Table of Contents
The first quarter of the shield depicts four stars as representative of the Southern Cross, then three ships symbolising the importance of New Zealand's sea trade; in the second quarter is a fleece representing the farming industry. The wheat sheaf in the third quarter represents the agricultural industry, whilst the crossed hammers in the fourth quarter represent the mining industry.
The supporters on either side of the shield consist of a Maori Chieftain holding a taiaha (a Maori war weapon) and a European woman holding the New Zealand Ensign.
Surmounting the Arms is the St. Edward's Crown which was used in the Coronation ceremony of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II. The crown symbolises the fact that Her Majesty is Queen of New Zealand under the New Zealand Royal Titles Act 1953.
(These Arms may not be used except with the consent of the Minister of Internal Affairs.)
New Zealand's economic progress is comprehensively recorded in the facts and figures of this volume, and other characteristics of the country are also covered. This annual compendium brings as nearly up to date as possible a wide range of statistical and general information for current reference and historical purposes.
This, the sixty-sixth issue of the Yearbook, has been entirely reset and the opportunity has been taken to revise the order of the subject matter as well as make even more substantial revision than usual to text and tables. Changes have been made in the order of some sections to bring allied subjects within the following broad groups; physiography, demography, and social characteristics; transport and communications; production; trade, prices, and consumption; finance; labour; and general.
The first section on physiography has been enlarged by general surveys on climate, geology, and earthquakes. The general farming section has been supplemented by a survey on soils and land use, and a review of the tourist industry has been added to the miscellaneous section. New sections have been created for communications and marketing.
A special article deals with university education for science and technology, a subject of growing importance to New Zealand's development.
The set of photographs illustrates some New Zealand buildings.
With the resetting, a new set of symbols in the statistical tables has been introduced and changes of format have been made.
I desire to express my appreciation to officers of this and other Government Departments for their assistance in preparing material and to the Government Printer and his staff for cooperation in the printing of this volume. The complete resetting of the Yearbook has made additional exacting demands both in printing and in editing. My thanks for their comprehensive contribution to the production of the Yearbook are extended to Mr J. B. McKinney, M.A., ADMIN, PROF., Editor of Publications, and members of the Editorial Branch and Statistical Draughting Unit of the Department of Statistics.

GOVERNMENT STATISTICIAN
Department of Statistics,
Wellington,
30 June 1961.
SYMBOLS
The interpretation of the symbols used in the tables throughout this publication is as follows:
| – | nil or zero |
| .. | figures not available |
| not yet available = space left blank | |
| … | not applicable |
| – – | amount too small to be expressed |
VALUES
All values are shown in New Zealand currency.
MEASURES
Unless otherwise stated, a ton is a long ton (2,240 1b).
ROUNDING
On occasions figures are rounded off to the nearest thousand or some other convenient unit. This may result in a total disagreeing slightly with the total of the individual items as shown in tables. Where figures are rounded the unit is in general expressed in words below the table headings, but where space does not allow this the unit may be shown as 000 for thousand, etc.
FISCAL YEARS
Figures for fiscal years ended 31 March (the fiscal year) are indicated in the text and headings of tables; otherwise figures are mainly for calendar years.
ABBREVIATIONS
| bd. ft. | board feet |
| ctd. | continued |
| cu. ft. | cubic feet |
| cwt | hundredweight |
| E | east |
| ft | feet |
| g | gramme |
| gal | gallon |
| h | hour |
| h.p. | horsepower |
| in. | inch |
| kW | kilowatt |
| kWh | kilowatt-hour |
| lb | pound |
| min | minute |
| mm | millimetre |
| N | north |
| oz | ounce |
| £(000) | thousand pounds |
| £(m) | million pounds |
| S | South |
| sq. ft. | square feet |
| W | west |
| y | yard |
GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION – The islands of New Zealand have been shaped from the projecting crests of earth folds which rise as broad ridges from the floor of the South Pacific Ocean, 1,000 miles east of the continent of Australia. There are three main islands – North, South, and Stewart separated only by relatively narrow straits – with adjacent islets and a small group called Chatham Islands, 536 miles to the east. Dating from 1842 the administrative boundaries of New Zealand, exclusive of island territories, extend from 33 degrees to 53 degrees south latitude and from 162 degrees east longitude to 173 degrees west longitude. Inhabited outlying minor islands are Raoul Island in the Kermadec Group, 614 miles north-east of the Bay of Islands, and Campbell Island, 320 miles south of Stewart Island.
New Zealand is also responsible for the administration of four island groups in the south-west Pacific – the Cook Islands, Niue Island, the Tokelau Islands, and Western Samoa. The first three are incorporated within the boundaries of New Zealand, while Western Samoa has been administered as a trust territory since 1946. The principal island of the Cook Group, Rarotonga, is 1,638 miles north of Auckland, and Niue to the west of the Cook Islands is a similar distance away. Lying to the north-west of the Cook Islands are the Tokelau Islands. The Trust Territory of Western Samoa is some 1,600 miles north-east from Auckland. In all, there are 23 islands scattered over a vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean making up New Zealand's island territories. The territorial area reaches to within 8 degrees of the Equator and extends south to the Tropic of Capricorn, while in longitude it covers nearly 20 degrees (156 degrees west to 173 degrees west).
The Ross Dependency, some 1,400 miles to the south, has been under New Zealand's jurisdiction since 1923 and comprises the sector of the Antarctic continent between 160 degrees east and 150 degrees west longitude, together with the islands lying between those degrees of longitude and south of latitude 60 degrees south.
The administrative area of New Zealand can be classified as follows. In this volume, in general, New Zealand refers to the group of islands shown in (a) only, unless it is expressly stated that the other islands as a whole or in part are included.
| New Zealand: | Area in Square Miles |
|---|---|
*Situated off North Island. †Situated off South Island. | |
| (a) Exclusive of island territories– | |
| North Island | 44,281 |
| South Island | 58,093 |
| Stewart Island | 670 |
| Chatham Island | 372 |
| Minor islands – | |
| Inhabited – | |
| Kermadec Islands* | 13 |
| Campbell Island† | 44 |
| Uninhabited (areas in parentheses) | 263 |
| Three Kings* (3); Snares† (1); Solander† (1/2); Antipodes† (24); Bounty† (1/2); Auckland† (234). | |
| Total New Zealand, exclusive of island territories | 103,736 |
| (b) Island territories – | |
| Tokelau Islands, comprised of – | |
| Fakaofo Island, Nukunono Island, Atafu Island | 4 |
| Cook and associated islands, comprised of – | |
| Southern Group | 78 |
| Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Mangaia, Mauke, Atiu, Takutea, Mitiaro, Manuae and Te-au-o-tu. | |
| Northern Group | 12 |
| Palmerston, Pukapuka, Penrhyn, Suwarrow, Manihiki, Nassau, Rakahanga. | |
| Niue Island | 100 |
| Total island territories | — 194 |
| (c) Ross Dependency (Estimated) | 160,000 |
| Total New Zealand, inclusive of island territories and Ross Dependency | 263,930 |
| Trust Territory of Western Samoa | 1,133 |
The total area of the foregoing groups, exclusive of the Ross Dependency and the Trust Territory of Western Samoa, is 103,930 square miles. Elsewhere in this issue – viz, in the section on land tenure, settlement, etc. – the aggregate area of New Zealand appears as 66,390,700 acres – i.e., 103,736 square miles. The latter area does not include the Cook and associated islands or the Tokelau Islands. Western Samoa is likely to become an independent territory from 1 January 1962.
The relevant Proclamations, defining from time to time the administrative area of New Zealand, are briefly referred to in Section 2.
GEOGRAPHICAL FEATURES: Coastline – Since the combined length of the North and South Islands extends just over a thousand miles, and since the width of neither Island exceeds 280 miles at its broadest point, New Zealand possesses a very lengthy coastline in proportion to its area. With the exception of the low-lying North Auckland Peninsula, the New Zealand land mass lies along a south-westerly and north-easterly axis, parallel to the direction of its mountain chains.
By reason of the latter fact the coastline is, on the whole, not greatly indented; and, as a consequence, New Zealand is not well endowed with natural harbours. In the North Island, Auckland and Wellington are the only two safe natural harbours of which the fullest commercial use can be made. On the east coast of the North Auckland Peninsula several deep and sheltered harbours exist, but as production from the hinterland is limited they are of little economic consequence at present. In the South Island the Marlborough Sounds and the West Coast Sounds form perfect land-locked harbours, but owing to their situations and to the rugged nature of the terrain they have – with the exception of Queen Charlotte Sound – little or no commercial utility. Where vital localities have not been endowed with ideal harbours it has been necessary to improve existing facilities by dredging and by breakwater construction, etc. In this manner efficient ports, capable of accommodating overseas vessels, have been formed in Lyttelton, Otago, and Bluff Harbours. On the west coast of both Islands the strong ocean drifts and high seas cause shoaling at river mouths and harbour entrances, while on the east coast of the South Island similar circumstances prevail, due to the large quantities of shingle brought down by the rivers being spread along the coast by ocean currents. The mountainous nature of the country makes the haulage of goods to and from the better equipped natural harbours both costly and difficult, and the construction and maintenance of further ports at various points along the coasts of both Islands has been necessary, either by dredging river mouths or by harbour-construction work.
Mountains – The mountainous nature of New Zealand is one of its most striking physical characteristics, less than one-quarter of the land surface lying below the 650 ft contour. In the North Island the higher mountains occupy approximately one-tenth of the surface; but, with the exception of the four volcanic peaks of Egmont (8,260 ft), Ruapehu (9,175 ft), Ngauruhoe (7,515 ft), and Tongariro (6,458 ft), they do not exceed an altitude of 6,000 ft. Of these four volcanoes only the first named can be classed as dormant. Ruapehu was particularly active from March 1945 to the end of that year, being responsible for considerable deposits of volcanic ash over a very wide area, while spectacular activity was exhibited by Ngauruhoe in 1949 and again in 1953 and 1954. In both cases violent eruptions alternated with quieter periods. Other volcanoes include Mount Tarawera and White Island, each of which has, upon one occasion within historical times, erupted with disastrous consequences. Closely connected with the volcanic system are the multitudinous hot springs and geysers.
The mountain system of the North Island runs generally in a south-west direction, parallel to the coast, from East Cape to Turakirae Head, and includes the following ranges from the north: Raukumara, Huiarau, Ruahine, Tararua, and Rimutaka. This chain is flanked on the west between the Huiarau and Ruahine by the Ahimanawa, Kaweka, and Kaimanawa Ranges, while west of the Kaimanawa is the National Park volcanic group comprising Mounts Ruapehu, Ngauruhoe, and Tongariro. The Hauhangaroa and Rangitoto Ranges run in a northerly direction from the National Park group. In the east the Moehau Range parallels the length of the Coromandel Peninsula. Mount Egmont forms the only country above 4,000 ft on the west coast of this Island.
The South Island is much more mountainous than the North, but shows fewer manifestations of recent volcanic activity. Along almost the entire length of the Island runs the massive chain known as the Southern Alps, which attains its greatest height in Mount Cook (12,349 ft), while no fewer than 17 peaks exceed 10,000 ft. West and north-west of the main portion of the Southern Alps are the Victoria, Brunner, and Lyell Ranges and the Tasman Mountains, the Victoria Range being flanked by the Paparoa Range. To the north run the St. Arnaud and Richmond Ranges, while to the north-east are the Spenser Mountains and the Kaikoura and Seaward Kaikoura Ranges, the two latter ranges running parallel to the east coast. The south portion of the Southern Alps breaks up into a miscellany of ranges dominating the mountainous Fiord and north-western Southland regions.
As might be expected, the higher mountains of the South Island have exerted a greater influence on the economic development of the country than those of the North Island. For many years the Southern Alps were an effective barrier to communication by land between the east and west coasts, while their climatic effects on the Canterbury plains and Otago plateaus determined the types of cultivation undertaken. Moreover, the existence of much elevated open country led to the development of pastoral holdings on a large scale. While the mountains in the North Island are not as high nor as extensive as those of the South Island, in the early days they effectively isolated various portions of the coastal plains and valleys. Their effect on climatic conditions, however, is considerably less, the rainfall being more evenly distributed. Owing to this more even distribution of the rainfall, and to the existence of considerable areas of lower relief, the foothills of the mountain systems were heavily wooded, and so proved a hindrance to agrarian development.
There are at least 223 named peaks of 7,500 ft or more in altitude. Below is a list of the peaks restricted to the four largest volcanic cones in the North Island and to mountains of a minimum height of 9,000 ft in the South Island.
| Mountain or Peak | Height (Feet) |
|---|---|
| NORTH ISLAND | |
| Ruapehu | 9,175 |
| Egmont | 8,260 |
| Ngauruhoe | 7,515 |
| Tongariro | 6,458 |
| SOUTH ISLAND | |
| Kaikoura Ranges – | |
| Tapuaenuku | 9,465 |
| Alarm | 9,400 |
| Southern Alps – | |
| Cook | 12,349 |
| Tasman | 11,475 |
| Dampier | 11,287 |
| Silberhorn | 10,757 |
| Lendenfeldt | 10,450 |
| David's Dome | 10,443 |
| Malte Brun | 10,421 |
| Torres | 10,376 |
| Teichelmann | 10,370 |
| Sefton | 10,359 |
| Haast | 10,294 |
| Elie de Beaumont | 10,200 |
| Douglas Peak | 10,107 |
| La Perouse | 10,101 |
| Haidinger | 10,059 |
| De la Beche | 9,815 |
| Aspiring | 9,957 |
| Hamilton | 9,915 |
| Glacier Peak | 9,865 |
| Arguilles Rouges | 9,731 |
| Nazomi | 9,716 |
| Darwin | 9,715 |
| Chudleigh | 9,686 |
| Annan | 9,667 |
| Low | 9,653 |
| Haeckel | 9,649 |
| Le Receveur | 9,562 |
| Goldsmith | 9,532 |
| Big Mac | 9,511 |
| Conway Peak | 9,510 |
| Bristol Top | 9,508 |
| Walter | 9,507 |
| Grey | 9,490 |
| Green | 9,307 |
| Hutton | 9,297 |
| D'Archiac | 9,279 |
| Ronald Adair | 9,276 |
| Hochstetter Dom | 9,258 |
| Earnslaw | 9,250 |
| Nathan | 9,200 |
| Barnicoat | 9,183 |
| Sibbald | 9,181 |
| Arrowsmith | 9,171 |
| Spencer | 9,167 |
| The Footstool | 9,073 |
| Rudolf | 9,039 |
| The Dwarf | 9,025 |
| Darran Range – | |
| Tutoko | 9,042 |
Glaciers – In keeping with the dimensions of the mountain system, New Zealand possesses, in the South Island, a glacial system of some magnitude. Of the glaciers the largest is the Tasman, which, with others of comparable size, rises in the more elevated area surrounding Mount Cook. Flowing down the eastern slope of the range, the Tasman Glacier has a length of 18 miles and a width of 11/4 miles. In common with other glaciers on the eastern slope, of which the more important are the Murchison (11 miles), the Mueller (8 miles), the Godley (8 miles), and the Hooker (71/4 miles), its rate of flow is slow, while its terminal face is at an altitude of somewhat over 2,000 ft. On the western slope of the range, owing to the greater snow precipitation, the glaciers are more numerous and descend to lower levels, while the steeper slope gives them a more rapid rate of flow. The two largest of these are the Fox and the Franz Josef, with lengths of 93/4 miles and 81/2 miles respectively, and terminal faces at altitudes of 670 ft and 690 ft.
As will be realised, these glaciers are an important tourist attraction, and as such have definite economic significance. Moreover, those glaciers on the eastern slopes which feed rivers utilised for irrigation and hydro-electric purposes are valuable in that they help to ensure a steady volume of water throughout the year.
Rivers – Of the numerous New Zealand rivers few are of sufficient length or volume to be navigable. Moreover, owing to the high relief of the country, they are mostly swift-flowing, while, as mentioned previously, nearly all are obstructed at their mouths by bars. For the purpose of internal communication, therefore, they are of little economic utility, and only in two or three isolated instances have they been thus consistently used. With improved roading conditions, however, their traffic has become negligible even in these cases.
As sources of hydro-electric power New Zealand rivers are of considerable importance, since their rapid rate of flow and dependable volume of ice-free water make them eminently suitable for this purpose. At the present time the Waikato and the Mangahao in the North Island and the Waitaki, Cobb, Clutha, and Waipori in the South are used for major hydro-electric schemes. The characteristics just mentioned are also important for purposes of irrigation, but, owing to the country's reliable rainfall, there are few areas other than in Canterbury and Otago where the rivers are so utilised.
Following is a list of the more important rivers. For purposes of uniformity, the length of a river is taken to be the distance from the mouth to the farthest point in the system, whether this should happen to bear the same name or that of an affluent, and is inclusive of the estimated course of a river flowing into and emerging from any lake in the system.
NORTH ISLAND
| Flowing into the Pacific Ocean– | Miles |
|---|---|
| Piako | 65 |
| Waihou (or Thames) | 95 |
| Rangitaiki | 95 |
| Whakatane | 65 |
| Waiapu (from source, Mata River) | 75 |
| Waipaoa (from source, Waipapa Stream) | 70 |
| Wairoa (from source, Hangaroa River) | 85 |
| Mohaka (from source, Taharua River) | 95 |
| Ngaruroro | 90 |
| Tukituki | 70 |
| Flowing into Cook Strait – | |
| Ruamahanga | 90 |
| Hutt | 35 |
| Otaki | 30 |
| Manawatu | 120 |
| Rangitikei | 130 |
| Turakina | 70 |
| Wangaehu | 100 |
| Wanganui | 180 |
| Waitotara | 55 |
| Patea | 75 |
| Flowing into the Tasman Sea – | |
| Waitara | 85 |
| Mokau | 85 |
| Waikato (from source, Upper Waikato River) | 270 |
| Wairoa (from source, Waiotu Stream) | 115 |
| Hokianga (from source, Waihou River | 45 |
SOUTH ISLAND
| Flowing into Cook Strait – | Miles |
|---|---|
| Aorere (from source, Spee River) | 45 |
| Takaka (from source, Cobb River) | 45 |
| Motueka | 70 |
| Waimea (from source, Wai-iti River) | 30 |
| Pelorus | 40 |
| Wairau | 105 |
| Awatere | 70 |
| Flowing into the Pacific Ocean – | |
| Clarence | 130 |
| Conway | 30 |
| Waiau-uha (or Waiau) | 105 |
| Hurunui | 90 |
| Waipara | 40 |
| Ashley | 60 |
| Waimakariri | 100 |
| Selwyn | 50 |
| Rakaia | 90 |
| Ashburton | 70 |
| Rangitata (from source, Clyde River) | 75 |
| Opihi | 50 |
| Pareora | 35 |
| Waihao | 45 |
| Waitaki (from source, Hopkins River) | 135 |
| Kakanui | 40 |
| Shag | 45 |
| Taieri | 175 |
| Clutha (from source Makarora River) | 210 |
| Flowing into Foveaux Strait – | |
| Mataura | 140 |
| Oreti | 120 |
| Aparima (Jacobs River) | 70 |
| Waiau (from source, Clinton River) | 135 |
| Flowing into the Tasman Sea – | |
| Hollyford | 50 |
| Cascade | 40 |
| Arawhata | 45 |
| Haast | 60 |
| Karangarua | 25 |
| Cook | 25 |
| Waiho (from source, Callery River) | 20 |
| Whataroa | 35 |
| Wanganui | 35 |
| Waitaha | 25 |
| Hokitika | 40 |
| Arahura | 35 |
| Taramakau | 50 |
| Grey | 75 |
| Buller (from source, Travers River) | 110 |
| Mokihinui | 35 |
| Karamea | 50 |
| Heaphy | 25 |
The discovery in 1861 that the beds of numerous rivers in the South Island contained extensive deposits of alluvial gold was of considerable importance in the economic development of the country. Not only did it lead to an increase in population and in wealth, but, through the following of the numerous streams to their sources, it also led to the rapid exploration of large tracts of remote country. The exploitation of these deposits has been carried on with varying degrees of success up to the present time by both manual and mechanical means, but the amount of gold now extracted is comparatively small.
A further factor in connection with the rivers is that, owing to the very successful acclimatisation of freshwater fish, notably trout, many of them now provide exceptionally fine fishing.
Lakes – In considering New Zealand's numerous lakes a distinction can be made, especially from the scenic viewpoint, between the lakes of the two Islands. Surrounded by extremely rugged country the larger lakes of the South Island are distinguished by the grandeur of their alpine settings, while those of the North Island, situated on a volcanic plateau, are of interest by reason of the neighbouring thermal activity. Owing to the excellence of their fishing, the North Island lakes possess an added tourist attraction. In both Islands the larger lakes are situated at high altitudes, and their consequent remoteness renders them unsuitable as a means of communication. In their functions as reservoirs the lakes of both Islands are of vital importance for the maintenance of the streams draining them and as a means of flood prevention. More especially is this case where hydro-electric schemes are involved, Lakes Waikaremoana and Taupo in the North Island, and Lakes Coleridge, Pukaki, Tekapo, Wanaka, Hawea, and Wakatipu in the South Island, being of particular significance in this respect. A series of narrow man-made lakes have been produced in connection with hydro-electric development along some of the rivers.
Some particulars of the more important lakes are given in the following table.
| Lake | Length, in Miles | Greatest Breadth, in Miles | Area, in Square Miles | Drainage Area, in Square Miles | Approximate Volume of Discharge, in Cubic Feet per Second | Maximum Height Above Sea Level in Feet (Range in Brackets)* | Greatest Depth, in Feet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *The range in lake levels is not available for all lakes. | |||||||
| NORTH ISLAND | |||||||
| Natural | |||||||
| Taupo | 25 | 17 | 234 | 1,270 | 4,490 | 1,172 (5) | 522 |
| Rotorua | 71/2 | 6 | 31 | 203 | .. | 920 (2) | 84 |
| Rotoiti | 10 | 3 | 13 | 248 | 852 | 916 (2) | 230 |
| Tarawera | 7 | 51/2 | 14 | 72 | 273 | 981 (2) | 285 |
| Rotoaira | 3 | 13/4 | 5 | 50 | 240 | 1,852 (3) | .. |
| Waikaremoana | 12 | 6 | 21 | 165 | 623 | 2,015 (45) | 840 |
| Wairarapa | 12 | 4 | 31 | 1,236 | .. | 5 | 64 |
| Rotoehu | 3 | 2 | 3 | 17 | .. | 968 (4) | .. |
| Rotoma | 31/4 | 21/4 | 41/2 | 12 | .. | 1,036 (6) | .. |
| Okataina | 4 | 3 | 4 | 25 | .. | 1,018 (9) | .. |
| Okareka | 11/2 | 11/4 | 11/4 | 8 | .. | 1,160 (4) | .. |
| Rotomahana | 4 | 13/4 | 31/2 | 27 | .. | 1,116 (22) | .. |
| Rerewhakaitu | 21/2 | 13/4 | 3 | .. | .. | 1,441 (4) | .. |
| Tikitapu | 1 | 3/4 | 1/2 | .. | .. | 1,364 | .. |
| Rotokakahi | 21/2 | 1 | 13/4 | 11 | 40 | 1,298 | .. |
| Artificial | |||||||
| Ohakuri | 21 | 1/4 | 51/2 | 1,850 | 5,540 | 942 | .. |
| Atiamuri | 4 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1,980 | 5,830 | 826 | .. |
| Whakamaru | 131/2 | 1/2 | 3 | 2,155 | 6,160 | 742 | .. |
| Maraetai | 41/2 | 1/2 | 11/2 | 2,390 | 6,730 | 618 | .. |
| Waipapa | 6 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 2,500 | 7,010 | 417 | .. |
| Arapuni | 10 | 1/2 | 5 | 2,655 | 7,310 | 363 (2) | .. |
| Karapiro | 15 | 1/4 | 3 | 2,880 | 7,820 | 176 | .. |
| Whakamarino | 1/2 | 1/4 | 1/10 | 900 | .. | ||
| SOUTH ISLAND | |||||||
| Natural | |||||||
| Rotoiti | 9 | 11/2 | 4 | 71 | 440 | 2,020 (6) | 250 |
| Rotoroa | 51/2 | 2 | 9 | 145 | 960 | 1,462 (5) | 499 |
| Brunner | 51/2 | 51/2 | 15 | 160 | .. | 280 | 357 |
| Kanieri | 6 | 11/4 | 6 | 11 | .. | 429 | 646 |
| Coleridge | 11 | 2 | 14 | 216 | .. | 1,672 | 680 |
| Sumner | 6 | 11/2 | 51/2 | 130 | .. | .. | .. |
| Tekapo | 11 | 31/2 | 37 | 550 | 3,060 | 2,347 (25) | 620 |
| Pukaki | 91/2 | 5 | 32 | 523 | 4,520 | 1,640 (30) | .. |
| Ohau | 11 | 3 | 23 | 460 | 2,310 | 1,730 (9) | .. |
| Hawea | 19 | 5 | 46 | 567 | 2,240 | 1,133 (53) | 1,285 |
| Wanaka | 28 | 3 | 74 | 982 | 7,150 | 915 (14) | .. |
| Wakatipu | 48 | 3 | 113 | 1,150 | 6,160 | 1,017 (7) | 1,239 |
| Te Anau | 38 | 6 | 136 | 1,275 | 9,730 | 686 (15) | 906 |
| Manapouri | 18 | 5 | 55 | 1,785 | 13,630 | 608 (21) | 1,455 |
| Monowai | 12 | 1 | 11 | 105 | 495 | 643 (13) | .. |
| Hauroko | 22 | 11/2 | 271/2 | 225 | 1,100 | 513 (6) | .. |
| Poteriteri | 18 | 11/2 | 18 | 160 | 1,050 | 96 | .. |
| Waihola | 4 | 11/4 | 3 | 2,200 | .. | (Tidal) | 52 |
| Ellesmere | 14 | 8 | 70 | 745 | .. | (Tidal) | 7 |
| Artificial | |||||||
| Cobb | 3 | 1/4 | 3/4 | 28 | 198 | 2,650 (50) | .. |
| Waitaki | 3 | 1/2 | 21/2 | 3,750 | 12,150 | 753 | .. |
| Roxburgh | 20 | 1/4 | 21/4 | 6,012 | 17,270 | 430 | .. |
| Mahinirangi | 9 | 1 | 8 | 120 | 230 | 1,282 | .. |
GEOLOGY – In New Zealand, ancient rocks (intensely deformed and indurated Paleozoic and Mesozoic geosynclinal sediments and Paleozoic metamorphic and intrusive rocks) form a “core” which is buried, over about half the country, by geologically young (late Cretaceous and Cenozoic) sedimentary and volcanic rocks. In most parts of the country major unconformity separates these younger rocks from the older ones. The present structure has been developed by vigorous deformation during the Cenozoic era. A feature of the country's structure are the numerous lengthy, active, transcurrent faults. Volcanic activity continues; the largest accumulations of volcanic rocks are geologically very young (late Tertiary and Quaternary), and most of them lie in the central North Island.
A Descriptive Atlas of New Zealand contains geological maps of New Zealand and summaries of New Zealand's geology and landscape development. New Zealand Geological Survey Bulletin 66, The Geological Map of New Zealand, 1 : 2,000,000 is a lengthier summary with a more detailed geological map and cross sections. Other Geological Survey bulletins and maps are mentioned in Section 17 of this Yearbook. Numerous geological articles are contained in the New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, New Zealand Journal of Science and Technology, and Transactions of the Royal Society of New Zealand.
EARTHQUAKES: Geophysical Background – Earthquakes are geographically associated with active volcanoes and with major earth movements such as mountain building; these three types of disturbance are confined, for the most part, to certain limited regions of the world. Such disturbed regions, of which New Zealand is one, are evidently the site of some kind of development affecting the outer shell of the Earth. Little is yet known about the internal processes that give rise to these geophysical disturbances, nor are the relations connecting them understood in any detail.
Formerly earthquakes were believed to be caused by volcanic activity, but it is now recognised that volcanic earthquakes are restricted to small shocks in the immediate vicinity of the volcanism. In New Zealand, tremors of this kind are experienced in the zone of active volcanism that extends from Mount Ruapehu to White Island.
In some places geological faulting at the surface gives visible evidence that a major earth movement has occurred. Occasionally movement on a fault has been observed to occur simultaneously with an earthquake in the same vicinity. New Zealand provided one of the earliest examples of this to become generally known, when movement took place on the Wairarapa Fault at the time of the great Wellington earthquake of 1855. Such events as this have led to the idea that earthquakes in general are caused by fault movements, but it has proved difficult to find convincing evidence in support of this theory. It is noteworthy that there seems to be little earthquake activity along much of the Alpine Fault, which has been traced for 300 miles from Milford Sound to Lake Rotoiti and is classed by geologists as one of the largest and most active faults in the world. The nature of the connection between earthquakes and faulting is still somewhat obscure.
The great majority of the world's earthquakes occur at depths of less than 40 miles, and in many earthquake zones there are no shocks at any greater depth. A moderate number of New Zealand earthquakes are classed as intermediate in depth, i.e., originating at between 40 miles and 190 miles deep. The two deepest New Zealand earthquakes recorded so far occurred six minutes apart on 23 March 1960, with a common focus 370 miles deep under north Taranaki; this is about 80 miles shallower than the deepest earthquake known.
It is difficult to compare the degree of earthquake activity in New Zealand with that in other regions because of the many differences that arise in earthquake type and mode of occurrence. New Zealand and California are often regarded as roughly similar, with an activity very much less than, for example, Japan or Chile.
Regional Distribution – There are two separate regions of earthquake activity in New Zealand. The larger, northern region may be roughly defined as lying between latitude 361/2°S and 431/2°S. It thus includes the northern half of the South Island, and all the North Island apart from the North Auckland peninsula; but the area from Kaipara Harbour to the lower Waikato River should be excluded. The southern active region lies to the west of longitude 1691/2°E, and incorporates Southland, western Otago, and southern Westland. Earthquakes have only occasionally been located in the parts of New Zealand lying outside these two regions.
Within the active regions the occurrence of shallow earthquakes is widely scattered. There has been a tendency, however, for the larger shallow earthquakes to lie towards the Pacific side of the northern active region and towards the Tasman side of the southern active region. Earthquakes with deeper foci are mostly confined to a narrow belt in the northern region, extending from the Bay of Plenty south-westwards to Tasman Bay.
The historical record is too brief to support a quantitative assessment of the frequency with which one might expect earthquakes to be felt at a given intensity in various parts of New Zealand. Considering the distances to which major earthquakes can be effective, in relation to the size of New Zealand, it would be imprudent to regard any part of the country, except perhaps the far north, as permanently exempt from the possibility of earthquake damage.
Outside the active regions there are many areas, however, where no damaging intensity has actually been experienced in historical times. Moreover, since the major shallow earthquakes on record have been rather widely distributed within the active regions, there appears to be no particular area of markedly intense seismicity.
The Hawke's Bay earthquake of 3 February 1931 resulted directly or indirectly in 255 deaths. The total of deaths that have been recorded as due to other earthquakes since 1848 is 29.
Seismological Observatory – Earthquake recorders are operated continuously at the following stations by the Seismological Observatory, Wellington: Apia and Afiamalu (Samoa); Raoul Island (Kermadecs); Suva (Fiji); Onerahi, Auckland, Karapiro, Tuai, Taranaki, Tongariro, Bunnythorpe, and Wellington (North Island); Cobb, Kaimata, Gebbies Pass, Roxburgh, and Monowai (South Island); Hallett Station and Scott Base (Antarctica). The installations at the following stations include instruments for recording distant earthquakes: Apia, Suva, Auckland, Wellington, Roxburgh, Hallett, Scott Base. At the Samoan and Antarctic stations preliminary readings are made locally and notified by radiogram. The analysis of records from all stations is carried out at the Observatory in Wellington.
The Observatory publishes regular reports of all significant earthquakes occurring in the New Zealand region; in a normal year there are about 200 such earthquakes, and about 100 of these are reported felt. The analysis involves using observations from stations in other countries as well as those from the local network, and the Observatory likewise contributes data to the international seismological agencies about distant earthquakes as well as large local ones. Details of tremors felt in New Zealand are supplied to the public and the press. In the study of felt earthquakes the instrumental results are augmented by “felt reports”; these are supplied by a large number of voluntary observers throughout New Zealand in response to a standard questionnaire issued by the Observatory.
Earthquake data are used by the Observatory for studying the fundamental characteristics of the Earth's crust in New Zealand, Antarctica, and the neighbouring oceanic regions, and also for contributing to geophysical knowledge of the Earth's deep interior.
Principal Earthquakes During the Year 1960 – On 25 May 1960 an earthquake of magnitude M=7 occurred at sea about 20 miles north of Milford Sound. This was the largest shallow earthquake in the New Zealand region since the Wairarapa shock of 24 June 1942. A great many aftershocks occurred during the ensuing week. This earthquake caused minor damage at several places, as also did the earthquake on 21 February, which was centred in north Canterbury. A few other shocks caused isolated damage.
An unusual occurrence was the tsunami (seismic seawave) that originated from the great Chilean earthquake of 23 May and caused minor damage at various places along the east coast, in both the North and South Islands.
The two deepest earthquakes so far recorded in New Zealand (370 miles deep) occurred under north Taranaki on 23 March, as has been mentioned above. The interest attaching to these shocks is enhanced by the fact that the only previously recorded New Zealand earthquake of comparable depth, that of 24 March 1953, occurred in the same locality and at almost the same depth.
WEATHER INFORMATION – The collection of weather information and the provision of weather forecasts and climatic data for diverse interests in aviation, shipping, agriculture, Government Departments, and the general public are functions of the New Zealand Meteorological Service. By arrangement with the administrations concerned the Service performs similar functions for British territories in the Pacific.
Weather reports for use in forecasting are made at about 110 places within New Zealand and 50 in Pacific islands and collected by telegraph and radio, along with measurements of winds at upper levels made at eight radar wind-measuring stations and of temperatures made at seven radio-sonde stations. Daily observations are made for climatological purposes at about 150 places in New Zealand and 60 in the islands. Rainfall measurements are made at a total of about 1,200 places within New Zealand and 110 outside the country.
Detailed climatological statistics are published annually in the Meteorological Observations. Current statistics appear monthly in a climatological table included in the New Zealand Gazette.
CLIMATE – Situated between 34°S and 47°S the main islands lie within the broad belt of strong westerly winds which encircles the hemisphere south of about latitude 35°S. Just to the north is the high-pressure ridge of the subtropics from which barometric pressure decreases southwards over New Zealand to the deep low-pressure trough located near latitude 60°S.
In the Australasian region there is no semipermanent anticyclone, as exists in subtropical latitudes in the Indian and eastern Pacific Oceans. Instead, a continual eastward migration of anticyclones takes place, roughly at weekly intervals. Most of the centres pass over or to the north of the North Island. The low-pressure troughs which separate successive anticyclones are associated with deep depressions centred far to the south. A period of disturbed weather accompanies the trough with a change to cold southerly or south-westerly winds as it advances north-eastwards over New Zealand. Conditions improve again with the approach of the next anticyclone from the west. While this simple progression dominates the day-to-day weather, the situation frequently becomes much more complex. The troughs are unstable systems where depressions commonly form, some of which develop into vigorous storms that travel south-eastwards across New Zealand.
The anticyclones themselves continually vary in size, intensity, and rate of movement. Their tracks are furthest north in the spring, on the average, and reach their southern limit in late summer or early autumn when most of the centres cross central or southern New Zealand. At this time of the year, too, northern and eastern districts of the North Island occasionally come under the influence of deep cyclones of tropical origin.
The other main factors which influence the climate of New Zealand are, first, its position in the midst of a vast ocean, and second, the shape and topography of the country itself.
Australia, the nearest continent, is 1,000 miles to the west; Antarctica is 1,400 miles to the south. Hot air masses from the interior of Australia in summer, or freezing air masses from the Antarctic, which occasionally reach New Zealand, retain little of their original character after their long ocean passage. Thus, there is an absence of extreme variations of temperature. On the other hand, since abundant supplies of moisture are supplied by evaporation from the oceans, and depressions are frequent and vigorous, the average precipitation is high.
The chain of high mountains, which extends from south-west to north-east through the length of the country, rises as a formidable barrier in the path of the prevailing westerly winds. The effect is to produce much sharper climatic contrasts from west to east than in the north-south direction. In some inland areas of the South Island just east of the mountains the climate is distinctly continental in character, despite the fact that no part of New Zealand is more than 90 miles from the sea.
Winds – Winds from a westerly quarter prevail in all seasons, with a general tendency to increase in strength from north to south. However, considerable local modifications to the general air flow occur during its passage across the mountainous terrain. Approaching the main ranges the westerly flow turns towards the north-east and on descending on the eastern side swings towards the southeast. This results in an increased number of south-westerlies in Westland and a predominance of north-westerlies in inland districts of Otago and Canterbury, where strong gales from this quarter occur at times in the late spring and summer. Daytime sea breezes usually extend from the coast inland for 20 miles or more during periods of settled weather in summer. On the Canterbury coast, north-easterlies are almost as frequent as the predominant south-westerlies, mainly as a result of a persistent sea breeze. Cook Strait, the only substantial gap in the main mountain chain, acts as a natural funnel for the air flow and is a particularly windy locality afflicted by gales from the south-east as well as the north-west. This “funnel” effect is also in evidence about Foveaux Strait. North of Taranaki the general air flow is more south-westerly, and there is a noticeable reduction in windiness in the summer.
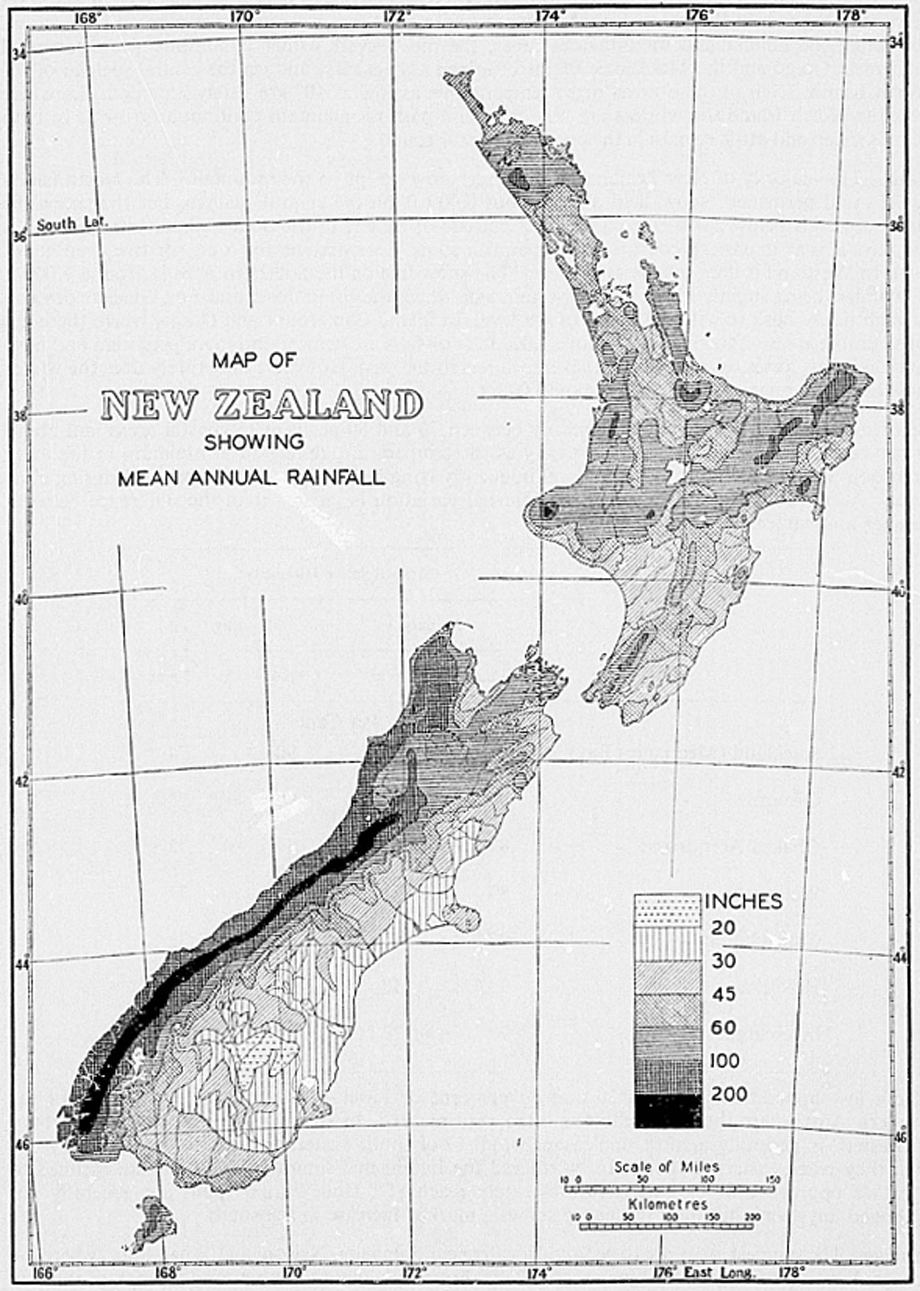
Rainfall – The distribution of rainfall is mainly controlled by mountain features, and the highest rainfalls occur where the mountains are exposed to the direct sweep of the westerly and north-westerly winds. The mean annual rainfall (see map) ranges from as little as 13 in. in a small area of Central Otago to over 300 in. in the Southern Alps. The average for the whole country is high, but for the greater part it lies between 25 and 60 in., a range regarded as favourable for plant growth in the temperate zone. The only areas with under 25 in. are found in the South Island, to the east of the main ranges. These include most of Central and North Otago, and South Canterbury. In the North Island, the driest areas are southern Hawke's Bay, Wairarapa, and Manawatu where the average rainfall is 30–40 in. a year. Of the remainder, much valuable farm land, chiefly in northern Taranaki and Northland, has upwards of 60 in. Over a sizeable area of both Islands rainfall exceeds 100 in. a year but, with the exception of Westland, this is mountainous and unoccupied, much of it being forest covered.
For a large part of the country the rainfall is spread evenly through the year, although its effectiveness in summer is, of course, much reduced. The greatest contrast is found in the north, where winter has almost twice as much rain as summer. This predominance of winter rainfall diminishes southwards. It is still discernible over the northern part of the South Island but, over the southern half, winter is the season with least rainfall, and a definite summer maximum is found inland due to the effect of convectional showers. The rainfall is also influenced by seasonal variations in the strength of the westerly winds. Spring rainfall is increased in and west of the ranges as the westerlies rise to their maximum about October, while a complementary decrease occurs at the same time in the lee of the ranges.
Areas which are exposed to the west and south-west experience much showery weather, and rain falls on roughly half the days of the year. Over most of the North Island rain can be measured on at least 150 days a year except to the east of the ranges where there are, in places, fewer than 125 rain days. Those areas of the South Island with annual rainfall under 25 in. generally have about 100 rain days a year. In the far south the frequency of rain increases sharply; in Stewart Island and Fiordland rain days exceed 200 a year. Over most of the country between 55 and 65 per cent of the rain days also qualify as wet days (0.10 in. of rain). The percentage increases to over 70 in Westland, but in the low rainfall area of inland Otago there are only about 40 wet days a year compared with 100 rain days.
On the whole the seasonal rainfall does not vary greatly from year to year, the reliability in spring being particularly advantageous for agricultural purposes. It is least reliable in late summer and autumn when very dry conditions may develop east of the ranges, particularly in Hawke's Bay.
The highest daily rainfall on record is 22 in., which occurred at Milford Sound where the mean annual rainfall is 250 in. Other areas with considerably lower rainfall are also subject to very heavy daily falls; such areas are to be found in northern Hawke's Bay and in north-eastern districts of the Auckland Province. By contrast, in the Manawatu district and in Otago and Southland daily falls reaching 3 in. are very rare.
Thunderstorms – Thunderstorms are not numerous. Their frequency is greatest in the north and west where thunder is heard on 15 to 20 days a year; east of the ranges the figure is five or less.
Hail – Hail is most frequent in the south-west where it is reported on about 20 days a year, but for the greater part of the country it occurs on about five days a year or less. Most of the hailstones are small, but occasionally large stones cause local damage to glasshouses, and to orchards and market gardens, chiefly in Canterbury and Hawke's Bay.
Frost – It is well known that local variations in frostiness are considerable, even within quite small areas. On a calm, clear night the cold air in contact with a sloping surface gravitates slowly downhill to collect in valleys and depressions, and it is these “Katabatic” drifts which are mainly responsible for local temperature variations at night. Gently sloping ground with a northerly aspect tends to be least affected by frost. Favourable sites in coastal areas of Northland are free of frost, although further inland light frosts occur frequently in the winter months. At Albert Park, Auckland, the screen minimum thermometer (4 ft above the ground) has registered below 32° F only once in nearly 50 years, yet across the harbour at Whenuapai Aerodrome there are eight screen frosts per annum on the average. Excluding the uninhabited mountainous areas, the most severe winter conditions are experienced in Central Otago and the Mackenzie Plains of inland Canterbury, and on the central plateau of the North Island. Even in these areas night temperatures as low as 10° are rarely recorded. Elsewhere over the North Island the winters are very mild and pastures maintain continuous growth. In both Islands sheep and cattle remain in the open all the year round.
Snow – The majority of New Zealanders rarely see snow except on the mountains. The North Island has a small permanent snow field above about 8,000 ft on the central plateau, but the snow line rarely descends below 2,000 ft even for brief periods in winter. In the South Island snow falls on a few days a year in eastern coastal districts and in some years may lie for a day or two even at sea level. In Westland it does not lie at sea level. The snow line on the Southern Alps is around 7,000 ft in summer, being slightly lower on the western side where the Franz Josef and Fox Glaciers descend through heavy bush to within 1,000 ft of sea level. In inland Canterbury and Otago, where there are considerable areas of grazing lands above 1,000 ft, snowfalls are heavier and more persistent and have caused serious losses of sheep during severe winters in the past. However, only rarely does the winter snow line there remain permanently below 3,000 ft.
Relative Humidity – Humidity is commonly between 70 and 80 per cent in coastal areas and about 10 per cent lower inland. It varies inversely as the temperature, falling to a minimum in the early afternoon when temperature is highest and frequently lying between 90 and 100 per cent during clear nights. As the following table shows, the diurnal variation is greater than the difference between summer and winter.
| Station | Mean Relative Humidity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | July | |||
| 3 a.m. | 3 p.m. | 3 a.m. | 3 p.m. | |
| Per Cent | ||||
| Auckland (Mechanics Bay) | 85 | 63 | 90 | 74 |
| Gisborne | 89 | 62 | 90 | 72 |
| Ohakea Aerodrome | 87 | 62 | 89 | 72 |
| Wellington | 89 | 71 | 87 | 77 |
| Christchurch | 87 | 61 | 89 | 73 |
| Hokitika | 95 | 78 | 93 | 75 |
| Invercargill | 90 | 72 | 91 | 78 |
Very low humidities – between 20 and 30 per cent or lower – occur at times in the lee of the Southern Alps where the Föhn effect is often very marked. In summer the hot, dry “Canterbury Norwester” is generally a most unpleasant wind. Cool south-westerlies are also at times very dry when they reach eastern districts. In Northland the humid mid-summer conditions are inclined to be rather oppressive though temperatures rarely reach 85°. Dull, humid spells are generally not prolonged anywhere, but their frequency shows a marked increase in the south.
Sunshine – The sunniest areas are to be found locally near Blenheim, Nelson, and Whakatane, where the average duration of bright sunshine exceeds 2,400 hours per annum. Napier and the rest of the Bay of Plenty are only slightly less sunny. A large portion of the country is favoured with at lease 2,000 hours. Even Westland, despite its high rainfall, has 1,800 hours. Southland, where sunshine drops sharply to 1,700 hours per annum, lies on the northern fringe of a broad zone of increasing cloudiness. Four hundred miles further to the south at Campbell Island the sunshine has the extremely low value of 650 hours per annum. A pleasant feature of the New Zealand climate is the high proportion of sunshine during the winter months. To eliminate the effect of varying day-length the summer and winter sunshine at a few selected stations have been expressed as a percentage of the possible sunshine.
| Summer | Winter | |
|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||
| Auckland | 57 | 49 |
| Hamilton | 52 | 44 |
| New Plymouth | 53 | 47 |
| Napier | 57 | 52 |
| Wellington | 52 | 42 |
| Nelson | 58 | 57 |
| Hokitika | 43 | 44 |
| Christchurch | 46 | 45 |
| Dunedin | 41 | 43 |
| Invercargill | 42 | 35 |
As these figures indicate, there is a marked increase in cloudiness in the North Island in winter, but little seasonal change in the South Island, except in Southland.
Temperature – Mean temperatures at sea level decrease steadily southwards from 59°F in the far north to 54° about Cook Strait, then to 49° in the south. With increasing altitude, temperatures drop about 3° per 1,000 ft. January and February, with approximately the same mean temperature, are the warmest months of the year; July is the coldest. Some temperature statistics for selected places are included in the table on page 16. Highest temperatures are recorded east of the main ranges, where they rise to the nineties on a few afternoons in most summers, usually in association with a north-westerly Föhn wind. The extremes for New Zealand (measured in a standard thermometer screen) are 101° at Ashburton and—3° at Ophir (Central Otago).
As is to be expected, there is a small annual range of temperature (difference between mean temperature of the warmest and coldest months). In Northland and in western districts of both Islands the annual range is about 15°F. For the remainder of the North Island, and east coast districts of the South Island, it is 17°–19°. Further inland it exceeds 20° in places, reaching a maximum of 25° in Central Otago where there is an approach to a continental type of climate.
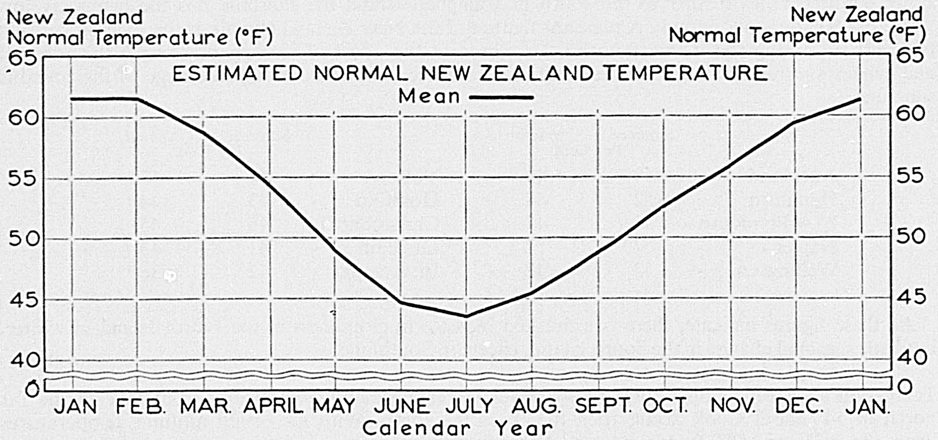
Normal Seasonal Temperature Pattern – A feature of the seasonal pattern of temperature for New Zealand is the near symmetry about either the hottest summer months or the coldest winter months. In other words the summer-winter decline is an almost identical reversal of the winter-summer rise. This shows up clearly when temperatures for 100 climatological stations are averaged month by month. The first two months of the calendar year, the summer months of January and February, display the same average temperature, that of 61.3°F. This temperature is the highest average for any month, being approached by only the December average of 59.2°F. Once February is past a decline sets in, the estimated average New Zealand temperature falling by 2.5°F from February to March to give a March average of 58.8°F. Thereafter, successive inter-monthly temperature drops of 4.4°, 5.4°, 4.2°, and 1.2°F finally produce a July average of 43.6°F, which makes this month the coldest of the year. Progressing through and past July the temperature steadily rises, the increments being successively, 1.8°, 3.4°, 3.8°, 3.2°, 3.4°, and 2.1°F, finally returning to the January mark of 61.3°F.
ESTIMATED NORMAL NEW ZEALAND TEMPERATURE (°F)*
| Calendar Month | Mean Temperature |
|---|---|
| *Based on temperature normals for 100 climatological stations. | |
| January | 61.3 |
| February | 61.3 |
| March | 58.8 |
| April | 54.4 |
| May | 49.0 |
| June | 44.8 |
| July | 43.6 |
| August | 45.4 |
| September | 48.8 |
| October | 52.6 |
| November | 55.8 |
| December | 59.2 |
The following diagram illustrates the seasonal temperature pattern.
Brief Review of 1960:Year – Rainfall was below average by up to 30 per cent over western and inland districts of the South Island from Queenstown northward, and also in South Canterbury, central Marlborough, Manawatu, Taihape, and most of Wairarapa. It was up to 70 per cent above average in Hawke's Bay, Gisborne, Coromandel, and most of Northland. Greatest departures above normal were recorded in some inland areas north of Gisborne city.
Temperatures were above average by up to 11/2 degrees in the South Island, except for most of Canterbury and parts of Marlborough. It was also about a degree warmer than normal over the greater part of the Auckland and Taranaki provinces. Elsewhere, temperatures were close to or slightly above normal. The average positive departure over the whole country was about half a degree, the same as in 1959.
The distribution of sunshine in the east-west direction was a complete reversal of the normal pattern, with Westland receiving more than Hawke's Bay and Canterbury. East of the North Island ranges it was the cloudiest year on record; Napier's total of 1,954 hours was the lowest in 54 years of observations. Gisborne and Masterton also had record low sunshine. The only areas to reach average values were the extreme north and south, and the West Coast, where there was an excess of 100–200 hours. The greatest deficiencies were in eastern districts of the North Island and in Rotorua - Bay of Plenty, where sunshine was 200–300 hours or more below average.
Seasonal Notes – January was warm and windy, and in many places too dry for pastures. Temperatures well over 90 degrees were reported in parts of Auckland and Hawke's Bay at the end of the month. In February good rains were welcomed in all districts; and over the northern half of the North Island it was particularly wet, cloudy, and warm.
The autumn season was mainly favourable for growth and stock. March was cloudy and cool and unsettled in the last three weeks. April was dry and sunny, except in Gisborne and Hawke's Bay. May was mild and cloudy.
The winter was particularly mild in the South Island, with much less snow than usual on the ranges; and this mild weather was appreciated by the farmers. Conditions were mainly favourable for stock except that the ground became rather too wet in June in Northland, Gisborne, Hawke's Bay, and Southland; and this wetness persisted in Northland during July. Flooding was reported in Northland and Gisborne on 8 June; in parts of Canterbury, Otago, and Southland from 19 to 22 June; and in Northland and the Hauraki Plains on 28 June. A vigorous cold front which crossed the country on 25–26 July brought the coldest weather of the year, with snow to low levels in the South Island and the high country of the North Island and strong gale-force southerly winds in north Taranaki. August was a drier month for most districts than June or July, and a spell of settled weather in the last 10 days was very welcome. Snow was reported to low levels in parts of Otago and Southland on 10 and 11 August.
September was unusually cloudy, especially in the North Island, and persistent north-easterly winds brought exceptionally wet weather to the Auckland Provincial District, adversely affecting stock. Serious flooding occurred in the Hauraki Plains on 15 September, with some flooding also in parts of Waikato and Northland. October, like September, was warmer than usual, but in the North Island it was also much sunnier than the previous month. It was drier than usual, but in most districts moisture was still adequate, and conditions were considered very favourable for stock and crops. On 5 October there was flooding again in Northland and Coromandel and also in Bay of Plenty.
November and December were marked by an unusually high frequency of south-easterly winds over the North Island with very wet, cloudy conditions in Gisborne and Hawke's Bay, but exceptionally dry weather in Taranaki and on the West Coast. It was also a very sunny period on the West Coast. Heavy and persistent rains in Gisborne and Hawke's Bay from 18 to 20 November caused flooding and disruption of road transport; serious losses of newly shorn sheep were reported. South-easterly winds continued through the first half of December with unusually cool temperatures. By the end of the year, in many districts conditions were considered rather too dry for satisfactory growth, affecting especially the hay crop.
The observations from which the following summary was compiled for the year 1960 were taken at 0900 hours New Zealand standard time, i.e., 2100 hours Greenwich mean time.
| Station | Air Temperature (Degrees Fahrenheit) | Bright Sunshine (Hours) | Rainfall, Total Fall (Inches) | No. of Rain Days | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Daily Maximum | Mean Daily Minimum | Approximate Mean Temp. | Extremes for 1960 | Extremes* | ||||||||
| Maximum | Month | Minimum | Month | Absolute Maximum | Absolute Minimum | |||||||
| *Highest and lowest temperature for the duration of records. | ||||||||||||
| Te Paki, Te Hapua | 67.2 | 52.3 | 59.8 | 80.6 | Feb | 29.0 | Jul | 82.8 | 27.0 | 2,233 | 63.04 | 183 |
| Auckland | 66.0 | 53.3 | 59.7 | 83.2 | Feb | 37.0 | Jul | 90.2 | 31.5 | 2,131 | 55.70 | 179 |
| Tauranga | 65.7 | 49.1 | 57.4 | 89.0 | Jan | 30.8 | Jul | 91.9 | 22.5 | 2,165 | 59.30 | 154 |
| Ruakura, Hamilton | 65.6 | 45.8 | 55.8 | 85.0 | Feb | 22.0 | Jul | 94.4 | 14.2 | 2,068 | 51.44 | 177 |
| Whakarewarewa | 63.6 | 45.3 | 54.4 | 90.3 | Jan | 26.2 | Jul | 98.0 | 21.3 | 1,793 | 56.10 | 156 |
| Onepoto, Lake Waikaremoana | 58.9 | 45.0 | 52.0 | 86.0 | Jan | 31.3 | Jul | 88.1 | 22.2 | 118.77 | 220 | |
| Gisborne | 65.5 | 48.3 | 56.9 | 96.1 | Feb | 31.0 | Aug | 99.8 | 25.9 | 1,987 | 55.32 | 188 |
| New Plymouth | 63.5 | 50.1 | 56.8 | 78.2 | Jan | 31.0 | Jul | 86.0 | 28.0 | 2,096. | 57.66 | 150 |
| Napier | 65.2 | 49.2 | 57.2 | 88.0 | Jan | 29.9 | Jul | 96.5 | 27.5 | 1,954 | 34.65 | 142 |
| Wanganui | 63.4 | 48.6 | 56.0 | 84.6 | Feb | 31.1 | Aug | 88.0 | 28.6 | 2,077 | 30.18 | 140 |
| Palmerston North (D.S.I.R.) | 63.6 | 46.9 | 55.3 | 84.9 | Feb | 27.8 | Jul | 87.0 | 21.2 | 1,745 | 30.68 | 164 |
| Waingawa, Masterton | 62.9 | 44.4 | 53.6 | 87.7 | Jan | 26.0 | Aug | 95.4 | 19.5 | 1,779 | 33.64 | 183 |
| Kelburn, Wellington | 59.9 | 49.2 | 54.5 | 78.8 | Feb | 33.9 | Aug | 88.0 | 28.6 | 1,971 | 47.23 | 175 |
| Nelson Airfield | 62.9 | 45.3 | 54.1 | 86.1 | Jan | 27.2 | Aug | 92.0 | 21.0 | 2,410 | 37.01 | 118 |
| Blenheim | 64.0 | 45.4 | 54.7 | 94.7 | Jan | 27.0 | Aug | 94.7 | 16.1 | 2,286 | 21.74 | 112 |
| Hanmer Forest | 61.0 | 38.9 | 49.9 | 91.0 | Jan | 17.0 | Jul | 97.0 | 8.2 | 1,789 | 41.39 | 144 |
| Hokitika South | 61.0 | 44.3 | 52.7 | 77.1 | Feb | 27.9 | Aug | 84.5 | 25.0 | 2,105 | 100.30 | 167 |
| Lake Coleridge | 60.4 | 40.3 | 50.3 | 89.0 | Jan | 20.5 | Jul | 97.0 | 10.0 | 21.80 | 118 | |
| Christchurch | 61.8 | 44.4 | 53.1 | 97.0 | Jan | 23.3 | Jul | 97.0 | 19.3 | 1,862 | 22.86 | 122 |
| Timaru | 61.4 | 43.3 | 52.4 | 94.3 | Jan | 26.4 | Jul | 99.0 | 19.8 | 1,813 | 20.92 | 119 |
| Milford Sound | 59.1 | 44.2 | 51.6 | 76.0 | Jan | 28.2 | Jun | 81.8 | 23.1 | 196.31 | 174 | |
| Queenstown | 59.2 | 41.0 | 60.1 | 85.6 | Jan | 23.6 | Jun | 93.4 | 19.2 | 1,917 | 25.11 | 119 |
| Alexandra | 62.2 | 41.0 | 51.6 | 91.0 | Jan | 15.5 | Jul | 99.0 | 11.0 | 1,968 | 12.61 | 92 |
| Musselburgh, Dunedin | 58.3 | 45.5 | 51.9 | 86.8 | Jan | 28.0 | Jun | 94.0 | 23.0 | 1,678 | 30.61 | 166 |
| Invercargill Airfield | 58.3 | 40.6 | 4.95 | 79.1 | Jan | 25.3 | Jun | 90.0 | 19.0 | 1,739 | 39.01 | 175 |
For 1960 the mean sea-level pressure values in millibars at 0900 hours New Zealand standard time were: Auckland 1015.7; Kelburn, Wellington 1015.0; Nelson Airfield 1015.2; Hokitika South 1015.1; Christchurch 1014.1; and Dunedin 1013.4.
The following table provides a brief summary of the main climatological elements for selected locations.
CLIMATOLOGICAL AVERAGES
| Station | Altitude | Average Annual Rainfall | Annual Averages of | Air Temperature (Degrees Fahrenheit) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rain Days (0.01 in. or more) | Bright Sunshine | Mean Temp. | Mean Daily Maximum | Mean Daily Minimum | Mean Annual | ||||||
| Jan | Jul | Jan | Jul | Maximum | Minimum | ||||||
| ft | in. | hours | |||||||||
| Te Paki, Te Hapua | 200 | 56.8 | 187 | 2,150 | 59.1 | 72.8 | 59.2 | 57.0 | 45.9 | 78 | 30 |
| Auckland | 160 | 48.9 | 173 | 2,150 | 60.5 | 72.8 | 56.7 | 60.0 | 46.1 | 81 | 37 |
| Tauranga | 12 | 51.2 | 152 | 2,350 | 56.9 | 74.5 | 57.4 | 54.7 | 40.1 | 85 | 29 |
| Ruakura, Hamilton | 131 | 45.9 | 168 | 2,070 | 55.2 | 74.6 | 55.9 | 51.7 | 37.1 | 85 | 23 |
| Rotorua | 975 | 53.7 | 151 | 2,060 | 54.4 | 74.3 | 53.6 | 51.3 | 36.9 | 86 | 26 |
| Gisborne | 12 | 39.8 | 158 | 2,220 | 57.0 | 75.7 | 55.8 | 53.8 | 39.5 | 90 | 29 |
| Onepoto, Lake Waikaremoana | 2,100 | 76.9 | 196 | 51.6 | 68.1 | 47.6 | 42.0 | 37.7 | 82 | 29 | |
| New Plymouth | 160 | 61.2 | 166 | 2,130 | 56.0 | 69.1 | 54.8 | 55.2 | 42.9 | 77 | 33 |
| Napier | 5 | 31.2 | 124 | 2,320 | 56.9 | 73.9 | 55.1 | 57.0 | 39.4 | 89 | 29 |
| Wanganui | 72 | 34.4 | 146 | 2,150 | 56.1 | 71.0 | 54.2 | 55.9 | 41.0 | 83 | 30 |
| Palmerston North (D.S.I.R.) | 110 | 39.0 | 172 | 1,890 | 54.8 | 70.5 | 53.1 | 54.3 | 39.1 | 82 | 27 |
| Waingawa, Masterton | 340 | 38.0 | 172 | 2,040 | 53.7 | 74.3 | 53.3 | 50.5 | 35.8 | 89 | 25 |
| Kelburn, Wellington | 415 | 49.2 | 158 | 2,010 | 54.1 | 67.6 | 51.2 | 54.4 | 41.5 | 79 | 33 |
| Nelson Airfield | 6 | 35.9 | 125 | 2,430 | 52.9 | 70.4 | 53.3 | 52.9 | 33.8 | 81 | 23 |
| Blenheim | 14 | 25.8 | 108 | 2,490 | 54.5 | 72.0 | 53.0 | 52.7 | 35.1 | 89 | 24 |
| Hanmer Forest | 1,270 | 45.3 | 143 | 1,940 | 50.4 | 71.6 | 48.2 | 47.8 | 29.0 | 89 | 15 |
| Hokitika South | 12 | 108.8 | 194 | 1,840 | 51.7 | 65.3 | 51.7 | 50.9 | 35.6 | 75 | 27 |
| Lake Coleridge | 1,195 | 33.0 | 118 | 50.8 | 70.1 | 48.1 | 48.6 | 29.8 | 87 | 18 | |
| Christchurch | 22 | 26.3 | 116 | 1,980 | 52.5 | 70.2 | 50.0 | 52.7 | 34.7 | 88 | 25 |
| Timaru | 56 | 23.5 | 112 | 1,920 | 51.8 | 70.0 | 49.4 | 51.4 | 33.4 | 90 | 24 |
| Milford Sound | 20 | 253.3 | 193 | 50.0 | 64.4 | 48.3 | 50.0 | 34.2 | 76 | 27 | |
| Queenstown | 1,100 | 32.0 | 132 | 2,000 | 50.0 | 69.8 | 45.6 | 49.0 | 30.9 | 85 | 23 |
| Alexandra | 520 | 13.2 | 100 | 2,110 | 50.6 | 72.6 | 44.6 | 50.8 | 28.0 | 89 | 18 |
| Musselburgh, Dunedin | 5 | 31.0 | 167 | 1,770 | 51.6 | 65.2 | 49.3 | 51.2 | 36.2 | 88 | 26 |
| Invercargill Airfield | 0 | 42.8 | 199 | 1,670 | 49.1 | 64.1 | 49.3 | 46.5 | 32.8 | 83 | 22 |
| NOTE: Averages of rainfall, 1921–50; rain days, 1950–59; sunshine, 1935–55; temperature, various periods – all exceeding 10 years. | |||||||||||
FLORA OF NEW ZEALAND – Those desiring information on the flora and plant covering of New Zealand are referred to the article which appeared in the 1940 and previous issues of the Yearbook. For more detailed information the following works may be consulted: Manual of the New Zealand Flora, 2nd ed., by T. F. Cheesman, 1925: Students' Flora of New Zealand…, by T. Kirk, 1889; Vegetation of New Zealand, 2nd ed., by L. Cockayne, 1928 (3rd reprint ed., 1958); New Zealand Plants and Their Story, 3rd ed., by L. Cockayne, 1927; Plants of New Zealand, 6th ed., by R. M. Laing and E. W. Blackwell, 1957; Handbook of the Naturalised Flora of New Zealand, by H. H. Allan, 1940; New Zealand Native Plant Studies, by W. C. Davies, 1956; New Zealand Ferns, 5th ed., by H. B. Dobbie and M. M. Crookes, 1953; Book of Ferns, by G. B. Stevenson, 2nd ed., 1959; Handbook of the New Zealand Mosses, by G. O. K. Sainsbury, 1955; Introduction to the Grasses of New Zealand, by H. H. Allan, 1936; Grasslands of New Zealand, 2nd ed., by E. B. Levy, 1955; Pasture Plants and Grasses of New Zealand, 7th ed., by F. W. Hilgendorf and J. W. Calder, 1952; Weeds of New Zealand…, 5th ed., by F. W. Hilgendorf and J. W. Calder, 1952; Poisonous Plants of New Zealand, by H. E. Connor, 1951; Trees of New Zealand, 4th ed., by L. Cockayne and E. P. Turner, 1958; New Zealand Trees and Shrubs and How to Identify Them, by H. H. Allan, 1928; Forest Flora of New Zealand, by T. Kirk, 1889; Forest Trees and Timbers of New Zealand, by H. V. Hinds and J. S. Reid, 1957; Exotic Forest Trees in New Zealand, by G. C. Weston, 1957; Forest Fungi, by M. E. Lancaster, 1955; The Marine Algae of New Zealand, Part I: Myxophyceae and Chlorophyceae, by V. J. Chapman, 1956.
FAUNA OF NEW ZEALAND – A brief article on the fauna of New Zealand is contained in the 1940 and earlier editions of the Yearbook. Other publications dealing with this topic include: Native Animals of New Zealand, by A. W. B. Powell, 1947; Animals of New Zealand, 4th ed., by F. W. Hutton and J. Drummond, 1923; Introduced Mammals of New Zealand, by K. A. Wodzicki, 1950; New Zealand Birds, 2nd ed., by W. R. B. Oliver, 1955; New Zealand Birds and How to Identify Them, 5th ed., by P. Moncrieff, 1957; Birds of New Zealand, by A. M. Bailey, 1955; Focus on New Zealand Birds, by G. J. H. Moon, 1957; Moas of Australia and New Zealand, by W. R. B. Oliver, 1949; Bird Islands of New Zealand, by R. A. Wilson, 1959; Treasury of New Zealand Fishes, 2nd ed., by D. H. Graham, 1956; Fresh Water Fishes of New Zealand, by G. Stokell, 1955; Sea Anglers' Fishes of New Zealand and Big Game Fishes and Sharks of New Zealand, by A. W. Parrott, 1957 and 1958; Shells of New Zealand, 3rd ed., by A. W. B. Powell, 1957; Manual of New Zealand Mollusca Plus Atlas, by H. Suter, 1913 and 1915; Insects of Australia and New Zealand, by R. J. Tillyard, 1926; Butterflies and Moths of New Zealand plus Supplement by G. V. Hudson, 1928 and 1939; Bibliography of New Zealand Entomology, 1775–1952, by D. Miller, 1956; New Zealand Beetles and Their. Larvae, by G. V. Hudson, 1934; Native Insects, by D. Miller, 1955; Aphids of New Zealand, by W. Cottier, 1953; New Zealand Neuroptera, by G. V. Hudson, 1904; Fragments of New Zealand Entomology, by G. V. Hudson, 1951; Acalypterate Diptera of New Zealand, by R. A. Harrison 1959; The Earthworm Fauna of New Zealand, by K. E. Lee, 1959.
EARLY HISTORY: General - When New Zealand was discovered by Europeans in 1642 it was found to be inhabited by a race of Polynesians called Maoris, who had migrated to these islands at least 300 years previously. It is generally accepted that the Maoris came originally from South East Asia, whence, as proto-Polynesians, they moved eastwards from island to island until they reached the eastern Pacific, where they settled the islands now known collectively as Polynesia. From Polynesia the ancestors of the Maori sailed south-west in ocean-going canoes to reach New Zealand and these voyages were probably spread over several generations, perhaps several centuries. Oral Maori history and genealogy support the view that there was a final wave of migration of considerable magnitude about A.D. 1350. Adapting themselves to a new physical environment, in isolation from the outside world, the Maoris produced forms of social and economic organisation and material culture which were significantly different from their Polynesian prototypes.
Coming from tropical latitudes, the Maoris mainly confined themselves to the warmer North Island, and when discovered by Europeans were in a high state of neolithic civilisation, with marked superiority in the arts of wood carving and military engineering. Their principal social unit was the family group, and from combinations of the numerous groups were formed the subtribes and tribes. With highly developed social and ritualistic customs, their system of land tenure and methods of cultivation were communal within the subtribes. Inter-tribal and intra-tribal warfare was common, and as individuals they displayed exceptional courage and intelligence.
The immediate effect of European contacts on the Maoris was the outburst of a series of tribal wars waged with greater ferocity and a vastly greater loss of life than was customary in pre European tribal engagements. The high mortality could, of course, be credited to the acquisition of a more lethal weapon, the musket. The advantage lay originally with the coastal tribes as a result of their earlier contact with Europeans, the wars continuing until all tribes were equally well armed. These wars were later followed by wars against the colonists, but after 1870 the story has been one of unbroken peace between Maoris and Europeans.
The introduction of European diseases and firearms, and the impact of European civilisation on the traditional way of life and customs of the Maoris, had such an adverse effect that their numbers must have been reduced by over half during the nineteenth century. However, the virility of the race gradually asserted itself, and from the beginning of the twentieth century the Maori population has been rapidly increasing.
Other island groups, such as the Cook Islands, Niue Island, and the Tokelau Islands, had also long been inhabited by Polynesians from various successive migrations extending over considerable periods prior to their discovery by Europeans.
Discovery by Europeans- On 13 December 1642, Abel Janszoon Tasman, a navigator of the Dutch East India Company, discovered the country to which he gave the name of Staten Land, and which later became known as “Nieuw Zeeland”. Tasman had left Batavia on 14 August 1642, and, after having discovered Tasmania, he steered eastward and sighted the west coast of the South Island, described by him as a high mountainous country. Sailing north, he had the misfortune to come into conflict with the Maoris at Golden Bay, on the north coast of the South Island, so that, though he continued his northward journey until he reached the northern tip of the country, he did not again attempt to land. His exploration was of necessity very cursory, for having explored only part of one coast he had no knowledge of the country's extent or shape.
There is no record of any European visit to New Zealand after Tasman's departure until Captain Cook sighted land on 6 October 1769, at Young Nick's Head, near Gisborne. On his first voyage Cook spent six months exploring the New Zealand coastline, and he completely circumnavigated the North and South Islands. His activities can be best described by saying “he found New Zealand a line on the map, and left it an archipelago”. Not only was Cook's ability shown by his cartographical accuracy, but also in his peaceful dealings with the truculent Maoris. He returned to New Zealand again in 1773, in 1774, and in 1777.
Several other explorers also visited New Zealand during the latter portion of the eighteenth century, amongst whom may be mentioned M. de Surville 1769, M. Marion du Fresne 1772, Captains Vancouver and Broughton 1791, Captain Raven 1792-93, Alejandro Malaspina and Jose de Bustamentey Guerra 1793, Lieutenant Hanson 1793.
The European discovery of many of the islands of the Cook Group was made by Captain Cook in 1773. Rarotonga and Mauke were not officially discovered for another 50 years, although there were records of earlier visits by the Bounty under the control of the mutineers in 1789 and later, in 1814, by the Cumberland. Niue Island was discovered by Cook in 1774. The first recorded discovery of the Tokelau Islands was made by Quiros in 1606. Of the remaining islands of the group, Atafu was discovered in 1765, Nukunono in 1791, and Fakaofa in the 1840s.
European Settlement and Colonisation - So far as is known, the first instance of Europeans being left in New Zealand to their own resources occurred in 1792, when Captain Raven of the Britannia landed a sealing party at Facile Harbour, on the west coast of the South Island, where they remained a little over 12 months before being called for.
In the years that followed, whaling stations sprang up along the coast, and a trade with New South Wales began not only in whale oil and seal skins, but also in flax and timber. Attracted to New Zealand were deserters from whaling vessels and escaped convicts from Australia, who, in the absence of any jurisdiction, soon became notorious for their extreme lawlessness. In 1814 Samuel Marsden, chaplain to the Governor of New South Wales, obtained permission to send two of his proteégés, Kendall and Hall, to the Bay of Islands to consider the desirability of establishing a mission station. Later they returned to Sydney for Marsden, who arrived in New Zealand to preach his first sermon at the Bay of Islands on Christmas Day, 1814. Of the many admirable activities undertaken by the missionaries, their action in having the Maori language “reduced to a rational orthography” deserves special mention.
In 1825 three separate, but abortive, attempts were made to found colonies; however for some years the only settlements were those round the principal whaling stations, although a number of Europeans gradually penetrated inland and resided there permanently, many marrying Maori women.
The first body of immigrants under a definite scheme of colonisation arrived in Port Nicholson in January 1840, there to found the town of Wellington, just one week before Captain William Hobson arrived at the Bay of Islands as Governor to proclaim British sovereignty (see page 22). These settlers were brought out from England by the New Zealand Company, whose moving spirit was Edward Gibbon Wakefield.
It was hoped that, by producing a proper balance of capitalists and artisans, self-contained communities could be successfully established. However, owing to the unsatisfactory nature of the land purchases, considerable difficulty was experienced in these initial settlements, and friction grew up not only between the settlers and the Maoris, but also between the Governor and the settlers. Before his death in 1842 Governor Hobson had transferred his capital from Russell to Auckland, but this transfer was of little assistance to the colonists, who had extended their settlements to Wanganui, New Plymouth, and Nelson.
Following the death of Hobson, the existence of the colony became precarious, for, through lack of funds and weak administration, Maori aggression became a real menace. To cope with the situation, the Colonial Office appointed Captain George Grey as Governor. Being well equipped with troops and funds, as well as being a man of vigour and perception, Grey soon restored order and won the confidence of both the settlers and the Maoris. During Grey's term two further organised settlements were made. In cooperation with the New Zealand Company the Free Church of Scotland sponsored the Dunedin Settlement of 1848, and the Church of England the Canterbury Settlement of 1850. These settlements, owing to their more favoured situations, their satisfactory land-purchase agreements, and their freedom from trouble with the Maoris, achieved a greater measure of success in carrying out the company's avowed aims.
After Grey's departure the question of relationship with the Maoris again came to the fore through the land-purchasing activities of the settlers - a situation aggravated by subsequent lack of consideration for the Maori system of land tenure. Following an incident at Waitara in the Taranaki district, where a dispute arose concerning land titles, war broke out in 1860 and lasted spasmodically till 1870. The recall of Grey did not solve the problem, as Grey, an autocrat, could not work with the elected Ministers, nor did his presence prevent the confiscation of land belonging to the Maoris, whether friendly or hostile. It was under the sympathetic administration of Sir Donald McLean as Minister for Maori Affairs that the dispute finally died down.
These hostilities were confined to the North Island; and, in the meantime, in 1861, large alluvial deposits of gold had been discovered in the South Island - leading to a tremendous influx of population and an alteration of the economic structure of the country.
No organised form of European colonisation has at any time taken place in the Cook Islands, Niue Island, or the Tokelau Islands.
SUBSEQUENT HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT (1870 ONWARDS) - The discovery of gold, by its increase of wealth, allowed the South Island to obtain a lead in commercial and political development which it long maintained. Moreover, with the subsequent agrarian expansion, especially in the development of the large pastoral holdings, the country ceased to be merely self-sufficient agriculturally, but began to develop a substantial export trade, mainly in wool, which it has maintained to the present day.
These factors, together with freedom from strife with the Maori population, led after 1870 to a quickening in political activities. Under the leadership of Sir Julius Vogel a policy of extensive borrowing for railway and road construction was begun. The provincial system which really commenced in 1853 had largely outlived its usefulness; in fact, the parochialism of their assemblies had frequently proved obstructive, and in consequence the provincial system was abolished in 1875, local administration being provided for by the Counties Act and the Municipal Corporations Act of 1876.
Of great social significance was the passing in 1877 of the Education Act, making education free, compulsory, and secular, while the laying during that decade of the first cable between Australia and New Zealand was a major advance in communications. At this time party politics began to enter into the parliamentary system, and the slump conditions which prevailed in the eighties (due to a fall in the world price level) intensified the political atmosphere. By the abolition of plural voting in 1889, and the introduction of female suffrage in 1893, the way was opened for a practical expression of political convictions by all adult members of the community.
In 1891 Ballance, as Leader of the Liberal Party, became Premier, to be followed on his death in 1893 by Seddon, and during the next decade the legislative essays of this party evoked world-wide interest. The main aim of the legislation was social justice, and its principal manifestations were in land division, the establishment of the Court of Arbitration, and the introduction of old-age pensions. The policy of land division aimed at closer land settlement, and it was achieved by the compulsory subdivision of large estates, with subsequent loans to small independent farmers wishing to establish themselves. In inaugurating the Court of Arbitration the object was to eliminate strikes by giving labour a recognised bargaining status; and the enactment was in accord with the enlightened code of labour legislation passed at that time.
With the commencement of the refrigerated trade in 1882, the policy of closer settlement progressed rapidly, since the production of frozen meat and dairy produce for export encouraged more intensive farming. There thus arose a new farming class which in 1911, some five years after Seddon's death, was mainly responsible for the overthrow of the Liberal regime.
The policy of the succeeding Reform Party under Massey was one favouring agricultural production. Farming interests were given constant encouragement by a series of enactments of which the extension of rural credit was typical. Three years after the advent of the Reform Party the First World War, 1914-18, broke out, leading to the formation of a Coalition Government and an Imperial commandeer of exports. War activities were marked by heavy casualty lists, in proportion to the population, and by enhanced cordiality in Imperial relations. One noteworthy outcome of the war commandeer was the precedent given for the establishment, after the war, of control boards to regulate the export of pastoral products.
Though the effects of the post-war depression during the period 1921-24 showed themselves in an increase in unemployment and slight wage reductions, no drastic legislation was necessary to stabilise economic conditions. During the following years the price level rose; and from the administrative side, it was characterised by extensive public works expenditure, with particular attention to hydro-electric schemes and highways.
Owing to the encouragement given to farming, pastoral production constantly expanded, so that New Zealand became one of the world's greatest exporters of pastoral produce. As a consequence, her national income was extremely sensitive to price fluctuations of these products; so that, with the advent of the depression in 1930, her economic position became extremely vulnerable. In order to produce balanced budgets, both public and private, various legislative remedies were attempted. In particular, enactments were provided for unemployment relief, for the suspension, in effect, of compulsory arbitration, for the establishment of a Reserve Bank, for a mortgage moratorium, for raising the exchange rate, and for reduction in interest rates and wages. With the recovery in price levels and consequent general economic revival, amendments were made to several of these Acts, removing the more stringent measures. The election of a Labour Government in 1935 led to a change in administrative policy, the preoccupation being mainly with social problems. Further amendments were made to the depression legislation, certain restrictive measures were removed, and other temporary adjustments made permanent.
The general climate of opinion and gradual maturity of outlook furnish the background in which certain distinctive trends appear in legislation passed since 1936.
The first major influence was a humanitarian attitude reinforced by a progressive economic policy. Evidence of this is implicit in the provision for a basic wage, and later for a minimum wage, employment-promotion legislation, amendments to workers' compensation, industrial conciliation and arbitration, mining, etc., legislation, the system of guaranteed prices for certain primary produce, the creation of farm industry reserves, and the rationalisation of production and marketing by the establishment of boards for certain items of primary produce.
The second major influence on legislation was conditioned by the outbreak of the Second World War, 1939-45. A vast body of legislation was placed on the statute book during the war period dealing with the control of manpower and materials, stabilisation of prices, wages, and rents, conditions of employment and suspension of certain peacetime features of industrial activity, discouragement of some industries and diversion to or encouragement of other industries, provision for rehabilitation, etc.
A third dominant trend was the acceptance of the principle that society should take active steps towards the improvement of the working, living, and social circumstances of its members. Foremost in this category was the Social Security Act and its later extensions providing for monetary benefits such as age, superannuation, family allowances, sickness, and unemployment, and by the provision of a system of medical, pharmaceutical, hospital, maternity, and other related benefits.
Other legislative enactments under this heading include the provision for paid annual holidays, reduction of working hours, extension of workers' compensation insurance, improvement in safety and health and welfare conditions in industry, and extension of educational facilities and opportunities.
A fourth approach to law making resulting from maturity of outlook has been the increased participation by New Zealand in international affairs consequent on its acceptance of responsibility in the wider issues of the present era. Legislation authorising participation in United Nations activities generally and in particular emergencies, such as military service in Korea, Malaya, and elsewhere; the extension of New Zealand representation in overseas countries and with the United Nations; the greater frequency of Commonwealth consultation; extension of aid to less developed countries, e.g., participation in the Colombo Plan, all bear witness to this change in outlook.
Another influence on legislation presents some parallels to that last mentioned, but is more concerned with the domestic sphere. It is exemplified in the increasing interest taken in welfare and social development generally of both the rapidly growing Maori population and the inhabitants of New Zealand's island and trust territories, such as the Cook Islands and Western Samoa.
Contemporaneously with the expansion of the field of legislative interest, other economic and industrial development of the country has proceeded with marked impetus in recent years. Expansion and diversification of manufacturing and servicing industries have provided avenues of employment for the growing labour force. At the same time the basic industries of the country, those concerned with primary production, have increased output, assisted by the rapid application of technological improvements and research findings.
The history of New Zealand's island territories has been largely one of wise paternal oversight, particularly in the earlier periods, by the New Zealand Government and by the various missions established in the islands. More recently, successive Governments have in various ways encouraged the inhabitants to take an increasing share in the administration of their communities, thus paving the way for some form of self-government. Much attention has been paid to combating tropical diseases and to health problems generally; such island industries as citrus fruit, and banana growing have been fostered and encouraged in various ways, with outlets being found for produce available for export. By and large, however, their economy is necessarily one of a subsistence type only, with financial and other assistance provided from Government sources for the expansion of educational facilities and opportunities, public works such as reading, conservation of water supplies by reservoir construction, communication facilities, etc.
Owing to limitations of space, the foregoing is but a brief résumé of New Zealand history. For detailed information, reference should be made to the many excellent books dealing with the subject, of which the more recent ones are listed in the General Bibliography appearing in Appendix (c) of this Yearbook, and others in earlier issues.
SOVEREIGNTY - Following representations from Maori chiefs for protection from the prevailing turmoil and lawlessness caused by tribal warfare and the rough element around the whaling stations, the New South Wales Government appointed, in 1832, Mr James Busby as British Resident at Russell. Owing to the failure to supply him with any means of exerting authority, his appointment was largely ineffective. Finally the disorder, and the friction between the two races, became so intolerable that even the missionaries, who were opposed to annexation, made representations for British sovereignty.
On 29 January 1840, Captain William Hobson, RN, arrived at the Bay of Islands, empowered, with the consent of the Maoris, to proclaim the sovereignty of Queen Victoria over the Islands of New Zealand, and to assume the government thereof. Hobson formally read his commissions at Kororareka on 30 January 1840, and on 6 February of the same year a compact called the Treaty of Waitangi was entered into, whereby all rights and powers of sovereignty were ceded to the Queen, all territorial rights being secured to the chiefs and their tribes.
On 21 May 1840 Governor Hobson proclaimed British sovereignty in the case of the North Island by virtue of the Treaty of Waitangi, and in the case of the South Island and Stewart Island by right of discovery. New Zealand remained a dependency of New South Wales until 3 May 1841, when it was created a separate colony by Royal Charter dated 16 November 1840. The capital was at first transferred by Hobson from Russell to Auckland, but in 1865 it was again transferred, on this occasion to Wellington, where the seat of Government has since remained.
During Governor Grey's term, steps were taken to draft a constitution for the colony. An Act granting representative institutions was passed by the Imperial Parliament on 30 June 1852, and was published in New Zealand by Proclamation on 17 January 1853. Under it provision was made for the constitution of a General Assembly consisting of a Legislative Council and a House of Representatives. Provision was also made for the division of the country into provinces, each province having an elected Council and Superintendent. (The provincial system was abolished in 1875 and the Legislative Council in 1950.) In the first General Assembly of 27 August 1854 certain members of this body were associated with the permanent members of the executive but they did not hold any portfolios. It was not until 7 May 1856 that responsible government was actually established.
With the gradual development of the country's economy, the acquisition of political and administrative experience, and the increasing desire for self-reliance in political matters, the degree of self-government became more complete. In recognition of this and of a nascent sense of nationality, New Zealand was given the title of Dominion in lieu of Colony, the new title taking effect on 26 September 1907.
Of the constitutional events in recent years the passing by the United Kingdom Parliament of the Statute of Westminster in December 1931 was of major importance. The draft of this statute was submitted for the confirmation of the various Commonwealth Legislatures before its passage through the United Kingdom Parliament. The statute granted complete autonomy to the various self-governing member countries, but it did not automatically apply to Australia or New Zealand. In other words, its operation in the latter self-governing members of the Commonwealth was declared to require specific adoption by the Legislature of that country. It was not until 1947 that the New Zealand Government formally adopted the Statute of Westminster.
As far as the island territories are concerned, the Cook Islands were proclaimed a British protectorate in 1888, and in 1901 were annexed and proclaimed part of New Zealand under the Colonial Boundaries Act 1895. Niue Island is part of the Cook Islands, though separately administered, and became part of New Zealand in 1901 with the extension of boundaries to include the Cook Islands. The Tokelau Islands were placed under the protection of Great Britain in 1877, formally annexed at the inhabitants' request in 1916, and from 1925 were administered by New Zealand at the request of the United Kingdom Government. From 1949 they became part of New Zealand by virtue of the Tokelau Islands Act 1948.
NEW ZEALAND'S INTERNATIONAL ACTIVITIES - Though in the nineteenth century Sir Julius Vogel and the Right Hon. R. J. Seddon had original views about the policy which Britain and New Zealand should pursue in the Pacific area - views which they announced with vigour - New Zealand did not acquire the right to conduct an independent foreign policy until the end of the First World War when the full nationhood of the “Dominions” was recognised. For some years after this, however, successive New Zealand Governments chose not to exercise this right and (pursuing a passive role in the League of Nations and refraining from establishing diplomatic relations with foreign Governments, or with other members of the Commonwealth apart from Britain) preferred to make known any views on matters of foreign affairs only to the British Government and through the confidential channels of intra-Commonwealth consultation.
Few pressures existed in the 1920s and early 1930s to impel New Zealand towards enunciating an independent foreign policy. The population was mainly British in composition and comparatively few were concerned to distinguish between the interests of New Zealand and those of the Mother Country. Nor had they much cause to do so: New Zealand had established a fruitful economic partnership with Britain, upon which country nearly all her material and cultural links were centred; and New Zealand's surest protector against dangers which it was incapable of meeting alone was the Royal Navy. It was, moreover, realised that New Zealand in her own right could make little impact on world affairs, whereas Britain was a great power capable of affecting the pattern of world events. New Zealand “foreign policy” therefore consisted chiefly in seeking to modify British policy in those few cases where New Zealand had a strong interest or a viewpoint rather different from that of Britain. A standing opportunity was provided by the system of confidential intra-Commonwealth consultation whereby Britain provided full information to the Dominions and sought their comments upon issues of international policy as they arose. In this way New Zealand tended to prefer a share of great power status to “independence” of foreign policy; this sufficed until the middle of the 1930s.
In practice, during the first 16 years after the First World War the New Zealand Government on only a few occasions thought it necessary to make significant efforts to bring about a modification of British policy. This situation resulted chiefly from the factors earlier outlined which made for an identity of interest and viewpoint between Britain and New Zealand. In part also it arose because few problems directly affecting New Zealand remained to be settled; in part it was because of a considered reluctance to give advice when the main consequences of accepting that advice fell upon Britain, not New Zealand; in part it was because New Zealand Governments tended to approach problems pragmatically rather than on grounds of principle, and were conscious of having no expert New Zealand Department organised to collect and appraise the facts on equal terms with the British Foreign Office; in part it was because New Zealand Governments, supplied by the Foreign Office with very much the same information as that on which the United Kingdom Cabinet based its judgments, viewed problems from a similar standpoint to that of the British Government. In short, most New Zealanders thought of external affairs in terms of Imperial unity and relied on British leadership of the Empire.
The emergence of an independent New Zealand foreign policy is usually held to date from 1935. Some Ministers in the new Government were deeply interested in world affairs in general, and the Government's approach was influenced by theory and principle. In particular, they held strong views on the principle of collective security and upon the League of Nations as the embodiment of that principle. In its method of championing the principles of collective security, pressing for the restoration of the authority of the League of Nations and, at a time when the United Kingdom Government was pursuing the policy which came to be known as appeasement, urging positive League action over Abyssinia, Spain, and China, the Government came to depart from the pattern of the previous 16 years: for, in addition to making its views known in confidential communications to the United Kingdom Government, it also stated them with vigour in the international forum of the Council and the Assembly of the League of Nations.
There was, however, no fundamental departure from the traditional policy of association with Britain. Moreover, the course that would be followed in the event of war was never in doubt. As early as 16 May 1938 a leading member of the Government had said, “If the Old Country is attacked, we are too . . . we will assist her to the fullest extent possible.” When war broke out the Prime Minister, the Right Hon. M. J. Savage, expressed New Zealand's position in terms that were as true in 1939 as they would have been in 1914:
“Behind the sure shield of Britain we have enjoyed and cherished freedom and self-government. Both with gratitude for the past, and with confidence in the future, we range ourselves without fear behind Britain. Where she goes, we go. Where she stands, we stand. We are only a small and young nation, but we are one and all a band of brothers, and we march forward with a union of hearts and wills to a common destiny.”
