Table of Contents
THIS is the twelfth issue of the New Zealand Official Year-book.
Thirteen pamphlets of “Advance Sheets” have been already published, which together form the whole of the work.
The Introductory and Official Part was included in the first of these pamphlets; the eight following contained the statistical information belonging to Part II.; and the last four were devoted to the descriptive portion of the book.
All these pamphlets have been circulated as far as deemed necessary in the colony, and a full supply of each was forwarded to the Agent-General in London as soon as issued.
E. J. VON DADELSZEN.
Registrar-General's Office, Wellington. N.Z., 30th September, 1903.
CORRIGENDA ET ADDENDA.
ON page 21, Supreme Court Judges: E. T. Conolly resigned, 10th September, 1903; F. R. Chapman appointed, 10th September, 1903.
On page 28. Foreign Consuls: Read—“United States, Consul-General, Frank Dillingham, Auckland; Consular Agents, William Reid, Wellington: Frank Graham, Christchurch.”
On page 28, Honours held by Colonists: To list of K.C.M.G. add—“Cadman, Hon. Sir Alfred Jerome, 1903.”
On page 29, Companions of Most Distinguished Order of St. Michael and St. George: Walter Kennaway, for “1897” read “1891.”
On page 30: To list of holders of the New Zealand Cross add—“Wrigg, Harry Charles William, 1898.”
On page 32: From list of members of Executive Council erase name of Hon. William C. Walker, resigned, and add names of Hon. Albert Pitt, M.L.C., Attorney-General, and Hon. Mahuta Tawhiao Potatau te Wherowhero, M.L.C. (without portfolio). The portfolios vacated by Hon. W. C. Walker are now held by the Prime Minister.
On page 33: Add to Roll of Members of the Honourable the Legislative Council—Hon. Mahuta Tawhiao Potatau te Wherowhero, 22nd May, 1903; Hon. Thomas Kennedy Macdonald, Wellington, 22nd June, 1903; Hon. Henry Francis Wigram, Canterbury, 22nd June, 1903; Hon. William Beehan, Auckland, 22nd June, 1903; Hon. Seymour Thorne George, Auckland, 22nd June, 1903.
On page 291: To first paragraph under heading of Imports add—“In estimating the value of imports, ad valorem goods are taken at their invoice value increased by 10 per cent., and include the value of case, cask, or covering (sec. 39, ‘Customs Laws Consolidation Act, 1882’). Value of all other goods includes freight and charges to time of arrival at port of discharge.”
On page 330: In first line following table of Butter and Cheese exported, for “£1,782,485” read “£782,485.”
On pages 516, 517: Heading of table to read, “Area Acquired and Handed over by Board.”
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
THE Colony of New Zealand consists of three main islands, with several groups of smaller islands lying at some distance from the principal group. The main islands, known as the North, the Middle, and Stewart Islands, have a coast-line 4,330 miles in length: North Island, 2,200 miles; Middle Island, 2,000 miles; and Stewart Island, 130 miles. Other islands included within the colony are the Chatham, Auckland, Campbell, Antipodes, Bounty, and Kermadec Islands. The annexation of the Cook or Hervey Group and sundry other islands has recently necessitated an enlargement of the boundaries of the colony, which will be specially treated of further on.
New Zealand is mountainous in many parts, but has, nevertheless, large plains in both North and Middle Islands. In the North Island, which is highly volcanic, is situated the famous Thermal-Springs District, of which a special account will be given. The Middle Island is remarkable for its lofty mountains, with their magnificent glaciers, and for the deep sounds or fiords on the western coast.
New Zealand is firstly a pastoral, and secondly an agricultural country. Sown grasses are grown almost everywhere, the extent of land laid down being nearly twelve millions of acres. The soil is admirably adapted for receiving these grasses, and, after the bush has been burnt off, is mostly sown over without previous ploughing. In the Middle Island a large area is covered with native grasses, all used for grazing purposes. The large extent of good grazing-land has made the colony a great wool and meat-producing country; and its agricultural capabilities are, speaking generally, very considerable. The abundance of water and the quantity of valuable timber are other natural advantages.
New Zealand is, besides, a mining country. Large deposits of coal are met with, chiefly on the west coast of the Middle Island. Gold, alluvial and in quartz, is found in both islands, the yield having been over sixty-one millions sterling in value to the present time. Full statistical information on this subject is given further on, compiled up to the latest dates.
The first authentic account of the discovery of New Zealand is that given by Abel Jansen Tasman, the Dutch navigator. He left Batavia on the 14th August, 1642, in the yacht “Heemskirk,” accompanied by the “Zeehaen” (or “Sea-hen”) fly-boat. After having visited Mauritius, and discovered Tasmania, named by him “Van Diemen's Land,” in honour of Anthony van Diemen, Governor of the Dutch possessions in the East Indies, he steered eastward, and on the 13th December of the same year sighted the west coast of the Middle Island of New Zealand, described by him as “a high mountainous country, which is at present marked in the charts as New Zealand.”
Tasman, under the belief that the land he saw belonged to a great polar continent, and was part of the country discovered some years before by Schouten and Le Maire, to which the name of Staaten Land had been given, gave the same name of Staaten Land to New Zealand; but within about three months afterwards Schouten's “Staaten Land” was found to be merely an inconsiderable island. Upon this discovery being announced, the country that Tasman had called Staaten Land received again the name of “New Zealand,” by which it has ever since been known. Tasman sailed along the coast to a bay, where he anchored. To this he gave the name of Murderers (now Massacre) Bay, on account of an unprovoked attack on a boat's crew by the natives, and the massacre of four white men. Thence he steered along the west coast of the North Island, and gave the name of Cape Maria van Diemen to the north-western extremity thereof. After sighting the islands of the Three Kings he finally departed, not having set foot in the country.
There is no record of any visit to New Zealand after Tasman's departure until the time of Captain Cook, who, after leaving the Society Islands, sailed in search of a southern continent then believed to exist. He sighted land on the 6th October, 1769, at Young Nick's Head, and on the 8th of that month cast anchor in Poverty Bay. After having coasted round the North Island and the Middle and Stewart Islands—which last he mistook for part of the Middle Island—he took his departure from Cape Farewell on the 31st March, 1770, for Australia. He visited New Zealand again in 1773, in 1774, and in 1777.
M. de Surville, a French officer in command of the vessel “Saint Jean Baptiste,” while on a voyage of discovery, sighted the northeast coast of New Zealand on the 12th December, 1769, and remained for a short time. A visit was soon after paid by another French officer, M. Marion du Fresne, who arrived on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand on the 24th March, 1772, but was, on the 12th June following, treacherously murdered at the Bay of Islands by the Natives.
In 1793 the “Dædalus,” under the command of Lieutenant Hanson, was sent by the Government of New South Wales to New Zealand, and two chiefs were taken thence to Norfolk Island. There was after this an occasional intercourse between the islands of New Zealand and the English settlements in New South Wales.
In 1814 the first missionaries arrived in New Zealand—Messrs. Hall and Kendall—who had been sent as forerunners by Mr. Marsden, chaplain to the New South Wales Government. After a short stay they returned to New South Wales, and on the 19th November of that year again embarked in company with Mr. Marsden, who preached his first sermon in New Zealand on Christmas Day, 1814. He returned to Sydney on the 23rd March, 1815, leaving Messrs. Hall and Kendall, who formed the first mission station at Rangihoua, Bay of Islands, under the auspices of the Church Missionary Society. Six years later, in 1821, the work of evangelization was put on a more durable basis; but the first station of the Wesleyan mission, established by Mr. Leigh and his wife, at the valley of the Kaeo, Whangaroa, was not taken possession of until the 10th June, 1823.
The first attempt at colonisation was made in 1825 by a company formed in London. An expedition was sent out under the command of Captain Herd, who bought two islands in the Hauraki Gulf and a strip of land at Hokianga. The attempt, however, was a failure, owing to the savage character of the inhabitants. In consequence of frequent visits of whaling-vessels to the Bay of Islands, a settlement grew up at Kororareka—now called Russell—and in 1833 Mr. Busby was appointed British Resident there. A number of Europeans gradually settled in different parts of the country, and married Native women.
In 1838 a colonisation company, known as the New Zealand Company, was formed to establish settlement on systematic principles. A preliminary expedition, under the command of Colonel William Wakefield, was despatched from England on the 12th May, 1839, and arrived in New Zealand in the following August. Having purchased land from the Natives, Colonel Wakefield selected the shore of Port Nicholson, in Cook Strait, as the site of the first settlement. On the 22nd January, 1840, the first body of immigrants arrived, and founded the town of Wellington. About the same time—namely, on the 29th January, 1840—Captain Hobson, R.N., arrived at the Bay of Islands, empowered, with the consent of the Natives, to proclaim the sovereignty of Queen Victoria over the islands of New Zealand, and to assume the government thereof. A compact called “The Treaty of Waitangi,” to which in less than six months five hundred and twelve names were affixed, was entered into, whereby all rights and powers of sovereignty were ceded to the Queen, all territorial rights being secured to the chiefs and their tribes. New Zealand was then constituted a dependency of the Colony of New South Wales, but on the 3rd May, 1841, was proclaimed a separate colony. The seat of Government had been previously established at Waitemata (Auckland), round which a settlement was formed.
The New Zealand Company having decided to form another settlement, to which the name of “Nelson” was to be given, despatched a preliminary expedition from England in April, 1841, for the purpose of selecting a site. The spot chosen was the head of Blind Bay, where a settlement was established. About the same time a number of pioneers arrived in Taranaki, despatched thither by the New Plymouth Company, a colonising society which had been formed in England, and had bought 50,000 acres of land from the New Zealand Company.
The next important event in the progress of colonisation was the arrival at Port Chalmers, on the 23rd March, 1848, of the first of two emigrant ships sent out by the Otago Association for the foundation of a settlement by persons belonging to or in sympathy with the Free Church of Scotland.
In 1849 the “Canterbury Association for founding a Settlement in New Zealand” was incorporated. On the 16th December, 1850, the first emigrant ship despatched by the association arrived at Port Cooper, and the work of opening up the adjoining country was set about in a systematic fashion, the intention of the promoters being to establish a settlement complete in itself, and composed entirely of members of the then United Church of England and Ireland.
Prior to the colonisation of New Zealand by Europeans, the earliest navigators and explorers found a race of people already inhabiting both islands. Papers written in 1874 by Mr. (afterwards Sir) William Fox, and Sir Donald McLean, then Native Minister, state that at what time the discovery of these islands was made by the Maoris, or from what place they came, are matters of tradition only, and that much has been lost in the obscurity enveloping the history of a people without letters. Nor is there anything on record respecting the origin of the Maori people themselves, beyond the general tradition of the Polynesian race, which seems to show a series of successive migrations from west to east, probably by way of Malaysia to the Pacific. Little more can now be gathered from their traditions than that they were immigrants, and that they probably found inhabitants on the east coast of the North Island belonging to the same race as themselves—the descendants of a prior migration, whose history is lost. The tradition runs that, generations ago, the Maoris dwelt in a country named Hawaiki, and that one of their chiefs, after a long voyage, reached the northern island of New Zealand. Returning to his home with a flattering description of the country he had discovered, this chief, it is said, persuaded a number of his kinsfolk and friends, who were much harassed by war, to set out with a fleet of double canoes for the new land. The names of most of the canoes are still remembered, and each tribe agrees in its account of the doings of the people of the principal canoes after their arrival in New Zealand; and from these traditional accounts the descent of the numerous tribes has been traced. Calculations, based on the genealogical staves kept by the tohungas, or priests, and on the well-authenticated traditions of the people, indicate that about twenty-one generations have passed since the migration, which may therefore be assumed to have taken place about five hundred and twenty-five years ago. The position of the legendary Hawaiki is unknown, but many places in the South Seas have been thus named in memory of the motherland. The Maoris speak a very pure dialect of the Polynesian language, the common tongue, with more or less variation, in all the Eastern Pacific Islands. When Captain Cook first visited New Zealand he availed himself of the services of a native from Tahiti, whose speech was easily understood by the Maoris. In this way much information respecting the early history of the country and its inhabitants was obtained which could not have otherwise been had.
For results of recent researches as to probable origin and present numbers of the Maoris, see Year-book for 1901.
The Proclamation of Captain Hobson on the 30th January, 1840, gave as the boundaries of the colony the following degrees of latitude and longitude: On the north, 34° 30' S. lat.; on the south, 47° 10' S. lat.; on the east, 179° 0' E. long.; on the west, 166° 5' E. long. These limits excluded small portions of the extreme north of the North Island and of the extreme south of Stewart Island.
In April, 1842, by Royal Letters Patent, and again by the Imperial Act 26 and 27 Vict., c. 23 (1863), the boundaries of the colony were altered so as to extend from 33° to 53° of south latitude and from 162° of east longitude to 173° of west longitude. By Proclamation bearing date the 21st July, 1887, the Kermadec Islands, lying between the 29th and 32nd degrees of south latitude and the 177th and 180th degrees of west longitude, were declared to be annexed to and to become part of the Colony of New Zealand.
By Proclamation bearing date the 10th June, 1901, the Cook Group of islands, and all the other islands and territories situate within the boundary-lines mentioned in the following Schedule, were included in the Colony of New Zealand:—
A line commencing at a point at the intersection of the twenty-third degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-fifty-sixth degree of longitude west of Greenwich, and proceeding due north to the point of intersection of the eighth degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-fifty-sixth degree of longitude west of Greenwich; thence due west to the point of intersection of the eighth degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-sixty-seventh degree of longitude west of Greenwich; thence due south to the point of intersection of the seventeenth degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-sixty-seventh degree of longitude west of Greenwich; thence due west to the point of intersection of the seventeenth degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-seventieth degree of longitude west of Greenwich; thence due south to the point of intersection of the twenty-third degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-seventieth degree of longitude west of Greenwich; and thence due east to the point of intersection of the twenty-third degree of south latitude and the one-hundred-and-fifty-sixth degree of longitude west of Greenwich.
The following now constitute the Colony of New Zealand:—
The island commonly known as the North Island, with its adjacent islets, having an aggregate area of 44,468 square miles, or 28,459,520 acres.
The island known as the Middle Island, with adjacent islets, having an aggregate area of 58,525 square miles, or 37,456,000 acres.
Stewart Island, and adjacent islets, having an area of 665 square miles, or 425,390 acres.
The Chatham Islands, situate 536 miles eastward of Lyttelton in the Middle Island, with an area of 375 square miles, or 239,920 acres.
The Auckland Islands, about 200 miles south of Stewart Island, extending about 30 miles from north to south, and nearly 15 from east to west, the area being 210,650 acres.
The Campbell Islands, in latitude 52° 33' south, and longitude 169° 8' west, about 30 miles in circumference, with an area of 45,440 acres.
The Antipodes Islands, about 458 miles in a south-easterly direction from Port Chalmers, in the Middle Island. These are detached rocky islands, and extend over a distance of between 4 and 5 miles from north to south. Area, 12,960 acres.
The Bounty Islands, a small group of islets, thirteen in number, lying north of the Antipodes Islands, and about 415 miles in an east-south-easterly direction from Port Chalmers. Area, 3,300 acres.
The Kermadec Islands, a group lying about 614 miles to the north-east of Russell, in the Bay of Islands. Raoul or Sunday Island, the largest of these, is about 20 miles in circuit. The next in size is Macaulay Island, about 3 miles round. Area of the group, 8,208 acres.
Islands forming the Cook Group:—
Rarotonga.—Distance from Auckland, 1,638 miles; circumference, 20 miles; height, 2,920 ft.
Mangaia.—Distance from Rarotonga, 116 miles; circumference, 30 miles; height, 656 ft.
Atiu.—Distance from Rarotonga, 116 miles: circumference, 20 miles; height, 374 ft.
Aitutaki.—Distance from Rarotonga, 140 miles; circumference, 12 miles: height, 366 ft.
Mauke.—Distance from Rarotonga, 150 miles; circumference, 6 miles; height, about 60 ft.
Mitiaro.—Distance from Rarotonga, 140 miles; circumference, 5 miles; height, about 50 ft; also,
Takutea.—Distant from Rarotonga, 125 miles.
The Herveys (Manuae and Aoutu).—Distant from Rarotonga, 120 miles.
Total area of above group, 150 square miles.
Islands outside the Cook Group:—
Savage or Niue.—Distance from Rarotonga, 580 miles; circumference, 40 miles; height, 200 ft.; area, about 100 square miles.
Palmerston.—Distance from Rarotonga, 273 miles; an atoll, 4 miles by 2 miles.
Penrhyn, or Tongareva.—Distance 735 miles from Rarotonga; an atoll, 12 miles by 7 miles.
Humphrey, or Manahiki.—Distance from Rarotonga, 650 miles; an atoll, 6 miles by 5 miles.
Rierson, or Rakaanga.—Distance from Rarotonga, 670 miles; an atoll, 3 miles by 3 miles.
Danger, or Pukapuka.—Distance from Rarotonga, 700 miles; an atoll, 3 miles by 3 miles.
Suwarrow.—Distance from Rarotonga, 530 miles; an atoll.
Total area of islands outside the Cook Group, 130 square miles.
The total area of the colony is thus about 104,751 square miles, of which the aggregate area of the outlying groups of islands that are practically useless for settlement amounts to about 498 square miles.
The areas of the several Australian States, as stated by different authorities, vary considerably. The total area of the Australian Continent is given as 2,944,628 square miles, according to a computation made by the late Surveyor-General of Victoria, Mr. J. A. Skene, from a map of Continental Australia compiled and engraved under his direction; but the following areas are taken from the latest official records of each colony:—
| Square Miles. | |
|---|---|
| Queensland | 668,497 |
| New South Wales | 310,700 |
| Victoria | 87,884 |
| South Australia | 903,690 |
| Western Australia | 975,920 |
| Total, Continent of Australia | 2,946,691 |
| Tasmania | 26,215 |
| Total, Commonwealth of Australia | 2,972,906 |
The size of these States (with New Zealand) may be better realised by comparison of their areas with those of European countries. The areas of the following countries—Austria-Hungary, Germany, France, Belgium, Holland, Denmark, Sweden and Norway, Portugal, Spain, Italy (including Sardinia and Sicily), Switzerland, Greece, Roumania, Bulgaria, Servia, Eastern Roumelia, and Turkey in Europe—containing on the whole rather less than 1,600,000 square miles, amount to little more than half the extent of the Australian Continent. If the area of Russia in Europe be added to those of the other countries the total would be about one-seventh larger than the Australian Continent, and about one-twelfth larger than the Australian States, with New Zealand.
The area of the Colony of New Zealand is about one-seventh less than the area of Great Britain and Ireland, the Middle Island of New Zealand being a little larger than the combined areas of England and Wales.
| United Kingdom. | Area in Square Miles. |
|---|---|
| England and Wales | 58,311 |
| Scotland | 30,463 |
| Ireland | 32,531 |
| Total | 121,305 |
| New Zealand. | Area in Square Miles. |
| North Island | 44,468 |
| Middle Island | 58,525 |
| Stewart Island | 665 |
| Chatham Islands | 375 |
| Other islands | 718 |
| Total | 104,751 |
The North Island extends over a little more than seven degrees of latitude, a distance in a direct line from north to south of 430 geographical or 498 statute miles; but, as the northern portion of the colony, which covers more than three degrees of latitude, trends to the westward, the distance in a straight line from the North Cape to Cape Palliser, the extreme northerly and southerly points of the island, is about 515 statute miles.
This island is, as a whole, hilly, and, in parts, mountainous in character, but there are large areas of plain or comparatively level country that are, or by clearing may be made, available for agricultural purposes. Of these, the principal are the plains in Hawke's Bay on the East Coast, the Wairarapa Plain in the Wellington District, and a strip of country along the West Coast, about 250 miles in length, extending from a point about thirty miles from the City of Wellington to a little north of New Plymouth. The largest plain in the North Island, Kaingaroa, extends from the shore of Lake Taupo in a north-north-easterly direction to the sea-coast in the Bay of Plenty; but a great part of it is covered with pumicesand, and is unfit for tillage or pasture. There are several smaller plains and numerous valleys suitable for agriculture. The level or undulating country in this island fit, or capable of being made fit, for agriculture has been roughly estimated at 13,000,000 acres. This includes lands now covered with standing forest, and swamps that can be drained; also large areas of clay-marl and pumice-covered land. The clay-marl in its natural state is cold and uninviting to the farmer, but under proper drainage and cultivation it can be brought to a high state of productiveness. This kind of land is generally neglected at the present time, as settlers prefer soils more rapidly remunerative and less costly to work. The larger portion of the North Island was originally covered with forest. Although the area of bush-land is still very great, yet year by year the amount is being reduced, chiefly to meet the requirements of settlement, the trees being cut down and burnt, and grass-seed sown on the ashes to create pasture. Hilly as the country is, yet from the nature of the climate it is especially suited for the growth of English grasses, which will flourish wherever there is any soil, however steep the land may be; once laid down in grass very little of the land is too poor to supply food for cattle and sheep. The area of land in the North Island deemed purely pastoral or capable of being made so, while too steep for agricultural purposes, is estimated at 14,200,000 acres. In the centre of the island is a lake, about twenty miles across either way, called Taupo. A large area adjacent to the lake is at present worthless pumice-country. The Waikato River, the largest in the North Island, flows out of the north-eastern corner of this lake, and runs thence north-westward until it enters the ocean a little distance south of the Manukau Harbour. This river is navigable for small steamers for about a hundred miles from its mouth. The Maori King-country, occupied by Natives who for several years isolated themselves from Europeans, lies between Lake Taupo and the western coast. The River Thames, or Waiho, having its sources north of Lake Taupo, flows northward into the Firth of Thames. It is navigable for about fifty miles, but only for small steamers. The other navigable rivers in this island are the Wairoa (Kaipara), the Wanganui, and the Manawatu, the two vast of which flow towards the south-west into Cook Strait.
The mountains in the North Island are estimated to occupy about one-tenth of the surface, and do not exceed 4,000ft. in height, with the exception of a few volcanic mountains that are more lofty. Of these, the three following are the most important:—
The Tongariro Mountain, situated to the southward of Lake Taupo. It consists of a group of distinct volcanic cones, the lava-streams from which have so overlapped in their descent as to form one compact mountain-mass at the base. The highest of these cones is called Ngauruhoe, and attains an elevation of 7,515ft. The craters of Ngauruhoe, the Red Crater (6,140ft.), and Te Mari (4,990ft.) are the three vents from which the latest discharges of lava have taken place, the most recent having occurred in 1868. These craters are still active, steam and vapour issuing from them with considerable force and noise, the vapours, charged with pungent gases and acids, making it dangerous to approach too near the crater-lips.
Ruapehu. This mountain lies to the south of Ngauruhoe and Tongariro. It is a volcanic cone in the solfatara stage, and reaches the height of 9,008ft., being in part considerably above the line of perpetual snow. The most remarkable feature of this mountain is the crater-lake on its summit, which is subject to slight and intermittent eruptions, giving rise to vast quantities of steam. Recently—in March, 1895—such an eruption took place, forming a few hot springs on the margin of the lake, and increasing the heat in the lake itself. This lake lies at the bottom of a funnel-shaped crater, the steep sides of which are mantled with ice and snow. The water occupies a circular basin about 500ft. in diameter, some 300ft. below the enclosing peaks, and is quite inaccessible except by the use of ropes. This lake, and the three craters previously mentioned on Tongariro, are all in one straight line, which, if produced, would pass through the boiling springs at Tokaanu on the southern margin of Lake Taupo, the volcanic country north-east of that lake, and White Island, an active volcano in the Bay of Plenty, situated about twenty-seven miles from the mainland.
Mount Egmont. This is an extinct volcanic cone, rising to a height of 8,260ft. The upper part is always covered with snow. This mountain is situated close to New Plymouth, and is surrounded by one of the most fertile districts in New Zealand. Rising from the plains in solitary grandeur, it is an object of extreme beauty, the cone being one of the most perfect in the world.
It is estimated that the area of mountain-tops and barren country at too high an altitude for sheep, and therefore worthless for pastoral purposes, amounts, in the North Island, to 300,000 acres.
Without a doubt the hot springs form the most remarkable feature of the North Island. They are found over a large area, extending from Tongariro, south of Lake Taupo, to Ohaeawai, in the extreme north—a distance of some 300 miles; but the principal seat of hydrothermal action appears to be in the neighbourhood of Lake Rotorua, about forty miles north-north-east from Lake Taupo. By the destruction of the famed Pink and White Terraces and of Lake Rotomahana during the eruption of Mount Tarawera on the 10th June, 1886, the neighbourhood has been deprived of attractions unique in character and of unrivalled beauty; but the natural features of the country—the numerous lakes, geysers, and hot springs, some of which possess remarkable curative properties in certain complaints—are still very attractive to tourists and invalids. The world-wide importance of conserving this region as a sanatorium for all time has been recognised by the Government, and it is now dedicated by Act of Parliament to that purpose.
Notwithstanding the length of coast-line, good harbours in the North Island are not numerous. Those on the west coast north of New Plymouth are bar-harbours, unsuitable for large vessels. The principal harbours are the Waitemata Harbour, on which Auckland is situated—this is rather a deep estuary than a harbour; several excellent havens in the northern peninsula; and Port Nicholson, on the borders of which Wellington is situated. This is a landlocked harbour, about six miles across, having a comparatively narrow but deep entrance from the ocean. The water is deep nearly throughout.
The Cape Colville Peninsula is rich in gold-bearing quartz.
Cook Strait separates the North and Middle Islands. It is some sixteen miles across at its narrowest part, but in the widest about ninety. The strait is invaluable for the purpose of traffic between different parts of the colony.
The extreme length of the Middle Island, from Jackson's Head, in Cook Strait, to Puysegur Point, at the extreme south-west, is about 525 statute miles; the greatest distance across at any point is in Otago (the southernmost) District, about 180 miles.
The Middle Island is intersected along almost its entire length by a range of mountains known as the Southern Alps. Some of the summits reach a height of from 10,000ft. to 12,000ft., Mount Cook, the highest peak, rising to 12,349ft.
In the south, in the neighbourhood of the sounds and Lake Te Anau, there are many magnificent peaks, which, though not of great height, are, owing to their latitude, nearly all crowned with perpetual ice and snow. Further north the mountains increase in height—Mount Earnslaw, at Lake Wakatipu; and Mount Aspiring, which has been aptly termed the New Zealand Matterhorn, 9,949 ft. in height, at Lake Wanaka. Northward of this again are Mount Cook (or Aorangi), Mount Sefton, and other magnificent peaks.
For beauty and grandeur of scenery the Southern Alps of New Zealand may worthily compare with, while in point of variety they are said actually to surpass, the Alps of Switzerland. In New Zealand few of the mountains have been scaled; many of the peaks and most of the glaciers are as yet unnamed; and there is still, in parts of the Middle Island, a fine field for exploration and discovery—geographical, geological, and botanical. The wonders of the Southern Alps are only beginning to be known; but the more they are known the more they are appreciated. The snow-line in New Zealand being so much lower than in Switzerland, the scenery, though the mountains are not quite so high, is of surpassing grandeur.
There are extensive glaciers on both sides of the range, those on the west being of exceptional beauty, as, from the greater abruptness of the mountain-slopes on that side, they descend to within about 700ft. of the sea-level, and into the midst of the evergreen forest. The largest glaciers on either side of the range are easily accessible.
The following gives the sizes of some of the glaciers on the eastern slope:—
| Name. | Area of Glacier. | Length of Glacier. | Greatest Width. | Average Width. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | Miles | ch. | Miles | ch. | Miles | ch. | |
| Tasman | 13,664 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 14 | 1 | 15 |
| Murchison | 5,800 | 10 | 70 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 66 |
| Godley | 5,312 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 55 | 1 | 3 |
| Mueller | 3,200 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 0 | 50 |
| Hooker | 2,416 | 7 | 25 | 0 | 54 | 0 | 41 |
The Alletsch Glacier in Switzerland, according to Ball, in the “Alpine Guide,” has an average width of one mile. It is in length and width inferior to the Tasman Glacier.
Numerous sounds or fiords penetrate the south-western coast. They are long, narrow, and deep (the depth of water at the upper part of Milford Sound is 1,270ft., although at the entrance only 130ft.), surrounded by giant mountains clothed with foliage to the snow-line, with waterfalls, glaciers, and snowfields at every turn. Some of the mountains rise almost precipitously from the water's edge to 5,000ft. and 6,000ft. above the sea. Near Milford, the finest of these sounds, is the great Sutherland Waterfall, 1,904ft. high.
The general surface of the northern portion of the Middle Island, comprising the Provincial Districts of Nelson and Marlborough, is mountainous, but the greater part is suitable for grazing purposes. There are some fine valleys and small plains suitable for agriculture, of which the Wairau Valley or Plain is the largest. Deep sounds, extending for many miles, break the coast-line abutting on Cook Strait. The City of Nelson is situated at the head of Blind Bay, which has a depth inwards from Cook Strait of about forty statute miles.
The Provincial District of Canterbury lies to the south of the Marlborough District, and on the eastern side of the island. Towards the north the land is undulating; then there is a stretch of almost perfectly level country extending towards the south-west 160 miles, after which, on the south, the country is undulating as far as the borders of the Otago District. On the east a block of hill-country rises abruptly from the plain and extends for some miles seaward. This is Banks Peninsula, containing several good harbours, the principal being Port Cooper, on the north, on which is situated Lyttelton, the chief port of the district: the harbour of Akaroa, one of the finest in the colony, is on the southern coast of this peninsula.
The District of Otago is, on the whole, mountainous, but has many fine plains and valleys suitable for tillage. The mountains, except towards the west coast, are generally destitute of timber, and suitable for grazing sheep. There are goldfields of considerable extent in the interior of this district. The inland lakes are also very remarkable features. Lake Wakatipu extends over fifty-four miles in length, but its greatest width is not more than four miles, and its area only 114 square miles. It is 1,070ft. above sea-level, and has a depth varying from 1,170ft. to 1,296ft. Te Anau Lake is somewhat larger, having an area of 132 square miles. These lakes are bounded on the west by broken, mountainous, and wooded country, extending to the ocean.
The chief harbours in Otago are Port Chalmers, at the head of which Dunedin is situated, and the Bluff Harbour, at the extreme south.
The District of Westland, extending along the west coast of the Middle Island, abreast of Canterbury, is more or less auriferous throughout. The western slopes of the central range of mountains are clothed with forest-trees to the snow-line; but on the eastern side timber is scarce, natural grasses covering the ground.
The rivers in the Middle Island are for the most part mountain torrents, fed by glaciers in the principal mountain ranges. When the snow melts they rise in flood, forming, where not confined by rocky walls, beds of considerable width, generally covered by enormous deposits of shingle. The largest river in the colony as regards volume of water is the Clutha. It is 154 miles in length, but is only navigable for boats or small river-steamers for about thirty miles. The Rivers Buller, Grey, and Hokitika, on the West Coast, are navigable for a short distance from their mouths. They form the only ports in the Westland District. In their unimproved state they admitted, owing to the bars at their mouths, none but vessels of small draught; but, in consequence of the importance of the Grey and Buller Rivers as the sole ports available for the coal-export trade, large harbour-works have been undertaken, resulting in the deepening of the beds of these rivers, and giving a depth of from 18ft. to 26ft. of water on the bar.
The area of level or undulating land in the Middle Island available for agriculture is estimated at about 15,000,000 acres. About 13,000,000 are suitable for pastoral purposes only, or may become so when cleared of forest and sown with grass-seed. The area of barren land and mountain-tops is estimated at about 9,000,000 acres.
Foveaux Strait separates the Middle from Stewart Island. This last island has an area of only 425,390 acres.
Stewart Island is a great tourist resort during the summer months, and is easily reached by steamer from the Bluff, distant about 25 miles.
The principal peak is Mount Anglem, 3,200ft. above sea-level, which has an extinct crater at its summit. Most of the island is rugged and forest-clad; the climate is mild, frost being seldom experienced; and the soil, when cleared of bush, is fertile.
The chief attractions are the numerous bays and fiords. Paterson Inlet is a magnificent sheet of water, about ten miles by four miles, situated close to Half-moon Bay, the principal port, where over two hundred people live. Horse-shoe Bay and Port William are within easy reach of Half-moon Bay. Port Pegasus, a land-locked sheet of water about eight miles by a mile and a half, is a very fine harbour. At “The Neck” (Paterson Inlet) there is a Native settlement of over a hundred Maoris and half-castes. The bush is generally very dense, with thick undergrowth. Rata, black-pine, white-pine, miro, and totara are the principal timber trees. Fish are to be had in great abundance and variety; oysters form an important industry. Wild pigeons, ducks, and mutton-birds are plentiful.
The outlying group of the CHATHAM ISLANDS, 480 statute miles east-south-east from Wellington, and 536 miles eastward of Lyttelton, consists of two principal islands and several unimportant islets. The largest island contains about 222,490 acres, of which an irregular-shaped lake or lagoon absorbs 45,960 acres. About one quarter of the surface of the land is covered with forest, the rest with fern or grass. The hills nowhere rise to a great height. Pitt Island is the next in size; the area is 15,330 acres. The greater portion of both islands is used for grazing sheep.
The KERMADEC GROUP of islands, four in number, is situated between 29° 10' and 31° 30' south latitude, and between 177° 45' and 179° west longitude. They are named Raoul or Sunday Island, Macaulay Island, Curtis Islands, and L'Espérance or French Rock. The principal island, Sunday, is 600 miles distant from Auckland. The islands are volcanic, and in two of them signs of activity are still to be seen. The rainfall is plentiful, but not excessive. The climate is mild and equable, and slightly warmer than the north of New Zealand. The following are the areas of the islands and islets of the group: Sunday Island, 7,200 acres; Herald group of islets, 85 acres; Macaulay Island, 764 acres; Curtis Islands, 128 acres and 19 acres; L'Espérance, 12 acres: total, 8,208 acres. Sunday Island is twenty miles in circumference, roughly triangular in shape, and at the highest point 1,723ft. above the sea-level. It is rugged and broken over a very large extent of its surface, and, except in a few places, covered with forest. The soil everywhere on the island is very rich, being formed by the decomposition of a dark-coloured pumiceous tuff and a black andesitic lava, with which is closely mixed a fine vegetable mould. The great luxuriance and richness of the vegetation bear witness to the excellence of the soil, which is everywhere—except where destroyed by eruptions, and on the steep cliffs—the same rich loam. Want of water is one of the drawbacks. Three of the four lakes on the island are fresh, but so difficult of approach as to be practically useless.
The AUCKLAND ISLANDS are about 290 miles south of Bluff Harbour, their position being given on the Admiralty chart as latitude 50° 31' 29" S., and longitude 166° 19' 12" E. They have several good harbours. Port Ross, at the north end of the principal island, was described by the eminent French commander, D'Urville, as one of the best harbours of refuge in the known world. At the southern end of the island there is a through passage extending from the east to the west coast. It has been variously named Adams Strait and Carnley Harbour, and forms a splendid sheet of water. The largest of the islands is about 27 miles long by about 15 miles broad, and is very mountainous, the highest part being about 2,000ft. above the sea. The west coast is bold and precipitous, but the east coast has several inlets. The wood on the island is, owing to the strong prevailing wind, scrubby in character. The New Zealand Government maintains at this island a dépôt of provisions and clothing for the use of shipwrecked mariners.
The COOK ISLANDS, with others recently annexed, are as under:—RAROTONGA (Cook Group): A magnificent island, rising to a height of 3,000 ft., clothed to the tops of the mountains with splendid vegetation. It has abundant streams, considerable tracts of sloping land, and rich alluvial valleys. The two harbours are poor.
MANGAIA, the south-easternmost of the Cook Group, is of volcanic origin, and about thirty miles in circumference. The productions, which are numerous and cheap, are obtained by assiduous labour.
ATIU (Cook Group) resembles Mangaia in appearance and extent. It is a mere bank of coral, 10 ft. or 12 ft. high, steep and rugged, except where there are small sandy beaches and some clefts, where the ascent is gradual.
AITUTAKI (Cook Group) presents a most fruitful appearance, its shores being bordered by flat land, on which are innumerable cocoanut and other trees, the higher ground being beautifully interspersed with lawns. It is eighteen miles in circuit.
MAUKE or Parry Island (Cook Group) is a low island; it is about two miles in diameter, well wooded, and inhabited.
MITIARO (Cook Group) is a low island, from three to four miles long and one mile wide.
HERVEY ISLANDS (Cook Group): This group consists of three islands, surrounded by a reef, which may be six leagues in circumference.
NIUE, or Savage Island, lying east of the Friendly Islands, is a coral island, thirty-six miles in circumference, rising to a height of 200 ft. It has the usual tropical productions.
PALMERSTON ISLAND, lying about 500 miles east of Niue and about 220 from the nearest island of the Cook Group (Aitutaki), is remarkable as the “San Pablo” of Magellan, the first island discovered in the South Sea. It has no harbour. The soil is fairly fertile, and there is some good hardwood timber.
PENRHYN ISLAND (Tongareva) lies about 300 miles north-east of Manahiki. It is one of the most famous pearl islands in the Pacific, and there is a splendid harbour, a lagoon with two entrances, fit for ships of any size.
MANAHIKI, lying about 400 miles eastward of Danger Island, is an atoll, about thirty miles in circumference, valuable from the extent of the cocoanut groves. The interior lagoon contains a vast deposit of pearl-shell.
RAKAANGA is an atoll, three miles in length and of equal breadth.
DANGER ISLAND (Pukapuka): Next to the 10th parallel, but rather north of the latitude of the Navigators, and east of them are a number of small atolls. Of these, the nearest to the Samoan Group—about 500 miles—is Danger Island, bearing north-west of Suwarrow about 250 miles.
SUWARROW ISLAND has one of the best harbours in the Pacific. It lies about 500 miles east of Apia, the capital of the Samoan Group. It is a coral atoll, of a triangular form, fifty miles in circumference, the reef having an average width of half a mile across, enclosing a land-locked lagoon twelve miles by eight. The entrance is half a mile wide, and there is accommodation for all the ships in the Pacific to ride in safety in all weathers, with depths of from three to thirty fathoms. It is out of the track of hurricanes, uninhabited, but capable by its fertility of supporting a small population. As a depot for the collection of trade from the various islands it ought to be very valuable.
British sovereignty was proclaimed over New Zealand in January, 1840, and the country became a dependency of New South Wales until the 3rd May, 1841, when it was made a separate colony. The seat of Government was at Auckland, and the Executive included the Governor, and three gentlemen holding office as Colonial Secretary, Attorney-General, and Colonial Treasurer.
The successors of these gentlemen, appointed in August, 1841, May, 1842, and January, 1844, respectively, continued in office until the establishment of Responsible Government on the 7th May, 1856. Only one of them—Mr. Swainson, the Attorney-General—sat as a member of the first General Assembly, opened on the 27th May, 1854. During the session of that year there were associated with the permanent members of the Executive Council certain members of the General Assembly. These latter held no portfolios.
The Government of the colony was at first vested in the Governor, who was responsible only to the Crown; but in 1852 an Act granting representative institutions to the colony was passed by the Imperial Legislature. Under it the constitution of a General Assembly for the whole colony was provided for, to consist of a Legislative Council, the members of which were to be nominated by the Governor, and of an elective House of Representatives. The first session of the General Assembly was opened on the 27th May, 1854, but the members of the Executive were not responsible to Parliament. The first Ministers under a system of Responsible Government were appointed on the 18th April, 1856. By the Act of 1852 the colony was divided into six provinces, each to be presided over by an elective Superintendent, and to have an elective Provincial Council, empowered to legislate, except on certain specified subjects. The franchise amounted practically to household suffrage. In each case the election was for four years, but a dissolution of the Provincial Council by the Governor could take place at any time, necessitating a fresh election both of the Council and of the Superintendent. The Superintendent was chosen by the whole body of electors of the province; each member of the Provincial Council by the electors of a district. The Provincial Governments, afterwards increased to nine, remained as integral parts of the Constitution of the colony until the 1st November, 1876, when they were abolished by an Act of the General Assembly, that body having been vested with the power of altering the Constitution Act. On the same day an Act of the General Assembly which subdivided the colony (exclusive of the areas included within municipalities) into counties, and established a system of local county government, came into force.
The Governor is appointed by the King. His salary is £5,000 a year, with an annual allowance of £1,500 on account of his establishment, and of £500 for travelling-expenses, provided by the colony.
Members of the Legislative Council hold their seats under writs of summons from the Governor. Till the year 1891 the appointments were for life; but in September of that year an Act was passed making appointments after that time tenable for seven years only, though Councillors may be reappointed. In either case seats may be vacated by resignation or extended absence. Two members of the Council are aboriginal native chiefs.
The members of the House of Representatives are elected for three years from the time of each general election; but at any time a dissolution of Parliament by the Governor may render a general election necessary. Four of the members are representatives of Native constituencies. For the purposes of European representation the colony is divided into sixty-eight electoral districts, four of which—the Cities of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin—return each three members, and all the other electorates one each, a total of seventy-six. The full number of members composing the House of Representatives is thus eighty. Members of the House of Representatives are chosen by the votes of the inhabitants in every electoral district appointed for that purpose. No person, who, being a bankrupt within the meaning of “The Bankruptcy Act, 1892,” has not obtained an order of discharge under that Act shall be qualified to be nominated as a candidate for election, or to be elected, or to take his seat as a member of the House of Representatives, anything in any other Act to the contrary notwithstanding.
In 1889 an amendment of the Representation Act was passed, which contained a provision prohibiting any elector from giving his vote in respect of more than one electorate at any election. “The Electoral Act, 1893,” extended to women of both races the right to register as electors, and to vote at the elections for members of the House of Representatives. The qualification for registration is the same for both sexes. No person is entitled to be registered on more than one electoral roll within the colony. Women are not qualified to be elected as members of the House of Representatives. The electoral laws are the subject of special comment further on in this work. Every man registered as an elector, and not specially excepted by the Electoral Act now in force, is qualified to be elected a member of the House of Representatives for any electoral district. For European representation every adult person, if resident one year in the colony and three months in one electoral district, can be registered as an elector. Freehold property of the value of £25 held for six months preceding the day of registration until 1896 entitled a man or woman to register, if not previously registered under the residential qualification. But the Amendment Act of 1896 abolished the property qualification (except in case of existing registrations), and residence alone now entitles a man or woman to have his or her name placed upon an electoral roll. For Maori representation every adult Maori resident in any Maori electoral district (of which there are four only in the colony) can vote. Registration is not required in Native districts. [The above provisions are now incorporated in “The Electoral Act, 1902,” which consolidates the electoral laws, with such amendments as were found necessary.]
Up to the year 1865 the seat of Government of New Zealand was at Auckland. Several attempts were made by members of Parliament, by motions in the Legislative Council and House of Representatives, to have it removed to some more central place; but it was not until November, 1863, that Mr. Domett (the then ex-Premier) was successful in carrying resolutions in the House of Representatives that steps should be taken for appointing some place in Cook Strait as the permanent seat of Government in the colony. The resolutions adopted were: “(1.) That it has become necessary that the seat of Government in the colony should be transferred to some suitable locality in Cook Strait. (2.) That, in order to promote the accomplishment of this object, it is desirable that the selection of the particular site in Cook Strait should be left to the arbitrament of an impartial tribunal. (3.) That, with this view, a Bill should be introduced to give effect to the above resolutions.” On the 25th November an address was presented to the Governor, Sir George Grey, K.C.B., by the Commons of New Zealand, requesting that the Governors of the Colonies of New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania, might each be asked to appoint one Commissioner for the purpose of determining the best site in Cook Strait. Accordingly, the Hon. Joseph Docker, M.L.C., New South Wales; the Hon. Sir Francis Murphy, Speaker of the Legislative Council, Victoria; and R. C. Gunn, Esq., Tasmania, were appointed Commissioners.
These gentlemen, having made a personal inspection of all suitable places, arrived at the unanimous decision “that Wellington, in Port Nicholson, was the site upon the shores of Cook Strait which presented the greatest advantages for the administration of the government of the colony.”
The seat of Government was, therefore, in accordance with the recommendation of the Commissioners, removed to Wellington in February, 1865.
Nearly all the public works of New Zealand are in the hands of the Government of the colony, and in the early days they simply kept pace with the spread of settlement. In 1870, however, a great impetus was given to the progress of the whole country by the inauguration of the “Public Works and Immigration Policy,” which provided for carrying out works in advance of settlement. Railways, roads, and water-races were constructed, and immigration was conducted on a large scale. As a consequence, the population increased from 267,000 in 1871 to 501,000 in 1881, and to 807,929 in December, 1902, besides whom there were 43,143 Maoris, and 12,292 persons belonging to the Cook and other Pacific Islands recently annexed to the colony.
Table of Contents
Captain William Hobson, R.N., from Jan., 1840, to 10 Sept., 1842.
[British sovereignty was proclaimed by Captain Hobson in January, 1840, and New Zealand became a dependency of the Colony of New South Wales until 3rd May, 1841, at which date it was proclaimed a separate colony. From January, 1840, to May, 1841, Captain Hobson was Lieutenant-Governor of New Zealand under Sir George Gipps, Governor of New South Wales, and from May, 1841, Governor of New Zealand; the seat of Government being at Auckland, where he died in September, 1842. From the time of Governor Hobson's death, in September, 1842, until the arrival of Governor Fitzroy, in December, 1843, the Government was carried on by the Colonial Secretary, Lieutenant Shortland.]
Lieutenant Shortland, Administrator, from 10 Sept., 1842, to 26 Dec., 1843.
Captain Robert Fitzroy, R.N., from 26 Dec., 1843, to 17 Nov., 1845.
Captain Grey (became Sir George Grey, K.C.B., in 1848), from 18 Nov., 1845, to 31 Dec., 1853.
[Captain Grey held the commission as Lieutenant-Governor of the colony until the 1st January, 1848, when he was sworn in as Governor-in-Chief over the Islands of New Zealand, and as Governor of the Province of New Ulster and Governor of the Province of New Munster. After the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act, Sir George Grey was, on the 13th September, 1852, appointed Governor of the colony, the duties of which office he assumed on the 7th March, 1853. In August, 1847, Mr. E. J. Eyre was appointed Lieutenant-Governor of New Munster: he was sworn in, 28th January, 1848. On 3rd January, 1848, Major-General George Dean Pitt was appointed Lieutenant-Governor of New Ulster: he was sworn in, 14th February, 1848; died, 8th January, 1851; and was succeeded as Lieutenant-Governor by Lieutenant-Colonel Wynyard, appointed 14th April, 1851; sworn in, 26th April, 1851. The duties of the Lieutenant-Governor ceased on the assumption by Sir George Grey of the office of Governor, on the 7th March, 1853.]
Lieutenant-Colonel Robert Henry Wynyard, C.B., Administrator, from 3 Jan., 1854, to 6 Sept., 1855.
Colonel Thomas Gore Browne, C.B., from 6 Sept., 1855, to 2 Oct., 1861.
Sir George Grey, K.C.B., Administrator, from 3 Oct., 1861; Governor, from 4 Dec., 1861, to 5 Feb., 1868.
Sir George Ferguson Bowen, G.C.M.G., from 5 Feb., 1868, to 19 Mar., 1873.
Sir George Alfred Arney, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 21 Mar. to 14 June, 1873.
Sir James Fergusson, Baronet, P.C., from 14 June, 1873, to 3 Dec., 1874.
The Marquis of Normanby, P.C., G.C.M.G., Administrator, from 3 Dec., 1874; Governor, from 9 Jan., 1875, to 21 Feb., 1879.
James Prendergast, Esquire, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 21 Feb. to 27 Mar., 1879.
Sir Hercules George Robert Robinson, G.C.M.G., Administrator, from 27 Mar., 1879; Governor, from 17 April, 1879, to 8 Sept., 1880.
James Prendergast, Esquire, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 9 Sept. to 29 Nov., 1880.
The Honourable Sir Arthur Hamilton Gordon, G.C.M.G., from 29 Nov., 1880, to 23 June, 1882.
Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 24 June, 1882, to 20 Jan., 1883.
Lieutenant - General Sir William Francis Drummond Jervois, G.C.M.G., C.B., from 20 Jan., 1883, to 22 Mar., 1889.
Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 23 Mar. to 2 May, 1889.
The Earl of Onslow, G.C.M.G., from 2 May, 1889, to 24 Feb., 1892.
Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 25 Feb., to 6 June, 1892.
The Earl of Glasgow, G.C.M.G., from 7 June, 1892, to 6 Feb., 1897.
Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice, Administrator, from 8 Feb., 1897, to 9th Aug., 1897.
The Earl of Ranfurly, G.C.M.G., from 10th Aug., 1897.
Table of Contents
Sir W. Martin, appointed Chief Justice, 10 Jan., 1842. Resigned, 12 June, 1857.
H. S. Chapman, appointed, 26 Dec., 1843. Resigned, 30 July, 1850. Reappointed, 23 Mar., 1864. Resigned, 31 Mar., 1875.
S. Stephen, appointed, 30 July, 1850. Appointed Acting Chief Justice, 20 Oct., 1855. Died, 13 Jan., 1858.
Daniel Wakefield, appointed, Oct., 1855. Died, Oct., 1857.
Hon. H. B. Gresson, appointed temporarily, 8 Dec., 1857. Permanently, 1 July, 1862. Resigned, 31 Mar., 1875.
Sir G. A. Arney, appointed Chief Justice, 1 Mar., 1858. Resigned 31 Mar., 1875.
A. J. Johnston, appointed, 2 Nov., 1858. Died, 1 June, 1888.
C. W. Richmond, appointed, 20 Oct., 1862. Died, 3 Aug., 1895.
J. S. Moore, appointed temporarily, 15 May, 1866. Relieved, 30 June, 1868.
C. D. R. Ward, appointed temporarily, 1 Oct., 1868. Relieved, May, 1870. Appointed temporarily, 21 Sept., 1886. Relieved, 12 Feb., 1889.
Sir J. Prendergast, appointed Chief Justice, 1 April, 1875. Resigned, 25 May, 1899.
T. B. Gillies, appointed, 3 Mar., 1875. Died, 26 July, 1889.
J. S. Williams, appointed, 3 Mar., 1875.
J. E. Denniston, appointed, 11 Feb., 1889.
E. T. Conolly, appointed, 19 Aug., 1889.
Hon. Sir P. A. Buckley, K.C.M.G., appointed, 20 Dec., 1895. Died, 18 May, 1896.
W. B. Edwards, appointed, 11 July, 1896.
F. W. Pennefather, appointed temporarily, 25 April, 1898. Resigned, 24 April, 1899.
Hon. Sir Robert Stout, K.C.M.G., appointed Chief Justice, 22 June, 1899.
J. C. Martin, acting Judge, appointed, 12 April, 1900. Resigned, 4 Dec., 1900.
Theophilus Cooper, appointed, 21 Feb., 1901.
Willoughby Shortland, Colonial Secretary, from 3 May, 1841, to 31 Dec., 1843; succeeded by Mr. Sinclair.
Francis Fisher, Attorney-General, from 3 May to 10 Aug., 1841; succeeded by Mr. Swainson.
George Cooper, Colonial Treasurer, from 3 May, 1841, to 9 May, 1842; succeeded by Mr. Shepherd.
William Swainson, Attorney-General, from 10 Aug., 1841, to 7 May, 1856.
Alexander Shepherd, Colonial Treasurer, from 9 May, 1842, to 7 May, 1856.
Andrew Sinclair, Colonial Secretary, from 6 Jan., 1844, to 7 May, 1856.
[The three gentlemen last mentioned were nominated by Her late Majesty as ex officio members of the Executive Council. Two of them, the Colonial Secretary and the Colonial Treasurer, were not members of the General Assembly, opened for the first time 27th May, 1854, but all three remained in office until the establishment of Responsible Government.]
James Edward FitzGerald, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 14 June to 2 Aug., 1854.
Henry Sewell, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 14 June to 2 Aug., 1854.
Frederick Aloysius Weld, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 14 June to 2 Aug., 1854.
Francis Dillon Bell, M.L.C., without portfolio, from 30 June to 11 July, 1854.
Thomas Houghton Bartley, M.L.C., without portfolio, from 14 July to 2 Aug., 1854.
Thomas Spencer Forsaith, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 31 Aug. to 2 Sept., 1854.
Edward Jerningham Wakefield, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 31 Aug. to 2 Sept., 1854.
William Thomas Locke Travers, M.H.R., without portfolio, 31 Aug. to 2 Sept., 1854.
James Macandrew, M.H.R., without portfolio, from 31 Aug. to 2 Sept., 1854.
| Parliament. | Date of Opening of Sessions. | Date of Prorogation. |
|---|---|---|
| First (dissolved 15th September, 1855) | 27 May, 1854 31 August, 1854 8 August, 1855 | 9 August, 1854. 16 September, 1854. 15 September, 1855. |
| Second (dissolved 5th November, 1860) | 15 April, 1856 (No session in 1857) 10 April, 1858 (No session in 1859) 30 July, 1860 | 16 August, 1856. 21 August, 1858. 5 November, 1860. |
| Third (dissolved 27th January, 1866) | 3 June, 1861 7 July, 1862 19 October, 1863 24 November, 1864 26 July, 1865 | 7 September, 1861. 15 September, 1862. 14 December, 1863. 13 December, 1864. 30 October, 1865. |
| Fourth (dissolved 30th December, 1870) | 30 June, 1866 9 July, 1867 9 July, 1868 1 June, 1869 14 June, 1870 | 8 October, 1866. 10 October, 1867. 20 October, 1868. 3 September, 1869. 13 September, 1870. |
| Fifth (dissolved 6th December, 1875) | 14 August, 1871 16 July, 1872 15 July, 1873 3 July, 1874 20 July, 1875 | 16 November, 1871. 25 October, 1872. 3 October, 1873 31 August, 1874. 21 October, 1875. |
| Sixth (dissolved 15th August, 1879) | 15 June, 1876 19 July, 1877 26 July, 1878 11 July, 1879 | 31 October, 1876. 10 December, 1877. 2 November, 1878. 11 August, 1879. |
| Seventh (dissolved 8th November, 1881) | 24 September, 1879 28 May, 1880 9 June, 1881 | 19 December, 1879. 1 September, 1880. 24 September, 1881. |
| Eighth (dissolved 27th June, 1884) | 18 May, 1882 14 June, 1883 5 June, 1884 | 15 September, 1882. 8 September, 1883. 24 June, 1884. |
| Ninth (dissolved 15th July, 1887) | 7 August, 1884 11 June, 1885 13 May, 1886 26 April, 1887 | 10 November, 1884. 22 September, 1885. 18 August, 1886. 10 July, 1887. |
| Tenth (dissolved 3rd October, 1890) | 6 October, 1887 10 May, 1888 20 June, 1889 19 June, 1890 | 23 December, 1887. 31 August, 1888. 19 September, 1889. 18 September, 1890. |
| Eleventh (dissolved 8th November, 1893) | 23 January, 1891 11 June, 1891 23 June, 1892 22 June, 1893 | 31 January, 1891. 25 September, 1891. 12 October, 1892. 7 October, 1893. |
| Twelfth (dissolved 14th November, 1896) | 21 June, 1894 20 June, 1895 11 June, 1896 | 24 October, 1894. 2 November, 1895. 19 October, 1896. |
| Thirteenth (dissolved 15th November, 1902) | 7 April, 1897 23 September, 1897 24 June, 1898 23 June, 1899 | 12 April, 1897. 22 December, 1897. 5 November, 1898. 24 October, 1899. |
| Fourteenth (dissolved 12th November, 1902) | 22nd June, 1900 1st July, 1901 1st July, 1902 | 22nd October, 1900. 8th November, 1901. 4th October, 1902. |
| Name of Ministry. | Assumed Office. | Retired. |
|---|---|---|
* Owing to the death of the Premier, the Hon. J. Ballance, on 27th April, 1893. | ||
| 1. Bell-Sewell | 7 May, 1856 | 20 May, 1856. |
| 2. Fox | 20 May, 1856 | 2 June, 1856. |
| 3. Stafford | 2 June, 1856 | 12 July, 1861. |
| 4. Fox | 12 July, 1861 | 6 August, 1862. |
| 5. Domett | 6 August, 1862 | 30 October, 1863. |
| 6. Whitaker-Fox | 30 October, 1863 | 24 November, 1864. |
| 7. Weld | 24 November, 1864 | 16 October, 1865. |
| 8. Stafford | 16 October, 1865 | 28 June, 1869. |
| 9. Fox | 28 June, 1869 | 10 September, 1872. |
| 10. Stafford | 10 September, 1872 | 11 October, 1872. |
| 11. Waterhouse | 11 October, 1872 | 3 March, 1873. |
| 12. Fox | 3 March, 1873 | 8 April, 1873. |
| 13. Vogel | 8 April, 1873 | 6 July, 1875. |
| 14. Pollen | 6 July, 1875 | 15 February, 1876. |
| 15. Vogel | 15 February, 1876 | 1 September, 1876. |
| 16. Atkinson | 1 September, 1876 | 13 September, 1876. |
| 17. Atkinson (reconstituted) | 13 September, 1876 | 13 October, 1877. |
| 18. Grey | 15 October, 1877 | 8 October, 1879. |
| 19. Hall | 8 October, 1879 | 21 April, 1882. |
| 20. Whitaker | 21 April, 1882 | 25 September, 1883. |
| 21. Atkinson | 25 September, 1883 | 16 August, 1884. |
| 22. Stout-Vogel | 16 August, 1884 | 28 August, 1884. |
| 23. Atkinson | 28 August, 1884 | 3 September, 1884. |
| 24. Stout-Vogel | 3 September, 1884 | 8 October, 1887. |
| 25. Atkinson | 8 October, 1887 | 24 January, 1891. |
| 26. Ballance | 24 January, 1891 | 1 May, 1893.* |
| 27. Seddon | 1 May, 1893. | |
| Name of Premier. |
|---|
| Henry Sewell. |
| William Fox. |
| Edward William Stafford. |
| William Fox. |
| Alfred Domett. |
| Frederick Whitaker. |
| Frederick Aloysius Weld. |
| Edward William Stafford. |
| William Fox. |
| Hon. Edward William Stafford. |
| George Marsden Waterhouse. |
| Hon. William Fox. |
| Hon. Julius Vogel, C.M.G. |
| Daniel Pollen, M.L.C. |
| Sir Julius Vogel, K.C.M.G. |
| Harry Albert Atkinson. |
| Harry Albert Atkinson (Ministry reconstituted). |
| Sir George Grey, K.C.B. |
| Hon. John Hall. |
| Frederick Whitaker, M.L.C. |
| Harry Albert Atkinson. |
| Robert Stout. |
| Harry Albert Atkinson. |
| Sir Robert Stout, K.C.M.G. |
| Sir Harry Albert Atkinson, K.C.M.G. |
| John Ballance. |
| Rt. Hon. Richard John Seddon, P.C. |
Table of Contents
| Name of Speaker. | Date of Appointment. | Date of Retirement or Death. |
|---|---|---|
| Hon. William Swainson | 16 May, 1854 | 8 August, 1855. |
| Hon. Frederick Whitaker | 8 August, 1855 | 12 May, 1856. |
| Hon. Thomas Houghton Bartley | 12 May, 1856 | 1 July, 1868. |
| Hon. Sir John Larkins Cheese Richardson, Kt. | 1 July, 1868 | 14 June, 1879. |
| Hon. Sir William Fitzherbert, K.C.M.G. | 14 June, 1879 | 23 January, 1891. |
| Hon. Sir Harry Albert Atkinson, K.C.M.G. | 23 January, 1891 | 28 June, 1892. |
| Hon. Sir Henry John Miller | 8 July, 1892. | |
| 6 October, 1897. |
Table of Contents
| Name of Speaker. | Date of Election. | Date of Retirement. |
|---|---|---|
| Sir Charles Clifford, Bart. | 26 May, 1854 | |
| 15 April, 1856 | 3 June, 1861. | |
| Sir David Monro, Kt. Bach. | 3 June, 1861 | |
| 30 June, 1866 | 13 Sept., 1870. | |
| Sir Francis Dillon Bell, K.C.M.G., C.B. | 14 August, 1871 | 21 October, 1875. |
| Sir William Fitzherbert, K.C.M.G. | 15 June, 1876 | 13 June, 1879. |
| Sir George Maurice O'Rorke, Kt. Bach. | 11 July, 1879 | |
| 24 September, 1879 | ||
| 18 May, 1882 | ||
| 7 August, 1884 | ||
| 6 October, 1887 | 3 October, 1890. | |
| Hon. Major William Jukes Steward | 23 January, 1891 | 8 November, 1893. |
| Hon. Sir George Maurice O'Rorke, Kt. Bach. | 21 June, 1894 | |
| 6 April, 1897. | ||
| 22 June, 1900. | 12 November, 1902. |
Table of Contents
| Country represented. | Office held. | Name. | Place of Residence. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria-Hungary | Consul | E. Langguth | Auckland. |
| Belgium | Consul - General for Australia and Fiji | Edouard Pollet | Melbourne. |
| Belgium | Consul | Hon. Charles John Johnston | Wellington. |
| Belgium | Consul | Joseph James Kinsey | Christchurch. |
| Belgium | Consul | John Burns | Auckland. |
| Belgium | Consul | George Lyon Denniston | Dunedin. |
| Brazil | Vice-Consul | A. H. Miles | Wellington. |
| Chili | Consul | William Brown | Sydney. |
| Denmark | Consul (for North Island); Chief Consular Officer in New Zealand | Francis Henry Dillon Bell | Wellington. |
| Denmark | Consul (for South Island) | Emil Christian Skog | Christchurch. |
| Denmark | Vice-Consul | Frederick Ehrenfrid Baume | Auckland. |
| Denmark | Vice-Consul | William Edward Perry | Hokitika. |
| Denmark | Vice-Consul | Peter Jorgen Wilhelm Holsted | Dunedin. |
| France | Consul (for New Zealand) | Count Louis Antoine Marie Joseph Henri De Courte | Auckland. |
| France | Hon. Vice-Consul | Percival Clay Neill | Dunedin. |
| France | Consular Agent | George Humphreys | Christchurch. |
| France | Consular Agent | George Dunnet | Auckland. |
| German Empire | Consul-General for Commonwealth of Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji | Paul Von Buri | Sydney. |
| German Empire | Consul | Carl Seegner | Auckland. |
| German Empire | Consul | Bendix Hallenstein | Dunedin. |
| German Empire | Consul | Philip Kippenberger | Christchurch. |
| German Empire | Consul | Friedrich August Krull | Wanganui. |
| German Empire | Vice-Consul | Eberhard Focke | Wellington. |
| Hawaiian Islands | Consul-General (for Australasia) | W. E. Dixon | Sydney. |
| Hawaiian Islands | Consul, Acting | George Dunnet | Auckland. |
| Italy | Consul-General for Commonwealth of Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji | C. Bertola | Melbourne. |
| Italy | Consular Agent | Thomas Wallace | Christchurch |
| Italy | Consular Agent | George Fisher | Wellington. |
| Italy | Consular Agent | Edward Bowes Cargill | Dunedin. |
| Italy | Consular Agent | Geraldo Giuseppe Perotti | Greymouth. |
| Italy | Consular Agent | Richard A. Carr | Auckland. |
| Japan | Consul | A. S. Aldrich | Wellington. |
| Liberia | Consul | A.M. Meyers | Auckland. |
| Netherlands | Consul - General for Commonwealth of Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji | W. L. Bosschart | Melbourne. |
| Netherlands | Consul | Hon. Charles John Johnston | Wellington. |
| Netherlands | Vice-Consul | Edward Bowes Cargill | Dunedin. |
| Netherlands | Vice-Consul | Ambrose Millar | Auckland. |
| Netherlands | Vice-Consul | Harold Featherston Johnston | Wellington. |
| Netherlands | Vice-Consul | G. de Vries | Christchurch. |
| Portugal | Consul | John Duncan | Wellington. |
| Portugal | Vice-Consul | Henry Rees George | Auckland. |
| Portugal | Vice-Consul | Ian G. Duncan | Wellington. |
| Portugal | Vice-Consul | Charles William Rattray | Dunedin. |
| Russia | Consul-General | Michel Oustinow | Melbourne. |
| Russia | Consul | Nicolas Passek | Melbourne. |
| Spain | Honorary Consul (with jurisdiction over Australia and New Zealand) | Henry Cave | Melbourne. |
| Spain | Vice-Consul | (Vacant) | Christchurch. |
| Spain | Honorary Vice-Consul | Alexander H. Turnbull | Wellington. |
| Sweden and Norway | Consul | Arthur Edward Pearce | Wellington. |
| Sweden and Norway | Vice-Consul | Frank Graham | Christchurch. |
| United States | Consul (for New Zealand) | Frank Dillingham | Auckland. |
| United States | Vice-Consul | Leonard A. Bachelder | Auckland. |
| United States | Consular Agent | Robert Pitcaithley | Christchurch. |
| United States | Consular Agent | John Duncan | Wellington. |
| United States | Consular Agent | Frederick Orlando Bridgman | Dunedin. |
The Hon. W. P. Reeves, Westminster Chambers, 13, Victoria Street, S.W. Secretary—Walter Kennaway, C.M.G.
Table of Contents
(DOWNING STREET, S.W., LONDON), WITH DATES OF APPOINTMENT.
Principal Secretary of State for the Colonies—The Right Hon. Joseph Chamberlain, M.P., 28th June, 1895.
Under-Secretaries: Parliamentary—The Right Hon. the Earl of Onslow, G.C.M.G., November, 1900. Permanent—Sir Montague Frederick Ommaney, K.C.B., K.C.M.G., 1900.
Assistant Under-Secretaries: Frederick Graham, C.B.; Charles P. Lucas, C.B.; H. B. Cox (Legal); and Reginald L. Antrobus, C.B.
Table of Contents
Buller, Sir Walter Lawry, 1886.
Hall, Hon. Sir John, 1882.
Hector, Sir James, 1887.
Perceval, Sir Westby Brook, 1894.
Stout, Hon. Sir Robert, 1886.
Ward, Hon. Sir Joseph George, 1901.
Campbell, Sir John Logan, 1902.
Miller, Hon. Sir Henry John, 1901.
O'Rorke, Hon. Sir George Maurice, 1880.
Prendergast, Hon. Sir James, 1881.
Russell, Sir William Russell, 1902.
Steward, Hon. Sir William Jukes, 1902.
Cradock, Major Montagu, 1901.
Davies, Brevet-Colonel R. H., 1901.
Newall, Brevet-Colonel Stewart, 1901.
Porter, Colonel T. W., 1902.
Robin, Brevet-Colonel Alfred William, 1901.
Bauchop, Major A., 1902.
Cadman, Hon. Alfred Jerome, 1901.
Gudgeon, Lieut.-Colonel Walter Edward, 1890.
Jowsey, Lieut.-Colonel Thomas, 1900.
Kennaway, Walter, 1897.
Richardson, Hon. Edward, 1879.
Roberts, John, 1891.
Walker, Hon. William Campbell, 1901.
Abbott, Major F. W., 1902.
Bartlett, Major E., 1902.
Hickey, Lieutenant D. A., 1902.
Hughes, Captain J. G., 1900.
Major, Major C. T., 1900.
Polson, Major D., 1900.
Stevenson, Captain R., 1902.
Todd, Captain D. J. M., 1900.
Townley, Lieutenant W. V., 1902.
Tudor, Lieutenant P. L., 1902.
Walker, Captain G. H., 1901.
Adamson, Thomas, 1869.
Black, Solomon, 1869.
Biddle, Benjamin, 1869.
Hill, George, 1869.
Lingard, William, 1869.
Mace, Francis Joseph, 1869.
Maling, Christopher, 1869.
Mair, Gilbert, 1870.
Preece, George, 1869.
Roberts, John Mackintosh, 1869.
Rodriguez, Antonio, 1869.
Shepherd, Richard, 1869.
Baigent, Private Ivanhoe.
Black, Sergeant-Major G. C.
Burr, Sergeant-Major W. T.
Cassidy, Sergeant W.
Fletcher, Sergeant-Major W. H.
Free, Private A.
Kent, Sergeant W.
Langham, Sergeant-Major J.
Lockett, Sergeant-Major E. B.
Pickett, Sergeant-Major M.
Rouse, Farrier-Sergeant G.
Travers, Quartermaster-Sergeant.
Wade, Private, H. B.
White, Sergeant-Major H.
By despatch from the Secretary of State for the Colonies, dated Downing Street, 15th June, 1893, His Excellency the Governor was apprised that the title of “Honourable,” appertaining to Members of the Executive and Legislative Councils in colonies possessing Responsible Government, whether confined to duration of office or continued for life, was approved by Her late Majesty for use and recognition throughout her dominions, either during office or for life, as the case may be.
By further despatch of 10th March, 1894, the Secretary of State announced that he was prepared in future to submit for the approval of the Sovereign the recommendation of the Governor of any colony having Responsible Government that the President of the Legislative Council or the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly may, on quitting office after three years' service in their respective offices, be permitted to retain the title of “Honourable.” This title is now held by Sir G. M. O'Rorke and Major Sir William Jukes Steward.
Besides the Members of the Executive and Legislative Councils, the following ex-Ministers are allowed, as such, to retain the title of “Honourable”: Bryce, John, 1884; Cadman, A. J., 1901; Fergus, Thomas, 1891; Hislop, Thomas W., 1891; Johnston, Walter W., 1884; Mitchelson, Edwin, 1891; Oliver, Richard, 1884; Reeves, William P., 1896; Richardson, George F., 1891; Thompson, Thomas, 1900; Tole, Joseph A., 1888.
RANFURLY, His Excellency The Right Honourable Sir Uchter John Mark, fifth Earl of (Ireland, 1831), Viscount Northland, (1791), Baron Welles (1781), Lord-in-Waiting to Her late Majesty (1895–97), Knight Grand Cross of the Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George; Knight of Justice and Member of the Council of the Order of St. John of Jerusalem; son of third earl, brother of fourth earl; born 14th August, 1856; succeeded, 1875; married, 1880, the Honourable Constance Elizabeth, only child of seventh Viscount Charlemont, C.B. Living issue: One son (Viscount Northland), two daughters (Ladies Constance and Eileen Knox). Appointed 6th April, 1897, and assumed office 10th August, 1897, as Governor and Commander-in-Chief in and over His Majesty's Colony of New Zealand and its Dependencies. Salary, £5,000. Allowance on account of establishment £1,500, and travelling-expenses £500 per annum. The allowance is not payable for any period during which the Governor is absent from the colony. Residences: Northland House, Dungannon, Ireland; Government House, Wellington; Government House, Auckland.
Private Secretary: Dudley Alexander (Major “The Prince of Wales's Own,” West Yorkshire Regiment).
Assistant Private Secretary: The Honourable Charles Edward Hill-Trevor.
Aide-de-Camp: Viscount Northland (Coldstream Guards).
ADMINISTRATOR OF (([0-9]+)).—The Chief Justice, appointed under a dormant Commission.
Table of Contents
THE annual appropriation for Ministers' salaries is fixed by statute at the sum of £8,900, of which £1,600 is for the Prime Minister, £1,300 for the Minister for Railways, and £1,000 for each of six other Ministers. All Ministers to whom salaries are appropriated are members of the Executive Council, holding one or more of the offices specified by law. Members of the Executive Council travelling within the colony on public service are entitled to allowance not exceeding £1 10s. per day when so engaged, but not during the time a Minister is attending a session of the General Assembly. The members of the Executive Council to whom salaries are payable, and who are not otherwise provided with residences at the seat of Government, are entitled to an allowance in lieu thereof at the rate of £200 a year.
The Executive Council now consists of:—
His Excellency the GOVERNOR presiding.
Rt. Hon. Richard John Seddon, P.C., Prime Minister, Colonial Treasurer, Minister of Defence, and Minister of Labour.
Hon. Sir Joseph George Ward, K.C.M.G., Minister for Railways, Colonial Secretary, Postmaster-General and Commissioner of Electric Telegraphs, Minister of Industries and Commerce, and Minister of Public Health.
Hon. James Carroll, Native Minister and Commissioner of Stamp Duties.
Hon. William Campbell Walker, C.M.G., Minister of Education and Minister of Immigration.
Hon. William Hall-Jones, Minister for Public Works and Minister of Marine.
Hon. James McGowan, Minister of Justice and Minister of Mines. (23rd January, 1900.)
Hon. Thomas Young Duncan, Minister of Lands and Minister for Agriculture. (2nd July, 1900.)
Hon. Charles Houghton Mills, Commissioner of Trade and Customs. (29th October, 1900.)
(Vacant) Attorney-General.
Clerk of the Executive Council—Alexander James Willis
Table of Contents
THE number of members at present constituting the Legislative-Council is forty-one. The number cannot be less than ten, but is otherwise unlimited. Prior to 1891 Councillors summoned by the Governor held their appointments for life; but on the 17th of September of that year an Act was passed giving the Council power to elect its own Speaker for a period of five years, and making future appointments to the Council tenable for seven years only, to be reckoned from the date of the writ of summons of the Councillor's appointment, though every such Councillor may be reappointed. The qualifications are that the person to be appointed be of the full age of twenty-one years, and a subject of His Majesty, either natural-born or naturalised by or under any Act of the Imperial Parliament or by or under any Act of the General Assembly of New Zealand. All contractors to the public service to an amount of over £50 and Civil servants of the colony are ineligible as Councillors. Payment of Councillors is at the rate of £200 a year, payable monthly. Actual travelling-expenses to and from Wellington are also allowed. A deduction of £1 5s. per sitting day is made in case of an absence, except through illness or other unavoidable cause. Under “The Legislative Council Act, 1891,” a seat is vacated by any member of the Council: (1.) If he takes any oath or makes any declaration or acknowledgment of allegiance, obedience, or adherence to any foreign Prince or Power; or (2), if he does, or concurs in, or adopts any act whereby he may become a subject or citizen of any foreign State or Power, or is entitled to the rights, privileges, or immunities of a subject of any foreign State or Power; or (3), if he is a bankrupt, or compounds with his creditors under any Act for the time being in force; or (4), if he is a public defaulter, or is attainted of treason, or is convicted of felony or any infamous crime; or (5), if he resigns his seat by writing under his hand addressed to and accepted by the Governor; or (6), if for more than one whole session of the General Assembly he fails, without permission of the Governor notified to the Council, to give his attendance in the Council. By the Standing Orders of the Council, the presence of one-fourth of the members of the Council, exclusive of those who have leave of absence, is necessary to constitute a meeting for the exercise of its powers. This rule, however, may be altered from time to time by the Council.
The ordinary sitting-days are Tuesdays, Wednesdays, Thursdays, and Fridays, from 2.30 p.m. to 5 p.m., resuming again at 7.30 p.m. when necessary.
| Speaker—The Hon. Sir HENRY JOHN MILLER, Kt. Chairman of Committees—The Hon. WILLIAM COWPER SMITH. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name. | Provincial District. | Date of Appointment. |
| *Life Members. | ||
| Arkwright, the Hon. Francis | Wellington. | 13 December, 1902. |
| Baillie, the Hon. William Douglas Hall | Marlborough. | 8 March, 1861.1 |
| Baldey, the Hon. Alfred | Otago. | 18 March, 1903. |
| Bolt, the Hon. William Mouat | Otago. | 16 October, 1899. |
| Bowen, the Hon. Charles Christopher | Canterbury. | 23 January, 1891.1 |
| Cadman, the Hon. Alfred Jerome, C.M.G. | Auckland. | 21 December, 1899. |
| Carncross, the Hon. Walter Charles Frederick | Taranaki. | 18 March, 1903. |
| Feldwick, the Hon. Henry | Otago. | 16 October, 1899. |
| Fraser, the Hon. Francis Humphris | Wellington. | 22 June, 1899. |
| Gourley, the Hon. Hugh | Dunedin. | 22 June, 1899. |
| Harris, the Hon. Benjamin | Auckland. | 3 February, 1897. |
| Holmes, the Hon. James | Westland. | 18 April, 1902. |
| Jenkinson, the Hon. John Edward | Canterbury. | 6 June, 1900. |
| Johnston, the Hon. Charles John | Wellington. | 23 January, 1891.1 |
| Jones, the Hon. George | Otago. | 13 December, 1902. |
| Kelly, the Hon. Thomas | Taranaki. | 16 October, 1899. |
| Kelly, the Hon. William | Auckland. | 3 February, 1897. |
| Kenny, the Hon. Courtney William Aylmer Thomas | Marlborough. | 15 May, 1885.1 |
| Louisson, the Hon. Charles | Canterbury. | 22 December, 1900. |
| McLean, the Hon. George | Otago. | 19 December, 1881.1 |
| Marshall, the Hon. James | Westland. | 18 April, 1902. |
| Miller, the Hon. Sir Henry John, Kt. (Speaker) | Otago. | 8 July, 1865.1 |
| Montgomery, the Hon. William | Canterbury. | 16 October, 1899. |
| Ormond, the Hon. John Davies | Hawke's Bay. | 20 January, 1891.1 |
| Peacock, the Hon. John Thomas | Canterbury. | 9 October, 1877.1 |
| Pinkerton, the Hon. David | Otago. | 3 February, 1897. |
| Pitt, the Hon. Albert, Lieut.-Colonel | Nelson. | 23 December, 1899. |
| Reeves, the Hon. Richard Harman Jeffares | Nelson. | 13 December, 1902. |
| Rigg, the Hon. John | Wellington. | 6 June, 1900. |
| Scotland, the Hon. Henry | Taranaki. | 24 February, 1868.1 |
| Smith, the Hon. Alfred Lee | Otago. | 18 June, 1898. |
| Smith, the Hon. William Cowper | Hawke's Bay. | 13 December, 1902. |
| Stevens, the Hon. Edward Cephas John | Canterbury. | 7 March, 1882.1 |
| Taiaroa, the Hon. Hori Kerei | Otago. | 15 May, 1885.1 |
| Thompson, the Hon. Thomas | Auckland. | 18 March, 1903. |
| Tomoana, the Hon. Henare | Hawke's Bay. | 24 June, 1898. |
| Trask, the Hon. Francis | Nelson. | 18 March, 1903. |
| Twomey, the Hon. Jeremiah Matthew | Canterbury. | 18 June, 1898. |
| Walker, the Hon. Lancelot | Canterbury. | 15 May, 1885.1 |
| Walker, the Hon. William Campbell, C. M. G. | Canterbury | 14 October, 1899. |
| Williams, the Hon. Henry | Auckland | 7 March, 1882.1 |
Clerk of Parliaments, Clerk of the Legislative Council, and Examiner of Standing Orders upon Private Bills—Leonard Stowe.
Clerk-Assistant—Arthur Thomas Bothamley.
Second Clerk-Assistant—George Moore.
Interpreter—Henry S. Hadfield.
The number of members constituting the House of Representatives is eighty—seventy-six Europeans and four Maoris. This number was fixed by the Act of 1900, which came for the first time into practical operation at the general election of 1902. Previously (from 1890) the House consisted of seventy-four members, seventy Europeans and four Maoris; and previously to that (from 1881) of ninety-five members, ninety-one Europeans and four Maoris. The North Island at present returns thirty-eight European members, and the Middle Island thirty-eight. The Cities of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin return each three members, and all other electoral districts one each. The elections are triennial, except in the case of a dissolution by the Governor. Every registered elector, being of the male sex, and free from any of the disqualifications mentioned in ‘The Electoral Act, 1902,’ is eligible for membership. All contractors to the public service of New Zealand to whom any public money above the sum of £50 is payable, directly or indirectly, in any one financial year, as well as the Civil servants of the colony, are incapable being elected as, or of sitting or voting as, members. The payment made to members of the House of Representatives is £25 per month, amounting to £300 per annum, subject to certain deductions for absence during session not due to sickness or other unavoidable cause. Travelling-expenses to and from Wellington are also allowed. This scale of payment came into force on the 7th November, 1901, under the provisions of “The Payment of Members Act, 1901.” Twenty members, inclusive of the Speaker, constitute a quorum. Unless otherwise ordered, the sitting-days of the House are Tuesdays, Wednesdays, Thursdays, and Fridays, from 2.30 p.m. to 5.30 p.m., resuming at 7.30 p.m. Order of admission to the Speaker's Gallery is by ticket obtained from the Speaker. The Strangers' Gallery is open free to the public.
| Speaker— | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chairman of Committees— | ||
| Name. | Electoral District. | Date of Notification of Return of Writ. |
| For European Electorates. | ||
| Aitken, John Guthrie Wood | City of Wellington | 10 December, 1902. |
| Alison, Ewen William | Waitemata | 10 December, 1902. |
| Allen, Edmund Giblett | Chalmers | 10 December, 1902. |
| Allen, James | Bruce | 10 December, 1902. |
| Arnold, James Frederick | City of Dunedin | 10 December, 1902. |
| Barber, William Henry Peter | Newtown | 10 December, 1902. |
| Banme, Frederick Ehrenfried | City of Auckland | 10 December, 1902. |
| Bedford, Harry Dodgshun | City of Dunedin | 10 December, 1902. |
| Bennet, James | Tuapeka | 10 December, 1902. |
| Bollard, John | Eden | 10 December, 1902. |
| Buchanan, Walter Clark | Wairarapa | 10 December, 1902. |
| Buddo, David | Kaiapoi | 10 December, 1902. |
| Carroll, Hon. James | Waiapu | 10 December, 1902. |
| Colvin, James | Buller | 10 December, 1902. |
| Davey, Thomas Henry | City of Christchurch | 10 December, 1902. |
| Duncan, Hon. Thomas Young | Oamaru | 10 December, 1902. |
| Dothie, John | City of Wellington | 10 December, 1902. |
| Ell, Henry George | City of Christchurch | 10 December, 1902. |
| Field, William Hughes | Otaki | 10 December, 1902. |
| Fisher, George | City of Wellington | 10 December, 1902. |
| Flatman, Frederick Robert | Geraldine | 10 December, 1902. |
| Fowlds, George | Grey Lynn | 10 December, 1902. |
| Fraser, Alfred Levavasour Durell | Napier | 10 December, 1902. |
| Fraser, William | Wakatipu | 10 December, 1902. |
| Graham, John | City of Nelson | 10 December, 1902. |
| Guinness, Arthur Robert | Grey | 10 December, 1902. |
| Hall, Charles | Waipawa | 10 December, 1902. |
| Hall-Jones, Hon. William | Timaru | 10 December, 1902. |
| Hanan, Josiah Alfred | Invercargill | 10 December, 1902. |
| Harding, Alfred Ernest | Kaipara | 10 December, 1902. |
| Hardy, Charles Albert Creery | Selwyn | 10 December, 1902. |
| Herdman, Alexa der Laurence | Mount Ida | 10 December, 1902. |
| Herries, William Herbert | Bay of Plenty | 10 December, 1902. |
| Hogg, Alexander Wilson | Masterton | 10 December, 1902. |
| Houston, Robert Morrow | Bay of Islands | 10 December, 1902. |
| Jennings, William Thomas | Egmont | 10 December, 1902. |
| Kidd, Alfred | City of Auckland | 10 December, 1902. |
| Kirkbride, Matthew Middlewood | Manukau | 10 December, 1902. |
| Lang, Frederic William | Waikato | 10 December, 1902. |
| Laurenson, George | Lyttelton | 10 December, 1902. |
| Lawry, Frank | Parnell | 10 December, 1902. |
| Lethbridge, Frank Yates | Oroua | 10 December, 1902. |
| Lewis, Charles | Courtenay | 10 December, 1902. |
| McGowan, Hon. James | Thames | 10 December, 1902. |
| McKenzie, Roderick | Motueka | 10 December, 1902. |
| Mackenzie, Thomas | Waikouaiti | 10 December, 1902. |
| McLachlan, John | Ashburton | 10 December, 1902. |
| McNab, Robert | Mataura | 10 December, 1902. |
| Major, Charles Edwin | Hawera | 10 December, 1902. |
| Mander, Francis | Marsden | 10 December, 1902. |
| Massey, William Ferguson | Franklin | 10 December, 1902. |
| Millar, John Andrew | City of Dunedin | 10 December, 1902. |
| Mills, Hon. Charles Houghton | Wairau | 10 December, 1902. |
| Moss, Edward George Britton | Ohmemuri | 10 December, 1902. |
| O'Meara, John | Pahiatua | 10 December, 1902. |
| Reid, Donald (jun.) | Taieri | 10 December, 1902. |
| Remington, Arthur Edward | Rangitikei | 10 December, 1902. |
| Rhodes, Robert Heaton | Ellesmere | 10 December, 1902. |
| Russell, Sir William Russell, Kt. Bach. | Hawke's Bay | 10 December, 1902. |
| Rutherford, Andrew William | Hurunui | 10 December, 1902. |
| Seddon, Rt. Hon. Richard John, P.C. | Westland | 10 December, 1902. |
| Sidey, Thomas Kay | Caversham | 10 December, 1902. |
| Smith, Edward Metcalf | Taranaki | 10 December, 1902. |
| Steward, Hon. Sir William Jukes, Kt. Bach. | Waitaki | 10 December, 1902. |
| Symes, Walter | Patea | 10 December, 1902. |
| Tanner, William Wilcox | Avon | 10 December, 1902. |
| Taylor, Thomas Edward | City of Christchurch | 10 December, 1902. |
| Thomson, James William | Clutha | 10 December, 1902. |
| Thomson, John Charles | Wallace | 10 December, 1902. |
| Vile, Job | Manawatu | 10 December, 1902. |
| Ward, Hon. Sir Joseph George, K.C.M.G. | Awarua | 10 December, 1902. |
| Wilford, Thomas Mason | Hutt | 10 December, 1902. |
| Willis, Archibald Dudingston | Wanganui | 10 December, 1902. |
| Witheford, Joseph Howard | City of Auckland | 10 December, 1902. |
| Witty, George | Riccarton | 10 December, 1902. |
| Wood, William Thomas | Palmerston | 10 December, 1902. |
| For Maori Electorates. | Day of Election. | |
| Heke, Hone | Northern Maori | 22 December, 1902. |
| Kaihau, Henare | Western Maori | 22 December, 1902. |
| Parata, Tame | Southern Maori | 22 December, 1902. |
| Pere, Wiremu | Eastern Maori | 22 December, 1902. |
Clerk of House of Representatives—H. Otterson.
Clerk-Assistant—A. J. Rutherfurd.
Second Clerk-Assistant—A. F. Lowe.
Sergeant-at-Arms—Major T. V. Shepherd.
Reader and Clerk of Bills and Papers—E. W. Kane.
Chief Hansard Reporter—Silas Spragg.
Interpreters—L. M. Grace, D. F. G. Barclay.
Clerk of Writs—H. Pollen.
Deputy Clerk of Writs—R. F. Lynch.
Chief Librarian—Charles Wilson.
Table of Contents
(1st April, 1903.)
Colonial Secretary—Hon. Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
Under-Secretary—Hugh Pollen
Chief Clerk—R. F. Lynch
Clerks—J. F. Andrews, A. R. Kennedy, F. A. de la Mare
Officer in Charge of Government Buildings—W. H. Hennah
Controller and Auditor-General—J. K. Warburton
Assistant Controller and Auditor—J. C. Gavin
Chief Clerk—L. C. Roskruge
Clerks—H. S. Pollen, W. G. Holdsworth, E. J. A. Stevenson, J. T. Dumbell, C. M. Georgeson, J. Skerrett, R. A. Gray
Cadets—C. E. Easton, G. V. Bogle
Cadette—E. A. Casey
Extra Clerks—D. C. Innes, J. Swift, A. E. Bybles, J. Ward, C. E. Briggs, E. E. Smythe, J. McC. Hamilton, T. S. Hamer, S. W. Thornton, G. G. Smith
Audit Officer, Agent-General's Office, London—C. F. W. Palliser
Audit Inspectors—P. P. Webb, A. H. Maclean, J. King, A. W. Eames, G. H. I. Easton, C. P. Johnson, H. A. Lamb, B. A. Meek, A. A. Bethune, J. H. Fowler
Registrar-General—E. J. Von Dadelszen
Chief Clerk and Deputy Registrar-General—G. Drury
Clerks—F. H. Machattie, W. W. Cook, Ben Keys
Index Clerk—S. Coffey
Government Printer, Stationery Office Manager, and Controller of Stamp Printing—John Mackay
Superintending Overseer—J. J. Gamble
Chief Clerk and Accountant—B. B. Allen
Clerk and Computer—N. B. K. Manley
Clerks—F. Barraud, J. W. Hall, R. Watts, A. Stace, A. Williams
Cadette—A. Paterson
Cadet—P. C. Jordan
Hansard Supervisor—M. F. Marks
Overseers—B. Wilson, J. F. Rogers
Overseer, Jobbing-room—G. Tattle
Night Foreman—D. Archibald
Readers—W. Fuller, H. S. Mountier, H. Lee, W. Sutherland
Overseer, Machine-room—J. Phillips
Sub-overseer, Machine-room—John Burns
Overseer, Binding Branch—W. Franklin
Sub-overseer, Binding Branch—G. H. Broad
Forewoman, Binding Branch—Miss O'Malley
Stamp Printer—H. Hume
Overseer, Lithographic Branch—D. Ross
Chief Draughtsman—G. N. Sturtevant
Stereotyper and Electrotyper—W.J. Kirk
Engineer—T. R. Barrer
Colonial Treasurer—Rt. Hon. R. J. Seddon, P.C.
Secretary to the Treasury, Receiver-General, Paymaster-General, and Registrar of New Zealand Consols—James B. Heywood
Accountant to the Treasury—Robert J. Collins
Cashier—C. E. Chittey
Corresponding Clerk—H. Blundell
Clerks—R. B. Vincent, W. E. Cooper, E. L. Mowbray, A. O. Gibbes, J. Holmes, H. N. W. Church, A. J. Morgan, T. J. Davis, F. H. Tuckey, H. Hawthorn, W. Wilson, G. C. Rodda, G. A. Fraser, E. Fisher
Cadets—W. Gillanders, J. Christie, W. L. Clapson, A. Hore, P. Dunstan
Cadettes—L. McIntosh, M. Ralston, D. M. Schramm, H. M. Batham, E. M. Taylor, E. A. C. Burrage, R. B. Banks
Officer for Payment of Imperial Pensions at Auckland—B. J. Daveney
Registrar and Actuary—George Leslie
Revising Barrister—L. G. Reid
Clerk—C. T. Benzoni
Registrar—J. Eman Smith
Chief Clerk—G. C. Fache
Clerks—F. M. Leckie, J. S. Lambert, R. S. Stokes, F. Twiss
Cadets—P. Cunningham, G. N. Morris
Deputy Registrars—
Auckland—S. Ruddock
Wellington—F. W. Mansfield, Registrar of Births, &c.
Christchurch—L. C. Williams, Registrar of Electors
Dunedin—Robert Hill
Invercargill—J. G. Petrie, Registrar of Electors
(In all other Pension Districts Clerks of the Magistrates' Courts are the Deputy Registrars)
Commissioner—John McGowan
Deputy Commissioner—G. F. C. Campell
Chief Clerk—F. J. M. D. Walmsley
Accountant—P. Heyes
Clerk in Charge—A. J. McGowan
Clerks—H. Nancarrow, D. R. Purdie, J. Stevenson, R. Hepworth, E. Randell, J. N. Grant, M. Fraser, J. Ferguson, H. S. Barron, C. E. J. Dowland, C. J. Lovatt
Minister of Justice—Hon. James McGowan
Under-Secretary—F. Waldegrave
Chief Clerk—C. B. Jordan
Translator—G. H. Davies
Clerks—C. E. Matthews, G. F. Dixon A. J. Thompson
Attorney-General—(vacant)
Solicitor-General—F. Fitchett, M.A., LL.D.
Assistant Law Officer—L. G. Reid
Law Draftsman—
Clerk—E. Y. Redward
Cadet—O. N. Gillespie
Registrar of Patents, Designs, and Trademarks—F. Waldegrave
Deputy Registrar—. C. Lewis
Clerk—Mary Eyre.
Cadet—J. T. Bishop
Chief Justice—
Wellington—Sir R. Stout, K.C.M.G.
Judges—
Wellington—W. B. Edwards, Theo. Cooper
Auckland—E. T. Conolly
Christchurch—J. E. Denniston
Dunedin—J. S. Williams
Wairarapa, Wanganui, New Plymouth, Hawera, and Palmerston North—C. C. Kettle
Nelson—H. W. Robinson
Ashburton, Timaru, Oamaru, Queenstown, Naseby, Lawrence, Invercargill, Hokitika, Greymouth, Westport, Reefton, and Kumara—C. D. R. Ward
Auckland—H. C. Brewer
New Plymouth—R. L. Stanford
Wanganui—C. C. Kettle
Napier—A. Turnbull
Gisborne—W. A. Barton
Wellington—D. G. A. Cooper
Nelson—H. W. Robinson
Blenheim—A. McArthur
Christchurch—A. R. Bloxam
Hokitika—V. G. Day
Dunedin—G. A. King
Invercargill—J. R. Colyer
Auckland—H. C. Brewer
Taranaki—A. H. Holmes
Hawke's Bay—A. Turnbull
Poverty Bay—W. A. Barton
Wellington—D. G. A. Cooper
Wairarapa—E. Rawson
Wanganui and Rangitikei—C. A. Barton
Nelson—W. Heaps
Westland North—E. C. Kelling
Central Westland—A. Askenbeck
Marlborough—J. Terry
Canterbury—A. R. Bloxam
Timaru—C. A. Wray
Westland—V. G. Day
Otago—G. A. King
Southland—J. R. Colyer
Auckland—Hon. J. A. Tole
New Plymouth—A. Standish
Gisborne—J. W. Nolan
Napier—H. A. Cornford
Wellington—F. H. D. Bell
Wanganui—S. T. Fitzherbert
Nelson—C. Y. Fell
Blenheim—R. McCallum
Christchurch—T. W. Stringer
Timaru—J. W. White
Dunedin—J. F. M. Fraser
Invercargill—T. M. Macdonald
Oamaru—A. G. Creagh
New Plymouth—A. Standish
Hawera—E. L. Barton
Wanganui and Palmerston North—S. T. Fitzherbert
Masterton—A. R. Bunny
Nelson—C. Y. Fell
Westport and Reefton—C. E. Harden
Hokitika—J. Park
Greymouth—M. Hannan
Timaru—J. W. White
Oamaru—J. G. Creagh
Queenstown—Wesley Turton
Invercargill—T. M. Macdonald
Auckland—H. W. Brabant
Pokeno, Waikato, &c.—H. W. Northcroft
Onehunga, &c.—T. Hutchison*
Russell, &c.—E. C. Blomfield
Tauranga, &c.—J. M. Roberts*
Thames, &c.—R. S. Bush*
Gisborne, &c.—W. A. Barton
New Plymouth—R. L. Stanford
Hawera, &c.—H. Eyre-Kenny
Wanganui, &c.—C. C. Kettle
Palmerston North, &c.—A. Greenfield
Wellington, &c.—W. R. Haselden
Wairarapa, &c.—W. P. James
Napier &c.—A. Turnbull
Nelson—H. W. Robinson*
Motueka, Collingwood, &c.—Wilson Heaps*
Blenheim, &c.—A. McArthur*
Christchurch, &c.—R. Beetham
Kaiapoi, &c.—H. W. Bishop
Timaru, &c.—C. A. Wray
Greymouth, Westport, &c.—R. S. Hawkins*
Hokitika, &c.—D. Macfarlane*
Dunedin, &c.—E. H. Carew* and C. C. Graham
Oamaru, &c.—J. Keddell*
Milton, &c.—G. Cruickshank*
Clyde, &c.—F. J. Burgess*
Naseby—J. McEnnis*
Invercargill, &c.—S. E. McCarthy*
Chatham Islands—R. S. Florance
Auckland—J. Lawson, J.P.
Wellington—J. Ashcroft, J.P.
Christchurch—G. L. Greenwood
Dunedin—C. C. Graham, S.M.
New Plymouth—A. H. Holmes
Hawera—A. Trimble
Wanganui—C. A. Barton
Palmerston North—W. Matravers
Masterton—E. Rawson
Nelson—C. H. Webb-Bowen
Hokitika—W. A. D. Banks
Kumara—T. M. Lawlor
Greymouth—B. Harper
Westport—E. C. Kelling
Reefton—A. Askenbeck
Timaru—T. Howley
Ashburton—T. W. Tayler
Oamaru—R. P. Ward
* Are also Wardens of Goldfields.
Invercargill—J. R. Colyer
Queenstown—A. A. Mair
Lawrence—A. M. Eyes
Naseby—F. Hart
Thames—J. Jordan
Coromandel—D. Banks
Paeroa—H. R. Bush
Waihi—E. W. Cave
Tauranga—W. A. Thom
Whangarei—T. Kirk
Havelock (Marlborough)—H. McArdle
Nelson—C. H. Webb-Bowen
Blenheim—John Terry
Motueka—H. E. Gilbert
Collingwood—W. Scale
Westport—E. C. Kelling
Charleston—R. V. McGlone
Reefton—A. Askenbeck
Ahaura—J. C. Malfroy
Greymouth—B. Harper
Kumara—T. M. Lawlor
Hokitika—W. A. D. Banks
Ashburton—T. W. Tayler
Naseby, &c.—F. Hart
Wyndham—D. Bogue
Clyde, Black's, and Alexandra—F. T. D. Jeffrey
Cromwell—E. D. Mosley
Queenstown and Arrowtown—A. A. Mair
Lawrence—A. M. Eyes
Gore—M. Foley
Riverton—A. G. Ashby
Auckland—H. G. Ralfe
Gisborne—G. J. Johnstone
Hamilton—W. Shanaghan
Napier—R. B. Mathias
Hastings—P. Skerrett
Wairoa—H. H. Carr
Stratford—J. B. Stoney
Dannevirke—S. Tansley
Marton, &c.—F. M. Deighton
Feilding—J. M. Rodgers
Wellington—A. D. Thomson
Christchurch—W. Martin
Lyttelton—J. Fitzgerald
Kaiapoi—M. Lynskey
Waimate—W. Y. Purchas
Dunedin—W. G. P. O'Callaghan
Port Chalmers—T. Hinchliff
Chief Judge—G. B. Davy
Judges—A. Mackay, D. Scannell, H. W. Brabant, W. J. Butler, H. F. Edger, W. G. Mair, H. D. Johnson, J. M. Batham
Registrars—Auckland, J. W. Browne; Gisborne, J. Brooking; Wellington, R. C. Sim
R. S. Bush, A. Turnbull, E. C. Blowfield, C. C. Kettle, J. M. Roberts, W. Stuart, H. W. Bishop, E. H. Carew, H. Eyre-Kenny, R. L. Stanford, T. Hutchison, H. W. Robinson, R. S. Florance: Sub - Commissioners—J. Brooking, W. A. Thom
Government Native Agent, Otorohanga—G. T. Wilkinson
Chief Judge—G. B. Davy
Judges—The Judges of the Native Land Court
Registrars—The Registrars of the Native Land Court
Auckland, T. Gresham, E. Baker; Coromandel, A. R. H. Swindley; Collingwood, E. Davidson; Foxton, E. S. Thynne; Hamilton, J. S. Bond; Hawera, C. E. Major; Marton, A. Ross; Otahuhu, S. Luke; Otaki W. H. Simcox; Paeroa, W. Forrest; Pahi, J. B. Ariell; Palmerston North, J. Mowlem; Port Albert, L. P. Becroft; Queenstown, L. Hotop; Raglan, W. H. Wallis; Midhirst, J. Mackay; Takaka, A. Sinclair; Thames, A. Bruce; Tauranga, A. C. H. Tovey; Te Awamutu, J. B. Teasdale; Te Kopuru, T. Webb; Waipawa, S. Johnson; Wellington, J. Ashcroft; Whangarei, J. M. Killen; Woodville, E. J. Gothard. All Stipendiary Magistrates are ex officio Coroners.
Commissioner—John Bennett Tunbridge
Chief Clerk—John Evans
Clerks—John Tasker, William John Mahoney, Walter Gollan
Inspector—Lieut.-Colonel Arthur Hume, N.Z.M.
Clerk—T. E. Richardson
Gaolers—Auckland, Francis Egerton Severne; Dunedin, John Henry Bratby; Hokitika, Thomas Rosson Pointon, Invercargill, Alexander Armstrong; Lyttelton, Matthew Michael Cleary; Napier, Michael Flannery; New Plymouth, Bartholomew Lloyd O'Brien; Wanganui, Robert T. N. Beasley; Wellington, Patrick Samuel Garvey; Wai-o-tapu, Jeremiah Charles Scanlon
Minister—Hon Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
Secretary—T. E. Donne
Acting Chief Clerk—G. S. Munro.
Minister—Hon. Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
Superintendent—T. E. Donne
Chief Clerk—C. R. C. Robieson
Inspector—F. Moorhouse
Accountant—R. E. Hayes
Journalist—J. Cowan
Clerks—H. Kirk, R. G. M. Park, J. W. Hill, S. J. Collett, W. M. Stevens, G. F. McGirr
Shorthand-writers and Typists—S. Dimant, N. Lambert
District Agents—Auckland, E. H. Montgomery; Rotorua, J. Andrews; Christchurch, W. R. Blow; Dunedin, (vacant); Invercargill, W. A. Saunders
Government Balneologist, Rotorua—A. S. Wohlmann, M.D., M.R.C.S., L.R.C.P.
House Surgeon, Rotorua—W. B. Craig, M.B.
Resident Medical Officer, Te Aroha—G. G. Kenny, M.B.
Manager, Hanmer Hot Springs—J. B. Gould
Minister of Labour—Rt. Hon. R. J. Seddon, P.C.
Secretary for Labour and Chief Inspector of Factories—E. Tregear
Chief Clerk and Deputy Chief Inspector of Factories—James Mackay
Clerks—F. Rowley, J. W. Collins, W. H. Hagger
Shorthand Writer and Typist—R. Ritson
Cadets—W. Linklater, Thomas McIntosh
Officer in Charge Women's Labour Department—H. Staveley
North Island—J. Shanaghan, H. Ferguson, J. Sinclair, W. J. Blake, W. H. Hagger, Margaret Hawthorne, and 75 local Inspectors
South Island—J. Shanaghan, J. Lomas, L. D. Browett, C. E. Aldridge, James Isdell, T. O'Grady, R. S. Bean, J. B. Lindsay, W. H. Hagger, Margaret Hawthorne, and 70 local Inspectors (There are also 200 Bureau Agents in different parts of the colony.)
Minister for Public Works—Hon. W. Hall-Jones
Under-Secretary—H. J. H. Blow
Engineer-in-Chief—W. H. Hales
Superintending Engineer—P. S. Hay, M.A., M.Inst.C.E.
Inspecting Engineer—R. W. Holmes, M.Inst.C.E.
Chief Clerk—W. D. Dumbell
Accountant—G. J. Clapham
Land-purchase Officer—H. Thompson
Record Clerk—H. W. H. Millais
Clerks—P. S. Waldie, E. McCarthy, A. Biddell, E. Bold, A. H. Kimbell, N. Jacobs, H. F. Curtis, A. Sampson, C. E. Crawford, G. C. Schmidt, W. McNamara, T. H. Hanna, J. J. Bennett, A. L. Goldfinch, L. White, E. Kidd, K. Webb
Chief Draughtsman—W. G. Rutherford
Architect—J. Campbell
Draughtsmen—T. Perham, E. Jackson, C. A. Lawrence, W. Withers, L. L. Richards, G. W. Phillips, J. Baird, W. G. C. Swan, J. H. Price, A. E. King, R. G. Applegarth, A. F. Macrae, T. S. Lambert, S. T. Silver, F. S. Marchant, W. J. C. Slane, S. W. M. Somerville, A. T. Ford
Head Storekeeper—John Young
Engineering Cadets—F. G. Hay, H. T. Thompson
Clerical Cadet—W. S. King
Clerical Cadettes—E. M. B. Lynch, E. J. Colquhoun
District Engineers—Auckland, C. R. Vickerman; Dunedin, E. R. Ussher, M.Inst.C.E.
Resident Engineers—Hunterville, G. L. Cook, M.Inst.C.E.; North Island Main Trunk Railway, J. D. Louch; Nelson, W. A. Shain; Westport, R. A. Young, Assoc.M.Inst.C.E.; Greymouth, J. Thomson, B.E.; Springfield, W. H. Gavin, Scargill, J. A. Wilson
Assistant Engineers—J. J. Hay, M.A.; S. J. Harding, J. H. Dobson, F. M. Hewson, J. Hannah, J. H. Lewis, G. C. McGlashan, C. E. Armstrong, F. H. Geisow, F. W. Furkert, W. Widdowson, H. Dickson, J. W. E. McEnnis, A. Ross, J. V. Haskell, C. A. Owen, J. W. Thomson, J. Meenan, A. Stewart, W. P. Moynihan, W. A. Jeff, W. Sherratt, C. J. McKenzie, F. P. Bartley
Engineering Cadets—J. J. Wilson, H. Vickerman, F. S. Dyson, J. Wood, L. B. Campbell, J. McNair, J. Norris, P. McNab, P. Keller, H. H. Sharp
Draughtsmen—C. Wood, W. A. Cumming, P. F. M. Burrows, W. H. Hislop, T. J. McCosker, J. J. Fraser, J. B. Robertson, H. C. W. Wrigg, A. Wood, W. G. Harding
Clerks—W. Black, C. T. Rushbrook, A. R. Stone, A. J. Sutcliffe, E. Waddell, J. H. Denton, J. B. Borton, L. P. Cabot, F. E. Banks, H. Grave, G. T. Grace, E. G. Beale, E. Crouch, J. A. White, P. P. Giesen, W. E. Fitzgerald, L. M. Shera, H. M. O'Donnell, S. A. Holland, A. D. Park, E. J. Edwards
Storekeepers—T. Douglas, J. C. Fulton, S. J. Moncrieff
Minister for Railways—Hon. Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
General Manager—T. Ronayne
Chief Clerk—R. W. McVilly
Clerks—E. J. Andrews, B. M. Wilson, W. S. Ridler, J. L. Day, W. Johnston, J. Hislop, C. G. Edwards, W. H. Gifford, J. V. Fogo, D. MacKellar, A. J. Will, W. A. Wellings, P. J. McGovern, W. H. Warren, A. N. Longton, S. S. Millington, J. D. Nash, H. Gerard, C. T. Reehal, F. C. Fraser, A. J. Levick, W. Rennie
Audit Inspectors—H. Baxter, D. Munro, R. Hislop, jun., I. Faris
Railway Accountant—A. C. Fife
Clerks—H. Davidson, J. H. Davies, G. S. P. Curtis, G. Wilson, J. McLean, E. Davy, A. Morris, C. Batten, J. Firth, W. B. Fisher, E. J. Fleming, H. H. Leopard, R. J. Loe, W. Bourke, T. Pattle, A. J. Belworthy, F. W. Lash, A. H. Hunt, W. E. Ahern, F. K. Porteous, A. D. C. Gosman, T. A. O'Connor, A. E. Wilson, J. W. Dayman, W. H. Simmons, J. B. Gauntlett, A. T. Parkes
Stores Manager—G. Felton
Stores Audit Inspector—F. J. Dawes
Clerks—M. C. Rowe, G. H. Norie, C. F. F. A. R. Isherwood, S. Alpe, H. W. Barbor, W. G. Wray, R. P. Bray, J. T. Bain, L. G. Porter, G. H. Stubbs, A. F. Spiller, J. R. Robertson, J. Kerr, J. Brabiner, J. Hayes, J. Ginnane, V. C. Hardie
Chief Traffic Manager—W. H. Gaw
Relieving District Traffic Manager—W. Stringleman
Clerks—J. E. Armstrong, G. A. C. Robieson, J. E. Widdop, T. T. Halbert
Traffic Superintendents—Wellington, T. Arthur; Dunedin, A. Grant
District Managers—Whangarei, E.E. Gillon; Auckland, H. Buxton; Wanganui, S. F. Whitcombe; Westland, F. W. Styles; Christchurch, T. W. Waite; Invercargill, C. A. Piper
Stationmasters in charge—Kawakawa, J. T. Parsons; Kaihu, R. B. Peat; Gisborne, G. G. Wellsted; Westport, T. Hay-Mackenzie; Nelson, E. G. Wilson; Picton, T. S. Edwards
Chief Engineer for Working Railways—J. Coom, M.Inst.C.E.
Inspecting Engineer—J. Burnett, M.Inst.C.E.
Signal Engineer—H.J. Wynne, A.M.Inst.C.E.
Railway Land Officer—E. G. H. Mainwaring
Inspector of Bridge Construction—A. H. Alabaster
Electrician—J. T. Fahy
Electric Mechanician—T. Hendry
Office Engineer—G. A. Troup
Draughtsmen—J. Besant, C. T. Jeffreys, W. R. B. Bagge, Ad. Howitt, L. Reynolds, A. S. Henderson, W. W. Fry, W. R. Davidson, G. G. Wilson, jun., E. Casey
Clerks—W. P. Hicks, J. T. Ford, W. A. Mirams, H. Jessup, T. H. Wilson, E. S. Kelly, H. W. Rowden, T. M. Lucy, H. H. Gardner, J. M. Robb, F. J. Rowden, E. D. Richards, W. B. O'Brien, G. P. Parrell, H. McAlister, J. A. F. Cundy, V. W. W. Venimore, F. T. A. Williams, W. B. Clark
District Engineers—Auckland, C. H. Biss; Wanganui, D. T. McIntosh; Wellington, A. C. Koch; Westport and Westland, F. J. Jones; Christchurch, H. Macandrew; Dunedin, F. W. MacLean; Invercargill, A. J. McCredie
Chief Mechanical Engineer—A.L. Beattie
Clerks—J. P. Kelly, R. Aekins, D. D. Weir, J. Rumgay, H. McKeowen, H. B. Sturmer, C. L. Pettit, A. J. Bland, J. H. Leopard, J. P. McKeowen, W. Somerville, E. S. Stringleman, N. E. White, J. Linehan
Chief Draughtsman—G. A. Pearson
Draughtsmen—R. Pye-Smith, G. Wilson, A. Smellie, F. H. Bell, J. M. Porteous
Boiler Inspector—J. W. Nichols
Locomotive Engineers—Auckland, A. V. Macdonald; Wellington-Napier-New Plymouth, T. A. Peterkin; Hurunui-Bluff, H. H. Jackson; Westport and Westland, G. E. Richardson, Relieving, J. D. Harris, F. T. Murison
Brake Engineer—J. H. Fox
Relieving Foreman—R. Simpson
H. Eyre-Kenny, Stipendiary Magistrate Chairman, appointed by the Governor
H. Davidson, Railway Accountant's Office, elected
T. Wilson, Engineman, elected
M. J. Mack, Guard, elected
W. Austin, Leading Carpenter, elected
W. Morrison, Ganger, elected
Postmaster-General and Electric Telegraph Commissioner—Hon. Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
Secretary—W. Gray
Superintendent of Electric Lines—J. K. Logan
Assistant Secretary and Inspector—T. Rose
Controller of Money-orders and Savings-banks, and Accountant—G. Gray
Chief Clerk—D. Robertson
Assistant Controller Money-Orders and Savings - Banks, and Assistant Accountant—W. R. Morris
Clerks, Secretary's Office—F. V. Waters, H. Plimmer, J. C. Williamson, W. Crow, V. J. Brogan, T. Ward, H. D. Grocott, J. C. Redmond, A. T. Markmann, W. J. Gow, F. W. Furby, J. B. Jordan, S. Macalister, J. P. P. Clouston, W. H. Barnett, A. Donovan
Mail Agents—W. Isbister, D. E. Lindsay (acting)
Clerks, Inspector's Branch—G. V. Hudson, J. Brennan, W. A. Tanner, F. S. Robins, S. M. Harrison, G. P. Edwards, H. McGill
Clerks, Accountant's Branch—J. L. H. Ledger, H. A. R. Huggins, G. W. Moorhouse, W. Callaghan, W. Chegwidden, R. J. Thompson, H. Cornwall, F. Perrin, J. J. Esson, D. A. Jenkins, H. N. McLeod, J. D. Avery, C. B. Harton, W. J. Drake, J. G. Roache, J. Coyle, F. W. Faber, F. E. Beamish, P. J. Kelleher, A. C. Elliott, G. H. Harris, H. C. Milne, C. W. J. Panting, H. C. Hickson, P. D. Hoskins, W. R. Wakelin, F. Stewart, G. G. Rose, G. T. Withers, H. E. Combs, J. E. Hull, A. Marshall, F. G. A. Eagles, C. G. Collins, T. M. Highet, E. C. Gamble, J. C. A. Dudley, T. H. N. Beasley, W. I. Dawson, W. K. Frethey, J. Snell, W. Gilbert, G. L. Messenger, T. A. Churches, C. H. Clinkard, J. M. Dale, H. A. Lamb, R. Porteous, D. Rutherford, A. Edwards, A. Baskiville, R. W. Penfold, W. A. Smith, R. H. Twose, E. White, C. Gamble, J. Madden, J. Alexander, P. Cutforth, A. Leeden, E. Bermingham, S. Brock, E. Harris, B. M. Kenny, V. Johnston, M. A. MacLeod, C. Smith, M. A. Asquith, E. E. Warren
Electrician—T. Buckley
Assistant Electrician—W. E. Chisholm
Mechanicians—R. Heinitz, F. Palmer
Storekeeper—J. Black
Assistant Storekeeper—C. B. Mann
Clerks in Store—C. Nicholls, T. Palmer, W. H. Carter, M. McGilvray, J. G. Howard, W. R. Aekins, J. L. Murphy
Auckland—J. W. Wilkin
*Thames—W. McHutcheson
*Gisborne—G. W. Sampson
Napier—D. Cumming
*New Plymouth—F. D. Holdsworth
*Wanganui—D. Miller
Wellington—S. J. Jago
*Blenheim—E. Northcroft
*Nelson—S. P. Stevens
*Westport—H. Logie
*Greymouth—C. J. Berry
*Hokitika—J. H. Sheath
Christchurch—J. F. McBeth
*Timaru—J. A. Hutton
*Oamaru—W. W. Beswick
Dunedin—E. Cook
*Invercargill—C. J. A. H. Tipping
Auckland—W. G. Meddings
Christchurch—J. W. Gannaway
Dunedin—J. Orchiston
Nelson—C. C. Robertson
Wellington—W. S. Furby
P. Curtis (Northern District), W. J. Chaney (Central District), W. St. G. Douglas (Midland District), T. T. King (Southern District)
Auckland—H. F. Seager
Napier—B. H. Keys
Wellington—H. W. Harrington
Christchurch—J. W. Mason
Dunedin—J. G. Ballard
Commissioner of Trade and Customs—Hon. C. H. Mills
Secretary and Inspector of Customs and Secretary of Marine—W. T. Glasgow
Chief Clerk—T. Larchin
Clerks, Customs—C. H. Manson, H. S. Cordery, W. A. Cameron
Cadet—G. F. McKellar
Audit—H. W. Brewer, H. Crowther (Writer)
Auckland—A. Rose
Poverty Bay—W. J. Hawley
New Plymouth—H. Bedford
Napier—E. R. C. Bowen
Wellington—D. Johnston
Wanganui—A. Elliott
Nelson—W. Heaps
Westport—H. R. Spence
Greymouth—C. Colebrook
Hokitika—W. Rose
Lyttelton and Christchurch—J. Mills
Timaru—C. S. Nixon
Oamaru—T. M. Cullen
Dunedin—C. W. S. Chamberlain
Invercargill and Bluff Harbour—A McDowell
Thames—T. C. Bayldon, Coastwaiter
Russell—H. Stephenson, Coastwaiter
Tauranga—C. C. Halliday, Officer in Charge
Whangaroa—A. G. Ratcliffe, Coastwaiter
Whangarei—J. Munro, Coastwaiter
Mongonui—H. G. Hunt, Officer in Charge
Hokianga—G. Martin, Coastwaiter
Kaipara—J. C. Smith, Officer in Charge
Waitara—J. Cameron, Coastwaiter
Patea—J. W. Glenny, Officer in Charge
Wairau—H. A. Jackman, Officer in Charge
Picton—T. W. Lecocq, Officer in Charge
Chatham Islands—R. S. Florance, Officer in Charge
Minister of Marine—Hon. W. Hall-Jones
Secretary—W. T. Glasgow
Chief Clerk—G. Allport
Clerks—J. J. D. Grix, G. Sinclair
Cadet—B. W. Millier
Marine Engineer for the Colony—W. H. Hales
* Combined post- and telegraph-offices.
Nautical Adviser and Chief Examiner of Masters and Mates—H. S. Blackburne
Weather Reporter—R. A. Edwin, Com. R.N.
Superintendent of Mercantile Marine and Examiner of Masters and Mates, Auckland—W. D. Reid
Superintendent of Mercantile Marine and Examiner of Masters and Mates—Wellington, G. G. Smith
Superintendent of Mercantile Marine and Examiner of Masters and Mates. Lyttelton—J. A. H. Marciel
Superintendent of Mercantile Marine and Examiner of Masters and Mates, Dunedin—C. E. W. Fleming
Master of s.s. “Tutanekai”—C. F. Post
Master of s.s. “Hinemoa”—J. Bollons
Wellington, Chief Inspector—L. F. Ayson
Russell—H. Stephenson
Whangarei—A. McDonnell
Wanganui—W. J. Campbell
Palmerston North—M. D. Stagpoole
Foxton—J. Forster
Hokitika—J. Duncan
Dunedin—J. McIntyre
Bluff—P. McGrath
Napier—C. H. Pratt
Chief Inspector of Machinery, Principal Engineer Surveyor, and Chief Examiner of Engineers—R. Duncan, Head Office, Wellington
Chief Clerk—R. P. Milne
Clerk—J. H. Macalister
Extra Clerks—R. G. Stone, W. D. Andrews, J. G. Macpherson, J. M. Healy
Cadet—H. Patterson
Inspectors of Machinery, Engineer Surveyors, and Examiners of Engineers:–
Auckland—H. Wetherilt, S. Dalrymple, G. McGregor
Wellington—H. A. McGregor, A. Calvert, W. R. Douglas, N. D. Hood
Nelson—A. McVicar
Christchurch—P. J. Carman
Timaru—J. Williamson
Dunedin—A. Walker, M. Sharp
Invercargill—A. W. Bethune
Board of Examiners of Stationary, Traction, Locomotive, and Winding Engine-Drivers—Robert Duncan, Chief Inspector of Machinery, M.Inst.Nav.A., M.Inst.Soc.A.Lond., Chairman; John Hayes, F.S.G.C., Inspecting Engineer of Mines; P. G. Hay, M.A., M.Inst.C.E.; R. P. Milne, Secretary
Commissioner of Stamp Duties—Hon. Jas. Carroll
Secretary for Stamps—C.A.St.G. Hickson
Chief Clerk and Accountant—H. O. Williams
Custodian and Issuer of Stamps—W. H. Shore
Record and Receiving Clerk—J. P. Murphy
Clerks—V. Willeston, J. Murray
Chief Stamper—C. Howe
Cadette—C. McIntosh
Auckland—E. Bamford
Gisborne—C. H. W. Dixon
Taranaki—R. L. Stanford
Hawke's Bay—Thos. Hall
Wellington—C. A. St. G. Hickson
Wanganui—D. Miller
Nelson—W. W. de Castro
Marlborough—C. E. Nalder
Canterbury—P. G. Withers
Timaru—J. A. Hutton
Otago—P. C. Corliss
Southland—W. Wyinks
Westland—V. G. Day
Registrar-General of Land and Deeds—G. B. Davy
Secretary, Land and Deeds—C. A. St. G. Hickson
* The more important harbours are controlled by local Boards, not by the Marine Department.
Auckland—E. Bamford
Taranaki—R. L. Stanford
Wellington—Wm. Stuart
Hawke's Bay—Thos. Hall
Poverty Bay—J. M. Batham
Nelson—H. W. Robinson
Marlborough—C. E. Nalder
Canterbury—G. G. Bridges
Otago—H. Turton
Southland—W. Wyinks
Westland—V. G. Day
Auckland—E. Bamford
Taranaki—R. L. Stanford
Wellington—H. Howorth
Hawke's Bay—Thos. Hall
Poverty Bay—J. M. Batham
Nelson—H. W. Robinson
Marlborough—C. E. Nalder
Canterbury—G. G. Bridges
Otago—H. Turton
Southland—W. Wyinks
Westland—V. G. Day
Auckland—E. Bamford
Taranaki—R. L. Stanford
Hawke's Bay—Thos. Hall
Wellington—H. O. Williams
Nelson—W. W. de Castro
Marlborough—C. E. Nalder
Canterbury—P. G. Withers
Otago—P. C. Corliss
Southland—W. Wyinks
Westland—V. G. Day
Poverty Bay—C. H. W. Dixon
Minister of Education (administering also Native schools, industrial schools, and the institution for deaf-mutes)—Hon. W. C. Walker, C.M.G.
Secretary for Education and Inspector-General of Schools—George Hogben, M.A.
Assistant Secretary—Sir E. O. Gibbes, Bart.
Clerks—F. K. de Castro, R. H. Pope, F. L. Severne, E. C. Banks, F. D. Thomson, B.A., H. J. Barrett, T. G. Gilbert, J. Beck, I. Davey, I. Robertson, C.T. Wild, M. G. D. Grant, G. P. Prichard, J. F. Cooper, F. W. Millar, A. J. H. Benge, J. Turner, K. McKenzie
Inspector of Native Schools—James H. Pope. Organizing Instructor—W. W. Bird, M.A.
Inspectors of Technical Instruction—M. H. Browne, E. C. Isaac
Assistant Inspectors of Industrial Schools—R. H. Pope (also clerk), T. A. Walker
Officer in charge of Public School Cadets—Major L. W. Loveday
Auckland—V. E. Rice
Taranaki—P. S. Whitcombe
Wanganui—W. J. Carson
Wellington—A. Dorset
Hawke's Bay—G. T. Fannin
Marlborough—J. Smith
Nelson—S. Ellis
Grey—H. Smith, B.A.
Westland—A. J. Morton, B.A.
Canterbury North—H. C. Lane
Canterbury South—J. H. Bamfield
Otago—P. G. Pryde
Southland—J. Neill
Auckland Industrial School—Miss S. E. Jackson, Manager
Wellington Receiving Home—Mrs. E. S. Dick, Manager
Burnham Industrial School (Canterbury)—T. Archey, Manager
Te Oranga Home (Canterbury)—Mrs. E. T. Branting, Manager
Christchurch Receiving Home—Miss A. B. Cox, Manager
Caversham Industrial School (Otago)—G. M. Burlinson, Manager
Inspector—Duncan MacGregor, M.A., M.B., C.M.*
Assistant Inspector—Mrs. Grace Neill
Medical Superintendent, Auckland Asylum—R. M. Beattie, M.B.
Medical Superintendent, Christchurch Asylum—E. G. Levinge, M.B.
Medical Superintendent, Porirua Asylum—Gray Hassell, M.D.
Medical Superintendent, Wellington Asylum—W. Baxter Gow, M.D.
Medical Superintendent, Seacliff Asylum—F. Truby King, M.B.
Superintendent, Hokitika Asylum—H. Gribben; Medical Officer, H. Macandrew, M.B.
Superintendent, Nelson Asylum—J. Morrison; Medical Officer, W. J. Mackie, M.D.
Ashburn Hall, Waikari (private asylum)—Proprietors, Dr. Alexander and Executor of James Hume; Medical Officer, Frank Hay, M.B.
Minister of Mines—Hon. James McGowan
Under-Secretary for Mines—H. J. H. Eliott
Inspecting Engineer—John Hayes
Chief Clerk—T. H. Hamer
Clerk—H. E. Radcliffe
Analyst—J. S. Maclaurin, D.Sc., F.C.S.
Geologist—Alexander McKay, F.G.S.
Assistant Geologist—W. A. McKay
Draughtsman—C. H. Pierard
Shorthand Writer—J. T. Watkins
Thames and Auckland Districts—James Coutts; Assistant Inspector, Thomas Ryan: Canterbury, Dunedin, and Southland Districts—E. R. Green; Assistant Inspector, Robert McIntosh; Cadet, H. Paton: West Coast Districts—R. Tennent; Assistant Inspector—A. H. Richards
Lecturers and Instructors: Thames—O. G. Adams; Assistant, A. H. V. Morgan, M.A.: Reefton—T. O. Bishop: Coromandel—D. V. Allen: Waihi—P. G. Morgan, M.A.
The Director of the Geological Survey of New Zealand: the Surveyor-General; the Inspecting Engineer of Mines; the Chief Inspector of Machinery, Wellington, James Bishop, Alfred Benjamin Lindop, and G. H. Broome
Same official members as above Board, excepting the Chief Inspector of Machinery, Wellington, with the following private members: H. A. Gordon, F.G.S., Auckland; Thomas Aitken Dunlop, Thames; Patrick Quirk Caples, Reefton; and Francis Hodge, Coromandel
The Director of the Geological Survey of New Zealand is Chairman of both Boards, and Mr. T. H. Hamer is the Secretary
Minister in Charge—The Hon. Minister of Mines
Director—Sir J. Hector, K.C.M.G., M.D., F.R.S.
Clerk, Curator, and Meteorological Observer for Wellington—A. H. Gore
* Also holds appointment of Inspector of Hospitals and Charitable Institutions.
Astronomical Observer—T. King
Meteorological Observer, Auckland—T. F. Cheeseman, F.L.S.
Meteorological Observer, Dunedin—H. Skey
Meteorological Observer, New Plymouth—G. W. Palmer
Meteorological Observer, Hokitika—A. D. Macfarlane
Meteorological Observer, Rotorua—Dr. Kenny
Meteorological Observer, Te Aroha—W. Hill
Meteorological Observer, Lincoln—Geo Gray
Meteorological Observer, Hanmer Plains—J. B. Gould
Minister of Defence—Rt. Hon. R. J. Seddon, P.C.
Under-Secretary—
Colonel James Melville Babington, H.M. General Staff (local Major-General)
Major N. L. D'A. Smith, N.Z.M.
Senior Clerk—T. F. Grey
Clerk—A. J. Baker
Lieut-Colonel Robert Haylock Owen, N.Z.M. (late Captain, H.M. South Lancashire Regiment)
Officer Commanding—Major St. Leger Montgomery Moore, N.Z.M. (Captain R.G.A.)
Captain J. E. Hume
Lieutenant H. E. Pilkington
Lieutenant W. P. Wall
Lieutenant M. M. Gardner
Lieutenant G. E. B. Mickle
Lieutenant R. O. Chesney
Lieutenant S. G. Sandle
Captain William Coyle, late Coast Brigade, R.E.
Lieutenant F. Symon
Lieutenant R. B. Smythe
Auckland—Brevet-Colonel Richard Hutton Davies, C.B., N.Z.M.
Wellington—Brevet - Colonel William Holden Webb, N.Z.M., late H.M. 109th Foot: Adjutant, Captain L. J. Joyce, N.Z.M.
Canterbury—Colonel Thomas William Porter, C.B., N.Z.M.
Otago—Brevet-Colonel Alfred William Robin, C.B., N.Z.M.
Nelson (temporary)—Major George Cecil Burleigh Wolfe, N.Z.M., late Captain R.M.L.I.; Adjutant. Lieut. Sydney Vincent Trask, N.Z.M.
Minister of Lands—Hon. Thomas Young Duncan
Surveyor-General and Secretary for Crown Lands—J. W. A. Marchant
Under-Secretary for Crown Lands—W. C. Kensington
Chief Draughtsman—F. W. Flanagan
Chief Clerk—F. T. O'Neill
Auditor of Land Revenue—W. G. Runcie
Accountant—R. A. Paterson
Superintendent of Village Settlements—J. E. March
Assistant Surveyor-General, Chief Surveyor, and Commissioner of Crown Lands—G. J. Mueller
District Surveyors—L. Cussen, J. Baber, jun., G. A. Martin, H. D. M. Haszard, T. K. Thompson
Assistant Surveyors—R. S. Galbraith, D. A. I. Barron, H. F. Edgecumbe, H. T. Mitchell
Chief Draughtsman—C. R. Pollen
Receiver of Land Revenue—T. M. Taylor
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—E. C. Gold Smith
District Land Officer, Gisborne, F. S. Smith
District Surveyors—F. S. Smith, James Hay, P. A. Dalziel
Assistant Surveyor—T. Brook
Chief Draughtsman—F. Simpson
Receiver of Land Revenue—F. Bull
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—J. Mackenzie
District Surveyors—H. M. Skeet, G. H. Bullard
Assistant-Surveyors—J. F. Frith, W. T. Morpeth, R. W. Watson
Chief Draughtsman—J. Langmuir
Receiver of Land Revenue—G. P. Doile
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—J. Strauchon
District Surveyors—J. D. Climie, F. A. Thompson, H. J. Lowe, W. J. Wheeler, J. McKay
Assistant Surveyors—J. R. Strachan, H. E. Girdlestone, E. A. Marchant
Chief Draughtsman—L. Smith
Receiver of Land Revenue—T. G. Waitt
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—W. G. Murray
District Surveyors—J. A. Montgomerie, J. Snodgrass, R. T. Sadd
Assistant Surveyors—J. D. Thomson, W. C. McAlister
Chief Draughtsman and Receiver of Land Revenue—H. Trent
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—C. W. Adams
District Surveyor—D. W. Gillies
Assistant Surveyor—H. Maitland
Chief Draughtsman and Receiver of Land Revenue—W. Armstrong
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—G. J. Roberts
Assistant Surveyor—W. Wilson
Chief Draughtsman—T. M. Grant
Receiver of Land Revenue—A. D. A. Macfarlane
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—T. Humphries
District Surveyors—T. N. Broderick, G. H. M. McClure
Chief Draughtsman—C. B. Shanks
Receiver of Land Revenue—A. A. McNab
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—David Barron
District Surveyors—E. H. Wilmot, D. M. Calder, W. T. Neill
Chief Draughtsman—S. Thompson
Receiver of Land Revenue—G. A. Reade
Chief Surveyor and Commissioner of Crown Lands—John Hay
District Surveyor—L. O. Mathias
Assistant Surveyor—A. Hodgkinson
Chief Draughtsman—G. Robinson
Receiver of Land Revenue—H. L. Welch
Auckland—G. J. Mueller, R. Thompson, D. Lundon, J. Renshaw, A. R. Harris
Hawke's Bay—E. C. Gold Smith, C. Hall, T. Hyde, R. R. Groom, G. Mathewson
Taranaki—J. Mackenzie, J. Heslop, James Rattenbury, J. B. Connett, J. McCluggage
Wellington—J. Strauchon, A. W. Hogg, A. Reese, J. Stevens, T. H. Robinson
Nelson—W. G. Murray, O. Lynch, R. Kerr, J. S. Wratt, G. Walker
Marlborough—C. W. Adams, J. Redwood, A. P. Seymour, H. M. Reader, G. Renner
Westland—G. J. Roberts, A. Matheson, J. Chesney, J. S. Lang, A. Cumming
Canterbury—T. Humphries, A. C. Pringle, J. Sealy, J. Allan, J. Stevenson
Otago—D. Barron, H. H. Kirkpatrick, H. Clark, J. Duncan, W. Dallas
Southland—J. Hay, A. Kinross, J. McIntyre, A. Baldey, D. King
Minister in Charge—Hon. T. Y. Duncan
Chief Engineer of Roads—C. W. Hurst-house
Chief Clerk—W. S. Short
Chief Accountant—H. J. Knowles
Road Surveyors—Auckland, A. B. Wright; Te Kuiti, T. Burd; Rotorua, A. C. Turner; Hawke's Bay, D. N. McMillan; Taranaki, G. T. Murray; Wanganui, R. H. Reaney; Wellington, G. F. Robinson; Marlborough, C. H. Williams; Canterbury, F. Wither; Otago, W. D. R. McCurdie; Southland, J. H. Treseder
Chairman of Board and Land Purchase Inspector—Alexander Barron.
The Board consists of the Land Purchase Inspector as Chairman, the Surveyor - General, the Commissioner of Taxes—these for the whole colony—with the Commissioners of Crown Lands and a member of the Land Board in each land district, who are members only for the business arising within their respective districts.
Minister in Charge—Hon. T. Y. Duncan
Secretary of Agriculture and Chief Inspector of Stock—John D. Ritchie
Chief Clerk—Richard Evatt
Clerk in Charge of Correspondence Branch—F. S. Pope
Clerk in Charge of Accounts Branch—J. E. D. Spicer
Compiler of Statistics—E. B. Burdekin
Clerks—Correspondence Branch: F. C. Hjorring, R. W. Atkinson, D. Sinclair, T. D. H. Hall, W. A. Pye. Accounts Branch—E. Fitzgibbon, F. C. Matthews, A. Calcott, T. R. Walton, S. T. K. Sharp, S. T. Evatt, A. McTaggart, O. Reid. Statistics Branch—A. C. Philpott
Pathologist and Chief Veterinarian—J. A. Gilruth, M.R.C.V.S.
Assistant Chief Veterinarian—C. J. Reakes, M.R.C.V.S.
Laboratory Assistant—G. H. Barker
Clerks—H. E. Carey, D. L. Luxford, C. Aston
Veterinarians (Ms. R.C.V.S.)—H. C. Wilkie (F.R.C.V.S., F.Z.S.), Dunedin; J. G. Clayton, J. Lyons, Auckland; A. R. Young, Hawera; S. Burton, Masterton; J. McKie, Wellington
Veterinarians and Meat Inspectors (Ms.R.C.V.S.)—A. Crabb, Christchurch; D. H. Rait, Hastings; C. R. Neale, Belfast; J. R. Charlton, Islington; T. G. Lilico, Timaru, J. A. R. Towers, Ngahauranga; D. Machattie, Ashburton; J. Kerrigan, Invercargill; V. A. Bankes, Wanganui; F. C. Robertson, Palmerston N.; W. H. Hawthorn, Gisborne; W. G. Taylor, Napier; W. D. Snowball, Dunedin; A. W. Barnes, Nelson; T. Cunningham, Mataura; D. Spilman, Petone; F. Glover, Picton
Meat Inspectors—H. S. S. Kyle, Invercargill; H. Marsack, Auckland; F. Beattie, Paeroa; W. A. P. Sutton, Thames; C. J. Barron, Blenheim; G. W. Mitchell, Lyttelton
Assistant Meat Inspectors—A. G. Howard, A. D. Gillies, E. T. B. Worthy, G. Thomson, J. Millea, J. Jarman, W. H. Rodney, G. W. Rait, B. Thomson, H. W. Binney, J. Preston, B. Ferguson, G. Thomson, T. J. Reakes, C. J. Stone, T. Anderson
Dairy Commissioner—J. A. Kinsella
Clerk—D. Bray
Dairy Instructors—D. J. McGowan, W. M. Singleton, A. G. Shirley
Dairy Instructors and Dairy - produce Graders, D. Cuddie, D. Dickie, Wellington; S. A. Dumbleton, T. C. Brash, New Plymouth
Dairy-produce Graders—A. A. Thornton, Lyttelton and Port Chalmers; J. Johnston, New Plymouth; E. Townshend, Auckland
Clerks to Graders—E. A. Dowden, G. W. Otterson, J. Hutton
Biologist—T. W. Kirk, F.L.S.
Clerks—J. H. Kingdon, B. Quirk
Viticultural Expert—R. Bragato
Assistant Entomologist—Auckland, Captain T. Broun, F.E.S.
Pomologists—North Island, W. J. Palmer, W. A. Boucher. South Island, J. C. Blackmore
Fruit Inspectors—Auckland, Captain T. Broun, F.E.S.; Wellington, H. Palethorpe; Christchurch, A. C. Smale; Dunedin, A. F. Cargill
Chemist—B. C. Aston, F.C.S.
Assistant Chemist—H. W. Lawrence, F.C.S.
Laboratory Assistant—G. B. Williams
Poultry Expert—D. D. Hyde
Clerk—A. E. Rowden
Poultry Graders—Auckland, R. W. Pounsford; Wellington, T. Burke; Christchurch, S. Newton; Dunedin, T. F. Leihy
Poultry-station Managers—Ruakura, C. Cussen; Momohaki, H. C. Collett; Burnham, W. S. McRae; Milton, J. W. Stewart
Chief Hemp Grader—C. J. Fulton.
Hemp Graders—Auckland, W. H. O. Johnston; Wellington, R. T. Bell; Bluff, W. J. Shea
Clerk, Wellington—H. Wynn-Williams
Overseers—Waerenga, N. Kensington; Ruakura, M. Mulcahy; Weraroa, G. Ross; Momohaki, F. Gillanders
Clerks—Ruakura, J. S. Edgecumbe; Weraroa, P. W. Goldsmith; Momohaki, J. Fleming
Caretakers—Auckland, A. Dickson; Wellington, J. P. Ross; Lyttelton, W. J. Thomas
(Inspectors under the Dairy Industry, Noxious Weeds, Rabbit Nuisance, Slaughtering and Inspection, and Stock Acts. Those marked* are also Registrars of Brands)
Auckland District—Ohaeawai, D. A. Graham; Whangarei, *J. T. Stone; Auckland, *E. Clifton (in charge of district), F. H. Brittain, R. Hull Hamilton, *D. Ross; Kihikihi, J. Kerr; Tauranga, A. H. Burkill
Hawke's Bay District—Gisborne, *C. Thomson and D. Fleming; Wairoa, *W. R. Rutherfurd; Napier, *W. Miller (in charge of district); Hastings, F. G. Wayne; Woodville, J. Harvey
Wairarapa District—Masterton, *G. H. Jenkinson (in charge of district); Carterton, T. C. Webb
Wellington District—Wellington, *A. Mills (in charge of district), J. Drummond (port)
Manawatu District—Palmerston North, *J. Duncan (in charge of district)
West Coast (North Island) District—Hunterville, V. A. Huddleston; Wanganui, *A. K. Blundell (in charge of district); Hawera, *J. W. Deem; Stratford, J. Budge; New Plymouth, R. Rowan
Marlborough District—Blenheim, *J. Moore (in charge of district)
Canterbury District—Rotherham, *J. Munro; Rangiora, C. A. Cunningham; Christchurch, *H. T. G. Turner (in charge of district); Lincoln, J. C, Miller; Ashburton, B. Fullarton; Timaru, J. C. Huddleston; Fairlie, W. Black
Southern District—Dunedin, T. A. Fraser, Assistant Chief Inspector (in charge of district). *J. E. Thomson (port); Kurow, W. Wills; Oamaru, *A. Ironside; Palmerston South, H. Hill; Mosgiel, R. I. Gossage; Naseby, C. Shaw; Clyde, *S. M. Taylor; Lawrence, *G. McLeod; Milton, T. Gillespie; Balclutha, J. L. Bruce; Gore, W. Dalgliesh; Invercargill, *R. Wright; Bluff, J. W. Raymond (port); Riverton, T. Gilmour; Queenstown, R. Fountain
Westland District—Hokitika, *C. C. Empson (in charge of district)
Nelson District—Richmond, G. S. Cooke; Nelson, *H. McN. Campbell (in charge of district)
Clerks—Auckland, W. C. Robinson (also Registrar of Brands); Napier, R. M. Miller; Masterton, R. J. Halcombe; Wellington, V. A. Mills: Palmerston North, G. A. Ross; Wanganui, D. Bell; Blenheim, G. H. Chrisp; Christchurch, J. Longton, R. F. Crosbie; Lawrence, E. Fowler; Invercargill, J. W. Bell, R. L. Johnston
(The Inspectors of Stock are also Inspectors under the Slaughtering Act.)
F. Beattie, Paeroa; W. A. P. Sutton, Thames; A. Macpherson, Christchurch
(The Inspectors of Stock are also Inspectors of Dairies.)
Auckland, G. M. Williamson; Paeroa, F. Beattie, Thames, W. A. P. Sutton; Napier, J. G. Parker; Wellington, J. Drummond; Lyttelton, G. W. Mitchell; Christchurch, A. Macpherson; Dunedin, W. R. Brown; Nelson, A. T. P. Hubbard
(The Inspectors of Stock are also Inspectors of Noxious Weeds.)
Napier, J. G. Parker; Eketahuna, J. Vile; Normanby, J. Heslop; Waitara, J. M. Hignett; Dunedin, W. R. Brown; Invercargill, M. O'Meara; Nelson, A. T. P. Hubbard.
Cambridge, J. S. Scott, R. Alexander; Kihikihi, B. Baylv; Pahiatua, T. Bacon; Masterton, J. Halligan; Alfredton, H. Munro; Carterton, H. S. Ussher; Wellington, W. Ross; Levin, A. C. Hackworth; Blenheim, G. Gee; Kaikoura, F. W. Sutton; Hanmer, D. Ross; Mount Somers, C. Watson; Temuka, W. R. Taylor; Timaru, D. Elliott; Waimate, E. F. Sullivan; Kurow, C. S. Dagleish; Maheno, F. McKenzie; Inch Valley, M. McLeod; Waikouaiti, A. Munro; Taieri, W. S. Goodall; Sutton, R. Irving; Waipiata, A. Clarke; Clyde, F. Urquhart; Roxburgh, A. F. Keach; Lawrence, W. Johnston; Pembroke, H. A. Munro: Milton, C. Branigan; Owaka, H. McLeod; Tapanui, A. C. Clapcott; Clinton, T. P. Short; Gore, A. Hughes; Lumsden, W. M. Munro; Wyndham, D. McLeod; Invercargill, J. McKellar; Riverton, T. N. Baxter.
Valuer General—John McGowan
Deputy Valuer-General—G. F. C. Campbell
Chief Clerk—F. J. M. D. Walmsley
Clerk in Charge—A. E. Fowler
Clerks—H. L. Wiggins, G. Halliday, T. T. Bolt, J. Atkinson, E. J. R. Cumming
Draughtsman—H. H. Seed
Supervising Valuers—W. Duncan, Auckland; A. P. O'Callaghan, Christchurch; A. McKerrow, Dunedin; H. Carswell, Invercargill
District Valuers—James I. Wilson, jun., Whangarei; W. Garrett, J. J. Reynolds, Auckland; W. H. Wallis, Hamilton; J. S. Simson, Gisborne; W. E. Griffin, Napier; H. J. C. Coutts, Hawera; S. Hill, New Plymouth; A. Barns, Wanganui; R. Gardner, Palmerston North; J. Fraser, Masterton; J. Ames, Wellington; T. W. Caverhill, Petone; E. Kenny, Picton; J. Glen, Nelson; J. Webster, Hokitika; A. D. Bayfield, Westport; D. Dick, Ashley; H. Murray, Christchurch; A. Freeman, Christchurch; A. Allan, Timaru; E. A. Atkinson, Oamaru; W. L. Craig, Palmerston South; W. Dallas, Balclutha; J. Wright, Dunedin; J. George, Queenstown; John Smaill, Gore; Charles Rout, A. Pyper, Invercargill
Clerks—Auckland, E. W. Watson, T. C. Somers; Christchurch, J. M. Wheeler, A. Millar; Dunedin, A. Clothier; Invercargill, T. Oswin, C. de R. Andrews
Cadets—Auckland, E. Panting; Wellington, F. C. Douglas; Invercargill, D. Corcoran
Commissioner—J. H. Richardson, F.F.A., F.I.A.V.
Assistant Commissioner—D. M. Luckie
Actuary—Morris Fox
Secretary—W. B. Hudson
Chief Medical Officer—T. Cahill, M.D.
Accountant—G. W. Barltrop
Assistant Actuary—P. Muter
Chief Clerk—R. C. Niven
Office Examiner—G. A. Kennedy
Clerks—J. W. Kinniburgh, A. Avery, W. S. Smith, A. H. Hamerton, F. B. Bolt, T. L. Barker, A. L. B. Jordan, H. S. Manning, C. E. Galwey, G. Webb, F. K. Kelling, J. B. Young, H. Rose, R. P. Hood, G. A. N. Campbell, A. T. Traversi, J. A. Thomson, A. de Castro, C. J. Alexander, R. T. Smith, H. L. Levestam, S. P. Hawthorne, J. G. Reid, C. H. E. Stichbury, J. R. Samson, R. F. Hamerton, A. H. Johnstone, W. H. Woon, G. S. Nicoll, R. S. Latta, T. Fouhy, J. R. Fraser, G. E. Sadd, W. Spence, J. J. Feeney, T. M. Dimant, W. J. Ewart, H. Wylie, M. L. Wilson, B. Trevithick
Chief Messenger—W. Archer
District Manager and Supervisor of New Business—G. Robertson
Chief Clerk—M. J. K. Heywood
Clerks—W. C. Marchant, A. M. McDonald
District Manager—J. C. Prudhoe
Chief Clerk—J. W. H. Wood
Clerks—G. J. Robertson, H. Mouat
Public Trustee—J. W. Poynton
Chief Clerk—A. A. K. Duncan
Solicitor—F. J. Wilson
Assistant Chief Clerk—T. S. Ronaldson
Accountant—T. D. Kendall
Clerks—T. Stephens, P. Fair, C. Zachariah, P. Hervey, E. C. Reeves, W. A. Fordham, A. Purdie, G. A. Smyth, A. J. Cross, E. A. Smythe, J. B. Jack, W. Barr, E. O. Hales, C. Morris, S. W. Smith, C. A. Goldsmith, H. Masters, R. Price, N. M. Chesney, H. Turner, C. M. Calders, O. Beck, M. E. Nash, J. Menzies, E. P. Hay, R. MacGibbon, J. Mackenzie, O. L. Bowley, G. Morris
District Agent, Christchurch—M. C. Barnett; Clerks, W. S. McGvern, G. Purnell, P. A. Devereux, A. R. Hadfield
District Agent, Auckland—E. F. Warren; Clerks, K. N. H. Browne, V. Adams, C. Robinson
District Agent, Dunedin—F. H. Morice; Clerks, J. Allen, T. Young, W. Layburn
District Agent, Greymouth—T. R. Saywell
District Agent, Nelson—E. P. Watkis
West Coast Settlement Reserves Agent and District Agent, New Plymouth—Thomas W. Fisher; Clerks, H. Oswin, G. Campbell
Superintendent—John McGowan
Deputy Superintendent—G. F. C. Campbell
Chief Clerk—F. J. M. D. Walmsley
Inspecting Accountant—P. Heyes
Clerk in Charge—W. Waddel
Clerks—M. J. Crombie, W. N. Hinchliffe, H. E. Williams, J. E. Thompson, C. B. Collins, W. Auld, A. A. Prichard, A. W. Knowles, T. W. Foote, H. O'Rourke, C. D. Wilson, J. B. Wallis. Typist—C. D. Fraser
Cadets—R. G. McLennan, A. Tudhope, J. F. O'Leary, T. W. Vickery, J. J. M. Harvey
Chief Valuers—W. Duncan, Auckland; A. P. O'Callaghan, Christchurch; A. McKerrow, Dunedin; H. Carswell, Invercargill
Clerk at Auckland—F. B. Robertson
Minister of Health—Hon. Sir J. G. Ward, K.C.M.G.
Director and Chief Health Officer—James M. Mason, M.D., D.P.H.
Assistant Chief Health Officer—Dr. Thomas H. Ambrose Valintine
Native Health Officer—Dr. Maui Pomare
Secretary—E. Horneman
Clerks—H. B. Magrath, T. P. Butler, H. Eastgate, J. W. Taylor, F. Willis. Typistes, Ethel Evans, Gwenllian Craig
Pathologist—J.A. Gilruth, M.R.C.V.S.
Analysts—Wellington, J. S. McLaurin; Auckland, J. A. Pond; Dunedin, J. G. Black; Christchurch, A. W. Bickerton
District Health Officers—Blenheim, Dr. W. Anderson (acting); Napier, Dr. F. I. De Lisle; Auckland, Dr. R. H. Makgill; Dunedin, Dr. F. Ogston; Nelson, Dr. J. P. Frengley; Christchurch, Dr. H. E. Finch; Greymouth, Dr. C. G. Morice
Port Health Officers—Picton, Dr. W. E. Redman; Oamaru, Dr. A. Douglas; Wanganui, Dr. R. C. Earle; Port Chalmers, Dr. G. Hodges; Wellington, Dr. H. Pollen; Westport, Dr. M. Mackenzie; Greymouth, Dr. C. G. Morice; Timaru, Dr. R. S. Reid; Onehunga, Dr. W. G. Scott; Auckland, Dr. E. W. Sharman; Kaipara, Dr. F. M. Purchas; Whangarei, Dr. G. B. Sweet; Bluff, Dr. J. Torrance; Lyttelton, Dr. C. H. Upham; Gisborne, Dr. J. W. Williams; Napier, Dr. T. C. Moore; New Plymouth, Dr. H. A. McClelland.
Sanitary Inspectors—Dunedin, J. G. Gunn; Wanganui, C. A. Schauer; New Plymouth, A. H. Kendall; Auckland, C. C. Winstanley; Napier, M. Kershaw; Nelson, C. Middleton; Christchurch, D. Munro; Invercargill, K. Cameron; Marton, F. C. Wilson; Masterton, G. H. Dolby.
Cadets in the Civil Service are required, after arriving at the age of eighteen years, to serve for three years in a Volunteer corps. Heads of departments are required to see that cadets who come within the regulations join the Volunteer Force, and serve for the period named, and also to notify the Under-Secretary for Defence of the appointment of all cadets coming within this regulation.
Table of Contents
THERE is no State Church in the colony, nor is State aid given to any form of religion. Government in the early days set aside certain lands as endowments for various religions bodies, but nothing of the kind has been done for many years past.
The Right Reverend Moore Richard Neligan, D.D., Auckland; consecrated 1903.
The Right Rev. William Leonard Williams, D.D., Waiapu; consecrated 1895.
The Right Rev. Frederic Wallis, D.D., Wellington; consecrated 1895.
The Right Rev. Charles Oliver Mules, M.A., Nelson; consecrated 1892.
The Right Rev. Churchill Julius, D.D., Christchurch; consecrated 1890.
The Right Rev. Samuel Tarratt Nevill, D.D., Dunedin; consecrated 1871, acting Primate.
The Right Rev. Cecil Wilson, M.A., Melanesia; consecrated 1894.
The Most Rev. Francis Redwood, S.M., D.D., Archbishop and Metropolitan, Wellington; consecrated 1874.
The principal present heads or officers of the various churches, and the places and times of holding the annual or periodical assemblies or meetings, are as follow:-
Church of England.—For Church purposes, the colony is divided into six dioceses, viz.: Auckland, Waiapu, Wellington, Nelson, Christchurch, and Dunedin. The General Synod meets every third year in one or other of the dioceses. Representatives attend from each diocese, and also from the diocese of Melanesia.—President, the Bishop of Dunedin, acting Primate. The Diocesan Synods meet once a year, under the presidency of the Bishop of the diocese. The next General Synod will be held in Auckland, on the 28th January, 1904.
Roman Catholic Church.—The diocese of Wellington, established in 1848, was in 1887 created an Archdiocese and the metropolitan see. There are three suffragan dioceses—Auckland, Christchurch, and Dunedin. A Retreat is held annually in each of the four dioceses, at the end of which a Synod is held, presided over by the Bishop, and at which all his clergy attend.
In January, 1899, the first Provincial Council of New Zealand was held in Wellington, under the presidency of the Metropolitan, and attended by all the Suffragan Bishops, and a number of priests elected specially in each diocese as representatives of the whole Catholic clergy in the colony. The decrees of this Council were approved by Rome in April, 1900, were published on 1st January, 1901, and are now binding in every diocese in New Zealand.
Presbyterian Church of New Zealand.—The General Assembly will meet on the second Tuesday of November, 1903, in First Church, Dunedin; and thereafter, on ordinary occasions, alternately in Wellington and Dunedin. Moderator, the Rev. James Paterson, Wellington; Clerk and Treasurer, Rev. David Sidey, D.D., Napier; Theological Professors, Rev. John Dunlop, M.A., D.D., and Rev. Michael Watt, M.A., D.D; and Mr. James Dunbar, tutor in Greek.
Methodist Church of Australasia in New Zealand.—The annual New Zealand Conference meets on or about the last Tuesday in February, the exact date being determined by the President, who holds office for one year. Each Conference determines where the next one shall assemble. President (1903–4), Rev. J. A. Luxford, Lyttelton; Secretary, Rev. S. Lawry, Palmerston North. The next Conference is to meet in Pitt Street Church, Auckland.
Primitive Methodist Church.—A Conference takes place every January. The next is to be held at Wanganui, commencing 7th January, 1904. The Conference officials for the present year are: President, Rev. G. Clement, Geraldine; Vice-President, Wm. King, Esq., Dunedin; Secretary, Rev. P. J. Cossum, Bluff; Hon. District Secretary, Mr. D. Goldie, Pitt Street, Auckland; Treasurer of Mission Funds, Mr. Joseph Watkinson, Mangere, Auckland.
Baptist Union of New Zealand.—President, Rev. R. S. Gray, Christchurch; Vice-President, H. M. Smeeton, Esq., Auckland; Treasurer, Mr. A. Chidgey, Kirwee. The Union comprises 35 churches, 21 preaching-stations, 3,721 members, and a constituency of 17,000. The denominational organ is the New Zealand Baptist, Editor, Rev. F. W. Boreham, Mosgiel. A Foreign Missionary Society, with an average income of £1,200, employs a doctor, a missionary, three zenana ladies, and 13 native helpers. The sphere of operations is in North Tipperah, East Bengal.
Congregational Union of New Zealand.—The annual meetings are held during the month of February, at such place as may be decided on by vote of the Council. Chairman for 1903–1904, Rev. W. A. Evans, Wellington; Chairman-elect, Rev. John Wilkins, Auckland; Secretary, Rev. A. T. Lee, Devonport, Auckland, Treasurer, Mr. W. H. Lyon, Auckland; Registrar, Mr. F. Meadowcroft, Wellington; Head Office, Auckland. In 1904 the meeting of the Council will be held at Wellington. The Committee of the Union meets in Auckland on the second Tuesday of each month.
Hebrews.—Ministers: Rev. S. A. Goldstein, Auckland; Rev. H. van Staveren, Wellington; Rev. I. Zachariah, Christchurch; Rev. A. T. Chodowski, Dunedin; Mr. Alexander Singer, Hokitika. Annual meetings of the general Congregations are usually held at these places during the month of Elul (about the end of August).
Table of Contents
THE defence forces consist of the Royal N.Z. Artillery and Royal N.Z. Engineers, and the auxiliary forces of Volunteers, Field Artillery, Garrison Artillery, Engineers (submarine mining and field), Mounted Rifles, Rifle, Cycle, Bearer companies, and Defence Rifle Clubs. There is a Commander of the Forces, who is an Imperial officer. A Royal Artillery officer is Staff Officer for Artillery. To the Under-Secretary for Defence all questions of expenditure are referred.
The two islands (North and Middle) are divided into five districts, each commanded by an officer of Field rank, with a staff of drill-sergeants.
This Force is divided into four detachments, which are stationed at Auckland, Wellington (head-quarters), Lyttelton, and Dunedin; their principal duties are to look after and take charge of all guns, ordnance stores, ammunition, and munitions of war at these four centres. The Force has an establishment of 240 rank and file.
This branch is divided between Auckland and Wellington, and has an establishment of 96 of all ranks. They have charge of two submarine mining steamers of the “Sir F. Chapman” class, and of all submarine mining stores.
There are five batteries of Field Artillery (two in the North Island and three in the Middle Island), with a total of 430 of all ranks. They are armed with 15-pounder B.L. and 6-pounder Nordenfeldts, on field-carriages, and go into camp annually for sixteen days.
There are five Garrison Artillery Corps in the North Island, and five in the Middle Island, comprising in all a total of 50 officers and 917 rank and file. They go into camp annually for sixteen days.
There are two corps of Submarine Miners in the North Island, of a total strength of 190. These corps also have cutters, &c., provided, and are instructed in rowing, knotting, splicing, signalling, and other duties pertaining to this branch of the service. Attendance at an annual camp is also compulsory.
This branch consists of four corps, with a total of 349 of all ranks, two in the North and two in the Middle Island. Besides carrying rifles they are provided with entrenching tools and all appliances for making and blowing up bridges or laying land-mines.
There are forty-one corps of Mounted Rifles in the North Island and thirty-one in the Middle Island, with a total strength of 5,478 of all ranks. These corps go into camp for an annual training of six days.
In this branch of the service there are a hundred and twenty corps, fifty-eight being in the North Island and sixty-two in the Middle Island, with a total strength of 7,750 of all ranks, including garrison bands.
There are Volunteer cycle corps at Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Nelson, and Dunedin, of a maximum strength of two officers and twenty-five non-commissioned officers, rank and file: they are attached to the infantry battalions at those centres.
Volunteer bearer corps at Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin are of a maximum strength of three officers and fifty non-commissioned officers, rank and file. There is also a bearer corps at Nelson of a maximum strength of two officers and twenty-five non-commissioned officers, rank and file.
There is a force of forty-one cadet corps—viz., twenty-one in the North Island and twenty in the Middle Island.
These have lately been established by the Government. Members can purchase rifles at cost price from Government. An annual grant of ammunition is made to those members who fulfil conditions as to quarterly drills. There are 111 rifle clubs, comprising about 2,300 men.
The whole of the adult portion of the Force have Lee-Enfield carbines or rifles; Cadets being armed with Martini-Enfield and Snider carbines. Defence rifle clubs are armed with Martini-Enfield rifles.
Members of the Permanent Forces are enrolled to serve for a period of eight years from enrolment, the last three years of such being in the Reserve; adult Volunteers for three years. The Permanent Forces are principally recruited from men who have one year's efficient service in the Volunteers. After passing the gunnery and other courses and serving three years in the Permanent Forces the men are eligible for transfer to police and prison services.
The Instructors for artillery and engineer and submarine mining corps are obtained from the School of Gunnery at Shoeburyness, and from the Royal Engineers, under a three years' engagement, on completion of which they return to their regiments.
An annual capitation of £2 10s. is granted to each efficient Volunteer, and 5s. to each efficient cadet. One hundred and fifty rounds of ball-cartridge are issued each year free to every adult Volunteer, and twenty-five rounds to each cadet over thirteen years of age.
The defence forces of New Zealand are administered under “The Defence Act, 1886,” and “The Defence Act Amendment Act, 1890.”
| Year. | Military Expenditure. | Harbour Defences. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1897–98 | 83,004 | 2,525 | 85,529 |
| 1898–99 | 114,789 | 10,158 | 124,947 |
| 1899–1900 | 184,970 | 5,328 | 190,298 |
| 1900–1901 | 156,218 | 3,960 | 160,178 |
| 1901–1902 | 250,478 | 6,678 | 257,156 |
| 1902–1903 | 292,081 | 6,126 | 298,207 |
| The special expenditure on account of contingents for South Africa is not included. | |||
ELEVEN of the crew of the barque “Spirit of the Dawn,” which was wrecked on Antipodes Island on the 4th September, 1893, remained on the island for eighty-eight days without becoming aware of the existence of the dépôt of provisions and clothing for castaways which is established there. Attention is now drawn to the fact that such dépôts are maintained by the New Zealand Government on that island, and on the Auckland, Campbell, Bounty, Kermadec, and Snares Islands.
The following are the positions of the dépôts:—
Auckland Islands.—A dépôt is placed on the south side of Erebus Cove, Port Ross, and another in Camp Cove, Carnley Harbour, and a third at the head of Norman Inlet. One boat is placed on the north-west end of Adams Island, another on Enderby Island, and another on Rose Island.
Campbell Island.—A dépôt is erected in Tucker Cove, Perseverance Harbour, and a boat has been placed at the head of that harbour.
Antipodes Islands.—A dépôt is placed abreast the anchorage on the north-east side of the principal island.
Bounty Islands.—There is a dépôt on the principal island.
Snares Island.—A dépôt has been established on this island in Boat Harbour.
Kermadec Islands.—A dépôt is established on Macaulay Island, near Lava Cascade, on the north-east end of the island, and another on Curtis Island, at the head of Macdonald Cove, on the northwestern end of the island.
Finger-posts to indicate the direction of the dépôts have also been put up.
The Government steamer visits the Auckland, Campbell, Antipodes, Bounty, and Snares Islands twice a year, and the Kermadec Islands once a year.
Table of Contents
VESSELS visiting New Zealand, and requiring docking or repairs, will find ample accommodation at the principal ports of the colony.
There are in New Zealand four graving-docks; two of these are situated in Auckland, one at Lyttelton, and one at Port Chalmers.
The Auckland Docks are the property of the Auckland Harbour Board, and cost, with machinery, appliances, &c., £250,300. The dimensions of the docks at Auckland are as follow:—
| Calliope Dock. | Auckland Dock. | |
|---|---|---|
| Length over all | 525 feet. | 312 feet. |
| Length on floor | 500 feet. | 300 feet. |
| Breadth over all | 110 feet. | 65 feet. |
| Breadth on floor | 40 feet. | 42 feet. |
| Breadth at entrance | 80 feet. | 43 feet. |
| Depth of water on sill at high water ordinary spring tides) | 33 feet. | 13 1/2 feet. |
Alterations are now being made to the lower altars of Calliope Dock which will enable vessels of 63 ft. beam to be docked without any difficulty.
The following is the scale of charges for the use of the Auckland and Calliope Graving Docks and appliances:—
| A(([0-9]+)) DOCK. | £ | s. | d. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entrance fee | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| For every vessel of 100 tons (gross register), or under, per day | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| For every vessel over 100 tons (gross register), for first 100 tons, per day | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| For every additional ton (gross register), per day | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| For two or more vessels docking at the same time, the tonnage of which together does not exceed 100 tons (gross register), per day each | 2 | 10 | 0 |
| For shores cut in docking or hanging the vessel, there must be paid, according to injury done, such amount as may be fixed by the Dockmaster. | |||
| For use of steam-kiln, 10s. per day. | |||
| For use of pitch furnace, 10s. per day. | |||
| C(([0-9]+)) DOCK. | £ | s. | d. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entrance fee | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 300 tons (gross register) | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 301 to 400 tons (gross register) | 22 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels 401 to 500 tons (gross register) | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 501 to 600 tons (gross register) | 27 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels 601 to 700 tons (gross register) | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 701 to 800 tons (gross register) | 32 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels 801 to 900 tons (gross register) | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 901 to 1,000 tons (gross register) | 37 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels 1,001 to 1,100 tons (gross register) | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 1,101 to 1,200 tons (gross register) | 45 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 1,201 to 1,300 tons (gross register) | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 1,301 to 1,500 tons (gross register) | 55 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 1,501 to 2,000 tons (gross register) | 60 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 2,001 to 3,000 tons (gross register) | 65 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 3,001 to 4,000 tons (gross register) | 70 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels 4,001 to 5,000 tons (gross register) | 75 | 0 | 0 |
The foregoing charges are for three days or less. After the third day in dock the following rates are charged:—
| For all vessels up to 500 tons (gross register) | 4d. per ton per diem. |
| For all vessels of 501 tons to 1,000 tons | 3d. per ton per diem. |
| For all vessels over 1,001 tons up to 2,000 tons | 2 1/2d. per ton per diem. |
| For all vessels over 2,001 tons and upwards | 2d. per ton per diem. |
Twenty per cent. reduction on Calliope Dock rates is allowed when two or three vessels can arrange to dock on the same tide, and remain in dock the same number of hours; but such reduction is not allowed if any of the Auckland Harbour Board's vessels are docked at the same time as another vessel.
For shores cut in docking or hanging the vessel, there is to be paid, according to injury done, such amount as may be fixed by the Dockmaster.
During the year 1902, 79 vessels of various descriptions, with a total of 26,089 tons, made use of the Auckland Graving Dock, occupying it in all 216 days, for repairs or painting.
In Calliope Dock 19 vessels were docked, with an aggregate tonnage of 44,174, and occupying the dock for 107 days.
Dock dues for the year amounted to £2,907 9s. 5d.
Under arrangement with the Admiralty, a complete plant of the most efficient and modern machinery has been provided at Calliope Dock-yard. The workshops are now erected, and all the machinery is placed in position, with the exception of the shear-legs. This plant includes 80-ton shear-legs complete, trolly to carry 80 tons and rails, 10-ton steam crane at side of dock, engines, boilers, overhead travellers; planing, shaping, and slotting machines; radial drills, vertical drills, band-saws for iron, punching and shearing machines, plate-bending rolls; 24 in.-centre gantry lathe, 70 ft. bed; 9 in. and 12 in. gantry lathes, milling - machines, emery - grinders, screwing - machines, ditto for pipes, horizontal boring - machines, Root's blower, smiths’ forges (six), coppersmith's forge, levelling-slabs, steam - hammers, lead-furnace, wall-cranes, zinc-bath, plate-furnace, jib-crane for foundry, circular-saw bench, band-saw for wood, lathe for wood, general joiner, carpenters’ benches (four), kiln for steaming boards, Fox's trimmer, cupola to melt 5 tons of metal, countersinking machine, pipe-bending machine, tools of various descriptions, moulders’ bins, force-pumps for testing pipes, vice-benches, electric-light engines, dynamos (two), &c.; and all other appliances and machinery required to render the plant adequate to repair any of His Majesty's ships upon the station, or any merchant vessel visiting the port. The dock and machinery will be available for use, when not required for His Majesty's vessels, in effecting repairs to any merchant vessel requiring same. Electric lights have been provided for workshops, dock, and dockyard. The dockyard is now connected by telephone with the central exchange. An abundant supply of the purest fresh water is available at Calliope Dock and Calliope Wharf; and a most complete establishment of up-to-date machinery and appliances has been provided.
The Port of Wellington has no dock; but there is a well-equipped patent slip at Evans Bay, on which vessels of 2,000 tons can be safely hauled up. This slip is the property of a private company, and is in no way connected with the Harbour Board. It is 1,070ft. long, with a cradle 260ft. in length. There is a depth of 32ft. at high water at the outer end of the slip. A dolphin and buoys are laid down for swinging ships in Evans Bay.
The company has convenient workshops, which contain machinery necessary for effecting all ordinary repairs to vessels using the slip.
During the year ending 31st March, 1902, ninety-six vessels of various sizes, of an aggregate of 50,037 tons, were taken up on the slip for repairs, cleaning, painting, &c. The charges for taking vessels on the slip and launching them are 1s. per ton on the gross tonnage for the first full twenty-four hours, and 6d. per ton per day afterwards, unless by special agreement.
The Graving-dock at Lyttelton, which is the property of the Harbour Board, is capable of docking men-of-war, or almost all of the large ocean steamers now running to the colony. Its general dimensions are: Length over all, 503ft.; length on floor, 450ft.; length inside caisson at a height of 4ft. above the floor, 462 ft.; breadth over all, 82ft.; breadth on floor, 46ft.; breadth at entrance, 62ft.; breadth where ship's bilge would be, on 6ft. blocks, 55ft.; depth of water on sill at high-water springs, 23ft.
The scale of charges for the use of the dock and pumping machinery are as follow:—
| £ | s. | d. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| For all vessels up to 300 tons, for four days or less | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 301 to 400 tons, for four days or less | 22 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 401 to 500 tons, for four days or less | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 501 to 600 tons, for four days or less | 27 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 601 to 700 tons, for four days or less | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 701 to 800 tons, for four days or less | 32 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 801 to 900 tons, for four days or less | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 901 to 1,000 tons, for four days or less | 37 | 10 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 1,001 to 1,100 tons, for four days or less | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 1,101 to 1,200 tons, for four days or less | 45 | 0 | 0 |
| For all vessels up to 1,201 tons and upwards, for four days or less | 50 | 0 | 0 |
After the fourth day in dock, the following rates are charged:—
| For all vessels up to 500 tons | 4d. per ton per day. |
| For all vessels of 501 tons to 1,000 tons | 3d. per ton per day. |
| For all vessels over 1,001 tons up to 2,000 tons | 2 3/4d. per ton per day. |
| For all vessels over 2,001 tons up to 3,000 tons | 2 1/2d. per ton per day. |
| For all vessels over 3,001 tons up to 4,000 tons | 2 1/4 per ton per day. |
| For all vessels over 4,001 tons up to 5,000 tons | 2d. per ton per day. |
Twenty per cent. reduction on the above rates is allowed when two or three vessels can arrange to dock on the same tide and remain in dock the same number of hours. Two vessels of 1,000 tons each can be docked at the same time. The 20-per-cent. rebate is not allowed if any of the Lyttelton Harbour Board's vessels are docked at the same time as another vessel. The twenty-four hours constituting the first day of docking commences from the time of the dock being pumped out.
Any vessel belonging to H.M. Navy or any colonial Government, or any commissioned ship belonging to any foreign nation, is admitted into the graving dock without payment of the usual dock dues, but is charged only such sum as is necessary for the reimbursement of actual expenditure of stores, wages, and materials.
There are electric lights, one on each side of the graving-dock; and there is a workshop alongside the dock, and several other engineering works within a short distance of it, where repairs and heavy foundry-work can be done.
The graving dock and machinery cost £105,000. The interest and sinking fund on that sum, at 6 1/2 per cent., amounts to £6,825 per annum. Since its construction, the dock dues for the twenty years, ended 31st December, 1902, amounted to £20,388 4s. 10d., and the working expenses to £12,249 13s. 5d., leaving a credit balance for twenty years, ended 31st December, 1902, of £8,138 11s. 5d.
During the year 1902 twenty-three vessels were docked, and the dock dues amounted to £1,266 19s. 3d. For the twenty years, ending 1902, 402 vessels were docked.
Alongside the graving dock is a patent slip, with a cradle 150ft. in length, suitable for vessels of 300 tons. It belongs to the Harbour Board.
The following is the scale of charges:—
Up to 75 tons gross register, £4 for five days, and 10s. per day after the fifth day.
Over 75 tons and up to 150 tons gross register, £6 for five days, and 15s. per day after fifth day.
Over 150 tons and up to 250 tons gross register, £8 for five days, and 20s. per day after fifth day.
Over 250 tons gross register, £10 for five days, and 20s. per day after fifth day.
A day to mean between sunrise and sunset.
The above rates cover the cost of all labour connected with hauling up and launching (the crew of the vessel to give their assistance as may be required), and the cost of blocking a vessel and shifting the blocks after hauling up.
The dock at Port Chalmers is vested in the Otago Dock Trust, a body entirely distinct from the Otago Harbour Board. Vessels of large size can be taken in the Otago Dock, as the following measurements will show:—
| Length over all | 335 feet. |
| Length on the floor | 328 feet. |
| Breadth over all | 68 feet. |
| Breadth on floor | 41 feet. |
| Breadth where ship's bilge would be | 43 feet. |
| Breadth at dock gates | 50 feet. |
| Depth of water on sill at high-water (ordinary spring tides) | 17 1/2 feet. |
Connected with the Otago Dock are a large machine-shop, steam-hammer, and forge, with all the appliances necessary for performing any work that may be required by vessels visiting the port. An 80-ton shear-legs has also been erected for heavy lifts.
There is also a patent slip, used for taking up small vessels.
All vessels using the Otago Graving Dock are liable to dock dues according to the following scale (unless under special contract), revised since the beginning of 1896:—
| £ | s. | d. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vessels under 200 tons, for the first three days, or part of three days | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Vessels of 200 tons, and under 800 tons | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| Vessels of 800 tons and upwards | 50 | 0 | 0 |
And for every day, or part of a day, after the first three days:—
| Vessels under 300 tons | 8d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 300 tons and under 400 tons | 7 3/4d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 400 tons and under 500 tons | 7 1/2d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 500 tons and under 600 tons | 7 1/4d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 600 tons and under 700 tons | 7d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 700 tons and under 800 tons | 6 3/4d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 800 tons and under 900 tons | 6 1/2d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 900 tons and under 1,000 tons | 6 1/4d. per register ton per day. |
| Vessels under 1,000 tons and upwards | 6d. per register ton per day. |
During the twelve months ended 31st December, 1902, the dock was in use 221 working-days. The number of vessels docked was fifty-two, having a total registered tonnage of 48,111.
Table of Contents
PILOTAGE, port charges, berthage charges, &c., at fourteen of the principal harbours in New Zealand, as on the 1st January, 1903 (compiled by Mr. C. Hood Williams, Secretary to the Lyttelton Harbour Board):—
Pilotage (not compulsory): Sailing-vessels, inwards and outwards, 3d. per ton each way.
Steamers, inwards and outwards, 2d. per ton each way when services of pilot are taken.
Pilotage includes the removal fee to or from the berth at 1d. per ton.
Port charges: 3d. per ton half-yearly (on all vessels over 15 tons) in one payment.
Harbourmaster's fees: 1d. per ton. Vessels paying pilotage are exempt.
Exemption berthage certificates are given to competent masters in the coastal and intercolonial trades, but not to those in foreign trade.
Berthage: Every person who shall use any wharf with any vessel shall pay for the use thereof—Ferry steamers, 10s. to £1 10s. per month; other vessels under 20 tons, 6d. and 1s. per day, not exceeding 10s. per quarter. For every vessel not included in the above, 1/4d. per ton per day. Outside berths, 1/8d. per ton per day.
Pilotage (not compulsory): Sailing-vessels over 100 tons, first 100 tons, 6d. per ton; every ton over 100 tons, 2d. per ton. Into and out of Turanganui River: Sailing-vessels, 3d. per ton; sailing-vessels towed, 2d. per ton; steamers, 2d. per ton.
Port charges: Steamers, sailing-vessels, or boats plying within the harbour or engaged in coasting only, 3d. per ton quarterly; steamers sailing-vessels, or boats plying within the harbour and not engaged in coasting, only on arrival (not to exceed 10d. per ton in any half-year), 1d. per ton; steamers or sailing-vessels from beyond the Australian States, on arrival, 4d. per ton.
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage alongside the wharves: Per day or part, under 50 tons, 5s.; over 50 tons and up to 75 tons, 7s. 6d.; over 75 tons up to 100 tons, 10s.; for every additional 50 tons or fraction thereof, 2s. 6d. Vessels discharging outside of bars to pay half foregoing dues. Steamers to pay double rates as per tonnage; and in all cases sailing-vessels to make way for steamers.
Pilotage (not compulsory): Into Inner Harbour—Sailing-vessels, 4d. per ton; steamers, 3d. per ton. To roadstead—First 100 tons, sailing-vessels, 6d. per ton; steamers, 3d. per ton. Every ton over 100 tons—Sailing-vessels, 2d. per ton; steamers, 1d. per ton. Into Breakwater Harbour—First 100 tons, sailing vessels, 6d. per ton; steamers, 3d. per ton. Every ton over 100 tons—Sailing-vessels, 2d. per ton; steamers, 1d. per ton. Outward pilotage, half rates.
Port charges: 6d. per ton quarterly in advance, vessels plying within port or engaged in coasting only; 2d. per ton on arrival of vessels not plying within port or not solely employed in coasting, but not to exceed 1s. per ton in any half-year. Ocean-going vessels (not being “colonial trading” or coasting vessels) returning to port within one month from date of first arrival are exempt from port charges for second or subsequent arrivals within one calendar month.
Harbourmaster's fees: 5s. per vessel of less than 60 tons. Steamers under 60 tons and licensed as lighters are exempt. 1d. per ton sailing-vessels 60 tons and upwards; 10s. per vessel steamers of 60 tons and under 120 tons; 1d. per ton steamers of 120 tons and upwards. Vessels paying for pilotage service inwards do not pay Harbourmaster's fees.
Berthage: Breakwater Harbour wharves—3d. per ton on cargo landed, shipped, or transhipped; 1s. each horse or large cattle shipped or transhipped; 1/2d. each sheep or small animal shipped or transhipped. Other wharves—10s. per vessel of 60 tons; £1 per vessel over 60 tons to 120 tons; 2d. per ton vessels over 120 tons. Half rates only charged where vessels entering the Inner Harbour pay for pilotage services. Vessels licensed as lighters or tow-boats shall, whilst actually employed at lighterage work, only pay one-third of the foregoing charges upon each and every trip.
Hawsers and moorings: Vessels at wharf in Breakwater Harbour—1/4 d. per ton per day, or part of a day, on registered tonnage. Vessels moored to buoys within Breakwater Harbour, 1/8d. per ton per day or part of a day.
Fenders: Vessels at wharves in Breakwater Harbour—5s. per day, vessels under 500 tons; 7s. per day, vessels of 500 tons and under 1,000 tons; 10s. per day vessels of 1,000 tons and under 1,500 tons; 15s. per day, vessels of 1,500 tons and under 2,000 tons; £1 per day, vessels of 2,000 tons; and so on, in proportion.
Pilotage (compulsory): Charged both inwards and outwards, intercolonial or coasting—Sailing-vessels, 3d. per ton; steamers, 1 1/2d. per ton; foreign sailing-vessel or steamer, 1/2 d. per ton.
Port charges: Intercolonial, 4d. per ton, payable half-yearly; foreign, 1/2d. per ton on arrival in roadstead.
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage rate: 3 1/2d. per ton on all cargo landed, shipped, or transhipped outwards; on registered tonnage also 1/2d. per ton.
Warps: 1d. per ton register for first 100 tons; 1/2d. per ton for excess.
Fenders: 1s. per day or part of day.
Water (minimum 3s.): 5s. per 1,000 gallons.
Pilotage: All vessels when piloted by signals from the staff only, 1d. per ton register. River pilotage, to be charged for any assistance rendered by the pilot or any of his crew inside the bar, 2d. per ton. When a pilot boards and conducts a vessel outside the bar, 3d. per ton. Steamers engaged in tendering ocean steamers at anchor in the roadstead charged half pilotage rates.
Port charges: Nil.
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage: For every steamer using any wharf, being berthed alongside, and whether discharging or loading cargo or not, 2d. per ton on gross register for first day of eight working hours, and 1d. for every succeeding day of eight working hours. For every sailing-vessel the charge to be 2d. for first day of eight working hours, and 1/2d. for every succeeding day of eight working hours, not exceeding five days. For every vessel occupying a berth outside another vessel, and loading or discharging cargo, 1/4d. per ton on gross register per day of eight working hours whilst loading or discharging. Ships’ dues on vessels detained in port by stress of weather will not be charged after the third day.
Pilotage (optional): Sailing-vessels inwards, 4d. per ton; sailing-vessels outwards, 3d. per ton; steamers inwards, 3d. per ton; steamers outwards, 2d. per ton. Pilotage includes the removal fee to or from the berth at 1d. per ton.
Port charges: 2d. per ton on arrival; not exceeding 6d. in any half-year. Half-yearly days, 1st January and July. Steamers arriving for coal, stores, water, or for receiving or landing mails or passengers and their luggage, which do not come to any wharf or receive or discharge cargo within the port, are exempt from port charges.
Harbourmaster's or berthing fee on vessels of 120 tons and upwards, 1d. per ton; under 120 tons, 10s. Vessels paying pilotage are exempt. Exemption berthage certificates are given to competent masters in the coastal and intercolonial trades, but not to those in foreign trade.
Berthage: None, unless vessels delay discharging or loading for an undue time.
Pilotage (compulsory): Steamers, inwards and outwards, 1d. per registered ton. Sailing-vessels, inwards and outwards, 3d. per ton. Minimum pilotage each way (in all cases), £1.
Port charges: For vessels not employing the pilot, to pay the following, upon first arrival, half-yearly: Vessels over 100 tons register, 1s. per ton; vessels under 100 tons register, 6d. per ton.
Harbour lights: Vessels not employing the pilot, over 100 tons register, 1d. per ton; under 100 tons register, 1/2d. per ton, on arrival.
Harbourmaster's fees: 120 tons and upwards, 1d. per ton; less than 120 tons, 10s. for each removal of any steamer or sailing vessel within the harbour.
Berthage, fenders, and warps: Nil.
Pilotage (not compulsory). Signal-station. Four pilots authorised: Vessels up to 120 tons register, 1d. per ton; over 120 tons, 2d. per ton inwards and outwards; minimum charge, 5s.; maximum charge, £10.
Port charges: Receiving and discharging ships’ ballast, 1s. per ton; minimum charge, 20s.; 1d. per ton for use of shoot.
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage: Use of wharf, for every vessel up to 1,400 tons lying at wharf, 1d. per ton net register per trip; for every vessel over 1,400 tons, 2d. per ton net register per trip; minimum charge, 5s. No vessel to be charged for more than one trip in any one week.
Pilotage: Free (signal-station).
Port charges: Discharging ships’ ballast, 6d. per ton
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage: Use of wharf, 6d. per ton net register per trip. Vessels in ballast for coal or timber, 1d. per ton net register for the first four days; maximum, £5 10s.; minimum, 5s.
Pilotage (compulsory): Pilotage, inwards and outwards, sailing-vessels 3 1/2d. per ton; steamers, 2 1/2d. per ton. Free on second call on same vovage.
Port charges: 2d. per ton, quarterly in advance, for vessels of 100 tons and upwards plying within the port or employed in coasting only, not to exceed 6d. per ton in any half-year; 2d. per ton for vessels of 100 tons and upwards not plying within the port or not solely employed in coasting, not to exceed 6d. per ton in any half-year. For exemptions from pilotage and harbour fees, see sections 132, 133, and 134 of “The Harbours Act, 1878.”
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthing charges: None.
Warps (21 in. coir hawsers): £1 per warp for use during a vessel's stay in port, not exceeding six months.
Fenders (soft wood): 10s. for first day, and 5s. er day after. 10s. for use of each hardwood fender.
Pilotage (compulsory): Sailing-vessels, 3d. per ton inwards and outwards; when tug used, 2d. per ton; steamers, 2d. per ton inwards and outwards. Foreign and intercolonial steamers under 3,500 cargo tons, working 800 tons or less, only one pilotage fee; 3,500 tons or over, working 1,000 tons cargo or less, one pilotage fee only.
Port charges: Coasters, 1 1/2d. per ton each trip; sailing-vessels, not coasters, 3d. per ton each trip; steam-vessels, not coasters, 6d. per ton on cargo worked; in all cases not to exceed 1s. 3d. per ton in any half-year. Intercolonial steamers coming coastwise 1 1/2d. per ton register, or 6d. per ton on cargo landed and shipped, whichever rate may be the lesser.
Harbourmaster's fees: 1d. per ton each service; vessels less than 120 tons, 10s.; steamers of 1,000 tons or over, which have loaded wholly in New Zealand or Australian ports, working 500 tons of cargo or less, only one harbourmaster's fee. This fee is charged to all vessels or steamers not paying pilotage.
Berthage: 3d. per ton on all cargo landed or shipped.
Hawsers and moorings: Vessels at wharves, 1/2d. per ton register for first seven days; subsequent days, 1/4d. per ton. Vessels at buoys, under 800 tons register, 1/8d. per ton; over 800 tons, 1/16d. per ton.
Fenders: Sailing-vessels under 500 tons register, 2s. per day; under 1,000 tons, 3s. per day; over 1,000 tons, 4s. per day. Steamers under 1,000 tons register, 4s. per day; under 1,500 tons, 10s. per day; under 2,000 tons, 15s. per day; over 2,000 tons, £1 per day.
Tonnage rate: On cargo, inwards or outwards—Coal, merchandise, stone, produce, and timber, 8d. per ton; wool, 2s. per ton; frozen sheep, 1d. per carcase; frozen lamb, 1d. per carcase; rabbits and hares, 3s. per ton, gross weight; all other frozen goods 3s. per ton, gross dead weight; live-stock, 1s. 8d. per ton. Note.—Collected in the same manner as berthage dues have been collected.
WARPS: 1/2d. per ton per day for seven days; 1/4d. per ton per day thereafter.
Pilotage (compulsory): Inwards and outwards, sailing-vesssls without tug, 6d. per ton; with tug, 4d. per ton; steamers, 4d. per ton. Foreign steamers calling twice on one voyage only charged once. All vessels holding exemption certificates, one annual pilotage. For every vessel under steam carrying an exempt pilot and employing a Board's pilot the charge shall be 1/2d. per ton for the Upper Harbour.
Port charges: 6d. per ton half-yearly, all vessels.
Harbourmaster's fees: Vessels less than 120 tons, 10s.; over 120 tons, 1d. per ton.
Berthage: Vessels trading within the port—10 tons, 5s. per quarter; 25 tons, 10s. per quarter; 50 tons, 15s. per quarter; 100 tons, £1 per quarter. Vessels trading beyond the port—Sailing-vessels 1/4d. per ton (maximum, eighteen days, £10); steam-vessels, 1/2d. per ton per day. Vessels laid up for less than a month, one-half the above rates; over a month, 1/2d. per ton per month.
Towage: When assistance is given to steam-vessels under steam, one-fourth usual towage, not exceeding £5 for Upper Harbour, and £7 for Lower Harbour.
NOTE.—Foreign steamers taking or discharging not more than 50 tons general cargo and 100 tons frozen produce, pay £50 for port charges, pilotage, and harbourmaster's fees; also maximum charges on any one vessel, £200.
Pilotage (compulsory): Steamers, inwards and outwards, 2 1/2d. per registered ton; sailing-vessels, 4 1/2d. inwards and outwards if tug not employed; 2 1/2d. per registered ton inwards and outwards if tug employed. Sailing-vessels in ballast, 2 1/2d. per registered ton inwards and outwards. Steamers in and out, 5d. per registered ton, payable yearly; sailing-vessels, in and out, 9d. per registered ton, payable yearly.
Port charges: On all vessels, per trip, 2d. per registered ton, or in one sum, half-yearly from date of entry, 6d. per registered ton.
Harbourmaster's fees: Free.
Berthage: Steamers, 2d. per ton net register for the first day, and 1d. per ton per week or part of a week thereafter. Sailing-vessels and hulks of over 50 tons register, 1d. per ton net register per week for the first four weeks, and 1/4d. per ton per week thereafter.
Towage assistance to steamers using their own motive power: Over 3,000 tons, £5; over 2,000 tons, £4; under 2,000 tons, £3.
Maximum charge for berthage dues, pilotage, and port charges, £180 in any one visit.
Steamers calling more than once on same voyage only charged one inward and outward pilotage.
Wharfage rates at fourteen of the principal harbours in New Zealand, as on 1st January, 1903 (compiled by Mr. C. Hood Williams, Secretary to the Lyttelton Harbour Board):—
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton imports; 1s. per ton exports.
Transhipments: Half-rates when declared before landing, or 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and seven days’ storage.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—1s. 6d. per ton landed; 1s. per ton shipped.
Transhipments: Half-rates when declared before landing, or 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and seven days’ storage.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—1s. 6d. per ton landed; 1s. per ton shipped.
Transhipments: Half-rates when declared, or 2s. 6d. per ton, including seven days’ storage and labour.
Wool.—6d. per bale, shipped or landed.
Transhipments: If landed, dumped, and re-shipped, 3d. per bale.
Coal.—1s. 3d. per ton landed; 6d. per ton shipped.
Transhipments: Shipped or discharged over side for steamer's use, free.
Timber.—Sawn, 2s. per 1,000 ft. landed; 1s. per 1,000 ft. shipped. Baulk or round (less 12 1/2 per cent.), 1s. per 1,000 ft. landed, 6d. per 1,000 ft. shipped.
Passengers’ luggage under half ton, goods carried by hand by passengers, and single packages under 5 ft. measurement, free.
General Merchandise.—Imports, 5s. to 6d.; exports, 2s. 6d. to 6d. By measurement, from 40 cubic feet to 4 cubic feet; same for weight. Ale, beer, and porter, per gallon—Import, 1 1/2d., export, 1/2d.; spirits and wine, per ton measurement, 7s. 6d. No export charges on goods that have paid inward wharfage.
Transhipments: Free.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—Grain—Imports, 5s.; exports, 1s. Grass seed—Imports, 5s.; exports, 2s. Potatoes—Imports, 5s.; exports, 2s. 6d. (12 sacks).
Transhipments: Free.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—Sheep, 2d. per carcase; lambs, 1d. per carcase; haunches, legs, &c., 2s. 6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Free.
Wool.—1s. 3d. per bale, export.
Transhipments: 3d. per bale if landed and reshipped. Free if transhipped into vessel.
Coal.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Coal for engines and freezing-ships, free.
Timber.—Sawn, 4s. per 1,000 ft.; baulk, 1s. per 1,000 ft., imports; 1s., and 6d., per 1,000 ft., exports.
Transhipments: Free.
General Merchandise.—2s. 6d. per ton imports, 1s. 3d. per ton exports, according to measurement or weight. If labour supplied, add on 9d. imports, and 3d. exports. Ballast, inwards, 1s. per ton; cutwards, 1s. per ton. Empties, half rates.
Transhipments: Quarter import rates, Outer Harbour; half import rates, Inner or Breakwater Harbours.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—2s. 6d. imports; 1s. 3d. exports, according to measurement or weight. If labour supplied, add on 9d. imports, and 3d. exports.
Transhipments: Quarter import rates, Outer Harbour; half import rates, Inner or Breakwater Harbours.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—Imports free; exports 2s. 6d. per ton. Tallow and pelts, imports free; exports 2s. 6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Quarter import rates, Outer Harbour; half import rates Inner or Breakwater Harbours.
Wool.—1s. per bale, exports only. Imports, free.
Transhipments: 3d. over side; 6d. per bale if landed for transhipment.
Coal.—2s. imports; 1s. exports.
Transhipments: Quarter rates, Outer Harbour; half rates, Inner or Breakwater Harbours. Coal for engines and freezing-ships, Outer Harbour, free, if declared so.
Timber.—3s. 4d. per 1,000 ft., imports; 1s. 3d. per 1,000 ft. exports.
Transhipments: Half rates, Inner or Breakwater Harbours; quarter rates, Outer Harbour.
NOTE.—Goods other than wool and flax landed on a wharf for transhipment to a vessel lying at another berth, charged inward wharfage only when declared at time of entry
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: 1s. 6d. per ton.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—2s. per ton; grass-seed, 2s. (20 sacks).
Transhipments: 1s. 6d. per ton.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: 1s. 6d. per ton.
Wool.—6d. per bale; five bales of 4 cwt., 2s. per ton; three bales of over 4 cwt. 2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Three-quarter rates.
Coal.—2s. per ton; brown coal, 1s. 9d., with labour.
Transhipments: Three-quarter rates, with labour.
Timber.—480 ft. per ton, 2s.; hardwood, 320 ft. per ton (rough or sawn), 2s., with labour.
Transhipments: Three-quarter rates.
General Merchandise.—Imports, 3s. per ton; exports, 2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Half-rates.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—Imports, 3s. per ton; exports, 2s. per ton. Potatoes, export, 1s. per ton.
Transhipments: Half-rates.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—Sheep, 1/2d. per carcase; lambs, 1/2d. per carcase; legs, shoulders, and loins calculated at so many to a carcase, according to freight.
Wool.—6d. per bale.
Transhipments: Half rates.
Coal.—1s. per ton. Coal for ship's use, outward, 6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Half-rates.
Timber.—6d. per 100 ft.; for shipment, 2d.; white pine, 1d.
Transhipments: Half rates.
General Merchandise.—2s per ton inwards, including labour and one night's storage. Inward cargo landed after noon on Friday is stored free till noon on following Monday; landed after noon on Saturday is stored free till 5 p.m. on the following Tuesday. 1s. per ton outwards, including labour. Railway wharfage—1s. inwards; 6d. outwards, without labour.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage. Over side of vessel lying at wharf, 6d. per ton.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—2s. per ton inwards, including labour and one night's storage; 1s. per ton outwards, including labour. Railway wharfage—1s. inwards; 6d. outwards, without labour.
Transhipments: 2s. per ton, including labour and seven days’ storage. Over side of vessel at wharf, 6d. per ton.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—1s. inwards; 1s. outwards, without labour. Railway wharfage—1s. inwards; 6d. outwards, without labour.
Transhipments: Meat, 1s. 3d. per ton, without labour; butter, 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and storage. Meat, butter, &c., over side of vessel at wharf, 6d. per ton.
Wool.—4d. per bale at Railway Wharf, without labour; 6d. per bale at other wharves, including labour.
Transhipments: 6d. per bale, including labour, and 3d. additional if stored. Over side of vessel to vessel at wharf, 3d. per bale.
Coal.—1s. per ton imports; 6d. per ton exports, without labour. Railway wharfage—1s. per ton inwards; 6d. per ton outwards, without labour.
Transhipments: Across wharf for steamer's use, free. From vessel or hulk to vessel at wharf, free.
Timber.—2d. per 100 ft. inwards; 1 1/2d. per 100 ft. outwards, without labour. If labour supplied, 2d. per 100 ft. added inwards, and 1 1/2d. outwards. Railway wharfage—2d. inwards; 1 1/2d. outwards, without labour.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including seven days’ storage and labour; and 6d. over vessel's side into another.
Harbour Improvement Rate.—The charge of 3d. per ton shall be made to and payable by ships to the Board, as a Harbour Improvement Rate on all goods landed on the wharves or landing-places under the control of the Board, except on coal and on ballast, and except on such goods as are the products of the Colony of New Zealand and are landed for the purpose of transhipment to vessels to be carried out of the colony: Provided that for the purposes of this by-law the following measurements shall be taken: Empties, half tonnage; wool, five bales to the ton; great cattle, each one ton; small cattle, twelve to the ton; timber, 500 ft. superficial measurement to the ton; bricks, slates, and tiles, 500 to the ton; carts and carriages, each two tons; loose hides, twenty-five to the ton.
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton, imports and exports, with labour.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; 2s. 6d. if landed.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—1s. 6d. per ton, imports and exports, with labour.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; 2s. 6d. if landed.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—None shipped.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Wool.—Exports, 1s. per bale; imports free.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Coal.—1s. per ton imports; 2s. with labour. Free exports.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, with labour. Free, when not landed on wharf.
Timber.—1d. per 100 ft. super., import; 1d. per 100 ft. super., export; 2s. per ton by measurement, with labour.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed on wharf. Re-shipments, 2s. 6d. per ton.
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage.
Wool.—6d. per bale.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
Coal.—6d. per ton.
Timber.—2d. per 100 ft. If for export and carried by rail, free.
General Merchandise.—3s. per ton. This charge includes 1s. a ton for receiving and delivering.
Transhipments; 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
rain and Agricultural Produce—3s. per ton. This charge includes 1s. a ton for receiving and delivering.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—3s. per ton. This charge includes 1s. a ton for receiving and delivering.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage.
Wool.—6d. per bale.
Transhipments: 2s. 6d. per ton, including labour and one week's storage; 1s. per ton if transhipped to vessel or lighter.
Coal.—6d. per ton inwards; 3d. outwards.
Timber.—2d. per 100 ft. If for export and carried by rail, free.
General Merchandise.—1s. 6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Free, whether landed on wharf or otherwise.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Free.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Free, whether landed on wharf or otherwise.
Wool.—6d. per bale.
Transhipments: Free.
Coal.—6d. per ton.
Transhipments: Free, whether landed on wharf or otherwise.
Timber.—3d. per 100 ft.
Transhipments: Free.
N.B.—All reshipments of goods from Lyttelton under declaration, free.
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Half rates.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—1s. 6d. par ton.
Transhipments: Half rates.
Frozen Meat.—1/2d. per carcase.
Transhipments: Half rates.
Wool.—1s. per bale.
Transhipments: Half rates.
Coal.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Half rates. For bunkering purposes, free.
Timber.—4d. per 100 ft.
Transhipments: Half rates.
General Merchandise.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Free.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Free.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—1/2d. per sheep. Butter, as merchandise, 2s. per ton. Other frozen goods, 2s. per ton
Transhipments: Free.
Wool.—6d. per bale.
Transhipments: Free.
Coal.—2s. per ton.
Transhipments: Free.
Timber.—5d. and 7d. per 100 ft. Fencing posts and rails, 4s. per 100. Palings, 7d. per 100.
Transhipments: Free.
Stone.—1/2d. per foot.
Live Cattle and Horses.—2s. 6d. each; yearlings, half rates. Sheep, 2d. each; pigs, 4d. each.
General Merchandise.—3s., 4s., and 5s. per ton, imports; 9d., 2s., and 3s. per ton, exports. (Classified.) Manufactured articles and articles which have paid an import duty, free.
Transhipments: 2s. per ton.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—1s. per ton, imports; 1s. 3d. per ton by weight, exports; bran and pollard, exports, free.
Transhipments: 1s. per ton.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—3s. per ton, exports; butter, imports, 4s. per ton; frozen meat, imports, 5s. per ton; sheep and lambs, 1d. per carcase, exports.
Transhipments: 2s. per ton.
Wool.—Exports, 3s. per ton by measurement; 4s. per ton, imports (three bales to ton).
Transhipments: 2s. per ton by measurement.
Coal.—3s. per ton, imports: 9d. per ton, exports.
Transhipments: 2s. per ton.
Timber.—6d. and 3d. per 100 superficial feet, imports; exports, free.
Transhipments: 2s. per ton by measurement. Notice of transhipment must be given within twenty-four hours after ship's arrival.
General Merchandise.—1s. 10d. per ton, imports and exports.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Grain and Agricultural Produce.—11d. per ton, imports and exports.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Frozen Meat, Butter, &c.—11d. per ton, exports; cheese, 1s. per ton.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Wool.—Exports, 9d. per bale; imports free.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed.
Coal.—1s. 6d. per ton, imports; free exports.
Transhipments: 1s. 6d. per ton when landed ex hulk; free when not landed on wharf.
Timber.—1s. per 1,000 ft. super., import; 1s. per 1,000 ft. super., export.
Transhipments: Free, when not landed on wharf; half rates if landed on wharf.
THE coasts of New Zealand are, considering their extent, fairly well lighted, but there are many places where lights are still required. Additions to the existing lights are made from time to time as funds are available.
There are twenty-nine coastal lights—eight of the first order, fifteen of the second, three of the third, and three of smaller orders, and a second order light is about to be erected on Kahurangi Point, on the west coast of the Middle Island, the tower for which is now being built.
There has been no special difficulty in the erection of lighthouses in New Zealand, apart from the trouble caused by indifferent landings. There are no lighthouses built in the sea, such as the well-known Eddystone or Bell Rock. That on The Brothers is the only one which it is considered necessary to keep as a rock-station: that is, the keepers are relieved from time to time, three being always at the station and one on shore.
The cost of the erection of the lighthouses is given by the Marine Department as about £181,600 (the Ponui Passage Lighthouse, having been built by the Provincial Government of Auckland, the cost is not given). The annual consumption of oil is about 21,700 gallons; and the cost of maintenance, irrespective of the cost of maintaining the lighthouse steamer, is about £16,100 a year. This amount includes cost of new houses at Farewell Spit, and sundry repairs at other stations.
Besides the coastal lighthouses, there are harbour-lights at most of the ports of the colony for the guidance of vessels into and out of the ports.
The following table shows the names of the lighthouses, indicating also their situation, the order of apparatus, description, period (in seconds) and colour of the lights, and of what material the respective towers are built:—
| Name of Lighthouse. | Order of Apparatus. | Description. | Period of Revolving Light. | Colour of Light. | Tower built of. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dioptric. | Seconds. | ||||||||
| Cape Maria van Diemen |  | 1st order | Revolving | 60 | White |  | Timber. | ||
| .. | Fixed | .. | Red, to show over-Columbia Reef | ||||||
| Moko Hinou | 1st order | Flashing | 10 | White | Stone. | ||||
| Tiri-Tiri (Auckland) | 2nd order | Fixed | 10 | White, with red arc over Flat Rock | Iron. | ||||
| Ponui Passage | 5th order | Fixed | .. | White and red | Timber | ||||
| Cuvier Island | 1st order | Revolving | 30 | White | Iron. | ||||
| East Cape | 2nd order | Revolving | 10 | White | Iron. | ||||
| Portland Island |  | 2nd order | Fixed | 30 | White |  | Timber | ||
| 2nd order | Fixed | .. | Red, to show over Bull Rock | ||||||
| Cape Palliser | 2nd order | Flashing | Twice every half-minute, with three seconds intervals between flashes | White | Iron. | ||||
| Pencarrow Head | 2nd order | Fixed | .. | White | Iron. | ||||
| Cape Egmont | 2nd order | Fixed | .. | White | Iron. | ||||
| Manukau Head | 3rd order | Fixed | .. | White | Timber. | ||||
| Kaipara Head | 2nd order | Flashing | 10 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Brothers (in Cook Strait) |  | 2nd order | Flashing | 10 | White |  | Timber. | ||
| .. | Fixed | .. | Red, to show over Cook Rock | ||||||
| Cape Campbell | 2nd order | Revolving | 60 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Godley Head (Lyttelton) | 2nd order | Fixed | .. | White | Stone. | ||||
| Akaroa Head | 2nd order | Flashing | 10 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Moeraki | 3rd order | Fixed | .. | White | Timber. | ||||
| Taiaroa Head | 3rd order | Fixed | Red | Stone. | |||||
| Cape Saunders | 2nd order | Revolving | 60 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Nugget Point | 1st order | Fixed | .. | White | Stone. | ||||
| Waipapapa Point | 2nd order | Flashing | 10 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Catadioptric. | |||||||||
| Dog Island | 1st order | Revolving | 30 | White | Stone. | ||||
| Dioptric. | |||||||||
| Centre Island | 1st order | Fixed | .. | White, with red arcs over inshore dangers | Timber. | ||||
| Puysegur Point | 1st order | Flashing | 10 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Cape Foulwind | 2nd order | Revolving | 30 | White | Timber. | ||||
| Farewell Spit | 2nd order | Revolving | 60 | White, with red arc over Spit end | Timber. | ||||
| Nelson | 4th order | Fixed | .. | White, with red arc to mark limit of anchorage | Iron. | ||||
| French Pass | 6th order | Fixed | .. | Red and white, with white light on beacon | Iron. | ||||
| Stephens Island | 1st order |  | Group flashing |  | 30 | White | Iron. | ||
Table of Contents
| Name. | Date from which Pension commenced. | Amount. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
* By an Act passed in 1871 the pension system was abolished in New Zealand, and in 1893 the Civil Service Insurance Act was passed. * Per diem. * Per diem. (a) 1s 6d. from 25th October, 1869; increased to 2s. 2d., 7th December, 1870. (b) 1s. from 17th December, 1868, to 17th December. 1869; 1s. 6d. from 17th December, 1869, to 17th December, 1870; 8d. from 17th December, 1870, to 30th September, 1874; increased to 1s. 6d 1st October, 1874. (c) 2s. from 5th June, 1867, to 5th June, 1868; 2s. from 5th June, 1868, to 5th June, 1869; permanent from 9th November, 1869. (d) 2nd October, 1869; ceased on 9th April, 1870; renewed, 22nd April, 1874. (e) 1s. 6d. from—, 1867; increased to 2s. from 14th February, 1868. (f) 1s. for twelve months, from 9th April, 1870; 2s. 8d., permanent, from 1st May, 1871. (g) 1s. 6d. for twelve months, from 18th October, 1869; 1s. 6d. for twelve months, from October, 1870; permanent, from 5th November, 1871. (h)1s. 6d. for eight months, from 20th September, 1869; 2s. 2d. for twelve months, from 11th June, 1870; 2s. 2d. for twelve months, from 11th June, 1871; 2s. 2d. from 11th June, 1872: permanent from 12th June, 1873. (i) 1s. from 10th May, 1865; renewed for twelve months, April, 1866 again renewed for twelve months; 8d. for twelve months, from 1868 to 10th May, 1869; 6d. for twelve months, from May, 1869; permanent from 11th May, 1870. | ||||
| Under “The Civil Service Act, 1866.”* | ||||
| £ | s. | d. | ||
| Andrews, A. | 1 May, 1896 | 141 | 12 | 0 |
| Anderson, I. G. | 6 Jan., 1896 | 261 | 18 | 1 |
| Bacon, T. | 1 Nov., 1901 | 96 | 4 | 0 |
| Baddeley, H. C. | 12 Jan., 1888 | 225 | 0 | 0 |
| Baker, E. | 1 Nov., 1880 | 214 | 17 | 1 |
| Barnes, G. H. | 16 Feb., 1896 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Batkin, C. T. | 1 April, 1890 | 533 | 6 | 0 |
| Bertrand, J. R. | 17 Feb., 1895 | 135 | 0 | 0 |
| Bicknell, F. | 1 Feb., 1882 | 96 | 13 | 4 |
| Blomfield, J. | 21 Mar., 1889 | 101 | 15 | 0 |
| Boers, W. G. | 24 Oct., 1901 | 73 | 13 | 7 |
| Bridson, W. | 1 Aug., 1893 | 146 | 8 | 7 |
| Browne, G. J. | 1 Mar., 1902 | 200 | 0 | 0 |
| Brown, W. R. E. | 1 Aug., 1892 | 265 | 16 | 8 |
| Bull, J. | 1 Nov., 1902 | 221 | 13 | 4 |
| Burgess, A. | 1 June, 1886 | 116 | 13 | 4 |
| Burke, J. | 1 July, 1899 | 89 | 0 | 11 |
| Burns, J. | 1 April, 1902 | 197 | 6 | 8 |
| Butts, E. D. | 1 April, 1893 | 258 | 6 | 8 |
| Calders, H. | 1 Nov., 1902 | 255 | 0 | 0 |
| Campbell, F. E. | 1 Mar., 1890 | 466 | 13 | 0 |
| Campbell, R. A. F. | 1 Aug., 1901 | 155 | 0 | 0 |
| Catley, J. T. | 1 Oct., 1898 | 223 | 6 | 8 |
| Cheesman, W. F. | 1 April, 1890 | 154 | 15 | 1 |
| Clarke, H. T. | 1 Jan., 1879 | 400 | 0 | 0 |
| Clarke, H. | 1 Oct., 1879 | 98 | 13 | 0 |
| Coney, J. C. | 1 Feb., 1902 | 283 | 0 | |
| S Cook, R. C. | 1 Sept., 1895 | 160 | 14 | 3 |
| Costall, J. | 10 July, 1892 | 131 | 3 | 10 |
| Creeke, W. | 1 April, 1891 | 52 | 15 | 8 |
| Crowe, A. | 31 Dec., 1885 | 63 | 12 | 3 |
| Culpan, W. | 1 Dec., 1868 | 62 | 10 | 0 |
| Cunningham, J. | 1 Feb., 1888 | 175 | 0 | 0 |
| Denham, E. | 1 Aug., 1902 | 316 | 13 | 4 |
| Dick, S. J. | 1 Feb., 1893 | 250 | 0 | 0 |
| Dickey, A. J. | 1 Nov., 1875 | 122 | 0 | 5 |
| Earle, J. | 13 Nov., 1888 | 104 | 10 | 0 |
| Elliott, S. | 1 July, 1898 | 110 | 11 | 4 |
| Falck, F. | 1 Mar., 1893 | 125 | 13 | 4 |
| Freeth, J. J. | 1 Mar., 1894 | 116 | 13 | |
| Gill, R. J. | 1 Sept., 1886 | 226 | 11 | 5 |
| Gore, R. B. | 1 Oct., 1902 | 276 | 0 | |
| Graham, G. H. | 8 Sept., 1891 | 52 | 10 | 0 |
| Giles, J. | 1 Feb., 1894 | 238 | 6 | 8 |
| Halliday, C. | 31 Aug., 1886 | 96 | 13 | 4 |
| Hamilton, M. | 11 July, 1880 | 200 | 0 | 0 |
| Hart, A. | 1 April, 1902 | 215 | 16 | 8 |
| Hart, J. T. | 12 Nov., 1890 | 193 | 7 | 0 |
| Haselden, C. J. A. | 1 July, 1896 | 255 | 19 | 1 |
| Heddell, P. | 17 Oct., 1894 | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| Henn, J. | 1 April, 1893 | 88 | 3 | 4 |
| Hill, C. J. | 9 Feb., 1895 | 72 | 0 | 0 |
| Holden, T. | 13 Oct., 1878 | 31 | 5 | 0 |
| Jackman, S. J. | 1 May, 1892 | 149 | 6 | 8 |
| Johnson, J. W. | 1 May, 1898 | 78 | 1 | 6 |
| Johnston, S. | 8 June, 1900 | 173 | 8 | 3 |
| Kaye, R. | 1 Dec., 1901 | 216 | 13 | 4 |
| Keetley, E. | 1 July, 1884 | 18 | 12 | 10 |
| Kissling, T. | 1 Jan., 1894 | 317 | 5 | 2 |
| Laing, E. B. | 1 April, 1887 | 112 | 10 | 0 |
| Laing, W. | 1 Feb., 1896 | 212 | 10 | 0 |
| Lang, A. | 1 Feb., 1893 | 75 | 15 | 3 |
| Lincoln, R. S. | 1 Mar., 1889 | 68 | 17 | 0 |
| Lodge, W. F. | 1 Oct., 1881 | 185 | 0 | 0 |
| Lubecki, A. D. | 1 April, 1896 | 200 | 0 | 0 |
| Marshed, E. T. | 1 Jan., 1902 | 185 | 0 | 0 |
| Millar, G. | 1 Feb., 1896 | 80 | 7 | 0 |
| Miller, F. | 1 April, 1899 | 141 | 13 | 4 |
| Mitford, G. M. | 1 Feb., 1869 | 196 | 15 | 0 |
| Monson, J. R. | 1 Oct., 1882 | 271 | 16 | 0 |
| Monro, H. A. H. | 1 Nov., 1880 | 342 | 17 | 2 |
| Morpeth, W. J. | 4 Aug., 1894 | 195 | 4 | 9 |
| Morrow, H. | 1 June, 1890 | 120 | 16 | 8 |
| McCulloch, H. | 1 Aug., 1890 | 233 | 0 | 0 |
| MacDonnell, R. T. | 23 July, 1890 | 150 | 0 | 0 |
| McKellar, D. | 1 Nov., 1901 | 347 | 13 | 9 |
| McKellar, H. S. | 1 Aug., 1892 | 433 | 6 | 8 |
| McPherson, D. | 1 Mar., 1903 | 179 | 1 | 10 |
| Nelson, J. | 1 Oct., 1901 | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| Norris, E. F. | 1 Oct., 1895 | 88 | 17 | 9 |
| Nuttall, J. | 1 July, 1897 | 74 | 13 | 4 |
| O'Connor, R. | 1 Sept., 1892 | 147 | 0 | 6 |
| Palmer, T. | 3 April, 1902 | 107 | 18 | 4 |
| Parris, R. | 1 Jan., 1877 | 314 | 5 | 8 |
| Pasley, E. W. | 1 Nov., 1901 | 215 | 16 | 8 |
| Pearson, W. H. | 30 Sept., 1884 | 340 | 9 | 6 |
| Phillips, W. M. | 1 Dec., 1894 | 69 | 4 | 5 |
| Pickett, R. | 1 Aug., 1866 | 209 | 10 | 6 |
| Pinwill, A. | 1 July, 1891 | 120 | 17 | 0 |
| Pitt, H. | 1 May, 1881 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Powell, D. | 1 July, 1893 | 44 | 1 | 8 |
| Rawson, C. E. | 1 Dec., 1895 | 244 | 0 | 11 |
| Reid, W. S. | 1 Nov., 1900 | 500 | 0 | 0 |
| Rennell, W. | 1 Dec., 1895 | 167 | 18 | 4 |
| Robertson, J. | 6 Oct., 1892 | 155 | 0 | 0 |
| Rodgerson, W. J. | 1 July, 1892 | 248 | 6 | 8 |
| Rowe, C. | 1 Oct., 1894 | 109 | 16 | 0 |
| Searancke, W. N. | 1 Feb., 1879 | 240 | 0 | 0 |
| Shrimpton, J. | 16 July, 1889 | 146 | 14 | 0 |
| Silvius, H. | 17 Jan., 1900 | 72 | 10 | 0 |
| Sinclair, A. | 1 June, 1878 | 195 | 0 | 0 |
| Slater, J. | 1 April, 1898 | 223 | 16 | 2 |
| Smith, J. | 1 June, 1894 | 49 | 5 | 6 |
| Smith, S. P. | 1 Nov., 1900 | 500 | 0 | 0 |
| Smith, T. H. | 1 July, 1876 | 371 | 8 | 7 |
| Stevens, P. | 1 Dec., 1892 | 183 | 0 | 0 |
| Stewart, J. T. | 1 May, 1889 | 300 | 0 | 0 |
| Swingland, P. | 1 Nov., 1899 | 96 | 0 | 0 |
| Teesdale, F. | 7 Oct., 1899 | 118 | 16 | 8 |
| Tennant, J. | 1 Jan., 1901 | 293 | 6 | 8 |
| Thomas, G. W. | 1 Nov., 1875 | 38 | 15 | 0 |
| Thompson, R. | 1 Mar., 1896 | 220 | 0 | 0 |
| Tizard, E. F. | 1 July, 1888 | 180 | 19 | 0 |
| Treseder, P. | 13 Oct., 1897 | 184 | 3 | 4 |
| Tucker, W. | 31 Dec., 1880 | 104 | 13 | 4 |
| Veale, J. S. | 1 Sept., 1887 | 56 | 2 | 10 |
| Von Sturmer, S. | 1 July, 1895 | 288 | 1 | 11 |
| Wardell, H. S. | 1 July, 1888 | 366 | 13 | 0 |
| Weetman, S. | 1 Mar., 1902 | 308 | 6 | 8 |
| White, C. | 8 Mar., 1902 | 93 | 6 | 8 |
| White, W. | 1 July, 1881 | 36 | 5 | 0 |
| White, W. B. | 1 July, 1873 | 375 | 4 | 9 |
| Williams, E. M. | 1 April, 1880 | 135 | 0 | 0 |
| Woon, J. G. | 1 July, 1892 | 209 | 10 | 6 |
| Wrigg, H. C. W. | 1 Aug., 1889 | 157 | 2 | 10 |
| Under “The Hamerton Pension Act, 1891.” | ||||
| Hamerton, R. C. | 11 Sept., 1891 | 250 | 0 | 0 |
| Under “The Meredith and Others Pensions Act, 1870.” | ||||
| Hamlin, Rhoda B. | —1865 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Under “The Military Pensions Act, 1866.” | ||||
| Adamson, T. | a | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Apera te Keunga | 14 May, 1864 | 0 | 2 | 6* |
| Barron, T. | 27 Aug., 1901 | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| Beamish, J. G. | b | 0 | 1 | 6* |
| Brown, M. R. | 75 | 0 | 0 | |
| Corbett, George | c | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Crawford, C. F. | 0 | 2 | 0* | |
| Gibbons, M. C. | 12 Oct., 1869 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Hamblyn, J. | 1 Oct., 1872 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Hastings, L. | 55 | 0 | 0 | |
| Kelly, T. | 9 April, 1870 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Kershaw, P. | 9 Aug., 1869 | 0 | 1 | 6* |
| Lacey, Garrett | 0 | 2 | 2* | |
| Lake, T. | 0 | 2 | 6* | |
| Lloyd, T. | d | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Marara, Ngakoa | 3 Dec., 1860 | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Matiu Whitish | 1 April, 1885 | 0 | 0 | 6* |
| Manparoa | 1 July, 1867 | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| McDonald, E. | 36 | 0 | 0 | |
| McDonnell, W. | 150 | 0 | 0 | |
| McDougall, T. R. | 1 April, 1898 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| McKay, G. | 0 | 1 | 0* | |
| McMahon, T. | e | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Mehaka Kepa | 2 Aug., 1865 | 0 | 0 | 9* |
| Morrison, Ann | 26 Oct., 1866 | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Pera Taitimu | 12 Oct., 1869 | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| Ross, Edward O. | 17 Nov., 1866 | 75 | 0 | 0 |
| Shanaghan, J. | 0 | 1 | 6* | |
| Shepherd, R. | f | 0 | 2 | 8* |
| Timms, W. | g | 0 | 1 | 6* |
| Tuffin, G. | 0 | 2 | 2* | |
| Vance, R. | 8 April, 1870 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Walsh, W. | 15 Nov., 1866 | 0 | 1 | 6* |
| Wasley, Edw. O. | h | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Williamson, F. | 1 June, 1869 | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Under “The Military Pensions Extension to Contingents Act, 1900.” | ||||
| £ | s. | d. | ||
| Anderson, L. C. | 27 Feb., 1902 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Atkinson, M. J. | 29 April, 1901 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Beath, A. M. | 10 Sept., 1902 | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Berry, Mrs. Charlotte, and children | 11 June, 1900 | 74 | 0 | 0 |
| Canavan, M. | 19 June, 1901 | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Clarke, J. L. | 18 Sept., 1902 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Clarke, M. | 14 Jan., 1901 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Collins, Lieut. Robert. W. G. | 16 Aug., 1901 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Connel, Mrs. M.A. | 17 Jan., 1901 | 26 | 0 | |
| Culling, J. | 7 July, 1901 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Donkin, A. | 1 June, 1901 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Dungan, M. | 4 Oct., 1901 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Fahey, J. V. | 27 Oct., 1901 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Foreman, R. G. | 15 Sept., 1902 | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Francis, C. J. (and four children) | 1 April, 1901 | 180 | 0 | 0 |
| Geddes, G. | 6 Sept., 1902 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Harvey, Mrs. M.P. | 16 Aug., 1900 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Leece, W. H. | 23 Aug., 1901 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| Lockett, E. B. | 22 Oct., 1902 | 54 | 0 | 0 |
| Love, Mrs. S., and children | 25 Aug., 1901 | 66 | 0 | 0 |
| Rees, H. | 8 Sept., 1902 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Roddick, H. | 21 Feb., 1902 | 26 | 0 | 0 |
| Sutherland, J. | 24 Sept., 1902 | 27 | 0 | 0 |
| Young, R. R. | 8 Sept., 1902 | 0 | 2 | 2* |
| Under “The Walsh and Other Pensions Act, 1869.” | ||||
| £ | s. | d. | ||
| Hewett, Ellen A. | 10 Feb., 1865 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Under “The Supreme Court Judges Act 1858 Amendment Act, 1874,” and “The Supreme Court Act, 1882.” | ||||
| Prendergast, Sir J. | 26 May, 1899 | 1133 | 6 | 8 |
| Under “The Militia Act Amendment Act, 1862.” | ||||
| Bending, W. | .. | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Bilton, F. | .. | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Cody, W. | .. | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| Dunn, A. J. N. | .. | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| King, E. M. | .. | 80 | 0 | 0 |
| Leaf, R. | i | 0 | 0 | 6* |
| Skinner, W. H. | .. | 0 | 2 | 6* |
| Vickery, W. | .. | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Woolfe, T. | .. | 0 | 2 | 0* |
| Under “The Schafer, McGuire, and Others Pensions Act, 1872.” | ||||
| McGuire, E. | 29 Sept., 1871 | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| Russell, W. | 1 July, 1871 | 0 | 1 | 0* |
| NEW ZEALAND CROSS GRATUITIES (£10 per Annum). | |
| Adamson, Thomas, 7th May, 1869. | Maling, Christopher, 10th March, 1869. |
| Black, Solomon, 10th March, 1869. | Mair, Gilbert, 7th February, 1870. |
| Biddle, Benjamin, 10th March, 1869. | Preece, George, 10th March, 1869. |
| Hill, George, 10th April, 1869. | Roberts, John Mackintosh, 10th March, 1869. |
| Lingard, William, 10th March, 1869. | Rodriguez, Antonio, 10th March, 1869. |
| Mace, Francis Joseph, 10th March, 1869. | Shepherd, Richard. 13th March, 1869. |
Pensions of late Provincial Government, Nelson—Mrs. Robinson's three daughters, £100.
Pension to Mrs. Elizabeth Ford, £46; pension of late F. G. Rawson continued to his widow, £45; pension to Aperahama Tahumirangi for wounds received when in the service of the New Zealand Government, £10.
THERE are (January, 1903) 206 publications on the register of newspapers for New Zealand. Of these, fifty-six are daily papers, twenty-eight are published three times a week, twenty-six twice a week, sixty-two once a week, one three times a month, three fortnightly, one three-weekly, and twenty-nine monthly.
The names of the newspapers, with the postal districts and towns in which they are printed, are given in the following list, the second column showing the day or period of publication.
M. signifies morning paper; E. evening paper:—
| AUCKLAND. | |
| Auckland— | |
| Auckland Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Auckland Weekly News and Town and Country Journal (M) | Saturday |
| Bible Standard (M.) | Monthly. |
| Catholic Chronicle (M.) | Monthly. |
| Christian Worker | Monthly. |
| Church Gazette (M.) | Monthly. |
| Danica (M.) | Thrice monthly (1st, 10th, 20th) |
| New Zealand ABC Guide | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Farmer, Bee and Poultry Journal (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Graphic, Ladies' Journal, and Youths' Companion | Wednesday. |
| New Zealand Herald (M.) | Daily. |
| New Zealand Illustrated Magazine | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Illustrated Sporting Review and Licensed Victualler's Gazette (M.) | Thursday. |
| New Zealand Illustrated Tit-Bits (M.) | Saturday. |
| New Zealand Joyful News | Monthly. |
| Observer (M.) | Saturday. |
| Pilot (M.) | Monthly. |
| Produce Circular and Monthly Report (M.) | Monthly. |
| Saturday Night (E.) | Saturday. |
| Sharland's Trade Journal | Saturday. |
| Coromandel— | |
| Coromandel County News (E). | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Dargaville— | |
| Wairoa Bell and Northern Advertiser (E.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Hamilton— | |
| Waikato Argus (E.) | Daily. |
| Waikato Times and Thames Valley Gazette (E.) | Daily. |
| Kawakawa— | |
| Northern Luminary (E.) | Friday. |
| Kawhia— | |
| Kawhia Settler and Raglan Advertiser (M.) | Saturday. |
| Onehunga— | |
| Manukau and Franklin Mail and Auckland Courier (E.) | Friday. |
| Manukau County Chronicle (M.) | Saturday. |
| Weekly Onehunga Independent and District Advertiser (M.) | Saturday. |
| Rotorua— | |
| Hot Lakes Chronicle (M.) | Saturday. |
| Warkworth— | |
| Rodney and Otamatea Times, Waitemata and Kaipara Gazette (M.) | Friday. |
| Whangarei— | |
| Northern Advocate (E.) | Daily. |
| Northern Chronicle (E.) | Saturday. |
| THAMES. | |
| Karangahake— | |
| Goldfields Advocate and Ohinemuri County Chronicle (M.) Tues., Thur., Sat. | |
| Opotiki— | |
| East Coast Guardian (E.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Opotiki Herald, Whakatane County and East Coast Gazette (E.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Paeroa— | |
| Ohinemuri Gazette (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Tauranga— | |
| Bay of Plenty Times and Thames Valley Warden (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Te Aroha— | |
| Te Aroha and Ohinemuri News and Upper Thames Advocate (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Thames— | |
| Thames Advertiser and Miners' News (M.) | Daily. |
| Thames Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Waihi— | |
| Waihi Daily Telegraph (E.) | Daily. |
| Waitekauri— | |
| Golden Age (E.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Gisborne— | |
| GISBORNE | |
| Gisborne Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Poverty Bay Herald (E.) | Daily. |
| NEW PLYMOUTH. | |
| Inglewood Record and Waitara Age (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| New Plymouth— | |
| Budget and Taranaki Weekly Herald (M.) | Saturday. |
| Daily News (M.) | Daily. |
| Taranaki Herald (E.) | Daily. |
| Taranaki News (M.) | Saturday. |
| Opunake— | |
| Opunake Times (E.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Stratford— | |
| Egmont Post (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Egmont Settler (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Waitara— | |
| Waitara Evening Mail and Clifton County Chronicle (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| NAPIER. | |
| Dannevirke Advocate (E.) | Daily. |
| Dannevirke Daily Press (E.) | Daily. |
| Hastings— | |
| Hastings Standard (E.) | Daily. |
| Napier— | |
| Daily Telegraph (E.) | Daily. |
| Hawke's Bay Herald (M.) | Daily. |
| New Zealand Fire and Ambulance Record (M.) | Monthly. |
| Waipawa— | |
| Waipawa Mail (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Wairoa— | |
| Wairoa Guardian and County Advocate (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| WANGANUI. | |
| Eltham Argus and Rawhitiroa and Kaponga Advertiser (E.) | Daily. |
| Hawera— | |
| Egmont Star (M.) | Saturday. |
| Hawera and Normanby Star, Patea County Chronicle, and Waimate Plains Gazette (E.) | Daily. |
| Hunterville— | |
| Hunterville Express, and Upper Rangitikei Advertiser (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Manaia— | |
| Waimate Witness (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Mangaweka— | |
| Settler (E.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Marton— | |
| Rangitikei Advocate and Manawatu Argus (E.) | Daily. |
| Patea— | |
| Patea County Press (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Taihape— | |
| Post (M.) | Thursday. |
| Wanganui— | |
| New Zealand Good Templar Watchword (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Tit Bits (M.) | Saturday. |
| Wanganui Chronicle and Patea-Rangitikei Advertiser (M.) | Daily. |
| Wanganui Herald (E.) | Daily. |
| Weekly Chronicle and Patea-Rangitikei Record (M.) | Saturday. |
| Yeoman (M.) | Friday. |
| WELLINGTON. | |
| Wairarapa Leader (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Wairarapa Observer, Featherston Chronicle, East Coast Advertiser, and South County Gazette (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Eketahuna— | |
| Eketahuna Express and North Wairarapa Courier (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Farmers Friend (M.) | Monthly (1st). |
| Feilding— | |
| Feilding Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Foxton— | |
| Manawatu Herald (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Greytown North— | |
| Te Puke ki Hikurangi (E.) | Tues., fortnightly. |
| Wairarapa Standard and Featherston Advocate (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Levin— | |
| Manawatu Farmer and Horowhenua County Chronicle (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Masterton— | |
| Wairarapa Age (M.) | Daily. |
| Wairarapa Daily Times (E.) | Daily. |
| Weekly Star and Wellington District Advertiser (M.) | Thursday. |
| Otaki— | |
| Otaki Mail and Horowhenua County and West Coast Advertiser (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Pahiatua— | |
| Pahiatua Herald (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Palmerston North— | |
| Manawatu Daily Standard, Rangitikei Advertiser, and West Coast Gazette (E.) | Daily. |
| Manawatu Daily Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Petone— | |
| Hutt and Petone Chronicle (E.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Wellington— | |
| Church Chronicle (M.) | Monthly. |
| Democrat (E.) | Friday. |
| Evening Post (E.) | Daily. |
| Mercantile Record (M.) | Saturday. |
| New Zealand Craftsman (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Dairyman and Farmers' Union Journal (E.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Field (M.) | Friday. |
| New Zealand Free Lance (M.) | Saturday. |
| New Zealand Mail, Town and Country Advertiser (M) | Wednesday. |
| New Zealand Mines Record (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Register and Property Investors' Guide (M). | Monthly. |
| Sport (M.) | Saturday. |
| Wellington Price Current and New Zealand Trade Review (M.) | Three-weekly. |
| Woodville— | |
| Woodville Examiner (E.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| BLENHEIM. | |
| Marlborough Daily Times and Town and Country Advertiser (M.) | Daily. |
| Marlborough Express (E.) | Daily. |
| Havelock— | |
| Pelorus Guardian and Miners' Advocate (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Picton— | |
| Marlborough Press, County of Sounds Gazette (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| NELSON. | |
| Golden Bay Argus (E.) | Thursday. |
| Motueka— | |
| Motueka Star (E) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Nelson— | |
| Colonist (M.) | Daily. |
| Nelson Evening Mail (E.) | Daily. |
| Takaka— | |
| Takaka News and Collingwood Advertiser (E.) | Thursday. |
| WESTPORT. | |
| Charleston Herald, Brighton Times, and Croninville Reporter (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Murchison— | |
| Buller Post (E.) | Tuesday. |
| Westport— | |
| Buller Miner (M.) | Friday. |
| Westport News (M.) | Daily. |
| Westport Times and Evening Star (E.) | Daily. |
| GREYMOUTH. | |
| Evening Star and Brunnerton Advocate (E.) | Daily. |
| Grey River Argus (M.) | Daily. |
| Weekly Argus (M.) | Weekly. |
| Reefton— | |
| Inangahua Herald and New Zealand Miner (M.) | Daily. |
| Inangahua Times and Reefton Guardian (E.) | Daily. |
| HOKITIKA. | |
| Hokitika Guardian and Evening Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Leader (M.) | Saturday. |
| West Coast Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Kumara— | |
| Kumara Times and Dillman's and Goldsborough Advertiser (M.) | Daily. |
| Ross— | |
| Ross and Okarito Advocate and Westland Advertiser (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| CHRISTCHURCH. | |
| Akaroa Mail and Banks Peninsula Advertiser (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Ashburton— | |
| Ashburton Guardian (E.) | Daily. |
| Ashburton Mail, Rakaia, Mount Somers, and Alford Forest Advertiser (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Ashburton Standard and Farmers' Advocate (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Cheviot— | |
| Cheviot News (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Christchurch— | |
| Canterbury Times (incorporating “Sportsman” and “New Zealand Cyclist”) (M.) | Wednesday. |
| Lyttelton Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Mercantile and Bankruptcy Gazette of New Zealand (E.) | Wednesday. |
| New Zealand Baptist (E.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Church News (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Fanciers' Chronicle (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Railway Review (E.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Schoolmaster (E.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand War Cry and Official Gazette of the Salvation Army (M.) | Saturday. |
| New Zealand Wheelman (M.) | Wednesday. |
| Press (M.) | Daily. |
| Prohibitionist (E.) | Fri., fortnightly. |
| Spectator (M.) | Tuesday. |
| Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Truth (E.) | Daily. |
| Weekly Press (incorporating “The Referee”) (M.) | Wednesday. |
| Kaikoura— | |
| Kaikoura Star and North Canterbury and South Marlborough News (E.) | Daily. |
| Rangiora— | |
| Standard and North Canterbury Guardian (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Southbridge— | |
| Ellesmere Guardian (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| TIMARU. | |
| Geraldine Guardian (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Temuka Leader (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Timaru— | |
| Timaru Herald (M.) | Daily. |
| Timaru Post (E.) | Daily. |
| Waimate— | |
| Waimate Advertiser (M.) | Saturday. |
| Waimate Times (M.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| OAMARU. | |
| North Otago Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Oamaru Mail (E.) | Daily. |
| DUNEDIN. | |
| Alexandra Herald and Central Otago Gazette (M.) | Thursday. |
| Balclutha— | |
| Clutha Leader (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Free Press (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Clyde— | |
| Dunstan Times, Vincent County Official Gazette, and General Goldfields Advertiser (M.) | Tuesday. |
| Cromwell— | |
| Cromwell Argus and Northern Goldfields Gazette (M.) | Tuesday. |
| Dunedin— | |
| Evening Star (E.) | Daily. |
| Farmers' Circular (M.) | Thur., fortn'ly |
| Katipo | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Guardian (M.) | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Journal of Education | Monthly. |
| New Zealand Mining, Engineering, and Building Journal (M.) | Thursday. |
| New Zealand Tablet (M.) | Friday. |
| Otago Daily Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Otago Witness (M.) | Thursday. |
| Otago Liberal and Workman (M) | Saturday |
| Outlook (M.) | Saturday. |
| Schoolmates | Monthly. |
| Trade Review and Farmers' Gazette (M.) | Thursday. |
| Triad (M.) | Monthly. |
| Weekly Budget (M.) | Saturday. |
| Lawrence— | |
| Tuapeka Times (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Milton— | |
| Bruce Herald (M.) | Tuesday, Friday |
| Mosgiel— | |
| Taieri Advocate (M.) | Wed., Saturday. |
| Naseby— | |
| Mount Ida Chronicle (M.) | Friday. |
| Palmerston— | |
| Palmerston and Waikouaiti Times (M.) | Friday. |
| Roxburgh— | |
| Mount Benger Mail (M.) | Saturday. |
| Tapanui— | |
| Tapanui Courier and Central Districts Gazette (M.) | Wednesday. |
| INVERCARGILL. | |
| Lake County Press (E.) | Thursday. |
| Gore— | |
| Mataura Ensign (E.) | Tues., Thur., Sat. |
| Southern Standard (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
| Invercargill— | |
| Southern Cross (M.) | Saturday. |
| Southlander (M.) | Friday. |
| Southland Daily News (E.) | Daily. |
| Southland Times (M.) | Daily. |
| Weekly Times (M.) | Friday. |
| Orepuki— | |
| Orepuki Advocate (M.) | Saturday. |
| Queenstown— | |
| Lake Wakatipu Mail (E.) | Saturday. |
| Riverton— | |
| Western Star and Wallace County Gazette (E.) | Tues., Friday. |
| Winton— | |
| Winton Record and Hokonui Advocate (M.) | Friday. |
| Wyndham— | |
| Wyndham Farmer (M.) | Mon., Wed., Fri. |
| Wyndham Herald (M.) | Tuesday, Friday. |
The foregoing towns are arranged according to the postal district in which they are situated.
Taking the provincial districts, Auckland has 45 publications registered as newspapers, Taranaki 13, Hawke's Bay 9, Wellington 42, Marlborough 4, Nelson 13, Westland 8, Canterbury 29, and Otago 43.
Table of Contents
THE headings of the respective classes in this Table and in the Table of Exemptions are used solely for convenience of classification, and shall not in any way affect the articles specified therein, or be construed to indicate the material of which any such article is made.
The word “iron” includes steel, or steel and iron combined.
Neither steam-engines, nor parts of steam-engines, nor steam-boilers (land or marine) are included in the expression “machines” or “machinery” in either this Table or the Table of Exemptions.
The abbreviation “n.o.e.” means not otherwise enumerated.
In computing “ad valorem” duties the invoice value of the goods is increased by 10 per cent.
1. Almonds, in shell, 2d. the lb.
2. Almonds, shelled, n.o.e., 3d. the lb.
3. Bacon and hams, 2d. the lb.
4. Biscuits, ships' plain and unsweetened, 3s. the cwt.
5. Biscuits, other kinds, 2d. the lb.
6. Boiled sugars, comfits, lozenges, Scotch mixtures, and sugar-candy, 2d. the lb., including internal packages.
7. Candied peel and drained peel, 3d. the lb.
8. Capers, caraway seeds, catsup, cayenne pepper, chillies, chutney, curry-powder and -paste, fish-paste, gelatine, isinglass, liquorice, olives, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
9. Chocolate confectionery, and all preparations of chocolate or cocoa—
In plain trade packages, 3d. the lb.
In fancy packages, or in small packages for retail sale, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
10. Confectionery n.o.e., 2d. the lb., including internal packages.
11. Currants, 1d. the lb.
12. Fish, dried, pickled, or salted, n.o.e., 10s. the cwt.
13. Fish, potted and preserved, 2d. the lb. or package of that reputed weight, and so in proportion for packages of greater or less reputed weight.
14. Fruit, fresh, viz.:—
Apples, pears, plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, medlars, apricots, quinces, tomatoes, 1d. the lb.
(No duty exceeding 1/2d. the lb. to be levied on apples and pears from 14th July to 31st December.)
Currants, raspberries, gooseberries, blackberries, and strawberries, 1/2d. the lb.
Lemons, 1/2d. the lb.
15. Fruits, dried, 2d. the lb.
16. Fruits, preserved in juice or syrup, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
17. Fruit-pulp, and partially preserved fruit n.o.e., 1 1/2d. the lb.
18. Fruits preserved by sulphurous acid, 1d. the lb.
19. Glucose, 1d. the lb.
20. Honey, 2d. the lb.
21. Jams, jellies, marmalade, and preserves, 2d. the lb. or package of that reputed weight, and so in proportion for packages of greater or less reputed weight.
22. Jellies concentrated in tablets or powder, 4d. the lb.
23. Maizena and cornflour, 1/4d. the lb.
24. Meats, potted or preserved, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
25. Milk, preserved, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
26. Mustard, 2d. the lb.
27. Nuts of all kinds, except cocoa-nuts, 2d. the lb.
28. Oysters, preserved, 2d. the lb. or package of that reputed weight, and so in proportion for packages of greater or less reputed weight.
29. Pearl barley, 1s. the cwt.
30. Peas, split, 2s. the cwt.
31. Pickles, 3s. the imperial gallon.
32. Provisions, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
33. Raisins, 1d. the lb.
34. Rice-flour, 6s. the cwt.
35. Sardines, including the oil, 2d. the lb.
36. Sauces, 4s. the imperial gallon.
37. Spices, including pepper and pimento, unground, 2d. the lb.
38. Spices, including pepper and pimento, ground, 4d. the lb.
39. Sugar, 1/2d. the lb.
40. Treacle and molasses, 1/2d. the lb.
41. Vegetables, fresh, dried, or preserved, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
42. Vinegar, table, not exceeding 6·5 per cent, of acidity, † 6d. the gallon.
C(([0-9]+)).
43. Cigarettes, not exceeding in weight 2 1/2 lb. per 1,000, 17s. 6d. the 1,000. And for all weight in excess of 2 1/2 lb. per 1,000, 6d. the oz.
44. Cigars, 7s. the lb.
45. Snuff, 7s. the lb.
46. Tobacco, 3s. 6d. the lb.
47. Tobacco, unmanufactured, entered to be manufactured in the colony in any licensed tobacco manufactory, for manufacturing purposes only, into tobacco, cigars, cigarettes, or snuff, 2s. the lb.
C(([0-9]+)) BEVERAGES, AND MATERIALS FOR M(([0-9]+)).
48. Ale, beer of all sorts, porter, cider, and perry, the gallon, or for six reputed quart bottles, or 12 reputed pint bottles, 2s. the gallon.
49. Cordials, bitters, and liqueurs, 16s. the liquid gallon.
50. Hops, 6d. the lb.
51. Malt, 2s. the bushel.
52. Rice malt, 1d. the lb.
53. Solid wort, 6d. the lb.
54. Spirits and strong waters, the strength of which can be ascertained by Sykes's hydrometer, 16s. the proof gallon.
(No allowance beyond 16·5 under proof shall be made for spirits or strong waters of a less hydrometer strength than 16·5 under proof.)
55. Spirits and strong waters, sweetened or mixed, when not exceeding the strength of proof, 16s. the liquid gallon.
56. Spirits and strong waters in cases shall be charged as follows, namely:—
Two gallons and under, as two gallons; over two gallons and not exceeding three, as three gallons; over three gallons and not exceeding four, as four gallons; and so on for any greater quantity contained in any case.
57. Spirits or strong waters, mixed with ingredients in any proportion exceeding 33 per cent. of proof spirit, and although thereby coming under any other designation, excepting patent or proprietary medicines, or tinctures and medicinal spirits otherwise enumerated, 16s. the liquid gallon.
* Vinegar exceeding 6·5 per cent. of acidity to be treated as acetic acid.
58. Wine, Australian, containing not more than 35 per cent. of proof spirit verified by Sykes's hydrometer, the gallon, or for six reputed quart bottles, or twelve reputed pint bottles, 5s. the gallon.
59. Wine, other than sparkling and Australian, containing less than 40 per cent. of proof spirit verified by Sykes's hydrometer, the gallon, or for six reputed quart bottles, or twelve reputed pint bottles, 6s. the gallon.
60. Wine, sparkling, 9s. the gallon.
C(([0-9]+))-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, (([0-9]+)) FOR MAKING SAME.
61. Aerated and mineral waters and effervescing beverages, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
62. Chicory, 3d. the lb.
63. Chocolate, 3d. the lb.
64. Cocoa, 3d. the lb.
65. Coffee, essence of, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
66. Coffee, roasted, 3d. the lb.
67. Syrups; lime- or lemon-juice sweetened; raspberry vinegar, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
68. Tea, 2d. the lb.
C(([0-9]+)), MEDICINES, CHEMICALS, (([0-9]+))' SUNDRIES.
69. Acid, acetic, n.o.e., containing not more than 30 per cent. of acidity, 1 1/2d. the lb.
For every 10 per cent. of acidity or fraction thereof additional, 1/2d. the lb.
70. Acid, tartaric, 1d. the lb.
71. Baking-powder, yeast preparations, and other ferments, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
72. Chemicals n.o.e., including photographic chemicals, and glacial acetic acid (B.P. standard), 15 per cent. ad valorem.
73. Cream of tartar, 1d. the lb.
74. Drugs and druggists' sundries and apothecaries' wares, n.o.e., 15 per cent. ad valorem.
75. Essences, flavouring, spirituous, 16s. the liquid gallon.
76. Essences, flavouring, n.o.e., 15 per cent.
77. Eucalyptus oil, in bulk or bottle, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
78. Glycerine, refined, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
79. Opium, 40s. the lb.
80. Patent medicines, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
81. Proprietary medicines, or medicaments, (1) bearing the name of the proprietor on label or package; (2) bearing a prefixed name in the possessive case; (3) n.o.e., prepared by any occult secret or art, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
82. Saccharine, except in the form of tabloids or tablets, 1s. 6d. the ounce.
83. Sarsaparilla, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
84. Soda, carbonate and bicarbonate, 1s. the cwt.
85. Soda, crystals, 2s. the cwt.
86. Tinctures and medicinal spirits of any recognised pharmacopœia, containing more than 50 per cent. of proof spirit, 1s. the lb.
87. Tinctures and medicinal spirits of any recognised pharmacopœia, containing 50 per cent. proof spirit or less, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)) GOODS.
88. Apparel and ready-made clothing, and all articles n.o.e. made up wholly or in part from textile or other piece-goods, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
89. Apparel made by British or foreign tailors, dress-, mantle-, or jacket-makers to the order of residents in the colony, and intended for the individual use of such residents, whether imported by the residents themselves or through an importing firm, 40 per cent. ad valorem.
90. Blankets, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
91. Collars and cuffs, of paper or other material, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
92. Cotton counterpanes, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
93. Cotton piece-goods, to include turkey twills, dress prints (hard-spun and plain-woven), where the invoice value does not exceed 4d. the yard; and cotton piece-goods n.o.e., 10 per cent. ad valorem.
94. Cotton piece-goods—namely, tapestry; cretonnes; chintz art crêpe, and serges; velveteens, velvets, and plushes, all kinds; damasks; moquette; sateens; linenettes; crepons; crimps; zephyrs; ginghams; turkey twills; prints; printed cottons; piqués; vestings; quiltings, and marcellas; muslins of all kinds; nets; window-nets; hollands, curtains, and blinds; diapers; ticks, including coloured Belgian; towellings; laces, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
95. Drapery n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
96. Feathers, ornamental (including ostrich), and artificial flowers, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
97. Forfar, dowlas, and flax sheeting, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
98. Furs, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
99. Haberdashery n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
100. Hats of all kinds, including straw hats, also caps, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
101. Hosiery n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
102. Lace, and laces, n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
103. Millinery of all kinds, including trimmed hats, caps, and bonnets, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
104. Ribbons and crape, all kinds, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
105. Rugs, woollen, cotton, opossum, or other, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
106. Shawls, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
107. Silks, satins, velvets, plushes, n.o.e., composed of silk mixed with any other material, in the piece, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
108. Textile piece-goods other than cotton or silk, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
109. Umbrellas, parasols, and sunshades, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
110. Yarns n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)) OF LEATHER.
111. Boots, shoes, and slippers, n.o.e.; goloshes, clogs, pattens, vamps, uppers, and laces, 22 1/2 per cent. ad valorem.
112. Heel-plates, and toe-stiffeners and plates, 22 1/2 per cent. ad valorem.
113. Leather—
Leather belting, and belt-leather, harness, bridle, legging, bag, kip (other than East India), 4d. the lb.
Buff and split, including satin hides and tweeds, 3d. the lb.
Cordovan, levanted leather, roans, sheepskins, morocco n.o.e., basils, 3d. the lb.
Sole-leather, 2d. the lb.
East India kip, Persians, lambskins and goatskins (dressed other than morocco), kangaroo and wallabi skins (dressed), tan and coloured calf, 2d. the lb.
Leather n.o.e., 1d. the lb.
114. Leather board or compo, 4d. the lb.
115. Leather bags and leather-cloth bags, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
116. Leather, chamois, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
117. Leather cut into shapes, 22 1/2 per cent. ad valorem.
118. Leather leggings, 22 1/2 per cent. ad valorem.
119. Leather manufactures n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
120. Portmanteaux; trunks; travelling-bags and brief-bags of leather or leather-cloth, 10 in. in length and upwards, and carpet-bags, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
121. Saddlery, and harness, whips and whip-thongs, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)) FURNISHING.
122. Basket- and wicker-ware n.o.e., not being furniture, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
123. Carpets, and druggets; floorcloth; mats, and matting, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
124. Desks, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
125. Furniture and cabinetware, n.o.e., and other than iron, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
126. Furniture-, knife-, and plate-powder and polish, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
127. Mantelpieces, other than stone, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
128. Upholstery n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)), GLASS, AND E(([0-9]+)).
129. Bricks, known as firebricks, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
130. China, porcelain, and parianware, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
131. Drainage pipes and tiles, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
132. Earthen flooring and garden-tiles, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
133. Earthenware, stoneware, and brownware, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
134. Filters, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
135. Fireclay, ground, and fireclay goods, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
136. Glass, crown, sheet, and common window, 2s. the 100 superficial feet.
137. Glassware; also plate-glass, and glass polished, coloured, and other kinds, n.o.e.; globes and chimneys for lamps, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
138. Lamps, lanterns, and lampwick, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
139. Plate-glass, bevelled or silvered; mirrors and looking-glasses, framed or unframed, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)) GOODS, MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS, ETC.
140. Artificial flies, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
141. Cards, playing, 6d. per pack.
142. Clocks, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
143. Dressing-cases, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
144. Fancy goods, and toys, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
145. Fishing tackle, including artificially-baited hooks other than flies, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
146. Jewellery; plate, gold or silver; greenstone, cut or polished, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
147. Mouldings in the piece for picture-frames, cornices, or ceilings 15 per cent. ad valorem.
148. Musical instruments of all kinds n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
149. Oil, perfumed, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
150. Papier-maché ware, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
151. Perfumery n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
152. Perfumed spirits and Cologne-water, £1 10s. the liquid gallon.
153. Photographic goods n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
154. Pictures, paintings, drawings, engravings, and photographs, framed or unframed; picture- or photograph-frames and -mounts, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
155. Platedware, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
156. Statues, statuettes, casts, and bronzes, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
157. Tobacco-pipes and -cases, cigar- and cigarette-holders and -cases, cigarette-papers and -cases, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
158. Toilet preparations n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
159. Watches, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
160. Walking-sticks, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
CLASS XI.—PAPER MANUFACTURES AND STATIONERY.
161. Calendars and show-cards, all kinds, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
162. Cardboard boxes complete, or cardboard cut and shaped for boxes (including match-boxes), 25 per cent. ad valorem.
163. Directories of New Zealand, or of any part thereof; also covers for directories, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
164. Handbills, programmes and circulars, playbills and printed posters, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
165. Ink, writing, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
166. Paper bags, coarse (including sugar-bags), 7s. 6d. the cwt
167. Paper bags n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
168. Paper-hangings, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
169. Paper wrapping—viz., blue candle, glazed cap, glazed casings, small hand, lumber hand, and tissue, 5s. the cwt.
170. Paper, wrapping, other kinds, including brown, cartridge, and sugar papers, 5s. the cwt.
171. Printing matter relating to patent or proprietary medicines; trade catalogues, price-lists, and fashion-plates of the goods of firms or persons in the colony, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
172. Stationery and writing-paper n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
173. Stationery, manufactured—viz., account-books; manuscript books; billhead, invoice, and statement forms; printed or ruled paper; counterbooks; cheque- and draft-forms; tags; labels; blotting-pads; sketchbooks; book-covers; copying letter-books; manifold writers; albums (other than for photographs); diaries; birthday-books; plain or faintlined ruled books; printed window-tickets; printed, lithographed, or embossed stationery; and Christmas, New Year, birthday, and Easter cards and booklets, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
174. Stereotypes and matrices, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)).
175. Bicycles, tricycles, and the like vehicles; also finished or partly finished or machined parts of same, n.o.e., including weldless steel tubing cut to short lengths, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
176. Boilers, land and marine, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
177. Brass cocks, valves, unions, lubricators, and whistles, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
178. Brass manufactures, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
179. Cartridges (shot), 10- to 24-bore, 1s. 6d. the 100.
180. Cartridge cases, 9d. the 100.
181. Cartridges n.o.e., 20 per cent ad valorem.
182. Cash-registering machines, 10 per cent. ad valorem.
183. Coffin-furniture, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
184. Composition-piping, 3s. 6d. the cwt.
185. Copper manufactures n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
186. Copying-presses, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
187. Crab-winches, cranes n.o.e., capstans, and windlasses, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
188. Cutlery, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
189. Firearms, all kinds, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
190. Galvanised iron manufactures n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
191. Gasometers, and other apparatus for producing gas; also gas-meters, 10 per cent. ad valorem.
192. Gaspipes, iron, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
193. Hardware, ironmongery, and holloware, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
194. Iron bridges, and iron material n.o.e. for the construction of bridges, wharves, jetties, or patent slips, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
195. Iron columns for buildings, and other structural ironwork, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
196. Iron doors for safes and vaults, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
197. Iron, galvanised corrugated sheets, screws, and nails, 2s. per cwt.
198. Iron galvanised tiles, ridging, guttering, and spouting, 20 per cent ad valorem.
199. Iron gates and gate-posts, staples, standards, straining posts and apparatus, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
200. Iron nails, 2s. per cwt.
201. Iron pipes, and fittings for same, including main-cocks, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
202. Iron, plain galvanised sheet and hoop, 1s. 6d. the cwt.
203. Iron tanks, exceeding 200 gallons and not exceeding 400 gallons, 10s. each.
204. Iron tanks of and under 200 gallons, 5s. each.
205. Iron work and wire work, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
206. Japanned and lacquered metal ware, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
207. Lawn-mowers, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
208. Lead, in sheets, 1s. 6d. the cwt.
209. Lead piping, 3s. 6d. the cwt.
210. Machinery n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
211. Machinery, electric, and appliances, 10 per cent. ad valorem.
212. Machinery for flour-mills, woollen-mills, paper-mills, rope- and twine-making, dredging, *saw-milling, *planing, oil-refining, boring; and also machinery for refrigerating or preserving meat, leather-splitting machines and band-knives for same, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
213. Manufactures, n.o.e., of metal, or of metal in combination with any other material, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
214. Nails n.o.e., 3s. the cwt.
215. Printing machines and presses, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
216. Pumps and other apparatus for raising water n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
217. Railway and tramway plant and materials n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
218. Sad-irons, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
219. Shot, 10s. the cwt.
220. Soda-water machines; also, machines for aerating liquids, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
221. Steam-engines and parts of steam-engines n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
222. Steam-engines, and parts thereof, including the boiler or boilers therefor, imported specially for mining or gold-saving purposes and processes, or for dairying purposes, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
223. Tinware, and tinsmiths' furniture n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
224. Waterworks pipes, iron, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
225. Weighbridges and weighing-machines, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
226. Wire mattresses and webbing, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
227. Zinc tiles, ridging, guttering, piping, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
228. Zinc manufactures n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)), AND ARTICLES MADE FROM TIMBER.
229. Bellows, other than forge, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
230. Blocks, wooden tackle, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
231. Buckets and tubs, of wood, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
232. Carriages, carts, drays, wagons, and perambulators, and wheels for the same, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
233. Carriage shafts, spokes, and felloes, dressed; bent carriage timber, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
234. Doors, glazed with ornamental glass, 4s. each.
235. Doors, plain, 2s. each.
236. Sashes, glazed, with ornamental glass, 4s. the pair.
237. Sashes, plain, 2s. the pair.
238. Timber, palings, 2s. the 100.
239. Timber, posts, 8s. the 100.
240. Timber, rails, 4s. the 100.
* See also item 418.
241. Timber, sawn, dressed, 4s. the 100 ft. superficial.
242. Timber, sawn, rough, 2s. the 100 ft. superficial.
243. Timber, shingles and laths, 2s. the 1,000.
244. Woodenware and turnery n.o.e, and veneers, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
C(([0-9]+)), PAINTS, ETC.
245. Axle-grease, and other solid lubricants, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
246. Harness oil and composition, and leather dressing, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
247. Naphtha, 6d. the gallon.
248. Oil, linseed, 6d. the gallon.
249. Oil, mineral, including shale-waste or unrefined mineral-oil n.o.e., 6d. the gallon.
250. Oil n.o.e., 6d. the gallon.
251. Oil, olive, in bulk, 6d. the gallon.
252. Oil vegetable, in bulk, n.o.e., 6d. the gallon.
253. Oil vegetable or other, in bottle, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
254. Paints and colours ground in oil or turpentine, 2s. 6d. the cwt.
255. Paints and colours mixed ready for use, 5s. the cwt.
256. Putty, 2s. the cwt.
257. Stearine, 1 1/2d. the lb.
258. Stearine for match-making, 3/4d. the lb.
259. Varnish; enamel paints; gold size, 2s. the gallon.
260. Whiting and chalk, 1s. the cwt.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)) PRODUCTS, ETC.
261. Animals, food for, of all kinds, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
262. Cattle (horned), 10s. each.
263. Chaff, £1 the ton.
264. Grain—namely, barley, 2s. the 100 lb.
265. Grain and pulse of every kind n.o.e., 9d. the 100 lb.
266. Grain and pulse of every kind, when ground or in any way manufactured, n.o.e., 1s. the 100 lb.
267. Horses, £1 each.
268. Linseed, £1 the ton.
269. Maize, 9d. the 100 lb.
270. Onions, £1 the ton.
271. Prepared calf-meal, £1 5s. the ton.
CLASS XVI.—MISCELLANEOUS.
272. Bags, flour, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
273. Bags, calico, forfar, hessian, and linen, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
274. Bagging and bags n.o.e., 15 per cent. ad valorem.
275. Blacking and boot-gloss, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
276. Blacklead, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
277. Blue, 2d. the lb.
278. Brooms, brushes, and brushware, n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
279. Brushes, hair, and combs; toilet- clothes- and hat-brushes, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
280. Candles, 1d. the lb. or package of that reputed weight, and so in proportion for packages of greater or less reputed weight.
281. Cement, 2s. the barrel.
282. Cordage and rope, n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
283. Cork, cut, including bungs, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
284. Fireworks n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
285. Flock, 10 per cent. ad valorem.
286. Glue and size, 1 1/2d. the lb.
287. Granite, sawn on not more than two sides, and not dressed or polished, 5 per cent. ad valorem.
288. Marble, granite, and other stone, dressed or polished, and articles made therefrom, including mantelpieces, 25 per cent. ad valorem.
289. Matches—
Wooden, in boxes containing not more than 60 matches, 1s. the gross of boxes.
In boxes containing over 60 and not more than 100 matches, 2s. the gross of boxes.
In boxes containing more than 100 matches, for every 100 matches or fraction thereof contained in one box, 2s. the gross of boxes.
Wax, “plaid vestas” in cardboard boxes containing under 100 matches, 1s. the gross of boxes.
“Pocket vestas” in tin or other boxes containing under 100 matches, 1s. 4d. the gross of boxes.
“Sportsman's,” “Ovals,” and “No. 4 tin vestas,” in boxes containing not more than 200 matches, 4s. 6d. the gross of boxes.
Wax, other kinds, for every 100 matches or fraction thereof contained in one box, 2s. 3d. the gross of boxes.
290. Nets and netting, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
291. Paraffin wax, 3/4d. the lb.
292. Powder, sporting, 6d. the lb.
293. Sacks, other than cornsacks and jute sacks, 15 per cent. ad valorem.
294. Sausage-skins and casings (including brine or salt), 3d. per lb.
295. Soap, common yellow, and blue mottled, 5s. the cwt.
296. Soap, n.o.e., 25 per cent. ad valorem.
297. Soap-powder, extract of soap, dry soap, and soft-soap, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
298. Spirits, methylated, 1s the liquid gallon.
299. Spirits, cleared from warehouse, methylated, under prescribed conditions, 6d. the liquid gallon.
300. Starch, 2d. the lb.
301. Tarpaulins, tents, rick- and wagon-covers, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
302. Twine n.o.e., 20 per cent. ad valorem.
303. Washing-powder, 20 per cent. ad valorem.
304. Wax, mineral, vegetable, and Japanese, 1 1/2d. the lb.
In addition to any duty chargeable by law on any goods imported into the colony, a further duty of 20 per cent. ad valorem shall be charged when the goods are prison-made.
TABLE OF EXEMPTIONS FROM DUTIES OF CUSTOMS.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
Names of Articles.305. Almonds, Barbary, Sicily, and French, used in confectioners' manufactures.
306. Anchovies, salted, in casks.
307. Arrowroot, sago, tapioca, macaroni, vermicelli, and prepared groats.
308. Salt.
309. Rice, dressed or undressed.
310. Rice manufactured into starch in bond.
C(([0-9]+))-(([0-9]+)), ETC.
311. Cocoa-beans.
312. Coffee, raw.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
313. Acids—viz.: boracic; carbolic, in bulk; fluoric; muriatic; nitric; oxalic; oleic; picric; pyrogallic; salicylic; sulphuric.
314. Concentrated extracts or essences in liquid form or preserved in fat for perfume-manufacturing purposes in manufacturing warehouses, in bottles of not less than 1 lb. in weight.
315. Disinfectants.
316. Drugs and chemicals—viz.: alum; sulphate of aluminium; sulphate of ammonia; anhydrous ammonia; aniline dyes; arsenic; bluestone, or sulphate of copper; borax; catechu; chloride of calcium; nitrate of silver; cochineal; creosote, crude or commercial; glycerine, crude; gum, arabic and tragacanth; gum benzoin; artificial gum arabic; gum damar; phosphorus; potash, caustic potash, and chlorate of potash; pearlash; prussiate of potash; cyanide of potassium; cyanide of sodium; liquid chlorine; sal-ammoniac; saltpetre; acetate of soda, crude; soda ash; caustic soda; nitrate of soda; silicate of soda; sulphate of soda; sulphide of sodium; hyposulphite of sodium; strychnine; sulphur; chloride of zinc; iron-sulphates; gall-nuts; turmeric; saffron; nitrousoxide gas; tree-washes; insecticides; maltine; chlorodyne.
317. Essential oils, except eucalyptus; cod-liver oil; oil of rhodium.
318. Horse-drenches.
319. Medicinal barks, leaves, herbs, flowers, roots and gums.
320. Scrub-exterminator.
321. Sheep-dip; sheep-drenches; sheep-licks.
322. Surgical and dental instruments and appliances.
323. Scientific and assay balances, retorts, flasks, and other appliances for chemical analysis and assay work.
324. Water-hardening chemicals for brewers' use.
C(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)).
325. Accoutrements for military purposes, excepting uniform clothing.*
326. Brace-elastic and brace-mountings.
327. Bunting, in the piece.
328. Butter- and cheese-cloth.
329. Buttons, tapes, wadding, pins, needles.
330. Calico, white and grey, also cotton sheetings, in the piece.
331. Corduroy, moleskin, and plain beaver-skin, of cotton, in the piece.
332. Coloured cotton shirtings; flannelette shirtings.†
333. Forfar, dowlas, and flax sheeting, when cut up under supervision in sizes not exceeding 47 in. x 36 in. for making flour-bags, and not exceeding 54 in. for lining wool mats.
334. Fur-skins, green or sun-dried.
335. Gold or silver lace or braid for military clothing.
336. Hatmakers' materials—viz.: silk plush; felt hoods; shellac; galloons; calicoes; spale-boards for hat-boxes; leathers and linings; blocks; moulds; frames; ventilators; and tassels.
337. Hessians, plain or striped, and scrim.
338. Leather-cloth.
339. Minor articles (required in the making-up of apparel, boots, shoes, hats caps, saddlery, umbrellas, parasols, and sunshades), enumerated in any order of the Commissioner, and published in the Gazette.
340. Sailcloth, canvas, and unbleached double-warped duck, in the piece.
341. Sewing cottons, silks, and threads; crochet, darning, and knitting cottons; angola mendings not exceeding 45 yards, on cards.
342. Silk for flour-dressing.
343. Silk twist (shoemakers' and saddlers').
* Subject to the provisions of section 28 of “The Defence Act, 1900,” as follows:—
Equipments to be admitted free of Customs Duty.
28. All military clothing, saddlery, and equipments imported into the colony for the boná fide use of a Volunteer corps shall, on the certificate in writing of the Minister of Defence that the same are or have been imported for such purpose, be admitted into the colony free of Customs duty.
* Subject to the provisions of section 28 of “The Defence Act, 1900,” as follows:—
† See note on page 95.
344. Staymakers' binding, eyelets, corset-fasteners, jean, ticks, lasting, sateen, and cotell.
345. Tailors' trimmings—viz.: plain-coloured imitation hair-cloth; canvas; plain Verona and plain diagonal, and such patterns of checked Italian cloth as may be approved of by the Commissioner of Customs; Italian cloth of cotton or wool; buckram; wadding and padding; silk, worsted, and cotton bindings and braids; stay-bindings; Russia braids; shoulder pads; buckles; silesias; drab, slate, and brown jeans; pocketings; slate, black, and brown dyed unions and linens.
346. Umbrella-makers' materials—viz.: reversible and levantine silk mixtures, gloria, and satin de chêne of not less than 44 in. in width; alpaca cloth, with border; zanella cloth, with border; also other piece-goods on such conditions as the Commissioner may approve; sticks, runners, notches, caps, ferrules, cups, ribs, stretchers, tips, and rings.
347. Union shirtings the invoice value of which does not exceed 6d. the yard.†
348. Waterproof material in the piece.
C(([0-9]+)), (([0-9]+)) USED IN LEATHER MANUFACTURES.
349. Boot elastic.
350. Bootmakers' linings, canvas, plain or coloured, bag and portmanteau linings, of such materials, qualities, and patterns as may be approved by the Commissioner.
351. Boots, shoes, and slippers—viz., children's, No. 0 to 3.
352. Cork soles, and sock soles.
353. East India kip, crust or rough-tanned, but undressed.
354. Goatskins, crust or rough-tanned, but undressed.
355. Grindery, except heel- and toe-plates.
356. Hogskins.
357. Kangaroo-, wallabi-skins, undressed.
358. Leather, japanned or enamelled; goatskins, dressed as morocco, coloured (other than black).
359. Saddle-trees.
360. Saddlers' ironmongery (except bits and stirrup-irons), hames, and mounts for harness; straining, surcingle, brace, girth, and roller webs; collar-check, and the same article plain, of such quality as may be approved by the Commissioner; legging-buckles.
361. Tanning materials, crude.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
362. Blind-webbing and tape.
363. Upholsterers' webbing, hair-seating, imitation hair-seating; curled hair; gimp and cord of wool, cotton, or silk; tufts, and studs.
C(([0-9]+)), GLASS, ETC.
364. Bottles, empty, plain glass, not being cut or ground; also, jars up to 3 in. in diameter at the mouth.
365. Glass plates (engraved) for photo-lithographic work.
366. Jars or other dutiable vessels, containing free goods or goods subject to a fixed rate of duty, and being ordinary trade packages for the goods contained in them.
C(([0-9]+)) GOODS, ETC.
367. Action-work and keys, in frames or otherwise, for manufacture of organs, harmoniums, and pianos; organ-pipes and stop-knobs.
* Whenever any dispute arises as to the application of the exemption in favour of coloured cotton, flannelette, or union shirtings, in the case of fabrics alleged to be such shirtings, the Commissioner has power to decide such dispute; and in case of doubt on his part, he may require the fabric in dispute to be cut up for shirt-making, under such conditions as he prescribes. (See section 6 of “The Customs and Excise Duties Act, 1895.”)
368. Artists' canvas, colours, brushes, and palette-knives.
369. Magic-lanterns, lenses, and slides.
370. Microscopes and astronomical telescopes, and lenses for same.
371. Musical instruments, specially imported for Volunteer bands.
372. Paintings, statuary, and works of art, presented to or imported by any public institution or art association registered as a body corporate, for display in the buildings of such institution or association, and not to be sold or otherwise disposed of.
373. Photographic cameras and lenses.
374. Photographs of personal friends in letters or packets.
375. Precious stones, cut or uncut and unmounted.
376. Sensitized surfaces for photographic purposes.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
377. Bookbinders' materials—viz., cloth, leather, thread, headbands, webbing, end-papers, tacketing-gut, marbling-colours, marble-paper, blue paste for ruling-ink, staple presses, wire-staples, staple-sticks.
378. Butter-paper, known as parchment paper or waxed paper.
379. Cardboard and pasteboard, of sizes not less than that known as “royal.”
380. Cardboard boxes, material for—viz., gold and silver paper, plain and embossed, gelatine and coloured papers, known as “box-papers.”
381. Cartridge-paper for drawing-books.
382. Cloth-lined boards, not less than “royal.”
383. Cloth-lined papers, enamelled paper; ivorite and gelatine; metallic paper; not less than “demy.”
384. Copy-books and drawing-books.
385. Copying-paper, medium and double-foolscap, in original mill wrappers and labels.
386. Hand-made cheque-paper.
387. Ink, printing.
388. Masticated para.
389. Millboard, and bookbinders' leather-board.
390. Paper, hand-made or machine-made book or writing, of sizes not less than the size known as “demy,” when in original wrappers.
391. Printing-paper.
392. Printed books, papers, and music, n.o.e.
393. School slates, and educational apparatus.
C(([0-9]+)).
394. All machinery for agricultural purposes, including chaff-cutters, corn-crushers; corn-shellers, also articles used in manufacturing the same—viz., chaff - cutting knives, tilt-rakes, fittings for threshing - mills, forgings for ploughs.
395. All agricultural implements.
396. All bolts and nuts, blank or screwed nuts, black or finished nuts.
397. Anchors.
398. Artificers' tools.
399. Axes and hatchets; spades, shovels, and forks; picks; mattocks; quartz and knapping-hammers; scythes, sheep-shears, reaping-hooks; soldering-irons; paperhangers' scissors; butchers' saws and cleavers.
400. Axles, axle-arms, and boxes.
401. Band-saws and folding-saws, including frames.
402. Bellows-nails.
403. Bicycles and tricycles, fittings for—viz., rubber-tires, pneumatic-tires, out-side covers, and inner tubes; rubber and cork handles, and pedal-rubbers; also drop-forgings and stampings, ball-bearings, weldless steel tube in full lengths, rims, forks, and spokes, in the rough.
404. Blacksmiths' anvils, forges, and fans.
405. Blowers.
406. Brass and copper, in pigs, bars, tubes, or sheets.
407. Brass tubing and stamped work, in the rough, for gasaliers and brackets.
408. Caps, percussion.
409. Card-clothing for woollen-mills.
410. Chain pulleys, and chains for same.
411. Chains, trace and plough chains; or metal articles required to repair or complete riding or driving harness or saddlery to be repaired or made in the colony.
412. Chamfering, crozing and howelling machine for cask-making.
413. Copper and composition, rod, bolts, sheathing, and nails.
414. Couch-roll jackets, machine-wires, beater-bars, and strainer-plates for paper-mills.
415. Crucibles.
416. Emery-grinding machines and emery-wheels.
417. Empty iron drums, not exceeding 10 gallons capacity.
418. Engineers', boilermakers', brass-finishers', smiths', and all metal- and wood-workers' machine and hand tools.
419. Engine governors.
420. Eyelets.
421. Fire-engines, including Merryweather's chemical fire-engines.
422. Fish-hooks.
423. Galvanising-baths, welded.
424. Gas-engines and hammers, and oil-engines.
425. Glassmakers' moulds.
426. Hydraulic cranes.
427. Iron- and brass-wove wire and wire gauze; also wire netting.
428. Iron boiler-plates and unflanged end-plates for boilers; boiler-tubes not exceeding 6 in. in diameter, and unflanged; Bowling's expansion rings; furnace-flues.
429. Iron, plain black sheet, rod, bolt, bar, plate, hoop, and pig.
430. Iron rolled girders.
431. Iron plates, screws, and castings for ships.
432. Iron wire n.o.e., including fencing-wire, plain and barbed.
433. Lead, in pigs and bars.
434. Locomotives.
435. Machine saws.
436. Machinery exclusively for the purpose of the manufacture of beet-root sugar.
437. Machinery for dairying purposes.
438. Machinery of every description for mining purposes, including machine pumps, but not including machinery for dredging.
439. Machinery for gold-saving purposes and processes.
440. Metal fittings for trunks, portmanteaux, travelling-bags, leggings, bags, and satchels.
441. Metal sheaves for blocks.
442. Metallic capsules.
443. Perambulators and the like vehicles, fittings for, n.o.e.
444. Perforated or cellular sheet zinc or iron.
445. Portable engines on four or any greater number of wheels, with boiler of locomotive type; also traction-engines.
446. Printing type and materials n.o.e.
447. Rails for railways and tramways.
448. Reapers and binders, and reaping and mowing machines, and extra parts for same; materials for manufacturing agricultural machinery, namely, reaper-knife sections, fingers, brass and steel springs, malleable castings, discs for harrows, mould-boards and plough-shares, mould-board plates, and steel-share plates cut to pattern, skeith-plates; ploughs and harrows; combined threshers.
449. Riddles and sieves.
450. Rivets and washers.
451. Separators and coolers for dairying purposes.
452. Set-screws, engineers' studs, and split-pins.
453. Sewing-, knitting-, and kilting machines.
454. Spiral springs (except sofa- and mattress-springs).
455. Steam and hydraulic pressure and vacuum gauges.
456. Steel rams, black or finished, for hydraulic cranes or jiggers.
457. Surveyors' steel bands and measuring-tapes.
458. Swords.
459. Tacks of all kinds.
460. Tea-packing lead.
461. Tin, in pigs, bars, or sheets.
462. Tinsmiths' fittings, including stamped or blocked tin, planished or unplanished.
463. Tins, tops of, ornamented.
464. Welded and flanged boiler-furnaces, plain or corrugated.
465. Wire, of brass, copper, or lead.
466. Zinc, plain sheet.
467. Zinc plates and copper plates for photo-lithographic work.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
468. Ash, hickory, and lancewood timber, unwrought.
469. Blacksmiths' bellows.
470. Brush woodware.
471. Carriage- and cart-shafts, spokes and felloes in the rough; hubs, of all kinds; poles if unbent and unplaned, of all kinds; bent wheel-rims.
472. Carriage- and cart-makers' materials—viz.: springs, mountings, trimmings, brass hinges, tire-bolts, shackle-holders, step treads, and other iron fittings (except steps, lamp-irons, dash-irons, seat-rails, and fifth wheels), rubber-cloth.
473. Churns.
474. Lignum-vitæ.
475. Sieves, hair.
476. Wooden handles for tools.
C(([0-9]+)), ETC.
477. Benzine in bulk.
478. Oils—viz.: candlenut, fish, kerosene, penguin, palm, seal, whale.
479. Paints and colours n.o.c.
480. Shale oil, once run, suitable for gas-making.
481. Spirits of tar.
482. Turpentine, driers, and terebene.
CLASS XV.—MISCELLANEOUS.
483. Apparatus and appliances solely for teaching purposes, as may be approved by the Commissioner.
484. Bags made of New Zealand tow or flax.
485. Belting for machinery, other than leather.
486. Binder-twine.
487. Bricks, other than fire-bricks.
488. Building materials n.o.e.
489. Brushes for cream-separators and combined screens.
490. Candlenuts and candlenut kernels.
491. Candle-wick.
492. Canvas aprons and elevators for reapers and binders.
493. Carpenters' baskets.
494. Charts and maps.
495. Confectioners' moulding-starch.
496. Cotton waste.
497. Dye-stuffs and dyeing materials, crude.
498. Felt sheathing.
499. Food preservative n.o.e.
500. Gum boots.
501. Hawsers of 12 in. and over.
502. Honey and brown Windsor soap composition.
503. Iron and steel cordage.
504. Jute bagging, bags, and sacks.
505. Manures.
506. Marble, and other stone, hewn or rough sawn, not dressed or polished.
507. Netmakers' cotton twine.
508. Official supplies for consular officers of countries where a similar exemption exists in favour of British Consuls.
509. Papermakers' felts.
510. Passengers' baggage and effects, including only wearing-apparel and other personal effects that have been worn or are in use by persons arriving in the colony; also implements, instruments, and tools of trade, occupation, or employment of such persons; and household or other effects not exceeding £100 in value, which have been in use for twelve months prior to embarkation by the persons or families bringing them to the colony, and not intended for any other person or persons or for sale *; also cabin-furnishings belonging to such persons.
511. Plaster of Paris.
512. Powder, blasting and meal.
513. Ship-chandlery n.o.e.
514. Ships' rockets, blue-lights, and danger-signals.
515. Stones, mill- grind- oil- and whet-.
516. Tobacco for sheepwash or for insecticide, after being rendered unfit for human consumption to the satisfaction of the Commissioner.
517. Treacle or molasses, mixed with bone-black in proportions to the satisfaction of the Commissioner.
518. Tubular woven cotton-cloth in the piece, for meat wraps.
519. Type-writers.
520. Wax, bottling.
521. Woolpacks and woolpockets.
522. Yarn—viz.: coir, flax, hemp.
523. Articles and materials (as may from time to time be specified by the Commissioner) which are suited only for, and are to be used solely in, the fabrication of goods within the colony. All decisions of the Commissioner in reference to articles so admitted free to be published from time to time in the Gazette.
524. And all articles not otherwise enumerated.
TABLE (([0-9]+)) DUTIES.
525. Tobacco, 1s. the lb.†
526. Cigars, cigarettes, and snuff, 1s. 6d. the lb.†
* Including bicycles which have been in use for twelve months.
† “The Tobacco Excise Duties Act, 1896,” section 2, enacts:—
“On and after the thirty-first day of December, one thousand eight hundred and ninety-six, section three of ‘The Customs and Excise Duties Act, 1891,' shall be deemed to be repealed, and in lieu of the duties imposed by that section there shall be levied, collected, and paid, on and after that day, upon tobacco manufactured in the colony, at the time of making the entry for home consumption thereof, the several duties of excise following, that is to say—
On tobacco One shilling the pound. On cigars and snuff One shilling and sixpence the pound On cigarettes— If manufactured by machinery Two shillings and sixpence the pound. If made by hand One shilling the pound.” 527. Beer, 3d. the gallon.
528. Articles in which spirit is a necessary ingredient, manufactured in a warehouse appointed under section 26 of “The Customs Laws Consolidation Act, 1882,” namely—
Pharmacopœia tinctures, essences, extracts, and medicinal spirits containing more than 50 per cent. of proof spirit, 9d. the lb.
Pharmacopœia tinctures, essences, extracts, and medicinal spirits containing less than 50 per cent. of proof spirit, 3d. the lb.
Culinary and flavouring essences, 12s. the liquid gallon, from 1st February, 1896.
Perfumed spirit, 20s. the liquid gallon, from 1st February, 1896.
Toilet preparations which are subject to 16s. the liquid gallon on importation, 12s. the liquid gallon.
Toilet preparations which are subject to 25 per cent. duty on importation, 6s. the liquid gallon.
Duties imposed by His Excellency the Governor under Section 17 of “The Customs and Excise Duties Act, 1888.”
529. Olive stones, ground (see New Zealand Gazette, 15th May, 1890), 4d. the lb.
530. Brewers' caramel (see New Zealand Gazette, 21st August, 1890), 3d. the lb.
531. Liquid hops (see New Zealand Gazette, 21st December, 1893), 6s. the lb.
532. The United Asbestos Patent Salamander Decorations (see New Zealand Gazette, 14th May, 1896), 15 per cent. ad valorem.
533. Matches of any material other than wood or wax, a duty corresponding to the duty payable on wooden matches (see New Zealand Gazette, 27th April, 1899).
534. Fibre conduit pipes and fittings for same (see New Zealand Gazette, 4th May, 1899), 5 per cent. ad valorem.
535. Caramel cereal (see New Zealand Gazette, 14th March, 1901), 1/2d. the lb.
536. Compo board (see New Zealand Gazette, 12th December, 1901), 4s. the 100 ft. super.
The “Opium Prohibition Act, 1901,” makes it unlawful for any person to import opium into the colony in any form suitable for smoking. Permits may be issued by the Commissioner of Trade and Customs for the importation of the drug in the following forms:—
Opium, crude.
Opium, in powder.
Opium, extract of, solid.
No permit shall be issued to any person of the Chinese race. Heavy penalties are prescribed for breaches of the above law.
“The Opium Prohibition Act Amendment Act, 1902,” makes it illegal to have opium in possession, except the kinds stated above, which can be held under permit.
“The Timber Export Act, 1901,” authorised the collection, by Order in Council, of the following duties:—
| SCHEDULE. | ||
| Logs, round | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. | Or such lesser duty as the Governor by Order in Council determines. |
| Logs, squared with axe or saw | ||
| Half logs | ||
| Flitches of any particular kind, or pieces of such size as the Governor by Order in Council from time to time determines | 3s. per 100 superficial feet | Or such lesser duty as the Governor by Order in Council determines. |
An Order in Council dated the 27th March, 1902, directs that there shall be levied, collected, and paid previous to exportation from New Zealand, duties upon white pine and kahikatea timber as under:—
| Logs, round | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. | |
| Logs, cut in half | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. | |
| Logs, squared with axe or saw, 10 in. by 10 in. or its equivalent or over | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. | |
| Flitches, any width, and not exceeding 10 in. thick | 2s. per 100 superficial feet. |
A further Order in Council, dated 10th April, 1902, directs that duties on kauri timber shall be charged as under:—
| Logs, round | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. |
| Logs, cut in half | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. |
| Logs, squared with axe or saw | 3s. per 100 superficial feet. |
| Flitches, exceeding 30 in. in width and 9 in. in thickness | 2s. per 100 superficial feet. |
Table of Contents
| FEES PAYABLE TO DISTRICT LAND REGISTRARS UNDER “THE L(([0-9]+)) ACT, 1885.” | |||
| For the bringing land under the provisions of this Act (over and above the cost of advertisements)— | £ | s. | d. |
| When the title consists of a Crown grant, and none of the land included therein has been dealt with | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| When the title is of any other description and the value exceeds £300 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| When the title is of any other description and the value exceeds £200 and does not exceed £300 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| When the title is of any other description and the value exceeds £100 and does not exceed £200 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| When the title is of any other description and when the value does not exceed £100 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Contribution to the Assurance Fund upon first bringing land under the Act,— | |||
| In the pound sterling | 0 | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Other fees— | |||
| For every application to bring land under the Act | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every certificate of title on transfer where the consideration does not exceed £100 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For every other certificate of title | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Registering memorandum of transfer, mortgage, incumbrance, or lease | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Registering transfer or discharge of mortgage or of incumbrance, or the transfer or surrender of a lease | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Registering proprietor of any estate or interest derived by settlement or transmission | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For every power of attorney deposited | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For every registration abstract | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| For cancelling registration abstract | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every revocation order | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Noting caveat | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Cancelling or withdrawal of caveat, and for every notice relating to any caveat | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every search | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| For every general search | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every map or plan deposited | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every instrument declaratory of trusts, and for every will or other instrument deposited | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For registering recovery by proceeding in law or equity or re-entry by lessee | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For registering vesting of lease in mortgagee, consequent on refusal of Trustee in Bankruptcy to accept the same | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For entering notice of marriage or death | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| For entering notice of writ or order of Supreme Court | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Taking affidavit or statutory declaration | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For the exhibition of any deposited instrument, or for exhibiting deeds surrendered by applicant proprietor | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For certified copy, not exceeding five folios | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every folio or part folio after first five | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| For every notice to produce deeds or instruments | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For every outstanding interest noted on certificate of title | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| When any instrument purports to deal with land included in more than one grant or certificate, for each registration memorial after the first | 0 | 2 | 0 |
All fees under the Act shall be due and payable in advance.
Where several properties are included in one form of application, there shall be charged in respect of each property an application fee, and a fee for bringing the land under the Act. Land included within one outer boundary shall be deemed one property for the purpose of this regulation.
In all cases a fee of one pound (£1) is hereby prescribed as the charge to be made for advertising notice of application; provided that, whenever it is necessary that unusual publicity shall be given to any application, the District Land Registrar may require payment of such additional sum as shall, in his judgment, be sufficient to defray the cost of such advertisements.
In all cases where application is made to bring land under the Act, and the certificate of title is directed to issue and is issued in the name of the applicant, the fees for bringing such land under the Act, with the exception of the “application fee,” may, at the request of the applicant, remain unpaid until such land is dealt with by him as registered proprietor. The District Land Registrar shall retain any such certificate of title until the fees due upon the same have been paid, and, until such payment, shall not register any dealing with the land included in such certificate of title.
Printed forms supplied by the Registrar for use under the Act shall be charged for at the rate of one shilling each. Solicitors, land-brokers, and others having forms printed for their own use, and at their own expense, shall, on approval of such forms by the Registrar, be entitled to have the same sealed free of charge.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
THE population of New Zealand, as estimated for the 31st December, 1902, with the increase for the year, is shown below:—
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated population, exclusive of Maoris (also Cook and other annexed Islands), on 31st December, 1901 |  | 787,657 | 414,223 | 373,434 |
| Increase during the year 1902:— | ||||
| By excess of births over deaths .. .. | 12,280 | 5,763 | 6,517 | |
| Excess of arrivals over departures .. .. | 7,992 | 5,922 | 2,070 | |
| Estimated population (exclusive of Maoris, also Cook and other annexed Islands), on 31st December, 1902 |  | 807,929 | 425,908 | 382,021 |
| Maori population, census, 1901 .. .. | 43,143 | 23,112 | 20,031 | |
| Population of Cook and other Pacific Islands .. | 12,292 | 6,369 | 5,923 | |
| Total estimated population of colony (including Maoris, also Cook and other Islands) on 31st December, 1902 |  | 863,364 | 455,389 | 407,975 |
The number of the Chinese in New Zealand at the end of the year 1902 was estimated to be 2,792 persons, of whom 31 were females.
Details showing the distribution of the Maori population and also of the Cook and other annexed Pacific Islands follow; but the figures in the succeeding portions of this section exclude these special features.
[Further particulars as to sex, age, &c., will be found in the section specially dealing with the Native population.]
| Counties. | Persons. |
|---|---|
| Mongonui | 2,093 |
| Whangaroa | 743 |
| Hokianga | 2,330 |
| Bay of Islands | 2,235 |
| Hobson | 984 |
| Whangarei | 739 |
| Otamatea | 186 |
| Rodney | 173 |
| Waitemata | 171 |
| Eden | 223 |
| Great Barrier Island | 37 |
| Waiheke Island | 70 |
| Manukau | 734 |
| Coromandel | 565 |
| Thames | 774 |
| Ohinemuri | 630 |
| Piako | 409 |
| Waikato | 983 |
| Waipa | 226 |
| Raglan | 1,499 |
| Kawhia | 1,649 |
| West Taupo | 1,130 |
| East Taupo | 651 |
| Rotorua | 971 |
| Tauranga | 1,301 |
| Whakatane | 3,170 |
| Waiapu | 2,474 |
| Cook | 1,803 |
| Clifton | 420 |
| Taranaki | 1,020 |
| Stratford | 43 |
| Hawera | 853 |
| Patea | 274 |
| Waitotara and Wanganui | 1,689 |
| Rangitikei | 459 |
| Oroua | 433 |
| Pohangina | 3 |
| Manawatu | 252 |
| Horowhenua | 1,035 |
| Wairoa | 1,991 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,605 |
| Waipawa | 403 |
| Patangata | 181 |
| Pahiatua | 24 |
| Wairarapa North | 337 |
| Wairarapa South | 476 |
| Hutt | 264 |
| Sounds | 263 |
| Marlborough | 79 |
| Kaikoura | 78 |
| Collingwood | 22 |
| Waimea | 107 |
| Buller | 23 |
| Westland | 60 |
| Ashley | 188 |
| Selwyn | 56 |
| Akaroa | 293 |
| Levels and Geraldine | 134 |
| Waimate | 65 |
| Waitaki | 117 |
| Waikouaiti | 168 |
| Peninsula | 92 |
| Taieri | 42 |
| Clutha | 22 |
| Southland | 2 |
| Wallace | 98 |
| Stewart Island | 112 |
| Chatham Islands | 211 |
| Persons. | |
|---|---|
* Results of census taken this year (1902). (a) Birthplaces.—Rarotonga, 1,517; Mangaia, 206; Aitutaki, 58; Mauke, 16: Atiu, 37; Mitiaro, 11; Society Islands, 73; other Pacific Islands, 58; United Kingdom, 30; America, 11: New Zealand, 21; China, 7; Germany, 5: Portugal, 5; Australia, 3; Jamaica, 1; New Guinea, 1. (b) Birthplaces.—Atiu, 913; Rarotonga, 3; Austria, 1; China, 1. (c) Not including 149 natives absent in ships or at the guano islands. (d) Whites and half-castes living as whites, 28 persons; absent in ships or at Tonga, 418 persons. (e) Birthplaces.—Palmerston atoll, 100; Manahiki, 10; Penrhyn, 3; Pukapuka, 1; Society Islands, 1. (f) Birthplaces.—Penrhyn, 312; Cook Islands, 25; Society Islands, 61; Arorai, 2; United Kingdom, 8; other places, 4. (g) Birthplaces.—Manahiki, 469; Pukapuka, 11; Society Islands, 2; England, 2. | |
| Rarotonga* | 2,060(a) |
| Mangaia | 1,541 |
| Atiu* | 918(b) |
| Aitutaki* | 1,170(c) |
| Mauke (or Parry Island) | 370 |
| Mitiaro | 165 |
| Hervey Islands | 10 |
| Total Cook group | 6,234 |
| Niue (or Savage Island)* | 4,079(d) |
| Palmerston* | 115(e) |
| Penrhyn (or Tongareva)* | 445(f) |
| Manahiki* | 484(g) |
| Rakaanga | 400 |
| Danger (or Pukapuka) | 505 |
| Suwarrow | 30 |
| Total other Islands | 6,058 |
| Total population of Islands included within the extended boundaries of the colony | 12,292 |
The increase for each quarter of the year 1902 was:—
| First Quarter. | |||
| Increase from: | Total. | Males. | Females. |
| Excess of births over deaths | 3,164 | 1,484 | 1,680 |
| Excess of departures over arrivals (decrease) | −825 | −1,044 | 219 |
| 2,339 | 440 | 1,899 | |
| Second Quarter. | |||
| Excess of births over deaths | 3,150 | 1,473 | 1,677 |
| Excess of departures over arrivals (decrease).. | −1,615 | −1,080 | −535 |
| 1,535 | 393 | 1,142 | |
| Third Quarter. | |||
| Increase from: | Total. | Males. | Females. |
| Excess of births over deaths | 2,823 | 1,299 | 1,524 |
| Excess of arrivals over departures | 3,758 | 3,347 | 411 |
| 6,581 | 4,646 | 1,935 | |
| Fourth Quarter. | |||
| Excess of births over deaths | 3,143 | 1,507 | 1,636 |
| Excess of arrivals over departures | 6,674 | 4,699 | 1,975 |
| 9,817 | 6,206 | 3,611 | |
| Year 1902. | |||
| Excess of births over deaths | 12,280 | 5,763 | 6,517 |
| Excess of arrivals over departures | 7,992 | 5,922 | 2,070 |
| 20,272 | 11,685 | 8,587 | |
The movement of population since 1885 is given next. Although the large increase in 1893 by excess of arrivals over departures was not maintained during the nine following years, the arrivals in the colony nevertheless exceeded the departures in each of these years, and the total excess of arrivals for the ten-year period 1893–1902 inclusive is found to be 38,712 persons, drawn from other states, colonies, or countries. The number may be somewhat greater than the actual fact, but probably not very much so. Reference to the possible source of error and its degree will be found further on.
| Year. | Estimated Population on the 31st December. | Increase during the Year | Centesimal Increase on Population of Previous Year. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Excess of Births over Deaths. | By Excess of Arrivals over Departures.* | Net Increase. | ||||
* Corrected where necessary in accordance with census results. The amount of loss by departures in the period 18–6–91, though correct in the aggregate, cannot be allocated with exactness to the respective years. † Loss. | ||||||
| 1885 | 575,172 | 13,612 | −2,744† | 10,868 | 1·93 | |
| 1886 | 589,386 | 13,164 |  | -17,194† | 58,886 | 10·24 |
| 1887 | 603,361 | 12,998 | ||||
| 1888 | 607,380 | 13,194 | ||||
| 1889 | 616,052 | 12,685 | ||||
| 1890 | 625,508 | 12,284 | ||||
| 1891 | 634,058 | 11,755 | ||||
| 1892 | 650,433 | 11,417 | 4,958 | 16,375 | 2·58 | |
| 1893 | 672,265 | 11,420 | 10,412 | 21,832 | 3·36 | |
| 1894 | 686,128 | 11,610 | 2,253 | 13,863 | 2·06 | |
| 1895 | 698,706 | 11,683 | 895 | 12,578 | 1·83 | |
| 1896 | 714,162 | 12,180 | 1,472 | 13,652 | 1·95 | |
| 1897 | 729,056 | 12,142 | 2,752 | 14,894 | 2·09 | |
| 1898 | 743,463 | 11,711 | 2,696 | 14,407 | 1·98 | |
| 1899 | 756,505 | 11,155 | 1,887 | 13,042 | 1·75 | |
| 1900 | 768,278 | 12,346 | 1,831 | 14,177 | 1·87 | |
| 1901 | 787,657 | 12,857 | 6,522 | 19,379 | 2·52 | |
| 1902 | 807,929 | 12,280 | 7,992 | 20,272 | 2·57 | |
The number of persons who arrived in the colony in the year 1902 was 30,293, an increase of 5,207 on the number for the previous year. Of the arrivals in 1902, 27,435 persons were classified as adults, being above the age of twelve years, and 2,858 as children. The total number of males was 21,522 and of females 8,771. The arrivals from the United Kingdom numbered 3,474, and from Australia 22,526. Besides these, 679 persons came from Fiji, and 3,614 from the South Seas and other ports, including arrivals by mail-steamers from San Francisco.
Classified in respect of birthplace, it is found that 10,283 of the arrivals were persons born in Australasia, 18,903 in the United Kingdom, and 38 in other British possessions. Of 1,069 persons born in foreign countries who arrived during 1902, 255 were born in Germany, 120 in Austria, 112 in France, 170 in the United States, 74 in Denmark, 41 in Sweden, 31 in Norway, 57 in Greece, 48 in Italy, 29 in Switzerland, 11 in Russia, 11 in Bavaria, 2 in Belgium, 1 in Spain, and 107 in other countries (China, Japan, Pacific Islands, Syria, Persia, and Asia Minor).
Among the arrivals in 1902 are noticed 102 “race-aliens,” or persons of other than European descent. Particulars of birthplace and sex are as under:—
| Birthplace. | M. | F. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia Minor | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| China | 69 | 0 | 69 |
| Syria | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Persia | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Pacific Islands | 9 | 3 | 12 |
| Fiji | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| India | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Japan | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| New Zealand | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 93 | 9 | 102 |
The practice of nominating immigrants to be brought out partly at the Government expense has been discontinued since the 16th December, 1890, and there was no free immigration in the year 1902. Certain reductions are, however, arranged by the Agent-General with the shipping companies in fares for men with moderate means who intend to take up land and settle in the colony.
Only 69 Chinese (all men) arrived in the colony during 1902, but 87 (all men) left, the departures thus exceeding the arrivals by 18.
The total departures in 1902 were 22,301 persons, being 3,737 more than in 1901. Thus, the movement of population both to and from the colony is found to have been greater than in the previous year.
The departures from the colony by the Union Steamship Company's boats, as given through the Customs Department, are checked by special returns kindly furnished by the pursers of the steamers, and, where persons who did not book their passages have been omitted, the necessary additions are made. The pursers' returns also serve to prevent the occasional omission of the full number of persons leaving by any one vessel, which sometimes had happened previous to the introduction of this check. Unless more passengers are at any time of great pressure taken away from New Zealand than can lawfully be carried, the returns of outgo of population should prove fairly correct, and indeed the last census shows that the estimated population even after five years' interval was a very close approximation to the truth.
Of the departures in 1902, 20,721 persons were over twelve years of age, and 1,580 children. More than twice as many males left the colony as females, the numbers being 15,600 and 6,701 respectively. The departures to the United Kingdom amounted to 1,497 persons, and those to Australia numbered 15,670. Besides these, 610 persons left for Fiji, and 4,524 for other ports (including passengers for San Francisco).
In 1891 the colony lost population by excess of departures over arrivals, but in each of the years 1892 to 1902, inclusive, New Zealand has drawn to itself more population than it has parted with, notwithstanding the attractions of Australian and other gold-fields.
The population of the colony (exclusive of Maoris), as returned in the census schedules for the night of the 31st March, 1901, was 772,719 persons, of whom 2,857 were Chinese, and 2,407 half-castes living amongst and as Europeans.
A census of the Maori population was taken during February of 1901, when, according to returns made by the enumerators, the number of the Native race was found to be 43,143 persons, including 3,133 half-castes living as Maoris. 196 Maori women were returned as married to European husbands. The complete population (European and Maori) of the colony was therefore 815,862 persons, as exhibited in the following statement, specifying the numbers for each sex:—
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| * Not including 352 persons, officers and crews of two British men-of-war. | |||
| Population (exclusive of persons of the aboriginal native race, of mixed European and Native blood, and Chinese) | 767,455 | 401,979 | 365,476 |
| Half-castes and persons of mixed race living as and among Europeans | 2,407 | 1,188 | 1,219 |
| Chinese | 2,857 | 2,825 | 32 |
| Aboriginal natives (including 196 Maori wives of Europeans) | 40,010 | 21,418 | 18,592 |
| Half-castes and persons of mixed race living among and as members of Maori tribes | 3,133 | 1,694 | 1,439 |
| Total population on 31st March, 1901 | *815,862 | 429,104 | 386,758 |
The total half-caste or mixed European and Native population was 5,540 persons. The number of half-castes living among Europeans increased since 1896 by 148, or at the rate of 6·55 per cent. In that year the number of Maori wives of Europeans was 229; in 1901 it was 196. The Chinese decreased from 3,711 at the time of the census of 1896 to 2,857 in March, 1901; or at the rate of 23·01 per cent., caused mainly by the excess of departures over arrivals.
The Maori population fell from 41,993 in 1891 to 39,854 in 1896, and increased to 43,143 in 1901, according to the returns.
The increase on the total European population between April, 1896, and 31st March, 1901, amounted to 69,359 persons, or a rate of 9·86 per cent. Between the census of 1891 and that of 1896 the numerical increase was 76,702 persons, or 12·24 per cent. The average annual increase in the period 1896–1901 was at the rate of 1·90 per cent.
The population of the principal divisions of the colony on 31st March, 1901, was—
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| North Island and adjacent islets (exclusive of Maoris) | 390,571 | 206,606 | 183,965 |
| Middle Island and adjacent islets (exclusive of Maoris) | 381,661 | 199,103 | 182,558 |
| Stewart Island | 272 | 166 | 106 |
| Chatham Islands (exclusive of Maoris) | 207 | 112 | 95 |
| Kermadec Islands | 8 | 5 | 3 |
| Total for the colony (exclusive of Maoris) | 772,719 | 405,992 | 366,727 |
The gradual equalization of the numbers of the sexes and growing density of population and dwellings in the colony are alluded to in a further table.
| Date of Enumeration. | Number of Females to 100 Males. | Number of Persons to a Square Mile. | Number of Persons to an Inhabited Dwelling. | Number of Inhabited Dwellings to a Square Mile. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| December, 1861 | 62·16 | 0·944 | 4·42 | 0·214 |
| February, 1871 | 70·52 | 2·456 | 4·48 | 0·548 |
| April, 1881 | 81·72 | 4·693 | 5·12 | 0·917 |
| April, 1891 | 88·26 | 0·024 | 5·06 | 1·191 |
| March, 1901 | 90·33 | 7·427 | 4·86 | 1·527 |
The increase of population of European descent at successive census periods has been:—
| Date of Enumeration. | Population. Persons. | Numerical Increase. Persons. | Centesimal Increase. |
|---|---|---|---|
| December, 1858 | 59,413 | 39,608 | 39·99 |
| December, 1861 | 99,021 | 73,137 | 73·86 |
| December, 1864 | 172,158 | 46,510 | 27·01 |
| December, 1867 | 218,668 | 37,725 | 17·25 |
| February, 1871 | 256,393 | 43,121 | 16·82 |
| March, 1874 | 299,514 | 114,898 | 38·36 |
| March, 1878 | 414,412 | 75,521 | 18·22 |
| April, 1881 | 489,933 | 88,549 | 18·07 |
| March, 1886 | 578,482 | 48,176 | 8·33 |
| April, 1891 | 626,658 | 76,702 | 12·24 |
| April, 1896 | 703,360 | 69,359 | 9·86 |
| March, 1901 | 772,719 |
These are stated as in March, 1901, and at the previous census. Taranaki stands first for rate of progress with an increase of 21·42 per cent. in five years, Wellington comes next with 16 per cent., Auckland third with 14·57, Marlborough and Nelson have increased from 6 to 7 per cent., Canterbury and Otago somewhat over 5 per cent.
| Provincial Districts. | Population, April, 1896. | Population, March, 1901. | Increase. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Persons. | Persons. | Numerical Persons. | Centesimal. | |
| (–) Decrease. | ||||
| Auckland | 153,564 | 175,938 | 22,374 | 14·57 |
| Taranaki | 31,175 | 37,855 | 6,680 | 21·42 |
| Hawke's Bay | 34,038 | 35,424 | 1,386 | 4·07 |
| Wellington | 121,854 | 141,354 | 19,500 | 16·00 |
| Marlborough | 12,483 | 13,326 | 843 | 6·75 |
| Nelson | 35,734 | 37,915 | 2,181 | 6·10 |
| Westland | 14,469 | 14,506 | 37 | 0·26 |
| Canterbury | 135,858 | 143,041 | 7,183 | 5·29 |
| Otago | 163,944 | 173,145 | 9,201 | 5·61 |
| Chatham Islands | 234 | 207 | −27 | −11·54 |
| Kermadec Islands | 7 | 8 | 1 | 14·28 |
| Totals | 703,360 | 772,719 | 69,359 | 9·86 |
New Zealand is, by “The Counties Act, 1876,” divided into counties and boroughs, excepting certain outlying islands, which are not within county boundaries. It is provided by the above-mentioned Act that boroughs shall not be included in counties. In March, 1901, the number of the counties was 86. Of these, the North Island had 52, with a population amounting altogether to 216,725 persons. The Middle Island had 33 counties, the population being 200,618 persons. Stewart Island is a county in itself, and had a population of 253 persons, exclusive of persons on shipboard. The names and populations of the various counties in the colony, with their interior boroughs set opposite, were as under at the date of the enumeration:—
| Counties. | Census, 1901. |
|---|---|
* Since reduced by creation of Waihi Borough. † Since reduced by creation of Egmont County, and Inglewood and Eltham Boroughs. ‡ Since reduced by creation of Kairanga County. § Since reduced by creation of Woodville County. | |
| Mongonui | 2,274 |
| On shipboard | 18 |
| Whangaroa | 927 |
| Hokianga | 1,767 |
| On shipboard | 22 |
| Bay of Islands | 2,587 |
| On shipboard | 26 |
| Hobson | 4,813 |
| On shipboard | 163 |
| Whangarei | 6,380 |
| On shipboard | 31 |
| Otamatea | 2,721 |
| Rodney | 3,678 |
| On shipboard | 17 |
| Waitemata | 7,035 |
| On shipboard | 27 |
| Eden | 19,314 |
| Manukau | 12,306 |
| Coromandel | 4,169 |
| On shipboard | 14 |
| Thames | 5,043 |
| On shipboard | 8 |
| *Ohinemuri | 9,978 |
| On shipboard | 50 |
| Piako | 2,436 |
| Waikato | 3,183 |
| Waipa | 3,580 |
| Raglan | 1,697 |
| Rawhia | 1,113 |
| On shipboard | 1 |
| West Taupo | 287 |
| East Taupo | 256 |
| Rotorua | 1,307 |
| Tauranga | 1,720 |
| Whakatane | 779 |
| Opotiki | 1,438 |
| On shipboard | 5 |
| Waiapu | 711 |
| Cook | 6,393 |
| Wairoa | 1,773 |
| Hawke's Bay | 6,833 |
| Clifton | 2,535 |
| †Taranaki | 11,194 |
| On shipboard | 92 |
| Stratford | 5,081 |
| †Hawera | 8,347 |
| Patea | 3,046 |
| Waitotara | 3,476 |
| Wanganui | 4,018 |
| Rangitikei | 7,570 |
| Kiwitea | 2,844 |
| ‡Oroua | 6,778 |
| Pohangina | 1,536 |
| Manawatu | 3,000 |
| Horowhenua | 4,654 |
| §Waipawa | 9,495 |
| Patangata | 2,376 |
| Boroughs. | Census, 1901. |
| Whangarei | 1,429 |
| Birkenhead | 1,057 |
| Devonport | 3,823 |
| On shipboard | 1 |
| Grey Lynn | 4,110 |
| Auckland | 34,213 |
| On shipboard | 874 |
| Parnell | 4,566 |
| Newmarket | 2,060 |
| Onehunga | 3,015 |
| On shipboard | 47 |
| Thames | 4,009 |
| On shipboard | 11 |
| Te Aroha | 888 |
| Hamilton | 1,253 |
| Cambridge | 989 |
| Tauranga | 945 |
| On shipboard | 1 |
| Gisborne | 2,737 |
| On shipboard | 58 |
| Napier | 8,774 |
| On shipboard | 211 |
| Hastings | 3,650 |
| New Plymouth | 4,405 |
| Stratford | 2,027 |
| Hawera | 2,131 |
| Patea | 691 |
| Wanganui | 7,329 |
| On shipboard | 5 |
| Marton | 1,101 |
| Feilding | 2,298 |
| Palmerston North | 6,534 |
| Foxton | 1,211 |
| Dannevirke | 2,315 |
| Woodville | 926 |
| Counties. | Census, 1901. |
|---|---|
* Boundaries since altered. † Since reduced by creation of Featherston County. ‡ Since reduced by creation of Mount Herbert County. § Since merged in Wellington. ∥Since merged in Christchurch. | |
| Pahiatua | 3,600 |
| *Akitio | 1,048 |
| *Castlepoint | 457 |
| *Eketahuna | 2,332 |
| *Mauriceville | 1,127 |
| *Masterton | 3,123 |
| †South Wairarapa | 5,419 |
| Hutt | 7,171 |
| Sounds | 946 |
| On shipboard | 2 |
| Marlborough | 6,518 |
| Kaikoura | 1,765 |
| Collingwood | 2,490 |
| On shipboard | 23 |
| Waimea | 7,833 |
| On shipboard | 3 |
| Buller | 4,868 |
| On shipboard | 1 |
| Inangahua | 4,595 |
| Grey | 4,971 |
| Westland | 4,405 |
| Amuri | 1,142 |
| Cheviot | 1,120 |
| *Ashley | 11,599 |
| *Selwyn | 30,787 |
| ‡Akaroa | 3,669 |
| Ashburton | 11,342 |
| Geraldine | 5,991 |
| Levels | 5,496 |
| Mackenzie | 1,642 |
| Waimate | 5,653 |
| Waitaki | 9,086 |
| Waihemo | 2,014 |
| Waikouaiti | 4,082 |
| Pahiatua | 1,209 |
| Masterton | 3,949 |
| Carterton | 1,205 |
| Greytown | 1,122 |
| Wellington | 43,638 |
| On shipboard | 333 |
| Onslow | 1,499 |
| §Melrose | 2,995 |
| Petone | 3,780 |
| Lower Hutt | 1,822 |
| Karori | 1,212 |
| Blenheim | 3,222 |
| Picton | 875 |
| On shipboard | 95 |
| Motueka | 886 |
| Richmond | 543 |
| Nelson | 7,010 |
| On shipboard | 157 |
| Westport | 2,922 |
| On shipboard | 236 |
| Brunner | 1,572 |
| Greymouth | 3,748 |
| On shipboard | 89 |
| Hokitika | 1,946 |
| On shipboard | 5 |
| Kumara | 1,121 |
| Ross | 614 |
| Kaiapoi | 1,795 |
| Rangiora | 1,768 |
| Lyttelton | 4,023 |
| On shipboard | 321 |
| Christchurch | 17,538 |
| New Brighton | 1,008 |
| ∥Sydenham | 11,404 |
| ∥Albans | 6,607 |
| ∥Linwood | 6,737 |
| Woolston | 2,532 |
| Sumner | 844 |
| Akaroa | 559 |
| On shipboard | 5 |
| Ashburton | 2,322 |
| Temuka | 1,465 |
| Timaru | 6,424 |
| On shipboard | 62 |
| Waimate | 1,359 |
| Oamaru | 4,836 |
| On shipboard | 17 |
| Hampden | 331 |
| Palmerston South | 738 |
| Hawksbury | 690 |
| Port Chalmers | 2,056 |
| On shipboard | 149 |
| North-east Valley | 3,527 |
| Maori Hill | 1,550 |
| West Harbour | 1,465 |
| Counties. | Census, 1901. |
|---|---|
* Boundaries since altered. [Chatham Islands, with a population of 207 at time of census of 1901, has since been created a county.] | |
| Peninsula | 2,561 |
| Taieri | 7,179 |
| Bruce | 4,762 |
| Tuapeka | 6,272 |
| *Clutha | 6,445 |
| Maniototo | 3,792 |
| Vincent | 4,362 |
| Lake | 2,535 |
| *Southland | 22,583 |
| Wallace | 7,989 |
| Fiord | 124 |
| Stewart Island | 253 |
| On shipboard | 19 |
| Boroughs. | Census, 1901. |
| Dunedin | 24,879 |
| On shipboard | 228 |
| Roslyn | 4,632 |
| Mornington | 4,008 |
| Caversham | 5,266 |
| St. Kilda | 1,700 |
| South Dunedin | 5,363 |
| Green Island | 667 |
| Mosgiel | 1,463 |
| Milton | 1,241 |
| Kaitangata | 1,463 |
| Lawrence | 1,159 |
| Roxburgh | 478 |
| Tapanui | 350 |
| Balclutha | 1,017 |
| Naseby | 505 |
| Cromwell | 642 |
| Alexandra | 818 |
| Arrowtown | 416 |
| Queenstown | 690 |
| Gore | 2,354 |
| Mataura | 867 |
| Winton | 474 |
| Invercargill | 6,215 |
| Invercargill North | 925 |
| Invercargill South | 1,874 |
| Invercargill East | 939 |
| Avenal | 355 |
| Gladstone | 329 |
| Campbelltown | 1,350 |
| On shipboard | 303 |
| Riverton | 815 |
The total county population amounted to 417,596, or 54·04 percent. of the total for the colony.†In counties are included all towns not constituted municipal boroughs; but, on the other hand, the people living in many of the boroughs can hardly be called town population. The population in boroughs was 350,202 persons, or 45·32 per cent. of the whole. For every 100 persons resident in counties in 1901 there were 84 residing in boroughs. In 1896 the counties had 391,735 persons, and the boroughs 307,294, or, in other words, for every 100 persons in counties, 78 were residents of the boroughs. Thus it will be seen that the proportion of the town to the county population was greater in 1901 than in 1896.
The Cities of Auckland, Christchurch, and Dunedin have considerable suburbs. The suburban population of Wellington is comparatively small. The following gives the names and populations of the several localities which may fairly be termed suburbs of the four principal cities:—
† For population of ridings, road districts, and localities, see Census volume, Part I.
| S(([0-9]+)) AUCKLAND. | |
|---|---|
| Population Census, 1901. | |
| Boroughs— | |
| Birkenhead | 1,057 |
| Devonport | 3,823 |
| Newmarket | 2,060 |
| Grey Lynn (Newton) | 4,110 |
| Parnell | 4,566 |
| Road Districts— | |
| Arch-hill | 1,671 |
| Eden Terrace | 2,011 |
| Epsom | 750 |
| Mount Albert | 2,085 |
| Mount Eden | 5,129 |
| Mount Roskill | 581 |
| One-tree Hill | 1,283 |
| Point Chevalier | 684 |
| Remuera | 2,186 |
| Northcote Riding | 767 |
| Outlying portion of Parnell Riding, being land in the Domain with hospital on it | 250 |
| Total suburbs | 33,013 |
| Auckland City | 34,213 |
| Total Auckland and suburbs | 67,226* |
| S(([0-9]+)) WELLINGTON.S(([0-9]+)) WELLINGTON. | |
|---|---|
| * Since merged in Wellington. | |
| Boroughs— | |
| Onslow | 1,499 |
| *Melrose | 2,995 |
| Karori | 1,212 |
| Total suburbs | 5,706 |
| Wellington City | 43,638 |
| Total Wellington and suburbs | 49,344 |
| S(([0-9]+)) CHRISTCHURCH. | |
|---|---|
| Population, Census, 1901. | |
| † Since merged in Christchurch. | |
| Boroughs— | |
| †Sydenham | 11,404 |
| †St. Albans | 6,607 |
| †Linwood | 6,737 |
| New Brighton | 1,008 |
| Woolston | 2,532 |
| Road Districts— | |
| Spreydon | 1,457 |
| Halswell (part) | 156 |
| Riccarton (part) | 4,371 |
| Avon (part) | 2,843 |
| Heathcote (part) | 2,388 |
| Total suburbs | 39,503 |
| Christchurch City | 17,538 |
| Total Christchurch and suburbs | 57,041 |
In laying off the suburbs of Christchurch the boundaries of the Christchurch Health District have been mainly followed.
| S(([0-9]+)) DUNEDIN. | |
|---|---|
| Boroughs– | |
| Caversham | 5,266 |
| Maori Hill | 1,550 |
| Mornington | 4,008 |
| North-East Valley | 3,527 |
| Roslyn | 4,632 |
| St. Kilda | 1,700 |
| South Dunedin | 5,363 |
| West Harbour | 1,465 |
| Total suburbs | 27,511 |
| Dunedin City | 24,879 |
| Total Dunedin and suburbs | 52,390 |
The increase of population for ten years at the four chief centres, with their suburbs, was:—
| Census, 1891. | Census, 1901 | Numerical Increase. | Increase per Cent. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland and suburbs | 51,287 | 67,226 | 15,939 | 31·08 |
| Wellington and suburbs | 34,190 | 49,344 | 15,154 | 44·32 |
| Christchurch and suburbs | 47,846 | 57,041 | 9,195 | 19·22 |
| Dunedin and suburbs | 45,869 | 52,390 | 6,521 | 14·22 |
Thus the two principal cities of the North Island are found to have progressed between 1891 and 1901 at a greater rate than those of the Middle Island, and Wellington in particular to have developed at more than three times the rate of Dunedin, and more than twice as fast as Christchurch.
While New South Wales and Victoria present what is termed by the statistician of the former State “the disquieting spectacle of capital towns growing with wonderful rapidity, and embracing in their limits one-third of the population of the territory of which they are the centre,” New Zealand is saved from this by the configuration of the country, which has resulted in the formation of four chief towns, besides others of secondary importance but nevertheless trading centres of considerable consequence.
Besides the boroughs, there were 35 town districts (including the special town district of Rotorua, constituted under “The Thermal-Springs Districts Act, 1881,”) which are portions of the counties in which they are situated. One only of these, Hampstead, has more than 1,000 inhabitants. A list of these town districts is subjoined, with populations, as in 1901:—
| Town Districts. | Population. |
|---|---|
* Constituted under “The Thermal-Springs Districts Act, 1881.” †Now a municipal borough. | |
| Kamo | 260 |
| Helensville | 531 |
| Papakura | 286 |
| Te Awamutu | 355 |
| Kihikihi | 222 |
| Ngaruawahia | 245 |
| Rotorua* | 914 |
| Opotiki | 627 |
| Waitara (Raleigh) | 765 |
| Opunake | 166 |
| Inglewood† | 719 |
| Normanby | 370 |
| Manaia | 447 |
| Waverley | 416 |
| Lethbridge | 230 |
| Bulls | 501 |
| Halcombe | 336 |
| Clyde (Wairoa) | 623 |
| Taradale | 763 |
| Ormondville | 459 |
| Waipawa | 669 |
| Kaikora North | 268 |
| Featherston | 629 |
| Johnsonville | 502 |
| Havelock | 316 |
| Amberley | 417 |
| Southbridge | 396 |
| Hampstead | 1,118 |
| Tinwald | 561 |
| Geraldine | 868 |
| Allanton (formerly Grey) | 227 |
| Outram | 420 |
| Clinton | 431 |
| Wyndham | 417 |
| Otautau | 443 |
In addition to the boroughs and town districts above referred to, the census results showed for 1901 throughout the colony no less than 683 places of the nature of townships, villages, or small centres without boundaries. It is impossible to say that the populations of these small centres are all strictly accurate, even for the census date, or given in such a way as to be fit for comparison one with another. In different cases more or less of surrounding country may have been considered as belonging to the centre, but there is at least at each place mentioned some sort of nucleus of population, if not a well-defined village or township. In making the statement the best has been done with a difficult matter, and the information is given as useful—in some cases, like that of Waihi and Reefton, important—even if open to objection here and there. The county in which each is situated is also given:—
| Population. | |
|---|---|
| * Now a municipal borough. | |
| Abbotsford, Taieri | 281 |
| Adair, Levels | 206 |
| Adams's Flat, Bruce | 76 |
| Adamson's, Southland | 69 |
| Addison's Flat, Buller | 208 |
| Ahaura, Grey | 219 |
| Albany, Waitemata | 87 |
| Albert Town, Vincent | 73 |
| Alford Forest, Ashburton | 221 |
| Alfredton (and vicinity), Masterton | 332 |
| Allandale, Waihemo | 115 |
| Allenton, Ashburton | 837 |
| Alma, Waitaki | 123 |
| Alton, Patea | 58 |
| Anderson's Bay, Peninsula | 567 |
| Annat, Selwyn | 105 |
| Antonio's Flat, Inangahua | 51 |
| Aongatete, Tauranga | 22 |
| Aoroa, Hobson | 373 |
| Apiti, Pohangina | 128 |
| Aramoho, Waitotara | 1,002 |
| Arapohu, Hobson | 189 |
| Aratapu, Hobson | 556 |
| Arden, Taieri | 87 |
| Argyle, Southland | 80 |
| Arthurtown, Westland | 74 |
| Arundel, Geraldine | 38 |
| Ashley, Ashley | 202 |
| Ashhurst (and vicinity), Oroua | 545 |
| Athol, Southland | 72 |
| Avondale, Eden | 826 |
| Awahuri, Manawatu | 42 |
| Awakino, Kawhia | 124 |
| Awanui, Waiapu | 51 |
| Awhitu, Manukau | 413 |
| Bainham, Collingwood | 126 |
| Bald Hill Flat, Vincent | 175 |
| Ballance, Pahiatua | 73 |
| Bannockburn, Vincent | 394 |
| Barkly, Southland | 63 |
| Barry's Bay, Akaroa | 154 |
| Basting's, Tuapeka | 28 |
| Beaconsfield, Levels | 122 |
| Beck's, Maniototo | 67 |
| Belfast, Selwyn | 613 |
| Belfield Village Settlement, Geraldine | 166 |
| Belgrove, Waimea | 156 |
| Bendigo, Vincent | 49 |
| Bennett's, Ashley | 77 |
| Berwick, Taieri | 87 |
| Blackball, Grey | 382 |
| Black's Point, Inangahua | 315 |
| lackwater, Inangahua | 149 |
| Blair Taieri, Taieri | 35 |
| Blue Spur, Westland | 135 |
| Bombay, Manukau | 363 |
| Bowentown, Tauranga | 24 |
| Brighton, Buller | 19 |
| Brighton, Taieri | 119 |
| Brightwater, Waimea | 391 |
| Broad Bay, Peninsula | 156 |
| Brockville, Taieri | 23 |
| Buckley, Cook | 164 |
| Buffalo (and vicinity), Coromandel | 574 |
| Bulltown, Ohinemuri | 27 |
| Bunnythorpe (and vicinity), Oroua | 148 |
| Burke's, Mackenzie | 143 |
| Burnside (and vicinity), Taieri | 469 |
| Burnveil and Lovell's Flat, Bruce | 89 |
| Burwood, Selwyn | 140 |
| Cabbage Bay, Coromandel | 18 |
| Callaghan's, Westland | 79 |
| Cambrian's, Maniototo | 103 |
| Cambridge West, Waipa | 238 |
| Cape Foulwind, Buller | 182 |
| Capleston, Inangahua | 153 |
| Cardrona, Lake | 126 |
| Castlecliffe, Waitotara | 412 |
| Castlepoint, Castlepoint | 22 |
| Centre Bush, Southland | 83 |
| Charleston, Buller | 199 |
| Charlton, Southland | 108 |
| Chatton, Southland | 32 |
| Cheltenham, Kiwitea | 39 |
| Chertsey, Ashburton | 99 |
| Clareville, Wairarapa South | 93 |
| Clarkville, Ashley | 253 |
| Clifden, Wallace | 93 |
| Clifton, Collingwood | 60 |
| Clyde, Vincent | 374 |
| Coal brookdale, Buller | 111 |
| Coal Creek, Tuapeka | 220 |
| Coalgate (and vicinity), Selwyn | 129 |
| Cobden, Grey | 423 |
| Collingwood, Collingwood | 16 |
| Cooptown, Akaroa | 96 |
| Coromandel, Coromandel | 663 |
| Courtenay, Selwyn | 161 |
| Crofton, Rangitikei | 148 |
| Cromarty, Fiord | 28 |
| Crushington, Inangahua | 152 |
| Cullensville, Marlborough | 84 |
| Culverden, Amuri | 87 |
| Dacre, Southland | 44 |
| Dalefield, Wairarapa South | 311 |
| Danieltown, Wallace | 68 |
| Darfield, Selwyn | 118 |
| Dargaville, Hobson | 505 |
| Deborah, Waitaki | 34 |
| Deborah Bay, Waikouaiti | 163 |
| Denlair, Wanganui | 61 |
| Denniston, Buller | 793 |
| Dillman's, Westland | 168 |
| Dipton, Southland | 68 |
| Doyleston, Selwyn | 154 |
| Dromore, Ashburton | 78 |
| Drummond, Wallace | 248 |
| Drury (and vicinity), Manukau | 364 |
| Dunback, Waihemo | 165 |
| Dunganville, Grey | 90 |
| Dunkeld, Tuapeka | 105 |
| Dunsandel, Selwyn | 236 |
| Duntroon, Waitaki | 181 |
| Durietown, Wanganui | 355 |
| Duvauchelle's Bay, Akaroa | 145 |
| East Clive, Hawke's Bay | 141 |
| East Dipton (and vicinity), Southland | 139 |
| Eastern Bush, Wallace | 17 |
| Eastown, Wanganui | 238 |
| East Winton, Southland | 155 |
| Edendale, Southland | 180 |
| Egmont, Taranaki | 33 |
| Eketahuna, Eketahuna | 340 |
| Ellesmere, Selwyn | 103 |
| Eltham, Hawera* | 400 |
| Enfield, Waitaki | 161 |
| Epworth, Geraldine | 105 |
| Ettrick, Tuapeka | 68 |
| Evansdale, Waikouaiti | 52 |
| Eweburn, Maniototo | 103 |
| Fairdown, Buller | 75 |
| Fairfax (and vicinity), Bruce | 183 |
| Fairfield, Taieri | 110 |
| Fairlie, Mackenzie | 597 |
| Feldwick, Wallace | 23 |
| Fendalton, Selwyn | 309 |
| Fernhills, Southland | 70 |
| Fernside (and vicinity), Ashley | 550 |
| Ferntown, Collingwood | 81 |
| Flax Swamp, Waikouaiti | 87 |
| Flaxton, Ashley | 17 |
| Fordell, Wanganui | 283 |
| Fortrose, Southland | 131 |
| Frankton, Lake | 265 |
| Frasertown, Wairoa | 175 |
| Galatea, Whakatane | 14 |
| Garfield, Wallace | 42 |
| Georgetown, Waitaki | 84 |
| German Bay, Akaroa | 155 |
| Gibbston, Lake | 158 |
| Gibbstown, Collingwood | 192 |
| Gimmerburn, Maniototo | 196 |
| Glenavy, Waimate | 98 |
| Gleniti (and vicinity), Levels | 99 |
| Glenorchy, Lake | 18 |
| Glenore, Bruce | 81 |
| Glentunnel, Selwyn | 153 |
| Golden Cross, Ohinemuri | 383 |
| Goldsborough, Westland | 146 |
| Gordon Special Settlement, Piako | 89 |
| Governor's Bay, Akaroa | 169 |
| Grahamstown, Whangarei | 60 |
| Granity Creek, Buller | 366 |
| Grassmere, Southland | 137 |
| Greatford (and vicinity), Rangitikei | 132 |
| Greendale, Selwyn | 340 |
| Green Island Bush, Taieri | 229 |
| Greenlane, Eden | 191 |
| Greenpark, Selwyn | 336 |
| Greerton, Tauranga | 99 |
| Grovetown, Marlborough | 352 |
| Gumtown, Coromandel | 107 |
| Hakaru, Otamatea | 44 |
| Hakataramea (and vicinity), Waimate | 264 |
| Hamilton, Maniototo | 27 |
| Hampden, Waipawa | 261 |
| Hamua, Pahiatua | 202 |
| Hanmer Springs, Amuri | 154 |
| Harwood, Southland | 81 |
| Hastings, Thames | 112 |
| Hastwell, Mauriceville | 220 |
| Hatter's, or Nelson Creek, Grey | 156 |
| Hawarahu, Manukau | 62 |
| Havelock, Hawke's Bay | 374 |
| Hawarden, Ashley | 66 |
| Hawea, Vincent | 39 |
| Hawthorndale, Southland | 42 |
| Heddon Bush, Wallace | 146 |
| Henderson (and vicinity), Waitemata | 357 |
| Henley, Taieri | 122 |
| Herbert, Waitaki | 282 |
| Herbertville, Patangata | 129 |
| Heriot (and vicinity), Tuapeka | 206 |
| Highcliffe, Peninsula | 222 |
| Hikurangi, Whangarei | 495 |
| Hikutaia, Thames | 152 |
| Hillgrove, Waitaki | 37 |
| Hindon, Taieri | 192 |
| Hirstfield, Wallace | 52 |
| Hobsonville, Waitemata | 194 |
| Hodgkinson, Wallace | 48 |
| Hohoura, Mongonui | 272 |
| Holmesdale, Wallace | 19 |
| Horndon, Selwyn | 188 |
| Hororata, Selwyn | 269 |
| Howick (and vicinity), Manukau | 617 |
| Huia, Taranaki | 54 |
| Huiakama, Stratford | 45 |
| Huirangi, Taranaki | 40 |
| Hukerenui, Whangarei | 110 |
| Hunterville, Rangitikei | 576 |
| Huntly, Waikato | 622 |
| Hurunui, Ashley | 58 |
| Hyde, Maniototo | 164 |
| Ida Valley, Vincent | 203 |
| Inangahua Junction, Inangahua | 98 |
| Inglewood, Southland | 46 |
| Islington, Selwyn | 289 |
| Jackeytown, Oroua | 85 |
| Josephville, Southland | 19 |
| Kaeo (and vicinity), Whangaroa | 324 |
| Kaihu, Hobson | 105 |
| Kai Iwi, Waitotara | 111 |
| Kaikohe, Bay of Islands | 115 |
| Kaikoura, Kaikoura | 516 |
| Kaitaia, Mongonui | 106 |
| Kaitawa, Pahiatua | 95 |
| Kakanui (North), Waitaki | 126 |
| Kakanui (South), Waitaki | 181 |
| Kakaramea, Patea | 117 |
| Kanieri, Westland | 149 |
| Kapanga, Coromandel | 328 |
| Karaka, Cook | 110 |
| Karangahake, Ohinemuri | 205 |
| Katu, Hokianga | 48 |
| Kaukapakapa, Waitemata | 543 |
| Kaurihohore, Whangarei | 191 |
| Kawakawa, Bay of Islands | 263 |
| Kawarau Gorge, Vincent | 40 |
| Kawhia, Kawhia | 158 |
| Keel, Ashley | 166 |
| Kennedy Bay, Coromandel | 89 |
| Kennington, Southland | 56 |
| Kereru (and vicinity), Horowhenua | 275 |
| Kerrytown, Levels | 156 |
| Killinchy, Selwyn | 77 |
| Kimberley, Selwyn | 149 |
| Kimbolton, Kiwitea | 219 |
| Kingsdown, Levels | 114 |
| Kingston, Lake | 61 |
| Kirwee (and vicinity), Selwyn | 333 |
| Kohinui, Pahiatua | 53 |
| Kohukohu, Hokianga | 128 |
| Kokonga, Maniototo | 45 |
| Komaka, Pohangina | 57 |
| Konini (vicinity), Pahiatua | 247 |
| Kopu, Thames | 166 |
| Koru, Taranaki | 93 |
| Kuaotunu, Coromandel | 375 |
| Kukunui (Brownstown), Eketahuna | 136 |
| Kumeroa, Waipawa | 148 |
| Kuri Bush, Taieri | 150 |
| Kuriwao, Clutha | 94 |
| Kurow, Waitaki | 264 |
| Kyeburn Diggings, Maniototo | 190 |
| Kyeburn, Upper, Maniototo | 78 |
| Lake Hayes, Lake | 194 |
| Larrikins, Westland | 90 |
| Lauder, Maniototo | 43 |
| Leedstown (and vicinity), Rangitikei | 269 |
| Leeston, Selwyn | 257 |
| Leithfield, Ashley | 298 |
| Lepperton, Taranaki | 36 |
| Levin, Horowhenua | 1,147 |
| Lichfield, Piako | 41 |
| Lime Hills, Southland | 96 |
| Lincoln (and vicinity), Selwyn | 464 |
| Lintley, Southland | 54 |
| Linton, Oroua | 61 |
| Little Akaloa, Akaroa | 233 |
| Livingstone, Waitaki | 123 |
| Longburn (and vicinity), Oroua | 358 |
| Long Bush, Southland | 215 |
| Longford, Inangahua | 25 |
| Longridge, Southland | 112 |
| Lowburn, Vincent | 133 |
| Lowther, Southland | 15 |
| Luggate, Vincent | 51 |
| Lumsden, Southland | 275 |
| Lumsden Extension, Southland | 162 |
| Lyell, Buller | 90 |
| Macandrew, Southland | 30 |
| Macetown, Lake | 113 |
| Mackaytown (and vicinity), Ohinemuri | 1,085 |
| Mackenzie, Cheviot | 113 |
| Macrae's (and vicinity), Waihemo | 59 |
| Maheno, Waitaki | 226 |
| Maitland, Southland | 22 |
| Makakahi, Pahiatua | 42 |
| Makarewa, Southland | 370 |
| Maketu, Tauranga | 41 |
| Makikihi, Waimate | 112 |
| Makomako (and vicinity), Pahiatua | 154 |
| Makuri, Pahiatua | 85 |
| Makutoku, Waipawa | 271 |
| Manakau, Horowhenua | 184 |
| Mandeville, Southland | 129 |
| Mangahao, Pahiatua | 43 |
| Mangamahoe, Mauriceville | 131 |
| Mangamaire, Pahiatua | 96 |
| Mangaonoho, Rangitikei | 342 |
| Mangare (and vicinity), Manukau | 702 |
| Mangatainoko, Pahiatua | 171 |
| Mangawai, Otamatea | 193 |
| Mangaweka (and vicinity), Rangitikei | 956 |
| Mansfordtown, Waikouaiti | 377 |
| Manurewa, Manukau | 70 |
| Manutahi, Patea | 72 |
| Maori Gully, Grey | 7 |
| Mapourika, Westland | 20 |
| Marima, Pahiatua | 50 |
| Marsden, Grey | 37 |
| Marshalltown, Kiwitea | 66 |
| Martinborough (and vicinity), Wairarapa South | 551 |
| Matakanui, Vincent | 219 |
| Matakana, Rodney | 172 |
| Matakohe, Otamatea | 338 |
| Matamau, Waipawa | 292 |
| Mauku (and vicinity), Manukau | 306 |
| Mauriceville, Mauriceville | 207 |
| Maxwelltown, Waitotara | 207 |
| Mayfield, Waitemata | 112 |
| Meanee, Hawke's Bay | 63 |
| Medbury Village Settlement, Ashley | 130 |
| Menzies' Ferry, Southland | 91 |
| Mercer (and vicinity), Manukau | 208 |
| Merryjigs, Inangahua | 68 |
| Merton, Waikouaiti | 170 |
| Methven, Ashburton | 296 |
| Middlemarch, Taieri | 226 |
| Midhirst, Stratford | 330 |
| Milford, Geraldine | 157 |
| Millwood, Southland | 75 |
| Mohaka, Wairoa | 119 |
| Mokau, Kawhia | 70 |
| Mokihinui, Buller | 29 |
| Mokoreta, Southland | 47 |
| Mongonui, Mongonui | 249 |
| Morley, Wallace | 70 |
| Morrinsville, Piako | 300 |
| Mosstown, Waitotara | 225 |
| Motu, Cook | 64 |
| Moutere, Waimea | 129 |
| Murawai, Cook | 23 |
| Murchison, Inangahua | 104 |
| Neavesville, Thames | 25 |
| Netherton, Ohinemuri | 155 |
| Nevis, Vincent | 168 |
| Newman, Eketahuna | 178 |
| Newport, Hobson | 129 |
| Ngahauranga, Hutt | 168 |
| Ngahere, Grey | 123 |
| Ngaire, Stratford | 81 |
| Ngakawau, Buller | 12 |
| Ngapara, Waitaki | 201 |
| Niagara, Southland | 87 |
| Nightcaps, Wallace | 373 |
| Nikau (and vicinity), Pahiatua | 114 |
| Nokomai, Southland | 113 |
| Nolan, Hawera | 129 |
| Normanby, Levels | 130 |
| Norsewood (and vicinity), Waipawa | 914 |
| Northcote, Waitemata | 767 |
| North Taieri (and vicinity), Taieri | 602 |
| No Town, Grey | 66 |
| Nukumaru, Waitotara | 61 |
| Oaklands, Peninsula | 76 |
| Oakura, Taranaki | 44 |
| Oban, Stewart Island | 80 |
| Ohaeawai, Bay of Islands | 112 |
| Ohau (and vicinity), Horowhenua | 309 |
| Ohaupo, Waipa | 250 |
| Ohinemutu, Rotorua | 107 |
| Ohingaiti (and vicinity), Raugitikei | 464 |
| Ohiwa, Opotiki | 19 |
| Ohoka, Ashley | 426 |
| Okaiawa, Hawera | 94 |
| Okaihau and Omapere, Bay of Islands | 273 |
| Okain's Bay, Akaroa | 273 |
| Okarito, Westland | 66 |
| Okato, Taranaki | 92 |
| Okoroire, Piako | 211 |
| Omahu, Thames | 268 |
| Omata, Taranaki | 41 |
| Ongaonga, Waipawa | 107 |
| Ophir, Vincent | 132 |
| Opitonui, Coromandel | 277 |
| Opua, Bay of Islands | 62 |
| Opuriao, Whakatane | 161 |
| Oraka, Wallace | 185 |
| Orari, Geraldine | 118 |
| Ormond (and vicinity), Cook | 482 |
| Oropi, Tauranga | 53 |
| Orwell Creek, Grey | 59 |
| Otahuhu, Manukau | 1,211 |
| Otaki (and vicinity), Horowhenua | 629 |
| Otakia, Taieri | 102 |
| Otara, Opotiki | 150 |
| Otara, Southland | 135 |
| Otawa, Manukau | 53 |
| Otekaike, Waitaki | 54 |
| Otiake, Waitaki | 118 |
| Otorohanga, Kawhia | 150 |
| Owaka, Clutha | 635 |
| Owen Junction, Inangahua | 28 |
| Owharoa (and vicinity), Ohinemuri | 485 |
| Oxford East, Ashley | 311 |
| Oxford West, Ashley | 176 |
| Paeroa, Ohinemuri | 1,504 |
| Pahia, Wallace | 151 |
| Pahautanui, Hutt | 104 |
| Paikakariki, Hutt | 160 |
| Pakawau, Collingwood | 39 |
| Pakington, Manukau | 69 |
| Panmure, Eden | 259 |
| Papanui, Selwyn | 270 |
| Paparata, Manukau | 180 |
| Papatoitoi (and vicinity), Manukau | 219 |
| Parangahatu, Akitio | 55 |
| Paraparaumu, Hutt | 198 |
| Parkville, Eketahuna | 202 |
| Patumahoe, Manukau | 148 |
| Patutahi (and vicinity), Cook | 228 |
| Peel (and vicinity), Geraldine | 170 |
| Pembroke, Lake | 130 |
| Pigeon Bay, Akaroa | 157 |
| Pihama, Hawera | 27 |
| Pine Hill, Waikouaiti | 41 |
| Pipiriki (and vicinity), Wanganui | 233 |
| Piritarau, Waiapu | 164 |
| Pirongia East, Waipa | 89 |
| Pleasant Point, Levels | 749 |
| Pleasant Valley, Waikouaiti | 50 |
| Pleckville, Eketahuna | 71 |
| Plimmerton, Hutt | 92 |
| Pohangina, Pohangina | 167 |
| Pokeno (and vicinity), Manukau | 460 |
| Porirua, Hutt | 80 |
| Porangahau, Patangata | 187 |
| Poro-o-torao, Clifton | 235 |
| Port Albert, Rodney | 241 |
| Port Awanui, Waiapu | 51 |
| Port Moeraki, Waitaki | 197 |
| Port Waikato, Raglan | 14 |
| Portobello Town, Peninsula | 50 |
| Puangi, Clifton | 40 |
| Puhoi, Rodney | 39 |
| Pukekohe East, Manukau | 331 |
| Pukekohe, Manukau | 611 |
| Pukerau, Southland | 129 |
| Pungarehu, Taranaki | 143 |
| Puni, Manukau | 212 |
| Purakanui, Waikouaiti | 31 |
| Puriri, Thames | 220 |
| Putara, Eketahuna | 29 |
| Putiki, Wanganui | 145 |
| Queensbury, Vincent | 54 |
| Raetihi (and vicinity), Wanganui | 433 |
| Raglan, Raglan | 114 |
| Rahotu, Taranaki | 80 |
| Rakaia, Ashburton | 439 |
| Rakaia Village Settlement, Ashburton | 187 |
| Rakaunui, Akitio | 46 |
| Rama Rama, Manukau | 204 |
| Rangiriri, Waikato | 76 |
| Rangiwahia (Pemberton), Kiwitea | 88 |
| Rata Settlement, Rangitikei | 210 |
| Raupo, Otamatea | 108 |
| Rawene, Hokianga | 103 |
| Redcliffe, Waimate | 86 |
| Redwood Town, Marlborough | 143 |
| Reefton, Inangahua | 1,722 |
| Reidston, Waitaki | 80 |
| Renwicktown, Marlborough | 292 |
| Reynolds, Waikouaiti | 35 |
| Riccarton, Selwyn | 313 |
| Richmond, Selwyn | 252 |
| Richmond Grove, Southland | 101 |
| Rikiorangi, Hutt | 138 |
| Rimu, Westland | 148 |
| Rimu, Southland | 56 |
| Riversdale, Southland | 312 |
| Riwaka, Waimea | 687 |
| Rockville, Collingwood | 102 |
| Rolleston, Selwyn | 85 |
| Rongotea, Manawatu | 229 |
| Rotherham, Amuri | 146 |
| Round Hill Diggings, Wallace | 178 |
| Ruapekapeka, Bay of Islands | 119 |
| Runciman, Manukau | 30 |
| Russell, Bay of Islands | 246 |
| Sandymount, Peninsula | 177 |
| Sanson, Manawatu | 210 |
| Sawyer's Bay, Waikouaiti | 305 |
| Scarborough, Levels | 54 |
| Scarborough (and vicinity), Pahiatua | 198 |
| Scotsburn, Geraldine | 24 |
| Sefton (and vicinity), Ashley | 620 |
| Selwyn, Selwyn | 33 |
| Serpentine, Maniototo | 44 |
| Shaftesbury, Piako | 85 |
| Shannon, Horowhenua | 272 |
| Shawfield, Waikouaiti | 125 |
| Sheffield, Selwyn | 153 |
| Shiel Hill, Peninsula | 86 |
| Shirley, Selwyn | 165 |
| Shortland, Thames | 1,217 |
| Silverstream, Mackenzie | 98 |
| Skippers, Lake | 92 |
| Southbrook (and vicinity), Ashley | 1,070 |
| Spring Creek (and vicinity), Marlborough | 264 |
| Springfield, Selwyn | 247 |
| Spring Grove, Waimea | 348 |
| Springston, Selwyn | 644 |
| Stafford, Westland | 116 |
| St. Andrew's, Waimate | 127 |
| St. Bathan's, Maniototo | 231 |
| St. Helier's Bay, Eden | 24 |
| St. Kilda, Buller | 16 |
| Stirling (and vicinity), Bruce | 232 |
| Stoke, Waimea | 511 |
| Strathmore, Stratford | 54 |
| Studholme Junction, Waimate | 138 |
| Swannanoa, Ashley | 100 |
| Swanson, Waitemata | 147 |
| Taheke, Hokianga | 21 |
| Taiaroa Heads, Peninsula | 45 |
| Taihape (and vicinity), Rangitikei | 461 |
| Taipa, Mongonui | 20 |
| Tairua, Thames | 360 |
| Taitapu, Selwyn | 268 |
| Takapau (and vicinity), Waipawa | 431 |
| Tamaki West (and vicinity), Eden | 351 |
| Tarras, Vincent | 158 |
| Tatararaki, Hobson | 348 |
| Taueru, Masterton | 139 |
| Tauherenikau, Wairarapa South | 113 |
| Taupaki, Waitemata | 131 |
| Taupiri, Waikato | 136 |
| Taupo, East Taupo | 79 |
| Tavistock, Waimate | 28 |
| Taylorville, Wanganui | 33 |
| Te Anui, Wallace | 16 |
| Te Aroha West, Piako | 158 |
| Te Aute, Waipawa | 120 |
| Teddington, Akaroa | 69 |
| Te Horo, Horowhenua | 98 |
| Te Kopuru, Hobson | 325 |
| Te Kuiti, Kawhia | 134 |
| Templeton, Selwyn | 67 |
| Teoneroa, Fiord | 37 |
| Te Puke (and vicinity), Tauranga | 477 |
| Te Teko, Whakatane | 20 |
| Thornbury, Wallace | 262 |
| Thorpe, Waimea | 100 |
| Tikorangi, Clifton | 29 |
| Tiniroto, Cook | 62 |
| Tinui, Castlepoint | 295 |
| Tokaanu, East Taupo | 55 |
| Toka-Toka, Otamatea | 96 |
| Toko, Stratford | 240 |
| Tokomaru, Horowhenua | 116 |
| Tokomaru (and vicinity), Waiapu | 196 |
| Totara, Whangaroa | 155 |
| Totara, Waitaki | 176 |
| Totara East, Grey | 188 |
| Tuakau, Manukau | 418 |
| Tuamarina, Marlborough | 44 |
| Tumai, Waikouaiti | 22 |
| Tutaekara, Pahiatua | 58 |
| Turua, Thames | 244 |
| Upper Hutt, Hutt | 309 |
| Urenui, Clifton | 165 |
| Utiku, Rangitikei | 297 |
| Vauxhall, Peninsula | 52 |
| Vogeltown, Taranaki | 176 |
| Waddington, Selwyn | 134 |
| Wade, Waitemata | 229 |
| Waianiwa, Southland | 52 |
| Waiau, Amuri | 153 |
| Waiau, Manukau | 63 |
| Waihi, Ohinemuri* | 3,813 |
| Waihola, Bruce | 190 |
| Waihou (and vicinity), Piako | 410 |
| Waikaia, Southland | 230 |
| Waikaka, Southland | 112 |
| Waikanae, Horowhenua | 149 |
| Waikare, Ashley | 417 |
| Waikawa, Southland | 44 |
| Waikiwi, Southland | 152 |
| Waikoikoi, Clutha | 13 |
| Waimangaroa, Buller | 151 |
| Waima, Hokianga | 43 |
| Waimata, Cook | 117 |
| Waimate, Bay of Islands | 105 |
| Waimatuku, Wallace | 166 |
| Waimea West, Waimea | 221 |
| Wainuiomata, Hutt | 48 |
| Waiomio, Bay of Islands | 74 |
| Waiorongomai, Piako | 154 |
| Waiotahi, Opotiki | 117 |
| Waipahi, Clutha | 130 |
| Waipara, Southland | 17 |
| Waipara, Ashley | 141 |
| Waipipi, Manukau | 135 |
| Waipiro (and vicinity), Waiapu | 118 |
| Waipori, Tuapeka | 211 |
| Waipu Central (and vicinity), Whangarei | 461 |
| Waipukurau, Waipawa | 565 |
| Wairaki, East Taupo | 25 |
| Wairio (and vicinity), Wallace | 271 |
| Waitahuna, Tuapeka | 301 |
| Waitati (and vicinity), Waikouaiti | 272 |
| Waitekauri, Ohinemuri | 441 |
| Waitotara, Patea | 173 |
| Waituna, Kiwitea | 53 |
| Waiwera, Waitemata | 59 |
| Waiwera, Clutha | 167 |
| Waiuku, Manukau | 205 |
| Wakefield, Waimea | 479 |
| Wallacetown, Southland | 160 |
| Wallingford, Patangata | 90 |
| Wangaehu, Wanganui | 19 |
| Wangamomona, Stratford | 23 |
| Wanstead, Patangata | 111 |
| Waotu, West Taupo | 71 |
| Warepa, Clutha | 217 |
| Warkworth, Rodney | 572 |
| Washdyke, Levels | 217 |
| Waterford, Tauranga | 50 |
| Waterton (and vicinity), Ashburton | 197 |
| Wayne's, Waihemo | 24 |
| Weber, Patangata | 159 |
| Weedon's, Selwyn | 106 |
| Wereroa, Horowhenua | 58 |
| West Clive, Hawke's Bay | 333 |
| West Melton, Selwyn | 280 |
| Weston, Waitaki | 237 |
| Whakataki, Castlepoint | 50 |
| Whakarewarewa, Rotorua | 48 |
| Whakatane, Whakatane | 239 |
| Whangapoua, Coromandel | 61 |
| Whangaroa, Whangaroa | 100 |
| Whare Flat, Taieri | 93 |
| Whenuakiti, Coromandel | 40 |
| Whitecliffs, Selwyn | 98 |
| Whitmore, Oroua | 80 |
| Whitstone, Waitaki | 51 |
| Wickliffe Bay, Peninsula | 30 |
| Wimbledon, Patangata | 90 |
| Winchester, Geraldine | 170 |
| Windsor, Waitaki | 130 |
| Woodbury, Geraldine | 111 |
| Woodend, Ashley | 365 |
| Woodend, Southland | 115 |
| Woodfield, Southland | 34 |
| Woodlands, Southland | 207 |
| Woodside, Taieri | 222 |
| Woodside, Wairarapa South | 23 |
| Woodstock, Westland | 189 |
| Woodstock Village Settlement, Ashley | 50 |
| Wrey's Bush, Wallace | 289 |
| Yaldhurst, Selwyn | 143 |
The names and populations of the islands adjacent to and included in the colony were, in March, 1901:—
| Islands | Total. | M. | F. |
|---|---|---|---|
| * Now a county. | |||
| Mokohinau Lighthouse | 8 | 5 | 3 |
| Tiritiri Lighthouse | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Motuhora | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| Great Barrier | 510 | 357 | 153 |
| Little Barrier | 11 | 1 | 10 |
| Kawau | 21 | 7 | 14 |
| Ponui | 27 | 11 | 16 |
| Ponui Lighthouse | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Ruthe's | 15 | 9 | 6 |
| Pakatoa | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| Pahiki | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Waiheke | 162 | 81 | 81 |
| Week's (Puketutu) | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Motuihi | 11 | 9 | 2 |
| Bean Rock Lighthouse | 1 | 1 | … |
| Motutapu | 11 | 7 | 4 |
| Rakino | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Rangitoto | 3 | 3 | .. |
| Brown's | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| Mercury | 14 | 5 | 9 |
| Cuvier and Lighthouse | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| Slipper | 3 | 3 | .. |
| Motiti | 2 | 2 | .. |
| East Island Lighthouse | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| Portland and Lighthouse | 21 | 13 | 8 |
| Kapiti | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Somes and Lighthouse | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| Stephen's | 18 | 9 | 9 |
| Brothers Lighthouse | 3 | 3 | .. |
| Quarantine | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Ruapuke | 9 | 9 | .. |
| Dog Island and Lighthouse | 16 | 9 | 7 |
| Centre and Lighthouse | 9 | 5 | 4 |
| Resolution | 2 | 2 | .. |
| Chatham Islands* | 207 | 112 | 95 |
| Kermadec Islands | 8 | 5 | 3 |
| Total | 1,158 | 706 | 452 |
The islands which are not included within the boundaries of the counties had in 1901 a population of 1,158 persons (exclusive of Maoris), against 950 in 1896. Only three of the islands had a population over 100 persons at last census. The population of the Great Barrier increased since 1896 from 307 to 510 persons; Waiheke showed a decrease from 166 to 162 persons. Europeans at the Chatham Islands decreased from 234 to 207.
The growth of population in Australasia over a period of forty years is shown in a comparative table. The total for March, 1901, being 4,557,323 persons, is greater than the population of Ireland or Scotland for 1900, and one-seventh part of the population of England and Wales for that year. Australasia has now twice the population of Denmark, over one-third more than Switzerland, and nearly that of the Netherlands.
| Persons, 1860 | Persons, 1870. | Persons, 1880. | Persons, 1890. | Census, March, 1901. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New South Wales | 348,546 | 498,659 | 747,950 | 1,121,860 | 1,362,200 |
| Victoria | 537,847 | 720,599 | 860,067 | 1,133,266 | 1,201,506 |
| Queensland | 28,056 | 115,567 | 226,077 | 392,965 | 503,266 |
| South Australia | 124,112 | 183,797 | 267,573 | 319,414 | 362,604 |
| Western Australia | 15,227 | 25,084 | 29,019 | 46,290 | 182,553 |
| Tasmania | 87,775 | 100,765 | 114,762 | 145,290 | 172,475 |
| New Zealand | 79,711 | 248,400 | 484,864 | 625,508 | 772,719 |
| Australasia | 1,221,274 | 1,898,871 | 2,730,312 | 3,784,593 | 4,557,323 |
Of the various religious denominations, the Church of England has most adherents in the colony. They numbered 314,024 at the date of the census; or, including 1,239 Protestants not more specifically described, 315,263 persons, being 40·84 out of every 100 of population. The Presbyterians numbered 176,503 persons, or 22·87 per cent., and the Roman Catholics came next with 108,960, or, including Catholics not further defined, 109,822, which gives a proportion of 14·23 per cent. The Methodists were 83,802, or 10·86 in every 100 persons. Of other denominations, the Baptists, of whom there were 16,035, and the Salvation Army, 7,999 persons, were those returning more than 1 per cent. of the total population, the proportions being 2·08 and 1·04 respectively. 18,295 persons objected to state their religious belief, or 2·38 in every 100.
The numbers and percentages for five censuses are given in tabular form, so as to allow of the degree of increase relatively to the population being observed:—
| Denominations. | Number of Adherents in 1901. | Proportion per Cent. of Population. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||
| 1881. | 1886. | 1891. | 1896. | 1901. | ||
| * “Unspecified” not taken into account. | ||||||
| Church of England and Protestants (undefined) | 315,263 | 41·50 | 40·17 | 40·51 | 40·27 | 40·84 |
| Presbyterians | 176,503 | 23·08 | 22·59 | 22·62 | 22·78 | 22·87 |
| Methodists | 83,802 | 9·53 | 9·55 | 10·14 | 10·44 | 10·86 |
| Baptists | 16,035 | 2·34 | 2·48 | 2·37 | 2·28 | 2·08 |
| Congregationalists | 6,699 | 1·37 | 1·35 | 1·07 | 0·97 | 0·87 |
| Lutherans | 4,833 | 1·18 | 1·02 | 0·90 | 0·79 | 0·63 |
| Salvation Army | 7,999 | .. | 0·91 | 1·50 | 1·50 | 1·04 |
| Society of Friends | 313 | 0·05 | 0·05 | 0·05 | 0·05 | 0·04 |
| Unitarians | 468 | 0·10 | 0·08 | 0·05 | 0·05 | 0·06 |
| Other Protestants | 16,877 | 1·26 | 1·55 | 1·82 | 2·16 | 2·19 |
| Roman Catholics and Catholics (undefined) | 109,822 | 14·08 | 13·94 | 13·96 | 14·07 | 14·23 |
| Greek Church | 189 | 0·01 | 0·01 | 0·01 | 0·02 | 0·02 |
| Hebrews | 1,611 | 0·31 | 0·27 | 0·23 | 0·22 | 0·21 |
| Buddhists, Confucians | 2,432 | 1·01 | 0·77 | 0·63 | 0·48 | 0·30 |
| Other Denominations | 1,347 | 0·11 | 0·10 | 0·12 | 0·16 | 0·17 |
| No Denomination | 8,240 | 0·89 | 1·05 | 1·32 | 1·22 | 1·07 |
| No Religion | 1,109 | 0·06 | 0·17 | 0·25 | 0·27 | 0·14 |
| Unspecified | 882 | 0·27 | 0·50 | * | * | * |
| Object to state | 18,295 | 2·85 | 3·44 | 2·45 | 2·27 | 2·38 |
| 772,719 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | |
Here the proportion belonging to the Church of England is shown to have been 40 per cent. since 1886, but a little higher previously. Presbyterians have been 22 or 23 per cent. of the whole at each enumeration, but the proportion of Methodists rose steadily from 9·53 to 10·86. Congregationalists declined from 1·37 per cent. in 1881 to 0·87 per cent. in 1901. Lutherans are fewer in proportion to the total at each succeeding census, while the Salvation Army increased from 0·91 in 1886 to 1·50 in 1891 and 1896, decreasing again to 1·04 in 1901.
Roman Catholics and Catholics undefined formed practically 14 per cent. of the people at each of the census years. The proportion of Buddhists and Confucians diminishes with the number of Chinese in the colony. In 1886 the percentage of persons objecting to state their religion was 3·44, which fell to 2·45 in 1891, and, further, to 2·27 in 1896, rising slightly in 1901 to 2·38 per cent.
A full statement of the particulars for all denominations, as at the census of 1896 and 1901, is given, with the numerical and centesimal increase or decrease in each case. Amongst 1,093 given as “Other Protestants,” 247 described themselves as “Church of God,” 201 as “Christians of no Denomination,” 145 as “Independents,” 41 as “Our Father's Church,” 33 as “Conditional Immortalists,” 31 as “Gospel Mission,” 29 as “Forward Movement,” 26 as “Central Mission,” and the remainder variously in very small numbers.
| NUMBERS FOR EACH DENOMINATION, AND INCREASE. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religious Denominations. | Census, 1901. | Census, 1896. | Increase or Decrease. | |||
 |  | |||||
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | Persons. | Numerical. | Centesimal. | |
| Total population | 772,719 | 405,992 | 366,727 | 703,360 | 69,359 | 9·86 |
| Total for specified religions | 771,837 | 405,372 | 366,465 | 702,238 | 69,599 | 9·91 |
| Episcopalians— | ||||||
| Church of England, and Episcopalians not otherwise defined | 314,024 | 165,100 | 148,924 | 281,166 | 32,858 | 11·69 |
| Protestants, undescribed | 1,239 | 742 | 497 | 1,643 | −404 | −24·59 |
| Presbyterians | 176,503 | 92,406 | 84,097 | 159,952 | 16,551 | 10·36 |
| Methodists— | ||||||
| Wesleyan Methodists | 71,034 | 35,362 | 35,672 | 63,373 | 7,661 | 12·09 |
| Primitive Methodists | 10,143 | 5,046 | 5,097 | 7,041 | 3,102 | 44·06 |
| Methodists (undefined) | 2,396 | 1,183 | 1,213 | 2,893 | −497 | −17·18 |
| Others | 229 | 122 | 107 | 60 | 169 | |
| Baptists | 16,035 | 7,574 | 8,461 | 16,037 | −2 | −0·01 |
| Congregationalists | 6,699 | 3,154 | 3,545 | 6,777 | −78 | −1·15 |
| Lutherans, German Protestants | 4,833 | 3,063 | 1,770 | 5,538 | −705 | −12·73 |
| Unitarians | 468 | 283 | 185 | 375 | 93 | 24·80 |
| Society of Friends | 313 | 195 | 118 | 321 | −8 | −2·49 |
| Church of Christ (Christian Disciples, Disciples of Christ, Disciples) | 6,105 | 2,860 | 3,245 | 5,859 | 246 | 4·20 |
| Brethren (Christian Brethren, Exclusive Brethren, Open Brethren, Plymouth Brethren) | 7,484 | 3,450 | 4,034 | 5,035 | 2,449 | 48·64 |
| Believers in Christ | 31 | 14 | 17 | 77 | −46 | −59·74 |
| Evangelists (Evangelical Union, Evangelical Church, Evangelical Christians, Evangelical Brethren) | 21 | 16 | 5 | 33 | −12 | −36·36 |
| Nonconformists | 61 | 36 | 25 | 95 | −34 | −35·79 |
| Salvation Army | 7,999 | 3,807 | 4,192 | 10,532 | −2,533 | −24·05 |
| Christadelphians | 989 | 497 | 492 | 952 | 37 | 3·89 |
| Swedenborgians (New Church, New Jerusalem Church) | 159 | 72 | 87 | 191 | −32 | −16·75 |
| Seventh day Adventists | 864 | 357 | 507 | 776 | 88 | 11·34 |
| Students of Truth | 33 | 17 | 16 | 340 | −307 | −90·29 |
| Dissenters | 3 | 3 | 65 | −62 | −95·38 | |
| Christian Israelites, Israelites | 34 | 19 | 15 | 61 | −27 | −44·26 |
| Other Protestants | 1,093 | 577 | 516 | 1,710 | −617 | |
| Roman Catholics | 108,960 | 56,490 | 52,470 | 97,525 | 11,435 | 11·73 |
| Catholics (undefined) | 862 | 480 | 382 | 1,279 | −417 | −32·60 |
| Greek Church | 189 | 134 | 55 | 116 | 73 | 62·93 |
| Catholic Apostolic | 326 | 140 | 186 | 247 | 79 | 31·98 |
| Other Sects— | ||||||
| Hebrews | 1,611 | 826 | 785 | 1,549 | 62 | 4·01 |
| Mormons, Latter-day Saints | 272 | 145 | 127 | 289 | −17 | −5·88 |
| Spiritualists | 499 | 240 | 259 | 376 | 123 | 32·71 |
| Buddhists, Confucians, &c. | 2,432 | 2,413 | 19 | 3,391 | −959 | −28·28 |
| Others | 250 | 162 | 88 | 187 | 63 | |
| No Denomination— | ||||||
| Freethinkers | 2,856 | 2,245 | 611 | 3,983 | −1,127 | −28·30 |
| Agnostics | 552 | 413 | 139 | 562 | −10 | −1·78 |
| Deists, Theists | 59 | 51 | 8 | 46 | 13 | 28·26 |
| No Denomination | 4,740 | 3,006 | 1,734 | 3,898 | 842 | 21·60 |
| Doubtful | 33 | 14 | 19 | 46 | −13 | −28·26 |
| No Religion— | ||||||
| No Religion | 1,012 | 752 | 260 | 1,605 | −593 | −36·95 |
| Atheists | 80 | 67 | 13 | 117 | −37 | −31·62 |
| Secularists | 17 | 12 | 5 | 153 | −136 | −88·88 |
| Object to state | 18,295 | 11,827 | 6,468 | 15,967 | 2,328 | 14·58 |
| Unspecified | 882 | 620 | 262 | 1,122 | −240 | −21·39 |
| NOTE.—The minus sign (–) indicates decrease. | ||||||
It will be seen by the table that, of the larger Protestant denominations, the Wesleyan Methodists increased since 1896 from 63,373 to 71,034 persons, being at the rate of 12·09 per cent.; Presbyterians from 159,952 to 176,503, or 10·35 per cent.; and the Church of England from 281,166 to 314,024, or 11·69 per cent. Baptists returned practically the same number of adherents as in 1896. The Salvation Army, which increased its numbers by 1,149 persons between 1891 and 1896, being at the rate of 12·25 per cent., now show a decrease of 2,533 persons, or 24·05 per cent. The numbers of the Brethren show an increase of 48·64 per cent., and the Seventh-day Adventists 11·34 per cent. increase; but the Congregationalists have decreased 1·15 per cent. and Lutherans 12·73 per cent. Of the Protestant bodies having but few members in the colony, the Unitarians increased from 375 to 468, and the Society of Friends fell in number from 321 to 313.
Roman Catholics added 11,435 to their number, being 11·73 per cent., a rate similar to that obtained by the Church of England.
Hebrews were 1,549 in 1896, and 1,611 in 1901, a difference of 62. Spiritualists progressed considerably, their numbers rising from 376 to 499, an increase of 32·71 per cent. Freethinkers decreased from 3,983 to 2,856, or 28·30 per cent., which is worthy of remark when contrasted with the increase of 14·01 per cent. gained between 1886 and 1891; and Agnostics, who numbered 562 in 1896, now show a decrease of 10.
While the number of males is found to be greater than that of the females in the Church of England, Presbyterian, Roman Catholic, and sundry other religious denominations, the contrary result is found in the following cases, the proportion per cent. being—
| Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|
| Wesleyan Methodists | 49·78 | 50·22 |
| Primitive Methodists | 49·75 | 50·25 |
| Baptists | 47·23 | 52·77 |
| Congregationalist | 47·08 | 52·92 |
| Church of Christ | 46·85 | 53·15 |
| Brethren | 46·10 | 53·90 |
| Salvation Army | 48·84 | 51·16 |
| Seventh-day Adventists | 41·32 | 58·68 |
Amongst those persons grouped as of “No Denomination,” “No Religion,” and “Object to state,” the proportion of females is very small, as will be seen by the next figures:—
| No Denomination— | Males. | Females. |
|---|---|---|
| Freethinkers | 78·60 | 21·40 |
| Agnostics | 74·82 | 25·18 |
| Deists, Theists | 86·44 | 13·56 |
| No Denomination | 63·42 | 36·58 |
| No Religion— | ||
| No Religion | 74·31 | 25·69 |
| Atheists | 83·75 | 16·25 |
| Secularists | 70·59 | 29·41 |
| Object to state | 64·70 | 35·30 |
Table of Contents
OF the population, exclusive of Maoris (772,719 persons), all but 442 were described as to birthplace on the census schedules. The number of the New Zealand-born was 516,106, and of those born in Australia, Tasmania, and Fiji, 27,215, making 543,321 born in Australasia. The New-Zealand-born increase in proportion to the whole with every successive census. In 1886, 51·89 per cent. of the population were born in this colony; in 1891, the percentage was 58·61; in 1896 it was 62·85; and in 1901 it had reached 66·83, adding to which 3·52 per cent. born in Australia, &c., makes 70·35 out of every 100 persons living in New Zealand who were born in Australasia.
205,111 persons, or 26·56 per cent. of the population, were born in the United Kingdom, which number was divided as under:—
| Born in United Kingdom— | Number of Persons. | Per Cent. of Population |
|---|---|---|
| England | 111,964 | 14·50 |
| Wales | 1,765 | 0·22 |
| Scotland | 47,858 | 6·20 |
| Ireland | 43,524 | 5·64 |
| 205,111 | 26·56 |
Besides these, there were 4,049 persons born in other British possessions.
Summarising these results, it is found that 752,481 of the population, or 97·43 per cent., were born in the British possessions, made up as follows:—
| Born in | Number of Persons. | Per Cent. of Population. |
|---|---|---|
| Australasia | 543,321 | 70·35 |
| United Kingdom | 205,111 | 26·56 |
| Other British Possessions | 4,049 | 0·52 |
| 752,481 | 97·43 |
There remained 18,593 persons born in foreign countries, or 2·41 per cent. of population; 1,203 born at sea; and 442 whose birthplaces were not specified.
The New Zealand-born population increased from 441,661 in 1896 to 516,106, or at the rate of 16·86 per cent., between 1896 and 1901, the numerical increase being 74,445 persons. The numbers born in the United Kingdom decreased altogether by 10,050 in the quinquennium.
| Born in | Persons. 1901. | Decrease since 1896. | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Numerical. | Centesimal. | ||
| England | 111,964 | 4,577 | 3·93 |
| Wales | 1,765 | 383 | 17·83 |
| Scotland | 47,858 | 2,577 | 5·11 |
| Ireland | 43,524 | 2,513 | 5·46 |
The numbers of Australian-born are found to have increased for each State. The number born in New South Wales, living in New Zealand, was 4,536 in the year 1896, and 6,430 in 1901, an increase of 41·75 per cent. There were 10,471 persons in this colony in 1896 born in Victoria, and 12,583 at last census, or an increase of 20·17 per cent. in five years. New Zealand also gained on the number born in Queensland, there being 1,271 in 1901, against 930 in 1896, or 36·36 per cent. increase. And similarly on the South Australian, Western Australian, and Tasmanian-born.
The number of the people born in foreign countries was found to be 18,593, being 2·41 per cent. of the whole. Besides these, 1,203 persons were returned as born at sea. The greatest number of foreigners were Germans (4,217). Next come persons born in China (2,902). Swedes and Norwegians numbered 2,827. There were 2,120 persons from Denmark and her possesions, and 1,874 persons from Austria-Hungary.
The numbers of those born in France, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, Denmark, Poland, Switzerland, Spain, Portugal, Greece, China, Africa, and North (so described) America all decreased since 1896.
The following table gives full details as to birthplace, and under the head of “Allegiance” the number of British and foreign subjects in New Zealand:—
| Where born. | Census, 1901. | Census, 1896. Persons. | Increase or Decrease. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||||
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | Numerical. | Centesimal. | ||
| NOTE.—The minus sign (-) indicates decrease. | ||||||
| Total population | 772,719 | 405,992 | 366,727 | 703,360 | 69,359 | 9·86 |
| Total for specified birthplaces | 772,277 | 405,690 | 366,587 | 702,756 | 69,521 | 9·89 |
| British:— | ||||||
| United Kingdom,— | ||||||
| England | 111,964 | 64,216 | 47,748 | 116,541 | −4,577 | −3·93 |
| Wales | 1,765 | 1,076 | 689 | 2,148 | −383 | −17·83 |
| Scotland | 47,858 | 27,516 | 20,342 | 50,435 | −2,577 | −5·11 |
| Ireland | 43,524 | 23,430 | 20,094 | 46,037 | −2,513 | −5·46 |
| Australasia and Fiji,— | ||||||
| New Zealand | 516,106 | 257,828 | 258,278 | 441,661 | 74,445 | 16·86 |
| Queensland | 1,271 | 645 | 626 | 930 | 341 | 36·36 |
| New South Wales | 6,430 | 3,395 | 3,035 | 4,536 | 1,894 | 41·75 |
| Victoria | 12,583 | 6,530 | 6,053 | 10,471 | 2,112 | 20·17 |
| South Australia | 1,575 | 807 | 768 | 1,222 | 353 | 28·88 |
| Western Australia | 230 | 103 | 87 | 112 | 78 | 69·64 |
| Tasmania | 19,70 | 2,084 | 1,636 | 3,160 | 560 | 17·72 |
| Australia (State not named) | 1,222 | 669 | 553 | 1,200 | 22 | 1·83 |
| Fiji | 224 | 98 | 126 | 151 | 73 | 48·34 |
| Other British Possessions,— | ||||||
| Gibraltar | 48 | 24 | 24 | 49 | −1 | −2·04 |
| Malta | 55 | 37 | 18 | 71 | −16 | −22·54 |
| India and Ceylon | 1,286 | 722 | 564 | 1,341 | −55 | −4·10 |
| Cape of Good Hope | 141 | 72 | 69 | 246 | −105 | −42·68 |
| St. Helena | 43 | 25 | 18 | 50 | −7 | −14·00 |
| British North America (Canada) | 1,544 | 947 | 597 | 1,412 | 132 | 9·35 |
| West Indies | 208 | 144 | 64 | 247 | −39 | −15·79 |
| Others | 724 | 408 | 316 | 334 | 390 | 116·76 |
| Foreign:— | ||||||
| Austria Hungary | 1,874 | 1,713 | 161 | 881 | 993 | 112·71 |
| Belgium | 117 | 84 | 33 | 138 | −21 | −15·22 |
| Denmark and Possessions | 2,120 | 1,384 | 736 | 2,125 | −5 | −0·24 |
| France and Possessions | 609 | 409 | 200 | 698 | −89 | −12·75 |
| Germany | 4,217 | 2,743 | 1,474 | 4,595 | −378 | −8·23 |
| Greece | 123 | 94 | 29 | 127 | −4 | −3·15 |
| Italy | 428 | 355 | 73 | 423 | 5 | 1·18 |
| Netherlands and Possessions | 116 | 105 | 11 | 132 | −16 | −12·12 |
| Poland | 97 | 65 | 32 | 101 | −4 | −3·96 |
| Portugal and Possessions | 172 | 151 | 21 | 173 | −1 | −0·58 |
| Russia and Possessions | 387 | 339 | 48 | 365 | 22 | 6·03 |
| Spain and Possessions | 59 | 41 | 18 | 88 | −29 | −32·95 |
| Sweden | 1,548 | 1,337 | 211 | 1,514 | 34 | 2·25 |
| Norway | 1,279 | 931 | 348 | 1,261 | 18 | 1·43 |
| Switzerland | 333 | 251 | 82 | 342 | −9 | −2·63 |
| Other European Countries | 30 | 20 | 10 | 30 | .. | .. |
| China | 2,902 | 2,866 | 36 | 3,719 | −817 | −21·97 |
| Africa | 103 | 54 | 49 | 134 | −31 | −23·13 |
| America, North America | 776 | 501 | 275 | 969 | −193 | −19·92 |
| United States of America | 881 | 592 | 289 | 780 | 101 | 12·95 |
| Other Foreign Countries | 422 | 289 | 133 | 485 | −63 | −12·99 |
| At sea | 1,203 | 590 | 613 | 1,322 | −119 | −9·00 |
| Unspecified | 442 | 302 | 140 | 604 | −162 | −26·82 |
| Allegiance. | ||||||
| British subjects | 761,104 | 396,052 | 365,052 | 690,003 | 71,101 | 10·30 |
| Foreign subjects | 11,615 | 9,940 | 1,675 | 13,357 | −1,742 | −13·04 |
Table of Contents
OF 403,167 males, exclusive of Chinese, 273,113 were returned as unmarried, 118,475 as husbands, 10,653 as widowers, and 926 were unspecified as to conjugal condition.
These figures show a proportion of 67·90 per cent. of males to have been unmarried, 29·45 as husbands, and 2·65 as widowers, or, eliminating all males under 14 years who were necessarily unmarried, 53·91 per cent. not married, 42·29 per cent. husbands, and 3·80 widowers.
Of females, numbering altogether 366,695, there were 230,510 unmarried, 117,821 wives, 17,902 widows, and 462 not specified as to condition. Or, represented proportionally, of females at all ages, 62·94 per cent. were not married, 32·17 were wives, and 4·89 widows. Shutting off those under 14 years, the proportions stand as 45·18 unmarried, 47·59 wives, and 7·23 widows.
The proportions for successive census periods exhibit on the male side a rise in the percentage of the married men and a steady increase in regard to widowers since the year 1878. On the female side the percentage of the unmarried rose with regularity until the year 1891, while the married diminished; but since that date there has been a marked increase in the percentage of the married. The percentage of widows increased steadily. Chinese are excluded from the calculations.
| Year. | Males. | Females. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||||
| Unmarried. | Married. | Widowed. | Unmarried. | Married. | Widowed. | |
| 1878 | 70·09 | 28·06 | 1·85 | 62·59 | 34·32 | 3·09 |
| 1881 | 70·39 | 27·73 | 1·88 | 63·64 | 33·05 | 3·31 |
| 1886 | 70·35 | 27·61 | 2·04 | 64·59 | 31·74 | 3·67 |
| 1891 | 70·02 | 27·61 | 2·37 | 64·95 | 30·94 | 4·11 |
| 1896 | 69·48 | 27·97 | 2·55 | 64·37 | 31·10 | 4·53 |
| 1901 | 67·90 | 29·45 | 2·65 | 62·94 | 32·17 | 4·89 |
The proportions at different age-periods show, for males, that the unmarried decrease from 99 per cent. at the period 17–20 to 65 per cent. at the period 25–30 years. At 30–35 years the husbands, who were only 34·61 per cent. at the previous period, exceeded the unmarried, the proportion being of husbands 58·54, unmarried, 40·30, divorced 0·08, and widowers 1·08 per cent. At 80–85 years the widowers were in the highest proportion per cent., the figures being 15·71 unmarried, 39·85 husbands, 0·19 divorced, and 44·25 widowers.
Of the females, 99 per cent. were spinsters at the period 14–18 years; thence onwards the proportion diminished and the wives and widows increased, until at 25–30 years the wives were in the highest proportion—i.e., 54·07 per cent., against 45·01 of unmarried females, 0·05 of divorced, and 0·87 widows. At 70–75 years the widows had increased so as to exceed the wives, being 52·31 per cent. against 43·53, whilst the spinsters had diminished to 4·16 per cent. At 85 and upwards the widows were 81·01 per cent. of the whole number of females.
The proportion of married women under 20 years of age is still steadily diminishing, while the proportion from 35 to 45 years has an increasing tendency. Women in New Zealand are therefore not now marrying at such early ages as they did in former years. The process brings the relative proportions closer to those that obtain in England:–
| Ages. | England. | New Zealand. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| 1881. | 1878. | 1881. | 1886. | 1891. | 1896. | 1901. | |
| Under 20 years | 1·10 | 2·45 | 2·16 | 1·81 | 1·19 | 1·12 | 0·98 |
| 20 and under 35 years | 59·32 | 61·90 | 60·53 | 60·03 | 60·12 | 59·57 | 59·94 |
| 35 and under 45 years | 39·58 | 35·65 | 37·31 | 38·16 | 38·69 | 39·31 | 39·08 |
| 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | |
The numbers and proportions according to conjugal condition for each age-period are exhibited in full detail:—
| Ages. | Total. | Unmarried. | Husbands. | Widowers. | Divorced. | Not stated. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All ages | 403,167 | 272,858 | 118,475 | 10,653 | 255 | 926 |
| Specified ages | 402,760 | 272,685 | 118,401 | 10,641 | 255 | 778 |
| 14 years and upwards | 280,786 | 150,711 | 118,401 | 10,641 | 255 | 778 |
| Under 14 years | 121,974 | 121,974 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 14 years to 15 years | 8,747 | 8,747 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 15 years to 16 years | 8,456 | 8,456 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 16 years to 17 years | 8,568 | 8,566 | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| 17 years to 18 years | 8,453 | 8,443 | 4 | .. | .. | 6 |
| 18 years to 19 years | 8,536 | 8,508 | 16 | .. | .. | 12 |
| 19 years to 20 years | 8,439 | 8,402 | 28 | .. | .. | 9 |
| 20 years to 21 years | 8,554 | 8,440 | 94 | 1 | .. | 19 |
| 21 years to 25 years | 32,607 | 29,482 | 2,953 | 34 | 4 | 134 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 35,145 | 22,730 | 12,121 | 156 | 10 | 128 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 29,463 | 11,845 | 17,206 | 317 | 24 | 71 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 23,983 | 6,854 | 16,577 | 445 | 41 | 66 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 21,128 | 4,898 | 15,434 | 706 | 26 | 64 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 18,647 | 3,730 | 13,956 | 859 | 47 | 55 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 14,948 | 2,788 | 11,098 | 970 | 34 | 58 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 13,450 | 2,423 | 9,699 | 1,259 | 24 | 45 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 12,571 | 2,320 | 8,711 | 1,484 | 17 | 39 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 10,074 | 2,347 | 5,927 | 1,756 | 15 | 29 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 5,317 | 1,094 | 2,931 | 1,267 | 7 | 18 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 2,277 | 444 | 1,105 | 709 | 3 | 16 |
| 80 years to 85 years | 1,048 | 164 | 416 | 462 | 2 | 4 |
| 85 years and upwards | 375 | 30 | 125 | 216 | 1 | 3 |
| Unspecified | 407 | 173 | 74 | 12 | .. | 148 |
| Ages. | Total. | Unmarried. | Wives. | Widows. | Divorced. | Not stated. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All ages | 366,695 | 230,361 | 117,821 | 17,902 | 149 | 462 |
| Specified ages | 366,487 | 230,284 | 117,746 | 17,881 | 149 | 427 |
| 14 years and upwards | 247,828 | 111,625 | 117,746 | 17,881 | 149 | 427 |
| Under 14 years | 118,659 | 118,659 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 14 years to 15 years | 8,358 | 8,358 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 15 years to 16 years | 8,376 | 8,375 | 1 | .. | .. | .. |
| 16 years to 17 years | 8,689 | 8,677 | 10 | .. | .. | 2 |
| 17 years to 18 years | 8,430 | 8,352 | 72 | .. | .. | 6 |
| 18 years to 19 years | 8,425 | 8,215 | 193 | 1 | 16 | |
| 19 years to 20 years | 8,438 | 7,924 | 501 | .. | .. | 13 |
| 20 years to 21 years | 8,583 | 7,593 | 963 | 5 | .. | 22 |
| 21 years to 25 years | 33,369 | 24,114 | 9,090 | 67 | 8 | 90 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 33,227 | 14,918 | 17,923 | 290 | 16 | 80 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 27,271 | 6,986 | 19,617 | 593 | 35 | 40 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 21,216 | 3,373 | 16,854 | 929 | 33 | 27 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 17,347 | 1,783 | 14,182 | 1,342 | 21 | 19 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 13,995 | 966 | 11,309 | 1,683 | 17 | 20 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 11,990 | 665 | 9,239 | 2,068 | 5 | 13 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 9,963 | 467 | 7,144 | 2,330 | 6 | 16 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 8,017 | 347 | 5,222 | 2,422 | 6 | 20 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 6,027 | 253 | 3,283 | 2,468 | 2 | 21 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 3,236 | 134 | 1,404 | 1,687 | .. | 11 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 1,679 | 86 | 515 | 1,074 | .. | 4 |
| 80 years to 85 years | 852 | 26 | 173 | 649 | .. | 4 |
| 85 years and upwards | 340 | 13 | 51 | 273 | .. | 3 |
| Unspecified | 208 | 77 | 75 | 21 | .. | 35 |
| Ages. | Unmarried. | Husbands. | Widowers. | Divorced. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All ages | 67·84 | 29·45 | 2·65 | 0·06 |
| Specified ages | 67·84 | 29·45 | 2·65 | 0·06 |
| 14 years and upwards | 53·82 | 42·29 | 3·80 | 0·09 |
| Under 14 years | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 14 years to 17 years | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 17 years to 18 years | 99·95 | 0·05 | .. | .. |
| 18 years to 19 years | 99·81 | 0·19 | .. | .. |
| 19 years to 20 years | 99·67 | 0·33 | .. | .. |
| 20 years to 21 years | 98·89 | 1·10 | 0·01 | .. |
| 21 years to 25 years | 90·79 | 9·09 | 0·11 | 0·01 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 64·91 | 34·61 | 0·45 | 0·03 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 40·30 | 58·54 | 1·08 | 0·08 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 28·66 | 69·31 | 1·86 | 0·17 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 23·25 | 73·27 | 3·35 | 0·13 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 20·06 | 75·07 | 4·62 | 0·25 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 18·72 | 74·53 | 6·52 | 0·23 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 18·08 | 72·35 | 9·39 | 0·18 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 18·51 | 69·51 | 11·84 | 0·14 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 23·37 | 59·00 | 17·48 | 0·15 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 20·65 | 55·31 | 23·91 | 0·13 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 19·64 | 48·87 | 31·36 | 0·13 |
| 80 years to 85 years | 15·71 | 39·85 | 44·25 | 0·19 |
| 85 years and upwards | 8·06 | 33·60 | 58·07 | 0·27 |
| Ages. | Unmarried. | Wives. | Widows. | Divorced. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All ages | 62·90 | 32·17 | 4·89 | 0·04 |
| Specified ages | 62·91 | 32·17 | 4·88 | 0·04 |
| 14 years and upwards | 45·12 | 47·59 | 7·23 | 0·06 |
| Under 14 years | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 14 years to 15 years | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 15 years to 16 years | 99·99 | 0·01 | .. | .. |
| 16 years to 17 years | 99·88 | 0·12 | .. | .. |
| 17 years to 18 years | 99·15 | 0·85 | .. | .. |
| 18 years to 19 years | 97·69 | 2·30 | 0·01 | .. |
| 19 years to 20 years | 94·05 | 5·95 | .. | .. |
| 20 years to 21 years | 88·69 | 11·25 | 0·06 | .. |
| 21 years to 25 years | 72·46 | 27·32 | 0·20 | 0·02 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 45·01 | 54·07 | 0·87 | 0·05 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 25·65 | 72·04 | 2·18 | 0·13 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 15·92 | 79·54 | 4·38 | 0·16 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 10·29 | 81·84 | 7·75 | 0·12 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 6·91 | 80·93 | 12·04 | 0·12 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 5·55 | 77·14 | 17·27 | 0·04 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 4·70 | 71·82 | 23·42 | 0·06 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 4·34 | 65·30 | 30·29 | 0·07 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 4·21 | 54·66 | 41·09 | 0·04 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 4·16 | 43·53 | 52·31 | .. |
| 75 years to 80 years | 5·13 | 30·75 | 64·12 | .. |
| 80 years to 85 years | 3·07 | 20·40 | 76·53 | .. |
| 85 years and upwards | 3·86 | 15·13 | 81·01 | .. |
Of 2,825 male Chinese living in the colony, 61 were stated as married and 13 widowed. The instruction on the census schedule was that Chinese not having wives in this colony or any Australian State should be returned as unmarried. Of 32 Chinese females, 18 were returned as married, 12 of the rest being young people under 14 years of age, and 2 from 25 to 29 years old. The half-caste Chinese are referred to on page 136.
Of 272,685 unmarried males of specified ages, 99,844 were over 20 years of age, and, of 230,284 unmarried females, 103,416 were found to be over 15 years; the excess of spinsters over bachelors was therefore 3,572. Accepting the above as the marriageable ages, the number of bachelors to every 100 spinsters was 97 (nearly).
That a process of equalisation in the numbers of bachelors and spinsters has been going on steadily during past years is proved by the results of previous censuses.
| NUMBER OF BACHELORS AGED 20 YEARS AND UPWARDS TO EVERY 100 (([0-9]+)) AGED 15 AND UPWARDS. | |
|---|---|
| Census 1874 | 238 |
| Census 1878 | 191 |
| Census 1881 | 162 |
| Census 1886 | 123 |
| Census 1891 | 105 |
| Census 1896 | 98 |
| Census 1901 | 97 |
The number of husbands of specified ages was 118,401, and of wives 117,746, giving an excess of husbands over wives amounting to 655. This excess of husbands is almost entirely accounted for by the arrival during the last few years of a number of Austrian gum-diggers in the Auckland Provincial District—married men, who did not bring their wives with them.
The widowers of specified ages numbered 10,641, and the widows 17,881, being a proportion of 60 widowers to every 100 widows. At the census of 1896 the proportion was 62 to every 100 widows.
Four hundred and four persons—namely, 255 men and 149 women—were entered on the census schedules as being divorced. These numbers are not likely to represent fully the actual facts, but are interesting as, no doubt, an approximation to the truth.
It was remarked in the report on the census of 1896 that the marriage rate in New Zealand, from being the highest in Australasia, had fallen among the lowest, and that the same process had been going on in regard to birth rates. The lapse of five years places New Zealand in a much better position, the marriage rate being only slightly lower than in Tasmania and Western Australia, but higher than in Victoria, New South Wales, South Australia, and Queensland.
| MARRIAGE RATES PER 1,000 OF POPULATION. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1874. | 1886. | 1891. | 1895. | 1900. | |
| Queensland | 8·62 | 8·67 | 7·18 | 6·23 | 6·88 |
| New South Wales | 7·70 | 7·99 | 7·39 | 6·35 | 7·38 |
| Victoria | 6·33 | 7·84 | 7·69 | 6·00 | 6·96 |
| South Australia | 8·00 | 6·24 | 7·31 | 5·88 | 6·50 |
| Western Australia | 6·96 | 7·98 | 8·00 | 6·83 | 10·27 |
| Tasmania | 6·83 | 7·26 | 6·63 | 5·32 | 7·71 |
| New Zealand | 8·81 | 5·99 | 6·04 | 5·94 | 7·67 |
In the year 1880, New Zealand had the highest birth rate in Australasia, but since 1887 the position has been exactly the opposite.
| BIRTH RATES PER 1,000 OF POPULATION. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1887. | 1891. | 1895. | 1900. | |
| Queensland | 38·09 | 36·35 | 32·85 | 30·21 |
| New South Wales | 36·42 | 34·50 | 30·66 | 27·43 |
| Victoria | 32·39 | 33·57 | 28·57 | 25·82 |
| South Australia | 34·63 | 33·92 | 30·23 | 25·78 |
| Western Australia | 37·34 | 34·85 | 25·62 | 31·46 |
| Tasmania | 33·87 | 33·37 | 30·10 | 28·25 |
| New Zealand | 32·09 | 29·01 | 26·78 | 25·60 |
The schedules showed that at the time of the census 43 European women were married to Chinese, the result of such unions being 106 children (60 males and 46 females). If these half-caste children be added to the number of pure-bred Chinese in the colony the result would be,—
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 2,857 | 2,825 | 32 |
| Chinese half-castes | 106 | 60 | 46 |
| 2,963 | 2,885 | 78 |
Table of Contents
THE number of persons under 21 years in March, 1901, was 359,723, and over 21 years 412,356, besides 640 unspecified as to age, but nearly all adults.
Comparison of the population under and over 21 years for 1886, 1891, 1896, and 1901, shows that the number over 21 years is increasing in proportion to the population at all ages.
| PROPORTIONS PER CENT. OF PERSONS—ALL AGES. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1886. | 1891. | 1896. | 1901. | |
| Under 21 years | 53·47 | 52·46 | 49·94 | 46·59 |
| Over 21 years | 46·53 | 47·54 | 50·06 | 53·41 |
| 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | |
The males under 21 years in 1901 were 181,753, and the adults 223,807, leaving 432 unspecified as to age, but of whom few were children. The females under 21 numbered 177,970, and adults 188,549, leaving 208 unspecified. The proportions per cent. of population over 21 years of age of each sex are higher for 1901 than for 1896.
| PROPORTIONS PER CENT. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | |||
| 1896. | 1901. | 1896. | 1901. | |
| Under 21 years | 47·72 | 44·77 | 52·39 | 48·53 |
| Over 21 years | 52·28 | 55·23 | 47·61 | 51·47 |
| 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | |
The proportion of aged people in the increases with time, and the progression is very important to notice. The figures for nine census years, extending from 1867 to 1901 are quoted:—
| PERSONS 65 YEARS AND UPWARDS PER CENT. OF POPULATION. | |
|---|---|
| 1867 | 0·8 |
| 1878 | 1·29 |
| 1891 | 2·29 |
| 1871 | 1·08 |
| 1881 | 1·41 |
| 1896 | 2·95 |
| 1874 | 1·22 |
| 1886 | 1·81 |
| 1901 | 4·06 |
The numbers at the periods most often in request may be described thus: Infancy extremé youth (under 5 years)—males, 44,324; females, 42,482: School age (5 to 15 years)—males, 86,414; females, 84,547: Women at the reproductive age (15 to 45 years)—183,387: The athletic age (21 to 40 years)—males, 121,939; females, 115,099: The militia age (17 to 55 years)—males only, 212,065: The elderly period of life (55 to 65 years)—males, 26,514; females, 17,980: Old-age (65 years and upwards)—males, 19,218; females, 12,135.
The total number of males liable to be called out for service in the militia in March, 1901, was, in round numbers, 129,000, consisting of all males between 17 and 40 years, with the unmarried between 40 and 55 years, less the exemptions, numbering about 37,880 persons. They are classified as under:—
| Class I. Unmarried, between 17 and 30 years | 86,327 |
| Class II. Married, between 17 and 30 years | 15,407 |
| Unmarried, between 30 and 40 years | 18,901 |
| Class III. Married, between 30 and 40 years | 34,545 |
| Unmarried, between 40 and 55 years | 11,700 |
| 166,880 | |
| Deduct exemptions | 37,880 |
| 129,000 |
Of married men between 40 and 55, there were 43,130.
For a person not born in New Zealand, the householder was required to state on the census schedule the length of his or her residence therein in years, and from the information thus obtained, a table has been compiled showing the number of persons at each year of age, and the length of their residence in the colony, and from this the following figures, which will no doubt be found interesting, are taken:—
On the 31st March, 1901, there were in New Zealand 26,563 persons of 65 years of age and upwards who had been twenty-five years and over resident in the colony, and, at the same time, no less than
| 3,537 persons 64 years of age and over, resident 24 years and upwards. |
| 3,602 persons 63 years of age and over, resident 23 years and upwards. |
| 3,831 persons 62 years of age and over, resident 22 years and upwards. |
| 3,532 persons 61 years of age and over, resident 21 years and upwards. |
| 5,978 persons 60 years of age and over, resident 20 years and upwards. |
| 4,180 persons 59 years of age and over, resident 19 years and upwards. |
| 4,676 persons 58 years of age and over, resident 18 years and upwards. |
| 4,567 persons 57 years of age and over, resident 17 years and upwards. |
| 5,277 persons 56 years of age and over, resident 16 years and upwards. |
| 5,030 persons 55 years of age and over, resident 15 years and upwards. |
In addition to the above, there were 925 persons of 65 years and over whose length of residence was not specified, 71 persons who had resided twenty-five years and over in the colony whose ages were not stated, and 273 adults unspecified both as to age and length of residence, as well as 163 adults born in New Zealand whose ages were not given.
Aliens are included in the foregoing figures, but Maoris are excluded. There were 11,615 foreign subjects (of all ages) in New Zealand on the 31st March, 1901.
Of the New Zealand born, 171 had reached or passed the age of 65 years at the time of the census; 22 were 64 years old; 43 were 63; 42 were 62; 43 were 61; 130 were said to be 60; 167 were 59; 243 were 58; 321 were 57; 386 were 56; and 410 were 55 years old. These have been included in the figures previously given.
Table of Contents
AT a Conference of Statisticians of the Australasian Colonies,* held in Sydney, February, 1900, a series of resolutions was passed, and a form of schedule agreed to, with the view of securing the uniformity so necessary for comparative purposes in system and heads of inquiry. The classification of occupations used in 1896 by this colony was, with minor amendments, generally adopted. This classification has been described as one devised “as a means of overcoming the great difficulties with which the systematic grouping of the occupations of the people of a country has always been found to be attended,” and may fairly be claimed to have attained its purpose.
The old classification of Dr. Farr, in use prior to 1891, purported to divide the population so as to distinguish the commercial from the industrial class; but, in allotting the various occupations to the different classes, the principle adopted was that of grouping all workers and dealers in different matters together according to the material dealt in or worked upon, and placing the whole in the industrial class. Thus the dealers, who are really commercial, went to swell the number of the industrial at the expense of the commercial class. General labourers were cast out of the industrial into the indefinite class, merely because the material on which they worked was not stated, &c. The classification used in 1891 and 1896, while preserving Farr's professional class nearly intact, transfers, among other changes, a large number of women and children from the domestic to the dependent class, and completes the commercial class by including “trade” among the agorici of Farr. The industrial class now consists of part of what was assigned to it by Farr, but includes general labourers. Miners and other primary producers are placed with the agricultural and pastoral class, as being engaged in obtaining raw materials from natural sources. The indefinite class is greatly reduced in number, and the class styled “dependent” introduced. A Conference (held in 1890) had agreed to a proposal for distinguishing “employers” from “employed”—a division first attempted in New Zealand, at the suggestion of the writer of this report, on the occasion of the census of 1886, and renewed in 1891 and 1896. The importance of affording the means of distinguishing persons in business from wage-earners is obvious, besides being absolutely essential to an improved classification of occupations.
* The names of the members of the Conference were as under: T. A. Coghlan, Government Statistician, New South Wales; J. Hughes, Registrar-General, Queensland; L. H. Sholl, Under-Secretary and Government Statist, South Australia; M. A. C. Fraser, Registrar-General, Western Australia; R. M. Johnston, Government Statistician and Registrar-General, Tasmania; E. J. von Dadelszen, Registrar-General, New Zealand.
It was also arranged for bringing out the occupations of the people in seven groups of ages, instead of merely distinguishing the number of each sex under and over 20 years of age as was done prior to 1891. (The full details will be found in the Census volume.)
The full description of the arrangement of occupations in the eight classes used under the new method is—
I. PROFESSIONAL.—Embracing all persons, not otherwise classed, mainly engaged in the government and defence of the country, and in satisfying the moral, intellectual, and social wants of its inhabitants.
II. DOMESTIC.—Embracing all persons engaged in the supply of board and lodging, and in rendering personal services for which remuneration is usually paid.
III. COMMERCIAL.—Embracing all persons directly connected with the hire, sale, transfer, distribution, storage, and security of property and materials.
IV. TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION.—Embracing all persons engaged in the transport of persons or goods, or in effecting communication.
V. INDUSTRIAL.—Embracing all persons, not otherwise classed, who are principally engaged in various works of utility, or in specialities connected with the manufacture, construction, modification, or alteration of materials so as to render them more available for the various uses of man, but excluding, as far as possible, all who are mainly or solely engaged in the service of commercial interchange.
VI. AGRICULTURAL, PASTORAL, MINERAL, (([0-9]+)) PRIMARY PRODUCERS.—Embracing all persons mainly engaged in the cultivation or acquisition of food products, and in obtaining other raw materials from natural sources.
VII. INDEFINITE.—Embracing all persons who derive incomes from services rendered, but the direction of which services cannot be exactly determined.
VIII. DEPENDENTS.—Embracing all persons dependent upon relatives or natural guardians, including wives, children, and others not otherwise engaged in pursuits for which remuneration is paid; and all persons depending upon private charity, or whose support is a burden on the public revenue.
In the professional class are included persons described as “officers of Government”; but the numbers given under this heading do not represent the whole number employed by the Government, the principle adopted having been to complete the other groups where the scheme of classification required it, rather than to show completely all persons paid by Government. Thus, Postal and Telegraph officers are classified in Class IV., “Transport and Communication.” Railway employees are similarly dealt with. It is highly important that persons making use of the tabulated results of the information as to occupations should be aware of and bear in mind the above facts.
The numbers under “Commercial” and “Industrial” include all persons whose occupations were sufficiently defined to enable them to be classified in connection with the business or industry in which they are engaged. Many, chiefly those whose employment was of the nature of unskilled clerical assistance, while entering “clerk” under the heading “Occupation,” did not state in what trade or industry they were employed. These, of course, could not be allotted to any special industry. Those engaged as agents or assistants in any occupation belonging to Classes III. to VII. have been, generally speaking, included with the principals. All persons stated as both manufacturers and dealers or sellers have been classed as makers only, under Class V. Persons out of employment are included under their ordinary or former occupations. Inmates of asylums, industrial schools, and refuges, together with all persons in gaols, have not been classed according to their ordinary occupations, but in Class VIII., as part of the dependent population.
The difficulty of tabulating the occupations of the people shown in the census is certainly lessened by the introduction of the card system; but there remains an unsatisfactoriness in the work on account of the different ways in which people return themselves when their occupation is virtually the same, and the number of instances in which unskilled labour is not defined as having to do with the industry on which it is temporarily employed. These causes prevent the published results from being what they ought to be, even with perfect care in the compilation-work. The basis of such work is often enough faulty or incomplete, and it is impossible to remedy the defect. One man may be a “carter at brewery,” and returns himself accordingly. Another omits the words “at brewery,” and thus the total number of persons employed in the brewing business becomes deficient. As continual instances of these irregularities are found, it arises that the census industrial statistics often differ materially as to “hands employed” from the results brought out under the head of “Occupation” in regard to labourers and others attached to various industries.
The population, specified as to occupation, is divided into two sections:—
| Totals. | Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breadwinners | 310,230 | 274,559 | 65,671 |
| Dependents, or non-breadwinners | 432,149 | 131,164 | 300,985 |
| Occupation not stated | 340 | 269 | 71 |
The dependent population consists chiefly of wives, relatives, and others employed in household duties but unpaid, children, persons supported by charity, &c. Its proportion to the whole increases with the process going on of equalisation in numbers of the sexes.
The male breadwinners were more than twice as numerous as the male dependents, who were mostly under fifteen years of age; but the female dependents were nearly five times as many as the breadwinners of that sex.
Breadwinners are divided into the seven classes previously alluded to:—
Primary Producers.—Males, 108,007; females, 3,914. This is the most important class numerically. It includes persons engaged in agricultural and pastoral pursuits, fishing, and mining.
Males 26·62, females 1·07 per cent. of population of either sex.
Industrial.—Males, 84,874; females, 16,310: persons engaged in manufacture or other processes where materials are employed combined.
Males 20·92, females 4·45 per cent.
Commercial.—Males, 34,409; females, 5,528.
The commercial group forms 8·48 per cent. of the male, and 1·51 per cent. of the female population.
Transport and Communication.—Males, 21,265; females, 485: persons engaged in the transport of passengers and goods, and in effecting communication.
Males 5·24, females 0·13 per cent.
Professional.—Males, 14,549; females, 8,960. These are persons, not otherwise classed, engaged in Government, defence, law and order, or ministering to religion, charity, health, education, art, science, or amusement.
Males 3·59, females 2·44 per cent.
Domestic (but directly earning money).—Males, 6,542; females, 27,852: persons supplying board and lodging, or personal services for which payment is rendered.
Males 1·61, females 7·60 per cent.
Indefinite.—Males, 4,913; females, 2,622: persons living on incomes earned in the past, or indefinitely described.
Males 1·21, females 0·71 per cent.
It will be observed from the appended table of occupations, that no less than 32·33 per cent. of the male population and 82·09 per cent. of the females are dependent. These consist of 127,916 males and 298,727 females dependent upon natural guardians; and 3,248 males and 2,258 females dependent upon the State, or upon public or private support. The greater number of those dependent upon natural guardians are scholars and students. There are also a large number of dependent relatives who were not stated to be performing domestic duties, and, of females, many persons performing domestic duties for which remuneration is not paid.
The population of each class, and the proportion per cent. of the total population, are:—
| Occupations. | Numbers. | Proportions per Cent. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | M. | F. | Persons. | M. | F. | |
| Total population | 772,719 | 405,992 | 366,727 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 |
| Section A.—Breadwinners. | ||||||
| Class I. Professional | 23,509 | 14,549 | 8,960 | 3·04 | 3·59 | 2·44 |
| Class II. Domestic | 34,394 | 6,542 | 27,852 | 4·45 | 1·61 | 7·60 |
| Class III. Commercial— | ||||||
| Sub-class A. Property and Finance | 5,631 | 5,046 | 585 | 0·72 | 1·24 | 0·16 |
| Sub-class B. Trade | 33,438 | 28,500 | 4,938 | 4·31 | 7·03 | 1·35 |
| Sub-class C. Storage | 868 | 863 | 5 | 0·10 | 0·21 | 0·00 |
| Class IV. Transport and Communication | 21,750 | 21,265 | 485 | 2·82 | 5·24 | 0·13 |
| Class V. Industrial | 101,184 | 84,874 | 16,310 | 13·10 | 20·92 | 4·45 |
| Class VI. Agricultural, Pastoral, and other Primary Producers— | ||||||
| Sub-class A. Agricultural | 67,812 | 65,723 | 2,089 | 8·78 | 16·20 | 0·57 |
| Sub class B. Pastoral | 21,410 | 19,600 | 1,810 | 2·77 | 4·83 | 0·50 |
| Sub-class C. Mineral | 17,816 | 17,808 | 8 | 2·31 | 4·39 | 0·00 |
| Sub-class D. Other Primary Producers | 4,883 | 4,876 | 7 | 0·63 | 1·20 | 0·00 |
| Class VII. Indefinite | 7,535 | 4,913 | 2,622 | 0·98 | 1·21 | 0·71 |
| Section B.—Non-Breadwinners (Dependents). | ||||||
| Class VIII. Dependents— | ||||||
| Sub-class A. Dependent on natural guardians | 426,643 | 127,916 | 298,727 | 55·23 | 31·53 | 81·47 |
| Sub-class B. Dependent upon the State, or upon public or private support | 5,506 | 3,248 | 2,258 | 0·72 | 0·80 | 0·62 |
| Occupations not stated | 340 | 269 | 71 | .. | .. | .. |
The breadwinners of the colony are also classified according to the grade of their occupations, by which means the entire population can be brought under six heads:—
| Males. | Per Cent. of Breadwinners. | Females. | Per Cent. of Breadwinners. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employers | 34,002 | 12·39 | 2,010 | 3·06 |
| Independent workers | 47,317 | 17·23 | 8,750 | 13·32 |
| Wage-earners | 166,432 | 60·62 | 48,088 | 73·23 |
| Unemployed | 8,467 | 3·08 | 1,359 | 2·07 |
| Relatives assisting, and not specified | 18,341 | 6·68 | 5,464 | 8·32 |
| Breadwinners | 274,559 | 100·00 | 65,671 | 100·00 |
| Dependents | 131,164 | .. | 300,985 | .. |
| Not stated | 269 | .. | 71 | .. |
| Totals | 405,992 | .. | 366,727 | .. |
The proportion of the male breadwinners who are employers (12·39 per cent.) is slightly higher than it was in 1896 (12·02 per cent.). On the female side the proportion of employers was 3·06 per cent. at both censuses. Male wage-earners, employed or unemployed, were 63·70 per cent., against 61·48 per cent. in 1896. Female wage-earners, whether in work or not, were 75·30 per cent. in 1901, against 75·01 per cent. in 1896, indicating a growing use of female labour.
Details of the numbers and proportions of persons of each sex (in the different classes of occupation) divided according to grade, i.e., employers, independent workers, wage-earners, unemployed, and relatives assisting, will be found on pp. 58 and 59 of the Registrar-General's Report on the Census of 1901.
Table of Contents
AN instruction was given in the census household schedule that in regard to all persons “laid up or unable to follow their usual occupation,” by reason of illness or accident, the fact was to be stated when the form was being filled up. And by means of the information thus obtained the proportion of persons incapacitated from work on the day of the census has been ascertained, and is shown in the tables according to age-periods.
Besides persons suffering from sickness or accident, those afflicted with certain infirmities are also distinguished. These include the “deaf-and-dumb,” “blind,” “lunatics,” “idiots,” “epileptics,” “paralytic,” “crippled and deformed,” “debilitated and infirm,” and “deaf only.”
The result of the investigation under this head shows that 9·28 persons in every 1,000 were suffering from sickness or accident on the 31st March, 1901, using the word “sickness” to mean inability to work on that day; and that, besides these, there were 7·20 persons in every 1,000 who were either affected with blindness, or deaf-and-dumb, lunatic, idiot, epileptic, &c., the proportion per 1,000 persons living stated to be suffering from sickness, accident, and infirmities being 16·48: for males, 20·09 per 1,000 living, and for females, 12·49.
The sickness and infirmity of the males is thus found to be higher than that of the females, as was the case in 1896, when the proportion was 20·92 for males and 14·36 for females.
The numbers and proportions of males and females suffering from sickness, accident, or specified infirmity in this colony, according to age-periods, will be found tabulated in the Report on the Census. In regard to males, after the period 35·40 the proportion of sickness rises steadily at each quinquennium of age; while under accident the proportion is highest at the period of 70·75 years. The rate of sickness per 1,000 males living at 35–40 years was 5·68, and this increased to 18·38 at 55–60, to 54·62 at 65–70, and to 70·18 at 80 and upwards. In regard to females, the sickness is not so great at 40–45 years as at 35–40, but from this point it increases, and from 50–55 very rapidly, though the numbers on which the proportions are based are admittedly small from this age onwards. The rates per 1,000 were 6·97 at 35–40 years, 13·95 at 55–60, and 47·82 at 80 years and upwards.
Females are proved to be very much less liable to accident than males, the proportions being 0·63 per 1,000 of females, and 3·03 per 1,000 of males; or better stated for this purpose, 6·27 per 10,000 females and 30·28 per 10,000 males. As with sickness, the proportions increase with advancing age: for instance, among males, 3·37 per 1,000 were suffering from accident at the group 20–25 years, 3·75 per 1,000 at 40–45, 10·24 at 65–70, and 12·90 at the group 70–75 years. Among females the highest proportion per 1,000 is found at 75–80 years, being a rate of 5·36, or 53·60 per 10,000 living.
Sickness and infirmity can be compared for New Zealand, in respect of persons over 15 years of age, with the results of the census of 1896 and previously. The proportions are:—
| PROPORTION PER 1,000 PERSONS OVER 15 YEARS. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sickness and Accident. | Specified Infirmities. | Total Sickness and Infirmity. | |
| Census 1874 | 12·64 | 5·32 | 17·96 |
| Census 1878 | 11·16 | 5·70 | 16·86 |
| Census 1881 | 11·20 | 7·22 | 18·42 |
| Census 1886 | 12·61 | 7·82 | 20·43 |
| Census 1891 | 12·78 | 11·08 | 23·86 |
| Census 1896 | 14·28 | 11·41 | 25·69 |
| Census 1901 | 12·72 | 10·29 | 23·01 |
The total of these under the various heads amounted to 5,574 of both sexes and all ages. The males were 3,466, and the females 2,108, the proportions for every 10,000 persons being 71·98: for males 85·21, and for females 57·35 per 10,000 of each sex respectively. These infirmities are specially treated of one by one in the succeeding paragraphs.
There were 226 persons—134 males and 92 females—returned as deaf and dumb, or dumb only: of these 45 were inmates of the Sumner Institution, leaving 181 deaf-mutes who were living at home or in some other private residence. The total shows a proportion of 2·91 persons per 10,000 living, against 2·86 ascertained in 1896. The proportions of the deaf and dumb taken according to the sexes did not differ much. The figures are given for six census years.
| DEAF AND DUMB (IN SEXES).—PROPORTIONS PER 10,000 OF POPULATION. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | |
| Census 1878 | 2·25 | 2·18 |
| Census 1881 | 2·23 | 2·45 |
| Census 1886 | 2·37 | 2·22 |
| Census 1891 | 2·80 | 2·49 |
| Census 1896 | 2·99 | 2·71 |
| Census 1901 | 3·28 | 2·51 |
The numbers at the census of 1901 for quinquennial age-periods are:—
| NUMBERS OF THE DEAF AND DUMB AT LAST CENSUS. | ||
|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | |
| All ages | 134 | 92 |
| — | — | |
| Under 5 years | .. | .. |
| 5 years to 10 years | 18 | 16 |
| 10 years to 15 years | 32 | 14 |
| 15 years to 20 years | 18 | 10 |
| 20 years to 25 years | 16 | 8 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 8 | 12 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 12 | 8 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 6 | 8 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 5 | 5 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 6 | 1 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 3 | 5 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 5 | 1 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 3 | 1 |
| 65 years to 70 years | .. | 1 |
| 70 years to 75 years | .. | .. |
| 75 years to 80 years | 1 | 2 |
| 80 years to and upwards | .. | .. |
| Unspecified | 1 | .. |
The highest numbers are shown at the ages 10 to 15.
The occupations (past or present) of the deaf and dumb were returned in 1901 as under:—
| OCCUPATIONS (PAST OR PRESENT) OF THE DEAF AND DUMB. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | ||||
 |  | ||||
| Persons. | Under 20. | Over 20. | Under 20. | Over 20. | |
| Draughtsman | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Hotel servant | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Domestic servant | 4 | 1 | .. | .. | 3 |
| Milkman | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Storekeeper's assistant | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Printer's assistant | 1 | 1 | .. | .. | .. |
| Saddler | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Tanner | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Cabinetmaker | 1 | 1 | .. | .. | .. |
| Tailor | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Dressmaker | 6 | .. | .. | 2 | 4 |
| Bootmaker | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Labourer at freezing-works | 1 | 1 | .. | .. | .. |
| Brewer's assistant | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Fellmonger | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Carpenter | 4 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. |
| Labourer | 4 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. |
| Farmer | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| Gardener | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Farm-labourer | 13 | 1 | 12 | .. | .. |
| Sheep-farmer | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Shepherd | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Dairy-farmer | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| Independent means | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| No occupation | 8 | .. | 8 | .. | .. |
| Domestic duties | 38 | .. | .. | 1 | 37 |
| Scholar, private school | 2 | 1 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Scholar, government school | 8 | 6 | .. | 2 | .. |
| Receiving tuition at home | 3 | 2 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Dependent on relatives | 41 | 20 | 5 | 11 | 5 |
| Inmate of deaf and dumb institution | 45 | 24 | 1 | 20 | .. |
| Industrial school | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. |
| Occupation not stated | 18 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 2 |
| 226 | 68 | 66 | 40 | 52 | |
There were 297 males and 156 females, making a total of 453 persons returned as blind, including 63 who were given in the schedules as “nearly” or “partly” blind. Of the above total number, 15 were inmates of the Jubilee Institute for the Blind at Auckland. It would thus appear that only one out of every thirty persons in the colony who suffered from blindness had been received into the institution. The number of blind persons in 1896 was 344. The proportions in every 10,000 of population show a continuous rise at successive censuses, and that there is more blindness amongst males than females.
| PROPORTIONS OF BLIND TO EVERY 10,000 PEOPLE. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
| 1874 | 2·34 | 2·45 | 2·18 |
| 1878 | 2·56 | 2·42 | 2·73 |
| 1881 | 2·82 | 2·93 | 2·68 |
| 1886 | 3·22 | 3·65 | 2·70 |
| 1891 | 4·37 | 4·91 | 3·74 |
| 1896 | 4·90 | 5·69 | 4·01 |
| 1901 | 5·87 | 7·32 | 4·26 |
The proportion of the blind per 10,000 persons living in the past has been: for England, about 8·79; for Ireland, 11·30; for Scotland, 6·95; for Germany, 7·93; for France, 8·37; and for Italy, 7·63. For the Australian States the figures are: Victoria, 8·72; New South Wales, 6·59; Australian Continent, 7·38.
The number of the blind in quinquennial periods of age is stated for each sex. Of 297 males, 100 were under and 197 upwards of 50 years old. Of 156 females, 63 were under 50, and 93 over that age.
| NUMBERS OF THE BLIND AT AGE-PERIODS. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | M. | F. | |
| All ages | 453 | 297 | 156 |
| — | — | — | |
| Under 5 years | 3 | .. | 3 |
| 5 years to 10 years | 16 | 9 | 7 |
| 10 years to 15 years | 17 | 11 | 6 |
| 15 years to 20 years | 15 | 11 | 4 |
| 20 years to 25 years | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 14 | 9 | 5 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 17 | 13 | 4 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 21 | 16 | 5 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 18 | 11 | 7 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 22 | 10 | 12 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 23 | 16 | 7 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 45 | 32 | 13 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 37 | 22 | 15 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 74 | 53 | 21 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 46 | 28 | 18 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 36 | 25 | 11 |
| 80 and upwards | 29 | 21 | 8 |
Of the total number of the blind, 453 persons, there were 43 in regard to whom no information as to occupation is given on the household schedule, 71 (females) were returned as engaged in domestic duties, 15 persons as inmates of the blind institute, 10 as dependent relatives, 132 as of no occupation, 21 as labourers, 21 as farmers, 9 as farm labourers, 6 as dairy farmers, 5 as sheep-farmers, 8 as carpenters, 10 as pensioners, 6 of independent means, and the rest (96) of various occupations in small numbers each. A complete statement is added, in regard to which it must be remarked that many of the occupations are evidently the past occupations of persons whom blindness has prevented from continuing to work at their usual calling.
| OCCUPATIONS (PAST OR PRESENT) OF THE BLIND. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male. | Female. | ||||
 |  | ||||
| Persons. | Under 20. | Over 20. | Under 20. | Over 20. | |
| Barrister (not in practice) | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Surgeon | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Teacher of the blind | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| School-teacher | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Musician | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Street musician | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Organ-grinder | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Comedian | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Boarding - house keeper | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Hotelkeeper | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Domestic servant | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Cook | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Capitalist | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Insurance agent | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Proprietor of houses | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| News vendor | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Butcher | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Assistant butcher | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Fish-hawker | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Fruiterer | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Grocer | .. | 3 | .. | 3 | .. |
| Seed merchant | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Hawker | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Storekeeper | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Commercial traveller | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Cab proprietor | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Mariner | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Waterman | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Lumper | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Compositor | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Piano-tuner | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Basketmaker | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| Saddler | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Shipwright | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Cabinetmaker | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Boot- and shoe-maker | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| Stonemason | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Carpenter | 8 | .. | 8 | .. | .. |
| Plumber | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Painter | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Contractor | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Labourer | 21 | .. | 21 | .. | .. |
| Farmer | 21 | .. | 20 | .. | 1 |
| Farm labourer | 9 | 9 | .. | .. | |
| Gardener | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Market-gardener | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Settler | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Dairy-farmer | 6 | .. | 5 | .. | 1 |
| Sheep-farmer | 5 | .. | 4 | .. | 1 |
| Shepherd | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Fisherman | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Bushman | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Gum-digger | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Miner | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Miner, coal | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Miner, quartz | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Miner, alluvial | 4 | .. | 4 | .. | .. |
| Inspector of minerals | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| No occupation | 132 | 11 | 80 | 2 | 39 |
| Independent means | 6 | .. | 4 | .. | 2 |
| Pensioner | 10 | .. | 9 | .. | 1 |
| Annuitant | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. |
| Domestic duties | .. | .. | 3 | 68 | |
| Scholar, Government school | 2 | 2 | .. | .. | .. |
| Scholar, private school | 1 | 1 | .. | .. | .. |
| Receiving tuition at home | 2 | 1 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Dependent on relative | 10 | 3 | .. | 7 | .. |
| Inmate of Blind Institute | 15 | 8 | .. | 7 | .. |
| Occupation not stated | 43 | 5 | 16 | .. | 22 |
| Totals | 453 | 31 | 266 | 20 | 136 |
The lunatics enumerated were 2,675 persons, 1,599 males and 1,076 females, nearly all of whom were inmates of the asylums for the insane in the colony. Departmental returns show 2,773 persons (including 22 Maoris, 10 males and 12 females) as the total number of inmates on the 31st December, 1901.
Comparison with the results of previous censuses shows a continually increasing proportion of lunatics to the population in respect of either sex, and that there is considerably more lunacy among the men than women.
| LUNATICS.—PROPORTIONS PER 10,000 OF POPULATION. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
| Census 1874 | 19·93 | 23·28 | 15·48 |
| Census 1878 | 20·85 | 25·07 | 15·54 |
| Census 1881 | 22·86 | 27·30 | 17·43 |
| Census 1886 | 26·50 | 31·03 | 21·18 |
| Census 1891 | 27·82 | 31·28 | 23·92 |
| Census 1896 | 31·13 | 35·70 | 26·02 |
| Census 1901 | 34·47 | 39·23 | 29·19 |
The number of males who were lunatics was highest at the period 45–50 years, and the females at 40–45, as will be found by the following statement:—
| LUNATICS.—NUMBERS AT QUINQUENNIAL AGE-PERIODS. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | M. | F. | |
| All ages | 2,675 | 1,599 | 1,076 |
| Under 5 years | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 years to 10 years | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| 10 years to 15 years | 19 | 11 | 8 |
| 15 years to 20 years | 43 | 22 | 21 |
| 20 years to 25 years | 114 | 63 | 51 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 186 | 108 | 78 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 245 | 141 | 104 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 257 | 145 | 112 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 312 | 176 | 136 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 333 | 213 | 120 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 296 | 177 | 119 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 298 | 191 | 107 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 244 | 139 | 105 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 162 | 109 | 53 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 88 | 60 | 28 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 35 | 21 | 14 |
| 80 years and upwards | 22 | 11 | 11 |
| Unspecified | 14 | 8 | 6 |
The proportion of lunatics per 10,000 males living at the above age-periods was only 5·18 at 15–20 years, but had advanced to 59·67 at 35–40 years, and reached its maximum at the period 55–60, when the proportion was 139·30. In the case of females, the proportion rose to a maximum of 130·97 at 60–65.
In 1900 one person in every 288, exclusive of Maoris, in New Zealand was afflicted with lunacy.
The number of idiots of both sexes enumerated in the census was 105, against 144 in 1896; the proportion to 10,000 of population being 1·36 against 2·02 at the previous census. As with lunacy, the proportion of idiocy amongst the males (1·43 per 10,000) is higher than amongst the females (1·28).
Table of Contents
THE replies given at the Census by householders showed that in every 100 persons living (excluding Chinese), 82·78 per cent. could read and write, 1·95 could read only, and 15·27 were unable to read. The proportion per cent. unable to read fell from 23·72 in 1878 to 21·19 in 1886, to 16·51 in 1896, and, further, to 15·27 in 1901. Of those who could read only, the proportion diminished from 6·76 in 1878 till in 1901 it stood at 1·95 per cent. The following shows the percentages at each census period:—
| Year. | Read and Write | Read only. | Cannot Read. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | |||||||
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | Persons. | Males. | Females. | Persons. | Males. | Females | |
| 1878 | 69·52 | 72·11 | 66·33 | 6·76 | 5·91 | 7·80 | 23·72 | 21·98 | 25·87 |
| 1881 | 71·32 | 73·31 | 68·94 | 5·63 | 5·01 | 6·39 | 23·05 | 21·68 | 24·67 |
| 1886 | 74·01 | 75·40 | 72·41 | 4·80 | 4·36 | 5·31 | 21·19 | 20·24 | 22·28 |
| 1891 | 77·27 | 77·97 | 76·48 | 3·97 | 3·74 | 4·24 | 18·76 | 18·29 | 19·28 |
| 1896 | 80·60 | 81·06 | 80·09 | 2·89 | 2·71 | 3·08 | 16·51 | 16·23 | 16·83 |
| 1901 | 82·78 | 83·08 | 82·44 | 1·95 | 1·81 | 2·10 | 15·27 | 15·11 | 15·46 |
Besides the improvement in the degree of education shown above, which is observed in respect of females as well as males, it will be noticed that whereas the difference in the percentage able to read and write is very considerably in favour of the male sex for the year 1878, the proportions approximate more closely at each successive census year, until in 1901 there are found to have been 82·44 per cent. of the female sex who could read and write, against 83·08 of males. The education of the females, taking as a standard the knowledge of reading and writing, is thus almost equal to that of the males. But with a system of free and compulsory education this would be expected in time, and the census results have no longer the degree of importance or interest they had years ago.
It is in considering the proportions of the population at different age-periods that the improvement in education is even more clearly proved, as seen by reference to the table dealing with those subjects.
Here it is found that in 1901, of persons at the age-period 10–15 years, 99·24 per cent, were able to read and write, while 0·34 per cent. could merely read, and 0·42 per cent. were unable to read. The proportion who could not read increased slowly with each succeeding quinquennial period of age, until at 50–55 years it stood at 3·23 per cent. At 75–80 years the proportion was 6·45, and at 80 and upwards it had advanced to 7·68. Similarly, the proportion of persons who could read only increased from 0·34 at 10–15 years to 1·86 at the period 50–55, and again to 7·75 at 80 and upwards. The better education of the people at the earlier ages is thus exhibited. The numbers upon which the above proportions are based are:—
| NUMBERS (EXCLUDING CHINESE). | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ages. | Persons. | Males. | Females. | |||||||||
 |  |  | ||||||||||
| Read and Write. | Read only. | Cannot Read. | Education unknown. | Read and Write. | Read only. | Cannot Read. | Education unknown. | Read and Write. | Read only. | Cannot Read. | Education unknown. | |
| All ages | 632,936 | 14,857 | 116,821 | 5,248 | 332,560 | 7,223 | 60,484 | 2,900 | 300,376 | 7,634 | 56,337 | 2,348 |
| Specified ages | 632,538 | 14,847 | 116,798 | 5,067 | 332,318 | 7,217 | 60,472 | 2,753 | 300,220 | 7,630 | 56,326 | 2,311 |
| Specified ages above 5 years | 632,538 | 14,570 | 30,350 | 4,996 | 332,318 | 7,082 | 16,324 | 2,720 | 300,220 | 7,488 | 14,026 | 2,276 |
| Under 5 years | .. | 277 | 86,448 | 68 | .. | 135 | 44,148 | 33 | .. | 142 | 42,300 | 35 |
| 5 years to 10 years | 53,408 | 9,181 | 21,647 | 1,491 | 26,528 | 4,803 | 11,206 | 771 | 26,880 | 4,378 | 10,441 | 720 |
| 10 years to 15 years | 84,316 | 287 | 357 | 258 | 42,586 | 164 | 210 | 137 | 41,730 | 123 | 147 | 121 |
| 15 years to 20 years | 84,167 | 97 | 351 | 195 | 42,041 | 58 | 238 | 115 | 42,126 | 39 | 113 | 80 |
| 20 years to 25 years | 82,210 | 136 | 494 | 273 | 40,570 | 90 | 342 | 159 | 41,640 | 46 | 152 | 114 |
| 25 years to 30 years | 67,458 | 158 | 478 | 278 | 34,564 | 94 | 325 | 162 | 32,894 | 64 | 153 | 116 |
| 30 years to 35 years | 55,721 | 177 | 489 | 347 | 28,856 | 100 | 315 | 192 | 26,865 | 77 | 174 | 155 |
| 35 years to 40 years | 44,020 | 277 | 591 | 311 | 23,342 | 129 | 357 | 155 | 20,678 | 148 | 234 | 156 |
| 40 years to 45 years | 37,065 | 347 | 726 | 337 | 20,373 | 149 | 421 | 185 | 16,692 | 198 | 305 | 152 |
| 45 years to 50 years | 31,059 | 461 | 780 | 342 | 17,812 | 176 | 459 | 200 | 13,247 | 285 | 321 | 142 |
| 50 years to 55 years | 25,299 | 495 | 860 | 284 | 14,185 | 171 | 436 | 156 | 11,114 | 324 | 424 | 128 |
| 55 years to 60 years | 21,670 | 613 | 850 | 280 | 12,596 | 231 | 463 | 160 | 9,074 | 382 | 387 | 120 |
| 60 years to 65 years | 18,871 | 661 | 825 | 231 | 11,729 | 243 | 481 | 118 | 7,142 | 418 | 344 | 113 |
| 65 years to 70 years | 14,156 | 767 | 1,001 | 177 | 9,099 | 314 | 564 | 97 | 5,057 | 453 | 437 | 80 |
| 70 years to 75 years | 7,529 | 464 | 451 | 109 | 4,806 | 196 | 246 | 69 | 2,723 | 268 | 205 | 40 |
| 75 years to 80 years | 3,408 | 249 | 252 | 47 | 2,017 | 90 | 146 | 24 | 1,391 | 159 | 106 | 23 |
| 80 and upwards | 2,181 | 200 | 198 | 36 | 1,214 | 74 | 115 | 20 | 967 | 126 | 83 | 16 |
| Unspecified age under 21 | 17 | 3 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Unspecified age over 21 | 381 | 7 | 12 | 176 | 233 | 4 | 4 | 142 | 148 | 3 | 8 | 34 |
Statistics showing the proportion of persons married in different years, and who signed the register with a mark, corroborate the census results as to advance in education. In the year 1881, 32 males and 58 females per 1,000 of either sex were found to be illiterate, as being not able to sign their names. These proportions fell to 19·21 males per 1,000 and 28·96 females per 1,000 of each sex in 1886, and again to 16·33 and 19·23 in 1890; in 1895 the proportions stood at 9·48 for males and the same for females, and in 1900 only 5·29 for males and 5·12 for females.
A table is next given to show particulars in respect of the various principal religious denominations, and of marriages by Registrars:—
| PERSONS IN EVERY 1,000 MARRIED WHO SIGNED BY MARK. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denomination. | 1881. | 1886. | 1890. | 1895. | 1900. | |||||
 |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | |
| Church of England | 16·59 | 27·15 | 9·33 | 12·00 | 6·08 | 4·86 | 3·21 | 3·21 | 3·01 | 5·27 |
| Presbyterians | 10·25 | 29·61 | 9·79 | 7·62 | 8·59 | 15·27 | 5·00 | 1·00 | 2·59 | 3·23 |
| Wesleyans and other Methodists | 32·41 | 41·79 | 6·33 | 14·78 | 15·20 | 10·14 | 4·65 | 4·65 | 3·98 | 3·98 |
| Roman Catholics | 117·78 | 133·33 | 46·45 | 65·57 | 35·26 | 42·82 | 17·39 | 28·26 | 9·46 | 6·31 |
| Other denominations | 10·36 | 20·72 | 11·49 | 22·99 | 15·00 | 0·00 | 10·00 | 10·00 | 0·00 | 0·00 |
| By Registrars | 39·22 | 93·51 | 35·98 | 62·03 | 29·77 | 40·60 | 22·02 | 20·73 | 13·29 | 10·22 |
| Total marriages | 32·04 | 57·98 | 19·21 | 28·96 | 16·33 | 19·23 | 9·48 | 9·48 | 5·29 | 5·12 |
In all the preceding proportions and numbers the Chinese have been excluded.
Occupiers of houses were directed, in filling up census schedules, to see that Chinese should be set down as unable to read or write unless they could read and write English. Out of a total of 2,857 Chinese, 385 were returned in conformity with these instructions as capable of reading and writing English, 20 as able to read only, and 2,452 as not able to read or write; but of these 2,452, no less than 823 are stated to be able to read and write Chinese, and 17 to read only in that language.
An inquiry was made as to the number of children attending schools of various kinds, besides those receiving tuition at home; also, as to the number of Sunday-school scholars and teachers. While information is always obtainable from the Educational Department as to children attending public schools, the number at private schools can only be got at by means of the census, or by special applications made for the purpose to the proprietors, which is done once a year. The census figures serve to check the returns received from private schools; while for Sunday-schools and tuition at home there is no other source of information.
The compiled tables give the attendance for March, 1901:—
| Total. | Boys. | Girls. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At Government primary schools | 132,911 | 68,360 | 64,551 |
| At college, high, grammar, or private schools | 19,837 | 8,994 | 10,843 |
| Being taught at home | 5,055 | 2,215 | 2,840 |
Comparison with former censuses shows increasing numbers at the schools, but latterly a decline in the home tuition. Possibly a gradually advancing density of population in the country districts accounts for the diminution in the children taught at home. The figures at last five successive censuses are:—
| At Government Primary Schools. | At College, High, Grammar or Private Schools. | Receiving Tuition at Home. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| April, 1881 | 87,811 | 13,538 | 7,348 |
| March, 1886 | 110,644 | 14,948 | 7,567 |
| April, 1891 | 124,063 | 17,047 | 8,178 |
| April, 1896 | 133,364 | 17,600 | 6,352 |
| March, 1901 | 132,911 | 19,837 | 5,055 |
As to attendance at Sunday-schools, a comparison can only be made if the teachers be included with the scholars. Proceeding on these lines a large development is found since 1878:—
| Census Year. | Totals. | Males. | Females. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1878 | 62,273 | 30,707 | 31,566 |
| 1886 | 99,884 | 48,509 | 51,375 |
| 1896 | 116,045 | 54,063 | 61,982 |
| 1901 | 118,412 | 54,834 | 63,578 |
The excess of females over males would seem to grow greater, considered numerically, as well as in proportion to the numbers, with time.
Comparing the results as to teachers and pupils separately for 1901 and 1896, an increase of 188 is found in the Sunday-school teachers, and of 2,179 in the number of scholars, the increase being more marked in the female than in the male sex.
| Census Year. | Teachers. | Pupils. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Males. | Females. | Total. | ||
| 1901 | 11,299 | 50,932 | 56,181 | 107,113 |
| 1896 | 11,111 | 50,096 | 54,838 | 104,934 |
| Increase | 188 | 836 | 1,343 | 2,179 |
It has been found impossible to collect the full statistics relating to schooling for the year 1902 in time for this work, and the figures for the previous year are accordingly given.
The number of schools, teachers, and scholars, as in December, 1901, are shown in the following summary:—
| Description of Schools. | Number of Schools. | Teachers. | Scholars. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUROPEAN. | |||||
| Public (Government) schools (scholars other than Maoris and half-castes) |  | 1,677 | 3,623* |  | 128,663 |
| Public (Government) schools (half-castes living among Europeans) | 1,072 | ||||
| Colleges, grammar, and high schools (aided or endowed) | 25 | 157 | 2,899 | ||
| Private and denominational schools (excluding Maori scholars) | 309 | 843 | 15,344 | ||
| Industrial schools and orphanages | .. | .. | 774 | ||
| Native village schools, European children attending | .. | .. | 338 | ||
| Private Native boarding - schools, European children attending | .. | .. | 14 | ||
| School for Deaf-mutes | 1 | .. | 49 | ||
| Jubilee Institute for Blind | 1 | 1 | 16 | ||
| Totals—European | 2,013 | 4,624 | 149,169† | ||
| Description of Schools. | Number of Schools. | Teachers. | Scholars. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* And 176 sewing-mistresses. † In addition to the above, the census results
showed that 5,055 children (2,215 boys, ‡ And 15 sewing-mistresses. | |||||
| NATIVE. | |||||
| Native village schools supported by Government (excluding European children stated above) | 91 | 157‡ | 2,935 | ||
| Private Native boarding-schools (maintenance of scholars paid by Government) |  | 4 | 11 |  | 78 |
| Private Native boarding-schools (maintenance of scholars paid from endowments) | 134 | ||||
| Private Native day-schools | 3 | 6 | 96 | ||
| Public (Government) schools, Maoris attending | .. | .. | 1,382 | ||
| Public (Government) schools, half-castes living as Maoris attending | .. | .. | 234 | ||
| Private and denominational schools for Europeans, Maoris attending | .. | .. | 53 | ||
| Totals—Native | 98 | 174 | 4,912 | ||
Thus at the end of 1901 there were 2,109 schools of all classes at which members of the European and Maori races were being educated. This was an increase of 9 on the number in 1900. The public primary schools numbered 1,677 in 1901, against 1,674 in 1900. The number of aided or endowed colleges, grammar, and high schools was 25, one less than in the previous year. The number of private schools from which returns were received by the Registrar-General was 309, an increase of 5. There were also ten industrial schools and orphanages, public and private, as well as a school for deaf-mutes subsidised by Government, and a school for the blind, which have not been included in the increase shown for the year.
The number of schools established for the education of the Native or Maori race was 98, two more than in 1900.
Education at the public schools is free (except that, at such as are also district high schools, fees are charged for the teaching of the higher branches) and purely secular. The attendance of all children between the ages of 7 and 13 is compulsory, except when special exemptions are granted, or a child is being otherwise sufficiently educated.
Compared with 1900 there was in 1901 an increase of 627 in the number of pupils belonging to the public schools at the end of the year, and the average attendance shows an increase of 50 for the whole year and 856 for the fourth quarter.
| SCHOOL ATTENDANCE AND YEARLY INCREASE FROM 1877 TO 1901. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | School Attendance. | Yearly Increase on | |||||||
| Number belonging at Beginning of Year. | Number belonging at End of Year. | Average Attendance* | Average Attendance expressed as Percentage of Roll-number. | Number belonging at Beginning of Year. | Number belonging at End of Year. | Average Attendance† | |||
| Fourth Quarter. | Whole Year. | Fourth Quarter. | Whole Year. | ||||||
* From 1877 to 1893 (inclusive) the
“strict” average is given, and for
subsequent years † From 1877 to 1894 (inclusive) the increase on
the “strict” average is given, and
for | |||||||||
| 1877 | … | 55,688 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 1878 | 50,849 | 65,040 | 49,435 | 45,521 | … | … | 9,352 | … | … |
| 1879 | 59,707 | 75,566 | 57,301 | 53,067 | 73·8 | 8,858 | 10,526 | 7,866 | 7,546 |
| 1880 | 68,124 | 82,401 | 62,946 | 60,625 | 74·6 | 8,417 | 6,835 | 5,645 | 7,558 |
| 1881 | 74,359 | 83,560 | 63,009 | 61,822 | 74·2 | 6,235 | 1,159 | 63 | 1,197 |
| 1882 | 76,309 | 87,179 | 66,426 | 63,709 | 73·6 | 1,950 | 3,619 | 3,417 | 1,887 |
| 1883 | 79,416 | 92,476 | 70,077 | 67,373 | 74·0 | 3,107 | 5,297 | 3,651 | 3,664 |
| 1884 | 84,883 | 97,238 | 74,650 | 72,657 | 75·1 | 5,467 | 4,762 | 4,573 | 5,284 |
| 1885 | 90,670 | 102,407 | 80,183 | 78,327 | 76·6 | 5,787 | 5,169 | 5,533 | 5,670 |
| 1886 | 95,377 | 106,328 | 83,361 | 80,737 | 76·1 | 4,707 | 3,921 | 3,178 | 2,410 |
| 1887 | 99,206 | 110,919 | 87,386 | 85,637 | 77·0 | 3,829 | 4,591 | 4,025 | 4,900 |
| 1888 | 103,534 | 112,685 | 90,849 | 90,108 | 79·3 | 4,328 | 1,766 | 3,463 | 4,471 |
| 1889 | 104,919 | 115,456 | 94,308 | 93,374 | 80·3 | 1,385 | 2,771 | 3,459 | 3,266 |
| 1890 | 108,158 | 117,912 | 96,670 | 94,632 | 79·9 | 3,239 | 2,456 | 2,362 | 1,258 |
| 1891 | 110,665 | 119,523 | 96,264 | 97,058 | 80·3 | 2,507 | 1,611 | [-406] | 2,426 |
| 1892 | 112,279 | 122,620 | 100,917 | 99,070 | 80·0 | 1,614 | 3,097 | 4,653 | 2,012 |
| 1893 | 114,305 | 124,686 | 99,872 | 98,615 | 78·5 | 2,026 | 2,066 | [-1,045] | [-455] |
| 1894 | 116,819 | 127,300 | 107,032 | 104,996 | 81·8 | 2,514 | 2,614 | 6,279 | 4,875 |
| 1895 | 119,900 | 129,856 | 108,708 | 108,394 | 82·8 | 3,081 | 2,556 | 1,676 | 3,398 |
| 1896 | 122,425 | 131,037 | 110,274 | 110,517 | 83·3 | 2,525 | 1,181 | 1,566 | 2,123 |
| 1897 | 123,533 | 132,197 | 111,952 | 112,328 | 83·9 | 1,108 | 1,160 | 1,678 | 1,811 |
| 1898 | 123,892 | 131,621 | 109,561 | 111,636 | 83·4 | 359 | [-576] | [-2,391] | [-692] |
| 1899 | 123,207 | 131,315 | 109,050 | 110,316 | 82·6 | [-685] | [-306] | [-511] | [-1,320] |
| 1900 | 123,416 | 130,724 | 111,498 | 111,747 | 84·1 | 209 | [-591] | 2,448 | 1,431 |
| 1901 | 122,727 | 131,351 | 112,354 | 111,797 | 84·1 | [-691] | 627 | 856 | 50 |
In the report of the Minister of Education the figures are thus commented upon:—
The average of the weekly roll-numbers throughout the year 1901 was almost the same as for the year 1900, the figures being 132,869 for 1901 and 132,897 for 1900. The number on the rolls at the end of the year 1901 shows an increase of 627 over the number on the rolls in December, 1900, the actual totals being respectively 131,351, for the former year and 130,724 for the latter. An analysis of these figures shows that there was an increase of 687 in the children under nine years of age, a decrease of 88 in the number between the ages of nine and fourteen, and a slight increase (28) in the number of children over fourteen years of age. The increase in the number of young children enrolled raises the expectation of an increased roll-number for the present year, 1902; while the establishment of district high schools should have the effect of increasing the number of pupils over fourteen years of age, an effect which will probably be somewhat more marked as time goes on.
The standard of regularity of attendance reached in 1900 was maintained in 1901, the total average attendance being again 84·1 per cent. of the average weekly roll-number, against 82·6 in 1899. There seems to be good reason to hope that, partly through the operation of the School Attendance Act of 1901, partly from other causes, attendance at public schools may still further improve. It is, however, interesting to note in this connection that for the primary day-schools in England in 1900 the average attendance was 82·1 per cent. of the number on the registers, in Scotland 70 per cent., and in Ireland 64·1 per cent. As nearly as can be ascertained, the average attendance in the primary schools of the various Australian Colonies during the year 1900, expressed as a percentage of the net enrolment, was as follows: New South Wales, 72·3; Victoria, 67·54; Queensland, 72·7; South Australia, 69·0; Western Australia, 81·2; Tasmania, 74·9. The significance of these figures and the importance of maintaining a high standard of regularity of school attendance will be better appreciated if it is remembered that the leading authorities on juvenile depravity and crime are agreed that these social faults have for the most part their origin in truancy and in the acquirement of the nomadic habit; and accordingly the margin between a low rate and a high rate of school attendance, although affected in some degree by sparse settlement, represents to a large extent those individual children who will, if still neglected, go to swell our industrial schools and reformatories, and, at a later age, our prisons, refuges, and lunatic asylums.
The subjects of instruction at the primary schools are required by the Education Act to be the following: Reading, writing, arithmetic, English grammar and composition, geography, history, elementary science and drawing, object-lessons, vocal music, and (in the case of girls) sewing and needlework, and the principles of domestic economy. Provision must also be made for the instruction in military drill of all boys in these schools.
“The Manual and Technical Instruction Act, 1900,” with its amendments of 1902, provides for manual and such subjects of technical instruction as are prescribed by regulations under this statute being included in the list of subjects named in the Education Act.
The Manual and Technical Instruction Act of 1900, and the amending Act of 1902, provides for public instruction in such manual and technical subjects as are set forth in the regulations thereunder. The same Acts provide also for the instruction in elementary handwork of pupils attending primary or secondary schools.
All classes recognised under the Act are eligible for grants in aid of necessary buildings, furniture, and apparatus, and for capitation. During 1902 capitation was paid on classes for drawing (various branches), painting, modelling, design, wood-carving, architecture, carpentry and joinery, plumbing, painters' and decorators' work, mechanical and electrical engineering, natural and experimental science (various branches), languages, mathematics, commercial subjects, cookery, laundry work, dressmaking, tailoring, wool-sorting, and singing.
Special classes maintained by Government grants for the training of public-school teachers in the subjects of manual and technical instruction prescribed for school classes have been established in several of the education districts of the colony.
The subjects taken up in school classes included cookery, woodwork, cottage gardening, swimming and life-saving, first aid and ambulance, dressmaking, and laundry work.
There were (1902) fifteen Technical or Art Schools, at which 360 recognised classes, attended by about 4,500 students, were conducted. Several new schools are in course of erection, while others are contemplated.
In connection with the Canterbury College there is an endowed School of Engineering and Technical Science, the students in which work for the university degree of B.Sc. in engineering. One hundred and ninety-two students attended in 1902.
The Canterbury Agricultural College has an endowment of over 60,000 acres of land, and possesses extensive buildings, and an experimental farm of a very complete character. The students work for the university degree of B.Sc. in agriculture. There were thirty students in 1902.
There are several Schools of Mines located in districts in which mining is actively carried on, and the Otago University maintains a professorial chair of mining and metallurgy, to which the Government makes an annual grant of £500. The number of students in mining in 1902 was over three hundred, sixty of whom were at the Otago University.
With the view of encouraging attendance at recognised technical schools and classes, arrangements have been made with the Railway Department by which teachers of classes registered with the Minister of Education may give certificates to their pupils which will enable them to obtain railway tickets at special rates.
The following table shows the results of examinations conducted in the colony on behalf of the Science and Art Department, London, and of the City and Guilds of London Institute:—
| LONDON TECHNICAL AND ART EXAMINATIONS, 1901. [“C” represents candidates; “P” passes.] | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects of Examination. | Auckland. | Wanganui. | Wellington. | Pahiatua. | Napier. | Christchurch. | Timaru. | Dunedin. | ||||||||
| SCIENCE AND ART DEPARTMENT. | C | P | C | P | C | P | C | P | C | P | C | P | C | P | C | P |
| Art. | ||||||||||||||||
| Drawing with chalk on the blackboard | 15 | 13 | … | … | … | … | … | … | 5 | 5 | 1 | .. | … | … | … | … |
| Geometrical drawing (art) | 5 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 3 | … | … | … | .. | 2 | 2 | … | … | 18 | 11 |
| Perspective | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | 3 | 1 | … | … | 10 | 1 |
| Model drawing | 22 | 20 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 27 | 22 |
| Freehand drawing in outline | 21 | 13 | 14 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 50 | 20 |
| Drawing in light and shade | 14 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 4 | … | … | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 13 | 10 |
| Principles of ornament | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 1 | … | … | … | 2 | 1 |
| Design | … | … | 1 | l | 7 | 2 | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … |
| Painting from still life | 5 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 4 | 3 | |
| Painting from still life ornament | .. | … | 1 | … | … | . | … | … | … | ... | 1 | 1 | … | … | 2 | 2 |
| Drawing from the antique | 6 | 6 | 1 | … | 2 | 2 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 5 | 3 |
| Drawing the antique from memory | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | .. | … | ... | ... | 1 | 1 |
| Drawing from life | .. | … | 3 | .. | 8 | 2 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | .. | … | 2 | 1 |
| Students' works | 19 | 9 | 15 | 6 | 22 | 6 | … | … | 13 | … | 4 | 2 | … | … | 3 | 1 |
| Science. | ||||||||||||||||
| Practical plane and solid geometry | … | … | 7 | 5 | 2 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | .. | 2 | … | 4 | 3 |
| Machine construction and drawing | 16 | 13 | … | … | 10 | 10 | … | … | … | … | … | … | .. | … | 20 | 14 |
| Building construction | 5 | 4 | 1 | … | 11 | 9 | … | … | … | … | 2 | 2 | … | … | 7 | 6 |
| Mathematics | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | … | .. | … | … | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Practical mathematics | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Steam | 9 | 7 | … | … | 5 | 3 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 |
| Magnetism and electricity | 6 | 2 | … | … | 2 | 2 | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … |
| Principles of agriculture | .. | .. | 2 | 2 | … | … | … | … | … | … | .. | … | … | … | … | … |
| CITY AND GUILDS OF LONDON INSTITUTE. | ||||||||||||||||
| Woodwork, final | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 6 | 5 | … | … | … | … |
| Carpentry and joinery (ordinary) | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 |
| Mechanical engineering | 3 | 2 | … | … | 4 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | 8 | 7 |
| Plumbing (preliminary) | … | … | … | … | 2 | 2 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Plumbing (ordinary) | .. | .. | … | … | 1 | 1 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Plumbing(honours) | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | .. | 5 | 4 |
| Painters' and decorators' work | 3 | … | … | … | … | … | . | … | … | … | 3 | 3 | … | … | … | … |
| Gas manufacture (honours) | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Electric light and power (preliminary) | … | … | … | … | 10 | 5 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Electric light and power | … | … | … | … | 6 | 3 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Telegraphy (honours) | … | … | … | .. | … | .. | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … |
| Lithography (preliminary) | … | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Lithography (ordinary) | … | … | … | 1 | 1 | .. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
| Totals | 157 | 111 | 69 | 33 | 118 | 71 | 7 | 2 | 41 | 22 | 44 | 33 | 10 | 6 | 186 | 115 |
| Total of papers, 632 total of passes, 393. | ||||||||||||||||
In the twenty-fifth annual report, the Minister of Education remarks on manual training and technical instruction:—
During the year steady progress has been in the formation of adult classes for technical instruction, and there has been a large increase—more than fivefold—in the classes for manual instruction in public schools, principally in the direction of introducing into the work of the preparatory classes and into the lower standard classes exercises based upon kindergarten methods. This feature is sound as far as it goes, as it seems to show that the spirit of the new movement is being rightly understood, for the change indicated by the introduction of hand-work into the school is not one affecting the mere details or machinery of school work, but is more fundamental in its character. Changes that affect only the externals of the school system, or only increase the number of disconnected subjects in the school syllabus, are sure to turn out in the end to be mere temporary devices. It has been the fashion to speak of that portion of a man's education that he receives at school as a preparation for life; in truth, a man's education goes on throughout his whole life, and the time spent at school is not merely a preparation for life, it is part of life itself. If the manual dexterity and the regular and easy co-ordination of hand and eye and brain that lead to the development of skill in the workman or the engineer, the artist or the surgeon, be not developed in youth, then there is a gap between the school-life and the after-life that is unnatural and prejudicial to the success of the adult; for there are few occupations in which some degree of manual skill is not at one time or another useful, and none in which men or women can afford to be without that all-round training of the mind that can be obtained only by combining the exercise of the muscular activities with that of the observation, reason, and memory. The instincts of the child herein guide him aright; he is constantly examining objects and seeking for some fresh outlet for his muscular activities. (As every instinct corresponds to some reality, no instinct should be overlooked; but every instinct should either be trained or be guided aright in the years of childhood.) These instincts are not such as mark the brute, but belong to the higher human intelligence, and they must therefore be taken seriously as indications of undeveloped powers, which need to be directed and disciplined, not suppressed, until they appear as scientific habit and manual skill in the youth and the adult. The new method of treatment accordingly extends not to one or two subjects of the curriculum, but, more or less, to nearly all. Besides the advantage derived from the fact that manual training brings into the school course a natural co-ordination by co-ordinating all the subjects of that course with life, its introduction into the schools gives opportunity to discover aptitudes that would otherwise perhaps be unsuspected, and to develop the pupils in such a way that they make intelligent use of this opportunity. It is evident that only a beginning can be made in the elementary school; hence the necessity for carrying on the work more completely in continuation and technical classes, and in the secondary schools and university colleges.
Professor John Dewey, one of the foremost men in matters of education in the United States at the present time, lays great stress on the points just referred to, and pertinently asks, “Now that the great value of manual training has come to be recognised in secondary” (and we may add, primary) “schools, why should not all the pupils have the benefit of it?” Again, he says, “Domestic science should be classed with science studies, and as such be provided with a laboratory.” And, if domestic science, why not, it may be added, agricultural science and the practical and scientific work that forms the basis of the other industries of life? In the elementary school all that can be done is to keep this aim in view, and to shape the course so that a firm foundation may be laid. A sound though rudimentary course of nature-study, the continuous training of hand and eye, and the development, by easy measurements, experiments, and observations performed by each child for himself or herself, of a habit of knowing things themselves, are the main characteristics that should mark this side of a pupil's work in the public school.
There are now (July, 1902) 360 classes established in various parts of the colony under the Manual and Technical Instruction Act, exclusive of school classes. The number last year was 293. Of the total of 360, 35 are continuation classes; the remainder are classes for manual or technical instruction. The number of school classes in operation last year was 132; the number in operation now (July, 1902) is 700. Of these, 18 are established in connection with secondary schools; the rest are in public elementary schools. Of the latter, 231 are connected with town schools, and 451 with schools in country districts. It is hoped that with the issue of the new standard syllabus shortly to be gazetted there will be a marked increase in the number of “hand-work” classes established in connection with the upper standards.
Last year (1901) special grants, amounting to £1,875 in all, were given to the Boards of Education to enable them to provide training for their teachers in those subjects prescribed by the regulations under the head of “Hand-work” in school classes. The grant, which is intended to cover the cost of the training in manual and technical work of pupil-teachers and normal-school students as well as of teachers already on the staffs of the schools, is to be renewed this year. From the reports that have been received, the several amounts seem to have been used in a careful and judicious way, and no doubt results will show that the money has been wisely expended.
New regulations were issued at the beginning of the present year, removing many of the restrictions that seemed necessary at first, and simplifying the mode in which grants are obtained. Further experience shows that still more simplification is possible, and the regulations will be further amended in this direction.
Many local bodies having shown a disposition to assist in promoting technical education, but being doubtful as to their right to representation on the bodies of managers of associated classes, a short Bill will be introduced to make it clear that such local bodies have the same powers as the associations already specifically named in the Manual and Technical Instruction Act of 1900. The result will probably be the formation of strong “associated classes” in all the chief centres, under the Boards of Education as controlling authorities, but having their own managers, representing all the bodies combining in the work. Such a course will probably tend both to efficiency and economy of money and of effort.
“The Manual and Technical Education Act, 1902,” gives effect to the powers indicated in the foregoing paragraph.
In the following table a statement is given of the expenditure upon manual and technical instruction during the year:—
| STATEMENT OF EXPENDITURE FOR YEAR ENDING 31ST DECEMBER, 1901. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | ||||
| Capitation | 2,805 | 12 | 11 | |||
| Subsidy of pound for pound on contributions | 729 | 13 | 5 | |||
| Grants:— | £ | s. | d. | |||
| Buildings and apparatus | 3,440 | 8 | 10 | |||
| Class material | 156 | 3 | 5 | |||
| 3,596 | 12 | 3 | ||||
| Training of Teachers:— | ||||||
| Auckland Education Board | 250 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Taranaki Education Board | 100 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Wanganui Education Board | 150 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Wellington Education Board | 200 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Hawke's Bay Education Board | 150 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Marlborough Education Board | 75 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Nelson Education Board | 125 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Grey Education Board | 75 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Westland Education Board | 75 | 0 | 0 | |||
| North Canterbury Education Board | 200 | 0 | 0 | |||
| South Education Board | 125 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Otago Education Board | 200 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Southland Education Board | 150 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 1,875 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Railway fares of teachers attending training-classes | 256 | 0 | 9 | |||
| Railway fares of instructors of training-classes | 47 | 3 | 11 | |||
| Railways fares of students attending registered classes of individuals | 175 | 8 | 8 | |||
| Expenses in connection with Examinations:— | ||||||
| Science and Art Board of Education, South Kensington | 63 | 10 | 0 | |||
| City and Guilds of London Institute | 13 | 12 | 10 | |||
| 77 | 2 | 10 | ||||
| Art posters | 25 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Inspectors:— | ||||||
| Salaries | 659 | 10 | 10 | |||
| Travelling-expenses | 203 | 19 | 3 | |||
| 863 | 10 | 1 | ||||
| Advertising and sundries | 56 | 10 | 3 | |||
| Total | £10,507 | 15 | 1 | |||
| MANUAL AND TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION, 1901. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School or Instructor. | Subjects of Instruction (grouped), and Average Attendance. | Payments. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Freehand (from Flat and Round) and Shading. | Drawing from Nature, Painting, and Modelling. | Mechanical Drawing and Engineering, and Machine Construction. | Geometry and Perspective. | Design and Ornament. | Architecture, and Building Construction. | Mathematics. | Natural and Experimental Science (Botany, Chemistry, and Physics). | Woodwork. | Plumbing (Theory and Practice). | Domestic Instruction. | English, and Commercial Subjects, and Latin and French. | Singing and Elocution. | Kindergarten Work. | Capitation. | Grants for Building Apparatus, and Material. | Pound-for-Pound Subsidy on Voluntary Contributions. | |||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |||||||||||||||
| Technical Classes Association, Auckland | 14 | .. | 2 | 4 | 8 | 14 | .. | .. | 23 | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 91 | 3 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| “Elam” School of Art, Auckland | 25 | .. | .. | 58 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .1 | 172 | 5 | 2 | .. | 150 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Payton, Mr. E. W., Auckland | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 7 | 1 | .. | .. | ||||
| Robinson, Mr. W. I., Auckland | .. | .. | 52 | 12 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11 | 10 | 1 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Auckland— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Devonport Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Wanganui— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical School, Wanganui | 19 | 28 | 11 | 21 | 2 | 10 | .. | .. | 22 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 121 | 14 | 6 | .. | 10 | 10 | 0 | ||
| Technical classes, Palmerston North | 17 | 19 | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | … | .. | 91 | 14 | 4 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical classes, Hawera | 8 | 15 | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 34 | 1 | 4 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical classes, Eltham | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9 | 13 | 1 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Wellington— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical School, Wellington | 34 | 266 | 23 | 107 | 29 | 32 | 35 | .. | 63 | 141 | 10 | 93 | .. | .. | 830 | 19 | 5 | 383 | 11 | 8 | 152 | 0 | 0 |
| Technical classes, Pahiatua | 17 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 2 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical classes, Carterton | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 4 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes Association, Masterton | 36 | .. | 18 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 8 | 30 | . | .. | 14 | .. | .. | 47 | 11 | 3 | .. | 149 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Caverhill, Miss L. L., Petone | 17 | 17 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 8 | 10 | 8 | .. | .. | ||||
| Anderson, Mr. R. N., Napier | .. | 42 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 19 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Napier— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical School, Napier | 17 | 18 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 34 | 19 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Napier Public School | 104 | .. | .. | .. | 104 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 48 | 11 | 7 | .. | .. | ||||
| Spit School | .. | .. | .. | .. | 45 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11 | 3 | 10 | .. | .. | ||||
| Port Ahuriri Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | 58 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20 | 11 | 0 | .. | .. | ||||
| Beecroft, Miss M., Hastings | 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Grey— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greymouth District High School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 15 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Westland— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kumara Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 19 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21 | 12 | 8 | .. | .. | ||||
| Canterbury College— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| School of Art, Christchurch | 162 | 95 | .. | 65 | 28 | 37 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 288 | 10 | 3 | 658 | 0 | 0 | .. | ||
| School of Engineering and Technical Science, Christchurch | 61 | .. | 58 | 63 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 108 | 10 | 3 | .. | .. | ||||
| School of Domestic Instruction, Christchurch | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 90 | .. | .. | .. | 134 | 11 | 0 | 66 | 7 | 6 | .. | ||
| Education Board, North Canterbury— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| School of Domestic Instruction | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 376 | .. | .. | .. | 61 | 12 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Christchurch School Classes | 56 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 6 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Amberley Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 25 | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 2 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Fendalton Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 3 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Addington Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 33 | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 3 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes, Leeston | 17 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9 | 1 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes, Lyttelton | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 100 | 0 | 0 | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes Association, Ashburton | .. | .. | .. | 6 | .. | .. | 2 | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 25 | .. | .. | 3 | 18 | 2 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes Association, Timaru | 16 | 13 | 18 | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | .. | .. | 81 | 152 | .. | .. | 63 | 1 | 5 | .. | 79 | 17 | 6 | ||
| High School Board, Timaru— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Classes at Timaru Girls' High School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 18 | 0 | .. | ||||
| Education Board, South Canterbury— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timaru Main Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 153 | 2 | 16 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Timaru South Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 70 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 14 | 0 | .. | ||
| Waimataitai Public School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 91 | 1 | 9 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Temuka District High School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 79 | 1 | 16 | 10 | .. | .. | ||||
| Technical Classes Association, Dunedin | .. | .. | 39 | .. | .. | 10 | 59 | 39 | 36 | 16 | 74 | 313 | 17 | .. | 91 | 9 | 10 | 2,232 | 18 | 10 | 179 | 18 | 3 |
| Education Board, Otago— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| School of Art, Dunedin | 110 | 63 | 24 | 80 | 20 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 354 | 16 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Classes at Tokomairiro District High School | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 29 | 3 | 8 | .. | ||||
| Kidston-Hunter, Mr. A., Dunedin | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 3 | 9 | .. | .. | ||||
| Education Board, Southland— | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Classes, Associated, Invercargill | 9 | 5 | 26 | .. | .. | 11 | 6 | 8 | 17 | .. | 51 | 56 | .. | .. | 42 | 7 | 0 | 114 | 18 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 6 |
| Technical Classes, Mataura | .. | .. | 8 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11 | 32 | .. | .. | 8 | 11 | 6 | .. | .. | ||||
| Totals | 754 | 581 | 279 | 427 | 294 | 130 | 110 | 73 | 251 | 166 | 768 | 685 | 17 | 393 | 2805 | 12 | 11 | 3596 | 12 | 3 | 729 | 13 | 5 |
The introduction of university education into New Zealand was effected by the Superintendent and Provincial Council of Otago, who in 1869 passed an Ordinance under which the University of Otago was established. Following closely on the founding of this institution was the establishment of the University of New Zealand under an Act of the General Assembly, “The New Zealand University Act, 1870.” This University subsequently received a Royal charter, whereby the degrees which it confers are declared entitled to “rank, precedence, and consideration” throughout the British Empire “as fully as if the said degrees had been conferred by any university of the United Kingdom.” It was apparently contemplated by Parliament (vide section 19 of the Act last quoted) that the New Zealand University and the Otago University should be amalgamated; but the negotiations for this purpose having failed the two institutions remained for some time distinct bodies. In the year 1874, however, the University of Otago surrendered or put in abeyance its power of conferring degrees, and became affiliated to the University of New Zealand, and at the same time it was stipulated that the University of New Zealand should not directly exercise functions of teaching.
In 1902 an amendment Act was passed reconstituting the Senate, which now consists of twenty-four members or Fellows, five to be elected by each of the four University College districts, that is to say—two by each governing body, two by each District Court of Convocation, and one by each Professorial Board. The remaining four members are nominated by the Governor in Council.
In the year 1873 the Superintendent and Provincial Council of Canterbury passed an Ordinance for founding “The Canterbury College,” and the college was accordingly established with the same standard of university education as that of the University of Otago, but without the power of conferring degrees.
In December, 1878, a Royal Commission on University and Secondary Education was appointed by the Governor, which met in July, 1879, and reported that two colleges, with an income of £4,000 each, ought to be established in Auckland and Wellington, and that suitable buildings, at a cost of £12,500 each, should be erected in those cities. In the following year the Royal Commission repeated these recommendations.
“The Auckland University College Act, 1882,” which became law on the 13th September in that year, definitely established the college, and endowed it with a statutory grant of £4,000 per annum. By “The Auckland University College Reserves Act, 1885,” three blocks of land, containing about 10,000 acres each, and a block containing about 354 acres, which had been devoted to the purpose of promoting higher education in the Province of Auckland, became vested in the Council of University College.
The Auckland University College was affiliated to the University of New Zealand by the Senate of the university on the 6th March, 1883, and on the 21st May in the same year the college was opened by the Governor.
Nothing was done for Wellington until the year 1894, when an Act was passed entitled “The Middle District of New Zealand University College Act, 1894,” which said “There shall be established in the City of Wellington a college to be connected with the University of New Zealand,” and provision was made for a governing body to be called the Council, but no provision was made for any pecuniary grant nor any endowment, and, though certain members of the Council were appointed, nothing could be done for want of funds.
Not until 1897 were the needs of Wellington actually attended to. In the session of Parliament that year the Right Hon. Mr. Seddon, P.C., Premier of the colony, introduced the Victoria College Act: an Act, as stated in the preamble, “to promote higher education by the establishment of a College at Wellington in commemoration of the sixtieth year of the reign of Her Majesty Queen Victoria,” the college being intended to embrace in its work the Provincial Districts of Wellington, Taranaki, Hawke's Bay, Nelson, Marlborough, and Westland. The Act was passed on the 22nd December, 1897, and the Council was formed as provided in the Act, and the work of organization was begun. The Act provides for the payment out of the Consolidated Fund of a grant of £4,000 a year, and also requires the Council to give six scholarships each year, called “Queen's Scholarships,” to persons of either sex under the age of fourteen years, upon the results of an examination under such conditions as the Council may provide. The Act further sets apart a parcel of land 4,000 acres in extent in the Nukumaru Survey District (Wellington Provincial District) as an endowment for the college.
The Council of the college has established six chairs: classics, English, mathematics and mathematical physics, chemistry, physics, and biology; and lectureships in modern languages, mental science, jurisprudence and constitutional history, general history, and political economy and law. It is intended as funds allow to add other subjects.
The New Zealand University is not a teaching body, as above explained, undergraduates hitherto for the most part keeping their terms at one or other of the affiliated institutions: the Auckland University College, the Victoria College, the Canterbury College, and the University of Otago, each of which has now a staff of professors and lecturers. On the 1st June, 1902, the number of graduates who had obtained direct degrees was 819.
The number of undergraduates on the roll of the University at that date was 2,637 (exclusive of such as had not performed any academical act for a period of ten years), but only 1,468 were keeping terms (not including undergraduates who had not, in the last two years, entered at a college or come up for any college or university examination), of whom 955 were males and 513 females. One hundred and four of the males and twenty-three of the females were medical students. The numbers of students attending lectures at the affiliated institutions during the year 1901–1902 were as follow: At the Auckland University College, 111 matriculated and 71 non-matriculated; at Canterbury College, 148 matriculated and 72 non-matriculated; at the Otago University, 210 matriculated and 27 non-matriculated. The Victoria College, before-mentioned, affords further facilities for university students, and in June, 1902, had a total of 144 students on the roll—112 matriculated and 32 non-matriculated.
There were 309 private schools in the colony at the end of 1901, an increase of 5 on the number in 1900: 30 were for boys, 74 for girls, and 205 for children of both sexes. The number of pupils attending them was 15,344—namely, 6,244 boys and 9,100 girls, not counting 53 Maoris, 23 boys and 30 girls. The number of European pupils at these schools was less than in 1900 by 211. Of the private schools, 129 were Roman Catholic, with an attendance of 10,448 pupils.
The following gives, for the past ten years, the number of private schools and of Europeans attending them, the number of Roman Catholic schools and pupils being also shown separately:—
| Year. | Number of Private Schools. | Pupils. | Included in Previous Numbers. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys. | Girls. | Totals. | Roman Catholic Schools. | Pupils at Roman Catholic Schools. | ||
| 1892 | 274 | 6,321 | 8,135 | 14,456 | 105 | 10,111 |
| 1893 | 299 | 6,431 | 8,491 | 14,922 | 111 | 10,263 |
| 1894 | 302 | 6,117 | 8,510 | 14,627 | 117 | 9,953 |
| 1895 | 298 | 6,187 | 8,472 | 14,659 | 114 | 10,458 |
| 1896 | 283 | 5,845 | 8,102 | 13,947 | 115 | 9,590 |
| 1897 | 278 | 5,974 | 8,473 | 14,447 | 120 | 9,642 |
| 1898 | 294 | 6,043 | 8,739 | 14,782 | 124 | 10,175 |
| 1899 | 307 | 6,219 | 9,076 | 15,295 | 133 | 10,526 |
| 1900 | 304 | 6,152 | 9,403 | 15,555 | 132 | 10,687 |
| 1901 | 309 | 6,244 | 9,100 | 15,344 | 129 | 10,448 |
The total number of children of European descent (including such half-castes as live among Europeans) known to be receiving education at school at the end of 1901 was 149,169; of these, 141,339 were from 5 to 15 years of age. The census showed also 5,055 children receiving tuition at home in 1901, against 6,352 in 1896. No doubt increased school accommodation in country places does away with the need for tutors and governesses to a certain extent.
The distribution of the private schools in the various provincial districts of the colony is shown in the next page:—
| PRIVATE AND DENOMINATIONAL SCHOOLS, 1901.—SUMMARY BY PROVINCIAL DSTRICTS. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial Districts. | Number of Schools. | Number of Teachers. | Number of Scholars. | Daily Average Attendance. | |||||||||
| Boys. | Girls. | Mixed. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | |
| * Exclusive of 53 Maoris (23 boys, 30 girls). | |||||||||||||
| Auckland | 4 | 19 | 59 | 82 | 31 | 168 | 199 | 1,270 | 2,009 | 3,279 | 1,081 | 1,780 | 2,861 |
| Taranaki | … | 2 | 11 | 13 | … | 28 | 28 | 195 | 333 | 528 | 164 | 289 | 453 |
| Hawke's Bay | 4 | 4 | 9 | 17 | 13 | 41 | 54 | 491 | 575 | 1,066 | 432 | 496 | 928 |
| Wellington | 6 | 15 | 36 | 57 | 42 | 148 | 190 | 1,318 | 1,913 | 3,231 | 1,191 | 1,730 | 2,921 |
| Marlborough | 1 | … | 5 | 6 | … | 12 | 12 | 155 | 145 | 300 | 125 | 123 | 248 |
| Nelson | 3 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 11 | 29 | 40 | 387 | 469 | 856 | 361 | 430 | 791 |
| Westland | 1 | 2 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 25 | 28 | 264 | 325 | 589 | 219 | 282 | 501 |
| Canterbury | 7 | 18 | 37 | 62 | 15 | 144 | 159 | 1,154 | 1,657 | 2,811 | 992 | 1,482 | 2,474 |
| Otago | 4 | 9 | 33 | 46 | 14 | 119 | 133 | 1,010 | 1,674 | 2,684 | 820 | 1,408 | 2,228 |
| Totals | 30 | 74 | 205 | 309 | 129 | 714 | 843 | 6,244 | 9,100 | 15,344* | 5,385 | 8,020 | 13,405 |
NOTE.—Denominational schools, such as Roman Catholic and Anglican, are included in the above as private schools. Particulars for the Roman Catholic schools in December, 1901, are as under:—
| SUMMARY OF ROMAN CATHOLIC SCHOOLS. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial Districts. | Number of Schools. | Number of Teachers. | Number of Scholars. | Daily Average Attendance. | |||||||||
| Boys. | Girls. | Mixed. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | |
| Auckland | 2 | 11 | 20 | 33 | 6 | 81 | 87 | 757 | 1,258 | 2,015 | 616 | 1,093 | 1,70 |
| Taranaki | … | 1 | 3 | 4 | … | 16 | 16 | 149 | 234 | 383 | 127 | 26 | 33 |
| Hawke's Bay | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 25 | 32 | 374 | 439 | 813 | 331 | 371 | 72 |
| Wellington | 3 | 5 | 10 | 18 | 20 | 66 | 86 | 841 | 1,119 | 1,960 | 766 | 1,02 | 1,90 |
| Marlborough | 1 | … | 2 | 3 | … | 7 | 7 | 134 | 113 | 247 | 106 | 95 | 201 |
| Nelson | 2 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 19 | 21 | 210 | 340 | 550 | 19 | 311 | 500 |
| Westland | 1 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 3 | 22 | 25 | 247 | 300 | 547 | 206 | 262 | 468 |
| Canterbury | 3 | 6 | 13 | 22 | 11 | 63 | 74 | 830 | 1,041 | 1,871 | 699 | 941 | 1,640 |
| Otago | 4 | 3 | 17 | 24 | 13 | 62 | 75 | 873 | 1,189 | 2,062 | 705 | 986 | 1,691 |
| Totals | 18 | 34 | 77 | 129 | 62 | 361 | 423 | 4,415 | 6,033 | 10,448 | 3,745 | 5,289 | 9,034 |
The number of Native village schools at the end of 1901 either supported or subsidised by the Government was 91, or two more than at the end of the previous year. In addition, there were four boarding-schools for Native children, the cost of whose maintenance was partly paid either by the Government or from endowments, and three private Native day-schools. The number of Maori children attending schools during the fourth quarter of 1901 was 4,912—namely, 2,791 males and 2,121 females. These included 303 half-castes at the Native village schools who were living as members of Maori tribes, and 234 at public European schools.
The numbers at the several schools in 1900 and 1901 were as under:—
| Schools. | Maori Children attending Schools. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys. | Girls. | Total of both Sexes. | ||||
| 1901. | 1900. | 1901. | 1900. | 1901. | 1900. | |
| At public European schools | 936 | 839 | 680 | 597 | 1,616 | 1,436 |
| At Native village schools | 1,641 | 1,576 | 1,294 | 1,186 | 2,935 | 2,762 |
| At subsidised or endowed boarding-schools | 122 | 111 | 90 | 91 | 212 | 202 |
| At private European or Native schools | 92 | 84 | 57 | 55 | 149 | 139 |
| Totals | 2,791 | 2,610 | 2,121 | 1,929 | 4,912 | 4,539 |
There was thus, in 1901, an increase of 181 in the number of Maori boys, and 192 in the number of Maori girls, attending, school.
Sixty-nine out of the ninety-one Native village schools in operation on 31st December, 1901, were under the charge of masters and seventeen under mistresses, and one under the joint control of a master and mistress; there were besides sixty-nine assistants, and fifteen sewing-mistresses. The salaries paid to the head-teachers range from £97 to £285, and those for assistants and sewing-mistresses from a nominal sum to £50.
The expenditure on Native schools for 1901 was as follows: Teachers' salaries and allowances, £14,273 1s.; books and school requisites, £440 18s.; repairs and small works, £519 15s. 6d.; inspection, £868 11s. 4d.; boarding-schools and scholarships, £1,990 6s. 11d.; buildings, fencing, furniture, &c., £4,312 3s. 8d.; technical instruction classes, £720 2s. 1d.; sundries, £285 11s. 6d.: total, £23,410 10s.
The total income of the various Education Boards for the year 1901 was £521,536. The grants by Government amounted to £473,379, an increase of £26,004 on the grants in 1900. These grants consist of (a) a statutory allowance of £3 15s. per child in daily average attendance, (b) a further capitation allowance of 1s. 6d. for scholarships, (c) a varying sum for school buildings, and (d) grants for technical education. The income from reserves amounted to £40,969, and that from local receipts, &c., to £7,188.
The total expenditure in 1901 amounted to £526,179, of which the sum of £427,660 was laid out on the maintenance of the schools.
The receipts and expenditure of the Education Boards, numbering thirteen altogether, are tabulated below, with further particulars:—
| RECEIPTS AND EXPENDITURE OF EDUCATION BOARDS. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts. | £ | s. | d. |
| To Balance, 1st January, 1901 | 11,565 | 8 | 8 |
| Government grants— | |||
| Rents from reserves | £40,969 | 0 | 2 |
| Balance of capitation | 413,381 | 2 | 11 |
| Total for maintenance | 454,350 | 3 | 1 |
| Buildings | 55,049 | 7 | 3 |
| Technical | 4,948 | 0 | 7 |
| Local receipts— | |||
| Fees, donations, &c. | 4,989 | 19 | 3 |
| Rents, &c. | 1,552 | 17 | 11 |
| Refunds, deposits, &c. | 645 | 14 | 8 |
| £533,101 | 11 | 5 | |
| Expenditure. | £ | s. | d. |
| By Boards' administration | 15,127 | 5 | 1 |
| Inspection and examination | 14,690 | 9 | 11 |
| Teachers' salaries and allowances | 382,061 | 4 | 9 |
| Incidental expenses of schools | 33,045 | 12 | 8 |
| Scholarships | 8,549 | 11 | 3 |
| Training of teachers | 4,003 | 4 | 9 |
| Buildings, sites, plans, &c. | 60,102 | 13 | 0 |
| Manual and technical instruction | 7,610 | 13 | 10 |
| Interest and exchanges | 241 | 11 | 9 |
| Refunds and sundries | 746 | 4 | 2 |
| Balance 31st December, 1901 | 6,923 | 0 | 3 |
| £533,101 | 11 | 5 | |
Particulars of the scholarships and the expenditure of the Boards thereon in 1901 are given in detail. The only institutions for the training of teachers are in North Canterbury and Otago. These two institutions have received grants-in-aid of £500 each.
| SCHOLARSHIPS. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education Districts. | Number held in Dec., 1901. | Boys. | Girls. | Period of Tenure. | Boards' Expenditure on Scholarships in 1901. | Annual Value, &c. | ||
| Years. | £ | s. | d. | |||||
| Auckland | 79 | 49 | 30 | 3 | 1,716 | 0 | 6 | 3 at £30, 22 at £25, 22 at £20, 32 at £15. |
| Taranaki | 13 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 295 | 15 | 9 | 2 at £35, 1 at £17, 1 at £16, 2 at £14, 6 at £10, 1 at £7 6s. |
| Wanganui | 17 | 8 | 9 | Varies | 622 | 13 | 3 | 11 at £40, 1 at £32, 5 at £15. |
| Wellington | 44 | 25 | 19 | 2 | 958 | 1 | 5 | 13 at £35, 31 at £15. |
| Hawke's Bay | 23 | 9 | 14 | 2 | 471 | 0 | 3 | 9 at £30 4s., 1 at £16 4s., 2 at £13 4s., 1 at £12 4s., 10 at £10 4s. |
| Marlborough | 10 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 139 | 0 | 0 | 2 at £40., 1 at £35, 7 at £10. |
| Nelson | 8 | 4 | 4 | Varies | 371 | 9 | 0 | 6 at £50 10s., 2 at £25. |
| Grey | 12 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 77 | 2 | 0 | 4 at £35, 8 at £10. |
| Westland | 7 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 100 | 10 | 0 | 1 at £23, 2 at £17 10s., 4 at £8. |
| North Canterbury | 38 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 1,317 | 0 | 4 | 21 at £40, 17 at £20. |
| South Canterbury | 34 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 326 | 15 | 11 | Varies from £22 10s. to £2 10s. |
| Otago | 52 | 35 | 17 | Varies | 1,332 | 0 | 9 | 13 at £40, 3 at £35, 2 at £24, 1 at £22, 15 at £20, 2 at £17, 16 at £15. |
| Southland | 21 | 14 | 7 | Varies | 604 | 1 | 3 | 13 at £35,3 at £20,5 at £15 |
| Totals, 1901 | 358 | 201 | 157 | 8,331 | 10 | 5 | ||
| Totals. 1900 | 349 | 197 | 152 | 8,142 | 10 | 9 | ||
A summary of the accounts of income and expenditure for the year 1901, as furnished by the governing bodies of the secondary or superior schools in the colony, shows the total receipts to have been £71,040. To this total, rents and sales of reserves contributed £28,509; interest on investments, and other receipts from endowments, £5,698; fees, £32,454; and miscellaneous, £4,379.
The total expenditure amounted to £84,725, of which sum office management and expenses absorbed £2,606; teachers' salaries, £34,924; scholarships and prizes, £2,511; buildings, furniture, insurance, rates, and rent, &c., £9,412; and other expenditure, £35,272. Included in the last item is a sum of £19,386, capital invested, which cannot be classed as ordinary expenditure.
A summary of the accounts for the year 1901, exhibiting further details, is given below:—
| SECONDARY OR SUPERIOR SCHOOLS, 1901. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts. | £ | s. | d. |
| To Credit balances on 1st January, 1901 | 21,724 | 17 | 10 |
| Endowment reserves sold | 5,040 | 10 | 7 |
| Mortgage moneys repaid | 2,870 | 0 | 0 |
| Rents of reserves | 23,468 | 8 | 11 |
| Interest on investments | 1,931 | 3 | 8 |
| Reserves Commissioners' payments | 3,766 | 15 | 1 |
| School fees (tuition) | 26,435 | 7 | 0 |
| Boarding-school fees | 6,019 | 8 | 0 |
| Books, &c., sold, and refunds | 263 | 4 | 0 |
| Sundries not classified | 1,245 | 12 | 8 |
| Debit balances, 31st December, 1901 | 1,357 | 1 | 10 |
| £97,122 | 9 | 7 | |
| Expenditure. | £ | s. | d. |
| By Liabilities on 1st January, 1901 | 2,467 | 4 | 10 |
| Expenses of management | 2,605 | 12 | 3 |
| School salaries | 34,923 | 19 | 3 |
| Boarding-school accounts | 5,168 | 8 | 0 |
| Examination expenses | 354 | 0 | 1 |
| Scholarships and prizes | 2,511 | 3 | 10 |
| Printing, stationery, fuel, light, &c. | 3,076 | 9 | 6 |
| Buildings, furniture, insurance, rent, and rates | 9,412 | 1 | 1 |
| Expenditure on endowments | 3,751 | 13 | 5 |
| Capital invested | 19,386 | 10 | 0 |
| Interest | 1,243 | 3 | 8 |
| Sundries | 2,291 | 13 | 3 |
| Credit balances, 31st December, 1901 | 9,930 | 10 | 5 |
| £97,122 | 9 | 7 | |
In December, 1901, the total number on the books of all the industrial schools was 1,765, or 62 more than at the close of the year 1900. On the books of the Government industrial schools there were 1,227, an increase of 64 over the corresponding number for 1900; on the books of the private industrial schools there were 538, or two less than at the end of the previous year. The number in residence at Government schools was 293, and at private industrial schools 348, so that 641 was the total number of “inmates” actually in residence. The number boarded out was 419, one being from a private school and the rest from Government schools. There were 17 girls maintained in various corrective institutions, 13 boys and girls in orphan homes, 1 boy at the Blind Institute, Auckland, and 1 at the School for Deaf-mutes, Sumner. The total number of inmates dependent on the schools for maintenance was therefore 1,092, or 56 more than the number at the end of 1900. The remaining 673, although still subject to control and supervision, were not dependent on the schools for maintenance. They may be classified as follows: Licensed to reside with friends, 155; at service, 448; in hospital, 4; in lunatic asylum, 5, in the Costley Training Institution, Auckland, on probation, 2; in other institutions without payment, 13; in gaol, 6; absent without leave, 40: namely, 29 from service and 11 from the schools.
There were six Government industrial schools in existence in 1901, and the numbers of inmates on their books at the end of the year were as follows: Auckland, 97; Receiving Home, Wellington, 69; Receiving Home, Christchurch, 226; Burnham, 281; Te Oranga Home, 46; Caversham, 508: total, 1,227. Those belonging to private industrial schools were distributed as follows: St. Mary's, Auckland, 130; St. Joseph's, Wellington, 76; St. Mary's, Nelson, 305; St. Vincent de Paul, Dunedin, 27: total, 538.
The cost of the Government schools and the amount recovered (from Charitable Aid Boards, from parents, from sale of farm produce, &c.) are next shown:—
| COST OF GOVEUNMENT INDUSTRIAL SCHOOLS, 1901. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School. | Gross Cost of School. | Cost of Boarding out (Included in preceding column). | Salaries of School Staff. (Included in first column.) | Recoveries. | Net Cost. | ||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Auckland | 3,427 | 18 | 6 | 705 | 16 | 10 | 295 | 11 | 8 | 478 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 6 | |
| Horowhenua (proposed) | 1,612 | 11 | 11 | .. | 62 | 8 | 0 | .. | 1,612 | 11 | 11 | ||||
| Burnham | 8,879 | 5 | 4 | 1,461 | 11 | 9 | 1,814 | 10 | 2 | 1,799 | 4 | 2 | 7,080 | 1 | 2 |
| Caversham | 8,189 | 8 | 3 | 3,045 | 8 | 5 | 1,089 | 6 | 0 | 4,933 | 12 | 1 | 3,255 | 16 | 2 |
| Te Oranga Home | 1,622 | 14 | 5 | .. | 330 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 19 | 3 | 1,600 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Receiving Home, Wellington | 626 | 14 | 4 | 129 | 6 | 8 | 183 | 5 | 0 | 126 | 7 | 10 | 500 | 6 | 6 |
| Receiving Home, Christchurch | 1,864 | 16 | 2 | 949 | 2 | 0 | 265 | 10 | 3 | 100 | 7 | 11 | 1,764 | 8 | 3 |
| Totals | 26,223 | 8 | 11 | 6,291 | 5 | 8 | 4,040 | 11 | 1 | 7,460 | 9 | 3 | 18,762 | 19 | 8 |
| Salaries and travelling-expenses of Assistant Inspector and Visiting Officers | 1,278 | 7 | 9 | ||||||||||||
| Travelling-expenses of other officers | 90 | 8 | 6 | ||||||||||||
| Contingencies | 64 | 16 | 3 | ||||||||||||
| Total | £20,196 | 12 | 2 | ||||||||||||
The next table shows payments made by the Government on account of inmates in private industrial schools, the recoveries, and the net expenditure by the Government. The contributions from Charitable Aid Boards to these schools, being made directly to the managers, are not included in the recoveries shown.
| GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE ON PRIVATE INDUSTRIAL SCHOOLS (R.C.), 1901. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School. | Payments. | Recoveries. | Net Expenditure by Government. | ||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| St. Mary's, Auckland | 1,427 | 9 | 0 | 122 | 15 | 0 | 1,304 | 14 | 0 |
| St. Joseph's, Wellington | 284 | 19 | 0 | 17 | 3 | 4 | 267 | 15 | 8 |
| St. Mary's, Nelson | 1,464 | 8 | 11 | 353 | 7 | 3 | 1,111 | 1 | 8 |
| St. Vincent de Paul's, Dunedin | 73 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 61 | 14 | 8 |
| Totals | 3,249 | 16 | 11 | 504 | 10 | 11 | 2,745 | 6 | 0 |
During 1901, inmates were maintained in eight other institutions, and the expenditure on this account was as follows: Mission Home, Jerusalem, Wanganui (Mother Aubert's), £96 4s.; St. Mary's, Richmond, Christchurch, £56 17s. 5d.; Samaritan Home, Christchurch, £18 2s.; Mount Magdala, Christchurch, £146 16s. 4d.; Levin Memorial Home, Wellington, £28 12s.; Rescue Home, Auckland, £2 2s.; St. Mary's Home, Karori, £23 8s.; and to a private home (for special treatment), £29 8s. 7d.
The total number of inmates of the two kinds of industrial schools is given for the years 1900 and 1901, and the variations in the numbers boarded out, in residence, or at service:—
| INMATES, 1900 AND 1901. | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Boarded out. | In Residence. | At Service, &c. | Totals. | ||||||||||||
| Dec., 1900. | Increase. | Decrease. | Dec., 1901. | Dec., 1900. | Increase. | Decrease. | Dec., 1901. | Dec., 1900. | Increase. | Decrease. | Dec., 1901. | Dec., 1900. | Increase. | Decrease. | Dec., 1901. | |
| Government Schools— | ||||||||||||||||
| Auckland | 46 | 2 | .. | 48 | 16 | 3 | .. | 19 | 32 | .. | 2 | 30 | 94 | 3 | .. | 97 |
| Receiving Home, Wellington | .. | 39 | .. | 39 | .. | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | 28 | .. | 28 | .. | 69 | .. | 69 |
| Receiving Home, Christchurch | .. | 147 | .. | 147 | .. | 10 | .. | 10 | .. | 69 | .. | 69 | .. | 226 | .. | 226 |
| Burnham | 162 | .. | 162 | .. | 108 | 7 | .. | 115 | 292 | .. | 126 | 166 | 562 | .. | 281 | 281 |
| Te Oranga Home, Christchurch | .. | .. | .. | .. | 12 | 5 | .. | 17 | 1 | 28 | .. | 29 | 13 | 33 | .. | 46 |
| Caversham | 194 | .. | 10 | 184 | 95 | 35 | .. | 130 | 205 | .. | 11 | 194 | 494 | 14 | .. | 508 |
| Private Schools— | ||||||||||||||||
| St. Mary's, Auckland | .. | .. | .. | .. | 100 | .. | 4 | 96 | 27 | 7 | .. | 34 | 127 | 3 | .. | 130 |
| St. Joseph's, Wellington | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | 49 | .. | 10 | 39 | 31 | 6 | .. | 37 | 82 | .. | 6 | 76 |
| St. Mary's, Nelson | 5 | .. | 4 | 1 | 202 | .. | 8 | 194 | 100 | 10 | .. | 110 | 307 | .. | 2 | 305 |
| St. Vincent de Paul's, South Dunedin | .. | .. | .. | .. | 16 | 3 | .. | 19 | 8 | .. | .. | 8 | 24 | 3 | .. | 27 |
| Totals | 409 | 188 | 178 | 419 | 598 | 65 | 22 | 641 | 696 | 148 | 139 | 705 | 1,703 | 351 | 289 | 1,765 |
In the Government schools the policy is to board out all children of suitable age and character. The authorities of the private schools do not adopt the boarding-out system.
The Jubilee Institute for the Blind is a private institution, and is not in any way under Government control, although it has received grants from time to time out of the Consolidated Revenue, and receives payment from the Education Department on account of pupils for whose tuition the department is responsible.
The payments made on behalf of such pupils to the Institute during the year amounted to £332 7s. 10d., towards which the parents contributed £41 8s. The number of pupils at the end of 1901 was fourteen. Attendance is now compulsory for all blind children of school age and sound mind.
The roll of this school includes all the known deaf-mutes of school age and of sound intellect in the colony who have been brought under the notice of the Education Department.
The inclusion in the School Attendance Act of 1901 of provisions dealing with blind and deaf children marks an important step in the education of these unfortunate members of the community. Hitherto many parents, either through carelessness or wilfully, have neglected to send such children to the institutions maintained for their special instruction; but now the Minister of Education has the power to enforce attendance, due provision being made for a contribution by parents towards the cost of maintenance or for free admission where parents are not in a position to contribute. The immediate consequence is an unusual increase in the number of candidates for admission to the Sumner School for Deaf-mutes.
The method of instruction used at Sumner is the oral method, in favour of which there is a vast predominance of expert opinion.
As regards the adoption of that system, the Minister of Education in his annual report remarks, “It is a matter for congratulation that this colony from the first adopted the oral method of teaching, in which children are taught to converse by watching the lips of others. In America, where manual and mixed methods were at first largely in vogue, they are being rapidly discarded in favour of oral instruction, and New Zealand has accordingly been saved the expense and inconvenience of changing from inferior systems of deaf-mute education to that which is now almost universally admitted to be the best.”
The number of libraries participating in the vote of £3,000 granted for subsidies shows an increase of twenty over the number aided in the previous year. In order that the purpose intended to be served by the vote may be attained, it is made a condition for participation that the whole of the subsidy granted to each library in the previous year shall have been expended in the purchase of books.
| Education Districts. | Number of Libraries. | Income. | Amount on which Subsidy is calculated. | Amount of Subsidy. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Auckland | 90 | 2,406 | 1 | 3 | 3,474 | 19 | 11 | 670 | 4 | 0 |
| Taranaki | 14 | 394 | 7 | 6 | 721 | 19 | 7 | 139 | 4 | 7 |
| Wanganui | 22 | 962 | 1 | 11 | 1,015 | 7 | 0 | 195 | 15 | 2 |
| Wellington | 21 | 2,221 | 11 | 3 | 1,137 | 2 | 11 | 219 | 4 | 10 |
| Hawke's Bay | 26 | 620 | 2 | 6 | 1,177 | 8 | 6 | 227 | 0 | 9 |
| Marlborough | 5 | 156 | 3 | 3 | 281 | 3 | 3 | 54 | 4 | 1 |
| Nelson | 24 | 561 | 17 | 3 | 1,034 | 8 | 6 | 199 | 9 | 3 |
| Grey | 5 | 181 | 4 | 0 | 306 | 4 | 0 | 59 | 0 | 7 |
| Westland | 5 | 101 | 12 | 6 | 226 | 12 | 6 | 43 | 13 | 11 |
| North Canterbury | 64 | 1,748 | 6 | 8 | 2,479 | 7 | 2 | 478 | 3 | 0 |
| South Canterbury | 18 | 515 | 17 | 4 | 848 | 3 | 4 | 163 | 10 | 7 |
| Otago | 47 | 803 | 10 | 0 | 1,820 | 0 | 0 | 350 | 19 | 1 |
| Southland | 27 | 295 | 7 | 6 | 995 | 7 | 6 | 191 | 19 | 9 |
| Special grant to Chatham Islands | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 10 | 5 |
| Totals | 369 | 10,982 | 2 | 11 | 15,557 | 4 | 2 | 3,000 | 0 | 0 |
Table of Contents
SITTINGS of the Supreme Court are held for trial of civil cases at Auckland, Gisborne, New Plymouth, Napier, Wellington, and Wanganui, in the North Island; and at Blenheim, Nelson, Hokitika, Christchurch, Timaru, Oamaru, Dunedin, and Invercargill, in the Middle Island.
The number of writs of summons issued in the Supreme Court in 1901 was 485, against 414 in 1900, 511 in 1899, 426 in 1898, 460 in 1897, 529 in 1896, and 511 in 1895. The number of civil cases tried decreased from 145 in 1900 to 116 in 1901. Of these last, 28 were tried before common juries, 5 by special jury, and 83 by Judge without jury. The total of amounts for which judgments were recorded in 1901 was £45,865. There were 54 writs of execution issued during the year.
Fifty-five cases were commenced at twelve District Courts in 1901. Seven of these cases were tried before juries, and 19 before a Judge only, making a total of 26 cases tried. Twenty-six cases lapsed or were discontinued, and in 3 cases judgments were pending. The total of amounts sued for was £9,686, and judgments were recorded for £1,035. Before the Magistrates' Courts 19,136 cases were tried, against 19,816 in 1900; the aggregate sum sued for during 1901 being £315,528, and the total for which judgment was given £175,604.
Five Crown (criminal) cases were reserved from the superior Courts to be brought before the Court of Appeal in 1901. In four cases the convictions were affirmed, and in one the conviction was quashed. There were appeals from 17 civil cases, of which 5 were allowed, 10 dismissed, and in 2 judgments were pending. Judgments were given on 7 other cases removed to the Court of Appeal.
The petitions in bankruptcy during 1901 numbered 222, of which 199 were made by debtors and 23 by creditors. This number is 82 fewer than the number of petitions for the preceding year.
Of the bankruptcies in 1901: in 11 cases the liabilities were under £50; in 44, from £50 to £100; in 66, from £100 to £250; in 45, from £250 to £500; in 30, from £500 to £1,000; in 17, from £1,000 to £2,000; in 7, from £2,000 to £5,000; in 2, £5,000 and upwards.
The following gives the number of petitions, the total amount of the unsecured assets, the amount of debts proved, and the amount paid in dividends and preferential claims for the years 1896 to 1901:—
| Year. | No. of Petitions in Bankruptcy. | Debtors' Statements of Assets, excluding Amounts secured to Creditors. | Amounts realised by Official Assignees. | Amount of Debts proved. | Amounts paid in Dividends and Preferential Claims. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1896 | 412 | 115,455 | 71,712 | 256,870 | 37,492 |
| 1897 | 415 | 73,466 | 40,942 | 133,344 | 45,015 |
| 1898 | 407 | 90,068 | 45,474 | 285,154 | 30,994 |
| 1899 | 389 | 59,434 | 34,268 | 158,931 | 30,084 |
| 1900 | 304 | 77,689 | 53,415 | 141,800 | 37,411 |
| 1901 | 222 | 58,658 | 49,781 | 84,452 | 30,358 |
A special article on the present bankruptcy law of New Zealand was printed in the Year-book of 1894. Reference is made in it to a mode of private assignment, which has come into such frequent use as to militate against conclusions being drawn from a comparison of the figures above given.
In 1898 the Legislature of New Zealand passed a Divorce Act, and the signification of Her Majesty's assent thereto was duly notified by His Excellency the Governor in a Proclamation dated the 1st April, 1899, bringing the Act into operation from the 1st June, 1899.
This Act places persons of either sex practically on an equality as regards petitions for dissolution of marriage; the same grounds, in substance, for a decree of divorce applying to man or woman.
Besides this important alteration of the law, the grounds for divorce are extended as under:—
Adultery, on either side.
Wilful desertion continuously during five years or more.
Habitual drunkenness on the part of husband, along with failing to support wife; or drunkenness and neglect, with unfitness to discharge household duties on the part of the wife.
Conviction, with sentence of imprisonment or penal servitude for seven years or upwards, for attempting to take life of petitioner.
Every decree for dissolution of marriage is in the first instance to be a decree nisi, not to be made absolute till after the expiration of such time, being not less than three months from the pronouncing thereof, as the Court shall by order from time to time direct.
The petitioner need not necessarily move to make absolute any decree nisi that may be pronounced.
A decree for a judicial separation may be obtained either by the husband or wife on the ground of adultery, or of cruelty, or of desertion without cause for a period of two years.
The petitions in 1901 under “The Divorce and Matrimonial Causes Act, 1867,” were 139 in number, being 23 in excess of those for 1900: 138 were for dissolution of marriage, and 1 for judicial separation; 103 decrees for dissolution of marriage were granted, and 1 for judicial separation. The proceedings under the Act for the years 1896 to 1901, were as follows:—
| Year. | Petitions for | Decrees for | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolution of Marriage. | Judicial Separation. | Dissolution of Marriage. | Judicial Separation. | |
| 1896 | 55 | 6 | 36 | 2 |
| 1897 | 48 | 10 | 33 | 1 |
| 1898 | 51 | 13 | 32 | 2 |
| 1899 | 112 | 1 | 46 | 16 |
| 1900 | 111 | 5 | 85 | 3 |
| 1901 | 138 | 1 | 103 | 1 |
The Act of 1898 has evidently operated in the direction of increasing largely (but probably in the main temporarily) the number of petitions and decrees for dissolution of marriage or judicial separation.
The proportion of petitions and decrees for dissolution of marriage to the number of marriages was up till 1898 higher in New Zealand than in England and Wales, but lower than in New South Wales or Victoria. The full effect of the operation of the new law in New Zealand has now, however, to be experienced.
As early as 1889 an Act was passed in Victoria to allow of divorces being granted for wilful desertion, habitual drunkenness with cruelty or neglect, imprisonment under certain circumstances of either party, and adultery on the part of the husband. This multiplication of the causes for divorce has largely increased the proportion of decrees in that State.
An Act of a similar tenor was passed in New South Wales in 1892, and brought into working in August of that year, under which, and an amending Act of 1893, in addition to adultery since marriage on the part of the wife, and adultery and cruelty on the part of the husband, petitions for divorce can now be granted in that State on any of the following grounds:—
Husband v. wife: Desertion for not less than three years; habitual drunkenness for a similar period; refusing to obey an order for restitution of conjugal rights; being imprisoned under a sentence of three years or upwards; attempt to murder or inflict grievous bodily harm, or repeated assaults on him within one year previously.
Wife v. husband: Adultery, provided that at the time of the institution of the suit the husband is domiciled in New South Wales; desertion for not less than three years; habitual drunkenness for the same period; refusing to obey an order for restitution of conjugal rights; being imprisoned for three years or upwards, or having within five years undergone various sentences amounting in all to not less than three years; attempt to murder, or assault with intent to inflict grievous bodily harm, or repeated assaults within one year previously.
To entitle either party to seek relief on these grounds, he or she must have been domiciled in the State at the time of instituting the suit for three years or upwards, and should not have resorted to the State for the purpose of the suit. When a wife seeks for a decree on the ground of three years' desertion, if she was domiciled in New South Wales when the desertion commenced, she shall not be deemed to have lost her domicile by reason of her husband having thereafter acquired a foreign domicile.
The divorces and separations in New South Wales and Victoria since the divorce law has been altered in the direction of increasing the grounds for decrees are as under. With these are given the figures for New Zealand under the old law up to 1898, and according to the new Act for 1899, 1900, and 1901. The figures for New South Wales tend to show that on altering the law there was a large accumulation of cases to get rid of, which increased the number of decrees to a degree which was not subsequently maintained.
| Year | New South Wales. | Victoria. | New Zealand. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | ||||
| Divorces. | Judicial Separations. | Divorces. | Judicial Separations. | Divorces. | Judicial Separations. | |
| * Act of 1898 in force in New Zealand. | ||||||
| 1893 | 306 | 9 | 85 | 7 | 25 | 1 |
| 1894 | 313 | 14 | 81 | 2 | 20 | 4 |
| 1895 | 301 | 11 | 85 | .. | 18 | 5 |
| 1896 | 234 | 8 | 106 | 2 | 36 | 2 |
| 1897 | 246 | 13 | 117 | .. | 33 | 1 |
| 1898 | 247 | 17 | 87 | .. | 32 | 2 |
| 1899* | 232 | 17 | 105 | 2 | 46 | 16 |
| 1900* | 219 | 14 | 93 | .. | 85 | 3 |
| 1901* | .. | .. | .. | .. | 103 | 1 |
The number of charges heard before the Magistrates' Courts in 1901 was 26,265. Repeated charges against the same person are counted as distinct. Of the charges in 1901, 440 were against persons of the aboriginal native race, an increase of 85 on the number for the previous year.
If the Maoris be excluded, the number of charges (exclusive of lunacy) in 1901 is found to have been 25,825, an increase of 1,741 upon the number for 1900; and the proportion per 1,000 of population was 33·20, against 31·54 in 1900.
Persons charged with lunacy and committed to asylums have been excluded from the calculations for this and previous years shown, so that the figures now given will differ somewhat from those appearing in former issues of this book.
The figures, both numerical and proportional, covering a period of twenty years are subjoined:—
| C(([0-9]+)) MAGISTRATES. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year. | Number. | Proportion per 1,000 of Mean Population. |
| 1882 | 21,622 | 42·45 |
| 1885 | 22,297 | 38·89 |
| 1888 | 18,370 | 30·35 |
| 1891 | 16,714 | 26·54 |
| 1894 | 16,820 | 24·76 |
| 1897 | 19,390 | 26·87 |
| 1898 | 21,668 | 29·42 |
| 1899 | 22,113 | 29·48 |
| 1900 | 24,084 | 31·54 |
| 1901 | 25,825 | 33·20 |
The summary convictions in 1901 numbered 20,624, including 298 Maoris. 756 persons, 47 of whom were Maoris, were committed for trial at the Supreme and District Courts, a decrease of 17 on the number committed in 1900.
Dealing with the summary convictions, and convictions in the superior Courts, for all offences, the figures for 1897 and onwards (excluding the Maoris) are:—
| SUMMARY CONVICTIONS. | CONVICTIONS IN SUPERIOR COURTS. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years. | Number. | Proportion per 1,000 of Mean Population. | Number. | Proportion per 1,000 of Mean Population |
| 1897— | ||||
| Offences against the person | 781 | 1·08 | 49 | 0·07 |
| Offences against property | 1,412 | 1·96 | 240 | 0·33 |
| Other offences | 12,205 | 16·91 | 14 | 0·02 |
| Totals | 14,398 | 19·95 | 303 | 0·42 |
| 1898— | ||||
| Offences against the person | 690 | 0·94 | 53 | 0·07 |
| Offences against property | 1,565 | 2·13 | 284 | 0·39 |
| Other offences | 13,917 | 18·90 | 14 | 0·02 |
| Totals | 16,172 | 21·97 | 351 | 0·48 |
| 1899— | ||||
| Offences against the person | 678 | 0·90 | 79 | 0·11 |
| Offences against property | 1,549 | 2·07 | 273 | 0·36 |
| Other offences | 14,583 | 19·44 | 24 | 0·03 |
| Totals | 16,810 | 22·41 | 376 | 0·50 |
| 1900— | ||||
| Offences against the person | 724 | 0·95 | 79 | 0·10 |
| Offences against property | 1,476 | 1·93 | 271 | 0·35 |
| Other offences | 16,285 | 21·33 | 19 | 0·02 |
| Totals | 18,485 | 24·21 | 369 | 0·47 |
| 1901— | ||||
| Offences against the person | 778 | 1·00 | 91 | 0·12 |
| Offences against property | 1,736 | 2·23 | 213 | 0·27 |
| Other offences | 17,812 | 22·90 | 24 | 0·03 |
| Totals | 20,326 | 26·13 | 328 | 0·42 |
Including 26 Maoris, the convictions in the superior Courts numbered 354 (persons). Particulars of sentences for these higher Courts, and of the punishments consequent on summary convictions in the lower Courts, are appended in two tables:—
| TABLE showing the Sentences of Criminals Tried and Convicted in the Supreme and District Courts during Five Years. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punishments. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. |
* Including 12 Maoris. † Including 35 Maoris. ‡ Including 7 Maoris. § Including 22 Maoris. ¶ Including 26 Maoris. | |||||
| Death | 2 | 3 | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Imprisonment with or without hard labour | 235 | 286 | 306 | 286 | 272 |
| Fined | 3 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 17 |
| Imprisonment with whipping | .. | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Released under “The First Offenders' Probation Act, 1886″ | 63 | 50 | 61 | 74 | 51 |
| Held to bail, or awaiting pleasure of Court | 12 | 21 | 12 | 25 | 12 |
| Sent to lunatic asylum | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. |
| Sent to industrial school | .. | 2 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Totals | *316 | †386 | ‡383 | §391 | ¶354 |
| TABLE showing the Punishments inflicted consequent on Summary Convictions during Five Years. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punishments. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. |
| Fine | 6,821 | 8,149 | 8,229 | 9,206 | 9,905 |
| Fine and imprisonment | 5 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Imprisonment in lieu of fine | 1,409 | 1,410 | 1,762 | 1,895 | 1,910 |
| Imprisonment and whipping | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Peremptory imprisonment | 1,579 | 1,616 | 1,683 | 1,723 | 1,948 |
| Recognisance | 123 | 111 | 118 | 121 | 105 |
| Whipping | 28 | 18 | 28 | 15 | 20 |
| Other | 4,432 | 4,868 | 4,990 | 5,525 | 6,438 |
| Totals | 14,398 | 16,172 | 16,810 | 18,485 | 20,326 |
| N.B.—Maoris have been excluded from this table. | |||||
During the five years, 1897 to 1901 inclusive, the consumption of beer in the colony per inhabitant would seem to have increased, the proportion having been 7·8 gallons in the earlier year, against 8·9 gallons in the later one. Excluding the Maoris, the same result is found to obtain, the figures being 8·2 for the year 1897 and 9·4 for 1901. Wine and spirits also show an increase in the consumption per head of population.
The following calculations are made to show the results, including and excluding Maoris:—
| CONSUMPTION OF BEER, WINE, AND SPIRITS PER HEAD OF POPULATION (INCLUDING AND EXCLUDING MAORIS). | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Including Maoris. | Excluding Maoris. | |||||
 |  | |||||
| Beer. Gal. | Wine. Gal. | Spirits. Gal. | Beer. Gal. | Wine. Gal. | Spirits. Gal. | |
| 1897 | 7·790 | 0·138 | 0·628 | 8·220 | 0·146 | 0·663 |
| 1898 | 7·995 | 0·139 | 0·634 | 8·427 | 0·146 | 0·668 |
| 1899 | 8·150 | 0·141 | 0·653 | 8·583 | 0·148 | 0·687 |
| 1900 | 8·696 | 0·145 | 0·684 | 9·150 | 0·152 | 0·720 |
| 1901 | 8·919 | 0·151 | 0·726 | 9·413 | 0·159 | 0·766 |
The actual quantities of beer, wine, and spirits used in the colony were, for the five years:—
| Beer for Consumption. Gals. | Wine for Consumption. Gals. | Spirits for Consumption. Gals. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1897 | 5,931,550 | 105,060 | 478,136 |
| 1898 | 6,204,700 | 107,595 | 491,846 |
| 1899 | 6,437,140 | 111,049 | 515,384 |
| 1900 | 6,986,900 | 116,188 | 549,932 |
| 1901 | 7,323,290 | 123,592 | 596,071 |
Excluding Maoris, the proportion of convictions for drunkenness per 1,000 of population was 9·18 in 1890, diminishing to 6·60 in 1895, 6·82 in 1896, 7·01 in 1897, 7·41 in 1898, and 8·26 in 1899, but increasing to 9·50 in 1900, and 10·32 in 1901. The number of convictions to which the proportions for the years 1896 to 1901 relate were as under:—
| Year. | Number. |
|---|---|
| 1896 | 4,822 |
| 1897 | 5,060 |
| 1898 | 5,458 |
| 1899 | 6,194 |
| 1900 | 7,252 |
| 1901 | 8,032 |
The totals of charges for drunkenness for the same years were:—
| Year. | Number. |
|---|---|
| 1896 | 4,916 |
| 1897 | 5,156 |
| 1898 | 5,559 |
| 1899 | 6,279 |
| 1900 | 7,319 |
| 1901 | 8,086 |
Among the New-Zealand-born population of European descent there is evidence of less drunkenness than among persons who have come to the colony from abroad. At the census of 1901, out of the total population of New Zealand over 15 years of age, 51·85 per cent. were found to have been born here; while the proportion of the convictions for drunkenness of New-Zealand-born Europeans to the total convictions was in the year 1900 about 17 per cent. only.
The prison statistics show for some years back the number of distinct prisoners received into gaol after being convicted of drunkenness. The figures for the years 1889–1901 are as follow (readmissions of the same person not counted):—
| DISTINCT PRISONERS CONVICTED OF D(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)). | |
|---|---|
| Year. | Number. |
| 1889 | 802 |
| 1890 | 808 |
| 1891 | 694 |
| 1892 | 638 |
| 1893 | 619 |
| 1894 | 457 |
| 1895 | 469 |
| 1896 | 515 |
| 1897 | 486 |
| 1898 | 520 |
| 1899 | 610 |
| 1900 | 674 |
| 1901 | 657 |
Here the decrease proceeds rapidly and uniformly from year to year until the year 1895, after which the figures rise somewhat. But conclusions cannot be drawn so safely from these prisons statistics as from the convictions for drunkenness previously stated, because the punishment is more often by fine than imprisonment. The convictions showed numbers rising from year to year, but along with the increase in the population of the colony.
In Australia the consumption per head of alcoholic liquors is greater than it is here. The average for three years, according to Mr. Coghlan, is given in the “Seven Colonies of Australasia,” and quoted below:—
| Spirits. Gal. Per Head. | Wine. Gal. Per Head. | Beer. Gal. Per Head. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| New South Wales | 0·77 | 0·66 | 10·43 |
| Victoria | 0·76 | 1·62 | 12·16 |
| Queensland | 1·08 | 0·44 | 11·41 |
| South Australia | 0·43 | 1·72 | 9·06 |
| Western Australia | 1·54 | 0·95 | 24·40 |
| Tasmania | 0·48 | 0·11 | 8·48 |
| New Zealand | 0·69 | 0·15 | 8·72 |
In each of these States, with the exception of Tasmania and South Australia, charges for drunkenness are, in proportion to population, far more numerous than in New Zealand. The order of the States for the year 1900 in this respect is, to quote from the same authority, as under:—
| C(([0-9]+)) DRUNKENNESS IN PROPORTION TO POPULATION. | |
|---|---|
| Queensland | 18·87 per 1,000 |
| Western Australia | 17·48 per 1,000 |
| New South Wales | 15·51 per 1,000 |
| Victoria | 13·30 per 1,000 |
| New Zealand | 9·59 per 1,000 |
Under this law, the Governor in Council may direct that any building or establishment which is the property of the Crown shall be an institution for inebriates; and he may appoint superintendents, with other officers.
Power is also given to make regulations for the management, supervision, and inspection of these institutions, any of which may be separated into two divisions, with different scales of accommodation, and fees to be paid by patients.
An inebriate may himself make application to a Judge or Magistrate for an order committing him to an institution. Or, if the husband, wife, or any relation or friend of any inebriate applies, the Judge or Magistrate may summon the inebriate to show cause why he should not be committed; when, if necessary, he may be compulsorily dealt with.
There are penalties for improper treatment of patients, and a patient is also liable if misconducting himself. It is also enacted that, during the continuance of an order, an escaped inebriate may be retaken.
A home has been established at Waitati, near Seacliff.
The Native population of the colony has hitherto been regarded as stationary, and comparisons of the numbers of summary convictions by the higher and lower Courts are given. The number for 1897 is swelled by 108 persons convicted of trespass. The figures relating to the convictions by the superior Courts are small and fluctuating, the proportionately large increase in 1898 being caused by the inclusion of sixteen convicted of conspiring to prevent the collection of taxes.
| S(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)). | |
|---|---|
| Year. | Number. |
| 1891 | 298 |
| 1892 | 293 |
| 1893 | 253 |
| 1894 | 321 |
| 1895 | 316 |
| 1896 | 332 |
| 1897 | 450 |
| 1898 | 349 |
| 1899 | 300 |
| 1900 | 253 |
| 1901 | 298 |
| CONVICTIONS OF MAORIS IN SUPERIOR COURTS. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year. | Convictions. | Number of Persons convicted. |
| 1891 | 7 | 7 |
| 1892 | 16 | 15 |
| 1893 | 13 | 12 |
| 1894 | 25 | 24 |
| 1895 | 17 | 15 |
| 1896 | 19 | 19 |
| 1897 | 16 | 12 |
| 1898 | 21 | 35 |
| 1899 | 8 | 7 |
| 1900 | 22 | 22 |
| 1901 | 26 | 26 |
The total number of prisoners received in the different gaols of the colony during the year 1901 was 4,302, including persons awaiting trial but not convicted within the year, and counting as distinct persons repeated admissions of the same person, as well as transfers-from gaol to gaol of convicts undergoing sentence. In 1900 the number received was 3,911, so that the figures for 1901 show an increase of 391. Of 4,302 admissions for 1901, 29 were for debt, and 53 on account of lunacy; while 126 were Maoris imprisoned for various offences. If the debtors, lunatics, and Maoris be excluded, the number of persons received into gaol is reduced to 4,094, against 3,670 in 1900.
The number of persons in gaol (including Maoris) at the end of the year 1901 was 713, or 145 more than in 1900.
| PRISONERS IN G(([0-9]+)) DECEMBER). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Undergoing Sentence. | Debtors and Lunatics | On Remand and a waiting Trial. | Total. |
| 1889 | 611 | 3 | 19 | 633 |
| 1891 | 494 | 4 | 36 | 534 |
| 1893 | 463 | 6 | 33 | 502 |
| 1895 | 531 | 5 | 46 | 582 |
| 1897 | 623 | .. | 51 | 674 |
| 1899 | 508 | .. | 58 | 566 |
| 1900 | 527 | .. | 41 | 568 |
| 1901 | 661 | 1 | 51 | 713 |
Of the prisoners previously convicted received in 1901, 426 men and 49 women had been convicted once; 210 men and 31 women twice; 1,053 men and 452 women three or more times: making a total of 1,689 men and 532 women.
Besides the returns from the Prisons Department, a separate card for each admission is furnished for every gaol. Such cards as show convictions are arranged alphabetically according to name of prisoner, and where several are found referring to the same person, all are thrown out but one; then the number of cards retained equals the actual number of distinct convicted prisoners received in the various gaols during the year. In 1901 this number (excluding Maoris) was 2,345, an increase of 229 on the number in 1900. These figures do not include children committed to the industrial schools simply on the ground that they are neglected or destitute.
The following table shows the number of distinct persons (exclusive of Maoris) received into gaol after conviction during 1901, classified according to nature of offence, religion, birthplace, and age:—
| D(([0-9]+)) P(([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)), 1901. | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [NOTE.—In this table a prisoner convicted of more than one offence during the year is reckoned once only, under the heading of the principal offence—e.g., a prisoner convicted three times of drunkenness, twice of vagrancy, and once of theft, is counted only once, under the heading “Theft.” Debtors and lunatics received into gaol, and children committed to the industrial schools not convicted of any crime, are omitted.] | ||||||||||||||||
| — | Offences against the Person. | Offences against Property. | Miscellaneous. | Totals. | ||||||||||||
| Convicted on Indictment. | Summarily convicted. | Theft and Deceit. | Mischief. | Vagrancy. | Drunkenness.* | Other Offences. | ||||||||||
* It must be remembered that drunkenness is punished more by fine than by imprisonment, so that the figures in the gaol tables do not represent the full number of persons punished for that offence. | ||||||||||||||||
| Religions— | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. |
| Church of England | 28 | 2 | 56 | 3 | 273 | 9 | 18 | 2 | 97 | 44 | 207 | 34 | 192 | 3 | 871 | 97 |
| Roman Catholic | 25 | 3 | 48 | 2 | 129 | 12 | 11 | 1 | 87 | 43 | 201 | 61 | 157 | 1 | 658 | 123 |
| Presbyterian | 15 | 1 | 25 | … | 73 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 49 | 18 | 87 | 15 | 82 | 2 | 337 | 44 |
| Wesleyan | 7 | 1 | 2 | … | 38 | 1 | 1 | … | 7 | … | 15 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 82 | 6 |
| Others | 6 | … | 8 | 1 | 29 | … | 4 | … | 8 | 5 | 32 | 2 | 32 | … | 119 | 8 |
| Totals | 81 | 7 | 139 | 6 | 542 | 29 | 40 | 4 | 248 | 110 | 542 | 115 | 475 | 7 | 2,067 | 278 |
| Birthplaces— | ||||||||||||||||
| England and Wales | 13 | … | 32 | 1 | 145 | 3 | 10 | … | 65 | 21 | 178 | 22 | 147 | 3 | 590 | 50 |
| Scotland | 4 | 1 | 16 | … | 32 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 37 | 6 | 72 | 9 | 66 | … | 232 | 20 |
| Ireland | 11 | 2 | 17 | 2 | 52 | 10 | 5 | … | 56 | 28 | 136 | 42 | 63 | 2 | 340 | 86 |
| New Zealand | 35 | 3 | 50 | 3 | 225 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 53 | 37 | 71 | 34 | 106 | 2 | 551 | 95 |
| Australian States | 7 | … | 2 | … | 47 | … | 2 | … | 15 | 8 | 22 | 5 | 25 | … | 120 | 13 |
| Other British possessions | 1 | … | 2 | .. | 2 | … | 1 | … | 6 | 3 | 15 | 1 | 12 | … | 39 | 4 |
| China | 1 | … | 1 | … | 2 | … | … | … | 1 | … | … | … | … | … | 5 | … |
| Other countries | 9 | 1 | 19 | … | 37 | … | 6 | … | 15 | 7 | 48 | 2 | 56 | … | 190 | 10 |
| Totals | 81 | 7 | 139 | 6 | 542 | 29 | 40 | 4 | 248 | 110 | 542 | 115 | 475 | 7 | 2,067 | 278 |
| Ages— | ||||||||||||||||
| Under 10 years | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 10 and under 12 years | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 12 and under 15 years | … | … | … | … | 5 | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 15 and under 20 years | 7 | .. | 5 | … | 68 | 3 | 4 | … | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 16 | … | 105 | 7 |
| 20 and under 25 years | 16 | 1 | 34 | 2 | 103 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 17 | 15 | 25 | 5 | 83 | … | 283 | 31 |
| 25 and under 30 years | 17 | 1 | 29 | … | 95 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 31 | 7 | 57 | 15 | 79 | … | 310 | 26 |
| 30 and under 40 years | 20 | 2 | 39 | 3 | 127 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 67 | 34 | 133 | 31 | 133 | … | 531 | 79 |
| 40 and under 50 years | 10 | .. | 17 | … | 77 | 5 | 7 | … | 56 | 29 | 135 | 32 | 81 | 4 | 383 | 70 |
| 50 and under 60 years | 6 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 45 | 5 | 5 | … | 45 | 19 | 120 | 21 | 58 | 2 | 287 | 50 |
| 60 years and over | 5 | 1 | 7 | … | 22 | … | 5 | … | 30 | 3 | 9 | 10 | 25 | 1 | 163 | 15 |
| Totals | 81 | 7 | 139 | 6 | 542 | 29 | 40 | 4 | 248 | 110 | 542 | 115 | 475 | 7 | 2,067 | 278 |
| Totals, 1900 | 52 | 5 | 126 | 1 | 495 | 26 | 41 | 5 | 190 | 80 | 552 | 122 | 398 | 17 | 1,854 | 262 |
The number of distinct persons (exclusive of Maoris) imprisoned after conviction, in the past twelve years, counting one offence only when the same person was imprisoned more than once, with the proportion per 10,000 persons living, is added:—
| Year. | Prisoners. | Proportion per 10,000 of Population. |
|---|---|---|
| 1890 | 2,397 | 38·61 |
| 1891 | 2,113 | 33·55 |
| 1892 | 2,164 | 33·69 |
| 1893 | 2,111 | 31·92 |
| 1894 | 1,955 | 28·78 |
| 1895 | 1,930 | 27·87 |
| 1896 | 1,936 | 27·11 |
| 1897 | 1,884 | 25·84 |
| 1898 | 1,982 | 26·92 |
| 1899 | 2,125 | 28·33 |
| 1900 | 2,116 | 27·71 |
| 1901 | 2,345 | 30·14 |
There has been since 1890 a decrease of 2·17 per cent. in the number of distinct convicted prisoners, and a reduction of 8·47 per 10,000 in the proportion to population. In New South Wales the proportion for 1898 was 66 per 10,000 persons.
It must be understood that the actual number of imprisonments was much in excess of the figures given, as many persons were several times imprisoned, either for offences differing in kind or for repetitions of the same offence. Thus, persons returned as imprisoned for larceny underwent other imprisonments for drunkenness, &c. Some returned as convicted of drunkenness were several times in gaol during the year for the same offence, or for another, such as assault, riotous or indecent conduct, &c. Often there were several charges preferred against the same person at the one time, of which the most serious followed by conviction has been selected.
The proportions in every 100 distinct convicted prisoners belonging to each of the four principal religious denominations, with proportions of prisoners at each age-period, and particulars as to birthplaces and ages, will be found in the Statistical Volume for 1901, on pages 487 and 489.
The prisoners in gaols during the year 1901 were maintained at a net cost to the State of £26 14s. 1d. per head, against £29 4s. 6d. in 1900.
While the New-Zealand-born formed at the last census 67 per cent. of the whole population of the colony, they contributed in 1901 only 28 per cent. of the prisoners received in gaol. Of the New-Zealand-born population, however, a large number are under 15 years of age, a period of life at which there are very few prisoners; and, therefore, another comparison is necessary. It is found that the New-Zealand-born over 15 years formed 52 per cent. of the total population above that age; but, as before stated, New-Zealanders constituted only 28 per cent. of the total number received in gaols.
The total number of New-Zealand-born distinct prisoners (excluding Maoris) received for the year 1901–646 persons—is found to be 49 in excess of the number for 1900. Of those received in 1901, 86 were under twenty years of age. As before stated, the plan adopted in preparing the foregoing tables is to count each prisoner only once, and to exclude all who are not convicted prisoners, besides dealing only with the number received during the year, instead of with the full number in gaol, which would, of course, include those brought forward from the previous year. The comparative results for a series of years given by this method are held to be more valuable than those brought out by one which includes prisoners merely awaiting trial, and continual repetitions of the same individuals.
In his report of the year 1902, the Inspector of Prisons thus comments on the work of the tree-planting prison at Waiotapu, the establishment of which was mentioned in previous Year-books:—
The Gaoler at Waiotapu gives some interesting details of the scheme of employing prisoners in the work of tree-planting. The success that has hitherto attended this experiment naturally leads to inquiry as to why the scheme is not extended to other localities. In the first place, it must be borne in mind that only prisoners of a fairly robust type, well conducted and of quiet habits, can be utilised. The ordinary criminal is, under present conditions, not available, for the reason that his first impulse would be to escape. Some men are safe only under lock and key and behind a fourteen-foot boundary-wall. The class of prisoner required for tree-planting or similar work in the country is the man who is determined to shorten his term of imprisonment by good conduct and industry, whose last thought is to escape, and who therefore needs little supervision. This class is, however, limited in number, and for that reason the scheme referred to cannot be extended as far as one could wish.
Ninety-seven persons were placed on probation in the year 1901, as against 112 in 1900. Of these, 21 were discharged after satisfactorily carrying out the conditions of their licenses, 5 were rearrested, and 71 remained under the supervision of Probation Officers.
Of the 1,329 persons placed on probation since the introduction of the Act in October, 1886, no less than 1,094 had, by the end of the year 1901, been discharged after satisfactorily carrying out the conditions of their licenses, 80 have been rearrested and sentenced to various terms of imprisonment, 1 committed suicide, 1 died, 32 absconded, 1 was sent to a lunatic asylum, and 119 remained fulfilling the conditions of their terms of probation. The Inspector of Prisons, in his report for the year 1900, made the following remarks, which will well bear repeating:—
From the foregoing it will be seen that a percentage of 83 have done well, while only a percentage of 2·41 have eluded the vigilance of the Probation Officers and absconded. These statistics speak for themselves, and show that the Probation Officers, who do the work gratuitously, have carefully inquired into and made judicious recommendations in the majority of cases, and are deserving of commendation.
The above-quoted results prove beyond doubt that the First Offenders' Probation Act, which was placed on the statute-book of the colony to put first offenders under a term of surveillance that is calculated to give them an extra incentive to good behaviour, and to check predilections that might end in a career of crime, is satisfactorily attaining that end. A probationer has ever before his mind the inevitable consequence which will ensue should he deviate from strictest rectitude of conduct during his probation, while he is not in a position to be contaminated by the evil associations which are almost inseparable from a prison life. The State is relieved of the expense of his support, and there is much more inducement to return to the paths of honesty and industry than there would be were he under bars and bolts inside the walls of a felon's cell; and, lastly, he is not branded as a “gaol-bird.”
The amount of costs which the various Courts directed to be paid during the year 1901 was £454, of which £216 6s. 6d. has been actually paid. The approximate cost of keeping these first offenders had they been sent to prison would have amounted to £3,908, which sum, added to the amount of costs, &c., actually paid, gives a saving of £4,124 6s. 6d.
The number of bodies on which inquests were held in 1901 was 980, including 24 Maoris. In 731 cases the bodies were of males, and in 249 of females.
The inquests on suicidal deaths in 1901 show an increase on the number for the previous year. The figures for each of the last six years were:—
| Year. | Inquests on Suicides. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Total. | |
| 1896 | 58 | 12 | 70 |
| 1897 | 42 | 11 | 53 |
| 1898 | 69 | 8 | 77 |
| 1899 | 61 | 13 | 74 |
| 1900 | 52 | 11 | 63 |
| 1901 | 71 | 13 | 84 |
The verdicts given at the inquests held in 1901 may be classified as under:—
| Nature of Verdict. | Inquests on Persons. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Total. | |
| Accident | 326 | 54 | 380 |
| Disease and natural causes | 308 | 174 | 482 |
| Intemperance | 5 | .. | 5 |
| Homicide | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Suicide | 71 | 13 | 84 |
| Execution | 1 | .. | 1 |
| Not classed | 16 | 2 | 18 |
| 731 | 249 | 980 | |
Of the accidental deaths, drowning is the most fatal form. The verdicts show that 129 bodies were found drowned, giving a percentage of 33·95 on the accidental deaths from all causes.
Table of Contents
THE census of the Maori population—that is, full-blooded Maoris, with all half-castes living as members of a Native tribe—was taken under the supervision of the officers of the Justice Department in the latter part of February, 1901. The enumeration of the Natives cannot be effected for one particular night, as is done with Europeans, but it is done as quickly and thoroughly as is possible under the circumstances existing.
The enumeration was made to state the names of the Natives in the Sub-Enumerator's books, besides information as to sex, age, principal tribe, sub-tribe, or hapu to which belonging, and particulars as to extent of cultivations owned individually or communally, with live stock.
Enumerators for the Maori census were directed to report on the health of the Natives, which is stated to have been generally good—that is, no epidemic disease was observed, though occasional outbreaks of influenza, fevers, &c., had happened since 1896.
The departmental report of 1st June, 1901, comments thus:—
As a knowledge of sanitary laws increases among the Maoris it may be expected that certain causes of disease will gradually disappear. But it is useless to expect the social habits of a people to conform to another standard all at once. While it it true that social conditions are susceptible of almost infinite modification, it is equally true that such modification can occur only after long periods of time.
The diffusion of knowledge must tend to uplift the Maoris. The transforming powers of education and association are at work, and must in time have their effect. The village schools are steadily improving the general standard of knowledge among the Maori people as a whole, while the higher schools turn out a number of intelligent young fellows who want only the opportunity to show the value of the training they have received. Suitable openings in the public service are limited, but the Government has displayed a sympathetic regard for deserving Maori youths wherever possible. There are now two Native medical students attending the Otago University, and the recent appointment of Dr. Pomare as Native Health Officer is expected to do much good in the direction of sanitary and social reform. Much also is hoped from the Maori Councils Act of last session, which confers on the Natives a limited measure of local self-government, and enables them to regulate and control habits and customs which are harmful alike to the individual and the community. Many of the older chiefs, as well as the educated younger generation, are showing a very intelligent interest in the reform movement, but they want to be shown what to do and how to do it. …
The reports of the Enumerators and Sub-enumerators contain much of interest. Crime does not prevail in any marked degree. The Natives as a whole are becoming more and more temperate every year. The drunken orgies that were once common are in a great measure things of the past. In several of the reports reference is made to their adoption of the European style of living; some are sheep-farmers, others cultivate their land, while others again engage in various forms of remunerative labour. Every year the spread of settlement brings them into closer touch with their pakeha neighbours, and subjects them to the influence of European example. Their ultimate destiny must remain a matter of speculation.
The proportion of the Maori population to that of European descent was in the years 1896 and 1901 one Maori to every eighteen Europeans. It is in the North Island that the proportion of Maoris to Europeans is by far the highest, being one in every ten, against one in one hundred and eighty-nine for the South and Stewart Islands.
The percentage of each race to the population was:—
| European Per Cent. | Maori Per Cent. | |
|---|---|---|
| North Island | 90·56 | 9·44 |
| Middle Island | 99·50 | 0·50 |
| Stewart Island | 70·83 | 29·17 |
| Chatham Islands | 49·52 | 50·48 |
In February, 1901, the number of Maoris on the principal islands of New Zealand was as shown hereunder:—
| Maoris. | Half-castes living as Members of Maori Tribes (included in the preceding Numbers). | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||||
| Persons. | Males. | Females. | Persons. | Males. | Females. | |
| North Island | 40,715 | 21,919 | 18,796 | 2,517 | 1,379 | 1,138 |
| Middle Island | 1,909 | 1,022 | 887 | 551 | 288 | 263 |
| Stewart Island | 112 | 66 | 46 | 13 | 5 | 3 |
| Chatham Islands— | ||||||
| Maoris | 180 | 90 | 90 | 34 | 14 | 20 |
| Morioris | 31 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 8 | 10 |
| Maori wives living with European husbands | 196 | .. | 196 | .. | .. | .. |
| Totals | 43,143 | 23,112 | 20,031 | 3,133 | 1,694 | 1,439 |
Besides the half-castes included in the above table, there were 2,407 half-castes (males, 1,188; females, 1,219) living with and enumerated as Europeans at the time of the census.
The above total of 43,143 shows an increase on the population as enumerated in 1896 of 3,289 persons. But the figures for 1896 showed a large decrease, and the increase for the period 1896–1901 is too great to be taken as an absolute fact—at least to the full extent shown. That some degree of increase has recently taken place is highly probable, although averaging the results of the different enumerations of Maoris made since 1878 conveys the idea of a stationary population.
| MAORI POPULATION AS ENUMERATED, 1874 TO 1901. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | Increase. | Decrease. | |
| 1874 (first census) | 45,470 | .. | .. |
| 1878 | 43,595 | .. | 1,875 |
| 1881 | 44,097 | 502 | .. |
| 1886 | 41,969 | .. | 2,128 |
| 1891 | 41,993 | 24 | .. |
| 1896 | 39,854 | .. | 2,139 |
| 1901 | 43,143 | 3,289 | .. |
The half-caste population consists of those who live as members of Maori tribes, and others living with and counted as Europeans in the census. Adding the numbers of the two kinds gives the following figures for three censuses:—
| Half-castes living as Members of Maori Tribes. | Half-castes living as Europeans. | Total Half-caste Population. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Census. | Persons. | Persons. | Persons. |
| 1891 | 2,681 | 2,184 | 4,865 |
| 1896 | 3,503 | 2,259 | 5,762 |
| 1901 | 3,133 | 2,407 | 5,540 |
Here the half-castes who were living as members of tribes are shown as decreasing in number since 1896, while those living as Europeans increased at both periods under review.
It has been stated that the increase shown by the census of 1901 in the Maori population can scarcely be considered a certainty to the full degree exhibited. The proportions of the people under and over fifteen years are now given for six successive census years, and the figures for 1896 and 1901 tend to show a growing proportion at the earlier ages.
| Males. | Females. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  | |||
| Under 15 Years. | Over 15 Years. | Under 15 Years. | Over 15 Years. | |
| 1901 | 35·75 | 64·25 | 37·89 | 62·11 |
| 1896 | 35·28 | 64·72 | 36·82 | 63·18 |
| 1891 | 33·22 | 66·78 | 35·22 | 64·78 |
| 1886 | 31·64 | 68·36 | 33·56 | 66·44 |
| 1881 | 33·65 | 66·35 | 34·64 | 65·36 |
| 1878 | 32·00 | 68·00 | 31·63 | 68·37 |
The proportions per cent. under 15 years of the young people of either sex are somewhat different from those found in the European population, viz.: Males under 15, 32·24; over 15 years, 67·76; and females under 15, 34·66; and over 15 years, 65·34.
Of the principal tribes residing in the North Island, the Ngapuhi again shows the greatest number of persons, and the next in importance was Ngatikahungunu. Waikato and Ngatiporou had over four thousand persons living. The Arawa had over three thousand, Ngatiraukawa, Rarawa, and Wanganui between two and three thousand each. A complete statement is given:—
| Principal Tribes in the North Island. | |
|---|---|
| Persons. | |
| Ngapuhi | 6,359 |
| Ngatikahungunu | 5,064 |
| Waikato | 4,457 |
| Ngatiporou | 4,152 |
| Arawa | 3,547 |
| Rarawa | 2,842 |
| Whanganui | 2,327 |
| Ngatiraukawa | 2,084 |
| Ngatiawa | 1,701 |
| Ngatimaniapoto | 1,570 |
| Ngatimaru | 1,350 |
| Urewera | 1,094 |
| Ngaiterangi | 913 |
| Ngatiruanui | 853 |
| Whanau-a-Apanui | 711 |
| Taranaki | 639 |
| Whakatohea | 598 |
| Ngatiwhatua | 356 |
| Unspecified | 98 |
| 40,715 | |
| Principal Tribes in the South Island. | |
|---|---|
| Persons. | |
| Ngatikahungunu | 1,549 |
| Ngatiawa | 211 |
| Waikato | 85 |
| Others | 64 |
| 1,909 | |
| Principal Tribe in Stewart Island. | |
|---|---|
| Persons. | |
| Ngatikahungunu | 112 |
| Principal Tribes in Chatham Islands. | |
|---|---|
| Persons. | |
| Ngatiawa | 180 |
| Moriori | 31 |
| 211 | |
The total number of Maoris in each county, being the localisation of the Natives throughout the colony, will be found on page 103.
Table of Contents
FOR purposes of local government New Zealand is divided into counties and boroughs. Although the boroughs, of which there were 103 in March, 1902, lie geographically within the counties, yet by the law they are not considered as part of them. On the 31st March, 1902, the counties numbered 91. The number is increased from time to time as need is found for further division. In the year 1878 there were only 63 counties. Interior to the counties are the road and town districts, but much of the country is outlying, many road districts having been merged, especially on goldfields territory.
There were, however, 225 road districts (three without Boards) in existence in March, 1902, and 35 town districts. One of these latter is the special Town District of Rotorua, constituted under “The Thermal-Springs Districts Act, 1881.” Besides the above there were 30 river protective districts (excluding Inch Clutha, in Bruce County, which is also a road district), 1 drainage district (Christchurch), 2 water-supply districts, and 16 land drainage districts under the Land Drainage Act of 1893 (one without Board). The Harbour Boards numbered 26, excluding Coromandel and Fortrose, for which the County Councils of Coromandel and Southland act as the Harbour Boards.
These bodies levied rates in the financial year 1901–1902 to the amount of £800,471, of which £548,859 consisted of general rates, and £251,612 special and separate rates. The sum of £78,617 was raised by licenses, and £17,736 by other taxes, making £896,824 altogether, which sum is equivalent to £1 2s. 11d. per head of the mean European population. In the year 1900–1901 the local taxation was £1 1s. 9d. per head, or 1s. 2d. less than in 1901–1902.
It will be seen from the table on the next page that since 1881 revenue derived from rates has more than trebled itself, having increased from £249,087 in 1880–81 to £800,471 in 1901–1902. Revenue from Government and other sources has, on the other hand, decreased in the same period, twenty-two years, from £352,540 to less than one-half, viz., £170,041. Receipts which cannot be classed as “revenue” were £889,705 in 1880–81, against £775,432 in 1901–1902; but these figures vary from year to year according to circumstances, such as large operations by way of construction of works, for which money has to be specially raised.
The receipts (distinguishing revenue from other sources of income) and expenditure of the various local bodies, with the amount of rates collected, and the amount of indebtedness on account of loans for each of the past twenty-two years, are shown in the following table:—
| LOCAL GOVERNING BODIES.—RATES, RECEIPTS, EXPENDITURE, AND LOANS, 1881 TO 1902.* | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year ended 31st March. | Receipts of Local Bodies. | Expenditure of Local Bodies.† | Outstanding Loans of Local Bodies (excluding Government Loans, for which see the following Columns). | Government Loans to Local Bodies. | ||||||
| Revenue from. | Receipts not Revenue. | Total Receipts. | Outstanding Debentures under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act, 1882.” | Net Indebtedness in February of each Year under “The Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1880” (including Debentures under the Roads and Bridges Construction Act, converted. | ||||||
| Rates. | Licenses, Tolls, Rents, and other Sources. | Government. | Total Revenue. | |||||||
* The figures for the Christchurch Drainage Board and Harbour Boards included are for the calendar years ended three months previous to the financial years. † Not including balances, deposits, or amounts paid to sinking funds and for redemption of debentures ‡ On the 30th June. | ||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1881 | 249,087 | 461,602 | 352,540 | 1,063,229 | 889,705 | 1,952,934 | 1,871,752 | 3,039,807 | .. | .. |
| 1882 | 297,328 | 476,473 | 218,179 | 991,980 | 419,608 | 1,411,588 | 1,637,337 | 3,277,584 | .. | .. |
| 1883 | 327,129 | 466,885 | 133,565 | 927,579 | 311,466 | 1,239,045 | 1,397,863 | 3,540,046 | .. | .. |
| 1884 | 398,659 | 502,969 | 241,558 | 1,143,186 | 331,994 | 1,475,180 | 1,499,117 | 3,962,330 | 77,439 | .. |
| 1885 | 401,393 | 477,813 | 364,082 | 1,243,288 | 430,561 | 1,673,849 | 1,653,706 | 4,313,223 | 123,086‡ | .. |
| 1886 | 410,639 | 504,807 | 377,811 | 1,293,257 | 514,728 | 1,807,985 | 1,644,706 | 4,943,270 | 134,534 | .. |
| 1887 | 434,237 | 447,631 | 342,432 | 1,224,300 | 992,633 | 2,216,933 | 1,885,001 | 5,620,747 | 113,072 | .. |
| 1888 | 433,832 | 460,210 | 334,857 | 1,228,899 | 511,594 | 1,740,493 | 1,819,787 | 5,812,803 | 18,635 | 191,687 |
| 1889 | 445,929 | 535,140 | 141,288 | 1,122,357 | 316,139 | 1,438,496 | 1,560,605 | 5,892,050 | 10,495 | 273,289 |
| 1890 | 460,303 | 568,405 | 139,320 | 1,168,028 | 206,688 | 1,374,716 | 1,476,540 | 5,978,059 | 9,676 | 319,603 |
| 1891 | 463,581 | 518,757 | 144,008 | 1,126,346 | 236,902 | 1,363,248 | 1,381,320 | 6,042,693 | 4,317 | 367,715 |
| 1892 | 488,824 | 584,274 | 109,022 | 1,182,120 | 214,124 | 1,396,244 | 1,400,467 | 6,081,934 | 4,245 | 449,532 |
| 1893 | 508,157 | 573,161 | 136,515 | 1,217,833 | 340,538 | 1,558,371 | 1,482,548 | 6,203,869 | 3,465 | 525,173 |
| 1894 | 551,412 | 547,560 | 134,271 | 1,233,243 | 623,038 | 1,856,281 | 1,589,124 | 6,614,824 | 2,685 | 547,679 |
| 1895 | 581,868 | 545,629 | 138,228 | 1,265,725 | 328,798 | 1,594,523 | 1,584,518 | 6,685,510 | 2,015 | 621,903 |
| 1896 | 592,903 | 581,966 | 156,180 | 1,331,049 | 269,145 | 1,600,194 | 1,627,079 | 6,737,578 | 1,442 | 667,451 |
| 1897 | 598,526 | 586,599 | 178,448 | 1,363,573 | 246,919 | 1,610,492 | 1,636,716 | 6,793,398 | 1,077 | 709,282 |
| 1898 | 644,552 | 608,436 | 182,166 | 1,435,154 | 304,645 | 1,739,799 | 1,733,016 | 6,834,361 | 712 | 742,530 |
| 1899 | 685,769 | 642,289 | 178,438 | 1,506,496 | 385,368 | 1,891,864 | 1,778,574 | 6,963,254 | 347 | 789,618 |
| 1900 | 714,151 | 695,988 | 152,044 | 1,562,183 | 372,028 | 1,934,211 | 1,960,073 | 7,057,350 | .. | 810,192 |
| 1901 | 734,023 | 751,046 | 168,785 | 1,653,854 | 825,039 | 2,478,893 | 2,250,572 | 7,563,069 | .. | 902,769 |
| 1902 | 800,471 | 848,983 | 170,041 | 1,819,495 | 775,432 | 2,594,927 | 2,547,286 | 7,839,695 | .. | 1,046,645 |
The indebtedness of local governing bodies on account of outstanding loans has increased in twenty-two years by nearly 158 per cent., from £3,039,807 to £7,839,695, exclusive of moneys borrowed from Government under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act, 1882,” and “The Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1886,” which represented a further indebtedness of £1,046,645 at the end of March, 1902.
| TABLE showing the Revenue of Local Governing Bodies derived from Rates, Licenses, and other Taxes during the Year 1901–1902. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local Bodies. | Rates. | Licenses. | Other Taxes. | Total. | |||||||||||
| General. | Special and Separate. | ||||||||||||||
* For year ended 31st March, 1902. † For year ended 31st December, 1901. ‡ Wharfage dues, charges, fees, tolls, rents, &c., amounting to £407,056 4s. 8d., have not been classed as taxation. § Equal to £1 2s. 11d. per head of the mean European population of the colony for the financial year 1901–1902. | |||||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Counties* | 209,493 | 15 | 11 | 39,350 | 15 | 8 | 18,374 | 6 | 5 | 9,955 | 16 | 11 | 277,174 | 14 | 11 |
| Boroughs* | 173,650 | 15 | 9 | 197,025 | 8 | 11 | 54,408 | 1 | 8 | 5,799 | 17 | 10 | 430,884 | 4 | 2 |
| Town Boards* | 3,161 | 13 | 6 | 207 | 18 | 8 | 3,602 | 0 | 6 | 213 | 13 | 8 | 7,185 | 6 | 4 |
| Road Boards* | 91,864 | 19 | 5 | 11,253 | 11 | 0 | 2,232 | 10 | 2 | 1,763 | 0 | 3 | 107,114 | 0 | 10 |
| River Boards* | 7,319 | 14 | 4 | 938 | 5 | 6 | … | 3 | 17 | 3 | 8,291 | 17 | 1 | ||
| Land-drainage Boards* | 2,724 | 17 | 9 | 1,126 | 16 | 5 | … | … | 3,851 | 14 | 2 | ||||
| Harbour Boards † | 41,370 | 13 | 9 | … | … | … | 41,370 | 13 | 9‡ | ||||||
| Christchurch Drainage Board † | 17,768 | 4 | 4 | … | … | … | 17,768 | 4 | 4 | ||||||
| Waimakariri-Ashley Water-supply Board* | 1,474 | 9 | 1 | 1,708 | 11 | 0 | … | … | 3,183 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Totals | 548,859 | 3 | 10 | 251,611 | 7 | 2 | 78,616 | 18 | 9 | 17,736 | 5 | 11 | 896,823 | 15 | 8§ |
A summary of all the transactions for the year 1901–1902 is given on pages 198 to 200. The total revenue of the local bodies for the financial year was £1,819,495, and they further received a sum of £775,432 which could not properly be termed “revenue,” making altogether a grand total of receipts amounting to £2,594,927. The rates formed 44 per cent. of the revenue proper. Licenses, rents, and other sources yielded 47 per cent., and 9 per cent. was granted by the General Government.
While the revenue proper of the counties amounted to £407,827, of which these bodies raised £248,845 by way of rates, the Road Boards' revenue was only £157,955, out of which £103,119 represented the result of their rating. The boroughs had the far larger revenue of £696,029, including £370,676 of rates, and their receipts under the heading of licenses, rents, and other sources amounted to the considerable sum of £309,467. In the matter of receipts from Government, of which a table is printed on the next page, the counties received the bulk of the money.
The details of amounts received, representing Government support to the various bodies, are stated in the following table:—
| LOCAL GOVERNING BODIES.—RECEIPTS FROM GOVERNMENT, 1901–1902. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Counties. | Boroughs. | Town Boards. | Road Boards. | River Boards (excluding Inch-Clutha, also Road Board). | Laud Drainage Boards. | Harbour Boards. | Drainage Board. | Waimakariri Water-supply Board. | Totals. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Rates on Crown and Native lands | 4 | 8 | 11 | 57 | 3 | 1 | … | 71 | 7 | 4 | … | … | … | … | … | 132 | 19 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| One-third receipts from land sold on deferred payment and from perpetual lease | 19,739 | 11 | 9 | … | 5 | 18 | 2 | 5,292 | 15 | 3 | … | … | … | … | … | 25,038 | 5 | 2 | ||||||||||||
| One-fourth of rents from small grazing-runs | 3,314 | 6 | 8 | … | … | 1,060 | 17 | 11 | … | … | … | … | … | 4,075 | 4 | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| Goldfields revenue and gold duty | 41,549 | 17 | 8 | 1,137 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 16 | 5 | 757 | 0 | 9 | … | … | … | … | … | 43,453 | 3 | 7 | ||||||||||
| Subsidies under the Local Bodies' Finance and Powers Act | 44,626 | 18 | 11 | 13,724 | 17 | 7 | 763 | 12 | 5 | 18,811 | 5 | 0 | … | … | … | … | … | 77,929 | 13 | 11 | ||||||||||
| Fees and fines under the Financial Arrangements Act | 970 | 18 | 3 | 489 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 18 | 11 | … | … | … | … | … | 1,470 | 19 | 11 | ||||||||||
| Other receipts | 440 | 1 | 3 | 477 | 19 | 10 | 207 | 5 | 0 | 7,781 | 5 | 2 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 10 | 0 | 8,511 | 17 | 9 | 256 | 8 | 10 | … | 17,941 | 7 | 10 | ||
| Total Revenue Account | 110,346 | 3 | 5 | 15,886 | 9 | 7 | 987 | 14 | 5 | 33,789 | 10 | 4 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 10 | 0 | 8,511 | 17 | 9 | 256 | 8 | 10 | … | 170,041 | 14 | 4 | ||
| Loans under Government Loans to Local Bodies Act | 70,623 | 12 | 6 | 43,962 | 17 | 9 | 600 | 0 | 0 | 23,090 | 3 | 9 | 5,500 | 0 | 0 | 1,400 | 0 | 0 | … | … | … | 145,170 | 14 | 0 | ||||||
| Grants for special works, &c. | 113,437 | 16 | 2 | 4,071 | 5 | 9 | … | 902 | 5 | 0 | 15 | 3 | 6 | … | … | … | … | 118,420 | 10 | 5 | ||||||||||
| Total receipts from Government | 294,407 | 12 | 1 | 63,920 | 13 | 1 | 1587 | 14 | 5 | 57,781 | 19 | 1 | 5,715 | 3 | 6 | 1,463 | 10 | 0 | 8,511 | 7 | 9 | 256 | 8 | 10 | … | 433,644 | 18 | 9 | ||
| LOCAL GOVERNING BODIES.—RECEIPTS FROM GOVERNMENT, 1901–1902. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Financial Year ended 31st March, 1902. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Counties. | Boroughs. | Town Boards. | Road Boards. | River Boards (excluding Inch-Clutha, also Road Board). | Land Drainage Boards. | Waimakariri Water-supply Board. | Totals. | |||||||||||||||||
* For amounts under various heads see preceding table; also for specification of loans under Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, and special grants, which are here included with “Receipts not revenue.” † Excluding loans under Roads and Bridges Construction Act and Government Loans to Local Bodies Act. For rates of interest see page 203. ‡ Not including loans, amounting to £1,046,645, repayable by instalments under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act. 1882,” and “The Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1886.” NOTE.—The return of receipts and expenditure in this summary represents the net receipts and expenditure of the year, exclusive of credit and debit balances, bank overdrafts, deposits, amounts paid to sinking funds, and for redemption of debentures | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Receipts:— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue from— | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| Rates | 248,844 | 11 | 7 | 370,676 | 4 | 8 | 3,369 | 12 | 2 | 103,118 | 10 | 5 | 8,287 | 19 | 10 | 3,851 | 14 | 2 | 3,183 | 0 | 1 | 741,331 | 12 | 11 |
| Licenses, rents, and other sources | 48,636 | 10 | 11 | 369,466 | 11 | 11 | 7,460 | 2 | 2 | 12,467 | 7 | 3 | 4,670 | 15 | 6 | 126 | 18 | 8 | 52 | 6 | 2 | 382,880 | 12 | 7 |
| Government* | 110,346 | 3 | 5 | 15,886 | 9 | 7 | 987 | 14 | 5 | 33,789 | 10 | 4 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 10 | 0 | … | 161,273 | 7 | 9 | ||
| County | … | … | 177 | 4 | 0 | 8,579 | 10 | 11 | … | … | … | 8,756 | 14 | 11 | ||||||||||
| Total revenue | 407,827 | 5 | 11 | 696,029 | 6 | 2 | 11,994 | 12 | 9 | 157,954 | 18 | 11 | 13,158 | 15 | 4 | 4,042 | 2 | 10 | 3,235 | 6 | 3 | 1,294,242 | 8 | 2 |
| Receipts not revenue | 209,895 | 2 | 11 | 350,598 | 5 | 4 | 1,249 | 7 | 3 | 30,873 | 4 | 2 | 5,936 | 12 | 5 | 1,485 | 0 | 10 | 24 | 9 | 6 | 600,062 | 1 | 7 |
| Total receipts | 617,722 | 8 | 10 | 1,046,627 | 11 | 6 | 13,244 | 0 | 0 | 188,828 | 3 | 1 | 19,095 | 7 | 9 | 5,527 | 2 | 10 | 3,259 | 15 | 9 | 1,894,304 | 9 | 9 |
| Expenditure:— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Public works | 444,514 | 14 | 10 | 502,614 | 1 | 4 | 7,488 | 11 | 7 | 138,553 | 13 | 7 | 16,442 | 12 | 3 | 3,635 | 5 | 4 | 1,236 | 8 | 10 | 1,114,485 | 7 | 9 |
| Charitable aid and hospitals | 37,645 | 17 | 1 | 28,198 | 15 | 0 | 264 | 7 | 0 | 9,899 | 9 | 7 | … | … | … | 76,008 | 8 | 8 | ||||||
| Management | 50,867 | 11 | 11 | 64,083 | 16 | 4 | 1,728 | 13 | 5 | 17,116 | 15 | 5 | 1,498 | 13 | 5 | 430 | 4 | 9 | 234 | 11 | 5 | 135,960 | 6 | 8 |
| Other expenditure | 68,066 | 8 | 11 | 423,578 | 12 | 7 | 2,429 | 9 | 0 | 29,327 | 3 | 5 | 6,580 | 17 | 8 | 1,308 | 3 | 2 | 1,396 | 15 | 0 | 532,687 | 9 | 9 |
| Total expenditure | 001,094 | 12 | 9 | 1,018,475 | 5 | 3 | 11,911 | 1 | 0 | 194,897 | 2 | 0 | 24,522 | 3 | 4 | 5,373 | 13 | 3 | 2,867 | 15 | 3 | 1,859,141 | 12 | 10 |
| Liabilities (including loans) | 946,209 | 6 | 3 | 3,916,891 | 19 | 9 | 6,128 | 18 | 7 | 305,653 | 8 | 9 | 89,046 | 13 | 7 | 30,570 | 0 | 4 | 22,213 | 0 | 9 | 5,316,713 | 8 | 0 |
| Loans † | 6,714 | 0 | 0 | 3,435,884 | 0 | 0 | 805 | 0 | 0 | 6,728 | 0 | 0 | 43,670 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 22,213 | 0 | 0 | 3,516,014 | 0 | 0‡ |
| — | Financial Year ended 31st December, 1901. | Totals—all Local Bodies. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbour Boards. | Drainage Boards. | ||||||||
* For amounts under various heads see preceding table; also for specification of loans under Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, and special grants, which are here included with “Receipts not revenue.” † Excluding loans under Roads and Bridges Construction Act and Government Loans to Local Bodies Act. For rates of interest see page 203. | |||||||||
| Receipts:— | |||||||||
| Revenue from— | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| Rates | 41,370 | 13 | 9 | 17,768 | 4 | 4 | 800,470 | 11 | 0 |
| Licenses, rents, and other sources | 457,053 | 5 | 3 | 291 | 19 | 3 | 840,225 | 17 | 1 |
| Government* | 8,511 | 17 | 9 | 256 | 8 | 10 | 170,041 | 14 | 4 |
| County | … | … | 8,756 | 14 | 11 | ||||
| Total revenue | 506,935 | 16 | 9 | 18,316 | 12 | 5 | 1,819,494 | 17 | 4 |
| Receipts not revenue | 166,298 | 12 | 0 | 9,071 | 9 | 2 | 775,432 | 12 | 9 |
| Total receipts | 673,234 | 8 | 9 | 27,383 | 11 | 7 | 2,594,927 | 10 | 1 |
| Expenditure:— | |||||||||
| Public works | 334,938 | 11 | 11 | 4,452 | 6 | 8 | 1,453,876 | 6 | 4 |
| Charitable aid and hospitals | … | … | 76,008 | 8 | 8 | ||||
| Management | 15,123 | 12 | 8 | 1,502 | 6 | 10 | 152,586 | 6 | 2 |
| Other expenditure | 319,187 | 17 | 8 | 12,939 | 11 | 4 | 864,814 | 18 | 9 |
| Total expenditure | 669,250 | 2 | 3 | 18,894 | 4 | 10 | 2,547,285 | 19 | 11 |
| Liabilities (including loans) | 4,285,973 | 10 | 4 | 205,577 | 3 | 5 | 9,808,204 | 1 | 9 |
| Loans† | 4,123,631 | 0 | 0 | 200,000 | 0 | 0 | 7,839,695 | 0 | 0 |
The expenditure of the local bodies amounted to £2,547,286. In the counties the cost of management, including salaries, travelling-expenses, rent, printing and advertising, collection of rates or tolls, legal expenses, and sundries, was £50,868. The Borough Councils expended in the same way £64,084, and the Road Boards £17,117.