Until 25 years ago New Zealand sought to protect and promote its interests solely through its association with Britain; in the world situation that then existed, and given New Zealand's small power and influence, this was certainly more economical and probably more effective than any other method of foreign policy. For a short period from 1935 New Zealand used the League of Nations as a supplement to the British association.
But the Second World War changed the pattern of power in the world and made it necessary for New Zealand gradually to revise its foreign policy and its method of implementing that policy. Even though the basic attachment of New Zealanders to the Mother Country was little affected, the fact became manifest that Britain was no longer a power able to determine events on a world scale and that, since New Zealand interests could no longer be protected by British actions alone, it did not suffice to confine New Zealand foreign policy to occasional attempts to persuade the British Government to take note of New Zealand views. Japanese aggression and, later, the rise of Communist China forced New Zealand to face the reality of its geographical location in the Pacific and to develop an additional relationship with the only other friendly power capable of protecting New Zealand -the United States of America - with the least possible prejudice to its association with the United Kingdom. To contribute to Anglo-American harmony is therefore a major preoccupation of New Zealand foreign policy.
To be woven into any post-war policy was the now traditional New Zealand belief in the principle of collective security and international justice, especially as symbolised by, though not yet embodied in, the United Nations. This was by no means an easy task in a world where the divisions of the cold war were reflected in competing regional alliances. There had to be a place, too, for belief in the ability of international cooperation to control armaments and to eliminate poverty, disease, and other economic and social causes of international tension.
During the war years New Zealand was admitted to the councils of the Allies and was expected to advance informed views. The Government honoured its responsibility and, having established in wartime the habit of participating in the making of international decisions, accepted it as natural that New Zealand should continue to participate in the development of a post-war world order and in subsequent international consultations. To this end New Zealand established (in effect from 1943) a professional Department of External Affairs and a career foreign service, and proceeded slowly to establish diplomatic missions in countries where New Zealand's interests merited protection. In particular, New Zealand sought increasingly to make its individual contribution to fostering good relationships with its neighbours in the Pacific and to increasing the measure of security and welfare in this area.
The threat to New Zealand's security, posed by the entry of Japan into the war at a time when the United Kingdom was fully committed in Europe, brought New Zealand into the closest relations with two of her Pacific neighbours, Australia and the United States. Recognition of the need for a greater measure of collaboration with Australia resulted in the signing in 1944 of the Canberra Pact which provided machinery for continuing consultation between the two Governments. Upon the entry of Japan into the war both New Zealand and Australia looked principally to the United States for protection. Relations among the three countries thus entered a new phase. The close association of wartime found expression in peacetime in the Anzus Treaty, in which, for the first time, New Zealand and Australia entered into a treaty of alliance and mutual defence with a foreign country. While neither Australia nor New Zealand was in favour of a vindictive or onerously restrictive peace settlement with Japan, they both made clear during the negotiation of the Japanese Peace Treaty their apprehension at the possibility of future aggression in the Pacific. The Anzus Treaty, which came into force in April 1952, was designed to allay these fears at the same time as it achieved the aim of both countries to enter into a close relationship with the major Pacific power. The treaty gives an assurance of United States support in the event of an armed attack from any quarter in the Pacific and so constitutes New Zealand's major safeguard from aggression in the area.
Since the signature of the Anzus Treaty, New Zealand has become a member of another regional defence system, the South-East Asia Treaty Organisation, SEATO. In joining SEATO, a body made necessary by the failure of the Great Powers to cooperate in carrying out the security functions entrusted to them by the United Nations Charter, New Zealand demonstrated further its new awareness of the international and strategic implications of its position in the South Pacific. In 1955, the Minister of External Affairs, the Hon. T. L. Macdonald, discussing New Zealand's foreign policy, said that the only possible threat to New Zealand's security could come from Asia, and in particular from the spread of Communist power in South-East Asia. “New Zealand's foreign policy grows,” he said, “from the need to reconcile geography and history, economic fact and strategic fact. In practical terms at present this means that, without weakening the many links which bind us to Britain and the whole Atlantic community, we must increase our concern with South-East Asia.”
This regional approach implied no weakening of the belief in the pre-eminent value of collective security organised on a world basis. New Zealand continued to place special importance upon its membership of the United Nations. It has been an active participant in the work of the General Assembly, has been a member of all Councils of the Organisation, has provided troops to the United Nations Force in Korea and military observers in Palestine, Kashmir, and Lebanon, and has endeavoured to assist all efforts to attain the political and social objectives outlined in the Charter.
At the time of the formation of SEATO, New Zealand's interest in South-East Asia had already been expressed in social and economic terms. In 1950, New Zealand, along with a group of other Commonwealth countries, became a member of the Colombo Plan established to assist the countries of South-East Asia to improve their standards of living. To New Zealand, a pioneer in the field of social legislation and a country where wealth is spread throughout all levels of the population, the Colombo Plan has a special significance and contributions, large by New Zealand standards (if small when measured against the potential need), have been made to it. Despite this new concentration on South-East Asia, New Zealand continued and developed its efforts (as will be seen later) to promote action on a world scale to deal with social and economic problems.
If, since the war, the facts of geography have had an important influence on New Zealand's attitudes towards foreign affairs, history and tradition continue nevertheless to mould its outlook. The historic links with the United Kingdom and with Western Europe and North America remain as strong as ever; and the economic links with the United Kingdom, New Zealand's best customer, remain strong. No situation is, however, constant. One of the key problems of external political, not merely economic, policy now presented to New Zealand grows out of the realisation that while New Zealand must expand the volume and value of its exports of primary products if the standard of living of its rapidly increasing population is to be maintained and improved, the United Kingdom market may be capable of only a limited expansion. New Zealand's foreign policy is likely to continue the endeavour to reconcile geography and history, economic fact and strategic fact.
Department of External Affairs-The External Affairs Act 1943 made provision for the appointment of a Minister of External Affairs* charged generally with the administration of external and foreign affairs, including relations with other countries, communications with other Governments, representation abroad, and representation of other countries in New Zealand. The Act also authorised the appointment of a Secretary of External Affairs and (superseding the High Commissioner Act of 1908) dealt with the appointment of High Commissioners and of overseas representatives.
The functions of the Department were defined at its inception as follows:
To act as a channel of communication between the Government and other British and foreign Governments on matters relating to external affairs.
To assist in negotiating treaties and international agreements.
To direct New Zealand's overseas diplomatic posts.
To deal with foreign diplomats, and to issue exequaturs to foreign consuls.
The Act thus established the Ministry of External Affairs as the normal channel of communication with the Governments of other countries. As, however, the new Department was in fact still a part of the Prime Minister's Department, no change in procedure, apart from the use of the changed nomenclature, was necessary.
Dealings with overseas Governments usually involve considerable interdepartmental coordination. Since the Prime Minister's Department has always been regarded primarily as a department of coordination, an intimate relationship has existed between the two Departments. The Prime Minister has for three periods found it appropriate to assume the portfolio of External Affairs and the Departments have in any case been run as a unit. The staff is held in common and, though some officers are engaged on work peculiar to one Department, the work of the majority involves both Departments. The Secretary of External Affairs is also Permanent Head of the Prime Minister's Department. In defence matters the two Departments have been closely associated. During the war, the Permanent Head was also Secretary of the War Cabinet. In that period the responsibility of the Prime Minister's Department for defence coordination was extended and developed; in discharging this responsibility the Permanent Head is now assisted by the Defence Secretariat of the Prime Minister's Department. This Secretariat works closely with the Defence Division of the Department of External Affairs, and the head of that Division is chairman of the body which coordinates military and civilian intelligence.
In the formulation and application of external affairs policy, close association with other Government Departments is necessary. Defence planning, for example, entails close liaison with the Service Departments, participation in the Colombo Plan with the Treasury and with the many Departments which supply experts and training facilities, consular questions with the Department of Labour, and legal questions with the Department of Justice. Moreover, the Department is a clearing house for a wide variety of material provided by overseas posts for other Departments. As well as fulfilling its major function of acting as a channel of communication with other Governments, the Department thus also acts as a coordinating centre for other Government Departments. The Department and its network of posts overseas also performs numerous services on behalf of Departments which are without overseas representatives of their own.
*The portfolio was assumed by the Prime Minister, the Right Hon. Peter Fraser.
In the Official Section at the end of the Yearbook the diplomatic and other New Zealand representatives overseas are listed, as well as the official representatives of other countries in New Zealand.
New Zealand in the Commonwealth - Despite the new emphasis in New Zealand's approach to international affairs resulting from its consciousness of the realities of its geographical position in the South Pacific, membership of the Commonwealth remains the central feature of its policy. Intimate association with the United Kingdom is the historical basis, and remains an important principle of New Zealand's external relations. The ties between New Zealand and the United Kingdom are embodied in the close association of the Commonwealth, membership of which has given New Zealand an international status that such a small and isolated community could not otherwise claim.
Although one of the oldest members, New Zealand, unlike some of its fellow members, did not seek to hasten the process of constitutional transition within the Commonwealth. At the Imperial Conference in 1930 the Prime Minister, the Right Hon. G. W. Forbes, stated that “We have felt that all times within recent years we have had ample scope for our national aspirations and ample freedom to carry out in their entirety such measures as have seemed to us to be desirable”. There was little interest in the adoption of the relevant provisions of the Statute of Westminster enacted in 1931 to give legal endorsement to the transformation that had taken place in the relationship between Britain and the Dominions. It was not, in fact, until 1947 that the necessary formalities were completed in New Zealand by the passing of the Statute of Westminster Adoption Act.
Since that time there have been many changes in the Commonwealth association both in constitutional respects and in numbers. Whereas at the beginning of the war there were only five members, there are now 13 and it is expected that more will join within the next few years. With the entry of India, Pakistan, Ceylon, the Federation of Malaya, Ghana, and Nigeria, the Commonwealth has become an entity embracing several continents and its relationships have taken on a new scope and emphasis. New Zealand, itself a country where two races live side by side, sees in the Commonwealth a special opportunity for multiracial cooperation and understanding.
New Zealand has as yet exchanged representatives with only five of the 13 members of the Commonwealth: Australia, Canada, India, the Federation of Malaya, and the United Kingdom.*
The importance New Zealand attaches to the Commonwealth association has been given practical expression in its membership of a number of Commonwealth organisations, including the Commonwealth Air Transport Council, the Commonwealth Telecommunications Board, the Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, the Imperial War Graves Commission, the Commonwealth Institute, the Commonwealth Economic Consultative Council, and the Commonwealth Scientific Office.
New Zealand in the United Nations - It has been noted earlier that the first significant expression of an independent New Zealand foreign policy occurred in the League of Nations and was directed to supporting the principle of collective security. Support for this principle later and through the United Nations has remained a cornerstone of New Zealand's foreign policy.
The purposes which motivated the policy in 1935 were strongly held beliefs, rather than a set of principles developed from any careful assessments by a national foreign service. The beliefs were nevertheless a reflection of widely held concern over world events, a concern which the succeeding years were to reinforce. It was, therefore, perhaps understandable that at San Francisco in 1945 New Zealand should argue so forcibly, if unsuccessfully, to eliminate the veto and to strengthen the collective security provisions of the United Nations Charter.
Despite its physical isolation New Zealand has felt unable to regard with unconcern the fate of other small countries helpless to defend themselves against a powerful aggressor and thus liable to be picked off one by one.
The United Nations does not, it is true, offer a complete guarantee of New Zealand's or any other small country's security against aggression. Nor has it yet achieved agreement on disarmament; but New Zealand Governments have acted upon the conviction that the United Nations, and it alone, contains the rudiments of a universal collective security system, and that it is through the United Nations, and not through its abandonment in favour of some alternative, that an effective and comprehensive collective security system may eventually be developed and agreement on disarmament achieved.
* The New Zealand High Commissioner in India is also appointed High Commissioner in Ceylon.
New Zealand has recognised that this objective must be a long-term one, and that the United Nations in its present form must be buttressed by regional defensive alliances. It has not taken the view that all multilateral diplomacy must be conducted within the United Nations. In general, however, New Zealand has regarded the United Nations as the natural centre of international diplomacy unless there were, in special cases, good reasons to work outside it.
Within the United Nations the expression of this policy has taken several forms. New Zealand has sought to remove the causes which might produce the need for recourse to collective security action. Its representatives have urged that the Assembly be used as a place for harmonising relations between nations: they have voiced the need for restraint in the pursuit of national objectives; they have consistently sought and supported responsible action in aid of an effective international organisation; they have reiterated the need for the early adoption of a broad programme of supervised disarmament. At the 1959 session of the General Assembly the Prime Minister, the Right Hon. W. Nash, welcomed the new disarmament proposals put forward by the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, and welcomed the reaffirmation they contained that total disarmament was the goal to be sought. He also reiterated New Zealand's concern to see the early conclusion of an international agreement to bring about the permanent cessation of nuclear weapons tests. Subsequently, New Zealand joined in the Assembly's appeal to all States to refrain from resuming or initiating testing programmes.
New Zealand has at the same time advocated adequate and timely preparations in case aggression should occur. When occasion has arisen New Zealand has been prepared to play its part: troops were provided to the United Nations Force in Korea and military observers to the United Nations Observer Groups in Palestine, Kashmir, and Lebanon. New Zealand representatives in the United Nations have also strongly supported the principle that all members must bear an equitable share of the cost of international action to meet aggression, e.g., the cost of supporting the United Nations Emergency Force in the Middle East.
To maintain the peace is the primary purpose of the United Nations, and for New Zealand the search for effective guarantees of international peace and security continues to be the first object of membership. It is not, however, the only object, nor is a system of collective security (or disarmament) the only means of giving effect to it.
The state of economic, social, and general political relations goes far to determine the urgency of the need for a collective security system. For New Zealand, geographically isolated and with limited direct diplomatic relations, the United Nations is inevitably one of the most important forums available, not only to influence the course of international events, but also to secure the friendship and understanding of the world community. For any country, its international reputation is a valuable asset. If New Zealand is better known and commands more influence in international affairs than some other small States similarly situated, this is in some measure, at least, due to New Zealand's record of active participation in the United Nations.
Economic and Social Council - New Zealand's interest in these questions-as well as the recognition by other countries that New Zealand has special experience to offer-is illustrated by its membership of the Economic and Social Council (an elective body of 18 members of the United Nations) from 1947 to 1949 and its re-election in 1958 for a further tern for the period 1959 to 1961. New Zealand is also a member of the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East (ECAFE), of the Executive Board of the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), of the Social and Statistical Commissions, and the Commission on International Commodity Trade. In the past New Zealand has also designated representatives on the Fiscal Commission and the Commission on the Status of Women.
In undertaking these responsibilities New Zealand may to some extent be regarded as “taking its turn”. In few cases, however, are the considerations in favour of representation so simple. New Zealand certainly shares with others an interest in ensuring that economic and social conditions are such as to permit ordered political progress. It is concerned to ensure that, where political principles are in issue, the beliefs which New Zealanders hold as essential should be recognised and, if possible, accepted by the world community. Sometimes there are strong reasons of self-interest; the weight of advantage received, in terms of professional benefit, and the contribution made are evenly balanced in the case of technical bodies such as the Statistical Commission. On the other hand some organs which were first designed to meet the emergency of post-war conditions, such as UNICEF, have developed programmes, e.g., the supply of milk powder and fish-liver oil, which are of economic interest to New Zealand.
The biggest single task now facing the Economic and Social Council is to promote and direct programmes for economic development in underdeveloped countries. New Zealand has always recognised the need for economic development and made its contributions to the appropriate funds, e.g., the Expanded Programme for Technical Assistance and the Special Fund. It has been concerned to ensure that international programmes in this field should be effective and realistic.
At present New Zealand representatives in the United Nations are called upon to deal with questions of economic development in three different fields. One is in the Economic Committee of the General Assembly, where the economic work of the Organisation is subject to general review; the second arises out of New Zealand's membership of ECAFE. In this setting, the detailed study of development programmes is closely related to the work of the Colombo Plan, and provides a significant counterpart to New Zealand's growing political interest in Asia.
Finally, within the Economic and Social Council, New Zealand is associated with activities affecting the lives and welfare of a considerable proportion of the world's population; moreover, the Council is responsible for the general direction of assistance programmes running at present at the rate of about $100 million a year.
Specialised Agencies -It is the responsibility of the Economic and Social Council under the Charter to coordinate the activities of the Specialised Agencies through consultations and recommendations. New Zealand is a member of all the Agencies except the International Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organisation. As a contributor to their budgets, it is concerned to ensure that activities are not duplicated and that the Secretariats of the United Nations and of the Agencies work closely together on matters of common interest. New Zealand has also been concerned to ensure that on political and administrative matters the policies of the Agencies are adjusted to those of the United Nations. As in the case of the different organs and subsidiary bodies of the United Nations, so with the Specialised Agencies, New Zealand's reasons for membership have ranged from motives of self-interest to its conviction of the value of international cooperation. In some cases non-membership would place New Zealand at a distinct disadvantage. Membership of the Universal Postal Union is essential to facilitate the efficient international movement of mails to and from this country. Similarly the International Telecommunications Union regulates international radio, telephone, and telegraphic traffic, and the need to belong to this body is universally accepted. The World Meteorological Organisation is the medium for setting standards and encouraging the free interchange of meteorological information. Wartime experience emphasised the fact that few countries have as direct an interest in international civil aviation as New Zealand; although the only international airline registered in New Zealand flies only regional routes, New Zealand is closely concerned with the efforts of the International Civil Aviation Organisation to foster the planning and development of international air transport and to ensure proper standards for the development of airways, airports, and air navigation facilities.
No clear line can, however, be drawn between the “technical” Agencies and others, and some degree of technical advantage is to be derived from membership of all the Specialised Agencies. Although its own health standards are high, New Zealand has nevertheless drawn benefits, particularly in its island territories, from its membership of the World Health Organisation. Each in its own field - the Food and Agriculture Organisation, the International Labour Organisation, the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation, and the International Atomic Energy Agency - constitutes an important international medium for the free interchange of knowledge and experience.
On occasion the Specialised Agencies provide the forum for advancement of a New Zealand interest. The FAO has played a prominent part in the formulation of measures to encourage the establishment of a stable international market for agricultural commodities, particularly in the enunciation of principles to govern the disposal of surplus commodities. At its Ninth Session in 1957 the conference adopted a resolution sponsored by New Zealand which recommended that FAO develop further ways of disposing of surplus products without impinging on existing or future channels of trade.
The International Labour Organisation, which was established in 1919 in association with the League of Nations, became a Specialised Agency of the United Nations in 1946, although retaining its autonomy. New Zealand is a member State with the Department of Labour as the liaison agency of the Government. New Zealand representatives regularly attend the annual International Labour Conference.
As well as the Commonwealth organisations mentioned earlier some regional organisations, particularly the South Pacific Commission, are of particular importance to New Zealand. Since the establishment of the Commission in 1947, New Zealand's island territories have derived much benefit from its work on fisheries, cooperatives, control of the rhinoceros beetle, and research upon filariasis.
New Zealand and the South-East Asia Treaty Organisation - New Zealand, together with other countries concerned at the deteriorating security situation in South-East Asia, followed with close attention the development of the Indo-China crisis during the first half of 1954. After a United States plea on 29 March for “united action” by the free world to resist further Communist expansion in South-East Asia, the following month the United Kingdom and French Governments made known their agreement with the United States that consideration should be given to the establishment as soon as possible of a collective security system in the area. In New Zealand the Minister of External Affairs stated on 14 April that the Government welcomed this proposal, and was prepared to participate in discussions for this purpose.
The clarification of the situation in Indo-China, as a result of the cease-fire agreements reached at Geneva on 21 July 1954, gave fresh impetus to the proposals for a collective security arrangement. After a further period of consultation, eight countries - Australia, France, New Zealand, Pakistan, the Philippines, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and the United States - announced on 14 August that they had agreed to attend a conference in the Philippines in September to consider the establishment of a system of collective defence for the area. On 8 September in Manila representatives of the eight Governments signed the South-East Asia Collective Defence Treaty. At the same time they agreed on a Pacific Charter setting out the principles upon which the signatories undertook to base their policies for maintenance of peace and stability in the treaty area. The Minister of External Affairs, the Hon. T. C. Webb, led the New Zealand delegation to the Manila Conference and signed the treaty on behalf of New Zealand. The implications for New Zealand of the new agreement were reported to Parliament when the Minister returned from the conference, and the treaty was ratified by New Zealand on 19 February 1955 and entered into force for all the parties on that date.
New Zealand and the Colombo Plan - Under the Colombo Plan, New Zealand, with Australia, Canada, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America, has joined with the countries of South and South-East Asia to help them improve their standards of living. The Colombo Plan is not a single plan, but a series of separate plans drawn up and administered by each country in the region; the external assistance required and made available to help implement these plans is negotiated on a bilateral basis. The Plan had its origin in, and took its name from, a meeting of Commonwealth Foreign Ministers held in January 1950 in Colombo to exchange views on world problems, particularly on the economic needs of the countries of South and South-East Asia. The meeting established a Consultative Committee to “ . . . survey the needs, to assess the resources available and required, to focus world attention on the development problems of the area, and to provide a framework within which an international cooperative effort could be promoted to assist the countries of the area to raise their living standards”. Since then the Consultative Committee has met consecutively in Sydney, London, Colombo, Karachi, New Delhi, Ottawa, Singapore, Wellington (1956), Saigon, Seattle, Jogjakarta, and Tokyo (1960).
A foundation member of the Plan and an active participant at every meeting, New Zealand has done its utmost, within the scope of its limited resources, to make significant grants of capital and technical assistance to the countries of the area.
Capital Assistance - By 31 March 1961 New Zealand had appropriated a total of £10,315,000 for capital and technical assistance under the Colombo Plan. Of this, at 30 June 1960, £6,059,937 had been transferred to the governments concerned or used at their request to buy equipment. Most of New Zealand's capital aid has been given in the form of direct transfers of overseas funds, but in appropriate cases it has been possible to supply equipment manufactured in New Zealand.
Among the capital-aid grants during 1960 were a further £45,000 for the Akkarayankulum irrigation tank in Ceylon, £6,000 for educational materials sent to Laos, and the provision of surveying equipment for North Borneo. A sum of £60,000 was set aside for land-development projects in Malaya. Substantial capital aid, combined in most cases with the provision of New Zealand technical personnel, was being considered for Pakistan's Jaipur Hat sugar mill, an artisan training centre in Rangoon, Burma, an agricultural faculty at the University of Northern Sumatra in Indonesia, further assistance for dairy projects at Jaipur and Lucknow in India, and a pasture-improvement project in Nepal. New Zealand has assisted regional projects in providing launches at a cost of £35,000, for the Mekong River Development Scheme, and is giving £100,000 annually to the Indus Water Scheme in India and Pakistan.
Technical Assistance - By 30 June 1960 New Zealand had spent £1,507,091 on Colombo Plan technical assistance, and 731 students had come to New Zealand to take training courses. The main fields in which training has been provided are education, engineering, health, agriculture, and general university studies. Steps are being taken to increase the proportion of New Zealand's Colombo Plan contribution that can be given in the form of technical assistance.
A new hostel in Christchurch, Warwick House, has been set up to help provide adequate accommodation for Colombo Plan students and an additional hostel is to be built at Massey Agricultural College for a similar purpose - in both cases care is being taken to see that the Colombo Plan Students are spread among the New Zealand students and are not kept together in the one hostel. An English Language Institute was set up at Victoria University of Wellington at the end of 1960 to provide practical training in English for Colombo Plan students. As a temporary measure a Summer School was held in January-February 1960 at Victoria University for Colombo Plan students who had an inadequate command of English. Other proposals to increase New Zealand's capacity to train Asian students include the expansion of training facilities in dairy technology.
The other form of technical aid, the sending of New Zealand experts to Asia, is also being expanded, and in the middle of 1960 there were 33 New Zealanders on assignment, compared with 30 in 1959. Twelve of the experts, comprising an English language team, are giving instruction in English teaching in training colleges and universities in 11 Indonesian cities. Another team consisting of 12 surveyors has left for Malaya in two groups, the first at the end of 1960 and the second early in 1961, to assist with large-scale land-development schemes.
General Aims - It is clear that, as New Zealand has assumed the international responsibilities appropriate to an independent country, its foreign policy has changed in emphasis and scope. The foundations of New Zealand's pre-war position in international affairs - its identification with Britain and its membership of the Commonwealth - have been modified and extended to meet the demands of an international situation greatly changed from that of 1939. As a country of predominantly European settlement, New Zealand retains its traditional loyalties to the United Kingdom and a sense of identity with Europe and of involvement in its destiny. As a Pacific power, it has sought security in friendship and formal defensive arrangements with Australia and the United States of America; at the same time it has developed its association with Asian countries. As a country concerned with the preservation of world peace and the organisation of defence against aggression it has placed prime importance upon development of the United Nations as an agency for peaceful settlement of international disputes and for the achievement of collective security. Pending the establishment of a broadly based United Nations security system, however, New Zealand has been prepared, in respect of South-East Asia, to participate in a protective grouping concerned with the defence of a single area. Moreover, while it sees aggressive Communism as the greatest threat to individual liberty at the present time, it is well aware of the powerful stirrings of other forces - the yearning for political emancipation, the antagonism to systems of racial discrimination, the demand of underprivileged countries for a greater share of the world's prosperity, for social advancement and opportunity. New Zealand's actions in the international field are designed to take account of these forces and, where possible, to assist the people of other countries in their striving for a better life. The limits of what it is able to do are those imposed by its size and capacity; its disposition is towards peaceful and friendly relations with all nations and (whatever the modifications which the needs of national security may impose) it is to that ultimate goal that its foreign policy is directed.
CONSTITUTION OF NEW ZEALAND: General - New Zealand is a monarchical State; it is also a constituent member of the Commonwealth. It is in this context that the preamble to the Royal Titles Act 1953 is significant “… whereas it is expedient that the style and titles at present appertaining to the Crown should be altered so as to reflect more clearly the existing relationships of the Members of the Commonwealth to one another and their recognition of the Crown as the Symbol of their free association and of the Sovereign as the Head of the Commonwealth …”
Constitutional elements besides that of the titular head, the Monarch, can be reviewed under the categories of legislative authority, the executive and administrative structure, and the judiciary. This division is a convenient one, even though there is no absolute line of demarcation between the three phases (e.g., legislation may and often does arise through the day-to-day experience of those responsible for administration and execution of policy, or through difficulties or anomalies made explicit in the course of dispensing justice or interpreting law). Conversely, in the exercise of the powers and functions of industrial and other tribunals, commissions, authorities, etc., both administrative and judicial elements may be discerned.
THE MONARCH - The New Zealand Parliament in the Royal Titles Act 1953 gave its assent to the use of the Royal style and titles as follows: Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God of the United Kingdom, New Zealand, and Her Other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith.
While the seat of the Monarch is normally in the United Kingdom, the Queen is represented in New Zealand by the Governor-General appointed by the Crown on the advice of Her New Zealand Ministers. The Governor-General has, however, an official existence, even in the country to which he has been appointed, only in the absence of the Queen from that country. In the island territories the Crown is represented by the Resident Commissioner or Resident Agent, and in the Trust Territory of Western Samoa by the High Commissioner. These officials carry out the constitutional functions of the Crown, but they also possess in varying degree certain executive and legislative powers, being responsible to the New Zealand Government for the administration and good government of the islands concerned.
Many powers held by the Monarch (or her representative) comprise but the means of giving effect to the public will. In New Zealand the Governor-General acts on the advice of the Ministers, which cannot be constitutionally ignored. Despite the long-term trend for powers to be assigned directly to Ministers without any necessity for vice-regal consultation, there are still many phases of Government which require Royal participation.
The Queen (in her absence the Governor-General) gives consent or approval prior to a Minister taking office or the formation of a Ministry; summons and prorogues Parliament; delivers the Speech from the Throne at the opening of a session; gives the Royal Assent to measures which have passed all stages in the House of Representatives, without which they have not the force of laws; makes appointments to most important State offices; confers knighthoods and other honours, etc.; and also provides that background of stability, continuity, and experience in many facets of government which is so desirable whenever there are sweeping changes in the dominance of political parties.
Besides those duties associated with the constitutional role, the Royal personage or representative makes an important contribution to the ceremonial life of the nation. This was particularly well illustrated during the sojourn of the Royal visitors to New Zealand in 1953-54. Both as the symbol of the nation and in virtue of her identification with the life and interests of her people, the Queen becomes the focus for all State occasions, as does the Governor-General in her absence.
LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY - The supreme law-making body with power to legislate for the whole country is the General Assembly, which now consists of the Governor-General and the House of Representatives, the former Legislative Council having been abolished since the close of 1950.
The powers of Parliament to make laws are legally untrammelled. This was not always so, for prior to the adoption by New Zealand of the Statute of Westminster in 1947 there was incapacity to make laws on certain matters which conflicted with United Kingdom statutes extending to New Zealand. There was also some doubt as to New Zealand's power to make laws possessing extra-territorial validity.
Although they do not limit the legal powers of Parliament as stated above, the provisions of the Electoral Act 1956 creating reserved sections in that Act are of great constitutional significance. The Act provides that certain of its sections may not be repealed except by a 75 per cent majority of the House of Representatives or following a referendum. These sections are those relating to:
The constitution and order of reference of the Representation Commission.
The number of European electoral districts and the basing of their boundaries on the total population.
The fixing of the tolerance within which the Commission must work at 5 per cent.
The age of voting.
The secret ballot.
The duration of Parliament.
This innovation is not legally effective in the sense that it does not prevent a subsequent Parliament from repealing it, since one Parliament cannot bind its successors. It should not be thought, however, that the new provision is a mere gesture. It records the unanimous agreement of both parties represented in Parliament that certain provisions have a fundamental character in the system of Government and should not be altered at the whim of a bare majority. Considered in this light the provision creating reserved sections introduces something in the nature of a formal convention which could not constitutionally be ignored.
While the law-making function is the prerogative of the members of Parliament, it must be remembered that, as in most democracies, laws are passed because of their acceptability to the majority party in Parliament - i.e., the Government party. Furthermore the initial acceptance will have probably been made in the deliberations of Cabinet.
With the increasing range and complexity of the statutory field, the multifarious concerns of a modern twentieth century government, and the necessity of conserving time for consideration of more important issues, much of the detailed procedural steps and other amplifying matter must become the subject of Orders in Council or of regulations made under the authority of some statute, rather than being incorporated in the statute itself. In this form of what has been termed legislation by delegation, the power to originate and sanction regulations rests with that comparatively small proportion of the majority party in Parliament individually known as Members of the Executive Council (or of Cabinet) and who collectively, together with the Governor-General, comprise the Executive Council. The same individuals, excluding the Governor-General, in New Zealand are members of the Cabinet, provided that each is the holder of a portfolio.
Cabinet may and often does function in a deliberate sense as well as in an executive or administrative sense. However, regulations, etc., though originating in Cabinet and becoming effective in the proceedings of the Executive Council, still remain subject eventually to the sovereign will of Parliament as a whole.
Meeting of Parliament - Parliament is summoned, prorogued, or dissolved by Proclamation issued by the Governor-General. A session is that period between the summoning of Parliament and its prorogation. Its length varies, but it usually occupies the months from June to November. When Parliament is prorogued all the business on hand lapses, and if this is to be proceeded with in the next session it must be re-introduced.
The course of a session may be interrupted by an adjournment.
Parliamentary Privileges - While in session these include freedom of speech and freedom from arrest, and also the right to engage in secret debate, if required, etc.
The Party System - There are two political parties represented in Parliament in New Zealand at present: National and Labour. At any general election these parties, together with any other political parties which may be desirous of so doing and also those standing as independents, state their respective policies before the electors. Each party normally puts forth one candidate for each of the 80 electorates into which the country is divided. The party which wins the majority of seats, although not necessarily the majority of votes, at the general election forms the Government. The leader of the elected members of the majority party becomes the Prime Minister, who makes Ministerial appointments from elected members of his party. The leader of the minority party in Parliament becomes the Leader of the Opposition. The effectiveness of the party system relies largely on the general agreement that the majority party is to govern and the minority is to criticise - so that there is ample time allocated for debate on Government measures in Parliament. While party control is exercised by national and local organisations outside Parliament, within the latter it is maintained by the respective party Whips.
Parliamentary Procedure - The House of Representatives has its Standing Orders, which govern its procedure and which are administered by Mr Speaker in the exercise of his control of the House. Mr Speaker's rulings on interpretation of the Standing Orders are followed in a similar manner to judicial decisions in the ordinary Courts of law. The main means by which Parliament does its work is through the system of debate and Committees. The election of a Speaker is the first business of a new House after the members have been sworn. A Chairman of Committees is elected as soon afterwards as is convenient. Twenty members, inclusive of the Speaker, constitute a quorum.
Parliamentary Functions and Control - The Parliament controls the Government in power in the last resort by its power to pass a resolution of no confidence in the Government, or to reject a proposal which the Government considers so necessary that it is made a matter of confidence, and thus force the Government to resign.
Financial control is exercised by the fact that expenditure of public money must be authorised by the House of Representatives in the form of an Appropriation Act, which authorises or grants money to the Government for the purposes approved. The authority for the raising of revenue by taxation or borrowing must also be given by Parliament. The functions of Parliament are, of course, the passing of legislation and taking action to make available finances or funds as required for State expenditure, while it also controls the Government. Legislation can be initiated from any member of Parliament, but in practice almost all Bills are introduced by the Government in power as a result of policy decisions taken in Cabinet, sometimes at the instigation of those Government Departments which will be responsible for their administration when the Bills become law. The chief exceptions are private Bills, which are designed for the particular interest or benefit of a person or body of persons, whether incorporated or not, and local Bills which relate largely to matters of local (as distinct from central) government business. The process of passing a public Bill is as follows: it receives a formal first reading on introduction, is then printed, and after some time it is given a second reading as a result of a debate on its general merits or principles. It may then be referred to one of the Select Committees, for consideration in the closest detail, before being considered by the whole House sitting in Committee. During these stages members have opportunities to suggest amendments which may be incorporated in the Bill if the majority so decide. The Bill is then reported to the House, and later read a third time, and passed; debate rarely occurs at these stages. The final stage is to send the Bill to the Governor-General for the Royal Assent and, unless provision is made for commencement on another date, it then becomes law. The Bills providing for receipt of moneys, such as the Finance Bill, and expenditure of moneys, such as the Appropriation Bill, are initiated only by a Minister of the Crown, normally the Minister of Finance.
Duration of Parliaments - Quinquennial Parliaments, instituted under the Constitution Act, were abolished by the Triennial Parliaments Act 1879, which fixed the term at three years. General elections have been held at three-yearly intervals since 1881, with a few exceptions. The term of the nineteenth Parliament was during the First World War extended to five years by special legislation, and that of the twenty-fourth (1931-35) and subsequent Parliaments to four years under the Electoral Amendment Act 1934. By the Electoral Amendment Act 1937 the three-year term was restored, but on account of war conditions the term of the twenty-sixth Parliament was extended to four years by the Prolongation of Parliament Act 1941. The Prolongation of Parliament Act 1942 extended the term still further to one year from the termination of the war, but with a proviso for a motion to be moved in the House of Representatives each year after the year 1942 either approving the continuation of the House or fixing an earlier date for its expiry. During the 1943 session a motion in favour of dissolution was carried, and Parliament was dissolved on 30 August 1943. Since then the duration of Parliaments has been of three years, with the exception that the twenty-ninth Parliament was dissolved after the expiration of approximately 20 months. The three-year limit was reenacted in the Electoral Act 1956, this being one of the reserved provisions referred to on page 31.
Number of Representatives - The number of members constituting the House of Representatives is 80 - 76 Europeans and four Maoris. They are designated “members of Parliament”. The number was originally fixed by the Constitution Act as not more than 42 and not less than 24, and the first Parliament called together in 1854 consisted of 40 members. Legislation passed in 1858 fixed the number of European members at 41; in 1860, at 53; in 1862, at 57; in 1865, at 70; in 1867, at 72; in 1870, at 74; in 1875, at 84; in 1881, at 91; in 1887, at 70; and in 1900, at 76. Since 1867 there have been four Maori representatives, and provision for this number was retained in the Electoral Act 1956. In 1952 the boundaries of the Maori electoral districts, which had remained unaltered since 1867, were changed by Proclamation so as to give a greater degree of equality of population among the four districts (in effect the Southern Maori Electoral District now includes a considerable area of the North Island).
Qualifications of Members -Under the Electoral Act 1956 every registered elector of either sex, but no other person, is qualified to be a parliamentary candidate. It is provided, however, that a person shall not be so elected who is disqualified as an elector under any of the provisions of the Act (see under “Franchise” later); or is an undischarged bankrupt; or is a contractor to the Public Service of New Zealand to whom any public money above the sum of £200 is payable, directly or indirectly (but not as a member of a registered company or incorporated body), in any one financial year. Although women have had the vote since 1893, they were not eligible as Parliamentary candidates until the passing of the Women's Parliamentary Rights Act 1919. Prior to 1936 a public servant was prohibited from being elected, but this prohibition was removed by the Political Disabilities Removal Act 1936. The present law is that if a public servant is elected to Parliament he vacates his office forthwith and he cannot resume employment in the Public Service within 12 months of ceasing to be a member of Parliament unless he had previously been a public servant for at least five years.
Salaries, etc. -In accordance with the recommendations contained in the report (issued in 1959) of the Royal Commission upon parliamentary salaries and allowances, the Prime Minister's salary, as from 1 July 1959, was increased to £4,250 with a tax-free allowance of £1,500 for the expenses of his office and the Ministerial residence. In addition, while travelling on official business he receives £4 4s. per day to meet expenses, and by virtue of his office is entitled to free cars, secretarial assistance, and free postage. The salary of each Minister holding a portfolio is £2,800 with a tax-free expense allowance of £450, and that of each Minister without portfolio £2,200, with £350 tax-free expense allowance. Where the office of Minister of External Affairs is held by a Minister other than the Prime Minister the expense allowance is increased to £615. Any Minister not occupying a Ministerial residence receives an allowance in lieu at the rate of £300 per annum. This allowance, or the assessed value of the residence where one is provided, is subject to income tax. Previously Ministers did not receive an expense allowance as such, but the Commissioner of Inland Revenue allowed a deduction from salary of £250 as an expense allowance. Ministers also receive an allowance of £4 4s. per day when travelling on official business within New Zealand.
The Civil List Amendment Act 1936 made provision for the appointment of Parliamentary Under-Secretaries, an innovation in executive control in New Zealand. The rate of salary attachable to such position is now £1,700, with the same house provision or allowances, and travel allowance while on official business, as for Ministers. An expense allowance of £400 is also payable. After the general election of November 1954, no appointments were made until 1960.
The Civil List Act 1950 provided that, on a recommendation of a Royal Commission, the salaries and allowances of Ministers and Members of Parliament may be fixed by Order in Council, in which event the salaries and allowances so fixed will be payable instead of those specified in the Civil List Act 1950. In conformity with the recommendations of the Royal Commission issued in 1959 the honorarium paid to members of the House of Representatives is now £1,400 per annum. Members are also paid an allowance to provide for expenses incurred in connection with parliamentary duties ranging from £275 per annum to £605 per annum, subject to the classification of electorates by the Representation Commission into the five classes of (a) a Wellington electorate, being a wholly urban electorate in or near Wellington or Lower Hutt, or (b) a wholly urban electorate other than a Wellington electorate, or (c) a substantially urban electorate, or (d) a substantially rural electorate, or (e) a wholly rural electorate; a special additional allowance of £100 per annum is paid to the member for Southern Maori and a special additional allowance of £50 per annum to the members representing the other three Maori electorates (for details see Parliamentary Salaries and Allowances Order 1959). Payment to members is subject to certain deductions for absence not due to sickness or other unavoidable cause. In addition to the honorarium, members are entitled to certain privileges in respect of railway and other forms of travel, a stamp allowance of £5 a month, etc. The Civil List Amendment Act 1955 provides that a Royal Commission shall be appointed to fix parliamentary salaries and allowances within three months after the date of every general election.
Part V of the Superannuation Act 1947, as amended by the Superannuation Amendment Act 1955, and consolidated in 1956, introduced a contributory superannuation scheme for members of the House of Representatives. The scheme now provides for a minimum retiring allowance of £350 per annum for a member with service of nine years (or eight years if a member has served throughout the duration of not less than three Houses of Representatives), the allowance increasing by £50 per annum for every year's service in excess of that period until a maximum allowance of £700 per annum is reached after 15 years' service.
A member must be 50 years of age before he qualifies, on ceasing to be a member, to receive the allowance. The annual contribution, which is compulsory, is £140 per annum, but a member may if he so desires receive a refund of his contributions upon ceasing to be a member.
In the case of a male member dying and leaving a widow surviving she becomes entitled during her widowhood to receive an annuity of two-thirds of the retiring allowance to which her husband was entitled at the time of his death.
Both the Speaker and Chairman of Committees hold office until a dissolution and receive payment until the first meeting of a new Parliament. The Speaker's remuneration is £2,400 per annum, in addition to which he receives an expense allowance of £600 and residential quarters in Parliament House. The honorarium of the Chairman of Committees is £1,825, and an allowance of £500 per annum to cover expenses incurred in connection with his parliamentary and official duties is also paid.
The Leader of the Opposition is paid a salary of £2,200 with an expense allowance of £490. In addition, a secretary and typist are provided by the State and an allowance of £215 is payable for travel outside his electorate. His stamp allowance is £12 10s. per month.
The Chief Whip of each party receives a salary of £1,450 per annum, and the Junior Whip of each party receives a salary of £1,430, together with the appropriate expense allowance in each case in accordance with the classification of his electorate.
ADMINISTRATION AND EXECUTIVE RESPONSIBILITY - After the election of a new Parliament, the Prime Minister, who is the leader of the majority party in the elected members, is given the task of selecting the members of the Executive Council (i.e., the new Ministry). Each of those members of Parliament to form the Government is entrusted by the Prime Minister with responsibility for administration of a specified field or aspect of government. This field is entitled a portfolio, e.g., all relevant matters relating to Customs would be allocated to one member, who is henceforth known as the Minister of Customs. He may also have other portfolios and the supervision of one or more Government Departments in which the activities carried out, though important, either do not rank as portfolios or are subsidiary aspects of the field -in these cases the Minister's responsibility will extend to being in charge of the named Department. One or other of the appointed Ministers in this way is responsible for the direction of activities and executive acts of each of the Government Departments and offices, etc., embracing the entire range of State activities. Thus arises the concept of Ministerial responsibility.
Executive Council-In the legal sense those members of Parliament who have been appointed Ministers, together with the Governor-General, comprise the Executive Council. The powers, duties, and responsibilities of the Governor-General and the Executive Council under the present system of responsible government are set out in Royal Letters Patent and Instructions thereunder of 11 May 1917, published in the New Zealand Gazette of 24 April 1919. The Royal Powers Act 1953 provides that the statutory powers conferred on the Governor-General may be exercised either by Her Majesty the Queen in person or by the Governor-General. In the execution of the powers and authorities vested in him the Governor-General must be guided by the advice of the Executive Council; but, if in any case he sees sufficient cause to dissent from the opinion of the Council, he may act in the exercise of his powers and authorities in opposition to the opinion of the Council, reporting the matter to Her Majesty without delay, with the reasons for his so acting.
In any such case any member of the Executive Council may require that there be recorded in the minutes of the Council the grounds of any advice or opinion that he may give upon the question.
A point of interest is that the Civil List Act 1950, in section 6, provided that no person shall be appointed a Minister or a member of the Executive Council unless he is a member of Parliament and that a person who ceases to be a member of Parliament cannot continue to be a Minister or a member of the Executive Council for more than 21 days. This gave statutory recognition for the first time to what had long been the convention.
At January 1961 the Executive Council consisted of 16 members in addition to the Governor-General. Two members, exclusive of His Excellency or the presiding member, constitute a quorum.
Under the Civil List Act 1950 and its amendments, His Excellency the Governor-General receives a salary of £6,500 per annum, and an allowance of £5,000 per annum for the salaries and expenses of his establishment (exclusive of the Official Secretary), plus all expenditure incurred in respect of the transport to and from New Zealand and the travel within or outside New Zealand of the Governor-General and his family and staff.
Cabinet - There is a close relationship between the Executive Council and the Cabinet. There are, however, significant differences in membership and functions.
The Council consists of all Ministers and is presided over by the Governor-General. Cabinet may or may not comprise all the Ministers, including a Minister without portfolio; the Governor-General is not a member. The Council (a statutory body) is one of the instruments for giving the imprint of legal form to policy determined by Cabinet (which is recognised only by constitutional convention).
Cabinet has been described as the directing body of national policy whose nature is more easily explained by analogy than by definition. It determines the policy to be submitted to Parliament. In it is vested the supreme control of national policy within the limits of Parliamentary approval. It coordinates and delineates the activities of the several Departments of State.
The juridical acts which are necessary to give legal force to certain of the decisions of Cabinet are taken by others - the Crown, the Executive Council, a Minister of the Crown, a Statutory Commission and the like. The preliminary review of proposed policy or of current administrative developments, which takes place in the informal atmosphere of Cabinet meetings, implies both deliberative or selective and administrative procedures on the part of this body.
Cabinet discussions are informal and confidential, anonymity being maintained as to the individual advocacy or opposition to particular proposals. The Cabinet system enables general agreement to be reached on any proposed line of action by either an individual Minister or by the Government as a whole. As a result the Executive Council confirmation can proceed smoothly and expeditiously.
In Parliament a Minister can be confident that his legislative or other proposals will have the unqualified support of the Government no matter what divergences of opinion may have been apparent before general agreement was reached in Cabinet. A consistent and agreed course of action on any particular issue can be determined. The work of Cabinet thus exemplifies the concept of the collective responsibility of the Government.
Certain questions are considered by committees of Cabinet composed of those Ministers primarily concerned. Some executive action may be undertaken by these committees within the lines of established Government policy. Their work is subject to periodical report to, and overall supervision by, the entire Cabinet. On occasions, ad hoc committees may be established to review or investigate particular questions and to present their conclusions and recommendations to Cabinet.
The Cabinet Secretariat is responsible for the servicing of Cabinet and its committees to ensure their smooth functioning. It is its purpose also to assist in the coordination and review of the work of the Departments of State.
Government Departments - The Minister as the political head of a Department of State may in fact have several Departments under his control. There are however some 44 different Departments with separate functions in New Zealand. Each of these has a permanent head who is responsible for the work and administration of the Department. He is of course responsible to the Minister in charge of the Department, while he also acts as adviser to the Minister on all matters within his appointed competence. Besides ensuring that the ministerial policy and directions communicated to him are effectively put into practice, his functions as the adviser include assessing the consequences of any executive action resulting from his departmental activity, evaluating the merits and demerits, whether political, social, or financial, of various modes of action, and making suggestions for improvements and for new policy measures as derived from departmental experience in the day-to-day execution of policy.
Departments can be broadly classified according to the administrative or regulatory, developmental, or social nature of their activities. Within the first group are the servicing subgroup, such as the Legislative, Prime Minister's Office, External Affairs, Printing and Stationery, Law Drafting, Valuation, Statistics, and Audit; the finance subgroup - Treasury, Customs, Inland Revenue; the regulatory subgroup - Public Service Commission, Internal Affairs, Island Territories, Labour, Marine; the defence and law and order subgroup - Navy, Army, Air, Justice, Crown Law, and Police; the publicity and research subgroup - New Zealand Broadcasting Service, Tourist and Publicity, Scientific and Industrial Research.
In the second group are the transport and communications subgroup, such as Transport, Post Office, and Railways; the developmental - Ministry of Works, Agriculture, Lands and Survey, Mines, Electricity, Maori Affairs, and Industries and Commerce; the commercial - Public Trust, Government Life Insurance, State Advances Corporation, and State Fire and Accident Insurance.
The third group comprises the Education, Health, and Social Security Departments.
This broad division serves merely to indicate in which field the dominant activity or purpose of the particular Department is engaged on or concerned with. Most Departments have servicing, informative, and regulatory functions, and many are equally regulatory and developmental in nature.
In addition to the system of direct administration in the form of Government Departments, there are other activities over which the State exercises some ultimate measure of control or ownership, though divorced in varying degrees from immediate supervision. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (the central bank), and one trading bank, are entirely State-owned, although the actual administration is quite independent, subject in the case of the Reserve Bank to the proviso that the Governor or Board of Directors is to give effect to any resolution of the House of Representatives in respect of the bank's functions or business.
Further instances of this principle are shown by the National Airways Corporation, which, although owned by the State, is administratively self-contained, and by the Tourist Hotel Corporation. In certain other avenues the type of administration is in between the normal departmental form and that evident in the corporation type; of such is the National Roads Board, which, though determining policy to a large degree, yet makes use of departmental administrative structures for implementation of policy.
Some administrative organisations have also quasi-judicial functions. Examples of this class are the Price Tribunal, Transport Charges Authority, Licensing Control Commission, and Local Government Commission.
JUDICIARY - The hierarchy of Courts in New Zealand comprises the Court of Appeal, the Supreme Court, and the Magistrates' Court. Apart from these Courts of general jurisdiction there are other Courts dealing with specific fields. In the latter category are the Court of Arbitration, concerned with awards and general orders governing wage determination and conditions of employment in industry; the Compensation Court dealing with workers' compensation; and the Land Valuation Court, which settles land valuation disputes and compensation claims where land is taken for public works. For further details refer to Section 8 (Justice) of this issue
ELECTORAL PROVISIONS - The law on these matters is now contained in the Electoral Act 1956. Following each population census, which is normally taken every five years, New Zealand is divided anew into 76 European electorates. In addition, there are four Maori electoral districts, three in the North Island and one covering a portion of the North Island together with the whole of the South Island, where the Maori population is comparatively small. The Governor-General may at any time by Proclamation alter the boundaries of the Maori electoral districts, but, as in the case of European electoral districts, any alterations are to come into force at the expiry of the Parliament existing when the Proclamation is issued.
The Government Statistician is required to supply population figures to the Surveyor-General as soon as possible after the census. The population used as the basis in obtaining the quota for each European electoral district is defined in section 2 (1) of the Electoral Act 1956.
The term “European population” means total population with the following exceptions:
Maoris:
Persons residing on board ship, whether as passengers or members of the crew or otherwise:
Persons residing temporarily as guests in any licensed hotel:
Persons residing temporarily in any naval, military, or air force camp, station, or establishment:
Persons residing as patients or inmates in any hospital:
Persons in respect of whom reception orders under the Mental Health Act 1911 are in force:
Persons detained pursuant to convictions in any penal institution.
After the population figures are supplied by the Government Statistician it is then the responsibility of the Representation Commission to define new electoral districts for Europeans. The Commission is constituted by virtue of section 15 of the Electoral Act 1956 and comprises seven members. Four of these, the Surveyor-General, the Government Statistician, the Chief Electoral Officer, and the Director-General of the Post Office, are official members. Two are unofficial members, being persons nominated by the House of Representatives, one nominated to represent the Government, and one to represent the Opposition. The seventh member is appointed, on the nomination of the official and unofficial members of the Commission or a majority of them, to be the Chairman of the Commission. The Chairman and unofficial members cease to be members on the date on which the first periodical census is taken after the date of their appointment.
The Commission determines the number of electoral districts in the North and in the South Islands so that the number of districts in the North Island bears, as nearly as possible, the same proportion to the number of districts in the South Island as the European population of the North Island bears to the European population of the South Island. Once this is done the next step is to determine the population quota for electoral districts in each Island by dividing the European population of each Island by the number of districts in that Island. In applying the quota, provision exists for an allowance by way of addition or subtraction of 5 per cent of the quota where districts containing the exact quota could not be formed consistently with consideration of topography, community of interest, communications, and existing electoral boundaries.
When the boundaries have been provisionally determined, maps are prepared illustrating the proposed electoral districts, and descriptions of each electoral district are published in the New Zealand Gazette. A time limit of one month is given thereafter in which objections to the proposed boundaries may be lodged. These objections are then considered by the Representation Commission and a final decision reached on boundaries which then become the new electoral districts.
In addition to determining new European electoral districts the Representation Commission is also charged with the responsibility of classifying them for the purpose of allowances as provided by section 14 of the Parliamentary Salaries and Allowances Order 1959. Under this section provision is made for an allowance based on the size, topography, and transport facilities of the electorate, the nature of its roads, the distribution of its population, and all other considerations that the Commission deems relevant.
The Act provides that all general elections and by-elections shall be held on a Saturday and for both European and Maori elections to be held on the same day. Polling hours in all electorates are from 9 a.m. to 7 p.m.
The Act provides that, if at any time Parliament is dissolved before it has been two years in existence, the main and supplementary rolls used in the previous general election, together with a further supplementary roll, may be used if in the opinion of the Chief Electoral Officer it is impracticable to print new main rolls. The same rolls, together with a further supplementary roll, are to be used for any by-election occurring before the next following general election.
Provision is made for the voting at elections and licensing polls by servicemen serving overseas, who are or will be of, or over the age of, 21 years before the date of the election or poll, whether or not registered as electors of any electoral district. Each such serviceman shall be qualified to vote as an elector of the electoral district in which is situated his usual place of residence before he last left New Zealand.
FRANCHISE - Since the abolition of plural voting in 1889 and the introduction of women's suffrage in 1893, every person 21 years of age or over (with certain obvious exceptions) has had the right to exercise one vote and one vote only in the election of members of the House of Representatives. The present law relating to electors and elections is contained in the Electoral Act 1956, and a note of some of the more important provisions of this Act is given below.
Qualification for Registration as Elector - To be qualified for registration as a parliamentary elector in New Zealand a person must have attained the age of 21 years and must (a) be a British subject or Irish citizen, (b) be ordinarily resident in New Zealand, (c) at some period have resided continuously in New Zealand for at least a year, and (d) except in special cases have resided continuously for three months or more in the electoral district in respect of which application for registration is made, and not have subsequently resided for three months or more in any other electoral district.
The Act defines what is meant by the term “ordinarily resident”. To be ordinarily resident in New Zealand, a person must be or have been actually resident in New Zealand with the intention of residing there indefinitely. If he is absent from New Zealand he must have had, ever since he left New Zealand, an intention to return to reside there indefinitely, and (except in the case of a public servant or the wife or husband of a public servant) must not have been absent from New Zealand for more than three years.
This new requirement that an elector must be ordinarily resident in New Zealand is an important departure from the previous position. Prior to 1957 any British subject who had been in New Zealand for a year was entitled to register and to vote, even though his residence might have been of a temporary nature and although he did not associate himself with the New Zealand community. Conversely, a New Zealander absent from New Zealand for more than a year lost the right to vote. Broadly speaking, the new qualifications restrict the right to vote to permanent residents, the test laid down being similar to the legal concept of domicile.
The following persons are disqualified from registration as electors: (a) Those in respect of whom reception orders under the Mental Health Act 1911 are in force, (b) those detained pursuant to a conviction in any penal institution, and (c) those whose names are on the Corrupt Practices List for any district. These qualifications and disqualifications apply alike to Maoris and Europeans.
Registration of Electors - A system of compulsory registration of electors has been in operation in respect of Europeans since 1924 and was introduced in respect of Maoris in 1956. Every person qualified to be registered as an elector of any district must, if he is in New Zealand, apply for registration within one month after the date on which he first becomes qualified to be registered as an elector. He must also apply for registration within three months after the issue of every Proclamation proclaiming the names and boundaries of electoral districts or within such later period as may be provided by Order in Council. Qualified electors who are outside New Zealand may apply for registration if they wish.
A European is not entitled to be registered as an elector of a Maori district and a Maori (other than a half-caste) is not entitled to be registered as an elector of a European district. A half-caste Maori may choose to be registered either for a Maori or European district, and special rules are laid down to govern a change from one to the other.
Voting at Elections - Voting at parliamentary elections is by secret ballot, a method which was first introduced in New Zealand in 1870. Recognition of the fundamental character which the secret ballot has attained in New Zealand was given in the Electoral Act 1956, which included the section providing for this method of voting among the reserved sections which may be repealed only by a 75 per cent majority vote of all the members of the House of Representatives or following a referendum.
In general, only those persons whose names are lawfully on the main and supplementary rolls of electors compiled prior to an election may vote at that election. The following classes of persons whose names are not on the roll are however entitled to vote:
Those who have applied for registration between writ day and polling day and have satisfied the Registrar that they became qualified for registration not earlier than one month before writ day.
Those who are qualified for registration and were at the last preceding election registered in that district or, where boundary changes have intervened, in some other district in which their then residence within the first-mentioned district was then situated.
Those who are qualified for registration and have since the last election and before 6 p.m. on writ day applied for registration in that district, or where boundary changes have intervened, in some other district in which their then residence within the first-mentioned district was then situated.
Servicemen outside New Zealand, if they are or will be 21 years of age or more on polling day and their place of residence before they left New Zealand is within the district.
Special Voters - A vote is normally cast by the elector at a polling booth within his district. An elector may, however, vote as a “special voter”, either at a polling booth outside his district or by post, in the following cases:
If his name does not appear on the main roll, or any supplementary roll for the district, or has been wrongly deleted from the roll.
If he will be outside New Zealand on polling day.
If he is or will be absent from the district on polling day.
If he will not be within 2 miles by the nearest practicable route of any polling place in the district during the hours of polling.
If he will be travelling during the hours of polling under conditions which will preclude him from voting at a polling place in the district.
If he is ill or infirm.
If, in the case of a woman, she is precluded from attending at a polling place by reason of approaching or recent maternity.
If he is a lighthouse keeper or a member of a lighthouse keeper's staff, or if she is the wife of a lighthouse keeper or of one of his staff.
If he has a religious objection to voting on the day of the week on which polling day falls.
If he satisfies the Returning Officer or Deputy Returning Officer that on any other ground he cannot vote at a polling place in the district without hardship or undue inconvenience.
These latter conditions replace the former classes of absentee, postal, and declaration voters, including servicemen outside New Zealand.
LOCAL GOVERNMENT - In 1876, following the abolition of the provinces, local government assumed the form it still basically retains. The Counties Act of 1876 divided the country into 63 counties, with provision for administration by elective councils having powers considerably less than those enjoyed by the Provincial Councils. In the same year the Municipal Corporations Act provided for the incorporation of the 36 boroughs then in existence and for the creation of new boroughs.
A description of the development of counties, boroughs, and town districts follows.
Counties - In general, the county organisation makes provision for the primary needs of a scattered population within a large area. With increasing settlement the original 63 counties were gradually subdivided until in 1920 the maximum of 129 was reached, although the number of councils formed never exceeded 126. Since 1955 the number of counties has been reduced by amalgamations and mergers under the Local Government Commission Act 1953. At April 1960 there were 121 counties, in 119 of which the Counties Act was in force.
Counties are now constituted under the Counties Act 1956, which consolidated earlier legislation relating to counties and road districts.
County councils may appoint county town committees for the purpose of advising the councils on the administration of county towns. The Counties Amendment Act 1959 amended the conditions for the constitution of county towns to provide that any part of a county not being part of a dependent town district in which there are not less than 60 houses with average density of not less than one house to every 3 acres may be constituted a county town.
The provisions relating to the persons eligible to act on a county town committee were also amended. The Act now provides that a member of the county council representing the riding in which the county town is situated, and any county elector having a residential or rating qualification in respect of an address or property within the county town, is eligible for appointment to the county town committee. Under the old legislation only ratepayers having a qualification in respect of property situated within the county town were eligible.
Boroughs - Dealing with the needs of a concentrated population, the borough organisation is concerned with a wide range of functions of a purely local nature. With the growth and centralisation of population the number of boroughs, despite numerous amalgamations of adjacent boroughs, steadily increased until 1955 when the total was 146. In April 1960 the total was 143.
Under the Municipal Corporations Act 1954 for the constitution of a borough there must be a population of at least 1,500 with an average density of population of at least one person per acre. A borough containing a population of 20,000 or more may be proclaimed a city, although the corporation remains unaltered.
Town Districts - The town district represents a form of local government intermediate between the county and the borough. It implies a certain concentration of population and the presence of interests which, from their purely local nature, cannot be satisfactorily met by the county organisation. In its early stages a town district usually remained subject to county control, although such control was practically confined to the main and county roads in the town district; in such circumstances it was known as a dependent town district. The Town Boards Amendment Act 1908 enabled town districts on reaching a population of more than 500 to become independent. On attaining its independence a town district becomes in all respects a separate entity, and, apart from its smaller population, is not essentially different from a borough. The constitution and powers of town districts have been brought into closer relationship to boroughs over the years, and independent town districts are now constituted under the Municipal Corporations Act 1954. The Act required that the area should not be more than 2 square miles, within which no two points are more than 4 miles distant and with a density of population of not less than one person to the acre. No new dependent town districts can be constituted. The number of town districts in April 1960 was 27 (15 independent and 12 dependent).
General Powers - Local authorities in New Zealand derive their powers from the Acts under which they are constituted, and also from special empowering Acts. In addition to legislation providing for particular types of local authority or for individual local authorities, there are several statutory measures which are more or less applicable to all local authorities, such as the Local Elections and Polls Act 1953 and the Local Authorities Loans Act 1956. For most harbour boards, there is in addition to the general Harbours Act a special Act for each board, which is subordinate to the general Act. Certain types of local authority - urban drainage boards, transport boards, the Auckland Harbour Bridge Authority, the Christchurch-Lyttelton Road Tunnel Authority, and the Waikato Valley Authority - derive their principal powers from special constituting Acts.
Local authorities have general powers of entering into contracts for any of the purposes for which they are constituted; of selling and leasing land; and of taking or purchasing any land which may be necessary or convenient for any public work.
The Local Authorities' Emergency Powers Act 1953 confers on local authorities certain powers (e.g., in respect of rescue, first aid, provision of relief and welfare, distribution of foodstuffs, information and advice to public, etc.) in emergencies arising from earthquake, fire, or flood, or in time of war from enemy action or from the action of enemy sympathisers.
Number of Local Authorities - Since the inception of the county system there has been a great expansion of local government throughout New Zealand. With the growth of population there has been a steady increase in the number of counties, boroughs, and town districts, while entirely new types of districts have been created to cater for special services. Geographically, New Zealand is divided into 121 counties, which comprise its total area, except for certain small islands which are not included within the boundaries of the adjacent counties. Administratively, boroughs and independent town districts, which are contained within the areas of the several counties, are regarded as separate entities. From an administrative point of view, therefore, the fundamental districts are counties, boroughs, and independent town districts. Upon this foundation a considerable superstructure of districts of other types has been erected. These overlapping districts may be divided into two broad classes, viz: (1) Districts formed from parts of counties, e.g., road districts; and (2) those which are composed of a group of adjacent districts of other types united for a common purpose, e.g., electric power districts.
The number of local authorities actively functioning at 1 April 1960 was 981 made up as follows: County councils, 119; borough (including city) councils. 143; town councils (independent), 15; town councils (dependent), 12; road boards, 3; river boards (3 boards also have the power of land drainage boards), 11; catchment boards, 13; land-drainage boards, 40; electric power boards, 41; water-supply board, 1; urban drainage boards, 5; transport boards, 2; local railway board, 1; electric power and gas boards, 2; milk boards (including 33 where the board is a borough council), 44; nassella tussock boards, 2; harbour bridge authority, 1; road tunnel authority, 1; valley authority, 1; plantation board, 1; underground water authorities, 3; rabbit boards, 209; fire boards (including 175 where the board is a borough or county council, etc.), 235; harbour boards (including 18 where the board is a borough or county council, etc.), 41; and hospital boards, 37. In addition to the 981 local authorities, there were 21 district councils of the National Roads Board constituted under the National Roads Act 1954. These district councils of the National Roads Board, although not local authorities in the strict sense of the term, are nevertheless intimately connected with certain aspects of local government, and have power to make recommendations of considerable importance.
Local Government Commission - The Local Government Commission Act 1953, which replaced the Local Government Commission Act 1946 and amendments, set up a Local Government Commission which is a permanent institution deemed to be a Commission of Inquiry under the Commissions of Inquiry Act 1908.
The Act provides that the Commission shall consist of a Chairman and two other members, one of whom shall have a special knowledge of urban local government, and the other a special knowledge of rural local government.
The functions of the Commission are to review the functions and districts of local authorities, and to inquire into proposals and prepare schemes for their reorganisation. Reorganisation schemes may provide for the union of adjoining districts, the merger, constitution, or abolition of districts, the alteration of boundaries, the conversion of a district into one of a different kind, the transfer of functions of one local authority to another or the dissolution of a local authority.
The Act provides for the appointment of a Local Government Appeal Authority whose function is to sit as a judicial authority to determine appeals made from decisions of the Commission. Any decision finally approving a scheme of reorganisation of districts may be appealed against only by the following parties:
The local authority of any district to which the scheme relates;
Any person or body having statutory authority to make decisions or recommendations in respect of the union, merger, constitution, alteration, or abolition of any district to which the scheme relates; and
The Minister, in any case where the scheme affects only one local authority, or only one local authority and an adjoining area that does not form part of a district, or does not affect any local authority.
Franchise - The franchise in local government is a variable one, differing materially in certain respects as between urban and country districts. Prior to the passing of the Local Elections and Polls Amendment Act 1941 the county franchise was based solely on property qualification, with a differential voting power according to the value of property possessed, whereas in boroughs and town districts every adult possessing the necessary residential qualifications was entitled to be enrolled as an elector for the election of the local-governing authority. On any proposal relating to loans or rates, however, a ratepaying qualification was, and still is, necessary.
An amendment passed in 1944 extended the franchise in counties and road districts to include a residential qualification on the same lines as for boroughs, but did not interfere with the multiple voting power conferred by a property qualification. One vote only is allowed in boroughs and town districts, but it is possible, by virtue of property qualification, to have a vote in more than one district. The 1944 amendment introduced compulsory registration of electors for boroughs and town districts, all adult persons not entitled to enrolment by virtue of a property qualification being required to make application for enrolment within a prescribed time. The Act also removed the disability which prevented persons in the employ of local authorities from becoming members thereof. The Local Elections and Polls Amendment Act 1946 provided that all general elections of local authorities were to be held on the third Wednesday in November of the year in which such elections were due, instead of in May as previously. The 1950 amendment altered this to the third Saturday in November. It also abolished the provisions of the 1946 amendment that any person could be entered on the local authority roll whose name appeared on the parliamentary roll with an address in that authority's district provided he or she had a residential qualification, and that, if not so entered, he or she could vote by declaration. The Local Elections and Polls Act 1953, which consolidated and amended previous Acts and amendments, provided that future elections are to be held on the third Saturday in November, commencing 1956, and every third year thereafter. The Act also extends the compulsory enrolment of residential electors to counties and road districts in addition to boroughs and town districts (for which provision had been made in 1944). Power is also given to make regulations to give full effect to the Act. Details of the franchise as it affects each type of local district are now given.
Counties - Any person of 21 years of age and over who possesses either of the following qualifications is entitled to be enrolled on the county electors roll:
Rating qualification, which may be held by any person whose name appears in the valuation roll as the occupier of any rateable property within a riding of the county. One vote is allowed where the rateable value does not exceed £1,000, two votes where the value is greater than £1,000 but not in excess of £2,000, and three votes where the value exceeds £2,000.
Residential qualification, which may be held by a person who is or has the status of a British subject or is an Irish citizen, and who has resided for one year in New Zealand and has had permanent residence of not less than three months in the riding of the county to which the roll relates.
Boroughs - Any person of 21 years of age and over who possesses any of the following qualifications is entitled to enrolment:
Freehold qualification - meaning the beneficial and duly registered ownership of a freehold estate in land of a capital value of not less than £25 situated in the borough, notwithstanding that any other person is the occupier thereof.
Rating qualification, which may be held by any person whose name appears in the valuation roll as the occupier of any rateable property within the borough.
Residential qualification, which may be held by a person who is or has the status of a British subject or is an Irish citizen, and who has resided for one year in New Zealand and who has had permanent residence during the last three months in the borough to which the roll relates.
Town Districts - The franchise is the same as for boroughs, except that for county electoral purposes in dependent town districts the county qualification is necessary.
Rabbit Districts - Where the rates of the district are based on the acreage and rateable value of land occupied by the ratepayer, the franchise is the same as that exercised for county council elections. Where the franchise is based on stock ownership, from one to five are allowed according to the number of stock units owned.
Other Districts - Road districts, river districts, land-drainage districts, water-supply districts, and the local railway district all have a franchise similar to that of counties except that the residential qualification applies to road districts only.
Districts composed of a grouping of districts of other types united for a common purpose have a franchise as for the component districts. Such districts are urban drainage districts, electric power districts, harbour districts, hospital districts, urban transport districts, and catchment districts. In some cases - e.g., the Auckland Metropolitan and Hutt Valley Drainage Boards - the members are appointed or elected by the territorial local authorities included in the district.
In addition to elected members, the constitution of harbour boards provided in most cases for certain nominated or appointed members (representatives of the Government, the waterfront industry, and the payers of harbour dues), but the Harbours Act 1950, which consolidated and amended previous legislation, provides that every harbour board shall now consist of members elected by the electors of constituent local authorities only.
TOWN AND COUNTRY PLANNING- The Town and Country Planning Act 1953 provides for the making and enforcement of regional and district planning schemes, and the detailed procedure to be followed in each case is amplified by the Town and Country Planning Regulations 1960. The Government administers the Act through the Minister of Works who may delegate his authority to the Commissioner of Works.
Regional Planning Schemes - Regional planning schemes must be preceded by a comprehensive survey of the natural resources of the areas concerned, and of the present and potential uses and values of all lands in relation to public activities or amenities. Regional schemes envisage the conservation and economic development of natural resources by classification of lands according to their best uses and by the coordination of all such public improvements, utilities, services, and amenities as are not limited to the territory of any one local authority. For the purposes of every regional planning scheme proposed to be prepared there is a Regional Planning Authority consisting of representatives of the several councils whose districts are wholly or partly within the region. Every local authority within the region other than the constituent councils may be represented by an associate member but is not entitled to a vote. Regional planning schemes are required to be reviewed at intervals of not more than 10 years.
District Schemes - Every district scheme is required to have for its general purpose the development of the area to which it relates (including where necessary the replanning and reconstruction of an area already built on) in such a way as will most effectively tend to promote and safeguard the health, safety and convenience, the economic and general welfare of its inhabitants, and the amenities of every part of the area. The council of every city, borough, county, and independent town district must provide and maintain a district scheme whether or not a regional planning scheme including its district has been prepared or become operative.
While a district scheme is being prepared a council may refuse its consent to the carrying out of any development that would be in contravention of the scheme and falls within the definition of a “detrimental work”, but the owner or occupier affected may appeal against such a decision to the Town and Country Planning Appeal Board, The Minister can require the council to exercise these powers where the development would or might adversely affect Government works or the public interest, and local authorities have similar rights in respect of their works. Any appeal proceedings lie against the Minister or the local authority concerned.
In the period before a district scheme becomes operative, any change of use of land that detracts or is likely to detract from the amenities of the neighbourhood is required to have the prior consent of the council. Where an application is made to the council for consent, the applicant and every person who claims to be affected by the proposed use has a right to be heard by the council and may appeal to the Appeal Board against the council's decision.
When completed and recommended by the council, copies of a district scheme are submitted to the Minister of Works and to adjoining councils and to local authorities within the area covered by the scheme for consideration, particularly in relation to their public works. When the Minister and each local authority is satisfied that all public works have been provided for in the scheme and have certified accordingly the district scheme is publicly notified for inspection for three months. Any owner or occupier of land affected may object to any provision of the scheme, and the Minister, other local authorities, professional, business, sporting or other such organisations, may also object to the scheme on grounds of public interest. In the event of an objection not being sustained by the council the objector may appeal to the Appeal Board whose decision is final.
The Minister of Works may prepare and obtain approval for a district scheme in any case where a local authority under an obligation to prepare such a scheme fails to do so after being notified in writing. The costs and expenses incurred by the Minister are recoverable from the local authority, or they may be deducted from any moneys payable to the local authority by the Crown.
When a district scheme has been finally approved and made operative the council and all local authorities having jurisdiction in the district are bound to observe, and enforce observance, of the requirements of the scheme. The provisions of an operative regional planning scheme are also obligatory, but a constituent council has a right of appeal to the Town and Country Planning Appeal Board where a provision of a proposed or operative district scheme conflicts with the regional scheme.
Operative district schemes may be altered at any time, and must be reviewed when any part of the scheme has been operative for five years. The procedure to be followed in the preparation, recommendation, and approval of an alteration or review of a scheme is the same as that for a new scheme commencing at the point where the scheme is ready to be recommended by the council.
Where a district scheme is operative the local authority may take under the Public Works Act 1928 any land in its district if in accordance with the scheme it considers it is necessary or expedient to do so for the proper development or use of the land, or for the provision or preservation of amenities, or for the improvement of areas that are too closely subdivided or are occupied by decadent buildings.
GENERAL REVIEW - A population census was taken as for the night of Tuesday, 18 April 1961, in New Zealand and it may be possible to give preliminary figures in the latest statistical information at the end of this Yearbook. Some figures are given in this section for the population census taken as for the night of Tuesday, 17 April 1956, and also later information on population. The 1956 census population of New Zealand, excluding island territories, was 2,174,062.
The minor islands (see page 1), other than the Kermadec Islands and Campbell Island, were uninhabited at the date of the census. The Ross Dependency had a population of 166 males at the 1956 census date and 137 males at 31 March 1960, these men being members of scientific expeditions.
A census of the island territories was conducted by the Department of Island Territories for the night of Tuesday, 25 September 1956, and the census figures were: Cook Islands and Niue Island, 21,387; Tokelau Islands, 1,619; Trust Territory of Western Samoa, 97,327. The total census population of New Zealand and island and trust territories was 2,294,395. Armed forces personnel overseas at the time of the census and not included in the population numbered 2,162 (Europeans, 1,972; Maoris, 190).
The following table gives a complete summary of New Zealand population.
| Date | Males | Females | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes population of the inhabited minor islands, i.e., Kermadec Islands, 9 (males); and Campbell Island, 9 (males). | ||||
| New Zealand: | ||||
| (a) Exclusive of island territories: | ||||
| Europeans | 30 June 1960 | 1,110,648 | 1,101,403 | 2,212,051* |
| Maoris | 30 June 1960 | 81,237 | 78,472 | 159,709 |
| Totals, New Zealand (excluding island territories) | 1,191,885 | 1,179,875 | 2,371,760 | |
| (b) Island territories: | ||||
| Tokelau Islands | 30 June 1960 | 900 | 1,029 | 1,929 |
| Cook Islands | 31 March 1960 | 9,293 | 8,881 | 18,174 |
| Niue Island | 30 June 1960 | 2,386 | 2,474 | 4,860 |
| Totals, New Zealand (including island territories) | 1,204,464 | 1,192,259 | 2,396,723 | |
| Western Samoa | 30 June 1960 | 54,980 | 52,053 | 107,033 |
| Ross Dependency | 31 March 1960 | 137 | - | 137 |
INCREASE OF POPULATION - Since the commencement of European settlement in New Zealand the European population has in every year shown an increase, though the rate of increase has fluctuated considerably, and the Maori population has increased continuously for over 50 years. Census records since 1901 are quoted in the succeeding table and include Maoris.
| Date of Census | Numbers | Intercensal Numerical Increase | Intercensal Percentage Increase | Average Annual Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excludes New Zealand armed forces personnel overseas. †Includes New Zealand armed forces personnel overseas. | ||||
| March 1901* | 815,853 | 72,646 | 977 | 1.89 |
| April 1906 | 936,304 | 120,451 | 14.76 | 2.75 |
| April 1911 | 1,058,308 | 122,004 | 13.03 | 2.52 |
| October 1916* | 1,149,225 | 90,917 | 8.59 | 1.50 |
| April 1921 | 1,271,664 | 122,439 | 10.65 | 2.27 |
| April 1926 | 1,408,139 | 136,475 | 10.73 | 2.06 |
| March 1936 | 1,573,810 | 165,671 | 11.77 | 1.13 |
| September 1945* | 1,702,298 | 128,488 | 8.16 | 0.83 |
| September 1945† | 1,747,679 | 173,869 | 11.05 | 1.11 |
| April 1951* | 1,939,472 | 237,174 | 13.93 | 2.37 |
| April 1951† | 1,941,366 | 193,687 | 11.08 | 1.91 |
| April 1956* | 2,174,062 | 234,590 | 12.10 | 2.31 |
| April 1956† | 2,176,224 | 234,858 | 12.10 | 2.31 |
In no fewer than five of the 10 censuses covered by the above table the figures are disturbed by the absence overseas of armed forces. Increase during the intercensal period preceding the census is thus diminished and in the period following is augmented by the return of such personnel. Numbers of armed forces personnel overseas at the respective dates were: 1901, 2,500 (approx.); 1916, 44,000 (approx.); 1945, 45,381; 1951, 1,894; and 1956, 2,162.
It will be noted that the growth of population has been substantial in each period. The lowest rates are those of 1926-36, a result of the great economic depression, and of 1936-45, which included six years of war.
Sources of population increase are threefold, viz, enlargement of territory, excess of arrivals over departures, and excess of births over deaths or natural increase. The first is inapplicable to New Zealand, the second is dealt with later in this section, and the third is discussed in the section relating to vital statistics. One aspect of the latter may, however, be given here. This is the reproduction index which, though not free from error, is a convenient indication of the growth or decline of a population. It is based on female children born (gross rate) and probably surviving to maturity (net rate). A net rate of 1.0 indicates a stationary population; above unity a rising population and below unity a falling population.
Reproduction rates during the latest five years were as follows, the figures relating only to the European population.
| Year | Gross Rate | Net Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1.817 | 1.749 |
| 1956 | 1.839 | 1.771 |
| 1957 | 1.893 | 1.822 |
| 1958 | 1.931 | 1.859 |
| 1959 | 1.950 | 1.878 |
POPULATION PROJECTIONS - An indication of future population growth, including Maoris, in New Zealand is given by the detailed projections for the period 1962-80 and the provisional projections for the five-yearly points 1985–2000 set out in the following table.
Projections of future population almost always involve an element of uncertainty owing to incomplete knowledge of the factors underlying changes in fertility, mortality, and migration levels, coupled with the difficulty of accurately forecasting the future course of the factors which are known to affect these components of population change. It should be understood, therefore, that these projections merely show the effect of the assumptions stated below the table on the future growth of the existing population. The assumptions, however, have been adopted only after careful studies of trends in the patterns of fertility, mortality, and migration and, in the light of available current information, are regarded as those most likely to produce realistic projections over the length of the projection period.
POPULATION PROJECTIONS (INCLUDINGMAORIS)
| Year | Assuming Net Immigration of | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 per Year | 10,000 per Year | |||||
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| (thousand) | ||||||
| 1962 | 1,233 | 1,220 | 2,453 | 1,240 | 1,224 | 2,464 |
| 1963 | 1,255 | 1,241 | 2,496 | 1,265 | 1,248 | 2,513 |
| 1964 | 1,277 | 1,262 | 2,539 | 1,291 | 1,272 | 2,563 |
| 1965 | 1,300 | 1,284 | 2,584 | 1,316 | 1,296 | 2,612 |
| 1966 | 1,325 | 1,306 | 2,631 | 1,344 | 1,321 | 2,665 |
| 1967 | 1,350 | 1,330 | 2,680 | 1,372 | 1,346 | 2,718 |
| 1968 | 1,375 | 1,354 | 2,729 | 1,399 | 1,374 | 2,773 |
| 1969 | 1,400 | 1,379 | 2,779 | 1,429 | 1,402 | 2,831 |
| 1970 | 1,426 | 1,405 | 2,831 | 1,459 | 1,432 | 2,891 |
| 1971 | 1,454 | 1,432 | 2,886 | 1,491 | 1,462 | 2,953 |
| 1972 | 1,483 | 1,459 | 2,942 | 1,524 | 1,493 | 3,017 |
| 1973 | 1,513 | 1,486 | 2,999 | 1,559 | 1,524 | 3,083 |
| 1974 | 1,544 | 1,517 | 3,061 | 1,594 | 1,556 | 3,150 |
| 1975 | 1,576 | 1,549 | 3,125 | 1,628 | 1,591 | 3,219 |
| 1976 | 1,610 | 1,581 | 3,191 | 1,664 | 1,626 | 3,290 |
| 1977 | 1,644 | 1,613 | 3,257 | 1,702 | 1,661 | 3,363 |
| 1978 | 1,679 | 1,646 | 3,325 | 1,741 | 1,697 | 3,438 |
| 1979 | 1,715 | 1,681 | 3,396 | 1,781 | 1,735 | 3,516 |
| 1980 | 1,750 | 1,716 | 3,466 | 1,821 | 1,776 | 3,597 |
| Provisional | ||||||
| 1985 | .. | .. | 3,760 | .. | .. | 3,926 |
| 1990 | .. | .. | 4,077 | .. | .. | 4,281 |
| 1995 | .. | .. | 4,418 | .. | .. | 4,664 |
| 2000 | .. | .. | 4,785 | .. | .. | 5,076 |
Assumptions - The two projections are linked to actual population numbers in 1960. The assumptions on which the more detailed projections for 1962-80 depend are as follows:
Birthrates for each quinquennial age and marital status (“married” and “not married”) group of females will continue at the average 1952-56 level.
The proportion of married females in each quinquennial age group will, in the future, vary in accordance with the rate of variation in the 1951-56 intercensal period.
Mortality rates for each quinquennial age group, male and female, will be maintained at the level shown by the New Zealand Life Tables, 1950-52.
Future net immigration will be at the rates of either 5,000 or 10,000 persons per annum, the age and sex distribution being based on the average 1937-58 pattern.
The provisional long-term projections for 1985–2000 are linked to the earlier projections. They are based on the following assumptions:
The rate of natural increase of population, excess of births over deaths, for the period 1980–2000 will be 15 persons per 1,000 living.
Net immigration will be as assumed for the period 1960-80.
The following diagram presented on a ratio scale shows the growth of actual population from 1880 to 1960 and projections through to 2000.
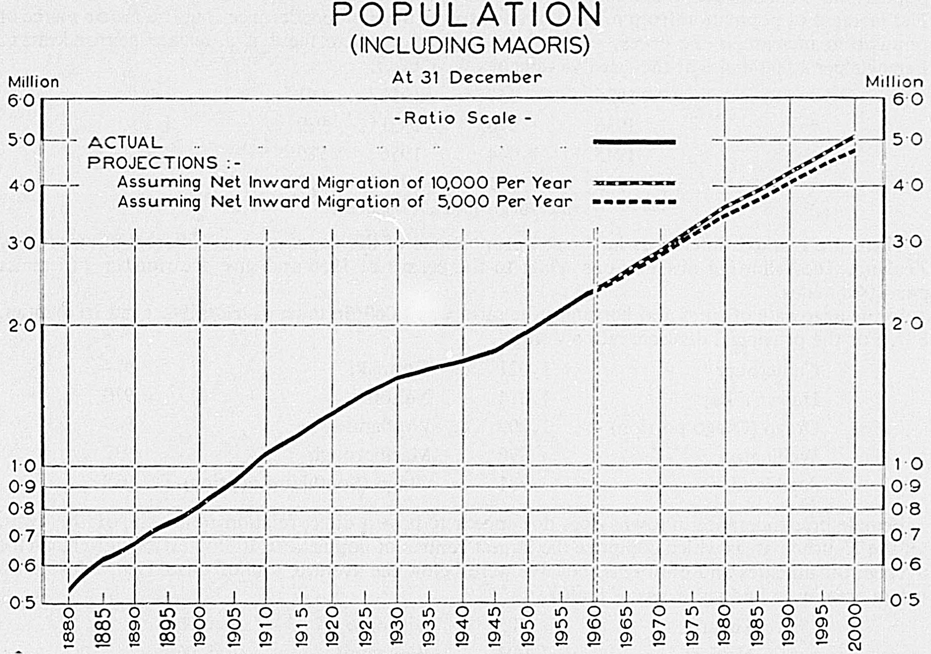
COMPARISON WITH OTHER COUNTRIES - In the following summary of certain selected countries the two most recent census years are quoted together with the annual average percentage increase of population during the respective intercensal periods.
| Country | Census Period | Average Annual Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|
*European population. †Including Hyderabad, but excluding Kashmir, Jammu, and the tribal areas of Assam. †Excluding full-blooded aborigines. §Including Newfoundland. | ||
| New Zealand | 1951-56 | 2.31 |
| England and Wales | 1931-51 | 0.46 |
| Scotland | 1931-51 | 0.26 |
| Northern Ireland | 1937-51 | 0.48 |
| Republic of Ireland | 1951-56 | -0.45 |
| Austria | 1939-51 | 0.33 |
| Denmark | 1950-55 | 0.77 |
| Finland | 1940-50 | 0.82 |
| France | 1946-54 | 0.90 |
| Hungary | 1941-49 | -0.15 |
| Netherlands | 1930-47 | 1.18 |
| Portugal | 1940-50 | 0.89 |
| Sweden | 1945-50 | 1.09 |
| Switzerland | 1941-50 | 1.12 |
| Union of South Africa* | 1946-51 | 2.18 |
| India† | 1941-51 | 1.26 |
| Pakistan | 1941-51 | 0.79 |
| Ceylon | 1946-53 | 2.84 |
| Australia† | 1947-54 | 2.46 |
| Canada§ | 1951-56 | 2.79 |
| United States of America | 1940-50 | 1.36 |
| NOTE—Minus sign (-) denotes a decrease. | ||
It is seen that Ceylon and Canada have the highest annual rates of increase. Both rates have increased substantially since the previous intercensal periods, the main factor in Ceylon being a fall in the death rate, and in Canada the increase in immigration.
The third highest rate of increase is that shown for Australia (2.46 per cent). New Zealand (2.31 per cent) and the Union of South Africa (2.18 per cent) show the next highest rates of increase. On the other hand, European countries show the lowest rates of increase - Hungary and the Republic of Ireland actually show a decrease - with the United Kingdom countries recording very low figures.
SEX PROPORTIONS - The figures for the census of 17 April 1956 show that males outnumber females by 9,333 in the European population, 3,027 in the Maori population, and 12,360 in the total population. Females per 1,000 males were: European, 991; Maori, 957; total population, 989. Net increase of population from migration adds to the male preponderance, but the major source of population increase is the excess of births over deaths, where there is a female preponderance. Females per 1,000 males at the last five censuses have been:
| *Including armed forces abroad. | |
|---|---|
| 1926 | 957 |
| 1936 | 970 |
| 1945 | 1,044 |
| 1945* | 991 |
| 1951 | 991 |
| 1951* | 989 |
| 1956 | 989 |
| 1956* | 987 |
There are marked differences in the sex proportions of the population of different parts of New Zealand. The following observations relate to the census of 1956 and give the number of females per 1,000 males.
In the aggregate of cities and boroughs the ratio was 1,060; in town districts, 962; and in counties, 887. For the provincial districts ratios were:
| Canterbury | 1,021 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,014 |
| Otago (Otago portion) | 1,009 |
| Wellington | 990 |
| Auckland | 981 |
| Taranaki | 974 |
| Nelson | 970 |
| Westland | 940 |
| Marlborough | 937 |
| Otago (Southland portion) | 935 |
Female preponderance in towns does not appear to have a direct relation to the size of the towns. Of the 15 urban areas which comprise the largest centres of population, 10 had ratios higher than the average for all cities and boroughs, but five were below the average, and of these Hutt, fifth largest urban area, even had an excess of males.
| Timaru | 1,105 |
| Napier | 1,093 |
| Hastings | 1,085 |
| New Plymouth | 1,084 |
| Dunedin | 1,082 |
| Nelson | 1,079 |
| Palmerston North | 1,077 |
| Christchurch | 1,072 |
| Gisborne | 1,067 |
| Wanganui | 1,066 |
| Invercargill | 1,051 |
| Auckland | 1,045 |
| Hamilton | 1,040 |
| Wellington | 1,039 |
| Hutt | 990 |
METHOD OF COMPILATION - In common with almost all countries, the basis for compiling population data in New Zealand is the census, which in this country in normal times is taken quinquennially. The details of the distribution of population, together with analyses of various population characteristics compiled from census data, will be found in the official publications compiled after each census.
The basis adopted for the census, and virtually throughout population statistics in New Zealand, is that of the population present, which may be defined as the population present at the place of enumeration at the time of the enumeration.
All references to New Zealand relate solely to geographic New Zealand, i.e., island territories are omitted except where their inclusion is specifically stated. Though Cook Islands, Niue Island, and Tokelau Islands are constitutionally part of New Zealand, for geographical reasons they are administered separately.
Maoris are included in all population data unless the contrary is stated. Maori-Europeans who are in half or greater degree of Maori origin are included with Maoris. For some purposes the population division into European and Maori is necessary or desirable and “European” is used, conveniently if not altogether accurately, as referring to all population other than Maori, a usage long established in New Zealand.
INTERCENSAL RECORDS - The intercensal statements of total population, prepared from the records of vital statistics and of external migration, have been, by virtue of the favourable position of New Zealand in this respect, relatively accurate. Discrepancies have in fact been so slight that no revisions of the intercensal figures between 1951 and 1956 were necessary.
The following population figures exclude members of New Zealand armed forces who were overseas, and also members of the armed forces of other countries who were in New Zealand.
| Year | Population (Including Maoris) at End of Year | Increase During Year | Mean Population for Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Numerical | Per Cent | ||
| Years Ended 31 March | ||||||
| 1950 | 955,427 | 947,456 | 1,902,883 | 38,323 | 2.06 | 1,881,317 |
| 1951 | 973,082 | 964,950 | 1,938,032 | 35,149 | 1.85 | 1,917,934 |
| 1952 | 997,468 | 987,262 | 1,984,730 | 46,698 | 2.41 | 1,958,729 |
| 1953 | 1,024,463 | 1,013,090 | 2,037,553 | 52,823 | 2.66 | 2,009,506 |
| 1954 | 1,049,963 | 1,037,777 | 2,087,740 | 50,187 | 2.46 | 2,061,376 |
| 1955 | 1,072,090 | 1,058,837 | 2,130,927 | 43,187 | 2.07 | 2,105,767 |
| 1956 | 1,094,283 | 1,081,090 | 2,175,373 | 44,446 | 2.09 | 2,150,290 |
| 1957 | 1,116,686 | 1,104,483 | 2,221,169 | 45,796 | 2.11 | 2,194,108 |
| 1958 | 1,144,670 | 1,130,845 | 2,275,515 | 54,116 | 2.45 | 2,246,093 |
| 1959 | 1,170,007 | 1,156,122 | 2,326,129 | 50,14 | 2.22 | 2,298,814 |
| 1960 | 1,191,399 | 1,178,767 | 2,370,166 | 44,037 | 1.89 | 2,345,602 |
| Years Ended 31 December | ||||||
| 1949 | 949,443 | 942,599 | 1,892,042 | 38,236 | 2.06 | 1,871,748 |
| 1950 | 967,308 | 960,321 | 1,927,629 | 35,587 | 1.88 | 1,909,092 |
| 1951 | 989,513 | 981,009 | 1,970,522 | 42,893 | 2.23 | 1,947,529 |
| 1952 | 1,017,874 | 1,006,682 | 2,024,556 | 54,034 | 2.74 | 1,996,149 |
| 1953 | 1,043,143 | 1,031,638 | 2,074,781 | 50,225 | 2.48 | 2,048,826 |
| 1954 | 1,065,490 | 1,052,944 | 2,118,434 | 43,653 | 2.10 | 2,094,910 |
| 1955 | 1,089,070 | 1,075,664 | 2,164,734 | 46,300 | 2.19 | 2,138,946 |
| 1956 | 1,111,176 | 1,097,956 | 2,209,132 | 44,398 | 2.05 | 2,182,833 |
| 1957 | 1,137,799 | 1,125,015 | 2,262,814 | 53,682 | 2.43 | 2,232,591 |
| 1958 | 1,165,568 | 1,150,332 | 2,315,900 | 53,086 | 2.35 | 2,285,852 |
| 1959 | 1,186,083 | 1,173,663 | 2,359,746 | 43,846 | 1.89 | 2,334,617 |
The figures given in the preceding table show the population inclusive of Maoris. The following table shows the population exclusive of Maoris.
| Year | Population (Excluding Maoris) at End of Year | Increase During Year | Mean Population for Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Numerical | Per Cent | ||
| Years Ended 31 March | ||||||
| 1950 | 897,618 | 892,710 | 1,790,328 | 35,730 | 2.04 | 1,770,130 |
| 1951 | 913,852 | 908,674 | 1,822,526 | 32,198 | 1.80 | 1,803,944 |
| 1952 | 936,338 | 929,104 | 1,865,442 | 42,916 | 2.35 | 1,841,332 |
| 1953 | 961,389 | 952,965 | 1,914,354 | 48,912 | 2.62 | 1,888,334 |
| 1954 | 984,822 | 975,534 | 1,960,356 | 46,002 | 2.40 | 1,936,202 |
| 1955 | 1,004,530 | 994,432 | 1,998,962 | 38,606 | 1.97 | 1,976,156 |
| 1956 | 1,024,427 | 1,014,367 | 2,038,794 | 39,832 | 1.99 | 2,016,067 |
| 1957 | 1,044,134 | 1,035,001 | 2,079,135 | 40,341 | 1.98 | 2,054,687 |
| 1958 | 1,069,666 | 1,058,731 | 2,128,397 | 49,262 | 2.37 | 2,101,543 |
| 1959 | 1,092,284 | 1,081,202 | 2,173,486 | 45,089 | 2.12 | 2,149,072 |
| 1960 | 1,110,850 | 1,100,961 | 2,211,811 | 38,325 | 1.76 | 2,190,101 |
| Years Ended 31 December | ||||||
| 1949 | 891,991 | 888,237 | 1,780,228 | 35,677 | 2.05 | 1.761,204 |
| 1950 | 908,479 | 904,467 | 1,812,946 | 32,718 | 1.84 | 1.795,830 |
| 1951 | 928,879 | 923,337 | 1,852,216 | 39,270 | 2.17 | 1,831,058 |
| 1952 | 955,354 | 947,102 | 1,902,456 | 50,240 | 2.71 | 1,875,940 |
| 1953 | 978,636 | 969,999 | 1,948,635 | 46,179 | 2.43 | 1,924,680 |
| 1954 | 998,544 | 989,084 | 1,987,628 | 38,993 | 2.00 | 1,966,454 |
| 1955 | 1,019,792 | 1,009,573 | 2,029,365 | 41,737 | 2.10 | 2,005,871 |
| 1956 | 1,039,303 | 1,029,206 | 2,068,509 | 39,144 | 1.93 | 2,044,752 |
| 1957 | 1,063,525 | 1,053,618 | 2,117,143 | 48,634 | 2.35 | 2,089,307 |
| 1958 | 1,088,606 | 1,076,158 | 2,164,764 | 47,621 | 2.25 | 2,137,483 |
| 1959 | 1,106,246 | 1,096,661 | 2,202,907 | 38,143 | 1.76 | 2,180,543 |
DISTRIBUTION OF POPULATION - Detailed population statistics are compiled for each census. Final figures for the 1956 census for provincial districts, urban areas, counties, cities, boroughs, town districts, extra-county islands, and shipping were published in Census, Vol. I, Increase and Location of Population.