The percentages borne by the cost of management to the total receipts and total expenditure were:—
| Cost of Management per Cent. of | Total Receipts | Total Expenditure. |
|---|---|---|
| Counties | 8·2 | 8·5 |
| Boroughs | 6·1 | 6·3 |
| Road Boards | 9·1 | 8·8 |
The amount of receipts and expenditure for each of the Harbour Boards in the colony for the year ended 31st December, 1901, also the liabilities at date of balancing, including outstanding loans, have been tabulated in another statement.
| Harbour Boards. | Receipts. | Expenditure (excluding Amounts paid to Sinking Fund and for Redemption of Debentures). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue from | Receipts not Revenue. | Total Receipts. | Works and Maintenance. | Other Expenditure, Interest, &c. | Out of Loan. | Total Expenditure. | Liabilities (including Outstanding Loans. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wharfage Dues, Charges, Fees, Tolls, &c. | Rates, Rents, and other Sources. | Total Revenue. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NOTE.—The figures relating to the Auckland Harbour Board and totals for the year 1901, differ from those published in the Statistical Volume, Welling to an error since discovered and now corrected. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Auckland | 39,528 | 6 | 2 | 14,758 | 4 | 2 | 54,286 | 10 | 4 | 40,458 | 16 | 7 | 94,745 | 6 | 11 | 39,675 | 5 | 1 | 31,778 | 4 | 3 | 55,405 | 12 | 0 | 126,856 | 1 | 4 | 449,971 | 8 | 9 |
| Bluff | 17,480 | 19 | 5 | 2,393 | 19 | 4 | 19,874 | 18 | 9 | 1,737 | 15 | 6 | 21,612 | 14 | 3 | 8,723 | 8 | 6 | 8,365 | 10 | 0 | … | 17,088 | 18 | 6 | 50,516 | 16 | 6 | ||
| Coromandel | 42 | 12 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 12 | 8 | … | 49 | 12 | 8 | 43 | 8 | 6 | … | … | 43 | 8 | 6 | … | ||||||||
| Fortrose | … | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | … | 10 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 10 | 0 | … | … | 12 | 10 | 0 | … | ||||||||||
| Gisborne | 8,972 | 19 | 5 | 5,970 | 16 | 3 | 14,913 | 15 | 8 | 6,316 | 1 | 6 | 21,289 | 17 | 2 | 868 | 6 | 3 | 11,113 | 11 | 0 | 7,376 | 13 | 11 | 19,358 | 11 | 2 | 204,018 | 16 | 2 |
| Greymouth | 24,720 | 9 | 6 | 913 | 5 | 11 | 25,633 | 15 | 5 | … | 25,633 | 15 | 5 | 15,793 | 9 | 6 | 12,109 | 12 | 5 | … | 27,903 | 1 | 11 | 214,103 | 6 | 5 | ||||
| Half-moon Bay and Horseshoe Bay | … | … | … | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | … | … | 100 | 0 | 0 | … | ||||||||||||
| Hokitika | 198 | 9 | 6 | 767 | 16 | 8 | 966 | 6 | 2 | 43 | 9 | 0 | 1,009 | 15 | 2 | 136 | 16 | 9 | 990 | 6 | 2 | … | 1,127 | 2 | 11 | 11,923 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Lyttelton | 42,388 | 15 | 7 | 2,203 | 15 | 11 | 44,592 | 11 | 6 | 1,333 | 17 | 4 | 45,926 | 8 | 10 | 9,499 | 10 | 5 | 24,533 | 3 | 6 | 6,924 | 5 | 11 | 40,956 | 19 | 10 | 262,302 | 17 | 0 |
| Mokau | 31 | 7 | 2 | … | 31 | 7 | 2 | … | 31 | 7 | 2 | … | 122 | 8 | 7 | … | 122 | 8 | 7 | 118 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||
| Napier | 20,091 | 13 | 9 | 21,296 | 16 | 3 | 41,388 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 41,407 | 14 | 1 | 6,886 | 3 | 2 | 28,316 | 2 | 9 | 835 | 3 | 5 | 36,037 | 9 | 4 | 501,696 | 9 | 3 |
| Nelson | … | 3,732 | 5 | 10 | 3,732 | 5 | 10 | … | 3,732 | 5 | 10 | 77 | 14 | 3 | 588 | 9 | 3 | … | 666 | 3 | 6 | … | ||||||||
| New Plymouth | 6,940 | 2 | 8 | 11,664 | 4 | 9 | 18,604 | 7 | 5 | 208 | 8 | 2 | 18,812 | 15 | 7 | 7,360 | 7 | 7 | 14,007 | 16 | 8 | … | 21,368 | 4 | 3 | 206,756 | 18 | 0 | ||
| New River | 732 | 9 | 6 | 99 | 9 | 4 | 831 | 18 | 10 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 906 | 18 | 10 | 553 | 13 | 8 | 986 | 6 | 6 | … | 1,540 | 0 | 2 | 18,231 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Oamaru | 7,539 | 7 | 5 | 8,206 | 0 | 7 | 15,745 | 8 | 0 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 15,765 | 18 | 0 | 2,549 | 14 | 7 | 12,070 | 2 | 11 | … | 14,619 | 17 | 6 | 325,159 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Otago | 67,768 | 0 | 11 | 13,423 | 0 | 9 | 81,191 | 1 | 8 | 12,156 | 7 | 6 | 93,347 | 9 | 2 | 21,272 | 18 | 2 | 48,705 | 9 | 10 | … | 69,978 | 8 | 0 | 709,475 | 4 | 10 | ||
| Patea | 2,025 | 11 | 8 | 442 | 3 | 5 | 2,467 | 15 | 1 | 130 | 6 | 4 | 2,598 | 1 | 5 | 846 | 4 | 0 | 1,633 | 0 | 1 | … | 2,479 | 4 | 1 | 14,269 | 12 | 9 | ||
| Riverton | … | 207 | 2 | 7 | 207 | 2 | 7 | … | 207 | 2 | 7 | 58 | 9 | 4 | 140 | 10 | 1 | … | 198 | 19 | 5 | 2,014 | 14 | 7 | ||||||
| Thames | 1,822 | 13 | 7 | 294 | 1 | 0 | 2,116 | 14 | 7 | … | 2,116 | 14 | 7 | 713 | 13 | 7 | 981 | 10 | 6 | … | 1,695 | 4 | 1 | 10,129 | 12 | 8 | ||||
| Timaru | 22,604 | 12 | 8 | 8,221 | 15 | 2 | 30,826 | 7 | 10 | 21,635 | 9 | 1 | 52,461 | 16 | 11 | 14,081 | 14 | 8 | 15,528 | 8 | 5 | 39,286 | 1 | 7 | 68,896 | 4 | 8 | 247,155 | 15 | 2 |
| Waimakariri | … | 270 | 6 | 4 | 270 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 272 | 11 | 4 | 27 | 4 | 6 | 164 | 10 | 9 | … | 191 | 15 | 3 | 454 | 6 | 8 | ||||
| Wairoa | 487 | 12 | 4 | 248 | 18 | 9 | 736 | 11 | 1 | 1,488 | 17 | 3 | 2,225 | 8 | 4 | 3,021 | 2 | 0 | 501 | 16 | 2 | … | 3,522 | 18 | 2 | 5,055 | 4 | 9 | ||
| Waitara | 1,500 | 9 | 2 | 512 | 15 | 0 | 2,013 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2,013 | 9 | 2 | 874 | 1 | 9 | 389 | 8 | 4 | … | 1,263 | 10 | 1 | 24,545 | 8 | 3 | ||
| Wanganui | 5,326 | 16 | 8 | 2,382 | 17 | 9 | 7,709 | 14 | 5 | 986 | 2 | 0 | 8,695 | 16 | 5 | 3,364 | 4 | 2 | 4,470 | 5 | 7 | … | 7,834 | 9 | 9 | 61,129 | 15 | 4 | ||
| Wellington | 85,982 | 17 | 8 | 1,780 | 16 | 0 | 87,763 | 13 | 8 | 49,504 | 0 | 2 | 137,207 | 13 | 10 | 10,010 | 14 | 9 | 70,856 | 8 | 11 | 49,185 | 0 | 10 | 130,052 | 4 | 6 | 319,371 | 8 | 1 |
| Westport | 50,411 | 15 | 8 | … | 50,411 | 15 | 8 | 30,050 | 8 | 10 | 80,462 | 4 | 6 | 88 | 2 | 5 | 44,666 | 0 | 10 | 30,050 | 8 | 10 | 74,804 | 12 | 1 | 647,403 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Whaingaroa | 146 | 14 | 6 | 37 | 2 | 0 | 183 | 16 | 6 | … | 183 | 16 | 6 | 21 | 18 | 7 | 156 | 4 | 4 | … | 180 | 2 | 11 | 164 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Whangarei | 311 | 7 | 1 | 34 | 18 | 4 | 346 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 347 | 14 | 1 | 298 | 11 | 2 | 53 | 0 | 7 | … | 351 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Totals | 407,056 | 4 | 8 | 99,879 | 12 | 1 | 506,935 | 16 | 9 | 166,298 | 12 | 0 | 673,234 | 8 | 9 | 146,961 | 7 | 4 | 333,228 | 8 | 5 | 189,060 | 6 | 6 | 669,250 | 2 | 3 | 4,285,973 | 10 | 4 |
In the succeeding table (page 203) will be found a summary of the amounts raised by loan, classified according to the rates of interest paid, distinguishing loans raised in the colony from those raised abroad. It will be noticed that the amount raised abroad (£5,552,100) is nearly three times as great as that raised in New Zealand (£2,287,595). The lowest rate of interest paid was 3 per cent., but the large sum of £2,828,201 was raised at 5 per cent., and £2,367,740 at 6 per cent., while £120,000 bore interest as high as 7 per cent.
| LOANS OF LOCAL BODIES, MARCH, 1902.—NET INDEBTEDNESS AND A(([0-9]+)). | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Amount of Debentures and Stock in Circulation. | Amount of Accrued Sinking Fund. | Not Indebtedness. | Annual Charge (excluding Exchange and Commission). | ||
| Interest. | Sinking Fund. | Total. | ||||
* Repayable by annual instalments of £64,343, representing 4 1/2 per cent. per annum on £918,808, 4 per cent. per annum on £16,322, and 3 1/2 per cent. per annum on £470,539, the amounts inscribed to 1st February, 1902. Repayments on the amount inscribed (£1,403,729, including £89,878 debentures under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act, 1882,” exchanged) would be £1,771,121. The actual repayments to date are £466,809, leaving £1,304,312 to be paid by way of interest and sinking fund on a present indebtedness of £1,046,645. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 6,714 | 932 | 5,782 | 325 | 108 | 433 |
| Boroughs | 3,435,884 | 378,529 | 3,057,355 | 176,829 | 12,401 | 189,290 |
| Town Boards | 805 | 107 | 698 | 44 | 30 | 74 |
| Road Boards | 0,728 | .. | 6,728 | 311 | 15 | 326 |
| River Boards | 43,670 | 10,785 | 33,885 | 2,249 | 564 | 2,813 |
| Water-supply Board | 22,213 | 1,119 | 21,094 | 1,125 | 200 | 1,325 |
| Harbour Boards | 4,123,631 | 393,904 | 3,729,727 | 203,574 | 21,259 | 224,833 |
| Drainage Boards | 200,050 | 37,687 | 162,363 | 12,003 | 2,125 | 14,128 |
| Totals | 7,839,095 | 823,063 | 7,016,632 | 396,400 | 36,762 | 433,222 |
| Inscribed debt of local bodies under “The Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1886” (including inscribed stock exchanged for debentures under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act, 1882”) | 1,046,645 | .. | 1,046,645* | .. | .. | 64,343 |
| Totals | 8,886,340 | 823,063 | 8,063,277 | 396,460 | 36,762 | 497,565 |
| LOANS OF LOCAL BODIES, RAISED WITHIN AND WITHOUT THE COLONY. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABLE showing the Amount of Indebtedness of Counties, Boroughs, Town, Road, River, and Water-supply Boards, as on the 31st March, 1902, and of Harbour and Drainage Boards as on the 31st December, 1901, classified according to the Rates of Interest paid, distinguishing Loans raised in the Colony from those raised elsewhere. (See note.) | |||||||||||||
| Loans raised in the Colony. | |||||||||||||
| Local Bodies. | No Interest. | 3 % | 3 1/2 % | 4 % | 4 1/4 % | 4 1/2 % | 5 % | 5 1/2 % | 6 % | 6 1/2 % | 7 % | Total. | |
* Including £500 at 4 3/8 per cent. and £2,500 at 4 3/4 per cent. † Including £2,000 at 5·7 per cent. and £3,000 at 5 3/4 per cent. ‡ Including £1,013 at 3 1/2 per cent. NOTE.—Not including loans, amounting to £1,040,645, repayable by annual instalments under “The Roads and Bridges Construction Act, 1882,” and “The Government Loans to Local Bodies Act. 1886.” | |||||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,214 | 4,500 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6,714 |
| Boroughs | 25,000 | .. | .. | 556,190 | 57,400 | 150,725* | 187,999 | 18,000 | 65,900† | 145,270 | 2,000 | 63,000 | 1,272,084 |
| Town Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 305 | .. | .. | .. | 500 | .. | .. | 805 |
| Road Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,956 | 1,752 | .. | .. | 20 | .. | .. | 6,728 |
| River Boards | .. | .. | .. | 3,200 | .. | 5,000 | 650 | .. | 3,320 | 5,500 | .. | .. | 17,670 |
| Water supply Boards | .. | .. | 1,013‡ | .. | .. | 6,000 | 12,200 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,000 | 22,213 |
| Harbour Boards | .. | 14,031 | 60,000 | 718,900 | .. | 38,300 | 98,650 | .. | 31,000 | 450 | .. | .. | 961,331 |
| Drainage Board | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 50 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 50 |
| Total raised in colony | 25,000 | 14,031 | 61,013‡ | 1,278,290 | 57,400 | 207,500* | 305,801 | 18,000 | 100,220† | 151,740 | 2,600 | 66,000 | 2,287,595 |
| Loans raised outside the Colony. | |||||||||||||
| Boroughs | .. | .. | .. | 33,000 | .. | 254,700 | 785,500 | .. | .. | 1,030,600 | .. | 60,000 | 2,103,800 |
| River Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21,000 | .. | .. | 5,000 | .. | .. | 26,000 |
| Harbour Boards | .. | .. | .. | 366,000 | .. | 100,00 | 1,715,900 | .. | .. | 980,400 | .. | .. | 3,162,300 |
| Drainage Board | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .200,000 | .. | .. | 200,000 |
| Total raised out of colony | .. | .. | .. | 399,00 | .. | 354,700 | 2,522,400 | .. | .. | 2,216,00 | .. | 60,000 | 5,552,100 |
| Total Loans raised. | |||||||||||||
| Counties | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,214 | 4,500 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6,714 |
| Boroughs | 25,000 | .. | .. | 589,190 | 57,400 | 405,425* | 973,499 | 18,00 | 65,900† | 1,175,870 | 2,600 | 123,000 | 3,435,884 |
| Town Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 305 | .. | .. | .. | 500 | .. | .. | 805 |
| Road Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,956 | 1,752 | .. | .. | 20 | .. | .. | 6,728 |
| River Boards | .. | .. | .. | 3,200 | .. | 5,000 | 21,650 | .. | 3,320 | 10,500 | .. | .. | 43,670 |
| Water-supply Board | .. | .. | 1,013‡ | .. | .. | 6,000 | 12,200 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,000 | 22,213 |
| Harbour Boards | .. | 14,031 | 60,000 | 1,081,900 | .. | 138,300 | 1,814,550 | .. | 31,000 | 980,850 | .. | .. | 4,123,631 |
| Drainage Boards | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 50 | .. | .. | 200,000 | .. | .. | 200,050 |
| Total loans raised | 25,000 | 14,031 | 61,013‡ | 1,677,290 | 57,400 | 562,200* | 2,828,201 | 18,000 | 100,220† | 2,367,740 | 2,600 | 126,000 | 17,839,695 |
From the tables on the preceding pages it will be seen that the total amount owing was, on the 31st March, 1902, £7,839,695. But against this accrued sinking funds to the value of £823,063 were held, leaving a net debt of £7,016,632, exclusive of moneys borrowed from the General Government and repaid by annual instalments.
The total annual charge (excluding exchange and commission) stood at £433,222, of which £396,460 was for interest, and the remainder, £36,762, contributions to sinking fund accounts.
Of the total net indebtedness in 1901–1902 the debt of the Harbour Boards, £3,729,727, formed the largest item, while the Borough Councils owed £3,057,355.
On referring to the comparative table on page 196, a great advance in the outstanding loans of local governing bodies will be noticed. Between 1892 and 1902 the gross indebtedness increased from £6,081,934 to £7,839,695, an addition of £1,757,761 or nearly 29 per cent. during the ten years. During the same period the population advanced at the rate of 24 per cent., and the value of land and improvements (1891–1902) from £122,000,000 to £155,000,000, or at the rate of 27 per cent.
The aggregate interest-charge for the year under review was £396,460, and £295,200 of this was payable on loans raised outside the colony. The average rate of interest payable to bondholders was rather more than £5 1s. 6d. per cent.
While the average rate of interest on the above-mentioned debt is found to be slightly more than 5 per cent., over two millions and three-quarters were raised at 5 per cent., and nearly two and a half millions at 6 per cent. or over.
The above Act consolidates certain measures dealing with loans to local bodies. As to Government loans, it contains the same provision as the Amendment Act of 1899 in respect of the debentures of any future loan, and offers, instead of interest payable at 5 per cent. for a term of twenty-six years, one or other of the following alternatives:—
Four and a half per cent. per annum for a term of twenty-six years;
Four per cent. per annum for thirty-two years; or
Three and a half per cent. per annum for forty-one years.
“The Local Bodies' Loans Amendment Act, 1902,” empowers the Colonial Treasurer to lend to small boroughs, having at the time of the last preceding census a population of less than 2,000 persons, any sum not exceeding £2,000 in any year for the purpose of making streets within the borough.
“The Municipal Corporations Act, 1900,” with its amending Act of 1902, deals with the franchise in the case of boroughs, and provides that, in addition to the persons who are already entitled to be enrolled, every person shall be so entitled who possesses the freehold or residential qualifications stated in the Act.
The possession of the freehold qualification is defined as being the beneficial and duly registered owner of a freehold estate in land of the capital value of not less than £25, situated in the borough, notwithstanding that any other person is the occupier thereof, or part thereof, under any tenancy.
Every person is deemed to possess a residential qualification within a borough if he is, and for at least three months last past has been, a residential occupant within such borough.
No person may be entered in the burgess lists in respect of more qualifications than one; but any person who has more than one qualification may select the one in respect of which he wishes to be entered.
In the case of husband and wife, any qualification possessed by one of them is deemed to be possessed by each.
No person enrolled on a burgess roll has more than one vote, and no person enrolled by virtue of the residential qualification can vote on any proposal relating to loans or rates.
A special article on this system of rating (which it is optional with local governing bodies to adopt or not) is given in Part III. of this work.
Up to the end of April, 1903, fifty-one local governing bodies (thirty boroughs, twelve counties, one town district, and eight road districts) had notified in the New Zealand Gazette that the proposal to levy rates on the unimproved value of land had been carried, while in eight cases (boroughs) the proposal had been rejected.
A county having decided to levy rates on the unimproved value, makes it compulsory for all interior Town and Road Boards to adopt the same system of rating. But in counties where the Counties Act is suspended, or where a general rate is not levied, the ratepayers of any Road Board may take a poll on the question. It is also permissible for any Town Board within a county not rating on the unimproved value to adopt that system, the decision to do so having been carried by vote of the ratepayers. The date of the polling did not, in some instances, allow of a rate on the unimproved value being struck for the year ended 31st March, 1902.
The amount of rates levied by the various Borough Councils, County Councils, Town Boards, and Road Boards, with other particulars, as returned by these bodies for the 31st March, 1902, will be found on the following pages:—
| BOROUGHS, 1901–1902. | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of Borough | Estimated Area (including Town Belt) in Acres. | Population. | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound. | Estimated Annual (or renting) Value of Rateable Property, March, 1902. | Capital Value of Rateable Property, March, 1902. | Unimproved Value of Rateable Property, March, 1902. | |||||||||||
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | General. | Separate. | Special. | Water. | Library. | |||||||||||
(1) For domestic supply; stores, nil. (2) Rate levied by Hawera County Council. (3) 1s. 3d. per 1,000 gallons by meter. (4) Consumption rate, 5 per cent., 2 1/2 per cent., or 1 1/4 per cent. (5) On capital value, £521,574. (6) On animal value. (7) On capital value (for charitable aid purposes). (8) Fee of 10s. per annum for sanitation; special, 1/2d., 1/20d., /16d., over special areas; 3/8d., 3/4d., Christchurch Drainage Board. (9) On capital value, £799,465; Christchurch drainage rate—Sewage area 3/4d. on capital value, rural area 17/32d. on unimproved value; Waimakariri River rate, 1/10d. on unimproved value. (10) Christchurch drainage rate, 3/8d.; South Waimakariri rate, 2/64d. (11) 2 1/3 per cent. on unconnected property. (12) West District only. (13) Maximum under “Municipal Corporations Act, 1900.” (14) In terms of section 102 of “Municipal Corporations Act, 1900.” (15) Under £12 10s., 10s.; under £300, 5 per cent.; over £300, 4 per cent.; land and buildings, half these rates. (16) Sanitation rate, over part of district. (17) Dunedin Drainage Board, 2d.; water rate, as per scale, “Municipal Corporations Act, 1900.” * Waihi: In first year. | ||||||||||||||||||
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | £ | £ | £ | ||||||
| Whangarei | 2,038 | 1,600 | 340 | 350 | .. | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 134,606 | .. | |||
| Birkenhead | 2,700 | 1,100 | 242 | 252 | 278 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 1/4 | 0 | 3 | .. | .. | 7,312 | .. | .. | ||
| Devonport | 640 | 3,823 | 746 | 663 | 1,205 | 0 | 1 1/2 | .. | 1/2 d., 3/4 d., & 1d. | 6d., or 2 1/2 per cent | .. | .. | .. | 211,394 | ||||
| Auckland | 1,762 | 35,284 | 7,507 | 5,307 | 7,308 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1/4 to 2 1/2 per cent. | 0 0 1/2 | 351,821 | .. | .. | ||
| Grey Lynn (01) | 900 | 4,120 | 800 | 670 | 884 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 4 to 6 per cent. | .. | 25,886 | .. | .. | ||
| Newmarket | 150 | 2,060 | 416 | 312 | 392 | 1 | 4 | .. | 0 | 6 | 4 to 6 per cent. | .. | 13,566 | .. | .. | |||
| Parnell | 480 | 4,575 | 963 | 615 | 863 | 1 | 5 | .. | 0 | 10 | 4 per cent. | .. | 31,455 | .. | .. | |||
| Onehunga | 1,200 | 3,015 | 820 | 603 | 1,000 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | 4 per cent. | 0 | 0 1/2 | 17,868 | .. | .. | |||
| Thames | 2,560 | 4,200 | 1,078 | 863 | 1,239 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | .. | 2 1/2 per cent. | 0 | 1 | 26,408 | .. | .. | ||
| Te Aroha | 200 | 888 | 198 | 208 | 320 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | 0 | 7 | .. | 6,303 | .. | .. | |||
| Waihi* | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | |||||
| Hamilton | 1,600 | 1,260 | 420 | 390 | 650 | 0 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 62,000 | ||||
| Cambridge | 1,083 | 1,000 | 263 | 200 | 688 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6,489 | .. | .. | ||||
| Tauranga | 1,000 | 1,050 | 386 | 416 | 591 | 2 | 0 | .. | 0 | 3 | .. | .. | 4,717 | .. | .. | |||
| Gisborne | 1,200 | 2,750 | 550 | 475 | 820 | 1 | 9 | .. | 0 | 3 | .. | .. | 35,000 | .. | .. | |||
| New Plymouth | 850 | 4,500 | 910 | 820 | 1,200 | 1 | 9 | .. | 0 | 10 | (1)0 | 0 | .. | 40,307 | .. | .. | ||
| Stratford | 1,920 | 2,023 | 450 | 567 | 1,020 | 0 | 1 | .. | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | 239,585 | .. | |||
| Hawera (1901) | 500 | 2,131 | 443 | 412 | 610 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17,134 | .. | .. | ||||
| Eltham | 1,590 | 1,018 | 250 | 240 | 500 | 2) | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | |||||
| Patea | 1,420 | 700 | 260 | 197 | 380 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 3/8 | .. | 0 | 1 3/4 | .. | 5,945 | .. | .. | ||
| Wanganui | 1,000 | 7,550 | 1,560 | 1,295 | 1,720 | 0 | 10 | .. | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | 61,000 | .. | .. | |||
| Marton | 1,423 | 1,101 | 238 | 249 | 406 | 1 | 0 | .. | 1 | 6 | .. | 0 | 0 1/2 | 9,953 | .. | .. | ||
| Feilding | 3,500 | 2,500 | 475 | 463 | 880 | 1 | 3 | .. | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 1 | 19,182 | .. | .. | ||
| Palmerston N. | 4,593 | 7,154 | 1,461 | 1,217 | 2,567 | 0 | 1 3/4 | .. | 1/16d., 1/10d., 2 1/8 d. | 2 per cent. under max. | 0 | 0 1/8 | .. | .. | 331,314 | |||
| Foxton | 5,760 | 1,212 | 286 | 320 | 656 | 1 | 3 | .. | 0 | 1 1/4 | .. | 0 | 1 | 8,710 | .. | .. | ||
| Hastings | 5,740 | 3,700 | 825 | 838 | 1,321 | 1 | 2 | .. | 0 | 10 | .. | .. | 41,340 | .. | .. | |||
| Napier | 879 | 8,774 | 1,885 | 984 | 2,574 | 0 | 9 | .. | 5d. & 10d. | (3)1 to 2 1/2 per cent. | .. | 86,252 | .. | .. | ||||
| Dannevirke | 1,222 | 2,500 | 470 | 453 | 1,305 | 1 | 3 | .. | 3d. & 7d. | 2 1/2 & 3 3/4 per cent. | .. | 16,265 | .. | .. | ||||
| Woodville | 1,240 | 950 | 230 | 472 | 472 | 0 | 3 5/8 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 41,286 | ||||
| Pahiatua | 740 | 1,209 | 350 | 410 | 460 | 0 | 2 1/2 | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 61,734 | ||
| Masterton | 4,311 | 4,000 | 622 | 667 | 1,104 | 1 | 1 | .. | .. | (4) | .. | 36,200 | .. | .. | ||||
| Carterton | 1,880 | 1,205 | 280 | 250 | 371 | 0 | 0 15/16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 109,597 | .. | ||||
| Greytown | 3,907 | 1,122 | 250 | 230 | 374 | 1 | 6 | 3d. & 6d. | 0 | 2 | .. | 0 | 1 | 9,148 | .. | .. | ||
| Lower Hutt | 3,225 | 1,950 | 382 | 383 | 529 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 3/16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 343,507 | .. | |||
| Petone | 952 | 3,780 | 844 | 587 | 1,494 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 5 | .. | .. | 29,720 | .. | |||
| Onslow | 2,870 | 1,450 | 322 | 360 | 650 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 1/6 | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 144,944 | ||
| Wellington | 1,100 | 43,638 | 9,260 | 5,100 | 9,958 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 3/4 | 0 | 9 3/5 | 0 | 1 | 473,599 | .. | .. |
| Karori | 5,127 | 1,217 | 220 | 320 | 545 | 0 | 1 91/200 | 0 | 0 5/32 | 0 | 1 1/11 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 151,625 | ||
| Melrose | 3,962 | 3,805 | 761 | 1,050 | 1,483 | (5)0 | 1 3/4 | (5)0 | 0 1/4 | 0 | 0 1/6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 332,688 | ||
| Picton | 560 | 875 | 170 | 269 | 980 | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 0 1/5 | .. | 1/4 d. and 1/2 d. | .. | .. | 70,725 | .. | |||
| Blenheim | 1,571 | 3,250 | 755 | 580 | 1,450 | 1 | 1 1/4 | 0 | 2 1/4 | 0 | 2 1/2 | .. | .. | 24,890 | .. | .. | ||
| Nelson | 4,800 | 7,040 | 1,482 | 1,175 | 2,352 | 1 | 3 | .. | 0 | 3 7/8 | 2 to 3 1/2 per cent. | .. | 56,954 | .. | .. | |||
| Richmond | 2,300 | 590 | 130 | 133 | 151 | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | (6)4 per cent. | .. | .. | 85,012 | .. | ||||
| Motueka | 5,643 | 886 | 168 | 175 | 175 | 0 | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 91,851 | .. | ||||
| Westport | 713 | 3,000 | 800 | 977 | 1,130 | 1 | 8 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 22,000 | .. | .. | ||||
| Greymouth | 2,000 | 4,000 | 799 | 628 | 1,052 | 0 | 4 | .. | (7)0 | 0 9/16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 78,955 | |||
| Brunner | 5,700 | 1,570 | 340 | 272 | 320 | 1 | 6 | 6d. & 9d. | 0 | 10 | .. | .. | 3,900 | .. | .. | |||
| Kumara | 842 | 1,120 | 296 | 321 | 427 | 0 | 0 15/16 | 0 | 1 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 27,658 | .. | |||
| Hokitika | 1,280 | 2,000 | 650 | 580 | 670 | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 1 3/8 | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 39,311 | ||
| Ross | 4,196 | 650 | 300 | 350 | 414 | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 0 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 30,996 | .. | |||
| Rangiora | 1,040 | 1,768 | 400 | 347 | 567 | 0 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 172,097 | .. | ||||
| Kaiapoi | 1,020 | 1,795 | 416 | 365 | 627 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,325 | .. | .. | ||||
| Christchurch | 1,249 | 18,538 | 4,265 | 2,950 | 4,789 | 1 | 7 | 2d. & 1s. | 2 1/4d. & 2d. | .. | .. | 246,086 | .. | .. | ||||
| Linwood | 659 | 7,000 | 1,514 | 1,201 | 1,504 | 0 | 1 1/8 | 0 | 0 1/8 | (8) | .. | .. | .. | .. | 169,251 | |||
| St. Albans | 1,500 | 6,650 | 1,490 | 1,395 | 1,783 | 0 | 1 1/4 | 0 | 0 3/32 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 756,372 | .. | |||
| Sydenham | 1,190 | 11,816 | 2,472 | 2,009 | 2,449 | 0 | 3 1/4 | .. | (9)0 | 0 1/9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 247,924 | |||
| Woolston | 1,276 | 2,600 | 530 | 565 | 667 | 0 | 1 1/4 | 0 | 0 5/32 | (10) | .. | .. | .. | 200,919 | .. | |||
| Sumner | 4,876 | 856 | 228 | 295 | 410 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 | (11)2 1/2 per cent. | .. | 7,030 | .. | .. | ||
| New Brighton | 1,500 | 1,000 | 220 | 565 | 713 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 | .. | .. | 6,914 | .. | .. | ||
| Lyttelton | 2,014 | 4,021 | 840 | 611 | 797 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 25,216 | .. | .. | ||||
| Akaroa | 221 | 580 | 136 | 130 | 190 | 0 | 0 15/16 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 48,182 | .. | ||||
| Ashburton | 680 | 2,300 | 520 | 586 | .. | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 22,627 | .. | .. | ||||
| Temuka | 794 | 1,500 | 345 | 404 | 639 | 0 | 1 1/2 | (12)0 | 0 3/8 | .. | .. | .. | 86,872 | .. | .. | |||
| Timaru | 1,100 | 6,500 | 1,503 | 950 | 1,825 | 1 | 6 | .. | 0 | 8 | 1s. or 6d. | .. | 51,635 | .. | .. | |||
| Waimate | 649 | 1,400 | 350 | 348 | 500 | 0 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 45,356 | ||||
| Oamaru | 1,111 | 4,836 | 1,270 | 1,304 | 1,547 | 2 | 0 | .. | 1 | 3 | (13) | .. | 30,529 | .. | .. | |||
| Hampden | 640 | 310 | 95 | 117 | 120 | 0 | 1 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15,633 | .. | ||||
| Palmerston S. | 800 | 738 | 184 | 248 | 360 | 0 | 1 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 41,598 | .. | ||||
| Hawksbury | 2,700 | 690 | 164 | 240 | 440 | 0 | 0 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 45,644 | .. | ||||
| Pert Chalmers | 335 | 2,056 | 495 | 508 | 576 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | (14) | .. | 12,262 | .. | .. | ||||
| North-East Valley | 5,980 | 3,825 | 760 | 1,000 | 1,172 | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 6 | .. | .. | 19,060 | .. | .. | |||
| Maori Hill | 3,700 | 1,600 | 336 | 362 | 392 | 1s., 1s. 3d., & 1s. 6d. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,948 | .. | .. | |||||
| West Harbour | 1,670 | 1,480 | 302 | 480 | 639 | 1 | 0 | .. | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | 8,934 | .. | .. | |||
| Dunedin | 1,800 | 25,114 | 6,000 | 3,200 | 4,900 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 9 | (15) | .. | 268,965 | .. | .. | ||
| Roslyn | 2,000 | 4,700 | 961 | 1,027 | 1,137 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 1/2 | (16)0 | 3 | .. | .. | 32,855 | .. | .. | ||
| Mornington | 654 | 4,095 | 819 | 810 | 1,002 | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 1 | .. | .. | 22,772 | .. | .. | |||
| Caversham | 1,073 | 5,340 | 1,048 | 870 | 1,056 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 per cent. | .. | 32,727 | .. | .. | ||
| St. Kilda | 463 | 1,800 | 375 | 483 | 688 | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 6 | 6 per cent. | .. | 11,129 | .. | .. | |||
| South Dunedin | 413 | 5,810 | 1,162 | 915 | 1,173 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | (17)0 | 6 | 5s. to 6 per cent. | .. | 24,689 | .. | .. | ||
| Green Island | 103 | 667 | 138 | 184 | 195 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,926 | .. | .. | ||||
| Mosgiel | 967 | 1,500 | 330 | 328 | 533 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 8,939 | .. | .. | ||||
| Milton | 265 | 1,400 | 270 | 215 | 323 | 1 | 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6,989 | .. | .. | ||||
| Kaitangata | 1,158 | 1,462 | 308 | 282 | 528 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | .. | .. | .. | 6,778 | .. | .. | |||
| Balclutha | 568 | 1,040 | 270 | 264 | 310 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | 0 | 1 | 5,252 | .. | .. | |||
| Lawrence | 640 | 1,165 | 240 | 355 | 300 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | 3d. and 6d. | .. | 8,088 | .. | .. | ||||
| Roxburgh | 400 | 500 | 122 | 81 | 126 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | 6d. | .. | 1,736 | .. | .. | ||||
| Tapanui | 126 | 500 | 140 | 80 | 150 | 1 | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,013 | .. | .. | ||||
| Naseby | 113 | 550 | 155 | 147 | 167 | 0 | 9 | .. | .. | 2 1/2, 3 1/2, 6, and 7 per cent. | .. | 2,333 | .. | .. | ||||
| Cromwell | 640 | 653 | 140 | 135 | 242 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | 1 | 2 | .. | 4,969 | .. | .. | |||
| Alexandra | 840 | 818 | 202 | 170 | 265 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 | .. | 6,280 | .. | .. | |
| Arrowtown | 390 | 386 | 94 | 101 | 212 | 1 | 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,010 | .. | .. | ||||
| Queenstown | 923 | 690 | 196 | 175 | 714 | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | .. | 4,850 | .. | .. | ||
| Gore | 1,150 | 2,500 | 540 | 610 | 1,337 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17,624 | .. | .. | ||||
| Mataura | 1,530 | 950 | 239 | 216 | 491 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,866 | .. | .. | ||||
| Winton | 160 | 500 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,021 | .. | .. | ||||
| Invercargill | 1,040 | 6,300 | 1,225 | 1,100 | 1,800 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | (13) | .. | 61,644 | .. | .. | ||
| North Invercargill | 326 | 925 | 200 | 253 | 320 | 1 | 4 | .. | 1 | 4 | .. | .. | 4,036 | .. | .. | |||
| South Invercargill | 4,000 | 1,950 | 381 | 618 | 907 | 1 | 6 | .. | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | 6,330 | .. | .. | |||
| East Invercargill | 121 | 939 | 192 | 225 | 225 | 1 | 9 | .. | 0 | 9 | .. | .. | 4′,253 | .. | .. | |||
| Avenal | 80 | 355 | 75 | 104 | 104 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | 1,912 | .. | .. | |||
| Gladstone | 240 | 335 | 70 | 140 | 140 | 1 | 0 | .. | 0 | 6 | .. | .. | 3,792 | .. | .. | |||
| Campbelltown | 2,000 | 1,450 | 356 | 360 | 650 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9,479 | .. | .. | ||||
| Riverton | 718 | 850 | 252 | 230 | 423 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,264 | .. | .. | ||||
| COUNTIES, 1901–1902. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [NOTE.—For value of land and improvements see Section XXVI.] | ||||
| COUNTIES. | Area in Square Miles (including Boroughs). | Population, Census, March, 1901, (excluding Boroughs). | Rates struck by County. | |
| General. | Other. | |||
* On unimproved value. † Outlying, 3/4d.; road districts, 3/4d. | ||||
| Mongonui (no return) | 934 | 2,274 | .. | |
| Whangaroa | 160 | 927 | 1d. | |
| Hokianga | 972 | 1,767 | 2 1/2d.* | |
| Bay of Islands | 826 | 2,587 | 1d. | |
| Hobson | 688 | 4,813 | 1 1/2d. | |
| Whangarei | 928 | 6,380 | 3/4d | 3/4d. separate. |
| Otamatea | 364 | 2,721 | 3/4d. | 3/4d. and 3/4d. separate in outlying districts. |
| Rodney | 560 | 3,67 | 3/4d. | 3/4d. H. and C.A.; 3/4d. separate in Hoteo district. |
| Waitemata | 613 | 7,035 | 3/4d | 1/2d. separate in three outlying districts, 3/4d. in five; 5/16d. special in Mairetahi Riding. |
| Eden | 43 | 19,314 | .. | |
| Manukau | 791 | 12,306 | .. | |
| Coromandel | 403 | 4,169 | 1 1/2d. | 3/4d. on Native lands. |
| Thames | 494 | 5,043 | 1 1/2d. | |
| Ohinemuri | 478 | 9,978 | d. | 3/4d. over special water-rate district. |
| Piako | 1,095 | 2,436 | 1/2d. | Separate, d.; Patetere, 1/4d.; Te Aroha special, 1/10d. Taotaoroa and Patetere Ridings. |
| Waikato | 591 | 3,183 | 1/4d. | |
| Waipa | 282 | 3,580 | 1/2d., 3/4d. | 3/4d. separate Hamilton, Mangapiko, and Alexandra outlying districts. |
| Raglan | 824 | 1,697 | 1/2d. | 1/2d. H. and C.A. |
| Kawhia | 1,515 | 1,113 | .. | |
| West Taupo | 1,594 | 287 | .. | |
| East Taupo | 2,581 | 256 | .. | |
| Rotorua | 984 | 1,307 | .. | |
| Tauranga | 577 | 1,720 | 1 1/4d. 1 3/8d. 1 d.* | 1/10d. H. and C.A.; 1/4 d., d. special.* |
| Whakatane (no return) | 1,716 | 779 | .. | |
| Opotiki | 1,440 | 1,438 | 3/4d. | 3/4d. separate in outlying district. |
| Waiapu | 1,121 | 711 | 1d. | 3/4d. special, Tokomaru-Tuakau. |
| Cook | 1,950 | 6,393 | 3/4d. | Various. |
| Clifton | 1,518 | 2,535 | 1d. | 1/2d. special, Junction Road loan; d. special, Onaero Road loan. |
| Taranaki (1901) | 386 | 19,541 | 2/3d. | 1/1 1/2d. for Eltham Road loan (small portion of county only). |
| Hawera | 381 | 3/4d. | 1/4d. separate over Mangatoki, Okaiawa, and Eltham outlying districts. | |
| Egmont | 254 | |||
| Stratford | 784 | 5,081 | 1/2d., 3/4d. | 1/2d. separate, South, East, and West Ridings; special various. |
| Patea | 691 | 3,046 | 3/4d. | d. special, Kapara loan, 3/4d. Omuoa loan; 3/4d. separate, Kapara Riding. |
| Waitotara | 343 | 3,476 | 1d. | |
| Wanganui | 1,942 | 4,018 | .. | d., 3/8d. special, Long Acre; 7/16d. Denlair, d. Waikupu Subdivisions. |
| Rangitikei | 852 | 7,570 | 7/8d. | Special, various, in twenty-seven special-rating districts. |
| Kiwitea | 336 | 2,844 | 3/4d. | Separate and special, various. |
| Kairanga | 184 | 6,778 | .. | |
| Oroua | 213 | |||
| Pohangina | 295 | 1,536 | 1/2 d. | 1/4d., 1/2d. separate; special, various. |
| Manawatu | 267 | 3,00 | d. | Separate and special, various. |
| Horowhenua | 591 | 4,654 | 1/2d., d., 3/4d. | Special, various. |
| Wairoa | 1,887 | 1,773 | 3/4d. | Special, d., d., d. in portions of county. |
| Hawke's Bay | 3,232 | 6,833 | 3/4d. | |
| Waipawa | 990 | 9,495 | d., d. d.* | Special, various.* |
| Woodville | 164 | d. special, for loans.* | ||
| Patangata | 747 | 2,376 | 1/2d., 3/4d., 1d., 1 1/4d. | d. special, Oero Riding; d. special, Taumumu Riding. |
| Pahiatua | 302 | 3,600 | d. | Fifty-one special, various. |
| Akitio | 328 | 1,048 | 1/2d. | |
| Castlepoint | 150 | 457 | 1 1/2d. | Special, various. |
| Eketahuna | 170 | 2,332 | 2 1/4d.* | Special various.* |
| Mauriceville | 125 | 1,127 | 1d. | Special rates over small rating areas. |
| Masterton | 670 | 3,123 | 7/8d. | Separate various. |
| Wairarapa South | 445 | 5,419 | .. | 1/8d. H. and C.A. |
| Featherston | 965 | d. | Special, various. | |
| Hutt | 590 | 7,171 | 1/4d. 1/2d., 3/4d. | 1/2d., d. separate; special, various. |
| Sounds | 573 | 946 | .. | |
| Marlborough | 3,812 | 6,518 | .. | |
| Kaikoura | 673 | 1,765 | 3/4d. | |
| Collingwood | 1,029 | 2,490 | d. | |
| Waimea | 1,662 | 7,833 | 3/4d. | d. H. and C.A.; d. and d. special for loans. |
| Buller | 1,818 | 4,68 | 3/4d. | d. special, Charleston Riding; d. H. and C.A. |
| Inangahua | 2,256 | 4,595 | 3d. 3 1/2d.* | Two special, 5/16d., 1/2d., Reefton Town; 2 1/4d. Boatman's Irrigation District.* |
| Grey | 1,452 | 4,971 | 1 1/2d. | d. H. and C.A. |
| Westland | 4,420 | 4,405 | 1 1/2d. | |
| Amuri | 2,62 | 1,142 | 1/2d. | d., 7/16d., d., special, for interest on loans. |
| Cheviot | 322 | 1,120 | 1d., 7/8d.* | d. special annual recurring rate on £103,630.* |
| Ashley | 1,627 | 11,599 | .. | |
| Selwyn | 2,597 | 30,787 | .. | 1/. H. and C.A. |
| Akaroa | 353 | 3,669 | d. | 1/4d. special. |
| Ashburton | 2,542 | 11,342 | 1/4d. | 1/2d. Ashburton Forks Public Works District; d. Mount Somers tramway; 1 1/2d. Ruapuna No. 1 and No. 2 Districts; d. Wakanui Public Works District. |
| Geraldine | 945 | 5,991 | 1/4d. | 3/8d. to 9/16d. |
| Levels | 273 | 5,496 | 1d. | |
| Mackenzie | 2,537 | 1,642 | 5/8d. | |
| Waimate | 1,343 | 5,653 | 7/8d.* | d., d., 1d. separate.* |
| Waitaki | 2,333 | 9,086 | 1/2d. | Separate, 1/8d. Otepopo, 1/4d. Kakanui, d. Moeraki and Waiareka Ridings. |
| Waihemo | 336 | 2,014 | d. | |
| Waikouaiti | 318 | 4,082 | 4/3d. | |
| Peninsula | 37 | 2,561 | .. | |
| Taieri (1991) | 930 | 7,179 | 3/4d. | 1/4d. H. and C.A. |
| Bruce | 503 | 4,762 | 3/8d., 3/4d.† | d. H. and C.A.; 1/6d. and d. separate; special, various. |
| Clutha | 946 | 6,445 | 3/4d. | d. H. and C.A.; d. separate, Catlin's and South Molyneux Ridings; special, various. |
| Tuapeka | 1,365 | 6,272 | 3/4d. | |
| Maniototo | 1,239 | 3,792 | d. | |
| Vincent | 2,684 | 4,362 | 1d. | 1 1/2d., 2 1/2d., special. |
| Lake | 3,712 | 2,535 | 1 1/4d. | d. special. |
| Southland | 3,852 | 22,583 | 1 1/4d. | 1/8d. H. and C.A.; 1/16d. small-birds destruction; 1/4d., d., 5/12d. special in special-rating districts. |
| Wallace | 3,404 | 7,989 | 3/4d. | d. H. and C.A.; separate rates in four ridings; special 1/20d. |
| Fiord | 3,040 | 124 | .. | |
| Stewart Island | 651 | 253 | 1/2d. | 1/4d. H. and C.A. |
| Chatham Islands | .. | .. | .. | |
| TOWN DISTRICTS, 1901–1902. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Town Districts. | Estimated Population 31st March, 1902. | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value of Property. | |||
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | ||||
* On the annual value. † On the unimproved value. (1) Special rate, 1/8d. (2) County rate, 1/4d. (3) Special rate, 1 3/4d. (4) Special rate, 1/4d. (5) Special rate, 1/8d. (6) Special rate, 1/4d.; separate, 1/16d. (7) Water rate 7 per cent. on annual value where water supplied. (8) Special rate, 3/8d. | ||||||
| s. | d. | |||||
| Kamo | 244 | 74 | 78 | 102 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Helensville | 550 | 104 | 100 | 124 | *0 | 4 |
| Papakura | 280 | 76 | 155 | 202 | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Te Awamutu | 350 | 50 | 63 | 75 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Kihikihi | 263 | 62 | 99 | 141 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Ngaruawahia | 300 | 100 | 146 | 140 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Rotorua | 1,000 | 250 | .. | .. | .. | |
| Opotiki | 700 | 260 | 185 | 280 | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Waitara (Raleigh) (1901) | 765 | 169 | 273 | .. | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Opunake (1901) | 466 | 98 | 163 | 478 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Inglewood | 829 | 193 | 173 | 262 | 0 | 0 3/4(1) |
| Normanby | 356 | 85 | 126 | 126 | †0 | 5 |
| Manaia | 430 | 70 | 153 | 341 | 0 | 0 3/4(2) |
| Waverley | 416 | 108 | 118 | 118 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Lethbridge (Turakina) | 229 | 54 | 63 | 63 | *0 | 8 |
| Bull's | 550 | 122 | 130 | 179 | *1 | 0 |
| Halcombe | 376 | 90 | 147 | 730 | *1 | 0(3) |
| Clyde (Wairoa) | 700 | 130 | 165 | 300 | 0 | 0 1/2(4) |
| Taradale | 800 | 160 | 190 | 198 | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Ormondville | 458 | 104 | 151 | 215 | 0 | 2 3/8 |
| Waipawa | 669 | 165 | 125 | 194 | †0 | 1 7/8(5) |
| Kaikora North | 269 | 60 | 105 | 135 | *1 | 0 |
| Featherston | 629 | 120 | 150 | 190 | 0 | 0 3/4(6) |
| Johnsonville | 500 | 108 | 113 | .. | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Havelock | 316 | 76 | 79 | 153 | 0 | 1 |
| Amberley | 417 | 96 | 89 | 130 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Southbridge | 396 | 120 | 240 | .. | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Hampstead | 1,234 | 250 | 270 | 320 | 0 | 0 1/2 |
| Tinwald | 560 | 111 | 160 | 233 | 0 | 0 5/8 |
| Geraldine | 900 | 210 | 208 | 315 | 0 | 0 3/4 |
| Greytown (Allanton), (no return) | 227 | .. | .. | .. | .. | |
| Outram | 420 | 61 | 66 | 110 | 0 | 0 1/4(7) |
| Clinton | 480 | 95 | 124 | 136 | *0 | 6 |
| Wyndham | 417 | 115 | 116 | 354 | *1 | 0 |
| Otautau | 475 | 106 | 122 | 186 | 0 | 0 3/4(8) |
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) 1/8d. separate. (2) On annual value; 4 1/2d. special. (3) 5/8d. special. (4) Hospital and charitable aid rate, d. (5) 1/8d. special, for lighting. (6) 17/32d., 2 1/8d., special, in special districts. (7) On unimproved value. (8) 5/16d. and 1/2d. special. (9) 1/2d. special. (10) 1/16d. special. (11) 1/3d. special. (12) 1/4d. special. | |||||||
| d. | |||||||
| Mongonui |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Whangaroa | |||||||
| Bay of Islands | |||||||
| Hokianga | |||||||
| Hobson | |||||||
| Whangarei— | |||||||
| Hikurangi | 495 | 80 | 120 | 135 | 3/4 | ||
| Kaurihohore | 191 | 51 | 56 | 68 | 3/4 | ||
| Kensington | 49 | 9 | 18 | 18 | 3/4 | ||
| Maungakaramea | 288 | 70 | 121 | 121 | 3/4 | ||
| Marua | 274 | 63 | 85 | 112 | 3/4 | ||
| Maunu | 584 | 150 | 142 | 154 | 3/4 | ||
| Otonga | 300 | 52 | 57 | 59 | 3/4 | ||
| Parua Bay | 215 | 50 | 200 | 255 | 3/4 | ||
| Ruarangi | 103 | 23 | 60 | 65 | 3/4 | ||
| Waikiekie | 205 | 27 | 92 | 211 | 3/4 | ||
| Waipu North | 224 | 55 | 55 | 120 | 3/4 | ||
| Whareora | 92 | 64 | 64 | 80 | 3/4 | ||
| Otamatea— | |||||||
| Mangawai | 268 | 50 | 90 | 95 | 3/4 | ||
| Matakohe | 423 | 80 | 168 | 250 | 3/4 | ||
| Mareretu (in first year) | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | ||
| Whakapirau (no Board) | 264 | .. | .. | .. | .. | ||
| Rodney— | |||||||
| Albertland North | 65 | 12 | 43 | 43 | 3/4 | ||
| Albertland South | 322 | 78 | 145 | 190 | 3/4 | ||
| Ahuroa | 41 | 14 | 42 | 72 | 3/4 | ||
| Komokoriki | 62 | 15 | 39 | 44 | 3/4 | ||
| Mahurangi East | 151 | 33 | 96 | 96 | 1/2 | ||
| Mahurangi Upper | 947 | 195 | 320 | 431 | |||
| Mainene | 74 | 11 | 26 | 82 | 3/4 | ||
| Matakana East | 132 | 21 | 35 | 35 | 3/4 | ||
| Matakana West | 172 | 57 | 67 | 150 | 3/4 | ||
| Omaha | 357 | 92 | 143 | 204 | 3/4 | ||
| Puhoi | 596 | 77 | 130 | .. | 3/4 | ||
| Tauhoa | 371 | 59 | 92 | .. | 3/4 | ||
| Wharehine | 96 | 20 | 32 | 35 | 3/4 | ||
| Waitemata— | |||||||
| Kaukapakapa | 543 | 100 | 182 | 392 | 3/4 | ||
| Pukeatua | 560 | .. | 220 | 260 | 3/4 | ||
| Whangaparaoa | 66 | 25 | 35 | 53 | 3/4 | ||
| Eden— | d. | ||||||
| Avondale | 1,075 | 225 | 380 | 452 | 3/4(1) | ||
| Arch Hill | 1,671 | 362 | 289 | 467 | 1s.(2) | ||
| Eden Terrace | 2,011 | 42 | 315 | 458 | 3/4(3) | ||
| Epsom | 750 | 145 | 144 | 163 | 3/4 | ||
| Mount Albert | 2,085 | 320 | 480 | 647 | 3/4(4) | ||
| Mount Eden | 5,129 | 1150 | 1,033 | 1,200 | 3/4(5) | ||
| Mount Roskill | 581 | 120 | 179 | 255 | 1/2 | ||
| Mount Wellington | 954 | 198 | 200 | 576 | 5/8 | ||
| One-tree Hill | 1,283 | 190 | 177 | 264 | 1/2 | ||
| Panmure Township | 259 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 1/2 | ||
| Point Chevalier | 684 | 33 | 42 | 53 | 3/4 | ||
| Remuera | 2,186 | 445 | 406 | 533 | 3/4 | ||
| Tamaki West | 375 | 102 | 115 | 157 | 5/8 | ||
| Manukau— | |||||||
| Awhitu | 413 | 102 | 130 | 157 | 3/4 | ||
| Drury | 382 | 80 | 151 | 170 | 3/4 | ||
| Howick Town | 224 | 71 | 120 | 132 | 3/4 | ||
| Hunua | 266 | 55 | 131 | 244 | 1 17/128(6)(7) | ||
| Karaka | 188 | 40 | 147 | 236 | 3/4 | ||
| Mangere | 702 | 200 | 205 | 209 | 1/2 | ||
| Manurewa | 260 | 59 | 82 | 141 | 1/2 | ||
| Maraetai | 82 | 22 | 30 | 36 | 1 1/4(7) | ||
| Mauku | 380 | 100 | 160 | 160 | 1/2(8) | ||
| Maungatawhiri | 378 | 50 | 62 | 95 | 1/2 | ||
| Mercer Township | 229 | 50 | 52 | 84 | 3/4 | ||
| Opaheke | 369 | 85 | 114 | 280 | 3/4(9) | ||
| Otahuhu | 1,211 | 346 | 289 | 366 | 3/4 | ||
| Pakuranga | 271 | 65 | 74 | 99 | 3/4 | ||
| Papakura | 373 | 84 | 106 | 117 | 1 33/100(7) | ||
| Paparata | 373 | 87 | 114 | 160 | 3/4 | ||
| Paparoa | 166 | 46 | 70 | 93 | 3/4 | ||
| Papatoetoe | 176 | 38 | 39 | 49 | 3/4 | ||
| Pokeno | 398 | 71 | 96 | 109 | 3/4(10) | ||
| Pollok Settlement | 88 | 20 | 37 | 46 | 3/4 | ||
| Pukekohe East | 942 | 216 | 232 | 257 | 3/4 | ||
| Pukekohe West | 1,153 | 231 | 263 | … | 3/4 | ||
| Tamaki East | 580 | 115 | 123 | 146 | 3/4 | ||
| Turanga | 227 | 44 | 67 | 75 | 3/4(11) | ||
| Waipipi | 905 | 220 | 250 | 300 | 3/4(12) | ||
| Wairoa | 792 | 190 | 203 | 310 | 3/4 | ||
| Waiuku | 492 | 195 | 215 | 225 | 3/4 | ||
| Coromandel |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Thames | |||||||
| Ohinemuri | |||||||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) No rate struck. (2) On unimproved value. (3) 3/d. and 1/2d. special. (4) No general rate; 1/2d. 1d., and 2d. special. | |||||||
| Piako— | d. | ||||||
| Matamata | 262 | 50 | 44 | 66 | 1/2 | ||
| Waitoa | 1,322 | 244 | 244 | 351 | 3/4 | ||
| Waikato— | |||||||
| Cambridge | 562 | 95 | 123 | 123 | 1/2 | ||
| Kirikiriroa | 964 | 153 | 251 | 251 | 1/2 | ||
| Tamahere | 248 | 26 | 52 | 52 | 3/4 | ||
| Whangamarino | 443 | 80 | 209 | 421 | 3/4 | ||
| Huntly | 966 | 100 | 196 | 196 | 3/4 | ||
| Waipa— | |||||||
| Newcastle | 391 | 82 | 152 | 170 | 3/4 | ||
| Pukekura | 810 | 176 | 270 | 420 | 3/4 | ||
| Rangiaohia | 507 | 81 | 107 | 120 | 3/4 | ||
| Tuhikaramea | 98 | 19 | 60 | 60 | 3/4 | ||
| Raglan— | |||||||
| Karamu (no Board) | 78 | .. | .. | .. | .. | ||
| Onewhero | 197 | 44 | 60 | 62 | ..(1) | ||
| Te Akau (no Board) | 32 | .. | .. | .. | .. | ||
| Kawhia |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| West Taupo | |||||||
| East Taupo | |||||||
| Rotorua | |||||||
| Tauranga— | |||||||
| Katikati | 409 | 82 | 143 | 263 | 17/18(2) | ||
| Te Puke | 477 | 140 | 180 | 208 | (1) | ||
| Te Puna | 169 | 36 | 135 | 140 | (1) | ||
| Whakatane |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Waiapu | |||||||
| Opotiki | |||||||
| Cook— | |||||||
| Aroha | 58 | 10 | 11 | 11 | (1) | ||
| Kaiti | 700 | 155 | 184 | 280 | 3/4(3) | ||
| Ngatapa | 489 | 116 | 94 | 101 | (1) | ||
| Ormond | 482 | 82 | 94 | 138 | 1/2 | ||
| Hangaroa (in first year) | .. | 14 | 19 | 28 | (1) | ||
| Patutahi | 638 | 75 | 99 | 230 | (1) | ||
| Pouawa | 85 | 45 | 74 | 110 | (4) | ||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) No general rate; 3/16d. special. (2) No rate struck. (3) No general rate; 1/2d. special. (4) 1/2d. special; 1/4d., 1/2d., 1d., 1 1/2d., separate. (5) 1/3d. special. (6) 1/6d. special; 1/3d. 1/3d., and 3/4d. separate. (7) 1/9d. special. (8) 3/4d. special over special-rating area. (9) 1/2d. special (10) Special, various. (11) County rate, 1/3d.; special various. (12) No general rate; 1/8d special. | |||||||
| Poverty Bay | 1,050 | 129 | 131 | 121 | (1) | ||
| Taruheru | 225 | 48 | 56 | 56 | (2) | ||
| Te Arai | 294 | 54 | 74 | 188 | (2) | ||
| Titirangi | 44 | 10 | 19 | 30 | (3) | ||
| Waikohu | 328 | 68 | 68 | 188 | (2) | ||
| Waimata | 264 | 48 | 48 | 50 | (2) | ||
| Waipaoa | 80 | 9 | 9 | 16 | (2) | ||
| Whataupoko | 1,148 | 215 | 278 | 320 | 3/4(4) | ||
| Clifton. (No road districts.) | |||||||
| Taranaki— | |||||||
| Barrett (1901) | 439 | 77 | 77 | 125 | 1/2 | ||
| Carrington (1901) | 341 | 66 | 85 | 85 | 1/2(5) | ||
| Egmont (1901) | 635 | 156 | 157 | 301 | 3/4(6) | ||
| Elliot (1901) | 235 | 43 | 51 | 60 | 5/8 | ||
| Frankley (1901) | 231 | 60 | 67 | 67 | 3/4 | ||
| Henui (1901) | 393 | 80 | 100 | 133 | 3/4 | ||
| Hurford, Upper (1901) | 56 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 1/2 | ||
| Mangorei (1901) | 276 | 47 | 66 | 68 | 3/4 | ||
| Moa (1901) | 2,836 | 470 | 550 | 600 | 2/3(7) | ||
| Oakura (1901) | 333 | 100 | 102 | 404 | 1/4(8) | ||
| Okato (1901) | 345 | 61 | 80 | 137 | 1/4 | ||
| Omata (1901) | 294 | 62 | 57 | 70 | 1/4 | ||
| Parihaka (1901) | 1,514 | 251 | 352 | 820 | 1/2 | ||
| Tataraimaka (1901) | 152 | 26 | 38 | 38 | 1/4 | ||
| Waitara West (1901) | 814 | 170 | 170 | 475 | 1/2(9) | ||
| Waiwakaiho (1901) | 350 | 75 | 99 | 183 | 1/2 | ||
| Egmont. (No road districts.) | |||||||
| Stratford— | |||||||
| Manganui | 1,734 | 340 | 380 | 500 | 1/2(10) | ||
| Hawera— | |||||||
| Waimate | 2,619 | 480 | 520 | 712 | 1/2(11) | ||
| Patea— | |||||||
| Kohi | 166 | 32 | 30 | 30 | 3/4 | ||
| Motoroa | 60 | 18 | 20 | 20 | 3/4 | ||
| Okotuku | 134 | 24 | 29 | 33 | 1/4 | ||
| Patea East | 401 | 70 | 84 | 355 | (2) | ||
| Patea West | 777 | 190 | 196 | 630 | (12) | ||
| Wairoa | 105 | 22 | 30 | 30 | 3/4 | ||
| Waitotara-Momohaki | 496 | 105 | 111 | 160 | 3/4 | ||
| Whenuakura-Waitotara | 313 | 40 | 42 | 42 | 1/4 | ||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) On unimproved value. (2) Special and separate, various. (3) Special, various. (4)2/3d. and 9/16d. special. (5) No rate struck. (6) 1/2d. special. | |||||||
| Waitotara. (No road districts). | d. | ||||||
| Wanganui— | |||||||
| Kaukatea | 198 | 45 | 41 | 108 | 1/2 | ||
| Kaitoke | 606 | 125 | 104 | 216 | 1/2 | ||
| Mataongaonga (in first year) | .. | 200 | 180 | 301 | 3/4 | ||
| Mangawhero | 973 | 450 | 400 | 700 | 1/2 | ||
| Purua | 904 | 200 | 170 | 272 | 3/4 | ||
| Wangaehu Upper (no return) | 695 | .. | .. | .. | .. | ||
| Rangitikei. | (No road districts.) | ||||||
| Oroua— | |||||||
| Manawatu | 2,405 | 470 | 551 | 850 | 1(1) | ||
| Manchester | 3,313 | 764 | 690 | 2,155 | 1/2(2) | ||
| Fitzherbert | 724 | 137 | 278 | 405 | 3/4 | ||
| Kairanga |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Pohangina | |||||||
| Kiwitea | |||||||
| Manawatu | |||||||
| Horowhenua— | |||||||
| Otaki | 1,280 | 290 | 310 | 1,171 | 1/2(3) | ||
| Te Horo | 512 | 100 | 135 | 500 | 5/8(4) | ||
| Wirokino | 2,862 | 775 | 750 | 1,100 | 1/2(3) | ||
| Wairoa |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Hawke's Bay | |||||||
| Waipawa— | |||||||
| Norsewood | 1,206 | 210 | 280 | 300 | 1 3/8(1) | ||
| Ruataniwha North | 651 | 108 | 86 | 97 | 1/2(1) | ||
| Takapau | 608 | 110 | 66 | 90 | 7/8(1) | ||
| Waipawa | 274 | 58 | 64 | 78 | 3/8(1) | ||
| Waipukurau | 741 | 121 | 128 | 192 | 1(1) | ||
| Patangata— | |||||||
| Oero | 305 | .. | 67 | 74 | 1/2 | ||
| Patangata | 294 | 47 | 51 | 99 | 3/16 | ||
| Porangahau | 433 | 90 | 76 | 153 | 1/2 | ||
| Taumumu | 185 | 20 | 17 | 18 | 2/5 | ||
| Wallingford | 192 | 25 | 28 | 36 | 1/4 | ||
| Wanstead | 143 | 21 | 57 | .. | (5) | ||
| Weber | 556 | 84 | 131 | 201 | 1/2(6) | ||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) On unimproved value. (2) Special, various. (3) 1/4d. special. (4) 3/4d. special. (5) No rate struck. | |||||||
| Pahiatua |  | (No road districts.) | d. | ||||
| Castlepoint | |||||||
| Eketahuna | |||||||
| Mauriceville | |||||||
| Woodville | |||||||
| Masterton | |||||||
| Wairarapa South— | |||||||
| Taratahi-Carterton | 2,523 | 560 | 475 | 632 | 5/16, 1(1)(2) | ||
| Featherston. | (No road districts.) | ||||||
| Hutt— | |||||||
| Makara | 257 | 39 | 43 | 60 | 1/2(3) | ||
| Seatoun | 432 | 150 | 168 | 168 | 3/4 | ||
| Sounds. | (No road districts.) | ||||||
| Marlborough— | |||||||
| Awatere | 785 | 150 | 210 | 224 | 3/4 | ||
| Omaka | 1,603 | 326 | 394 | 487 | 5/8 | ||
| Pelorus | 1,218 | 230 | 264 | 423 | 1 3/4(4)(1) | ||
| Picton | 847 | 188 | 161 | 254 | 5/8 | ||
| Spring Creek | 819 | 136 | 136 | 175 | 1/2 | ||
| Wairau | 930 | 200 | 195 | 215 | 3/4 | ||
| Kaikoura. | (No road districts.) | ||||||
| Collingwood— | |||||||
| Collingwood | 1,078 | 335 | 302 | 550 | 3/4 | ||
| Takaka | 1,342 | 341 | 329 | 783 | 3/4 | ||
| Waimea— | |||||||
| Dovedale | 286 | 48 | 54 | 88 | 3/4 | ||
| Moutere Upper | 397 | 105 | .. | .. | (5) | ||
| Riwaka | 687 | 145 | .. | .. | (5) | ||
| Stoke | 1,183 | 210 | .. | .. | (5) | ||
| Suburban North | 559 | 120 | .. | .. | (5) | ||
| Waimea West | 460 | 73 | 86 | 86 | (5) | ||
| Buller |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Inangahua | |||||||
| Grey | |||||||
| Westland | |||||||
| Amuri | |||||||
| Cheviot (no Board). | |||||||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) Eyre Water-race, 2 1/2d. per acre; View Hill Water-race, 1d. in the pound. (2) 6d. special; 1/2d., 2d., and 6d. separate. (3) 1/8d. H. and C.A.; 2/64d. Waimakariri; 3/8d. drainage. (4) 2/64d. Waimakariri; 1/5d. separate. (5) 1/4d. and 3/4d. drainage; 2/64d. and 3/64d. Waimakariri. (6) 1/8d. H. and C.A. (7) 2/64d. Waimakariri. (8) No rate struck. (9) 1/4d. special. | |||||||
| Ashley— | d. | ||||||
| Ashley | 726 | 500 | 200 | 280 | 3/4 | ||
| Cust | 713 | 161 | 140 | 192 | 3/8 | ||
| Eyreton | 1,566 | 335 | 277 | 277 | 5/8 | ||
| Eyreton West | 401 | 85 | 77 | 77 | 1/4 | ||
| Kowai | 1,851 | 540 | 650 | 771 | 5/8 | ||
| Mandeville and Rangiora | 2,257 | 530 | 431 | 672 | 5/8 | ||
| Oxford | 1,973 | 550 | 473 | 839 | 3/4(1) | ||
| Waipara | 1,695 | 332 | 310 | 540 | 1/2 | ||
| Selwyn— | |||||||
| Avon | 3,889 | 1130 | 852 | 1,097 | 1s.(2) | ||
| Courtenay | 2,560 | 428 | 463 | 754 | 7/16 | ||
| Ellesmere | 3,497 | .. | 608 | 609 | 1/2 | ||
| Halswell | 1,278 | 220 | 190 | 240 | 3/4 | ||
| Heathcote | 2,995 | 500 | 844 | 900 | 3/4(3) | ||
| Lake Coleridge | 177 | 37 | 30 | 83 | 1/4 | ||
| Lincoln | 1,213 | 372 | 248 | 317 | 1/2(4) | ||
| Malvern | 965 | 164 | 156 | 309 | 1/2 | ||
| Malvern East | 625 | 139 | 161 | 290 | 1/4 | ||
| Malvern South | 428 | 82 | 210 | 340 | 1/2 | ||
| Rakaia | 825 | 197 | 192 | 336 | 3/8 | ||
| Riccarton | 5,713 | .. | 1,093 | 1,334 | 3/4(5) | ||
| Spreydon | 1,457 | 293 | 374 | 415 | 3/4(6) | ||
| Springs | 1,872 | 460 | 408 | 540 | 1/2(7) | ||
| Taitapu | 324 | 90 | 67 | 76 | 3/4 | ||
| Templeton | 2,338 | 505 | 589 | 650 | 7/16(7) | ||
| Waimakariri Upper | 235 | 21 | 13 | 41 | (8) | ||
| Akaroa— | |||||||
| Akaroa and Wainui | 1,308 | 230 | 256 | 256 | 11/16 | ||
| Le Bon's Bay | 316 | 58 | 91 | 91 | 3/4(9) | ||
| Little River | 816 | 270 | 180 | 160 | 5/8 | ||
| Okain's Bay | 520 | 100 | 96 | 116 | 3/4(9) | ||
| Pigeon Bay | 258 | 57 | 53 | 60 | 5/8 | ||
| Port Levy | 159 | 31 | 49 | 56 | 1/2 | ||
| Port Victoria | 292 | 55 | 60 | 60 | 3/4 | ||
| Ashburton— | |||||||
| Anama | 75 | 77 | 124 | 1/4 | |||
| Ashburton Upper | 2,002 | 380 | 600 | 680 | 3/8 | ||
| Coldstream | 319 | 65 | 76 | 94 | 1/2 | ||
| Longbeach | 1,335 | .. | 350 | .. | 13/32 | ||
| Mount Hutt | 1,500 | 275 | 266 | 399 | 1/4 | ||
| County and District. | Population (Census, 1901). | Number of | Amount of Rate levied in the Pound on the Capital, Annual, or Unimproved Value. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwellings. | Ratepayers. | Rateable Properties. | |||||
(1) No rate struck. (2) 1/2d. separate. | |||||||
| Mount Somers | 928 | 200 | 230 | 230 | 1/2 | ||
| Rangitata | 797 | 108 | 147 | 155 | 3/8 | ||
| South Rakaia | 1,480 | 330 | 345 | 500 | 1/4 | ||
| Wakanui | 1,230 | 228 | 280 | 324 | 5/16 | ||
| Geraldine— | |||||||
| Geraldine | 2,250 | 480 | 520 | 844 | 3/4 | ||
| Mount Peel | 493 | 120 | 122 | 175 | 1/2 | ||
| Temuka | 2,380 | 512 | 504 | 765 | 3/4 | ||
| Levels |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Mackenzie | |||||||
| Waimate | |||||||
| Waihemo | |||||||
| Waikouaiti | |||||||
| Peninsula— | |||||||
| Otago Heads | 304 | 44 | 57 | 101 | 3/4 | ||
| Peninsula | 1,324 | 219 | 333 | 393 | 3/4 | ||
| Portobello | 796 | 365 | 361 | 371 | 3/4 | ||
| Tomahawk | 137 | 22 | 33 | 44 | 3/4 | ||
| Taieri. | (No road districts.) | ||||||
| Bruce— | |||||||
| Balmoral | 476 | 68 | 86 | 95 | (1) | ||
| Inch-Clutha (Road and River) | 344 | 60 | 62 | 73 | 1/2 | ||
| Mount Stuart | 618 | 112 | 129 | 129 | 1/2 | ||
| Clutha |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Tuapeka | |||||||
| Maniototo | |||||||
| Vincent | |||||||
| Lake | |||||||
| Southland— | |||||||
| Knapdale | 1,596 | 293 | 333 | 396 | 5/8 | ||
| Oteramika | 2,249 | 368 | 461 | 461 | 1/2(2) | ||
| Tuturau | 733 | 127 | 148 | 164 | 1/2 | ||
| Wallace |  | (No road districts.) | |||||
| Fiord | |||||||
| Stewart Island | |||||||
| Chatham Islands | |||||||
Table of Contents
THE colony is at present (July, 1903) divided into sixty-eight districts for purposes of European representation—sixty-four rural districts having one member each, and four city electorates three members each. This division was made on the basis of the results of the census of 1901. The Electoral Act of 1902 directs that, in computing for electoral purposes the population of the colony, 28 per cent. shall be added to the country population—i.e., all persons living outside towns of 2,000 inhabitants and over. The total population of the colony (other than Maoris), with the addition aforesaid, having been ascertained, is then divided by the number of members (76), and the quotient thus obtained forms the quota. The four city electoral districts (which have three members each) are so defined in extent that the population shall be three times the quota. Inasmuch as it would be impossible to divide the country into a given number of districts all having exactly the precise quota of population, the law permits the Commissioners to make an allowance of 550 persons by way of addition to or deduction from the population of rural districts, and of 100 in case of city electorates, with special provision for districts where the population is partly city and partly rural, so that more consideration can be given to community of interest, facilities of communication, and topographical features, in constructing the districts.
But, although the above describes the existing state of affairs, the present electoral districts were formed in accordance with the laws in force prior to 2nd October, 1902, when the allowance by way of addition to or deduction from the population of rural districts was 1,250.
The Act provides for two permanent Commissions, called the “North” and “South” Island Representation Commissions. These sit together as a joint Commission for the purpose of fixing the number of districts for the North and South Islands respectively, but afterwards act separately and independently of one another, the duties and functions of each being confined to their respective island.
The North Island with its adjacent islands includes 34 electoral districts, having 38 members; the South and Stewart Islands having also 34 districts and 38 members. In 1896 and in 1899 the North Island returned 34 and the South Island 36 members; but since then six new rural districts have been created, by which the North Island has gained four and the South Island two members.
These districts are, as before stated, for purposes of European representation. But the colony is again divided into four districts for purposes of Maori representation, under the electoral law, each district having one Native member elected by the Maoris; making the House of Representatives consist of 80 members altogether—76 Europeans and 4 Maoris.
By the Act which came into force in 1893 the great step was taken of admitting women to the franchise. The Amendment Act of 1896 abolished the non-residential or property qualification, with a saving clause in favour of then-existing registrations in respect of such qualification. “The Electoral Act, 1902,” consolidates the whole of the electoral laws, and amends the same where necessary.
Electors are enrolled on sending to the Registrar a claim and declaration according to a prescribed form. There are no fixed periods for making up fresh electoral rolls, but the rolls are revised and printed before a general election, and also for any district in which a by-election is to take place. Nor are there any fixed periods for the revising and purifying of the rolls. It is the duty of the Registrar of each electoral district to keep the rolls revised and complete.
Dealing with the population of both sexes, it is found that the total number of persons on the rolls was 415,789, out of a total adult population estimated at 429,385. These figures give a proportion of 96·83 per cent. of adults who were registered as electors, as against 96·79 at the previous election in 1899, 95·11 in 1896, and 94·98 in 1893. The number of persons who voted, or who went to the poll, was 318,859, or 76·69 per cent. of the number on the rolls, a slightly smaller proportion than obtained in 1899, which was 77·59 per cent.
| Date of General Election. | Estimated Total Adult Persons. | Number on Rolls. | Proportion of Adult Persons registered as Electors. | Number of Persons who voted. | Proportion of Persons on Rolls who voted. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Excluding figures for three electorates in which there was no contest. † Including 4,974 informal votes. | |||||
| 1893 | 319,010 | 302,997 | 94·98 | 220,082 | 75·25* |
| 1896 | 356,658 | 339,230 | 95·11 | 258,254 | 76·13 |
| 1899 | 386,146 | 373,744 | 96·79 | 279,330 | 77·59* |
| 1902 | 429,385 | 415,789 | 96·83 | 318,859† | 76·69 |
Dealing with men only, the number on the rolls was 229,845, or only 3,757 short of the full number of adult males in the colony as estimated for the day of the election. The males who voted in 1902 were 180,294, or 78·44 per cent. of those on the rolls, against 79·06 per cent. in 1899.
| Date of General Election. | Estimated Total Adult Males. | Number of Men on Rolls. | Proportion of Adult Males registered as Electors. | Number who voted. | Proportion of Males on Rolls who voted. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Excluding figures for three electorates in which there was no contest. † The number on the rolls was in excess of the estimated adult male population at the date of the election. ‡ Including informal. | |||||
| 1893 | 179,539 | 193,536 | † | 129,792 | 69·61* |
| 1896 | 197,002 | 196,925 | 99·96 | 149,471 | 75·90 |
| 1899 | 214,773 | 210,529 | 98·02 | 159,780 | 79·06* |
| 1902 | 233,602 | 229,845 | 98·39 | 180,294‡ | 78·44 |
The figures relating to women show that a lesser proportion (94·97 per cent.) of adults were registered as electors in 1902 than in 1899 (95·24 per cent.). The number of women who voted, 138,565, is 74·52 per cent. of the females on the rolls, while in 1899 there were 119,550 who voted, giving the higher proportion of 75·70 per cent.; so that (assuming the figures to be correct) there is no evidence of a greater willingness now on the part of the females to go to the poll.
| Date of General Election. | Estimated Total Adult Females. | Number of Women on Rolls. | Proportion of Adult Females registered as Electors. | Number who voted. | Proportion of Females on Rolls who voted. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Excluding figures for three electorates in which there was no contest. † Including informal. | |||||
| 1893 | 139,471 | 109,461 | 78·48 | 90,290 | 85·18* |
| 1896 | 159,656 | 142,305 | 89·13 | 108,783 | 76·44 |
| 1899 | 171,373 | 163,215 | 95·24 | 119,550 | 75·70* |
| 1902 | 195,783 | 185,944 | 94·97 | 138,565† | 74·52 |
The following table shows for the different districts the number of electors of each sex on the rolls, with the voters (including those whose votes were informal), and the population as at last Census:—
| Electoral Districts. | Number of Members. | Population as at Census, 31st March, 1901. | Number of Electors on Roll. | Number of Voters who recorded Votes (including informal). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Total. | Males. | Females. | Total. | |||
| Bay of Islands | 1 | 8,372 | 2,430 | 1,586 | 4,016 | 1,753 | 1,052 | 2,805 |
| Kaipara | 1 | 9,519 | 3,099 | 1,635 | 4,734 | 2,309 | 1,270 | 3,579 |
| Marsden | 1 | 9,798 | 2,896 | 1,990 | 4,886 | 2,358 | 1,515 | 3,873 |
| Waitemata | 1 | 10,782 | 3,244 | 2,534 | 5,778 | 2,430 | 1,730 | 4,160 |
| Eden | 1 | 9,553 | 2,559 | 2,543 | 5,102 | 1,918 | 1,776 | 3,694 |
| Auckland, City of | 3 | 35,687 | 10,424 | 9,552 | 19,976 | 8,267 | 6,849 | 15,116 |
| Grey Lynn | 1 | 9,716 | 2,487 | 2,932 | 5,419 | 1,956 | 2,196 | 4,152 |
| Parnell | 1 | 10,511 | 2,980 | 3,208 | 6,188 | 2,030 | 1,919 | 3,949 |
| Manukau | 1 | 10,364 | 2,746 | 3,106 | 5,852 | 2,231 | 2,379 | 4,610 |
| Franklin | 1 | 9,523 | 2,766 | 2,085 | 4,851 | 2,089 | 1,346 | 3,435 |
| Thames | 1 | 10,708 | 2,820 | 2,681 | 5,501 | 2,275 | 1,967 | 4,242 |
| Ohinemuri | 1 | 9,834 | 3,453 | 1,828 | 5,281 | 2,527 | 1,367 | 3,894 |
| Waikato | 1 | 9,491 | 3,008 | 2,228 | 5,236 | 2,548 | 1,732 | 4,280 |
| Bay of Plenty | 1 | 10,897 | 4,045 | 1,683 | 5,728 | 2,815 | 1,596 | 4,411 |
| Waiapu | 1 | 9,905 | 3,930 | 2,351 | 6,281 | 3,139 | 1,835 | 4,974 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1 | 10,701 | 3,406 | 2,174 | 5,580 | 2,096 | 1,165 | 3,261 |
| Napier | 1 | 11,343 | 2,591 | 2,892 | 5,483 | 2,161 | 1,899 | 4,060 |
| Waipawa | 1 | 10,572 | 3,153 | 2,025 | 5,178 | 2,279 | 1,314 | 3,593 |
| Pahiatua | 1 | 9,444 | 2,755 | 1,863 | 4,618 | 2,201 | 1,354 | 3,555 |
| Masterton | 1 | 10,283 | 3,084 | 2,248 | 5,332 | 2,412 | 1,586 | 3,998 |
| Wairarapa | 1 | 8,408 | 2,861 | 1,889 | 4,750 | 2,465 | 1,609 | 4,074 |
| Egmont | 1 | 9,582 | 3,092 | 1,912 | 5,004 | 2,303 | 1,278 | 3,581 |
| Taranaki | 1 | 9,820 | 2,959 | 2,584 | 5,543 | 2,542 | 2,037 | 4,579 |
| Hawera | 1 | 10,132 | 3,347 | 2,430 | 5,777 | 2,669 | 1,834 | 4,503 |
| Patea | 1 | 10,568 | 3,948 | 2,439 | 6,387 | 3,034 | 1,832 | 4,866 |
| Rangitikei | 1 | 8,480 | 3,352 | 1,744 | 5,096 | 2,457 | 1,114 | 3,571 |
| Wanganui | 1 | 11,196 | 3,678 | 2,826 | 6,504 | 2,741 | 2,215 | 4,956 |
| Oroua | 1 | 9,435 | 2,816 | 1,899 | 4,715 | 1,782 | 1,461 | 3,243 |
| Palmerston | 1 | 10,555 | 3,450 | 2,666 | 6,116 | 2,638 | 2,028 | 4,666 |
| Manawatu | 1 | 9,057 | 2,752 | 1,726 | 4,478 | 2,014 | 1,238 | 3,252 |
| Otaki | 1 | 8,347 | 2,117 | 1,626 | 3,743 | 1,559 | 1,017 | 2,576 |
| Hutt | 1 | 10,451 | 2,775 | 2,289 | 5,064 | 2,157 | 1,763 | 3,920 |
| Wellington, City of | 3 | 35,836 | 11,063 | 10,155 | 21,218 | 8,669 | 7,312 | 15,981 |
| Newtown | 1 | 11,701 | 3,418 | 3,247 | 6,665 | 2,670 | 2,447 | 5,117 |
| Nelson, City of | 1 | 11,284 | 2,717 | 2,800 | 5,517 | 2,267 | 2,075 | 4,342 |
| Motueka | 1 | 9,872 | 2,703 | 1,757 | 4,460 | 1,796 | 907 | 2,703 |
| Buller | 1 | 10,747 | 3,355 | 2,076 | 5,431 | 2,665 | 1,487 | 4,152 |
| Grey | 1 | 10,255 | 3,415 | 2,096 | 5,511 | 2,297 | 1,154 | 3,451 |
| Westland | 1 | 8,662 | 2,862 | 1,806 | 4,668 | 2,124 | 1,153 | 3,277 |
| Wairau | 1 | 10,784 | 3,121 | 2,234 | 5,355 | 2,643 | 1,779 | 4,422 |
| Hurunui | 1 | 8,847 | 2,807 | 1,712 | 4,519 | 2,279 | 1,298 | 3,577 |
| Kaiapoi | 1 | 8,500 | 2,479 | 2,246 | 4,725 | 2,134 | 1,852 | 3,986 |
| Avon | 1 | 10,394 | 2,672 | 2,989 | 5,661 | 2,130 | 2,155 | 4,285 |
| Christchurch, City of | 3 | 35,826 | 9,663 | 10,106 | 19,769 | 8,367 | 8,458 | 16,825 |
| Riccarton | 1 | 8,475 | 1,922 | 2,409 | 4,331 | 1,404 | 1,908 | 3,312 |
| Ellesmere | 1 | 8,338 | 2,116 | 1,774 | 3,890 | 1,724 | 1,242 | 2,966 |
| Lyttelton | 1 | 10,465 | 2,502 | 2,364 | 4,866 | 1,960 | 1,982 | 3,942 |
| Courtenay | 1 | 8,430 | 2,335 | 1,892 | 4,227 | 1,801 | 1,352 | 3,153 |
| Selwyn | 1 | 9,231 | 2,608 | 1,731 | 4,339 | 2,017 | 1,222 | 3,239 |
| Ashburton | 1 | 10,497 | 3,422 | 2,454 | 5,876 | 2,772 | 1,962 | 4,734 |
| Geraldine | 1 | 8,787 | 2,387 | 1,918 | 4,305 | 2,058 | 1,575 | 3,633 |
| Timaru | 1 | 10,651 | 2,988 | 2,869 | 5,857 | 2,679 | 2,245 | 4,924 |
| Waitaki | 1 | 8,654 | 2,685 | 1,760 | 4,445 | 2,043 | 1,422 | 3,465 |
| Oamaru | 1 | 10,098 | 2,764 | 2,457 | 5,221 | 2,382 | 2,025 | 4,407 |
| Mount Ida | 1 | 8,361 | 2,721 | 1,575 | 4,296 | 2,174 | 1,180 | 3,354 |
| Waikouaiti | 1 | 8,912 | 2,324 | 2,009 | 4,333 | 1,767 | 1,336 | 3,103 |
| Chalmers | 1 | 10,945 | 3,016 | 3,015 | 6,031 | 2,345 | 2,324 | 4,669 |
| Dunedin, City of | 3 | 35,297 | 11,016 | 12,117 | 23,133 | 8,436 | 8,968 | 17,404 |
| Caversham | 1 | 11,533 | 3,100 | 3,242 | 6,342 | 2,727 | 2,808 | 5,535 |
| Taieri | 1 | 9,027 | 2,556 | 2,171 | 4,727 | 2,132 | 1,690 | 3,822 |
| Bruce | 1 | 8,405 | 2,686 | 2,185 | 4,871 | 2,103 | 1,826 | 3,92 |
| Tuapeka | 1 | 8,557 | 2,895 | 1,804 | 4,699 | 2,307 | 1,384 | 3,691 |
| Clutha | 1 | 9,481 | 2,827 | 2,147 | 4,974 | 2,245 | 1,476 | 3,721 |
| Wakatipu | 1 | 10,226 | 3,066 | 1,881 | 4,947 | 2,536 | 1,422 | 3,958 |
| Mataura | 1 | 10,710 | 3,524 | 2,531 | 6,055 | 2,943 | 2,016 | 4,959 |
| Awarua | 1 | 10,286 | 2,816 | 2,019 | 4,835 | 2,195 | 1,580 | 3,775 |
| Invercargill | 1 | 11,159 | 3,163 | 3,176 | 6,339 | 2,660 | 2,556 | 5,216 |
| Wallace | 1 | 10,237 | 3,108 | 2,046 | 5,154 | 2,688 | 1,714 | 4,402 |
Particulars are given for the four city electorates, where the electors have the right of voting for three members. The number of votes exercisable is more than twenty-eight thousand in excess of those recorded, so that some of the electors evidently voted for only one or two candidates. It is interesting to note, that for the two northern cities (Auckland and Wellington) in the number of electors on the rolls and the number who recorded their votes the males exceeded the females, while for the two city electorates in the South Island (Christchurch and Dunedin) the women voters outnumbered the men.
| City. | No. of Members returned. | Electors on Rolls. | Voters who recorded Votes. | No. of Votes recorded. | No. of Votes exercisable by persons who voted. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men. | Women. | Total. | Men. | Women. | Total. | ||||
| Auckland | 3 | 10,424 | 9,552 | 19,976 | 8,267 | 6,849 | 15,116 | 40,119 | 45,348 |
| Wellington | 3 | 11,063 | 10,155 | 21,218 | 8,669 | 7,312 | 15,981 | 42,365 | 47,943 |
| Christchurch | 3 | 9,663 | 10,106 | 19,769 | 8,367 | 8,458 | 16,825 | 45,056 | 50,475 |
| Dunedin | 3 | 11,016 | 12,117 | 23,133 | 8,436 | 8,968 | 17,404 | 39,567 | 52,212 |
| Total | 12 | 42,166 | 41,930 | 84,096 | 33,739 | 31,587 | 65,326 | 167,107 | 195,978 |
A return is added showing the number of votes recorded for each candidate, and from this it will be seen that in thirteen instances the deposits were forfeited, the number of votes received in each case having been less than one-tenth of the number polled by the successful candidate. One candidate, Mr. F. W. Isitt, was nominated for ten separate districts, and one, Mr. D. Whyte, for two districts:—
| Electoral Districts and Names of Candidates. | Number of Votes recorded. | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| For each Candidate. | Total. | |
| Bay of Islands: | ||
| Houston, R. M. | 1,593 | |
| Glass, A. G. C. | 1,183 | 2,776 |
| Kaipara: | ||
| Harding, A. E. | 1,183 | |
| Stallworthy, J. | 824 | |
| Peacocke, G. L. | 730 | |
| Bassett, T. | 529 | |
| Newman, C. | 288 | 3,554 |
| Marsden: | ||
| Mander, F. | 1,951 | |
| Thompson, R. | 1,893 | 3,844 |
| Waitemata: | ||
| Alison, E. W. | 2,409 | |
| Hatfield, A. J. | 1,695 | 4,104 |
| Eden: | ||
| Bollard, J. | 2,628 | |
| Cheal, P. E. | 1,000 | 3,628 |
| City of Auckland: | ||
| Witheford, J. H. | 7,854 | |
| Baume, F. E. | 7,540 | |
| Kidd, A. | 5,786 | |
| Richardson, W. | 4,852 | |
| Napier, W. J. | 4,271 | |
| Rosser, A. | 3,504 | |
| French, R. | 3,055 | |
| Hanan, J. H. | 2,016 | |
| Fawcus, J. | 966 | |
| Bradly, A. P. | 217 | |
| Simson, H. N. | 58 | 40,119 |
| Grey Lynn: | ||
| Fowlds, G. | 2,108 | |
| Masefield, T. T. | 1,990 | 4,098 |
| Parnell: | ||
| Lawry, F. | 1,996 | |
| Shera, J. M. | 1,872 | 3,868 |
| Manukau: | ||
| Kirkbride, M. M. | 2,372 | |
| O'Rorke, Sir G. M. | 2,145 | 4,517 |
| Franklin: | ||
| Massey, W. F. | 2,297 | |
| Harris, A. R. | 1,121 | 3,418 |
| Thames: | ||
| McGowan, J. | 2,458 | |
| Lucas, W. H. | 1,573 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 36 | 4,067 |
| Ohinemuri: | ||
| Moss, E. G. B. | 1,527 | |
| Palmer, J. | 1,341 | |
| Poland, H. | 996 | 3,864 |
| Waikato: | ||
| Lang, F. W. | 2,234 | |
| Greenslade, H. J. | 2,009 | 4,243 |
| Bay of Plenty: | ||
| Herries, W. H. | 2,110 | |
| Lundon, D. | 1,434 | |
| Jordan, C. | 429 | |
| Taylor, J. E. | 387 | 4,360 |
| Waiapu: | ||
| Carroll, J. | 3,232 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 1,562 | 4,794 |
| Hawke's Bay: | ||
| Russell, Sir W. R. | 2,330 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 887 | 3,217 |
| Napier: | ||
| Fraser, A. L. D. | 2,739 | |
| Eames, R. J. | 1,249 | 3,988 |
| Waipawa: | ||
| Hall, C. | 2,556 | |
| Taylor, J. | 988 | 3,544 |
| Pahiatua: | ||
| O'Meara, J. | 1,796 | |
| Bolton, S. | 1,459 | |
| Gould, A. W. | 268 | 3,523 |
| Masterton: | ||
| Hogg, A. W. | 2,451 | |
| Cooper, J. C. | 1,503 | 3,954 |
| Wairarapa: | ||
| Buchanan, W. C. | 2,049 | |
| Hornsby, J. T. M. | 1,983 | 4,032 |
| Egmont: | ||
| Jennings, W. T. | 1,765 | |
| Leech, C. | 1,750 | 3,515 |
| Taranaki: | ||
| Smith, E. M. | 2,419 | |
| Okey, H. J. H. | 2,105 | 4,524 |
| Hawera: | ||
| Major, C. E. | 2,233 | |
| McGuire, F. | 2,212 | 4,445 |
| Patea: | ||
| Symes, W. | 2,638 | |
| Haselden, F. H. | 2,187 | 4,825 |
| Rangitikei: | ||
| Remington, A. E. | 1,399 | |
| Birch, W. J. | 1,152 | |
| Reardon, M. J. | 537 | |
| Hornblow, R. E. | 358 | |
| Smith, J. | 69 | 3,515 |
| Wanganui: | ||
| Willis, A. D. | 2,866 | |
| Baker, J. W. | 1,428 | |
| Lundon, G. | 586 | 4,880 |
| Oroua: | ||
| Lethbridge, F. Y. | 1,911 | |
| Tompkins, A. H. | 1,293 | 3,204 |
| Palmerston: | ||
| Wood, W. T. | 2,230 | |
| Hodder, T. R. | 1,896 | |
| Manson, H. J. | 511 | 4,637 |
| Manawatu: | ||
| Vile, J. | 1,691 | |
| Stevens, J. | 1,515 | 3,206 |
| Otaki: | ||
| Field, W. H. | 2,006 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 496 | 2,502 |
| Hutt: | ||
| Wilford. T. M. | 2,115 | |
| Pirani, F. | 1,674 | |
| Collier, J. H. | 90 | 3,879 |
| City of Wellington: | ||
| Aitken, J. G. W. | 7,808 | |
| Duthie, J. | 6,886 | |
| Fisher, G. | 6,685 | |
| O'Regan, P. J. | 6,304 | |
| Atkinson, A. R. | 6,094 | |
| Findlay, J. G. | 4,764 | |
| Godber, J. | 1,437 | |
| Jellicoe, E. G. | 1,384 | |
| McLaren, D. | 1,003 | 42,365 |
| Newtown: | ||
| Barber, W. H. P. | 1,385 | |
| Hislop, T. W. | 1,357 | |
| Luke, C. M. | 1,100 | |
| Chapple, W. A. | 1,017 | |
| Tustin, W. G. | 159 | 5,018 |
| City of Nelson: | ||
| Graham, J. | 2,156 | |
| Atmore, H. | 1,633 | |
| Piper, J. | 521 | 4,310 |
| Motueka: | ||
| McKenzie, R. | 2,256 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 418 | 2,674 |
| Buller: | ||
| Colvin, J. | 3,370 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 769 | 4,139 |
| Grey: | ||
| Guinness, A. R. | 2,764 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 619 | 3,383 |
| Westland: | ||
| Seddon, Rt. Hon. R. J. | 2,983 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 237 | 3,220 |
| Wairau: | ||
| Mills, C. H. | 2,401 | |
| Duncan, J. | 1,990 | 4,391 |
| Hurunui: | ||
| Rutherford, A. W. | 1,577 | |
| Reece, H. F. | 880 | |
| Meredith, R. | 834 | |
| Forbes, G. W. | 205 | |
| Pulley, G. T. | 68 | 3,564 |
| Kaiapoi: | ||
| Buddo, D. | 2,558 | |
| Hassall, A. D. | 1,302 | 3,860 |
| Avon: | ||
| Tanner, W. W. | 1,680 | |
| Brunt, J. R. | 1,632 | |
| Loughrey, A. | 871 | |
| Myers, J. S. | 37 | 4,220 |
| City of Christchurch: | ||
| Taylor, T. E. | 8,122 | |
| Ell, H. G. | 7,924 | |
| Davey, T. H. | 6,331 | |
| Collins, W. W. | 5,982 | |
| Smith, G. J. | 5,980 | |
| Turnbull, A. H. | 4,648 | |
| Taylor, C. | 4,491 | |
| Allison, C. | 1,393 | |
| Baynes, B. | 185 | 45,056 |
| Riccarton: | ||
| Witty, G. | 1,776 | |
| Russell, G. W. | 1,491 | 3,267 |
| Ellesmere: | ||
| Rhodes, R. H. | 1,719 | |
| Thornton, C. R. | 1,218 | 2,937 |
| Lyttelton: | ||
| Laurenson, G. | 3,041 | |
| Rollitt, W. | 869 | 3,910 |
| Courtenay: | ||
| Lewis, C. | 1,535 | |
| Rennie, J. | 1,185 | |
| Barrett, J. | 401 | 3,121 |
| Selwyn: | ||
| Hardy, C. A. C. | 1,594 | |
| Ivess, J. | 1,051 | |
| Wilson, K. | 554 | 3,199 |
| Ashburton: | ||
| McLachlan, J. | 2,132 | |
| Studholme, J., jun. | 1,693 | |
| Brock, W. | 783 | |
| Ager, A. | 60 | 4,668 |
| Geraldine: | ||
| Flatman, F. R. | 2,275 | |
| Maslin, W. S. | 1,303 | 3,578 |
| Timaru: | ||
| Hall-Jones, W. | 3,046 | |
| Smith, F. H. | 1,395 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 348 | 4,789 |
| Waitaki: | ||
| Steward, Sir W. J. | 1,992 | |
| Campbell, J. | 1,400 | 3,392 |
| Oamaru: | ||
| Duncan, T. Y. | 2,141 | |
| Brown, J. M. | 1,261 | |
| Macpherson, J. A. | 717 | |
| Crawford, H. B. | 138 | 4,257 |
| Mount Ida: | ||
| Herdman, A. L. | 1,731 | |
| Ewing, J. | 1,600 | 3,331 |
| Waikouaiti: | ||
| Mackenzie, T. | 2,424 | |
| Isitt, F. W. | 578 | 3,002 |
| Chalmers: | ||
| Allen, E. G. | 2,614 | |
| White, J. | 2,002 | 4,616 |
| City of Dunedin: | ||
| Bedford, H. D. | 10,088 | |
| Millar, J. A. | 9,396 | |
| Arnold, J. F. | 8,393 | |
| Barclay, A. R. | 7,072 | |
| Chisholm, R. | 4,618 | 39,567 |
| Caversham: | ||
| Sidey, T. K. | 2,939 | |
| Earnshaw, W. | 2,495 | 5,434 |
| Taieri: | ||
| Reid, D., jun. | 1,503 | |
| Ramsay, J. J. | 1,149 | |
| Marshall, A. | 589 | |
| Samson, C. | 407 | |
| Wright, J. | 134 | 3,782 |
| Bruce: | ||
| Allen, J. | 2,505 | |
| Scott, J. A. | 1,392 | 3,897 |
| Tuapeka: | ||
| Bennet, J. | 1,864 | |
| Gilkison, R. | 1,798 | 3,662 |
| Clutha: | ||
| Thomson, J. W. | 1,671 | |
| Stewart, D. | 1,031 | |
| Quin, W. | 820 | |
| McNeil, J. | 176 | 3,698 |
| Wakatipu: | ||
| Fraser, W. | 1,971 | |
| Ross, R. B. | 1,522 | |
| Murdoch, A. | 324 | |
| Kelly, J. | 65 | 3,882 |
| Mataura: | ||
| McNab, R. | 2,669 | |
| Raymond, I. W. | 2,231 | 4,900 |
| Awarua: | ||
| Ward, Sir J. G. | 2,795 | |
| Whyte, D. | 913 | 3,708 |
| Invercargill: | ||
| Hanan, J. A. | 3,322 | |
| Whyte, D. | 1,814 | 5,136 |
| Wallace: | ||
| Tnomson, J. C. | 2,589 | |
| Glifedder, M. | 1,796 | 4,385 |
A summary of the population, number of electors on the rolls, and the total number of votes recorded at each of the last four general elections is next given:—
| — | 1902. | 1899. | 1896. | 1893. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Total number of electors who recorded their votes: 318,859 in 1902, 279,330 in 1899, 258,254 in 1896, and 220,082 in 1893. | ||||
| Number of votes recorded for members elected | 235,083 | 202,324 | 184,929 | 153,663 |
| Number of votes recorded for defeated candidates | 181,879 | 185,305 | 174,475 | 149,413 |
| Total votes recorded* | 416,962 | 387,629 | 359,404 | 303,076 |
| Number of names on rolls in districts uncontested | .. | 13,726 | .. | 10,539 |
| Number of names on rolls in districts where elections were contested | 415,789 | 360,018 | 339,230 | 292,458 |
| Total number of electors on rolls | 415,789 | 373,744 | 339,230 | 302,997 |
| Total population at last census | 772,504 | 703,119 | 703,119 | 626,359 |
The names of the members returned at the last general election arranged in alphabetical order are next shown, with the electoral district represented by each.
| Name. | Electoral District. |
|---|---|
| Aitken, John Guthrie Wood | City of Wellington. |
| Alison, Ewen William | Waitemata. |
| Allen, Edmund Giblett | Chalmers. |
| Allen, James | Bruce. |
| Arnold, James Frederick | City of Dunedin. |
| Barber, William Henry Peter | Newtown. |
| Baume, Frederick Ehrenfried | City of Auckland. |
| Bedford, Harry Dodgshun | City of Dunedin. |
| Bennet, James | Tuapeka. |
| Bollard, John | Eden. |
| Buchanan, Walter Clark | Wairarapa. |
| Buddo, David | Kaiapoi. |
| Carroll, Hon. James | Waiapu. |
| Colvin, James | Buller. |
| Davey, Thomas Henry | City of Christchurch. |
| Duncan, Hon. Thomas Young | Oamaru. |
| Duthie, John | City of Wellington. |
| Ell, Henry George | City of Christchurch. |
| Field, William Hughes | Otaki. |
| Fisher, George | City of Wellington. |
| Flatman, Frederick Robert | Geraldine. |
| Fowlds, George | Grey Lynn. |
| Fraser, Alfred Levavasour Durell | Napier. |
| Fraser, William | Wakatipu. |
| Graham, John | Nelson. |
| Guinness, Arthur Robert | Grey. |
| Hall, Charles | Waipawa. |
| Hall-Jones, Hon. William | Timaru. |
| Hanan, Josiah Alfred | Invercargill. |
| Harding, Alfred Ernest | Kaipara. |
| Hardy, Charles Albert Creery | Selwyn. |
| Herdman, Alexander Laurence | Mount Ida. |
| Herries, William Herbert | Bay of Plenty. |
| Hogg, Alexander Wilson | Masterton. |
| Houston, Robert Morrow | Bay of Islands. |
| Jennings, William Thomas | Egmont. |
| Kidd, Alfred | City of Auckland. |
| Kirkbride, Matthew Middlewood | Manukau. |
| Lang, Frederic William | Waikato. |
| Laurenson, George | Lyttelton. |
| Lawry, Frank | Parnell. |
| Lethbridge, Frank Yates | Oroua. |
| Lewis, Charles | Courtenay. |
| McGowan, Hon. James | Thames |
| McKenzie, Roderick | Motueka. |
| Mackenzie, Thomas | Waikouaiti. |
| McLachlan, John | Ashburton. |
| McNab. Robert | Mataura. |
| Major, Charles Edwin | Hawera. |
| Mander, Francis | Marsden. |
| Massey, William Ferguson | Franklin. |
| Millar, John Andrew | City of Dunedin. |
| Mills, Hon. Charles Houghton | Wairau. |
| Moss, Edward George Britton | Ohinemuri. |
| O'Meara, John | Pahiatua. |
| Reid, Donald (jun.) | Taieri. |
| Remington, Arthur Edward | Rangitikei. |
| Rhodes, Robert Heaton | Ellesmere. |
| Russell, Sir William Russell, K.C.M.G. | Hawke's Bay. |
| Rutherford, Andrew William | Hurunui. |
| Seddon, Rt. Hon. Richard John, P.C. | Westland. |
| Sidev, Thomas Kay | Caversham. |
| Smith, Edward Metcalf | Taranaki. |
| Steward, Sir William Jukes, K.C.M.G. | Waitaki. |
| Symes, Walter | Patea. |
| Tanner, William Wilcox | Avon. |
| Taylor, Thomas Edward | City of Christchurch. |
| Thomson, James William | Clutha. |
| Thomson, John Charles | Wallace. |
| Vile, Job | Manawatu. |
| Ward, Hon. Sir Joseph George, K.C.M.G. | Awarua. |
| Wilford, Thomas Mason | Hutt |
| Willis, Archibald Dudingston | Wanganui. |
| Witheford, Joseph Howard | City of Auckland. |
| Witty, George | Riccarton. |
| Wood, William Thomas | Palmerston. |
The occupations of members elected in 1902 show an increase in the number of the representatives of the farmer class as compared with 1899. The table also shows that farmers or runholders furnish more members than any other class of occupation. There were twenty-one of these (besides four given as “settlers”) returned in 1902. There were ten barristers or solicitors, and five journalists. The number of members returned in 1902 was seventy-six, against seventy in 1896 and 1899:—
| Occupations. | 1896. | 1899. | 1902. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Professional— | |||
| Barrister, solicitor | 9 | 10 | |
| Journalist | 9 | 8 | 5 |
| Mining advocate, interpreter, lecturer, teacher | 4 | 1 | |
| Chemist | .. | .. | 1 |
| Domestic— | |||
| Hotelkeeper | .. | .. | 1 |
| Commercial— | |||
| Land-broker, estate agent | .. | .. | 2 |
| Auctioneer | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Director of financial company | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Native agent | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Stationer, bookseller, draper, grocer, butcher | 3 | 6 | 5 |
| Merchant, iron merchant, timber merchant | 3 | ||
| Storekeeper | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Commission agent, clerk, accountant, commercial traveller | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Transport and Communication— | |||
| Coach proprietor | .. | .. | 1 |
| Industrial— | |||
| Tailor, shoemaker, dyer | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Mill-owner, ship-rigger, builder, metallurgical engineer, mine-manager | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Blacksmith | .. | .. | 1 |
| Printer | .. | .. | 2 |
| Farmer | 11 | 13 | 12 |
| Sheep-farmer, runholder, grazier, stock-owner | 14 | 7 | 9 |
| Contractor | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Others— | |||
| Settler, gentleman, &c. | 8 | 7 | 5 |
Of a Maori population amounting to 43,143 persons at the census of 1901, 14,271 voted at the general election held in December, 1902, an increase of 643 on the number who voted at the election of 1899. In 1893 the voters numbered 11,269, or 1,739 persons fewer than in 1896, when 13,008 Maoris recorded their votes, while at the general election held in December, 1899, the number of Maoris who voted was 13,628. As the Native population increased but slightly between 1891 and 1901, it would appear that Maoris are taking more interest as to their representation in Parliament than formerly, or perhaps there is now more convenience for attending to vote, or better knowledge of political affairs. The numbers of voters for the several districts in December, 1902, were:—
| Electoral Districts. | Population: Census 1901. | Number who voted. | Per Cent. of Population at all Ages. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Totals. | |||
| North Island— | |||||
| Northern Maori | 5,400 | 4,478 | 9,878 | 2,134 | 21·60 |
| Eastern Maori | 7,465 | 6,510 | 13,975 | 5,265 | 37·67 |
| Western Maori | 9,054 | 7,994 | 17,048 | 6,266 | 36·76 |
| South Island— | |||||
| Southern Maori | 1,193 | 1,049 | 2,242 | 606 | 27·03 |
| Totals | 23,112 | 20,031 | 43,143 | 14,271 | 33·08 |
The votes recorded for each candidate were:—
| Electoral Districts and Names of Candidates. | Number of Votes recorded. | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| For each Candidate. | Total. | |
| Northern Maori Electoral District: | ||
| Hone Heke | 1,665 | |
| Hamiora Mangakahia | 268 | |
| Kipa te Whatanui | 119 | |
| Hapeta Henare | 74 | |
| Eru Ihaka | 2,134 | |
| Eastern Maori Electoral District: | ||
| Wiremu Pere | 2,182 | |
| Pirimi Mataiawhea | 1,568 | |
| Mohi te Atahikoia | 1,515 | 5,265 |
| Western Maori Electoral District: | ||
| Henare Kaihau | 3,324 | |
| Ngarangi Katitia | 954 | |
| Te Heuheu Tukino | 840 | |
| Eruera te Kahu | 673 | |
| Te One Tuhi | 399 | |
| Te Weraroa Kingi | 76 | 6,266 |
| Southern Maori Electoral District: | ||
| Tame Parata | 343 | |
| Hone Tare Tikao | 263 | 606 |
| Total | 14,271 | |
On the succeeding page will be found a tabular statement giving the results of each general election since the year 1853 for purposes of European representation.
| GENERAL ELECTIONS FOR EUROPEAN REPRESENTATIVES HELD FROM THE YEAR 1853. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parliament. | Date of General Election. | Number of Names on Roll of Electors. | Number of Members returned. | Number of Members returned unopposed. | Numbers of Votes recorded (or of Voters recording Votes). | Population of the Colony at end of Year. | Average Number of | ||
| Persons to each Member. | Persons to each Elector. | Electors to each Member. | |||||||
* Information not obtainable. 1 Including 100, the estimated number in Akaroa District, for which there is no return. 2 Including 800, the estimated number in the electorates of Town of New Plymouth, Grey, and Bell, and Omata, for which districts there are no returns. 3 Electors for the Electoral District of “The Otago Goldfields” not included. 4 Men and women. 5 Voters recording votes. | |||||||||
| First | 1853 | 1 5,934 | 37 | * | * | 30,000 | 811 | 5·1 | 160 |
| Second | 1855 | 2 10,324 | 37 | * | * | 37,192 | 1,005 | 3·6 | 279 |
| Third | 1861 | 13,466 | 53 | * | * | 79,711 | 1,504 | 5·9 | 254 |
| Fourth | 1866 | 3 33,338 | 72 | * | * | 190,607 | 2,647 | 5·7 | 463 |
| Fifth | 1871 | 47,275 | 74 | * | * | 248,400 | 3,357 | 5·3 | 639 |
| Sixth | 1875 | 61,755 | 84 | * | * | 375,856 | 4,474 | 6·1 | 735 |
| Seventh | 1879 | 82,271 | 84 | 14 | 43,776 | 463,729 | 5,521 | 5·6 | 979 |
| Eighth | 1881 | 120,972 | 91 | 11 | 69,985 | 500,910 | 5,505 | 4·1 | 1,329 |
| Ninth | 1884 | 137,686 | 91 | 11 | 74,672 | 564,304 | 6,201 | 4·1 | 1,513 |
| Tenth | 1887 | 175,410 | 91 | 5 | 111,911 | 603,361 | 6,630 | 3·4 | 1,928 |
| Eleventh | 1890 | 183,171 | 70 | 6 | 136,337 | 625,508 | 8,936 | 3·4 | 2,617 |
| Twelfth | 1893 | 4302,997 | 70 | 3 | 45220,082 | 672,265 | 9,604 | 2·2 | 4,328 |
| Thirteenth | 1896 | 4339,230 | 70 | .. | 45258,254 | 714,162 | 10,202 | 2·1 | 4,853 |
| Fourteenth | 1899 | 4373,744 | 70 | 3 | 45279,330 | 756,505 | 10,807 | 2·0 | 5,339 |
| Fifteenth | 1902 | 4415,789 | 76 | .. | 45318,859 | 807,929 | 10,631 | 1·9 | 5,471 |
Table of Contents
DURING the year ended the 31st March, 1902, 2,492 licenses for the sale of intoxicating liquors were granted. Of these, 1,513 were publicans' and accommodation licenses, 6 New Zealand wine, 77 packet, 155 wholesale, and 741 conditional licenses. The fees paid amounted to £54,514, and formed part of the revenue of the local governing bodies of the districts in which the licenses were issued. Particulars are given in the following table:—
| NUMBER OF LICENSES GRANTED DURING (([0-9]+)) 1901–1902, AND THE AMOUNT OF FEES PAID TO LOCAL BODIES THEREFOR. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Licenses. | In Counties. | In Boroughs. | Total. |
| Publicans' licenses | 607 | 690 | 1,297 |
| Accommodation licenses | 216 | .. | 216 |
| Total licensed houses | 823 | 690 | 1,513 |
| New Zealand wine licenses | .. | 6 | 6 |
| Packet licenses | 16 | 61 | 77 |
| Wholesale licenses | 11 | 144 | 155 |
| Conditional licenses | 569 | 172 | 741 |
| Total licenses granted | 1,419 | 1,073 | 2,492 |
| Amount of license-fees paid to local bodies | £19,917 | £34,597 | £54,514 |
The average number of persons to each licensed house in counties and boroughs respectively, for 1901–1902, is next shown:—
| Number of Licensed Houses.* | Census Population. | Average Number of Persons to each Licensed House. | |
|---|---|---|---|
* I.e., houses holding publicans' or accommodation licenses. † Excluding persons on shipboard and adjacent islands. | |||
| Counties | 823 | 417,596 | 507 |
| Boroughs | 690 | 350,202 | 508 |
| Totals | 1,513 | 767,798† | 507 |
In 1900–1901 the number of licensed houses in counties was 832, and those in boroughs 690, giving a total of 1,522 houses, or 9 more than in 1901–1902. The average number of persons to a licensed house increased from 502 in 1900–1901 to 507 in 1901–1902 in counties, and in boroughs the average was 508 for both years.
The annual fees paid for licenses are—
| * Between the hours of six in the morning and ten at night. For an eleven o'clock license an additional £5 must be paid. | |
|---|---|
| (1.) For a publican's license— | £ |
| (a.) Within the limits of a borough or town district | 40* |
| (b.) Outside the aforesaid limits | 25 |
| (2.) For a New Zealand wine license | 1 |
| (3.) For an accommodation license, a sum to be determined by the Licensing Committee, not exceeding | 20 |
| (4.) For a packet license— | |
| (a.) For a vessel exceeding 50 tons register | 10 |
| (b.) For a vessel not exceeding 50 tons register | 5 |
| (5.) For a wholesale license | 20 |
| (6.) For a conditional license, according to duration of license, a sum not exceeding | 30 |
The approximate capital value of the licensed houses in the counties was stated at £755,687, and the same for certain of the boroughs at £323,398. There was, besides, an annual value of £106,345 for other licensed houses in the boroughs, which, capitalised at 6 per cent., would represent £1,772,417. The capital value of all licensed houses would therefore be about £2,851,502.
The total number of persons engaged in or connected with the sale or manufacture of wine, spirits, beer, cordials, &c., was returned at the census of 1901 as under:—
| Males. | Females. | Persons. | |
|---|---|---|---|
*Between the hours of six in the morning and ten at night. For an eleven o'clock license an additional £5 must be paid. | |||
| Hotelkeepers | 1,341 | 215 | 1,556 |
| Relative assisting | 133 | 631 | 764 |
| Manager, clerk | 104 | 22 | 126 |
| Hotel servant, cook | 1,376 | 2,557 | 3,933 |
| Barman, barmaid | 178 | 349 | 527 |
| Manager, secretary, steward of club-house | 115 | 27 | 142 |
| Wine, spirit, merchant | 3 | 53 | |
| Assistant | 10 | *1 | 11 |
| Clerk, storeman | 55 | 56 | |
| Traveller | 31 | .. | 31 |
| Cordial, &c., seller | 6 | .. | 6 |
| Brewer, bottler, and others engaged in brewing | 606 | 4 | 610 |
| Relative assisting | 8 | 1 | 9 |
| Maltster and assistants | 147 | .. | 147 |
| Wine manufacturer | 16 | .. | 16 |
| Cordial, &c., maker, bottler | 231 | 7 | 238 |
| Assistant, clerk, traveller, &c. | 130 | 2 | 132 |
| Totals | 4,537 | 3,820 | 8,357 |
Under “The Alcoholic Liquors Sale Control Act, 1893,” each electoral district constituted for the election of a member of the House of Representatives is a licensing district, and electors for the House of Representatives are also electors under the Licensing Acts.
Under the Amendment Act of 1895 the licensing poll is taken at the same time as the general election of members of the House of Representatives. The questions for the decision of the voters are,—
Whether the number of licenses existing in the district shall continue?
Whether the number shall be reduced?
Whether any licenses whatever shall be granted?
The voter may vote for one or two of these proposals, but no more.
The method of determining the result of the poll in each district by the Returning Officer is as follows:—
If the number of votes recorded in favour of the continuance of existing licenses is an absolute majority of all the voters whose votes were recorded, the proposal is deemed to be carried, and the licenses continue until the next poll, subject to certain provisions in special cases.
If the number of votes recorded in favour of a reduction in the number of licenses is an absolute majority of all the voters whose votes were recorded, the proposal is deemed to be carried, and supersedes the proposal for continuance of licenses. The Licensing Committee then reduces publicans' licenses by not less than 5 per cent. or more than 25 per cent. of the total number existing, excluding forfeitures. Provision is made that when a reduction vote is carried the licenses shall be reduced by one at least when the total number does not exceed ten, two when not over thirty, and three at least when the licenses exceed thirty.
If the number of votes recorded in favour of the proposal that no license shall be granted is not less than three-fifths of all the voters whose votes were recorded, the proposal is declared to be carried, and supersedes the proposal for reduction and for continuance, and no licenses can be granted.
If none of the proposals respecting licenses is carried by the prescribed majority the licenses continue as they are until next poll, subject to certain provisions in special cases.
The result of the poll taken on the 25th November, 1902, as made up from returns received from the officer in charge of the poll in each licensing district, is as follows:—
| District. | Number of Persons on Roll | Votes recorded for | Total Number of Persons who recorded Valid Votes. | Number of Men and Women who recorded Votes (including Informal). | Result of Poll. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuance. | Reduction. | No License. | Men. | Women. | Total. | ||||
† For restoration. ‡ For non-restoration. § Not including 8,900 informal votes. * Election since declared void. | |||||||||
| Bay of Islands | 4,016 | 1,759 | 567 | 850 | 2,750 | 1,753 | 1,052 | 2,805 | Continuance carried. |
| Marsden | 4,886 | 1,738 | 1,709 | 2,032 | 3,844 | 2,358 | 1,515 | 3,873 | No proposal carried. |
| Kaipara | 4,734 | 2,037 | 1,037 | 1,353 | 3,560 | 2,309 | 1,270 | 3,579 | Continuance carried. |
| Waitemata | 5,778 | 2,234 | 1,627 | 1,648 | 4,035 | 2,430 | 1,730 | 4,160 | Continuance carried. |
| City of Auckland | 19,976 | 7,345 | 6,683 | 6,524 | 14,594 | 8,267 | 6,849 | 15,116 | Continuance carried. |
| Grey Lynn | 5,419 | 1,829 | 2,197 | 2,175 | 4,107 | 1,956 | 2,196 | 4,152 | Reduction carried. |
| Eden | 5,102 | 1,754 | 1,693 | 1,638 | 3,537 | 1,918 | 1,776 | 3,694 | No proposal carried. |
| Parnell | 6,188 | 2,062 | 1,538 | 1,435 | 3,852 | 2,030 | 1,919 | 3,949 | Continuance carried. |
| Manukau | 5,852 | 2,268 | 1,964 | 1,927 | 4,478 | 2,231 | 1,379 | 4,610 | Continuance carried. |
| Franklin | 4,851 | 1,584 | 1,588 | 1,737 | 3,361 | 2,089 | 1,346 | 3,435 | No proposal carried. |
| Thames | 5,501 | 1,996 | 1,768 | 2,090 | 4,178 | 2,275 | 1,967 | 4,242 | No proposal carried. |
| Ohinemuri | 5,281 | 1,956 | 1,255 | 1,808 | 3,795 | 2,527 | 1,367 | 3,894 | Continuance carried. |
| Waikato | 5,236 | 2,506 | 1,387 | 1,587 | 4,165 | 2,548 | 1,732 | 4,280 | Continuance carried. |
| Bay of Plenty | 5,728 | 2,077 | 1,182 | 1,838 | 4,225 | 2,815 | 1,596 | 4,411 | No proposal carried. |
| Waiapu | 6,281 | 2,295 | 1,970 | 2,568 | 4,879 | 3,139 | 1,835 | 4,974 | No proposal carried. |
| Hawke's Bay | 5,580 | 1,636 | 1,157 | 1,417 | 3,133 | 2,096 | 1,165 | 3,261 | Continuance carried. |
| Napier | 5,483 | 1,749 | 2,080 | 2,006 | 3,854 | 2,161 | 1,899 | 4,060 | Reduction carried. |
| Waipawa | 5,178 | 1,802 | 1,239 | 1,640 | 3,544 | 2,279 | 1,314 | 3,593 | Continuance carried. |
| Pahiatua | 4,618 | 1,601 | 1,058 | 1,800 | 3,464 | 2,201 | 1,354 | 3,555 | No proposal carried. |
| Masterton | 5,332 | 1,945 | 1,396 | 1,906 | 3,930 | 2,412 | 1,586 | 2,998 | No proposal carried. |
| Wairarapa | 4,750 | 2,015 | 1,245 | 1,727 | 3,972 | 2,465 | 1,609 | 4,074 | Continuance carried. |
| Egmont | 5,004 | 1,862 | 863 | 1,403 | 3,414 | 2,303 | 1,278 | 3,581 | Continuance carried. |
| Taranaki | 5,543 | 2,347 | 1,542 | 2,021 | 4,402 | 2,542 | 2,037 | 4,579 | Continuance carried. |
| Hawera | 5,777 | 2,112 | 1,659 | 2,133 | 4,295 | 2,669 | 1,834 | 4,503 | No proposal carried. |
| Patea | 6,387 | 2,195 | 1,842 | 2,265 | 4,611 | 3,034 | 1,832 | 4,866 | No proposal carried. |
| Rangitikei | 5,096 | 1,863 | 707 | 1,342 | 3,371 | 2,457 | 1,114 | 3,571 | Continuance carried. |
| Wanganui | 6,504 | 2,409 | 1,885 | 2,267 | 4,745 | 2,741 | 2,215 | 4,956 | Continuance carried. |
| Oroua | 4,715 | 1,570 | 1,081 | 1,505 | 3,100 | 1,782 | 1,461 | 3,243 | Continuance carried. |
| Palmerston | 6,116 | 2,365 | 1,473 | 1,976 | 4,637 | 2,638 | 2,028 | 4,666 | Continuance carried. |
| Manawatu | 4,478 | 1,587 | 1,096 | 1,400 | 3,109 | 2,014 | 1,238 | 3,252 | Continuance carried. |
| Otaki | 3,743 | 1,345 | 955 | 1,062 | 2,464 | 1,559 | 1,017 | 2,576 | Continuance carried. |
| Hutt | 5,064 | 1,674 | 1,585 | 1,920 | 3,721 | 2,157 | 1,763 | 3,920 | No proposal carried. |
| City of Wellington | 21,218 | 6,749 | 7,325 | 7,496 | 15,175 | 8,669 | 7,312 | 15,981 | No proposal carried. |
| Newtown* | 6,665 | 1,869 | 2,777 | 2,995 | 4,985 | 2,670 | 2,447 | 5,117 | No license carried. |
| City of Nelson | 5,517 | 2,515 | 1,527 | 1,327 | 4,243 | 2,267 | 2,075 | 4,342 | Continuance carried. |
| Motueka | 4,460 | 1,745 | 595 | 799 | 2,657 | 1,796 | 907 | 2,703 | Continuance carried. |
| Buller | 5,431 | 2,413 | 1,149 | 1,593 | 4,102 | 2,665 | 1,487 | 4,152 | Continuance carried. |
| Grey | 5,511 | 1,746 | 1,399 | 1,524 | 3,393 | 2,297 | 1,154 | 3,451 | Continuance carried. |
| Westland | 4,668 | 2,179 | 835 | 888 | 3,220 | 2,124 | 1,153 | 3,277 | Continuance carried. |
| Wairau | 5,355 | 2,303 | 1,671 | 1,869 | 4,323 | 2,643 | 1,779 | 4,422 | Continuance carried. |
| Hurunui | 4,519 | 1,784 | 1,395 | 1,632 | 3,472 | 2,279 | 1,298 | 3,577 | Continuance carried. |
| Kaiapoi | 4,725 | 1,601 | 2,132 | 2,319 | 3,936 | 2,134 | 1,852 | 3,986 | Reduction carried. |
| Riccarton | 4,331 | 1,646 | 1,306 | 1,365 | 3,236 | 1,404 | 1,908 | 3,312 | Continuance carried. |
| Avon | 5,661 | 1,898 | 2,021 | 2,187 | 4,169 | 2,130 | 2,155 | 4,285 | No proposal carried. |
| City of Christchurch | 19,769 | 7,897 | 7,484 | 7,888 | 16,298 | 8,367 | 8,458 | 16,825 | No proposal carried. |
| Lyttelton | 4,866 | 1,782 | 1,900 | 2,012 | 3,874 | 1,960 | 1,982 | 3,942 | No proposal carried. |
| Ellesmere | 3,890 | 1,489 | 1,162 | 1,336 | 2,890 | 1,724 | 1,242 | 2,966 | Continuance carried. |
| Courtenay | 4,227 | 1,320 | 1,512 | 1,644 | 3,040 | 1,801 | 1,352 | 3,153 | No proposal carried. |
| Selwyn | 4,339 | 1,258 | 1,608 | 1,804 | 3,081 | 2,017 | 1,222 | 3,239 | Reduction carried. |
| Ashburton | 5,876 | 1,734 | 2,489 | 2,870 | 4,625 | 2,772 | 1,962 | 4,734 | No license carried. |
| Geraldine | 4,305 | 1,683 | 1,580 | 1,796 | 3,578 | 2,058 | 1,575 | 3,633 | No proposal carried. |
| Timaru | 5,857 | 2,175 | 2,427 | 2,637 | 4,856 | 2,679 | 2,245 | 4,924 | No proposal carried. |
| Waitaki | 4,445 | 1,481 | 1,674 | 1,896 | 3,411 | 2,043 | 1,422 | 3,465 | No proposal carried. |
| Oamaru | 5,221 | 1,801 | 2,144 | 2,459 | 4,319 | 2,382 | 2,025 | 4,407 | No proposal carried. |
| Mount Ida | 4,296 | 1,596 | 1,319 | 1,569 | 3,251 | 2,174 | 1,180 | 3,354 | No proposal carried. |
| Waikouaiti | 4,333 | 1,311 | 1,524 | 1,698 | 3,017 | 1,767 | 1,336 | 3,103 | Reduction carried. |
| Chalmers | 6,031 | 1,676 | 2,669 | 2,773 | 4,558 | 2,345 | 2,324 | 4,669 | No license carried. |
| City of Dunedin | 23,133 | 7,269 | 8,937 | 8,518 | 17,240 | 8,436 | 8,968 | 17,404 | Reduction carried. |
| Caversham | 6,342 | 2,399 | 2,862 | 2,938 | 5,397 | 2,727 | 2,808 | 5,535 | Reduction carried. |
| Taieri | 4,727 | 1,626 | 1,729 | 2,031 | 3,695 | 2,132 | 1,690 | 3,822 | No proposal carried. |
| Bruce* | 4,871 | 1,525 | 2,157 | 2,372 | 3,869 | 2,103 | 1,826 | 3,929 | No license carried. |
| Tuapeka | 4,699 | 1,628 | 1,642 | 1,841 | 3,587 | 2,307 | 1,384 | 3,691 | No proposal carried. |
| Clutha | 4,974 | 1,368† | .. | 2,245‡ | 3,613 | 2,245 | 1,476 | 3,721 | Non-restoration carried. |
| Mataura | 6,055 | 1,877 | 2,353 | 2,939 | 4,825 | 2,943 | 2,016 | 4,959 | No license carried. |
| Wakatipu | 4,947 | 2,090 | 1,359 | 1,654 | 3,837 | 2,536 | 1,422 | 3,958 | Continuance carried. |
| Wallace | 5,154 | 1,957 | 1,836 | 2,323 | 4,201 | 2,688 | 1,714 | 4,402 | No proposal carried. |
| Invercargill | 6,339 | 2,043 | 2,855 | 3,079 | 5,147 | 2,660 | 2,556 | 5,216 | Reduction carried. |
| Awarua | 4,835 | 1,499 | 1,858 | 2,208 | 3,713 | 2,195 | 1,580 | 3,775 | |
| Totals | 415,789 | 148,449 | 132,240 | 151,524 | 309,959§ | 180,294 | 138,565 | 318,859 | |
From the foregoing table it will be seen that 148,449 votes were recorded in favour of continuing existing licenses—including one district, that of Clutha, where the vote (1,368) was for restoration of the licenses cancelled at the poll taken in 1899–132,240 for reduction, and 151,524 for no license (including 2,245 votes cast for non-restoration in the Clutha district).
In twenty-nine of the sixty-eight licensing districts the majority of the voters was in favour of continuance, in twenty-four no proposal was carried, in nine reduction, and in six no-license was carried, but in two of these latter the poll on petition was declared invalid. In twenty-four of the districts—Marsden. Grey Lynn, Franklin, Thames, Waiapu, Napier, Pahiatua, Hutt, Waitaki, Oamaru, Waikouaiti, Kaiapoi, Avon, Lyttelton, Courtenay, Selwyn, Geraldine, Timaru, Caversham, Taieri, Tuapeka, Wallace, Invercargill, and Awarua—a majority of the votes polled was for no-license, but not in sufficient number to make up the three-fifths required to carry that issue. Of the total number of persons, 318,859, including those whose votes were informal, 180,294, or 56·54 per cent., were men, and 138,565, or 43·46 per cent., were women. Compared with the polling in the year 1899, this shows a numerical increase of 19,335, or 12·01 per cent., on the part of the men, and 17,702, or 14·65 per cent., on the part of the women, clearly showing that the latter are now taking greater interest in local-option matters than they formerly did.
A comparison with 1899 of the votes recorded and the number of persons who went to the poll, with the numerical and centesimal increase in each case, is shown in the next table:—
| Year | Number of Persons on Rolls. | Votes recorded for | Number of Persons who recorded Votes (including informal). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuance. | Reduction. | No License. | Males. | Females. | Totals. | ||
*Many had been struck off for not voting at the general election for Parliament. | |||||||
| 1894 | 248,194* | 73,771 | 25,919 | 84,435 | 74,372 | 47,862 | 122,234 |
| 1896 | 339,230 | 139,580 | 94,555 | 98,312 | 151,235 | 108,663 | 259,898 |
| 1899 | 373,744 | 142,443 | 107,751 | 118,575 | 160,959 | 120,863 | 281,822 |
| 1902 | 415,789 | 148,449 | 132,240 | 151,524 | 180,294 | 138,565 | 318,859 |
The large increases in the number of votes recorded for no-license or reduction are prominent features in the above table. It is also interesting to note the substantial increase shown in the number of persons who went to the poll, though these latter must not be accepted as absolutely correct throughout.
Table of Contents
THE results of the compilation of the special returns relating to the various manufactories, works, &c., in the colony are compared with those shown for previous censuses in certain of the tabulated statements given with these remarks.
It must be observed, however, that whereas up till the time of last census the term “factory” was rather held to mean an establishment where manufacture was carried on wholesale, where machinery was employed, and where several hands worked together; in the returns for 1901 a “factory” has been interpreted to mean any concern where two or more persons work together at making articles for disposal, wholesale or retail, and without reference to machinery being used or not. Thus the return seems to be rather one showing industrial workers (and their production) where two or more are found together, than one of manufactories to supply the wholesale traders, or making for export. But the attempt has been made to approximate the census results to those of the Labour Department, according to special direction. To make the comparison with previous census figures as true as possible, the results for all the dressmaking, tailoring, shirt-making, millinery, and other establishments which were not included until 1901, have been deducted from the totals at foot of the summary table. Any roughness in the comparison caused by small concerns employing two persons only, and doing a retail business in making or repairing, having been included at the last census, but not before, cannot be avoided. And indeed it will become clear to any one reading the following remarks that the large increase in money value of manufactures is obtained mostly on items in respect of which moving down to a limit of two persons engaged would not materially alter the comparison.
The totals for the industries do not include mining and quarrying, which are dealt with separately.
Deducting, as above mentioned, from the total value of manufactures for the year 1900 the results for such industries as were not included in 1895, a most satisfactory increase is found on analysis of items, which has been mainly brought about by developments on a large scale in the following industries:—
| Value of Output for Year 1895 compared with 1900. | |
|---|---|
| Increase in 5 years. £ | |
| Meat freezing, preserving, &c. | 2,182,616 |
| Butter and cheese factories | 1,033,876 |
| Tanning, fellmongering, and wool-scouring | 650,855 |
| Foundries, boiler-making, range-making, and engineering | 621,356 |
| Sawmills, with sash and door making | 369,882 |
| Printing establishments (not Government) | 315,161 |
| Clothing (with boot and shoe) factories | 242,122 |
| Breweries and malt-houses | 240,468 |
| Flaxmills | 170,946 |
| Gasworks | 91,542 |
| Chaff-cutting works | 90,816 |
| Biscuit factories | 79,010 |
| Bacon-curing establishments | 73,542 |
| Coach-building and painting | 67,108 |
| Woollen-mills | 56,959 |
| Brick, tile, and pottery works | 56,090 |
| Aerated-water factories | 53,202 |
| Cycle factories | 46,230 |
| Lime and cement works | 29,261 |
If to these be added the value of the grass-seed after dressing, £241,239 for the year 1900, the greater part of the increase in the total for all manufactured articles (£7,591,789) is accounted for. There are a large number of smaller amounts of increase than those above stated, but the main lines of development are sufficiently indicated.
The addition of the figures in the column for total value of manufactures is not absolutely justified to the fullest extent of the amount shown (seventeen million pounds sterling); but in the present state of New Zealand industries it appears that the degree of repetition of value is not so great as to prevent the total given being of great help in judging of development. No doubt seventeen million pounds is over the fact, because, for instance, butter frozen for export is included in returns for meat freezing establishments, and also in the butter factory returns; timber cut is valued under saw-milling, and some again in the furniture-making line. Also, leather is valued in the tanning returns, and some part of it again in the boot and saddlery items. But, of the material operated upon, a great deal is imported.
The great primary industries of meat-freezing, butter and cheese making, with some others, do not mainly provide materials for making other wares.
The iron which is used at the foundries and engineering works is imported to New Zealand.
But it must be admitted that, as the colony advances in primary industries, deductions will have to be made with great discrimination from the figures in the column “Value of all manufactures,” in respect of the amounts given in the returns.
As yet it is held that the addition is not so much affected by repetitions as to render the result other than useful; although, as before remarked, the total figures are admittedly in excess of the actual fact. The comparison with previous census results is still considered valuable.
The special tables which follow the summaries will show clearly that quantities have risen, as well as the value of manufactures, so that the development is not merely a question of market prices but of actual output.
In 1896 the actual increase in five years of the annual output was found to be only £775,523. But it was noticed that there were special causes for this amount being so small; and also that quantities showed then in many cases a certain degree of development of industries, though values had not been maintained throughout.
The year 1895 was admittedly a time when great results could not be looked for. Severe financial troubles had happened shortly before. The phormium and rope industries, iron-working (implements and other) were not thriving, and in other lines matters were not altogether what could have been wished. The inquiry for the year 1900 has been made after a period of great prosperity.
| Manufactories and Works, 1896 and 1901. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| April, 1896. No. | March, 1901.† No. | Increase, 1896–1901. No. | |
* Omitting Government Railway Workshops and Government Printing Office. † Excluding dressmaking, tailoring, shirt-making, millinery, &c., for which no returns in 1896. | |||
| Number of establishments* | 2,459 | 3,163 | 704 |
| Hands employed— | |||
| Males | 22,986 | 35,438 | 12,452 |
| Females | 4,403 | 6,288 | 1,885 |
| Totals† | 27,389 | 41,726 | 14,337 |
| Wages paid— | £ | £ | £ |
| To Males | 1,776,076 | 2,895,279 | 1,119,203 |
| Females | 131,516 | 203,282 | 71,766 |
| Totals† | 1,907,592 | 3,098,561 | 1,190,969 |
| H.-p. | H.-p. | H.-p. | |
| Horse-power | 28,096 | 39,052 | 10,956 |
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Total approximate value of— | |||
| Land | 1,063,989 | 1,713,254 | 649,265 |
| Buildings | 1,743,073 | 2,419,803 | 676,730 |
| Machinery and plant | 2,988,955 | 3,826,574 | 837,619 |
| Totals | 5,796,017 | 7,959,631 | 2,163,614 |
Under the heading “Hands employed,” the males increased from 22,986 in 1896 to 35,438, or at the rate of nearly 54·17 per cent. in five years. The females employed increased at the rate of 42·81 per cent.
The wages paid in the factories or large industrial works dealt with in the census returns were returned for 1895 at £1,907,592, and for 1900 £3,098,561.
The average annual amount of wages paid to male hands was £77·2 in 1895 and £81·7 in 1900. For females, £29·8 in 1895 against £32·3 at the last census. The wages of both would seem to have been more than maintained.
The increase for the year 1901 over 1896 in the horse-power stated in the returns was 10,956, against 6,400 for 1896.
The approximate value of the land used for purposes of the factories and industries increased from £1,063,989 in 1896 to £1,713,254 in 1901. The value of the lands used for mining is not included in the above figures, and the value of Crown lands has been omitted throughout.
A very satisfactory development will be found in the value of the machinery and plant, from £2,988,955 in 1896 to £3,826,574 in 1901, being at the rate of 28·02 per cent. for the period. The value of the buildings also increased greatly.
All the various industries for which returns were received in 1901 are given in the statement below, which thus enumerates completely the manufactories and works in operation in the colony, specifying the provincial districts in which they are situated:—
| Industries in Provincial Districts. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufactories, Works, &c. | Number of Industries in Provincial Districts. | Total Number of Industries. | ||||||||
| Auckland. | Taranaki. | Hawke's Bay. | Wellington. | Marlborough. | Nelson. | Westland. | Canterbury. | Otago. | ||
| Animal food— | ||||||||||
| Meat freezing and preserving works | 7 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | .. | .. | 4 | 13 | 34 |
| Ham- and bacon-curing establishments | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | .. | 4 | .. | 10 | 12 | 39 |
| Fish curing and preserving works | 8 | .. | .. | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | .. | 13 | 28 |
| Butter and cheese factories | 27 | 102 | 8 | 37 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 17 | 42 | 247 |
| Rabbit-packing | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Condensed-milk factory | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Vegetable food— | ||||||||||
| Grain-mills | 8 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 5 | .. | 23 | 27 | 78 |
| Biscuit-factories | 5 | .. | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | .. | 2 | 7 | 20 |
| Fruit-preserving and jam-making works | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | 2 | 13 |
| Sugar-boiling and confectionery works | 8 | .. | 3 | 4 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 4 | 26 |
| Sugar-refining works | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Fruit-canning works | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Baking-powder factories | 8 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 | 11 |
| Drinks, narcotics, and stimulants— | ||||||||||
| Breweries | 9 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 16 | 15 | 74 |
| Malthouses | 4 | .. | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 8 | 33 |
| Colonial-wine making | 4 | .. | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | .. | 14 |
| Aerated-water factories | 22 | 11 | 8 | 24 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 27 | 17 | 125 |
| Coffee and spice works | 4 | .. | .. | 4 | .. | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 18 |
| Tobacco manufactories | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| Cigarette manufactories | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 |
| Sauce and pickle factories | 9 | 1 | 1 | 5 | .. | 1 | .. | 4 | 2 | 23 |
| Vinegar works | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 4 |
| Ice factories | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| Animal matters (not otherwise classed)— | ||||||||||
| Bone-mills | 2 | 3 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | 8 |
| Soap and candle works | 7 | .. | 1 | 4 | .. | 2 | .. | 6 | 4 | 24 |
| Glue factory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Sausage-skin factory | 1 | .. | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| Boiling-down works | 5 | .. | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 14 |
| Manure-works | 1 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Oleomargarine-works | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 1 |
| Fat-refining works | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Working in wood— | ||||||||||
| Cooperages | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 4 | 23 |
| Saw-mills, sash and door factories | 48 | 23 | 26 | 66 | 8 | 46 | 29 | 18 | 70 | 334 |
| Barrow and ladder factory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Woodware and turnery factories | 10 | 1 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 6 | 28 |
| Vegetable produce for fodder— | ||||||||||
| Chaff-cutting establishments | 15 | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 12 | .. | 25 | 1 | 55 |
| Grass-seed-dressing establishments | .. | 4 | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9 | 11 | 25 |
| Paper-manufacture— | ||||||||||
| Paper-mills | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 3 |
| Paper bag and box factories | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 | 7 | |
| Gas-works | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 30 |
| Electric-lighting works | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Processes relating to stone, clay, glass, &c.— | ||||||||||
| Lime and cement works | 6 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 2 | 1 | .. | 5 | 15 |
| Brick, tile, and pottery works | 24 | 5 | 8 | 18 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 20 | 25 | 108 |
| Tobacco-pipe factory | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Monumental masonry | 8 | .. | 1 | 3 | .. | 2 | .. | 6 | 7 | 27 |
| Glassworks | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 2 |
| Glass-bevelling works | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| Electro-plating works | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 2 |
| Pumice-works | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Metals, other than gold and silver— | ||||||||||
| Tinware-factories | 12 | .. | .. | 13 | .. | 4 | 2 | 18 | 11 | 60 |
| Iron and brass foundries, boiler-making, machinists, &c. | 13 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 14 | 65 |
| Heel- and toe-plate factories | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 |
| Engineering-works | 10 | .. | .. | 9 | .. | 2 | .. | 8 | 8 | 37 |
| Range-making works | 5 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 9 |
| Spouting and ridging factories | 6 | 8 | 2 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 9 | 35 |
| Lead-headed-nail works | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Iron-pipe and fluming works | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Books and publications— | ||||||||||
| Printing offices | 35 | 12 | 4 | 40 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 35 | 49 | 188 |
| Musical instruments— | ||||||||||
| Musical-instrument factories | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 3 |
| Ornaments, minor art products, and small wares— | ||||||||||
| Picture-frame makers | 2 | .. | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 9 |
| Basket and perambulator factories | 6 | .. | .. | 6 | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 5 | 21 |
| Cork-cutting | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Lapidaries | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 3 |
| Equipment for sports and games— | ||||||||||
| Billiard-table factories | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 3 |
| Designs, medals, type, and dies— | ||||||||||
| Rubber-stamp making | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| Arms and explosives— | ||||||||||
| Ammunition factory | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Machines, tools, and implements— | ||||||||||
| Agricultural - implement factories | 6 | .. | 2 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 10 | 12 | 33 |
| Brush and broom factories | 6 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 2 | 12 |
| Cutlery factory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Bellows factory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Carriages and vehicles— | ||||||||||
| Coach building and painting works | 33 | 11 | 12 | 44 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 26 | 20 | 160 |
| Cycle factories | 8 | 2 | 3 | 10 | .. | 2 | .. | 25 | 21 | 71 |
| Harness, saddlery, and leather-ware— | ||||||||||
| Saddlery and harness factories | 22 | 7 | 7 | 29 | .. | 5 | 1 | 24 | 20 | 115 |
| Whip-thong factories | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 |
| Portmanteau factories | 2 | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 6 |
| Tanning, fellmongering, and wool - scouring establishments | 16 | 4 | 15 | 14 | 4 | 4 | .. | 29 | 33 | 119 |
| Ships, boats, and their equipment— | ||||||||||
| Ship- and boat-building yards | 17 | .. | .. | 3 | .. | 1 | .. | 2 | 9 | 32 |
| Graving-docks and patent slips | 3 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Block and pump factory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Sail and oilskin factories | 9 | 1 | 2 | 4 | .. | 1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 30 |
| Furniture— | ||||||||||
| Furniture and cabinetmaking | 26 | 14 | 7 | 36 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 32 | 144 |
| Venetian-blind works | 2 | .. | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 3 | 12 |
| Mattress factories | 3 | .. | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 4 | 12 |
| Wool, rug, and mat making | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Chemicals and by-products— | ||||||||||
| Perfumery manufactory | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 |
| Varnish manufactories | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 4 |
| Ink manufactories | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 |
| Starch manufactories | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | 2 | 3 |
| Chemical works | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 5 | 8 |
| Haematite-paint factories | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | 3 | 4 |
| Sheep-dip factories | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 |
| Match factories | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 |
| Herbal-remedies factories | 1 | .. | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 8 |
| Blacking factories | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 3 |
| Cocoanut-oil mill | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 |
| Textile fabrics— | ||||||||||
| Woollen-mills | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Flock-mills | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Cleaning and dyeing works | 5 | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 1 | 11 |
| Dress— | ||||||||||
| Tailoring establishments | 32 | 12 | 3 | 67 | .. | 10 | 7 | 22 | 22 | 175 |
| Dressmaking and millinery establishments | 41 | 8 | 12 | 78 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 69 | 65 | 290 |
| Shirt-making establishments | 4 | 1 | .. | 7 | .. | 1 | .. | 4 | 8 | 25 |
| Corset and belt manufactories | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | .. | 6 |
| Clothing factories | 7 | .. | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 8 | 21 |
| Waterproof factories | 1 | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Boot and shoe factories | 31 | 4 | .. | 24 | .. | 2 | 3 | 27 | 35 | 126 |
| Hat and cap factories | 5 | .. | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 3 | 13 |
| Hosiery factories | 1 | .. | .. | 3 | .. | 1 | .. | 5 | 7 | 17 |
| Fibrous materials— | ||||||||||
| Rope and twine works | 3 | 1 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 4 | 17 |
| Bag and sack factory | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Flax-mills | 23 | 6 | 2 | 25 | 14 | 7 | .. | 8 | 16 | 101 |
| Returns not included in above | 40 | 5 | 3 | 4 | .. | 6 | .. | 13 | 3 | 74 |
| Totals, Census, 1901 | 752 | 267 | 160 | 707 | 61 | 198 | 78 | 648 | 809 | 3680 |
| Deduct tailoring, dressmaking, shirt-making, and monumental masons' establishments, not included in accounts taken for 1896 and 1891 | 85 | 21 | 16 | 155 | 5 | 22 | 10 | 101 | 102 | 517 |
| Totals, Census, 1901 (less deductions shown above) | 667 | 246 | 144 | 55 | 56 | 176 | 68 | 547 | 707 | 3163 |
| Totals, Census, 1896 | 573 | 128 | 147 | 396 | 50 | 154 | 47 | 448 | 516 | 2459 |
| Totals, Census, 1891 | 577 | 68 | 85 | 333 | 77 | 142 | 51 | 380 | 541 | 2254 |
The provincial districts, arranged according to the number of industries belonging to each, specified in the last census returns, stand as under:—
| Number of Industries, excluding Mines and Quarries. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 1896 | 1891 | |
| Otago | 707 | 516 | 541 |
| Auckland | 667 | 573 | 577 |
| Wellington | 552 | 396 | 333 |
| Canterbury | 547 | 448 | 380 |
| Taranaki | 246 | 128 | 68 |
| Nelson | 176 | 154 | 142 |
| Hawke's Bay | 144 | 147 | 85 |
| Westland | 68 | 47 | 51 |
| Marlborough | 56 | 50 | 77 |
The principal industries returned at the census of 1901, and particulars relating thereto, are given in detail in the following table. These industries are arranged in classes according to their nature:—
| Nature of Industries. | Total Nature of Industries. | Number of Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Amount of Power employed (Horse-power). | Value of all Materials used or operated upon during 1900. | Value of all Manufactures or Produce (including Repairs) for the Year 190.* | Approximate Value of Land, Buildings, Machinery, and Plant. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Total. | Males. | Females. | Total. | ||||||
* For information as to quantities manufactured or produced, see special tables. Value of output, wages, &c., not shown where the number of establishments is so small that particulars might be identified. † For full particulars respecting these industries, see special tables Note.—See note at end of Table. ‡ Value of manufactures at Government Railway Workshops not included. § Value of manufactures at Government Printing Office not included. | |||||||||||
| Animal food— | £ | £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Meat freezing and preserving works† | 34 | 2,172 | 49 | 2,221 | 198,306 | 1,419 | 199,725 | 7,057 | 252,290 | 3,720,475 | 893,720 |
| Ham and bacon curing establishments† | 39 | 185 | 11 | 196 | 13,891 | 496 | 14,387 | 250 | 115,656 | 159,564 | 62,192 |
| Fish curing and preserving works† | 28 | 135 | 2 | 137 | 7,445 | 73 | 7,518 | .. | 7,714 | 25,173 | 17,235 |
| Butter and cheese factories† | 247 | 1,165 | 23 | 1,188 | 95,461 | 972 | 96,433 | 2,399 | 1,195,600 | 1,535,150 | 388,750 |
| Rabbit-packing | 7 | 62 | .. | 62 | 3,200 | .. | 3,200 | .. | .. | .. | 362 |
| Condensed-milk factory | 1 | 17 | 16 | 33 | .. | .. | .. | 39 | .. | .. | .. |
| Vegetable food— | |||||||||||
| Grain-mills† | 78 | 513 | 2 | 515 | 49,254 | 110 | 49,364 | 2,422 | 545,642 | 682,884 | 358,656 |
| Biscuit factories† | 20 | 454 | 213 | 667 | 34,231 | 4,545 | 38,776 | 291 | 117,383 | 197,989 | 90,243 |
| Fruit-preserving and jam-making works† | 13 | 85 | 82 | 167 | 6,317 | 1,758 | 8,075 | 117 | 42,404 | 58,092 | 20,935 |
| Sugar-boiling and confectionery works | 26 | 158 | 147 | 305 | 11,128 | 3,600 | 14,728 | 19 | 47,150 | 88,580 | 56,955 |
| Sugar-refining works | 1 | 256 | .. | 256 | .. | .. | .. | 922 | .. | .. | |
| Fruit-canning works | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 10 | .. | .. | |
| Baking-powder factories | 11 | 19 | 10 | 29 | 1,074 | 181 | 1,255 | 17 | 9,318 | 18,163 | 18,200 |
| Drinks, narcotics, and stimulants— | |||||||||||
| Breweries† | 74 | 677 | 5 | 682 | 83,493 | 77 | 83,570 | 632 | 158,212 | 553,627 | 294,592 |
| Malthouses† | 33 | 145 | .. | 145 | 14,994 | .. | 14,994 | 110 | 72,211 | 105,671 | 75,038 |
| Colonial-wine making† | 14 | 49 | 10 | 59 | 2,320 | 92 | 2,412 | 14 | 3,019 | 10,330 | 18,183 |
| Aerated-water factories† | 125 | 437 | 15 | 452 | 31,771 | 284 | 32,055 | 250 | 63,835 | 151,811 | 105,178 |
| Coffee and spice works | 18 | 63 | 15 | 78 | 4,959 | 235 | 5,194 | 83 | 32,091 | 45,628 | 47,572 |
| Tobacco manufactories | 2 | 11 | 9 | 20 | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | .. | .. |
| Cigarette manufactories | 3 | 1 | 17 | 18 | .. | .. | .. | 6 | .. | .. | .. |
| Sauce and pickle factories† | 23 | 77 | 51 | 128 | 4,628 | 1,760 | 6,388 | 71 | 20,505 | 31,258 | 36,715 |
| Vinegar works | 4 | 13 | 10 | 23 | 1,179 | 258 | 1,437 | 4 | 3,284 | 6,824 | 4,480 |
| Ice-factories | 2 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 35 | .. | .. | .. |
| Animal matter (not otherwise classed)— | |||||||||||
| Bone-mills | 8 | 17 | .. | 17 | 453 | .. | 453 | 77 | 1,080 | 2,529 | 6,230 |
| Soap and candle works† | 24 | 224 | 8 | 232 | 19,009 | 239 | 19,248 | 346 | 112,623 | 158,649 | 66,809 |
| Glue factory | 1 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 28 | .. | .. | .. |
| Sausage-skin factories | 10 | 98 | .. | 98 | 8,689 | .. | 8,689 | .. | 17,845 | 30,674 | 3,949 |
| Boiling-down works† | 14 | 61 | .. | 61 | 5,910 | .. | 5,910 | 93 | 92,693 | 114,416 | 26,838 |
| Manure works | 5 | 30 | .. | 30 | 1,872 | .. | 1,872 | 63 | 31,652 | 37,769 | 10,266 |
| Oleomargarine-works | 1 | 9 | .. | 9 | .. | .. | .. | 50 | .. | .. | .. |
| Fat-refining works | 1 | 14 | .. | 14 | .. | .. | .. | 18 | .. | .. | .. |
| Working in wood— | |||||||||||
| Cooperages† | 23 | 137 | 1 | 138 | 10,884 | 39 | 10,923 | 177 | 19,942 | 37,521 | 21,787 |
| Saw-mills, sash and door factories† | 334 | 6,805 | 7 | 6,812 | 513,622 | 266 | 513,888 | 8,744 | .. | 1,268,689 | 703,620 |
| Barrow and ladder factory | 1 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Woodware and turnery factories | 28 | 154 | 2 | 156 | 11,779 | 82 | 11,861 | 176 | 19,146 | 37,552 | 28,227 |
| Vegetable produce for fodder— | |||||||||||
| Chaff-cutting establishments | 55 | 265 | 1 | 266 | 9,829 | 26 | 9,855 | 391 | 130,507 | 169,313 | 46,786 |
| Grass-seed dressing establishments | 25 | 60 | .. | 60 | 5,310 | .. | 5,310 | 189 | 197,846 | 241,239 | 48,195 |
| Paper manufacture— | |||||||||||
| Paper-mills | 3 | 79 | 19 | 98 | .. | .. | .. | 705 | .. | .. | .. |
| Paper bag and box factories | 7 | 24 | 57 | 81 | 1,312 | 1,936 | 3,248 | 13 | 4,471 | 14,217 | 11,499 |
| Gasworks† | 30 | 568 | 4 | 572 | 70,388 | 185 | 70,573 | 242 | 83,612 | 290,567 | 971,559 |
| Electric-lighting works | 6 | 52 | .. | 52 | 6,226 | .. | 6,226 | 2,158 | 4,603 | 23,234 | 64,156 |
| Processes relating to stone, clay, glass, &c.— | |||||||||||
| Lime and cement works† | 15 | 184 | .. | 184 | 16,577 | .. | 16,577 | 466 | 18,397 | 45,142 | 38,436 |
| Brick, tile, and pottery works† | 108 | 838 | .. | 838 | 63,336 | .. | 63,336 | 659 | .. | 122,230 | 114,567 |
| Tobacco-pipe factory | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Monumental masonry | 27 | 81 | .. | 81 | 7,072 | .. | 7,072 | 13 | 8,689 | 22,313 | 17,391 |
| Glassworks | 2 | 9 | .. | 9 | .. | .. | .. | 13 | .. | .. | .. |
| Glass-bevelling works | 2 | 7 | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. | 13 | .. | .. | .. |
| Electro-plating works | 2 | 11 | .. | 11 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. |
| Pumice-works | 1 | 27 | 1 | 28 | .. | .. | .. | 15 | .. | .. | .. |
| Metals, other than gold and silver— | |||||||||||
| Tinware factories† | 60 | 336 | 1 | 337 | 23,107 | 36 | 23,143 | 23 | 52,553 | 98,587 | 56,914 |
| Iron and brass foundries, boiler-making, machinists, &c.† | 65 | 1,950 | 5 | 1,955 | 162,477 | 170 | 162,647 | 983 | 240,578 | 508,906 | 211,282 |
| Heel- and toe-plate factories | 3 | 7 | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. | 23 | .. | .. | .. |
| Engineering works†‡ | 37 | 1,437 | 5 | 1,442 | 127,374 | 261 | 127,635 | 541 | 186,208 | 361,958 | 155,081 |
| Range-making works | 9 | 193 | .. | 193 | 16,927 | .. | 16,927 | 53 | 19,721 | 53,307 | 27,919 |
| Spouting and ridging factories | 35 | 261 | .. | 261 | 20,584 | .. | 20,584 | 35 | 70,643 | 112,691 | 52,687 |
| Lead-headed-nail works | 1 | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Iron-pipe and fluming works | 2 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Books and publications— | |||||||||||
| Printing offices†§ | 188 | 2,627 | 507 | 3,134 | 268,041 | 16,564 | 284,605 | 956 | 200,243 | 704,285 | |
| Musical instruments— | |||||||||||
| Musical-instrument factories | 3 | 11 | .. | 11 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Ornaments, minor art products, and smallwares— | |||||||||||
| Picture-frame makers | 9 | 19 | 3 | 22 | 1,234 | 69 | 1,303 | 1 | 2,497 | 5,771 | 11,750 |
| Basket and perambulator factories | 21 | 107 | 11 | 118 | 6,517 | 494 | 7,011 | 9 | 6,902 | 17,942 | 18,180 |
| Cork-cutting | 1 | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Lapidaries | 3 | 8 | .. | 8 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. |
| Equipment for sports and games— | |||||||||||
| Billiard-table factories | 3 | 7 | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Designs, medals, type, and dies— | |||||||||||
| Rubber-stamp making | 2 | 3 | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Arms and explosives— | |||||||||||
| Ammunition-factory | 1 | 21 | 84 | 105 | .. | .. | .. | 39 | .. | .. | |
| Machines, tools, and implements— | |||||||||||
| Agricultural implement factories | 33 | 584 | 2 | 586 | 53,879 | 62 | 53,941 | 360 | 49,072 | 138,094 | 61,339 |
| Brush and broom factories | 12 | 86 | 42 | 128 | 5,965 | 1,190 | 7,155 | 32 | 10,158 | 21,131 | 13,829 |
| Cutlery-factory | 1 | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. |
| Bellows-factory | 1 | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Carriages and vehicles— | |||||||||||
| Coach-building and painting works† | 160 | 1,185 | .. | 1,185 | 83,356 | .. | 83,356 | 128 | 88,229 | 216,077 | 150,811 |
| Cycle-factories† | 71 | 378 | 17 | 395 | 20,873 | 570 | 21,443 | 95 | 26,824 | 65,047 | 65,403 |
| Harness, saddlery, and leatherware— | |||||||||||
| Saddlery and harness factories† | 115 | 629 | 23 | 652 | 40,808 | 1,026 | 41,834 | 3 | 75,724 | 147,626 | 96,559 |
| Whip-thong factories | 2 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Portmanteau factories | 6 | 19 | 3 | 22 | 1,206 | 117 | 1,323 | .. | 2,741 | 5,483 | 6,460 |
| Tanning, fellmongering, and wool-scouring establishments† | 119 | 1,957 | 6 | 1,963 | 159,180 | 162 | 159,342 | 1,108 | 1,391,323 | 1,888,107 | 235,952 |
| Ships, boats, and their equipment— | |||||||||||
| Ship- and boat-building yards† | 32 | 211 | .. | 211 | 13,476 | .. | 13,476 | 49 | 20,389 | 45,811 | 15,198 |
| Graving docks and patent slips | 7 | 32 | .. | 32 | 2,864 | .. | 2,864 | 435 | .. | 7,264 | 230,165 |
| Block and pump factory | 1 | 2 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. |
| Sail and oilskin factories† | 30 | 150 | 81 | 231 | 10,446 | 1,996 | 12,442 | .. | 24,628 | 44,854 | 40,893 |
| Furniture— | |||||||||||
| Furniture and cabinet-making† | 144 | 1,243 | 67 | 1,310 | 88,843 | 2,262 | 91,105 | 369 | 101,595 | 241,024 | 170,338 |
| Venetian-blind works | 12 | 49 | 2 | 51 | 3,567 | 65 | 3,632 | 19 | 5,896 | 13,233 | 7,469 |
| Mattress-factories | 12 | 55 | .. | 55 | 3,260 | .. | 3,260 | 20 | 9,212 | 16,296 | 13,165 |
| Wool, rug, and mat making | 2 | 9 | 8 | 17 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Nature of Industries. | Total Nature of Industries. | Number of Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Amount of Power employed (Horse-power). | Value of all Materials used or operated upon during 1900. | Value of all Manufactures or Produce (including Repairs) for the Year 190.* | Approximate Value of Land, Buildings, Machinery, and Plant. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Females. | Total. | Males. | Females. | Total. | ||||||
Note.—Two or more distinct industries were carried on at some establishments. In such cases particulars of power, hands, and plant employed, and wages paid, unless stated separately for each branch of industry, have been treated as belonging to the most important work. * or information as to quantities manufactured or produced, see special tables. Value of output, wages, &c. not shown where the number of establishments is so small that particulars might be identified. † For full particulars respecting these industries, see special tables. § See remarks on page 242. | |||||||||||
| Chemicals and by-products— | £ | £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Perfumery-manufactory | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Varnish-manufactories | 4 | 19 | .. | 19 | 1,474 | .. | 1,474 | 37 | 4,227 | 6,732 | 5,765 |
| Ink-manufactories | 3 | 5 | .. | 5 | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | .. | .. |
| Starch-manufactories | 3 | 24 | 8 | 32 | .. | .. | .. | 16 | .. | .. | .. |
| Chemical-works | 8 | 76 | 19 | 95 | 7,551 | 504 | 8,055 | 92 | 42,479 | 64,834 | 37,793 |
| Haematite-paint factories | 4 | 12 | .. | 12 | 609 | .. | 609 | 28 | 1,030 | 2,578 | 5,943 |
| Sheep-dip factories | 3 | 6 | 1 | 7 | .. | .. | .. | 10 | .. | .. | .. |
| Match-factories | 2 | 37 | 146 | 183 | .. | .. | .. | 19 | .. | .. | .. |
| Herbal-remedies factories | 8 | 13 | 10 | 23 | 1,134 | 581 | 1,715 | 12 | 3,994 | 18,396 | 10,305 |
| Blacking-factories | .. | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | .. | .. |
| Cocoanut-oil mills | .. | 2 | 10 | .. | 10 | .. | .. | .. | 54 | .. | .. |
| Textile fabrics— | |||||||||||
| Woollen-mills† | 10 | 769 | 924 | 1,693 | 71,454 | 40,547 | 112,001 | 1,554 | 196,081 | 359,382 | 277,422 |
| Flock-mills | 5 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 559 | 12 | 571 | 55 | 1,459 | 4,105 | 2,650 |
| Cleaning and dyeing works | 11 | 28 | 23 | 51 | 1,816 | 837 | 2,653 | 13 | 2,141 | 7,855 | 9,635 |
| Dress— | |||||||||||
| Tailoring establishments | 175 | 722 | 899 | 1,621 | 65,695 | 37,251 | 102,946 | 8 | 122,853 | 301,356 | 211,016 |
| Dressmaking and millinery establishments | 290 | 23 | 2,865 | 2,888 | 2,236 | 76,270 | 78,506 | .. | 173,211 | 312,436 | 193,998 |
| Shirt-making establishments | 25 | 28 | 503 | 531 | 1,911 | 13,651 | 15,562 | 40 | 45,319 | 75,879 | 26,528 |
| Corset and belt manufactories | 6 | 1 | 24 | 25 | 9 | 542 | 551 | .. | 959 | 2,249 | 5,659 |
| Clothing-factories† | 21 | 431 | 2,081 | 2,512 | 37,778 | 63,023 | 100,801 | 67 | 177,828 | 329,026 | 89,247 |
| Waterproof-factories† | 6 | 22 | 92 | 114 | 1,807 | 2,822 | 4,629 | 3 | 6,285 | 13,378 | 7,845 |
| Boot and shoe factories† | 126 | 1,906 | 790 | 2,696 | 165,227 | 27,216 | 192,443 | 184 | 273,325 | 529,254 | 176,992 |
| Hat and cap factories | 13 | 37 | 80 | 117 | 2,641 | 2,748 | 5,389 | 20 | 11,463 | 25,641 | 19,217 |
| Hosiery-factories† | 17 | 17 | 265 | 282 | 1,328 | 6,702 | 8,030 | 71 | 18,032 | 31,265 | 19,997 |
| Fibrous materials— | |||||||||||
| Rope and twine works† | 17 | 192 | .. | 192 | 13,136 | .. | 13,136 | 494 | 46,378 | 87,63 | 55,309 |
| Bag and sack factory | 1 | .. | 6 | 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Flax-mills† | 101 | 1,698 | .. | 1,698 | 101,046 | .. | 101,046 | 1,190 | 53,064 | 203,492 | 64,446 |
| Values for industries of which less than four of any one sort were found in the returns | .. | .. | .. | .. | 53,927 | 9,235 | 63,162 | .. | 526,252 | 694,896 | 258,885 |
| Returns not included in above | 74 | 140 | 156 | 296 | 10,952 | 4,836 | 15,788 | 138 | 28,834 | 61,749 | 59,659 |
| Totals, Census, 1901 | 3,680 | 36,292 | 10,555 | 46,847 | 2,972,193 | 330,454 | 3,302,647 | 39,113 | 7,749,770 | 17,853,133§ | 8,408,564 |
| Deduct tailoring, dressmaking, shirtmaking, and monumental masons' establishments, not included in accounts taken for 1896 and 1891 | 517 | 854 | 4,267 | 5,121 | 76,914 | 127,172 | 204,086 | 61 | 350,072 | 711,984 | 448,933 |
| Totals, Census, 1901 (loss deductions shown above) | 3,163 | 35,438 | 6,288 | 41,726 | 2,895,279 | 203,282 | 3,098,561 | 39,052 | 7,399,698 | 17,141,149 | 7,959,631 |
| Totals, Census, 1896 | 2,459 | 22,986 | 4,403 | 27,389 | 1,776,076 | 131,516 | 1,907,592 | 28,096 | 3,285,247 | 9,549,360 | 5,796,017 |
| Totals, Census, 1891 | 2,254 | 22,664 | 2,969 | 25,663 | 1,705,641 | 102,999 | 1,808,640 | 21,696 | .. | 8,773,837 | 5,261,826 |
The succeeding statement shows the most important industries in operation in 1901, ranged in order of the values of their output for 1900, and compared with the results obtained for the years 1895, 1890, and 1885:—
| Total Value of all Manufactures or Produce, including Repairs. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 1895 | 1890 | 1885 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Meat-freezing and preserving and boiling-down works | 3,834,891 | 1,652,275 | 1,464,659 | 543,878 |
| Tanning, fellmongering, and wool-scouring | 1,888,107 | 1,237,252 | 1,026,349 | 634,915 |
| Butter and cheese factories | 1,535,150 | 501,274 | 150,957 | 43,094 |
| Sawmills, sash and door factories | 1,268,689 | 898,807 | 832,959 | 1,177,713 |
| Iron and brass foundries, boiler-making, machinists, &c. (not including Government Railway Workshops) | 924,171 | 302,815 | 403,635 | 368,919 |
| Clothing and boot-and-shoe factories | 858,280 | 616,158 | 570,315 | 514,506 |
| Printing establishments (not including Government Printing Office) | 704,285 | 389,124 | 354,559 | 273,886 |
| Grain mills | 682,884 | 874,656 | 991,812 | 754,830 |
| Breweries and malthouses | 659,298 | 418,830 | 380,849 | 421,197 |
| Woollen mills | 359,382 | 302,423 | 279,175 | 194,311 |
| Gasworks | 290,567 | 199,025 | 178,947 | 194,653 |
| Grass-seed dressing establishments | 241,239 | .. | .. | .. |
| Furniture and cabinetmaking | 241,024 | 85,327 | 131,314 | 162,375 |
| Coach - building and painting works | 216,077 | 148,969 | 139,660 | 128,346 |
| Flax-mills | 203,492 | 32,546 | 234,266 | 20,059 |
| Biscuit factories | 197,989 | 118,979 | 127,147 | 47,784 |
| Chaff-cutting works | 169,313 | 78,497 | 63,236 | 54,440 |
| Bacon-curing establishments | 159,564 | 86,022 | 83,435 | 58,799 |
| Soap and candle works | 158,649 | 152,298 | 155,714 | 130,745 |
| Aë-water factories | 151,811 | 98,609 | 91,691 | 94,098 |
| Saddlery and harness factories | 147,626 | 63,735 | 37,347 | .. |
| Agricultural implement factories | 138,094 | 102,054 | 144,472 | 111,823 |
| Brick, tile, and pottery works | 122,230 | 66,140 | 56,830 | 91,797 |
| Spouting and ridging works | 112,691 | 23,762 | 33,140 | 25,478 |
| Tinware factories | 98,587 | 63,723 | 14,297 | 8,500 |
| Sugar-boiling and confectionery works | 88,580 | 33,235 | 17,248 | 17,130 |
| Rope and twine works | 87,863 | 52,400 | 76,711 | 56,413 |
| Cycle factories | 65,047 | 18,817 | 5,655 | 1,301 |
| Chemical works | 64,834 | 75,320 | 41,568 | 34,283 |
| Fruit-preserving and jam-making works | 58,092 | 36,108 | 27,255 | 32,292 |
| Ship and boat-building works | 45,811 | 25,233 | 35,847 | 56,132 |
| Coffee and spice works | 45,628 | 74,339 | 64,024 | 98,234 |
| Lime and cement works | 45,142 | 15,881 | 19,416 | 16,928 |
| Sail, tent, and oilskin factories | 44,854 | 30,166 | 31,083 | 25,574 |
| Bone-mills and other manure works | 40,298 | 12,246 | 4,628 | 8,337 |
| Woodware and turnery factories | 37,552 | 18,276 | 9,050 | .. |
| Cooperages | 37,521 | 19,233 | 11,540 | 11,862 |
| Hosiery factories | 31,265 | 9,357 | 5,650 | 6,200 |
| Sauce and pickle works | 31,258 | 13,417 | 6,407 | 3,145 |
| Sausage-skin factories | 30,674 | 13,472 | 10,582 | .. |
| Hat and cap factories | 25,641 | 10,902 | 21,628 | 13,695 |
| Fish - curing and preserving works | 25,173 | 10,292 | 19,537 | 12,182 |
| Electric-lighting works | 23,234 | .. | .. | .. |
| Brush and broom factories | 21,131 | 23,363 | 13,340 | 7,786 |
| Herbal-remedies factories | 18,396 | .. | .. | .. |
| Baking-powder factories | 18,163 | 10,153 | 5,637 | 4,120 |
| Basket and perambulator factories | 17,942 | 11,920 | 7,381 | 4,375 |
| Mattress factories | 16,296 | .. | .. | .. |
| Paper-bag and cardboard box factories | 14,217 | 7,698 | 4,497 | .. |
| Waterproof factories | 13,378 | 22,354 | .. | .. |
| Venetian blind factories | 13,233 | 9,878 | 4,776 | 6,470 |
| Colonial-wine works | 10,330 | 8,963 | 3,456 | 3,626 |
| Other industries in respect of which the value of the manufactures was less than £8,000, and sundry | 805,606 | 473,037 | 380,156 | 235,148 |
The order of the principal industries, ranged according to the number of hands employed, is as follows:—
| Number of Hands. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 1896 | 1891 | |
| Sawmills, sash and door factories | 6,812 | 4,059 | 3,266 |
| Clothing and boot and shoe factories | 5,208 | 4,407 | 3,233 |
| Iron and brass foundries, boiler-making, machinists, &c. | 3,590 | 1,642 | 1,787 |
| Printing establishments (excluding Government Printing Office) | 3,134 | 2,351 | 2,569 |
| Meat freezing, preserving, and boiling-down works | 2,282 | 2,037 | 1,568 |
| Tanning, fellmongering, and wool-scouring establishments | 1,963 | 1,629 | 1,196 |
| Flax-mills | 1,698 | 647 | 3,204 |
| Woollen-mills | 1,693 | 1,416 | 1,175 |
| Furniture and cabinet-making factories | 1,310 | 496 | 585 |
| Butter and cheese factories | 1,188 | 576 | 269 |
| Coach-building and painting works | 1,185 | 807 | 678 |
| Brick, tile, and pottery works | 838 | 455 | 494 |
| Breweries and malt uses | 827 | 560 | 563 |
| Biscuit factories | 667 | 425 | 331 |
| Saddlery and harness factories | 652 | 266 | 184 |
| Agricultural implement factories | 586 | 581 | 528 |
| Gasworks | 572 | 295 | 249 |
| Grain-mills | 515 | 419 | 499 |
| Aerated-water factories | 452 | 347 | 261 |
| Cycle factories | 395 | 125 | 31 |
| Tinware factories | 337 | 289 | 93 |
| Sugar-boiling and confectionery works | 305 | 69 | 53 |
| Hosiery factories | 282 | 133 | 51 |
| Chaff-cutting works | 266 | 212 | 205 |
| Spouting and ridging works | 261 | 90 | 100 |
| Sugar-refining works | 256 | 160 | 110 |
| Soap and candle works | 232 | 190 | 209 |
| Sail, tent, and oilskin factories | 231 | 143 | 124 |
| Ship- and boat-building yards | 211 | 108 | 145 |
| Bacon-curing establishments | 196 | 123 | 84 |
| Rope and twine works | 192 | 150 | 222 |
| Lime and cement works | 184 | 79 | 98 |
| Match factories | 183 | 121 | .. |
| Fruit-preserving and jam-making works | 167 | 193 | 117 |
| Woodware and turnery factories | 156 | 81 | 51 |
| Cooperages | 138 | 76 | 53 |
| Fish-curing and preserving works | 137 | 75 | 140 |
| Brush and broom factories | 128 | 92 | 81 |
| Sauce and pickle works | 128 | 68 | 41 |
| Basket and perambulator factories | 118 | 76 | 63 |
| Hat and cap factories | 117 | 72 | 112 |
| Waterproof factories | 114 | 93 | .. |
| Ammunition factories | 105 | 90 | 80 |
| Sausage-skin factories | 98 | 56 | 73 |
| Paper mills | 98 | 84 | 48 |
| Chemical works | 95 | 114 | 55 |
| Paper-bag and cardboard-box factories | 81 | 86 | 35 |
| Coffee and spice works | 78 | 119 | 81 |
| Rabbit preserving and packing works | 62 | 32 | .. |
| Grass-seed dressing establishments | 60 | .. | .. |
| Colonial-wine works | 59 | 53 | 24 |
| Mattress factories | 55 | .. | .. |
| Electric-lighting works | 52 | .. | .. |
| Venetian-blind factories | 51 | 45 | 29 |
| Cleaning and dyeing works | 51 | 58 | 48 |
| Bone-mills and other manure works | 47 | 46 | 25 |
| Condensed-milk factory | 33 | .. | .. |
| Graving docks and patent slips | 32 | 29 | 64 |
| Starch and soda works | 32 | 27 | 13 |
| Baking-powder factories | 29 | .. | .. |
| Pumice works | 28 | 20 | .. |
| Corset and belt manufactories | 25 | .. | .. |
| Herbal-remedies factories | 23 | .. | .. |
| Vinegar works | 23 | .. | .. |
| Portmanteau factories | 22 | .. | .. |
| Picture-frame makers | 22 | .. | .. |
| Tobacco manufactories | 20 | .. | .. |
| Sheep-dip factories | 7 | 29 | .. |
| Industries employing under 20 hands | 532 | 268 | 36 |
The establishments increased from 43 in 1896 to 48 in 1901, and the hands employed from 2,037 to 2,282. The value of output for 1900 is returned as more than double that for 1895, the figures being £3,834,891 against £1,652,275, a rise of £2,182,616. From 1890 to 1895 the increase was only £187,616. Of the total value for 1900 (£3,834,891), sheep and lambs frozen were valued at £2,103,166, and legs of mutton at £85,361. The beef frozen, preserved meats, tallow, bonedust, &c., also show largely increased business in the quinquennium, 1895–1900; frozen butter and rabbits most markedly so.
The table given below shows quantities as well as values in the comparisons, which speak for themselves as to the great development that has been proceeding of late.
| Census Year. | No of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Output, 1900 and 1895. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep and Lambs frozen. | |||||||||||
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Oil | Carcases. | Value. | |||
| £ | £ | No. | £ | ||||||||
| 1901 | 48 | 2,233 | 49 | 204,216 | 1,419 | 50 | .. | 1 | 7,450 | *3,348,123 | *2,103,166 |
| 1896 | 43 | 1,985 | 52 | 180,471 | 304 | 42 | 3 | .. | 7,492 | *2,362,535 | *1,213,559 |
| Increase | 5 | 248 | .. | 23,745 | 1,115 | 8 | .. | 1 | .. | 985,588 | 889,607 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | .. | 42 | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Output for the Years 1900 and 1895—continued. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beef frozen and chilled. | Frozen Rabbits. | Preserved Meats. | Tallow. | |||||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quan. | Value. | |
| Lb. | £ | No. | £ | Lb. | £ | Tons. | £ | |
| 1901 | 34,285,328 | 381,210 | 6,040,047 | 144,616 | 7,867,440 | 171,151 | 14,767 | 298,821 |
| 1896 | 1,954,495 | 21,425 | .. | .. | 4,999,640 | 74,369 | 10,958 | 172,310 |
| Incr. | 32,330,833 | 359,785 | 6,040,047 | 144,616 | 2,867,800 | 96,782 | 3,809 | 126,511 |
| Census Year. | Output for the Years 1900 and 1895-continued. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonedust. | Other Manures. | Neatsfoot and Trotter Oil. | Bones, Horns, Hoots, &c. | |||||
| Quan. | Value. | Quan. | Value. | Quan. | Value. | Quan. | Value. | |
* Also 21,994 cwt. of legs of mutton frozen in 1895, valued at £16,373, and 64,203 cwt. of frozen legs of mutton in 1900, valued at £85,361. | ||||||||
| Tons. | £ | Tons. | £ | Galls. | £ | Tons. | £ | |
| 1901 | 6,514 | 31,037 | 5,721 | 25,824 | 30,174 | 3,450 | 530 | 3,085 |
| 1896 | 3,248 | 11,865 | 2,206 | 9,424 | 15,067 | 2,097 | 113 | 188 |
| Increase | 3,266 | 19,172 | 3,515 | 16,400 | 15,107 | 1,353 | 417 | 2,897 |
| Census Year. | Output, 1900 and 1895—continued. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Products. | Frozen Produce (Butter and all other frozen): Value. | Total Value of Output, 1900 and 1895. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |
| Value. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 82,345 | 503,430 | 3,834,891 | 87,776 | 428,075 | 404,707 |
| 1896 | 64,889 | 65,776 | 1,652,275 | 67,504 | 326,224 | 317,323 |
| Increase | 17,456 | 437,654 | 2,182,616 | 20,272 | 101,851 | 87,384 |
These were 39 in number, employing 196 hands, against 37 with 123 hands in 1895. The output increased in value from £86,022 for 1895 to £159,564 in 1900, the business done in hams having progressed very greatly.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | Horsepower. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | |||||||
| 1901 | 39 | 185 | 11 | 13,891 | 496 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 250 |
| 1896 | 37 | 118 | 5 | 7,314 | 80 | 7 | 1 | .. | 49 |
| Increase | 2 | 67 | 6 | 6,577 | 416 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 201 |
| Census Year. | Value of Material used. | Output for Year 1900. | Total Value of Output. | Approximate Value of*† | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacon. | Hams. | Lard. | Other Products. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
* Value of land and buildings given with butter-factory in one case. † Value of land buildings, and plant not stated in one case. | |||||||||
| £ | Cwt. | Cwt. | Cwt. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 115,656 | 34,103 | 21,836 | 2,082 | 4,182 | 159,564 | 19,377 | 25,960 | 16,855 |
| 1896 | 65,867 | 33,260 | 800 | 20 | .. | 86,022 | 6,823 | 11,090 | 4,605 |
| Incr. | 49,789 | 843 | 21,036 | 2,062 | 4,182 | 73,542 | 12,554 | 14,870 | 12,250 |
There was a considerable decrease shown in the quantity of fish cured in 1900 as compared with 1895, but the value of the lesser output was set down as £4,778 more than in the earlier year. The quantity cured in 1900 was 1,082,820 lb., against 1,719,512lb. in 1895. The output of tinned fish increased from 113,304 lb. to 288,849lb., and the total value of all products of the 28 establishments rose from £10,292 to £25,173.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Value of Materials used 1900 and 1895. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 28 | 135 | 2 | 7,445 | 73 | 7,714 |
| 1896 | 27 | 74 | 1 | 3,229 | 13 | 2,124 |
| Increase | 1 | 61 | 1 | 4,216 | 60 | 5,590 |
| Census Year. | Fish cured. | Fish tinned. | Value of other Produce. | Total Value of Output. | Approximate value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| lb | £ | lb | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 1,082,820 | 13,182 | 288,849 | 6,206 | 5,785 | 25,173 | 9,937 | 3,858 | 3,440 |
| 1896 | 1,719,512 | 8,404 | 113,304 | 1,888 | .. | 10,292 | 3,902 | 3,782 | 2,045 |
| Incr. | .. | 4,778 | 175,545 | 4,318 | 5,785 | 14,881 | 6,035 | 76 | 1,395 |
| Decr. | 636,692 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
Here a most excellent result is shown by the comparison. Not only did the number of factories increase from 170 to 247 between 1896 and 1901, besides skimming stations and creameries in connection with them—202 against 105; but the number of persons employed was more than doubled (1,188 against 576), and the value of the output rose to three times the amount for 1895. The figures are, £1,535,150 for 1900, against £501,274 for 1895.
The produce of factory-made butter for 1900 was set down at 29,758,310lb., and for 1895 at 11,336,776lb., while cheese made similarly increased from 86,460cwt. to 139,687 cwt. in the same period.
It is to be regretted that there is no estimate of butter and cheese made on farms, so that the total produce for the colony could be arrived at.
By far the greater number of factories for making butter are in the North Island, the number having been 174, out of a total of 247, which turned out 24,500,000 lb. of butter in the year 1900, leaving somewhat over 5,000,000lb. as the output for the Middle Island. Taranaki is the provincial district in which the operations are by far the largest, 12,500,000 lb. of butter being the result of the factory operations, and nearly 32,000 cwt. of cheese. Wellington factories show for 1900 a total of over 7,500,000lb. of butter and 32,000 cwt. of cheese. Otago makes more cheese (52,000 cwt.) in her factories than any other district. The butter was found to be a little short of 3,000,000lb. for the year.
The money invested for purposes of this industry in land, buildings, machinery, and plant has largely increased. Full particulars are given in the subjoined table:—
| Census Year. | No. of Factories. | Hands Employed. | Amount paid in Wages. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam | Water | Gas and Oil. | Horse. | Hand. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | |||||||||
| 1901 | 247 | 1,165 | 23 | 95,461 | 972 | 223 | 37 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 2,399 |
| 1896 | 170 | 548 | 28 | 39,716 | 441 | 234 | 33 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 1,531 |
| Increase | 77 | 617 | .. | 55,745 | 531 | .. | 4 | 7 | .. | .. | 868 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | 5 | .. | .. | 11 | .. | .. | 2 | 5 | .. |
| Census Year. | Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheese. | Butter. | Other Produce. | Total Value of all Produce. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| Quan. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Value. | |||||
| Tons. | £ | Lb. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 6,984 | 303,758 | 29,758,310 | 1,203,520 | 27,872 | 1,535,150 | 38,780 | 147,307 | 202,663 |
| 1896 | 4,323 | 146,158 | 11,336,776 | 355,116 | .. | 501,274 | 27,335 | 91,601 | 115,070 |
| Incr. | 2,661 | 157,600 | 18,421,534 | 848,404 | 27,872 | 1,033,876 | 11,445 | 55,706 | 87,593 |
In 1896 it was remarked in the Census report that the result of a five year's comparison was to show a decrease in the number of grain-mills in operation, and decline of hands employed, also in grain operated upon. The result for 1900 is more satisfactory.
Although the number of mills working fell from 90 in 1896 to 78 in 1900, the hands employed increased from 419 to 515, and the wheat used from 3,815,433 bushels to 4,004,789 bushels, besides a slight increase in other kinds of grain. The total value of the output, however, declined from £874,656 to £682,884. A statement is given, to exhibit full details:—
| Census Year. | Number of Mills. | Number of Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Number of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Wind. | Gas. | Pairs of Stones. | Sets of Rollers. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | ||||||||||
| 1901 | 78 | 513 | 2 | 49,254 | 110 | 45 | 35 | .. | 3 | 2,422 | 83 | 429 |
| 1896 | 90 | 419 | .. | 40,890 | .. | 51 | 45 | 1 | 1 | 2,333 | 144 | 406 |
| Increase | .. | 94 | 2 | 8,364 | 110 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 89 | .. | 23 |
| Decrease | 12 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 10 | 1 | .. | .. | 61 | .. |
| Census Year. | Grain operated upon during the Years 1900 and 1895. | Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||||
| Wheat. | Other Grain. | Value. | Flour. | Meal. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |
| Bushels. | Bushels. | £ | Tons. | Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 4,004,789 | 762,340 | 545,642 | 83,017 | 7,418 | 682,884 | 44,688 | 132,817 | 181,151 |
| 1896 | 3,815,433 | 731,448 | 653,219 | 81,033 | 16,482 | 874,656 | 41,730 | 134,714 | 179,403 |
| Incr. | 189,356 | 30,892 | .. | 1,984 | .. | .. | 2,958 | .. | 1,748 |
| Decr. | .. | .. | 107,577 | .. | 9,064 | 191,772 | .. | 1,897 | .. |
Twenty factories are shown as in operation in 1901 against 17 five years previously. But 109 more males and 133 more females were employed in the later year. The comparison shows that not much more was done in biscuit-making during the year 1900 than in 1895, the figures being 3,267 tons against 3,003 tons. But the returns for 1900 shows also confectionery made valued at £55,039, and other products to the value of £38,474. The total output came to £197,989, while in 1895 the sum was only £118,979.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands. | Wages. | Machine-power used. | Horsepower. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water and Gas. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | ||||||
| 1901 | 20 | 454 | 213 | 34,231 | 4,545 | 11 | 5 | 291 |
| 1896 | 17 | 345 | 80 | 18,801 | 1,355 | 10 | 4 | 134 |
| Increase | 3 | 109 | 133 | 15,430 | 3,190 | 1 | 1 | 157 |
| Census Year. | Biscuits made. | Total Value of Manufactures for 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
* Including 1,286 tons confectionery, valued at £55,039, and other products valued at £38,474. | |||||
| Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 3,267 | 197,989* | 14,940 | 35,567 | 39,736 |
| 1896 | 3,003 | 118,979 | 11,340 | 21,575 | 25,951 |
| Increase | 264 | 79,010 | 3,600 | 13,992 | 13,785 |
The weight of fruit bottled or preserved in New Zealand during 1900 was returned at 84,500 lb, against 72,790lb. in 1895. The jam manufacture increased considerably, the figures being 3,303,395lb., and 1,930,058lb. for 1895. Other preserves were also made in 1900 to the extent of 179,532 lb. How it arises that the returns show fewer hands and factories at the time of last census than at the previous collection cannot be explained.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Value of Materials used, 1900 and 1895. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | ||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 13 | 85 | 82 | 6,317 | 1,758 | 9 | 2 | 117 | 42,404 |
| 1896 | 22 | 103 | 90 | 5,101 | 1,450 | 6 | .. | 77 | 20,542 |
| Increase | .. | .. | .. | 1,216 | 308 | 3 | 2 | 40 | 21,862 |
| Decrease | 9 | 18 | 8 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures, 1900 and 1895. | Other Preserves. | Value of all Manufactures, 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit, bottled or preserved. | Jam made. | |||||||||
| Quantity | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity | Value | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| Lb. | £ | Lb. | £ | Lb. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 84,500 | 950 | 3,303,395 | 54,120 | 179,532 | 3,022 | 58,092 | 5,160 | 9,835 | 5,940 |
| 1896 | 72,790 | 1,676 | 1,930,058 | 33,355 | 52,118 | 1,077 | 36,108 | 4,504 | 9,865 | 4,498 |
| Incr. | 11,710 | .. | 2,373,337 | 20,765 | 127,414 | 1,945 | 21,984 | 656 | .. | 1,442 |
| Decr. | .. | 726 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 30 | .. |
This industry is becoming an important one. The value of the manufactured articles for the year 1900 reached the sum of £88,580, which is £55,345 in excess of the value returned for 1895. The number of establishments was 26, and the hands employed show an increase from 69 to 305, of whom 147 were females.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive-power. | Horsepower. | Value of Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | ||||
* Information not available. | |||||||||
| £ | £ | H.p. | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 26 | 158 | 147 | 11,128 | 3,600 | 1 | 2 | 19 | 47,150 |
| 1896 | 12 | 39 | 30 | 2,253 | 561 | * | * | 21 | 14,887 |
| Incr. | 14 | 119 | 117 | 8,875 | 3,039 | .. | .. | .. | 32,263 |
| Decr. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | .. |
| Census Year. | Sugar used. | Other Materials used. | Total Value of Output for 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
* Information not available. | |||||||
| Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 1,400 | 28,440 | 18,710 | 88,580 | 21,271 | 17,709 | 17,975 |
| 1896 | * | * | * | 33,235 | 2,610 | 3,850 | 2,465 |
| Increase | .. | .. | .. | 55,345 | 18,661 | 13,859 | 15,510 |
Although the number of breweries in the colony in 1901 was fewer than that for 1896, the hands employed were more numerous, and the quantity of beer manufactured considerably greater.
While in the year 1895 there were 5,249,278 gallons brewed, the output for 1900 amounted to 7,379,581 gallons, being over two millions of gallons of increase in a five-year period; and the value increased proportionately.
The quantities of beer on which excise duty was paid for consumption were, for 1895, 4,936,400 gallons, and 6,811,280 gallons for 1900, being in each case a somewhat lesser quantity than that returned as manufactured.
It was noticed in the report on the Census of 1896 that consumption of beer per head of population had fallen since 1891 from 7·899 gallons in 1890 to 7·421 gallons in 1895, and the quantity manufactured showed very little increase. But from 1895 to 1900, as shown above, the brewing proceeded at a considerable rate, and the consumption per head has advanced from 7·421 gallons to 9·150 gallons. No doubt prosperous times have brought about this result.
The imported beer entered at the Customs for home consumption decreased in quantity from 201,770 gallons in 1895 to 175,620 gallons in 1900, proving that the colonial-made article is more and more taking the place of the beer brought from abroad. In the year 1892 261,394 gallons were brought into New Zealand.
| Census Year. | No of Breweries. | Hands. | Wages paid. | Motive-power employed. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Wind. | Horse. | Hand. | ||
| £ | £ | ||||||||||
| 1901 | 74 | 677 | 5 | 83,493 | 77 | 56 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 1896 | 85 | 465 | .. | 57,327 | .. | 56 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 14 |
| Increase | .. | 212 | 5 | 26,166 | 77 | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. |
| Decrease | 11 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 2 | 11 |
| Census Year. | Amount of Horsepower. | Number of | Materials used during Years 1900 and 1895. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horses employed. | Drays employed. | Sugar. | Malt. | Hops. | Value. | ||
| Lb. | Bush. | Lb. | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 632 | 176 | 149 | 2,424,505 | 455,035 | 562,245 | 158,212 |
| 1896 | 441 | 180 | 149 | 1,607,144 | 328,059 | 424,839 | 125,706 |
| Increase | 191 | .. | .. | 817,361 | 126,976 | 137,406 | 32,506 |
| Decrease | .. | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Beer made, 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant | |
| Gal. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 7,379,581 | 553,627 | 78,694 | 139,014 | 76,884 |
| 1896 | 5,249,278 | 336,734 | 51,533 | 115,033 | 63,850 |
| Increase | 2,130,303 | 216,893 | 27,161 | 23,981 | 13,034 |
At 33 malthouses, which were in connection with the breweries before mentioned, 623,686 bushels of barley were malted, being in excess of the quantity for 1895 by 267,278 bushels, or nearly 75 per cent. The large additional quantity of beer made in 1900 required increased operations in malting.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands Employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Horse. | Hand. | |||||
| £ | H.-p. | ||||||||
| 1901 | 33 | 145 | 14,994 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 21 | 110 |
| 1896 | 31 | 95 | 9,398 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 25 | 59 |
| Increase | 2 | 50 | 5,596 | 2 | .. | 3 | 1 | .. | 51 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4 | .. |
| Census Year. | Value of Materials used. | Barley malted, 1900, 1895. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| Note.—In some cases the value of land, buildings, and plant has been included in the returns furnished by proprietors of breweries to which the malthouses belong. | ||||||
| £ | Bushels. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 72,211 | 623,686 | 105,671 | 23,920 | 41,110 | 10,008 |
| 1896 | 52,881 | 356,408 | 82,096 | 6,685 | 27,910 | 2,909 |
| Increase | 19,330 | 267,278 | 23,575 | 17,235 | 13,200 | 7,099 |
Besides 26,513 gallons of colonial wine made in 1900, and also 400 gallons of brandy used to fortify the wine, 27,537 gallons of cider were manufactured. These results are satisfactory on comparison with those of 1895, when the wine amounted to 15,860 gallons. The quantity of cider increased from 19,178 gallons to 27,537 gallons. The value of produce increased from £8,963 in 1895 to £10,330 in 1900.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands. | Wages. | Machine-power used: Steam | Horsepower | Wine made. | Cider. | Value of Products, 1900–1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||||||
| £ | £ | H-p. | Galls. | Galls. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |||||
| 1901 | 14 | 49 | 10 | 2,320 | 92 | 2 | 14 | 26,513 | 27,537 | 10330 | 10156 | 5,074 | 2,953 |
| 1896 | 19 | 41 | 12 | 1,925 | 95 | 2 | 6 | 15,860 | 19,178 | 8,963 | 8,224 | 2,929 | 1,679 |
| Incr. | .. | 8 | .. | 395 | .. | .. | 8 | 10,653 | 8,359 | 1,367 | 1,932 | 2,145 | 1,274 |
| Decr. | 5 | .. | 2 | .. | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
Although the number of factories under this head slightly decreased between the censuses of 1896 and 1901, the operations were very much greater in the year 1900 than in 1895, and with this is shown increase of value of manufactures, as well as quantity, to a considerable extent, besides a greater number of persons employed.
The money value of all manufacture for 1900 amounted to £151,811, against £98,609 in 1895; an increase of nearly 54 per cent. Over £10,000 of additional money was paid in wages during the later year, while an increase from 1,091,580 dozen of aerated-water bottled to 1,886,024 dozen, besides a greatly enlarged business in cordials, tonic beer, and other drinks is recorded. The full particulars are tabulated below:—
| Census Year. | No. of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Horsepower. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Horse. | Gas. | Hand, Oil, and Electrical. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | |||||||||
| 1901 | 125 | 437 | 15 | 31,771 | 284 | 49 | 10 | 21 | 34 | 12 | 250 |
| 1896 | 132 | 330 | 17 | 21,184 | 261 | 46 | 17 | 11 | 24 | 35 | 216 |
| Incr. | .. | 107 | .. | 10,587 | 23 | 3 | .. | 10 | 10 | .. | 34 |
| Decr. | 7 | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | 7 | .. | .. | 23 | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Cider. | Total Value of Manufactures | Approximate Value of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerated Waters. | Cordials. | Tonic Beer. | Miscellaneous. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| Quan. | Value. | |||||||||
* Including 6,000 gallons vinegar. † Casks. | ||||||||||
| Doz. | Doz. | Doz. | Gals. | £ | Gals. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 1,886,024 | 25,478 | 89,821 | 13,356 | 5,356 | 9,950 | 151,811 | 33,037 | 34,875 | 37,266 |
| 1896 | 1,091,580 | 20,720 | 17,415 | 8,907* | 1,350 | †50 | 98,609 | 19,476 | 32,439 | 37,429 |
| Inc. | 794,444 | 4,758 | 72,406 | 4,449 | 4,006 | .. | 53,202 | 13,561 | 2,436 | .. |
| Dec. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 163 |
The number of these works was 18, the same as in 1896, but the hands fell from 119 to 78. The value of manufactured goods declined from £74,339 to £45,628 in the five years.
This industry progresses steadily. It employed 77 males and 51 females in 1901. Sauces and pickles were manufactured to the value of £31,258 in the previous year, more than double the amount made five years ago.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Value of Materials used. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam | ||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | |||||
| 1901 | 23 | 77 | 51 | 4,628 | 1,760 | 4 | 71 | 20,505 |
| 1896 | 24 | 44 | 24 | 1,835 | 622 | 3 | 57 | 7,934 |
| Increase | .. | 33 | 27 | 2,793 | 1,138 | 1 | 14 | 12,571 |
| Decrease | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sauces. | Pickles. | Other Condiments. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | ||||||
| Doz. Pnts | £ | Doz. Pnts | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 44,604 | 11,128 | 31,110 | 10,378 | 9,752 | 31,258 | 17120 | 12,375 | 7,220 |
| 1896 | 20,539 | 6,229 | 9,949 | 3,793 | 3,395 | 13,417 | 5175 | 5,160 | 1,574 |
| Increase | 24,065 | 4,899 | 21,161 | 6,585 | 6,357 | 17,841 | 11945 | 7,215 | 5,646 |
The development of these works was at a moderate rate only between 1896 and 1901, the value of manufactures of all kinds reaching to £158,649 for the year 1900, and £152,298 for 1895. In 1900, 92,321 cwt. of soap were made, and 26,690 cwt. of candles, besides other manufactures to the value of £20,611.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Value of Materials used. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water, Gas, Hand. | ||||
| £ | £ | H, p. | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 24 | 224 | 8 | 19,009 | 239 | 20 | 4 | 346 | 112,623 |
| 1896 | 22 | 187 | 3 | 16,882 | 21 | 17 | .. | 252 | 98,194 |
| Increase | 2 | 37 | 5 | 2,127 | 218 | 3 | 4 | 94 | 14,429 |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soap. | Candles. | Value of other Manufactures | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| Quantity. | Value. | Value. | ||||||
| Cwt. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 92,321 | 76,591 | 61,447 | 20,611 | 158,649 | 10,432 | 27,184 | 29,193 |
| 1896 | 85,637 | 71,382 | 58,512 | 22,404 | 152,298 | 9,884 | 20,110 | 28,832 |
| Increase | 6,684 | 5,209 | 2,935 | .. | 6,351 | 548 | 7,074 | 361 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | 1,793 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
These numbered 23, according to the returns for 1901. 47,072 casks were made in 1900, against 33,418 in 1895, and the manufacture of kegs increased greatly. The 1901 returns show also the construction of butter-boxes to the number of 159,147, and of cheese-cases 33,165, against 78,378 and 3,660 respectively for 1896.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages. | Machine-power used. | Horsepower. | Value of Materials used. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | |||||
| £ | H.-p. | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 23 | 137 | 1 | 10,923 | 16 | 1 | 177 | 19,942 |
| 1896 | 21 | 76 | .. | 4,250 | 10 | .. | 110 | 10,281 |
| Increase | 2 | 61 | 1 | 6,673 | 6 | 1 | 67 | 9,661 |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Output. | Approximate Value of | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kegs. | Casks. | Butter boxes. | Cheese-cases. | Land. | Buildings | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| No. | No. | No. | No. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 12,585 | 47,072 | 159,147 | 33,165 | 37,521 | 5,669 | 7,815 | 8,303 |
| 1896 | 1,680 | 33,418 | 78,378 | 3,660 | 19,233 | 3,297 | 3,353 | 4,525 |
| Increase | 10,905 | 13,654 | 80,769 | 29,505 | 18,288 | 2,372 | 4,462 | 3,778 |
There has been a very great development of this industry since 1896. Although only 35 additional mills were returned as working in 1901, the hands employed increased from 4,059 to 6,812, and the (first-cut) sawn timber from 191,053,466 ft. to 261,583,518 ft., an addition of 70,530,052 ft. The figures given for resawing, moulding, &c., show a retrograde movement, but the number of doors and sashes made increased from 61,550 to 91,376 in five years; and the total money value of all manufactures or produce of the sawmills reached the sum of £1,268,689 against £898,807 at the previous census. The value of the plant largely increased.
The quantity of first-cut sawn timber for the year 1900 was far greater in the Auckland Provincial District than in any other, the order being as follows:—
| Feet of Timber sawn (first cutting). | |
|---|---|
| Auckland | 109,124,543 |
| Wellington | 41,375,471 |
| Otago | 40,482,149 |
| Hawke's Bay | 22,382,990 |
| Westland | 13,971,951 |
| Nelson | 12,212,951 |
| Taranaki | 11,881,139 |
| Marlborough | 5,437,365 |
| Canterbury | 4,714,959 |
The increase at Auckland in five years is from 79,464,526 ft. to 109,124,543 ft. At Westland also the increase is noticeably great, considering the magnitude of the industry there.
| Census Year. | No. of Mills. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | |||||||
| 1901 | 334 | 6,805 | 7 | 513,622 | 266 | 317 | 24 | 3 | 8,744 |
| 1896 | 299 | 4,055 | 4 | 323,223 | 274 | 29 | 1 | 6,409 | |
| Increase | 35 | 2,750 | 3 | 190,665 | 43 | .. | 2 | 2,335 | |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5 | .. | .. | |
| Census Year. | Output for the Years 1900 and 1895. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sawn Timber. | Value of Posts, Rails, &c. | Re-sawing, Planed, Flooring, Skirting, &c. | Mouldings. | ||||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value | ||
| Ft. | £ | £ | Ft. | £ | Run. ft. | £ | |
| 1901 | 261,583,518 | 971,048 | 19,277 | 34,824,246 | 172,127 | 9,152,598 | 42,970 |
| 1896 | 191,053,466 | 627,959 | 10,998 | 41,026,223 | 173,765 | 12,653,368 | 44,104 |
| Inc. | 70,530,052 | 343,089 | 8,279 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Dec. | .. | .. | .. | 6,201,977 | 1,638 | 3,500,770 | 1,134 |
| Census Year. | Output for 1900 and 1895—continued. | Total Value of all Output. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doors and Sashes. | Land. | Buildings | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| Quantity. | Value. | |||||
| No. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 91,376 | 63,267 | 1,268,689 | 187,398 | 108,015 | 408,207 |
| 1896 | 61,550 | 41,981 | 898,807 | 186,958 | 100,667 | 298,797 |
| Inc. | 29,826 | 21,286 | 369,882 | 440 | 7,348 | 109,410 |
The operations of the gasworks in the colony for the year 1900, contrasted with those for 1895 and 1890, show such expansion as must be considered highly satisfactory, and this notwithstanding the increased use of electricity in substitution for gas.
There were 30 gasworks at the time of the census of 1901, employing 572 hands, against 27, with 295, in 1896. The wages paid in 1900 amounted to over £70,000 sterling, against £38,000 in 1895, and the value of all produce was £290,567, against £199,025.
In quantity, 786 million cubic feet of gas are shown to have been manufactured in 1900, against 532 million feet for 1895, besides increased quantities of coke, tar, and other residuals.
| Census Year. | No. of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horsepower. | Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas made. | |||||||||||
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam | Water. | Gas. | Quantity. | Value. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | Cubic feet. | £ | |||||||
| 1901 | 30 | 568 | 4 | 70,388 | 185 | 24 | 1 | 12 | 242 | 786,531,150 | 245,000 |
| 1896 | 27 | 293 | 2 | 37,747 | 102 | 19 | 1 | 8 | 126 | 532,060,300 | 178,196 |
| Increase | 3 | 275 | 2 | 32,641 | 83 | 5 | .. | 4 | 116 | 254,470,850 | 66,804 |
| Census Year. | Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895—continued. | Total Value of all Produce. | Approximate Value of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coke. | Tar. | Other Residuals: Value | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and plant. | ||||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | ||||||
| Tons. | £ | Gallons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 38,830 | 32,968 | 693,181 | 11,665 | 934 | 290,567 | 65,555 | 88,874 | 817,130 |
| 1896 | 17,339 | 14,446 | 345,632 | 4,649 | 1,734 | 199,025 | 41,422 | 79,610 | 645,641 |
| Incr. | 21,491 | 18,522 | 347,549 | 7,016 | .. | 91,542 | 24,133 | 9,264 | 171,489 |
| Decr. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 800 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
Fifteen of these works, employing 184 hands, were in operation in 1901. In 1896, only 79 hands were returned. The value of manufacture for 1900 was three times as great as that for 1895, and that of machinery used more than doubled during the five years.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | Horsepower. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Males. | Steam. | Horse. | |||
| £ | H.-p. | |||||
| 1901 | 15 | 184 | 16,577 | 8 | 2 | 466 |
| 1896 | 14 | 79 | 5,560 | .. | .. | 289 |
| Increase | 1 | 105 | 11,017 | .. | .. | 177 |
| Census Year. | Value of Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures for 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 18,397 | 45,142 | 3,881 | 10,218 | 24,337 |
| 1896 | 4,631 | 15,831 | 3,181 | 7,270 | 11,968 |
| Increase | 13,766 | 29,261 | 700 | 2,948 | 12,369 |
These works employed in 1900 close on double the number of hands that were engaged in 1895, and the number of bricks rose from 18,800,000 to 40,900,000 for those years. The value of pottery made, including drain-pipes, rose from £31,503 to £34,810; and the total value of all the manufactures from £66,140 to £122,230. Otago shows first in the output of bricks made, Canterbury next, then Auckland, while Wellington takes the fourth place. The number of brick, stone, or concrete houses increased between the last two censuses from 6,490 to 7,517, a rate of 13·66 per cent., while those of cob, sod, huts, &c., decreased substantially in number. Houses built of wood or iron increased from 134,092 to 153,945, the rate, 14 per cent., being slightly higher than that which obtained for brick and stone dwellings.
| Census Year | Number of Works. | Hands employed | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horse-power. | Number of Machines used. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | Horse. | Water. | Hand. | For tempering or crushing Clay. | For Making Bricks or Pottery. | |||
| £ | £ | H.p. | |||||||||||
| 1901 | 108 | 838 | .. | 63,336 | .. | 63 | 139 | 1 | 4 | 659 | 109 | 77 | |
| 1896 | 108 | 454 | 1 | 28,179 | 50 | 38 | 170 | .. | 1 | 519 | 108 | 92 | |
| Increase | 384 | 35,157 | 25 | .. | 1 | 3 | 140 | 1 | .. | ||||
| Decrease | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 50 | .. | 31 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15 | |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bricks made. | Pottery, &c., made. | |||||
| Common. | Firebricks. | Value. | Drain-pipes. | Tiles. | Flower pots. | |
| No. | No. | £ | No. | No. | Doz. | |
| 1901 | 40,976,765 | 313,551 | 86,578 | 1,226,296 | 310,076 | 3,111 |
| 1896 | 18,805,715 | 193,600 | 34,637 | 1,175,065 | 464,851 | 8,347 |
| Increase | 22,171,050 | 119,951 | 51,941 | 51,231 | .. | .. |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | 154,775 | 5,236 |
| Census Year. | Manufactures, 1900 and 1895—continued. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pottery, &c., made. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| Miscellaneous: Value. | Total Value of Pottery, &c. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 7,475 | 34,810 | 122,230 | 41,123 | 37,718 | 35,726 |
| 1896 | 4,249' | 31,503 | 66,140 | 24,074 | 24,917 | 27,594 |
| Increase | 3,226 | 3,307 | 56,090 | 17,049 | 12,801 | 8,132 |
A large development is observed in respect of this industry. The value of the manufacture rose from £63,723 in 1895 to £98,587 in 1900. In 1890 the value of the goods was only £14,297. The number of hands increased from 289 to 337 in five years, and the establishments from 34 to 60, and the wages paid from £19,742 to £23,107. But the increase shown in this industry is largely due to the inclusion in the later year of small establishments of which no account was taken in 1896.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | ||
| £ | £ | |||||||
| 1901 | 60 | 336 | 1 | 23,107 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 1896 | 34 | 288 | 1 | 19,742 | .. | |||
| Increase | 26 | 48 | .. | 3,365 | 36 | .. | .. | |
| Census Year. | Horse-power. | Value of Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures and Repairs in 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
* Information not available. | ||||||
| H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 23 | 52,553 | 98,587 | 24,907 | 22,100 | 9,907 |
| 1896 | 27 | 32,835 | 63,723 | 10,660 | 7,475 | 7,714 |
| Increase | .. | 19,718 | 34,864 | 14,247 | 14,625 | 2,193 |
| Decrease | 4 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
The total value of the manufacture (including repairs) in connection with these industries was returned for the year 1900 at £924,171, or more than three times the amount for 1895, which was £302,815. This great increase is nearly all found in the figures for Otago, where the value of manufacture given at last census had reached £512,021, no doubt being swelled by the dredge-making work. There were 1,948 more hands employed in 1901 than five years previously, or an increase of 118·64 per cent., the actual number of persons being 3,590, against 1,642 for the earlier year. That a considerable development of the business would be exhibited was of course expected, on account of the stimulus given by the growing requirement for dredges in procuring gold from river-beds, &c.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Horse-power. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male. | Female. | Male. | Female. | |||
| Note.—The above table does not include fifteen Government Railway and Maintenance workshops (eight Railway workshops and seven Maintenance workshops): Hands employed in year 1900, 1,626; wages paid, £185,355; horse-power employed 760; materials used, £192,050; manufactures and repairs (3 locomotives, 34 bogie carriages, 20 bogie brake-vans, 441 wagons, 1,102 tarpaulins, and repairs to the value of £36,306); the total value of manufactures and repairs in the Railway workshops being £365,946, and the value of machinery and plant, £97,659. The value of materials used and value of repairs are not stated in Maintenance workshops returns. | ||||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | ||||
| 1901 | 111 | 3,580 | 10 | 306,778 | 431 | 1,577 |
| 1896 | 90 | 1,639 | 3 | 129,699 | 64 | 1,093 |
| Increase | 21 | 1,941 | 7 | 177,079 | 367 | 484 |
| Census Year. | Value of Materials used or operated on. | Total Value of Manufactures (including Repairs). | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 446,507 | 924,171 | 127,346 | 89,001 | 177,935 |
| 1896 | 100,273 | 302,815 | 70,811 | 55,152 | 126,172 |
| Increase | 346,234 | 621,356 | 56,535 | 33,849 | 51,763 |
There is an ammunition factory in the Auckland District, where 105 hands are actively employed. To give more details might be considered a breach of confidence.
Although the numbers of factories and hands employed as shown in the latest returns do not indicate development, the total value of all manufacture appears to have increased from £102,054 to £138,094, including repairs. The number of implements made during 1900 is greater under nearly all descriptions than for 1895.
From whatever cause it may arise that the hands are returned as only 584, against 581 in 1895, the fact remains that the operations in the factories were very much greater in 1900 than five years before. This is clearly shown, both as to money value for the total and as to number of implements, under a long series of descriptive headings:—
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive-power. | Horse-power. | Value of all Materials used. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | |||||||
| 1901 | 33 | 584 | 2 | 53,879 | 62 | 23 | 1 | 360 | 49,072 |
| 1896 | 34 | 581 | .. | 44,581 | .. | 23 | .. | 217 | 26,904 |
| Increase | .. | 3 | 2 | 9,298 | 62 | .. | 1 | 143 | 22,168 |
| Decrease | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for Years 1900 and 1895. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ploughs. | Harrows. | Disc and Spade Harrows. | Horse - hoes, Cultivators, and G b-bers. | Sowers and Drills. | Rollers. | Farm Drays and Wagons. | Horse Hayrakers. | Chaff-cutters. | |
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |
| 1901 | 869 | 864 | 344 | 292 | 219 | 242 | 358 | 22 | 196 |
| 1896 | 590 | 578 | 208 | 377 | 182 | 104 | 169 | 18 | 38 |
| Increase | 279 | 286 | 136 | .. | 37 | 138 | 189 | 4 | 158 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | 85 | .. | .. | .. | .. | |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for Years 1900 and 1895—continued. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnip-cutters | Seed Threshing and Cleaning Machinery | Straw elevators. | Windmills. | Wool-presses | Swingle rees and Yokes. | Sheep-racks. | Various Machines Unspecified (Value). | |
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | £ | |
| 1901 | 46 | 25 | 17 | 75 | 89 | 1,845 | .. | 15,157 |
| 1896 | 18 | 6 | 4 | 69 | 95 | 69 | 31 | 12,743 |
| Increase | 28 | 19 | 13 | 6 | .. | 1,776 | .. | 2,414 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6 | .. | 31 | |
| Census Year. | Total Value of Manufactures (including Repairs). | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 138,094 | 19,591 | 21,504 | 20,244 |
| 1896 | 102,054 | 19,900 | 21,336 | 30,031 |
| Increase | 36,040 | .. | 168 | .. |
| Decrease | .. | 309 | .. | 9,787 |
This industry ranks amongst the first in respect of employment of hands. 2,627 males and 507 females were returned as engaged in it at last census, the males increasing from 2,123 in 1896 to 2,627 in 1901. Female hands have increased greatly. In 1891 there were only 196; in 1896 the number was 228, while in 1901 it had risen to 507, women and girls. As to the value of product it was set down for the year 1900 at £704,285, against £389,124 five years earlier; but how far these last figures can be relied on is uncertain. There is difficulty in making them up.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | ||
| Note.—The table does not include particulars for Government Printing Office. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | |||||||
| 1901 | 188 | 2,627 | 507 | 268,041 | 16,564 | 19 | 14 | 93 |
| 1896 | 154 | 2,123 | 228 | 204,165 | 12,137 | 22 | 16 | 50 |
| Increase | 34 | 504 | 279 | 63,876 | 4,427 | .. | .. | 43 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 2 | .. |
| Census Year. | Machine-power used—continued. | Horse-power. | Value of all Products. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric. | Oil. | Hand. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| H. p. | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 5 | 8 | 73 | 956 | 704,285 | 109,130 | 160,787 | 289,621 |
| 1896 | .. | 3 | 64 | 532 | 389,124 | 68,847 | 124,369 | 203,699 |
| Increase | 5 | 5 | 9 | 424 | 315,161 | 40,283 | 36,418 | 85,922 |
The value of the manufacture and repairs rose from £148,969 in 1895, to £216,077 in 1900, an increase of £67,108, or a rate of 45·05 per cent. The hands employed also increased from 807 to 1,185.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | M. | Steam. | Gas. | Water. | ||
| £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 160 | 1,185 | 83,356 | 17 | 9 | 2 |
| 1896 | 116 | 807 | 57,377 | 19 | 4 | 2 |
| Increase | 44 | 378 | 25,979 | .. | 5 | .. |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Amount of Horse-power. | Total Value of Manufactures (including Repairs). | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1901 | 128 | 216,077 | 70,622 | 55,972 | 24,217 |
| 1896 | 119 | 148,969 | 41,376 | 40,076 | 24,350 |
| Increase | 9 | 67,108 | 29,246 | 15,896 | .. |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | 133 |
A very great advance has been made since 1896, as the number of works was found to be 71 against 19, and 378 males besides 17 females were engaged, being an increase of 270 persons on the number previously shown. The value of the manufacture and repairs rose from £18,817 for the year 1895 to £65,047 for 1900, or at the rate of 245·7 per cent. Cycles being now used not only for pleasure and exercise, but also in business to a certain extent, the industry of making and repairing these articles is necessarily found expanding with time.
Among the establishments shown for 1901 there are indeed a considerable number of purely repairing-shops, and these were not taken into account at the previous census. But apart from this qualification the returns show a large genuine increase in the operations.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands. | Wages. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horse-power. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | Water. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | |||||||
| 1901 | 71 | 378 | 17 | 20,873 | 570 | 4 | 15 | 1 | 95 |
| 1896 | 19 | 125 | .. | 5,952 | .. | 4 | 4 | .. | 33 |
| Increase | 52 | 253 | 17 | 14,921 | 570 | .. | 11 | 1 | 62 |
| Census Year. | Value of Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | Number of Cycles manufactured in 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures (including Repairs), 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1901 | 26,824 | 1,988 | 65,047 | 31,465 | 24,431 | 9,507 |
| 1896 | 7,696 | 734 | 18,817 | 7,925 | 12,240 | 4,666 |
| Increase | 19,128 | 1,254 | 46,230 | 23,540 | 12,191 | 4,841 |
Of these, 115 were returned. In the total value of manufacture and repairs there is an increase, caused chiefly by the inclusion in 1901 of small saddlers' shops which were not reckoned as factories in 1896.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Value of Materials used, 1900. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | |||
* Including a number of small saddlery and harness-making concerns, which were not dealt with as “factories'' at the previous census. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901* | 115 | 629 | 23 | 40,808 | 1,026 | 75,724 |
| Census Year. | Total Value of Manufactures (including Repairs), 1900. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
* Including a number of small saddlery and harness-making concerns, which were not with as “factories'' at the previous census. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901* | 147,626 | 54,380 | 37,035 | 5,144 |
These works numbered 12 in 1901, against 15 in 1896. The hands employed numbered 128 at last census, and the value of manufactured articles for the year 1900 was returned at £21,131.
Good progress was made in this industry between 1896 and 1901, not so much in the direction of increasing the number of establishments, but in hands employed, with quantity and value of manufacture. The hands increased from 1,629 to 1,963, and the wool scoured or sliped from 19,723,481 lb. to 25,793,239 lb. The value of all produce or manufacture for 1900 was £1,888,107, against £1,237,252 in 1895, or more than 50 per cent. in five years.
| Census Year. | No. of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | House-power. | Number of Tanpits. | Value of Hides, Skins, &c., operated on. | Value of Bark, Coal, Soap, &c. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Oil. | ||||||
| No. | No. | £ | £ | H.-p. | No. | £ | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 119 | 1,957 | 6 | 159,180 | 162 | 57 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1,108 | 1,216 | 1,161,965 | 229,358 |
| 1896 | 117 | 1,623 | 6 | 116,715 | 268 | 49 | 8 | .. | 1 | 686 | 1,252 | .. | 134,176 |
| Increase | 2 | 334 | .. | 42,465 | .. | 8 | 1 | 1 | .. | 422 | .. | .. | 95,182 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | .. | 106 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 36 | .. | .. |
| Census | Tons of Bark used, and Kind. | Manufactures or Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wattle. | New Zealand. | Other Kinds. | Total. | |||||
| Australia. | Tasmania. | Wool Scoured and Sliped. | Skins stripped of Wool. | Hides tanned. | ||||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Lb. | No. | No. | |
| 1901 | 3,384 | 305 | 465 | 1,177 | 5,331 | 25,793,239 | 4,026,598 | 178,075 |
| 1896 | 3,419 | 1,423 | 359 | 24 | 5,225 | 19,723,481 | 3,879,560 | 154,505 |
| Increase | .. | .. | 106 | 1,153 | 106 | 6,069,758 | 147,038 | 23,570 |
| Decrease | 35 | 1,118 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures or Produce for the Years 1900 and 1895—cont. | Total Value of Produce and Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skins tanned. | Pelts Salted or Preserved. | Other Products. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| No. | No. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 272,775 | 4,031,974 | 54,296 | 1,888,107 | 52,319 | 2,855 | 80,778 |
| 1896 | 856,918 | 1,418,792 | .. | 1,237,252 | 41,490 | 77,186 | 52,729 |
| Increase | .. | 2,613,182 | .. | 650,855 | 10,829 | 25,669 | 28,049 |
| Decrease | 584,143 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
The reports on the censuses of 1891 and 1896 were to the effect that this industry was not shown as a thriving one by the returns. In the table now put forward the results are better, as to number of hands employed, vessels built, and total value of all manufacture for the year 1900. But the number of establishments has fallen from 40 to 32, and boat-building is shown to have declined.
| Census Year. | Number of Yards. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Total Value of all Manufactures (including Repairs), 1900 and 1895. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | M. | |||
| £ | £ | |||
| 1901 | 32 | 211 | 13,476 | 45,811 |
| 1896 | 40 | 108 | 6,724 | 25,233 |
| Increase | .. | 103 | 6,752 | 20,578 |
| Decrease | 8 | .. | .. | .. |
As with the ship and boat-building yards, these industries show a decrease in the number of works, but a considerable increase in the number of hands employed, and in the value of the output. The total value of manufactures in 1900 was returned at £44,854, against £30,166, in 1895.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Value of Materials used. | Total Value of all Manufactures, 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 30 | 150 | 81 | 10,446 | 1,996 | 24,628 | 44,854 | 22,976 | 15,700 | 2,217 |
| 1896 | 39 | 92 | 51 | 5,660 | 1,361 | .. | 30,166 | 13,105 | 9,825 | 693 |
| Increase | .. | 58 | 30 | 4,786 | 635 | .. | 14,688 | 9,871 | 5,875 | 1,524 |
| Decrease | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
In this branch of industrial work fuller returns have been obtained for 1901 than were secured in 1896. It may be taken, however, as a fact that a substantial rise took place during the five years in the operations of these establishments.
| Census Year. | No. of Factories. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive-power. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Oil. | Electric. | ||
| £ | £ | |||||||||
| 1901 | 144 | 1,243 | 67 | 88,843 | 2,262 | 17 | 4 | 29 | 2 | 3 |
| Census Year. | Horse-power. | Value of Material used. | Total Value of all Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 369 | 101,595 | 241,024 | 75,200 | 71,884 | 23,254 |
There was up to 1896 a steady growth in the value of the manufacture, from £34,283 in 1885 to 41,586 in 1890, and to £75,320 in 1895; but the value of output for 1900 was £64,834 only. Ninety-five hands were employed at last census in eight establishments.
The woollen mills of the colony are now ten in number, and employed 1,693 persons in 1901, 769 being males, and 924 females. These factories, therefore, provide more occupation for women and girls than for the male sex. The increase in male hands employed is from 655 in 1896 to 769 in 1901, and in females from 761 to 924. In 1891 there were only 373 women and 200 girls.
As to value of manufacture of all kinds, the increase is at the rate of 19 per cent. for five years; the figures being £302,423 for 1895 and £359,382 for 1900.
The increase in quantity of tweed made, from 1,297,012 yards in 1895 1,445,867 yards in 1900, or about 12 per cent., is not so great that in flannel, the production of which reached 1,191,234 yards for 1900. The production of blankets has also greatly developed, the figures being 28,576 pairs in 1895, and 49,523 pairs in 1900. Rugs, shawls, hosery, and yarn also show high increase:—
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages. | Machine-power used. | Horse-power. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | |||
† “Other manufactures'' in 1900 consisted of 234,843 lb. yarn and 53,920 dozen hosiery; and in 1895, of 168,802 lb. and 5,122 spindles of yarn, 21,447 dozen and 28,000 lb. of hosiery, 2,592 knitted garments, and 13,000 mats. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | ||||||
| 1901 | 10 | 769 | 924 | 71,454 | 40,547 | 9 | 2 | 1,554 |
| 1896 | 9 | 655 | 761 | 59,583 | 32,036 | 9 | 2 | 1,400 |
| Increase | 1 | 114 | 163 | 11,871 | 8,511 | .. | .. | 154 |
| Census Year. | Wool used in 1900 and 1895. | Value of Other Materials used. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Tweed. | Cloth. | Flannel. | Blankets. | ||
| Lb. | £ | £ | Yds. | Yds. | Yds. | Pairs. | |
| 1901 | 3,257,319 | 162,920 | 33,161 | 1,445,867 | .. | 1,191,234 | 49,523 |
| 1896 | 3,485,893 | 100,135 | 39,182 | 1,297,012 | 357,228 | 554,256 | 28,576 |
| Increase | .. | 62,785 | .. | 148,855 | .. | 636,978 | 20,947 |
| Decrease | 228,574 | .. | 6,021 | .. | 357,228 | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for Years 1900 and 1895—contd. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shawls and Rugs. | Shirting. | Other Manufactures. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| No. | Yds. | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1901 | 26,806 | .. | † | 359,382 | 11,264 | 93,454 | 172,704 |
| 1896 | 20,020 | 15,384 | † | 302,423 | 11,050 | 68,358 | 144,065 |
| Increase | 6,786 | .. | .. | 56,959 | 214 | 25,096 | 2,639 |
| Decrease | .. | 15,384 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| * One mill not in operation. | |||||||
The number of hands increased from 307 males and 1,751 females to 431 males and 2,081 females in five years. Employing, as it now does, about 2,500 persons, this industry ranks high in regard to the absorption of labour, especially that of the female sex, of whom over two thousand are required, as above shown.
The value of all manufacture for the year 1900 was returned at £329,026, against £258,352, in 1895.
The making of waterproof garments is also shown to have developed considerably, whether conducted in combination with clothing factory work of the ordinary kind, or as independent establishments.
| Census Year. | Number of Factories. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Amount of Horse-power. | Total Value of Manufactures, 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 21 | 431 | 2,081 | 37,778 | 63,023 | 67 | 329,026 | 31,200 | 46,615 | 11,432 |
| 1896 | 27 | 307 | 1,751 | 26,450 | 46,789 | 62 | 258,352 | 18,550 | 29,900 | 8,254 |
| Increase | .. | 124 | 330 | 11,328 | 16,234 | 5 | 70,674 | 12,650 | 16,715 | 3,178 |
| Decrease | 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
In addition to clothing factories, six establishments were in 1901 engaged in the manufacture of waterproof garments only. These in 1900 turned out 15,384 waterproofs, valued at £13,378; besides which 25,196 waterproof garments were made in the clothing factories.
| Census Year. | Number of Factories. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Amount of Horse-power. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1901 | 6 | 22 | 92 | 1,807 | 2,822 | 3 | 3,020 | 3,655 | 1,170 |
| 1896 | 4 | 15 | 78 | 1,344 | 2,540 | 2 | 2,650 | 1,900 | 766 |
| Increase | 2 | 7 | 14 | 463 | 282 | 1 | 370 | 1,755 | 404 |
The total value of all manufactures, as brought out, is £529,254 for 1900. The output from the factories during 1900 was 1,161,873 pairs of boots and shoes, 104,583 pairs of slippers, and 166,027 pairs of uppers.
Excluding gum-boots, during 1900 boots and shoes to the value of £187,629 were imported into the colony, nearly the whole being subject to a duty of 22 1/2 per cent. The United Kingdom supplied to the value of £126,705, and the United States of America £42,658. Besides these were imported boot and shoe vamps and uppers, valued at £8,100. The exports of leather, the produce of the colony, during the same period, were valued at £112,867, and of boots and shoes made in New Zealand, £534.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Power. | Horse-power. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Hand and Oil. | |||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | ||||||||
| 1901 | 126 | 1,906 | 790 | 165,227 | 27,216 | .. | 2 | 26 | 98 | 184 |
| Census Year. | Value of Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | Manufactures for the Years 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Approximate Value of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boots and Shoes. | Slippers. | Uppers. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| £ | Pairs. | Pairs. | Pairs. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 273,325 | 1,161,873 | 104,583 | 166,027 | 529,254 | 57,415 | 70,189 | 49,386 |
| *Including a number of small bootmaking concerns which were not dealt with as `factories'' at the previous census. | ||||||||
At the census of 1896 returns were obtained from 7 stocking-weaving factories, employing 1 male and 132 females. The wages paid amounted to £2,541, and the value of the output to £9,357. The census of 1901 shows a very large increase on these figures, as will be seen in the statement given herewith.
| Census Year. | Number of Factories. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | Horse-power. | Value of Material used. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | Steam. | Gas. | ||||
| £ | £ | H.-p. | £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 17 | 17 | 265 | 1,328 | 6,702 | 2 | 5 | 71 | 18,032 |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for the Year 1900. | Approximate Value of | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half-hose. Quantity. | Hose. Quantity. | Shirts and Pants. Quantity | Other Knitted Goods. Value. | Total Value of Manufactures. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |
Note.—The above table does not include 53,920 dozen hose, half-hose, under-shirts, pants, and other knitted garments which are given in “Woollen-factories'' return. * One factory not in operation in 1900, and one factory in operation six months only. | ||||||||
| Dozen. | Dozen. | Dozen. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 39,601 | 9,529 | 1,053 | 480 | 31,265 | 4,605 | 6,790 | 8,602 |
Rope and twine making would appear to have advanced since 1895, to judge from the value of all manufactures given in the returns, which amounted to £87,863 for the year 1900, against £52,400 five years before. Nevertheless, the actual quantity of rope made represented in weight is shown as slightly less than at the earlier census year. As to materials used, phormium comes by far the first, 1,502 tons for 1900 being utilised, against 1,452 tons in 1895. Of manila only 291 tons were used, against 169 in 1895.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Motive Power. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | M. | Steam. | Water. | Gas. | Horse. | Horse-power. | ||
| £ | H.-p. | |||||||
| 1901 | 17 | 192 | 13,136 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 494 |
| 189y | 24 | 150 | 6,840 | 5 | 6 | .. | .. | 280 |
| Increase | 42 | 6,296 | 1 | .. | 1 | 1 | 214 | |
| Decrease | 7 | .. | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Materials used in 1900 and 1895. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phormium. | Manila. | Other Materials. | Total Value. | ||||
| Tons. | £ | Tons. | £ | Tons. | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 1,502 | 28,663 | 291 | 13,140 | 87 | 4,575 | 46,378 |
| 1896 | 1,452 | 19,251 | 169 | 4,664 | 85 | 4,335 | 28,250 |
| Increase | 50 | 9,412 | 122 | 8,476 | 2 | 240 | 18,128 |
| Census Year. | Manufactures for 1900 and 1895. | Total Value of all Manufactures. | Approximate Value of. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ropes. | Lines. | Twine. | Other Manufactures. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | |||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 85 | 1,727 | 295 | 87,863 | 6,546 | 9,313 | 39,450 | |
| 1896 | 289 | 27 | 7 | 37 | 52,400 | 7,247 | 6,855 | 26,859 |
| Increase | .. | 58 | 00 | 258 | 35,463 | .. | 2,458 | 12,591 |
| Decrease | 15 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 701 | .. | .. |
A complete collapse in this industry was shown by the returns of 1896. At that time only 52 mills were left in operation, and the hands employed had fallen in number to 484 men and 163 boys. The returns for 1901 show a revival in the mills to 101 in operation, with 1,519 men and 179 boys. In 1891 there were 177 mills with 2,169 men and 1,029 boys, so that the development obtained 10 years ago has not been recovered in full, though the position has improved greatly since 1896. The wages paid stood at £101,046 for the year 1900; nearly 100,000 tons of raw material were used, and 12,000 tons of fibre dressed, besides 1,000 tons of tow produced. The money value of the total output was £203,492, against £32,546 in 1895, and £234,266 in 1890.
The export of phormium for twelve years has been as under:—
| Year | Exported. Tons. | Value. £ |
|---|---|---|
| * This is greater than the quantity returned as dressed in 1900. | ||
| 1890 | 21,158 | 381,789 |
| 1891 | 15,809 | 281,514 |
| 1892 | 12,793 | 214,542 |
| 1893 | 12,587 | 219,375 |
| 1894 | 4,677 | 66,256 |
| 1895 | 1,806 | 21,040 |
| 1896 | 2,968 | 32,985 |
| 1897 | 2,769 | 30,674 |
| 1898 | 4,850 | 74,556 |
| 1899 | 10,371 | 184,411 |
| 1900 | 15,906* | 332,182 |
| 1901 | 10,171 | 195,728 |
The uncertainty that has attended enterprise in the matter of flax-milling still remains, but an Act has been passed forbidding the shipping of phormium for exportation from New Zealand unless it has been previously inspected by a Government official, and graded under regulations which have been made for the purpose. This will have the effect of preventing badly-dressed flax of an inferior quality from being sent away, and thus injuring the reputation of the article generally by depreciation.
The most important particulars given in the returns are tabulated below:—
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men. | Boys. | Steam. | Water. | |||
| £ | ||||||
| 1901 | 101 | 1,519 | 179 | 101,046 | 75 | 34 |
| 1896 | 52 | 484 | 163 | 17,544 | 23 | 30 |
| Increase | 49 | 1,035 | 16 | 83,502 | 52 | 4 |
| Census Year. | Amount of Horse-power. | No. of Machines used. | Raw Material used. 1900 and 1895. | Fibre dressed, 1900 and 1895. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | |||
| H.-p. | Tons. | £ | Tons. | £ | ||
| 1901 | 1,190 | 105 | 96,571 | 53,064 | 12,035 | 201,235 |
| 1896 | 553 | 65 | 21,770 | 7,775 | 2,999 | 31,771 |
| Increase | 637 | 40 | 74,801 | 45,289 | 9,036 | 169,464 |
| Census Year. | Tow produced. | Total Value of Output, 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity. | Value. | Land. | Buildings. | Machinery and Plant. | ||
| Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 1,062 | 2,257 | 203,492 | 24,644 | 11,212 | 28,590 |
| 1896 | 406 | 775 | 32,546 | 12,448 | 6,531 | 12,380 |
| Increase | 656 | 1,482 | 170,946 | 12,196 | 4,681 | 16,210 |
Returns were received for 120 gold-quartz mining and crushing works in 1901. In 1896 there were 168 of these returned, and 135 in 1891. Of 120 quartz-crushing works in 1901, employing 4,333 hands, 78, with 3,370 persons employed, belonged to Auckland Provincial District, being located at the Thames, Waihi, and surrounding country.
The census tables she £796,871 as the total value of the gold obtained by quartz-crushing in the year 1900. Comparison with the two previous censuses shows the output in 1895 (£492,478) to have been higher than that of 1890, but considerably less than that for 1900, quoted above.
The value of the machinery and plant for quartz-crushing increased from £241,715 in 1890, and £335,474 in 1895, to £735,927 in 1900.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Wages paid. | Machine-power used. | Horse-power. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | M. | Steam. | Water. | |||
| £ | H.-p. | |||||
| 1901 | 120 | 4,333 | 382,658 | 148 | 74 | 5,919 |
| 1896 | 168 | 2,814 | 226,791 | 49 | 70 | 3,688 |
| Increase | 1,519 | 155,867 | 99 | 4 | 2,231 | |
| Decrease | 48 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Quartz crushed. | Gold produced 1900 and 1895. | Silver produced 1900 and 1895. | Value of Gold and Silver produced 1900 and 1895. | Approximate Value of Machinery and Plant. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tons. | Oz. | Oz. | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 356,058 | 214,789 | 326,457 | 796,871 | 735,927 |
| 1896 | 163,743 | 149,612 | 81,302 | 492,478 | 335,474 |
| Increase | 192,315 | 65,177 | 245,155 | 304,393 | 400,453 |
Returns for the purposes of the table showing results of hydraulic gold-mining were obtained from public companies and parties of miners operating on a large scale; but, so far as the numbers of persons employed are concerned, nothing like the actual facts are disclosed, and the quantity of gold shown to have been won must fall far short of the true total. The number of men engaged in all kinds of alluvial gold-mining during the year ended 31st March, 1901, was 7,659 Europeans and 1,576 Chinese. Of these nearly 1,000 were employed in dredging. The hands employed shown in the tables for the two classes of alluvial mining number 1,927, so that there must be some 7,300 Europeans and Chinese whose earnings are not included in the tables.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horse-power. | Claims working Day and Night, or Day only. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | Water. | Electricity. | ||||
| H.-p. | ||||||
| 1901 | 130 | 962 | 21 | 2 | 342 | Day and night, 37 |
| Day only, 87 | ||||||
| 1896 | 105 | 744 | 28 | 2 | 156 | Day and night, 32 |
| Day only, 73 | ||||||
| Increase | 25 | 218 | .. | .. | 186 | .. |
| Decrease | .. | .. | 7 | .. | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Expenditure during 1900 and 1895. | Yield of Gold. | Value of Gold. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour. | Water. | Plant and Repairs. | Management. | Total. | |||
* Six mines were not in operation during 1900. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | Oz. | £ | |
| 1901 | 76,008 | 19,398 | 26,373 | 6,652 | 128,431 | 35,059 | 135,944 |
| 1896 | 48,964 | 17,414 | 40,183 | 7,208 | 113,769 | 31,161 | 122,871 |
| Increase | 27,044 | 1,984 | .. | .. | 14,662 | 3,898 | 13,073 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | 13,810 | 556 | .. | .. | .. |
During the quinquennial period 1895–1900 this class of industry has become of great importance, not only as a gold-producer, but from the fact that all the works in connection with the building and repairing of dredges is done in the colony. The number of dredges increased from 35 in 1895 to 145 in 1900, and the hands employed from 258 to 965. The yield of gold during 1900 was 71,778 oz., valued at £287,061, against 18,124 oz. and £70,016 in 1895. The expenditure in 1900 was as follows:—
| £ | |
|---|---|
| Labour | 78,238 |
| Coal, plant, and repairs | 188,046 |
| Management | 16,308 |
| Total | £282,592 |
The capital invested in dredging is £690,430, and the value of machinery and plant £528,600. Of the total number, 121 dredges belonged to the Otago Provincial District, 23 to Nelson and Westland, and 1 to Marlborough.
| Census Year. | Number of Works. | Hands employed. | Machine-power used. | Amount of Horse-power. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | Steam. | Water. | Unspecified. | |||
* Including 31 dredges not in operation during 1900 and 10 dredges for which no particulars of operations could be obtained. Three of the dredges were working a few months only. | ||||||
| H.-p. | ||||||
| 1901 | 145* | 965 | 134 | 2 | 9 | 3,041 |
| 1896 | 35 | 258 | 30 | 3 | .. | 963 |
| Increase | 130 | 707 | 104 | .. | 9 | 2,078 |
| Decrease | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Census Year. | Expenditure during 1900 and 1895. | Yield of Gold. | Value of Gold. | Approximate Value of Machinery and Plant. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour. | Coal, Plant, and Repairs. | Management. | Total. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | Oz. | £ | £ | |
| 1901 | 78,238 | 188,046 | 16,308 | 282,592 | 71,778 | 287,061 | 528,600 |
| 1896 | 27,124 | 25,159 | 4,264 | 56,547 | 18,124 | 70,016 | 86,003 |
| Increase | 51,114 | 162,887 | 12,044 | 226,045 | 53,654 | 217,045 | 442,597 |
It must be remembered that a great part of the gold yield in the colony is obtained from alluvial workings, of which no returns are required by the Census Act to be rendered, so that the figures given above must not be regarded as showing any approach to the total production, which amounted to £1,439,602, or, with silver, £1,478,481, for the year 1900.
The returns for quartz-mining and gold-dredging are believed to be fairly correct, but those for hydraulic mining fall far short of the total. No attempt has been made to obtain returns from individual miners or small parties, and these comprise the bulk of the alluvial miners.
The table shows the full output of all the collieries in the colony during 1900. The quantity mined was 1,093,990 tons, against 726,654 in 1895, an increase of 367,336 tons or over 50 per cent. The quantity imported during 1900 was 124,033 tons, and the export amounted to 114,358 tons, 112,707 tons of which were New Zealand produce. The number of persons employed in coal-mining increased from 1,799 in 1895 to 2,460 in 1900, and the value of machinery and plant from £148,367 in 1896 to £372,093 in 1901.
| Census Year. | Number of Coal-Mines. | Hands Employed. | Wages Paid. | Motive Power. | Horse-power. | Quality of Coal mined during the Year 1900. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males. | Males. | Steam. | Water. | Horse. | Wind. | Brown. | Pitch. | |||
Note.—Several private mines worked by owners for their own requirements are not included in the above. | ||||||||||
| £ | H.-p. | Tons. | Tons. | |||||||
| 1901 | 145 | 2,460 | 242,089 | 32 | 9 | 23 | 2 | 2,852 | 339,786 | 37,804 |
| Census Year. | Quality of Coal mined during the Year 1900 —contd. | Total Quantity of Coal won. | Total Cost of Production. | Total Value of Output. | Approximate Value of Machinery and Plant. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lignite. | Bituminous and Semi-bituminous. | |||||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | £ | £ | ||
| 1901 | 42,538 | 673,862 | 1,093,990 | 365,787 | 540,778 | 372,093 |
A summary of all the information obtained under the Census Act relating to mines and quarries is appended:—
| — | Number of Works. | Number of Hands employed. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 1896 | 1891 | 1900 | 1895 | 1890 | |
| Gold-quartz mining and crushing works | 120 | 168 | 135 | 4,333 | 2,814 | 1,971 |
| Hydraulic gold-mining | 130 | 105 | 74 | 962 | 744 | 495 |
| Gold-dredging | 145 | 35 | 965 | 258 | ||
| Collieries § | 145 | 164 | 95 | 2,460 | 1,799 | 1,655 |
| Stone (building) quarries | 8 | 12 | 9 | 58 | 59 | 35 |
| Stone (road-metal, &c.) quarries | ||||||
| Totals | 548 | 484 | 313 | 8,778 | 5,674 | 4,156 |
| — | Approximate Value of Output. | Approximate Value of Machinery and Plant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 1895 | 1890 | 1900 | 1895 | 1890 | |
* Value of machinery and plant used in hydraulic gold-mining not returned; capital invested, £505,674. † Capital invested, information incomplete. ‡ Capital invested. £161,990. § Figures for 1895–96 taken from Mines Report; census returns found incomplete, and results not reliable. Value of output taken at 10s. per ton. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Gold-quartz mining and crushing works | 796,871 | 492,478 | 278,893 | 735,927 | 335,474 | 241,715 |
| Hydraulic gold-mining | 135,944 | 113,769 | 73,713 | 207,750 | * | 154,270 |
| Gold-dredging | 287,061 | 70,016 | 528,600† | ‡86,003 | ||
| Collieries§ | 540,778 | 370,400 | 279,777 | 372,093 | 148,367 | 155,671 |
| Stone (building) quarries | 2,793 | 6,041 | 4,487 | 4,660 | 4,070 | 6,744 |
| Stone (road-metal, &c.) quarries | ||||||
| 8,371 | ||||||
| Totals | 1,771,818 | 1,052,704 | 636,870 | 1,849,030 | 573,914* | 558,400 |
Table of Contents
THE quantities and values of imports used in making up the figures given in this portion of the statistical information are obtained from Customs entries, verified where necessary, as with goods subject to an ad valorem duty, by examination. For exports, the “free on board in New Zealand” value is given; but, as regards the main items, the Collector of Customs examines carefully the amounts stated, and compares them with current price-lists, to prevent any over-estimate. Goods transhipped at a foreign port are regarded as imported from the country where they were originally shipped, and exports as destined for the country where it is intended to land them. The countries named, however, may not be those of origin or destination, as no attempt is made to trace the goods beyond the ports disclosed by the documents presented to the Customs. Very little cargo in transitu passes through New Zealand.
The total declared values of the imports in 1902 amounted to £11,326,723, being a decrease on the corresponding total in 1901 of £491,192. These figures, however, include specie. The value of coin brought into the colony in 1902 was £368,685, against £464,499 in the previous year, and if these amounts are excluded, the decrease on the values of all other articles will be only £395,378.
The value of imports for each of the past fifteen years was:—
| Year. | Imports, inclusive of Specie. | Imports, exclusive of Specie. |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1888 | 5,941,900 | 5,430,050 |
| 1889 | 6,308,863 | 5,980,583 |
| 1890 | 6,260,505 | 5,928,625 |
| 1891 | 6,503,849 | 6,431,101 |
| 1892 | 6,943,056 | 6,742,544 |
| 1893 | 6,911,515 | 6,494,279 |
| 1894 | 6,788,020 | 5,990,177 |
| 1895 | 6,400,129 | 6,115,953 |
| 1896 | 7,137,320 | 7,035,379 |
| 1897 | 8,055,223 | 7,994,201 |
| 1898 | 8,230,600 | 8,211,409 |
| 1899 | 8,739,633 | 8,613,656 |
| 1900 | 10,646,096 | 10,207,326 |
| 1901 | 11,817,915 | 11,353,416 |
| 1902 | 11,326,723 | 10,958,038 |
Thus a check has been experienced in the expansion movement observed to have been going on from 1894 to 1901. But in 1901 the Government imported railway plant to the value of about half a million of money, against which the import for 1902 was only about £120,000.
It will be seen that the value of imports, exclusive of specie, rose from £5,430,050 in 1888 to £6,742,544 in 1892, then fell to £5,990,177 in 1894, after which there ensued a steady advance year by year to £11,353,416 in 1901, with a slight falling off in 1902. The movement for the period 1894–1902 is a rise at the rate of 83 per cent. in money value, or a sum of £4,967,861. In quantities of various imports the increases vary, and full particulars of every kind of article imported in 1902 are to be found in detail further on, which may be critically examined with those in similar tables given in the previous Year-books.
The degree of expenditure of loan moneys by the general and local Governments may somewhat affect the question when considering the rise of imports. And, when consulting the figures relating to expenditure out of loan accounts, the matter of aids from the Consolidated Fund (which are included) presents itself, besides other features in connection with this subject.
The expansion of imports is still further to be considered in connection with the condition of the manufactures of the colony, for an increase of imports arising from a decline of internal manufactures would scarcely be regarded as a satisfactory position. But Section XIV., preceding this, exhibits a most substantial general development of the manufactures of New Zealand since 1895, not only in the great primary industries, but throughout.
It is desirable to consider not only the total value of the import trade for different years by comparing figures, but to ascertain the rates per capita of population, to judge whether the imports are relatively greater or less than they have been. The fairest comparisons are from calculations made after deducting specie imported, for in the year 1894, as an instance, no less than £797,843 was brought to the colony in coin.
The figures for each year from 1888 stand thus:—
| Years. | Imports per head of mean Population, excluding Maoris. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Including Specie. | Excluding Specie. | |||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1888 | 9 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 19 | 5 |
| 1889 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 6 |
| 1890 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 11 | 0 |
| 1891 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 3 |
| 1892 | 10 | 16 | 3 | 10 | 9 | 11 |
| 1893 | 10 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 16 | 5 |
| 1894 | 9 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 16 | 5 |
| 1895 | 9 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 16 | 8 |
| 1896 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 9 | 19 | 1 |
| 1897 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 7 |
| 1898 | 11 | 3 | 7 | 11 | 3 | 1 |
| 1899 | 11 | 13 | 1 | 11 | 9 | 8 |
| 1900 | 13 | 18 | 10 | 13 | 7 | 4 |
| 1901 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 14 | 11 | 11 |
| 1902 | 14 | 3 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 8 |
Using the figures exclusive of the specie, it will be seen that, though comparisons for years since 1888 do not show by any means a steady rise since that year, the position is, that whereas the imports proper were only £8 19s. 5d. per head of population in the first period of the table, they had increased by £4 15s. 3d. per head in 1902, and, until last year, increase is observed in each year's figures since 1894.
By means of the accompanying table, in which the articles imported are arranged in groups according to their nature, the increases in value can be traced to their specific heads:—
I(([0-9]+)) FIVE YEARS.
| Imports for Five Years. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group of Principal Articles imported. | 1898 | 1899 | 1900 | 1901 | 1902 |
* Includes methylated and perfumed spirits, and spirits of wise. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Apparel and slops | 354,940 | 393,689 | 451,879 | 463,194 | 511,397 |
| Boots and shoes | 130,912 | 151,593 | 194,811 | 211,215 | 202,931 |
| Cotton piece-goods | 417,733 | 447,495 | 514,607 | 470,568 | 498,485 |
| Drapery | 343,820 | 395,696 | 438,299 | 443,863 | 449,503 |
| Haberdashery | 85,985 | 84,808 | 95,401 | 110,746 | 102,569 |
| Hats and caps | 66,416 | 68,184 | 66,799 | 70,013 | 75,222 |
| Hosiery | 75,736 | 90,545 | 103,291 | 101,481 | 115,071 |
| Linen manufactures | 56,572 | 69,167 | 83,206 | 89,915 | 71,170 |
| Millinery | 36,074 | 36,932 | 43,313 | 43,380 | 45,701 |
| Silks | 79,910 | 87,639 | 97,922 | 121,937 | 139,522 |
| Woollens | 286,911 | 297,387 | 330,713 | 348,666 | 393,033 |
| Totals | 1,935,009 | 2,123,135 | 2,420,241 | 2,474,978 | 2,604,604 |
| Agricultural implements | 17,234 | 17,063 | 13,508 | 10,744 | 11,518 |
| Cutlery | 22,722 | 19,764 | 23,089 | 27,149 | 29,993 |
| Hardware and ironmongery | 248,665 | 255,701 | 330,314 | 315,239 | 334,965 |
| Rails and railway bolts, &c. | 42,773 | 63,557 | 118,464 | 148,344 | 85,163 |
| Iron and steel, other, pig, wrought, wire, &c. | 554,124 | 632,182 | 865,361 | 682,906 | 815,260 |
| Machinery | 422,011 | 405,551 | 536,429 | 600,019 | 561,640 |
| Nails | 36,792 | 31,363 | 48,050 | 40,034 | 44,114 |
| Railway plant | 57,224 | 63,807 | 63,128 | 514,511 | 122,303 |
| Sewing-machines | 30,618 | 30,801 | 37,429 | 38,227 | 37,005 |
| Tools, artificers' | 70,631 | 59,066 | 77,447 | 84,523 | 88,273 |
| Totals | 1,502,794 | 1,578,855 | 2,113,219 | 2,461,696 | 2,130,243 |
| Sugar | 425,270 | 354,925 | 451,522 | 489,936 | 402,138 |
| Tea | 183,717 | 183,691 | 199,934 | 219,089 | 197,127 |
| Totals | 608,987 | 538,616 | 651,456 | 709,025 | 599,265 |
| Beer | 37,844 | 39,166 | 34,296 | 34,949 | 43,627 |
| Spirits* | 187,020 | 215,685 | 198,282 | 243,824 | 235,369 |
| Tobacco | 161,836 | 184,173 | 198,861 | 221,889 | 212,634 |
| Wine | 48,514 | 51,640 | 55,098 | 63,837 | 60,350 |
| Totals | 435,214 | 490,664 | 486,537 | 564,499 | 551,980 |
| Paper | 133,901 | 135,482 | 174,111 | 184,986 | 181,486 |
| Printed books | 109,961 | 132,260 | 136,891 | 140,347 | 149,194 |
| Stationery | 98,469 | 100,875 | 96,408 | 113,422 | 112,676 |
| Totals | 342,331 | 368,617 | 407,410 | 438,755 | 443,35 |
| Bags and sacks | 111,116 | 123,596 | 141,810 | 214,987 | 135,674 |
| Coals | 105,223 | 92,815 | 120,406 | 151,334 | 125,732 |
| Fancy goods | 103,786 | 110,114 | 128,339 | 145,356 | 148,072 |
| Fruits (including fresh, preserved, bottled, dried) | 181,447 | 180,590 | 226,128 | 248,985 | 175,366 |
| Oils | 162,523 | 126,967 | 206,770 | 238,396 | 251,415 |
| Other imports (excluding specie) | 2,722,979 | 2,879,687 | 3,305,010 | 3,705,405 | 3,792,331 |
| Total Imports (excluding specie) | 8,211,409 | 8,613,65 | 10,207,326 | 11,353,416 | 10,958,038 |
| Specie imported | 19,191 | 125,977 | 438,770 | 464,499 | 368,685 |
| Total Imports | 8,230,600 | 8,739,633 | 10,646,096 | 11,817,915 | 11,326,723 |
Of £10,958,038 the total value of goods imported during 1902, the chief items were as under:—
| Articles. | Value. | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| £ | per Cent. | |
| Clothing, drapery, &c. | 2,604,604 | 23·77 |
| Metal, machinery, and implements | 2,130,243 | 19·44 |
| Tea and sugar | 599,265 | 5·47 |
| Wine, beer, spirits, and tobacco | 551,980 | 5·04 |
| Paper, books, and stationery | 443,356 | 4·04 |
| Other imports | 4,628,590 | 42·24 |
| £10,958,038 | 100·00 |
The declared value of the clothing, drapery, &c., imported increased from £2,474,978 in 1901 to £2,604,604 in 1902. In 1898 the value of these imports was £1,935,009. The iron, machinery, and implements imported in 1902 were valued at £2,130,243, an increase of £627,449 on the corresponding figures for 1898 (£1,502,794). The value of sugar and tea imported in 1902 shows a decrease, when compared with 1901, of £109,760. Beer, wine, spirits, and tobacco show a decrease of £12,519, from £564,499 in 1901 to £551,980 in 1902.
To the total value of “Other imports (excluding specie),” in 1902 (£3,792,331), shown in the table above, arms, ammunition, and explosives contributed a sum of £129,733; bicycles, tricycles, and fittings, £134,177; drugs, chemicals, and druggists' wares, £240,841; patent medicines, £40,953; manures, £154,964; musical instruments, £110,663; glass and glassware, £138,908; earthenware, £66,975; floorcloth and oilcloth, £74,556; furniture and upholstery, £62,842; cement, £54,811; leather and leather manufactures, £72,789; seeds, £70,720; and timber, £146,561.
Goods imported by means of the “Parcels post” system during 1902 were valued at £123,912.
Goods received from the Cook and other annexed Islands are now treated as New Zealand produce, and not as imports. The total in 1902 was valued at £32,163, and the principal articles of produce as follows: Bêche-de-mer, £117; limejuice, £814; raw coffee, £334; copra, £8,429; raw cotton, £5; fruit, £19,204; candlenuts, £616; cocoanuts, £388; vanilla beans, £84; hats, £1,235.
The values of the imports into New Zealand during the years 1901 and 1902 are given in the next table, classified according to the duties to which they were liable, and arranged so as to show the declared value of goods on which specific or ad valorem duties at various rates are payable, and of those admitted free of duty:—
| Duties to which Imports liable. | Value of Imports, 1901. | Value of Imports, 1902. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Specific duties | .. | 2,404,581 | .. | 2,395,274 |
| Ad valorem duties— | ||||
| 5 per cent. | 252,513 | 176,607 | ||
| 10 per cent. | 170,433 | 226,994 | ||
| 15 per cent. | 156,777 | 177,041 | ||
| 20 per cent. | 2,359,311 | 2,496,376 | ||
| 22 1/2 per cent. | 208,205 | 201,967 | ||
| 25 per cent. | 994,472 | 1,084,133 | ||
| 40 per cent. | 1,085 | 1,166 | ||
| Various | 8,875 | 1,584 | ||
| Parcels-post (various) | 109,683 | 123,912 | ||
| 4,261,354 | 4,489,780 | |||
| Duty-free (excluding specie) | 4,687,481 | 4,072,984 | ||
| Specie imported | .. | 464,499 | 368,685 | |
| Totals | .. | 11,817,915 | 11,326,723 |
The proportions of free and dutiable goods imported during 1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902 are compared with similar figures for 1894, the year preceding that in which the altered tariff came into force:—
| — | 1894 | 1899 | 1900 | 1901 | 1902 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Including excise duties levied on certain imports manufactured in bond. | |||||
| Merchandise— | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Free | 1,871,772 | 2,942,999 | 3,727,926 | 4,687,481 | 4,072,984 |
| Dutiable | 4,118,405 | 5,670,657 | 6,479,400 | 6,665,935 | 6,885,054 |
| Imports (less specie) | 5,990,177 | 8,613,656 | 10,207,326 | 11,353,416 | 10,958,038 |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Total net duty received* | 1,572,467 | 2,046,452 | 2,174,498 | 2,196,767 | 2,289,783 |
| Duty, per cent. of imports— | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent |
| (a.) On dutiable imports | 38·18 | 36·09 | 33·56 | 32·96 | 33·26 |
| (b.) On all merchandise | 26·25 | 23·76 | 21·30 | 19·35 | 20·30 |
The value of sugar (including glucose, molasses, and treacle) imported in 1902 was £402,138, a decrease of £87,798 on the amount for 1901 (£489,936). The value of this import for the last three years has averaged only £447,865 per annum; but for the three years, 1882, 1883, and 1884, the average, with a much smaller population, was £615,207 for each year. The smaller average amount for the last three years is due, not so much to a reduction in the quantity imported as to the fall in the price of sugar, and partly to the fact that the proportion of refined to raw sugar has vastly decreased.
The following figures, giving the consumption per head of sugar in Australasia, are, saving those for New Zealand—and excluding a proportion (30 lb. per head) deducted on account of Maoris—taken from Mr. Coghlan's “Seven Colonies of Australasia, 1901–1902.” The figures stating the consumption of tea, given further on, are also taken from the same source:—
| Annual Consumption of Sugar per Head in Australasia. | |
|---|---|
| Lb. | |
| Queensland | 123·8 |
| Western Australia | 114·5 |
| New South Wales | 107·8 |
| New Zealand | 104·8 |
| South Australia | 100·2 |
| Victoria | 93·0 |
| Tasmania | 90·5 |
The quantity of tea entered for consumption in 1902 was 5,088,581 lb. Supposing Maoris to use, on an average, 1 lb. per. head per annum, the consumption of tea per head of the population, exclusive of Maoris, would be 6·3 lb. in 1902.
| Annual Consumption of Tea per Head in Australasia. | |
|---|---|
| Lb. | |
| Western Australia | 9·8 |
| South Australia | 8·1 |
| New South Wales | 7·9 |
| Queensland | 7·4 |
| Victoria | 6·9 |
| New Zealand | 6·3 |
| Tasmania | 6·2 |
During 1902 excise duty was paid on 7,179,360 gallons of beer; and 201,523 gallons of beer, 602,021 gallons of spirits, and 126,450 gallons of wine were entered at the Customs for home consumption.
The actual quantity of beer made and used in the colony has increased from 4,243,760 gallons in 1886 to 7,179,360 gallons in 1902:—
| Beer manufactured in New Zealand on which Excise Duty was paid. | |
|---|---|
| Gal. | |
| 1886 | 4,243,760 |
| 1887 | 4,264,160 |
| 1888 | 4,050,560 |
| 1889 | 4,402,480 |
| 1890 | 4,676,240 |
| 1891 | 4,567,920 |
| 1892 | 4,752,720 |
| 1893 | 4,873,600 |
| 1894 | 4,807,360 |
| 1895 | 4,936,400 |
| 1896 | 5,382,960 |
| 1897 | 5,741,200 |
| 1898 | 6,013,120 |
| 1899 | 6,261,200 |
| 1900 | 6,811,280 |
| 1901 | 7,134,800 |
| 1902 | 7,179,360 |
The following table gives the consumption per head of alcoholic liquors by the people, excluding and including Maoris, showing separately the proportions of beer, wine, and spirits from 1883 to 1902. To the amount of beer manufactured in the colony in each year on which excise duty was paid has been added the amount brought into consumption from imports:—
| Year. | Beer. | Spirits. | Wine. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excluding Maoris. | Including Maoris. | Excluding Maoris. | Including Maoris. | Excluding Maoris. | Including Maoris. | |
| Gal. | Gal. | Gal. | Gal. | Gal. | Gal. | |
| 1883 | 9·435 | 8·709 | 1·088 | 1·005 | 0·315 | 0·291 |
| 1886 | 7·861 | 7·333 | 0·820 | 0·765 | 0·212 | 0·198 |
| 1889 | 7·624 | 7·136 | 0·598 | 0·560 | 0·176 | 0·165 |
| 1892 | 7·807 | 7·328 | 0·708 | 0·664 | 0·174 | 0·163 |
| 1895 | 7·421 | 6·996 | 0·629 | 0·593 | 0·135 | 0·127 |
| 1898 | 8·427 | 7·995 | 0·668 | 0·634 | 0·146 | 0·139 |
| 1899 | 8·583 | 8·150 | 0·687 | 0·653 | 0·148 | 0·141 |
| 1900 | 9·150 | 8·696 | 0·720 | 0·684 | 0·152 | 0·145 |
| 1901 | 9·413 | 8·919 | 0·766 | 0·726 | 0·159 | 0·151 |
| 1902 | 9·252 | 8·777 | 0·755 | 0·716 | 0·158 | 0·150 |
A comparison of the annual consumption of beer, spirits, and wine per head in Australasia is added:—
| — | Beer. | Spirits. | Wine. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gal. | Gal. | Gal. | |
| Queensland | 11·41 | 1·08 | 0·44 |
| New South Wales | 10·43 | 0·77 | 0·66 |
| Victoria | 12·16 | 0·76 | 1·62 |
| South Australia | 9·06 | 0·43 | 1·72 |
| Western Australia | 24·40 | 1·54 | 0·95 |
| Tasmania | 8·48 | 0·48 | 0·11 |
| New Zealand (including Maoris) | 8·72 | 0·69 | 0·15 |
The tobacco entered for consumption in 1902 was 1,969,285 lb., and the consumption per head of population, including Maoris, 2·34 lb.
| Average Annual Consumption per Head of Tobacco in various Countries.* | |
|---|---|
* See “The Seven Colonies of Australasia, 1901–1902.'' | |
| Lb. | |
| Holland | 6·92 |
| United States | 4·40 |
| Western Australia | 4·39 |
| Turkey | 4·37 |
| Austria-Hungary | 3·77 |
| Denmark | 3·70 |
| Switzerland | 3·24 |
| Belgium | 3·15 |
| Germany | 3·00 |
| Queensland | 3·00 |
| New South Wales | 2·67 |
| New Zealand | 2·34 |
| Tasmania | 2·13 |
| Victoria | 2·13 |
| Canada | 2·11 |
| France | 2·05 |
| South Australia | 1·91 |
| Sweden | 1·87 |
| Spain | 1·70 |
| United Kingdom | 1·41 |
| Italy | 1·34 |
| Russia | 1·23 |
The imports from the United Kingdom to New Zealand in 1902 were valued at £6,851,452, or a decrease of £34,379 on the value of goods imported from the Home-country during the previous year. From British colonies and possessions the imports were £2,569,505, a decrease of £344,361 on the amount in 1901.
The following are the values of imports from different countries or places in 1902 and 1901, given in the order of the increase or decrease from each:—
| Country, Colony, State, &c. | 1902 | 1901 | Increase. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Victoria | 748,313 | 641,431 | 106,882 |
| Belgium | 86,236 | 63,083 | 23,153 |
| Ocean Island | 13,500 | 1,266 | 12,234 |
| Germany | 210,560 | 198,521 | 12,039 |
| British Columbia | 19,858 | 8,640 | 11,218 |
| Japan | 56,087 | 45,465 | 10,622 |
| France | 35,572 | 27,714 | 7,858 |
| South Australia | 47,135 | 39,319 | 7,816 |
| Sweden | 19,243 | 11,809 | 7,434 |
| Western Australia | 7,336 | 4,846 | 2,490 |
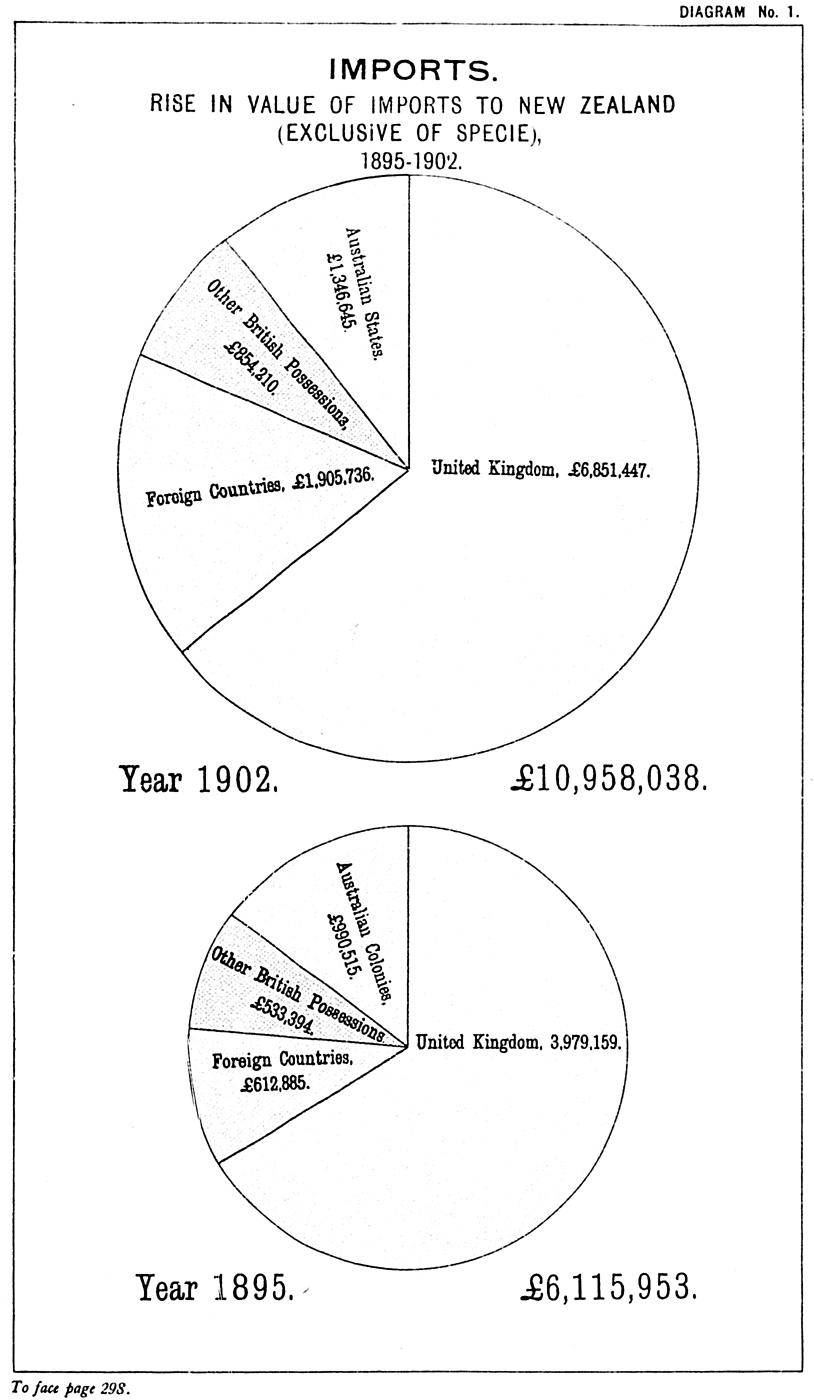
IMPORTS. RISE IN VALUE OF IMPORTS TO NEW ZEALAND (EXCLUSIVE OF SPECIE), 1895–1902.
| Country, Colony, State, &c. | 1902 | 1901 | Increase. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Italy | 11,129 | 9,211 | 1,918 |
| West Indies | 3,019 | 1,517 | 1,502 |
| Denmark | 1,800 | 309 | 1,491 |
| Burmah | 2,234 | 1,072 | 1,162 |
| Navigator's Island | 3,597 | 2,692 | 905 |
| Cape Colony | 843 | 330 | 513 |
| Hongkong | 18,670 | 18,245 | 425 |
| Friendly Islands | 9,756 | 9,487 | 269 |
| West Indies (British) | 190 | .. | 190 |
| Norway | 300 | 154 | 146 |
| Turkey | 136 | .. | 130 |
| New Guinea | 82 | .. | 82 |
| Natal | 135 | 56 | 79 |
| Sandwich Islands | 90 | 35 | 55 |
| Portugal | 600 | 552 | 48 |
| Egypt | 700 | 657 | 43 |
| New Caledonia | 23 | .. | 23 |
| Transvaal Colony | 19 | .. | 19 |
| Russia | 10 | .. | 10 |
| Norfolk Island | 43 | 38 | 5 |
| Country, Colony, State. &c. | 1902 | 1901 | Decrease. |
|---|---|---|---|
* The value of goods shipped from New Zealand to the Cook and other Islands lately annexed was, in 1902, £32,163. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| New South Wales | 871,593 | 1,222,026 | 350,433 |
| United States (West Coast) | 172,362 | 240,515 | 68,153 |
| Bengal | 284,742 | 331,188 | 46,446 |
| United Kingdom | 6,851,452 | 6,885,831 | 34,379 |
| Cook and Savage Islands | * | 32,669 | 32,669 |
| Java | 55,005 | 83,416 | 28,411 |
| United States (East Coast) | 1,146,575 | 1,174,745 | 28,170 |
| Fiji | 327,972 | 349,706 | 21,734 |
| Queensland | 6,991 | 26,858 | 19,867 |
| Malden Island | 15,665 | 29,398 | 13,733 |
| Tasmania | 33,927 | 44,840 | 10,913 |
| Ceylon | 125,891 | 134,742 | 8,851 |
| Philippine Islands | 8,103 | 15,739 | 7,636 |
| Society Islands | 5,983 | 13,150 | 7,167 |
| Holland | 10,363 | 17,314 | 6,951 |
| Greece | 14,097 | 19,758 | 5,661 |
| China | 12,500 | 15,324 | 2,824 |
| Singapore | 23,113 | 25,538 | 2,425 |
| Asia Minor | 15,250 | 16,910 | 1,660 |
| Surprise Island | 8,206 | 9,242 | 1,036 |
| Spain | 988 | 1,650 | 662 |
| Austria | 1,655 | 2,316 | 661 |
| Switzerland | 2,198 | 2,650 | 452 |
| Mauritius | .. | 442 | 442 |
| Madras | 872 | 1,084 | 212 |
| Chesterfield Island | .. | 167 | 167 |
| Canary Islands | 41 | 149 | 108 |
| Lord Howe Island | .. | 47 | 47 |
| Bombay | 447 | 475 | 28 |
| New Hebrides | .. | 25 | 25 |
| Canada | 33,516 | 33,538 | 22 |
| Aden | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Argentine Republic | .. | 7 | 7 |
The following table gives the value of the imports for each port in New Zealand for the last two years, arranged in order of magnitude for 1902:—
| 1902 | 1901 | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Wellington | 3,124,771 | 3,046,707 |
| Auckland | 3,087,460 | 3,023,566 |
| Dunedin | 1,956,235 | 2,203,824 |
| Lyttelton | 1,745,272 | 2,072,186 |
| Invercargill and Bluff | 341,798 | 328,727 |
| Napier | 211,297 | 218,140 |
| Timaru | 148,033 | 176,967 |
| Wanganui | 134,158 | 153,679 |
| Nelson | 122,555 | 135,779 |
| New Plymouth | 81,488 | 73,631 |
| Greymouth | 69,514 | 74,842 |
| Oamaru | 51,428 | 55,393 |
| Poverty Bay | 39,902 | 49,745 |
| Westport | 35,218 | 32,254 |
| Patea | 17,227 | 16,038 |
| Wairau | 15,861 | 14,376 |
| Hokitika | 13,105 | 22,023 |
| Kaipara | 4,568 | 7,114 |
| Tauranga | 2,441 | 1,875 |
| Picton | 479 | 1,366 |
The values of imports in each provincial district during 1892 and 1902 were as under:—
| 1892 | 1902 | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Auckland | 1,667,499 | 3,134,371 |
| Taranaki | 43,269 | 98,715 |
| Hawke's Bay | 221,499 | 211,297 |
| Wellington | 1,607,053 | 3,258,929 |
| Marlborough | 18,254 | 16,340 |
| Nelson | 151,141 | 157,773 |
| Westland | 43,885 | 82,619 |
| Canterbury | 1,304,862 | 1,893,306 |
| Otago | 1,860,733 | 2,349,461 |
The value of imports by parcel-post (£24,861 in 1892 and £123,912 in 1902) must be added to the above figures in order to make up the totals (including specie) of £6,943,056 and £11,326,723 for the respective years.
Separating the value of the imports for the North Island from that of the Middle Island, it is found that while in 1892 the former received imported goods to the value of £3,539,320, against £3,378,875 for the Middle Island, in the year 1902 the North Island imports exceeded those of the other to a far greater extent, the values being respectively £6,703,312 and £4,499,499, or an excess for the North Island of £2,203,813, or 48·98 per cent.
Details of all imports for 1902, giving quantities and values of articles introduced into the colony, with the amounts entered for Home consumption, and the amount of duty received, are next shown:—
| General Imports into the Colony of New Zealand during the Year 1902. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (For rates of duty, see Tariff, pp. 85 to 101.) | ||||||
| Articles. | Total Quantities Imported. | Value of Total Imports. | Entered for Home Consumption on Importation and ex Warehouse. | Amount of Duty received. | ||
| Acid— | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Acetic | 382,481 lb. | 3,982 | 464,000lb. | 2,899 | 19 | 9 |
| Carbolic | 34,715 lb. | 651 | .. | .. | ||
| Salicylic | 4,446 lb. | 306 | .. | .. | ||
| Sulphuric | 142,345 lb. | 1,367 | .. | .. | ||
| Tartaric | 101,985 lb. | 4,886 | 100,087 lb. | 417 | 0 | 7 |
| Unenumerated | 95,609 lb. | 1,719 | .. | .. | ||
| Alkali— | ||||||
| Potash and caustic potash | 1,972 cwt. | 3,021 | .. | .. | ||
| Soda ash | 12,395 cwt. | 4,411 | .. | .. | ||
| Soda, carbonate and bicarbonate | 15,737 cwt. | 5,311 | 15,487 cwt. | 774 | 6 | 7 |
| Soda, caustic | 13,987 cwt. | 10,203 | .. | .. | ||
| Soda crystals | 46 cwt. | 19 | 46 cwt. | 4 | 13 | 0 |
| Soda silicate | 4,189 cwt. | 1,578 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 5,551 cwt. | 3,440 | .. | .. | ||
| Alum | 1,825 cwt. | 646 | .. | .. | ||
| Animals, Living— | ||||||
| Bears | 2 No. | 30 | .. | .. | ||
| Birds | 1,639 cwt. | 294 | .. | .. | ||
| Cats | 4 cwt. | 7 | .. | .. | ||
| Cattle, horned | 24 cwt. | 1,260 | 24 No. | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| Deer | 24 cwt. | 154 | .. | .. | ||
| Dogs | 70 cwt. | 309 | .. | .. | ||
| Donkeys | 2 cwt. | 400 | .. | .. | ||
| Goats | 41 cwt. | 342 | .. | .. | ||
| Hares | 42 cwt. | 11 | .. | .. | ||
| Horses | 179 cwt. | 9,432 | 167 No. | 167 | 0 | 0 |
| Leeches | .. | 2 | .. | .. | ||
| Mice | 6 No. | 3 | .. | .. | ||
| Monkeys | 4 No. | 15 | .. | .. | ||
| Opossums | 2 No. | 2 | .. | .. | ||
| Pigs | 8 No. | 40 | .. | .. | ||
| Poultry | 384 No. | 738 | .. | .. | ||
| Rabbits | 4 No. | 3 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheep | 933 No. | 7,904 | .. | .. | ||
| Turtles | 15 No. | 27 | .. | .. | ||
| Apparel and slops n.o.e. | 510,231 | £507,026 | 120,756 | 8 | 1 | |
| Apparel made to the order of residents in the colony | .. | 1,166 | £1,172 | 468 | 14 | 7 |
| Arms, ammunition, and explosives— | ||||||
| Accoutrements | .. | 2,140 | .. | .. | ||
| Gaps, percussion | 8,292,350 No. | 1,142 | .. | .. | ||
| Cartridges, 10- to 24-bor | 5,126,681 No. | 16,602 | 5,096,800 No. | 3,822 | 11 | 11 |
| Cartridges n.o.e. | 12,475,840 No. | 11,327 | £7,086 | 1,417 | 3 | 3 |
| Cartridge-cases | 210,980 No. | 383 | 208,700 No. | 78 | 5 | 8 |
| Detonator for dynamite | .. | 1,577 | .. | .. | ||
| Dynamite | 87,250 lb. | 5,007 | .. | .. | ||
| Firearms | 9,987 No. | 15,535 | £14,102 | 2,820 | 6 | 11 |
| Fuse | 138,187 coils | 4,041 | .. | .. | ||
| Lithofracteur and cordite | 502,271 lb | 23,039 | .. | .. | ||
| Ordnance stores | .. | 24,753 | .. | .. | ||
| Powder, blasting | 691,675 lb. | 17,433 | .. | .. | ||
| Powder, sporting | 15,070 lb. | 2,243 | 13,568 lb. | 339 | 4 | 0 |
| Shot | 171 cwt. | 451 | 166 cwt. | 83 | 5 | 0 |
| Swords | 164 No. | 258 | .. | .. | ||
| Other explosives | 15,740 lb. | 840 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 2,962 | .. | .. | ||
| Asphalt | 57,833 cwt. | 12,874 | .. | .. | ||
| Bacon and hams | 3,581 lb. | 140 | 912 lb. | 7 | 12 | 1 |
| Bags and sacks— | ||||||
| Cornsacks | 596,267 doz. | 124,231 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 75,978 doz. | 11,443 | £2,887 | 577 | 10 | 0 |
| Bagging and sacking | .. | 977 | £34 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
| Basketware and wickerware | .. | 3,024 | £3,057 | 611 | 6 | 10 |
| Beer | 225,442 galls. | 43,627 | 201,523 galls. | 20,152 | 6 | 11 |
| Belting, leather | 32,564 lb. | 3,778 | 31,195 lb. | 519 | 18 | 5 |
| Belting, other than leather | .. | 19,895 | .. | .. | ||
| Beverages, non-alcoholic— | ||||||
| Aerated and mineral waters | 6,606 doz. | 1,637 | £1,728 | 345 | 13 | 0 |
| Coffee essence | .. | 8,978 | £8,354 | 1,670 | 17 | 1 |
| Limejuice, sweetened | 4,927 galls. | 1,155 | £1,264 | 252 | 17 | 0 |
| Limejuice, unsweetened | 12,579 galls. | 2,085 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 436 | £477 | 119 | 3 | 7 |
| Bicycles and tricycles | 7,752 No. | 52,633 | £52,097 | 10,419 | 8 | 11 |
| Materials for | .. | 81,544 | £40,042 | 8,008 | 7 | 7 |
| Biscuits— | ||||||
| Fancy, and other kinds | 109,384 lb. | 5,290 | 109,537 lb. | 912 | 16 | 2 |
| Ships', plain | 28 cwt. | 33 | 27 cwt. | 4 | 0 | 7 |
| Blacking | .. | 7,331 | £7,397 | 1,479 | 7 | 2 |
| Blacklead | .. | 2,660 | £2,871 | 574 | 3 | 9 |
| Blue | 190,583 lb. | 4,968 | 198,930 lb. | 1,657 | 15 | 0 |
| Boats | 31 No. | 836 | .. | .. | ||
| Books, printed | .. | 149,194 | .. | .. | ||
| Boots and shoes | 89,802 doz. pr | 192,794 | £193,990 | 43,647 | 16 | 8 |
| Gum-boots | 1,002 doz. pr | 10,137 | .. | .. | ||
| Borax | 2,624 cwt. | 2,873 | .. | .. | ||
| Brass— | ||||||
| Pigs, bars, tubes, or sheets | 813 cwt. | 3,157 | .. | .. | ||
| Tubing or stamped work in the rough | 126 cwt. | 546 | .. | .. | ||
| Manufactures | .. | 9,559 | £9,635 | 1,927 | 1 | 10 |
| Bricks— | ||||||
| Building | 88,200 No. | 247 | .. | .. | ||
| Fire | 150,408 No. | 656 | £656 | 131 | 5 | 8 |
| Other kinds | 38,048 No. | 113 | .. | .. | ||
| Brushware and brooms— | ||||||
| Brooms | 2,566 doz. | 1,666 | £1,547 | 386 | 14 | 1 |
| Brushes (clothes, hair, hat, and toilet) | .. | 8,253 | £8,316 | 1,663 | 5 | 4 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 6,685 | £6,829 | 1,707 | 6 | 11 |
| Materials for | .. | 6,675 | .. | .. | ||
| Buckets and tubs— | ||||||
| Iron | 817 doz. | 476 | £463 | 115 | 13 | 2 |
| Wood | 222 doz. | 107 | £107 | 21 | 8 | 0 |
| Building materials, unenumerated | .. | 7,303 | .. | .. | ||
| Butter | 31 cwt. | 171 | .. | .. | ||
| Candles | 2,268,914 lb. | 40,758 | 2,234,171 lb. | 9,309 | 0 | 11 |
| Canes and rattans | .. | 1,362 | .. | .. | ||
| Canvas | .. | 39,202 | .. | .. | ||
| Caramel, brewers' | 16,107 lb. | 242 | 15,967 lb. | 199 | 11 | 9 |
| Caramel, cereal | 192 lb. | 3 | 192 lb. | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Cards, playing | 70,502 packs | 1,361 | 65,894 packs | 1,647 | 7 | 0 |
| Carpeting and druggeting | 43,347 | £41,799 | 8,359 | 14 | 2 | |
| Carriages, &c.— | ||||||
| Carriages | 384 No. | 9,592 | £9,570 | 1,913 | 18 | 0 |
| Carts, drays, and wagons | 302 No. | 2,853 | £2,880 | 576 | 0 | 0 |
| Perambulators and go-carts | 165 No. | 173 | £173 | 34 | 12 | 0 |
| Materials for | .. | 7,903 | £7,965 | 1,593 | 1 | 1 |
| Materials for axles, axle-arms, and boxes | .. | 17,538 | .. | .. | ||
| Materials for carriage and cart shafts, spokes, and felloes in the rough | .. | 8,329 | .. | .. | ||
| Carriage and cart makers materials | .. | 15,525 | .. | .. | ||
| Casks, empty | 2,254 No. | 2,963 | £2,959 | 591 | 17 | 0 |
| Cement | 121,150 barrels | 54,811 | 117,637 barrels | 11,763 | 14 | 0 |
| Chains and chain cables | 7,174 cwt. | 8,183 | .. | .. | ||
| Charcoal | 6,088 cwt. | 2,785 | .. | .. | ||
| Cheese | 31 cwt. | 137 | £137 | 27 | 8 | 0 |
| China, porcelain, and parianware | .. | 25,986 | £26,072 | 5,214 | 7 | 11 |
| Clocks | 43,297 No. | 13,011 | £12,833 | 2,566 | 10 | 1 |
| Coal | 127,853 tons | 125,732 | .. | .. | ||
| Cocoa and chocolate | 409,500 lb. | 40,840 | 421,793 lb. | 5,272 | 8 | 4 |
| Cocoa beans | 180,675 lb. | 6,208 | .. | .. | ||
| Coffee— | ||||||
| Raw | 220,878 lb. | 8,217 | .. | .. | ||
| Roasted | 862 lb. | 46 | 1,169 lb. | 14 | 12 | 3 |
| Coke | 1,039 tons | 2,597 | .. | .. | ||
| Combs | .. | 1,757 | £1,741 | 348 | 3 | 1 |
| Confectionery— | ||||||
| Chocolate in plain trade packages | 130,540 lb. | 6,443 | 136,800 lb. | 1,710 | 0 | 0 |
| Chocolate, fancy packages | .. | 9,300 | £9,392 | 1,878 | 6 | 7 |
| Unenumerated | 379,875 lb. | 12,246 | 396,225 lb. | 3,301 | 17 | 7 |
| Copper— | ||||||
| Nails | 309 cwt. | 1,301 | .. | .. | ||
| Pig, bar, sheet, and tube | 5,393 cwt. | 20,973 | .. | .. | ||
| Rod and bolt | 267 cwt. | 1,015 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheathing | 426 cwt. | 1,573 | .. | .. | ||
| Manufactures | .. | 286 | £286 | 57 | 4 | 0 |
| Copra | 58 tons | 786 | .. | .. | ||
| Cordage | 4,978 cwt. | 14,170 | £14,126 | 2,805 | 5 | 2 |
| Hawsers of 12 in. and over | 470 cwt. | 781 | .. | .. | ||
| Iron and steel | 11,134 cwt. | 25,640 | .. | .. | ||
| Cork, cut | .. | 10,405 | £10,348 | 2,069 | 11 | 2 |
| Cork, in the rough | 68 cwt. | 113 | .. | .. | ||
| Cotton piece-goods— | ||||||
| Butter and cheese cloth | .. | 3,232 | .. | .. | ||
| Calico, white and grey | .. | 163,675 | .. | .. | ||
| Corduroy, moleskin, and beaver-skin | .. | 3,139 | .. | .. | ||
| Leather-cloth | .. | 6,134 | .. | .. | ||
| Shirtings, coloured cotton | .. | 32,513 | .. | .. | ||
| Shirtings, flannelette | .. | 4,332 | .. | .. | ||
| Shirtings, union, of 6d. per yard and under | .. | 2,232 | .. | .. | ||
| Tubular woven cotton cloth | .. | 7,447 | .. | .. | ||
| Waterproof material | .. | 23,270 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 252,511 | £246,189 | 38,290 | 7 | 0 |
| Cotton— | ||||||
| Raw | 8,443 lb. | 159 | .. | .. | ||
| Waste | 4,335 cwt. | 6,085 | .. | .. | ||
| Wick | 70,648 lb. | 3,092 | .. | .. | ||
| Cutlery | .. | 29,993 | £31,204 | 6,024 | 14 | 2 |
| Doors, plain | 360 No. | 194 | 360 No. | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Drapery | .. | 277,513 | £275,912 | 55,182 | 6 | 1 |
| Lace and laces | .. | 52,516 | £52,509 | 13,127 | 4 | 9 |
| Ribbons and crape | .. | 18,422 | £18,311 | 4,577 | 13 | 3 |
| Tailors' trimmings | .. | 101,052 | .. | .. | ||
| Drugs— | ||||||
| Baking-powder and yeast preparations | .. | 179 | £187 | 37 | 8 | 0 |
| Chemicals n.o.e. | .. | 5,916 | £5,878 | 881 | 15 | 4 |
| Cream of tartar | 877,034 lb. | 31,200 | 850,991 lb. | 3,545 | 15 | 11 |
| Drugs, druggists'sundries, and apothecaries' wares | .. | 75,476 | £75,697 | 11,354 | 11 | 1 |
| Glycerine, refined | .. | 1,859 | £1,883 | 376 | 10 | 2 |
| Tinctures and medicinal spirits | 18,211 lb. | 1,308 | 18,916 lb. | 945 | 16 | 7 |
| Washing-powder | .. | 238 | £238 | 47 | 12 | 0 |
| Anhydrous ammonia | .. | 6,586 | .. | .. | ||
| Arsenic | 1,924 cwt. | 1,795 | .. | .. | ||
| Disinfectants | .. | 5,209 | .. | .. | ||
| Food preservative | .. | 4,565 | .. | .. | ||
| Gums | .. | 2,319 | .. | .. | ||
| Insecticides and tree-washes | .. | 1,608 | .. | .. | ||
| Maltine | .. | 831 | .. | .. | ||
| Medicinal barks, leaves, &c. | .. | 1,594 | .. | .. | ||
| Phosphorus | .. | 804 | .. | .. | ||
| Potassium cyanide | 9,674 cwt. | 50,655 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheep-dip | .. | 34,686 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheep and horse drenches | .. | 459 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 13,554 | .. | .. | ||
| Dyes | .. | 16,531 | .. | .. | ||
| Earthenware | .. | 66,975 | £66,387 | 13,277 | 9 | 8 |
| Eggs | 12 doz. | 15 | .. | .. | ||
| Engine-packing | 3,236 cwt. | 11,138 | .. | .. | ||
| Essences, flavouring— | ||||||
| Spirituous | 1,694 gals. | 4,475 | 1,722 gals. | 1,377 | 10 | 2 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 170 | £140 | 20 | 18 | 10 |
| Essential oils— | ||||||
| Eucalyptus | 10,743 lb. | 2,276 | £2,392 | 478 | 8 | 0 |
| Other kinds | 32,163 lb. | 5,027 | .. | .. | ||
| Fancy goods and toys | .. | 148,072 | £145,549 | 29,109 | 14 | 10 |
| Felt sheathing | .. | 7,342 | .. | .. | ||
| Fire-engines | 159 No. | 2,333 | .. | .. | ||
| Fire-hose and other appliances | .. | 4,557 | .. | .. | ||
| Fireworks | .. | 1,061 | £919 | 183 | 15 | 6 |
| Fish— | ||||||
| Anchovies, salted | 34 cwt. | 63 | .. | .. | ||
| Dried, pickled, and salted | 2,872 cwt. | 5,448 | 2,713 cwt. | 1,356 | 13 | 6 |
| Potted and preserved | 1,933,188 lb. | 42,234 | 1,759,001 lb. | 14,658 | 6 | 10 |
| Fish-ova | .. | 667 | .. | .. | ||
| Fishing-tackle— | ||||||
| Artificial flies | .. | 237 | £237 | 59 | 7 | 6 |
| Fish-hooks | .. | 888 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 4,290 | £4,301 | 860 | 3 | 1 |
| Flock | 83 cwt. | 83 | 83 cwt. | 8 | 6 | 0 |
| Floorcloth and oilcloth | .. | 74,556 | £73,129 | 14,625 | 15 | 6 |
| Flour | 99,069 centals | 39,446 | 93,212 centals | 4,660 | 12 | 5 |
| Foods, animal— | ||||||
| Chaff | 1/4 ton | 2 | 1/4 ton | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 1,892 | £1,911 | 382 | 4 | 0 |
| Foods, farinaceous— | ||||||
| Arrowroot | 46,027 lb. | 615 | .. | .. | ||
| Macaroni and vermicelli | 137,355 lb. | 1,847 | .. | .. | ||
| Maizena and corn-flour | 1,025,940 lb. | 12,326 | 965,216 lb. | 1,005 | 8 | 8 |
| Sago and tapioca | 18,841 cwt. | 10,421 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 2,353 | .. | .. | ||
| Fruits, bottled and preserved | 43,517 doz. | 11,075 | £11,524 | 2,881 | 1 | 4 |
| Fruits, dried— | ||||||
| Currants | 2,347,712 lb. | 19,008 | 2,546,719 lb. | 10,611 | 6 | 7 |
| Raisins | 2,441,590 lb. | 38,169 | 2,504,405 lb. | 10,435 | 0 | 5 |
| Unenumerated | 1,139,917 lb. | 15,969 | 1,206,347 lb. | 10,052 | 17 | 10 |
| Fruits, fresh— | ||||||
| Apples, pears, and plums | 495,600 lb. | 7,928 | 495,433 lb. | 2,064 | 6 | 1 |
| Apples and pears | 575,312 lb. | 5,342 | 575,312 lb. | 1,198 | 11 | 4 |
| Lemons | 419,182 lb. | 5,018 | 412,198 lb. | 858 | 14 | 11 |
| Other kinds | 12,687,912 lb. | 70,380 | .. | .. | ||
| Lemon and orange peel, in brine | 432,579 lb. | 2,334 | .. | .. | ||
| Preserved in sulphurous acid | 7,186 lb. | 83 | 7,186 lb. | 29 | 18 | 10 |
| Pulp and partially preserved fruit | 6,753 lb. | 60 | 6,753 lb. | 42 | 4 | 1 |
| Fungus | 1 cwt. | 5 | .. | .. | ||
| Furniture and upholstery | .. | 35,203 | £35,279 | 8,819 | 13 | 3 |
| Kapok | 6,268 cwt. | 21,767 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 5,872 | .. | .. | ||
| Furniture, knife, and plate powder and polish | .. | 5,328 | £5,333 | 1,066 | 12 | 3 |
| Furs | .. | 6,686 | £6,688 | 1,672 | 1 | 10 |
| Gelatine and isingiass | 109,667 lb. | 6,687 | £6,558 | 1,311 | 10 | 5 |
| Glass— | ||||||
| Bottles, empty | .. | 40,959 | .. | .. | ||
| Mirrors and looking-glasses | .. | 6,342 | £6,376 | 1,593 | 17 | 10 |
| Plate, bevelled, &c. | .. | 5,335 | £5,293 | 1,323 | 6 | 5 |
| Plate, other kinds | 314,936 sup. ft. | 9,348 | £9,468 | 1,893 | 11 | 0 |
| Window | 3,417,142 sup. ft. | 31,866 | 3,401,850 sup. ft. | 3,401 | 17 | 1 |
| Glassware | .. | 45,058 | £36,931 | 7,386 | 2 | 1 |
| Glue and size | 118,571 lb. | 2,469 | 118,509 lb. | 740 | 13 | 7 |
| Gold-leaf | .. | 698 | .. | .. | ||
| Grain and pulse— | ||||||
| Barley | 23 centals | 17 | 7 centals | 0 | 13 | 6 |
| Beans and peas | 1,229 centals | 670 | 1,229 centals | 46 | 1 | 8 |
| Oats | 1,429 centals | 431 | 39 centals | 1 | 9 | 8 |
| Wheat | 14,081 centals | 4,549 | 14,052 centals | 526 | 19 | 5 |
| Unenumerated | 4,099 centals | 2,806 | 4,091 centals | 153 | 8 | 6 |
| Ground, unenumerated | 5,502 centals | 4,594 | 5,575 centals | 278 | 15 | 3 |
| Grease | 4,463 cwt. | 3,494 | £3,297 | 659 | 8 | 2 |
| Grindery— | ||||||
| Heel and toe plates | .. | 2,470 | £2,471 | 556 | 0 | 6 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 17,362 | .. | .. | ||
| Haberdashery | .. | 20,466 | £20,342 | 4,068 | 9 | 2 |
| Buttons | .. | 30,635 | .. | .. | ||
| Sewing-cottons, &c. | .. | 48,251 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 3,217 | .. | .. | ||
| Hair | 359 cwt. | 1,284 | .. | .. | ||
| Hardware, hollow-ware, and ironmongery | .. | 277,938 | £274,124 | 54,824 | 15 | 11 |
| Coffin furniture | .. | 2,147 | £2,153 | 430 | 13 | 0 |
| Hardware | .. | 3,227 | .. | .. | ||
| Hats and caps | 73,291 doz. | 75,222 | £74,261 | 18,565 | 7 | 3 |
| Hatters' materials | .. | 18,896 | .. | .. | ||
| Hemp | 105 tons | 4,793 | .. | .. | ||
| Hides | 11,252 No. | 7,399 | .. | .. | ||
| Honey | 210 lb. | 2 | 210 lb. | 1 | 15 | 0 |
| Hops | 78,245 lb. | 4,435 | 66,226 lb. | 1,655 | 13 | 0 |
| Hosiery | .. | 115,071 | £115,118 | 23,023 | 13 | 3 |
| Indiarubber and gutta-percha goods | .. | 8,888 | £68 | 13 | 12 | 0 |
| Ink— | ||||||
| Printing | 167,268 lb. | 6,627 | .. | .. | ||
| Writing | .. | 1,721 | £1,385 | 277 | 0 | 10 |
| Instruments, musical— | ||||||
| Harmoniums and organs | 542No. | 5,889 | £5,779 | 1,155 | 14 | 0 |
| Pianos | 3,813 No. | 84,841 | £86,383 | 17,276 | 12 | 1 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 17,797 | £18,154 | 3,630 | 15 | 8 |
| For Volunteer bands | .. | 256 | .. | .. | ||
| Materials for | .. | 1,880 | £294 | 58 | 16 | 0 |
| Instruments, other kinds— | ||||||
| Optical | .. | 2,616 | .. | .. | ||
| Scientific | .. | 4,165 | .. | .. | ||
| Surgical and dental | .. | 23,969 | .. | .. | ||
| Surveying | .. | 1,384 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 177 | .. | .. | ||
| Iron and steel— | ||||||
| Angle | 389 tons | 3,065 | .. | .. | ||
| Bar, bolt, and rod | 12,432 tons | 118,032 | .. | .. | ||
| Bolts and nuts | 17,772 cwt. | 19,431 | .. | .. | ||
| Castings for ships | 15 tons | 967 | .. | .. | ||
| Galvanised manufactures | .. | 920 | £903 | 225 | 15 | 11 |
| Hoop | 1,695 tons | 16,300 | .. | .. | ||
| Hoop, galvanised | 3,110 cwt. | 2,143 | 3,107 cwt. | 233 | 0 | 8 |
| Pig | 6,519 tons | 29,462 | .. | .. | ||
| Pipes and fittings | 12,049 tons | 113,363 | £112,783 | 5,639 | 3 | 0 |
| Rails | 9,846 tons | 62,735 | .. | .. | ||
| Railway bolts and fastenings | 2,436 tons | 22,428 | £995 | 199 | 0 | 0 |
| Sheet and plate | 5,522 tons | 50,369 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheet, galvanised, corrugated | 277,967 cwt. | 220,947 | 275,089 cwt. | 27,508 | 18 | 5 |
| Sheet, galvanised, plain | 53,439 cwt. | 44,517 | 53,189 cwt. | 3,989 | 3 | 3 |
| Staples and standards | 1,105 tons | 6,236 | £6,180 | 1,236 | 0 | 4 |
| Tanks | 3,384 No. | 10,054 | 3,343 No. | 1,468 | 5 | 0 |
| Wire, fencing, barbed | 4,665 tons | 61,009 | .. | .. | ||
| Wire, fencing, plain | 8,644 tons | 84,001 | .. | .. | ||
| Wire, telegraphic and telephonic | 106 tons | 1,624 | .. | .. | ||
| Wire-netting | .. | 32,648 | .. | .. | ||
| Wire, unenumerated | 896 tons | 11,091 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 38 tons | 102 | .. | .. | ||
| Jams, jellies, and preserves | 328,630 lb. | 5,885 | 347,940 lb. | 2,899 | 10 | 0 |
| Jellies, concentrated | 92,400 lb. | 3,745 | 87,454 lb. | 1,457 | 11 | 5 |
| Jewellery | .. | 23,106 | £21,192 | 4,238 | 8 | 6 |
| Lamps, lanterns, and lampwick | .. | 22,300 | £22,165 | 4,433 | 0 | 7 |
| Lead— | ||||||
| Pigs and bars | 777 tons | 9,522 | .. | .. | ||
| Pipe | 748 cwt. | 764 | 744 cwt. | 130 | 2 | 0 |
| Sheet | 19,726 cwt. | 15,009 | 17,687 cwt. | 1,326 | 10 | 5 |
| Manufactures | .. | 307 | £307 | 61 | 8 | 0 |
| Leather | 417,272 lb. | 63,139 | 370,675 lb | 2,387 | 11 | 7 |
| Chamois | .. | 534 | £521 | 104 | 3 | 5 |
| Leather manufactures— | ||||||
| Boot and shoe vamps, uppers, and laces | .. | 7,520 | £7,488 | 1,684 | 17 | 10 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 1,596 | £1,686 | 358 | 4 | 4 |
| Lighthouses materials | .. | 560 | .. | .. | ||
| Linen piece-goods— | ||||||
| Forfar, dowlas, and flax sheeting | .. | 12,056 | £1,833 | 366 | 12 | 0 |
| Forfar, dowlas, &c., cut up under supervision | .. | .. | £8,621 | .. | ||
| Linens n.o.e. | .. | 16,558 | £16,063 | 3,212 | 13 | 0 |
| Hessians and serim | .. | 42,556 | .. | .. | ||
| Linseed | 8 tons | 150 | 8 tons | 8 | 6 | 9 |
| Liquorice | .. | 3,006 | £3,050 | 610 | 0 | 2 |
| Machinery and machines— | ||||||
| Agricultural | .. | 73,386 | .. | .. | ||
| Ploughs and harrows | .. | 11,518 | .. | .. | ||
| Dairying | .. | 46,156 | .. | .. | ||
| Dairying engines for | 60 No. | 2,990 | £4,064 | 203 | 4 | 0 |
| Dairying boilers for | 52 No. | 2,892 | £4,429 | 221 | 9 | 0 |
| Dredging | .. | 9,677 | £9,460 | 473 | 0 | 6 |
| Electric | .. | 127,998 | £86,142 | 8,614 | 4 | 0 |
| Engines, steam | 135No. | 20,635 | £17,841 | 3,568 | 6 | 0 |
| Engines, gas | 587 No. | 39,355 | .. | .. | ||
| Engines, boilers for | 99 No. | 11,473 | £8,712 | 1,742 | 8 | 0 |
| Flour-milling | .. | 4,715 | £4,452 | 222 | 12 | 3 |
| Gas-making | .. | 23,865 | £22,264 | 2,226 | 7 | 6 |
| Mining | .. | 32,555 | .. | .. | ||
| Mining engines for | 18 No. | 1,620 | £3,220 | 161 | 0 | 0 |
| Paper-milling | .. | 495 | £180 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Portable and traction engines | 64 No. | 25,570 | .. | .. | ||
| Printing | .. | 15,229 | £14,620 | 731 | 0 | 6 |
| Refrigerating | .. | 7,059 | £4,502 | 225 | 1 | 6 |
| Sewing and knitting | 9,857 No. | 37,005 | .. | .. | ||
| Wood-working | .. | 15,708 | .. | .. | ||
| Woollen-milling | .. | 18,947 | £15,832 | 791 | 12 | 0 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 72,678 | £53,283 | 9,953 | 13 | 0 |
| Materials for and parts of | .. | 8,646 | £1,561 | 258 | 13 | 0 |
| Malt | 3,693 bush. | 1,101 | 3,694 bush. | 369 | 7 | 9 |
| Rice-malt | 14,198 lb. | 123 | 14,198 lb. | 59 | 3 | 2 |
| Manures— | ||||||
| Bone-dust | 14,026 tons | 70,637 | .. | .. | ||
| Guano | 13,114 tons | 40,306 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 12,590 tons | 44,621 | .. | .. | ||
| Marble— | ||||||
| Dressed and polished, and manufactures | .. | 7,193 | £7,203 | 1,800 | 14 | 0 |
| Hewn, or rough-sawn | 280 tons | 2,248 | .. | .. | ||
| Matches and vestas— | ||||||
| Wax (boxes) | 59,432 gross | 7,634 | 58,884 gross | 3,454 | 19 | 5 |
| Wooden .. (boxes) | 34,440 gross | 2,660 | 34,816 gross | 1,781 | 4 | 4 |
| Mats and matting | .. | 9,192 | £9,132 | 1,826 | 7 | 3 |
| Meats, potted and preserved | 52,801 lb. | 2,377 | £2,165 | 433 | 1 | 8 |
| Medicines, patent and proprietary | .. | 40,953 | £38,544 | 5,781 | 13 | 1 |
| Metal, manufactures— | ||||||
| Japanned and lacquered metalware | .. | 1,198 | £1,225 | 306 | 6 | 0 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 15,956 | £14,894 | 2,978 | 17 | 8 |
| Weighbridges and weighing machines | .. | 3,253 | £3,226 | 645 | 6 | 4 |
| Anchors | 829 No. | 1,042 | .. | .. | ||
| Rivets and washers | 8,402 cwt. | 8,335 | .. | .. | ||
| Tacks | 1,781 cwt. | 2,734 | .. | .. | ||
| Type-writers | 738 No. | 10,690 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 56,871 | .. | .. | ||
| Metal sheathing, other than copper | 347 cwt. | 1,151 | .. | .. | ||
| Milk, preserved | 997,809 lb. | 18,949 | £17,170 | 4,292 | 9 | 8 |
| Millinery— | ||||||
| Feathers, ornamental | .. | 2,557 | £2,535 | 633 | 14 | 9 |
| Other kinds | .. | 43,144 | £43,172 | 10,793 | 1 | 5 |
| Minerals— | ||||||
| Antimony-ore | 4 cwt. | 12 | .. | .. | ||
| Mica | .. | 1 | .. | .. | ||
| Mustard | 195,914 lb. | 11,124 | 200,162 lb. | 1,668 | 0 | 4 |
| Nails— | ||||||
| Iron | 76,808 cwt. | 43,793 | 76,777 cwt. | 7,677 | 13 | 9 |
| Unenumerated | 194 cwt. | 321 | 179 cwt. | 26 | 17 | 5 |
| Nuts— | ||||||
| Almonds, in shell | 17,728 lb. | 315 | 18,129 lb. | 151 | 1 | 6 |
| Almonds, shelled | 32,861 lb. | 2,582 | 30,280 lb. | 378 | 9 | 11 |
| Almonds, Barbary, &c. | 126,333 lb. | 4,847 | .. | .. | ||
| Cocoa | 48,560 No. | 241 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 70,713 lb. | 1,066 | 69,041 lb. | 575 | 6 | 10 |
| Oakum | 369 cwt. | 446 | .. | .. | ||
| Oars | 4,053 No. | 662 | .. | .. | ||
| Oils— | ||||||
| Castor, bulk | 138,085 galls. | 17,628 | 94,878 galls. | 2,371 | 19 | 0 |
| Castor, bottled | 1,787 doz. pt. | 635 | £656 | 98 | 8 | 5 |
| Cod liver | 8,921 galls. | 1,990 | .. | .. | ||
| Colza | 13,477 galls. | 2,005 | 12,612 galls. | 315 | 6 | 0 |
| Fish, penguin, and seal | 31,477 galls. | 3,198 | .. | .. | ||
| Linseed | 297,548 galls. | 46,635 | 280,277 galls. | 7,006 | 18 | 8 |
| Mineral, kerosene | 3,329,648 galls. | 116,880 | .. | .. | ||
| Mineral, other kinds | 236,097 galls. | 18,459 | 205,820 galls. | 5,145 | 10 | 0 |
| Neatsfoot | 471 galls. | 45 | 471 galls. | 11 | 15 | 6 |
| Olive, bulk | 9,307 galls. | 1,715 | 9,176 galls. | 229 | 7 | 10 |
| Olive, bottled | 3,053 doz. pts | 1,553 | £1,595 | 239 | 5 | 0 |
| Unenumerated, bulk | 280,588 galls. | 28,682 | 259,042 galls. | 6,476 | 1 | 0 |
| Unenumerated, bottled | 5,594 doz.pts | 2,286 | £2,467 | 370 | 0 | 3 |
| Unenumerated | 171,462 galls. | 9,704 | .. | .. | ||
| Oilmen's stores | .. | 7,314 | £7,415 | 1,483 | 0 | 1 |
| Onions | 19,871 cwt. | 7,264 | 19,444 cwt. | 972 | 3 | 9 |
| Opium | 85 lb. | 98 | 135 lb. | 270 | 11 | 6 |
| Paints and colours— | ||||||
| Ground in oil | 41,858 cwt. | 49,506 | 40,475 cwt. | 5,059 | 6 | 4 |
| Mixed, ready for use | 5,771 cwt. | 13,417 | 4,926 cwt. | 1,231 | 11 | 5 |
| Unenumerated | 12,921 cwt. | 13,782 | .. | .. | ||
| Paper— | ||||||
| Bags, coarse | 23 cwt. | 24 | 23 cwt. | 8 | 13 | 2 |
| Bags, other kinds | 2,914 cwt. | 4,731 | £4,960 | 1,239 | 19 | 11 |
| Butter-paper | 3,372 cwt. | 6,255 | .. | .. | ||
| Paperhangings | .. | 33,422 | £33,639 | 5,045 | 17 | 11 |
| Printing | 117,128 cwt. | 108,439 | .. | .. | ||
| Wrapping | 5,235 cwt. | 5,897 | 5,305 cwt. | 1,326 | 8 | 5 |
| Writing | 11,572 cwt. | 20,051 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 1,394 cwt. | 2,667 | .. | .. | ||
| Peas, split | 1,123 cwt. | 643 | 1,123 cwt. | 112 | 6 | 11 |
| Peel, candied and dried | 19,469 lb. | 381 | 18,271 lb. | 228 | 7 | 9 |
| Perfumery— | ||||||
| Perfumed spirits | 1,325 galls. | 5,330 | 1,310 galls. | 1,964 | 17 | 10 |
| Toilet preparations | .. | 7,345 | £7,153 | 1,788 | 6 | 4 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 1,500 | £1,476 | 369 | 2 | 5 |
| Photographic goods | .. | 6,163 | £5,996 | 1,199 | 2 | 10 |
| Cameras and lenses | .. | 8,256 | .. | .. | ||
| Copper, glass, and zinc plates for photo-litho graphic purposes | .. | 903 | .. | .. | ||
| Sensitised surfaces for photographic purposes | .. | 13,813 | .. | .. | ||
| Pickles | 6,421 galls. | 1,673 | 5,986 galls. | 897 | 16 | 10 |
| Pictures, paintings, drawings, engravings, and photographs | .. | 7,155 | £6,612 | 1,322 | 9 | 4 |
| Family portraits | .. | 323 | .. | .. | ||
| Paintings, &c., for museums, &c. | .. | 504 | .. | .. | ||
| Picture frames and mounts | .. | 1,275 | £1,308 | 261 | 13 | 0 |
| Pitch | 2,833 cwt. | 995 | .. | .. | ||
| Plants, trees, and shrubs | .. | 4,302 | .. | .. | ||
| Plaster of Paris | 6,512 cwt. | 1,242 | .. | .. | ||
| Plate and plated ware | .. | 47,263 | £48,150 | 9,629 | 18 | 11 |
| Portmanteaux | .. | 5,204 | £5,099 | 1,274 | 16 | 6 |
| Leather and leather-cloth bags | .. | 29 | £25 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Potatoes | 35 1/2 tons | 211 | £153 | 30 | 12 | 0 |
| Printing material—Stereotypes and matrices | .. | 61 | £62 | 15 | 12 | 6 |
| Type and materials.n.o.e. | .. | 12,655 | .. | .. | ||
| Provisions n.o.e. | .. | 7,745 | £7,641 | 1,528 | 2 | 3 |
| Pumps | .. | 7,991 | £4,594 | 913 | 15 | 3 |
| Putty | 4,602 cwt. | 2,309 | 4,607 cwt. | 460 | 14 | 6 |
| Quicksilver | 11,678 lb. | 1,490 | .. | .. | ||
| Rags | 61 cwt. | 237 | .. | .. | ||
| Railway plant—Locomotives | 5 No. | 11,831 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 110,472 | £5,284 | 1,050 | 16 | 0 |
| Resin | 10,280 cwt. | 5,502 | .. | .. | ||
| Rice | 63,548 cwt. | 38,964 | .. | .. | ||
| Rice-flour | 101 cwt. | 82 | 103 cwt. | 30 | 18 | 4 |
| Rugs | .. | 12,872 | £12,687 | 2,537 | 6 | 7 |
| Saccharine | 11,733 oz. | 338 | 8,217 oz. | 617 | 16 | 3 |
| Saddlery and harness | .. | 30,697 | £30,810 | 6,162 | 0 | 8 |
| Harness and oil-composition | .. | 2,460 | £2,300 | 459 | 18 | 9 |
| Saddlers' ironmongery and materials | .. | 21,104 | .. | .. | ||
| Collar-check | .. | 5,331 | .. | .. | ||
| Salt | 15,972 tons | 34,885 | .. | .. | ||
| Rock | 421 ton | 962 | .. | .. | ||
| Saltpetre | 266 ton | 1,736 | .. | .. | ||
| Sashes, plain | 6 pairs | 37 | 6 pairs | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Sauces | 12,769 gals. | 8,925 | 12,076 galls. | 2,415 | 3 | 2 |
| Sausage-skins | 216,696 lb. | 11,150 | 192,516 lb. | 2,406 | 9 | 0 |
| Seeds— | ||||||
| Grass and clover | 17,317 cwt. | 46,626 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 24,094 | .. | .. | ||
| Shale | 399 tons | 1,192 | .. | .. | ||
| Shells | 99 cwt. | 365 | .. | .. | ||
| Ship-chandlery | .. | 6,658 | .. | .. | ||
| Silks | .. | 139,522 | £137,634 | 34,408 | 9 | 6 |
| For flour-dressing | .. | 155 | .. | .. | ||
| Silver | 2,362 oz. | 322 | .. | .. | ||
| Skins and pelts— | ||||||
| Fur-skins | 3,008 No. | 108 | .. | .. | ||
| Kangaroo and wallabi | 3,971 No. | 105 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | 19,817 No. | 2,316 | .. | .. | ||
| Slates, roofing | 174,887 No. | 1,608 | .. | .. | ||
| Soap— | ||||||
| Common | 6 cwt. | 11 | 6 cwt. | 1 | 11 | 3 |
| Soap powder, extract of soap, &c. | .. | 6,422 | £6,419 | 1,283 | 17 | 7 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 27,518 | £27,074 | 6,768 | 10 | 9 |
| Specie— | ||||||
| Gold | .. | 346,030 | .. | .. | ||
| Silver | .. | 21,402 | .. | .. | ||
| Copper | .. | 1,253 | .. | .. | ||
| Specimens illustrative of natural science | .. | 359 | .. | .. | ||
| Spices— | ||||||
| Ground | 23,974 lb. | 955 | 19,389 lb. | 323 | 3 | 0 |
| Unground | 457,377 lb. | 14,006 | 458,802 lb. | 3,823 | 7 | 1 |
| Bitter and liqueurs | 3,106 galls. | 3,271 | 3,302 galls. | 2,641 | 8 | 6 |
| Brandy | 75,562 galls. | 31,385 | 71,783 galls. | 57,426 | 4 | 8 |
| Geneva and gin, unsweetened | 78,562 galls. | 19,572 | 67,210 galls. | 53,767 | 17 | 8 |
| Methylated | 1,423 galls. | 177 | 1,423 galls. | 71 | 3 | 0 |
| Rum | 17,794 galls. | 3,149 | 18,747 galls. | 14,997 | 15 | 2 |
| Sweetened | 6,243 galls. | 1,821 | 7,388 galls. | 5,910 | 1 | 3 |
| Whisky | 459,480 galls. | 165,803 | 427,827 galls. | 342,261 | 7 | 11 |
| Unenumerated | 2,375 galls | 1,647 | 2,291 galls. | 1,833 | 0 | 4 |
| Spirits of wine | 47,332 galls. | 3,214 | 1,753 galls. | 1,402 | 3 | 9 |
| Methylated, in bond | .. | .. | 43,034 galls. | 1,075 | 17 | 3 |
| Sponges | .. | 272 | £198 | 29 | 13 | 6 |
| Starch | 811,476 lb. | 8,937 | 874,601 lb. | 7,288 | 6 | 10 |
| Moulding | 4,480 galls. | 37 | .. | .. | ||
| Stationery— | ||||||
| Manufactured | .. | 49,375 | £41,343 | 10,335 | 16 | 5 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 36,232 | £35,990 | 7,198 | 1 | 10 |
| Apparatus for teaching | .. | 4,710 | .. | .. | ||
| Bookbinders' materials | .. | 6,006 | .. | .. | ||
| Cardboard-boxes, materials for | .. | 10,577 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 5,776 | .. | .. | ||
| Stearine | 112 lb. | 3 | 112 lb. | 0 | 14 | 0 |
| For match-making | 247,417 lb. | 5,948 | 258,208 lb. | 806 | 14 | 0 |
| Stone— | ||||||
| Building | 4,419 tons | 8,248 | .. | .. | ||
| Flagging | 5 tons | 23 | .. | .. | ||
| Granite and other stone, dressed, or polished | .. | 3,826 | £3,826 | 956 | 10 | 0 |
| Granite, unwrought | 1 ton | 6 | £6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Grind-, mill-, oil-, and whet-stones | .. | 2,429 | .. | .. | ||
| Sugar— | ||||||
| Raw | 630,260 cwt. | 341,410 | .. | .. | ||
| Refined | 74,598 cwt. | 50,112 | 84,878,074 lb. | 176,829 | 6 | 5 |
| Glucose | 6,855 cwt. | 4,467 | 762,309 lb. | 3,176 | 5 | 9 |
| Molasses and treacle | 166 cwt. | 149 | 2,629,932 lb. | 5,479 | 0 | 6 |
| Molasses and treacle, mixed with bone-black | 192 lb. | 25 | .. | .. | ||
| Sulphur | 5,667 cwt. | 1,760 | .. | .. | ||
| Tanning materials— | ||||||
| Crude bark | 4,348 tons | 38,465 | .. | .. | ||
| Other kinds | .. | 4,771 | .. | .. | ||
| Tar | .. | 2,118 | .. | .. | ||
| Tarpaulins and tents | .. | 461 | £461 | 92 | 4 | 0 |
| Tea | 5,210,375 lb. | 197,127 | 5,088,581 lb. | 12,404 | 16 | 9 |
| Textile piece-goods other than silk, cotton, linen, or woollen | .. | 18, 109 | £17,134 | 3,426 | 17 | 5 |
| Articles made up from, other than apparel | .. | 11,439 | £11,192 | 2,797 | 18 | 11 |
| Timber— | ||||||
| Laths and shingles | 547,249 No. | 552 | 547,240 No. | 54 | 14 | 6 |
| Logs | 1,906 No. | 9,122 | .. | .. | ||
| Logs, hewn | 5,355,357 sup. ft | 65,631 | .. | .. | ||
| Palings | 498,095 No. | 3,118 | 498,095 No. | 498 | 1 | 9 |
| Posts | 11,281 No. | 413 | 11,281 No. | 45 | 2 | 5 |
| Rails | 3,615 No. | 115 | 3,615 No. | 7 | 5 | 1 |
| Sawn, undressed | 7,045,373 sup. ft. | 65,154 | 5,448,800 sup. ft. | 5,448 | 16 | 0 |
| Sawn, dressed | 69,057 sup. ft. | 1,577 | 69,057 sup. ft. | 138 | 2 | 4 |
| Unenunerated | .. | 879 | .. | .. | ||
| Tin— | ||||||
| Block | 2,944 cwt. | 18,468 | .. | .. | ||
| Foil | 21,704 lb. | 1,108 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheet | 59,620 cwt. | 52,185 | .. | .. | ||
| Tinware | .. | 12,275 | £12,272 | 3,067 | 18 | 10 |
| Tinsmiths' furnishings and fittings | .. | 1,754 | .. | .. | ||
| Tobacco— | ||||||
| Unmanufactured | 49,929 lb. | 2,417 | 42,580 lb. | 4,258 | 0 | 9 |
| Manufactured | 1,759,636 lb. | 137,990 | 1,657,223 lb. | 290,014 | 4 | 9 |
| Cigars | 79,447 lb. | 27,312 | 78,453 lb. 76,152,000 No. | 27,458 | 10 | 4 |
| Cigarettes | 183,850 lb. | 44,692 | 10,380 oz. | 259 | 10 | 0 |
| Snuff | 2,121 lb. | 223 | 1,832 lb. | 641 | 4 | 0 |
| Tobacco-pipes and cases, &c. | .. | 24,550 | £24,665 | 6,160 | 5 | 0 |
| Tools and implements— | ||||||
| Axes and hatchets | .. | 10,670 | .. | .. | ||
| Engineers' machine tools | .. | 25,336 | .. | .. | ||
| Scythes | .. | 1,455 | .. | .. | ||
| Sheep-shears | .. | 2,685 | .. | .. | ||
| Spades, shovels, and forks | .. | 13,654 | .. | .. | ||
| Unenumerated | .. | 88,273 | .. | .. | ||
| Tramway plant | .. | 24,917 | £24,065 | 4,813 | 0 | 0 |
| Turpentine, driers, and terebine | 109,040 lb. | 14,492 | .. | .. | ||
| Twine | 473,259 lb. | 15,538 | £14,014 | 2,082 | 16 | 0 |
| Binder | 83 cwt. | 274 | .. | .. | ||
| Nets and netting | .. | 1,302 | £1,344 | 268 | 18 | 0 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 270 | .. | .. | ||
| Umbrellas and parasols | .. | 18,574 | £18,646 | 3,729 | 5 | 2 |
| Materials for | .. | 3,473 | .. | .. | ||
| Varnish and gold-size | 36,931 galls. | 18,500 | 35,313 galls. | 3,531 | 6 | 10 |
| Vegetables, fresh, dried, and preserved | .. | 1,357 | £1,153 | 230 | 12 | 1 |
| Vinegar | 58,635 galls. | 6,628 | 59,032 galls. | 1,475 | 15 | 10 |
| Watches | 31,706 No. | 18,009 | £18,218 | 3,643 | 11 | 4 |
| Watchmakers' materials | .. | 554 | .. | .. | ||
| Wax— | ||||||
| Beeswax | 74 cwt. | 486 | .. | .. | ||
| Paraffin | 1,262,720 lb. | 14,903 | 1,262,700 lb. | 3,945 | 18 | 9 |
| Unenumerated | 2,074 cwt. | 66 | 1,762 lb. | 11 | 0 | 3 |
| Whiting and chalk | 10,825 cwt. | 1,168 | 10,825 cwt. | 541 | 4 | 9 |
| Wine— | ||||||
| Australian | 52,350 galls. | 18,376 | 54,475 galls. | 13,618 | 14 | 4 |
| Sparkling | 11,422 galls. | 21,391 | 10,225 galls. | 4,601 | 8 | 3 |
| Other kinds | 59,133 galls. | 20,583 | 61,747 galls. | 18,524 | 4 | 0 |
| Wooden ware | .. | 40,947 | £32,001 | 5,545 | 9 | 8 |
| Wool— | ||||||
| Greasy | 80,456 lb. | 4,003 | .. | .. | ||
| Scoured | 17,012 lb. | 910 | .. | .. | ||
| Washed | 784 lb. | 10 | .. | .. | ||
| Woollen piece-goods | .. | 363,798 | £367,412 | 73,482 | 9 | 10 |
| Blankets | 21,587 pairs | 8,736 | £8,621 | 1,724 | 5 | 6 |
| Woolpacks | 86,598 doz. | 31,568 | .. | .. | ||
| Woolpockets | 784 doz. | 394 | .. | .. | ||
| Yarns | .. | 7,627 | £7,667 | 1,533 | 8 | 0 |
| Coir, flax, and hemp | .. | 6,620 | .. | .. | ||
| Zinc manufactures— | ||||||
| Tiles, ridging, &c. | .. | 148 | £148 | 29 | 12 | 0 |
| Unenumerated | .. | 69 | £66 | 16 | 10 | 0 |
| Perforated sheet | 491 cwt. | 979 | .. | .. | ||
| Plain sheet | 6,860 cwt. | 8,441 | .. | .. | ||
| Spelter | 5,675 cwt. | 5,926 | .. | .. | ||
| Minor articles | .. | 7,900 | .. | .. | ||
| Articles and materials suited only for and to be used solely in the fabrication of goods in the colony | .. | 20,622 | .. | .. | ||
| Materials for cartridge-making | .. | 6,872 | .. | .. | ||
| Miscellaneous goods— | ||||||
| Manufactured | .. | 15,137 | .. | .. | ||
| Unmanufactured | .. | 4,733 | .. | .. | ||
| Vanilla beans | 10,431 lb. | 1,947 | .. | .. | ||
| Parcels-post | .. | 123,912 | .. | 22,737 | 7 | 5 |
| Excise Duties. | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Tobacco, manufactured | .. | .. | 2,095 | 12 | 0 | |
| Cigars | .. | .. | .. | 177 | 10 | 6 |
| Cigarettes made by hand | .. | .. | .. | 11 | 17 | 0 |
| Pharmacopœia tinctures, essences, extracts, and medicinal spirits containing more than 50 per cent. of proof spirit | .. | .. | .. | 2,248 | 3 | 7 |
| Pharmacopœia tinctures, &c., containing less than 50 per cent. of proof spirit | .. | .. | .. | 16 | 17 | 11 |
| Culinary and flavouring | .. | .. | .. | 182 | 18 | 10 |
| Perfumed spirits | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Toilet preparations | .. | .. | .. | 0 | 18 | 0 |
The Cook and Savage Islands, now part of New Zealand, have not been considered in the table of imports made up by the Department of Trade and Customs. Details of goods received from those islands in 1902 are given on page 295.
The Customs and excise duties received during the last five years are shown in detail, also the rate of revenue per head of mean population, inclusive and exclusive of Maoris, for each year:—
| — | 1898 | 1899 | 1900 | 1901 | 1902 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Including £89 excise duty on culinary and flavouring essences. † Including £149 excise duty on culinary and flavouring essences, and £11 on perfumed spirits. ‡ Including £89 excise duty on culinary and flavouring essences. § Including £173 duty on culinary and flavouring essences, and £19 on perfumed spirits. || Including £183 excise duty on culinary and flavouring essences, £5 perfumed spirits, and £1 toilet preparations. | |||||
| Customs Duties. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Spirits | 395,513 | 414,395 | 442,090 | 478,816 | 483,582 |
| Wine | 31,138 | 32,045 | 33,614 | 35,864 | 36,745 |
| Ale, Beer, &c. | 19,158 | 17,594 | 17,562 | 18,849 | 20,152 |
| Cigars, Cigarettes, and Snuff | 71,430 | 77,810 | 82,357 | 90,490 | 94,992 |
| Tobacco | 257,516 | 263,057 | 279,651 | 296,016 | 294,272 |
| Tea | 78,676 | 79,975 | 68,960 | 45,905 | 42,405 |
| Coffee, Cocoa, &c. | 5,463 | 6,968 | 5,285 | 4,647 | 5,288 |
| Sugar and Molasses | 154,355 | 162,787 | 168,876 | 173,055 | 185,484 |
| Opium | 5,501 | 6,139 | 6,426 | 6,618 | *271 |
| Other Goods by Weight | 187,758 | 192,987 | 178,554 | 151,286 | 166,687 |
| Other Goods by Weight ad valorem | 637,506 | 682,722 | 775,649 | 808,531 | 867,209 |
| Other Duties | 105,987 | 91,155 | 94,687 | 59,316 | 65,219 |
| Parcels-post | 11,725 | 14,368 | 16,643 | 22,405 | 22,737 |
| Totals, Customs Duties | 1,961,726 | 2,042,002 | 2,170,354 | 2,191,798 | 2,285,043 |
| Tinctures—New Zealand | *1,244 | †2,036 | ‡1,638 | §2,198 | ||2,454 |
| Cigars, Cigarettes, and Snuff — New-Zealand-manufactured | 152 | 91 | 129 | 174 | 190 |
| Tobacco — New - Zealand - manufactured | 2,282 | 2,323 | 2,376 | 2,596 | 2,096 |
| Beer—New Zealand | 75,164 | 78,265 | 85,141 | 89,185 | 89,742 |
| Totals, Excise Duties | 78,842 | 82,715 | 89,284 | 94,153 | 94,482 |
| £ | s. d. £ | s. d. £ | s. d. £ | s. d. £ | d. s. d. |
| Revenue from Customs Duties per head of mean population (excluding Maoris) | 2 13 3 | 2 14 5 | 2 16 10 | 2 16 10 | 2 17 3 |
| Ditto (including Maoris) | 2 10 6 | 2 11 8 | 2 14 0 | 2 13 5 | 2 14 4 |
| Revenue from Excise Duties per head of mean population (excluding Maoris | 0 2 1·7 | 0 2 2·5 | 0 2 4 | 0 2 5 | 0 2 4·4 |
| Ditto (including Maoris) | 0 2 0·4 | 0 2 1·1 | 0 2 2·7 | 0 2 3·5 | 0 2 3·5 |
The Customs revenue for the year 1902 amounted to £2,285,043, and the excise duties to £94,482. The revenue from Customs was £2 17s. 3d. per head of population excluding Maoris, and £2 14s. 4d. if they be included. In 1888 the Customs revenue was £2 6s. 2d. per head of European population, and from that time the proportion increased slowly year by year until 1892, when it reached £2 11s. 6d. per head. During the next two years there was a falling-off; but 1895 and following years, except for a slight fall in 1901, show increases, the proportion for 1902 being higher than in any year since 1882. Details for thirteen years are given:—
| Customs Revenue per Head of European Population. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | |
| 1890 | 2 | 9 | 3 |
| 1891 | 2 | 9 | 7 |
| 1892 | 2 | 11 | 6 |
| 1893 | 2 | 10 | 4 |
| 1894 | 2 | 6 | 4 |
| 1895 | 2 | 6 | 9 |
| 1896 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| 1898 | 2 | 13 | 3 |
| 1897 | 2 | 13 | 0 |
| 1899 | 2 | 14 | 5 |
| 1900 | 2 | 16 | 10 |
| 1901 | 2 | 16 | 4 |
| 1902 | 2 | 17 | 3 |
Dating from 1890, the taxation by way of Customs and excise duties together increased from £2 11s. 2d. in that year to £2 11s. 11d. in 1896, to £2 15s. 1d. in 1897, to £2 15s. 5d. in 1898, to £2 16s. 8d. in 1899, to £2 19s. 2d. in 1900, declined to £2 18s. 9d. in 1901, increasing again to £2 19s. 7d. in 1902.
There was an alteration of tariff in 1895 in certain items, but the amount of duty paid in 1902 bears a lesser proportion to the total value of imports (less specie) for that year than the duty paid in 1894, prior to the new tariff, to the imports of that year.
In the year 1900 certain duties were lowered and exemptions granted. Tea is now charged only 2d. per pound, instead of 4d.; currants and raisins are lowered to 1d. per pound; candles are 1d.; cocoa and roasted coffee, 3d. There is also reduction on stearine for match-making, on paraffin-wax, and wax matches. Patent and proprietary medicines bear 15 per cent. duty, also certain drugs and chemicals. Steam-engines, or parts thereof, are charged 5 per cent. The new exemptions are various.
With these circumstances there has been a greater import of taxable articles, which would seem to indicate that purchasing power had increased. It is at least certain that the value of imports rose from £5,990,177 (excluding specie), in 1894, to £10,958,038 in 1902, while the changes of tariff were being effected.
The tariff has been given in full in this book (see pages 85 to 101). The rates of duty levied include 16s. per gallon on spirits; 30s. per gallon on perfumed spirits; 7s. per pound on cigars and snuff; 17s. 6d. per 1,000 of 2 1/2 lb. and under, and 6d. per ounce weight over 2 1/2 lb. per 1,000, on cigarettes; 3s. 6d. per pound on manufactured and 2s. on unmanufactured tobacco. Sparkling wine is charged 9s. a gallon; Australian, 5s.; other kinds, 6s.; ale and beer, 2s. The duty on tea is 2d. the pound; on cocoa, chocolate, and chicory, 3d.; raw coffee, 2d.; roasted, 3d. Sugar, molasses, and treacle pay 1/2 d., and glucose 1d. per pound. Opium is charged 40s. per pound, but this article, in a form suitable for smoking, cannot now be legally imported. The Opium Prohibition Acts, 1901 and 1902, make the importation or possession of opium suitable for smoking illegal. The remainder of the Customs revenue, with small exception, is made up of charges on goods by weight, ad valorem duties, ranging from 5 to 40 per cent., and receipts from the foreign parcels-post. There is also an excise duty of 1s. per pound on tobacco; 1s. 6d. per pound on cigars, cigarettes, and snuff; 3d. per gallon on beer; 9d. per pound on tinctures, &c., manufactured in the colony, containing more than 50 per cent. of proof spirit, and 3d. per pound when less than 50 per cent. Also, 12s. per gallon on culinary flavouring-essences; and 20s. on perfumed spirits.
By “The Tobacco Excise Duties Act, 1896,” the excise duty on cigarettes made in the colony is now (from the 31st December, 1896) 2s. 6d. per pound on machine-made and 1s. per pound on hand-made cigarettes.
“The Tobacco Act Amendment Act, 1896,” enacts that all packages of manufactured tobacco shall be labelled before leaving the manufactory, and provides for the issue of warrants to use cutting-machines for cutting duty-paid manufactured tobacco for sale (or to be used in the manufacture of cigarettes by hand), and to manufacture cigarettes by hand, under certain conditions.
The duties authorised by “The Timber Export Act, 1901,” will be found given on page 100 in detail with the full tariff.
Table of Contents
THE value of all the exports in 1902, exclusive of horses and forage sent to South Africa with the New Zealand Contingents, but inclusive of specie (£9,518), was £13,644,977; the value of New Zealand produce exported, £13,498,599: an average of £16 18s. 5d. per head of population, against £16 6s. 3d. for the previous year. The increase in the value of exports of New Zealand produce for 1902 in respect of that for 1901 amounts to £808,139, or 6·37 per cent.
The values of exports for the years 1892 and 1902 to the United Kingdom, the Australian States, with other British possessions, and to foreign countries, show the extent and development of outward trade in regard to its distribution:—
| Countries. | 1892 | 1902 |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 7,483,618 | 9,450,648 |
| New South Wales | 699,933 | 1,118,193 |
| Victoria | 520,646 | 1,295,233 |
| Queensland | 52,944 | 62,988 |
| Western Australia | 32,949 | 132,907 |
| South Australia | 31,695 | 34,033 |
| Tasmania | 29,147 | 40,996 |
| Other British possessions (excluding Hongkong, Norfolk Island, and Fiji) | 4,426 | 763,887 |
| China (including Hongkong) | 4,109 | 66,396 |
| United States | 520,797 | 489,964 |
| Other foreign ports | 154,587 | 189,732 |
| £9,534,851 | £13,644,977 |
A comparative table showing the values of New Zealand domestic exports, according to their nature, for fifteen years will be found further on, with comments. The continuous rise observed from 1895 to 1900 was, as remarked last year, arrested in 1901, but the decline in that year is more than balanced by the large increase in 1902, which shows the highest value of goods exported yet recorded in the annals of the colony.
But first a comparative statement of exports according to value for the last two years is given, showing the amounts for various principal articles, being the produce or manufacture of the colony, classified in groups:—
| Year 1901. | Year 1902. | Increase in 1902. | Decrease in 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Mine. | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Coal | 142,176 | 154,747 | 12,571 | .. |
| Gold | 1,753,784 | 1,951,426 | 197,642 | .. |
| Silver and minerals | 74,003 | 77,038 | 3,035 | .. |
| Total | 1,969,963 | 2,183,211 | 213,248 | .. |
| The Fisheries. | ||||
| Fish | 17,851 | 16,015 | .. | 1,836 |
| Oysters | 3,201 | 2,867 | .. | 334 |
| Other | 965 | 1,542 | 577 | .. |
| Total | 22,017 | 20,424 | .. | 1,593 |
| The Forest. | ||||
| Fungus | 12,453 | 10,257 | .. | 2,196 |
| Kauri-gum | 446,114 | 450,223 | 4,109 | .. |
| Timber— | ||||
| Sawn and hewn | 294,699 | 208,005 | .. | 86,694 |
| Other | 1,191 | 2,477 | 1,286 | .. |
| Total | 754,457 | 670,962 | .. | 83,495 |
| Animals and Produce. | ||||
| Bacon and hams | 17,732 | 18,590 | 858 | .. |
| Beef and pork (salted) | 10,225 | 9,837 | .. | 388 |
| Butter | 882,406 | 1,205,802 | 323,396 | .. |
| Cheese | 238,685 | 103,539 | .. | 75,146 |
| Hides | 43,470 | 44,546 | 1,076 | .. |
| Live-stock | 16,518 | 113,959 | 97,441 | .. |
| Preserved meats | 87,683 | 123,534 | 35,851 | .. |
| Frozen meat | 2,253,262 | 2,718,763 | 465,501 | .. |
| Rabbit-skins | 57,046 | 52,566 | .. | 4,480 |
| Sausage-skins | 39,498 | 61,167 | 21,669 | .. |
| Sheepskins and pelts | 264,579 | 375,876 | 111,297 | .. |
| Tallow | 351,710 | 550,131 | 198,421 | .. |
| Wool | 3,699,103 | 3,354,563 | .. | 344,540 |
| Other | 7,280 | 11,995 | 4,715 | .. |
| Total | 7,969,197 | 8,804,868 | 835,671 | .. |
| Agricultural Products. | ||||
| Bran and sharps | 15,294 | 39,523 | 24,229 | .. |
| Chaff | 92 | 1,705 | 1,613 | .. |
| Flour | 8,495 | 3,613 | .. | 4,882 |
| Grain— | ||||
| Barley | 13,241 | 25,062 | 11,821 | .. |
| Beans and peas | 20,028 | 22,097 | .. | 3,931 |
| Maize | 15,085 | 40,417 | 25,332 | .. |
| Malt | 32,252 | 705 | .. | 31,547 |
| Oats | 922,301 | 666,664 | .. | 255,637 |
| Wheat | 270,111 | 31,074 | .. | 245,037 |
| Hops | 17,189 | 14,292 | .. | 2,897 |
| Oatmeal | 27,591 | 21,578 | .. | 6,013 |
| Potatoes | 90,658 | 72,807 | .. | 17,851 |
| Seeds (grass and clover) | 69,937 | 84,861 | 14,924 | .. |
| Other | 18,112 | 21,588 | 3,476 | .. |
| Total | £1,532,386 | £1,045,986 | .. | £486,400 |
| Manufactures. | ||||
| Apparel | 7,227 | 2,267 | .. | 4,960 |
| Leather | 112,400 | 92,636 | .. | 19,761 |
| Phormium (New Zealand hemp) | 195,728 | 534,031 | 338,303 | .. |
| Woollen manufactures | 13,759 | 6,664 | .. | 7,095 |
| Other manufactures | 96,028 | 119,634 | 23,606 | .. |
| Total | 425,142 | 755,232 | 330,090 | .. |
| Miscellaneous | 17,298 | 17,916 | 618 | .. |
| Total exports (colonial produce and manufactures) | 12,690,460 | 13,498,599 | 808,139 | .. |
| Specie | 11,614 | 9,518 | .. | 2,096 |
| Other exports (British and foreign) | 179,350 | 136,860 | .. | 42,490 |
| Total exports | £12,881,424 | £13,644,977 | £763,553 | .. |
The class designated “Animals and Produce” shows by far the greatest value, the sum for 1902 being £8,804,868, which includes £3,354,563 for wool and £2,718,763 for frozen meat. The total value of exports in this class increased during the year by £835,671, on a total of £7,969,197 in 1901.
Although the value of wool exported in 1902 is less than that for the previous year, the quantity will be found greater.
“The Mine” takes second place among the classes for total value, with an export of coal, gold, silver, and other minerals amounting to £2,183,211 for 1902, being an increase of £213,248 on £1,969,963, the export for the previous year.
“Agricultural Products,” principally grain, potatoes, and seeds, take third place, but show a decrease of £486,400 on the value exported in 1901, oats and wheat falling off considerably.
“The Forest” shows an export for last year valued at £670,962, which gives a decrease of £83,495 on the figures for the previous year, timber being accountable for nearly the whole shortage.
“Manufactures” are set down at £755,232 in 1902, being £330,090 more than in the previous year. Phormium shows the remarkable increase on the operations for 1901 of £338,303. Woollen manufactures sent abroad decreased by £7,095, and leather by £19,764.
The smallest group in respect to value is “The Fisheries.” The total for the group was £20,424 last year.
The exports of New Zealand produce or manufacture for the two last years have also to be considered in relation to quantity, and the articles are again grouped in the next table according to the same classification as that used for purposes of comparing the values.
| Quantities of the Principal Articles of New Zealand Produce exported. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items. | Year 1901. | Year 1992. | Increase in 1902. | Decrease in 1902. | |
* At 20 lb. to the bushel. | |||||
| The Mine:— | |||||
| Coal | Tons | 159,643 | 188,677 | 29,034 | .. |
| Gold | Oz. | 455,558 | 507,852 | 52,294 | .. |
| Silver | Oz. | 571,134 | 674,196 | 103,062 | .. |
| Minerals | Tons | 945 | 607 | .. | 338 |
| The Fisheries:— | |||||
| Fish | Cwt | 11,020 | 9,611 | .. | 1,409 |
| Oysters | Doz. | 383,680 | 339,685 | .. | 43,995 |
| Whalebone | Lb. | 1,232 | 1,680 | 448 | .. |
| The Forest:— | |||||
| Fungus | Cwt. | 5,902 | 4,632 | .. | 1,270 |
| Gum (kauri) | Tons | 7,541 | 7,430 | .. | 111 |
| Timber (sawn and hewn) | Ft. | 71,822,369 | 49,251,549 | .. | 22,570,820 |
| Animals and Produce:— | |||||
| Bacon and hams | Cwt. | 5,500 | 5,910 | 410 | .. |
| Beef and pork (salted) | Cwt. | 8,281 | 8,020 | .. | 261 |
| Butter | Cwt. | 201,591 | 253,998 | 52,407 | .. |
| Cheese | Cwt. | 104,294 | 74,746 | .. | 29,548 |
| Hides | No. | 47,875 | 45,038 | .. | 2,837 |
| Live-stock (cattle, horses, sheep, pigs) | No. | 4,298 | 52,743 | 48,445 | .. |
| Meats (preserved) | Cwt. | 35,258 | 54,271 | 19,013 | |
| Meats (frozen) | No. | 1,857,547 | 2,138,557 | 281,010 | .. |
| Sausage-skins | No. | 9,133 | 13,398 | 4,265 | .. |
| Skins (rabbit) | No. | 7,112,008 | 6,139,794 | .. | 972,214 |
| Skins (sheep) and pelts | No. | 4,601,531 | 6,144,680 | 1,543,149 | .. |
| Tallow | Cwt. | 335,360 | 424,060 | 88,700 | |
| Wool | Lb. | 146,820,079 | 160,419,023 | 13,598,944 | |
| Agricultural Products:— | |||||
| Bran and sharps | Tons | 4,754 | 7,737 | 2,983 | .. |
| Chaff | Tons | 28 | 356 | 328 | .. |
| Flour | Tons | 1,305 | 370 | .. | 935 |
| Grain, barley | Bush. | 119,779 | 151,360 | 31,581 | .. |
| Grain, beans and peas | Bush | 166,184 | 102,314 | .. | 63,870 |
| Grain, maize | Bush | 124,447 | 225,829 | 100,382 | .. |
| Grain, malt | Bush | 141,324 | 2,865 | .. | 138,459 |
| Grain, oats | Bush | 10,514,924 | 5,185,812 | .. | 5,329,112 |
| Grain, wheat | Bush | 2,301,092 | 194,671 | .. | 2,106,421 |
| Hops | Cwt. | 4,298 | 4,311 | 13 | .. |
| Oatmeal | Tons | 3,323 | 1,804 | .. | 1,519 |
| Potatoes | Tons | 22,062 | 17,715 | .. | 4,347 |
| Seeds (grass and clover) Bush* | 294,347 | 246,389 | .. | 47,958 | |
| Manufactures:— | |||||
| Ale and beer | Gals. | 19,449 | 25,892 | 6,443 | .. |
| Cordage | Cwt. | 647 | 820 | 173 | .. |
| Leather | Cwt. | 18,281 | 15,469 | .. | 2,812 |
| Phormium (New Zealand hemp) | Tons | 10,171 | 20,852 | 10,681 | .. |
| Soap | Cwt. | 6,014 | 5,770 | .. | 244 |
The numerical increases in such articles as butter, wool, coal, silver, gold, live-stock, frozen and preserved meat, tallow, sheepskins and pelts, barley, maize, beer, and phormium, are all most satisfactory, and in some cases very considerable; while, on the other hand, the export of timber, cheese, rabbitskins, malt, wheat, and oats, with some other items, declined in 1902. The rates of increase and decrease for the principal articles are exhibited in the table following:—
| Increases. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Export of | Rate of Increase per Cent. in 1902 over Quantity in 1901. | |
| Chaff | Tons | Over 100 |
| Live-stock | No. | Over 100 |
| Phormium | Tons | 105·01 |
| Maize | Bush. | 80·66 |
| Bran and sharps | Tons | 62·75 |
| Meats (preserved) | Cwt. | 53·93 |
| Sausage-skins | Cwt. | 46·70 |
| Whalebone | Lb. | 36·36 |
| Sheepskins and pelts | No. | 33·54 |
| Ale and beer | Gals. | 33·13 |
| Cordage | Cwt. | 26·74 |
| Tallow | Cwt. | 26·45 |
| Barley | Bush. | 26·37 |
| Butter | Cwt. | 26·00 |
| Coal | Tons | 18·19 |
| Silver | Oz. | 18·04 |
| Meat (frozen) | Cwt. | 15·13 |
| Gold | Oz. | 11·48 |
| Wool | Lb. | 9·26 |
| Bacon and hams | Cwt. | 7·45 |
| Hops | Cwt. | 0·30 |
| Decreases. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Export of | Rate of Decrease per Cent. in 1902 over Quantity in 1901. | |
| Malt | Bush. | 97·97 |
| Wheat | Bush. | 91·54 |
| Flour | Tons | 71·65 |
| Oats | Bush. | 50·68 |
| Oatmeal | Tons | 45·71 |
| Beans and peas | Bush. | 38·43 |
| Minerals | Tons | 35·77 |
| Timber | Ft. | 31·43 |
| Cheese | Cwt. | 28·33 |
| Fungus | Cwt. | 21·52 |
| Potatoes | Tons | 19·70 |
| Seeds | Bush. | 16·29 |
| Leather | Cwt. | 15·38 |
| Rabbitskins | No. | 13·67 |
| Fish | Cwt. | 12·79 |
| Oysters | Doz. | 11·47 |
| Hides | No. | 5·93 |
| Soap | Cwt. | 4·06 |
| Beef and pork (salted) | Cwt. | 3·15 |
| Gum (Kauri) | Tons | 1·47 |
The position as to value in respect of a period of fifteen years, 1888 to 1902 inclusive, is presented in a table giving the domestic exports for each. The most important items of export given under the heading “Other New Zealand Produce” are coal, silver, minerals, fish, oysters, fungus, kauri-gum, timber, bacon and hams, salted and preserved meats, tallow, sheep and rabbit skins, hides, sausage-skins, and live-stock. The aggregate value of these in 1902 was £2,274,377.
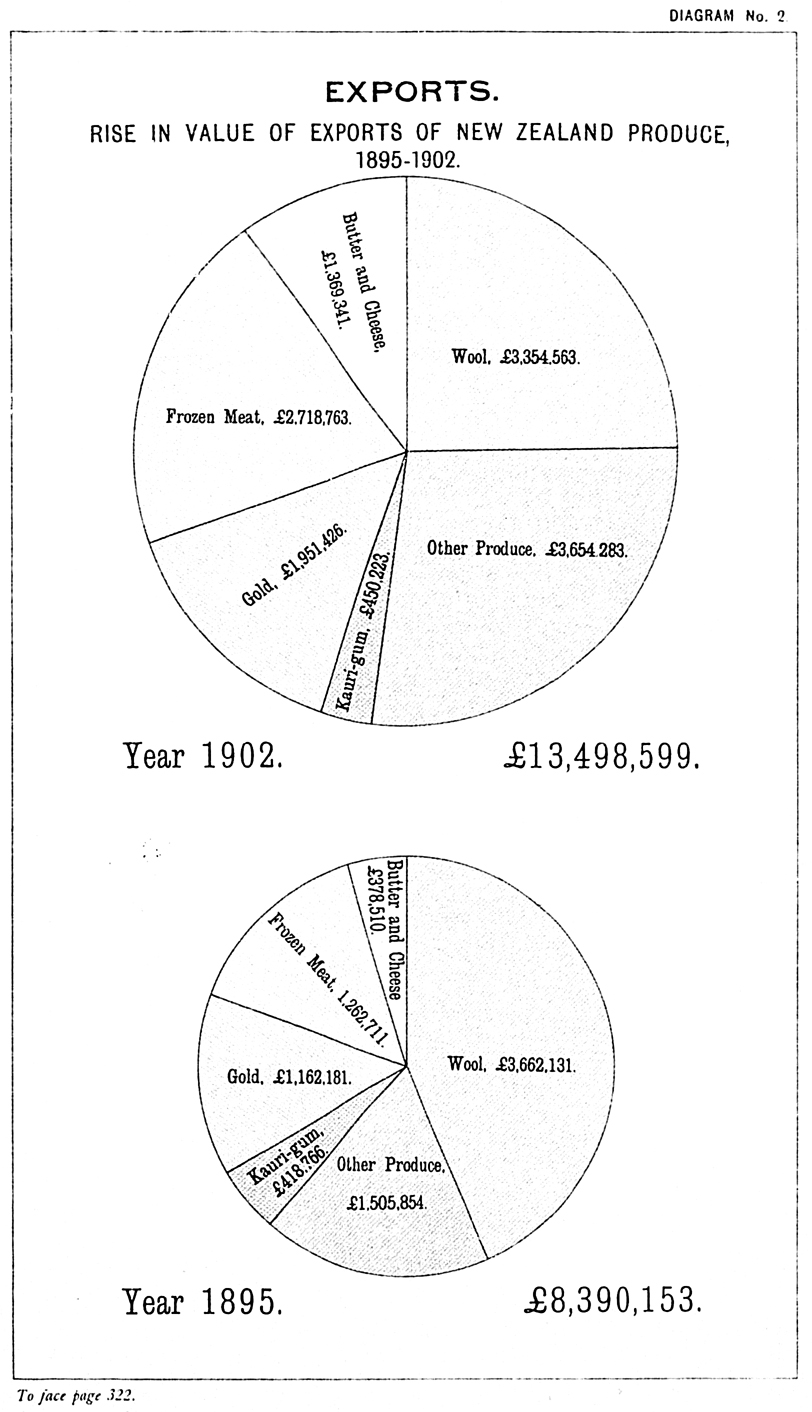
EXPORTS. RISE IN VALUE OF EXPORTS OF NEW ZEALAND PRODUCE, 1895–1902.
| Exports of New Zealand Produce. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calender Year. | Wool. | Gold. | Frozen Meat. | Butter and Cheese. | Agricultural Produce. | Manufactures | Other N.Z. Produce. | Total. |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1888 | 3,115,098 | 914,309 | 628,800 | 197,170 | 905,907 | 233,383 | 1,260,461 | 7,250,128 |
| 1889 | 3,976,375 | 785,490 | 783,374 | 213,945 | 1,424,297 | 569,880 | 1,288,647 | 9,042,008 |
| 1890 | 4,150,599 | 751,360 | 1,087,617 | 207,687 | 1,289,864 | 547,947 | 1,393,687 | 9,428,761 |
| 1891 | 4,129,686 | 1,007,172 | 1,194,724 | 236,933 | 894,467 | 420,357 | 1,516,755 | 9,400,094 |
| 1892 | 4,313,307 | 951,963 | 1,033,377 | 318,204 | 1,035,637 | 367,677 | 1,345,703 | 9,365,868 |
| 1893 | 3,774,738 | 915,921 | 1,085,107 | 354,271 | 716,546 | 345,636 | 1,365,164 | 8,557,443 |
| 1894 | 4,827,016 | 887,865 | 1,194,545 | 366,483 | 317,655 | 224,958 | 1,266,626 | 9,085,148 |
| 1895 | 3,662,131 | 1,162,181 | 1,262,711 | 378,510 | 326,029 | 188,702 | 1,409,889 | 8,390,153 |
| 1896 | 4,391,848 | 1,041,428 | 1,251,993 | 411,882 | 572,355 | 198,081 | 1,309,749 | 9,177,330 |
| 1897 | 4,443,144 | 980,204 | 1,566,286 | 553,122 | 495,175 | 197,601 | 1,360,735 | 9,596,267 |
| 1898 | 4,645,804 | 1,080,691 | 1,698,750 | 539,466 | 410,677 | 253,805 | 1,695,795 | 10,324,988 |
| 1899 | 4,324,627 | 1,513,180 | 2,088,856 | 713,617 | 913,678 | 378,066 | 1,867,716 | 11,799,740 |
| 1900 | 4,749,196 | 1,439,602 | 2,123,881 | 969,731 | 1,230,565 | 549,342 | 1,992,932 | 13,055,249 |
| 1901 | 3,699,103 | 1,753,784 | 2,253,262 | 1,121,091 | 1,532,386 | 425,142 | 1,905,692 | 12,690,400 |
| 1902 | 3,354,563 | 1,951,426 | 2,718,763 | 1,869,341 | 1,045,986 | 755,232 | 2,302,288 | 13,498,599 |
The preceding table shows that the value of the exports of New Zealand produce fell from £9,428,761 in 1890 to £8,390,153 in 1895, rose in 1896 to £9,177,336, in 1897 to £9,596,267, in 1898 to £10,324,988, in 1899 to £11,799,740, in 1900 to £13,055,249, in 1901 declined to £12,690,460, but in 1902 increased to £13,498,599, the highest value yet attained in any one year.
Thus there was a net increase of exports, since 1895, to the value of £5,108,446, all New Zealand produce, and far more than a recovery to the figures for 1890 and 1891 (after which had followed a decrease in values). With the amount of increase in money must be considered the state of prices of the various kinds of produce.
The export of wool, measured by quantity, rose from 102,817,077 lb. in 1890 to 160,419,023 lb. in 1902, or at the rate of 56·02 per cent., and that of frozen meat from 898,894 cwt. to 2,138,557 cwt.
Gold, too, which was exported to the quantity of 187,641 oz. in 1890, increased to 507,852 oz. in 1902, the rate of increase being 170·65 per cent.
The re-export trade of the colony would seem from the subjoined figures to have been almost stationary for the last thirteen years, the figures for 1890 and 1902 only differing by a sum of £3,695. The re-exports of merchandise in 1902 were valued at £136,860, or only 1 per cent. of the total exports, excluding specie.
| Exports of British, Foreign, and other Colonial Produce (excluding Specie). | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1890 | 140,555 |
| 1891 | 160,765 |
| 1892 | 125,052 |
| 1893 | 123,402 |
| 1894 | 136,402 |
| 1895 | 127,900 |
| 1897 | 144,955 |
| 1998 | 124,850 |
| 1899 | 123,682 |
| 1900 | 168,009 |
| 1901 | 179,350 |
| 1902 | 136,680 |
| 1896 | 122,571 |
With these sums may be contrasted the re-export trade of New South Wales—a State having somewhat less than double the population of New Zealand—which, exclusive of specie, amounted in 1901 to £3,458,023, or no less than 15·04 per cent. of the value of all goods exported.
The exports from the North and Middle Islands respectively, excluding “Parcels-post,” during the last four years were as under:—
| Year. | North Island. | Middle Island. | Proportion to North Island. | Total Export. Middle Island. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |||
| 1899 | 6,011,239 | 5,916,290 | 50·40 | 49·60 |
| 1900 | 6,707,964 | 6,526,397 | 50·70 | 49·30 |
| 1901 | 6,077,724 | 6,787,546 | 47·24 | 52·70 |
| 1902 | 7,085,275 | 6,543,389 | 51·99 | 48·01 |
The North Island exported in 1902 more than half of the total for the two Islands.
The following are the values of exports to different countries or places in 1902 and 1901, arranged in order of magnitude of increase or decrease in later year to each:—
| Country, Colony, State, &c. | 1902 | 1901 | Increase. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Victoria | 1,295,233 | 754,833 | 540,400 |
| United Kingdom | 9,450,648 | 9,295,375 | 155,273 |
| United States (East Coast) | 447,623 | 332,175 | 115,448 |
| New South Wales | 1,118,193 | 1,024,065 | 94,128 |
| Queensland | 62,988 | 23,411 | 39,577 |
| Western Australia | 132,907 | 95,319 | 37,588 |
| Hongkong | 66,354 | 29,792 | 36,502 |
| Fiji | 59,690 | 43,709 | 15,981 |
| Friendly Islands | 36,980 | 30,502 | 6,478 |
| Navigator Islands | 36,537 | 25,047 | 5,490 |
| Brazil | 4,909 | 252 | 4,657 |
| British Columbia | 4,348 | 1,371 | 2,977 |
| Canada | 3,018 | 747 | 2,271 |
| Philippine Islands | 2,193 | .. | 2,193 |
| Japan | 3,780 | 1,640 | 2,140 |
| Uruguay | 1,877 | 126 | 1,751 |
| Denmark | 5,966 | 4,888 | 1,078 |
| Norfolk Island | 3,549 | 2,485 | 1,064 |
| Portuguese East Africa | 1,045 | 611 | 434 |
| Belgium | 394 | 14 | 380 |
| New Caledonia | 2,011 | 1,735 | 276 |
| Sandwich Islands | 1,713 | 1,524 | 189 |
| Marshall Islands | 140 | .. | 140 |
| Transvaal Colony | 122 | .. | 122 |
| New Hebrides | 125 | 23 | 102 |
| Singapore | 284 | 211 | 73 |
| Java | 40 | .. | 40 |
| Caroline Islands | 453 | 425 | 33 |
| Italy | 32 | .. | 32 |
| Falkland Islands | 15 | .. | 15 |
| Rhodesia | 13 | .. | 13 |
| Bombay | 54 | 42 | 12 |
| Surprise Island | 22 | 10 | 12 |
| New Britain | 595 | 585 | 10 |
| Guam | 32 | 16 | 6 |
| Chili | 4 | .. | 4 |
| Orange River Colony | 3 | .. | 3 |
| Norway | 3 | .. | 3 |
| Peru | 2 | .. | 2 |
| Country, Colony, State, &c. | 1902 | 1901 | Decrease. |
|---|---|---|---|
* These Islands are now annexed to New Zealand. The value of goods forwarded to them last year was £22,973. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| United States (West Coast) | 42,341 | 186,904 | 144,563 |
| Cape Colony | 79,213 | 119,758 | 40,545 |
| Natal | 674,708 | 705,107 | 30,399 |
| Cook Islands* | .. | 21,849 | 21,849 |
| China | 42 | 15,407 | 15,365 |
| Tasmania | 40,996 | 53,260 | 12,264 |
| South Australia | 34,033 | 42,943 | 8,910 |
| Bengal | 1,728 | 9,550 | 7,822 |
| Spain | .. | 7,261 | 7,261 |
| Canary Islands | 44 | 5,740 | 5,696 |
| Society Islands | 23,393 | 27,612 | 4,219 |
| Savage Island* | .. | 1,883 | 1,883 |
| Germany | 9,389 | 10,470 | 1,081 |
| Sweden | 166 | 692 | 526 |
| Ceylon | 377 | 596 | 219 |
| Argentine Republic | 542 | 760 | 218 |
| Maiden Island | 1 | 205 | 204 |
| Switzerland | 42 | 132 | 90 |
| West Indies | .. | 90 | 90 |
| Antarctic Regions | 62 | 62 | |
| Holland | 42 | 100 | 58 |
| Austria | 12 | 59 | 47 |
| France | 15 | 36 | 21 |
| Asia Minor | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Madras | 2 | 6 | 4 |
| Burmah | 1 | 2 | 1 |
The quantity of wool exported in 1902, as previously shown, was 160,419,023 lb., valued at £3,354,563, an increase of 13,598,944 lb., or 9·26 per cent. on the quantity exported in the previous year, but a decrease of £344,540, or 9·31 per cent. on the value. The annual production of wool is best estimated by taking the exports for the twelve months immediately preceding the commencement of shearing, and adding thereto the quantity used in the colony for manufacturing purposes.
The following shows the produce for each of the last fifteen years ending on the 30th September:—
| Year ending 30th September. | Quantity exported. | Quantity purchased by Local Mills. | Total Annual Produce. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lb. | Lb. | Lb. | |
| 1888 | 89,276,268 | 4,079,563 | 93,355,831 |
| 1889 | 95,618,507 | 3,556,004 | 99,174,511 |
| 1890 | 102,522,185 | 2,979,293 | 105,501,478 |
| 1891 | 108,619,473 | 2,918,073 | 111,537,546 |
| 1892 | 110,860,050 | 3,388,954 | 114,249,004 |
| 1893 | 119,643,874 | 2,629,855 | 122,273,729 |
| 1894 | 128,480,457 | 2,476,155 | 130,956,612 |
| 1895 | 129,333,769 | 3,299,132 | 132,632,901 |
| 1896 | 128,309,673 | 3,989,934 | 132,299,607 |
| 1897 | 134,410,955 | 3,298,469 | 137,709,424 |
| 1898 | 150,401,399 | 3,763,831 | 154,165,230 |
| 1899 | 143,644,203 | 4,258,505 | 147,902,708 |
| 1900 | 144,829,515 | 3,223,392 | 148,052,907 |
| 1901 | 143,064,789 | 4,629,924 | 147,694,713 |
| 1902 | 155,652,563 | 4,203,312 | 159,855,875 |
From these figures it appears that, notwithstanding the apparent decrease from 1898 to 1901, the wool-clip has increased by over 71 per cent. during the last fifteen years.
To arrive at a perfectly correct estimate of the increase in wool-production it would be necessary to take into consideration the proportion of greasy, scoured (and sliped), and washed wool exported each year, the washing process of course greatly reducing the weight. The percentages of greasy, scoured, and washed wool to the total quantities exported during the last five years are:—
| Years. | Greasy. Per Cent. | Scoured and Sliped. Per Cent. | Washed. Per Cent. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1898 | 78·62 | 20·36 | 1·02 |
| 1899 | 77·54 | 21·64 | 0·82 |
| 1900 | 78·62 | 20·10 | 1·28 |
| 1901 | 78·25 | 20·61 | 1·14 |
| 1902 | 73·82 | 24·26 | 1·92 |
The increase in the wool-production is, of course, mainly due to the greater number of sheep—namely, 20,342,727 in April, 1902, against 15,423,328 in May, 1889. A comparative statement for several years is supplied, showing the number of flocks in groups of sizes:—
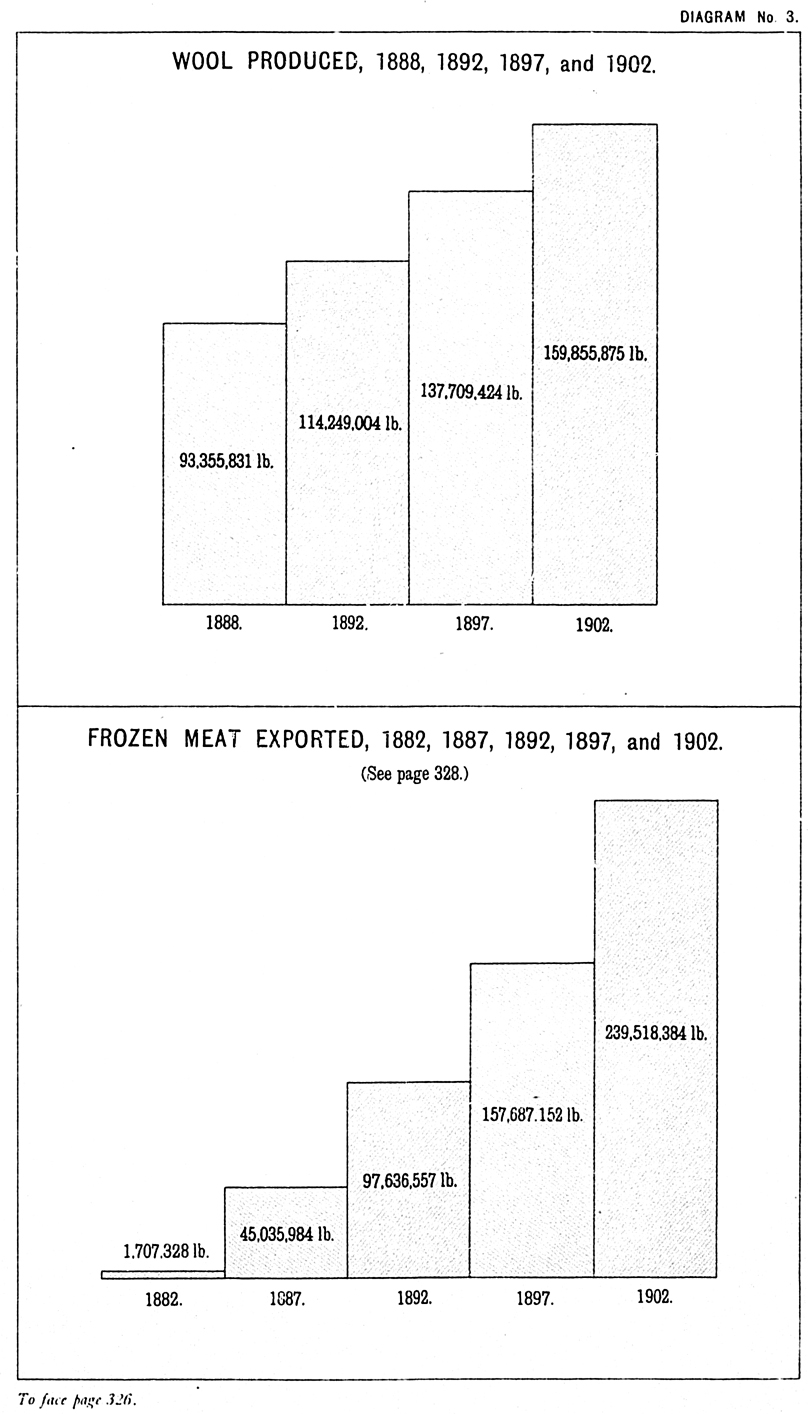
WOOL PRODUCED, 1888, 1892, 1897, and 1902. FROZEN MEAT EXPORTED, 1882, 1887, 1892, 1897, and 1902. (See page 328.)
| Number of Flocks, 1890 to 1902. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* From 1,000 to 2,500, 1,798 flocks; from 2,500 to 5,000, 614 flocks. † From 1,000 to 2,500, 1,971 flocks; from 2,500 to 5,000, 650 flocks. ‡ From 1,000 to 2,500, 2,232 flocks; from 2,500 to 5,000, 730 flocks. | |||||||
| Size of Flocks. | 1890 | 1892 | 1894 | 1896 | 1898 | 1900 | 1902 |
| Under 500 | 7,662 | 8,822 | 10,314 | 12,028 | 12,886 | 12,239 | 11,961 |
| 500 and under 1,000 | 1,528 | 2,033 | 2,427 | 2,605 | 2,708 | 2,810 | 3,158 |
| 1,000 and under 2,000 | 854 | 1,193 | 1,409 | 1,460 | 2,412* | 2,621† | 2,962‡ |
| 2,000 and under 5,000 | 586 | 761 | 933 | 892 | 2,412* | 2,621† | 2,962‡ |
| 5,000 and under 10,000 | 283 | 314 | 345 | 340 | 341 | 352 | 385 |
| 10,000 and under 20,000 | 236 | 231 | 230 | 231 | 231 | 196 | 206 |
| 20,000 and upwards | 160 | 176 | 179 | 147 | 144 | 139 | 131 |
| Totals | 11,309 | 13,530 | 15,837 | 17,703 | 18,722 | 18,357 | 18,803 |
It will be apparent that the general tendency of increase since the year 1890 is towards the multiplication of the smaller flocks, whose owners are better able to cope with the rabbit difficulty than the large runholders.
Prior to 1878 rabbit-skins were a very small item in the exports, but in that year the number sent out of the colony amounted to 3,951,209. Ten years after (1888) the export had risen to 11,809,407, from which it increased to 17,041,106 in 1893, the greatest number as yet exported in a year. From 1895 the fall was rapid, and the export for 1898 only reached 6,607,934 skins. In 1899 there was a slight upward tendency, the number exported being 7,891,648, which, however, fell to 5,690,893 in the year 1900. In 1901 7,122,008 skins were exported, and in 1902 only 6,139,794 skins.
The figures for the years in which there has been decline are quoted:—
| Year. | Number of Rabbit-skins exported. |
|---|---|
| 1893 | 17,041,106 |
| 1894 | 14,267,385 |
| 1895 | 15,229,314 |
| 1896 | 10,828,612 |
| 1897 | 8,099,334 |
| 1898 | 6,607,934 |
| 1899 | 7,891,648 |
| 1900 | 5,690,893 |
| 1901 | 7,112,008 |
| 1902 | 6,139,794 |
From the above it will be seen that the importance of the export has very much diminished. The fall, represented in money value, has been:—
| Year. | Value of Rabbit-skins exported. |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1893 | 138,952 |
| 1894 | 87,993 |
| 1895 | 85,022 |
| 1896 | 65,599 |
| 1897 | 47,472 |
| 1898 | 51,607 |
| 1899 | 81,118 |
| 1900 | 41,689 |
| 1901 | 57,046 |
| 1902 | 52,566 |
While the amount of money received for this produce of the colony shows less profit than formerly, it may be a satisfactory result, as seemingly indicating some abatement of the rabbit-pest. Large quantities of frozen rabbits are now exported, and are alluded to in the remarks on the frozen-meat industry on the next page.
These form a more important article of export at the present time than the rabbit-skins, though in the year 1888 the position was the reverse as regards value in money. In 1888 the number of sheepskins and pelts sent away from New Zealand was 1,646,401, against 6,144,680 in 1902, a rise of 273·22 per cent. for the period between those years. The value increased from £83,574 to £375,876, or 349·75 per cent. Figures for the last nine years are quoted:—
| Year. | Export of Sheepskins and Pelts. No. |
|---|---|
| No. | |
| 1894 | 2,681,552 |
| 1895 | 3,230,539 |
| 1896 | 3,001,791 |
| 1897 | 3,688,051 |
| 1898 | 4,995,325 |
| 1899 | 4,960,054 |
| 1900 | 4,669,430 |
| 1901 | 4,601,531 |
| 1902 | 6,144,680 |
Besides wool and meat, tallow is largely exported, and since the year 1888, when 136,460 cwt. were sent away, the export has increased to 424,060 cwt. in 1902. In value this export considerably exceeds that of either sheepskins or rabbit-skins, and the money is indeed more than the total for those two articles taken together. The nine latest years show the following results:—
| Tallow exported. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Years. | Cwt. | £ |
| 1894 | 199,400 | 204,499 |
| 1895 | 263,560 | 260,999 |
| 1896 | 222,540 | 208,821 |
| 1897 | 310,200 | 259,964 |
| 1898 | 347,160 | 302,141 |
| 1899 | 338,620 | 311,649 |
| 1900 | 367,780 | 368,473 |
| 1901 | 335,360 | 351,710 |
| 1902 | 424,060 | 550,131 |
Frozen meat now takes second place among the exports of New Zealand produce. In 1902, 2,138,557 cwt., valued at £2,718,763, were shipped in the colony. An account of the development of the industry was given in a special article in the Year-book, 1894. The total export for each year since the commencement of the trade has been:—
| Year. | Lb. |
|---|---|
| 1882 | 1,707,328 |
| 1883 | 9,853,200 |
| 1884 | 28,445,228 |
| 1885 | 33,204,976 |
| 1886 | 38,758,160 |
| 1887 | 45,035,984 |
| 1888 | 61,857,376 |
| 1889 | 73,564,064 |
| 1890 | 100,934,756 |
| 1891 | 110,199,082 |
| 1892 | 97,636,557 |
| 1893 | 100,262,453 |
| 1894 | 114,827,216 |
| 1895 | 127,018,864 |
| 1896 | 123,576,544 |
| 1897 | 157,687,152 |
| 1898 | 173,798,576 |
| 1899 | 208,972,624 |
| 1900 | 206,621,072 |
| 1901 | 208,045,264 |
| 1902 | 239,518,384 |
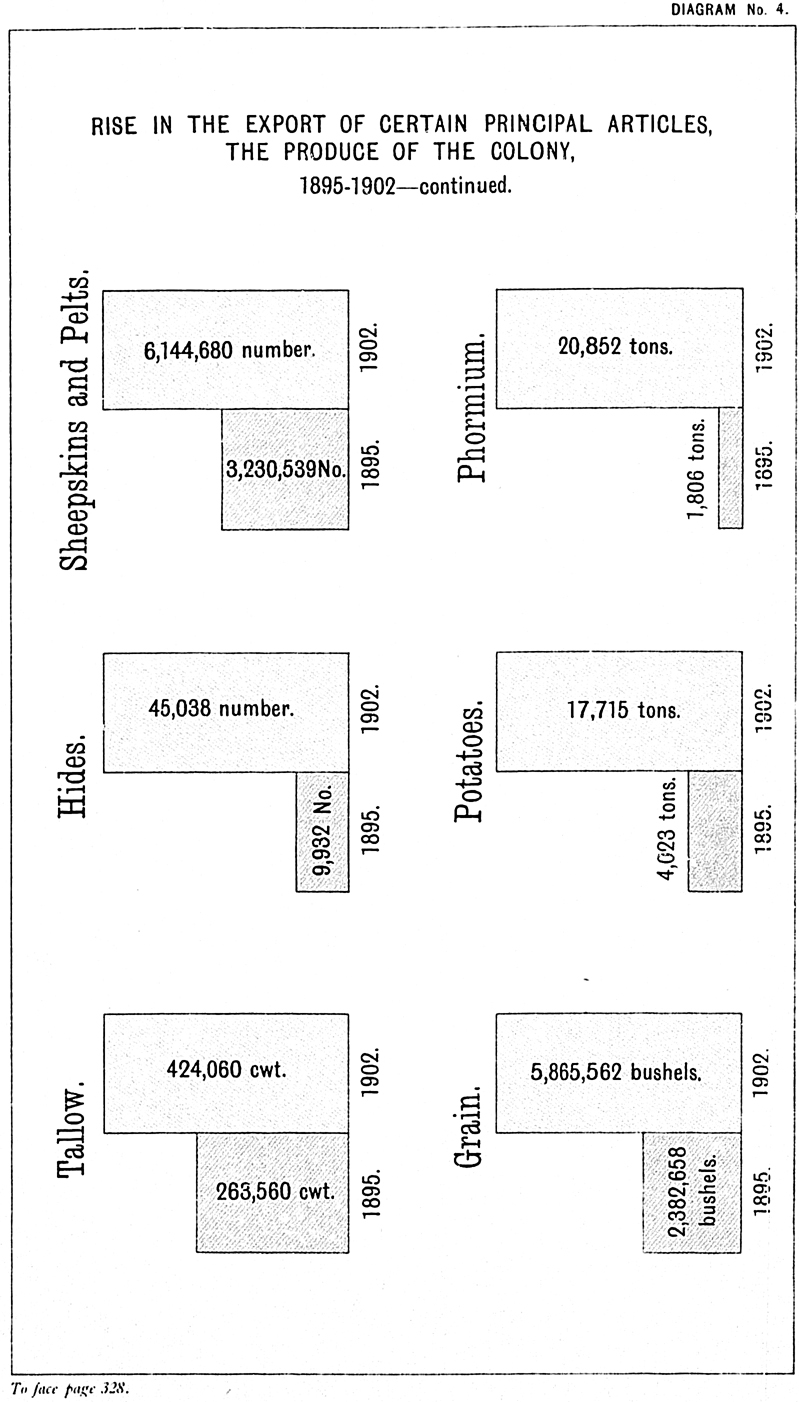
RISE IN THE EXPORT OF CERTAIN PRINCIPAL ARTICLES, THE PRODUCE OF THE COLONY, 1895–1902—
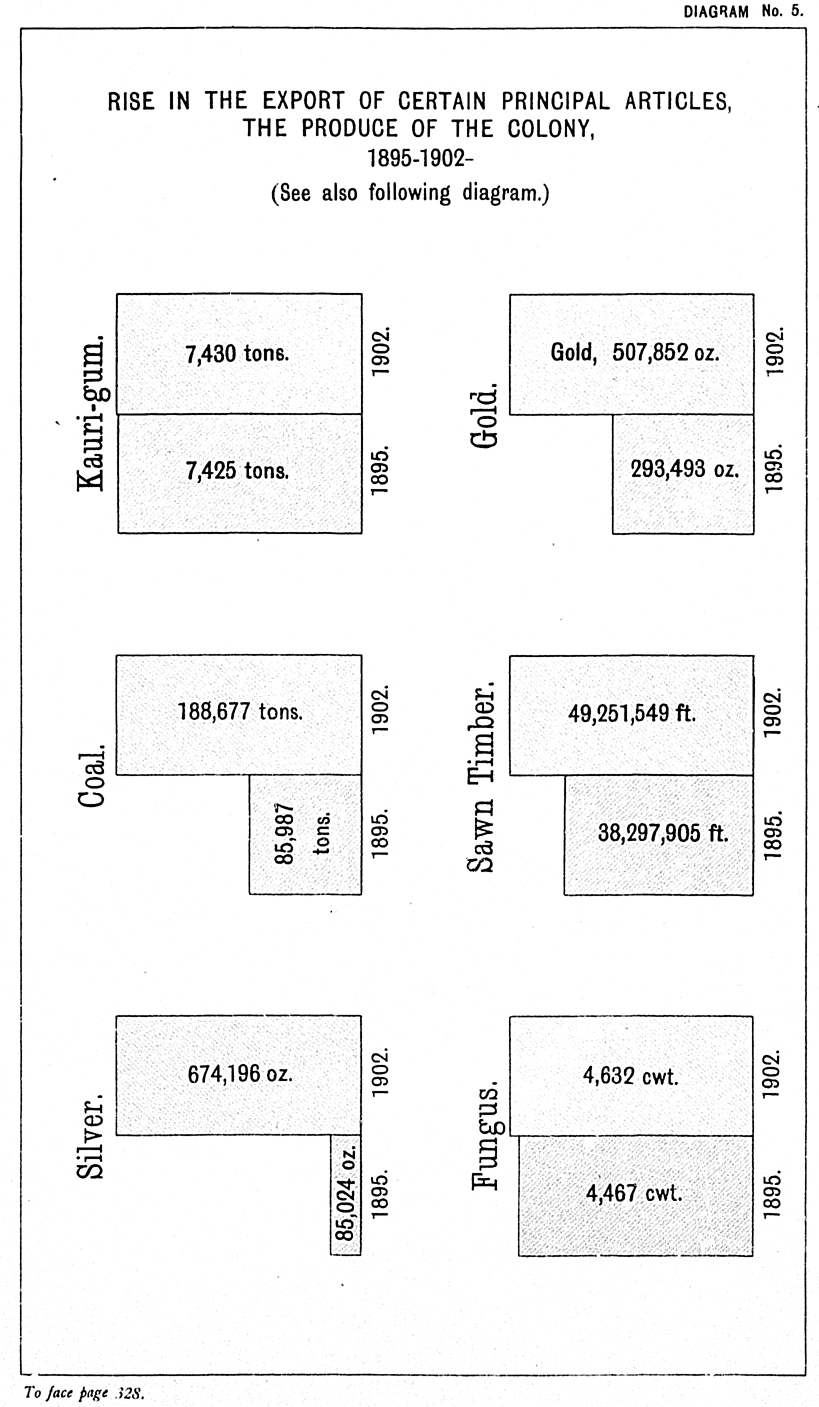
RISE IN THE EXPORT OF CERTAIN PRINCIPAL ARTICLES, THE PRODUCE OF THE COLONY, 1895–1902-(See also following diagram.)
The above figures for 1899 include 129,224 cwt., or 4,876,534 (number) of frozen rabbits and hares in the skin; those for 1900 include 12,260 (731 cwt.) of hares, and 6,501,997 rabbits, weighing 167,971 cwt., valued at £154,856, those for 1901, include 42,202 (2,943 cwt.) of hares, and 4,830,669 (124,353 cwt.) of rabbits, valued at £117,813, and those for 1902 include 23,421 (1,643 cwt.) of hares, and 4,776,914 (123,229 cwt.) rabbits, valued at £118,884, so that rabbits can hardly now be looked upon as wholly worthless, especially when the export of the skins, previously remarked upon, is further considered.
To ascertain the total value of the meat export in 1902 it is necessary to take into consideration, with the amount of £2,718,763, value of frozen meat before stated, £10,245 for frozen fish; also the value of preserved meats, £123,534; of salted beef and pork, £9,837; and of bacon and hams, £18,590.
The amount of gold exported in 1902 was 507,852 oz., an increase of 52,294 oz. on the quantity exported in 1901.
The total quantity of gold entered for duty to the 31st December, 1902, which may be reckoned as approximately the amount obtained in the colony, was 15,572,507 oz., of the value of £61,111,316. For fuller information, see special section on mining.
The value of the grain exported in 1902 was £786,548. The grain exports for 1901 and 1902 were made up as under:—
| 1901 | 1902 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushels. | £ | Bushels. | £ | |
| Wheat | 2,301,092 | 276,111 | 194,671 | 31,074 |
| Oats | 10,514,924 | 922,301 | 5,185,812 | 666,664 |
| Barley | 119,779 | 13,241 | 151,360 | 25,062 |
| Malt | 141,324 | 32,252 | 2,865 | 705 |
| Maize | 124,447 | 15,085 | 225,829 | 40,417 |
| Peas and beans | 166,184 | 26,028 | 102,314 | 22,097 |
| Rye and unenumerated | 5,765 | 793 | 2,711 | 529 |
| Total quantity and value | 13,373,515 | £1,285,811 | 5,865,562 | £786,548 |
Compared with the previous year the quantity and value of grain exported in 1902 show a considerable decrease.
From the year 1890 to 1898, inclusive, the decline in the export of wheat was very great, while for 1899–1900 and 1901 there was a revival, as will be seen by the following figures. But for 1902 the quantity sent out of the colony fell to less than 200,000 bushels:—
| Year. | Wheat exported. Bushels. |
|---|---|
| Bushels. | |
| 1890 | 4,467,026 |
| 1892 | 2,460,774 |
| 1894 | 228,904 |
| 1896 | 453,123 |
| 1898 | 10,090 |
| 1899 | 2,901,676 |
| 1900 | 2,867,069 |
| 1901 | 2,301,092 |
| 1902 | 194,671 |
The imports of wheat during 1898 exceeded the exports by upwards of 50,000 bushels, but in 1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902 the imports were practically nil, the small quantity introduced into the colony being for seeding purposes only.
In oats, the quantity exported in 1902 shows a large decrease over that for the previous year:—
| Year. | Export of Oats. Bushels. |
|---|---|
| 1891 | 4,052,414 |
| 1892 | 3,830,444 |
| 1894 | 1,963,288 |
| 1896 | 2,247,053 |
| 1898 | 816,210 |
| 1899 | 3,520,734 |
| 1900 | 5,818,648 |
| 1901 | 10,514,924 |
| 1902 | 5,185,812 |
The acreages under cereals for the last four years have been:—
| 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Land in wheat (for threshing) | 269,749 | 206,465 | 163,462 | 194,355 |
| Land in oats (for threshing) | 398,243 | 449,534 | 405,924 | 483,659 |
| Land in barley (for threshing) | 48,003 | 30,831 | 26,514 | 27,921 |
The total quantity of butter and cheese exported in the past fourteen years, and the amount of either commodity sent to the United Kingdom is tabulated:—
| Year. | Total Export of Butter. | Butter Exported to the United Kingdom. | Total Export of Cheese. | Cheese Exported to the United Kingdom. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cwt. | Cwt. | Cwt. | Cwt. | |
| 1889 | 37,955 | 21,099 | 26,558 | 7,633 |
| 1890 | 34,816 | 26,579 | 40,451 | 31,043 |
| 1891 | 39,430 | 28,989 | 39,770 | 29,565 |
| 1892 | 53,930 | 41,509 | 41,493 | 30,000 |
| 1893 | 58,149 | 52,363 | 46,201 | 41,567 |
| 1894 | 60,771 | 58,845 | 55,655 | 54,540 |
| 1895 | 57,964 | 55,194 | 76,743 | 73,369 |
| 1896 | 71,353 | 60,092 | 71,372 | 58,692 |
| 1897 | 99,002 | 79,849 | 77,683 | 67,681 |
| 1898 | 96,801 | 80,814 | 68,711 | 41,412 |
| 1899 | 136,086 | 121,502 | 69,440 | 40,901 |
| 1900 | 172,583 | 165,871 | 102,849 | 81,908 |
| 1901 | 201,591 | 170,903 | 104,294 | 74,510 |
| 1902 | 253,998 | 170,207 | 74,746 | 50,325 |
Of the butter exported in 1902, 170,207 cwt., valued at £1,782,485, were shipped to the United Kingdom; 20,688 cwt., value £107,506, to New South Wales; 43,898 cwt., value £214,337, to Victoria; 1,763 cwt., value £9,711, to Tasmania; 7,056 cwt., value £35,860, to Western Australia; 299 cwt., value £1,475, to South Australia; 3,098 cwt., value £17,544 to Queensland; 559 cwt., value £2,856, to Fiji; 5,315 cwt., value £27,963, to Cape Colony and Natal; 797 cwt., value £4,482, to the South Sea Islands; 200 cwt., value £1,032, to Portuguese East Africa; 112 cwt., value £521, to British Columbia; and 6 cwt., valued at £30, to Bengal and Ceylon.
ON page 330, tenth line from bottom of page, for £1,782,485 read £782,485.
[To face page 330
EXPORT OF BUTTER, 1890, 1893, 1896, 1899, 1902. EXPORT OF CHEESE, 1890, 1893, 1896, 1899, 1902.
Of the cheese exported, 50,325 cwt., valued at £105,663, were sent to the United Kingdom; 7,047 cwt., value £16,588, to New South Wales; 6,050 cwt., value £13,542, to Victoria; 6,175 cwt., value £14,990, to Western Australia; and 4,001 cwt., value £9,923, to the other Australian States. While the quantity of butter exported in 1902, 253,998 cwt., shows an increase of 569 per cent. on the quantity exported in 1889, the increase in the export of cheese during the fourteen years has been at the rate of 181 per cent.— 74,746 cwt. in 1902, as against 26,558 cwt. in 1889.
Phormium, of which 20,852 tons (excluding 1,335 tons of tow), valued at £534,031, were exported in 1902, shows a very great increase in the export, on comparing the figures for last year with those for 1901, when the quantity sent away was 10,171 tons. Outside of the question of prices, a large permanent development of this industry depends on the cultivation and careful selection of the plants used, and on improvements in the method of preparing the fibre.
The export for 1902 (7,430 tons) is a substantial one. The value was £450,223, or an average of £60 11s. 11d. per ton. Full information as to the uses of this resin and the kauri-gum industry generally is given in a special article in Part III. of the Year-book for 1900. It embraces interesting matter from the report of the Royal Commission which investigated the whole subject in 1898.
The following table gives the values of the exports from each port in New Zealand for the last two years, arranged in order of magnitude for 1902:—
| 1902 | 1901 | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Wellington | 2,567,268 | 1,943,963 |
| Lyttelton | 2,382,429 | 2,489,470 |
| Auckland | 2,091,016 | 1,922,792 |
| Dunedin | 1,618,294 | 1,463,237 |
| Invercargill and Bluff | 938,599 | 1,005,278 |
| Napier | 838,910 | 806,110 |
| Timaru | 685,759 | 849,986 |
| New Plymouth | 413,911 | 436,580 |
| Greymouth | 411,115 | 406,966 |
| Poverty Bay | 397,039 | 373,817 |
| Wanganui | 307,345 | 284,162 |
| Patea | 249,750 | 49,190 |
| Oamaru | 154,252 | 260,903 |
| Wairau and Picton | 143,094 | 127,705 |
| Kaipara | 131,789 | 192,316 |
| Westport | 97,206 | 61,965 |
| Waitara | 88,247 | 68,794 |
| Nelson | 70,080 | 87,218 |
| Hokitika | 42,561 | 34,818 |
The decrease of exports during 1902 was £66,679 at Invercargill and Bluff, and £107,041 at Lyttelton.
| Details of all Exports, 1902. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Articles exported. | Quantities. | Value in Sterling. | ||||
| Produce and Manufactures of the Colony. | British, Foreign, and other Colonial Produce and Manufactures. | Produce and Manufactures of the Colony. | British, Foreign, and other Colonial Produce and Manufactures. | Total. | ||
| Acid— | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Unenumerated | lb. | .. | 234 | .. | 13 | 13 |
| Alkali— | ||||||
| Soda, carbonate and bicarbonate | cwt. | 8 | .. | 3 | .. | 3 |
| Potash | cwt. | .. | 10 | .. | 20 | 20 |
| Animals, living— | ||||||
| Birds | No. | 4 | .. | 2 | .. | 2 |
| Bees | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | 8 |
| Dogs | No. | 26 | 1 | 77 | 10 | 87 |
| Donkeys | No. | 5 | .. | 30 | .. | 30 |
| Cattle (horned) | No. | 3,062 | .. | 39,263 | .. | 39,263 |
| Horses | No. | 1,308 | 3 | 28,394 | 45 | 28,439 |
| Pigs | No. | 326 | .. | 531 | .. | 531 |
| Poultry | No. | 5,680 | .. | 815 | .. | 815 |
| Sheep | No. | 48,047 | .. | 44,839 | .. | 44,839 |
| Apparel and slops | .. | 2,267 | 2,836 | 5,103 | ||
| Arms, ammunition, and explosives— | ||||||
| Caps, percussion | No. | .. | 26,000 | .. | 5 | 5 |
| Cartridges | No. | 14,450 | 23,175 | 86 | 125 | 211 |
| Detonators | No. | .. | 16,500 | .. | 34 | 34 |
| Dynamite | lb. | .. | 2,350 | .. | 176 | 176 |
| Firearms | No. | .. | 101 | .. | 421 | 421 |
| Fuse | coils | .. | 500 | .. | 17 | 17 |
| Ordnance stores | .. | .. | .. | .. | 159 | 159 |
| Powder, blasting | lb. | .. | 400 | .. | 16 | 16 |
| Powder, sporting | lb. | .. | 1,200 | .. | 115 | 115 |
| Shot | cwt. | .. | 1 | .. | 5 | 5 |
| Swords | No. | .. | 27 | .. | 44 | 44 |
| Bacon and hams— | ||||||
| Bacon | cwt. | 1,368 | .. | 4,395 | .. | 4,395 |
| Hams | cwt. | 4,542 | .. | 14,195 | .. | 14,195 |
| Bags and sacks— | ||||||
| Cornsacks | doz. | 750 | 18,592 | 188 | 3,761 | 3,949 |
| Unenumerated | doz. | 28 | 4,175 | 3 | 418 | 421 |
| Basketware and wickerware | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Bêohe-de-mer | cwt. | 20 | .. | 61 | .. | 61 |
| Beer | galls. | 25,892 | 6,053 | 3,139 | 1,534 | 4,673 |
| Belting, leather | lb. | .. | 28 | .. | 8 | 8 |
| Beverages, non-alcoholic— | ||||||
| Aerated and mineral waters | doz. | 923 | 462 | 191 | 20 | 211 |
| Coffee essence | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | 1 |
| Limejuice, unsweetened | galls. | .. | 7,943 | .. | 547 | 547 |
| Unenumerated | galls. | .. | .. | 15 | .. | 15 |
| Bicycles and tricycles | No. | 1 | 157 | 20 | 1,488 | 1,508 |
| Materials for | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1,031 | 1,032 |
| Biscuits— | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Fancy, and other kinds | lb. | 4,771 | .. | 109 | .. | 109 |
| Ship's plain | cwt. | 4,082 | .. | 3,441 | .. | 3,441 |
| Blacklead | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Boats | No. | 6 | .. | 236 | .. | 236 |
| Bones | tons | 4 | .. | 16 | .. | 16 |
| Books, printed | .. | .. | .. | 2,231 | 2,730 | 4,961 |
| Boots and shoes | doz. prs. | 83 | 485 | 303 | 1,183 | 1,486 |
| Bran | tons | 6,432 | .. | 31,684 | .. | 31,684 |
| Brass— | ||||||
| Pigs, bars, tubes, or sheets | cwt. | .. | 14 | .. | 70 | 70 |
| Manufactures | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 84 | 90 |
| Bricks, Fire | No. | 7,586 | .. | 59 | .. | 59 |
| Brushware and brooms— | ||||||
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 10 | 14 |
| Butter | cwt. | 253,998 | .. | 1,205,802 | .. | 1,205,802 |
| Carpeting and druggeting | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1,155 | 1,155 |
| Carriages, &c.— | ||||||
| Carriages | No. | 12 | .. | 422 | .. | 422 |
| Carts and wagons | No. | 47 | .. | 531 | .. | 531 |
| Perambulators | No. | 3 | .. | 8 | .. | 8 |
| Materials for | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 36 | 43 |
| Casks, empty | No. | 2 | 701 | 3 | 457 | 460 |
| Cement | barrels. | 13 | 156 | 7 | 94 | 101 |
| Chaff | tons | 356 | .. | 1,705 | .. | 1,705 |
| Chains | cwt. | .. | 6 | .. | 8 | 8 |
| Cheese | cwt. | 74,746 | .. | 163,539 | .. | 163,539 |
| Chinaware | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 227 | 232 |
| Clocks | No. | .. | 26 | .. | 164 | 164 |
| Coals | tons | 188,677 | 3,427 | 154,747 | 3,895 | 158,642 |
| Cocoa and Chocolate | lb. | .. | 3,154 | .. | 165 | 165 |
| Coffee— | ||||||
| Raw | lb. | 1,824 | 6,268 | 50 | 387 | 427 |
| Roasted | lb. | 307 | 484 | 15 | 26 | 41 |
| Confectionery— | ||||||
| Chocolate in fancy packages | .. | .. | .. | .. | 37 | 37 |
| Unenumerated | lb. | 11,350 | .. | 319 | .. | 319 |
| Copper nails | cwt. | .. | 2 | .. | 10 | 10 |
| Copra | tons | .. | 319 | .. | 4,264 | 4,294 |
| Cordage | cwt. | 820 | 238 | 1,655 | 552 | 2,207 |
| Iron and steel | cwt. | .. | 97 | .. | 305 | 305 |
| Cotton piece-goods— | ||||||
| Calico, white and grey | .. | .. | .. | .. | 984 | 984 |
| Shirtings | .. | .. | .. | .. | 133 | 133 |
| Waterproof material | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15 | 15 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 5,152 | 5,157 |
| Cotton— | ||||||
| Raw | lb. | .. | 1,590 | .. | 37 | 37 |
| Waste | cwt. | .. | 2 | .. | 4 | 4 |
| Cutlery | .. | .. | .. | .. | 86 | 86 |
| Doors | No. | 1,086 | .. | 851 | .. | 851 |
| Drapery | .. | .. | .. | 92 | 1,959 | 2,051 |
| Drugs, chemicals, and druggists' wares— | ||||||
| Anhydrous ammonia | .. | .. | .. | 25 | .. | 25 |
| Chemicals n.o.e. | .. | .. | .. | 598 | 188 | 786 |
| Disinfectants | .. | .. | .. | 82 | 65 | 147 |
| Drugs, and druggists' sundries | .. | .. | .. | 622 | 3,120 | 3,742 |
| Dyes | .. | .. | .. | .. | 197 | 197 |
| Insecticides | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 11 | 15 |
| Sheep-dip | .. | .. | .. | 524 | 536 | 1,060 |
| Earthenware | .. | .. | .. | 266 | 834 | 1,100 |
| Eggs | doz. | 2,152 | .. | 141 | .. | 141 |
| Engine-packing | cwt. | .. | 13 | 5 | 111 | 116 |
| Essential oils | lb. | .. | 2,837 | .. | 178 | 178 |
| Fancy-goods and toys | .. | .. | .. | 1,024 | 2,160 | 3,184 |
| Curiosities | .. | .. | .. | 64 | .. | 64 |
| Fire-clay | tons | 15 | .. | 39 | .. | 39 |
| Fish— | ||||||
| Dried, pickled, and salted | cwt. | 22 | 40 | 47 | 90 | 137 |
| Potted and preserved | lb. | 195,871 | 75,309 | 5,723 | 2,041 | 7,764 |
| Frozen | cwt. | 7,840 | .. | 10,245 | .. | 10,245 |
| Ova | No. | 330,000 | .. | 333 | .. | 333 |
| Fishing-tackle | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Floorcloth and oilcloth | .. | .. | .. | .. | 49 | 49 |
| Flour | tons | 370 | 11 | 3,613 | 122 | 3,735 |
| Foods, Animal— | ||||||
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 1,605 | .. | 1,605 |
| Foods, farinaceous— | ||||||
| Maizena and cornflour | lb. | .. | 3,120 | .. | 40 | 40 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 104 | .. | 104 |
| Fruits— | ||||||
| Bottled and preserved | doz. | 96 | 171 | 34 | 59 | 93 |
| Dried: Currants | lb. | .. | 27,697 | .. | 261 | 261 |
| Raisins | lb. | .. | 21,893 | .. | 406 | 406 |
| Unenumerated | lb. | .. | 24,473 | .. | 388 | 388 |
| Fresh | lb. | 106,526 | 1,920 | 1,097 | 9 | 1,106 |
| Pulp and partially preserved fruit | lb. | 152,171 | .. | 2,010 | .. | 2,010 |
| Fungus | cwt. | 4,632 | .. | 10,257 | .. | 10,257 |
| Furniture and upholstery | .. | .. | .. | 718 | 364 | 1,082 |
| Furniture, knife, and plate polish and powder | .. | .. | .. | .. | 177 | 17 |
| Furs | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20 | 20 |
| Gelatine and Isinglass | lb. | .. | 807 | .. | 88 | 88 |
| Glass bottles, empty | .. | .. | .. | 24 | 172 | 196 |
| Glassware | .. | .. | .. | 83 | 484 | 567 |
| Glue and size | cwt. | 179 | .. | 98 | .. | 98 |
| Glycerine | cwt. | 523 | .. | 890 | .. | 890 |
| Gold | oz. | 507,852 | .. | 1,951,426 | .. | 1,951,426 |
| Gold-leaf | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21 | 21 |
| Grain and pulse— | ||||||
| Barley | bush. | 151,360 | .. | 25,062 | .. | 25,062 |
| Beans and peas | bush. | 102,314 | 10 | 22,097 | 3 | 22,100 |
| Maize | bush. | 225,829 | .. | 40,417 | .. | 40,417 |
| Oats | bush. | 5,185,812 | .. | 666,664 | .. | 666,664 |
| Rye | bush. | 2,148 | .. | 363 | .. | 363 |
| Wheat | bush. | 194,671 | .. | 31,074 | .. | 31,074 |
| Unenumerated | bush. | 563 | .. | 166 | .. | 166 |
| Grease | cwt. | 44 | 62 | 117 | 47 | 164 |
| Grindery | .. | .. | .. | 17 | .. | 17 |
| Gum, kauri | tons | 7,430 | .. | 450,223 | .. | 450,223 |
| Haberdashery | .. | .. | .. | 4 | 308 | 312 |
| Buttons | .. | .. | .. | .. | 301 | 301 |
| Sewing-cottons, &c. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1,280 | 1,280 |
| Hair | cwt. | 740 | .. | 3,831 | .. | 3,831 |
| Hardware, hollow-ware, and ironmongery | .. | .. | . | 120 | 2,995 | 3,115 |
| Hats and caps | doz. | 8 | 59 | 16 | 150 | 166 |
| Hatters' materials | .. | .. | .. | .. | 217 | 217 |
| Hay and straw | tons | 1,280 | .. | 4,998 | .. | 4,998 |
| Hides | No. | 45,038 | .. | 44,546 | .. | 44,546 |
| Honey | lb. | 37,390 | .. | 677 | .. | 677 |
| Hops | cwt. | 4,311 | 81 | 14,292 | 269 | 14,561 |
| Horns and hoofs | tons | 1,602 | .. | 1,186 | .. | 1,186 |
| Hosiery | .. | .. | .. | 736 | 539 | 1,275 |
| Indiarubber goods | .. | .. | .. | .. | 612 | 612 |
| Ink, writing | .. | .. | .. | .. | 24 | 24 |
| Instruments, musical— | ||||||
| Harmoniums, &c. | No. | .. | 2 | .. | 115 | 115 |
| Pianofortes | No. | .. | 18 | .. | 583 | 583 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | .. | 541 | 541 |
| Instruments— | ||||||
| Scientific | .. | .. | .. | .. | 225 | 225 |
| Surgical and dental | .. | .. | .. | .. | 372 | 372 |
| Surveying | .. | .. | .. | 20 | 117 | 137 |
| Iron and steel— | ||||||
| Bar, bolt, and rod | tons | .. | 27 | .. | 429 | 429 |
| Bolts and nuts | cwt. | .. | 21 | .. | 20 | 20 |
| Castings for ships | tons | 1 | 5 | 43 | 459 | 502 |
| Galvanised manufactures | .. | .. | .. | 350 | 447 | 797 |
| Pipes and fittings | tons | .. | 2 | 3 | 30 | 33 |
| Sheet, galvanised and corrugated | cwt. | .. | 3,252 | .. | 2,786 | 2,786 |
| Sheet, galvanised plain | cwt. | .. | 94 | .. | 103 | 103 |
| Tanks, 400 galls. | No. | .. | 18 | .. | 61 | 61 |
| Tanks, 200 galls. | No. | .. | 1 | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Wire, fencing, barbed | tons | .. | 112 | .. | 307 | 307 |
| Wire, fencing, plain | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Wire netting | .. | .. | .. | .. | 39 | 39 |
| Wire, n.o.e. | tons | 208 | .. | 418 | .. | 418 |
| Unenumerated | tons | .. | 49 | .. | 55 | 55 |
| Jams, jellies, and preserves | lb. | 5,066 | 5,705 | 97 | 86 | 183 |
| Jellies, concentrated | lb. | 32 | 1,661 | 2 | 51 | 53 |
| Jewellery | .. | .. | .. | 675 | 162 | 837 |
| Lamps, lanterns, and lampwick | .. | .. | .. | .. | 206 | 206 |
| Lard | cwt. | 986 | .. | 2,470 | .. | 2,470 |
| Lead, pipe | cwt. | 9 | .. | 10 | .. | 10 |
| Leather | cwt. | 15,469 | 26 | 92,636 | 526 | 93,162 |
| Leather manufactures, unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 33 | 470 | 503 |
| Lime | bush. | 1,100 | .. | 55 | .. | 55 |
| Linen piece-goods | .. | .. | .. | .. | 45 | 45 |
| Linseed | cental. | 10,948 | .. | 6,146 | .. | 6,146 |
| Machinery— | ||||||
| Agricultural | .. | .. | .. | 5,557 | 3,031 | 8,588 |
| Dairying | .. | .. | .. | 47 | 773 | 820 |
| Brickmaking | .. | .. | .. | .. | 200 | 200 |
| Dredging | .. | .. | .. | 7,395 | 917 | 8,312 |
| Electric | .. | .. | .. | 6 | 1,004 | 1,010 |
| Engines, steam | No. | .. | 2 | .. | 77 | 77 |
| Engines, steam parts of | .. | .. | .. | .. | 113 | 113 |
| Engines, gas and oil | No. | .. | 4 | .. | 307 | 307 |
| Flour-milling | .. | .. | .. | 44 | 906 | 950 |
| Gas-making | .. | .. | .. | .. | 303 | 303 |
| Mining | .. | .. | .. | 2,650 | 88 | 2,738 |
| Paper-milling | .. | .. | .. | .. | 50 | 50 |
| Portable and traction engines | No. | .. | 2 | .. | 750 | 750 |
| Printing | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1,072 | 1,072 |
| Refrigerating | .. | .. | .. | .. | 260 | 260 |
| Sewing and knitting | No. | .. | 144 | .. | 709 | 709 |
| Wood-working | .. | .. | .. | 60 | .. | 60 |
| Woollen-milling | .. | .. | .. | .. | 35 | 35 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 840 | 6,690 | 7,530 |
| Materials for, and parts of | .. | .. | .. | .. | 152 | 152 |
| Malt | bush. | 2,865 | .. | 705 | .. | 705 |
| Manures— | ||||||
| Bonedust | tons | 34 | .. | 186 | .. | 186 |
| Unenumerated | tons | 96 | 5 | 477 | 15 | 492 |
| Marble | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 72 | 85 |
| Matches and vestas— | ||||||
| Wax | gross | .. | 456 | .. | 195 | 195 |
| Wooden | gross | .. | 2,571 | .. | 197 | 197 |
| Mats and matting | .. | .. | .. | 91 | 22 | 113 |
| Meal— | ||||||
| Oaten | centals | 36,085 | .. | 21,578 | .. | 21,578 |
| Wheatmeal | centals | 45 | .. | 36 | .. | 36 |
| Meats— | ||||||
| Beef, fresh | cwt. | 40 | .. | 56 | .. | 56 |
| Beef, frozen | cwt. | 286,699 | .. | 370,691 | .. | 370,691 |
| Beef, salted | cwt. | 7,963 | .. | 9,708 | .. | 9,708 |
| Kidneys, frozen | cwt. | 6,214 | .. | 10,722 | .. | 10,722 |
| Lamb, frozen | carcases | 1,852,050 | .. | 898,534 | .. | 898,534 |
| = cwt. | 586,837 | |||||
| Mutton (whole car- cases), frozen | carcases | 2,058,622 | 1,183,072 | .. | 1,183,072 | |
| = cwt. | 1,028,737 | |||||
| Mutton (joints), frozen | cwt. | 93,164 | .. | 109,030 | .. | 109,030 |
| Pork, frozen | cwt. | 4,164 | .. | 9,729 | .. | 9,729 |
| Pork, salted | cwt. | 57 | .. | 129 | .. | 129 |
| Poultry, frozen | cwt. | 2,775 | .. | 8,101 | .. | 8,101 |
| Veal, frozen | cwt. | 1,191 | .. | 1,682 | .. | 1,682 |
| Other kinds, frozen | cwt. | 3,932 | .. | 8,318 | .. | 8,318 |
| Rabbits, frozen in the skins | No. | 4,776,914 | .. | 116,996 | .. | 116,996 |
| cwt. | 123,229 | |||||
| Hares, frozen in the skins | No. | 23,421 | .. | 1,888 | .. | 1,888 |
| = cwt. | 1,643 | |||||
| Potted and preserved | No. | 54,271 | 87 | 124,534 | 99 | 124,633 |
| Extract of meat | lb. | 110,156 | .. | 17,951 | .. | 17,951 |
| Unenumerated | cwt. | 227 | .. | 552 | .. | 552 |
| Medicines, patent | .. | .. | .. | 263 | 296 | 559 |
| Metal, Manufactures of— | ||||||
| Anchors | No. | .. | 1 | .. | 10 | 10 |
| Metal sheathing | cwt. | .. | 9 | .. | 36 | 36 |
| Typewriters | No. | .. | 6 | .. | 52 | 52 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 1,682 | 5,276 | 6,958 |
| Metal, old | cwt. | 29,100 | .. | 6,326 | .. | 6,326 |
| Milk, preserved | lb. | 614,708 | 47,078 | 12,305 | 995 | 13,300 |
| Millinery— | ||||||
| Feathers, ornamental | .. | .. | .. | 274 | 12 | 286 |
| Other kinds | .. | .. | .. | 12 | 41 | 53 |
| Minerals— | ||||||
| Auriferous ore | tons | 231 | .. | 2,560 | .. | 2,560 |
| Chrome ore | tons | 175 | .. | 525 | .. | 525 |
| Hæmatite | tons | 17 | .. | 116 | .. | 116 |
| Scheelite ore | tons | 39 | .. | 1,200 | .. | 1,200 |
| Silver ore | tons | 1 | .. | 1 | .. | 1 |
| Sulphur | tons | 100 | .. | 475 | .. | 475 |
| Unenumerated | tons | 44 | .. | 186 | .. | 186 |
| Mustard | lb. | .. | 348 | .. | 13 | 13 |
| Nails | cwt. | .. | 339 | .. | 283 | 283 |
| Nuts— | ||||||
| Almonds in shell | lb. | .. | 6 | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Oakum | cwt. | .. | 9 | .. | 19 | 19 |
| Oil— | ||||||
| Castor, bulk | galls. | .. | 399 | .. | 45 | 45 |
| Castor, bottled | doz. pts. | .. | 106 | .. | 43 | 43 |
| Cod-liver | galls. | .. | 3 | .. | 8 | 8 |
| Colza | galls. | .. | 1,189 | .. | 181 | 181 |
| Cocoanut | galls. | 3,124 | .. | 339 | .. | 339 |
| Linseed | galls. | .. | 3,317 | .. | 545 | 545 |
| Mineral, kerosene | galls. | .. | 126,776 | .. | 5,742 | 5,742 |
| Mineral, other kinds | galls. | .. | 4,979 | .. | 333 | 333 |
| Neatsfoot | galls. | 292 | 15 | 16 | 3 | 19 |
| Olive, bulk | galls. | .. | 599 | .. | 86 | 86 |
| Whale | galls. | 7,696 | .. | 608 | .. | 608 |
| Unenumerated | galls. | 97 | 14,360 | 25 | 1,370 | 1,395 |
| Oilmen's stores | .. | .. | .. | 130 | 1,755 | 1,885 |
| Onions | cwt. | 16,137 | .. | 4,493 | 1,370 | 4,493 |
| Oysters | doz. | 339,685 | .. | 2,867 | .. | 2,867 |
| Paints and colours— | ||||||
| Ground in oil | cwt. | 27 | 671 | 36 | 940 | 976 |
| Mixed ready for use | cwt. | 1 | 223 | 3 | 923 | 926 |
| Unenumerated | cwt. | 135 | 69 | 48 | 39 | 87 |
| Paper bags | cwt. | 1,200 | .. | 1,021 | .. | 1,021 |
| Paper— | ||||||
| Butter | cwt. | 12 | .. | 61 | .. | 61 |
| Printing | cwt. | 110 | .. | 117 | 117 | |
| Paperhangings | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 1 |
| Wrapping | cwt. | 575 | 25 | 455 | 38 | 493 |
| Perfumery— | ||||||
| Perfumed spirits | galls. | .. | 18 | .. | 27 | 27 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | .. | 103 | 103 |
| Phormium | tons | 20,852 | .. | 534,031 | .. | 534,031 |
| Tow | tons | 1,335 | .. | 5,359 | .. | 5,359 |
| Photographic goods | .. | .. | .. | 53 | 506 | 559 |
| Pickles | galls. | 14 | .. | 3 | .. | 3 |
| Pictures | .. | .. | .. | 1,419 | 421 | 1,840 |
| Picture-frames and mounts | .. | .. | .. | .. | 18 | 18 |
| Pitch | cwt. | .. | 383 | .. | 88 | 88 |
| Plants and shrubs | .. | .. | .. | 502 | .. | 502 |
| Plate and platedware | .. | .. | .. | 10 | 2,580 | 2,590 |
| Pollard and sharps | tons | 1,314 | .. | 7,839 | .. | 7,839 |
| Portmanteaux | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Potatoes | tons | 17,715 | .. | 72,807 | .. | 72,807 |
| Printing materials | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 328 | 330 |
| Provisions n.o.e. | .. | .. | .. | 1,861 | 559 | 2,420 |
| Pumps | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 54 | 57 |
| Rags | cwt. | 439 | 18 | 434 | 3 | 437 |
| Rice | cwt. | .. | 655 | .. | 499 | 499 |
| Rugs | .. | .. | .. | 3,337 | 126 | 3,463 |
| Saddlery | .. | .. | .. | 601 | 63 | 664 |
| Harness oil | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | 8 |
| Salt | ton | .. | 1 | .. | 3 | 3 |
| Sashes | pairs | 831 | .. | 540 | .. | 540 |
| Sauces | galls. | 34 | 283 | 14 | 186 | 200 |
| Sausage-skins | cwt. | 13,398 | 77 | 61,167 | 258 | 61,425 |
| Seeds— | ||||||
| Grass and clover | cwt. | 43,998 | 80 | 84,861 | 189 | 85,050 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 1,511 | 596 | 2,107 |
| Shell— | ||||||
| Pearl | cwt. | .. | 114 | .. | 327 | 327 |
| Ship-chandlery, n.o.e. | .. | .. | .. | 255 | 1,036 | 1,291 |
| Silk piece-goods | .. | .. | .. | .. | 440 | 440 |
| Silver | oz. | 674,196 | .. | 71,975 | .. | 71,975 |
| Skins— | ||||||
| Calf and other | No. | 18,575 | .. | 711 | .. | 711 |
| Rabbit | No. | 6,139,794 | .. | 52,566 | .. | 52,566 |
| Sheep, with wool | No. | 441,078 | .. | 57,549 | .. | 57,549 |
| Sheep, without wool | No. | 5,703,602 | .. | 318,327 | .. | 318,327 |
| Pelt pieces | lb. | 339,360 | .. | 738 | .. | 738 |
| Soap— | ||||||
| Common | cwt. | 5,770 | .. | 5,172 | .. | 5,172 |
| Powder | .. | .. | .. | 1 | 91 | 92 |
| Unenumerated | lb. | .. | .. | .. | 139 | 139 |
| Specie— | ||||||
| Gold | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,718 | 3,718 |
| Silver | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,800 | 5,800 |
| Specimens, illustrative of natural science | .. | .. | .. | 483 | 5 | 488 |
| Spices— | ||||||
| Ground | lb. | .. | 36 | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Unground | lb. | .. | 7,631 | .. | 1,703 | 1,703 |
| Spirits— | ||||||
| Bitters, cordials, &c. | galls. | .. | 28 | .. | 38 | 38 |
| Brandy | galls. | .. | 932 | .. | 463 | 463 |
| Geneva and gin, unsweetened | galls. | .. | 1,121 | .. | 357 | 357 |
| Rum | galls. | .. | 180 | 56 | .. | 56 |
| Sweetened, &c. | galls. | .. | 16 | .. | 8 | 8 |
| Whisky | galls. | .. | 8,039 | .. | 3,059 | 3,059 |
| Unenumerated | galls. | .. | 4 | .. | 6 | 6 |
| Spirits of wine | galls. | .. | 52 | .. | 4 | 4 |
| Sponges | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5 | 5 |
| Starch | lb. | 56 | .. | 1 | .. | 1 |
| Stationery | .. | .. | .. | 1,263 | 654 | 1,917 |
| Stone— | ||||||
| Building | tons | 650 | .. | 628 | .. | 628 |
| Wrought | .. | .. | .. | 103 | 34 | 137 |
| Greenstone | cwt. | 91 | .. | 569 | .. | 569 |
| Jade | cwt. | 24 | .. | 45 | .. | 45 |
| Pumice | tons | 683 | .. | 1,794 | .. | 1,794 |
| Sugar— | ||||||
| Refined | lb. | 727,328 | 84,624 | 5,901 | 684 | 6,585 |
| Tallow | tons | 19,733 | .. | 497,018 | .. | 497,018 |
| Mutton stock, and oleomargarine | tons | 1,464 | .. | 52,947 | .. | 52,947 |
| Oil | tons | 6 | .. | 166 | .. | 166 |
| Tarpaulins and tents | .. | .. | .. | 20 | .. | 20 |
| Tanning materials— | ||||||
| Bark | tons | 105 | .. | 880 | .. | 880 |
| Other kinds | .. | .. | .. | .. | 121 | 121 |
| Tea | lb. | .. | 109,487 | .. | 4,662 | 4,662 |
| Textile piece-goods, other than silk, cotton, linen, or woollen | .. | .. | 7 | 179 | 186 | |
| Articles made up from, other than apparel | .. | .. | .. | 8 | 164 | 172 |
| Timber— | ||||||
| Logs | No. | 114 | .. | 395 | .. | 395 |
| Logs hewn | sup. ft. | 644,263 | .. | 1,950 | .. | 1,950 |
| Sawn, undressed | sup. ft. | 47,013,669 | 4,981 | 193,902 | 72 | 193,974 |
| Sawn, dressed | sup. ft. | 1,593,587 | .. | 12,153 | .. | 12,153 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 1,202 | .. | 1,202 |
| Tin— | ||||||
| Block | cwt. | .. | 147 | .. | 128 | 128 |
| Foil | lb. | .. | 560 | .. | 20 | 20 |
| Sheet | cwt. | .. | 152 | .. | 146 | 146 |
| Tinware | .. | .. | .. | 167 | 87 | 254 |
| Tobacco— | ||||||
| Manufactured | lb. | .. | 70,890 | .. | 5,937 | 5,937 |
| Cigars | lb. | .. | 3,327 | .. | 937 | 937 |
| Cigarettes | lb. | .. | 3,318 | .. | 1,228 | 1,228 |
| Tobacco-pipes, &c. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | 2 |
| Tools— | ||||||
| Engineers' machine | .. | .. | .. | .. | 296 | 296 |
| Sheep-shears | .. | .. | .. | .. | 18 | 18 |
| Unenumerated | .. | .. | .. | 82 | 376 | 458 |
| Tramway plant | .. | .. | .. | 33 | 131 | 164 |
| Turpentine, driers, and terebine | gals. | .. | 42 | .. | 7 | 7 |
| Twine | cwt. | 3 | .. | 125 | 125 | |
| Nets and netting | .. | .. | .. | .. | 12 | 12 |
| Reaper and binder | cwt. | 6,225 | .. | 10,303 | .. | 10,303 |
| Umbrellas and parasols | .. | .. | .. | .. | 168 | 168 |
| Varnish and gold size | gals. | .. | 700 | .. | 266 | 266 |
| Vegetables | .. | .. | .. | 162 | 21 | 183 |
| Vinegar | gals. | 30 | .. | 2 | .. | 2 |
| Watches | No. | .. | 237 | .. | 313 | 313 |
| Wax— | ||||||
| Beeswax | cwt. | 16 | .. | 87 | .. | 87 |
| Paraffin, &c. | lb. | 308 | 6 | 6 | ||
| Whalebone | cwt. | 15 | .. | 540 | .. | 540 |
| Wine— | ||||||
| Australian | gals. | .. | 1,694 | .. | 658 | 658 |
| Sparkling | gals. | .. | 413 | .. | 800 | 800 |
| Other kinds | gals. | 103 | 898 | 58 | 550 | 608 |
| Woodenware | .. | .. | .. | 1,059 | 752 | 1,811 |
| Wool—- | ||||||
| Greasy | lb. | 118,428,418 | .. | 2,230,739 | .. | 2,230,739 |
| Scoured | lb. | 20,289,134 | .. | 610,066 | .. | 610,066 |
| Sliped | lb. | 18,624,189 | .. | 450,178 | .. | 450,178 |
| Washed | lb. | 3,077,282 | .. | 63,580 | .. | 63,580 |
| Woollen piece-goods | .. | .. | .. | 2,816 | 746 | 3,562 |
| Woollen blankets | pairs | 433 | .. | 503 | .. | 503 |
| Yarns | .. | .. | .. | 8 | .. | 8 |
| Zinc— | ||||||
| Plain sheet | cwt. | .. | 43 | .. | 27 | 27 |
| Spelter | cwt. | 999 | 44 | 673 | 27 | 700 |
| Goods, miscellaneous— | ||||||
| Manufactured | .. | .. | .. | 470 | 93 | 563 |
| Unmanufactured | .. | .. | .. | 1,603 | 547 | 2,150 |
| Parcels Post | .. | .. | .. | 16,313 | .. | 16,313 |
A table is appended giving details of goods forwarded in the year 1902 to the Cook and other Pacific Islands annexed to New Zealand in 1901. These do not appear as exports from the colony, being merely part of the internal trade or transactions between one portion of what is now New Zealand and another.
| Articles. | Quantities. | Value. |
|---|---|---|
| £ | ||
| Animals, living— | ||
| Cattle, horned | 12 No. | 148 |
| Sheep | 149 No. | 128 |
| Apparel and slops | .. | 573 |
| Bags and sacks, cornsacks | 1,161 doz. | 286 |
| Biscuits | 2,049 cwt. | 936 |
| Boots and shoes | 76 1/2 doz. | 261 |
| Butter and cheese | 50 cwt. | 274 |
| Coal | 1,515 tons | 1,577 |
| Calico piece-goods | .. | 1,703 |
| Drapery, hosiery, haberdashery, millinery, hats | .. | 2,050 |
| Fish, dried and preserved | 12,369 lb. | 321 |
| Flour | 77 tons | 816 |
| Hardware, cutlery, nails, tools | .. | 795 |
| Iron and steel | 671 cwt. | 582 |
| Meats, salted and preserved | 1,028 1/2 cwt. | 1,953 |
| Oils | 9,710 gals. | 459 |
| Oilmen's stores | .. | 429 |
| Provisions, unenumerated | .. | 262 |
| Soap, common | 600 cwt. | 451 |
| Specie, silver | .. | 1,475 |
| Spirits | 950 gals. | 282 |
| Sugar, refined | 105,724 lb. | 937 |
| Timber | 553,938 sup. ft. | 2,880 |
| Tobacco, cigars, cigarettes | 4,839 lb. | 316 |
| Miscellaneous | .. | 3,079 |
| Total value of goods cleared outwards from Auckland | 22,973 |
Particulars of goods cleared outwards from these annexed islands to Auckland in 1902 will be found in Section XV.
The value of the total trade of New Zealand advanced from £13,431,804 in the year 1886 to £24,971,700 in 1902. But of these amounts some portion was coin. Excluding the specie, the figures for 1886 are £12,853,736, and for 1902, £24,593,497.
| Year. | Total Trade. | Imports. | Exports. | Imports (excluding Specie). | Exports (excluding Specie). | Excess of Exports over Imports (excluding Specie). |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1886 | 13,431,804 | 6,759,013 | 6,672,791 | 6,319,223 | 6,534,513 | 215,290 |
| 1887 | 13,111,684 | 6,245,515 | 6,866,169 | 6,064,281 | 6,680,772 | 616,491 |
| 1888 | 13,709,225 | 5,941,900 | 7,767,325 | 5,430,050 | 7,403,206 | 1,972,156 |
| 1889 | 15,650,727 | 6,308,863 | 9,341,864 | 5,980,583 | 9,183,954 | 3,203,371 |
| 1890 | 16,072,245 | 6,260,525 | 9,811,720 | 5,928,895 | 9,569,316 | 3,640,421 |
| 1891 | 16,070,246 | 6,503,849 | 9,566,397 | 6,431,101 | 9,560,859 | 3,129,758 |
| 1892 | 16,477,907 | 6,943,056 | 9,534,851 | 6,742,544 | 9,490,920 | 2,748,376 |
| 1893 | 15,896,879 | 6,911,515 | 8,985,364 | 6,494,279 | 8,680,845 | 2,186,566 |
| 1894 | 16,019,067 | 6,788,020 | 9,231,047 | 5,990,177 | 9,221,550 | 3,231,373 |
| 1895 | 14,950,353 | 6,400,129 | 8,550,224 | 6,115,953 | 8,518,119 | 2,402,166 |
| 1896 | 16,458,425 | 7,137,320 | 9,321,105 | 7,035,379 | 9,299,907 | 2,264,528 |
| 1897 | 18,072,216 | 8,055,223 | 10,016,993 | 7,994,201 | 9,741,222 | 1,747,021 |
| 1898 | 18,748,555 | 8,230,600 | 10,517,955 | 8,211,409 | 10,449,838 | 2,238,429 |
| 1899 | 20,677,968 | 8,739,633 | 11,938,335 | 8,613,656 | 11,923,422 | 3,309,766 |
| 1900 | 23,892,257 | 10,646,096 | 13,246,161 | 10,207,326 | 13,223,258 | 3,015,932 |
| 1901 | 24,699,339 | 11,817,915 | 12,881,424 | 11,353,416 | 12,869,810 | 1,516,394 |
| 1902 | 24,971,700 | 11,326,723 | 13,644,977 | 10,958,038 | 13,635,459 | 2,677,421 |
The trade for these years has been selected for exhibition in tabular form because during each of the series there was an excess of exports over imports, whereas previously the reverse obtained, and the colony was purchasing to an extent not covered by the value of the export. During the last seventeen years the excess of exports over imports, excluding money sent to and from the colony, amounted to a total sum of £40,115,459.
How different the foregoing conditions were from those previously obtaining will be seen by observing the balance of trade for the years 1881 to 1885 inclusive:—
| Year. | Excess of Imports over Exports. |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1881 | 1,406,898 |
| 1882 | 1,948,485 |
| 1883 | 761,938 |
| 1884 | 235,981 |
| 1885 | 539,239 |
The gradually declining excess of imports turned in 1886 and 1887 to a small excess of exports, but subsequently the excess of exports was very great, and attained the sum of £3,640,421 in the year 1890.
Again considering the results for the seventeen years, 1886–1902, during which the balance was in favour of the exports, the external trade is shown for each year per head of population, the calculations being made exclusive as well as inclusive of specie, for the purpose of arriving at exact conclusions as regard trade in goods. In the year 1894 the imported money amounted to a sum of £797,843, making a substantial difference in the rates.
Excluding specie, the trade per head of population increased from £22 1s. 7d., in 1886, to £30 16s. 6d. in 1902: imports from £10 17s. 1d. to £13 14s. 8d., and exports from £11 4s. 6d. to £17 1s. 10d.
| Year. | Including Specie. | Excluding Specie. | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Trade per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | Imports per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | Exports per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | Total Trade per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | Imports per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | Exports per Head of Mean Population (excluding Maoris). | |||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1886 | 23 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 12 | 2 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 22 | 1 | 7 | 10 | 17 | 1 | 11 | 4 | 6 |
| 1887 | 21 | 19 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 11 | 10 | 3 | 21 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 4 | 1 |
| 1888 | 22 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 16 | 4 | 12 | 16 | 7 | 21 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 19 | 5 | 12 | 4 | 7 |
| 1889 | 25 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 15 | 4 | 5 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 9 | 15 | 6 | 15 | 0 | 3 |
| 1890 | 25 | 13 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 15 | 13 | 8 | 24 | 19 | 4 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 15 | 8 | 4 |
| 1891 | 25 | 10 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 15 | 3 | 7 |
| 1892 | 25 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 16 | 3 | 14 | 16 | 11 | 25 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 15 | 7 |
| 1893 | 24 | 0 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 0 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 22 | 18 | 11 | 9 | 16 | 5 | 13 | 2 | 6 |
| 1894 | 23 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 19 | 11 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 22 | 7 | 11 | 8 | 16 | 5 | 13 | 11 | 6 |
| 1895 | 21 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 4 | 10 | 12 | 7 | 0 | 21 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 0 |
| 1896 | 23 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 13 | 3 | 9 | 23 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 19 | 1 | 13 | 3 | 1 |
| 1897 | 25 | 0 | 11 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 13 | 17 | 8 | 24 | 11 | 7 | 11 | 1 | 7 | 13 | 10 | 0 |
| 1898 | 25 | 9 | 3 | 11 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 5 | 8 | 25 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 3 | 10 |
| 1899 | 27 | 11 | 5 | 11 | 13 | 1 | 15 | 18 | 4 | 27 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 15 | 18 | 0 |
| 1900 | 31 | 5 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 10 | 17 | 6 | 11 | 30 | 13 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 4 | 17 | 6 | 4 |
| 1901 | 31 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 16 | 11 | 2 | 31 | 2 | 9 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 16 | 10 | 10 |
| 1902 | 31 | 6 | 0 | 14 | 3 | 11 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 30 | 16 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 8 | 17 | 1 | 10 |
The highest record of trade (excluding specie) was that for 1874, when the rate per head was £41 4s. 5d., the imports, in consequence of the large expenditure of borrowed money, amounting at that time to £24 17s. per head, against £13 14s. 8d. in 1902.
It has been customary to leave out the Maoris in estimating the sum per head, for their industries and necessities swell the volume of trade in comparatively so slight a measure that the amount per head of European population can be more truly ascertained by omitting them altogether.
The trade with the United Kingdom in 1902 amounted to £16,302,100, comprising 65·29 per cent. of the total.
With the Australian States, trade was done during 1902 to the value of £4,399,645; of which New South Wales claimed £1,989,786, and Victoria £2,043,546, made up as follows:—
| Exports from New Zealand. | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| To New South Wales, 1902 | 1,118,193 |
| To Victoria, 1902 | 1,295,233 |
| Imports into New Zealand. | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| From New South Wales, 1902 | 871,593 |
| From Victoria, 1902 | 748,313 |
The latter amounts, in each case, represent the declared values the imports into New Zealand from the States mentioned, not their export value as given in the New South Wales and Victorian returns.
Included in the exports to New Zealand from New South Wales is coal to the quantity of 126,548 tons, valued at £124,430.
Both imports from and exports to the United States in 1902 show a decrease when compared with the previous year's figures.
Of the exports to the United States in 1902 the values of the principal New Zealand products were: Coal, £2,009; kauri-gum, £322,976; hides, £1,099; sheepskins, £33,758; rabbit-skins, £5,195; sausage-skins, £37,867; onions, £770; grass-seed, £3,680; wool, £14,372; and phormium, £64,129.
The following table shows the value of the total trade with the United States for each of the past ten years, 1893 to 1902 inclusive, during which period the trade has increased considerably. But the increase is entirely on the side of the imports from those States, and especially from the Atlantic ports, from which there is a far greater output to New Zealand than from the Pacific side.
| Trade with the United States. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Imports from | Exports to | Total Trade. | ||
| Atlantic Ports. | Pacific Ports. | Atlantic Ports. | Pacific Ports. | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1893 | 345,743 | 33,635 | 430,842 | 65,706 | 875,926 |
| 1894 | 359,196 | 35,495 | 230,829 | 56,367 | 681,887 |
| 1895 | 351,823 | 42,410 | 298,536 | 18,103 | 710,872 |
| 1896 | 419,689 | 73,151 | 263,564 | 63,025 | 819,429 |
| 1897 | 521,939 | 106,105 | 252,013 | 123,083 | 1,003,140 |
| 1898 | 700,555 | 99,856 | 337,059 | 286,074 | 1,423,544 |
| 1899 | 687,906 | 87,403 | 387,614 | 45,885 | 1,208,808 |
| 1900 | 958,286 | 103,587 | 424,314 | 34,482 | 1,520,669 |
| 1901 | 1,174,745 | 240,515 | 332,175 | 186,904 | 1,934,339 |
| 1902 | 1,146,575 | 172,362 | 447,623 | 42,341 | 1,808,901 |
The development in the decennial period is at the rate of over 100 per cent., or an increase in value of £932,975.
The trade with India and Ceylon reached a total of £416,348, against £478,757 in 1901. The imports—tea, rice, castor-oil, wool-packs, &c.—were reckoned at £414,186, leaving a balance of only £2,162 for exports.
A monthly passenger and cargo service to South Africa has been established, controlled by the “New Zealand and African Steamship Company,” and subsidised by the New Zealand Government. The steamers are from 9,000 to 14,000 tons measurement cargo-capacity.
The contractors nominate four loading ports in this colony, but the Government may, under a condition of the contract, add to these, or substitute others. The ports of discharge are Durban, Port Elizabeth, and Capetown, but the boats must call at Fremantle. Western Australia, en route.
An important and increasing trade has, so far, grown out of this service, indeed it has been found necessary on a recent occasion to despatch a second steamer during the month.
To exhibit the nature and dimensions of the trade as at present, the main items comprising the cargo of the s.s. “Essex,” which sailed from Wellington on the 14th June, 1903, are given: 49,046 carcases frozen mutton, 220 carcases lamb, 2,200 quarters beef, 500 sides pork, 708 cases meats, 179 cases poultry, 298 cases fish, 3,808 boxes butter, 94 cases cheese, 45,106 sacks oats, 1,472 sacks bran, 1,987 sacks potatoes, 17,535 superficial feet timber, 3,094 live sheep, 3 horses, 480 packages sundries.
Shipments of live sheep are becoming regular. The demand for poultry is greater than the supply, and practically all the frozen beef now sent from the colony is carried by this line of steamers.
Experimental shipments of timber for the Capetown railways and harbour works are being made, and some 3,000 bags of pumice for insulation have been supplied to a freezing company at the same place.
A feature of the service is the creation of a trade with Fremantle in frozen meat and live sheep.
The value of the South African trade from 1893 to 1902 is as follows:—
| Year. | Imports from | Exports to | Total Trade. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1893 | 1,563 | 3,779 | 5,342 |
| 1894 | 16 | 2,545 | 2,561 |
| 1895 | 58 | 10,255 | 10,313 |
| 1896 | 129 | 12,508 | 12,637 |
| 1897 | 87 | 6,795 | 6,882 |
| 1898 | 72 | 2,766 | 2,838 |
| 1899 | 215 | 90,187 | 90,402 |
| 1900 | 502 | 405,419 | 405,921 |
| 1901 | 386 | 825,476 | 825,862 |
| 1902 | 997 | 754,059 | 755,056 |
The following table gives the value of the imports and exports of what is now the Commonwealth of Australia and the Colony of New Zealand for the year 1901:—
| State or Colony. | Total Value of | Excess of Exports over Imports. | Excess of Imports over Exports. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imports. | Exports. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Queensland | 6,376,239 | 9,249,366 | 2,873,127 | 0 |
| New South Wales | 26,928,218 | 27,351,124 | 422,906 | .. |
| Victoria | 18,927,340 | 18,646,097 | .. | 281,243 |
| South Australia | 7,371,588 | 8,015,889 | 644,301 | .. |
| Ditto, Northern Territory | 106,700 | 302,931 | 196,231 | .. |
| Western Australia | 6,454,171 | 8,515,623 | 2,061,452 | .. |
| Tasmania | 1,965,199 | 2,945,757 | 980,558 | .. |
| New Zealand | 11,817,915 | 12,881,424 | 1,063,509 | .. |
In the preceding table is given the total trade inwards and outwards of each State and colony, counting twice over the value of goods produced in one State or colony and carried thence into another, and reckoning the same goods three times where they are imported from without into one State or colony and re-exported thence in the same year into another. But, in order to form a just idea of the trade of Australasia as a whole, it is necessary to eliminate the inter-state traffic altogether. From the following table the value of imports and exports exchanged between the various States has accordingly been excluded:—
| External Trade of Australasia. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Total Trade. | Imports. | Exports. | Excess of Imports. | Excess of Exports. |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1885 | 72,220,444 | 41,136,038 | 31,084,406 | 10,051,632 | .. |
| 1890 | 75,143,818 | 38,451,160 | 36,692,658 | 1,758,502 | .. |
| 1891 | 84,565,778 | 41,325,033 | 43,240,745 | .. | 1,915,712 |
| 1892 | 75,325,933 | 34,529,501 | 40,796,432 | .. | 6,266,931 |
| 1893 | 67,788,738 | 27,925,990 | 39,862,748 | .. | 11,936,758 |
| 1894 | 65,192,202 | 26,063,630 | 39,128,572 | .. | 13,064,942 |
| 1895 | 67,624,317 | 27,425,725 | 40,198,592 | .. | 12,772,867 |
| 1896 | 74,511,262 | 34,420,596 | 40,090,666 | .. | 5,670,070 |
| 1897 | 83,569,568 | 37,862,741 | 45,706,827 | .. | 7,844,086 |
| 1898 | 85,600,442 | 37,310,583 | 48,289,859 | .. | 10,979,276 |
| 1899 | 97,637,194 | 39,990,123 | 57,647,071 | .. | 17,656,948 |
| 1900 | 104,298,717 | 48,351,933 | 55,946,784 | .. | 7,594,851 |
| 1901 | 109,651,267 | 50,506,802 | 59,144,465 | .. | 8,637,663 |
It will be observed that in the year 1885 the excess of imports over exports for Australasia amounted to no less a sum than £10,051,632, and that five years later the excess of imports had fallen to £1,758,502. In 1891 the position was completely reversed, the exports exceeding the imports by £1,915,712. This excess increased to £6,266,931 in the following year (1892), and to £13,064,942 in 1894, but decreased to £12,772,867 in 1895, to £5,670,070 in 1896. It was £7,844,086 in 1897, £10,979,276 in 1898, and in 1899 the excess of exports over imports amounted to £17,656,948. In 1900 there was a falling-off in the value of exports, and the excess amounted to only £7,594,851, but in 1901 the balance in favour of exports was £8,637,663.
The trade per head of the population in each of the States of the Australian Commonwealth and New Zealand in 1901 was:—
| Trade per Head of the Population in 1901. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State or Colony. | Mean Population. | Imports. | Exports. | Total Trade. | ||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Queensland | 505,695 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 18 | 5 | 10 | 30 | 18 | 0 |
| New South Wales | 1,372,145 | 19 | 12 | 6 | 19 | 18 | 8 | 39 | 11 | 2 |
| Victoria | 1,202,960 | 15 | 14 | 8 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 31 | 4 | 8 |
| South Australia | 357,556 | 20 | 12 | 4 | 22 | 8 | 4 | 43 | 0 | 8 |
| Ditto, Northern Territory | 4,624 | 23 | 1 | 6 | 65 | 10 | 3 | 88 | 11 | 9 |
| Western Australia | 188,603 | 34 | 4 | 5 | 45 | 3 | 0 | 79 | 7 | 5 |
| Tasmania | 173,606 | 11 | 6 | 5 | 16 | 19 | 4 | 28 | 5 | 9 |
| New Zealand | 777,968 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 16 | 11 | 2 | 31 | 15 | 0 |
But the values of the exports of the Australian States, more especially New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia, are largely increased by the inclusion of articles the produce or manufacture of other States, colonies, and countries.
The value of home productions or manufactures exported from each State or colony in 1901, and the rate per head of mean population, were as follow:—
| State or Colony. | Home Produce exported. | Per Head of Population. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | |
| Queensland | 9,009,696 | 17 | 16 | 4 |
| New South Wales | 19,915,884 | 14 | 10 | 3 |
| Victoria | 14,134,028 | 11 | 14 | 11 |
| South Australia | 4,216,601 | 11 | 15 | 10 |
| Ditto, Northern Territory | 301,709 | 65 | 5 | 0 |
| Western Australia | 8,216,718 | 43 | 11 | 4 |
| Tasmania | 2,933,878 | 16 | 18 | 0 |
| New Zealand | 12,690,460 | 16 | 6 | 3 |
The next table sets forth the amount of the trade of each of the above-named States and colony with the United Kingdom in 1901:—
| State or Colony. | Imports from the United Kingdom. | Exports to the United Kingdom. | Total Trade with the United Kingdom. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Queensland | 2,474,784 | 3,354,854 | 5,829,638 |
| New South Wales | 10,102,941 | 7,647,963 | 17,750,904 |
| Victoria | 7,221,801 | 5,425,772 | 12,647,573 |
| South Australia | 2,234,982 | 2,288,286 | 4,523,268 |
| Ditto, Northern Territory | 7,745 | 18,661 | 26,406 |
| Western Australia | 2,566,162 | 5,625,459 | 8,191,621 |
| Tasmania | 628,617 | 833,928 | 1,462,545 |
| New Zealand | 6,885,831 | 9,295,375 | 16,181,206 |
The statement appended shows the relative importance of Australasia as a market for the productions of the United Kingdom:—
| Exports of Home Productions from the United Kingdom, in 1901, to— | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| British India and Ceylon | 36,513,040 |
| Australasia | 26,955,763 |
| Germany | 23,573,785 |
| United States | 18,393,883 |
| Cape of Good Hope and Natal | 17,154,380 |
| France | 16,472,068 |
| Holland | 9,089,149 |
| Russia | 8,673,334 |
| Belgium | 8,156,203 |
| Japan | 8,132,223 |
| Dominion of Canada | 7,785,472 |
| Sweden and Norway | 7,699,985 |
| Italy | 7,612,562 |
The exports to other countries did not amount to £7,000,000 in any one case.
Australasia as a whole, with a population of about 4,600,000, thus takes the second place in importance for consumption of British produce, the exports thereto being two-thirds the value of similar exports to British India, with its 294,000,000 inhabitants.
Value of imports and exports of the Cook and other Islands from the year 1892 to 1900 [in 1901 these islands were annexed to New Zealand]:—
| Year. | From New Zealand | From Tahiti. | Other Places. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1892 | 10,998 | 5,251 | .. | 16,249 |
| 1893 | 10,200 | 9,084 | .. | 19,284 |
| 1894 | 13,152 | 9,283 | .. | 22,435 |
| 1895 | 16,861 | 6,408 | .. | 23,269 |
| 1896 | 17,167 | 5,911 | .. | 23,068 |
| 1897 | 22,455 | 4,406 | .. | 26,861 |
| 1898 | 15,332 | 2,323 | .. | 18,155 |
| 1899 | 9,768 | 2,330 | 1,457 | 13,555 |
| 1900 | 17,700 | 2,230 | 1,251 | 21,181 |
The value of the exports for the same period is as follows:—
| Year. | From Cook Islands. | From other Places. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1892 | 15,394 | 4,943 | 20,337 |
| 1893 | 18,703 | 905 | 19,668 |
| 1894 | 18,937 | 1,728 | 20,665 |
| 1895 | 19,084 | 1,054 | 20,138 |
| 1896 | 15,486 | 1,333 | 16,819 |
| 1897 | 21,751 | 2,381 | 24,132 |
| 1898 | 11,209 | 1,408 | 12,617 |
| 1899 | 11,199 | 3,020 | 14,219 |
| 1900 | 19,310 | 3,069 | 22,379 |
Table of Contents
THE shipping entered inwards during 1902 comprised 638 vessels, of 1,089,179 tonnage; while entered outwards were 611 vessels, of 1,048,770 tons. Comparison with the figures for the previous year shows in the entries a decrease of 50 vessels and an increase of 25,905 tons, and in the clearances a decrease of 80 vessels and 27,136 tons. Of the vessels inwards, 172, of 496,203 tons, were British; 395, of 429,467 tons, colonial; and 71, of 163,509 tons, foreign. Those outwards numbered 152, of 447,351 tons, British; 385, of 437,489 tons, colonial; and 74, of 163,930 tons, foreign. Compared with the figures for 1901 there was a decrease of 3 vessels and an increase of 47,515 tons in British vessels entered, a decrease in the colonial shipping entered of 46 vessels and 32,262 tons. Foreign shipping shows a decrease of 1 in the number of vessels entered, and an increase of 10,652 tons. Of the entries in 1902, 228, of 123, 186 tons, were sailing-vessels, and 410, of 965,993 tons, steamers. Of the clearances, 213, of 113,950 tons, were sailing-vessels, and 398, of 934,820 tons, steamers. The shipping inwards and outwards for ten years is given in the table following:—
| Vessels entered, 1893–1902. | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Total Number. | British. | Colonial. | Foreign. | ||||||||
| Vessels. | Tons. | Crews. | Vessels. | Tons. | Crews. | Vessels. | Tons. | Crews. | Vessels. | Tons. | Crews. | |
Note.—Coasting-vessels are not included in the above table. | ||||||||||||
| 1893 | 617 | 615,604 | 20,935 | 166 | 290,323 | 7,289 | 405 | 272,250 | 11,745 | 46 | 53,031 | 1,901 |
| 1894 | 609 | 631,100 | 21,834 | 141 | 271,994 | 6,456 | 423 | 306,547 | 13,279 | 45 | 52,559 | 2,099 |
| 1895 | 611 | 672,951 | 22,074 | 146 | 299,667 | 6,837 | 420 | 319,313 | 13,209 | 45 | 53,971 | 2,028 |
| 1896 | 589 | 614,097 | 19,857 | 126 | 249,601 | 5,495 | 395 | 300,176 | 12,210 | 68 | 64,320 | 2,152 |
| 1897 | 600 | 686,899 | 21,542 | 133 | 276,020 | 6,086 | 395 | 340,793 | 13,138 | 72 | 70,086 | 2,318 |
| 1898 | 620 | 765,255 | 24,081 | 152 | 329,065 | 7,910 | 399 | 369,840 | 13,897 | 69 | 66,350 | 2,274 |
| 1899 | 609 | 811,183 | 23,929 | 149 | 350,861 | 6,986 | 388 | 392,671 | 14,666 | 72 | 67,651 | 2,277 |
| 1900 | 616 | 854,632 | 23,791 | 156 | 392,394 | 7,183 | 393 | 392,519 | 14,135 | 67 | 69,719 | 2,473 |
| 1901 | 688 | 1,063,274 | 29,724 | 175 | 448,688 | 7,713 | 441 | 461,729 | 16,063 | 72 | 2,857 | 5,948 |
| 1902 | 638 | 1,089,179 | 30,264 | 172 | 496,203 | 8,871 | 395 | 421,467 | 15,305 | 71 | 163,509 | 6,088 |
| Vessels cleared, 1893–1902. | ||||||||||||
| 1893 | 635 | 642,466 | 21,448 | 186 | 317,130 | 7,839 | 400 | 270,308 | 11,665 | 5,028 | 1,944 | |
| 1894 | 614 | 631,250 | 21,934 | 140 | 270,464 | 6,437 | 432 | 310,050 | 13,527 | 42 | 50,736 | 1,970 |
| 1895 | 597 | 648,946 | 21,619 | 134 | 281,840 | 6,528 | 420 | 315,171 | 13,068 | 43 | 51,935 | 2,023 |
| 1896 | 592 | 627,659 | 20,217 | 123 | 259,064 | 5,637 | 402 | 305,926 | 12,448 | 67 | 62,669 | 2,132 |
| 1897 | 587 | 675,333 | 21,409 | 140 | 280,229 | 6,240 | 378 | 327,068 | 12,881 | 69 | 68,036 | 2,288 |
| 1898 | 622 | 765,793 | 24,130 | 150 | 322,150 | 7,898 | 403 | 377,102 | 13,948 | 69 | 66,541 | 2,284 |
| 1899 | 604 | 807,866 | 24,117 | 152 | 355,442 | 7,194 | 379 | 386,219 | 14,656 | 73 | 66,205 | 2,267 |
| 1900 | 613 | 825,275 | 23,481 | 149 | 368,241 | 6,978 | 397 | 388,436 | 14,153 | 67 | 68,598 | 2,350 |
| 1901 | 691 | 1,075,906 | 30,028 | 177 | 462,179 | 7,954 | 441 | 458,994 | 16,106 | 73 | 154,733 | 5,968 |
| 1902 | 611 | 1,048,770 | 29,294 | 152 | 447,351 | 7,983 | 385 | 437,489 | 15,171 | 74 | 163,930 | 6,140 |
The noticeable feature in the operations for the decennium is a considerable increase of tonnage inwards and outwards, but not in the numbers of vessels, showing that larger ships are now used than those of ten years ago.
The figures given apply to the external trade only; but in a new country such as New Zealand, as yet deficient in roads, but having an extensive seaboard and a number of good harbours, the coastal trade must be relatively very large, as is evidenced by the figures next given:—
| SHIPPING ENTERED COASTWISE, 1902. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number. | Tons. | |
| Sailing-vessels | 4,797 | 306,965 |
| Steamers | 17,007 | 7,942,658 |
| SHIPPING CLEARED COASTWISE, 1902. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number. | Tons. | |
| Sailing-vessels | 4,758 | 304,523 |
| Steamers | 17,011 | 8,005,112 |
The total number of vessels entered coastwise was thus 21,804, of 8,249,623 tons, an increase of 324 vessels and 405,810 tons on the figures for 1901. The total clearances coastwise were 21,769 vessels, of 8,309,635 tons, an increase of 347 vessels and 509,738 tons on the number for the previous year.
The number and tonnage of the registered vessels belonging to the several ports on the 31st December, 1902 (distinguishing sailing-vessels and steamers), was as under:—
| Registered Vessels, 31st December, 1902. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ports. | Sailing-vessels. | Steam-vessels. | ||||
| Vessels. | Gross Tonnage. | Net Tonnage. | Vessels. | Gross Tonnage. | Net Tonnage. | |
| Auckland | 194 | 17,639 | 16,488 | 93 | 12,179 | 7,341 |
| Napier | 8 | 591 | 578 | 17 | 1,543 | 844 |
| Wellington | 22 | 3,462 | 3,343 | 25 | 4,473 | 2,409 |
| Nelson | 7 | 180 | 180 | 9 | 820 | 517 |
| Lyttelton | 30 | 6,046 | 5,771 | 9 | 2,178 | 911 |
| Dunedin | 49 | 15,233 | 14,881 | 68 | 81,648 | 49,950 |
| Invercargill | 15 | 1,619 | 1,565 | 3 | 211 | 55 |
| Totals | 325 | 44,770 | 42,806 | 224 | 103,052 | 62,027 |
The history and progress of railways in New Zealand was specially described in the Year-book of 1894, as was also the line partly built by the New Zealand Midland Railway Company. An account of the line belonging to the Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company was published in the Year-book for 1895.
The length of Government railways open for traffic on the 31st March, 1903, was 2,291 miles, of which 868 were situated in the North Island and 1,423 in the Middle Island.
The sections of the North Island lines consist of the Kawakawa, 8 miles; Whangarei, 23; Kaihu, 17; Auckland, 341; Gisborne–Karaka, 13 miles; and the Wellington–Napier–New Plymouth, 466 miles. The Middle Island sections comprise the Hurunui–Bluff, with branches, 1,213 miles; Westland, 112; Westport, 31; Nelson, 33; Picton, 34 miles. The total cost of construction, including Public Works loan expenditure on harbour works forming part of the railway system, has been £19,081,735 (besides £1,133,200 spent on unopened lines), and the average cost per mile of open line £8,436.
The following statement shows the number of miles of Government railways open, the number of train-miles travelled and of passengers carried, and the tonnage of goods traffic, for the past thirteen years:—
| Year. | Length open. | Train-mileage. | Passengers. | Season Tickets issued. | Goods and Live-stock. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1890–91 | 1,842 | 2,894,776 | 3,433,629 | 13,881 | 2,134,023 |
| 1891–92 | 1,869 | 3,010,489 | 3,555,764 | 16,341 | 2,122,987 |
| 1892–93 | 1,886 | 3,002,174 | 3,759,044 | 16,504 | 2,258,235 |
| 1893–94 | 1,948 | 3,113,231 | 3,972,701 | 17,226 | 2,128,709 |
| 1894–95 | 1,993 | 3,221,620 | 3,905,578 | 28,623 | 2,123,343 |
| 1895–96 | 2,014 | 3,307,226 | 4,162,426 | 36,233 | 2,175,943 |
| 1896–97 | 2,018 | 3,409,218 | 4,439,387 | 43,069 | 2,461,127 |
| 1897–98 | 2,055 | 3,666,483 | 4,672,264 | 48,660 | 2,628,746 |
| 1898–99 | 2,090 | 3,968,708 | 4,955,553 | 55,027 | 2,744,441 |
| 1899–1900 | 2,104 | 4,187,893 | 5,468,284 | 63,335 | 3,251,716 |
| 1900–1901 | 2,212 | 4,620,971 | 6,243,593 | 82,921 | 3,461,331 |
| 1901–1902 | 2,235 | 5,066,360 | 7,356,136 | 100,778 | 3,667,039 |
| 1902–1903 | 2,291 | 5,443,333 | 7,575,390 | 118,431 | 3,730,394 |
The traffic in local products for the past thirteen years was:—
| Year. | Wool. | Timber. | Grain. | Minerals. | Horses and Cattle. | Sheep and Pigs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* The equivalent tonnage for live-stock has been given. | ||||||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Number. | Number. | |
| 1890–91 | 87,701 | 153,078 | 528,683 | 828,079 | 44,999 | 1,313,155 |
| 1891–92 | 85,888 | 170,521 | 442,277 | 873,899 | 47,618 | 1,117,253 |
| 1892–93 | 96,842 | 169,910 | 523,637 | 884,031 | 46,590 | 1,359,860 |
| 1893–94 | 101,340 | 183,192 | 4,191 | 864,538 | 51,573 | 1,394,456 |
| 1894–95 | 103,328 | 198,578 | 3,356 | 857,917 | 52,075 | 1,563,213 |
| 1895–96 | 99,363 | 213,132 | 374,699 | 878,659 | 50,766 | 1,893,058 |
| 1896–97 | 98,958 | 257,825 | 423,888 | 1,032,252 | 47,256 | 2,016,437 |
| 1897–98 | 103,055 | 313,073 | 427,448 | 1,048,868 | 54,871 | 2,399,379 |
| 1898–99 | 97,396 | 310,266 | 420,071 | 1,147,353 | 66,226 | 2,552,745 |
| 1899–1900 | 104,621 | 334,677 | 764,033 | 1,218,698 | 76,537 | 2,559,836 |
| 1900–1901 | 96,519 | 380,803 | 772,571 | 1,366,241 | 84,289 | 2,463,250 |
| 1901–1902 | 101,878 | 427,153 | 813,345 | 1,443,792 | 95,384 | 2,780,019 |
| 1902–1903 | 116,309 | 436,008 | 718,376 | 1,604,426 | 115,198 | 3,883,177 |
The cash revenue for the year 1902 – 1903 amounted to £1,974,038; and the total expenditure to £1,343,415. The net cash revenue—£630,623—was equal to a rate of £3 6s. 1d. per cent. on the capital cost; the percentage of expenditure to revenue was 68·05. The earnings on some of the lines ranged as high as £6 1s. 9d., and even £16 2s. 7d., per cent.
The particulars of the revenue and expenditure for the past thirteen years are given herewith:—
| Year. | Passenger Fares. | Parcels Luggage and Mails. | Goods and Live-stock. | Rents and Miscellaneous. | Total. | Expenditure. | Net Revenue. | Percentages of Expenditure to Revenue. | Percentages Revenue to Capital Cost. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Note.—For 1895–96 and subsequent years the railways have been credited with the value of services performed for other Government departments, and debited with the value of work done for the railways by other departments. | |||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | % | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1890–91 | 353,593 | 38,997 | 690,779 | 38,332 | 1,121,701 | 700,703 | 420,998 | 62·47 | 2 | 18 | 11 |
| 1891–92 | 364,617 | 41,795 | 671,469 | 37,550 | 1,115,431 | 706,517 | 408,914 | 63·34 | 2 | 15 | 9 |
| 1892–93 | 390,619 | 44,801 | 707,785 | 38,316 | 1,181,521 | 732,141 | 449,380 | 61·97 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 1893–94 | 402,019 | 45,206 | 686,469 | 39,098 | 1,172,792 | 735,358 | 437,434 | 62·70 | 2 | 17 | 9 |
| 1894–95 | 385,149 | 43,270 | 683,726 | 38,706 | 1,150,851 | 732,160 | 418,691 | 63·62 | 2 | 14 | 6 |
| 1895–96 | 389,234 | 54,736 | 698,115 | 40,956 | 1,183,041 | 751,368 | 431,673 | 63·51 | 2 | 16 | 0 |
| 1896–97 | 410,160 | 58,084 | 774,163 | 43,751 | 1,286,158 | 789,054 | 497,104 | 61·35 | 3 | 3 | 10 |
| 1897–98 | 433,430 | 60,872 | 837,589 | 44,117 | 1,376,008 | 857,191 | 518,817 | 62·30 | 3 | 4 | 10 |
| 1898–99 | 475,553 | 66,418 | 882,077 | 45,617 | 1,469,665 | 929,737 | 539,928 | 63·26 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| 1899–00 | 515,020 | 68,488 | 985,723 | 54,660 | 1,623,891 | 1,052,358 | 571,533 | 64·80 | 3 | 8 | 5 |
| 1900–01 | 544,976 | 72,712 | 1,051,694 | 57,854 | 1,727,236 | 1,127,847 | 599,389 | 65·30 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
| 1901–02 | 621,019 | 79,561 | 1,110,575 | 63,431 | 1,874,586 | 1,252,237 | 622,349 | 66·80 | 3 | 8 | 6 |
| 1902–03 | 625,698 | 87,273 | 1,189,101 | 71,966 | 1,974,038 | 1,343,415 | 630,623 | 68·05 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
The revenue per (average) mile of railway open during the year was £873, and the expenditure £591; equal to 7s. 3d. and 4s. 11d. per train-mile respectively.
The total number of miles travelled by trains was 5,443,333.
In addition to the above railways, there were 113 miles of private lines open for traffic on the 31st March, 1903—including the Wellington–Manawatu Railway, 84 miles.
The cost of the construction of the Wellington–Manawatu Railway is now returned as £793,575, being at the rate of £9,447 per mile. The term “cost of construction,” as applied to railways, includes value of equipment, rolling-stock, &c., not merely the road-line and buildings. The gross earnings for the twelve months ended the 28th February, 1903, amounted to £111,398, and the working-expenses to £60,129, equivalent to 53·97 per cent. of the revenue.
The following statement gives the average number of miles of Government railways open for traffic in Australasia in 1901–1902:—
| Railways (State only). | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State or Colony. | Year ended | Average Miles open. | Train Miles Run. | Cost of Construction of Open Lines. | Gross Receipts. | Working Expenses. | Percentage of Net Revenue to Cost. | Number of | ||
| Locomotives. | Vehicles. | |||||||||
| Passenger. | Goods and Livestock. | |||||||||
* Includes 7 1/2 miles private lines worked by Government. † State railways only. | ||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | % | |||||||
| Queensland | 30 June, 1902 | 2,801 | 5,666,058 | 20,119,143 | 1,382,179 | 992,751 | 1·94 | 362 | 419 | 7,058 |
| New South Wales | 30 June, 1902 | 2,953 | 11,649,059 | 40,565,073 | 3,668,686 | 2,267,369 | 3·48 | 518 | 794 | 12,514 |
| Victoria | 30 June, 1902 | 3,265 | 11,284,944 | 40,613,784 | 3,367,843 | 2,072,374 | 3·19 | 542 | 1,189 | 10,101 |
| South Australia | 30 June, 1902 | 1,882 | 4,226,413 | 14,435,784 | 1,097,697 | 724,166 | 2·59 | 351 | 438 | 6,525 |
| Western Australia | 30 June, 1902 | 1,356 | 4,507,919 | 7,410,426 | 1,521,429 | 1,256,370 | 3·58 | 274 | 260 | 5,285 |
| Tasmania | 31 Dec., 1901 | *459 | 895,682 | †3,799,098 | 205,791 | 173,400 | 0·85 | 71 | 171 | 1,439 |
| New Zealand | 31 Mar., 1903 | 2,262 | 5,443,333 | 19,081,735 | 1,974,038 | 1,343,415 | 3·30 | 372 | 751 | 12,992 |
In addition to the Government lines open for traffic in 1902, New South Wales had, in 1901, 85 miles of private railway; Western Australia, 623 miles; Tasmania, 14 miles, 7 1/2 miles of which are worked by Government; and New Zealand, on 31st March, 1903, 113 miles.
There were 1,807 post-offices in New Zealand at the end of 1902.
The number of letters, letter-cards, post-cards, books, and pattern-packets, newspapers, and parcels dealt with during the year, compared with the number handled in 1901, was as under:—
| Total Number dealt with. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1902 | 1901 | ||
| Letters | 56,689,256 | 51,544,265 | 5,144,991 Increase. |
| Letter-cards | 1,025,375 | 1,023,295 | 2,080 Increase. |
| Post-cards | 1,302,167 | 1,522,377 | 220,210 Decrease. |
| Books and pattern-packets | 18,626,324 | 17,801,066 | 825,258 Increase. |
| Newspapers | 18,517,276 | 18,973,632 | 456,356 Decrease. |
| Parcels | 291,670 | 273,442 | 18,228 Increase. |
The average number of letters, &c., posted per head of the population in each of the past five years was,—
| 1898 | 1899 | 1900 | 1901 | 1902 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Letters and letter-cards | 45·34 | 47·77 | 49·01 | 63·49 | 68·07 |
| Post-cards | 1·90 | 2·12 | 2·43 | 1·88 | 1·55 |
| Books and parcels | 19·72 | 21·68 | 21·10 | 21·09 | 21·45 |
| Newspapers | 14·77 | 15·13 | 16·17 | 17·81 | 16·79 |
The facilities afforded for the transmission of parcels through the Post Office to places within and without the colony have proved of much convenience to the public. The regulations admit of parcels up to 11 lb. in weight being sent to almost all the important countries of the world.
The following table shows the number of parcels exchanged with the United Kingdom, the Australian States, &c., in 1901 and 1902:—
| Country. | Number of Parcels. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Received. | Despatched. | |||
* Four months only. † Five months only. ‡ Seven months only. § Six months only. | ||||
| 1901 | 1902 | 1901 | 1902 | |
| United Kingdom and foreign countries viâ London | 24,011 | 28,881 | 5,787 | 6,225 |
| United States | 3,019 | 4,123 | 833 | 1,085 |
| Vancouver | 221 | 303 | 131 | 168 |
| Victoria | 2,853 | 4,071 | 1,456 | 1,961 |
| New South Wales | 7,260 | 7,705 | 2,386 | 2,704 |
| South Australia | 284 | 680 | 245 | 246 |
| Queensland | 408 | 507 | 342 | 359 |
| Tasmania | 217 | 237 | 377 | 464 |
| Western Australia | 211 | 235 | 264 | 310 |
| Samoa | .. | *12 | 155 | 143 |
| Rarotonga | 32 | †21 | 86 | †27 |
| Fiji | 60 | 48 | 168 | 251 |
| Ceylon | 487 | 209 | 101 | 54 |
| Uruguay | .. | .. | 17 | 24 |
| Cape Colony | 814 | 390 | 537 | 407 |
| Transvaal | .. | .. | 378 | ‡151 |
| Natal | §72 | 174 | §26 | 64 |
| Malta | 2 | .. | .. | .. |
| India | .. | 352 | *47 | 136 |
| Totals | 39,951 | 47,654 | 13,336 | 14,779 |
The declared value of the parcels received from places outside the colony was £123,912, on which the Customs duty amounted to £22,737.
The number and weight of parcels dealt with from 1895 to 1902 are given. The word “parcels” in the first-named table includes the parcels herein mentioned:—
| — | 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parcels, No. | 176,206 | 186,611 | 197,554 | 204,603 | 223,350 | 233,456 | 273,442 | 291,670 |
| Weight, lb. | 582,193 | 654,333 | 676,054 | 698,301 | 765,836 | 794,994 | 928,237 | 1,034,342 |
The number of offices open for the transaction of money-order business at the end of 1902 was 494.
During 1902, 367,207 money-orders, for a total sum of £1,277,059 2s. 3d., were issued at the various post-offices in the colony. The money-orders from places beyond New Zealand and payable in the colony numbered 28,259, for the amount of £103,530 3s. 11d.
The number of offices open for the sale of postal notes at the end of 1902–1903 was 575: 616,264 postal notes were sold, value £191,904 13s. Commission amounted to £4,195 17s. 10d.
The notes paid numbered 610,464, value £190,374 14s. 6d.
The cost of the various mail-services between England and New Zealand was, in 1902, as follows:—
| S(([0-9]+)) SERVICE. | 1902. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Payments— | £ | s. | d. |
| Subsidies, &c. | 22,258 | 0 | 1 |
| Interprovincial and other charges | 5,813 | 8 | 5 |
| £28,071 | 8 | 6 | |
| Receipts— | |||
| Contributions from Fiji | 96 | 5 | 7 |
| Postages collected in the colony | 13,290 | 2 | 2 |
| £13,386 | 7 | 9 | |
| Loss to the colony | £14,685 | 0 | 9 |
| PENINSULAR AND ORIENTAL AND ORIENT LINES SERVICES. | |||
| Payments— | £ | s. | d. |
| To P. and O. and Orient Lines | 3,209 | 11 | 11 |
| Transit across Australia | 156 | 8 | 2 |
| Transit across European Continent | 375 | 4 | 6 |
| Intercolonial services | 1,787 | 10 | 5 |
| £5,528 | 15 | 0 | |
| Receipts— | |||
| Postages collected from England and from foreign effects | 1,381 | 18 | 5 |
| Postages collected in the colony | 1,743 | 4 | 11 |
| £3,125 | 3 | 4 | |
| Loss to the colony | £2,403 | 11 | 8 |
The total amount of postages collected and contributions received for these services in 1902 was £16,511 11s. 1d.
The average number of days in 1902 within which the mails were delivered between London and each of the undermentioned ports in New Zealand was:—
| San Francisco Service. | P. and O. Line. | Orient Line. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| London to— | |||
| Auckland | 30·94 | 37·27 | 39·15 |
| Wellington | 32·44 | 39·35 | 40·08 |
| Dunedin | 33·72 | 39·29 | 39·52 |
| Bluff | 34·47 | 38·54 | 38·77 |
There were 7,749 miles of telegraph-line open at the end of March, 1903, carrying 22,672 miles of wire. 4,559,304 telegrams were transmitted during the year; of these, the private and Press messages numbered 4,271,218, which, together with telephone exchange and other telegraph receipts, yielded a revenue of £222,494 16s. 6d.
There were twenty-six telephone central exchanges and forty-four sub-exchanges on the 31st March, 1903. The number of connections increased from 9,260 in March, 1902, to 10,633 in March, 1903. The subscriptions to these exchanges during the financial year amounted to £62,151 8s. 11d.
The capital expended on the equipment, &c., of the several telephone exchanges up to the 31st March, 1903, was £213,966 10s. 8d.
“The Pacific Cable Authorisation Act, 1899,” empowered the Government of New Zealand to co-operate with the Governments of Great Britain, Canada, New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland in raising the required capital for constructing and maintaining a Pacific cable—the cable to be jointly owned and maintained by the contributing Governments; New Zealand to join such of the Australian States as were prepared to do likewise, upon the basis of a guarantee of four-ninths of the cost of construction and annual deficiency (if any) by such States, New Zealand's proportion of the guarantee not to exceed in any case one-ninth of the whole cost
Arrangements having been finally concluded, the work of construction proceeded, with the result that the cable, which was opened for traffic between New Zealand and Australia and Fiji on the 9th April of last year, was completed to Bamfield, Vancouver Island, on the 31st October following, and opened for international business on the 8th December, 1902.
The route is from Doubtless Bay, New Zealand, to Vancouver, Canada, viâ Norfolk Island, Fiji, and Fanning Island. The Australian connection is at Norfolk Island. The deep-sea portion of the Vancouver–Fanning Island cable is stated to be the longest in the world. It was laid in twenty days. Following the opening of the cable a much faster service between the colony, America, and Europe has resulted.
Table of Contents
The natural mineral resources of New Zealand are very great, and have exercised in the past a most important influence on the development and progress of the colony. Gold to the value of £61,111,316 was obtained prior to the 31st December, 1902; the value of the produce for the year 1902 having been £1,951,433. In the earliest years the gold was obtained from alluvial diggings, but at the present time much is taken from gold-bearing quartz, which is distributed widely through several parts of the colony, and thus there is a much better prospect of the permanency of this industry than alluvial diggings alone could give.
The yield of silver to the end of 1902 amounted to £452,781 in value, the quantity mined in 1902 having been 674,196 oz., valued at £71,975.
Of other minerals, the value of the product to the same date amounts to £20,718,489, of which kauri-gum yielded £11,226,168, and coal, with coke, £9,200,139.
The quantities and values of precious metals and minerals obtained during the year 1902, and the total value of all mining produce since 1853, are:—
| 1902. | Total Value since 1853. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oz. | £ | £ | |
| Gold | 508,045 | 1,951,433 | 61,111,316 |
| Silver | 674,196 | 71,975 | 452,781 |
| 1,182,241 | 2,023,408 | 61,564,097 | |
| Tons. | |||
| Copper-ore | .. | .. | 18,088 |
| Chrome-ore | 175 | 525 | 38,002 |
| Antimony-ore | .. | .. | 52,598 |
| Manganese-ore | .. | .. | 60,846 |
| Hæmatite-ore | 17 | 116 | 342 |
| Mixed minerals | 415 | 4,422 | 115,113 |
| Coal | 1,362,702 | 741,759 | 9,175,335 |
| Shale | 2,338 | 1,169 | 7,193 |
| Coke (exported) | .. | .. | 24,804 |
| Kauri-gum | 7,430 | 450,223 | 11,226,168 |
| £3,221,622 | £82,282,586 | ||
Of the gold entered for exportation during the year ended the 31st March, 1903—viz., 527,372 oz., representing a value of £2,024,731—about 60 per cent. came out of quartz-mines; but, if the total yield of gold obtained in the colony be taken, the value of which to 31st March, 1903, is £61,561,313, about 25 per cent. came from quartz-mines, and 75 per cent. from alluvial workings.
The total value of mineral production for Australasia to the end of the year 1901 is shown in the following table. The figures, except those for New Zealand, are taken from Mr. Coghlan's “Statistics of the Six States of Australia and New Zealand,” 1901–1902:—
| State or Colony. | Gold. | Silver and silver-lead. | Copper. | Tin. | Coal. | Other Minerals. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Inclusive of kauri-gum to the value of £10,775,945. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| New S'th Wales | 49,661,815 | 32,341,577 | 5,857,073 | 6,601,806 | 39,494,844 | 4,299,947 | 138,257,062 |
| Victoria | 260,489,201 | 856,539 | 206,395 | 715,498 | 1,042,358 | 346,031 | 263,656,022 |
| Queensland | 52,751,675 | 788,042 | 2,249,692 | 4,693,866 | 2,821,989 | 320,410 | 63,625,674 |
| South Australia | 2,388,197 | 118,630 | 22,822,046 | 32,680 | ... | 509,542 | 25,871,095 |
| W'st'n Australia | 30,149,712 | 11,453 | 326,972 | 198,199 | 150,972 | 414,534 | 31,251,842 |
| Tasmania | 4,893,588 | 2,384,886 | 3,921,495 | 7,276,294 | 445,465 | 336,932 | 19,258,660 |
| New Zealand | 59,159,883 | 380,806 | 18,088 | ... | 8,433,576 | 11,068,611* | 79,060,964 |
| Australasia | 459,494,071 | 36,881,933 | 35,401,761 | 19,518,343 | 52,389,204 | 17,296,007 | 620,981,319 |
The history of the finding of gold in this colony was briefly sketched in the Year-books for 1893 and 1894, and need not, therefore, be repeated here, but a word may be said on recent developments in mining. Great changes have taken place since the early days, when a man wanted but a pick and shovel, tin dish and cradle, to enable him to earn a livelihood on the diggings. The rich shallow gravels have been to all appearances worked out, the ground is getting deeper, the inroads of water more troublesome, and greatly improved appliances are needed in order to pump the water or wash away the masses of drift that overlie the gold-bearing layers on the bottom.
The difficulty for many years experienced in working the beds of the larger rivers has been at last overcome by the use of dredging machinery. Dredging has not only been adopted for working river-beds, but has also been applied with advantage to alluvial flats, which cannot be otherwise profitably worked. The total number of dredges at the end of the year 1902 was: Working, 201; being built, 23; not working, 52; undergoing removal, &c., 16: total, 292.
The importance of this class of gold-mining is best illustrated by the fact that, during the five weeks ending 30th May, 1903, the quantity of gold won by 115 dredges for which returns are available was 104 oz. 17 dwt. per dredge, the average time worked by each dredge being three weeks and a half. There are many private owners, who do not make public their returns.
The following are the averages for five months of dredges that publish returns:—
| (Approximate.) Return per Dredge. | (Approximate.) Average Working Period.* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oz. | dwt. | gr. | |||
*Or periods for which returns were furnished. †Averaged for four weeks. ‡Averaged for five weeks. | |||||
| 4 weeks ending January 31, 1903 | 96 dredges† | 74 | 15 | 0 | 3 weeks. |
| 4 weeks ending February 28, 1903 | 106 dredges ‡ | 83 | 0 | 0 | 3 weeks. |
| 4 weeks ending March 28, 1903 | 105 dredges † | 74 | 10 | 0 | 3 weeks. |
| 4 weeks ending April 25, 1903 | 110 dredges † | 79 | 3 | 0 | 3 weeks. |
| 5 weeks ending May 30, 1903 | 115 dredges ‡ | 104 | 17 | 0 | 3 1/2 weeks. |
It may be calculated that 10 oz. per week will pay working-expenses—big dredges more, say 12 oz.; little dredges less, say 6 oz. to 8 oz. Repairs are very costly, in some cases up to as high as £500 per annum, in others perhaps not more than £100. If £300 allowed on the average it would probably cover cost—not, of course, of removal from one claim to another, which is often very expensive, according to distance, as from Central Otago to Waimumu or Charlton, in Southland, or from Otago to the West Coast.
An average of 15 oz. per week would probably cover working-expenses and repairs, taking small dredges with the large ones.
The recovery of gold from river-beds and wet alluvial flats is an established industry in New Zealand. The success of some of the ventures in the earlier stages of what was at first a comparatively novel form of mining led to rash speculation, but this undesirable condition has ceased to exist, and dredging is now regarded as a good field for investment.
The small amount of capital required and low working-expenses are advantages which tend to popularise dredging, and secure the working of gold-deposits which would otherwise lie untouched.
The total number of gold-miners employed in 1902 was 11,398, as against 12,732 for the previous year. In some places, more especially in Otago, Nelson, and the West Coast, many of the miners do not depend entirely on mining, but employ a part of their time in farming and other pursuits.
In 1901 an Act was passed reducing the fee payable for a miner's right from 10s. to 5s.
The total quantity of gold entered for export during the years ending 31st March, 1902, and 31st March, 1903, for the several districts, and the total quantity and value of the gold exported from the colony from the 1st January, 1857, to the 31st March, 1903, are shown hereunder; but this does not necessarily include the whole of the gold produced, as no doubt much has been taken out of the colony from time to time by people who have evaded the duty, and a good deal has been used for making jewellery and ornaments:—
| Table showing the Quantity and Value of Gold entered for Exportation from New Zealand for the Years ended the 31st March, 1902 and 1903, and the Total Quantity and Value from January, 1857, to 31st March, 1903. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District. | Year ending 31st March, 1902. | Year ending 31st March, 1903. | Increase for Year ending 31st March, 1903. | Total Quantity and Value from January, 1857, to 31st March, 1903. | |||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | ||||
| * Decrease. | |||||||
| Oz. | £ | Oz. | £ | Oz. | Oz. | £ | |
| Auckland | 201,861 | 728,498 | 203,158 | 724,892 | 1,297 | 3,055,462 | 11,398,344 |
| Wellington | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 188 | 706 |
| Marlborough | 277 | 1,108 | 401 | 1,604 | 124 | 87,500 | 340,902 |
| Nelson | 4,207 | 17,118 | 6,235 | 24,704 | 2,028 | 273,597 | 1,080,199 |
| West Coast | 104,441 | 418,322 | 125,399 | 501,639 | 20,958 | 6,228,870 | 24,769,757 |
| Canterbury | 19 | 71 | .. | .. | – 19* | 123 | 483 |
| Otago | 128,200 | 515,265 | 192,079 | 771,892 | 63,879 | 6,044,721 | 23,970,922 |
| Totals | 439,005 | 1,680,382 | 527,272 | 2,024,731 | 88,267 | 15,690,461 | 61,561,313 |
It will be seen from the above table that there was last year an increase in the yield of gold of 88,267 oz. on the figures for the preceding twelve months.
Of the total quantity of gold entered for exportation last year Auckland contributed 38·53 per cent.; Marlborough, 0·08 per cent.; Nelson, 1·18 per cent.; West Coast, 23·78 per cent.; and Otago, 36·43 per cent.
The gold yield of Australasia for 1898, 1899, 1900, and 1901, was as under:—
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oz. | Oz. | Oz. | Oz. | |
| Queensland | 920,048 | 946,894 | 963,189 | 835,553 |
| New South Wales | 340,493 | 496,196 | 345,650 | 267,061 |
| Victoria | 837,257 | 854,500 | 807,407 | 789,562 |
| South Australia | 31,961 | 23,122 | 24,086 | 26,952 |
| Western Australia | 1,050,184 | 1,643,877 | 1,580,950 | 1,879,390 |
| Tasmania | 74,233 | 83,992 | 81,125 | 75,831 |
| New Zealand | 280,175 | 389,558 | 373,616 | 455,561 |
| 3,534,351 | 4,438,139 | 4,176,023 | 4,329,910 |
The increase for the period is 795,559 oz. The mint value of Australasian gold averages £3 16s. per ounce, and a comparison of value is therefore as follows: 1898, £13,430,533; 1899, £16,864,927; 1900, £15,868,887; 1901, £16,453,658: increase, 1898 to 1901, £3,023,125.
Gold-production of the World for each of the Five Years 1897–1901.
(From a table compiled in the Government Statistician's Office, Perth, Western Australia.)
| Countries and Continents. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australasia. | ||||||
| Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | ||
| Western Australia | .. | 603,847 | 939,490 | 1,470,605 | 1,414,311 | 1,703,416 |
| Victoria | .. | 765,365 | 788,429 | 789,368 | 751,211 | 731,276 |
| Queensland | .. | 601,060 | 647,487 | 668,150 | 676,058 | 598,412 |
| New Zealand | .. | 230,759 | 254,416 | 356,231 | 338,911 | 412,876 |
| New South Wales | .. | 265,593 | 292,940 | 412,412 | 281,214 | 216,888 |
| Tasmania | .. | 68,093 | 68,624 | 77,110 | 74,445 | 69,491 |
| South Australia | .. | 28,285 | 22,377 | 18,633 | 19,418 | 21,946 |
| New Guinea, &c. | .. | 5,890 | 5,627 | 10,402 | 7,560 | 8,693 |
| Total ounces | .. | 2,568,892 | 3,019,390 | 3,802,911 | 3,563,128 | 3,762,998 |
| Total value | £ | 10,911,960 | 12,825,553 | 16,153,739 | 15,135,206 | 15,984,200 |
| Africa. | ||||||
| The Transvaal | .. | 2,743,518 | 3,823,367 | 3,637,713 | 348,761 | 258,033 |
| Other countries and colonies | 48,479 | 57,579 | 130,257 | 194,049 | 256,449 | |
| Total ounces | .. | 2,791,997 | 3,880,946 | 3,767,970 | 542,810 | 514,482 |
| Total value | £ | 11,859,649 | 16,485,211 | 16,005,319 | 2,305,710 | 2,185,381 |
| America. | ||||||
| United States of America | .. | 2,774,935 | 3,118,398 | 3,437,210 | 3,829,897 | 3,880,578 |
| Canada | .. | 291,582 | 666,445 | 1,028,620 | 1,350,176 | 1,183,465 |
| Mexico | .. | 481,362 | 587,548 | 281,471 | 455,204 | 499,725 |
| Columbia | .. | 107,736 | 109,473 | 89,231 | 57,804 | 100,145 |
| South America | .. | 394,584 | 414,114 | 493,456 | 563,045 | 584,786 |
| Total ounces | .. | 4,050,199 | 4,895,978 | 5,329,988 | 6,256,126 | 6,248,699 |
| Total value | £ | 17,204,152 | 20,796,793 | 22,640,350 | 26,574,334 | 26,542,786 |
| Europe. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | Fine oz. | |
| Russia | .. | 1,073,798 | 1,073,525 | 1,083,543 | 1,072,434 | 1,253,592 |
| Other European countries | .. | 214,280 | 203,844 | 203,446 | 230,400 | 210,873 |
| Total ounces | .. | 1,288,078 | 1,277,369 | 1,286,989 | 1,302,834 | 1,464,465 |
| Total value | £ | 5,471,407 | 5,425,919 | 5,466,782 | 5,534,087 | 6,220,652 |
| British India | .. | 369,154 | 378,674 | 405,045 | 444,585 | 452,743 |
| China | .. | 298,486 | 261,655 | 269,783 | 208,031 | 231,058 |
| Other Asiatic countries | .. | 88,584 | 99,630 | 157,751 | 207,864 | 273,798 |
| Total ounces | .. | 756,224 | 739,959 | 832,579 | 860,480 | 957,599 |
| Total value | £ | 3,212,235 | 3,143,146 | 3,536,571 | 3,655,087 | 4,067,622 |
| The World. | ||||||
| Total ounces | .. | 11,455,390 | 13,813,642 | 15,020,437 | 12,525,378 | 12,948,243 |
| Value, pounds sterling | £ | 48,659,403 | 58,676,622 | 63,802,761 | 53,204,424 | 55,000,641 |
By a statute passed in December, 1897, and termed “The Cyanide Process Gold-extraction Act, 1897,” an agreement was approved by Parliament under which the Government arranged to purchase the patent rights in New Zealand of the Cassel Gold-extracting Company, thus rendering the said patent rights available for mining purposes at reasonable rates of royalty. The process used under the patent is what is commonly known as the cyanide process, and the operation of the Act should prove highly important in the development of low-grade ores, and otherwise promote the mining industry. The royalties received by the Government up to the 31st March, 1903, amounted to £5,586 15s. 2d. The payment of royalties will cease when the total amount disbursed for the purchase of the patent rights has been repaid to the Consolidated Fund.
At the annual meeting of the Waihi Gold-mining Company held at London in April last the chairman remarked:—
“At the last annual meeting I claimed the year 1901, which we were then dealing with, to be the record year in our history. It was our best year up to that point. It was notable, among other things, for that year's bullion return of £461,000, an increase of £144,000 upon the previous year's return. We became producers of bullion in 1890 with a sum of £13,628. Every year since, with unfailing regularity, we have produced an increased amount, until in 1902 we have recorded a return of £521,574, or £60,000 better than 1901, making an increased realisation of upwards of £200,000 in two years, so that the bullion return of 1902 has made that year the record year; but the monthly returns of this current year seem to indicate that 1903 may yield an improved return upon the large yield of 1902.”
The mine-manager, in his report, gives the experience in respect of the Waihi Mine:—
“The gold found in our lodes is very fine, and intimately mixed with the stone. The finer the stone can be ground, the more gold is liberated. Wet crushing prevailed at Waihi many years before the Waihi Company was formed, and tens of thousands of tons of Martha ore were treated there by wet crushing, in which process the best results did not give a saving of 30 per cent. of the assay value of the gold. This result did not pay the cost of mining and milling, and wet crushing of Waihi ore, after ample trial for upwards of ten years, proved a complete failure. The ore used then was as good and as rich as that we are crushing now, but no process then known in New Zealand would save the gold. The use of solutions of cyanide for gold-saving was then unknown, and by the ordinary wet-crushing process this fine gold was carried away by the water. The mine was therefore a failure. After it came into our hands, in order to solve these questions, specimens of our ore were sent to experts in America, and I went there myself. After investigation we found that the Americans had met with the same difficulties with similar fine gold at several of their mills: the water had carried the gold away as it had done with us, and so the ore had to be crushed dry and very fine—the finer the better. By the adoption of dry crushing at Waihi, and afterward treating the finely ground ore in Howell's pans with quicksilver, we saved over 60 per cent. of the gold. This was a great step in advance, and enabled us to pay a small dividend; but the discovery which was soon after made of the use of cyanide of potassium in gold-saving enabled us to increase our saving of gold to about 90 per cent. of the assay value. Here, then, in dry crushing we had found the only process which then met the requirements of our case, saved a large percentage of the gold, and was applicable to the abundant supplies of oxidized ores which were contained in the mine. Had oxidized ore continued downwards dry crushing would have continued at Waihi; but the intrusion of sulphide ore in the lower levels raised a practical difficulty, for when sulphide ore got into the cyanide-vats it interfered with our extraction, and losses of gold followed. This difficulty ultimately led to the present system, but only after a series of inexpensive experiments made in small experimental plants at Waihi. We have not vacillated; we have boldly grappled with great difficulties. We obtained and imported dry-crushing machinery from America, and with it saved the situation and pulled Waihi into the front mining rank. When cyanide became a factor in gold-saving we purchased the right to use it for this company, and have been greatly benefited by its use; and now we believe we have, at a comparatively small cost, the most complete and permanent plant in the Southern Hemisphere, and one entirely suitable for the requirements of our mine. I make no apology for this somewhat lengthened notice of wet and dry crushing. The subject is of the highest importance. You will see from what I have said how deliberate and careful we have been, and how essential it is that the facts connected with this vital question should be fully known. While we have two processes working side by side at our mills the expense of treatment has been greater than if we had only one kind of plant. Now that we have only one mode of treatment at all the mills we expect to obtain two results—(1) cheaper treatment, and (2) to be able to treat a much larger quantity of ore, and so secure larger bullion returns. We do not expect a better extraction, but so far we have obtained good results, and we hope for improved extraction from time to time.”
The extent of the coal - measures in New Zealand will make coal-mining one of the large industries in the colony, especially on the west coast of the Middle Island, where bituminous coal exists equal, if not superior, in quality to coal of the same class in any part of the world.
The progressive increase in the output of coal from 1878 to the end of 1902 is shown below:—
| Year. | Raised in the Colony. | Imported. | Total raised in the Colony and imported per Annum. | Exported (excluding Coal for Fuel by Ocean Steamers). | Total Consumption of Coal within the Colony. | Yearly Increase in Consumption within the Colony. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total. | Yearly Increase. | ||||||
| * Decrease. | |||||||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | |
| 1873 | 162,218 | .. | 174,148 | 336,366 | 3,921 | 332,445 | .. |
| 1879 | 231,218 | 69,000 | 158,076 | 389,294 | 7,195 | 382,099 | 49,654 |
| 1880 | 299,923 | 68,705 | 123,298 | 423,221 | 7,021 | 416,200 | 34,101 |
| 1881 | 337,262 | 37,339 | 129,962 | 467,224 | 6,626 | 460,598 | 44,398 |
| 1882 | 378,272 | 41,010 | 129,582 | 507,854 | 4,245 | 503,609 | 43,011 |
| 1883 | 421,764 | 43,492 | 123,540 | 545,304 | 7,172 | 538,132 | 34,523 |
| 1884 | 480,831 | 59,067 | 148,444 | 629,275 | 6,354 | 622,921 | 84,789 |
| 1885 | 511,063 | 30,232 | 130,202 | 641,265 | 2,371 | 638,894 | 15,973 |
| 1886 | 534,353 | 23,290 | 119,873 | 654,226 | 2,862 | 651,364 | 12,470 |
| 1887 | 558,620 | 24,267 | 107,230 | 665,850 | 12,951 | 652,899 | 1,535 |
| 1888 | 613,895 | 55,275 | 101,341 | 715,236 | 27,678 | 687,558 | 34,659 |
| 1889 | 586,445 | −27,450* | 128,063 | 714,508 | 39,290 | 675,218 | 12,340 |
| 1890 | 637,397 | 50,952 | 110,939 | 748,336 | 33,404 | 714,932 | 39,74 |
| 1891 | 668,794 | 31,397 | 125,318 | 794,112 | 29,093 | 764,019 | 49,087 |
| 1892 | 673,315 | 4,521 | 125,453 | 798,768 | 28,169 | 770,599 | 6,580 |
| 1893 | 691,548 | 18,233 | 117,444 | 808,992 | 24,288 | 784,704 | 14,105 |
| 1894 | 719,546 | 27,998 | 112,961 | 832,507 | 25,449 | 807,058 | 22,354 |
| 1895 | 726,654 | 7,108 | 108,198 | 834,852 | 26,151 | 808,701 | 1,643 |
| 1896 | 792,851 | 66,197 | 101,756 | 894,607 | 27,974 | 866,633 | 57,932 |
| 1897 | 840,713 | 47,862 | 110,907 | 951,620 | 26,639 | 924,981 | 58,348 |
| 1898 | 907,033 | 66,320 | 115,427 | 1,022,460 | 18,348 | 1,004,112 | 79,131 |
| 1899 | 975,234 | 68,201 | 99,655 | 1,074,889 | 14,146 | 1,060,743 | 56,631 |
| 1900 | 1,093,990 | 118,756 | 124,033 | 1,218,023 | 36,699 | 1,181,324 | 120,581 |
| 1901 | 1,227,638 | 133,648 | 149,764 | 1,377,402 | 77,563 | 1,299,839 | 118,515 |
| 1902 | 1,362,702 | 135,064 | 127,853 | 1,490,555 | 110,666 | 1,379,889 | 80,050 |
It will be seen from the above that, with the exception of 1889, there has been a steady increase in the output of coal from the mines in the colony year after year since records have been kept by the Mines Department. The yearly increase in output is principally due to the growing demand for consumption within the colony. During a period of twenty-five years the annual consumption of coal in New Zealand has increased to the extent of 1,047,444 tons, showing that new industries are quickly springing up, requiring fuel for generating motive-power.
The total output from the mines last year was 1,362,702 tons, as against 1,227,638 tons for 1901, an increase of 135,064 tons. The coal imported from other countries was 127,853 tons, against 149,764 tons in 1901, a decrease in the importation last year of 21,911 tons. The imports were 126,548 tons from New South Wales, 1,300 tons from Victoria, and 5 tons from the United Kingdom. The total export of coal was 192,104 tons, of which 188,677 tons were colonial produce, and 3,427 tons imported coal from other countries. Of the coal exported, 81,438 tons were for coaling direct steamers trading between the colony and the United Kingdom, and has been treated as coal consumed within the colony, these steamers trading wholly between New Zealand and Great Britain. Taking, therefore, the output from the mines and the coal imported, there is a total of 1,490,555 tons, of which 110,666 tons were exported, leaving the consumption within the colony last year 1,379,889 tons, as against 1,299,839 tons for 1901, an increased consumption of 80,050 tons.
The largest increase in the output last year was in the Westport district—namely, 73,405 tons. There was also an increased production from the mines in the Otago District of 18,988 tons, in the Southland district of 11,487 tons, in the Greymouth district of 10,426 tons, in the Waikato district of 7,455 tons, in the Kawakawa and Hikurangi district of 7,308 tons, in the Reefton district of 2,658 tons, in the Malvern district of 3,347 tons, in the Miranda district of 3,063 tons, in the Mokau district of 737 tons; but there was a decline in the West Wanganui district of 2,208 tons, and in the Whangarei, Kamo, Ngunguru, and Whauwhau district of 1,602 tons.
The quantities of coal produced in each district are as under:—
| Name of District. | Output of Coal. | Increase or Decrease. | Approximate Total Output of Coal up to the 31st December, 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1902. | 1901. | |||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | |
| Kawakawa and Hikurangi | 60,606 | 53,298 | + 7,308 | 1,250,424 |
| Whangarei, Kamo, Ngunguru, and Whauwhau | 32,155 | 33,757 | − 1,602 | 499,774 |
| Waikato | 91,541 | 84,086 | + 7,455 | 1,342,795 |
| Mokau | 4,250 | 3,513 | + 737 | 33,784 |
| Miranda | 3,493 | 430 | + 3,063 | 3,923 |
| Pelorus | .. | .. | .. | 711 |
| West Wanganui | .. | 2,208 | − 2,208 | 55,183 |
| Westport | 523,462 | 455,057 | +73,405 | 4,710,012 |
| Reefton | 8,760 | 6,102 | + 2,658 | 99,006 |
| Greymouth | 216,594 | 206,168 | +10,426 | 3,299,882 |
| Malvern | 19,445 | 16,098 | + 3,347 | 418,929 |
| Timaru | .. | .. | .. | 10,657 |
| Otago | 308,310 | 289,322 | +18,988 | 4,670,969 |
| Southland | 89,086 | 77,599 | +11,487 | 747,161 |
| Totals | 1,362,702 | 1,227,638 | +135,064 Net. | 17,143,210 |
The following table, constructed from “Laboratory Reports of the Geological Survey” (Sir J. Hector) gives the composition of samples of New Zealand coals freshly taken from the principal mines:—
| Number. | Description. | Locality. | Analysis. | Evaporative Power.* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Carbon. | Hydrocarbon. | Water. | Ash. | 1. | 2. | |||
| * The second column headed “Evaporative Power” is obtained by the use of a multiple computed from the results of Professor Liversedge's experiments upon the coals of New South Wales. The multiple used for the first column is the one which has long been generally used for computing the evaporative power of coals; but, to prevent any unfair and prejudicial comparison of our coals with those of New South Wales, the second column is given. | ||||||||
| 1 | Anthracite | Acheron, Canterbury | 84·12 | 1·96 | 1·80 | 12·12 | 10·93 | 18·50 |
| 2 | Bituminous | Coalbrookdale | 7·83 | 20·50 | 1·16 | 3·51 | 9·70 | 16·45 |
| 3 | Bituminous | Coalbrookdale | 70·00 | 22·15 | 2·52 | 5·33 | 9·10 | 15·40 |
| 4 | Bituminous | Banbury | 69·97 | 25·71 | 0·99 | 3·33 | 9·09 | 15·38 |
| 5 | Altered brown coal | Malvern Hills | 68·54 | 19·89 | 4·15 | 7·42 | 8·27 | 12·50 |
| 6 | Bituminous | Tyneside | 65·59 | 29·18 | 0·82 | 4·41 | 8·52 | 13·55 |
| 7 | Glance coal | Rakaia Gorge | 64·51 | 21·27 | 6·76 | 7·46 | 8·30 | 13·20 |
| 8 | Bituminous | Wallsend | 62·87 | 31·64 | 1·66 | 3·83 | 8·17 | 13·82 |
| 9 | Bituminous | Grey River | 62·37 | 29·44 | 1·99 | 6·20 | 8·01 | 13·22 |
| 10 | Pitch coal | Kawakawa | 61·16 | 28·00 | 2·51 | 8·33 | 7·95 | 12·55 |
| 11 | Bituminous | Preservation Inlet | 60·88 | 28·60 | 4·33 | 6·19 | 7·91 | 12·80 |
| 12 | Pitch coal | Blackball, Grey River | 60·20 | 29·97 | 8·01 | 1·82 | 7·82 | 12·20 |
| 13 | Bituminous | Mokihinui | 59·75 | 32·14 | 3·97 | 4·14 | 7·76 | 11·80 |
| 14 | Bituminous | Coalpit Heath | 58·81 | 38·98 | 1·02 | 1·19 | 7·64 | 12·96 |
| 15 | Bituminous | Mokihinui | 57·92 | 34·94 | 3·96 | 3·18 | 7·50 | 12·75 |
| 16 | Bituminous | Brunner Mine | 56·62 | 35·68 | 1·59 | 6·11 | 7·36 | 12·46 |
| 17 | Bituminous | Brunner Mine | 56·21 | 37·73 | 1·50 | 4·56 | 7·30 | 12·36 |
| 18 | Bituminous | Westport | 56·01 | 37·17 | 2·60 | 4·22 | 7·28 | 12·30 |
| 19 | Bituminous | Mokihinui | 55·59 | 38·86 | 3·16 | 2·39 | 7·20 | 12·22 |
| 20 | Bituminous | Brunner | 54·16 | 35·85 | 2·50 | 7·49 | 7·04 | 11·91 |
| 21 | Altered brown coal | Malvern Hills | 53·29 | 32·04 | 12·65 | 2·02 | 6·92 | 11·50 |
| 22 | Bituminous | Wallsend | 53·10 | 35·47 | 1·41 | 10·02 | 6·90 | 11·68 |
| 23 | Bituminous | Otamataura Creek | 52·89 | 36·63 | 2·19 | 8·29 | 6·90 | 11·70 |
| 24 | Bituminous | Near Cape Farewell | 51·37 | 38·72 | 4·38 | 5·53 | 6·31 | 11·60 |
| 25 | Pitch coal | Kawakawa | 50·15 | 42·63 | 4·18 | 3·04 | 6·50 | 11·80 |
| 26 | Glance coal | Whangarei | 50·11 | 38·68 | 8·01 | 3·20 | 6·50 | 11·75 |
| 27 | Pitch coal | Kamo | 50·01 | 37·69 | 9·61 | 2·69 | 6·50 | 11·17 |
| 28 | Brown coal | Malvern Hills | 49·99 | 35·42 | 11·79 | 2·80 | 6·49 | 10·90 |
| 29 | Brown coal | Fernhill | 49·95 | 36·95 | 12·00 | 1·10 | 6·49 | 10·99 |
| 30 | Brown coal | Allandale | 47·31 | 34·26 | 12·41 | 6·02 | 6·15 | 10·96 |
| 31 | Brown coal | Kaitangata | 46·48 | 33·48 | 14·66 | 5·38 | 6·04 | 10·22 |
| 32 | Brown coal | Shag Point | 46·21 | 32·65 | 16·02 | 5·12 | 6·00 | 10·16 |
| 33 | Brown coal | Homebush | 44·92 | 36·00 | 15·83 | 3·25 | 5·83 | 9·87 |
| 34 | Pitch coal | Hikurangi, Whangarei | 44·50 | 47·00 | 5·99 | 2·51 | 5·78 | 9·79 |
| 35 | Brown coal | Hokonui | 44·28 | 38·22 | 16·50 | 1·00 | 5·75 | 9·77 |
| 36 | Brown coal | Kaitangata | 44·11 | 38·32 | 15·44 | 2·13 | 5·74 | 9·96 |
| 37 | Brown coal | Nightcaps | 43·62 | 33·68 | 18·33 | 4·37 | 5·67 | 9·59 |
| 38 | Pitch coal | Shag Point | 43·19 | 30·05 | 15·82 | 10·94 | 5·61 | 9·52 |
| 39 | Brown coal | Springfield | 42·68 | 33·66 | 18·65 | 5·01 | 5·55 | 9·38 |
| 40 | Brown coal | Orepuki | 42·64 | 36·26 | 14·44 | 6·66 | 5·54 | 9·38 |
| 41 | Brown coal | Kaitangata | 38·29 | 32·43 | 17·50 | 11·78 | 4·87 | 8·32 |
| 42 | Brown coal | Shag Point | 35·76 | 30·86 | 13·22 | 20·16 | 4·64 | 7·85 |
| 43 | Brown coal | Allandale | 34·72 | 41·43 | 18·99 | 4·86 | 4·51 | 7·63 |
| 44 | Pitch coal | Grey River | 34·72 | 56·48 | 6·20 | 2·60 | 4·51 | 7·63 |
| For Comparison. | ||||||||
| Newcastle, N.S.W. | Best | 58·33 | 34·17 | 1·83 | 5·67 | 7·50 | 12·82 | |
| Newcastle, N.S.W | Worst | 53·34 | 26·66 | 3·33 | 16·67 | 6·90 | 11·72 | |
As regards the quality of the coal, it cannot be surpassed. The late Sir John Coode, in his presidential address to the Institute of Civil Engineers, London, stated: “The bituminous coal found on the west coast of the Middle Island is declared by engineers to be fully equal, if not superior, to the best description from any part of the world.”
The quantity of each class of coal produced in 1901 and 1902 was:—
| Class of Coal. | Output of Coal. | Increase. | Approximate Total Output of Coal up to the 31st December, 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1901. | 1902. | |||
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | |
| Bituminous and semi-bituminous | 754,953 | 845,046 | 90,093 | 9,546,823 |
| Pitch | 14,584 | 25,245 | 10,661 | 1,837,956 |
| Brown | 405,152 | 427,172 | 22,020 | 5,151,271 |
| Lignite | 52,949 | 65,239 | 12,290 | 607,160 |
| Totals | 1,227,638 | 1,362,702 | 135,064 | 17,143,210 |
It has been computed that to deliver coal at the pit-mouth costs in labour 6s. a ton. The number of persons employed in all the coalmines last year was 2,885, and the output of coal 1,362,702 tons: the average earning for each person would thus be £141 14s. per annum, or about £2 14s. 6d. per week.
For some years slight exudations of petroleum have been noticed in the locality of Lake Brunner, between Greymouth and the mouth of the Otira Gorge.
It has been found that when shallow holes have been dug and allowed to fill with water small quantities of crude petroleum could be skimmed off the top of the water. This has led to further investigation, and several leases have been taken up with a view to prospecting for the oil in quantity. Boring operations have been commenced by the Kotuku Oil Association and the Lake Brunner Oil Company.
Crude petroleum was also obtained in a borehole near Dobson (Greymouth). This bore was one of a series put down to prove the coal-measures.
Fairly extensive deposits of phosphate rock have been discovered as a fringe to the limestone at Clarendon, near Milton, Otago. The Ewing Phosphate Company (Limited) has been formed, and operations of quarrying and burning on a commercial scale have been undertaken. After burning, the rock is crushed and chemically treated. The value of this phosphate as a fertiliser has been satisfactorily proved, and there is every indication of a growing industry in quarrying the rock and preparing it for use. With such a valuable material at our very doors, there is no doubt that in future the importation of phosphate manures will cease, or at least be greatly reduced, whilst the question of export from this colony is within the range of possibility.
A considerable amount of development and prospecting work was undertaken during the year 1902 at the Point Elizabeth property near Greymouth and the Seddonville Colliery in the Westport district. The tunnels being driven to win the coal are approaching completion, and other necessary works are well advanced.
Very little has been done in the colony to prospect and develop mines other than for gold and silver. The only exports last year of metalliferous products, excluding gold and silver, were 231 tons of auriferous ore, 175 tons of chrome-ore, 100 tons of sulphur, 39 tons of scheelite-ore, 17 tons of hæmatite, and small parcels of other minerals, representing an aggregate value of £5,063.
Table of Contents
Until 1895 the agricultural statistics were collected and compiled by the Registrar-General, under authority of “The Census Act, 1877,” annually in the month of February, except in census years, when the collection was made with the enumeration of the people. Under this Act statistics of the acreage in grass and in all kinds of cultivation were taken, and at the same time the estimated yields of all the principal crops were obtained from the farmers. themselves.
By the Agricultural and Pastoral Statistics Act, passed in 1895, the duty of collecting the returns devolved upon the Department of Agriculture. The plan now adopted under the Act of 1895 is similar to that used in the United Kingdom, the account of land laid down in crop being made up much earlier than formerly, while estimates of produce are made after the results of threshing are known.
Statistics of the land in cultivation were accordingly collected in October, 1902, and an interim return of the compiled results was published in detail in the New Zealand Gazette of the 18th December, 1902, while the corrected acreages under each description of crop were made public on the 19th February following. A summary of the particulars then given is shown in the accompanying tables, with the finally corrected statements of yield of the principal crops; but in comparing these figures with the results obtained in former years it must be remembered that, under the new Act, statistics of the acreage and crops of land held and cultivated by Maoris are included, whereas previously information about the farming carried on by Maoris was obtained only when a census of the Native race was taken.
Full remarks on the progress of agriculture in New Zealand, in respect of all its features in detail, are supplied in the special article devoted to the subject which appears as the first of Section II., in Part III.
| Acreage and Actual Yield in Principal Corn-crops, 1903. | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial Districts. | Wheat. | Oats. | Barley. | Maize. | Bye. | |||||||||||
| Acres. | Yield per Acre, in Bushels. | Total Bushels. | Acres. | Yield per Acre, in Bushels. | Total Bushels. | Acres. | Yield per Acre, in Bushels. | Total Bushels. | Acres | Yield per Acre, in Bushels. | Total Bushels. | Acres. | Yield per Acre, in Bushels. | Total Bushels. | ||
| * Not included in the averages. | ||||||||||||||||
| Auckland | 2,599 | 29·74 | 77,027 | 7,063 | 29·53 | 208,584 | 893 | 35·44 | 31,646 | 10,983 | 50·75 | 557,405 | 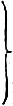 | 1,279 | 30·00 | 38,370 |
| Taranaki | 1,075 | 40·00 | 43,000 | 5,390 | 42·00 | 226,380 | 633 | 41·00 | 25,953 | 101 | 35·00 | 3,535 | ||||
| Hawke's Bay | 701 | 26·74 | 18,750 | 5,914 | 35·08 | 207,434 | 1,259 | 37·95 | 47,778 | 723 | 55·00 | 39,765 | ||||
| Wellington | 5,969 | 36·79 | 219,610 | 27,881 | 42·13 | 1,174,861 | 1,514 | 35·44 | 53,660 | 212 | 30·00 | 6,360 | ||||
| Marlborough | 3,750 | 30·00 | 112,500 | 2,903 | 39·00 | 113,217 | 6,522 | 35·00 | 228,270 | ... | ... | ... | ||||
| Nelson | 1,666 | 31·96 | 53,252 | 5,068 | 43·66 | 221,245 | 3,237 | 34·58 | 111,937 | 17 | 32·00 | 544 | ||||
| Westland | ... | ... | ... | 9* | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ||||
| Canterbury | 135,907 | 39·24 | 5,333,588 | 199,346 | 49·03 | 9,773,662 | 9,553 | 50·06 | 478,197 | 2* | ... | ... | ||||
| Otago | 42,688 | 37·48 | 1,600,188 | 230,082 | 42·77 | 9,841,325 | 4,310 | 36·84 | 158,791 | ... | ... | ... | ||||
| Totals | 194,355 | 38·37 | 7,457,915 | 483,659 | 45·00 | 21,766,708 | 27,921 | 40·69 | 1,136,232 | 12,038 | 50·48 | 607,609 | 1,279 | 30·00 | 38,370 | |
| Number of Acres under Cultivation in each Provincial District, 1903. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial Districts | In Grass or Clover, sown after Land ploughed | In Grass, surface-sown: Land not ploughed. | In Hay, included in either or both of the Previous Columns. | In Bare Fallow. | In Grain-crops. | In Green and other Crops. | In Garden | In Orchard or Vineyard. | Total in Grass, Crop, and Fallow. | In Plantations of Forest Trees. | Tussock or Native Grass, and Unimproved. |
| Auckland | 612,503 | 1,517,041 | 14,328 | 11,578 | 23,698 | 97,318 | 3,850 | 11,978 | 2,277,966 | 10,093 | 3,513,607 |
| Taranaki | 155,466 | 634,644 | 6,728 | 106 | 7,458 | 16,165 | 871 | 850 | 815,560 | 1,186 | 237,960 |
| Hawke's Bay | 401,415 | 1,376,773 | 8,892 | 198 | 8,921 | 29,401 | 1,136 | 1,505 | 1,819,349 | 4,406 | 1,449,310 |
| Wellington | 276,701 | 2,323,928 | 11,443 | 1,942 | 37,373 | 57,379 | 2,317 | 3,703 | 2,703,343 | 3,982 | 1,145,629 |
| Marlborough | 93,281 | 283,818 | 1,525 | 196 | 15,376 | 19,015 | 260 | 481 | 412,427 | 1,438 | 1,889,710 |
| Nelson | 116,508 | 337,798 | 3,143 | 367 | 10,832 | 29,283 | 397 | 3,033 | 498,218 | 1,760 | 1,546,368 |
| Westland | 9,424 | 49,479 | 346 | .. | 42 | 997 | 65 | 124 | 60,131 | 7 | 494,641 |
| Canterbury | 1,443,066 | 414,137 | 13,655 | 9,674 | 354,028 | 254,124 | 4,951 | 3,211 | 2,483,191 | 25,162 | 3,980,272 |
| Otago | 1,449,982 | 312,251 | 9,282 | 20,433 | 278,955 | 264,626 | 3,785 | 2,306 | 2,332,338 | 5,754 | 8,173,639 |
| Totals | 4,558,346 | 7,249,869 | 69,342 | 44,494 | 736,683 | 768,308 | 17,632 | 27,191 | 13,402,523 | 53,788 | 22,431,136 |
| Acreage under Sown Grasses, and Cultivation generally, for each County, as on the 15th October, 1902. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counties. | In Sown Grasses, after having been ploughed. | In Sown Grasses, not previously ploughed. | Land broken up but not under Crop. | Total under Crop. | In Garden. | In Orchard. | Plantations of Forest Trees. |
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Mongonui | 6,997 | 24,026 | 242 | 1,225 | 83 | 172 | 4 |
| Whangaroa | 695 | 4,149 | 1 | 194 | 30 | 103 | 1 |
| Bay of Islands | 5,647 | 35,560 | 145 | 1,011 | 76 | 314 | 20 |
| Hokianga | 433 | 21,949 | 9 | 754 | 134 | 316 | 47 |
| Rodney | 11,354 | 83,677 | 647 | 1,114 | 144 | 1,153 | 128 |
| Whangarei | 23,225 | 92,052 | 220 | 2,194 | 129 | 1,217 | 437 |
| Otamatea | 5,909 | 64,724 | 347 | 556 | 58 | 367 | 42 |
| Hobson | 837 | 59,484 | 700 | 950 | 208 | 233 | 160 |
| Waitemata | 22,201 | 33,520 | 1,284 | 1,606 | 349 | 2,166 | 256 |
| Eden | 16,573 | 4,607 | 150 | 1,473 | 1,052 | 689 | 322 |
| Manukau | 108,606 | 93,585 | 5,149 | 21,272 | 397 | 1,471 | 807 |
| Coromandel | 2,354 | 9,619 | 40 | 454 | 58 | 111 | 18 |
| Thames | 4,697 | 8,055 | 67 | 1,051 | 70 | 412 | 14 |
| Ohinemuri | 6,770 | 10,507 | 49 | 1,469 | 267 | 136 | 48 |
| Waikato | 78,456 | 30,616 | 496 | 11,391 | 74 | 556 | 4,817 |
| Raglan | 15,218 | 87,466 | 125 | 3,689 | 83 | 223 | 41 |
| Waipa | 61,153 | 10,292 | 295 | 14,090 | 134 | 629 | 624 |
| Piako | 120,420 | 55,232 | 556 | 23,845 | 116 | 309 | 1,086 |
| West Taupo and Kawhia | 16,040 | 65,358 | 322 | 4,523 | 42 | 97 | 177 |
| East Taupo and Rotorua | 4,218 | 6,404 | 162 | 1,164 | 24 | 65 | 481 |
| Tauranga | 30,737 | 18,748 | 215 | 8,815 | 100 | 439 | 248 |
| Whakatane | 5,866 | 9,130 | 60 | 2,983 | 8 | 45 | 27 |
| Opotiki | 12,564 | 10,786 | 243 | 4,077 | 30 | 78 | 8 |
| Waiapu | 16,755 | 180,745 | .. | 2,741 | 18 | 140 | 8 |
| Cook | 34,778 | 496,750 | 54 | 8,375 | 166 | 537 | 272 |
| Wairoa | 19,778 | 262,759 | 6 | 2,322 | 153 | 180 | 128 |
| Hawke's Bay | 192,314 | 414,708 | 83 | 19,398 | 646 | 801 | 1,843 |
| Waipawa | 109,109 | 307,606 | 36 | 11,207 | 201 | 218 | 1,633 |
| Woodville | 3,763 | 71,759 | 40 | 1,017 | 17 | 201 | 61 |
| Patangata and Weber | 76,451 | 319,941 | 33 | 4,378 | 119 | 105 | 741 |
| Clifton | 13,018 | 51,913 | .. | 2,433 | 103 | 71 | 25 |
| Taranaki and Egmont | 53,758 | 149,790 | 9 | 6,914 | 345 | 414 | 252 |
| Stratford | 1,269 | 165,360 | .. | 910 | 24 | 16 | 35 |
| Hawera | 50,537 | 147,536 | 52 | 8,269 | 321 | 137 | 277 |
| Patea | 36,884 | 120,045 | 45 | 5,097 | 78 | 212 | 597 |
| Waitotara | 21,614 | 84,085 | .. | 3,299 | 207 | 228 | 171 |
| Wanganui and Waimarino | 15,902 | 176,298 | 39 | 4,207 | 221 | 236 | 229 |
| Rangitikei | 57,174 | 237,645 | 156 | 16,047 | 182 | 428 | 1,025 |
| Kiwitea | 2,194 | 147,624 | 26 | 2,900 | 37 | 165 | 44 |
| Pohangina | 171 | 83,826 | .. | 453 | 16 | 120 | 2 |
| Oroua | 8,787 | 86,198 | 22 | 6,591 | 79 | 329 | 178 |
| Kairanga | 10,354 | 76,524 | 24 | 6,340 | 165 | 467 | 182 |
| Manawatu | 50,335 | 50,059 | 547 | 14,803 | 67 | 159 | 261 |
| Horowhenua | 9,169 | 97,807 | 28 | 3,080 | 163 | 334 | 64 |
| Hutt | 7,568 | 166,606 | 35 | 1,996 | 612 | 322 | 326 |
| Featherston | 44,948 | 175,416 | 253 | 11,053 | 89 | 127 | 595 |
| Wairarapa South | 22,286 | 186,922 | 483 | 9,332 | 96 | 153 | 282 |
| Masterton | 21,361 | 304,866 | 156 | 11,735 | 187 | 212 | 398 |
| Castlepoint | 2,699 | 96,823 | 123 | 497 | 23 | 45 | 124 |
| Akitio | 273 | 108,814 | 30 | 231 | 78 | 42 | 34 |
| Pahiatua | 1,258 | 139,921 | 20 | 1,327 | 62 | 243 | 46 |
| Eketahuna | 608 | 62,653 | .. | 588 | 20 | 66 | 17 |
| Mauriceville | .. | 41,841 | .. | 273 | 13 | 27 | 4 |
| Marlborough | 61,363 | 124,571 | 139 | 29,296 | 155 | 282 | 1,191 |
| Sounds | 2,871 | 98,489 | 50 | 1,418 | 81 | 173 | 43 |
| Kaikoura | 29,047 | 60,758 | 7 | 3,677 | 24 | 26 | 204 |
| Collingwood | 3,335 | 36,382 | 1 | 1,339 | 19 | 279 | 7 |
| Waimea | 30,291 | 164,864 | 242 | 21,488 | 226 | 2,383 | 259 |
| Buller | 899 | 6,349 | .. | 151 | 49 | 139 | .. |
| Inangahua | 4,863 | 29,056 | 54 | 859 | 16 | 93 | 2 |
| Amuri | 51,535 | 97,530 | 70 | 7,982 | 64 | 31 | 1,122 |
| Cheviot | 25,585 | 3,617 | .. | 8,296 | 23 | 108 | 370 |
| Grey | 4,292 | 18,482 | .. | 460 | 33 | 76 | 7 |
| Westland | 5,132 | 30,997 | .. | 579 | 32 | 48 | .. |
| Ashley | 249,200 | 140,981 | 2,494 | 89,963 | 659 | 444 | 2,596 |
| Selwyn | 297,165 | 25,788 | 1,970 | 139,682 | 2,167 | 1,357 | 6,483 |
| Akaroa and Mount Herbert | 24,839 | 161,566 | 345 | 3,375 | 147 | 378 | 359 |
| Ashburton | 396,981 | 29,499 | 1,529 | 174,687 | 689 | 377 | 11,315 |
| Geraldine | 130,937 | 11,727 | 801 | 57,918 | 233 | 242 | 1,680 |
| Levels | 86,028 | 1,285 | 221 | 43,427 | 418 | 241 | 1,339 |
| Waimate | 201,547 | 39,837 | 2,214 | 82,803 | 569 | 141 | 746 |
| Mackenzie | 56,369 | 3,454 | 100 | 16,297 | 69 | 31 | 644 |
| Waitaki | 197,291 | 35,807 | 1,592 | 68,640 | 382 | 201 | 958 |
| Waihemo | 33,589 | 4,880 | 254 | 10,511 | 81 | 69 | 122 |
| Waikouaiti | 18,903 | 46,302 | 95 | 7,021 | 64 | 102 | 114 |
| Peninsula | 2,519 | 13,601 | 17 | 1,633 | 195 | 39 | 59 |
| Taieri | 86,914 | 13,737 | 356 | 27,359 | 597 | 351 | 414 |
| Bruce | 104,028 | 5,338 | 294 | 38,493 | 173 | 77 | 347 |
| Clutha | 175,632 | 31,143 | 1,195 | 53,616 | 443 | 96 | 511 |
| Tuapeka | 101,904 | 18,908 | 1,582 | 37,113 | 256 | 427 | 1,256 |
| Maniototo | 46,691 | 2,633 | 325 | 20,035 | 221 | 19 | 204 |
| Vincent | 20,037 | 2,527 | 1,355 | 13,360 | 139 | 237 | 93 |
| Lake | 9,636 | 6,926 | 3,370 | 11,877 | 108 | 91 | 237 |
| Southland | 494,659 | 81,863 | 8,817 | 195,954 | 942 | 498 | 1,096 |
| Wallace and Fiord | 158,142 | 48,187 | 1,181 | 57,957 | 170 | 96 | 340 |
| Stewart Island | 37 | 399 | .. | 12 | 14 | 3 | 3 |
| Total | 4,558,346 | 7,249,869 | 44,494 | 1,504,991 | 17,632 | 27,191 | 53,788 |
The extent of land in cultivation (including sown grasses and land broken up but not under crop) amounted to 13,402,523 acres. Of this area, land under artificial grasses comprised 88·10 per cent.; land under grain-crops, 5·50 per cent.; land under root and green crops, 5·73 per cent.; land in garden and orchard, 0·34 per cent.; and land in fallow, 0·33 per cent. Full details for the last sixteen years are tabulated.
| Number of Acres in Grass, under each Class of Crop, and in Bare Fallow, 1888 to 1903. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | In Grass or Clover, sown after Land ploughed. | In Grass or Clover, surface-sown: Land not ploughed. | In Hay, included in either or both of the Previous Columns. | In Bare Fallow. | In Grain-crops. | In Green and other Crops. | In Garden. | In Orchard or Vineyard. | Total in Grass, Crop, Fallow, Garden, and Orchard. | In Plantations of Forest Trees. |
| 1888 | 2,884,007 | 3,053,052 | 67,812 | 154,266 | 738,603 | 454,824 | 8,608 | 16,329 | 7,309,689 | 28,565 |
| 1889 | 2,941,888 | 3,337,423 | 50,656 | 142,747 | 793,866 | 454,243 | 8,561 | 15,246 | 7,693,974 | 33,938 |
| 1890 | 3,027,912 | 3,497,137 | 45,889 | 149,979 | 826,505 | 513,893 | 8,568 | 15,771 | 8,039,765 | 28,928 |
| 1891 | 3,250,543 | 3,715,675 | 44,045 | 210,509 | 703,329 | 582,439 | 9,810 | 17,047 | 8,489,352 | 35,310 |
| 1892 | 3,327,755 | 4,076,126 | 46,652 | 140,454 | 769,778 | 579,112 | 9,608 | 19,627 | 8,922,460 | 38,723 |
| 1893 | 3,611,393 | 4,650,652 | 61,811 | 154,254 | 753,091 | 544,355 | 9,763 | 20,085 | 9,743,593 | 40,401 |
| 1894 | 3,865,348 | 4,833,549 | 60,740 | 142,342 | 669,850 | 551,962 | 9,951 | 21,109 | 10,094,111 | 39,826 |
| 1895 | 3,908,581 | 4,921,136 | 56,614 | 140,494 | 560,179 | 597,686 | 10,263 | 21,401 | 10,159,740 | 55,386 |
| 1896 | 4,254,983 | 5,030,247 | 96,818 | 58,039 | 674,850 | 680,750 | 17,749 | 19,362 | 10,735,980 | 43,246 |
| 1897 | 4,308,720 | 5,733,138 | 109,466 | 57,158 | 688,297 | 762,762 | 16,924 | 22,291 | 11,589,290 | 47,630 |
| 1898 | 4,123,304 | 5,743,245 | 67,865 | 60,792 | 727,038 | 790,184 | 16,177 | 22,387 | 11,483,127 | 52,546 |
| 1899 | 4,065,860 | 6,178,879 | 75,620 | 51,164 | 892,468 | 796,235 | 16,930 | 22,983 | 12,024,519 | 47,216 |
| 1900 | 4,337,594 | 6,515,708 | 68,234 | 78,751 | 745,685 | 796,773 | 16,890 | 24,401 | 12,515,802 | 48,942 |
| 1901 | 4,425,738 | 6,656,174 | 68,023 | 67,747 | 721,325 | 765,051 | 17,411 | 25,777 | 12,679,223 | 49,394 |
| 1902 | 4,695,200 | 6,924,978 | 62,984 | 55,947 | 634,879 | 772,967 | 17,684 | 26,836 | 13,128,491 | 48,770 |
| 1903 | 4,558,346 | 7,249,869 | 69,342 | 44,494 | 736,683 | 768,308 | 17,632 | 27,191 | 13,402,523 | 53,788 |
The wheat harvest of 1903 showed an average yield of 38·37 bushels per acre, the crop realised being 7,457,915 bushels, against 4,046,589 bushels in 1902.
The quantity of wheat of the previous season's harvest held by farmers in October, 1902, as shown by the gazetted figures, was 1,230,780 bushels, an amount which excludes stocks of grain and flour held by merchants and millers. The total amount of wheat exported during the year 1902 was 194,671 bushels, while the imports were 23,395 bushels, most probably for seeding purposes.
The imports of flour during 1902 were 99,069 centals (4,953 1/2 tons), and the exports 381 tons.
The area under wheat for threshing increased from 163,462 acres in 1902 to 194,355 acres in 1903; and this increase of 30,893 acres was shared by all the provincial districts excepting Hawke's Bay. In addition to the area cut for threshing, 389 acres were cut for chaff, and 15 acres for ensilage, while 496 acres were fed down with stock, so that the total area sown in wheat was 195,255 acres.
Of the 194,355 acres in wheat (for threshing) this year, no less than 135,907 acres were in Canterbury, and 42,688 acres in Otago.
The area under wheat for grain, the estimated gross produce in bushels, and the average yield per acre for each of the last thirteen years were:—
| Year. | Land under Wheat. | Estimated Gross Produce. | Average Yield per Acre. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | Bushels. | Bushels. | |
| 1891 | 301,460 | 5,723,610 | 18·99 |
| 1892 | 402,273 | 10,257,738 | 25·50 |
| 1893 | 381,245 | 8,378,217 | 21·98 |
| 1894 | 242,737 | 4,891,695 | 20·15 |
| 1895 | 148,575 | 3,613,037 | 24·32 |
| 1896 | 245,441 | 6,843,768 | 27·88 |
| 1897 | 258,608 | 5,926,523 | 22·92 |
| 1898 | 315,801 | 5,670,017 | 17·95 |
| 1899 | 399,034 | 13,073,416 | 32·76 |
| 1900 | 269,749 | 8,581,898 | 31·81 |
| 1901 | 206,465 | 6,527,154 | 31·61 |
| 1902 | 163,462 | 4,046,589 | 24·76 |
| 1903 | 194,355 | 7,457,915 | 38·37 |
The following gives the area in wheat, and the estimated produce, for the Australian States for the season of 1902:—
| State. | Wheat-crop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | Bushels. | Bushels per Acre. | |
| Queensland | 87,232 | 1,692,222 | 19·40 |
| New South Wales | 1,392,070 | 14,808,703 | 10·64 |
| Victoria | 1,754,417 | 12,127,382 | 6·91 |
| South Australia | 1,743,452 | 8,012,762 | 4·60 |
| Western Australia | 93,707 | 933,101 | 9·96 |
| Tasmania | 44,084 | 963,662 | 21·86 |
The estimated wheat-crop of the world for last year, compared with the actual returns for the previous four years, has been arrived at from figures published in the Statist of 30th August, 1902 (in bushels of 60 lb., 000's omitted).
| 1902. | 1901. | 1900. | 1899. | 1898. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Including Slavonia and Croatia. † Including Poland and Siberia. | |||||
| Austria | 46,000 | 44,000 | 40,800 | 49,600 | 46,400 |
| Hungary* | 176,000 | 138,000 | 152,000 | 150,000 | 140,000 |
| Belgium | 14,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 | 14,000 |
| Bulgaria | 40,000 | 32,000 | 24,000 | 28,000 | 40,000 |
| Denmark | 3,200 | 2,000 | 2,600 | 4,000 | 4,000 |
| France | 336,000 | 304,000 | 325,200 | 366,000 | 364,000 |
| Germany | 140,000 | 96,000 | 156,000 | 157,600 | 150,400 |
| Greece | 6,000 | 5,200 | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 |
| Holland | 6,000 | 5,200 | 4,000 | 5,200 | 4,800 |
| Italy | 116,000 | 128,000 | 116,000 | 134,000 | 132,000 |
| Portugal | 6,000 | 4,800 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 6,000 |
| Roumania | 72,000 | 70,000 | 54,000 | 26,000 | 56,000 |
| Russia† | 376,000 | 344,000 | 328,000 | 344,000 | 352,000 |
| Caucasus | 56,000 | 56,000 | 56,000 | 52,000 | 48,000 |
| Servia | 12,000 | 10,000 | 8,000 | 13,200 | 12,000 |
| Spain | 108,000 | 112,000 | 98,000 | 95,200 | 120,000 |
| Sweden | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,400 |
| Switzerland | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 |
| Turkey (Europe) | 40,000 | 32,000 | 32,000 | 24,000 | 28,000 |
| United Kingdom | 52,000 | 56,000 | 54,400 | 66,000 | 80,000 |
| Totals for Europe | 1,613,200 | 1,459,200 | 1,481,000 | 1,544,800 | 1,612,000 |
| Algeria | 28,000 | 26,000 | 24,000 | 20,000 | 28,000 |
| Tunis | 8,000 | 8,000 | 10,000 | 8,000 | 6,000 |
| Argentine Republic | 80,000 | 56,000 | 68,000 | 104,000 | 96,000 |
| Australasia | 32,000 | 43,200 | 55,200 | 44,000 | 54,000 |
| Asia Minor | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 | 48,000 |
| Canada | 96,000 | 88,000 | 52,000 | 64,000 | 64,000 |
| Cape Colony | 4,000 | 2,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,400 |
| Chili | 12,000 | 8,800 | 8,000 | 12,000 | 16,000 |
| Egypt | 12,000 | 10,000 | 8,800 | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| India | 224,000 | 252,000 | 184,000 | 236,000 | 248,000 |
| Persia | 20,000 | 20,000 | 24,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| Syria | 20,000 | 16,000 | 16,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 |
| United States of America | 656,000 | 752,000 | 600,000 | 656,000 | 720,000 |
| Uruguay | 8,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 | 7,200 | 12,000 |
| Mexico | 14,000 | 14,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 |
| Totals out of Europe | 1,254,000 | 1,342,000 | 1,112,000 | 1,249,200 | 1,350,400 |
| Grand total | 2,867,200 | 2,801,200 | 2,593,000 | 2,794,000 | 2,962,400 |
The yearly consumption of wheat per head of population in New Zealand has been estimated at 6 bushels, and the quantity required for seed at 2 bushels to the acre.
Using these figures, the Department of Agriculture estimates that there will be a large surplus quantity after providing for this year's wants.
| Wheat: Estimated Surplus, 1903. | ||
| Bushels. | ||
| The area for threshing was 194,355 acres, and the total yield computed at | 7,457,915 | |
| Amount of wheat on hand, 31st October, 1902 (as per returns) | 1,230,780 | |
| Amount of wheat and flour imported from 1st November, 1902, to 28th February, 1903 | 59,520 | |
| 8,748,215 | ||
| Bushels. | ||
| Wheat and flour exported from 1st November, 1902, to 28th February, 1903 | 76,940 | |
| Consumption for same period for population of 850,000, at the rate of 6 bushels per head per annum | 1,700,000 | |
| 1,776,940 | ||
| Leaving available for all purposes as at 28th February, 1903 | 6,971,275 | |
| Estimated quantity required for seed (say, 200,000 acres at 2 bushels per acre) | 400,000 | |
| Estimated consumption of 860,000 persons, at 6 bushels per head, from 1st March, 1903, to 28th February, 1904 | 5,160,000 | |
| 5,560,000 | ||
| Apparent surplus | 1,411,275 | |
The difficulty of correctly computing the consumption of breadstuffs is shown by the great differences in the estimates arrived at.
The average quantity required per head of the population (exclusive of that used for seed) has been calculated at 5·9 bushels for New South Wales, and 5·2 bushels for Victoria, by statisticians in those States.
The average consumption of wheaten breadstuffs in New Zealand thus appears to be somewhat higher than in New South Wales and Victoria.
The following is the average annual consumption of wheat per inhabitant in some of the principal countries of the world:—
| United Kingdom | 5·6 bushels. |
| Canada | 6·6 bushels. |
| France | 8·1 bushels. |
| Germany | 3·0 bushels. |
| Russia | 2·1 bushels. |
| Italy | 5·4 bushels. |
| United States | 4·5 bushels. |
The English consumption during the last twenty-five years appears to have ranged from 5 1/2 to 6 bushels per head of population.
The extent of land in oats grown for grain in 1903 was 483,659 acres, against 405,924 acres in the preceding year, an increase of 77,735 acres. The Provincial Districts of Otago (230,082 acres) and Canterbury (199,346 acres) account for 429,428 acres of the total area, Wellington taking third place with 27,884 acres. The breadth of land in oats for chaffing, ensilage, or feeding down with stock was 205,357 acres, an increase of 5,849 acres on the figures for 1902.
The average yield per acre was, in 1903, 45 bushels, and in 1902, 37·06 bushels, the quantity of produce increasing from 15,045,233 bushels to 21,766,708 bushels.
The oat-crop for 1902 in the Australian States was as follows:—
| Acres. | Bushels. | Average per Acre. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Queensland | 1,535 | 42,208 | 27·49 |
| New South Wales | 32,245 | 687,179 | 21·31 |
| Victoria | 329,150 | 6,724,900 | 20·43 |
| South Australia | 34,660 | 469,254 | 13·54 |
| Western Australia | 9,641 | 158,638 | 16·77 |
| Tasmania | 54,089 | 1,702,659 | 31·48 |
This is a very important crop. In 1903 there were 12,038 acres sown for grain, the yield being 607,609 bushels of corn, an average of 50·48 bushels per acre. Maize is grown only in the North Island, with the exception of a few acres in Nelson and Otago. The Provincial District of Auckland had 10,983 acres; Hawke's Bay, 723 acres; Taranaki, 101 acres; and Wellington, 212 acres, in 1903. As considerable interest is taken in this crop, the group of counties where it is chiefly grown is stated, viz.: Hobson, Manukau, Thames, Ohinemuri, Rodney, Whangarei, Mongonui, Waikato, Waipa, West Taupo and Kawhia, Hokianga, Tauranga, Whakatane, Opotiki, Waiapu, Cook, Wairoa, and Hawke's Bay. Small acreages are found in all the counties of the Auckland, and in most of the counties in the Taranaki, Hawke's Bay, and Wellington Districts.
Under barley, 27,921 acres were returned in 1903, the crop. being 1,136,232 bushels, an average yield per acre of 40·69 bushels. In 1902 the area under barley was 26,514 acres, and the yield 855,993 bushels, or 32·28 bushels per acre.
There were 1,279 acres in rye, yielding 38,370 bushels, or at the rate of 30 bushels per acre, in 1903, against 1,090 acres and 27,250 bushels, the rate being 25 bushels per acre, in 1902.
The area under peas for threshing in the season 1903 was 8,600 acres, yielding 300,675 bushels, or an average of 34·96 bushels per acre, against 7,242 acres and 164,712 bushels, or 22·88 bushels per acre, in the previous year.
Under beans there were 3,037 acres, giving a return of 90,346 bushels, the average being 29·71 bushels per acre, against 3,504 acres and 88,905 bushels (25·65 bushels per acre) in 1902.
The area under potatoes was 31,408 acres in 1903, yielding the return of 193,267 tons, or a rate of 6·15 tons per acre, against 31,259 acres in 1902, and 206,815 tons (or 6·61 tons per acre), an increase of 149 acres but a decrease in the yield of 13,548 tons.
A comparison of the gross yield of potatoes with the amount exported in each of the twelve years 1883–94 showed that for such period an average of 597 lb. per head of population was retained in the colony. Allowing for waste, pig-feed, and seed, the average amount retained for human consumption was found to be 449 lb. a head.
Turnips and rape form a most important crop in a sheep-breeding country such as New Zealand, and in 1892 the area of land under this crop amounted to 422,359 acres. The returns for 1895 gave only 385,788 acres, but for the present year 512,686 acres (392,830 acres in turnips and 119,856 in rape) were set down as under these crops; and there were 10,350 acres in addition, in mangolds (8,141 acres), beet (376 acres), and carrots (1,833 acres).
The cost of growing turnips sown broadcast and in drills may be: Broadcast—Ploughing, 5s. 6d. per acre; harrowing, 3s. per acre; rolling, 1s. per acre; seed and sowing, 1s. 6d. per acre: total, 11s. per acre. Drill—Ploughing, 5s. 6d.; grubbing, 3s.; harrowing, 3s.; rolling, 1s.; drilling, 3s. 6d.; hand-hoeing, 10s.; horse-hoeing, 5s.; seed and sowing, 2s. 6d.; manure, 10s. to 15s.: total, £2 3s. 6d. to £2 8s. 6d. per acre.
There were 790 acres under hops in 1903, as against 844 acres last year. No account of the produce for the last eight years was taken, but in 1895 the yield was 7,556 cwt. In 1900 the total quantity used by the breweries in the colony amounted to 5,020 cwt. Of the land under hops in 1903, 702 acres were in the Waimea County and 73 in Collingwood, both in the Provincial District of Nelson. The import of hops in 1902 amounted to 693 cwt., and the exports, the produce of the colony, to 4,311 cwt.
The growing of tobacco does not progress in New Zealand. In 1889, 34 acres were being cultivated; in 1890, 25 acres; in 1891, 16 acres; in 1892, 6 acres; in 1893, 4 acres; in 1894, 4 acres; and in 1895, 5 acres, producing 1,599 lb. of dried leaf. Statistics of this crop have not been taken since 1895.
The extent of land in garden was 17,632 acres, of which 14,062 acres were private gardens and 3,570 acres market gardens. In plantations of forest trees there were 53,788 acres.
There were 26,486 acres in orchard in 1903, an increase of 192 acres on the area so returned in the previous year, and 705 acres were returned as “vineyard.” The fruit-crop of the colony is supplemented by a considerable import from the Australian States and Fiji.
New Zealand is essentially suited for grazing purposes. Wherever there is light and moisture English grasses thrive when the natural bush and fern are cleared off—in fact, the white clover gradually overcomes the fern; and, from the mildness of the winter season, there are few places where there is not some growth, even in the coldest months of the year. In all parts of the colony stock live, although in varying condition, without other food than such as they can pick up. Sown-grass land, as might be expected, heads the list of cultivations.
At the beginning of the year 1903 there were 11,808,215 acres under artificial grasses. Of these, 4,558,346 acres had been previously ploughed, presumably under grain or other crops, while 7,249,869 acres had not been ploughed. Much of the latter area was bush or forest land, sown down in grass after the timber had been wholly or partially burnt off.
The area under ryegrass for seed in the season of 1903 was 27,881 acres, yielding 576,931 bushels of 20 lb., or a rate of 20·69 bushels per acre, against 16,244 acres and 356,765 bushels, an average of 21·97 bushels per acre, in 1902.
In cocksfoot there were 27,884 acres, which yielded 6,786,844 lb., or an average of 243 lb. per acre, against 27,876 acres and 4,481,340 lb. (a rate of 161 lb. per acre) in the previous year.
Seeds for sowing pasture lands are used much as in Great Britain, the following being a common mixture: Perennial ryegrass, 25 lb. to 30 lb. per acre; cocksfoot, 2 lb.; alsike, 2 lb.; timothy, 3 lb.; cowgrass, 2 lb.; red clover, 2 lb.; white clover, 2 lb.; rape, 1 lb.: total, 39 lb. to 44 lb. per acre. Pastures are renewed at intervals of from four to eight years, according to the nature of the land.
The following shows the acreage in sown grasses in Australasia in 1901–1902:—
| Acres. | |
|---|---|
| Queensland | 34,679 |
| New South Wales | 467,839 |
| Victoria (1900) | 207,896 |
| South Australia | 23,510 |
| Western Australia | 11,132 |
| Tasmania | 314,422 |
| New Zealand | 11,620,178 |
It will be observed that the acreage of land under sown grasses was eleven times as great in New Zealand as in the whole of Australia and Tasmania. When compared in size with the States of Australia, New Zealand is not large—about one-thirtieth of their total area—but in respect of grazing capabilities the relative importance of this country is much greater. Australia is generally unsuitable, owing to conditions of climate, for the growth of English grasses, and the amount of feed produced by the natural grasses throughout the year is very much less per acre than is obtained from the sown-grass lands in New Zealand; indeed, it may be said that the average productiveness of grassland is about nine times as great here as in Australia, or, in other words, that land in this colony covered with English grasses may be considered equal for grazing purposes to an area of Australian land about nine times as great.
In addition to the artificially-sown pastures, the returns for 1903 show that 22,431,136 acres of unimproved land, including that in tussock or native grass, belonged to the occupied holdings, and were available for stock-feeding by the sheep-farmers and cattle-farmers of the colony.
Table of Contents
The occupation of land must not be confused with ownership,* because there are large parcels of lands held which are unused and unoccupied. Neither can lands occupied be properly compared with the returns of Crown lands alienated or in process of alienation, for certain lands have passed into the hands of Europeans which were never made waste lands of the Crown.
The occupied lands of the colony for 1902–1903 have been returned by the Department of Agriculture at 35,887,447 acres, including Crown lands leased for pastoral purposes only, or 379,558 acres in excess of the area for the preceding year.
Tables are given showing the numbers and acreages of holdings, grouped according to size, for the last five years in which the Department of Agriculture has compiled the information.
In 1895 the holdings of over 1 acre in extent, as returned to the Registrar-General, numbered only 46,676. Holdings occupied by Maoris were excluded, besides holdings of exactly 1 acre, also gardens and orchards attached to residences.†
| Occupied Lands: Holdings. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [This and the succeeding statement deal with the full extent of occupied land, including Crown pastoral leases.] | |||||
| Sizes of Holdings. | No. of Holdings. | ||||
 | |||||
| 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. | |
| * The latest information in reference to ownership of land which is available gives figures up to the 31st March, 1902. It is contained in Parliamentary Return B.-20 of that year, and states the total number of owners of land (town and country holdings of all sizes) to be 115,713 for the colony. The most important figures (showing ownership of productive land) are those of freeholders outside boroughs and town districts, and excluding holdings of under 5 acres. These figures are:— | |||||
| 1 acre to 10 acres, inclusive | 17,230 | 17,454 | 17,468 | 17,817 | 18,348 |
| 10 acres to 50 acres, inclusive | 11,426 | 11,505 | 11,399 | 11,531 | 11,348 |
| 50 acres to 100 acres, inclusive | 7,276 | 7,195 | 7,162 | 7,130 | 7,239 |
| 100 acres to 200 acres, inclusive | 9,164 | 9,177 | 9,080 | 9,332 | 9,400 |
| 200 acres to 320 acres, inclusive | 5,584 | 5,675 | 5,751 | 5,898 | 5,998 |
| 320 acres to 640 acres, inclusive | 5,555 | 5,830 | 6,023 | 6,201 | 6,387 |
| 640 acres to 1,000 acres, inclusive | 1,946 | 2,128 | 2,212 | 2,324 | 2,449 |
| 1,000 acres to 5,000 acres, inclusive | 2,589 | 2,667 | 2,802 | 2,854 | 3,003 |
| 5,000 acres to 10,000 acres, inclusive | 369 | 352 | 392 | 393 | 366 |
| 10,000 acres to 20,000 acres, inclusive | 220 | 233 | 233 | 234 | 217 |
| 20,000 acres to 50,000 acres, inclusive | 175 | 169 | 167 | 165 | 175 |
| 50,000 acres and over | 105 | 100 | 97 | 103 | 104 |
| 61,639 | 62,485 | 62,786 | 63,982 | 65,034 | |
| New Zealand Owners (Over 5 Acres). | |
|---|---|
| Year 1902 | 43,735 |
| Year 1892 | 38,935 |
| Year 1889 | 37,432 |
| Year 1886 | 34,450 |
| Year 1883 | 30,764 |
† At the census of April, 1901, the actual number of persons described in the census schedules as having occupations necessitating their occupying holdings of land was 40,144. This number includes 28,337 farmers, 3,220 runholders, 895 market-gardeners, 2,388 horticulturists or gardeners, 4,702 dairy-farmers, 345 fruit-growers, 29 vignerons, 159 poultry-farmers, 35 bee-farmers, and 34 others.
The holdings are shown to have increased by the number of 3,395 since 1898–99.
The total acreage of occupied land for each of the last five years is shown:—
| Occupied Lands: Acreages. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sizes of Holdings in Acres. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. |
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| 1 to 10 inclusive | 68,671 | 70,290 | 71,387 | 73,954 | 73,726 |
| 10 to 50 inclusive | 315,651 | 322,936 | 320,158 | 324,620 | 314,940 |
| 50 to 100 inclusive | 570,503 | 568,716 | 556,868 | 560,888 | 566,406 |
| 100 to 200 inclusive | 1,401,171 | 1,404,581 | 1,389,120 | 1,431,532 | 1,424,265 |
| 200 to 320 inclusive | 1,469,859 | 1,475,195 | 1,493,761 | 1,543,749 | 1,550,548 |
| 320 to 640 inclusive | 2,568,462 | 2,688,231 | 2,772,325 | 2,836,787 | 2,908,745 |
| 640 to 1,000 inclusive | 1,649,580 | 1,731,636 | 1,843,235 | 1,924,982 | 1,960,730 |
| 1,000 to 5,000 inclusive | 5,364,539 | 5,495,467 | 5,715,047 | 5,849,516 | 6,195,878 |
| 5,000 to 10,000 inclusive | 2,579,773 | 2,451,073 | 2,591,497 | 2,525,849 | 2,600,348 |
| 10,000 to 20,000 inclusive | 3,274,623 | 3,201,355 | 3,272,741 | 3,285,879 | 3,146,714 |
| 20,000 to 50,000 inclusive | 5,448,033 | 5,535,541 | 5,417,990 | 5,578,887 | 5,272,922 |
| 50,000 and over inclusive | 9,675,403 | 9,477,632 | 9,467,444 | 9,571,246 | 9,872,225 |
| 34,386,268 | 34,422,653 | 34,911,573 | 35,507,889 | 35,887,447 | |
In regard to holdings, out of a total of 65,034 in 1903 the large proportion of 36,935, or 56·79 per cent., were from 1 to 100 acres in extent; 46,335, or 71·25 per cent., were from 1 to 200 acres; and 52,333, or 80·47 per cent., were from 1 to 320 acres in size. The total number over 320 acres was only 12,701, or 19·53 per cent. of the whole, thus indicating a considerable degree of moderately close settlement, although the area of the holdings over the 320-acres limit necessarily shows as very large in a table which includes the Crown pastoral leases.
The plan of excluding these leases from the table showing the holdings in classes has its advantages, though not now adopted.
From the total extent of occupied land shown for the colony, such of the area of the Crown pastoral leases as has been distinguished by the enumerators can be deducted, and comparison then made for the census years 1886 and 1891, and the Agricultural Department returns for 1902–1903. The figures are:—
| — | Census Results, March, 1886. | Census Results, April, 1891. | Figures returned by Department of Agriculture, 1902–1903. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Total area of occupied land (after deducting Crown pastoral leases) | 17,077,074 | 19,951,925 | 27,099,082 |
The acreage shown in the returns as held on Crown pastoral lease would appear to have been understated in the returns rendered by occupiers, for the table (which is given hereunder) shows less than nine millions of acres. The figures in the previous column headed “Held from Crown under Various Tenures” seem greater than they should be, judging from the Lands Department returns. Possibly there may have been some misplacements, and caution is advised in using the numbers in the last two columns.
| Occupation of Land: Tenure. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial Districts. | Total Area of Holdings. | Freehold. | Leased from Private Individuals or Public Bodies. | Leased from Natives. | Held from Crown under Different Tenures. | Held under Pastoral Lease |
| * For remarks as to the accuracy of the figures in the columns see above. | ||||||
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Auckland | 5,801,666 | 3,965,533 | 416,176 | 501,039 | 878,070 | 40,848 |
| Taranaki | 1,054,706 | 568,883 | 200,276 | 98,282 | 187,265 | .. |
| Hawke's Bay | 3,273,065 | 1,793,283 | 316,178 | 829,423 | 293,274 | 40,907 |
| Wellington | 3,852,954 | 2,490,557 | 490,690 | 253,333 | 502,161 | 116,213 |
| Marlborough | 2,303,575 | 800,682 | 99,904 | 23,957 | 791,754 | 587,278 |
| Nelson | 2,046,346 | 1,004,704 | 122,877 | 21,136 | 261,761 | 635,868 |
| Westland | 554,779 | 60,467 | 6,210 | 2,741 | 317,191 | 168,170 |
| Canterbury | 6,488,625 | 2,716,711 | 838,036 | 14,542 | 521,823 | 2,397,513 |
| Otago | 10,511,731 | 2,890,473 | 1,041,599 | 10,472 | 1,767,619 | 4,801,568 |
| Totals | 35,887,447 | 16,291,293 | 3,531,946 | 1,754,925 | 5,520,918* | 8,788,365* |
It would appear that holders of their lands from the Crown do not return to collectors so much as the quantity on which they pay rent to Government. The acreages stated to be held under Crown pastoral lease do not agree with the tables of the Lands Department. Arranged according to the number of holdings, the provincial districts stand in order as under:—
| Auckland | 16,324 holdings. |
| Otago | 13,757 holdings. |
| Canterbury | 11,273 holdings. |
| Wellington | 10,685 holdings. |
| Taranaki | 4,499 holdings. |
| Hawke's Bay | 3,191 holdings. |
| Nelson | 3,148 holdings. |
| Marlborough | 1,433 holdings. |
| Westland | 724 holdings. |
The occupied holdings of the North Island now considerably outnumber those of the Middle Island, the numbers being—North Island, 34,699; Middle Island, 30,335. For the year 1896–97 the returns showed 29,535 holdings for the Middle Island, against 29,369 for the North, besides 36 holdings at the Chatham Islands of which no account was taken for the last five years.
The full details of holdings and acreages, classified according to size, for the year 1902–1903 will be found in the table on the following page:—
| Occupation of Land: Number and Area of Holdings (including Crown Pastoral Leases). | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As compiled by the Department of Agriculture. | ||||||||||||||
| Table showing for the Year 1902–1903 the Occupied Holdings and the Acreages (including Crown Pastoral Leases) in Groups of Sizes, according to the Provincial Districts. | ||||||||||||||
| Provincial Districts. | Total of Holdings. | 1–10 Acres, inclusive. | Over 10–50 Acres, inclusive. | Over 50–100 Acres, inclusive. | Over 100–200 Acres, inclusive. | Over 200–320 Acres, inclusive. | Over 320–640 Acres, inclusive. | Over 640–1,000 Acres, inclusive. | Over 1,000–5,000 Acres, inclusive. | Over 5,000–10,000 Acres, inclusive. | Over 10,000–20,000 Acres, inclusive. | Over 20,000–25,000 Acres, inclusive. | Over 50,000 Acres. | |
| Auckland: Area in acres | 5,801,666 | 17,804 | 82,761 | 156,561 | 350,657 | 395,482 | 677,668 | 476,158 | 1,281,659 | 591,661 | 419,482 | 570,876 | 780,897 | |
| Number of holdings | 16,324 | 4,648 | 2,867 | 2,022 | 2,365 | 1,533 | 1,496 | 602 | 639 | 92 | 33 | 17 | 10 | |
| Taranaki: Area in acres | 1,054,706 | 3,151 | 16,921 | 59,118 | 170,393 | 162,783 | 215,604 | 109,394 | 288,368 | 6,070 | 22,904 | ... | ... | |
| Number of holdings | 4,499 | 622 | 566 | 750 | 1,140 | 635 | 482 | 140 | 161 | 1 | 2 | ... | ... | |
| Hawke's Bay: Area in acres | 3,273,065 | 4,677 | 16,823 | 19,939 | 38,746 | 47,256 | 125,117 | 89,962 | 503,614 | 342,338 | 554,370 | 898,858 | 631,365 | |
| Number of holdings | 3,191 | 1,093 | 645 | 261 | 267 | 177 | 272 | 122 | 230 | 52 | 33 | 32 | 7 | |
| Wellington: Area in acres | 3,852,954 | 12,765 | 47,372 | 95,885 | 277,241 | 238,389 | 519,667 | 372,846 | 998,290 | 435,129 | 450,604 | 215,347 | 189,419 | |
| Number of holdings | 10,685 | 2,921 | 1,712 | 1,169 | 1,758 | 921 | 1,135 | 459 | 511 | 60 | 30 | 7 | 2 | |
| Marlborough: Area in acres | 2,303,575 | 1,557 | 4,044 | 8,621 | 22,371 | 26,370 | 85,936 | 71,941 | 269,257 | 93,859 | 243,417 | 383,864 | 1,092,338 | |
| Number of holdings | 1,433 | 449 | 170 | 115 | 149 | 101 | 182 | 90 | 126 | 14 | 16 | 12 | 9 | |
| Nelson: Area in acres | 2,046,346 | 3,037 | 18,721 | 31,520 | 68,258 | 69,471 | 131,787 | 99,999 | 270,123 | 22,911 | 93,149 | 403,146 | 834,724 | |
| Number of holdings | 3,148 | 787 | 648 | 401 | 459 | 269 | 292 | 124 | 138 | 4 | 6 | 13 | 7 | |
| Westland: Area in acres | 554,779 | 680 | 3,990 | 6,438 | 17,531 | 16,253 | 25,714 | 9,589 | 43,780 | 73,769 | 171,684 | 185,351 | ... | |
| Number of holdings | 724 | 217 | 127 | 86 | 114 | 62 | 55 | 12 | 22 | 11 | 11 | 7 | ... | |
| Canterbury: Area in acres | 10,488,625 | 14,801 | 62,853 | 89,028 | 190,320 | 224,684 | 419,240 | 276,473 | 1,123,508 | 396,266 | 487,079 | 983,844 | 2,220,529 | |
| Number of holdings | 11,273 | 3,724 | 2,269 | 1,154 | 1,284 | 871 | 922 | 336 | 562 | 54 | 35 | 36 | 26 | |
| Otago: Area in acres | 10,511,731 | 15,254 | 61,455 | 99,296 | 288,748 | 369,860 | 708,012 | 454,368 | 1,417,279 | 638,345 | 704,025 | 1,631,636 | 4,123,453 | |
| Number of holdings | 13,757 | 3,887 | 2,344 | 1,281 | 1,864 | 1,429 | 1,551 | 564 | 614 | 78 | 51 | 51 | 43 | |
Totals | Area in acres | 35,887,447 | 73,726 | 314,940 | 566,406 | 1,424,265 | 1,550,548 | 2,908,745 | 1,960,730 | 6,195,878 | 2,600,348 | 3,146,714 | 5,272,922 | 9,872,225 |
| Number of holdings | 65,034 | 18,348 | 11,348 | 7,239 | 9,400 | 5,998 | 6,387 | 2,449 | 3,003 | 366 | 217 | 175 | 104 | |
A comparative table is presented showing the increase in livestock since the year 1858. The figures are taken from the census as far as 1891, but for 1895–96 and following years the results of the enumeration made annually by the Department of Agriculture under “The Agricultural and Pastoral Statistics Act, 1895,” have been made use of.
| Year. | Horses. | Asses and Mules. | Cattle. | Sheep. | Goats. | Pigs. | Poultry. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Not enumerated. † Numbers for April, 1895, 1896, 1897, 1898, 1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902. | |||||||
| 1858 | 14,912 | 122 | 137,204 | 1,523,324 | 11,797 | 40,734 | * |
| 1861 | 28,275 | 153 | 193,285 | 2,761,383 | 12,191 | 43,270 | 236,098 |
| 1864 | 49,409 | 339 | 249,760 | 4,937,273 | 12,005 | 61,276 | 378,414 |
| 1867 | 65,715 | 323 | 312,835 | 8,418,579 | 11,964 | 115,104 | 676,065 |
| 1871 | 81,028 | 397 | 436,592 | 9,700,629 | 12,434 | 151,460 | 872,174 |
| 1874 | 99,859 | 267 | 494,917 | 11,704,853 | 14,276 | 123,921 | 1,058,198 |
| 1878 | 137,768 | 241 | 578,430 | 13,069,338 | 14,243 | 207,337 | 1,323,542 |
| 1881 | 161,736 | 362 | 698,637 | 12,985,085 | 11,223 | 200,083 | 1,566,114 |
| 1886 | 187,382 | 297 | 853,358 | 16,564,595 | 10,220 | 277,901 | 1,679,021 |
| 1891 | 211,040 | 348 | 831,831 | 18,128,186 | 9,055 | 308,812 | 1,790,070 |
| 1895–96 | 237,418 | 426 | 1,047,901 | 19,826,604† | * | 239,778 | * |
| 1896–97 | 249,813 | 434 | 1,138,067 | 19,138,493† | * | 209,834 | * |
| 1897–98 | 252,834 | 393 | 1,209,165 | 19,687,954† | * | 186,027 | * |
| 1898–99 | 258,115 | 534 | 1,203,024 | 19,673,725† | * | 193,512 | * |
| 1899–1900 | 261,931 | 459 | 1,222,139 | 19,348,506† | * | 249,751 | * |
| 1900–1901 | 266,245 | 480 | 1,256,680 | 19,355,195† | * | 250,975 | * |
| 1901–1902 | 279,672 | 406 | 1,361,784 | 20,233,099† | * | 224,024 | * |
| 1902–1903 | 286,955 | 464 | 1,460,663 | 20,342,727† | * | 193,740 | * |
The stock owned by Maoris in the year 1901, which is included above, comprised 317,436 sheep and 36,943 head of cattle. The number of horses is not specified, but is known to be large.
| Table showing for each County in New Zealand the Number of Horses, Cattle, Sheep, and Pigs in 1902. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County. | Horses, October, 1902. | Cattle, including Calves, October, 1902. | Dairy Cows, included in foregoing. | Sheep, including Lambs, April, 1902. | Pigs, October, 1902. |
| * Not including 43,390 heifers over two years old intended for dairying. | |||||
| Mongonui | 2,122 | 8,859 | 1,469 | 25,289 | 2,175 |
| Whangaroa | 564 | 1,686 | 158 | 8,344 | 804 |
| Bay of Islands | 2,549 | 11,277 | 2,120 | 32,708 | 2,115 |
| Hokianga | 2,692 | 7,084 | 1,893 | 11,945 | 2,756 |
| Rodney | 2,292 | 14,189 | 3,568 | 78,696 | 562 |
| Whangarei | 4,524 | 29,616 | 7,780 | 37,805 | 1,709 |
| Otamatea | 1,610 | 12,711 | 2,550 | 48,581 | 691 |
| Hobson | 2,140 | 20,183 | 3,191 | 21,084 | 3,972 |
| Waitemata | 2,494 | 12,316 | 3,836 | 40,659 | 1,262 |
| Eden | 6,383 | 7,105 | 3,694 | 4,250 | 1,690 |
| Manukau | 8,345 | 50,558 | 18,657 | 95,153 | 5,297 |
| Coromandel | 898 | 4,136 | 800 | 13,644 | 689 |
| Thames | 1,793 | 5,237 | 1,849 | 4,749 | 1,163 |
| Ohinemuri | 1,722 | 5,856 | 1,983 | 4,138 | 1,949 |
| Waikato | 3,315 | 22,490 | 6,642 | 66,159 | 2,572 |
| Raglan | 3,328 | 26,510 | 4,180 | 92,643 | 2,177 |
| Waipa | 3,654 | 24,315 | 7,722 | 34,011 | 2,806 |
| Piako | 2,926 | 31,172 | 4,588 | 176,591 | 1,345 |
| West Taupo and Kawhia | 5,533 | 21,247 | 1,960 | 33,972 | 7,922 |
| East Taupo and Rotorua | 1,872 | 3,137 | 532 | 30,491 | 1,651 |
| Tauranga | 2,572 | 15,108 | 2,794 | 4,015 | 1,357 |
| Whakatane | 826 | 4,474 | 1,134 | 22,992 | 566 |
| Opotiki | 1,525 | 7,151 | 1,694 | 16,762 | 758 |
| Waiapu | 4,407 | 16,932 | 559 | 372,242 | 3,757 |
| Cook | 7,193 | 48,056 | 4,538 | 941,421 | 2,888 |
| Wairoa | 3,037 | 10,824 | 1,380 | 558,988 | 913 |
| Hawke's Bay | 7,769 | 35,254 | 4,274 | 1,272,956 | 3,806 |
| Waipawa | 4,507 | 32,543 | 5,822 | 728,783 | 1,791 |
| Woodville | 1,105 | 11,358 | 4,486 | 1,191 | |
| Patangata and Weber | 2,743 | 32,271 | 1,256 | 731,932 | 565 |
| Clifton | 1,415 | 18,762 | 4,894 | 27,149 | 1,223 |
| Taranaki and Egmont | 5,923 | 71,176 | 32,550 | 28,763 | 6,471 |
| Stratford | 2,758 | 44,280 | 18,011 | 115,276 | 2,940 |
| Hawera | 5,795 | 78,086 | 34,074 | 156,417 | 7,331 |
| Patea | 3,010 | 27,606 | 8,218 | 225,228 | 1,650 |
| Waitotara | 2,028 | 13,818 | 3,828 | 149,659 | 1,217 |
| Wanganui and Waimarino | 5,044 | 19,507 | 4,924 | 418,772 | 3,490 |
| Rangitikei | 5,540 | 34,801 | 8,194 | 566,948 | 2,658 |
| Kiwitea | 2,218 | 18,576 | 6,172 | 284,806 | 2,014 |
| Pohangina | 999 | 9,562 | 3,585 | 128,940 | 1,194 |
| Oroua | 2,333 | 15,579 | 7,576 | 301,109 | 2,677 |
| Kairanga | 3,275 | 17,809 | 7,908 | 3,067 | |
| Manawatu | 2,628 | 22,013 | 7,215 | 170,166 | 2,817 |
| Horowhenua | 2,908 | 24,843 | 7,733 | 135,200 | 3,183 |
| Hutt | 5,203 | 15,586 | 7,990 | 217,007 | 2,525 |
| Featherston | 3,069 | 24,848 | 3,362 | 623,550 | 2,079 |
| South Wairarapa | 2,277 | 21,067 | 5,050 | 1,996 | |
| Masterton | 3,369 | 23,579 | 3,635 | 543,897 | 1,161 |
| Castlepoint | 516 | 7,150 | 426 | 152,976 | 58 |
| Akitio | 1,204 | 12,424 | 1,539 | 162,484 | 439 |
| Pahiatua | 2,065 | 21,759 | 9,114 | 228,680 | 2,751 |
| Eketahuna | 947 | 8,251 | 4,320 | 71,644 | 1,242 |
| Mauriceville | 398 | 4,697 | 2,064 | 66,672 | 451 |
| Marlborough | 3,477 | 4,962 | 2,205 | 522,783 | 1,513 |
| Sounds | 855 | 5,129 | 1,838 | 164,657 | 1,213 |
| Kaikoura | 1,198 | 2,686 | 876 | 161,728 | 425 |
| Collingwood | 1,271 | 7,515 | 553 | 44,878 | 2,050 |
| Waimea | 4,791 | 12,892 | 5,315 | 209,321 | 3,615 |
| Buller | 508 | 3,680 | 1,468 | 2,084 | 474 |
| Inangahua | 942 | 6,968 | 1,402 | 23,670 | 754 |
| Westland | 1,472 | 10,299 | 2,327 | 17,204 | 767 |
| Grey | 850 | 5,613 | 1,325 | 11,033 | 645 |
| Amuri | 1,343 | 4,805 | 340 | 395,257 | 156 |
| Cheviot | 919 | 1,339 | 556 | 196,882 | 570 |
| Ashley | 8,324 | 17,064 | 6,911 | 801,164 | 6,204 |
| Selwyn | 15,455 | 29,642 | 15,419 | 706,610 | 17,608 |
| Akaroa and Mount Herbert | 2,682 | 23,842 | 5,749 | 246,645 | 2,261 |
| Ashburton | 9,478 | 9,819 | 3,644 | 876,274 | 7,452 |
| Geraldine | 4,178 | 5,941 | 2,176 | 689,571 | 2,775 |
| Levels | 3,343 | 5,229 | 2,145 | 1,536 | |
| Waimate | 5,305 | 8,757 | 2,687 | 602,424 | 2,712 |
| Mackenzie | 1,504 | 2,836 | 1,003 | 418,854 | 557 |
| Waitaki | 6,290 | 20,396 | 8,713 | 563,724 | 3,043 |
| Waihemo | 1,381 | 4,460 | 1,770 | 120,200 | 486 |
| Waikouaiti | 1,514 | 9,927 | 5,443 | 79,217 | 1,531 |
| Peninsula | 873 | 7,560 | 4,346 | 2,470 | 816 |
| Taieri | 7,011 | 25,529 | 9,158 | 208,074 | 3,853 |
| Bruce | 3,684 | 10,880 | 3,470 | 172,640 | 1,402 |
| Clutha | 4,862 | 17,576 | 5,834 | 325,679 | 1,453 |
| Tuapeka | 3,826 | 6,485 | 2,182 | 374,304 | 890 |
| Maniototo | 2,174 | 5,894 | 1,319 | 323,043 | 323 |
| Vincent | 2,368 | 5,009 | 1,290 | 295,699 | 861 |
| Lake | 1,467 | 3,768 | 894 | 148,278 | 446 |
| Southland | 17,106 | 63,735 | 19,737 | 895,636 | 6,645 |
| Wallace and Fiord | 5,130 | 20,655 | 5,099 | 454,690 | 1,155 |
| Stewart Island | 12 | 337 | 88 | 1,688 | 16 |
| Totals | 286,955 | 1,460,663 | 428,773* | 20,342,727 | 193,740 |
The following gives the number of the principal kinds of livestock in Australasia for the year 1901–1902:—
| State or Colony. | Sheep. | Cattle. | Horses. | Pigs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Queensland | 10,030,971 | 3,772,707 | 462,119 | 121,641 |
| New South Wales | 41,857,099 | 2,047,454 | 486,716 | 265,730 |
| Victoria | 10,841,790 | 1,602,384 | 392,237 | 350,370 |
| South Australia | 5,060,540 | 479,863 | 178,199 | 89,875 |
| Western Australia | 2,542,844 | 394,580 | 73,830 | 61,025 |
| Tasmania | 1,792,481 | 168,661 | 32,399 | 58,716 |
| April, 1901. | Nov., 1901. | Nov., 1901. | Nov., 1901. | |
| New Zealand | 20,233,099 | 1,361,784 | 279,672 | 224,024 |
New Zealand thus takes second place in order for number of sheep, and fourth for the number of her cattle and horses.