North and South Islands - In 1858 the North Island had a larger population than the South, but this position was reversed at the succeeding enumeration, and the South Island had the larger population (exclusive of Maoris) at each census from 1861 to 1896. In 1901 the North Island was found to have slightly the larger total and since then has steadily increased its lead.
The following table gives the population of the North and South Islands as disclosed by each census since 1901.
| Census Year | Population (Excluding Maoris) | Proportions Per Cent | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Island | South Island | Total | North Island | South Island | |
| 1901 | 388,626 | 381,678 | 770,304 | 50.45 | 49.55 |
| 1906 | 474,605 | 411,390 | 885,995 | 53.57 | 46.43 |
| 1911 | 561,281 | 444,304 | 1,005,585 | 55.82 | 44.18 |
| 1916 | 648,439 | 447,789 | 1,096,228 | 59.15 | 40.85 |
| 1921 | 741,255 | 477,658 | 1,218,913 | 60.81 | 39.19 |
| 1926 | 831,813 | 512,656 | 1,344,469 | 61.87 | 38.13 |
| 1936 | 938.939 | 552.545 | 1.491,484 | 62.95 | 37.05 |
| 1945 | 1,050,984 | 552,570 | 1,603,554 | 65.54 | 34.46 |
| 1951 | 1,202,357 | 621,439 | 1,823,796 | 65.93 | 34.07 |
| 1956 | 1,365,470 | 671,441 | 2,036,911 | 67.04 | 32.96 |
The natural increase of European population (i.e., excess of births over deaths) for the North Island during the 1951-56 intercensal period was 103,999, and the total net increase 163,113. For the South Island the natural increase was 45,832, and the total net increase 50,002. The population of the North Island increased at a greater proportionate rate than that of the South Island between the 1951 and 1956 censuses. Inclusive of Maoris, the North Island increase was 183,495, or 13.97 per cent, and the South Island increase 51,095, or 8.17 per cent.
At the 1956 census the North Island population was 1,497,364, inclusive of 131,894 Maoris, and the South Island population 676,698, inclusive of 5,257 Maoris.
At 31 March 1960 the North Island population was 1,642,461, inclusive of 152,697 Maoris, and the South Island population 727,705, inclusive of 5,658 Maoris.
Provincial Districts - The approximate areas and the estimated populations, inclusive of Maoris, of the various provincial districts are given in the next table.
For the guidance of overseas readers it is necessary to explain that there have been no provinces in New Zealand since 1875. Provincial districts are simply the former provinces, but they have no functions and are now merely historic divisions serving as useful units for a primary geographical breakdown. There is no Southland Provincial District and the “Southland portion of Otago” has little resemblance in area to the former Southland Province.
| Provincial District | Area (Square Miles) | Estimated Population 1 April 1960 |
|---|---|---|
| Auckland | 25,420 | 972,061 |
| Hawke's Bay | 4,260 | 110,900 |
| Taranaki | 3,750 | 100,100 |
| Wellington | 10,870 | 459,400 |
| Marlborough | 4,220 | 28,400 |
| Nelson | 10,870 | 74,200 |
| Westland | 4,880 | 18,700 |
| Canterbury | 13,940 | 336,705 |
| Otago: | ||
| Otago portion | 14,070 | 176,200 |
| Southland portion | 11,460 | 93,500 |
| New Zealand | 103,740 | 2,370,166 |
The foregoing table illustrates the wide disparities in the size of the provincial districts, whether measured by area or by population.
Urban and Rural Population - On 17 April 1956 somewhat over two-fifths (43.3 per cent) of the population of New Zealand (excluding Maoris) were included in the five principal urban areas - Auckland, Hutt, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin - and over one-half (57.7 per cent) in all the urban areas. In the following table urban population means the population in cities and boroughs, while rural population covers counties, all town districts, and extra-county islands. It will be observed that there was a marked slackening in the rate of the urban drift between 1926 and 1936, but the 1945 figures, due no doubt to wartime influences, disclosed a substantial increase in the urban population, whereas the rural population for the first time recorded a decrease. In the 1945-51 period a substantial gain was recorded in the rural population, but it was insufficient to prevent further deterioration of its ratio to total population. This drop in the ratio of rural population continued in the period 1951-56.
| Census | Population | Percentage of Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural | Urban | Migratory | Rural | Urban | Migratory | |
*Figures exclude military and internment camps. †Figures include armed services in New Zealand at census date and internment camps, but exclude members of the United States forces present in New Zealand and also enemy prisoners of war. ‡Inclusive of Maori half-castes (3,221 in 1916 and 4,236 in 1921) living as Europeans, as they cannot be distinguished separately for these two censuses. | ||||||
| Excluding Maoris: | ||||||
| 1901 | 416,701 | 349,842 | 3,761 | 54.09 | 45.42 | 0.49 |
| 1906 | 457,297 | 424,251 | 4,447 | 51.61 | 47.89 | 0.50 |
| 1911 | 495,577 | 505,003 | 5,005 | 49.28 | 50.22 | 0.50 |
| 1916*‡ | 501,956 | 585,306 | 3,463 | 46.02 | 53.66 | 0.32 |
| 1921‡ | 531,694 | 681,988 | 5,231 | 43.62 | 55.95 | 0.43 |
| 1926 | 552,344 | 785,040 | 7,085 | 41.08 | 58.39 | 0.53 |
| 1936 | 602,519 | 884,293 | 4,672 | 40.40 | 59.29 | 0.31 |
| 1945† | 591,855 | 1,008,534 | 3,165 | 36.91 | 62.89 | 0.20 |
| 1951 | 654,921 | 1,163,090 | 5,785 | 35.91 | 63.77 | 0.32 |
| 1956 | 704,536 | 1,327,996 | 4,379 | 34.59 | 65.20 | 0.21 |
| Including Maoris: | ||||||
| 1926 | 610,446 | 790,555 | 7,138 | 43.35 | 56.14 | 0.51 |
| 1936 | 677,087 | 892,024 | 4,699 | 43.02 | 56.68 | 0.30 |
| 1945† | 674,821 | 1,024,292 | 3,185 | 39.64 | 60.17 | 0.19 |
| 1951 | 748,922 | 1,184,672 | 5,878 | 38.62 | 61.08 | 0.30 |
| 1956 | 809,267 | 1,360,347 | 4,448 | 37.22 | 62.57 | 0.21 |
Another conception of urban and rural population is presented in the next table. For this purpose urban population has been taken as that enumerated in cities, boroughs, or town districts with a minimum population of 1,000. Migratory population is excluded.
| Including Maoris | Excluding Maoris | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1926 | 1956 | 1926 | 1956 | |
| Numbers | ||||
| Urban - towns of: | ||||
| 1,000- 2,500 | 104,360 | 65,931 | 102,201 | 71,249 |
| 2,500- 5,000 | 86,408 | 158,605 | 85,430 | 155,068 |
| 5,000-10,000 | 82,644 | 133,600 | 82,144 | 116,592 |
| 10,000–25,000 | 186,545 | 297,699 | 185,580 | 289,271 |
| 25,000 or over | 338,213 | 701,948 | 337,221 | 690,231 |
| Totals, urban | 798,170 | 1,357,783 | 792,576 | 1,322,411 |
| Rural | 602,831 | 811,831 | 544,808 | 710,121 |
| Totals, New Zealand (excluding migratory) | 1,401,001 | 2,169,614 | 1,337,384 | 2,032,532 |
| Percentages | ||||
| Urban - towns of: | ||||
| 1,000- 2,500 | 7.45 | 3.04 | 7.64 | 3.50 |
| 2,500- 5,000 | 6.17 | 7.31 | 6.39 | 7.63 |
| 5,000-10,000 | 5.90 | 6.16 | 6.14 | 5.74 |
| 10,000-25,000 | 13.31 | 13.72 | 13.88 | 14.23 |
| 25,000 or over | 24.14 | 32.35 | 25.21 | 33.96 |
| Totals, urban | 56.97 | 62.58 | 59.26 | 65.06 |
| Rural | 43.03 | 37.42 | 40.74 | 34.94 |
| Totals, New Zealand | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Some apparent anomalies, where the numbers exclusive of Maoris exceed those inclusive of Maoris, arise from the transfer of towns to other population categories.
An important characteristic of the distribution of urban population in New Zealand is what may be termed its decentralisation. In place of one great metropolis containing a huge proportion of the population, the more highly urbanised portion of the community is localised in four widely separated centres. An interesting feature is the wide gap which has long existed between the four major centres and the next largest towns.
Urban and rural communities are not evenly distributed. The South Island, for example, contains proportionately more rural population than does the North Island.
RECENT MOVEMENTS IN TOWNS AND COUNTIES: Urban Areas - These are statistical conceptions and not administrative units. Their purpose is to provide definite, stable, and comparable boundaries for the larger centres of population. In addition to the central city, they include neighbouring boroughs and parts of counties which are regarded as suburban to the centre of population.
Urban areas were formed in 1917 and, except for two additions and one deletion, remained unaltered until 1951, when a revision of boundaries was made and the new areas used in the 1951 census. From census records and maps, revised population figures were prepared on the basis of the new boundaries. In the case of European population the figures were revised for each census back to 1911, and on the basis of population including Maoris the revision was possible back to the 1926 census. The most significant change resulting from this revision was the division of the former Wellington Urban Area, plus additional areas to the north, into the two adjacent urban areas of Hutt and Wellington. The two areas in a sense form a single conurbation, and for some purposes it may still be convenient to use a combined figure. However, the extent and pattern of development in the Hutt Valley have been such as to establish it as a centre complementary to Wellington but no longer suburban to it. In Auckland the boundaries were extended considerably, but in most other cases it was found that little change was necessary.
| Urban Area | Population (Including Maoris) | Population Increase 1951-56 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1936 | 1945 | 1951 | 1956 | Numerical | Percentage | |
| Auckland | 226,366 | 286,767 | 329,123 | 381,063 | 51,940 | 15.78 |
| Hamilton | 20,096 | 27,319 | 33,137 | 40,646 | 7,509 | 22.66 |
| Gisborne | 15,878 | 16,995 | 19,774 | 22,622 | 2,848 | 14.40 |
| Napier | 19,170 | 20,741 | 24,538 | 27,507 | 2,969 | 12.10 |
| Hastings | 17,920 | 20,306 | 23,797 | 27,787 | 3,990 | 16.77 |
| New Plymouth | 18,597 | 21,057 | 24,923 | 28,292 | 3,369 | 13.52 |
| Wanganui | 25,750 | 26,262 | 29,717 | 32,100 | 2,383 | 8.02 |
| Palmerston North | 24,372 | 27,820 | 32,908 | 37,775 | 4,867 | 14.79 |
| Hutt | 37,295 | 55,786 | 74,878 | 86.053 | 11,175 | 14.92 |
| Wellington | 122,062 | 132,305 | 133,414 | 138,297 | 4,883 | 3.66 |
| Nelson | 13,493 | 16,523 | 20,497 | 22,503 | 2,006 | 9.79 |
| Christchurch | 133,515 | 151,068 | 174,221 | 193,367 | 19,146 | 10.99 |
| Timaru | 18,771 | 19,672 | 22,851 | 24,694 | 1,843 | 8.07 |
| Dunedin | 85,607 | 87,587 | 95,457 | 99,370 | 3,913 | 4.10 |
| Invercargill | 25,912 | 27,755 | 31,613 | 35,107 | 3,494 | 11.05 |
| Totals | 804,804 | 937,963 | 1,070,848 | 1,197,183 | 126,335 | 11.80 |
In the 20 years covered by the table all urban areas have consistently recorded increases in population. In the years 1951-56 Auckland had the greatest numerical growth, while Hamilton and Hastings had the highest proportionate increases.
Wellington Urban Area's increase of nearly 4 per cent between 1951 and 1956, compared with under 1 per cent in the previous intercensal period, resulted mainly from housing development in the Titahi Bay and Porirua areas. The rate of growth of Hutt Urban Area slowed down in the last intercensal period. For Hutt and Wellington Urban Areas combined the increase rate was 7.71 per cent, a rate exceeded by all urban areas except Dunedin.
Of particular interest is the marked increase in the Maori population in urban areas during the last 20 years. In Auckland the number of Maoris increased from 1,863 in 1936 to 11,361 in 1956. In the 15 urban areas there were 5,371 Maoris in 1936, as compared with 22,825 in 1956.
The next table contains the population (Maoris included) of the 15 urban areas as estimated for 1 April 1960. The component parts of the five largest centres of population are given in detail, while for the remaining 10 areas totals only are quoted. In most of the 10 cases the urban area comprises the central city plus the urban portion of the adjoining county. At 1 April 1960 the five largest urban areas had a total population of 981,400, this being equivalent to 41.41 per cent of the New Zealand total. The total for all urban areas at the same date was 1,309,900, or 55.27 per cent of the total population of New Zealand.
| Urban Area | Estimated Population (Including Maoris) 1 April 1960 |
|---|---|
| Auckland | |
| Auckland city | 141,900 |
| East Coast Bays borough | 8,440 |
| Takapuna borough | 20,500 |
| Devonport borough | 11,750 |
| Northcote borough | 4,120 |
| Birkenhead borough | 6,740 |
| Henderson borough | 3,210 |
| Glen Eden borough | 4,870 |
| New Lynn borough | 8,510 |
| Newmarket borough | 1,920 |
| Mt. Albert borough | 25,700 |
| Mt. Eden borough | 18,650 |
| Mt. Roskill borough | 29,600 |
| Onehunga borough | 16,750 |
| One Tree Hill borough | 13,150 |
| Ellerslie borough | 4,760 |
| Mt. Wellington borough | 14,950 |
| Howick borough | 5,810 |
| Otahuhu borough | 8,840 |
| Papatoetoe borough | 15,800 |
| Manurewa borough | 7,150 |
| Papakura borough | 7,030 |
| Remainder of urban area | 42,750 |
| Total | 422,900 |
| Hutt | |
| Lower Hutt city | 53,600 |
| Upper Hutt borough | 15,100 |
| Petone borough | 10,500 |
| Eastbourne borough | 2,740 |
| Remainder of urban area | 13,560 |
| Total | 95,500 |
| Wellington | |
| Wellington city | 123,000 |
| Tawa borough | 5,960 |
| Remainder of urban area | 15,940 |
| Total | 144,900 |
| Christchurch | |
| Christchurch city | 151,500 |
| Riccarton borough | 7,930 |
| Lyttelton borough | 3,600 |
| Heathcote county | 5,860 |
| Remainder of urban area | 45,910 |
| Total | 214,800 |
| Dunedin | |
| Dunedin city | 72,400 |
| Port Chalmers borough | 3,210 |
| West Harbour borough | 2,230 |
| St. Kilda borough | 6,850 |
| Green Island borough | 5,210 |
| Mosgiel borough | 5,750 |
| Remainder of urban area | 7,650 |
| Total | 103,300 |
| Hamilton | 46,700 |
| Gisborne | 24,600 |
| Napier | 30,300 |
| Hastings | 31,000 |
| New Plymouth | 31,100 |
| Wanganui | 34,000 |
| Palmerston North | 41,600 |
| Nelson | 24,200 |
| Timaru | 26,100 |
| Invercargill | 38,900 |
Counties - The following table gives the estimated population (including Maoris) of individual counties at 1 April 1960, together with the approximate area of each. It should be noted that “Administrative Counties” do not include boroughs or town districts independent of county control, but include town districts which form parts of counties.
| Administrative County | Estimated Population (Including Maoris) 1 April 1960 | Approximate Area, in Square Miles |
|---|---|---|
| North Island: | ||
| Mangonui | 7,960 | 958 |
| Whangaroa | 2,500 | 240 |
| Hokianga | 7,270 | 613 |
| Bay of Islands | 13,070 | 823 |
| Whangarei | 15,050 | 1,039 |
| Hobson | 7,080 | 745 |
| Otamatea | 7,260 | 421 |
| Rodney | 7,070 | 477 |
| Waitemata | 43,100 | 600 |
| Great Barrier Island | 300 | 110 |
| Manukau | 24,100 | 238 |
| Franklin | 19,240 | 550 |
| Raglan | 12,600 | 931 |
| Waikato | 18,430 | 643 |
| Waipa | 21,090 | 444 |
| Otorohanga | 8,640 | 762 |
| Waitomo | 9,740 | 1,297 |
| Taumarunui | 9,200 | 1,853 |
| Coromandel | 2,940 | 444 |
| Thames | 3,440 | 414 |
| Hauraki Plains | 6,010 | 233 |
| Ohinemuri | 4,530 | 241 |
| Piako | 12,600 | 444 |
| Matamata | 22,700 | 994 |
| Tauranga | 22,200 | 716 |
| Rotorua | 18,850 | 1,040 |
| Taupo | 12,500 | 3,040 |
| Whakatane | 17,100 | 1,681 |
| Opotiki | 5,380 | 1,326 |
| Matakaoa | 1,840 | 295 |
| Waiapu | 6,330 | 793 |
| Uawa | 1,750 | 261 |
| Waikohu | 3,850 | 1,014 |
| Cook | 9,670 | 822 |
| Wairoa | 8,220 | 1,385 |
| Hawke's Bay | 20,800 | 1,668 |
| Waipawa | 4,140 | 524 |
| Patangata | 3,790 | 651 |
| Waipukurau | 1,360 | 128 |
| Dannevirke | 4,960 | 546 |
| Woodville | 1,870 | 156 |
| Clifton | 2,920 | 443 |
| Taranaki | 7,540 | 227 |
| Inglewood | 3,360 | 199 |
| Stratford | 6,430 | 866 |
| Egmont | 6,540 | 240 |
| Eltham | 3,690 | 207 |
| Waimate West | 3,100 | 83 |
| Hawera | 5,460 | 190 |
| Patea | 4,180 | 591 |
| Waimarino | 2,740 | 829 |
| Waitotara | 3,380 | 468 |
| Wanganui | 3,580 | 460 |
| Rangitikei | 13,600 | 1,730 |
| Kiwitea | 2,400 | 359 |
| Pohangina | 1,310 | 259 |
| Oroua | 4,990 | 190 |
| Manawatu | 7,880 | 265 |
| Kairanga | 6,390 | 184 |
| Horowhenua | 10,050 | 544 |
| Hutt | 25,900 | 443 |
| Makara | 13,900 | 98 |
| Pahiatua | 2,910 | 236 |
| Akitio | 1,190 | 321 |
| Eketahuna | 1,960 | 318 |
| Mauriceville | 550 | 115 |
| Masterton | 4,400 | 808 |
| Wairarapa South | 3,160 | 440 |
| Featherston | 3,840 | 954 |
| Totals, North Is. counties | 587,880 | 43,677 |
| South Island: | ||
| Sounds | 1,000 | 457 |
| Marlborough | 8,620 | 1,946 |
| Awatere | 1,840 | 1,030 |
| Kaikoura | 3,420 | 905 |
| Amuri | 3,110 | 2,285 |
| Cheviot | 1,570 | 327 |
| Golden Bay | 4,130 | 1,011 |
| Waimea | 14,300 | 1,533 |
| Buller | 4,630 | 1,885 |
| Murchison | 1,450 | 1,372 |
| Inangahua | 3,300 | 942 |
| Grey | 4,940 | 1,579 |
| Westland | 4,690 | 4,410 |
| Waipara | 3,050 | 937 |
| Kowai | 2,230 | 157 |
| Ashley | 740 | 309 |
| Rangiora | 3,880 | 96 |
| Eyre | 1,650 | 175 |
| Oxford | 1,670 | 318 |
| Tawera | 750 | 941 |
| Malvern | 4,150 | 250 |
| Paparua | 16,650 | 133 |
| Waimairi | 34,900 | 43 |
| Heathcote | 5,860 | 13 |
| Halswell | 2,230 | 39 |
| Mt. Herbert | 620 | 66 |
| Akaroa | 1,990 | 170 |
| Chatham Island | 560 | 372 |
| Wairewa | 930 | 170 |
| Springs | 2,540 | 92 |
| Ellesmere | 3,660 | 232 |
| Selwyn | 1,710 | 954 |
| Ashburton | 12,050 | 2,460 |
| Geraldine | 5,470 | 578 |
| Levels | 5,850 | 263 |
| Mackenzie | 3,320 | 2,852 |
| Waimate | 6,440 | 1,383 |
| Waitaki | 10,450 | 2,412 |
| Waihemo | 1,130 | 338 |
| Waikouaiti | 4,010 | 315 |
| Peninsula | 3,850 | 40 |
| Taieri | 7,630 | 901 |
| Bruce | 4,190 | 520 |
| Clutha | 6,410 | 1,045 |
| Tuapeka | 5,500 | 1,388 |
| Maniototo | 2,780 | 1,340 |
| Vincent | 4,450 | 2,922 |
| Lake | 1,980 | 3,871 |
| Southland | 29,910 | 3,703 |
| Wallace | 10,450 | 3,728 |
| Fiord | 10 | 3,035 |
| Stewart Island | 540 | 670 |
| Totals, South Island counties | 273,190 | 58,913 |
| Totals, all counties | 861,070 | 102,590 |
During the year three counties had estimated increases of 1,000 or more, viz, Waitemata (2,800), Waimairi (2,200), and Hutt (1,500). These counties serve, respectively, as dormitory suburbs for Auckland, Christchurch, and Wellington.
Substantial losses in population were recorded by Whangarei, Manukau, and Taranaki counties because of losses of territory to neighbouring local authorities.
Waikato and Vincent counties also had substantial losses, the result of the departure of construction workers from Meremere steam power station and Hawea works camp respectively. Most of the other losses by counties were minor, territorial boundary changes being responsible in some cases and camp closings, etc., in other cases.
Boroughs - Similar information as in the case of counties is now given for cities and boroughs.
| Borough | Estimated Population (Including Maoris) 1 April 1960 | Approximate Area, in Acres |
|---|---|---|
| North Island: | ||
| Kaitaia | 2,710 | 1,310 |
| Kaikohe | 2,470 | 1,342 |
| Whangarei | 17,200 | 6,510 |
| Dargaville | 3,670 | 2,800 |
| Helensville | 1,190 | 1,315 |
| East Coast Bays | 8,440 | 3,850 |
| Takapuna | 20,500 | 3,280 |
| Devonport | 11,750 | 1,100 |
| Northcote | 4,120 | 1,190 |
| Birkenhead | 6,740 | 3,084 |
| Henderson | 3,210 | 1,278 |
| Glen Eden | 4,870 | 1,244 |
| New Lynn | 8,510 | 1,393 |
| Auckland (city) | 141,900 | 18,493 |
| Newmarket | 1,920 | 182 |
| Mt. Albert | 25,700 | 2,430 |
| Mt. Eden | 18,650 | 1,477 |
| Mt. Roskill | 29,600 | 4,604 |
| Onehunga | 16,750 | 1,876 |
| One Tree Hill | 13,150 | 2,430 |
| Ellerslie | 4,760 | 745 |
| Mt. Wellington | 14,950 | 4,075 |
| Howick | 5,810 | 1,534 |
| Otahuhu | 8,840 | 1,345 |
| Papatoetoe | 15,800 | 2,241 |
| Manurewa | 7,150 | 1,727 |
| Papakura | 7,030 | 2,010 |
| Pukekohe | 5,450 | 3,471 |
| Waiuku | 1,560 | 1,465 |
| Tuakau | 1,420 | 1,091 |
| Huntly | 4,520 | 1,678 |
| Cambridge | 5,120 | 2,646 |
| Ngaruawahia | 3,070 | 1,112 |
| Hamilton (city) | 40,700 | 6,576 |
| Te Awamutu | 5,160 | 1,162 |
| Otorohanga | 2,100 | 560 |
| Te Kuiti | 4,240 | 1,668 |
| Taumarunui | 4,800 | 3,234 |
| Thames | 5,260 | 2,712 |
| Paeroa | 2,980 | 1,419 |
| Waihi | 3,110 | 1,330 |
| Te Aroha | 3,040 | 2,783 |
| Morrinsville | 4,260 | 1,177 |
| Matamata | 2,990 | 934 |
| Putaruru | 3,420 | 975 |
| Mt. Maunganui | 4,570 | 3,475 |
| Tauranga | 10,950 | 3,535 |
| Te Puke | 2,200 | 1,047 |
| Rotorua | 14,100 | 3,611 |
| Taupo | 4,480 | 2,290 |
| Whakatane | 6,630 | 1,539 |
| Kawerau | 3,800 | 1,718 |
| Opotiki | 2,620 | 772 |
| Gisborne (city) | 21,300 | 3,610 |
| Wairoa | 4,140 | 1,603 |
| Napier (city) | 22,700 | 3,955 |
| Taradale | 4,260 | 1,002 |
| Hastings (city) | 21,700 | 3,211 |
| Havelock North | 3,220 | 1,165 |
| Waipawa | 1,750 | 1,710 |
| Waipukurau | 3,140 | 971 |
| Dannevirke | 5,710 | 1,300 |
| Woodville | 1,510 | 1,054 |
| Waitara | 4,190 | 1,587 |
| New Plymouth (city) | 28,800 | 5,722 |
| Inglewood | 1,780 | 703 |
| Stratford | 5,000 | 2,016 |
| Eltham | 2,330 | 1,599 |
| Hawera | 7,260 | 1,270 |
| Patea | 2,020 | 1,420 |
| Ohakune | 1,700 | 2,079 |
| Raetihi | 1,230 | 958 |
| Wanganui (city) | 31,700 | 6,184 |
| Taihape | 2,590 | 1,923 |
| Marton | 4,200 | 1,415 |
| Feilding | 7,570 | 2,031 |
| Foxton | 2,680 | 757 |
| Palmerston N. (city) | 39,300 | 6,943 |
| Shannon | 1,290 | 844 |
| Levin | 7,560 | 1,332 |
| Otaki | 2,900 | 1,396 |
| Upper Hutt | 15,100 | 2,165 |
| Lower Hutt (city) | 53,600 | 11,004 |
| Petone | 10,500 | 2,553 |
| Eastbourne | 2,740 | 1,546 |
| Tawa | 5,960 | 1,037 |
| Wellington (city) | 123,000 | 18,226 |
| Pahiatua | 2,470 | 720 |
| Eketahuna | 790 | 948 |
| Masterton | 14,200 | 3,116 |
| Carterton | 2,850 | 1,265 |
| Greytown | 1,490 | 1,093 |
| Featherston | 1,330 | 759 |
| Martinborough | 1,320 | 1,070 |
| Totals, North Island cities and boroughs | 1,038,820 | 234,107 |
| South Island: | ||
| Picton | 2,270 | 1,052 |
| Blenheim | 11,500 | 2,497 |
| Nelson (city) | 22,700 | 8,255 |
| Richmond | 3,010 | 2,600 |
| Motueka | 3,050 | 2,523 |
| Westport | 5,590 | 760 |
| Runanga | 1,850 | 1,204 |
| Greymouth | 9,030 | 2,594 |
| Brunner | 1,120 | 5,700 |
| Kumara | 510 | 842 |
| Hokitika | 3,080 | 674 |
| Ross | 550 | 3,800 |
| Rangiora | 3,440 | 877 |
| Kaiapoi | 3,140 | 786 |
| Riccarton | 7,930 | 728 |
| Christchurch (city) | 151,500 | 25,698 |
| Lyttelton | 3,600 | 2,560 |
| Ashburton | 11,200 | 2,601 |
| Geraldine | 1,790 | 745 |
| Temuka | 2,310 | 795 |
| Timaru (city) | 24,500 | 3,668 |
| Waimate | 3,290 | 771 |
| Oamaru | 11,900 | 2,811 |
| Hampden | 320 | 630 |
| Palmerston | 880 | 900 |
| Waikouaiti | 710 | 1,958 |
| Port Chalmers | 3,210 | 954 |
| West Harbour | 2,230 | 2,181 |
| Dunedin (city) | 72,400 | 13,942 |
| St. Kilda | 6,850 | 463 |
| Green Island | 5,210 | 1,789 |
| Mosgiel | 5,750 | 965 |
| Milton | 1,980 | 315 |
| Kaitangata | 1,300 | 1,280 |
| Balclutha | 3,890 | 1,258 |
| Tapanui | 440 | 129 |
| Lawrence | 580 | 615 |
| Roxburgh | 860 | 515 |
| Naseby | 170 | 188 |
| Alexandra | 2,300 | 815 |
| Cromwell | 920 | 972 |
| Arrowtown | 200 | 457 |
| Queenstown | 1,460 | 998 |
| Gore | 7,180 | 2,276 |
| Mataura | 2,040 | 1,272 |
| Winton | 1,430 | 505 |
| Invercargill (city) | 34,200 | 8,995 |
| Bluff | 3,240 | 2,111 |
| Riverton | 1,220 | 997 |
| Totals, South Island cities and boroughs | 449,830 | 122,021 |
| Totals, all cities and boroughs | 1,488,650 | 356,128 |
Five cities and boroughs had estimated increases of 1,000 or more during the year. Whangarei, Papatoetoe, and New Plymouth gained substantially from territorial boundary changes during the year to enable them to record increases of 1,100, 3,300, and 3,400 respectively. Whangarei gained an estimated 850 persons from Whangarei county on 1 April 1960, Papatoetoe an estimated 2,940 persons from Manukau county on 1 October 1959, and New Plymouth an estimated 3,000 persons from Taranaki county on 1 April 1960. Christchurch and Mt. Roskill had estimated gains of 2,100 and 1,000 respectively. There were very few decreases in boroughs and the decreases themselves were small.
Town Districts - As stated earlier, the population of independent town districts - i.e., those contained in section (a) of the following table - is not included with that of the county in which the town district is located, but the population of dependent town districts - section (b) - is included in that of the respective parent county.
| Town District | Estimated Population (Including Maoris) 1 April 1960 | Approximate Area, in Acres |
|---|---|---|
| *Parent county shown in parentheses. | ||
| (a) Town Districts Not Forming Parts of Counties | ||
| North Island: | ||
| Kawakawa | 820 | 280 |
| Hikurangi | 1,070 | 960 |
| Kamo | 1,270 | 852 |
| Warkworth | 1,050 | 1,427 |
| Ohura | 630 | 815 |
| Manunui | 960 | 1,251 |
| Murupara | 1,450 | 530 |
| Manaia | 770 | 510 |
| Waverley | 900 | 484 |
| Mangaweka | 350 | 955 |
| Hunterville | 620 | 791 |
| Totals, North Island | 9,890 | 8,855 |
| South Island: | ||
| Lumsden | 670 | 1,264 |
| Wyndham | 680 | 680 |
| Nightcaps | 680 | 285 |
| Otautau | 840 | 490 |
| Totals, South Island | 2,870 | 2,719 |
| Totals | 12,760 | 11,574 |
| (b) Town Districts Forming Parts of Counties* | ||
| North Island: | ||
| Kohukohu (Hokianga) | 240 | 1,020 |
| Rawene (Hokianga) | 480 | 280 |
| Russell (Bay of Islands) | 620 | 1,066 |
| Mercer (Franklin) | 340 | 890 |
| Te Kauwhata (Waikato) | 730 | 1,290 |
| Ohaupo (Waipa) | 330 | 1,281 |
| Kihikihi (Waipa) | 960 | 523 |
| Te Karaka (Waikohu) | 390 | 700 |
| Patutahi (Cook) | 260 | 1,275 |
| Kaponga (Eltham) | 550 | 558 |
| Normanby (Hawera) | 520 | 260 |
| Totals, North Island | 5,420 | 9,143 |
| South Island: | ||
| Edendale (Southland) | 610 | 696 |
| Totals, South Island | 610 | 696 |
| Totals | 6,030 | 9,839 |
During the year the independent town district of Leeston was absorbed by Ellesmere county, while the dependent town districts of Southbridge (in Ellesmere county) and Outram (in Taieri county) lost their identities.
Extra-county Islands and Migratory Population - In addition to the populations quoted for administrative counties, cities and boroughs, and independent town districts, the New Zealand totals include migratory population and persons located on islands not within the boundaries of any county. The two latter categories comprised an estimated total of 7,686 people as at 1 April 1960.
Of the islands concerned, Waiheke, with an estimated population of 2,280 as at 1 April 1960, was the only one of any size.
AGE DISTRIBUTION - The following table shows the estimated age distribution of the population at 31 December 1959 and of the mean population for the year 1959. The figures are based on the 1956 census data and brought up to date from statistics of births, ages of persons dying, and ages of persons arriving in or departing from New Zealand.
| Age Group in Years | Excluding Maoris | Maoris | Total Population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| As at 31 December 1959 | |||||||||
| Under 5 | 130,626 | 124,571 | 255,197 | 15,532 | 15,162 | 30,694 | 146,158 | 139,733 | 285,891 |
| 5 and under 10 | 116,100 | 111,700 | 227,800 | 12,660 | 11,960 | 24,620 | 128,760 | 123,660 | 252,420 |
| 10 ,, 15 | 109,000 | 104,400 | 213,400 | 10,100 | 9,760 | 19,860 | 119,100 | 114,160 | 233,260 |
| 15 ,, 20 | 84,700 | 80,600 | 165,300 | 8,240 | 8,000 | 16,240 | 92,940 | 88,600 | 181,540 |
| 20 ,, 25 | 69,200 | 66,700 | 135,900 | 6,660 | 6,690 | 13,350 | 75,860 | 73,390 | 149,250 |
| 25 ,, 30 | 70,200 | 65,900 | 136,100 | 5,630 | 5,720 | 11,350 | 75,830 | 71,620 | 147,450 |
| 30 ,, 35 | 77,500 | 71,300 | 148,800 | 4,780 | 4,720 | 9,500 | 82,280 | 76,020 | 158,300 |
| 35 ,, 40 | 74,500 | 72,800 | 147,300 | 3,620 | 3,680 | 7,300 | 78,120 | 76,480 | 154,600 |
| 40 ,, 45 | 67,800 | 69,300 | 137,100 | 3,130 | 3,170 | 6,300 | 70,930 | 72,470 | 143,400 |
| 45 ,, 50 | 67,200 | 66,100 | 133,300 | 2,740 | 2,500 | 5,240 | 69,940 | 68,600 | 138,540 |
| 50 ,, 55 | 60,400 | 58,400 | 18,800 | 2,310 | 1,890 | 4,200 | 62,710 | 60,290 | 123,000 |
| 55 ,, 60 | 50,300 | 49,500 | 99,800 | 1,560 | 1,330 | 2,890 | 51,860 | 50,830 | 102,690 |
| 60 ,, 65 | 39,000 | 43,000 | 82,000 | 1,160 | 950 | 2,110 | 40,160 | 43,950 | 84,110 |
| 65 ,, 70 | 30,900 | 37,700 | 68,600 | 750 | 610 | 1,360 | 31,650 | 38,310 | 69,960 |
| 70 ,, 75 | 26,010 | 32,190 | 58,200 | 495 | 435 | 930 | 26,505 | 32,625 | 59,130 |
| 75 ,, 80 | 18,530 | 23,290 | 41,820 | 265 | 205 | 470 | 18,795 | 23,495 | 42,290 |
| 80 and over | 14,280 | 19,210 | 33,490 | 205 | 220 | 425 | 14,485 | 19,430 | 33,915 |
| Totals | 1,106,246 | 1,096,661 | 2,202,907 | 79,837 | 77,002 | 156,839 | 1,186,083 | 1,173,663 | 2,359,746 |
| Totals: | |||||||||
| Under 14 | 336,826 | 322,471 | 659,297 | 36,522 | 35,162 | 71,684 | 373,348 | 357,633 | 730,981 |
| Under 16 | 373,426 | 357,471 | 730,897 | 40,002 | 38,542 | 78,544 | 413,428 | 396,013 | 809,441 |
| Under 21 | 455,326 | 435,671 | 890,997 | 48,042 | 46,322 | 94,364 | 503,368 | 481,993 | 985,361 |
| 21 and over | 650,920 | 660,990 | 1,311,910 | 31,795 | 30,680 | 62,475 | 682,715 | 691,670 | 1,374,385 |
| 16 and under 21 | 81,900 | 78,200 | 160,100 | 8,040 | 7,780 | 15,820 | 89,940 | 85,980 | 175,920 |
| 65 and over | 89,720 | 112,390 | 202,110 | 1,715 | 1,470 | 3,185 | 91,435 | 113,860 | 205,295 |
| Mean Population for Year 1959 | |||||||||
| Under 5 | 128,545 | 122,808 | 251,353 | 15,141 | 14,763 | 29,904 | 143,686 | 137,571 | 281,257 |
| 5 and under 10 | 115,300 | 110,700 | 226,000 | 12,470 | 11,860 | 24,330 | 127,770 | 122,560 | 250,330 |
| 10 ,, 15 | 106,200 | 101,700 | 207,900 | 9,870 | 9,510 | 19,380 | 116,070 | 111,210 | 227,280 |
| 15 ,, 20 | 83,400 | 79,300 | 162,700 | 8,160 | 7,900 | 16,060 | 91,560 | 87,200 | 178,760 |
| 20 ,, 25 | 68,400 | 65,600 | 134,000 | 6,560 | 6,600 | 13,160 | 74,960 | 72,200 | 147,160 |
| 25 ,, 30 | 71,000 | 66,300 | 137,300 | 5,560 | 5,640 | 11,200 | 76,560 | 71,940 | 148,500 |
| 30 ,, 35 | 77,500 | 71,300 | 148,800 | 4,660 | 4,620 | 9,280 | 82,160 | 75,920 | 158,080 |
| 35 ,, 40 | 73,700 | 72,400 | 146,100 | 3,580 | 3,620 | 7,200 | 77,280 | 76,020 | 153,300 |
| 40 ,, 45 | 67,700 | 69,000 | 136,700 | 3,090 | 3,130 | 6,220 | 70,790 | 72,130 | 142,920 |
| 45 ,, 50 | 66,800 | 65,500 | 132,300 | 2,730 | 2,450 | 5,180 | 69,530 | 67,950 | 137,480 |
| 50 ,, 55 | 59,600 | 57,500 | 117,100 | 2,250 | 1,840 | 4,090 | 61,850 | 59,340 | 121,190 |
| 55 ,, 60 | 49,700 | 48,900 | 98,600 | 1,540 | 1,310 | 2,850 | 51,240 | 50,210 | 101,450 |
| 60 ,, 65 | 38,200 | 42,600 | 80,800 | 1,130 | 930 | 2,060 | 39,330 | 43,530 | 82,860 |
| 65 ,, 70 | 31,000 | 37,600 | 68,600 | 740 | 610 | 1,350 | 31,740 | 38,210 | 69,950 |
| 70 ,, 75 | 26,060 | 31,860 | 57,920 | 485 | 420 | 905 | 26,545 | 32,280 | 58,825 |
| 75 ,, 80 | 18,490 | 23,050 | 41,540 | 265 | 210 | 475 | 18,755 | 23,260 | 42,015 |
| 80 and over | 14,070 | 18,760 | 32,830 | 210 | 220 | 430 | 14,280 | 18,980 | 33,260 |
| Totals | 1,095,665 | 1,084,878 | 2,180,543 | 78,441 | 75,633 | 154,074 | 1,174,106 | 1,160,511 | 2,334,617 |
| Totals: | |||||||||
| Under 14 | 331,745 | 317,808 | 649,553 | 35,741 | 34,443 | 70,184 | 367,486 | 352,251 | 719,737 |
| Under 16 | 367,245 | 351,408 | 718,653 | 39,151 | 37,773 | 76,924 | 406,396 | 389,181 | 795,577 |
| Under 21 | 447,945 | 428,508 | 876,453 | 47,111 | 45,453 | 92,564 | 495,056 | 473,961 | 969,017 |
| 21 and over | 647,720 | 656,370 | 1,304,090 | 31,330 | 30,180 | 61,510 | 679,050 | 686,550 | 1,365,600 |
| 16 and under 21 | 80,700 | 77,100 | 157,800 | 7,960 | 7,680 | 15,640 | 88,660 | 84,780 | 173,440 |
| 65 and over | 89,620 | 111,270 | 200,890 | 1,700 | 1,460 | 3,160 | 91,320 | 112,730 | 204,050 |
DENSITY OF POPULATION - The relation of population to area, which is commonly referred to as “density of population”, is a subject of much interest and a source of serious misconceptions. Generally speaking, a dense population must depend upon land utilisation or industrialisation. In New Zealand there is a great area of high mountainous country, particularly in the South Island, while there are also large areas of water or of broken, swampy, or hilly country which is either incapable of effective use or which can be used profitably only for pastoral purposes, afforestation, or the like.
Most of the land that can still be brought into occupation requires special methods or heavier capital expenditure to develop it. The Departments of Lands and Survey and Maori Affairs are grassing annually quite large areas of what was, until recently, regarded as useless land. The development of unimproved land for farming purposes can be expected to continue steadily, but the accompanying growth of mechanisation in farming tends to stabilise the size of the labour force engaged in farming operations.
While industrial development has made very marked growth in New Zealand over the years, and extensive further development appears certain, there are factors unfavourable to the growth of industry to a point where dense populations could be supported - not the least of which are a lack of mineral resources, relative smallness of the home market (even with an expanded population), and distance from export markets.
Within New Zealand there are wide variations in density of population. The North Island, with an area of 44,297 square miles, had a population density of 33.80 persons per square mile at the 1956 census date, and the South Island, with an area of 59,439 square miles, had a population density of 11.38 persons per square mile at the same date.
The following table provides comparative density figures on a provincial district basis.
| Provincial District | Area, in Square Miles | Persons per Square Mile | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1911 | 1921 | 1936 | 1951 | 1956 | ||
| Auckland | 25,420 | 11.75 | 16.00 | 21.52 | 29.31 | 34.29 |
| Hawke's Bay | 4,260 | 12.46 | 14.94 | 18.07 | 21.41 | 24.02 |
| Taranaki | 3,750 | 14.44 | 17.40 | 20.71 | 23.17 | 25.10 |
| Wellington | 10,870 | 18.80 | 23.43 | 29.11 | 35.94 | 39.48 |
| Marlborough | 4,220 | 3.90 | 4.33 | 4.54 | 5.42 | 6.09 |
| Nelson | 10,870 | 4.48 | 4.39 | 5.47 | 6.23 | 6.52 |
| Westland | 4,880 | 3.24 | 2.92 | 3.83 | 3.72 | 3.79 |
| Canterbury | 13,940 | 12.52 | 14.34 | 16.81 | 20.09 | 22.06 |
| Otago: | ||||||
| Otago | 14,070 | 9.46 | 9.76 | 10.76 | 11.33 | 12.00 |
| Southland | 11,460 | 5.17 | 5.44 | 6.35 | 6.76 | 7.44 |
| Totals | 103,740 | 10.20 | 12.26 | 15.17 | 18.70 | 20.96 |
MAORI POPULATION - The first official general census of Maoris was taken in 1857-58, and others occurred in regular sequence from 1874 onwards. Owing to inherent difficulties the earlier census records make no pretence towards complete accuracy.
According to census records the Maori population suffered a period of almost unbroken decline from 1858 to 1896. The following causes no doubt contributed to this decline - warfare amongst the tribes and with the European settlers; the susceptibility of the Maori to epidemic and other diseases introduced with the white race; and the mental outlook of the Maori under the new conditions.
During the last 50 years, however, the Maori population has increased continuously, at first steadily and of later years at a fairly rapid rate. In fact, the vitality exhibited by the Maori race in recent years is a most outstanding feature. The rate of natural increase of the Maori population is more than double that of the European.
A statement of Maori population is now given for each census from 1901 to 1956.
| Year | Maori Population | Intercensal Increase | Intercensal Increase | Average Annual Increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes members of armed forces overseas at census date. | ||||
| Number | Number | Per Cent | Per Cent | |
| 1901 | 45,549 | 3,436 | 8.2 | 1.6 |
| 1906 | 50,309 | 4,760 | 10.5 | 2.0 |
| 1911 | 52,723 | 2,414 | 4.8 | 1.0 |
| 1916 | 52,997 | 274 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| 1921 | 56,987 | 3,990 | 7.5 | 1.6 |
| 1926 | 63,670 | 6,683 | 11.7 | 2.2 |
| 1936 | 82,326 | 18,656 | 29.3 | 2.6 |
| 1945 | 98,744 | 16,418 | 19.9 | 1.9 |
| 1945* | 100,044 | 17,718 | 21.5 | 2.1 |
| 1951 | 115,676 | 16,932 | 17.1 | 2.9 |
| 1951* | 115,740 | 15,696 | 15.7 | 2.7 |
| 1956 | 137,151 | 21,475 | 18.6 | 3.5 |
| 1956* | 137,341 | 21,601 | 18.7 | 3.5 |
The average annual percentage increase from 1951 to 1956 was 3.47, which is considerably higher than the corresponding figure for the European population, viz, 2.24 per cent. The natural increase ratios for the year 1960 shown below afford a better illustration.
| European | Maori | |
|---|---|---|
| Birthrate | 25.00 | 46.41 |
| Death rate | 8.81 | 8.56 |
| Natural-increase rate | 16.19 | 37.85 |
Of the 137,151 Maoris at the 1956 census, 131,894 were in the North Island. Auckland Provincial District contains the bulk of the Maoris, particularly in the Auckland peninsula and Waikato - Bay of Plenty regions. In the South Island Maoris do not attain any numerical significance. Maoris have always been residents in rural communities and this is still substantially true. A marked change has, however, taken place during and since the war as a result of employment conditions. As late as the 1936 census only 8,249 Maoris (10.02 per cent) dwelt in cities, boroughs, or independent town districts. By the 1956 census the comparative figure was 33,424 (24.37 per cent). The largest concentration is in Auckland Urban Area, where 11,361 Maoris were enumerated. The total Maori population at 1 April 1960 was 158,355.
Numbers of persons wholly or partly of Maori blood as disclosed by the censuses of 1951 and 1956 are set out in the following table.
| Counted in the Maori population: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 1956 | |
| *This category, first introduced in 1956, covers those cases of “Maori - other races” mixtures where there is half or more Maori blood involved; it accounts for the decline in most classes counted in the population other than Maori. | ||
| Full Maori | 76,918 | 88,440 |
| Maori-Europeans: | ||
| Three-quarter-caste | 15,201 | 18,624 |
| Half-caste | 23,183 | 28,492 |
| Maori-other Polynesian | 374 | 775 |
| Maori-other races* | .. | 820 |
| Totals | 115,676 | 137,151 |
| Counted in the population other than Maori: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 1956 | |
| †Includes Maori-Arab. | ||
| Maori-European quarter-caste | 18,421 | 25,108 |
| Maori-Japanese | 16 | 9 |
| Maori-Chinese | 369 | 64 |
| Maori-Indian | 220 | 64 |
| Maori-Syrian or Lebanese | 73 | 27† |
| Maori-American Indian | - | 3 |
| Maori-Negro | 11 | 2 |
| Maori-Filipino | 10 | 1 |
| Maori-West Indian | 13 | 6 |
| Maori-Melanesian | 33 | 23 |
| Totals | 19,166 | 25,307 |
In 1956 there were recorded in New Zealand some 162,458 persons wholly or partly of Maori origin, compared with 134,842 in 1951.
EXTERNAL MIGRATION - Statistics of external migration are compiled from individual statements obtained from each person entering or leaving New Zealand.
Including crews of vessels, 183,237 persons from overseas arrived in New Zealand during the year ended 31 March 1960 which, compared with 1958-59 shows an increase of 12,810. During the same period 180,438 persons departed. This figure, compared with the corresponding one for 1958-59, shows an increase of 20,340.
In addition to the figures just quoted there were also 35,637 through passengers and tourists on cruising liners, who called in at New Zealand in the course of their voyages.
The excess of total arrivals over total departures for 1959-60 was 2,799, compared with an excess of 10,329 during 1958-59.
The numbers of arrivals and departures during the last 11 years are given in the table following. Crews of vessels, through passengers, tourists on cruising liners and members of the armed forces, etc., have not been taken into account in this table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Arrivals | Departures | Excess of Arrivals Over Departures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | ||
| 1950 | 26,190 | 24,690 | 50,880 | 21,471 | 21,529 | 43,000 | 7,880 |
| 1951 | 28,309 | 26,335 | 54,644 | 23,411 | 23,711 | 47,122 | 7,522 |
| 1952 | 33,162 | 29,336 | 62,498 | 24,009 | 22,825 | 46,834 | 15,664 |
| 1953 | 35,574 | 30,666 | 66,240 | 22,399 | 21,809 | 44,208 | 22,032 |
| 1954 | 32,266 | 29,579 | 61,845 | 24,176 | 22,228 | 46,404 | 15,441 |
| 1955 | 32,496 | 29,114 | 61,610 | 28,593 | 25,987 | 54,580 | 7,030 |
| 1956 | 34,789 | 31,683 | 66,472 | 30,336 | 28,044 | 58,380 | 8,092 |
| 1957 | 40,836 | 35,219 | 76,055 | 34,518 | 30,045 | 64,563 | 11,492 |
| 1958 | 42,859 | 36,807 | 79,666 | 34,464 | 29,794 | 64,258 | 15,408 |
| 1959 | 44,955 | 38,693 | 83,648 | 39,917 | 33,739 | 73,656 | 9,992 |
| 1960 | 47,894 | 41,483 | 89,377 | 46,467 | 39,697 | 86,164 | 3,213 |
A substantial increase of 9,583 was recorded in arrivals for 1956-57, and this was attributable, in part, to the fact that the Olympic Games held in Australia in November 1956 stimulated traffic both to and from New Zealand. This high level of arrivals has been maintained, with increases of 3,611 in 1957-58, 3,982, or 5 per cent, in 1958-59, and 5,729, or 7 per cent, in 1959-60.
From 1 April 1953 departures showed a steady increase year by year until 1957-58 when a slight drop of 305 occurred. However, 1958-59 showed a large increase of 9,398 or 15 per cent, on the 1957-58 figure, while 1959-60 showed an increase of 12,508, or 17 per cent, on 1958-59.
In the 10-year period ended 31 March 1960 the net gain from passenger migration was 115,886, while if movement of crews is taken into account this decreased to 113,931.
Classes of Arrivals and Departures - The following table gives an analysis of all classes of arrivals during the last five years, including through passengers, tourists on cruising liners, and crews. In classifying arrivals or departures as permanent the commonly used international rule is applied - i.e., residence or absence of one year or more.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes 856 persons on working holidays. Information not known for earlier years. †Includes 1,431 persons on working holidays. | |||||
| Immigrants intending permanent residence | 20,878 | 23,030 | 26,254 | 24,852 | 20,294 |
| New Zealand residents returning | 21,915 | 25,046 | 23,640 | 27,623 | 32,526 |
| Visitors - | |||||
| Tourists | 16,884 | 19,368 | 20,723 | 21,927 | 24,794 |
| On business | 3,154 | 3,712 | 4,025 | 3,655 | 4,241 |
| Theatrical, entertaining, etc. | 696 | 879 | 850 | 764 | 943 |
| Educational purposes | 191 | 227 | 220 | 233 | 247 |
| Others, officials, etc. | 1,943 | 2,941 | 2,950 | 3,675* | 5,307† |
| In transit | 811 | 852 | 1,004 | 919 | 1,025 |
| Through passengers and tourists on cruising liners | 8,264 | 20,718 | 31,468 | 26,045 | 35,637 |
| Crews | 67,908 | 73,738 | 87,324 | 86,779 | 93,860 |
| Totals | 142,644 | 170,511 | 198,458 | 196,472 | 218,874 |
The succeeding table gives a similar analysis of departures.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand residents departing - | |||||
| Permanently | 9,436 | 9,220 | 8,108 | 10,985 | 13,420 |
| Temporarily | 23,287 | 26,162 | 24,510 | 28,674 | 34,667 |
| Temporary residents departing | 25,657 | 29,181 | 31,640 | 33,997 | 38,077 |
| Through passengers and tourists on cruising liners | 8,264 | 20,718 | 31,468 | 26,045 | 35,637 |
| Crews | 67,331 | 74,375 | 86,147 | 86,442 | 94,274 |
| Totals | 133,975 | 159,656 | 181,873 | 186,143 | 216,075 |
Ages - The following table gives the age-distribution of immigrants and emigrants for the 12 months ended 31 March 1960.
| Age, in Years | Permanent Arrivals | Permanent Departures | Excess of Arrivals Over Departures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Totals | Males | Females | Totals | ||
| 0-14 | 2,257 | 2,135 | 4,392 | 1,390 | 1,198 | 2,588 | 1,804 |
| 15-24 | 2,405 | 2,487 | 4,892 | 1,784 | 1,907 | 3,691 | 1,201 |
| 25-34 | 2,643 | 2,590 | 5,233 | 1,917 | 1,558 | 3,475 | 1,758 |
| 35-44 | 1,314 | 1,245 | 2,559 | 900 | 798 | 1,698 | 861 |
| 45-59 | 871 | 1,099 | 1,970 | 621 | 669 | 1,290 | 680 |
| 60 and over | 438 | 810 | 1,248 | 259 | 419 | 678 | 570 |
| Totals | 9,928 | 10,366 | 20,294 | 6,871 | 6,549 | 13,420 | 6,874 |
Of the permanent arrivals during the year 1959-60, 22 per cent were under 15 years of age, 46 per cent under 25 years, 72 per cent under 35 years, and 84 per cent under 45 years. Permanent departures represented a similar age distribution, with percentages of 19, 47, 73, and 85 respectively.
Origin - The following table shows for the last three years the birthplaces of immigrants intending permanent residence and of New Zealand residents departing permanently.
| Country of Birth | Immigrants Intending Permanent Residence | New Zealand Residents Departing Permanently | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
| *Includes arrival of Hungarian refugees, 451 in 1957-58 and 49 in 1958-59. | ||||||
| Commonwealth Countries | ||||||
| England and Wales | 10,507 | 9,995 | 7,392 | 1,858 | 2,755 | 3,282 |
| Scotland | 1,879 | 2,231 | 1,479 | 316 | 458 | 555 |
| Northern Ireland | 420 | 501 | 314 | 49 | 107 | 108 |
| United Kingdom (other or undefined) | 310 | 298 | 193 | 40 | 82 | 70 |
| India | 315 | 227 | 252 | 93 | 152 | 103 |
| Canada | 232 | 234 | 261 | 94 | 121 | 98 |
| Australia | 2,407 | 2,169 | 1,672 | 644 | 937 | 1,037 |
| Cook Islands and Niue | 498 | 474 | 339 | 25 | 50 | 37 |
| Western Samoa | 180 | 157 | 206 | 38 | 50 | 41 |
| Fiji | 263 | 203 | 216 | 72 | 70 | 63 |
| New Zealand | 3,916 | 3,904 | 3,789 | 4,028 | 5,060 | 6,659 |
| Other Commonwealth countries in the Pacific | 81 | 77 | 88 | 48 | 40 | 55 |
| Other countries within the Commonwealth | 506 | 509 | 471 | 81 | 133 | 163 |
| Totals, Commonwealth countries | 21,514 | 20,979 | 16,672 | 7,386 | 10,015 | 12,271 |
| Other Countries | ||||||
| Austria | 87 | 64 | 72 | 15 | 36 | 25 |
| China | 132 | 106 | 81 | 17 | 31 | 34 |
| Denmark | 218 | 183 | 119 | 19 | 22 | 61 |
| Germany | 240 | 154 | 143 | 27 | 49 | 58 |
| Hungary* | 476 | 67 | 56 | 6 | 15 | 13 |
| Indonesia | 85 | 125 | 91 | 16 | 30 | 49 |
| Netherlands | 1,605 | 1,466 | 1,632 | 170 | 209 | 268 |
| Republic of Ireland | 652 | 492 | 325 | 91 | 147 | 202 |
| Switzerland | 139 | 88 | 86 | 25 | 24 | 27 |
| United States of America | 371 | 467 | 439 | 157 | 198 | 176 |
| Yugoslavia | 101 | 103 | 150 | 8 | 11 | 18 |
| Others | 632 | 555 | 424 | 169 | 197 | 216 |
| Totals, other countries | 4,738 | 3,870 | 3,618 | 720 | 969 | 1,147 |
| At sea | 2 | - | 3 | 2 | - | 1 |
| Not specified | - | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| Grand totals | 26,254 | 24,852 | 20,294 | 8,108 | 10,985 | 13,420 |
Assisted Immigration - Various systems of assisted immigration have been in force since 1871, with the exception of the period 1892 to 1903 (inclusive). Assistance to immigrants was largely suspended between 1927 and 1947, and only 50 immigrants received financial assistance during the 10 years ended 31 March 1946.
To alleviate the shortage of staff in mental hospitals the Government decided in 1946 to recruit labour in the United Kingdom, and the number of arrivals under this scheme totalled 240 (all females).
In July 1947 a comprehensive free and assisted-passage scheme was introduced by the Government. Under this scheme certain categories of immigrants were given free passages to New Zealand provided they had served in the United Kingdom armed forces (including the Merchant Navy) during the Second World War, while others selected under the scheme were required to contribute only .10 towards the cost of their fares. Eligibility was confined to single residents of the United Kingdom (with no dependants) between the ages of 20 and 35 years who were suitable for, and willing to accept employment in, a wide variety of occupations. All assisted immigrants were required to enter into a contract with the New Zealand Government that they would engage in approved employment for two years after their arrival in New Zealand.
A scheme of child migration from the United Kingdom was in operation from June 1949 to May 1953. Arrivals of British children between the ages of five and 17 years totalled 169 in 1949-50, 107 in 1950-51, 99 in 1951-52, 87 in 1952-53, and 68 up to terminating date during 1953-54.
In May 1950 a new immigration policy was announced by the Government, the main changes being as follows:
The existing scheme in regard to unmarried British immigrants, including nominations, to continue, but with an extension of the age limit from 35 to 45 years of age and abolition of the requirement of .10 contribution towards cost of fare.
The extension of the free-passage scheme to certain categories of married British immigrants with up to two children - later extended to up to four dependent children.
The acceptance of a number of single non-British men and women between the ages of 20 and 35 years. Dutch, Danish, Swiss, Austrian, and German nationals were selected.
At the end of 1958, it was decided to cut back assisted immigration by limiting male workers from the United Kingdom to skilled tradesmen, experienced farm workers, and experienced workers required in essential industries. Married workers accepted in these categories were limited to those with not more than two children. At the same time, the recruitment of German, Austrian, Danish, and Swiss migrants was terminated.
In 1960 steps were taken to increase the recruitment of skilled workers required for the expansion of essential industries. These steps included the acceptance of married men in approved categories with up to four dependent children. In March 1961 the Government announced a plan to bring to New Zealand in 1961-62 up to 5,000 assisted immigrants.
The numbers of assisted immigrants (exclusive of displaced persons and Hungarian refugees) arriving in New Zealand since the reintroduction of the scheme in 1947 are as follows.
| British | Dutch | Austrian | German | Danish | Swiss | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year ended 31 March 1947 | 158 | - | - | - | - | - | 158 |
| ,, 1948 | 1,140 | - | - | - | - | - | 1,140 |
| ,, 1949 | 1,527 | - | - | - | - | - | 1,527 |
| ,, 1950 | 2,532 | - | - | - | - | - | 2,532 |
| ,, 1951 | 2,873 | 55 | - | - | - | - | 2,928 |
| ,, 1952 | 3,849 | 1,100 | - | - | - | - | 4,949 |
| ,, 1953 | 4,872 | 2,709 | - | - | - | - | 7,581 |
| ,, 1954 | 5,611 | 688 | - | - | - | - | 6,299 |
| ,, 1955 | 3,880 | 452 | - | - | - | - | 4,332 |
| ,, 1956 | 4,732 | 391 | - | - | - | - | 5,123 |
| ,, 1957 | 4,172 | 252 | 139 | 30 | - | - | 4,593 |
| ,, 1958 | 4,070 | 245 | 44 | 69 | 106 | 45 | 4,579 |
| ,, 1959 | 4,343 | 141 | 36 | 35 | 92 | 31 | 4,678 |
| ,, 1960 | 2,360 | 90 | 25 | 39 | 13 | 22 | 2,549 |
In the preceding migration tables assisted immigrants are included in the totals of “Immigrants intending permanent residence”.
Displaced Persons - Commencing with the year 1949-50 the Government agreed to accept drafts of displaced persons from Europe, who were brought to New Zealand in shipping provided by the International Refugee Organisation. These settlers were chosen by a New Zealand Selection Mission, and arrivals totalled 941 in 1949-50, 978 in 1950-51, and 2,663 in 1951-52, made up of young single men and women, widows with one child, family groups, orphans, and a number of elderly people. This scheme was brought to an end with the arrival in April 1952 of the final two displaced persons accepted by the Government.
HUNGARIAN REFUGEES - Following the uprising in Hungary, the Government agreed to accept a quota of 1,000 Hungarian refugees. This quota was subsequently increased to 1,300. The first draft arrived by air in December 1956 and a total of 1,117 finally arrived, the last of them reaching New Zealand during the year ended 31 March 1959.
OTHER REFUGEES - Apart from displaced persons, New Zealand has accepted and continues to accept refugees from Europe and the mainland of China. In 1958 it was decided to offer resettlement opportunities to 20 “hard core” refugee families from Europe who, because of handicapped persons in each family unit, were unacceptable elsewhere. These families arrived during 1959. In 1959 it was decided to accept a further 100 “hard core” families. These were selected and arrived during 1960.
PASSPORTS - Authority for the issue of passports in New Zealand and by New Zealand representatives overseas is contained in the Passports Act 1946 and the Passport Regulations 1946.
New Zealand passports are issued by the Department of Internal Affairs at Wellington, Auckland, and Christchurch. United Kingdom, Canadian, Australian, and Indian passports are issued by the respective High Commissioners for those countries. The representatives of New Zealand at London, Washington, New York, San Francisco, Ottawa, Canberra, Paris, The Hague, Tokyo, Singapore, Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur, and New Delhi are authorised to issue and renew New Zealand passports.
Entry into New Zealand - Apart from British subjects and the wives of British subjects arriving from Australia, no person 16 years of age or over may land in New Zealand unless in possession of a valid passport or other recognised travel document. Exemption (which is additional to the requirements of the Immigration Restriction and Undesirable Immigrants Exclusion Acts) may be granted by the Minister of Internal Affairs. With the exception of nationals of those countries with which New Zealand has concluded agreements for the mutual abolition of visas, all aliens require a British visa.
People born in the Cook Islands and the Tokelau Islands are British subjects and New Zealand citizens. They require to obtain formal exit permission from the Resident Commissioner if they wish to proceed to New Zealand.
Citizens of Western Samoa are New Zealand protected persons. If they wish to visit New Zealand as temporary visitors for periods of up to three months they must obtain prior permission from the High Commissioner for Western Samoa. Those desiring to enter New Zealand for longer periods than three months are required in addition to make prior application to the Secretary of Labour, Department of Labour, Wellington.
A British subject who is the master or a member of the crew of the vessel in which he arrives does not need to produce a passport.
Departure from New Zealand - All persons leaving New Zealand, with the exception of British subjects travelling to Australia or making the round trip to New Zealand's island territories, should be in possession of a valid passport or other travel document.
IMMIGRATION RESTRICTION - The legislation respecting the restriction of immigration into New Zealand is contained in the Immigration Restriction Act 1908 and its amendments, and the Undesirable Immigrants Exclusion Act 1919.
The Immigration Restriction Act is administered by the Department of Labour, while the Undesirable Immigrants Exclusion Act is administered by the Department of Justice.
Subject to certain exemptions, the following classes of persons are prohibited from landing in New Zealand.
Persons not of British birth, unless in possession of permits issued by the Department of Labour, (NOTE - A person is not deemed to be of British birth by reason that he or his parents or either of them is a naturalised British subject, or by reason that he is an aboriginal native or the descendant of an aboriginal native of any dominion (other than New Zealand), colony, possession, or protectorate of Her Majesty.)
Idiots or insane persons.
Persons suffering from contagious diseases which are loathsome or dangerous.
Persons who have been convicted of an offence for which they have been sentenced to a term of imprisonment or other form of detention for one year or more.
Persons who are considered by the Attorney-General to be disaffected or disloyal, or of such a character that their presence in New Zealand would be injurious to the peace, order, and good government of the country.
To obtain permits to enter New Zealand as permanent residents, application must be made by the intending immigrants themselves to the Secretary of Labour, Wellington. The application must be made in the prescribed form and must be supported by documents duly attested in the country of origin, in which country the applicant must have resided for at least 12 months prior to the date of application. Each application is considered individually on its own merits.
Provision is made in the law to permit persons covered by clause (1) above to pay temporary visits to New Zealand for the purposes of business, pleasure, or health. Temporary permits are normally restricted to some period not exceeding six months, but may be extended if the proper authorities consider that the circumstances warrant such action. A deposit may be required in respect of such temporary permit, and is returned on the departure of the visitor if the conditions of the temporary permit have been complied with. A deed to be entered into by some approved person or persons resident in New Zealand guaranteeing to pay all expenses that may be incurred by the Crown or any public body for the visitor's maintenance, relief, arrest, or detention in New Zealand or his deportation therefrom may also be required.
Provision is also made whereby, under certain conditions, students may be allowed to enter New Zealand temporarily.
Restricted Immigrants - When persons who are lunatic, idiotic, deaf, dumb, blind, or infirm arrive in New Zealand and are likely to become a charge upon the public or upon any public or charitable institution, the master, owner, or charterer of the ship by which such persons came to New Zealand may be called on to enter into a bond of .100 for each such person, guaranteeing payment of any expenses which may be incurred for their support and maintenance by or in any such institution within a period of five years.
Declaration by Persons Arriving in New Zealand - Every person of and over the age of 15 years who lands in New Zealand must, unless exempted by the Minister of Immigration, make and deliver to an officer of Customs a declaration giving the following particulars: Name, age, marital status, occupation, birthplace, nationality, race, particulars of children under 15 years of age arriving with him, residence, etc.
NATIONALITY AND NATURALISATION - The basic nationality law is the British Nationality and New Zealand Citizenship Act 1948 as amended. The original Act came into force on 1 January 1949 and was enacted following a conference of nationality experts of Commonwealth countries in February 1947 to discuss the basis of new nationality legislation. The scheme of the legislation accepted by Commonwealth Governments is the “common status” of all British subjects, namely, that in each Commonwealth country all persons are recognised as British subjects who possess citizenship under the citizenship laws of any of the members of the Commonwealth. (NOTE - The Act states that “British subject” and “Commonwealth citizen” have the same meaning.)
Upon the commencement of the Act, New Zealand citizenship was automatically conferred on the following classes of British subjects: (a) those born in New Zealand; (b) those naturalised in New Zealand; (c) those ordinarily resident in New Zealand throughout the whole of the year 1948; (d) those whose fathers were British subjects born or naturalised in New Zealand; and (e) women married before the commencement of the Act to men who become citizens under the various provisions of the Act.
Since the commencement of the Act, New Zealand citizenship may be acquired in the following ways: (a) by birth in New Zealand; (b) by descent; (c) by registration; and (d) by naturalisation.
Citizens of other Commonwealth countries acquire New Zealand citizenship by registration. The requirement is three years residence reducible to 12 months at the Minister's discretion. A British woman married to a New Zealand citizen may be registered without any residential qualification. Applicants for New Zealand citizenship by registration must satisfy the Minister that they are of good character and have an adequate knowledge of English and of the duties and responsibilities of New Zealand citizenship.
The principal conditions governing the grant of naturalisation to aliens under the 1948 Act are that the applicant shall satisfy the Minister of Internal Affairs (a) that he has resided in New Zealand for a period of five years, (b) that he is of good character and has a sufficient knowledge of the English language, (c) that if his application is granted he intends to reside permanently in New Zealand, (d) that the applicant gives a year's notice of his intention to apply, and (e) that the applicant possesses a sufficient knowledge of the responsibilities and privileges of New Zealand citizenship. There is discretionary provision for the Minister to allow residence in other Commonwealth countries to be reckoned for the purposes of the first condition, but in such cases a minimum of two years' residence in New Zealand is essential.
Naturalisation granted to a married man does not automatically confer New Zealand citizenship on his wife and children, if they are aliens. These dependants may apply to be registered as New Zealand citizens after the head of the family has been naturalised. An alien woman marrying a British subject does not acquire her husband's nationality on marriage, but may apply to be registered as a British subject and New Zealand citizen. Acquisition of citizenship by naturalisation or registration automatically confers the status of a British subject, and the two methods of acquiring citizenship are differences in legal procedure only.
A British woman marrying an alien does not lose her nationality under the present Act.
Alien adults acquiring New Zealand citizenship by naturalisation or registration, and alien minor children over 16 years of age acquiring it by registration, are required to take the oath of allegiance. The Minister may also at his discretion require persons other than aliens acquiring New Zealand citizenship to take the oath of allegiance. Recognising the importance both to this country and to the new settlers themselves of their acquisition of New Zealand citizenship, the Government decided that ceremonies should be held at which applicants should, in an atmosphere of dignity and solemnity, take the oath of allegiance to Her Majesty and be presented with their certificates of naturalisation or registration as New Zealand citizens. Local authorities agreed to arrange such ceremonies. The first was presided over by the Mayor of Wellington on 24 May 1955. During the 1959-60 year there were 80 such ceremonies.
New Zealand citizens are liable at the discretion of the Minister to deprivation of New Zealand citizenship if they voluntarily acquire a foreign nationality by any formal act other than marriage; or if they voluntarily exercise the privileges or perform any of the duties of a foreign nationality possessed by them. In addition, persons naturalised or registered as New Zealand citizens are liable to deprivation if citizenship was obtained by fraud or false representation.
The numbers of naturalisations, registrations, etc., during the year ended 31 March 1960 were as follows.
| Country of Birth | Certificates of Naturalisation (Aliens and British-protected Persons) | Certificates of Registration as a New Zealand Citizen (British Subjects, Irish Citizens, British-protected Persons, and Aliens) | Certificates of Registration as a New Zealand Citizen—Minor Children (British Subjects and Aliens) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | |
| Bulgaria | 10 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| China | 127 | 8 | 1 | 47 | 13 | 4 |
| Czechoslovakia | 14 | 1 | - | 6 | 1 | - |
| Denmark | 27 | 2 | - | 16 | 9 | 5 |
| Germany | 6 | 3 | - | 15 | 11 | 9 |
| Greece | 7 | 1 | - | 5 | 4 | - |
| Hungary | 7 | 2 | - | 4 | - | - |
| Indonesia | 36 | 1 | - | 24 | 5 | 8 |
| Italy | 15 | 1 | - | 7 | - | 2 |
| Latvia | 21 | 5 | - | 10 | 6 | - |
| Lithuania | 8 | 2 | - | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| Netherlands | 478 | 11 | - | 200 | 58 | 43 |
| Norway | 8 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Poland | 41 | 8 | - | 19 | 1 | 2 |
| Republic of India | - | - | 20 | 20 | - | - |
| Rumania | 31 | 3 | - | 21 | 7 | 8 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 18 | 4 | - | 13 | - | - |
| United Kingdom | - | - | 100 | 77 | - | - |
| Yugoslavia | 37 | 2 | - | 20 | 2 | 5 |
| Other countries | 67 | 4 | 29 | 75 | 44 | 47 |
| Totals | 958 | 59 | 150 | 585 | 165 | 136 |
Of the certificates of registration granted to adult males, 148 were to British subjects or Irish citizens who acquired New Zealand citizenship by virtue of one year's residence in the country immediately preceding the date of application, and two to British subjects generally resident outside New Zealand who were registered as New Zealand citizens by virtue of their close association by way of descent, residence, or otherwise, with New Zealand.
The certificates of registration granted to adult females were 93 to British subjects who acquired New Zealand citizenship by virtue of one year's residence in the country immediately preceding the date of application, 44 to British wives of New Zealand citizens, and 448 to alien women married to New Zealand citizens by birth or naturalisation.
Certificates of registration granted to minor children were 276 (149 males, 127 females) to children of New Zealand citizens by naturalisation or registration, and 25 (16 males, nine females) who lodged applications independently.
REGISTRATION OF ALIENS - The registration of aliens in New Zealand is provided for by the Aliens Act 1948. The Aliens Amendment Act 1957 transferred, from 1 April 1958, the administration of the principal Act from the Police Department to the Department of Justice.
The number of aliens on the New Zealand register at 1 April 1960 was 27,643, comprising 17,072 males and 10,571 females. This is not the complete number in New Zealand, as certain classes are not required to register, including the following: (a) children under 16 years of age; (b) persons holding diplomatic status, consuls, or employees of embassies, legations, and consulates who are resident in New Zealand solely for the purpose of performing official duties; (c) certain temporary visitors to New Zealand; (d) Western Samoans, except in special circumstances. Under the British Nationality and New Zealand Citizenship Act 1948 a citizen of the Republic of Ireland, though not possessing the status of British subject (or, in alternative phraseology, Commonwealth citizen), is nevertheless not classed as an alien and is not required to register.
The following table shows the numbers on the register at 1 April 1959 and 1 April 1960.
| Country of Nationality | 1 April 1959 | 1 April 1960 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Austria | 343 | 110 | 453 | 340 | 118 | 458 |
| Belgium | 51 | 33 | 84 | 47 | 32 | 79 |
| Bulgaria | 124 | 11 | 135 | 108 | 9 | 117 |
| China | 2,246 | 1,192 | 3,438 | 2,081 | 1,185 | 3,266 |
| Czechoslovakia | 133 | 48 | 181 | 111 | 40 | 151 |
| Denmark | 623 | 291 | 914 | 605 | 294 | 899 |
| Estonia | 49 | 61 | 110 | 42 | 52 | 94 |
| Finland | 65 | 45 | 110 | 60 | 45 | 105 |
| France | 103 | 103 | 206 | 85 | 100 | 185 |
| Germany | 286 | 348 | 634 | 308 | 362 | 670 |
| Greece | 572 | 486 | 1,058 | 535 | 465 | 1,000 |
| Hungary | 731 | 375 | 1,106 | 732 | 382 | 1,114 |
| Indonesia | 43 | 10 | 53 | 27 | 1 | 28 |
| Italy | 254 | 185 | 439 | 248 | 184 | 432 |
| Japan | 10 | 50 | 60 | 5 | 50 | 55 |
| Latvia | 154 | 154 | 308 | 129 | 131 | 260 |
| Lebanon | 15 | 13 | 28 | 13 | 14 | 27 |
| Lithuania | 51 | 52 | 103 | 44 | 47 | 91 |
| Netherlands | 8,401 | 5,111 | 13,512 | 8,325 | 5,265 | 13,590 |
| Norway | 122 | 43 | 165 | 118 | 43 | 161 |
| Poland | 899 | 595 | 1,494 | 837 | 563 | 1,400 |
| Rumania | 35 | 19 | 54 | 35 | 20 | 55 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 79 | 53 | 132 | 73 | 47 | 120 |
| Sweden | 79 | 37 | 116 | 76 | 43 | 119 |
| Switzerland | 429 | 220 | 649 | 443 | 219 | 662 |
| United States of America | 752 | 369 | 1,121 | 812 | 356 | 1,168 |
| Yugoslavia | 659 | 395 | 1,054 | 676 | 406 | 1,082 |
| Other countries | 104 | 60 | 164 | 107 | 62 | 169 |
| Stateless | 55 | 39 | 94 | 50 | 36 | 86 |
| Totals | 17,467 | 10,508 | 27,975 | 17,072 | 10,571 | 27,643 |
The number of aliens on the register at 1 April 1960 shows a decrease of 332 as compared with 12 months earlier. An increase during the year was shown by Netherlands (78), United States of America (47), Germany (36), and Yugoslavia (28). Decreases were shown by several countries, the largest being China (172), Poland (94), Greece (58), and Latvia (48).
Tables showing for aliens registered at 1 April 1956, ages, occupational groups, and geographical location by countries of nationality, will be found on pages 44–47 of the 1957 Yearbook.
STATISTICS OF THE 1956 CENSUS - Publications containing the results of the census taken for the night of 17 April 1956 are included in the list on the page preceding the Index of this Yearbook.
The following pages give details relating to Marital Status, Dependent Children, and Religious Professions. Information on Age Distribution, Racial Origins, Birthplaces, Duration of Residence of Overseas-born, and Overseas War Service was given on pages 56–65 of the 1958 Yearbook.
MARITAL STATUS-The marital status of persons aged 16 years and over as returned at the census of 1956 is summarised in the following tables.
| Age (Years) | Never Married | Married | Legally Separated | Widowed | Divorced | Not Specified | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | |||||||
| 16-19 | 59,642 | 454 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 7 | 60,112 |
| 20 | 12,660 | 799 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 13,471 | |
| 21-24 | 39,939 | 15,547 | 124 | 25 | 30 | 44 | 55,709 |
| 25-29 | 28,231 | 50,409 | 512 | 108 | 210 | 53 | 79,523 |
| 30-34 | 14,594 | 62,191 | 742 | 220 | 635 | 47 | 78,429 |
| 35-39 | 8,947 | 60,033 | 704 | 345 | 846 | 38 | 70,913 |
| 40-44 | 7,439 | 60,664 | 682 | 633 | 1,021 | 33 | 70,472 |
| 45-49 | 6,392 | 57,326 | 650 | 957 | 1,130 | 47 | 66,502 |
| 50-54 | 5,229 | 47,232 | 576 | 1,414 | 1,046 | 38 | 55,535 |
| 55-59 | 4,563 | 38,738 | 423 | 2,056 | 842 | 32 | 46,654 |
| 60-64 | 3,430 | 28,825 | 303 | 2,652 | 642 | 29 | 35,881 |
| 65-69 | 3,350 | 24,909 | 247 | 4,009 | 582 | 19 | 33,116 |
| 70-74 | 2,705 | 18,816 | 262 | 4,950 | 392 | 24 | 27,149 |
| 75-79 | 1,966 | 11,123 | 130 | 4,951 | 235 | 15 | 18,420 |
| 80-84 | 948 | 4,195 | 55 | 3,379 | 87 | 12 | 8,676 |
| 85-89 | 350 | 1,105 | 42 | 1,630 | 28 | 2 | 3,157 |
| 90 and over | 66 | 221 | 6 | 484 | 6 | 1 | 784 |
| Not specified adults | 166 | 346 | 10 | 41 | 14 | 208 | 785 |
| Totals, 1956 | 200,617 | 482,933 | 5,475 | 27,859 | 7,747 | 657 | 725,288 |
| Totals, 1951 | 194,701 | 433,091 | 6,663 | 27,178 | 7,039 | 1,239 | 669,911 |
| Females | |||||||
| 16-19 | 54,433 | 4,133 | 23 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 58,601 |
| 20 | 8,985 | 4,127 | 29 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 13,156 |
| 21-24 | 19,612 | 33,181 | 372 | 82 | 77 | 11 | 53,335 |
| 25-29 | 11,232 | 60,757 | 843 | 250 | 399 | 21 | 73,502 |
| 30-34 | 7,693 | 65,415 | 917 | 591 | 729 | 16 | 75,361 |
| 35-39 | 6,504 | 62,859 | 888 | 1,166 | 1,003 | 21 | 72,441 |
| 40-44 | 6,462 | 59,506 | 862 | 2,113 | 1,214 | 13 | 70,170 |
| 45-49 | 6,548 | 51,430 | 718 | 3,297 | 1,233 | 20 | 63,246 |
| 50-54 | 5,810 | 40,414 | 583 | 4,768 | 1,099 | 16 | 52,690 |
| 55-59 | 5,446 | 33,299 | 449 | 7,251 | 938 | 15 | 47,398 |
| 60-64 | 4,994 | 25,262 | 364 | 9,818 | 756 | 16 | 41,210 |
| 65-69 | 4,674 | 19,524 | 305 | 12,780 | 622 | 13 | 37,918 |
| 70-74 | 3,951 | 12,521 | 214 | 13,627 | 369 | 13 | 30,695 |
| 75-79 | 2,912 | 6,414 | 109 | 11,836 | 182 | 9 | 21,462 |
| 80-84 | 1,487 | 2,059 | 26 | 6,986 | 60 | 7 | 10,625 |
| 85-89 | 556 | 472 | 6 | 3,272 | 9 | 1 | 4,316 |
| 90 and over | 149 | 117 | 1,006 | 3 | 2 | 1,277 | |
| Not specified adults | 165 | 653 | 6 | 162 | 17 | 24 | 1,027 |
| Totals, 1956 | 151,613 | 482,143 | 6,714 | 79,020 | 8,715 | 225 | 728,430 |
| Totals, 1951 | 153,199 | 431,176 | 7,803 | 71,835 | 7,891 | 686 | 672,590 |
The proportional distribution of the population aged 16 years or over according to marital status is given in the following summary.
| Marital Status | 1951 | 1956 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | |
| Never married | 29.12 | 22.80 | 27.69 | 20.82 |
| Married | 64.77 | 64.17 | 66.64 | 66.21 |
| Legally separated | 1.00 | 1.16 | 0.76 | 0.92 |
| Widowed | 4.06 | 10.69 | 3.84 | 10.85 |
| Divorced | 1.05 | 1.18 | 1.07 | 1.20 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
DEPENDENT CHILDREN - Married men, widowers, and widows were asked at the census in 1956 to state the number of their living children under 16 years (including stepchildren and children adopted by them). Married women, divorced and legally separated persons were not asked to supply the information as this would have created the risk of duplication of children counted.
The numbers of persons having dependent children, including Maoris, are shown with comparative figures from the 1951 census. The category “nil” includes those cases where members of the family were 16 years of age and over, as well as those cases where there were no children in the family.
| Number of Dependent Children Under 16 Years | 1951 Census | 1956 Census | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Married Men | Widowers | Widows | Married Men | Widowers | Widows | |
| Nil | 186,712 | 24,417 | 65,541 | 195,413 | 25,381 | 72,579 |
| 1 | 83,217 | 1,301 | 3,182 | 86,730 | 1,139 | 3,094 |
| 2 | 79,155 | 705 | 1,526 | 92,899 | 654 | 1,678 |
| 3 | 45,222 | 315 | 707 | 57,937 | 329 | 824 |
| 4 | 21,118 | 220 | 369 | 28,080 | 165 | 407 |
| 5 | 9,130 | 98 | 197 | 11,664 | 84 | 223 |
| 6 | 4,080 | 52 | 80 | 5,253 | 36 | 86 |
| 7 | 1,974 | 19 | 74 | 2,451 | 23 | 41 |
| 8 | 1,076 | 10 | 18 | 1,164 | 15 | 23 |
| 9 and over | 818 | 7 | 15 | 988 | 12 | 21 |
| Not specified | 589 | 34 | 126 | 354 | 21 | 44 |
| Totals | 433,091 | 27,178 | 71,835 | 482,933 | 27,859 | 79,020 |
The numbers of dependent children in each of the three groups in 1956 were: dependent on married men, 684,846; dependent on widowers, 5,131; and dependent on widows, 12,862; a total of 702,839 dependent children out of a 1956 census total of 720,190 children under 16 years of age. The difference is accounted for mainly by the exclusion of children whose parents were legally separated; those whose parents where divorced and had not remarried; children who had lost both parents; and ex nuptial children (the last two classes excluding cases of adoption).
Comparable numbers of dependent children in the three groups in 1951 were: dependent on married men, 562,401; dependent on widowers, 5,621; and dependent on widows, 12,108; a total of 580,130 out of a total of 596,876 children under 16 years.
Between the 1951 and 1956 censuses the total number of dependent children of married men increased from 562,401 to 684,846, a rise of 21.8 per cent. The number of married men increased by 49,842, or 11.5 per cent. Those recording “nil” dependent children increased by only 4.7 per cent, while those with dependent children increased by 16.8 per cent.
Married men with two children recorded the largest numerical increase, rising from 79,155 to 92,899, this representing a 17.4 per cent increase. The greatest percentage increase, however, was recorded by married men with four children, this group increasing from 21,118 in 1951 to 28,080 in 1956 a rise of 6,962, or 33 per cent.
The next table shows within each group, the average number of dependent children, firstly for all persons within the group, and then for persons with dependent children in that group.
| Average Number of Dependent Children | 1951 Census | 1956 Census |
|---|---|---|
| Married men - | ||
| Per person | 1.30 | 1.42 |
| Per person with dependent children | 2.29 | 2.38 |
| Widowers - | ||
| Per person | 0.21 | 0.18 |
| Per person with dependent children | 2.06 | 2.09 |
| Widows - | ||
| Per person | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| Per person with dependent children | 1.96 | 2.01 |
The most significant point from the table is the marked rise in the average number of dependent children of married men. This is a reflection of the sharp increases recorded, since 1951, in the numbers of married men having from two to seven dependent children.
RELIGIOUS PROFESSIONS - The following summary presents the main religious professions returned at the 1956 census.
| Religious Profession | Number of Adherents, 1956 Census |
|---|---|
| Church of England | 780,999 |
| Presbyterian | 483,884 |
| Roman Catholic (including Catholic undefined) | 310,723 |
| Methodist | 161,823 |
| Protestant (undefined | 47,999 |
| Baptist | 33,910 |
| Brethren | 22,444 |
| Ratana | 19,570 |
| Salvation Army | 14,122 |
| Latter Day Saints | 13,133 |
| Church of Christ | 10,852 |
| Christian (undefined) | 7,662 |
| Congregational | 7,448 |
| Seventh Day Adventist | 7,219 |
| Ringatu | 5,092 |
| Lutheran | 4,012 |
| Christian Scientist | 3,992 |
| Jehovah's Witness | 3,844 |
| Hebrew | 3,823 |
| Eastern Orthodox Catholic | 2,728 |
| Undenominational | 2,062 |
| Undenominational Christian | 1,765 |
| Agnostic | 1,748 |
| Freethinker | 1,661 |
| Hindu | 1,597 |
| Christadelphian | 1,459 |
| Atheist | 1,316 |
| Rationalist | 1,188 |
| Apostolic Church | 969 |
| Dutch Reformed Church | 829 |
| Commonwealth Covenant Church | 813 |
| Spiritualist | 748 |
| Assemblies of God | 747 |
| Society of Friends | 721 |
| Non-conformist | 596 |
| Pentecostal | 567 |
| Missions | 513 |
| Unitarian | 449 |
| Liberal Catholic | 385 |
| Confucian | 384 |
| Theosophist | 332 |
| No religion (so returned) | 12,651 |
| All other religious professions | 5,462 |
| Object to state | 173,569 |
| Not specified | 16,252 |
| Totals | 2,174,062 |
The four main churches - Church of England, Presbyterian, Roman Catholic, and Methodist - retained the adherence of the great bulk of the population, although their combined proportion fell from 82.2 per cent of the total population in 1951 to 79.9 per cent in 1956. All four churches increased in numbers, though only the Roman Catholic church increased its ratio to total population - 13.6 per cent in 1951 to 14.3 per cent in 1956.
The large increase in the numbers recorded as “Protestant (undefined)” may have resulted from the wording of the questionnaire. Formerly the public were asked not to use indefinite terms such as “Protestant” or “Catholic”, but in 1956 no such request was made and it would appear that many persons used these terms without any further indication of their religious profession.
The category recorded as “Object to state” represents those persons availing themselves of the special statutory right of objecting to answer a question on this subject. The proportion of the population in this class increased from 7.1 per cent in 1951 to 8.0 per cent in 1956. It is probable that the “not specified” group includes a number of persons objecting to the question.
The proportional distribution according to number of adherents is as shown below.
| Religious Profession | Percentage of Total Population | |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 1956 | |
| Church of England | 37.47 | 35.92 |
| Presbyterian | 23.01 | 22.26 |
| Roman Catholic (including Catholic undefined) | 13.64 | 14.29 |
| Methodist | 8.05 | 7.44 |
| Protestant (undefined) | 0.74 | 2.21 |
| Baptist | 1.62 | 1.56 |
| Brethren | 1.10 | 1.03 |
| Ratana | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| Salvation Army | 0.70 | 0.65 |
| Latter Day Saints | 0.52 | 0.60 |
| Church of Christ | 0.62 | 0.50 |
| No religion (so returned) | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| Object to state | 7.09 | 7.98 |
| All other (including not specified) | 3.95 | 4.08 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 |
STATISTICS OF WORLD POPULATION - The area and estimated population of the continents and some of the principal countries of the world at 1 July 1959 are shown in the following table. (Source: United Nations Population and Vital Statistics Report for July 1960 and Demographic Yearbook 1959.)
| Continents and Countries | Area | Population |
|---|---|---|
*1958 Estimate. †Former Belgian Congo. | ||
| sq. miles | ||
| (000) | (000) | |
| Continents | ||
| Europe | 1,903 | 423,000 |
| Asia | 10,480 | 1,622,000 |
| U.S.S.R. | 8,650 | 210,500 |
| Africa | 11,670 | 236,000 |
| North America | 9,359 | 261,000 |
| South America | 6,870 | 137,000 |
| Oceania | 3,304 | 16,100 |
| Totals, world | 52,236 | 2,905,600 |
| Selected Countries | ||
| Europe - | ||
| United Kingdom | 94 | 52,157 |
| Republic of Ireland | 27 | 2,846 |
| Belgium | 12 | 9,104 |
| Denmark | 17 | 4,547 |
| France | 213 | 44,970 |
| Federal Republic of Germany | 96 | 52,837 |
| Eastern Germany | 41 | 16,213 |
| Italy | 116 | 49,062 |
| Netherlands | 13 | 11,346 |
| Norway | 125 | 3,557 |
| Spain | 194 | 29,894 |
| Sweden | 174 | 7,454 |
| Switzerland | 16 | 5,235 |
| Oceania - | ||
| Australia | 2,975 | 10,061 |
| New Zealand | 103 | 2,331 |
| Asia - | ||
| China | 3,769 | 669,000* |
| India | 1,267 | 402,600 |
| Japan | 143 | 92,740 |
| Pakistan | 365 | 86,823 |
| Federation of Malaya | 51 | 6,698 |
| Indonesia | 576 | 89,600 |
| Africa - | ||
| Union of South Africa | 472 | 14,673 |
| Congo (Leopoldville)† | 905 | 13,840 |
| Ghana | 92 | 4,911 |
| Federation of Nigeria | 339 | 33,663 |
| Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland | 484 | 7,990 |
| United Arab Republic | 457 | 29,632 |
| North America - | ||
| United States of America | 3,022 | 177,702 |
| Canada | 3,851 | 17,442 |
| South America - | ||
| Argentina | 1,073 | 20,614 |
| Brazil | 3,287 | 64,216 |
Table of Contents
GENERAL - Statistical data presented in this subsection cover the entire population of New Zealand. Europeans and Maoris are dealt with separately in later subsections.
Since 1 April 1952 all Maori marriages have been solemnised in the same manner and registration effected in the same way as European marriages. As regards births and deaths, however, separate registers for Maoris and Europeans are used, and in the case of Maoris the information required is not as detailed as that for Europeans. It is probable that the standard of registration of Maori vital events is now very little inferior, if at all, to that of Europeans.
BIRTHS - Registration of Maori births is somewhat less accurate (although improvement has been manifest in recent years) than those of the European population. Owing to the extensive time lag in the receipt by the Registrar-General of a considerable number of registrations, the statistics of Maori births relate to the number of registrations received by the Registrar-General during the year, whereas the European figures cover the actual registrations effected during the year.
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European | Maori | Total | European | Maori | Total | |
| 1950 | 44,309 | 5,105 | 49,414 | 24.67 | 45.07 | 25.88 |
| 1951 | 44,651 | 5,238 | 49,889 | 24.39 | 44.97 | 25.62 |
| 1952 | 46,469 | 5,459 | 51,928 | 24.77 | 45.41 | 26.01 |
| 1953 | 46,414 | 5,529 | 51,943 | 24.12 | 44.54 | 25.35 |
| 1954 | 48,431 | 5,700 | 54,131 | 24.63 | 44.37 | 25.84 |
| 1955 | 49,869 | 5,807 | 55,676 | 24.86 | 43.64 | 26.03 |
| 1956 | 50,430 | 6,163 | 56,593 | 24.67 | 44.64 | 25.93 |
| 1957 | 51,852 | 6,632 | 58,484 | 24.82 | 46.29 | 26.20 |
| 1958 | 53,774 | 6,861 | 60,635 | 25.16 | 46.24 | 26.53 |
| 1959 | 54,739 | 7,130 | 61,869 | 25.10 | 46.28 | 26.50 |
| 1960 | 55,435 | 7,415 | 62,850 | 25.00 | 46.41 | 26.44 |
The inclusion of Maoris raised the level of the birth rate all through the period covered, but in no case does it reverse the trend of the rate for New Zealand, exclusive of Maoris. In an international comparison for the quinquennium 1955-59 the inclusion of Maoris does not alter New Zealand's position of seventh in a total of 27 countries covered.
NATURAL INCREASE - The birth and death rates of the population are not subject to violent fluctuation, and consequently the natural-increase rate, i.e., excess of births over deaths, shows, in the period covered by the next table, a decline until 1951 and a continuous increase since. The following table shows the numbers gained by natural increase, together with the rate per 1,000 of mean population, for the last 11 years.
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European | Maori | Total | European | Maori | Total | |
| 1950 | 27,594 | 3,736 | 31,330 | 15.36 | 32.98 | 16.41 |
| 1951 | 27,139 | 3,914 | 31,053 | 14.83 | 33.60 | 15.94 |
| 1952 | 29,056 | 3,976 | 33,032 | 15.49 | 33.07 | 16.54 |
| 1953 | 29,405 | 4,184 | 33,589 | 15.28 | 33.70 | 16.39 |
| 1954 | 30,764 | 4,491 | 35,255 | 15.65 | 34.96 | 16.83 |
| 1955 | 31,916 | 4,535 | 36,451 | 15.91 | 34.08 | 17.04 |
| 1956 | 32,027 | 4,870 | 36,897 | 15,67 | 35.28 | 16.90 |
| 1957 | 32,441 | 5,181 | 37,622 | 15.53 | 36.16 | 16.85 |
| 1958 | 34,760 | 5,574 | 40,334 | 16.26 | 37.57 | 17.65 |
| 1959 | 34,925 | 5,816 | 40,741 | 16.02 | 37.75 | 17.45 |
| 1960 | 35,911 | 6,047 | 41,958 | 16.20 | 37.85 | 17.65 |
In the 10 years to 31 December 1960 New Zealand has gained by natural increase of the population a total of 336,932, comprising 318,344 Europeans and 48,588 Maoris.
MARRIAGES - The following table shows the numbers of marriages contracted during each of the last 11 years. Maori marriages are included.
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 17,099 | 8.96 |
| 1951 | 16,915 | 8.78 |
| 1952 | 17,061 | 8.55 |
| 1953 | 17,224 | 8.41 |
| 1954 | 17,557 | 8.38 |
| 1955 | 17,795 | 8.32 |
| 1956 | 17,531 | 8.03 |
| 1957 | 17,614 | 7.89 |
| 1958 | 18,305 | 8.01 |
| 1959 | 18,315 | 7.84 |
| 1960 | 18,909 | 7.96 |
DEATHS - The effect of including Maoris is to increase slightly, except for the latest years, the total death rate for New Zealand, as is seen in the following table.
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European | Maori | Total | European | Maori | Total | |
| 1950 | 16,715 | 1,369 | 18,084 | 9.31 | 12.09 | 9.47 |
| 1951 | 17,512 | 1,324 | 18,836 | 9.56 | 11.37 | 9.67 |
| 1952 | 17,413 | 1,483 | 18,896 | 9.28 | 12.34 | 9.47 |
| 1953 | 17.009 | 1,345 | 18,354 | 8.84 | 10.84 | 8.96 |
| 1954 | 17.667 | 1,209 | 18,876 | 8.98 | 9.41 | 9.01 |
| 1955 | 17.953 | 1,272 | 19,225 | 8.95 | 9.56 | 8.99 |
| 1956 | 18,403 | 1,293 | 19,696 | 9.00 | 9.37 | 9.02 |
| 1957 | 19,411 | 1,451 | 20,862 | 9.29 | 10.13 | 9.34 |
| 1958 | 19,014 | 1,287 | 20,301 | 8.90 | 8.67 | 8.88 |
| 1959 | 19,814 | 1,314 | 21,128 | 9.09 | 8.53 | 9.05 |
| 1960 | 19,524 | 1,368 | 20,892 | 8.81 | 8.56 | 8.79 |
Although the Maori death rate was consistently higher than the European rate, the continuous decline of the former has now brought it to a position below the European rate. The net result now is that the inclusion of Maoris reduces the general death rate to slightly lower than the European rate. Countries with lower death rates (in 1959) than New Zealand included Israel, 5.9; Netherlands, 7.1; Canada, 8.1; Union of South Africa (European population only), 8.6; and Australia, 8.9.
TOTAL DEATHS BY CAUSES - Although the incidence of different diseases as causes of death varies considerably between the Maori and European sections of New Zealand's population, the only important disease to show a marked influence on the general death rate by the inclusion of Maoris is tuberculosis. The average death rate for the total population from tuberculosis (all forms) for the five years 1955-59 was 102 per million of population, compared with 77 for Europeans alone. New Zealand has for many years had a comparatively low tuberculosis death rate for the European section of its population, but when Maoris are included the latest triennial international figures available (1955-57) show New Zealand to be eleventh out of a total of 37 countries. With Maoris excluded, New Zealand's position would be eighth.
Total deaths for the years 1956-59, classified according to the Abbreviated List of the sixth and seventh (1948 and 1955) revisions of the International Classification of Diseases, are contained in the following table. Similar tables for the European and Maori populations separately may be found by reference to Sections 4D and 4E respectively. (The 1955 revision of the International Classification was adopted in New Zealand in 1958.)
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | Rate per Million of Mean Population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Tuberculosis of respiratory system | 208 | 226 | 168 | 118 | 95 | 101 | 73 | 51 |
| Tuberculosis, other forms | 30 | 28 | 32 | 19 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 8 |
| Syphilis and its sequelae | 23 | 33 | 22 | 17 | 11 | 15 | 10 | 7 |
| Typhoid fever | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - |
| Dysentery, all forms | 4 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | - |
| Scarlet fever and streptococcal sore throat | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Diphtheria | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| Whooping cough | 10 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 5 | - | 4 | 3 |
| Meningococcal infections | 20 | 22 | 18 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 5 |
| Acute poliomyelitis | 51 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 23 | 1 | 3 | - |
| Measles | 9 | 1 | 10 | 16 | 4 | - | 4 | 7 |
| Malaria | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| All other diseases classified as infective and parasitic | 93 | 105 | 91 | 116 | 43 | 47 | 40 | 50 |
| Malignant neoplasms, including neoplasms of lymphatic and haematopoietic tissues | 3,153 | 3,213 | 3,297 | 3,339 | 1,444 | 1,439 | 1,442 | 1,430 |
| Benign and unspecified neoplasms | 48 | 45 | 37 | 34 | 22 | 20 | 16 | 15 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 229 | 286 | 286 | 240 | 105 | 128 | 125 | 103 |
| Anaemias | 74 | 57 | 51 | 48 | 34 | 26 | 22 | 21 |
| Vascular lesions affecting central nervous system | 2,316 | 2,519 | 2,606 | 2,570 | 1,061 | 1,128 | 1,140 | 1,101 |
| Non-meningococcal meningitis | 45 | 35 | 46 | 50 | 21 | 16 | 20 | 21 |
| Rheumatic fever | 17 | 17 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 3 |
| Chronic rheumatic heart disease | 222 | 255 | 271 | 234 | 102 | 114 | 119 | 100 |
| Arteriosclerotic and degenerative heart disease | 5,177 | 5,342 | 5,305 | 5,615 | 2,372 | 2,393 | 2,321 | 2,405 |
| Other diseases of the heart | 753 | 770 | 808 | 922 | 345 | 345 | 353 | 395 |
| Hypertension with heart disease | 561 | 573 | 461 | 470 | 257 | 257 | 202 | 201 |
| Hypertension without mention of heart | 145 | 130 | 144 | 123 | 66 | 58 | 63 | 53 |
| Influenza | 89 | 181 | 37 | 190 | 41 | 81 | 16 | 81 |
| Pneumonia | 803 | 950 | 751 | 1,059 | 368 | 426 | 329 | 454 |
| Bronchitis | 441 | 507 | 477 | 560 | 202 | 227 | 209 | 240 |
| Ulcer of stomach and duodenum | 179 | 207 | 170 | 177 | 82 | 93 | 74 | 76 |
| Appendicitis | 30 | 35 | 29 | 36 | 14 | 16 | 13 | 15 |
| Intestinal obstruction and hernia | 134 | 180 | 151 | 146 | 61 | 81 | 66 | 63 |
| Gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and colitis, except diarrhoea of the newborn | 139 | 154 | 134 | 152 | 64 | 69 | 59 | 65 |
| Cirrhosis of liver | 68 | 75 | 56 | 61 | 31 | 34 | 24 | 26 |
| Nephritis and nephrosis | 131 | 160 | 158 | 119 | 60 | 72 | 69 | 51 |
| Hyperplasia of prostate | 169 | 150 | 135 | 137 | 77 | 67 | 59 | 59 |
| Complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium | 31 | 44 | 31 | 36 | 14 | 20 | 14 | 15 |
| Congenital malformations | 285 | 277 | 354 | 343 | 131 | 124 | 155 | 147 |
| Birth injuries, post-natal asphyxia, and atelectasis | 326 | 369 | 318 | 294 | 149 | 165 | 139 | 126 |
| Infections of the newborn | 51 | 55 | 67 | 61 | 23 | 25 | 29 | 26 |
| Other diseases peculiar to early infancy, and immaturity unqualified | 283 | 302 | 333 | 373 | 130 | 135 | 146 | 160 |
| Senility without mention of psychosis, ill-defined, and unknown causes | 152 | 8 | 117 | 118 | 70 | 48 | 51 | 51 |
| All other diseases | 2,039 | 2,076 | 1,963 | 2,030 | 934 | 930 | 859 | 870 |
| Motor-vehicle accidents | 334 | 407 | 405 | 362 | 153 | 182 | 177 | 155 |
| All other accidents | 610 | 731 | 684 | 683 | 279 | 327 | 299 | 293 |
| Suicide and self-inflicted injury | 199 | 215 | 220 | 204 | 91 | 96 | 96 | 87 |
| Homicide and operations of war | 11 | 15 | 25 | 25 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 11 |
| Totals | 19,696 | 20,862 | 20,301 | 21,128 | 9,023 | 9,344 | 8,881 | 9,050 |
TOTAL INFANT MORTALITY - The inclusion of the Maori population in New Zealand vital statistics has a significant influence upon the infant-mortality rate. The infant-mortality rate of the European population of New Zealand was the lowest in the world for a long period, and recently has declined to a particularly low level. The Maori rate, on the other hand, always a high one, has not shown any noticeable improvement until recent years. It is also subject to violent fluctuations owing to the ravages of certain epidemic diseases, which have relatively very little effect on the European rate. The European, Maori, and total infant-mortality figures for the last 21 years are given in the next table.
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European | Maori | Total | European | Maori | Total | |
| 1940 | 990 | 372 | 1,362 | 30.21 | 87.22 | 36.78 |
| 1941 | 1,045 | 517 | 1,562 | 29.77 | 125.06 | 39.81 |
| 1942 | 964 | 424 | 1,388 | 28.71 | 97.92 | 36.62 |
| 1943 | 951 | 399 | 1,350 | 31.37 | 89.86 | 38.85 |
| 1944 | 1,012 | 461 | 1,473 | 30.12 | 102.26 | 38.65 |
| 1945 | 1,036 | 413 | 1,449 | 27.99 | 88.93 | 34.79 |
| 1946 | 1,093 | 431 | 1,524 | 26.10 | 74.62 | 31.99 |
| 1947 | 1,122 | 365 | 1,487 | 25.04 | 73.18 | 29.86 |
| 1948 | 970 | 380 | 1,350 | 21.95 | 76.67 | 27.47 |
| 1949 | 1,046 | 422 | 1,468 | 23.78 | 85.82 | 30.02 |
| 1950 | 1,008 | 356 | 1,364 | 22.75 | 69.74 | 27.60 |
| 1951 | 1,017 | 357 | 1,374 | 22.78 | 68.16 | 27.54 |
| 1952 | 1,014 | 461 | 1,475 | 21.82 | 84.45 | 28.40 |
| 1953 | 931 | 404 | 1,335 | 20.06 | 73.07 | 25.70 |
| 1954 | 968 | 34 | 1,302 | 19.99 | 58.60 | 24.05 |
| 1955 | 1,002 | 33 | 1,365 | 20.09 | 62.51 | 24.52 |
| 1956 | 978 | 335 | 1,313 | 19.39 | 54.36 | 23.20 |
| 1957 | 1.036 | 384 | 1,420 | 19.98 | 57.90 | 24.28 |
| 1958 | 1,043 | 373 | 1,416 | 19.40 | 54.37 | 23.35 |
| 1959 | 1.089 | 388 | 1,477 | 19.89 | 54.42 | 23.87 |
| 1960 | 1,090 | 330 | 1,420 | 19.66 | 44.50 | 22.59 |
The inclusion of Maoris not only places the infant-mortality rate for New Zealand on a considerably higher level, but also replaces the general downward movement by a much more fluctuating trend.
It also has a considerable effect on the position occupied by New Zealand among the countries of the world. In the quinquennium 1954-58 New Zealand's infant-mortality rate (exclusive of Maoris), with an average of 20, was the third lowest of 35 countries for which reliable figures were available, whereas the inclusion of the Maori population relegated it to fifth place, below Sweden, the Netherlands, Australia, and Norway.
INQUESTS - An inquest may be held for the purpose of establishing: (a) The fact that a person has died; (b) The identity of the deceased person; (c) When, where, and how the death occurred.
All inquests are held in public, but under the Coroners Act 1951 there is power to exclude persons from an inquest and to prohibit the publication of any part of the evidence.
The next table classifies inquests for the latest five years according to the verdict returned and recorded in the Deaths Register of the Registrar-General.
| Year | Disease and Natural Causes | Accident | Homicide | Suicide | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | |
| 1955 | 248 | 118 | 659 | 177 | 12 | 5 | 135 | 50 | 1,054 | 350 |
| 1956 | 232 | 124 | 615 | 170 | 6 | 5 | 127 | 65 | 980 | 364 |
| 1957 | 215 | 127 | 700 | 207 | 6 | 6 | 151 | 62 | 1,072 | 402 |
| 1958 | 200 | 77 | 704 | 206 | 15 | 8 | 163 | 56 | 1,082 | 347 |
| 1959 | 158 | 103 | 611 | 182 | 12 | 12 | 153 | 47 | 934 | 344 |
In the table above, it will be seen that almost the whole of the decrease in 1959 inquests (compared to those for 1958) is in one group - accidents. A further notable feature is the decrease in the number of suicides during 1959. These were 19, or 8.7 per cent, below the 1958 figure.
(NOTE - The term European, used in the context of this subsection, means the population exclusive of Maoris.)
REGISTRATION - The law as to registration of European births is embodied in the Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951. The provisions generally as to registration are that a birth may be registered within two months without fee. After two months and within six months a birth is registrable only after a statutory declaration of the particulars required to be registered has been made before the Registrar by the parent or some person present at birth, and on payment of the prescribed fee. A birth may be registered after six months only upon the direction of the Registrar-General, who may authorise registration in any case within two years after the date of birth. An information for neglect to register must be laid within two years of date of birth. In cases of neglect or refusal to give the Registrar information in respect of any birth the Registrar-General may at any time within two years after the birth of the child authorise some person to give the Registrar the information required to enable him to register the birth, and to sign as informant the entry in the register, upon which the Registrar shall register the birth.
Notwithstanding the foregoing provisions, power is given by the Act for the Registrar-General to register an unregistered birth which occurred in New Zealand, irrespective of the time that may have elapsed. Satisfactory evidence on oath, and such other proof as the Registrar-General may deem necessary, are required. This provision does not, however, relieve any person from liability to prosecution for failure to register in the proper manner.
Although two months are allowed for the registration of a birth, it is compulsory to notify the birth to the Registrar within a much shorter interval. The occupier of any premises in which a child is born is to give notice to the Registrar according to the best of the knowledge and belief of the occupier of the fact of the birth, the date on which it occurred, the name and address of the mother or father of the child, and of such other particulars as the Registrar-General may require. Any such notice is to be in writing, signed by the occupier and endorsed by some other person, if any, in attendance at the confinement, and is to be delivered or posted to the Registrar within 48 hours after the birth if in a borough, or seven days in any other case. Births are to be registered by the Registrar whose office is nearest to the place of birth.
Particulars required to be registered are: date and place of birth; name and sex of child; names, ages, and birthplaces of parents; occupation of father; maiden name of mother; date and place of parents' marriage; and ages and sex of previous issue (distinguishing living and dead) of the marriage. The father of an ex-nuptial child is not required to give information, nor is his name entered in the register unless at the joint request of the mother and himself, or unless he subsequently marries the mother. A child born out of New Zealand but arriving before attaining the age of 18 months may be registered within six months of arrival. The Registrar-General may authorise registration of such a child who is over 18 months but under three years of age. Additional information required on notification of birth - but not registration - includes (a) weight of child at birth, and (b) period of gestation of mother. These particulars are required for statistical purposes.
Birth statistics are compiled from the records of the Registrar-General. The births covered by a year's statistics are those registered during the year irrespective of the year of birth. The figures do not include still births, except where specified on pages 84 and 85. A special classification of still births is given on page 90.
Registration of Maori Births - Registrations of the births of Maoris are effected with the Maori Registrars in the various districts set up for this purpose. Statistics relating to the births of Maoris will be found in Section 4E.
NUMBERS AND RATES - The long-term trend of the birthrate in New Zealand was downward until recent years. A reference to the diagram on page 83 and to the table on page 82, indicates this trend very clearly. After the pioneering days of the nineteenth century, when the population consisted very largely of young immigrants faced with the raising of a family, the birthrate began to decline appreciably. A further migration wave at the turn of the century reversed the trend temporarily, but in 1909 the downward movement was again resumed. With minor fluctuations in the earlier stages and in the years influenced by the First World War this decline continued until 1936. In that year a slight upward movement began, and by 1940 some of the deficit had been made up by the gradual rise. This was accelerated during the Second World War (with minor fluctuations) until successive record high totals (as regards the numbers of births) were established in 1945-47. In 1948 a decline in births was shown with a further recession in 1949. The decreases were not large, and in 1950-52 increases were again in evidence. A very small decrease was shown in 1953. Increases followed in the next seven years. The numbers and rates of births (children born alive) for each of the last 20 years are given in the following table.
| Year | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1941 | 35,100 | 22.81 |
| 1942 | 33,574 | 21.73 |
| 1943 | 30,311 | 19.70 |
| 1944 | 33,599 | 21.59 |
| 1945 | 37,007 | 23.22 |
| 1946 | 41,871 | 25.26 |
| 1947 | 44,816 | 26.47 |
| 1948 | 44,193 | 25.59 |
| 1949 | 43,988 | 24.98 |
| 1950 | 44,309 | 24.67 |
| 1951 | 44,651 | 24.39 |
| 1952 | 46,469 | 24.77 |
| 1953 | 46,414 | 24.12 |
| 1954 | 48,431 | 24.63 |
| 1955 | 49,869 | 24.86 |
| 1956 | 50,430 | 24.67 |
| 1957 | 51,852 | 24.82 |
| 1958 | 53,774 | 25.16 |
| 1959 | 54,739 | 25.10 |
| 1960 | 55,435 | 25.00 |
Comparisons of birthrates over a series of years or between different countries are usually made on the basis of the “crude” rates - i.e., the number of births per 1,000 of the mean population, irrespective of sex or age.
The “crude” rates do not permit of allowance being made for variations in the proportion of women of the child-bearing ages, and it is advisable and of interest to supplement the table of “crude” rates with a computation of the legitimate birthrate per 1,000 married women of 15 and under 45 years of age, or the total birthrate per 1,000 of all women of these ages. The following table gives both rates for each census year (on the basis of the births registered in that year and the population as at the census) from 1901 to 1956 together with the “crude” rate for the year.
| Census Year | Birthrate per 1,000 Women 15 and Under 45 Years | “Crude” Birthrate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legitimate* | Total | ||
| *Per 1,000 married women. | |||
| 1901 | 246.2 | 111.7 | 26.34 |
| 1906 | 235.3 | 114.1 | 27.08 |
| 1911 | 211.7 | 109.5 | 25.97 |
| 1916 | 193.6 | 106.7 | 25.94 |
| 1921 | 181.6 | 99.0 | 23.38 |
| 1926 | 166.9 | 90.9 | 21.06 |
| 1936 | 136.6 | 72.2 | 16.64 |
| 1945 | 166.5 | 99.8 | 23.22 |
| 1951 | 172.8 | 116.9 | 24.39 |
| 1956 | 176.5 | 124.1 | 24.66 |
The proportion of married women in the child-bearing ages is now much higher than in former years; in fact the percentage in 1901 was 43.3 as compared with 67.1 in 1956. A study of the figures for successive censuses reveals considerable changes in the age constitution of married women within the child-bearing ages. As the birthrate varies with age, the change in age constitution over the period is a factor which should be taken into account.
NATURAL INCREASE - Recent increases in the birthrate have tended to result in a rise in the rate of natural increase, as shown in the following table.
| Year | Numbers | Rate per 1,000 Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Births | Deaths | Natural Increase | Births | Deaths | Natural Increase | |
| 1950 | 44,309 | 16,715 | 27,594 | 24.67 | 9.31 | 15.36 |
| 1951 | 44,651 | 17,512 | 27,139 | 24.39 | 9.56 | 14.83 |
| 1952 | 46,469 | 17,413 | 29,056 | 24.77 | 9.28 | 15.49 |
| 1953 | 46,414 | 17,009 | 29,405 | 24.12 | 8.84 | 15.28 |
| 1954 | 48,431 | 17,667 | 30,764 | 24.63 | 8.98 | 15.65 |
| 1955 | 49,869 | 17,953 | 31,916 | 24.86 | 8.95 | 15.91 |
| 1956 | 50,430 | 18,403 | 32,027 | 24.66 | 9.00 | 15.66 |
| 1957 | 51,852 | 19,411 | 32,441 | 24.82 | 9.29 | 15.53 |
| 1958 | 53,774 | 19,014 | 34,760 | 25.16 | 8.90 | 16.26 |
| 1959 | 54,739 | 19,814 | 34,925 | 25.10 | 9.09 | 16.01 |
| 1960 | 55,435 | 19,524 | 35,911 | 25.00 | 8.81 | 16.19 |
The natural increase rate provides a useful guide to population increase and a further method is that of the net reproduction index, which is based on female children born and probably surviving. Details of gross and net reproduction rates for recent years will be found in Section 3 of this issue.
The movements that have taken place since 1880 are well illustrated in the accompanying diagram, which shows the rates at annual intervals.
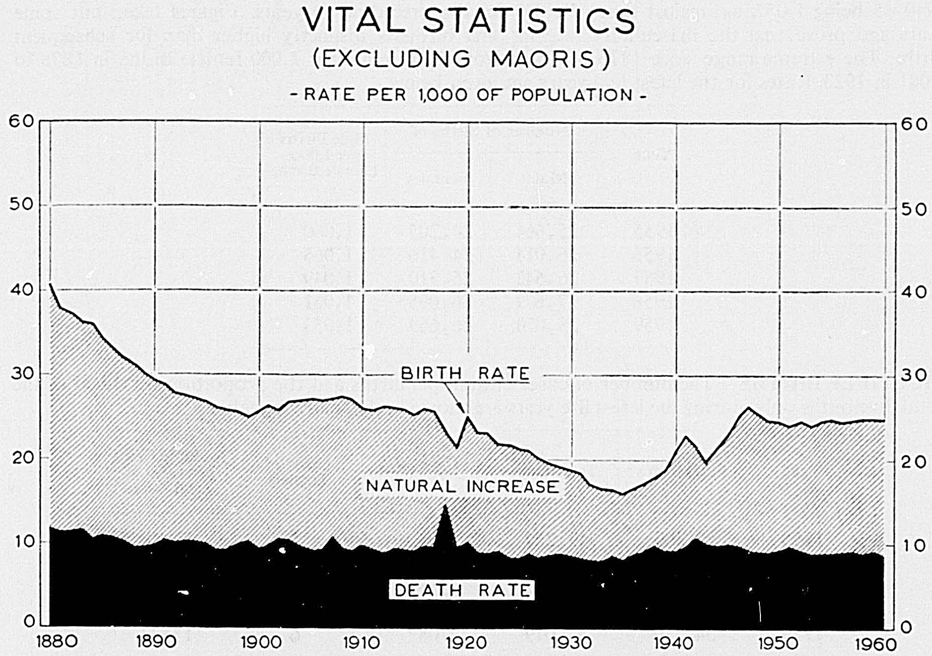
COMPARISON WITH OTHER COUNTRIES - An international comparison of birth- and natural-increase rates is made in the following table. New Zealand's position is higher on the basis of natural increase than it is on that of the birthrate. The rates, which are the average of the five years 1955-59, are taken from the Monthly Bulletin of Statistics issued by the United Nations.
| Country | Rate per 1,000 of Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Births | Natural Increase | |
| Mexico | 46.4 | 33.8 |
| Peru | 36.1 | 25.3 |
| Puerto Rico | 33.3 | 26.2 |
| Canada | 28.0 | 17.9 |
| Israel | 27.9 | 21.7 |
| New Zealand | 25.2 | 16.1 |
| Union of South Africa | 24.9 | 16.4 |
| Yugoslavia | 24.7 | 14.3 |
| United States of America | 24.6 | 15.2 |
| Portugal | 23.4 | 12.4 |
| India | 23.3 | 12.3 |
| Australia | 22.6 | 13.8 |
| Netherlands | 21.4 | 13.9 |
| Spain | 21.4 | 12.0 |
| Republic of Ireland | 21.1 | 9.1 |
| Finland | 19.8 | 10.7 |
| France | 18.4 | 6.6 |
| Norway | 18.2 | 9.5 |
| Italy | 18.1 | 8.4 |
| Japan | 18.1 | 10.3 |
| Switzerland | 17.5 | 7.6 |
| Austria | 16.8 | 4.4 |
| Denmark | 16.8 | 7.7 |
| Germany (Western) | 16.8 | 5.8 |
| United Kingdom | 16.4 | 4.7 |
| Sweden | 14.5 | 4.9 |
SEXES OF CHILDREN BORN - With the exception of one year (1860), there has always been a preponderance of males in the number of children born in New Zealand. The proportions are usually shown by stating the number of births of male children to every 1,000 female births. This number has been as high as 1,113 (in 1859), and as low as 991 (in 1860), but little significance can be attached to any figures prior to 1870, on account of the comparatively small number of births. It is a popular idea that the proportion of male births tends to increase considerably in war years, but the experience in this country does little to bear out this theory, the average over the six years 1940-45 being 1,057, as against that of 1,050 for the preceding 10 years. Figures taken out some years ago prove that the masculinity rate for first births is distinctly higher than for subsequent births. The extreme range since 1870 has been from 1,016 male per 1,000 female births in 1878 to 1,081 in 1923. Rates for the latest five years are given below.
| Year | Number of Births of | Male Births per 1,000 Female Births | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | ||
| 1955 | 25,664 | 24,205 | 1,060 |
| 1956 | 26,014 | 24,416 | 1,065 |
| 1957 | 26,542 | 25,310 | 1,049 |
| 1958 | 27,679 | 26,095 | 1,061 |
| 1959 | 28,070 | 26,669 | 1,053 |
MULTIPLE BIRTHS - The number of cases of multiple births and the proportion per 1,000 of the total (live births only) during the latest five years are shown in the following table.
| Year | Total Births | Total Cases | Cases of Twins | Cases of Triplets | Multiple Cases per 1,000 of Total Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes two cases where triplets would have been recorded had not one child been still born. | |||||
| 1955 | 49,869 | 49,254 | 605 | 5 | 12.38 |
| 1956 | 50,430 | 49,803 | 619 | 4 | 12.51 |
| 1957 | 51,852 | 51,285 | 555 | 6 | 10.94 |
| 1958 | 53,774 | 53,138 | 620 | 8 | 11.82 |
| 1959 | 54,739 | 54,019 | 708* | 6 | 13.22 |
Counting only cases where both children were born alive, there were 708 cases of twin births registered in 1959. There were also six cases of triplets.
The total number of confinements resulting in live births was 54,019, and on the average one mother in every 76 gave birth to twins (or triplets).
When still births are taken into account, the total number of confinements for the year 1959 is increased to 54,771, and the number of cases of multiple births to 764. On this basis the proportion of mothers giving birth to twins or triplets is increased to one in 73.
Although the incidence of multiple births has not varied greatly in recent years, as may be seen from the following summary, a considerable increase was recorded in 1959.
| Year | Cases of Twins | Cases of Triplets | Total Multiple Cases | Rate per 1,000 Confinements | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both Born Alive | One Born Alive, One Still Born | Both Still Born | Total | All Born Alive | One Born Alive, Two Still Born | Two Born Alive, One Still Born | All Still Born | Total | |||
| 1955 | 605 | 46 | 7 | 658 | 5 | 1 | - | - | 6 | 664 | 13.3 |
| 1956 | 619 | 49 | 17 | 685 | 4 | - | - | - | 4 | 689 | 13.6 |
| 1957 | 555 | 51 | 9 | 615 | 6 | - | - | - | 6 | 621 | 11.9 |
| 1958 | 620 | 21 | 10 | 651 | 8 | - | - | - | 8 | 659 | 12.2 |
| 1959 | 706 | 41 | 8 | 755 | 6 | 1 | 2 | - | 9 | 764 | 14.0 |
| Average of five years | 621 | 42 | 10 | 673 | 6 | - | - | - | 6 | 679 | 13.0 |
The likelihood of still births occurring is much greater in cases of multiple births than in single cases. This is exemplified in the following table. The figures in respect of multiple cases include all cases where one or more of the children were still born.
| Year | Still-birth Cases per 100 of Total Cases (Including Still Births) | |
|---|---|---|
| Single Cases | Multiple Cases | |
| 1955 | 1.49 | 8.13 |
| 1956 | 1.55 | 9.58 |
| 1957 | 1.49 | 9.66 |
| 1958 | 1.46 | 4.70 |
| 1959 | 1.36 | 6.81 |
| Average of five years | 1.47 | 7.78 |
During the five years 1955-59 there were 3,107 cases of live twin births (including ex-nuptial), and of these in 1,007 instances, or 32.4 per cent, both children were males; in 986, or 31.7 per cent, both were females; and in the remaining 1,114, or 35.9 per cent, the children were of opposite sexes.
The six cases of triplets in 1959 comprised one of three males, one of three females, two of two males and one female, and two of one male and two females.
AGES OF PARENTS - Information as to the relative ages of parents of legitimate living children whose births were registered in 1959 is shown in the following table.
| Age of Mother, in Years | Age of Father, in Years | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 21 | 21 and Under 25 | 25 and Under 30 | 30 and Under 35 | 35 and Under 40 | 40 and Under 45 | 45 and Under 50 | 50 and Under 55 | 55 and Under 65 | 65 and Over | Total Cases | |
*Including 39 legitimate cases where twins would have been registered had not one child been still born. †Including C cases of triplets. | |||||||||||
| Single Births | |||||||||||
| Under 21 | 671 | 2,360 | 1,190 | 224 | 44 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 1 | - | 4,505 |
| 21 and under 25 | 137 | 3,832 | 7,016 | 1,903 | 316 | 63 | 28 | 7 | 2 | - | 13,304 |
| 25 “ 30 | 10 | 573 | 7,127 | 6,425 | 1,600 | 308 | 106 | 25 | 14 | 1 | 16,189 |
| 30 “ 35 | 2 | 37 | 983 | 4,727 | 3,118 | 844 | 297 | 57 | 26 | 3 | 10,094 |
| 35 “ 40 | 2 | 6 | 100 | 743 | 2,175 | 1,364 | 500 | 148 | 55 | 3 | 5,096 |
| 40 “ 45 | - | - | 7 | 49 | 191 | 548 | 347 | 133 | 39 | 3 | 1,317 |
| 45 and over | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | 12 | 36 | 18 | 14 | - | 86 |
| Totals | 822 | 6,808 | 16,423 | 14,074 | 7,447 | 3,148 | 1,315 | 393 | 151 | 10 | 50,591* |
| Multiple Births | |||||||||||
| Under 21 | 5 | 28 | 15 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 50 |
| 21 and under 25 | 2 | 35 | 72 | 28 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 140 |
| 25 “ 30 | 1 | 33 | 78 | 84 | 17 | 4 | 2 | - | - | - | 219 |
| 30 “ 35 | - | 1 | 19 | 72 | 50 | 10 | 9 | 2 | - | - | 163 |
| 35 “ 40 | - | - | 1 | 12 | 35 | 27 | 8 | 1 | - | - | 84 |
| 40 “ 45 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2 | - | - | 18 |
| 45 and over | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Totals | 8 | 97 | 185 | 198 | 106 | 50 | 26 | 5 | - | - | 675† |
| Grand totals | 830 | 6,905 | 16,608 | 14,272 | 7,553 | 3,198 | 1,341 | 398 | 151 | 10 | 51,266 |
PREVIOUS ISSUE OF PARENTS - Tables are given in the annual Report on Vital Statistics containing detailed information as to number of previous issue in conjunction with (1) age of mother and (2) duration of marriage. The table under the first heading for the year 1959 is here summarised.
| Age of Mother, in Years | Number of Previous Issue | Total Legitimate Cases | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 and Under 10 | 10 and Under 15 | 15 and Over | ||
| *This number represents 50,591 single cases and 675 multiple cases. | ||||||||||
| Under 21 | 3,308 | 1,043 | 177 | 25 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 4,555 |
| 21 and under 25 | 6,293 | 4,573 | 1,869 | 532 | 145 | 31 | 1 | - | - | 13,444 |
| 25 “ 30 | 3,465 | 5,057 | 4,446 | 2,162 | 820 | 297 | 160 | 1 | - | 16,408 |
| 30 “ 35 | 1,331 | 1,993 | 2,700 | 2,137 | 1,150 | 507 | 425 | 14 | - | 10,257 |
| 35 “ 40 | 543 | 749 | 1,048 | 1,080 | 753 | 433 | 528 | 45 | 1 | 5,180 |
| 40 “ 45 | 144 | 141 | 210 | 230 | 212 | 132 | 229 | 33 | 4 | 1,335 |
| 45 and over | 8 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 16 | 11 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 87 |
| Totals | 15,092 | 13,561 | 10,465 | 6,173 | 3,098 | 1,411 | 1,361 | 99 | 6 | 51,266* |
In computing previous issue, multiple births have been given their full significance, the numbers at the head of the columns relating to children born alive. In the following table this procedure has been followed not only for the previous issue, but also for children covered by the 1959 registrations, who are also taken into account in the computation of the averages.
| Age of Mother, in Years | Total Mothers | Total Issue | Average Issue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 21 | 4,555 | 6,085 | 1.34 |
| 21-24 | 13,444 | 24,233 | 1.80 |
| 25-29 | 16,408 | 42,856 | 2.66 |
| 30-34 | 10,257 | 34,346 | 3.35 |
| 35-39 | 5,180 | 20,670 | 3.99 |
| 40-44 | 1,335 | 6,119 | 4.58 |
| 45 and over | 87 | 476 | 5.47 |
| Totals | 51,266 | 134,785 | 2.63 |
It should be stressed that the averages are no more than they purport to be - viz, the average number of children (including those registered in 1959) born up to the present time to those mothers of legitimate children whose births were registered during the year. They do not purport to represent, nor do they represent, the average issue of all women of the ages shown. Furthermore, they include issue born to the existing marriages only. The averages for recent years were as follows: 1954, 2.54; 1955 and 1956, 2.58; 1957, 2.60; and 1958, 2.62. In 1915, the earliest year for which reliable comparative figures are available, the average issue was 3.11.
FIRST BIRTHS - Of a total of 290,797 confinements resulting in legitimate births during the six years 1954–1959, the issue of no fewer than 86,955, or 30 per cent, were first-born children. In 38,223, or 44 per cent, of these cases the birth occurred within 12 months, and in 64,153, or 74 per cent, within two years after the marriage of the parents. In the remaining 26 per cent of cases where there was any issue to the marriage two years or more had elapsed before the birth of the first child.
Statistics of first births indicate that the proportion occurring within one year after marriage is gradually increasing. There has been little fluctuation during the same period in the proportion of first births occurring within two years after marriage. The decline in the marriage rate in recent years has been accompanied by a downward movement in the actual proportion of first births to total births.
| Year | Total Legitimate Cases | Total Legitimate First Cases | Proportion of First Cases to Total Cases | First Cases Within One Year After Marriage | First Cases Within Two Years After Marriage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Proportion to Total First Cases | Number | Proportion to Total First Cases | ||||
| Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | |||||
| 1954 | 45,743 | 14,066 | 30.75 | 5,998 | 42.64 | 10,296 | 73.20 |
| 1955 | 47,015 | 14,130 | 30.01 | 6,156 | 43.57 | 10,562 | 74.75 |
| 1956 | 47,514 | 14,403 | 30.31 | 6,339 | 44.01 | 10,637 | 73.85 |
| 1957 | 48,772 | 14,402 | 29.53 | 6,314 | 43.84 | 10,600 | 73.60 |
| 1958 | 50,487 | 14,862 | 29.44 | 6,678 | 44.93 | 10,934 | 73.57 |
| 1959 | 51,266 | 15,092 | 29.44 | 6,738 | 44.65 | 11,124 | 73.71 |
| Totals for six years | 290,797 | 86,955 | 29.90 | 38,223 | 43.96 | 64,153 | 73.78 |
The period of time elapsing before the birth of the first child has varied considerably during recent years mainly as a result of war and post-war influences. The following table compares the 1959 figures with those for earlier years, and illustrates the movement in the duration-of-marriage factor in first births.
| Duration of Marriage in Years | Proportion Per Cent of Total First Births | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1924 | 1934 | 1944 | 1954 | 1959 | |
| Under 1 year | 50.06 | 46.25 | 38.47 | 42.64 | 44.65 |
| 1 and under 2 years | 26.64 | 26.79 | 26.30 | 30.56 | 29.06 |
| 2 “ 3 “ | 10.43 | 10.24 | 11.28 | 11.56 | 11.08 |
| 3 “ 4 “ | 5.51 | 6.16 | 7.88 | 5.95 | 5.68 |
| 4 “ 5 “ | 3.03 | 3.96 | 7.18 | 3.30 | 3.42 |
| 5 “ 10 “ | 3.36 | 5.49 | 7.36 | 5.05 | 4.94 |
| 10 years and over | 0.97 | 1.11 | 1.53 | 0.94 | 1.17 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
For the years covered by the foregoing table the average duration of marriage before the birth of the first child was -1924, 1.76 years; 1934, 1.85 years; 1944, 2.22 years; 1954, 1.87 years; and 1959, 1.86 years.
An item of interest extracted from the birth statistics is a table of first births occurring to mothers in different age groups, expressed as a proportion per cent of the total first births. A comparison has also been computed on this basis for the years 1924, 1934, 1944, 1954, and 1959.
FIRST BIRTHS, BY AGE OF MOTHER
| Age of Mother, in Years | First Births, Proportion Per Cent at Each Age Group to Total First Births | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1924 | 1934 | 1944 | 1954 | 1959 | |
| Under 20 | 7.55 | 8.90 | 7.33 | 9.08 | 13.12 |
| 20 and under 25 | 38.16 | 40.39 | 41.79 | 47.71 | 50.50 |
| 25 and under 30 | 32.59 | 32.79 | 29.54 | 27.79 | 22.96 |
| 30 and under 35 | 14.68 | 13.10 | 14.61 | 10.39 | 8.82 |
| 35 and under 40 | 5.33 | 3.79 | 5.36 | 3.92 | 3.60 |
| 40 and under 45 | 1.59 | 0.99 | 1.34 | 1.02 | 0.95 |
| 45 and over | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
The figures of average ages of mothers at the birth of their first child are as follows for the above years: 1924, 26.39; 1934, 25.90; 1944, 25.18; 1954, 25.32; and 1959, 24.69.
EX-NUPTIAL BIRTHS — The numbers of ex-nuptial births registered during each of the years 1949–1959, with the percentages they bear to total births registered, were as follows.
| Year | Number | Percentage of Total Births |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 1,671 | 3.80 |
| 1950 | 1,768 | 3.99 |
| 1951 | 1,935 | 4.33 |
| 1952 | 2,104 | 4.53 |
| 1953 | 1,997 | 4.30 |
| 1954 | 2,100 | 4.34 |
| 1955 | 2,264 | 4.54 |
| 1956 | 2,310 | 4.58 |
| 1957 | 2,549 | 4.92 |
| 1958 | 2,689 | 5.00 |
| 1959 | 2,792 | 5.10 |
The long-term trend in the rate of ex-nuptial births is indicated by the movement in the proportion of ex-nuptial births per 1,000 unmarried women — i.e., spinsters, widows, and divorced women — at the reproductive ages. The figures for each census year from 1911 to 1956 are as follows.
| Census Year | Unmarried Women 15 and Under 45 years of Age | Ex-nuptial Births | Ex-nuptial Birth-rate per 1,000 Unmarried Women |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1911 | 120,778 | 1,078 | 8.93 |
| 1916 | 125,461 | 1,159 | 9.24 |
| 1921 | 136,539 | 1,258 | 9.21 |
| 1926 | 148,551 | 1,473 | 9.92 |
| 1936 | 167,781 | 1,126 | 6.71 |
| 1945 | 156,326 | 1,824 | 11.67 |
| 1951 | 130,343 | 1,935 | 14.85 |
| 1956 | 129,877 | 2,310 | 17.79 |
Included in the total of 2,792 ex-nuptial births in 1959 were 39 cases of twins, the number of confinements being thus 2,753. From the following table it will be seen that of the 2,753 mothers 1.001, or 36 per cent, were under 21 years of age.
| Age | Cases |
|---|---|
| 13 | 1 |
| 14 | 7 |
| 15 | 40 |
| 16 | 87 |
| 17 | 183 |
| 18 | 220 |
| 19 | 244 |
| 20 | 219 |
| 21 | 198 |
| 22 | 168 |
| 23 | 136 |
| 24 | 139 |
| 25–29 | 501 |
| 30–34 | 350 |
| 35–39 | 212 |
| 40–44 | 43 |
| 45 and over | 5 |
| Total | 2,753 |
The Legitimation Act — The Legitimation Act of 1939 stipulates that every ex-nuptial child whose parents have intermarried shall be deed to have been legitimated from birth by reason of such marriage. The Act requires the parents or surviving parent of any person legitimated under the Act to register with the Registrar-General the particulars of the birth of that person, showing that person as the lawful issue of the parents. Application for registration must be made within three months after the date of the marriage.
Where the Registrar-General has reason to believe that any person has been legitimated under the terms of the Act, and no application for registration has been made within the prescribed time, he may require the responsible parents or parent to make an application within a specified period of not less than seven days after receiving notice to do so. Any failure to comply with the notice requiring application for registration within the time specified renders the person or persons responsible liable on summary conviction to a fine of £5. If no application for registration is made within the appropriate time specified in the Act or in the notice received from the Registrar-General, application for registration of the particulars of the birth of any legitimated person may be made by that person, or by one of his parents, or by any other person.
The numbers of legitimations of Europeans registered in each of the latest five years were as follows; 1955, 463; 1956, 545; 1957, 555; 1958, 526, and 1959, 620.
ADOPTIONS — The Adoption Act 1955 sets out the provisions regarding the adoption of children. The Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951 contains provision for the registration of adopted children. The Registrar of the Court by which any adoption order is made is required to furnish to the Registrar-General particulars of the order, including the full name and place of birth of the child, as well as the full names and addresses of both the natural and the adopting parents. An entry is made in the prescribed form in the register of births, particulars of the adopting parents being given in lieu of those of the natural parents. If the child's birth has previously been registered in New Zealand a note of the adoption order is made on the original entry. An amendment to the Infants Act in 1939 extended the age at which a child might be legally adopted from under 15 years to under 21 years.
The adoption of a Maori child is required to be registered in the same manner as that of a European child.
The Adoption Act 1955 requires interim orders to be made in the first instance, and for these to remain in force for six months before adoption orders become effective. This legislative change would account for the low total of 887 recorded in 1956.
The following table shows the number of adoptions (exclusive of Maori children) which have been registered during the latest five years.
| Year | Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |
| 1955 | 744 | 711 | 1,455 |
| 1956 | 428 | 459 | 887 |
| 1957 | 901 | 790 | 1,691 |
| 1958 | 856 | 815 | 1,671 |
| 1959 | 958 | 1,011 | 1,969 |
Of the 1,969 adoptions registered in 1959, 808 were children under the age of one year, 675 were between one and five years, 237 were between five and 10 years, and 249 were aged 10 years or over In addition, 333 Maori children (178 males and 155 females) were adopted in 1959.
Statistics of adoptions registered have been available in New Zealand since 1919, and these indicate that the numbers are considerably influenced by the economic condition of the country, the lowest total, 329, being recorded in 1931.
STILL BIRTHS — The registration of still births was made compulsory in New Zealand as from 1 March 1913. Although it is necessary to effect a birth-registration entry for a still-born child, no entry is made in the register of deaths. The Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951 stipulates, however, that a medical practitioner or a midwife in attendance at the confinement where a still birth occurs must furnish a certificate stating to the best of his or her knowledge and belief the cause of the still birth. Particulars of causes of still births will be found in Section 4D relating to deaths. A stillborn child is defined as one “which has issued from its mother after the expiration of the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy and which was not alive at the time of such issue”. Still births are not included either as births or as deaths in the various numbers and rates shown in this subsection and in that relating to deaths. The rate of 1.45 per 100 total births in 1959 is the lowest rate recorded since the registration of still births was made compulsory in 1913.
The registrations of European still births during each of the latest five years were as follows.
| Year | Males | Females | Total | Male Still Births per 1,000 Female Still Births | Percentage of Still Births to— | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Living Births | All Births | |||||
| 1955 | 430 | 366 | 796 | 1,175 | 1.60 | 1.57 |
| 1956 | 461 | 397 | 858 | 1,161 | 1.70 | 1.67 |
| 1957 | 452 | 382 | 834 | 1,183 | 1.61 | 1.58 |
| 1958 | 466 | 353 | 819 | 1,320 | 1.52 | 1.50 |
| 1959 | 415 | 390 | 805 | 1,064 | 1.47 | 1.45 |
Masculinity is in general much higher among still births than among living births, the rate for still births in 1959 being 1,064 males per 1,000 females as compared with 1,053 for living births.
The percentage of ex-nuptials among still-born infants was in 1959, 6.83, and among infants born alive, 1.97.
Of the living legitimate births registered in 1959, 29 per cent were first births, while of legitimate still births 36 per cent were first births. Statistics over many years indicate that there is a considerably greater probability of still births occurring to mothers having their first confinement than to those having subsequent confinements. In addition to the 805 European still births in 1959, there were 137 Maori still births registered, comprising 78 males and 59 females.
FOETAL DEATHS — The Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951 stipulates that in the case of a foetal death where the child has issued from its mother after the twentieth week, and up to and including the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy, a medical practitioner or a midwife who was in attendance at the confinement shall sign and supply a certificate stating to the best of his or her knowledge and belief the cause of the foetal death, and such other particulars as may be required by the Registrar-General. A foetal death is not required to be registered as in the case of a still-born child.
GENERAL — Marriage may be solemnised in New Zealand either by a person whose name is on the list of officiating ministers under the Marriage Act, or before a duly appointed Registrar or Deputy Registrar of Marriages. A licence must be obtained from a Registrar of Marriages before a marriage by an officiating minister can be solemnised. Marriage by an officiating minister may be solemnised at any time between 6 o'clock in the morning and 8 o'clock in the evening. Marriage before a Registrar can be solemnised at any time during the hours the office of the Registrar is open for the transaction of public business.
Notice of intended marriage must be given to a Registrar of Marriages by one of the parties to the proposed marriage. In the case of a person under 21 years of age, not being a widow or widower, the consent of parents or guardian is necessary. Consent of the Court may also be given in cases of refusal by any person whose consent is required.
The system of notice and licence has operated in New Zealand since 1855. Officiating ministers and Registrars are required to send to the Registrar-General returns of all marriages solemnised, and as the returns come in they are checked off with the entries in the Registrars' lists of notices received. In case of the non-arrival of a marriage return corresponding to any entry in the list of notices, inquiries are made with a view to obtaining the return if the marriage has been solemnised.
Marriage is forbidden between persons within certain degrees of relationship, any such marriage being declared void. The prohibition applies whether the relationship is by the whole blood or by the half-blood, and whether the relationship is nuptial or ex-nuptial. The present law on this matter is contained in the Marriage Act 1955.
Section 34 of this Act provides that proxy marriages may be authorised by a Magistrate in New Zealand of any person who is resident in New Zealand to any person who is outside New Zealand, if the Magistrate is satisfied that the person who is outside the country is unable to come to New Zealand by reason of the existence of a state of war or armed conflict, or by reason of the conditions of his service as a member of the armed forces of any Commonwealth country, or of any country for the time being allied with any Commonwealth country.
Any New Zealand citizen who intends to be married in a country other than New Zealand according to the law of that country, and who desires to obtain a certificate for the purpose of complying with the law of that country, may give notice to the Registrar-General who, upon receiving the notice, shall make such searches and inquiries and give such notices as may be prescribed under the Act. If no caveat is entered within 14 days of the receipt by the Registrar-General, a certificate may be issued, after proper notices have been given that no lawful impediment to the marriage has been shown to the Registrar-General to exist.
Any New Zealand representative who has attended the marriage of a New Zealand citizen in a country other than New Zealand, and is satisfied that the marriage has been solemnised in accordance with the formalities of the law of that other country, may give a certificate and forward a duplicate copy to the Registrar-General, who shall bind the duplicate in a special register kept by him for the purpose.
Since 1933 the minimum age for marriage has been 16 years of age. No marriage shall be deemed to be void, however, by reason only of an infringement of the minimum age.
The Maori Purposes Act 1951 stipulated that after 1 April 1952 every marriage to which a Maori is a party shall be solemnised in the same manner, and its validity shall be determined by the same law, as if each of the parties was a European.
As a result of this legislative change, marriage statistics from the year 1952 are inclusive of Maoris and Maori marriage figures as a separate feature have lapsed. Figures quoted in this subsection for years prior to 1952 are all exclusive of Maoris.
Particulars regarding divorce will be found at the close of this subsection.
NUMBERS AND RATES — The movement of the marriage rate over a lengthy period of time may be observed from the statistical summary appearing towards the end of this Yearbook. The numbers and rates of marriages during each of the last 20 years are here given.
| Year | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Population |
|---|---|---|
| *Inclusive of Maoris. | ||
| 1941 | 13,313 | 8.65 |
| 1942 | 12,219 | 7.91 |
| 1943 | 11,579 | 7.53 |
| 1944 | 13,125 | 8.43 |
| 1945 | 16,160 | 10.14 |
| 1946 | 20,535 | 12.39 |
| 1947 | 18,525 | 10.94 |
| 1948 | 17,192 | 9.96 |
| 1949 | 16,785 | 9.53 |
| 1950 | 16,504 | 9.19 |
| 1951 | 16,359 | 8.93 |
| 1952* | 17,061 | 8.55 |
| 1953* | 17,224 | 8.41 |
| 1954* | 17,557 | 8.38 |
| 1955* | 17,795 | 8.32 |
| 1956* | 17,531 | 8.03 |
| 1957* | 17,614 | 7.89 |
| 1958* | 18,305 | 8.01 |
| 1959* | 18,315 | 7.84 |
| 1960* | 18,909 | 7.96 |
Both the marriage rate and the number of marriages in 1946 were the highest on record. The main reason for this was the return from overseas of many thousands of men in the age groups of high marriage rates. An appreciable decline, however, in both the number of marriages and in the marriage rate took place in 1947 and 1948. The number continued to decline until 1951. Separate figures for European marriages are not available after 1951.
Comparison with Other Countries — Marriage rates for certain countries for 1959 are given below (these particulars have been taken from the Monthly Bulletin of Statistics, issued by the Statistical Office of the United Nations).
| Country | Rate per 1,000 Mean Population |
|---|---|
| Yugoslavia | 8.7 |
| Puerto Rico | 8.6 |
| United States of America | 8.5 |
| Portugal | 8.4 |
| Austria | 8.3 |
| Spain | 8.1 |
| Israel | 7.8 |
| Italy | 7.8 |
| Netherlands | 7.8 |
| New Zealand | 7.8 |
| Switzerland | 7.7 |
| United Kingdom | 7.5 |
| Australia | 7.4 |
| Canada | 7.3 |
| Chile | 7.2 |
| Denmark | 7.2 |
| Finland | 7.2 |
| France | 7.1 |
| Norway | 6.5 |
| Sweden | 6.3 |
| Republic of Ireland | 5.4 |
MARITAL STATUS — The total number of persons married during the year 1959 was 36,630, of whom 32,470 were single, 1,603 widowed, and 2,557 divorced. The figures for the five years 1955 to 1959, showing the sexes separately, are given in the table following.
| Year | Single | Widowed | Divorced | Total Persons Married | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bridegroom | Bride | Bridegroom | Bride | Bridegroom | Bride | ||
| 1955 | 15,858 | 15,819 | 803 | 748 | 1,134 | 1,228 | 35,590 |
| 1956 | 15,513 | 15,580 | 837 | 752 | 1,181 | 1,199 | 35,062 |
| 1957 | 15,634 | 15,625 | 837 | 798 | 1,143 | 1,191 | 35,228 |
| 1958 | 16,198 | 16,226 | 810 | 789 | 1,297 | 1,290 | 36,610 |
| 1959 | 16,264 | 16,206 | 811 | 792 | 1,240 | 1,317 | 36,630 |
The position is more easily seen by studying the percentages given in the next table.
| Year | Bridegrooms | Brides | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Widowed | Divorced | Single | Widowed | Divorced | |
| Per Cent | ||||||
| 1955 | 89.12 | 4.51 | 6.37 | 88.90 | 4.20 | 6.90 |
| 1956 | 88.49 | 4.77 | 6.74 | 88.87 | 4.29 | 6.84 |
| 1957 | 88.76 | 4.75 | 6.49 | 88.71 | 4.53 | 6.76 |
| 1958 | 88.48 | 4.43 | 7.09 | 88.64 | 4.31 | 7.05 |
| 1959 | 88.80 | 4.43 | 6.77 | 88.49 | 4.32 | 7.19 |
Divorce statistics at the end of this subsection show the numbers of decrees granted in recent years, the numbers varying from 1,400 to 1,900 a year. The number of widowed persons remarrying, which was 39 per 1,000 in 1940, rose to 44 per 1,000 in 1959.
The relative marital status of bridegrooms and brides for each of the latest five years is next given.
| Year | Marriages Between Bachelors and | Marriages Between Widowers and | Marriages Between Divorced Men and | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinsters | Widows | Divorced Women | Spinsters | Widows | Divorced Women | Spinsters | Widows | Divorced Women | |
| 1955 | 14,892 | 292 | 674 | 305 | 321 | 177 | 622 | 135 | 377 |
| 1956 | 14,607 | 264 | 642 | 339 | 335 | 163 | 634 | 153 | 394 |
| 1957 | 14,661 | 291 | 682 | 316 | 354 | 167 | 648 | 153 | 342 |
| 1958 | 15,191 | 273 | 734 | 310 | 346 | 154 | 725 | 170 | 402 |
| 1959 | 15,228 | 303 | 733 | 300 | 329 | 182 | 678 | 160 | 402 |
The relative proportions of divorced men and divorced women remarrying during the last three years has changed but little compared with 10 years earlier. During the three years 1938–40 the number of male divorcees remarrying was 2,066, as compared with 2,169 females, which gives a rate of 95 males for every 100 females. In 1957–59 the respective numbers were 3,680 males and 3,798 females, and the corresponding rate 97 males for every 100 females. In the case of widowed persons remarrying, however, there has been a marked change in the figures. In the three-year period 1938–40, 2,420 widowers remarried but only 1,619 widows, whereas in 1957–59 there were 2,458 widowers and 2,379 widows who remarried, the number of widowers per 100 widows being 149 in the former period and 103 in the latter period.
AGES OF PERSONS MARRIED — Of the 36,630 persons married in 1959, 8,260, or 23 per cent, were under 21 years of age; 13,299, or 36 per cent, were returned as 21 and under 25; 7,102, or 19 per cent, as 25 and under 30; 4,608, or 13 per cent, as 30 and under 40; and 3,361, or 9 per cent, as 40 years of age or over. The following table relates to the year 1959.
| Age of Bridegroom, in Years | Age of Bride, in Years | Total Bridegrooms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 21 | 21 and Under 25 | 25 and Under 30 | 30 and Under 35 | 35 and Under 40 | 40 and Under 45 | 45 and Over | ||
| Under 21 | 1,298 | 253 | 25 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1,578 |
| 21 and under 25 | 3,600 | 3,019 | 336 | 40 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7,002 |
| 25 and under 30 | 1,435 | 2,258 | 942 | 204 | 62 | 10 | - | 4,911 |
| 30 and under 35 | 293 | 572 | 571 | 354 | 135 | 36 | 20 | 1,981 |
| 35 and under 40 | 40 | 135 | 209 | 226 | 197 | 67 | 33 | 907 |
| 40 and under 45 | 11 | 30 | 61 | 101 | 130 | 110 | 76 | 519 |
| 45 and over | 5 | 30 | 47 | 87 | 178 | 202 | 868 | 1,417 |
| Total brides | 6,682 | 6,297 | 2,191 | 1,013 | 707 | 427 | 998 | 18,315 |
The recent trend is for persons to marry at younger ages. The following table shows since 1920 the proportions of men and women married at each age group to every 100 marriages.
| Period | Under 21 | 21 and Under 25 | 25 and Under 30 | 30 and Under 35 | 35 and Under 40 | 40 and Under 45 | 45 and Over | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Inclusive of Maoris. | ||||||||
| Males | ||||||||
| 1920–24 | 3.13 | 24.66 | 32.21 | 17.73 | 10.24 | 5.43 | 6.60 | 100.00 |
| 1925–29 | 3.49 | 28.04 | 34.49 | 14.33 | 7.70 | 4.48 | 7.47 | 100.00 |
| 1930–34 | 3.46 | 27.28 | 37.02 | 15.14 | 6.10 | 3.61 | 7.39 | 100.00 |
| 1935–39 | 2.68 | 25.91 | 38.26 | 16.46 | 6.75 | 3.22 | 6.72 | 100.00 |
| 1950–54* | 5.05 | 35.42 | 31.21 | 10.95 | 5.86 | 3.56 | 7.95 | 100.00 |
| 1955–59* | 7.18 | 36.68 | 29.44 | 11.21 | 4.81 | 2.97 | 7.71 | 100.00 |
| Females | ||||||||
| 1920–24 | 15.99 | 35.47 | 26.21 | 10.66 | 5.53 | 2.98 | 3.16 | 100.00 |
| 1925–29 | 18.61 | 37.88 | 23.67 | 8.93 | 4.65 | 2.82 | 3.44 | 100.00 |
| 1930–34 | 18.67 | 38.51 | 24.79 | 8.22 | 3.85 | 2.40 | 3.56 | 100.00 |
| 1935–39 | 17.10 | 38.26 | 26.30 | 8.86 | 3.91 | 2.02 | 3.55 | 100.00 |
| 1950–54* | 25.78 | 38.65 | 16.85 | 6.96 | 4.12 | 2.59 | 5.05 | 100.00 |
| 1955–59* | 32.99 | 35.71 | 13.76 | 6.11 | 3.65 | 2.49 | 5.29 | 100.00 |
For many years the average age (arithmetic mean) at marriage for both males and females, more particularly the latter, showed a tendency to increase. However, in recent years there has been a tendency towards a slight fall. The figures for each of the years 1950–59 are as follows.
| Year | Bridegrooms (Years) | Brides (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| *Inclusive of Maoris. | ||
| 1950 | 29.67 | 26.14 |
| 1951 | 29.42 | 25.96 |
| 1952* | 29.52 | 26.19 |
| 1953* | 29.31 | 25.90 |
| 1954* | 29.20 | 25.85 |
| 1955* | 28.99 | 25.67 |
| 1956* | 29.07 | 25.59 |
| 1957* | 28.97 | 25.48 |
| 1958* | 29.97 | 25.30 |
| 1959* | 28.70 | 25.26 |
The average ages of bachelors and spinsters at marriage are considerably lower than those shown in the preceding table, which covers all parties and is naturally affected by the inclusion of remarriages of widowed and divorced persons. The average ages of grooms and brides for each of the latest five years according to marital status were as shown below.
| Year | Bridegrooms | Brides | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelors | Divorced | Widowers | Spinsters | Divorced | Widows | |
| 1955 | 26.74 | 41.67 | 55.46 | 23.76 | 37.01 | 47.42 |
| 1956 | 26.65 | 41.81 | 56.02 | 23.60 | 36.97 | 48.85 |
| 1957 | 26.55 | 42.13 | 56.19 | 23.46 | 37.04 | 47.78 |
| 1958 | 27.78 | 41.37 | 55.80 | 23.20 | 36.94 | 49.38 |
| 1959 | 26.32 | 41.82 | 56.35 | 23.10 | 37.45 | 49.03 |
The foregoing figures give the average age at marriage, but these do not correspond with the modal or popular age, if the age at which the most marriages are celebrated may be so termed. The modal age for brides (21) has remained unchanged for very many years, but in the case of bridegrooms the most popular age has varied, and for recent years it has been 22 to 24.
Marriages of Minors — Of every 1,000 men married in 1959, 86 were under 21 years of age, while 365 in every 1,000 brides were under 21.
In 1,298 marriages in 1959 both parties were given as under 21 years of age, in 5,384 marriages the bride was returned as a minor and the bridegroom as an adult, and in 280 marriages the bridegroom was a minor and the bride an adult.
The proportion of minors among persons marrying has been increasing over a fairly long period, and in the table below figures are given for the last five years. In the latest available year (1959) one bride in every three was under 21 years of age, the proportion for grooms being one in 12.
| Year | Age, in Years | Totals | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | Number | Rate per 100 Marriages | |
| Bridegrooms | |||||||
| 1955 | 7 | 36 | 125 | 267 | 572 | 1,007 | 5.66 |
| 1956 | 4 | 33 | 135 | 353 | 605 | 1,130 | 6.45 |
| 1957 | 9 | 50 | 169 | 360 | 652 | 1,240 | 7.04 |
| 1958 | 7 | 58 | 223 | 433 | 758 | 1,479 | 8.08 |
| 1959 | 5 | 73 | 228 | 497 | 775 | 1,578 | 8.62 |
| Brides | |||||||
| 1955 | 196 | 526 | 1,015 | 1,534 | 1,856 | 5,127 | 28.81 |
| 1956 | 213 | 569 | 1,134 | 1,681 | 1,909 | 5,506 | 31.41 |
| 1957 | 266 | 636 | 1,165 | 1,706 | 1,989 | 5,762 | 32.71 |
| 1958 | 281 | 672 | 1,319 | 1,975 | 2,219 | 6,466 | 35.32 |
| 1959 | 271 | 669 | 1,316 | 2,070 | 2,356 | 6,682 | 36.48 |
MARRIAGES BY MINISTERS OF VARIOUS CHURCHES — Of the 18,315 marriages registered in 1959, Church of England clergymen officiated at 4,464, Presbyterians at 4,650, Roman Catholics at 2,801, and Methodists at 1,465, while 3,609 marriages were solemnised by Registrars.
The following table shows the proportions of marriages by ministers of the largest churches and before Registrars in each of the years 1953–59.
| Church | Percentage of Marriages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Church of England | 25.04 | 26.21 | 25.63 | 25.88 | 24.63 | 25.12 | 24.37 |
| Presbyterian | 27.04 | 26.23 | 26.27 | 25.32 | 26.24 | 25.08 | 25.39 |
| Roman Catholic | 14.52 | 14.4 | 15.05 | 14.84 | 15.19 | 15.12 | 15.29 |
| Methodist | 8.16 | 7.96 | 8.08 | 8.35 | 8.31 | 7.78 | 8.00 |
| Others | 6.39 | 6.56 | 6.73 | 6.79 | 6.82 | 7.28 | 7.24 |
| Before Registrars | 18.85 | 18.64 | 18.24 | 18.82 | 18.81 | 19.62 | 19.71 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
The foregoing figures must not be taken as an exact indication of the religious professions of the parties married, as it does not necessarily follow that both (or even one) of the parties are adherents of the Church whose officiating minister performed the ceremony, and persons married before Registrars may belong, in greater or lesser proportion, to any or none of the churches. Of the total population (inclusive of Maoris) at the general census of 1956, 35.9 per cent were recorded as adherents of the Church of England, 22.3 per cent Presbyterian, 14.3 per cent Roman Catholic, 7.4 per cent Methodist, and 20.1 per cent of other religions or of no religion, or who objected to state their religious profession.
NUMBER OF OFFICIATING MINISTERS — The number of names on the list of officiating ministers under the Marriage Act was (January 1960) 3,244, and the churches to which they belong are shown hereunder.
| Church | Number |
|---|---|
| Roman Catholic Church | 761 |
| Church of England | 565 |
| Presbyterian Church of New Zealand | 513 |
| Methodist Church of New Zealand | 356 |
| Ratana Church of New Zealand | 169 |
| Salvation Army | 168 |
| Baptist | 146 |
| Brethren | 70 |
| Latter Day Saints | 53 |
| Ringatu Church | 45 |
| Associated Churches of Christ | 42 |
| Seventh Day Adventist | 40 |
| Congregational Independent | 35 |
| Assemblies of God | 30 |
| Jehovah's Witness | 24 |
| Apostolic Church | 21 |
| Commonwealth Covenant Church | 19 |
| Liberal Catholic Church | 17 |
| Evangelistic Church of Christ | 13 |
| Churches of Christ | 11 |
| Evangelical Lutheran Concordia Conference | 11 |
| Church of Te Kooti Rikirangi | 10 |
| Spiritualist Church of New Zealand | 9 |
| Church of God | 9 |
| Hebrew Congregations | 7 |
| United Maori Mission | 5 |
| Others | 96 |
| Total | 3,244 |
The Ratana Church of New Zealand, the Ringatu Church, the United Maori Mission, and the Church of Te Kooti Rikirangi are Maori organisations.
DIVORCE AND NULLITY — The present law is contained in the Divorce and Matrimonial Causes Act 1928 and its amendments and a résumé of its principal provisions is now given.
Grounds for Divorce — These are set out as follows:
Adultery since the celebration of the marriage;
Wilful and continuous desertion for three years or more;
Habitual drunkenness for four years, coupled with (wife's petition) failure to support or habitual cruelty, or with (husband's petition) neglect of, or self-caused inability to discharge, domestic duties;
Conviction for attempted murder of petitioner or of any child of petitioner or respondent or for an offence under section 197 of the Crimes Act 1908 against petitioner or any such child;
Conviction for murder;
Insanity and confinement as a lunatic for seven out of 10 years preceding the petition;
Insanity for seven years, and confinement for three years immediately preceding the petition;
Insanity and confinement as a lunatic for the five years immediately preceding the petition;
Failure for three years or more to comply with a decree for restitution of conjugal rights;
Separation under an agreement, written or verbal, which has been in full force for not less than three years;
Separation by decree of judicial separation or separation order (or their equivalent in any country), which has been in force for not less than three years;
Parties living apart for not less than seven years and unlikely to be reconciled;
Husband guilty of rape, sodomy, or bestiality since marriage.
In cases based on separation of the parties, whether by order or agreement or otherwise, the Court must dismiss the petition if the respondent opposes it and the Court is satisfied that the separation was due to the wrongful act or conduct of the petitioner. In these cases, and in cases where the ground is failure to comply with a decree for restitution of conjugal rights, the Court has in any event a discretion whether or not to grant a divorce. In practice, however, where the petition is not opposed the Court rarely exercises this discretion against a petitioner.
Jurisdiction — The Court has jurisdiction in divorce only in cases where the petitioner is domiciled in New Zealand. In petitions based on grounds (i) above, the petitioner must have been domiciled in New Zealand for at least three years at the time when the petition is filed.
Under the common law a married woman takes her husband's domicile and is incapable of acquiring a separate domicile while the marriage subsists. As a result of a series of statutory amendments, however, a wife who is living in New Zealand apart from her husband has in effect the capacity to acquire a separate domicile for the purposes of the divorce and nullity law as if she were unmarried.
Overseas Divorces — The common law relating to the recognition of overseas divorces was clarified and extended by an amendment in 1953, and further extended in 1958. New Zealand Courts will recognise divorces granted in any country by Courts exercising jurisdiction there on the basis of the domicile of either party in that country, or of the residence in that country of the wife for at least two years, or of the domicile of the husband in that country before a desertion or separation, or that either party was a national or citizen of that country.
Nullity — The first New Zealand legislation on the subject of nullity was enacted in 1953. It replaces and extends the common law on this topic.
The Court has jurisdiction to make a decree of nullity of marriage if either of the parties is domiciled in New Zealand when the petition is filed or if the marriage was solemnised in New Zealand.
A petition for a nullity decree may be presented in the case of either a void or a voidable marriage. Void marriages are those which are of no effect whether or not a decree is obtained. Voidable marriages are those which are valid unless and until a decree is obtained.
The following are the cases in which a marriage is void by the law of New Zealand:
Where at the time of the ceremony either party to the marriage was already married;
Where, whether by reason of duress or mistake or insanity or otherwise, there was at the time of the marriage an absence of consent by either party to marriage to the other party;
Where the parties are within the prohibited degrees of relationship as set out in the Marriage Act 1955;
Where the marriage was not solemnised in due form.
A marriage is voidable in New Zealand on the following grounds:
Incapacity or wilful refusal of the respondent to consummate the marriage;
Mental deficiency of either party within the meaning of the Mental Health Act 1911, although that party was capable of consenting to the marriage;
Venereal disease (of the respondent) in a communicable form;
Pregnancy of the respondent by some person other than the petitioner.
In cases (b), (c), and (d) the facts alleged must have existed at the time of the marriage and proceedings must be instituted within a year of the marriage. Furthermore the Court must be satisfied —
That the petitioner was at the time of the marriage ignorant of the facts;
That marital intercourse with the petitioner's consent has not taken place since the discovery of the existence of the grounds for a decree.
With the exception of inability to consummate the marriage there was no ground on which a marriage was voidable before the passing of the 1953 amendment.
A decree of nullity in a voidable marriage puts an end to the marriage from the date of the decree only and not from the date of the marriage. The principal effect of this is to ensure the legitimacy of any children of the marriage.
Statistical Data — Figures showing the operations of the Supreme Court in its divorce jurisdiction during recent years are as follows. A number of the decrees granted in any year relate to petitions filed in earlier years.
| Year | Dissolution or Nullity of Marriage | Judicial Separation | Restitution of Conjugal Rights | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petitions Filed | Decrees Nisi | Decrees Absolute | Petitions Filed | Decrees for Separation | Petitions Filed | Decrees for Restitution | |
| 1949 | 2,001 | 1,824 | 1,892 | 15 | 1 | 331 | 262 |
| 1950 | 1,912 | 1,707 | 1,633 | 11 | 4 | 304 | 217 |
| 1951 | 1,882 | 1,666 | 1,582 | 11 | 7 | 263 | 210 |
| 1952 | 1,960 | 1,727 | 1,684 | 15 | 8 | 296 | 204 |
| 1953 | 1,897 | 1,643 | 1,540 | 10 | 3 | 227 | 197 |
| 1954 | 1,886 | 1,479 | 1,536 | 12 | 3 | 28 | 19 |
| 1955 | 1,799 | 1,379 | 1,472 | 14 | 3 | 24 | 8 |
| 1956 | 1,891 | 1,568 | 1,449 | 8 | 5 | 22 | 6 |
| 1957 | 1,998 | 1,719 | 1,400 | 21 | 10 | 23 | 10 |
| 1958 | 2,084 | 1,805 | 1,751 | 19 | 13 | 14 | 5 |
| 1959 | 1,912 | 1,648 | 1,639 | 21 | 6 | 19 | 9 |
The passing in November 1953 of the Divorce and Matrimonial Causes Amendment Act had a marked effect as regards petitions and decrees for restitution of conjugal rights.
The next table gives the grounds (dissolution or nullity cases) of petitions and decrees during 1958 and 1959.
| Grounds | Petitions Filed | Decrees Absolute Granted | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Husbands' Petitions | Wives' Petitions | Husbands' Petitions | Wives' Petitions | |||||
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Adultery | 410 | 325 | 175 | 196 | 268 | 257 | 132 | 147 |
| Desertion | 153 | 144 | 115 | 96 | 134 | 115 | 95 | 78 |
| Drunkenness with cruelty, failure to maintain, etc. | 2 | - | 10 | 6 | - | - | 7 | 3 |
| Attempted murder | - | - | 3 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Insanity | 9 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| Non-compliance with order for restitution of conjugal rights | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| Separation for not less than three years | 455 | 408 | 591 | 583 | 357 | 318 | 454 | 436 |
| Separation by Court order | 22 | 16 | 103 | 83 | ||||
| Living apart for not less than seven years | 67 | 66 | 64 | 58 | 80 | 71 | 68 | 79 |
| Presumption of death | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Sodomy, etc. | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nullity | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | - | - | - | 7 |
| Non-consummation | 9 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| Bigamy | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Totals | 1,111 | 962 | 973 | 950 | 877 | 798 | 874 | 841 |
The figures shown for decrees absolute cover all such granted during the year, whether the antecedent decree nisi was granted in the same or in a previous year.
Over the five-year period 1955–59 inclusive, the average percentage of decrees absolute granted on wives' petitions (83.5), was greater than the percentage granted on husbands' petitions (76.3). It is interesting to note that 1958 was the only occasion since 1952 in which the number of decrees absolute granted on husbands' petitions was greater than the total granted on wives' petitions.
In 493 of the 1,639 cases where decrees absolute were granted during 1958 there was no living issue of the marriage. The number of living issue was one in 375 cases, two in 376 cases, three in 229 cases, and four or more in 166 cases.
The table which follows shows the duration of marriage in all cases for which decrees absolute were granted in the five years 1955 to 1959.
| Duration of Marriage, in Years | Husbands' Decrees Absolute Granted | Wives' Decrees Absolute Granted | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Under 5 | 65 | 61 | 51 | 76 | 65 | 69 | 44 | 39 | 54 | 48 |
| 5 and under 10 | 204 | 217 | 184 | 228 | 233 | 234 | 255 | 242 | 275 | 245 |
| 10 and under 15 | 155 | 140 | 164 | 227 | 207 | 163 | 174 | 203 | 228 | 228 |
| 15 and under 20 | 123 | 105 | 106 | 129 | 102 | 138 | 113 | 96 | 134 | 123 |
| 20 and under 30 | 110 | 120 | 125 | 153 | 133 | 112 | 127 | 110 | 132 | 151 |
| 30 and over | 49 | 57 | 40 | 64 | 58 | 50 | 36 | 40 | 51 | 46 |
| Totals | 706 | 700 | 670 | 877 | 798 | 766 | 749 | 730 | 874 | 841 |
The number of living issue affected by the decrees absolute of their parents during each of the last five years was as follows: 1955, 2,294; 1956, 2,365; 1957, 2,269; 1958, 2,737; and 1959, 2,655.
(NOTE — The term European used in the context of this subsection means the population exclusive of Maoris.)
REGISTRATION — The law as to registration of deaths is embodied in the Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951. Particulars required in the registration of a death include date, place of residence and domicile, name, occupation, sex, age, cause of death, birthplace, duration of residence in New Zealand, whether cremated or not, marital status, living issue of married persons, race (European or Maori), medical attendant by whom certified, particulars as to burial, and, in the case of married males, age of widow.
Every death occurring in New Zealand is required to be registered within three days after the day of the burial. There is a penalty up to £10 for neglect, the funeral director in charge of the burial being solely responsible for registration. When an inquest is held the Coroner becomes responsible for registration, the time allowed being three days after the conclusion of the inquest. The Coroner may, in writing, authorise an agent to attend to registration on his behalf. Registrations must not be effected before the conclusion of the inquest.
Where the Coroner decides not to hold an inquest the funeral director is responsible for registration of the death.
The law does not impose any limit of time after which a death may not be registered as it does in the case of a birth. Although it is necessary to effect a birth-registration entry in the case of a still-born child, no entry is made in the register of deaths. The principal Act stipulates, however, that a medical practitioner or a midwife in attendance at a confinement where a still birth occurs must furnish a certificate stating to the best of his or her knowledge and belief the cause of the still birth.
Provision is made for the registration of the death of a person whose body is removed for anatomical examination under Part II of the Medical Act 1908, or is removed for burial outside New Zealand.
Any person, burying, or permitting or taking part in the burial of the body of any deceased person without a certificate of cause of death signed by a duly registered medical practitioner, or a Coroner's order to bury the body, renders himself liable to a fine of £50. Burial at sea of a person dying in New Zealand is prohibited except on the authority of a Coroner.
It is incumbent upon a medical practitioner to give the certificate of cause of death to the person required to supply information for the purpose of registering the death (the funeral director in charge of the burial). The practitioner is required to report forthwith to the Coroner any case where, in his opinion, the death has occurred in any circumstances of suspicion.
The Births and Deaths Registration Amendment Act 1955 provides that — where the death of any person occurs outside New Zealand and the death takes place on board a New Zealand ship within the meaning of the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952, or on board an aircraft registered in New Zealand pursuant to the Civil Aviation Act 1948, or as the result of any occurrence on board any such aircraft during its operation — the Registrar-General may authorise any Registrar to register the death in accordance with the provisions of the Act relating to the registration of deaths taking place in New Zealand.
Deaths of Members of the Forces While Overseas — The Births and Deaths Registration Act 1951 requires the Registrar-General to compile a register containing particulars of all persons who have died while out of New Zealand on service with any Commonwealth force within the meaning of the Army Act 1950 and who at the time of their deaths were domiciled in New Zealand. Deaths registered in the War Deaths Register from 1940 onwards were not taken into account in arriving at the number and rate of deaths in New Zealand, nor were deaths of visiting overseas servicemen or prisoners of war in New Zealand. Deaths of New Zealand servicemen which occurred in New Zealand were, however, included.
Registration of Maori Deaths — Registration of the deaths of Maoris are effected with the Maori Registrars in the various districts set up for this purpose. Statistics relating to the deaths of Maoris are not included in this subsection, but are fully covered in Section 4E.
NUMBERS AND RATES — The following table shows the number of deaths and the death rate per 1,000 of the mean population during each of the last 20 years.
| Year | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1941 | 15,146 | 9.84 |
| 1942 | 16,385 | 10.60 |
| 1943 | 15,447 | 10.04 |
| 1944 | 15,363 | 9.87 |
| 1945 | 16,051 | 10.07 |
| 1946 | 16,093 | 9.71 |
| 1947 | 15,904 | 9.39 |
| 1948 | 15,812 | 9.16 |
| 1949 | 16,012 | 9.09 |
| 1950 | 16,715 | 9.31 |
| 1951 | 17,512 | 9.56 |
| 1952 | 17,413 | 9.28 |
| 1953 | 17,009 | 8.84 |
| 1954 | 17,667 | 8.98 |
| 1955 | 17,953 | 8.95 |
| 1956 | 18,403 | 9.00 |
| 1957 | 19,411 | 9.29 |
| 1958 | 19,014 | 8.90 |
| 1959 | 19,814 | 9.09 |
| 1960 | 19,524 | 8.81 |
New Zealand has had for many years a favourable death rate. The fact that the death rate is still comparatively very low, despite the older age constitution of the population, is probably due, inter alia, to improvements in medical techniques, expansion of health services, etc. This progress has been reflected, for example, in a relatively low incidence of serious outbreaks of the more important epidemic diseases (which were much more prevalent in the early years of colonisation) and in a remarkably low infant-mortality rate.
The general trend of the death rate in New Zealand was for many years downwards, reaching its lowest level during the depression years of the early thirties. After that an upward trend was in evidence for some years, the figures recorded during the war years being the highest for a long time. It is possible that the absence overseas of considerable numbers of men of early adult age, at which mortality experience is the most favourable, would have some effect on the rates established. The strains of wartime would also have some effect on deaths in the older age groups; in fact, the high rate of 1942 disclosed a sharp rise in deaths resulting from diseases of the heart and nervous system. For four years following 1945 a downward trend was again in evidence and, although small increases were recorded in 1950 and 1951, the 1952 and 1953 rates again showed decreases, the figure of 8.84 for 1953 being the lowest recorded rate since 1936 (8.75). A contributing factor to the slight rise in the rate recorded in 1954 was the registration during the year of the deaths of the victims of the Tangiwai railway disaster.
The death rates of males and females for the last 11 years are shown separately in the next table.
| Year | Deaths per 1,000 of Mean Population | Male Deaths to Every 100 Female Deaths | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | ||
| 1950 | 10.23 | 8.38 | 9.31 | 123 |
| 1951 | 10.50 | 8.62 | 9.56 | 122 |
| 1952 | 10.12 | 8.44 | 9.28 | 121 |
| 1953 | 9.80 | 7.86 | 8.84 | 126 |
| 1954 | 9.96 | 8.00 | 8.98 | 126 |
| 1955 | 9.86 | 8.03 | 8.95 | 124 |
| 1956 | 9.99 | 8.00 | 9.00 | 126 |
| 1957 | 10.35 | 8.22 | 9.29 | 127 |
| 1958 | 9.73 | 806 | 8.90 | 122 |
| 1959 | 9.98 | 8.19 | 9.09 | 123 |
| 1960 | 9.67 | 7.93 | 8.81 | 123 |
COMPARISON WITH OTHER COUNTRIES — An international comparison of death rates is made in the following table. They are the average of the five years 1955–59 and are taken from the Monthly Bulletin of Statistics issued by the United Nations.
| Country | Rates per 1,000 of Population |
|---|---|
| *European population only. | |
| Israel | 6.2 |
| Puerto Rico | 7.1 |
| Netherlands | 7.5 |
| Japan | 7.8 |
| Canada | 8.1 |
| Union of South Africa* | 8.5 |
| Norway | 8.7 |
| Australia | 8.8 |
| Denmark | 9.1 |
| Finland | 9.1 |
| New Zealand | 9.1 |
| Spain | 9.4 |
| United States of America | 9.4 |
| Costa Rica | 9.6 |
| Sweden | 9.6 |
| Italy | 9.7 |
| Switzerland | 9.9 |
| Yugoslavia | 10.4 |
| Peru | 10.8 |
| Germany (Western) | 11.0 |
| India | 11.0 |
| Portugal | 11.2 |
| United Kingdom | 11.7 |
| France | 11.8 |
| Republic of Ireland | 12.0 |
| Austria | 12.4 |
| Mexico | 12.6 |
DISTRIBUTION OF DEATHS OVER THE YEAR — An examination of the total number of deaths registered in each quarter of the period 1949–59 gives the following averages: March quarter, 3,768; June quarter, 4,435; September quarter, 5,310; and December quarter, 4,390.
A classification according to month of death shows that in 1959 the months during which the greatest number of deaths occurred were July, June, and May, with totals of 2,081, 1,953, and 1,894 respectively. Excluding December, a proportion of deaths occurring in that month not being registered till January, February had the least number of deaths, 1,247, followed by March and November with 1,395 and 1,457 respectively.
The lowest number of deaths on any one day, again excluding December, was 32, this number occurring on 27 January. The greatest number (79) occurred on 24 June.
AGE AT DEATH — The deaths registered during the year 1959 are tabulated below according to age.
| Age | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 month | 422 | 341 | 763 |
| 1–2 months | 65 | 33 | 98 |
| 3–5 months | 63 | 49 | 112 |
| 6–11 months | 59 | 57 | 116 |
| 1 year | 50 | 62 | 112 |
| 2 years | 30 | 19 | 49 |
| 3 years | 22 | 24 | 46 |
| 4 years | 16 | 14 | 30 |
| 5–9 years | 55 | 38 | 93 |
| 10–14 years | 54 | 23 | 77 |
| 15–19 years | 84 | 31 | 115 |
| 20–24 years | 109 | 34 | 143 |
| 25–29 years | 96 | 49 | 145 |
| 30–34 years | 120 | 62 | 182 |
| 35–39 years | 142 | 101 | 243 |
| 40–44 years | 188 | 137 | 325 |
| 45–49 years | 353 | 233 | 586 |
| 50–54 years | 479 | 283 | 762 |
| 55–59 years | 716 | 402 | 1,118 |
| 60–64 years | 933 | 594 | 1,527 |
| 65–69 years | 1,169 | 837 | 2,006 |
| 70–74 years | 1,546 | 1,190 | 2,736 |
| 75–79 years | 1,739 | 1,543 | 3,282 |
| 80–84 years | 1,359 | 1,390 | 2,749 |
| 85–89 years | 755 | 910 | 1,665 |
| 90–94 years | 251 | 345 | 596 |
| 95–99 years | 52 | 74 | 126 |
| 100 years | 1 | 6 | 7 |
| 101 years | - | 1 | 1 |
| 102 years | 1 | - | 1 |
| 103 years | 1 | - | 1 |
| 104 years | - | 1 | 1 |
| 106 years | 1 | - | 1 |
| Totals | 10,931 | 8,883 | 19,814 |
The following table indicates the changes that have occurred since 1930 in the age distribution of persons dying. The movement in the proportions of deaths occurring at the different age groups is very striking. The results of three main factors are illustrated, viz, health measures, which have achieved an immense saving of young life; the fluctuations in the birthrate over the period; and the great increase in the proportion of old people in the community.
| Age, in Years | Number of Deaths | Percentage of Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1959 | 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1959 | |
| Under 1 | 924 | 990 | 1,008 | 1,089 | 7.57 | 6.93 | 6.03 | 5.50 |
| 1 and under 5 | 327 | 205 | 199 | 237 | 2.68 | 1.44 | 1.19 | 1.20 |
| 5 and under 10 | 167 | 98 | 87 | 93 | 1.37 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| 10 and under 15 | 105 | 108 | 64 | 77 | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| 15 and under 20 | 222 | 151 | 120 | 115 | 1.82 | 1.06 | 0.72 | 0.58 |
| 20 and under 25 | 315 | 247 | 158 | 143 | 2.58 | 1.73 | 0.95 | 0.72 |
| 25 and under 30 | 337 | 270 | 142 | 145 | 2.76 | 1.89 | 0.85 | 0.73 |
| 30 and under 35 | 337 | 290 | 191 | 182 | 2.76 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 0.92 |
| 35 and under 40 | 374 | 320 | 275 | 243 | 3.07 | 2.24 | 1.65 | 1.23 |
| 40 and under 45 | 478 | 362 | 328 | 325 | 3.92 | 2.53 | 1.96 | 1.64 |
| 45 and under 50 | 640 | 472 | 522 | 586 | 5.25 | 3.30 | 3.12 | 2.96 |
| 50 and under 55 | 794 | 798 | 697 | 762 | 6.51 | 5.59 | 4.17 | 3.84 |
| 55 and under 60 | 881 | 1,145 | 1,021 | 1,118 | 7.22 | 8.02 | 6.11 | 5.64 |
| 60 and under 65 | 1,003 | 1,461 | 1,503 | 1,527 | 8.22 | 10.23 | 8.99 | 7.71 |
| 65 and under 70 | 1,077 | 1,697 | 2,170 | 2,006 | 8.83 | 11.88 | 12.98 | 10.12 |
| 70 and under 75 | 1,171 | 1,772 | 2,536 | 2,736 | 9.60 | 12.41 | 15.17 | 13.81 |
| 75 and under 80 | 1,242 | 1,556 | 2,316 | 3,282 | 10.18 | 10.89 | 13.86 | 16.56 |
| 80 and over | 1,805 | 2,340 | 3,378 | 5,148 | 14.80 | 16.38 | 20.21 | 25.98 |
| Totals | 12,199 | 14,282 | 16,715 | 19,814 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
During the earlier period covered by the next table the fall in the death rate was common to all ages and to both sexes. In more recent years, however, there have been some fluctuations in the rates for the higher age groups. Of special significance are the low rates recorded in the childhood and early adult life age groups in recent years. The female rate for the various age groups is now lower than the male rate in all instances, with the exception of the one and under five years group. The increase in the death rate (per 1,000 of population) at successive age groups from 15 years onwards is well exemplified.
| Year | Under 1* | 1 and Under 5 | 5 and Under 15 | 15 and Under 25 | 25 and Under 35 | 35 and Under 45 | 45 and Under 55 | 55 and Under 65 | 65 and Under 75 | 75 and Over |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Per 1,000 live births in this case. | ||||||||||
| (rates per 1,000 of mean population) | ||||||||||
| Males | ||||||||||
| 1901 | 78.60 | 6.81 | 1.89 | 3.52 | 3.97 | 6.16 | 11.94 | 23.12 | 50.59 | 141.67 |
| 1911 | 63.48 | 5.36 | 1.91 | 2.42 | 3.87 | 6.27 | 11.02 | 20.83 | 53.22 | 130.58 |
| 1921 | 53.10 | 4.78 | 1.85 | 2.44 | 3.56 | 5.55 | 9.61 | 19.96 | 46.17 | 128.60 |
| 1931 | 38.21 | 2.83 | 1.35 | 2.28 | 2.77 | 4.64 | 8.69 | 18.25 | 44.18 | 130.57 |
| 1941 | 32.55 | 2.14 | 0.99 | 1.98 | 2.62 | 3.76 | 8.79 | 20.67 | 46.31 | 137.85 |
| 1951 | 26.49 | 1.40 | 0.64 | 1.54 | 1.82 | 2.93 | 7.20 | 20.04 | 46.90 | 127.33 |
| 1959 | 21.70 | 1.05 | 0.49 | 1.27 | 1.45 | 2.33 | 6.58 | 18.76 | 47.58 | 125.93 |
| Females | ||||||||||
| 1901 | 63.87 | 5.50 | 1.64 | 3.58 | 4.72 | 6.70 | 10.62 | 19.44 | 43.32 | 127.98 |
| 1911 | 48.74 | 5.37 | 1.48 | 2.76 | 4.34 | 4.92 | 8.38 | 17.89 | 40.44 | 119.60 |
| 1921 | 42.31 | 4.49 | 1.31 | 2.34 | 3.38 | 4.46 | 8.00 | 14.88 | 36.81 | 120.23 |
| 1931 | 25.67 | 2.47 | 0.97 | 1.85 | 3.20 | 3.81 | 6.84 | 15.36 | 36.83 | 122.87 |
| 1941 | 26.85 | 2.04 | 0.71 | 1.35 | 2.05 | 3.14 | 6.58 | 14.55 | 38.06 | 116.57 |
| 1951 | 18.81 | 1.19 | 0.36 | 0.73 | 1.17 | 2.04 | 5.29 | 13.27 | 32.35 | 113.75 |
| 1959 | 18.00 | 1.10 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.81 | 1.68 | 4.20 | 10.89 | 29.18 | 101.09 |
| Both Sexes | ||||||||||
| 1901 | 71.40 | 6.17 | 1.77 | 3.55 | 4.33 | 6.40 | 11.37 | 21.63 | 47.87 | 135.71 |
| 1911 | 56.31 | 5.36 | 1.70 | 2.58 | 4.09 | 5.64 | 9.82 | 19.55 | 47.74 | 126.13 |
| 1921 | 47.82 | 4.64 | 1.58 | 2.39 | 3.47 | 5.10 | 8.85 | 17.59 | 41.90 | 124.84 |
| 1931 | 32.15 | 2.65 | 1.17 | 2.07 | 2.98 | 4.22 | 7.80 | 16.88 | 40.56 | 126.87 |
| 1941 | 29.77 | 2.09 | 0.85 | 1.65 | 2.32 | 3.44 | 7.65 | 17.68 | 42.20 | 126.76 |
| 1951 | 22.77 | 1.30 | 0.50 | 1.15 | 1.49 | 2.49 | 6.26 | 16.52 | 39.36 | 119.96 |
| 1959 | 19.89 | 1.07 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 1.14 | 2.01 | 5.40 | 14.74 | 37.48 | 111.99 |
The average (arithmetic mean) age at death of persons of each sex at 10-yearly intervals since 1901 and during each of the last four years was as follows.
| Year | Males | Females |
|---|---|---|
| age (years) | ||
| 1901 | 41.64 | 37.68 |
| 1911 | 46.17 | 42.37 |
| 1921 | 48.45 | 46.97 |
| 1931 | 54.14 | 55.48 |
| 1941 | 58.65 | 59.60 |
| 1951 | 61.58 | 65.25 |
| 1956 | 63.89 | 66.69 |
| 1957 | 63.78 | 67.37 |
| 1958 | 63.25 | 67.24 |
| 1959 | 63.95 | 67.54 |
There has been a striking upward movement in the average age at death since 1901. A noticeable feature is that in the earlier years the age for females was considerably lower than that for males, the margin gradually narrowing until virtual equality was reached in 1927–28, since when the female average age at death has been higher than the male.