The losses in Australia have raised this colony to the second position in regard to sheep. To illustrate this, the case of Queensland shows 19,856,959 sheep in 1895, falling to 10,030,971 in 1901, and further to 7,213,985 in 1902; cattle fell in number from 7,012,997 in 1894 to 3,772,707 in 1901, and again to 2,543,471 in 1902.
The returns made to the Department of Agriculture show a smaller number of sheep for the years 1886 and 1891 than the census figures given previously, because the account was taken later in the year. The particulars are given for seventeen years, distinguishing the number for the North from that in the Middle Island.
According to these returns, the flocks of the North Island increased from 5,285,907 sheep in the year 1886 to 10,286,346 in 1902, or at the rate of over 94 per cent., while sheep in the Middle Island increased from 9,888,356 to 10,056,381, a gain of 1·70 per cent. in the same period. For the North Island the increase during the seventeen years was 5,000,439 sheep, while in the Middle Island there was an increase of 168,025.
| Year. | North Island | Middle Island. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1886 | 5,285,907 | 9,888,356 | 15,174,263 |
| 1887 | 5,506,485 | 9,649,141 | 15,155,626 |
| 1888 | 5,668,996 | 9,373,202 | 15,042,198 |
| 1889 | 5,990,244 | 9,433,084 | 15,423,328 |
| 1890 | 6,588,346 | 9,527,767 | 16,116,113 |
| 1891 | 7,159,927 | 9,593,825 | 16,753,752 |
| 1892 | 8,204,029 | 10,366,723 | 18,570,752 |
| 1893 | 8,685,361 | 10,695,008 | 19,380,369 |
| 1894 | 9,169,352 | 11,061,477 | 20,230,829 |
| 1895 | 8,994,646 | 10,831,958 | 19,826,604 |
| 1896 | 9,131,736 | 10,006,757 | 19,138,493 |
| 1897 | 9,540,717 | 10,147,237 | 19,687,954 |
| 1898 | 9,864,945 | 9,808,780 | 19,673,725 |
| 1899 | 9,953,399 | 9,395,107 | 19,348,506 |
| 1900 | 9,998,173 | 9,357,022 | 19,355,195 |
| 1901 | 10,218,945 | 10,014,154 | 20,233,099 |
| 1902 | 10,286,346 | 10,056,381 | 20,342,727 |
There was an increase of 109,628 in the total number of sheep since April, 1901, by the above figures, and an increase between 1892 and 1902 amounting to 1,771,975, or at a rate of 9·54 per cent. The export and local consumption of wool developed from 111,537,546 lb. for the year ended September, 1891, to 159,855,875 lb. for the corresponding year of 1902. The export of sheepskins and pelts, which in 1890 was 2,292,521 in number, rose to 6,144,680 in 1902.
Over a series of years the number of sheep has been well maintained, although the slaughter needed for the export of frozen mutton increased to nearly four millions of sheep and lambs in 1902.
The proportion of small flocks of sheep until 1902 increased very considerably, and with smaller flocks the rabbit difficulty is easier to master than with large ones.
| Number of Flocks, 1886, 1891, 1896, 1900, 1901, and 1902. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size of Flocks. | 1886. | 1891. | 1896. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
| Under 500 | 6,024 | 8,272 | 12,028 | 12,239 | 11,700 | 11,961 |
| 500 and under 1,000 | 1,189 | 1,691 | 2,605 | 2,810 | 3,059 | 3,158 |
| 1,000 and under 2,000 | 747 | 969 | 1,460 892 | 2,621 | 2,877 | 2,962 |
| 2,000 and under 5,000 | 532 | 666 | ||||
| 5,000 and under 10,000 | 263 | 287 | 340 | 352 | 397 | 385 |
| 10,000 and under 20,000 | 228 | 239 | 231 | 196 | 189 | 206 |
| 20,000 and upwards | 166 | 169 | 147 | 139 | 138 | 131 |
| 9,149 | 12,293 | 17,703 | 18,357 | 18,360 | 18,803 | |
| 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| * From 1,000 to 2,500 | 1,971 | 2,189 | 2,232 |
| * From 2,500 to 5,000 | 650 | 688 | 730 |
| 2,621 | 2,877 | 2,962 |
The average size of the flocks is found to have been 1,659 sheep for 1886, 1,363 for 1891, 1,081 in 1896, 1,040 in 1899, 1,054 in 1900, 1,102 in 1901, and 1,082 in 1902.
Of the provincial districts, that of Canterbury had most sheep in 1902, Wellington came next, and Otago occupied the third place. The full particulars, with increases or decreases since 1901, are:—
| Provincial Districts. | No. of Sheep in 1902. | No. of Sheep in 1901. | Increase. | Decrease. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canterbury | 4,341,542 | 4,318,887 | 22,655 | .. |
| Wellington | 4,222,510 | 4,239,538 | .. | 17,028 |
| Otago | 3,965,342 | 3,978,011 | .. | 12,669 |
| Hawke's Bay | 3,292,659 | 3,298,431 | .. | 5,762 |
| Auckland | 2,218,344 | 2,116,594 | 101,750 | .. |
| Nelson | 872,092 | 868,808 | 3,284 | .. |
| Marlborough | 849,168 | 821,812 | 27,356 | .. |
| Taranaki | 552,833 | 564,392 | .. | 11,559 |
| Westland | 28,237 | 26,636 | 1,601 | .. |
| 20,342,727 | 20,233,099 | 109,628 | Net increase. |
Five of the provincial districts show an increase in the number of sheep in 1902 when compared with the previous year's returns, aggregating 156,646, to which gain Canterbury contributed 22,655, Auckland 101,750, Marlborough 27,356, Nelson 3,284, and Westland 1601. The other four provincial districts show decreases (Wellington 17,028, Otago 12,669, Hawke's Bay 5,762, and Taranaki 11,559), and thus reduce the gain for the whole colony to 109,628, as shown above.
The number of breeding ewes in the colony in April, 1901, was returned at 9,906,616, and in April, 1902, at 9,610,149, thus showing a substantial decrease of 296,467 for the year—a matter for serious consideration. The annual export and consumption of sheep during the last five years has been:—
| Year. | Export of Frozen Mutton and Lamb, including Pieces at 60 lb. to a Sheep. | Live Sheep exported. | Estimated Consumption in the Colony: Carcases. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898 | 3,005,720 | 6,270 | 1,744,000 | 4,755,990 |
| 1899 | 3,468,431 | 4,362 | 1,780,000 | 5,252,793 |
| 1900 | 3,055,135 | 3,840 | 1,800,000 | 4,858,975 |
| 1901 | 3,400,138 | 3,668 | 1,834,000 | 5,237,806 |
| 1902 | 4,084,578 | 48,047 | 1,904,000 | 6,036,625 |
It has been estimated that the annual consumption of mutton in New Zealand is equivalent to 2·25 sheep per inhabitant, and that the number of sheep required in the present year (1903) for food will be about 1,932,000. (Maoris, for the purposes of this calculation, have been included.)
Two important advantages that sheep-farming has in New Zealand are (1) the low cost of the production of mutton, and (2) the high percentage of natural increase. With regard to the high percentage of increase, there need only be cited a few average returns from well-known flocks to show what excellent lambings New Zealand farmers obtain under good management.
| Lambing Returns.—Averages. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locality. | Breed of Flock. | Breed of Rams. | Breed of Ewes. | No. of Ewes. | Percentage of Lambs. | Remarks. | |
| North Island | Lincoln | Lincoln | Lincoln | 7,517 | 81·04 |  | Land merely surface-sown in English-grass pasture. |
| North Island | Lincoln | Lincoln | Lincoln | 5,301 | 85·05 | ||
| North Island | Lincoln | Lincoln | 7/8 Lincoln | 12,177 | 100·00 | ||
| North Island | Romney | Romney | Romney | 1,141 | 96·17 | ||
| North Island | Lincoln | Southd'n | Lincoln | 2,033 | 94·71 | ||
| Middle Island | Merino | Merino | Merino | 14,765 | 75·36 |  | Mountainous country in n'tive past're, unimproved. |
| Middle Island | Merino | B. Leic'str | Merino | 4,235 | 88·94 | ||
| Middle Island | Cross-bred | B. Leic'str | Cross-bred | 8,624 | 80·82 |  | In English-grass pasture. |
| Middle Island | Half-bred | B. Leic'str | Half-bred | 2,747 | 82·79 | ||
| Middle Island | B. Leic'str | B. Leic'str | B. Leic'str | 778 | 90·77 | ||
| Middle Island | Lincoln | Lincoln | Lincoln | 452 | 88·08 | ||
| Middle Island | R. Marsh | R. Marsh | R. Marsh | 253 | 111·46 | ||
| Middle Island | E. Leic'str | E. Leic'str | E. Leic'str | 464 | 93·34 | ||
| Middle Island | Shropshire | Shropshire | Shropshire | 168 | 97·41 | ||
| Middle Island | Southd'n | Southd'n | Southd'n | 114 | 96·87 | ||
The above returns are fair average ones, but much higher might have been shown if exceptional cases had been selected.
The increase of cattle between 1891 and 1896 was 216,070, or at the rate of 25·98 per cent. The rapid development of the butter and cheese industry, represented in great part by the export figures given in the comparative table on page 330, created a requirement for milch cows, which increased in number from 206,906 in 1891 to 276,217 in 1896, or at the rate of 33·50 per cent.
The cattle as enumerated in 1902–1903 for each provincial district are given in the next table. Here is shown the substantial increase of 98,879 head of all classes over the number returned in 1901–1902, and of no less than 51,670 in the number of cows and heifers for dairy purposes.
| Provincial District. | Bulls for Stud Purposes. | Steers over Two Years Old. | Cows and Heifers for Dairy Purposes. | Cows and Heifers for Breeding Purposes. | Cows and Heifers for Fattening. | Steers and Heifers under Two Years not otherwise enumerated. | Totals. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Including heifers over two years old intended for dairying: 39,001 in 1901–1902, and 43,390 in 1902–1903. For actual number of dairy cows in each county see table on pages 369 to 391. | |||||||
| Auckland | 6,528 | 72,492 | 102,403 | 60,341 | 13,738 | 155,903 | 411,405 |
| Taranaki | 3,895 | 28,706 | 106,582 | 5,584 | 5,505 | 89,638 | 239,910 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,890 | 22,026 | 19,080 | 35,421 | 3,704 | 40,129 | 122,250 |
| Wellington | 5,616 | 44,371 | 102,929 | 46,015 | 8,809 | 108,129 | 315,869 |
| Marlborough | 251 | 1,140 | 5,188 | 350 | 407 | 5,441 | 12,777 |
| Nelson | 589 | 4,594 | 12,882 | 1,666 | 2,262 | 15,206 | 37,199 |
| Westland | 249 | 3,242 | 4,531 | 2,368 | 895 | 4,627 | 15,912 |
| Canterbury | 1,637 | 9,433 | 42,871 | 2,561 | 4,105 | 42,523 | 103,130 |
| Otago | 3,394 | 24,655 | 75,697 | 16,335 | 7,736 | 74,394 | 202,211 |
| Totals, 1902–1903 | 24,049 | 210,659 | 472,163* | 170,641 | 47,161 | 535,990 | 1,460,663 |
| Totals, 1901–1902 | 21,228 | 202,810 | 420,493* | 166,126 | 50,267 | 500,860 | 1,361,784 |
| Increase, 1902–1903 | 2,821 | 7,849 | 51,670 | 4,515 | .. | 35,130 | 98,879 |
| Decrease, 1902–1903 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,106 | .. | .. |
Classified according to breed, the numbers for the two years under review are:—
| Pure-bred— | 1902–1903. | 1901–1902. |
| Shorthorn | 73,030 | 63,476 |
| Hereford | 11,315 | 6,598 |
| Polled Angus | 12,359 | 8,836 |
| Ayrshire | 4,987 | 4,705 |
| Jersey | 4,193 | 4,586 |
| Other pure-breds | 4,341 | 9,101 |
| Crosses | 1,350,438 | 1,264,482 |
| Totals | 1,460,663 | 1,361,784 |
Out of a total of 1,460,663 cattle in the colony, the North Island is shown to have had 1,089,434, or 75 per cent., while the Middle Island had 371,229, or 25 per cent. Similarly, the dairy cows and heifers intended for dairying in the North Island numbered 330,994, and in the Middle Island 141,169.
Thus, the North Island, which now leads as regards number of sheep, contains more than twice as many dairy cows and other cattle as the Middle Island.
Of the total number of cattle (1,460,663) given above, 428,773 were dairy cows. It is found impossible to give a statement of the actual amount of butter and cheese made, even at the factories only. All that can be said is that there were in September, 1902, 276 cheese and butter factories and creameries, with 319 skimming-stations, reported to the Department of Agriculture. But very few of these factories made any return to the Department of their output for the previous year, and it is therefore impossible to arrive at the total quantity of cheese and butter made. The census returns for March, 1901, show there were then 247 factories and 202 creameries, the annual output during the year 1900 amounting to 29,758,310 lb. of butter and 139,687 cwt. of cheese.
The increase in horses is shown for four census years:—
| Census Years. | Number of Horses. | Numerical Increase. | Increase per Cent. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1886 | 187,382 | 23,658 | 12·63 |
| 1891 | 211,040 | 26,378 | 12·50 |
| 1896 | 237,418 | 28,827 | 12·14 |
| 1901 | 266,245 |
At the enumeration made in 1902–1903 (October to January), the number of horses was found to have increased to 287,419 (including 464 mules and asses), for which particulars are given. It will be seen that the Provincial District of Auckland had by far the most horses, Otago and Canterbury following, Wellington taking fourth place.
| Provincial District. | Entires. | Geldings. | Mares over Two Years old. | Mares with Foal at Foot, or to foal this Season. | Colts and Fillies under Two Years old. | Totals. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Including 464 mules and asses in 1903, and 406 in 1902. | ||||||
| Auckland | 858 | 33,703 | 23,587 | 8,955 | 10,415 | 77,518 |
| Taranaki | 133 | 7,994 | 6,387 | 1,961 | 2,428 | 18,903 |
| Hawke's Bay | 211 | 8,648 | 6,312 | 1,897 | 2,131 | 19,199 |
| Wellington | 530 | 20,034 | 14,744 | 5,292 | 5,438 | 46,038 |
| Marlborough | 58 | 2,388 | 1,879 | 466 | 744 | 5,535 |
| Nelson | 109 | 4,148 | 3,305 | 989 | 1,226 | 9,777 |
| Westland | 41 | 1,145 | 710 | 195 | 242 | 2,333 |
| Canterbury | 407 | 21,757 | 17,301 | 4,634 | 6,275 | 50,374 |
| Otago | 437 | 24,697 | 19,180 | 5,392 | 8,036 | 57,742 |
| Totals, 1902–1903 | 2,784 | 124,514 | 93,405 | 29,781 | 36,935 | 287,419* |
| Totals, 1901–1902 | 2,596 | 124,869 | 93,188 | 27,249 | 32,176 | 280,078* |
| Increase, 1902–03 | 188 | .. | 217 | 2,532 | 4,759 | 7,341 |
| Decrease, 1902–03 | .. | 355 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
Classified according to breed, the numbers for the two years under review are:—
| 1902–1903. | 1901–1902. | |
|---|---|---|
| Thoroughbred | 6,661 | 6,545 |
| Hunter and hackney | 23,483 | 26,736 |
| Carriage and trotting | 19,897 | 19,899 |
| Light ordinary | 120,284 | 114,321 |
| Draught | 104,146 | 99,604 |
| Ponies under 14 hands | 12,484 | 12,567 |
| Mules and asses | 464 | 406 |
| Totals | 287,419 | 280,078 |
It has long been expected that the export of New Zealand horses to Australia and India would assume large proportions. So far, however, the trade has not developed to the extent anticipated. The opinion has been often expressed that more might be done than has been in the past. The following figures will show the position for the years 1885, 1890, 1895, 1896, 1898, and 1900 to 1902:—
| Exported to | 1885. | 1890. | 1895. | 1896. | 1898. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
| Victoria | 133 | 92 | 10 | 22 | 41 | 29 | 38 | 40 |
| New South Wales | 2,687 | 197 | 53 | 53 | 39 | 19 | 5 | 56 |
| Queensland | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2 | .. | .. |
| Tasmania | 113 | 27 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 5 | 4 |
| Fiji | 32 | 57 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 16 | 50 | 27 |
| Bengal | 34 | 235 | 94 | 151 | 116 | 69 | 106 | 147 |
| Brazil | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| South Sea Islands | 13 | 18 | 15 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 3 |
| United Kingdom | .. | .. | 5 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 1 | .. |
| United States of America (W. Coast) | 10 | .. | 3 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Cape Colony | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 600 | 2 | .. |
| Natal | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1,031 |
| 3,022 | 628 | 193 | 249 | 210 | 756 | 265 | 1,308 |
Pigs have decreased since 1891, when the number was 308,812, against 193,740 in 1902–1903. The figures given in the accompanying table are those compiled by the Agricultural Department, and for 1902–1903 show a decrease of 30,284 in the total number of pigs kept in the previous year. The Auckland Provincial District has far more pigs than any other.
| Number of Pigs in each Provincial District. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial District. | Boars for Stud Purposes. | Barrows and Sows over One Year old, for Fattening. | Sows kept solely for Breeding Purposes. | Barrows and Sows under One Year old. | Totals. |
| Auckland | 1,511 | 8,881 | 8,352 | 35,888 | 54,633 |
| Taranaki | 474 | 1,516 | 2,843 | 14,782 | 19,615 |
| Hawke's Bay | 207 | 864 | 1,178 | 6,017 | 8,266 |
| Wellington | 952 | 2,138 | 5,383 | 26,546 | 35,019 |
| Marlborough | 75 | 410 | 429 | 2,237 | 3,151 |
| Nelson | 173 | 631 | 985 | 5,830 | 7,619 |
| Westland | 37 | 335 | 148 | 892 | 1,412 |
| Canterbury | 744 | 1,759 | 5,119 | 33,483 | 41,105 |
| Otago | 543 | 2,416 | 2,772 | 17,189 | 22,920 |
| Totals, 1902–1903 | 4,716 | 18,950 | 27,210 | 142,864 | 193,740 |
| Totals, 1901–1902 | 4,983 | 21,955 | 30,150 | 166,936 | 224,024 |
| Decrease, 1902–03 | 267 | 3,005 | 2,940 | 24,072 | 30,284 |
The approximate numbers of the different breeds were:—
| 1902–1903. | 1901–1902. | |
| Pure Berkshire | 30,192 | 34,891 |
| Pure Yorkshire | 2,798 | 3,549 |
| Other pure-breds | 1,182 | 2,194 |
| Crosses | 159,568 | 183,390 |
| Totals | 193,740 | 224,024 |
Table of Contents
The number of births registered in the colony during 1902 was 20,655, or 25·89 in every 1,000 persons living. The rate is lower than in 1901, though slightly higher than those for the three years 1900, 1899, and 1898. From 1882 until the year 1899 there was a regular fall. The number of births registered in a year reached 19,846 in 1884, after which it fell to 17,876 in 1892, rising year by year to 18,955 in 1898, falling in 1899 to 18,835, but again rising to 19,546 in 1900, 20,491 in 1901, and 20,655 in 1902.
The figures for each year from 1882 are worthy of notice, especially in connection with the subsequent particulars given as to marriages solemnised and the growth of population:—
| Year. | Number of Births. | Rate per 1,000 of Population. |
|---|---|---|
| 1882 | 19,009 | 37·32 |
| 1883 | 19,202 | 36·28 |
| 1884 | 19,846 | 35·91 |
| 1885 | 19,693 | 34·35 |
| 1886 | 19,299 | 33·15 |
| 1887 | 19,135 | 32·09 |
| 1888 | 18,902 | 31·22 |
| 1889 | 18,457 | 30·07 |
| 1890 | 18,278 | 29·44 |
| 1891 | 18,273 | 29·01 |
| 1892 | 17,876 | 27·83 |
| 1893 | 18,187 | 27·50 |
| 1894 | 18,528 | 27·28 |
| 1895 | 18,546 | 26·78 |
| 1896 | 18,612 | 26·33 |
| 1897 | 18,737 | 25·96 |
| 1898 | 18,955 | 25·74 |
| 1899 | 18,835 | 25·12 |
| 1900 | 19,546 | 25·60 |
| 1901 | 20,491 | 26·34 |
| 1902 | 20,655 | 25·89 |
The marriages have increased numerically, and the population of the colony also.
| Year. | Number of Marriages. | Mean Population (excluding Maoris). |
|---|---|---|
| 1881 | 3,277 | 493,482 |
| 1882 | 3,600 | 509,309 |
| 1883 | 3,612 | 529,292 |
| 1884 | 3,800 | 552,590 |
| 1885 | 3,813 | 573,362 |
| 1886 | 3,488 | 582,117 |
| 1887 | 3,563 | 596,374 |
| 1888 | 3,617 | 605,371 |
| 1889 | 3,632 | 612,716 |
| 1890 | 3,797 | 620,780 |
| 1891 | 3,805 | 629,783 |
| 1892 | 4,002 | 642,245 |
| 1893 | 4,115 | 661,349 |
| 1894 | 4,178 | 679,196 |
| 1895 | 4,110 | 692,417 |
| 1896 | 4,843 | 706,846 |
| 1S97 | 4,928 | 721,609 |
| 1898 | 5,091 | 736,260 |
| 1S99 | 5,461 | 749,984 |
| 1900 | 5,860 | 763,594 |
| 1901 | 6,095 | 777,968 |
| 1902 | 6,394 | 797,793 |
In the year 1881 there were in New Zealand 5·72 births to every marriage in the previous year, in 1901 the proportion had fallen to 3·50 births to each marriage, and in 1902 to 3·23.
In the Australian States a similar decrease is noticeable. In Victoria the number of children to a marriage for the year 1880 was 4·99, but fell to 4·05 in 1898. In New South Wales the figures are 5·0 and 4·11 for the same years respectively.
The average number of children born to a marriage for the decennial period 1891–1900 was, in New South Wales, 4·79; Victoria, 4·39; and in New Zealand, 3·87. In England and Wales for the period 1890–99 the average was 4·09, in Scotland 4·36, and in Ireland 4·83.
New Zealand had in 1880 the highest birth-rate (40·78); in 1900 the case was reversed; but in 1901 and 1902 the New Zealand rate was higher than that of Victoria and South Australia.
The fall over ten years is calculated as under:—
| Birth-rates per 1,000 of Population. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State or Colony. | 1893. | 1894. | 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
| Queensland | 33·73 | 31·86 | 32·85 | 30·06 | 29·92 | 28·28 | 27·31 | 30·21 | 28·28 | 27·68 |
| New South Wales | 33·33 | 31·48 | 30·66 | 28·35 | 28·42 | 27·14 | 27·10 | 27·43 | 27·60 | 27·17 |
| Victoria | 31·23 | 29·16 | 28·56 | 27·33 | 26·59 | 25·72 | 26·71 | 25·82 | 25·77 | 25·23 |
| South Australia | 31·76 | 30·49 | 30·23 | 28·46 | 26·97 | 24·98 | 25·51 | 25·78 | 25·39 | 24·85 |
| Western Australia | 34·22 | 28·27 | 26·30 | 22·65 | 25·82 | 29·35 | 30·64 | 31·46 | 30·32 | .. |
| Tasmania | 33·92 | 31·11 | 30·09 | 28·16 | 27·73 | 26·24 | 25·98 | 28·25 | 28·40 | 33·05 |
| New Zealand | 27·50 | 27·28 | 26·78 | 26·33 | 25·96 | 25·74 | 25·12 | 25·60 | 26·34 | 25·89 |
This table also shows that although New Zealand had in 1900 the lowest birth-rate in Australasia, the fall has been much less in this colony since 1892 than in the others, with the exception of Tasmania.
A declining birth-rate is noticeable in many civilised countries, and attention has been drawn by statisticians and political economists to the serious consequences that may result. That fertility among women in New Zealand is decreasing, from whatever causes, further facts will tend to show.
Taking the number of married women in New Zealand at what may be considered the child-bearing ages (i.e., from fifteen to forty-five years, inclusive) as shown by each census since 1878, and for the same years the number of legitimate births (excluding plural) registered, the birth-rate per 1,000 married women of the above-stated ages is easily found, and is shown to be steadily declining. In 1878 the rate was 337 per 1,000, in 1896 it had fallen to 252, and in 1901 to 244; or, in other words, in 1878 one married woman of the ages specified in every three gave birth to a child, while in 1901 the rate was one in four only. The figures for each census year are given below, and are followed by a table showing the declining birthrate, and the increase in the marriage-rate, in the United Kingdom.
| Birth-rates (Legitimate) per 1,000 Married Women at Child-bearing Ages for each Census Year, 1878 to 1901. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year (Census). | Number of Married Women between 15 and 45 Years of Age. | Number of Legitimate Births (Confinements). | Birth-rate per 1,000 Married Women of from 15 to 45 Years of Age. |
| 1878 | 50,995 | 17,196 | 337·2 |
| 1881 | 57,458 | 18,003 | 313·3 |
| 1886 | 62,704 | 18,532 | 295·5 |
| 1891 | 63,165 | 17,455 | 276·3 |
| 1896 | 69,807 | 17,596 | 252·1 |
| 1901 | 79,406 | 19,355 | 243·8 |
| Birth and Marriage Rates in the United Kingdom, 1887, 1891, 1896, and 1901. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Births. | Marriages. | ||||
 |  | ||||
| Year. | Mean Population. | Number. | Rate per 1,000 of Population. | Number. | Rate per 1,000 of Population. |
| 1887 | 36,599,143 | 1,123,149 | 30·69 | 246,339 | 6·73 |
| 1891 | 37,806,773 | 1,148,259 | 30·37 | 275,970 | 7·30 |
| 1896 | 39,644,147 | 1,152,144 | 29·06 | 296,089 | 7·47 |
| 1901 | 41,546,698 | 1,162,414 | 27·98 | 312,532 | 7·52 |
The above figures are taken from the “Statistical Abstract for the United Kingdom” (49th number), published in August, 1902.
The birth-rates for ten years in Great Britain and certain countries of the European Continent are given from the report of the Registrar-General of England. The rates in England and Wales, and in Scotland, are higher than those in New Zealand, but the rate for Ireland is lower. For 1891 and following years France has the lowest rate of all quoted:—
| Birth-rates in European Countries, 1891 to 1900. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Countries. | Number of Births per 1,000 of Mean Population. | |||||||||
| 1891. | 1892. | 1893. | 1894. | 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | |
| Hungary | 42·3 | 40·4 | 42·6 | 41·5 | 41·9 | 40·5 | 40·3 | 37·7 | 39·3 | 39·3 |
| Austria | 37·0 | 36·2 | 37·9 | 36·7 | 38·1 | 38·0 | 37·5 | 36·2 | 37·1 | .. |
| Italy | 37·0 | 36·1 | 36·4 | 35·4 | 34·7 | 34·7 | 34·6 | 33·4 | 33·8 | 32·9 |
| German Empire | 37·0 | 35·7 | 36·8 | 35·9 | 36·1 | 36·3 | 36·0 | 36·1 | 35·8 | 35·6 |
| Netherlands | 33·7 | 32·0 | 33·8 | 32·7 | 32·8 | 32·7 | 32·5 | 31·9 | 32·0 | 31·5 |
| Scotland | 31·2 | 30·7 | 30·8 | 29·9 | 30·0 | 30·4 | 30·0 | 30·1 | 29·8 | 29·6 |
| Norway | 30·9 | 29·6 | 30·7 | 29·8 | 30·6 | 30·4 | 30·0 | 30·3 | 30·9 | 30·1 |
| England and Wales | 31·4 | 30·4 | 30·7 | 29·6 | 30·2 | 29·6 | 29·5 | 29·3 | 29·1 | 28·7 |
| Belgium | 29·6 | 28·9 | 29·5 | 29·0 | 28·5 | 29·0 | 29·0 | 28·6 | 28·8 | 28·9 |
| Sweden | 28·3 | 27·0 | 27·4 | 27·1 | 27·5 | 27·2 | 26·7 | 27·1 | 26·4 | 26·9 |
| Switzerland | 27·8 | 27·4 | 27·7 | 27·1 | 27·1 | 27·9 | 28·1 | 28·4 | 28·9 | 28·6 |
| Ireland | 23·1 | 22·5 | 23·0 | 22·9 | 23·2 | 23·6 | 23·5 | 23·2 | 22·9 | 22·7 |
| France | 22·6 | 22·3 | 22·7 | 22·3 | 21·7 | 22·5 | 22·3 | 21·8 | 21·9 | 21·4 |
From the year 1895 marriages have shown an increase, the rate being then 5·94 per 1,000 of population. In 1902 the rate rose to 8·01, the highest record since 1876, when it was 8·25 per 1,000 of mean population. The number of marriages solemnised in 1902 was 6,394, an increase of 299 on the number for 1901.
| Marriage-rates in Australasia per 1,000 of Population. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1874. | 1886. | 1891. | 1896. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | |
| Queensland | 8·62 | 8·67 | 7·18 | 6·05 | 6·03 | 6·78 | 6·88 | 6·61 |
| New South Wales | 7·70 | 7·99 | 7·39 | 6·59 | 6·66 | 6·89 | 7·38 | 7·68 |
| Victoria | 6·33 | 7·84 | 7·69 | 6·48 | 6·53 | 7·01 | 6·96 | 6·99 |
| South Australia | 8·00 | 6·24 | 7·31 | 6·20 | 6·18 | 6·24 | 6·50 | 6·44 |
| Western Australia | 6·96 | 7·98 | 8·00 | 8·45 | 9·89 | 9·89 | 10·27 | 9·65 |
| Tasmania | 6·83 | 7·26 | 6·63 | 5·88 | 6·29 | 6·37 | 7·71 | 7·68 |
| New Zealand | 8·81 | 5·99 | 6·04 | 6·85 | 6·91 | 7·28 | 7·67 | 7·83 |
In April, 1896, New Zealand had 83,659 children living under the age of five years, and in March, 1901, the number was 86,806, an increase of 3,147, although the population at all ages increased in the quinquennium by 9·86 per cent. Between 1886 and 1891 the children living under five years actually decreased in number by 3,624, the increase of population of all ages (8·33 per cent.) being less than between 1891 and 1896 (12·24 per cent.), or 1896 and 1901 (9·86 per cent.). The number of children under one year to the total population at all ages, according to the results of four censuses, was:—
| Children under One Year. | Total Population (all Ages). | |
|---|---|---|
| Census 1886 | 18,355 | 578,482 |
| Census 1891 | 16,443 | 626,658 |
| Census 1896 | 17,070 | 703,360 |
| Census 1901 | 18,381 | 772,719 |
Thus, in 1886, with a population of 578,482 persons, there were 18,355 children under one year, against 18,381 children of that age in 1901, with a population of 772,719 persons.
The births registered in 1885 were 19,693, against 19,546 in 1900. The birth-rate fell from 34·35 per 1,000 of the population in 1885 to 25·60 in 1900.
Deducting 1,469, the number of deaths of children under one year registered in 1900, from 19,546, the number of births for that year, leaves 18,077, or within 304 of the living children under one year at the time of the last census.
There were 220 cases of twin births (440 children), and triplets were registered in two instances, in 1902. The number of children born was 20,655; the number of mothers was 20,431: thus, on an average, one mother in every 93 gave birth to twins, against 107 in 1901, 102 in 1900, 106 in 1899, 97 in 1898, and 101 in 1897 and 1896. In 1895 the proportion was one in 93, and in 1894 one in 103.
The births of 921 children were illegitimate: thus 45 in every 1,000 children born were born out of wedlock, against 46 in 1901.
The following table gives the rates of illegitimacy in Australasia. The rate in 1901 in New Zealand is less than in any of the Australian States except Western Australia and South Australia:—
| Proportion of Illegitimate Births in every 100 Births. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Queensland. | New South Wales. | Victoria. | South Australia. | Western Australia. | Tasmania. | New Zealand. |
| 1890 | 4·85 | 5·26 | 5·09 | 2·50 | .. | 4·05 | 3·30 |
| 1891 | 4·65 | 5·36 | 5·36 | 2·93 | .. | 3·72 | 3·49 |
| 1892 | 5·05 | 5·71 | 5·59 | 2·93 | 5·89 | 4·75 | 3·32 |
| 1893 | 4·97 | 6·16 | 5·46 | 2·84 | 4·17 | 4·41 | 3·70 |
| 1894 | 4·52 | 6·14 | 5·50 | 3·05 | 4·66 | 5·09 | 3·80 |
| 1895 | 4·93 | 6·51 | 5·33 | 3·13 | 4·47 | 4·97 | 4·50 |
| 1896 | 5·22 | 5·71 | 5·63 | 3·45 | 5·61 | 5·91 | 4·48 |
| 1897 | 6·02 | 6·58 | 5·42 | 3·53 | 5·27 | 5·74 | 4·41 |
| 1898 | 6·04 | 6·93 | 5·29 | 3·62 | 4·99 | 5·09 | 4·23 |
| 1899 | 5·97 | 7·15 | 5·49 | 3·95 | 4·91 | 6·08 | 4·40 |
| 1900 | 6·40 | 7·01 | 5·91 | 4·24 | 4·82 | 5·43 | 4·63 |
| 1901 | 5·93 | 7·16 | 5·58 | 3·98 | 3·88 | 5·94 | 4·57 |
| 1902 | 6·04 | 6·60 | 5·51 | 4·36 | .. | 5·36 | 4·46 |
These figures show a rise in the proportion of illegitimate births to every 100 births for this colony, amounting to 1·16 for the period 1890–1902.
The total number of births registered was 19,299 in 1886 and 20,655 in 1902, while the illegitimate births rose from 602 to 921. The causes that led to the fall in the birth-rate certainly did not greatly affect the number of illegitimate children.
The number of spinsters in the colony between 15 and 45 increased during the ten years from 65,035 (census 1891) to 100,310 (census 1901), or at the rate of 55·9 per cent., while the illegitimate births increased from 638 to 937, or at the rate of 46·9 per cent. only.
It would therefore appear that the larger proportion of illegitimate births now obtaining cannot with any certainty be taken as indicative of increased looseness of living on the part of the people.
The following figures, taken from “The Wealth and Progress of New South Wales, 1900–1901,” showing the rate of illegitimacy per 100 births in Australasia and in the United Kingdom, are based on statistics for a period of five years:—
| Country. | Illegitimate Births per Cent. |
|---|---|
| New South Wales | 6·88 |
| Victoria | 5·55 |
| Queensland | 5·94 |
| South Australia | 3·76 |
| Western Australia | 5·06 |
| Tasmania | 5·65 |
| New Zealand | 4·42 |
| England and Wales | 4·15 |
| Ireland | 2·65 |
| Scotland | 6·97 |
Of the total number of children born in Australasia during the five years ended 1901, 5·75 per cent. were illegitimate, as compared with 4·42 per cent. in the United Kingdom for the period 1896–1900.
The figures in the next table, which give the percentages of illegitimate births in a number of foreign countries, also cover in most cases a period of five years, 1897–1901.
| Country. | Illegitimate Births per Cent. |
|---|---|
| Germany | 9·08 |
| Prussia | 7·68 |
| Bavaria | 13·43 |
| Saxony | 12·89 |
| Austria | 14·20 |
| Hungary | 9·13 |
| France | 8·82 |
| Belgium | 7·67 |
| Netherlands | 2·60 |
| Sweden | 11·13 |
| Norway | 7·43 |
| Italy | 6·45 |
For England and Wales the proportion of illegitimate births to the total births in 1900 was 4 per cent., having gradually diminished from 7 per cent. in 1845. The minimum rate was 2·7 per cent., in Essex, and the maximum 6·7 per cent., in Westmoreland. For London the percentage was 3·6.
The average proportion of illegitimate births in Scotland in 1901 was 6·3 per cent., the rate varying from 3·4 per cent. in Dumbartonshire to 13·7 in Wigtownshire: but in Ireland in that year the extremely low average of 2·6 per cent. obtained, the rate varying from 0·7 in Connaught to 3·4 in Ulster.
An important Act was passed in 1894, entitled the Legitimation Act, which makes provision for the legitimation of children born before marriage on the subsequent marriage of their parents. Under this Act any child born out of wedlock, whose parents afterwards marry, is deemed to be legitimised by such marriage on the birth being registered in the manner prescribed by the Act. For legitimation purposes Registrars must register a birth when called upon to do so by any person claiming to be the father of an illegitimate child; but such person is required to make a solemn declaration that he is the father, and that at the time of the birth there existed no legal impediment to his marriage with the mother of the child. He has also to produce the evidence of his marriage. It will thus be seen that in cases dealt with under the Act registration becomes the test of legitimacy. In the December quarter of 1894, 11 children were legitimised; in 1895 the number was 68; in 1896, 56; in 1897, 48; in 1898, 59; in 1899, 41; in 1900, 62; in 1901, 47; and in 1902, 96; making altogether 488, legitimations since the passing of the law.
By this statute it has been rendered unlawful for a person to take charge, for payment, of an infant to maintain or nurse for more than three days without holding a license as an infants' home keeper. The house of such a person must be registered as an infants' home.
The administration of this law is a matter entirely managed by the police. The licensed homes are periodically inspected, and the results have shown that licensees generally comply with the required conditions, the homes and infants being well looked after.
The Commissioner in his report for the year ended 31st March, 1902, writes:—
During the year there were 565 registered homes throughout the colony, representing 943 infants, against 548 homes and 872 infants in 1900.
Twenty-nine deaths occurred in the homes during the year, against twenty-six in the preceding year, being equal to 30·75 per thousand, against 29·81 per thousand in 1900.
The mortality throughout the colony of infants under four years of age (the age to which the Act applies) was 26·37 per thousand, or only 4·38 less than in the homes. This, I submit, may be regarded as satisfactory, considering that the infants in the homes are reared artificially, and that a very large percentage, through being illegitimate, have not received, prior to being admitted to the homes, the careful nurturing that infants brought into the world under more favourable conditions are likely to receive, and are weakly in consequence.
Eleven licensees were prosecuted for breaches of the Act during the year, of whom ten were convicted, and two licenses were cancelled.
The total number of births registered as occurring in the four chief centres and suburbs in 1902 was 5,347, as against 5,234 for the previous year.
The births in the four cities rose from 3,161 in 1901 to 3,196 in 1902, and in the suburban boroughs from 2,073 to 2,151. The birth-rates for 1902 were:—
| Birth-rates per 1,000 of Mean Population. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Auckland City | 30·80 | |
| Auckland City and five suburban boroughs | .. | 29·64 |
| Wellington City | 25·29 | |
| Wellington City and three suburban boroughs | .. | 25·92 |
| Christchurch City | 25·84 | |
| Christchurch City and four suburban boroughs | .. | 26·36 |
| Dunedin City | 19·96 | |
| Dunedin City and eight suburban boroughs | .. | 23·08 |
Thus, by the inclusion of the suburbs the rate is raised at Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin, but lowered at Auckland. It will be observed that Auckland has the highest rate, Christchurch next highest, Wellington and Dunedin following with intervals. The difference between the Auckland rate (29·64) and the Dunedin rate (23·08) is considerable. The birth-rate for the whole colony for 1902 was 25·89 per thousand. Auckland, Christchurch, and Wellington are thus over the average, and Dunedin below it.
Taking the births in the four chief boroughs without their suburbs, and comparing the numbers for 1902 and 1901, an increase for 1902 is observed at Auckland of 60, at Christchurch of 50, but a decrease of 24 at Wellington and of 51 at Dunedin. The figures for the last five years are:—
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
| Auckland (without suburbs) | 916 | 988 | 1,028 | 1,037 | 1,097 |
| Wellington (without suburbs) | 1,065 | 1,036 | 1,127 | 1,150 | 1,126 |
| Christchurch (without suburbs) | 390 | 340 | 417 | 423 | 473 |
| Dunedin (without suburbs) | 507 | 490 | 526 | 551 | 500 |
The birth-rates for two of the chief boroughs in 1902 show a rise, and for two a decrease, when compared with 1901. In Auckland the rate rose from 30·00 to 30·80, and in Christchurch from 24·12 to 25·84; but fell in Wellington from 26·35 to 25·29, and in Dunedin from 22·04 to 19·96. The rates for five years, 1898 to 1902, are as follows:—
| Births per 1,000 of Population. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
| Auckland (without suburbs) | 26·96 | 25·77 | 29·31 | 30·00 | 30·80 |
| Wellington (without suburbs) | 25·75 | 24·24 | 25·76 | 26·35 | 25·29 |
| Christchurch (without suburbs) | 22·07 | 18·74 | 21·51 | 24·12 | 25·84 |
| Dunedin (without suburbs) | 21·61 | 20·82 | 22·07 | 22·04 | 19·96 |
Aliens residing in the colony may, on taking the oath of allegiance to His Majesty, obtain letters of naturalisation entitling them to enjoy all the rights and privileges that a natural-born subject of the United Kingdom can enjoy or transmit within this colony. Three hundred and twenty-two aliens (310 men and 12 women) were naturalised in 1902.
The number belonging to each nationality was as under:—
| Number of Aliens naturalised in 1902. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Natives of— | M. | P. |
| German Empire | 76 | 6 |
| Norway and Sweden | 71 | 1 |
| Denmark | 31 | 4 |
| Russia, Poland, and Finland | 29 | 0 |
| France and possessions | 11 | 0 |
| Italy | 16 | 0 |
| Austria-Hungary | 39 | 1 |
| China | 5 | 0 |
| United States of America | 9 | 0 |
| Netherlands | 3 | 0 |
| Switzerland | 5 | 0 |
| Belgium | 2 | 0 |
| Portugal and possessions | 9 | 0 |
| Turkey and Syria | 2 | 0 |
| Brazil | 1 | 0 |
| West Indies | 1 | 0 |
The number of natives of each country naturalised during the last twenty years is next shown,—
| Natives of— | |
| Germany | 1,495 |
| Sweden and Norway | 1,115 |
| Denmark | 793 |
| China | 326 |
| Italy and Sicily | 194 |
| Switzerland | 163 |
| Russia in Europe | 213 |
| Austria-Hungary | 225 |
| France | 124 |
| Netherlands | 53 |
| Greece | 45 |
| Portugal | 53 |
| United States of America | 71 |
| Belgium | 28 |
| Other countries | 88 |
| Total | 4,986 |
By section 2 of “The Aliens Act Amendment Act, 1882,” repealed and re-enacted by section 2 of “The Aliens Act Amendment Act, 1892,” it is provided that when the father, or mother being a widow, has obtained naturalisation in the colony, every child who during infancy has become resident with them in New Zealand shall be deemed to be naturalised, and shall have the rights and privileges of a natural-born subject.
The marriages for 1902 show an increase on the number for the previous year. The number was 6,394, or 299 more than in 1901. The marriage-rate rose from 7·83 per 1,000 persons living in 1901 to 8·01 in 1902, the rate for the latter year being the highest obtained since 1876, when it stood at 8·25 per 1,000 persons. The improvement shown during the last seven years sets New Zealand in a good position relatively to the Australian States.
The rates for a series of fifteen consecutive years were:—
| Marriages per 1,000 of the Population. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Queensland. | New South Wales. | Victoria. | South Australia. | Western Australia. | Tasmania. | New Zealand. |
| 1888 | 8·63 | 7·37 | 8·03 | 6·70 | 7·18 | 6·58 | 5·97 |
| 1889 | 8·37 | 6·76 | 8·14 | 6·47 | 6·99 | 6·50 | 5·94 |
| 1890 | 8·49 | 7·14 | 8·21 | 7·06 | 5·80 | 6·64 | 6·12 |
| 1891 | 7·18 | 7·39 | 7·69 | 7·31 | 8·00 | 6·63 | 6·04 |
| 1892 | 6·67 | 6·77 | 6·64 | 6·51 | 7·29 | 6·51 | 6·23 |
| 1893 | 5·91 | 6·40 | 5·99 | 6·26 | 6·34 | 5·51 | 6·22 |
| 1894 | 5·70 | 6·20 | 5·98 | 6·09 | 6·24 | 5·43 | 6·15 |
| 1895 | 6·23 | 6·35 | 6·00 | 5·88 | 6·83 | 5·32 | 5·94 |
| 1896 | 6·05 | 6·59 | 6·48 | 6·20 | 8·45 | 5·88 | 6·85 |
| 1897 | 6·05 | 6·72 | 6·36 | 5·46 | 10·73 | 6·23 | 6·83 |
| 1898 | 6·03 | 6·66 | 6·53 | 6·18 | 9·89 | 6·29 | 6·91 |
| 1899 | 6·78 | 6·89 | 7·01 | 6·24 | 9·89 | 6·37 | 7·28 |
| 1900 | 6·88 | 7·38 | 6·96 | 6·50 | 10·27 | 7·71 | 7·67 |
| 1901 | 6·61 | 7·68 | 6·99 | 6·44 | 9·65 | 7·68 | 7·83 |
| 1902 | 6·31 | 7·53 | 7·02 | 6·61 | .. | 7·47 | 8·01 |
But the improved rate for this colony is still lower than the rate for some few European countries.
| Marriages in every 1,000 of the Population. | ||
|---|---|---|
| German Empire | 1900 | 8·5 |
| Belgium | 1900 | 8·6 |
| Hungary | 1900 | 8·9 |
| England and Wales | 1900 | 8·0 |
| Switzerland | 1900 | 7·7 |
| Austria | 1900 | 8·0 |
| Spain | 1900 | 8·9 |
| Denmark | 1900 | 7·6 |
| Scotland | 1900 | 7·3 |
| France | 1900 | 7·8 |
| Netherlands | 1900 | 7·6 |
| Italy | 1900 | 7·2 |
| Norway | 1900 | 7·0 |
| Sweden | 1900 | 6·2 |
| Ireland | 1900 | 4·8 |
Of the marriages solemnised in 1902, 5,803 were between bachelors and spinsters, 199 between bachelors and widows, 292 between widowers and spinsters, and 100 between widowers and widows.
Divorced men and women have been classified as bachelors or spinsters: 25 divorced men and 51 divorced women were married during the year.
Included amongst spinsters are ten married women, and amongst the bachelors two married men, who elected to go through the form of marriage with other persons under the protection of the provisions of section 204, subsection (5), of “The Criminal Code Act, 1893,” which runs: “No one commits bigamy by going through a form of marriage if he or she has been continually absent from his or her wife or husband for seven years then last past, and is not proved to have known that his wife or her husband was alive at any time during those seven years.”
The total number of marriages solemnized (6,394) does not include marriages where both parties are of the aboriginal native race, such persons being exempted from the necessity of complying with the provisions of the Marriage Act, although at liberty to take advantage thereof. Eleven marriages in which both parties were Maoris were contracted in 1902 in terms of the Act: 4 by Registrars, 6 by clergymen of the Church of England, and 1 by a Wesleyan minister.
The results of three censuses in respect of the number of bachelors cf 20 years and upwards, and spinsters of 15 years and upwards, in the colony show some interesting features. In 1891 there was an excess of bachelors over the spinsters amounting to 3,497 men. But by 1896 not only had the preponderance of the male element been lost, but an excess of spinsters over bachelors was reported amounting to 1,786 women, while in 1901 this excess had risen to 3,572 women.
It is noticeable how differently the numbers for the provincial districts have been affected by the process in operation. An excess of bachelors was preserved in Auckland, Taranaki, Hawke's Bay, Wellington, Marlborough, Nelson, and Westland from 1891 to 1901. In Canterbury, however, an excess of spinsters was found in 1891 of 2,516, which increased to 3,997 in 1896 and to 4,918 in 1901; while in Otago an excess of 773 spinsters in 1891 increased to 2,066 in 1896, and diminished slightly in 1901, when there were 1,899 more spinsters than bachelors. These two important districts of the Middle Island have lost large numbers of bachelors by departures to the North Island.
The following table exhibits the particulars for each provincial district:—
| Provincial Districts. | Census, 1891. | Census, 1896. | Census, 1901. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excess of Bachelors over Spinsters. | Excess of Bachelors over Bachelors. | Excess of Bachelors over Spinsters. | Excess of Bachelors over Bachelors. | Excess of Bachelors over Spinsters. | Excess of Bachelors over Bachelors. | |
| Total excess | 3,497 | .. | .. | 1,786 | .. | 3,572 |
| Auckland | 156 | .. | 703 | .. | 521 | .. |
| Taranaki | 121 | .. | 524 | .. | 805 | .. |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,337 | .. | 1,142 | .. | 425 | .. |
| Wellington | 2,129 | .. | 637 | .. | 32 | .. |
| Marlborough | 644 | .. | 183 | .. | 158 | .. |
| Nelson | 1,486 | .. | 580 | .. | 637 | .. |
| Westland | 900 | .. | 501 | .. | 666 | .. |
| Canterbury | .. | 2,516 | .. | 3,997 | .. | 4,918 |
| Otago | .. | 773 | .. | 2,066 | .. | 1,899 |
| Chatham Islands | 15 | .. | 7 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Kermadec Islands | .. | 2 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
Of the marriages in the year 1902, 24·58 per cent. were solemnised by ministers of the Church of England, 25·95 per cent. by ministers of the Presbyterian Churches, 12·95 per cent. by ministers of the Wesleyan and other Methodist Churches, 9·94 per cent. by ministers of the Roman Catholic Church, 10·07 per cent. by ministers of other denominations, and 16·51 per cent. by Registrars.
The following shows the proportions of marriages by ministers of the principal denominations in the past eight years, and the percentages of these denominations to the total population:—
| Denomination. | Percentage of Marriages. | Percentage of Denomination to Total Population in 1901. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | ||
| Church of England | 22·74 | 22·86 | 23·00 | 23·37 | 24·17 | 22·68 | 24·91 | 24·58 | 40·84 |
| Presbyterians | 24·32 | 25·01 | 25·44 | 26·02 | 25·30 | 26·38 | 24·48 | 25·95 | 22·87 |
| Methodists | 15·69 | 17·92 | 17·61 | 13·98 | 12·91 | 13·23 | 13·19 | 12·95 | 10·86 |
| Roman Catholics | 11·19 | 10·26 | 10·12 | 10·37 | 10·87 | 10·82 | 10·53 | 9·94 | 14·23 |
| Other denominations | 7·29 | 6·05 | 5·86 | 9·25 | 9·34 | 10·20 | 10·20 | 10·07 | 11·20 |
| By Registrars | 18·77 | 17·90 | 17·97 | 17·01 | 17·41 | 16·69 | 16·69 | 16·51 | .. |
| 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | |
Marriage by the Registrar is found to be less frequent than it was eight years ago, the percentage falling from 18·77 in 1895 to 16·51 in 1902.
Of the men married in 1902, 16, or 2·50 in every 1,000, and of the women 28, or 4·38 per 1,000, signed the register by marks.
The illiteracy of the people, as measured by the proportion of married persons who affix marks instead of signatures to the marriage register, has greatly decreased of late, having fallen since 1881 from 32·04 per 1,000 among men to 2·50 per 1,000, and from 57·98 per 1,000 to 4·38 per 1,000 among women. This is shown in a very striking manner by the following table:—
| Persons in every 1,000 married who signed by Mark. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denomination. | 1881. | 1891. | 1901. | 1902. | ||||
| M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | |
| Church of England | 16·59 | 27·15 | 8·29 | 10·66 | 1·32 | 3·29 | 1·91 | 1·91 |
| Presbyterians | 10·25 | 29·61 | 5·79 | 8·69 | 2·68 | 4·69 | 1·81 | 1·81 |
| Wesleyans and other Methodists | 32·41 | 41·79 | 8·93 | 10·71 | 3·73 | 3·73 | 1·21 | 6·04 |
| Roman Catholics | 117·78 | 133·33 | 31·33 | 18·28 | 6·23 | 7·79 | .. | 4·72 |
| Other denominations | 10·36 | 20·72 | 9·26 | .. | 1·61 | 3·22 | 8·00 | 4·00 |
| By Registrars | 39·22 | 93·51 | 27·42 | 43·08 | 13·77 | 15·73 | 6·63 | 12·31 |
| Total marriages | 32·04 | 57·98 | 13·93 | 16·82 | 4·59 | 6·23 | 2·50 | 4·38 |
The proportion of illiterates in 1901 and 1902 was greatest among those married before Registrars. Previously the proportion was largest among Roman Catholics; but since 1881 it has, as shown by the table, most remarkably decreased.
Of the persons married in 1902, 89 bridegrooms and 1,061 brides were under 21 years of age—one of the bridegrooms was between 17 and 18, and six between 18 and 19. Of the brides, one was under 15 years of age, four were between 15 and 16, and twenty-seven between 16 and 17 years of age. The proportion of men married is greatest at the ages of 25 to 30, and of women at from 21 to 25 years.
The following are the proportions of men and women married at each age-period to every 100 marriages in the years 1891, 1901, and 1902:—
| Age. | 1891. | 1901. | 1902. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | |
| Under 21 years | 1·55 | 20·79 | 1·93 | 17·16 | 1·39 | 16·59 |
| 21 and under 25 | 26·99 | 43·99 | 24·94 | 39·97 | 24·93 | 40·60 |
| 25 and under 30 | 36·19 | 22·97 | 37·08 | 26·89 | 38·43 | 26·90 |
| 30 and under 40 | 25·94 | 8·72 | 27·12 | 12·73 | 27·18 | 12·84 |
| 40 and under 50 | 6·44 | 2·71 | 6·04 | 2·44 | 5·14 | 2·00 |
| 50 and under 60 | 2·26 | 0·66 | 1·77 | 0·57 | 1·86 | 0·72 |
| 60 and under 70 | 0·55 | 0·16 | 0·92 | 0·24 | 0·88 | 0·30 |
| 70 and upwards | 0·08 | .. | 0·20 | .. | 0·19 | 0·05 |
Registrars of Marriages are prohibited by law from issuing certificates for the marriage of minors without the consent of their parents or lawful guardians, if there be any in the colony. If a declaration be made in any case that there is no parent or lawful guardian in the colony, then a certificate may be issued after the expiration of fourteen days following the date on which the notice of intended marriage is given.
A marriage may not be solemnised except after the delivery to the minister or Registrar who officiates of a certificate issued by a Registrar authorising such marriage, and if any persons knowingly and wilfully intermarry without such certificate the marriage is null and void; and no clergyman or minister of any denomination is empowered to solemnise marriages until his name has been placed on the Registrar-General's list of officiating ministers for the year.
Marriage with a deceased wife's sister in New Zealand was legalised in the year 1880, and an Act was passed in the year 1900 which legalised marriage with the brother of a deceased husband. This Act is retrospective, including in its provisions marriages between such parties which had previously been solemnised as well as those contracted after the statute was passed, and declaring all these to be valid, and the issue born prior or subsequent to the passing of the Act to be deemed born in lawful wedlock.
The measure was reserved for the signification of her late Majesty's pleasure. The Royal assent has since been given, and the Act came into force in New Zealand by Proclamation dated the 22nd May, 1901.
The ages at which persons may contract binding marriages are the same as in England—12 years for females and 14 for males. Marriage may be contracted at earlier ages than those stated, but would be voidable at the discretion of either of the parties upon reaching the age of 12 or 14, as the case may be, and without the necessity of proceedings in Court.
Although in New Zealand the age at which girls may legally marry is as above, nevertheless, by the criminal law, to unlawfully carnally know a girl under the age of 16 years is now a punishable offence. The age of consent was raised from 15 to 16 by statute passed in 1896.
The average age of the men married in this colony in 1902 was 28·89 years, and of the women 25·63 years. In England the mean age of those whose ages were stated was (in the year 1900) 28·41 years for men, and 26·29 years for women. Thus the average age at marriage in the colony is higher for men, but lower for women, than in England.
The proportion of bridegrooms under 21 is much greater in England than in New Zealand; but the proportion of brides under 21 is greater in the colony.
In England, in 1900, of every 1,000 bridegrooms whose ages were stated, 51 were under 21 years of age, and of every 1,000 brides 163 were under 21 years of age. In New Zealand, in 1902, the proportions were 14 bridegrooms and 166 brides of similar ages in every 1,000 married:—
| Year. | Bridegrooms under 21 in every 100. | Brides under 21 in every 100. |
|---|---|---|
| 1888 | 1·85 | 24·30 |
| 1890 | 1·89 | 22·75 |
| 1892 | 1·62 | 20·14 |
| 1894 | 1·44 | 19·53 |
| 1896 | 1·96 | 19·51 |
| 1898 | 1·57 | 18·13 |
| 1899 | 2·10 | 18·81 |
| 1900 | 1·67 | 17·34 |
| 1901 | 1·93 | 17·16 |
| 1902 | 1·39 | 16·59 |
The number of names on the list of officiating ministers under the Marriage Act is (May, 1903) 1,024, and the denominations to which they belong are shown hereunder:—
| Denomination. | No. |
|---|---|
| Church of England | 322 |
| Presbyterian Church of New Zealand | 220 |
| Roman Catholic Church | 169 |
| Methodist Church of Australasia | 167 |
| Congregational Independents | 22 |
| Baptists | 30 |
| Primitive Methodist Connexion | 37 |
| Lutheran Church | 8 |
| Hebrew Congregations | 6 |
| Church of Christ | 14 |
| Free Methodist Church of New Zealand | 4 |
| Auckland Society of the New Church | 1 |
| Auckland Central Mission | 1 |
| Wellington Central Mission | 1 |
| Independent Free Church | 1 |
| The Forward Movement | 1 |
| Salvation Army | 10 |
| Catholic Apostolic Church | 4 |
| Seventh-day Adventists | 3 |
| Unitarian Church | 1 |
| Pilgrims of Peace | 1 |
| Scots Church | 1 |
| Total | 1,024 |
The deaths in 1902 numbered 8,375, being equivalent to a rate of 10·50 in every 1,000 persons living, as against 9·81 in 1901. The lowest rate experienced since the year 1887, when the deaths were 10·29 per 1,000 of the population, was that for 1896 (9·10).
| Comparative Death-rate for the Period 1892 to 1902. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country. | 1892. | 1893. | 1894. | 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
| * Excluding the Northern Territory. | |||||||||||
| New Zealand | 10·06 | 10·23 | 10·19 | 9·91 | 9·10 | 9·14 | 9·84 | 10·24 | 9·43 | 9·81 | 10·50 |
| Queensland | 12·66 | 13·34 | 12·08 | 11·38 | 12·10 | 11·33 | 12·66 | 12·07 | 11·73 | 11·88 | 12·08 |
| New South Wales | 12·20 | 13·24 | 12·36 | 11·79 | 12·30 | 10·88 | 12·48 | 11·82 | 11·16 | 11·68 | 11·95 |
| Victoria | 13·63 | 14·11 | 13·14 | 13·25 | 13·35 | 12·90 | 15·94 | 14·28 | 12·75 | 13·22 | 13·40 |
| South Australia* | 11·41 | 13·44 | 11·64 | 11·25 | 11·48 | 11·24 | 13·06 | 12·14 | 10·64 | 11·11 | 11·79 |
| Western Australia | 16·67 | 15·31 | 14·40 | 17·78 | 16·45 | 16·97 | 16·05 | 13·76 | 12·92 | 13·36 | .. |
| Tasmania | 13·53 | 13·47 | 12·42 | 11·38 | 11·63 | 11·53 | 13·51 | 13·25 | 11·05 | 10·45 | 10·84 |
| England and Wales | 19·0 | 19·1 | 16·5 | 18·7 | 17·0 | 17·4 | 17·5 | 18·2 | 18·2 | .. | .. |
| Scotland | 18·5 | 19·3 | 17·1 | 19·4 | 16·6 | 18·4 | 18·0 | 18·1 | 18·5 | .. | .. |
| Ireland | 19·4 | 17·9 | 18·2 | 18·4 | 16·6 | 18·4 | 18·1 | 17·6 | 19·6 | .. | .. |
| Denmark | 19·4 | 18·8 | 17·4 | 16·8 | 15·6 | 16·5 | 15·5 | 17·3 | 16·9 | .. | .. |
| Norway | 17·8 | 16·3 | 16·9 | 15·7 | 15·2 | 15·3 | 15·3 | 16·9 | 15·8 | .. | .. |
| Sweden | 17·9 | 16·8 | 16·4 | 15·2 | 15·6 | 15·4 | 15·1 | 17·7 | 16·8 | .. | .. |
| Austria | 28·8 | 27·2 | 27·8 | 27·7 | 26·4 | 25·6 | 24·9 | 25·4 | .. | .. | .. |
| Hungary | 35·1 | 31·2 | 30·5 | 29·7 | 28·9 | 28·5 | 28·0 | 27·2 | 26·9 | .. | .. |
| Switzerland | 18·8 | 19·9 | 19·9 | 19·1 | 17·7 | 17·6 | 18·2 | 17·6 | 19·3 | .. | .. |
| German Empire | 24·1 | 24·6 | 22·3 | 22·1 | 20·8 | 21·3 | 20·5 | 21·5 | 22·1 | .. | .. |
| Netherlands | 21·0 | 19·2 | 18·5 | 18·6 | 17·2 | 16·9 | 17·0 | 17·1 | 17·8 | .. | .. |
| France | 22·8 | 22·5 | 21·2 | 22·2 | 20·0 | 19·5 | 20·9 | 21·1 | 21·9 | .. | .. |
| Italy | 26·1 | 25·1 | 24·9 | 25·0 | 24·0 | 21·9 | 22·9 | 21·8 | 23·7 | .. | .. |
As will be seen from the preceding table, covering a series of years, the death-rate in New Zealand contrasts very favourably with that in the Australian States and in European countries.
In this statement New Zealand is conspicuous as showing the lowest death-rate. The rates for the principal Australian States are a little higher, but, generally speaking, far below those for the United Kingdom or the European Continental States mentioned in the table.
Perfect accuracy in comparing one country or colony with another can only be attained by the use of what is termed an “index of mortality.” The proportions of the living vary in regard to the different age-groups, and the ordinary death-rate—which is calculated on the population as a whole—does not afford a true means of judging of the relative healthiness of the places compared. But by taking a population like that of Sweden, and applying the percentage at each age-group to the death-rates, a standard of health or index of mortality can be arrived at. This has been done for New Zealand, in accordance with a resolution of the Statistical Conference held at Hobart in 1902, and the result is expressed in tabular form. When similar results are published by the States of Australia, comparisons will be given.
| Index of Mortality in New Zealand for 1902. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ages. | Estimated Mean Population, 1902. | Number of Deaths, 1902. | Death-rate per 1,000, 1902. | Percentage of Population of Sweden, 1890 (Standard). | Index of Mortality in New Zealand per 1,000. |
| Under 1 year | 18,987 | 1,712 | 90·17 | 2·55 | 2·30 |
| 1 and under 20 years | 334,914 | 1,194 | 3·57 | 39·80 | 1·42 |
| 20 and under 40 years | 262,713 | 1,311 | 4·99 | 26·96 | 1·35 |
| 40 and under 60 years | 127,248 | 1,458 | 11·46 | 19·23 | 2·20 |
| 60 years and upwards | 53,931 | 2,700 | 50·06 | 11·46 | 5·74 |
| Totals | 797,793 | 8,375 | 10·50 | 100·00 | 13·01 |
In the earlier annual reports on the vital statistics of the four chief towns the central boroughs alone were dealt with, particulars respecting the suburbs not having been obtained. But this omission was held to be a grave defect, as the suburban death-rate may differ much from the death-rate at the centre. Steps were therefore taken early in 1895 to collect statistics of the suburban boroughs as well as of the four chief cities. As regards Auckland and Christchurch, the whole of the area usually recognised as suburban has not yet been brought under municipal government, and the statistics given below do not deal with such portions as still remain in road districts. The omission, however, is not very important, for there are in either case quite enough suburbs included within borough boundaries to give a fair idea of the death-rate of greater Auckland and greater Christchurch. As further boroughs are formed the vital statistics will be made to include them.
The total number of deaths registered for the four centres in 1902 was 2,598—viz., 1,694 in the cities, and 904 in the suburbs. In 1901 the number was 2,275: 1,465 in the cities, and 810 in the suburbs.
By including the suburbs the death-rate for last year is lowered at each of the four centres. The rates for the year are:—
| Death-rates per 1,000 of Mean Population. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Auckland City | 17·21 | |
| Auckland City and five suburban boroughs | 15·27 | |
| Wellington City | 12·58 | |
| Wellington City and three suburban boroughs | 12·24 | |
| Christchurch City | 12·24 | |
| Christchurch City and four suburban boroughs | 12·14 | |
| Dunedin City | 11·86 | |
| Dunedin City and eight suburban boroughs | 11·29 | |
If the suburbs are included, the death-rate is found to be highest in Auckland and lowest in Dunedin; Wellington and Christchurch taking second and third places respectively. The death-rate for the colony was 10·50 per 1,000 of mean population. The four centres might be expected to show a higher average than this.
If the number of deaths of infants under one year be excluded, the mortality among the rest of the population is found to have been for 1901 and 1902 in the following ratio to the 1,000 living:—
| 1901. | 1902. | |
| Auckland (including suburbs) | 8·65 | 11·10 |
| Wellington (including suburbs) | 7·60 | 8·87 |
| Christchurch (including suburbs) | 9·89 | 9·04 |
| Dunedin (including suburbs) | 9·70 | 9·23 |
The degree of infantile mortality is perhaps best shown in the proportion of deaths of children under one year of age to every 100 births. For 1901 and 1902 the proportions at the chief centres were,—
| 1901. | 1902. | |
| Auckland (including suburbs) | 9·88 | 14·07 |
| Wellington (including suburbs) | 10·03 | 13·02 |
| Christchurch (including suburbs) | 11·02 | 11·76 |
| Dunedin (including suburbs) | 7·89 | 8·91 |
Thus in 1902 the proportions for Dunedin and Christchurch are less than those found at either of the other two chief cities. Again, the percentage of deaths of children under 5 years to the total number of deaths is—in Auckland, 38·47; in Wellington, 37·98; in Christchurch, 31·29; and in Dunedin, only 21·85. The total of deaths under 5 is 855, or 32·91 per cent. of all deaths, as against 618 and 27·16 per center for 1901. The deaths of persons of 65 and upwards numbered 59 st year; in 1901 they were 586.
Excluding suburbs, and dealing with the deaths at all ages in the four cities or central boroughs only, the rates for 1902 are found to be higher in Auckland and Wellington, but lower in Christchurch and Dunedin, than in the previous year. The total number of deaths, and the death-rates, for four years are given:—
| Cities (excluding Suburbs). | Deaths, 1899. | Deaths, 1900. | Deaths, 1901. | Deaths, 1902. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Per 1,000 of Population. | No. | Per 1,000 of Population. | No. | Per 1,000 of Population. | No. | Per 1,000 of Population. | |
| Auckland | 499 | 13·02 | 480 | 13·69 | 453 | 13·10 | 613 | 17·21 |
| Wellington | 477 | 11·16 | 401 | 9·17 | 465 | 10·66 | 560 | 12·58 |
| Christchurch | 230 | 12·68 | 206 | 10·62 | 231 | 13·11 | 224 | 12·24 |
| Dunedin | 317 | 13·47 | 292 | 12·25 | 316 | 12·64 | 297 | 11·86 |
By omitting the deaths of infants under one year, and calculating the rate on the population of one year of age and upwards, the death-rates for the two North Island cities are found to be higher in 1902 than in the previous year, but they are lower at Christchurch and Dunedin in the South Island.
| Deaths per 1,000 of Population, excluding Infants (under One Year of Age). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
| Auckland (excluding suburbs) | 9·53 | 9·72 | 9·93 | 12·86 |
| Wellington (excluding suburbs) | 8·39 | 7·65 | 8·12 | 9·54 |
| Christchurch (excluding suburbs) | 9·16 | 8·22 | 10·69 | 9·03 |
| Dunedin (excluding suburbs) | 11·59 | 10·64 | 10·88 | 10·35 |
Subjoined is a table showing the rates of infant mortality in the four cities for each of the past five years, together with the mean rates for the period.
| Deaths of Children under One Year to every 100 Births. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | Mean of Five Years. | |
| Auckland (excluding suburbs) | 17·14 | 14·47 | 14·49 | 11·57 | 14·07 | 14·35 |
| Wellington (excluding suburbs) | 13·71 | 12·26 | 6·65 | 10·43 | 13·02 | 11·21 |
| Christchurch (excluding suburbs) | 10·00 | 19·71 | 11·99 | 11·35 | 11·76 | 12·96 |
| Dunedin (excluding suburbs) | 9·66 | 10·20 | 8·37 | 9·07 | 8·91 | 9·24 |
While treating of the death-rates at the chief cities and surroundings, it is desirable to refer to the causes of mortality, which is done in the remarks that follow. The deaths for the whole colony, classified according to their cause, are treated of at length a little further on.
The total mortality from these diseases at Auckland and Wellington centres, with their suburbs, was higher in 1902 than in the previous year. The total deaths in this class at the four towns were 209 for 1901, and 356 for 1902.
| Deaths from Febrile and Zymotic Diseases. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland and Suburbs. | Wellington and Suburbs. | Christchurch and Suburbs. | Dunedin and Suburbs. | Total. | |
| 1902 | 165 | 108 | 48 | 35 | 356 |
| 1901 | 70 | 46 | 54 | 39 | 209 |
Of the above, diarrhœal diseases caused most deaths in 1902 at the four centres taken together, the total number being 125. Measles came next, with 92 deaths, whooping-cough 38, influenza 29, diphtheria 19, typhoid fever 17, scarlet fever 11, and other zymotic complaints 25.
Comparison of the deaths for each city shows,—
| Zymotic, &c., Diseases. | Auckland and Suburbs. | Wellington and Suburbs. | Christchurch and Suburbs. | Dunedin and Suburbs. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1902. | 1901. | 1902. | 1901. | 1902. | 1901. | 1902. | 1901. | |
| Diarrhœal diseases | 67 | 31 | 19 | 10 | 31 | 10 | 8 | 6 |
| Influenza | 10 | 14 | 9 | 14 | 3 | 25 | 7 | 21 |
| Typhoid fever | 10 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 |
| Measles | 40 | .. | 49 | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 2 |
| Scarlet fever | 1 | 1 | 1 | .. | 5 | 1 | 4 | .. |
| Bubonic plague | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Diphtheria | 12 | 2 | .. | 7 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| Whooping-cough | 18 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Chicken-pox | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. |
| Other zymotic diseases | 4 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
Hydatids and worms were fatal at Auckland (1 death each).
These numbered 24, 7 being due to want of breast-milk, or malnutrition, 16 to alcoholism and delirium tremens, and 1 to infantile scurvy.
The deaths at the four towns numbered 481 in 1902. The first in importance of these diseases, and of all causes of death, is tubercle. The figures for 1901 and 1902 show 263 and 254 deaths for each year respectively.
| Phthisis and other Tubercular Diseases (at Four Chief Centres). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1902. | 1901. | |||
| Phthisis. | Other Tubercular Diseases. | Phthisis. | Other Tubercular Diseases. | |
| Auckland and suburbs | 42 | 11 | 41 | 9 |
| Wellington and suburbs | 49 | 19 | 55 | 25 |
| Christchurch and suburbs | 57 | 12 | 43 | 11 |
| Dunedin and suburbs | 44 | 20 | 68 | 11 |
| 192 | 62 | 207 | 56 | |
The mortality from tubercular diseases for 1902 is 9·78 per cent. of the total deaths at the four boroughs and their suburbs from all causes.
Deaths from cancer rose at the chief towns from 154 in 1901 to 165 in 1902. The latter number is 6·35 per cent. of deaths for the year from all causes.
The number of deaths from cancer at the four chief towns and their suburbs for each of the last five years was as under:—
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland and suburbs | 25 | 40 | 32 | 32 | 44 |
| Wellington and suburbs | 43 | 27 | 36 | 38 | 37 |
| Christchurch and suburbs | 43 | 40 | 32 | 41 | 25 |
| Dunedin and suburbs | 49 | 44 | 45 | 43 | 59 |
| 160 | 151 | 145 | 154 | 165 |
Diabetes shows 26 deaths in 1902, against 24 in 1901.
There were 255 deaths in this class, of which 106 were from premature births, 122 from old age, and 27 from other causes.
Deaths in this class were 141 more than in 1901, the figures being 1,266, against 1,125. Diseases of the respiratory system show 337 deaths for 1902, or more than one-fourth of the whole mortality in the class, against 308 in the former year. Bronchitis, pneumonia, congestion of lungs, pleurisy, and allied diseases form this group.
Under the head of “Diseases of the Digestive System” there were 250 deaths at the four centres, including 94 from enteritis, peritonitis 18, gastritis 18, cirrhosis of liver 18, jaundice 9, and dentition 22.
Diseases of the urinary system caused 92 deaths. The remaining deaths were: 267 from nervous diseases, 1 disease of organs of special sense, 262 of organs of the circulatory, 9 of the lymphatic, 31 of the reproductive systems, 13 of the organs of locomotion, and 4 of the integumentary system.
There were 109 violent deaths, 80 of which were classed as accidental. Three of these latter were caused by fractures, and 8 by falls. In 6 cases deaths resulted from the deceased being run over by a cart, tram, train, &c. Five deaths were from burns or scalds, 18 by drowning, 11 by suffocation, 2 by poisoning, 3 by misadventure with chloroform; besides 7 from accident at birth, and 17 others.
Of 29 suicides, 9 were by shooting, 5 by cutting throat, 7 by poison, 2 by hanging, 3 by drowning, 1 by an explosive, 1 by strangling, and 1 by throwing himself from a window.
The vital statistics of the chief cities, with their suburbs, of Australasia show that the death-rate in Wellington (N.Z.) for 1901 was lower than that of any other of the principal towns for the same year.
| Capital Cities (including Suburbs). | Estimated Mean Population. | Births. | Deaths. | Excess of Births over Deaths. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number. | Rate per 1,000 of Population. | Total Number. | Rate per 1,000 of Population. | |||
* Ten-mile radius. † Census, 1901. | ||||||
| Melbourne | 498,030 | 12,375 | 24·85 | 7,515 | 15·09 | 4,860 |
| Sydney | 491,220 | 12,601 | 25·65 | 6,197 | 12·62 | 6,404 |
| Adelaide | 162,195 | 3,930 | 24·23 | 2,130 | 13·13 | 1,800 |
| Brisbane* | 119,428† | 3,457 | 28·95 | 1,522 | 12·74 | 1,935 |
| Perth | 37,156 | 1,304 | 35·10 | 622 | 16·74 | 682 |
| Hobart | 34,654 | 909 | 26·23 | 501 | 14·46 | 408 |
| Wellington | 49,344 | 1,326 | 26·87 | 508 | 10·29 | 818 |
The average age at death of persons of either sex, in each of the eight years 1895–1902, was as follows:—
| Males. | Females. | |
|---|---|---|
| 1895 | 36·21 years. | 30·17 years. |
| 1896 | 36·80 years. | 32·41 years. |
| 1897 | 38·80 years. | 34·77 years. |
| 1898 | 39·29 years. | 35·69 years. |
| 1899 | 37·73 years. | 33·54 years. |
| 1900 | 40·31 years. | 36·14 years. |
| 1901 | 41·64 years. | 37·68 years. |
| 1902 | 41·07 years. | 34·88 years. |
The average expectation of life at each year of age has been compiled from a table given in a paper on the rates of mortality in New Zealand which was recently published by Mr. George Leslie, now Registrar of Friendly Societies. This is the best and most up-to-date information procurable, but it is not guaranteed by the authorities of the Government Life Insurance Department.
The table shows, on comparison with New South Wales figures (Coghlan's), that at birth the expectation of life to the male infant in New Zealand is considerably greater than in the State, the figures being 54·41 years (N.Z.), against 49·60 (N.S.W.), and for females 57·26 and 52·90.
At 21 years of age the expectation in New Zealand for males is 43·77 years, against 41·35 (N.S.W.), and for females 45·59, against 43·62.
At age 45 the comparison is, for males, 25·23 years (N.Z.), 23·27 (N.S.W.); females, 27·46 years (N.Z.), against 25·34 (N.S.W.)
At the age of 70, the limit of a normal life, the figures for New Zealand are—males 9·48 years, females 10·23, against 8·64 for both sexes in New South Wales.
Throughout the comparison is in favour of this country.
| Expectation of Life in New Zealand. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age. | Average Duration of Life: Years. | Age. | Average Duration of Life: Years. | Age. | Average Duration of Life: Years. | |||
| Male. | Female. | Male. | Female. | Male. | Female. | |||
| 0 | 54·44 | 57·260 | 35 | 32·829 | 34·954 | 70 | 9·481 | 10·227 |
| 1 | 59·102 | 61·214 | 36 | 32·054 | 34·215 | 71 | 8·988 | 9·673 |
| 2 | 59·169 | 61·220 | 37 | 31·282 | 33·475 | 72 | 8·504 | 9·130 |
| 3 | 58·626 | 60·647 | 38 | 30·511 | 32·734 | 73 | 8·035 | 8·604 |
| 4 | 57·924 | 59·934 | 39 | 29·744 | 31·990 | 74 | 7·586 | 8·095 |
| 5 | 57·167 | 59·148 | 40 | 28·979 | 31·243 | 75 | 7·1 | 7·614 |
| 6 | 56·396 | 58·343 | 41 | 28·220 | 35·493 | 76 | 6·758 | 7·164 |
| 7 | 55·606 | 57·520 | 42 | 27·465 | 29·739 | 77 | 6·379 | 6·742 |
| 8 | 54·791 | 56·680 | 43 | 26·715 | 28·981 | 78 | 6·022 | 6·349 |
| 9 | 53·956 | 55·825 | 44 | 25·971 | 28·221 | 79 | 5·683 | 5·982 |
| 10 | 53·094 | 54·953 | 45 | 25·231 | 27·458 | 80 | 5·362 | 5·636 |
| 11 | 52·212 | 54·069 | 46 | 24·499 | 26·694 | 81 | 5·055 | 5·312 |
| 12 | 51·315 | 53·180 | 47 | 23·773 | 25·927 | 82 | 4·765 | 5·005 |
| 13 | 50·425 | 52·294 | 48 | 23·055 | 25·163 | 83 | 4·489 | 4·714 |
| 14 | 49·539 | 51·415 | 49 | 22·344 | 24·399 | 84 | 4·229 | 4·439 |
| 15 | 48·663 | 50·545 | 50 | 21·636 | 23·640 | 85 | 3·982 | 4·180 |
| 16 | 47·803 | 49·690 | 51 | 20·932 | 22·885 | 86 | 3·747 | 3·935 |
| 17 | 46·960 | 48·847 | 52 | 20·231 | 22·135 | 87 | 3·525 | 3·705 |
| 18 | 46·139 | 48·016 | 53 | 19·530 | 21·392 | 88 | 3·313 | 3·487 |
| 19 | 45·336 | 47·198 | 54 | 18·836 | 20·655 | 89 | 3·110 | 3·283 |
| 20 | 44·551 | 46·393 | 55 | 18·150 | 19·926 | 90 | 2·914 | 3·089 |
| 21 | 43·775 | 45·593 | 56 | 17·478 | 19·202 | 91 | 2·723 | 2·905 |
| 22 | 43·005 | 44·803 | 57 | 16·822 | 18·485 | 92 | 2·525 | 2·731 |
| 23 | 42·235 | 44·021 | 58 | 16·183 | 17·776 | 93 | 2·323 | 2·564 |
| 24 | 41·463 | 43·244 | 59 | 15·560 | 17·077 | 94 | 2·101 | 2·400 |
| 25 | 40·684 | 42·474 | 60 | 14·949 | 16·386 | 95 | 1·843 | 2·238 |
| 26 | 39·899 | 41·708 | 61 | 14·348 | 15·705 | 96 | 1·553 | 2·082 |
| 27 | 39·108 | 40·946 | 62 | 13·754 | 15·037 | 97 | 1·247 | 1·931 |
| 28 | 38·319 | 40·187 | 63 | 13·170 | 14·386 | 98 | 0·960 | 1·774 |
| 29 | 37·526 | 39·431 | 64 | 12·600 | 13·752 | 99 | 0·677 | 1·600 |
| 30 | 36·736 | 38·678 | 65 | 12·046 | 13·135 | 100 | 0·500 | 1·424 |
| 31 | 35·949 | 37·928 | 66 | 11·512 | 12·534 | 101 | ... | 1·195 |
| 32 | 35·165 | 37·181 | 67 | 10·994 | 11·945 | 102 | ... | 0·889 |
| 33 | 34·384 | 36·438 | 68 | 10·486 | 11·365 | 103 | ... | 0·500 |
| 34 | 33·605 | 35·695 | 69 | 9·981 | 10·792 | |||
Subjoined is a classified statement of the deaths of infants under one year during 1902, with the ratio of the deaths in each class to the 1,000 births during the year:—
| Year. | Sex. | Under 1 Month. | 1 and under 3 Months. | 3 and under 6 Months. | 6 and under 12 Months. | Total under 12 Months. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Deaths. | |||||||
| 1902 |  | Male | 379 | 185 | 169 | 219 | 952 |
| Female | 286 | 159 | 144 | 171 | 760 | ||
| Deaths to the 1,000 Births. | |||||||
| 1902 |  | Male | 35·57 | 17·37 | 15·86 | 20·56 | 89·36 |
| Female | 28·58 | 15·90 | 14·40 | 17·10 | 75·98 | ||
Eighty-nine out of every thousand of male children born, and seventy-six of every thousand females, are found to have died before attaining the age of one year. The mortality is thus one in eleven of male children and one in thirteen of females, even in New Zealand, where conditions are far more favourable to infant life than in Australia, at least as far as relates to the cities.
It will also be seen from the figures that the chances of living during the first year of age are far greater for female than for male infants. Thus, during the year 1902 there were—
| 100 deaths of males to 80 deaths of females under 1 month of age; |
| 100 deaths of males to 92 deaths of females from 1 to 3 months of age; |
| 100 deaths of males to 91 deaths of females from 3 to 6 months of age; |
| 100 deaths of males to 83 deaths of females from 6 to 12 months of age; |
| 100 deaths of males to 85 deaths of females under 12 months of age. |
The rates of infantile mortality—that is, the proportion the deaths of children under one year of age bear to the births—are higher in the Australian States than in New Zealand.
The deaths registered in the colony during the last five years, when distributed among the several classes according to their assigned causes, give the rates shown hereunder:—
| Causes of Death. | Rate per 10,000 living. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
| Zymotic diseases | 10·99 | 12·41 | 9·23 | 7·83 | 10·52 |
| Parasitic diseases | 0·37 | 0·38 | 0·30 | 0·24 | 0·10 |
| Dietetic diseases | 0·87 | 1·03 | 0·93 | 0·88 | 0·85 |
| Constitutional diseases | 18·81 | 18·75 | 17·76 | 18·83 | 19·30 |
| Developmental diseases | 8·80 | 9·64 | 9·15 | 10·05 | 10·60 |
| Local diseases | 46·86 | 48·69 | 45·63 | 48·95 | 51·66 |
| Violence | 7·43 | 7·23 | 7·53 | 7·48 | 7·58 |
| Ill-defined and not-specified causes | 4·26 | 4·27 | 3·76 | 3·87 | 4·36 |
| All causes | 98·39 | 102·40 | 94·29 | 98·13 | 104·97 |
The next table shows that forty-nine in every one hundred deaths in 1902 were from local diseases, of which diseases of the respiratory system formed 13 per cent., diseases of the circulatory system 11 per cent., and of the nervous system 10 per cent., while diseases of the digestive system contributed 9 per cent. Constitutional diseases, including, with others, phthisis and cancer, comprised 18 per cent. of the total mortality. Ten per cent. of deaths were from zymotic causes, including 5·77 per cent. from miasmatic diseases, and 3·27 per cent. from diarrhœal. Deaths from developmental diseases caused 10·10 per cent. of the whole, and violent deaths accounted for 7·22 per cent.
| Causes of Death. | Number of Deaths. | Proportion to Total Deaths. | Proportion per 10,000 living, 1902. | Proportion per 10,000 living 1901. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male. | Female. | Total. | Male. | Female. | Total. | |||
| Class I. Specific febrile or zymotic diseases,— | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | |||||
| Order 1. Miasmatic diseases | 267 | 216 | 483 | 5·45 | 6·20 | 5·77 | 6·05 | 5·04 |
| Order 2. Diarrhœal diseases | 139 | 136 | 275 | 2·85 | 3·90 | 3·27 | 3·45 | 1·79 |
| Order 3. Malarial diseases | 2 | ... | 2 | 0·04 | ... | 0·03 | 0·03 | ... |
| Order 4. Zoogenous diseases | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Order 5. Venereal diseases | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0·11 | 0·29 | 0·18 | 0·19 | 0·23 |
| Order 6. Septic diseases | 22 | 42 | 64 | 0·45 | 1·20 | 0·77 | 0·80 | 0·77 |
| Total Class I. | 435 | 404 | 839 | 8·90 | 11·59 | 10·02 | 10·52 | 7·83 |
| Class II. Parasitic diseases | 6 | 2 | 8 | 0·12 | 0·06 | 0·10 | 0·10 | 0·24 |
| Class III. Dietetic diseases | 50 | 18 | 68 | 1·02 | 0·52 | 0·81 | 0·85 | 0·88 |
| Class IV. Constitutional diseases | 817 | 723 | 1,540 | 16·71 | 20·74 | 18·39 | 19·30 | 18·83 |
| Class V. Developmental diseases | 476 | 370 | 846 | 9·73 | 10·62 | 10·10 | 10·60 | 10·05 |
| Class VI. Local diseases,— | ||||||||
| Order 1. Diseases of nervous system | 523 | 335 | 858 | 10·69 | 9·61 | 10·25 | 10·75 | 10·54 |
| Order 2. Diseases of organs of special sense | 2 | 6 | 8 | 0·04 | 0·17 | 0·10 | 0·10 | 0·04 |
| Order 3. Diseases of circulatory system | 578 | 376 | 954 | 11·82 | 10·79 | 11·39 | 11·96 | 12·00 |
| Order 4. Diseases of respiratory system | 641 | 417 | 1,058 | 13·11 | 11·96 | 12·64 | 13·26 | 12·61 |
| Order 5. Diseases of digestive system | 408 | 326 | 734 | 8·34 | 9·36 | 8·74 | 9·20 | 7·89 |
| Order 6. Diseases of lymphatic system | 10 | 18 | 28 | 0·20 | 0·52 | 0·34 | 0·35 | 0·41 |
| Order 7. Diseases of urinary system | 229 | 99 | 328 | 4·68 | 2·84 | 3·92 | 4·11 | 3·65 |
| Order 8. Diseases of reproductive system,— | ||||||||
| (a.) Of organs of generation | 1 | 26 | 27 | 0·02 | 0·74 | 0·32 | 0·34 | 0·35 |
| (b.) Of parturition | ... | 85 | 85 | ... | 2·44 | 1·02 | 1·07 | 0·89 |
| Order 9. Diseases of locomotive system | 21 | 9 | 30 | 0·45 | 0·26 | 0·36 | 0·38 | 0·35 |
| Order 10. Diseases of integumentary system | 8 | 3 | 11 | 0·16 | 0·09 | 0·13 | 0·14 | 0·22 |
| Total Class VI. | 2,421 | 1,700 | 4,121 | 49·51 | 48·78 | 49·21 | 51·66 | 48·95 |
| Class VII. Violence,— | ||||||||
| Order 1. Accident or negligence | 408 | 115 | 523 | 8·34 | 3·30 | 6·24 | 6·56 | 6·35 |
| Order 2. Homicide | ... | 2 | 2 | ... | 0·06 | 0·02 | 0·02 | 0·10 |
| Order 3. Suicide | 75 | 5 | 80 | 1·54 | 0·14 | 0·96 | 1·00 | 1·02 |
| Order 4. Execution | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 0·01 |
| Total Class VII. | 483 | 122 | 605 | 9·88 | 3·50 | 7·22 | 7·58 | 7·48 |
| Class VIII. Ill-defined and not-specified causes | 202 | 146 | 348 | 4·13 | 4·19 | 4·15 | 4·36 | 3·87 |
| Grand totals | 4,890 | 3,485 | 8,375 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 100·00 | 104·97 | 98·13 |
The next table shows, for either sex, the number of deaths from each cause registered during the year 1902:—
| CAUSES OF DEATH. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class. | Causes of Death. | Males. | Females. | Total. |
| Orders and Diseases. | ||||
| I.---SPECIFIC FEBRILE OR ZYMOTIC DISEASES. | ORDER 1.---Miasmatic. | |||
| Small-pox | ... | ... | ... | |
| Chicken-pox | ... | ... | ... | |
| Measles | 82 | 52 | 134 | |
| Epidemic rose-rash, rubeola | ... | ... | ... | |
| Scarlet fever, scarlatina | 14 | 25 | 39 | |
| Typhus | ... | ... | ... | |
| Bubonic plague | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Dengue | ... | ... | ... | |
| Relapsing fever | ... | ... | ... | |
| Influenza | 62 | 55 | 117 | |
| Whooping-cough | 42 | 41 | 83 | |
| Mumps | ... | ... | ... | |
| Diphtheria | 29 | 25 | 54 | |
| Cerebro-spinal, fever | ... | ... | ... | |
| Simple and ill-define fever | ... | ... | ... | |
| Enteric fever, typhoid | 35 | 18 | 53 | |
| Other miasmatic diseases | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Order 1 | 267 | 216 | 483 | |
| ORDER 2.---Diarrhœal. | ||||
| Simple cholera | 9 | 8 | 17 | |
| Diarrhœa | 108 | 109 | 217 | |
| Dysentery | 22 | 19 | 41 | |
| Total Order 2 | 139 | 136 | 275 | |
| ORDER 3.---Malarial. | ||||
| Remittent fever | ... | ... | ... | |
| Ague | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Beriberi | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Total Order 3 | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| ORDER 4.---Zoogenous. | ||||
| Hydrophobia | ... | ... | ... | |
| Glanders | ... | ... | ... | |
| Splenic fever | ... | ... | ... | |
| Cow-pox and other effects of vaccination | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Order 4 | ... | ... | ... | |
| ORDER 5.---Venereal. | ||||
| Syphilis | 3 | 10 | 13 | |
| Gonorrhœa, stricture of urethra, ulcer of groin | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Total Order 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| ORDER 6.---Septic. | ||||
| Phagedæa | ... | ... | ... | |
| Erysipelas | 8 | 7 | 15 | |
| Pyæmia, septicæmia | 14 | 10 | 24 | |
| Puerperal fever, pyæmia, septicæmia | ... | 25 | 25 | |
| Total Order 6 | 22 | 42 | 64 | |
| Total Class I. | 435 | 404 | 839 | |
| II.---PARASITIC DISEASES. | Thrush | 1 | ... | 1 |
| Other diseases from vegetable parasites | ... | ... | ... | |
| Hydatid disease | 4 | 2 | 6 | |
| Worms | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Other diseases from animal parasites | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Class II. | 6 | 2 | 8 | |
| III.---DIETETIC DISEASES. | Starvation, exposure | 6 | ... | 6 |
| Want of breast-milk | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| Scurvy | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Intemperance--- | ||||
| Chronic alcoholism | 26 | 7 | 33 | |
| Delirium tremens | 9 | 1 | 10 | |
| Other dietetic diseases | 6 | 9 | 15 | |
| Total Class III. | 50 | 18 | 68 | |
| IV.---CONSTITUTIONAL DISEASES. | Rheumatic fever | 21 | 22 | 43 |
| Rheumatism | 6 | 13 | 19 | |
| Gout | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Rickets | 3 | 2 | 5 | |
| Cancer | 296 | 240 | 536 | |
| Tabes mesenterica, tubercular peritonitis | 20 | 25 | 45 | |
| Tubercular meningitis, acute hydrocephalus | 34 | 32 | 66 | |
| Phthisis | 339 | 278 | 617 | |
| Other forms of tuberculosis, scrofula | 35 | 39 | 74 | |
| Purpura, hæmorrhagic diathesis | 4 | 7 | 11 | |
| Anæmia, chlorosis, leucocythæmia | 25 | 21 | 46 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 25 | 43 | 68 | |
| Other constitutional diseases | 7 | 1 | 8 | |
| Total Class IV. | 817 | 723 | 1,540 | |
| V.---DEVELOPMENTAL DISEASES. | Premature birth | 177 | 126 | 303 |
| Atelectasis | 14 | 19 | 33 | |
| Cyanosis | 5 | 6 | 11 | |
| Spina bifida | 7 | 9 | 16 | |
| Imperforate anus | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Cleft palate, hare-lip | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Other congenital defects | 8 | 8 | 16 | |
| Old age | 262 | 202 | 464 | |
| Total Class V. | 476 | 370 | 846 | |
| VI.---LOCAL DISEASES. | ORDER 1.---Diseases of Nervous System. | |||
| Inflammation of the brain or its membranes | 72 | 60 | 132 | |
| Cerebro-spinal meningitis | 5 | 4 | 9 | |
| Apoplexy | 157 | 108 | 265 | |
| Softening of brain | 17 | 6 | 23 | |
| Hemiplegia, brain paralysis | 27 | 22 | 49 | |
| Paralysis (undescribed) | 56 | 22 | 78 | |
| Paralysis agitans | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Insanity, general paralysis of insane | 32 | 10 | 42 | |
| Chorea | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Epilepsy | 19 | 14 | 33 | |
| Convulsions | 61 | 54 | 115 | |
| Laryngismus stridulus | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Idiopathic tetanus | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Paraplegia, diseases of spinal cord | 22 | 8 | 30 | |
| Locomotor ataxia | 8 | 1 | 9 | |
| Other diseases of nervous system | 41 | 23 | 64 | |
| Total Order 1 | 523 | 335 | 858 | |
| ORDER 2.---Diseases of Organs of Special Sense. | ||||
| Otitis, otorrhœa | 2 | 6 | 8 | |
| Epistaxis, and diseases of nose | ... | ... | ... | |
| Ophthalmia, and diseases of eye | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Order 2 | 2 | 6 | 8 | |
| ORDER 3.---Diseases of Circulatory System. | ||||
| Endocarditis, valvular disease | 385 | 261 | 646 | |
| Pericarditis | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
| Hypertrophy of heart | ... | ... | ... | |
| Fatty degeneration of heart | 28 | 25 | 53 | |
| Angina pectoris | 27 | 9 | 36 | |
| Syncope | 80 | 48 | 128 | |
| Aneurism | 34 | 2 | 36 | |
| Senile gangrene | 4 | 2 | 6 | |
| Embolism, thrombosis | 15 | 22 | 37 | |
| Phlebitis | ... | 3 | 3 | |
| Varicose veins, piles | ... | ... | ... | |
| Other diseases of circulatory system | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Total Order 3 | 578 | 376 | 954 | |
| ORDER 4.---Diseases of Respiratory System. | ||||
| Laryngitis | 16 | 10 | 26 | |
| Croup | 11 | 4 | 15 | |
| Other diseases of larynx and trachea | ... | 1 | 1 | |
| Asthma, emphysema | 17 | 3 | 20 | |
| Bronchitis | 203 | 161 | 364 | |
| Pneumonia | 320 | 195 | 515 | |
| Pleurisy | 34 | 20 | 54 | |
| Other diseases of respiratory system | 40 | 23 | 63 | |
| Total Order 4 | 641 | 417 | 1,058 | |
| Stomatitis, cancrum oris | 3 | 2 | 5 | |
| Dentition | 25 | 18 | 43 | |
| Sore throat, quinsy | 4 | 1 | 5 | |
| Dyspepsia | 5 | 2 | 7 | |
| Hæmatemesis | 6 | 1 | 7 | |
| Melæna | 5 | 1 | 6 | |
| Diseases of stomach, gastritis | 49 | 60 | 109 | |
| Enteritis | 124 | 108 | 232 | |
| Ulceration, perforation, of intestine | 10 | 6 | 16 | |
| Ileus, obstruction of intestine | 35 | 16 | 51 | |
| Stricture or strangulation of intestine | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Intussusception of intestine | 6 | 1 | 7 | |
| Hernia | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| Fistula | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Peritonitis | 38 | 36 | 74 | |
| Ascites | ... | 1 | 1 | |
| Gall-stones | 3 | 6 | 9 | |
| Cirrhosis of liver | 28 | 15 | 43 | |
| Other diseases of liver, hepatitis, jaundice | ... | 23 | 52 | |
| Other diseases of digestive system | 31 | 17 | 48 | |
| Total Order 5 | 408 | 326 | 734 | |
| ORDER 6.---Diseases of Lymphatic System and Ductless Glands. | ||||
| Diseases of lymphatic system | 5 | 2 | 7 | |
| Diseases of spleen | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Bronchocele | ... | 11 | 11 | |
| Addison's disease | 3 | 5 | 8 | |
| Total Order 6 | 10 | 18 | 28 | |
| ORDER 7.---Diseases of Urinary System. | ||||
| Acute nephritis | 30 | 16 | 46 | |
| Bright's disease | 107 | 56 | 163 | |
| Uræmia | 14 | 3 | 17 | |
| Suppression of urine | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Calculus | 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| Hæmaturia | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Diseases of bladder and prostate | 61 | 10 | 71 | |
| Other diseases of urinary system (kidney diseases undescribed) | 9 | 12 | 21 | |
| Total Order 7 | 229 | 99 | 328 | |
| ORDER 8.---Diseases of Reproductive System. | ||||
| (a.) Diseases of organs of generation,--- | ||||
| Ovarian disease | ... | 6 | 6 | |
| Diseases of uterus and vagina | ... | 18 | 18 | |
| Disorders of menstruation | ... | 2 | 2 | |
| Pelvic abscess | ... | ... | ... | |
| Perineal abscess | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Diseases of testes, penis, scrotum, &c. | ... | ... | ... | |
| (b.) Diseases of parturition,--- | ||||
| Abortion, miscarriage | ... | 16 | 16 | |
| Puerperal mania | ... | ... | ... | |
| Puerperal metritis | ... | ... | ... | |
| Puerperal convulsions | ... | 11 | 11 | |
| Placenta prævia (flooding) | ... | 18 | 18 | |
| Phlegmasia dolens | ... | ... | ... | |
| Other accidents of childbirth | ... | 40 | 40 | |
| Total Order 8 | 1 | 111 | 112 | |
| ORDER 9.---Diseases of Organs of Locomotion. | ||||
| Caries, necrosis | 10 | 3 | 13 | |
| Arthritis, ostitis | 4 | 2 | 6 | |
| Other diseases of organs of locomotion | 7 | 4 | 11 | |
| Total Order 9 | 21 | 9 | 30 | |
| ORDER 10.---Diseases of Integumentary System. | ||||
| Carbuncle | ... | ... | ... | |
| Phlegmon, cellulitis | 3 | 1 | 4 | |
| Lupus | ... | ... | ... | |
| Ulcer, bed-sore | 1 | ... | 1 | |
| Eczema | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Pemphigus | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Other diseases of integumentary system | ... | 1 | 1 | |
| Total Order 10 | 8 | 3 | 11 | |
| Total Class VI. | 2,421 | 1,700 | 4,121 | |
| VII.---VIOLENCE. | ORDER 1.---Accident or Negligence. | |||
| Fractures, contusions | 185 | 21 | 209 | |
| Gunshot wounds | 14 | 4 | 18 | |
| Cut, stab | 13 | 3 | 16 | |
| Burn, scald | 18 | 30 | 48 | |
| Sunstroke | 2 | ... | 2 | |
| Poison | 8 | 10 | 18 | |
| Drowning | 125 | 21 | 146 | |
| Suffocation | 18 | 12 | 30 | |
| Otherwise | 25 | 11 | 36 | |
| Total Order 1 | 40 | 115 | 523 | |
| ORDER 2.---Homicide. | ||||
| Murder, manslaughter | ... | 2 | 2 | |
| Wounds in battle | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Order 2 | ... | 2 | 2 | |
| ORDER 3.---Suicide. | ||||
| Gunshot wounds | 21 | ... | 21 | |
| Cut, stab | 15 | 1 | 16 | |
| Poison | 13 | 1 | 14 | |
| Drowning | 9 | 3 | 12 | |
| Hanging | 10 | ... | 10 | |
| Otherwise | 7 | ... | 7 | |
| Total Order 3 | 75 | 5 | 80 | |
| ORDER 4.---Execution. | ||||
| Hanging | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Class VII. | 483 | 122 | 605 | |
| VIII.---ILL-DEFINED AND NOT-SPECIFIED CAUSES. | Dropsy | ... | ... | ... |
| Marasmus, &c. | 180 | 143 | 323 | |
| Mortification, gangrene | ... | ... | ... | |
| Tumour | 5 | 1 | 6 | |
| Abscess | 3 | ... | 3 | |
| Hæmorrhage | ... | ... | ... | |
| Sudden (cause unascertained) | 14 | 2 | 16 | |
| Other ill-defined and not-specified causes | ... | ... | ... | |
| Total Class VIII. | 202 | 146 | 348 | |
| General totals | 4,890 | 3,485 | 8,375 | |
The deaths in 1902 from specific febrile or zymotic diseases amounted to 839, a proportion of 10·52 in every 10,000 persons living, an increase of 230 on the number of deaths in 1901, when the proportion was 7·83. A heavier mortality from measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, whooping-cough, and diarrhœal diseases were the main causes of the increased death-rate in this class.
The following are the diseases in this class that have caused the greatest mortality during the past ten years:—
| Diseases. | 1893. | 1894. | 1895. | 1896. | 1897. | 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measles | 525 | 14 | .. | 1 | 1 | 56 | 137 | 9 | 6 | 134 |
| Scarlet fever and scarlatina | 1 | 5 | .. | 4 | 2 | 2 | .. | 10 | 17 | 39 |
| Diphtheria | 128 | 92 | 76 | 74 | 49 | 45 | 58 | 63 | 44 | 54 |
| Whooping-cough | 55 | 190 | 150 | 24 | 2 | 6 | 123 | 90 | 9 | 83 |
| Influenza | 106 | 233 | 125 | 89 | 120 | 219 | 135 | 181 | 219 | 117 |
| Diarrhoea diseases | 193 | 207 | 232 | 334 | 257 | 275 | 298 | 199 | 139 | 275 |
| Enteric or typhoid fever | 97 | 115 | 94 | 124 | 106 | 120 | 93 | 68 | 95 | 53 |
| Puerperal fever | 24 | 38 | 32 | 10 | 18 | 19 | 15 | 24 | 20 | 25 |
Measles, which was epidemic in 1893, caused only 16 deaths in the four succeeding years; but in 1898 the mortality rose to 56 and in 1899 to 137 deaths, falling again to 9 deaths in 1900 and to 6 deaths in 1901, again rising to 134 in 1902. From scarlet fever and scarlatina there were 39 deaths last year. The mortality from diphtheria rose from 45 deaths in 1898 to 58 in 1899 and 63 in 1900, fell to 44 deaths in 1901, and rose again to 54 in 1902.
Whooping-cough in 1894 destroyed 190 lives, and 150 in 1895, but was in 1896, 1897, and 1898 much less fatal. In 1899 the mortality sprang up again to a total of 123 deaths, against 90 in 1900, 9 in 1901, and £3 in 1902. In 1891 there were 242 deaths from this cause.
Influenza, the deaths from which were 89 in 1896, 120 in 1897, and 219 in 1898, caused 135 deaths in 1899, 181 in 1900, 219 in 1901, and 117 in 1902.
From diarrhœal complaints the deaths in 1902 were 275, against 139 in 1901; while in 1896 the mortality reached the height of 334 deaths, and in 1889 was even higher (355), with a much smaller population than in 1902. Diarrhœal diseases were the most fatal of the order “febrile and zymotic” (275 deaths), measles coming second, for the year 1902, influenza third, and whooping-cough fourth.
Enteric or typhoid fever was not so fatal in 1902 as in 1901, the figures being 53 deaths, against 95 for the former year. The highest mortality during the decennium was in 1896, when the deaths numbered 124 for the colony.
The year 1900 saw the outbreak of the disease known as the bubonic plague, in Sydney and other parts of Australia. In that year there was one death from plague in New Zealand, which occurred at Auckland. None happened in the year 1901, but three deaths from this cause, all males, were registered at Auckland during 1902. The Public Health Department is taking every possible precaution.
From small-pox there were no deaths in 1902. The vaccinations registered for the last ten years are as under:—
| Year. | Total Vaccinations registered. | Number of Births registered. | Proportion of Successful Vaccinations of | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Children under 1 Year of Ago to Total Births. Per Cent. | Children under 14 Years of Age to Total Births. Per Cent. | |||
| 1902 | 8,763 | 20,655 | 12·64 | 42·43 |
| 1901 | 3,768 | 20,491 | 9·68 | 18·39 |
| 1900 | 4,525 | 19,546 | 16·12 | 23·15 |
| 1899 | 5,133 | 18,835 | 17·94 | 27·25 |
| 1898 | 10,349 | 18,955 | 29·05 | 54·60 |
| 1897 | 12,440 | 18,733 | 32·89 | 66·41 |
| 1896 | 11,917 | 18,612 | 30·78 | 64·03 |
| 1895 | 8,523 | 18,546 | 31·72 | 44·34 |
| 1894 | 9,322 | 18,528 | 32·42 | 50·31 |
| 1893 | 7,412 | 18,187 | 28·09 | 40·75 |
The number of successful vaccinations registered in 1902 was 8,763, against 3,768 in 1901, 4,525 in 1900, 5,133 in 1899, and 10,349 in 1898. The fall prior to 1902 was consequent on the alteration of the law relative to vaccination in England, and subsequently in this colony.
One child in every eight born in 1902 is shown to have been successfully vaccinated in that year. The procedure under the new law as regards vaccination is similar to that previously in force. The Registrar issues a notice when a birth is registered, with forms for certificate as to the result of vaccination attached. Vaccination is still compulsory, if exemption is not secured in four months from date of birth. But everything is now subject to the provisions of the “exemption clause,” which is the main feature, and governs the rest. Any parent or custodian who has conscientious objections—believing that vaccination would be injurious to the child's health—can apply for a certificate of exemption to a Magistrate or Registrar of Births; and, when the child's parent or guardian is resident outside of a borough, the application may be made to and certificate granted by a Justice of the Peace.
Four thousand three hundred and twenty-seven exemption certificates were issued from the 13th October, 1900, when the Act came into force, to the end of the year 1902.
When no exemption certificate is obtained, the law now allows to the parent twelve months instead of six from date of birth in which to vaccinate, and a similar period from date of taking charge of child in case of a custodian. There are penalties for not vaccinating, as before. One conviction for neglecting to vaccinate a child removes liability until the child is four years of age.
The main features of the new English law include a system of domiciliary visitation by public vaccinators, in substitution for that requiring children to be taken to vaccination stations, and exemption of parents and others from any penalty for not vaccinating children on production to the proper officer of a Magistrate's certificate to the effect that he is satisfied as to the conscientious objections raised. Vaccination with glycerinated calf-lymph or other lymph issued by Local Government Boards is offered by the Government. The Act continues in force until the beginning of the year 1904.
There were 8 deaths from parasitic diseases, the proportion per 10,000 living being 0·10. Deaths from hydatids numbered 6 in 1902.
Under the class “Dietetic diseases” are included 43 deaths from intemperance. But these cannot be said to represent the full extent of the mortality really caused by the abuse of alcoholic liquors. Many deaths of intemperate persons are attributed to disease of the liver, kidneys, &c., in the medical certificates.
The deaths from constitutional diseases in 1902 numbered 1,540, or 19·30 per 10,000 of population, and 18 out of every 100 deaths from all causes. This class of disease is more fatal than any other except that defined as “Local diseases,” on account of the great numbers of deaths from cancer and phthisis, with other tubercular complaints, which are classed as “Constitutional.”
From phthisis there are more deaths than from any other cause. The number of deaths was 617 in 1902. The deaths in 1902 were in the proportion of 7·73 in every 10,000 persons living, against 7·66 in the previous year.
Figures for ten years are quoted, showing that the total number of deaths from this disease in 1902 was the highest recorded during the decennium, though the rate had been higher in some of the previous years.
| Year. | Deaths from Phthisis. | Rate per 10,000. |
|---|---|---|
| 1893 | 545 | 8·24 |
| 1894 | 576 | 8·48 |
| 1895 | 553 | 7·99 |
| 1896 | 523 | 7·40 |
| 1897 | 596 | 8·26 |
| 1898 | 597 | 8·11 |
| 1899 | 593 | 7·91 |
| 1900 | 577 | 7·56 |
| 1901 | 596 | 7·66 |
| 1902 | 617 | 7·73 |
In Australasia the rate is materially increased by the deaths of persons who have come out either already suffering from phthisis or predisposed thereto. There is no reason for believing that this circumstance has more effect on the death-rate in Australia than in New Zealand; so that the lower rate referred to in previous issues of this work as obtaining in this colony may be taken as proof of the superiority of its climate for withstanding consumptive tendencies.
The death-rate of England and Wales from phthisis, though declining, is far higher than that of New Zealand. In 1900 it stood at 13·32 per 10,000.
Phthisis is now known to be and is treated as an infectious preventable disease caused by the bacillus tuberculosis, which is communicable in many ways. Certain constitutions are far more predisposed than others to receive this bacillus, especially under conditions of life unfavourable to robust health, when a nidus is formed for the development of the bacillus. The Government has established a sanatorium for consumptives at Hamilton in the Waikato, and further institutions are contemplated.
From other forms of tuberculosis the deaths in 1902 were 185, or 2·32 per 10,000 of population. Thus a large addition has to be made to the deaths from phthisis to appreciate the full mischief done by tubercular disease.
The mortality from all forms of tubercular disease, taken together, has been at the average rate of about 10 1/2 persons per 10,000 living for the last ten years. This rate is far lower than that which obtained in England during the year 1900, when the proportion was 19·00 per 10,000 living.
A table is supplied showing the results for each of ten years in New Zealand. Besides the death-rate from tubercular diseases, it also shows the percentage of deaths by tubercle to those from all causes, which was from 9 1/2 to 11 1/2 per cent. for the decennial period 1893–1902.
| Decennial Table, 1893–1902, showing the Death-rate from Tubercle per 10,000 Living and Percentage of Total Deaths. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Mean Population. | Number of Deaths from Tubercular Diseases. | Rate per 10,000. | Percentage of Total Deaths from All Causes. |
| 1893 | 661,349 | 729 | 11·02 | 10·77 |
| 1894 | 679,196 | 752 | 11·07 | 10·87 |
| 1895 | 692,417 | 761 | 10·99 | 11·09 |
| 1896 | 706,846 | 680 | 9·62 | 10·57 |
| 1897 | 721,609 | 763 | 10·57 | 11·57 |
| 1898 | 736,260 | 769 | 10·44 | 10·62 |
| 1899 | 749,984 | 795 | 10·60 | 10·35 |
| 1900 | 763,594 | 752 | 9·85 | 10·44 |
| 1901 | 777,968 | 775 | 9·96 | 10·15 |
| 1902 | 797,793 | 802 | 10·05 | 9·58 |
| Decennial Table, 1893–1902.—Deaths from various Tubercular Diseases registered in New Zealand, specifying the Number under and over Five Years of Age. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | |||||||||||
| Year. | Tabes Mesenterica, Tubercular Peritonitis. | Tubercular Meningitis, Acute Hydrocephalus | Phthisis. | Other Forms of Tuberculosis, Scrofula. | Total Deaths from Tuberculosis. | Total All Ages. | |||||
| Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | ||
| 1893 | 35 | 14 | 33 | 39 | 8 | 537 | 21 | 42 | 97 | 632 | 729 |
| 1894 | 36 | 13 | 33 | 30 | 7 | 569 | 16 | 48 | 92 | 660 | 752 |
| 1895 | 47 | 15 | 25 | 37 | 5 | 548 | 28 | 56 | 105 | 656 | 761 |
| 1896 | 36 | 11 | 30 | 28 | 5 | 518 | 19 | 33 | 90 | 590 | 680 |
| 1897 | 35 | 9 | 33 | 32 | 7 | 589 | 13 | 45 | 88 | 675 | 763 |
| 1898 | 37 | 12 | 37 | 38 | 10 | 587 | 11 | 37 | 95 | 674 | 769 |
| 1899 | 43 | 19 | 32 | 40 | 10 | 583 | 12 | 56 | 97 | 698 | 795 |
| 1900 | 20 | 20 | 24 | 55 | 13 | 564 | 9 | 47 | 66 | 6 | 752 |
| 1901 | 30 | 22 | 30 | 31 | 10 | 586 | 14 | 52 | 84 | 691 | 775 |
| 1902 | 26 | 19 | 36 | 30 | 5 | 612 | 8 | 66 | 75 | 727 | 802 |
Eight deaths from “lupus” recorded during the decennium have not been included in the above table. They were all deaths of adult persons (4 males and 4 females).
It will be seen that the term “tubercular diseases” includes “phthisis,” “tabes mesenterica,” “tubercular peritonitis,” “tubercular meningitis,” “acute hydrocephalus,” with other forms of tuberculosis (scrofula, &c.). Of these the mortality from phthisis forms by far the greatest part of the whole. Thus, in 1902 there were 617 deaths from phthisis out of a total of 802 deaths from all tubercular complaints. Of 617 deaths by phthisis, only 5 were of persons under 5 years of age.
Examination of the next table, giving the full series of ages of persons who died from tubercular disease during the year 1902, shows that of 45 deaths from tabes mesenterica, with tubercular peritonitis, 26 were of children under 5 years. Also that, of 66 deaths from tubercular meningitis, with acute hydrocephalus, 36 were of persons under 5 years, and 20 from 5 to 20 years. Under “other forms of tuberculosis” (excepting phthisis) the greater numbers of deaths are at ages under 25 years.
The mortality from phthisis is heaviest at 20–30 years, being 227 deaths out of 617 of all ages; but large numbers are found in the columns as far as that for the advanced term of 65 to 70 years, at which the deaths for 1902 were 20, and 10 deaths from this cause are of persons of 70 years and upwards.
| Table showing the Number of Deaths from Tubercular Diseases registered in New Zealand during the Year 1902, arranged in Groups of Ages. | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| — | Under 1 Year. | Under 5 Years. | 5 to 10. | 10 to 15. | 15 to 20. | 20 to 25. | 25 to 30. | 30 to 35. | 35 to 40. | 40 to 45. | 45 to 50. | 50 to 55. | 55 to 60. | 60 to 65. | 65 to 70. | 70 to 75. | 75 to 80. | 80 and upwards. | Total, 5 Years and over. | All ages. |
| Tabes Mesenterica, Tubercular Peritonitis | 23 | 26 | ... | 2 | ... | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | ... | ... | 2 | ... | ... | 1 | ... | ... | ... | 19 | 45 |
| Tubercular Meningitis, Acute Hydrocephalus | 9 | 36 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 8 | ... | 2 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 30 | 66 |
| Phthisis | 2 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 64 | 102 | 125 | 77 | 70 | 43 | 30 | 25 | 17 | 19 | 20 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 612 | 617 |
| Other forms of Tuberculosis, Scrofula | 3 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ... | 2 | 2 | 1 | ... | ... | 66 | 74 |
| Totals | 37 | 75 | 14 | 24 | 79 | 127 | 146 | 87 | 73 | 44 | 31 | 30 | 17 | 21 | 23 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 727 | 802 |
To show the mortality from tuberculosis in various parts of the colony, a table giving the deaths in the various provincial districts is added, which, however, only shows that the mortality is distributed very much according to population. The deaths in the North Island are, however, found to be 46 fewer than those for the South Island, or 378 deaths and 424 deaths for those divisions respectively:—
| Table showing the Number of Deaths from Tubercular Disease registered in each Provincial District of New Zealand during the Year 1902. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial District. | Tabes Mesenterica, Tubercular Peritonitis. | Tubercular Meningitis, Acute Hydrocephalus. | Phthisis. | Other Forms of Tuberculosis, Scrofula. | Total Deaths from Tuberculosis. |
| Auckland | 11 | 13 | 146 | 11 | 181 |
| Taranaki | 2 | 1 | 11 | 3 | 17 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1 | 3 | 27 | 1 | 32 |
| Wellington | 8 | 18 | 107 | 15 | 148 |
| Marlborough | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 8 |
| Nelson | 2 | 4 | 29 | 5 | 40 |
| Westland | .. | 1 | 10 | .. | 11 |
| Canterbury | 10 | 6 | 128 | 17 | 161 |
| Otago | 10 | 66 | 154 | 21 | 204 |
| Totals | 45 | 66 | 617 | 74 | 802 |
Legislative action has been recommended to safeguard the life and health of the people from tubercle; and the complete isolation of consumptive patients, with the disinfecting of their sputa and of everything that has been in contact with them, is suggested from time to time as a necessary measure.
The deaths from cancer during the year 1902 were 536. There were more deaths of males than of females, the numbers being—males 296, females, 240. The rate of mortality per 10,000 living was 6·72. The apparent increase in deaths from this disease is shown further on and compared with that of England. But the increase is not believed by all authorities to be a fact to the extent represented, but partly the result of more careful certification of the causes of death, and of improved diagnosis in cases of what is termed inaccessible cancer.
It is certain, however, that out of a total of 8,375 deaths from all causes in New Zealand during 1902, 536, or 6·40 per cent., were caused by cancer.
The death-rate from cancer is not so great as that from tubercular diseases, but is nevertheless a most alarming matter, not only on account of the number of deaths, but because of its progressive increase.
A decennial table shows that the deaths per 10,000 persons living rose from 5·02 in 1892 to 6·72 in 1902; and that whereas 4·91 out of every 100 deaths were attributable to cancer ten years ago, the proportion had grown to 6·40 last year.
| Table showing for each of the Ten Years 1893 to 1902 the Number of Persons registered as having died from Cancer, the Proportion of Deaths from Cancer per 10,000 living, and the Percentage of all Deaths attributed to Cancer. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Estimated Mean Population. | Deaths from Cancer. | Total Deaths, all Causes. | Deaths from Cancer per 10,000. | Percentage of Total Deaths due to Cancer. |
| 1893 | 661,349 | 332 | 6,767 | 5·02 | 4·91 |
| 1894 | 679,196 | 408 | 6,918 | 6·01 | 5·90 |
| 1895 | 692,417 | 383 | 6,863 | 5·53 | 5·58 |
| 1896 | 706,846 | 389 | 6,432 | 5·50 | 6·05 |
| 1897 | 721,609 | 395 | 6,595 | 5·47 | 5·99 |
| 1898 | 736,260 | 471 | 7,244 | 6·40 | 6·50 |
| 1899 | 749,984 | 468 | 7,680 | 6·24 | 6·09 |
| 1900 | 763,594 | 430 | 7,200 | 5·63 | 5·97 |
| 1901 | 777,968 | 515 | 7,634 | 6·62 | 6·75 |
| 1902 | 797,793 | 536 | 8,375 | 6·72 | 6·40 |
To exhibit how cancer affects the different parts of the human body in respect of each sex, the experience of four years (1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902) is shown in a succeeding table. Of any single organ affected, the stomach is the one most liable to be the seat of cancer among males, although with this sex the disease is apparently to about the same extent located in the mouth, lips, tongue, and throat, taking these parts all together. Next to the stomach, the liver is with males the part which is most often attacked, to judge by mortality records, and next in order come the intestines and rectum. Afterwards, but at a considerable distance, follow the kidneys, bladder, and urethra.
Amongst the females, the organs of generation, ovaries, uterus, and vagina, as a group, show by far most cases of mortality from cancer; but, as with the males, the stomach is, of any single organ, the one most affected, the liver coming next, then the breast, and then the intestines and rectum. Females do not contract cancer in the mouth (judging by the returns of deaths), tongue, lips, and throat to nearly the same extent as prevails among males. Whatever may be the cause, the figures are remarkable, being only 6 out of every 100 deaths from cancer among females, against 27 out of every 100 of males dying from the same cause; or, expressed in numbers, 45 deaths of females occurred against 256 of males from cancer in the mouth, &c., in a four years' experience of mortality.
| Table showing the Number of Deaths of Males and Females from Cancer during the Years 1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902, classified according to the Part of the Body affected. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part affected. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | ||||
| Number of Deaths. | Proportion of Specified. | Number of Deaths. | Proportion of Specified. | Number of Deaths. | Proportion of Specified. | Number of Deaths. | Proportion of Specified. | |
| Males. | ||||||||
| Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | Per Cent. | |||||
| Mouth, lip, tongue, throat, neck, &c. | 65 | 27·43 | 68 | 31·78 | 60 | 24·69 | 63 | 24·14 |
| Stomach | 87 | 36·71 | 80 | 37·38 | 97 | 39·92 | 112 | 42·91 |
| Intestines, rectum | 20 | 8·44 | 26 | 12·15 | 32 | 13·17 | 32 | 12·26 |
| Liver | 40 | 16·88 | 25 | 11·68 | 37 | 15·23 | 38 | 14·56 |
| Kidneys, bladder, urethra, &c. | 17 | 7·17 | 9 | 4·21 | 13 | 5·35 | 12 | 4·60 |
| Leg, foot, &c. | 6 | 2·53 | 4 | 1·87 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Lung | 2 | 0·84 | 2 | 0·93 | 4 | 1·64 | 4 | 1·53 |
| 237 | 100·00 | 214 | 100·00 | 243 | 100·00 | 261 | 100·00 | |
| Not specified | 34 | .. | 32 | .. | 22 | .. | 35 | .. |
| Totals | 271 | .. | 246 | .. | 265 | .. | 296 | .. |
| Females. | ||||||||
| Mouth, tongue, throat, &c. | 17 | 9·71 | 6 | 3·73 | 6 | 2·77 | 16 | 7·44 |
| Breast | 20 | 11·43 | 17 | 10·56 | 38 | 17·51 | 33 | 15·35 |
| Stomach | 40 | 22·86 | 28 | 17·39 | 61 | 28·11 | 43 | 20·00 |
| Intestines, rectum | 14 | 8·00 | 21 | 13·04 | 19 | 8·76 | 33 | 15·35 |
| Kidneys, bladder | 4 | 2·29 | 5 | 3·11 | 2 | 0·92 | 8 | 3·72 |
| Ovary, uterus, vagina | 50 | 28·57 | 54 | 33·54 | 55 | 25·35 | 44 | 20·46 |
| Liver | 25 | 14·29 | 25 | 15·53 | 29 | 13·36 | 33 | 15·35 |
| Gall-bladder, spleen, pancreas | 3 | 1·71 | 2 | 1·24 | 2 | 0·92 | 3 | 1·40 |
| Lung, spine, thigh, shoulder | 2 | 1·14 | 3 | 1·86 | 5 | 2·30 | 2 | 0·93 |
| 175 | 100·00 | 161 | 100·00 | 217 | 100·00 | 215 | 100·00 | |
| Not specified | 22 | .. | 23 | .. | 33 | .. | 25 | .. |
| Totals | 197 | .. | 184 | .. | 250 | .. | 240 | .. |
Considering the numbers of persons dying at the different age-periods, the following table of ten years' results shows the age of 30 years to be the time of life at which deaths from cancer begin to be numerous (it is really 35 for males and 30 for females). The maximum of deaths is reached at the period 60 to 65 for males, and 55 to 60 for females. These remarks are given without reference to the numbers of persons living at the various ages.
Deaths from cancer, it will be observed, are very rare among children under 5 years, and not frequent in those above that age.
| Deaths from Cancer.—Decennial Return. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table showing the Number of Persons (Males and Females) at Different Ages registered as having died from Cancer in New Zealand during the Ten Years 1893 to 1902. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year. | Under 1 Year. | Total under 1 Year. | 1 to 2. | 2 to 3. | 3 to 4. | 4 to 5. | Total under 5 Years. | 5 to 10. | 10 to 15. | 15 to 20. | 20 to 25. | 25 to 30. | 30 to 35. | 35 to 40. | 40 to 45. | 45 to 50. | 50 to 55. | 55 to 60. | 60 to 65. | 65 to 70. | 70 to 75. | 75 to 80. | 80 and upwards. | Total 5 Years and over | All Ages. | |||
| Under 1 Month. | 1 to 3 Months. | 3 to 6 Months. | 6 to 12 Months. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1893 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | ... | 3 | 1 | 6 | 9 | 22 | 32 | 61 | 54 | 57 | 36 | 25 | 13 | 6 | 329 | 332 |
| 1894 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 1 | ... | 1 | 1 | ... | 3 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 15 | 27 | 41 | 64 | 73 | 71 | 38 | 26 | 24 | 7 | 407 | 408 |
| 1895 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 2 | ... | ... | 3 | 1 | 6 | 11 | 25 | 47 | 61 | 64 | 63 | 38 | 37 | 19 | 6 | 383 | 383 |
| 1896 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 21 | 36 | 59 | 74 | 67 | 49 | 29 | 14 | 7 | 387 | 389 |
| 1897 | ... | ... | 1 | ... | 1 | ... | 1 | ... | 1 | 3 | ... | 2 | 1 | 1 | ... | 7 | 10 | 22 | 41 | 42 | 71 | 74 | 49 | 35 | 29 | 8 | 392 | 395 |
| 1898 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 2 | ... | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 36 | 47 | 47 | 77 | 79 | 69 | 35 | 30 | 9 | 469 | 471 |
| 1899 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 1 | 3 | 3 | ... | 1 | 4 | 6 | 15 | 21 | 42 | 48 | 82 | 64 | 87 | 45 | 27 | 19 | 467 | 468 |
| 1900 | ... | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ... | ... | 1 | ... | 2 | ... | ... | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 16 | 40 | 35 | 75 | 78 | 59 | 51 | 31 | 20 | 428 | 430 |
| 1901 | ... | ... | 1 | ... | 1 | ... | ... | ... | ... | 1 | 2 | ... | 4 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 20 | 31 | 53 | 60 | 65 | 80 | 74 | 63 | 33 | 11 | 514 | 515 |
| 1902 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 1 | ... | 3 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 22 | 35 | 49 | 50 | 72 | 88 | 86 | 67 | 31 | 15 | 536 | 536 |
The numbers of deaths of persons from cancer in each provincial district are given in another table, according to age-groups, but the result merely shows the disease to be one found everywhere throughout the colony—at least, there is no sufficient evidence of climatic conditions affecting the mortality to a great extent in any particular part of the country.
| Table showing the Number of Deaths from Cancer registered in each Provincial District of the Colony of New Zealand during the Years 1899–1902. | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |||||||||
| Provincial Districts. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Total | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Total | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Total. | Under 5 Years. | Over 5 Years. | Total. |
| Auckland | ... | 89 | 89 | 1 | 107 | 108 | 1 | 91 | 92 | ... | 115 | 115 |
| Taranaki | ... | 25 | 25 | ... | 9 | 9 | ... | 24 | 24 | ... | 24 | 24 |
| Hawke's Bay | ... | 26 | 26 | ... | 15 | 15 | ... | 16 | 16 | ... | 15 | 15 |
| Wellington | ... | 70 | 70 | ... | 79 | 79 | ... | 83 | 83 | ... | 95 | 95 |
| Marlborough | ... | 6 | 6 | ... | 11 | 11 | ... | 7 | 7 | ... | 7 | 7 |
| Nelson | ... | 26 | 26 | ... | 19 | 19 | ... | 34 | 34 | ... | 33 | 33 |
| Westland | ... | 12 | 12 | ... | 11 | 11 | ... | 26 | 26 | ... | 19 | 19 |
| Canterbury | ... | 96 | 96 | ... | 74 | 74 | ... | 98 | 98 | ... | 98 | 98 |
| Otago | 1 | 117 | 118 | 1 | 103 | 104 | ... | 135 | 135 | ... | 130 | 130 |
| Totals | 1 | 467 | 468 | 2 | 428 | 430 | 1 | 514 | 515 | ... | 536 | 536 |
The increase since 1881 is well exhibited in respect of each sex, and in regard to the higher ages, which are the periods at which the most cancer deaths occur, by a proportional statement:—
| Proportions of Deaths from Cancer per 10,000 Males and Females living at Three Age-periods. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | 40 to 50. | 50 to 60. | 60 to 70. | |||
| Males. | Females. | Males. | Females. | Males. | Females. | |
| 1881 | 5·58 | 9·80 | 11·10 | 22·57 | 22·86 | 43·78 |
| 1898 | 9·07 | 16·59 | 21·64 | 26·09 | 55·21 | 47·44 |
| 1902 | 11·86 | 10·53 | 18·90 | 28·73 | 46·18 | 44·12 |
The death-rates for cancer in respect of each sex are given for each of seven years, selected to show the position as from 1886 to 1902:—
| Deaths from Cancer in every 10,000 Persons of each Sex living in New Zealand. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year. | Males. | Females. |
| 1886 | 3·69 | 3·67 |
| 1890 | 4·72 | 4·79 |
| 1894 | 6·65 | 5·27 |
| 1898 | 6·77 | 5·98 |
| 1899 | 6·85 | 5·56 |
| 1900 | 6·12 | 509 |
| 1901 | 6·48 | 6·77 |
| 1902 | 7·05 | 6·35 |
The mortality was higher among the males than among the females (with the exception of 1901), which is the reverse of English experience, where the rate was 6·72 per 10,000 of males and 9·75 of females for the year 1900. In the United Kingdom, however, the rate of increase is so much higher among males than with females that the Registrar-General calculates equilibrium will be reached in about the year 1932, and thereafter the rate among males would exceed the rate among females.
The increase in the numbers for the sexes together for England and New Zealand is represented in the proportions below:—
| Deaths from Cancer in every 10,000 Persons living. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year. | New Zealand. | England. |
| 1881 | 2·69 | 5·20 |
| 1886 | 3·68 | 5·90 |
| 1891 | 4·68 | 6·92 |
| 1896 | 5·50 | 7·64 |
| 1899 | 6·24 | 8·29 |
| 1902 | 5·63 | 8·28 |
The actual number of deaths of persons of either sex and all ages registered in New Zealand during the last twelve years was:—
| Males. | Females. | Totals. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1891 | 154 | 141 | 295 |
| 1892 | 173 | 134 | 307 |
| 1893 | 188 | 144 | 332 |
| 1894 | 240 | 168 | 408 |
| 1895 | 208 | 175 | 383 |
| 1896 | 205 | 184 | 389 |
| 1897 | 210 | 185 | 395 |
| 1898 | 263 | 208 | 471 |
| 1899 | 271 | 197 | 468 |
| 1900 | 246 | 184 | 430 |
| 1901 | 265 | 250 | 515 |
| 1902 | 296 | 240 | 536 |
| Totals | 2,719 | 2,210 | 4,929 |
The total of deaths from developmental diseases was 846, or 10·60 per 10,000 persons living. The mortality from premature birth comprised 303 deaths, and that from atelectasis, cyanosis, and other congenital defects 79 deaths. The proportion of deaths from premature birth varies from 11 to 15 out of every 1,000 births, and that from congenital defects from 2 to 4 per 1,000 births. Particulars for seven years exhibit the annual rates:—
| Number and Proportions per 1,000 Births. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Deaths from No. | Premature Birth. per 1,000. | Deaths from No. | Congenital Defects. Proportion per 1,000. |
| 1896 | 230 | 12·36 | 46 | 2·47 |
| 1897 | 211 | 11·26 | 52 | 2·78 |
| 1898 | 251 | 13·24 | 54 | 2·85 |
| 1899 | 261 | 13·86 | 47 | 2·50 |
| 1900 | 276 | 14·12 | 55 | 2·81 |
| 1901 | 264 | 12·88 | 63 | 3·07 |
| 1902 | 303 | 14·66 | 79 | 3·82 |
Stating the result in another way, there was one death from premature birth to every 68 births in 1902, and one death from congenital defect to every 261 births. In England the proportion of deaths from premature birth to every 1,000 births was as high as 19·93 in the year 1900.
Deaths by diseases of the nervous system were 858, or 10·25 out of every 100 deaths from all causes, and 10·75 out of every 10,000 persons living. Of the 858 deaths, 265 were credited to apoplexy, 115 to convulsions, and 132 to inflammation of the brain and its membranes. Paralysis, including hemiplegia and paralysis of the insane, caused 169 deaths, and locomotor ataxia 9 deaths. Paraplegia, with diseases of the spinal cord, caused 30. Deaths from nervous diseases (excluding convulsions of children) numbered 747, or 9·36 per 10,000 persons living.
Diseases of the circulatory system resulted in 954 deaths, being 11·39 out of every 100 from all causes, and 11·96 per 10,000 persons living. Of the total number in this order, endocarditis and valvular disease of the heart contributed 646 deaths. From angina pectoris there were 36 deaths, from syncope 128, from aneurism 36, and from other forms of heart-disease (hypertrophy, fatty degeneration, and pericarditis) 97.
Diseases of the respiratory system show 1,058 deaths, of which 879 were attributable to bronchitis and pneumonia. Taken together, these two complaints were the cause of more deaths than was phthisis; and adding 54 from pleurisy, 15 from croup, 26 from laryngitis, and 84 from other respiratory diseases, the mortality in the order is found to be 12·64 per cent. of the total deaths, and 13·26 per 10,000 of the population.
Deaths from diseases of the digestive system also formed a large proportion of the whole (8·74 per cent.), the number being 734. Enteritis was most fatal, showing 232 deaths, gastritis (109) and liver-diseases (95) coming next.
Of 328 deaths from diseases of the urinary system in 1902, the deaths from Bright's disease of the kidneys (albuminuria) numbered 163.
Deaths by violence form a large item in the total mortality. In 1902 the proportion per 10,000 of persons living was 7·58, the total number of deaths having been 605.
Of 483 males who died violent deaths, 75 were suicides. The deaths of females by violence were far fewer than those of males, amounting to 122, and out of these only 5 committed suicide. A table given previously states the full list of deaths from external or violent causes for the year 1902.
Accidental deaths numbered 523—males 408 and females 115. Of the total male deaths, 185 resulted from fractures or contusions, and 125 from drowning. Of the female deaths, 21 were due to drowning.
Prior to the abolition of provinces the hospitals of the colony were supported mainly out of provincial revenues. After that event the expenditure for hospitals was for the most part charged against the revenue of counties and municipal corporations, until October, 1885, when “The Hospitals and Charitable Institutions Act, 1885,” came into force.
The portion of the colony included within the three principal islands—the North, Middle, and Stewart Islands—is by the above Act divided into thirty hospital districts, each consisting of one or more counties with the interior boroughs, to be presided over by elective Boards, designated “Hospital and Charitable Aid Boards.”
The revenues of these Boards accrue from the following sources:—
Rents and profits of land and endowments vested in the Board, or set apart for the benefit of particular institutions;
Voluntary contributions;
Grants from contributory local authorities; and
Subsidies from the Consolidated Fund (these being at the rate of 10s. for every £1 of bequests, but in no case exceeding £500 in respect of any one bequest; £1 4s. for every £1 of voluntary contributions; and £1 for every £1 received from any local authority).
The contributory local authorities (being the County and Borough Councils, and Boards of road and town districts where the Counties Act is not in force) are empowered by the Act to raise by special rates the amounts assessed by the Hospital District Boards as their proportionate contributions to the Hospital and Charitable Aid Fund.
The District Boards undertake the general management and control of those hospitals that are not incorporated in terms of the Act, and are required to contribute to the support of the incorporated hospitals. To be incorporated a hospital must have as many as 100 subscribers contributing not less than £100 annually by amounts of not less than 5s., and must have been declared by the Governor in Council, after receipt by him of a duly signed petition, to be a body politic and corporate, under the government of trustees.
There are 45 hospitals in the colony, of which 23 are incorporated institutions, while 22 are directly managed and controlled by District Boards. In 1902 these hospitals afforded accommodation for 1,139 male and 677 female patients, a total of 1,816. The number of cubic feet of space included within the walls of all the sleeping-wards was 2,575,532, which gave an average of 1,363 cubic feet to each bed. 9,042 males and 4,504 females were admitted as patients during the year 1902, and 779 male and 364 female patients were inmates at the end of the year. The total number of indoor patients during the year was 14,659—viz., 9,825 males and 4,834 females.
Outdoor relief was also given to a very large number of persons; but, as in some of the hospitals no records are kept of the outdoor patients, it is impossible to state the number of distinct persons who received such relief.
The total revenues of the various hospitals as at five different annual periods were:—
| — | 1897–98. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Voluntary contributions and bequests | 11,521 | 11,991 | 9,188 | 7,330 | 11,154 |
| Payments by patients | 12,728 | 13,066 | 16,503 | 15,998 | 18,083 |
| From Government | 38,687 | 41,052 | 44,815 | 47,074 | 54,387 |
| From Hospital Boards and local authorities | 31,524 | 33,864 | 35,006 | 36,812 | 40,638 |
| Rents and other sources | 5,429 | 5,523 | 5,097 | 6,908 | 7,58S |
| Totals | 99,889 | 105,496 | 1100,609 | 114,122 | 131,850 |
The various benevolent asylums and charitable institutions are placed on a similar footing to the hospitals. Most of the Boards of hospital districts are also Charitable Aid Boards; but, for the purpose of distributing charitable aid only, some of the hospital districts have been united into larger districts, so that, although there are thirty Boards for hospital purposes, there are only twenty-three for charitable-aid purposes.
Returns were received from nineteen benevolent asylums (not including orphanages), established for the support of indigent persons. The number of inmates in these institutions at the end of 1902 was 1,222, of whom 725 were males and 497 females. Outdoor relief was given by three of these institutions to 1,944 persons (including 1,206 children).
There is a Sailors' Home at Auckland for the use of seafaring men resident in or visiting the town. The late Edmund Costley having left a large sum for charitable purposes, it was resolved to employ the bequest in building and endowing an institution where sailors might be received without distinction of race or religious belief, and board, lodging, and refreshments provided for them, together with such instruction and amusements as might tend to promote their social comfort and general welfare.
The Home, built in 1887, has room for 35 inmates, who are charged 15s. a week for board and lodging. It is managed by a council of eight members elected by the subscribers to the institution. The late Primate of New Zealand, who first originated the scheme, was Life President.
There were in 1902 four orphan asylums in the colony, one maintained by a District Hospital Board, one by the Church of England authorities, and two by clergy of the Roman Catholic Church; three of them receiving, at the charge of the State, orphan, destitute, and other children committed to them by a Stipendiary Magistrate.
Exclusive of the children so committed, 17 male and 30 female orphans were received during the year 1902, and 53 male and 83 female orphans remained as inmates at the end of the year.
Orphanages receiving committed children are, for that purpose, constituted “industrial schools.”
There are seven public lunatic asylums in the colony, maintained wholly or in part out of the public revenue. There is also one private asylum, licensed by the Governor for the reception of lunatics.
The amount of sleeping-accommodation provided in each of the public asylums is shown in tabular form, giving separately the number and cubic contents of the sleeping-rooms intended for one person only, and of the dormitories occupied by several inmates conjointly, together with the number of patients actually in the asylums on the 31st December, 1902:—
| — | Sleeping-rooms for One Person only. | Dormitories for more than One Persons. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number. | Aggregate Number of Cubic Feet. | Inmates (Patients) on 31st December, 1902. | Number. | Aggregate Number of Cubic Feet. | Inmates (Patients) on 31st December 1902 | |
| Auckland | 133 | 119,280 | 133 | 25 | 252,672 | 405 |
| Wellington | 77 | 72,509 | 77 | 16 | 100,173 | 200 |
| Porirua | 68 | 63,217 | 68 | 14 | 307,512 | 434 |
| Nelson | 38 | 32,228 | 38 | 14 | 65,112 | 100 |
| Hokitika | 31 | 23,223 | 31 | 8 | 69,302 | 88 |
| Christchurch | 80 | 69,651 | 80 | 34 | 227,010 | 476 |
| Seacliff | 176 | 144,839 | 176 | 46 | 263,534 | 486 |
| Totals | 603 | 524,947 | 603 | 157 | 1,285,315 | 2,189 |
At Ashburn Hall, Waikari, there are 66 rooms, each for one person only, with an aggregate cubic content of 64,913 ft. The number of patients on the 31st December, 1902, was 42.
At the end of 1902, 1,695 male and 1,111 female patients (including 14 out on trial) were under the care of the asylum officers of the colony. Of these, 1,604 males and 1,043 females were regarded as incurable, 6 males and 8 females were out on trial, and 85 males and 60 females were supposed to be curable. 160 male and 116 female patients were discharged during the year.
The following shows the proportion of insane—or, rather, of inmates of lunatic asylums and those out on trial—to the population (exclusive in each case of Maoris) at the end of the years stated:—
| 1884, 1 insane person to every 393 of population. |
| 1886, 1 insane person to every 370 of population. |
| 1888, 1 insane person to every 365 of population. |
| 1890, 1 insane person to every 348 of population. |
| 1892, 1 insane person to every 339 of population. |
| 1894, 1 insane person to every 316 of population. |
| 1896, 1 insane person to every 308 of population. |
| 1898, 1 insane person to every 300 of population. |
| 1899, 1 insane person to every 296 of population. |
| 1900, 1 insane person to every 288 of population. |
| 1901, 1 insane person to every 286 of population. |
| 1902, 1 insane person to every 286 of population. |
It must not be overlooked that the proportions are increased by the admission into the asylums of inebriates, idiots, and others, who should not properly be there.
Information as to lunacy, extracted from the results of the census, will be found on pp. 150 and 151.
Table of Contents
(From Tables prepared by Sir James Hector.)
| THE OBSERVATIONS WERE TAKEN AT 9.30 A.M. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stations and Months. | Temperature in Shade. | Rainfall. | Mean Height of Barometer. | Prevailing Wind. | ||
| Highest. | Lowest. | Wet Days. | Fall. | |||
| ° Fahr. | ° Fahr. | No. | Inches. | Inches. | ||
| Auckland (lat. 36° 50’ S.; long. 174° 50’ 40” E.; alt. 125 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 78·0 | 52·0 | 11 | 1·580 | 29·930 | SW. |
| February | 79·0 | 54·0 | 7 | 0·440 | 30·100 | SW. |
| March | 79·5 | 53·0 | 10 | 3·340 | 30·140 | NE, SW. |
| April | 73·0 | 46·0 | 19 | 6·270 | 30·140 | SW, NE. |
| May | 67·0 | 45·0 | 25 | 6·300 | 29·950 | SW, S. |
| June | 62·0 | 40·0 | 12 | 3·220 | 30·160 | NE. |
| July | 60·0 | 38·0 | 17 | 2·140 | 30·180 | SW, SE. |
| August | 62·0 | 39·0 | 16 | 2·330 | 30·130 | SW, SE. |
| September | 63·0 | 41·0 | 22 | 6·210 | 29·900 | SW. |
| October | 68·0 | 41·0 | 16 | 2·740 | 30·040 | SW. |
| November | 72·0 | 48·0 | 12 | 0·880 | 30·060 | SW. |
| December | 75·0 | 50·0 | 17 | 2·830 | 30·010 | SW, NE. |
| Rotorua (lat. 38° 9’ S.; long. 176° 15’ E.; alt. 990 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 90·5 | 42·0 | 12 | 2·690 | 29·120 | SW. |
| February | 90·0 | 40·0 | 7 | 3·080 | 30·220 | SW, N. |
| March | 79·5 | 36·5 | 9 | 5·680 | 30·230 | SW. |
| April | 75·5 | 30·0 | 12 | 8·960 | 30·210 | SW. |
| May | 71·0 | 28·0 | 10 | 4·300 | 29·960 | SW, W. |
| June | 64·0 | 27·0 | 11 | 6·550 | 30·240 | SW, S. |
| July | 62·0 | 26·0 | 4 | 0·450 | 30·220 | SW. |
| August | 61·0 | 27·0 | 11 | 4·110 | 30·200 | SW. |
| September | 64·0 | 26·0 | 16 | 5·200 | 29·930 | SW. |
| October | 74·0 | 28·5 | 11 | 5·330 | 30·150 | W. |
| November | 75·0 | 33·0 | 7 | 0·920 | 30·130 | SW, W. |
| December | 85·0 | 36·0 | 10 | 1·450 | 30·160 | W. |
| New Plymouth (lat. 39° 3’ 35” S.; long. 174° 4’ 58” E.; alt. 100 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 83·0 | 46·0 | 19 | 3·600 | 29·990 | SW. |
| February | 84·0 | 46·0 | 13 | 2·590 | 30·110 | SW, NW. |
| March | 80·0 | 41·0 | 14 | 2·630 | 30·190 | SE. |
| April | 83·0 | 34·0 | 24 | 6·340 | 30·080 | SE, SW. |
| May | 84·0 | 36·0 | 25 | 5·960 | 29·880 | SW, SE. |
| June | 83·0 | 32·0 | 18 | 5·030 | 30·152 | SE. |
| July | 84·0 | 29·0 | 21 | 1·490 | 30·180 | SE, SW. |
| August | 82·0 | 30·0 | 16 | 3·800 | 30·157 | SE, SW. |
| September | 86·0 | 31·0 | 26 | 5·830 | 29·904 | W, NW, SE. |
| October | 84·0 | 30·0 | 22 | 5·580 | 30·078 | SW, NW. |
| November | 85·0 | 36·0 | 22 | 3·540 | 30·100 | SW. |
| December | 90·0 | 40·0 | 25 | 5·650 | 30·017 | NW, SW. |
| Wellington (lat. 41° 16’ 25” S.; long. 174° 46’ 20” E.; alt. 140 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 81·0 | 48·0 | 13 | 2·270 | 29·879 | NW, S. |
| February | 76·5 | 47·0 | 12 | 1·380 | 29·947 | NW, S. |
| March | 77·0 | 43·0 | 10 | 3·100 | 30·017 | NW, S. |
| April | 73·0 | ·0 | 20 | 4·700 | 29·993 | S. |
| May | 64·0 | 33·0 | 21 | 5·190 | 29·721 | NW, S. |
| June | 60·0 | 33·0 | 24 | 4·840 | 30·122 | SW, NW. |
| July | 62·0 | 32·0 | 1 | 2·340 | 30·082 | NW. |
| August | 61·0 | 35·0 | 19 | 2·060 | 30·067 | NW, SW. |
| September | 60·0 | 34·0 | 21 | 3·110 | 29·753 | NW, SW. |
| October | 65·0 | 35·0 | 13 | 3·060 | 29·878 | NW, SW. |
| November | 69·0 | 38·0 | 15 | 2·960 | 29·840 | NW. |
| December | 71·0 | 41·0 | 19 | 3·740 | 29·844 | NW, SW. |
| Hokitika (lat. 42° 41’ 30” S.; long. 170° 49’ E.; alt. 12 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 82·0 | 44·5 | 11 | 16·110 | 29·846 | SW, NW. |
| February | 71·5 | 44·0 | 15 | 9·140 | 29·964 | SW, NW. |
| March | 82·0 | 39·0 | 7 | 4·950 | 29·988 | SW, E. |
| April | 73·5 | 36·0 | 14 | 3·600 | 29·987 | E, SW. |
| May | 66·5 | 2·0 | 16 | 7·120 | 29·740 | SW, E. |
| June | 64·0 | 28·0 | 9 | 8·790 | 30·105 | E. |
| July | 58·5 | 26·0 | 13 | 4·140 | 30·112 | E, SW. |
| August | 61·5 | 28·0 | 11 | 6·350 | 30·048 | SW, E. |
| September | 62·0 | 28·0 | 17 | 6·280 | 29·810 | SW. |
| October | 69·0 | 30·0 | 18 | 9·160 | 29·911 | SW, NW. |
| November | 67·0 | 32·0 | 19 | 9·950 | 29·887 | SW, NW. |
| December | 71·0 | 38·0 | 16 | 10·480 | 29·825 | SW, NW. |
| Lincoln, College, Canterbury (lat. 43° 32’ 16” S.; long. 172° 38’ 59” E.; alt. 65 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 88·0 | 39·0 | 7 | 0·840 | 29·794 | NE, SW, NW. |
| February | 88·0 | 42·7 | 10 | 1·625 | 29·907 | NE. |
| March | 84·4 | 34·5 | 14 | 4·300 | 29·971 | NE, SW. |
| April | 71·6 | 32·6 | 17 | 1·355 | 29·999 | NE, SW. |
| May | 63·5 | 28·6 | 20 | 2·770 | 29·658 | SW, NE. |
| June | 66·3 | 26·2 | 14 | 1·710 | 30·130 | SW, NE. |
| July | 65·5 | 27·5 | 0 | 1·175 | 30·007 | NE. |
| August | 66·5 | 27·0 | 8 | 1·090 | 30·037 | NE. SW. |
| September | 64·5 | 25·9 | 12 | 1·465 | 29·718 | SW, NE. |
| October | 81·6 | 29·6 | 8 | 1·295 | 29·811 | NE. |
| November | 81·4 | 35·4 | 9 | 1·115 | 29·733 | SE, NW. |
| December | 83·8 | 33·2 | 25 | 5·750 | 29·836 | NE, SE, SW. |
| Dunedin (lat. 45° 52’ 11” S.; long. 170° 31’ 7” E.; alt. 300 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 78·0 | 42·0 | 14 | 3·598 | 29·720 | W. |
| February | 86·0 | 38·0 | 15 | 6·406 | 29·813 | NE, SW. |
| March | 75·0 | 42·0 | 15 | 14·386 | 29·929 | NE. |
| April | 70·0 | 38·0 | 18 | 4·206 | 29·938 | SW. |
| May | 58·0 | 32·0 | 17 | 2·702 | 29·612 | SW. |
| June | 60·0 | 29·0 | 13 | 4·310 | 30·045 | SW, NE. |
| July | 60·0 | 33·0 | 13 | 1·492 | 29·933 | SW. |
| August | 55·0 | 32·0 | 9 | 1·374 | 29·917 | SW. |
| September | 61·0 | 33·0 | 20 | 5·174 | 29·648 | SW, NE. |
| October | 70·0 | 32·0 | 13 | 2·210 | 29·729 | SW. |
| November | 75·0 | 38·0 | 16 | 2·302 | 29·657 | W, SW. |
| December | 71·0 | 38·0 | 21 | 5·404 | 29·734 | SW, W. |
| Chatham Islands (lat. 43° 52’ S.; long. 176° 42’ W.; alt. 100 ft.)— | ||||||
| January | 72·0 | 43·0 | 10 | 1·200 | 29·690 | SW. |
| February | 71·0 | 42·0 | 12 | 3·750 | 29·820 | NW. |
| March | 69·0 | 43·0 | 17 | 2·930 | 29·870 | SE. |
| April | 66·0 | 41·0 | 21 | 5·980 | 29·730 | SW. |
| May | 61·0 | 36·0 | 23 | 5·720 | 29·260 | SW, W. |
| June | 57·0 | 37·0 | 20 | 2·460 | 29·920 | SW. NW. |
| July | 57·0 | 33·0 | 26 | 2·860 | 29·640 | SW. |
| August | 61·0 | 32·0 | 24 | 4·100 | 29·830 | SE. |
| September | 59·0 | 36·0 | 23 | 4·810 | 29·370 | SW. |
| October | 59·0 | 34·0 | 14 | 1·610 | 29·620 | SW. |
| November | 62·0 | 34·0 | 19 | 3·160 | 29·530 | SW. |
| December | 64·0 | 39·0 | 14 | 1·140 | 29·590 | SW. |
| Stations | Temperature in Shade. | Rainfall. | Mean Heights of Barometer. | Prevailing Wind. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highest, and Date. | Lowest, and Date. | Days on which Rain fell. | Greatest Fall. and Date. | |||
| ° Fahr. | ° Fahr. | No. | Inches. | Inches. | ||
| Auckland | 79·5, 1 Mar. | 38·0, 17 July | 18 | 2·280, 8 April | 30·061 | SW, NE. |
| Rotorua | 90·5, 20 Jan. | 26·0, 11 July, 10 Sept. | 120 | 3·6, 2 April | 30·064 | SW, W. |
| New Plymouth | 90·0, 26 Dec. | 29·0, 16, 17 July | 245 | 1·180, 24 June | 30·070 | SE, SW. |
| Wellington | 81·0, 13 Jan. | 32·0, 17 July | 201 | 1·980, 11 May | 29·928 | NW, SW. |
| Hokitika | 82·0, 10, 15 Jan., 8 Mar. | 26·0, 15 July | 166 | 3·930, 23 Jan. | 29·934 | SW, E, NW |
| Lincoln | 88·0, 10,18 Jan., 4 Feb. | 25·9, 3 Sept. | 154 | 0·840, 24 Jan. | 29·883 | NE, SW. |
| Dunedin | 80·0, 3 Feb. | 29·0, 18 June | 181 | 3·960, 24 Mar. | 29·806 | SW, W. |
| Chatham Islands | 72·0, 19 Jan. | 32·0, 1 Aug. | 223 | 1·250, 9 Sept. | 29·656 | SW, NW. |
The comparative tables of the amount of sunshine recorded in Surrey and in Christchurch respectively during last year, and published in the Christchurch Press, afford valuable proof of the brightness of this climate as compared with that of England. The English records were taken at a place near Hindhead, on the Surrey highland, first made known by Professor Tyndall selecting a site for a house there. The district has since become famous as one of the healthiest and sunniest in England, and these characteristics, coupled with its comparative proximity to London, have made it a popular residential district. It is a case, then, of one of the most sunny districts in England being compared with a New Zealand town, which we can hardly suppose to be more blessed with sunshine than many other places in the colony. This being so, it will be admitted that Christchurch comes splendidly out of the test with 1,749·59 hours of sunshine during the year, as against Surrey's 1,492·2 hours, a difference in favour of New Zealand of 257 hours. Nor is this the most striking comparison. The sun shone here on all but thirty-nine days in the year, while at Hindhead there were no less than eighty-one absolutely sunless days. The monthly average of days on which the sun shone in Christchurch was twenty-seven, in Surrey it was under twenty-four. The winter comparisons are still more forcible. Taking the four months from November to February as the English winter months, and those from May to August as the corresponding months out here, we find that whereas three of the months in England had but sixteen days each on which sunshine was recorded, and the fourth had only fifteen days, in Christchurch during the winter months the sun was seen on twenty-eight, twenty, thirty, and twenty-nine days respectively. Our worst month was June, with little more than fifty-five hours of sunshine; but in Surrey December had only forty-two sunny hours, January had fifty-four, and February fifty-five. On the other hand, the best English summer record beats ours. July in Surrey had 229 hours of sunshine, our January had 217; but it must be remembered that summer days in England are longer than with us, just as our winter days are longer than with them.
| GRAYSHOT, SURREY, ENGLAND. | CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months, 1902. | Days with Sun. | Days no Sun. | Total Hours. | Corresponding Months in New Zealand. | Days with Sun. | Days no Sun. | Total Hours. |
| Spring— | Spring— | ||||||
| February | 15 | 13 | 55·7 | August | 29 | 2 | 146·16 |
| March | 26 | 5 | 118·5 | September | 29 | 1 | 149·58 |
| April | 28 | 2 | 165·3 | October | 31 | 0 | 191·50 |
| Summer— | Summer— | ||||||
| May | 28 | 3 | 179·0 | November | 28 | 2 | 203·20 |
| June | 27 | 3 | 189·6 | December | 27 | 4 | 143·58 |
| July | 30 | 1 | 229·4 | January | 29 | 2 | 217·75 |
| Autumn— | Autumn— | ||||||
| August | 30 | 1 | 136·9 | February | 25 | 3 | 154·08 |
| September | 29 | 1 | 178·0 | March | 23 | 8 | 121·25 |
| October | 23 | 8 | 78·8 | April | 27 | 3 | 97·08 |
| Winter— | Winter— | ||||||
| November | 16 | 14 | 64·0 | May | 28 | 3 | 110·58 |
| December | 16 | 15 | 42·8 | June | 20 | 10 | 55·75 |
| January | 16 | 15 | 34·2 | July | 30 | 1 | 159·08 |
| Total | 284 | 81 | 1492·2 | Total | 326 | 39 | 1749·59 |
The following table, compiled from information published in the Statistical Abstract for the Colonial Possessions of the United Kingdom, shows the shade temperature for each month in New Zealand and other British States and Colonies. The figures given are the means of four years (H signifies highest, and L lowest):—
| British Possessions (Stations and Height in Feet above Sea Level where known) | Jan. | Feb. | March. | April. | May. | June. | July. | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Year. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | H. | L. | |
| °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | °F. | |
| New Zealand— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wellington (140) | 78 | 45 | 78 | 47 | 76 | 44 | 70 | 43 | 66 | 38 | 62 | 34 | 59 | 33 | 62 | 34 | 65 | 37 | 69 | 41 | 74 | 33 | 75 | 44 | 78 | 33 |
| Queensland— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brisbane (130) | 92 | 64 | 93 | 63 | 91 | 61 | 85 | 54 | 80 | 50 | 76 | 42 | 75 | 39 | 78 | 41 | 85 | 46 | 91 | 50 | 94 | 57 | 97 | 61 | 97 | 39 |
| New South Wales— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sydney (155) | 92 | 59 | 89 | 58 | 84 | 59 | 79 | 51 | 72 | 48 | 67 | 44 | 63 | 39 | 70 | 42 | 77 | 45 | 88 | 48 | 87 | 54 | 94 | 57 | 94 | 39 |
| Victoria— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melbourne (91) | 101 | 48 | 99 | 47 | 99 | 45 | 86 | 40 | 74 | 37 | 64 | 37 | 62 | 32 | 68 | 34 | 74 | 34 | 81 | 40 | 94 | 44 | 96 | 45 | 101 | 32 |
| South Australia— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adelaide (140) | 108 | 49 | 106 | 50 | 100 | 48 | 89 | 45 | 78 | 40 | 67 | 38 | 65 | 36 | 74 | 9 | 79 | 41 | 86 | 41 | 96 | 45 | 101 | 48 | 108 | 36 |
| Western Australia— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perth (47) | 107 | 50 | 102 | 53 | 98 | 52 | 96 | 57 | 81 | 40 | 70 | 38 | 70 | 37 | 73 | 38 | 80 | 42 | 83 | 42 | 93 | 48 | 100 | 51 | 107 | 37 |
| Tasmania— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hobart (160) | 91 | 45 | 94 | 45 | 93 | 44 | 75 | 38 | 71 | 37 | 61 | 34 | 59 | 33 | 66 | 33 | 72 | 35 | 77 | 35 | 92 | 40 | 86 | 43 | 94 | 33 |
| Natal— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Durban (150) | 99 | 63 | 95 | 61 | 94 | 60 | 94 | 58 | 89 | 52 | 86 | 49 | 88 | 48 | 91 | 49 | 96 | 50 | 91 | 53 | 97 | 57 | 98 | 59 | 99 | 49 |
| Cape Town— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Royal Observatory (37) | 94 | 54 | 90 | 51 | 92 | 49 | 86 | 45 | 80 | 42 | 76 | 39 | 74 | 37 | 76 | 37 | 83 | 39 | 86 | 44 | 89 | 48 | 90 | 52 | 94 | 37 |
| Hongkong— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Observatory (110) | 73 | 47 | 78 | 46 | 77 | 49 | 84 | 58 | 89 | 68 | 91 | 73 | 91 | 74 | 91 | 74 | 92 | 70 | 90 | 66 | 82 | 55 | 79 | 49 | 91 | 46 |
| Straits Settlements— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singapore (30) | 88 | 70 | 90 | 70 | 91 | 71 | 91 | 73 | 90 | 73 | 90 | 72 | 90 | 72 | 89 | 72 | 89 | 71 | 89 | 71 | 8 | 71 | 89 | 70 | 91 | 70 |
| Mauritius— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Royal Alfred Observatory (179) | 84 | 69 | 84 | 71 | 84 | 70 | 82 | 70 | 80 | 62 | 77 | 60 | 75 | 59 | 75 | 59 | 77 | 62 | 80 | 62 | 82 | 66 | 84 | 68 | 84 | 59 |
| Canada— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toronto (350) | 47 | -3 | 45 | -3 | 51 | 6 | 71 | 22 | 78 | 31 | 86 | 44 | 88 | 46 | 89 | 47 | 82 | 41 | 71 | 27 | 56 | 13 | 45 | -1 | 89 | -3 |
| Montreal (187) | 45 | -14 | 42 | -13 | 44 | 0 | 69 | 24 | 81 | 32 | 87 | 43 | 88 | 50 | 86 | 50 | 81 | 39 | 70 | 27 | 59 | 11 | 43 | -11 | 88 | -13 |
| St. John (N.B.) (116) | 49 | -7 | 46 | -7 | 47 | 4 | 62 | 22 | 69 | 33 | 81 | 42 | 79 | 49 | 77 | 48 | 73 | 37 | 60 | 26 | 56 | 16 | 49 | -3 | 81 | -7 |
| Halifax (122) | 50 | -1 | 46 | -3 | 50 | 10 | 63 | 22 | 73 | 32 | 83 | 39 | 84 | 48 | 84 | 49 | 80 | 36 | 69 | 29 | 60 | 21 | 51 | 3 | 84 | -3 |
| Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island (38) | 47 | -6 | 4 | -9 | 47 | 5 | 60 | 20 | 70 | 31 | 77 | 39 | 80 | 49 | 79 | 49 | 75 | 39 | 66 | 30 | 58 | 19 | 47 | 1 | 80 | -9 |
| Winnipeg, Manitoba (764) | 34 | -37 | 32 | -37 | 49 | -25 | 76 | 8 | 82 | 20 | 90 | 35 | 87 | 40 | 91 | 34 | 86 | 30 | 73 | 17 | 53 | -16 | 39 | -29 | 91 | -37 |
| Victoria, British Columbia (10) | 51 | 14 | 55 | 22 | 60 | 30 | 67 | 29 | 73 | 38 | 76 | 39 | 79 | 43 | 76 | 44 | 71 | 38 | 64 | 35 | 55 | 30 | 51 | 23 | 79 | 14 |
| St. John's, Newfoundland(125) | 48 | -6 | 50 | -8 | 50 | 11 | 61 | 15 | 71 | 27 | 76 | 33 | 81 | 41 | 79 | 42 | 78 | 33 | 65 | 24 | 62 | 19 | 51 | 9 | 81 | -8 |
| Barbados— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Joes River (430) | 81 | 67 | 81 | 67 | 83 | 69 | 84 | 70 | 84 | 71 | 85 | 72 | 84 | 70 | 85 | 70 | 85 | 71 | 85 | 71 | 84 | 70 | 83 | 69 | 85 | 67 |
| Bahamas— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Military Hospital | 77 | 63 | 79 | 68 | 79 | 67 | 84 | 69 | 89 | 72 | 88 | 73 | 89 | 78 | 89 | 73 | 87 | 75 | 86 | 77 | 82 | 70 | 77 | 67 | 89 | 63 |
| Jamaica— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingston (60) | 91 | 63 | 90 | 63 | 90 | 62 | 91 | 68 | 91 | 70 | 92 | 71 | 95 | 71 | 93 | 73 | 92 | 70 | 93 | 69 | 91 | 67 | 90 | 63 | 95 | 62 |
| Trinidad (130) | 86 | 67 | 87 | 68 | 88 | 69 | 88 | 70 | 89 | 70 | 86 | 71 | 86 | 71 | 86 | 70 | 89 | 70 | 88 | 70 | 87 | 70 | 85 | 69 | 89 | 67 |
Table of Contents
IN December, 1902, five banks of issue were doing business in New Zealand, the Bank of New Zealand and the Colonial Bank having amalgamated in 1895. Two of the five banks, the Bank of New Zealand and the National Bank of New Zealand (Limited), were wholly New Zealand institutions, with a paid-up capital of £750,000, besides which the Bank of New Zealand has £2,000,000 of 4 per cent. stock guaranteed by the Government of the colony. The total average liabilities of all five banks for the year 1902 in respect of New Zealand transactions were £18,701,063, and the average assets £18,999,180. The average amount on deposit during the year was £17,231,767, of which sum £1,090,174 belonged to the General Government. Excluding those belonging to Government, deposits to the value of £8,531,614 were bearing interest, and £7,609,979 at call. The value of the notes in circulation of these banks was £1,375,788.
The development of banking in New Zealand since the year 1857 has been very great. Taking for each year the average of the four quarters’ returns made by the banks of issue, the figures for 1857, 1870, 1880, 1890, 1900, and 1902 are:–
| Year. | Deposits. | Assets. | Liabilities. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1857 | 343,316 | 419,860 | 432,494 |
| 1870 | 3,127,769 | 6,315,354 | 3,819,670 |
| 1880 | 8,538,935 | 14,220,275 | 9,550,177 |
| 1890 | 12,368,610 | 17,735,259 | 13,356,598 |
| 1900 | 15,570,610 | 17,314,535 | 16,964,582 |
| 1902 | 17,231,767 | 18,999,180 | 18,701,063 |
In 1880 the deposits of these banks were £18·00 per head of the mean population; in 1890 they were £19·92 per head; and in 1902, £21·60. The ratio of advances to deposits, which was 132·34 per cent. in 1880, reached its maximum in 1883, when it stood at 173·35 per cent. The proportion since that year fell, till in 1897 it was only 76·21 per cent. In 1898, however, the ratio had advanced to 80·52 per cent., and in 1899 still further, to 80·92 per cent. In 1900 there was again a decline, to 77·61 per cent.; in 1901 a substantial advance to 81·74 per cent. was shown, the highest proportion since 1895; but in 1902 the ratio again fell to 79·31 per cent.
The following figures, which are taken from the published returns for the December quarter of each year, show that the value of the coin and bullion held by all the banks of issue doing business in New Zealand rose steadily from 1891 to 1895, in which year the value stood at £3,333,272. Since that date the value gradually decreased year by year to £2,636,177 in December quarter, 1899, but rose again to £2,802,232 in December, 1900, to £3,063,843 in December, 1901, and further to £3,292,090 in 1902:—
| Quarter ended 31st December | Coin. | Gold and Silver in Bullion or Bars. | Total Coin and Bullion. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1890 | 2,421,530 | 169,659 | 2,591,189 |
| 1891 | 2,231,242 | 126,346 | 2,357,588 |
| 1892 | 2,381,319 | 141,406 | 2,522,725 |
| 1893 | 2,480,453 | 121,496 | 2,601,949 |
| 1894 | 3,103,355 | 118,121 | 3,221,476 |
| 1895 | 3,199,889 | 133,383 | 3,333,272 |
| 1896 | 3,171,702 | 122,901 | 3,294,603 |
| 1897 | 2,848,183 | 107,635 | 2,955,818 |
| 1898 | 2,625,896 | 126,349 | 2,752,245 |
| 1899 | 2,511,102 | 125,075 | 2,636,177 |
| 1900 | 2,658,207 | 144,025 | 2,802,232 |
| 1901 | 2,921,268 | 142,575 | 3,063,843 |
| 1902 | 3,124,916 | 167,174 | 3,292,090 |
The figures shown for each quarter of the year 1902 are:—
| Coin. | Bullion. | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| March quarter, 1902 | 2,967,730 | 151,813 |
| June quarter, 1902 | 2,986,222 | 174,489 |
| September quarter, 1902 | 3,081,713 | 153,236 |
| December quarter, 1902 | 3,124,916 | 167,174 |
In 1886 the average amount of advances made by the banks was £15,853,420, equal to £27·23 per head of the mean population. The advances gradually declined in amount and proportion to population until 1891, when they were in value £11,549,145, or £18·34 per head. During the years 1892 and 1893, however, there was a rise, but in 1894 a fall to £12,031,537 (£17·71 per head), and in 1897 to £10,892,111, or £15·09 per head, which is the lowest average since the year 1872. In 1898 an increase both in the average amount of advances and in the rate per head of population (£11,387,321 and £15·47 respectively) was observed; in 1899 there was a further increase to £11,806,859, or £15·74 per head; in 1900 to £12,084,744, or £15·83 per head; in 1901 to £13,106,909, or £16·85 per head; and in 1902 to £13,666,457, or £17·13 per head. The discounts in 1902 amounted to £1,814,639, or £2·27 per head of mean population. The largest amount of discounts in any year was £6,061,959 in 1879, a rate of £13·53 per head. From 1879 there was a fall year by year until 1896, when the sum was £1,756,791, or £2·49 per head. In 1897 they totalled £1,768,845, but, with a comparatively larger population, the rate per head was only £2·45. In 1898 the amount fell to £1,719,715, and the rate per head to £2·34. In 1899 there was a further decline, in the amount to £1,692,201 and in the rate per head to £2·26; but in 1900 a rise to £1,730,809, or £2·27 per head, and in 1901 to £1,896,869, the rate being £2·44 per head. In 1902 the amount declined to £1,814,639, and the rate to £2·27 per head.

The deposits, as stated in the returns for the March quarters of the years 1903 and 1902, were:—
| £ | |
|---|---|
| Deposits not bearing interest, March quarter, 1903 | 8,259,884 |
| Deposits not bearing interest, March quarter, 1902 | 7,087,161 |
| An increase of | £1,172,723 |
in the amount held at call. The fixed deposits show a similar movement, but of lesser magnitude:—
| £ | |
|---|---|
| Deposits bearing interest, March quarter, 1903 | 8,736,644 |
| Deposits bearing interest, March quarter, 1902 | 8,318,439 |
| An increase of | £418,205 |
Besides the above, the Government had with the Bank of New Zealand £1,451,651 on deposit in March, 1903, as against £1,255,294 in March, 1902.
An account of the special banking legislation of 1893 and its subsequent developments will be found in the previous issues of the Year-book. (See page 400, Year-book 1902.)
The number of post-offices open for the transaction of savings-bank business at the end of 1902 was 481.
There were 53,587 new accounts opened in the year, and 38,558 accounts were closed. The total number of open accounts at the end of 1902 was 227,465, or 1 in every 3·55 of the population.
The deposits received during the year amounted to £5,069,619 6s. 2d., and the withdrawals to £4,708,771 11s. 2d., the excess of deposits over withdrawals having thus been £360,847 15s. The total sum standing at credit of all accounts on the 31st December, 1902, was £6,883,787 5s. 9d., which gave an average of £30 5s. 3d. to the credit of each open account.
The number of open accounts (as on the 31st December) for the last five years are classified according to amounts at credit of each:—
| 1898. | 1899. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not exceeding £20 | 125,190 | 133,851 | 142,368 | 153,593 | 161,989 |
| Exceeding £20 and up to £50 | 18,001 | 20,206 | 22,333 | 23,743 | 25,520 |
| Exceeding £50 and up to £100 | 11,238 | 12,286 | 13,704 | 14,705 | 16,621 |
| Exceeding £100 and up to £200 | 9,641 | 10,403 | 11,173 | 12,797 | 14,657 |
| Exceeding £200 and up to £300 | 3,573 | 3,915 | 5,151 | 4,765 | 5,473 |
| Exceeding £300 and up to £400 | 1,111 | 1,145 | 1,238 | 1,394 | 1,619 |
| Exceeding £400 and up to £500 | 639 | 654 | 773 | 768 | 860 |
| Exceeding £500 | 575 | 586 | 668 | 671 | 726 |
| Totals | 169,968 | 183,046 | 197,408 | 212,436 | 227,465 |
The following were the securities, &c., standing in the name of the Postmaster-General on account of the Post-Office Savings-Bank Fund on the 31st December, 1902:—
| Description of Securities. | Nominal Value. | Value at Cost Price. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| “Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1896,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 100,000 | 0 | 0 | 100,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1899,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 125,000 | 0 | 0 | 125,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Acts, 1896 and 1897, Debentures, 3 per cent. | 65,000 | 0 | 0 | 65,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1902,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 100,000 | 0 | 0 | 100,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Consolidated Loan Act, 1867,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 13,000 | 0 | 0 | 12,480 | 0 | 0 |
| “Consolidated Stock Act, 1884,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 629,100 | 0 | 0 | 629,100 | 0 | 0 |
| “Dairy Industry Act, 1898,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 1,781 | 0 | 0 | 1,781 | 0 | 0 |
| “Defence and other Purposes Loan Act, 1870,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 75,000 | 0 | 0 | 72,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Defence and other Purposes Loan Act, 1870,” Debentures, 4 1/2 per cent. | 8,100 | 0 | 0 | 8,100 | 0 | 0 |
| District Railways Purchasing Acts, 1885 and 1886, Debentures, 4 per cent. | 42,000 | 0 | 0 | 36,076 | 17 | 8 |
| District Railways Purchasing Acts, 1885 and 1886, Scrip, 4 per cent. | 34,100 | 0 | 0 | 34,100 | 0 | 0 |
| Dunedin Garrison Hall Debentures, 5 per cent. | 6,000 | 0 | 0 | 6,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “General Purposes Loan Act, 1873,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 5,200 | 0 | 0 | 4,342 | 0 | 0 |
| “Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1886,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 231,500 | 0 | 0 | 231,500 | 0 | 0 |
| Greymouth Harbour Board Debentures, 4 per cent. | 105,000 | 0 | 0 | 105,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Hamilton Borough Debentures, 4 1/2 per cent. | 3,000 | 0 | 0 | 3,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Hokitika Harbour Board Debentures, 5 per cent. | 10,000 | 0 | 0 | 10,000 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | ||||||
| “Immigration and Public Works Loan Act, 1870,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 174,200 | 0 | 167,272 | 0 | 0 | |
| ‘‘Immigration and Public Works Loan Act, 1870,” Debentures, 4 1/2 per cent. | 20,900 | 0 | 0 | 20,527 | 10 | 0 |
| “Immigration and Public Works Loan Act, 1870,” Debentures, 4 per cent. (Imperial guaranteed) | 400,000 | 0 | 0 | 400,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Inscribed Stock, 3 per cent. | 2,134,940 | 0 | 0 | 2,129,614 | 0 | 0 |
| “Land for Settlements Act, 1894,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 731,066 | 0 | 0 | 731,066 | 0 | 0 |
| Land for Settlements Act Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 62,000 | 0 | 0 | 62,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Lands Improvement and Native Lands Acquisition Act, 1894,” Debentures, 4 per cent. | 264,000 | 0 | 0 | 264,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Lands Improvement and Native Lands Acquisition Act, 1894,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent | 35,000 | 0 | 0 | 35,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Local Bodies’ Loans Act, 1901,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 245,000 | 0 | 0 | 245,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Oamaru Borough Consolidated Loan 1893 Debentures, 5 per cent. | 13,800 | 0 | 0 | 13,800 | 0 | 0 |
| Oamaru Harbour Bonds, 5 1/2 per cent. | 31,000 | 0 | 0 | 31,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Patea Harbour Board Debentures, 4 1/2 per cent. | 13,000 | 0 | 0 | 13,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “State Coal-mines Act, 1901,” Debentures, 3 1/2 per cent. | 30,000 | 0 | 0 | 30,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Thames Harbour Board Debentures, 4 per cent. | 10,000 | 0 | 0 | 10,000 | 0 | 0 |
| “Public Revenues Act, 1893” (Treasury Bills), 3 1/2 per cent. | 749,200 | 0 | 0 | 749,200 | 0 | 0 |
| Westport Harbour Board Debentures, 4 per cent. | 489,500 | 0 | 0 | 489,500 | 0 | 0 |
| Totals | 6,957,387 | 0 | 0 | 6,934,459 | 7 | 8 |
Practically nearly the whole of this fund is invested in securities of the New Zealand General Government. Summarising the figures shows the investments to be:—
| £ | |
|---|---|
| In New Zealand Government securities | 6,276,087 |
| In local bodies’ securities | 675,300 |
| In other securities | 6,000 |
| Total | £6,957,387 |
There are five savings-banks in the colony not connected with the Post Office. The total amount deposited in them in 1902 was £747,764 0s. 9d., of which the deposits by Maoris comprised £152 11s. 9d. The withdrawals reached the sum of £701,262 10s. 5d., or less than the total deposits by £46,501 10s. 4d. The total amount to the credit of the depositors at the end of the year was £993,090 7s. 2d., of which sum £143 13s. 1d. belonged to Maoris.
If the total deposits at the end of the year be assumed to be equal to the average for the last quarter, then it may be affirmed that, exclusive of Government moneys, the deposits in the several banks of issue and in the two classes of savings-banks amounted at the end of 1902 to £24,018,470. In addition, there are the deposits with building societies, which in 1900 were £249,530, and it is known that there were also deposits with financial companies of which no particulars have been supplied to the Department. The known deposits reach an average of £30 0s. 9d. per head of the population, exclusive of Maoris.
There were 68 registered building societies in operation in the colony at the end of 1900. Of these, 33 were terminable societies, the rest were permanent.
The total receipts by these societies during their financial year were £659,367, of which deposits comprised £237,542.
The assets at the end of the year were valued at £1,137,642. The liabilities were: To shareholders, reserve fund, &c., £864,860; to depositors, £249,530; and to bankers and other creditors, £23,252.
During the year ended 31st December, 1902, 183 joint-stock companies, with a total nominal capital of £1,924,865, and two guarantee companies, were registered under the provisions of “The Companies Act, 1882.”
The Registrar of Friendly Societies received returns for the year 1901 from 445 lodges, courts, tents, &c., of various friendly societies throughout the colony. The number of members at the end of 1901 was 41,236.
The total value of the assets of these societies was £804,753, equivalent to £19 10s. 4d. per member. Of the total assets, the value of the sick and funeral benefit funds was £744,089.
The receipts during the year on account of the sick and funeral funds amounted to £100,487, and the expenditure to £67,363, of which the sick-pay to members reached the sum of £43,921. In addition to the sick-pay, the sum of £37,840 was paid out of the medical and management expenses fund for attendance given and medicine supplied to the members and their families.
The Registrar of Friendly Societies has supplied particulars of the number of members of friendly societies, the amount of their accumulated capital, and the average capital per member in Australasia, according to the latest published statistics, arranged in order of membership:—
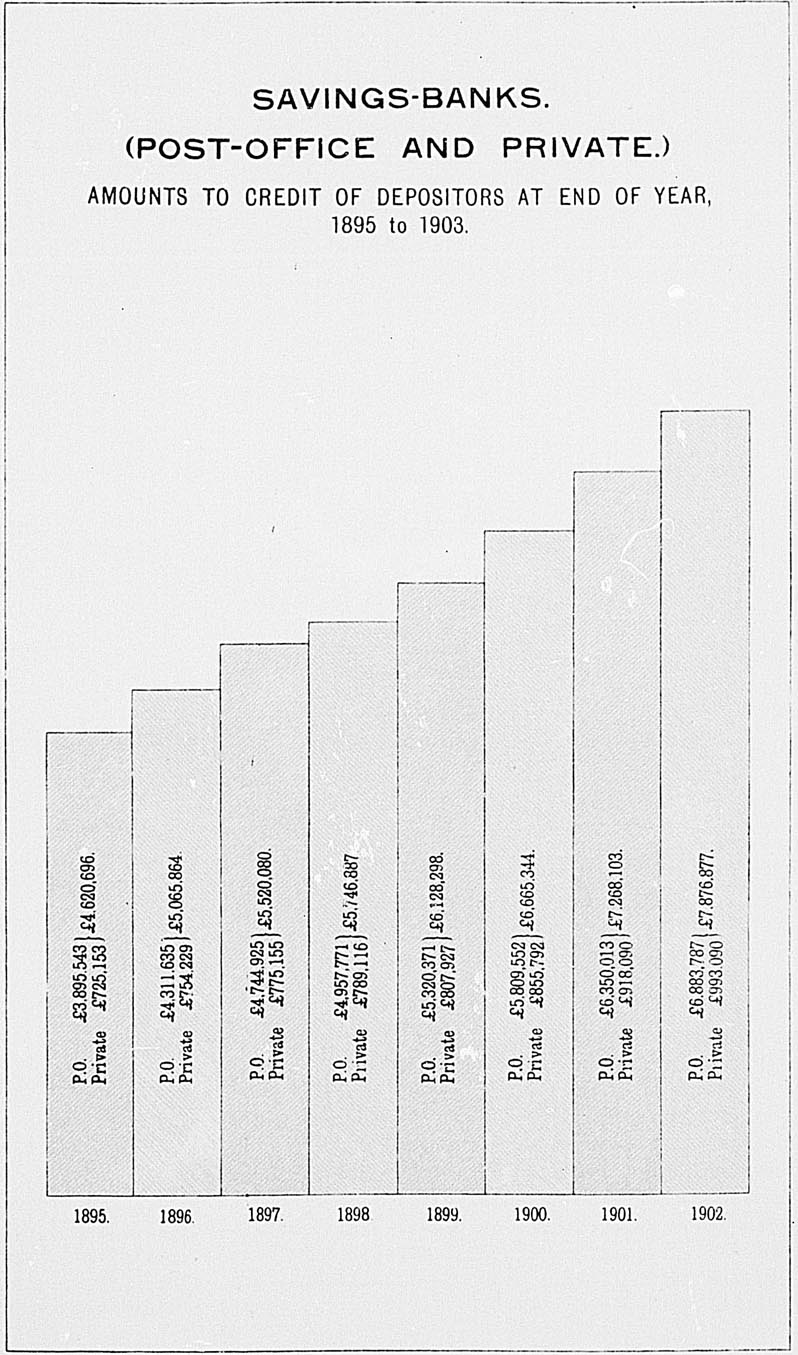
| State or Colony. | Date of Return. | Number of Lodges. | Number of Members. | Amount of Funds. | Capital per Member. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | ||||
| Victoria | 31st Dec., 1900 | 1,111 | 97,937 | 1,316,370 | 13 | 8 | 10 |
| New South Wales | 31st Dec., 1897 | 817 | 69,124 | 596,463 | 8 | 12 | 7 |
| New Zealand | 31st Dec., 1901 | 445 | 41,236 | 804,753 | 19 | 10 | 4 |
| South Australia | 31st Dec., 1899 | 396 | 39,346 | 535,198 | 13 | 12 | 1 |
| Queensland | 31st Dec., 1901 | 361 | 31,167 | 269,111 | 8 | 12 | 8 |
| Tasmania | 31st Dec., 1899 | 117 | 12,883 | 100,562 | 7 | 16 | 1 |
| Western Australia | 31st Dec., 1900 | 108 | 6,890 | 46,306 | 6 | 14 | 5 |
New Zealand shows by far the highest average of capital per member, South Australia and Victoria following, but not closely, while the averages of New South Wales, Queensland, Western Australia, and Tasmania are less than half the sum shown for this colony.
In a return to an order of the House of Representatives it is stated that during the year ended 31st March, 1902, mortgages to the value of £8,256,913 were registered in the several land registration districts of the colony, while the monetary value of those paid off amounted to £5,924,368. Compared with a similar return for the year 1900–1901 the mortgages registered show an increase of £825,215, the total amount for the earlier year having been £7,431,698.
The total amounts represented in the mortgages registered and paid off in each registration district during 1900–1901 and 1901–1902 were:—
| 1901–1902 | 1900–1901 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| District. | Mortgages registered. | Mortgages paid off. | Mortgages registered. | Mortgages paid off. |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Auckland | 768,556 | 596,475 | 663,121 | 507,886 |
| Poverty Bay | 254,649 | 184,839 | .214,394 | 169,279 |
| Taranaki | 781,287 | 688,165 | 872,111 | 498,149 |
| Hawke's Bay | 866,311 | 452,948 | 685,395 | 494,964 |
| Wellington | 2,042,942 | 1,411,388 | 2,108,812 | 1,257,352 |
| Marlborough | 242,866 | 156,143 | 132,106 | 140,648 |
| Nels | 145,104 | 87,927 | 183,022 | 127,172 |
| Westland | 36,950 | 22,033 | 25,821 | 14,305 |
| Canterbury | 1,932,005 | 1,651,569 | 1,424,780 | 1,057,458 |
| Otago | 661,035 | 409,536 | 569,442 | 552,289 |
| Southland | 525,208 | 263,345 | 552,694 | 263,115 |
| Totals | £8,256,913 | £5,924,368 | £7,431,698 | £5,082,617 |
Classified according to the various rates of interest, the amounts in the mortgage deeds registered during the two years were:—
| 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | Rate of Interest. |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
(a.) Including £700 at 4 1/4 per cent. (b.) Including £22,000 at 4 3/5 per cent. (c.) Including £300 at 5 1/3 per cent. (d.) Including £2,360 at 6 5/12 per cent. (e.) Including £100 at 7 1/4 per cent. (f.) Including £200 at 7 2/3 per cent. (g.) Including £30 at 8 1/4 per cent. (h.) Including £12,000 at 4 3/13 per cent., £14,000 at 4 5/16 per cent., and £150 at 4 1/3 per cent. (i.) Including £6,500 at 4 5/8 per cent. | ||
| 78,319 | 119,626 | at 4 per cent or under. |
| 1,652,410a. | 1,876,506h. | at 4 1/2 per cent. |
| 80,310b. | 79,994i. | at 4 3/4 per cent. |
| 2,242,362 | 2,889,148 | at 5 per cent. |
| 19,520 | 13,435 | at 5 1/4 per cent. |
| 421,578c. | 481,913 | at 5 1/2 per cent. |
| 5,300 | 4,895 | at 5 3/4 per cent. |
| 670,472 | 651,315 | at 6 per cent. |
| 4,071d. | 590 | at 6 1/4 per cent. |
| 135,793 | 84,736 | at 6 1/2 per cent. |
| 100 | 450 | at 6 3/4 per cent. |
| 244,248e. | 244,891 | at 7 per cent. |
| 22,619f. | 40,902 | at 7 1/2 per cent. |
| 188,102g. | 193,757 | at 8 per cent. |
| 66,142 | 95,005 | at 8 1/2 per cent. and over. |
| 1,600,352 | 1,475,075 | at rates not specified. |
| .. | 4,675 | free. |
| £7,431,698 | £8,256,913 | |
Comparison of the foregoing with the amounts at the various rates of interest in the mortgages registered during 1895–96 shows the lowering of the rates that has taken place:—
| Year 1895–96. | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 26,285 | in small sums at less than 5 per cent. |
| 833,226 | at from 5 per cent. to 5 1/4 per cent. |
| 732,764 | at 5 1/2 per cent. |
| 116,600 | at 5 3/4 per cent. |
| 1,372,261 | at from 6 per cent. to 6 1/4 per cent. |
| 371,896 | at from 6 1/2 per cent. to 6 3/4 per cent. |
| 599,542 | at from 7 per cent. to 7 1/4 per cent. |
| 111,651 | at 7 1/2 per cent. |
| 382,348 | at 8 per cent. |
| 173,416 | in small sums, at rates above 8 per cent. |
| 853,801 | at rates which are not specified. |
| £5,573,790 |
The total amount shown in deeds as secured by mortgage under the Land Transfer Act on 31st March, 1902, was £40,587,169, as against £37,767,650 in March, 1901, £35,303,728 in March, 1900, £33,035,337 in March, 1899, £32,152,288 in March, 1898, and £31,112,921 in March, 1897; but in respect of some transactions the same money may be included more than once.
There were existing in the colony at the close of the year 1901 94,429 life insurance policies, an average of 120 in every 1,000 persons living. The gross amount represented by these policies was £23,567,427, an average of £249 11s. 7d. for each policy, and of £29 18s. 5d. for every European inhabitant of the colony at the end of the year.
The distribution of these policies shows that nearly one-half are held in the Government Life Insurance Department:—
| Name of Office. | Number of Years of Business in the Colony. | New Zealand Business only. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Existing Policies at End of Year 1901. | Gross Amount insured by Policies at End of Year 1901. | ||
| £ | |||
| Australian Mutual Provident Society | 40 | 28,196 | 7,709,232 |
| Australian Widows’ Fund Life Assurance Society (Limited) | 4 | 1,502 | 407,298 |
| Citizens’ Life Assurance Company (Limited) | 8 | 3,563 | 539,170 |
| Colonial Mutual Life Assurance Society (Limited) | 18 | 4,653 | 1,224,768 |
| Equitable Life Assurance Society of the United States | 17 | 1,272 | 501,967 |
| Mutual Life Association of Australasia | 25 | 5,802 | 1,488,538 |
| National Mutual Life Association of Australasia (Limited) | 22 | 8,004 | 1,898,750 |
| New York Life Insurance Company | 15 | 146 | 55,602 |
| Life Insurance Department of the New Zealand Government | 32 | 41,291 | 9,742,102 |
| Totals, December, 1901 | .. | 94,429 | £23,567,427 |
| Totals, December, 1900 | .. | 89,849 | £22,629,255 |
The rate at which life insurance increased is evidenced by the difference between the amounts insured at the end of each of the two years 1900 and 1901, being a sum of £938,172, or 4·15 per cent., while for the same twelve months the population increased by 2·52 per cent. only.
In addition to the ordinary life insurance transactions alluded to above, there were in 1901 two industrial life assurance offices doing business in New Zealand. The number of policies in existence and the gross amount insured by such policies at the end of the year were:—
| Name of Office. | Number of Years of Business in the Colony. | New Zealand Business only. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Existing Policies at End of Year 1901. | Gross Amount insured by Policies at End of Year 1901. | ||
| £ | |||
| The Citizens’ Life Assurance Company (Limited) | 8 | 17,376 | 376,784 |
| The Provident and Industrial Insurance Company of New Zealand | 12 | 8,735 | 194,008 |
| Totals, December, 1901 | .. | 26,111 | £570,792 |
| Totals, December, 1900 | .. | 24,562 | £544,116 |
Here an increase of £26,676, or 4·90 per cent., is shown to have taken place in twelve months.
By this statute the Commissioner of Life Insurance is given power to insure persons from accident, and specially employers against liability for accident to any person employed, besides generally doing the business of an insurer against accident.
The Act provides for capital for the accident insurance business by empowering the Governor in Council to raise by debentures or scrip, or by issue of inscribed stock, sums of money not exceeding £25,000 altogether. To redeem at maturity the securities issued in respect of capital raised there are provisions for a sinking fund.
The funds, assets, and liabilities of the Government Life Insurance Department belonging to its accident insurance branch are to be kept separately and distinct from the main life insurance business, and powers are vested in the Governor to make regulations in regard to tables fixing rates of premiums, and other details, for the conduct of accident insurance.
The income and expenditure for the initial period, June to December, 1901, and the year 1902, were:—
| Year. | Income. | Expenditure. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premiums. | Other Receipts. | Total. | Claims. | Management. | Other Expenses. | Total. | |
| * The expenses were unavoidably heavy, and include commission £2,236, salaries £1,674, other expenses of management £1,433. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1901 (7th June to 31st December) | 11,856 | 41 | 11,897 | 2,428 | *5,343 | 30 | 7,801 |
| 1902 | 14,100 | 70 | 14,170 | 7,364 | 5,836 | 40 | 13,240 |
During last year the premium income amounted to £14,100, an increase of £2,244 over the premiums received during the previous period.
The total claims, including provision for those not actually settled at the close of the year, amounted to £7,364, as against £2,428 in 1901, the rate in proportion to the premiums earned showing a marked increase. A sum of £4,363 is held as a reserve on account of claims accrued but unsettled as at 31st December. The total expenses show a decrease of about 4 per cent. on the premium income as compared with 1901.
A further sum of £240 has been carried to the unearned premium reserve, which now stands at £4,020.
The funds show an increase of £691, and now stand at £1,007.
This institution was described in full detail in the Year-book for 1898, page 454.
Classifying the business as on the 31st March, 1902 and 1903, the results are:—
| 1902. | 1903. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Estates. | Value of Estates. | Number of Estates. | Value of Estates. | |
| £ | £ | |||
| Wills and trusts (including sinking funds accounts) | 651 | 1,122,404 | 744 | 1,279,743 |
| Intestate estates | 923 | 163,304 | 989 | 197,368 |
| Real estates | 69 | 7,317 | 71 | 7,585 |
| Lunatic estates | 728 | 163,306 | 802 | 170,585 |
| Native reserves | 143 | 366,000 | 143 | 375,000 |
| West Coast Settlement Reserves | 309 | 625,000 | 312 | 655,000 |
| Unclaimed lands | 226 | 20,283 | 253 | 21,504 |
| Total | 3,049 | £2,467,614 | 3,314 | £2,706,785 |
The capital funds of the Public Trust Office invested amounted, on the 31st March, 1903, to £1,861,308. The investments are as follow:—
| £ | |
|---|---|
| New Zealand Government securities | 578,343 |
| Local bodies’ debentures | 31,129 |
| Mortgages of freehold property | 1,251,836 |
| Total | £1,861,308 |
By the Amendment Act of 1885 the Schedule of Duties payable under the principal Act of 1881 has been repealed, and the following imposed in lieu thereof:—
| 1. When the value does not exceed £100 | No duty. |
| 2. Upon any amount exceeding £100 but not exceeding £1,000— | |
| On the first £100 | No duty. |
| And on the remainder | £2 1/2 per cent. |
| 3. Upon any amount exceeding £1,000 but not exceeding £5,000 | £3 1/2 per cent. |
| 4. Upon any amount exceeding £5,000, but not exceeding £20,000 | £7 per cent. |
| Upon £20,000 and any amount over that sum | £10 per cent. |
| Strangers in blood, excepting adopted children | £3 per cent. additional. |
These duties are leviable upon the final balance of the real and personal estates.
The exemption in respect of property passing absolutely to widow at death of husband is now extended vice versá.
There are also special provisions in the law affecting children, grandchildren, step-children, and adopted children inheriting property.
The above duties also apply to deeds of gift.
The number and value of estates of deceased persons finally certified, on which duty was paid during the years 1900, 1901, and 1902, are shown, classified according to amount:—
| Value of Estates. | 1900. | 1901. | 1902. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Estates. | Aggregate Value on which Duty was Paid. | Number of Estates. | Aggregate Value on which Duty was Paid. | Number of Estates. | Aggregate Value on which Duty was Paid. | |
| £ £ | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Under 500 | 752 | 146,105 | 856 | 158,551 | 768 | 161,471 |
| 500 to 1,000 | 224 | 158,392 | 225 | 163,186 | 254 | 176,148 |
| 1,000 to 2,000 | 172 | 246,012 | 159 | 232,961 | 167 | 239,166 |
| 2,000 to 3,000 | 66 | 161,724 | 54 | 130,069 | 84 | 208,451 |
| 3,000 to 4,000 | 37 | 129,079 | 33 | 113,269 | 36 | 126,275 |
| 4,000 to 5,000 | 26 | 115,295 | 29 | 125,701 | 26 | 117,013 |
| 5,000 to 7,500 | 20 | 121,080 | 30 | 181,849 | 39 | 235,539 |
| 7,500 to 10,000 | 16 | 139,792 | 29 | 248,644 | 17 | 148,727 |
| 10,000 to 15,000 | 13 | 156,649 | 18 | 227,423 | 19 | 223,970 |
| 15,000 to 20,000 | 4 | 69,350 | 10 | 167,620 | 4 | 68,859 |
| 20,000 and over | 15 | 517,472 | 14 | 603,425 | 25 | 1,008,618 |
| Totals | 1,345 | 1,960,950 | 1,457 | 2,352,698 | 1,439 | 2,714,237 |
Of the 1,457 estates dealt with in 1901, 448, of an aggregate value of £291,145, were devised by females, an average of about £650 for each estate, while in 1902 the estates of females on which duty was paid numbered 414, the declared value being £322,839, an average of nearly £780 each. The estates left by males in the first of the two years under review numbered 1,009, of an aggregate value of £2,061,553, or about £2,043 for each estate; and in the second, 1,025 estates, valued at £2,391,398, an average of £2,333 each.
The number of estates admitted to probate and the number of adult deaths in each year 1898 to 1902 are given, and it will be seen that 26 out of every 100 adults who died during the year 1902 left property subject to estate duty.
| Year. | Number of Estates. | Number of Adult Deaths. | Proportion per Cent. of Adults who died leaving Property on which Duty paid. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1898 | 1,287 | 4,696 | 27·41 |
| 1899 | 1,327 | 4,719 | 28·12 |
| 1900 | 1,345 | 4,683 | 28·72 |
| 1901 | 1,457 | 5,134 | 28·38 |
| 1902 | 1,439 | 5,413 | 26·58 |
The private wealth of the colony has been estimated on the basis of the probate returns, the calculation being made on the assumption that the wealth of the living is proportionally equal to that left by the dead. Dividing the aggregate amount admitted to probate during a series of years by the number of deaths occurring within the same period, the average value of property left by each person dying is obtained. Then, assuming that the average wealth owned by each person living is equal to that left by each person dying, the total aggregate private wealth may readily be found. For a calculation of this kind it is necessary to take the average results for a series of years, as any inference drawn from the figures of a single year would be untrustworthy; for an increase in the death-rate must necessarily give a corresponding decrease in the estimated wealth, unless the value of estates admitted to probate maintains year by year the same ratio to the number of deaths. An epidemic among young children who have no property to leave would unduly lower the average; while, on the other hand, the deaths of a few wealthy persons would raise it abnormally. By putting the figures for several years together, and taking the average for that term, fairly reliable results may be arrived at, thus:—
| Years, inclusive. | Amount sworn to. | Total Number of Deaths. | Average Amount left by each Person. | Average Number of Persons living. | Average Total Wealth for each Year of the Period. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | |||
| 1898–1902 | 11,329,747 | 38,133 | 297 | 2 | 3 | 765,120 | 227,325,797 |
It is manifest, however, that this average does not exhibit with sufficient accuracy the actual present amount of wealth. If the average amount per head were the same at the end of the year 1902 as for the period 1898–1902—viz., £297·111—then the total wealth possessed by the 807,929 persons in the colony on the 31st December of that year would be £240,054,835.
These figures, however, fail short of the full amount of private wealth, as the values sworn to do not include those estates on which no stamp duty is payable—viz., land and goods passing to the husband or wife of the deceased, and a great number of properties under £100. The aggregate value of such estates must be considerable, and should give a substantial increase to the average amount per head, and therefore to the total wealth. But, on the other hand, less than 35 per cent. of the deaths in 1902 were of persons under twenty years of age, and the census of 1901 showed that 44 per cent. of the population living at that time were under twenty: so that, in assuming the average wealth per head of the living to be the same as the average left by each one dying, the aggregate is somewhat unduly swelled, because, as a rule, persons under twenty have little or no property.
The estimated private wealth for each of the last ten years is shown by the following figures:—
| Year. | Amount. | Average per Head. |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1893 | 156,058,273 | 232 |
| 1894 | 154,715,821 | 225 |
| 1895 | 152,918,021 | 219 |
| 1896 | 170,007,843 | 238 |
| 1897 | 183,781,780 | 252 |
| 1898 | 201,154,323 | 271 |
| 1899 | 217,587,481 | 288 |
| 1900 | 228,236,158 | 296 |
| 1901 | 229,587,916 | 291 |
| 1902 | 240,054,835 | 297 |
Of the total amount of private wealth given above for 1902—viz., £240,054,835—about £130,000,000 would be the value of real estate privately owned, subtracting which leaves, approximately, £110,000,000 as representing personal property. Although this may appear a high estimate, a very large development in the taxable personal estate during the last ten years is absolutely demonstrated by the returns showing the amounts of income-tax paid, which rose from £67,367 in 1892–93 to £200,634 in 1902–1903.
The Government Statistician of New South Wales estimated the private wealth of Australasia for the year 1901 at £1,083,838,000, an average of £240 per inhabitant; and the same authority has returned the private wealth for the State of New South Wales as £358,934,000 sterling for the year 1901.
An attempt to arrive at the value of the public property (exclusive of lessees’ interests in land and improvements) in the colony, with the assistance of the Valuer-General, has led to the following result:—
Public property—i.e., land and improvements not owned by individuals, exclusive of Government railways:—
| £ | £ | |
|---|---|---|
| Crown lands | 15,303,184 | |
| Local authorities’ lands | 4,319,539 | |
| Educational lands | 3,181,739 | |
| Church and other lands | 2,249,378 | |
| 25,053,840 | ||
| Government railways, open and under construction, 31st March, 1902 | 19,606,248 | |
| Other public works—viz., telegraphs, lighthouses, harbours, and water-supply on goldfields | 4,810,399 | |
| Total public property | £49,470,487 | |
This amount of £49,470,487, with the sum of £240,054,835 previously shown as the private wealth, estimated from probate returns, gives a total of £289,525,322. If to this be added £7,490,521, the value of Native lands with their improvements (exclusive of lessees’ interests), a final total of £297,015,843 is reached.
So much of this sum as represents private wealth may be considered as net wealth, because stamp duty is paid after subtracting liabilities on estates. But the debt of the General Government and that of the local bodies (so far as raised abroad) must be deducted. These amounts were, in the year 1902, £46,611,726 and £5,552,100 respectively. Allowing for these, it is found that the colony had in 1902 at least £244,852,017 value of public and private wealth. No doubt there is more, but full information as to public wealth other than property owned by the Government is not procurable.
The amount of the aggregate annual earnings of the people of New Zealand is given in the Year-book of 1897 (p. 283). To arrive at this estimate the method adopted was to allot to each person the probable income earned in respect of the occupation set down against his or her name in the household schedules collected at the census of 12th April, 1896. Exception may no doubt be taken to the plan of basing a calculation on a series of arbitrary assumptions, but there is precedent for such a course. The results of the calculation were given without any guarantee of accuracy, similar figures having been called for in the past. Indeed, it is important to make clear that the figures must only be considered as put forward with the greatest diffidence, and rather of necessity than otherwise. They may, indeed, give a fair idea of the facts, but the responsibility of using them for any particular purpose is not accepted by the Registrar-General.
The aggregate of wages paid in the colony for the year 1896, as given in the Year-book of 1897 (p. 284), was arrived at by assigning to each wage-earner the probable annual income each would derive from the profession or occupation followed. As in the case of income, the calculations made were put forward merely by way of an attempt to get as closely as possible to the facts, and because asked for; but no assurance whatever can be given as to the exactness of the conclusions stated, and the Registrar-General does not accept any responsibility in regard to their use.
An estimate was made in 1894 of the cost of living in New Zealand, including, besides what was spent on necessaries, the additional outlay on what may be termed luxuries, and on things of occasional necessity. The rate arrived at per head of population was £35 6s. 1d. per annum for that year. Fuller particulars are given in former issues of the Year-book.
The average income per head, previously referred to, was believed to be from £37 12s. to £44 per annum.
Mr. Mulhall, in his “Dictionary of Statistics,” gives the average expenditure per head of population for certain specified countries as follows:—
| Country. | Average Annual Expenditure per Head. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | |
| United Kingdom | 29 | 14 | 9 |
| France | 23 | 19 | 4 |
| Germany | 20 | 3 | 4 |
| Russia | 10 | 1 | 11 |
| Austria | 14 | 4 | 9 |
| Italy | 11 | 11 | 0 |
| Spain | 15 | 12 | 6 |
| Portugal | 11 | 5 | 6 |
| Sweden | 20 | 8 | 4 |
| Norway | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Denmark | 28 | 11 | 5 |
| Holland | 20 | 17 | 4 |
| Belgium | 25 | 8 | 2 |
| Switzerland | 18 | 0 | 0 |
| United States | 32 | 16 | 2 |
| Canada | 23 | 2 | 2 |
| Argentina | 27 | 9 | 1 |
The estimate for Australia, made by the Government Statistician of New South Wales, for the present time is £38 per head.
The quantities used per head of population in New Zealand of some of the main articles of consumption will be found in the Year-book for 1898. The figures are averages for five years.
The average prices of produce, live-stock, provisions, &c., in each provincial district are given for the year 1902 in tabular form on pages 463 and 464. While the variations for the different districts are such as to render it in most cases inadvisable to show averages for the colony, this has nevertheless been done for the staples of food—i.e., bread, meat, and milk—also for tea and sugar, which may almost be called necessaries. Averages for the colony, taken out for the years 1878, 1888, 1898, and 1902, indicate in some cases a decline in prices with the advance of time. In striking these, prices on the goldfields have not been taken into account:—
| — | 1878. | 1888. | 1898. | 1902. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | |
| Bread per lb. | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 3/4 | 0 | 1 1/2 | 0 | 1 3/4 |
| Beef per lb. | 0 | 5 1/2 | 0 | 3 3/4 | 0 | 3 3/4 | 0 | 5 |
| Mutton per lb. | 0 | 3 3/4 | 0 | 3 1/4 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 1/2 |
| Sugar per lb. | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 1/4 | 0 | 2 3/4 | 0 | 2 3/4 |
| Tea per lb. | 2 | 9 | 2 | 3 1/2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 9 |
| Butter (fresh) per lb. | 1 | 4 | 0 | 9 1/4 | 0 | 9 3/4 | 1 | 0 |
| Cheese (colonial) per lb. | 0 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 5 1/2 | 0 | 7 |
| Milk per quart. | 0 | 4 1/2 | 0 | 3 1/4 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 1/2 |
The average rates of wages paid in 1902 in each provincial district for agricultural, pastoral, artisan, and servants’ labour are given on pages 465 to 467.
| AVERAGE P(([0-9]+)) PRODUCE, LIVE-STOCK, PROVISIONS, ETC., (([0-9]+)) PROVINCIAL D(([0-9]+)) NEW Z(([0-9]+))THE YEAR 1902. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Produce, &c. | Auckland. | Taranaki. | Hawke's Bay. | Wellington. | Marlborough. | Nelson. | Westland (Goldfield). | Canterbury | Otago (Part Goldfield). |
* Per ton. † Per 100lb. | |||||||||
| I. A(([0-9]+)). | |||||||||
| Wheat per bushel (60lb.) | 4/6 to 5/ | 4/ to 5/6 | 5/ to 5/6 | 5/3 to 6/ | 4/6 | 5/2 to 5/6 | 4/6 to 6/ | 5/ to 5/6 | 4/ to 6/ |
| Barley per bushel (47lb.) | 4/ to 4/6 | 3/6 | 3/ to 3/6 | 3/3 to 4/6 | 3/6 | 4/6 | 4/ to 5/ | 3/ to 3/9 | 3/ to 4/ |
| Oats per bushel (40lb.) | 3/3 to 3/9 | 3/6 to 3/9 | 2/9 to 4/ | 2/9 to 4/ | 4/ | 3/3 | 3/ to 3/9 | 2/6 to 3/ | 2/2 to 3/ |
| Maize per bushel (56lb.) | 4/ to 5/ | 4/ to 6/ | 4/ to 5/ | 4/ to 6/ | 4/6 | 5/3 | .. | 5/ to 6/ | 2/3 to 5/6 |
| Bran per bushel (20lb.) | 1/4 to 2/3 | 1/6 | 1/6 to 2/6 | 1/3 to 2/6 | £7/10* | 1/9 to 2/ | 1/6 to 1/10 | 1/3 to 2/ | 1/ to 1/6 |
| Hay per ton | £4 to £5 | £4/10 to £5 | £3/10 to £4 | £3/5 to £5/10 | £4 | £4 to £6 | £5 to £6 | £3 to £4/10 | 52/6 to 100/ |
| II. F(([0-9]+)) BREAD. | |||||||||
| Flour, wholesale per ton of 2,000lb. | £11/10 to £15 | 190/ to 250/ | £10 to £15 | 250/ to 330/ | £12/10 | 280/ to 290/ | 280/ to 290/ | 240/ to 290/ | £11 to £14 |
| Flour, retail per bag of 50lb. | 6/9 to 8/ | 6/ to 8/ | 6/6 to 8/6 | 7/6 to 8/6 | 7/ | 7/6 to 8/6 | 7/6 to 8/6 | 7/3 to 9/ | 6/6 to 7/6 |
| Bread per 4lb. loaf | 7d. to 8d. | 8d. | 7d. to 8d. | 7d. to 8d. | 8d. | 8d. | 8d. to 9d. | 7d. to 8d. | 6 1/2 d. to 8d. |
| III. LIVE-(([0-9]+)) MEAT. | |||||||||
| Horses, draught per head | £20 to £40 | £30 to £35 | £25 to £40 | £35 to £45 | £20 to £45 | £30 to £40 | £45 to £60 | £25 to £45 | £25 to £50 |
| Horses, saddle and harness per head | £7 to £15 | £15 to £20 | £10 to £25 | £10 to £25 | £10 to £35 | £18 to £20 | £10 to £20 | £15 to £30 | £10 to £30 |
| Cattle, fat per head | £7 to £11 | £6 to £8 | £9 to £10 | £8 to £12 | 25/† | 150/ to 210 | £12 to £19 | £8 to £12 | £7 to £13 |
| Cattle, milch cows per head | £6 to £7/10 | £5 to £9 | £6 to £10 | £7 to £10 | £7/10 | £8 to £9 | £6 to £10 | £7 to £9 | £6 to £10 |
| Sheep, fat per head | 13/ to 17 | 12/ to 15/ | 13/ to 15/ | 12/6 to 18/ | 16/ | 13/to16/6 | 16/ to £1 | 15/6 to £1 | 14/ to £1 |
| Lambs, fat per head | 10/ to 11/ | 10/6 | 10/ to 11/6 | 10/ to 15/ | 12/ | 11/ to 14/ | 10/ to 15/ | 12/ to 16/ | 10/ to 15/ |
| Butchers' meat:— | |||||||||
| Beef per lb. | 5d. to 7d. | 5d. | 4 1/2d. to 6d. | 4 1/2d. to 7d. | 4 1/2d. to 6d. | 6d. to 8d. | 6d. to 7d. | 4d. to 8d. | 4d. to 8d. |
| Mutton per lb. | 3 1/2d. to 7d. | 4d. to 5d. | 3d. to 4 1/2d. | 4 1/2d. to 6d. | 5d. to 6d. | 5d. to 6d. | 5d. to 7d. | 3 1/2d. to 6d. | 4d. to 6d. |
| Veal per lb. | 4d. to 6d. | 4d. to 5d. | 5d. to 5 1/2d. | 4 1/2d. to 7d. | 6d. | 5d. to 6d. | 6d. to 7d. | 5d. to 6d. | 5d. to 10d. |
| Pork per lb. | 5d. to 7d. | 5d. to 6d. | 5d. to 6d. | 6d. to 8d. | 6d. | 6d. to 8d. | 6d. to 8d. | 6d. to 7d. | 6d. to 9d. |
| Lamb per lb. | 5d. to 7d. | 5 1/5d. to 6d. | 5 1/2d. to 7d. | 6d. to 9d. | 3/6 to 4/ | 6d. to 9d. | 6d. to 9d. | 5d. to 7d. | 5d. to 8d. |
| IV. D(([0-9]+)) | per qr. | ||||||||
| Butter, fresh per lb. | 11d. to 1/3 | 11d. to 1/ | 7d. to 1/ | 8d. to 1/ | 1/1 | 9d. to 1/2 | 10d. to 1/ | 9d. to 1/ | 7d. to 1/1 |
| Butter, salt per lb. | 7d. to 10d. | 10d. | 8d. to 10d. | 8d. to 9d. | 9d. | 7d. to 9d. | 9d. to 1/ | 7d. to 10d. | 7 1/2d. to 1/ |
| Cheese, colonial per lb. | 6 1/2d. to 8d. | 6d. to 7d. | 8d. to 10d | 5 1/2d. to 8d. | 7d. | 7d. | 7d. to 8d. | 7d. to 8d. | 5 1/2d. to 8d. |
| Cheese, imported per lb. | 7d. to 1/ | 1/4 | 1/ to 2/3 | 1/6 to 2/6 | 2/ | 2/6 | 10d. | 1/2 to 1/8 | 9d. to 1/6 |
| Milk per quart | 3d. to 4d. | 3d. | 3d. to 4d. | 3d. to 4d. | 3d. | 4d to 5d. | 4d. to 5d. | 3d. to 4d. | 2 1/2d. to 6d. |
| V. FARM-(([0-9]+)). | |||||||||
| Geese per pair | 6/ to 9/ | 7/ to 8/ | 7/ to 10/ | 6/ to 10/ | 5/6 | 4/6 to 8/ | 8/ to 12/6 | 4/3 to 6/ | 5/ to 11/6 |
| Ducks per pair | 3/ to 5/ | 5/ | 3/9 to 5/ | 4/ to 6/6 | 4/ | 5/ to 5/6 | 5/ to 7/ | 3/6 to 5/6 | 2/6 to 6/6 |
| Fowls per pair | 2/6 to 4/ | 3/6 to 4/6 | 2/6 to 4/ | 3/6 to 5/ | 2/6 | 3/6 to 4/ | 4/ to 5/ | 3/ to 3/6 | 2/ to 4/ |
| Turkeys per head | 4/ to 8/ | 5/ to 5/6 | 5/ to 9/ | 4/ to 10/ | 5/ | 7/ | 5/ to 15/ | 4/ to 10/ | 5/ to 14/ |
| Bacon per lb. | 8d. to 10d. | 9d. | 9d. to 1/1 | 8 1/2d. to 1/2 | 9d. | 9d. to 11d. | 10d. to 11d. | 6d. to 11d. | 6d. to 10d. |
| Ham per lb. | 8 1/2d. to 1/ | 10 1/2d. to 11d. | 10d. to 1/1 | 9d. to 1/3 | 11d. | 10d. to 11d. | 10 1/2d. to 1/ | 8d. to 11d. | 8d. to 11d. |
| Eggs per doz. | 10d. to 1/2 | 10d. to 1/1 | 1/ to 1/3 | 9d. to 1/6 | 1/2 | 11d. to 1/6 | 1/6 | 9d. to 1/2 | 8d. to 1/4 |
| VI. G(([0-9]+)). | |||||||||
| Potatoes, wholesale per ton | 100/ to 220/ | 80/ to 170/ | 90/ to 210/ | 70/ to 180/ | 140/ | 120/ to 160/ | 160/ to 240/ | 85/ to 200/ | 70/ to 300/ |
| Potatoes, retail per cwt. | 6/3 to 14/ | 6/ to 9/ | 10/ to 12/6 | 5/ to 11/ | 8/ | 9/ to 10/ | 9/ to 14/ | 7/6 to 13/6 | 4/6 to 15/ |
| Onions per lb. | 1d. to 3d. | 1 1/2d. to 3d. | 1 1/2d. to 2d. | 1 1/2d. to 3d. | 1d. | 1 1/2d. to 1 3/4d. | 1d. to 2d. | 1d. to 2d. | 1d. to 3d. |
| Carrots per doz. bnchs. | 1/ to 2/ | 1/ to 3/ | 1/ to 3/ | 1/ | 6d. | 2/ to 2/6 | 1/6 to 3/ | 1/3 to 3/ | 1/ to 6/ |
| Turnips per doz. bnchs. | 1/ to 2/ | 1/ to 2/ | 1/ to 3/ | 1/ | 6d. | 2/ to 2/6 | 2/ to 3/ | 1/3 to 3/ | 1/ to 6/ |
| Cabbages per doz. | 1/6 to 3/ | 3/3 to 4/ | 2/ to 3/ | 1/ to 3/ | 1/ | 2/6 to 3/ | 3/ to 3/6 | 1/ to 3/ | 1/ to 6/ |
| VII. (([0-9]+)). | |||||||||
| Tea per lb. | 1/4 to 2/ | 1/9 to 2/ | 1/9 to 2/6 | 1/2 to 2/6 | 2/ | 1/10 to 2/ | 1/8 to 2/ | 1/3 to 2/6 | 1/3 to 2/4 |
| Coffee per lb. | 1/3 to 1/11 | 1/8 | 1/6 to 2/ | 1/6 to 2/ | 2/ | 1/9 to 1/10 | 1/9 to 2/ | 1/3 to 1/8 | 1/6 to 2/ |
| Sugar per lb. | 2d. to 3d. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 3d. | 3d. | 3d. | 2d. to 2 1/2d. | 1 1/2d. to 3d. |
| Rice per lb. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 2 1/2d. to 3d. | 2d. to 3d. | 3d. | 3d. | 3d. | 2d. to 2 1/2d. | 1 1/2d. to 3d. |
| Salt per lb. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | 1d. | |
| Soap per cwt. | 13/6 to 23/ | 20/ to 32/6 | 13/ to 26/ | 11/ to 25/ | 21/ | 9/ to 27/ | 12/ to 25/ | 10/ to 20/ | 12/ to 24/ |
| Candles per lb. | 6d. to 8d. | 7d. | 5d. to 9d. | 7d. to 8d. | 7d. | 7d. to 8d. | 6d. to 8d. | 5d. to 7d. | 5d. to 8d. |
| Tobacco per lb. | 5/3 to 5/9 | 5/6 to 6/ | 5/3 to 6/ | 5/3 to 6/ | 5/3 | 5/6 | 5/ to 5/6 | 5/ to 6/ | 5/ to 6/6 |
| Coal per ton | 26/ to 55/ | 40/ | 35/6 to 52/6 | 38/ to 50/ | 40/ | 22/6 to 40/ | 22/ to 36/ | 36/ to 52/ | 18/ to 39/6 |
| Firewood per cord | 20/ to 30/ | 19/ to 25/ | 18/ to 32/ | 18/ to 36/ | 30/ | 28/ to 30/ | 16/ to 30/ | 28/ to 40/ | 18/ to 50/ |
| VIII. BEER, WINES, SPIRITS. | |||||||||
| Beer, colonial | 80/ to 92/ | 80/ to 90/ | 90/ to 110/ | 80/ to 100/ | 80/ | 85/ to 100/ | 80/ to 95/ | 80/ to 108/ | 60/ to 120/ |
| Beer, English, bottl'd per doz. qts. | 12/ to 15/ | 15/ to 16/ | 14/6 to 15/6 | 14/6 to 17/ | 14/ | 14/ to 15/ | 15/ to 16/ | 12/6 to 18/ | 13/6 to 18/ |
| Brandy per gallon | 25/ to 30/ | 30/ to 35/ | 28/6 to 30/ | 26/ to 34/ | 30/ | 26/ to 32/ | 22/ to 25/ | 25/6 to 30/ | 25/ to 28/ |
| Rum per gallon | 22/6 to 27/ | 28/ | 26/ to 30/ | 24/6 to 32/6 | 27/6 | 24/6 to 25/ | 22/ to 25/ | 23/ to 30/ | 23/ to 33/ |
| Whisky per gallon | 24/ to 30/ | 27/6 to 30/ | 30/ to 35/ | 28/ to 32/6 | 30/ | 25/ to 28/ | 22/ to 25/ | 25/ to 28/6 | 24/ to 28/ |
| Gin per gallon | 20/ to 24/ | 22/ to 24/ | 17/6 to 27/6 | 20/ to 26/ | 27/6 | 25/ to 28/ | 18/ to 20/ | 22/ to 28/6 | 20/ to 30/ |
| Wine, Australian per gallon | 15/ to 22/6 | 18/ to 20/ | 16/ to 22/6 | 14/ to 30/ | 16/ | 14/ | 13/6 to 17/ | 15/ to 20/ | 14/ to 21/ |
| Wine, European per gallon | 17/ to 25/ | 30/ | 20/ to 27/6 | 22/ to 40/ | 20/ | 21/ | 12/6 to 20/ | 20/ to 25/ | 16/ to 30/ |
| 1. AGRICULTURAL LABOUR. | |||||||||
| Farm-labourers: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 15/ to 22/ | 15/ to 25/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ | 20/ | 20/ to 30/ | 15/ to 25/ | 15/ to 20/ |
| Without board, per day | 6/ to 7/ | 7/ to 8/ | .. | .. | .. | 7/ | .. | 6/ to 7/6 | 6/ to 8/ |
| Ploughmen: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 20/ to 25/ | 15/ to 25/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 25/ | 20/ | 25/ to 30/ | 20/ to 27/6 | 20/ to 25/ |
| Without board, per day | 7/ | 7/ to 8/ | .. | .. | .. | 7/ | .. | .. | .. |
| Harvesters: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 25/ to 48/ | 40/ | 20/ | 20/ to 30/ | 30/ to 35/ | 40/ | .. | 40/ to 50/ | 25/ to 40/ |
| Without board, per day | 10/ | 1/ to 1/3 | 1/ per hour | 1/ to 1/3 | 8/ | 12/ | .. | 1/per hour | 9d. to 1/ |
| Men-cooks on farms: | per hour | per hour | per hour | ||||||
| With board, per week | 25/ to 40/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 15/ to 30/ | 25/ | 30/ | .. | 20/ to 40/ | 20/ to 40/ |
| Female farm-servants: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 10/ to 15/ | 8/ to 15/ | 10/ to 20/ | 12/6 to 20/ | 12/ | 10/ | .. | 10/ to 15/ | 8/ to 20/ |
| 2. P(([0-9]+)). | |||||||||
| Shepherds, with board, per annum | £50 to £70 | £50 to £65 | £58/10 to £78 | £50 to £78 | £65 to £78 | £70 | .. | £52 to £80 | £52 to £70 |
| Stock-keepers, with board, per annum | £50 to £70 | £50 to £65 | £58/10 to £78 | £50 to £78 | £50 to £65 | £70 | .. | £60 | £50 to £70 |
| Station-labourers: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 20/ to 25/ | 15/ to 25/ | 17/6 to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ | .. | 15/ to 20/ | 15/ to 20/ |
| Without board, per day | 7/ | 8/ | 7/ | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Shearers, with board, per 100 sheep shorn | 17/6 to 20/ | 16/8 to 20/ | 17/6 to 20/ | 16/8 to 20/ | 16/8 | 16/8 | .. | 16/6 to 20/ | 16/8 to 20/ |
| Men-cooks on stations, with board, per week | 20/ to 27/6 | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 40/ | 30/ to 40/ | 25/ | .. | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 30/ |
| 3. ARTISAN LABOUR (per day, without board). | |||||||||
| Masons | 10/ to 14/ | 9/ to 10/ | 11/ to 14/ | 10/ to 12/6 | 14/ | 12/ | 14/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 12/ |
| Plasterers | 10/ to 14/ | 9/ to 10/ | 12/ to 14/ | 10/ to 14/ | 14/ | 12/ | 12/6 to 15/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 14/ |
| Bricklayers | 9/ to 14/ | 9/ to 12/ | 11/ to 14/ | 10/ to 14/ | 14/ | 12/ | 10/ to 14/ | 12/ | 12/ to 14/ |
| Carpenters | 9/ to 11/6 | 10/ to 12/ | 8/ to 10/ | 10/ to 12/ | 9/ | 9/ to 11/ | 10/ to 12/6 | 10/ to 12/ | 8/ to 12/ |
| Smiths | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 9/ | 8/ to 12/ | 7/ to 12/ | 10/ | 10/ to 11/ | 10/ | 9/ to 10/ | 7/ to 12/ |
| Shipwrights | 10/ to 11/ | 8/ to 10/ | 12/ | 10/ to 12/ | .. | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ | 10/ to 12/ | 9/ to 12/ |
| Plumbers | 8/ to 12/ | 10/ | 8/ to 11/ | 9/ to 12/ | 10/ | 10/ | 10/ to 13/ | 9/ to 10/6 | 9/ to 12/ |
| Painters | 7/6 to 12/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 12/ | 9/ to 12/ | 9/ | 8/ to 11/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 10/6 | 7/ to 12/ |
| Saddlers | 8/6 to 10/ | 7/ to 9/ | 8/ to 10/ | 7/ to 10/ | 8/ | 8/ to 9/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 8/6 | 8/ to 10/ |
| Shoemakers | 7/6 to 8/ | 7/ to 8/ | 7/6 to 8/6 | 7/ to 10/ | 8/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/6 to 10/ | 7/ to 8/ | 6/ to 10/ |
| Coopers | 9/ to 10/ | 7/ to 10/6 | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 11/ | 9/ | 12/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 10/6 | 8/ to 10/ |
| Watchmakers | 9/6 to 11/ | 7/ to 8/ | 8/ to 10/ | 7/ to 12/ | 10/ | 8/ | 9/ to 12/ | 7/ to 9/ | 8/ to 10/ |
| Wheelwrights | 10/ to 11/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ to 10/ | 7/ to 12/ | 10/ | 10/ to 11/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 12/ | 9/ to 12/ |
| 4. SERVANTS. | |||||||||
| Married couples without family, with board, per annum | £60 to £80 | £80 to £85 | £80 to £90 | £60 to £80 | £70 to £80 | £75 | .. | £65 to £75 | £52 to £80 |
| Married couples with family, with board, per annum | £55 to £85 | .. | £80 | £52 to £80 | £65 to £75 | £70 | .. | £60 to £70 | £50 to £80 |
| Grooms, with board, per week | 15/ to 25/ | 15/ to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ | 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 25/ | 15/ to 25/ |
| Gardeners: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 20/ to 25/ | 25/ to 30/ | 20/ to 25/ | 20/ to 35/ | 25/ to 35/ | 25/ | 20/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 30/ |
| Without board, per day | 5/ | 7/ to 8/ | .. | 8/ | 7/ to 8/ | 8/ | 8/ to 10/ | 8/ | 7/ to 8/ |
| Cooks, with board, per week | 15/ to 25/ | 20/ to 30/ | 15/ to 25/ | 15/ to 35/ | 15/ to 20/ | 15/ to 20/ | 15/ to 40/ | 15/ to 20/ | 15/ to 30/ |
| Laundresses, with board, per week | 12/ to 20/ | 15/ to 30/ | 10/ to 17/6 | 15/ to 25/ | 10/ to 15/ | 10/ to 15/ | 15/ to 20/ | 12/ to 20/ | 12/ to 20/ |
| General house servants, with board, per week | 8/ to 15/ | 8/ to 12/ | 10/ to 15/ | 8/ to 20/ | 10/ to 12/ | 8/ to 10/ | 10/ to 15/ | 10/ to 12/6 | 10/ to 15/ |
| Housemaids, with board, per week | 7/ to 15/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 15/ | 8/ to 20/ | 10/ to 12/ | 8/ to 17/6 | 10/ to 15/ | 9/ to 12/6 | 8/ to 15/ |
| Nursemaids, with board, per week | 5/ to 10/ | 4/ to 5/ | 5/ to 7/6 | 7/ to 15/ | 5/ to 8/ | 6/ to 7/ | 6/ to 8/ | 5/ to 10/ | 5/ to 10/ |
| Needlewomen: | |||||||||
| With board, per week | 15/ to 21/ | 30/ to 35/ | 21/ | 14/ to 20/ | .. | 15/ | .. | 15/ | 10/ to 20/ |
| Without board, per day (lunch always provided) | 2/6 to 4/ | 3/ to 3/6 | 3/6 to 4/ | 3/6 to 5/ | 3/ | 3/ | 3/ to 6/ | 3/6 to 5/ | 3/ to 6/ |
| 5. MISCELLANEOUS. | |||||||||
| General labourers, without board, per day | 5/ to 8/6 | 7/ to 8/ | 6/ to 8/ | 7/ to 9/ | 6/ to 8/ | 7/ to 9/ | 9/ to 10/ | 6/ to 7/6 | 6/ to 8/ |
| Stonebreakers without board, per cubic yard | 2/3 to 6/ | 3/6 to 3/9 | 2/ | 2/6 to 5/ | 3/ | 1/ | 3/6 to 5/ | 2/6 to 4/ | 1/7 1/2 to 5/ |
| Seamen, with board, per month | £4 to £6 | £5 to £6 | £6 10s.£5 to £7 | .. | £6 | .. | £4 to £8 | £5 to £6 | |
| Miners, without board, per day | 7/6 to 10/ | 8/ | .. | 9/ | 9/ | 9/ to 11/ | 9/ to 10/ | 8/6 | 7/ to 12/ |
| Engine-drivers, without board, per day | 9/ to 10/ | 9/ to 10/ | 8/ to 10/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 12/ | 10/ to 14/ | 8/ to 15/ |
| Tailors, without board, per day | 8/ to 10/ | 7/ to 10/ | 6/8 to 15/ | 6/8 to 10/ | 8/–10/ | 7/6 to 10/ | 7/6 to 10/ | 8/ to 10/ | 6/8 to 10/ |
| Tailoresses, without board, per week | 12/ to 27/ | 20/ to 30/ | 25/ to 40/ | 25/ to 40/ | .. | 20/ to 36/ | 24/ to 30/ | 17/6 to 30/ | 18/ to 30/ |
| Dressmakers, without board, per week | 17/6 to 24/ | 36/ to 48/ | 20/ to 50/ | 10/ to 40/ | .. | 20/ to 45/ | 21/ to 40/ | 18/ to 25/ | 20/ to 40/ |
| Milliners, without board, per week | 27/ to 36/ | 30/ to 36/ | 25/ to 60/ | 12/6 to 60/ | 40/–50/ | 24/ to 45/ | 25/ to 50/ | 21/ to 50/ | 20/ to 48/ |
| Machinists, without board, per week | 20/ to 30/ | 30/ to 36/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/–25/ | 24/ to 30/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 30/ | 20/ to 36/ |
| Storekeepers, without board, per week | 27/6 to 60/ | 40/ to 55/ | 60/ | 50/ to 60/ | .. | 50/ | 50/ to 60/ | 50/ to 60/ | 45/ to 65/ |
| Storekeepers, assistants, without board, per week | 25/ to 48/ | 25/ to 42/ | 30/ to 45/ | 45/ to 60/ | 40/–50/ | 40/ to 48/ | 40/ to 50/ | 40/ to 48/ | 35/ to 50/ |
| Drapers' assistants, without board, per week | 25/ to 48/ | 45/ to 60/ | 50/ to 60/ | 45/ to 65/ | 40/–60/ | 40/ to 50/ | 30/ to 60/ | 25/ to 60/ | 40/ to 60/ |
| Grocers' assistants, without board, per week | 25/ to 48/ | 36/ to 55/ | 40/ to 55/ | 35/ to 55/ | 35/–42/ | 40/ to 48/ | 50/ | 35/ to 60/ | 35/ to 48/ |
| Butchers, without board, per week | 20/ to 60/ | 30/ to 60/ | 40/ to 50/ | 40/ to 60/ | 45/ | 40/ to 50/ | 40/ to 60/ | 35/ to 54/ | 25/ to 55/ |
| Bakers, without board, per week | 40/ to 60/ | 36/ to 50/ | 20/ to 55/ | 40/ to 60/ | 55/ | 45/ to 50/ | 42/ to 60/ | 35/ to 60/ | 25/ to 55/ |
| Storemen, without board, per week | 40/ to 50/ | 40/ to 48/ | 40/ to 60/ | 40/ to 55/ | 50/ | 50/ | 50/ to 60/ | 40/ to 50/ | 45/ to 50/ |
| Compositors, without board, per week | 36/ to 60/ | 36/ to 60/ | 42/ to 50/ | 30/ to 70/ | 50/ | 40/ to 50/ | 40/ to 60/ | 50/ to 60/ | 40/ to 70/ |
The legislation passed by the General Assembly of New Zealand and termed the “labour laws” comprises the undermentioned statutes and regulations made under various Acts:—
“The Accidents Compensation Act, 1901.”
“The Alcoholic Liquors Sale Control Act Amendment Act, 1895": Section 10.
Bankruptcy: Sections 112 and 120 of Act of 1892.
“The Coal-mines Act, 1891": Sections 18 to 58 and 64 to 88.
“The Coal-mines Act Amendment Act, 1901": Sections 3, 4, and 6.
“The Companies Acts Amendment Act, 1893": Sections 8 and 9.
“The Conspiracy Law Amendment Act, 1894.”
“The Contractors’ and Workmen's Lien Act, 1892.”
“The Criminal Code Act, 1893": Sections 150 and 213.
“The Deaths by Accidents Compensation Act, 1880.
“The Electoral Act Amendment Act, 1900": Section 10.
“The Employers’ Liability Act, 1882,” with amendments of 1891 and 1892.
“The Factories Act, 1901,” with amendments of 1902.
“The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, 1900,” with amendments of 1901.
“The Inspection of Machinery Act, 1902.”
“The Kauri-gum Industry Act, 1898,” and Amendment Acts of 1899 and 1902.
“The Labour Day Act, 1899.”
“The Land for Settlements Act Amendment Act, 1896” (provision for workmen's homes).
“The Legitimation Act, 1894": Section 6.
“The Licensing Act, 1881": Section 131.
“The Master and Apprentice Act, 1865.” Master and Apprentice: Extract from “The Criminal Code Act, 1893,” sections 150 and 213.
“The Mining Act, 1898,” and Amendment Acts, 1900, 1901, and 1902.
“The Public Contracts Act, 1900.”
“The Servants’ Registry Offices Act, 1895.”
“The Shearers’ Accommodation Act, 1898.”
“The Shipping and Seamen's Act, 1877,” with Amendment Acts of 1885, 1890, 1894, 1895, 1896, and 1899.
“The Shops and Shop-assistants Act, 1894,” with Amendment Acts of 1895, 1896, and 1901.
“The Sunday Labour in Mines Prevention Act, 1897.”
“The Threshing-machine Owners’ Lien Act, 1895.”
“The Trade-Union Act, 1878,” and Amendment Act, 1896.
“The Truck Act, 1891.”
“The Wages Attachment Act, 1895.”
“The Wages Protection Act, 1899” (forming part of and to be read with “The Truck Act, 1891”).
“The Workers’ Compensation for Accidents Act, 1900,” with amendments of 1902.
“The Workmen's Wages Act, 1893.”
The labour laws have been passed in the effort to regulate certain conditions affecting employer and employed. Their scope embraces many difficult positions into which the exigencies of modern industrial life have forced those engaged in trades and handicrafts. The general tendency of these laws is to ameliorate the position of the worker by preventing social oppression through undue influences, or through unsatisfactory conditions of sanitation. It will undoubtedly be found that, with the advance of time, these laws are capable of improvement and amendment; but they have already done much to make the lives of operatives of fuller and more healthy growth, and their aim is to prevent the installation of abuses before such abuses attain formidable dimensions.
The manufacturing population in New Zealand differs from that in some of the Australian States by its wide dispersion. The capital city has hitherto been unable to draw to itself the industrial ability of the other provincial centres; and not only do Auckland, Christchurch, and Dunedin vie with Wellington as centres of population, but also as nuclei of commercial activity. In the second-class towns, such as Nelson, Napier, Invercargill, &c., many important works are being carried on, while even in the villages and rural districts the progress of new settlement necessitates the manufacture of articles which in older communities are produced in specialised localities. Men scattered widely at the numerous occupations of colonial country life, shearing, harvesting, bush-felling, road-making, or sailing coastal vessels, &c., require legal protection against the dangers and disabilities to which their callings expose them. This general dispersion of industry necessitates not only a wide system of supervision, but legislative measures of a peculiar character, at once sufficiently elastic to comprehend many varieties of function, and yet rigid to crush any apparent abuse.
The most important of these laws, in its general significance, is that dealing with compulsory arbitration in labour disputes. “The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, 1894” (with its amending Acts of 1895, 1896, and 1898), were consolidated and further amended by the Acts of 1900 and 1901, now in force, and which are for the purpose of encouraging industrial association, and to facilitate the settlement of trade difficulties. Societies consisting of two or more employers, or of seven or more workers, may be registered and become subject to the jurisdiction of the Board and Court appointed by the Act of 1900. Any such society, after complying with stated conditions, may bring a disputed case before the Board of Conciliation appointed for that industrial district, and, if the Board fails to effect a settlement, the dispute may be referred to the Court of Arbitration, whose award may be enforced in the same manner as an award of the Supreme Court. The amending Act of 1901 gives the right to either party to a trade dispute to refer the matter directly to the Arbitration Court. The amount for which such an award may be enforced against an association is limited to £500.
“The Factories Act, 1901,” is a consolidation of previous legislation, with some important amendments. New Zealand has been divided into factory districts under the charge of a Chief Inspector and 150 local Inspectors. As a “factory” or “work-room” includes any place in which two or more persons are engaged in working for hire or reward in any handicraft, there are few operatives who do not come within the scope of the Act. Children under fourteen years of age are not allowed to be employed, and the hours of labour, holidays, &c., of women and youths under sixteen are strictly regulated. Good ventilation, sanitary accommodation, and general cleanliness of buildings are points dwelt upon; while machinery has to be properly guarded, fire-escapes provided, and dangerous occupations especially classified. In order to assist the system of free general education which prevails in the colony, young persons are not allowed to work in factories till they have passed the Fourth Standard of the State schools, or an equivalent examination. To prevent the introduction of “sweating” into our commercial centres, articles made, or partly made, in private dwellings, or unregistered workshops, have to be labelled when offered for sale, so that goods so manufactured (often in unsanitary premises) may not be placed in the market in competition with work done in properly inspected factories. Any person removing such labels is liable to a heavy fine. The Factory Inspectors also exercise supervision over the sleeping accommodation provided for shearers in country districts. As the sheep-runs and farms are widely scattered, sometimes in the rough and remote back country, this part of the work of inspection is no easy task. A woman Inspector of Factories also gives her assistance to the duties of the Department, travelling from place to place, and particularly looking into the condition of the operative women and girls. There is an amendment Act, passed in 1902, relative to the granting of overtime permits, the minimum wages of persons under twenty years of age, and the health of persons working in the manufacture of textile fabrics.
The duration of the hours of business in shops is limited by “The Shops and Shop-assistants Act, 1894,” and the Shops and Shop-assistants Act Amendment Acts, 1895, 1896, and 1901. These provide for the closing of all shops in towns and boroughs for one afternoon half-holiday in each week. A few shops, such as those of fishmongers, fruiterers, eating-house keepers, &c., are exempted from the general closing on account of their convenience to the public; but assistants in such establishments, in the bars of hotels, and in country stores, must have a half-holiday on some day of the week. Very small shops carried on by Europeans without paid assistants are also exempt from closing on the general half-holiday, but must close on one afternoon in each week. The hours of work for women and young persons are defined; sitting accommodation must be provided, and precautions as to the necessary time for meals, sanitary accommodation, &c., are enforced; the Act also enumerates the working-hours, holidays, &c., of clerks employed in banks, mercantile offices, &c.
“The Employers’ Liability Act, 1882,” added to and amended in 1891 and 1892, is designed to protect workmen from negligence on the part of employers, by defining under what circumstances compensation for injury or death may be recoverable. The Act covers all employments except that of domestic servant, and does not allow of any “contracting out” by agreement on the part of employer and employed. Another Act of this character has regard to the payment of workmen's wages, and states that if a workman shall demand payment of wages twenty-four hours or more after they are due, and the contractor does not pay such wages, the workman may legally attach all moneys due to the contractor by the employer until such wages are paid. “The Truck Act, 1891,” requires that payment of wages shall not be made in goods or “truck,” but in money, any contra account notwithstanding; but there are a few exemptions, such as for advances for food, tools, &c., to men engaged in felling bush. In order to minimise the number of cases wherein fraudulent or unfortunate contractors victimised their labourers, “The Contractors’ and Workmen's Lien Act, 1892,” was brought into existence. This entitles a person who has done work upon any land, building, or chattel to a lien upon such property. The lien is only to be exercised under certain restrictions, and for a limited amount, but it gives priority of claim for wages against other service, and enables legal proceedings for recovery to be taken before the attached property can be disposed of or alienated.
“The Workers’ Compensation for Accidents Act, 1900,” will probably almost altogether supersede the Employers’ Liability Act, because, while an accident to a workman had not to be compensated by an employer under the latter Act unless it had occurred through his carelessness or that of his agent, under the former all accidents are to be compensated unless they are caused by the serious and wilful misconduct of the person injured. To meet the difficulty of too great expense falling on an employer through his having to pay large accident compensation, “The Government Accident Insurance Act, 1899.” was passed, which insures employers against risk of paying compensation. “The Workers’ Compensation for Accidents Act Amendment Act, 1902,” extends the application of the principal Act to workers in all branches of agriculture, and reduces the term during which the employer is not liable to pay for accident from two weeks to one week.
“The Accidents Compensation Act, 1901,” provides that an independent medical examination of the injured person may be ordered by the Judge before whom a claim of compensation for accident is brought.
“The Servants’ Registry Offices Act, 1895,” regulates the licensing of registry offices for domestic or farm servants. It prevents friendless or uneducated people from becoming the prey of unscrupulous persons, who formerly collected fees by duping the applicants for situations. The registry-office keepers have to pay a licensing fee to the Government, and to present a certificate of good character when applying for a license. Proper ledgers and books open to inspection must be provided, and the lending or hiring of licenses is not permitted. Registry-office keepers are not allowed to keep lodging-houses for servants, or have any interest in such houses.
There are sundry Acts for the supervision of shipping, and the protection of sailors and passengers. They relate to the appointment of pilots and ships’ officers; the engagement and discharge of sailors; the sanitation, ventilation, and overloading of vessels; and the number of duly rated hands engaged in proportion to tonnage. They endeavour to prevent injustice to the sailor as to advance-notes, or payments in foreign money, and also specify penalties to be inflicted for desertion, disobedience, &c.
Combinations or associations of persons for regulating the relations between masters and masters, or masters and workmen, or workmen and workmen, are directed by “The Trade Union Act, 1878.” In this Act the different statutes which do not apply to trade-unions (such as the Joint Stock Act, the Friendly Societies Act, &c.) are enumerated, and the manner in which such societies may register, hold property, &c., is set out, together with the necessary provisions as to returns, penalties, &c. [An Amendment Act was passed in 1896, altering the age of membership.] “The Conspiracy Law Amendment Act, 1894,” permits any combination of persons in furtherance of a trade dispute, provided that any act performed by such combination or society would not be unlawful if done by one person. Such action must not include riot, sedition, or crime against the State.
“The Wages Attachment Act, 1895,” prevents wages below £2 a week being attached for debt. It does not interfere with any workman being sued for debt in the ordinary course, but prevents a grasping creditor from stepping in before others and seizing wages in advance before they are earned. [There is also “The Wages Protection Act, 1899,” which has to be read with “The Truck Act, 1891,” previously alluded to.]
“The Master and Apprentice Act, 1865,” applies mainly to the indenturing of apprentices by the State, such apprentices being children of destitute parents. In other respects the law of England is held to be the law governing the relations between masters and apprentices in this colony; but special sections of the Act apply to the punishment of apprentices for absenting themselves from duty, and to the fine on a master for neglecting or ill-using his apprentice. Sections 150 and 213 of “The Criminal Code Act, 1893,” also relate to the proper care of apprentices by their masters.
“The Mining Act, 1898,” consolidates and repeals all statutes of a similar nature, and includes various amendments suggested by the Conference of Wardens of Goldfields, and by mining associations. The mining legislation refers to labour in any kind of mine, and deals with the position of tributers and wagesmen, the examination for certificates for mine-managers, &c., provision for ventilation, precautions against accident by blasting, &c. There are amending Acts of 1900, 1901, and 1902, providing for the inspection of mines by workmen, limiting the number of hours of working underground, and making provision for the payment of overtime.
In or about coal-mines women and boys are not allowed to be engaged. There is provision for the appointment of inspectors, mine-managers, engine-drivers, &c., and rules are furnished as to the ages and working-hours of those employed in attending engines, machinery, winding-gear, &c. The ventilation of mines is provided for, and the necessary safeguards imposed as to blasting operations, working in foul air, protecting lights, &c. There are regulations for the management and administration of funds and moneys, which relate chiefly to the withdrawal of moneys from the Sick and Accident Fund, and returns demanded from trustees of the fund.
There is also “The Deaths by Accident Compensation Act, 1880.”
“The Public Contracts Act, 1900,” provides that any person entering into a contract exceeding the value of twenty pounds with the Government, any Education Board, Harbour Board, or local authority, and employing skilled or unskilled manual labour in the execution of such contract, shall be bound to pay wages at the rate ruling in the locality of the work, but in no case lower than the rates fixed by the Arbitration Court. The maximum length of the working-day on any public contract is not to exceed eight hours. A penalty not exceeding £10 is recoverable by summary proceedings for every breach of the provisions of the Act.
Remarks on the co-operative system of constructing public works were given in a special article in the Year-book of 1894. The numbers of workmen employed in this manner under Government departments during each month of the financial year 1902–1903 were:—
| Roads and Lands and Survey Departments. | Public Works Departments. | Total. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| April, 1902 | 748 | 846 | 1,594 |
| May, 1902 | 813 | 1,102 | 1,915 |
| June, 1902 | 943 | 1,173 | 2,116 |
| July, 1902 | 1,117 | 1,261 | 2,378 |
| August, 1902 | 1,105 | 1,317 | 2,422 |
| September, 1902 | 1,229 | 1,569 | 2,798 |
| October, 1902 | 1,211 | 1,715 | 2,926 |
| November, 1902 | 1,324 | 1,865 | 3,189 |
| December, 1902 | 1,573 | 1,881 | 3,454 |
| January, 1903 | 1,512 | 2,386 | 3,898 |
| February, 1903 | 1,910 | 2,771 | 4,681 |
| March, 1903 | 2,338 | 2,913 | 5,251 |
The average number of men employed in each year was as follows:—
| Year. | Roads and Lands and Survey Departments. | Public Works Departments. | Total. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1891–92 | 261 | 527 | 788 |
| 1892–93 | 280 | 842 | 1,122 |
| 1893–94 | 933 | 1,015 | 1,948 |
| 1894–95 | 1,103 | 962 | 2,065 |
| 1895–96 | 1,572 | 764 | 2,336 |
| 1896–97 | 1,459 | 854 | 2,313 |
| 1897–98 | 1,552 | 890 | 2,442 |
| 1898–99 | 1,613 | 1,194 | 2,807 |
| 1899–1900 | 1,825 | 1,243 | 3,068 |
| 1900–1901 | 1,820 | 2,090 | 3,910 |
| 1901–1902 | 1,894 | 2,673 | 4,567 |
| 1902–1903 | 1,319 | 1,733 | 3,052 |
| Annual average last twelve years | 1,303 | 1,232 | 2,535 |
The total number of men for whom employment has been found by the Department of Labour up to the end of March, 1903, is given below. The statement also exhibits the number of persons dependent upon the men assisted:—
| Men. | Dependents. | |
|---|---|---|
| June, 1891, to 31st March, 1892 | 2,593 | 4,729 |
| 1st April, 1892, to 31st March, 1893 | 3,874 | 7,802 |
| 1st April, 1893, to 31st March, 1894 | 3,341 | 7,942 |
| 1st April, 1894, to 31st March, 1895 | 3,030 | 8,883 |
| 1st April, 1895, to 31st March, 1896 | 2,871 | 8,424 |
| 1st April, 1896, to 31st March, 1897 | 1,718 | 4,719 |
| 1st April, 1897, to 31st March, 1898 | 2,035 | 4,928 |
| 1st April, 1898, to 31st March, 1899 | 2,115 | 4,759 |
| 1st April, 1899, to 31st March, 1900 | 2,147 | 4,471 |
| 1st April, 1900, to 31st March, 1901 | 3,124 | 5,432 |
| 1st April, 1901, to 31st March, 1902 | 1,830 | 2,747 |
| 1st April, 1902, to 31st March, 1903 | 3,704 | 5,934 |
| 32,382 | 70,770 |
Table of Contents
THE revenue for the year ended 31st March, 1903, was £6,447,435, and the ordinary expenditure £6,214,019, leaving an excess of revenue over expenditure of £233,416. Adding to this the balance brought forward from the previous year (1901–1902), of £270,489, gives a sum of £503,905. A transfer of £200,000 was made to the Public Works Fund, leaving at the close of the year a balance amounting to £303,905.
The chief heads of revenue and expenditure are shown hereunder:—
| REVENUE AND EXPENDITURE. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue. | £ | £ | Expenditure. | £ | £ |
| Balance on 31st March, 1902 | .. | 270,489 | His Excellency the Governor | 7,000 | |
| Customs duties | 2,335,643 | Legislative | 49,987 | ||
| Beer duty | 90,400 | Ministers' salaries and allowances | 12,931 | ||
| Stamps (including postal and telegraph cash receipts) | 978,939 | Interest and sinking fund charges | 1,900,979 | ||
| Land-tax | 296,062 | Exchange and commission | 20,525 | ||
| Income-tax | 200,684 | ||||
| Railways | 1,982,551 | Pensions, civil and military | 47,446 | ||
| Registration and other fees | 83,881 | Old-age pensions | 212,962 | ||
| Marine dues | 32,968 | Railways | 1,357,385 | ||
| Miscellaneous | 133,204 | Public instruction | 566,568 | ||
| Territorial revenue | 252,277 | Postal and telegraph services | 485,860 | ||
| 6,386,609 | |||||
| Other receipts— | Judicial and legal | 258,633 | |||
| Proceeds of debentures for increases of sinking fund | 57,500 | Hospitals and charitable institutions | 109,071 | ||
| Defence | 214,226 | ||||
| Recoveries in respect of expenditure of previous years | 3,326 | Subsidies to local bodies | 71,049 | ||
| Department of Agriculture | 101,134 | ||||
| 60,826 | Lunatic asylums | 66,002 | |||
| Valuation Department | 26,248 | ||||
| Customs | 36,045 | ||||
| Marine (including harbours and lights) | 44,064 | ||||
| Printing and stationery | 35,847 | ||||
| Land and Income Tax Department | 19,596 | ||||
| Registration of land and deeds, births, deaths, and marriages | 21,765 | ||||
| Public buildings and domains | 21,019 | ||||
| Miscellaneous expenditure | 283,208 | ||||
| Territorial expenditure | 241,469 | ||||
| 6,214,019 | |||||
| Other expenditure— | |||||
| Transferred to Public Works Fund | 200,000 | ||||
| Balance on 31st March, 1903 | 303,905 | ||||
| £6,717,924 | £6,717,924 | ||||
The ordinary revenue shows an increase for the year 1902–1903 of 5·70 per cent. over the figures for 1901–1902. When considering the figures given it must be remembered that population increased at the rate of 3·15 per cent., so that any rate above this means a higher ratio of revenue. Taking the items in order of their magnitude, the advance is shown below:—
| Heads of Revenue. | Ordinary Revenue. | Increase. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1901–1902. | Per Cent. of Total. | 1902–1903. | Per Cent. of Total. | Numerical. | Centesimal. | |
| * Decrease. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent. | |||
| Customs duties | 2,201,116 | 37·93 | 2,335,643 | 38·07 | 134,527 | 6·11 |
| Railways | 1,869,489 | 32·21 | 1,982,551 | 32·32 | 113,062 | 6·05 |
| Stamps (including postal and telegraph cash receipts) | 908,671 | 15·66 | 978,939 | 15·96 | 70,268 | 7·73 |
| Land-tax | 312,836 | 5·39 | 296,062 | 4·83 | - 16,774* | - 5·36* |
| Income-tax | 179,397 | 3·09 | 200,684 | 3·27 | 21,287 | 11·87 |
| Beer duty | 90,233 | 1·55 | 90,400 | 1·47 | 167 | 0·19 |
| Registration and other fees | 76,492 | 1·32 | 83,881 | 1·37 | 7,389 | 9·66 |
| Marine | 31,456 | 0·54 | 32,968 | 0·54 | 1,512 | 4·81 |
| Miscellaneous | 133,761 | 2·31 | 133,204 | 2·17 | - 557* | - 0·42* |
| Ordinary revenue | 5,803,451 | 100· | 6,134,332 | 100·00 | 330,881 | 5·70 |
The amount derived from Customs duties was 6·11 per cent. greater than that shown for 1901–1902, beer duty 0·19 per cent., income-tax 11·87 per cent., stamps, &c., 7·73 per cent., and railway revenue shows an advance of 6·05 per cent. While the population of the colony increased by 3·15 per cent. during 1902–1903, the ordinary revenue advanced at the much higher rate of 5·70, as shown above.
The Customs and excise duties in 1902–1903 accounted for £39 10s. 10d. out of every £100 of ordinary revenue collected; railways, £32 6s. 5d.; and stamps, &c., £15 19s. 2d. Of other items, the land-tax yielded 4·83 per cent. and income-tax 3·27 per cent. of the revenue.
Territorial revenue belonging to the Consolidated Fund increased from £249,619 in 1901–1902 to £252,277 in 1902–1903, or at the rate of 1·06 per cent. In the previous year, 1901–1902, there was a decrease of 7·62 per cent. Details for the last two years are:—
| — | Territorial Revenue. | Increase or Decrease, 1901–1903. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1901–1902. | Per Cent. of Total. | 1902–1903. | Per Cent. of Total. | Numerical. | Centesimal. | |
| * Exclusive of revenue derived from land set apart for State forests, £3,871; lands for close settlement. £109,820; and of the Cheviot Estate, £14,603. These moneys are credited in the separate loan accounts to which they belong. The amount of all moneys taken by the Receivers of Land Revenue during the year ended 31st March, 1903, will be found stated, under each head, in Section XXV., “Crown Lands.” | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent. | |||
| Cash land sales | 59,576 | 23·87 | 37,446 | 14·84 | - 22,130 | - 37·15 |
| Deferred-payment land sales | 8,435 | 3·38 | 6,702 | 2·66 | - 1,733 | - 20·55 |
| Pastoral runs, rents, miscellaneous | 181,608 | 72·75 | 208,129 | 82·50 | 26,521 | 14·60 |
| Territorial revenue | 249,619 | 100·00 | 252,277* | 100·00 | 2,658 | 1·06 |
By the foregoing table the cash land sales for 1902–1903 are shown to have decreased by 37 per cent., and to supply nearly 15 per cent. of the whole territorial revenue of the Consolidated Fund; while rents and miscellaneous, which constitute over 82 per cent. of the total, have increased by 14·60 per cent.
The total ordinary and territorial revenue is found to have increased from £6,053,070 in 1901–1902 to £6,386,609 in 1902–1903, at the rate of 5£51 per cent., or 2£36 per cent. more than the rate at which population increased:—
| Ordinary. | Territorial. | Total. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Year 1902–1903 | 6,134,332 | 252,277 | 6,386,609 |
| Year 1901–1902 | 5,803,451 | 249,619 | 6,053,070 |
| Increase | 330,881 | 2,658 | 333,539 |
After allowing for alteration in system of charging interest and sinking fund, the charges of the public debt paid out of the Consolidated Fund, in proportion to the ordinary and territorial revenue, are found to have fallen from 41·6 per cent. in 1890–91 to 29·77 per cent. in 1902–1903.
If the sum of £44,148, the amount of territorial revenue received by way of land sales in 1902–1903, is deducted from the total revenue the charges of the public debt will be found to have absorbed 29·97 per cent. of the revenue, reduced by the sum derived from relinquishment of real estate of the Crown.
The whole of the revenue of the General Government arising from taxation as well as from other sources for the last eight financial years exhibits great progress. The rates of taxation and of revenue-per head of mean population are given to illustrate this:—
| Year ended 31 March. | Revenue. | Taxation per Head of Mean Population. | Revenue per Head of Mean Population. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From Taxation. | From other Sources. | Total. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1896 | 2,335,760 | 2,220,255 | 4,556,015 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 10 |
| 1897 | 2,521,911 | 2,276,797 | 4,798,708 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 1 |
| 1898 | 2,678,576 | 2,400,654 | 5,079,230 | 3 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 2 |
| 1899 | 2,707,099 | 2,551,129 | 5,258,228 | 3 | 13 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 3 |
| 1900 | 2,891,126 | 2,808,492 | 5,699,618 | 3 | 16 | 10 | 7 | 11 | 6 |
| 1901 | 3,042,890 | 2,864,026 | 5,906,916 | 3 | 19 | 6 | 7 | 14 | 4 |
| 1902 | 3,113,079 | 3,039,760 | 6,152,839 | 3 | 19 | 8 | 7 | 17 | 6 |
| 1903 | 3,277,964 | 3,169,471 | 6,447,435 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 8 |
The total revenue is shown to have increased from £4,556,015 in 1895–96 to £6,447,435 in 1902–1903, a difference of £1,891,420, while the proportion to population has increased by nearly £1 10s. per head.
The greater yield from the sources of taxation exhibited by the above figures can be regarded as indicative of increased prosperity enjoyed by the people of the colony.
The expenditure for 1902–1903 (exclusive of expenditure properly belonging to territorial purposes) amounted to £6,214,019, of which the largest item, after the charges of the public debt, £1,900,979, was on account of railways, £1,357,385. Public instruction cost £556,568, of which £465,348 was for carrying on the Board schools, £23,578 for technical and higher education, £20,397 for Native schools, £20,113 for industrial schools, and £27,854 for school-buildings. The postal and telegraph services cost £485,860. Under the heading “Judicial and Legal” the total sum expended was £258,633, of which the largest item was the police, £123,804; the next, District and Magistrates' Courts, £47,169; and, thirdly, prisons, £32,070. Hospitals and charitable institutions cost £109,071, and the lunatic asylums £66,002. Defence required £214,226; the Department of Agriculture £101,134; and the Valuation Department £26,248. Payments of old-age pensions required £212,962 for the year.
The chief items of expenditure under this head are the Lands and Survey Department, £129,795, and Mines, £12,578; while there was paid to local bodies £93,496 (£33,163 being “thirds” and “fourths” under the Land Act, and £16,608 for the Greymouth, £3,602 for the New Plymouth, £39,647 for the Westport, and £476 for the Nelson Harbour Boards); besides £5,145 expended in management of water-races, and £457 in rates on Crown lands.
The expenditure out of ordinary and territorial revenue during the last six financial years is tabulated, specifying the chief heads of expenditure. It must be noted that the old-age pensions become a large item for the years 1899–1900, 1900–1901, 1901–1902, and 1902–1903. The development of the Departments of Agriculture, Public Health, &c., also contributed to raising the expenditure latterly:—
| Expenditure. | Financial Years (ended 31st March). | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1897–98. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Charges of the public debt | 1,741,413 | 1,767,468 | 1,749,394 | 1,745,616 | 1,803,939 | 1,900,979 |
| Railways | 849,923 | 968,917 | 1,039,412 | 1,145,088 | 1,280,997 | 1,357,385 |
| Public instruction (including school-buildings, industrial and Native schools, and deaf-and-dumb institution) | 466,925 | 475,218 | 472,653 | 481,087 | 539,317 | 566,568 |
| Postal and telegraph | 362,993 | 388,546 | 388,582 | 416,364 | 463,817 | 485,860 |
| Militia and Volunteers | 91,388 | 119,051 | 162,940 | 229,704 | 191,250 | 214,226 |
| Old-age pensions | .. | 3,124 | 157,095 | 199,708 | 210,045 | 212,962 |
| Crown lands and surveys | 119,920 | 114,469 | 123,441 | 137,838 | 122,278 | 129,795 |
| Police and Armed Constabulary | 104,214 | 115,293 | 115,752 | 117,744 | 120,629 | 123,804 |
| Other expenditure | 865,596 | 906,425 | 930,858 | 1,006,555 | 1,163,643 | 1,222,440 |
| Totals | 4,602,372 | 4,858,511 | 5,140,127 | 5,479,704 | 5,895,915 | 6,214,019 |
In addition to the expenditure above referred to, there were also—excluding operations on debentures, &c.—disbursements during the financial year ended 31st March, 1903, out of the Public Works Fund to the amount of £1,514,445, chiefly for roads, railway construction, and for public buildings; also out of the Land for Settlements Account the large sum of £372,925 for purchase of estates to be cut up for close settlement, including contingent expenses. This account also aided the Consolidated Fund by reducing the interest to be paid to the extent of £93,599. The sum of £39,424 was expended in the opening up and management of State coal-mines. The Loans to Local Bodies Account, which deals with moneys used chiefly for roading the more inaccessible country and for water-supply, shows an expenditure of £253,448; and for interest on debentures, surveys, roads, &c., in connection with the Cheviot Estate £9,037 was paid. Details of all these are given. The total expenditure out of loan accounts was £2,283,198, or, adding £425,100 for redemption of debentures and for temporary advances repaid, £2,708,298. As previously explained, this account was aided by a transfer from revenue of £200,000 to the Public Works Fund.
| EXPENDITURE OUT OF LOAN ACCOUNTS, 1902–1903. | ||
| £ | £ | |
| Public Works Fund— | ||
| Immigration | 142 | |
| Public works, departmental | 12,819 | |
| Railways | 759,753 | |
| Roads | 283,169 | |
| Development of goldfields | 24,213 | |
| Purchase of Native lands | 15,783 | |
| Telegraph extension | 68,578 | |
| Public buildings | 197,455 | |
| Lighthouses, harbour-works, and defences | 13,581 | |
| Tourist and health resorts | 10,949 | |
| Rates on Native lands | 471 | |
| Contingent defence | 37,004 | |
| Lands improvement | 2,348 | |
| Charges and expenses of raising loans | 88,180 | |
| 1,514,445 | ||
| Cheviot Estate Account— | ||
| Interest (including arrears) | 8,866 | |
| Surveys, roading, &c. | 171 | |
| 9,037 | ||
| Lands for Settlement Account— | ||
| Purchase of estates | 353,462 | |
| Expenses | 19,263 | |
| Interest recouped to Consolidated Fund | 93,599 | |
| Charges and expenses on issue of debentures under the Act | 320 | |
| Services not provided for | 200 | |
| 466,844 | ||
| State Coal-mines Account— | ||
| Salaries and other charges | 39,424 | |
| Loans to Local Bodies Account— | ||
| Grants to local bodies | 234,870 | |
| Roads to open up Crown lands | 18,578 | |
| 253,448 | ||
| Total | 2,283,198 | |
| Lands for Settlement Account— | ||
| Renewal of debentures | 250,000 | |
| Debentures paid off | 10,100 | |
| Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Acts— | ||
| Temporary advances repaid | 165,000 | |
| 425,100 | ||
| Total | £2,708,298 | |
The expenditure out of loan accounts for five years may be summarised as given in the next table:—
| Heads of Expenditure out of Loan Accounts. | Financial Years. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. | |
* Including sums expended in the purchase of land for settlements—viz., £518,459 in 1898–99; £469,331 in 1899–1900; in 1900–1901, £251,837; in 1901–1902, £498,124; and in 1902–1903, £466,844. † Including sums expended under Loans to Local Bodies Acts—viz., £16,972 in 1898–99; £31,363 in 1899–1900; in 1900–1901, £37,390; in 1901–1902, £31,979; and in 1902–1903, £18,578. NOTE.—Excluding amounts applied to investments by way of advances to settlers with charges and expenses, besides amounts for debentures redeemed and advances repaid. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Charges and expenses of raising loans | 225 | 28,322 | 1,460 | 5,620 | 88,180 |
| Cheviot Estate purchase and expenses | 16,497 | 8,917 | 8,937 | 8,881 | 9,037 |
| Contingent defence | 13,867 | 42,810 | 37,650 | 146,876 | 37,004 |
| Immigration | 105 | 385 | 214 | 140 | 142 |
| Land purchases | *571,642 | *501,355 | *280,575 | *516,385 | *482,627 |
| Lighthouses, harbour-works, and defences | 15,662 | 9,026 | 6,517 | 12,159 | 13,581 |
| Public buildings | 107,267 | 115,427 | 121,364 | 145,600 | 197,455 |
| Public Works departmental expenditure | 10,090 | 12,572 | 12,933 | 16,404 | 12,819 |
| Railway-construction and other works connected with railway-extension | 374,141 | 417,937 | 717,723 | 1,333,941 | 759,753 |
| Rates on Native lands | 347 | 744 | 673 | 570 | 471 |
| Roads | †312,506 | †316,753 | †353,131 | †435,669 | †301,747 |
| Telegraph-extension | 28,551 | 26,771 | 50,101 | 31,729 | 68,578 |
| Development of goldfields | 17,355 | 21,815 | 15,907 | 15,325 | 24,213 |
| Tourist and health resorts | .. | .. | .. | 11,260 | 10,949 |
| Lands improvement | .. | .. | .. | 1,677 | 2,348 |
| State coal-mines | .. | .. | .. | .. | 39,424 |
| Payments to local bodies under Government Loans to Local Bodies Acts | 75,428 | 68,770 | 138,956 | 208,531 | 234,870 |
| Totals | 1,543,683 | 1,571,604 | 1,746,141 | 2,890,767 | 2,283,198 |
The total amount of actual loan-moneys under various heads raised from the beginning is roughly shown further on in a table dealing with the public debt of the colony.
Although the Public Works Fund forms the main source of the expenditure out of loan accounts, all the money included in it has not been raised from loans. Amounts from the revenue of the Consolidated Fund were paid to the Public Works Fund during the last twelve financial years as follows:—
| £ | |
| 1891–92 | 30,000 |
| 1892–93 | 200,000 |
| 1893–94 | 250,000 |
| 1894–95 | 250,000 |
| 1895–96 | 150,000 |
| 1896–97 | 150,000 |
| 1897–98 | 300,000 |
| 1898–99 | 425,000 |
| 1899–1900 | 450,000 |
| 1900–1901 | 500,000 |
| 1901–1902 | 500,000 |
| 1902–1903 | 200,000 |
| Total | £3,405,000 |
The expenditure each year since 1884 on services provided for by the Public Works Fund has been:—
| Year. | Immigration. | Railways. | Roads. | Development of Goldfields. | Telegraph Extension. | Public Buildings. | Lighthouses, &c. | Other Services. | Totals. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Exclusive of moneys spent on roads under Lands Improvement, Native Lands Purchase, and Government Loans to Local Bodies Accounts: £103,076 in 1894–95, £162,757 in 1895–96, £173,358 in 1896–97. † The expenditure on roads under the first two Acts mentioned above (*) is included as part of Public Works Fund; the sum of £18,770 was also spent out of Loans to Local Bodies Account on roads to open up Crown lands in 1897–98, £16,972 in 1898–99, £31,363 in 1899–1900, £37,390 in 1900–1901, £31,979 in 1901–1902, and £18,578 in 1902–1903. These moneys have been excluded, as have also small sums expended in roading, &c., the Cheviot Estate. | |||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1884–85 | 57,148 | 603,063 | 317,043 | 8,029 | 25,799 | 117,361 | 34,033 | 114,251 | 1,336,727 |
| 1885–86 | 11,675 | 725,496 | 335,904 | 9,032 | 36,016 | 86,859 | 133,975 | 136,435 | 1,475,386 |
| 1886–87 | 12,454 | 615,265 | 278,617 | 7,665 | 18,952 | 89,598 | 148,705 | 162,228 | 1,333,484 |
| 1887–88 | 15,598 | 403,726 | 219,519 | 1,016 | 22,984 | 90,529 | 76,825 | 135,962 | 966,159 |
| 1888–89 | 8,791 | 272,077 | 106,440 | 55 | 12,047 | 34,592 | 47,593 | 132,344 | 613,939 |
| 1889–90 | 867 | 289,572 | 84,126 | 284 | 16,346 | 35,473 | 9,434 | 46,362 | 482,464 |
| 1890–91 | 1,823 | 180,020 | 71,289 | 821 | 16,292 | 22,819 | 2,666 | 39,026 | 334,756 |
| 1891–92 | 817 | 154,416 | 101,605 | 2,257 | 27,773 | 34,791 | 7,347 | 62,495 | 391,501 |
| 1892–93 | 242 | 220,894 | 105,506 | 3,811 | 29,245 | 31,101 | 11,205 | 60,502 | 462,506 |
| 1893–94 | 343 | 176,304 | 147,418 | 5,272 | 16,127 | 44,032 | 6,588 | 10,713 | 406,797 |
| 1894–95 | 101 | 247,545 | 61,757* | 5,865 | 19,229 | 54,190 | 3,145 | 9,578 | 401,410* |
| 1895–96 | Cr. 10 | 197,105 | 66,774* | 9,345 | 35,538 | 76,529 | 7,410 | 19,639 | 412,330* |
| 1896–97 | 301 | 207,231 | 64,292* | 10,508 | 36,791 | 70,579 | 11,600 | 26,683 | 427,985* |
| 1897–98 | 70 | 351,600 | 290,777† | 33,117 | 29,384 | 73,585 | 5,295 | 81,715 | 865,543† |
| 1898–99 | 105 | 374,141 | 295,534† | 17,354 | 28,551 | 107,267 | 15,662 | 77,713 | 916,327† |
| 1899–1900 | 385 | 417,937 | 285,532† | 21,815 | 26,771 | 115,427 | 9,026 | 116,330 | 993,223† |
| 1900–1901 | 214 | 717,723 | 315,791† | 15,907 | 50,101 | 121,364 | 6,517 | 81,404 | 1,309,021† |
| 1901–1902 | 140 | 1,333,941 | 403,690† | 15,325 | 31,729 | 145,600 | 12,159 | 200,668 | 2,143,252† |
| 1902–1903 | 142 | 759,753 | 283,169† | 24,213 | 68,578 | 197,455 | 13,581 | 167,554 | 1,514,445† |
Three-per-cent. stock to the value of £230,040 was inscribed during the year 1902–1903, which began with a credit balance of £4,704 in this account. Of this sum, £52,000 was applied to pay off debentures, £165,000 was transferred to the Public Works Fund for repayment of advance made on security of short-dated debentures, and £800 was exchanged for debentures under “The Canterbury Loan Ordinance, 1862” (6 per cent.). Premiums amounting to £240 were paid on these conversions. Expenses, the chief items of which were discount (£11,104), stamp duty (£3,032), brokerage and commission (£574), office expenses, rents, law charges, &c. (£331), absorbed £15,041, leaving a credit balance in this account of £1,662 on the 31st March, 1903.
A notable feature in the legislation of the year 1894 was the passing of the Government Advances to Settlers Act, a description of which, with its amending Acts and the loan operations under the same, will be found in Part III.
The loans authorised to the 31st March, 1903, classified according to provincial districts, are shown in tabular form:—
| Provincial Districts. | Loans authorised. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Applications. | Amount applied for. | Amount of Advances authorised. | |
| £ | £ | ||
| Auckland | 2,509 | 822,946 | 719,168 |
| Taranaki | 1,862 | 828,272 | 729,759 |
| Hawke's Bay | 845 | 267,370 | 238,260 |
| Wellington | 3,302 | 1,271,462 | 1,117,738 |
| Marlborough | 419 | 176,517 | 160,005 |
| Nelson | 190 | 59,370 | 52,705 |
| Westland | 156 | 42,045 | 36,695 |
| Canterbury | 1,045 | 332,857 | 290,235 |
| Otago | 2,594 | 1,102,676 | 972,375 |
| Totals | 12,922 | 4,903,515 | 4,316,940 |
Of the 12,922 advances authorised, 1,629 applicants declined the grants (£735,280) offered them, so that the net advances to the 31st March, 1903, numbered 11,293, and amounted to £3,581,660.
Of the total advances authorised, 10,534 were for advances under £500 in value, and 2,388 over.
The number of applications received to the 31st March, 1903, was 16,643, for an aggregate amount of £5,927,495.
The advances authorised on fixed loans, according to provincial districts, to the 31st March, 1903, were:—
| Provincial Districts. | Number. | Amount of Mortgage. | Value of Security. |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | ||
| Auckland | 50 | 16,290 | 41,498 |
| Taranaki | 63 | 45,935 | 106,975 |
| Hawke's Bay | 18 | 6,750 | 15,668 |
| Wellington | 82 | 59,340 | 139,548 |
| Marlborough | 1 | 1,200 | 2,005 |
| Nelson | 3 | 250 | 963 |
| Westland | 6 | 670 | 2,113 |
| Canterbury | 17 | 14,725 | 31,804 |
| Otago | 89 | 76,235 | 117,732 |
| Totals | 329 | 221,395 | 458,306 |
The liabilities and assets at 31st March, 1903, of the Government Advances to Settlers Office were:—
| DR. | Liabilities. | £ | s. | d. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | ||||
| 3-per-cent. Loan, redeemable 1st April, 1945, “A” | 1,500,000 | |||
| 3-per-cent. Loan, redeemable 1st April, 1945, “B” | 500,000 | |||
| 3-per-cent. sundry loans | 740,000 | |||
| Advances on account of loan | 200,000 | |||
| 2,940,000 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Assurance Fund | 67,911 | 16 | 8 | |
| Suspense Account | 4,411 | 17 | 7 | |
| Accrued interest payable | 49 | 14 | 1 | |
| Profit and Loss Account | 3,167 | 11 | 1 | |
| £3,015,540 | 19 | 5 |
| CR. | Assets. | £ | s. | d. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Account— | ||||
| Advances on mortgage | £ s. d. | |||
| 3,516,285 0 0 | ||||
| Less repayments | 925,741 19 0 | |||
| 2,590,543 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Temporary investments, Bank of New Zealand guaranteed stock | 4,836 | 17 | 0 | |
| Sinking Fund investment with Public Trustee | 125,867 | 7 | 10 | |
| Assurance Fund investment with Public Trustee | 67,911 | 16 | 8 | |
| Mortgage instalments receivable, overdue | 1,385 | 8 | 8 | |
| Bills receivable | 890 | 11 | 7 | |
| Interest receivable, overdue | 6,043 | 17 | 0 | |
| Interest receivable, accrued | 27,173 | 8 | 2 | |
| Cash in hand and in bank | 33,007 | 8 | 1 | |
| Loan-flotation charges | 157,881 | 3 | 5 | |
| £3,015,540 | 19 | 5 | ||
“The Government Advances to Settlers Act Amendment Act, 1899,” as an encouragement to the early payment of the prescribed instalments of interest on fixed loans, and of interest and principal on loans under the instalment principle, provides for a rebate to the mortgagor, which reduces his interest to 4 1/2 per cent. in lieu of 5 per cent. per annum.