EXPECTATION OF LIFE — Life tables depicting the pattern of mortality over the age span of life for the non-Maori* component of New Zealand's population have been constructed at various times since 1880. The most recent tables are based on the 1956 population census, together with mortality statistics for 1955–57. As the pattern of mortality among non-Maoris has stabilised in recent years, these latest life tables give an accurate statistical summary of current mortality experience.
Life tables contain a measure of the degree of longevity of the population called the “expectation of life”. The expectation of life at any age is the average remaining lifetime for persons of this age, assuming that mortality rates at each age continue at the level shown by the life table. The life expectancy at selected ages at the present time, for the non-Maori population in New Zealand, is shown in the table below. The overall longer span of life enjoyed by females, compared with males, is evident, as is the improvement in life expectancy once the first year of life is survived.
LIFE EXPECTANCY FOR NON-MAORI POPULATION, SELECTED AGES
| Exact Age (Years) | Life Expectancy (Years) | |
|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | |
| 0 | 68.88 | 73.88 |
| 1 | 69.47 | 74.17 |
| 2 | 68.60 | 73.29 |
| 3 | 67.69 | 72.38 |
| 4 | 66.76 | 71.44 |
| 5 | 65.81 | 70.49 |
| 10 | 60.98 | 65.60 |
| 15 | 56.12 | 60.72 |
| 20 | 51.44 | 55.87 |
| 25 | 46.87 | 51.02 |
| 30 | 42.19 | 46.17 |
| 40 | 32.84 | 36.65 |
| 50 | 23.93 | 27.53 |
| 60 | 16.19 | 19.16 |
| 70 | 10.08 | 11.91 |
| 80 | 5.71 | 6.47 |
| 90 | 2.86 | 3.09 |
| 100 | 1.18 | 1.19 |
Improvement in non-Maori life expectancy since 1880, for both sexes, has been most striking for the younger ages, but has been relatively small for the advanced ages. Progress in medical science, coupled with improved social conditions, has resulted in substantial reductions in mortality among infants and children from infectious diseases; on the other hand, diseases of middle and old age are less amenable to control. It is unlikely, therefore, that increases in life expectancy in the future will occur on the scale of the past, but will be quite small and will happen very slowly. The table below displays the life expectancy revealed by each life table compiled since 1880 for the three exact ages of 0, 20, and 60 years.
IMPROVEMENT IN NON-MAORI LIFE EXPECTANCY SINCE 1880
| Life Table | Life Expectancy (Years) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males Aged | Females Aged | |||||
| 0 | 20 | 60 | 0 | 20 | 6 | |
| 1880–92 | 54.44 | 44.55 | 14.95 | 57.26 | 46.39 | 16.39 |
| 1891–95 | 55.29 | 45.47 | 15.06 | 58.09 | 47.19 | 16.55 |
| 1896–1900 | 57.37 | 46.34 | 15.33 | 59.95 | 47.91 | 16.54 |
| 1901–05 | 58.09 | 46.74 | 15.40 | 60.55 | 48.23 | 16.64 |
| 1906–10 | 59.17 | 47.20 | 15.51 | 61.76 | 48.77 | 16.77 |
| 1911–15 | 60.96 | 47.61 | 15.54 | 65.48 | 49.14 | 16.72 |
| 1921–22 | 62.76 | 48.66 | 16.03 | 65.43 | 50.36 | 17.29 |
| 1925–27 | 63.99 | 48.93 | 15.79 | 66.57 | 50.96 | 17.23 |
| 1931 | 65.04 | 49.61 | 16.22 | 67.88 | 51.28 | 17.30 |
| 1934–38 | 65.46 | 49.89 | 16.06 | 68.45 | 52.02 | 17.49 |
| 1950–52 | 68.29 | 51.15 | 16.19 | 72.43 | 54.64 | 18.53 |
| 1955–57 | 68.88 | 51.44 | 16.19 | 73.88 | 55.87 | 19.16 |
*A table showing the expectation of life of the Maori population is given in Section 4E.
Prior to the Second World War the New Zealand non-Maori population were probably the longest lived of any national population group in the world. This pre-eminent position has not been maintained, however, although New Zealand still takes a very high place in the international ranking list. The table below compares the life expectancy at birth for the non-Maori population with that for selected overseas countries. In all cases the expectancies are the most recent available.
LIFE EXPECTANCY AT BIRTH, SELECTED COUNTRIES
| Country | Period | Life Expectancy at Birth (Years) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | ||
*Non-Maori population. †White population. | |||
| New Zealand* | 1955–57 | 68.88 | 73.88 |
| Australia | 1953–55 | 67.14 | 72.75 |
| Canada | 1950–52 | 66.33 | 70.83 |
| Denmark | 1951–55 | 69.87 | 72.60 |
| England and Wales | 1956 | 67.76 | 73.36 |
| France | 1952–56 | 65.04 | 71.15 |
| Netherlands | 1953–55 | 71.0 | 73.9 |
| Norway | 1951–55 | 71.11 | 74.70 |
| Sweden | 1951–55 | 70.49 | 73.43 |
| Union of South Africa† | 1945–47 | 63.78 | 68.31 |
| United States of America | 1956 | 67.3 | 73.7 |
| U.S.S.R. | 1955–56 | 63 | 69 |
INFANT MORTALITY — Over a long period of years New Zealand has been renowned for its low rate of infant mortality, a fact attributable partly to such matters as climate, virility of the race, comparative absence of densely settled areas, etc., and partly legislative and educative measures — the latter conducted by the State as well as by various organisations (one of the most important of these is the Royal New Zealand Society for the Health of Women and Children which was founded in 1907).
Particulars of deaths of infants under one year of age for each of the years 1950–60 are shown in the following table.
| Year | Number | Rate per 1,000 Live Births | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| 1950 | 569 | 439 | 1,008 | 25.1 | 20.3 | 22.8 |
| 1951 | 611 | 406 | 1,017 | 26.5 | 18.8 | 22.8 |
| 1952 | 553 | 461 | 1,014 | 23.2 | 20.4 | 21.8 |
| 1953 | 549 | 382 | 931 | 23.0 | 16.9 | 20.1 |
| 1954 | 556 | 412 | 968 | 22.3 | 17.6 | 20.0 |
| 1955 | 599 | 403 | 1,002 | 23.3 | 16.6 | 20.1 |
| 1956 | 542 | 436 | 978 | 20.8 | 17.7 | 19.4 |
| 1957 | 605 | 431 | 1,036 | 22.8 | 17.0 | 20.0 |
| 1958 | 608 | 435 | 1,043 | 22.0 | 16.7 | 19.4 |
| 1959 | 609 | 480 | 1,089 | 21.7 | 18.0 | 19.9 |
| 1960 | 610 | 479 | 1,089 | 21.4 | 17.8 | 19.7 |
In the following table New Zealand's infant-mortality rate is shown in comparison with that of other countries. The figures are taken from the United Nations Demographic Yearbook 1959. It is interesting to observe that the distinction of having the lowest infant-mortality rate in the world belongs to Sweden, which achieved the phenomenally low ratio of 17 infant deaths per 1,000 live births in 1954–58, as compared with New Zealand's 20 for the same quinquennium. In the case of the United States of America, the Union of South Africa, and New Zealand the European population only has been taken into account.
| Country | Quinquennia | Deaths Under 1 Year Per 1,000 Live Births |
|---|---|---|
| Sweden | 1954–58 | 17 |
| Netherlands | 1954–58 | 19 |
| New Zealand (excluding Maoris) | 1954–58 | 20 |
| Norway | 1953–57 | 21 |
| Australia | 1954–58 | 22 |
| United Kingdom | 1954–58 | 24 |
| Switzerland | 1954–58 | 25 |
| Denmark | 1953–57 | 26 |
| United States of America (excluding coloured population) | 1954–58 | 26 |
| Finland | 1954–58 | 28 |
| Union of South Africa (excluding coloured population) | 1954–58 | 31 |
| Canada | 1954–58 | 31 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1954–58 | 33 |
| China (Taiwan) | 1954–58 | 34 |
| Cyprus | 1954–58 | 35 |
| France | 1954–58 | 36 |
| Republic of Ireland | 1954–58 | 36 |
| Israel | 1954–58 | 38 |
| Belgium | 1954–58 | 38 |
| West Germany | 1954–58 | 39 |
| Japan | 1954–58 | 40 |
| Austria | 1954–58 | 44 |
| East Germany | 1954–58 | 47 |
| Italy | 1954–58 | 50 |
| Spain | 1954–58 | 53 |
| U.S.S.R. | 1953–57 | 56 |
| Argentina | 1954–58 | 62 |
| Venezuela | 1954–58 | 68 |
| Ceylon | 1953–57 | 70 |
| Mexico | 1954–58 | 79 |
| Portugal | 1954–58 | 87 |
| Peru | 1954–58 | 96 |
| Yugoslavia | 1954–58 | 100 |
| India | 1953–57 | 103 |
| Chile | 1954–58 | 122 |
The male rate of infant mortality is considerably above the female rate, the average for New Zealand over the five-year period 1955–59 being 23.4 male deaths per 1,000 male births and 17.2 female deaths per 1,000 female births.
The rates per 1,000 births for the two sexes combined at different ages during the first year of life are now given for each of the last 11 years.
INFANT-MORTALITY RATES, 1949–59 (PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS)
| Year | Under 1 Day | 1 Day and Under 2 Days | 2 Days and Under 1 Week | Total Under 1 Week | 1 Week and Under 2 Weeks | 2 Weeks and Under 3 Weeks | 3 Weeks and Under 1 Month | Total Under 1 Month | 1 Month and Under 12 Month | Total Under 1 Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 8.2 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 15.2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 17.0 | 6.8 | 23.8 |
| 1950 | 7.3 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 14.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 16.6 | 6.2 | 22.8 |
| 1951 | 6.9 | 2.9 | 4.9 | 14.7 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 16.2 | 6.6 | 22.8 |
| 1952 | 6.3 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 13.0 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 15.1 | 6.7 | 21.8 |
| 1953 | 5.9 | 2.1 | 4.1 | 12.1 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 14.3 | 5.8 | 20.1 |
| 1954 | 6.0 | 2.4 | 4.2 | 12.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 14.4 | 5.6 | 20.0 |
| 1955 | 6.4 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 11.8 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 14.1 | 6.0 | 20.1 |
| 1956 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 3.6 | 11.6 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 13.3 | 6.0 | 19.4 |
| 1957 | 6.9 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 12.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 13.8 | 6.1 | 20.0 |
| 1958 | 6.8 | 1.8 | 3.0 | 11.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 13.6 | 5.8 | 19.4 |
| 1959 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 12.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 13.9 | 6.0 | 19.9 |
Infants who die in the first year of life may be grouped roughly into two main classes, viz, those dying within one month of birth and those surviving the first month of life but dying before the first anniversary of their birth. Deaths amongst the first class, called neo-natal deaths, are due principally to pre-natal and natal influences. The second group covers those infants who have succumbed in the main to causes arising from post-natal influences such as the various epidemic diseases, diseases of the respiratory system, faulty feeding, and other environmental factors.
The next table shows that, whereas in the quinquennium 1951–55 the death rate for children under one month of age was 50 per cent lower than in the quinquennium 1881–85, the rate for children who had survived the first month of life was only approximately one-tenth as high as in the eighties. In other words, whereas formerly over 60 children out of every 1,000 who survived the first month of life died before reaching one year of age, now only six such deaths occur. While the decline in the under-one-month group has been progressive for some years, it was among infants who had survived the first month of life that the most marked reductions were achieved. In the thirties, however, the reduction of this rate was arrested, and in the quinquennium 1941–45 an increase was recorded for the first time. For some years it had been considered that any further substantial decrease in the total infant-mortality rate would have to be achieved in the under-one month group. The figures for 1951–55, however, indicate that, whereas this group recorded a decrease of 26 per cent from the 1941–45 rate, the one-month-and-over group declined by 36 per cent.
| Period | Deaths per 1,000 Births | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 Year | Under 1 Month | Between 1 and 12 Months | |
| 1881–1885 | 90.60 | 29.77 | 60.83 |
| 1886–1890 | 84.09 | 27.57 | 56.52 |
| 1891–1895 | 87.60 | 30.34 | 57.26 |
| 1896–1900 | 80.06 | 30.38 | 49.68 |
| 1901–1905 | 74.77 | 30.64 | 44.13 |
| 1906–1910 | 69.62 | 30.28 | 39.34 |
| 1911–1915 | 53.63 | 29.28 | 24.35 |
| 1916–1920 | 48.62 | 28.16 | 20.46 |
| 1921–1925 | 42.75 | 27.48 | 15.27 |
| 1926–1930 | 36.70 | 24.82 | 11.88 |
| 1931–1935 | 31.88 | 22.34 | 9.54 |
| 1936–1940 | 31.83 | 22.51 | 9.32 |
| 1941–1945 | 29.53 | 20.01 | 9.52 |
| 1946–1950 | 23.92 | 17.31 | 6.61 |
| 1951–1955 | 20.95 | 14.84 | 6.11 |
| 1956–1959 | 19.67 | 13.92 | 5.97 |
The accompanying diagram further illustrates the reduction in the infant-mortality rate that has taken place over a long period, and the relatively steady low rate of recent years.
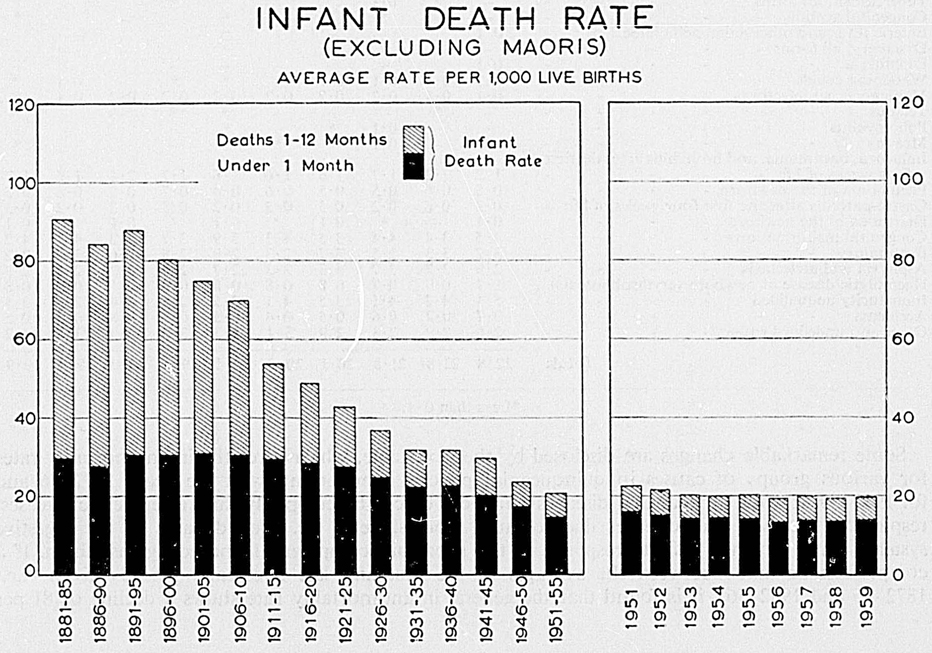
Causes of Infant Mortality — The principal causes of infant mortality over the last 10 years, showing both numbers and rates per 1,000 live births, are shown in the following table. The classification is according to the Sixth (1948) and Seventh (1955) Revisions of the International List.
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1951 | 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Tuberculosis, all forms | - | 1 | 4 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 |
| Congenital syphilis | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Enteric fever and other salmonella infections | 3 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Dysentery, all forms | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| Diphtheria | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | —- |
| Whooping cough | 12 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 6 | 2 |
| Meningococcal infections | 2 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 5 | 2 |
| Tetanus | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Poliomyelitis | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Measles | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Influenza, pneumonia, and bronchitis after the first four weeks of life | 53 | 96 | 79 | 73 | 77 | 79 | 84 | 107 | 87 | 91 |
| Pneumonia of the newborn | 22 | 30 | 22 | 24 | 28 | 21 | 35 | 26 | 31 | 30 |
| Gastro-enteritis after the first four weeks of life | 15 | 26 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 9 | 16 |
| Diarrhoea of the newborn | 3 | - | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| Congenital malformations | 198 | 151 | 205 | 163 | 208 | 196 | 186 | 165 | 223 | 231 |
| Birth injury | 142 | 146 | 118 | 127 | 110 | 144 | 143 | 135 | 123 | 119 |
| Asphyxia and atelectasis | 128 | 164 | 174 | 152 | 110 | 137 | 128 | 172 | 134 | 124 |
| Haemolytic disease of newborn (erythroblastosis) | 50 | 38 | 34 | 37 | 40 | 40 | 39 | 26 | 50 | 43 |
| Immaturity unqualified | 225 | 191 | 191 | 162 | 198 | 162 | 143 | 176 | 132 | 167 |
| Accidents | 30 | 33 | 26 | 24 | 17 | 27 | 26 | 39 | 27 | 27 |
| Other and undefined causes | 122 | 131 | 129 | 136 | 152 | 164 | 166 | 167 | 213 | 228 |
| Totals | 1,008 | 1,017 | 1,014 | 931 | 968 | 1,002 | 978 | 1,036 | 1,043 | 1,089 |
| Causes of Death | Rates per 1,000 Live Births | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1951 | 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Less than 0.1. | ||||||||||
| Tuberculosis, all forms | - | * | 0.1 | * | - | * | * | * | - | * |
| Congenital syphilis | - | - | * | - | - | * | - | - | - | * |
| Enteric fever and other salmonella infections | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | - | - |
| Dysentery, all forms | - | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | - | - |
| Whooping cough | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | - | - | * | 0.1 | * |
| Meningococcal infections | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | * |
| Tetanus | - | * | - | - | - | * | * | - | - | * |
| Poliomyelitis | - | - | 0.1 | * | - | * | - | - | - | - |
| Measles | * | - | 0.1 | * | * | - | - | - | - | * |
| Influenza, pneumonia, and bronchitis after the first four weeks of life | 1.2 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| Pneumonia of the newborn | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| Gastro-enteritis after the first four weeks of life | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Diarrhoea of the newborn | 0.1 | - | * | 0.1 | * | 0.1 | * | 0.1 | * | 0.1 |
| Congenital malformations | 4.5 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 3.5 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| Birth injury | 3.2 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| Asphyxia and atelectasis | 2.9 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
| Haemolytic disease of newborn (erythroblastosis) | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Immaturity unqualified | 5.1 | 4.3 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 3.1 |
| Accidents | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Other and undefined causes | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 4.2 |
| Totals | 22.8 | 22.8 | 21.8 | 20.1 | 20.0 | 20.1 | 19.4 | 20.0 | 19.4 | 19.9 |
Some remarkable changes are disclosed by the next table, which gives the infant-mortality rates for various groups of causes in quinquennial periods commencing with the years 1872–76 and for 1957–59. It would appear that diseases which can be combated openly, such as epidemic diseases, respiratory diseases, and diseases due to faulty nourishment, etc. (i.e., diseases of the digestive system), have shown a definite response to the strenuous campaigns launched against them. If a comparison be made between the averages of the first and last five-yearly periods given — i.e., 1872–76 and 1952–56 — it is found that the general infant-mortality rate shows a decline of 81 per cent, while even greater decreases are recorded for tuberculosis (99 per cent), convulsions (100 per cent), gastric and intestinal diseases (98 per cent), epidemic diseases (97 per cent), and respiratory diseases (81 per cent). The rate for epidemic diseases still continues to decline, and it is interesting to note that over 46 per cent of the total under this heading in the years 1952–56 was due to meningococcal infections, with 17 per cent assigned to influenza, and 16 per cent to whooping cough. During the five-year period 1952–56 there were only two deaths from streptococcal sore throat and no deaths at all from scarlet fever or diphtheria.
In 1957–59, 45 per cent of deaths from epidemic diseases were due to influenza, 27 per cent to meningococcal infections, 13 per cent to whooping cough, 7 per cent to infectious encephalitis, 7 per cent to chickenpox, and 1 per cent to other epidemic diseases.
The increase shown for malformations and the decrease for tuberculosis are probably somewhat less than is indicated by the figures. In the earlier years covered by the table the latter heading included all deaths from hydrocephalus, many of which were no doubt due to congenital hydrocephalus, which is now included among the malformations. A proportion of the deaths from hydrocephalus in the earlier years would also probably be due to meningitis. The following table shows quinquennial average death rates of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births. To enable the comparison with past years to be maintained, the infant deaths for 1950 onwards have been reassembled to conform to the former classifications for the purposes of this table — i.e., influenza deaths have been included under epidemic diseases, while both pneumonia and diarrhoea of the newborn have been included under respiratory and gastric and intestinal diseases respectively, and not as diseases of early infancy.
| Period | Epidemic Diseases | Tuberculosis | Infantile Convulsions | Respiratory Diseases | Gastric and Intestinal Diseases | Malformations | Early Infancy | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Less than 0.1. | |||||||||
| 1872–1876 | 13.5 | 5.5 | 9.7 | 12.9 | 24.2 | 1.2 | 25.0 | 17.3 | 109.3 |
| 1877–1881 | 10.2 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 12.3 | 19.8 | 1.4 | 21.9 | 15.3 | 93.6 |
| 1882–1886 | 9.3 | 4.7 | 7.9 | 11.8 | 19.1 | 1.2 | 25.5 | 12.3 | 91.8 |
| 1887–1891 | 8.9 | 3.7 | 6.3 | 10.5 | 18.5 | 1.3 | 24.7 | 8.8 | 82.7 |
| 1892–1896 | 9.8 | 3.3 | 6.6 | 11.0 | 16.6 | 1.4 | 24.9 | 11.2 | 84.8 |
| 1897–1901 | 6.1 | 2.6 | 5.6 | 10.0 | 17.2 | 1.5 | 26.2 | 9.7 | 78.9 |
| 1902–1906 | 5.5 | 1.5 | 4.1 | 9.7 | 15.3 | 1.3 | 27.6 | 7.9 | 72.9 |
| 1907–1911 | 5.9 | 1.3 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 15.5 | 1.9 | 26.7 | 6.3 | 68.5 |
| 1912–1916 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 5.1 | 7.4 | 3.9 | 26.2 | 3.5 | 52.5 |
| 1917–1921 | 3.2 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 26.1 | 2.9 | 48.1 |
| 1922–1926 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 22.4 | 3.3 | 41.1 |
| 1927–1931 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 5.0 | 19.4 | 3.1 | 35.2 |
| 1932–1936 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 17.5 | 2.4 | 31.7 |
| 1937–1941 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 5.5 | 17.4 | 2.5 | 31.6 |
| 1942–1946 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 16.1 | 2.6 | 28.7 |
| 1947–1951 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 13.6 | 2.1 | 23.3 |
| 1952–1956 | 0.4 | * | - | 2.4 | 0.6 | 4.0 | 11.0 | 1.8 | 20.3 |
| 1957–1959 | 0.4 | * | - | 2.2 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 10.5 | 1.9 | 19.8 |
It is convenient to consider still births and deaths in the first week of life together, as they are largely the result of common causes. The combined group is termed perinatal mortality. The term is particularly appropriate when we consider how deaths in the newborn crowd closely towards the day of birth. This is clearly shown in the table on page 106. Still births, deaths in the first week of life, and perinatal deaths (still births plus deaths in the first week) are shown in the following table. The still births and the perinatal mortality rate are calculated per 1,000 total births (still births plus live births), while the death rate for the first week of life is calculated per 1,000 live births.
| Year | Still Births | Deaths Under 1 Week | Perinatal Mortality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Rate | Number | Rate | Number | Rate | |
| 1955 | 796 | 15.71 | 588 | 11.79 | 1,384 | 27.31 |
| 1956 | 858 | 16.73 | 584 | 11.58 | 1,442 | 28.11 |
| 1957 | 834 | 15.83 | 638 | 12.30 | 1,472 | 27.93 |
| 1958 | 819 | 15.00 | 624 | 11.60 | 1,443 | 26.43 |
| 1959 | 805 | 14.49 | 663 | 12.11 | 1,468 | 26.43 |
The combined rate has shown a steady improvement, due principally to the reduction in the still-birth rate. It is observed that a considerable proportion of the live-born babies who would previously have been still births would be delicate, immature infants with a high risk of dying in the first week of life. Consequently the death rate for the first week has not changed noticeably.
CAUSES OF STILL BIRTH — A still-born child is defined in New Zealand as one “which has issued from its mother after the expiration of the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy and which was not alive at the time of such issue”.
The registration of still births has been effected in New Zealand since 1913, but no information regarding the causes of still births was required for registration purposes until 1947. As from 1 July 1952 a certificate of the cause of death in cases of intermediate foetal deaths — i.e., deaths after the end of the twentieth but before the end of the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy — was also required to be furnished. The certificates of causes of still birth and foetal death provide for both maternal and foetal causes to be entered.
The following table shows the 805 still births registered during 1959 classified (a) according to maternal causes and (b) according to foetal causes.
| Causes of Still-Birth | Number of Cases | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |
| (a) Maternal Causes | |||
| Chronic disease in mother | 13 | 8 | 21 |
| Acute disease in mother | 3 | 9 | 12 |
| Diseases and conditions of pregnancy and childbirth | 94 | 70 | 164 |
| Difficulties in labour | 39 | 43 | 82 |
| Other causes in mother | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| Totals | 152 | 133 | 285 |
| (b) Foetal Causes | |||
| Placental and cord conditions | 122 | 119 | 241 |
| Birth injury | 5 | 4 | 9 |
| Congenital malformation of foetus | 38 | 38 | 76 |
| Diseases of foetus and ill defined causes | 98 | 96 | 194 |
| Totals | 263 | 257 | 520 |
| Totals, all causes | 415 | 390 | 805 |
PERINATAL MORTALITY AND PREMATURITY — Approximately three out of every four infants who die in the first year of life do so in the first month, and of those dying in the first month 50 per cent die in the first day of life and 85 per cent in the first week.
A principal factor in the loss of this new life is prematurity. This is seen in the following table, where causes of neo-natal deaths for 1959 are set out in accordance with the International List of 1955.
| Causes of Death | Under 1 Day | 1 Day and Under 1 Week | 1 Week and Under 2 Weeks | 2 Weeks and Under 3 Weeks | 3 Weeks and Under 1 Month | Total Under 1 Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital malformations | 42 | 56 | 17 | 12 | 9 | 136 |
| Injury at birth | 37 | 33 | 5 | 1 | - | 76 |
| Injury at birth with prematurity | 23 | 20 | - | - | - | 43 |
| Post-natal asphyxia and atelectasis | 23 | 17 | 2 | - | - | 42 |
| Post-natal asphyxia and atelectasis, with prematurity | 55 | 24 | 1 | - | - | 80 |
| Pneumonia of newborn | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 21 |
| Pneumonia of newborn, with prematurity | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 9 |
| Disorders arising from maternal toxaemia | 4 | 3 | - | - | - | 7 |
| Disorders arising from maternal toxaemia, with prematurity | 22 | 9 | - | - | - | 31 |
| Haemolytic disease of newborn (erythroblastosis) | 12 | 7 | 2 | 1 | - | 22 |
| Haemolytic disease of newborn (erythroblastosis), with prematurity | 9 | 8 | 2 | - | - | 19 |
| Haemorrhagic disease of newborn | 2 | 5 | - | 1 | - | 8 |
| Haemorrhagic disease of newborn, with prematurity | 1 | 4 | 2 | - | - | 7 |
| Diarrhoea of newborn | - | - | 2 | - | - | 2 |
| Diarrhoea of newborn with prematurity | - | - | 1 | 2 | - | 3 |
| Ill-defined diseases peculiar to early infancy | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | 14 |
| Ill-defined diseases peculiar to early infancy, with prematurity | 17 | 17 | 1 | - | - | 35 |
| Immaturity with mention of any other subsidiary condition | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 4 |
| Immaturity, unqualified | 116 | 48 | 3 | - | - | 167 |
| Pemphigus neonatorum | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Umbilical sepsis | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Umbilical sepsis with prematurity | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Other sepsis of newborn | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 3 |
| Other sepsis of newborn, with prematurity | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| External causes | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 3 |
| Other causes | 9 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 26 |
| Totals | 387 | 276 | 52 | 27 | 20 | 762 |
A total of 167, or 22 per cent, of all neo-natal deaths are directly attributed to immaturity, and a further 233 deaths are associated with it. The principal conditions of early infancy with which immaturity is associated are: (1) asphyxia in 80 cases (10.5 per cent of all neo-natal deaths); (2) birth injury in 56 cases (7.3 per cent); and (3) diseases peculiar to early infancy in 35 cases (4.6 per cent).
In the case of still births, out of 805 in 1959 there were 479 cases, or 59 per cent, where gestation fell short of full term.
It is not possible to assess what the reduction in perinatal mortality would be if every pregnancy were to go to full term, but there is no doubt that it would be considerable.
As a first step in the campaign to reduce this grave loss of new life, details of the birth weight and gestation period of all infants born alive or dead after 1 July 1952 were required to be furnished to the Registrars of Births and Deaths. These will provide essential basic data for further studies on prematurity. It will give a measure of the extent of the problem in different localities according to the age and parity of the mother and the occupation of the father and it will enable cohorts of infants to be followed through their first year of life so that their mortality and morbidity experience may be shown according to their degree of maturity at birth.
CAUSES OF DEATH — Since 1908 the classification of causes of death in New Zealand has been on the basis of the international classification. Almost all countries are member States of the World Health Organisation, and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Injuries, and Causes of Death has world-wide application.
The Seventh (1955) Revision of the Classification was applied to New Zealand in 1958. Like the Sixth Revision, this assigns the cause of death to the underlying cause. This is defined as (a) the disease or injury which initiated the train of morbid events leading directly to death, or (b) the circumstances of the accident or violence which produced the fatal injury. The responsibility for indicating the train of events is placed on the physician or surgeon signing the medical certificate of death.
The following table shows the numbers of deaths and death rates per million of mean population according to the Abbreviated List of 50 causes.
The statistics for tuberculosis, cancer, puerperal causes, and violent causes, which are of special interest and significance, are discussed later in this subsection. Certain diseases (cholera, plague, smallpox, typhus, and typhoid fever) are not listed in the table below as there were no deaths from these causes in the years shown.
| Causes of Death | Numbers align="center" | Rates per Million of Mean Population | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Less than one. | ||||||||||
| Tuberculosis of respiratory system | 195 | 146 | 163 | 121 | 85 | 97 | 71 | 78 | 57 | 39 |
| Tuberculosis, other forms | 23 | 14 | 21 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 6 |
| Syphilis and its sequelae | 26 | 17 | 28 | 18 | 14 | 13 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 6 |
| Dysentery, all forms | 4 | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | 2 | * | - | 1 | * |
| Scarlet fever and streptococcal sore throat | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | * | * | - | * | - |
| Diphtheria | 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | * |
| Whooping cough | 2 | 2 | - | 7 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 3 | 1 |
| Meningococcal infections | 16 | 16 | 16 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| Acute poliomyelitis | 29 | 50 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 14 | 24 | 1 | 2 | * |
| Measles | 8 | 3 | - | 8 | 8 | 4 | 1 | - | 4 | 4 |
| Malaria | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | - |
| All other diseases classified as infective and parasitic | 85 | 77 | 84 | 71 | 96 | 42 | 38 | 40 | 33 | 44 |
| Malignant neoplasms, including neoplasms of lymphatic and haematopoietic tissues | 3,077 | 3,051 | 3,110 | 3,192 | 3,220 | 1,534 | 1,492 | 1,489 | 1,493 | 1,477 |
| Benign and unspecified neoplasms | 35 | 43 | 43 | 35 | 31 | 17 | 21 | 21 | 16 | 14 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 205 | 215 | 271 | 273 | 232 | 102 | 105 | 130 | 128 | 106 |
| Anaemias | 77 | 69 | 56 | 49 | 45 | 38 | 34 | 27 | 23 | 21 |
| Vascular lesions affecting central nervous system | 2,281 | 2,256 | 2,457 | 2,550 | 2,517 | 1,137 | 1,103 | 1,176 | 1,193 | 1,154 |
| Non-meningococcal meningitis | 27 | 31 | 24 | 31 | 35 | 13 | 15 | 11 | 15 | 16 |
| Rheumatic fever | 5 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Chronic rheumatic heart disease | 202 | 171 | 201 | 218 | 197 | 101 | 84 | 96 | 102 | 90 |
| Arteriosclerotic and degenerative heart disease | 4,770 | 5,023 | 5,185 | 5,166 | 5,476 | 2,378 | 2,456 | 2,482 | 2,417 | 2,511 |
| Other diseases of the heart | 702 | 707 | 716 | 747 | 851 | 350 | 346 | 343 | 350 | 390 |
| Hypertension with heart disease | 630 | 546 | 557 | 443 | 447 | 314 | 267 | 267 | 207 | 205 |
| Hypertension without mention of heart | 122 | 140 | 126 | 140 | 118 | 61 | 68 | 60 | 66 | 54 |
| Influenza | 23 | 83 | 129 | 30 | 174 | 11 | 41 | 62 | 14 | 80 |
| Pneumonia | 480 | 657 | 784 | 621 | 865 | 239 | 321 | 375 | 291 | 397 |
| Bronchitis | 407 | 384 | 462 | 433 | 516 | 203 | 188 | 221 | 203 | 237 |
| Ulcer of stomach and duodenum | 172 | 177 | 202 | 167 | 170 | 86 | 87 | 97 | 78 | 78 |
| Appendicitis | 18 | 27 | 33 | 25 | 35 | 9 | 13 | 16 | 12 | 16 |
| Intestinal obstruction and hernia | 93 | 126 | 164 | 143 | 132 | 46 | 62 | 78 | 67 | 61 |
| Gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and colitis, except diarrhoea of newborn | 87 | 99 | 100 | 92 | 103 | 43 | 48 | 48 | 43 | 47 |
| Cirrhosis of liver | 70 | 64 | 70 | 52 | 59 | 35 | 31 | 34 | 24 | 27 |
| Nephritis and nephrosis | 160 | 119 | 142 | 143 | 107 | 80 | 58 | 68 | 67 | 49 |
| Hyperplasia of prostate | 142 | 165 | 144 | 132 | 136 | 71 | 81 | 69 | 62 | 62 |
| Complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium | 22 | 20 | 35 | 22 | 27 | 11 | 10 | 17 | 10 | 12 |
| Congenital malformations | 266 | 255 | 240 | 316 | 307 | 133 | 125 | 115 | 148 | 141 |
| Birth injuries, post-natal asphyxia, and atelectasis | 281 | 271 | 307 | 257 | 243 | 140 | 133 | 147 | 120 | 111 |
| Infections of the newborn | 27 | 44 | 41 | 49 | 45 | 13 | 21 | 20 | 23 | 21 |
| Other diseases peculiar to early infancy, and immaturity unqualified | 254 | 241 | 256 | 273 | 322 | 127 | 118 | 123 | 128 | 148 |
| Senility without mention of psychosis, ill defined, and unknown causes | 161 | 143 | 96 | 111 | 111 | 80 | 70 | 46 | 52 | 51 |
| All other diseases | 1,684 | 1,916 | 1,918 | 1,850 | 1,924 | 840 | 937 | 918 | 865 | 882 |
| Motor-vehicle accidents | 313 | 294 | 336 | 353 | 308 | 156 | 144 | 161 | 165 | 141 |
| All other accidents | 571 | 525 | 662 | 610 | 611 | 285 | 258 | 317 | 285 | 280 |
| Suicide and self-inflicted injury | 181 | 194 | 209 | 211 | 198 | 90 | 95 | 100 | 99 | 91 |
| Homicide and operations of war | 17 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 18 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Totals | 17,953 | 18,403 | 19,411 | 19,014 | 19,814 | 8,950 | 9,000 | 9,291 | 8,896 | 9,087 |
TUBERCULOSIS — The death toll from tuberculosis of the respiratory system has declined steadily for many years and is still doing so. During the last 10 years the fall has been particularly steep, as is shown in the following average rates for the past five quinquennia: 1933–37, 333 per million of population; 1938–42, 323 per million; 1943–47, 294 per million; 1948–52, 186 per million; 1953–57, 87 per million. The rate of 39 for 1959 is a reduction of 50 per cent of the 1957 rate.
The latest triennial figures available show New Zealand in eighth place out of 37 countries for which death rates from respiratory tuberculosis were compiled. The countries with lower rates than New Zealand were Denmark, 4.4; Netherlands, 4.6; Israel, 5.5; Australia, 6.6; Union of South Africa (white), 6.8; Canada, 6.9; United States of America, 8.1. The New Zealand rate was 8.2 per 100,000.
In addition to the 85 deaths from tuberculosis of the respiratory system during 1959, there were 13 deaths from other forms of tuberculosis, comprised of:
| Tuberculosis of meninges and nervous system | 4 |
| Tuberculosis of intestines, peritoneum, and mesentery | 2 |
| Tuberculosis of bones and joints | 4 |
| Tuberculosis of lymphatic system | 1 |
| Tuberculosis of genito-urinary system | 1 |
| Tuberculosis of adrenal glands | 1 |
Deaths from tuberculosis of sites other than pulmonary have also declined greatly in recent years, the death rate from these causes having been reduced from 82 per million of population in 1933–37 to 7 per million in 1958–59. The principal factor in this reduction has been tuberculosis of the meninges and central nervous system. In 1933 there were 43 deaths from this cause, compared with only 4 in 1959.
The following table shows the number of deaths from tuberculosis in 1959, classified according to sex and age groups. Of those dying from this cause in 1959, persons under the age of 45 years formed 18 per cent.
| Age, in Years | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 and under 10 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 10 and under 15 | - | 1 | 1 |
| 15 and under 20 | - | - | - |
| 20 and under 25 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 25 and under 30 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 30 and under 35 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| 35 and under 40 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 40 and under 45 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 45 and under 50 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| 50 and under 55 | 7 | 6 | 13 |
| 55 and under 60 | 10 | - | 10 |
| 60 and under 65 | 12 | 3 | 15 |
| 65 and under 70 | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| 70 and under 75 | 6 | 3 | 9 |
| 75 and under 80 | 7 | 3 | 10 |
| 80 and over | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Totals | 67 | 31 | 98 |
CANCER — A detailed report on cancer mortality and morbidity in New Zealand was issued in 1958 by the Medical Statistics Branch of the Department of Health. This report covers mortality from cancer from 1941 to 1955, and also surveys all cases reported to the National Cancer Register by the various cancer clinics established in New Zealand under the auspices of the British Empire Cancer Campaign Society. In addition to discussion of the total cancer picture in New Zealand, an analysis, with discussion, is made by specific sites broken down under the following subheadings: the age and sex of new cases registered, incidence, survival experience, treatment, stage of disease at time of diagnosis, and period elapsing between first symptoms and diagnosis. Under each of these headings a comparison is made between the local figures and those available from other countries, while in the principal sites the New Zealand mortality is contrasted with that of generally 24 other countries of the world.
Attention is drawn to the transference, under the 1948 Revision of the International Classification, of Hodgkin's disease, leukaemia, etc., into the category of malignant diseases. This classification was introduced in 1950, and all cancer figures quoted for that and subsequent years include these conditions.
Cancer is annually responsible for more deaths in New Zealand than can be assigned to any cause other than diseases of the heart. While it is most prevalent in middle and old age, it exacts a heavy toll throughout the lifespan. With the inclusion of Hodgkin's disease and leukaemia under the cancer heading, the disease assumes a very high position as a cause of death among children and adolescents. It is interesting to compare the decline in the death rate from tuberculosis with the rise in the cancer death rate. These rates are set out in the following table and diagram. The fall in the tuberculosis rate may be said to reflect the achievements of the public health service, whilst the rise in the cancer rate portrays the increasing age of the population.
This is illustrated by the following figures.
| Average Death Rates per 10,000 of Population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Period | Tuberculosis | Cancer |
| 1880–89 | 12.35 | 3.42 |
| 1890–99 | 10.62 | 5.44 |
| 1900–09 | 9.10 | 6.79 |
| 1910–19 | 6.99 | 8.22 |
| 1920–29 | 5.69 | 9.30 |
| 1930–39 | 4.17 | 11.17 |
| 1940–49 | 3.46 | 13.56 |
| 1950–59 | 1.20 | 14.91 |
The relative movements in the death rates from cancer and tuberculosis are further illustrated in the following diagram, which shows the rates at five-yearly intervals since 1875, and annually since 1950.
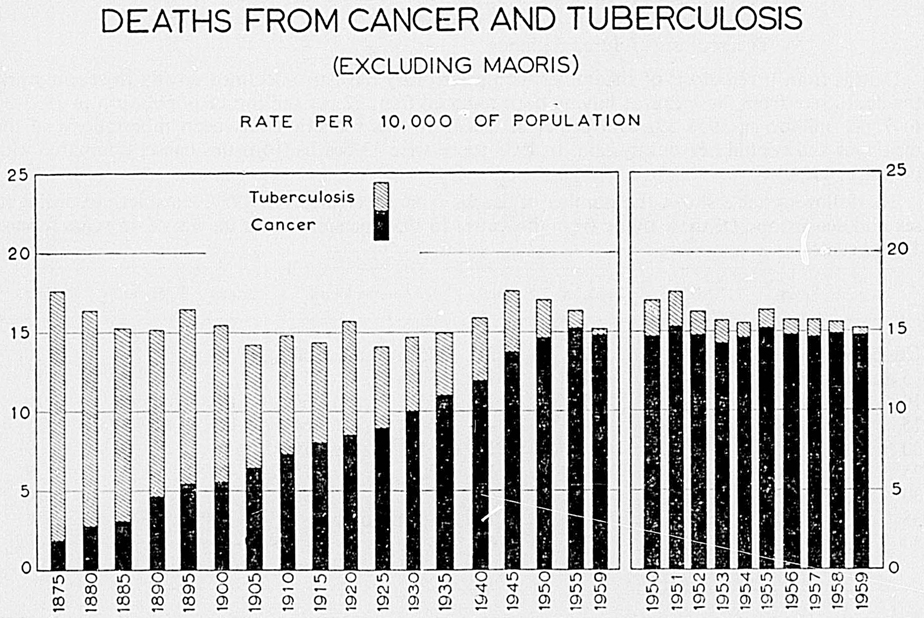
In 1959 there were 3,220 deaths from cancer in New Zealand, a proportion of 14.77 per 10,000 of mean population. Figures in this table are all inclusive of Hodgkin's disease, leukaemia, etc. A summary for the latest 11 years is given below.
| Year | Number of Deaths from Cancer | Recorded Death Rate | Standardised Death Rate* |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Standard population used for standardised rates — England and Wales 1901. | |||
| 1949 | 2,472 | 14.04 | 9.08 |
| 1950 | 2,652 | 14.77 | 8.98 |
| 1951 | 2,836 | 15.49 | 9.49 |
| 1952 | 2,799 | 14.92 | 9.02 |
| 1953 | 2,786 | 14.48 | 8.86 |
| 1954 | 2,878 | 14.64 | 8.98 |
| 1955 | 3,077 | 15.34 | 9.35 |
| 1956 | 3,051 | 14.92 | 9.12 |
| 1957 | 3,110 | 14.89 | 9.08 |
| 1958 | 3,192 | 14.93 | 9.24 |
| 1959 | 3,220 | 14.77 | 9.14 |
A summary showing the location of the disease in deaths from cancer during 1959 is given in the following table.
| Site of Disease | Numbers | Rates per Million of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Buccal cavity and pharynx | 42 | 17 | 59 | 38 | 16 | 27 |
| Oesophagus | 35 | 32 | 67 | 32 | 29 | 31 |
| Stomach | 232 | 145 | 377 | 212 | 134 | 173 |
| Intestine, except rectum | 163 | 195 | 358 | 149 | 180 | 164 |
| Rectum | 95 | 73 | 168 | 87 | 67 | 77 |
| Larynx | 14 | 2 | 16 | 13 | 2 | 7 |
| Trachea, and of bronchus and lung specified as secondary | 352 | 54 | 406 | 321 | 50 | 186 |
| Breast | 1 | 280 | 281 | 1 | 258 | 129 |
| Cervix uteri | - | 103 | 103 | - | 95 | 47 |
| Other and unspecified parts of uterus | - | 47 | 47 | - | 43 | 22 |
| Prostate | 204 | - | 204 | 186 | - | 94 |
| Skin | 42 | 30 | 72 | 38 | 28 | 33 |
| Bone and connective tissue | 17 | 12 | 29 | 16 | 11 | 13 |
| All other and unspecified sites | 407 | 381 | 788 | 371 | 351 | 361 |
| Leukaemia and aleukaemia | 85 | 75 | 160 | 78 | 69 | 73 |
| Lymphosarcoma and other neoplasms of lymphatic and haematopoietic system | 56 | 29 | 85 | 51 | 27 | 39 |
| Totals | 1,745 | 1,475 | 3,220 | 1,593 | 1,360 | 1,477 |
The standardised figures for recent years suggest that cancer, while undoubtedly increasing in numerical incidence, is not doing so out of proportion to the population exposed to the cancer risk. Improvement in diagnosis has been responsible for some of the numerical increase in the recorded deaths from cancer, though this factor has now become more stabilised. A classification according to sex and age groups for 1959 is now given.
| Age, in Years | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 5 | 9 | 16 | 25 |
| 5 and under 10 | 12 | 8 | 20 |
| 10 and under 15 | 12 | 5 | 17 |
| 15 and under 20 | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| 20 and under 25 | 11 | 5 | 16 |
| 25 and under 30 | 13 | 13 | 26 |
| 30 and under 35 | 23 | 23 | 46 |
| 35 and under 40 | 24 | 34 | 58 |
| 40 and under 45 | 31 | 57 | 88 |
| 45 and under 50 | 89 | 99 | 188 |
| 50 and under 55 | 104 | 106 | 210 |
| 55 and under 60 | 133 | 134 | 267 |
| 60 and under 65 | 206 | 165 | 371 |
| 65 and under 70 | 224 | 182 | 406 |
| 70 and under 75 | 287 | 193 | 480 |
| 75 and under 80 | 303 | 208 | 511 |
| 80 and over | 260 | 221 | 481 |
| Totals | 1,745 | 1,475 | 3,220 |
Ninety per cent of the deaths from cancer during 1959 were at ages 45 years and upwards, and 58 per cent at ages 65 years and upwards. Approximately one death in every six of persons who die after the age of 50 years is due to cancer.
PUERPERAL CAUSES — In point of numbers of deaths, puerperal accidents and diseases do not rank high among causes of death. Nevertheless, deaths from puerperal causes are of special importance and significance. The rate per 1,000 live births in each of the latest 20 years is shown in the following table.
| Year | Proportion per 1,000 Live Births |
|---|---|
| 1940 | 2.93 |
| 1941 | 3.36 |
| 1942 | 2.53 |
| 1943 | 2.21 |
| 1944 | 2.71 |
| 1945 | 2.24 |
| 1946 | 2.05 |
| 1947 | 1.07 |
| 1948 | 1.26 |
| 1949 | 1.02 |
| 1950 | 0.90 |
| 1951 | 0.69 |
| 1952 | 0.71 |
| 1953 | 0.54 |
| 1954 | 0.51 |
| 1955 | 0.44 |
| 1956 | 0.40 |
| 1957 | 0.67 |
| 1958 | 0.41 |
| 1959 | 0.49 |
A survey of the death rate from puerperal causes since 1872 shows that for a period in the early part of the twentieth century there was a tendency for the rate to decline. Then followed a definite upward movement, culminating in a rate of 6.48 per 1,000 live births in 1920, the third highest on record, this figure having been exceeded only in 1884 and 1885. Comparatively high rates persisted until 1931, since when the decline has been more or less steady. The efficacy of new drugs and methods of treatment is reflected in the extremely low rates recorded in recent years, the figure for 1956 of 0.40 being a new record. This low rate has been achieved mainly by a reduction in the number of deaths from septic abortion and puerperal sepsis. Deaths from complications of childbirth have also been few since 1949, but the 13 deaths in this category in 1957, as well as the 10 deaths attributed to toxaemic conditions, were the main factors in bringing the 1957 rate up to the highest since 1952.
It is generally conceded that in years of high birth rates the maternal-mortality rate tends to rise, probably due to the abnormally high proportion of first births in the total of births, upon which the death rate for these causes is based. In common with most countries for which recent figures are available, the reverse has been the experience in New Zealand during recent years. Possibly a contributory factor in this reversal has been the rise in the proportion of births taking place in institutions, more particularly in special annexes attached to the larger hospitals, where every facility for the care of the patient is more readily available.
Details of deaths from deliveries and complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium for the three years 1957 to 1959 are shown in the following summary.
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | Rate per 10,000 Live Births | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Toxaemias of pregnancy | 7 | 8 | 5 | 1.35 | 1.48 | 0.91 |
| Placenta praevia | - | 1 | - | - | 0.18 | - |
| Other haemorrhage of pregnancy | 1 | 2 | - | 0.19 | 0.37 | - |
| Ectopic pregnancy | 1 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Other complications arising from pregnancy | 3 | - | 1 | 0.58 | - | 0.18 |
| Abortion without mention of sepsis or toxaemia | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.73 |
| Abortion with sepsis | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.73 |
| Abortion with toxaemia | 1 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Delivery complicated by placenta praevia or antepartum haemorrhage | 3 | 1 | - | 0.58 | 0.18 | - |
| Delivery complicated by retained placenta | 2 | - | - | 0.39 | - | - |
| Delivery complicated by other post-partum haemorrhage | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.37 |
| Delivery complicated by disproportion or malposition of foetus | - | - | 1 | - | - | 0.18 |
| Delivery complicated by prolonged labour of other origin | 2 | - | - | 0.39 | - | - |
| Delivery with trauma | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0.58 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| Delivery with other complications of childbirth | 1 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Sepsis of childbirth and the puerperium | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.37 |
| Puerperal phlebitis and thrombosis | - | 1 | 2 | - | 0.18 | 0.37 |
| Puerperal pulmonary embolism | - | 1 | 3 | - | 0.18 | 0.55 |
| Puerperal eclampsia | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Puerperal toxaemia | 2 | - | - | 0.39 | - | - |
| Other and unspecified complications of the puerperium | 1 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Mastitis and other disorders of lactation | 1 | - | 1 | 0.19 | - | 0.18 |
| Totals, including septic abortion | 35 | 22 | 27 | 4.75 | 4.09 | 4.93 |
| Totals, excluding septic abortion | 32 | 21 | 23 | 6.17 | 3.90 | 4.20 |
A summary of maternal mortality from all puerperal causes, in triennial periods since 1933, is now given.
| Causes of Death | 1933–35 | 1936–38 | 1939–41 | 1942–44 | 1945–47 | 1948–50 | 1951–53 | 1954–56 | 1957–59 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puerperal sepsis | 39 | 44 | 46 | 30 | 12 | 6 | 3 | - | 4 |
| Eclampsia and other toxaemias | 93 | 94 | 80 | 58 | 62 | 42 | 30 | 20 | 20 |
| Septic abortion | 91 | 68 | 58 | 61 | 33 | 20 | 7 | 12 | 8 |
| Accidents, haemorrhage, and other mortality | 104 | 91 | 135 | 94 | 110 | 73 | 49 | 35 | 52 |
| Total maternal mortality | 327 | 297 | 319 | 243 | 217 | 141 | 89 | 67 | 84 |
| Maternal mortality, excluding septic abortion | 236 | 229 | 261 | 182 | 184 | 121 | 82 | 55 | 76 |
In all four disease divisions there has been a steady downward trend in the numbers, despite the fact that in the quarter century covered the total of confinements has approximately doubled. This position has been brought about by improvements in the standard of ante-natal care and obstetrical skill as well as advances in medical science.
DEATHS FROM EXTERNAL CAUSES — Deaths from external causes, apart from suicide, claim approximately 6 per cent of the total deaths. The following table shows deaths from external causes for the three years 1957, 1958, and 1959 according to the Intermediate List of the 1955 Revision of the International Classification. It is necessary to refer to the detailed list of circumstances of accident or means of injury if a comparison with years prior to 1949 is required, as the inclusions under the headings below differ considerably from past practice — e.g., drowning from boats and ships or from horseback whilst crossing rivers are included below as transport fatalities, as also are falls on board ship and from horseback.
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | Rate per Million of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Motor-vehicle accidents | 336 | 364 | 308 | 161 | 170 | 141 |
| Other transport accidents | 87 | 90 | 57 | 42 | 42 | 26 |
| Accidental poisoning | 26 | 18 | 32 | 12 | 8 | 15 |
| Accidental falls | 250 | 204 | 268 | 120 | 95 | 123 |
| Accident caused by machinery | 40 | 39 | 27 | 19 | 18 | 12 |
| Accident caused by fire and explosion of combustible material | 28 | 30 | 17 | 13 | 14 | 8 |
| Accident caused by hot substance, corrosive liquid, steam, and radiation | 8 | 13 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 3 |
| Accident caused by firearm | 15 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 5 |
| Accidental drowning and submersion | 107 | 81 | 83 | 51 | 38 | 38 |
| All other accidental causes | 101 | 108 | 110 | 48 | 51 | 50 |
| Homicide and injury purposely inflicted by other persons (not in war) | 13 | 13 | 18 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| Totals | 1,011 | 977 | 937 | 484 | 457 | 430 |
The number of deaths recorded from all accidental causes in 1959 was 919, corresponding to a rate of 4.21 per 10,000 of population.
Drownings are a leading cause of accidental death in New Zealand. Included in the preceding table as transport accidents are a further 21 deaths due to drowning. Twelve of these were from the capsize of small boats, whilst the remaining 9 deaths involved principally the larger type of boat. The year 1959 shows a fall in the death rate from external causes; this is due mainly to a reduction in the number of deaths in transport accidents.
Transport Accidents — In classifying deaths attributable to transport accidents under the various subheadings shown in the following table the rule of assignment is that in fatalities due to collisions of railway trains and electric tram cars with motor vehicles, the death is assigned to the railway train or electric tram car as being the heavier and more powerful vehicle. In the case of collisions between motor vehicles and horse-drawn vehicles, the death is assigned to the motor vehicle.
The number and rate of deaths resulting from railway, tramway, motor vehicle, and aircraft accidents during each of the last 11 years are as follows.
| Year | Deaths Due to Accident | Rate per 10,000 of Mean Population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Railway | Tramway | Motor Vehicle | Aircraft | Railway | Tramway | Motor Vehicle | Aircraft | |
| *Less than 0.01. | ||||||||
| 1949 | 28 | 7 | 190 | 25 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 1.08 | 0.14 |
| 1950 | 30 | 7 | 198 | 6 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 1.10 | 0.03 |
| 1951 | 39 | 9 | 254 | 9 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 1.39 | 0.05 |
| 1952 | 32 | 2 | 240 | 14 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 1.28 | 0.07 |
| 1953 | 26 | 2 | 269 | 28 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 1.40 | 0.15 |
| 1954 | 180 | 4 | 269 | 16 | 0.92 | 0.02 | 1.37 | 0.08 |
| 1955 | 42 | 2 | 295 | 9 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 1.47 | 0.04 |
| 1956 | 21 | 3 | 281 | 10 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 1.37 | 0.05 |
| 1957 | 31 | 2 | 318 | 22 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 1.52 | 0.11 |
| 1958 | 23 | 1 | 353 | 23 | 0.11 | * | 1.65 | 0.11 |
| 1959 | 27 | 1 | 294 | 9 | 0.12 | * | 1.34 | 0.04 |
Deaths occurring as a result of the Tangiwai railway disaster were not registered till 1954, and consequently were not included in the 1953 totals. These deaths numbered 154, and of course account for the large increase in the number of deaths due to railway accidents shown for 1954. Of this number one was a Maori, and seven were registered as unidentified bodies.
New Zealand's worst air disaster occurred in 1949, when 15 lives were lost in a crash at Waikanae. In recent years the wide use of aircraft in agricultural operations such as aerial topdressing has resulted in a number of deaths from aircraft accidents.
Deaths from motor-vehicle accidents recorded an appreciable increase up to 1930, but this trend was reversed during the depression years, largely owing to a great reduction in the number of motor vehicles on the roads during that period. With the advent of more prosperous times, the toll of the motor vehicle again mounted, although, fortunately, not in proportion to the tremendous increase in motor-vehicular traffic on the highways. An appreciable drop, however, was experienced during the war years as there was less traffic on the roads owing to restrictions on the use of motor spirits and the supply of rubber tyres. Since the war the number of fatalities from motor-vehicle accidents progressively increased up to 1958, with the exception of small declines in 1952 and again in 1956. The year 1958 was a particularly bad year from the accident point of view, especially those involving motor vehicles.
The figures given in the above table for deaths from motor-vehicle accidents (which do not include deaths of Maoris) are exclusive of accidents where persons have been killed in collisions between motor vehicles and trains or trams, these being assigned to the heavier vehicle. For 1959 there were 14 deaths from such accidents, bringing the total number of deaths in cases where a motor vehicle was involved up to 308. The corresponding figure for 1958 was 364.
Non-transport Accidents — The 1955 Revision of the International List makes provision for non-transport accidents (excluding therapeutic misadventure in treatment, complications following vaccination or inoculation, and late effects of injury and poisoning) to be grouped according to the place where the accident or poisoning occurred. The following table shows the deaths, both numbers and rates, for each of the three years 1957, 1958, and 1959 according to this classification.
| Place of Occurrence | Number | Rate per Million of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Home (including home premises and vicinity and non-institutional place of residence) | 294 | 222 | 260 | 141 | 104 | 119 |
| Farm (including buildings and land under cultivation, but excluding farm and home premises) | 45 | 57 | 35 | 22 | 27 | 16 |
| Mine and quarry | 6 | 14 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
| Industrial place and premises | 18 | 28 | 29 | 9 | 13 | 13 |
| Place for recreation and sport | 5 | 6 | 14 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Street and highway | 24 | 9 | 18 | 11 | 4 | 8 |
| Public building (building used by the general public particular group of the public) | 10 | 10 | 14 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| Resident institution (homes, hospitals, etc.) | 51 | 50 | 55 | 24 | 23 | 25 |
| Other specified places | 101 | 80 | 92 | 48 | 37 | 42 |
| Place not specified | 11 | 25 | 16 | 5 | 12 | 7 |
| Totals | 565 | 501 | 539 | 270 | 234 | 247 |
One in every two fatal non-traffic accidents occurs in or about the home. The year 1957 was a particularly bad one for this type of mishap.
The chief killer in the home is falls, which exacts a heavy toll of the aged and infirm. This is clearly illustrated in a special report on domestic accidents issued by the Department of Health in 1960. The second important cause of death in the home is asphyxia from regurgitation of food and inhalation of other objects, or mechanically from pillows and bedclothes; this is the principal hazard of the first six months of life, though a proportion of these deaths is probably due to some undisclosed respiratory infection. Almost all the home drowning fatalities are amongst toddlers between one and two years of age who fall into rivers, creeks, and ponds in the vicinity of the home.
Nineteen of the 35 accidental deaths on farms in 1959 were caused by farm machinery (usually tractors). Further data regarding accidents will be found elsewhere in this volume (see Index). A later section is devoted wholly to statistics of industrial accidents.
Suicide — There were 198 suicidal deaths in 1959 — 151 males and 47 females — the death rates per 100,000 of population being 13.8 for males and 4.3 for females.
Rates per 100,000 of population showing the age distributions, averaged over the years 1957, 1958, and 1959 are shown next.
| Sex | 10/14 | 15/19 | 20/24 | 25/29 | 30/34 | 35/39 | 40/44 | 45/49 | 50/54 | 55/59 | 60/64 | 65/69 | 70/74 | 75/79 | 80+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | 1.1 | 6.0 | 11.8 | 11.9 | 15.8 | 17.7 | 18.2 | 28.2 | 39.1 | 24.2 | 25.1 | 37.7 | 31.6 | 43.7 | 51.2 |
| Females | - | 0.9 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 14.2 | 13.4 | 16.2 | 9.8 | 15.1 | 7.6 | 5.9 |
These figures show the typical increase in the suicide rates with increasing age and the fall in the female rate after the age of 75.
The next table presents the average, over three-yearly periods since 1921, of standardised suicide rates per 100,000 of mean population.
| Annual Average During | Males | Females |
|---|---|---|
| 1921–23 | 18.0 | 4.5 |
| 1924–26 | 17.5 | 4.5 |
| 1927–29 | 20.5 | 5.4 |
| 1930–32 | 20.6 | 4.6 |
| 1933–35 | 15.3 | 4.7 |
| 1936–38 | 13.4 | 4.9 |
| 1939–41 | 13.0 | 4.3 |
| 1942–44 | 10.9 | 4.9 |
| 1945–47 | 10.5 | 4.5 |
| 1948–50 | 11.1 | 4.6 |
| 1951–53 | 11.8 | 4.1 |
| 1954–56 | 10.6 | 4.2 |
| 1957–59 | 11.8 | 3.9 |
The male rate fell sharply after the depression years, while the female rate has remained fairly constant.
The following table provides an international comparison of suicide rates for various countries. The figures have been calculated from material in the United Nations Demographic Yearbooks.
| Country | Triennium | Rate per 100,000 of Population |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | 1954–56 | 1.3 |
| Republic of Ireland | 1955–57 | 2.5 |
| Union of South Africa (coloured) | 1955–57 | 2.8 |
| Guatemala | 1955–57 | 3.0 |
| Northern Ireland | 1955–57 | 3.6 |
| United States of America (coloured) | 1954–56 | 3.9 |
| New Zealand (Maori) | 1955–57 | 4.1 |
| Bulgaria | 1954–56 | 5.9 |
| Netherlands | 1955–57 | 6.1 |
| Italy | 1955–57 | 6.7 |
| Canada | 1955–57 | 7.0 |
| Norway | 1955–57 | 7.3 |
| Ceylon | 1955–57 | 7.6 |
| Scotland | 1955–57 | 7.9 |
| New Zealand (European) | 1955–57 | 9.5 |
| Union of South Africa (Asiatic) | 1955–57 | 9.7 |
| United States of America (white) | 1954–56 | 10.1 |
| Uruguay | 1953–55 | 10.9 |
| Australia | 1955–57 | 11.1 |
| Union of South Africa (white) | 1955–57 | 11.2 |
| England and Wales | 1954–56 | 11.5 |
| Belgium | 1955–57 | 14.3 |
| Southern Rhodesia | 1954–56 | 14.9 |
| Alaska | 1954–56 | 15.6 |
| France | 1955–57 | 16.4 |
| West Germany | 1955–57 | 18.8 |
| Sweden | 1955–57 | 19.2 |
| Hungary | 1955–57 | 20.6 |
| Finland | 1955–57 | 21.4 |
| Switzerland | 1955–57 | 21.4 |
| Denmark | 1955–57 | 22.6 |
| Austria | 1955–57 | 23.4 |
| Japan | 1955–57 | 24.5 |
GENERAL — Unless specially stated to the contrary, in the preceding Subsections 4B and 4D, Maoris have been excluded from the statistical tables presented. The standard of registration of Maoris was, for many years, below that of the European section of the population of New Zealand. This was due partly to difficulties of language, educational status, etc., and partly to problems of access. This latter difficulty arose from the fact that the greater portion of the Maori population is resident in country districts not so well served with modern facilities as regards transport, medical, and nursing services, etc. Consequently registration of vital facts regarding the Maori race as a whole was not quite at the same high level of accuracy as obtains for the European population, but very considerable improvement has been effected in recent years, and it is now believed that Maori registrations are very little inferior, if at all, to those of Europeans.
MAORI BIRTHS — Maori births and deaths became registrable as from 1 March 1913. The number of Registrars of Maori births and deaths in New Zealand is over 230, most of these being in the North Island, where over 96 per cent of the Maori population is located. Every Maori settlement of any size is within reach of one of these Registrars. Maori registrations are entered in a separate register, which does not, however, make provision for as many particulars as is the case with registrations of Europeans.
The number of births of Maoris registered during 1960 was 7,415 (3,774 males, 3,641 females). The Maori birth rate in 1960 was almost twice the European birth rate (25.00 per 1,000). Registrations of Maori births in each of the last 11 years were as follows.
| Year | Number of Maori Births | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Maori Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | ||
| 1950 | 2,606 | 2,499 | 5,105 | 45.07 |
| 1951 | 2,746 | 2,492 | 5,238 | 44.97 |
| 1952 | 2,856 | 2,603 | 5,459 | 45.41 |
| 1953 | 2,884 | 2,645 | 5,529 | 44.54 |
| 1954 | 2,934 | 2,766 | 5,700 | 44.37 |
| 1955 | 2,984 | 2,823 | 5,807 | 43.64 |
| 1956 | 3,133 | 3,030 | 6,163 | 44.64 |
| 1957 | 3,333 | 3,299 | 6,632 | 46.29 |
| 1958 | 3,464 | 3,397 | 6,861 | 46.24 |
| 1959 | 3,672 | 3,458 | 7,130 | 46.28 |
| 1960 | 3,774 | 3,641 | 7,415 | 46.41 |
For registration purposes a Maori is defined as “a person belonging to the aboriginal race of New Zealand, and includes a half-caste and a person intermediate in blood between half-castes and persons of pure descent from that race”. Only registrations relating to persons possessing half or more Maori blood are made in the register of Maori births or Maori deaths. All registrations in respect of persons possessing less than half Maori blood must be made in the European register.
MAORI MARRIAGES — From 1 April 1952 all Maori marriages have been subject to the ordinary laws affecting European marriages, and no marriage according to Maori custom subsequent to that date is held valid. As a result it is not now possible to distinguish marriages of Maoris from those of Europeans, and Maori marriage statistics as a separate feature have lapsed.
MAORI DEATHS — Registrations of Maori deaths during each of the last 11 years have been as follows.
| Year | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Maori Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| 1950 | 734 | 635 | 1,369 | 12.62 | 11.52 | 12.09 |
| 1951 | 739 | 585 | 1,324 | 12.38 | 10.31 | 11.37 |
| 1952 | 803 | 680 | 1,483 | 13.04 | 11.60 | 12.34 |
| 1953 | 760 | 585 | 1,345 | 11.97 | 9.65 | 10.84 |
| 1954 | 680 | 529 | 1,209 | 10.35 | 8.43 | 9.41 |
| 1955 | 694 | 578 | 1,272 | 10.19 | 8.90 | 9.56 |
| 1956 | 708 | 585 | 1,293 | 10.03 | 8.67 | 9.36 |
| 1957 | 804 | 647 | 1,451 | 10.99 | 9.22 | 10.13 |
| 1958 | 728 | 559 | 1,287 | 9.63 | 7.68 | 8.67 |
| 1959 | 717 | 597 | 1,314 | 9.14 | 7.89 | 8.53 |
| 1960 | 775 | 593 | 1,368 | 9.54 | 7.55 | 8.56 |
The rates for the two sexes are more nearly equal for Maoris than for the rest of the population, the female rate being actually higher than the male in 1949. The total Maori death rate has shown considerable improvement during recent years. The rate in 1960 is the second lowest ever recorded for Maoris, and indeed is lower than that recorded for Europeans. Further improvement in the infant-mortality rate for Maoris could result in an even lower death rate in the near future.
Apart from mere numbers by sex, statistics of Maori deaths are not available prior to 1920, but annual tabulations are now made on the bases of age and cause of death. The ages of Maoris whose deaths were registered during the year 1959 were as shown in the following table.
| Age, in Years | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 | 224 | 164 | 388 |
| 1 and under 5 | 48 | 40 | 88 |
| 5 and under 10 | 13 | 14 | 27 |
| 10 and under 15 | 12 | 5 | 17 |
| 15 and under 20 | 17 | 12 | 29 |
| 20 and under 25 | 23 | 12 | 35 |
| 25 and under 30 | 19 | 9 | 28 |
| 30 and under 35 | 17 | 17 | 34 |
| 35 and under 40 | 22 | 19 | 41 |
| 40 and under 45 | 17 | 28 | 45 |
| 45 and under 50 | 30 | 35 | 65 |
| 50 and under 55 | 33 | 33 | 66 |
| 55 and under 60 | 47 | 38 | 85 |
| 60 and under 65 | 30 | 34 | 64 |
| 65 and under 70 | 47 | 32 | 79 |
| 70 and under 75 | 36 | 32 | 68 |
| 75 and under 80 | 29 | 31 | 60 |
| 80 and under 85 | 26 | 21 | 47 |
| 85 and under 90 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 90 and under 95 | 9 | 6 | 15 |
| 95 and under 100 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| 100 and over | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| Totals | 717 | 597 | 1,314 |
EXPECTATION OF LIFE — The expectation of life at various ages for the Maori population is shown below. These expectations are taken from Maori Life Tables, 1955–57.
| Age (Years) | Life Expectancy (Years) | |
|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | |
| 0 | 57.23 | 58.68 |
| 1 | 60.30 | 60.80 |
| 2 | 59.89 | 60.35 |
| 3 | 59.17 | 59.63 |
| 4 | 58.36 | 58.80 |
| 5 | 57.52 | 57.91 |
| 10 | 53.15 | 53.24 |
| 20 | 44.12 | 44.14 |
| 30 | 35.57 | 35.20 |
| 40 | 27.31 | 26.55 |
| 50 | 19.43 | 19.28 |
| 60 | 13.03 | 13.38 |
| 70 | 8.84 | 9.12 |
| 80 | 5.44 | 5.75 |
Life expectancy at birth for a Maori male increased by 3.18 years in the interval 1950–52 to 1955–57, with that for females increasing by 2.80 years. This was a substantial increase in a short period and is evidence that, although Maori life expectancy is relatively low, it is improving at a fast rate. In this interval between the construction of the first and second sets of Maori life tables the improvement was not so spectacular at higher ages, however.
The expectation of life of Maoris is much shorter than that of the European population. A comparison at age 0 shows a life expectation which is 11.65 years longer for European males and 15.20 years longer for European females.
A similar table to the above for Europeans will be found in Section 4D.
Causes of Maori Deaths — With the exception of diphtheria and scarlet fever, epidemic and infectious diseases generally exact a much heavier toll proportionately among Maoris than among the European population, the most noteworthy example being tuberculosis, particularly of the respiratory system. Other diseases of the respiratory system also show much higher rates for Maoris than for Europeans, and the same state of affairs is disclosed for diarrhoeal diseases and stomach complaints.
The rates set out in the following table are crude rates, i.e., the number of deaths attributed to the disease per 10,000 of the total Maori population. Taken at their face value the figures show the Maori as having a very low mortality from certain diseases which rank high as causes of death among the European population. These diseases are those which generally affect persons of more advanced ages, such as cancer, diabetes, vascular lesions of the central nervous system, arteriosclerotic and degenerative heart disease, and kidney disease. The Maori population has a comparatively small proportion of its total in the older age groups, and if allowance is made for the low numbers who would be susceptible to these conditions, it is apparent that the Maori is affected in much the same proportion as the European. This position is revealed by the calculation of age-specific rates, which are the number of deaths from a disease in a specified age group per 10,000 of the population in that age group. It is unfortunate that both the absolute numbers of deaths as well as the population at risk in the older ages is too small to permit of the calculation, for the Maori, of standardised rates which smooth out these age-structure disparities.
The Introduction of the Sixth (1948) Revision of the International Classification of Causes of Death in 1950, together with the change to assignment according to the underlying cause of death, prevent accurate comparisons being made between the 1950 and subsequent mortality tabulations and those for earlier years. The following table shows the Maori deaths for 1957 to 1959 classified according to the Abbreviated List of the 1948 and 1955 Revisions.
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | Rate per 10,000 of Mean Maori Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Tuberculosis of respiratory system | 63 | 47 | 33 | 4.40 | 3.17 | 2.14 |
| Tuberculosis, other forms | 7 | 15 | 6 | 0.49 | 1.01 | 0.39 |
| Syphilis and its sequelae | 5 | 4 | 3 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.19 |
| Typhoid fever | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| Dysentery, all forms | 1 | 3 | - | 0.07 | 0.20 | - |
| Whooping cough | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.39 |
| Meningococcal infections | 6 | 8 | 3 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.19 |
| Acute poliomyelitis | - | 1 | - | - | 0.07 | - |
| Measles | 1 | 2 | 8 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.52 |
| All other diseases classified as infective and parasitic | 21 | 20 | 20 | 1.47 | 1.35 | 1.30 |
| Malignant neoplasms, including neoplasms of lymphatic and haematopoietic tissues | 103 | 105 | 119 | 7.19 | 7.01 | 7.72 |
| Benign and unspecified neoplasms | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 15 | 13 | 8 | 1.05 | 0.88 | 0.52 |
| Anaemias | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| Vascular lesions affecting central nervous system | 62 | 56 | 53 | 4.33 | 3.77 | 3.44 |
| Non-meningococcal meningitis | 11 | 15 | 15 | 0.77 | 1.01 | 0.97 |
| Rheumatic fever | 9 | 5 | 3 | 0.63 | 0.34 | 0.19 |
| Chronic rheumatic heart disease | 54 | 53 | 37 | 3.77 | 3.57 | 2.40 |
| Arteriosclerotic and degenerative heart disease | 157 | 139 | 139 | 10.96 | 9.36 | 9.02 |
| Other diseases of the heart | 54 | 61 | 71 | 3.77 | 4.12 | 4.61 |
| Hypertension with heart disease | 16 | 18 | 23 | 1.12 | 1.21 | 1.49 |
| Hypertension without mention of heart | 4 | 4 | 5 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.32 |
| Influenza | 52 | 7 | 16 | 3.63 | 0.47 | 1.04 |
| Pneumonia | 166 | 130 | 194 | 11.59 | 8.76 | 12.59 |
| Bronchitis | 45 | 44 | 44 | 3.14 | 2.97 | 2.86 |
| Ulcer of stomach and duodenum | 5 | 3 | 7 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.45 |
| Appendicitis | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| Causes of Death | Number of Deaths | Rate per 10,000 of Mean Maori Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Intestinal obstruction and hernia | 16 | 8 | 14 | 1.12 | 0.54 | 0.91 |
| Gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and colitis, except diarrhoea of the newborn | 54 | 42 | 49 | 3.77 | 2.83 | 3.18 |
| Cirrhosis of liver | 5 | 4 | 2 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.13 |
| Nephritis and nephrosis | 18 | 15 | 12 | 1.26 | 1.01 | 0.78 |
| Hyperplasia of prostate | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0.42 | 0.20 | 0.06 |
| Complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.58 |
| Congenital malformations | 37 | 38 | 36 | 2.58 | 2.56 | 2.34 |
| Birth injuries, post-natal asphyxia, and atelectasis | 62 | 61 | 51 | 4.33 | 4.11 | 3.31 |
| Infections of the newborn | 14 | 18 | 16 | 0.98 | 1.21 | 1.04 |
| Other diseases peculiar to early infancy, and immaturity unqualified | 46 | 60 | 51 | 3.21 | 4.04 | 3.31 |
| Senility without mention of psychosis, ill-defined, and unknown causes | 12 | 6 | 7 | 0.84 | 0.40 | 0.45 |
| All other diseases | 158 | 113 | 106 | 11.03 | 7.62 | 6.88 |
| Motor-vehicle accidents | 71 | 52 | 54 | 4.96 | 3.50 | 3.50 |
| All other accidents | 69 | 74 | 72 | 4.82 | 4.99 | 4.67 |
| Suicide and self-inflicted injury | 6 | 9 | 6 | 0.42 | 0.61 | 0.39 |
| Homicide and operations of war | 2 | 11 | 7 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.45 |
| Totals | 1,451 | 1,287 | 1,314 | 101.27 | 86.74 | 85.28 |
The 1957 Maori death rate was the highest recorded since 1953. The influenza epidemic, as well as substantial increases in the totals for pneumonia and motor-vehicle accidents, contributed to the rise.
MAORI INFANT MORTALITY — As regards infant mortality, the Maori rate is much higher and more variable than the European, principally owing to the ravages of epidemic diseases, tuberculosis, respiratory diseases, and diarrhoeal diseases. The infant-mortality rate for the first year of life was 56.7 per 1,000 births in the case of Maoris for the five years 1955–59, as compared with 19.8 per 1,000 among European infants. There has, however, been a substantial decrease in Maori infant mortality in recent years.
The numbers and rates per 1,000 live births for the last 11 years are given in the next table.
| Year | Maoris | Europeans | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Deaths Under One Year | Rate per 1,000 Live Births | Number of Deaths Under One Year | Rate per 1,000 Live Births | |
| 1950 | 356 | 69.74 | 1,008 | 22.75 |
| 1951 | 357 | 68.16 | 1,017 | 22.78 |
| 1952 | 461 | 84.45 | 1,014 | 21.82 |
| 1953 | 404 | 73.07 | 931 | 20.06 |
| 1954 | 334 | 58.60 | 968 | 19.99 |
| 1955 | 363 | 62.51 | 1,002 | 20.09 |
| 1956 | 335 | 54.36 | 978 | 19.39 |
| 1957 | 384 | 57.90 | 1,036 | 19.98 |
| 1958 | 373 | 54.37 | 1,043 | 19.40 |
| 1959 | 388 | 54.42 | 1,089 | 19.89 |
| 1960 | 330 | 44.50 | 1,090 | 19.65 |
The next table shows for the year 1959 the principal causes of death of Maori infants in the various subdivisions of the first year of life. The classification is according to the Seventh (1955) Revision of the International Classification of Causes of Death.
| Causes of Death | Under 1 Day | 1 Day and Under 2 Days | 2 Days and Under 1 Week | 1 Week an Under 2 Weeks | 2 Weeks and Under 3 Weeks | 3 Weeks and Under 1 Months | 1 Week an Under 2 Weeks | 2 Months an Under 3 Months | 3 Months and Under 6 Months | 6 Months and Under 9 Months | 9 Months and Under 12 Months | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuberculosis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Whooping cough | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | 5 |
| All other diseases classified as infective and parasitic | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| Non-meningococcal meningitis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | 7 |
| Influenza | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 5 |
| Pneumonia, except of newborn | - | - | - | - | - | - | 11 | 13 | 43 | 36 | 22 | 125 |
| Bronchitis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 15 |
| Intestinal obstruction and hernia | - | - | - | 1 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 7 |
| Gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and colitis, except diarrhoea of newborn | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 7 | 14 | 11 | 4 | 41 |
| Congenital malformations | 7 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 28 |
| Birth injuries | 14 | 7 | 5 | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 31 |
| Post-natal asphyxia and atelectasis | 11 | 3 | 5 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 20 |
| Infections of the newborn | 1 | - | 1 | 5 | 3 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - | 16 |
| Immaturity unqualified | 24 | 7 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 34 |
| Other diseases peculiar to early infancy | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 17 |
| Accidents | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 4 | - | 2 | 9 |
| Other diseases | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 17 |
| Totals | 63 | 24 | 21 | 13 | 5 | 11 | 22 | 31 | 88 | 67 | 43 | 388 |
Immaturity unqualified accounted for 34 infant deaths, but in a further 33 deaths due to diseases of early infancy, prematurity was an associated condition.
The great achievement in reducing the infant-mortality rate for the European population has been accomplished during the period after the first month of life up to the end of the first year. Conversely, the causes of the high Maori mortality rates are to be found in the same period of life. In recent years the Maori rate for the under one month group has been in the proportion of one and a half times that of the European, whereas in those between one and 12 months, the Maori rate is over six times that of the European. This is indicated in the next table, which contrasts the mortality rates per 1,000 live births for European and Maori infants respectively for the last 21 years.
| Year | Europeans | Maoris | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under One Month | One and Under Twelve Months | Total Under One Year | Under One Month | One and Under Twelve Months | Total Under One Year | |
| 1939 | 21.85 | 9.29 | 31.14 | 32.07 | 82.85 | 114.92 |
| 1940 | 22.03 | 8.18 | 30.21 | 23.92 | 63.30 | 87.22 |
| 1941 | 20.00 | 9.77 | 29.77 | 26.85 | 98.21 | 125.06 |
| 1942 | 18.73 | 9.98 | 28.71 | 19.40 | 78.52 | 97.92 |
| 1943 | 21.27 | 10.10 | 31.37 | 18.92 | 70.94 | 89.86 |
| 1944 | 20.60 | 9.52 | 30.12 | 19.30 | 82.96 | 102.26 |
| 1945 | 19.59 | 8.40 | 27.99 | 26.05 | 62.88 | 88.93 |
| 1946 | 19.08 | 7.02 | 26.10 | 18.35 | 56.27 | 74.62 |
| 1947 | 18.08 | 6.96 | 25.04 | 25.46 | 47.72 | 73.18 |
| 1948 | 15.80 | 6.15 | 21.95 | 28.85 | 47.82 | 76.67 |
| 1949 | 17.01 | 6.77 | 23.78 | 22.78 | 63.04 | 85.82 |
| 1950 | 16.57 | 6.18 | 22.75 | 28.41 | 41.33 | 69.74 |
| 1951 | 16.22 | 6.56 | 22.78 | 25.01 | 43.15 | 68.16 |
| 1952 | 15.15 | 6.67 | 21.82 | 25.82 | 58.63 | 84.45 |
| 1953 | 14.26 | 5.80 | 20.06 | 26.95 | 46.12 | 73.07 |
| 1954 | 14.39 | 5.60 | 19.99 | 19.83 | 38.77 | 58.60 |
| 1955 | 14.14 | 5.95 | 20.09 | 19.64 | 42.87 | 62.51 |
| 1956 | 13.35 | 6.05 | 19.39 | 19.96 | 34.40 | 54.36 |
| 1957 | 13.85 | 6.13 | 19.98 | 20.36 | 37.55 | 57.90 |
| 1958 | 13.59 | 5.80 | 19.40 | 22.01 | 32.50 | 54.51 |
| 1959 | 13.92 | 5.97 | 19.89 | 19.21 | 35.20 | 54.42 |
The principal causes of death of Maori infants responsible for the high mortality rates after the first month of life are diarrhoea and enteritis, broncho-pneumonia, pneumonia, and other diseases of the respiratory system.
Comparing the average rates for the first five-year period in the above table. 1940–44, with those for the five years, 1955–59, it is seen that European neo-natal mortality has been reduced by 33 per cent over the period in contrast to a much lower reduction in the Maori of 7 per cent; for those aged between one and 12 months the European reduction of 37 per cent is less favourable than that in the Maori at 54 per cent.
Birth injury and prematurity are two diseases in the neo-natal group in which Maori rates are considerably higher than the European. Contributing towards this disparity is the higher proportion of Maori confinements outside of hospital as well as a reluctance on the part of many Maori mothers to seek ante-natal care.
The Maori infant who survives the first month of life is especially susceptible to gastro-intestinal disorders such as diarrhoea, colitis, and gastro-enteritis, and to respiratory conditions such as influenza, pneumonia, and bronchitis. Certain environmental conditions and circumstances are known to underlie these diseases, such as unsatisfactory feeding associated with the failure to seek or heed skilled advice from Plunket or district nurses, and in many instances poor housing and sanitary conditions.
GENERAL — Comparisons of healthiness of a community over a period of years which are based on death rates do not fully take into account the effect of the advance of medical science in recent years. It is common knowledge that many diseases regarded a few decades ago as incurable now show a fair proportion of recoveries. Similarly, the death rates in epidemics are in general much lower now than formerly, owing partly to the steps taken to prevent the spread of the disease, partly to the necessity of early notification in most countries, and partly to increased medical knowledge. Again, many diseases seldom if ever result fatally. Death-rate statistics are therefore supplemented by data relating to illness.
The principal source of statistics of illness in New Zealand, apart from that resulting in death, comes from the public hospitals, to which some 85 per cent of all hospital inpatients are admitted. Information concerning every person discharged from a public hospital is collected and tabulated in accordance with the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Injuries, and Causes of Death, and published annually in the Department of Health publication Medical Statistics. Similar information was formerly published in the Annual Report on Vital Statistics issued by the Department of Statistics. Other morbidity statistics in New Zealand are those concerning certain notifiable diseases, shown in Section 5A, those about industrial accidents reported in Section 37B, those concerning benefits granted under the Social Security Act reported in Section 6A, those of sick members of friendly societies mentioned in Section 6E, and those about people in mental hospitals reported in Section 5C.
NOTIFICATION OF DISEASES — The numbers of all notifiable diseases reported during the calendar year 1959 are shown in the following table; the total figures (including Maoris) are given month by month, with the totals for Maoris being shown in the last column.
| Disease | All Cases | Mao | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | Totals | Totals Only | |
| Diphtheria | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | 18 | 7 |
| Enteric fever— | ||||||||||||||
| Typhoid | 10 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 60 | 48 |
| Paratyphoid | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 6 | - |
| Tuberculosis— | ||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary | 68 | 94 | 100 | 102 | 104 | 81 | 126 | 103 | 95 | 105 | 116 | 109 | 1,203 | 406 |
| Other forms | 17 | 15 | 14 | 22 | 8 | 14 | 24 | 23 | 13 | 24 | 13 | 16 | 203 | 75 |
| Cerebrospinal meningitis | 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 2 | 87 | 21 |
| Poliomyelitis | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 16 | 1 |
| Pneumonic influenza | 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | - | 50 | 5 |
| Ornithosis (psittacosis) | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - |
| Puerperal fever— | ||||||||||||||
| Ordinary | 2 | 2 | - | 4 | - | 4 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 16 | 7 |
| Following abortion | 4 | 3 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 19 | - |
| Eclampsia | 2 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 64 | 3 |
| Tetanus | 5 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 | - | 2 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 39 | 5 |
| Hydatids | 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 69 | 18 |
| Trachoma | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 4 | 4 |
| Ophthalmia neonatorum | 11 | 8 | 20 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 16 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 127 | 20 |
| Food poisoning | 62 | 14 | 15 | 9 | 7 | 132 | 16 | 8 | 14 | 8 | 14 | 11 | 310 | 47 |
| Dysentery— | ||||||||||||||
| Bacillary | 11 | 23 | 30 | 38 | 46 | 29 | 61 | 145 | 145 | 62 | 45 | 39 | 679 | 81 |
| Amoebic | - | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | - | 9 | - |
| Undulant fever | 3 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 36 | 4 |
| Leptospirosis | 8 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 4 | - | 5 | 13 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 117 | 2 |
| Salmonellosis | 55 | 17 | 16 | 14 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 131 | 15 |
| Malaria | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | - |
| Actinomycosis | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Lethargic encephalitis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Anchylostomiasis | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| Infective hepatitis | 163 | 165 | 158 | 132 | 116 | 167 | 149 | 209 | 137 | 174 | 225 | 178 | 1,973 | 134 |
| Pemphigus neonatorum | 25 | 14 | 38 | 21 | 24 | 9 | 17 | 7 | 13 | 10 | 12 | 9 | 199 | 26 |
| Staphylococcal pneumonia and septicaemia | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | - | 2 | 20 | 1 |
| Septicaemia (following abortion or miscarriage) | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Taeniasis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - |
| Leprosy | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Beriberi | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Totals | 472 | 406 | 434 | 414 | 365 | 494 | 454 | 554 | 494 | 456 | 496 | 429 | 5,468 | 934 |
Total notifications for each of the latest five years for all cases and for Maoris for some of the notifiable diseases are shown in the following table. Attention is drawn to the fact that these figures are not considered to be a complete coverage of the incidence of these diseases as medical practitioners frequently overlook the necessity of notifying the Medical Officer of Health.
| Disease | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diphtheria | All cases | 51 | 31 | 31 | 16 | 18 |
| Maori | 10 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 7 | |
| Typhoid and paratyphoid fever | All cases | 60 | 67 | 49 | 44 | 66 |
| Maori | 41 | 51 | 36 | 14 | 48 | |
| Pulmonary tuberculosis | All cases | 1,640 | 1,565 | 1,530 | 1,425 | 1,203 |
| Maori | 501 | 524 | 521 | 497 | 406 | |
| Cerebrospinal meningitis | All cases | 91 | 72 | 102 | 53 | 87 |
| Maori | 23 | 16 | 33 | 14 | 21 | |
| Poliomyelitis | All cases | 703 | 897 | 63 | 57 | 16 |
| Maori | 34 | 42 | 4 | 5 | 1 | |
| Puerperal fever and septic abortion | All cases | 39 | 46 | 40 | 58 | 35 |
| Maori | 1 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 7 | |
| Tetanus | All cases | 32 | 23 | 33 | 32 | 39 |
| Maori | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | |
| Hydatids | All cases | 36 | 38 | 56 | 61 | 69 |
| Maori | 10 | 12 | 10 | 17 | 18 | |
| Food poisoning | All cases | 198 | 184 | 384 | 285 | 310 |
| Maori | 12 | 32 | 16 | 37 | 47 | |
| Bacillary dysentery | All cases | 457 | 201 | 165 | 438 | 679 |
| Maori | 62 | 28 | 22 | 72 | 81 | |
| Undulant fever | All cases | 44 | 32 | 23 | 38 | 36 |
| Maori | 2 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 4 | |
| Infective hepatitis | All cases | .. | .. | 1,443 | 1,893 | 1,973 |
| Maori | .. | .. | 97 | 156 | 134 | |
Diphtheria — In 1959 the number of cases, 18, was the second lowest on record.