There are new alternative modes of disposing of moneys paid in advance laid down in this measure, but it is optional with mortgagors to adopt the new system instead of that previously in operation in respect of moneys paid before the commencement of the new Act, and which are held under the original arrangements.
Provision is made for the readjustment of loans by memorandum of adjustment, which gives elasticity to the system by treating the balance of principal due as a fresh loan granted for a new term.
The margin of security on loans is provided for as follows: In the case of fixed loans the amount of the loan is not to exceed three-fifths of the value of the security, while in case of loans under the instalment system on freehold security of first-class agricultural land the amount of the loan is not to exceed two-thirds the value of the security; on other rural freeholds the limit is three-fifths.
Advances may now be made on the security of urban or suburban land, but on the instalment system only, and with limitation of amount to a maximum of £2,000 and a minimum of £25.
Urban land is defined as that situate in a borough having a population of at least two thousand persons, and which is not used for farming, dairying, or market gardening; and suburban land means that which is situate in a borough having under two thousand people, or any town or vicinity, and which is not used for agricultural or dairying purposes as above referred to.
As to security for loans: In the case of urban lands on which there are buildings, the amount of the loan is not to exceed three-fifths of the value of the land apart from the buildings, plus one-half of the value of the buildings apart from the land. When the land is suburban, having buildings thereon, the loan is not to exceed one-half of the value of the land apart from the buildings, plus one-half of the value of the buildings separately.
When the land is urban or suburban, but has no buildings, the loan is not to exceed one-half of the value of the land, and there is not to be any loan except for the erection of buildings, and to be by way of instalments as erection proceeds.
There is a further subdivision of the Act, under which special provisions are made for protecting the interests of the Advances to Settlers Department with respect to other than freehold securities.
The legislation for authorisation of loan moneys for Advances to Settlers has been: Under the principal Act of 1894, £3,000,000; under the Amendment Act of 1901, £1,000,000.
Another important financial Act, termed the New Zealand Consols Act, was passed in 1894, with the intention of providing further means of investment for the savings of persons resident in the colony. Some progress is being made in this class of deposits, which tends to show that the public may in time recognise the system as a means of safe and profitable investment of their savings. It is singular that deposits of moneys belonging to trust funds or minors are not more freely made. It is thought that the advantage of such an investment at a fair rate of interest and of a permanent character is not widely enough known.
Up to the 31st March, 1899, deposits amounting to £385,925 had been received, in sums ranging from £5 to £150,000. During 1899–1900 the deposits inscribed totalled £55,562; in 1900–1901, £17,902; in 1901–1902, £8,935; and in 1902–1903, £4,232: making the sum invested to the 31st March, 1903, £472,556.
The system of making deposits in New Zealand Consols is fully described in Part III.
“The Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1896,” empowered the Colonial Treasurer to raise £1,000,000—in aid of the Public Works Fund to the extent of £500,000, and the Lands Improvement Account and the Native Lands Purchase Account £250,000 each.
The Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act Amendment Act, passed in 1897, authorised the raising of an additional sum of £250,000, to be applied for the purpose of procuring £200,000 for further rolling-stock for railways, and for the repair of damages to lines by floods or otherwise; £25,000 for erection and repair of public-school buildings, and another sum of £25,000 for purposes building and equipment of technical schools.
The Act of 1898 provided for raising £500,000, of which £175,000 was allocated to railways-construction, £200,000 was for new rolling-stock for open railways, and £125,000 for the construction of roads, bridges, and other works authorised.
Under another Act of 1899, the sum of £1,000,000 was authorised—£300,000 for railway-construction, £225,000 for rolling-stock, £350,000 for land settlement and goldfields development, £50,000 for school-buildings, £50,000 for purchase of Native lands, and £25,000 for harbour defence.
A further Act of 1900 provided for the raising of £1,000,000, of which £500,000 was allocated to railway-construction, £300,000 for rolling-stock, £150,000 for land settlement, and £50,000 for goldfields development.
Again, an Act of 1901 authorised raising the sum of £1,250,000. Of this, £600,000 was applied to railway-construction, £400,000 for rolling-stock, £200,000 for land settlement, and £50,000 to development of goldfields.
“The Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1902,” authorised raising, in the colony or elsewhere, of sums not exceeding £1,750,000 altogether, by debentures or scrip, or by the creation or issue of inscribed stock under “The New Zealand Consolidated Stock Act, 1877.”
Provision was made for obtaining funds pending the raising of the money authorised, by the sale, &c., of short-dated debentures, bearing interest not exceeding 4 per cent. per annum, and having a currency of not more than seven years.
All the money raised under this Act is applied to the following purposes:—
| £ | |
| 1. Railways— | |
| Railway-construction | 750,000 |
| Additional rolling-stock, &c., for open lines | 450,000 |
| 2. Land settlement and goldfields development— | |
| Construction of roads, tracks, and bridges to open up back blocks, and other work in connection therewith | 450,000 |
| For developing goldfields | 50,000 |
| 3. For telegraph extension | 50,000 |
| £1,750,000 | |
The moneys raised under these Acts and the operations by way of purchasing estates to be cut up for close settlement form the subject of a special section of this part of the Year-book (No. XXVI.).
The above Act consolidates all former measures dealing with the borrowing-powers of local bodies. It does not affect the securities issued for any loan raised under any Act repealed.
As to Government loans to local bodies, the yearly rate of interest and the period during which interest is payable by the local authority shall, at the option of such authority, be—
Four and a half per centum per annum for a period of twenty-six years; or
Four per centum per annum for a period of thirty-two years; or
Three and a half per centum per annum for a period of forty-one years.
The interest payable in respect of every existing loan the period of which is twenty-six years shall be 4 1/2 per centum per annum, unless such loan be adjusted under either of the alternatives (b) or (c) mentioned above. These readjustments may be applied to any loan existing at the time of the passing of the Act, should the local authority interested so elect.
At the expiration of the period during which interest is payable the liability of the local authority shall cease without further payment.
THE direct taxation prior to 1892 consisted of a property-tax of 1d. in the pound on all assessed real and personal property (with an exemption of £500), and the stamp duties; but in 1891 a Land and Income Assessment Act was passed repealing the property-tax. A full description of the system of the land and income tax will be found in a special article in Part III. of this work. The leading features only are briefly stated here.
The Assessment Act of 1891 provided for an ordinary land-tax on the actual value of land, allowing an owner to deduct any amount owing by him secured on a registered mortgage. Under the original Act the deduction for improvements might not exceed £3,000; but by the Amendment Act of 1893 the value of all improvements whatsoever was exempted from liability to land-tax. Besides this, an exemption of £500 was allowed when the balance, after making deductions as above stated, was not above £1,500 and beyond that a smaller exemption was granted, but ceasing when the balance amounted to £2,500. There is a consolidation Act passed in 1900 now in force. Mortgages are subject to the land-tax, but in 1902–1903 the rate was lowered from the full amount to 3/4d. in the pound. The revenue from the ordinary land-tax is, in round numbers, about £220,000 per annum, being somewhat lessened by the reduction of the mortgage-tax, notwithstanding increased valuations. The rate of ordinary land-tax for 1902–1903 was 1d. in the pound. Native land occupied by Europeans is taxed 1/2d. in the pound on the unimproved value.
In addition to the ordinary land-tax, there is a graduated land-tax, which commences when the unimproved value is £5,000. For the graduated land-tax the present value of all improvements is deducted; but mortgages are not deducted. The Act of 1893, while reducing the ordinary taxation on land by exempting all improvements, increased the graduated tax, and the revised rates are now one-eighth of a penny in the pound sterling when the value is £5,000 and is less than £10,000, from which the rate increases with the value of the property by further steps of an eighth of a penny until the maximum of 2d. in the pound is reached, payable when the value is £210,000, or exceeds that sum.
This graduated tax yields, in round numbers, £80,000 per annum, which is not included in the sum of £220,000 given above. Twenty per cent. additional tax is levied in case of persons who have been absent from the colony for not less than one year prior to the passing of the yearly taxing Act. This amounts to about £1,000, and is included in the £80,000 shown above.
The taxable balances of real estates for purposes of the graduated tax according to the latest information were:—
| Rate. | Taxable Balance. | Tax. | Rate. | Taxable Balance. | Tax. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1/8d. | 8,728,499 | 4,547 | 11/4d. | 1,004,810 | 5,233 |
| 1/4 d. | 4,706,951 | 4,903 | 13/8 d. | 939,166 | 5,381 |
| 3/8 d. | 2,480,025 | 3,875 | 1 1/2 d. | 287,162 | 1,795 |
| 1/2 d. | 1,979,768 | 4,125 | 1 5/8 d. | 472,972 | 3,202 |
| 5/8 d. | 1,745,783 | 4,546 | 1 3/4 d. | 369,013 | 2,691 |
| 3/4 d. | 1,912,581 | 5,977 | 1 7/8 d. | 197,329 | 1,542 |
| 7/8 d. | 1,598,467 | 5,828 | 2 d. | 1,021,827 | 8,515 |
| 1 d. | 2,521,968 | 10,925 | |||
| 1 1/8 d. | 1,012,695 | 4,747 | .. | 30,979,016 | 77,832 |
Besides the land-tax (ordinary and graduated) there is also levied by way of further direct taxation an income-tax on all incomes above £300. From the yearly income of every taxpayer there is deducted by way of special exemption the sum of £300, and from taxable incomes a further deduction up to £50 per annum for life-insurance premiums is allowed. The rate of income-tax for 1902–1903 was 6d. in the pound on the first taxable £1,000, and 1s. in the pound on any excess of £1,000.
Companies pay 1s. in the pound, and are not allowed exemption. The Act of 1893 further disallowed the £300 exemption in the case of persons not domiciled in New Zealand.
The revenue derived from income-tax may be roughly set down at £200,000 per annum.
The indirect taxation is made up of Customs duties, and excise duty on beer made in the colony.
The following statement shows the total amount raised by the General Government taxation in 1885, 1890, and the last eight financial years ending 31st March:—
| Amount of Revenue raised by Taxation. | Amount per Head of Population (excluding Maoris). | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1885 | 2,016,730 | 3 | 10 | 10 |
| 1890 | 2,173,985 | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| 1895–96 | 2,335,761 | 3 | 7 | 1 |
| 1896–97 | 2,521,911 | 3 | 11 | 0 |
| 1897–98 | 2,678,576 | 3 | 13 | 11 |
| 1898–99 | 2,707,099 | 3 | 13 | 3 |
| 1899–1900 | 2,891,126 | 3 | 16 | 10 |
| 1900–1901 | 3,042,890 | 3 | 19 | 6 |
| 1901–1902 | 3,113,079 | 3 | 19 | 8 |
| 1902–1903 | 3,277,964 | 4 | 1 | 8 |
The average annual amount of revenue raised by taxation during the period 1895–96 to 1902–1903 has been £3 15s. 4d.
It may be well to call attention to the fact that a rise in the amount of taxation yielded per head of population may indicate (outside the question of increasing the rate of any particular tax levied) a satisfactory condition of business, as showing activity.
As the Maoris contribute somewhat to the Customs revenue, an allowance should be made on that account to ascertain more correctly the amount of taxation per head of the rest of the people. By including Maoris the Customs and excise duties per head of the rest of the population would be reduced by 3s. 1d. for the year 1902–1903. If this amount be deducted from the taxation per head given for that year, the rate would be reduced from £4 1s. 8d. to £3 18s. 7d. This latter rate may fairly be used for comparison with the rates in the States of Australia.
Of the total amount of taxation stated for the year 1902–1903, the indirect taxation—i.e., Customs and excise duties—amounted to £2,426,043, while land and income tax, with stamps for taxation, yielded £851,921, which constitutes direct taxation. So that the colony still raises 74 per cent. of its taxation revenue by means of the indirect method.
A table of the Customs tariff is given in detail in Part I. of this book (pp. 85–101), and the duties leviable upon estates of deceased persons on page 457.
The amounts paid by way of income-tax, under a uniform rate of taxation, show great increase year by year, and afford satisfactory evidences of prosperity. These are quoted with a caution in regard to the figures for 1892 to 1895. The full number of persons properly liable to the tax may not have been ascertained at such time.
| Income-tax paid. | |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1892–93 | 67,367 |
| 1893–94 | 75,238 |
| 1894–95 | 89,891 |
| 1895–96 | 92,778 |
| 1896–97 | 105,504 |
| 1897–98 | 115,210 |
| 1898–99 | 115,480 |
| 1899–1900 | 128,721 |
| 1900–1901 | 173,809 |
| 1901–1902 | 179,397 |
| 1902–1903 | 200,684 |
The increase from 1895–96 to 1902–1903 is £107,906, being a rate of 116·31 per cent., while the population increased during the same period by 16 per cent.
The various local bodies levied taxation during the year ended 31st March, 1902, to the amount of £896,824, or £1 2s. 11d. per head of European population. Of the total sum, £548,859 was raised by general rates, £251,612 by special and separate rates, £78,617 by licenses, and £17,736 by other taxes.
The following were the amounts and rates of General Government taxation per head of population in Australasia for 1901–1902, specifying the proportions derived from Customs and other taxes:—
| State or Colony. | Amount of Revenue raised by Taxation. | Proportion of Taxation from Customs and Excise Duties. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customs and Excise. | Other Taxes. | Total. | ||
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent. | |
| Queensland | 1,297,662 | 276,771 | 1,574,433 | 82·42 |
| New South Wales | 2,812,722 | 1,148,942 | 3,961,664 | 71·00 |
| Victoria | 2,376,483 | 716,446 | 3,092,929 | 76·84 |
| South Australia | 699,608 | 267,786 | 967,394 | 72·32 |
| Western Australia | 1,335,114 | 173,582 | 1,508,696 | 88·49 |
| Tasmania | 424,443 | 111,515 | 535,958 | 79·19 |
| New Zealand | 2,291,349 | 821,730 | 3,113,079 | 73·60 |
| State or Colony. | Rate of Taxation per Head of Mean Population. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customs and Excise. | Other Taxes. | Total. | |||||||
| * Or, including Maoris, £3 16s. 7 1/4d. (See remarks on previous page.) | |||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Queensland | 2 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 8 |
| New South Wales | 2 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 16 | 10 |
| Victoria | 1 | 19 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 11 | 2 |
| South Australia | 1 | 18 | 4 | 0 | 14 | 8 | 2 | 13 | 0 |
| Western Australia | 6 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 16 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| Tasmania | 2 | 8 | 11 | 0 | 12 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 9 |
| New Zealand (excluding Maoris) | 2 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 19 | 8* |
THE gross public debt of the colony on the 31st March, 1903, was £55,899,019, an increase of £2,932,572 on the amount owing at the end of the preceding financial year.
Of this increase, £338,700 was devoted to the purchase of lands for settlement; £450,000 was used for purposes of advances to settlers; £278,000 for loans to local bodies; £4,232 for New Zealand Consols deposits; and £52,000 for purchase and development of State coal-mines: making a total of £1,122,932 invested in a directly reproductive manner, outside of money used for railway and telegraph construction, which might almost be considered as of a similar nature.
The following table states the debentures and stock in circulation on 31st March, 1903, under the several Loan Acts or Ordinances of the Colonial and old Provincial Governments, the dates when redeemable, the sinking funds accrued in respect of the same, and the annual charge thereon for interest and sinking fund:—
| PUBLIC DEBT ON 31ST MARCH, 1903. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ... | Amount outstanding. | Due Date. | Sinking Funds accrued. | Not Indebtedness. | Annual Charge. | Remarks. | ||||
| Rate. | Amount. | When payable. | ||||||||
| Int. | S.F. | |||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ |  c. c. |  c. c. | £ | ||||
| New Zealand Loan Act, 1863 | ... | 266,300 | 15 July, 1914 | 146,492 | 119,808 | 5 | 1 | 15,978 | 15 Jan. and 15 July. | |
| Consolidated Loan Act, 1867 | ... | 236,400 | Ann. drawing | ... | 236,400 | 5 | ... | 11,820 | Quarterly, 15 Jan., &c. | |
| Immigration and Public Works Loan Act, 1870 | ... | *1,000,000 | 1 June, 1907 | 756,158 | 243,842 | 4 | 2·4 | 64,000 | 1 June and 1 Dec. | Sinking fund payable 13 Mar. and 13 Sept. *Only £200,000 has actually been issued to the public. |
| Canterbury Loan Ordinance, 1862 | 3,000 | 15,200 | 2 Jan., 1915 | 14,258 | 942 | 6 | 1 | 1,120 | 30 June and 31 Dec. | |
| 12,200 | 2 July, 1916 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Loan Act, 1867 | ... | 13,000 | 15 April, 1913 | ... | 13,000 | 4 | ... | 520 | 15 April and 15 Oct. | |
| Immigration and Public Works Loan Act, 1870 | 363,000 | 390,900 | 15 April, 1913 | ... | 363,000 | 4 | ... | 14,520 | 15 April and 15 Oct. | |
| 27,900 | 15 April, 1913 | ... | 27,900 | 4 1/2 | ... | 1,256 | 15 April and 15 Oct. | |||
| Defence and other Purposes Loan Act, 1870 | 25,000 | 100,000 | 1 July, 1910 | ... | 25,000 | 4 1/2 | ... | 1,125 | 30 June and 31 Dec. | |
| 75,000 | 15 April, 1913 | ... | 75,000 | 4 | ... | 3,000 | 15 April and 15 Oct. | |||
| General Purposes Loan Act, 1873 | 17,400 | 82,900 | 15 Oct., 1913 | ... | 17,400 | 4 | ... | 696 | 15 April and 15 Oct. | |
| 10,800 | 15 May, 1914 | ... | 10,800 | 4 | ... | 432 | 15 May and 15 Nov. | |||
| 54,700 | 28 Nov., 1914 | ... | 54,700 | 5 | ... | 2,735 | 15 May and 15 Nov. | † The sinking fund is payable on £2,022,100 (1 1/2 per cent. on £1,402,435. 1 per cent. on £35,225, and 1/2 per cent. on £584,440); the Land Assurance Fund, is also charged with 1/2 per cent. as a contribution towards sinking fund. | ||
| District Railways Purchasing Acts, 1885-86 | 40,000 | 137,100 | 1 July, 1909 | ... | 40,000 | 6 | ... | 2,400 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |
| 97,100 | 1 April, 1905 | ... | 97,100 | 4 | ... | 3,884 | ||||
| Government Loans to Local Bodies Act, 1886 | ... | 250,300 | 1 Sept., 1907 | ... | 250,300 | 3 1/2 | † | 33,071 | 1 Mar. and 1 Sept. | |
| Consolidated Stock Act, 1877 | 29,150,302 | 44,824,466 | Nov., 1929 | ... | 29,150,302 | 4 | ... | 1,166,012 | 1 May and 1 Nov. | |
| 6,161,167 | 1 Jan., 1940 | ... | 6,161,167 | 3 1/2 | ... | 215,641 | 1 Jan. and 1 July. | |||
| 9,512,997 | 1 April, 1945 | ... | 9,512,997 | 3 | ... | 285,390‡ | 1 April and 1 Oct. | ‡ £89,700 of this amount will be recouped by the Government Advances to Settlers Office. | ||
| Consolidated Stock Act, 1884-Colonial issue | 272,000 | 781,500 | 1 Sept., 1905 | ... | 781,500 | 3 1/2 | ... | 27,352 | 1 Mar. and 1 Sept. | |
| 509,500 | 31 Dec., 1907 | ... | ||||||||
| Native Land Purchases Act, 1892 | ... | 125,000 | 31 Oct., 1906 | ... | 125,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 4,375 | 30 April and 31 Oct. | |
| (Renewed under the Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1899) | ||||||||||
| Land for Settlements Act, 1892 | ... | 45,276 | 31 Oct., 1906 | ... | 45,276 | 3 1/2 | ... | 1,585 | 30 April and 31 Oct. | |
| (Renewed under the Land for Settlements Acts Amendment Act, 1899) | ||||||||||
| Lands Improvement and Native Lands Acquisition Act, 1894 | ... | 400,000 | 30 Sept., 1908 | ... | 283,000 | 4 | ... | 11,320 | 31 Mar. and 30 Sept. | |
| 117,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 4,095 | 31 Mar. and 30 Sept. | ||||||
| New Zealand Consols Act, 1894 | ... | 472,556 | 1 Feb., 1910 | ... | 472,556 | 3 1/2 | ... | 16,540 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |
| Land for Settlements Acts, 1894, 1897, 1899, and 1900 | 769,490 | 2,722,340 | 31 Oct., 1906 | ... | 769,490 | 3 1/2 | ... | 26,932 | 30 April and 31 Oct. | |
| 349,000 | 1 April, 1909 | ... | 349,000 | 3 3/4 | ... | 13,088 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 62,000 | 1 April, 1909 | ... | 62,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 2,170 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 56,000 | 1 April, 1905 | ... | 56,000 | 4 | ... | 2,240 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 10,000 | 1 April, 1906 | ... | 10,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 350 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 527,950 | 1 May, 1904 | ... | 527,950 | 4 | ... | 21,118 | 1 May and 1 Nov. | |||
| 21,000 | 1 Nov., 1904 | ... | 21,000 | 4 | ... | 840 | 1 May and 1 Nov. | |||
| 412,900 | 1 Feb., 1905 | ... | 412,900 | 4 | ... | 13,528 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |||
| 2,100 | 1 Feb., 1905 | ... | 2,100 | 3 1/2 | ... | 73 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |||
| 100,000 | 1 Dec., 1906 | ... | 100,000 | 4 | ... | 4,000 | 1 June and 1 Dec. | |||
| 161,900 | 1 Feb., 1908 | ... | 161,900 | 4 | ... | 6,476 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |||
| 250,000 | 1 April, 1904 | ... | 250,000 | 4 | ... | 10,000 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| Carried forward | ... | ... | 51,863,238 | ... | 916,908 | 50,946,330 | ... | ... | 1,989,682 | |
| Brought forward | ... | ... | 51,863,238 | ... | 916,908 | 50,946,330 | ... | ... | 1,989,682 | |
| Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Acts, 1896, 1897, 1898, 1899, 1900, 1901, and 1902 | 500,000 | 3,430,000 | 15 Aug., 1921* | ... | 500,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 17,500 | 15 Feb. and 15 Aug. | * Loan may be paid off at any time after 15th February. 1907, on six months' notice being given. |
| 15,000 | 31 Oct., 1903 | ... | 15,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 525 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |||
| 150,000 | 4 Jan., 1904 | ... | 150,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 5,250 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |||
| 100,000 | 15 Jan., 1905 | ... | 500,000 | † | ... | ... | ... | † No interest paid. | ||
| 100,000 | 15 Feb., 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 100,000 | 15 Mar., 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 100,000 | 17 April 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 100,000 | 15 May. 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 100,000 | 15 June, 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 100,000 | 16 July, 1905 | ... | 300,000 | ‡ | ... | 10,500 | 31 Mar. and 30 Sept. | ‡ 1/4 per cent. over bank rate; varying interest, calculated at 3 1/2 per cent. | ||
| 100,000 | 15 Aug., 1905 | ... | ||||||||
| 465,000 | 1 April, 1903 | ... | 465,000 | 4 | ... | 18,600 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 500,000 | 1 April, 1904 | ... | 500,000 | 4 | ... | 20,000 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |||
| 250,000 | 1 Dec., 1904 | ... | 250,000 | 4 | ... | 10,000 | 1 June and 1 Dec. | |||
| 750,000 | 1 Dec., 1906 | ... | 750,000 | 4 | ... | 30,000 | 1 June and 1 Dec. | |||
| Government Advances to Settlers Act, 1894 | ... | 200,000 | ... | ... | 200,000 | § | ... | 7,000 | ... | § Short - dated debentures since paid off. |
| Dairy Industry Act, 1898 | 438 | 1,781 | 1 Aug., 1908 | ... | 1,781 | 3 1/2 | ... | 62 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |
| 843 | 1 Jan., 1911 | ... | ||||||||
| 500 | 1 Jan., 1916 | ... | ||||||||
| Government Accident Insurance Act, 1898 | ... | 2,000 | 1 Feb., 1911 | ... | 2,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 70 | 1 Feb. and 1 Aug. | |
| Local Bodies' Loans Act, 1901 | ... | 350,000 | 1 Jan., 1909 | ... | 350,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 12,520 | 1 Mar. and 1 Sept. | |
| State Coal-mines Act, 1901 | ... | 52,000 | 1 April, 1907 | ... | 52,000 | 3 1/2 | ... | 1,820 | 1 April and 1 Oct. | |
| Add- | 916,908 | 54,982,111 | ||||||||
| Accrued sinking fund in respect of the Government Loans to Local Bodies Acts | ... | ... | ... | 314,964|| | ||Represents the accrued sinking fund held by Public Trustee in respect of the total amount issued under the Government Loans to Local Bodies Acts, of which £1,421,800 has been converted into consolidated stock. | |||||
| Sinking fund, Government Advances to Settlers Office Account | ... | ... | ... | 125,867 | ||||||
| Investments in securities included above on account New Zealand Consols Investment Account | ... | ... | ... | 455,500 | ||||||
| Debentures held by Public Trustee as security for stock issued in respect of preferred shares | ... | ... | ... | 500,000 | ||||||
| Totals | ... | 55,899,019¶ | ... | 2,313,239 | 53,585,780 | ... | ... | 2,123,529 | ¶ Treasury bills amounting to £700,000 are not included. | |
A condensation of this table shows at a glance the amount of money that will be required in the near future for meeting the liabilities arising at the expiration of the terms of the loans. Taking the position as at present, and dealing with the term of five years 1903–1907, the total sum falling due is found to be £7,430,616.
From the year 1908 onwards to 1921 the amounts becoming due annually are comparatively small.
In 1929 (26 years hence) and from then the bulk of the debt will have to be dealt with—that is, nearly forty-five millions of money out of a total of close on fifty-six millions.
| Due Date. | Amount. |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1903 | 480,000 |
| 1904 | 1,698,950 |
| 1905 | 1,640,100 |
| 1906 | 1,799,766 |
| 1907 | 1,811,800 |
| 1908 | 562,338 |
| 1909 | 801,000 |
| 1910 | 497,556 |
| 1911 | 2,843 |
| 1913 | 496,300 |
| 1914 | 331,800 |
| 1915 | 3,000 |
| 1916 | 12,700 |
| 1921 | 500,000 |
| 1929 | 29,150,302 |
| 1940 | 6,161,167 |
| 1945 | 9,512,997 |
| Annual drawing | 236,400 |
| Short - dated debentures (since paid off) | 200,000 |
| £55,899,019 |
The net public debt, after deducting the accrued sinking fund (£2,313,239), was on 31st March, 1903, £53,585,780, an increase of £1,748,149 during the year. More than eight years' revenue, ordinary and territorial, at the present rate would thus be required to pay off the net debt of the colony. The net indebtedness per head of population for 1902–1903 is greater than in 1901–1902 by 2s. 11d. In March, 1890, it stood at £60 5s. 3d.; in 1891, £59 11s. 10d.; in 1892, £59 2s.; in 1893, £58 2s. 7d.; in 1894, £57 8s. 10d.; in 1895, £57 9s. 9d.; in 1896, £60 2s. 4d.; in 1897, £60 13s. 9d.; in 1898, £60 4s. 11d.; in 1899, £61 14s. 4d.; in 1900, £61 17s. 3d.; in 1901, £62 16s. 10d.; in 1902, £65 12s. 4d.; and in 1903, £65 15s. 3d. But, in considering the increase of the amount of debt per head as a burden on the people, attention should be given to the remarks following the table showing amounts paid by way of charges of the public debt out of the revenue year by year. Besides these remarks, under the head of “Interest and Sinking Funds” there are others bearing on the subject, given previously, under “Revenue,” which is shown to have been relieved substantially since the year 1890.
| Years ended 31st March. | Estimated or Census Population. | Amount of Debentures and Stock in Circulation. | Gross Indebtedness per Head of European Population. | Amount of Sinking Fund accrued. | Net Indebtedness. | Net Indebtedness per Head of European Population. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * With these figures (taken from the detailed table showing the public debt) the Hon. Colonial Treasurer explained in his Financial Statement that “in addition to the customary deduction made for sinking funds accrued, there had been this year included the accrued sinking funds of the Government Advances to Settlers Act, an item heretofore not shown in the table. The gross debt is also further reduced by taking off the amount of Government securities in which the New Zealand Consols deposits are invested, as both amounts appear in the table of the public debt. For the same reason £500,000 held by the Public Trustee in trust for the payment at maturity of the stock inscribed for the purchase of the preferred shares of the Bank of New Zealand, represented by debentues of like amount issued under ‘The Aid to Public Works and Land Settlement Act, 1899,’ is also deducted.” | ||||||||||
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||
| 1890 | 618,657 | 38,667,950 | 62 | 10 | 1 | 1,386,185 | 37,281,765 | 60 | 5 | 3 |
| 1891 | 626,658 | 38,830,350 | 61 | 19 | 4 | 1,487,042 | 37,343,308 | 59 | 11 | 10 |
| 1892 | 637,472 | 38,713,068 | 60 | 14 | 8 | 1,037,862 | 37,675,206 | 59 | 2 | 0 |
| 1893 | 656,187 | 39,257,840 | 59 | 16 | 7 | 1,113,770 | 38,144,070 | 58 | 2 | 7 |
| 1894 | 676,747 | 39,826,415 | 58 | 17 | 0 | 951,924 | 38,874,491 | 57 | 8 | 10 |
| 1895 | 689,475 | 40,386,964 | 58 | 11 | 6 | 751,932 | 39,635,032 | 57 | 9 | 9 |
| 1896 | 703,187 | 43,050,780 | 61 | 4 | 5 | 778,891 | 42,271,889 | 60 | 2 | 4 |
| 1897 | 717,649 | 44,366,618 | 61 | 16 | 5 | 814,294 | 43,552,324 | 60 | 13 | 9 |
| 1898 | 731,713 | 44,963,424 | 61 | 9 | 0 | 881,903 | 44,081,521 | 60 | 4 | 11 |
| 1899 | 746,673 | 46,938,006 | 62 | 17 | 3 | 857,279 | 46,080,727 | 61 | 14 | 4 |
| 1900 | 758,616 | 47,874,452 | 63 | 2 | 2 | 944,375 | 46,930,077 | 61 | 17 | 3 |
| 1901 | 772,719 | 49,591,245 | 64 | 3 | 7 | 1,033,494 | 48,557,751 | 62 | 16 | 10 |
| 1902 | 789,994 | 52,966,447 | 67 | 0 | 11 | 1,128,816 | 51,837,631 | 65 | 12 | 4 |
| 1903 | 814,842 | 55,899,019 | 68 | 12 | 0 | 2,313,239* | 53,585,780* | 65 | 15 | 3 |
The debt of the colony as above stated does not include the unpaid loans raised by the several local bodies, amounting at the end of March, 1902, to £7,839,695, of which sum £5,552,100 was raised outside the colony. These are referred to in dealing with the finance of local bodies.
The increase of the gross public debt since the 31st March, 1891, amounts to £17,068,669. A schedule of items composing this sum is subjoined. It shows the purposes to which the money raised has been or is being devoted. The second largest item is £3,190,000 raised for advances to settlers, which represents investments by the Government bearing interest and lent on continually improving security, the principal being repaid by instalments.
Other items which may be considered to represent interest-bearing investments are those under the heads “Land settlement,” “Native land purchases,” “Loans to local bodies,” “Lands improvement,” “N.Z. Consols,” and “Bank of N.Z. preferred shares.”
| £ | |
| Gross public debt, 31st March, 1903 | 55,899,019 |
| Gross public debt, 31st March, 1891 | 38,830,350 |
| Increase | £17,068,669 |
| £ | ||
| Native land purchases | 649,700 | |
| Land settlement (including Cheviot) | 3,111,416 | |
| Loans to local bodies | 1,697,100 | |
| Lands improvement | 500,000 | |
| Advances to settlers | 3,190,000 | |
| Bank of N.Z. preferred shares | 500,000 | |
| N.Z. Consols | 472,556 | |
| District railways | 47,000 | |
| Public works | 6,335,000 | |
| Increase by conversions | 666,469 | |
| Sinking fund accretions | 1,522,200 | |
| Naval and military settlers | 27,226 | |
| Government accident insurance | 2,000 | |
| Advances to dairy companies | 1,781 | |
| State coal-mines | 52,000 | £ |
| 18,774,448 | ||
| Less Redemptions— | ||
| Consolidated Stock Act, 1884, debentures | 1,260,420 | |
| Other debentures | 445,359 | |
| 1,705,779 | ||
| Total net increase | .. | £17,068,669 |
Of the total amount of outstanding public debt at the end of March, 1903—viz., £55,899,019—more than thirty-four millions sterling bore interest at the rate of 4 per cent., over ten millions sterling at 3 1/2 per cent., and more than nine millions sterling at 3 per cent. The following are the rates of interest payable on the complete public debt:—
| Rates of Interest. | Amount at each Rate. |
|---|---|
| * Including £500,000 on which the interest paid was 1/4 per cent. over bank rate: varying rate, averaging 3 1/2 per cent. | |
| £ | |
| 6 percent. | 55,200 |
| 5 per cent. | 557,400 |
| 4 1/2 per cent. | 52,900 |
| 4 per cent. | 34,504,352 |
| 3 3/4 per cent. | 349,000 |
| 3 1/2 per cent. | 10,367,170* |
| 3 per cent. | 9,512,997 |
| No interest | 500,000 |
| Total | £55,899,019 |
The total amount of interest payable to bondholders on the full amount of the public debt as quoted above is £2,072,347, which gives an average rate of £3 14s. 10d. per £100. On the total public debt outstanding on the 31st March, 1891, the average interest charge was £4 10s. 3d. per £100. During the period 1891–1903. therefore, the average rate is found to have declined 17 per cent.
The foregoing refers to interest payable to bondholders only, and has nothing to do with sinking-fund requirements, which are included in the whole annual charge of the public debt.
The actual payments during nine years for interest and sinking fund out of the Consolidated Fund are shown hereunder, together with the percentage of ordinary and territorial revenue absorbed by the public-debt charges:—
| Year ended 31st March | Amounts actually paid for Interest and Sinking Fund out of the Consolidated Fund. | Rate per Head of Mean Population. | Percentage of Revenue absorbed by Public Debt Charges. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Debt. | Treasury Bills. | Total. | |||||||
| Interest. | Sinking Fund. | Total. | Interest. | ||||||
| NOTE.—The alteration made in 1894–95 of the system which previously obtained in dealing with the drawing loan of 1867 has affected the comparison of the figures for the last nine years with those preceding. The total amount actually paid for interest and sinking fund in 1889–90 was, under the old system, £1,897,602. The figures for each of the years ended March, 1890 to 1894 inclusive, will be found in the Year-book for 1899. | |||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||
| 1895 | 1,619,925 | 57,979 | 1,677,904 | 38,985 | 1,716,889 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 38·96 |
| 1896 | 1,602,933 | 41,183 | 1,644,116 | 39,659 | 1,683,775 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 36·96 |
| 1897 | 1,630,577 | 41,858 | 1,672,435 | 37,034 | 1,709,469 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 35·62 |
| 1898 | 1,668,697 | 43,380 | 1,712,077 | 29,336 | 1,741,413 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 34·28 |
| 1899 | 1,689,749 | 44,651 | 1,734,400 | 33,068 | 1,767,468 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 33·61 |
| 1900 | 1,674,618 | 46,073 | 1,720,691 | 28,703 | 1,749,394 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 31·07 |
| 1901 | 1,671,552 | 46,364 | 1,717,916 | 27,700 | 1,745,616 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 29·83 |
| 1902 | 1,722,819 | 47,724 | 1,770,543 | 33,396 | 1,803,939 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 29·80 |
| 1903 | 1,817,701 | 50,464 | 1,868,165 | 32,814 | 1,900,979 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 29·77 |
The above amounts shown as interest and sinking fund do not comprise the whole of the interest and sinking fund paid by the Government in respect of moneys raised by the issue of loans. Thus, in respect of loans raised under the Land for Settlements Acts, the Government Advances to Settlers Acts, and for the purchase of the Cheviot Estate, the interest, although made a charge upon the Consolidated Fund, is recovered from the receipts derived from the leasing of the lands, or from instalments paid by borrowers. The amount of interest thus charged and recovered during last year was £192,206 (under the Land for Settlements Acts, £93,600; Advances to Settlers Act, £89,700; Cheviot Estate, £8,866; Government Accident Insurance Act, £40). Such interest does not become a burden upon the taxpayer, and consequently is not included in the figures upon which the rate per head of mean population is calculated.
The amount actually paid for interest and sinking fund out of the Consolidated Fund during 1902–1903 was £97,040 more than that for the previous year, and the rate of charge per head of population increased somewhat.
The securities in which the sinking funds were held as on the 31st March, 1903, are specified in the statement following:—
| STATEMENT OF THE SECURITIES in which the SINKING FUNDS of the several LOANS were invested on the 31st March, 1903. | |||
| £ | s. | d. | |
| Investments in— | |||
| New Zealand 5-per-cent. Debentures | 3,470 | 0 | 0 |
| New Zealand 4 1/2-per-cent. Debentures | 1,700 | 0 | 0 |
| New Zealand 3 1/2-per-cent. Debentures | 1,250 | 0 | 0 |
| New Zealand 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 129,754 | 19 | 6 |
| New Zealand 3 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 2,571 | 3 | 7 |
| New Zealand 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 270 | 5 | 11 |
| New South Wales 4-per-cent. Debentures | 20,800 | 0 | 0 |
| New South Wales 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 5,486 | 6 | 7 |
| New South Wales 3 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 84,269 | 13 | 4 |
| New South Wales 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 70,673 | 12 | 11 |
| Victoria 4-per-cent. Debentures | 15,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Victoria 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 43,233 | 17 | 4 |
| Victoria 3 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 83,341 | 9 | 6 |
| Victoria 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 27,158 | 9 | 10 |
| South Australia 4-per-cent. Debentures | 24,700 | 0 | 0 |
| South Australia 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 4,851 | 0 | 5 |
| South Australia 3 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 38,068 | 11 | 6 |
| South Australia 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 114,819 | 12 | 6 |
| Canada 4-per-cent. Debentures | 18,200 | 0 | 0 |
| Canada 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 60,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Canada 3 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 34,022 | 11 | 8 |
| Canada 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 33,226 | 12 | 3 |
| Canada 2 1/2-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 13,666 | 15 | 11 |
| Tasmania 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 6,645 | 15 | 1 |
| Queensland 4-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 1,433 | 8 | 8 |
| Ceylon 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 6,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Leeds Corporation 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 14,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiff Corporation 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 24,444 | 1 | 9 |
| Gold Coast 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 6,511 | 8 | 3 |
| Reading Corporation 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 6,500 | 0 | 0 |
| Sheffield Corporation 3-per-cent. Inscribed Stock | 13,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Aid to Public Works and Land Settlements Act 4-percent. Debentures | 330 | 0 | 0 |
| Land for Settlements Act 4-per-cent. Debentures | 2,510 | 0 | 0 |
| Local Bodies' Loans Act 3 1/2-per-cent. Debentures | 400 | 0 | 0 |
| County of Tauranga 5-per-cent. Debentures | 60 | 0 | 0 |
| Borough of Brunner 6-per-cent. Debentures | 840 | 0 | 0 |
| Borough of Hokitika 6-per-cent. Debentures | 1,860 | 0 | 0 |
| Borough of Patea 4 1/2-per-cent. Debentures | 200 | 0 | 0 |
| Borough of Tauranga 5-per-cent. Debentures | 200 | 0 | 0 |
| Westport Harbour Board 4-per-cent. Debentures | 550 | 0 | 0 |
| Waimakariri-Ashley Water-supply Board 5-per-cent. Debentures | 320 | 0 | 0 |
| Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company 5-per-cent. Debentures | 540 | 0 | 0 |
| 916,879 | 16 | 6 | |
| Sinking funds in respect of Local Bodies' Loans Act, 1901, and Government Advances to Settlers Act, 1894— | |||
| Mortgages | 67,900 | 0 | 0 |
| In common fund, Public Trust Office— | |||
| At 4 per cent. £6,000 0 0 | |||
| At 3 1/2 per cent. 366,931 1 2 | |||
| 372,931 | 1 | 2 | |
| 1,357,710 | 17 | 8 | |
| Cash balance on 31st March, 1903 27 16 3 | |||
| Amount overinvested by trustees 25 0 0 | |||
| 2 | 16 | 3 | |
| Total | £1,357,713 | 13 | 11 |
Of the total amount, £540,482 is represented by stock and debentures of the Australian States, and £165,116 by those of Canada and Ceylon; £142,256 was invested in similar securities of the New Zealand Government; £57,944 in inscribed stock of English corporations; £4,030 in debentures of various local governing bodies; other securities, £7,052; £67,900 on mortgage; and £372,931 is in the hands of the Public Trustee.
Of the gross public debt of the colony outstanding on 31st March, 1903, £47,892,366 was raised in London, £568,100 in Australia, and £7,438,553 in New Zealand; and of the total amount £45,297,022 was held as inscribed stock, and £10,601,997 in the form of debentures. Details are given hereunder:—
| Kind of Stock. |  | Total. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Debentures | 3,067,900 | 568,100 | 6,965,997 | 10,601,997 |
| Inscribed stock | 44,824,466 | .. | 472,556 | 45,297,022 |
| Total | 47,892,366 | 568,100 | 7,438,553 | 55,899,019 |
The highest and lowest London prices for the New Zealand 4, 3 1/2, and 3 per cent. stock, taken over a range of fourteen years, are quoted:—
| QUOTATIONS, NEW ZEALAND STOCK. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-per-cents. | 3 1/2-per-cents. | 3-per-cents. | ||||
| Year. | Highest. | Lowest. | Highest. | Lowest. | Highest. | Lowest. |
| 1888 | 104 1/2 | 96 1/4 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1889 | 109 1/4 | 99 5/8 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1890 | 109 1/8 | 102 1/4 | 98 5/8 | 93 1/4 | .. | .. |
| 1891 | 107 1/2 | 100 | 98 1/4 | 91 1/8 | .. | .. |
| 1892 | 106 5/8 | 100 | 98 | 91 1/2 | .. | .. |
| 1893 | 107 1/4 | 97 | 97 1/2 | 90 | .. | .. |
| 1894 | 109 7/8 | 105 3/8 | 103 1/2 | 96 1/4 | .. | .. |
| 1895 | 113 1/2 | 105 5/8 | 107 1/2 | 100 | 95 3/4 | 91 |
| 1896 | 118 1/4 | 106 1/2 | 110 3/8 | 101 1/2 | 103 1/2 | 90 |
| 1897 | 117 | 112 3/8 | 111 | 104 3/4 | 102 | 99 1/2 |
| 1898 | 116 7/8 | 108 | 109 7/8 | 103 | 101 1/2 | 96 1/2 |
| 1899 | 116 1/2 | 105 1/2 | 109 | 102 | 99 1/4 | 94 1/4 |
| 1900 | 113 1/4 | 109 | 106 3/4 | 103 3/8 | 98 1/2 | 95 1/4 |
| 1901 | 115 3/8 | 110 3/4 | 109 3/4 | 104 1/8 | 99 1/2 | 93 1/8 |
| 1902 | 113 1/4 | 109 | 109 1/2 | 102 1/8 | 97 | 93 5/8 |
The following figures, which, with the exception of those for New Zealand, are taken from Mr. Coghlan's Australasian Statistics, show the public debt of each State or colony in 1901–1902:—
| State or Colony. | Date. | Public Debt. | Debt per Head of Population. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Debt. | Floating Debt. | Total. | |||||
| * As shown previously (see page 496), the amount of accrued sinking fund reduces this by £1 8s. 7d. per head. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Queensland | 30 June, 1902 | 38,807,427 | 531,000 | 39,338,427 | 76 | 8 | 6 |
| New South Wales | 30 June, 1902 | 66,108,359 | 5,484,126 | 71,592,485 | 51 | 6 | 0 |
| Victoria | 30 June, 1901 | 51,636,275 | 1,435,000 | 53,071,275 | 44 | 1 | 5 |
| South Australia | 30 June, 1902 | 26,423,045 | 849,500 | 27,272,545 | 75 | 2 | 10 |
| Western Australia | 30 June, 1902 | 14,942,310 | .. | 14,942,310 | 71 | 14 | 6 |
| Tasmania | 31 Dec., 1901 | 9,095,735 | .. | 9,095,735 | 52 | 4 | 1 |
| New Zealand | 31 Mar., 1902 | 52,966,447 | .. | 52,966,447 | 67 | 0 | 11* |
The amount of indebtedness per head of population in June, 1902, in South Australia, Western Australia, and Queensland was thus greater than that for New Zealand in March, 1902.
The burden of a public debt depends greatly on the measure in which it is expended on reproductive works, and on the degree of prosperity enjoyed by the people. The generally rugged character of this country, and the natural difficulties appertaining to the sites of many of the towns, soon necessitated a large outlay on roads and public works. The need was fully recognised, and to some extent met, by the Provincial Governments, which have justly received great credit for their far-seeing and liberal exertions. A great deal of road-making, often of a very costly character, was accomplished, harbour and other improvements begun, and immigration encouraged. Some railways were made in Canterbury, Otago, and Southland. The City of Christchurch and the Canterbury Plains were connected with the Port of Lyttelton by a railway, which required the construction of a long and very costly tunnel through the intervening range of hills. In Otago private enterprise, backed by the guarantee of the Provincial Government, built a railway from Dunedin to Port Chalmers, and some miles of line were made in Southland from the Town of Invercargill into the interior; but no general and comprehensive scheme of public works could be carried out by the separate exertions of the Provincial Governments. In 1870, therefore, the General Government brought forward its public-works and immigration policy, by which it was proposed to raise a loan of ten millions for the construction of main trunk railways, roads, and other public works of importance to the colony as a whole, as well as for the promotion of immigration on a large scale, the expenditure to be spread over a period of ten years. This policy was accepted by the Legislature, and embodied in “The Immigration and Public Works Act, 1870.”
The demands for local railways and other works soon caused the original proposals to be exceeded, and entailed an expenditure at a much more rapid rate and to a far greater amount than was originally contemplated. Although many of the works undertaken have been directly unremunerative, yet the effect of the policy as a whole has been largely to develop the settlement of the country, and to increase enormously the value of landed property; land in parts which before the construction of railways was valued at from £1 to £2 per acre having been subsequently sold at prices varying from £10 to £20 per acre. Moreover, the railway and telegraph lines yield a revenue which covers a large portion of the interest on their cost after paying working-expenses.
A statement is supplied, based on figures taken from the Colonial Treasurer's Budget of 1897 (to which the necessary additions have been made), showing the purposes for which the money forming the public debt of the colony was raised or voted.
But the amounts in the items must be regarded as only approximations to the actual facts. The information is merely indicative of the truth, and is a revision of what was given in the Year-book, 1899, which was found to be not as near to correctness as possible in places.
| PUBLIC DEBT OF NEW ZEALAND, MARCH, 1903, SHOWING APPROXIMATELY (([0-9]+)) RAISED OR VOTED UNDER VARIOUS HEADS, ARRANGED IN THREE CLASSES. | |
|---|---|
| On 31st March, 1903. | |
| * NOTE.—Only a portion of expenditure of old Provincial Governments on railways became public debt of the colony. The total expenditure on railways (Provincial and General Government) to 31st March, 1903, was over twenty millions sterling, which includes £1,104,281 spent by the Provincial Governments, of which £82,259 was for the Dunedin and Port Chalmers line. | |
| (a.) Services— | £ |
| Railways | 17,960,000* |
| Lands improvement (roads and bridges) | 5,400,000 |
| Public works and buildings | 4,160,000 |
| Land-purchases | 2,190,000 |
| Immigration | 2,460,000 |
| Maori war | 2,360,000 |
| Defence | 1,840,000 |
| Telegraphs | 950,000 |
| Goldfields and coal-mines | 780,000 |
| Lighthouses and harbours | 520,000 |
| State coal-mines | 50,000 |
| Tourist and health resorts | 20,000 |
| Investments— | £ | |
|---|---|---|
| Advances to settlers | 3,000,000 | |
| Loans to local bodies | 1,980,000 | |
| Purchase of lands for settlement | 3,110,000 | |
| Bank of New Zealand preferred shares | 500,000 | |
| New Zealand Consols | 470,000 | |
| (c.) Other— | ||
| Deficiencies in revenue, charges and expenses of raising loans, provincial liabilities, miscellaneous expenditure, and unexpended |  | 8,145,000 |
It will be found that on the 31st March, 1903, out of a total debt of £55,899,019, the amounts allocated for services formed approximately the following proportions of the whole:—
| Per Cent. | |
|---|---|
| For Railways | 32·13 |
| For Lands improvement (roads and bridges) | 9·66 |
| For Public works and buildings | 7·44 |
| For Land-purchases | 3·92 |
| For Immigration | 4·40 |
| For Maori war | 4·22 |
| For Defence | 3·29 |
| For Telegraphs | 1·70 |
| For Goldfields and coal-mines | 1·40 |
| For Lighthouses and harbours | 0·93 |
| For State coal-mines | 0·09 |
| For Tourist and health resorts | 0·04 |
The total sum is divided into three classes in the table, of which (a) is composed of the various services above referred to, and the total of which forms 69·22 per cent. of the whole debt in 1903; class (b) consists of moneys devoted to what may be termed investments, being 16·21 per cent. of the total; (c) moneys paid away in charges and expenses of raising loans, also to meet deficiencies of revenue, besides old provincial liabilities, and miscellaneous expenditure, forming 12·93 per cent. of the debt, along with unexpended balance of loans raised, 1·64 per cent.
The figures given as to railways do not include all the sums spent by the Provincial Governments, as stated in the note to the table, nor do the figures in some other items agree with those given elsewhere, made up from tables showing the expenditure out of the Public Works Fund, which, as previously explained, is augmented by contributions from the Consolidated Revenue Account.
The net expenditure, under all heads, of the Public Works Fund from 1870 to the 31st March, 1903, can be given correctly, but this fund, as stated previously, is not altogether composed of money charged to the public debt. It had received £33,914,187 from loans and £4,369,207 by way of receipts in aid on the latter date. The money received by way of aid included £3,405,000 transferred from the Consolidated Fund during the last twelve financial years, out of surplus revenue. Nearly thirty-eight millions sterling were spent since the year 1870 up to March last, and the items given below exhibit the nature of the works, &c., with amount for each.
| NET EXPENDITURE OF PUBLIC WORKS FUND FROM 1870 TO 31ST MARCH, 1903. | |
| Expenditure on— | £ |
| Immigration | 2,148,000 |
| Public works, departmental | 491,037 |
| Railways, including surveys of new lines | 19,261,719 |
| Roads | 6,248,248 |
| Land-purchases | 1,999,014 |
| Development of goldfields | 725,892 |
| Telegraph extension | 1,006,465 |
| Public buildings | 2,852,705 |
| Lighthouses, harbour-works, and defences | 991,353 |
| Contingent defence | 733,839 |
| Rates on Native lands | 65,268 |
| Thermal springs | 14,600 |
| Tourist and health resorts | 22,209 |
| Lands improvement | 4,090 |
| Charges and expenses of raising loans | 1,151,055 |
| Coal-mines | 10,835 |
| Interest and sinking fund | 218,500 |
| Total | £37,944,829 |
The railway expenditure during each of six quinquennial periods, and for the years ended 31st March, 1901, 1902, and 1903, since the initiation of the public-works policy, has been:—
| £ | |
| 1st July, 1870, to 30th June, 1875 | 3,575,362 |
| 1st July, 1875, to 31st March, 1880 | 4,919,712 |
| 1st April, 1880, to 31st March, 1885 | 3,120,680 |
| 1st April, 1885, to 31st March, 1890 | 2,308,319 |
| 1st April, 1890, to 31st March, 1895 | 978,498 |
| 1st April, 1895, to 31st March, 1900 | 1,547,732 |
| 1st April, 1900, to 31st March, 1901 | 717,723 |
| 1st April, 1901, to 31st March, 1902 | 1,333,941 |
| 1st April, 1902, to 31st March, 1903 | 759,752 |
| Total | £19,261,719 |
New Zealand's expenditure on railways is, with one exception (that of Tasmania) the lowest per head of the population of any of the Australian States. The next table shows the cost of railway-works, the mileage, the average cost per mile, the population, and the cost per head of the population in New Zealand and the several States referred to:—
| State or Colony. | Year ended | Cost of Construction of Open Lines. | Average No. of Miles of Line open. | Average Cost per Mile. | Estimated Population | Cost per Head of Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Including Northern Territory. † Maoris included. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | ||||
| Queensland | 30 June, 1902 | 20,119,143 | 2,801 | 7,184 | 510,515 | 39 | 8 | 2 |
| New South Wales | 30 June, 1902 | 40,565,073 | 2,953 | 13,407 | 1,395,600 | 29 | 1 | 4 |
| Victoria | 30 June, 1902 | 40,613,784 | 3,265 | 12,298 | 1,206,749 | 33 | 13 | 2 |
| South Australia* | 30 June, 1902 | 14,435,784 | 1,882 | 7,670 | 364,795 | 39 | 11 | 6 |
| West'n Australia | 30 June, 1902 | 7,410,426 | 1,356 | 5,465 | 208,325 | 35 | 11 | 5 |
| Tasmania | 31 Dec., 1901 | 3,799,098 | 459 | 8,304 | 174,233 | 21 | 16 | 1 |
| New Zealand | 31 Mar., 1903 | 19,081,735 | 2,262 | 8,436 | 857,985 | 22 | 4 | 10† |
In the foregoing table the cost per head of population for railway-construction is shown to have been between £33 and £36 in the States of Victoria and Western Australia; over £39 in South Australia and Queensland; in New South Wales it was over £29; but in New Zealand the cost has been £22, and in Tasmania over £21, per head of population.
The Assets Realisation Board was established for the purchase, in connection with the affairs of the Bank of New Zealand, of all the assets of the Estates Company and of the Auckland Agricultural Company.
The General Manager reports that during the year ended 31st March last (1903)—
“The business of the Board in all departments has been satisfactory.
“The results of the year's working, apart from the special £101,135 paid by the Bank in excess of the statutory £50,000, shows full provision for payment of debenture interest, and a clear surplus of £19,660.”
Sales to the extent of £138,498 have been made, a decrease of £1,400 over those of the previous year. Of the total value (£138,498), £119,740 represents country, £9,333 town lands, and £9,425 stock, implements, &c., sold on properties finally realised.
The sales for the period 1895–1903, including stock, show a total of £963,678 received.
On 31st March, 1903, the proportion of total sales from time of starting to the book-cost of all estates (£2,731,706) was 35·27 per cent.; and to land-tax valuation, plus 10 per cent. for sundry properties, with the manager's valuation for station properties (which together total £1,895,179), it was 50·85 per cent.
Particulars of operations are—
| £ | |
| Sales of properties finally realised, 1895–1903 (including stock), (net amount) | 484,265 |
| Properties partially realised, 1895–1903 | 479,413 |
| £963,678 |
The book-cost of the estates in respect of which the sales were finally closed was £690,249. These properties are shown above to have realised £484,265, leaving a deficiency of £205,984, including the realisation expenses, &c.
The localities of the sales are as follows:—
| Estates. | Farms. | Town Sections. | Suburban Sections. | £ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland | 5 | 206 | 684 | 270 | 301,568 |
| Canterbury | 3 | 78 | 19 | 63 | 246,059 |
| Hawke's Bay | 2 | .. | 10 | .. | 104,250 |
| Otago | 2 | 10 | 565 | 182 | 70,729 |
| Marlborough | 1 | 4 | 65 | 6 | 20,414 |
| Wellington | 1 | 17 | 31 | 1 | 156,631 |
| 899,651 | |||||
| Proceeds: realisation of sundry assets | 8,280 | ||||
| Stock sales on properties finally realised | 55,747 | ||||
| £963,678 | |||||
A SUMMARY of the transactions during the year ended 31st March, 1903, will be found in the following table, which shows under all descriptions of tenure the number of selectors and the area selected:—
| Nature and Tenure of Lands selected during the Year ended the 31st March, 1903. | Number of Purchasers or Selectors. | Area. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Including thirty-three endowments: area, 7,281 acres 2 roods 8 perches; and thirty five selections under the Thermal Springs Districts Act, comprising 304 acres 3 roods 35 perches. | |||||||||
| Selectors. | Area. | ||||||||
| A. | R. | P. | A. | R. | P. | ||||
| Town lands sold for cash | 154 | 168 | 1 | 20 | 371 | 17,188 | 2 | 17 | |
| Suburban lands sold for cash | 83 | 273 | 2 | 31 | |||||
| Rural lands sold for cash | 134 | 16,746 | 2 | 6 | |||||
| Occupation with right of purchase | 403 | 118,556 | 3 | 6 | |||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 285 | 108,065 | 1 | 33 | |||||
| Agricultural lease | 3 | 35 | 3 | 37 | |||||
| Village settlement, cash | 19 | 9 | 1 | 35 | |||||
| Village settlement, lease in perpetuity | 39 | 598 | 2 | 4 | |||||
| Village-homestead special settlement | 34 | 1,511 | 3 | 23 | |||||
| Special settlement associations | 29 | 5,761 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Improved-farm special settlement (lease in perpetuity and occupation with right of purchase) | 30 | 4,031 | 3 | 25 | |||||
| Occupation leases, Mining Act | 52 | 2,433 | 2 | 5 | |||||
| Small-grazing-runs | 35 | 93,525 | 1 | 14 | |||||
| Pastoral runs | 129 | 1,050,779 | 3 | 18 | |||||
| Miscellaneous leases and licenses | 434 | 106,859 | 3 | 35 | |||||
| Cheviot Estate— | |||||||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 2 | 34 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| Grazing-farms | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | |||||
| Miscellaneous | 2 | 8 | 0 | 4 | |||||
| Land for Settlements Acts— | |||||||||
| Cash lands | 3 | 5 | 0 | 32 | |||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 286 | 53,645 | 3 | 38 | |||||
| Lease in perpetuity, village | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Small grazing-runs | 9 | 20,393 | 2 | 19 | |||||
| Miscellaneous | 45 | 5,890 | 2 | 13 | |||||
| Endowments— | |||||||||
| Cash lands | 7 | 83 | 0 | 20 | |||||
| Occupation leases, Mining Act | 6 | 51 | 2 | 36 | |||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 6 | 1,092 | 3 | 39 | |||||
| Small grazing-runs | 2 | 2,641 | 3 | 6 | |||||
| Miscellaneous | 12 | 3,411 | 3 | 27 | |||||
| Thermal Springs District leases | 35 | 304 | 3 | 35 | |||||
| Totals | *2,280 | *1,596,949 | 0 | 1 | |||||
Particulars of the number of Crown tenants at present holding lands under the several tenures, together with the yearly rental payable, are given in the next statement.
| STATEMENT showing the TOTAL NUMBER (([0-9]+)) TENANTS, with Area selected or held, and the Yearly Rent payable, as on the 31st March, 1903. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenures. | Total Number of Tenants. | Total Area held by such Tenants. | Total Yearly Rental or Instalment payable. | ||||
| O(([0-9]+)) LANDS. | A. | R. | P. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Deferred payment | 485 | 79,664 | 1 | 37 | 3,774 | 16 | 8 |
| Perpetual lease | 831 | 161,578 | 0 | 11 | 6,235 | 19 | 3 |
| Occupation with right of purchase | 3,774 | 1,016,626 | 1 | 31 | 36,997 | 13 | 4 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 3,569 | 1,052,365 | 2 | 9 | 33,976 | 6 | 2 |
| Agricultural lease | 17 | 555 | 1 | 37 | 30 | 19 | 3 |
| Homestead | 3 | 188 | 0 | 37 | ... | ||
| Mining Districts Land Occupation Act | 383 | 15,945 | 2 | 9 | 940 | 8 | 4 |
| Village settlements— | |||||||
| Deferred payment | 23 | 443 | 1 | 36 | 44 | 15 | 10 |
| Perpetual lease | 153 | 2,427 | 1 | 37 | 369 | 19 | 8 |
| Occupation with right of purchase | 38 | 30 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 2 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 460 | 6,537 | 0 | 12 | 620 | 5 | 0 |
| Village-homestead special settlements— | |||||||
| Perpetual lease | 335 | 5,759 | 1 | 7 | 848 | 2 | 11 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 692 | 17,316 | 3 | 24 | 2,453 | 13 | 0 |
| Special settlement associations— | |||||||
| Deferred payment | 7 | 726 | 1 | 20 | 8 | 1 | 4 |
| Perpetual lease | 23 | 1,932 | 3 | 31 | 130 | 13 | 6 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 637 | 118,357 | 1 | 0 | 6,061 | 15 | 3 |
| Improved-farm special settlements | 452 | 48,315 | 2 | 31 | 3,206 | 2 | 8 |
| Small grazing-runs | 624 | 1,274,470 | 0 | 27 | 26,070 | 8 | 1 |
| Pastoral runs | 821 | 11,510,611 | 2 | 37 | 73,448 | 18 | 6 |
| Miscellaneous leases | 2,484 | 491,132 | 0 | 22 | 10,914 | 10 | 8 |
| Totals | 15,811 | 15,804,984 | 2 | 19 | 206,146 | 10 | 7 |
| CHEVIOT ESTATE— | |||||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 119 | 24,403 | 1 | 9 | 6,456 | 5 | 0 |
| Village-homestead special settlement | 72 | 2,480 | 1 | 0 | 870 | 0 | 4 |
| Grazing-farms | 48 | 45,977 | 2 | 9 | 6,624 | 7 | 2 |
| Pastoral runs | 1 | 1,642 | 0 | 0 | 193 | 3 | 8 |
| Miscellaneous | 74 | 1,525 | 0 | 11 | 290 | 17 | 3 |
| LAND FOR S(([0-9]+))— | |||||||
| Lease in perpetuity | 2,110 | 346,146 | 2 | 14 | 104,113 | 7 | 7 |
| Lease in perpetuity, village | 46 | 448 | 1 | 36 | 341 | 1 | 10 |
| Special-settlement associations | 11 | 2,114 | 1 | 9 | 162 | 7 | 8 |
| Small grazing-runs | 54 | 90,089 | 2 | 16 | 12,328 | 4 | 10 |
| Pastoral runs | 2 | 953 | 2 | 38 | 121 | 13 | 0 |
| Miscellaneous | 128 | 8,855 | 1 | 24 | 752 | 13 | 5 |
| THERMAL-SPRINGS (ROTORUA) | 282 | 6,059 | 3 | 28 | 1,939 | 6 | 4 |
| Grand totals | 18,758 | 16,335,680 | 3 | 13 | 340,339 | 18 | 8 |
| Endowments | 647 | 164,860 | 2 | 34 | 8,107 | 3 | 8 |
| Native townships | 189 | 583 | 3 | 7 | 786 | 3 | 4 |
Tables I. and II., which follow, exhibit the acreage of land taken up for settlement, and the number of holdings under each description of tenure. The lands held under pastoral license and miscellaneous leases, such as for timber and flax-cutting, coal-mining, &c., are not included in these tables. Tables III. and IV. show the total acreage taken up year by year since 1893 in each land district, and the number of holdings grouped according to size, the areas varying from less than one acre in extent to 1,000 acres and over.
The forfeitures and surrenders in respect of the lands taken up for settlement (excluding, as already remarked, pastoral and miscellaneous leases) for the last seven years were:—
| 1896–97 | 815 holdings | 228,978 acres. |
| 1897–98 | 658 holdings | 130,380 acres. |
| 1898–99 | 567 holdings | 180,957 acres. |
| 1899–1900 | 510 holdings | 164,003 acres. |
| 1900–1901 | 354 holdings | 106,690 acres. |
| 1901–1902 | 192 holdings | 75,368 acres. |
| 1902–1903 | 329 holdings | 106,390 acres. |
Forfeited and surrendered lands are again thrown open for selection as soon as possible, and in the majority of cases are taken up again by fresh selectors within a short time.
A full description of the various tenures under which land is dealt with in the colony is given in the article entitled “The Land System of New Zealand, in Part III. of this book.
| I.—COMPARATIVE STATEMENT SHOWING ACREAGE OF LANDS SELECTED UNDER SETTLEMENT CONDITIONS (EXCLUDING PASTORAL RUNS, MISCELLANEOUS LEASES AND LICENSES, AND THERMAL SPRINGS DISTRICT LEASES) (([0-9]+)) OF THE YEARS ENDED 31ST MARCH, 1893–1903. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | 1892–93. | 1893–94. | 1894–95. | 1895–96. | 1896–97. | 1897–98. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. |
* Lease in perpetuity. NOTE.—The forfeitures and surrenders for the last seven of the years dealt with in the table were—for the year 1896–97, 228,978 acres; 1897—98, 130,380 acres; 1898–99, 180,957 acres; 1899–1900, 164,003 acres; 1900–1901, 106,690 acres; 1901–1902, 75,368 acres; and for 1902–1903, 106,390. But it must not be supposed that these relate to the acreages taken up during the same years; on the contrary, forfeitures may have their origin in selections of long standing and various dates. | |||||||||||
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Cash lands | 36,327 | 34,999 | 38,695 | 26,575 | 28,485 | 22,525 | 37,400 | 23,936 | 58,700 | 27,290 | 17,277 |
| Deferred payments | 21,084 | 12,669 | 5,454 | 456 | .. | .. | 13 | .. | .. | 52 | .. |
| Perpetual lease and small areas | 122,558 | 3,854 | 1,263 | 1,427 | 9,106 | 651 | 640 | 624 | 2,499 | 10 | .. |
| Occupation with right of purchase | 54,271 | 108,133 | 75,478 | 84,968 | 59,648 | 81,414 | 109,950 | 117,771 | 262,729 | 128,893 | 118,557 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 55,320 | 179,993 | 91,799 | 122,350 | 104,927 | 117,938 | 159,415 | 153,531 | 144,208 | 116,445 | 162,839 |
| Agricultural lease | 194 | 365 | 45 | 36 | 13 | 258 | 114 | 70 | 23 | 28 | 36 |
| Occupation lease under “The Mining Districts Land Occupation Act, 1894” | .. | .. | .. | 2,931 | 2,817 | 1,285 | 1,449 | 2,295 | 2,123 | 2,644 | 2,485 |
| Village settlement— | |||||||||||
| Cash | 528 | 2 | 24 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 30 | 4 | 22 | 10 | 9 |
| Deferred payment | 391 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Perpetual lease | 2,636 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Occupation with right of purchase | .. | 1 | 23 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Lease in perpetuity | 4 | 3,953 | 4,050 | 3,365 | 1,317 | 1,426 | 2,115 | 1,762 | 1,082 | 456 | 619 |
| Village-homestead special settlement | 494 | 2,550 | 2,743 | 793 | 360 | 42 | 134 | 31 | 376 | 469 | 1,512 |
| Special-settlement associations | 157,381* | 68,852* | 51,346 | *44,237 | 28,084* | *442 | *607 | *2 | .. | .. | *5,761 |
| Homestead | 38 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Special-settlement improved farms | .. | .. | 9,731 | 28,348 | 4,882 | 9,007 | 4,823 | 7,393 | 1,936 | 1,618 | 4,032 |
| Small grazing-runs and grazing-farms | 92,927 | 252,693 | 117,846 | 46,407 | 68,934 | 149,458 | 77,632 | 155,109 | 86,076 | 128,060 | 116,567 |
| Totals | 544,153 | 668,064 | 398,497 | 361,904 | 308,581 | 384,449 | 394,324 | 462,529 | 559,774 | 405,976 | 429,694 |
| II.—COMPARATIVE STATEMENT SHOWING NUMBER OF SELECTORS OF LAND UNDER SETTLEMENT CONDITIONS (EXCLUDING PASTORAL RUNS, MISCELLANEOUS LEASES AND LICENSES, AND THERMAL SPRINGS DISTRICT LEASES) DURING EACH OF THE YEARS (([0-9]+)) MARCH, 1893–1903. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | 1892–3. | 1893–4. | 1894–5. | 1895–6. | 1896–7. | 1897–8. | 1898–9. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. |
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |
| For cash | 552 | 497 | 392 | 476 | 388 | 272 | 534 | 491 | 363 | 489 | 381 |
| Deferred payments | 169 | 96 | 47 | 6 | .. | .. | 1 | .. | .. | 1 | .. |
| Perpetual lease and small areas | 385 | 17 | 3 | 7 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | .. |
| Occupation with right of purchase | 161 | 461 | 398 | 431 | 277 | 380 | 458 | 395 | 673 | 447 | 403 |
| Lease in perpetuity | 126 | 612 | 372 | 696 | 659 | 599 | 675 | 647 | 489 | 502 | 579 |
| Agricultural lease | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Occupation lease under “The Mining Districts Land Occupation Act, 1894” | .. | .. | .. | 69 | 48 | 23 | 31 | 64 | 53 | 78 | 58 |
| Village settlement— | |||||||||||
| Cash | 75 | 3 | 23 | 16 | 4 | 2 | 21 | 6 | 35 | 21 | 19 |
| Deferred payment | 29 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Perpetual lease | 164 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Occupation with right of purchase | .. | 5 | 30 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | .. | 1 | .. |
| Lease in perpetuity | 2 | 203 | 232 | 193 | 102 | 92 | 106 | 80 | 97 | 33 | 40 |
| Village-homestead special settlement | 33 | 118 | 60 | 19 | 18 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 7 | 30 | 34 |
| Special-settlement associations | 838 | 290 | 262 | 238 | 142 | 5 | 5 | 1 | .. | .. | 29 |
| Homestead | 1 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Improved-farm special settlement | .. | .. | 107 | 315 | 45 | 77 | 64 | 41 | 13 | 9 | 30 |
| Small grazing-runs and grazing-farms | 39 | 142 | 60 | 32 | 27 | 71 | 40 | 64 | 35 | 48 | 47 |
| Totals | 2,578 | 2,454 | 1,988 | 2,504 | 1,735 | 1,539 | 1,953 | 1,803 | 1,769 | 1,661 | 1,623 |
| NOTE.—The forfeitures and surrenders for the last seven of the years dealt with in the table were—for the year 1896–97, 815 holdings; 1897–98; 658 holdings; 1898–99,567 holdings; 1899–1900, 510 holdings; 1900–1901, 354 holdings; 1901–1902, 192 holdings; and in 1902–1903, 329 holdings. See note to previous table as to the origin of these failures. | |||||||||||
| III.—LANDS TAKEN UP UNDER SETTLEMENT CONDITIONS DURING EACH OF (([0-9]+)) ENDED 31ST MARCH, 1894–1903 (EXCLUSIVE OF PASTORAL RUNS, MISCELLANEOUS LEASES AND LICENSES, AND THERMAL SPRINGS DISTRICT LEASES).* | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land District. | 1893–94. | 1894–95. | 1895–96. | 1896–97. | 1897–98. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. |
| * See notes as to forfeitures and surrenders on previous tables. | ||||||||||
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | |
| Auckland | 134,992 | 99,313 | 67,831 | 49,522 | 56,295 | 90,160 | 78,677 | 201,355 | 108,761 | 153,741 |
| Hawke's Bay | 24,356 | 20,141 | 16,353 | 22,858 | 19,876 | 36,222 | 36,451 | 90,625 | 71,902 | 38,505 |
| Taranaki | 13,954 | 35,113 | 55,850 | 22,002 | 16,786 | 18,867 | 54,960 | 71,000 | 23,942 | 39,353 |
| Wellington | 84,871 | 49,586 | 79,478 | 63,801 | 48,909 | 63,746 | 41,387 | 48,530 | 14,301 | 15,048 |
| Nelson | 36,739 | 34,906 | 19,421 | 14,462 | 13,600 | 18,673 | 10,211 | 18,918 | 29,520 | 11,289 |
| Marlborough | 8,227 | 18,353 | 15,858 | 20,858 | 54,581 | 51,973 | 74,311 | 33,063 | 64,624 | 56,681 |
| Canterbury | 94,861 | 33,744 | 14,827 | 22,654 | 75,041 | 52,839 | 34,218 | 20,744 | 11,981 | 4,112 |
| Westland | 1,346 | 1,826 | 1,765 | 3,865 | 437 | 352 | 792 | 709 | 27,214 | 45,464 |
| Otago | 159,050 | 80,439 | 70,238 | 79,212 | 77,345 | 40,599 | 68,436 | 49,901 | 29,232 | 51,038 |
| Southland | 109,668 | 25,076 | 20,283 | 9,347 | 21,579 | 20,893 | 63,086 | 24,929 | 24,499 | 14,463 |
| Totals | 668,064 | 398,497 | 361,904 | 308,581 | 384,449 | 394,324 | 462,529 | 559,774 | 405,976 | 429,694 |
| IV.—HOLDINGS TAKEN UP UNDER SETTLEMENT CONDITIONS DURING EACH OF (([0-9]+)) ENDED 31ST MARCH, 1894–1903 (EXCLUSIVE OF PASTORAL RUNS, MISCELLANEOUS LEASES AND LICENSES, AND THERMAL SPRINGS DISTRICT LEASES), CLASSIFIED ACCORDING TO SIZE. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size. | 1893–94. | 1894–95. | 1895–96. | 1896–97. | 1897–98. | 1898–99. | 1899–1900. | 1900–1901. | 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. |
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |
| Under 1 acre | 176 | 256 | 259 | 154 | 103 | 293 | 345 | 158 | 195 | 187 |
| 1 to 50 acres | 739 | 696 | 719 | 588 | 496 | 571 | 501 | 466 | 569 | 475 |
| 51 to 250 acres | 933 | 757 | 1,198 | 709 | 616 | 633 | 492 | 522 | 475 | 498 |
| 251 to 500 acres | 341 | 169 | 232 | 178 | 197 | 277 | 262 | 333 | 245 | 240 |
| 501 to 1,000 acres | 150 | 70 | 70 | 84 | 63 | 128 | 116 | 181 | 113 | 158 |
| 1,001 acres and upwards | 115 | 40 | 26 | 22 | 64 | 51 | 87 | 109 | 64 | 65 |
| Totals | 2,454 | 1,988 | 2,504 | 1,735 | 1,539 | 1,953 | 1,803 | 1,769 | 1,661 | 1,623 |
The following is a statement of the gross amounts collected by Receivers of Land Revenue for the years 1901–1902 and 1902–1903:—
| 1901–1902. | 1902–1903. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Territorial revenue | 249,619 | 1 | 6 | 252,277 | 15 | 1 |
| Lands for settlement | 90,053 | 5 | 6 | 110,632 | 8 | 8 |
| Cheviot Estate | 14,061 | 0 | 8 | 14,609 | 9 | 9 |
| State forests | 17,188 | 11 | 5 | 3,870 | 14 | 10 |
| North Island Main Trunk Railway | 6,670 | 14 | 5 | 9,396 | 14 | 7 |
| Thermal springs | 414 | 8 | 6 | 77 | 4 | 9 |
| Rotorua Town Council | 1,094 | 2 | 4 | 1,846 | 2 | 0 |
| Lakes Ellesmere and Forsyth | 1,615 | 12 | 2 | 1,631 | 17 | 10 |
| Crown-grant fees | 914 | 12 | 5 | 804 | 1 | 6 |
| Native townships | 310 | 8 | 1 | 702 | 2 | 10 |
| Mining district land occupation | 641 | 12 | 4 | 911 | 10 | 9 |
| Miscellaneous | 1,753 | 17 | 3 | 1,550 | 6 | 7 |
| Mount Cook Hermitage | 190 | 5 | 6 | .. | ||
| Hanmer Sanatorium | 1,344 | 1 | 2 | .. | ||
| Government loans to local bodies | 21,420 | 15 | 7 | 28,301 | 7 | 4 |
| Endowments | 17,638 | 9 | 8 | 20,053 | 19 | 9 |
| Survey vote | 2,207 | 16 | 1 | 1,713 | 19 | 9 |
| Totals | £427,138 | 14 | 7 | £448,379 | 16 | 0 |
A FULL description is given, in a special article belonging to Section 1, Part III., of the objects and method of the Land for Settlements Acts, under which the acquirement by Government is authorised, through purchase from private owners, of properties for subdivision into small farms to meet the want felt of Crown lands for disposal in places where they are specially in demand.
The report of the Chairman of the Board of Land Purchase Commissioners on the transactions for the twelve months ended the 31st March, 1903, states:—
About 150 properties were offered for sale, aggregating 740,871 acres. The Board dealt with 108, and recommended the purchase or exchange of 59, containing 404,426 acres.
The Government having approved, negotiations were completed with the owners of 11 estates, containing 29,910 acres, which cost £142,460; and 8 estates, containing 82,696 acres, valued at £208,708, were acquired, but not wholly paid for within the year.
The Arbitration Court sat at Napier on the 29th January, and awarded the Crown 28,857 acres of the Milbourne Estate for £142,262, including costs of one side. The Court also allowed the vendors to retain 600 acres and one homestead. The amount which the Government offered for 29,550 acres was £118,200.
The purchase of 8,542 acres of the Longbush and Tablelands Estate was completed, but the negotiations for taking a portion of the estate, the freehold of which is held by Native owners, failed, the Supreme Court deciding that Native land, although held under a Crown title, could not be taken compulsorily. The value of the purchase is somewhat injuriously affected by this unexpected decision.
The estates wholly paid for during the year are Argyll (Milbourne and Te Reinga), in Hawke's Bay; Spotswood, in Taranaki; Linton, Longbush, and Tablelands, in Wellington; Kokatahi, in Westland; Eccleston, Mead, Chamberlain (Opawa), and Squires, in Canterbury; and Windsor Park (two parts) and Duncan, in Otago.
The total completed purchases for the year comprise 14 estates, containing 69,273 acres, which cost £349,452.
Besides these, negotiations were completed for the Bickerstaffe Estate (Colbeck's), in Auckland; Wigan (Takapau), in Hawke's Bay; Normandale (Western Hutt), in Wellington; Annan (Highfield), in Canterbury; and St. Helen's (Kenton), in Otago. Exchanges were also completed at Birchhill and Awatere, in Marlborough, and Ruangarehu, in Hawke's Bay.
The Levels Estate, containing 38,247 acres, was recommended for purchase and approved by the Government, but, as the owners declined to sell, proceedings were commenced to take the estate compulsorily. Since the close of the year, however, an agreement was arrived at to buy at £6 9s. per acre, and the estate will be taken possession of on the 31st March, 1904.
The Mount Vernon Estate, proceedings to take which compulsorily were commenced some time ago, has not yet been before the Court.
At Birchhill the New Zealand Land Association held freeholds of the best of the land in Mount Patriarch, Ragan, and Manuka Island Runs, and so practically prevented the Crown from leasing the large areas of pastoral country adjacent. The association agreed to sell these freeholds for one block of Crown lands, the advantage being as nearly as possible equal to the Crown and to the association.
| SUMMARY OF ALL LANDS OFFERED TO GOVERNMENT UNDER “THE LAND FOR S(([0-9]+)) ACT, 1900,” AND HOW DEALT WITH, FROM 1ST APRIL, 1902, (([0-9]+)) MARCH, 1903. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land District where Land situated. | Number of Estates offered. | Area offered. | Area declined without going to Board. | Area not recommended by Board. | Area recommended by Board. | Area under Consideration. | Area withdrawn. | Total. |
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | ||
| Auckland | 33 | 270,435 | .. | 169,566 | 78,518 | 22,251 | 100 | 270,435 |
| Hawke's Bay | 11 | 36,987 | 4,074 | .. | 22,548 | 10,365 | 1,200 | 36,987 |
| Taranaki | 29 | 9,752 | 681 | 25 | 306 | 8,740 | .. | 9,752 |
| Wellington | 27 | 75,681 | 5,308 | 15,447 | 7,370 | 47,556 | .. | 75,681 |
| Marlborough | 1 | 246 | .. | .. | .. | 246 | .. | 246 |
| Westland | 1 | 111 | .. | .. | .. | 111 | .. | 111 |
| Canterbury | 23 | 117,811 | 7,290 | 42,018 | 50,551 | 17,952 | 400 | 117,811 |
| Otago | 18 | 85,480 | 18,465 | .. | 10,425 | 56,590 | .. | 85,480 |
| Southland | 7 | 144,368 | 9,000 | .. | 18,085 | 117,283 | .. | 144,368 |
| Total | 150 | 740,871 | 44,818 | 227,056 | 187,803 | 281,094 | 1,700 | 740,871 |
| SUMMARY OF ESTATES ACQUIRED UP TO (([0-9]+)) MARCH, 1903, AND AMOUNTS OF PURCHASE-MONEY. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of Land District. | No. of Estates acquired before 31st March, 1902. | Areas acquired before 31st March, 1902. | No. of Estates acquired from 1st April, 1902, to 31st March, 1903. | Area acquired from 1st April, 1902, to 31st March, 1903. | Total Numbers of Estates to 31st March, 1903. | Total Area to 31st March, 1903. | Purchase-money. | ||||||||
* Includes Ruangarehu exchange, 2,380 acres. † Acquired by way of exchange. | |||||||||||||||
| A. | B. | P. | A. | R. | P. | A. | R. | P. | £ | s. | d. | ||||
| Auckland | 12 | 36,949 | 1 | 35 | 2 | 12,543 | 1 | 19 | 14 | 49,492 | 3 | 14 | 142,359 | 14 | 10 |
| Hawke's Bay | 11 | 71,658 | 2 | 12 | 3 | 46,568 | 0 | 19* | 14 | 118,226 | 2 | 31 | 637,342 | 0 | 11 |
| Taranaki | 1 | 1,505 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 306 | 2 | 25 | 2 | 1,812 | 0 | 33 | 46,817 | 17 | 2 |
| Wellington | 8 | 15,772 | 3 | 15 | 4 | 10,717 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 26,490 | 0 | 25 | 185,348 | 9 | 4 |
| Marlborough | 7 | 68,135 | 2 | 0 | .. | 22,480 | 3 | 4† | 7 | 90,616 | 1 | 4 | 165,444 | 5 | 9 |
| Westland | 1 | 3,230 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1,879 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 5,109 | 3 | 26 | 8,343 | 2 | 2 |
| Canterbury | 48 | 156,755 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 50,359 | 2 | 18 | 53 | 207,115 | 0 | 23 | 1,008,877 | 13 | 11 |
| Otago | 14 | 60,396 | 3 | 15 | 4 | 7,177 | 0 | 29 | 18 | 67,574 | 0 | 4 | 392,821 | 10 | 6 |
| Southland | 5 | 34,388 | 0 | 39 | .. | .. | 5 | 34,388 | 0 | 39 | 88,132 | 15 | 9 | ||
| Totals | 107 | 448,792 | 3 | 15 | 20 | 152,032 | 2 | 24 | 127 | 600,825 | 1 | 39 | 2,675,487 | 10 | 4 |
At Awatere the Assets Realisation Board held freeholds interspersed with the Crown lands formerly held by them under pastoral lease, and it was arranged that the Board should transfer all its freeholds in one block to the Crown, and the Crown granted the Board all the Crown lands within the other block retained by the Board.
The exchange of Ruangarehu, near Waipiro, consists in the transfer to Mr. J. N. Williams of four small isolated blocks of Crown land, in exchange for about an equal area of his freehold in one block, which is ready for occupation, and is situated on the Tologa-Waipiro inland track.
For workmen's homes and small farms near towns two properties were purchased and opened for lease, with rather disappointing results. The properties purchased last year, and offered for lease during the year, also failed in finding anything like full occupation.
There was a very great desire expressed by the representatives of labour that land should be acquired. At Dunedin, although the principle of providing land for workmen's homes was fully expressed, it was found that very few indeed would definitely state that they would themselves take up any land on the statutory terms if it were offered to them. I believe workmen find it more convenient to live near their work, and that few care to undertake the trouble or cost of living out of town, unless there are frequent rapid and cheap means of communication.
The following is a summary of the transactions under the Land for Settlements Acts to the 31st March, 1903:—
| No. | Area. Acres. | Prime Cost £ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchased or exchanged and opened for selection | 116 | 497,683 | 2,250,961 |
| Paid for, but not opened for selection | 6 | 42,990 | 215,818 |
| Purchased, but not paid for nor opened | 5 | 60,152 | 208,708 |
| 127 | 600,825 | 2,675,487 | |
| Under negotiation | 17 | 320,638 | 1,098,160 |
The income for the year amounts to £120,967, and the outlay for interest on money borrowed is £93,599. Other outlay is charged to capital. There are also 19,544 acres not yet let, valued at £3,401 yearly, and 8,338 acres taken up by roads and reserves, from which no revenue was derived.
The result of the year's operations shows a profit of £27,369. The accumulated and invested credit balance up to the end of the year is £117,546, besides uncollected rents, on the 31st March last, amounting to £10,489, but a considerable part of which has since been received. The arrears are principally in Taranaki, Hawke's Bay, Wellington, Marlborough, and Southland, the greatest being in Hawke's Bay; but three large estates account for more than half of the whole indebtedness.
The Secretary for Crown Lands and Surveyor-General's report to the Hon. the Minister of Lands on the condition and settlement of the lands acquired and handed over to his department under the above-mentioned Acts gives the particulars of the estates offered for selection as follows:—
During the year the Land Purchase Board transferred to the control of this Department 91,724 acres 2 roods 4 perches, comprised in twelve estates, one homestead site, and portions of the Birch Hill and Awatere freehold properties. The latter were acquired in exchange for Crown lands. Of these, eight estates, one homestead site, and the Awatere and Birch Hill lands, containing in all an area of 49,162 acres and 14 perches, were opened for selection, together with ten other estates comprising an area of 29,639 acres and 15 perches, which had been handed over prior to the 31st March, 1902, but were not ready for settlement on that date. The properties were all surveyed, subdivided, valued, and submitted for lease on carefully considered and designed schemes, and were readily quitted, except the areas noted in the fourth column of the table hereunder.
The five Auckland hamlets were opened as “Workmen's Homes,” and are situated in the vicinity of the City of Auckland. The Kumeroa and Forest Gate Estates were acquired under the compulsory provisions of “The Land for Settlements Consolidation Act, 1900,” and, notwithstanding, the result may so far be classed as satisfactory. The small Linton Settlement, near Halcombe, was all selected. The Kokatahi Settlement, in Westland, is in a better position than shown, inasmuch as the balance of 1,246 acres have been taken up since the 31st March last. The five Canterbury properties constitute a large proportion of the whole; and of the Lyndon Estate (Amuri) and the Chamberlain (Opawa) Settlement, near Albury, not an acre has been left on the Land Board's hands. The Windsor Park Estates (Otago) all went off.
Given a continuance of the present favourable conditions affecting farming and grazing, it is anticipated that these later acquisitions under the Land for Settlements Act will prove as beneficial and satisfactory to the colony and tenants as the majority of the previous purchases have been.
| ESTATES OFFERED for SELECTION during the Year ended 31st March, 1903, under “The Land for Settlements Consolidation Act, 1900.” | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land District, and Name of Estate. | Area of Estate. | Number of Selectors. | Area unselected 31st March, 1903. | Annual Rental payable on Lands leased. | Date of Opening. | ||||||
| Auckland— | A. | R. | P. | A. | R. | P. | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Cradock Hamlet | 33 | 0 | 9 | 3 | 22 | 0 | 25 | 17 | 14 | 0 | 22 April, 1902. |
| Hetana Hamlet | 451 | 1 | 34 | 7 | 377 | 1 | 6 | 14 | 5 | 4 | 22 April, 1902. |
| Kitchener Hamlet | 26 | 3 | 35 | 1 | 20 | 3 | 14 | 5 | 12 | 0 | 22 April, 1902. |
| Methuen Hamlet | 77 | 3 | 14 | 7 | 45 | 2 | 7 | 33 | 17 | 9 | 22 April, 1902. |
| Plumer Hamlet | 74 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 54 | 2 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 22 April, 1902. |
| Hawke's Bay— | |||||||||||
| Kumeroa | 3,774 | 2 | 38 | 14 | 726 | 0 | 0 | 1,425 | 9 | 10 | 12 May, 1902. |
| Forest Gate | 8,822 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 81 | 2 | 13 | 2,587 | 17 | 6 | 19 May, 1902. |
| Wellington— | |||||||||||
| Linton | 551 | 1 | 36 | *5 | ... | 309 | 13 | 6 | 17 Sept., 1902. | ||
| Westland— | |||||||||||
| Kokatahi | 1,879 | 2 | 20 | 3 | 1,246 | 1 | 30 | 100 | 17 | 10 | 4 Nov., 1902. |
| Canterbury— | |||||||||||
| Lyndon No. | 15,887 | 0 | 0 | 10 | ... | 2,281 | 10 | 2 | 21 April, 1902. | ||
| Maytown | 391 | 3 | 32 | 12 | ... | 286 | 16 | 2 | 28 April, 1902. | ||
| R.S. 30791 (pt.) | 100 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ... | 17 | 0 | 0 | 23 April. 1902. | ||
| Eccleston | 1,246 | 1 | 5 | 4 | ... | 569 | 11 | 2 | 12 May, 1902. | ||
| R.S. 36226 | 46 | 1 | 26 | 1 | ... | 5 | 3 | 0 | 16 Oct., 1902. | ||
| Mead | 5,914 | 3 | 17 | 21 | ... | 975 | 18 | 0 | 21 Jan., 1903. | ||
| Chamberlain | 10,500 | 1 | 9 | 21 | ... | 2,169 | 19 | 10 | 9 March, 1903. | ||
| Otago— | |||||||||||
| Windsor Park | 3,821 | 2 | 16 | 38 | ... | 1,655 | 8 | 2 | 28 May, 1902. | ||
| Windsor Park (No. 2) | 2,179 | 2 | 17 | 10 | ... | 875 | 16 | 8 | 28 Oct., 1902. | ||
| Duncan | 633 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 210 | 0 | 22 | 181 | 16 | 8 | 29 Dec., 1902. |
| Totals | 56,412 | 2 | 31 | 194 | 2,784 | 2 | 9 | 13,524 | 17 | 9 | |
The estates, &c., acquired in each district under the Land for Settlements Acts to the 31st March, 1903, are next shown:—
| Name of Estate. | Area acquired. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland— | A. | R. | P. |
| Opouriao | 7,604 | 0 | 0 |
| Okauia | 5,920 | 0 | 0 |
| Rangiatea | 4,004 | 0 | 0 |
| Karapiro | 2,334 | 0 | 9 |
| Fencourt | 7,105 | 3 | 5 |
| Whitehall | 8,959 | 0 | 0 |
| Cradock Hamlet | 33 | 0 | 9 |
| Hetana Hamlet | 451 | 1 | 34 |
| Kitchener Hamlet | 26 | 3 | 35 |
| Methuen Hamlet | 77 | 3 | 14 |
| Plumer Hamlet | 74 | 0 | 0 |
| 36,590 | 0 | 26 | |
| Hawke's Bay— | |||
| Raureka | 427 | 2 | 0 |
| Elsthorpe | 9,740 | 0 | 0 |
| Waimarie | 430 | 2 | 10 |
| Pouparae | 337 | 3 | 4 |
| Tomoana | 111 | 3 | 38 |
| Mahora | 1,133 | 3 | 0 |
| Willows | 775 | 1 | 36 |
| Hatuma | 26,522 | 3 | 20 |
| Manga-a-toro | 19,581 | 3 | 12 |
| Kumeroa | 3,774 | 2 | 38 |
| Forest Gate | 8,822 | 0 | 13 |
| 71,658 | 2 | 11 | |
| Taranaki— | |||
| Tokaora | 1,505 | 2 | 8 |
| Wellington— | |||
| Paparangi | 322 | 3 | 32 |
| Ohakea | 1,745 | 1 | 30 |
| Te Matua | 702 | 0 | 19 |
| Aorangi | 1,785 | 0 | 0 |
| Langdale | 9,405 | 0 | 0 |
| Mangawhata | 1,240 | 2 | 36 |
| Epuni Hamlet | 100 | 3 | 14 |
| Maungaraki | 470 | 3 | 4 |
| Linton | 551 | 1 | 36 |
| 16,324 | 1 | 11 | |
| Marlborough | |||
| Blind River | 5,507 | 0 | 0 |
| Omaka | 3,898 | 0 | 0 |
| Puhipuhi | 320 | 0 | 0 |
| Starborough | 35,906 | 0 | 0 |
| Richmond Brook | 5,854 | 0 | 0 |
| Waipapa | 3,755 | 2 | 0 |
| North Bank | 12,895 | 0 | 0 |
| 68,135 | 2 | 0 | |
| Westland— | |||
| Poerua | 3,230 | 1 | 6 |
| Kokatahi | 1,894 | 2 | 20 |
| 5,124 | 3 | 26 | |
| Canterbury— | |||
| Pareora | 620 | 2 | 13 |
| Studholme Junction | 109 | 0 | 7 |
| Kapua | 574 | 1 | 22 |
| Rosebrook | 600 | 1 | 8 |
| Otaio | 373 | 3 | 14 |
| Patoa | 4,535 | 3 | 14 |
| The Peaks | 2,811 | 0 | 9 |
| Roimata | 48 | 3 | 27 |
| Kereta | 105 | 2 | 29 |
| Braco | 27 | 2 | 4 |
| Epworth | 21 | 0 | 3 |
| Ashley Gorge | 1,165 | 3 | 6 |
| Omihi Valley | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Orakipaoa | 384 | 0 | 31 |
| Highbank | 9,121 | 3 | 8 |
| Otarakaro | 39 | 3 | 9 |
| Wharenui | 73 | 1 | 10 |
| Rakitairi | 3,526 | 1 | 26 |
| Waiapi | 1,124 | 2 | 36 |
| Horsley Down | 3,982 | 3 | 35 |
| Albury | 19,539 | 1 | 24 |
| R.S. 1862 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| R.S. 2682 (part | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| R.S. 36469 | 154 | 3 | 2 |
| R.S. 36231 | 98 | 3 | 30 |
| R.S. 36056 and 36057 | 58 | 0 | 16 |
| R.S. 36228 | 100 | 3 | 23 |
| R.S. 36278 | 618 | 2 | 0 |
| R.S. 30791 (part) | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| R.S. 36226 (part) | 46 | 1 | 26 |
| Marawiti | 2,028 | 2 | 33 |
| Hekeao | 2,254 | 2 | 11 |
| Pawaho | 52 | 0 | 18 |
| Waikakahi | 48,205 | 2 | 34 |
| Tamai | 41 | 0 | 28 |
| Takitu | 9,713 | 0 | 37 |
| Pareora No. 2 | 8,132 | 0 | 31 |
| Rautawiri | 113 | 0 | 7 |
| Papaka | 1,561 | 2 | 25 |
| Punaroa | 7,029 | 3 | 5 |
| Lyndon | 4,243 | 3 | 28 |
| Kohika | 3,864 | 1 | 10 |
| Tarawahi | 31 | 3 | 0 |
| Raincliff | 745 | 2 | 0 |
| Puhuka | 39 | 2 | 7 |
| Kaimahi | 100 | 2 | 1 |
| Kapuatohe | 49 | 3 | 37 |
| Rapuwai | 2,247 | 2 | 11 |
| Lyndon No. 2 | 15,887 | 0 | 0 |
| Maytown | 391 | 3 | 32 |
| Eccleston | 1,246 | 1 | 5 |
| Mead | 5,914 | 3 | 17 |
| Chamberlain | 10,500 | 1 | 9 |
| 174,463 | 1 | 22 | |
| Otago— | |||
| Pomahaka | 7,478 | 2 | 2 |
| Tahawai | 70 | 1 | 35 |
| Maerewhenua | 11,163 | 3 | 31 |
| Puketapu | 509 | 0 | 6 |
| Ardgowan | 4,268 | 3 | 28 |
| Makareao | 2,383 | 0 | 4 |
| Makareao Extension | 2,589 | 2 | 12 |
| Momona | 224 | 1 | 16 |
| Toka-rahi | 11,259 | 2 | 36 |
| Janefield | 147 | 0 | 2 |
| Elderslie | 11,618 | 2 | 4 |
| Barnego | 7,078 | 2 | 1 |
| Earnscleugh | 1,269 | 3 | 5 |
| Windsor Park | 3,821 | 2 | 16 |
| Windsor Park No. 2 | 2,179 | 2 | 17 |
| Duncan | 633 | 2 | 3 |
| 67,047 | 1 | 17 | |
| Southland— | |||
| Merrivale | 9,998 | 0 | 0 |
| Otahu | 6,153 | 0 | 36 |
| Beaumont | 4,484 | 0 | 4 |
| Ringway | 2,253 | 2 | 8 |
| Glenham | 11,484 | 2 | 10 |
| 34,373 | 1 | 18 | |
| SUMMARY. | |||
| Auckland | 36,590 | 0 | 26 |
| Hawke's Bay | 71,658 | 2 | 11 |
| Taranaki | 1,505 | 2 | 8 |
| Wellington | 16,324 | 1 | 11 |
| Marlborough | 68,135 | 2 | 0 |
| Westland | 5,124 | 3 | 26 |
| Canterbury | 174,463 | 1 | 22 |
| Otago | 67,047 | 1 | 17 |
| Southland | 34,373 | 1 | 18 |
| Totals | 475,223 | 0 | 19 |
Since the initiation of the policy under “The Land for Settlements Act, 1892” it will be found that, including special purchases to provide homesteads and low country for a few Crown tenants, the number of settlements, exclusive of the Birch Hill and Awatere exchanges, is 116, comprising in all 475,223 acres, and the result is that 2,335 tenants—or 7,200 souls in all—have been placed upon 447,334 acres, for which they are liable for an annual rental of £116,979. The area absorbed by roads and reserves is 8,338 acres, and on the 31st March last the total area still in the hands of the Land Boards, inclusive of forfeited and surrendered sections, amounted to 19,544 acres, with an estimated annual rental of £3,401, whilst 278 lessees, holding 61,680 acres, were in arrear £10,489. This amount has been since greatly reduced. The holdings which fall back into the hands of the Crown are reopened as expeditiously as possible, and are as a rule promptly taken up, but difficulty is still experienced in quitting portions of some of the Auckland hamlets, the Waipapa Settlement (Marlborough), the Pomahaka and Barnego Settlements (Otago), and the Beaumont and Glenham Settlements (Southland). The Northbank Estate (Marlborough) was held back for mining.
Table of Contents
IN the year 1896 an Act intituled the Government Valuation of Land Act was passed, providing for the appointment of a Valuer-General, and for the periodical valuation of all land in the colony. The Valuer-General is the Commissioner of Taxes for the time being. The valuations on the district roll are used for the assessment of land-tax, stamp duties, and duties on deceased persons' estates; for local rates, except in places where these are levied on the annual value; also, for the purposes of advances and investments on mortgage of land by the Post Office, Government Insurance Department, Public Trust Office, Government Advances to Settlers Office.
The term “land” means and includes all lands, tenements, buildings, and hereditaments, whether corporeal or incorporeal, and also includes all chattel interests in land.
A certified copy of any entry in the district valuation-roll is supplied by the Department on payment of the prescribed fee.
The district valuation-roll continues in force until a fresh roll is made, but whilst in force it may be altered and amended from time to time. The rolls for rating purposes are supplied to local bodies by the Valuer-General on the request of the local authority. The aim is to insure a standard valuation for taxation, local rating, and loan purposes.
Owners and occupiers dissatisfied with their valuations have the right of objection, the procedure being that laid down by “The Rating Act, 1894,” and the regulations under “The Government Valuation of Land Act, 1896.” The cost of making the valuation is divided proportionally between the Departments mostly using it and the local authorities, while separate fees are provided for by regulation for supplying individual valuations to persons requiring them.
The district valuation-roll shows the capital value of the property, of improvements, and the unimproved value of the land.
The surface-value only of gold mines is included, and the value of the Government railways has been excluded.
All land is included, whether occupied or unoccupied, whether owned by private individuals, by the Crown, by Natives, by local authorities, Education Boards, School Commissioners, Churches, corporations, companies, or societies of all kinds, and whether subject to or exempt from taxation or rates.
The result of the general valuation of land as in March, 1898, is given in the report of the Valuer-General, presented to both Houses of Parliament. Since this general valuation a revision has been made in many districts, which brings the figures as corrected to represent the values on the 31st March, 1903. Comparative figures are here given for 1891 and 1903 showing the increase, and stating separately the unimproved value and the value of improvements.
| COMPARISON OF CAPITAL VALUES. 1891 AND 1903. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1891. | 1903. | Increase, 1891 to 1903. | |
| * In several cases the unimproved value, together with the value of improvements, does not equal the capital value. This is chiefly owing to alterations made by Assessment Courts. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Unimproved value | 75,787,895 | 103,476,204 | 27,688,309 |
| Value of improvements | 46,365,297 | 63,373,177 | 19,007,880 |
| Total | 122,225,029* | 168,849,381 | 46,624,352* |
In the figures for the North and South Islands the relative degree of increase is exhibited, and the rapid rate of progress in the North Island shows in strong contrast to that of the other Island. There has been great spread of settlement in the Wellington and Taranaki Districts.
| CAPITAL VALUES. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1891. | 1903. | Increase. | |
| £ | £ | £ | |
| North Island | 57,441,115 | 92,781,648 | 35,340,533 |
| South Island | 64,783,914 | 76,067,733 | 11,283,819 |
| Totals | 122,225,029 | 168,849,381 | 46,624,352 |
The increase for the North Island of £35,340,533 represents an advance of 61·52 per cent. on the value in 1891, and that of £11,283,819, for the South Island, 17·42 per cent. The increase for the whole colony, as shown previously, was £46,624,352, or 38·14 per cent.
The following statement gives the capital value of land and improvements in counties and boroughs as for 1891 and 1903.
| CAPITAL VALUE OF LAND (([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)) (([0-9]+)). | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1891. | 1903. | |
| £ | £ | |
| Counties | 85,818,167 | 113,126,818 |
| Boroughs | 36,406,862 | 55,722,563 |
| Totals | 122,225,029 | 168,849,381 |
The increase in the capital value of land, with improvements, in counties for the twelve years is £27,308,651, or 31·82 per cent., while that for boroughs is £19,315,701, or 53·05 per cent.; but the value of property in boroughs was added to between 1891 and 1903 by the constitution of fourteen new boroughs, and that of the counties correspondingly reduced, so that the actual rate of increase in the value of country lands is higher than indicated by the above figures, and in urban lands considerably less.
Comparisons are given in detail in the tables which follow.
| COUNTIES, 1891 AND 1903. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABLE SHOWING THE CAPITAL VALUE OF LAND, WITH IMPROVEMENTS (AND DISTINGUISHING UNIMPROVED VALUE OF LAND), IN EACH COUNTY IN NEW ZEALAND ACCORDING TO THE RESULTS OF GENERAL VALUATION MADE IN 1891, AND THAT OF 1898 CORRECTED TO 1903:— | ||||||||
| [* No valuation made. R signifies valuation revised.] | ||||||||
| County. | Capital Value, Land and Improvements. | Unimproved Value of Land (included in previous columns). | ||||||
| As in Year 1891. | As in 1898, revised to 31st March, 1903. | As in Year 1891. | As in 1898, revised to 31st March, 1903. | |||||
(a) Exclusive of Borough of Whangarei, which in 1891 formed part of county. (b) Exclusive of Borough of Waihi, which in 1891 formed part of county. (c) Exclusive of Borough of Te Aroha, which in 1891 formed part of county. (d) Exclusive of County of Opotiki, which in 1891 formed part of the County Whakatane. (e) Formed part of Whakatane County. (f) Exclusive of the County of Woodville and of Dannevirke Borough, which in 1891 formed parts of the County of Waipawa. (g) Formed part of Waipawa County. (h) Exclusive of Weber County, which in 1891 formed part of Patangata County. (i) Formed part of Patangata County. (j) Exclusive of the Borough of Inglewood and of a portion of Egmont County, which in 1891 formed parts of Taranaki County. (k) Formed parts of the Counties of Taranaki and Hawera. (l) Exclusive of the Borough of Stratford, which in 1891 formed part of county. (m) Exclusive of the Borough of Eltham, which in 1891 formed part of county; also exclusive of a portion of the Egmont County. (n) Exclusive of Waimarino County, which in 1891 formed part of the Wanganui County. (o) Formed part of Wanganui County. (p) Formed part of Oroua County. (q) Exclusive of Counties of Kiwitea, Pohangina, and Kairanga, which in 1891 formed parts of Oroua County. (r) Late Wairarapa North County. (s) Exclusive of Featherston County, which in 1891 formed part of Wairarapa South County. (t) Formed part of Wairarapa South County. (u) Exclusive of Motueka Borough, which in 1891 formed part of county. (v) Exclusive of Linwood, Woolston, and New Brighton Boroughs, which in 1891 formed part of county. (w) Exclusive of Mount Herbert County, which in 1891 formed part of Akaroa County. (x) Formed part of Akaroa County. (y) Exclusive of Levels County and Temuka Borough, which in 1891 formed part of county. (z) Formed part of Geraldine County. (†) Approximate only. † Exclusive of Borough of Maura, which in 1891 formed part of county. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |||||
| Mongonui | 196,158 | 226,975 | 152,151 | 155,969 | ||||
| Whangaroa | 63,825 | 77,543 | 41,379 | 47,241 | ||||
| Bay of Islands | 365,069 | 352,782 | 247,612 | 225,908 | ||||
| Hokianga | 422,365 | 414,448 | 365,957 | 338,211 | ||||
| Whangarei | 523,420 | 576,783(a) | 316,003 | 332,896(a) | ||||
| Hobson | 325,974 | R 430,674 | 241,880 | R 269,548 | ||||
| Otamatea | 258,496 | R 437,678 | 156,975 | R 263,257 | ||||
| Rodney | 293,235 | R 328,622 | 173,313 | R 154,260 | ||||
| Waitemata | 632,012 | R 735,700 | 388,568 | R 400,545 | ||||
| Eden | 2,002,677 | R 3,027,838 | 991,380 | R 1,530,822 | ||||
| Manukau | 1,385,330 | R 1,772,701 | 664,272 | R 898,733 | ||||
| Islands (Great and Little Barrier) | 55,284 | 61,732 | 42,574 | 39,621 | ||||
| Waiheke, &c. | 71,343 | 87,021 | 40,211 | 45,005 | ||||
| Waikato | 682,774 | R 710,103 | 282,655 | R 335,844 | ||||
| Raglan | 357,941 | R 758,948 | 280,945 | R 474,380 | ||||
| Waipa | 464,086 | R 721,726 | 197,900 | R 347,719 | ||||
| Kawhia | 354,269 | 473,979 | 350,051 | 415,617 | ||||
| Coromandel | 217,120 | R 334,560 | 166,483 | R 227,311 | ||||
| Thames | 253,013 | R 382,022 | 168,442 | R 246,075 | ||||
| Ohinemuri | 204,704 | R 421,284(b) | 164,182 | R 257,263(b) | ||||
| Tauranga | 282,723 | R 398,372 | 172,078 | R 260,183 | ||||
| Piako | 689,384 | R 995,370(c) | 427,889 | R 525,878(c) | ||||
| Rotorua | 168,371 | 479,479 | 114,289 | 395,998 | ||||
| Whakatane | 663,785 | 301,724(d) | 548,221 | 257,195(d) | ||||
| Opotiki | (e) | 445,339 | (e) | 357,019 | ||||
| East Taupo | 301,681 | 299,039 | 292,106 | 288,249 | ||||
| West Taupo | 235,997 | 250,205 | 226,406 | 224,939 | ||||
| Islands (Mayor and Motiti) | 5,780 | 3,696 | ||||||
| Waiapu | 472,548 | R 994,630 | 341,062 | R 568,437 | ||||
| Cook | 1,885,856 | R 3,341,793 | 1,175,712 | R 2,012,676 | ||||
| Wairoa | 1,101,072 | R 1,383,541 | 786,032 | R 914,450 | ||||
| Hawke's Bay | 3,673,889 | R 4,209,481 | 2,558,583 | R 3,062,313 | ||||
| Waipawa | 2,179,812 | R 2,331,424(f) | 1,249,695 | R 1,426,667 | ||||
| Woodville | (g) | R 727,220 | (g) | R 453,501 | ||||
| Patangata | 1,863,936 | R 2,059,947(h) | 1,154,909 | R 1,490,210(h) | ||||
| Weber | (i) | R 302,821 | (i) | R 162,513 | ||||
| Clifton | 441,325 | R 772,289 | 385,252 | R 573,097 | ||||
| Taranaki | 969,579 | R 1,739,941 (j) | 604,091 | R 1,023,220(j) | ||||
| Egmont | (k) | R 675,032 | (k) | R 418,201 | ||||
| Stratford | 560,345 | R 1,392,315(l) | 447,502 | R 855,612(l) | ||||
| Hawera | 1,247,436 | R 2,783,611(m) | 807,887 | R 1,866,485(m) | ||||
| Patea | 823,675 | R 1,383,409 | 522,322 | R 850,075 | ||||
| Waitotara | 731,668 | R 1,034,808 | 460,842 | R 696,222 | ||||
| Wanganui | 1,176,106 | R 1,264,402(n) | 830,519 | R 875,943(n) | ||||
| Waimarino | (o) | 568,277 | (o) | 510,522 | ||||
| Rangitikei | 1,475,473 | R 2,614,639 | 870,091 | R 1,511,584 | ||||
| Kiwitea | (p) | R 1,100,850 | (p) | R 651,632 | ||||
| Pohangina | (p) | R 571,303 | (p) | R 333,784 | ||||
| Manawatu | 810,171 | R 1,201,527 | 445,416 | R 853,460 | ||||
| Oroua | 2,268,854 | R 1,182,392(q) | 1,298,417 | R 770,963(q) | ||||
| Kairanga | (p) | R 1,171,374 | (p) | R 799,000 | ||||
| Horowhenua | 858,648 | R 1,433,344 | 551,248 | R 863,864 | ||||
| Islands (Kapiti, Chatham, and Mana) | 113,541 | 69,216 | ||||||
| Pahiatua | 511,400 | R 1,205,806 | 331,634 | R 665,978 | ||||
| Akitio |  | (r) 1,831,209 |  | R498,458 |  | (r) 1,057,393 |  | R 304,615 |
| Castlepoint | R384,129 | R 216,556 | ||||||
| Eketahuna | R 547,110 | R 295,490 | ||||||
| Mauriceville | R 318,277 | R 152,759 | ||||||
| Masterton | R 1,789,129 | R 1,050,020 | ||||||
| Wairarapa South | 1,872,035 | R 1,116,906(s) | 1,104,064 | R 685,109(s) | ||||
| Featherston | (t) | R 1,893,261(†) | (t) | R 1,248,600(†) | ||||
| Hutt | 1,030,745 | R 1,675,527 | 520,005 | R 884,376 | ||||
| Collingwood | 323,910 | 366,033 | 223,376 | 196,233 | ||||
| Waimea | 1,196,226 | 1,310,015(u) | 740,668 | 769,868(u) | ||||
| Sounds | 171,095 | R 359,090 | 124,480 | R 213,820 | ||||
| Marlborough | 1,837,632 | R 2,088,938 | 1,344,120 | R 1,493,794 | ||||
| Kaikoura | 350,521 | 448,856 | 209,082 | 346,401 | ||||
| Buller | 651,129 | R711,759 | 483,407 | R 491,271 | ||||
| Inangahua | 874,948 | 864,357 | 598,963 | 623,829 | ||||
| Grey | 861,890 | 826,216 | 670,528 | 581,881 | ||||
| Westland | 1,048,158 | 825,936 | 964,461 | 673,226 | ||||
| Cheviot | 486,765 | R 706,216 | 413,852 | R 561,290 | ||||
| Amuri | 921,221 | R 901,422 | 762,518 | R 677,418 | ||||
| Ashley | 3,801,341 | R 4,096,608 | 2,861,083 | R 3,212,362 | ||||
| Selwyn | 7,446,756 | R 7,756,749(v) | 4,897,419 | R 5,424,834(v) | ||||
| Akaroa | 1,169,379 | R 1,286,151(w) | 775,316 | R 941,116(w) | ||||
| Mount Herbert | (x) | R 211,582 | (x) | R 150,398 | ||||
| Ashburton | 3,630,383 | R 4,631,097 | 2,691,466 | R 3,591,071 | ||||
| Geraldine | 3,257,696 | R 1,850,259(y) | 2,316,183 | R 1,425,895(y) | ||||
| Levels | (z) | R 1,463,208 | (z) | R 1,130,315 | ||||
| Mackenzie | 736,021 | 796,073 | 589,528 | 641,521 | ||||
| Waimate | 2,462,433 | R 2,904,617 | 1,968,587 | R 2,412,960 | ||||
| Waitaki | 2,709,379 | R 2,758,532 | 2,060,640 | R 2,188,661 | ||||
| Maniototo | 449,650 | 568,929 | 358,342 | 371,142 | ||||
| Waihemo | 417,887 | 417,749 | 277,792 | 276,203 | ||||
| Waikouaiti | 602,015 | R 687,584 | 309,077 | R 379,259 | ||||
| Peninsula | 414,146 | 435,233 | 193,301 | 239,695 | ||||
| Taieri | 1,330,718 | R 1,472,808 | 931,554 | R 1,040,786 | ||||
| Tuapeka | 938,701 | R 917,566 | 642,394 | R 611,331 | ||||
| Bruce | 957,438 | R 997,628 | 600,771 | R 667,620 | ||||
| Clutha | 1,151,046 | R 1,274,848 | 772,352 | R 843,113 | ||||
| Vincent | 791,595 | R 460,380 | 637,287 | R 293,707 | ||||
| Lake | 382,722 | R 339,061 | 274,791 | R 249,289 | ||||
| Fiord | 131,391 | 124,986 | ||||||
| Wallace | 1,364,016 | R 1,926,518 | 943,777 | R 1,323,037 | ||||
| Southland | 3,739,513 | R 4,868,546† | 2,446,830 | R 3,345,270† | ||||
| Stewart Island | 85,021 | 160,042 | 79,690 | 133,880 | ||||
| Islands (Antipodes, &c.) | * | 13,880 | * | 13,880 | ||||
| BOROUGHS, 1891 AND 1903. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABLE SHOWING THE CAPITAL VALUE OF LAND, WITH IMPROVEMENTS (AND DISTINGUISHING THE UNIMPROVED VALUE OF LAND), IN EACH BOROUGH IN NEW ZEALAND ACCORDING TO THE RESULTS OF THE GENERAL VALUATION MADE IN 1891, AND THAT OF 1898 CORRECTED TO 1903. | ||||
| [R Signifies valuation revised.] | ||||
| Borough. | Capital Value, Land and Improvements. | Unimproved Value of Land, (included in previous columns). | ||
| As in Year 1891. | As in 1898, revised to 31st March, 1903. | As in Year 1891. | As in 1698, revised to 31st March, 1903. | |
(a) Formed part of Whangarei County. (b) Formed part of Piako County. (c) Formed part of Ohinemuri County. (d) Formed part of Waipawa County. (e) Formed part of Stratford County. (f) Formed part of Hawera County. (g) Formed part of Taranaki County. (h) Now Melrose Ward of Wellington City. (i) Formed part of Pahiatua County. (j) Formed part of Waimea County. (k) Now St. Albans Ward of Christchurch City. (l) Now Sydenham Ward of Christchurch City. (m) Now Linwood Ward of Christchurch City. (n) Formed part of Selwyn County. (p) Value of coal-mines excluded. (q) Formed part of Geraldine County. (s) Value of railway-station (£80,000), included in 1898, excluded in 1898. (t) Formed part of Southland County. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Whangarei | (a) | R 147,831 | (a) | R 58,954 |
| Birkenhead | 77,532 | 108,533 | 42,333 | 49,490 |
| Devonport | 407,333 | 577,939 | 163,468 | 242,062 |
| Auckland | 4,934,288 | R 7,049,904 | 2,471,496 | R 3,696,430 |
| Parnell | 366,098 | 456,523 | 138,775 | 191,576 |
| Newmarket | 182,353 | 218,298 | 82,327 | 83,975 |
| Grey Lynn (late Newton) | 222,355 | R 461,287 | 135,607 | R 198,921 |
| Onehunga | 250,634 | 282,898 | 111,406 | 128,601 |
| Hamilton | 90,142 | R 156,809 | 44,584 | R 69,284 |
| Cambridge | 70,279 | 85,930 | 25,521 | 27,360 |
| Thames | 227,171 | 232,902 | 76,547 | 91,437 |
| Tauranga | 63,026 | 86,590 | 25,153 | 29,267 |
| Te Aroha | (b) | 55,757 | (b) | 24,189 |
| Waihi | (c) | R 137,340 | (c) | R 64,587 |
| Gisborne | 317,989 | R 515,774 | 148,511 | R 311,297 |
| Napier | 1,275,853 | 1,289,457 | 667,157 | 585,955 |
| Hastings | 372,458 | R 567,460 | 230,592 | R 320,256 |
| Dannevirke | (d) | 153,331 | (d) | 81,405 |
| Woodville | 102,226 | 98,037 | 57,852 | 43,824 |
| New Plymouth | 341,117 | R 966,861 | 165,621 | R 616,768 |
| Hawera | 84,834 | R 328,239 | 37,914 | R 178,725 |
| Patea | 43,378 | R 64,291 | 12,055 | R 22,000 |
| Stratford | (e) | R 270,537 | (e) | R 161,215 |
| Eltham | (f) | R 171,130 | (f) | R 98,105 |
| Inglewood | (g) | 91,445 | (g) | 33,175 |
| Wanganui | 543,403 | R 1,330,648 | 290,321 | R 854,898 |
| Marton | 83,915 | 116,287 | 33,736 | 40,507 |
| Fielding | 146,884 | R 331,954 | 68,199 | R 167,520 |
| Palmerston North | 489,618 | R 815,676 | 310,293 | R 353,506 |
| Foxton | 85,743 | R 121,247 | 39,755 | R 61,362 |
| Onslow | 144,053 | R 277,826 | 70,803 | R 150,589 |
| Karori | 118,728 | R 321,347 | 74,595 | R 211,012 |
| Wellington | 5,865,778 | R 10,935,689 | 3,440,182 | R 6,590,278 |
| Melrose(h) | 203,517 | R 609,582 | 129,429 | R 355,125 |
| Pahiatua | (i) | R 148,970 | (i) | R 71,737 |
| Masterton | 356,860 | R 636,040 | 159,861 | R 339,566 |
| Carterton | 88,650 | R 163,996 | 31,315 | R 82,332 |
| Greytown | 115,649 | R 146,912 | 34,095 | R 57,580 |
| Lower Hutt | 244,075 | R 419,631 | 159,178 | R254,403 |
| Petone | 268,358 | R 489,799 | 145,221 | R 253,683 |
| Richmond | 84,285 | 87,431 | 43,375 | 46,268 |
| Nelson | 942,370 | 861,873 | 389,397 | 348,276 |
| Picton | 88,195 | R 109,527 | 41,189 | R 52,340 |
| Blenheim | 378,943 | R 306,721 | 167,481 | R 133,744 |
| Motueka | (j) | 98,345 | (j) | 52,690 |
| Westport | 166,987 | 199,899 | 57,782 | 82,584 |
| Greymouth | 299,077 | R 370,260 | 114,543 | R 97,142 |
| Brunner | 115,892 | 70,330(p) | 16,166 | 11,539(p) |
| Kumara | 33,565 | 37,552 | 6,945 | 5,581 |
| Hokitika | 102,708 | R 167,857 | 18,054 | R 66,068 |
| Ross | 16,961 | R 20,975 | 5,250 | R 5,382 |
| Rangiora | 158,017 | 186,968 | 71,161 | 74,945 |
| Kaiapoi | 134,055 | 163,891 | 47,023 | 48,475 |
| St. Albans(k) | 524,822 | R 895,761 | 284,938 | R 365,087 |
| Christchurch | 3,403,566 | R 4,534,565 | 1,820,770 | R 2,279,807 |
| Sydenham(l) | 821,060 | 869,040(s) | 333,876 | 288,304(s) |
| Linwood(m) | (n) | 546,659 | (n) | 171,361 |
| Woolston | (n) | 234,877 | (n) | 99,758 |
| New Brighton | (n) | 100,081 | (n) | 46,245 |
| Sumner | 102,145 | R 132,953 | 60,246 | R 66,832 |
| Lyttelton | 851,730 | 850,949 | 150,490 | 238,912 |
| Akaroa | 49,407 | 54,323 | 19,628 | 17,738 |
| Ashburton | 223,091 | 260,688 | 90,733 | 97,285 |
| Temuka | (q) | 111,941 | (q) | 32,130 |
| Timaru | 442,830 | R 866,357 | 151,661 | R 323,560 |
| Waimate | 75,399 | R 140,298 | 18,759 | R 51,658 |
| Oamaru | 612,571 | R 522,507 | 279,113 | R 179,307 |
| Hampden | 13,195 | R 21,157 | 5,229 | R 7,460 |
| Naseby | 24,186 | 33,939 | 2,440 | 4,169 |
| Palmerston | 51,182 | R 56,446 | 16,771 | R 14,309 |
| Hawksbury | 45,716 | R 60,000 | 19,823 | R 28,555 |
| Port Chalmers | 200,043 | 234,988 | 60,946 | 61,456 |
| West Harbour | 137,015 | 135,144 | 68,240 | 61,675 |
| North-east Valley | 276,835 | 280,651 | 130,271 | 106,409 |
| Maori Hill | 142,890 | R 201,009 | 67,348 | R 86,573 |
| Roslyn | 360,962 | R 587,118 | 169,610 | R 249,816 |
| Mornington | 284,875 | 326,438 | 125,414 | 113,978 |
| Dunedin | 4,193,422 | R 5,452,589 | 2,124,467 | R 2,605,199 |
| Caversham | 466,074 | 497,422 | 217,158 | 189,222 |
| South Dunedin | 223,534 | R 350,372 | 82,609 | R 103,970 |
| St. Kilda | 118,477 | R 194,406 | 76,842 | R 97,773 |
| Green Island | 36,962 | R 39,396 | 13,585 | R 11,234 |
| Mosgiel | 122,625 | R 157,583 | 53,441 | R 65,200 |
| Roxburgh | 20,123 | 30,535 | 3,167 | 3,438 |
| Lawrence | 79,066 | 98,147 | 18,584 | 23,184 |
| Tapanui | 16,155 | 16,174 | 2,575 | 2,550 |
| Milton | 76,207 | R 142,756 | 14,012 | R 38,886 |
| Balclutha | 53,210 | R 93,530 | 14,547 | R 32,829 |
| Kaitangata | 54,976 | 62,464 | 21,133 | 28,081 |
| Arrowtown | 24,586 | 27,233 | 5,012 | 4,754 |
| Queenstown | 65,153 | 69,663 | 13,524 | 12,562 |
| Cromwell | 22,168 | 37,734 | 4,658 | 9,196 |
| Alexandra | 13,578 | 45,713 | 2,955 | 10,257 |
| Gore | 142,708 | R 280,600 | 66,171 | R 104,833 |
| Mataura | (t) | R 123,232 | (t) | R 50,011 |
| Winton | 20,195 | R 48,856 | 7,965 | R 19,613 |
| Gladstone | 26,541 | 39,105 | 13,825 | 16,060 |
| Avenal | 15,269 | 27,089 | 6,687 | 8,441 |
| North Invercargill | 28,293 | 41,586 | 15,640 | 17,169 |
| East Invercargill | 42,996 | 58,279 | 18,385 | 17,615 |
| Invercargill | 959,140 | R 1,215,162 | 517,879 | R 500,010 |
| South Invercargill | 79,526 | R 117,702 | 42,813 | R 44,922 |
| Riverton | 59,626 | 60,779 | 22,024 | 15,206 |
| Campbelltown | 97,380 | 164,231 | 49,430 | 75,721 |
| LOCAL DISTRICTS, 1903. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABLE showing the CAPITAL VALUE of LAND with IMPROVEMENTS (and distinguishing the UNIMPROVED VALUE of LAND), in each RIDING, ROAD DISTRICT, and TOWN DISTRICT in NEW ZEALAND according to the results of the General Valuation made in 1898, revised to 1903. | ||||
| County and Riding. | Road District. | Town District. | Capital Value, Land and Improvements. | Unimproved Value of Land (included in previous column). |
* Formerly part of Parihaka Road District. *Approximate. NOTE.—No valuations were made for the Cook or Kermadec Islands. | ||||
| Mongonui County— | .. | .. | £ | £ |
| Kaitaia | .. | .. | 52,484 | 35,084 |
| Mongonui | .. | .. | 37,553 | 24,265 |
| Hohoura | .. | .. | 39,615 | 23,343 |
| Herekino | .. | .. | 30,923 | 28,021 |
| Victoria Valley | .. | .. | 24,836 | 14,382 |
| Oruru | .. | .. | 41,564 | 30,874 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £226,975 | £155,969 |
| Whangaroa County— | ||||
| Whangaroa | .. | .. | 25,328 | 15,512 |
| Totara | .. | .. | 20,262 | 12,705 |
| Kaeo | .. | .. | 31,953 | 19,024 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £77,543 | £47,241 |
| Bay of Islands County— | ||||
| Waimate | .. | .. | 109,295 | 65,368 |
| Russell | .. | .. | 46,150 | 33,794 |
| Kawakawa | .. | .. | 73,502 | 34,886 |
| Pakaraka | .. | .. | 123,835 | 91,860 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £352,782 | £225,908 |
| Hokianga County— | ||||
| Whangape | .. | .. | 60,333 | 50,653 |
| Kohukohu | .. | .. | 55,077 | 41,573 |
| Waihou | .. | .. | 67,498 | 61,204 |
| Tahaka | .. | .. | 62,450 | 57,166 |
| Horeke | .. | .. | 21,835 | 17,519 |
| Rawene | .. | 30,040 | 18,773 | |
| Omapere | .. | .. | 117,215 | 91,323 |
| Waipoua | ||||
| Total of county | .. | .. | £414,448 | £338,211 |
| Whangarei County— | ||||
| Otonga | Otonga | .. | 18,703 | 8,489 |
| Outlying | .. | 30,182 | 20,479 | |
| Kiripaka | (Marua | .. | 29,931 | 21,798 |
| Outlying | .. | 36,537 | 25,351 | |
| Hikurangi | Hikurangi | .. | 38,996 | 24,778 |
| Kaurihohore | .. | 13,962 | 6,392 | |
| Outlying | .. | 17,577 | 11,725 | |
| Wairua | .. | Kamo | 22,453 | 7,872 |
| Outlying | .. | 60,892 | 30,957 | |
| Maunu | Maunu | .. | 72,238 | 42,613 |
| Outlying | .. | 46,322 | 33,696 | |
| Manaia | Whareora | .. | 9,627 | 4,929 |
| Parua | .. | 23,318 | 11,346 | |
| Outlying | .. | 23,516 | 14,122 | |
| Manganpai | Maungakaramea | .. | 25,468 | 10,194 |
| Ruarangi | .. | 11,700 | 6,162 | |
| Waikiekie | .. | 24,445 | 15,159 | |
| Outlying | .. | 14,249 | 8,087 | |
| Waipu | Waipu North | .. | 16,813 | 6,101 |
| Outlying | .. | 39,854 | 20,646 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £576,783 | £332,896 |
| Hobson County— | ||||
| Dargaville | .. | .. | 54,115 | 26,605 |
| Kaihu | .. | .. | 43,225 | 33,768 |
| Tangowahine | .. | .. | 85,057 | 78,494 |
| Wairoa | .. | .. | 53,357 | 42,620 |
| Okahu | .. | .. | 47,382 | 22,291 |
| Aratapu | .. | .. | 74,686 | 27,980 |
| Te Kopuru | .. | .. | 72,852 | 37,790 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £430,674 | £269,548 |
| Otamatea County— | ||||
| Tokatoka | .. | .. | 109,508 | 73,274 |
| Matakohe | Matakohe | .. | 50,461 | 32,731 |
| Outlying | .. | 50,461 | 8,965 | |
| Mareretu | .. | .. | 26,113 | 13,845 |
| Paparoa | .. | .. | 48,968 | 22,666 |
| Wairau | .. | .. | 49,735 | 26,933 |
| Whakapirau | Whakapirau | .. | 70,874 | 44,411 |
| Kaiwaka | Mangawai | .. | 25,886 | 14,289 |
| Outlying | .. | 42,073 | 26,143 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £437,678 | £263,257 |
| Rodney County— | ||||
| Albert | Albertland North | .. | 7,046 | 4,493 |
| Mainene | .. | 7,083 | 3,823 | |
| Albertland South | .. | 27,132 | 8,628 | |
| Wharehine | .. | 13,474 | 7,649 | |
| Hoteo | .. | .. | 42,140 | 20,890 |
| Tauhoa | Tauhoa | .. | 25,862 | 10,979 |
| Komokoriki | .. | 11,997 | 6,893 | |
| Ahuroa | .. | 5,703 | 3,563 | |
| Omaha | Omaha | .. | 36,011 | 20,944 |
| Matakana | Matakana West | .. | 17,501 | 6,459 |
| Matakana East | .. | 9,200 | 5,378 | |
| Eastern Mahurangi | .. | 11,373 | 4,694 | |
| Mahurangi | Upper Mahurangi | .. | 35,048 | 15,126 |
| Warkworth | .. | 43,879 | 15,510 | |
| Puhoi | Puhoi | .. | 35,173 | 19,231 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £328,622 | £154,261 |
| Waitemata County— | ||||
| Mairetahi | .. | Helensville | 27,392 | 5,143 |
| Outlying | .. | 76,557 | 37,948 | |
| Kaukapakapa | Kaukapakapa | .. | 47,787 | 26,536 |
| Kumeu | .. | .. | .41,304 | 23,646 |
| Wainui | Whangaparoa | .. | 7,856 | 3,941 |
| Pukeatua | .. | 29,832 | 17,791 | |
| Outlying | .. | 30,085 | 14,356 | |
| Waitemata County— | ||||
| Takapuna | .. | .. | 150,982 | 87,365 |
| Birkenhead | .. | .. | 30,584 | 20,807 |
| Northcote | .. | .. | 86,431 | 42,516 |
| Waitakerei | .. | .. | 93,958 | 58,144 |
| Waikomiti | .. | .. | 106,932 | 62,352 |
| Total of county | £735,700 | £400,545 | ||
| Eden County— | ||||
| Newton | Arch Hill | .. | 103,623 | 40,466 |
| Grafton | Eden Terrace | .. | 127,369 | 43,346 |
| Whau | Point Chevalier | .. | 118,649 | 27,114 |
| Mount Albert | .. | 257,626 | 118,746 | |
| Avondale | .. | 141,595 | 70,150 | |
| Mount Roskill | .. | 171,049 | 115,736 | |
| Epsom | Mount Eden | .. | 655,856 | 253,802 |
| Epsom | .. | 234,121 | 125,680 | |
| One Tree Hill | .. | 316,143 | 199,454 | |
| Parenell | Remuera | .. | 563,310 | 329,375 |
| Orakei | .. | 10,896 | 9,322 | |
| Tamaki | Tamaki West | .. | 128,609 | 86,179 |
| Panmure Township | .. | 15,248 | 4,306 | |
| Mount Wellington | .. | 183,744 | 107,146 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £3,027,838 | £1,530,822 |
| Manukau County— | ||||
| Awhitu | Awhitu | .. | 38,549 | 18,884 |
| Pollock Settlement | .. | 14,536 | 6,815 | |
| Waiuku | Waipipi | .. | 148,087 | 75,687 |
| Waiuku | .. | 74,476 | 39,256 | |
| Howick | Pakuranga | .. | 60,840 | 44,613 |
| Howick Township | .. | 15,861 | 6,029 | |
| Paparoa | .. | 22,334 | 11,108 | |
| East Tamaki | .. | 108,211 | 53,351 | |
| Turaoga | .. | 27,324 | 12,070 | |
| Maraotai | .. | 12,625 | 6,933 | |
| Otahuhu | Otahuhu | .. | 105,101 | 51,076 |
| Mangere | .. | 200,348 | 119,188 | |
| Papatoitoi | .. | 60,231 | 39,860 | |
| Manurewa | .. | 36,608 | 20,109 | |
| Papakura | Papakura | .. | 70,900 | 36,726 |
| Wairoa | .. | 96,286 | 46,959 | |
| Drury | .. | 48,921 | 21,866 | |
| Papakura | .. | 22,246 | 8,415 | |
| Hunua | .. | 25,439 | 16,832 | |
| Pukekohe | Mauku | .. | 56,745 | 29,658 |
| Karaka | .. | 36,969 | 19,313 | |
| Pukekohe West | .. | 150,808 | 70,569 | |
| Pukekohe East | .. | 126,671 | 54,033 | |
| Maungatawhiri | Opaheke | .. | 41,356 | 18,989 |
| Paparata | .. | 39,639 | 17,482 | |
| Pokeno | .. | 35,366 | 17,636 | |
| Maungatawhiri | .. | 28,814 | 12,758 | |
| Mercer | .. | 18,849 | 8,755 | |
| Outlying | .. | 48,581 | 40,412 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,772,701 | £898,733 |
| Islands— | ||||
| Great Barrier | .. | .. | 61,732 | 39,621 |
| Little Barrier | ||||
| Kawau | .. | .. | 87,021 | 45,005 |
| Motuhora | ||||
| Moturoa | ||||
| Motutikatika | ||||
| Mokohinau | ||||
| Taranga | ||||
| Week's Island | ||||
| Tiritiri | ||||
| Waiheke | ||||
| Motutapu | ||||
| Ponui | ||||
| Rangitoto | ||||
| Motuihi | ||||
| Cuvier | ||||
| Great Mercury | ||||
| White | .. | .. | Not | valued. |
| Whale | ||||
| Total of islands | .. | .. | £148,753 | £84,626 |
| Waikato County— | ||||
| Whangamarino | Whangamarino | .. | 98,502 | 56,991 |
| Huntly | Huntly | .. | 92,481 | 55,147 |
| Kirikiriroa | Kirikiriroa | .. | 270,668 | 100,619 |
| Tamahere | Tamahere | .. | 88,064 | 42,480 |
| Cambridge | Cambridge | .. | 160,388 | 80,607 |
| Total of county | .. | £710,103 | £335,844 | |
| Raglan County— | ||||
| Onewhero | .. | .. | 149,853 | 91,293 |
| Whangape | .. | .. | 167,345 | 106,948 |
| Waingaro | .. | .. | 134,086 | 73,706 |
| Te Akau | Te Akau | .. | 108,029 | 87,858 |
| Karioi | .. | .. | 62,702 | 33,101 |
| Whaingaroa | .. | .. | 60,538 | 31,815 |
| Karamu | Karamu | .. | 28,240 | 17,799 |
| Outlying | .. | 14,927 | 10,688 | |
| Pirongia | .. | .. | 33,228 | 21,172 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £758,948 | £474,380 |
| Waipa County— | ||||
| Newcastle | Newcastle | .. | 78,825 | 43,072 |
| .. | Ngaruawahia | 20,593 | 5,774 | |
| Hamilton | .. | .. | 97,442 | 50,468 |
| Tuhikaramea | Tuhikaramea | .. | 45,154 | 25,907 |
| Pukekura | Pukekura | .. | 182,678 | 91,154 |
| Mangapiko | .. | .. | 125,919 | 56,877 |
| Rangiaohia | Rangiaohia | .. | 124,131 | 57,826 |
| .. | Te Awamutu | 31,181 | 11,616 | |
| .. | Kihikihi | 15,803 | 5,025 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £721,726 | £347,719 |
| Kawhia County | .. | .. | £473,979 | £415,617 |
| Coromandel County— | ||||
| Harataunga | .. | .. | 253,685 | 168,971 |
| Mercury Bay | .. | .. | 80,875 | 58,340 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £334,560 | £227,311 |
| Thames County— | ||||
| Hastings | .. | .. | 74,131 | 59,498 |
| Kauaeranga | .. | .. | 48,453 | 15,486 |
| Parawai | .. | .. | 42,333 | 17,750 |
| Totara | .. | .. | 217,105 | 153,341 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £382,022 | £246,075 |
| Ohinemuri County— | ||||
| Waitoa | .. | .. | 80,666 | 66,411 |
| Paeroa | .. | .. | 206,803 | 114,511 |
| Waitekauri | .. | .. | 56,465 | 38,316 |
| Karangahake | .. | .. | 77,350 | 38,025 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £421,284 | £257,263 |
| Tauranga County— | ||||
| Katikati | Katikati | .. | 60,036 | 38,154 |
| Outlying | .. | 18,955 | 17,084 | |
| Te Puna | Te Puna | .. | 39,666 | 30,134 |
| Outlying | .. | 1,759 | 879 | |
| Te Puna Township | ||||
| Waimapu | .. | .. | 87,849 | 57,534 |
| Maketu | Te Puke | .. | 86,656 | 53,346 |
| Outlying | .. | 103,451 | 63,052 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £398,372 | £260,183 |
| Piako County— | ||||
| Waitoa | Waitoa | .. | 424,291 | 210,619 |
| Te Aroha | .. | .. | 85,836 | 52,795 |
| Matamata | Matamata | .. | 163,450 | 89,615 |
| Taotaoroa | .. | .. | 54,981 | 32,799 |
| Patetere | .. | .. | 266,812 | 140,050 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £995,370 | £525,878 |
| Rotorua County— | ||||
| North | .. | .. | 233,239 | 188,429 |
| South | .. | .. | 246,240 | 207,569 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £479,479 | £395,998 |
| Whakatane County— | ||||
| Matata | .. | .. | 98,931 | 89,984 |
| Omataroa | .. | .. | 62,869 | 43,401 |
| Opouriao | .. | .. | 108,828 | 98,194 |
| Waimana | .. | .. | 31,096 | 25,616 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £301,724 | £257,195 |
| Opotiki County— | ||||
| Waioeka | .. | .. | 386,600 | 328,057 |
| Ohiwa | .. | .. | 23,732 | 15,220 |
| Opotiki | .. | Opotiki | 35,007 | 13,742 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £445,339 | £357,019 |
| East Taupo County | .. | .. | £299,039 | £288,249 |
| West Taupo County | .. | .. | £250,205 | £224,939 |
| Mayor and Motiti Islands | .. | .. | £5,780 | £3,696 |
| Matakaoa | .. | .. | 93,352 | 78,608 |
| Awanui | .. | .. | 86,370 | 61,678 |
| Piritarau | .. | .. | 297,127 | 162,944 |
| Waipiro | .. | .. | 251,579 | 130,493 |
| Tokomaru | .. | .. | 266,202 | 134,714 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £994,630 | £568,437 |
| Cook County— | ||||
| Tolago | .. | .. | 495,778 | 282,045 |
| Waikohu | Waikohu | .. | 363,267 | 220,819 |
| Waipaoa | .. | 137,429 | 70,543 | |
| Ngatapa | .. | 426,194 | 271,747 | |
| Waimata | Waimata | .. | 234,722 | 125,924 |
| Pouawa | .. | 178,322 | 97,277 | |
| Gisborne | Ormond | .. | 77,876 | 47,411 |
| Poverty Bay | .. | 235,379 | 167,424 | |
| Taruheru (Subdivisions 1, 2) | .. | 80,763 | 57,510 | |
| Whataupoko | Taruheru Subdivision 3) | .. | 52,135 | 25,788 |
| Whataupoko | .. | 117,688 | 49,018 | |
| Kaiti | .. | 102,683 | 60,460 | |
| Titirangi | .. | 33,679 | 27,066 | |
| Patutahi | Patutahi | .. | 222,766 | 141,228 |
| Hangarea | Hangaroa | .. | 71,548 | 42,848 |
| Aroha | .. | 75,787 | 40,234 | |
| Outyling | .. | 106,842 | 78,201 | |
| Arai | Arai | .. | 328,935 | 207,133 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £3,341,793 | £2,012,676 |
| Wairoa County— | ||||
| Waikaremoana | .. | .. | 617,233 | 408,407 |
| Clyde | .. | Clyde | 58,190 | 29,344 |
| Outlying | .. | 280,473 | 184,876 | |
| Mohaka | .. | .. | 427,645 | 291,823 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,383,541 | £914,450 |
| Hawke's Bay County— | ||||
| Petane | .. | .. | 331,192 | 215,589 |
| Puketapu | .. | .. | 451,500 | 312,613 |
| Okawa | .. | .. | 604,650 | 428,836 |
| Meanee | .. | Taradale | 67,118 | 34,041 |
| Outlying | .. | 201,997 | 128,310 | |
| Erehwon | .. | .. | 212,150 | 181,065 |
| Maraekakaho | .. | .. | 450,544 | 313,341 |
| Heretaunga | .. | .. | 781,685 | 586,211 |
| Clive | .. | .. | 376,956 | 294,591 |
| Havelock | .. | .. | 731,689 | 567,716 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £4,209,481 | £3,062,313 |
| Waipawa Country— | ||||
| Waipawa | North Ruataniwha | .. | 301,116 | 183,396 |
| Waipawa | .. | 62,293 | 40,279 | |
| .. | Waipawa | 74,232 | 27,844 | |
| Ruataniwha | Takapau | .. | 251,659 | 152,957 |
| Outlying | .. | 463,299 | 260,651 | |
| Waipukurau | Waipukurau | .. | 372,663 | 253,372 |
| Norsewood | Norsewood | .. | 172,720 | 92,883 |
| Ormondville | .. | Ormondville | 30,989 | 7,477 |
| Outlying | .. | 100,387 | 59,268 | |
| Dannevirke | .. | .. | 502,066 | 348,540 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,331,424 | £1,426,667 |
| Woodville County— | ||||
| Woodville | .. | 178,894 | 105,674 | |
| Maungaatua | .. | .. | 159,142 | 109,232 |
| Kumeroa | .. | .. | 215,553 | 122,816 |
| Maharahara | .. | .. | 173,631 | 115,779 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £727,220 | £453,501 |
| Patangata County— | ||||
| Patangata | Patangata | .. | 171,064 | 118,790 |
| .. | Kaikora North | 26,007 | 11,293 | |
| Oero | Oero | .. | 371,737 | 285,715 |
| Taumumu | Taumumu | .. | 600,164 | 444,454 |
| Eparima | Wanstead | .. | 147,963 | 107,015 |
| Wallingford | .. | 379,968 | 265,399 | |
| Porangahau | Porangahau | .. | 363,044 | 257,544 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,059,947 | £1,490,210 |
| Weber County— | ||||
| Weber | .. | .. | 98,248 | 54,041 |
| Titree Point | .. | .. | 85,305 | 49,208 |
| Wimbledon | .. | .. | 119,268 | 59,264 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £302,821 | £162,513 |
| Clifton County— | ||||
| Mokau | .. | .. | 380,473 | 323,144 |
| Urenui | .. | .. | 103,654 | 66,606 |
| Tikorangi | .. | .. | 76,624 | 45,923 |
| Waihi | .. | .. | 79,920 | 57,135 |
| Ngatimaru | .. | .. | 131,618 | 80,289 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £772,289 | £573,097 |
| Taranaki Country— | ||||
| Waitara | Waitara West | .. | 188,186 | 108,920 |
| .. | Raleigh | 47,605 | 19,157 | |
| Egmont | .. | 135,877 | 78,926 | |
| Henui | .. | 115,668 | 79,471 | |
| Moa | Moa | .. | 462,572 | 230,577 |
| Mangorei | .. | 53,339 | 34,476 | |
| Waiwakaiho | .. | 71,301 | 38,940 | |
| Omata | Elliott | .. | 55,395 | 39,083 |
| Carrington | .. | 99,808 | 64,566 | |
| Frankley | .. | 72,986 | 45,501 | |
| Barrett | .. | 114,390 | 76,671 | |
| Omata | .. | 90,611 | 63,919 | |
| Upper Hurford | .. | 14,648 | 8,627 | |
| Tataraimaka | .. | 36,740 | 21,383 | |
| Oakura | .. | 77,216 | 50,983 | |
| Okato | .. | 80,357 | 47,255 | |
| Outyling)* | .. | 23,242 | 14,765 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,739,941 | £1,023,220 |
| Stratford County— | ||||
| North | Manganui | .. | 311,071 | 173,704 |
| East | .. | .. | 651,571 | 407,705 |
| West | .. | .. | 212,800 | 133,977 |
| South | .. | .. | 216,873 | 140,226 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,392,315 | £855,612 |
| Egmont County— | ||||
| Rahotu | Parihaka | .. | 372,056 | 236,380 |
| Opunake | .. | Opunake | 48,143 | 23,850 |
| Oeo | .. | .. | 254,833 | 157,971 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £675,032 | £418,201 |
| Hawera County— | ||||
| Waimate | Waimate | .. | 810,406 | 540,571 |
| .. | Manaia | 39,850 | 14,078 | |
| Mangatoki | .. | .. | 344,910 | 229,927 |
| Okaiawa | .. | .. | 256,278 | 188,642 |
| Eltham | .. | .. | 272,624 | 168,347 |
| Hawera | .. | Normanby | 27,289 | 11,008 |
| Outlying | .. | 757,997 | 528,046 | |
| Mokoia | .. | .. | 274,257 | 185,866 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,783,611 | £1,866,485 |
| Patea Country— | ||||
| Otoia | Patea West | .. | 361,430 | 230,183 |
| Patea East | .. | 210,772 | 138,714 | |
| Outlying | .. | 5,514 | 5,514 | |
| Kapara | .. | .. | 137,739 | 81,963 |
| Waverley | Kohi | .. | 72,286 | 44,934 |
| Wairoa | .. | 84,516 | 51,568 | |
| Motoroa | .. | 37,643 | 20,908 | |
| Waitotara-Momohaki | .. | 164,679 | 82,785 | |
| Okutuku | .. | 79,666 | 54,590 | |
| Whenuakura-Waitotara | .. | 196,235 | 129,084 | |
| .. | Waverley | 32,929 | 9,832 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,383,409 | £850,075 |
| Waitotara County— | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Tokomaru | .. | .. | 160,688 | 114,641 |
| Waitotara | .. | .. | 341,799 | 241,932 |
| Brunswick | .. | .. | 301,578 | 200,385 |
| Westmere | .. | .. | 230,743 | 139,264 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,034,808 | £696,222 |
| Wanganui County— | ||||
| Mangawhero | Mangawhero | .. | 285,930 | 190,706 |
| Upper Wangaehu | Upper Wangaehu | .. | 379,724 | 293,975 |
| Mataongaonga | Mataongaonga | .. | 142,669 | 101,354 |
| Kaukatea | Kaukatea | .. | 75,445 | 46,426 |
| Purua | Purua | .. | 213,030 | 131,365 |
| Kaitoke | Kaitoke | .. | 167,604 | 112,117 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,264,402 | £875,943 |
| Waimarino County— | ||||
| Huikumu | .. | .. | 178,371 | 162,916 |
| Manganui | .. | .. | 106,771 | 102,174 |
| Ruapehu | .. | .. | 49,896 | 47,320 |
| Karioi | .. | .. | 41,197 | 36,629 |
| Parapara | .. | .. | 109,976 | 87,982 |
| Raetihi | .. | .. | 8,254 | 4,574 |
| Ohakune | .. | .. | 73,812 | 68,927 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £568,277 | £510,522 |
| Rangitikei County— | ||||
| Ohingaiti | .. | .. | 592,127 | 343,545 |
| Otairi | .. | .. | 319,806 | 161,948 |
| Maungahoe | .. | .. | 184,956 | 103,348 |
| Paraekaretu | .. | .. | 295,614 | 170,529 |
| Wangaehu | .. | .. | 210,083 | 133,825 |
| Maungaraupi | .. | .. | 247,328 | 138,816 |
| Porewa | .. | .. | 256,243 | 137,975 |
| Otakapu | .. | Lethbridge | 27,024 | 11,143 |
| Outlying | .. | 267,581 | 184,197 | |
| Rangitoto | .. | Bulls | 38,948 | 11,790 |
| Outlying | .. | 174,929 | 114,468 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,614,639 | £1,511,584 |
| Kiwitea County— | ||||
| Hautapu | .. | .. | 133,031 | 79,995 |
| Rangiwahia | .. | .. | 147,695 | 84,405 |
| Peep-o'-day | .. | .. | 113,070 | 58,733 |
| Ongo | .. | .. | 118,203 | 72,513 |
| Kiwitea | .. | .. | 112,537 | 73,118 |
| Waituna | .. | .. | 116,451 | 69,913 |
| Cheltenham | .. | .. | 116,380 | 73,039 |
| Kimbolton | .. | .. | 105,995 | 56,436 |
| Pakihikura | .. | .. | 137,488 | 83,480 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,100,850 | £651,632 |
| Pohangina County— | ||||
| Mangapikopiko | .. | .. | 90,369 | 49,750 |
| Umutoi | .. | .. | 91,220 | 57,856 |
| Coal Creek | .. | .. | 87,492 | 45,729 |
| Tamaki | .. | .. | 67,264 | 46,878 |
| Pohangina | .. | .. | 51,950 | 28,419 |
| Mangaone | .. | .. | 100,498 | 59,154 |
| Awahou | .. | .. | 82,510 | 45,998 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £571,303 | £333,784 |
| Manawatu County— | ||||
| Sandon | .. | .. | 159,436 | 104,684 |
| Mount Stewart | .. | .. | 152,305 | 105,819 |
| Waitohi | .. | .. | 157,280 | 106,100 |
| Campbell | .. | .. | 198,173 | 137,064 |
| Carnarvon | .. | .. | 194,196 | 152,144 |
| Kawakawa | .. | .. | 174,891 | 120,810 |
| Awahou | .. | .. | 165,246 | 126,839 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,201,527 | £853,460 |
| Oroua County— | ||||
| Waituna | Halcombe | 21,443 | 5,428 | |
| Manchester, Wards 1, 2, 3, 4 | .. | 580,492 | 390,503 | |
| Ashhurst | Manchester, Wards 5,6,7 | .. | 580,457 | 375,032 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,182,392 | £770,963 |
| Kairanga County— | ||||
| Taonui | .. | .. | 801,596 | 565,377 |
| Fitzherbert | .. | .. | 369,778 | 233,623 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,171,374 | £799,000 |
| Horowhenua County— | ||||
| Tokomaru | Wirokino, Wards 1, 2, 3 | .. | 313,478 | 170,949 |
| Wirokino | Wirokino, Wards 4, 5, 6 | .. | 596,431 | 390,336 |
| Otaki | Otaki | .. | 290,741 | 164,081 |
| Te Horo | Te Horo | .. | 232,694 | 138,498 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,433,344 | £863,864 |
| Islands— | ||||
| Kapiti | .. | .. | 17,984 | 13,378 |
| Mana | ||||
| Somes | ||||
| Chatham | .. | .. | 90,557 | 55,836 |
| Total of islands | .. | .. | £113,541 | £69,216 |
| Pahiatua County— | ||||
| Mangahao | .. | .. | 411,710 | 240,775 |
| Pukemiku | .. | .. | 134,991 | 77,230 |
| Makuri | .. | .. | 210,770 | 111,428 |
| Mangaone | .. | .. | 190,265 | 111,569 |
| Puketoi | .. | .. | 258,070 | 124,976 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,205,806 | £665,978 |
| Akitio County— | ||||
| Akitio | .. | .. | 151,128 | 91,429 |
| Waihi | .. | .. | 81,066 | 47,532 |
| Rakaunui | .. | .. | 40,531 | 25,257 |
| Pongaroa | .. | .. | 117,191 | 69,416 |
| Mataikona | .. | .. | 108,542 | 70,981 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £498,458 | £304,615 |
| Castlepoint County— | ||||
| East | .. | .. | 170,209 | 99,222 |
| West | .. | .. | 213,920 | 117,334 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £384,129 | £216,556 |
| Eketahuna County— | ||||
| West | .. | .. | 286,626 | 161,538 |
| East | .. | .. | 260,484 | 133,952 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £547,110 | £295,490 |
| Mauriceville County— | ||||
| West | .. | .. | 159,044 | 77,281 |
| East | .. | .. | 159,233 | 75,478 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £318,277 | £152,759 |
| Masterton County— | ||||
| Alfredton | .. | .. | 259,508 | 114,690 |
| Upper Taueru | .. | .. | 166,760 | 90,943 |
| Rangitumau | .. | .. | 284,703 | 170,859 |
| Opaki | .. | .. | 372,875 | 215,656 |
| Te Whiti | .. | .. | 168,750 | 114,392 |
| Wainuioru | .. | .. | 536,533 | 343,480 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,789,129 | £1,050,020 |
| Wairarapa South County— | ||||
| Belvedere | .. | .. | 198,074 | 114,737 |
| Dalefield | .. | .. | 181,312 | 110,809 |
| Parkvale | .. | .. | 195,246 | 122,453 |
| Maungaraki | .. | .. | 542,274 | 337,110 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,116,906 | £685,109 |
| Featherston County— | ||||
| Pahaoa | .. | .. | Details not yet. | available as |
| Greytown | .. | .. | ||
| Martinborough | .. | .. | ||
| Western Lake | .. | .. | ||
| Kahutara | .. | .. | ||
| Featherston | .. | Featherston | ||
| Outlying | .. | |||
| Otaraia | .. | .. | ||
| Turanganui | .. | .. | ||
| Awhea | .. | .. | ||
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,893,261* | £1,248,600* |
| Hutt County— | ||||
| Whareroa | .. | .. | 174,940 | 86,992 |
| Horokiwi | Plimmerton | .. | 19,541 | 7,631 |
| Outlying | .. | 180,816 | 78,074 | |
| Porirua | .. | Johnsonville | 68,022 | 31,211 |
| Outlying | .. | 408,166 | 146,057 | |
| Mungaroa | .. | .. | 230,939 | 135,242 |
| Epuni | .. | .. | 181,275 | 125,467 |
| Wainuiomata | .. | .. | 180,126 | 126,427 |
| Makara | Makara | .. | 87,185 | 44,655 |
| Seatoun | .. | 144,517 | 102,620 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,675,527 | £884,376 |
| Collingwood County— | ||||
| Aorere | Collingwood | .. | 150,273 | 86,200 |
| Outlying | .. | 9,864 | 9,864 | |
| Takaka | .. | .. | 205,896 | 100,169 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £366,033 | £196,233 |
| Waimea County— | ||||
| Moutere | Upper Moutere | .. | 48,085 | 22,899 |
| Outlying | .. | 43,797 | 26,026 | |
| Motueka | Riwaka | .. | 92,102 | 59,329 |
| Outlying | .. | 112,900 | 61,362 | |
| Stoke | Stoke | .. | 235,643 | 154,985 |
| Wai-iti | Dovedale | .. | 36,673 | 21,892 |
| Waimea West | .. | 78,586 | 52,821 | |
| Outlying | .. | 297,399 | 157,975 | |
| Wangapeka | .. | .. | 101,163 | 62,560 |
| Motupiko | .. | .. | 141,474 | 77,797 |
| Wangamoa | Suburban North | .. | 105,546 | 56,421 |
| Outlying | .. | 6,146 | 5,577 | |
| Maitai portion | .. | 12,501 | 10,224 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,310,015 | £769,868 |
| Sounds County— | ||||
| Pelorus Sound portion (Croixelles to Cape Lambert) | .. | .. | 256,738 | 145,985 |
| Queen Charlotte Sound and Port Underwood portion | .. | .. | 102,352 | 67,835 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £359,090 | £213,820 |
| Marlborough County— | .. | .. | ||
| Pelorus | Pelorus | .. | 243,884 | 136,939 |
| Havelock | .. | Havelock | 24,040 | 7,070 |
| Picton | Picton | .. | 219,556 | 134,012 |
| Spring Creek | Spring Creek | .. | 206,353 | 159,069 |
| Omaka | Omaka | .. | 355,784 | 264,130 |
| Wairau | Wairau | .. | 471,544 | 353,564 |
| Awatere | Awatere | .. | 567,777 | 439,010 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,088,938 | £1,493,794 |
| Kaikoura County— | ||||
| Clarence | .. | .. | 90,882 | 82,585 |
| Suburban | .. | .. | 97,590 | 68,383 |
| Peninsula | .. | .. | 47,125 | 20,410 |
| Conway | .. | .. | 162,650 | 132,939 |
| Hundalee | .. | .. | 50,609 | 42,084 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £448,856 | £346,401 |
| Buller County— | ||||
| Karamea | .. | .. | 267,975 | 241,235 |
| Wareatea North | .. | .. | 258,075 | 113,336 |
| Wareatea South | .. | .. | 93,307 | 67,370 |
| Lyell | .. | .. | 28,149 | 17,347 |
| Charleston | .. | .. | 64,253 | 51,983 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £711,759 | £491,271 |
| Inangahua County— | ||||
| Hampden | .. | .. | 397,776 | 355,934 |
| Boatman's | .. | .. | 99,543 | 71,755 |
| Reefton | .. | .. | 196,034 | 57,803 |
| Murray | .. | .. | 15,543 | 10,272 |
| Crushington | .. | .. | 54,310 | 48,779 |
| Antonio's | .. | .. | 101,151 | 79,286 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £864,357 | £623,829 |
| Grey County— | ||||
| Cobden | .. | .. | 96,152 | 69,580 |
| Brunnerton | .. | .. | 139,602 | 104,461 |
| Waipuna | .. | .. | 165,094 | 109,817 |
| Nelson Creek | .. | .. | 67,400 | 46,507 |
| Red Jack's | .. | .. | 117,364 | 89,489 |
| Maori Creek | .. | .. | 51,176 | 26,549 |
| Paroa | .. | .. | 35,726 | 20,767 |
| Marsden | .. | .. | 20,358 | 17,655 |
| Hohonu | .. | .. | 133,344 | 97,056 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £826,216 | £581,881 |
| Westland County— | ||||
| Arahura | .. | .. | 80,890 | 46,726 |
| Kanieri | .. | .. | 220,166 | 116,370 |
| Southern | .. | .. | 524,880 | 510,130 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £825,936 | £673,226 |
| Cheviot County— | ||||
| Hawkeswood | .. | .. | 166,871 | 139,490 |
| Kaiwara | .. | .. | 88,500 | 83,150 |
| Waiau | .. | .. | 114,280 | 90,620 |
| Lowry | .. | .. | 126,153 | 92,166 |
| Hurunui | .. | .. | 98,229 | 79,825 |
| Seaward | .. | .. | 112,183 | 76,039 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £706,216 | £561,290 |
| Amuri County— | ||||
| Hanmer | .. | .. | 205,791 | 144,937 |
| Pahau | .. | .. | 227,732 | 164,502 |
| Waiau | .. | .. | 350,936 | 279,127 |
| Rotherham | .. | .. | 116,963 | 88,852 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £901,422 | £677,418 |
| Ashley County— | ||||
| Waipara | Waipara | .. | 1,350,253 | 1,144,727 |
| Mount Thomas | Ashley | .. | 326,189 | 248,851 |
| Kowai | Kowai | .. | 524,558 | 377,603 |
| .. | Amberley | 31,148 | 10,426 | |
| Oxford | Oxford | .. | 408,998 | 297,675 |
| Cust | Cust | .. | 175,102 | 130,413 |
| Mandeville | Mandeville-Rangiora | 636,684 | 497,014 | .. |
| West Eyreton | West Eyreton | .. | 195,014 | 161,524 |
| Eyreton | Eyreton | .. | 448,662 | 344,129 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £4,096,608 | £3,212,362 |
| Selwyn County— | ||||
| Avon | Avon | .. | 608,396 | 385,414 |
| Riccarton | Riccarton | .. | 1,137,247 | 707,130 |
| Templeton | .. | 520,421 | 315,304 | |
| Courtenay | Courtenay | .. | 864,185 | 632,071 |
| Malvern | Malvern | .. | 141,970 | 104,062 |
| East Malvern | .. | 150,410 | 115,297 | |
| South Malvern | .. | 97,004 | 65,597 | |
| Upper Waimakariri | .. | 65,444 | 52,404 | |
| Heathcote | Heathcote | .. | 530,025 | 307,780 |
| Halswell | Taitapu | .. | 123,641 | 96,250 |
| Spreydon | .. | 175,886 | 95,729 | |
| Halswell | .. | 395,092 | 277,457 | |
| Coleridge | Lake Coleridge | .. | 228,432 | 179,175 |
| Rakaia | .. | 352,268 | 259,913 | |
| Lincoln | Springs | .. | 630,412 | 470,067 |
| Lincoln | .. | 375,108 | 281,619 | |
| Ellesmere | Ellesmere | .. | 1,342,066 | 1,066,574 |
| .. | Southbridge | 36,742 | 12,991 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £7,756,749 | £5,424,834 |
| Mount Herbert County— | ||||
| Port Victoria | .. | .. | 81,201 | 52,026 |
| Port Levy | .. | .. | 130,381 | 98,372 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £211,582 | £150,398 |
| Akaroa County— | ||||
| Port Levy | Pigeon Bay | .. | 150,473 | 108,930 |
| Little River | Little River | .. | 444,123 | 344,647 |
| Okain's Bay | Okain's Bay | .. | 135,472 | 98,859 |
| Le Bon's Bay | Le Bon's Bay | .. | 103,774 | 75,802 |
| Wainui | Town of Akaroa and Wainui | .. | 452,309 | 312,878 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,286,151 | £941,116 |
| Ashburton County— | ||||
| Mount Hutt | Mount Hutt | .. | 935,999 | 756,767 |
| South Rakaia | South Rakaia | .. | 777,153 | 604,340 |
| Mount Somers | Mount Somers | .. | 260,978 | 211,558 |
| Anama | .. | 268,462 | 223,005 | |
| Upper Ashburton | Upper Ashburton | .. | 751,455 | 574,229 |
| Wakanui | Wakanui | .. | 477,005 | 353,581 |
| .. | Hampstead | 66,588 | 30,630 | |
| Rangitata | Rangitata | .. | 226,609 | 175,548 |
| Ashburton | Longbeach | .. | 581,771 | 464,530 |
| Coldstream | .. | 228,680 | 166,168 | |
| .. | Tinwald | 56,397 | 30,715 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £4,631,097 | £3,591,071 |
| Geraldine County— | ||||
| Mount Peel | Mount Peel | .. | 411,887 | 331,168 |
| Raukapuka | Geraldine | .. | 613,644 | 478,293 |
| .. | Geraldine | 59,411 | 14,671 | |
| Temuka | Temuka | .. | 765,317 | 601,763 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,850,259 | £1,425,895 |
| Levels County— | ||||
| Tengawai | .. | .. | 288,372 | 233,238 |
| Point | .. | .. | 202,372 | 160,895 |
| Waimataiti | .. | .. | 216,586 | 163,045 |
| Seadown | .. | .. | 213,352 | 176,649 |
| Claremont | .. | .. | 165,677 | 132,252 |
| Gleniti | .. | .. | 158,998 | 89,384 |
| Otipua | .. | .. | 217,851 | 174,852 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,463,208 | £1,130,315 |
| Mackenzie County— | ||||
| Te Kapo | .. | .. | 238,339 | 216,548 |
| Fairlie | .. | .. | 245,877 | 167,078 |
| Albury | .. | .. | 311,857 | 257,985 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £796,073 | £641,521 |
| Waimate County— | ||||
| Upper Pareora | .. | .. | 297,825 | 259,266 |
| Lower Pareora | .. | .. | 248,749 | 209,164 |
| Hakataramea | .. | .. | 236,256 | 193,953 |
| Otaio | .. | .. | 374,016 | 318,422 |
| Makikihi | .. | .. | 294,046 | 235,763 |
| Deep Creek | .. | .. | 457,533 | 367,196 |
| North Waihao | .. | .. | 996,192 | 829,196 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,904,617 | £2,412,960 |
| Waitaki County— | ||||
| Ahuriri | .. | .. | 119,899 | 110,105 |
| Otakaika | .. | .. | 263,470 | 186,769 |
| Awamoko | .. | .. | 406,519 | 356,935 |
| Papakaio | .. | .. | 528,623 | 400,387 |
| Waiareka | .. | .. | 551,443 | 435,922 |
| Incholme | .. | .. | 194,785 | 168,375 |
| Kakanui | .. | .. | 313,855 | 257,905 |
| Otepopo | .. | .. | 227,708 | 156,229 |
| Moeraki | .. | .. | 152,230 | 116,034 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £2,758,532 | £2,188,661 |
| Maniototo County— | ||||
| St. Bathan's | .. | .. | 75,659 | 41,354 |
| Idaburn | .. | .. | 63,176 | 42,848 |
| Mount Ida | .. | .. | 173,883 | 104,367 |
| Kyeburn | .. | .. | 64,564 | 43,235 |
| Puketoi | .. | .. | 96,944 | 66,041 |
| Hyde | .. | .. | 38,369 | 23,576 |
| Serpentine | .. | .. | 56,334 | 49,721 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £568,929 | £371,142 |
| Waihemo County— | ||||
| Green Valley | .. | .. | 44,712 | 29,803 |
| Dunback | .. | .. | 56,104 | 35,597 |
| Macrae's | .. | .. | 90,236 | 59,994 |
| Blue Mountain | .. | .. | 73,997 | 48,783 |
| Meadowbank | .. | .. | 28,768 | 23,182 |
| Bushy | .. | .. | 68,998 | 44,726 |
| Goodwood | .. | .. | 54,934 | 34,118 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £417,749 | £276,203 |
| Waikouaiti County— | ||||
| Hawkesbury | .. | .. | 194,178 | 139,149 |
| Merton | .. | .. | 252,660 | 116,773 |
| Blue-kin | .. | .. | 163,486 | 80,107 |
| North-east Valley | .. | .. | 77,260 | 43,230 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £687,584 | £379,259 |
| Peninsula County— | ||||
| Portobello Bay | Otago Heads | .. | 53,705 | 23,731 |
| Portobello (Portobello Ward) | .. | 56,344 | 34,579 | |
| Broad Bay | Portobello (Broad Bay Ward) | .. | 45,456 | 26,280 |
| North East Harbour | Portobello (Northeast Harbour Ward) | .. | 51,574 | 27,453 |
| Sandymount | Peninsula (Sandymount Ward) | .. | 47,743 | 30,957 |
| Highcliff | Peninsula (Highcliff Ward) | .. | 60,669 | 34,796 |
| Anderson's Bay | Peninsula (Anderson's Bay Ward) | .. | 92,120 | 44,355 |
| Tomahaw | Tomahawk | .. | 27,622 | 17,544 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £435,233 | £239,695 |
| Taieri County— | ||||
| Strath Taieri | .. | .. | 170,705 | 122,793 |
| Deep Stream | .. | .. | 152,842 | 126,748 |
| Manogatua | .. | .. | 188,736 | 144,211 |
| Outram | Outram | 44,645 | 22,016 | |
| Outlying | .. | 212,288 | 180,632 | |
| East Taieri | .. | .. | 169,899 | 124,537 |
| North Taieri | Half-way Bush | .. | 20,756 | 9,749 |
| Outlying | .. | 145,090 | 92,558 | |
| Kaikorai | .. | .. | 203,394 | 106,481 |
| Otokia | .. | Grey | 10,156 | 3,540 |
| Outlying | .. | 154,297 | 107,521 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,472,808 | £1,040,786 |
| Tuapeka County— | ||||
| Teviot | .. | .. | 140,350 | 93,251 |
| James | .. | .. | 247,792 | 175,897 |
| Beaumont | .. | .. | 46,453 | 34,342 |
| Gabriel's | .. | .. | 40,348 | 21,239 |
| Waipori | .. | .. | 43,579 | 33,173 |
| Tapanui | .. | .. | 190,671 | 131,613 |
| Brown's | .. | .. | 92,018 | 55,742 |
| Clark's | .. | .. | 55,621 | 33,452 |
| Waitahuna | .. | .. | 60,734 | 32,622 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £917,566 | £611,331 |
| Bruce County— | ||||
| Clarendon | .. | .. | 59,535 | 40,663 |
| Mount Stuart | Mount Stuart | .. | 102,143 | 72,493 |
| Waihola | .. | .. | 75,060 | 40,388 |
| Balmoral | Balmoral | .. | 232,835 | 155,632 |
| Tokomairiro | .. | .. | 217,612 | 145,918 |
| Glenledi | .. | .. | 36,442 | 26,826 |
| Crichton | .. | .. | 74,222 | 56,383 |
| Kaitangata | .. | .. | 62,623 | 43,249 |
| Matau | Inch-Clutha | .. | 67,235 | 43,433 |
| Outlying | .. | 69,921 | 42,635 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £997,628 | £667,620 |
| Clutha County— | ||||
| Glenkenich | .. | .. | 156,445 | 105,060 |
| Waipahi | .. | .. | 140,221 | 92,770 |
| Clydevale | .. | .. | 104,708 | 78,633 |
| Pomahaka | .. | .. | 178,078 | 132,462 |
| .. | Clinton | 20,344 | 6,356 | |
| Clinton | Outlying | .. | 63,726 | 49,074 |
| Clutha | .. | 139,845 | 100,899 | |
| Richardson | .. | .. | 155,207 | 99,880 |
| South Molyneux | .. | .. | 128,942 | 78,449 |
| Catlin's | .. | .. | 187,337 | 99,530 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,274,848 | £843,113 |
| Vincent County— | ||||
| Hawea | .. | .. | 87,196 | 64,664 |
| Clutha | .. | .. | 44,820 | 24,006 |
| Lindis | .. | .. | 22,279 | 15,540 |
| Matakanui | .. | .. | 58,893 | 37,164 |
| Manuherikia | .. | .. | 71,221 | 46,494 |
| Dunstan | .. | .. | 99,178 | 58,050 |
| Carrick | .. | .. | 35,434 | 24,243 |
| Earnscleugh | .. | .. | 41,359 | 23,546 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £460,380 | £293,707 |
| Lake County— | ||||
| Matukituki | .. | .. | 23,827 | 19,245 |
| Shotover | .. | .. | 20,644 | 17,066 |
| Greenstone | .. | .. | 48,270 | 38,487 |
| Cardrona | .. | .. | 43,302 | 27,205 |
| Queenstown | .. | .. | 54,981 | 36,213 |
| Arrow | .. | .. | 89,430 | 62,238 |
| Kingston | .. | .. | 58,607 | 48,835 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £339,061 | £249,289 |
| Fiord County | .. | .. | £131,391 | £124,986 |
| Wallace County— | ||||
| Mararoa | .. | .. | 331,378 | 259,836 |
| Waiau | .. | .. | 292,872 | 222,755 |
| Wairio | .. | .. | 400,078 | 258,834 |
| Otautau | .. | Otautau | 30,759 | 9,140 |
| Outlying | .. | 373,922 | 264,545 | |
| Orepuki | .. | .. | 188,052 | 101,887 |
| Aparima | .. | .. | 309,457 | 206,040 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £1,926,518 | £1,323,037 |
| Southland County— | ||||
| Oreri | .. | .. | 431,974 | 315,844 |
| Wakaia | .. | .. | 308,653 | 228,727 |
| Winton | .. | .. | 964,228 | 614,177 |
| Hokonui (Waimumu portion) | .. | .. | 234,710 | 189,754 |
| Hokonui (northern portion and Mabel subdivision) | .. | .. | 401,804 | 281,286 |
| Mataura | Knapdale | .. | 349,451 | 254,872 |
| Tuturau | .. | 188,486 | 133,374 | |
| Outlying | .. | 148,195 | 102,720 | |
| Wallacetown | .. | .. | 335,046 | 228,566 |
| Awarua | Invercargill | .. | 164,494 | 85,819 |
| Outlying | .. | 334,758 | 199,237 | |
| Waihopai | Oteramika | .. | 410,365 | 302,167 |
| Toetoes | .. | Wyndham | 35,278 | 11,663 |
| Outlying—Wyndham portion | .. | 90,506 | 63,739 | |
| Other outlying | .. | 470,598 | 333,325 | |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £4,868,546 | £3,345,270 |
| Stewart Island | ||||
| County— | ||||
| North | .. | .. | 62,327 | 42,175 |
| South | .. | .. | 97,715 | 91,705 |
| Total of county | .. | .. | £160,042 | £133,880 |
| Islands— | ||||
| Antipodes | .. | .. | £13,880 | £13,880 |
| Auckland | ||||
| Campbell | ||||
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
THE Crown lands of New Zealand are administered under. “The Land Act, 1892,” together with its amendments and the regulations made thereunder.
The distinguishing features of the present land system are the outcome of ideas which have been gradually coming to maturity for some years past in this colony. These features involve the principle of State ownership of the soil, with a perpetual tenancy in the occupier. This, whatever may be the difference in detail, is the prevailing characteristic of the several systems under which land may now be selected. In New Zealand this tendency to State ownership has taken a more pronounced form than in any of the Australian States. In point of fact, most of the Crown lands are now disposed of for 999 years. The rentals are based on the assessed value of the land at the time of disposal, without increase or recurring valuations. Under this system there is a fixity of tenure practically equal to freehold, and which, like freehold, necessarily carries with it the power of sale, sub-lease, mortgage, or disposition by will. At the same time the improvements made in the soil by cultivation, &c., are secured to the tenant should he from any cause be obliged to forfeit or surrender his lease.
The advantages of this system to the selector are manifest. When it is taken into consideration that, with few exceptions, the Crown lands are, in their prairie condition, incapable of profitable use, the advantage to the settler of setting free his capital to develop the capabilities of the soil, rather than having to expend it in the purchase of a freehold, is very apparent. One of the most striking benefits of this system is the advantage it gives to the man who, with little more capital than his strong right arm, is enabled to make a home for himself; which, under the freehold system, he would be unable to accomplish.
The values placed on the Crown lands are, as a rule, low, for the State does not so much seek to raise a revenue directly therefrom as to encourage the occupation of the lands by the people; this occupation secures an indirect increased revenue, besides the other advantages resulting from a numerous rural population.
Again, underlying the whole of the New Zealand land system is a further application of the principle of “the land for the people"—viz., the restriction in area which any man may hold. This subject has been forced upon the attention of the Legislature by defects in former systems, under which one individual with means at his command could appropriate large areas, to the exclusion of his less wealthy fellow-settler. Under existing conditions, where the price at which land is offered is fixed for ever, and where choice of selection is by ballot, every would-be settler has the same chance, and may hold under the Crown an equal area of land. The quantity that a selector may hold is so fixed as to encourage the class of moderate farmers, for up to the statutory limit the amount he may select is left almost entirely to himself. The Act defines the amount of land any one may hold at 640 acres of first-class or 2,000 acres of second-class land. These limits apply to lands which are thrown open for optional selection, but in some cases, where the quality of the land is very good and the selectors many, the limit is by regulation made smaller.
In addition to the many advantages offered by the lease-in-perpetuity system, the Land Act provides others, to meet the wants of different classes. The general rule is that land thrown open for optional selection is offered to the public under three different tenures, the choice of which is left to the would-be settler.
The three tenures are:—
Cash, in which one-fifth of the purchase-money is paid down at once, and the remainder within thirty days. The final title is not given until certain improvements have been made on the land.
Lease with a purchasing clause, at a 5-per-cent. rental on the value of the land; the lease being for twenty-five years, with the right to purchase at the original upset price at any time after the first ten years and within twenty-five years, or to convert into a lease in perpetuity (3rd tenure).
Lease in perpetuity, at a rental of 4 per cent. on the capital value.
The present land-laws have been in force since the 1st November, 1892, and, therefore, the returns of the Department of Lands and Survey for the year ending the 31st March, 1903, in respect of lands the tenure of which is optional, will give a fair idea of that tenure most favoured by the public. The figures are:—
Cash: 134 selections, 16,747 acres.
Occupation with right of purchase: 403 selections, 118,557 acres.
Lease in perpetuity: 285 selections, 108,065 acres.
“The Land Act, 1892,” provides for a special class of settlement called small - farm associations, which found favour with the public to a very considerable extent during the first three years after the Act of 1892 came into force, but is now superseded to a large extent by the improved - farm settlement system. The small - farm association system provides that, where not less than twelve individuals have associated themselves together for mutual help, such an association can, with the approval of the Minister of Lands, select a block of land of not more than 11,000 acres, but there must be a selector to each 200 acres in the block. The extreme limit that one person may hold is fixed at 320 acres. Settlements of this class are held on lease in perpetuity, in a similar way to lands under the same tenure when thrown open for optional selection. The conditions of residence and improvement are the same. The system offers many advantages to the settler, so long as the blocks of land are judiciously chosen, having regard to quality of land, access, markets, and the probability of employment being obtained in the neighbourhood. In the eagerness to obtain lands on such easy terms these points have, in the past, not received sufficient attention by some of the associations, and in consequence they are not all successful.
Under “The Land Act, 1885,” there was a somewhat similar system, but it allowed of the acquisition of the freehold. This is now being taken advantage of to a considerable extent.
The following figures show the amount of settlement by associations under both Acts on the 31st March, 1903. At that date there were 678 selectors, holding 123,131 acres under various tenures and in different parts of the country. Many of the settlements, which were carefully selected, are doing well. Others, where long and expensive roads have to be made to them, are as yet not very productive, and many selections have been abandoned.
The village-settlement system of New Zealand has excited much inquiry. This system provides: 1st, villages of one acre sections; 2nd, small farms of 100 acres. There has not been any great extension of this system in recent years. On the 31st March last there were 1,781 settlers holding 36,963 acres, and the total number of persons residing in these settlements was 1,204 and 577 non-resident, the amount advanced by Government for houses, clearing, &c., being £15,115, of which £3,916 had been returned. The total value of improvements on the lands at the same date was £168,041. The above figures include the settlement on reserves and endowments.
The improved - farm settlement system was first begun in order to find work for the people. Considerable areas of forest-clad Crown lands were set aside, and small contracts for the clearing, burning, and sowing these with grass have been let. In most cases the farms are selected or balloted for in their primitive state, and the settler is for a time paid for the improvements he makes, or, in other words, the cost of converting forest lands into grass lands is advanced from time to time by the Government. In other cases a piece of forest land is taken in hand, and men are employed at fixed rates in felling, burning, and grassing. When so much grass is laid down as will give a good start, the land is opened for selection in sections of 50 to 200 acres and balloted for among the applicants. The farms are let on lease in perpetuity at a rental sufficient to cover the cost of clearing, &c., together with a fair rental of the land. Up to the 31st March, 1903, 47 settlements had been allocated, covering an area of 65,859 acres, situate in various parts of the colony. At that date 452 settlers had been allotted sections, who, together with their families, numbered 1,731 persons who were residing on the lands. They had felled and grassed 26,542 acres. The amount paid to the settlers up to the 31st March, 1903, was £53,727, and the total value of improvements on the land (including the Government advances) was £94,515.
The size of holdings averages about 100 acres.
In the earlier years of the settlement of New Zealand there were opportunities for men of capital and judgment to acquire large estates, and while there were plenty of good Crown lands to select from this was of great advantage to the colony when money was needed for administration and roads and bridges. These large estates employed hired labour, and most of them did little towards cultivating their lands, and consequently progress beyond the pastoral stage ceased in the districts in which they were situated. As the best lands in the course of years passed from the Crown, the country became a series of agricultural communities interspersed with large properties occupied by a manager and a few shepherds, and the people pressed that they and their sons should be allowed to occupy these large estates instead of being compelled to go into inaccessible back country without roads or railways. To meet this the Hon. (later Sir) John McKenzie, then Minister of Lands, introduced into the Legislature in the session of 1892 a Bill intituled “The Land for Settlements Act,” which authorised the purchase from private individuals of suitable properties for subdivision into farms. Under the provisions of this Act and the amending Acts, which are now consolidated into the Act of 1900, properties have been acquired, and divided into small farms and leased in perpetuity at a 5-per-cent. rental, on a capital value fixed at a rate sufficient to cover first cost, together with survey, administration, and roads (if required). The usual process of acquisition is as follows: Whenever a property is offered to the Government, if it is so situated as to meet the object of the Act, a report on it is obtained from a Government officer, and, should his report be favourable, the question of purchase is then considered by a Board of Land Purchase Commissioners, composed of the Inspector, who is the permanent Chairman, three other Government officers, whose training and duties qualify them to advise the Government as to whether the purchase is a suitable one, and as to the price which should be given for the property, and a member nominated by the Government from residents in the district where the land to be dealt with is situated. It is only on the advice of this Board that the Government acts. In nearly all cases the properties acquired have been improved to a certain extent by fencing and buildings, and were situated in the neighbourhood of closely settled districts. The amount which may be expended per annum under the Act is £500,000. The Act also provides for the exchange of high-lying pastoral Crown lands for low-lying agricultural lands suitable for small holdings.
Lands may also be taken compulsorily in cases where the Board cannot agree with the owner as to price, &c., and where the Governor in Council decides to acquire the land for closer settlement. The amount payable to the owner is decided by a Compensation Court, composed of a Judge of the Supreme Court and two Assessors, one appointed by Government, the other by the owner of the property. Four properties have hitherto been acquired compulsorily, and they have been disposed of on satisfactory terms.
The acquisition of lands under the Land for Settlements Acts has proved beneficial in providing homes for a large class of men of moderate capital who shrink from the rough work of breaking in new country or who, having accumulate capital (cash, stock, and implements), prefer open country near civilisation. Sons of farmers begin life near the old home, and help from there is given in many ways. The system also affords to the small-farmer class of the Old Country an opening for building up homes for themselves where their previous experience will be of use, instead of having to learn the methods adapted to a new and wild country.
Preference is given to landless people, and applicants for rural land have to satisfy the Land Board as to their means to stock and cultivate the property applied for and erect suitable buildings thereon. The Board, in fact, has a discretion as to who may become tenants.
Land may also be compulsorily taken for workmen's homes within a borough having a population of at least 15,000 persons, or within a radius of fifteen miles from the border thereof, for the purposes of providing workmen's homes or villages; but the area is restricted to not more than 100 acres every year within any such borough, or within the radius named above from the boundary of the borough.
The owner is left with right to retain an area of not more than 10 acres if in a borough, or 50 acres in any other case.
A workmen's allotment is not to exceed 5 acres, and advances up to £50 are made by Government to successful applicants in aid of the cost of fencing and building dwellinghouses.
Regulations giving full directions to applicants under this Act have been issued from time to time, which should be in the hands of every one before applying for lands under this Act.
An account of the operations under the Land for Settlements Acts will be found in Part II. of this work.
From about the year 1823 (which is the date of the first recorded deed) until the 6th February, 1840, the date of the Treaty of Waitangi, lands in New Zealand were acquired by direct purchase from the Maoris by individual members of the white races. During the years 1837 to 1839, or about the time it became probable that the sovereignty of the islands would be assumed by the United Kingdom, the greater number of these purchases were made, and they extended to most parts of the country. These purchases are technically known as “the old land claims,” and their total number (including pre-emptive claims), as estimated by Commissioner F. Dillon Bell in 1862, was 1,376, covering an area of about 10,322,453 acres, out of which large area grants were recommended for 292,475 acres. These figures have been slightly added to since, but not to any very large extent. The large area shown above was reduced on survey to about 474,000 acres, situated principally to the north of Auckland. The difference in area between the amount granted and the total area surveyed became what are termed “surplus lands of the Crown.” It was held that the Native title had been fully extinguished over the whole area surveyed; but, as by statute the claimants could only be granted 2,560 acres each, the balance became vested in the Crown on the assumption of the sovereignty, the Native title having been fully extinguished.
In many cases the titles did not issue to those to whom the land was awarded, as they were compensated by scrip issued by the Government, with the understanding that such tip was to be exercised in the purchase of Crown lands in the neighbourhood of Auckland, to which place it was desirable—so soon as the capital was founded—to draw a population. The lands thus paid for in scrip became Crown lands, and these, together with the surplus lands, have from time to time been disposed of by the Crown and settled on. The amount of scrip, &c., issued up to 1862 was over £109,000.
On the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi on the 6th February, 1840, the pre-emptive right was ceded to the Government, and consequently private purchase ceased. This remained the law until the passing of “The Native Land Act, 1862,” when the Crown relinquished its right of pre-emption, whilst at the same time the purchase of Native lands for the Crown did not abate, but continued side by side with the private purchases up to the passing of “The Native Land Court Act, 1894.”
“The Maori Lands Administration Act, 1900,” is a measure intended to restrain Natives from pauperising themselves in the future by parting with the freehold of the balance of their lands (about five millions of acres). Its main provisions are—
Prohibition of further alienation of the freehold of Native lands, either to the Crown or private purchasers, except as to inchoate transactions at the date of the passing of the Act and certain limited areas which were then comprised in separate titles or held by not more than two owners.
Leasing of Native lands through partly elected and partly nominated Councils possessing all the powers and, where authorised, exercising all or any of the functions of the Native Land Court.
Advances to Natives to road and otherwise improve their surplus lands for their own use and occupation.
From time to time since 1840 various sums were appropriated by Government or by Parliament for the acquisition of a Crown estate. Up to the date of passing of “The Native Land Act, 1862,” these operations were conducted by officers of the Government specially appointed, who, from a knowledge of the Maoris, their customs and disposition, were successful in securing large areas of land for settlement. It must be conceded that their operations as a whole were successful, and that the number of disputed cases arising out of their labours was exceedingly small. The Waitara purchase is, however, here excluded, for there were reasons of general policy affecting that sale which did not prevail in other cases. This purchase was the ostensible cause of the war of 1860 and following years, but the motives which led to it were far deeper than the mere purchase of a few acres—there was a great principle at stake.
The difference effected in the mode of purchase by “The Native Land Act, 1862,” was this: Previously, the title of the Maoris who were to receive payment for the land was decided by the Land Purchase officers; but the Act quoted set up a Court, presided over by able Judges, who determined the titles, which were afterwards registered in a special Court. Purchases have since been effected with the registered owners.
It is difficult to obtain figures showing the actual area acquired by the Crown from the Maoris up to 1870, but in round numbers it was 6,000,000 acres in the North Island; whilst the whole of the Middle Island, with the exception of reserves for the original Native owners, was acquired prior to the passing of “The Native Land Act, 1862.” Stewart Island was purchased from the Native owners by deed dated 29th June, 1864.
The Native rebellion of 1860–69 brought Native-land purchases, for the time being, practically to a standstill.
The Immigration and Public Works Acts of 1870 and 1873 appropriated £200,000 and £500,000 respectively for the purchase of lands in the North Island; and these amounts have, up to the 31st of March, 1903, been augmented by further annual appropriations from the public funds and other loan-moneys, covering altogether a total expenditure since 1870 of £2,000,013, with the following results: Area finally acquired in the North Island from Natives, from 1870 to 31st March, 1903, 7,940,027 acres. Area under negotiation in the North Island on 31st March, 1903, 114,530 acres; interests therein finally acquired, 14,385 acres.
The Crown lands are administered, under the authority of “The Land Act, 1892,” by the Hon. the Minister of Lands at Wellington. For convenience the colony is divided into ten land districts, each being under the local direction of a Commissioner and a Land Board. The Commissioner's office is known as the principal land office, and in some of the larger districts there are one or more local land offices. It is with these land offices the selector has to transact all business, from the first consultation of the maps to the final receipt of the Crown title.
The names of the land districts and of the towns where each principal office is situated are, beginning with the most northerly and taking them geographically, as under:—
| Land District. | Town where Principal Land Office is situated. |
|---|---|
| Auckland | Auckland. |
| Taranaki | New Plymouth. |
| Hawke's Bay | Napier. |
| Wellington | Wellington. |
| Nelson | Nelson. |
| Marlborough | Blenheim. |
| Westland | Hokitika. |
| Canterbury | Christchurch. |
| Otago | Dunedin. |
| Southland | Invercargill. |
Crown lands are divided into three classes:—
Town and village lands, the upset prices of which are, respectively, not less than £20 and £3 per acre; such lands are sold by auction:
Suburban lands, the upset price of which may not be less than £2 an acre; these lands are also sold by auction:
Rural lands, which may be disposed of at not less than £1 per acre for first-class, and 5s. an acre for second-class lands; such lands may be sold or leased by auction, or sold or leased on application.
No rural section may be larger than 640 acres in extent if first-class land, or 2,000 acres if second-class land, whether offered by auction or application. No person can select more than 640 acres of first-class or 2,000 acres of second-class land, including therein any land which he then holds. Small grazing-runs, first-class, may not exceed 5,000 acres, and second-class 20,000 acres. Pastoral runs are limited to areas which will carry 20,000 sheep or 4,000 cattle. No person can select more than one run.
Crown lands may be acquired as follows:—
By auction, after survey, in which case one-fifth of the price is paid down at the time of sale, the balance within thirty days:
By application, after the lands have been notified as open for selection, in which case the applicant fills up a form (to be obtained at any of the Land Offices) and makes the declaration and undertaking required by the particular system he wishes to select under.
All applications, whether for surveyed or unsurveyed lands, are deemed to be simultaneous if made on the same day, and, if there be more than one applicant for the same land, the right of selection is determined by ballot.
Lands thrown open for application may be either surveyed or unsurveyed, and those not selected the first day remain open.
Lands for selection are notified as open for application on and after a stated day, and, at the option of the applicant, may be obtained on any of the three following tenures: (a) Freehold; (b) Occupation with the right of purchase; (c) Lease in perpetuity.
If the land is surveyed, one-fifth of the price is to be paid down when the application is granted, and the balance within thirty days; or, if the land is not completely surveyed, the survey-fee is deposited when the application is agreed to, and goes towards the purchase of the land; the balance must be paid within thirty days of notice that the survey is completed.
A certificate of occupation will issue to the purchaser on final payment, which will be exchanged for a Crown title so soon as the Board is satisfied that the improvements mentioned on the next page have been completed.
Lands selected on this tenure are held under a license for twenty-five years. At any time subsequent to the first ten years, and before the expiration of the license, after having resided and made the improvements hereinafter described, the licensee can, on payment of the upset price of the land, acquire the freehold. If the land be not purchased, the license may be exchanged for a lease in perpetuity.
The rent is 5 per cent. on the cash price of the land; a half-year's rent has to be paid at the time the application is approved, if surveyed land, which represents the half-year's rent due in advance on the 1st day of January or July following the selection. If the land is unsurveyed, the cost of survey is to be paid, and is credited to the selector as so much rent paid in advance, counted from the 1st day of January or July following thirty days’ notice of the completion of survey.
Residence and improvement of the land are compulsory, as hereinafter described.
Lands selected on this tenure are leased for 999 years, subject to the conditions of residence and improvements described below. The rental is 4 per cent. on the cash price of the land, and applications are dealt with in the same way as under the previous tenure (b), but there is at no time a right to purchase the freehold.
Two or more persons may make a joint application to hold as tenants in common under either of the two last-named tenures.
Under the two last-mentioned tenures, the conditions as to residence and improvements are:—
RESIDENCE—
Must commence on bush or swamp lands within four years, and in open or partly open land within one year, from the date of selection:
Must be continuous for six years on bush or swamp land, and for seven years on open or partly open land, on lands occupied with a right of purchase:
Must be continuous for a term of ten years on lease-in-perpetuity lands.
The Board has power to dispense with residence in certain cases, such as where the selector is residing on adjacent lands, or is a youth or unmarried woman living with parents, and in a few other cases.
RESIDENCE implies the erection of a habitable house to be approved of by the Board.
IMPROVEMENTS which must be made are as follows:—
Freehold-tenure lands must be improved within seven years to an amount of £1 an acre for first-class land, and 10s. an acre for second-class land.
Lands held on lease with right of purchase, or on lease in perpetuity, must be improved to an amount equal to 10 per cent. of the value of the land within one year from the date of the license or lease; within two years must be improved to the amount of another 10 per cent.; within six years must be improved to the value of another 10 per cent., making 30 per cent. in all within the six years. In addition to the above, the land must be further improved to an amount of £1 an acre for first-class land, and on second-class land to an amount equal to the net price of the land, but not more than 10s. an acre.
Improvements may consist of reclamation from swamps, clearing of bush, planting with trees or hedges, cultivation of gardens, fencing, draining, making roads, wells, water-tanks, water-races, sheep-dips, embankments or protective works, or in any way improving the character or fertility of the soil; or the erection of any building, &c.; and cultivation includes the clearing of land for cropping, or clearing and ploughing for laying down with artificial grasses, &c.
Under the existing regulations any number of persons, not less than twelve, may select and apply for a block of land of not less than 1,000 acres or more than 11,000 acres in extent, but the number of members must be such that there shall be one for every 200 acres in the block, and no one can hold more than 320 acres, except in swamp lands, where the area may be 500 acres.
The capital value of lands within a special settlement is fixed after survey by special valuation, but may not be less than 10s. an acre; the rental is not less than 4 per cent. on the capital value, and the tenure is a lease in perpetuity.
Residence, occupation, and improvements are generally the same as already described, and applications have to be made in manner prescribed by regulations.
Applicants should apply to a Commissioner for a copy of the regulations, as they are liable to change at any time.
Suitable land for small settlement of this kind is now scarce.
Special regulations are in force for this class of settlement, which should be applied for, but briefly the terms are as follow: Applicants are selected by the Commissioner of Crown Lands, preference being given to married men. The areas of the farms may vary from 10 acres to 200 acres, according to locality; no settler can select more than one farm. Contracts are made with the settler to fell the forest, burn it, and sow with grass-seed up to 100 acres, the cost being paid by the Government, and £10 may be advanced to a single man and £30 to a married man to help to build a house. The rates allowed for felling are those current in the district. The land is then leased for 999 years at a rental of 4 per cent. on the unimproved capital value, plus the actual cost of the felling and grassing. As a rule, the settlers can get employment on the roadworks in the neighbourhood, but Government does not guarantee this.
Residence for the first ten years is compulsory, and improvements must be made in terms of Part III. of “The Land Act, 1892.” (See ante.)
Village settlements are disposed of under regulations made from time to time by the Governor, but the main features are as follow:—
Such settlements may be divided into:—
Village allotments not exceeding one acre each, which are disposed of either by auction among the applicants or by application, as already described, with option of tenure, the cash price being not less than £3 per allotment:
Homestead allotments not exceeding 100 acres each, which are leased in perpetuity at a 4-per-cent. rental on a capital value of not less than 10s. per acre.
Residence, improvements, and applications are the same as already described. The leases are exempt from liability to be seized or sold for debt or bankruptcy.
The Colonial Treasurer is empowered in certain cases to advance small sums for the purpose of enabling selectors to profitably occupy their allotments.
Small grazing-runs are divided into two classes: First-class, not exceeding 5,000 acres; second-class, not exceeding 20,000 acres in area. The rental in both cases is not less than 2 1/2 per cent. on the capital value per acre, but such capital value cannot be less than 5s. per acre. Small grazing-runs are based for terms of twenty-one years, with right of renewal for other twenty-one years, at a rent of 2 1/2 per cent. on the then value of the land. The runs are declared open for selection, and applications and declarations on the forms provided have to be filled in and left at the Land Office, together with the deposit of one half-year's rent, which represents that due on the 1st day of March or September following the selection.
No holder of a pastoral run, and no holder of freehold or leasehold land of any kind whatever, over 1,000 acres in area, exclusive of the small grazing-run applied for, may be a selector under this system; and only one small grazing-run can be held by any one person.
The lease entitles the holder to the grazing rights, and to the cultivation of any part of the run, and to the reservation of 150 acres round his homestead through which no road may be taken; but the runs are subject to the mining laws.
Residence is compulsory, if bush or swamp land, within three years; if open, within one year; and must be continuous to the end of the term, but may in a few cases be relaxed. Improvements necessary are as follow: Within the first year, to the amount of one year's rent; within the second year, to another year's rent; and, within six years, to the value of two other years’ rent: making in all a sum equal to four years’ rental, which must be expended within six years. In addition to these improvements, bush-covered first-class runs must be improved to an amount of 10s. an acre, and second-class bush-clad runs to an amount of 5s. an acre.
These runs may be divided, after three years’ compliance with the conditions, amongst the members of the selector's family.
Pastoral country is let by auction for varying terms not exceeding twenty-one years; and, excepting in extraordinary circumstances, runs must not be of a greater extent than will carry 20,000 sheep or 4,000 head of cattle. Runs are classified from time to time by special Commissioners into: (1) Pastoral lands, which are suitable only for depasturing more than 5,000 sheep; (2) pastoral-agricultural lands, suitable for subdivision into areas of under 5,000 acres, which may be either let as pastoral runs, generally for short terms, or cut up for settlement in some other form. Leases of pastoral lands may not be resumed; leases of pastoral-agricultural lands may be resumed at any time after twelve months’ notice, without compensation.
No one can hold more than one run; but, in case of any one holding a run of a carrying-capacity less than 10,000 sheep, he may take up additional country up to that limit.
Runs are offered at auction from time to time, and half a year's rent has to be paid down at the time of sale, being the amount due in advance on the 1st day of March or September following the sale, and the purchaser has to make the declaration required by the Act. All leases begin on the 1st day of March, and they entitle the holder to the grazing rights, but not to the soil, timber, or minerals; and the lease terminates over any part of the run which may be leased for some other purpose, purchased, or reserved. The tenant has to prevent the burning of timber or bush; in open country to prevent the growth of gorse, broom, or sweetbriar; and to destroy the rabbits on his run. With the consent of the Land Board, the interest in a run may be transferred or mortgaged, but power of sale under a mortgage must be exercised within two years.
In case it is determined again to lease any run on expiry of the lease, the new lease must be offered by auction twelve months before the end of the term, and if, on leasing, it shall be purchased by some one other than the previous lessee, valuation for improvements, to be made by an appraiser, shall be paid by the incoming tenant, but to a value not greater than three times the annual rent—excepting in the case of a rabbit-proof fence, which is to be valued separately. If the run is not again leased, the value of rabbit-proof fencing is paid by the Crown, but the tenant has no claim against the Crown beyond the value of the rabbit-proof fence; he may, however, within three months of sale, remove fences, buildings, &c. Runs may also be divided with the approval of the Board.
The following is the scale of charges for surveys of unsurveyed lands:—
Not exceeding 30 acres, £6.
Exceeding 30 and up to 50 acres, 3s. 6d. per acre, but not less than £6.
Exceeding 50 and up to 100 acres, 3s. per acre, but not less than £8 15s.
Exceeding 100 and up to 200 acres, 2s. 6d. per acre, but not less than £15.
Exceeding 200 and up to 300 acres, 2s. per acre, but not less than £25.
Exceeding 300 and up to 500 acres, 1s. 8d. per acre, but not less than £30.
Exceeding 500 and up to 1,000 acres, 1s. 4d. per acre, but not less than £41 10s.
Exceeding 1,000 and up to 2,000 acres, 1s. per acre, but not less than £66 10s.
For the survey of any area of rural land, being open land, the scale of charges shall be two-thirds the foregoing rates.
The Chief Surveyor may vary the above charges by substituting a rate per mile or per day for such work as may not come under the foregoing scale.
Table of Contents
THE Government Advances to Settlers Act was a Government policy measure in the legislation of 1894. It was designed to afford relief to a numerous class of colonists who were struggling under the burden of high rates of interest and heavy legal expenses of mortgages. These were established when prices of agricultural produce were high and profits large; and, so long as business continued to be prosperous, they attracted but little, if any, attention. For several years preceding 1894 commerce and agriculture had suffered from world-wide depression; settlers were becoming embarrassed in their circumstances; and the high rates of interest still charged were felt to be a burden on the industry of the people not easily borne, and a hindrance to the settlement and development of the farming lands of the colony. Under these circumstances the Government brought in the Government Advances to Settlers Act. It was passed towards the close of the session of 1894, and immediately came into operation, with results which have proved beneficial to the farming community. A general decline in the rates of interest at once set in, and it is not too much to claim that the Act has been instrumental in lowering these to a considerable extent on several millions of money invested on mortgage of the farming lands of the colony. This result, while it may have diminished the incomes of a few persons resident within the colony, has benefited thousands of deserving settlers and led to large areas of land being brought under cultivation that, but for the Advances to Settlers Act, would still be in their natural state.
The Act authorised the raising of three million pounds sterling within two years, in sums of a million and a half per annum, at a rate of interest not higher than 4 per cent. In May, 1895, tenders were invited in London for £1,500,000 of 3-per-cent. inscribed stock of the Government of New Zealand, and applications were received for £5,960,400 at prices ranging from £100 to £90. The million and a half was placed at an average price of £94 8s. 9d.
An amending Act, passed in 1895, extended the time for raising the residue of the three millions to three years from the coming into operation of the amending Act. In 1898 this term was extended for a further period of three years, and in 1901 the time-limit restriction was removed altogether, power being given at the same time to raise an additional loan of £1,000,000.
To carry out the objects of the Act, an office was established called the “Government Advances to Settlers Office”; at the same time a General Board was constituted to co-operate with and assist the Superintendent, the title by which the chief administrative officer is known.
The business of the office is the advancing of money in New Zealand on first mortgage of lands and improvements held under any of the following classes of tenure, free from all encumbrances, liens, and interests other than leasehold interests, that is to say:—
Freehold land held in fee-simple under “The Land Transfer Act, 1885,” or freehold land held in fee-simple the title to which is registered under “The Deeds Registration Act, 1868.”
Crown land held on perpetual lease under “The Land Act, 1885.”
Crown land held under Parts III. and IV. of “The Land Act, 1892.”
Crown land held on lease as a small grazing-run under “The Land Act, 1885,” or under “The Land Act, 1892.”
Crown land held on agricultural lease under “The Mining Act, 1891.”
Crown land held on lease (not being for mining purposes) under “The Westland and Nelson Coalfields Administration Act, 1877.”
Native land held on lease under “The West Coast Settlement Reserves Act, 1881,” or under the Act of 1892.
Land held on lease under “The Westland and Nelson Native Reserves Act, 1887.”
Land held under “The Thermal-Springs Districts Act, 1881.”
Educational and other reserves which are subject to the provisions of “The Land Act 1877 Amendment Act, 1882,” by virtue of Proclamation made under section 50 thereof, or “The Land Act, 1885,” by virtue of Proclamation made under section 237 thereof, or “The Land Act, 1892,” by virtue of Proclamation made under section 243 thereof, and are held on perpetual lease or lease in perpetuity, or on deferred-payment or small grazing-run systems.
Crown land held by license on the deferred-payment system under Part III. of “The Land Act, 1885.”
Land held under lease from a leasing authority, as defined by “The Public Bodies’ Powers Act, 1887,” and providing for the payment by the incoming tenant of valuation for improvements made upon the land, whether by the lessee named in such lease or any former lessee, as tenant.
With regard to classes 10 and 12, a lease is not eligible if it provides for absolute forfeiture (without compensation) for breach of conditions, or if on the determination of the lease compensation is to be allowed for certain improvements only.
Mortgages are granted either on the instalment or the fixed-loan system (fully described hereafter); and the margins of security required by the Act are as follow:—
On freeholds (other than urban or suburban) three-fifths of the value may be advanced either on the instalment or fixed-loan system: Provided that in the case of first-class agricultural freeholds instalment loans may be advanced up to two-thirds of the value.
On leaseholds (other than urban or suburban) one-half of the value of the lessee's interest in the lease may be advanced on the instalment system. No loans are granted on leaseholds on the fixed-loan system.
On urban and suburban freeholds, loans are granted on the instalment system only, and the amounts of loan are limited as follow:—
On urban freehold on which buildings exist, three-fifths of the value of the land, plus one-half the value of the buildings, may be advanced;
On suburban freehold on which buildings exist, one-half the value of the land, plus one-half the value of the buildings, may be advanced:
On urban or suburban freehold on which no buildings exist, one-half the value of the land may be advanced, but on such security no loan shall be granted except for the erection of buildings on the land: the loan to be advanced by instalments at the discretion of the Board, as the erection of the buildings proceeds.
“Urban land” means land which is situate in a borough having a population of at least two thousand inhabitants and is not used for farming, dairying, or market-gardening purposes.
“Suburban land” means land which is situate in a borough having a population of less than two thousand inhabitants, or in any town, or in the vicinity of any town or borough, and is not used for farming, dairying, or market-gardening purposes.
Lands situated within towns, and are used for farming, dairying, or market-gardening, are treated in accordance with paragraphs (1) and (2) above.
The right of determining what land may be considered “urban” or “suburban,” or “first-class agricultural,” is imposed by the Act on the General Lending Board.
The security which the applicant offers for the loan must consist of one or more holdings of the several classes of tenure above mentioned, and must, of course, be of the necessary value; and, if the security is leasehold, all the covenants and conditions of the lease, including the payment of rent, must have been regularly complied with.
Any person desiring an advance is required to make a written application on the prescribed form, a copy of which can be obtained from any Postmaster in the colony. The Postmaster also supplies an envelope in which the application may be forwarded free of post-age, and affords to the applicant any explanation which may be required respecting the filling-in of the application.
In the case of an application for an advance on the security of an interest in land held under a lease or license issued from the Lands Department (and belonging to one or more of the classes of tenure numbered 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11), a notice of the application must be forwarded to the Commissioner of Crown Lands for the district in which the land is situated. The requisite form, and an envelope for forwarding it free of postage, may be obtained from any Postmaster in the colony.
No loan of less than £25 or more than £3,000 can be granted, and in the case of “urban” or “suburban” lands the maximum loan is fixed at £2,000.
All applications must be accompanied by a valuation-fee according to the following scale:—
| £ | s. | d. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| On an application for a loan not exceeding £100 | 0 | 10 | 6 |
| Exceeding £100 but not exceeding £250 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Exceeding £250 but not exceeding £500 | 1 | 11 | 6 |
| Exceeding £500 but not exceeding £3,000 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
If the applicant has already obtained any advance under the Act and is desirous of obtaining a further advance, either on the same security or on a separate security, the amount of the application, added to the amount of the advances already obtained, must not exceed the limit mentioned above—£3,000 for farming and £2,000 for urban or suburban lands.
Mortgages granted on the fixed-loan system may be for any period not exceeding and the principal is repayable at the of the term. They may also be repaid in whole or in part on any half-yearly due date during the term, as explained hereafter. Interest at the rate of 5 per cent. is payable half-yearly, reducible to per cent. provided payment is made not later than fourteen days after due date and no arrears remain outstanding.
Mortgages granted on the instalment system are repayable by seventy-three half-yearly payments of principal and interest combined. They may also be repaid in whole or in part at any time. Interest charged at the rate of 5 per cent., reducible to 4 1/2 per cent. provided payment is made not later than fourteen days after due date and no arrears remain outstanding.
Every half-yearly instalment, except the last, is at the rate of £3 (less the rebate of interest in case of prompt payment) for every £100 of the loan. The following table shows, taking a loan of £100 as an instance, how much of each instalment is applied to repaying the principal, and how much is in payment of interest. It shows also the amount of rebate in respect of each instalment, and the balance of principal remaining due after payment of the respective instalments until the loan is entirely repaid in thirty-six years and a half:—
| TABLE OF PRESCRIBED HALF-YEARLY INSTALMENTS FOR EVERY O(([0-9]+)) POUNDS OF THE LOAN. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half-year. | Prescribed Half-yearly Instalment. | Apportioned thus: | 1/2 per Cent. Rebate of Interest. | Balance of Principal owing. | |||||||||||
| On Account of Interest at 5 per Cent. | On Account of Principal. | ||||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 99 | 10 | 0 |
| 2nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 98 | 19 | 9 |
| 3rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 98 | 9 | 3 |
| 4th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 0 | 10 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 97 | 18 | 6 |
| 5th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 97 | 7 | 6 |
| 6th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 96 | 16 | 2 |
| 7th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 96 | 4 | 7 |
| 8th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 95 | 12 | 8 |
| 9th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 95 | 0 | 6 |
| 10th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 12 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 94 | 8 | 0 |
| 11th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 12 | 10 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 93 | 15 | 2 |
| 12th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 0 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 93 | 2 | 1 |
| 13th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 92 | 8 | 8 |
| 14th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 13 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 91 | 14 | 11 |
| 15th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 91 | 0 | 9 |
| 16th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 14 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 90 | 6 | 3 |
| 17th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 14 | 10 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 89 | 11 | 5 |
| 18th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 15 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 88 | 16 | 2 |
| 19th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 15 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 88 | 0 | 7 |
| 20th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 87 | 4 | 7 |
| 21st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 16 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 86 | 8 | 2 |
| 22nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 16 | 10 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 85 | 11 | 4 |
| 23rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 17 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 84 | 14 | 1 |
| 24th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 17 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 83 | 16 | 5 |
| 25th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 82 | 18 | 4 |
| 26th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 81 | 19 | 10 |
| 27th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 81 | 0 | 10 |
| 28th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 19 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 80 | 1 | 4 |
| 29th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 79 | 1 | 4 |
| 30th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 11 | 78 | 0 | 10 |
| 31st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 11 | 76 | 19 | 10 |
| 32nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 75 | 18 | 4 |
| 33rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 74 | 16 | 4 |
| 34th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 73 | 13 | 9 |
| 35th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 72 | 10 | 7 |
| 36th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 71 | 6 | 10 |
| 37th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 70 | 2 | 6 |
| 38th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 68 | 17 | 7 |
| 39th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 67 | 12 | 0 |
| 40th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 66 | 5 | 10 |
| 41st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 64 | 19 | 0 |
| 42nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 63 | 11 | 6 |
| 43rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 9 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 62 | 3 | 3 |
| 44th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 60 | 14 | 4 |
| 45th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 59 | 4 | 8 |
| 46th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 57 | 14 | 3 |
| 47th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 56 | 3 | 1 |
| 48th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 54 | 11 | 2 |
| 49th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 12 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 52 | 18 | 5 |
| 50th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 51 | 4 | 11 |
| 51st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 49 | 10 | 7 |
| 52nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 47 | 15 | 4 |
| 53rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 45 | 19 | 3 |
| 54th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 44 | 2 | 3 |
| 55th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 42 | 4 | 4 |
| 56th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 18 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 40 | 5 | 5 |
| 57th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 19 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 38 | 5 | 7 |
| 58th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 36 | 4 | 9 |
| 59th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 34 | 2 | 10 |
| 60th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 31 | 19 | 11 |
| 61st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 29 | 15 | 11 |
| 62nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 11 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 27 | 10 | 10 |
| 63rd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 25 | 4 | 7 |
| 64th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 22 | 17 | 2 |
| 65th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 20 | 8 | 7 |
| 66th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 17 | 18 | 10 |
| 67th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 15 | 7 | 10 |
| 68th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 12 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 6 |
| 69th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 11 |
| 70th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| 71st | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 8 |
| 72nd | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 17 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 0 |
| 73rd | 1 | 13 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | .. | ||
The mortgagor under the instalment system may pay to the Superintendent at any time, and under the fixed-loan system on any half-yearly due date, the whole balance of principal owing, with interest to date of payment, and obtain a discharge of the mortgage on payment of the fee prescribed for such discharge.
The mortgagor may also from time to time pay to the Superintendent, in addition to the half-yearly payments, sums of £5 or a multiple of £5, and in the case of fixed loans such deposits are applied in reduction of the advance, and interest is charged on the balance only; or, if the mortgagor so directs, such deposits are held on his behalf and applied in payment of the half-yearly instalments of interest as they fall due.
In the case of an instalment loan, money paid in advance by a mortgagor is applied in one of the following methods, according as he directs:—
It may be held on his behalf and applied in payment of the half-yearly instalments (consisting partly of interest and partly of principal) as they fall due, until the deposit is exhausted.
It may be applied at once in payment of as many future half-yearly instalments of principal (but not of interest) as it will cover, and, as far as such instalments are concerned, the corresponding interest will not be charged. On the next half-yearly date, however, the mortgagor will be required to continue his payments as before, the advance payment having the effect of reducing the period (thirty-six years and a half) during which he would have to pay such instalments. For instance, a mortgagor has a loan of £100: On the due date of his eighth half-yearly instalment he pays, in addition to the amount due, a sum of £5. This is applied in payment of his ninth, tenth, eleventh, twelfth, thirteenth, fourteenth, and fifteenth instalments of principal—12s. 2d., 12s. 6d., 12s. 10d., 13s. 1d., 13s. 5d., 13s. 9d., 14s. 2d. (see table), making a total of £4 11s. 11d.—and the corresponding interest, £2 7s. 10d., £2 7s. 6d., £2 7s. 2d., £2 6s. 11d., £2 6s. 7d., £2 6s. 3d., £2 5s. 10d., is not charged. A balance of 8s. 1d. remains in his favour. Then on the next due date he has to make the half-yearly payment as usual (less 8s. 1d.), but, instead of being the ninth, it counts as the sixteenth instalment, and by this means the whole loan is repaid three years and a half earlier (seven half-yearly payments) than it otherwise would be.
It may be applied as explained in the next paragraph.
On the due date of any instalment, after at least one-tenth of the loan has been repaid, by means of the half-yearly instalments or of moneys repaid in advance, or both, the mortgagor (provided he is not in arrear with any instalment or other payment due under the mortgage) may, with the consent of the Superintendent, readjust the loan by treating the balance of principal then unpaid as a fresh loan duly granted on that date for a fresh term. But no readjustment is allowed unless the balance of unpaid principal amounts to at least £100. Under this arrangement the mortgagor will be relieved of paying interest on the original amount of the loan, and will pay only on the balance of principal not repaid.
Advance payments in reduction of the mortgage, unless made on the due date of a half-yearly payment, take effect only from the next due date.
The law-costs payable for preparing and completing the mortgages under the Act are as follow:—
Law-costs of perusing title, preparing and registering mortgage (to be deducted from the advance),—
| £ | s. | d. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| If advance be not exceeding £250 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| Exceeding £250, but not exceeding £500 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Exceeding £500, but not exceeding £750 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Exceeding £750, but not exceeding £1,000 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Exceeding £1,000, but not exceeding £1,500 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
| Exceeding £1,500, but not exceeding £2,000 | 1 | 11 | 6 |
| Exceeding £2,000, but not exceeding £3,000 | 1 | 17 | 6 |
With cash disbursements, which are the same in every case, namely,—
| Mortgage-forms | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Search-fee (with an additional 2s. for every certificate of title after the first) | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Registration (with an additional 2s. for every certificate of title after the first) | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Law-costs of perusing title, preparing and registering mortgage (to be deducted from the advance),—
| £ | s. | d. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| If advance be not exceeding £150 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Exceeding £150, but not exceeding £250 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| Exceeding £250, but not exceeding £500 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| Exceeding £500, but not exceeding £750 | 1 | 13 | 0 |
| Exceeding £750, but not exceeding £1,000 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| Exceeding £1,000, but not exceeding £1,500 | 2 | 13 | 0 |
| Exceeding £1,500, but not exceeding £2,000 | 3 | 13 | 0 |
| Exceeding £2,000, but not exceeding £3,000 | 4 | 13 | 0 |
With cash disbursements,—
| Fee chargeable by solicitor not residing in registration centre for employing agent to register mortgage | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Solicitor's charge for obtaining Land Board's consent to mortgage of leasehold land— | |||
| If advance be not exceeding £250 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Exceeding £250 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Fee for partial or total discharge of mortgage | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Fee for execution of consent by the Superintendent to any document | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Fee for production of title-deeds held by the Superintendent | 0 | 5 | 6 |
Solicitors are entitled to charge moderately for any services mortgagors may require and above those provided for in the scale—such services, for example, as clearing encumbered titles, obtaining and registering titles, &c.
Valuation reports on the securities offered are made on behalf of the Department by expert land-valuers; and these reports, together with the corresponding valuations appearing in the district valuation-rolls, prepared in accordance with the provisions of “The Government Valuation of Land Act, 1896,” and reports from the Commissioners of Crown Lands in the case of Crown leaseholds, are considered by the General Board. Board meetings are held weekly, or as occasion requires, and the Superintendent is bound by the resolutions of the Board. A resolution is taken with regard to every application placed before the General Board, so that on the Board rests the responsibility of granting loans or of refusing to grant them.
Some applicants offer securities which are obviously not eligible; and in that event the valuation-fees paid are returned, the securities are not reported on, and the applications do not go before the Board.
By arrangements made with the Post Office, mortgagors are enabled to pay their instalments and interest to the credit of the Superintendent at any money-order office throughout the colony, and free of all costs for remitting the money to Wellington. This is an arrangement at once convenient and economical for the large number of persons scattered all over the colony who have financial dealings with the Advances to Settlers Office. Loans may also be repaid in full through the Post Office.
The officials of the Government Advances to Settlers Office are bound by declaration to observe secrecy respecting applications for advances, and are forbidden to give any information respecting the business of the Department except to officers appointed to assist in carrying out the provisions of the Act.
The Act provides penalties for persons employed in the business of the Advances to Settlers Office taking any fee or reward from an applicant for a loan under the Act; for persons acting as valuers of land in which they have a pecuniary interest; and for persons who may attempt to bribe any one employed under the Act. It should be understood that no commission, charge, or procuration fee is payable in connection with an application for a loan.
The first meeting of the General Board for the purpose of considering applications for loans was held on 23rd February, 1895; and up to the 31st March, 1903, the Board had authorised 12,922 advances, amounting to £4,316,940. The total amount applied for in the 12,922 applications granted in full and partially was £4,903,515. 1,629 applicants declined the partial grants offered to them, amounting to £735,280; so that the net advances authorised at 31st March, 1903, numbered 11,293, and amounted to £3,581,660. The security for the net authorised advances was valued at £7,849,728. The number of applications received up to 31st March, 1903, was 16,643, for an aggregate amount of £5,927,495.
Table of Contents
BY “The Land and Income Assessment Act, 1891,” a system of taxation was instituted on the unimproved value of land and the capital value of mortgages of land, in conjunction with a tax on incomes in excess of £300 a year. Various amending Acts were passed from time to time, and in 1900 the law was consolidated in one measure—"The Land and Income Assessment Act, 1900.”
Eleven years’ taxation on this basis has now been collected to date, and it may be safely claimed that the system has, from a financial point of view, been a success, and that the revenue is collected practically without friction.
In 1902–1903 the rate of land-tax in respect of mortgages was reduced from one penny in the pound to three farthings. This represented a reduction of revenue to the extent of £30,000. Part of this loss was recouped by revised valuations made, which produced an increase of £13,000, and the yield for 1902–1903 was, in round figures, £296,000, of which the ordinary land-tax was £217,000 and the graduated tax (including the special tax on absentee land-owners) £79,000. It will therefore be seen from these figures that if the mortgage-tax had not been reduced the yield from the land-tax would have been £326,000, as against £313,000 in 1901–1902.
For the purposes of the “ordinary” land-tax, owners are allowed under the Act to deduct from the total unimproved value of their land the amount of any registered mortgage thereon, and the mortgagees are required to make a return of all their mortgages. In the case of uncompleted sales, where the title has not been transferred the amount of unpaid purchase-money is treated as a mortgage—that is, it may be deducted by the purchaser and must be included in the return made by the vendor.
An owner of land the unimproved value of which, together with mortgages owing to him, does not exceed £1,500 (after deducting mortgages owing by him) is allowed an exemption of £500, but where such value exceeds £1,500 the exemption diminishes by £1 for every £2 that such value increases, so that no exemption is allowable when £2,500 is reached.
The Act contains a provision that in cases where the income from any land or mortgages, plus income from all other sources, is less than £200 per annum, and the owner is incapacitated by age or infirmity from supplementing such income, a further exemption may be allowed by the Commissioner upon his being satisfied that the payment of the tax would entail hardship on such owner. This discretionary power has been exercised in a considerable number of instances, especially in the case of widows and orphans with small means, and much hardship prevented.
All mortgages are assessed at their full nominal value, except where it is satisfactorily shown that owing to depreciation of the security or other cause such value has been diminished. In the case of mixed mortgages—that is, mortgages which are secured on both real and personal property—the amount of the mortgage chargeable with land-tax is taken to be the assessed value of the land included in the security, the interest derived from the balance of mortgage being liable to income-tax.
It will be readily seen that the deductions and exemptions which have been referred to materially reduce the number of taxpayers as compared with the number of land-owners, the latter being upwards of 115,000, whilst the former only number about 18,500.
If the unimproved value of land in any assessment amounts to £5,000 or over, graduated tax is payable thereon according to the scale given on another page. Mortgages, however, are not chargeable with the graduated tax; but, on the other hand, no deduction is allowed in an assessment for graduated tax in respect of any mortgage owing on the land.
Twenty per cent. additional on the amount of the graduated tax is levied where the owners have been resident out of the colony for a period of not less than one year next preceding the date of the passing of the annual taxing Act.
Native lands which are occupied by Europeans are subject to the ordinary tax, it being considered that as such lands have benefited equally with the lands of Europeans by the expenditure of public money, they should bear some proportion of the taxation. But, recognising that in some instances, where the interests of the Native owners are small, the collection of the tax might possibly entail some hardship, the Legislature decided that only half the usual rate should be collected on such lands. Graduated tax is not chargeable on Native land.
Both the number of income-tax payers and the amount of tax received may appear at first sight smaller than might be expected from the population of New Zealand, but it should be remembered that incomes from land and mortgages are exempt, the unimproved value of the former and the capital value of the latter being chargeable with land-tax in the manner hereinbefore explained. The statutory exemption of £300, plus life-insurance premiums up to £50, renders a very large number of employees and small traders exempt from the tax. Companies pay the tax on profits, and dividends are not returnable by their shareholders. These circumstances will account for the smallness of the number (7,200) subject to income-tax and, to a certain extent, the comparatively inconsiderable contribution to the revenue.
Objections to income assessments are heard in private before the Stipendiary Magistrate.
It is impossible to indicate the number and variety of questions which arise daily in connection with income assessments, or to give a full account of how they are dealt with.
Amongst the questions to which special attention has been given is that of the depreciation of plant and machinery, and the amount to be allowed as a deduction under this heading. The Amendment Act of 1894 admitted, amongst deductions, an allowance for depreciation of plant and machinery over and above what may be claimed as repairs and renewals, and this allowance is maintained in the Act of 1900. The allowance is, by law, fixed at what may be considered just by the Commissioner; but the Chief Inspector of Machinery is, in this matter, the expert adviser of the Department, and he fixes the rates to be allowed. There have been naturally some differences of opinion between owners of machinery and the Department, but only in the case of steam-vessels has the Inspector found it necessary to alter the scale first laid down. The rule formulated for the Inspector's guidance is as follows:—
An allowance to be made of such an amount (over and above what is expended in renewals and repairs) as will equal the annual loss of profit-earning power.
This is not intended to provide for the loss of capital invested, but simply represents the annual loss through wear and tear (as affecting income-earning capacity), other than that which can be made good by renewals of parts and repairs.
Obsolete machinery is also allowed for when the machinery has been actually discarded; and here the amount to be allowed must bear the same proportion to the whole loss as the time the tax has been in operation bears to the life of the machine. An engine discarded in the tenth year of the tax—the life of the engine being, say, twenty years—would be allowed for to one-half of the loss incurred, less the annual amounts that have been allowed by the Department for depreciation during ten years. Machinery superseded by something better, but kept in reserve in case of a breakdown, is not allowed for.
In the consolidating Act of 1900, before referred to, a further allowance is made to taxpayers who occupy their own freehold or leasehold premises. Such taxpayers are now entitled to deduct a sum at the rate of 5 per cent. on the capital value of their interest in the land or improvements thereon. This concession is intended to remove an anomaly which previously existed as between a taxpayer in business who occupied premises for which he paid rent and one who occupied his own freehold, or premises erected on leasehold ground. In the first case rent was deducted, and in the hands of the landlord was not taxable, being income derived from land; in the second case the allowance was limited under the then existing law to 5 per cent. on the amount on which land-tax was paid. This might be nothing, and in the case of premises on leasehold land no allowance could then be made. As an equivalent of the rent paid by a tenant, a freeholder is now allowed a deduction of 5 per cent. on the capital value of his business premises; while a leaseholder, who was previously entitled to deduct his ground-rent only, is now allowed a further deduction of 5 per cent. on the capital value of any leasehold interest he may own in his business premises. Mortgage interest, however, is not now deductible. The deduction of 5 per cent. on the capital value of the taxpayer's interest in his business premises precludes any further deduction. The effect of the provision is to exclude land, with its profit or loss, from the income-tax system.
It should be mentioned here that the statutory exemption of £300 is not allowed to absentees, whether firms or individuals, nor in any case to companies.
Regulations have been issued for levying income-tax on the profits earned by shipowners whose headquarters are beyond the colony. The plan adopted is to require a return of the outward freight and passenger lists, and to levy tax at the rate of one shilling in the pound upon 5 per cent. of the total returned.
The yield of land-tax and income-tax for the last five years has, in round figures, been as follows:—
| Year. | Land-tax. | Income-tax. |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1898–9 | 298,000 | 115,500 |
| 1899–1900 | 294,000 | 129,000 |
| 1900–1 | 294,000 | 173,000 |
| 1901–2 | 313,000 | 179,000 |
| 1902–3 | 296,000 | 201,000 |
The rates of tax at present are as follow: The ordinary land-tax is 1d. in the pound; the graduated tax commences at £5,000, at 1/2d. in the pound on the unimproved value, and rises to 2d. where the unimproved value of an owner's land is £210,000, or exceeds that sum. The ordinary tax on Native land occupied by Europeans is 1/2d. in the pound. For taxpayers other than companies the rate of income-tax is 6d. in the pound on the first taxable £1,000—that is, after deducting the £300 exemption—and 1s. in the pound on any excess over £1,000. A person having an annual income of £1,900 would be thus taxed: £300 would be exempted; £1,000 would pay 6d. in the pound; and the remaining £600, 1s. in the pound: making a total of £55 a year. The tax on an income of £400 would be at 6d. on £100, equal to £2 10s. Income-tax is payable by companies, at the uniform rate of 1s. in the pound.
The schedule of rates of graduated land-tax is as follows:—
| Where the value is £5,000 and is less than £10,000, | one-eighth of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £10,000 and is less than £15,000, | two-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £15,000 and is less than £20,000, | three-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £20,000 and is less than £25,000, | four-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £25,000 and is less than £30,000, | five-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £30,000 and is less than £40,000, | six-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £40,000 and is less than £50,000, | seven-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £50,000 and is less than £70,000, | one penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £70,000 and is less than £90,000, | one penny and one-eighth of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £90,000 and is less than £110,000, | one penny and two-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £110,000 and is less than £130,000, | one penny and three-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £130,000 and is less than £150,000, | one penny and four-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £150,000 and is less than £170,000, | one penny and five-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £170,000 and is less than £190,000, | one penny and six-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £190,000 and is less than £210,000, | one penny and seven-eighths of a penny in the pound sterling. |
| Where the value is £210,000 or exceeds that sum, | twopence in the pound sterling. |
THE above Act provides for the periodical valuation of all landed properties in New Zealand, and for that purpose the colony is divided into special districts.
The first valuation was made as at 31st March, 1898, since which date valuations in many parts of the colony have been revised as circumstances required. An Amendment Act passed during the session of 1900 contains the amendments which four years’ experience of the original Act showed to be desirable. As the principle of the original Act remains unaltered, the amendments are practically confined to the machinery clauses and the clearer definition of terms.
The valuations are used for the following purposes: Land-tax, local rates (in cases where rates are levied on the capital or on the unimproved value), stamp duties, and duties under “The Deceased Persons’ Estates Duties Act, 1881”; for advances and investments on mortgage of land made by the Post Office, Government Insurance Department, Public Trust Office, Government Advances to Settlers Office, and the Commissioners of the Public Debts Sinking Funds. The valuation is also used for the guidance of the Government in transactions under “The Land for Settlements Act, 1894,” and “The Public Works Act, 1894.”
Valuations are supplied by the Department on payment of the prescribed fee.
The cost of making the valuation is borne principally by the Valuation Department, the Land- and Income-tax Department, the Advances to Settlers Office, and the local authorities using the valuation, while separate fees, for supplying individual valuations to those requiring them, are charged by regulation.
Table of Contents
“THE Rating on Unimproved Value Act, 1896,” was passed by the General Assembly to afford local bodies the opportunity of adopting the principle of rating which is expressed in the title of the measure. It is entirely at the option of the bodies to adopt the system, and provision is made for a return to the old system of rating, if desired, after three years’ experience of the new one. The Act provides that a proportion of the ratepayers on the roll, varying from 25 per cent. where the total number does not exceed 100, to 15 per cent. where the number exceeds 300, may by demand in writing, delivered to the chairman of the district, require that a proposal to rate property on the basis of the unimproved value may be submitted to the ratepayers, whose votes shall be taken between twenty-one and twenty-eight days after delivery of the demand. The poll is to be taken in the same manner as in case of a proposal to raise a loan in the district under “The Local Bodies’ Loans Act, 1886.”
Under the original Act it was necessary for a minimum number of one-third of the ratepayers to vote, and a majority of their votes carried the proposal. Now, under “The Municipal Corporations Act, 1900,” the question of adoption or otherwise is decided by a bare majority of the valid votes recorded, irrespective of the number of ratepayers who have voted.
A rescinding proposal can be carried at a poll by the same means as one for adoption, but not until after three years have elapsed, and, vice versa, rejection of a proposal bars its being again brought forward for a similar period. However, in the case of past polls at which the proposal to adopt the Act was rejected solely on account of an insufficient number of ratepayers recording their votes, it is now provided that a new poll may be held at any time.
The valuation-roll is supplied to the local authority by the Valuer-General under the provisions of “The Government Valuation of Land Act, 1896,” and its amendment of 1900, and the definitions of “capital value,” “improvements,” “unimproved value,” and “value of improvements” found in these Acts apply also to the Rating on Unimproved Value Act. Provision is made for adjustment of rating powers given under previous Acts to the Act of 1896 by fixing equivalents. Thus a rate of 1s. in the pound on the annual value under former Acts is to be considered equal to 3/4d. in the pound on the capital value under the Act of 1896.
The adjustments are to be made so that the rates on the unimproved value shall be such as to produce as much as, but not more than, the rates under “The Rating Act, 1894.” For instance, supposing a local authority has a rating power up to 3/4d. in the pound on the capital value, then it can levy any rate in the pound on the unimproved value of land in its district so long as the producing capacity of such rate is not greater than would be the producing capacityof a 3/4d. rate on the capital value of the district. When a fixed rate, under the older system of rating, is security for a loan, the Controller and Auditor-General is given power to interfere and fix the new rate himself if of opinion that the new rate on the unimproved value does not afford equally good security to the one to be given up.
The operation of the Act does not apply to water, gas, electric light, sewage, nor hospital and charitable aid rates.
Up to the present time (31st March, 1903) the local bodies that have submitted the question of the adoption of the Act to the ratepayers are as follow:—
| **Results of Polls. | Votes recorded. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| For. | Against. | Informal. | ||
* Date of polls will be found in a special table in Statistical Vol. for 1902. † New poll taken under Act of 1900. * New poll taken under Act of 1900. | ||||
| Ashburton Borough | Rejected | 102 | 199 | 4 |
| Auckland City | Rejected | 753 | 1,697 | .. |
| Balclutha Borough | Carried | 60 | 33 | .. |
| Cheviot County | Carried | 165 | 41 | .. |
| Christchurch Borough | Carried | 596 | 512 | .. |
| Devonport Borough | Carried | 356 | 109 | .. |
| Eketahuna County | Carried | 149 | 21 | 1 |
| Feilding Borough | Carried | 268 | 56 | 1 |
| Foxton Borough | Rejected | 53 | 98 | 4 |
| Gore Borough | Carried | 122 | 67 | 5 |
| Grey Lynn Borough | Carried | 140 | 71 | 2 |
| Greymouth Borough | Carried | 214 | 48 | 1 |
| Hamilton Borough | Carried | 77 | 52 | .. |
| Hastings Borough | Rejected | 250 | 265 | 15 |
| Hokianga County | Carried | 109 | 25 | 6 |
| Hokitika Borough | Carried | 212 | 53 | 3 |
| Hunua Road District | Carried | 60 | 2 | .. |
| Inangahua County | Carried | 284 | 11 | 2 |
| Invercargill Borough | Carried | 386 | 174 | 4 |
| Karori Borough | Carried | 93 | 3 | 1 |
| Linwood Borough | Carried | 276 | 38 | 2 |
| Lower Hutt Borough | Carried | 94 | 68 | 4 |
| Manawatu Road District | Carried | 105 | 10 | .. |
| Maraetai Road District | Carried | 16 | .. | .. |
| Mareretu Road District | Carried | 24 | .. | .. |
| Masterton Borough | Carried | 221 | 139 | 6 |
| Melrose Borough | Carried | 236 | 40 | 6 |
| Mosgiel Borough | Rejected | 58 | 87 | 1 |
| Normanby Town District | Carried | 82 | 56 | 3 |
| North Invercargill Borough | Carried | 107 | 24 | 2 |
| Onslow Borough | Carried | 140 | 8 | .. |
| Pahiatua Borough | Carried | 136 | 38 | 1 |
| Pahiatua County | Carried | 350 | 31 | 3 |
| Palmerston North Borough | Carried | 402 | 12 | 3 |
| Papakura Road District | Carried | 30 | 1 | .. |
| Pelorus Road District | Carried | 98 | 41 | .. |
| Petone Borough | † Rejected | 100 | 134 | 4 |
| Picton Borough | †Rejected | 27 | 73 | 1 |
| Raglan County | †Carried | 116 | 85 | 2 |
| St. Albans Borough | †Carried | 350 | 218 | 15 |
| South Invercargill Borough | †Carried | 106 | 54 | 1 |
| Southland County | †Carried | 919 | 574 | .. |
| Spreydon Road District | †Carried | 141 | 57 | 4 |
| Stratford County | Carried | 399 | 23 | 2 |
| Stratford Borough | Carried | 137 | 64 | 1 |
| Sumner Borough | Carried | 91 | 19 | .. |
| Sydenham Borough | Carried | 353 | 193 | .. |
| Tauranga County | Carried | 90 | 13 | 2 |
| Taratahi–Carterton Road District | Carried | 261 | 53 | .. |
| Timaru Borough | Rejected | 93 | 246 | 5 |
| Waimate Borough | Carried | 235 | 61 | 14 |
| Waimate County | Carried | 368 | 162 | .. |
| Waipawa County | Carried | 462 | 28 | 3 |
| Wairarapa North County | Rejected | 331 | 68 | 10 |
| Wairarapa South County | Carried | 187 | 8 | .. |
| Wellington City | Carried | 1,261 | 591 | .. |
| Winton Borough | Carried | 39 | 33 | 1 |
| Woodville Borough | Carried | 175 | 7 | 1 |
| Woolston Borough | Carried | 252 | 190 | 7 |
IN 1898 a Bill, introduced into Parliament by the Right Hon. R. J. Seddon, Prime Minister, became law,* which provided for the payment of an old-age pension out of the Consolidated Fund (revenue of the General Government) to persons duly qualified, without contribution by the beneficiaries. The Act, however, only provided for payments out of revenue, for the purposes of the pensions, until the close of the second session of the late Parliament. [By amendment passed in 1900 the limit as to time of the operation of the principal Act is rescinded, and the authority to pay made absolute.] The conditions under which pension is granted are set forth in sections 7, 8, and 64 of the statute, as under:—
7. Subject to the provisions of this Act, every person of the full age of sixty-five years or upwards shall, whilst in the colony, be entitled to a pension as hereinafter specified.
8. No such person shall be entitled to a pension under this Act unless he fulfils the following conditions, that is to say:—
That he is residing in the colony on the date when he establishes his claim to the pension; and also
That he has so resided continuously for not less than twenty-five years immediately preceding such date:
Provided that continuous residence in the colony shall not be deemed to have been interrupted by occasional absence therefrom unless the total period of all such absence exceeds two years; nor, in the case of a seaman, by absence therefrom whilst serving on board a vessel registered in and trading to and from the colony if he establishes the fact that during such absence his family or home was in the colony [By amendment passed in 1900, as an alternative condition in respect of residence an absence of four years from the colony is allowed, provided that the claimant was not absent during the year ended 31st October, 1898, and provided that the total period of actual residence is not less than twenty-five years]; and also
* A Bill had been previously introduced in 1897, which, as amended by the lower branch of the Legislature, was transmitted to the Legislative Council, but thrown out by that body.
As a preliminary to the introduction of the Bill in 1897, an Act entitled “The Registration of People's Claims Act” was passed in 1896, under which persons aged sixty-five years or upwards, having resided twenty years in the colony, and whose income did not exceed £50 per annum, were allowed for a limited time to send in pension-claims. This Act was subsequently repealed, and all certificates granted under it cancelled, by the Old-age Pensions Act of 1898.
(3.) That during the period of twelve years immediately preceding such date he has not been imprisoned for four months, or on four occasions, for any offence punishable by imprisonment for twelve months or upwards, and dishonouring him in the public estimation; and also
(4.) That during the period of twenty-five years immediately preceding such date he has not been imprisoned for a term of five years with or without hard labour for any offence dishonouring him in the public estimation; and also
(5.) That the claimant has not during the period of twelve years immediately preceding such date (Amendment Act, 1902), for a period of six months or upwards, if a husband, deserted his wife, or without just cause failed to provide her with adequate means of maintenance, or neglected to maintain such of his children as were under the age of fourteen years; or, if a wife, deserted her husband or such of her children as were under that age:
Provided that, if the pension-certificate is issued, the pensioner's rights thereunder shall not be affected by any disqualification contained in this subsection unless the fact of such disqualification is established at any time to the satisfaction of a Stipendiary Magistrate; and also
(6.) That he is of good moral character, and is, and has for five years immediately preceding such date been, leading a sober and reputable life; and also
(7.) That his yearly income does not amount to fifty-two pounds or upwards, computed as hereinafter provided [By amendment passed in 1900 the property and income of husband and wife is to be computed as belonging to them jointly, and their united yearly incomes, including the pension, is limited to £78]; and also
(8.) That the net capital value of his accumulated property does not amount to two hundred and seventy pounds or upwards, computed and assessed as hereinafter provided; and also
(9.) That he has not directly or indirectly deprived himself of property or income in order to qualify for a pension. [By amendment passed in 1901, it is provided that, if during the currency of a pension a pensioner becomes possessed of any property or income in excess of what is allowed in respect of the amount of pension granted, the pension can on application be confirmed, cancelled, or varied in amount by the Magistrate. Provision is also made for the recovery of sums paid in pensions exceeding the amount allowed by law. The Amendment Act of 1902 provides that where the applicant is owner of his (her) residence, not over £300 value, it may be conveyed to the Public Trustee, and the value deducted from the capital value of the accumulated property in computing the pension. The Public Trustee permit the pensioner to reside on the property rent free during life, and, if he or she dies leaving wife or husband who is entitled to a pension, then during life of survivor. Provision is made for dealing with such property on death of pensioner or survivor, and for retransfer of property to pensioner if desired]; and also
(10.) That he is the holder of a pension-certificate as hereinafter provided.
64. This Act, in so far as it provides for the granting of pensions, shall not apply to—
Aboriginal natives of New Zealand to whom moneys other than pensions are paid out of the sums appropriated for Native purposes by “The Civil List Act, 1863”; nor to
Aliens; nor to
Naturalised subjects, except such as have been naturalised for the period of five years next preceding the date on which they establish their pension-claims [By amendment passed in 1900, in the case of naturalised persons the term of qualification preceding the establishment of a pension-claim is reduced from five years to one]; nor to
Chinese or other Asiatics, whether naturalised or not.
If, in the opinion of a Magistrate adjudicating, it would be more advantageous for a Maori applying for a pension to receive an allowance out of the moneys appropriated for Native purposes, he may, in lieu of granting pension, make recommendation accordingly to the Native Minister. A Magistrate may, in granting a pension to a Maori, direct that it be paid to some Government officer for the benefit of the applicant.
The full pension is £18 a year, payable in twelve monthly instalments; but for each £1 of income above £34, also for each £15 of accumulated property above £50, £1 is deducted from the amount of the pension.
The first instalment of the pension is payable on the first day of the month next but one following the date of the certificate.
For the administration of the Act the colony is divided into seventy-four districts, for each of which there is a Deputy Registrar, controlled by a Chief Registrar at Wellington.
All applicants for a pension have now to fill in the answers to a set of questions on a new claim form, and to come before the Deputy-Registrar if physically fit to do so. The Deputy-Registrar then verifies the answers given by a set of inquiry forms provided for the purpose, and when this has been done to the satisfaction of that officer the applicant appears, as required by the Act, before the Stipendiary Magistrate, who may grant or reject the claim according to the evidence. All pensioners already on the books are being given the opportunity, when they come for renewal this year, to answer a similar set of questions, the answers to which are verified as in the case of a new claim.
The particulars of pensions granted are entered on a weekly return form, which, with the Magistrate's certificate, is sent to the Chief Registrar for entry in the General Register of Old-age Pensions.
The particulars of instalments falling due are advised to the General Post Office on a schedule. Advice, authorising payment, is then issued to the Postmaster at the money-order office at which the pensioner desired the instalment to be paid. At frequent intervals the Accountant of the General Post Office furnishes a statement of the payments made, from which the monthly instalments are entered on a card bearing the name of the pensioner.
At the due date of the instalment the pensioner may present his certificate for payment at the money-order office named in the certificate. A pensioner failing to collect his instalment within twenty-one days forfeits the amount, but may apply for a warrant of waiver within fourteen days of such forfeiture. [By amendments passed in 1900 and 1901 the currency of each instalment is for one calendarmonth, with power to the Colonial Treasurer to extend the period in special cases.] If a pensioner is unable, through sickness or other reasonable cause, to collect his pension, he may apply to ave an agent appointed to receive the instalments on his behalf. Should a pensioner desire to change the office of payment an application is to be made to the Deputy Registrar for the district in which the pension is registered. The change is advised to the Chief Registrar by telegram, who notifies the postal authorities. A transfer of a pension-certificate from one district to another is effected by the Deputy Registrar for the district in which the pension is registered sending a warrant to the Deputy Registrar for the district to which the transfer is made.
The decease of all persons of the age of sixty-five years and upwards is notified to the Chief Registrar by the Registrars of Deaths in the various districts. By amendment passed in 1900 the right of pensioners to admission to charitable institutions is protected.
All matters affecting the payment of pensions are reported by the Deputy Registrars from time to time.
The Act came into force on 1st November, 1898. The appointment of a Registrar followed; and in December the old-age pension districts were constituted, and Deputy Registrars appointed for them. By the 31st March, 1899, there were 7,443 pensions, which represented a yearly payment of £128,082. A year later the number of pensions in force was 11,285, representing a yearly payment of £193,718. On the 31st March, 1901, the number in force was 12,405, the yearly payment for these being £211,965; on the 31st March, 1902, there were 12,776 pensions, and the amount was £217,192; and on the 31st March, 1903, the number in force was 12,481 (including 892 Maoris), representing a liability of £211,594.
The number of pensions in force in each of the old-age pension districts was:—
| NUMBER AND ANNUAL VALUE OF PENSIONS GRANTED TO EUROPEANS AND MAORIS (([0-9]+)) ON THE 31ST MARCH, 1903. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District. | Number. | Annual Value. | |||
| European. | Maoris. | ||||
| £ | s. | d. | |||
| Auckland | 974 | 8 | 16,556 | 0 | 0 |
| Coromandel | 86 | 37 | 2,183 | 0 | 0 |
| Dargaville | 64 | .. | 1,114 | 0 | 0 |
| Hamilton | 149 | 11 | 2,659 | 0 | 0 |
| Helensville | 240 | 6 | 4,252 | 0 | 0 |
| Kaitaia | 17 | 44 | 1,013 | 0 | 0 |
| Mangonui | 10 | 19 | 489 | 0 | 0 |
| Maungaturoto | 39 | .. | 598 | 0 | 0 |
| Otahuhu | 222 | 13 | 3,738 | 0 | 0 |
| Raglan | 9 | 50 | 1,009 | 0 | 0 |
| Rawene | 14 | 87 | 1,678 | 0 | 0 |
| Rotorua | 6 | 51 | 1,019 | 0 | 0 |
| Russell | 61 | 96 | 2,581 | 0 | 0 |
| Taupo | 33 | 573 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Warkworth | 68 | 2 | 1,086 | 0 | 0 |
| Whangarei | 138 | 3 | 2,405 | 0 | 0 |
| Whangaroa | 15 | 28 | 745 | 0 | 0 |
| Thames | 247 | 11 | 4,413 | 0 | 0 |
| Opotiki | 13 | 24 | 642 | 0 | 0 |
| Paeroa | 55 | 6 | 1,065 | 0 | 0 |
| Tauranga | 32 | 43 | 1,293 | 0 | 0 |
| Te Aroha | 35 | 1 | 624 | 0 | 0 |
| Whakatane | 8 | 65 | 1,312 | 0 | 0 |
| Gisborne | 62 | 34 | 1,603 | 0 | 0 |
| Port Awanui | 5 | 16 | 378 | 0 | 0 |
| Napier | 269 | 2 | 4,589 | 0 | 0 |
| Dannevirke | 146 | 1 | 2,447 | 0 | 0 |
| Waipawa | 23 | .. | 401 | 0 | 0 |
| Wairoa | 9 | 54 | 975 | 0 | 0 |
| New Plymouth | 185 | 20 | 3,429 | 0 | 0 |
| Stratford | 30 | .. | 494 | 0 | 0 |
| Wanganui | 193 | 16 | 3,587 | 0 | 0 |
| Hawera | 59 | 4 | 1,116 | 0 | 0 |
| Marton | 77 | 10 | 1,476 | 0 | 0 |
| Patea | 20 | 3 | 403 | 0 | 0 |
| Wellington | 534 | 4 | 9,382 | 0 | 0 |
| Feilding | 92 | 7 | 1,653 | 10 | 0 |
| Greytown | 82 | 2 | 1,412 | 0 | 0 |
| Masterton | 51 | 1 | 1,483 | 0 | 0 |
| Otaki | 51 | 13 | 1,089 | 0 | 0 |
| Pahiatua | 32 | .. | 504 | 0 | 0 |
| Palmerston North | 162 | 7 | 2,852 | 0 | 0 |
| Nelson | 267 | 4 | 4,364 | 0 | 0 |
| Motueka | 80 | .. | 1,291 | 0 | 0 |
| Blenheim | 163 | 3 | 2,747 | 0 | 0 |
| Havelock | 8 | .. | 135 | 0 | 0 |
| Christchurch | 1,208 | 20,384 | 0 | 0 | |
| Akaroa | 41 | 808 | 0 | 0 | |
| Amberley | 9 | .. | 158 | 0 | 0 |
| Ashburton | 195 | .. | 3,340 | 0 | 0 |
| Culverden | 4 | .. | 63 | 0 | 0 |
| Kaiapoi | 274 | 6 | 4,628 | 0 | 0 |
| Kaikoura | 22 | 2 | 402 | 0 | 0 |
| Timaru | 146 | .. | 2,504 | 0 | 0 |
| Fairlie | 6 | .. | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Geraldine | 126 | 7 | 2,227 | 0 | 0 |
| Waimate | 102 | 2 | 1,711 | 0 | 0 |
| Greymouth | 473 | .. | 8,173 | 0 | 0 |
| Reefton | 156 | .. | 2,748 | 0 | 0 |
| Hokitika | 496 | 2 | 8,771 | 0 | 0 |
| Westport | 232 | 4 | 4,130 | 0 | 0 |
| Oamaru | 236 | 3 | 4,151 | 0 | 0 |
| Dunedin | 963 | 1 | 16,403 | 0 | 0 |
| Balclutha | 138 | .. | 2,364 | 0 | 0 |
| Clyde | 100 | .. | 1,776 | 0 | 0 |
| Lawrence | 206 | .. | 3,487 | 0 | 0 |
| Milton | 131 | .. | 2,157 | 0 | 0 |
| Naseby | 98 | .. | 1,694 | 0 | 0 |
| Palmerston South | 60 | .. | 994 | 0 | 0 |
| Port Chalmers | 177 | 6 | 2,970 | 0 | 0 |
| Invercargill | 605 | 1 | 10,197 | 0 | 0 |
| Queenstown | 112 | .. | 1,944 | 0 | 0 |
| Riverton | 131 | 5 | 2,363 | 0 | 0 |
| Chatham Islands | 4 | 1 | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 11,589 | 892 | £211,594 | 10 | 0 |
With the above, a statement of the cost of administration year by year is furnished, to show the initial and consequent expense. The Deputy Registrars of Old-age Pensions are mostly Clerks of Stipendiary Magistrate's Courts; the adjudication on claims is by the Magistrates; and the payments are made through the Postal Department.
| COST OF ADMINISTRATION OF “THE OLD-(([0-9]+)) ACT, 1898,” FOR THE FINANCIAL YEARS ENDED | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | 31 March, 1899. | 31 March, 1900. | 31 March, 1901. | 31 March, 1902. | 31 March, 1903. |
| * Registrar and two clerks. | |||||
| Salaries— | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Registrar | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 621* |
| Deputy Registrars | 40 | 150 | 200 | 219 | 279 |
| Other expenses— | |||||
| Advertising and printing | 16 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Clerical assistance | 248 | 1,124 | 1,209 | 1,328 | 1,730 |
| Travelling-expenses and interpreters’ fees | 84 | 309 | 194 | 190 | 384 |
| Shorthand-writer (S.M. Courts) | 19 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Contributions to Post Office | 466 | 500 | 500 | 500 | |
| Contingencies | 3 | 211 | 176 | 138 | 245 |
| Rent of offices | .. | .. | 36 | 60 | 46 |
| Total | 510 | 2,360 | 2,415 | 2,535 | 3,805 |
The following remarks are taken from the Registrar's report on the transactions for the year ended 31st March, 1903:—
“The number of pensions in force on the 31st March, 1903, was 12,481, representing a liability of £211,594—an average per pension of £16 19s. Of this number, 892 were Maoris.
“During the financial year just ended the number of new pensions granted was 1,386, including 62 Maoris. Five pensions, cancelled in the previous year, were reinstated.
“The total number of pensions voided during the year was 1,686, made up as follows: Deaths, 1,064; renewals not applied for, 278; renewals refused, 198; cancellations, 146. Maoris are represented in these figures by 103 deaths, 79 renewals not applied for, 38 renewals refused, and 11 cancellations.
“The total payments on account of pensions during the year amounted to £210,140 16s. 6d. Refunds direct to the Public Account of pension overpaid totalled £984 11s. 1d., leaving the net charge against the Act as £209,156 5s. 5d. A further refund of pension overpaid, totalling £55, was also obtained in stamps.
“The total amount of instalments for the year unpaid on the 31st March was £1,667 10s. 2d. Of this amount, £1,577 16s. 10d. represents absolutely forfeited instalments, the balance of £89 13s. 4d. being instalments the payment of which is in abeyance.”
| NUMBER OF PENSIONS GRANTED SINCE THE ACT CAME INTO OPERATION; NUMBER OF DEATHS, CERTIFICATES CANCELLED, PENSIONS LAPSED, AND RENEWALS REFUSED DURING EACH YEAR; (([0-9]+)) OF PENSIONS IN FORCE AT END OF EACH YEAR. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year ended | Number of Pensions granted. | Number of Deaths of Pensioners. | Number of Pension-certificates cancelled. | Number of Renewals refused. | Number of Pensions lapsed. | Number of Pensions in Force at End of Year. |
| * Including five cancellations of the previous year reinstated. | ||||||
| 31 Mar., 1899 | 7,487 | 38 | 6 | .. | .. | 7,443 |
| 31 Mar., 1900 | 4,699 | 786 | 28 | 37 | 6 | 11,285 |
| 31 Mar., 1901 | 2,227 | 815 | 25 | 202 | 65 | 12,405 |
| 31 Mar., 1902 | 1,694 | 935 | 54 | 152 | 182 | 12,776 |
| 31 Mar., 1903 | 1,391* | 1,064 | 146 | 198 | 278 | 12,481 |
| Total | 17,498 | 3,638 | 259 | 589 | 531 | .. |
| COMPARATIVE STATEMENT OF PENSIONS IN FORCE, AND PAYMENTS MADE IN EACH FINANCIAL YEAR SINCE ACT CAME INTO OPERATION. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date. | Number of Pensions in Force. | Payments to End of Financial Year. | Annual Increase in Expenditure. | Increase in Number of Pensions. | Decrease in Number of Pensions. |
| £ | £ | ||||
| At March 31, 1899 | 7,443 | 3,124 | .. | .. | .. |
| At March 31, 1900 | 11,285 | 157,342 | 154,218 | 3,842 | .. |
| At March 31, 1901 | 12,405 | 197,292 | 39,950 | 1,120 | .. |
| At March 31, 1902 | 12,776 | 207,468 | 10,176 | 371 | .. |
| At March 31, 1903 | 12,481 | 210,140 | 2,672 | .. | 295 |
| £ | ||
| * Gross increase in expenditure during the financial year 1902–1903 | ... | 2,672 |
| Less—(1.) Refunds to Public Account by Court proceedings | £984 | |
| (2.) Refunds by way of fine | 55 | |
| (3.) Instalments due in 1901–1902 paid in 1902–1903 | 629 | |
| — | 1,668 | |
| Net increase in expenditure | ... | £1,004 |
| AGES OF EUROPEAN PENSIONERS ON THE ROLLS (([0-9]+)) MARCH, 1903. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At Age | Number | At Age | Number | At Age | Number |
| 65 | 492 | 78 | 320 | 91 | 12 |
| 66 | 707 | 79 | 261 | 92 | 12 |
| 67 | 876 | 80 | 237 | 93 | 3 |
| 68 | 1,114 | 81 | 164 | 94 | 1 |
| 69 | 1,355 | 82 | 174 | 95 | 1 |
| 70 | 1,197 | 83 | 176 | 96 | 1 |
| 71 | 825 | 84 | 83 | 97 | 1 |
| 72 | 921 | 85 | 54 | 98 | 1 |
| 73 | 642 | 86 | 52 | 99 | 1 |
| 74 | 541 | 87 | 56 | 100 | 1 |
| 75 | 471 | 88 | 28 | 101 | 1 |
| 76 | 421 | 89 | 22 | — | |
| 77 | 347 | 90 | 18 | 11,589 | |
Table of Contents
THE purpose of “The New Zealand Consols Act, 1894,” is, by providing for an inscription of such Consols, to give further facilities for the safe investment of savings. Practically, it establishes another branch of the Government Savings-Bank, with extended power of investment. Under section 3 the Colonial Treasurer is authorised to receive by way of deposits from persons in the colony sums of money up to £500,000 [increased by £250,000 under provisions of section 2, Amendment Act, 1900]; but the amount deposited in any one year must not be more than £250,000. The currency of such deposits is not to exceed forty years. The present issue matures 1st February, 1910. The rate of interest must not exceed 4 per cent. The actual rate being paid is 3 1/2 per cent. per annum.
Post-office money-order offices throughout the colony are made use of to receive applications for inscription, and also for payment of the half-yearly interest on the amounts deposited. The Receivers are the Postmasters, and the Registrar under the Act is the Secretary to the Treasury, Wellington.
Regulations have been issued, under which every deposit of money for inscription is to be accompanied by an application according to the form given further on, which is to be signed by the applicant and countersigned by the Receiver (Postmaster) taking the deposit. The person paying the money receives an interim receipt pending official acknowledgment from the Registrar at Wellington. The receipt subsequently given by the Registrar to the Consols-holder is not a negotiable document, or of monetary value, beyond its being proof of the deposit for purposes of inscription. A holder of Consols can obtain from the Registrar, on application and payment of 5s., a certified copy of any entry in the register relating to his deposit.
There is provision for the transfer of Consols from one holder to another on application being made to the Registrar according to the second form given, and payment of 1s. fee.
In case an inscriber desires to make use of his deposit, or any portion of it, to the extent of £5, or a multiple of £5, he can obtain a Consols certificate which is payable to bearer, and is transferable by delivery. This certificate entitles the holder to receive interest half-yearly at the same rate as the original inscription, and also to payment of the principal sum on the due date.
The application for the certificate must be according to the form appended, and the fee payable is 1s. for every one hundred pounds or aliquot part thereof expressed in the certificate. There is also a fee at the above rate for inscribing the amount of a Consols certificate. The form of Consols certificate is also given.
Interest on Consols for which no certificate has been issued is payable by warrant, and such warrants are transferable by indorsement in the manner provided in the form.
Interest on Consols for which a certificate has been issued is payable to the bearer of the certificate on presentation at any post-office money-order office, or at the Treasury, Wellington (see the last form).
The Act provides for the deposit of money by minors, which may be acceptable to parents as encouraging habits of thrift in children.
As stated previously, the present issue of Consols has a currency to the 1st February, 1910, and carries interest at the rate of three pounds ten shillings for every one hundred pounds deposited; and an assured investment of moneys bearing a fair rate of interest for so long a term should secure, when well known, a large portion of the deposits of our thrifty population.
To the Registrar of Inscribed Consols,
Treasury, Wellington.
I [We],, of, having this day deposited at the sum of pounds shillings and pence, for investment in -per-cent. New Zealand Consols, hereby request that the same may be duly inscribed in the books of your office in the name of.
Signature of depositor:
Full address of depositor, together with name of nearest money-order office:
Dated at, this day of, 19.
Deposit duly received as above.
Signature of Receiver:.
IN consideration of the sum of, the receipt whereof is hereby acknowledged, I [we], of, do assign the sum of pounds shillings and pence, being my [our] interest or share in the New Zealand -per-cent. Inscribed Consols, under “The New Zealand Consols Act, 1894,” and all my [our] property, right, and interest in and to the same, and the dividends thereon, unto, of, his [their] executors administrators, or assigns, and the Registrar is hereby requested to transfer the same accordingly. The prescribed fee of is enclosed herewith.
Witness my [our] hand, this day of, 19 .
Witnessed by—Signature: .
Signature: .
Occupation: .
Address: .
I [We], of, do hereby accept the above Consols, and apply for the transfer thereof to me [us].
Signature: .
Witnessed by—
Signature: .
Place: .
Date:, 19 .
To the Registrar of Inscribed Consols,
Treasury, Wellington.
I [We], of, being the holder of New Zealand Inscribed Consols to the amount of pounds shillings and pence, do hereby make application for a Consols certificate in favour of bearer for the sum of pounds, to be issued to me [us] in accordance with and subject to the provisions contained in “The New Zealand Consols Act, 1894.” The prescribed fee of is enclosed herewith.
Witness—Signature: .
Signature:
Occupation
Address:
No. . £ .
THE bearer of this certificate will be entitled to payment of the sum of pounds sterling upon presentation hereof at the Treasury at Wellington, New Zealand, on the day of, 19, together with such interest, computed at the rate of sterling per centum per annum, as may be found to be unpaid on the before-mentioned date in accordance with the indorsements of interest-payments made hereon.
The principal and interest are a charge upon and shall be paid out of the accruing income of the Consolidated Fund of the colony.
Interest hereon at the rate of sterling per centum per annum is payable half-yearly, on the and in each year, at any post-office money-order office within the colony.
The amount of interest paid is to be indorsed on the back hereof by the person making such payment.
Dated at the office of the Registrar of Inscribed Consols, Wellington, 19 .
, Registrar.
Countersigned—
, Controller and Auditor-General.
Entered, folio .
[On the back, indorsements of the half-yearly dividends paid by the Postmaster are to be duly made.]
To the Treasury at Wellington, or to the Postmaster at any post-office money-order office throughout the colony.
PLEASE pay or order the sum of pounds shillings and pence, being interest for half-year due, 19, on £ -per-cent. New Zealand Consols.
£::., Registrar.
I hereby acknowledge to have received the above-mentioned sum in full payment of interest for half-year due as above.
Signature: .
Table of Contents
IT is generally admitted that there is no part of the British dominions where agriculture, in its widest sense, can be carried on with so much certainty and with such good results as in New Zealand. The range of latitude, extending as it does from 34° to 47° South, secures for the colony a diversity of climate which renders it suitable for all the products of subtropical and temperate zones, while an insular position protects it from the continuous and parching droughts which periodically inflict such terrible losses on the agriculturist and pastoralist of Australia and South America.
Again, the climate, although somewhat variable, never reaches the extremes of heat or cold. So genial, indeed, is it that most animals and plants, when first introduced to the colony, assume a vigour unknown to them before.
All the best forage-plants and grasses thrive most admirably, continuing to grow throughout the year with little intermission. Stock of every sort thrive and fatten rapidly on the pastures, coming to maturity at an early age without the aid of roots or condimental foods. All cereals flourish equally well, more especially Indian corn, which produces from fifty to eighty bushels per acre.
So full is the soil of plant-food that several continuous crops of potatoes or cereals may be taken with little apparent exhaustion. Wheat, oats, and barley thrive where the soil is not too rich; otherwise they produce enormous crops of straw, without a corresponding yield of corn. The tobacco-plant thrives well, as do also hops and sorghum, broom-corn, peanut, hemp, ramee or rhea (China grass), together with a large variety of economic plants, the growth of which will one day afford employment for a large population. In addition to these, all the British, Chinese, and Japanese fruits, with oranges, lemons, limes, olives, and vines (in the northern part), flourish abundantly, requiring but ordinary care. Potatoes are largely grown, and yield heavy crops.
Much of the country along the south-west and west coast is now taken up, and the primeval forest is fast disappearing before the settler's axe. For the most part, the soil is fertile, and the growth of grass and clover is extremely rapid and vigorous when sown on the surface after the felled timber has been destroyed by fire.
To the British husbandman it will seem almost incredible that the best pasture-grasses grow and thrive as they do with no other preparation than the ashes resulting from the burnt timber—no ploughing and no previous loosening of the soil—yet, in less than a year from the date of scattering the seed, this same land will fatten from five to six sheep per acre.
So rapidly are these fertile forest-lands being cleared and converted into pastures that the demand for stock (principally dairy) has greatly increased, and this demand must continue for a series of years before it is fully met.
Those who in the past have watched the progress of New Zealand, especially of the North Island, have always maintained that when the Maori difficulties and other impediments to settlement were over, the prosperity of the country would advance at a very rapid rate. The time has now come, and all that is required to expedite the coming prosperity is the settlement of our lands by a thrifty class of settlers.
There are millions of acres yet unoccupied, a great portion of which is of good quality, and only waiting the hand of man to make it carry, with very little cost, large herds of dairy stock, with flocks of long-wool and crossbred sheep. The west coast of the island is essentially a cattle-country. Considerable areas in the midland districts are adapted to long-wool sheep, as is also the country along the east coast. Much of the country may be described as being good sheep-land, a large portion of which is quite capable of carrying two sheep to the acre, and some of it as many as three or four.
If the North Island has a splendid inheritance in her forests, the Middle Island can boast of her magnificent plain-lands, rolling downs, and vast mountain ranges, all of which, to a greater or less degree, have already been made to contribute to the wealth of the colony.
The central portion of the Middle Island presented to the first-comers a vast plain, covered only with waving tussock-grass, offering little or no obstruction to the plough.
Travelling south, the country assumes a different character: easy, undulating downs, well watered, here and there interspersed with fertile plains, the greater portion admirably adapted for agriculture, and all of it suitable for pastoral purposes.
The climate of the Middle Island is not so warm in summer nor so mild in winter as that experienced in the North Island. However, as has already been stated, there are no extremes of heat or cold. Much more might be said in praise of this portion of the colony. It is deemed necessary to say so much in order that readers may better comprehend the comparative ease with which every kind of farming is carried on in New Zealand as compared with other countries less favourably situated.
The following resumé of the statistics, as published in the Gazette for the past season, is sufficient to indicate the trend of the agricultural and pastoral industries; fuller particulars will be found in the statistical portion of this book. It will be seen that there has been a material increase in the areas devoted to cereal crops and grasses throughout the colony.
The increase in cereals is as follows: Wheat, 30,893 acres; oats, 77,735 acres; barley, 1,407 acres. There is, however, a decrease in maize of 465 acres. The land laid down in pasture increased by 188,037 acres, but in turnips there were 5,678 acres less.
The stock statistics show that horses have increased by 7,341 head, and cattle by 98,879. Pigs have decreased, the probable explanation of this being that the demand for dairy stock has been so increasingly ....rge that the greater portion of the separated milk from the factories has been used for rearing calves.
The sheep returns for 1902 afford convincing evidence of the phenomenal productiveness of our flocks; for, notwithstanding the enormous drain upon these, to sustain the ever-increasing demand of the frozen-meat trade, it will be found that the increase over the previous returns was 109,628, the total number being 20,342,727, the highest total yet reached by the colony. But the figures for March, 1903, will show reduction on account of large requirements of live sheep for replenishing Australian flocks after losses by drought, and also for South Africa, besides a greatly increased export of frozen carcases. And later, losses by snowstorm will affect the figures.
Before the advent of the freezing-chamber, sheep-farming could only be carried on profitably on large areas, with large flocks, for the reason that wool and tallow were the only marketable products, the sale of fat sheep and lambs being confined to supplying the demand for local consumption. The new order has completely altered the condition of things from an agricultural point of view. Almost every farmer, small and large, now keeps his flock of breeding ewes for the production of lambs for freezing, thereby necessitating the growth of root and forage crops, and so bringing about a greatly improved style of farming throughout the colony when compared with the previous system of universal corn-growing.
The season of 1902–3 was remarkable for the lowness of temperature which for the most part prevailed throughout the colony during the summer months, notwithstanding which the cereal crops may fairly be described as phenomenal. Feed has been plentiful. The dairy industry has had a most successful season. The capacity of the frozen-meat works has been taxed to the utmost. New Zealand may well claim the premier position amongst British colonies as a field for agricultural settlement on small holdings. It is true that land is more plentiful and cheaper in Canada and South America; nevertheless, the favourable conditions upon which agricultural land may now be obtained under the land regulations more than compensate for the cheaper land in other countries, when we consider our immunity from droughts, together with our usually abundant rainfall and ever-verdant pastures. Referring to the season of 1902–3 “Ovis” writes,—
We have had a bountiful harvest, and yet, in view of the light stocks of old wheat at the end of the year, it is doubtful whether the wheat-crop will be much more than sufficient for our own wants. Any surplus that we have will not go very far towards making up the deficiency in Australia. The wheat-crop of New Zealand does not bulk up very largely in the world's annual production of that cereal. The largest crop we have ever grown would not amount to more than about 1/2 per cent. of the estimated total wheat-crop of the world. We are in the fortunate position of not being compelled to grow wheat on land of inferior quality. In general it is only the most fertile land that is sown to wheat, and this largely accounts for our high average yields. As things have turned out, there are, no doubt, many farmers who regret not having sown a larger breadth of wheat, but the fact of the wheat-crop being kept within such relatively narrow limits is sufficient proof that it has not in the past been found, on an average, a highly profitable crop, and it shows also that there are other branches of agricultural industry which have been found profitable. The special market which existed for oats during the two or three seasons past has led to considerable expansion in the growth of that crop, but indications at present seem to point in the direction of a glutted market. The oat-crop is one that is easily grown: it does not require such good land as wheat, nor does the land need the same special preparation, and it works in very conveniently with other farming operations. There is a large extent of grass which must be annually renewed, and there is a saving of tillage in laying the land down with a crop of oats. The oat-crop is an indispensable part of the economy of the farm, and its value is not wholly dependent on the selling price. It would appear from the statistics of the past two or three years, deducting the quantity actually exported from the quantity estimated to have been grown, that the present annual consumption of oats within the colony is something like 10,000,000 bushels when the price is at a figure which renders it unlikely that any considerable quantity of oats would be used for feeding sheep. When the price goes very low, when, as sometimes occurs, oats are at a price which leaves little or no margin of profit, then the home consumption goes up largely. This is especially the case when there happens to be a shortage of other feed. During the past two or three seasons the sheep-feeding boxes have been practically thrown aside, but next winter they will probably come into use again, and a not inconsiderable part of the oat-crop will find its way to the market in the shape of mutton and wool, and also dairy-produce. A country owning 20,000,000 sheep, 1,400,000 cattle (including nearly 400,000 dairy cows), and 300,000 horses, should, with mutton and dairy-produce at fairly good prices, have no difficulty in putting a few million bushels of oats to profitable use. As a matter of fact, farmers are quite willing to starve both their sheep and cattle in order to make an immediate profit on the oat-crop, but when the price of oats goes below paying-level, the stock begin to profit by it, and the farmer is not so badly off as he takes himself to be. There is the further consideration that grain sold in the bag is fertility parted with, but grain fed to the stock is in a large measure fertility conserved.
The unusual lateness of the harvest has had the effect of hampering sheep operations this season. The stubbles are full of undergrowth, but the crops were so long in ripening that, except in very early districts, feed of this description was not available for weaning purposes at the proper time. This, for a while, had considerable influence on the lamb market, but from this time forward there is every prospect of abundance of feed all over the country. The export of fat lambs this season will probably be exceptionally heavy. Last autumn it was thegeneral outcry that the lambs were not doing well, and yet, in comparison with the previous year, there was an increase in the export of lambs of about 400,000 carcases. But it is a question whether there was not some falling-off in quality. The average price on the Smithfield Market for New Zealand lamb for the year is given at 5d. per pound, which seems to show that the lamb trade must have been profitable to the country generally. It is to be remarked, however, that the import of River Plate lamb to the London market last year showed the substantial increase of over 100,000 carcases, though the quantity is still insignificant in comparison with the number received from New Zealand. Australia, notwithstanding the drought, was able to increase its output of fat lambs by upwards of a quarter of a million, a fact which seems rather surprising, though its decrease in mutton export was more than 600,000. There seems little likelihood of Australia ever becoming a serious competitor in the lamb market, though the sudden increase of the River Plate lamb trade may be an earnest of much larger numbers to follow. But it is not to be taken for granted that we are going to be driven out of the London market by the South American product. The New Zealand lamb trade has been a profitable one for years past, a fact which has, doubtless, not been overlooked by South American producers and exporters, and had there not been great natural difficulties in the way of fattening lambs in that country the South American lamb trade would long before now have assumed much greater dimensions. It is a fact well within the experience of New Zealand sheep-farmers that fattening lambs and fattening mature sheep are two different things. It is uphill work fattening lambs in districts where the climate, soil, and other conditions are such that they do not fatten well naturally, and it is also an undertaking of considerable relative expense. New Zealand has many advantages from a pastoral point of view, and yet the area which may be described as good lamb-fattening country is very limited. It may be remarked that last year the heaviest shipments of Australian lamb came on the London market during the first two months of the year, a time at which importations from this colony are exceptionally light. Unfortunately, New Zealand shipments come on the market in very irregular quantities, and the price fluctuates in accordance with the arrivals. In connection with this aspect of what is one of our most important industries, and which, with more judicious handling, might become still more valuable, the remarks of Mr. Gilbert Anderson at the annual meeting of the Christchurch Meat Company are well worth repeating: “The table of shipments shows the erratic manner in which the shipments are made, and how difficult it is for either the freezing companies or the shipping companies, or those who have to meet the daily supply in London, to cater for a business carried on in this erratic manner. Some day, no doubt, the farmers will be satisfied to leave the entire shipping in the hands of the freezing companies, so that regular supplies can be sent forward as the market requires them.”
The Canterbury Plains, the great wheat-growing district of the Middle Island, extend 150 miles north and south, running inland from the sea for forty miles, the whole forming an area of over 3,000,000 acres. A great portion of this vast plain is admirably adapted for the production of wheat, barley, and oats, and all the best cultivated grasses, the growing of which has been carried on extensively since the foundation of the colony. The total area under wheat for threshing in the colony for the season 1902–1903 was 194,355 acres (exclusive of 389 acres cut for chaff and 496 acres fed off with stock), of which 135,907 acres were grown in Canterbury, the average yield throughout the colony being 38·37 bushels per acre. The land is for the most part free from stones or impediments of any kind. Single-furrow ploughs are now rarely seen, double- and three-furrow ploughs being in general use, and an occasional steam plough. Three horses, occasionally four, with a man or a boy, can turn over three acres per day on the plains, at a cost of 5s. or 6s. per acre. A stroke of the disc or other harrow, followed by the seed-drill and light harrows, completes the operation of sowing.
Seed-sowing commences in May, and can be continued as weather permits through the winter, and in the heavy swamp-land (drained) on into September and even October. From 1 1/4 to 1 1/2 and 2 bushels of seed per acre are usually sown, the quantity increasing as the season advances.
Otago and Southland districts excel in the production of oats, which is their principal cereal crop. The total area sown for grain under this cereal for the season 1902–1903 was 483,659 acres, being an increase as compared with the previous season of 77,735 acres.
The yield of oats in Otago and Southland varies from 40 to 80 bushels per acre, the cost of production being about the same as wheat—viz., £2 per acre when grown from grass-land, and £1 10s. from stubble.
Malting barley, of very superior quality, is grown in Nelson and Marlborough, where the soil and climate appear to be particularly adapted to its culture.
The growing of this cereal (barley) for malting purposes requires more attention than it has yet received in this colony. It is claimed for this crop that it will show a better result than wheat, for the following reasons: (1) It is less exhaustive to the soil; (2) it gives an average yield of from 10 per cent. to 20 per cent. more than wheat; (3) the growing crop in favourable seasons can be fed off twice, or even three times, to the advantage of the subsequent yield of grain. Land of a light and calcareous nature, but unsuitable for wheat, will give a barley thin in the skin, and particularly suited for malting purposes. Barley is not a difficult crop to raise, but there are certain points that need careful attention, which, if neglected, would probably result in the production of an inferior sample, which would hardly pay for growing.
Potatoes: Potatoes are largely grown throughout New Zealand. On suitable soils very heavy crops are raised, it being no uncommon thing to dig from 8 to 10 and 15 tons per acre, although the general average is much lower, for the reason that unsuitable land is frequently devoted to this crop. The area under potatoes in 1902–1903 was 31,408 acres, as against 31,259 acres grown in 1902. The bulk of the crop is planted without manure, but, where used, bonedust, superphosphate, blood-manure, or animal guano (which may be procured of first quality from the local manure manufactories), from 1 cwt. to 2 cwt. per acre, is applied with good results.
The potato is, however, an expensive crop to grow, costing from £5 to £6 per acre, and it is perhaps the most precarious of all crops, being materially affected by drought, but more particularly so by early and late frosts. The crop in Canterbury for the past season, 1903, was damaged by a frost in April to the extent of one-fourth of the expected yield. Potato growers admit that £1 10s. per ton off the fork will pay better than £2 after being stored for any time.
Land for potatoes is usually broken out of grass, skim-ploughed in autumn, ploughed deeply in spring, and thoroughly tilled; or potatoes may be grown in drills opened and closed with a double-furrow plough. The seed—15 cwt. per acre—is then ploughed in under every third furrow, the after-culture consisting of harrowing just as the crop is appearing over ground (by this means myriads of seedling weeds are destroyed); drill-grubbing, hoeing, horse-hoeing, and earthing-up being the subsequent operations. Heavy crops of wheat, oats, barley, beans, or peas can always be relied upon after potatoes, season permitting.
Turnips:* The turnip crop of this season has been an indifferent one. On the plains of Canterbury the want of sufficient warmth and moisture at the critical period of turnip growth had an injurious effect on thousands of acres. In the southern portion of the Island the crop will be sufficient for the requirements of stock-owners. The area under this crop for the season 1902–1903 was 392,830 acres.
Rape is largely grown as sheep-feed, and may be sown either in early spring or immediately after harvest, the stubble being skim-ploughed or broken up with the spring-tined cultivator. This crop is invaluable in the early spring, and may be fed-off in time for oats or barley. Dairy-cattle, however, should not be fed on rape, as doing so destroys the flavour of the milk. This fodder plant ranks next in value to the turnip for fattening sheep and lambs, and forms a most valuable adjunct to that crop.