Typhoid and Paratyphoid Fever — In 1959 the incidence was somewhat greater than in 1958.
Cerebrospinal Meningitis — The notifications in 1959 showed an increase on the 1958 figures.
Poliomyelitis — There was a considerable drop in incidence in 1959. Vaccination against poliomyelitis has been completed in the age groups up to 21 years, and is now practically confined to the infants under 12 months of age and expectant mothers.
Hydatids — There are two main sources of information about hydatid disease in New Zealand: patients admitted to public hospitals, and cases notified to the district offices of the Department of Health. A register of hydatid disease patients treated in public hospitals is kept by the Medical Statistics Branch, Department of Health. Reference to the register makes it possible to distinguish between new cases and readmissions. Until recently the number of new public hospital cases registered each year has been considerably greater than the number of cases notified to District Health Officers in the same year. This apparent discrepancy was caused through incomplete notification. A recent study showed that in some districts less than one-third of new cases treated in public hospitals had been notified to the District Health Office.
The following table, which includes Maoris, shows the number of new public hospital cases admitted, the number of public hospital cases readmitted, and the number of notifications for the latest 10 years.
| Year | Number of New Public Hospital Cases | Public Hospital Cases Readmitted | Total Public Hospital Cases | Notifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional figures. | ||||
| 1949 | 85 | 47 | 132 | 43 |
| 1950 | 84 | 53 | 137 | 38 |
| 1951 | 101 | 62 | 163 | 58 |
| 1952 | 89 | 69 | 158 | 39 |
| 1953 | 103 | 78 | 181 | 61 |
| 1954 | 80 | 63 | 143 | 41 |
| 1955 | 85 | 62 | 147 | 36 |
| 1956 | 80 | 59 | 139 | 38 |
| 1957 | 76 | 69 | 145 | 56 |
| 1958 | 69* | 47* | 116* | 61 |
The numbers of deaths from hydatid disease in New Zealand for the years 1948–59 are shown below by site of disease. The figures include Maoris. The numbers of deaths have been much lower since 1957.
| Year | Liver | Lung | Other Sites | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 15 |
| 1949 | 8 | - | 5 | 13 |
| 1950 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 19 |
| 1951 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 14 |
| 1952 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 10 |
| 1953 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 15 |
| 1954 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 13 |
| 1955 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 14 |
| 1956 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 14 |
| 1957 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| 1958 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 |
| 1959 | 5 | - | - | 5 |
| Totals | 74 | 29 | 40 | 143 |
The educational activities of the Department of Health, carried out in conjunction with the Department of Agriculture, were continued and farmers are more conscious of the need to control this disease.
Food Poisoning — Notifications in 1959 were similar in number to those in 1958. It is certain, however, that while outbreaks involving numbers of people are generally reported there must be many sporadic cases and family outbreaks which are dismissed as “summer sickness” or “gastric ‘flu”.
Infective Hepatitis — During 1959 there were 1,973 cases reported, an increase of 80 over the total for 1958. This disease continues to gain ground and is becoming one of the most serious public health problems.
5—Ybk.
Bacillary Dysentery — There was a further marked increase in notifications during 1959. This disease is one of the most infectious diseases.
Tuberculosis — With an intensification of case finding by all tuberculosis workers in recent years the notification of tuberculosis has improved to a degree that enables a reasonable picture of the disease to be presented as it affects this country. Annual notifications are now on the decline. The Department of Health is continuing its efforts to reduce further both incidence and mortality. In fact the mortality per 100,000 of population has decreased from 28.3 in 1951 to 5.9 in 1959. The number of public health nurses available for tuberculosis case-finding work has been increased, and hospital clinics in the charge of chest specialists have been provided to give a wide coverage. The responsibilities of the Department of Health in case finding and domiciliary care are coordinated with those of the hospital boards, which are responsible for diagnosis and treatment.
Medical officers of the Department of Health assist the public health nurses in the examination of contacts and arrange tuberculin tests and X-ray examinations. There are at present some 10 mass miniature X-ray units strategically sited throughout the country. In 1959 nine of these carried out a total of 256,332 chest X-ray examinations, and found that 1.08 in every thousand examined required supervision and treatment for tuberculous disease. In addition to tuberculosis, many other conditions of lungs and heart were discovered and, where necessary, were referred to the individual's private doctor for further investigation and follow-up.
As a contribution to prophylaxis, B.C.G. vaccination against tuberculosis, which was commenced in hospital staffs, contacts, and adolescents, is being maintained in these groups. During 1959 vaccinations were performed in 34,669 persons after preliminary Mantoux testing, and the results of this activity should become manifest in the years to come.
The Department of Health maintains a Tuberculosis Register, which classifies all notified cases, and a clearer conception of the type, form, and extent of the disease is being obtained. The number of cases on the Register (inclusive of Maoris) at 31 December 1959 was 13,035, of which 12,080 were respiratory and 955 non-respiratory. The number of new cases notified in 1959 was 1,406, of which 925 were European and 481 Maori. Of the European cases, 797 were respiratory and 128 non-respiratory, and in the Maori cases the figures were 406 and 75 respectively. Some of these cases may have since been proved non-tuberculous and subsequently deregistered.
The total number of European persons on the Register at the end of 1959 amounted to 39.1 per 10,000 of the European population and the Maori rate was 292 per 10,000 of the Maori population. The combined figure was 55.9 per 10,000.
PUBLIC HOSPITALS — Detailed statistical information is supplied to the Department of Health about every patient, except normal maternity cases, discharged from or dying in public hospitals in New Zealand. The following tables have been compiled from that information for the years specified below.
Patients Treated — The following table shows the number of patients treated in public hospitals for the latest five years.
| Year | Remaining on 1 January from Previous Year | Admissions | Discharges | Deaths | Total Number of Indoor Patients | Remaining on 31 December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Does not include seven patients in hospitals from which returns were not collected after 31 December 1954. †Does not include 16 patients in hospitals from which returns were not collected after 31 December 1955. †Does not include 75 psychiatric patients in Queen Mary Hospital, Hanmer Springs, previously included in the total remaining on 31 December 1958. | ||||||
| 1955 | 8,348* | 156,063 | 148,025 | 8,410 | 164,411 | 7,976 |
| 1956 | 7,960† | 160,684 | 151,881 | 8,824 | 168,644 | 7,939 |
| 1957 | 7,939 | 169,729 | 160,009 | 9,576 | 177,668 | 8,083 |
| 1958 | 8,083 | 174,790 | 165,481 | 9,248 | 182,873 | 8,144 |
| 1959 | 8,069‡ | 184,195 | 174,202 | 10,020 | 192,264 | 8,042 |
Age and Sex of Patients — The age and sex of patients discharged from or dying in public hospitals during 1958 are shown below.
| Age Groups | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 year | 4,287 | 3,095 | 7,382 |
| 1 and under 2 years | 2,285 | 1,615 | 3,900 |
| 2 and under 3 years | 1,982 | 1,363 | 3,345 |
| 3 and under 4 years | 1,802 | 1,245 | 3,047 |
| 4 and under 5 years | 1,834 | 1,430 | 3,264 |
| 5 and under 10 years | 8,462 | 6,492 | 4,954 |
| 10 and under 15 years | 6,155 | 4,388 | 10,543 |
| 15 and under 20 years | 6,079 | 6,838 | 12,917 |
| 20 and under 25 years | 5,448 | 7,600 | 13,048 |
| 25 and under 30 years | 4,532 | 7,146 | 11,678 |
| 30 and under 35 years | 4,282 | 6,530 | 10,812 |
| 35 and under 40 years | 3,953 | 5,661 | 9,614 |
| 40 and under 45 years | 3,855 | 5,107 | 8,962 |
| 45 and under 50 years | 4,179 | 4,732 | 8,911 |
| 50 and under 55 years | 4,375 | 4,130 | 8,505 |
| 55 and under 60 years | 4,425 | 3,565 | 7,990 |
| 60 and under 65 years | 3,944 | 3,597 | 7,541 |
| 65 and under 70 years | 4,056 | 3,529 | 7,585 |
| 70 and under 75 years | 4,108 | 3,498 | 7,606 |
| 75 and under 80 years | 3,746 | 3,056 | 6,802 |
| 80 and under 85 years | 2,016 | 1,950 | 3,966 |
| 85 years and over | 1,216 | 1,141 | 2,357 |
| Totals | 87,021 | 87,708 | 174,729 |
Although there is little overall difference in the totals of males and females, there is a well defined pattern when figures for each sex are compared, age group by age group. In all ages under 15 years there is a preponderance of males. This difference is common to most disease groups but is mere marked in diseases of the digestive and respiratory systems, in congenital malformations, and in accidental injuries. For the ages between 15 and 50 years there are more females than males. This age group covers the child-bearing ages in women, and the higher proportion of female patients is a reflection of this fact. Apart from conditions associated with pregnancy, abortion, delivery, and the puerperium, female patients outnumbered male patients in both malignant and non-malignant tumours and in diseases of the genito-urinary system. In the remaining age group, that for ages over 50 years, the males once more predominate, particularly in diseases of the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems, and in infective and parasitic diseases.
Principal Diseases — The following summary shows the principal diseases treated, together with the number of deaths and the fatality rate per cent in public hospitals in 1958. The disease headings are the subtitles of the International Classification of Diseases. More detailed information is published annually in Medical Statistics.
5*
It should be noted that the disease or condition for which a patient is admitted to hospital is not necessarily that which would rank as the cause of death in mortality statistics. Congestive heart failure, for instance, is comparatively highly ranked in hospital cases as the condition immediately affecting the patient, but is frequently only the consequence of some underlying disease, which would take precedence over congestive heart failure in the statistics of causes of death. Hospital returns show each disease for which the patient was treated while in hospital, but the classification for statistical purposes has been made on the basis of the principal disease for which the patient was admitted, regardless of what other unrelated diseases may have been present or developed during the stay in hospital. In mortality statistics, on the other hand, the underlying cause of death is of paramount importance. In the summary below a patient admitted on account of an injury is classified according to the nature of the injury. Should the patient die, however, the death would be classified in the mortality statistics according to the cause of the injury, e.g., motor-vehicle accident, accidental fall, etc.
SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL DISEASES TREATED IN PUBLIC HOSPITALS DURING 1958
| Diseases | Total Discharges and Deaths in Public Hospitals | Deaths in Public Hospitals | Fatality Rate Per Cent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tuberculosis of respiratory system | 2,257 | 104 | 4.6 |
| Tuberculosis — other forms | 595 | 28 | 4.7 |
| Syphilis and its sequelae | 114 | 16 | 14.0 |
| Gonococcal infection and other venereal diseases | 49 | - | - |
| Infectious diseases commonly arising in intestinal tract | 331 | 6 | 1.8 |
| Other bacterial diseases | 525 | 74 | 14.1 |
| Spirochaetal diseases except syphilis | 91 | - | - |
| Diseases attributable to viruses | 1,654 | 44 | 2.7 |
| Malaria | 19 | - | - |
| Other infective and parasitic diseases | 375 | 1 | 0.3 |
| Cancer, malignant disease | 7,447 | 1,797 | 24.1 |
| Benign neoplasm | 3,663 | 26 | 0.7 |
| Neoplasm of unspecified nature | 105 | 3 | 2.9 |
| Allergic disorders | 1,718 | 41 | 2.4 |
| Diseases of thyroid gland | 844 | 10 | 1.2 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1,639 | 144 | 8.8 |
| Diseases of other endocrine glands | 236 | 10 | 4.2 |
| Avitaminoses and other metabolic diseases | 325 | 15 | 4.6 |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs | 761 | 45 | 5.9 |
| Psychoses | 1,405 | 59 | 4.2 |
| Psychoneurotic disorders | 1,727 | 4 | 0.2 |
| Disorders of character, behaviour and intelligence | 1,094 | 13 | 1.2 |
| Vascular lesions affecting central nervous system | 3,034 | 1,344 | 44.3 |
| Inflammatory diseases of central nervous system | 560 | 80 | 14.3 |
| Other diseases of central nervous system | 1,577 | 183 | 11.6 |
| Diseases of nerves and peripheral ganglia | 345 | 8 | 2.3 |
| Inflammatory diseases of eye | 564 | 3 | 0.5 |
| Other diseases and conditions of eye | 2,678 | 13 | 0.5 |
| Diseases of ear and mastoid process | 1,489 | 9 | 0.6 |
| Rheumatic fever | 536 | 15 | 2.8 |
| Chronic rheumatic heart disease | 400 | 76 | 19.0 |
| Arteriosclerotic and degenerative heart disease | 4,027 | 1,045 | 25.9 |
| Other heart diseases | 1,927 | 530 | 27.5 |
| Hypertensive disease | 1,165 | 151 | 13.0 |
| Disease of arteries | 837 | 215 | 25.7 |
| Diseases of veins and other diseases of circulatory system | 4,323 | 61 | 1.4 |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 1,714 | 8 | 0.5 |
| Influenza | 472 | 7 | 1.5 |
| Pneumonia | 4,804 | 515 | 10.7 |
| Bronchitis | 1,810 | 137 | 7.6 |
| Other diseases of respiratory system | 12,623 | 87 | 0.7 |
SUMMARY OF PRINCIPAL DISEASES TREATED IN PUBLIC HOSPITALS DURING 1958
| Diseases | Total Discharges and Deaths in Public Hospitals | Deaths in Public Hospitals | Fatality Rate Per Cent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases of buccal cavity and oesophagus | 1,953 | 13 | 0.7 |
| Diseases of stomach and duodenum | 2,560 | 133 | 5.2 |
| Appendicitis | 6,047 | 27 | 0.4 |
| Hernia of abdominal cavity | 4,253 | 39 | 0.9 |
| Other diseases of intestine and peritoneum | 4,136 | 216 | 5.2 |
| Diseases of liver, gallbladder, and pancreas | 3,161 | 126 | 4.0 |
| Nephritis and nephrosis | 637 | 96 | 15.1 |
| Other diseases of urinary system | 2,339 | 106 | 4.5 |
| Diseases of male genital organs | 2,454 | 138 | 5.6 |
| Diseases of breast, ovary, Fallopian tube, and parametrium | 1,210 | 4 | 0.3 |
| Diseases of uterus and other female genital organs | 6,240 | 12 | 0.2 |
| Complications of pregnancy | 2,710 | 6 | 0.2 |
| Abortion | 4,702 | 1 | - |
| Delivery without complications | 595 | - | - |
| Delivery with specified complications | 1,144 | 5 | 0.4 |
| Complications of the puerperium | 1,116 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Infections of skin and subcutaneous tissue | 4,591 | 14 | 0.3 |
| Other diseases of skin and subcutaneous tissue | 1,984 | 25 | 1.3 |
| Arthritis and rheumatism, except rheumatic fever | 2,141 | 66 | 3.1 |
| Osteomyelitis and other diseases of bone and joint | 3,549 | 37 | 1.0 |
| Other diseases of musculoskeletal system | 2,135 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Congenital malformations | 2,402 | 191 | 8.0 |
| Birth injuries, asphyxia, and infections of newborn | 627 | 110 | 17.5 |
| Other diseases peculiar to early infancy | 1,171 | 105 | 9.0 |
| Ill defined symptoms referable to systems and organs | 8,580 | 12 | 0.1 |
| Senility and ill defined diseases | 1,224 | 232 | 19.0 |
| Fracture of skull, spine, and trunk | 2,292 | 127 | 5.5 |
| Fracture of upper limb | 3,397 | 9 | 0.3 |
| Fracture of lower limb | 4,142 | 272 | 6.6 |
| Dislocation without fracture | 670 | - | - |
| Sprains and strains of joints and adjacent muscles | 556 | - | - |
| Head injuries (excluding skull fracture) | 4,989 | 74 | 1.5 |
| Internal injury of chest, abdomen, and pelvis | 292 | 39 | 13.4 |
| Laceration and open wound of face, neck, and trunk | 995 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Laceration and open wound of upper limb | 2,553 | 1 | - |
| Laceration and open wound of lower limb | 1,121 | - | - |
| Laceration and open wounds of multiple location | 122 | - | - |
| Superficial injury | 288 | - | - |
| Contusion and crushing with intact skin surface | 1,175 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Effects of foreign body entering through orifice | 768 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Burns | 1,494 | 39 | 2.6 |
| Injury to nerves and spinal cord without bone injury | 101 | 1 | 1.0 |
| Effects of poisons | 1,377 | 23 | 1.7 |
| Effects of weather, exposure, and related conditions | 56 | 2 | 3.6 |
| Other and unspecified injuries and reactions | 766 | 6 | 0.8 |
| Special conditions and examinations without sickness | 2,020 | - | - |
| Admission for convalescent care, plastic treatment, and prosthetic devices | 35 | - | - |
| Totals | 174,729 | 9,248 | 5.3 |
Deaths in Public Hospitals — The proportion of deaths in public hospitals to all deaths has increased over the last 30 years. Examination of the following table shows the trend.
| Year | Deaths in Public Hospitals | Total Deaths | Proportion of Deaths in Public Hospitals to Total Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1929 | 4,125 | 13,220 | 31.2 |
| 1930 | 3,979 | 13,145 | 30.3 |
| 1931 | 3,822 | 13,062 | 29.3 |
| 1932 | 3,882 | 12,875 | 30.2 |
| 1933 | 4,036 | 12,862 | 31.4 |
| 1934 | 4,383 | 13,810 | 31.7 |
| 1935 | 4,497 | 13,664 | 32.9 |
| 1936 | 4,952 | 14,658 | 33.8 |
| 1937 | 5,274 | 15,215 | 34.7 |
| 1938 | 5,959 | 16,874 | 35.3 |
| 1939 | 5,568 | 15,933 | 34.9 |
| 1940 | 5,825 | 15,875 | 36.7 |
| 1941 | 6,511 | 17,047 | 38.2 |
| 1942 | 7,073 | 18,117 | 39.0 |
| 1943 | 7,372 | 17,122 | 43.0 |
| 1944 | 7,478 | 17,049 | 43.9 |
| 1945 | 7,939 | 17,686 | 44.9 |
| 1946 | 7,710 | 17,720 | 43.5 |
| 1947 | 17,442 | ||
| 1948 | 7,352 | 17,285 | 42.5 |
| 1949 | 7,595 | 17,578 | 43.2 |
| 1950 | 7,742 | 18,084 | 42.8 |
| 1951 | 8,163 | 18,836 | 43.3 |
| 1952 | 8,119 | 18,896 | 43.0 |
| 1953 | 7,926 | 18,354 | 43.2 |
| 1954 | 8,140 | 18,876 | 43.1 |
| 1955 | 8,410 | 19,225 | 43.7 |
| 1956 | 8,824 | 19,696 | 44.8 |
| 1957 | 9,576 | 20,862 | 45.9 |
| 1958 | 9,248 | 20,301 | 45.6 |
| 1959 | 10,020 | 21,128 | 47.4 |
Duration of Stay in Public Hospitals — The average duration of stay of patients in public hospitals is shown for selected diseases in the following table.
SUMMARY OF SELECTED DISEASES TREATED IN PUBLIC HOSPITALS, SHOWING AVERAGE DURATION OF STAY, 1958
| Diseases | Total Discharges and Deaths in Public Hospitals | Average Stay (Days) |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory tuberculosis | 2,257 | 129.0 |
| Non-respiratory tuberculosis | 595 | 75.5 |
| Infective and parasitic diseases other than tuberculosis | 3,158 | 21.5 |
| Otitis media and mastoiditis | 1,111 | 12.4 |
| Rheumatic fever | 536 | 60.6 |
| Chronic rheumatic heart disease | 400 | 32.3 |
| Acute upper respiratory infections, influenza, and acute bronchitis | 2,887 | 7.9 |
| Pneumonia | 4,804 | 18.1 |
| Chronic or unqualified bronchitis | 1,109 | 26.3 |
| Hypertrophied tonsils and adenoids, and quinsy | 9,991 | 4.1 |
| Appendicitis | 6,047 | 10.5 |
| Gastro-enteritis (acute) | 1,227 | 9.0 |
| Infections of skin and subcutaneous tissue | 4,591 | 10.6 |
| Osteomyelitis and periostitis | 1,069 | 36.2 |
| Malignant neoplasms | 7,447 | 26.5 |
| Benign tumours of uterus, ovary, and female genital organs | 1,639 | 12.1 |
| Allergic disorders | 1,718 | 21.4 |
| Thyrotoxicosis | 421 | 20.8 |
| Diabetes | 1,639 | 33.3 |
| Psychoneurotic disorders | 1,727 | 29.5 |
| Vascular lesions of central nervous system | 3,034 | 54.3 |
| Arteriosclerotic, hypertensive and degenerative heart disease, and general arteriosclerosis | 5,526 | 39.0 |
| Varicose veins and phlebitis | 2,364 | 15.1 |
| Haemorrhoids | 818 | 12.5 |
| Dental caries and other diseases of teeth and supporting structures | 1,447 | 2.5 |
| Peptic ulcer | 2,141 | 23.1 |
| Hernia | 4,253 | 12.2 |
| Gallbladder disease | 2,754 | 16.9 |
| Nephritis and nephrosis | 637 | 34.9 |
| Urinary infections and calculus | 1,559 | 15.8 |
| Hyperplasia of prostate | 1,225 | 30.8 |
| Disease of female genital organs (excluding tumours) | 6,918 | 9.6 |
| Arthritis | 1,874 | 60.8 |
| Muscular rheumatism, neuralgia, and neuritis | 567 | 18.7 |
| Synovitis and other inflammatory diseases of tendons and fascia | 768 | 9.3 |
| Symptoms, senility, and ill defined conditions | 9,804 | 19.3 |
| Accidents, poisoning, and violence | 27,154 | 14.6 |
| Deliveries and complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium | 10,267 | 8.4 |
| Remainder | 37,246 | 20.9 |
| Total | 174,729 | 19.9 |
Accident Cases — A summary is given below of accident cases treated as inpatients in public hospitals during 1958.
| Type of Accident | Total Cases | Percentage of All Accident Cases | Aggregate Stay (Days) | Average Stay (Days) | Aggregate Stay as Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transport— | |||||
| Railway | 126 | 0.4 | 2,688 | 21.3 | 0.6 |
| Motor-vehicle traffic | 5,271 | 18.3 | 84,241 | 16.0 | 19.1 |
| Motor-vehicle non-traffic | 148 | 0.5 | 2,343 | 15.8 | 0.5 |
| Other road vehicles | 1,699 | 5.9 | 16,159 | 9.5 | 3.7 |
| Water | 192 | 0.7 | 3,379 | 17.6 | 0.8 |
| Aircraft | 19 | 0.1 | 321 | 16.9 | 0.1 |
| Total transport | 7,455 | 25.9 | 109,131 | 14.6 | 24.8 |
| Non-transport— | |||||
| Accidental poisoning | 1,060 | 3.7 | 3,194 | 3.0 | 0.7 |
| Accidental falls | 7,110 | 24.7 | 164,362 | 23.1 | 37.3 |
| Other accidents | 10,431 | 36.3 | 119,228 | 11.4 | 27.1 |
| Total non-transport | 18,601 | 64.7 | 286,784 | 15.4 | 65.1 |
| Complications due to non-therapeutic medical and surgical procedures | 85 | 0.3 | 349 | 4.1 | 0.1 |
| Therapeutic misadventure and late complications of therapeutic procedures | 1,570 | 5.5 | 28,598 | 18.2 | 6.5 |
| Late effects of injury and poisoning | 335 | 1.2 | 9,445 | 28.2 | 2.1 |
| Suicide and self-inflicted injury | 360 | 1.3 | 3,137 | 8.7 | 0.7 |
| Homicide and injury purposely inflicted by other persons | 353 | 1.2 | 3,263 | 9.2 | 0.7 |
| Injury resulting from operations of war | 2 | - | 4 | - | - |
| Grand totals | 28,761 | 100.0 | 440,711 | 15.3 | 100.0 |
Most cases come under the heading “Non-transport — Other accidents”, which includes accidents caused by cutting and piercing instruments, machinery, falling objects, fire and hot objects, and so on. Of these most occurred in the home.
The second largest group is “Accidental falls”, which has an aggregate stay greater than any other group. This is due to the long periods spent in hospital by elderly people who have sustained serious falls.
Motor-vehicle traffic accidents comprise the third largest group, and have the third largest aggregate stay. It is interesting to note that there were three and a half times as many admissions to hospital and nearly three and a half times as many beds occupied by people injured in non-transport accidents as there were for motor-vehicle traffic accidents.
DEVELOPMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICES IN NEW ZEALAND - The Public Health Act 1900 placed public health administration in New Zealand on an efficient basis. A separate Department of Public Health was set up under its own Minister; the country was divided into a number of health districts, and properly trained and qualified staff were appointed to administer the Act. In the years following the establishment of the Department steady progress was made in the building up of a public health organisation. Acts were passed dealing with the sale of food and drugs; the registration of medical practitioners, pharmacists, nurses and midwives, plumbers; the prevention of quackery; and the control of venereal disease. Sanatoria were established to help in the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis. Attention was given to problems of maternal welfare. Medical supervision of school children came into operation, at first under the control of the Department of Education, then after 1921 under the Department of Health.
In 1909 a closer link between curative and preventive medicine was forged by merging the Hospitals and Charitable Aid Department into the Department of Public Health's organisation.
During the years 1900 to 1920 there was an increasing public interest taken in health matters. As a result a number of voluntary health organisations were established with the objects of diffusing knowledge of infant welfare, first aid, and home nursing.
The 1918–19 influenza epidemic brought to light a number of defects in the public health organisation, particularly the need for a simplification of existing health legislation and the need for a clear definition of the duties of local authorities, hospital boards, and the Department of Health. The result of this experience was the passing of the Health Act 1920 under which, with its amendments, the Department of Health operated until 1956.
Following the passing of this Act new health districts were created and the existing activities of the Department were expanded. Among the more important of the new activities of the Department were the establishment of a School Dental Service in 1920, the building up of health education work, and, in 1937, the institution of the Medical Research Council. Registration was widened to include dentists, opticians, and masseurs.
Developments since the Second World War included a more positive attack on tuberculosis marked by the passing of the Tuberculosis Act 1948, the establishment as a Government agency of the Dominion X-ray and Radium Laboratory existing at Christchurch, and the creation of the National Health Institute in Wellington. At the end of 1947 the Mental Hospitals Department ceased to be a separate Government Department, and became the Division of Mental Hygiene of the Department of Health. Occupational therapists and dietitians are further professional classes with legislation providing for national registration.
The Health Act 1956 consolidated and amended the law relating to public health.
A more detailed outline of the development of public health services in New Zealand up to 1939 will be found in the annual report of the Department of Health for that year.
PRESENT ORGANISATION OF PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICES - Local Authorities: Part II of the Health Act 1956 lays definite obligations on local authorities in regard to public health. Each local authority must either appoint its own health inspectors or contribute to the salary of an inspector of the Department of Health. Each inspector must hold a certificate of the Royal Society for the Promotion of Health (or certain equivalents) before he can be appointed. A local authority's responsibility in health matters is wide. It must promote and conserve the public health within its district - a function which includes regular inspections of its district; abatement of nuisances as defined in the Health Act; provision of efficient refuse, nightsoil, and sanitary services; protection and purification of water supplies; closing and demolition of insanitary buildings; registration and regulation of cattle saleyards; and the enforcement of certain minimum sanitary requirements for residences and business premises. It may also make bylaws dealing with public health matters.
Department of Health: The chief administrative officer of the Department is the Director-General of Health. He is assisted by two Deputy Director-Generals, and the work of the Department is divided among the following divisions: Public Health, Hospitals, Child Health, Nursing, Clinical Services, Tuberculosis, Health Education, Maternal Welfare, Dental Health, and Physical Medicine. There is also the Division of Mental Health, the activities of which are described in Section 5c. New Zealand as a whole is divided into 19 health districts, each under the control of a medical officer of health, a medical practitioner with special qualifications in sanitary science.
The Department is required to secure the preparation, effective carrying out, and coordination of measures necessary to promote public health. It administers all Acts relating to public health; it advises local authorities on public health; it must do whatever is possible to prevent, limit, or suppress disease; it promotes research into public health fields and the prevention and treatment of disease; it conducts health publicity and organises and controls medical, dental, and nursing services paid from public funds. With the authority of the Minister, a medical officer of health may exercise very wide powers in the event of an epidemic or serious outbreak of infectious disease, including the requisitioning of land and buildings, prohibition of public gatherings, and controlling the movements of cases and contacts of any infectious disease. Certain diseases, mostly infectious, but including some non-communicable, must be notified by medical practitioners. Provisions relating to quarantine are included in the Health Act; and extensive power is given to make regulations relating to the conservation and promotion of public health.
The Department's organisation includes a Board of Health. The Health Act 1956 reconstituted the Board of Health and widened the scope of its functions. While the former Board of Health was principally concerned with water supply and drainage, the new Board, in addition to its responsibilities in relation to local authorities and their sanitary works, has the much wider function of giving the Minister authoritative advice on the broad aspects of public health policy and the relationship between the various health services.
In addition to the Health Act 1956, the following Acts are administered by the Department:
| Cemeteries Act 1908 |
| Dangerous Drugs Act 1927 |
| Dentists Act 1936 |
| Dietitians Act 1950 |
| Food and Drugs Act 1947 |
| Hospitals Act 1957 |
| King George the Fifth Memorial |
| Children's Health Camps Act 1953 |
| Medical Act 1908 (Part II) |
| Medical Advertisements Act 1942 |
| Medical Practitioners Act 1950 |
| Medical Research Council Act 1950 |
| Mental Health Act 1911 |
| Nurses and Midwives Act 1945 |
| Occupational Therapy Act 1949 |
| Opticians Act 1928 |
| Physiotherapy Act 1949 |
| Plumbers Registration Act 1953 |
| Poisons Act 1960 |
| Radioactive Substances Act 1949 |
| Social Security Act 1938 (Part III) |
| Tuberculosis Act 1948 |
A detailed report of the activities of the Department of Health is given in the annual report of the Director-General of Health (parliamentary paper H. 31).
The net expenditure of the Department (excluding capital expenditure from the Public Works Account) for the years ended 31 March 1959 and 1960 is given in the following table.
| Item | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vote “Health”– | £ | £ | £ |
| General health services | 1,594,342 | 1,592,907 | – 1,435 |
| Dental health | 945,483 | 1,042,341 | 96,858 |
| Departmental hospitals and institutions (other than mental health) | 519,466 | 562,489 | 43,023 |
| Mental health | 3,479,621 | 3,777,632 | 298,011 |
| Health education | 28,655 | 29,596 | 941 |
| Medical Research Council | 104,872 | 107,623 | 2,751 |
| Homes for the aged | 209,539 | 479,035 | 269,496 |
| Pensioners housing: Local authorities | 176,019 | 203,008 | 26,989 |
| Youth hostels | 12,219 | 8,325 | – 3,894 |
| Plunket Society subsidies | 120,956 | 128,113 | 7,157 |
| Miscellaneous grants and subsidies | 90,520 | 94,778 | 4,258 |
| Bursaries | 42,594 | 42,487 | – 107 |
| Totals | 7,324,286 | 8,068,334 | 744,048 |
| Vote “Public Hospitals”– | |||
| Grants to hospital boards | 15,774,324 | 17,204,751 | 1,430,427 |
| Vote “Medical, Hospital, etc., Benefits” | 18,650,601 | 19,886,957 | 1,236,356 |
| Grand totals | 41,749,211 | 45,160,042 | 3,410,831 |
NOTE - Minus sign (–) denotes a decrease.
PUBLIC HEALTH ACTIVITIES – This account covers measures relating to “preventive” medicine, as distinct from activities in “curative” medicine, which are dealt with elsewhere in this volume – see Section 5B (Hospitals) and Section 5C (Mental Hospitals). Information on medical, hospital, and other related benefits, which are administered by the Department of Health, is given in Section 6A (Social Security).
It is convenient to consider public health activities under headings which correspond generally to certain of the divisions within the Department of Health. These headings are:
| Public Health |
| Occupational Health |
| Tuberculosis |
| Child Health |
| Dental Health |
| Health Education |
| Maternal Welfare |
| Radiation Protection |
| Physical Medicine |
| Nursing |
PUBLIC HEALTH – The Health Act places responsibility for the maintenance of the public health largely on the Department, but local authorities have powers and duties to perform in a number of sanitary and inspection services. Each of the 19 health districts in New Zealand is under the control of a medical officer whose duties include the administration of all enactments relating to public health and who can provide local governing bodies with expert advice in this field. Public hygiene is concerned more particularly with the control of infectious disease, environmental hygiene, food and drugs, poisons and addiction-producing drugs, and burial and cremation.
Disease: The control of disease is based on a system of notification which has long been in force. The present list of notifiable diseases is as follows.
| Notifiable Infectious Diseases: |
| Anthrax |
| Cerebro-spinal fever (cerebro-spinal meningitis) |
| Cholera |
| Cysticercosis |
| Diphtheria |
| Dysentery (amoebic and bacillary) |
| Encephalitis lethargica |
| Enteric fever (typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever) |
| Fulminant influenza |
| Infective hepatitis |
| Leprosy |
| Leptospiral infections |
| Ophthalmia neonatorum |
| Ornithosis (psittacosis) |
| Pemphigus neonatorum, impetigo, or pustular lesions of the skin of the newborn infant |
| Plague (bubonic or pneumonic) |
| Pneumonic influenza |
| Poliomyelitis |
| Other Notifiable Diseases: |
| Actinomycosis |
| Anchylostomiasis (hookworm disease) |
| Beriberi |
| Bilharziasis (endemic haematuria, Egyptian haematuria) |
| Chronic lead poisoning |
| Compressed-air illness arising from occupation |
| Damage to eyesight arising from occupation |
| Dengue |
| Diseases of the respiratory system arising from occupation |
| Eclampsia |
| Food poisoning |
| Puerperal fever involving any form of septicaemia, sepsis, or sapraemia |
| Relapsing fever |
| Salmonella infections |
| Septicaemia, sepsis, or sapraemia, in any form, following abortion or miscarriage |
| Septicaemic influenza |
| Smallpox (variola, including varioloid and alastrim) |
| Staphylococcal pneumonia of the newborn infant |
| Staphylococcal septicaemia of the newborn infant |
| Taeniasis |
| Trachoma (granular conjunctivitis, granular ophthalmia, granular eyelids) |
| Typhus |
| Undulant fever |
| Yellow fever |
| Hydatid disease |
| Impaired hearing arising from occupation |
| Malaria |
| Phosphorus poisoning |
| Poisoning from any insecticide, weedicide, fungicide, or animal poison met with at work |
| Poisoning from any gas, fumigant, or refrigerant met with at work |
| Poisoning from any solvent met with at work |
| Poisoning from any metal or salt of any metal met with at work |
| Skin diseases arising from occupation |
| Tetanus |
All forms of tuberculosis are notifiable under the Tuberculosis Act 1948.
Venereal Diseases: Venereal diseases are only notifiable if the patient discontinues treatment before cure is effected. The Venereal Diseases Regulations 1941 give adequate powers for the examination and treatment of persons suspected of suffering from the diseases. Free treatment has been established in the larger cities and treatment is available to seamen at the main ports in accordance with the Brussels Agreement. Restrictions are also placed on the nature of the employment such persons may undertake if they are suffering from the diseases in a communicable form.
In the administration of the regulations, every precaution is taken to ensure the avoidance of publicity.
Environmental Hygiene is concerned with the provision and proper maintenance of public water supplies and sewerage systems, the disposal of refuse, the condition of dwellinghouses, the control of offensive trades, and the hygiene of premises in which food is manufactured and sold, including eating houses. These matters are primarily the responsibility of the local authorities, but the Department of Health acts in a general advisory capacity. In the case of many of the smaller local authorities the necessary inspections are made by departmental inspectors on behalf of and by arrangement with the local authorities.
Food and Drugs: The Food and Drugs Act 1947 provides for the analysis, by analysts appointed under the Act, of any article of food or drink, or of any drug, which may be sold, offered for sale, or exposed for sale, and for the inspection of any place where there is any food or drug intended for sale. If any such article is proved to be unfit for human consumption heavy penalties may be inflicted on the person or persons responsible. Stringent measures are provided for the prevention of adulteration of food, drink, or drugs, and for the inspection of places where such goods are manufactured or packed. Control is also established over all utensils and appliances coming into contact with food and drugs.
Considerable progress has been made in implementing the purposes of the Act. All the common foodstuffs are standardised, and the labelling of packages is controlled by regulations, which are revised and added to as the necessity arises. Regular sampling of foods, particularly milk, is undertaken by departmental inspectors, and these samples are analysed in the Dominion Laboratory and its branch laboratories.
An important provision of the Act controls all kinds of publicity concerning any food or drug whereby a purchaser would possibly be deceived in regard to the properties of such food or drug, whether or not it is standardised by regulation. This matter is also covered by the Medical Advertisements Act 1942, which is referred to later.
The definition of “drug” includes medicines used externally or internally by man, anaesthetics, soaps, and disinfectants.
Any person may, on payment of the prescribed fee, together with the cost of the sample, require any authorised officer to purchase a sample of any food and submit it for analysis.
A power contained in the 1947 Act enables any drug to be withheld from the public except when prescribed by a doctor, dentist, or veterinary surgeon.
Dangerous Drugs and Poisons: In order to carry out New Zealand's obligations under international conventions relating to addiction-producing drugs, the Dangerous Drugs Act 1927 was enacted. The dealing in and the use of prepared opium, cocaine, and marihuana are prohibited, and the production, manufacture, sale, and distribution of other dangerous drugs are restricted to persons licensed by the Director-General of Health. The importation of these drugs is controlled by the Department of Health. Suitable regulations, the Dangerous Drugs Regulations 1951, are in force to give effect to the provisions of the Act, and are similar to the regulations in the United Kingdom and Australia.
The Poisons Act 1960 controls the distribution, use, labelling, and packing of all poisons and toxic substances. It is an offence to pack poisons in bottles that are ordinarily used for food, drink, or medicine. The Act also provides for the control of certain poisonous drugs by preventing their sale to the public except on the prescription of a doctor, a dentist, or a veterinary surgeon. There is power to introduce special safeguards for certain dangerous chemicals used in horticulture. Labels for poisons in this “Deadly Poison” group must bear statements of the precautions to be taken in using the poison, the symptoms of poisoning, and the remedial treatment, and must be approved by the Director-General of Health.
Hydatids Eradication: The Hydatids Act 1959 provides new and more positive methods of attack in the campaign for the eradication of hydatid disease. The Act is administered by the Department of Agriculture and set up a National Hydatids Council on which the Department of Health has representation.
Medical Advertisements Act 1942: This Act came into force in January 1943. Under it the word “advertisement” is defined broadly, but does not include any advertisement or scientific matter distributed only to members of the medical and allied professions.
The Act set up a Medical Advertisements Board, which was given power as a quasi judicial body to examine statements made in any medical advertisement. The Board may require the claims or statements made or implied to be substantiated to its satisfaction. Subsequent publication of such an advertisement is prohibited until the Board has notified its decision, and the veto on publication becomes permanent if the Board decides the claim or statement has not been proved.
Regulations issued under the Act limit the claims which may be included in any medical advertisement, and include a list of diseases concerning which no advertisement may make a claim to cure.
Cemeteries: The law governing burial and cremation in New Zealand is found in the Cemeteries Act 1908 and its amendments. The registration by local authorities of funeral directors and mortuaries operated by them is provided for in the Health (Burial) Regulations 1946.
Widespread provision for cemeteries has been made in the past by the reservation of areas of Crown land for this purpose, but apart from this the Cemeteries Act makes it clear that local authorities are charged with ensuring that in their districts there exists adequate provision for the disposal of the dead.
In most rural areas and in the smaller centres the local authority either acts as trustee or else has been delegated the power of appointing individual trustees to carry out the provisions of the Act. For some cemeteries established on Crown reserves trustees are appointed by the Governor-General. In the larger centres local authorities have acquired land for the establishment of cemeteries.
The law provides that cremation may be carried out subject to the conditions that the deceased was not known to have left any written direction to the contrary and that the cremation is effected in conformity with the regulations. The latter imposed stringent precautions against cremation being used for any criminal purpose. Crematoria have been established in Auckland (2), Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, Hastings, Wanganui, Nelson, and Palmerston North.
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH – The Factories Act 1946, section 78, gives to medical officers of health or other authorised officers of the Department of Health the same powers and authorities as inspectors of factories with regard to the health and welfare sections of the Act. Towards the end of 1956 the functions of the Division of Occupational Health became one of the functions of the Division of Public Hygiene and, whereas they were previously discharged in the field by five district industrial medical officers, they are now discharged by all medical officers of health.
The objective of the programme is to work with labour, management, the medical profession, and other groups to assist in improving the health of the worker. In the promotion of this programme it is evident that clearly defined arrangements are necessary to avoid duplication of effort so far as the Department of Labour and some other Departments are concerned, there being very necessary joint activities in this field of worker health.
The principle arrived at is that the Department of Labour is responsible for accident prevention, hours of work, employment of women and children, etc., but calls to the attention of the Department of Health any health problems which the factory inspectors may encounter. The enforcement of statutes and regulations is undertaken by the Department of Labour. The suspension of workers on health grounds, approval of respirators and similar protective equipment, and the arrangements for medical examinations are undertaken by the Department of Health, which also investigates health hazards referred to it from the Department of Labour or disclosed as a result of investigations into notified occupational disease, complaints, surveys, etc. Resulting from this cooperation, clearly established codes of practice are developing, as are also a series of regulations dealing with health hazards, many of the latter being administered by the two Departments, each in its own sphere.
A somewhat similar understanding has been established with the Waterfront Industry Commission and New Zealand Railways, and illustrates the general pattern of arrangements between the Department of Health and other Government Departments or agencies concerned with particular aspects of workers' health.
Occupational Disease: The notifiable occupational diseases are scheduled in the Health Act 1956 and details of diseases notified are published annually in the report of the Director-General of Health.
Control of Health Hazards: An increasing number of specific health hazards are coming under formal control, namely lead processes, electroplating, spray painting, sand blasting (siliceous blasting agents in factories are prohibited), fumigation, aerial application of poisons, where in conjunction with the Civil Aviation Administration a special rating is required by pilots, and agricultural chemicals. The organisation of radiation protection is dealt with by the Dominion X-ray and Radium Laboratory, while a number of other specific hazards are currently receiving consideration.
Medical, Nursing, and First-aid Services: While there are no statutory obligations on industry to provide medical and nursing services, an increasing number of Government and private factories do provide such services, details of which are published in the annual report of the Director-General of Health.
To meet the needs of small plants the Department has developed and is developing industrial health centres with financial support from the Waterfront Industry Commission in the case of harbour areas, and the Workers' Compensation Board in the case of general industry.
Minimal first-aid requirements have been laid down by the Department, which generally endeavours to encourage both the development of medical and nursing services and the raising of first-aid standards throughout industry generally.
Pre-employment Examinations: Pre-employment medical examinations are required for young workers before entering factory employment.
Air Pollution – The air pollution provisions of Part V of the Health Act have been enforced since 1958. A senior chemical inspector is resident in Wellington with a deputy in Auckland.
The classes of process requiring registration were increased from 20 to 26 by the Chemical Works Order of 1960 and now include, for the control of odours, supervision of rending processes. Most registrable processes are governed by the requirement to adopt the best practicable means, but there are limiting standards for lead and acid gases. All new installations or extensions of these registrable processes require approval by the Department of Health.
Air pollution committees in Auckland and Christchurch, in association with the Air Pollution Committee of the Board of Health, have established surveys to determine the extent of air pollution in these cities and the need for further action.
TUBERCULOSIS – Legislation for the control of tuberculosis in New Zealand is provided for in the Tuberculosis Act 1948, which is administered by the Department of Health. The Act provides for notification and registration of tuberculosis cases; compulsory medical examination and hospitalisation of recalcitrant tuberculosis patients; Government financial and housing assistance to tuberculosis patients; worker's compensation to hospital and other institutional employees who contract tuberculosis in the course of their employment.
The Department's programme for control of the disease is based on adequate case-finding and notification procedures, the proper treatment and surveillance of notified cases, investigation and control of contacts. This calls for close coordination of the staff and services of hospital boards (which are responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis) and officers of the Department of Health who deal with the social and epidemiological aspects of the disease. The latter involves supervision of tuberculosis families, tracing of contacts, and the maintenance of tuberculosis statistics.
Mass miniature radiography is now an established and important feature of the Department's case-finding programme and during the years 1956 to 1958, 679,542 persons were X-rayed in the nine mass X-ray units then operated by the Department. This resulted in the discovery of 1,153 active cases.
B.C.G. vaccination is also undertaken by the Department and, in particular, is offered to the contacts of registered cases, post-primary-school children, and hospital workers partly exposed to infection.
Over the past decade, the results achieved are marked by a steady decrease each year in new notifications together with a marked decrease in mortality.
CHILD HEALTH – The Division of Child Health is responsible for the supervision of all measures for safeguarding the health of pre-school and school children, and also for ensuring a satisfactory environment at school. Priority is given to the health of the pre-school child.
The Division consists of a Director, who is a medical practitioner, with a staff of full-time and part-time medical officers. The medical officer of health in charge of a health district is responsible, within the limits of the policy laid down and the instructions he receives, for the direction and control of all child health work in his district.
An effort is being made to have every child examined in infancy and twice more before school entry. The examination of pre-school children is carried out by medical officers of the division in Plunket rooms in conjunction with Plunket nurses, and at kindergartens, day nurseries, and other pre-school organisations assisted by public health nurses.
The Division aims at giving each primary school child three physical examinations during primary-school life. Each infant not recorded as having been examined at a pre-school clinic by a medical officer within the preceding calendar year is examined by the public health nurse, who selects those children who require examination by the medical officer. During the remainder of primary school life two other examinations are carried out by the public health nurse. These are in Standard 2 and Form II. As in the case of new entrants not seen by a medical officer at a pre-school clinic, the nurse refers any departure from normal for a special examination by the medical officer. Special medical examinations by the medical officer are also made whenever parents, teachers, the public health nurse, or the medical officer considers them to be necessary. The children found to be suffering from defects are kept under observation until the necessary treatment is obtained from the private practitioner or the hospital.
Mentally backward and feeble-minded children are given special attention, arrangements being made in conjunction with the Department of Education for their entry into a special school or other institution as may be necessary.
A start has been made on the more detailed medical examination of post-primary-school children. Physically handicapped children enrolled with the Correspondence School are also thoroughly examined.
Throughout its work the Division tries to secure the interest and cooperation of parents and family doctors, because only in this way can the work be made effective. With this object in view parents are invited to be present at the medical examination of their children, an opportunity of which the majority take advantage.
Prevention of Disease: The activities of the Division are not confined to the routine medical examination of school children. In addition, certain positive measures are taken to prevent disease and correct physical defects. The more important of these measures are:
Poliomyelitis Vaccination – Immunisation against poliomyelitis has been carried out by the Division's staff for the past four years.
Diphtheria Immunisation – Protection against diphtheria is a routine procedure, and protection against whooping cough is generally given at the same time by use of a combined vaccine. It is preferable that immunisation be done by the family doctor, and the course of injections should be commenced as soon as possible after the third month of infant life. Arrangements can be made for mothers who are unable to have the immunisation done privately to attend with the infant at a departmental clinic. Where necessary in country areas the public health nurse will visit the home to immunise the child. Booster doses are given after the child's fourth birthday. If this booster dose has been missed it is given as soon as possible after the child commences school.
Typhoid Inoculations – Maori children in the North Island are inoculated annually against the typhoid group of diseases.
Goitre Control – The use of iodised salt and iodine-rich foods are advocated by the officers of the Division.
The Milk-in-schools Scheme aims at maintenance of nutrition.
Health Camps are established to which children are admitted for convalescence or correction of malnutrition.
Health camps were originally established to cater for the needs of delicate and undernourished children in the age group of five to 12 years. Now children suffering from minor emotional, psychological, and behaviour problems are also helped by the change in their environment which a camp provides. The service selects the children to attend the camps (which are maintained by an independent organisation – the King George the Fifth Memorial Children's Health Camps Federation) and, as necessary, re-examines them before admission and after discharge. In the camps the children live under an orderly and disciplined routine, they eat plain, well cooked food, and they get plenty of rest, fresh air, and sunshine. In practically all cases a child who attends a health camp benefits both physically and mentally. The opportunity is taken to impart health education by practising healthful living. There are six permanent and two part-time health camps in New Zealand.
For children with emotional or psychological disturbances and behaviour problems, child health clinics have been established in the larger centres and elsewhere. These are staffed by a team consisting of a pediatrician, psychiatrist, psychologist, play therapist, and social worker. Children are referred to these clinics through the family doctor if there is one.
DENTAL HEALTH – The Division of Dental Health, which was instituted in 1921, is concerned with the administration of the various dental activities of the Government, and in particular –(a) The National Dental Service, which comprises (i) the School Dental Service and (ii) the Adolescent Dental Service; (b) the Social Security (Dental Benefits) Regulations; (c) the Dentists Act 1936 and regulations; (d) dental bursaries; (e) dental research; (f) dental health education.
The Division of Dental Health has at its head a Director (a dental surgeon) who is responsible to the Minister of Health, through the Director-General of Health. There is a Deputy Director and two Assistant Directors. A senior executive officer is responsible for the secretarial services. Also attached to the Director's staff is a dental research officer, who is seconded from the New Zealand Medical Research Council
The service is organised in 12 units, each of which is controlled by a senior dental officer, who is directly responsible to the Director. These officers are: the principals of the schools for dental nurses at Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch, and the principal dental officers in charge of the nine dental districts into which New Zealand is divided.
The School Dental Service is staffed by trained school dental nurses and the Adolescent Service by dental surgeons.
The School Dental Service – Briefly, the functions of the service are to improve the standard of dental health of school children (and of pre-school children) by affording them regular and systematic treatment at six-monthly intervals, commencing from the primer classes (or earlier where possible), and continuing through to the highest class of the primary (or intermediate) school. Thereafter they are eligible for enrolment in the Adolescent Service. At present an unprecedented increase in the school population is being experienced as a result of the unusually high birthrate of late years. Until the number of dental nurses can be increased proportionately, children are being transferred to the “adolescent” service at an earlier stage, in order to enable the dental nurses to maintain six-monthly treatment for the younger children. This is a temporary phase, pending the training of more dental nurses.
The other main function of the School Dental Service is health education – the instruction of the children and of the general public in the principles of oral hygiene and the prevention of dental disease. For this purpose there is within the Division an organisation for health education, to which further reference is made under a later heading.
Two years are devoted to the theoretical and practical training of school dental nurses. Approximately 400 student dental nurses are in training at the one time. The course is carefully graduated, and is in the hands of a staff of dental surgeons and dental tutor sisters. Private dental practitioners are represented on the examining board for the final examination. During the period of training, student dental nurses reside in hostels owned and controlled by the Department of Health.
On completing her training, a school dental nurse is posted to a school dental clinic, where she becomes responsible to the principal dental officer of her district for the dental treatment of a group of approximately 500 patients. She is visited at intervals by the principal dental officer or one of his staff, who discusses current problems, and assists the dental nurse to maintain a high standard in the conduct of her work.
Dental treatment comprises fillings in both temporary teeth and permanent teeth, cleaning and scaling of the teeth, extractions where necessary, and sodium fluoride treatment. There were 374,116 children under regular treatment by the school dental nurses during the year 1959–60. The aim of the service is to promote dental health by conserving the natural teeth and preventing dental decay. Only a small number of teeth have to be extracted as unsavable, about four for every 100 saved by conservative treatment.
Orthodontic treatment is carried out principally in Wellington, where an orthodontic unit is established at the Children's Dental Clinic, which is associated with the School for Dental Nurses. Dental officers in field clinics undertake a limited amount of orthodontic treatment of a simple nature.
Adolescent Dental Service – In addition to the service provided by a number of clinics controlled by the Department of Health, dental care for adolescents is being provided by private practitioners as a dental benefit under the Social Security Act, the practitioners being reimbursed on a fee-for-service basis.
Eligibility for dental treatment as an adolescent is contingent upon a person having undergone regular dental care up to within three months of the time of application, either at a school dental clinic or from a private dental practitioner.
Treatment of adolescents is in effect a continuation of the treatment provided by the School Dental Service, and is continued until a patient has reached his sixteenth birthday.
Treatment is essentially of a nature designed to conserve the natural teeth. Dental supervision of adolescents is on a basis of examination and treatment at six-monthly intervals. There is free choice of dentists, and dentists have the right to decline patients.
The treatment (other than treatment requiring special approval) which may be provided as dental benefits, and the fees payable, are indicated in the Schedule to the Social Security (Dental Benefits) Regulations 1960. Dentists are free to exercise their professional judgment, and, if in their opinion a case demands a form of treatment that is not provided for in the Schedule, there is provision, with certain limitations, for such treatment to be approved as a charge on the Social Security Fund.
At 31 March 1960 there were 160,121 children enrolled for dental benefits, and the amount paid for their treatment for the year 1959–60 was £1,000,877. A further 11,328 children were enrolled at departmental clinics.
Dental Health Education – The dental health education activities of the Department include the production of posters, pamphlets, sound films, filmstrips, radio talks, newspaper advertisements, and all other types of advertising media.
Officers of the service are kept in touch with health education and other matters by means of the School Dental Service Gazette, which is published bi-monthly.
Dental officers and school dental nurses are expected to impress on their patients the necessity of maintaining a high standard of oral health. To further this end every opportunity is taken of distributing health educational literature, displaying posters, and devoting reasonable clinical time to instruction in oral hygiene. Opportunities to address meetings of various kinds are availed of wherever possible.
Dental Research – By arrangement with the New Zealand Medical Research Council, a dental research officer is attached to the service. Primarily this officer is engaged in a long-term programme of research on dental problems, but his services are also available to assist the dental administration in carrying out short-term research projects when information is required for a specific purpose.
In addition to this work, the investigation of dental materials and methods of using them goes on constantly, and provides useful data for the selection and use of materials for the service.
Dental Bursaries – The Government grants up to 20 bursaries each year to selected students to assist them to qualify as dentists. The bursaries are of a value of £80 per annum, plus free tuition, the value of which is approximately £50, and are tenable for five years, subject to satisfactory reports from the university authorities. An additional allowance of £50 per annum is payable to students who have to live away from home in order to pursue their studies. Students who are granted bursaries must enter into an agreement to pursue their studies diligently and, on graduating, to enter the service of the Crown or of a hospital board appointed by the Crown for a specified period not exceeding three years.
HEALTH EDUCATION – The aim is to work with the public and to encourage action that will improve personal, family, and community health. The Division has a Director who is a medical practitioner with training in health education, a small staff of writers, technicians, and clerks at Head Office, and lay health education officers who are seconded to district offices and are responsible to the Director through their medical officers of health.
Medical and dental officers, public health nurses, dental nurses, and inspectors of health all devote some of their time to health education. The health education officer acts as a coordinator and stimulates and extends health teaching and health programmes in the district. All the health education officers are women and several hold the diploma in health education issued jointly by Victoria University of Wellington and the Department of Health. All are given special training before taking up their appointments. Various media are used to make the teaching as attractive, as direct, and as acceptable as possible. Daily newspapers and national periodicals carry regular advertisements in health subjects. Radio broadcasts are given at least twice a week and leaflets, pamphlets, and posters are available on many health topics.
The Division also publishes the Department's official bulletin Health which has a circulation of over 50,000 and is issued free to the public four times a year. It gives health information and publicises various aspects of the Department's work.
To assist field officers in their health education work, visual aids, displays, and other publicity material is provided and in addition district offices are encouraged to produce their own.
Voluntary organisations, too, are assisted in their work by the supply of teaching aids and other materials and by assistance with their training programmes.
Each district office has a health education committee consisting of senior administrative and professional officers which plans and budgets local health programmes. A central committee at Head Office largely plans and budgets for overall national requirements.
MATERNAL WELFARE – Maternal and infant welfare work in New Zealand is based on co-operation between the Department of Health, hospital boards, the medical and nursing professions, and the Royal New Zealand Society for the Health of Women and Children (Plunket Society).
The Director of the Division is a medical practitioner who, while not concerned with the particulars of day-to-day administration of maternity hospitals, is responsible for maternal welfare generally in its broadest sense. He keeps abreast of overseas and local developments and is regarded as a consultant on matters of national significance. For instance, in the event of an outbreak of infection affecting mothers or infants, he conducts and directs any necessary investigations as to causes and remedial measures required, in consultation with such other divisions as may be necessary.
The Director has the benefit of the advice of the Maternity Services Committee of the Board of Health, of which he is a member. This committee was formed to advise the Minister on matters relating to obstetric and maternal welfare generally.
The medical officers of health, through their staff of nurse inspectors, exercise a general supervision over the work of midwives and closely control the private hospitals throughout the country. All private hospitals are required to be licensed under the Hospitals Act 1957, and the Department of Health sees that standards regarding buildings, equipment, and staff are observed.
Except in an emergency, no persons other than registered medical practitioners and registered midwives are allowed to conduct confinements, and only registered midwives and registered maternity nurses are permitted to nurse women in childbirth. Approximately 98 per cent of all confinements (European over 99 per cent, Maori over 90 per cent) take place in the various types of maternity hospital – a maternity annex to a public hospital, a State (St. Helens) hospital, or a private maternity hospital.
Important contributions to maternal welfare are made by the Division of Nursing, which includes in its duties the supervision of the training of midwives and maternity nurses, and by the Hospitals Division, which includes in its duties the approval of plans for accommodation to be provided by the various types of maternity hospital. The work of these two Divisions is surveyed elsewhere in this section.
RADIATION PROTECTION – Under the Radioactive Substances Act 1949 the protection of the population from radiation hazards is solely the responsibility of the Department of Health, and the Department has established the Dominion X-ray and Radium Laboratory to provide the administrative and technical services required, and in addition the educational programme, without which effective cooperation in any safety field is not likely to be achieved. An important feature of the Act was the setting up of the Radiological Advisory Council on whose advice the Minister of Health may take action on radiation problems concerning the welfare of the people. Further legislation by way of regulations followed in 1951 and these include the Radiation Protection Regulations and the Transport of Radioactive Substances Regulations.
The Dominion X-ray and Radium Laboratory is required to maintain the primary X-ray standard for New Zealand and also reference standards for the accurate measurement of radioactive substances used in clinical work. Control of radiation sources is effectively obtained by licensing operators at each place where ionising sources are used, and the Electrical (X-ray) Wiring Regulations 1944 provide for the compulsory registration of all X-ray plants in the country. The importation and use of radioactive materials is strictly controlled and requests for such materials on overseas suppliers must be authorised by the laboratory, which acts as the procurement agency for most of the radioisotopes required.
The laboratory operates a field service whereby trained physicists regularly visit all places where ionising sources are used. During these visits measurements are taken, protection problems discussed, and everything possible is done to ensure that persons associated with the ionising sources adopt safe working habits. Apart from the obvious groups, e.g., medical and dental users, the laboratory is also concerned with specialised equipment, such as mass X-ray units, X-ray apparatus used in schools, radar and television equipment, X-ray diffraction units, electron microscopes, research accelerators, etc. Good protection, of course, depends not only on careful working habits but also on material protection.
In recent years the Department of Health has undertaken responsibility for the monitoring of air, rainwater, and soil for the incidence of radioactive contamination from fall-out.
PHYSICAL MEDICINE – The Division of Physical Medicine is concerned with potentially disabling conditions such as rheumatic diseases, cerebral palsy, and other disorders of the locomotor system. The Division is responsible for the general organisation and development of physiotherapy and occupational therapy services throughout the country. The Director is a medical practitioner with special training and experience in these fields.
The centre for the treatment of rheumatism is established at Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Rotorua, which has approximately 100 beds set aside for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Clinical research is also carried out there. Use is made of the thermal waters of Rotorua, the chief establishment for hydrotherapy treatment at the moment being the Main Bath House which is administratively combined with the Queen Elizabeth Hospital. A proportion of the inpatients of Queen Elizabeth Hospital receive treatment at the Main Bath House and outpatients can also be referred for treatment. A large number of outpatients referred from all parts of New Zealand are seen every year.
Admission of patients to the hospital is arranged with the Medical Superintendent, who also arranges for outpatient consultations. The investigation of rheumatic patients and the application of specific measures, including physiotherapy for preventing and controlling deformity, have been developed considerably at Queen Elizabeth Hospital. Occupational therapy has been developed to teach people how to live with their disabilities. Social workers assist in bridging the gap between rehabilitation and vocational and social resettlement.
A cerebral palsy unit is also situated at Queen Elizabeth Hospital providing residential accommodation for 20 children. At this unit the activities of a team of physiotherapists, occupational therapists, teachers, and speech therapists are coordinated by the supervisor of the unit working under a physician. In addition to treatment, post-graduate courses are given to physiotherapists, occupational therapists, teachers, and speech therapists. Patients can be referred by their doctors to the physician in charge of the unit for advice only, or for admission and treatment. Cerebral palsy visiting therapist services are now operating in Christchurch, Wellington, and Palmerston North health districts. These have proved so successful that it is hoped to extend the service to other districts as qualified staff become available.
Cerebral palsy day schools have been established in Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill. Parents of cerebral palsy cases who seek their children's admission first apply to the appropriate medical officer of health or education board. The Director of the Division is often able to advise if cases are referred to him by medical practitioners. The schools are administered by education boards under the Department of Education, but close liaison exists between the schools, the Division, and the Rotorua unit.
The Division is closely associated with the Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy Boards, and the Divisional Director deputises for the Director-General of Health as chairman of these Boards.
The selection of candidates for training at the School of Physiotherapy, Dunedin, is carried out by the Physiotherapy Council of the Otago Hospital Board, and the Departmental Inspector of Physiotherapy who also interviews applicants for bursaries which are awarded to suitable candidates. Such bursaries carry with them conditions that on qualification the bursar will work in a public hospital or departmental institution for two years. The training school for occupational therapists is situated at Auckland Mental Hospital and is administered by the Mental Hospitals Division. Trainees are paid a salary while training, and have to agree to work in a departmental or public hospital for two years after qualification.
6*
The Division is actively concerned in the problem of the rehabilitation of the physically disabled, the organisation of which is at present being developed by an inter-departmental committee.
NURSING DIVISION – Training of nurses commenced in New Zealand in 1886, and registration of nurses was introduced in 1901 and of midwives in 1904. In 1921 the Division of Nursing was set up in the Department of Health and the Nurse Inspector of Hospitals was appointed Director of the Division. In 1928 a post-graduate course for the purpose of providing nurses for executive, teaching, and public health positions was established. Today a block and study day system of organisation of theoretical and practical work operates in all nursing schools.
The training of all nurses and midwives is governed by the Nurses and Midwives Act 1945. This Act is administered by the Nurses and Midwives Board, which comprises mainly nurse members who are in active practice, and is independent of political and departmental control, although the Director-General of Health is the Chairman, and the Director, Division of Nursing, is the Registrar. The current regulations under the Act are the Nurses Registration Regulations 1958. Provision has been made for a three-year basic nursing curriculum which will include obstetric nursing, a three-year curriculum for male nurses, a three-year course in psychopaedic nursing, a lowering of the age at which nurses and male nurses may register – from 21 to 20 years, and for nurse aids from 19 to 18 years.
The Division is responsible for the maintenance of an adequate and efficient nursing service and the supervision of conditions, including health for nurses and other staff and recruitment of nurses.
The Nurses and Midwives Board through the Registrar supervises hospitals and nursing schools in all aspects of training, and also the examination and registration of nurses. The nurse inspector who makes a visit to a hospital carries out the dual purpose, therefore, of making reports both to the Director-General of Health through the Nursing Division, and to the Nurses and Midwives Board through the Registrar. This integration of work is a feature which has preserved good relationships in the hospitals, and has enabled the practical and theoretical training of nurses as well as their conditions to be maintained at a uniformly high standard.
The control of most of the public health nursing services and of district (home) nursing is exercised from the Division, although the specialised infant-welfare and mothercraft work of the Plunket Society is under the control of that organisation; close cooperation with that society is, however, maintained.
Another part of the work is the selection and placement of nurses in the various groups of Pacific islands for which the New Zealand Government is responsible. These nurses for hospital and public health work are seconded from the New Zealand service for periods of two years, pension rights being continuous. The supervision of this service is exercised by regular visits to the islands.
Close liaison exists between the nursing services organised for the armed services and the division, while any organisation for emergency nursing is carried out by the division.
The organisation of refresher courses for all groups is another responsibility, while the post-graduate course is a special feature of its work. As already stated this was organised in 1928 and is controlled by a committee on which the Department of Health, the Universities, and Hospital Boards Association are represented. Courses are followed in hospital and nursing school administration, public health nursing, medical social work, industrial nursing, and teaching and administration in obstetric nursing. A new course in pediatric nursing for sisters in charge of children's wards was instituted in 1957.
Up to 60 students take the nine months' post-graduate course annually, and with few exceptions they are specially selected and attend on bursaries from the Department of Health, hospital boards, and voluntary organisations, while during recent years there has been an increasing number from overseas countries. The school has its own building, library, classrooms, offices, and hostel. The full-time instructors at the school conduct the refresher courses during the school recess, and also carry out supervision of hospitals, nursing schools, and public health work, thus keeping up to date with the practical needs of the field.
The New Zealand Nurses Association is an active body having relationships with the Nursing Division; it is represented by four members on the Nurses and Midwives Board, two members on the Matrons Grading Committee, and by two on the Nurses Salaries Board, while at the annual conference and more frequent executive meetings various matters are brought to the notice of the authorities concerned.
New Zealand with its small population, good climate, and good standard of living, should have a comparatively healthy people, but has its particular health and social needs. The administration on the nursing side has expanded to meet these and the increasing opportunities for service in the fields of human welfare.
MEDICAL STATISTICS – The Medical Statistics Branch is responsible for the compilation of the statistics included in the Annual Report on the Medical Statistics of New Zealand. The Branch also prepares special statistics for the various Divisions of the Department and for research workers in different fields both in New Zealand and overseas. A constant liaison is maintained with the World Health Organisation, which is supplied with statistical material giving a picture of health trends in New Zealand. In addition from time to time special statistical investigations are made into important aspects of public health and diseases that warrant specific study.
NATIONAL HEALTH INSTITUTE – Opened in 1954, the National Health Institute is the Department of Health's centre for the study of public health problems. It contains an Epidemiology Section, an Occupational Health Unit and Public Health Laboratories.
The Epidemiology Section conducts field research into matters of public health interest and also is responsible for conducting the course of training for the diploma of the Royal Society for the Promotion of Health and, in addition, refresher courses for health inspectors.
The recently established Occupational Health Unit will provide consultant and laboratory services in this field.
The Public Health Laboratories provide diagnostic and reference services in bacteriology and virology for medical officers of health and hospital laboratories as well as for the other sections of the institute. The institute is the national centre for those reference services which are organised on an international basis.
MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL – Under the Medical Research Council Act 1950 a Medical Research Council was established as a corporate body with the following functions.
To foster medical research and to prepare and publish such reports on these matters as may in its opinion be necessary or of value to teachers or other persons:
To furnish information, advice, and assistance to persons and organisations concerned with medical research.
This Council took over and developed the work of the departmental committee, bearing the same name, which had been in existence since 1938. At the end of 1960 research in the following fields was in progress: chest diseases; clinical medicine; dentistry; endocrinology; hydatids; Island Territories research; microbiology; neuropathology and neurophysiology; nutrition; obstetrics; psychiatry; surgery; toxicology; pathology.
The Council maintains liaison with the research work being carried out by the Travis Trust Laboratory for tuberculosis research, the New Zealand Branch of the British Empire Cancer Campaign Society, and medical research foundations established in Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch.
The Council administers the Medical Research Endowment Fund, from which an annual expenditure of £100,000 is incurred in supporting research projects at the University of Otago, the University of Auckland, and the institutions of the Auckland Hospital Board.
The Council employs a staff of 90 full-time workers and some 40 associated workers contribute to the activities of the 14 research committees established by the Council.
The Council is empowered to receive bequests and donations to the fund for furthering the objects of the Council as set out in the Medical Research Council Act 1950.
MEDICAL COUNCIL – The Medical Council of New Zealand, constituted under the Medical Practitioners Act 1950, consists of the Director-General of Health, the Dean of the Faculty of Medicine in the University of Otago, and five other registered medical practitioners. One of the five members is appointed on the recommendation of the New Zealand Branch of the British Medical Association.
The Council deals with all applications for registration under the Act, which prescribes that every person shall be entitled to conditional registration who satisfies the Council that he is a graduate in medicine and surgery of the University of New Zealand; or registered on the register kept in accordance with the provisions of the Acts regulating the registration of medical practitioners in the United Kingdom or the Republic of Ireland; or the holder, after a course of not less than six years, of an overseas diploma approved by the Council. The Council may, however, refuse to approve any diploma (even in the case of persons registered in the United Kingdom or the Republic of Ireland) unless it appears that New Zealand graduates are, without further examination, entitled to registration in the country granting the diploma. It may also require the holder of a foreign diploma to attend a course and pass an examination in medicine and surgery. Until an applicant is able to satisfy the Council that he has obtained house officer experience, in a resident medical capacity, of not less than 12 months or has otherwise obtained comparable experience, registration is on a conditional basis. Persons registered conditionally may practise only in an approved hospital.
The fee for registration is £5, which is payable on deposit of evidence of qualifications. An applicant who is refused registration has the right of appeal to the Supreme Court. Each year every registered medical practitioner who is not specially exempted under the Act and who is actually practising medicine in New Zealand is required to obtain an annual practising certificate, the fee payable being £1.
The Medical Council is vested with certain disciplinary powers. Right of appeal to the Supreme Court is provided. The Supreme Court, on the motion of the Medical Council, may order the removal of a name from the register in cases where a medical practitioner is guilty of grave impropriety or infamous conduct in a professional respect, or is convicted of an indictable offence punishable by imprisonment for a term of two years or upwards. The Medical Council is also given power to hear appeals against the decisions of the Medical Practitioners Disciplinary Committee set up under the Medical Practitioners Act 1950. Any person involved who feels aggrieved by the decision of the Medical Council on an appeal from the Disciplinary Committee may appeal to the Supreme Court against the Council's decision.
The Medical Council was given power to institute an internship scheme in New Zealand. This became effective from 1 December 1952.
The number of medical practitioners on the register at 30 June 1960 was 3,396, and, of this number, approximately 2,800 were actively engaged in medical practice in New Zealand.
Investigation Committee: Complaints Against Registered Medical Practitioners – The Medical Council Amendment Act 1957 introduced the Investigation Committee and established a procedure for the reception and investigation of complaints amounting to infamous conduct and grave impropriety against registered medical practitioners. Briefly, the procedure requires that a complainant should direct his complaint to a Crown Solicitor of a Supreme Court district, and the Crown Solicitor is required to further the matter by calling upon two registered medical practitioners, from a duly appointed panel of four such practitioners, to sit with the Crown Solicitor to investigate the complaint and to submit a report thereon to the Solicitor-General. The Solicitor-General is required to act in accordance with the recommendation of the committee as set out in the report referred to him. The Medical Council must hear a complaint submitted to it by the Solicitor-General.
The complaints amounting to professional misconduct must be referred to the secretary of the Disciplinary Committee and the Disciplinary Committee exercises certain disciplinary powers in relation to complaints amounting to professional misconduct.
REGISTRATION COUNCILS AND BOARDS – Dentists: The Dentists Act 1936 provides for the constitution of a Dental Council, the functions of which are to examine and approve of the qualifications of applicants desiring registration as dentists and to exercise disciplinary control over registered dentists.
The Dentists Register is kept by the Director-General of Health, to whom applications for registration are addressed. The applications are submitted by the Director-General of Health to the Dental Council for consideration and direction regarding acceptance for registration. The Director-General of Health may issue to any person who has applied for registration as a dentist a provisional practising certificate which entitles the person to practise dentistry pending consideration of his application by the Dental Council.
Any adult person is entitled to be registered as a dentist who satisfies the Dental Council that he is the holder of a qualification in dentistry obtained from the University of New Zealand; or that he is the holder of a qualification approved by the Dental Council and obtained from a university or other institution in the United Kingdom or in some other part of the British Commonwealth (in the latter case, however, the Council may require a further examination); or is the holder of an approved foreign qualification, but the Council may refuse to approve any foreign qualification if New Zealand graduates in dentistry are not accepted for registration without further examination in the country concerned, or the Council may require the applicant to pass a further examination.
The fee for initial registration is £5. If a provisional practising certificate is required, there is a further fee of 5s. A fee of £1 per annum is payable for an annual practising certificate.
The number of private dental practitioners holding annual practising certificates at 1 June 1960 was 827, and in addition there were 110 dentists in Government and university employment.
Nurses and Midwives: Under the Nurses and Midwives Act 1945 is constituted the Nurses and Midwives Board, consisting of the Director-General of Health (Chairman), the Director, Division of Mental Health, the Director, Division of Nursing (Registrar), one registered medical practitioner, a representative of the Hospital Boards Association of New Zealand, two registered nurses, one registered midwife, and one registered psychiatric nurse. Members other than official members are appointed on the recommendation of the Minister of Health, the nursing personnel being nominated by the New Zealand Registered Nurses Association.
The functions of the Board are:
To determine the courses of training and instruction to be undergone by candidates for examination.
To approve hospitals and other institutions at which training or any portion of training may be received.
To conduct examinations; to appoint examiners and make all necessary arrangements for examinations; to issue suitable certificates of registration.
To receive applications for registration and to authorise registration in proper cases.
To have regard to the conduct of persons registered under the Act, and, within the scope of its authority, to do whatever may be necessary for the effective administration of the Act.
Under the Act, regulations authorised by the Governor-General by Order in Council may be made, the current regulations being the Nurses and Midwives Regulations 1958.
Registration – The Nurses and Midwives Act 1945 requires that the following registers be kept by the Registrar: (a) Nurses, (b) Midwives and Maternity Nurses, (c) Male Nurses, (d) Psychiatric Nurses, and (e) Nursing Aids.
Every person trained in New Zealand who satisfies the Board that she or he has served the stipulated training period, has passed the prescribed qualifying examination, and has complied with the other conditions laid down by the Act, is entitled to have her or his name entered in the appropriate register. In addition, persons trained outside New Zealand who satisfy the Board that their training and qualifications are equal to the equivalent New Zealand training and qualifications are entitled to be registered in the appropriate New Zealand registers.
In the case of New Zealand trained nurses the fee payable for the qualifying examination includes the registration fee. Overseas-trained nurses whose applications for registration have been approved by the Board are required to pay a fee of £2 for the initial qualification and a further fee of $1 for each additional qualification. A practising fee of 5s. is payable annually.
Physiotherapists: Under the Physiotherapy Act 1949 is constituted the New Zealand Physiotherapy Board. The Board is concerned with the training, examination, and registration of candidates for physiotherapy practice, and the conduct of those registered under the Act.
The training period for physiotherapists is three years. Full-time training is conducted at the New Zealand School of Physiotherapy, Dunedin, administered by the Otago Hospital Board, and eight months of the final year are spent at one of the subsidiary training schools in various parts of New Zealand. All students are required to pass the State final examination in physiotherapy to qualify for registration. The fees payable for examination and registration are prescribed by regulations under the Act.
Every person registered under the Act and engaged in the practice of physiotherapy must hold an annual practising certificate. The fee payable is 10s. per annum.
The Act provides for the admission to the register of overseas personnel whose standard of training is acceptable to the Board.
Occupational Therapists: Under the Occupational Therapy Act 1949 is constituted the Occupational Therapy Board. The Board is concerned with the training, examination, registration, and conduct of persons engaged in the practice of occupational therapy in New Zealand. The training period is three years, and is undertaken at the School of Occupational Therapy, Avondale, Auckland.
Every person registered under the Act and engaged in the practice of occupational therapy in New Zealand must hold an annual practising certificate, the fee payable being 5s. The Act provides for the admission to the register of persons trained outside New Zealand whose standard is acceptable to the Board.
Dietitians: Under the Dietitians Act 1950 is constituted the Dietitians Board. The functions of the Board are (a) to advise and make recommendations to the Minister of Health in respect of any matter affecting the profession of dietetics, (b) to determine courses of training and instruction to be undergone by candidates for examinations, (c) to approve hospitals and other institutions as training schools, (d) to conduct examinations, (e) to effect registration, (f) to have regard to the conduct of persons registered under the Act, and (g) to effectively administer the Act.
The training period for a dietitian is, in the case of the holder of a degree of bachelor of home science conferred by the University of New Zealand or of the holder of a diploma in home science of the University of Otago, 12 months in a hospital training school. In the case of a registered nurse, the training period is two academic years in the School of Home Science, University of Otago, together with two periods totalling 10 months in a hospital training school.
At the conclusion of training all students are required to pass the State examination for dietitians in order to qualify for registration. The fees payable for examination and registration are prescribed by regulations under the Act.
Every person registered under the Act and engaged as a practising dietitian must hold an annual practising certificate. The fee payable is 10s. per annum.
The Act also provides for admission to the Register of overseas personnel whose standard of training is acceptable to the Board.
Opticians: The Opticians Act 1928 provides for the constitution of an Opticians Board, consisting of the Director-General of Health (the Registrar), three persons engaged in practice as opticians in New Zealand (one of whom must be practising as an employee of another registered optician), and a registered medical practitioner with special knowledge of diseases of the eyes.
The Board deals with all applications for registration under the Act. On payment of the prescribed fee (£5), every person is entitled to registration as an optician who satisfies the Board that:
He has received satisfactory training qualifying him to practise as an optician and is the holder of a certificate of qualification recognised by the Board; or
He has passed an examination under the Act, both theoretical and practical, after a course of not less than three years' approved training in New Zealand as prescribed by regulations, or produces evidence of satisfactory training overseas.
An annual practising certificate fee of £1 is required.
Regulations pursuant to the Opticians Act 1928 prescribe the conditions and period of training and the syllabus for the examination conducted by the Opticians Board.
There are approximately 268 opticians registered, but not all are engaged in active practice as opticians.
Plumbers: The Plumbers Board of New Zealand consists of five members – the Director-General of Health or his deputy (Chairman), the Director of Education, a city or borough engineer nominated by the Municipal Association of New Zealand, and both a master plumber and a journeyman plumber elected by their respective associations.
The Board is concerned with the examination and registration of plumbers and once registered a plumber is issued with an annual practising certificate which is renewable on 31 March each year while he is engaged in sanitary plumbing.
Serving as an apprentice for about five years is the most frequent method of gaining entry to the written and practical examinations of the Board, although there is some limited reciprocity in recognition of plumbing qualifications obtained overseas, e.g., United Kingdom, Australia.
In many parts of New Zealand, especially the more populous and urban areas, all sanitary plumbing as defined in the Plumbers Registration Act 1953 must be performed only by registered plumbers. This restriction on the personal qualifications of plumbers is additional to specifications and standards of workmanship, etc., which have been prescribed for sanitary plumbing. Disciplinary action could be taken against a registered plumber who does unsatisfactory work. During the year ended 31 March 1960, 3,061 registered plumbers renewed their practising certificates.
Pharmaceutical Chemists: There are about 1,550 names on the Register of Pharmaceutical Chemists in New Zealand. All registered pharmaceutical chemists, except those who notify the Registrar that they have conscientious objection to membership, automatically become members of the Pharmaceutical Society of New Zealand, the society's affairs being managed by the Pharmacy Board constituted by the Pharmacy Act 1939.
The Board consists of 12 members, 11 being chemists, and one a barrister appointed by the Minister of Health. Nine members are elected on a district basis by registered pharmaceutical chemists who are either proprietors or enrolled managers of pharmacies and two by persons, not necessarily registered pharmaceutical chemists, who have served an approved apprenticeship and who, at the time of the election, are employed in pharmacy. The main function of the Pharmacy Board is to administer the Pharmacy Act and generally to protect and promote the interests of the profession of pharmacy and the interests of the public in relation thereto.
It is a specific requirement of the Pharmacy Act that pharmacies in New Zealand be at all times maintained under the immediate supervision and control of a registered pharmaceutical chemist, either in the capacity of proprietor or enrolled manager.
The Board has reciprocal arrangements with the pharmaceutical authorities of Great Britain, Northern Ireland, Republic of Ireland, and all the Australian States in the matter of registration. Any person registered as a pharmaceutical chemist in any of these places is eligible for registration in New Zealand. Persons registered as pharmaceutical chemists in New Zealand, similarly, are eligible for registration in the countries mentioned.
The Board conducts the examinations prescribed in the Pharmacy Regulations. Any adult person completing these examinations, as well as an approved apprenticeship of four years, qualifies for registration as a pharmaceutical chemist.
The College of Pharmacy in Wellington was taken over as a function of the society at the beginning of 1944, after having been conducted privately for a period of 11 years. All persons indentured after 1 October 1944 are obliged to attend personally at the college for a period of three weeks during their final year of apprenticeship.
With the commencement in 1960 of a new system of pharmacy education, the society's college will continue in existence only for as long as is necessary to afford existing students reasonable opportunities to qualify under the conditions that obtained at the time of entry into the profession. The new system involves full-time attendance for two years at the School of Pharmacy, Petone, followed by two years of apprenticeship. Commencing in 1960 also there is a four-year degree course in pharmacy at the University of Otago. It is proposed that graduates will be required to serve one year's apprenticeship before becoming eligible for registration as chemists.
Any chemist or company in which not less than 75 per cent of the share capital is owned by a chemist or chemists may establish one pharmacy. Unqualified persons or companies in which less than 75 per cent of the share capital is chemist-owned must, however, secure the consent of the Pharmacy Authority, set up under the Act, before commencing business, and in all cases the establishment of more than one pharmacy under the same ownership is subject to the consent of the Authority. All pharmacies must be registered with the Board.
VOLUNTARY WELFARE ORGANISATIONS – Over the years voluntary welfare organisations have made valuable contributions to certain aspects of the field of public health. In many cases they are encouraged and assisted in their work by grants from public funds. Among the more important of these organisations are the Plunket Society, the King George the Fifth Memorial Children's Health Camps Federation, St. John Ambulance (N.Z.), the New Zealand Red Cross Society, the Crippled Children Society, and the New Zealand Federation of Tuberculosis Associations.
The Plunket Society – the Royal New Zealand Society for the Health of Women and Children – is concerned with the welfare of all babies. The society trains its own infant-welfare nurses, conducts infant-welfare clinics, and maintains Karitane hospitals throughout the country for premature babies or difficult feeders. In rural areas where there is no Plunket clinic, public health nurses do infant-welfare work.
The King George the Fifth Memorial Children's Health Camps Federation maintains a chain of permanent health camps for delicate and undernourished children. The federation works in close cooperation with the Department of Health. It is the means whereby the voluntary nature of the various organisations is preserved, while ensuring that the available resources are utilised to the best advantage. Much of the finance for the federation's activities is derived from the proceeds of the annual health-stamp appeal.
The St. John Ambulance (N.Z.) has divisions throughout the country carrying out free ambulance work and instruction in first aid and home nursing. It is a branch of the Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem.
The New Zealand Red Cross Society, a part of the International Red Cross Committee, has centres and subcentres throughout the country. It gives training in first aid, home nursing, hygiene and sanitation, and emergency transportation of the injured. Graduates of these classes form voluntary-aid detachments that in peacetime are recruited as aids in hospitals, and in wartime may be recruited for service overseas as well.
The Crippled Children Society keeps a register of all crippled children, helps them to acquire all possible medical treatment, and undertakes vocational training and home education where these are required.
The New Zealand Federation of Tuberculosis Associations looks after the interests of patients suffering from tuberculosis. It assists the Department of Health with health education of the public regarding tuberculosis and concerns itself with after-care and vocational training and guidance of patients.
NATIONAL PHYSICAL WELFARE AND RECREATION – Because of the abundant natural facilities for popular recreation, New Zealand citizens have always been characterised by a love of outdoor sporting and recreational activity. Although, compared with the older countries of the world, there are large areas available as playing fields, even in the cities, the demand still exceeds the supply. On the other hand, the long coastlines and frequent mountain ranges enable most people to enjoy outdoor life. A temperate, equable climate ensures the use of facilities on a year-round basis.
The most popular summer sports are swimming and surfing, tennis, cricket, athletics, lawn bowls, softball, rowing, and cycle touring.
Rugby football is the premier sport in winter, but there are enthusiastic and numerically large followings for hockey, association football, tramping, ski-ing and mountaineering, outdoor and indoor basketball, badminton, and table tennis. Both professional and amateur boxing and wrestling are quite popular winter sports, whilst the game of indoor bowls, hitherto confined to isolated areas, is attracting increasing numbers.
Generally speaking, facilities for indoor sports are inadequate in the face of the growing interest and participation in such sports as indoor basketball, badminton, table tennis, and indoor bowls. There is a growing realisation of this inadequacy, and steps are being taken, usually in conjunction with community-centre movements, to provide and maintain indoor sporting facilities of a high standard.
All sporting activities in New Zealand are organised on a district basis, with representatives from each district forming a national controlling body. In this way every sport has a number of associations, unions, subassociations, etc., which control the sport in each district from the strictly local aspect, while a New Zealand association (or union) is the controlling body in all matters of nation-wide significance in that particular sport.
An exception to this arrangement, whereby each sport is responsible for its own administration, is that of selection of representatives for the Olympic and the Empire Games. There exists in New Zealand an Olympic Council made up of representatives of all sports bodies interested in Olympic and Empire Games competition.
Organisational and Practical Assistance in Learn to Swim Campaigns – Extensive “Learn to Swim” campaigns are conducted each summer by the Department of Education (for school children) and by the Physical Welfare and Recreation Branch of the Department of Internal Affairs in conjunction with swimming associations. Frequently the two organisations combine in specific district campaigns.
In recent years an extensive publicity campaign has been conducted in an effort to decrease the incidence of deaths by drowning.
Financial Assistance – Provision was made in the Physical Welfare and Recreation Act 1937 for the making of grants by the Government in aid of the development of sporting and recreational facilities. Such grants are not made for honoraria, travelling expenses, personal uniforms, or general administrative expenses, nor where it is considered that an organisation can carry out a project without grant assistance. In the main, grants are restricted to national organisations for the extension of sporting and recreational facilities and to leadership groups for the furtherance of their activities in the training of leaders.
HISTORY – The Government in 1846 granted money for the erection of hospitals in each of the four centres – Auckland, Wellington, Wanganui, and Taranaki – for the treatment of sick and destitute Europeans and free treatment for all Maoris. The foundation stone of the Wellington Hospital was laid in November 1846, whilst the Auckland Hospital was founded the following year. The first Dunedin Hospital was built in 1851, and Christchurch was first served by a hospital at Lyttelton known to have been operating in 1853. In 1854 control of public hospitals was vested in the six Provincial Councils of Auckland, Taranaki, Wellington, Nelson, Canterbury, and Otago, but in 1876, following the abolition of the provinces, control reverted to the General Government.
Hospitals generally remained under Government control until 1885, when the first Hospitals and Charitable Institutions Act was passed. By it New Zealand was divided into 38 hospital districts, each under the control of its own board. The number of districts gradually increased until by 1926 there were 47; amalgamations since that date have reduced the number to 37, at which it now stands.
A Consultative Committee on Hospital Reform was appointed in May 1953 to inquire into and report on matters affecting the administrative control of public hospitals and other services provided by hospital boards and, after taking evidence, it made recommendations to the Government for the reform of the hospital system. A new Hospitals Act passed in 1957 broke new ground in the central principle of its operation. The Act came into force on 1 April 1958. It incorporated as a basic principle the main recommendation of the Consultative Committee on Hospital Reform that the Minister of Health on behalf of the Government should have the responsibility of ensuring the provision by hospital boards of hospital and associated services. Government assumed complete financial responsibility for hospitals. Consonant with the new responsibilities the Minister was given wide powers of direction and regulation to ensure the establishment of a comprehensive and integrated hospital service for the whole country. Elected boards were retained to manage institutions and administer the services provided under the Act and no reduction was made in the number of boards.
A Hospitals Advisory Council, comprising three departmental members (Health, Treasury, and Works) and three hospital board members, is provided for by the Act. Primarily the function of the Advisory Council is to consider and make recommendations on matters referred to it by the Minister but it may also initiate business on matters covered by the Hospitals Act. Provision is also made for the appointment of technical or advisory committees to assist in the administration of the Act.
CONSTITUTION – A “hospital district” comprises one or more counties and includes boroughs, road and town districts within the boundaries of the county or counties. Districts vary in size from Auckland, with a population of 480,920, down to Maniototo, which has only 2,970 people.
A board consists of one or more representatives of each constituent district, or combined districts of two or more constituent districts where these do not justify independent representation, the number being fixed by the Governor-General by Order in Council, having regard to the relative populations of the districts. The total number of members of any board must in no case be less than eight or more than 14.
Board members are elected by the electors of the various constituent districts or combined districts in the hospital district, and the term of office is three years. Formerly, electors in counties required a ratepayer's qualification, whereas electors in boroughs and town districts required only a residential qualification, and this applied even though the elected members sat on the same board. Legislation in 1946 made the residential qualification universal.
POWERS – A hospital board has power to establish, control, and manage any of the following institutions: hospitals, relief institutions, maternity homes, convalescent homes, sanatoria, institutions for children, residential or day nurseries, and institutions of any kind which the Governor-General by Order in Council may declare that boards may establish. Power is given to boards to establish preventive health services and to combine for the purpose of establishing institutions or services which a board may establish.
AUTHORITY OF MINISTER OF HEALTH – It is the duty of every hospital board to provide and maintain such institutions, hospital accommodation, and medical, nursing, and other services as the Minister of Health considers necessary in any part of the district for the reception, relief, care, treatment, isolation, and removal to hospital or “other place” of persons who are suffering from infectious or other disease or from injury and for maternity cases. The Minister is specifically charged with the function of ensuring the provision of these services and of coordinating, guiding, and supervising the activities of hospital boards.
The consent of the Minister of Health is required before a hospital board may:
Borrow money.
Spend more than £500 for capital purposes such as adding to or altering buildings, erecting new buildings, purchasing land or equipment.
Make appointments to certain specified staff positions (but the Minister may veto appointments only on the advice of the Hospitals Advisory Council).
Close an institution or restrict services (subject to a recommendation of the Hospitals Advisory Council).
Make grants to medical or nursing associations or to hospitals, and allied services; grant bursaries or study and conference leave.
Sell or exchange land.
The Minister may issue directions to boards as he considers necessary or expedient for the purposes of the Act; in particular he may direct boards as to the manner in which, and the conditions subject to which, any duty, power, or function is to be exercised. Where any duty, power, or function is to be exercised with the prior consent of the Minister, he may refuse consent or grant his consent subject to such conditions and restrictions as he thinks fit. Notice of any direction or consent of the Minister must be given to the board in writing, signed by the Minister or the Director-General. The Minister may fix from time to time the maximum amount a board may expend on any item or class of expenditure and may require a board to amend its financial estimates.
A board must appoint such number of medical practitioners, dentists, nurses, dental nurses, midwives, and other officers as the Minister may from time to time deem necessary for the efficient performance of the functions of the board, whether within an institution under the control of the board or elsewhere within the district.
The Director-General is authorised to visit and inspect hospitals and to appoint assistant inspectors, and is required to report to Parliament through the Minister on the administration of the Hospitals Act.
FINANCE – When boards were first established in 1885 they obtained their revenue from the following sources: (a) voluntary contributions and bequests; (b) Government subsidy £1 for £1 on voluntary contributions and bequests; (c) patients' fees; (d) levy on contributory local authorities by rate on the capital value of land; and (e) Government subsidy on levies paid from general taxation.
Voluntary contributions and bequests and subsidy thereon at no time formed an important part of board revenue, and in 1932 the subsidy in this connection was abolished.
In the earliest days public hospitals were meant only for the destitute sick, but as time went on the standard of service was greatly improved and gradually they were availed of by all sections of the community. The hospitals charged a fee which covered cost of maintenance, and patients able to pay were expected to do so. Fees collected were usually found to form about one-third of a board's total revenue.
Until 1923 the subsidy on levy was paid at the rate of £1 for £1 for both capital and maintenance purposes, but in that year the subsidy on account of maintenance was amended to a scale which had relation to the burden of levy on the rates of local authorities; the board with the highest burden was paid 26s. subsidy; the board with the lowest burden was paid 14s. subsidy; the average of all boards remained at 20s. subsidy.