Mangolds and Carrots are largely grown in some districts. They cost more money per acre than turnips to produce, as they must be hand-hoed; nor are they so suitable a crop for cleaning the land. Turnip-sowing does not commence till November or December, affording ample time for the destruction of seedling weeds; this important opportunity is largely lost in the culture of the mangold, which is usually sown in October. Mangolds are, however, an invaluable crop on a stock-farm, as they do not reach their primest condition until the turnip-supply is exhausted, usually in August. From 30 to 60 tons per acre is not an uncommon yield of these roots, often without the aid of manure, on rich swamp land.
Carrots are also a valuable crop, especially for horses; on sandy loams the yield reaches 15 to 20 tons per acre. Carrots impart a pleasant flavour to butter, and should be largely grown for dairy stock.
*Valuable information on the growing of this crop will be found under this heading in the Year-book for 1901, page 478.
Clover: Saving clover for seed in favourable seasons is a lucrative industry, adding materially to the farmers’ income. Clover is sown with a spring crop, usually of corn, lightly grazed in the following autumn, and then reserved for a crop of hay, which, according to the season, yields from 2 to 3 tons per acre when cut in November or early in December. Most farmers prefer feeding off with sheep in preference to mowing for hay. The after-growth is then allowed to flower and seed, which it does very freely. Thousands of humble-bees may be seen in the clover-fields during the months of January, February, and March. The seed ripens in March, and is then cut and dried, and threshed out by machines known as clover-shellers. An acre of clover may yield in hay and seed from £8 to £10. It must, however, be stated that, while a good crop of clover-seed is a most lucrative one, it is nevertheless a most precarious one. Owing to the lateness of the season of ripening, it sometimes happens that the fertilisation is imperfect, resulting in a majority of barren heads. This has given rise to a controversy as to whether the proper bee has been introduced. The point was referred to the late Miss Ormerod, the English entomologist, who settled the question in the affirmative.
White and alsike clover are now grown in considerable quantities. White clover yields enormously: as much as 300 lb. of alsike seed has been obtained per acre. These clovers are not so dependent on the action of the humble-bee for their fertilisation. They mature earlier, and are more easily threshed and cleaned than cow-grass or clover.
Grass-seed Saving: All the most valuable British grasses flourish throughout New Zealand. Cocksfoot has been for many years a staple product of Banks Peninsula (Akaroa County), where the soil for the most part consists of decomposed volcanic rocks and vegetable mould. Large quantities of this seed are now raised in the North Island and in many other parts of the colony as well. The seed is of the finest description, frequently weighing 20 lb. to the bushel, 12 lb. being a standard bushel. Cocksfoot thrives on a very wide range of soil, from the richest to the poorest, preferring, of course, the former. It may be found on the dry stony plains of the interior, green and healthy, when the surrounding herbage, introduced or indigenous, has given in to the heat of the summer sun.
Growing ryegrass for seed is also an important industry. The seed is usually gathered by stripping; sometimes the grass is cut and tied and afterwards threshed by machinery. The average yield is from 15 to 20 bushels per acre, weighing from 25 lb. to 32 lb. per bushel, 20 lb. being the standard weight. A common practice is to graze the land till midsummer; to take the stock off for a few weeks, and then to run the stripper over the ground. By this primitive method 10 bushels per acre are sometimes secured, being of the finest quality. Ryegrass-seed is usually in good demand; the price varies according to the season; the usual price, however, is from 2s. 6d. to 3s. 6d. and 4s. per bushel.
Many of the indigenous grasses of New Zealand are possessed of considerable feeding value, but, unfortunately, few of them will stand too close feeding. The action of fire is especially injurious to most of them. Of recent years a great deal is being written about Danthonia semiannularis (one of the native oat-grasses) as a grass particularly adapted to some of the poorer soils in the North Island, where it is said to thrive admirably; it is also said to be able to resist the action of occasional grass-fires. There are many varieties of Danthonias, from the giant, coarse-growing snow-grass or oat-grass, to the fine-leaved varieties found in almost all the natural permanent pastures.
Small Seeds: New Zealand, from the nature of her soil and climate, offers a fine field for growing all kinds of farm and garden seeds. This circumstance has already attracted the attention of some of the larger seed-merchants of Great Britain, whose agents occasionally visit the colony with a view to inducing farmers and others to grow certain kinds of seeds. The industry is peculiarly adapted to small holdings, and well suited to young persons, the work being light and of an interesting character. Ready sale can be found for carefully-grown and carefully-cleaned garden seeds.
Pulse: Peas and beans are largely grown for pig and horse feed, and for export; they form an excellent preparation for wheat. An extensive trade in peas of a certain description is done in the manufacturing towns of Great Britain; and efforts are now being made to secure a share of this trade for the colony by producing peas suitable for splitting for human food. The business should prove a most remunerative one. Thirty bushels of peas per acre are considered a fair crop, while 40 to 70 bushels of beans are often secured. As showing the extraordinary fertility of some of the lands in the Canterbury District, it may be mentioned that beans and wheat have been grown alternately on Kaiapoi Island for thirty years without any apparent diminution of yield, the crops of recent years being as abundant as those grown years ago; 40 to 50 bushels of wheat and 60 to 70 bushels of beans being the usual return per acre.
Cape Barley and Winter Oats: The demand for early spring feed has resulted in the growing of these plants for forage. Their extreme hardiness renders them well adapted for autumn sowing. If sown in March they are ready for feeding-off in May; they may be fed off again in July, and on till the beginning of October, when, if allowed to run to seed, they will produce 40 to 60 bushels per acre, or they may be ploughed in for turnips.
Tares are also grown, but not so largely as they deserve to be, especially for dairy stock. Mixed with oats, barley, or rye, they are excellent milk-producers; and when grown luxuriantly they destroy all kinds of weeds, and leave the land in fine condition for a spring corn-crop.
Lucerne: This permanent fodder-plant thrives admirably in most parts of New Zealand, yielding three to five cuttings in the year; and, if properly cultivated and well attended to, particularly in its early stage of growth, it will continue to yield liberal cuttings for seven or eight years, or even longer. This is a most excellent crop for the small or large farmer, furnishing, as it does, an abundant supply of succulent fodder, in deeply-cultivated soils, during the drier months of midsummer, as well as in the early spring. All farm animals are partial to lucerne; pigs thrive admirably upon it. No farm should be without a well cultivated plot of this plant. In deeply-cultivated land lucerne will yield several cuttings during the season, no matter how hot and dry the weather may be. It is this drought-resisting quality which renders lucerne such a valuable fodder plant in Queensland and New South Wales, where it is extensively grown for pasture purposes.
When comparing the cost of working a farm in England with one of the same size in the colony, several points have to be taken into account, such as the climate, the soil, labour, and machinery. In Australasia wages are higher than in Britain; as a set-off against this, New Zealand can claim, firstly, that there are more fine working days in the year, that the fields are much larger, that the latest improvements in machinery have been introduced, that the soil is more easily worked, and that the genial nature of the climate renders it unnecessary to house stock during the winter months, at least in the North Island, thus saving the cost of attendance; secondly, that farming operations may be carried on continuously throughout the ploughing and sowing season; and, thirdly, that the paddocks are so large, and usually so level, that the double- and treble-furrow plough may be worked by one man or youth with three horses, thus equalising the cost of labour, as we have shown that one man, or even a boy, will be quite equal to two men or boys in the Old Country, so that after all the difference in the rate of wages is not so great as might appear at first sight.
The hay-crop is simply cut one day, raked into windrows the next, and in a couple more it is ready for stacking.
Wheat is cut and tied by machinery, the stooks requiring no capping. It is frequently threshed out of the stook in favourable seasons, thereby saving the cost of stacking and thatching; but this method, although very general, is not recommended except in hot or dry seasons. When stacked, the stacks are rarely thatched, except, perhaps, on the weather side. This is a wise precaution, the neglect of which sometimes entails serious loss.
The manure bill, which is such a heavy item of annual expenditure with the British farmer, presses as yet very lightly on the farmers of the colony. It is, however, a notable fact that the use of fertilisers is becoming more general; 1 cwt. to 1 1/2 cwt. of superphosphates per acre is used with the turnip and other root-crops, for the purpose of forcing the young plant into the rough leaf, when it will be out of one danger—the turnip-fly. It will therefore be seen that the colonial farmer has many advantages over the farmer of the Old Country.
It may also be pointed out that the application of one or two hundredweight per acre of superphosphate of lime produces better results in colonial soils than double the quantity would do in England, showing clearly that the natural richness of colonial soils is not yet exhausted.
Cattle: The total number of cattle in the colony for 1902–1903 was 1,460,663, an increase of 98,879 over the previous year.
Horses: The number of horses in the colony for 1902–1903 was 287,419.
Sheep: The returns made up to the 30th April, 1903, show a falling off of 1,340,678. It must not, however, be assumed that this shortage arises from any diminution in the power of production in the colony in this direction; but rather to the continually increasing export of maiden ewe lambs, regardless of the requirements for the up-keeping of the breeding flocks of the colony. As will be seen by the following figures, the export of lambs for the year ended 31st March, 1903, amounted to 2,104,544, as against 1,684,091 in 1902, or an increased output of 420,453. The export of mutton shows a large increase as well—viz., 866,371 carcases, or a total increase for the year of mutton and lamb of 1,286,824. The total exports for the year ending 31st March amounted to 2,531,993 sheep and 2,104,544 lambs, a total of 4,636,537, as against 3,349,713 in 1902. Again, the number of live sheep exported in 1901–1902 was only 3,579, as compared with 48,447 in 1902–1903. In addition to these causes it must be remembered that the lambing in certain districts was most unsatisfactory. It will therefore be seen that the shortage of sheep is principally due to the indiscriminate slaughter for the freezing-works, induced by the extremely remunerative prices offered for sheep and lambs suitable for the purpose.
The returns made up to the 30th April, 1903, show the distribution of the flocks of the colony to be as follows: In the North Island, 9,512,527; and in the South Island, 9,489,522: total, 19,002,049.
Sheep: New Zealand has proved itself admirably adapted for the breeding of all classes of sheep, from the fine-combing merino to the strongest type of Lincoln. The merino occupies and thrives on the wild lands of the colony, from the snow-line to the border of the plains, as well as on the drier portions of the plains. The merino ewe furnishes the foundation for all the crossbred varieties. On the rich moist soils the Lincoln and Romney Marsh sheep flourish, while the finer English and Border Leicesters and Downs sheep occupy the drier lands.
Crossbred Sheep: Those bred from merino ewes and longwool rams, or from crossbred ewes with Down rams, are the most suitable for the frozen-meat trade, and are known as “freezers.”
The dapper little Southdown flourishes wherever crossbreds thrive. Their more ponderous cousins, the Shropshire and Hampshire Downs, have their admirers, especially the Shropshire, which are largely used for crossing, with a view to producing early-maturing lambs. English Leicesters are also much sought after for this purpose, particularly in the Middle Island, where “prime Canterbury” mutton is produced.
Shearing commences in September, and is continued till January. The usual price per hundred is from 17s. 6d. to 20s. Shearing-machines are not so largely used as was expected when first introduced.
The average clips for the various breeds of sheep are approximately: Merino, from 4 lb. to 7 lb.; quarter-breds, about 6 1/2 lb.; half-breds, 7 1/2 lb.; three-quarter-breds, 8 1/2 lb.; Leicester, 10 1/2 lb.; Lincoln, 11 lb. Of course, very much larger clips are obtained from special flocks, as much as 25 lb. to 30 lb. per sheep; but the above figures represent general averages.
The staple of New Zealand wool, especially the long-wool and cross-bred, is remarkable for its freedom from breaks and other imperfections incidental to countries subject to long droughts and scarcity of feed.
The most profitable sheep for New Zealand is that which combines the best fleece and the most suitable carcase for freezing purposes, together with early maturity. This is the class of sheep which some sheep-breeders have set themselves to produce. Whether such an animal, having fixity of type, can be evolved, remains to be proved; so much depends on the feed, situation, and soil.
The capability of New Zealand for producing mutton has not yet reached its limit. When the frozen-meat trade was first seriously considered, an assertion to the effect that the colony could soon find 1,000,000 sheep per annum for freezing without impairing the breeding-flocks was treated as highly chimerical by sheep-breeders of long experience. The annual output of sheep and lambs is now over four millions and a half. But, while congratulating the colony on the rapid development of the frozen-meat trade, it must be borne in mind that in Argentina strenuous efforts are being made to secure a share of the frozen-mutton trade carried on by New Zealand with Great Britain; Australia is also striving hard to share the trade with New Zealand. It must be admitted that with cheaper land, and a closer proximity to the markets of the world, Argentina will necessarily be a very formidable rival to Australasia. The only way to keep command of the market is to ship nothing but first quality graded mutton and lamb.
“The New Zealand Flock-book,” published in 1895, is now thoroughly established, and is of great value to the owners of pure pedigree flocks. The Royal Agricultural Society of Victoria also publishes a Flock-book for British breeds of sheep. This is a step in the right direction, as flock-masters in South America demand a certificate to the effect that the cattle and sheep purchased by them are duly registered in an authorised Herd- or Flock-book. The value of these books is now so fully recognised that all the distinctive breeds of sheep in Britain and elsewhere have their recognised registers.
The climate of New Zealand is admirably adapted for the breeding and rearing of horses of all kinds, especially draught-horses. Indeed it would be difficult to find better Clydesdale horses than those bred on the limestone soils of Oamaru and elsewhere. Some of the best blue-blood of this breed has from time to time been imported from Scotland, with the result that the breed is now well established in the colony.
The light-horse stock of the colony has risen into note through the production of animals which have rendered themselves famous on the colonial turf. The demand for horses suitable for remounts for the cavalry service in India is a continuous one, affording a ready market for the proper stamp of animal; shipments are periodically made to that country with varying results.
With a view to bringing the use of pure-bred sires within the reach of small selectors in the outlying blocks the Government have imported a few first-class horses of the most approved types, which cannot fail to have a beneficial effect on the stock of the country. The Canterbury Agricultural and Pastoral Association publish a Draught-horse Stud-book, which is largely used by breeders of that class of horse.
The colony possesses all the best strains of blood, and this is evidenced by the superior class of cattle to be met with throughout the settled districts, especially in the show yards. There are now four herd-books published in the colony—viz., the “Shorthorn,” “Other Breeds,” published by the Canterbury Agricultural and Pastoral Association, the “Hereford Herd-book,” published by the Hereford breeders, and the “Jersey Herd-book,” published in Palmerston North. The value of properly kept herd-books is now fully recognised. Purchasers of animals for export or otherwise now demand that they shall be duly registered in some authorised Herd-book as a guarantee of pure breed. New Zealand is free from many of the diseases so disastrous to horned stock in other countries. It is said that Iceland is the only other spot on the earth which enjoys a similar immunity. With a view to maintaining this enviable position, the Government have prohibited vessels carrying live-stock from infected colonies touching at any of the ports of New Zealand except under certain conditions. This action is deemed necessary, owing to the prevalence of pleuro-pneumonia in Australia.
The breeding of first-class dairy stock offers a field for profitable investment. Milking-cattle now command a high price, and will continue to do so, owing to the increasing development of the dairy industry. There are now 428,773 cows kept exclusively for dairy purposes. The rearing of well - bred heifer calves will repay all the time and trouble bestowed thereon. Separated milk, although relieved of its butter-fat, loses little of its feeding value; the addition of a little linseed meal will restore the fatty constituents, which, however, are not the most valuable for feeding purposes. Ground oats, wheat, or barley added to the linseed mucilage will render calves fit for the butcher in a comparatively short time. An acre or so of European flax should be grown upon every farm where stock-rearing is carried on. The fattening of calves for export has not yet been attempted in the colony, although there is a very large and lucrative market for veal calves in London, ranging from £4 to £6 and £7 per head. Much has still to be done in the way of improving the dairy stock of the colony. The yield of milk from fairly good milking-cattle is approximately 500 gal. per annum, although 700 gal. per head are frequently obtained from selected herds. The average quantity of milk obtained will no doubt be increased as more attention is paid to breeding, and proper feeding. The general management and feeding of dairy stock is a question demanding every attention. Kind treatment is essential to success; clean pastures, clear running water, and grasses of the best quality are all factors fully recognised wherever dairying is successfully carried out; and, last but not least, warmth and shelter during the cold wet months of winter.
The average yield of butter from milk passed through the separator is 1 lb. for every 2 1/2 gal. of milk of 10 1/2 lb.; so that the average cow produces annually 200 lb. of butter, or 500 lb. of cheese, which, estimated at 4 1/2d. per pound, will be worth about as much as the butter.
This industry continues to flourish throughout New Zealand. The export of butter for the year ended 31st March, 1903, reached 263,196 cwt., valued at £1,268,759; and of cheese, 74,611 cwt., value £181,604: or a total of £1,450,363. This industry is capable of much greater expansion without even increasing the number of milch cattle, but by improvement in breeding. The Government continues to spend large sums of money in teaching the art of butter-making, the proper method of packing, and shipping. Till recently nothing was done in the way of encouraging the breeding of better strains of cattle for the production of milk of superior quality as well as quantity. The Government, recognising the importance of this matter, have imported a few first-class sires for the use of those dairy farmers who are not in a position to secure the best bulls for their purpose. The service of these bulls has been fixed at a nominal scale, and is only available for selected animals. It will thus be seen that dairy farming has now developed into one of the settled industries of the colony. Graders are employed examining all butter and cheese for export, who brand each packet with its proper quality. Factory-owners now recognise the fact that it is folly to pay freight on any but the best quality; and this remark applies to grain and meat as well. We have to compete against Canada, the United States, Denmark, Australia, and the Argentine. New Zealand dairymen must, therefore, endeavour to raise dairy cattle which will yield the maximum of milk of the best quality; in fact, nothing but intense farming will pay in the future, applied to every branch.
It is interesting and instructive to note the progress of our dairy industry—judging from the exports of butter and cheese for the year ending March, 1903—viz., butter, 13,160 tons; cheese, 3,730 tons: showing an increase in butter of 2,185 tons. Cheese, however, shows a decrease of 593 tons. This falling-off, however, is accounted for by the fact that several factories have been closed and turned into creameries in connection with butter factories, and for the supply of milk for condensing. Compared with the frozen-meat industry it is also interesting to note that the total value of the dairy produce exported for the past year amounted to £1,450,363, as against £1,173,216 for the year ended 31st March, 1902. The total value of the dairy produce exported in 1895 amounted to only £378,570. The value of the frozen meat for the same period was £1,262,711. It is therefore very probable that the former industry will equal—if it does not excel—the latter in value in a very few years.
Side by side with this rapidly developing industry, we have to bear in mind the fact that the Argentina is also increasing its export of butter and meat to the British market. Statistics show that while in 1900 her export of butter was only 102 tons, in 1902 it had increased to 3,018 tons, 562 tons of which was sent to South Africa.
The complete sterilising of milk to destroy the germs of diseases like tuberculosis is a wise precaution. The operation consists of heating milk up to a certain temperature, and cooling it rapidly, a process which has been found to destroy the bacillus of tuberculosis known to be present in the milk of affected cattle. The Government veterinaries are employed examining the cattle, and a large number are annually tested with tuberculin, and when found affected they are destroyed, compensation being allowed.
These useful adjuncts to the dairy should hold a much more important position on all dairy farms in New Zealand than they do at present. The last statistics show that there has been a considerable falling-off in numbers. The favourite breed in New Zealand is the improved Berkshire. The large and small breeds of White Yorkshire are also to be met with, but are not so generally approved of as the black pigs. The Tamworth pig has its admirers amongst pig-breeders, as they answer admirably for crossing with black pigs. They produce good bacon pigs, making more lean meat and longer sides than the pure Berkshires. Pigs require no better attention than a good grass paddock, with a liberal supply of roots, and a little unthreshed pea-haulm for a few weeks before killing, with plenty of water, and shelter from the sun during the warmest summer months.
The breeding, rearing, and fattening of pigs is a source of wealth which is capable of considerable expansion. Several plants for the mild curing of bacon have been set up at the various freezing-factories, and by private persons and firms. The establishment of properly appointed pig-farms is a somewhat costly undertaking, as all the fences must be pig-proof. Doubtless this consideration has had a deterrent effect upon some, while others find the rearing of young stock for the dairy and the breeding of lambs a sufficiently profitable undertaking, besides causing less trouble.
The stock of pigs in the colony is estimated at 193,740. There is room for an enormous extension of this industry.
The efforts being made by the Government to foster this industry are gradually producing the hoped-for results. The distribution of a better class of poultry is showing good results already. Farmers are beginning to see that their poultry-yard should form no mean auxiliary to the general return from the products of the farm. With such a climate as we have, there need be no difficulty in raising hundreds where dozens are now produced. The Department is doing much to foster this industry, with what success may be gathered from the following statement of facts: During the last financial year 75,000 birds were killed, dressed, and graded at the Government depots, the majority of them for the South African market, as against 38,000 for the year ending 31st March, 1902. In addition to the poultry which passed through the depots during the last financial year, several thousand birds were exported without being graded by the Government experts. The Agricultural Department intends to seek legislation to prevent the export of any poultry unless it has been graded by a Government official. This is a step in the right direction.
From the North Cape to the Bluff Hill, in the extreme south of the Middle Island, the climate and soil are, for the most part, eminently adapted for the growth of a large variety of fruits. Generally speaking, pears, plums, quinces, apricots, figs, walnuts, cherries, gooseberries, currants, strawberries, and raspberries grow luxuriantly, producing abundant crops of fruit. In the Auckland District, oranges, lemons, and limes flourish: many groves are now bearing, and afford light and pleasant employment to a large number of persons. This employment will go on increasing as the plantations throughout the colony become older. The olive flourishes in the North Island; bearing heavy crops, and the manufacture of oil will assume important dimensions at no distant date.
Vine-growing is also carried on with tolerable success in many districts; tons of fruit grown under glass are sold in the Auckland markets annually. Signor Bragato, an Italian wine expert, has given it as his opinion that there are numerous localities in both Islands suited for growing vines for the manufacture of wine.
Away in the far north the banana grows and ripens its fruit, but it is not thought that it will ever enter into successful competition with those grown and imported at so cheap a rate from the Pacific Islands.
Extensive orchards of apples have existed in Auckland for many years, and are still capable of producing an abundance of fruit, if kept free from codlin-moth and other pests. Orchard-planting is progressing, and must one day be a very important industry. Central Otago will also become a large fruit-producing district, being free from violent and scorching north-west winds. The total area under orchards in the colony is 27,191 acres, including 705 acres of vineyard.
The manufacture of cider is already assuming considerable dimensions, opening up a ready market for surplus fruit. The colonial-made article is rapidly coming into favour with the general public.
The drying of fruit has been fostered by the authorities, who sent an expert through some of the apple-growing districts, giving practical lessons in the art of artificial fruit-drying. A great deal more might also be done in bottling fruits, and the manufacture of fruit-wine, if only for home consumption. The manufacture of jam is successfully carried on; there is, however, plenty of room for further developments in this direction.
Those who have watched the course of events in other countries, so far as they affect the agricultural interests of New Zealand, have come to the conclusion that New Zealand will have to pay great attention to the quality of her agricultural exports. Our farmers cannot hope to compete with such countries as Australia and South America, where land is so much cheaper, and where mutton and beef of good quality can be produced; for cheap meat these must command the markets of the world. Happily for New Zealand, our climate and pastures are such that we can not only produce mutton equal to the finest English or Scotch, but we can produce more per acre than can be done in Australia. Our dairy-produce is now second to none, which is largely due to the system of manufacture and Government grading.
Owing to her humid climate and fertile soil New Zealand is peculiarly well adapted for small holdings. Men of slender means can easily make homes for themselves and their families, always provided they know something of the work they undertake, and are, with their families, willing to work hard and live frugally for a few years. It is quite possible for a man with a few cows and pigs, together with poultry and bees, to make a good living, as markets for these products are now being opened up in England and elsewhere; there is also a good local market if the goods are properly prepared, and a continuous demand for the supply of coastal and ocean-going steamers. The facilities now given for obtaining land and money at reasonable rates offer great inducements to persons to settle upon the land. This is amply illustrated at Cheviot, where a fine estate has been cut up into moderate-sized farms, and let to farmers on perpetual lease at a rental representing 4 percent, on the purchase-money. Prosperous homes have sprung up, and tree-planting is being carried on by some of the settlers, which is an earnest of the stability of the settlement.
Table of Contents
ALMOST every country in the world has one or two trees that are very largely relied on for timber-supply, both for home use as well as for export. In New Zealand the kauri and rimu are used much more than any other trees. In Northern Europe the Scotch pine and larch are the mainstay, spruce occupying almost the same position there as white-pine does here. In Greece and Southern Europe Pinus laricio supplies large quantities of timber. In the Eastern States of America and Canada, white-pine (Pinus strobus) is the chief timber tree, with spruce taking second place. The Southern States of the Union rely on Pinus australis, known in the market as Georgia pitch-pine, with Pinus mitis taking second place as the soft-leaved pine. In the mining districts of the interior Pinus ponderosa and its varieties is the great lumber tree, while in California and British Columbia several trees grow in sufficient quantity and size to be largely used as sawn timber; but even here two trees stand out beyond the rest as sources of supply—in California, the redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), and further north the Oregon pine (Abies douglasii), are each converted into sawn timber in enormous quantities, and exported to the ends of the earth. And so I might go on mentioning the spruce of Norway, the stringy-bark gum of Tasmania, the red-gum of Victoria, and the cedar of India; but as all those, and many more species of trees, have been introduced into New Zealand, our chief inquiry will be which of the many trees introduced will be likely to prove the most profitable to plant here. Nothing can be more important than this, for, if useless trees are planted, the loss to the individual and the colony will be enormous. Many grave mistakes in planting have been made, and are still being made. For the early mistakes there are good excuses, but for the blunders that are every year made now no excuse is possible.
For those who take an interest in forestry it is very pleasing to find that the Forest Department of New Zealand is every year increasing the number of trees raised and planted, and it seems hardly possible to conceive that any labour union will complain of the prisoners being employed in planting trees on the poor pumice lands of the interior of the North Island. The possibilities of the pumice lands for growing timber are astonishing. I have been informed that some larch planted last year had made a growth of 3 ft. during the year, and that in a plantation made five years ago larch trees were to be found 25 ft. high. This growth is wonderful, and proves without doubt that the pumice plains, which have always been spoken of as being perfectly useless, will yet become a very valuable asset to the country if planted with suitable trees, and where the larch will grow no better tree can be planted, its good qualities being well known; and it has this advantage, that seeds can be procured from Europe at a low rate, and the plants, when raised, can be removed with the greatest ease and success. Mr Matthews, State Forester, tells me that he has imported 6 cwt. of larch-seed this year, and if, as we are told, there are 68,000 seeds in a pound, it means that there are over four millions of seeds of this one tree alone to be sown in the spring. I suppose not more than fifty per cent. will grow, but even then it means millions of trees to plant out. It is only in the very best places in Canterbury that the larch will grow, and it cannot be recommended for general planting, several other trees promising better results.
For planting on the Canterbury Plains, Pinus laricio, Pinus ponderosa, and the Austrian pine will be found far more suitable than the larch. Of the other great timber-producing trees of the world the Scotch pine may be dismissed as being of very little value in any part of New Zealand. The same may be said of the Norway spruce, a good specimen being very rare, and even where it will grow other trees of more value should always be planted. Nor does the Pinus strobus, the tree so much lauded in the Eastern States of America and Canada as the tree of trees, promise much in New Zealand. Now and again a fairly good specimen may be seen, but generally they have a very thin and shabby appearance. Pinus australis and Pinus mitis, valuable trees in the Southern States of America, grow very slowly, and show no promise of being of any value here for their timber; but Pinus australis may be grown for its distinct and peculiar appearance. Sequoia sempervirens, the redwood of California, will probably be found to be a profitable tree in some parts of New Zealand, especially where the larch succeeds; there I think that the redwood will grow, and where it will grow it is very desirable that it should be largely planted, as it is not only ornamental, but the wood is one of the most useful, and is now imported for certain special purposes, as for window-sashes, proving the most suitable of all woods. The tree is a very rapid grower, but is very subject to lose its leading shoot. There is a very fine specimen standing by the monkey-puzzle in the Public Gardens, Christchurch, which has been seeding freely for many years. The Oregon pine (Abies douglasii), also known as Pseudotsuga douglasii, is a grand tree, and will succeed over a much wider range of climate than the redwood, as good specimens may be seen in every provincial district of New Zealand.
The opinion seems to be widely held that the indigenous trees cannot be propagated and grown as other trees are, but it is not so, as totara, kauri, and all the other native timber trees can be grown in the nurseries with ease; but it is very doubtful whether a timber-supply could be secured from them so economically as from species that have been introduced from other countries, and yet it is to be hoped that our Chief Forester will make plantations of each of our best timber trees, and give them a trial. As the kauri lives in Christchurch, it might be tried over a much wider range than it now occupies in its native state with good prospect of success, as, for instance, all down the west coast of the North Island. Totara, one of the most durable woods known, can be grown almost everywhere, and as it grows readily from cuttings, and is quite ornamental, it should be seen much oftener than it is. I have succeeded in raising a large number from seed gathered in Nelson District. The rimu is more difficult to grow than either kauri or totara, and I have never yet been able to get any seeds. Plants taken from the bush, if planted in a cool sheltered place, will succeed, and make lovely specimen trees, but there seems little probability of its ever succeeding as a profitable forest tree in cultivation. White-pine seeds freely, and is easy to grow in a damp place, but under the most favourable circumstances can hardly be called ornamental, and the wood is of little value except for such purposes as our fast-growing trees, such as Pinus insignis, would more quickly supply. On the whole, as introduced grasses have to a large extent supplanted the native grasses, so it seems likely that the introduced trees will be found to grow more successfully than the indigenous ones do under cultivation.
In planting for profit there are other considerations to be thought of than which tree will grow best in a particular locality. For instance, larch is generally held to be superior to anything else for mine-props; consequently if larch will grow, although not quite so well as some other good tree, in the neighbourhood of a mining district, the larch would most likely prove the more profitable tree, since it would find a market on the spot.
There are certain valuable trees which have proved themselves everywhere of good constitution, and it appears to me that these are the trees which should he planted largely in New Zealand; other trees more particular about soil and climate may be found’ to do equally well, but in the meantime it will be safer to plant those trees that have everywhere proved successful, and have given the same promise of success here. Among these I may mention the three cedars, Cedrus atlantica, Cedrus deodara, Cedrus libani, and Picca pinsapo, among the more ornamental timber trees, and Pinus laricio and Pinus ponderosa as the most valuable timber trees which seem to thrive everywhere. Of Pinus laricio a standard American author says, after giving an account of its vigorous growth, “As it is a native of warm climates many persons suppose it will prove too tender for this section, but so far as we have been able to ascertain it has given entire satisfaction. The long wavy leaves are of a bright green colour, and the perfect shape of them has always produced a favourable impression with us, and we wish it were more extensively known.” The wood is quite valuable for lumber, being long-grained, white, easily worked, and, according to some authorities, very durable. English authors are all equally emphatic with respect to the value of this tree. Webster says, “Whether in an ornamental or economic sense this must be considered as one of if not the most valuable species that is cultivated in this country.” The author of “Pinacæ” says of the Corsican pine, “All thing considered, it is one of the most valuable and generally useful species of the genus Pinus which has yet been planted in the British Isles, being thoroughly hardy, sound in constitution, of tolerably large dimensions, and of a very rapid and regular growth; and will not only grow, but will produce both quantity and quality of timber equal to any, and superior to many, of its congeners, when grown under the same conditions.” Many other authorities might be quoted as to the value of this tree in other parts of the world, and our own experience quite confirms it, as the most likely tree to produce the best and most generally useful timber of all the trees as yet introduced. Seeds of it can be bought in Europe at a low rate, and of good quality, fifty per cent. of which may be expected to germinate. There are about 41,000 seeds to the pound. There is one objection to Pinus laricio—-viz., it is more difficult to transplant than some of the other pines, and that is my experience; but a tree of so much value is worth the little extra care required in its removal. It is not always the tree that is the easiest to plant that will be of most value to the planter. I was very annoyed to find last winter a public body planting a worthless pine on the recommendation of a nurseryman, and for no other reason than that the percentage of failures would be small; surely it would be better to pay 10 per cent, more for a valuable tree that a less price for a tree that, when full grown, will not make even decent firewood. Had the Pinus laricio been a nurseryman's tree, I have no doubt it would oftener be recommended, and more extensively planted.
The planting of the waste places of the earth with suitable trees is occupying the attention of every civilised country, and it is well that, while New Zealand is borrowing money annually for the development of the country, she should, at the same time, annually plant a few million trees on the uncultivatable portions of the land, as a sort of sinking fund to ease the burden of the “unborn millions” of whom we have often heard, and who will be responsible for the interest at least on the borrowed money. And that this may be a good way of providing a sinking fund, if the work is now well done, is proved by the price—about £10 each—now paid for kauri trees in the North of Auckland.
Table of Contents
* I must express my great indebtedness to Sir James Hector and to Professor Maclaurin for the numerous analyses they have placed at my disposal.
THERE is no district in the world containing a larger number and a greater variety of hot mineral springs than Rotorua. Their total number is enormous and practically impossible to estimate, for while the number of the large springs must run into hundreds, in some areas small ones bubble up from under the lee of every little rock and wash the roots of every tuft of hardy manuka, until the ground is literally a sieve, where one must walk warily, and where to stray from the beaten track after dark is to court disaster. Such areas as the Kuirau Reserve, the lake-shore from the Sanatorium grounds to beyond the Postmaster Baths, and parts of Whakarewarewa and Ohinemutu are simply riddled, and to form a fresh spring all that is required is a few moments' work with a spade. Stories have got about, which have obtained a wide credence, that the ground is in a constant tremble, that the air always reeks of sulphur, that the place is a veritable Gehenna, to be gazed at and sniffed at with awe—and swiftly departed from. These are “travellers' tales.” There are whiffs of sulphur in the air certainly, especially on damp days, but the ground does not tremble, and though earthquakes are not uncommon they are less severe than in other parts of the country. The average visitor, unless he is stopping to take a course of the baths, is whisked off every day by enterprising caterers to see the wonders of the distant districts, ignorant of those that lie at his very door. At Ohinemutu, at Whakarewarewa, even in the Sanatorium grounds, may be seen as fine examples of thermal activity as could be wished, while the Sanatorium gardens afford an endless feast of floral colouring. Here one may take one's tea al fresco, sitting at daintily-spread tables, and attended by Maori maidens in picturesque native dress, while a band discourses music, or if more energetically inclined may repair to the beautiful bowling-green, the tennis or the croquet-lawn. Or here the lazy man or the contemplative may sit on a shady seat and smoke his pipe at ease, watching the shadows purple the woods of ever-beautiful Mokoia lying like a jewel on the breast of Rotorua.
The Township of Rotorua has been well laid out. Broad straight streets, planted with avenues of English trees, intersect each other at right angles, lined with little villas each surrounded by its own garden, giving plenty of light and air and space, while the public gardens will more than bear comparison with the finest in the country. Besides the usual public buildings there is an excellent public library, while the town boasts, in addition to easy access by rail, such conveniences of up-to-date civilisation as electric light and a telephone exchange.
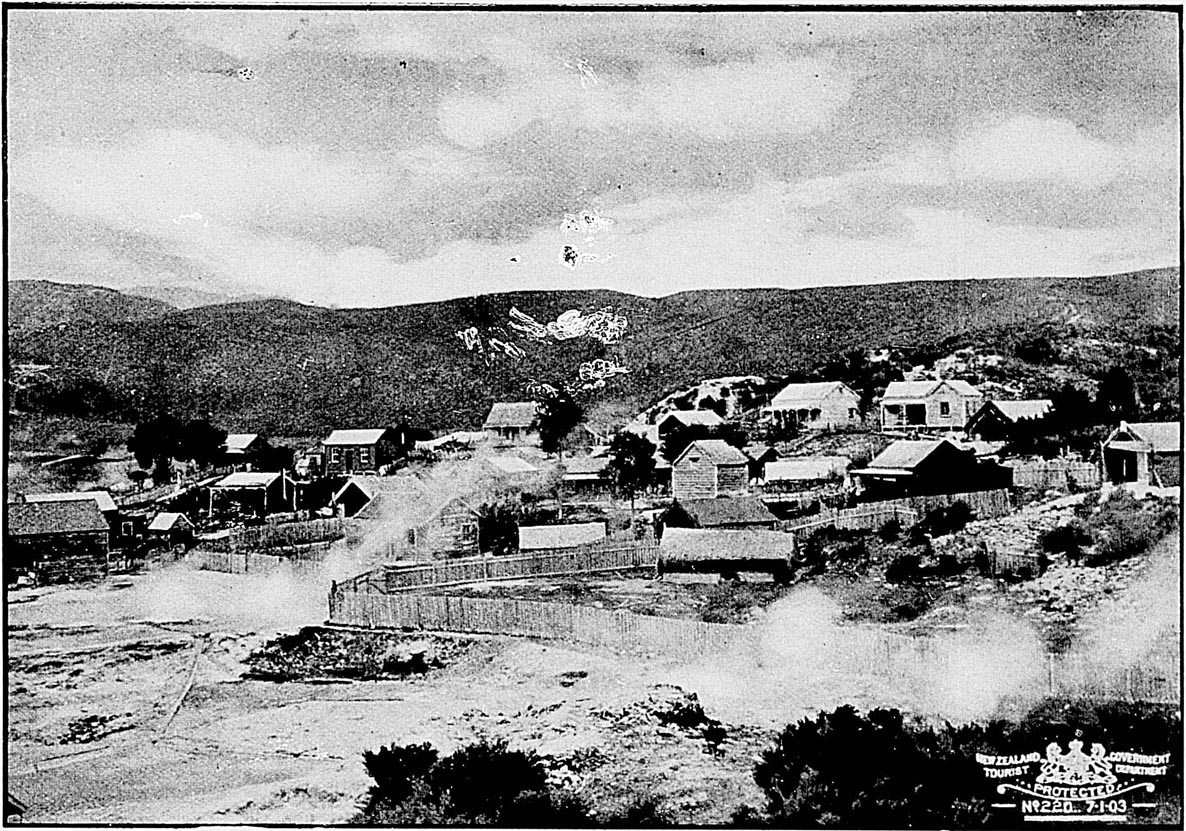

WHAKAREWAREWA
To add to its value as a health resort, Rotorua possesses a bright, sunny, bracing climate. Standing as it does, on an inland plateau, at an altitude of nearly 1,000 ft., by a wide expanse of lake, there is nearly always a keen air, and visitors will do well to bring with them warm clothing, and not be misled by such a geographical expression as latitude.
Turning our backs on the lake and following the broad main street of Rotorua for a couple of miles, we come to Whakarewarewa, perhaps the most interesting spot in the whole thermal district. The ground seems fairly alive with every kind of hot spring and hot mud-pools of every size, shape, and colour. The beautifully shaped cones of the mud geysers are especially interesting, as here you may see in the actual process of formation perfect models of the craters of the great volcanoes. Here, too, may be seen several very fine geysers. The action of the largest of these is intermittent. At Whakarewarewa the amount of hot mineral water is simply enormous, millions of gallons bubbling and hissing and seething all around. Finally, here is a Native village of surpassing interest. Women, in crimson and green and purple, puffing stolidly at the inevitable pipe, the inevitable baby slung across their backs; piccaninnies of all shapes and sizes and colours, active bright little beggars, here, there, and everywhere, dodging between the legs of the pakeha, diving from the high bridge for the coins he may throw, shrilly clamorous to dance a haka for him, or sing to him. Anything, alas, to extract the tourist's cash. There are several primitive but very enjoyable baths at Whakarewarewa, notably the Spout Bath, which is practically a hot waterfall, part of the overflow of an enormous spring, and the Oil Bath, somewhat resembling the Rachel.
At Ohinemutu, the old township of Rotorua, one may see, with the exception of the geysers, pretty much the same sights as at Whakarewarewa, but everything is, so to speak, on a softer scale. The Native village seems a thought more civilized; the boiling springs are curbed to a decorous bubble, even the sullen black mud geysers look less blatantly diabolical. Here as at Whakarewarewa one may see the Natives cooking by natural steam over a banked-up spring, and may also, for a consideration, throb to the fierce stamping of a haka in the carved meeting-house, or be lulled by the rhythmic grace of the poi dance.
As a contrast to so much hot water, a trip across the lake to Hamurana is well worth doing. A river of purest water wells up with great force through a shaft of rock—whose iridescent walls sparkle and scintillate with colour—and runs a short swift course to-the lake. The picture of hanging willows and blue waters mantled with red water-weed is one to haunt the memory. But you must go on a fine day.
From Hamurana the steamer proceeds to Mokoia, an island stored with Maori legend, and on to Te Ngae, where the coach takes one to Tikitere and Rotorua.
At Tikitere are the same thermal phenomena as at Rotorua, but the mud volcanoes are in a state of even fiercer activity. A short walk along a pretty bush track takes one to the Blue Lake, a sheet of fresh water nestling calmly beautiful in the hollow of a crater of verdure-clad hills.
No one should leave this district without visiting the great fresh-water lakes, Rotoiti, Rotoehu, and Rotoma. Rotoiti can be reached either by road or by water, and is worth going a long way to see. The road, after leaving Tikitere, skirts the lake for miles, here giving a panoramic view of the blue waters, there running round a miniature bay where tiny waves lap a white sandy beach and promontories of rock and forest are mirrored in the calm waters they shelter. Should time permit, passing Rotoehu and along Hongi's Track through the forest, a luxurious bath may be taken in the hot effervescing springs of Waitangi, and a glimpse obtained of Rotoma, perhaps the loveliest of all the lakes. Or, going by steamer, one reaches Rotoiti by the Ohau Channel from Rotorua, and, winding along the other shore of the lake, pries into a succession of exquisite nooks, rich with the luxuriant beauty of native bush down to the water's edge. Leaving the steamer at the far end of Rotoiti, the journey may be continued home by coach viâ Tikitere.
Perhaps the most interesting, and certainly the most enthralling excursion of the whole district is that known as the “round trip.” This takes one round the scene of the Tarawera eruption of 1886, past the buried village of Wairoa, and past the mighty geyser of Waimangu. Part of the trip is by road and part by water, the interest increasing with every step of the journey till it culminates in Waimangu itself.
Leaving Rotorua by coach, proceeding across the pumice plain, and passing through a narrow belt of bush left undestroyed by the eruption, one suddenly comes on Lake Tikatapu, of an almost unnatural blue, and beyond it Rotokakihi, of an equally fantastic greenish shade. The curious colour of these lakes is due to the suspended mineral matter in the water. Passing these lakes, Wairoa is reached, the village buried by the eruption of Tarawera in 1886. Ruins of the old mill, the hotel, Sophia's whare, and here and there parts of the walls of a cottage still remain; but Nature is busily and successfully engaged in covering up the pathetic relics of the past. From Wairoa a pleasant row or sail across Lake Tarawera lands one at the foot of the volcano, in a wilderness of dried mud, furrowed to an extraordinary degree with storm-water. A short walk, and weembark again on Lake Rotomahana, and row past the sites of the Pink and White Terraces, the former still in a state of fierce thermal activity. Boiling springs and steam-holes riddle the hillside, while numerous hot springs rise from the floor of the lake, so that one may enjoy the somewhat uncanny experience of rowing over boiling water and feeling the boat vibrate as to the propeller of a steamer. Disembarking where a deep gorge marks the cleft of the eruption, we follow the course of the overflow water of Waimangu up a fairly stiff incline, till we reach the shelter hut overlooking the geyser, usually hot and panting and more than ready for lunch. Hundreds of feet below us lies a small lake, rather over an acre in extent, looking absolutely quiet and innocent. That this apparently harmless sheet of water may suddenly shoot a thousand feet into the air, bearing with it tons of mud and boulders, seems quite incredible, and it requires all the photographs of the guides to convince the doubters who are disappointed in a display that Waimangu is really a geyser at all. Beside the actual geyser is a boiling lake, the Echo Crater Lake, which looks much more formidable and geyser-like. Though there is a rough periodicity about Waimangu of about thirty hours, yet this is by no means absolute, and however carefully one may plan a visit it is impossible to insure seeing a display. To get over the difficulty, the Government have just erected a handsome “accommodation house,” which is really a hotel, commanding a fine view of the geyser and a panorama of Tarawera mountain and the district for miles around.
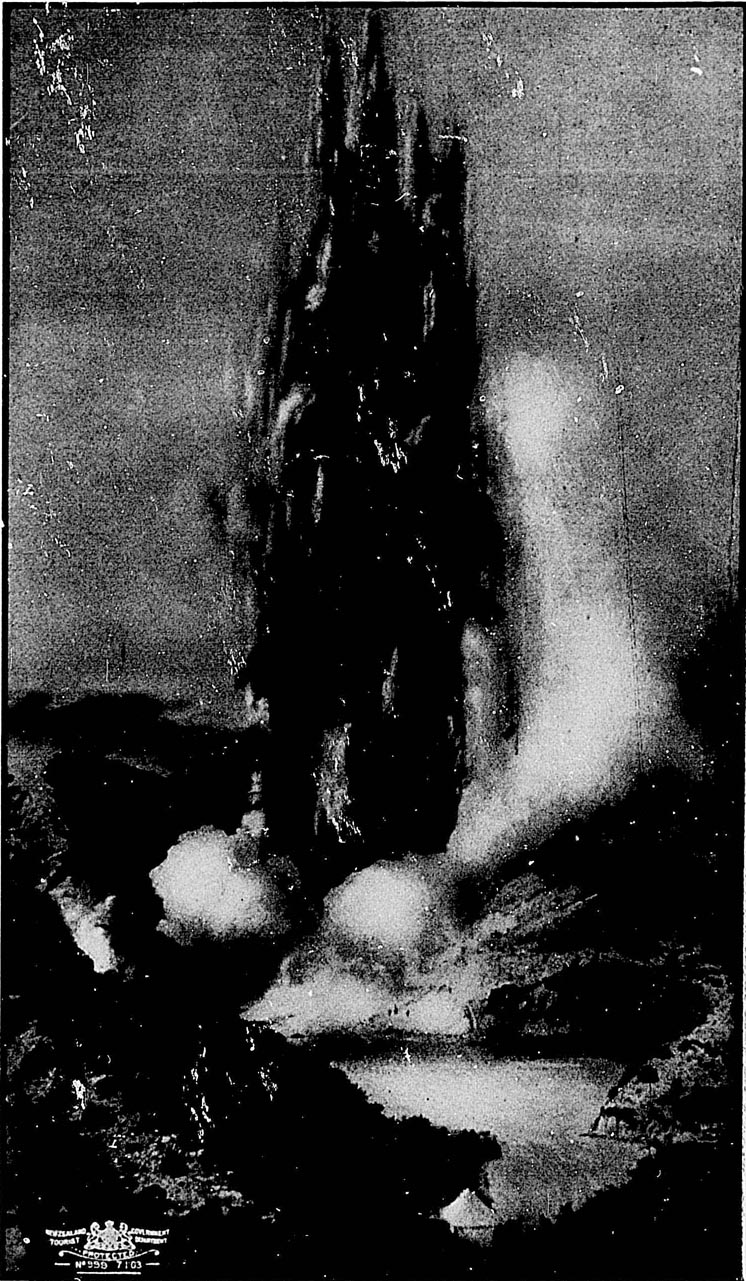
WAIMANGU
Before proceeding to a description of the mineral waters and baths of Rotorua, it may not be out of place to preface the account with a few words on the action of mineral waters generally. There is a largely prevalent idea that the mineral matters dissolved in thermal waters are absorbed through the skin of the bather, enter into his system, and so directly attack the disease. Unfortunately—or perhaps fortunately, for the results in every-day life would be disastrous—this is by no means the case. The skin, partly from the greasy secretions on its surface and partly from the nature of its construction, is quite incapable of absorbing substances in watery solution, except under special conditions. Substances dissolved in a fatty medium may undoubtedly penetrate the skin, and so may certain gases, such as sulphuretted hydrogen, which is abundantly present in the waters, or very finely powdered substances such as the sulphur which is deposited on the skin after a sulphur-vapour bath. Probably, too, a certain amount of mineral water is absorbed when directed on to the skin in fine spray under pressure, more especially if massage is used at the same time, as in the Aix massage douche. A very much larger amount may be absorbed through the lungs and respiratory tract by inhaling the vapours and fumes arising from the waters, and this will explain why it is that silver articles about the clothing may be blackened by the sulphur exuded through the skin several days after leaving a sulphur district. But when all is said and done, the amount absorbed by the skin and lungs is so infinitesimal that it plays quite a minor part in the therapeutics of thermal bathing, and it is only when taken by the mouth in carefully graduated doses that the medicinal effect of the dissolved salts can be obtained. It is to the mechanical, chemical, and possibly electrical, stimulation of the skin by the thermal waters that the balnealogist trusts for all those curative processes which it is his function to direct, aiding them with massage, passive movements, gymnastics, or electricity, as the case demands.
The skin must be conceived as a structure exceedingly rich in blood-vessels, which, though minute in themselves, are, when taken in the aggregate, capable of containing a large proportion of the whole blood-supply of the body. Remembering, too, that these vessels are capable both of great dilatation and active contraction, and that they can readily be made to dilate or contract by using various mineral waters and varying the temperature of the water, it will at once be seen how profoundly a properly selected mineral bath may modify the circulation, can be made to draw blood to the surface, relieving an inward congestion, or by constricting the skin may flush the deep vessels. It can readily be seen, too, how this action of the skin, which has been termed the “skin heart,” may greatly help on the action of a heart perhaps diseased and overloaded, or, again, by injudicious use may thwart that organ and cause fainting or even death. For this reason alone it is about as reasonable a thing to take baths “on one's own” for the cure of disease as to go into a chemist's shop and reach down the nearest bottle “on spec.”
The nature of the mineral waters of Rotorua and their source are described below, and full analyses of the principal springs given:—
While amongst the countless springs arising in the Rotorua district there are, as might be expected, considerable numbers of varieties, and although it is no uncommon thing to observe two springs of almost diametrically opposite chemical properties arising side by side, yet there are certain features common to all.
In the first place, all the mineral springs in the district are hot, and where at times there may appear to be exceptions to the rule it will always be found that the coolness of the water is due either to admixture with fresh water or to evaporation in a basin comparatively large and fed only by a small spring. Without exception, too, the waters contain in solution either sulphuretted hydrogen, sulphurous acid, or both gases. Another invariable ingredient is silica, either in the form of silica, silicic acid, or a combination of that acid with various bases. This is a special characteristic of the waters of geyser regions, and is noticeable in Iceland and in the Yellowstone Park, U.S.A. To this silica is due the formation of those wonderful terraces for which New Zealand has long been famous. The hot water, as it cools and concentrates, being no longer able to keep in solution its dissolved salts, these are deposited in layers, either horizontal and delicately rippled or in stalactite masses, the colour varying generally from white through every shade of grey to pink, according to the nature of the metals present with the silica. The waters, which may therefore be classed under the heading of sulphurous siliceous thermal waters, may be roughly divided into two main groups—acid and alkaline—with various subdivisions, and it is to the close juxtaposition of these entirely unlike waters that Rotorua owes its unique importance.
The distinguishing characteristic of these waters is the presence of free hydrochloric acid, free sulphuric acid, or both, in considerable quantity. In addition, they contain a large amount of alum, sulphate of soda, and iron-oxides, and in the somewhat cumbersome nomenclature of modern science would be classed as acid sulphurous sulphated siliceous waters, a type which does not exist in Europe, though found in the Yellowstone Park, U.S.A., and in Tuscarora, Canada.
Such waters are more suitable for external than for internal use, and for baths of what are known as the “simple immersion” kind they are especially valuable.
In addition to the therapeutic action which they exert in common with all other thermal baths, these waters possess a very powerful rubefacient action in virtue of the free acids they contain. By rapidly withdrawing large quantities of blood to the skin over the whole surface of the body, they profoundly modify the circulation, relieving congestion of internal organs and inflamed joints and nerves, easing pain and stiffness, resolving exudations, and promoting glandular activity. They act, in fact, in medical parlance, as powerful alteratives.
Besides their use as baths, some of these waters, more especially those containing a large proportion of alum, have been used with great success as astringents, especially as gargles in cases of relaxed and congested throat. The Egg-pot, a small but powerful spring near the Postmaster Baths, has long had a reputation for this purpose.
The best-known examples of the acid waters are the springs supplying the Priest and Postmaster Baths.
This spring percolates through a layer of hot pumice a few feet beneath the surface of the ground, and flows into the lake. The water has a greenish tinge, a very acid taste, an odour of sulphuretted-hydrogen and sulphurous-acid gases, and issues from the earth at a temperature of from 98° to 110° Fahr. The total output it is impossible to estimate, on account of the numerous sources of leakage, but it is very large. The analysis is as follows:—
| Grains per Gallon. | |
|---|---|
| Sulphate of soda | 19·24 |
| Sulphate of potash | Traces. |
| Sulphate of lime | 7·41 |
| Sulphate of magnesia | 3·03 |
| Sulphate of alumina | 21·67 |
| Sulphate of iron | 1·24 |
| Sulphuric acid | 22·12 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 3·65 |
| Silica | 18·41 |
| Total | 96·77 |
Also sulphuretted hydrogen, 2·98 grains; carbonic-acid gas, 2·16 grains.
The Postmaster.—This spring bears a very close resemblance to the Priest, both in its situation and in its chemical properties, and differs only in containing an even larger proportion of free sulphuric and hydrochloric acids. It may, in fact, be looked upon as a stronger Priest water. It issues from the ground at a temperature varying from 98° Fahr. to 110° Fahr., and the total outflow is about the same as, or rather less than, the Priest spring. The following is the analysis of the water:—
| Grains per Gallon. | |
|---|---|
| Sulphate of soda | 32·87 |
| Sulphate of potash | 1·24 |
| Sulphate of lime | 4·93 |
| Sulphate of magnesia | 1·83 |
| Sulphate of alumina | 33·22 |
| Iron-oxides | 4·42 |
| Sulphuric acid (free) | 30·32 |
| Hydrochloric acid (free) | 6·14 |
| Silica | 17·61 |
| Total | 132·58 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 3·02 |
Two springs near the Postmaster, and at present supplying some unenclosed and almost disused baths, are the Waikupapapa and Ngaruapuia. The waters, as will be seen from the analysis, are practically identical with the Priest water, but considerably weaker.
| Waikupapapa. | |
|---|---|
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Sulphate of soda | 33·18 |
| Sulphate of potash | 0·26 |
| Sulphate of lime | 2·44 |
| Sulphate of magnesia | 0·24 |
| Sulphate of alumina | 0·32 |
| Iron-oxides | Trace. |
| Sulphuric acid (free) | 4·29 |
| Hydrochloric acid (free) | 7·49 |
| Silica | 8·23 |
| Total | 56·45 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 3·61 |
| Ngaruapuia. | |
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Sulphate of soda | 29·80 |
| Sulphate of soda potash | 0·64 |
| Sulphate of soda lime | 6·87 |
| Sulphate of soda magnesia | 0·31 |
| Sulphate of alumina | .. |
| Iron-oxides | Trace. |
| Sulphuric acid (free) | 3·11 |
| Hydrochloric acid (free) | 6·76 |
| Silica | 12·01 |
| Total | 59·50 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | Traces. |
All the above springs are typical examples of acid, sulphurous thermal water, and form a pale-green solution, perfectly clear, except that on standing exposed to the air there is a tendency to the precipitation of floculent sulphur.
There is another class of acid water, constituting a connecting-link between the foregoing and the hot mud-springs—that is to say, an acid water containing a considerable and varying amount of mineral mud in suspension. Such a spring is the Coffee-pot—a spring which it is hard to know whether to class under the head of mud or water—and the Cameron Spring arising a few yards from it. These waters, while owing their virtues partly to the salts and free acids in solution, act still more powerfully from the amount of mineral mud in suspension. They had a great reputation among the Maoris, and have fallen into an altogether undeserved neglect. It is hoped that when the new buildings are erected increased use will be made of them for immersion baths.
| Coffee-pot. | |
|---|---|
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Silica | 13·86 |
| Sulphate of soda | 23·71 |
| Chloride of potassium | 0·77 |
| Chloride of aluminium | 1·46 |
| Chloride of calcium | 2·04 |
| Chloride of magnesium | 1·62 |
| Chloride of iron | 1·47 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 7·66 |
| Sulphuric acid | 7·60 |
| Total | 60·19 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 3·19 |
| CAMERON SPRING. | |
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Sulphate of soda | 44·54 |
| Chloride of potassium | 1·67 |
| Chloride of sodium | 12·04 |
| Chloride of calcium | 5·22 |
| Chloride of magnesium | 1·28 |
| Chloride of aluminium | 0·62 |
| Silica | 9·22 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 5·92 |
| Total | 80·51 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 4·42 |
| Painkiller. | |
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Chloride of sodium | 46·42 |
| Chloride of potassium | 1·71 |
| Chloride of calcium | 2·66 |
| Chloride of magnesium | 1·47 |
| Chloride of iron and aluminium | 4·22 |
| Sulphate of soda | 29·14 |
| Hydrochloric acid | 6·84 |
| Silica | 18·02 |
| Total | 110·48 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 4·84 |
These springs find their way through a thick stratum of mineral mud, which generally reaches to the surface of the ground, but may be entirely overlaid by a thick rocky crust of silica. As a rule they are also characterized by a very large evolution of gas, chiefly sulphuretted hydrogen and sulphurous acid, with a certain amount of carbonic acid, while they differ from the Priest water in the small quantity of alum in solution.
We have seen that the acid waters are without parallel in Europe, and possess certain unique advantages for external use. The alkaline waters represent a type common to many of the most famous spas of Europe, and are suitable both for bathing and drinking. They differ from the majority of European waters in being more siliceous.
These waters are characterized by their very high temperature (180° Fahr. to boiling point), perfect clearness, and soft emollient feel. As a rule they contain somewhat less sulphuretted hydrogen than the acid waters. Springing as they do from greater depths than the acid waters this is only what might be anticipated, as the gas is believed to be formed by the reduction of the sulphates of the alkaline earths by organic matter under the influence of pressure and heat. Seen in bulk, in a perfectly fresh condition, they present every gradation of colour between a faint blue and a delicate green, but on standing exposed to the air for some time the water is apt to become opalescent as a result of oxidation.
Used for bathing purposes these waters possess certain medical attributes which may be considerably modified by the method of bathing employed. And herein lies their great utility. Taken as simple immersion baths about the body-temperature they act as nervous sedatives, an effect greatly increased by the action of the sulphuretted hydrogen present. Prolonging the immersion, the action of the alkaline salts and the dissolved gases removes the greasy secretions and dead cells of the skin at the same time flushing it with blood, while the silicates in the water exert a bland emollient action. Hence the value of these waters in certain forms of skin-disease. But it is for douche purposes that these waters are most of all valuable, more especially for that combination of douching and massage known as Aix massage. For this the bland nature of the water, combined with an almost slippery feel, a quality permitting the masseur's hands to glide easily over the bather's skin, and which is really due to a soapy material formed by the action of the alkaline water on the sebaceous secretions of the skin, renders the alkaline waters particularly suitable. Doubtless, too, the siliceous nature of the water increases this effect. At Aix-les-Bains the same quality appears to be due to a low form of vegetable growth in the water called glairine.
For internal administration the alkaline sulphurous waters have valuable properties, and also certain drawbacks, the most serious of the latter being their extremely nauseous taste. Happily, however, if the water is taken at first in small doses, which are gradually increased from day to day, the distate not only steadily lessens but is often replaced by a positive enjoyment. The water should be taken as fresh and as hot as possible, sipped rather than gulped down, and should be taken on an empty stomach either before meals or in the cooling-room after or before a bath, according to the special effect desired. Thus taken before meals it cleanses the stomach, neutralises acidity, and stimulates the flow of gastric juice in virtue of its alkalinity. In addition, the sulphides, sulphates, and chlorides in solution exert a specific influence on the digestive glands, more especially stimulating the liver, so that the water relieves engorgement of the liver, hæmorrhoids, and, indirectly, constipation. At the same time the amount of iron present, though small, is sufficient to exert a distinctly tonic influence. There remains one important ingredient whose action must be regarded as still open to question—the silica. What therapeutic action, if any, the silicates exert is still a moot point, and my own experience in their use has been hardly long enough for me to venture a positive opinion.
It will be seen from the above that the alkaline sulphurous waters—such as the Rachel—are fairly potent medicines, and not to be taken in indiscriminate quantities without medical advice. More especially patients with greatly enfeebled digestion, profound anæmia, or persons suffering from functional disturbances of the heart should avoid their internal use.
One other application of these waters remains to be considered—their use, in the form of vapour, for inhalation and for vapour baths. At present no facilities exist for inhaling the vapour, but in the new baths I hope to see installed a complete inhalatorium. By increasing the mucous secretions, relaxing the respiratory tissues, and softening and disquamating the epithelium, inhalation of these vapours would be distinctly beneficial in certain cases of chronic bronchitis and asthma.
While on the subject of inhalation it may be remarked that a good deal of involuntary inhalation goes on during a bath, especially when, as in the old form of baths, these are built directly over the source. The amount of sulphuretted hydrogen that bubbles up through the water in the Priest and Postmaster Baths is very considerable, and is largely responsible for the not infrequent cases of fainting in those baths. While not without its use as a skin-stimulant in the water, and for its action on the nervous system when inhaled, the good is so much more than counterbalanced by the evil that it would be better in all future baths not to build them over the springs, but always to lead the waters to them. The carbonic-acid gas which is present in several of the springs is hardly in sufficient quantity to have any marked therapeutic or toxic effect.
Vapour baths in which the body or part of the body is immersed in the steam arising from the mineral water form a part of the armamentarium of nearly every spa in Europe, and ample provision for them has been made in the designs for the new bath buildings. But, while at present deficient in this respect, Rotorua possesses a “sulphur-vapour bath” which is believed to be unique. From a hot sulphur cavern immediately below the floor of the Blue Bath, steam and hot fumes, principally sulphur-dioxide in a very concentrated form, are led into a vapour “cabinet” of the ordinary type, in which the patient sits immersed with his head projecting through an aperture. It is hardly possible to exaggerate the value of this bath in certain cases. While possessing all the properties of an ordinary vapour bath, the sulphurous fumes of themselves have an intensely stimulating effect on the skin; while, in addition, sulphur in the finest possible powder is deposited on the whole surface of the body. Under such a combination of circumstances quite an appreciable amount of sulphur is absorbed into the system, while at the same time all the effects mentioned before as attributable to immersion in Priest water are brought about.
| Analyses of the Alkaline Waters, in Grains per Gallon. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rachael. | Oil Bath. (Whakarewarewa). | Waikiti (Ohinemutu, 1903). | |
| Sodium-chloride | 69·43 | 66·34 | 38·75 |
| Potassium-chloride | 3·41 | 1·46 | .. |
| Lithium-chloride | Traces | Traces | .. |
| Sodium-sulphate | 11·80 | 7·49 | 2·72 |
| Potassium-sulphate | .. | .. | 2·70 |
| Sodium-bicarbonate | .. | .. | 20·03 |
| Calcium-bicarbonate | .. | .. | 0·82 |
| Magnesium-bicarbonate | .. | .. | 0·74 |
| Iron and alumina oxides | 2·41 | .. | .. |
| Alumina | .. | .. | 0·16 |
| Silica | 5·87 | .. | 24·36 |
| Sodium-silicate | 18·21 | 2·08 | .. |
| Calcium-silicate | 4·24 | 3·16 | .. |
| Magnesium-silicate | 1·09 | 0·76 | .. |
| Ferr. silicate | .. | 0·85 | .. |
| Totals | 116·46 | 82·14 | 90·28 |
| Also sulphuretted hydrogen and carbonic acid. | |||
The appearance of an acid and an alkaline spring alongside flashes at once across the mind the inevitable query “Why?” How is it that two such antagonistic waters can outflow so closely together without mixing and neutralising one another? Evidently their sources, or at any rate one of their sources, must be far distant from their outlet. Very deep vertical or sinuous fissures in the earth's crust might account for the phenomenon, or one vertical shaft penetrating a horizontal and superficial water-bearing stratum. A close examination of a large number of springs inclined me to the latter opinion.
The foreshore of Lake Rotorua for more than a mile is riddled with acid springs, which seem, so to speak, to ooze from the surface pumice. By digging down a few feet in almost any part of this area one strikes a layer of acid sulphurous water closely resembling the Priest water. It is significant, too, that the temperature of the Priest Baths is materially lowered by a heavy rainfall. The alkaline waters in this area, on the other hand, are ejected with a certain amount of force from deep shafts, whose walls are lined with a silicate deposit soft under the water, of stony hardness where exposed and dry. It is impossible to measure the depth of these shafts, as their walls are not vertical, but they are certainly of considerable depth—the Rachel Spring, for instance, has been sounded to a depth of 150 ft. There is a close resemblance, both in the nature of the outlet-shaft and in the character of the water, between these springs and the geysers of Whakarewarewa; and even the quietest and most placid pools—such as the Rachel—will exhibit geyser action if the pressure on them is suddenly lowered, as by rapidly running off a large quantity of water.
The physical configuration of the springs, then, would point to the supposition that the Priest water is a superficial layer separated from a deeper level of alkaline water by some impervious stratum, pierced here and there by vertical shafts which allow the alkaline water under a considerable degree of pressure, to reach the surface. To test the truth of this theory shafts were sunk in various parts of the Sanatorium grounds, both in sulphur-beds, where one might expect to obtain hot water, and in apparently sound places overgrown with trees 30 ft. high. In all cases hot, acid, sulphurous water was obtained at a distance varying from 5 ft. to 12 ft. below the surface. Certain strata, more especially a black-cinter layer, contained water in larger quantities and higher temperatures than others, the thermometer registering anything from 110° Fahr. to 160° Fahr. An analysis of one of these “artificial springs” will be seen below under heading A. On digging through the floor of spring A we came upon a dense stratum of white clay some 12 ft. thick, and boring through this with a 6 in. iron pipe we came on a plentiful supply of a neutral water, richer in chlorides, of a temperature of 187° Fahr., and altogether more approximating in character to Rachel water (analysis B).
| Analysis, in Grains per Gallon. | ||
|---|---|---|
| A. | B. | |
| Silica | 16·80 | 16·80 |
| Alumina | 20·36 | 4·10 |
| Iron-oxide | 1·10 | 0·15 |
| Lime | 0·56 | 0·56 |
| Magnesia | 0·61 | 0·20 |
| Soda | 2·46 | 13·33 |
| Potash | 0·40 | 0·80 |
| Chloride | 3·55 | 14·41 |
| Sulphuric acid | 57·40 | 12·60 |
| Total | 103·24 | 62·95 |
| Sulphuretted hydrogen | 6·2 | 2·98 |
| Acidity, calculated as sulphuric acid | 11·31 | Neutral. |
Spring B bears a close analogy with the Spout Bath at Whakarewarewa, which is also a nearly neutral spring.
| Spout Bath.—Analysis, in Grains per Gallon. | |
|---|---|
| Silicate of sodium | 16·32 |
| Silicate of calcium | 1·61 |
| Silicate of magnesium | 1·14 |
| Silicate of iron | 0·39 |
| Sulphate of sodium | 13·47 |
| Chloride of potassium | 1·24 |
| Chloride of sodium | 53·61 |
| Phosphate of alumina | Traces |
| Total | 87·78 |
The baths of Rotorua are designed expressly to cater for the needs of two distinct types of bathers—those who come for pleasure and those who come for “the cure.” For the former there are hot swimming-baths whïch are amongst the finest in existence. The enormous supplies of hot mineral water available enable us to keep up three large swimming-baths, always filled with water at the body-temperature. These are entirely emptied and cleaned out every week, while a constant stream of clean hot water is always flowing in, and bathers have this additional guarantee of the purity of the water: that unless this constant inflow of fresh hot water is kept up the temperature of the bath must inevitably and rapidly sink.
The Duchess Bath is a fine swimming-bath 40 ft. long and 20 ft. broad, enclosed in a building lofty enough to prevent any feeling of stuffiness. Here one may get a luxurious swim and a cold shower in independence of the weather. On either side of the swimming-bath is a suite of private rooms containing a bath-room, and a really sumptuous dressing-room, lavatory, cold shower, and hot douche. These baths, which are open to ladies one half the day and gentlemen the other, are all supplied by the Rachel spring, which is noted for the soft emollient nature of its water.
The ladies' swimming-bath, also supplied by the Rachel spring, is open to the sky, and measures 48 ft by 24 ft.
The third swimming-bath, the Blue Bath, 62 ft. by 23 ft., is reserved for gentlemen, is also open-air, and is fed by the water from the Malfroy geysers.
In the same building is the sulphur-vapour bath already described.
The main block of buildings, the Pavilion Baths, is divided into separate wings for ladies and gentlemen. Here are situated, in addition to the ladies' swimming-bath, the immersion baths supplied by the famous “Priest” water and suites of public and private baths supplied from the Rachel spring. Under the same roof are the mud baths, comprising “complete immersion” and “local” mud baths.
At the ticket-office may be obtained hot Rachel water free for drinking purposes, and cold Te Aroha water—a strongly alkaline saline—at 1d. per glass. It is hoped to be able before long to retail here several of the more important waters of the colony at a nominal price.
Behind the Duchess Bath, in an unpretentious wooden building, are the ladies' and gentlemen's Aix massage baths. These are very comfortably fitted up with cooling-rooms and private dressing-rooms, while the walls of the bath-rooms are lined with plate glass to insure absolute cleanliness. The Rachel water, under hydraulic pressure of about 40 lb. to the square inch, supplies the various douches, and the whole is in charge of a thoroughly experienced masseur and masseuse, who, in addition to a knowledge of massage and douching, are expert in the Swedish movements and gymnastics.
Half a mile away along the lake-shore, in the direction of Whakarewarewa, are the Postmaster Baths, similar in construction to the Priest Baths, with a male and female side, but open to the air. Their special use and nature have already been touched upon.
At Whakarewarewa are the Spout Bath already mentioned, and several other baths at present in private hands.
Tariff.—The cost of the baths is really remarkably low, and varies from 6d. for certain public baths to 2s. 6d. for the Aix massage.
The season may be said to last all the year round, for while the great majority of visitors crowd to Rotorua during the summer there are large and increasing numbers who have learned from past experience that Rotorua is much more comfortable in the autumn and winter, when we enjoy week after week of still, clear, bracing days, with a genial sun and an absence of that gusty wind which is the chief drawback of the climate in early summer.
Rotorua may most easily be reached by rail from Auckland. The express leaves Auckland every morning, arriving in Rotorua in comfortable time for dinner in the evening. As a dining-car is now to be attached to this train the journey will be made very much more comfortably than heretofore. This train connects with the Australian boat from Sydney to Auckland.
Another route is overland via the Wanganui River and Taupo; a most interesting and charming way in summer, but, owing to the long coaching journey, somewhat uncomfortable in winter.
There are four hotels and about twenty boardinghouses, and the number of the latter is steadily increasing; but during the height of the season, especially if some special function such as the Carnival or a public holiday is on, it would be wise to engage rooms in advance.
This it is impossible to state, so much depending on the nature and severity of the case, but, striking an average, a month would be a very fair allowance. Indeed in very severe cases it is as a rule better not to prolong a stay over several months, but rather to go away after six weeks or so and return later.
The sufferer must not expect a Pool of Bethesda at Rotorua: we do not profess to do impossibilities, and are only too well aware of our limitations; but this much may be affirmed with absolute sincerity, that nowhere in the known world exist finer bathing-waters for the relief of suffering humanity.
Taking coach at Rotorua, and turning sharply to the right from Whakarewarewa, a drive of twenty-one miles brings one to Waiotapu. From the time the first gorge is left, with boulder-strewn Puarenga rushing far below, the conduit supplying Rotorua with water winding snakily beside it, the road is comparatively uninteresting until Kakaramea is reached.
Maunga Kakaramea—Rainbow Mountain—owes its name to the extraordinary richness and variety of colouring of its steeper slopes, due to the coloured earths of which it is largely composed. In a single roadside cutting one may pick up specimens of earth of the most intense red, purple, and orange, with every gradation through delicate pinks, greys, and greens to pure white. There is an easy track to the summit.
Passing an intensely green still lake at the foot of Kakaramea, a short drive brings one to the Waiotapu Hotel.
Many people look upon Waiotapu as merely a place to halt at for lunch on the road to Taupo, but it is well worth spending a few days here. Space forbids anything like an adequate description of this wonderful valley. Here may be seen on a gigantic scale every kind of hydro-thermal activity: enormous boiling cauldrons, mud geysers on a scale nowhere else attempted, hot cascades and waterfalls, steam-holes, alum caves, and an immense variety of mineral waters.
From Waiotapu the road leads across an interminable pumice plain to Taupo. The Waikato River, now rolling majestically, now thundering over falls and rapids, alone breaks the monotony of the journey. Away to the left can be seen the steam from the Ohaki spring, while in the far distance rise the snowy peaks of the volcanoes Ruapehu and Ngauruhoe.
A few miles before reaching Taupo we come to Wairakei, a veritable oasis in the desert of pumice, fern, and manuka. On no account should the traveller miss Wairakei. Waiotapu holds us with its weirdness, but Wairakei is magnificent. Through the hotel gardens, fed by innumerable springs, runs literally a river of hot water, in which you can swim under the overarching trees, a cold stream running alongside for the delectation of the hardier spirits; at points along the stream cascades of hot water form natural shower-baths amid fern and moss and shrub. Finally, in one high fall, the mineral water serves a purpose which is, I believe, unique—to drive a water-wheel and cut chaff.
There are two main groups of springs in two distinct valleys: one, the smaller, consisting of a large number of springs of an aluminous, sulphurous, and chalybeate nature, the overflow of which constitutes the hot river; and the other, and larger, the “Geyser Valley,” in which most of the waters are of an alkaline saline nature. Here may be seen a large number of geysers of all sizes, which differ from those of Whakarewarewa in the extreme frequency and regularity of their action and in their beautiful surroundings. Any one with half an hour to spare may be quite certain of his patience being rewarded by seeing at least one geyser play.
Many miles before reaching Wairakei the landscape is dominated by the frowning extinct crater of (Tau Hara.) As the road twists and turns round the low hills at its base, the great mountain seems ever elusive, never getting nearer, and, in fact, even when we reach Taupo after hours of driving, we seem still as far off the mountain as ever. This peculiarity of a conical mountain is due of course to the fact that one face of it is so much like another as to be indistinguishable; we have simply driven round it. The same phenomenon is very noticeable in passing Mount Egmont.
The Aratiatia Rapids are best visited from Wairakei, but a splendid view of the Huka Falls may be obtained from the coach-road between Wairakei and Taupo. It is a really magnificent sight to see the huge mass of purest water, of the most delicious green colour, pour thunderously over the falls. One realises what an immense force it is the electrical engineers propose to harness.
Taupo is a pretty little place overlooking the lake, and commanding quite a Swiss view of the snowy giants opposite.
There is a choice of three hotels for the traveller: the Lake Hotel, most convenient for the steamer and the through route to Wanganui; the Spa, and the Terraces, with hot mineral baths attached.
Taupo, standing as it does at an altitude of 1,250 ft. in the very centre of the North Island, with a fine bracing climate, a magnificent lake, and absolutely unlimited supplies of hot mineral water, can hardly fail to become in the future one of the foremost health resorts of the country.
The Spa Hotel consists of a series of cottages grouped about a pretty garden, through which runs a stream of hot mineral water. There are a number of comfortable baths, and several kinds of mineral water flowing in astounding quantities. The whole is in a sheltered sunny valley, and should prove a perfect haven for those in search of a quiet restful winter resort.
Some 200 ft. above Taupo is the Terraces Hotel. In its grounds is a deep and picturesque ravine in which arise a large number of springs of different kinds. The outflow of mineral water here is really enormous, and many of the springs possess valuable medicinal properties.
In addition to several hot springs which arise from the shore of the lake between the Terraces and the Lake Hotel, there is another group along the bank of the Waikato River, including some exceedingly interesting geysers.
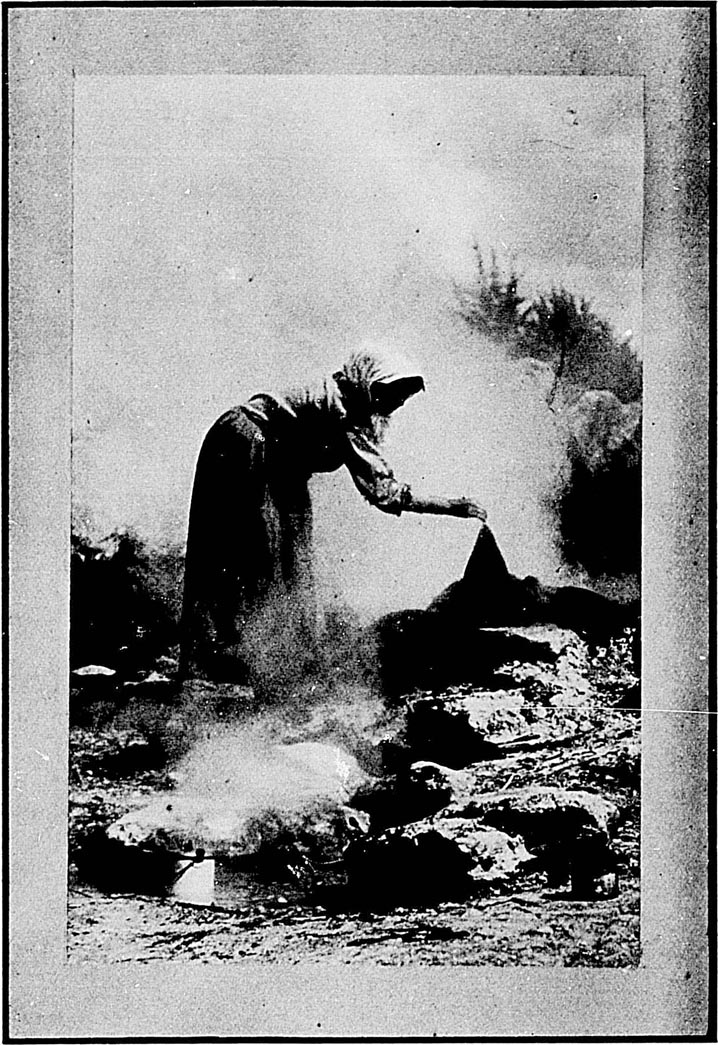

Maori Woman Cooking.
At Tokaanu, across the lake, are several very large hot springs, of varying nature, which on account of the enormous number of springs in this district have been comparatively neglected. Had they been situated in any European country they would long ago have obtained worldwide reputation.
Orakei Korako may be reached either by driving over from Wairakei or by riding from Atiamuri by the new road beside the Waikato, a most picturesque route.
There are two objects at the springs which are alone well worth going to see—the Terraces, which since the destruction of the Pink and White Terraces are the finest in the colony, and the Alum Cave. Surely if any spot deserved the epithet “fairy” it is this grotto. In a cliff overlooking the Waikato, with the everlasting dingy scrub and scrubby fern around, one suddenly comes on an opening in the cliff half-hidden with vegetation. Descending by a rough boulder-strewn track, one enters fairyland. A hundred feet overhead the cliff-face shelves into the grotto. Purple and orange, green and crimson, the roof is iridescent with every colour, while at the very bottom of the grotto, where painted roof meets painted floor, is an exquisitely beautiful pool of hot water, delicately green, its perfectly still surface reflecting the coloured walls. The sloping floor of the cave is filled with stately nikau palms, growing luxuriantly in the warm steamy atmosphere. To the left of the pool is a narrow opening leading into a large cave, whose floor is a pool of hot water, and whose atmosphere is like the hottest room of a Turkish bath. Here the guide will momentarily disappear, to appear torch in hand in the mysterious depths, lighting up the cave with weird effect. The atmosphere, however, does not invite too long a sojourn.
There are a very large number of valuable mineral springs at Orakei Korako, but on account of the inaccessibility of the spot they have hitherto been used only by the Maori.
These springs may be reached from Rotorua either by rail or road. In either case, the route passes through charming scenery.
Taking the coach by preference, and skirting the foot of Ngongotaha along the western side of the lake, we reach the bush some ten miles from Rotorua, after a long pull uphill. Thenceforward the road runs for miles through beautiful bush scenery, and by the time the mid-day halt is made the keen air—we are some 2,000 ft. up—has made lunch a welcome duty. As the coach begins the descent of the opposite face of the mountain-chain the scenery gets finer and finer, until it culminates in a magnificent panorama of wooded ridge and rocky crest, with deep luxuriant gorges in between, and beyond the broad valleys of Thames and Waikato, the far horizon serrated with blue hills. A few miles across the plain and we come to Okoroire.
Here the River Waihou forces its way through a narrow cleft of rock, foaming into a broad basin, on whose margin are situated the springs, overhung with trees and banks of fern. Close behind is the hotel with its lazy verandahs, its orchards, and its farmyard. The waters, which are mildly saline and comfortably hot, have been led into the baths close to the river-side, and constitute a particularly pleasant and inviting dip. Jammed in the narrowest cleft of the river's course is all that is left of a large Maori canoe which tradition says was wrecked in its present situation during a foolhardy and fatal attempt by a visiting tribe to paddle through the rapids. There is good trout-fishing in the river, and altogether for the angler, and for the bather in search of quiet comfort, Okoroire is a charming spot. Within driving distance of Okoroire are the fine hot springs of Mata Mata, which are well worth a visit and a bathe in.
| Upper No. 2 Bath—Analysis. | |
|---|---|
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Calcium-sulphate | 2·77 |
| Magnesium-chloride | 0·69 |
| Sodium-chloride | 9·48 |
| Sodium-carbonate | 17·18 |
| Potassium-carbonate | 1·42 |
| Iron-oxide | 1·10 |
| Silica and silicates | 9·70 |
| Total | 42·34 |
Flow, 1,300 gallons per hour. Temperature, 113° Fahr.
| Fairy or Open-air Bath.—Analysis. | |
|---|---|
| Grains per Gallon. | |
| Calcium-sulphate | 2·42 |
| Calcium-carbonate | 1·84 |
| Magnesium-carbonate | 1·03 |
| Sodium-chloride | 4·34 |
| Alkaline oxide | 11·41 |
| Iron-oxide | 0·70 |
| Silica and silicates | 9·82 |
| Total | 31·56 |
Flow, 4,100 gallons per hour. Temperature, 99° Fahr.
One of the best and certainly one of the prettiest resorts in New Zealand is Te Aroha. Nestling at the foot of a high richly-wooded mountain, on the edge of a wide plain, the first view of it from the railway recalls irresistibly one of those pleasant little watering-places one finds in quiet nooks on the Continent of Europe. Only a chalet or two perched among the pines is wanted to make the illusion complete.
Situated in a large garden, prettily terraced on the hillside, are dotted about a large number of baths. Some of these are small buildings erected either over or alongside a spring, as, for instance, No. 1, which is reserved for ladies; but the central block constitutes quite a handsome and picturesque bath-house, with a large number of private baths, and, with the exception of the Aix massage bath at Rotorua, is the most up-to-date bathing establishment in the colony.
Te Aroha differs from most of the spas of New Zealand in this important particular: that, while their most striking feature is their enormous outflow, at Te Aroha the flow is distinctly limited. Luckily this limitation is more than counterbalanced by the medicinal properties of the water. While Rotorua is a bathing resort, Te Aroha is essentially a place for drinking the waters, and when we speak of a “limited supply” the term is comparative only, for there is ample to supply the needs of the whole of Australasia.
The waters much resemble those of Vichy (France), but are distinctly stronger. A gallon of Vichy water, for instance, contains 319 grains of sodium-carbonate, while Te Aroha spring No. 6 contains 499 grains. Drinking the water is of value in many cases of dyspepsia, and in certain forms of liver and kidney disease; but sufferers are warned that the waters are not suitable for each and every case, and it is better to take medical advice before starting on a course.
Another small spring has lately been discovered, the analysis of which is appended below as No. 19.
| Analysis of Eighteen Mineral Waters from Te Aroha.—No. 4423.Alkaline Waters 1 to 15, 17 to 18. | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Temp. in deg. Fah. | Dimensions of Bath. | Quantity of Water in each. | Chloride of Sodium. | Chloride of Potassium. | Sulphate of Soda. | Carbonate of Lime. | Carbonate of Magnesia. | Carbonate of Soda. | Alumina. | Iron Oxide. | Silica. | Total Grains per Gallon. | |
| Ft. in. Ft. in. | Gals. | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 102 | 9 10 x 7 0 | 1,607 | 60·25 | 1·72 | 38·32 | 10·77 | 6·86 | 461·56 | Trace | Trace | 7·56 | 586·96 | |
| 2 | 112 | 9 7 x 8 5 | 1,725 | 60·45 | 1·90 | 32·67 | 7·12 | 4·21 | 426·29 | Trace | Trace | 7·12 | 539·76 | |
| 3 | 112 | ... | ... | 60·51 |  | 32·82 | 7·24 | 4·20 | 429·19 | Trace | Trace | 7·21 | 541·17 | |
| 4 | 92 | 11 0 x 9 0 | 1,771 | 34·24 | 19·16 | 4·62 | 2·14 | 246·49 | Trace | Trace | 5·17 | 311·82 | ||
| 5 | 100 | 6 7 x 5 8 | 998 | 68·77 | 36·92 | 6·91 | 3·15 | 476·58 | Trace | Trace | 6·10 | 598·43 | ||
| 6 | 104 | 11 0 x 9 0 | 2,650 | 66·23 | 35·14 | 7·12 | 2·99 | 499·75 | Trace | Trace | 7·14 | 618·37 | ||
| 7 | 86 | 7 6 x 5 0 | 1,009 | 67·13 | 34·04 | 7·46 | 4·34 | 444·20 | Trace | Trace | 7·01 | 564·18 | ||
| 8 | 109 | ... | ... | 66·14 | 1·96 | 32·91 | 7·47 | 4·21 | 451·97 | Trace | Trace | 8·60 | 573·26 | |
| 9 | 112 | ... | ... | 41·29 | ... | 22·16 | 4·94 | 2·61 | 301·17 | Trace | Trace | 6·44 | 378·61 | |
| 10 | 96 | ... | ... | 35·24 | ... | 19·19 | 4·67 | 2·31 | 276·19 | Trace | Trace | 6·00 | 343·60 | |
| 11 | 88 | ... | ... | 34·69 | ... | 20·12 | 5·11 | 2·56 | 261·44 | Trace | Trace | 6·11 | 330·03 | |
| 12 | 88 | ... | ... | 41·66 | ... | 22·96 | 5·12 | 2·99 | 300·97 | Trace | Trace | 7·11 | 380·81 | |
| 13 | 120 | ... | ... | 40·67 | ... | 21·86 | 6·11 | 3·13 | 301·64 | Trace | Trace | 6·86 | 380·27 | |
| 14 | 122 | ... | ... | 42·61 | ... | 23·16 | 7·14 | 3·49 | 321·64 | Trace | Trace | 6·66 | 404·70 | |
| 15 | 139 | ... | ... | 43·11 | ... | 22·16 | 6·91 | 3·61 | 331·76 | Trace | Trace | 7·05 | 414·60 | |
| 17 | ... | ... | ... | 2·71 | ... | 3·92 | 0·64 | 0·27 | 9·36 | Trace | Trace | 4·21 | 21·11 | |
| 18 | ... | ... | ... | 16·12 | ... | 8·16 | 1·97 | 1·01 | 131·72 | Trace | Trace | 13·14 | 172·12 | |
| 19. | Sodium-chloride | 26·57 | Sodium-sulphate | 18·19 | Magnesium - bicarbonate | 11·24 | ||||||||
| Potassium-chloride | 1·08 | Sodium-bicarbonate | 179·81 | ate | ||||||||||
| Lithium-chloride | traces | Calcium-bicarbonate | 31·82 | Ferrous bicarbonate | ·12 | |||||||||
| Silica | 3·92 | |||||||||||||
| Total solids, 272·75. | ||||||||||||||
| Free carbonic acid, 71 grains. | ||||||||||||||
In addition to these springs there are several in private hands. This year (1903) the springs and baths were transferred from the Domain Board to the Department of Tourist and Health Resorts, and placed in charge of Dr. Kenny, late of Rotorua, who may be consulted at a fixed fee.
Table of Contents
The Hanmer hot mineral springs, on a plateau of North Canterbury, 1,218 ft. above sea-level, are one day's journey from Christchurch by rail and coach. The train leaves Christchurch daily for Culverden, thence coach to Hanmer. There is good accommodation at the Government Spa, Mr. J. B. Gould, manager. Natural hot mineral water and private baths are provided at the spa. Hot-air and douche baths and massage are available. The baths are sulphuretted saline water, valuable for both external and internal use in cases of rheumatism, gout, and certain forms of indigestion, kidney-complaints, and skin-diseases. Inhalation, in certain forms of bronchitis and asthma, is also found effective.
A tennis-court, croquet-lawn, and bowling-green are provided for the use of visitors. There is good trout-fishing in a number of streams within easy reach of the spa.
The Mount Cook Hermitage Hotel—under the control of the Government Tourist Department—is situated in the heart of the Southern Alps. The Hermitage is 2,506 ft. above sea-level. It is reached from Christchurch or Dunedin by rail and coach. Trains connect at Timaru for Fairlie, thirty-nine miles. At Fairlie the traveller changes to the coach for the rest of his journey (ninety-six miles). A night is spent en route from Fairlie to the Hermitage at Lake Pukaki, where there is a Government hotel. Guides and horses are obtainable at the Hermitage. The hotel is a building of thirty-five rooms, with stabling and paddocks for horses. Cook's coupons are accepted at the Hermitage. The glaciers within easy distance include the great Tasman Glacier (one of the largest in the world), the Murchison, Godley, Mueller, and Hooker. Mount Cook (12,349 ft.) and the surrounding mountains are within convenient distance of the Hermitage. From the Ball Hut (3,404 ft.) and Malte Brun Hut (5,700 ft.), erected for the shelter of climbers, in the vicinity of Mount Tasman, many alpine excursions may be made. The Ball Hut is twelve miles, and the Malte Brun about twenty miles from the Hermitage. The west coast may be reached from here, viâ the Hooker Glacier, Fitzgerald's Pass, and the valleys of the Copland and Karangarua Rivers.
The most easily accessible of the Otago lakes is Wakatipu, which is fifty-four miles long, 1,069 ft. above sea-level, and has a depth of 1,252 ft. Queenstown, on the shores of this lake, is reached in one day from Dunedin or Invercargill by rail (174 miles or eighty-seven miles) to Kingston, thence by Government steamer twenty-five miles. From Queenstown, where there is good hotel accommodation, the ascent of Ben Lomond (5,747 ft.) and other mountains may be made on horseback. The Government steamers run to Kinloch and Glenorchy, at the head of the lake, whence excursions may be made to Mount Earnslaw (9,300 ft.), by horse and on foot, to Paradise (by buggy), and to the Routeburn Valley, the Dart River, Rere Lake, &c. There is an alpine route through from Greenstone on the shores of the lake, via the Hollyford River, to Martin's Bay on the west coast (sixty-three miles), also a track from Mount Nicholas to Lake Te Anau via the Keys.
Lake Wanaka (928 ft. above sea-level and thirty-five miles in length) may be conveniently visited from Wakatipu. A coach runs from Queenstown to Pembroke, on Lake Wanaka, a distance of forty-one miles. The service is bi-weekly in summer and weekly in winter. There are hotels at Pembroke, and an accommodation house at Makarora (the head of the lake). Steamers ply on the lake and may be hired as required. Lake Hawea (131 ft. above Wanaka) is ten miles distant by a vehicle-road. There is good red-deer stalking in the vicinity; trout abound in the streams and in Lakes Wanaka and Hawea. A track leads from the head of Lake Wanaka over the Haast Pass (sixteen miles distant) to the west coast, connecting with the road to Hokitika.
Lake Te Anau, forty-two miles long, and 694 ft. above the sea, is reached by train and coach from either Dunedin or Invercargill—train to Lumsden, thence a coach journey of fifty-two miles to Te Anau, occupying a day. There is a comfortable hotel at the coach terminus on the shores of the lake. A small steamer runs to the head of the lake, where there is an accommodation house. From here visitors may walk to Sutherland Falls and Milford Sound. The track leads up the Clinton Valley, over Mackinnon's Pass to the Sutherland Falls (nineteen miles), and Milford Sound (thirty-five miles). The Sutherland Falls (1,904 ft.) are the highest in the world. There are shelter huts at convenient distances along the route. Guides are obtainable at Te Anau. There is an accommodation house at Sutherland's, Milford Sound, opposite Mitre Peak. An oil-launch is available for excusions on the Sound. From the upper part of Lake Te Anau there is a good track to George Sound (thirteen miles), viâ Lakes Hankinson and Thompson. A rowing-boat is available on the Sound, and huts are provided for visitors.
Manapouri Lake (elevation 597 ft.) is visited from Lake Te Anau. The distance between the lakes is six miles, but the accommodation houses are thirteen miles apart. A coach traverses the intervening distance, in connection with the steamers on the lakes and the coaches from Lumsden. Manapouri may also be reached by coach (thirty-eight miles) from Otautau, which is thirty-two miles from Invercargill by rail. Manapouri is the deepest of the New Zealand lakes, having an extreme depth of 1,452 ft. There is a small steamer on the lake; it may be engaged by visitors as required. This lake is regarded by many as the most picturesque in New Zealand.
Stewart Island is reached by steamer (weekly service) from the Bluff, a distance of twenty-four miles. There are accommodation-houses at Oban (Half-moon Bay), where the steamer calls, and at the bays round the coast. An auxiliary oil-ketch and other boats may be hired at Oban for coastal cruises, and excellent fishing is to be obtained. Bathing, boating, and deep-sea-fishing excursions are the chief attractions of the island. Walking-tours may also be made to the summits of Mounts Anglem (3,200 ft.) and Rakiahua (2,217 ft.), and other wooded peaks.
Small coasting-boats (sail and screw) take visitors when required to Paterson Inlet, the Neck, and other scenic resorts. Two of the most attractive spots, Port Adventure and Lords River, may be visited in one day from Oban. The boardinghouses at Oban are capable of accommodating a large number of visitors; there are several stores in the township.
Table of Contents
Distant from Auckland, 1,638 miles; circumference, 20 miles; height, 2,920 ft.; area, 30 square miles; population, 2,060.
Rarotonga is, beyond all doubt, the most fertile and valuable of the Cook Group, and it has the largest population. The island has been exceptionally favoured by nature, not only with delightful scenic attractions, but also with a remarkably rich and productive soil—the source of abundant wealth. The secret of its great fertility is its excellent water-supply, which is due to its elevation. The climate, too, is most favourable, not only to vegetable but also to animal life. The island is, however, one of the least planted, for there are many tracts of land of the best quality on the south, west, and north-west coasts that produce little if anything. It must have supported at one time a population of many thousands, but they are now reduced to about 2,100 natives and whites.
At present the country is overrun with noxious weeds, some of them of very recent introduction; and they are spreading with a rapidity that necessitates the most persistent efforts to keep cultivated areas free from them. The cotton scale blight has also made its appearance in this and other islands.
The land-tenure of Rarotonga is as follows: In very ancient times the land was divided amongst the crew of the canoe that first took possession of the island, and the representatives of the eldest branch of each family are now known as Arikis, or Mataiapos, according to their original rank on landing. These chiefs have at all times been recognised as trustees for the descendants of the original ancestor who resided on the land; but they now claim the right to expel any man who dares to assert his independence, or act in any manner contrary to the views of his overlord. In olden days, when it was essential to the existence of a tribe that all should be of one mind and obedient to the chief, any one disputing his will might well have been turned off the land with the consent of the whole tribe. Now, however, this consent is not always deemed necessary by either Ariki or Mataiapo.
The aborigines of Rarotonga are very closely akin to the Maoris of New Zealand, and probably at one time had frequent intercourse with them. They are not naturally industrious, nor have they had any reason for becoming so; but as they are quite aware of the value of European goods, it may be concluded that they would work willingly enough if inducement offered. Industry would probably follow good land regulations; but these, it is considered, should compel a certain amount of fencing to be done every year.
The seat and centre of the government of the Cook Islands—the double township of Avarua and Avatiu—is situated on the north or lee side of the Island of Rarotonga, opposite two small openings in the coral reef. The former has the advantage of a boat harbour, where small craft can be moored in safety when the wind is not blowing in from the sea. The residence of the Commissioner and the establishment of the ex-queen are situated here.
Though the dwellings of the natives are built of coral concrete, the Government offices are constructed of wood, and are not imposing in appearance.
The value of goods imported into Rarotonga for the Cook and other islands for six years gives an average as under: From New Zealand, £15,137; from Tahiti, £7,724: total, £22,861.
Exports for the same period from the Cook Group: To New Zealand, £17,000; to Tahiti, £2,904: total, £19,904 per annum. From Penrhyn and other islands, via Rarotonga, £1,956.
The exports from Cook Islands comprise: Copra, 33 per cent.; fruit, including limejuice, 33 per cent.; coffee, 30 per cent.; cotton and other goods, 4 per cent. From Penrhyn and other islands: Pearlshell, 90 per cent.; copra, 10 per cent.
Distant from Rarotonga, 116 miles; circumference, 30 miles; height, 656 ft.; area, 30 square miles; population, 1,541.
Mangaia is the most southerly island of the Cook Group, and is second in importance to Rarotonga only on account of its difficult and dangerous coast. A fringing reef closely surrounds the island, and there is no break or passage through which a boat can reach the shore. The sea-face of the reef is so steep that vessels can only with the greatest difficulty obtain an anchorage. Communication between them and the islanders is carried on by the latter in canoes, which they navigate most skilfully through the surf on the reef.
Mangaia is almost circular. Around it, rising gently from the shallow lagoon within the reef, is a narrow, sandy beach. From this there rises, almost abruptly, a steep cliff about 100 ft. in height of jagged and broken coral rock, pierced and tunnelled with numerous fissures and caves. On the top of this rise is a level plateau, known as the “makatea,” which extends, about a mile in average width, nearly all round the island. The inner edge of this flattened ring descends again almost to sea-level, enclosing an ancient crater. In the midst of this rise several volcanic mounds, the highest having an elevation of 656 ft. The hollow area is drained by natural subterranean channels under the “makatea” into the sea. The eastern side of the island is a desert of basalt rock.
Cocoanuts, bananas, oranges, limes, citrons and other fruits grow plentifully. The annual export of copra is large, as is also that of perishable fruits. The natives have cultivated much of the land, and owing to their industry the productions of the island have a favourable name. The coffee is the best produced in the Cook Group, not from any superiority of soil or climate, but because of the care exercised in picking and drying the berries.
As the general fertility of the land is below that of the other islands of the group, the natives produce better results because of the consequent necessity for cultivation. The “makatea” is especially suitable for the citrus family. Unfortunately the uncertainty of communication has prevented the development of the limejuice industry. In former years cotton was grown in large quantities and exported.
Mangaia is one of the few places in the world of which it can be said that every man, woman, and child owns land on defined boundaries sufficient for his or her support. From the most ancient times the soil has been most minutely subdivided.
Distant from Rarotonga, 116 miles; circumference, 20 miles; height, 374 ft.; area, 32 square miles; population, 918.
Atiu resembles Mangaia in formation, being a raised mass of coral with high jagged cliffs facing the sea. It has a similar barrier to shipping round its shores, and communication with vessels must be by canoes launched over the sea-wall through the breakers. Every inch of Atiu is worthy of cultivation, though it has not that appearance of fertility that is so characteristic of Rarotonga and Aitutaki. The bare central ridge, with its red soil and low-growing fern, is deceptive, for it is really the best land.
On the highest point of the ridge cocoanuts, bananas, oranges, and coffee grow with the utmost luxuriance; and the kumara, most valuable and uncertain of South Sea vegetables, yields large crops. The cocoanut-palm grows well everywhere, but especially so on the coral rock formation, though only a few hundred trees are to be found there. Coffee and oranges grow vigorously, but very few trees are to be seen. There is, however, an excuse for the non-cultivation of the orange, for men can hardly be expected to cultivate fruit for which there is no demand. It is only within the last two years that any anxiety has been shown to purchase the oranges of this island, except at the end of the season, when fruit has become scarce and therefore valuable. That the people of Atiu should have neglected to plant the cocoanut-palm extensively is, however, astonishing, for perishable fruits are unsuitable, inasmuch as a very moderate sea from the north or west will prevent their being shipped. With copra this would matter but little, for the cargo would receive no damage by delay. The result of this apathy or neglect is that the tribes of Atiu are about the most poverty-stricken people of the group. For this state of affairs the land tenure of the island may be in a measure responsible, as the old tribal system of New Zealand holds sway. There are but nine hundred people, and this being so it is obvious that under the most favourable circumstances this number of Polynesians could not occupy and cultivate two square miles of their island.
Mauke, Mitiaro, and Takutea belong to the Atiuans.
Distant from Rarotonga, 150 miles; circumference, 6 miles; height, about 60 ft.; area, 4 1/2 square miles; population, 370.
Mauke is a low circular island about two miles across, lying to the north-east of Rarotonga. Like Mangaia and Atiu, it is surrounded by an unbroken fringing reef. It is marvellously fertile, and in value and quantity the produce exported is greater than that of Atiu; but the limit of production has not nearly been reached. Here also the “makatea,” or coral zone, remains unplanted.
The value of a South Sea island can hardly be calculated by reference to the surface area, for the warm damp climate develops exceedingly active growth, whether the land be planted with cocoanuts, oranges, bananas, vanilla, or coffee. Large quantities of oranges are annually produced on Mauke.
Distant from Rarotonga, 140 miles; circumference, 5 miles; height, about 50 ft.; area, 4 square miles; population, 165.
This island is a good instance of an elevated coral reef, thinly coated with sand and gravel of the same material. The surface is not more than six feet above high-water mark, and on those rare occasions when the group is visited by a hurricane, there is but one spot on which the inhabitants can find safety, for the sea then breaks right across the island.
Copra is the only article of regular export, but in the centre of the island there is a fertile patch whereon oranges and bananas are grown with moderate success. The people live almost entirely on cocoanut and fish, and their appearance is such as to justify the Polynesian belief that no better food can be obtained for man. A few oranges are occasionally exported, but the wants of the inhabitants are supplied by the sale of some 40 tons of copra per annum. This amount might, however, be increased to 80 tons, or even more.
Distant from Rarotonga, 125 miles; area, 2 square miles.
This island is uninhabited, but belongs to the tribes of Atiu, who visit it for a few weeks in each year to make copra. It is a coral island, and is moderately fertile. It is probably capable of producing 100 tons of copra per annum, but at present the production is only 10 tons.
Distant from Rarotonga, 140 miles; circumference, 12 miles; height, 366 ft.; area, 7 square miles; population, 1,170.
The name includes the island anciently known as “Arahura,” and some seven or eight smaller islands on the vast barrier reef. Some of these are volcanic, and would seem to have been small peaks on the lip of an extinct volcano, now submerged.
The island itself is pear-shaped, about four miles by two; its highest part (366 ft.) being situated near the centre of the enclosing triangle, with a long, low stalk curving round and joining the reef wall at the apex. This is a good illustration of an atoll in process of formation—the highest part of the original island not yet sunk beneath the waves. Through the western sea-wall is a narrow opening, out of which the sea is always running with considerable force, for it is the only escape for the water driven over the reef on the windward side. The channel is shallow and tortuous, and is the only means of landing on the island.
Some of the best oranges in the New Zealand market, known as “Tahiti,” are from Aitutaki, while the best pineapples in the Eastern Pacific are from the same place. The remaining articles of export are copra, and limejuice of very good quality. Much of the former is produced on the islets.
The land-tenure of this island leaves nothing to be desired, for the soil has been minutely subdivided and each family well provided for. All that is now required is a properly constituted land tribunal to settle questions of title.
The Aitutakians are naturally a hardy race, and industrious when away from their own homes; but on their native soil much time is taken up with disputes over succession to intestate estates.
They are said to be the best sailors in the Cook Group, and their services are much in demand for working the cargo on vessels at Tahiti. They make fans and mats, and are expert at plaiting various fibres for hatmaking. Independent and conservative, they have preserved their right to prohibit the importation of intoxicants.
Some of the inhabitants have commenced to cultivate the land, and the produce of the island has nearly doubled in the last two years, being now greatly in excess of that of any other island if calculated on the basis of population.
Distant from Rarotonga, 120 miles; area of Manuae, 1 1/2 square miles; population, 10.
These two small islands are better known as the Hervey Group. They are situated about midway between Atiu and Aitutaki, and are owned by the people of the latter place, whose title is indisputable. They destroyed all of the original people except a few women, whose descendants have been admitted to have a certain claim apart from, but not superior to, the conquerers, as represented by the Arikis.
The islands have been leased to a European firm, with the result that the export of copra has risen from 36 tons in 1898 to 64 tons in 1901. During the same period the Cook Island Trading Company has planted thirty thousand young palms, and Manuae now bids fair to be the leading copra island of the Cook Group within the next ten or twelve years.
Distant from Rarotonga 580 miles; circumference, 40 miles; height, 200 ft.; area, about 100 or 110 square miles; population, 4,079.
Niue, or Savage Island, is a long, low island, fringed with a misty cloud of fine spray caused by the breakers ceaselessly beating upon its jagged coasts. The shores being too deep and steep to support a barrier reef, the coast-line is deprived of its protection. It is fertile, and is probably three times as large as Rarotonga (being about seventeen miles in length and seven miles and a half in depth), but not more valuable. The soil is not volcanic, for the whole island is but an upheaval of coral reef, seamed and tunnelled in all directions. The coral has been more or less decomposed by atmospheric action, and the land is, therefore, fertile even where the rock is seen peeping from beneath the surface.
In consequence of the porous nature of the rock there are no streams in Niue, and fresh water is therefore very scarce. There are many deep caverns and stalactite caves, however, whence a supply of cool water is obtainable, but most of it is said to get brackish after a spell of dry weather.
Much of the land is encumbered with a dense scrub of guava bush, a few of these plants introduced into the island having increased and spread over large areas, from which it seems almost impossible to eradicate them.
The orange, the cocoanut, sugar-cane, cotton, and other tropical products grow well, and the lemon flourishes on the rocky shores. Notwithstanding these advantages, Niue appears to be condemned to depend almost entirely on the cocoanut for its export. The shores of the island are so precipitous that the few landing-places are not always approachable even in fine weather, and one—Mutulau—can only be negotiated when the wind is westerly, that is, during three weeks in the year. Under these circumstances perishable fruit could not be shipped successfully.
The great want of the island is a main road connecting all the villages with Alofi. Unfortunately, there are difficulties in this matter, it being necessary to blast out the face of a cliff if Mutulau is to be connected with the chief town. Without good roads Niue can never make the most of its natural fertility, for at the present time most of the produce is carried on men's backs; and as the fixed price of labour at Niue is 4s. per diem, it would cost £6 per ton to carry copra from Mutulau to Alofi.
On account of their isolation, the natives of Niue are somewhat different in character from other Polynesians. They are very industrious, and the men are often engaged at Tonga and elsewhere as labourers. The girls and women plait hats, which are exported to New Zealand and Australia. They are keen traders, but are much averse to strangers obtaining a foothold in the island itself.
[A fuller and more special description of this island by Mr. S. Percy Smith, who acted as Special Commissioner for several months, will be found in the Year-book for 1902.]
Distant from Rarotonga, 273 miles; area, 1 square mile; population, 115.
The Palmerstons are situated upon an irregular ring of coral reef, measuring outside about four miles and a half by two miles and a half, just awash with the tide. This narrow ring is about half a mile in width, and it supports eight little islets, nearly all covered with cocoanut palms. The largest of these is little more than half a mile in length and about a quarter of a mile wide. Under its grove of palms is the settlement of the entire population of the group. The lagoon and reef abound with fish, and turtles are caught in plenty.
The group is leased to the family of the late William Masters, an old sailor from one of the Midland Counties, who was one of the first to plant the islets with the cocoanut palm. The lagoon is large, but does not produce pearl-shell; though it seems possible that if spawn were introduced it might thrive.
Copra is the only article of export, and this product is likely to increase in quantity, for the Masters family is still planting the waste lands and thinning out the palms where they have been too thickly planted.
Distant 735 miles from Rarotonga; area, 3 square miles; population, 445.
This atoll is known to the Polynesians under the names of Tongareva or Ma-ngaro-ngaro, and is valuable only by reason of the existence of pearl-shell beds in the extensive lagoon, which has a surface area of not less than a hundred square miles. The extent and value of these shell-beds is only imperfectly known, for the native population is small, and they do no more work than will provide them with food and clothing. It is not possible to do more than estimate the yield of shell, but it is safe to say that not less than 70 tons is annually exported, and that the value is probably £200 per ton.
The cocoanut crop is small, though there are many trees on the long strip of coral sand that separates the ocean from the lagoon. The soil of Penrhyn does not apparently suit the cocoanut palm, or it may be, as the natives assert, that the rats destroy the young nuts. Whatever the cause, not more than 15 tons of copra is annually produced by this atoll.
Fresh water is very scarce at Penrhyn.
Distant from Rarotonga, 530 miles; area, 1/2 square mile; population, 30.
Suwarrow is an atoll with a splendid lagoon. The entrance will admit of vessels drawing from 15 ft. to 20 ft. of water passing through, and the lagoon itself forms an excellent harbour. The atoll is under lease to the Pacific Trading Company, but its only value is the lagoon, which produces a very good class of pearl-shell, taken by the aid of diving-dresses in water averaging from 20 to 28 fathoms in depth. The present yield of shell is nearly 50 tons per annum, but the beds are about to be given a long rest.
In October, 1901, there were about forty persons on the island, natives of Manahiki or Tahiti, but it is doubtful if there has ever been an indigenous or native population, for the islets of the reef are small, and no old cocoanut palms are to be seen.
The copra made on Suwarrow does not exceed 6 tons per annum, as many nuts are used by the pearl-shell fishers, and on several of the islets the trees are too young to bear fruit.
Distant from Rarotonga, 650 and 670 miles respectively; area, each 2 square miles: population, Manakihi, 484; Rakahanga, 400.
Manahiki, or Humphrey, is nearly circular, but there is no opening large enough for a boat to pass into the lagoon. The people are amiable and industrious, and are expert swimmers, as indeed are all the South Sea Islanders. Beche-de-mer is obtained from the lagoon. The island occasionally suffers from drought.
Rakahanga, or Rierson, is also an atoll. The inhabitants are much like those of Manahiki, and are happy and contented. Turtle are plentiful round the reef.
These islands may be treated as one, for they are not more than twenty-five miles apart, and belong to the same people, who are governed by two Arikis. The former has until lately produced a limited amount of pearl-shell, but about the end of 1900 it was found that the beds were exhausted by over-fishing. The lagoon was therefore closed to give it a much needed rest.
The only industry is now that of copra-making. Both islands are overplanted—indeed the yield of nuts would be greatly increased if three out of every four trees were cut down.
Pukapuka is a small solitary atoll about three miles in diameter, which produces pearl-shell. It is about seven hundred miles from Rarotonga, and has an area of two square miles. The population is 505 persons.
Nassau is also a small island within the extended boundaries. It is said to be uninhabited.
The education of the children living in the Cook Group is in the bands of the London Mission Society, a non-sectarian but Protestant association, which provides some one thousand eight hundred children in the Cook and Northern Islands with a sound and useful education. At Tereora, in Rarotonga, there is a very useful institution at which the mission supplies an English education for the children of those leading men that are willing to pay a small fee per annum. At the present time there are forty children at Tereora under a qualified teacher, and in aid of this establishment a subsidy of £2 10s. per head is paid by the Islands Government. The school is capably managed, and it is a rule of the mission that the boys shall raise their own vegetable food.
In Mangaia there has until lately been a school of the Tereora type under a European lady, and it will probably resume operations when the new missionary arrives to take charge of that island.
At Aitutaki the natives have built a very fine schoolhouse, and a certificated teacher is now (February, 1902) on his way from England to take up the training of the children of that island.
To sum the educational work now being done by the London Mission Society: 1,575 children are being taught to read and write Maori, 250 are receiving an elementary English education, and forty are receiving a Fifth Standard education. To the above must be added the good work done by the Sisters of St. Joseph, a Roman Catholic institution of French and Irish ladies, who have established themselves in Rarotonga, and have perhaps fifty pupils, drawn from all the denominations and nationalities to be found in the South Seas.
Oranges and bananas have heretofore been the chief exports; but for some years past have barely cleared expenses during the months of May, June, July, and August, though there have occasionally been fair returns for the remaining four months of the orange season. Not only is there no improvement, but the trade is slowly and surely becoming less remunerative, owing to the competition of Tahiti, Tonga, Fiji, Samoa, and New South Wales, and will shortly reach the point at which export must cease. The Tahiti orange competes with that of Rarotonga on equal terms, although prohibitive duties are imposed at Tahiti on all goods or produce from places outside the French sphere of influence. So also the oranges of New South Wales are admitted free to New Zealand, though the coffee and limejuice from the islands is prohibited in Australia by the Federal tariff. That the islands could, if necessary, supply all New Zealand with bananas seems quite certain, and during the past twelve months hundreds of acres have been planted with this object in view; but the competition of Fiji and the expenses of shipping have put an end to any hope of expansion of this export.
As regards coffee, there is no market in New Zealand, for since the duty on that article was removed the colony has been flooded with an inferior bean from Costa Rica that can be sold more cheaply. Hence only the market of Tahiti is open, and there the duty is approximately 31 per cent, of the selling-value. Under these circumstances dependence can only be placed on copra, and even this industry is not capable of immediate expansion. The planting of the cocoanut-palm has been neglected for many years, and eight years more must elapse before any benefit can be derived from the trees lately planted.
Throughout the Eastern Pacific it will be noticed that all the cocoanut-palms are from sixty to eighty years' growth. Young trees may be seen of from two to five years, but half-grown trees seldom, if ever. The result of this, in the event of a real hurricane, will be that all of the old and partially worn-out trees will be uprooted, and many of the islands will have no export worth mentioning for the ensuing ten years.
The following statement will show the present and estimated possible yield of copra and the yield of pearl-shell for each island:—
| Copra. | Pearl-shell. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Production. | Estimated Possible Production. | Present Production. | |
| Tons. | Tons. | Tons. | |
| Rarotonga | 150 | 2,000 | .. |
| Mangaia | 150 | 500 | .. |
| Atiu | 125 | 1,800 | .. |
| Mauke | 160 | 350 | .. |
| Mitiaro | 40 | 80 | .. |
| Takutea | 10 | 100 | .. |
| Aitutaki | 350 | 450 | .. |
| Manuae | 60 | 400 | .. |
| Niue | 500 | 3,500 | .. |
| Palmerston | 100 | 180 | 50 |
| Penrhyn | 15 | 100 | 70 |
| Suwarrow | 25 | 100 | .. |
| Manahiki | 100 | 200 | 10 |
| Rakahanga | 100 | 200 | .. |
| Pukapuka | 100 | 200 | .. |
With reference to this unsatisfactory coinage, it is reported that the natives of the group have refused to accept the dollar in payment for island produce. The result of this action has been most satisfactory, for both Mangaia and Aitutaki have banished the Chili dollar and have replaced it with British coin. In Rarotonga, which is the trade centre of the Cook Islands, it has not yet been abolished, but most of the business is now transacted with British money. The trade of Penrhyn, Manahiki, and Rakahanga is still in the hands of Tahiti firms, with whom the Chili dollar is the only medium of exchange. The dollar is at present worth about 1s. 9d. in English money.
This little article will give some account of the social organization and life of the Maori people of New Zealand, as known to have obtained among them prior to the advent of Europeans.
The Maori people, like others in a similar culture-stage, were ever incapable of forming themselves into a nation, of combining for the purpose of advancing the public weak except in the case of single tribes, the members of which would unite to present a front when threatened by a common enemy. These Natives formed themselves into tribes. Each tribe would be the descendants of a common ancestor, whose name the tribe usually took as a tribal name, though not so in all cases. Each of these tribes was subdivided into clans or sub-tribes, and these again into what may be termed the “gens” or family group. Observe, the unit of Maori social life appears to have been neither the individual, nor yet the family, but the family group. This will be noted when we survey their social customs and consanguineous nomenclature.
There was not a great deal of cohesion among the various clans of a tribe, except in case of war. Indeed these clans, or sub-tribes, often fought fiercely among themselves, one against the other. As a rule the people lived in fortified places, the defensive works thereof consisting of earthworks, ditches, escarpments, and palisading. Such a fort would be occupied by a family group, or a clan, or in some cases by several clans, in which latter case it often occurred that the fortified area would be subdivided by means of earthworks and palisades, as between the different clans, in case of inter-clan fighting.
From these forts they would issue forth each day in order to perform various necessary labours, as the cultivation of their crops, fishing, hunting, &c., each clan and each family group cultivating, or hunting over, only such lands as lay within their own boundaries. These boundaries were clearly defined, and trespass for the purpose of hunting, fishing, or cultivation, or the collection of any of the products of the land of another branch of the tribe, would at once be taken as a casus belli.
In time of war each clan would gather under its own chiefs, and all clans would assemble at a common rendezvous in order to march against the tribal enemies, or await their attack. In expeditions against other tribes, each clan pleased itself as to whether or not it took part in the foray. Unless the whole of the clans agreed to place themselves beneath the command of a famous war chief, or fighting priest, there was often much bickering, jealousy, and want of cohesion among the various clans, with consequent loss of fighting power.
During the long nights the Natives would collect in large houses within these forts, and amuse themselves by singing, posture dancing, the relation of their ancient racial myths and folk-lore, together with various games of skill. The kite, the whip-top, and the humming-top are ancient Maori toys.
Social etiquette was a strong point among these neolithic people, who were most punctilious in their observance of the numberless rules pertaining thereto; indeed a breach of such might lead to severe and prolonged fighting. The Maori is naturally of a dignified demeanour and a born orator.
The people may be said to have been divided into three principal classes—(1) the chiefs (although various grades of such existed), (2) the common people, (3) slaves.
The chiefs and priests were the influential persons of the tribe, and the first-born of a high chief's family was a most important person, and was also endowed with a great amount of tapu. His, or her, prestige was great, and such first-born were considered to be imbued with considerable power of a supernatural nature. Primogeniture was ever an active and a powerful force in Maoridom. The priests and chiefs were the repository of the unwritten archives of the tribe. They preserved, and taught to carefully selected youths, the tribal history, mythology, ritual, &c, which were thus conserved orally from generation to generation. But every individual, even commoners, had much to learn, as land-boundaries, the genealogy of his family, and numerous charms, invocations, &c., for many purposes.
As observed, the family group was practically the social unit. Hence we note, in the consanguineous nomenclature of these people, that such terms as “father,” “mother,” “sister,” and “brother,” have not the same restricted meaning as they have with us. The term papa means father, also uncle, &c. The word for mother (whaea) also denotes aunts, &c. Tuahine—a sister—is also used to describe a female cousin, and so on.
There was, and is, no family life, as we know it, among the Maori people. The relations between parents and children are also totally different. Brothers and sisters, &c., of the parents would appear to have as much say in matters affecting the children as have the true parents, indeed often much more. The Maori family is by no means cohesive. The family group, or sub-clan, is much more so.
In regard to marriage, such matters were often arranged (and are still) by the uncles and aunts of a girl, the parents taking little or no part therein. The marriage of near relatives, such as first cousins, was abhorred, and looked upon as incest, for such cousins are termed brothers and sisters, in accordance with the native conception of the social unit. Thus the Maori was exogamous as regards the family group, or gens, but usually endogamous in regard to the tribe; usually, but not always so. Marriages with members of other tribes, and also with slaves, were by no means uncommon. Children of a slave mother by a free man would themselves be free, and be looked upon as members of the tribe. The taint of such an origin would, however, run down the generations.
When a man died, his younger brother often married the widow, and it was considered the correct thing so to do.
Children were often adopted by their aunts, or more distant relatives; nor does the change appear to grieve them as a rule. Children are very seldom chastised among the Natives, nor, to give them due credit, do they appear to need it.
Some most singular customs obtained respecting birth. When a woman of rank was in childbed for the first time, she became intensely tapu, and was not allowed to remain in the village, nor in a house. She was taken away from the village, and a rude shed, termed the “fœtus house,” was built for her reception, where she remained with one attendant until the child was about two days old—i.e., when the tua rite had been performed over it by the priest, and the tapu lifted from mother and child.
Both birth and death were sacred matters to the Maori, and neither were allowed to take place in the houses of the people, but the woman, or invalid, as the case might be, was taken away outside the fort or village, and a rough shelter provided for them. Forts stained with the blood of the defenders thereof shed in battle were often deserted on account of being thus rendered tapu, and new ones built elsewhere. Should a person chance to die in a dwelling-place, that house must be deserted. The sacredness of death is upon it. It must, however, be observed, that the term tapu in many of these cases should rather be taken as meaning “unclean” than “sacred.”
When, in former times, a chief was near his end, he would call his people around him, and proceed to make a last speech to them, urging them to preserve their tribal unity, to be strenuous in avenging all insults and injuries which he had not already equalised, and to uphold the tribal dignity in all ways. After which he would bid them farewell, and proceed to die without loss of time.
On the death of a person, preparations are made for a funeral feast, to which many come, and lamentations, speech-making and feasting last for several days, during which the corpse, in olden times, lay in state, surrounded by his fine garments and weapons.
Related peoples among other tribes will often form a mourning-party and march long distances in order to wail over a person, or persons, who have been dead and buried for years. These singular mourning-rites are really much enjoyed by the Natives. Their grief does not prevent them from having a thoroughly good time. It may be remarked that the sick are shown but little attention; care and solicitude for such are not prominent traits in the Maori character. But as soon as death ensues, then the most extravagant protestations of grief are made. That is, to the Maori mind, the only way of avenging a natural death. For what says the Maori orator? “By tears and lamentations alone may the stroke of misfortune be avenged.”
In Maoridom, when visitors are being received, great outcry is made, waving of garments, loud wailing cries of welcome, as the challengers fall back on the homestead. Then follows a prolonged scene of weeping, the two parties standing in two closely-arranged masses opposite to each other. After this comes speech-making and feasting, cooked food being borne to the guests by a procession of people, who sing loudly as they advance.
But when a party is leaving a village, no such demonstration is made, excepting a few cries of farewell.
Feasts are given by a tribe, or clan, at intervals, to which many people are invited and at which, in former times, some very singular rites were performed. At such meetings matters affecting the tribe are discussed.
Such were some of the social rules and customs of the old-time Maori, and many of them are still in force at this day. Many other items remain to be noted, and these we will treat of in the years that lie before.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
THE Auckland Land District covers about four and a half degrees of latitude, with an area of 13,858,000 acres, extending from 34° 30' to 39° S., its greatest length being about 365 miles, from the North Cape to the 39th parallel, south of Lake Taupo, while its greatest width is about 180 miles. In the peninsula north of Auckland, indented as it is on either side by harbours and arms of the sea, and with a mean width between the Pacific Ocean and Tasman Sea of little over forty miles, the range of temperature is remarkably small. The thermometer seldom registers above 80° in the shade in the middle of summer, whilst the heat is always tempered by a cool breeze, bringing the mean summer temperature to under 70° in the shade. The frosts are hardly worth mentioning, as the minimum register is seldom below 40°; but south of Auckland sharp white frosts occur very often, more especially beyond 38° of latitude, and snow lies upon the summits of some of the highest hills or mountains in winter.
This land district may be said to have no real mountains, as the most prominent peaks of the several scattered ranges or hills seldom exceed 3,000 ft. in height above the sea-level, an altitude just enough—south of 38°—to clothe the last 1,000 ft. with snow in the depth of winter. North of Hokianga and the Bay of Islands there is one well-defined range of hills rising to a height of 2,463 ft.; whilst south of these places, and extending to the Wairoa River on one side and the Whangarei Harbour upon the other, the country is all more or less broken into ranges from 1,000 ft. to 2,000 ft. in height, with valleys between. The next really well developed main range lies within the Coromandel and Thames Peninsula. With a length of over 150 miles, it has an average height of over 2,800 ft., commencing with Moehau, or Cape Colville, 2,935 ft.; next, Te Aroha, a peak of 3,176 ft.; and ending at Weraiti with a height of 2,527 ft. There are two other well-defined ranges—namely, Tawairoa and Hauturu—lying between the West Coast and the Waipa basin, with their highest peak at Pirongia, which rises to 3,156 ft., and is often snow-capped. There are other ranges forming the watershed between the basins of the Waikato and Waipa Rivers, and dividing both from the streams running into the western side of Lake Taupo. Their highest peak is Pureora, rising to 3,793 ft. The eastern side of the land district is occupied by a very broken, forest-clad country, known as the Urewera country, the average height of which is about 2,500 ft. It is practically unexplored, and, being still in the hands of the Natives, is not as yet available for settlement. To the east of Lake Taupo lie the Kaimanawa Ranges, of about 4,500 ft., and generally open on the ridges, with valleys clothed in beech forests. Nearly the whole of the Auckland Land District is indented on both coasts with harbours and arms of the sea, forming a cheap and easy means of access. Of rivers, properly so called, there are only two of any great length—namely, the Wairoa and Waikato. The first empties itself into the Kaipara Harbour, a large arm, or rather succession of ams, of the sea, giving hundreds of miles of inland water-carriage to all parts of the Counties of Hobson, Otamatea, Rodney, and Waitemata. This river is navigable from its mouth to its junction with its tributaries Wairua and Mangakahia, a distance of ninety-one miles from the sea, and for forty miles it is navigable for ships of large burden. The River Waikato has a course of 200 miles, measured from its source in the Ruapehu Mountain through Lake Taupo to the sea on the West Coast. It is navigable for river-steamers for seventy-five miles from its mouth, and its tributary, the Waipa, for twenty miles from its confluence with the Waikato at Ngaruawahia. Another river—the Thames, or Waihou—though of no great length, affords a valuable means of inland water-carriage, and is navigable for small steamers for twenty-five miles. Generally speaking, every part of the district has an abundant water-supply, now and then lessened for a short time at the end of a very dry summer.
Of plains proper, this district has only the stretch of country called Kaingaroa, extending from the eastern side of Lake Taupo towards the Bay of Plenty, all more or less of a pumice formation; the valley of the Thames, and the delta between the Thames and Piako Rivers, which is generally level, the quality of the soil varying very much in different parts; and the Central Waikato basin, already thickly settled. Here and there in the North there are level plateaux of volcanic soil, more or less densely wooded, and along the main rivers there are stretches of level country, but there are no large plains of alluvial soil such as the Middle Island can show.
Of these, which add so much to the scenery of a country, this district possesses a fair share, there being eight principal lakes, with some twenty or more smaller ones. To the north of Auckland, in the Bay of Islands district, there is only one lake of any size, called Omapere, three miles by two miles, an old crater. In the Waikato are Lakes Waikare and Whangape, the first six miles and a half long by three miles across, and the second five miles by one mile. These lakes are generally covered with numerous wild swans and ducks, and, being both connected with the Waikato River by navigable creeks, form a convenient waterway for transport of goods to settlers living around their shores. All the remaining lakes of large size are within the watershed of the Thermal-springs District, and are mostly from seven to eight miles long, and from three to six miles wide, except Taupo Moana, the queen of the North Island lakes, which is twenty-five miles long and eighteen miles broad, with a depth of 500 ft. The scenery round its western shore is of the most romantic kind.
The greater part of the Auckland Land District has been covered in the past with dense forests, which are now fast disappearing under the axe of the settler and being transformed into rich pasture-land. The only really good Crown lands fit for settlement in the North are still all covered with forest, and must be cleared and sown before any returns can follow. The area of forest land in the Auckland District at the present time is about 1,800,000 acres north of Auckland, and 3,420,000 acres south of it. The forests contain a mixture of trees of all kinds, from the giant kauri to scrubby tea-tree or manuka, but all the bush is useful for building, fencing, and household purposes, or at any rate may be converted into charcoal for sale. Of kauri (the most valuable tree in New Zealand) great quantities, worth as much as £1,000,000 per annum, are being yearly cut, and exported or use for home consumption. To give some idea of the size of these trees, and the amount of timber contained in them, it is estimated that upon the Crown lands in the Auckland Land District there are still remaining 1,185,000,000 ft., of a value, as the timber stands, of over a million sterling.
With respect to the soils of Auckland, nowhere in New Zealand within such short distances is there such a diversity in the quality—a distance of half a mile often makes all the difference between rich alluvial and barren pipeclay. To the north of the Bay of Islands and Hokianga the lands are chiefly clay and sandstone, with here and there a volcanic area intervening. In and about the valley of the Mangonuiowae River, in the Hokianga County, there is some of the richest alluvial soil in the district; and, taking the whole Crown land remaining to the north of a line between the Hokianga and Bay of Islands Harbours, the really available good land fit for settlement would be about 40,000 acres. There are large areas outside of this which will carry good grass and feed one or two sheep to the acre, after clearing and laying down in grass; and there is also land highly suitable for fruit-growing. South of Hokianga, and between that place and the Wairoa River, the soil is, generally speaking, very good, being both volcanic and alluvial. Here the Crown has probably 150,000 acres of such land fit for settlement. Immediately south of the Bay of Islands, and extending thence to Whangarei, the soil is, for the most part, clay lying upon sandstone or marl, with alluvial flats in the bottoms of the valleys; but these are, as a rule, very narrow. Within the Puhipuhi State Forest there is an area, say, of 16,000 acres, more or less, of volcanic soil. Approaching Whangarei, at Hikurangi, the limestone crops out, overlying coal-deposits, and round Whangarei itself the soil becomes a rich volcanic, in a high state of cultivation. South of Whangarei Harbour, and from thence to Auckland, the Crown lands generally are of a broken character, with soil varying from alluvial swamps—as in the case of the Tokatoka Swamp of 16,000 acres—to the limestone areas round Maungaturoto, the sandstone and clay lands of Rodney County, and the poorer clay lands lying north of the City of Auckland, which have, however, proved eminently suitable for fruit-growing.
For about 200 miles south of Auckland the land (with the exception of the Cape Colville Ranges) is, generally speaking, far less broken, and gradually opens out into large tracts of level country in the Waikato and Waipa basins. Immediately south of Auckland the soil is rich volcanic until it is gradually superseded by the prevailing clays; the greater portion of Manukau County, for thirty miles south of Auckland, may be classed as pastoral, and is under occupation as such. The Crown areas available for settlement—say, 16,000 acres—are chiefly in the Otau Parish, varying from volcanic clay to ordinary clay land, forest-clad, and well adapted for pastoral purposes. In the Counties of Waikato, Raglan, Waipa, Piako, West Taupo, and Kawhia, there is a still greater diversity of soils; Raglan County contains large areas of good limestone country, broken, but with rich black soil, and carrying most luxuriant grass. The lower Waikato country consists of clay soil and extensive swamps, almost undrainable, but at a distance of eighty miles from Auckland is found a flat and undulating country, lying partly within the Waikato and Waipa basins, and partly within the valleys of the Piako and Waihou Rivers, formed mainly of alluvial deposits of rhyolite sands brought down from the volcanic districts. In the Kawhia County there are some 300,000 acres of excellent limestone land, a large portion of which is heavily timbered, with numerous warm valleys. Most of this land has now been acquired by the Government from the Native owners, and is being opened for settlement. Beyond this there is a large stretch of country consisting alternately of open valleys and forest-clad hills, a fair proportion of which is good land, both pastoral and agricultural. The County of Coromandel, with portions of Thames and Ohinemuri Counties, is chiefly devoted to the mining industry. The soil is nearly all clay, the land very broken, but suitable for pastoral purposes if cleared of the dense forest that now covers it. The western portion, however, of the Thames and Ohinemuri Counties contain large areas of alluvial and swamp lands, now in the hands of the Crown, but, through want of drainage, not yet available for settlement.
In the County of Tauranga, the clay lands extend from Te Aroha Mountain to Katikati entrance, changing, near Tauranga, to sandstone and black pumice soil of rich character, which improves towards Te Puke and Maketu, where the land is all good, and more or less volcanic. In Whakatane and Opotiki Counties there are very extensive swamps, of which large portions are drainable, and back from the coast seven miles or so are large areas of Crown lands, broken and forest-covered, opened ready for settlement. The soil is chiefly clay or light loam, with alluvial flats in the valleys, and all well watered. This kind of country extends to the boundary of the land district. The coastal lands are nearly all alluvial flats in a high state of cultivation, and the settlers mostly well-to-do.
Briefly to set forth the capabilities of the Crown lands in the district, it will suffice to say that north of the Bay of Islands and Hokianga the land is suitable chiefly for two classes of persons—the gum-digger, and the fruit-grower or small farmer. The former has the range over large areas of Crown lands upon paying a small fee, and his earnings average from 5s. to 10s. a day. As for the latter, in and around Hokianga, with its 250 miles of water-frontage, almost anything can be grown, from the tropical banana to the more prosaic potato, whilst oranges and lemons flourish side by side with all kinds of apples, pears, and plums. Wheat does fairly well, and maize gives a return of 50 to 60 bushels an acre. Sheep also thrive; and most of the lands, when properly grassed with artificial grasses, will carry two or three sheep to an acre, but ordinary rough-grassed lands only one and a half to two sheep per acre. The Messrs. Williams, at Pakaraka, are feeding four sheep to the acre upon land sown with furze. The clearing of forest lands, ring-fencing and grassing them, will cost about £3 to £3 10s. per acre. The same remarks apply to the Bay of Islands and Whangarei, and to the country as far south as Auckland. Round about Whangarei district, and under similar conditions of culture, the average return for good agricultural or pastoral lands might reach 12s. an acre per annum. South of Auckland, throughout the Waikato, Piako, Waipa, and Raglan Counties, and thence south to the district boundaries, the land is both agricultural and pastoral. All the cereals do well, wheat averaging 27 to 30 and up to 40 bushels per acre, and oats 26 bushels per acre. Potatoes average from 5 to 7 tons per acre. Dairy-farming is carried on, yielding (upon well-cultivated farms) a net profit of 15s. to 20s. an acre per annum; whilst sheep-farming yields a profit of from 5s. to 7s. 6d. a sheep per annum on very large estates; allowing for greater losses from disease, &c., the average return would still be 4s. per sheep. The cost of clearing fern and scrub is generally from 7s. to 10s. an acre, and laying down fern land by surface-sowing and harrowing, about 17s. an acre.
The seaward counties of Tauranga, Whakatane, and Opotiki are both agricultural and pastoral, growing wheat and maize alike to perfection. In fact, these counties, upon their alluvial shores and uplands, grow the greater portion of the maize produced in the district, and from the ports of Whakatane and Opotiki in one year some 34,000 sacks have been exported. In these counties the average yield of wheat is from 22 to 25 bushels per acre, oats about 29 bushels per acre, and maize 45 to 60 bushels per acre. It is quite possible within this district to select land early in the winter, fell and burn off by the ensuing summer, sow in grass in the autumn, and put on stock within twelve months from selection.
The rainfall during the year averages about 39 in., the greater portion of which, as a rule, falls between the 1st of May and 1st of November, or during the winter and spring months. Owing to the constant changes of wind, caused by the configuration of the coast-line, the shortness of the distance between the two coasts, and the influence, greater or less, of the trade-winds, it is quite common for one neighbourhood to have double the rainfall of another, even though the two be only twenty miles apart. Droughts of more than a couple of months are practically unknown, and grass is always abundant.
One of the chief means whereby the great healthiness of the climate is maintained is the constant presence of fine breezes, blowing both summer and winter, the prevailing winds being north-east and south-west, and very seldom passing into really heavy gales. In the middle of summer, the sea-breeze during the day and the land-breeze at night are almost unvarying.
Timber.—The vast forests of kauri and other valuable trees have given this district the foremost place for production and export of timber. There are many safe and sheltered harbours for shipping, while streams and rivers without number form convenient highways for conveying logs to the mills or ports. Some idea of the extent of this industry may be given by quoting from the official returns made at the time of census of 1901. There were then forty-eight sawmills situated in various parts of the district, with engines of a total of some 3,100-horse power. These mills employed over 2,000 men, and produced yearly some 109,000,000 ft. of sawn timber, valued at £459,128; of timber resawn into flooring, skirting, &c., some 14,000,000 ft., valued at upwards of £79,000, not to mention posts and rails, mouldings, sashes, and doors. Besides this output, in the remoter parts of the district large quantities of timber are hand-sawn. The durable puriri is converted into railway-sleepers, for which there is a great demand, and the totara is largely sought after for telegraph-posts and wharf-piles.
Kauri-gum.—The most unique production of this portion of the colony is kauri-gum, obtained for the most part from the country north of Auckland. It is formed by the hardening of the exuded turpentine from the kauri tree, and is dug out of ground from which the forest has been burnt off. The Royal Commission appointed in 1893 elicited the fact that the procuring of the gum gave employment then to no less than 6,897 persons. Last year 7,430 tons were exported, valued at £450,223. The kauri-gum is extensively used in the manufacture of varnish, and also for glazing calico. Nearly two-thirds of the varnishes in the market are produced from this gum. The average earnings of a digger may be taken as from £1 7s. to £1 10s. per week.
Flax (Phormium tenax).—An industry, which has assumed large proportions, is the conversion of the broad leaves of the Phormium tenax into marketable flax suitable for the manufacture of rope, twine, mats, mattresses, and numerous other articles. The flax-mills are scattered over different parts of the district, as near rail or water carriage as possible, and employ a considerable number of men and boys, whilst the local rope and twine works give work to a good many more. The export from Auckland Land District of phormium for the year 1902–1903 was 4,105 tons, valued at £111,091.
Gold.—This district has in the past produced large quantities of gold, but the area over which auriferous quartz-reefs has been discovered is limited to the Counties of Coromandel, Thames, Ohinemuri, and a small portion of Piako. In 1902–1903 the output of this neighbourhood was 39 per cent. of all the gold produced in New Zealand. The total estimated value of the gold was £724,892 for 1902–1903. All the gold won was obtained by battery amalgamation and the cyanide process. There is a large amount of English capital being expended in developing new discoveries in out-districts away from the goldfield, but it will be some time yet before these discoveries have reached their full development. At the Thames there is a School of Mines, well attended and showing good results.
Coal.—Coal is found in most parts of this district, and is being worked with more or less success at Kawakawa, Hikurangi, Kamo, and Ngunguru, to the north of Auckland; whilst in the south there are three mines at Huntly, all turning out a good household coal.
Fruit.—The climate of the Auckland District is well adapted for the growth of the orange, lemon, vine, and olive, as also for the fruits of England, America, and Japan. The subtropical kinds flourish about Hokianga, in the north; those of the temperate regions, in the Waikato and neighbourhood. Now that the problem of how to land fruit in good condition in the London market has been solved, orchard planting is rapidly progressing, and it has been found that the culture of the hard varieties of the apple will repay export to England. Of late years a demand has set in for the poor clay land that used to contain gum, as it is admirably suited for fruit-growing. Orchards are now planted in neighbourhoods where the soil has lain idle for years, for it has been proved that apples grown on this poor soil keep longer than those grown on richer land. What can be done by cultivation and care on poor lands is evidenced at the Waerenga Government Experimental Plantation in the Waikato, where the two orchards of fruit trees and vines show most luxuriant growth. More attention is being just now paid to stone fruits, for which there is always a steady local market, than to apples, which have of late years been heavily handicapped by blight. The fruit industry in Auckland is yet in its infancy, and is capable of great extension. At present peaches are the only fruit canned, though there is also a good deal done in the way of drying fruits and vegetables by the process of evaporation.
Fishing.—The sea and harbours abound in fish. At least eighteen different varieties suitable for the table are caught with little labour, and settlers living near the sea-coast or any one of the many harbours and tidal rivers can always obtain enough for all necessities. At present the canning industry is confined to mullet, of which there is a large amount exported, and an equal quantity used for home consumption. The rock-oyster is found over a large area on these coasts, and large quantities are sent both to the southern ports of the colony and also to Australia.
The City of Auckland lies on the southern shore of the Waitemata Harbour, one of the finest havens in the colony, on a narrow neck of land between the Waitemata and the Manukau. Alike from the sea and from the neighbouring hills the city and surrounding country present a charming picture. Especially fine is the view from Mount Eden, a low volcanic hill in the suburbs. Facing the town are the green hills and white houses of the North Shore, and the remarkable island peak of Rangitoto; beyond lie the many islands of the Hauraki Gulf, with the blue hills of Coromandel and the Great Barrier in the far distance. Clustered near the foot of the hill, and scattered for many miles to the southward, are charming villa-like houses, with tasteful gardens and shrubberies, while to the north-west the view is closed by high wooded ranges. The city has an excellent commercial position; it has communication by sea with both sides of the Island, while the Kaipara and Wairoa Rivers leading far into the northern peninsula, and to the south the Waikato and Thames Rivers leading into the heart of the Island, give it natural facilities for inland communication. In March, 1901, the population of the city and suburbs amounted to 67,226 persons. The city is well supplied with gas and water, and amongst public buildings may be noticed Government House, the new Government Offices, Post and Telegraph Offices, Supreme Court, &c. There is a Free Public Library and Art Gallery, and a good Museum, containing what is probably the best Maori collection in the world. The Auckland University College is affiliated to the New Zealand University. The Victoria Arcade, the Exchange, Harbour Board Offices, hotels and clubs, as well as many commercial buildings, compare favourably with those in other parts of the colony. There are admirable recreation-grounds, including the Government Domain of about 180 acres, as well as the Botanic Garden and the Albert Park in the centre of the city. There is an electric tramway system extending through the suburbs. Auckland has numerous industries, including, amongst others, ship-building, sugar-refining, timber-converting, sash and door manufactories; rope and twine, pottery, brick and tile, and varnish works; printing-offices, &c.
The City of Auckland is the centre from which radiate all railways, road, and steamer routes. From it, by rail, lies the way to all Crown lands south of the Waitemata, while the Kaipara Railway connects it with the country north of Helensville. All lands to the north and along the Bay of Plenty are reached from its wharves by the Northern Company's steamers. The chief centres to the north are:—
Warkworth, on the East Coast, forty miles from Auckland, with communication by coach and steamer nearly every day. It is a thriving township, with post and telegraph office, public halls, hotels, &c. It is also the site of important hydraulic-lime and cement works. A good deal of agricultural and pastoral farming is carried on in its neighbourhood.
On the West Coast an important centre is Helensville, on the Kaipara Harbour, distant thirty-eight miles from Auckland, with which it is connected by rail. It has all the conveniences required by travellers in the shape of good hotels, stores, &c., and is the starting-point of the river-steamers running to all places in the Otamatea and Hobson Counties. It is also one of the main centres for the export of balk timber.
North of Helensville the railway has been opened to Ahuroa, fifty-seven miles from Auckland. The line is under construction to Hotea, and will eventually be carried on to Maungaturoto.
Dargaville, on the Wairoa River, is a town of about 500 inhabitants, with all conveniences for travellers. It may be reached by rail and steamer from Auckland three times a week. Dargaville is the starting-point of the Kaihu Valley Railway, which is open for traffic for seventeen miles from the town, and from the terminus of the railway all the Crown lands in the neighbourhood are reached, even so far north as Hokianga. The town is also the centre of a very large timber export. There are only two townships on the west of any importance north of Dargaville—Port Rawene, or Hokianga, and Kohukohu, about four miles further up. Both have post and telegraph stations, and comfortable hotels, with fortnightly steam-communication from Auckland.
Whangarei, on the East Coast, is distant seventy-five miles from Auckland, with which it has steam-communication twice a week. The town is a thriving and important place, having a population of about 1,500, and is the centre of a large agricultural and pastoral country. In the neighbourhood is also a large coal-bearing and gum-producing district, while the export of oranges and lemons, which thrive magnificently on the rich volcanic soil, is on the increase. From here, all lands within a radius of thirty to forty miles may be visited by horse, carriage, or ail. Opau Wharf, about three miles south of Whangarei, is the present commencing point of the railway-line passing through Whangarei and Kamo to Hukerenui, a distance of about twenty-three miles. This line will ultimately join that now being constructed in a southerly direction from Kawakawa. A bridge is also being built over the Whangarei River, in order that the railway may be extended from Opan Wharf to deep water at Grahamsfern, three miles distant.
Kawakawa, at the head of the tidal portion of the river of the same name, is connected by a short railway-line with Opua, the calling-place of steamers from Auckland. Kawakawa possesses good inns. From it coaches run weekly to Hokianga and Whangarei. It is the centre of a coal and gum industry, and a port of lading for those products. The old town of Russell is situated further down the bay, and has a good hotel, besides having a post and telegraph office. To Whangaroa, Mangonui, Awanui, Hohoura, and Parengarenga the Northern Company's steamers run every week. Whangaroa is famed for its exquisite scenery, and is the centre of a large timber and gum export trade. Mangonui is the starting-point and centre from which to visit, by carriage or horse, all the Crown lands in the Mangonui County.
South of Auckland, along the Waikato Railway, there are numerous townships of more or less importance, but no starting-point for Crown lands until Mercer is reached at a distance of forty-three miles. It is situated at the borders of what is known as the Waikato Country, upon the Waikato River, which is tidal up to this point, and the township has a post and telegraph office and other conveniences. At sixty-five miles from Auckland by rail is Huntly, also on the Waikato River, a flourishing township, with a large output of valuable coal. It has also pottery, brick, and tile works. On the opposite side of the Waikato River large areas of Crown lands are being brought into use, and are carrying numbers of sheep and cattle. The next town is Ngaruawahia, or Newcastle, seventy-four miles from Auckland, situated at the junction of the Waikato and Waipa Rivers, with hotels, bank, post and telegraph office. It is a centre from which portions of Crown lands in Raglan County are reached, and also from it river-steamers run north and south to the various settlements. Ngaruawahia has a flourishing creamery, a brewery, and a cooperage. At eighty-five miles from Auckland the train reaches Frankton Junction, where a line branches off to Hamilton, Te Aroha, Paeroa, Thames, and Rotorua, the main line going through Te Awamutu, 100 miles from Auckland, to Poro-o-tarao, 146 miles. The line has been formed to Taumaranui, and may be open for traffic up to that point (174 miles from Auckland) about November, 1903, by which date the bridge over the Wanganui river will have been completed. This will enable platelaying and ballasting to be carried on over the Whakapapa and Owhango sections, which are now under formation for a further distance of about 14 miles. The summit of the line is reached at Waimarino (206 miles from Auckland). Te Awamutu is a thriving town; but to reach available lands for future settlement the traveller passes on by rail to Otorohanga (114 miles). Te Kuiti and Poro-o-tarao, twelve and thirty-two miles further on respectively, are both places at which there are accommodation-houses, forming convenient centres for visiting the fertile undulating limestone lands in the vicinity. Hamilton is a busy, flourishing town, situated on both sides of the Waikato River, with a population of about 1,300 persons, and is the centre of an agricultural and pastoral district. It possesses a creamery, flax-mill, brewery, and two soap-factories, besides other local industries. Cambridge, about thirteen miles by road and fifteen miles by rail from Hamilton, has a population of about 1,000, and is the headquarters of the Farmers' Club. It is a busy, thriving township, surrounded by good farming country. Between Hamilton and Cambridge, and in the country round, there are numerous creameries, cheese and butter factories. Wine and cider making is also successfully pursued, and there are several apiaries, from which large quantities of honey are produced. There are three flour-mills in the district, one at Cambridge, one at Hamilton, and the third at the terminus of one of the before-mentioned branch lines. One hundred and fifteen miles from Auckland by rail is Te Aroha, a quiet township, celebrated for its thermal springs, with good hotels. Another thirteen miles brings the traveller to Paeroa, a centre of mining industry, whence a branch line 12 ½ miles long is under construction to Waihi, a gold-mining town, and in another twenty miles the Thames Borough is reached.
The settlements at the Thames and Coromandel are essentially mining townships. The first is situated thirty-eight miles by steamer from Auckland, on the Firth of Thames, and at the mouth of the Waihou River. It has a population of about 4,000 persons. There is daily rail and steam communication with Auckland, and a railway connecting it with Paeroa and Te Aroha. Coromandel is about thirty-five miles from Auckland, with which it has constant communication by steamer; it is another mining centre, situated at the head of a picturesque harbour. Tauranga, with a population of about 1,000, is situated on the harbour of that name in the Bay of Plenty. Coaches run thither from the Thames, and from Rotorua; it has also constant communication by steamer with Auckland, and with Matata, Whakatane, and Opotiki. From the fact of the harbour being the only one on the East Coast between Coromandel Peninsula and Gisborne capable of receiving large vessels, the town is bound to be of importance in the future.
Opotiki, the second town of importance in the Bay of Plenty, is situated about sixty-five miles by steamer or road from Tauranga. It has weekly steam communication with Auckland, and is connected with Gisborne by a bridle-track. It is the headquarters of the maize-producing district, and has rich alluvial lands, from which good returns are obtained. It is a starting-point from which large blocks of Crown lands suitable for pastoral purposes may be reached.
The Township of Rotorua is situated on the shores of Rotorua Lake, at a distance of 171 miles by rail from Auckland. Travellers can reach Rotorua in one day from Auckland. It is the chief township in the hot-lakes district, and has also a large area of fairly good Crown land near, adapted for pastoral purposes. Considerable quantities of sulphur are obtained from the neighbourhood.
In the Mangonui County there are open about 15,662 acres, surveyed into sections of fairly good forest land, tolerably easy of access.
In the Bay of Islands County there are about 9,074 acres of Crown lad surveyed, both forest and open, but the Natives still own some 152,000 acres, chiefly forest land, except about Kaikohe, where it is open and rich volcanic land, most of it broken, but fit for settlement.
In Hokianga County there are 23,752 acres of available Crown land, surveyed into sections, of good quality, nearly all covered with forest, and fit for immediate settlement. The Natives still own some 104,650 acres, almost all good land, and fit for settlement.
In Whangarei County there are about 6,443 acres of available surveyed land, mostly broken and forest-clad. The Natives still retain some 28,850 acres of land, part of it very rich.
In the Otamatea County about 408 acres surveyed, a good deal of this being alluvial swamp, and now well drained. The Natives still own about 20,000 acres, but not much of it is fit for settlement.
In the Rodney and Waitemata Counties about 6,832 acres of Crown lands are surveyed, most of it fit only for pastoral or fruit-growing purposes. The Natives still own about 14,000 acres in these two counties, some of it very good land.
In the Manukau County the Crown has some 1,703 acres surveyed of broken forest land, fit for pastoral purposes. The Natives still own about 15,000 acres, a portion of which is fairly good.
In the Waikato and Raglan Counties the Crown lands open and surveyed are about 9,573 acres, all fairly good land, mostly forest, and easy of access. In Raglan County the Natives still own the freehold of 150,000 acres, all good land.
In the Coromandel, Thames, and Ohinemuri Counties there are about 6,525 acres of Crown lands surveyed, a great deal of it too broken for settlement. In the last two counties a good deal of the land is swampy, and requires draining. The Natives still own 97,200 acres, much of which is very good.
In Tauranga, Whakatane, Opotiki, and Rotorua Counties the Crown has 12,671 acres open and surveyed, nearly all forest-clad, and generally broken; but in the last-named county the Natives retain a very large area, the greater part too broken or too much covered with pumice or volcanic ash to be fit for settlement.
In the Kawhia and West Taupo Counties about 32,938 acres surveyed and open, really first-class land, all suitable for pastoral purposes, and accessible from the Main Trunk Railway-line.
In addition to the above lands open and surveyed there are about 419,381 acres open of unsurveyed land. Month by month additional land is surveyed and placed on the market so that the demand can be satisfied.
The progress made by the dairy industry in Auckland during the last few years is remarkable. The numbers of factories and skimming-stations for 1902 in the provincial district are 52 and 69 respectively, against 33 and 59 in 1901. The North Island shows an increase of 27 factories and 37 skimming-stations, the increase being by far the largest in Auckland—19 and 10. There is also a “tinning-house” in the district. Of the 52 factories in operation, 44 are butter and the remainder cheese factories. The larger companies own between them over 50 separate creameries, where milk is collected to supply the factories. The butter exported since the beginning of the 1902 season up to January, 1903, was 40,459 boxes of 56 lb. each and 3,638 kegs of 112 lb. each, totalling 23,867 ½ cwt., this season's output being 3,647 ½ cwt. more than that of last season at the same date.
Several creameries, &c., are now being erected, and are in their initiatory stages. When in full working-order they will greatly add to the returns.
The increase in the export of factory butter from Auckland to London for 1903 season is 1,356 packages, valued at £3,000. To this must be added Australian shipments, South African, and local requirements. New factories have been opened at Te Rau-a-Moa, Waihou, Hunua, Tauranga, Matakohe, and Matakana. The New Zealand Dairy Association have also largely extended their operations.
The industry increases in a satisfactory ratio as new land is opened for settlement and laid down in grass.
The recent drought has been the means of compelling the Australian States to look to this colony for a considerable portion of their butter supply. Regular shipments also have been made to South Africa, so it may be supposed that a market has been established there.
The output for next season will be largely increased, as during the last few years a great number of settlers have been placed on lands in the King Country, where they have cleared and grassed their holdings.
Table of Contents
The Taranaki Land District is situated on the western side of the North Island of New Zealand, at about its widest part, and may be said to be the most compact and fertile district of the colony, for, with the exception of the upper half of Mount Egmont, and of the ranges adjoining, which absorb about 36,000 acres, the whole of the area—minus what is taken up by the rivers, streams, and lakes—is suitable for settlement, and certainly two-thirds of the district is good land. The gross area of the district is 2,430,000 acres.
Of mountains, the principal one is the beautiful volcanic cone from which the district takes its name, Taranaki, otherwise called Mount Egmont, which has an altitude of 8,260 ft. This mountain is the centre of distribution for a radius of twenty miles of the volcanic formation known as the “drift,” which covers the volcanic rocks below an altitude of 3,000 ft. Hummocks composed of trachyte boulders and cement crop up here and there and make excellent metal-quarries.
Beyond the volcanic formation—that is, from about Urenui on the north and Hawera on the south—the country is generally broken, and the formation is known as papa, a calcareous blue clay, capped in many places by shelly limestone.
The northern portion, between the Tongaporutu and the Mokau Rivers, contains also limestone, greensands, and coal outcrops. At Panirau, a small tributary of the Mokau, about thirty miles from the sea, there is an isolated patch of volcanic agglomerate and tufas, and a similar formation is found at the north-eastern corner of the district.
Eastward of the base of Mount Egmont there are few, if any, mountains worthy of the name, although there are many ranges varying in height from 1,000 ft. to 1,500 ft. above sea-level, and, in a few instances—such as the Matemateonga and Waiaria Ranges—they run up to 2,500 ft.
The principal river is the Wanganui, which bounds the district on the east between Taumaranui and Pipiriki, a distance of about ninety miles. Its average width varies from 2 to 3 chains. For nearly the whole distance it is shut in by high precipitous hills, and in many places by perpendicular walls of rock. The scenery is very grand and beautiful. There are numerous rapids, but few of them are dangerous to skilful canoeists. Steamers run regularly from Wanganui to Pipiriki, a distance of fifty-five miles.
Messrs. Hatrick and Co. are running a steamer between Pipiriki and Putikituna, some twelve miles up the Tangarakau River. From this point a road (nine miles in length) has been constructed to join the Ohura (or East) Road at a point about forty-seven miles from Stratford, and in the middle of the Whangamomona Improved-farm Settlement, the settlers in which and surrounding blocks will thus have double communication, with Wanganui on the one hand and Stratford on the other. When the road is completed through to Auckland, tourists can enjoy a trip up the Wanganui River as far as Ohura, then back, and up Tangarakau River across to Ohura Road, then on to Auckland, or back to Stratford, as they desire. The dimensions of the steamer are 40 ft. long by 8 ft. beam, with a light draft of 9 in. and passenger capacity for forty, the amount of cargo depending on quantity of water in river from time to time. The time-table as at present arranged is: Leave Putikituna for Pipiriki and Wanganui every Tuesday morning at 10 o'clock, and every Sunday leave Pipiriki for Putikituna. The principal tributaries flowing into the Wanganui on the Taranaki side are the Whangamomona, at eighty-two miles; Tangarakau, at eighty-five miles; Ohura, at 114 miles; Ongaruhe, at 143 miles respectively from the Town of Wanganui.
The next river in size is the Mokau, bounding the district on the north. It is navigable for handy steamers drawing from 7 ft. to 8 ft. of water as far as the coalmines, about twenty miles from its mouth, and for canoes as far as Totoro, twenty-six miles further up. Several outcrops of coal are found on its banks, and, as limestone is also present, the river is likely to become an important waterway of the district. The scenery on either side, although not on quite so grand a scale as may be seen on the Wanganui, is very beautiful.
The other large rivers are the Waitara and Patea. The former has its source about midway between the coast and the Wanganui River, in an easterly direction from Pukearuhe, between New Plymouth and the Mokau. It is about a hundred miles in length, and runs out at the Town of Waitara, some ten miles north-east from New Plymouth. There is a bar at the mouth, but steamers of 300 tons can enter safely in calm weather, and, although there are numerous rapids on its course it is navigable for canoes for about ninety miles.
The Patea River rises in Mount Egmont, and, after traversing a tortuous course of about 110 miles, runs out at the extreme southern end of the provincial district. It has a bar-harbour, with a depth of 13 ft. to 14 ft. at spring-tides. Steamers of from 40 tons to 50 tons trade regularly to the town of Patea, which is situated a mile or so north of the mouth. The Patea is navigable for canoes for fifty miles.
Besides these rivers there are many smaller ones, and streams innumerable—in fact, no district in the world could be better watered and at the same time be so secure from disastrous floods. It is estimated that between the Mokau and the Patea there are no fewer than eighty-five named streams emptying themselves into the Tasman Sea, fully sixty of which flow from Mount Egmont.
Excepting the Ngaire Swamp, a block of open land near Eltham, 3,700 acres in extent, now partially drained and recently disposed of for settlement purposes, there are no plains, properly so called, in the district, although the stretch of very fertile country lying between the Waingongoro and Otakeho Rivers, comprising an area of about 25,000 acres, is known as the Waimate Plains. Of this area 13,500 acres have been disposed of, and the remainder, 11,500 acres, has been handed back to the Natives as a reserve.
There are no lakes worthy of the name. The largest sheet of water is Rotokare, situate about twelve miles from Eltham; it is about half a mile in length, with an average width of six chains. There are also a few small lakes inland from Waverley, at the southern end of the district.
The whole of the district, with the exception of a fringe of open country along the coast from Pukearuhe to Patea, averaging three miles in width, and containing about 250,000 acres, and some valleys at the north-eastern corner of the district, about 150,000 acres in extent, was originally covered with heavy forest, but this is rapidly disappearing under progress of settlement and erection of sawmills to deal with such timber.
The larger timber is chiefly rata, rimu, matai, tawa, kahikatea, kohekohe, pukatea, rewarewa, hinau, with a few totara scattered here and there. Among the smaller trees may be mentioned the kotukutuku or fuchsia, karaka, and mahoe.
As regards the timber industry, there are altogether thirty-nine sawmills, and the total quantity cut in 1902 was 22,187,995 ft., chiefly rimu, 15,530,000 ft.; kahikatea, 5,272,709 ft.; totara, 620,000 ft.; and matai, 765,286 ft. Most of these mills work together under Association rules and prices, their output for the year being 14,062,686 superficial feet. The others work independently, and their output amounted to 8,125,309 ft. for the same period.
An area of 72,565 acres, measuring six miles on every side from the summit of Mount Egmont, was originally set apart as a forest-reserve. To this has now been added 1,040 acres on the lower slopes of Pouakai Range, with an additional 5,500 acres on the Patua Range, making a total of about 79,000 acres, which has now by Act of Parliament been set apart as the “Egmont National Park,” the internal affairs of which are administered by a partly elected and partly nominated Board of ten members. At about three miles within the reserve the forest begins to get stunted; and at four and a half miles it gives place to low wiry scrub, which ceases at five miles, or an elevation of about 4,000 ft. At 5,000 ft. the moss ends; beyond this point to the summit the mountain is composed of loose scoria and lava.
A comfortable house, known as the Egmont Mountain-house, has been built at an elevation of 3,200 ft. on the northern face of the mountain, at a distance of twenty miles from New Plymouth by the Junction and Egmont Roads. Eighteen miles can be driven over, and the remaining two ridden. This house is maintained by the Egmont National Park Board, and is open for the accommodation of visitors from about the 20th of December to the middle or end of April in each year. The keeper acts as guide also. The time usually occupied in the ascent from the house is from three to four hours for men, and four to six hours for ladies. There are two women's rooms at one end of the house, and two men's at the other, with large common living and dining-room in the centre. Visitors have now the option of being supplied with meals at a cost of 1s. 6d. each, or they may provide and cook their own food. Horse feeds, 1s. 6d. each; paddocking, 6d. daily, or 2s. 6d. a week. A small charge for use of house is made to visitors of 1s. per night or 5s. per week throughout the visit. In addition to the mountain-house, the Board has erected a cottage of three rooms, comprising two bedrooms (fitted with four bunks each), and one living room in between. This cottage is intended for renting by the week to family parties, only one such party occupying it at a time, the minimum charge per week being two pounds sterling for a party of four adults; over that number and up to eight (the limit allowed), 7s. 6d. each per week; children over five and under twelve years, half rates. The cottage is not let to any one party for a longer period than two weeks while there are other applicants. The Board provides cooking and other utensils, firewood, and water, also mattresses and pillows; but visitors must take their own blankets, and provide and cook their own food. The caretaker at the mountain-house keeps a small stock of the principal lines of food usually wanted for sale to visitors. The cottage is within 60 or 70 yards of the mountain-house, and in charge of the same caretaker, but parties desirous of renting it should communicate with the Honorary Secretary to Committee for Northern Division of Egmont National Park, New Plymouth, giving dates between which they require it. These applications are booked in order of priority of receipt (after notification that offers will be received, usually in the early part of December). The cottage is opened and closed on same dates as the mountain-house. Guide's fee for mountain, £1 per party. During the past season there were 1,022 visitors, remaining various periods of from one or two days to as many weeks. The view from the top is superb, including as it does, volcanic cones of Ruapehu, Ngauruhoe, and Tongariro, the whole of Taranaki, and a considerable portion of Auckland and Wellington Districts, also across Cook Strait to the mountains of Marlborough and Nelson Districts of the Middle Island. In fine weather, when the snow is off, the mountain can be ascended without risk. A considerable sum has been expended in improving the accommodation at the house.
The mountain can also easily be ascended from Stratford side, the return journey occupying about thirteen hours, including stoppages. Tourists can ride over the first eleven miles to the Pembroke Road Mountain-house (three rooms) above the bush-line, altitude 3,720 ft.: time occupied, about two and a half hours. A new two-roomed cottage has been erected, and is now in use. Here the horses are left, and the remaining climb has to be done on foot: time required for a fair walker, three hours, although, coming down, the distance can be done in two hours. Three hundred and fifty persons visited the mountain by this route during the season. Good hotel-accommodation, guide, and horses can be obtained in Stratford. Provisions are kept on reasonable terms by the caretaker at the house. The return trip can be varied by visiting Dawson's Falls and Kendle's Cascade, or by a run across to the Egmont Mountain-house. Those who do not care to attempt the summit will be amply repaid by the pleasure of the ride through the forest and by the magnificent views to be obtained from the house. The houses have sleeping accommodation for about thirty persons.
Another route now coming into favour is from Hawera or Eltham viâ Manaia or Kaponga and Dawson's Falls. At the latter place a comfortable shelter-house, capable of accommodating over forty people, has been erected, and is known as the Falls Mountain-house (altitude, 2,990 ft.). This house, which is close to the Falls (65 ft.), is within an easy two hours' ride of Kaponga. During the season the house is in charge of a caretaker, and food, horse-feed, and paddocking can be obtained. There were 1,084 visitors to Falls and mountain by this route during last season. A comfortable three-roomed cottage has been erected in connection with this house. Water is obtained from the adjoining creek by means of a ram. From the house to summit of Mount Egmont occupies from four to six hours' climbing at a moderate pace, the time being in accordance with strength and composition of party. From the top the tourist can, instead of returning by the same route, drop down to the mountain-house on the north or New Plymouth side of the mountain. The walk would not occupy over two hours, easy walking, or he could go out viâ Stratford.
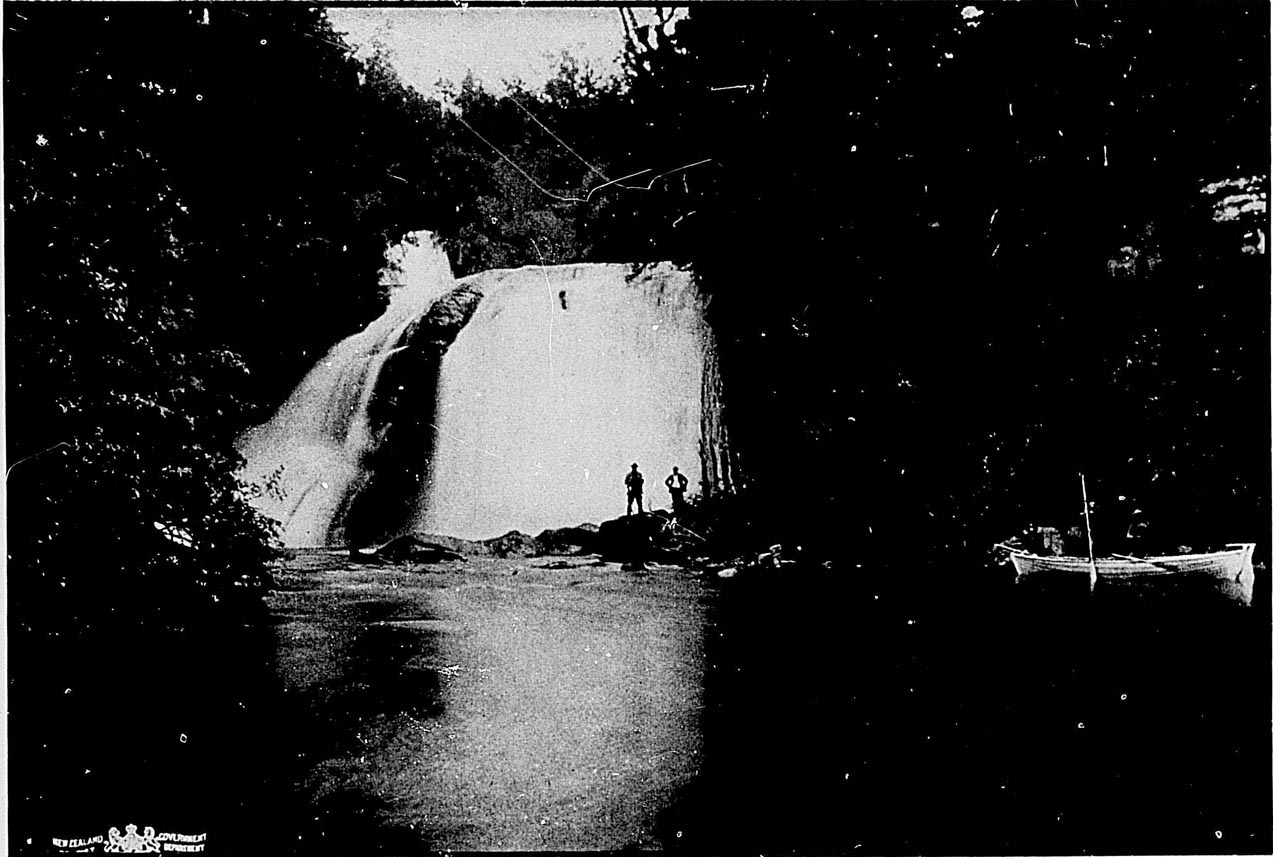

Waterfall, Waikaremoana.
Recently a track has been partly made from the western side of the mountain, enabling 200 tourists to ascend via Rahotu. A small accommodation-house has been erected, 32 ft. by 14 ft., consisting of a general room and two sleeping rooms, each containing twelve bunks. Tables, forms, and utensils have also been provided.
The volcanic soil, the boundaries of which have been already described, varies a good deal in quality. The best is believed to be on the south side of the mountain, between Stratford, Hawera, and Opunake, but not less than two or three miles from the forest-reserve boundary. It is thought that the country now being opened to the north and east of the volcanic deposit—that is, the papa and limestone formation—will, from the presence of lime, be much richer and more lasting as pasture-land than that around the mountain. The carrying-capacity of the land is, on an average, two and a half to three sheep to the acre.
Taranaki is essentially a grazing and dairying district, its chief products being butter and cheese.
There are 97 dairy factories and 78 skimming stations scattered over the district. Of these factories, 83 produce butter only, 9 butter and cheese combined, while 5 produce cheese only. Sixty-nine factories and creameries are owned by proprietory companies, while 106 are run on co-operative principles. There are also in this district 14 registered packing-houses for milled butter, 251 registered private dairies for butter-making, and 2 for cheese only, besides many small plants run on individual farms of which no record is obtainable.
In September, 1896, a new work in connection with the dairying and meat industries was started in the shape of the Taranaki Freezing Works. They are situated at Moturoa, near the breakwater, and close alongside the railway-line. Substantial buildings have been erected, and a railway siding laid down. The machinery consists of a “Paxman” compound surface-condensing engine of forty indicated horse-power, driving a “Livide” compressor, capable of freezing 400 sheep per diem: although up to the present time the company has confined its attention wholly to the freezing of dairy produce. During the year 1902 the output from the works has been—Butter, 154,567 packages, weighing 3,864 tons net; cheese, 8,741 packages, net weight 586 tons. During the hot season the factories ad railway-vans carrying butter have been supplied with ice from the works at a nominal cost. Most of the butter from the southern end of the district now goes to Patea.
At the Taranaki Bacon Factory, Fitzroy, substantial buildings have been erected, and a 6-horse-power “Livide” machine fitted up, and the owner has the works in full swing. The pigs are purchased from the farmers in the district and delivered at the styes in connection with the factory, where they are topped off with corn-feeding for fourteen days before being slaughtered. The number of pigs put through during past season—a slack one—was 2,025; price paid, £2,050. The hams and bacon exhibited by this factory have always taken first-class honours in the various agricultural shows. An industry like this cannot but prove of great assistance to settlers in the district, and should receive their most cordial support.
There are in the Taranaki District 18,903 horses, 239,910 cattle, 552,833 sheep, and 19,615 swine. These figures include all kinds and ages.
Agriculture has not hitherto been carried on to any great extent in this district. The total area under corn-crops and cut for threshing during season 1902–1903 was 7,363 acres; corn- and grass-crops cut for hay, chaff, or ensilage, 12,142 acres; corn- and green-crops for feeding to, or down with, stock, 1,043 acres; sown grasses and clovers for feeding down, 782,102 acres; sown grasses for seed, 766 acres; potatoes, 1,440 acres; beet, 10 acres: turnips, 7,617 acres; mangolds, 753 acres; rape, 2,136 acres; carrots, 501 acres; other crops, 82 acres; total area under crops of all kinds, including gardens, orchards, vineyards, 820,831 acres. Plantations, 1,186 acres; fallow, 106 acres.
The average yield of different grain-crops in bushels per acre for season of 1902–1903 was: Wheat, 40·0; oats, 42·0; barley, 41·0.
The only mining going on at present is at the Mokau Coal-mines, which are situated on the Mokau River, about twenty-three miles from the sea, the river being navigable right up to the mines for vessels of 7 ft. 6 in. draught. The coal is the best class of pitch-brown, and is excellent for household and steam purposes.
Ironsand is found in great abundance on the seashore from Mokau to Patea, a distance of 130 miles. It produces, when smelted, from 50 to 60 per cent. of iron of the finest quality. The first attempt to smelt this sand was made in 1848, and several trials have been made since, but the heavy cost of production and the absence of capital and modern appliances have, so far, retarded the industry. Strong efforts are now being made to remedy this by the introduction of outside capital, and it is hoped these will shortly be successful.
The climate of Taranaki is remarkably healthy, without any extremes of temperature. Below is given a table of mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures in shade for each month of the year ending December, 1902:—
| Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | April. | May. | June. | July. | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature | 66 | 66 | 65 | 63 | 61 | 55·6 | 56 | 55·6 | 58 | 58·7 | 61·5 | 64·6 |
| Extreme maximum temperature | 83 | 84 | 80 | 83 | 84 | 83 | 84 | 82 | 86 | 84 | 85 | 90 |
| Extreme minimum temperature | 46 | 46 | 41 | 34 | 36 | 32 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 36 | 40 |
| Number of days on which rain fell | 19 | 13 | 14 | 24 | 25 | 18 | 21 | 16 | 26 | 22 | 22 | 23 |
| Total rainfall per month in inches and decimals | 3·600 | 2·590 | 2·630 | 6·340 | 5·690 | 5·030 | 1·490 | 3·800 | 5·830 | 5·580 | 3·540 | 5·650 |
| Mean barometric reading for the month | 29·99 | 30·11 | 30·19 | 30·21 | 29·88 | 30·152 | 30·18 | 30·157 | 29·904 | 30·078 | 30·10 | 30·017 |
The mean barometric reading was 30·080 in. for the year. Total rainfall, 51·770 in. on 243 days. The rainfall varies considerably, as, for instance, at Norfolk Road, three miles south of Inglewood, the rainfall for the year 1902 was 78·33 in. on 198 days; the maximum fall was 2·85 in. on 21st June. The average rainfall at New Plymouth during the past eight years was 61·712 in., and at Norfolk Road for same period 98·485 in.
The principal town of the district is New Plymouth (population about 4,885), situate on the seashore, about two miles from and to the north-east of the picturesque rocky islets known as the Sugar Loaves. The general appearance of the town is very attractive, and it abounds in neatly-kept gardens. The Recreation Grounds, from which a good view of Mount Egmont is obtained, form a favourite resort.
New Plymouth is 251 miles by rail from Wellington, the railway running in a northerly direction through the district from Patea to Sentry Hill, where it turns at right-angles westward for eight miles to New Plymouth. From Sentry Hill there is a branch line to Waitara, four miles distant.
The Port of New Plymouth is situated at the Sugar Loaves, two miles from the town. Protection for shipping is afforded by a concrete mole or breakwater running in a north-east direction for a distance of 1,900 ft. Under the lee of this there is wharf-accommodation provided for the coastal trade. Steamers of 1,000 tons can be berthed here in almost all weathers. The wharf is connected with New Plymouth by both rail and road. The breakwater was built at a cost of £200,000, borrowed under security of one-fourth of the land revenue of the Provincial District of Taranaki, and the right to levy a rate over certain lands. The present rate levied is ¼d. in the pound on the capital value. The principal over-sea exports from breakwater for the year (exclusive of all coastal trade) were: Bacon and hams, 1,007 cwt., value £3,491; butter, 81,009 cwt., value £374,089; cheese, 9,547 cwt., value £20,998; fungus, 1,064 cwt., value £2,106; leather, 262 cwt., value £1,201; tallow, 335 tons, value, £7,184; total value, £495,658. Imports (oversea): value, £81,488. Customs duties for the year, £24,894. During the year 629 steamers entered and left the port: tonnage, 233,482, with crews numbering 12,393. The number of passengers to and from the breakwater by sea, 27,747, being 4,800 more than the preceding year.
Manufactures in New Plymouth are represented by a sash-and-door, a boot, butter-keg, and three coach factories, a brewery, a cordial factory, a flour-mill, tannery, fellmongery, bone-mill, and iron-foundry, with freezing-works and bacon-factory in the suburbs. The town has both water and gas laid on.
Hawera, the next largest town, is situate on the eastern edge of the Waimate Plains. The population is 2,131, and the town is lit with gas. The Wellington—New Plymouth Railway runs close to it, the distance by rail from New Plymouth being about forty-eight miles. Hawera is surrounded by a first-class dairying and grazing country, capable of carrying a very large population. On 1st December, 1898, an up-to-date bacon-factory, costing some £1,200, commenced the work of killing and curing in Hawera, and this industry is now well supported.
The Town of Patea is situated on the coast, at the extreme southern end of the district, and has a population of 691. There is a splendid grazing district inland, with a large area of land yet to be opened up. There is a dairy factory, which has two branch creameries in the country. A bacon-factory has also been established. Exports for 1902 were: Wool, 5,716 bales; fungus, 1,178 bags; tallow, 425 casks; pelts, 182 casks; loose hides, 3,720; grass-seed, 70 sacks; butter, 79,800 cases; flax, 81 bales; meat, 155 cases; sheep, 200; sundries, 500 packages; bacon, 35 cases; empties, 936; transhipment, 525 tons. Imports: Ordinary, 7,702 tons; coals, 2,016 tons. Wharfages amounted to £1,293, dumping dues £412, tonnage dues £349. The number of steamers in and out were 174. The Harbour Board has an up-to-date wool-dumping press and hydraulic pumps. The width between the east and west pier-heads is 260 ft.; width of channel about 180 ft., gradually narrowing to 100 ft. as the beacons are approached. The pilot reports the depth of water at not less than 12 ft. at high-water springs, and 9 ft. at high-water neaps, with a straight channel.
Stratford, a comparatively young town, lies about midway between Patea and New Plymouth. It has already a population of over 2,000, and is growing fast The height above sea-level is 1,000 ft., and the climate is bracing though somewhat moist. The main road to Auckland—known as the Stratford—Ongarue (now Ohura Road)—starts here. It has been formed as a cart-road for fifty-six miles, and as a bridle-road to sixty-one miles. If the work is continued energetically, communication with Auckland should be opened up in about three years' time. A commencement has been made with the construction of the railway line between Stratford and Auckland viâ Ongarue, the line being completed as far as Toko. A bacon-factory has been started at Stratford under very favourable circumstances, and is likely to prove a public benefit, and also a financial success to the proprietary company. The works are on a fair scale and up to date. The machinery is driven by a 30-horse-power Victor turbine, the power being obtained from the Patea River through a tunnel 865 ft. long, cut across a bend in the river. The refrigerating engine is a 6-ton British Linde, while hot water is supplied from a high-pressure boiler in an adjoining building. The chilling-chamber holds about 120 carcases (or one day's killing); here they remain overnight, and are then passed on to the curing-room, a spacious compartment of 80 ft. by 26 ft., capable of holding 1,000 carcases; from here they pass to the drying-room, of same size and capacity, on the upper story. A brick smoke-house, capable of dealing with 600 pieces at a time, has also been erected. The piggeries and slaughter-house are about a mile from the works, and are connected by tramway. The former consist of twenty compartments holding ten pigs each, and are conveniently arranged for feeding, &c. The output during the past season was 3,109 pigs, costing £5,886. On the Eltham—Opunake Road another factory, called the “Pioneer Bacon Factory,” was started in 1897, and put through during part of last year 1,866 pigs—costing £3,662.
Waitara, a seaport town of 765 inhabitants, is situated on the river of the same name, a mile up from the sea, and about ten miles north-east from New Plymouth. The Mount Egmont Freezing-works have passed into the hands of a company styled the “Waitara Freezing and Cool Storage Company, Limited,” who have rebuilt and greatly enlarged the works, the storage capacity now being for 25,000 carcases of mutton, together with five freezing rooms, capable of hanging 1,200 carcases, also a beef-chilling room and a mutton-chilling room. Provision is made at the slaughterhouse for accommodation of fourteen mutton and three beef butchers. The freezing-plant is a 60-ton Hercules, and is guaranteed to freeze 1,500 sheep per day. The boiling-down and tallow department is most complete and up-to-date, and a large manure plant is now in course of erection. The works are fitted throughout with electric light. The following produce was dealt with during the year: 18,443 quarters of beef, 19,865 carcases of mutton, 19,686 carcases of lamb, 175 carcases 271 sides and 280 quarters of veal: total weight, 2,309 tons. All produce is conveyed on board the New Zealand Shipping Company's ocean-going steamers (which anchor in Waitara roadstead) in specially constructed and insulated bags. These works are gazetted as Government grading and cool stores, which is a great convenience for outside dairy factories, as it avoids risk of injury to their produce after it has been graded. The exports from the port for the year 1902 were; Wool, 1,437,524 lb.; grain, 162 tons; grass-seed, 1,220 sacks; hides, 1,698; skins, 55 bundles; timber, 22,051 super. feet; flour, 38 tons; potatoes, 487 sacks; tallow, 751 casks; pelts, 58 casks; cattle, 282 head; horses, 12; sheep, 155; frozen mutton and lambs, 709 tons; frozen meat, 1,340 tons; butter, 94 boxes; fungus, 5 bales; general cargo, 627 ¼ tons. Total tonnage of exports for year was 3,930 tons. Imports for same period were: Grain, 35 tons; manure, 1,504 tons; lime, 37 tons; timber, 297,108 super. feet; coal, 4,211 ¾ tons; wool, 264 bales; fungus, 9 bales; hides, 42; skins, 27 bundles; flour, 498 tons; horse, 1; sheep, 366; flax, 305 bales; butter, 629 boxes; general cargo, 3,934 tons. Total tonnage of imports, 9,628 tons; making in all a gross total of 13,558 tons of cargo handled at the port during the year.
Inglewood, situated on the railway-line, sixteen miles south-east of New Plymouth, is a flourishing little town of some 720 inhabitants, rapidly coming to the front. The bacon-factory during the year put through 1,915 pigs, costing £3,860. The factory is worked by a 24 in. turbine, the water being conveyed in a race 10 chains long. It is provided with a four-horse-power tubular boiler, a Lard jacket, and Californian pump. There is also a size “D” ammonia refrigerating machine.
Eltham, a rising borough of 800 inhabitants, is making very rapid progress. The bacon-factory during the year put through 1,866 pigs, costing £3,662, exactly the same as Stratford.
Opunake, a seaport town of 466 inhabitants, was visited during the year by 35 steamers. Imports, 708 tons; exports, 108 tons; but more than half the trade of the district does not come or go through the port; in fact, the goods carried by road are on the increase. If the railway from Eltham is made this town should make rapid strides, as it is intended to improve the harbour.
The only other towns of importance are Manaia, population, 447; and Normanby, population, 370.
The chief means of communication is the railway from Wellington, which traverses the district between Patea and New Plymouth—a distance of sixty-six miles. Through trains run every day, except Sunday, between New Plymouth and Wellington, and vice versa, a distance of 251 miles. As already stated, a railway from Stratford to Whangamomona has been commenced, and is already open so far as the village of Toko, six miles and a half from Stratford. This line will eventually be extended to connect with the North Island Main Trunk Railway at Ongarue Station.
The Main North Road runs from New Plymouth, passing through the Towns of Waitara and Urenui; and is formed as a cart-road to Mokau, the northern boundary of the district. All the streams are bridged with the exception of the Mokau River, on which is a good ferry. From Mokau there is a dray-road right through to Te Kuiti, on the Auckland railway system. About midway between New Plymouth and Waitara the Mountain Road diverges and runs almost due south, and chiefly along the railway, for a distance of forty miles, connecting with the Main South Road at the Town of Hawera. This is at present the principal road in the district, tapping, as it does, large numbers of district roads, and passing through the Towns of Inglewood, Midhirst, Stratford, Eltham, Normanby, and Hawera.
The Ohura Road branches from the Mountain Road at Stratford. It is formed and open for traffic as a dray-road for fifty-six miles from Stratford and for horse-traffic to sixty-one miles. A coach runs in summer time every Monday and Thursday (returning on following days) between Stratford and Whangamomona Village, a distance of forty-one miles, and the road is now being extended into the interior so as eventually to connect with Auckland, and will open up a large area of fertile country.
The Main South Road from New Plymouth follows the trend of the coast to the south, and was at one time the coach-road to Wellington. It passes through the Villages of Omata, Oakura, Okato, Rahotu, Otakeho, Manutahi South, and Kakaramea, and the Towns of Opunake, Manaia, Hawera, and Patea.
The Junction Road runs south-east from New Plymouth, and crosses the Mountain Road and railway at Inglewood, thirteen miles out; it is metalled for thirty-six miles and a quarter, formed as a dray-road to forty-four miles and a half, thence as a bridle-road to forty-five miles and three-quarters, where it connects with the Ohura Road at a distance of thirty miles from Stratford. This road crosses a number of district roads; hence its name.
The Opunake Road runs from Stratford to Opunake, twenty-six miles, skirting the southern base of Mount Egmont. It is formed and metalled for twelve miles from Stratford; the remainder is open for horse-traffic only. Vehicular traffic turns down the Manaia Road to Kaponga, thence along the Eltham—Opunake Road to the latter place. This route is metalled throughout.
The Eltham Road runs from Eltham to Opunake, twenty-five miles, connecting with the Opunake Road at Punehu, seven miles from Opunake. This is formed and metalled throughout.
The other main roads in course of construction are the Rawhitiroa Road, leaving the Mountain Road near Eltham; the Otaraoa, Moki, and Okoke Roads.
In the Ohura and Aria Survey Districts, and lying near the Ohura Road, between Tuhara and Ongarue: Seven allotments, comprising 6,761 acres; generally slopes and spurs covered with mixed forest, good soil, on a papa formation, and well watered; elevation, 450 ft. to 1,800 ft. above sea-level. The land is suitable for cattle and sheep raising, while small portions will be found suitable for dairying.
Forty-five allotments, comprising 46,271 acres lying inland of Waverley, Patea, and Waitotara, also to the east of Eltham, and tapped by the Eltham—Waitotara Road and branch roads, also by the various roads leading from the towns mentioned. As a rule the land is rough, and in some places swampy, wholly covered with mixed forest; soil, varying from fair to good; well watered. When the best portions have been cleared they will be found suitable for cattle and sheep raising, and small portions on the river flats may be found suitable for dairying.
Forty-one allotments, comprising 40,879 acres, lying inland of the Mokau Road and Tongaporutu River, extending also along the Moki Road and its branches towards the Ohura Road, and embracing the land in the valleys of the upper waters of the Waitara River. Generally comprising rough pastoral country, suitable for cattle and sheep raising, with portions suitable for dairying; fair to good soil, wholly covered with mixed forest; papa formation, well watered.
Six allotments, comprising 5,737 acres, at the back of settled districts of Strath-more, Pohokura, and Whangamomona. Rough pastoral country, wholly covered with mixed forest; soil fair to good, on a papa formation, and well watered. The country is adapted for sheep and raising young cattle, while small portions may be found suitable for dairying operations.
In the Ohura and King Country: 110,000 acres, comprising mixed open and forest land of good quality, varying from undulating to hilly, and lying to the south of Mokau-iti, and between it and the Ohura River.
In Upper Tongaporutu District: 19,000 acres, comprising hilly country, covered with heavy forest, fair to good soil, on a papa formation.
Near Whangamomona, and lying to the north-west and south-east of the township, comprising hilly country covered with heavy forest; 36,800 acres.
In the Upper Whenuakura District, lying at the headwaters of the Whenuakura and Moeawatea Streams, and comprising rough and broken country, wholly covered with forest; soil fair to good, on a papa formation, and well watered; 12,604 acres.
Various forfeited sections in the Upper Waitara, Omona, Cape. Mimi, and Mahoe Survey Districts; 11,472 acres.
Total, 189,876 acres. All the lands will be found suitable for mixed occupation, such as raising young cattle and sheep, and in the more favoured localities for dairying.
In addition, 333,689 acres are in the hands of the Crown partially explored, a good deal of which will be suitable for settlement.
There are 239,600 acres of land in this district still in the hands of the Natives.
A guide, giving particulars of any Crown lands open for selection, will be supplied free to any one applying personally or by letter to the Lands and Survey Department, New Plymouth.
It may be said, in conclusion, that there is every sign of genuine prosperity throughout the district, which has advanced rapidly during the last few years, and will no doubt continue to do so.
Table of Contents
The Land District of Hawke's Bay comprises that portion of the east coast of the North Island from Cape Turnagain, in latitude 40° 30', northwards to Lottin Point, about thirty miles beyond the East Cape, and contains the Waiapu, Cook, Wairoa, Hawke's Bay, Waipawa, Patangata, Woodville, and Weber Counties.
It has a seaboard of 300 miles, with an average depth from the coast of forty-five miles, and embraces an area of 6,063,000 acres. Its western limit is defined by the Ruahine, Kaweka, Ahimanawa, Raukumara, and other high ranges that form the watershed between the rivers flowing through it to the sea, and those that run to the west coast and the Bay of Plenty.
The Ruahine Range extends northwards for about sixty miles from the Manawatu Gorge as far as the valley of the Ngaruroro River. Its altitude varies from 3,000 ft. to 6,000 ft., and for a considerable distance its summit is snow-clad during the winter months.
The Kaweka, a shorter range, divided from the Ruahine by the Ngaruroro River, attains an altitude of 5,650 ft., is very rugged and steep, and a prominent feature in the landscape in winter, covered as it then is with snow.
From these two ranges, which fall very abruptly on the Hawke's Bay side the land slopes gradually to the sea, forming in some parts fine rolling hills—the essence of a sheep-country—in others extensive plains, with comparatively little poor soil.
Northwards from the Kaweka there is a series of forest-clad ranges of varying height, stretching away in the direction of the East Cape. Hikurangi, the highest point, is a bold peak with an elevation of 5,606 ft., rising so abruptly on all sides that the ascent can be made only at one point, and that with difficulty.
The only lake in the district of any extent is Waikaremoana, so famous for its magnificent scenery. It lies about thirty-five miles inland of Wairoa (Clyde), and is eleven miles in length, with a breadth at the widest part of about eight miles. Nestled among precipitous mountain-ranges, wooded to the water's edge, with numerous bays and inlets, it has a natural beauty hardly to be surpassed.
From Wairoa there is a formed road to the lake, and twenty-five miles round it, as far as the Oporuahine River.
The principal plains are: (1.) The Ruataniwha, some fifty miles south of Napier. This is 120 square miles in extent, is for the most part occupied as sheep-runs, and carries a large quantity of stock. (2.) The Heretaunga Plain, with an area of ninety square miles, lying immediately to the south of Napier. This is rich alluvial land; a large portion is thickly settled, the remainder used for grazing and agriculture. The only other plain of any extent is at Poverty Bay. It has an area of sixty-five square miles, is very fertile, well cultivated, and has a large population.
The district is well watered throughout by numerous rivers and streams, but none are navigable except the Wairoa and Turanganui, and these only for vessels of light draught. They are both tidal, and serve as ports to the Towns of Wairoa (Clyde) and Gisborne.
The chief outlets from Napier are three in number. First the Napier—Wellington Railway, which traverses the centre of the southern half of the district for its whole length of 100 miles, and may be called the main artery of communication. Parallel to it throughout runs an excellent gravelled road, which was made before the construction of the railway. On either side there are numerous branch roads, which act as feeders, making a very complete system of internal transit. Another main road runs in a westerly direction to Kuripapanga, distant forty-five miles, a favourite resort in the summer time, removed as it is from the heat of the country near the coast. A coach runs thither twice a week, and on thence to Inland Patea, where the Napier Road meets the roads to Hunterville, Tokaanu, and the Wanganui River.
The part of the district served by these two main lines—viz., that between Napier and Woodville—contains the greater portion of the population, and from the extent of arable land within it is likely in the future to be very thickly peopled. Notwithstanding that so much of the Native land in this part is unoccupied and in its natural state, there are nearly a million of acres of land in sown grasses.
The main road northwards from Napier is the coach route to Taupo, which, soon after leaving the fertile Petane Valley, begins to traverse poor country, and twenty-five miles out enters the light pumice soil.
The Napier - Wairoa Road has been completed, with the exception of bridges at Waikare and Matahouroa Streams, and there is a weekly mail-coach service between the two towns. The coach is stopped occasionally by floods at the streams mentioned, and until the bridges are completed the heavy traffic between the two places will be done by a small steamer.
From the Wairoa a main road runs northward, through the Village of Tiniroto and on to Gisborne, a distance of seventy-five miles. For a considerable distance it runs through hilly country, and, as it has not been gravelled, wheeled traffic is suspended during the winter months; but a coach runs weekly for nine or ten months out of the year. The road from Wairoa to Gisborne viâ Nuhaka Hot Springs is completed and open for wheeled traffic.
Between Gisborne and Opotiki, in the Bay of Plenty, communication is not good. The road, which is 120 miles in length, has been formed to the Motu Township, a distance of sixty miles. In the neighbourhood of the forest a large area of Crown lands has been taken up and settled during the last few years. The rest of the journey must be done on horseback. A railway is being constructed from Gisborne in the direction of Motu. The portion from Gisborne to Ormond, a distance of ten miles, and for three miles beyond, is open for traffic. The continuation of this line is being pushed forward, and will greatly assist the progress of the district.
The country to the north of Gisborne is being rapidly opened up, the coastal road being open for traffic as far as Port Awanui, while several of the arterial roads are being extended.
Small steamers trade regularly along the coast, calling in at Tolago and Tokomaru Bays, Waipiro, Tuparoa, Awanui, Kawakawa, and other small bays.
The Hawke's Bay District is pre-eminently a sheep-grazing country, and the large area of 2,527,216 acres has been improved and sown in English grasses, clover, &c. In April, 1902, there were 4,606,322 sheep in the district, and the numbers of other stock were as follows: Horses, 30,761; cattle, 187,238; and swine, 14,911. The value of the wool exported from Hawke's Bay for the year ended 30th June, 1902, is £440,908, a considerable increase over last year.
Freezing works are established at Tomoana, Port Ahuriri, and Gisborne, and the export of frozen meat for the year ended 30th June, 1902, was as follows: Beef, 3,052 tons, valued at £76,300; 146,019 carcases of mutton, valued at £91,262; 102,141 carcases of lamb, valued at £56,178; preserved meats, 55 tons, valued at £2,750. Though the exports quoted show a decrease on the previous year's figures, a marked increase is recorded for the total exportations from the district, such increase for the year being no less than £95,969.
As showing the importance of this industry, there are numerous sawmills in the district, and, outside of wool, frozen meats, tallow, and pelts, sawn timber ranks first in the value of the exports. Timber to the value of £26,365 was exported for the year ended 30th June last, as against £15,850 for the previous twelve months. It is satisfactory to note that sawmills have been established at Pohui and Puketitiri, in which districts there are large areas of valuable forest. As the bulk of the sawn timber from these places must necessarily come through Napier, it follows that the port and trade of the town will reap immense benefits from the further development of the industry in its vicinity.
Twenty-three tons of fish, representing a value of £230, were exported last year. It is a matter for regret that what at one time gave every promise of becoming a large and promising industry should be in the position these figures disclose. The trouble appears to be that fish are not now present in the same numbers as when the industry was first started.
Agriculture is not carried on to the extent it might be with so much land suitable for root- and grain-crops. No doubt this is due to the profits made in sheep-farming. It is chiefly confined to the Heretaunga Plains and the flat lands near Gisborne. The soil is favourable to root-crops; potatoes range from 12 to 15 tons to the acre, and in some instances exceed this amount. Only a moderate quantity of grain is grown; barley, for which the soil seems well adapted, returning from 20 to 60 bushels of good sample to the acre.
Settlers are now turning their attention to dairying, and factories have been established in the bush districts at Norsewood, Ormondville, Maharahara, Hastings, Gisborne, and Woodville, whilst several others are in contemplation. At the last-mentioned town a cheese-factory has been in existence for some years, and turns out an excellent article much sought after in other parts of the colony. There can be no doubt that the further development of the dairying industry must materially benefit the farming class—especially the small farmer, who may find it difficult to make a living out of sheep.
Other industries, such as fellmongeries, soap-works, boot, coach, and sash-and-door factories, &c., are established in the principal towns. During the year 1901 the Hawke's Bay Woollen Manufacturing Company commenced operations in their factory at Napier, and now gives employment to a large number of hands.
The climate is generally of a mild character, and, though hot along the coastlands in the height of summer, it is, owing to the dryness of the atmosphere, not so relaxing as in parts of the island farther north. The rainfall is light, excepting in the bush districts and high inland country.
Napier itself is recommended by many medical men as a resort for invalids suffering from pulmonary complaints, chiefly on account of the mildness of its winter season. The average rainfall for thirty-four years is 37·070 in.
Napier is pleasantly situated on the peninsula known as Scinde Island, which is joined to the mainland by a narrow shingle-bank several miles in length. It is a busy town, with a population of about 9,500. The business part is on the flat land at the foot of the group of hills that take up the greater part of the peninsula. These hills, formerly barren and waste, are now occupied by numerous private residences, and the very general tree-planting has given the upper town a distinctive and pleasing character. There is an excellent water-supply, derived wholly from artesian wells of large size, and pumped by machinery to reservoirs on the tops of the hills. The shipping trade, as the large exports show, is especially active during the wool and frozen-meat season. It is still carried on at Port Ahuriri, about a mile from the town; but has recently, in a large measure, been transferred to the fine breakwater which is now almost completed. During the year ending 30th June, 1903, the imports amounted in value to £214,886, and the exports to £971,599.
Gisborne, the trade-centre and port of what is known as the Poverty Bay District, is a prosperous town of about 2,700 inhabitants, exclusive of Maoris, rapidly increasing in size and importance, as the large quantity of unimproved land in the Cook County is fast becoming settled and made productive. There are 1,313,663 sheep in Cook and Waiapu Counties, and Gisborne's exports amounted to £533,166 in value for the year ended June, 1903.
Clyde, the county town and port of the Wairoa County, is picturesquely situated on the Wairoa River, about three miles from the mouth. The river is navigable for small craft as far as the village of Frasertown, twelve miles further up.
With a few exceptions, the towns and villages to the south of Napier are all situated on the line of railway running from that city to Wellington. The principal are: Hastings, a rising town of about 3,700 inhabitants, Waipawa, Waipukurau, Dannevirke, and finally Woodville, about three miles from the Manawatu Gorge, and distant ninety-eight miles from Napier. It is at this end of the district that the Crown has, in the last few years, successfully planted settlement, and, in place of the continuous forest known as the Seventy-mile Bush of earlier days, there are now prosperous townships, with various thriving industries established.
The land held by tenants of the Crown, of whom there are 972 in the district, under the various systems of tenure, amounts to 655,298 acres, and there remain about 194,080 acres not yet dealt with in any manner.
The latter is, for the most part, suitable for pastoral purposes only, any fit for agriculture lying in small, isolated spots, widely scattered, and such as could not be selected independently of the surrounding inferior land. Nearly the whole is broken forest country, fitted more for sheep than cattle, and having an average carrying-capacity, when cleared, of about one sheep to the acre, though the best of it might possibly graze from two to three. The land is chiefly in the Hangaroa, Koranga, Mangatoro, Norsewood, and Motu Districts, and the back-country of the Waiapu County.
About 67,228 acres are now open for selection. This area includes lands open under the small grazing-run system.
The following is a short description of some of the areas to be dealt with in the future:—
Waitahaia Block, Waiapu County.—16,350 acres. Nearly all forest country, with soil varying from light to good.
Mata Survey District.—1,756 acres, being the Aorangiwai No. 1 Block; broken forest country; soil fair.
Tutamoe Survey District.—7,750 acres, being the Huiarua No. 1 and Tutamoe Blocks; all bush, broken, soil medium. Situated about thirty miles from Tokomaru.
Urutawa Survey District.—9,140 acres, being the Whitikau No. 1 and Whakapaupakihi Blocks. Broken forest country, soil fair.
Koranga and Ngatapa Survey Districts.—About 42,684 acres, being part of the Tahora No. 2 Block, situated north of Waipaoa and Ruakituri Rivers, and between them and the Koranga River. It comprises some very hilly country, but, though nearly all the land is covered with bush or scrub, there is some fair soil, and would make fair pastoral country. All well watered. North of this portion the Crown has some 70,000 acres in the Auckland Land District, west of the Waioeka River.
Hangaroa Survey District.—25,004 acres cut up into five small grazing-runs, comprising undulating and broken country with light soil on papa formation. Forty-two miles from Gisborne.
Motu Survey District.—23,900 acres, being the Motu Block. Part undulating country, rest broken. One-third open fern and scrub, remainder forest clad. Soil light. About sixty miles from Gisborne, along the Opotiki Road.
Patoka Survey District.—4,028 acres, chiefly forest country, with light soil. Part river-bed.
Puketapu Survey District.—320 acres, in Block I. Waste land, north of the Pokopoko Stream, and west of Sections 16 to 20. Chiefly gullies.
Tahoraite and Norsewood Districts.—About 7,366 acres, being the Tamaki No. 1 Block. Bush country, all covered with heavy forest. A good proportion undulating land. All well watered. It will probably be some time before this block is opened for selection.
Norsewood Survey District.—Piripiri Block, 17,056 acres. Part of this block is in the Wellington Land District. It will probably be some time before this land is in the market.
In addition to the foregoing, there is an area of 17,345 acres, principally small blocks scattered over various districts, as follows: Mata, 1,074 acres; Hikurangi, 1,931 acres; Tokomaru, 216 acres; Waingaromia, 4,522 acres; Uawa, 372 acres; Hangaroa, 1,218 acres; Waiapu, 798 acres; Matakaoa, 145 acres; Opoiti, 3,676 acres; and Nuhaka North, 575 acres agricultural and 3,025 acres pastoral.
Of the Native lands in this district, a very considerable portion has been leased to Europeans, but there still remains in the hands of the Maoris a valuable estate, comprising both agricultural and pastoral country, and including some 800,000 acres of excellent land. This land lies for the most part in the Waiapu County, towards the East Cape.
Table of Contents
The Wellington District is bounded towards the north by the Auckland District; towards the east by the Hawke's Bay District, to the sea; thence by the sea to the Patea River on the West Coast; and thence bounded towards the west by the Taranaki District. The area contained within these limits is about 6,810,958 acres. It lies between the parallels of 39° and 41° 30' south latitude; its greatest length north and south is about 180 miles, and its mean width east and west about sixty miles.
The district is divided into two well-defined parts by a mountain range, which forms part of the backbone of the North Island. At its northern end this range—there known by the name of Ruahine, and averaging a height of about 4,000 ft.—divides Wellington from Hawke's Bay; but after passing the point where it is intersected by the Manawatu River, the range takes the name of Tararua for many miles, until, at about forty miles from the termination on the shores of Cook Strait, it divides into two main ranges, known respectively under the general names of Rimutaka and Tararua, both ranges averaging from 2,500 ft. to 3,500 ft. in height, the highest point being 5,154 ft. Parallel to the main range, and divided from it by the Wairarapa Plain and the undulating country to the north, is a series of ranges at a few miles inland from the East Coast, known as the Puketoi, Taipo, Maungaraki, and Haurangi Ranges. Lying on the northern border of the district are the Kaimanawa Ranges, for the most part open and grass-covered, rising to a mean height of about 4,500 ft. Westward from the latter mountains, and divided from them by a deep, broad valley, in which flow the Waikato and Wangaehu Rivers, is the volcanic chain of mountains containing Ruapehu, 9,008 ft., and Ngauruhoe, an active volcano, 7,515 ft. high. The long sweeping curve of Cook Strait, forming the south-western limit of the district, is bordered, from the Patea River to within thirty miles of Wellington, by a comparatively level and undulating country, now nearly all under cultivation, having an average width of about fifteen miles. This is one of the finest parts of the colony, and is celebrated for its stock-raising capabilities. It was originally in a great measure open, though the southern part, where the plain is narrowed in between the sea and the Tararua Range, has a good deal of forest on it, now fast disappearing under the axe of the settler.
Inland of this coastal plain, at varying distances from the sea, the country gradually rises to a mean height of about 1,500 ft. to 1,800 ft., and becomes a good deal broken in character. It was originally forest-clad almost throughout. It is much cut up by rivers and streams flowing from the interior to the sea, of which the principal, commencing from the north, are these: The Waitotara, the Wanganui, the Wangaehu, the Rangitikei, the Oroua, the Pohangina, and the Manawatu, which last, after leaving the gorge in the Ruahine Ranges, runs through level land to its mouth in Cook Strait. This broken country, being everywhere composed of papa, or marly formation, which takes grass excellently, promises in the near future to be a large sheep-carrying district.
At about fifteen miles south of the volcanic peaks of Ruapehu Mountain the papa country terminates in a fairly well-marked escarpment, giving place to a more level and undulating country formed of volcanic matter, the greater portion of which is forest-clad, though on the south-east, east, and west sides of that mountain there are open grassy plains, of no great fertility, but yet suited to pastoral pursuits.
To the eastward of the main range formed by the Rimutaka and Tararua Ranges is the great depression known at its southern end as the Wairarapa Plain, which gradually rises northwards from the lake of that name into wooded, somewhat broken country, of no great height, at a distance of some forty-five miles from the sea. From here the country falls again slightly to the Upper Manawatu River, the depression in this part being marked by the extensive flats in the neighbourhood of Pahiatua, and by the shallow valleys of the Mangahao, Mangatainoko, and Tiraumea Rivers and their branches. For thirty miles from the sea this great valley is mostly open, with patches of forest here and there, but becomes more plentifully wooded at the base of the Rimutaka and Tararua Ranges. The quality of the soil varies from light and stony, on the Wairarapa Plains proper, to rich papa country, as the northern end is approached. The southern end of this country is watered by the Ruamahanga River and its tributaries. Generally the district is a pastoral one, though agriculture is also pursued successfully. The neighbourhood of the Puketoi Ranges is in many places composed of limestone, and promises in the future to become a very rich pastoral district, such as will support a considerable population. In the forks formed by the Tararua and Rimutaka Ranges the Hutt River takes its rise, and runs in a southerly direction through an undulating or level country, finally falling into Port Nicholson. The valley contains some very fine land, generally held in small holdings.
The two most important of these have already been mentioned. On the eastern side of the main range the Wairarapa extends northward from the lake of that name for about forty-seven miles, with an average width of about nine miles. In some parts, especially on the flats along the Ruamahanga River, the soil is alluvial and rich; in others, though stony and unfit for cultivation, it is nevertheless grassed, and carries stock well in the winter and rainy seasons. The plain is watered by the Waiohine, Waingawa, and Ruamahanga Rivers, and contains altogether about 200,000 acres, much of which is good agricultural land. On the other side of the district, west of the Tararua and Ruahine Ranges, there is a large block of land so nearly level that it may be called a plain, extending from Paikakariki (twenty-seven miles from Wellington) to Marton (a few miles north of the Rangitikei River), and contains about half a million acres. Starting as a narrow strip between the hills and the sea, the plain widens out by degrees until at Feilding it is at least twenty miles in breadth. Along the beach runs a fringe of sandhills, but behind this is to be found some of the best farming and grazing land in the colony. There are two plains inland—Murimotu and Waimarino—both lying some 2,200 ft. above sea-level, in the neighbourhood of Mount Ruapehu, the former to the south and the latter to the north-west of the mountain. The soil is covered with a coarse native tussock, and, though capable of carrying stock, is of a light porous nature, and cannot be classed as agricultural land.
First among these is the Wanganui—“the Rhine of New Zealand”—with a length of 136 miles from its source, near Mount Tongariro, to its outlet. The Manawatu is next in importance. Rising in the Ruahine Range, it flows through the picturesque Manawatu Gorge, joining the sea at the port of Foxton. The Rangitikei, the third in size, rises in the Ruahine Mountains, and flows through the Awarua country, where it is joined by the Hautapu and other large tributaries. After a course of over a hundred miles it reaches the sea some little distance below the Township of Bulls, on the West Coast. Lesser rivers on the West Coast are the Waitotara (north of Wanganui), the Wangaehu (which takes its rise in Mount Ruapehu, and from its source to its mouth is so strongly impregnated with sulphur that fish cannot live in it), the Turakina, and the Otaki. The only other rivers of any size are the Hutt (Heretaunga), emptying itself into the Wellington Harbour, the Ruamahanga, flowing through the Wairarapa Valley and lakes into Palliser Bay, and on the East Coast the Pahaoa, Aohanga, and Akit.
The only lake of any size in the Wellington District is the Wairarapa, lying between the Rimutaka and Haurangi Ranges, towards the southern end of the Wairarapa Valley. It is about twelve miles long and four broad, and is connected by the Ruamabanga River with Onoke, a small lake separated from Palliser Bay by a narrow shingle spit only. A passage through the spit is opened from time to time when the lake rises above its natural level and overflows the low-lying flats along its margin. Water-fowl of every kind—among them numbers of black swans—are to be found round about these lakes.
The views obtained from the railway-line in the ascent and descent of the Rimutaka Range are among the best in the neighbourhood of Wellington, and the road through the Forty-mile Bush was long considered one of the most beautiful drives in the North Island; but its beauty has been diminished by the felling of the bush consequent on the increase of settlement. The same may be said of the Manawatu Gorge, famed in the old coaching days for its lovely scenery, but now sadly marred by the construction of the railway-line. The most beautiful drive now left is through the Awarua Bush, from Ohingaiti to Moawhango. From this road, as it winds round the spurs, most charming glimpses are obtained of the Rangitikei River and the blue hills beyond, and at other points the traveller looks up deep ravines where the graceful fern-tree stands out in bright relief against the dark green of the native bush. Another road from Pipiriki, on the Wanganui River, to the Murimotu Plain, traverses one of the most magnificent forests in the North Island. Here the bushman's axe has felled only the timber standing on the road-line, and the track runs beneath the shade of the largest and stateliest maire and rimu known. Beautiful as these drives are, the scenery on the Wanganui River is still more lovely. A few miles below Taumaranui the river enters a series of gorges, shut in by high precipitous cliffs. Sometimes the canoe glides slowly through quiet reaches, sometimes shoots rapids which make the traveller hold his breath till they are passed, and then again traverses places where the water is ever in turmoil, boiling and eddying in whirlpools, taxing the energies of the most skilful Native steersman, and testing the nerve of the most courageous tourist. These experiences, with the views obtained of the banks, densely wooded even where the papa rock rises almost straight from the water's edge, make the eighty miles journey from Taumaranui to Pipiriki an event not easily effaced from the memory. Between Pipiriki and Wanganui excellent steamers are now running, so that the beauties of the lower part of the river may be seen by all without trouble or discomfort.
The Wellington District is essentially a forest country, for out of the 6,810,958 acres contained within its borders about 3,000,000 are still under bush. By far the largest forest is the Waimarino, having an area of at least three-quarter million acres, a large portion of it being nearly level land, containing magnificent timber, principally totara, maire, matai, rimu, and other pines. This forest is as yet hardly touched, though timber is being cut at Raetihi for the settlers now making their homes in the neighbourhood. The distance from the settled districts or any port will render the timber in this part useless as a marketable commodity until the country is opened up by the Auckland Main Trunk Railway now in course of construction.
The next in size is the Rangitikei-Hautapu Forest, containing an area of about 350,000 acres, a considerable portion in the Awarua Block being first-class milling timber, which will be available as soon as the extension of the Hunterville Railway-line taps it. Between this and the Waimarino Forest there is a large extent of bush-land, drained by the Turakina, Mangamahu, and Wangaehu Rivers, extending up to the Wanganui River, and containing about 300,000 acres. Very little of this, from its inaccessibility, will be utilised for sawmilling purposes, but a great deal of it, together with a further block of 230,000 acres on the west side of the Wanganui River, will be cleared by the settlers and sown down with grass. A further block of about 100,000 acres of forest-land lies in the Pohangina Valley and on the slopes of the Ruahine Range. A large portion of this has been taken up and is now being settled. The forest-land on the West Coast extends from Pukerua to the Manawatu Gorge, on the west side of the Tararua Range, and contains an area of about 300,000 acres, the bulk of it being fit only for turning into pasture. The most available part of it, alongside the Wellington-Manawatu Railway, is being extensively cut into by sawmillers at Levin and other places on the line.
After this' in size is the forest on the eastern slopes of the Tararua Ranges, extending from Featherston to the Manawatu Gorge, which includes what remains, of the well-known Forty-mile Bush, containing probably about 175,000 acres. Portion of this area is being quickly denuded of timber by the sawmills established at Pahiatua, Newman, Hukanui, Eketahuna, and by settlers. A tract of about 50,000 acres lying to the east of the Puketoi Range cannot be utilised for milling purposes, as it is not tapped by any branch railway-line, and its distance from the main line would probably render the business unprofitable except for local purposes. Nor are there any suitable ports along the coast where timber could be shipped.
The other forests are, one near Lake Taupo, and the Haurangi Forest on the east side of the Wairarapa Lake. These consist for the most part of birch-covered hills, and cannot be considered as valuable for milling purposes.
It may be said that the Wellington Land District contains within its borders a greater quantity of good land than any other in the North Island, very little, except the mountain-tops, being unfitted for use, while some of it is of very superior quality, suited for the growth of the productions of every temperate climate. As much of it is still forest-clad, settlers must look forward to having to make their farms by felling and burning the bush before grass can be sown, and, as it takes from ten to fifteen years before the plough can be used in bush-land, grazing, for which the climate and soil is admirably adapted, will be the principal industry for some time to come. It is generally calculated that the cost of felling and burning ordinary bush varies from 25s. to 35s. an acre. To this must be added about 20s. for seed and fencing. It is no uncommon thing for a return to be received at from twelve to eighteen months after felling. The usual practice is to put sheep on to the new lands soon after the grass has obtained a good hold. The process of improving the lands by the gradual “logging up” and burning of the fallen tree-trunks is a long one, but it pays in the end, for in this way fine pasture-lands are obtained on the hills, and agricultural lands on the flats.
The climate of Wellington District is healthy and mild, the mean annual temperature (in the city) being 55·4, whilst the mean rainfall is 48·49 in. per annum. The rainfall differs, however, according to locality. Inland and near the ranges it is much greater. The top of Ruapehu Mountain is covered with perpetual snow, which lies also on the tops of Kaimanawa, Ruahine, and Tararua in the winter. Frosts are heavy in the interior.
The coasts of Wellington are not so well supplied in this respect as are some other parts of the colony; but what is lost in number is made up in a great measure by the excellence of the chief haven—Port Nicholson—which, from the position it occupies, at the meeting-point, as it were, of the coastal traffic of both Islands, and from its sheltered position and depth of water, may be considered one of the most convenient harbours in the world. The Wanganui River, which has been considerably improved by artificial means, is the second port in the district, and has a considerable trade carried on by coastal steamers. The Patea and Manawatu Rivers are also used by coastal steamers, whilst several other places along the shoreafford shelter and stopping-places, according to the direction of the wind. The extension of railways along both coasts has, in a large measure, done away with the inconveniences arising from want of harbours.
The capital of the colony—Wellington—is situated in the south-west angle of Port Nicholson, on Lambton Harbour. The wharfage accommodation here is second to none in the colony, and the wharves present always a busy scene of life with the numerous steamers and sailing-vessels continuously loading or discharging. As many as six ocean-going steamers are frequently seen alongside, loading with wool, frozen meat, and other products, for conveyance to Europe. The port possesses a patent slip at Evans' Bay, within a short distance of the city. Founded in 1840 by the New Zealand Company, the city occupies the flats skirting the original shore-line, long since obliterated by the reclamation of the foreshore, which is now mostly covered with fine buildings. Rising close behind the old shore-line is a range of hills, the lower parts of which are all built over. The population of the city at the present time is about 49,500, including the suburb of Melrose, which now forms part of Wellington. Being the seat of Government, the city contains the residence of the Governor and the headquarters of the Government departments, which are placed in what is said to be the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere. There are several noticeable public buildings, amongst which must be mentioned the Parliamentary Buildings, containing a valuable library, General Post Office, Government Life Insurance Offices, Government Printing Office, Government Railway Offices, Public Library, School of Art, and Harbour Board Offices. The Colonial Museum and the Botanical Gardens are also worthy of notice. The city is lighted by electricity, and its streets are to be paved with wooden blocks, whilst an excellent supply of water is obtained from the Wainui-o-mata River, on the other side of the harbour. The installation of a system of electric trams is proceeding. The principal industries are represented by iron- and brass-foundries, sawmills, soap-and-candle works, boot-factories, aërated water, meat-freezing works, coachbuilding, rope-and-twine works, sash-and-door factories, brick-, tile-, and pottery-works, besides a match-factory and innumerable other smaller works of various kinds. The city is increasing with rapid strides; its excellent position, together with the fine back-country, places it in the front rank of New Zealand towns. Its principal suburbs are Onslow and Karori, containing 1,750 and 1,500 inhabitants respectively.
Petone is situated near the mouth of the Hutt River, seven miles from Wellington, on the railway-line. It has a population of 3,780, and is a rising township, containing the Government Railway Workshops, a woollen factory, and a meat-freezing and preserving establishment. The Lower Hutt, almost immediately adjoining, has also a large population, and some well-built residences with beautiful gardens. The Upper Hutt, situated at the head of the valley, has many small farms, owned by some of the very early settlers. The railway here starts the ascent of the Rimutaka Range.
Featherston, situated at the foot of the Wairarapa Valley, forty-six miles by rail from Wellington, is a small township, with butter- and cheese-factories in the neighbourhood. Roads lead from it to Martinborough and the East Coast, and also down the Wairarapa Valley to Palliser Bay.
Greytown North is situated three miles off the main line of railway, and near the middle of the Wairarapa Valley, fifty-four miles from Wellington by rail. The chief industries are sawmilling and coachbuilding. The population is 1,122 persons.
A few miles further north is the Town of Carterton, where are to be found timber-mills, cheese-factories, &c., and a population of 1,205 persons. There is some splendid farming land in this locality on the banks of the Ruamahanga River.
Masterton is situated at the head of the Wairarapa Valley, on the Wellington-Napier Railway, sixty-seven miles from the capital. It is the centre of an agricultural and pastoral country, and has a population of 3,949. It is lit with gas, and has several industries, such as fellmongery, rope-making, flax-mills, coach-factory, &c., and, in addition, has some excellent fish-breeding ponds, from which many of the rivers in the colony have been supplied with trout. An important coach-road leads from here through a fine pastoral district to Te Nui, and on to Castlepoint on the East Coast, where a large quantity of wool is annually shipped to Wellington for export.
North of Masterton is the Opaki Plain, and beyond is the entrance of the once famous Forty-mile Bush, which is now a thriving pastoral, agricultural, and dairying district. Butter-factories have been established at numerous centres.
Eketahuna is, by rail and road, eighty-nine miles from Wellington. From there a main road leads to Alfredton, and up the Tiraumea Valley, through the East Puketoi country, to Weber, and Dannevirke, on the Napier Railway-line.
Pahiatua, a township eighteen miles beyond Eketahuna, has a resident population of 1,209. It is the county and market-town of a large and improving district, and will probably also become the centre of a large dairying industry. Several branch roads run from Pahiatua into the adjoining country, the principal one leading to Makuri through a beautifully-wooded gorge. From there another branch road passes over the Makuri saddle into the East Puketoi country.
On the West Coast, Pahautanui, at the head of the Porirua Harbour, is the centre of a small agricultural community of early settlers, the old coach-road to the West Coast running through it; and there is a branch-road leading over to Hayward's in the Hutt Valley. Paikakariki, twenty-seven miles from Wellington, may be considered the commencing-point of the West Coast settlements, which are springing up in every available valley along the coast. At Otaki, forty-seven miles from Wellington, by rail and road, there is a township, and a large Native settlement. At Manukau, Levin, and Shannon, thriving townships have arisen since the Manawatu Railway Company opened up the land round about, much of it being rich farming and grazing country. Between Shannon and the Manawatu River there is a large raupo or flax swamp, named Makurerua, containing at least 15,000 acres of fine alluvial soil, which is being gradually drained, and will probably at some future period become grazing-land.
Foxton, a township at the mouth of the Manawatu River, is a small shipping port, containing about 1,200 inhabitants. It is connected with Palmerston North by a branch railway, and is the outlet for a large area of good agricultural land.
Palmerston North is an inland town at the junction of the Wellington-New Plymouth and the Palmerston-Napier Railways, situated on a fine plain in the midst of a most excellent farming district at a point eighty-seven miles from Wellington, and 110 miles from Napier. Its population is now upwards of 7,800. It is lit with gas, and has a good water-supply. A fine bridge across the Manawatu River connects it with the Fitzherbert Block, a tract of rich agricultural land. Nine miles from Palmerston is the Township of Ashhurst, at the mouth of the Pohangina Valley, up which settlement has now extended for a distance of twenty-two miles. Several large farm-homestead association blocks have been selected up this valley.
Feilding, ninety-nine miles from Wellington by rail, with a population of 2,298, is becoming one of the most important towns on the West Coast, as it is the centre of a very fine locality, and the outlet for a large tract of inland country, the forest on which is fast being felled. A coach-road connects it with Birmingham (Kimbolton) and Pemberton, about thirty-two miles distant. On the seaward side for a distance of twenty miles there is also much good agricultural land, extending on the north-west to the Rangitikei River, and including the Township of Halcombe. There are several dairy factories established in the neighbourhood.
Marton, 116 miles from Wellington by rail, with a population of 1,100, one of the earliest of the West Coast settlements, is also the centre of an agricultural country. The Township of Bulls, on the north side of the Rangitikei River, lies between Marton and the coast. From Marton Junction the southern part of the North Island Main Trunk Railway extends up the Rangitikei Valley to Hunterville, a good-sized township in the centre of a grazing district, and from thence as far as Mangaweka, thirty-two miles from Marton, by way of the Makohine Viaduct. A short distance beyond Mangaweka is the viaduct of the same name, 964 ft. long, now rapidly approaching completion. The line is in a well advanced state to Taihape, and it is expected will be opened next year. The construction of the line is proceeding between Taihape and Turangarere. The distance from Marton Junction to the summit at Waimarino is about 104 miles. The coach-road has been made to Turangarere, and from thence to Tokaanu, on Lake Taupo, in the Auckland District.
Wanganui, situated near the mouth of the river of that name, is the oldest town after Wellington, from which it is 150 miles by rail—the distance by sea being only a hundred and twenty miles. It is the centre of an excellent farming district, and has a considerable trade, and several manufactories. Near the mouth of the river are freezing-works, the meat from which is conveyed by lighters to the large English steamers which lie off the mouth of the river. The town is lit with gas, and has a good water-supply. Not far from it are some extensive railway workshops. Altogether it is a thriving place, with a population of about 7,300. The Wanganui River is navigable for a light-draught steamer up to Pipiriki, a distance of fifty-six miles, and for canoes a further distance of eighty miles to Taumaranui. A branch road extends from Pipiriki through the Waimarino Forest to Ohakune, and on to Karioi on the Murimotu Plains, thence by way of Turangarere and Moawhango to Napier.
Town Land.—Further sections in Piriaka, Raetihi, Ohakune, Mowhanau, Taihape, Mataroa, and Pongaroa Townships will probably be opened for sale at Wanganui, Pahiatua, and Wellington on dates due notice of which will be given in the local papers.
About 20,000 acres, known as the Retaruke Block, on the Wanganui River. It is proposed to open this under the small grazing-run system during next summer.
Awarua Block.—There is an area of about 101,000 acres purchased by the Crown in this block available for future subdivision and disposal. This area for the most part consists of the rougher portion of the block, and will probably be occupied as pastoral country. It is proposed to offer an area east of Utiku at an early date.
Puketotara, Ahu-ahu, and Te Tuhi Blocks.—These blocks, situated about thirty miles up the Wanganui River, comprise about 35,600 acres, and will shortly be offered for selection as second-class unsurveyed land on optional systems.
Taonui, Maraetana, Pukewhakapu Blocks.—These blocks, which comprise about 12,500 acres, situated between the Mangawhero and Wangaehu Rivers, are now under survey. It is proposed to offer them shortly on optional systems.
All the available land suitable for holding under the improved-farm conditions has now been allotted, but if any of the sections now held under this system should be forfeited, they will probably be ballotted for amongst applicants in the district who are known to be of good character and likely to make good settlers. If further blocks of suitable land for this system are found, they will be cut up and opened on the same conditions.
Waitotara.—The Te Ngae Block, 1,546 acres of second-class pastoral land, is now open for selection in two small grazing-runs.
Waimarino.—A block of about 46,550 acres, on the Retaruke, Oio, and Kaitieke Rivers, has had roads surveyed through it, and portion of it lately surveyed is now open for selection on small grazing-run system. The remainder of this block will shortly be open as unsurveyed land on optional system. 32,000 acres at the head of the Retaruke and Makino Streams have also been roaded. The rest of the Waimarino country, containing about 250,000 acres, is more or less broken, and will probably be opened later on as second-class pastoral country or small grazing-runs, to enable it to be taken up in larger sections.
A number of forfeited sections are now open for selection in the following blocks: Marton No. 3, Marton No. 1, Umutoi, Waimarino, Hunterville No. 2, Dannevirke Centennial, &c.
Tauakira No. 1 Block.—Nine sections, of an area of 10,041 acres, are open for selection on optional systems. This block is situated on Wanganui River, about 28 miles from Wanganui.
Victoria College Endowment Block.—One lot of 2,200 acres is open for selection on the small grazing-run system.
Wanganui River Trust Endowment Block.—This block of 9,733 acres is subdivided into four lots, open for selection on the small grazing-run system.
Mangapapa 1c Block.—One section, 797 acres, is open for selection on optional systems.
Waimarino Block.—An area of 8,100 acres of Crown land and State forest is open for application as a grazing lease for a term of three years.
Rangipo-Waiau-Murimotu Block.—An area of 100,301 acres in this block, subdivided into three runs, is open for selection as pastoral leases under Part VI. of “The Land Act, 1892.”
Kaitieke Block.—Nineteen lots, comprising an area of 10,218 acres, are open for selection on the small grazing-run system.
Ohotu Block.—Seventy-one lots, comprising an area of 57,455 acres of Maori land, about forty-five miles up the Wanganui River, in the Ohotu Block, have been offered for selection for terms of twenty-one years with right of renewal. Particulars as to the lots still open can be obtained from the President, Aotea Maori Council, Wanganui.
Pipiriki Township.—Leases of several forfeited allotments for the term of twenty-one years, with right of renewal for a further term of twenty-one years, will be open for application by tender shortly.
Tokaanu Township.—Leases of ninety-nine allotments for the term of twenty-one years, with right of renewal for a further term of twenty-one years, are open for application by tender.
Potaka Township.—Leases of forty-four allotments for the term of twenty-one years, with right of renewal for a further term of twenty-one years, are open for application by tender.
Hokio Township.—Leases of forty-seven allotments for the term of twenty-one years, with right of renewal for a further term of twenty-one years, are open for application by tender.
Wharangi (Foxton Sanatorium).—Leases of twenty-three allotments for the term of fourteen years are open for application by tender.
Tongariro, Rangipopo, and Kaimanawa Blocks.—105,000 acres have been acquired by the Crown, but none of it is likely to be taken up for settlement for a long time to come.
“Crown Land Guides” and sale lithographs, giving full particulars of lands open for selection in this Land District, will be forwarded to any one on application to the Commissioner of Crown Lands, Wellington.
Townships are now surveyed at Pipiriki, Tokaanu, Parata, Potaka and Hokio; sections in all of which are open for leasing under “The Native Townships Act, 1895.”
The allocation of the Crown's purchases in the Raketapauna, Rangiawaea, Tupapanui, Puketotara, Ahuahu, Pukewhakapu, Maraetana, Taonui, Motukawa Nos. 1 and 2, Te Tuhi Nos. 1, 2, 3, and 4, has been made by the Land Court; and the surveys of the land allotted are in hand, and they should be available for settlement soon after the surveys are completed.
The blocks under lease to Europeans contain about 374,700 acres, the principal being the Owhaoko, Mangohane, and Ruanui, occupied by Mr. Studholme; and the Oroumatua, leased to Mr. Birch. Of others passed through the Native Land Court there are about 562,415 acres which are fit for settlement, the principal being the balance of the Awarua and the Motukawa, Raketapauma, Te Tuhi, Ahu-Ahu, Rangiwaea, and Puketotara Blocks in the central district; Raetihi in the Waimarino district; Tauakira and Ohotu, on the Wanganui River; Tupapanui, Maraetaua, Taonui, and Kaha-kaha, between the Wanganui and Wangaehu Rivers. Those not suitable for settlement at present are the Te Hautu, Ohuanga, and Kaimanawa, on the east side, and the Oahukura on the west side, of Tongariro Mountain, containing an area of about 345,000 acres.
The Native lands which have not passed the Native Land Court contain an area of about 130,000 acres, the principal being the Mairekura, Okehu, Tawhitinui, and Papahaua Blocks, on and between the Wangaehu and Wanganui Rivers, and some others on the west side of the latter river.
The pastoral industry is by far the more important, the total area in grass in 1903 being 2,600,629 acres as compared with 102,714 acres under crop, garden, or orchard. Of the area in crop, 5,969 acres were in wheat, 27,884 in oats, and 38,520 acres in turnips or rape, the rest being in potatoes or other crops.
The following figures will show the average return per acre of grain, for the year 1903: Wheat, 36·79 bushels; oats, 42·13 bushels; barley, 35·44 bushels.
The area in sown grass now exceeds that in any other district in the colony, though the area under crop is very small as compared with either the Otago or Canterbury Districts. In April, 1902, there were 4,222,510 sheep; and in October, 1902, the cattle numbered 315,869, and horses 46,038. The total area in gardens is given as 2,317 acres; in orchards, 3,703 acres; and in plantations, 3,982 acres.
Both soil and climate are well adapted for the production of butter and cheese, and hence we find creameries and butter-factories increasing in number very considerably each year, and the export constantly augmenting.
Forty-eight butter and cheese factories were returned in September, 1902, as at work in the Wellington Provincial District.
The principal flax-mills working are at Featherston, Carterton, and Martinborough, in the Wairarapa, and at Foxton on the West Coast. This industry fluctuates greatly, in accordance with the price ruling for the dressed article. In 1901 twenty-five mills were at work, employing 580 men and 25 boys; the machines driven by water-wheel or engine working up to 365-horse power.
Sawmills are to be found in different parts of the district where the means of communication are sufficient, the timbers cut being principally totara and red pine, both of which are largely used in house construction and other works. Others of the native woods are very beautiful, but are utilised only to a small extent.
The principal mills are at Pahiatua, Eketahuna, Masterton, and Carterton, in the Forty-mile Bush and Wairarapa districts, and at Levin on the West Coast. besides which there are several mills in Wellington for dressing the rough material, In the whole district there were in 1901 sixty-six mills, of an aggregate of 1,114-horse power, engaged in this industry, employing 1,114 hands, the output of sawn timber being 41,375,471 ft., and the total value, including posts and rails, resawn timber, doors, sashes, &c., 210,589, which, next to Auckland, is the highest for any provincial district in the colony.
The numbers of the other principal industries in this provincial district, as given in Census, 1901, were as follow: Meat-freezing and preserving works, 5; ham and bacon curing establishments, 3; fish-curing works, 4; grain-mills, 8; sugar-boiling and confectionery works, 4; breweries, 10; aerated-water factories, 24; sauce and pickle factories, 5; soap and candle works, 4; cooperages, 4; wood ware factories, 5; gasworks, 6; brick, tile, and pottery works, 18; tinware factories, 13; iron and brass foundries, 13; printing offices, 40; basket and perambulator factories, 6; coachbuilding and painting works, 44; cycle-factories, 10; saddlery and harness factories, 29; tanning, fellmongering, &c., establishments, 14; sail and oilskin factories, 4; furniture and cabinet-making, 36; tailoring establishments, 67; dressmaking and millinery, 78; shirt-making, 7; boot and shoe factories, 24.
Table of Contents
The Marlborough Land District, occupying the north-east corner of the Middle Island, and containing about 2,635,000 acres of land, is bounded generally on the north and east by Cook Strait and the East Coast as far as the Conway River; thence by that river to its junction with the Towy River; from this point, by straight lines, rivers, and the summits of watersheds to the western side of Tennyson Inlet, Pelorus Sound. From the Conway to the Acheron River it abuts on to the Canterbury Land District, and from that river to Pelorus Sound it is bounded by the Land District of Nelson.
The widest part of the district is from Cape Campbell to Tophouse, a distance of about sixty-seven miles, and the extreme length from Cape Jackson to the Conway is 120 miles.
The district throughout is generally mountainous, but none even of the highest peaks are covered with perpetual snow, although Tapuaenuku, the highest of the inland Kaikouras, attains an altitude of 9,462 ft. Of the Seaward Kaikouras, or Looker-on Mountains, the highest points are Kaitarau and Whakari, which are 8,700 ft. and 8,500 ft respectively. There are several lesser peaks, from 4,000 ft. upwards.
The view from Kahautara Bluff, south of Kaikoura Settlement, looking northwards, when the Looker-on Mountains are snow-capped, is said to be one of the finest in New Zealand.
Geologically, the district may be briefly described as follows: North of the Wairau River the rocks belong chiefly to the Upper and Lower Devonian series, with a belt of Silurian between them, embracing the country along the west of Queen Charlotte Sound to Cook Strait. Within these series auriferous deposits are found, and at present worked at Mahakipawa, Wakamarina, and Wairau Valley. In Endeavour Inlet an antimony-mine was worked for some time. But operations have been discontinued and the machinery removed. The country south of the Wairau River may be said to belong chiefly to the Carboniferous Age, with patches, along the coast and up the Clarence Valley, of Cretaceo-Tertiary and Lower Greensand formations; while along and between the Awatere and Clarence Rivers volcanic formation and numerous intrusive dykes occur. The Red Hills also, at the head of the Wairau Valley, are of volcanic origin.
Coal has been discovered in the neighbourhood of Picton, and in the Clarence Valley, but none has been as yet successfully worked within the district. A narrow belt of Tertiary limestone, suitable for building purposes, extends, with small interruptions, from Cape Campbell to the boundary of the Canterbury Provincial District. The Marlborough land may be divided into three classes: Open land, generally covered with associated grasses; forest-land; and intermediate, or land partly forest, partly covered with scrub, fern, or other rank vegetation. This original condition of the soil naturally gave rise to a localisation of industries, and a very unequal distribution of settlement. Thus the open country was taken up for pastoral purposes; in the forest country the timber industry was developed, and the intermediate land passed into the hands of farmers. Though agriculture is now extending into the pastoral and forest country, and considerable areas of forest-land have been cleared and laid down in grass, the portions of the district characterized by these respective industries are still well defined.
In the northern part of the district, bounded by Cook Strait, numerous deep fiords and bays run far into the land. The principal of these are Pelorus and Queen Charlotte Sounds, Tory Channel, Port Underwood, and Port Gore.
These Sounds are very picturesque, but the hills surrounding them are not so rugged and precipitous as are those of the thirteen celebrated Sounds on the west coast of Otago and Southland.
Though generally steep, the land is not too rough to be used for pastoral purposes, and nearly all the land in the Sounds is occupied by thriving settlers.
Pelorus Sound, the most extensive and picturesque, is thirty-four miles long, following the course of the main channel, with the Town of Havelock at its head. There are many bays and inlets branching off in all directions; the largest of these is Kenepuru Sound, fourteen miles long. Pelorus Sound, including its branches, has a shore line of over 300 miles in length, not counting islands.
Queen Charlotte Sound is the next in length, being thirty miles from its entrance to its head; it also has many bays and inlets, one of which is Picton Harbour, twenty-five miles from the entrance.
Tory Channel is ten miles long, and forms the most direct line of communication between Picton and Wellington. The distance from Wellington Wharf to the entrance of Tory Channel is about forty miles, and about twenty more to Picton.
The shore-line of Queen Charlotte Sound and Tory Channel is over 200 miles in length. The entrance of Queen Charlotte Sound is about twenty miles distant from that of Pelorus Sound, and this latter is about twelve miles from the French Pass. Generally there is deep water in all the sounds and bays, and good anchorage can be found near the shore. The country is hilly everywhere in the neighbourhood of the Sounds, the highest point being Mount Stokes, 3,951 ft. above sea level.
Four considerable rivers, the Wairau, Awatere, Clarence, and Conway, rise towards the western boundary of the district; the two former, running east and north, fall into Cook Strait; the two latter, taking a southerly and easterly course, discharge into the sea on the eastern side of the Island. These rivers water large and fertile valleys, but none can be entered by vessels except the Wairau, which is navigable for small steamers for about ten miles from its mouth.
The Wairau Plain, containing about 65,000 acres, on which stands Blenheim, the capital of Marlborough, is the principal block of agricultural land within the district. The soil, generally good, is, on the lower or seaward side of the plain, extremely fertile, especially in the neighbourhood of Tua Marina, Spring Creek, and near Blenheim, which is surrounded by numerous gardens, with rich deep mould, and well sheltered with trees. The average yield of wheat for the plain is about 25 bushels per acre; of oats and barley, 35; of peas, 30; and of potatoes, 10 tons per acre. Hops have been successfully grown for many years in the neighbourhood of the town, but, owing to the high price of labour, their cultivation has not extended. The plain, traversed in all directions by good macadamised roads, and dotted over with numerous comfortable homesteads, standing in clumps of trees amidst well-cultivated fields, has already an old-world appearance. More than half the population of the Marlborough Land District—about 13,000, according to the last census—is centred in the Town of Blenheim and on the Wairau Plain. Besides this plain there are several thousand acres of terrace flats and valleys along the larger rivers, notably at Starborough, on the Lower Awatere.
There are not any lakes worthy the name. The largest is Kapara te Hau, more familiarly known as Grassmere, situate on the coast between the Awatere River and Cape Campbell. It is about three miles in diameter, and very shallow, being, indeed, no more than a lagoon, as during a dry season there is little or no water in it.
There are two other lakes of small size, viz.,—Lake Elterwater, four miles south of Lake Grassmere, and Lake McRae, situate in the open country between the Awatere and the Clarence Rivers.
The portion of Marlborough north-west of the Wairau River, extending to the boundary of the Nelson Land District, and including the County of Sounds, in all about 280,000 acres, was originally covered with dense forest. In the valleys and on the lower hill-slopes, rimu, kahikatea, matai, totara, miro, and tawa were the principal forest-trees. The higher portion of the hills and steep spurs are clothed with the various species and variety of birch (beech), to which along the shores of the Sounds were added pukatea and kohekohe, the latter locally called cedar.
Since 1860 sawmills have been at work in various parts of the district. Thirty-two mills have been erected, and have worked for longer or shorter periods. Havelock, on the Pelorus Sound, is at present the headquarters of the timber trade.
The hills along the shores of the Sound will, for many years, furnish birch sleepers. There are other timbers left in places, but nowhere sufficient to justify the erection of a mill, unless pukatea wood, hitherto neglected, could be utilised. It is a light, tough timber, well adapted for boat-building and for packing-cases. The quantity of pine timber remaining in the Kaituna and Onamalutu Valleys is small, but there is a good supply of birch and other wood, suitable for fencing and firewood. On these valleys the Wairau Plain is mainly dependent for timber.
The Pelorus Valley, with its tributaries the Wakamarina, Rai, Ronga, and Opouri Valleys, still contain about 300,000,000 ft. of convertible timbers, exclusive of the birch, of which there is a large amount of the best quality on the hills and terraces. The Wairau, Blenheim, and other districts extending southwards must depend for the future on this source for all their building material.
In the neighbourhood of Kaikoura, along the base of Mount Fyffe, and in the Hapuku Valley, there is another small block of forest-land in which three small sawmills have been erected. The quantity of timber suitable for sawmill purposes in this block is very limited, but it will furnish the neighbouring country with firewood and fencing for many years.
The Wairau Plain, which is the principal block of agricultural land, has been already dealt with. The second agricultural centre is in the neighbourhood of Kaikoura. The land extending along the base of Mount Fyffe, between the Kohai and Hapuku Rivers, about 13,000 acres in extent, is held in small or moderate-sized farms; the soil is good, the block known as “The Swamp,” between Mount Fyffe and the Peninsula, being particularly rich. In the Pelorus, Kaituna, and Onamalutu Valleys, and in the Sounds, settlers following in the wake of the sawmills have already converted much of the land worked over into grazing-farms. The land is of three descriptions—alluvial flats, terraces, and hill-sides. On the flats in the larger valleys the soil is rich, producing heavy crops of oats, peas, beans, and potatoes, wherever it has been brought into cultivation. The terrace-land varies much in quality, but generally grows good grass, as do also the hills on which tawa formerly grew; the birch country being very barren. On the small bush-farms cattle-grazing is the chief pursuit. Out of 12,000 head kept in Marlborough, 4,300 belong to the forest country.
About 1,680,000 acres of the Marlborough Land District are at present devoted to keeping sheep. The leaseholds in the northern parts of the district contain a large extent of scrub- and fern-covered country, now producing little or no food for sheep, but capable of improvement. The total number of sheep depastured is 849,168, distributed as follows amongst the counties into which the land district is divided: Marlborough County, 522,783; Sounds County, 164,657; Kaikoura County, 161,728. On the natural pasture of the open country merino sheep are kept almost exclusively, the land carrying from half to one sheep per acre. In the forest country, on sown grass, the land keeps from two to four crossbred sheep per acre. Along the shores of the Sounds large areas of hill-land have been taken up on lease, and are now being cleared and laid down in grass expressly for keeping sheep, but generally throughout the forest country the holdings are small or of moderate size; hence this is, after the Wairau Plain, the most populous portion of the district.
Gold-mining has been carried on for some years, principally at Mahakipawa, Wakamarina, and Wairau Valley. At present not much gold is being obtained.
One dredge is at work in the Wakamarina River, with satisfactory results; but the two at Top Valley have suspended operations—the returns not being payable—and one of them is being removed to Armchair Creek.
Twelve sawmills are at work within the district: one at Kaikoura, and the others in the Pelorus, Kaituna, Onamalutu, and Wakamarina Valleys, and in the Pelorus and Queen Charlotte Sounds. The principal one is Messrs. Brownlee and Co., in the Pelorus Valley, their tramway being some fifteen miles long, the output last year being about 3,142,000 ft. Messrs. Brownlee and Co. have sixty men employed, and keep two vessels running between Havelock and Lyttelton.
During the year the flax industry employed eleven mills, and the quantity of hemp shipped was 1,300 bales and 570 bales tow.
There are three flour-mills at work, two of them being owned by Messrs. Redwood Bros. The one at Spring Creek is a complete roller-mill, driven by water-power, and can turn out about 14 tons of flour in twenty-four hours. It is electric-lighted, and the sack-working machinery is driven by electric motor. The other two mills are in the Town of Blenheim; one is worked by water-power and the other by steam.
There is a dairy factory at Spring Creek which contains all the latest improvements in machinery; 19 tons of butter were produced in 1902.
There is a first-class cheese-factory at Tuamarina. Last season 82 tons were turned out. There are also cheese-factories at Kaikoura and Havelock. The latter had an output of 52 tons.
Marlborough possesses one of the finest climates in the world; and at Blenheim it is fine weather nearly all the year round. There is almost a total absence of the boisterous winds that so frequently visit Wellington.
The original distribution of the open and forest lands was entirely due to climatic causes. At Cape Campbell, one of the barest places in the district, the annual rainfall is only 23·25 in.; in the Pelorue Valley, the centre of the forest country, it is over 65 in. This difference between the climates of the northwestern and south-eastern portions of the district explains why the artificial pasture-land, when compared with the natural pasture, supports such a large amount of stock. Winter and spring are the wettest seasons, hence the dry climate is not unfavourable for agriculture. Wherever the soil is suitable, crops sown in winter and harvested in early summer can be successfully grown. Everywhere near the coast the range of temperature, considering the latitude, is very small. The thermometer seldom falls below 30 deg., or rises above 78 deg. Along the shores of the Sounds the mildness of the winter, owing to the curious distribution of land and water, allows lemons, oranges, passion-fruit, figs, and other sub-tropical fruits to be grown in favourable situations. On the lower hills and terraces of the forest country the chestnut (Castanea vulgaris) grows rapidly, and commences to bear fruit in five or six years. A few trees planted in the Pelorus Valley some twenty years ago are now yielding annually about 2 cwt. of nuts a tree. In all parts of the low country the common English fruit-trees—apple, plum, pear, cherry, &c.—yield abundantly, the fruit, owing to the clearness of the atmosphere, being of excellent quality. In the high country, where snow falls occasionally during winter, red, white, and black currants can be produced in such quantities that with little labour they might be made an article of export to the warmer parts of Australia.
The chief town, Blenheim, is situate on the Wairau Plain, at the junction of the Opawa and Omaka Rivers—a third river, the Taylor, would join at about the same point were it not that when not in flood it disappears beneath the surface, about three miles south of the town. Blenheim has been termed a miniature Christchurch, doubtless from its extreme flatness. Considering this, its streets are not so straight and wide as they should be. The Government Buildings, which comprise the Post and Telegraph Offices, Lands and Survey Offices, Courts of Justice, &c., form a handsome edifice in the centre of the town, which is well planted with deciduous and evergreen trees. It is about eighteen miles and a half from Picton by range and about twelve miles from the sea by the Opawa River, which is navigable for small steamers. Blenheim is lit by gas, and is supplied with water principally by artesian wells. The population is 3,222.
The next town in importance is Picton, the principal port, only fifty-three miles by sea from Wellington. This little town, both in position and appearance, may be said to be the antithesis of Blenheim, being most picturesquely situated at the head of Queen Charlotte Sound, and nestling among hills, some of the higher ones still densely covered with birch and other forest. There is frequent communication with Wellington and Nelson by steamers averaging 500 tons, and vessels of large size can lie at the wharf at low-water. The direct exportation of frozen meat from Picton commenced in 1892, when 16,433 carcases were shipped. The Christchurch Meat Company exported from Picton for the year ended 31st March, 1903, mutton, 41,705 carcases, and lambs, 37,617 carcases. Picton possesses a malting establishment also, producing for export, as the excellent quality of the barley grown on the Wairau Plain insures a ready market. A small quantity of oysters, mostly procured in Queen Charlotte Sound, is annually exported from Picton; with culture the supply might be almost indefinitely increased, many of the sheltered bays in both sounds being well adapted for the purpose. What is now being done along the Marlborough coast is a mere trifle compared with what might be accomplished if capital and knowledge were brought to bear on the fishing industry. Around the whole coast, from the mouth of the Conway to near the French Pass, the sea abounds in fish. Within the Sounds and amongst the islands of Cook Strait, hapuku, schnapper, moki, barracouta, raturi, kahawai, and rock-cod are extremely plentiful. Immense shoals of the southern herring (Clupea sagax) and of anchovies (Engranlis encrasicholus) frequent the inlets at certain seasons of the year, and quantities of fresh fish are exported from thence to various places within the colony. As steamers arrive at and leave Picton almost daily, shipments can be made without delay to all parts. Picton possesses a good gravitation water-supply. Its population is about 900 persons.
Havelock, situate at the head of Pelorus Sound, is, as has been already stated, the present headquarters of the timber trade, Messrs. Brownlee and Co.'s steam sawmill, at the mouth of the Pelorus River, being only a mile or so from the town. Between Picton and Havelock there is a mail-service twice a week, viâ Cullensville, on the Mahakipawa Goldfields. The population of Havelock is about 300 persons.
The Town of Kaikoura, the greater part of which is built on a raised shingle-beach, is situate at Kaikoura Peninsula, near the southern boundary of the district. The town, with the adjoining settlement of small farms, forms one of the most picturesque spots in New Zealand, lying as it does under the Seaward Kaikouras, or Looker-on Mountains. At the back of the town the peninsula, which is composed of Cretaceo-tertiary limestone, rises abruptly for about 100 ft., and affords splendid sites for dwelling-houses. Kaikoura is connected with Blenheim by a weekly coach service, the distance being about ninety-five miles. There is also direct steamer communication with Wellington and Lyttelton. The population of the town is about 500.
The only railway is that between Picton and Seddon, a distance of thirty-three miles and a half. Three train run daily between Picton and Blenheim, about eighteen miles, and one train between Blenheim and Seddon on five days in the week. A substantial railway and traffic bridge over the Awatere River, costing 22,500, is a very great boon to the district.
The Main North Road to Nelson, distant seventy-eight miles, is a good metalled road nearly the whole way. It runs up the Wairau Valley from Blenheim for about six miles, crosses the Wairau River into the Kaituna Valley, which it follows as far as Havelock—about twenty-eight miles. It then runs up the Pelorus and Rai Valleys, and ascends by easy gradients to the Brown Saddle, where it crosses the boundary into Nelson. An excellent coach-service—probably the best in the colony—has been established for some years, the coach running to and from Nelson on alternate days, covering the distance in eleven hours, and another coach-service twice a week has been established between Blenheim and Havelock.
The Main South Road, running over the Taylor Pass into the Awatere Valley, and through the Starborough, Flaxbourne, Kekerangu, and other properties, connects Blenheim with Kaikoura and the south, and is a good road during dry weather, although it might be much improved in places. Since the acquisition of the Starborough Estate by the Government the bulk of the traffic now goes viâ the Redwood Pass, as it is a more direct route to the town of Seddon.
The portion between the Clarence River—over which a fine bridge was built some years ago—and the Hapuku River runs along the coast under steep and picturesque hills covered with forest. A road to the south of Kaikoura, between the Kahautara and Conway Rivers, is now completed and forms part of the main Cheviot—Kaikoura Road, and, besides its great usefulness in opening up the country through which it passes, will also become a favourite route for tourists, as in many places it passes through most picturesque scenery.
A good road has been formed up the Wairau Valley, passing through the Bankhouse, Erina, Lansdowne, Hillersden, and Birch-hill properties, and connecting with Tophouse, just outside the boundary, and distant fifty-six miles from Blenheim. At Tophouse there is an hotel and a telegraph-station, and thence a good road leads to Belgrove, on the Nelson Railway line.
A coach runs twice a week between Blenheim and Wairau Valley—twenty-five miles—where there is an hotel, a post- and telegraph-office, and one or two stores.
There is also a good cart-road running up the Awatere River—which it crosses and recrosses several times—as far as Molesworth Station, about seventy miles from Blenheim. Between these points there is a weekly coach and mail service.
There are other minor roads and bridle-tracks throughout the district too numerous to specify.
The area of Crown lands at present available for settlement is about 140,000, acres, but of this area 100,000 acres are of very poor quality, being chiefly the summits of high, rugged country. The balance of available area lies principally in the Pelorus, Rái, and Wakamarina Valleys, and in the Sounds, and will doubtless be readily taken up when thrown open for selection.
Table of Contents
The Nelson Land District comprises the north and north-western portion of the Middle Island, the greater part being high and mountainous, and on the western and inland ranges covered with dense forest to the bush-limit, at from 4,000 ft. to 4,500 ft. Cape Farewell, the northernmost point, is situated at the western entrance of Cook Strait, on the south side of which lie Golden or Massacre Bay, and Tasman Bay, more commonly called Blind Bay. The former derives its name from the massacre of a boat's crew belonging to Tasman, who visited it on the occasion of his discovery of New Zealand in 1642. At the head of the latter, which has a depth of fifty-four miles from its entrance, stands the town of Nelson. From Separation Point, on the western side of Blind Bay, a range of mountains from 3,000 ft. to 4,000 ft. in height extends southward to Mount Murchison. It consists of a granitic formation, with slate, limestone, and sandstone belts. From Pelorus Sound, on the east, commences another range—a portion of which is serpentine, forming a mineral belt immediately south of Nelson City. It reaches an elevation of 6,000 ft., and runs in a south-westerly direction to the St. Arnaud Range, terminating in the Spencer Mountains, a large central mass attaining a height of 8,000 ft. above the sea-level. To the westward of the Spencer Ranges and those on the further side of Blind Bay are the Brunner, Lyell, Marine, and Tasman Mountains, from 5,000 ft. to 6,500 ft. in height. Still further westward along the coast are the Paparoa, Buckland Peaks, and Papahaua Mountains, about 4,500 ft. at their highest point, and the Whakamarama Range, extending from Rocks Point to Cape Farewell. There are also a number of isolated mountain-masses here and there through the district.
The inland Spencer Mountains are the source of the principal rivers of the district south of the Buller River, and are thus described by the late Sir Julius von Haast: “On the southern slopes of this wild alpine-stack we find the principal sources of the Grey, or Pohaturoa; on its north-east side the sources of the Wairau; on its eastern side those of the Acheron and Clarence; and in the deep recesses of these snow-clad giants those of the Waiau-ua, or Dillon: so we may say that, with the exception of the Takaka and Aorere, which fall into Massacre Bay, the Wangapeka and Motueka, which run into Blind Bay, the Karamea and smaller streams, which reach the sea on the West Coast to the north of the Buller River, all the rivers of any size in the northern part of this island take their rise in this magnificent chain.”
The Buller River (Kawtiri) has its source at a point about sixty miles southwest from Nelson, where it flows out of the beautiful alpine lake Rotoiti, lying 1,800 ft. above sea-level at the foot of the lofty St. Arnaud Range. This river breaks through the massive mountain chains of the interior in a transverse or easterly direction, forming, where it receives no tributaries, a succession of magnificent rocky gorges, and, after a course of about one hundred miles, finally discharges its waters into the ocean on the West Coast. The Gowan River, a tributary, has its source in another exquisite lake, Rotoroa, 1,623 ft. above sea-level. Other tributaries of the Buller are: the Matakitaki, Maruia, Owen, Matiri, and Inangahua, all of which take their rise in the snowy ranges.
The lakes of the district are alpine in character, surrounded by grand mountain and bush scenery. The principal are: Rotoiti, lying east, and Rotoroa south-east, of Mount Murchison; Matiri, to the west of Owen Range, 980 ft. above the sea.
The Waimea Plains, near Nelson, with the Lower Motueka, Riwaka, and Takaka Valley lands, formed part of the original settlement of the New Zealand Company, and are occupied mostly by small settlers. Inland are the Tiraumea Plains, 1,100 ft. above sea-level, and the Maruia, 1,300 ft. These are, together, about 30,000 acres in extent. They are surrounded by high mountains heavily timbered, and the land is of only second-rate quality. On the West Coast the level lands are Totara Flat and Ikamatua Plains, Mawhera-iti, and Inangahua Valleys, lying on the eastern flanks of the Paparoa coastal range. There are also open pakihi at Addison's Flat, on the south side of the Buller, and low swampy lands on the north side; northward is the heavily timbered country of the special settlement at the mouth of the Karamea.
The area of the District is estimated at 4,686,000 acres, of which the open land under 2,000 ft. in altitude is, approximately, 915,000 acres; the area of forestland under 2,000 ft., about 1,382,000 acres; and the open land above that altitude, about 581,000 acres, inclusive of bare mountain summits. The wooded country is estimated at 3,200,000 acres; of this area probably about 900,000 acres is scrub and stunted bush; and of the remainder, not 700,000 acres at the outside would be available for clearing. The timber on the western side consists of red- and white-pine, matai (or black-pine), totara, kawhaka (or cedar), rata, and occasional silver-pine, besides black- and red-birch (Fagus fusca). These varieties are also found, but in smaller areas, on the eastern side; birch preponderating. A large amount of timber is used in the mining industry for props and planking, and throughout the districts generally for shingles, fencing, firewood, sleepers, &c.
On the Waimea Plains is grown excellent barley, a small quantity of which is exported. Oats and chaff are sent in large amounts to the West Coast and elsewhere. Hops also form one of the chief exports. Wheat, maize, rye, and root-crops of most varieties are grown, and fruit is plentiful. The weekly wage of a farm-labourer is 20s. with board; without board he would receive 6s. a day. Ploughmen can get 20s. per week with board; without, 7s. 6d. a day.
The total area of pastoral lands held under the Crown by 77 tenants on the 31st March, 1903, amounted to 317,060 acres. As the agricultural land is limited, settlers are turning their attention to the timbered mountain-slopes for grazing purposes. These, when the timber is felled and burnt, and the ground sown with suitable grass, will, after three to four years, carry about two sheep to an acre on fair soil, and more on the limestone country. The cost of felling and burning green timber is from 15s. to 20s. per acre; cost of mixed grass-seeds and sowing, about 15s. per acre; and a good paling-fence on ordinary bush-lands with double No. 8 wires at top and bottom, with ½ in. palings and 7 in. posts sunk 2 ft. in the ground, can be erected at about 12s. per chain.
The western side of the Nelson District was a terra incognita till about the year 1863, when gold was first discovered in large quantities. Miners flocked in at first from the other goldfields in New Zealand, then from Australia, California, and other parts of the world, until in 1865 the whole coast-line was peopled from Broken River in the north to Jackson's Bay in the south. Mining, at first altogether alluvial, developed into quartz-reefing, and hydraulic-sluicing of large areas. The agricultural lands about the Grey and Inangahua were taken up and cultivated; and, as mining became a more settled industry, the miners occupied and tilled the non-auriferous alluvial flats in the many valleys: hence at the present time a number of homesteads are scattered throughout the district.
Reefton and its neighbourhood forms one of the chief quartz-mining districts in New Zealand; and the West Coast, including Westland, has produced about 45 per cent. of the total gold raised in the colony. The oldest alluvial field is at Collingwood. Among other minerals found in the district are: silver, copper, chrome, antimony, manganese, and hæmatite. Extensive deposits of coal are found on the West Coast, within the areas of the Grey and Buller Coalfields Reserves. Coal is also found in Collingwood, in Blind Bay, and in West Wanganui Inlet; and there are numerous smaller areas of coal-bearing strata here and there throughout the district. The output from the mines at work within the district during the year ending 31st December, 1902, was 537,222 tons. Copper-ore is found in a serpentine rock-formation near Nelson, but the companies which have worked the ore have not hitherto been successful—the last one, “The Champion,” failing from want of sufficient capital. Deposits of chrome-ore are also found here. Silver-ore has been worked in the Collingwood District; and at Parapara, in Blind Bay, there are widespread deposits of hæmatite iron-ore, combined with limestone and coal, waiting only for capital to develop them. It will be readily gathered from the above brief description that mining is the chief industry of the Nelson District. A great many river and beach-dredging claims have been taken up, and in many instances a large amount has been expended in the purchase and erection of dredges. A high degree of ultimate success in these ventures is looked for.
The timber industry in this district has now become an important trade. There are thirty-eight sawmills working, and during the past year about 9,000,000 ft. of various kinds of wood, principally red- and black-pine, have been cut in this district for export, and silver-pine has been largely in demand for railway-sleepers for home consumption.
A small industry in flax is also carried on.
The chief town is Nelson, situated at the head of Blind Bay, in 41° 16' S., and surrounded on all sides, except the north, by mountains reaching an elevation of 3,500 ft. With a mean temperature of 54·8° Fahr. it possesses a climate almost unequalled for its beneficial effects on invalids suffering from pulmonary diseases. There are many picturesque spots in the suburbs, and the city itself, with its cleanly-looking buildings and well-kept gardens, is one of the most charming spots in New Zealand. There is an old-established Boys' College, a High School for Girls, and a School of Music, besides Government and other schools. The Anglican Pro-Cathedral, built on the summit of a central hill, memorable as being the site of fortifications erected in the early days of the settlement for defence against an expected attack of the Natives, is a striking feature. The Roman Catholic Church, Convent, and school-buildings cover a large extent of ground. There is also at Stoke, a small village three miles from Nelson, a central Catholic Orphanage, surrounded by grounds of considerable area. There is a good supply of excellent water from a reservoir in the hills at the back of the town, and the streets are well lighted with gas. The several Government departments are housed in one roomy building, containing a large hall used for Supreme Court sittings and other public purposes. The principal industries are represented by iron foundries, fruit preserving and canning works, breweries, biscuit-factory, coachbuilding, sawmills, and sash and door factories, boot factories, and many other small works. Nelson has a small natural harbour, formed by a boulder-bank running for eight miles parallel to the shore, deep enough at high tide to admit vessels of 1,000 tons burden. It is a port of call for the Union Steamship Company's coastal steamers, and has a small local fleet plying between the West Coast, Blind Bay, Picton, and Wellington. The town is reached from the eastward by a good main road from Marlborough. A railway-line has been constructed up country to the southward for thirty-one miles to Motupiko, passing through the farming villages of Stoke, Richmond (borough), Brightwater, Wakefield, Foxhill, and Belgrove, and is being extended for a further distance of ten miles, crossing the Motueka River by means of a combined railway and traffic bridge, and proceeding up the Tadmor Valley as far as Tadmor Settlement. The section will probably be open for traffic within a year. Leaving for the West Coast by a good main road, the traveller starts from the Motupiko Station on one of Cobb and Co.'s coaches, and proceeding up the Valleys of the Motupiko and Clarke, crosses the Hope saddle and thence down the Hope Valley to its junction with the Buller, about sixty-seven miles from town. He then enjoys a succession of views of mountain-gorge scenery, and, after traversing a gorge of seventeen miles in length, arrives at the Lyell, 107 miles from his starting-point. This is an alpine township, in a small quartz-mining neighbourhood. Here is a fine lattice-girder bridge, spanning a rocky gorge of the Buller, and springing boldly from a bluff on the northern side. It is about 347 ft. long, two of the spans being 108 ft. and 168 ft. respectively. The roadway is 100 ft. above the river-bed. At 116 miles the junction of the Inangahua with the Buller is reached, the main road continuing to Reefton, with a branch road twenty-eight miles to Westport, which for twelve miles passes through some of the grandest river-gorge scenery in New Zealand.
Westport, the town next in importance to Nelson, is situated at the mouth of the Buller River. The harbour is sheltered from southerly gales by Cape Foulwind and its outlying rocks, and is accessible in nearly all weathers. A large sum has been spent on a system of harbour-works, designed by the late Sir John Coode. Westport is the place of shipment for the coal-mines lying northward as far as the Mokihinui River. The character of this coal for steam purposes stands almost unrivalled. The long line of coal-staiths and wharves on the northern bank of the river, with a fleet of steam-colliers loading alongside, does not fail at once to impress a visitor with a sense of the importance of the trade. Though much has already been done, yet the industry, from the extent of the coal-bearing strata, is capable of much larger expansion when the necessary capital can be found. The Westport—Mokihinui Mine Railway connects with the mines and conveys the coal to the port. At the foot of the Mount Rochfort plateau, nine miles from Westport, is Waimangaroa, and on the plateau itself is Denniston—both coal-mining villages. The latter, built at an elevation of 1,960 ft., is said to be the highest township in New Zealand. On a clear day it is well worth a visit, for the sake of enjoying the magnificent panoramic view of the southern Alps, which reach their highest point in Mount Cook, 12,349 ft. high, about 100 miles south. South of Westport are the alluvial gold-mining centres of Addison's Flat, Croninville, Nine-mile Beach, and Charleston.
Motueka is a thriving town situate near the mouth of the Motueka River. It is the centre of a considerable agricultural and fruit-growing district. It has two bacon-factories, fruit pulping and canning works, and dairy factory.
From the Inangahua Junction, the main road continues southward through the Inangahua Valley, passing through cultivated lands, which are being gradually won from the heavy bush, and at a distance of 136 miles from Nelson reaches the township of Reefton. Here, as at Westport, are good hotels, and, as in every one of the larger coast towns, a hospital receiving a Government grant-in-aid. This town was the first in New Zealand to be lighted by electricity. Through the Midland Railway extension of the Grey—Brunner line, Reefton is now connected by rail with Greymouth, from whence it is for the most part supplied. The continuation of the line down the Inangahua Valley is being carried on at present. About two miles inland from Reefton is Black's Point mining township, with several batteries at work in and about the place, a visit to which is generally paid by tourists wishing to see something of the gold-mining industry. Other small mining townships are: Boatman's, Capleston, and Antonio's.
Leaving Reefton by rail, and passing into the Grey Valley through a short tunnel, and by a bridge over the Grey River, Totara Flat is reached, nineteen miles distant. This brings us into the Westland District, to which refer for the balance of the journey to Greymouth.
Situate on the coast, fifty miles north of Westport, is the Karamea Special Settlement, principally settled from the Nelson and Motueka Valley districts. This part of the district contains some excellent but heavily-timbered land, and is reached from Westport by a road, connecting with the Westport—Mokihinui Railway at the Mokihinui River. There is a bridle-track, also, connecting with Collingwood and Golden Bay. This track passes along the coast northwards, thence up the Heaphy Valley to the Golden Downs, and down the Aorere Valley to Golden Bay. Here again is another coal-basin, which, though of inferior value to the older deposits on the western side, is likely to become of importance, having at the present time one mine in full work. Another coal-basin exists at West Wanganui and Pakawau.
In the Aorere Valley, of which Collingwood is the port, alluvial mining is still found to be payable, and the country contains some valuable timber in the upper part not yet utilised. Nineteen miles south, in Blind Bay, lies the small port of Waitapu, from which a considerable amount of sawn timber is exported, drawn from the Takaka Valley, and brought down by a steam tramway from the upper mills. From the head of this valley the main road is carried over a pass in the Pikikirunga Range, 3,476 ft. high, through the villages of East and West Takaka, Riwaka, Motueka, and Moutere to the town of Richmond, eight miles from Nelson. Inland are also the villages of Ngatimoti, Dovedale, Tadmor, and Sherry, each the centre of a number of small farms, and all connected by fairly-good dray-roads.
An inland road, partly bridle-track and partly dray-road, has been made from Nelson to Canterbury, by way of Tophouse, Wairau Gorge, Tarndale, Clarence Valley, Jollie's Pass, and the Hanmer Plains. Here there are hot mineral springs, much visited by persons suffering from rheumatism and skin-diseases.
About 3,000,000 acres of Crown lands still remain unoccupied in the northern part of the Nelson District; they consist principally of high bush-country, with occasional patches of good valley-lands, the greater part being classed as second-class land. The area open for selection to date comprises 9,048 acres of surveyed lands, and 244,937 acres unsurveyed lands, of which the location, nature of soil, &c., have been briefly described in the foregoing pages.
Table of Contents
The Westland District occupies the central portion of the western watershed of the Middle Island, joining Canterbury on the east; its north and south boundaries with Nelson and Otago being the Pororari, Otututu, Grey, and Awarua Rivers. The mean length is 250 miles, and its average width twenty-seven miles. The area is 6,750 square miles, composed, for the most part, of the great central snow-clad mountain chain and its out-running ranges, intersected by narrow bush-clad valleys, and subsiding westward into undulating plateaux, river straths, and shelving coasts.
The great dividing range, which constitutes the eastern boundary from the head of the Grey River to Mount Aspiring, presents a magnificent spectacle of snow and ice-clad summits, representing every aspect of mountain grandeur—masses of rock protruding from ice and snow; precipices of enormous height, with cascades; drifted expanses of snow-fields, feeding glaciers; cañons and ravined foothills covered to the top with forest.
A few of these lead from the foothills, and are of small volume; the others are snow-fed streams descending from the central range, at first in narrow gorges amongst the mountains, but spreading widely on reaching the sea-board country. They are shallow, shingly streams in winter, but swift and deep in summer. In the northern district all the larger rivers are bridged; and, southward, ferries are placed on all the main streams, which, from the melting of the snow, are practically unfordable from September to January. They will all, more or less, be available for electric-power purposes.
The principal lakes are Lakes Christabel, Hochstetter, Ahaura, Haupiri, Brunner, Poerua, Kanieri, Mahinapua, Ianthe, Rotokino, Whahapo, Mapourika, Paringa, Moerak, and Ellery, with Saltwater and Okarito Lagoons. These and a considerable number of smaller ones are dotted over the district, all varying in character—mountain tarns; coastal tidal lagoons; shallow reedy sheets; deep mountain-girt waters, all more or less forest-locked, and presenting every form of lacustrine beauty. In conjunction with their effluents they form valuable waterways for light transport to adjacent districts.
Generally speaking the whole of the district is covered with dense forest, from the sea-beach to the grass-grown tops of the high ranges, even the broken mountain-faces being wrapped with exuberant foliage. The varieties of trees differ considerably according to soil and altitude. Kamahi and rata are the chief timbers, very useful for firewood, and, being spread over the whole district, constitute an almost inexhaustible supply. Rimu is the chief milling timber, and this also is widely distributed from the sea-board to the interior uplands. Valuable stretches of white-pine belt the low lying depression of the coastal lands, and the same may be remarked concerning the imperishable silver-pine. Clumps of black-pine of good quality are met with, also rarer patches of marketable totara, while serviceable cedars are scattered along the flanks of the inland ranges and all over the lower hills and plateaux. The approximate area of forest equals 2,394,951 acres, of which a fair portion carries timber fit for the sawmill; the remainder is mainly firewood and mining timbers.
The high pastoral uplands have a coating of rich mould, and this continues fairly good down to the any timber lands. The alpine forest is readily cleared, and imported grasses grow luxuriantly, cocksfoot being the best, as it withstands fire and frosts. The lower flanks of the mountains hold a thinner soil, which at present hardly pays the heavy labour of felling the bush, while the lower heights are somewhat abrupt and unfitted for cultivation. A margin, varying in width, of fertile slopes and fans fringes the basis of the hills, and having a natural drainage constitutes an area of excellent agricultural land.
The upland soils of the coastal undulations and terraces are light loams of moderate fertility, which rest upon transported gravels, the drifted accumulations of eroded hills. On these plateaux are numerous “pakihi,” or natural clearings, which are mostly extensive tracts of swampy lands, with a peaty soil, resting on thin layers of impervious clay and non-porous gravels, or, in a few cases, on impacted glacial moraines; these formations all overlying loose drifts. The reclamation of these areas if only a matter of time, as the bulk of them are quite drainable.
Stretches of good alluvium border the rivers, streams, and sea-coast, and form the favorite location to settlers.
The climate is equable and temperate, remarkably free from storms and fogs, and immediately after bad weather the clouds roll inland, and there is a prevailing clearness of sky. The rain-bearing winds are mostly from the northwest and north-east. The southerly winter gales usually coat the ranges with snow, which, however, rarely falls below 2,000 ft. The rainfall averages 109·89 in. per annum.
The total area of pastoral lands amounts to 2,002,577 acres, 103,801 of which constitute high mountain grass districts, the balance (1,898,776 acres) being the ordinary bush-clad country, much of which is quite inaccessible to stock. All over the coastal lands, along the slopes of the lower hills, and in the bottoms of the valleys, large herds of cattle are bred and fattened on the dense undergrowth of the forest. The tussock herbage of the high lands is being gradually used by sheep-farmers, and in the near future these natural pastures will support large flocks.
The agricultural lands comprise some 219,400 acres of forest and 11,500 acres of open surface, such as swamps, grass-grown river-beds, and fringes, &c. The bulk of these lands, when cleared of bush, grow root-crops, especially turnips, which are much used for fattening purposes. The even and moist temperature encourages the almost uninterrupted growth of grass and clover, which are very luxuriant, and favour stock-raising. Oats are also grown abundantly for local consumption, and for the most part are cut into chaff. Year by year the imports of potatoes, fruits, butter, and fat stock are decreasing, owing to increased local production.
The district is fairly well provided with means of communication. The railway now extends from Hokitika, viâ Greymonth, to Reefton, branching at Stillwater to Otira, near Arthur's Pass. An extension to Ross of the Greymouth—Hokitika line is now in course of construction. Coaches twice a week connect with Canterbury, viâ Arthur's Pass, and ply daily between Ross, Hokitika, Kumara, Greymouth, and the neighbouring towns; while once a week a mail is conveyed on horseback southward to Gillespie's Beach, and once a fortnight to Jackson's Bay. A subsidised steamer runs between Hokitika and the southern ports as far as Jackson's Bay, plying every two months, thus enabling settlers to obtain supplies and to ship their cattle and produce to market. The Government steamer also calls at Big, Jackson's, and Bruce Bays on her quarterly trips from Dunedin. Steamers also trade regularly between Hokitika and Greymouth and other parts of the colony. The Main South Road, which for many miles skirts the foot of the Main Range, has been so greatly improved of late years that the traveller can now ride comfortably and safely, viâ Haast Pass, right through into Otago. Numerous bridle-tracks branch from the trunk line to various points, while the large open river-beds likewise give access to the country on either hand. From Jackson's Bay horse-tracks have been made, viâ Cascade River and Barn Bay, to open up the southernmost country. Sundry dips and cols, varying in height from 1,800 ft. to over 7,000 ft., leading down the central range, have been explored and mapped, and during the summer months are crossed from time to time by experienced mountaineers. Of these depressions the only sub-alpine saddle is Haast Pass, all the others being liable to blocks by winter snows. A coach-road over Arthur's Pass and a horse-track through Haast Pass have been made. Another bridle-road is also in course of construction across Whitcombe's Pass, but between these points no trans-insular road exists. Tracks have also been constructed giving easy access to the Franz Josef and Fox Glaciers, and in the future, as population increases, doubtless tourist and stock tracks will be constructed along many of the intervening routes. From Okarito northward the district is in telegraphic communication with the rest of the colony.
Greymouth.—This, the largest town in Westland, containing a population of 4,200, has progressed most remarkably during the last few years. It is situated on the south bank of the Grey River, close to its mouth, and is the main shipping port for northern Westland. Four railway-lines radiate from Greymouth to the State Coal-mine, Reefton, Otira, and Hokitika. Extensions of the three last-mentioned lines are in course of construction. The town has a Telephone Exchange, good Public Library, first-class drainage, an abundant water-supply, and is well paved and lighted, the water and gas works belonging to the Corporation. One of the Government Railway workshops is located here, and amongst other local industries are a foundry, breweries, sawmills, sash and door factories, furniture manufactories, meat-preserving works, lime and cement works, coachbuilding establishments, &c.
Hokitika.—This town is situated at the north mouth of the Hokitika River, bordering the sea-beach. It contains a population of about 2,000, and is mainly dependent on the adjacent saw and flax mills, farming settlements, and goldmines. A considerable trade is also done by sea with the miners and settlers in South Westland, for which district it is the shipping port. The town enjoys grand views of Mount Cook and other peaks; and from the terrace on the town hill the panorama of snow-capped mountains is one of the finest in the world. The town possesses a good library, reading-room, and museum; it is lit with gas, and has a telephone exchange. It is well laid out, the main streets being 99 ft. wide and very clean. There is a central park, and as the suburban dwellings are surrounded by gardens the town has a very pleasing aspect. A fine clock-tower, with chimes, has lately been erected in memory of the Westland troopers who fell in the Boer War. The local industries comprise saw and flax mills, sash and door and furniture factories, foundry and engineering shops, coach building, fish cannery, breweries, and coffee and spice works. A very handsome building encloses the High and State Schools.
Brunner.—Picturesquely situated on the banks of the Grey River, seven miles above Greymouth, includes the villages of Dobson, Taylorville, and Wallsend, and contains 1,570 people. This town is wholly dependent on the adjacent Brunner and Tyneside coal-mines and their allied industries of coke-burning, brick and tile making. The output of these mines and manufactories is sent by rail to Greymouth, where the bulk of it is shipped. The mineral traffic causes this short branch to be the best-paying railway-line in the colony. Two fine suspension bridges across the Grey River link the townships together, one being a railway and the other a foot bridge.
Kumara.—This compact little town, with its suburbs of Dillmanstown and Larrikins, of 1,120 inhabitants is placed on the skirts of the largest alluvial goldfield in New Zealand. Main roads to Hokitika, Greymouth, and Christchurch radiate from this place, and a fine turnpike of four miles connects it with the railway. The town is finely situated on a high tableland, and enjoys interesting views of mountains and bush-clad plateaux, river, valley and ocean. Hydraulic gold-mining is carried on here on an extensive scale, the greater portion of the water-supply coming many miles from the inland mountains. Large sludge-channels have been made to carry away the tailings. This industry gives employment to a large number of men, and also provides lucrative work for sawmillers and mechanical engineers. It has finely-equipped and well-built schools and a hospital.