Under the Social Security Act 1938 a charge was made on all salaries and wages and other income, and the proceeds were paid into a special fund named the Social Security Fund. The charge was fixed at 1s. in the pound, and in 1946 it was raised to 1s. 6d. in the pound. The Act was to provide, inter alia, “a system whereby medical and hospital treatment will be made available to persons requiring such treatment”. Hospital benefits for inpatients were inaugurated in 1939. The effect of this change was to transfer the liability for payment of patients' fees from the patient to the Social Security Fund. The charge on the Fund was initially fixed at 6s. per patient per day if for more than one day, being the average collection made by the boards from patients. To keep up with the rising cost of maintenance the rate in 1943 was increased to 9s. per day. As from 1 April 1961 the rate has been £1 8s. in a Class A hospital, £1 2s. for a Class B hospital, and £1 15s. 6d. per day in maternity hospitals.
In 1943 the proportions of revenue derived from the three main sources of Social Security Fund, levy on local authorities, and Government subsidy from general taxation, were almost even. Rising costs led to increases in the levies on local authorities, and property owners complained that they were being asked to carry an unfair burden as compared with other sections of the community. As a result legislation was passed in 1946 limiting the levy on contributory local authorities to 0-5d. in the pound of rateable capital value, and this had the immediate effect of transferring a substantial portion of boards' cash requirements from levy to the subsidy paid from general taxation. Also it followed that any further increases in cost would fall solely on the subsidy except to the extent that increases in rateable capital value of property increased the amount of levy. In consequence of this development and the increased benefits payments already mentioned, the proportions of revenue derived from the main sources have changed. The approximate position for 1950–51 was: Social Security Fund, 25 per cent; levy, 15 per cent; subsidy, 55 per cent. The Hospitals Amendment Act 1951 provided for the abolition of the levy on contributory local authorities by an annual reduction of the rate of levy during the next five years. The first reduction was made for the year ended 31 March 1953, when the rate was 5/12d. on the capital value. For the final year ended 31 March 1957 the levy was 1/12d. per pound of rateable capital value. In 1959–60 revenue was derived from Government grants, 70 per cent (£17,204,751); Social Security Fund, 26 per cent (£6,516,959); and sundry receipts, 4 per cent (£912,850).
From 1 April 1958 the Government assumed complete financial responsibility for the public hospitals, apart from the raising by hospital boards of loans for major capital construction.
Income – The following is a comparative statement of moneys received by hospital boards and sanatorium committees from Government and local authority funds.
| Year | From Government Funds | From Local Authority Funds Levies | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grants | Social Security Benefits | |||
| *Includes £14,606 payments to hospital boards for administration of medical services in special areas. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955–56 | 10,703,689 | 5,404,402 | 1,079,828 | 17,187,919 |
| 1956–57 | 12,895,674 | 5,402,653 | 657,698 | 18,956,025 |
| 1957–58 | 15,390,252 | 5,508,781 | - | 20,899,033 |
| 1958–59 | 15,774,324 | 6,380,653 | - | 22,154,977 |
| 1959–60 | 17,204,751 | 6,516,959* | - | 23,721,710 |
Loans – Boards have been authorised by the Minister of Health to raise loans to cover a very extensive building programme. The position of loan liability is as under.
| Year | Amount Raised | Repayment | Balance | Reducible by Sinking Fund |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955–56 | 1,982,010 | 697,486 | 12,898,629 | 70,470 |
| 1956–57 | 3,518,260 | 837,893 | 15,578,997 | 74,188 |
| 1957–58 | 2,767,420 | 988,923 | 17,357,492 | 77,375 |
| 1958–59 | 2,961,760 | 1,056,581 | 19,288,673 | 121,953 |
| 1959–60 | 7,015,730 | 1,201,560 | 25,012,838 | 205,856 |
Expenditure - Hospital board expenditure is subject to a measure of control by the Minister of Health. Boards are required in the month of April each year to make an estimate of their expenditure for both capital and maintenance purposes and to have the estimates confirmed at a special meeting of the board. The Minister may, if he thinks it necessary so to do, require the board to amend the estimate submitted. He may also require a board by notice to limit expenditure of whatever kind he may specify. Expenditure for the two latest years is now given.
| Item of Expenditure | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Institutional maintenance | 17,928,731 | 19,504,268 |
| Outdoor relief | 31,287 | 32,552 |
| Grants to private hospitals | 42,137 | 42,316 |
| Other grants | 7,427 | 6,822 |
| Transport of patients | 209,870 | 235,971 |
| District nursing (including grants thereto) | 200,830 | 222,325 |
| Administration | 518,391 | 545,809 |
| Superannuation | 147,343 | 928,473 |
| Miscellaneous | 292,182 | 299,270 |
| Interest on loans | 744,508 | 158,161 |
| Repayment of loans | 1,127,367 | 1,306,893 |
| Capital works other than “loan” | 1,817,895 | 1,529,674 |
| Totals, excluding loans | 23,067,968 | 24,812,534 |
| Loan works | 3,407,591 | 5,256,333 |
| Totals | 26,475,559 | 30,068,867 |
Institutional Operating Expenditure - The average operating expenditure per occupied bed relating to hospitals of all types and old people's homes for the last three years and for general hospitals for the last five years was as follows:
| Year | Treatment | Institutional Maintenance | Heat, Light, Power, and Water | Household Expenses | Buildings and Grounds | Miscellaneous | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Institutions | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1957-58 | 501.9 | 94.7 | 112.9 | 504.7 | 79.0 | 1.3 | 1,294.5 |
| 1958-59 | 519.3 | 98.5 | 119.3 | 531.2 | 78.9 | 1.4 | 1,348.6 |
| 1959-60 | 572.1 | 107.4 | 127.2 | 562.4 | 83.2 | 1.5 | 1,453.8 |
| General Hospitals | |||||||
| 1955-56 | 437.9 | 96.7 | 103.7 | 471.3 | 66.4 | 1.2 | 1,177.2 |
| 1956-57 | 491.2 | 98.4 | 106.7 | 503.8 | 73.0 | 1.2 | 1,274.3 |
| 1957-58 | 551.1 | 108.3 | 119.6 | 537.4 | 79.9 | 1.2 | 1,397.5 |
| 1958-59 | 572.2 | 112.8 | 123.8 | 565.8 | 79.4 | 1.2 | 1,455.2 |
| 1959-60 | 626.3 | 122.0 | 130.4 | 595.7 | 81.5 | 1.5 | 1,557.4 |
Each of these averages includes the direct expenditure of each activity for labour, materials, and incidental expenses, but excludes overheads such as depreciation and interest on capital.
PATIENTS: Public Institutions - Section 4F contains statistics of inpatients other than normal maternity cases treated at public hospitals. The statistics given in the following table relate to patients and inmates in all institutions (general, maternity, special hospitals, and old people's homes) including institutions under the control of the Department of Health. The number of beds in public institutions available at 31 March 1960 and the average number occupied during the year were as follows.
| Types of Bed | Beds Available | Average Number of Occupied Beds per Day | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | |
| General | 12,992 | 5.5 | 9,679.7 | 4.2 |
| Maternity | 2,535 | 1.1 | 1,704.4 | 0.7 |
| Total hospital beds | 15,527 | 6.6 | 11,384.1 | 4.9 |
| Non-hospital beds | 1,168 | 0.5 | 1,027.5 | 0.4 |
| Totals | 16,695 | 7.1 | 12,411.6 | 5.3 |
In addition to the 15,527 hospital beds in public institutions there were 2,662 (2,270 general and 392 maternity) in the 158 licensed private hospitals. If the beds in licensed private hospitals are included, the ratios of beds per 1,000 of population become 6.5 for general beds and 1.3 for maternity beds.
The average number of occupied hospital beds per 1,000 of population in hospital districts varies from 3.6 to 9.6. This variation can be accounted for in the main by the fact that many hospitals to a varying extent draw patients from other districts. Other factors which influence the figures are the availability of medical practitioners and their habits in sending patients to hospital or retaining them for home treatment, the availability of private-hospital beds, housing facilities, domestic assistance, private or district nursing assistance, and the efficiency of the outpatient departments.
The number of institutions coming under the heading of public institutions for the year ended 31 March 1960 was 224, comprising 78 general hospitals (7 of which were also old people's homes), 2 homes for cripples, 6 non-acute hospitals, 4 convalescent hospitals, 105 maternity hospitals, 4 tuberculosis sanatoria, a hospital for physical disorders and a neurological hospital (both of which are under the control of the Department of Health), 22 old people's homes, and 1 children's home.
The following statistics for the latest two years relate to all institutions:
| 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of beds of all descriptions for patients or inmates in all public institutions, including institutions under the control of the Department of Health | 16,365 | 16,695 |
| Number of such beds per 1,000 of population | 7.1 | 7.1 |
| Average number occupied per 1,000 of population | 5.4 | 5.3 |
| Number of persons who, as inpatients or inmates, availed themselves of institutional services during year | 245,509 | 255,195 |
| Number per 1,000 of population who, as inpatients or inmates, availed themselves of institutional services during the year | 106.8 | 108.8 |
| Number of attendances by outpatients (including 87,633 attendances for 1959-60 for dental treatment) during year | 1,866,257 | 1,924,944 |
| Number per 1,000 of population of attendances (including dental) by outpatients | 811.8 | 820.7 |
The Appendix to the Annual Report of the Director-General of Health on Hospital and Relief Statistics contains further detail on public institutions.
General Hospitals - In the following table the figures relate only to general hospitals under the control of hospital boards.
| Year | Inpatients Treated | Average Number of Occupied Beds per Day | Average Turnover of Patients Treated per Occupied Bed | Available Beds | Outpatient Attendances (Including Dental) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | Number | Proportion per 1,000 of Population | ||
| 1955-56 | 175,925 | 80.9 | 8,659.8 | 4.0 | 20.3 | 11,080 | 5.1 | 1,529,557 | 703.5 |
| 1956-57 | 186,186 | 84.9 | 8,827.0 | 4.0 | 21.1 | 11,119 | 5.1 | 1,609,096 | 733.4 |
| 1957-58 | 194,588 | 86.6 | 8,860.0 | 3.9 | 22.0 | 11,550 | 5.1 | 1,647,668 | 733.6 |
| 1958-59 | 200,795 | 87.3 | 8,886.2 | 3.9 | 22.6 | 11,557 | 5.0 | 1,757,644 | 764.6 |
| 1959-60 | 210,454 | 89.7 | 9,049.7 | 3.9 | 23.3 | 11,690 | 5.0 | 1,792,531 | 764.2 |
Private Hospitals - The control and licensing of private hospitals is provided for in Part V of the Hospitals Act 1957. With specified exceptions such as institutions controlled by hospital boards and the State, any premises in which two or more patients are maintained at the same time must be licensed. No premises may be licensed unless the Director-General of Health is satisfied that they are suitable. Staffing and other requirements are governed by regulations and all private hospitals are subject to regular inspection by the Department of Health.
The total number of private hospitals licensed in New Zealand at 31 December 1959 was 158, providing 392 maternity beds and 2,270 beds for general cases.
The Social Security Act, inter alia, provides for the payment to licensees of private hospitals of prescribed amounts in respect of hospital treatment afforded by them. Particulars are contained in section 6A.
MATERNITY SERVICES: Benefits Under the Social Security Act 1938 - The Social Security Act, inter alia, makes provision for payments from the Social Security Fund to hospitals, medical practitioners, and nurses for services in connection with maternity cases. Particulars of maternity benefits provided under the Act will be found in section 6A.
At the end of 1959 available hospital-bed accommodation for maternity cases was 2,898, made up as follows:
| Public hospitals | 2,341 |
| Private hospitals | 404 |
| State (St. Helens) hospitals | 133 |
| Alexandra Home (Wellington) | 20 |
| Total | 2,898 |
The total number of confinements in maternity hospitals in 1959 was 61,046, of which 48,361 were in public maternity hospitals, 8,761 in private hospitals, 3,455 in St. Helens Hospitals, and 469 in the Alexandra Home, Wellington. There were 5,344 admissions for ante-natal treatment. All these figures are inclusive of Maoris.
State Maternity Hospitals - There were three State maternity (St. Helens) hospitals operating at 31 December 1960, these being located in Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch. Prior to the advent of the maternity benefits under the Social Security Act the use of these hospitals was restricted to cases where the husband's income did not exceed £5 per week, and in cases of large families £6 per week. There are now no restrictions in this respect, and all service is free to the patient. The main function now served by these hospitals is to provide extended training for maternity nurses, so that they may qualify for the more responsible work of midwives.
This service is given under the supervision of a medical superintendent, who is also responsible for the conduct of all abnormal cases and for the supervision of the ante-natal and post-natal care of all patients attending. There is also an outpatient department attached to each hospital which provides nursing services for patients not entering the institution.
Domiciliary Midwifery Services - Public health nurses and hospital board district nurses carry out some pre-natal work and a limited amount of obstetrical work in back-country areas. In general, however, most of the population is within reach of a maternity hospital, and home deliveries are not encouraged. There remain, however, a few midwives who contract with the Department of Health to give home maternity service under the Social Security Act.
Ante-natal Services - Since maternity benefits have been provided free to patients under the Social Security Act and medical practitioners have been paid a fee under that Act for giving ante-natal, neo-natal, and post-natal attention, the bulk of the ante-natal attendance and instruction has been provided by the patient's own medical attendant, this being one part of the service for which he receives a fee. The doctor's attendance, if desired, is supplemented by that of the midwife in charge of an ante-natal clinic. These free ante-natal clinics are established in connection with the three St. Helens Hospitals, all public maternity hospitals or maternity wards, and a number of clinics conducted by the Plunket Society. Ante-natal classes to prepare mothers for the baby's arrival are also being developed and doctors can refer patients to these to supplement their own ante-natal instructions. In the case of women living far from the main centres of population, ante-natal work is supplemented by the public health nurses, who are employed by the Department of Health, or by hospital board district nurses.
The majority of women now realise that ante-natal care is as essential to their welfare as attendance, during their delivery and lying-in period, by a doctor and trained maternity nurse or midwife. The Department has supplemented the service by the free distribution of a pamphlet Suggestions to Expectant Mothers.
Every effort is being made to impress parents with the importance of personal hygiene and systematic ante-natal care throughout pregnancy. Addresses and lectures are delivered by medical officers of the Department of Health to nurses and societies interested in this subject. So that there will be definite cooperation between the midwife and the ante-natal clinic, and in order that the midwife may be informed of the clinical methods adopted by the Department, refresher courses of lectures, particularly on ante-natal work, are available to all registered midwives and maternity nurses.
FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE FOR ACCOMMODATION AND SERVICES (Old People's Homes, Youth Hostels, and Short-stay Homes for Intellectually Handicapped Children - The extent to which Government assistance is offered to religious and voluntary organisations and local authorities in providing accommodation and services for elderly people and others whom it is considered are in special need, has increased steadily over the past decade. Under this partnership with Government, the social service agencies of all the major religious bodies, as well as other welfare organisations, have established additional accommodation for sick and infirm old people. Where it is not possible to meet the need of elderly people through these agencies, the provision of care and nursing for the aged becomes a hospital board responsibility. Religious and welfare organisations at present provide approximately 3,350 home and hospital beds for the elderly, and hospital boards some 1,950 beds.
For the elderly who are ambulant and are able to care for themselves and whose main need is that of housing, local authorities are encouraged and assisted by Government to build specially designed flats or cottages which enable age beneficiaries and those with limited means to retain their independence.
Other measures which are of importance in assisting elderly people to remain in their homes as long as possible are receiving increased attention. Chief amongst these are the provision of district nursing services, home aid, meals-on-wheels, laundry services, and occupational therapy. In general, the services are provided by hospital boards with voluntary organisations and the Aged People's Welfare Council assisting in various ways.
Old People's Homes - From April 1950 to July 1955, subject to certain conditions, religious or charitable institutions could be granted up to 50 percent of the cost of providing accommodation for old people. In August 1955 the maximum amount of the subsidy offered was increased to 75 percent. In February 1960 the rate of subsidy was increased to 100 percent of the approved capital cost. The administration of this policy is the responsibility of the Department of Health.
During the year 1959-60 subsidies totalling £256,892 were approved to assist in the provision of accommodation for 229 old people. From April 1950 to 31 March 1960, subsidies totalling £2,222,800 have been approved and buildings erected as a result will accommodate 2,070 old people.
Pensioners' Flats - Since 1950 the Government has encouraged local authorities to undertake the provision of accommodation for age beneficiaries by offering subsidy and loan finance. The present policy is to offer a subsidy of up to 50 per cent of the cost of erecting accommodation such as flats or cottages for old people and to provide the balance from loan moneys at 3 1/2 percent. The maximum subsidy available for a two-person flat is £850 and for a one-person flat £700. Since the policy was first initiated in 1951 a total of £950,111 had been made available as subsidy up to 31 March 1960. As a result 1,944 old people will be provided with suitable accommodation.
Youth Hostels - In June 1951 the Government decided that, subject to certain conditions, it would assist religious or welfare organisations to establish hostels for young people by granting subsidies of up to 50 percent of the cost of erecting or acquiring hostels. The object of this decision is to assist young men and women who are living away from their homes and are having difficulty in finding suitable living accommodation. The Department of Health was made responsible for the administration of this policy.
During the year 1959-60 subsidies of £3,288 were approved to assist in the provision of hostels for 17 young people. Since the policy was approved, subsidies totalling £301,537 had been granted up to 31 March 1960 to assist in the provision of hostel accommodation for 503 young people.
Short-stay Homes for Intellectually Handicapped Children - In 1954 the Government approved the payment, under certain conditions, of a subsidy of up to 50 percent on the capital cost of approved buildings and furnishings acquired for the purpose of providing short-stay homes for intellectually handicapped children. The intention was to assist the Intellectually Handicapped Children's Parents Association in the provision of homes where eligible children could be placed for up to two months in one continuous period during the illness of a parent, absence of parents from the family home, or for other similar reasons. The administration of the policy is the responsibility of the Department of Health.
The total amount expended on capital subsidies for short-stay homes during the year ended 31 March 1960 was £9,213. In addition £1,641 was paid by way of maintenance subsidy during the same period.
GENERAL - Mental hospitals are administered under the direction of the Minister of Health by the Mental Health Division of the Department of Health. Hospital boards have no jurisdiction over mental hospitals.
The newer hospitals are built on the villa system with accommodation provided in pleasant detached units of about 50 beds each. Each villa is surrounded by lawns and gardens and is largely self-contained. The older hospitals are being modernised. There are facilities for recreation and entertainment in addition to provision for modern methods of therapy. In common with mental health services in other parts of the world, the Mental Health Division has had to contend with shortages of staff, particularly medical and nursing staff. The minimum of three years' training is required before nursing staff, male and female, become eligible to sit examinations of the Nurses and Midwives Board for qualification as psychiatric nurses.
In 1959 there were in New Zealand 11 public mental hospitals and one private mental hospital (Ashburn Hall, Dunedin). The figures in the following tables refer to people treated in these 12 institutions and have been summarised from the Fifth Report on Mental Health Statistics, 1959, issued by the Medical Statistics Branch of the Department of Health. The report contains both administrative and clinical data about first admissions and readmissions (including replacements from probation), transfers, discharges, and deaths, for each mental hospital. The report also presents information about psychiatric disorders in terms of age and sex, etiological factors, country of birth, marital status, religion, race, family history, treatment, response to treatment, and length of stay.
Definitions: Patient - A patient is a person in a mental hospital who may not discharge himself.
Voluntary Boarder - A voluntary boarder is a person in a mental hospital who may discharge himself. In the following tables where there is information about both patients and voluntary boarders, the term “patient” has this special meaning and should not be regarded as being synonymous with the term “patient” as applied to general or public hospitals.
HISTORICAL SUMMARY: Average Number on Registers - Since 1942 the number of patients on the registers has increased by 24.4 percent and the number of voluntary boarders has increased by 210.2 percent. The increase for all cases combined was 30.9 percent. There has been little change in the number of patients during the latest four years including 1959. The increase in overall numbers for these four years, has occurred in the registers of voluntary boarders.
First Registrations - The average number of first registrations for the five years 1935-39 was 1,155. The rate per 100,000 mean population was 72.5. In 1959 the number was 2,719 and the rate was 116.5 per 100,000. This represents an increase of 135.4 percent in numbers and 60.7 percent in rate over the 1935-39 figures.
The rate for patients was highest during 1950-54, when it reached 68.5 per 100,000. It has declined steadily since. The 1959 rate for voluntary boarders was for the first time higher than that for patients. This is a reflection of a more enlightened attitude on the part of the public and the medical profession towards early treatment of mental disorders.
The percentage of first registrations in total registrations has decreased from 80.1 percent for the five years 1935-39 to 64.7 percent in 1959. The percentage of voluntary boarders in first registrations has increased from 18.3 percent to 50.3 percent over the same period.
Reregistrations - The number of patients reregistered has increased by 219.1 percent from the 1935-39 average of 178 to 568 in 1959. During the same time the number of voluntary boarder reregistrations has increased from 112 to 917, or by 718.8 percent. The rates have increased from 11.1 per 100,000 to 24.3 for patients and from 7.0 to 39.3 for voluntary boarders. For all cases the increase in numbers has been from 290 to 1,485, or 408.6 percent, and in rates from 18.1 to 63.6, or by 251.4 percent.
The proportion of reregistrations in total registrations has increased from 20.0 in 1935-39 to 35.3 in 1959. The percentage of voluntary boarders in reregistrations has increased over the same period from 38.6 percent to 61.8 percent.
Removals The number of patients discharged has increased from an average of 536 for 1935-39 to 1,111 in 1959, an increase of 107.3 percent. Over the same period the deaths of patients increased from 481 to 775, or by 61.1 percent. The rates for discharges per 100,000 mean population increased from 33.6 in 1935-39 to 47.6 in 1959, or by 41.7 percent. For deaths the rates increased by 9.9 percent from 30.2 in 1935-39 to 33.2 in 1959. For all patient removals the rates increased by 26.6 percent from 63.8 to 80.8.
The number of voluntary boarder removals has increased much more spectacularly. In 1935-39 the average number of voluntary boarders discharged each year was 271. In 1959 it was 2,098, an increase of 647.2 percent. For deaths the figure increased from 23 to 56, or by 143.5 percent. For discharges and deaths combined the figure increased from 294 to 2,154, or by 632.7 percent.
The rates per 100,000 mean population for voluntary boarder discharges have increased from 17.0 to 89.9, or by 428.8 percent. The rates for deaths showed little change from 1.4 to 2.4.
The total number of discharges (patients and voluntary boarders combined) has increased from 807 in the period 1935-39 to 3,209 in 1959; the deaths from 504 to 831. The rates per 100,000 have increased for discharges from 50.6 to 137.5. For deaths the rates have increased more modestly from 31.6 to 35.6. For all removals, the rate has increased from 82.2 to 173.0, an increase of 110.5 percent: this includes discharges and deaths of both patients and voluntary boarders.
During 1935.39 the annual rate of registration was 90.6 per 100,000; the rate of removal was 82.2, a difference of 8.4 per 100,000. In 1959 the rate of registration was 180.1; the rate of removal was 173.0, a difference of 7.1 per 100,000.
Conclusion - The conclusion to be drawn from these figures is that, although about twice as many New Zealanders are currently entering and leaving mental hospitals as was the case 25 years ago, fewer are staying in mental hospitals for long periods of time.
The length of stay in hospital for first admissions continues to decline, and far greater use is being made of periods of trial leave in the course of rehabilitation.
AVERAGE NUMBERS ON THE REGISTERS - The average number of patients and voluntary boarders who were either resident or were absent on leave during 1959 is shown for each hospital in the following table.
| Hospital | Resident | Absent on Leave | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Patients | |||||||||
| Auckland | 542 | 560 | 1,102 | 88 | 167 | 255 | 630 | 727 | 1,357 |
| Kingseat | 434 | 433 | 867 | 35 | 35 | 70 | 469 | 468 | 937 |
| Raventhorpe | 9 | 262 | 271 | - | 3 | 3 | 9 | 265 | 274 |
| Tokanui | 427 | 415 | 842 | 34 | 51 | 85 | 461 | 466 | 927 |
| Lake Alice | 306 | - | 306 | 3 | - | 3 | 309 | - | 309 |
| Levin Farm | 341 | 182 | 523 | 23 | 14 | 37 | 364 | 196 | 560 |
| Porirua | 520 | 747 | 1,267 | 25 | 52 | 77 | 545 | 799 | 1,344 |
| Nelson | 539 | 417 | 956 | 19 | 44 | 63 | 558 | 461 | 1,019 |
| Seaview | 204 | 292 | 496 | 10 | 11 | 21 | 214 | 303 | 517 |
| Sunnyside | 720 | 667 | 1,387 | 51 | 105 | 156 | 771 | 772 | 1,543 |
| Seacliff | 646 | 474 | 1,120 | 55 | 81 | 136 | 701 | 555 | 1,256 |
| Ashburn Hall | 8 | 10 | 18 | - | 1 | 1 | 8 | 11 | 19 |
| Totals | 4,696 | 4,459 | 9,155 | 343 | 564 | 907 | 5,039 | 5,023 | 10,062 |
| Voluntary Boarders | |||||||||
| Auckland | 65 | 83 | 148 | 3 | 11 | 14 | 68 | 94 | 162 |
| Kingseat | 37 | 30 | 67 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 39 | 33 | 72 |
| Raventhorpe | 1 | 6 | 7 | - | - | - | 1 | 6 | 7 |
| Tokanui | 36 | 47 | 83 | 5 | 8 | 13 | 41 | 55 | 96 |
| Lake Alice | 3 | - | 3 | - | - | - | 3 | - | 3 |
| Levin Farm | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Porirua | 66 | 95 | 161 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 68 | 97 | 165 |
| Nelson | 20 | 19 | 39 | 15 | 38 | 53 | 35 | 57 | 92 |
| Seaview | 7 | 12 | 19 | - | - | - | 7 | 12 | 19 |
| Sunnyside | 61 | 55 | 116 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 63 | 56 | 119 |
| Seacliff | 56 | 49 | 105 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 60 | 55 | 115 |
| Ashburn Hall | 22 | 39 | 61 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 24 | 41 | 65 |
| Totals | 374 | 435 | 809 | 35 | 71 | 106 | 409 | 506 | 915 |
| All Cases | |||||||||
| Auckland | 607 | 643 | 1,250 | 91 | 178 | 269 | 698 | 821 | 1,519 |
| Kingseat | 471 | 463 | 934 | 37 | 38 | 75 | 508 | 501 | 1,009 |
| Raventhorpe | 10 | 268 | 278 | - | 3 | 3 | 10 | 271 | 281 |
| Tokanui | 463 | 462 | 925 | 39 | 59 | 98 | 502 | 521 | 1,023 |
| Lake Alice | 309 | - | 309 | 3 | - | 3 | 312 | - | 312 |
| Levin Farm | 341 | 182 | 523 | 23 | 14 | 37 | 364 | 196 | 560 |
| Porirua | 586 | 842 | 1,428 | 27 | 54 | 81 | 613 | 896 | 1,509 |
| Nelson | 559 | 436 | 995 | 34 | 82 | 116 | 593 | 518 | 1,111 |
| Seaview | 211 | 304 | 515 | 10 | 11 | 21 | 221 | 315 | 536 |
| Sunnyside | 781 | 722 | 1,503 | 53 | 106 | 159 | 834 | 828 | 1,662 |
| Seacliff | 702 | 523 | 1,225 | 59 | 87 | 146 | 761 | 610 | 1,371 |
| Ashburn Hall | 30 | 49 | 79 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 32 | 52 | 84 |
| Totals | 5,070 | 4,894 | 9,964 | 378 | 635 | 1,013 | 5,448 | 5,529 | 10,977 |
The average number on the registers in 1959 was 10,062 for patients and 915 for voluntary boarders. For the previous year the figures were 10,006 for patients and 796 for voluntary boarders.
In the following table the average number on the registers is shown for certain years.
| Year | Resident | Absent on Leave | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Patients | |||||||||
| 1942 | 4,190 | 3,443 | 7,633 | 221 | 236 | 457 | 4,411 | 3,679 | 8,090 |
| 1947 | 4,313 | 3,750 | 8,063 | 254 | 332 | 586 | 4,567 | 4,082 | 8,649 |
| 1952 | 4,475 | 4,115 | 8,590 | 308 | 488 | 796 | 4,783 | 4,603 | 9,386 |
| 1956 | 4,643 | 4,544 | 9,187 | 313 | 539 | 852 | 4,956 | 5,083 | 10,039 |
| 1957 | 4,659 | 4,530 | 9,189 | 310 | 557 | 867 | 4,969 | 5,087 | 10,056 |
| 1958 | 4,651 | 4,508 | 9,159 | 312 | 535 | 847 | 4,963 | 5,043 | 10,006 |
| 1959 | 4,696 | 4,459 | 9,155 | 343 | 564 | 907 | 5,039 | 5,023 | 10,062 |
| Voluntary Boarders | |||||||||
| 1942 | 143 | 150 | 293 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 144 | 151 | 295 |
| 1947 | 171 | 205 | 376 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 172 | 209 | 381 |
| 1952 | 215 | 265 | 480 | 3 | 8 | 11 | 218 | 273 | 491 |
| 1956 | 276 | 325 | 601 | 19 | 31 | 50 | 295 | 356 | 651 |
| 1957 | 288 | 373 | 661 | 21 | 57 | 78 | 309 | 430 | 739 |
| 1958 | 312 | 388 | 700 | 18 | 78 | 96 | 330 | 466 | 796 |
| 1959 | 374 | 435 | 809 | 35 | 71 | 106 | 409 | 506 | 915 |
| All Cases | |||||||||
| 1942 | 4,333 | 3,593 | 7,926 | 222 | 237 | 459 | 4,555 | 3,830 | 8,385 |
| 1947 | 4,484 | 3,955 | 8,439 | 255 | 336 | 591 | 4,739 | 4,291 | 9,030 |
| 1952 | 4,690 | 4,380 | 9,070 | 311 | 496 | 807 | 5,001 | 4,876 | 9,877 |
| 1956 | 4,919 | 4,869 | 9,788 | 332 | 570 | 902 | 5,251 | 5,439 | 10,690 |
| 1957 | 4,947 | 4,903 | 9,850 | 331 | 614 | 945 | 5,278 | 5,517 | 10,795 |
| 1958 | 4,963 | 4,896 | 9,859 | 330 | 613 | 943 | 5,293 | 5,509 | 10,802 |
| 1959 | 5,070 | 4,894 | 9,964 | 378 | 635 | 1,013 | 5,448 | 5,529 | 10,977 |
FIRST ADMISSION In 1959 there were 2,719 first admissions to mental hospitals. Of these 1,311 were males and 1,408 were females. For the first year ever, the number of voluntary boarders (1,367) exceeded the number of patients (1,352).
The numbers and rates of first admissions, together with the percentage of first admissions in total admissions and the percentage of voluntary boarders in first admissions for 1935 to 1959, are shown in the next table.
| Years | Patients | Voluntary Boarders | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| *Average over five years* | |||||||||
| Numbers | |||||||||
| 1935-39* | 481 | 462 | 943 | 115 | 97 | 212 | 596 | 559 | 1,155 |
| 1940-44* | 470 | 526 | 996 | 110 | 126 | 236 | 580 | 652 | 1,232 |
| 1945-49* | 544 | 607 | 1,151 | 235 | 267 | 502 | 779 | 874 | 1,653 |
| 1950-54* | 625 | 746 | 1,371 | 349 | 384 | 733 | 974 | 1,130 | 2,104 |
| 1955 | 639 | 768 | 1,407 | 406 | 437 | 843 | 1,045 | 1,205 | 2,250 |
| 1956 | 668 | 753 | 1,421 | 492 | 543 | 1,035 | 1,160 | 1,296 | 2,456 |
| 1957 | 700 | 767 | 1,467 | 445 | 570 | 1,015 | 1,145 | 1,337 | 2,482 |
| 1958 | 649 | 705 | 1,354 | 481 | 587 | 1,068 | 1,130 | 1,292 | 2,422 |
| 1959 | 690 | 662 | 1,352 | 621 | 746 | 1,367 | 1,311 | 1,408 | 2,719 |
| Years | Patients | Voluntary Boarders | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Rates | |||||||||
| 1935-39* | 59.5 | 58.9 | 59.2 | 14.2 | 12.4 | 13.3 | 73.7 | 71.3 | 72.5 |
| 1940-44* | 58.5 | 62.8 | 60.8 | 13.7 | 15.0 | 14.4 | 72.2 | 77.8 | 75.2 |
| 1945-49* | 61.1 | 67.5 | 64.5 | 26.2 | 29.6 | 27.9 | 87.3 | 97.1 | 92.4 |
| 1950-54* | 62.2 | 74.9 | 68.5 | 34.6 | 38.5 | 36.6 | 96.8 | 113.4 | 105.1 |
| 1955 | 59.4 | 72.3 | 65.8 | 37.7 | 41.1 | 39.4 | 97.1 | 113.4 | 105.2 |
| 1956 | 60.9 | 68.4 | 65.1 | 44.8 | 50.0 | 47.4 | 105.7 | 118.4 | 112.5 |
| 1957 | 62.3 | 69.1 | 65.7 | 39.6 | 51.3 | 45.4 | 101.9 | 120.4 | 111.1 |
| 1958 | 56.4 | 62.1 | 59.2 | 41.8 | 51.7 | 46.7 | 98.2 | 113.8 | 105.9 |
| 1959 | 58.8 | 57.0 | 57.9 | 52.9 | 64.3 | 58.6 | 111.7 | 121.3 | 116.5 |
| Percentage of First Admissions in Total Admissions | Percentage of Voluntary Boarders in First Admissions | |
|---|---|---|
| *Average over five years. | ||
| 1935-39* | 80.1 | 18.3 |
| 1940-44* | 76.7 | 19.0 |
| 1945-49* | 75.6 | 30.1 |
| 1950-54* | 74.0 | 34.7 |
| 1955 | 71.2 | 37.5 |
| 1956 | 69.4 | 42.1 |
| 1957 | 67.7 | 40.9 |
| 1958 | 64.7 | 44.1 |
| 1959 | 64.7 | 50.3 |
Age - The age and age-specific rates, per 100,000 in each age group shown, of first admissions in 1959 are shown in the following table. In general terms the age-specific rates are higher for the older age groups, the principal exception being the 30 to 39 years group which was higher than any other group aged under 60 years.
| Age in Years | Numbers | Percentage of Total | Age-specific Rates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Under 10 | 62 | 51 | 113 | 4.7 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 22.8 | 19.6 | 21.3 |
| 10 and under 20 | 126 | 85 | 211 | 9.6 | 6.0 | 7.8 | 60.7 | 42.8 | 52.0 |
| 20 and under 30 | 201 | 207 | 408 | 15.3 | 14.7 | 15.0 | 132.7 | 143.6 | 138.0 |
| 30 and under 40 | 239 | 290 | 529 | 18.2 | 20.6 | 19.5 | 149.9 | 190.9 | 169.9 |
| 40 and under 50 | 198 | 205 | 403 | 15.1 | 14.6 | 14.8 | 141.1 | 146.3 | 143.7 |
| 50 and under 60 | 150 | 159 | 309 | 11.4 | 11.3 | 11.4 | 132.6 | 145.1 | 138.8 |
| 60 and under 70 | 116 | 138 | 254 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 163.2 | 168.8 | 166.2 |
| 70 and under 80 | 125 | 162 | 287 | 9.5 | 11.5 | 10.6 | 275.9 | 291.7 | 284.6 |
| 80 and over | 94 | 111 | 205 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 658.3 | 584.8 | 616.4 |
| Total | 1,311 | 1,408 | 2,719 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 111.7 | 121.3 | 116.5 |
Diagnosis - The five leading diagnoses in 1959 were: schizophrenia, 477 cases; senile psychosis, 447 cases; manic-depressive reaction, 441 cases; neurotic-depressive reaction, 391 cases; and mental deficiency, 236 cases. These five diagnoses accounted for nearly three-quarters (73.3 percent) of first admissions.
The number of patients and voluntary boarders together with the percentage of voluntary boarders in all first admissions are now shown for 1959.
| Diagnosis | Patients | Voluntary Boarders | Percentage of Voluntary Boarders in All First Admissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psychoses | |||
| General paralysis of insane | 1 | - | - |
| Other syphilis of central nervous system | 1 | - | - |
| Schizophrenia | 278 | 199 | 42 |
| Manic-depressive reaction | 137 | 304 | 69 |
| Involutional melancholia | 6 | 29 | 83 |
| Paranoia and paranoid states | 22 | 10 | 31 |
| Senile psychosis | 416 | 31 | 7 |
| Presenile psychosis | 6 | 3 | 33 |
| Psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | 39 | 8 | 17 |
| Alcoholic psychosis | 21 | 11 | 34 |
| Psychosis of other demonstrable etiology | 38 | 13 | 25 |
| Puerperal psychosis | 17 | 19 | 53 |
| Other and unspecified psychoses | 27 | 5 | 16 |
| Psychoneuroses | |||
| Anxiety reaction | - | 113 | 100 |
| Hysterical reaction | 5 | 44 | 90 |
| Neurotic-depressive reaction | 19 | 372 | 95 |
| Other and unspecified psychoneurotic disorders | 1 | 37 | 97 |
| Disorders of Character, Behaviour, and Intelligence | |||
| Pathological and immature personality | 44 | 43 | 49 |
| Alcoholism | 14 | 92 | 87 |
| Mental deficiency | 225 | 11 | 5 |
| Other and unspecified character, behaviour, and intelligence disorders | 3 | 8 | 73 |
| Other Conditions | |||
| Late effects of acute infectious encephalitis | - | 1 | 100 |
| Multiple sclerosis | - | 1 | 100 |
| Epilepsy | 17 | 13 | 43 |
| Other diseases of the brain | 2 | - | - |
| Observation | 13 | - | - |
| Totals | 1,352 | 1,367 | 50 |
Changes in first admission numbers and rates per million of mean population over the last three years are shown in the following table. The rate for all first admissions fell from 1,112 in 1957 to 1,060 in 1958. In 1959, however, the rate rose to 1,165 per million, the highest on record. All diagnoses did not conform to this pattern, the most notable exception being senile psychosis, which showed a decline in both numbers and rates for each successive year.
| Diagnosis | Numbers | Rates per Million of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Psychoses | ||||||
| Syphilis of central nervous system | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Schizophrenia | 416 | 391 | 477 | 186 | 171 | 204 |
| Manic-depressive reaction | 431 | 414 | 441 | 193 | 181 | 189 |
| Involutional melancholia | 43 | 27 | 35 | 19 | 12 | 15 |
| Paranoia and paranoid states | 40 | 32 | 32 | 18 | 14 | 14 |
| Senile psychosis | 489 | 454 | 447 | 219 | 199 | 191 |
| Presenile psychosis | 9 | 13 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| Psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | 62 | 56 | 47 | 28 | 24 | 20 |
| Alcoholic psychosis | 58 | 34 | 32 | 26 | 15 | 14 |
| Psychosis of other demonstrable etiology | 43 | 32 | 51 | 19 | 14 | 22 |
| Puerperal psychosis | 10 | 18 | 36 | 4 | 8 | 15 |
| Other and unspecified psychoses | 21 | 33 | 32 | 9 | 14 | 14 |
| Psychoneuroses | ||||||
| Anxiety reaction | 104 | 133 | 113 | 47 | 58 | 48 |
| Hysterical reaction | 45 | 72 | 49 | 20 | 31 | 21 |
| Neurotic-depressive reaction | 296 | 280 | 391 | 133 | 122 | 167 |
| Other and unspecified psychoneurotic disorders | 28 | 21 | 38 | 13 | 9 | 16 |
| Disorders of Character, Behaviour, and Intelligence | ||||||
| Pathological and immature personality | 38 | 60 | 87 | 17 | 26 | 37 |
| Alcoholism | 65 | 63 | 106 | 29 | 28 | 45 |
| Mental deficiency | 224 | 245 | 236 | 100 | 107 | 101 |
| Other and unspecified character, behaviour, and intelligence disorders | 7 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
| Other Conditions | ||||||
| Epilepsy | 33 | 19 | 30 | 15 | 8 | 13 |
| Other defined conditions | 14 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 |
| Observation | 3 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Totals | 2,482 | 2,422 | 2,719 | 1,112 | 1,060 | 1,165 |
Etiological Factors - Information about the causes of mental disorders was reported in only 60 percent of first admissions. It should also be noted that several factors can be reported for one case. For example, a person might be admitted because of a combination of old age and excessive use of alcohol. The principal factors were reported as old age, peculiarities in the structure of the personality, subnormal intelligence, alcohol, and congenital factors. The information is analysed in the following table.
| Etiological Factors | Number of First Admissions |
|---|---|
| Heredity | 17 |
| Congenital | 184 |
| Birth injury | 12 |
| Other natal and prenatal conditions | 3 |
| Factors in structure of personality | 303 |
| Family relations | 103 |
| Adolescence | 13 |
| Pregnancy and puerperium | 78 |
| Climacteric | 36 |
| Old age | 498 |
| Religion | 3 |
| Loneliness | 18 |
| Sickness of near relative | 14 |
| Unhappy love affair | 13 |
| Sex trauma and difficulties | 12 |
| Other stress | 16 |
| Alcohol | 211 |
| Drug addiction | 9 |
| Financial difficulty | 11 |
| Business worry | 16 |
| Subnormal intelligence | 271 |
| Tuberculosis | 2 |
| Syphilis | 5 |
| Acute infectious encephalitis | 5 |
| Neoplasm of brain | 2 |
| Endocrine disorders | 14 |
| Epilepsy | 69 |
| Other diseases of central nervous system | 47 |
| Arteriosclerosis | 56 |
| Other circulatory diseases | 21 |
| Respiratory diseases | 12 |
| Congenital malformation | 24 |
| Injury | 15 |
| Adverse therapeutic reaction | 7 |
| Other illness | 49 |
| Other factors | 12 |
| Totals | 2,181 |
READMISSIONS - A readmission is a person admitted to a New Zealand mental hospital who has previously been in a New Zealand mental hospital.
Age and Sex - The following table shows the readmissions for 1959 by age and sex, the percentage of cases in age groups, and the age-specific rates per 100,000 of mean population.
| Age in Years | Numbers | Percentage of Total | Age-specific Rates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Under 10 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| 10 and under 20 | 30 | 17 | 47 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 14.4 | 8.6 | 11.6 |
| 20 and under 30 | 133 | 108 | 241 | 16.3 | 10.6 | 13.2 | 87.8 | 74.9 | 81.5 |
| 30 and under 40 | 184 | 259 | 443 | 22.6 | 25.5 | 24.2 | 115.4 | 170.5 | 142.3 |
| 40 and under 50 | 173 | 218 | 391 | 21.2 | 21.5 | 21.4 | 123.3 | 155.6 | 139.4 |
| 50 and under 60 | 151 | 177 | 328 | 18.5 | 17.4 | 17.9 | 133.5 | 161.6 | 147.3 |
| 60 and under 70 | 82 | 140 | 222 | 10.1 | 13.8 | 12.1 | 115.4 | 171.3 | 145.3 |
| 70 and under 80 | 56 | 76 | 132 | 6.9 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 123.6 | 136.8 | 130.9 |
| 80 and over | 5 | 18 | 23 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 35.0 | 94.8 | 69.2 |
| Total | 815 | 1,015 | 1,830 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 69.4 | 87.5 | 78.4 |
The principal difference in the age profiles between first admissions and readmissions is that there are fewer young and fewer old people in the readmissions.
Diagnosis - The number of males and females readmitted during 1959, together with the proportion which were voluntary admissions, is shown below. The leading causes of readmission were manic-depressive reaction (538 cases), schizophrenia (512 cases), and neurotic-depressive reaction (193 cases). These three diagnoses accounted for 67.9 percent of all readmissions.
| Diagnosis | Numbers | Proportion Which Were Voluntary Admissions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | ||
| Psychoses | ||||
| General paralysis of insane | 3 | - | 3 | 33.3 |
| Other syphilis of central nervous system | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| Schizophrenia | 208 | 304 | 512 | 34.6 |
| Manic-depressive reaction | 200 | 338 | 538 | 54.5 |
| Involutional melancholia | 4 | 17 | 21 | 71.4 |
| Paranoia and paranoid states | 13 | 13 | 26 | 26.9 |
| Senile psychosis | 36 | 50 | 86 | 34.9 |
| Presenile psychosis | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
| Psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14.3 |
| Alcoholic psychosis | 12 | 10 | 22 | 31.8 |
| Psychosis of other demonstrable etiology | 12 | 9 | 21 | 38.1 |
| Puerperal psychosis | - | 16 | 16 | 37.5 |
| Other and unspecified psychoses | 5 | 11 | 16 | 6.3 |
| Psychoneuroses | ||||
| Anxiety reaction | 39 | 30 | 69 | 97.1 |
| Hysterical reaction | 6 | 21 | 27 | 59.3 |
| Neurotic-depressive reaction | 82 | 111 | 193 | 90.2 |
| Other and unspecified psychoneurotic disorders | 5 | 8 | 13 | 92.3 |
| Disorders of Character, Behaviour, and Intelligence | ||||
| Pathological and immature personality | 24 | 11 | 35 | 57.1 |
| Alcoholism | 89 | 7 | 96 | 84.4 |
| Drug addiction | 4 | - | 4 | 50.0 |
| Mental deficiency | 42 | 39 | 81 | 17.3 |
| Other Conditions | ||||
| Post-encephalitic Parkinsonism | 1 | - | 1 | 100.0 |
| Epilepsy | 17 | 12 | 29 | 58.6 |
| Observation | 4 | - | 4 | - |
| Totals, all conditions | 815 | 1,015 | 1,830 | 52.0 |
In the following table the numbers of readmissions and rates per million of mean population are shown for the latest three years.
| Diagnosis | Numbers | Rates per Million of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Psychoses | ||||||
| Syphilis of central nervous system | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Schizophrenia | 454 | 460 | 512 | 203 | 201 | 219 |
| Manic-depressive reaction | 453 | 527 | 538 | 203 | 231 | 230 |
| Involutional melancholia | 32 | 25 | 21 | 14 | 11 | 9 |
| Paranoia and paranoid states | 31 | 25 | 26 | 14 | 11 | 11 |
| Senile psychosis | 104 | 70 | 86 | 47 | 31 | 37 |
| Presenile psychosis | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | 6 | 9 | 14 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Alcoholic psychosis | 18 | 19 | 22 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| Psychosis of other demonstrable etiology | 22 | 22 | 21 | 10 | 10 | 9 |
| Puerperal psychosis | 3 | 5 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Other and unspecified psychoses | 16 | 12 | 16 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| Psychoneuroses | ||||||
| Anxiety reaction | 37 | 58 | 69 | 17 | 25 | 30 |
| Hysterical reaction | 28 | 35 | 27 | 13 | 15 | 12 |
| Neurotic-depressive reaction | 159 | 194 | 193 | 71 | 85 | 83 |
| Other and unspecified psychoneurotic disorders | 11 | 4 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 |
| Disorders of Character, Behaviour, and Intelligence | ||||||
| Pathological and immature personality | 23 | 21 | 35 | 10 | 9 | 15 |
| Alcoholism | 63 | 74 | 96 | 28 | 32 | 41 |
| Mental deficiency | 65 | 64 | 81 | 29 | 28 | 35 |
| Other and unspecified character, behaviour, and intelligence disorders | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Other Conditions | ||||||
| Epilepsy | 17 | 27 | 29 | 8 | 12 | 12 |
| Other defined conditions | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Observation | 1 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Totals | 1,556 | 1,670 | 1,830 | 697 | 731 | 784 |
Both numbers and rates have increased steadily over the last three years. Diagnoses showing the greatest increases are manic-depressive reaction, alcoholism, schizophrenia, and anxiety reaction.
DISCHARGES - There are four principal ways of being discharged from mental hospital: (a) outright discharge, which means being formally discharged at the time of leaving hospital; (b) trial discharge; (c) probation leave, being authorised leave of more than three months' duration for any other purpose; (d) discharged “not committed”, which means being discharged from a mental hospital on the grounds that the patient's mental condition does not warrant his being detained in a mental hospital.
There were 3,662 discharges in 1959. Of these 2,164 were outright discharges, 1,035 were on trial discharge, 342 were probation leavers, and 121 were discharged “not committed”.
The principal diagnoses were: manic-depressive reaction, 899 cases; schizophrenia, 898 cases; and neurotic-depressive reaction, 560 cases.
The following table shows the number of discharges for 1959 by diagnosis.
| Diagnosis | Outright Discharge | Trial Discharge | Probation Leave | Not Committed | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psychoses | |||||
| General paralysis of insane | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Schizophrenia | 375 | 398 | 103 | 22 | 898 |
| Manic-depressive reaction | 593 | 234 | 63 | 9 | 899 |
| Involutional melancholia | 33 | 20 | 6 | 1 | 60 |
| Paranoia and paranoid states | 21 | 20 | 8 | 2 | 51 |
| Senile psychosis | 42 | 56 | 40 | - | 138 |
| Presenile psychosis | 2 | 4 | 2 | - | 8 |
| Psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | 7 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 22 |
| Alcoholic psychosis | 27 | 13 | 4 | 3 | 47 |
| Psychosis of other demonstrable etiology | 19 | 20 | 4 | 3 | 46 |
| Puerperal psychosis | 29 | 14 | 3 | - | 46 |
| Other and unspecified psychoses | 19 | 12 | 4 | 2 | 37 |
| Psychoneuroses | |||||
| Anxiety reaction | 169 | 14 | 8 | 1 | 192 |
| Hysterical reaction | 60 | 16 | 9 | - | 85 |
| Phobic reaction | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Obsessive-compulsive reaction | 13 | 2 | 1 | - | 16 |
| Neurotic-depressive reaction | 450 | 89 | 16 | 5 | 560 |
| Psychoneurosis with somatic symptoms affecting circulation | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Psychoneurosis with somatic symptoms affecting digestive system | 1 | 1 | - | - | 2 |
| Psychoneurosis with somatic symptoms affecting other systems | 2 | 1 | - | - | 3 |
| Other and unspecified psychoneurotic disorders | 18 | 2 | 1 | - | 21 |
| Disorders of Character, Behaviour, and Intelligence | |||||
| Pathological personality without psychosis | 23 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 44 |
| Immature personality | 32 | 5 | 2 | 18 | 57 |
| Non-psychotic alcoholism | 158 | 10 | 1 | 13 | 182 |
| Drug addiction | 6 | 3 | - | - | 9 |
| Primary childhood behaviour disorders | - | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| Mental deficiency | 24 | 63 | 56 | 14 | 157 |
| Other and unspecified character, behaviour, and intelligence disorders | 6 | - | - | - | 6 |
| Other Conditions | |||||
| Multiple sclerosis | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Epilepsy (without psychosis) | 31 | 14 | 3 | 1 | 49 |
| Observation without need for further medical care | - | 1 | - | 16 | 17 |
| Totals | 2,164 | 1,035 | 342 | 121 | 3,662 |
Duration of stay - Nearly a quarter (24.4 percent) of those discharged left hospital within a month of admission. A further 38.9 percent left in the next two months, and a further 16.9 percent were discharged in the subsequent three months. The average stay for all discharges was 43 weeks.
DEATHS - In 1959 there were 758 deaths in mental hospitals. In addition 72 people died while on probation and one died while on escape.
The principal diagnosis was senile psychosis, 380 cases. Next came mental deficiency, 90 cases, and schizophrenia, 89 cases.
In 1959, 94 people died during the first month in hospital and a further 101 deaths occurred in people who had been in hospital one but under three months. In the following table the number of deaths in mental hospitals during 1959 are shown for selected diagnoses by sex and duration of stay.
| Selected Diagnosis | Sex | Under 1 Month | 1-3 Months | 3-6 Months | 6-12 Months | 1-2 Years | 2-3 Years | 3-5 Years | 5-10 Years | 10-20 Years | 20 Years and Over | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia (including paraphrenia) | Male | 3 | 6 | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | 5 | 27 | 46 |
| Female | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 7 | 10 | 20 | 43 | |
| Both sexes | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | - | 8 | 15 | 47 | 89 | |
| Manic-depressive psychosis and involutional melancholia | Male | 3 | - | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 26 |
| Female | 3 | 7 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 34 | |
| Both sexes | 6 | 7 | 1 | - | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 60 | |
| Senile and presenile psychosis and psychosis with cerebral arteriosclerosis | Male | 38 | 41 | 22 | 33 | 24 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 182 |
| Female | 34 | 29 | 26 | 40 | 34 | 32 | 21 | 33 | 8 | - | 257 | |
| Both sexes | 72 | 70 | 48 | 73 | 58 | 37 | 29 | 38 | 13 | 1 | 439 | |
| Alcoholism, all forms | Male | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 |
| Female | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 3 | |
| Both sexes | - | - | - | 3 | 2 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 13 | |
| Psychoneurosis | Male | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 4 |
| Female | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 4 | |
| Both sexes | 3 | - | 1 | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 8 | |
| Mental deficiency | Male | 1 | 4 | - | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 9 | 18 | 47 |
| Female | 1 | 5 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 43 | |
| Both sexes | 2 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 13 | 14 | 32 | 90 | |
| All other diseases | Male | 5 | 5 | 4 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 8 | 38 |
| Female | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 21 | |
| Both sexes | 6 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 59 | |
| Totals, all deaths | Male | 51 | 56 | 28 | 38 | 36 | 13 | 19 | 16 | 34 | 62 | 353 |
| Female | 43 | 45 | 29 | 44 | 39 | 37 | 29 | 60 | 32 | 47 | 405 | |
| Both sexes | 94 | 101 | 57 | 82 | 75 | 50 | 48 | 76 | 66 | 109 | 758 |
EXPENDITURE, ETC. - The total expenditure on public mental hospitals (not including the cost of new buildings and additions) and particulars of receipts during the last 11 financial years are shown in the next table. As from 1 April 1939 free maintenance and treatment of patients have been provided in all public mental hospitals in accordance with the provisions of the Social Security Act 1938. The Mental Health Amendment Act 1950 provides that the cost of maintenance of any person who is not ordinarily resident in New Zealand and who is detained in any public institution shall be a debt due to the Crown.
| Year Ended 31 March | Total Expenditure | Receipts | Net Expenditure | Gross Average Cost per Patient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients' Fees | Sale of Produce, etc. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1950 | 1,766,659 | 1,602 | 177,152 | 1,587,905 | 203 | 0 | 0 |
| 1951 | 1,810,285 | 2,956 | 125,771 | 1,681,558 | 206 | 2 | 0 |
| 1952 | 2,288,589 | 4,983 | 138,465 | 2,145,141 | 257 | 6 | 0 |
| 1953 | 2,446,344 | 1,849 | 55,210 | 2,389,285 | 272 | 2 | 0 |
| 1954 | 2,510,886 | 1,218 | 71,528 | 2,438,140 | 231 | 8 | 8 |
| 1955 | 2,549,733 | 3,104 | 68,437 | 2,478,192 | 262 | 4 | 10 |
| 1956 | 2,805,877 | 629 | 66,962 | 2,738,286 | 283 | 19 | 4 |
| 1957 | 3,036,431 | 874 | 75,193 | 2,960,364 | 312 | 8 | 2 |
| 1958 | 3,366,820 | 560 | 95,990 | 3,270,270 | 344 | 12 | 2 |
| 1959 | 3,583,237 | 664 | 102,951 | 3,479,622 | 355 | 17 | 3 |
| 1960 | 3,889,910 | 815 | 111,463 | 3,777,632 | 392 | 15 | 7 |
As already stated, the expenditure included in the foregoing table does not include amounts spent on new buildings, additions, etc., the cost of which is met by the Ministry of Works. The sums spent in this connection fell away considerably in the later war years. Expenditure for the last four financial years, however, has amounted to £708,828 in 1956-57, £841,609 in 1957-58, £783,548 in 1958-59, and £697,398 in 1959-60.
Table of Contents
DEVELOPMENT - Social security is a comprehensive plan of State assistance by a system of monetary benefits for cases of need and free or subsidised medical and hospital provisions for the safeguarding of health.
The Social Security Act 1938, which came into operation on 1 April 1939, is the basic legislation. Its principal objects were (a) to substitute for the system of non-contributory civil pensions - e.g, old age, widows', and other pensions - a system of extended monetary benefits on a contributory basis; (b) the inauguration of a system of medical and hospital benefits and of other related benefits.
The Social Security Amendment Act 1945 introduced a further important addition to the social legislation of New Zealand. It established the principle of universal family benefits, and from 1 April 1946 each mother has received a benefit in respect of each of her dependent children irrespective of the family income or property.
There is reciprocity of social security benefits with Australia, and with Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Under the Social Security (Reciprocity with Australia) Act 1948 the classes of benefits cover the following: age pensions and age benefits, invalid pensions (including wives' and children's allowances) and invalids' benefits, widows' pensions and widows' benefits, child endowment and family benefits, unemployment benefits, and sickness benefits. The Social Security (Reciprocity with the United Kingdom) Act 1956 provides for reciprocity between the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland and New Zealand to cover age, superannuation, widows', orphans', invalids', sickness, and unemployment benefits. Family benefits have been payable on a reciprocal basis since 1948.
Earlier Yearbooks should be referred to for details of social welfare benefits paid prior to the passing of the Social Security Act 1938.
ADMINISTRATION - The Social Security Act 1938 established the Social Security Department, which is under the control of a Commission. The Department administers, under the direction of the Minister of Social Security, Part II of the Act dealing with monetary benefits, while Part III of the Act, dealing with medical, hospital, and other related benefits, is administered by the Department of Health under the direction of the Minister of Health.
The War Pensions Act 1954 is also administered by the Social Security Department, one of whose officers is designated Secretary for War Pensions.
Owing to the continued decline in volume of rehabilitation work now that the needs of most ex-servicemen have been met, it was decided in 1959-60 to merge the Rehabilitation Division (formerly attached to the Department of Internal Affairs) with the War Pensions Branch of the Social Security Department.
FINANCIAL PROVISIONS - Finance to enable the provisions of the Act to be carried out was provided for by the establishment within the Public Account of the Social Security Fund. The principal revenue of the fund was derived from a charge (collected by the Inland Revenue Department) on salaries, wages, and other income, including the income of companies, but the Act also made provision for the payment to the fund of such other moneys as might be appropriated by Parliament from time to time, and a substantial amount has been transferred from the Consolidated Fund each year except 1957-58.
The social security charge, which had been at the rate of 1d. for every 1s. 8d. or part thereof of income since the inception of the scheme, was increased in 1946 to 1d. for every 13 1/3d. or part thereof - i.e., 1s. 6d. in the pound. The increase, in the case of salaries and wages, became effective from and including 13 May 1946, while “other” income received during the year ended 31 March 1946 was subject to the increased rate.
The Income Tax Assessment Act 1957, which introduced the Pay As You Earn system of taxation from 1 April 1958, provided for the imposition of a social security income tax in the place of the social security charge. This tax has also been written into the deduction tables under the PAYE system at the rate hitherto obtaining (i.e., 1s. 6d. in the pound). It forms part of the pay-period tax. By the Social Security Amendment Act 1958 all social security income tax was payable into the Consolidated Fund in 1958-59 and 1959-60, and the amount necessary for administering the Social Security Act was appropriated out of that fund. The Finance Act 1959 provided for the payment into the Social Security Fund, from 1 April 1960, of an amount computed at the rate of 1s. 6d. for each £1 of the total national private income for the preceding year, as estimated by the Government Statistician.
In the case of salaries and wages the amount of the tax is deducted by the employer or other person by whom the wages or salaries are paid, while the tax on other income is payable by the recipient in three instalments on 7 June, 7 November, and 7 February in the income year.
Receipts - Receipts of the Social Security Fund for financial years are given in the following table.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social security income tax | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| On salary and wages | - | - | - | 5,739,381 | - |
| On other income of persons | - | - | - | 11,185,226 | - |
| On company income | - | - | - | 8,142,140 | - |
| PAYE | - | - | - | 55,547,918 | - |
| Charge on salaries and wages | 35,272,654 | 37,262,667 | 40,317,504 | - | - |
| Charge on other income of persons | 16,706,970 | 16,655,458 | 18,008,194 | - | - |
| Charge on company income | 7,931,093 | 7,717,099 | 7,930,406 | - | - |
| Grants from Consolidated Fund (Social Security Act) | 14,000,000 | 14,000,000 | - | 24,600,000 | 106,500,000 |
| Maintenance recoveries against defaulting husbands | 92,674 | 92,233 | 104,195 | 115,558 | 131,180 |
| Interest on investments | 77,432 | 80,738 | 83,082 | - | - |
| Reciprocity arrangements: Recoveries from Australian Government | 4,332 | 11,058 | 7,978 | 7,643 | 7,891 |
| Other receipts | 25,826 | 37,266 | 58,230 | 62,190 | 94,359 |
| Total revenue | 74,110,981 | 75,856,519 | 66,509,589 | 105,400,056 | 106,733,430 |
Payments - Particulars of payments of the Social Security Fund during the same five financial years are contained in the next table.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monetary benefits | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Superannuation | 7,771,406 | 7,908,795 | 8,279,199 | 8,940,752 | 15,460,047 |
| Age | 22,831,089 | 23,305,383 | 24,304,077 | 26,104,992 | 27,291,008 |
| Widows' | 2,849,308 | 2,934,265 | 3,279,683 | 3,642,351 | 3,915,785 |
| Orphans' | 30,688 | 31,599 | 36,129 | 38,195 | 39,441 |
| Family | 18,860,866 | 19,444,421 | 20,152,619 | 25,995,315 | 31,791,986 |
| Invalids' | 1,680,111 | 1,672,438 | 1,799,823 | 1,942,490 | 2,118,411 |
| Miners' | 127,351 | 121,048 | 124,589 | 119,205 | 112,832 |
| Unemployment | 4,247 | 20,578 | 52,067 | 111,723 | 189,898 |
| Sickness | 1,302,868 | 1,221,409 | 1,368,360 | 1,436,913 | 1,719,343 |
| Emergency | 534,104 | 729,309 | 819,451 | 849,461 | 931,429 |
| Supplementary assistance | 163,334 | 184,276 | 218,201 | 252,758 | 273,010 |
| Advances for repairs to homes | - | - | - | 4,054 | 46,687 |
| Capitalisation of family benefit | - | - | - | - | 3,879,889 |
| Total monetary benefits | 56,155,372 | 57,573,521 | 60,434,198 | 69,438,209 | 87,769,766 |
| Medical benefits | |||||
| Medical | 3,548,080 | 3,797,062 | 3,927,892 | 3,969,646 | 4,243,361 |
| Hospital | 4,764,666 | 4,869,453 | 4,930,424 | 5,774,519 | 5,650,253 |
| Maternity | 1,376,564 | 1,414,767 | 1,449,359 | 1,542,493 | 1,561,861 |
| Pharmaceutical | 4,039,145 | 4,572,557 | 4,466,541 | 5,112,343 | 5,956,302 |
| Supplementary | 1,818,699 | 2,118,873 | 2,284,091 | 2,256,374 | 2,479,850 |
| Total, medical benefits | 15,547,154 | 16,772,712 | 17,058,307 | 18,655,375 | 19,891,627 |
| Reciprocity benefits | |||||
| Australia | 4,035 | 10,245 | 9,977 | 9,191 | 10,699 |
| Great Britain | 186 | Cr.17 | 90 | - | - |
| Balance of maintenance moneys | 267 | 114 | 300 | 291 | 112 |
| Administration expenses | 1,176,779 | 1,249,542 | 1,398,244 | 1,360,302 | 1,522,130 |
| Total payments | 72,883,793 | 75,606,117 | 78,901,116 | 89,463,368 | 109,194,334 |
| Balance of fund at end of year | 16,805,828 | 17,056,230 | 4,664,703 | 20,601,391 | 18,140,487 |
MONETARY BENEFITS - A summarised account of the changes in monetary benefits from the inception of the social security scheme to 1957 was given on pages 205-206 of the 1958 issue of the Yearbook. Since 1939 the original provisions have been considerably amended and enlarged to correct anomalies and to cover more comprehensively the needs of the people. In addition the rates of benefits have been increased from time to time, mainly as a result of the increased cost of living. In December 1959 additional payments of £6 to single beneficiaries and £12 to married couples were made. These payments covered the period from 12 October 1959 - when a general wage order came into effect - to 29 March 1960.
The Social Security Amendment Act 1960 increased the rates payable in respect of age, invalids' widows' (and mothers' allowances), and miners' benefits by £13 a year and sickness and unemployment benefits by 5s. a week from 30 March 1960. The amendment abolished the means tests on property, formerly applicable to age, invalids', orphans', and unemployment benefits, and increased the amount of income allowable before reduction of age, widows', and invalids' benefits from £104 to £156 a year, and the allowable income for sickness and unemployment benefits from £2 to £3 a week from 12 October 1960. From the same date provision was made for an allowable income of £52 a year before reduction in the rate of orphans' benefit which was formerly reducible by £1 for every complete £1 of an orphan's income.
Also from 12 October 1960 the amendment increased the rate payable in respect of a superannuation benefit by £13 a year and gave the Social Security Commission discretionary power to grant on application an additional £26 a year to single, widowed, separated, or divorced superannuation beneficiaries.
For the purpose of determining eligibility for benefit on grounds of residence, persons employed outside New Zealand will be deemed to be resident in New Zealand if employed on Government business, and may be so deemed at the Commission's discretion if employed otherwise, for the purposes of Part II of the principal Act, where liable for the payment of social security income tax on their earnings. In each case the wife and children are also included. The 1950 amendment provided that persons employed by the Governments of Western Samoa and the Cook Islands are exempted from payment of the social security income tax unless they remain ordinarily resident in New Zealand.
The receipt of a war disablement pension or a basic war widow's pension does not render a person ineligible to receive a social security benefit.
SUMMARY OF RATES OF SOCIAL SECURITY BENEFITS - The list below gives a summary of the annual and weekly rates for monetary benefits as at January 1961.
| Benefit | Annual Rate | Weekly Rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * According to circumstances, but in general, standard rates will be increased by 20s. a week for beneficiary, 10s a week for his wife, and 5s. a week for each dependent child. | ||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Superannuation | ||||||
| Unmarried person | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Married person | 221 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Age | ||||||
| Unmarried person | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Married couple if both eligible (each) | 221 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Married woman whose husband is not eligible | 221 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Married man whose wife is not eligible | 442 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Widows' | ||||||
| Widow | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Additional mother's allowance where widow has | ||||||
| One dependent child | 156 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Two dependent children | 182 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Three dependent children | 208 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Four dependent children | 234 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 0 |
| Five dependent children | 260 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Six or more dependent children | 286 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| Orphans' (each child) | 117 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 |
| Family (each child) | 39 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | |
| Invalids' | ||||||
| Unmarried person, 20 years or over | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Unmarried person under 20 years | 208 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Married man with wife included | 442 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Married woman | 221 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Limit of income, including benefits, where domestic or nursing assistance required for a married woman | 702 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 10 | 0 |
| Miners' | ||||||
| Unmarried person | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Married man with wife included | 442 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Miner's widow | 214 | 10 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| Sickness or Unemployment | ||||||
| Person under 20 years without dependants | 182 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Married man with wife included | 442 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Married woman | 221 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Others | 247 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Supplementary Assistance | According to circumstances | |||||
| Emergency | According to circumstances | |||||
| Emergency - Sufferers from tuberculosis* | ||||||
Superannuation Benefits - Every person over the age of 65 years who satisfies the prescribed residential qualifications is entitled to a superannuation benefit without conditions as to income or property. The superannuation benefit is, however, regarded as assessable income for income-tax purposes but is exempt from the social security income tax. The residential qualifications require, in general, a period of residence in New Zealand of 20 years immediately preceding application for benefit, but in the case of a person who was resident in New Zealand on 15 March 1938 the qualifying period is 10 years only. Allowances are made for occasional absences.
For the 10 years' requirement, continuous residence is not deemed to be interrupted by absence -
If the total period of absence from New Zealand does not exceed one year; or
If the total period of absence from New Zealand exceeds one year but does not exceed that period by more than six months for every year of residence in New Zealand in excess of a period of 10 years, and the applicant is ordinarily resident in New Zealand at the date of his application.
A similar proviso for the 20 years' requirement applies -
If the total period of absence from New Zealand does not exceed two years; or
If the total period of absence from New Zealand exceeds two years but does not exceed that period by more than six months for every year of residence in New Zealand in excess of a period of 20 years, and the applicant is ordinarily resident in New Zealand at the date of his application.
Provision is made to cover absence by a seaman serving on board any ship registered or owned in New Zealand and absence in any capacity as a member of any of Her Majesty's Forces.
A superannuation benefit is not payable in addition to any other cash benefit except a family benefit. For example, a superannuation benefit and an invalid's benefit cannot be paid to the one person. Similarly, a superannuation benefit and an age benefit are not payable to the one person.
At the date of commencement on 1 April 1940, and for the remainder of the year, the rate of benefit was £10 a year, thereafter being increased by £2 10s. a year. As from 1 October 1951, however, the amount payable for the balance of the year 1951-52 was raised from £37 10s. to £75 a year, this amount increasing by £5 a year on 1 April of each succeeding year to £110 a year in 1958. From 1 April 1959 the rate increased to £156 a year, from 30 March 1960 to £208 a year, and from 12 October 1960 to £221 a year for a married person and to £247 a year for an unmarried person on application.
The number of superannuation benefits in force at 31 March 1960 was 87,959, an increase of 3,576 above the total for the previous year. Expenditure on these benefits rose from £8,940,752 in 1958-59 to £15,460,047 in 1959-60.
Age Benefits - Every person who has attained the age of 60 years is entitled to receive an age benefit, subject to satisfying certain qualifications in regard to residence and character. The residential qualifications are the same as those set out under the preceding heading in regard to superannuation benefits. The character qualifications mainly relate to desertion of wife or husband or wilful failure in the case of a married man or widower to provide adequate maintenance for wife or for children under 16 years of age.
The basic rate of the benefit is £221 a year, subject to certain deductions on account of income. Particulars of additions to and deductions from the basic rate are as follows:
Unmarried applicants: The basic rate is increased to £247, although reduced by £1 for every complete £1 of income in excess of £156 a year.
Married applicants: Where husband and wife are both entitled to the benefit the basic rate is reduced by 10s. for every complete £1 of their combined incomes in excess of £156 a year. In cases where only one of them is entitled to the benefit the reduction is at the rate of £1 for every complete £1 of their total income (excluding a family benefit) in excess of £377 a year. A further provision allows of an extra payment, not exceeding £221 a year, to a male recipient when his wife is ineligible for any benefit under the Act. This is payable only up to a limit of the total income of the couple, plus benefit, of £598 a year.
For the above purposes, income is deemed not to include amounts received by way of war disablement pension or basic war widow's pension.
From 1 August 1955 an age benefit may be granted to unmarried women between 55 and 60 years of age who are unable to engage in regular employment.
Age beneficiaries are entitled to surrender their benefits while their earnings are excessive and to apply for reinstatement immediately the employment ceases. The earnings received during the period that both husband and wife were not in receipt of age benefits are not taken into account.
Any deduction from the maximum rate of benefit because of excess income may be diminished by £6 10s. for each year that an applicant, on having attained the age of 65 years, has deferred applying for the benefit between the ages of 60 and 65 years, provided that he was residentially qualified to receive the benefit during that period.
During 1959-60, 1,077 existing beneficiaries and new applicants received additional benefit for the first time on account of the deferment concession. The periods of deferment were: one year, 66; two years, 77; three years, 101; four years, 110; and five years, 723.
In computing the allowable income of any female beneficiary or the wife of any beneficiary no account is taken of her personal earnings from domestic or nursing services in private homes or in hospitals or charitable institutions up to £78 a year.
A special allowance not exceeding £26 a year may be paid to any person in receipt of an age benefit who served as a member of a New Zealand contingent in connection with the South African War or in any of Her Majesty's forces in that war if he had been born in New Zealand or was domiciled therein at the commencement of the war.
The Commission may also, in its discretion, increase by an amount not exceeding £26 a year the rate of any benefit under Part II of the Act (including the age benefit) payable to any beneficiary who was one of the parents of a deceased member of any of Her Majesty's forces established in New Zealand whose death was attributable to service with the forces. Similar powers exist in respect of a parent of a deceased member of the New Zealand mercantile marine whose death was attributable to the Second World War. The provision also covers from 1 April 1949 the case of a deceased member of any force or of the mercantile marine of any part of the British Commonwealth other than New Zealand who was domiciled in New Zealand at the commencement of the Second World War and whose death was directly attributable to that war. At 31 March 1960 there were 2,546 of these allowances in force, this representing a decrease of 88 from the figure of 2,634 for 1959.
Where an applicant for an age benefit is totally blind, the rate of the benefit, together with any benefits and allowances payable to or in respect of the wife or husband of the applicant, is not to be less than the total of benefits and allowances that would have been paid if the applicant had been eligible for an invalid's benefit.
The number of age benefits in force at 31 March 1960 was 116,077, a decrease of 2,425 as compared with the figure at the end of March 1959. The 1960 total was inclusive of 4,451 husbands receiving benefits on account of dependent wives who were not eligible for benefits in their own right, and of 162 males receiving the additional allowance of up to £26 a year paid to veterans of the South African War. Expenditure on age benefits increased from £26,104,992 in 1958-59 to £27,291,008 in 1959-60.
The following table shows the estimated age distribution of (a) persons who were granted new age benefits during the calendar year 1959 (including transfers from widows' and invalids' benefits), and (b) total age beneficiaries at 31 December 1959.
| Age, in Years | Persons Granted New Age Benefits During 1959 | Total Age Beneficiaries at 31 December 1959 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| 60 | 1,080 | 2,080 | 3,160 | 872 | 1,266 | 2,138 |
| 61 | 330 | 430 | 760 | 1,089 | 2,327 | 3,416 |
| 62 | 170 | 300 | 470 | 959 | 2,685 | 3,644 |
| 63 | 180 | 320 | 500 | 904 | 3,021 | 3,925 |
| 64 | 200 | 200 | 400 | 1,187 | 3,075 | 4,262 |
| Totals, 60-64 | 1,960 | 3,330 | 5,290 | 5,011 | 12,374 | 17,385 |
| 65-69 | 770 | 740 | 1,510 | 8,237 | 16,771 | 25,008 |
| 70-74 | 490 | 420 | 910 | 10,783 | 19,044 | 29,827 |
| 75 and over | 290 | 270 | 560 | 15,772 | 27,616 | 43,388 |
| Totals | 3,510 | 4,760 | 8,270 | 39,803 | 75,805 | 115,608 |
Widows' Benefits - Every widow who is the mother of one or more children under 16 years of age is entitled to a benefit in respect of widowhood. In addition, any widow not being the mother of children under 16 years of age who satisfies the following conditions is also entitled to the benefit:
A widow who has had one or more children, provided that the duration of her marriage was not less than 15 years or, in the alternative, that the aggregate of the period of the duration of her marriage and any subsequent period during which she had the care of at least one of her children under 16 years of age was not less than 15 years:
A widow who, on the expiration of not less than five years after the date of her marriage, became a widow after she attained the age of fifty years:
A widow of not less than 50 years of age who became a widow after she had attained the age of 40 years, provided that the duration of her marriage was not less than 10 years and that not less than 15 years have expired since the date of her marriage.
It will be noted that no widow under 50 years of age who has not had one or more children can qualify for the benefit.
Provision is also made for other classes of women (not being widows) to receive benefits as if they were widows. Particulars are as follows:
Any married woman who satisfies the Commission that she has been deserted by her husband and that she has taken proceedings against him for a maintenance order under the Destitute Persons Act 1910. Either the beneficiary or the Commission may institute and prosecute proceedings for the enforcement of the order, or for an order cancelling, varying, or suspending the maintenance order. Any moneys paid by a husband, whether by way of maintenance order or otherwise, are set off against any benefit so granted. Benefits for deserted wives may be continued after divorce:
Any married woman in respect of whose husband a reception order is in force under the Mental Health Act 1911 (whether or not he is detained in an institution under the Act), or whose husband is for the time being detained in an institution under that Act, whether as a voluntary boarder or otherwise.
The two paragraphs which follow also apply in such cases, reference to the date of death being deemed to be reference to date of desertion by the husband or to the making of a reception order.
Except in the case of widows with one or more children under 16 years of age, no widow is entitled to receive a widow's benefit unless she and her husband were both resident in New Zealand for not less than three years immediately preceding the death of the husband or, unless either of them, being ordinarily resident in New Zealand at the date of the husband's death, has resided continuously in New Zealand for not less than five years.
The term “children” does not include any child born out of New Zealand unless at least one of the following conditions is satisfied - namely, that -
The mother of the child was only temporarily out of New Zealand at the time of its birth; or
Both parents were resident in New Zealand for the three years immediately preceding the date of the death of the husband of the applicant; or
One of the parents, being ordinarily resident in New Zealand at the date of the husband's death, has resided continuously in New Zealand for not less than five years.
The term “child” includes a stepchild or a child adopted during the lifetime of the husband of the applicant (in cases where the husband is dead) or adopted while the husband and wife were living together (in cases of desertion, etc.). It may also (at the discretion of the Commission) include any child who is being maintained by the applicant or was at any time maintained by the husband of the applicant.
No woman shall be entitled to receive a widow's benefit unless the Commission is satisfied that she is of good moral character and sober habits.
The rate of benefit payable to a widow is £247 a year plus a supplementary benefit (mother's allowance) of £156 a year in cases where there is one dependent child and £182 a year where there are two dependent children under sixteen years of age. For a widow with three dependent children the rate of mother's allowance is £208; with four children £234; with five children £260; and with six or more children £286 a year.
Any income received, exclusive of war disablement or basic war widow's pension, is taken into account in computing the benefit payable, and where such income exceeds £156 the annual rate of benefit is reduced by £1 for every complete £1 of such excess. The maximum of income plus benefit in the case of a widow without dependent children is £403 a year and for a widow with one dependent child is £559 a year. This maximum is increased by 126 a year for each additional dependent child up to and including the sixth. A widow with dependent children will, of course, receive in addition the universal family benefit of 15s. a week for each child.
The provision relating to the allowable income of £78 a year gained from domestic or nursing services in private homes or in hospitals and charitable institutions without affecting the amount of the benefit payable to women age-beneficiaries also applies to widows' benefits. Widows' benefits cease on remarriage.
At 31 March I960 there were 13,049 benefits in force, an increase of 216 during the year Expenditure totalled £3,915,785 in 1959-60, compared with £3,642,351 in 1958-59. Offset against these amounts were the sums of £131,180 and £115,558 respectively, being recoveries of maintenance from defaulting husbands.
The following table affords an analysis of widows' benefits in force at 31 March 1960.
| With One Dependent | With Two or More Dependent Children | Without Dependent Children | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Widows | 2,427 | 2,543 | 6,611 | 11,581 |
| Deserted wives | 278 | 676 | 342 | 1,296 |
| Wives of mental hospital patients | 33 | 79 | 60 | 172 |
| Totals | 2,738 | 3,298 | 7,013 | 13,049 |
Orphans' Benefits - A benefit in respect of complete orphanhood is payable in the case of a child under 16 years of age who was born in New Zealand or whose last surviving parent was resident in New Zealand for a period of not less than three years preceding the date of his or her death. A stepchild or an adopted child comes within the definition of the term, and payment may be made to any person for the time being having the care and control of the child. No payment is made on account of any orphan maintained in a State institution. but payment may be made to the governing bodies of homes and orphanages of religious or other organisations.
The rate of an orphan's benefit is £117 a year reduced by £1 for each complete £1 of income received by or for the benefit of the orphan in excess of £52 a year. In any case where the benefit of the orphan falls below £39 a year application may be made for a family benefit of 15s, a week in lieu of orphan's benefit. For the purpose of assisting in the further education of any child, the Commission may grant or continue the benefit until the end of the year in which the child reaches the age of eighteen years.
The number of benefits in force at the end of March 1960 was 277 (in respect of 372 children), an increase of 13 during the year. Expenditure increased from £38,195 in 1958-59 to £39,441 in 1959-60.
Family Benefits - As from 1 April 1946 the father or mother of any child or children under 16 years of age may apply for a family benefit, irrespective of the income or property of the parents or children. Prior to 1 April 1946 family benefits were payable subject to a means test.
The rate of the benefit is 15s. a week for each child, and in every ease is paid to the mother of the children, unless in special circumstances the Commission considers that it should be paid to the father or to some other person for the benefit of the children.
If a beneficiary in receipt of an age or other monetary benefit is the parent of dependent children, payment in respect of the children is made by way of a separate family benefit.
The term “children” includes stepchildren and adopted children, but docs not include -
Any child who has attained the age of 16 years unless such child is continuing its education AS a full-time day pupil at a school or college, in which case the Commission may grant or continue the benefit until the end of the year in which it reaches the age of 18 years.
Any child who is not in fact maintained as a member of the family of the applicant.
Any child in respect of whom any other benefit or pension, etc., is payable out of public moneys.
The Commission may regard as a member of the applicant's family any child who, although not a child of the applicant, is being maintained as a member of the family. A benefit may also be continued beyond the age of 16 years in respect of any child who is totally incapacitated from earning a living by reason of some physical or mental defect.
In order to qualify for a family benefit at least one of the following conditions must be satisfied, namely -
The child was born in New Zealand.
The mother of the child was only temporarily absent from New Zealand at the time of its birth.
The Commission is satisfied that the child is likely to remain permanently in New Zealand.
The child has resided continuously in New Zealand for not less than 12 months.
A benefit is not payable in respect of any child committed to the care of the Child Welfare Division of the Department of Education nor in respect of any child residing in an institution under the care of the Division of Mental Hygiene of the Department of Health. Family benefits are payable to children of a member of any of Her Majesty's naval, military, or air forces.
A family benefit or portion of a family benefit may be paid in a lump sum in advance for a period not exceeding 52 weeks in respect of the first child of a marriage or a child who has commenced his first year of post-primary instruction.
Under the provisions of the Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act 1958, family benefits may be capitalised and paid in advance to assist parents with the purchase of home properties, additions or alterations to existing homes, or the repayment of mortgages and other obligations on family homes. In outline, the measure provides for the capitalisation of the family benefit in respect of one or more children from the age of one year up to the age of 16 years, provided that the total of the advance or advances in the case of any one family is not less than £200 or more than £1,000.
The Act came into force on 1 April 1959 and during the first year's operations, 15,265 applications for capitalisation were approved in respect of the benefits of 27,473 children. The aggregate capitalised value of the benefits involved was £9,363,563.
A family benefit may be paid in cash, or to the credit of the Post Office Savings Bank account of the mother. The number of family benefits being paid to Post Office Savings Bank accounts decreased from 123,818 at 31 March 1959 to 120,569 at 31 March 1960, the amount lodged increasing from £8,985,703 to £11,835,911 this being due to the increase in rate of benefit from 10s. to 15s. a week from 1 October 1958.
The total number of benefits in force at 31 March 1960 was 343,193 covering 820,000 children, compared with corresponding figures of 333,413 and 796,529 at 31 March 1959. Included in the 1959-60 total of children were 15,358 pupils and 42 incapacitated minors over the age of 16 years. Expenditure increased from £25,995,315 in 1958-59 to £31,791,986 in 1959-60.
Invalids' Benefits - Subject to certain residential and other qualifications, every person of the age of 16 years and upwards who is not qualified to receive an age benefit is entitled to an invalid's benefit if he -
Is totally blind; or
Is permanently incapacitated for work as the result of an accident or by reason of illness or of any congenital defect.
The other qualifications referred to are as follows:
That he has fulfilled certain residential qualifications, these in the main being the same as for superannuation benefits described on page 178.
That incapacity for work was not self-induced or in any way brought about with a view to qualifying for an invalid's benefit.
Applicant must be of good moral character and sober habits.
Provision is made for a medical examination, when necessary, to determine the extent of incapacity. In the event of an application being declined on medical grounds, the applicant has the right of appeal, within three months after the decision of the Commission has been communicated to him, to a board of three medical practitioners nominated by the Department. An invalid's benefit may be paid in respect of a period of absence from New Zealand not exceeding two years in the aggregate, if the Commission is satisfied that such absence was for the purpose of obtaining any special medical or surgical treatment, or in the case of blindness, for the purpose of undertaking vocational training or treatment in respect of the eyes.
The prescribed rates for invalids' benefits, together with the amounts of allowable income, exclusive of war disablement or basic war widows' pensions, are as follows.
| Class of Person | Rate of Benefit | Allowable Income | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekly | Yearly | Weekly | Yearly | |||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Person under 20 years without dependants | 4 | 0 | 0 | 208 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 156 | 0 | 0 |
| Married man | 4 | 5 | 0 | 221 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 156 | 0 | 0 |
| Wife | 4 | 5 | 0 | 221 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| All other persons | 4 | 15 | 0 | 247 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 156 | 0 | 0 |
As in the case of other benefits, dependent children are provided for by way of the family benefit at 15s. a week each.
In each case the amount of the benefit is reduced by £1 for every complete £1 of income, exclusive of war disablement or basic war-widow's pension, in excess of the amounts stated as allowable. In computing the income of any blind person no account is taken of his personal earnings. In addition, personal earnings of such blind persons are subsidised to the extent of 25 percent so long as the total income, including any benefit received, does not exceed £533 a year (£559 if unmarried).
Where an applicant is a married woman and, by reason of incapacity, necessary nursing or domestic assistance is required to be paid for, the Commission may increase the rate of any benefit which may have been reduced on account of income to an amount not in excess of £221 a year, but so that the total income of applicant and husband, inclusive of the benefit, does not exceed £13 10s. a week.
Any person in receipt of an invalid's benefit who, on the attainment of age 60, becomes entitled to receive an age benefit is required to relinquish his invalid's benefit and is granted an age benefit in lieu thereof, but the aggregate amount payable for a blind beneficiary and his wife (if any) is not altered by this transfer.
Of 827 new benefits granted in 1959 the marital status of the recipients was single 352 (175 males, 177 females), married 318 (308 males, 10 females), widowed 50 (30 males, 20 females), and apart, separated, divorced 107 (54 males, 53 females). By far the greatest number were aged 50 years or over, 437, the numbers for other age groups being as follows: under 20 years, 128; 20 and under 40 years, 123; and 40 and under 50 years, 139.
Invalids' benefits in force at 31 March 1960 numbered 8,024, a decrease of 8 on the March 1959 figure, while expenditure rose from £1,942,490 in 1958-59 to £2,118,411 in 1959-60.
Miners' Benefits - Subject to the qualifications set out hereunder, a miner's benefit is payable to any person who, while engaged as a miner in New Zealand, contracted miner's phthisis and is there by permanently and seriously incapacitated for work, or to any person who contracted, while engaged as a miner in New Zealand, any other occupational or heart disease and is thereby permanently and totally incapacitated for work. The term “miner's phthisis” means pneumoconiosis and includes tuberculosis of the lungs or any other disease of the respiratory organs commonly associated with, or a sequel to, pneumoconiosis. The necessary qualifications are-
Employment as a miner in New Zealand for not less than two and a half years:
Continuous residence in New Zealand for not less than five years immediately preceding the date of his application for a benefit. Continuity of residence is not deemed to have been interrupted by occasional absences aggregating not more than six months:
Good moral character and sober habits and must not have deserted or wilfully failed to provide for his wife and children during the period of five years immediately preceding the date of application:
That compensation under the Workers' Compensation Act in respect of the same disability is not being received.
The rates of miners' benefits are £4 5s. a week or £221 a year (or £247 if unmarried), increased by £4 5s. a week, or £221 a year, for a wife. Dependent children under 16 years are provided for by way of family benefit at the rate of 15s. a week each.
There is no reduction in the benefit on account of the income or property of the applicant and/or his wife.
Provision is made for medical examination where necessary to determine whether the applicant is permanently incapacitated for work, or the extent of his incapacity.
An applicant whose claim has been declined on medical grounds has a right of appeal to a board consisting of three registered medical practitioners appointed by the Department.
A special provision is made for the payment from the Social Security Fund of a reasonable contribution towards the funeral expenses of any person who dies while in receipt of a miner's benefit. The amount to be paid is at the discretion of the Commission.
If a person in receipt of a miner's benefit dies leaving a widow, such widow is entitled to a benefit of £4 2s. 6d. a week, or £214 10s. a year, during widowhood. This benefit is payable regardless of the circumstances of the widow, her income or property not being considered in the granting of a benefit.
Payment of benefits is not affected by a period or periods of absence from New Zealand not exceeding two years in the aggregate.
Miners' benefits in force at 31 March 1960 numbered 353 (including 89 widows), 33 fewer than at the corresponding date in 1959. During 1959-60 the expenditure on this class of benefit was £112,832, compared with £119,205 in 1958-59.
Unemployment Benefits - Subject to the conditions set out below, every person over the age of 16 years who is not qualified to receive an age benefit is entitled to a benefit in respect of unemployment. An applicant is required to satisfy the Commission in respect of the following:
That he is unemployed:
That he is capable of undertaking and is willing to undertake suitable work:
That he has taken reasonable steps to obtain suitable employment:
That he has resided continuously in New Zealand for not less than 12 months.
An unemployment benefit is not payable in respect of the first seven days of any period of unemployment, except in special circumstances. In addition, the Commission may postpone, for a period not exceeding six weeks, the commencement of the benefit, or it may terminate the benefit in any of the following circumstances:
If the applicant has voluntarily become unemployed without good and sufficient reason:
If the applicant has lost his employment by reason of any misconduct as a worker:
If the applicant or beneficiary has refused or failed, without a good and sufficient reason, to accept any offer of suitable employment:
In the case of a seasonal worker if his earnings for the season are sufficient for the maintenance of himself and his family notwithstanding a period of temporary unemployment.
Unemployment benefits are payable in accordance with the following scale:
| Weekly Benefit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | |
| Person under 20 years without dependants | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Married man with wife included | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Others | 4 | 15 | 0 |
Dependent children are paid for by way of family benefit at the rate of 15s. per week each.
The benefit is payable so long as the beneficiary is unemployed or until he becomes eligible to receive another class of benefit, other than a family benefit - e.g., an age benefit.
A married woman is entitled to receive the benefit of up to £4 5s. a week only if her husband is unable to maintain her. If a beneficiary is not receiving a benefit in respect of a wife, an allowance may be paid in respect of any person who has the care of his home.
The foregoing rates of benefits may be reduced, having regard to the income received by the applicant or his wife.
The numbers of applications for unemployment benefits dealt with during the years ended 31 March 1959 and 1960 were 3,559 and 5,228 respectively, 2,584 persons being granted a benefit in 1958-59, and 3,588 in 1959-60. At the end of March 1960 312 benefits were in force, compared with 341 at the end of the previous year. Payment of additional benefit for a dependent wife was included in 1,729 of the benefits granted during 1959-60 and in 160 of the benefits in force at 31 March 1960. Expenditure for the year 1959-60 amounted to £189,898, as against £111,723 in 1958-59.
Sickness Benefits - Every person over the age of 16 years who has resided continuously in New Zealand for not less than 12 months and who satisfies the Commission that he is temporarily incapacitated for work through sickness or accident, and that by reason thereof he has suffered a loss of salary, wages, or other earnings, is entitled to a sickness benefit. The amount of the benefit is limited to the amount by which the weekly earnings of the applicant have been reduced by reason of his incapacity or to a maximum of £8 10s. a week payable to a man and his wife. Where a person is engaged in business on his own account and by reason of sickness or accident is obliged to employ a substitute during the period of incapacity, the remuneration paid to the substitute is regarded as loss of earnings. Every application for a benefit must be supported by a medical certificate, and no benefit is payable for the first seven days of incapacity except under special circumstances.
A married woman shall be entitled to receive a sickness benefit of up to £4 5s. a week, only if the Commission is satisfied that her husband is unable to maintain her.
Subject to the foregoing remarks concerning amount of benefit, the rates of sickness benefits are as follows:
| Weekly Benefit | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | |
| Person under 20 years without dependants | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Married man with wife included | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Others | 4 | 15 | 0 |
Any applicant who is maintaining a home and who is not drawing a benefit in respect of a wife, may receive a benefit at a rate not exceeding that for a wife, in respect of any person who has the care of his home.
Dependent children are provided for by way of family benefit.