Ross.—Population, 650. A very picturesque township, situated at the foot of the northern slopes of Mount Greenland, 150 ft. above and one mile distant from the sea. It occupies a very sunny sheltered position, and is faced for fruit and flowers. It is essentially a gold-mining centre, and extensive sluicing is carried on. Right under the town area are various layers of auriferous drifts, partly worked, but at present water-logged. In the near future it is expected that these deep levels will be worked again and the town renew its old prosperity. The early completion of the railway from Hokitika will greatly benefit Ross and the surrounding district.
Cobden.—Population, 423. This town is at the northern mouth of the Grey River, and immediately opposite the Borough of Greymouth, to which it is linked by a fine bridge. It is principally occupied by the residences of Greymouth merchants and tradesmen.
Blackball.—Population probably 800. A prosperous and rising township, mainly dependent on the splendid coal-mines in its vicinity. A fine railway and traffic bridge is in course of construction over the Grey River, and a branch about two and a half miles long will connect the town with the main line.
In addition to the towns already enumerated, there are many small mining and sawmilling centres, such as Ahaura, Hatter's Terrace, No Town, Stillwater, Kokiri, Nelson Creek, Moana, Nobles, Orwell Creek, Twelve-mile, Stafford, Kanieri, Woodstock, Rimu, Blue Spur, Okarito, Gillespie's, &c. In the near future an important town will be established in connection with the State coalmines near Greymouth, which are being connected by rail with that town.
The harbours and ports of Westland are the following:—
Greymouth, twenty-four miles north-east of Hokitika: Extensive harbour-works have been carried out. A breakwater or sea-wall extends some 3,542 ft. seaward from the mouth of the river on the south side, and on the north side 1,125 ft., with internal half-tide training walls, the result being an average depth of water on the bar of 20 ft. 10 in. at high water, and of from 8 ft. to 16 it. at low water. Vessels of 1,500 tons can now come alongside the wharf. There is berthage accommodation of 2,030 ft., with a minimum depth of 12 ft. to 16 ft. at low water. The principal exports are gold, coal, coke, and timber. The number of vessels that entered the port during the year 1902 was: 591 steamers, tonnage, 201,844; 40 sailing vessels, tonnage, 4,412: being a total tonnage of 206,256 for the year. The train runs down the wharf, and the coal-trucks, specially made for the purpose, are lifted and emptied into the vessel's hold by means of powerful hydraulic and steam cranes, of which there are six, with capacities of from 1 ½ tons to 12 tons, so that every encouragement is given to quick despatch. 179,934 tons of coal, 2,108 tons of coke, 1,375 tons of bricks, and 15,604,303 superficial feet of sawn timber, and 142,172 sleepers were exported during the year.
Hokitika: Two training walls have been constructed, the one on the north side being about 2,000 ft. long, while that on the south is 677 ft. The bar is of shifting sand, and the depth at high water varies from 9 ft. to 15 ft., while inside the depth is from 6 ft. to 22 ft. for three-quarters of a mile from the entrance. For ten months out of the twelve the port is usually safe for vessels drawing 8 ft. to 10 ft. of water. The berthage space amounts to 1,000 ft., with from 18 ft. to 22 ft. of water. The principal exports are gold and timber.
Okarito, fifty-five miles south-west of Hokitika: A bar harbour, sometimes completely blocked by a high sandbank thrown up by heavy seas. When open, the entrance is good, with a maximum depth of 10 ft. There is a small jetty about half a mile from the entrance.
Bruce Bay, ninety-five miles south-west of Hokitika: An open roadstead, well sheltered from the south and south-westerly winds by Heretaniwha Point, which juts out fully a mile to the northward. Good anchorage in 1 ft. of water opposite the Green rock, which stands up out of the water. Good boat-landing with above-mentioned winds on a smooth sandy beach.
Paringa River, one hundred and four miles south-west of Hokitika: Open roadstead. Vessels coming in and out should give Harata Reef (off the north head) a wide berth. There is also a sunken reef, awash at low water, in the middle of the Bay, and a dangerous sunken rock just off the south head, two or three chains away, facing a small sandy bay and right abreast of the trig. station. Vessels lie inside and a little to the northward of this rock, about a quarter of a mile from shore, and are quite safe with southerly winds.
Haast River, one hundred and eighteen miles south-west of Hokitika: A constantly shifting bar at entrance, which is nearly opposite and a little to the southward of the Alhambra Rock. This rock stands well out of the water, and vessels entering can go on either side with safety. Average depth of water on bar from 6 ft. to 8 ft.
Okuru and Turnbull Rivers, one hundred and thirty-eight miles south-west of Hokitika: These rivers join just inside the entrance. Good straight channel: average depth, 8 ft. to 10 ft. The port is well sheltered by Open Bay Islands, which lie about three miles away, just opposite the entrance, bearing a trifle west of north. A dangerous reef lies about two miles and a half from the south-west point of the smaller island, and immediately to the north-west of a line drawn from the last-named point to the extreme end of Jackson's Head.
Jackson's Bay, one hundred and fifty-three miles south-west of Hokitika: Good shelter and anchorage open only to north-east, with 12 ft. of water within a few chains of shore. Jackson's Head runs out about one mile and a half in a north-easterly direction from the southern end of the Bay. This is the only ocean harbour on the coast of Westland, and could be converted into a first-class port at comparatively small cost. No doubt Jackson's Bay will eventually form a coal port, as indications of coal are found from the bay to Tauperikaka, a distance of thirty miles. Moreover, the recent discovery of a practicable pass through the Main Range, via the Waiatoto and Axius Rivers, will make it in the near future the natural outlet for the Lake Wanaka country.
Big, or Awarua Bay, two hundred miles south-west of Hokitika: At the extreme south-west corner of Westland. An open roadstead, sheltered from east and south-west winds: 24 ft. of water on south side anchorage and 30 ft. on north side, just opposite Crayfish Rock, in a spot sheltered from northerly winds.
Steamers have also in past years entered the Taramakau, Waitaha, Wataroa, Wanganui, Waiatoto, and Arawata Rivers, all of which have bar-entrances. The Cascade River is likewise navigable, though no steamer has as yet been in; and goods and passengers are also landed at he roadsteads of Saltwater, Gillespie's Beach, and Abbey Rocks.
The District of Westland contains the greatest area of alluvial auriferous ground on the West Coast.
All the Westland rivers carry down more or less gold, but the three great gold-yielding rivers are the Grey, Arahura, and Waiho, the bars and beaches of which appear to be replenished with fresh deposits of the metal after each flood. We may safely assert that every large or small stream in the Grey Valley is auriferous, and the gold-bearing nature of the adjoining gravels is evidenced by the old and new workings which are scattered all over the watershed. Again, if one stands on the summit of Mount Turiwhate, the ancient beds of the Arahura can be easily traced northward to the Kumara and southward to the Rimu diggings. Similarly, the Waiho has in olden times flowed both northward down the present valley of the Okarito River and southward to the Omoeroa River, the lateral terraces in both directions being well defined and gold-bearing.
There are three main gold-bearing deposits in Westland. The first, which may be called riverine leads, run generally westward. These are ancient river-beds, often lying at a considerable elevation, of which the bulk has been washed away, leaving detached portions, as Kumara and Rimu. The second are beach-leads, both those along the present coast-line and others running parallel thereto at distances varying from one quarter to four miles inland, and at levels from a few feet below to a couple of hundred feet above sea-level. The third are extensive masses of gravel, &c., occurring in large isolated patches, as at Bell Hill, Big Dam Hill, Humphrey's Gully, and Bald Hill, north of the Haast. These drifts have all one noticeable peculiarity—namely, that they invariably coat the seaward faces of the hills, and neither gold nor drift is to be found on the inland slopes. Gold-bearing fans from Mount Greenland have been found at different levels on Ross Flat, having probably been deposited in deep water by successive land slides.
Hydraulic mining on a large scale is successfully carried on in various portions of the northern districts, and is rapidly being extended to many other localities. Kanieri Lake is being again utilised, and an abundant quantity of water is now available for the sluicers in the Kanieri Valley. The extension now proposed of that race to Back Creek would develop a very large field. The tapping of the Arahura River will enable the miners at Blue Spur to obtain an unfailing supply of water and command a large area of auriferous country at present unworkable from want of water at a sufficient altitude. A large acreage of alluvial drift has been pegged out as dredging claims. Some companies are at work, with more or less profit; many more are busy erecting plants, while others are completing the preliminary surveys, inspections, and borings essential before placing their properties on the market. Experts are assured that a large extent of auriferous gravels exist all over the low-lying country which will yield remunerative returns by this new treatment. Undoubtedly great areas of swampy, undrainable, and hitherto unavailable lands will be thoroughly prospected, and it is confidently predicted that valuable finds will be made in such districts. Numerous and costly experiments have been made with dredges of different types in the endeavour to work economically the gold-bearing sands which lie along the sea-beaches for a distance of a hundred and forty miles; but very few have proved a success. A considerable number of miners (“black-sanders”) work on some of the beaches, and seem to make a fair living, many of them having been so employed in one neighbourhood for over twenty years.
Gold-bearing quartz has been found throughout the district, the most promising finds being at Paparoa, Mount Alexander, Taipo Range, Browning's Pass, and Cedar Creek. Silver ores, associated with gold, have also been found, notably at Rangitoto.
As noted before, great quantities of coal are obtained from the mines at Brunner, and also from the fine seams at Blackball, higher up the Grey Valley. It would appear that the greater portion of the seaward country hereabouts contains practically inexhaustible coal-fields. Extensive seams are now being developed at the “State Coal-mine,” in the Seven-mile Creek Basin, and further along the coast, and on the higher slopes of the Paparoa Range large outcrops are being prospected. This region contains the greater area of coal-bearing strata, but all the way down the coast to Jackson's Bay, wherever the coal-measures have been protected from the scour of the ice-streams of the great glacial period, isolated patches of coal exist; possibly borings would prove the lower coal-beds to be intact under the overlying drifts.
Specimens of nearly all the known minerals have been discovered in various parts of Westland District. The Paparoa Range contains many varieties, and eventually will hold a large mining population. Slate has recently been found here. Copper lodes have also been discovered throughout the district, the finest outcrops being on the western slope of the Matakitaki Range, with good seams and beds of coal and limestone adjacent. Petroleum has been found in the Arnold Valley, and borings are now being made to test and develop what is hoped may be a good oil-bearing basin.
This industry is steadily progressing; there are thirty-four mills in operation, and about 16,000,000 ft. of timber and 143,000 silver-pine sleepers were exported last year. There are over five hundred hands engaged in the lumber trade, either at the sawmills or as sleeper and firewood cutters, &c. The completion of the railway to Ross will give a considerable impetus to this business.
It may be stated that every available strip of flex in this district has been lately taken up. There are three mills in full swing, employing over ninety hands, and as other sixteen leases have been granted by the Land Board, on condition that mills are erected within a reasonable period, a large expansion of the industry may be expected.
Table of Contents
The Land District of Canterbury comprises the central portion of the Middle Island, and lies between the Conway River, Barefell Pass, and Mt. Franklin on the northward; the Spenser Mountains, Travers Peak, Mt. Barron, the Amuri, Hope, and Hurunui Passes, the summit of the Southern Alps, and the western watershed of the River Hopkins and Lake Ohau on the westward; the Rivers Ohau and Waitaki on the southward; and the South Pacific Ocean on the eastward. It lies between south latitudes 42° 5' and 44° 55', and east longitudes 169° 45' and 173° 30'. The length of the district north-east and south-west is about 220 miles; the breadth W.N.W. and E.S.E., from the summit of the Alps to the sea, averages seventy miles. The sea-board has a length of about 300 miles, consisting generally of low-lying beaches, broken by the projection eastward of Banks Peninsula, which contains the only large natural harbours. That portion of the district which fronts the ocean between the Ashley and Opihi Rivers is flat land, about 2,500,000 acres in extent; north and south of those limits the plain is interspersed with undulating and hilly country. This great plain stretches westwards, rising and merging into downs and hills, which again extend westward and merge into the Southern Alps and the offshoots therefrom. Banks Peninsula, which has an area of about 250,000 acres, is wholly composed of ridges and hills, deeply intersected by basins and gullies, the result of volcanic action.
The Southern Alps, which form the backbone of the island, are a continuous chain of mountains, with a succession of magnificent peaks, attaining their culminating point in Mount Cook, or Aorangi, 12,349 ft. above sea-level; there are, besides, numerous peaks ranging in altitude between 7,000 ft. and 10,000 ft. Offshoots, extending to great distances eastward and south-eastward from the main range, attain elevations of 6,000 ft. to 9,000 ft. On these mountain-ranges are numerous and extensive glaciers, from which emanates the river-system of the district, comprising the Waiau-ua, about 100 miles in length; Hurunui, 85 miles; Waimakariri, 90 miles; Rakaia, 85 miles; Ashburton, 64 miles; Rangitata, 74 miles; the Waitaki and its main feeders, 140 miles. These rivers rush down from the mountain-gorges, through the intervening ranges and hills, and traverse the plains to the sea. The channels on the plains are shallow, and extend in some instances over a mile in width.

Lyttelton Harbour.
These rivers serve as outlets for a portion of the Lake system of the Middle Island, Lake Sumner being connected with the Hurunui, Lakes Coleridge and Heron with the Rakaia, and the Mackenzie Country lakes—Tekapo, Pukaki, and Ohau—with the Waitaki. Another important lake is that known as Lake Ellesmere, west of Banks Peninsula; it is separated from the ocean by a narrow shingle-spit only 5 chains across at one point, through which, at certain seasons, the flood waters force a channel to the sea. Lake Tennyson is situated on the eastern flank of the Spenser Mountains, 3,614 ft. above sea-level.
The climate of Canterbury is well suited to Europeans. It resembles that of Great Britain, but on the plains is far more equable, the mean daily range of temperature being 17·10° Fahr. Observations taken at Lincoln (fourteen miles from Christchurch) for a period of ten years, ending December, 1892, give the following results: Barometer, reduced to 32° Fahr. and sea-level, 30·06 in.; mean maximum daily temperature, 61·47°; mean minimum daily temperature, 43·27°; mean average temperature, 52·37°. The extremes of temperature were 92° and 22° Fahr. The rainfall for the same period averaged 26·809 in. per annum, the extremes being 35·287 in. in 1886 and 14·836 in. in 1890. The average annual number of days on which rain fell was 123, the extremes being 149 in 1887 and 98 in 1891. Snowfalls are very light on the plains, but in the high uplands the climate is much colder and more severe. The changes of weather and temperature are sudden, calms and gales, rain and sunshine, heat and cold alternating. The prevailing winds are north-east, south-west, and north-west—the last a hot wind. The climate, as a whole, splendidly healthy, bracing, and most enjoyable.
The district was occupied, in the first instance, by settlers sent out by the Canterbury Association, which was formed in 1848, and incorporated by Royal Charter in 1849, under the auspices of prominent men in England, including the Archbishop of Canterbury and Lord Lyttelton. The step was not taken until after due inquiry as to the most suitable part in which to establish a settlement. Captain (afterwards Sir George) Grey, at that time Governor, recommended the Wairarapa, but it was finally decided to take over from the New Zealand Company a tract of the Canterbury Plains, in the neighbourhood of Port Cooper. Captain Thomas, the agent of the association, who had advised the selection, superintended the surveys and the preparations for receiving intending settlers. The original intention of the founders was that the settlement should be independent and complete in itself, and should embrace only such persons as were members of the Church of England and were approved of by the association. This was frustrated by the influx of numbers of persons of all classes and beliefs. The first body of emigrants arrived at Port Cooper on the 16th December, 1850, and the settlement remained under the control of the association, as directed by a committee of management in England, and under the active personal supervision of Mr. John Robert Godley, until 1853, when the whole of Canterbury became a province of New Zealand by the provisions of “The Constitution Act, 1852.”
Thenceforward the control of the settlement was vested in the Superintendent and the Provincial Council. The first Superintendent was Mr. James Edward FitzGerald, who held office till 1857; he was followed in succession by Mr. William Sefton Moorhouse, 1857–1863; Mr. Samuel Bealey, 1863–1866; Mr. Moorhouse again till 1868; and Mr. William Rolleston till the abolition of the provinces in 1876, when the district came directly under the control of the General Government.
In no part of New Zealand are the means of communication better than in Canterbury. The natural facilities of the country have been abundantly supplemented by railways and roads. Lyttelton, the chief port, is connected by rail with Christchurch, the heart and centre of the whole district. From Christchurch the main line extends northwards to Culverden, a distance of 69 miles, with a branch from Waipara to Scargill (about fifteen miles) open for traffic. It is proposed to extend this branch to Mackenzie, in the Cheviot District. Southward the main trunk line runs through Waitaki, 139 miles to Dunedin. These lines tap and serve the whole coastal district, and the lands adjoining on the western side. As feeders to these trunk lines, eight branch lines have been constructed westward, and two lines south-eastward; the former, in most instances, extending to the foot of the hills.
Combined with the railway system is a complete network of main, district, and subsidiary roads, extending into all parts of Canterbury. The total length of railways is 460 miles, and the roads probably exceed 10,000 miles in the aggregate. The completion of this splendid system is due, partly to the foresight of the original settlers, partly to the exertions of the Provincial Government, and partly to the railway and public-works policy of the late Sir Julius Vogel.
According to Sir James Hector, the main western ranges are composed of Upper Palæozoic rocks, having at their base extensive plains of Tertiary fluviatile formation, with occasional protruding ridges of Upper Mesozoic, forming low mountain-ranges subordinate to the main axis. Banks Peninsula consists of basic volcanic rocks.
The area of the Canterbury Land District is 9,604,045 acres, of which the estimated area of forest-land is 516,030 acres. Forest-lands are found in Banks Peninsula and in the Mount Peel and Waimate districts, where the timber consists chiefly of rimu, totara, and matai; at the sources of the Waiau-ua, Ashley, Waimakariri, Rakaia, and Hopkins Rivers, at Lakes Ohau and Sumner, and near Springfield and Methven. the timber in these localities being mostly native beech; and near Oxford, where the beech is intersperaed with rimu, totara, matai, &c.
The lands of Canterbury may be classed approximately as follows: First class, 2,046,071 acres; second class, 5,207,173 acres; third class (barren lands and lands of small value), 2,350,801 acres: total, 9,604,045 acres.
| The disposition of lands was in 1903 as follows:— | No. of Holders. | Area in Acres. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Crown lands disposed of for cash (including land granted under Midland Railway Act, 572,000 acres, but deducting lands repurchased for settlement—174,463 acres) | ... | 3,995,335 |
| 2. | Lands held on deferred payments | 21 | 11,339 |
| 3. | Lands held on perpetual lease | 78 | 4,279 |
| 4. | Lands held as leaseholds in perpetuity | 1,273 | 229,738 |
| 5. | Lands held in occupation with right of purchase | 21 | 1,454 |
| 6. | Lands held as village-homestead special settlements | 407 | 12,440 |
| 7. | Lands held as small grazing-runs | 82 | 172,437 |
| 8. | Lands held as grazing-farms (on Cheviot Estate) | 48 | 45,978 |
| 9. | Pastoral licenses | 148 | 3,521,091 |
| 10. | Special-settlement associations | 41 | 4,653 |
| 11. | Reserves and Crown lands held under temporary occupation licenses (area, 94,565 acres, included in 12 and 16) | 639 | ... |
| 12. | Area of land reserved and granted under various Acts (exclusive of Midland Railway land, included in 1) | ... | 970,734 |
| 13. | Land purchased and disposed of under Land for Settlements Acts (included in 4, 7, 10, and 11; 917 holders, 173,167 acres) | ... | ... |
| 14. | Crown lands open for selection | ... | 3,958 |
| 15. | Crown lands being prepared for selection | ... | 8,174 |
| 16. | Barren lands, and lands for future disposal | ... | 622,435 |
| Total | 2,758 | 9,604,045 |
In explanation, it may be noted that No. 1 comprises the freehold lands conveyed, and that tenants of Nos. 2, 3, and 5 have the right of acquiring the freehold, which is not the case with tenants of Nos. 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, and 13. Crown lands proper are: 14, open for selection; 15, being prepared for selection.
The Southern Alps and mountains adjoining are, owing to their great altitude, subject to disintegration, and form for the most part rocky barren wastes.
The lower ranges and hills, the high tablelands, and the light stony portions of the plain form the pastoral areas.
In the northern and southern districts and in the great central plain are the agricultural areas. This latter class of land comprises rich alluvial tracts about Cheviot, Rangiora, Kaiapoi, Lincoln, Ellesmere, Longbeach, Temuka, and Waimate, and the splendid plain- and down-lands which extend from Cheviot to the Waitaki.
Banks Peninsula, where the soil is of a rich volcanic nature, though exceedingly hilly, has alluvial areas in the valleys and about the bays.
Below a certain level, the mountainous and hilly regions, and the high upland country in the western and northern part, are covered by native grasses, with an admixture of English forage-plants where the character of the soil and other circumstances are favourable.
The pasturage, which is very suitable for sheep-farming, is taken full advantage of by the pastoral tenants of the Crown, and is used to some extent by freeholders. The light stony portions of the plain also contain native grass lands, well adapted to merino sheep.
The lower hills, downs, and better kinds of plain-country have been widely cultivated, and have proved well fitted for the production both of cereals and of grasses.
The chief crops grown in Canterbury District are wheat, oats, barley, turnips, rape, clover- and grass-seed; while amongst other crops produced are rye, peas, beans, mangolds, beet, carrots, and potatoes.
Of the cereals, wheat is the most largely grown, and was for many years a large item of export. In the season 1902–1903 the area under crop for threshing was 136,316 acres, being over two-thirds of the total wheat area of the colony. The total yield was 5,349,130 bushels, being an average of 39·24 bushels per acre.
Oats also are very successfully grown, the figures for the same period being 200,581 acres, or about five-twelfths of the total area of this crop in the colony. The total yield was 9,481,587 bushels, being an average of 49·06 bushels per acre.
Barley of superior quality is also produced, the figures being 9,650 acres, equal to over one-third of the total area of barley crop in the colony. The total yield was 480,234 bushels, being an average of 49·76 bushels per acre.
Grass-seeds are abundantly grown, cocksfoot mainly on the splendid Banks Peninsula country, and ryegrass throughout the land district.
Potatoes, which yield crops of excellent quality, were grown in 1902–1903 on 9,408 acres; turnips and rape were grown on 196,917 acres, and the combined area of other crops grown, including rye, peas, beans, mangolds, beet, carrots, and onions, was 14,214 acres. The area of wheat, oats, and barley for fodder was 57,344 acres. The area ploughed and laid down in English grasses was 1,520,186 acres. Surface-sown lands comprised 515,284 acres. The total area under crop was 624,430 acres, and the area broken up but not in crop, 9,744 acres. Plantations, exclusive of private gardens, occupied an area of 26,654 acres. The aggregate area of private and market gardens, orchards, and vineyards over quarter of an acre in extent was 8,388 acres.
The pastoral and agricultural lands provide grazing and fodder for a large-number of sheep, cattle, horses, and other stock. Of late years the value of the plains has been much enhanced and the carrying-capacity thereof greatly increased by the water-race system, which supplies water throughout the length and breadth of the dry areas, and enables the country to be occupied in smaller holdings than would otherwise be possible.
The following table shows the extent, cost, and other particulars regarding the water-race system in the several counties in 1903:—
| County. | Area watered | Miles of Races. | Total Cost. | Cost per Acre watered. | Amount of Water distributed every Twenty-four Hours. | Annual Charge for Use of Water. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acres. | £ | s. d. | Gal. | |||
| Amuri | 24,162 | 54 | 4,800 | 3 11 ⅔ | ... | Races are maintained by an annual charge in proportion to area watered. |
| Ashley | 122,000 | 500 | 25,000 | 4 1 | 27,000,000 | From ¾d. to 6d. per acre, in addition to special rates for interest on loans. |
| Selwyn | 326,888 | 1,119 | 73,819 | 4 5 | 90,940,960 | 8s. 4d. to £1 5s. per 100 acres. |
| Ashburton | 586,000 | 1,350 | 43,300 | 1 5 ¾ | 86,000,000 | From £2 to £3 per mile of race. |
| Geraldine | 71,212 | 260 | 9,010 | 2 6 ½ | 29,520,000 | About 7d. per acre, including a rate for payment of principal and interest on loans, and a rate for maintenance. |
| Levels | 19,000 | 71 | 5,500 | 5 9 ½9 | 6,480,000 | 1 ½d. per acre, and on part of area an interest-rate of ¼d. in the pound on capital-value. |
| Mackenzie | 9,000 | 32 | 1,885 | 4 2 ¼ | 7,516,800 | 2 11/16d. per acre on part of district and ⅝d. in the pound on capital value in remainder of district. |
| Waimate | 35,700 | 157 | 8,125 | 4 7 | 8,500,000 | Races are maintained by an annual charge on the value of lands watered. |
The sheep in the District of Canterbury, in April, 1902, numbered 4,933,681. In October, 1902, there were 52,637 horses, 109,274 cattle, and 41,831 pigs.
The district has a well-deserved reputation for the classes and splendid quality of its sheep. On the mountains and higher lands the merino still predominates; but on the richer low-lying ranges, hills, and plains the prevailing types are crosses between the merino and Leicester, Lincoln. Romney Marsh, and other breeds. In proof of the superior character of the flocks, pasturage, and climatic conditions in the Middle Island, the following percentages of lambing returns are quoted—these are “fair average returns, but much higher might have been exhibited”: Mountain native pasture—pure merino, 75·36; pure merino and Border Leicester, 88·94: English-grass pasture—crossbred and Border Leicester, 80·8; half-bred Border Leicester, 82·79; Border Leicester, 90·77; Lincoln, 88·08; Romney Marsh, 111·46; English Leicester, 93·34; Shropshire, 97·41; Southdowns, 96·87. It must be borne in mind that the flocks and herds are supported by the natural and artificial pastures without housing.
Owing to the development of the frozen-meat trade a great impetus has been given to sheep-breeding. The bulk of the primest meat exported from the colony is sud by this district, with Marlborough, and commands the highest price in the London markets. In the year ended 31st December, 1902, the number of carcases frozen was 2,004,682, valued at £1,316,433. There were also produced 15,867 cases of preserved meats, 15,480 casks of allow, 6,555 tons of bonedust and manures, besides neatsfoot-oil, oleo, &c.
The total quantity of frozen meat exported from Canterbury during the year ended 31st March, 1903, was 866,190 cwt., valued at £1,213,967. At Belfast, Fairfield (near Ashburton), Islington, and Timaru, freezing-works are established, each containing a complete plant for carrying on the industry, as well as departments for curing, preserving, boiling-down, tallow rendering, fellmongering, and the manufacture of manures. The Belfast Freezing Works, owned by the Canterbury Frozen Meat and Dairy Produce Export Company, contain engines of 710-horse-power, and employ 300 men. They have storage for 90,000 carcases, and can put through 5,500 carcases in a day. The same company has a factory at Fairfield (near Ashburton), where 65,000 carcases can be stored and 4,000 dealt with in a day, and another factory is being built in South Canterbury. The Islington and Timaru works, which are owned by the Christchurch Meat Company, employ in all about 750 men, and have engines representing 403-horse-power. The former can put through 8,00) carcases per diem, and have storage for 140,000 carcases. The latter can deal with 6,000 carcases in a day, and have storage for 100,000 carcases. At Hornby there has been established by Messrs. Nelson Brothers (Limited) a well-equipped factory for freezing only, with engines of 300-horse-power, and a capacity of dealing with 1,000 sheep per diem. The factory has storage-room for 50,000 sheep, but is not now in operation.
During the year ended 31st March, 1903, there were shipped at Lyttelton and Timaru 42,068,584 lb. wool, valued at £1,222,021; and to this must be added the amount (about 1,000,000 lb.), bought for manufacture by the woollen-mills in the district. The Kaiapoi Woollen Manufacturing Company, Limited, owns large woollen mills at Kaiapoi, and clothing factories at Christchurch. These are fitted with modern machinery and appliances, and the company's products have obtained a considerable reputation. The company employs about 1,020 hands, pays about £58,000 in wages per annum, and uses about 3,200 bales of wool and £6,000 worth of other colonial products in a year. The staple of the New Zealand wool, especially the long-wool and cross-bred, is remarkable for its freedom from breaks and other imperfections. The average clips are approximately as follows: Merino, 4 lb. to 7 lb.; quarter-breds, 6 ½ lb.; half-breds, 7 ½ lb.; three-quarters, 8 ½ lb.; Leicesters, 10 ½lb.; Lincoln, 11 lb. From special flocks clips up to 25 lb. and 30 lb. are obtained.
Banks Peninsula and the rich tracts of country previously mentioned are excellently suited for dairy farming. The pasturage and climatic conditions are favourable, and a great increase in the production of butter and cheese may be looked for, more especially as housing and hand-feeding are in some districts unnecessary. A central co-operative dairy factory has been established at Addington, served by twelve creameries, situate at Marshlands, Oxford, Halswell, Springston, Doyleston, Little River, Ladbrooks, Lakeside, Kaiapoi, Green Park, Brookside, and Ashburton, each capable of dealing with the milk of 1,000 cows. There are also very complete dairy factories at Taitapu, Sefton, Cheviot, Timaru, Temuka, South-brook, Belfast, Tinwald and Le Bon's Bay, as well as cheese-factories at Flemington and German Bay. The number of cheese and butter factories in the district in 1900 was 17, and of creameries 14; the number of hands employed was 75; the output of butter and cheese amounted to 2,906,715lb.; and the total value of the output was £108,332.
The sawmilling industry finds its development chiefly in the Oxford, Little River, Mount Somers, and Waimate districts. The number of mills in Canterbury in 1901 was eighteen, employing 260 hands, the horse-power being 317. The output in 1900 was 4,714,959 ft., valued at £22,277. The number is, however, diminishing, owing to the working-out of the available timber. The timber comprises birch, totara, red-and white-pine. The first-named is used chiefly for sleepers and fencing, the totara and pine for building purposes. Including the work done by the planing-and moulding-mills the value of all the manufactures under this head was £45,866.
The district is eminently adapted for the growth of a large variety of fruits, especially all that flourish in Great Britain. Attention has recently been directed to landing supplies of fruit in London; the attempts so far have proved satisfactory, and point to the possibility of a large trade being established.
Brown coal is found at the Malvern Hills, Homebush, Whitecliffs, Springfield, Mount Somers, Albury, and various other places. Lignite is also commonly distributed. For the year 1902, the output from 15 collieries, employing about 60 hands, was 19,445 tons, bringing the total amount raised from 26 collieries up to the 31st December, 1902, to 429,586 tons. The seams worked vary from 16 ft. to 2 ft. 3 in., the average width being 8 ft. At Acheron, near Lake Coleridge, a true anthracite is found, the other pits in the district being of brown coal or lignite.
The building-stones of Canterbury comprise some excellent varieties. The Halswell quarries produce an exceedingly hard and close-grained stone of a dull leaden-grey colour. Granular trachytes are obtained from Governor's Bay, Lyttelton; porphyrites at Malvern Hills; good limestone at Malvern Hills, Waikari, Mount Somers, and various other places; bluestone rock is found at Timaru suitable for millstones. There is abundance of limestone in North Canterbury, Mount Somers, Castle Hill, and various other parts, which is well adapted for making lime.
Deep-sea fishing is carried on from Lyttelton and Akaroa, the kinds of fish chiefly caught being groper (hapuku), ling, conger eels, moki, butterfish, barracouta, soles, whiting, red-cod, herrings, and garfish. From Lake Ellesmere and the river estuaries excellent flounders are obtained.
Trout thrive amazingly in the rivers and fresh-water lakes, affording excellent sport.
Excluding mines and quarries, the total number of manufactories in Canterbury at the date of the census in 1901 was 648, employing 7,050 males and 2,754 females.
Included in the above were 35 printing, 10 agricultural-implement, 26 coach building and painting, 29 fellmongering, tanning, currying, and wool-scouring establishments, 5 sail- and oilskin-factory. 27 boot-and-shoe factories, 7 rope-and-twine works, 8 flax-mills, 4 boiling-down, eat-preserving, and freezing works, 10 bacon-curing works, 17 cheese- and butter-factories, 23 grain-mills, 34 chaff-cutting and grass-seed-dressing works, 16 breweries, 10 malt-houses, 27 aerated waters and cordial works, 4 sauce- and pickle-making factories, 6 soap- and candle-works, 18 sawmills and sash-and-door factories, 4 gasworks, 20 brick, tile, and pottery manufactories, 14 iron- and brass-foundries, 25 cycle-works, 20 furniture-factories, and 8 engineering-works.
The census returns also showed that in 1900, the value of land, machinery, and buildings used for factory purposes was £1,489,096, and the total value of manufactures £4,701,304.
Primary Schools.—The district is divided into two parts, termed North and South Canterbury, each presided over by an Educational Board. Under the control of the Boards schools have been established throughout the whole country wherever population warrants their erection.
The number of children attending the public primary schools in Canterbury, on 31st March, 1903, was 24,786. Average daily attendance, 20,612. Number of teachers—males, 250; females, 403: total, 653. Number of schools, 277.
There is a Normal School at Christchurch for the training of teachers.
Secondary Education.—For the further education of children ample provision has been made by the establishment of secondary schools. The principal schools of this class are the Boys' and Girls' High Schools at Christchurch, Rangiora, Ashburton, and Timaru. For more advanced students Canterbury College, Christchurch, is available. This institution was founded and endowed by the Provincial Government in 1873. It is presided over by a Board of Governors. The teaching staff comprises twelve professors and lecturers, and the number of students attending lectures is 224. The School of Engineering, Electricity, and Technical Science, recently established as a special branch of the college, is well equipped, and is attended by a large number of students. The School of Art is also a special branch of the college work, and the popularity of both these branches has been met by the recent erection of considerable additions to the building accommodation.
It should be recorded here that the Provincial Government of Canterbury was fully alive to its duties as regards higher education. It made reserves for the purpose of endowment for the following objects: (1) College, 101,640 acres, reserved June, 1873; (2) technical science, 103,000 acres, reserved July, 1873; (3) School of Agriculture, 100,950 acres, reserved June, 1873; (4) Boys' High School, 9,220 acres, reserved at various dates; (5) Classical School, 8,953 acres, reserved at various dates. To these were subsequently added the following: (6) Girls' High School, 2,578 acres, reserved January, 1878; (7) Medical School, 5,000 acres, reserved December, 1877.
Private Schools.—There are numerous private schools, independent of the State, the chief amongst them being Christ's College, Christchurch, connected with the Church of England. The Roman Catholics support schools of their own in Christchurch, Pleasant Point, Lyttelton, Timaru, Addington, Papanui, Ashburton, Akaroa, Rangiora, Sheffield, Temuka, Leeston, and Waimate. There are besides, in Christchurch, some excellent private boarding- and day-schools for both boys and girls.
Canterbury has the advantage of possessing many flourishing public institutions. The School of Art, Christchurch, was established by the College Governors in 1882; the Art Gallery owes its origin to the Art Society, the site being the gift of the Government. The Canterbury Agricultural College, Lincoln, also founded by the College Governors, is surrounded by 660 acres of land. The commodious buildings, which cost over £20,000, provide accommodation for the Director and teaching-staff, and for forty-five students. The fees are on a low scale. The farm buildings are complete, and include a well-equipped dairy. Instruction is given in agriculture, chemistry, botany, mechanics, physics, surveying, &c.
The Public Library, Christchurch, under the control of the College Governors, contains reading-rooms, a circulating library of 21,728 books, and a reference library of 14,371 volumes. One hundred and seventy-two magazines and newspapers are provided. The number of subscribers is 1,950, and the average daily attendance between 900 and 1,000. A spacious free reading-room, 60 ft. by 36 ft., has recently been erected, and is supplied with 127 English, American, and colonial newspapers and periodicals.
The Museum, Christchurch, is a handsome pile of stone buildings; the collections are large and varied. They are separated into two groups: (1) Those from New Zealand; (2) those from foreign countries. In the New Zealand department the skeletons of whales and moas, as well as the collections of shells (tertiary and fossils) and rocks, are specially good; and the Maori collection, exhibited in a Maori house, is also of considerable interest. In the foreign department, the geological, mineralogical, and ethnological collections are the most extensive, but there is also a good illustrative series of Egyptian and Roman antiquities, as well as of the remains of prehistoric man in Europe and America.
This institution owes its origin and success to the foresight, skill, and energy of the late Sir Julius von Haast, and to the munificence of the Provincial Government.
The philanthropic institutions embrace the Christchurch, Akaroa, Ashburton, Timaru, and Waimate Hospitals; the Sunnyside Asylum for the Insane; the Rhodes Convalescent Home; the Memorial Home for the Aged at Woolston; the City Mission and Destitute Men's Home, Christchurch; the Deaf-and-Dumb Asylum at Sumner; the Orphanage, Lyttelton; the Industrial School at Burnham; and the Mount Magdala Asylum, Samaritan Home, and St. Mary's Home, in the vicinity of Christchurch.
Christchurch, the capital city of the Canterbury District, is situated on the plains. It is practically level, the original portion of the city being laid out in rectangular form, two miles by one mile and a quarter, and intersected diagonally by a street. All the principal streets are 66 ft. in width. There are numerous open spaces, including the Cathedral Square in the centre, and Cranmer and Latimer Squares. The Avon, a pretty stream, overhung by willows, runs through the town, presenting from all points charming vistas. The city is surprisingly Eng its appearance, architecture, and surroundings. The central portion, where standing the Cathedral, Government offices, and other substantial structures, has a handsome, well-built look. Other parts contain fine public buildings, such as the Museum, Canterbury College, High Schools, &c. The whole is admirably set off by Hagley Park, 400 acres in extent, the Domain and Botanical Gardens, 79 acres, Lancaster Park, the Town Belts, and other public and private gardens and plantations. The suburbs can show many handsome houses and beautifully kept grounds.
On the 1st April, 1903, the suburbs of Sydenham, Linwood, and St. Albans were amalgamated with the original city proper into what is known as “Greater Christchurch,” comprising a total population (according to the census of March, 1901) of 42,286, in 8,515 houses. Including the adjacent Borough of Woolston, and the suburbs of Papanui, Fendalton, Riccarton, &c., the total population amounts to about 57,000. Tramways connect the centre of the city with the outlying areas of Addington, Sydenham, the Port Hills, and Papanui, and with the seaside villages of New Brighton and Sumner. The city has been drained at considerable expense, the sewage being conveyed three miles and discharged on the sand wastes near the sea. A pure and copious water-supply has been provided by nature, and is obtained by artesian wells. For the purposes of municipal government the city is divided into four wards, and its affairs are controlled by the City Council, presided over by the Mayor. Christchurch is the centre of trade and commerce for the North Canterbury agricultural and pastoral country, and the headquarters of many manufacturing industries, including carriage, boot, and clothing-factories, flour-mills, breweries, meat preserving and freezing, biscuit, planing and moulding, bicycle, and other works.
There are large and well-equipped show-grounds at Addington.
The Canterbury Agricultural and Pastoral Association and the Industrial Association, operating through a public company, have recently erected a fine block of buildings in brick and stone, comprising a large hall capable of seating three thousand persons (and known as the Canterbury Hall), together with smaller halls and suites of offices. It is proposed to establish an industrial and agricultural museum of a permanent character in the building, which should form a most useful reference to the productions and capabilities of the district. The opening of the building was inaugurated by the holding of the “Canterbury Jubilee Industrial Exhibition, 1900,” commemorating the establishment of the province fifty years before, and forming an excellent index to the progress of the district since that time. The exhibition was confined to colonial products, but the bulk of the exhibits were produced in the district. It remained open for three months—from the 1st November, 1900, to the 31st January, 1901—was visited during that time by about 250,000 persons, and yielded a profit to the Industrial Association (as promoters) of about £3,000.
Recreation and amusement are provided for by the Canterbury Hall (already referred to), Theatre Royal, Opera House, and various public halls, the famous Riccarton racecourse, the numerous cricket and football grounds, &c., while boating men have the River Avon and the Heathcote estuary.
Christchurch is connected with the outside world by Port Lyttelton, seven miles distant. The railway-tunnel of 1 ⅝ miles in length, through the Port Hills, is on this line. Christchurch is not only the centre of the splendid Canterbury Plains, but is also one of the chief railway centres of the colony. Addington railway-workshops are extensive and fully equipped.
Lyttelton, the chief port of the district, is situated on the northern shores of the inlet of that name, sometimes called Port Cooper. The surrounding country consists of high precipitous hills, which separate the harbour from Christchurch and the plains; but by the construction of the railway and tunnel the natural difficulties have been overcome, with the result that the whole of the imports and exports of northern and central Canterbury pass through Lyttelton. The origination and accomplishment of this great engineering work is due to the late William Sefton Moorhouse, at that time Superintendent of the Province. The natural advantages of the port have been enhanced by reclamation and harbour-works, which include two breakwaters, 2,010 ft. and 1,400 ft. in length respectively, extending from Officer and Naval Points, enclosing about 107 acres; long lengths of wharf accommodation, 10,041 ft.; a patent slip for ships up to 400 tons; and a splendid graving-dock 450 ft. long, width on top and bottom 82 ft. and 46 ft. respectively, the entrance being 62 ft. wide, well equipped with machinery and all requisites for repairs. Ships drawing up to 25 ft. can berth alongside the spacious wharves and sheds. The railway, electric-light, machinery, and appliances are available throughout, which renders loading and unloading practicable both by day and by night. As an indication of the volume of trade dealt with at the port, it may be noted that for the year ended March 31, 1903, the imports were valued at £1,782,508 and the exports at £2,778,984. The town nestles on the side of the range, the streets being generally steep, flanked by solid stone buildings; and a background of green spurs and bold rocky faces gives to the whole a charming and picturesque appearance. The water-supply is obtained from artesian wells on the Christchurch side of the hills. To Christchurch there is a bridle-track over the range, and a carriage-rad viâ Sumner. The harbour is well defended by fortifications and batteries on Ripa Island and the mainland. The population at last census was 4,023 persons.
Timaru, the third town in importance, is situated on the coast and railway-line between Christchurch (100 miles) and Dunedin (131 miles). The boundaries of this borough were extended in 1898, the estimated area, including town belt, being now 1,100 acres. It has a well-constructed artificial harbour, the port of shipment for the agricultural and pastoral districts of Geraldine, Timaru, and Waimate. The harbour is enclosed by a breakwater built of blocks of concrete; a rubble wall—the North Mole—starts from the shore a quarter of a mile away to the north, and extends easterly to a point 350 ft. from the breakwater. The enclosed space is 50 acres. During the year ended March 31, 1903, the value of goods imported here was £147,036 and of produce exported £810,352. The town is picturesquely situated on rolling hills overlooking the sea. The streets are irregular, but the public and commercial buildings, churches, and private houses are generally well and handsomely built of stone. The chief industries are meat-freezing, saw-milling, flour-milling, &c. The town has a good high-pressure water-supply, and is connected by well-made roads with the surrounding districts, and by rail with Fairlie, the route to the Mackenzie Country and Mount Cook. The population at last census was 6,424 persons.
Of other towns in Canterbury the following deserve mention: Rangiora, population, 1,768 persons, twenty miles from Christchurch by northern line of railway, is situated in the centre of a fine farming country, and possesses manufactories, including flax-mills, flour-mill, and brewery. The town and neighbourhood are much benefited by plantations.
Kaiapoi, on the Waimakariri, population 1,795, about fourteen miles from Christchurch by the northern railway-line, lies in a rich farming country, rendered pleasing and attractive by the extent and variety of plantations and gardens. There are factories and various industries, including ham- and bacon-curing, sawmills, brewery, and agricultural-implement works. Here also is the famed Kaiapoi Woollen-mill, which employs 600 hands when trade is brisk. The Waimakariri is navigable for small vessels to the centre of the town.
Ashburton, the newest of the towns, has a population of 2,322, and is fifty-three miles from Christchurch on the southern trunk line. It is a well-built town, with extensive and beautiful recreation-grounds and gardens. It owes its existence to the settlement of the plains, the surrounding country being well adapted for farming. There are meat-freezing works, a cordial-factory, flour-mills, gasworks, ironworks, woollen-mill, brickworks, &c.
Geraldine, population 868, is situated on the Waihi River, four miles from Orari Railway-station, about eighty-six miles south-west from Christchurch. It is a neat and pretty town, in a first-class farming district, and has a beautiful park of native forest-trees.
Temuka, eighty-eight miles from Christchurch, on the southern railway-line, is a well-built town, with good agricultural land all round. It possesses flour-mills, a butter- and cheese-factory, brewery, foundry, fellmongery and paper-mill. There is a beautiful park and domain. The population of the borough is 1,465 persons.
Waimate, population 1,359, is situated on the Waihao Forks Railway, about four miles from Studholme Junction, some 111 miles from both Christchurch and Dunedin. This town is the centre for an extensive back-country, and a splendid agricultural area. It owes its origin to the sawmill industry of the Waimate bush. Industries: saw-milling, flour-milling, &c.
Akaroa, population 559, situated on the noble harbour of that name, was founded in 1840, in the first instance by the French. It is a quiet, picturesque little place, much patronised by Christchurch residents and others as a summer resort and watering-place. It was here that Captain Stanley hoisted the British flag on 11th August, 1840, when he took possession of the Middle Island on behalf of the Crown, forestalling the French by a few hours only. A suitable obelisk commemorating this event has been erected on the spot.
Table of Contents
The Otago Land District lies between the 44th and 47th parallels of south latitude, and extends from 167° 20' to 171° 10' of east longitude. It is bounded on the north by the Canterbury Land District; on the south-east and south by the ocean; on the west and south by the Waikawa, Mokoreta, Slopedown, Waikaka, Chatton, Wendon, Waikaia, Gap, Rockyside, and Kingston Survey Districts, the western and southern shores of Lake Wakatipu, the Mid-Wakatipu, Mavora, Swinton, Eglinton, Arran and Doon Survey Districts, and a straight line from the north-east corner of the last-mentioned district to the nearest arm of George Sound, and by George Sound to the ocean; and on the north-west by the ocean to Big Bay.
The district measures about 160 miles from Milford Sound on the west coast to Waikouaiti Bay on the east coast, and the same distance from north to south. Its area is 9,482,800 acres.
The country generally is mountainous, the highest land being to the north-west, and culminating in Mount Aspiring, 9,960 ft. above the level of the sea.
The west coast mountains are remarkably rugged and grand; and of the thirteen sounds that pierce (is coast, three are within the limits of the Otago and District, the remaining ten being on the west coast of the Southland District. These three are Milford Sound, Bligh Sound, and George Sound. Milford Sound though only eight miles in length, contains some of the grandest scenery in the world; and fourteen miles inland from its head is the great Sutherland Waterfall, 1,904 ft. high, possibly the highest waterfall known. Bligh Sound is smaller than Milford, and not nearly so interesting; but George Sound is larger, and very picturesque.

Hagley Park.
A tourist track has been opened from the head of Te Anau Lake to Milford Sound, and a practicable route has also been discovered, and a track formed, from the north-west arm of the middle fiord of Te Anau Lake to the head of George Sound.
Te Anau Track.—A guide works on this track from December to April. He carries a fortnightly mail between Lake Te Anau and Milford Sound, and also meets each trip of the “Waikare.” There is ample accommodation for tourists who wish to make the journey in short stages, as there are huts erected at six different places on the track.
For nearly one hundred miles inland from the west coast the country is very mountainous, but at a distance of sixty or seventy miles from the south-east coastline it begins to get gradually lower, taking the form of rolling hills and downs along the sea-shore.
The largest rivers are the Clutha, Taieri, and Waitaki: the first-named drains Lakes Wakatipu, Wanaka, and Hawea; the last, Lakes Ohau, Pukaki, and Tekapo, in the Canterbury District. Te Anau, the largest lake in the Middle Island, lies partly in the Otago and partly in the Southland District. The dimensions of these lakes are as follows:—
| Lakes. | Length in Miles. | General Breadth in Miles. | Area in Square Miles. | Height above Sea-level in Feet. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Te Anau | 38 | 1 to 6 | 132 | 694 |
| Wakatipu | 50 | 1 to 3 ½ | 114 | 1,069 |
| Wanaka | 29 | 1 to 3 | 75 | 928 |
| Hawea | 19 | 3 | 48 | 1,062 |
| Ohau | 11 | 1 to 3 | 23 | 1,720 |
| Pukaki | 11 | 2 ½ to 5 | 31 | 1,588 |
| Tekapo | 15 | 1 to 3 ½ | 32 ½ | 2,325 |
These lakes are situated in mountainous country; they are of glacial origin, and all very deep.
On Wakatipu there are large Government steamers, which run from Kingston, at the southern end, to Glenorchy and Kinloch, at the head of the lake.
On Lakes Wanaka and Te Anau smaller steamers are in use.
The Clutha River is the largest in New Zealand, and is estimated to discharge over 1,000,000 cubic feet per minute. It has a rapid current, but is navigable for small steamers for a distance of forty miles from its mouth. The Waitaki is not a navigable river. For some seventeen miles from its mouth the Taieri River is affected by tides, which run up one branch into Waihola Lake, and up the other branch as far as Allanton (Greytown).
There is a small steamer on Waihola Lake, and another on the Taieri River at Henley. During the summer season both run excursion trips to the mouth of the river when required. The distance in each case is about eight miles.
There are some considerable areas of tolerably level land in the interior, the largest being the Maniototo Plains, the Idaburn, Manuherikia, and Upper Clutha Valleys. Their dimensions are approximately as follows: Maniototo Plains, length, twenty-eight miles; average breadth, ten miles; Idaburn Valley, twenty-five miles by four miles; Manuherikia Valley, thirty-five miles by four miles; Upper Clutha Valley, thirty-three miles by five miles.
The Taieri Plain, nearer the coast, is about the same size as the Idaburn Valley, and is very fertile. Other plains are the Waitaki in the north, the Tokomairiro, the Strath-Taieri, the Tapanui, and the fertile Inch-Clutha, lying between the two branches of the Clutha River, and consisting entirely of alluvial deposit. There is also a good deal of low country, chiefly rolling downs, on the south-west side of the Clutha near the sea.
The forest-land lies mostly along the sea-coast, the largest area of bush being Tautuku Forest, about forty miles in length and fifteen miles in breadth. The western part of this forest is in the Southland District. The other principal forest areas are in the following localities, viz.: north of Dunedin, east of the Tapanui mountains, in the upper valley of the Waikaia River, and towards the north-west coast.
The forests of Otago contain a large variety of useful timber, both hard and soft wood; some being suitable for building purposes, while other varieties are highly ornamental, and much prized for cabinet-work.
Building-stones of good quality are found in various places throughout Otago. The Port Chalmers quarries afford an inexhaustible supply of bluestone, a basaltic stone of great hardness and durability; and the neighbourhood of Hindon furnishes a bluestone of superior quality. In Otago central a hard, close sandstone is obtained near Kokonga. A hard freestone of excellent quality is found at Waikawa, where there is a large hill of it close to the water's edge. Blocks of very great size can be obtained. There is also a freestone of superior quality on the property lately owned by the late Hon. W. J. M. Larnach at the Peninsula. A dense dark granite is obtainable on Ruapuke Island; specimens, both tooled and polished, may be seen in the base and pilasters of the new Government Life Insurance Buildings at Dunedin. A soft white building-stone—the well-known Oamaru limestone—is found in large quantities along the railway-line near Oamaru, from whence a good deal is exported to other parts of New Zealand and to the Australian States. A similar kind of stone is found at Otekaike, about two miles from the railway-station, and it may be interesting to note that during the years 1891–93 about 3,000 tons of stone were sent from the Otekaike quarries to form the facings of the Melbourne Fish-market.
Limestone is found in the following places: Oamaru, Otekaike, Otepopo, Waihemo Maniototo Plains, Waikouaiti, Lower Harbour, Peninsula, Waihola, Millburn, and Wakatipu.
The Millburn Lime and Cement Company burn large quantities of lime at their Millburn works, whence it is sent to all parts of Otago, for building purposes, gasworks, &c. It is also largely used in farming, and the productiveness of the Tokomairiro Plain has been greatly increased of late years by its application to the soil. Large cement-works belonging to the same company have been open for some years on the reclaimed land in Otago Harbour, near Dunedin. The cement manufactured at these works is considered fully equal, if not superior, to the best imported, and is largely used in building and other constructive works.
The Government have constructed a branch railway to the lime deposits on the Makareao Estate, Waihemo, having tested the same with satisfactory results, the lime produced being of exceptionally good quality.
No first-class coals have yet been discovered in Otago suitable for ocean-going steamships. In the southern portion of the district and in part of Southland thin seams of coal of a bituminous character exist, but so far nothing of a commercial value has been found. These coals are of Mesozoic age. First-class brown coals are worked in several parts of Otago and Southland, the principal seats of the industry being Shag Point, Green island, Kaitangata, and Nightcaps. Considerable quantities of brown coal are now being mined in Central Otago, the dredging requirements having considerably increased the output in this district.
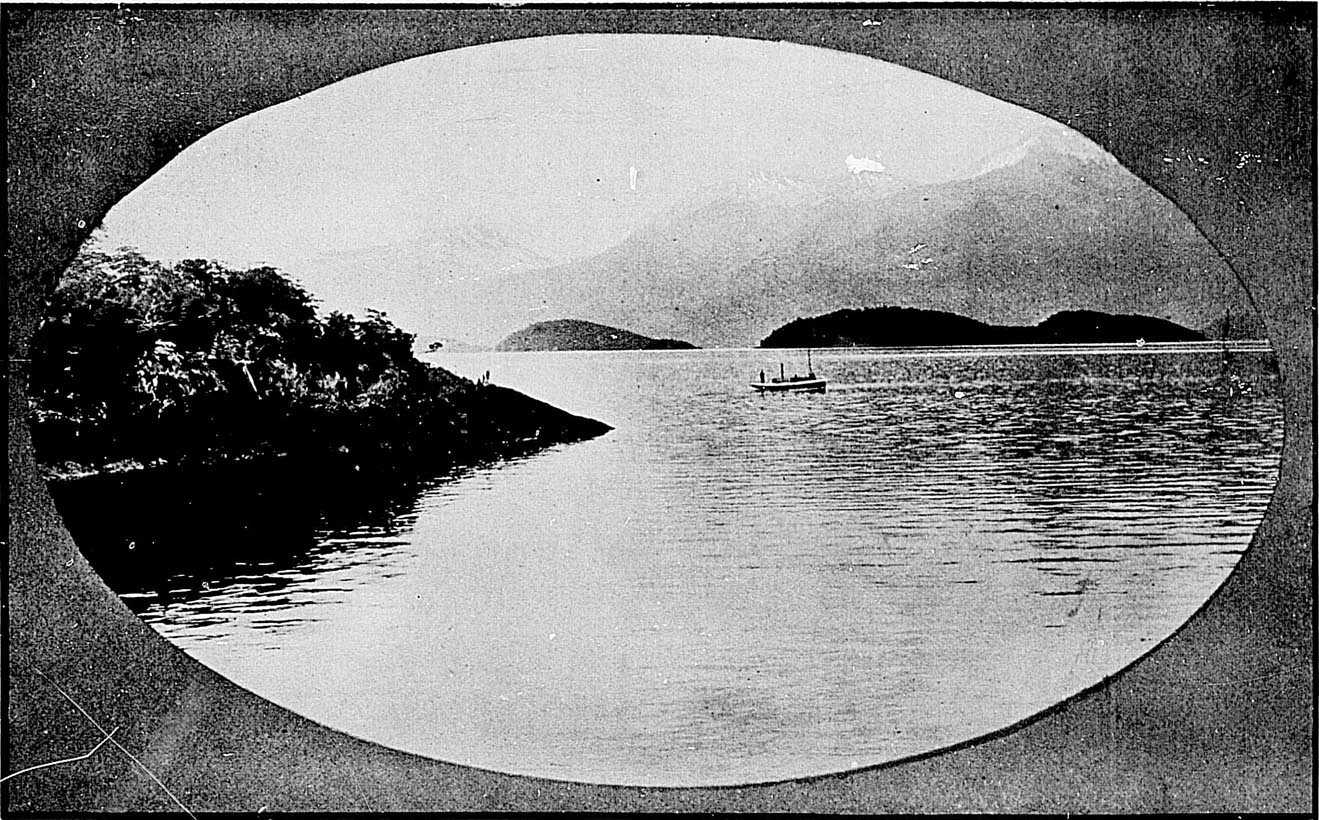

Cathedral Peaks, Manapouri.
Beds of lignite are also found in numerous localities, chiefly round the margins of the old lake-basins and along the courses of the older river-valleys, and are worked on a sufficient scale to supply local requirements.
The output of coal and lignite in Otago and Southland for 1902 was 397,396 tons, an increase of 30,475 tons on previous year. In addition, 2,338 tons of oil-shale were raised at the Orepuki Mine for reduction at the works on the premises.
The climate of Otago varies greatly in different neighbourhoods, and sometimes a distance of a few miles only separates districts very dissimilar in this respect. A large area in the interior of Otago has what may be called a dry climate. This area includes the Maniototo Plains, the Idaburn and Manuherikia Valleys, and extends to Lakes Wakatipu, Wanaka, Hawea, and Ohau on the west and north, and to the Waitaki River on the north-east. From Oamaru the direction would be across country to the Lammerlaw Ranges, and thence to Mount Benger and the southern end of Lake Wakatipu. This part of the country is well adapted for sheep of all kinds, especially merinos. Some of the runs in the hilly country are capable of carrying 20,000 sheep.
In marked contrast to central Otago is the West Coast District, which may be described as having a wet climate. Not that the number of wet days in the year is very great, but it is subject to very heavy rains from the north-west, the fall generally exceeding 100 in. per annum. But, although wet, the climate is mild, and the vegetation is consequently luxuriant. The only settlers of this part of the country are Mr. and Mrs. Sutherland, who keep a house of accommodation for tourists at the head of Milford Sound. There are very few visitors to the Sounds during winter, but in summer the tourist traffic is considerable. Towards the south-east and south coasts of the district the climate is moist, being somewhat similar to that of Dunedin, where the average rainfall is 35 in., distributed over 163 days in the year.
There are some fine fruit-growing districts in the valley of the Clutha, from below Roxburgh right up to Lake Wanaka. The summers are dry and warm, and the soil suitable. Apricots, peaches, &c., come to maturity fully a month before they do at Dunedin, and grapes ripen in the open air. There is a great future for this neighbourhood in the growing of those varieties of fruit which agree with and a dry climate. The grape might be cultivated either for wine-making or for the table, and some varieties could be made into good raisins. The dryness of the atmosphere is favourable for preserving all kinds of fruit, while the Otago Central Railway will bring the neighbourhood into direct communication with a market.
Cereals of all kinds do very well over nearly the whole of the provincial district, which includes Southland. The following are the agricultural statistics:—
Total area under cultivation in the provincial district, including sown grasses and fallow land, 2,332,338 acres. Corn crops sown for threshing, comprising wheat, oats, barley, rye, maize, peas, beans, 278,955 acres; land broken up and grassed, 1,446,575 acres, and 3,407 acres in clover, while 312,251 acres have been surface sown with grass without the land being first broken up; green-crops, comprising potatoes, turnips, mangolds, rape, beet, carrots, &c., 264,626 acres; plantations, &c. including private gardens, market gardens, orchards, and vineyards of a quarter-acre and upwards, 11,845 acres, and 20,433 acres ploughed but not planted. The area in tussock, or native grass, is 8,173,639 acres.
| Acres.] | Estimated Yield per Acre. | Total. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat for threshing | 42,688 | 37 bushels | 1,600,188 bushels. |
| Oats threshing | 230,082 | 42 bushels. | 9,841,325 bushels. |
| Barley threshing | 4,310 | 36 bushels. | 158,791 bushels. |
The total number of sheep in Otago Provincial District, which includes Southland, on the 30th April, 1902, was 3,965,342, of which number about 700,000 were merinos. On an average, about one-third of the flocks consist of breeding-ewes. The shearing is mostly done by hand, but the Wolseley shearing-machines have been introduced on about ten stations, the number of machines in each wool-shed varying generally from ten to fifteen, though there is one shed at Benmore, near Lake Ohau, where there are twenty-eight machines driven by a turbine.
The above-mentioned district had also, in October last, 57,698 horses; 202,211 cattle; and 22,920 pigs.
The rabbit-pest is still a severe tax on the stockowners. The number of skins exported last year from Otago was 5,897,367; the monetary value being £50,396.
There are nine meat-freezing and preserving-works in Otago. The principal freezing establishments are at Oamaru, at Burnside, and at Port Chalmers. At Oamaru there are two Bell-Coleman machines, and a 60-ton Hercules refrigerator, capable of freezing 1,200 sheep a day, and there is storage-room for 20,000 carcases. At Burnside there is a 70-ton Hercules machine, capable of freezing 2,000 carcases per day, and storage-room for 50,000 carcases. The Port Chalmers freezing-works, erected in 1896 by the Otago Dock Trust, cost £4,500. They are used principally for the storage of butter prior to shipment, but the freezing-chambers have also been used for sheep, rabbits, and fish. The refrigerating machinery includes a 12-ton Hercules refrigerator. The capacity of the building is 30,000 cubic feet, and 50 tons of butter can be handled per week. The capacity has lately been nearly trebled, at an additional cost of £8,500. These additions include a 35-ton Hercules refrigerator.
There are four woollen-mills at work in Otago, employing some 974 hands. The amount paid in wages is about £64,594 per annum, and the machinery is 800-horse-power. £80,000 worth of wool and other materials are used per annum, and the turn-out of manufactured goods exceeds £181,000 yearly. The woollen industry in Otago is of greater magnitude than in any other district of New Zealand, notwithstanding the fact that the Bruce Woollen-mill, one of the newest and smallest, was totally destroyed by fire on the 28th April, 1901. It is now restored.
Besides supplying local needs Otago Provincial District exported last year 23,860,360 lb. of wool, having a value of £552,414.
In clothing-factories, also, Otago takes a prominent place, having eight, employing 778 hands, whose wages amount to £33,200 per annum.
The following is an extract from last annual report of the National Dairy Association of New Zealand (South Island):—
“There is no cheaper or surer way of keeping the land in good heart than by combining dairying with other farming branches, and the outlook as to future prices for dairy produce is at least as good as that for grain or meat. We cannot have closer settlement and prosperity if dairying is neglected.”
The Taieri and Peninsula Company continue to extend and increase, and have absorbed a good many of the smaller cheese-factories. The cheese-factories still, however, make progress.
Total amount of cheese and butter shipped to London during season 1902–1903 from Otago and Southland: Cheese, 2,083,087 lb.; butter, 1,284,418 lb.
Under this head the census returns of 31st March, 1901, gave within the Otago Provincial District—13 meat-preserving works; 12 bacon-curing establishments; 13 fish-curing establishments; 42 butter- and cheese-factories; 27 grain-mills; 7 biscuit-factories; 2 jam-factories; 4 confectionery-works; 15 breweries; 8 malt-houses; 17 aerated-water and cordial factories; 2 sauce- and pickle-factories; 4 soap- and candle-works; 4 cooperages; 70 sawmills and sash-and-door factories; 5 gasworks; 5 lime- and cement-works; 25 brick-, tile-, and pottery-works; 11 tinware-factories; 14 iron- and brass-foundries; 8 engineering-works; 12 agricultural-implement factories; 49 printing establishments; 20 coach building and painting establishments; 21 cycle-works; 20 saddlery- and harness-factories; 33 fellmongeries, tanning, currying, and wool-scouring establishments; 9 ship- and boatbuilding yards; 7 sail-, tent-, and oilskin-factories; 32 furniture-factories; 8 clothing-factories; 2 waterproof-factories; 7 hosiery-factories; 35 boot- and shoe-factories; 4 rope- and twine-works; and 16 flaxmills.
The total number of works of the above description in the Otago Provincial District was 809. The motive power employed comprised 295 steam-engines, 43 water-engines, 98 gas-engines, 4 oil-engines, 21 worked by horse and 3 by electricity, making a total of 464, with horse-power amounting to 8,390. The number of hands employed was 8,745 males and 3,057 females, who received in wages £733,671 and £96,069 respectively. The value of materials used or operated upon in 1900 was £1,741,981, while the approximate value of the manufactures, &c. (including repairs), was £3,749,497. The approximate value of the land, buildings, machinery, and plant totalled £1,862,858. The above amounts are exclusive of Government railway workshops.
Under the head of mining there were 26 gold quartz-mines, 68 hydraulic goldmines, 121 gold-dredges, and 105 coal-mines in operation.
Otago produces about one-third of all the gold taken out in New Zealand.
Gold is found very generally distributed throughout Otago, except in the southern portion of the district. The principal localities are: Clutha Valley, Tuapeka, Shotover, Cardrona, Tinker's, St. Bathan's, Mount Ida, Nevis, Bannockburn, and Maerewhenua.
Last financial year the Otago Provincial District produced 192,079 oz. of gold, having a value of £771,892.
The following are the chief towns of Otago, with their population at last census, including all having 1,000 inhabitants and upwards: Dunedin, and suburbs, 52,390; Oamaru, 4,836; Port Chalmers, 2,056; Mosgiel, 1,463; Milton, 1,241; Kaitangata, 1,463; Lawrence, 1,159; Balclutha, 1,017.
Dunedin, the capital city of Otago, is situated at the head of Otago Harbour, which is divided into two parts—the upper and lower. The lower harbour is six miles long from Taiaroa Heads to Port Chalmers. The upper harbour, from Port Chalmers to Dunedin, is seven miles in length. Dunedin and Port Chalmers are also connected by railway.
Although the hills surrounding Dunedin are rather tame in character and outline, the city itself is picturesquely situated. The business part of it is on level land near the harbour, and the residences occupy the sloping hills which rise on the west side of the city. The city proper is about two miles and a half long by seven-eighths of a mile wide, and is bounded on the land side by what is called the Town Belt. This reserve averages one-fifth of a mile in width, and comprises 500 acres, a great part of which is virgin bush. A pretty road, called the Queen's Drive, has been laid out through the Belt from end to end, from which many fine views of the town and harbour can be obtained.
It is thirteen miles down the harbour to the Heads in a north-easterly direction, but the Ocean Beach, lying to the south-east, is only two miles from the centre of the city, and the favourite seaside resort—St. Clair—is about three miles. Trams run to both these places at short intervals. The city is also connected with the suburban boroughs, lying on the hills overlooking the town, by excellent cable-tramways. The Botanical Gardens to the north of the city are well laid out, the native bush contrasting with the cultivated parts. The Reservoir also, which is within easy walking distance, and the drive to Blueskin Bay, have many beauties.
Dunedin is well supplied with elementary schools, there being six large schools in the city proper, with an attendance of 3,355 pupils, and ten more in the suburbs, with 3,624 pupils.
There is also in Dunedin a training-college for teachers. The students in training number seven men and ten women. They devote every fifth week during the session to practice in teaching and management of classes in the ten associated schools of the city and suburbs.
The School of Art and Design is in the same building as the Normal School, and has a staff of five teachers and a pupil-teacher. In 1902 there were 387 students in attendance.
The Otago Boys' High School stands on a commanding plateau 300 ft. above the business part of the city and the harbour. The school was opened on the 3rd August, 1863, in the building in Dowling Street now occupied as the Girls' High School. The new buildings in Arthur Street were opened by the late Sir William Jervois, Governor, in February, 1885. The teaching staff, including the Rector, numbers eleven; the attendance is about 236.
The Otago Girls' High School was opened on the 6th February, 1871, with a roll of 78 pupils. The present attendance is 152, with a teaching staff of 9, exclusive of visiting teachers. Otago holds the proud distinction of having established the first Girls' High School in Australasia. Among the earnest band of workers who laboured to establish this first High School for girls the name of Miss Dalrymple stands pre-eminent, and will ever be held in grateful remembrance by the people of Otago.
At the commencement of the present year the Board of Governors accepted the Government's offer in connection with providing free secondary education by admitting sixty-three boys and fifty-one girls who passed the sixth standard in the primary schools and were under fourteen years of age on 31st December last, on payment by the Government at the rate of £6 per annum per head.
The Board is also providing free education to twenty-three boys and twenty-four girls in terms of Government regulations.
It is probable that the number of Government scholars will be considerably augmented.
The Otago University was founded in 1869, and opened in 1871. It is well housed in a handsome pile of buildings in the domestic Gothic style. There are three separate faculties in the University—viz., Arts and Science, Medicine, and Mining. The School of Medicine provides the full course for a Medical degree of the University of New Zealand. There is a Medical Museum in the University buildings containing anatomical, pathological, and other preparations and models. The teaching staff numbers at present twenty-six professors and lecturers. The School of Mines occupies a separate (temporary) building. There are at present about sixty students going through the prescribed courses for the diplomas and certificates in the Mining, Metallurgical, Geological, Mine and Land-surveying and the Assaying Divisions. Of undergraduates keeping terms there are 248—viz., 191 men and 57 women. The University Library contains over 5,000 specially selected volumes, and is open to the public under certain conditions for purposes of reference. The Chemical and Physical Laboratories are well fitted up, and furnished with all necessary instruments and appliances. There are six scholarships tenable at the University, ranging in value from £15 to £30 per annum.
The public Museum, of which the Professor of Biology is Curator, is under the control of the University Council. It is situated in Great King Street, about five minutes' walk from the University. There is a public Art gallery attached, which contains some good works of art. Up to the present time only the central portion of the original design for the Museum building has been erected.
The Dunedin Athenæum and Mechanics' Institute possesses a fine library of over 21,000 volumes, and a membership of about 1,000 subscribers. Besides the Circulating Library there is a Reference Library, and a very large reading-room, well supplied with newspapers and magazines, and chess and smoking-rooms. During the past year the building has been greatly enlarged, over £2,000 having been spent on improvements.
There are some fine specimens of architecture in Dunedin, the buildings for the most part having an air of permanence and solidity. Some of the churches are very handsome. The First Church, in Moray Place, and Knox Church, in George street, are both handsome stone structures, and St. Joseph's Cathedral (Roman Catholic) is built of stone in the decorated Gothic style. The portion at present constructed will seat 1,000 persons, and has cost £23,000.
The Cargill Monument, which was erected to the memory of the late Captain Cargill, the founder of the Otago settlement, stands in the Triangle, between the Customhouse and the Bank of New Zealand. It is an ornate specimen of early decorated Gothic.
Port Chalmers (eight miles from Dunedin) situate on Otago Harbour, midway between the Heads and Dunedin, has a population of over 2,000. It is the chief port of Otago, and possesses every accommodation for Home vessels, including dry dock, 80-ton sheer-legs, steam-hammer, and other appliances, besides several private foundries, cool-storage chamber, &c. The Port Chalmers graving dock is described in the article on page 64.
Leaving Dunedin by the northern railway, winding in and out through the hills which surround the town, and skirting the precipitous cliffs of the coast-line, the first station of importance reached is Waitati, a favourite seaside resort in Blueskin Bay; distance, seventeen miles. Fifteen miles beyond is Waikouaiti; population, 690; pleasantly situated on the Hawksbury lagoon, the centre of a flourishing farming country. The next place of note is Palmerston, forty-one miles from Dunedin, with 738 inhabitants. A branch-line leaves Palmerston and runs nine miles up Shag Valley to Dunback. Six miles further on the main line there is a branch to Shag Point, a coalfield, with two pits being actively worked.
Oamaru (seventy-eight miles) is the second town in Otago, having a population of about 5,300. It is the centre of a large farming district, and has a good harbour, formed by a concrete breakwater, for the reception of ocean-going ships. The chief exports are wool and grain. A branch-line runs from the junction near Oamaru up the Waiareka Valley to Ngapara, seventeen miles, and Tokarahi, twenty-five miles from Oamaru, and another seven miles by road brings us to Livingstone.
Starting from Oamaru, and proceeding to Central Otago, viâ the valley of the Waitaki River, the first part of the journey is accomplished by rail across the fertile Papakaio Plains to Awamoko (ninety-six miles), and thence following up the Waitaki River past Duntroon to Kurow (120 miles from Dunedin). At Kurow the traveller leaves the railway and follows the course of the Waitaki through pastoral country to Rugged Ridges Station (133 miles); a little beyond Rugged Ridges the road leaves the Waitaki River, and crossing the Ahuriri Pass (141 miles), strikes the Ahuriri River, which it follows up past Omarama Station (158 miles) to the junction of Longslip Creek; it then ascends this creek until Lindis Pass saddle is reached (172 miles), at a height of 3,185 feet. Here begins the descent to the Clutha Valley viâ Morven Hills Station (181 miles) and Tarras Station (200 miles). From Tarras Station the road runs through settled farming country up the Clutha River, which is crossed by means of a punt at Newcastle (219 miles), and four miles more brings the traveller to Pembroke, on the southern shore of Lake Wanaka.
From Dunedin the main trunk railway runs southward to Invercargill, a distance of 139 miles. Passing through the Caversham Borough and tunnel the traveller reaches Burnside (four miles) and Abbotsford (five miles), industrial centres, with coalmining, tanning, iron-smelting, and other works. Four miles farther on is Wingatui, the junction of the Otago Central Railway; and ten miles from Dunedin is Mosgiel, a rising township with 1,463 inhabitants, noted for its woollen-mills. The railway-line now skirts the Taieri Plain, an alluvial flat eighteen miles long by five miles broad; the most fertile portion of Otago. A branch-line nine miles long from Mosgiel junction runs to Outram, on the farther side of the Taieri Plain. Passing the smaller Townships of Allanton (Greytown) and Henley, and Lakes Waihola and Waipori, the main line strikes Milton (thirty-six miles). Milton, in the middle of the Tokomairiro Plain, is a town of 1,241 inhabitants, with flour-mill, dairy factories, flax-mill, pottery works, and tannery. The next place of importance is Balclutha (fifty-three miles), on the banks of the Clutha River, with flax-mills, dairy factories, and chicory works; population 1,017. Kaitangata, situated lower down the Clutha River, and connected by a branch-line four miles long, has extensive coalfields, and a population of about 1,500. Leaving Balclutha, the main line runs through the Clutha downs, passing the small centres of Waitepeka, Warepa, Kaihiku, and Waiwera, and reaches Clinton (seventy-four miles), on the Waiwera stream, a favourite resort of anglers. The next station of note beyond Clinton is Waipahi Junction (eighty-four miles), on the Waipahi River, likewise a favourite fishing-ground. Further on is Gore (100 miles), on the Mataura River, in the Southland District. Gore is a fast-rising township of some 2,600 inhabitants, with paper-mill, flour-mill, freezing-works, dairy factory, coal-mines, &c.
A branch-line from Waipahi follows up and crosses the Pomahaka River and connects Tapanui (107 miles), Kelso (110 miles), and Heriot (114 miles). An extension of this line for a distance of over six miles to Edie's is under construction.
The Otago Central Railway starts from Wingatui, crosses the Taieri Plain, and then winds round to the Taieri River, which it follows up to the present terminus at Ida Valley. In its course along the river it runs for some distance through a rocky gorge, but after crossing the Sutton Stream enters Strath-Taieri—a comparatively flat, open country. Near Hindon Station (twenty-five miles from Dunedin), in the Taieri Gorge, and Barewood (thirty-seven miles), there are quartz-reefs being worked. In traversing the Strath-Taieri the line passes the Blair-Taieri Village Settlement (forty-four miles), Middlemarch, a rising township (forty-eight miles), and reaches Hyde (sixty-four miles). The present limit is Ida Valley (106 miles), but the line is under construction for a further distance of about fifteen miles, passing through the Poolburn Gorge and across the Manuherikia River to about a mile beyond Spottis Creek. The extension of the line to Clyde presents no engineering difficulties. Central Otago has a great future before it, as in the opinion of experts it is naturally adapted for producing fruit of all kinds in perfection.
Another means of access to Central Otago is by the Clutha Valley.
Two miles beyond Milton the Lawrence branch leaves Clarkesville Junction, runs up the Tokomairiro River and the gorge of Manuka Creek, and down to Waitahuna (fifty-three miles from Dunedin), and Lawrence (sixty miles), gold-mining centres, with an aggregate population of about 1,500. Gold was first discovered here in 1861, and the mines are still yielding freely. From Lawrence a coach runs to Beaumont (seventy-two miles), on the Clutha River. Crossing the Beaumont Bridge the road follows the west bank of the Clutha, passing numerous dredging-claims. At eighty-nine miles is Ettrick, and seven miles further on is Roxburgh—the Teviot—(ninety-six miles), a town of 478 inhabitants. Recrossing the Clutha River by the Roxburgh Bridge, and proceeding up the east bank, the traveller reaches Alexandra South (124 miles), at the junction of the Manuherikia River with the Clutha, and Clyde—the Dunstan—(130 miles), the chief town of Vincent County. The next place of importance is Cromwell (143 miles), at the junction of the Kawarau River with the Clutha. Cromwell is a small town of 642 inhabitants, and has a good bridge over the Clutha River. If the traveller wishes to pursue his journey farther he can either follow the road up the Clutha to Newcastle and Pembroke, on Lake Wanaka, or take the Kawarau Gorge road by way of the Crown Terrace to Queenstown, on Lake Wakatipu.
Queenstown, a picturesque township situated on the shores of Lake Wakatipu, has a population of 690, and is the centre of a large gold-mining district. The chief feature of Queenstown is the grand mountain and lake scenery in the neighbourhood, which attracts large numbers of tourists every year. There are two ways of reaching Queenstown—the one by the Clutha Valley and Kawarau Gorge, as above described, and the other by rail to Kingston, at the foot of Lake Wakatipu, and thence by steamer, which runs to suit the trains.
The Tautuku bush, in the south of Otago, has only lately been opened up, but already a large number of settlers are making their homes there. Starting from Balclutha the Catlin's River branch-line runs southwards to Romahapa (sixty-one miles from Dunedin) on the crossing of the main road to Port Molyneux, thence to Glenomaru (sixty-five miles), and Owaka (seventy-two miles from Dunedin), and is being constructed to Catlin's Bridge, four miles further on. The Catlin's—Waikawa main road is formed the whole way through, as are also numerous district roads, and the adjacent lands are being taken up as fast as they are thrown open.
The principal lines are as follows: (1.) The main trunk line from Dunedin to Christchurch, with branches from Oamaru to Hakataramea, forty-three miles; and Oamaru to Ngapara and Tokorahi, twenty-five miles; also, Palmerston to Dunback, nine miles. (2.) The main trunk line, Dunedin to Invercargill, with branches, Mosgiel to Outram, nine miles; Milton to Lawrence, twenty-four miles; Stirling to Kaitangata, five miles; Balclutha to Owaka, nineteen miles; and Waipahi to Heriot, twenty miles. (3.) The Otago Central, from Wingatui to Ida Valley, ninety-eight miles.
The total population of the Otago Provincial District on the 31st March, 1901, was 173,145.
Area of Otago Land District: Open land below 2,000 ft., 5,300 square miles; forest-land below 2,000 ft., 1,960 square miles; open land above 2,000 ft., 6,777 square miles; forest-land above 2,000 ft., 500 square miles; area of lakes, &c., 280 square miles: total, 14,817 square miles, or 9,482,800 acres.
The following table shows the disposition of the land in the Otago District on 31st March, 1903:—
| Holdings. | Acres. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Lands finally alienated, comprising freehold land and vested reserves | ... | 2,818,995 |
| 2. | Lands held on deferred payment, rural | 45 | 12,949 |
| 3. | Lands held on perpetual lease, rural | 251 | 48,595 |
| 4. | Lands held under occupation-with-right-of-purchase clause | 229 | 39,956 |
| 5. | Lands held on lease in perpetuity, ordinary Crown lands, rural | 638 | 165,182 |
| 6. | Lands held under agricultural lease on goldfields | 16 | 535 |
| 7. | Lands held under Mining Districts Land Occupation Act | 158 | 5,612 |
| 8. | Lands held under village settlement, deferred payment | 3 | 130 |
| 9. | Lands held under village settlement, perpetual lease | 17 | 364 |
| 10. | Lands held under village settlement, lease in perpetuity | 119 | 1,733 |
| 11. | Lands held under village-homestead special settlement, perpetual lease | 77 | 1,215 |
| 12. | Lands held by special-settlement associations, lease in perpetuity | 14 | 2,765 |
| 13. | Lands held as small grazing-runs | 266 | 534,338 |
| 14. | Lands held under pastoral license, not including bush | 237 | 4,519,101 |
| 15. | Lands held under lease and license for miscellaneous purposes, exclusive of gold-mining | 564 | 88,536 |
| 16. | Lands acquired and disposed of as lease in perpetuity under Land for Settlements Act. rural | 409 | 56,075 |
| 17. | Lands acquired and disposed of as small grazing-runs under Land for Settlements Act | 3 | 3,667 |
| 18. | Lands acquired and disposed of as pastoral homestead sites under Land for Settlements Act | 2 | 954 |
| 19. | Lands acquired and disposed of as miscellaneous licenses under Land for Settlements Act | 48 | 762 |
| 20. | Crown lands open for selection (including Land for Settlements Act), exclusive of pastoral lands | ... | 54,481 |
| 21. | Crown lands being prepared for selection (including 548 acres under Land for Settlements Act) | ... | 82,600 |
| 22. | Land open for application under pastoral licenses | ... | 42,287 |
| 23. | Lands held by aboriginal natives | ... | 16,500 |
| 24. | Lakes, and Clutha and Taieri Rivers | ... | 179,200 |
| 25. | Balance of Crown lands, including mining reserves, public reserves not vested, bush-lands, roads, barren country, &c. | ... | 873,315 |
| Total area of district (14,817 square miles), 9,482,800 | |||
Tenants of lands included in 2, 3, and 4 have the right of acquiring the freehold. There is no right of acquiring the freehold for tenants of lands included in 5, 6, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19. From item No. 1 should be deducted 67,047 acres, having been acquired under Land for Settlements Act, and absorbed in items Nos. 16, 17, 18, 19, and part 20. The summation of items exceeds total area of district by this amount.
Table of Contents
The Southland District, comprising the Counties of Fiord and Stewart Island, and parts of the Counties of Southland, Wallace, and Lake, is bounded on the north and east by the Otago District, and on the south and west by the Tasman Sea, and may be said to lie between south latitudes 45° and 47° and east longitudes 166° 15' and 169° 15'. For administrative purposes, however, the Snares, Auckland, Enderby, Campbell, Antipodes, Bounty, and all other islands within the limits of the colony south of the 47° parallel of south latitude are included in it.
The total area of the district, including Stewart Island, but exclusive of Solander, Ruapuke, and the other small islands enumerated above, is 6,966,592 acres, of which 500,000 are covered with bush. A considerable area in the Fiord County consists of immense alpine country with scrubby bush reaching to the snow-line. This little-known country extends to the western sea, and there presents the almost indescribable West Coast Sounds. The whole region is a paradise for the artist, and, indeed, for all enthusiastic lovers of nature, but has little attraction for the agriculturist or pastoralist. The bush land suitable for timber lies in the neighbourhood of Forest Hill, Hokonui, Waikawa, and on Stewart Island. The timbers of commercial value are totara, rimu, miro, matai, kahikatea, rata, and kamahi, in mixed bushes; but Fagus fusca and other beeches predominate on the high lands.
The open land in Southland and Wallace Counties, in its natural state, carries tussock and snow-grass, fern, flax, manuka, &c., and there is a considerable area of marshy land, interspersed here and there with peat bogs.
Perhaps the most striking feature, if we exclude the Fiord country, is the number of well-defined rivers and valleys of the district, the latter often widening out to such an extent as to form very extensive plains. Commencing with the eastern side, the Mataura, Oreti (or New River), Aparima (or Jacob's River), and Waiau are the most prominent illustrations of this; but these rivers by no means exhaust the list, as they all have numerous tributaries, which exhibit the same features on a smaller scale.
Speaking generally, the watersheds of these rivers do not attain any great height until followed far inland, and near the great lakes to be presently noticed. From what has been said above it follows that the extensive plains and valleys referred to are of alluvial formation, in many places of very rich and fertile quality, and capable of raising crops of every known product, subject, of course, to climatic limitations. Generally these plains and valleys rise from the river-levels in a very gradual slope, sometimes into a series of terraces from 10 ft. to 50 ft. in height, and sometimes into undulating hills, intersected at frequent intervals by lateral gullies, affording natural drainage and an abundant supply of water.
These hills are covered with an indigenous growth, consisting of tussock and other grasses, fern, flax, &c., and even in their native state afford excellent grazing for sheep.
Near the large lakes, such as Wakatipu, Te Anau, Manapouri, Hauroto, and others, and between these and the West Coast, the country becomes very high, often reaching 5,000 ft. and 6,000 ft. above sea-level, with very steep and rugged spurs—this is the Fiord country before referred to. The open country occasionally presents a number of ridges and lesser mountain-tops covered with tussock and other herbage, affording admirable pasture for sheep in summer; but stock have to be removed from April to October, during which period this country is generally covered with snow.
Southland does not contain so much forest as most of the North Island districts, and this will account for its early and extensive settlement; nevertheless there are considerable areas of forest in the eastern, southern, and western parts, and on Stewart Island, and a large export trade is done in the different kinds of pine and other timbers used for building, engineering, furniture-making, &c.
From what has been said of the river systems it will be evident that the country is well supplied with water, although none of the rivers can be used for purposes of internal communication; but the plains are traversed by railways for considerable distances from the principal towns, and where the railways end communication is continued by good roads, so that there is probably no part of the colony better off for means of transit; and with the Bluff Harbour the Southland District would seem to possess every facility.
Having already touched on the character of the soil, it only remains to say that the plains, terraces, and lower hills are well adapted for raising wheat, oats, and other cereals, turnips, mangolds, beets, and the various other crops common to temperate climates. Wheat is not so widely grown as it might be, for the reason, probably, that the pastoral branches of farming receive more attention than the agricultural, and wheat is not required for these; whereas oats are largely grown for export and to feed sheep in the form of chaff; turnips also are much cultivated for winter food. Where wheat is grown the yields are very satisfactory, ranging from 40 to 60 bushels per acre, while oats frequently give 80 to 100 bushels.
Linseed is now receiving some attention from farmers, as they find ready sale for it to the manufacturing chemists at remunerative prices, a fair crop yielding over £5 per acre.
Dairy-farming now forms a very important industry in this district, a number of factories having been established, the total number now in the district being 7 creameries, 6 cheese-factories, and 11 dairy factories, one being a large condensed-milk factory and one making first-class Stilton cheese.
By far the most important industries are those connected with the raising and export of mutton and wool. Some years ago sheep-farming was much hindered by the inroads of rabbits; but owing to the repressive measures adopted there has been a marked abatement of the pest. The hill-country, although it does not carry a large proportion of stock to area, is eminently healthy. The average carrying-capacity over the whole district would probably be slightly over one sheep to the acre. Until within the last few years most of the runs were stocked with merinos, but owing to the decline in price of merino wool, and to the carcase being unacceptable to the European market, these sheep have, generally speaking, been replaced by Leicesters, Lincolns, Romney Marsh, Cheviot, and crossbreds of various kinds, better suited to the existing demands. A number of large establishments for slaughtering and freezing sheep are at work. One of the latest of these, erected near the Bluff Harbour, is considered to be the most complete in the colony, being provided with all possible labour-saving machinery and appliances for working up the by-products into articles of commerce.
Extensive seams of coal and lignite are distributed over the district, and an extensive deposit of brown coal is being developed by the Nightcaps Coal Company. This coal is largely used throughout the district, and its utility has been recognised by the Railway Department of the colony, some 40,000 tons having been used on the Southland section of New Zealand railways during the past year. In many places the annual output is considerable. A deposit of shale covering a fair area exists at Orepuki, and extensive buildings with machinery have been erected to recover the oil, wax, and other products. Peat is also found in some up-country neighbourhoods, and is used for fuel where wood and coal are scarce. Gold is found all over the district, and is being obtained either by sluicing or dredging. A considerable amount of capital has been invested in river- and beach-dredges worked by steam. Payable gold-bearing reefs exist in Preservation Inlet and at Stewart Island. Among the lesser industries the preparation of the fibre of the native flax plant (Phormium tenax) is worthy of notice. The plant is found all over this district, and a number of mills set up, some forty-two in number. The more remunerative and regular prices obtained during the past year will, if upheld, make this a steady industry throughout the colony.
Salt-water fish abound in great numbers in the waters surrounding Stewart Island, and oysters are found on banks between that island and the Bluff. Fish are largely exported to Melbourne, as also the oysters during the open season. All the large rivers, and many of the tributaries, are well stocked with trout, while for heavy trout-fishing the Waiau River may be mentioned as one of the finest in New Zealand. One river—the Aparima—had salmon-spawn put into it some years ago, and, it is now believed, with success.
The small English fruits, such as gooseberries, currants, raspberries, strawberries, &c., grow in great profusion, as do also apples. Stone-fruits are not so common, although peaches, nectarines, apricots, &c., do well when trained against nursery-walls in favourable aspects.
The climate is bracing in winter, and warm and genial in spring and summer. The old residents state that there has been a marked decrease in the rainfall within the last decade. No regular observations have been recorded for the last few years, but it is believed that the average is about 30 in, a year. It may, however, be observed that more rain falls near the coast than inland, and also that the rainfall is more evenly distributed throughout the year than is the case in the northern part of the colony. The temperature varies from 40° in winter to 70° in summer.
Invercargill, the chief town, was from the first well laid out with wide streets, and liberal reserves in the town belts for recreation purposes. The Corporation exercises a paternal care in providing water, gas, and in disposing of sewage, &c., for the citizens; and the streets are well lighted, paved, and maintained. Artesian water is pumped to the top of a handsome brick tower—which, by the way, is a very conspicuous landmark—and stored there in a tank, from which most of the houses within the town boundaries are supplied. The population, including suburbs, is nearly 11,000. Five railways concentrate here, one from the famed Cold Lakes, another from Dunedin and Christchurch, a third line communicates with the agricultural and pastoral country lying east of the Mataura River, known as the Seaward Bush line, a fourth line opens communication with the extended area westward covered by the Wallace County and known as the Western District, while the short line to the Port of Bluff carries a heavy traffic—the main produce of the district—for export. There are rope-and-twine, carriage and implement-factories, flourmills, sawmills, fellmongeries, a boot-factory, bacon-factory, brick- and pottery-works, iron-foundries, and various other industries. Good beer is brewed here, and there are three first-class hotels. The Government Buildings, lately enlarged, are on a scale not often seen in a town of the same size. A clock and chimes of New Zealand make have been placed in the central tower. Although the Bluff is the principal port, Invercargill is provided with a lesser harbour in the New River Estuary, where there is a jetty with appliances for the use of small steamers and craft trading with Stewart Island and along the coast, the goods being handled within the town boundaries.
The Bluff Harbour, which is connected by rail with Invercargill, does a very large shipping business, accommodating steamers of the largest tonnage engaged in the frozen-meat and dairy export trade. Considerable additions have been made to the wharfage accommodation during the past year, and as an indication of the importance of the port it may be stated that the combined net tonnage of 408,756 has been entered inwards during the year, while for depth of water available one of the frozen-meat steamers, loaded up and drawing 27 ft. 5 in., passed out with ease. The port is well-known as being the first and last port of call for steamers trading with Victoria and Tasmania.
Next in size to Invercargill is the inland Town of Gore, situated on the Mataura River, and at the junction of the Main Trunk Railway with the Waimea Plains Branch. Owing to this fact, and to the fertility of the land in the neighbourhood, Gore is rapidly growing in size and importance.
Riverton is a pretty little town, about twenty-five miles from Invercargill, with which it is connected by rail, which runs through to Orepuki; it is situated on the estuary of Aparima, or Jacob's River. Riverton is the oldest settlement in Southland, and was a great resort for whalers in former years. The harbour is available for and used by coasting-vessels, but the principal carrying-trade is done by rail. There are several sawmills in the neighbourhood, this industry being largely carried on near the many timbered localities in the district.
Otautau, on the banks of the stream bearing the same name, is the county town of Wallace. It is the distributing centre of all that large area of agricultural and pastoral country lying between the Longwood range and the Waiau River, and northwards to the Mararoa River. It has direct communication by rail with Invercargill, Nightcaps, and Orepuki. In Otautau large grain stores are seen, flour-mills, and a dairy factory, while in the vicinity timber and flax mills are met with. The most direct inland communication with Lakes Manapouri and Te Anau is by road passing through the town and onwards.
The Village of Nightcaps is reached by a short line of railway from Thornbury, on the Invercargill—Riverton line. A large colliery exists here. (See Industrial, Coal, &c., ante.)
The Town of Winton is on the Invercargill—Kingston Railway, about twenty miles distant from Invercargill, and is the centre of a good farming, sawmilling, and coal-mining district. A short line of railway has been opened from here to Hedgehope, a locality lying some fifteen miles in a westerly direction.
Lumsden is the junction of the Kingston, Invercargill, and Waimea Plains lines. Coaches starting from here take passengers and mails to Lakes Manapouri and Te Anau and the surrounding country.
East of Invercargill are Edendale and Wyndham, both with railway connection, and surrounded by rich agricultural country reaching to Fortrose, with good roads. Fortrose is situated on the estuary of Mataura River, which can be entered by coasting steamers. This place is surrounded by exceedingly fertile agricultural country, as before mentioned.
Eastward of Fortrose and about midway between that place and Catlin's River is Waikawa, a newly-settled township with a harbour for coasters, and a large area of surveyed Crown land around, with good timber, available for settlement. Steamers trading with Dunedin and Invercargill call here and at Fortrose at regular intervals. A good export of timber occurs at Waikawa.
The total area of surveyed lands remaining open to selection as on the 31st March, 1903, was 73,646 acres, comprising the following lands:—
| A. | R. | P. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Town and suburban | 866 | 3 | 25 |
| Village-homestead settlements | 986 | 1 | 18 |
| Rural | 62,171 | 0 | 26 |
| Rural, lease in perpetuity only | 1,595 | 3 | 19 |
| Lands for settlement, L.I.P. and S.G.R. | 8,025 | 2 | 34 |
| 73,646 | 0 | 2 | |
| Unsurveyed pastoral runs | 1,153,871 | 0 | 0 |
| Gross total | 1,227,517 | 0 | 2 |
During the current year it is proposed to open to selection about 9,500 acres in the Waiau and Longwood Districts, the survey of which is now nearly completed, and about 2,000 acres in the Alton and Lillburn Survey Districts. If the proposed withdrawal of land from State forest reservation be approved, a considerable area will be placed in the market. On Stewart Island, if the land be found suitable for settlement after careful examination, a block of a few thousand acres may be opened. The whole of these lands are forest-clad.
DATES OF SOME OF THE PRINCIPAL EVENTS IN THE HISTORY OF NEW ZEALAND.
Dec. 13, 1642.—Discovery of New Zealand by Abel Jansen Tasman.
Oct. 8, 1769.—Captain Cook landed at Poverty Bay on his first visit.
June 30, 1788.—Macaulay and Curtis Islands, of the Kermadec Group, discovered by Captain Sever, of H.M. transport “Lady Penrhyn.”
Nov. 29, 1790.—Chatham Islands discovered by Lieutenant Broughton, in H.M.S. “Chatham.”
Nov. 17, 1793.—Captain d'Entrecasteaux, with the “La Recherche” and “L'Espérance,” discovered Raoul or Sunday Island. (The latter name was given by Captain Raven, of the transport “Britannia,” who visited the island 6th Nov., 1796.)
Nov., 1793.—Lieutenant-Governor King's (of Norfolk Island) visit to Doubtless Bay.
1795.—The ship “Endeavour,” Captain Bampton, sunk at Facile Harbour, Dusky Sound.
1800.—Antipodes Island discovered by Captain Pendleton.
1806.—Auckland Isles discovered by Captain Briscow, ship “Ocean,” one of Enderby's whalers.
1806.—Ship “Venus” visited East Coast of New Zealand. She was taken by convicts at Port Dalrymple, Tasmania. Their visits gave rise to the Nga-Puhi southern expedition.
1807.—Defeat of Hongi and Nga-Puhi tribe at Moremonui, 10 miles south of Maunganui Bluff, Kaipara.
1809.—The taking and burning of the transport “Boyd” at Whangaroa.
1810.—Campbell Island discovered by Captain F. Haselburg, of brig “Perseverance.”
1814.—First arrival of the Rev. Mr. Marsden at Bay of Islands, and introduction of Christianity. Horses, oxen, sheep, and poultry first brought to the colony.
Aug., 1815.—Attempted capture of the “Trial” and “Brothers” at Kennedy Bay.
1818.—Hongi's and Te Morenga's great expedition to East Cape.
1819–20.—Patuone, Nene, and Te Rauparaha's raid on Taranaki and Port Nicholson.
1820.—Hongi visited England; returned to New Zealand July, 1821.
1820.—H.M. store-ship “Coromandel” visited Coromandel.
1820.—Rev. S. Marsden travelled from Wai-te-mata viâ Kaipara to the Bay of Islands—the first white man to do so.
Aug., 1820.—The “Prince Regent” entered Auckland Harbour—the first vessel to do so.
Nov., 1821.—Fall of Mauinaina Pa, Auckland Isthmus, to Hongi.
Nov., 1821.—Ngati-Toa migration from Kawhia to Otaki under Te Rauparaha.
Dec., 1821.—Fall of Te Totara Pa, Thames, to Hongi.
May, 1822.—Fall of Matakitaki Pa, Waikato, to Hongi.
May, 1823.—Fall of Mokoia Pa, Rotorua Lake, to Hongi.
1823, 1828.—Acts passed by the Imperial Parliament extending the jurisdiction of the Courts of justice in New South Wales to all the British subjects in New Zealand.
1824.—Fall of Te Whetumatarau Pa, near East Cape, to Pomare.
1825.—First attempt at colonisation by an expedition under the command of Captain Herd, who bought two islands in the Hauraki Gulf.
Feb., 1825.—Great defeat of Ngati-Whatua at Te Ikaaranganui, Kaipara, by Hongi.
1827.—Destruction of mission-station at Whangaroa by Hongi's forces.
Feb., 1827.—Admiral (then Captain) Dumont D'Urville anchored in Auckland Harbour.
1828.—Hongi died at Whangaroa, from wounds received at Hokianga.
1828.—The “Maquarie,” Captain Kent, the first vessel to enter Kawhia.
March, 1829.—Brig “Hawes” captured at Whakatane by Maoris.
1830.—Battle of Taumata-wiwi, near Cambridge.
1830.—Fall of Kaiapohia Pa, Canterbury.
March 6, 1830.—Battle of Kororareka, between two Nga-Puhi tribes.
Dec., 1830.—Death of Tama-i-hara-nui at the hands of Te Rauparaha's people. He was brought from Port Cooper by Captain Steward, brig “Elizabeth.”
1831.—Tory Channel whaling-station established.
1831.—Application of thirteen chiefs for the protection of King William the Fourth.
Dec., 1831.—Pukerangiora Pa, Waitara, fell to Waikato.
Feb., 1832.—Repulse of Waikato at Nga-motu Pa, under Dicky Barrett.
1833.—Mr. Busby appointed British Resident, to live at the Bay of Islands.
1834.—Battle of Haowhenua and Pakakutu, near Otaki.
1834.—Bishop Williams's first visit to East Cape.
April 29, 1834.—“Harriet” wrecked at Cape Egmont.
Oct. 1, 1834.—H.M.S. “Alligator” shelled and took Waimate Pa, near Opunake. First occasion of H.M. troops being employed in New Zealand.
1835.—Declaration of independence of the whole of New Zealand as one nation, with the title of “The United Tribes of New Zealand.”
Nov. and Dec., 1835.—Ngati-Awa tribes migrated to and conquered the Chatham Islands.
March 28, 1836.—Maketu Pa, Bay of Plenty, fell to Waikato.
May 9, 1836.—Te Tumu Pa, Bay of Plenty, fell to Te Arawa.
Aug. 5, 1836.—Battle at Matai-puku, Rotorua—Waikato beat Te Arawa.
Oct., 1836.—Siege of Toka-a-kuku, Te Kaha, Bay of Plenty.
1838.—The Roman Catholic Bishop Pompallier, with several priests, arrived at Hokianga.
Sept. 1, 1838.—H.M.S. “Pelorus” discovers Pelorus Sound.
April, 1839.—Taking of the French whaler “Jean Bart” at Chatham Islands by Maoris.
May 12, 1839.—Departure of the preliminary expedition of the New Zealand Company from England.
June, 1839.—Issue of Letters Patent authorising the Governor of New South Wales to include within the limits of that colony any territory that might be acquired in sovereignty by Her Majesty in New Zealand.
Sept. 16, 1839.—First body of New Zealand Company's emigrants sailed from Gravesend.
Sept. 20, 1839.—Arrival in Port Nicholson of the preliminary expedition of the New Zealand Company under Colonel Wakefield.
Oct. 16, 1839.—Battle of Te Kuititanga, Otaki.
Jan. 20, 1840.—First steamer arrived in New Zealand.
Jan. 22, 1840.—Arrival of first body of immigrants at Port Nicholson.
Jan. 29, 1840.—Captain Hobson, R.N., arrived at the Bay of Islands. On the following day (Jan. 30) he hoisted the Union flag, and read the commission, under the Great Seal of the United Kingdom, which extended the boundaries of the Colony of New South Wales so as to embrace and comprehend the Islands of New Zealand; also his own commission as Lieutenant-Governor over territory that might be acquired in sovereignty.
Feb. 5, 1840.—Treaty of Waitangi signed.
May 21, 1840.—Date of Proclamations of sovereignty over the Islands of New Zealand.
June 17, 1840.—The Queen's sovereignty over the Middle Island formally proclaimed at Cloudy Bay, by Major Bunbury, H.M. 80th Regiment, and Captain Nias, R.N.
Aug. 11, 1840.—The British flag hoisted at Akaroa by Captain Stanley, R.N., and British authority established. The French frigate “L'Aube” arrived there on the 13th August, and the vessel “Comte de Paris,” with fifty-seven immigrants, on the 16th August, in order to establish a French colony.
Sept. 18, 1840.—The British flag hoisted at Auckland. The Lieutenant-Governor's residence established there.
1840.—Formation of Wanganui settlement under the name of “Petre.”
Feb. 12, 1841.—Issue of charter of incorporation to the New Zealand Company.
Mar. 31, 1841.—Arrival of first New Plymouth settlers.
May 3, 1841.—New Zealand proclaimed to be independent of New South Wales.
Oct., 1841.—Selection of site for settlement at Nelson.
Feb. 1, 1842.—Settlement founded at Nelson.
May 29, 1842.—Arrival of Bishop Selwyn in the colony.
Sept. 10, 1842.—Death of Governor Hobson. Lieutenant Shortland, R.N., Colonial Secretary, became Acting-Governor until the arrival of Captain Fitzroy.
June, 1843.—Affray with Natives at the Wairau, and massacre by Rangihaeata of Captain Wakefield, R.N., agent at Nelson of the New Zealand Company, and others, who had surrendered.
Dec. 1, 1843.—Arrival of Captain Fitzroy, R.N., as Governor.
July 8, 1844.—The Royal flagstaff at Kororareka cut down by Heke.
March 10, 1845.—Attack on and destruction of Town of Kororareka by Heke.
Oct. 1, 1845.—Receipt of despatch notifying recall of Governor Fitzroy.
Nov. 14, 1845.—Arrival of Captain Grey, as Lieutenant-Governor of the colony, from South Australia.
Jan. 11, 1846.—Capture of pa at Ruapekapeka, Bay of Islands, and termination of Heke's war.
Mar. 3, 1846.—Commencement of Native hostilities in the Hutt Valley, near Wellington.
May 16, 1846.—Attack by Natives on a military outpost in the Hutt Valley.
July 23, 1846.—Capture of Te Rauparaha at Porirua, near Wellington. He was detained for a year as a prisoner on board a ship of war.
Aug. 28, 1846.—The New Zealand Government Act passed by the Imperial Parliament, under which a charter was issued dividing the colony into two provinces, and granting representative institutions.
May 19, 1847.—Attack by Natives on settlement of Wanganui.
Jan. 1, 1848.—Captain Grey sworn in as Governor-in-Chief over the Islands of New Zealand, also as Governor of the Province of New Ulster and Governor of the Province of New Munster.
Jan. 3, 1848.—Major-General Pitt appointed by Governor Grey to be Lieutenant-Governor of the Province of New Ulster.
Jan. 28, 1848.—Assumption by Lieutenant-Governor E. J. Eyre, at Wellington, of the administration of the Government of the Province of New Munster.
Feb. 21, 1848.—Peace ratified at Wanganui.
Mar. 7, 1848.—Suspension by Imperial statute of that part of the New Zealand Government Act which had conferred representative institutions.
Mar., 1848.—Otago founded by a Scotch company under the auspices of the Free Church of Scotland.
Oct., 1848.—Severe earthquake at Wellington.
July, 1850.—Surrender of the New Zealand Company's charter, all its interests in the colony reverting to the Imperial Government.
Dec., 1850.—Canterbury founded by the Canterbury Association in connection with the Church of England.
Jan. 8, 1851.—Death of Major-General Pitt, Lieutenant-Governor of the Province of New Ulster.
April 14, 1851.—Lieutenant-Colonel Wynyard appointed Lieutenant-Governor of the Province of New Ulster.
1852.—Discovery of gold at Coromandel by Mr. Charles Ring.
June 30, 1852.—The Constitution Act passed by the Imperial Parliament, granting representative institutions to the colony, and subdividing it into six provinces.
Jan., 1853.—Promulgation of the Constitution Act.
Mar. 7, 1853.—Assumption by Sir George Grey, K.C.B., of the duties of Governor of the colony, in terms of the appointment after the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act, and cessation of the duties of the Lieutenant-Governors of New Ulster and New Munster.
Dec. 31, 1853.—Departure of Governor Sir George Grey.
Jan. 3, 1854.—Lieutenant-Colonel Wynyard assumed the administration of the Government.
May 27, 1854.—Opening at Auckland of the first session of the General Assembly by Lieutenant-Colonel Wynyard, Administrator of the Government.
Jan., 1855.—Very severe earthquake on each side of Cook Strait.
Sept. 6, 1855.—Arrival of Governor Colonel T. Gore Browne, C.B.
Nov. 12, 1855.—First members elected to House of Representatives under system of Responsible Government.
Aug. 8, 1855.—General Assembly opened.
Sept. 15, 1855.—General Assembly prorogued.
May 7, 1856.—Appointment of the first Ministry under the system of Responsible Government, under Mr. Sewell, Colonial Secretary.
May 14, 1856.—Defeat of Mr. Sewell's Ministry.
May 20, 1856.—Appointment of a Ministry under presidency of Mr. W. Fox, as Attorney-General.
May 28, 1856.—Defeat of Mr. Fox's Ministry, by a majority of one, on a direct vote of want of confidence.
June 2, 1856.—Appointment of a Ministry under the presidency of Mr. E. W. Stafford.
1857.—First payable goldfield in the colony opened at Collingwood, in the Nelson Province.
Aug. 21, 1858.—New Provinces Act passed.
Nov. 1, 1858.—Establishment of the Province of Hawke's Bay.
Dec. 22, 1858.—The Austrian exploring frigate “Novara” arrived in Auckland Harbour. Dr. Ferdinand von Hochstetter, at the request of the New Zealand Government, was commissioned to make geological surveys of the greater part of Auckland and Nelson Provinces.
March, 1859.—Te Teira offered land at Waitara for sale to the Government.
Nov. 1, 1859.—Establishment of the Province of Marlborough.
Mar., 1860.—Commencement of hostilities against Wiremu Kingi te Rangi-take at Waitara.
Mar. 18, 1860.—Capture of Maori pa at Waitara.
Mar. 28, 1860.—Engagement at Waireka.
June 27, 1860.—Engagement of Puketakauere at Waitara.
Nov. 6, 1860.—Defeat at Mahoetahi, with heavy loss, of a force of Waikato Natives, who had crossed the Waitara River to join Wiremu Kingi.
Dec. 31, 1860.—Capture of the Matarikoriko Pa, and defeat of a large body of Waikato Natives.
Jan. 23, 1861.—The Natives made a determined attack on the redoubt at Huirangi occupied by Imperial troops, and were repulsed with heavy loss.
April 1, 1861.—Establishment of Province of Southland.
May 21, 1861.—A truce agreed to.
May, 1861.—Discovery of gold at Gabriel's Gully, Otago.
July 5, 1861.—Defeat of Mr. Stafford's Ministry, by a majority of one, on a vote of want of confidence.
July 12, 1861.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. Fox.
July 29, 1861.—Incorporation of the Bank of New Zealand.
Sept. 26, 1861.—Arrival of Sir George Grey, K.C.B., at Auckland, from the Cape Colony, to succeed Governor Gore Browne. Sir George Grey was sworn in as Governor on the 3rd October.
Oct. 2, 1861.—Departure of Governor Gore Browne.
June 28, 1862.—Coromandel proclaimed a goldfield.
June 29, 1862.—Wreck of s.s. “White Swan” on East Coast (with loss of many public records, in transit from Auckland).
July 28, 1862.—Defeat of Mr. Fox's Ministry by the casting-vote of the Speaker, on a proposed resolution in favour of placing the ordinary conduct of Native affairs under the administration of the Responsible Ministers.
Aug. 6, 1862.—Appointment of a Ministry under the leadership of Mr. Alfred Domett.
Feb. 7, 1863.—Wreck of H.M.S. “Orpheus” on Manukau Bar; 181 lives lost.
Feb. 26, 1863.—Definite relinquishment by the Imperial Government of control over administration of Native affairs.
May 4, 1863.—Treacherous assault near Tataraimaka by Natives on a military escort. Murder of Lieutenant Tragett, Dr. Hope, and five soldiers of the 57th Regiment.
June 4, 1863.—Defeat of Natives at Katikara, by a force under Lieut.-General Cameron.
July 17, 1863.—Action at Koheroa, in the Auckland Province. Commencement of the Waikato War.
Oct. 27, 1863.—Resignation of the Domett Ministry, in consequence of difficulties experienced in connection with arrangements for finding a fitting representative of the Government in the Legislative Council.
Oct. 30, 1863.—Appointment of the Ministry formed by Mr. Fox, under the premiership of Mr. F. Whitaker.
Nov., 1863.—Acceptance by the General Assembly of colonial responsibility in Native affairs.
Nov. 20, 1863.—Battle of Rangiriri. Defeat of Natives and unconditional surrender of 183.
Dec. 1, 1863.—The first railway in New Zealand opened for traffic by W. S. Moorhouse, Superintendent of Canterbury. The line was from Christchurch to Ferrymead Junction.
Dec. 3, 1863.—The New Zealand Settlements Act passed, giving the Governor power to confiscate the lands of insurgent Natives.
Dec. 8, 1863.—Occupation of Ngaruawahia. The British flag hoisted on the Maori king's flagstaff.
Feb. 11, 1864.—Engagement with Natives on Mangapiko River. Major (then Captain) Heaphy, of the New Zealand Forces, won the Victoria Cross for distinguished bravery on this occasion.
Feb. 22, 1864.—Defeat of Natives at Rangiaohia.
April 2, 1864.—Attack on and capture of pa at Orakau, Waikato.
April 21, 1864.—Engagement near Maketu, Bay of Plenty. Tribes of the Rawhiti defeated by Arawa Natives, under Captain McDonnell.
April 29, 1864.—Assault on Gate Pa, Tauranga, Bay of Plenty, and repulse of large British force by the Maoris. The pa was abandoned by the Natives during the following night.
April 30, 1864.—Repulse of attack by rebel Hauhau Natives on redoubt at Sentry Hill, Taranaki.
May 14, 1864.—Battle of Moutoa, an island in the Wanganui River, between friendly and rebel Hauhau Natives. Complete defeat of rebels.
June 21, 1864.—Engagement at Te Ranga, near Tauranga, by Lieut.-Colonel Greer, 68th Regiment. Severe defeat of the Natives.
1864.—Discovery of gold on the west coast of the Middle Island.
Sept. 10, 1864.—Escape of Maori prisoners from Kawau.
Oct. 3, 1864.—Wellington chosen as the seat of Government.
Nov. 24, 1864.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. F. A. Weld, the Whitaker Fox Ministry having resigned during the recess.
Dec. 17, 1864.—Confiscation of Native lands in Waikato by Sir George Grey.
Feb., 1865.—Removal of the seat of Government to Wellington.
March 2, 1865.—Barbarous murder of the Rev. Mr. Volkner, a Church of England missionary, at Opotiki, by Hauhau fanatics, under Kereopa.
June 8, 1865.—Submission of the Maori Chief Wiremu Tamihana te Waharoa (William Thompson).
June 17, 1865.—Murder of Mr. Fulloon, a Government officer, and his companions, at Whakatane, by Hauhau fanatics.
July 22, 1865.—Capture of the Wereroa Pa, near Wanganui.
Aug. 2, 1865.—Assault and capture of the Pa Kairomiromi, at Waiapu, by Colonial Forces under Captain Fraser, and Native Contingent under the chief Te Mokena. Eighty-seven rebels killed.
Sept. 2, 1865.—Proclamation of peace issued by Governor Sir George Grey, announcing that the war, which commenced at Oakura, was at an end.
Sept. 30, 1865.—Murder by Hauhaus, at Kakaramea, of Mr. Broughton, when sent as friendly messenger to them by Brigadier-General Waddy.
Oct. 12, 1865.—Resignation of Mr. Weld's Ministry, on account of a resolution adverse to the Government policy, having been defeated only by the casting-vote of the Speaker.
Oct. 16, 1865.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. E. W. Stafford.
Dec. 25, 1865.—Defeat of rebel Natives at Wairoa, Hawke's Bay, by Colonial Forces and Native Contingent.
Jan. 4, 1866.—Defeat of Natives at Okotuku Pa, on the west coast of the North Island, by force under Major-General Chute.
Jan. 7, 1866.—Assault on and capture of Putahi Pa, by force under Major-General Chute.
Jan. 13, 1866.—Assault on and capture of Otapawa Pa, by force under Major-General Chute.
Jan. 17, 1866, to Jan. 25, 1866.—Period of Major-General Chute's march through the bush to New Plymouth.
Jan., 1866.—Escape of a large number of Native prisoners from the hulk at Wellington; many were drowned in trying to swim ashore.
March 29, 1866.—Submission of the rebel chiefs Te Heuheu and Herekiekie, of Taupo district.
Mar., 1866.—A detachment of Maori prisoners sent to the Chatham Islands.
June 15, 1866.—Commencement of Panama steam mail-service.
Aug. 26, 1866.—The Cook Strait submarine telegraph cable laid.
Oct. 2, 1866.—Engagement with rebel Natives at Pungarehu, West Coast, by Colonial Forces, under Major McDonnell.
Oct. 8, 1866.—First Act passed to impose stamp duties.
Oct. 12, 1866.—Defeats of rebel Natives at Omaranui and at Petane, Hawke's Bay, by Colonial Forces.
Oct. 10, 1867.—An Act passed to establish an institute for the promotion of science and art in the colony.
Oct. 10, 1867.—An Act passed for the division of the colony into four Maori electorates, and the admission of four Maori members to the House of Representatives.
Jan., 1868.—Establishment of the County of Westland.
Feb. 5, 1868.—Arrival of Governor Sir George F. Bowen, G.C.M.G.
July 4, 1868.—Seizure by Maori prisoners, under the leadership of Te Kooti, of the schooner “Rifleman,” and their escape from the Chatham Islands.
July 12, 1868.—Night attack by Natives on redoubt at Turuturu Mokai. Sub-Inspector Ross and seven Europeans killed. Natives driven off by the arrival of a force under Major Von Tempsky.
Aug. 8, 1868.—Pursuit by Lieut.-Colonel Whitmore of escaped Chatham Island prisoners, and indecisive engagement in the gorge of the Ruake Ture.
Aug. 21, 1868.—Attack on Ngutu-o-te-Manu by force under Lieut.-Colonel McDonnell. Defeat of Natives; four Europeans killed and eight wounded.
Sept. 7, 1868.—Engagement in bush at Ngutu-o-te-Manu. Major Von Tempsky, Captains Buck and Palmer, Lieutenants Hunter and Hastings, and fourteen men killed.
Oct. 19, 1868.—Bishop Selwyn left New Zealand.
Nov. 7, 1868.—Attack on Moturoa. Repulse of Colonial Forces, with severe loss.
Nov. 10, 1868.—Massacre of thirty-two Europeans at Poverty Bay by Te Kooti's band of Natives, who had escaped from the Chatham Islands.
Nov. 24, 1868, Dec. 3, 1868, Dec. 5, 1868.—Engagements between friendly Natives and rebels under Te Kooti, at Patutahi, Poverty Bay district.
Jan. 5, 1869.—Assault on and capture of Ngatapa Pa, Poverty Bay district, after a siege of six days, by the Colonial Forces of Europeans and friendly Natives under Colonel Whitmore and Major Ropata. Dispersion and pursuit of Te Kooti's band. More than 136 rebel Natives were killed.
Feb. 13, 1869.—Treacherous murder of the Rev. John Whitely and seven other Europeans at the White Cliffs, Taranaki.
Feb. 18, 1869.—Attack by rebel Natives on a foraging-party at Karaka Flat; one sergeant and six men killed.
Mar. 3, 1869.—Termination of Panama mail-service.
Mar. 13, 1869.—Attack on and defeat of Titokowaru's force at Otauto.
April 10, 1869.—Native pa at Mohaka taken by Te Kooti, who killed forty friendly Natives and several Europeans in the neighbourhood.
April 12, 1869.—First arrival of H.R.H. the Duke of Edinburgh in Wellington, in H.M.S. “Galatea.”
May 6, 1869.—Surprise and capture of Ahikereru and Oamaru Teangi Pas, Waiwera country. Defeat of Te Kooti.
June 13, 1869.—Surrender to Major Noake and Mr. Booth, R.M., of the chief Tairua, with 122 men, women, and children of the Pakakohe Tribe, near Wanganui.
June 24, 1869.—Defeat of Mr. Stafford's Ministry on a want-of-confidence motion.
June 28, 1869.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. W. Fox.
Sept. 3, 1869.—An Act passed providing Government life insurance and annuities.
Oct., 1869.—Seventy-four prisoners from the bands of Te Kooti and Titokowaru sentenced to death, after trial, for treason. The sentences of seventy-three were commuted to penal servitude for various terms.
Oct. 4, 1869.—Pourere Pa stormed and taken by Lieut.-Colonel McDonnell, with a mixed force of Europeans and Natives.
Jan., 1870.—Three hundred friendly Natives under Topia, and three hundred under Major Keepa (known as Kemp), started up the Wanganui River in pursuit of Te Kooti, who retreated into the Urewera country.
Jan. 25, 1870.—Capture of Tapapa Pa, occupied by Te Kooti.
Feb. 24, 1870.—The last detachment of the Imperial troops left the colony.
Mar. 25, 1870.—Major Keepa, with Native force, captured the position held by Te Kooti at Maraetahi, in Urewera country; nineteen rebels killed and seventy-three of Te Kooti's men taken prisoners. Te Kooti escaped with twenty followers.
Mar. 26, 1870.—Commencement of San Francisco mail-service.
June 28, 1870.—Enunciation in the House of Representatives of the public-works policy by the Colonial Treasurer, Mr. Vogel.
July, 1870.—Thirty prisoners of Te Kooti's band sentenced to death. The sentences were commuted to penal servitude.
Aug. 27, 1870.—Arrival in Wellington of H.R.H. the Duke of Edinburgh in H.M.S. “Galatea.” Second visit.
Sept. 12, 1870.—An Act passed to establish the New Zealand University.
Sept. 12, 1870.—The Land Transfer Act passed, to simplify the title to land and dealings with real estates.
Oct. 6, 1870.—Southland Province reunited with Otago.
Dec. 5, 1870.—Honiani te Puni, the chief of the Ngatia was, a staunch friend of the Europeans, died at Petone, near Wellington, aged ninety years.
Mar., 1871.—Commencement of railway-construction under the public-works policy.
Aug. 4, 1871.—Death of Tamati Waka Nene, the great Ngapuhi chief and friend of the Europeans.
Nov., 1871.—Capture of the notorious rebel Kereopa, the murderer of the Rev. Mr. Volkner, by the Ngatiporous.
Jan. 5, 1872.—Execution of Kereopa at Napier.
Jan., 1872.—Remission of sentences on fifty-eight Native prisoners then undergoing imprisonment for rebellion.
Feb. 22, 1872.—Visit of William King, the Maori chief of Waitara, to New Plymouth, and resumption of amicable relations with the Europeans.
May 9, 1872.—A general thanks giving day for the recovery of H.R.H. the Prince of Wales.
Sept. 6, 1872.—Defeat and resignation of Mr. Fox's Ministry.
Sept. 10, 1872.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of the Hon. E. W. Stafford.
Oct. 4, 1872.—Defeat of the Stafford Ministry on a vote of want of confidence moved by Mr. Vogel.
Oct. 11, 1872.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of the Hon. G. M. Waterhouse, M.L.C.
Oct. 11, 1872.—First appointment of Maori chiefs (two) to be members of the Legislative Council.
Oct. 25, 1872.—The Public Trust Office Act passed.
Jan., 1873.—Establishment of the New Zealand Shipping Company.
Mar. 3, 1873.—The Hon. W. Fox appointed Premier on the resignation of that office by the Hon. G. M. Waterhouse, the other members of the Ministry being confirmed in their offices.
Mar. 19, 1873.—Departure of Governor Sir G. F. Bowen, G.C.M.G.
Mar. 21, 1873.—Assumption of the Government by Sir G. A. Arney, Chief Justice, as Administrator.
April 8, 1873.—Resignation of the premiership by the Hon. W. Fox, on the return of the Hon. J. Vogel, C.M.G., from Australia. Appointment of Mr. Vogel as Premier, the other Ministers being confirmed in their offices.
June 14, 1873.—Arrival of Governor Sir J. Fergusson, P.C.
Aug. 22, 1874.—The Imprisonment for Debt Abolition Act passed.
Nov. 27, 1874.—Sir James Fergusson left New Zealand.
Dec. 3, 1874.—Arrival of Governor the Marquis of Normanby, P.C.
1874.—31,774 immigrants were introduced this year under the immigration and public-works policy.
Jan. 3, 1875.—Visit of Sir Donald McLean to the Maori king; resumption of amicable relations.
July 6, 1875.—Resignation of the Ministry, in consequence of the absence of Sir J. Vogel, K.C.M.G., in England, and his being unable to attend the session of Parliament. Reconstitution thereof, under the premiership of the Hon. Dr. Pollen, M.L.C.
July, 1875.—Establishment of the Union Steam Shipping Company of New Zealand.
1875.—18,324 immigrants were introduced this year under the immigration and public-works policy.
Oct. 12, 1875.—The Abolition of Provinces Act passed.
Feb. 15, 1876.—Resignation of the Hon. Dr. Pollen's Ministry, and reconstitution under the premiership of Sir J. Vogel, K.C.M.G.
Feb. 18, 1876.—Completion of the work of laying the telegraph cable between New Zealand and New South Wales.
June, 1876.—Death of Dr. Isaac Earl Featherston, while acting as Agent-General for the colony in England. He was the first to hold that office, and had previously been Superintendent of the Province of Wellington from the time of the first establishment of provincial representative institutions.
Sept. 1, 1876.—Resignation of Sir J. Vogel's Ministry in view of the appointment of Sir J. Vogel as Agent-General. Formation of a Ministry under the premiership of Major Atkinson.
Sept. 13, 1876.—Resignation of Major Atkinson's Ministry in consequence of doubts being entertained as to the constitutional position thereof. Reconstruction of the Ministry under the premiership of Major Atkinson.
Nov. 1, 1876.—“The Abolition of Provinces Act, 1875,” came into full operation. Complete abolition of provincial institutions. The colony subdivided into counties and municipal boroughs.
Oct. 8, 1877.—Defeat of the Atkinson Ministry on a vote of want of confidence moved by Mr. Larnach.
Oct. 15, 1877.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Sir George Grey, K.C.B.
Nov. 29, 1877.—The Education Act, providing for the free and compulsory education of children, passed.
April 11, 1878.—Bishop Selwyn died, in England.
Oct. 29, 1878.—Sir George Grey's first land-tax passed.
Feb. 29, 1879.—Departure of Governor the Marquis of Normanby, P.C.
Mar., 1879.—Removal of surveyors from the Waimate Plains by Natives acting under Te Whiti's orders.
Mar. 27, 1879.—Arrival of Governor Sir Hercules G. R. Robinson, G.C.M.G.
May 25, 1879.—The Natives from Parihaka, by order of Te Whiti, began ploughing up lands occupied by Europeans.
June, 1879.—Arrest and imprisonment of 180 of these Natives for causing disturbances.
July 29, 1879.—Defeat of the Grey Ministry on an amendment to the Address in Reply, moved by Sir William Fox, followed by a dissolution of Parliament.
Oct. 3, 1879.—Defeat and subsequent resignation of Sir George Grey's Ministry.
Oct. 8, 1879.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of the Hon. John Hall.
Dec. 19, 1879.—An Act passed to assess property for the purpose of taxation.
Dec. 19, 1879.—The Triennial Parliament Act passed.
Dec. 19, 1879.—An Act passed to qualify every resident male of twenty-one years of age and upwards to vote.
June, 1880.—First portion of the Parihaka Maori prisoners released by the Government.
July 9, 1880.—Bounty Island taken possession of by Captain George Palmer, H.M.S. “Rosario.”
Sept. 8, 1880.—Departure of Governor Sir Hercules G. R. Robinson, G.C.M.G.
Oct. 1880.—Release of the last portion of the Parihaka Maori prisoners.
Oct. 26, 1880.—Sir Francis Dillon Bell appointed Agent-General.
Nov. 29, 1880.—Arrival of Governor Sir A. H. Gordon, G.C.M.G.
April 29, 1881.—“Tararua,” steamer, wrecked; 130 lives lost.
June 26, 1881.—Severe earthquakes in Wellington.
Nov. 5, 1881.—March of force of Constabulary and Volunteers on Parihaka, and arrest of Te Whiti and Tohu, without bloodshed.
Feb. 15, 1882.—First shipment of frozen meat made from Port Chalmers. (See Year-book, 1893, p. 192.)
April 21, 1882.—Resignation (during the recess) of the Hon. J. Hall's Ministry, and its reconstruction under the premiership of the Hon. F. Whitaker, M.L.C.
June 23, 1882.—Departure of Governor Sir A. H. Gordon.
June 24, 1882.—Assumption of the Government by Sir J. Prendergast, Chief Justice.
Jan. 20, 1883.—Arrival of Governor Sir W. F. D. Jervois, G.C.M.G., C.B.
Jan. 26, 1883.—A direct line of steam-communication between England and New Zealand inaugurated by the New Zealand Shipping Company.
Feb. 13, 1883.—Proclamation of amnesty to Maori political offenders.
Feb. 19, 1883.—Liberation of Te Whiti and Tohu.
Sept. 25, 1883.—Resignation of the office of Premier and his seat in the Ministry by the Hon. F. Whitaker, and the appointment of the Hon. Major H. A. Atkinson to be Premier, the members of Mr. Whitaker's Ministry being confirmed in their offices.
June 11, 1884.—Defeat of Major Atkinson's Government.
June 27, 1884.—Dissolution of the General Assembly.
Aug. 16, 1884.—Resignation of Major Atkinson's Ministry in consequence of the result of the general election. Formation of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. Robert Stout.
Aug. 20, 1884.—Defeat of Mr. Stout's Ministry by an amendment, expressive of want of confidence, to the Address in Reply being carried.
Aug. 28, 1884.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Major Atkinson.
Aug. 29, 1884.—Defeat of Major Atkinson's Ministry on a vote of want of confidence.
Sept. 3, 1884.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Mr. Robert Stout.
Nov. 8, 1884.—An Act passed to enable certain loans of the New Zealand Government to be converted into inscribed stock and the accrued sinking funds released.
Aug. 1, 1885.—The New Zealand Industrial Exhibition opened at Wellington.
June 10, 1886.—Volcanic eruptions at Tarawera, and destruction of the famed Pink and White Terraces; 101 lives lost.
May 28, 1887.—Defeat of Sir Robert Stout's Ministry.
July 15, 1887.—Dissolution of the General Assembly, after prorogation, on the 10th June.
July 21, 1887.—A Proclamation issued declaring the Kermadec Islands to be annexed to and form part of the Colony of New Zealand.
Aug. 17, 1887.—Kermadec Group annexed to New Zealand. Flag hoisted and proclamation read at Sunday Island.
Oct. 8, 1887.—Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of Major H. A. Atkinson, Sir Robert Stout's Ministry having resigned in consequence of the result of the election.
Dec. 19, 1887.—An Act passed to reduce the number of members of the House of Representatives, after the expiration of the General Assembly then sitting, to seventy-four, including four Maori representatives.
Dec. 23, 1887.—The Australian Naval Defence Act, being an Act to provide for the establishment of an additional naval force on the Australian station, at the joint charge of the Imperial and the several Colonial Governments, was passed by the New Zealand Legislature.
Oct. 27, 1888.—Formal Proclamation of British Protectorate of Cook group of islands, by Captain Bourke, R.N., of H.M.S. “Hyacinth.”
Mar. 22, 1889.—Departure of Governor Sir W. F. D. Jervois, G.C.M.G., C.B., from the colony.
Mar. 23, 1889.—Assumption of the Government by Sir James Prendergast.
May 2, 1889.—Arrival of the Earl of Onslow, G.C.M.G.
Sept. 2, 1889.—Electors prohibited by statute from voting in respect of more than one electorate at any election for the House of Representatives.
Nov. 26, 1889.—Opening of South Seas Exhibition, Dunedin.
Dec. 5, 1890.—First election of members of the House of Representatives under a practical manhood suffrage, and on the one-man-one-vote principle.
Jan. 24, 1891.—Notification by Governor of acceptation of resignation (during the recess) of the Hon. Sir H. A. Atkinson's Ministry. Appointment of a Ministry under the premiership of the Hon. John Ballance.
April 22, 1891.—Proclamation by Governor of New Zealand to inhabitants at Rarotonga of appointment of British Resident for the Protectorate of the Cook Islands.
May 25, 1891.—Adhesion of Australia to Postal Union.
Aug. 19, 1891.—Labour-laws: Passing of Employers' Liability Act 1882 Amendment Act
Aug. 29, 1891.—Labour-laws: Passing of Truck Act, to prohibit payment of wages in goods or otherwise than in money.
Sept. 8, 1891.—Passing of Land and Income Assessment Act for purposes of taxation, and repeal of property-tax.
Sept. 21, 1891.—Labour laws: Passing of an Act for supervising and regulating of factories and workrooms. [Repealed by Act of 1894.]
Jan. 19, 1892.—Electoral districts of the colony based on population as ascertained by the results of the census of 1891 proclaimed.
Feb. 2, 1892.—Departure of Governor the Earl of Onslow.
Feb. 25, 1892.—Assumption of the Government by Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice.
June 7, 1892.—Arrival of Governor the Earl of Glasgow, G.C.M.G.
June 28, 1892.—Death of Sir H. A. Atkinson, K.C.M.G., Speaker of the Legislative Council, and previously four times Premier.
Oct. 1, 1892.—Labour-laws: Passing of Contractors' and Workmen's Lien Act.
Oct. 8, 1892.—Passing of Dairy Industry Act. [Repealed by Act of 1894.]
Oct. 11, 1892.—Passing of first Land-tax and Income-tax Act on the basis of the Assessment Act of previous year.
Oct. 11, 1892.—“Land Act, 1892”: Lease in Perpetuity without revaluation system introduced: occupation with right of purchase: optional method of selection: small farms associations.
Oct. 8, 1892.—“Land for Settlements Act, 1892,” authorising purchase of lands from individuals for purposes of subdivision. [Repealed by Act of 1894. See post.]
April 19, 1893.—Cheviot Estate taken over by Government under the Land and Income Assessment Act.
April 27, 1893.—Death of Hon. John Ballance, Premier of New Zealand.
May 1, 1893.—Resignation of the Ministry in consequence of the death of the Hon. John Ballance, and appointment of a new Ministry under the premiership of the Hon. R. J. Seddon.
June 23, 1893.—Death of Sir William Fox, K.C.M.G., four times Premier of New Zealand.
Sept. 2, 1893.—Passing of Bank-note Issue Act, to make bank-notes a first charge on assets and to enable the Government to declare them to be a legal tender, &c.
Sept. 8, 1893.—The Legislative Council of New Zealand passed, by a majority of two, the Bill conferring the franchise on women.
Sept. 14, 1893.—Banks and Bankers Act Amendment Act passed, to permit of increase of capital by issue of new shares.
Sept. 19, 1893.—“The Electoral Act, 1893,” extending franchise to women.
Oct. 2, 1893.—Alcoholic Liquors Sale Control Act passed: New licenses to be granted subject to the votes of the electors: reduction or abolition of licenses if desired.
Oct. 6, 1893.—Passing of “Criminal Code Act, 1893.”
Oct. 6, 1893.—Labour-laws: Passing of “Workmen's Wages Act, 1893.”
Oct. 6, 1893.—Native Land Purchase and Acquisition Act.
Oct. 20, 1893.—Sir James Prendergast appointed temporarily Deputy of the Governor.
Nov. 28, 1893.—A general election took place, being the first occasion on which women exercised the franchise.
Dec. 28, 1893.—Death of Right Rev. Dr. Henry John Chitty Harper, formerly Bishop of Christchurch and Primate of New Zealand.
Mar. 19, 1894.—Sir James Prendergast appointed temporarily Deputy of the Governor.
June 30, 1894.—Passing of Act to extend operation of Bank-note Issue Act, and another Act to control the transfer of bank shares.
June 30, 1894.—“Bank of New Zealand Share Guarantee Act, 1894,” to guarantee special issue of shares to amount of £2,000,000, and purchase of Assets Estates Company by Assets Board. [Amended on July 20.]
July 20, 1894.—Passing of an Act to limit number of bank directors and power of shareholders to transfer their shares.
Aug. 21, 1894.—Labour-laws: Passing of Conspiracy Law Amendment.
Aug. 31, 1894.—Labour-laws: Passing of an Act to encourage the formation of industrial unions and associations, and to facilitate the settlement of industrial disputes by conciliation and arbitration.
Oct. 18, 1894.—“New Zealand Consols Act, 1894.”
Oct. 18, 1894.—“Government Advances to Settlers Act, 1894,” for relief of settlers burdened by high charges of interest, &c.
Oct. 18, 1894.—Passing of “Land for Settlements Act, 1894,” authorising acquisition of private lands for purposes of settlement, with compulsory powers, and repealing Act of 1892; also “Lands Improvement and Native Lands Acquisition Act, 1894.”
Oct. 18, 1894.—Labour-laws: Passing of “Shops and Shop-assistants Act, 1894,” for limiting hours of business in shops.
Oct. 23, 1894.—Passing of “Banking Act, 1894.”
Oct. 23, 1894.—Dairy Industry Act, to regulate manufacture of butter and cheese, with inspection and grading for export, and provide for purity of milk.
Oct. 28, 1894.—Wreck of s.s. “Wairarapa” at Great Barrier Island; 135 lives lost.
Mar. 29, 1895.—Death of Right Reverend Andrew Burn Suter, D.D., formerly Bishop of Nelson, and Primate of New Zealand.
May 27, 1895.—Government assumed management of the Midland Railway.
Aug. 3, 1895.—Death of C. W. Richmond, Puisne Judge of Wellington.
Aug. 20, 1895.—Trustees cemeteries authorised to provide for cremation of dead.
Sept. 4, 1895.—“Bank of New Zealand and Banking Act, 1895,” providing for writing off paid-up capital with proceeds of first call on reserve liability. Also for new capital and Assets Realisation Board, &c. Also to purchase business of any other bank.
Sept. 20, 1895.—Labour-laws: Passing of an Act to regulate attachment of wages.
Sept. 20, 1895.—Labour-laws: Passing of Servants' Registry Office Act.
Sept. 20, 1895.—“Family Homes Protection Act, 1895,” to secure homes for the people and to prevent them from mortgage or sale for debt.
Oct. 18, 1895.—Amended tariff passed.
Oct. 31, 1895.—Bank of New Zealand and Banking Act Amendment Act: Sale of Colonial Bank business to Bank of New Zealand.
Dec. 20, 1895.—Appointment of Sir P. A. Buckley, K.C.M.G., as a Judge of Supreme Court.
Jan. 10, 1896.—Hon. W. P. Reeves appointed Agent-General in London.
Mar. 26, 1896.—Brunner Mine explosion; sixty-seven deaths.
April 12, 1896.—General census of colony taken for Sunday night.
May 18, 1896.—Death of Sir Patrick Buckley, K.C.M.G.
July 11, 1896.—Appointment of Mr. W. B. Edwards as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
July 19, 1896.—Death of Hon. Robert Pharazyn, M.L.C.
Aug. 2, 1896.—Death of James Edward FitzGerald, C.M.G., Controller and Auditor-General.
Oct. 16, 1896.—Land for Settlements Act amended: Special provision made for disposal of highly improved lands acquired: preference given to landless people: Boards may select applicants, &c.
Oct. 17, 1896.—Alteration of franchise by abolition of non-residential or property qualification.
Oct. 17, 1896.—Government Valuation of Land Act passed.
Dec. 4, 1896.—General election of members of House of Representatives for the new districts as fixed by the Representation Commissioners on basis of Census, 1896.
Feb. 6, 1897.—Departure of the Earl of Glasgow, G.C.M.G.
Feb. 8, 1897—Sir James Prendergast Administrator of Government.
June 22, 1897.—Diamond Jubilee of reign of Her Majesty Queen Victoria. Hon. R. J. Seddon, Premier of New Zealand, called to Privy Council, on occasion of his visit to England with contingent New Zealand Forces.
July 29, 1897.—Wreck of s.s. “Tasmania” at Mahia Peninsula, ten lives lost.
Aug. 10, 1897.—The Earl of Ranfurly assumed office as Governor.
Dec. 22, 1897.—Act to establish at Wellington the Victoria College, in connection with the New Zealand University.
July 15, 1898.—Hon. Sir Francis Dillon Bell, K.C.M.G., C.B., died.
1898.—Death of Sir George Grey, K.C.B.
1898.—Death of Bishop Selwyn, of Melanesia.
Oct. 15, 1898.—The Municipal Franchise Reform Act passed.
1898.—The Divorce Bill passed both Houses. Her Majesty's assent thereto gazetted 13th April, 1899.
Nov. 1, 1898.—An Act to provide for Old-age Pensions passed.
Feb. 10, 1899.—Rev. William Colenso died at Napier.
March 13, 1899.—Sir Julius Vogel, K.C.M.G., died.
April, 1899.—Victoria University College opened in Wellington.
May 25, 1899.—Resignation of Sir James Prendergast, Chief Justice.
June 1, 1899.—“The Divorce Act, 1898” (assented to by Her Majesty the Queen), came into operation.
June 22, 1899.—Sir Robert Stout, K.C.M.G., appointed Chief Justice.
Oct. 19, 1899.—Act passed constituting Labour Day. The second Wednesday in the month of October in each year to be a public holiday.
Oct. 21, 1899.—N.Z. Contingent (the first) consisting of 215 officers and men, left in s.s. “Waiwera” for Algoa Bay to assist the British in the Transvaal war.
Nov. 16, 1899.—General Assembly dissolved.
Dec. 6, 1899.—General Election of Members of House of Representatives.
Jan. 21, 1900.—The Second N.Z. Contingent (258 officers and men) left for South Africa in s.s. “Waiwera.”
Feb. 5, 1900.—Hon. Thomas Dick died.
Feb. 17, 1900.—The Third N.Z. Contingent (264 officers and men) left for South Africa in s.s. “Knight Templar.”
March 24 and 31, 1900.—The Fourth and Fifth Contingents (1,060 officers and men) left for South Africa in s.s.'s “Monowai,” “Gymeric,” “Waimate,” and “Maori.”
June 28, 1900.—“Bubonic Plague Prevention Act, 1900,” passed.
Aug. 8, 1900.—“Immigration Restriction Act, 1899,” assented to by Her Majesty in Council, came into operation.
Oct. 13, 1900.—Public Health Act passed.
Oct. 18, 1900.—The Maori Councils Act passed.
Oct. 20, 1900.—“The Representation Act, 1900,” passed, increasing number of European representatives to seventy-six.
Dec. 29, 1900.—Hon. Sir James Prendergast, Kt., appointed Deputy-Governor.
Jan. 1, 1901.—Universal penny postage adopted by New Zealand.
Jan. 22, 1901.—Queen Victoria died.
Jan. 28, 1901.—Accession of King Edward VII. proclaimed in New Zealand.
Jan. 30, 1901.—Sixth N.Z. Contingent (578 officers and men) sailed for South Africa in s.s. “Cornwall.”
Feb. 21, 1901.—Appointment of Mr. Theo. Cooper as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
March 31, 1901.—General census of the Colony taken for Sunday night.
April 6, 1901.—Seventh N.Z. Contingent (600 officers and men, roughriders) sailed for South Africa, per s.s. “Gulf of Taranto.”
May 22, 1901.—Deceased Husband's Brother Marriage Act came into operation after Royal assent.
June 10, 1901.—Duke and Duchess of Cornwall and York arrived in New Zealand.
June 10, 1901.—Boundaries of Colony extended to include Cook and other Pacific Islands.
Aug. 6, 1901.—Sir John McKenzie, K.C.M.G., died.
Nov. 7, 1901.—State Coal-mines Act passed.
Feb. 1, 1902.—North Island division of the Eighth N.Z. Contingent sailed from Auckland for South Africa per s.s. “Surrey.”
Feb. 8, 1902.—South Island division of the Eighth Contingent sailed from Lyttelton per s.s. “Cornwall.”
March 12, 1902. South Island division of the Ninth N.Z. Contingent sailed from Port Chalmers for South Africa per s.s. “Kent.”
March 19, 1902.—North Island division of the Ninth Contingent sailed from Auckland per s.s. “Devon.”
April 14, 1902.—North Island division of the Tenth N.Z. Contingent sailed from Auckland for South Africa per s.s. “Drayton Grange.”
April 14, 1902.—Right Hon. R. J. Seddon sailed for London to attend Conference of Colonial Premiers, and to represent New Zealand at His Majesty the King's Coronation.
April 19, 1902.—South Island division of the Tenth Contingent sailed for South Africa per s.s. “Norfolk.”
June 26, 1902.—Death of Most Rev. Bishop William Garden Cowie, Primate of New Zealand.
Aug. 9, 1902.—Celebration in New Zealand on the occasion of the Coronation of His Majesty King Edward VII.
Aug. 1902.—Return of N.Z. troopers from South Africa (Eighth Contingent left Durban 5th July; Ninth, 9th July; Tenth, 15th July).
Nov. 12, 1902.—General Assembly dissolved.
Nov. 25, 1902.—General Election of Members of House of Representatives.
Dec. 8, 1902.—Pacific (all red) Cable-service opened for international business.
Dec. 31, 1902.—Export of frozen-meat for year valued at £2,718,763.
Dec. 31, 1902.—Export butter and cheese for year valued at £1,369,341.
Feb. 8, 1903.—Hon. W. Rolleston died.
Mar. 16, 1903.—Sir George Whitmore, K.C.M.G., died.
May 22, 1903.—Mahuta Tawhiao Potatau te Wherowhero (formerly known as the Maori King), summoned to the Legislative Council, and sworn in as a member of the Executive Council of the Colony.
May 24, 1903.—Empire Day proclaimed in New Zealand (anniversary of birth of late Queen Victoria).
- Development of Banking 447
- Loans for 482, 562
- Table showing how repaid 566
- Titles eligible 483, 563
- Valuation-fees 565
- Ages at Death Average 418
- Average, of Persons married 410
- Of Prisoners 187
- Of the People 137
- Acreage under Wheat, Oats, &c., in Provincial Districts 373
- Barley 381, 593
- Cape Barley and Winter Oats 596
- Cattle 394, 600
- Cereals 373, 590
- Consumption of Wheat 380
- Cost of growing Oats 593
- Cost of working a Farm 597
- Dairy Industry, The 601
- Dairy Stock 395, 601
- Fertilisers 598
- Fruit Industry, The 604
- Gardens and Orchards 383
- Grass-seeds 383, 595
- Hops 382
- Horses 396, 598
- Lambing Returns, Averages 394
- Mangolds and Carrots 594
- Maize 381
- Oats 381, 593
- Pigs 397, 603
- Potatoes 382, 593
- Poultry 603
- Rape 594
- Root-crops 593
- Sheep 392, 598
- Tree-planting 605
- Turnips and Rape 382, 594
- Wheat-crop of Australian States 379
- Wheat-crop of the World 379
- Wheat, Estimated Surplus of 380
- Wheat for Threshing 378
- Wheat held by Farmers, 1902 378
- Wheat, Seed per Acre 593
- Wheat, Yield per Acre 373, 592
- Live-Stock 389, 598
- Dates of certain Principal Events in the History of New Zealand 717
- Of Cook Islands 7
- Of North, Middle, Stewart, Chatham, and other Islands 6
- Of United Kingdom compared with New Zealand 8
- Compared with European Countries 7
- Chinese 107
- Departures, how Numbers ascertained 107
- Lunatic 439
- Orphan 430
- Exports 331
- General description 650
- Imports 300
- Meteorology 441
- Population 114
- Value of Property 524
- Vital Statistics 405, 413
- Graving-dock Charges 61
- Debt of 501
- Friendly Societies in 452
- Mineral Production of 361
- Railways in 355
- Live-Stock in 391
- Oat-crop of 355
- Population 123
- Taxation in 490
- Trade 347
- Wheat-crop of 379
- Petitions, &c., Six Years 178
- Transactions in 1901 177
- Advances and Discounts 448
- In all Classes of Banks, Average per Head 452
- Assets and Liabilities 447
- In all Classes of Banks, Average per Head 452
- Deposits 447, 449
- In all Classes of Banks, Average per Head 452
- Notes in Circulation, &c. 447
- Post-Office Savings 449
- Deposits, Withdrawals, Open Accounts, Amounts to Credit 449
- Securities held 450
- Deposits, Withdrawals 451
- Private Savings 451
- Deposits, Withdrawals 451
- Yield in Bushels 373
- Export of 329
- Numbers of each Nationality and Increase 129
- Illegitimate 403
- Illegitimacy in Australasia 493
- Legitimation Act 401
- Of Twins 402
- Proportion to Population, 1882–1902 399
- To Marriages, Proportion of 490
- Expenditure of 190
- Auckland, with suburbs 114
- Christchurch, with suburbs 114
- Dunedin, with suburbs 114
- Wellington, with suburbs 114
- In Colony 110
- Auckland, with suburbs 114
- Christchurch, with suburbs 114
- Dunedin, with suburbs 114
- Wellington, with suburbs 114
- Indebtedness of 202
- Population of 110
- Rateable Value of Property in 206
- Revenue of 199
- Value of Land and Improvements in 524
- Amounts deposited with 452
- Income, Assets, Liabilities, Reserve Funds 432
- Export to United Kingdom, Fourteen Years 330
- Grading 602
- Industry 601
- Decennial Return 432
- Part of Body affected 433
- Proportion of Deaths per 10,000 living, 1893–1902 432
- In Provincial Districts 395
- At Four Centres 415
- Cancer 431
- Developmental Diseases, 436
- Dietetic Diseases 427
- Local Diseases 436
- Measles 425
- Old Age 436
- Parasitic Diseases 427
- Phthisis 428
- Proportion of Deaths from each 421
- Typhoid Fever 425
- Violence 437
- Half-castes 136
- Immigration and Emigration of 107
- Number in Colony 103
- Exports 331
- General Description 700
- Imports 300
- Population 114
- Value of Property 525
- Vital Statistics 405, 414
- Sunshine in New Zealand 414
- Temperature in New Zealand, Australia, and other British Possessions 441 446
- Classes of, in New Zealand 370
- Consumption of 367
- Export of 367
- Found in Colony, Analysis of 369
- Import of 367
- Output of 367
- Crown Agents for the 28
- Population of the 103
- Bachelors and Spinsters 134
- Divorced Persons 135
- Husbands and Wives 135
- Marriage-rates in Australasia 135
- Widowers and Widows 135
- Government 17
- For Drunkenness 183
- Summary 181
- Education 639
- Future Trade Prospects 639
- Nine Island 636
- Population 104
- Management of Local Governing Bodies 200
- Railways 353
- Working a Farm in New Zealand 597
- Legislative, Roll of Members of the 35
- Successive Speakers of the Legislative 25
- Land under Cultivation in 375
- Value of Land and Improvements in 521, 526
- Civil Cases, Supreme and District 177
- Charges for Offences before 180
- Committals 181
- Punishment on Summary Convictions (five years) 182
- Summary Convictions before 181
- Divorce and Separation 177
- Charges for Offences before 180
- Committals 181
- Punishment on Summary Convictions (five years) 182
- Summary Convictions before 181
- Magistrates', Civil Cases 177
- Charges for Offences before 180
- Committals 181
- Punishment on Summary Convictions (five years) 182
- Summary Convictions before 181
- Sentences, Supreme and District (five years) 182
- Supreme and District, Convictions 181
- Mode of acquiring 556
- Agriculture.
- Revenue from 315
- Proportion of Taxation in Australasia derived from, 1901–2 490
- Produce, Export of 330
- Stock 395, 601
- Causes of 420
- Congenital Defects 436
- Nervous Diseases 436
- From Phthisis 428
- From Typhoid Fever 425
- In Four Principal Cities 414
- In Principal Cities of Australasia 418
- At various Age-periods 418
- Inquests on 190
- Number of, in 1902 412
- Of Infants 419
- Of Infants to every 1,000 Births 419
- Violent 437
- Of Local Bodies 202
- Duties Payable on 457
- Administration; Artillery, New Zealand Royal; Bearer Corps, Volunteers; Cadet Corps, Volunteers; Capitation; Cycle Corps, Volunteers; Defence Rifle Clubs; Engineers, New Zealand Royal; Engineers, Volunteers; Enrolment, &c.; Expenditure and Maintenance; Field Artillery, Volunteers; Instructors; Militia and Volunteer Districts; Mounted Rifles, Volunteers; Naval and Garrison Artillery, Volunteers; Arms, &c.; Rifle Corps, Volunteers; Submarine Mining Engineers, Volunteers 57
- Grounds for 178
- Persons convicted of 183
- Exports 331
- General Description 707
- Imports 300
- Meteorology 443
- Population 114
- Value of Property 525
- Vital Statistics 405, 414
- Wages 465–467
- Public (Government) Schools 157
- School of Engineering and Technical Science 159
- Technical 158
- University, New Zealand 166
- Victoria College 167
- Improvement in 152
- In Cook and other Islands 639
- Representation.
- Immigration and Emigration.
- Duties Payable on 457
- Charges of Public Debt 497
- General Government 474
- Local Bodies 199
- On Railways 353
- Out of Public Works Fund by General Government 479
- Butter and Cheese to United Kingdom, for Fourteen Years 330
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Coal 321, 367
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Details of all Exports 332
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- From different Ports 331
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- From North and Middle Islands 324
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- From United Kingdom to various Countries and Colonies 349
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Frozen Meat 328
- Quantity, Twenty-one Years 328
- Value, Fifteen Years 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Gold, Silver, and other Minerals to 31st December, 1902 360
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Gold, 1902 329
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Grain 329
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Home Produce, Value of 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Increase and Decrease on Principal Articles 322
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Kauri-gum 331
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Of Australasia, 1901 347
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Phormium 331
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Quantities of Principal Articles, 1901 and 1902 321
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Rabbitskins 327
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Re-exports, exclusive of Specie 323
- Of New South Wales compared with New Zealand 324
- Sheepskins and Pelts 328
- Tallow 328
- To United States 345
- Value of principal Articles of New Zealand Produce 319
- Wool, Fifteen Years 326
- Manufactories and Works.
- Of the North Island 8
- Municipal 204
- In Australasia 452
- Lodges, &c., Assets, Receipts of Sick and Funeral Funds, Expenditure, Sick Pay, Management Expenses 452
- Drying 604
- Industry, The 604
- Coal-mining 366
- Composition of 369
- Consumption of 367
- Output of 370
- Total Quantity and Value entered for Exportation, 31st March, 1903 363
- Gold exported 329
- Total Quantity and Value entered for Exportation, 31st March, 1903 363
- Gold produced in Australia 364
- Gold production of the World 364
- Remarks on 361
- Advances authorised 482
- Business of Office 483, 562
- Conditions of Advance 483, 564
- Costs and Fees 565, 569
- Fixed Loans 482, 565
- Half-yearly Repayments, Table of 566
- Instalments of Loans payable at Post-offices 570
- Instalment Mortgages 565
- Officials bound to Secrecy 570
- Terms of Loans 565
- Titles eligible for Advances 563
- Capital Values, North and South Islands 520
- Comparison of Capital Values, 1891 and 1903 520
- Cost of making Valuation, How Borne 519, 575
- Increase in Values 520
- Objection, Right of 519
- Purposes for which Valuation-rolls used 519, 575
- Values in Boroughs 524
- Values in Counties 521
- Grown in each Provincial District 373
- In Australasia, 1901–2 384
- Sown, per Acre 383
- Auckland Docks 60
- Lyttelton Dock and Patent Slip 63
- Port Chalmers Dock 64
- Wellington Patent Slip 62
- Export of 331
- Price of 331
- In Provincial Districts 396
- Accommodation and Indoor Patients 438
- General Management 437
- Number of Districts 437
- Revenues of Boards, how raised 437
- Thermal Springs
- Speakers of the 26
- Of Chinese 107
- Each Australian State, 1901 347
- Beer, Spirits, and Wine, Consumption of 297
- South Africa 346
- United Kingdom 299
- United Kingdom to Australasia 349
- United States, Ten Years 345
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Clothing, &c. 293
- South Africa 346
- United Kingdom 299
- United Kingdom to Australasia 349
- United States, Ten Years 345
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Coal 294, 367
- South Africa 346
- United Kingdom 299
- United Kingdom to Australasia 349
- United States, Ten Years 345
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Free and Dutiable Imports, Value of 295
- South Africa 346
- United Kingdom 299
- United Kingdom to Australasia 349
- United States, Ten Years 345
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- From different Countries, 1901 and 1902, Values of 298
- South Africa 346
- United Kingdom 299
- United Kingdom to Australasia 349
- United States, Ten Years 345
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Inclusive and exclusive of Specie, Fifteen Years 291
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Into Australasia 347
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Per Head of Population 292
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Spirits 297
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Sugar and Tea, Imports of 296
- Consumption of, per Head of Population 296
- Tobacco, Consumption of 298
- Trade per Head of Population, Australasia 348
- Exemptions 571, 572
- Rates of Tax 574
- Yield of Tax 574
- Growth of Amount Paid 489
- Of Local Bodies 199–203
- For Twenty-two Years 196
- To Persons outside Colony 203
- Manufactories and Works.
- Fire 190
- Companies in New Zealand 455
- Area of Australasia 7
- Colony of New Zealand 8
- Middle Island 11
- Boundaries and Area of New Zealand 5
- Middle Island 11
- Colonisation 3
- Middle Island 11
- Constitution 16
- Middle Island 11
- Cook Strait 11
- Middle Island 11
- Discovery and Early Settlement 2
- Middle Island 11
- Foveaux Strait 13
- Middle Island 11
- Glaciers in Middle Island 11
- Middle Island 11
- Government 17
- Middle Island 11
- Maoris, The 4
- Middle Island 11
- Outlying Islands 14
- Middle Island 11
- Physical Features of the North Island 8
- Middle Island 11
- Public Works 19
- Seat of Government 18
- Average Price of 331
- Quantities and Values exported 331
- In New Zealand. (See Year-book, 1894, p. 362.)
- Prices of Provisions, Live-stock, &c., 1902 463, 464
- Wages, Average Rates of 465–467
- Acts of Parliament composing 468
- Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration 469
- Coal-mines Act 471
- Conspiracy Law 471
- Factories Act 469
- Master and Apprentice 471
- Mining 471
- Public Contracts Act 471
- Servants' Registry Offices 470
- Shipping Acts 471
- Shops and Shop-assistants 469
- Trades-Union Act 471
- Wages Attachment 471
- Workers' Compensation for Accidents 470
- Remarks on 468
- Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration 469
- Coal-mines Act 471
- Conspiracy Law 471
- Factories Act 469
- Master and Apprentice 471
- Mining 471
- Public Contracts Act 471
- Servants' Registry Offices 470
- Shipping Acts 471
- Shops and Shop-assistants 469
- Trades-Union Act 471
- Wages Attachment 471
- Workers' Compensation for Accidents 470
- Acreage of, under Crop 374
- Graduated 487, 572
- And Income-tax 487, 570
- Graduated 487, 572
- Crown, open for Selection.
- Graduated 487, 572
- Fit for Agriculture and Pasture 9
- Graduated 487, 572
- Government Valuation of 519, 575
- Graduated 487, 572
- Grass-sown 383
- Graduated 487, 572
- Held as Pastoral Runs 508
- Graduated 487, 572
- Held as Small Grazing-runs 508
- Graduated 487, 572
- Held under Pastoral and Miscellaneous Leases 508
- Graduated 487, 572
- Holdings in Provincial Districts 387
- Graduated 487, 572
- Holdings taken up 385
- Graduated 487, 572
- Holdings taken up, Sizes of 386
- Graduated 487, 572
- Improved Farm Settlements 508, 559
- Graduated 487, 572
- Occupation of 385, 558
- Graduated 487, 572
- On Perpetual Lease, Lease in Perpetuity, and Occupation with Right of Purchase 508
- Graduated 487, 572
- Rating on Unimproved Value 576
- Graduated 487, 572
- Revenue from 572
- Graduated 487, 572
- Sold for Cash 512
- Graduated 487, 572
- Sold on Deferred Payments 508
- Graduated 487, 572
- Taken up under various Tenures, Eleven years 509
- Graduated 487, 572
- Taken up in each Land District 511
- Graduated 487, 572
- Tax 487, 571
- Graduated 487, 572
- Village Settlements, Land held 508, 551
- Village Settlements, sold on Deferred Payments, &c. 508
- Estates offered for Selection during Year ended 31st March, 1903 514
- Transactions under 513
- Administration 556
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Classification of Lands, &c. 556
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Grazing-runs, Small 560
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Improved-farm Settlements 559
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Land Districts and Principal Land Offices 556
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Mode of Acquiring Crown Lands 556
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Optional System of Selection 557
- Freehold Tenure 557
- Leases in Perpetuity 558
- Occupation with Right of Purchase 557
- Pastoral Runs 560
- Residence and Improvements 558
- Special-settlement Associations 559
- Survey Charges on Unsurveyed Lands 561
- Village-homestead Settlements 559
- Native, Purchase of, by Government 554
- Survey Charges on Unsurveyed 561
- In Boroughs 524
- In Colony 520
- In Counties 521
- In Local Districts 526
- Native Members of the 17
- Roll of Members of the 33
- Number and Fees paid 235
- Proportion to Population 235
- Alcoholic Liquors Sale Control Act 237
- Annual Fees 236
- Revenue from Licenses 235
- Average Prices of 463
- Export of 332
- In Australasia 391
- In each County 389
- Average Consumption per Head of Foods, &c. (See Year-book, 1898, p. 289.)
- In various Countries 462
- Expenditure, 1902–3 478
- Public Debt 491
- For Advances to Settlers 482
- Public Debt 491
- General Government
- Public Debt 491
- Of Local Bodies, Outstanding, at various Rates of Interest 203
- Of Local Bodies, Net Indebtedness 202
- “Local Bodies' Loans Act, 1901” 204
- Cost of Management 200
- Expenditure of 199–201
- Indebtedness: Twenty-two Years 196
- Number of 195
- Outstanding Loans at various Rates of Interest 203
- Rates collected in Twenty-two Years 196
- Revenue and Expenditure of Boroughs, Counties, Drainage Board, Harbour Boards, River Boards, Road Boards, Town Boards 199–201
- Taxation by 197
- Aerated-water and Cordial 267
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Agricultural Implement 275
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Ammunition 275
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Bacon-curing 260
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Biscuit 263
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Boot and Shoe 283
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Breweries 265
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Brick, Tile, and Pottery 272
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Brush and Broom 279
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Butter and Cheese 261
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Chemical 281
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Clothing and Waterproof 282
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Coach Building and Painting 277
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Coffee and Spice 268
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Colonial Wine 267
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Comparison of, 1896 and 1901 243
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Comparison, Number of Hands employed, 1891, 1896, 1901 257
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Comparison, Value of Product, 1885, 1890, 1895, and 1900 256
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Confectionery 264
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Cooperages 269
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Cycle 278
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Details of Principal Industries 249
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Fellmongering, Tanning, Currying, and Wool-scouring 279
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Fish Curing and Preserving 260
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Fruit-preserving and Jam-making 263
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Furniture 281
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Gasworks 271
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Grain-mills 262
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Hosiery 284
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Increase in Value of Output, 1895–1900 242
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Industries in Provincial Districts 245
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Iron and Brass Foundries, Boiler and Range Making, with Engineering 274
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Lime and Cement 272
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Malthouses 266
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Meat Freezing and Preserving, with Boiling-down 258
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Mines and Quarries 287
- Collieries 289
- Gold-dredging 288
- Gold-quartz Mining and Crushing 287
- Hydraulic Gold-mining 288
- Phormium 285
- Printing and Bookbinding 276
- Rope and Twine 285
- Saddlery and Harness 278
- Sail, Tent, and Oilskin 280
- Sauce and Pickle 268
- Sawmills and Sash and Door 270
- Ship and Boat Building 280
- Soap and Candle 269
- Summarised Results 243
- Tinware 274
- Woollen-mills 281
- Charged with Offences 185
- Children attending Schools 170
- Contribute towards Revenue 489
- Convicted of Offences, 1891–1901 185
- Distribution of 103
- Enumeration of 191
- Half-castes 193
- Population a Last Census 192
- Representation 17, 34, 222, 232
- Sociology 641
- Decrees for Dissolution of 179
- Decrees for Judicial Separation 179
- Rates in New Zealand, Australian States, and European Countries 407
- Ages at which Marriage may be contracted 411
- Ages of Persons Married 410
- Of Aborigines 408
- Percentage of Persons under 21 Years 410
- Proportion by each Denomination 409
- Proportion of each Sex signing Register by Mark 410
- Average Yield of Butter from 601
- Average Yield per Cow 601
- Thermal-springs Districts.
- Remarks on 361
- Amounts borrowed at various rates of interest 454
- Egmont 10
- Ruapehu 10
- Tongariro 9
- Consumption per head. (See Year-book, 1898, p. 289.)
- Posted 356
- Abolition of Provincial Governments in 17
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- “Accident Insurance Act, 1899” 456
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Area of, Boundaries and 5
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Arrival of Missionaries in 3
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Captain Cook's Visits to 2
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Colonisation of 3
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Colony divided into Six Provinces 17
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Company 3
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Consols 484
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- County Government in 17
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Cook Islands, Inclusion of 5
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Discovery and Early Settlement of 2
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Electoral Division of 222
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- General Assembly of 32
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Government Advances to Settlers 562
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Governor of 30
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Governors of, Successive 19
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Land System of 549
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Lieutenant Hanson's Visit to 3
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Made a Separate Colony 4
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Manufactories and Works 241
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Newspapers 79
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Premiers of 25
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Provincial Governments abolished 17
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Rainfall in 441
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Representative Government granted in 16
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Settlement at Port Nicholson 3
- Canterbury 4
- Nelson 4
- New Plymouth 4
- Otago 4
- Sovereignty of Queen proclaimed 3
- Stock, Quotations of 500
- Surville, and Marion du Fresne, Visits of 2
- Tasman's Visit 2
- Temperature 441
- Treaty of Waitangi 4
- University of 166
- Currency of Deposits 585
- Deposits in 484
- Forms of Application 586
- Rate of Interest 585
- Regulations 585
- The purpose of 585
- Acreage and Actual Yield in Provincial Districts 373
- Export of 329
- Charges for, before Magistrates' Courts 180
- Convicted before Supreme and District Courts 185
- Summarily convicted 185
- Committals for 181
- Convicted before Supreme and District Courts 185
- Summarily convicted 185
- Convictions for 181
- Convicted before Supreme and District Courts 185
- Summarily convicted 185
- Maoris charged with 185
- Convicted before Supreme and District Courts 185
- Summarily convicted 185
- Amount of Pension 580
- Applications, how made 580
- Deductions 580
- How, when, and where paid 580
- Number granted to 31st March, 1903 581
- Qualifications 578
- Value of Imports by 300
- Lands held under 508, 560
- Receipts from 508
- Tenants of 508
- Export of 331
- Deaths from, 1893 to 1902 428
- Middle Island 11
- In Counties 389
- In Provincial Districts 398
- Arrivals and Departures 106
- From and to United Kingdom 106
- Of Chinese 107
- Census, 1901 108
- Chinese 103
- Cook and other Islands 104
- European 103
- Increase in each Quarter, 1902 105
- In adjacent Islands 122
- In Principal Cities and Suburbs 114
- In Provincial Districts 110
- Maori 191
- Of Australasia 123
- Of Boroughs 110
- Of Capital City 114
- Of Counties 110
- Of Town Districts and Small Centres 115
- Average Number of Days within which Mails from London delivered 358
- Books and Parcels, &c. 356
- Increase of Correspondence 356
- Letters posted, per Head of Population 356
- Mail-service, England and New Zealand, Cost of 357
- Money-orders 357
- Newspapers 356
- Parcels 356
- Postal Notes 357
- Post-cards 356
- Savings-banks 449
- Securities 450
- Cost of Growing 594
- Cultivation of 593
- Export of 319, 321
- Yield of 382
- Ages of Distinct, convicted 187
- Birthplaces of 187
- Convicted, Number of 186
- Cost of maintaining 188
- Distinct convicted, Classified 187
- New Zealand-born, convicted, 1901 188
- Previously convicted 186
- Religious Denominations of 187
- Annual Charge 497
- Securities in which invested 499
- Comparison with Past Years 495
- Securities in which invested 499
- Details of Loans 492
- Securities in which invested 499
- Flotation of Loans 500
- Securities in which invested 499
- Increase of 496
- Securities in which invested 499
- Net Indebtedness 495
- Securities in which invested 499
- Of Australasia 501
- Securities in which invested 499
- Purposes of Money composing Debt 502
- Securities in which invested 499
- Rates of Interest on 497
- Securities in which invested 499
- Sinking Fund accrued, Amount of 496
- Securities in which invested 499
- Stock Quotations 500
- Industrial Schools 172
- Secondary Schools, Income and expenditure of 172
- Technical Schools 158
- Number and Value of Estates administered 457
- Expenditure on 478
- Australian States, Miles of, in 355
- Length and Cost 353
- Particulars of Revenue from 354
- Passengers 353
- Profit on Working 354
- Revenue and Expenditure 354
- Train-miles 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Comparison of Traffic, Revenue, and Expenditure for Thirteen Years 353, 354
- Length and Cost 353
- Particulars of Revenue from 354
- Passengers 353
- Profit on Working 354
- Revenue and Expenditure 354
- Train-miles 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Government, Goods and Live-stock carried 353
- Length and Cost 353
- Particulars of Revenue from 354
- Passengers 353
- Profit on Working 354
- Revenue and Expenditure 354
- Train-miles 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- In New Zealand, their History and Progress. (See Year-book, 1894, p. 377.)
- Wellington-Manawatu Railway 354
- Cultivation of 594
- In Road Districts 214
- Town Districts 213
- Method of taking Poll 576
- Ratepayers may demand Poll to be taken 576
- Rating Powers 576
- Result of Polls taken by Local Bodies 577
- System Optional 576
- Numbers of each denomination and increase 125
- Proportion of each denomination, 1881, 1886, 1891, 1896, 1901 124
- Proportion of the sexes in the various denominations 127
- Duties and Functions of Representation Commissions 222
- “Electoral Act, 1902” 18
- Electoral Acts 223
- Electoral Divisions of the Colony 222
- General Election of 1902 223
- Maori Members 232
- Qualifications of Electors, European 18
- Maori 18
- Representation Commissions 222
- Woman's Franchise 18, 223
- Government Railways 354
- Land-tax and Income-tax, Revenue from 487, 489
- Loan Expenditure, 1902–3 479
- Of Boroughs, Counties, Drainage Boards, Harbour Boards, River Boards, Road Boards, and Town Boards 199, 200
- Ordinary Revenue 475
- Ordinary Revenue Expenditure 477
- Territorial Revenue Expenditure 477
- Territorial Revenue 475
- Legislative Council 33
- Rotorua 610
- Te Aroha 626
- Private 451
- Deaf and Dumb 175
- Cost of 173
- Inmates, 1900 and 1901 174
- Industrial 172
- Cost of 173
- Inmates, 1900 and 1901 174
- Engineering 159
- Mines 159
- Native 170
- Primary or Public 157
- Private 168
- Roman Ca 169
- Sunday 155
- Technical 158
- Acquisition of Land under 515
- Estates offered for Selection during Year 1902–1903 514
- Expenditure authorised 552
- Government Aid to Settlers 553
- Preference given to Landless People 553
- Process of Acquisition 552
- Special Provisions for Workmen's Homes 553
- Transactions of Board for Year 1902–1903 513
- In Australasia, 1900–1901 391
- In Colony, Seventeen Years 392
- In Counties 389
- In Provincial Districts, April, 1901 and 1902 393
- Number and Size of Flocks 327, 393
- Numbers in North and Middle Islands, Seventeen Years 392
- Clips, Average Weight of 599
- Grass-seed sown per Acre 383
- Lambing Returns 394
- New Zealand Flock-book 600
- Coastwise, Inwards 352
- Coastwise, Outwards 352
- Inwards and Outwards, Ten Years 351
- Laws 471
- Registered Vessels 352
- Amounts paid for interest and 497
- Securities of 499
- Legislative Council 33
- Land Districts.
- In Counties 375
- New Zealand, compared with Australia 384
- Legislative Council, Successive 25
- Schools.
- Civil Cases 177
- In Australasia 391
- Ministries 24
- Premiers 25
- Judges, Past and Present 21
- By Local Bodies 197
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Deductions and Exemptions under Land- and Income-tax 487, 571, 572
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Growth of Amount paid in Income-tax 489
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Incidence of Land- and Income-tax 487, 571, 572
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Income-tax 488, 572
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Land-tax (ordinary) 487, 571
- Graduated 487, 572
- In Australasia 490
- Per Head in New Zealand, for Ten Years (excluding Maoris) 488
- In Australasia 490
- Proportion derived from Customs, 1902–1903 489
- Rate of, per Head, including Maoris 489
- Rates of Land-tax 487, 574
- Yield of Land and Income-tax 487, 574
- Analysis of Springs 627
- Description of Waters 627
- Agricultural, Art, Engineering and Technical Science 159
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Canterbury Agricultural College 159
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Examinations 160
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Manual and Technical Instruction, 1901 164
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Metallurgy 159
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Remarks on 160
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- School of Engineering and Technical Science 159
- Medicine, Otago 708
- Mines, Otago 159
- Messages transmitted 358
- Miles of Line 358
- Receipts 358
- At different Stations of New Zealand 441–444
- Highest and Lowest in Shade, in New Zealand, the Australian States, and other British Possessions 446
- Hanmer 628
- Rotorua 610
- Te Aroha 626
- Local Bodies.
- Towns, Villages, &c., Populations of 115
- Australasia as Market for Great Britain, Importance of 349
- Shipping.
- External, in Australasia 347
- Shipping.
- Of Australasia, Value of, per Head 348
- Shipping.
- Of Australasia with United Kingdom 349
- Shipping.
- (See Exports.)
- Shipping.
- (See Imports.)
- Shipping.
- (See Shipping.)
- Shipping.
- Of Cook and other Islands 350
- Per Head of Population, Seventeen Years 344
- With Atlantic and Pacific Ports of United States, Ten Years 345
- With Australia 344
- With India 345
- With United Kingdom 344
- Electric Telegraph 358
- Australasian 355
- Cost of 353
- Number of Miles travelled 353
- Revenue and Expenditure for Thirteen Years 354
- Traffic for Thirteen Years 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Mail-services 357
- Australasian 355
- Cost of 353
- Number of Miles travelled 353
- Revenue and Expenditure for Thirteen Years 354
- Traffic for Thirteen Years 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Postal and Electric Telegraph 356
- Australasian 355
- Cost of 353
- Number of Miles travelled 353
- Revenue and Expenditure for Thirteen Years 354
- Traffic for Thirteen Years 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Railways 352
- Australasian 355
- Cost of 353
- Number of Miles travelled 353
- Revenue and Expenditure for Thirteen Years 354
- Traffic for Thirteen Years 353
- Traffic in Local Products for Thirteen Years 353
- Cost of growing 382
- Students 167
- Undergraduates 167
- Calculated from Probate Returns 459
- Of Australasia 460
- Exports 331
- General Description 670
- Imports 300
- Meteorology 442
- Population 114
- Value of Property 524
- Vital Statistics 405, 414
- Acreage and Actual Yield in Provincial Districts 373
- Annual Average, Principal Countries 380
- Area under, and Produce, Thirteen Years 378
- Annual Average, Principal Countries 380
- Consumption of, in New Zealand 380
- Annual Average, Principal Countries 380
- Crops of Australian States 379
- Crop of the World 379
- Export in 1902 329
- Seed Sown per Acre 593
- Yield per Acre 596
- Exported 325
- Production of, Fifteen Years 326
- Proportions of Greasy, Scoured, and Washed Wool exported, Five Years 326
- Used at Local Mills 326
Table of Contents
| Year | Population of European Descent (excluding the Military and their Families.)* | Trade. | Revenue and Expenditure. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imports | Exports. | Revenue from Customs. | Revenue from Land Sales and Crown Lands. | Revenue from Post Office, Fees, Fines, Licenses, and other Incidental Sources. | Total Revenue from Previous Sources. | Parliamentary Grant, or Receipts in aid of Revenue. | Appropriations from the Commissariat Chest for Military and Naval Expenditure.† | Total Expenditure. | ||
*The Maori population was estimated at 56,400 persons in the year 1853. † The data are drawn from several official sources, and the information is only approximate. ‡ Raised by debentures at different issues. | ||||||||||
| Persons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1840 | 2,050 | .. | .. | 926 | .. | .. | 926 | .. | .. | 926 |
| 1841 | 5,000 | 85,062 | 10,836 | 6,407 | 28,540 | 2,443 | 37,390 | 43,347 | 804 | 81,541 |
| 1842 | 10,992 | 166,783 | 18,670 | 18,568 | 11,723 | 2,298 | 32,589 | 17,494 | 1,426 | 51,509 |
| 1843 | 11,848 | 191,207 | 53,945 | 16,241 | 1,613 | 3,544 | 21,398 | 9,562 | 8,093 | 39,053 |
| 1844 | 12,447 | 111,619 | 49,647 | 11,099 | 405 | 2,445 | 13,949 | 30,815‡ | 9,782 | 54,546 |
| 1845 | 12,774 | 116,980 | 76,911 | 8,899 | 155 | 3,845 | 12,899 | .. | 200,000 | 212,899 |
| 1846 | 13,274 | 155,478 | 82,656 | 21,319 | 615 | 4,711 | 26,645 | 35,673‡ | 190,000 | 252,318 |
| 1847 | 14,477 | 202,355 | 45,485 | 36,472 | 835 | 5,958 | 43,265 | 37,752 | 153,038 | 234,055 |
| 1848 | 17,166 | 233,844 | 44,215 | 38,366 | 3,337 | 5,779 | 47,482 | 36,000 | 155,653 | 239,135 |
| 1849 | 19,543 | 254,679 | 133,662 | 41,931 | 3,600 | 4,877 | 50,408 | 20,000 | 151,455 | 221,863 |
| 1850 | 22,108 | .. | .. | 43,612 | 8,559 | 7,127 | 52,298 | 41,730 | 131,100 | 232,128 |
| 1851 | 26,707 | .. | .. | 49,208 | 12,261 | 5,580 | 67,049 | 20,000 | 110,600 | 197,649 |
| 1852 | 27,633 | .. | .. | 50,527 | 14,281 | 10,956 | 75,764 | 10,000 | 91,600 | 177,364 |
The following are particulars respecting the European population, their cultivations, and live stock for the year 1851:—
Religious Denominations.—Church of England, 14,179 persons; Presbyterians, 4,124; Wesleyans, 2,529; Primitive Methodists, 226; Independents, 333; Baptists, 400; Unitarians, 74; Lutherans, 186; Quakers, 8; Protestants not specifically defined, 614; Roman Catholics, 3,473; Jews, 65; refused to state, 496.
Education.—Could not read, 7,818 persons; read only, 4,353; read and write, 14,536.
Land in Cultivation.—Acres—in wheat, 5,514; barley, 1,329; oats, 2,324; maize, 259; potatoes, 2,256; grass, 15,589; gardens or orchard, 1,188; other crops, 679: total under crop, 29,140 Acres fenced, 40,025.
Live Stock.—Horses, 2,890; mules and asses, 60; cattle, 34,787; sheep, 233,043; goats, 12,121; pigs, 16,214.
| (For Summary, Years 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year. | Population (exclusive of Maoris) on 31st December. | Births. | Deaths. | Marriages. | Crown Lands.*(See note as to lands acquired for purposes of close settlement.) | Occupied and Cultivated Holdings over One Acre in Extent. | Land (including Sown Grasses) under Cultivation. Horses. | Horses | ||||||||||||
| Males. | Females. | Totals. | Waste Lands sold for Cash in each Year. | Cash realised. | Lands finally alienated under the Deferred-payment System. | Free Grants.* | Let on Perpetual Lease. | Taken up during the Year.. | ||||||||||||
| Land taken up. | In Occupation on 31 Dec. | Under Occupation with Right of Purchase.|| | On Lease in Perpetuity.§ | Improved Farms.§ | Special-: settlement Associates.§ | Small Grazing-runs and Grazing-farms.§ | ||||||||||||||
*The waste or Crown lands sold or granted in each year prior to 1856 cannot be accurately stated. The total gross quantity of land disposed of by Crown grants up to the end of March, 1903, including both grants for public purposes, Native reserves, and old land-claims; also, from the year 1872, grants to Natives under the provisions of the Native Land Acts. On 31st March, 1903, 11,513,207 acres, in 824 runs || The population of the colony (other than Maoris) according to the census of 31st March railways; there are, besides, 113 miles of private lines. § Financial year ended 31st March of the year following. aUnder deferred-payment system. ‡ Corrected by results of census taken in April, 1891. bHeld under perpetual lease. cArea included previously as held under lease in perpetuity, and occupancy NOTE.—The area acquired by the Board under the Land for Settlements Acts to 31st March, 1903, was 600,825 acres, of which 447,334 acres were under lease to 2,335 selectors, 8,338 acres occupied by roads and | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Acres. | £ | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Number. | Acres. | ||||||||
| 1853 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1854 | 17,914 | 14,640 | 32,554 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1855 | 20,781 | 16,411 | 37,192 | 1460 | 470 | 406 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1856 | 25,356 | 20,184 | 45,540 | 1722 | 406 | 404 | 51,972 | 33,156 | .. | 14 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1857 | 27,606 | 22,196 | 49,802 | 1966 | 434 | 478 | 141,159 | 79,060 | .. | 6169 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 121,648 | .. |
| 1858 | 33,679 | 25,734 | 59,413 | 2272 | 582 | 534 | 239,128 | 150,839 | .. | 6277 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 141,007 | 14–912 |
| 1859 | 41,107 | 30,486 | 71,593 | 2647 | 704 | 603 | 477,021 | 222,885 | .. | 45,730 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 156,940 | .. |
| 1860 | 45,394 | 34,317 | 79,711 | 3146 | 1092 | 690 | 424,254 | 204,113 | .. | 47,016 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1861 | 61,062 | 37,959 | 99,021 | 3441 | 1109 | 878 | 449,358 | 285,365 | .. | 18,834 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 226,621 | 28,27 |
| 1862 | 79,680 | 46,132 | 125,812 | 4064 | 1231 | 1091 | 658,337 | 506,657 | .. | 40,335 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1863 | 105,978 | 58,070 | 164,048 | 5115 | 1983 | 1485 | 529,437 | 380,998 | .. | 66,853 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1864 | 106,580 | 65,578 | 172,158 | 6501 | 2921 | 1878 | 691,174 | 595,858 | .. | 47,198 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 382,655 | 49,40 |
| 1865 | 117,376 | 73,231 | 190,607 | 7490 | 2757 | 1908 | 503,112 | 341,094 | .. | 62,681 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1866 | 125,080 | 79,034 | 204,114 | 8466 | 2540 | 2038 | 603,406 | 528,028 | .. | 55,975 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1867 | 131,929 | 86,739 | 218,668 | 8918 | 2702 | 2050 | 288,917 | 287,416 | .. | 76,743 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 676,909 | 65,715 |
| 1868 | 134,621 | 91,997 | 226,618 | 9391 | 2662 | 2085 | 199,309 | 182,065 | .. | 42,205 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11,932 | 783,435 | .. |
| 1869 | 140,112 | 97,137 | 237,249 | 9718 | 2721 | 1931 | 112,211 | 115,941 | .. | 145,449 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13,476 | 997,477 | .. |
| 1870 | 145,732 | 102,668 | 248,400 | 10,277 | 2703 | 1851 | 76,766 | 88,419 | .. | 37,256 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,211 | 1,140,279 | .. |
| 1871 | 156,431 | 110,555 | 266,986 | 10,592 | 2642 | 1864 | 92,642 | 110,973 | .. | 123,796 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 14,874 | 1,226,222 | 81,028 |
| 1872 | 162,404 | 117,156 | 279,560 | 10,795 | 3192 | 1873 | 338,516 | 389,107 | .. | 183,673 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15,304 | 1,416,933 | .. |
| 1873 | 170,406 | 125,540 | 295,946 | 11,222 | 3645 | 2276 | 790,245 | 980,758 | .. | 484,541 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15,883 | 1,651,712 | .. |
| 1874 | 194,349 | 147,511 | 341,860 | 12,844 | 4161 | 2828 | 648,800 | 860,471 | .. | 238,581 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 16,092 | 1,943,653 | 99,261 |
| 1875 | 213,294 | 162,562 | 375,856 | 14,438 | 5712 | 3209 | 318,682 | 448,697 | .. | 486,335 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17,250 | 2,377,402 | .. |
| 1876 | 225,580 | 173,495 | 399,075 | 16,168 | 4904 | 3196 | 497,416 | 846,831 | .. | 31,145 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 18,750 | 2,940,711 | .. |
| 1877 | 227,681 | 180,937 | 408,618 | 16,856 | 4685 | 3114 | 777,862 | 1,314,480 | .. | 40,314 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20,519 | 3,523,277 | .. |
| 1878 | 240,627 | 191,892 | 432,519 | 17,770 | 4645 | 3377 | 642,667 | 1,252,993 | 79,324 | 54,861 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21,048 | 3,982,866 | 137,768 |
| 1879 | 257,894 | 205,835 | 463,729 | 18,070 | 5583 | 3352 | 79,575 | 146,733 | .. | 37,953 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 23,129 | 4,506,889 | .. |
| 1880 | 268,364 | 216,500 | 484,864 | 19,341 | 5437 | 3181 | 131,798 | 184,488 | 18,978 | 41,972 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 24,147 | 4,768,192 | .. |
| 1881 | 274,986 | 225,924 | 500,910 | 18,732 | 5491 | 3277 | 235,815 | 351,430 | 39,494 | 530,650 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 26,298 | 5,189,104 | 161,736 |
| 1882 | 283,303 | 234,404 | 517,707 | 19,009 | 5701 | 3600 | 138,512 | 209,004 | 27,487 | 122,100 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 27,352 | 5,651,255 | .. |
| 1883 | 294,665 | 246,212 | 540,877 | 19,202 | 6061 | 3612 | 113,500 | 141,251 | 24,229 | 1,228,698 | 26,786 | 26,364 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 28,587 | 6,072,949 | .. |
| 1884 | 306,667 | 257,637 | 564,304 | 19,846 | 5740 | 3800 | 96,267 | 124,928 | 40,023 | 121,611 | 20,975 | 41,561 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 29,814 | 6,550,399 | .. |
| 1885 | 312,125 | 263,101 | 575,226 | 19,693 | 6081 | 3813 | 59,613 | 84,282 | 34,637 | 456,080 | 24,441 | 51,367 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 31,763 | 6,668,920 | .. |
| 1886 | 317,646 | 271,740 | 589,386 | 19,299 | 6135 | 3488 | 39,964 | 43,836 | 29,292 | 185,764 | 50,329§ | 93,868 | .. | .. | .. | 43,873a | 105,857 | 33,332 | 6,845,177 | 187,382 |
| 1887 | 324,558 | 278,803 | 603,361 | 19,135 | 6137 | 3563 | 21,154 | 25,330 | 18,496 | 316,488 | 72,401§ | 150,218 | .. | .. | .. | 31,740a | 156,482 | 34,743 | 7,284,752 | .. |
| 1888 | 324,948 | 282,432 | 607,380 | 18,902 | 5708 | 3617 | 64,898 | 52,379 | 23,630 | 142,351 | 205,371§ | 312,495 | .. | .. | .. | 19,905a | 161,652 | 35,747 | 7,670,167 | .. |
| 1889 | 328,588 | 287,464 | 616,052‡ | 18,457 | 5772 | 3632 | 42,617 | 47,950 | 24,773 | 60,708 | 238,634§ | 544,914 | .. | .. | .. | 4,970a | 60,340 | 38,178 | 8,015,426 | .. |
| 1890 | 332,557 | 292,951 | 625,508‡ | 18,278 | 5994 | 3797 | 98,479 | 108,959 | 46,808 | 135,763 | 289,871§ | 798,571 | .. | .. | .. | 71a | 86,161 | 38,083 | 8,462,495 | .. |
| 1891 | 336,174 | 297,884 | 634,058 | 18,273 | 6518 | 3805 | 56,060 | 53,568 | 52,021 | 209,432 | 283,440§ | 1,019,405 | .. | .. | .. | 1,923b | 159,464 | 41,224 | 8,893,225 | 211,040 |
| 1892 | 345,146 | 305,287 | 650,433 | 17,876 | 6459 | 4002 | 33,659 | 34,156 | 41,726 | 243,008 | 125,194§ | 1,188,071 | 54,271 | 212,705 | .. | 157,381c | 92,926 | 42,768 | 9,713,745 | .. |
| 1893 | 357,635 | 314,630 | 672,265 | 18,187 | 6767 | 4115 | 26,275 | 26,786 | 44,779 | 198,323 | 3,854§ | 1,100,537 | 108,134 | 252,798 | .. | 68,852c | 252,693 | 45,290 | 10,063,051 | .. |
| 1894 | 363,763 | 322,365 | 686,128 | 18,528 | 6918 | 4178 | 38,695§ | 47,033§ | 53,577§ | 89,516§ | 1,263§ | 864,212§ | 75,501 | 156,926 | 9,731c | 51,346c | 117,845 | 46,676 | 10,128,076 | .. |
| 1895 | 369,725 | 328,981 | 698,706 | 18,546 | 6863 | 4110 | 26,584§ | 21,117§ | 62,287§ | 143,107§ | 1,427§ | 746,403§ | 84,970 | 198,300 | 28,348c | 44,237c | 46,407 | .. | 10,698,809 | 237,418 |
| 1896 | 376,987 | 337,175 | 714,162 | 18,612 | 6432 | 4843 | 28,489§ | 20,825§ | 57,015§ | 223,871§ | 9,106§ | 632,046§ | 59,652 | 139,210 | 4,882c | 28,084c | 68,934 | 58,904d | 11,550,075 | 249,813 |
| 1897 | 384,703 | 344,353 | 729,056 | 18,737 | 6595 | 4928 | 22,526§ | 18,226§ | 41,683§ | 25,602§ | 651§ | 543,535§ | 81,416 | 128,813 | 9,007c | 442c | 149,458 | 60,759d | 11,444,563 | 252,834 |
| 1898 | 392,124 | 351,339 | 743,463 | 18,955 | 7244 | 5091 | 37,430§ | 26,829§ | 39,506§ | 438,257§ | 640§ | 440,089§ | 109,952 | 166,960 | 4,823c | 607c | 77,632 | 62,639d | 11,984,606 | 258,115 |
| 1899 | 398,679 | 357,826 | 766,505 | 18,835 | 7680 | 5461 | 23,940§ | 21,057§ | 26,370§ | 703,799§ | 624§ | 336,183§ | 117,772 | 162,688 | 7,393c | 2c | 155,109 | 62,485d | 12,474,511 | 261,931 |
| 1900 | 403,628 | 364,650 | 768,278 | 19,546 | 7200 | 5860 | 58,725§ | 34,019§ | 22,569§ | 40,151§ | 2,499§ | 267,576§ | 262,729 | 147,223 | 1,936c | .. | 86,076 | 62,786d | 12,636,035 | 266,245 |
| 1901 | 414,223 | 373,434 | 787,657 | 20,491 | 7634 | 6095 | 27,300§ | 22,498§ | 14,286§ | 354,487§ | 10§ | 204,842§ | 128,893 | 118,519 | 1,618c | .. | 128,060 | 63,982d | 13,083,971 | 279,67 |
| 1902 | 425,908 | 382,021 | 607,929 | 20,655 | 8375 | 6394 | 17,203§ | 12,694§ | 16,953§ | 57,807§ | .. | 161,578§ | 118,557 | 167,489 | 4,032c | 5761 | 116,568 | 65,034d | 13,357,700 | 286,955 |
| (For Summary, Years 1840 to 1852, see separate sheet.) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lands acquired for purposes of close settlement.) | Occupied and Cultivated Holdings over One Acre in Extent. | Land (including Sown Grasses) under Cultivation. | Live-stock.† | Postal. | Electric T | |||||||||||||
| Perpetual Lease. | Taken up during the Year. | Horses. | Horned Cattle. | Sheep. | Pigs. | Letters (received and despatched). | Newspapers (received and despatched). | Postal Revenue. | Money Orders issued. | Amount of Money Orders issued. | Miles of Line. | Number of Message | ||||||
| In Occupation on 31 Dec. | Under Occupation with Right of Purchase.§ | On Lease in Perpetuity.§ | Improved Farms.§ | Special-:settlement Associations.§ | Small Grazing-runs and Grazing-farms.§ | |||||||||||||
tal gross quantity of land disposed of by Crown grants up to the end of March, 1903, including both lands sold and lands disposed of without sale, was 23,949,142 statute acres. The figures under the head “Free Grasses under the provisions of the Native Land Acts. On 31st March, 1903, 11,513,207 acres, in 824 runs, were held from Government on depasturing licenses, and 1,410,537 acres, as small grazing-runs, by 726 persons. Following. ¶ The population of the colony (other than Maoris) according to the census of 31st March, 1901, was 772,719 at that date; the Maori population was 43,143, and of the Cook and other Pacific islands 12,292 per head under perpetual lease. cArea included previously as held under lease in perpetuity, and occupation with right of purchase. dHoldings of exactly one acre, besides certain Maori holdings, are included. e0,825 acres, of which 447,334 acres were under lease to 2,335 selectors, 8,338 acres occupied by roads and reserves, 19,544 acres unlet, and the balance under survey. The Cheviot Estate, comprising 84,755 acres, was also purchased | ||||||||||||||||||
| Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Acres. | Number. | Acres. | Number. | Number. | £ | Number. | £ | ||||||
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 119,039 | 177,583 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 138,482 | 201,381 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 171,407 | 238,522 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 196,760 | 271,254 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 121,648 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 337,721 | 498,163 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 141,007 | 14,912 | 137,204 | 1,523,324 | 40,734 | 482,856 | 684,348 | 6024 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 156,940 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 707,870 | 839,385 | 7812 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 890,369 | 1,029,356 | 10,068 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 226,621 | 28,275 | 193,285 | 2,761,383 | 43,270 | 1,236,768 | 1,428,351 | 14,108 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,122,232 | 2,064,123 | 22,710 | 1410 | 6590 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,403,248 | 3,397,669 | 32,329 | 11,586 | 55,703 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 382,655 | 49,409 | 249,760 | 4,937,273 | 61,276 | 4,151,142 | 4,306,017 | 39,302 | 16,591 | 78,556 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,443,473 | 4,206,992 | 46,475 | 17,236 | 78,576 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,758,644 | 4,373,039 | 49,598 | 22,710 | 108,779 | 699 | 48,2 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 676,909 | 65,715 | 312,835 | 8,418,579 | 115,104 | 4,811,240 | 3,060,888 | 55,331 | 24,473 | 115,610 | 714 | 87,43 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11,932 | 783,435 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,977,199 | 3,283,615 | 57,107 | 25,854 | 118,211 | 1471 | 134,6 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13,476 | 997,477 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,016,595 | 3,563,147 | 58,007 | 28,427 | 127,218 | 1611 | 173,7 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,211 | 1,140,279 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,645,879 | 3,889,662 | 55,780 | 31,864 | 140,454 | 1887 | 238,1 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 14,874 | 1,226,222 | 81,028 | 436,592 | 9,700,629 | 151,460 | 6,081,697 | 4,179,784 | 70,249 | 36,291 | 157,397 | 2015 | 369,0 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15,304 | 1,416,933 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 6,958,543 | 4,411,091 | 94,733 | 44,660 | 191,009 | 2312 | 491,2 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 15,883 | 1,651,712 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7,915,985 | 5,269,195 | 94,706 | 52,351 | 219,258 | 2389 | 637,9 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 16,092 | 1,943,653 | 99,261 | 494,113 | 11,674,863 | 123,741 | 9,058,456 | 6,306,692 | 104,371 | 62,712 | 263,164 | 2632 | 844,3 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17,250 | 2,377,402 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,427,851 | 6,811,277 | 122,496 | 73,027 | 293,481 | 3156 | 993,3 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 18,750 | 2,940,711 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 11,770,737 | 7,962,748 | 129,263 | 80,255 | 310,268 | 3170 | 1,100,5 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20,519 | 3,523,277 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13,054,870 | 8,066,311 | 143,600 | 90,672 | 334,973 | 3307 | 1,182,9 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21,048 | 3,982,866 | 137,768 | 578,430 | 13,069,338 | 207,337 | 15,524,761 | 9,410,366 | 158,998 | 101,017 | 368,255 | 3434 | 1,260,3 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 23,129 | 4,506,889 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20,957,818 | 10,057,944 | 141,448 | 117,999 | 428,673 | 3512 | 1,448,9 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 24,147 | 4,768,192 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 22,824,468 | 10,272,917 | 149,517 | 135,648 | 465,405 | 3758 | 1,304,71 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 26,298 | 5,189,104 | 161,736 | 698,637 | 12,985,085 | 200,083 | 25,557,931 | 12,248,043 | 156,579 | 135,556 | 452,182 | 3824 | 1,438,77 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 27,352 | 5,651,255 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 30,525,579 | 13,313,099 | 168,325 | 148,162 | 499,368 | 3974 | 1,570,1 |
| 26,364 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 28,587 | 6,072,949 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 33,588,408 | 13,030,563 | 172,665 | 172,556 | 541,133 | 4074 | 1,599,4 |
| 41,561 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 29,814 | 6,550,399 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 35,257,846 | 14,093,742 | 188,772 | 186,052 | 572,666 | 4264 | 1,654,3 |
| 51,367 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 31,763 | 6,668,920 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 35,829,855 | 14,233,878 | 197,456 | 188,622 | 581,395 | 4463 | 1,774,2 |
| 93,868 | .. | .. | .. | 43,873a | 105,857 | 33,332 | 6,845,177 | 187,382 | 853,358 | 16,564,595 | 277,901 | 38,084,592 | 14,324,047 | 206,029 | 155,680 | 547,755 | 4546 | 1,836,2 |
| 150,218 | .. | .. | .. | 31,740a | 156,482 | 34,743 | 7,284,752 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 39,377,774 | 15,381,323 | 213,355 | 159,579 | 555,744 | 4646 | 1,835,39 |
| 312,495 | .. | .. | .. | 19,905a | 161,652 | 35,747 | 7,670,167 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 40,398,020 | 16,202,849 | 212,247 | 162,387 | 555,996 | 4790 | 1,765,8 |
| 544,914 | .. | .. | .. | 4,970a | 60,340 | 38,178 | 8,015,426 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 42,301,233 | 16,721,016 | 222,978 | 172,076 | 589,545 | 4874 | 1,802,9 |
| 798,571 | .. | .. | .. | 71a | 86,161 | 38,083 | 8,462,495 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 43,917,200 | 17,912,734 | 229,867 | 176,427 | 602,077 | 5060 | 1,961,1 |
| 1,019,405 | .. | .. | .. | 1,923b | 159,464 | 41,224 | 8,893,225 | 211,040 | 831,831 | 18,128,186 | 308,812 | 47,612,864 | 18,501,912 | 245,395 | 195,239 | 651,990 | 5349 | 1,968,26 |
| 1,188,071 | 54,271 | 212,705 | .. | 157,381c | 92,926 | 42,768 | 9,713,745 | .. | .. | 18,570,752 | .. | 50,610,742 | 18,557,565 | 252,494 | 199,438 | 694,847 | 5479 | 190,414 |
| 1,100,537 | 108,134 | 252,798 | .. | 68,852c | 252,693 | 45,290 | 10,063,051 | .. | 885,305 | 19,380,369 | .. | 52,085,449 | 19,556,030 | 253,457 | 210,957 | 750,929 | 5513 | 2,069,79 |
| 864,212§ | 75,501 | 156,926 | 9,731c | 51,346c | 117,845 | 46,676 | 10,128,076 | .. | 964,034 | 20,230,829 | .. | 52,168,336 | 19,271,590 | 254,800 | 222,678 | 776,783 | 5823 | 2,046,8 |
| 746,403§ | 84,970 | 198,300 | 28,348c | 44,237c | 46,407 | ¶ | 10,698,809 | 237,418 | 1,047,901 | 19,826,604 | 239,778 | 29,586,949e | 12,675,973e | 242,615 | 243,497 | 812,604 | 6245 | 2,124,21 |
| 632,046§ | 59,652 | 139,210 | 4,882c | 28,084c | 68,934 | 58,904d | 11,550,075 | 249,813 | 1,138,572 | 19,138,493 | 209,853 | 30,442,053e | 13,216,521e | 262,482 | 269,566 | 902,160 | 6285 | 2,520,16 |
| 543,535§ | 81,416 | 128,813 | 9,007c | 442c | 149,458 | 60,759d | 11,444,563 | 252,834 | 1,209,165 | 19,687,954 | 186,027 | 33,030,095e | 14,261,345e | 272,163 | 293,659 | 970,831 | 6484 | 2,696,23 |
| 440,089§ | 109,952 | 166,960 | 4,823c | 607c | 77,632 | 62,639d | 11,984,606 | 258,115 | 1,203,024 | 19,673,725 | 193,512 | 35,654,947e | 15,095,487e | 304,947 | 318,370 | 1,029,241 | 6736 | 2,960,73 |
| 336,183§ | 117,772 | 162,688 | 7,393c | 2c | 155,109 | 62,485d | 12,474,511 | 261,931 | 1,222,139 | 19,348,506 | 249,751 | 38,484,371e | 15,717,388e | 325,301 | 344,664 | 1,118,808 | 6910 | 3,469,6 |
| 267,576§ | 262,729 | 147,223 | 1,936c | .. | 86,076 | 62,786d | 12,636,035 | 266,245 | 1,256,680 | 19,355,195 | 250,975 | 39,898,479e | 17,045,715e | 316,858 | 369,834 | 1,214,853 | 7249 | 3,898, |
| 204,842§ | 128,893 | 118,519 | 1,618c | .. | 128,060 | 63,982d | 13,083,971 | 279,672 | 1,361,784 | 20,233,099 | 224,024 | 52,567,560e | 18,973,632e | 281,097 | 405,967 | 1,286,508 | 7469 | 4,167,9 |
| 161,578§ | 118,557 | 167,489 | 4,032c | 5761 | 116,568 | 65,034d | 13,357,700 | 286,955 | 1,460,663 | 20,342,727 | 193,740 | 57,714,631e | 18,517,276e | 302,604 | 367,207 | 1,277,059 | 7749 | 4,559,3 |
| See separate sheet.) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postal. | Electric Telegraph. | Miles of Railway. | Shipping. | |||||||||||||||
| Sheep. | Pigs. | Letters (received and despatched). | Newspapers (received and despatched). | Postal Revenue. | Money Orders issued. | Amount of Money Orders issued. | Miles of Line. | Number of Messages. | Cash and Cash Values, including Telephones. | Open for Traffic. | Under Construction. | Railway Receipts. | Inwards. | Outwards. | Registered Vessels belonging to the Colony. | |||
| Number of Vessels. | Tonnage. | Number of Vessels. | Tonnage. | Number of Vessels. | Gross Tonnage. | |||||||||||||
lands disposed of without sale, was 23,949,142 statute acres. The figures under the head “Free Grants” represent in each year the total area of free grants to immigrants and naval and military settlers, Government on depasturing licenses, and 1,410,537 acres, as small grazing-runs, by 726 persons. † Prior to 1892 this information is given for the years in which a census of the colony was taken. 719 at that date; the Maori population was 43,143, and of the Cook and other Pacific islands 12,292 persons. ¶ Information not similarly compiled by Department of Agriculture. **Government of purchase. dHoldings of exactly one acre, besides certain Maori holdings, are included. eNew system; counted once only. cres unlet, and the balance under survey. The Cheviot Estate, comprising 84,755 acres, was also purchased for settlement, and 76,028 acres are now under lease to 314 tenants. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number. | Number. | £ | Number. | £ | £ | £ | ||||||||||||
| .. | .. | 119,039 | 177,583 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 238 | 65,504 | 229 | 62,891 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | 138,482 | 201,381 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 293 | 74,831 | 293 | 76,718 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | 171,407 | 238,522 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 378 | 88,614 | 341 | 79,825 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | 196,760 | 271,254 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 326 | 85,748 | 323 | 82,991 | .. | .. |
| .. | .. | 337,721 | 498,163 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 289 | 78,309 | 283 | 76,524 | 186 | 6662 |
| 1,523,324 | 40,734 | 482,856 | 684,348 | 6024 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 339 | 90,118 | 322 | 82,293 | 189 | 6852 |
| .. | .. | 707,870 | 839,385 | 7812 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 438 | 136,580 | 398 | 120,392 | 213 | 7883 |
| .. | .. | 890,369 | 1,029,356 | 10,068 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 398 | 140,276 | 398 | 140,293 | 238 | 8527 |
| 2,761,383 | 43,270 | 1,236,768 | 1,428,351 | 14,108 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 596 | 197,986 | 546 | 205,350 | 252 | 9144 |
| .. | .. | 2,122,232 | 2,064,123 | 22,710 | 1410 | 6590 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 813 | 301,365 | 783 | 288,647 | 287 | 10,825 |
| .. | .. | 3,403,248 | 3,397,669 | 32,329 | 11,586 | 55,703 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1154 | 419,935 | 1094 | 394,665 | 343 | 15,189 |
| 4,937,273 | 61,276 | 4,151,142 | 4,306,017 | 39,302 | 16,591 | 78,556 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1117 | 426,004 | 1089 | 433,253 | 423 | 22,573 |
| .. | .. | 4,443,473 | 4,206,992 | 46,475 | 17,236 | 78,576 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 862 | 295,625 | 783 | 283,020 | 466 | 24,484 |
| .. | .. | 4,758,644 | 4,373,039 | 49,598 | 22,710 | 108,779 | 699 | 48,231 | 9114 | .. | .. | .. | 1019 | 330,303 | 986 | 306,979 | 493 | 26,787 |
| 8,418,579 | 115,104 | 4,811,240 | 3,060,888 | 55,331 | 24,473 | 115,610 | 714 | 87,436 | 14,295 | .. | .. | .. | 944 | 309,568 | 950 | 308,169 | 366 | 23,240 |
| .. | .. | 4,977,199 | 3,283,615 | 57,107 | 25,854 | 118,211 | 1471 | 134,647 | 26,224 | .. | .. | .. | 851 | 277,105 | 873 | 287,710 | 372 | 24,539 |
| .. | .. | 5,016,595 | 3,563,147 | 58,007 | 28,427 | 127,218 | 1611 | 173,746 | 32,649 | .. | .. | .. | 764 | 250,731 | 771 | 247,764 | 381 | 25,990 |
| .. | .. | 5,645,879 | 3,889,662 | 55,780 | 31,864 | 140,454 | 1887 | 238,195 | 27,422 | .. | .. | .. | 756 | 273,151 | 766 | 265,407 | 384 | 26,743 |
| 9,700,629 | 151,460 | 6,081,697 | 4,179,784 | 70,249 | 36,291 | 157,397 | 2015 | 369,085 | 37,203 | .. | .. | .. | 729 | 274,643 | 709 | 265,618 | 371 | 27,107 |
| .. | .. | 6,958,543 | 4,411,091 | 94,733 | 44,660 | 191,009 | 2312 | 491,205 | 44,669 | .. | .. | .. | 775 | 300,302 | 743 | 285,366 | 364 | 23,963 |
| .. | .. | 7,915,985 | 5,269,195 | 94,706 | 52,351 | 219,258 | 2389 | 637,941 | 55,195 | 145 | 434 | .. | 739 | 289,297 | 704 | 281,847 | 411 | 30,035 |
| 1,674,863 | 123,741 | 9,058,456 | 6,306,692 | 104,371 | 62,712 | 263,164 | 2632 | 844,301 | 62,322 | 209 | 621 | 21,198 | 856 | 399,296 | 822 | 385,533 | 471 | 38,935 |
| .. | .. | 10,427,851 | 6,811,277 | 122,496 | 73,027 | 293,481 | 3156 | 993,323 | 74,420 | 542 | 464 | 72,073 | 926 | 416,727 | 940 | 417,820 | 502 | 42,025 |
| .. | .. | 11,770,737 | 7,962,748 | 129,263 | 80,255 | 310,268 | 3170 | 1,100,599 | 80,841 | 718 | 427 | 469,051 | 878 | 393,180 | 866 | 393,334 | 538 | 44,401 |
| .. | .. | 13,054,870 | 8,066,311 | 143,600 | 90,672 | 334,973 | 3307 | 1,182,955 | 85,589 | 1052 | 251 | 569,898 | 812 | 388,568 | 848 | 400,609 | 533 | 42,479 |
| 3,069,338 | 207,337 | 15,524,761 | 9,410,366 | 158,998 | 101,017 | 368,255 | 3434 | 1,260,324 | 92,433 | 1089 | 142 | 758,096 | 926 | 456,490 | 886 | 428,493 | 541 | 46,965 |
| .. | .. | 20,957,818 | 10,057,944 | 141,448 | 117,999 | 428,673 | 3512 | 1,448,943 | 112,351 | 1171 | 284 | 762,572 | 894 | 473,940 | 908 | 475,752 | 563 | 64,457 |
| .. | .. | 22,824,468 | 10,272,917 | 149,517 | 135,648 | 465,405 | 3758 | 1,304,712 | 100,023 | 1288 | 192 | 836,077 | 730 | 395,675 | 786 | 424,041 | 559 | 66,316 |
| 2,985,085 | 200,083 | 25,557,931 | 12,248,043 | 156,579 | 135,556 | 452,182 | 3824 | 1,438,772 | 101,566 | 1333 | 187 | 892,026 | 765 | 420,134 | 762 | 413,487 | 572 | 72,387 |
| .. | .. | 30,525,579 | 13,313,099 | 168,325 | 148,162 | 499,368 | 3974 | 1,570,189 | 102,378 | 1371 | 171 | 953,347 | 795 | 461,285 | 769 | 438,551 | 584 | 76,196 |
| .. | .. | 33,588,408 | 13,030,563 | 172,665 | 172,556 | 541,133 | 4074 | 1,599,400 | 102,958 | 1404 | 224 | 961,304 | 805 | 494,926 | 851 | 507,565 | 579 | 84,903 |
| .. | .. | 35,257,846 | 14,093,742 | 188,772 | 186,052 | 572,666 | 4264 | 1,654,305 | 101,482 | 1479 | 158 | 1,045,712 | 852 | 529,188 | 872 | 534,242 | 583 | 92,696 |
| .. | .. | 35,829,855 | 14,233,878 | 197,456 | 188,622 | 581,395 | 4463 | 1,774,273 | 112,778 | 1613 | 179 | 1,047,418 | 786 | 519,700 | 780 | 513,000 | 597 | 95,887 |
| 6,564,595 | 277,901 | 38,084,592 | 14,324,047 | 206,029 | 155,680 | 547,755 | 4546 | 1,836,266 | 115,666 | 1721 | 171 | 998,768 | 725 | 502,572 | 707 | 488,331 | 571 | 94,196 |
| .. | .. | 39,377,774 | 15,381,323 | 213,355 | 159,579 | 555,744 | 4646 | 1,835,394 | 116,211 | 1753 | 169 | 994,843 | 653 | 489,754 | 675 | 493,583 | 557 | 94,027 |
| .. | .. | 40,398,020 | 16,202,849 | 212,247 | 162,387 | 555,996 | 4790 | 1,765,860 | 104,116 | 1777 | 163 | 997,615 | 683 | 526,435 | 701 | 531,478 | 524 | 86,132 |
| .. | .. | 42,301,233 | 16,721,016 | 222,978 | 172,076 | 589,545 | 4874 | 1,802,987 | 106,462 | 1809 | 176 | 1,095,569 | 781 | 602,634 | 762 | 593,252 | 520 | 87,411 |
| .. | .. | 43,917,200 | 17,912,734 | 229,867 | 176,427 | 602,077 | 5060 | 1,961,161 | 110,697 | 1842 | 132 | 1,121,701 | 744 | 662,769 | 745 | 649,705 | 521 | 98,907 |
| 8,128,186 | 308,812 | 47,612,864 | 18,501,912 | 245,395 | 195,239 | 651,990 | 5349 | 1,968,264 | 117,634 | 1869 | 170 | 1,115,432 | 737 | 618,515 | 744 | 625,807 | 521 | 102,068 |
| 8,570,752 | .. | 50,610,742 | 18,557,565 | 252,494 | 199,438 | 694,847 | 5479 | 1,904,143 | 103,813 | 1886 | 188 | 1,181,522 | 686 | 675,223 | 689 | 656,100 | 491 | 101,156 |
| 9,380,369 | .. | 52,085,449 | 19,556,030 | 253,457 | 210,957 | 750,929 | 5513 | 2,069,791 | 112,466 | 1948 | 148 | 1,172,792 | 617 | 615,604 | 635 | 642,466 | 478 | 100,388 |
| 230,829 | .. | 52,168,336 | 19,271,590 | 254,800 | 222,678 | 776,783 | 5823 | 2,046,839 | 114,510 | 1993 | 127 | 1,150,851 | 609 | 631,100 | 614 | 631,250 | 475 | 99,588 |
| 9,826,604 | 239,778 | 29,586,949e | 12,675,973e | 242,615 | 243,497 | 812,604 | 6245 | 2,124,211 | 123,112 | 2014 | 114 | 1,183,041 | 611 | 672,951 | 597 | 648,946 | 479 | 100,988 |
| 9,138,493 | 209,853 | 30,442,053e | 13,216,521e | 262,482 | 269,566 | 902,160 | 6285 | 2,520,169 | 129,635 | **2,018 | 124 | 1,286,158 | 589 | 614,097 | 592 | 627,659 | 492 | 105,553 |
| 9,687,954 | 186,027 | 33,030,095e | 14,261,345e | 272,163 | 293,659 | 970,831 | 6484 | 2,696,233 | 136,221 | **2,055 | 92 | 1,376,008 | 600 | 686,899 | 587 | 675,333 | 506 | 119,713 |
| 9,673,725 | 193,512 | 35,654,947e | 15,095,487e | 304,947 | 318,370 | 1,029,241 | 6736 | 2,960,738 | 145,295 | **2,090 | 113 | 1,469,665 | 620 | 765,255 | 622 | 765,793 | 518 | 126,113 |
| 9,348,506 | 249,751 | 38,484,371e | 15,717,388e | 325,301 | 344,664 | 1,118,808 | 6910 | 3,469,631 | 162,945 | **2,104 | 111 | 1,623,891 | 609 | 811,183 | 604 | 807,866 | 522 | 129,583 |
| 9,355,195 | 250,975 | 39,898,479e | 17,045,715e | 316,858 | 369,834 | 1,214,853 | 7249 | 3,898,128 | 186,978 | **2,212 | 208 | 1,727,236 | 616 | 854,632 | 613 | 825,275 | 520 | 137,767 |
| 233,099 | 224,024 | 52,567,560e | 18,973,632e | 281,097 | 405,967 | 1,286,508 | 7469 | 4,167,981 | 207,476 | **2,235 | 212 | 1,874,586 | 688 | 1,063,274 | 691 | 1,075,906 | 520 | 143,183 |
| 342,727 | 193,740 | 57,714,631e | 18,517,276e | 302,604 | 367,207 | 1,277,059 | 7749 | 4,559,304 | 222,495 | **2,291 | 194 | 1,974,038 | 638 | 1,089,179 | 611 | 1,048,770 | 549 | 147,822 |
| Year. | Exports (the Produce of New Zealand). | Exports (the Produce of New Zealand). | Imports. | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wool. | Grain. | Frozen Meat. | Butter. | Cheese. | Flax (Phormium). | Gold. | Gum (Kauri). | Provisions, Tallow, Timber, &c. | |||||||||||
| Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Value. | Total Value. | Total Value. | |
*Post-Office Savings-Banks were first opened in 1867. † Statistics of schools and scholars not being complete for years prior to 1874, no figures are entered. § There was in March, 1903, an accrued sinking fund amounting to £2,313,239, leaving a net indebtedness of £53,585,780. || Excluding Maoris. ¶ An accident-insurance branch was 1899, was £3,124; in 1900, £157,095; in 1901, £197,293; in 1902, £207,509; and in 1903 £209,156. aFinancial year ended 31st March of year following. bDuring the last twelve years the Public Works Fund has been assisted by contributions from the revenue of the Consolidated Fund to the £425,000; in 1899–1900, £450,000; in 1900–1901, £500,000; in 1901–1902, £500,000; in 1902–1903, £200,000. Further receipts in aid have been given since the year 1870 by way of contributions of stamp | |||||||||||||||||||
| Lb. | £ | Bushels. | £ | Cwt. | £ | Cwt. | £ | Cwt. | £ | Tons. | £ | Oz. | £ | Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1853 | 1,071,340 | 66,507 | 59,959 | 19,042 | .. | .. | 1039 | 7507 | 808 | 4092 | 46 | 1046 | .. | .. | 829 | 15,971 | 189,107 | 303,272 | 597,82 |
| 1854 | 1,254,416 | 70,103 | 93,700 | 41,019 | .. | .. | 807 | 7399 | 169 | 975 | 48 | 1563 | .. | .. | 1660 | 28,864 | 170,967 | 320,890 | 891,2 |
| 1855 | 1,772,344 | 93,104 | 150,352 | 82,302 | .. | .. | 785 | 5786 | 406 | 2163 | 150 | 4674 | .. | .. | 355 | 4514 | 173,324 | 365,867 | 813,4 |
| 1856 | 2,559,618 | 146,070 | 66,150 | 24,032 | .. | .. | 647 | 3837 | 290 | 1414 | 22 | 552 | .. | .. | 1440 | 18,591 | 123,937 | 318,433 | 710,8 |
| 1857 | 2,648,716 | 176,579 | 81,757 | 29,676 | .. | .. | 382 | 2102 | 549 | 1818 | 38 | 710 | 10,436 | 40,442 | 2521 | 35,250 | 82,817 | 369,394 | 992,9 |
| 1858 | 3,810,372 | 254,022 | 71,403 | 20,680 | .. | .. | 532 | 2838 | 934 | 3995 | 64 | 1516 | 13,533 | 52,443 | 1810 | 20,036 | 78,419 | 433,949 | 1,141,27 |
| 1859 | 5,096,751 | 339,779 | 118,740 | 39,016 | .. | .. | 859 | 5588 | 1067 | 4296 | 77 | 1593 | 7336 | 28,427 | 2010 | 20,776 | 81,833 | 521,308 | 1,551,0 |
| 1860 | 6,665,880 | 444,392 | 55,683 | 13,112 | .. | .. | 1026 | 6623 | 810 | 3535 | 61 | 1240 | 4538 | 17,585 | 1046 | 9851 | 52,795 | 549,133 | 1,548,33 |
| 1861 | 7,855,920 | 523,728 | 8118 | 2518 | .. | .. | 25 | 126 | 404 | 1844 | 2 | 43 | 194,234 | 752,657 | 856 | 9888 | 48,437 | 1,339,241 | 2,493,8 |
| 1862 | 9,839,265 | 674,226 | 6602 | 1821 | .. | .. | Butter and cheese not separately given for years 1862 to 1865. Then total export for this period was 617 cwt., value £2,976 | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 261 | 410,862 | 1,591,389 | 1103 | 11,107 | 77,835 | 2,358,020 | 4,626,08 |
| 1863 | 12,585,980 | 830,495 | 3238 | 1160 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 251 | 628,450 | 2,431,723 | 1400 | 27,027 | 52,105 | 3,342,891 | 7,024,6 |
| 1864 | 16,691,666 | 1,070,997 | 3580 | 722 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7 | 170 | 480,171 | 1,857,847 | 2228 | 60,590 | 59,089 | 3,050,634 | 7,000,6 |
| 1865 | 19,180,500 | 1,141,761 | 25,447 | 6076 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3 | 75 | 574,574 | 2,226,474 | 1867 | 46,060 | 82,729 | 3,503,421 | 5,594,97 |
| 1866 | 22,810,776 | 1,354,152 | 32,610 | 7297 | .. | .. | 232 | 1590 | 13 | 65 | 45 | 996 | 735,376 | 2,844,517 | 2535 | 70,572 | 116,901 | 4,396,090 | 5,894,8 |
| 1867 | 27,152,966 | 1,580,608 | 158,811 | 26,986 | .. | .. | 38 | 192 | 90 | 362 | 126 | 4256 | 686,753 | 2,700,275 | 2685 | 77,491 | 89,294 | 4,479,464 | 5,344,6 |
| 1868 | 28,875,163 | 1,516,548 | 632,556 | 114,125 | .. | .. | 138 | 532 | 335 | 1240 | 534 | 8137 | 637,474 | 2,504,326 | 2690 | 72,493 | 51,361 | 4,268,762 | 4,985,7 |
| 1869 | 27,765,636 | 1,371,230 | 520,556 | 96,441 | .. | .. | 2705 | 14,679 | 2331 | 8040 | 2028 | 45,245 | 614,281 | 2,362,995 | 2850 | 111,307 | 80,197 | 4,090,134 | 4,976,12 |
| 1870 | 37,039,763 | 1,703,944 | 854,399 | 141,135 | .. | .. | 3435 | 12,995 | 2735 | 9327 | 5471 | 132,578 | 544,880 | 2,157,585 | 4391 | 175,074 | 212,044 | 4,544,682 | 4,639,0 |
| 1871 | 37,793,734 | 1,606,144 | 1,032,902 | 164,087 | .. | .. | 4342 | 12,426 | 1619 | 4023 | 4248 | 90,611 | 730,029 | 2,787,520 | 5054 | 167,958 | 338,335 | 5,171,104 | 4,078,19 |
| 1872 | 41,886,997 | 2,537,919 | 1,058,480 | 178,886 | .. | .. | 1629 | 4462 | 1362 | 4379 | 3985 | 99,405 | 445,370 | 1,730,992 | 4811 | 154,167 | 396,976 | 5,107,186 | 5,142,95 |
| 1873 | 41,535,185 | 2,702,471 | 598,431 | 136,832 | .. | .. | 722 | 2342 | 1993 | 6625 | 6454 | 143,799 | 505,337 | 1,987,425 | 2833 | 85,816 | 412,660 | 5,477,970 | 6,464,68 |
| 1874 | 46,848,735 | 2,834,695 | 1,162,782 | 291,103 | .. | .. | 357 | 1168 | 1326 | 4408 | 2038 | 37,690 | 376,388 | 1,505,331 | 2568 | 79,986 | 397,762 | 5,152,143 | 81,218 |
| 1875 | 54,401,540 | 3,398,155 | 1,276,927 | 231,417 | .. | .. | 104 | 660 | 442 | 1862 | 639 | 11,742 | 355,322 | 1,407,770 | 3230 | 138,523 | 285,715 | 5,475,844 | 8,029,17 |
| 1876 | 59,853,454 | 3,395,816 | 2,172,098 | 337,878 | .. | .. | 871 | 3910 | 885 | 3488 | 897 | 18,285 | 318,367 | 1,268,559 | 2888 | 109,234 | 351,731 | 5,488,901 | 6,905,17 |
| 1877 | 64,481,324 | 3,658,938 | 1,323,910 | 276,452 | .. | .. | 5206 | 23,458 | 4999 | 16,713 | 1053 | 18,826 | 366,955 | 1,476,312 | 3632 | 118,348 | 469,670 | 6,058,717 | 6,973,41 |
| 1878 | 59,270,256 | 3,292,807 | 2,112,214 | 508,767 | .. | .. | 3106 | 12,111 | 3019 | 9368 | 622 | 10,666 | 311,437 | 1,244,190 | 3445 | 132,975 | 573,735 | 5,784,619 | 8,755,66 |
| 1879 | 62,220,810 | 3,126,439 | 3,470,344 | 660,557 | .. | .. | 339 | 1631 | 172 | 628 | 445 | 7874 | 284,100 | 1,134,641 | 3228 | 147,535 | 484,150 | 5,563,455 | 8,374,58 |
| 1880 | 66,860,150 | 3,169,300 | 5,540,445 | 898,997 | .. | .. | 2717 | 8350 | 717 | 1983 | 894 | 15,617 | 303,215 | 1,220,263 | 4725 | 242,817 | 544,973 | 6,102,300 | 6,162,0 |
| 1881 | 59,415,940 | 2,909,760 | 5,815,960 | 986,072 | .. | .. | 2426 | 8496 | 3056 | 6112 | 1308 | 26,285 | 250,683 | 996,867 | 5460 | 253,778 | 574,880 | 5,762,250 | 7,457,04 |
| 1882 | 65,322,707 | 3,118,554 | 4,310,984 | 907,961 | 15,244 | 19,339 | 11,264 | 52,088 | 3553 | 10,130 | 2040 | 41,955 | 230,893 | 921,664 | 5533 | 260,369 | 921,290 | 6,253,350 | 8,609,27 |
| 1883 | 68,149,430 | 3,014,211 | 6,723,303 | 1,286,724 | 87,975 | 118,328 | 8869 | 42,020 | 2519 | 6892 | 2013 | 36,761 | 222,899 | 892,445 | 6518 | 336,606 | 1,121,257 | 6,855,244 | 7,974,03 |
| 1884 | 81,139,028 | 3,267,527 | 5,489,635 | 766,824 | 254,069 | 345,090 | 15,766 | 66,593 | 10,342 | 25,074 | 1525 | 23,475 | 246,392 | 988,953 | 6393 | 342,151 | 1,116,799 | 6,942,486 | 7,663,88 |
| 1885 | 86,507,431 | 3,205,275 | 4,597,645 | 513,697 | 296,473 | 373,857 | 24,923 | 102,387 | 15,245 | 35,742 | 1063 | 16,316 | 222,732 | 890,056 | 5876 | 299,762 | 1,154,819 | 6,591,911 | 7,479,92 |
| 1886 | 90,853,744 | 3,072,971 | 3,523,324 | 463,549 | 346,055 | 427,193 | 23,175 | 105,537 | 16,429 | 45,657 | 1112 | 15,922 | 235,578 | 939,648 | 4920 | 257,653 | 1,058,552 | 6,386,682 | 6,759,01 |
| 1887 | 88,824,382 | 3,321,074 | 4,126,836 | 443,780 | 402,107 | 455,870 | 17,018 | 54,921 | 23,913 | 54,562 | 1578 | 25,094 | 187,938 | 747,878 | 6790 | 362,434 | 1,085,468 | 6,551,081 | 6,245,51 |
| 1888 | 83,225,733 | 3,115,008 | 5,101,167 | 668,859 | 552,298 | 628,800 | 29,995 | 118,252 | 36,682 | 78,918 | 4042 | 75,269 | 229,608 | 914,309 | 8482 | 380,933 | 1,274,780 | 7,255,128 | 5,941,90 |
| 1889 | 10,222,7354 | 3,976,375 | 6,120,202 | 985,224 | 656,822 | 783,374 | 37,955 | 146,840 | 26,558 | 67,105 | 17,084 | 361,182 | 197,492 | 785,490 | 7519 | 329,590 | 1,606,828 | 9,042,008 | 6,308,86 |
| 1890 | 10,281,7077 | 4,150,599 | 8,287,024 | 1,030,415 | 898,894 | 1,087,617 | 34,816 | 122,701 | 40,451 | 84,986 | 21,158 | 381,789 | 187,641 | 751,360 | 7438 | 378,563 | 1,440,731 | 9,428,761 | 6,260,52 |
| 1891 | 1,061,87,114 | 4,129,686 | 5,877,059 | 676,338 | 1,000,307 | 1,194,724 | 39,430 | 150,258 | 39,770 | 86,675 | 15,809 | 281,514 | 251,161 | 1,172 | 8388 | 437,056 | 1,436,671 | 9,400,094 | 6,503,84 |
| 1892 | 118,180,912 | 4,313,307 | 6,625,525 | 816,272 | 869,600 | 1,033,377 | 53,930 | 227,162 | 41,493 | 91,042 | 12,793 | 214,542 | 237,393 | 1,963 | 8705 | 517,678 | 1,200,525 | 9,365,868 | 6,943,05 |
| 1893 | 109,719,684 | 3,774,738 | 4,855,368 | 583,397 | 903,836 | 1,085,167 | 58,149 | 254,645 | 46,201 | 99,626 | 12,587 | 219,375 | 227,502 | 1,921 | 8317 | 510,775 | 1,113,799 | 8,557,443 | 6,911,51 |
| 1894 | 144,295,154 | 4,827,016 | 2,434,295 | 226,183 | 1,025,243 | 1,194,545 | 60,771 | 251,280 | 55,655 | 115,203 | 4677 | 66,256 | 221,614 | 1,865 | 8338 | 404,567 | 1,112,233 | 9,085,148 | 6,788,02 |
| 1895 | 116,015,170 | 3,662,131 | 2,381,837 | 215,783 | 1,134,097 | 1,262,711 | 57,964 | 227,601 | 76,743 | 150,909 | 1806 | 21,040 | 293,493 | 1,1,181 | 7425 | 418,766 | 1,269,031 | 8,390,153 | 6,400,12 |
| 1896 | 129,151,624 | 4,391,848 | 2,941,821 | 346,197 | 1,103,362 | 1,251,993 | 71,353 | 281,716 | 71,372 | 130,166 | 2968 | 32,985 | 263,694 | 1,0,428 | 7126 | 431,323 | 1,269,680 | 9,177,336 | 7,137,32 |
| 1897 | 135,835,117 | 4,443,144 | 1,919,887 | 235,429 | 1,407,921 | 1,566,286 | 99,002 | 402,605 | 77,683 | 150,517 | 2769 | 30,674 | 251,647 | 980,204 | 6641 | 398,010 | 1,389,398 | 9,596,267 | 8,055,223 |
| 1898 | 149,385,815 | 4,645,804 | 1,045,980 | 136,120 | 1,551,773 | 1,698,750 | 96,801 | 403,690 | 68,711 | 135,776 | 4850 | 74,556 | 280,175 | 1,080,691 | 9905 | 586,767 | 1,562,834 | 10,324,988 | 8,230,600 |
| 1899 | 147,169,497 | 4,324,627 | 6,985,999 | 721,817 | 1,865,827 | 2,088,856 | 136,086 | 571,799 | 69,440 | 141,818 | 10,371 | 184,411 | 389,570 | 1,513,180 | 11,116 | 607,919 | 1,645,313 | 11,799,740 | 8,739,633 |
| 1900 | 140,706,486 | 4,749,196 | 9,529,847 | 1,034,014 | 1,844,831 | 2,123,881 | 172,583 | 740,620 | 102,849 | 229,111 | 15,906 | 332,182 | 373,614 | 1,439,602 | 10,159 | 622,293 | 1,784,350 | 13,055,249 | 10,646,096 |
| 1901 | 146,820,079 | 3,699,103 | 13,373,515 | 1,285,811 | 1,857,547 | 2,253,262 | 201,591 | 882,406 | 104,294 | 238,685 | 10,171 | 195,728 | 455,558 | 1,753,784 | 7541 | 446,114 | 1,935,567 | 12,690,460 | 11,817,915 |
| 1902 | 160,419,023 | 3,354,563 | 5,865,562 | 786,548 | 2,138,557 | 2,718,763 | 253,998 | 1,205,802 | 74,746 | 163,539 | 20,852 | 534,031 | 507,852 | 1,951,426 | 7430 | 450,223 | 2,333,704 | 13,498,599 | 11,326,723 |
| Exports (the Produce of New Zealand). | Imports. | Coal-mines, Output from. | Revenue of General Government. | Expenditure of General Government. | Public Debt: Debentures and Stock in Circulation. (Prior to 1880 the figures are for Calendar Years.) | Debt of Local Bodies. | Banks. (Average of Four Quarters.) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax (Phormium). | Gold. | Gum (Kauri). | Provisions, Tallow, Timber, &c. | Liabilities. | ||||||||||||||
| Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Quantity. | Value. | Value. | Total Value. | Total Value. | Out of Revenue Account. | Out of Loan Accounts. | Deposits. | Assets. | |||||
and scholars not being complete for years prior to 1874, no figures are entered. ‡ In addition to these there were in December, 1902, 3,742 children attending the Native schools, nearly indebtness of £53,585,780. || Excluding Maoris. ¶ An accident-insurance branch was opened on 7th June, 1901. For the year ending 31st December, 1902, premiums amounting to £14,100 had been re Public Works Fund has been assisted by contributions from the revenue of the Consolidated Fund to the extent of £3,405,000; the payments in each financial year were-in 1891–92, £30,000; in 1892–93, £200,000; in 1893–94, £200,000. Further receipts in aid have been given since the year 1870 by way of contributions of stamp duties, release of sinking funds, &c. cAnd securing annuities amounting to £36,392 per annum. | ||||||||||||||||||
| £ | Tons. | £ | Oz. | £. | Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | Tons. | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| 4092 | 46 | 1046 | .. | .. | 829 | 15,971 | 189,107 | 303,272 | 597,827 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 975 | 48 | 1563 | .. | .. | 1660 | 28,864 | 170,967 | 320,890 | 891,201 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 2163 | 150 | 4674 | .. | .. | 355 | 4514 | 173,324 | 365,867 | 813,460 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1414 | 22 | 552 | .. | .. | 1440 | 18,591 | 123,937 | 318,433 | 710,868 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1,818 | 38 | 710 | 10,436 | 40,442 | 2521 | 35,250 | 82,817 | 369,394 | 992,994 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 343,316 | 419,860 | 432,494 |
| 3995 | 64 | 1516 | 13,533 | 52,443 | 1810 | 20,036 | 78,419 | 433,949 | 1,141,273 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 448,078 | 705,738 | 616,769 |
| 4296 | 77 | 1593 | 7336 | 28,427 | 2010 | 20,776 | 81,833 | 521,308 | 1,551,030 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 541,213 | 1,003,584 | 678,474 |
| 3535 | 61 | 1240 | 4538 | 17,585 | 1046 | 9851 | 52,795 | 549,133 | 1,548,333 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 644,521 | 992,082 | 801,588 |
| 1844 | 2 | 43 | 194,234 | 752,657 | 856 | 9888 | 48,437 | 1,339,241 | 2,493,811 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 882,754 | 1,235,952 | 1,097,162 |
| .. | 13 | 261 | 410,862 | 1,591,389 | 1103 | 11,107 | 77,835 | 2,358,020 | 4,626,082 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 836,000 | .. | 1,596,446 | 2,691,117 | 2,092,497 |
| .. | 13 | 251 | 628,450 | 2,431,723 | 1400 | 27,027 | 52,105 | 3,342,891 | 7,024,674 | Prior to 1878, 709–931 | .. | .. | .. | 1,289,750 | .. | 2,092,090 | 4,028,766 | 2,962,585 |
| .. | 7 | 170 | 480,171 | 1,857,847 | 2228 | 60,590 | 59,089 | 3,050,634 | 7,000,655 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,219,450 | .. | 2,480,303 | 5,063,458 | 3,343,172 |
| .. | 3 | 75 | 574,574 | 2,226,474 | 1867 | 46,060 | 82,729 | 3,503,421 | 5,594,977 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,368,681 | .. | 2,638,414 | 5,455,289 | 3,522,146 |
| 65 | 45 | 996 | 735,376 | 2,844,517 | 2535 | 70,572 | 116,901 | 4,396,090 | 5,894,863 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,435,728 | .. | 3,097,473 | 5,891,532 | 4,010,110 |
| 362 | 126 | 4256 | 686,753 | 2,700,275 | 2685 | 77,491 | 89,294 | 4,479,464 | 5,344,607 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,781,193 | .. | 2,904,594 | 5,947,160 | 3,737,695 |
| 1240 | 534 | 8137 | 637,474 | 2,504,326 | 2690 | 72,493 | 51,361 | 4,268,762 | 4,985,748 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7,182,743 | .. | 3,102,727 | 5,734,745 | 3,838,220 |
| 8040 | 2028 | 45,245 | 614,281 | 2,362,995 | 2850 | 111,307 | 80,197 | 4,090,134 | 4,976,126 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7,360,616 | .. | 3,174,831 | 6,231,416 | 3,863,006 |
| 9327 | 5471 | 132,578 | 544,880 | 2,157,585 | 4391 | 175,074 | 212,044 | 4,544,682 | 4,639,015 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7,841,891 | .. | 3,127,769 | 6,315,354 | 3,819,670 |
| 4023 | 4248 | 90,611 | 730,029 | 2,787,520 | 5054 | 167,958 | 338,335 | 5,171,104 | 4,078,193 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 8,900,991 | .. | 3,334,672 | 5,871,888 | 3,988,400 |
| 4379 | 3985 | 99,405 | 445,370 | 1,730,992 | 4811 | 154,167 | 396,976 | 5,107,186 | 5,142,951 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 9,985,386 | .. | 3,919,838 | 5,429,747 | 4,628,819 |
| 6625 | 6454 | 143,799 | 505,337 | 1,987,425 | 2833 | 85,816 | 412,660 | 5,477,970 | 6,464,687 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 10,913,936 | .. | 4,713,806 | 7,267,720 | 5,538,030 |
| 4408 | 2038 | 37,690 | 376,388 | 1,505,331 | 2568 | 79,986 | 397,762 | 5,152,143 | 8,121,812 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13,366,936 | .. | 5,564,434 | 9,954,216 | 6,490,504 |
| 1862 | 639 | 11,742 | 355,322 | 1,407,770 | 3230 | 138,523 | 285,715 | 5,475,844 | 8,029,172 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 17,400,031 | .. | 5,967,205 | 10,987,178 | 6,987,318 |
| 3488 | 897 | 18,285 | 318,367 | 1,268,559 | 2888 | 109,234 | 351,731 | 5,488,901 | 6,905,171 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 18,678,111 | .. | 6,238,471 | 11,776,070 | 7,221,399 |
| 16,713 | 1053 | 18,826 | 366,955 | 1,476,312 | 3632 | 118,348 | 469,670 | 6,058,717 | 6,973,418 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 20,691,111 | .. | 7,185,106 | 12,992,104 | 8,152,230 |
| 9368 | 622 | 10,666 | 311,437 | 1,244,190 | 3445 | 132,975 | 573,735 | 5,784,619 | 8,755,663 | 162,218 | .. | .. | .. | 22,608,311 | .. | 8,960,369 | 15,393,630 | 10,031,009 |
| 628 | 445 | 7874 | 284,100 | 1,134,641 | 3228 | 147,535 | 484,150 | 5,563,455 | 8,374,585 | 231,218 | .. | .. | .. | 23,958,311 | .. | 8,021,073 | 16,054,295 | 9,057,463 |
| 1983 | 894 | 15,617 | 303,215 | 1,220,263 | 4725 | 242,817 | 544,973 | 6,102,300 | 6,162,011 | 299,923 | .. | .. | .. | 28,185,711 | .. | 8,538,935 | 14,220,275 | 9,550,177 |
| 6112 | 1308 | 26,285 | 250,683 | 996,867 | 5460 | 253,778 | 574,880 | 5,762,250 | 7,457,045 | 337,262 | .. | .. | .. | 28,479,111 | 3,039,807 | 9,069,377 | 14,863,645 | 10,083,188 |
| 10,130 | 2040 | 41,955 | 230,893 | 921,664 | 5533 | 260,369 | 921,290 | 6,253,350 | 8,609,270 | 378,272 | .. | .. | .. | 29,445,011 | 3,277,584 | 8,945,346 | 17,162,234 | 10,015,273 |
| 6892 | 2013 | 36,761 | 222,899 | 892,445 | 6518 | 336,606 | 1,121,257 | 6,855,244 | 7,974,038 | 421,764 | .. | .. | .. | 31,071,582 | 3,540,046 | 8,659,477 | 17,794,761 | 9,706,700 |
| 25,074 | 1525 | 23,475 | 246,392 | 988,953 | 6393 | 342,151 | 1,116,799 | 6,942,486 | 7,663,888 | 480,831 | .. | .. | .. | 32,195,422 | 3,962,330 | 9,643,214 | 18,442,139 | 10,691,599 |
| 35,742 | 1063 | 16,316 | 222,732 | 890,056 | 5876 | 299,762 | 1,154,819 | 6,591,911 | 7,479,921 | 511,063 | .. | .. | .. | 33,880,722 | 4,313,223 | 10,083,296 | 18,811,567 | 11,130,244 |
| 45,657 | 1112 | 15,922 | 235,578 | 939,648 | 4920 | 257,653 | 1,058,552 | 6,386,682 | 6,759,013 | 534,353 | .. | .. | .. | 35,741,653 | 4,943,270 | 10,579,711 | 19,041,827 | 11,603,194 |
| 54,562 | 1578 | 25,094 | 187,938 | 747,878 | 6790 | 362,434 | 1,085,468 | 6,551,081 | 6,245,515 | 558,620 | .. | .. | .. | 36,758,437 | 5,620,747 | 11,031,614 | 18,799,847 | 11,995,495 |
| 78,918 | 4042 | 75,269 | 229,608 | 914,309 | 8482 | 380,933 | 1,274,780 | 7,255,128 | 5,941,900 | 613,895 | .. | .. | .. | 38,375,050 | 5,812,803 | 11,155,778 | 18,709,444 | 12,108,353 |
| 67,105 | 17,084 | 361,182 | 197,492 | 785,490 | 7519 | 329,590 | 1,606,828 | 9,042,008 | 6,308,863 | 586,445 | .. | .. | .. | 38,667,950 | 5,892,050 | 11,528,424 | 17,652,915 | 12,486,717 |
| 84,986 | 21,158 | 381,789 | 187,641 | 751,360 | 7438 | 378,563 | 1,440,731 | 9,428,761 | 6,260,525 | 637,397 | .. | .. | .. | 38,830,350 | 5,978,059 | 12,368,610 | 17,735,259 | 13,356,598 |
| 86,675 | 15,809 | 281,514 | 251,161 | 1,172 | 8388 | 437,056 | 1,436,671 | 9,400,094 | 6,503,849 | 668,794 | .. | .. | .. | 38,713,068 | 6,042,693 | 12,796,098 | 16,814,518 | 13,820,458 |
| 91,042 | 12,793 | 214,542 | 237,393 | 1,963 | 8705 | 517,678 | 1,200,525 | 9,365,868 | 6,943,056 | 673,315 | .. | .. | .. | 39,257,840 | 6,081,934 | 13,587,062 | 17,558,168 | 14,623,335 |
| 99,626 | 12,587 | 219,375 | 227,502 | 921 | 8317 | 510,775 | 1,113,799 | 8,557,443 | 6,911,515 | 691,548 | .. | .. | .. | 39,826,415 | 6,203,869 | 14,433,777 | 18,255,534 | 15,489,633 |
| 115,203 | 4677 | 66,256 | 221,614 | 865 | 8338 | 404,567 | 1,112,233 | 9,085,148 | 6,788,020 | 719,546 | .. | .. | .. | 40,386,964 | 6,614,824 | 13,927,217 | 17,746,421 | 14,930,791 |
| 150,909 | 1806 | 21,040 | 293,493 | 1,181 | 7425 | 418,766 | 1,269,031 | 8,390,153 | 6,400,129 | 726,654 | 4,556,015a | 4,370,481a | .. | 43,050,780 | 6,685,510 | 13,544,415 | 18,159,781 | 14,491,627 |
| 130,166 | 2968 | 32,985 | 263,694 | 1,428 | 7126 | 431,323 | 1,269,680 | 9,177,336 | 7,137,320 | 792,851 | 4,798,708a | 4,509,981a | 1,089,590ab | 44,366,618 | 6,737,578 | 14,490,827 | 16,900,199 | 15,520,431 |
| 150,517 | 2769 | 30,674 | 251,647 | 980,204 | 6641 | 398,010 | 1,389,398 | 9,596,267 | 8,055,223 | 840,713 | 5,079,230a | 4,602,372a | 1,134,812ab | 44,963,424 | 6,793,398 | 14,290,512 | 17,276,771 | 15,380,248 |
| 135,776 | 4850 | 74,556 | 280,175 | 1,080,691 | 9905 | 586,767 | 1,562,834 | 10,324,988 | 8,230,600 | 907,033 | 5,258,228a | 4,858,511a | 1,543,683ab | 46,938,006 | 6,834,361 | 14,143,229 | 17,013,404 | 15,299,058 |
| 141,818 | 10,371 | 184,411 | 389,570 | 1,513,180 | 11,116 | 607,919 | 1,645,313 | 11,799,740 | 8,739,633 | 975,234 | 5,699,618a | 5,140,127a | 1,571,604ab | 47,874,452 | 6,963,254 | 14,591,223 | 17,190,433 | 15,834,858 |
| 229,111 | 15,906 | 332,182 | 373,614 | 1,439,602 | 10,159 | 622,293 | 1,784,350 | 13,055,249 | 10,646,096 | 1,093,990 | 5,906,916a | 5,479,704a | 1,746,141ab | 49,591,245 | 7,057,350 | 15,570,610 | 17,314,535 | 16,964,582 |
| 238,685 | 10,171 | 195,728 | 455,558 | 1,753,784 | 7541 | 446,114 | 1,935,567 | 12,690,460 | 11,817,915 | 1,227,638 | 6,152,839a | 5,895,915a | 2,890,767ab | 52,966,447 | 7,563,069 | 16,034,848 | 18,422,274 | 17,490,035 |
| 163,539 | 20,852 | 534,031 | 507,852 | 1,951,426 | 7430 | 450,223 | 2,333,704 | 13,498,599 | 11,326,723 | 1,362,702 | 6,447,435a | 6,214,019a | 2,285,198ab | 55,899,019§ | 7,839,695 | 17,231,767 | 18,999,180 | 18,701,063 |
| Out of Loan Accounts. | Public Debt: Debentures and Stock in Circulation. (Prior to 1880 the figures are for Calendar Years.) | Debt of Local Bodies. | Banks. (Average of Four Quarters.) | Savings-Banks. | Insurances in Force in the Government Insurance Department at end of Year.¶ | Old-age Pensions, 31st March. | Friendly Societies from which returns received. | Schools and Scholars.† | Crime. | Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Schools. | Private Schools. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits. | Assets. | Liabilities. | Number of Depositors. | Balance to credit on 31st Dec. | No. of Policies. | Sums Assured and Bonuses. | No. of Pensions in force. | Amount represented. | No. of Lodges, &c. | No. of Members. | Schools. | Scholars. | Schools. | Scholars. | Convictions a Superior Courts.|| | Convictions in Magistrates' Courts.|| | ||||
there were in December, 1902, 3,742 children attending the Native schools, nearly all maintained by Government, 746 at industrial schools and orphanages, and 3,072 scholars at high schools. || For the year ending 31st December, 1902, premiums amounting to £14,100 had been received, while claims paid totalled £7,364. **The actual amount paid in pensions on the 31st March, payments in each financial year were– in 1891–92, £30,000; in 1892–93, £200,000; in 1893–94, £250,000; in 1894–95, £250,000; in 1895–96, £150,000; in 1896–97, £150,000; in 1897–98, £300,000; in 1898–99 ......... ds, &c. cAnd securing annuities amounting to £36,392 per annum. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||||||||||
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 13 | 1373 | 1853 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 21 | 1955 | 1854 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 31 | 2154 | 1855 |
| .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 28 | 2005 | 1856 |
| .. | .. | .. | 343,316 | 419,860 | 432,494 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 27 | 2010 | 1857 |
| .. | .. | .. | 448,078 | 705,738 | 616,769 | 715 | 7862 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 62 | 2589 | 1858 |
| .. | .. | .. | 541,213 | 1,003,584 | 678,474 | 802 | 7996 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 70 | 2749 | 1859 |
| .. | .. | .. | 644,521 | 992,082 | 801,588 | 1104 | 12,450 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 91 | 2903 | 1860 |
| .. | .. | .. | 882,754 | 1,235,952 | 1,097,162 | 1144 | 22,921 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 100 | 3490 | 1861 |
| .. | 836,000 | .. | 1,596,446 | 2,691,117 | 2,092,497 | 1496 | 29,768 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 145 | 6371 | 1862 |
| .. | 1,289,750 | .. | 2,092,090 | 4,028,766 | 2,962,585 | 2371 | 44,117 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 234 | 9296 | 1863 |
| .. | 2,219,450 | .. | 2,480,303 | 5,063,458 | 3,343,172 | 4669 | 94,248 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 262 | 11,357 | 1864 |
| .. | 4,368,681 | .. | 2,638,414 | 5,455,289 | 3,522,146 | 4304 | 87,400 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 332 | 10,102 | 1865 |
| .. | 5,435,728 | .. | 3,097,473 | 5,891,532 | 4,010,110 | 4513 | 91,863 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 277 | 11,040 | 1866 |
| .. | 5,781,193 | .. | 2,904,594 | 5,947,160 | 3,737,695 | 6579 | 156,855 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 240 | 11,209 | 1867 |
| .. | 7,182,743 | .. | 3,102,727 | 5,734,745 | 3,838,220 | 8121 | 243,615 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 248 | 10,973 | 1868 |
| .. | 7,360,616 | .. | 3,174,831 | 6,231,416 | 3,863,006 | 10,103 | 320,383 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 277 | 11,695 | 1869 |
| .. | 7,841,891 | .. | 3,127,769 | 6,315,354 | 3,819,670 | 12,137 | 388,804 | 59 | 30,250 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 231 | 11,990 | 1870 |
| .. | 8,900,991 | .. | 3,334,672 | 5,871,888 | 3,988,400 | 14,275 | 454,966 | 454 | 200,611 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 180 | 11,506 | 1871 |
| .. | 9,985,386 | .. | 3,919,838 | 5,429,747 | 4,628,819 | 17,289 | 597,002 | 1689 | 625,421 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 190 | 10,801 | 1872 |
| .. | 10,913,936 | .. | 4,713,806 | 7,267,720 | 5,538,030 | 21,807 | 812,144 | 2634 | 995,986 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 189 | 11,992 | 1873 |
| .. | 13,366,936 | .. | 5,564,434 | 9,954,216 | 6,490,504 | 27,215 | 943,753 | 3953 | 1,453,496 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 544 | 38,215 | 188 | 8237 | 194 | 13,741 | 1874 |
| .. | 17,400,031 | .. | 5,967,205 | 10,987,178 | 6,987,318 | 30,310 | 897,326 | 4989 | 1,836,859 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 599 | 45,562 | 182 | 7316 | 257 | 17,110 | 1875 |
| .. | 18,678,111 | .. | 6,238,471 | 11,776,070 | 7,221,399 | 32,577 | 905,146 | 6153 | 2,282,129 | .. | .. | 89 | 8560 | 680 | 51,964 | 244 | 9357 | 249 | 15,902 | 1876 |
| .. | 20,691,111 | .. | 7,185,106 | 12,992,104 | 8,152,230 | 35,709 | 964,430 | 7149 | 2,716,907 | .. | .. | 88 | 8828 | 730 | 56,239 | 252 | 9992 | 250 | 16,103 | 1877 |
| .. | 22,608,311 | .. | 8,960,369 | 15,393,630 | 10,031,009 | 39,926 | 1,043,204 | 8711 | 3,251,220 | .. | .. | 110 | 9759 | 748 | 65,040 | 236 | 9206 | 292 | 16,119 | 1878 |
| .. | 23,958,311 | .. | 8,021,073 | 16,054,295 | 9,057,463 | 42,679 | 990,337 | 10,223 | 3,726,330 | .. | .. | 138 | 13,165 | 817 | 75,556 | 257 | 10,234 | 296 | 15,821 | 1879 |
| .. | 28,185,711 | .. | 8,538,935 | 14,220,275 | 9,550,177 | 47,462 | 1,148,992 | 11,656 | 4,171,504 | .. | .. | 179 | 14,484 | 836 | 82,401 | 278 | 11,238 | 330 | 14,778 | 1880 |
| .. | 28,479,111 | 3,039,807 | 9,069,377 | 14,863,645 | 10,083,188 | 61,054 | 1,549,515 | 12,411 | 4,471,182 | .. | .. | 272 | 18,634 | 869 | 83,560 | 266 | 9987 | 270 | 13,795 | 1881 |
| .. | 29,445,011 | 3,277,584 | 8,945,346 | 17,162,234 | 10,015,273 | 68,358 | 1,832,047 | 15,892 | 5,273,164 | .. | .. | 273 | 18,700 | 911 | 87,179 | 262 | 10,002 | 265 | 16,220 | 1882 |
| .. | 31,071,582 | 3,540,046 | 8,659,477 | 17,794,761 | 9,706,700 | 73,546 | 1,784,631 | 19,917 | 5,992,111 | .. | .. | 275 | 18,848 | 943 | 92,476 | 257 | 11,255 | 258 | 16,590 | 1883 |
| .. | 32,195,422 | 3,962,330 | 9,643,214 | 18,442,139 | 10,691,599 | 79,514 | 1,926,759 | 21,003 | 6,224,571 | .. | .. | 281 | 21,144 | 987 | 97,238 | 265 | 12,203 | 287 | 17,672 | 1884 |
| .. | 33,880,722 | 4,313,223 | 10,083,296 | 18,811,567 | 11,130,244 | 85,769 | 2,142,560 | 23,218 | 6,552,242 | .. | .. | 302 | 22,794 | 1021 | 102,407 | 280 | 11,989 | 266 | 17,566 | 1885 |
| .. | 35,741,653 | 4,943,270 | 10,579,711 | 19,041,827 | 11,603,194 | 91,296 | 2,133,861 | 24,715 | 7,053,276 | .. | .. | 290 | 21,679 | 1054 | 106,328 | 288 | 12,497 | 286 | 16,428 | 1886 |
| .. | 36,758,437 | 5,620,747 | 11,031,614 | 18,799,847 | 11,995,495 | 97,496 | 2,407,776 | 25,439 | 7,136,944 | .. | .. | 347 | 24,928 | 1093 | 110,919 | 299 | 13,417 | 347 | 15,278 | 1887 |
| .. | 38,375,050 | 5,812,803 | 11,155,778 | 18,709,444 | 12,108,353 | 103,046 | 2,691,693 | 26,168 | 7,362,488 | .. | .. | 353 | 24,938 | 1128 | 112,685 | 299 | 13,893 | 308 | 14,259 | 1888 |
| .. | 38,667,950 | 5,892,050 | 11,528,424 | 17,652,915 | 12,486,717 | 110,566 | 2,858,644 | 27,218 | 7,600,537 | .. | .. | 365 | 26,013 | 1155 | 115,456 | 293 | 13,458 | 276 | 13,861 | 1889 |
| .. | 38,830,350 | 5,978,059 | 12,368,610 | 17,735,259 | 13,356,598 | 118,344 | 3,137,023 | 28,102 | 7,807,792 | .. | .. | 357 | 26,379 | 1200 | 117,912 | 298 | 13,626 | 270 | 13,885 | 1890 |
| .. | 38,713,068 | 6,042,693 | 12,796,098 | 16,814,518 | 13,820,458 | 126,886 | 3,406,949 | 29,226 | 8,390,803 | .. | .. | 364 | 27,372 | 1255 | 119,523 | 281 | 14,142 | 283 | 13,051 | 1891 |
| .. | 39,257,840 | 6,081,934 | 13,587,062 | 17,558,168 | 14,623,335 | 135,827 | 3,580,544 | 30,316 | 8,580,817 | .. | .. | 379 | 28,754 | 1302 | 122,620 | 274 | 14,456 | 241 | 13,290 | 1892 |
| .. | 39,826,415 | 6,203,869 | 14,433,777 | 18,255,534 | 15,489,633 | 147,199 | 3,966,849 | 31,709 | 8,821,255 | .. | .. | 372 | 29,763 | 1355 | 124,690 | 299 | 14,922 | 304 | 13,457 | 1893 |
| .. | 40,386,964 | 6,614,824 | 13,927,217 | 17,746,421 | 14,930,791 | 154,405 | 4,066,594 | 32,907 | 9,232,543 | .. | .. | 369 | 29,963 | 1410 | 127,300 | 302 | 14,627 | 300 | 12,613 | 1894 |
| .. | 43,050,780 | 6,685,510 | 13,544,415 | 18,159,781 | 14,491,627 | 163,513 | 4,620,696 | 33,968 | 9,345,229 | .. | .. | 376 | 30,905 | 1464 | 129,856 | 298 | 14,659 | 344 | 13,067 | 1895 |
| 1,089,590ab | 44,366,618 | 6,737,578 | 14,490,827 | 16,900,199 | 15,520,431 | 175,173 | 5,065,864 | 34,772 | 9,415,693 | .. | .. | 392 | 31,825 | 1533 | 131,037 | 283 | 13,947 | 291 | 14,149 | 1896 |
| 1,134,812ab | 44,963,424 | 6,793,398 | 14,290,512 | 17,276,771 | 15,380,248 | 187,954 | 5,520,080 | 36,174 | 9,857,010 | .. | .. | 388 | 32,670 | 1585 | 132,197 | 278 | 14,447 | 303 | 14,875 | 1897 |
| 1,543,683ab | 46,938,006 | 6,834,361 | 14,143,229 | 17,013,404 | 15,299,058 | 199,464 | 5,746,887 | 37,848 | 10,124,227 | 7,443a | 128,082a | 410 | 35,501 | 1624 | 131,621 | 294 | 14,782 | 351 | 16,642 | 1898 |
| 1,571,604ab | 47,874,452 | 6,963,254 | 14,591,223 | 17,190,433 | 15,834,858 | 213,172 | 6,128,297 | 39,366 | 10,341,702 | 11,285a | 193,718a | 433 | 38,202 | 1645 | 131,315 | 307 | 15,295 | 376 | 17,286 | 1899 |
| 1,746,141ab | 49,591,245 | 7,057,350 | 15,570,610 | 17,314,535 | 16,964,582 | 228,883 | 6,665,344 | 40,368 | 10,639,978 | 12,405a | 211,965a | 444 | 40,257 | 1674 | 130,724 | 304 | 15,555 | 369 | 18,989 | 1900 |
| 2,890,767ab | 52,966,447 | 7,563,069 | 16,034,848 | 18,422,274 | 17,490,035 | 245,024 | 7,268,103 | 41,291 | 10,627,263c | 12,776a | 217,192a | 445 | 41,236 | 1677 | 131,351‡ | 309 | 15,344 | 328 | 20,326 | 1901 |
| 2,285,198ab | 55,899,019§ | 7,839,695 | 17,231,767 | 18,999,180 | 18,701,063 | 261,948 | 7,876,877 | 42,406 | 11,024,734c | 12,481a | 211,595a | .. | .. | 1757 | 132,262‡ | 297 | 15,624 | 334 | 22,300 | 1902 |
† Statistics of schools and scholars not being complete for years prior to 1874, no figures are entered. ‡ In addition to these there were in December, 1902, 3,742 children attending £2,313,239, leaving a net indebtedness of £53,585,780. || Excluding Maoris. ¶ An accident-insurance branch was opened on 7th June, 1901. For the year ending 31st December, 1902, premiums am £207,509; and in 1903 £209,156. During the last twelve years the Public Works Fund has been assisted by contributions from the revenue of the Consolidated Fund to the extent of £3,405,000; the payments in each financial year were—in 1891–92, £30,000; is 1901–1902, £500,000; in 1902–1903, £200,000. Further receipts in aid have been given since the year 1870 by way of contributions of stamp duties, release of sinking funds, &c. cAnd securing annuities amounting to £36 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 339 | 1631 | 172 | 628 | 445 | 7874 | 284,100 | 1,134,641 | 3228 | 147,535 | 484,150 | 5,563,455 | 8,374,585 | 231,218 | .. | .. | .. | 23,958,311 | .. | 8,021,073 |
| 2717 | 8350 | 717 | 1983 | 894 | 15,617 | 303,215 | 1,220,263 | 4725 | 242,817 | 544,973 | 6,102,300 | 6,162,011 | 299,923 | .. | .. | .. | 28,185,711 | .. | 8,538,935 |
| 2426 | 8496 | 3056 | 6112 | 1308 | 26,285 | 250,683 | 996,867 | 5460 | 253,778 | 574,880 | 5,762,250 | 7,457,045 | 337,262 | .. | .. | .. | 28,479,111 | 3,039,807 | 9,069,377 |
| 11,264 | 52,088 | 3553 | 10,130 | 2040 | 41,955 | 230,893 | 921,664 | 5533 | 260,369 | 921,290 | 6,253,350 | 8,609,270 | 378,272 | .. | .. | .. | 29,445,011 | 3,277,584 | 8,945,346 |
| 8869 | 42,020 | 2519 | 6892 | 2013 | 36,761 | 222,899 | 892,445 | 6518 | 336,606 | 1,121,257 | 6,855,244 | 7,974,038 | 421,764 | .. | .. | .. | 31,071,582 | 3,540,046 | 8,659,477 |
| 15,766 | 66,593 | 10,342 | 25,074 | 1525 | 23,475 | 246,392 | 988,953 | 6393 | 342,151 | 1,116,799 | 6,942,486 | 7,663,888 | 480,831 | .. | .. | .. | 32,195,422 | 3,962,330 | 9,643,214 |
| 24,923 | 102,387 | 15,245 | 35,742 | 1063 | 16,316 | 222,732 | 890,056 | 5876 | 299,762 | 1,154,819 | 6,591,911 | 7,479,921 | 511,063 | .. | .. | .. | 33,880,722 | 4,313,223 | 10,083,296 |
| 23,175 | 105,537 | 16,429 | 45,657 | 1112 | 15,922 | 235,578 | 939,648 | 4920 | 257,653 | 1,058,552 | 6,386,682 | 6,759,013 | 534,353 | .. | .. | .. | 35,741,653 | 4,943,270 | 10,579,711 |
| 17,018 | 54,921 | 23,913 | 54,562 | 1578 | 25,094 | 187,938 | 74,878 | 6790 | 362,434 | 1,085,468 | 6,551,081 | 6,245,515 | 558,620 | .. | .. | .. | 36,758,437 | 5,620,747 | 11,031,614 |
| 29,995 | 118,252 | 36,682 | 78,918 | 4042 | 75,269 | 229,608 | 914,309 | 8482 | 380,933 | 1,274,780 | 7,255,128 | 5,941,900 | 613,895 | .. | .. | .. | 38,375,050 | 5,812,803 | 11,155,778 |
| 37,955 | 146,840 | 26,558 | 67,105 | 17,084 | 361,182 | 197,492 | 785,490 | 7519 | 329,590 | 1,606,828 | 9,042,008 | 6,308,863 | 586,445 | .. | .. | .. | 38,667,950 | 5,892,050 | 11,528,424 |
| 34,816 | 122,701 | 40,451 | 84,986 | 21,158 | 381,789 | 187,641 | 751,360 | 7438 | 378,563 | 1,440,731 | 9,428,761 | 6,260,525 | 637,397 | .. | .. | .. | 38,830,350 | 5,978,059 | 12,368,610 |
| 39,430 | 150,258 | 39,770 | 86,675 | 15,809 | 281,514 | 251,161 | 1,172 | 8388 | 437,056 | 1,436,671 | 9,400,094 | 6,503,849 | 668,794 | .. | .. | .. | 38,713,068 | 6,042,693 | 12,796,098 |
| 53,930 | 227,162 | 41,493 | 91,042 | 12,793 | 214,542 | 237,393 | 963 | 8705 | 517,678 | 1,200,525 | 9,365,868 | 6,943,056 | 673,315 | .. | .. | .. | 39,257,840 | 6,081,934 | 13,587,062 |
| 58,149 | 254,645 | 46,201 | 99,626 | 12,587 | 219,375 | 227,502 | 921 | 8317 | 510,775 | 1,113,799 | 8,557,443 | 6,911,515 | 691,548 | .. | .. | .. | 39,826,415 | 6,203,869 | 14,433,777 |
| 60,771 | 251,280 | 55,655 | 115,203 | 4677 | 66,256 | 221,614 | 8,865 | 8338 | 404,567 | 1,112,233 | 9,085,148 | 6,788,020 | 719,546 | .. | .. | .. | 40,386,964 | 6,614,824 | 13,927,217 |
| 57,964 | 227,601 | 76,743 | 150,909 | 1806 | 21,040 | 293,493 | 1,1181 | 7425 | 418,766 | 1,269,031 | 8,390,153 | 6,400,129 | 726,654 | 4,556,015a | 4,370,481a | .. | 43,050,780 | 6,685,510 | 13,544,415 |
| 71,353 | 281,716 | 71,372 | 130,166 | 2968 | 32,985 | 263,694 | 1,0428 | 7126 | 431,323 | 1,269,680 | 9,177,336 | 7,137,320 | 792,851 | 4,798,708a | 4,509,981a | 1,089,590ab | 44,366,618 | 6,737,578 | 14,490,827 |
| 99,002 | 402,605 | 77,683 | 150,517 | 2769 | 30,674 | 251,647 | 980,204 | 6641 | 398,010 | 1,389,398 | 9,596,267 | 8,055,223 | 840,713 | 5,079,230a | 4,602,372a | 1,134,812ab | 44,963,424 | 6,793,398 | 14,290,512 |
| 96,801 | 403,690 | 68,711 | 135,776 | 4850 | 74,556 | 280,175 | 1,080,691 | 9905 | 586,767 | 1,562,834 | 10,324,988 | 8,230,600 | 907,033 | 5,258,228a | 4,858,511a | 1,543,683ab | 46,938,006 | 6,834,361 | 14,143,229 |
| 136,086 | 571,799 | 69,440 | 141,818 | 10,371 | 184,411 | 389,570 | 1,513,180 | 11,116 | 607,919 | 1,645,313 | 11,799,740 | 8,739,633 | 975,234 | 5,699,618a | 5,140,127a | 1,571,604ab | 47,874,452 | 6,963,254 | 14,591,223 |
| 172,583 | 740,620 | 102,849 | 229,111 | 15,906 | 332,182 | 373,614 | 1,439,602 | 10,159 | 622,293 | 1,784,350 | 13,055,249 | 10,646,096 | 1,093,990 | 5,906,916a | 5,479,704a | 1,746,141ab | 49,591,245 | 7,057,350 | 15,570,610 |
| 201,591 | 882,406 | 104,294 | 238,685 | 10,171 | 195,728 | 455,558 | 1,753,784 | 7541 | 446,114 | 1,935,567 | 12,690,460 | 11,817,915 | 1,227,638 | 6,152,839a | 5,895,915a | 2,890,767ab | 52,966,447 | 7,563,069 | 16,034,848 |
| 253,998 | 1,205,802 | 74,746 | 163,539 | 20,852 | 534,031 | 507,852 | 1,951,426 | 7430 | 450,223 | 2,333,704 | 13,498,599 | 11,326,723 | 1,362,702 | 6,447,435a | 6,214,019a | 2,285,198ab | 55,899,198ab | 7,839,695 | 17,231,767 |
| Public Trust Office. | Government Valuation of Land and Improvements: Comparison, years 1891 and 1903. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature of Business. | 1903. Number of Estates. | 1903. Value of Estates. | In Counties. | In Boroughs. | The Colon | ||
| £ | £ | £ | |||||
| Wills and trusts (including sinking funds accounts) | 744 | 1,279,743 | Unimproved value, 1903 | 76,097,894 | Unimproved value, 1903 | 27,378,310 | Unimproved value, 1903 |
| Intestate estates | 989 | 197,368 | Unimproved value, 1891 | 57,880,233 | Unimproved value, 1891 | 17,907,662 | Unimproved value, 1891 |
| Real estates | 71 | 7,585 | |||||
| Lunatic estates | 802 | 170,585 | Increase | 18,217,661 | Increase | 9,470,648 | Increase |
| Native reserves | 143 | 375,000 | |||||
| West Coast Settlement Reserves | 312 | 655,000 | Value of Improvements, 1903 | 37,028,924 | Value of improvements, 1903 | 28,344,253 | Value of improvements, |
| Unclaimed lands | 253 | 21,504 | Value of improvements, 1891 | 27,922,735 | Value of improvements, 1891 | 18,442,562 | Value of improvements, |
| Total | 3,314 | 2,706,785 | Increase | 9,106,189 | Increase | 9,901,691 | Increase |
74, no figures are entered. ‡ In addition to these there were in December, 1902, 3,742 children attending the Native schools, nearly all maintained by Government, 746 at industrial schools ¶ An accident-insurance branch was opened on 7th June, 1901. For the year ending 31st December, 1902, premiums amounting to £14,100 had been received, while claims paid totalled £7,364. m the revenue of the Consolidated Fund to the extent of £3,405,000; the payments in each financial year were—in 1891–92, £30,000; in 1892–93, £200,000; in 1893–94, £250,000; in 1894–95, £250,000; in 1895–96, £150,000; the year 1870 by way of contributions of stamp duties, release of sinking funds, &c. cAnd securing annuities amounting to £36,392 per annum. | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147,535 | 484,150 | 5,563,455 | 8,374,585 | 231,218 | .. | .. | .. | 23,958,311 | .. | 8,021,073 | 16,054,295 | 9,057,463 | 42,679 | 990,337 | 10,223 | 3,726,330 | .. | .. | 110 |
| 242,817 | 544,973 | 6,102,300 | 6,162,011 | 299,923 | .. | .. | .. | 28,185,711 | .. | 8,538,935 | 14,220,275 | 9,550,177 | 47,462 | 1,148,992 | 11,656 | 4,171,504 | .. | .. | 179 |
| 253,778 | 574,880 | 5,762,250 | 7,457,045 | 337,262 | .. | .. | .. | 28,479,111 | 3,039,807 | 9,069,377 | 14,863,645 | 10,083,188 | 61,054 | 1,549,515 | 12,411 | 4,471,182 | .. | .. | 272 |
| 260,369 | 921,290 | 6,253,350 | 8,609,270 | 378,272 | .. | .. | .. | 29,445,011 | 3,277,584 | 8,945,346 | 17,162,234 | 10,015,273 | 68,358 | 1,832,047 | 15,892 | 5,273,164 | .. | .. | 273 |
| 336,606 | 1,121,257 | 6,855,244 | 7,974,038 | 421,764 | .. | .. | .. | 31,071,582 | 3,540,046 | 8,659,477 | 17,794,761 | 9,706,700 | 73,546 | 1,784,631 | 19,917 | 5,992,111 | .. | .. | 275 |
| 342,151 | 1,116,799 | 6,942,486 | 7,663,888 | 480,831 | .. | .. | .. | 32,195,422 | 3,962,330 | 9,643,214 | 18,442,139 | 10,691,599 | 79,514 | 1,926,759 | 21,003 | 6,224,571 | .. | .. | 281 |
| 299,762 | 1,154,819 | 6,591,911 | 7,479,921 | 511,063 | .. | .. | .. | 33,880,722 | 4,313,223 | 10,083,296 | 18,811,567 | 11,130,244 | 85,769 | 2,142,560 | 23,218 | 6,552,242 | .. | .. | 302 |
| 257,653 | 1,058,552 | 6,386,682 | 6,759,013 | 534,353 | .. | .. | .. | 35,741,653 | 4,943,270 | 10,579,711 | 19,041,827 | 11,603,194 | 91,296 | 2,133,861 | 24,715 | 7,053,276 | .. | .. | 290 |
| 362,434 | 1,085,468 | 6,551,081 | 6,245,515 | 558,620 | .. | .. | .. | 36,758,437 | 5,620,747 | 11,031,614 | 18,799,847 | 11,995,495 | 97,496 | 2,407,776 | 25,439 | 7,136,944 | .. | .. | 347 |
| 380,933 | 1,274,780 | 7,255,128 | 5,941,900 | 613,895 | .. | .. | .. | 38,375,050 | 5,812,803 | 11,155,778 | 18,709,444 | 12,108,353 | 103,046 | 2,691,693 | 26,168 | 7,362,488 | .. | .. | 353 |
| 329,590 | 1,606,828 | 9,042,008 | 6,308,863 | 586,445 | .. | .. | .. | 38,667,930 | 3,892,050 | 11,528,424 | 17,652,915 | 12,486,717 | 110,566 | 2,858,644 | 27,218 | 7,600,537 | .. | .. | 365 |
| 378,563 | 1,440,731 | 9,428,761 | 6,260,525 | 637,397 | .. | .. | .. | 38,830,350 | 5,978,059 | 12,368,610 | 17,735,259 | 13,356,598 | 118,344 | 3,137,023 | 28,102 | 7,807,792 | .. | .. | 357 |
| 437,056 | 1,436,671 | 9,400,094 | 6,503,849 | 668,794 | .. | .. | .. | 38,713,068 | 6,042,693 | 12,796,098 | 16,814,518 | 13,820,458 | 126,886 | 3,406,949 | 29,226 | 8,390,803 | .. | .. | 364 |
| 517,678 | 1,200,525 | 9,365,868 | 6,943,056 | 673,315 | .. | .. | .. | 39,257,840 | 16,081,934 | 13,587,062 | 17,558,168 | 14,623,335 | 135,827 | 3,580,544 | 30,316 | 8,580,817 | .. | .. | 379 |
| 510,775 | 1,113,799 | 8,557,443 | 6,911,515 | 691,548 | .. | .. | .. | 39,826,415 | 6,203,869 | 14,433,777 | 18,255,534 | 15,489,633 | 147,199 | 3,966,849 | 31,709 | 8,821,255 | .. | .. | 372 |
| 404,567 | 1,112,233 | 9,085,148 | 6,788,020 | 719,546 | .. | .. | .. | 40,386,964 | 6,614,824 | 13,927,217 | 17,746,421 | 14,930,791 | 154,405 | 4,066,594 | 32,907 | 9,232,543 | .. | .. | 369 |
| 418,766 | 1,269,031 | 8,390,153 | 6,400,129 | 726,654 | 4,556,015a | 4,370,481a | .. | 43,050,780 | 6,685,510 | 13,544,415 | 18,159,781 | 14,491,627 | 163,513 | 4,620,696 | 33,968 | 9,345,229 | .. | .. | 376 |
| 431,323 | 1,269,680 | 9,177,336 | 7,137,320 | 792,851 | 4,798,708a | 4,509,981a | 1,089,590ab | 44,366,618 | 6,737,578 | 14,490,827 | 16,900,199 | 15,520,431 | 175,173 | 5,065,864 | 34,772 | 9,415,693 | .. | .. | 392 |
| 398,010 | 1,389,398 | 9,596,267 | 8,055,223 | 840,713 | 5,079,230a | 4,602,372a | 1,134,812ab | 44,963,424 | 6,793,398 | 14,290,512 | 17,276,771 | 15,380,248 | 187,954 | 15,520,080 | 36,174 | 9,857,010 | .. | .. | 388 |
| 586,767 | 1,562,834 | 10,324,988 | 8,230,600 | 907,033 | 5,258,228a | 4,858,511a | 1,543,683ab | 46,938,006 | 6,834,361 | 14,143,229 | 17,013,404 | 15,299,058 | 199,464 | 5,746,887 | 37,848 | 10,124,227 | 7,443a | 128,082a | 410 |
| 607,919 | 1,645,313 | 11,799,740 | 8,739,633 | 975,234 | 5,699,618a | 5,140,127a | 1,571,604ab | 47,874,452 | 6,963,254 | 14,591,223 | 17,190,433 | 15,834,858 | 213,172 | 6,128,297 | 39,366 | 10,341,702 | 11,285a | 193,781a | 433 |
| 622,293 | 1,784,350 | 13,055,249 | 10,646,096 | 1,093,990 | 5,906,916a | 5,479,704a | 1,746,141ab | 49,591,245 | 7,057,350 | 15,570,610 | 17,314,535 | 16,964,582 | 228,883 | 6,665,344 | 40,368 | 10,639,978 | 12,405a | 211,965a | 444 |
| 446,114 | 1,935,567 | 12,690,460 | 11,817,915 | 1,227,638 | 6,152,839a | 5,895,915a | 2,890,767ab | 52,966,447 | 7,563,069 | 16,034,848 | 18,422,274 | 17,490,035 | 245,024 | 7,268,103 | 41,291 | 10,627,263c | 12,776a | 217,192a | 445 |
| 450,223 | 2,333,704 | 13,498,599 | 11,326,723 | 1,362,702 | 6,447,435a | 6,214,019a | 2,285,198a | 55,899,019§ | 7,839,695 | 17,231,767 | 18,999,180 | 18,701,063 | 261,948 | 7,876,877 | 42,406 | 11,024,734c | 12,481a | 211,595a | .. |
| Government Valuation of Land and Improvements: Comparison, years 1891 and 1903. | Government Advances to Settlers. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Counties. | In Boroughs. | The Colony. | Loans authorised to 31st March, 1903. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Unimproved value, 1903 | 76,097,894 | Unimproved value, 1903 | 27,378,310 | Unimproved value, 1903 | 103,476,204 | ||
| Unimproved value, 1891 | 57,880,233 | Unimproved value, 1891 | 17,907,662 | Unimproved value, 1891 | 75,787,895 | ||
| Increase | 18,217,661 | Increase | 9,470,648 | Increase | 27,688,309 | Number of applications | 12,922 |
| Value of Improvements, 1903 | 37,028,924 | Value of improvements, 1903 | 28,344,253 | Value of improvements, 1903 | 65,373,177 | Amount applied for | £4,903,515 |
| Value of improvements, 1891 | 27,922,735 | Value of improvements, 1891 | 18,442,562 | Value of improvements, 1891 | 46,365,297 | Amount of advances authorised | £4,316,940 |
| Increase | 9,106,189 | Increase | 9,901,691 | Increase | 19,007,880 | ||