The rate of benefit computed as aforesaid is reduced by 1s. for every complete 1s. of the total income, exclusive of war disablement or basic war-widows' pensions, of the applicant and of his wife or her husband, as the case may be, in excess of £3 a week or, in any case where the applicant or his wife or her husband, as the case may be, is in receipt of a sick benefit from a friendly society or a like benefit from any other source, in excess of £4 a week.
The numbers of applications for sickness benefits dealt with during the years ended 31 March 1959 and 1960 were 29,211 and 31,748 respectively. The number of persons granted sickness benefits was 27,169 in 1958-59 and 29,542 in 1959-60. Benefits in force at 31 March 1960 totalled 4,064, compared with 4,190 at the end of March 1959. Total expenditure for 1959-60 amounted to £1,719,343, an increase of £282,430 on the 1958-59 figures.
In the following table sickness benefits which ceased during the calendar year 1959 are shown according to the duration of the sickness benefit.
| Duration of Sickness Benefit (Weeks) | Number of Benefits | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |
| 0-4 | 10,303 | 2,662 | 12,965 |
| 5-12 | 6,952 | 2,067 | 9,019 |
| 13-25 | 2,548 | 1,570 | 4,118 |
| 26-52 | 1,296 | 508 | 1,804 |
| 53-104 | 526 | 161 | 687 |
| Over 104 | 122 | 22 | 144 |
| Totals | 21,747 | 6,990 | 28,737 |
The following table gives a classification of sickness benefits according to the disease suffered by the beneficiary. The data are obtained from an analysis of the benefits which ceased during the calendar year 1959.
| Disease or Injury | Males | Females | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infective and parasitic diseases | 1,320 | 434 | 6.1 |
| Neoplasms | 402 | 214 | 2.1 |
| Allergic, endocrine system, metabolic, and nutritional diseases | 651 | 169 | 2.9 |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs | 56 | 66 | 0.4 |
| Mental, psychoneurotic, and personality disorders | 896 | 589 | 5.2 |
| Diseases of the nervous system and sense organs | 972 | 224 | 4.2 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | 1,962 | 329 | 8.0 |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | 3,972 | 997 | 17.3 |
| Diseases of the digestive system | 3,127 | 702 | 13.4 |
| Diseases of the genito-urinary system | 559 | 325 | 3.0 |
| Deliveries and complications of pregnancy | .. | 1,422 | 4.9 |
| Diseases of the skin and cellular tissue | 1,034 | 241 | 4.4 |
| Diseases of the bones and organs of movement | 1,713 | 457 | 7.6 |
| Congenital malformations | 68 | 32 | 0.3 |
| Senility, and ill-defined conditions | 929 | 333 | 4.4 |
| Accidents, poisonings, and violence (nature of injury) | 4,086 | 456 | 15.8 |
| Totals | 21,747 | 6,990 | 100.0 |
Emergency Benefits - An emergency benefit may be granted by the Commission on the grounds of hardship to any person who by reason of age, physical or mental disability, domestic circumstances, or any other reason is unable to earn a sufficient livelihood for himself and those dependent on him and is ineligible for any other monetary benefit.
The amount of the emergency benefit is at the discretion of the Commission, which fixes as nearly as possible an amount equal to that payable for the type of benefit for which the applicant most closely qualifies.
Payments of benefits for which tuberculosis sufferers may qualify are at the rates of £4 10s. a week for a single person under 20 years of age without dependants, £5 15s. a week for a single person 20 years and over, and £10 a week for a married couple. These rates are increased by 5s. a week for each dependent child.
Emergency benefits in force at 31 March 1960 numbered 3,136, compared with 3,039 at 31 March 1959. Expenditure in the 1959-60 year amounted to £931,429 and in 1958-59 to £849,461.
Supplementary Assistance - Since 1951 supplementary assistance has been available to social security beneficiaries and others who have special commitments which cannot be met out of current income, have insufficient other resources, and are unable to help themselves. Welfare and other organisations have been encouraged to assist in bringing this source of help to the knowledge of persons who might qualify, and departmental literature has included information on the purpose of supplementary assistance, the cost of which is now borne by the Social Security Fund. Continuing grants are made where the applicant's continuing commitments, e.g., food, fuel, rent, are in excess of the income received by the applicant, and lump sum grants are usually made to meet some nonrecurring expense. An analysis of these grants showing age, sex, marital status, rate and purpose of grants, type of living accommodation, and number of dependent children, is given in the parliamentary paper H. 9, 1960.
In the 1959-60 year, 9,333 applications for assistance were granted, expenditure totalling £273,010, compared with 8,166 grants totalling £252,758 in 1958-59. There were 5,525 continuing grants in force at 31 March 1960.
Domestic and Nursing Concession - Female social security beneficiaries or the wives of social security beneficiaries are allowed, in addition to the ordinary income exemption of £156 a year, to earn up to £78 a year in domestic or nursing service in private homes, hospitals, homes for the care of the aged, or charitable institutions approved by the Commission, without their benefits being reduced. During the year 1959-60, 416 applications were received for employment in private homes, of which 399 were granted, while at 31 March 1960 there were 892 concessions in force, compared with 1,097 at the end of March 1959. During the year 1959-60, 285 applications were received for employment in hospitals and institutions, of which 274 were granted, while at 31 March 1960 there were 448 concessions in force.
Reciprocity with Australia - The Social Security (Reciprocity with Australia) Act 1948, provided for reciprocity in relation to a wide range of benefits between New Zealand and the Commonwealth of Australia. The Act came into force on 1 July 1949. A similar Act was passed in Australia and came into force on the same date.
Part II of the Act covers the case of former residents of Australia and applies to any person who, having at any time resided in Australia, is permanently resident in New Zealand inasmuch as he either satisfies the Commission that he is so permanently resident or has been in continuous residence in New Zealand for not less than six months (unless in this case the appropriate authorities in both countries agree that the residence is not to be regarded as permanent).
For the purpose of any application for a benefit in respect of a person covered by this Act, residence in Australia or birth in Australia will be regarded as residence or birth in this country.
Applicants for age, invalids', or widows' benefits must be qualified on residential grounds to receive the corresponding pensions under the Social Services Act (Australia) as if their residence in New Zealand had been residence in Australia. No male person is entitled to receive an age benefit unless he has attained the age of 65 years. The Act also provides that the Commission shall treat blindness or permanent incapacity for work occurring in Australia as if it had occurred in New Zealand.
Part III of the Act deals with persons who, although ordinarily resident in New Zealand, are temporarily resident in Australia. Such residence is not a disqualification for a benefit. Benefits may be applied for and paid in Australia, although the Commission may, in its discretion, postpone payment of the whole or any part of the benefit until the return of the beneficiary to New Zealand.
The appropriate reciprocal provisions made in respect of Australia are contained in the Schedule to the Act.
Reciprocity exists in respect of the following classes of pensions, allowances, endowments, and benefits under the respective Acts governing social security provisions:
Age pensions and age benefits.
Invalid pensions (including wives' and children's allowances) and invalids' benefits.
Widows' pensions and widows' benefits.
Child endowment and family benefits.
Unemployment benefits.
Sickness benefits.
Reciprocal benefits in force in New Zealand as at 31 March 1960 numbered 363, as compared with 509 at 31 March 1959.
Reciprocity with United Kingdom - As mentioned earlier, reciprocity in respect of family benefits between New Zealand and Great Britain and Northern Ireland was provided for by legislation during 1948, reciprocal family benefits in force at 31 March 1960 numbering five, compared with the 1959 figure of 12. The Social Security Amendment Act 1951 contained a provision that a family benefit may be paid in respect of a child immediately on arrival in New Zealand if the Commission is satisfied that the child is likely to remain permanently in New Zealand. The fall in reciprocal family benefits from the 1952 figure of 787 is therefore accounted for by the substitution in most cases of ordinary family benefits.
The Social Security (Reciprocity with United Kingdom) Act 1956 brought into operation from 1 April 1956 an agreement providing for reciprocity in a comprehensive range of benefits between New Zealand and the United Kingdom.
General Principles of the Agreement - The general principle of the agreement is that persons migrating from one country to the other for permanent residence will be taken into the social security scheme of the receiving country and paid benefits by the receiving country under the laws and conditions applicable to other residents of that country.
This principle is modified to the extent that the United Kingdom has agreed to continue to pay retirement pensions and widows' pensions in New Zealand to former residents of the United Kingdom who are qualified under the United Kingdom scheme. In such cases, New Zealand will supplement such pensions to bring them up to the New Zealand rates where necessary.
United Kingdom Residents in New Zealand - In New Zealand the agreement applies to former residents of England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland, and the Isle of Man who claim age, superannuation, widows', orphans', invalids', sickness, and unemployment benefits under the Social Security Act.
The agreement modifies the residential requirements of the Social Security Act and enables persons who formerly lived in the United Kingdom to be treated as if they resided in New Zealand during any period they lived in the United Kingdom. Though the normal qualifying age for a grant of age benefit in New Zealand is 60, no man claiming age benefit by virtue of the agreement is entitled to receive it till he reaches 65.
The United Kingdom continues to pay retirement pensions and widows' pensions to persons in New Zealand who are qualified under the national insurance scheme and, in such cases, New Zealand, where necessary, supplements the national insurance pensions to bring them up to the rate of the appropriate New Zealand benefit. There is no supplementation in cases where the national insurance retirement or widow's pension is equal to, or greater than, the New Zealand social security benefit which could be paid.
New Zealand Residents in the United Kingdom - In the United Kingdom the agreement applies to former residents of New Zealand who claim retirement pensions, widows' pensions, widowed mother's and guardian's allowances, sickness and employment benefits under the National Insurance Act.
The United Kingdom scheme is a contributory scheme, and payment of benefits is dependent upon the satisfaction of specified contributory conditions.
The agreement modifies the provisions of the National Insurance Act of the United Kingdom and enables persons who formerly lived in New Zealand to be treated for the purpose of satisfying the contribution conditions of that Act as if they had paid contributions under the national insurance scheme for each week during which they had been resident in New Zealand. The qualifying age for retirement pension under the National Insurance Act is 60 for women and 65 for men. Consequently, no man will be entitled to retirement pension till he is 65.
Persons who were in receipt of superannuation, age, or widow's benefit when they left New Zealand will generally be regarded as having satisfied the contribution conditions under the United Kingdom scheme if they have reached pensionable age, and will receive the appropriate national insurance benefit from the date of their arrival in the United Kingdom.
Persons in receipt of social security benefits in New Zealand who go to the United Kingdom for the purpose of a visit will normally have their benefits suspended on departure, but if they return to New Zealand within 12 months they will be paid arrears of their social security benefit for the period of their absence. If they apply for, and receive, national insurance pensions while in the United Kingdom, the amount paid by the United Kingdom will be deducted from the arrears of social security benefit payable on their return.
MEDICAL, HOSPITAL, AND OTHER RELATED BENEFITS - The part of the Act dealing with medical and like benefits is of general application to all persons ordinarily resident in New Zealand, and makes provision for medical, pharmaceutical, hospital, maternity, and other related benefits.
The Act also gives authority for the inauguration of supplementary benefits as and when the occasion for providing such benefits arises. Among the supplementary benefits introduced are radiological services, dental services, home nursing services, and domestic assistance.
Medical Benefits - Under the provisions contained in the Act every person is entitled to such medical treatment as is ordinarily given by medical practitioners in the course of a general practice. Certain services are excluded, the principal of these being as follows:
Medical services afforded in relation to maternity cases. (These services are covered by maternity benefits and are described under a later heading):
Medical services involved in any medical examination of which the sole or primary purpose is the obtaining of a medical certificate:
Medical services other than anaesthetic services, involved in or incidental to the extraction of teeth by a medical practitioner:
Medical services in respect of which fees are payable under the Social Security (X-ray Diagnostic Services) Regulations 1941, Social Security (Physiotherapy Benefits) Regulations 1951, and Social Security (Laboratory Diagnostic Services) Regulations 1946-see later headings:
Medical services afforded by means of advice given by telephone, telegram, or letter except under circumstances specifically approved by the Director-General of Health, and medical services not afforded by a medical practitioner in person.
Every medical practitioner who renders any of the prescribed services is entitled to receive from the Social Security Fund a reasonable fee not exceeding 7s. 6d. for every occasion on which any such service is provided. Milage fees are also provided for in certain cases. Where the practitioner is called upon to provide, in response to an urgent request, services on a Sunday or holiday, or between the hours of 8 p.m. and 8 a.m., the appropriate fee shall be a reasonable one not exceeding 12s. 6d. For specialist services an amount not exceeding 7s. 6d. for each attendance is likewise recoverable. Doctors may claim directly from the Department of Health, or may require the patient to pay the fee and himself claim a refund from the Department of Health. There has been a steady swing towards the direct-claim system by doctors, and 77 per cent now follow this practice.
Pharmaceutical Benefits - This class of benefit was introduced on 5 May 1941. Persons claiming medical benefits are entitled to receive, without cost to themselves, all such prescribed medicines, prescribed drugs, prescribed materials, and prescribed appliances as are ordered for their use by a medical practitioner in the course of providing any medical services under the Act. There is a Drug Tariff, which sets out particulars of all medicines, drugs, appliances, etc., that may be supplied and charged against the fund. The proprietor of any pharmacy within the meaning of the Pharmacy Act 1939 or any other person entitled to sell any drugs or pharmaceutical requirements may be permitted to become a contractor under the scheme. Hospital boards are entitled to receive payment for pharmaceutical requirements supplied to outpatients, but not in respect of inpatients.
Hospital Benefits - The Act provides for the payment to hospital boards and the proprietors of licensed hospitals and to other approved institutions (who have entered into contracts under the Act) of prescribed amounts in respect of hospital treatment afforded by them. The amount paid to a hospital board is in full satisfaction of its claim for the treatment of patients; in the case of licensed hospitals and other institutions the amount paid is in partial satisfaction of claims against the patients or other persons liable for the hospital charges.
These benefits came into force on 1 July 1939, and the present rates from 1 April 1961, which vary for different classes of hospitals defined by regulations, are as follows:
Where treatment has been afforded in a Class A hospital on not more than two days, the sum of £2 16s.:
Where afforded in a Class A hospital on more than two days, the sum of £1 8s. for every day on which any treatment is afforded:
For treatment in a Class B hospital, the sum of £1 2s. for each day:
Provided that the day of admission to hospital and day of discharge therefrom shall together be counted as one day.
Class A hospitals are public or private hospitals with properly equipped facilities for surgical operations.
The Act also provides that in lieu of payment being made in respect of individual hospital patients the Minister may from time to time authorise the payment of a grant in respect of hospital treatment afforded in any private hospital or other approved institution.
In addition to the public hospitals and licensed private hospitals, there is another limited class of semi-public hospitals which, in accordance with the Act, has been approved for the purposes of hospital benefits. This class includes the Karitane Baby Hospitals (six), conducted by the Royal New Zealand Society for the Protection of Women and Children, more commonly known as the Plunket Society, and in addition a home for incurables operated under a charitable trust. Special rates were determined for these classes of hospital, and such payments must be accepted in full satisfaction of the claim of the institution authorities.
Hospital benefits are also available in respect of maintenance and treatment afforded to any inpatient of Queen Mary Neurological Hospital, Hanmer Springs, or of the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Rotorua. Treatment is free except that a small charge is made in respect of single-room accommodation at Queen Mary Hospital when obtained at the request of the patient.
The Social Security (Hospital Benefits for Outpatients) Regulations 1947 provide for free treatment of outpatients at public hospitals. “Hospital treatment” in relation to an outpatient of any public hospital covers the supply of artificial aids, including contact lenses (introduced 1 June 1947), hearing aids (1 November 1947), artificial limbs (1 April 1948), surgical footwear (1 December 1951), ileostomy and colostomy appliances (27 April 1955), urinals: men's (25 July 1955), women's (29 October 1959), and all medical, surgical, or other treatment afforded by the staff of the hospital; but does not include dental treatment or services in respect of which fees are payable under specific Social Security Regulations (X-ray diagnostic services, laboratory diagnostic services) referred to under later headings. In respect of artificial limbs and surgical footwear the conditions of supply provide for part payment by the patient.
Mental Hospitals - The principal Act made provision for the treatment of patients in public mental hospitals without charge as from 1 April 1939. By section 10 of the Social Security Amendment Act 1939 a licensed (private) mental hospital may be recognised and approved by the Minister as a hospital for the purposes of the Act, and hospital benefits in respect of treatment therein are payable accordingly. All expenditure since 1 April 1945 in connection with public mental hospitals has been borne by the Consolidated Fund.
Maternity Benefits - Maternity benefits include ante-natal and post-natal advice and treatment by medical practitioners, and the services of doctors and nurses at confinements in maternity hospitals or elsewhere.
These benefits came into force on 15 May 1939, but the maternity medical practitioner service was not in full operation until 1 October of that year. The amount calculated in accordance with the scale of fees for the time being in force shall be accepted by the medical practitioner in full satisfaction of his claims except in the case of a practitioner who is recognised as an obstetric specialist in accordance with the terms of the Act. Such a practitioner, in addition to the fees payable from the Social Security Fund, may recover additional fees from the patient. A medical practitioner may contract out of the maternity benefits provisions. In such cases the patient is responsible for all the fees.
The main provisions in regard to maternity benefits apart from the medical practitioner service are as follows:
State maternity (St. Helens) hospitals: No charge is made for any services in the St. Helens hospitals.
Public maternity hospitals or maternity wards under the control of hospital boards: Payment from Social Security Fund to hospital board -
£1 15s. 6d. in respect of the day of birth of the child and for each of the succeeding 14 days:
A fee of £2 where any patient is actually attended during labour and at delivery by a medical officer employed by the board.
These amounts are to be regarded as in full settlement of all claims in respect of the maternity benefits afforded by the board.
Licensed (private) maternity hospitals: Licensees of licensed maternity hospitals who have entered into contracts under the Act are entitled to receive fees from the Social Security Fund at the same rate as stated in (2) (a) in regard to hospital boards. The licensee's contract permits a specified additional charge to the patient.
Midwives and maternity nurses: Approved midwives and maternity nurses who are in attendance in cases where confinement takes place other than in a maternity hospital are entitled to receive from the fund fees at the rate of £1 10s. for the day or days of labour (£3 in the case of midwives) and £1 7s. per day for each of the 14 days succeeding the birth of the child or 10s. 6d. per day if a visiting obstetric nurse only. These amounts are to be regarded as in full satisfaction of a nurse's claims in respect of the nursing services.
X-ray Diagnostic Services - The benefits provided for comprise the following:
The making of X-ray examinations with the aid of a fluorescent screen:
The taking of X-ray photographs:
The supply and administration of any drugs or other substances for the purposes of any such examination or photograph:
The provision of medical services incidental to any such examination or photograph, except medical services of a kind not ordinarily performed by radiologists as such:
The provision of any other incidental services for the purposes of any such examinations or photographs.
X-ray photographs or X-ray examinations made or taken for dental purposes or for the purposes of life assurance, visas, emigration permits, and examinations for the sole or primary purpose of obtaining medical certificates for production to some other person, are not included in the services that may be provided. This does not exclude examinations for medical certificates for the purposes of benefits under the Social Security Act 1938 or “sickness benefits” from a friendly society, or group examinations approved by the Director-General of Health.
The scale of fees payable from the fund in respect of services rendered by recognised radiologists is prescribed in a schedule to the Social Security (X-ray Diagnostic Services) Regulations 1941, Amendment No. 5, issued on 26 January 1960. Where the service is rendered by a medical practitioner employed or engaged by a hospital board the prescribed fees are to be accepted by the board in full settlement, but in other cases the amount of such fees is deducted from the amount charged to the patient, who is responsible for the balance, if any.
Physiotherapy Benefits - Physiotherapy treatment by private physiotherapists are covered by the Social Security (Physiotherapy Benefits) Regulations 1951. The general arrangement for these benefits consists of contracts with registered physiotherapists under which they are paid from the Social Security Fund a fee of 3s. 6d. for each treatment and undertake not to charge the patient any additional fees in excess of 8s. for treatment afforded in their rooms or 13s. for treatment afforded elsewhere.
No physiotherapy treatment is recognised for the purpose of the benefits unless it is given on the recommendation of a medical practitioner, and not more than six weeks' treatment may be given on a single recommendation except in the case of certain specified diseases, illness, etc., approved by the Director-General of Health, when the period of treatment on any one recommendation may be extended up to six months.
Home-nursing Services - Home-nursing services free of cost to the recipients were introduced by the Social Security (District Nursing Services) Regulations 1944, which stipulate that no charge may be made for district nursing services provided by any Department of State, hospital board, or subsidised association elsewhere than in a hospital or other institution, but provision is made for payments to these organisations from the Social Security Fund.
Domestic Assistance - The provision of monetary assistance to approved incorporated associations formed for the purpose of providing domestic assistance in homes, or whose objects include the provision of such assistance, is made by the Social Security (Domestic Assistance) Regulations 1944. Assistance in this connection (commenced 20 December 1944) is restricted by the regulations to the following classes:
Cases where there are one or more children under 12 years of age permanently residing in a home and the mother or other woman in charge of the home is wholly or partially incapacitated from undertaking her ordinary domestic duties by reason of pregnancy or maternity, or by reason of accident, sickness, etc.:
Cases where there are three or more children under 12 years of age permanently residing in the home, and any member of the household requires special care and attention by reason of sickness or infirmity:
Cases where all members of the household of an age or condition to help in the home are wholly or partially incapacitated from work by sickness or otherwise:
Cases where lack of domestic assistance in the home is a cause of undue hardship.
Laboratory Diagnostic Services - The benefits concerning laboratory diagnostic services came into operation on 1 April 1946, and comprise the supply of all materials or substances required for the purpose of providing laboratory diagnostic services, and the provision of medical services incidental to any laboratory diagnostic service, except medical services of a kind that are not ordinarily performed by pathologists as such, and the provision of any other incidental services for the purposes of laboratory diagnostic services.
The following services are not included:
Examination of specimens for public health.
Post-mortem examinations.
Laboratory services for dental purposes or for the purposes of life insurance.
The preparation of sera and vaccines.
The schedule of fees payable from the fund covers fees payable to hospital boards and to recognised pathologists. The prescribed fee shall be accepted in full satisfaction in respect of the services provided.
Dental Services - The Social Security (Dental Benefits) Regulations 1960 provide for free dental treatment. These benefits commenced on 1 February 1947, and at present are confined to persons who are under 16 years of age.
The regulations provide that the services may be provided -
By a registered dentist in a State dental clinic; or
By a State dental nurse in a State dental clinic; or
By a contracting dentist pursuant to a contract under these regulations; or
By a contracting authority in the dental department of a public hospital or in a dental school, pursuant to a contract under these regulations.
A schedule to the regulations prescribes the nature of the benefits that may be provided and a scale of fees payable to contracting dentists and authorities in respect thereof.
Artificial Aids - The Social Security (Hospital Benefits for Outpatients) Regulations 1947 made provision for the supply of artificial aids, such as artificial limbs, hearing aids, and contact lenses.
Contact Lenses - These may be supplied in respect of the following optical disabilities: (a) conical cornea, (b) gas keratitis, (c) certain forms of irregular astigmatism and any other conditions which cannot be corrected by ordinary spectacle lenses and which show marked improvement with contact lenses. In each case the supply of such lenses must be recommended by an approved ophthalmologist.
Hearing Aids - Individual electrical hearing aids may be supplied subject to the following conditions:
The patient possesses a hearing loss of at least 35 decibels in the better ear over the significant frequencies of speech or such other loss of a lesser degree as, in the opinion of an otologist employed or engaged by a hospital board, renders the use of an aid necessary.
The patient's hearing loss is such that in the opinion of the otologist it is capable of correction or marked improvement by the use of the type of hearing aid supplied or approved for the purpose of the benefit.
It is provided that in respect of patients who satisfy these conditions but who do not wish to avail themselves of the hearing aid issued free of charge by hospital boards there may be paid a sum not exceeding £13 towards the purchase of any aid approved for the purposes of these benefits. If a patient has received a benefit for a hearing aid within the preceding five years, the hospital board may pay half (or up to a maximum of £6 10s.) of the cost of replacement, provided that the replacement aid will assist hearing more than the existing aid and that the patient is otherwise eligible.
Artificial Limbs - The supper of artificial limbs is subject to the following conditions:
The patient has not obtained or is not entitled to obtain a limb as an ex-serviceman under the provisions of the War Pensions Regulations 1956 or under the provisions of section 22 of the Workers' Compensation Act 1956:
The supply of the limb is recommended by an orthopaedic surgeon employed or engaged by a hospital board:
The limb is of an approved type and can, in the opinion of the supplier's orthopaedic adviser, be satisfactorily fitted:
Not more than 80 per cent of the cost of the limb shall be borne by the Social Security Fund.
For the purposes of the regulations “artificial limb” includes artificial arms, artificial hands, artificial legs, and artificial feet, and includes an initial supply of not more than six pairs of limb socks for such limbs.
Benefits and Pensions in Force - A summary showing particulars of the various social security benefits and the various pensions in force in each of the last three financial years is as follows.
| Class of Benefit or Pension | Number in Force at 31 March | Annual Value at 31 March 1960 | Payments During | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | ||
*The expenditure figures given under this heading are gross widows' benefits - i.e., not reduced by the amounts recovered under maintenance orders. †Excluding recoveries. | |||||||
| Social security benefits- | |||||||
| Monetary- | £ | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Superannuation | 83,577 | 84,383 | 87,959 | 13,693,016 | 8,279,199 | 8,940,752 | 15,460,047 |
| Age | 118,187 | 118,502 | 116,077 | 26,254,847 | 24,304,077 | 26,104,992 | 27,291,008 |
| Widows* | 12,168 | 12,833 | 13,049 | 3,792,433 | 3,279,683 | 3,642,351 | 3,915,785 |
| Orphans' | 260 | 264 | 277 | 40,999 | 36,129 | 38,195 | 39,441 |
| Family | 326,619 | 333,413 | 343,193 | 29,178,268 | 20,152,619 | 25,995,315 | 31,791,986 |
| Invalids' | 7,802 | 8,032 | 8,024 | 2,026,371 | 1,799,823 | 1,942,490 | 2,118,411 |
| Miners' | 405 | 386 | 353 | 108,635 | 124,589 | 119,205 | 112,832 |
| Unemployment | 128 | 341 | 312 | - | 52,067 | 111,723 | 189,898 |
| Sickness | 3,767 | 4,190 | 4,064 | - | 1,368,360 | 1,436.913 | 1,719,343 |
| Emergency | 3,060 | 3,039 | 3,136 | - | 819,451 | 849,461 | 931,429 |
| Supplementary assistance | 4,721 | 5,117 | 5,525 | 276,848 | 218,201 | 252,758 | 273,010 |
| Advances for repairs to homes | - | - | - | - | - | 4,054 | 46,687 |
| Capitalisation of family benefit | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3,879,889 |
| Totals | 560,694 | 570,500 | 581,969 | - | 60,434,198 | 69,438,209 | 87,769,766 |
| Medical, etc.- | |||||||
| Medical | - | - | - | - | 3,927,892 | 3,969,646 | 4,243,361 |
| Hospital | - | - | - | - | 4,930,424 | 5,774,519 | 5,650,252 |
| Maternity | - | - | - | - | 1,449,359 | 1,542,493 | 1,561,861 |
| Pharmaceutical | - | - | - | - | 4,466,541 | 5,112,343 | 5,956,302 |
| Supplementary | - | - | - | - | 2,284,091 | 2,256,374 | 2,479,851 |
| Totals† | - | - | - | - | 17,058,307 | 18,655,375 | 19,891,627 |
| War pensions, etc.- | |||||||
| First World War (1914-18) | 15,694 | 15,383 | 14,890 | 3,291,285 | 3,294,368 | 3,332,239 | 3,390,183 |
| Second World War (1939-45) | 24,330 | 24,423 | 24,430 | 2,790,590 | 2,566,816 | 2,721,444 | 2,837,898 |
| K Force | 203 | 199 | 209 | 18,308 | 19,386 | 17,519 | 17,701 |
| South African War | 21 | 21 | 21 | 5,581 | 5,088 | 5,405 | 5,502 |
| War veterans' allowances | 10,881 | 12,157 | 12,961 | 5,068,719 | 3,539,098 | 4,508,772 | 4,927,681 |
| Mercantile Marine | 26 | 28 | 24 | 3,549 | 3,590 | 4,006 | 3,852 |
| Emergency Reserve Corps | 9 | 9 | 9 | 2,243 | 2,101 | 2,267 | 2,149 |
| War pensions supplementary assistance | 116 | 127 | 9,310 | 7,102 | 9,055 | 9,580 | |
| Totals | 51,164 | 52,336 | 52,671 | - | 9,437,549 | 10,600,707 | 11,194,546 |
| Other: Sundry pensions and annuities | 555 | 598 | 620 | - | 78,748 | 83,694 | 86,733 |
| Grand totals | 612,413 | 623,434 | 635,260 | - | 87,008,802 | 98,777,985 | 118,942,672 |
The total number of persons in respect of whom social security benefits (including dependent wives and children) were payable at 31 March 1960 was 1,061,980, or 4,481 per 10,000 of population. For the previous year the corresponding figures were 1,037,435 and 4,473 respectively.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, £67,256,492, or 64.8 per cent of the total expenditure (£103,734,817) on monetary and medical benefits including supplementary assistance, was paid without a means test, the remaining amount being subject to a means test.
The following table gives details of expenditure on the various classes of medical benefits during the last five financial years.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Mainly on account of hospital benefits. | |||||
| Maternity benefits | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Public hospital fees | 753,404 | 776,321 | 780,364 | 873,755 | 892,692 |
| Private hospital fees | 200,532 | 190,613 | 180,222 | 181,254 | 185,978 |
| Medical practitioners' fees | 396,494 | 398,848 | 440,563 | 411,661 | 432,170 |
| Milage fees | 14,929 | 14,732 | 16,131 | 17,223 | 19,198 |
| Obstetric nurses' fees | 4,705 | 4,153 | 3,055 | 4,102 | 3,693 |
| Private hospital loans | 6,500 | 30,100 | 29,024 | 54,498 | 28,130 |
| Totals | 1,376,564 | 1,414,767 | 1,449,359 | 1,542,493 | 1,561,861 |
| Medical benefits- | |||||
| Capitation fees | 4,412 | 4,412 | 4,411 | 4,412 | 4,411 |
| Milage fees | 197,493 | 207,292 | 219,505 | 205,362 | 214,860 |
| General medical services | 3,275,171 | 3,510,971 | 3,626,825 | 3,680,520 | 3,931,273 |
| Special arrangements | 63,470 | 69,166 | 73,019 | 76,572 | 87,094 |
| Purchase of sites and erection of residences for medical officers | 7,534 | 5,221 | 4,132 | 2,780 | 5,723 |
| Totals | 3,548,080 | 3,797,062 | 3,927,892 | 3,969,646 | 4,243,361 |
| Hospital benefits- | |||||
| Public hospitals- | |||||
| Inpatients | 3,662,651 | 3,564,457 | 3,595,714 | 4,252,604 | 4,255,681 |
| Outpatients | 341,875 | 397,716 | 414,234 | 414,602 | 414,460 |
| Private hospitals | 579,542 | 601,126 | 616,964 | 755,215 | 770,358 |
| Approved institutions | 95,453 | 107,057 | 111,789 | 117,153 | 125,275 |
| Private hospital subsidies | 3,028 | - | - | - | - |
| Private hospital loans | 68,151 | 179,368 | 180,210 | 196,423 | 64,577 |
| Grants towards operating costs of Karitane hospitals | 13,966 | 19,729 | 11,513 | 38,522 | 19,901 |
| Totals | 4,764,666 | 4,869,453 | 4,930,424 | 5,774,519 | 5,650,252 |
| Pharmaceutical benefits- | |||||
| Chemists | 3,949,164 | 4,475,606 | 4,353,752 | 4,973,558 | 5,787,684 |
| Medical practitioners | 15,951 | 17,934 | 22,463 | 27,274 | 32,126 |
| Institutions | 74,030 | 79,017 | 90,326 | 111,511 | 136,492 |
| Totals | 4,039,145 | 4,572,557 | 4,466,541 | 5,112,343 | 5,956,302 |
| Supplementary benefits- | |||||
| Radiological services | 448,374 | 474,369 | 471,792 | 471,202 | 489,459 |
| Laboratory services | 277,458 | 338,673 | 414,863 | 471,795 | 585,644 |
| Physiotherapy services | 64,863 | 66,499 | 61,569 | 61,679 | 63,005 |
| Specialist services (neurosurgery) | 3,181 | 2,872 | 2,990 | 3,790 | 5,003 |
| District nursing services | 150,117 | 162,016 | 181,892 | 195,518 | 206,587 |
| Dental services | 798,756 | 906,420 | 932,451 | 940,590 | 1,000,877 |
| Domestic assistance | 7,744 | 9,977 | 12,560 | 12,365 | 14,757 |
| Artificial-aids benefits | 63,646 | 73,229 | 82,786 | 93,782 | 107,789 |
| Other | 4,560 | 84,818 | 123,188 | 5,653 | 6,727 |
| Totals | 1,818,699 | 2,118,873 | 2,284,091 | 2,256,374 | 2,479,851 |
| Grand totals | 15,547,154 | 16,772,712 | 17,058,307 | 18,655,375 | 19,891,627 |
| Recoveries* | 5,566 | 10,053 | 7,666 | 4,774 | 4,670 |
| Net totals | 15,541,588 | 16,762,659 | 17,050,641 | 18,650,601 | 19,886,957 |
A summary of social security (monetary and health benefits, special assistance and bonuses) and war and other pension payments during each of the last 11 years, together with the amount per head of mean population, is now given.
| Year Ended 31 March | Payments During Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Per Head of Mean Population | ||
| Social Security and Pensions | |||
| £(000) | £ | s. | |
| 1950 | 50,697 | 26 | 19 |
| 1951 | 53,859 | 28 | 2 |
| 1952 | 62,423 | 31 | 17 |
| 1953 | 64,310 | 32 | 0 |
| 1954 | 68,341 | 33 | 3 |
| 1955 | 73,821 | 35 | 1 |
| 1956 | 79,912 | 37 | 3 |
| 1957 | 82,989 | 37 | 16 |
| 1958 | 87,009 | 38 | 15 |
| 1959 | 98,778 | 42 | 19 |
| 1960 | 115,016 | 49 | 1 |
The following table gives a comparison of social security benefits and war pension payments with national income in the years quoted.
| Year Ended 31 March | Net National Income at Factor Cost | Expenditure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Benefits | Other Cash Benefits | All Cash Benefits | Cash and Health Benefits | War and Other Pensions | ||
*Includes bonus and supplementary assistance. †Includes supplementary assistance. | ||||||
| Amount £(Million) | ||||||
| 1955 | 802.2 | 18.2 | 35.3* | 53.5* | 66.1* | 7.8* |
| 1956 | 843.7 | 18.9 | 37.3† | 56.2† | 71.7† | 8.2† |
| 1957 | 886.0 | 19.5 | 38.1† | 57.6† | 74.3† | 8.6† |
| 1958 | 929.9 | 20.2 | 40.2† | 60.4† | 77.5† | 9.5† |
| 1959 | 964.5 | 26.0 | 43.4† | 69.4† | 88.1† | 10.7† |
| 1960 | 1,044.9 | 31.8 | 52.0† | 83.8† | 103.7† | 11.3† |
| Percentage of Expenditure to National Income | ||||||
| 1955 | 100 | 2.3 | 4.4 | 6.7 | 8.2 | 1.0 |
| 1956 | 100 | 2.2 | 4.4 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 1.0 |
| 1957 | 100 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 6.5 | 8.4 | 1.0 |
| 1958 | 100 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 6.5 | 8.3 | 1.0 |
| 1959 | 100 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 7.2 | 9.1 | 1.1 |
| 1960 | 100 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 9.9 | 1.1 |
MISCELLANEOUS PENSIONS, ETC. - In addition to the various classes of benefits enumerated in the foregoing part of this section there were 620 pensions at 31 March 1960 classed as “sundry pensions and annuities”. This class covers ex-officers of the Legislative Department, ex-members of the defence forces, certain ex-members of the Legislature, and others, by way of compassionate allowance, etc.
LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY - All pensions payable to or on account of members of the forces, the Mercantile Marine, and the Emergency Reserve Corps are governed by the War Pensions Act 1954.
ADMINISTRATION - The Secretary for War Pensions, who under the Act must be an officer of the Social Security Department, is charged with the administration of war pensions under the general direction and control of the Minister of Defence. The Act also provides for the appointment of a War Pensions Board (or boards), which has the responsibility of granting or declining claims for pensions and allowances. This board consists of not less than three and not more than four members, one of whom must be a registered medical practitioner and one a representative of returned servicemen. Claimants have the right of appeal to a War Pensions Appeal Board, also appointed under the Act. An appeal board consists of three members, two of whom must be registered medical practitioners, one of these being a representative of returned servicemen.
GROUNDS FOR PAYMENT OF WAR PENSIONS – Pensions in respect of the death or disablement of any member of the New Zealand forces are payable to the dependants of the member (in the case of death) and to the member and his dependants (in the case of disablement) in any of the following cases:
Where death or disablement occurred while on service overseas as a member of the forces in connection with any war in which Her Majesty was then engaged, or in connection with any emergency, whether arising out of the obligations undertaken by New Zealand under the Charter of the United Nations or otherwise (i.e., includes service rendered in Korea):
Where death or disablement is attributable to his service in New Zealand or overseas, e.g., in Malaya:
In any case where the condition which resulted in the death or disablement was aggravated by his service in New Zealand or overseas.
It is laid down that the onus of proving that death or disablement was attributable to service, or that the condition which resulted in death or disablement was aggravated by such service, shall not be on the claimant and that the War Pensions Board and the War Pensions Appeal Board shall give claimants the full benefit of all presumptions in their favour. A member who was graded fit for service when he entered the forces is deemed to have been absolutely fit at that time unless any defects were noted then or within the first two months of service. This presumption does not operate if the member failed to disclose any material fact to the medical examiner. The Act also states that the boards are not to be bound by technicalities or legal forms or rules of evidence shall determine all claims in accordance with their merits.
WAR PENSIONS AND ALLOWANCES, AND WAR VETERANS' ALLOWANCES: SUMMARY OF RATES – The list below summarises the rates of war and economic pensions and allowances at January 1961.
| Class of Pensions, Allowance, etc. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependants of Deceased Members of the Forces, Mercantile | |||
| Marine, or Emergency Reserve Corps – | Weekly Rate | ||
| *Ranges from £3 7s. 6d. for all ranks and ratings up to major (Army) and equivalent in other services, members of Mercantile Marine, and members of Emergency Reserve Corps; £3 16s. lieutenant-colonel and equivalent; £3 18s. colonel and equivalent; and £4 brigadier or upwards or equivalent in other services. | |||
| Widow – | £ | s. | d. |
| Basic rate* | 3 | 7 | 6 |
| Mother's allowance (where one child) | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Mother's allowance (where two children) | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Mother's allowance (where three children) | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Mother's allowance (where four children) | 4 | 10 | 0 |
| Mother's allowance (where five children) | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Mother's allowance (where six or more children) | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| Economic pension | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Allowable income | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Child – | |||
| Where both parents dead or if not under control of mother | 2 | 15 | 0 |
| Other children | 15 | 0 | |
| Widowed mother – | |||
| Basic rate | 3 | 7 | 6 |
| Economic (wholly dependent or mother of two or more sons being deceased members of the forces) | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Economic (partly dependent) | 3 | 12 | 6 |
| Other dependant | 3 | 7 | 6 |
| Guardian of children of deceased member | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Totally Disabled Members of the Forces, Mercantile Marine, or Emergency Reserve Corps – | Weekly Rate | ||
| Member – | £ | s. | d. |
| Basic disablement pension | 4 | 10 | 0 |
| Special increment for blindness, multiple or serious disabilities | 2 | 10 | 0 |
| Economic pension (if unmarried £4 15s.) | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Allowable income | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Attendant's allowance | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Wife | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Child | 15 | 0 | |
| Other dependant | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| War Veteran's Allowance – | |||
| Unmarried veteran (£247 a year) | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| Married male veteran (£442 a year) | 8 | 10 | 0 |
| Married female veteran (£221 a year) | 4 | 5 | 0 |
| Yearly Rate | |||
| £ | s. | d. | |
| Age supplement (maximum) payable to veteran or to his wife, or both, as each attains the age of 65 years | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Supplementary Assistance | According to circumstances | ||
| Clothing Allowance – | Yearly Rate | ||
| Loss of – | £ | s. | d. |
| Two limbs or parts | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| Leg or part | 27 | 10 | 0 |
| Arm or part | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Use of mechanical appliance apart from artificial limb | 20 | 0 | 0 |
The payment of 15s. a week to each child may be made either by way of family benefit or, alternatively, by way of war pension.
The earnings of women from domestic or nursing services in private homes or in hospitals or charitable institutions up to £78 a year are not taken into account.
In December 1959 an additional payment of £6 to single war pensioners and £12 to married couples was made. The additional payment covered the period from 12 October 1959 – when a general wage order came into effect – to 31 March 1960. The War Pensions Amendment Act 1960 provided for increases of 5s. a week in the rates of economic and wives' pensions, of mothers' allowances payable to widows with dependent children, and of war veterans' allowances from 1 April 1960.
Pensions payable for specific disabilities are assessed as a percentage of the full pension payable for total disablement. The following schedule sets out the relevant disabilities and percentages.
| Nature of Disability | Per Cent of Full Pension Payable |
|---|---|
| Total blindness | 100 |
| Loss of: two limbs; limb and eye; both hands; all fingers and thumbs; both feet; hand and foot | 100 |
| Incurable insanity | 100 |
| Very severe facial disfigurement | 100 |
| Amputation of – | |
| Right arm through shoulder joint; leg through hip joint; leg through upper third of thigh (without useful stump) | 100 |
| Left arm through shoulder joint | 95 |
| Leg through upper third of thigh (with useful stump) | 90 |
| Permanent loss of speech | 90 |
| Amputation of: arm at or above elbow; leg through knee joint or middle or lower third of thigh | 85 |
| Total deafness | 85 |
| Severe facial disfigurement | 80 |
| Amputation of – | |
| Arm below elbow; leg below knee; right hand | 75 |
| Left hand | 70 |
| Loss of – | |
| One eye; four fingers | 50 |
| Three fingers; thumb | 40 |
| Two fingers | 25 |
| Index finger of either hand | 20 |
If a member, while in receipt of a permanent pension of an amount of not less than 70 per cent of the maximum pension that would be payable in respect of total disablement, dies from any cause not attributable to service as a member of the forces, a pension may be granted to his widow or dependent children as if death was attributable to service.
Other grants and concessions which may be made include the following:
A free pass on the New Zealand Railways rail and road services to members in receipt of full permanent pensions:
A permit to travel first class at second-class rates on the New Zealand Railways to amputees and others suffering locomotive disabilities to a degree of over 50 per cent for which they receive permanent pensions:
Free medical and surgical treatment in respect of pensionable disabilities. Surgical appliances such as artificial limbs, etc., are also supplied free and kept in good order and repair:
Payment of an annual travelling allowance of up to £26 to totally disabled pensioners who are unfit to travel alone:
Payment of up to £100 towards the cost of structural alterations with a £25 provision for furniture to provide special accommodation for a pensioner suffering from pulmonary tuberculosis:
A maximum accommodation allowance of £2 a day is payable to war pensioners reporting for medical examination or treatment, while compensation of up to £2 per day is paid in respect of loss of earnings:
Interest-free loans to certain seriously disabled pensioners to purchase motorcars; payment of loadings on life-assurance policies where the loadings are due to war disabilities; gallantry awards to disablement pensioners; and funeral grants in respect of deceased ex-servicemen.
Pensions to Dependants (other than Wives or Children) – In addition to pensions for wives and children, a pension may be granted to any member of a deceased or disabled serviceman's family. “A member of the family” includes a parent, grandparent, step-parent, grandchild, stepchild, brother, sister, half-brother, half-sister, and mother-in-law. “Child,” in relation to any member of the forces, means a child under the age of 16 years, and includes an adopted child and an ex-nuptial child (subject to certain conditions). The parents of a male member of the forces are included in the definition of dependant in every case, without proof of preservice dependency. Also, except in the case of the wife, widow, children under 16, and parents, the eligibility of dependants is based on the expectation of dependency on the member.
Economic Pensions – An “economic pension” is defined as a supplementary pension granted on economic grounds and is in addition to any pension payable as of right in respect of death or disablement. In considering a claim for an economic pension a War Pensions Board is required to take into consideration the ability of the claimant to obtain and retain suitable employment, the personal income and ownership of any property, the cost of living, and other relevant matters.
The personal earnings of a disablement pensioner are disregarded in the assessment of an economic pension to an amount equivalent to that by which the disablement pension is less than the amount of pension for total disablement.
Servicemen pensioned for minor disablement do not receive economic pensions.
WAR VETERANS' ALLOWANCES – The object of war veterans' allowances was to make provision for members of the forces who, apart from any wounds or other injuries received during war service, were ageing prematurely or otherwise becoming unfit for permanent employment by reason of mental or physical incapacity. The term “veteran” includes –
Any male member of the New Zealand forces who has served as such in actual engagement with the enemy or, by reason of his period of overseas service and the arduous or dangerous nature of it, is considered a proper person for the grant of an allowance:
Any female member who has served overseas as a member of the New Zealand forces:
Any other person who, being a bona fide resident of New Zealand at the commencement of any war or emergency in which members of the New Zealand forces have served as such, has served in that war or emergency as a member of any of Her Majesty's forces, other than the New Zealand forces.
A condition precedent to the granting of a war veteran's allowance is a minimum of five years' continuous residence in New Zealand immediately preceding the date of the claim. Continuous residence is not deemed to be interrupted by occasional absences not exceeding six months in the aggregate, increased by one month for each year in excess of five that the veteran has resided in New Zealand; any absences as a member of the Commonwealth forces are also disregarded.
Whether or not a claimant for an allowance is unfit for permanent employment by reason of mental or physical infirmity is a question of fact to be determined by the War Pensions Board. Claimants have the right of appeal to a War Pensions Appeal Board.
No account is taken of the amount of war disablement pensions in the determination of the basic war veterans' allowances. In computing any war veteran's allowance no account is taken of the personal earnings of any woman from domestic or nursing services in a private home or hospital or charitable institution up to £78 per year.
The War Pensions Amendment Act 1960 extended the meaning of the term “veteran” to include an ex-serviceman of any Commonwealth country (other than New Zealand) provided that he has resided in New Zealand for at least 20 years and fulfils the service requirements for the grant of an allowance. Absences not exceeding two years in the aggregate during the 20 years preceding application are permitted, with a further allowance of six months for every year of residence in excess of 20. Under this amendment provision is also made for veterans of the South African War who served with the New Zealand forces and do not fulfil the service requirements but have attained the age of 75 years.
Where a veteran in receipt of an allowance dies leaving a widow in respect of whom an allowance is being paid a War Pensions Board may, in its discretion, grant the widow a gratuity equivalent to £422 10s. a year for two years or of such lesser amount as it thinks fit.
EMERGENCY RESERVE CORPS PENSIONS – These pensions are payable under the 1954 Act where death or disablement was suffered by a member of the Emergency Reserve Corps in the course of service (including training), or was directly attributable to such service.
MERCANTILE MARINE PENSIONS – The 1954 Act provides for the payment of pensions and allowances in respect of death or disablement of members of the mercantile marine as a result of the Second World War.
SUPPLEMENTARY ASSISTANCE – A fund was established in November 1951 to provide for similar cases to those set out under social security supplementary assistance (see page 186). During the year ended 31 March 1960 there were 260 grants totalling £9,580, compared with 242 grants totalling £9,055 in the previous year. Expenditure on supplementary assistance is now met from the Consolidated Fund.
WAR BURSARIES – Bursaries for educational purposes are available to children of war veterans, seriously and permanently disabled ex-servicemen, and of deceased ex-servicemen in respect of whose deaths war pensions are paid. Bursaries are paid at the following rates:
| Class of Bursary | Per Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | |
| (a) Secondary school children | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| (b) Full-time university students | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| (c) Part-time university students | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| (d) Part-time technical school children | 1 | 10 | 0 |
The rates payable under (a) and (b) are doubled in the case of an orphan child or a child whose father or mother is in receipt of an economic pension or a war veteran's allowance.
During 1959–60, 1,678 bursaries were granted, expenditure on this behalf being £60,899 for the year. The 1958–59 figures were 1,447 bursaries and £54,802.
WAR PENSIONS APPEAL BOARD – A claimant may appeal to a War Pensions Appeal Board from a decision of a War Pensions Board within six months of the date on which the decision of the latter was communicated to him. Such an appeal can only be made in so far as it consists of –
The rejection of any claim for a pension in respect of the death or disablement of a member of the forces on the ground that the death or disablement was not attributable to his service as a member of the forces or that the condition that resulted in his death or disablement was not aggravated by such service.
The assessment of a pension granted to any member of the forces in so far as the assessment is based on medical grounds.
The rejection of any claim for a war veteran's allowance on the ground that the applicant is not unfit for permanent employment.
The appeal board may confirm the decision of the War Pensions Board or may grant a pension, or, within the limits prescribed by the Act, may increase or reduce the amount of any pension. The number of appeals dealt with was 266 in 1959–60. Of these, 143 or 54 per cent were upheld, 108 disallowed, and 15 struck out or withdrawn.
STATISTICAL REVIEW OF WAR PENSIONS ALLOWANCES, ETC. – During the year ended 31 March 1960 the Department dealt with 3,526 applications for war pensions. Of these, 621 applications were lodged by ex-servicemen in respect of their own disabilities, the balance being made up of claims by dependants, applications for economic pensions, and war veterans' allowances. The total for the previous year was 4,450; of these, 618 were in respect of the applicants' own disability. In addition there were 129 claims received during the year in respect of disablement arising from service with peacetime armed forces, of which 78 were granted and 51 declined.
Summary of Disabilities for Which Pensions Granted, 1939–60 – The following is a summary of the disabilities attributed to war service from 1939 onwards and for which ex-service personnel had been granted pensions up to 31 March 1960.
| Class of Disability or Disease | Type of Service | Total | Percentage of Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overseas (1939–45) | K Force | J Force | New Zealand | |||
| Infections and infestations | 2,032 | 92 | 7 | 138 | 2,269 | 3.9 |
| Nervous system | 9,469 | 36 | 13 | 1,708 | 11,226 | 19.1 |
| Eye, ear, and nose | 6,772 | 77 | 20 | 1,406 | 8,275 | 14.0 |
| Circulatory and blood system | 2,251 | 8 | 2 | 1,041 | 3,302 | 5.6 |
| Metabolism and endocrine system | 420 | 2 | 1 | 177 | 600 | 1.0 |
| Respiratory system | 3,566 | 27 | 54 | 1,203 | 4,850 | 8.2 |
| Diseases of bones, joints, muscles tendons, and ligaments | 5,041 | 24 | 8 | 1,827 | 6,900 | 11.7 |
| Digestive system | 4,389 | 36 | 12 | 1,203 | 5,640 | 9.6 |
| Generative system | 338 | 1 | 1 | 121 | 461 | 0.8 |
| Gunshot wounds and accidental injuries to bones, joints, and soft tissues | 7,857 | 107 | 27 | 1,737 | 9,728 | 16.5 |
| Skin | 2,500 | 21 | 12 | 540 | 3,073 | 5.2 |
| Areolar tissue | 45 | 2 | - | 25 | 72 | 0.1 |
| Tumours and neoplastic growths | 190 | 1 | - | 53 | 244 | 0.4 |
| Malformations | 301 | 1 | - | 132 | 434 | 0.7 |
| Amputations | 501 | 3 | - | 22 | 526 | 0.9 |
| Urinary tract | 610 | 7 | 3 | 155 | 775 | 1.3 |
| Debility | 443 | - | - | 109 | 552 | 1.0 |
| Totals | 46,725 | 445 | 160 | 11,597 | 58,927 | 100.0 |
The following table shows for all classes of war pensions the number in force at the end of March in each year and the expenditure during the years given.
| Year Ended 31 March | First World War (1914–18) | Second World War (1939–45) | K Force | War Veterans | South African War | Mercantile Marine | Emergency Reserve Corps | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number in Force | ||||||||
| 1950 | 18,976 | 26,537 | - | 3,997 | 39 | 24 | 11 | 49,584 |
| 1951 | 18,573 | 25,901 | - | 4,776 | 37 | 26 | 11 | 49,324 |
| 1952 | 18,135 | 25,356 | 13 | 5,468 | 34 | 24 | 10 | 49,040 |
| 1953 | 17,786 | 25,141 | 85 | 5,964 | 32 | 24 | 9 | 49,041 |
| 1954 | 17,419 | 24,766 | 104 | 6,810 | 29 | 24 | 9 | 49,161 |
| 1955 | 17,074 | 24,703 | 164 | 7,616 | 28 | 24 | 9 | 49,618 |
| 1956 | 16,683 | 24,687 | 183 | 8,479 | 26 | 24 | 9 | 50,091 |
| 1957 | 16,317 | 24,519 | 200 | 9,520 | 24 | 27 | 9 | 50,616 |
| 1958 | 15,694 | 24,330 | 203 | 10,881 | 21 | 26 | 9 | 51,164 |
| 1959 | 15,383 | 24,423 | 199 | 12,157 | 21 | 28 | 9 | 52,220 |
| 1960 | 14,890 | 24,430 | 209 | 12,961 | 21 | 24 | 9 | 52,544 |
| Expenditure (£) | ||||||||
| 1950 | 2,271,371 | 2,010,852 | - | 743,999 | 3,826 | 2,403 | 1,588 | 5,034,039 |
| 1951 | 2,311,606 | 1,970,236 | - | 964,882 | 3,726 | 2,359 | 1,628 | 5,254,437 |
| 1952 | 2,711,710 | 2,071,829 | 671 | 1,282,094 | 4,429 | 2,872 | 1,973 | 6,075,578 |
| 1953 | 2,747,298 | 2,072,429 | 4,478 | 1,471,405 | 4,315 | 2,957 | 1,764 | 6,304,646 |
| 1954 | 2,776,891 | 2,107,575 | 9,377 | 1,822,018 | 4,528 | 2,384 | 1,618 | 6,724,391 |
| 1955 | 3,110,948 | 2,341,940 | 14,505 | 2,212,223 | 5,051 | 2,867 | 1,934 | 7,689,468 |
| 1956 | 3,043,395 | 2,357,355 | 14,833 | 2,707,308 | 5,363 | 2,668 | 1,978 | 8,132,900 |
| 1957 | 3,126,546 | 2,410,859 | 17,990 | 2,999,565 | 5,159 | 3,375 | 1,943 | 8,565,437 |
| 1958 | 3,294,368 | 2,566,816 | 19,386 | 3,539,098 | 5,088 | 3,590 | 2,101 | 9,430,447 |
| 1959 | 3,332,239 | 2,721,444 | 17,519 | 4,508,772 | 5,405 | 4,006 | 2,267 | 10,591,652 |
| 1960 | 3,390,183 | 2,837,898 | 17,701 | 4,927,681 | 5,502 | 3,852 | 2,149 | 11,184,966 |
The foregoing figures include the following: (a) travelling allowances of £26 a year paid to 1,157 pensioners at 31 March 1960; (b) clothing allowances, of which 1,390 were being paid at 31 March and expenditure on which for 1959–60 was £32,154; and (c) gallantry awards of an annual value of £1,714. The following are not included: (a) costs of certain medical treatment not available under social security amounting to £61,477 in 1959–60 and £59,917 in 1958–59, (b) railway and bus concessions to pensioners for total and permanent disablement and for locomotive disabilities for which a permanent pension of over 50 per cent disablement has been granted, costing £18,530 in 1959–60 and £18,459 in the previous year; (c) loadings on life-assurance policies where the loadings are due to war disabilities, expenditure under this heading being £1,602 in 1959–60; (d) funeral grants, which cost £22,950 in 1959–60; (e) 22 interest-free loans in 1959–60 totalling £7,100 towards the purchase of motor vehicles by certain seriously disabled pensioners; and (f) supplementary assistance of £9,580 in 1959–60 and £9,055 in 1958–59.
Administrative costs for 1959–60 in respect of war pensions and allowances amounted to £14,492, as against £13,383 in 1958–59.
The numbers of First and Second World War and K Force pensions in force as at 31 March of each of the last five years are given below.
| At 31 March | Disablement Pensions | Dependants of Disabled Ex-members | On Account of Death | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent | Temporary | Widows | Parents and Other Dependants | |||
| First World War, 1914–18 | ||||||
| 1956 | 11,405 | 315 | 2,197 | 2,654 | 112 | 16,683 |
| 1957 | 11,123 | 252 | 2,115 | 2,729 | 98 | 16,317 |
| 1958 | 10,599 | 235 | 2,018 | 2,763 | 79 | 15,694 |
| 1959 | 10,340 | 208 | 1,943 | 2,814 | 78 | 15,383 |
| 1960 | 9,890 | 234 | 1,810 | 2,886 | 70 | 14,890 |
| Second World War, 1939–45 | ||||||
| 1956 | 13,852 | 7,769 | 788 | 1,420 | 858 | 24,687 |
| 1957 | 14,497 | 7,004 | 785 | 1,453 | 780 | 24,519 |
| 1958 | 15,096 | 6,336 | 783 | 1,424 | 691 | 24,330 |
| 1959 | 15,804 | 5,692 | 798 | 1,494 | 635 | 24,423 |
| 1960 | 16,105 | 5,353 | 841 | 1,564 | 567 | 24,430 |
| K Force | ||||||
| 1956 | 16 | 164 | 3 | - | - | 183 |
| 1957 | 29 | 164 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 200 |
| 1958 | 41 | 156 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 203 |
| 1959 | 57 | 137 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 199 |
| 1960 | 66 | 136 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 209 |
The number of children for whom payments were made during 1959–60 but who were not included in the preceding table totalled 1,425, being 168 in respect of First World War pensions, 1,250 for Second World War pensions, and seven for K Force pensions.
The next table shows the number of disability pensions in force at 31 March 1960, classified according to percentage of disablement.
| Percentage of Disablement | First World War | Second World War | K Force | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent | Temporary | Permanent | Temporary | Permanent | Temporary | ||
| 100 | 1,855 | 51 | 1,052 | 492 | 7 | 5 | 3,462 |
| 90–99 | 107 | 5 | 80 | 35 | - | - | 227 |
| 80–89 | 307 | 20 | 278 | 135 | 1 | - | 741 |
| 70–79 | 697 | 20 | 442 | 186 | 2 | 4 | 1,351 |
| 60–69 | 545 | 20 | 407 | 241 | 2 | 3 | 1,218 |
| 50–59 | 1,212 | 11 | 923 | 425 | 3 | 9 | 2,583 |
| 40–49 | 1,560 | 20 | 996 | 442 | 5 | 10 | 3,033 |
| Under 40 | 3,607 | 87 | 11,927 | 3,397 | 46 | 105 | 19,169 |
| Totals | 9,890 | 234 | 16,105 | 5,353 | 66 | 136 | 31,784 |
Details of economic pensions payable at 31 March 1960 are now given, together with the totals as at 31 March 1959.
| Class of Pension | First World War 1914–18 | Second World War 1939–45 | K Force | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Annual Value | Number | Annual Value | Number | Annual Value | |
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Ex-members with permanent pensions | 2,507 | 532,547 | 795 | 167,029 | 4 | 830 |
| Ex-members with temporary pensions | 31 | 6,738 | 324 | 65,785 | 4 | 884 |
| Widows | 2,281 | 521,937 | 1,074 | 246,424 | 1 | 19 |
| Widowed mothers | 10 | 1,813 | 141 | 26,946 | - | - |
| Totals at 31 March 1960 | 4,829 | 1,063,035 | 2,334 | 506,184 | 9 | 1,733 |
| Totals at 31 March 1959 | 4,923 | 1,085,187 | 2,205 | 477,845 | 8 | 2,164 |
General – Superannuation for all Government employees is provided for under the authority of the Superannuation Act 1956, and provisions for members of the Judiciary and members of Parliament are also included in this measure. Members of the armed forces, Police, Post Office, Public Service, Railways, and teachers, are now contributing to the one fund, with slightly differing terms and conditions provided to meet the requirements of the various services.
Local Government employees and the permanent employees of all statutory bodies are provided for under the National Provident Fund Act 1950. For the operations of the National Provident Fund, see Section 6D.
There are also a considerable number of private superannuation funds in existence, some self-contained. Information respecting these is given at the end of this subsection.
The Government Superannuation Fund – The Government Superannuation Fund, came into being on 1 April 1948, replacing and absorbing the moneys belonging to the former Public Service Superannuation Fund, the Teachers' Superannuation Fund, and the Government Railways Superannuation Fund. Its revenues comprise contributions, subsidies from the Consolidated and other funds, interest accruing from investments, fines, all moneys that would have been paid into the earlier three funds, and all other moneys that may be payable into the Fund.
The Fund is administered by a board consisting of the Minister of Finance as chairman, the Secretary to the Treasury, the Chairman of the Public Service Commission, the General Manager of Railways, the Director of Education, the Director-General of the Post Office, the Commissioner of Police, and six members appointed on the nomination of the various service organisations.
The benefits of superannuation are now available for all Government servants, i.e., persons in the permanent service of the State. Employees of the Government Service, which includes the Education Service, Police, the Cook Islands Public Service, the Samoan Public Service, and the State Advances Corporation, in addition to the Departments of State under the control of the Public Service Commission, the Railways Department, and the Post Office, may all become contributors to the Fund. Separate provision is made for persons in the service of the Crown in respect of the Government of New Zealand in other than an honorary capacity – permanent members of the regular armed forces, Police, Magistrates and Maori Land Court Judges and members of the Judicature (Judges of the Supreme Court and Court of Arbitration), and members of Parliament.
Contributions range from 5 per cent of annual salary, if under 30 years of age at commencement of contributory service, to 10 per cent where the age exceeds 50 years, the increase being at the rate of 1 per cent for each five-year increase in age group. An alternative modified scheme, within the framework of the present standard scheme, was introduced in. 1955, under which contributors may elect to contribute only 60 per cent of the standard contribution rates and receive only 60 per cent of the standard benefits. Standard retiring allowances are computed at the rate of a one hundred and twentieth part of the annual salary for each year of contributory service, increased by a sum equal thereto (i.e., on a £1 for £1 basis) up to £500 per annum, reducing thereafter by £1 for each £2 by which the amount exceeds £500. In no case shall the added amount be computed on a lesser salary than £600 per annum. The annual salary for the purpose of this computation is deemed to be the average of that received during the five years immediately preceding retirement, although in special cases, so long as the first computed portion of the retiring allowance is a lesser amount than £150, the average salary received during the last three years may be used if it results in a more favourable computation.
Upon retirement a contributor entitled to a retiring allowance may elect (1) to take an increased allowance to age 65, reducing thereafter, (2) to surrender portion of his retiring allowance in favour of his widow or other approved dependant after his death, (3) to elect to surrender not more than one-quarter of his retiring allowance and to receive in lieu thereof a lump sum payment equivalent to nine times the amount of allowance surrendered, (4) to accept a refund of his contributions.
Payment of retiring allowances and annuities is now made in advance in instalments every 28 days, no recovery being made should the beneficiary die during the benefit period. When a married contributor dies, whether before or after becoming entitled to a retiring allowance, his widow may elect to receive a refund of the amount of his contributions less any sums received by him during his lifetime, or to receive an annuity at one-half of the rate of his retiring allowance at the date of his retirement (or, if he died before then, to which he would have been entitled if he had retired on the date of his death on the ground of being medically unfit for further duty) disregarding any election to take a variable allowance or to surrender part of the allowance to an approved dependant.
The amount of the widow's annuity is not to be less than £130 (£78 in modified scheme). In addition, £26 per annum (£15 12S. in modified scheme) is payable in respect of each child under 16 years of age left by a deceased contributor. The widow's benefit is payable only during widow-hood but is reinstated if subsequent to remarriage a person again becomes a widow.
The above are general provisions only and for a complete survey need to be supplemented by reference to other provisions in respect of age, length of service, sex, sickness, withdrawals, refunds, subsidiary benefits, etc., contained in the Act. Adjustments have been made from time to time in the allowances payable to retired contributors and also to widows of ex-contributors to assist in meeting the increased cost of living.
Contributory membership and retiring allowances as outlined apply generally to permanent members of the regular armed forces.
The Police Act 1958 provides for compulsory membership for the Police, with retirement at age 60. The rate of contribution varies from 5 per cent to 12 per cent. For computing the retiring allowance, each year in the Police is deemed to be one year and one-seventh where the contributory service commenced after age 25. Where contributory service commenced between 20 and 25 years a lesser proportion is added.
Members of the Judicature are entitled to a retiring allowance based on one twenty-fourth of their salary for each year of service, with a maximum of two-thirds, and they may elect to contribute 5 per cent of their salary to provide annuities for their widows, calculated as 15 per cent of the final salary. Magistrates and Judges of the Maori Land Court are also entitled to retiring allowances, subject to age and length of service qualifications, one-fortieth of the annual salary at the date of retirement being allowed for each year of service, but in no case is the retiring allowance to exceed two-thirds of that salary.
Members of Parliament contribute 10 per cent of salary, but if at the date of commencement of the retiring allowance contributions are less than £425 the deficiency must be paid into the Parliamentary Superannuation Account within such time and in such manner as the Minister of Finance may allow. Subject to service of nine years (or eight years if a member has served throughout the duration of not less than three Houses of Representatives) and attainment of the age of 50 years, retiring allowances are at the rate of £350 a year for the first eight-year period of service, and for each additional year of service an increase of £50, with a maximum rate of allowance of not more than £700 a year. A widow receives two-thirds of her husband's entitlement.
At 31 March 1960 there were 72,884 contributors, paying £3,500,495 per annum into the Fund. The pensioners at the same date numbered 21,024 and were entitled to £6,821,408 per annum, made up as follows.
| — | Number | Annual Allowances | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | ||
| £ | ||||
| Retired for age or length of service | 9,441 | 3,159 | 12,600 | 5,610,090 |
| Retired for ill health | 1,395 | 264 | 1,659 | 350,302 |
| Widows | - | 5,526 | 5,526 | 829,030 |
| Children | 644 | 595 | 1,239 | 31,986 |
| Totals | 11,480 | 9,544 | 21,024 | 6,821,408 |
Accumulated funds at 31 March 1960 amounted to £32,262,673. Total assets, which amounted to £32,362,269, included: Investments, £30,733,500; interest, due and accrued, £297,762; contributions in course of transmission, etc., £177,787, and cash in hand and at bank, £1,153,220.
The average effective interest earnings (per cent) of the Fund for the year ended 31 March 1960 was £3 16S. 7d.
The total revenue of the Fund for the year ended 31 March 1960 was £10,796,919, including members' contributions £3,514,402, interest on investments and on contributions £1,160,171, other items £20,365, and subsidy £6,101,981. The total amount expended during the year was £7,989,597, including retiring and other allowances £7,332,503, refunds of contributions £623,301, transfers to National Provident Fund £33,711, and investment charges £82.
The following statistics present a review of the operations of the Fund during the latest five years
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Contributors | Annual Contributions | Interest Receivable From Investments | Contributions From Government | Annual Value of Allowances | Accumulated Fund |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1956 | 63,116 | 2,504,605 | 657,579 | 3,599,066 | 5,096,199 | 21,774,651 |
| 1957 | 64,743 | 2,665,663 | 770,662 | 3,862,065 | 5,533,581 | 23,707,430 |
| 1958 | 68,380 | 3,116,414 | 902,000 | 4,617,809 | 5,908,895 | 26,500,249 |
| 1959 | 70,878 | 3,403,749 | 1,032,503 | 4,850,139 | 6,353,386 | 29,455,351 |
| 1960 | 72,884 | 3,500,495 | 1,160,171 | 4,971,000 | 6,821,408 | 32,262,673 |
Private Superannuation Funds – Most large and many small employers have established their own staff superannuation funds. Certain taxation concessions are available to an employer and his employees in respect of their contributions to a superannuation fund provided the fund is approved by the Commissioner of Inland Revenue, and it is probable that there are very few funds being administered which have not been approved.
NUMBER OF APPROVED FUNDS
| As at 31 March | Number to Date |
|---|---|
| 1953 | 2,587 |
| 1954 | 2,912 |
| 1955 | 3,147 |
| 1956 | 3,388 |
| 1957 | 3,625 |
| 1958 | 3,844 |
| 1959 | 3,967 |
| 1960 | 4,201 |
A few funds, particularly those of banks, oil companies, insurance companies, and large companies engaged in international trade, provide pensions on retirement, but approximately 95 per cent of all approved funds provide lump-sum payments on retirement.
Of every 95 lump-sum funds approximately two are invested in shares, debentures, and trustee securities, and the remaining 93 are invested in life-insurance policies taken out on the lives of the various employees.
The life-insurance companies regard superannuation funds as an important part of their business, and they have been responsible for a great increase in the number of approved funds in recent years.
GENERAL – The National Provident Fund came into operation on 1 March 1911 and is administered by a board comprising the Minister of Finance as chairman, the Secretary to the Treasury, the Director-General of Health, the Valuer-General, the Superintendent of the Fund, and three other members appointed by and holding tenure of office during the pleasure of the Governor-General. The present legislative authority is contained in the National Provident Fund Act 1950, and its amending Acts.
Provision has been made for local authorities to lodge with the National Provident Fund moneys which are not required immediately and for the board to hold sinking, depreciation, and other special funds on behalf of local authorities. The 1959 amendment Act extended these provisions enabling any local authority to invest funds held in the credit of any account, and also provided the same investment facilities for any body or person approved by the Minister. These surplus moneys would become available for lending to other local authorities. A special Investment Committee was set up to attend to the investment of moneys in the Fund. The National Provident Fund Account is kept at the Reserve Bank with appropriate provision for overdraft accommodation.
In addition to guaranteeing the benefits payable under the Act, the State provides a subsidy to the extent of one-fourth of the contributions paid into the Fund, and also meets all the administrative expenses.
The Fund now provides three distinct services:
Public Fund – Pensions and subsidiary benefits for members of the general public, with extensions for members of approved friendly societies and employees of firms, trade unions, etc.
Superannuation Fund – Superannuation for employees of all local authorities and other statutory bodies.
An Investment Pool – Local authorities may temporarily invest otherwise idle loan and other moneys in the pool.
Public Fund – Membership to the public portion of the Fund is open to any resident of New Zealand over the age of 16 years who wishes to purchase a retirement pension and obtain cover for the various other benefits offered.
Contributors have the option of joining one or both of the schemes offered. The Public Fund Scheme, as detailed in the National Provident Fund Act 1950 and subsequent amendments, provides a medium by which a predetermined amount of pension may be purchased by the payment of fixed regular contributions. After five years' membership subsidiary benefits in the form of an incapacity allowance, widows' and children's allowances attach to membership.
The Single Premium Scheme, introduced by authority of the 1958 amendment, enables residents to purchase a retirement pension by making contributions of varying amounts according to their ability to pay. At the end of each 12-monthly period the total contributions made during the previous 12 months are added up and from this total is calculated the value of the pension purchased during that year which together with purchases in other years becomes available at any age between 60 and 65 years. A variation of this scheme is now available for self-employed persons wishing to take advantage of the special income tax exemption on contributions made to such schemes.
Both the Public Fund Scheme and the Single Premium Scheme provide the contributor with optional benefits which become available on retirement. These include a variable pension from 60 to 65 years, the right to accept a joint and survivorship pension with the spouse, and an opportunity of surrendering up to one-quarter of the pension in return for a capital payment.
Both schemes are available without medical examination. The benefits to those contributing for five years or over include a liberal widow's allowance.
The Superannuation Fund – The board is empowered to entertain applications by local authorities for superannuation on behalf of their employees. Hospital boards are contributors on behalf of their nursing and clerical employees and, with the consent of the Minister of Finance, State Departments contribute for nurses and other specialist officers not adequately provided for in the normal Government superannuation scheme.
The conditions and benefits in the early schemes were fixed by negotiation between the board and the local authority. To achieve uniformity in benefits and make improved conditions of superannuation available to permanent employees of all local authorities, the board was empowered in 1946 to vary the conditions and benefits in the original schemes, and to issue a notice to all local authorities containing conditions and benefits under which any permanent employee might elect to become a contributing employee. Funds earlier established under the Local Authorities Superannuation Act 1908 have been merged with the National Provident Fund, and there is now operating one uniform superannuation scheme to which all local authorities in New Zealand contribute; employees may move more freely from employment in one local authority to another without sacrifice of accrued superannuation benefits.
The principle of voluntary membership introduced into State schemes extends to the National Provident Fund schemes and provision is made for the recognition, by agreement with the employing authority, of General or Local Government service within the British Commonwealth or within New Zealand. A further provision enacted authorises the board to protect accrued superannuation rights of New Zealanders moving from General or Local Government service to service with a United Nations organisation.
The Fund is the approved superannuation vehicle for all statutory corporations and also provides facilities whereby registered educational institutions may provide superannuation for teachers, thus removing another artificial barrier to the free interchange of teachers in the educational services.
The benefits and contributions are substantially the same as those operating in the Government Superannuation Fund, and there is provision whereby employees may transfer from local authority to State employment, and vice versa, without loss of accrued rights.
On retirement there are several options as to joint and survivorship or variable pensions, which enable the income payable after retirement to be arranged to meet individual needs. A superannuitant may elect to surrender his right to a proportion (not exceeding one-fourth) of the pension and to receive instead payment of a sum equal to nine times the amount by which his annual pension is reduced consequent on the surrender.
Local Authorities Investment Pool – The Investment Committee meets periodically, and up to the end of March 1960 over £15 m. had been lodged in the pool. A substantial portion of the amount is loan moneys and is only available for periods of three to six months pending its being utilised by the local authorities for the purpose for which it was raised, but it is anticipated that there will emerge a hard core of £4 m. to £5 m. available for long-term investment. The success of this venture depends largely upon the support accorded by the local authorities, for the Fund is not undertaking the raising of loans but merely endeavouring to make available to the smaller local authorities otherwise idle moneys.
During the last five years the Fund has invested practically all its available moneys in loans to local authorities, but its normal investable funds are only approximately £2 m., so that its activities must be considered more in the nature of assistance to local authorities in raising moneys than any attempts to satisfy their loan requirements.
Statistical Summary – The numbers of contributors as at 31 March 1960 were as follows.
| Fund | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual single premium | 384 | 38 | 422 |
| Public Fund | 10,104 | 719 | 10,823 |
| Superannuation | 6,974 | 3,463 | 10,437 |
| Totals | 17,462 | 4,220 | 21,682 |
Summarised figures set out for the years ended 31 December 1957 and 1958 and the 15 months ended 31 March 1960 form a useful basis for comparative analysis.
| Year Ended 31 December | Fifteen Months Ended 31 March 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | ||
| New contributors | 2,437 | 1,999 | 3,133 |
| Total contributors | 22,455 | 21,724 | 21,682 |
| Pensioners and other beneficiaries | 4,557 | 4,820 | 5,136 |
| Income— | £ | £ | £ |
| Contributions | 1,204,242 | 1,381,154 | 1,655,940 |
| Interest (including fines) | 733,926 | 812,967 | 1,182,568 |
| Total income (including State subsidy) | 2,316,320 | 2,638,948 | 3,233,277 |
| Outgo— | |||
| Pensions | 500,713 | 535,434 | 724,507 |
| Other benefits | 406,846 | 341,069 | 461,845 |
| Total outgo | 909,013 | 877,238 | 1,186,870 |
| Funds at end of year | 19,644,247 | 21,405,967 | 23,452,364 |
| Effective interest earnings (per cent) | 3 19S. 0d. | 4 0S. 10d. | 4 6S. 7d. |
The amount of the subsidy paid by the State on contributions paid to the Fund during the 15 months ended 31 March 1960 was £391,320.
The next table presents an alternative comparison, the periods covered on this occasion being the years ended 31 December until the end of 1958 and the 15 months ended 31 March 1960.
| Year | Number of Contributors | Annual Rate of Contributions Payable | Total Amount of Fund | Pensions and Allowances Paid During Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incapacity | Retiring | Widows' and Children's | ||||
* Estimated. † Actual. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1955 | 22,849 | 890,658* | 17,026,502 | 16,623 | 374,229 | 61,724 |
| 1956 | 22,571 | 946,140* | 18,236,940 | 21,818 | 453,651 | 70,500 |
| 1957 | 22,455 | 984,292* | 19,644,247 | 22,885 | 500,713 | 76,272 |
| 1958 | 21,724 | 1,381,154† | 21,405,957 | 28,028 | 535,434 | 79,612 |
| 1 Jan 1959–31 Mar 1960 | 21,682 | 1,655,940† | 23,452,364 | 37,987 | 724,507 | 103,490 |
Of the accumulated fund of £23,452,364, and the local authority loan and special reserve fund of £15,441,151 as at 31 March 1960, £38,412,277 was invested, the principal classes of investments being Government securities, £16,310,102; local authority securities, £21,156,241; mortgages, etc., £747,934; and debentures, shares, etc., £198,000.
The following table shows the details of investments of the Fund for the 15 months ended 31 March 1960.
| Class of Security | Investments, 1 January 1959 | Movements During Period | Investments, 31 March 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Investments | Realisations and Repayments | |||
| Government and State Advances | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Corporation stock | 9,242,305 | 8,774,594 | 1,706,797 | 16,310,102 |
| Local authority debentures | 18,461,888 | 4,666,084 | 1,971,731 | 21,156,241 |
| Mortgages | 1,063,670 | 32,026 | 361,373 | 734,323 |
| Company shares and debentures | 198,000 | - | - | 198,000 |
| Reversions | 14,568 | 1,925 | 2,882 | 13,611 |
| Totals | 28,980,431 | 13,474,629 | 4,042,783 | 38,412,277 |
THE legislation dealing with friendly societies is contained in the Friendly Societies Act 1909 and its amendments. Provision is made for the registration of all societies and branches with the Registrar of Friendly Societies, and also for the general superintendence by the Government of the administration of the funds of the societies.
LODGES AND MEMBERS – The table following gives the number of registrations (i.e., of friendly societies proper, or lodges, together with benevolent societies, working-men's clubs, etc., registered under the Act) and of lodge members as at 31 December of the years shown.
| Name of Order | Registrations | Lodge Members | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Membership figures relate to “actuarial” societies only. | ||||||
| Manchester Unity Independent Order of Oddfellows | 244 | 243 | 238 | 28,473 | 28,406 | 28,057 |
| Independent Order of Oddfellows | 188 | 190 | 187 | 7,762 | 7,573 | 7,338 |
| National Independent Order of Oddfellows | 1 | 1 | 1 | 64 | 55 | 52 |
| Ancient Order of Foresters | 134 | 130 | 130 | 10,879 | 10,684 | 10,434 |
| United Ancient Order of Druids | 140 | 138 | 138 | 14,384 | 14,086 | 13,743 |
| Independent Order of Rechabites | 48 | 46 | 46 | 2,834 | 2,745 | 2,655 |
| Order of Sons of Temperance | 7 | 7 | 6 | 390 | 386 | 377 |
| Sons and Daughters of Temperance | 1 | 1 | 1 | 78 | 75 | 71 |
| Hibernian-Australasian Catholic Benefit Society | 76 | 74 | 73 | 3,781 | 3,749 | 3,707 |
| Protestant Alliance Friendly Society of Australasia | 11 | 11 | 10 | 474 | 460 | 433 |
| Grand United Order of Oddfellows | 10 | 10 | 10 | 218 | 207 | 189 |
| Isolated friendly societies | 67 | 67 | 69 | 543* | 535* | 527* |
| Working-men's clubs | 24 | 24 | 24 | - | - | - |
| International Order of Good Templars | 11 | 11 | 11 | - | - | - |
| Specially authorised societies | 18 | 19 | 32 | - | - | - |
| Totals | 980 | 972 | 976 | 69,880 | 68,961 | 67,583 |
Annual returns of receipts, expenditure, etc., of lodges are required by law. For the year 1959 the Registrar of Friendly Societies received returns from 798 “actuarial” lodges, with an aggregate membership of 67,583 at the end of the year, as compared with 809 lodges and 68,961 members for 1958. During the year, 1,960 members were admitted by initiation, etc., and 662 by clearance; 1,361 died, 661 left by clearance, and 1,978 by arrears, etc.
The aggregate membership of lodges increased year by year, reaching a peak in 1930, when the total was 107,167. The economic depression probably accounted for the decrease in each of the following three years, the number at the end of 1933 being 100,237. A series of increases then commenced, the 1930 level being passed in 1936, and by 31 December 1938 a total of 113,709 had been reached. Each of the succeeding years, however, has witnessed a fall in membership, although the decrease in 1959 was comparatively slight. The number at the end of that year (67,583) was, however, 46,126, or 41 per cent less than in 1938. The various benefits under the social security scheme, particularly medical and hospital benefits (see Section 6A), have no doubt had a considerable effect on the membership of friendly societies.
The statistics given subsequently relate to the lodges (798 in 1959) for which returns were received and tabulated.
MORTALITY AND SICKNESS – In the following statement of the mortality experience for the last five years no account has been taken of age incidence.
| Year | Deaths of Members | Per 1,000 Members at Risk | Deaths of Members' Wives | Per 1,000 Members at Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1,315 | 18-35 | 334 | 4-66 |
| 1956 | 1,264 | 17-66 | 301 | 4-20 |
| 1957 | 1,356 | 19-12 | 333 | 4-69 |
| 1958 | 1,227 | 17-60 | 326 | 4-68 |
| 1959 | 1,361 | 19-74 | 323 | 4-68 |
The number of members sick during 1959 was 11,621, equal to 17-5 per 100 members at risk. The sickness experienced during 1959 was 284,966 weeks, equal to 24 weeks 3 days per sick member and 4 weeks 2 days for each member at risk.
FUNDS OF FRIENDLY SOCIETIES – The total funds of the societies and branches as at 31 December 1959 amounted to £9,524,723, made up as follows.
| Funds | Amount | Assets | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | ||
| Sick and funeral funds | 6,843,225 | Investments at interest | 8,493,889 |
| Surplus appropriation funds, etc. | 1,213,780 | Value of land and buildings | 719,434 |
| Management funds, goods, etc. | 563,476 | Cash not bearing interest | 260,021 |
| Distress, benevolent funds, etc. | 904,242 | Value of goods | 29,612 |
| Other assets | 13,284 | ||
| Owing by management funds | 8,483 | ||
| Total | 9,524,723 | Total | 9,524,723 |
The net income from investments credited to the sick and funeral funds for 1959 amounted to £344,226, the average rate being £5 5S. 0d. per cent, as against £5 1S. 4d. in 1958.
There has been over many years a continuous increase in the amount of accumulated funds standing to the credit of friendly societies, the increase in the last 10 years amounting to £2,818,010, or 42 per cent. The average capital per member has also appreciably increased, the gain in the last 10 years amounting to £52 14S. 3d. (60 per cent). The substantial fall in membership over the last 10 years has resulted in outstanding increases being shown for the average capital per member.
| Year | Total Funds | Average Capital per Member | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1949 | 6,706,713 | 88 | 4 | 5 |
| 1950 | 6,858,062 | 91 | 9 | 0 |
| 1951 | 7,126,449 | 95 | 16 | 8 |
| 1952 | 7,331,341 | 99 | 18 | 3 |
| 1953 | 7,523,883 | 103 | 8 | 3 |
| 1954 | 7,780,419 | 108 | 2 | 0 |
| 1955 | 8,078,280 | 113 | 6 | 11 |
| 1956 | 8,512,156 | 120 | 10 | 1 |
| 1957 | 8,840,887 | 126 | 10 | 4 |
| 1958 | 9,140,125 | 132 | 10 | 10 |
| 1959 | 9,524,723 | 140 | 18 | 8 |
The contributions and entrance fees paid to sick and funeral funds in 1959 amounted to £190,608. Divided by the mean number of members, the average for 1959 was £2 15s. 10d., as against £2 12s. 9d.
The interest and rent received by the lodges and central bodies amounted to £344,226 in 1959, equal to £5 0S. 10d. per member, as against £4 12S. 8d. for 1958.
The amount of sickness benefit paid was £147,609 in 1959, equal to £12 14S. 0d. per member sick and £2 3S. 3d. per member, as against £12 15S. 10d. and £2 0S. 11d. respectively for 1958. Viewing the amount paid in relation to the weeks of sickness, the average benefit per week is found to be 10S. 4d. in 1959, as against 10S. 3d. for 1958.
The funeral benefit paid amounted to £108,163 in 1959, equal to £1 11S. 8d. per member, as compared with £1 8S. 11d. for 1958.
The total worth of the sick and funeral funds at the beginning of 1959 was £6,613,449, and at the end of the year £6,843,225.
HISTORY AND ADMINISTRATION – The education system of New Zealand can be understood only when it is seen against its historical background. The first settlements in the new colony were relatively isolated units, each of which had to make its own provision for the education of its children. In some places the provision of schools was left to the churches, in some to private enterprise, and in others to public associations. When the provinces were established in 1852 the Provincial Councils took over education as one of their functions, but this brought no degree of uniformity to New Zealand schools, for each province tended to foster the type of school organisation already established in its area. The provinces varied considerably in the efficiency of their school systems but, in spite of some success in the face of difficulties in certain areas, at the end of the provincial period in 1876 not more than half the children between the ages of five and 15 were attending school at all.
The present national system of free, secular, and compulsory* education derives from the Education Act 1877. This Act followed upon the abolition of the provinces, but the provinces, though dead as political units, left their mark upon the school system. A fierce struggle between the protagonists of central and of local control ended in a victory for the provincialists, and the public schools were placed under the control of district education boards, which were for the most part the same bodies as the old provincial education boards. The Colonial Government, however, had to provide all the finance in the form of capitation grants, and a small Department of Education was set up in Wellington, very largely for the purpose of distributing the grants. For every school district constituted under the Act there was a school committee, elected by householders, which, subject to the control of the board, had “the management of educational matters within the school district”. The school committees elected the members of the education board.
As far as mere structure is concerned, this still remains the pattern of the system of school administration in New Zealand, but there have been, in the intervening years, great changes in the relative functions of the three authorities. The general tendency has been for final power and responsibility to shift from the committees to the boards and from the boards to the Department. The committees, in fact, through lack of professional executive officers and independent sources of revenue, from the very beginning were unable to take over the full powers that the 1877 Act obviously intended them to have, and for the first 20 years of national education the education boards were the predominant authorities in the system.
From just before the beginning of this century the Department of Education began to play an increasingly important part in educational administration, partly as a result of improved means of communication. Under the Act of 1877 the boards had been given wide powers: to administer funds from endowments and departmental grants, to appoint and remove teachers, to pay teachers' salaries according to their own scales, to establish scholarships and provide for secondary education in district high schools, and to control the inspectorate. Legislation, beginning with the establishment of a national scale of primary school salaries and staffing in 1901 and culminating in the Education Act 1914 (still the basic measure under which the education system is administered), concentrated these powers more and more in the hands of the Department, which began to take a more detailed interest in expenditure by the boards. The original freedom of the boards in the expenditure of building grants was taken away, and the present system, requiring special departmental authorisation for each new building, gradually became established. From 1901 onwards the Department paid over to the boards the exact sum required for teachers' salaries, thus leaving a much reduced capitation grant to be used by the local authorities at their own discretion. In 1914 the Department took over the control of the primary-school inspectorate.
*Every child (with certain statutory exemptions) between the ages of seven and 15 years has to be enrolled as a pupil of either a public or a registered school.
The centralisation of the inspectorate made possible a further change affecting the powers of the boards. In 1920 a New Zealand grading scheme was instituted under which all primary-school teachers were annually awarded grading marks by the inspectors. A teacher's total marks gave him a place on a numerically graded list. Since all ordinary appointments were to be decided on the basis of this list, the system of appointment was in effect a national one, and the boards had very limited powers of discretion although they made the appointments. In 1940 biennial grading was substituted for annual grading, thus freeing the inspectors of schools in alternate years to give more time to schools. The provision of an annual grading number for teachers was, however, retained. A new appointments scheme involving the classification of teachers in four broad divisions and triennial assessment was agreed upon in 1954. An Education Amendment Act giving legal effect to it was passed in 1955. Transition to the new scheme began in 1957, and was fully effective for all teachers by 1959. Under the new scheme appointments are recommended to education boards by three-man appointments committees (one in each education district) on which the Department, the board, and the teachers are represented. Thus teachers for the first time were given some voice in the making of appointments. The scheme is supervised by the Central Advisory Committee, representative of Department, boards, and teachers. This Committee reports annually to the Director and every five years to the Minister of Education. It acts as an arbitrator when a board and an appointments committee fail to agree on a recommendation for an appointment.
It does not follow, however, since the boards and the school committees have lost many of their original powers, that they have ceased to play an important part in the system. A school committee's primary function is the care of school buildings, grounds, and equipment, but, in addition to this, many interest themselves very keenly in the general activities of the school and provide in each district a focusing point for local opinion on educational matters. The education boards are still the initiating bodies on matters of buildings, sites, conveyance of pupils, consolidation, and provision of school facilities generally: and, although the final word often lies with the Minister of Education or the Department, the boards have no small influence in the fixing of policy within their districts. The schools are legally their schools and the teachers their teachers, although in general the boards' choices of applicants are limited under the system for making appointments. The teachers' classroom activities are under the control of the inspectors, but their general responsibility is to the boards, and their professional life tends to centre on the boards rather than on the Department. In spite of the apparent clumsiness of the administrative structure and of periods of strong feeling in the past, the system at present functions remarkably smoothly, and has achieved a balance, workable if not ideal, between the claims of local initiative and national efficiency. A certain degree of decentralisation was achieved in 1948 when a branch of the Department of Education was established at Auckland, and this was extended further by the establishment of a branch in Christchurch in 1960.
Post-primary education, with the exception of that given in the district high schools, was not brought by the Act of 1877 within the province of the education boards. Several secondary schools had been established in various ways before 1877, and these continued under their own boards of governors, which were in no way related to the education boards. The Education Reserves Act 1877 set aside one-fourth of the educational reserves for secondary education, vesting the remainder in the education boards for primary-school purposes. Thus there was introduced into the colony that cleavage between elementary and secondary education that was characteristic of the English system. In the years immediately following the Act of 1877 a series of Acts set up a number of local high school boards, each in control of its own land endowments. No effective provision was made for the inspection of these schools by any outside authority or for the coordination of their work with any other part of the school system.
Further secondary schools, and, from 1902 onwards, technical high schools, were from time to time established. Before 1901 fees had been charged even in district high schools. In that year free places were instituted in district high schools, and in 1902 secondary schools were offered special capitation grants if they would provide free places for deserving scholars. Under the Education Act 1908 free places at the technical schools were granted on a more liberal basis, and by 1914 all State post-primary schools were obliged to give free places for two years at least to any pupil who had passed the Proficiency Examination. In 1936 the Proficiency Examination was abolished, and free post-primary education to the end of the year in which he reached 19 years of age became available to every child who completed a primary-school course, or who attained 14 years of age by 31 March of the first year in which he attended a post-primary school.
A direct effect of this movement towards free post-primary education was that the Department began to exercise an increasing degree of control over the schools. The Education Amendment Act 1920 authorised the establishment of New Zealand staffing and salary scales for post-primary schools, and instituted the system – already operative in the case of the education boards – of paying over to the schools the exact sum required for salaries plus a capitation grant for incidental expenses, less the amount received from local secondary-school endowments. This, in effect, nationalised these endowments, and spread more evenly the benefits resulting from the foresight of the early settlers. As from 1 April 1949 all revenue received by the schools was handed over to the Crown and the total cost of salaries and incidental expenses met from the Consolidated Fund. The endowment reserves themselves were vested in the Crown as from the beginning of 1950.
COMMISSION ON EDUCATION IN NEW ZEALAND – On 15 February 1960 the Minister of Education announced that Sir George Currie, Vice-Chancellor of the University of New Zealand, had accepted the Government's invitation to serve as chairman on a broadly representative, 11-member commission on New Zealand education.
The terms of reference of the commission, which may extend its deliberations over two years, are as follows:
To consider the publicly controlled system of primary, post-primary, and technical education in relation to' the present and future needs of the Dominion, and, within the broad scope of this reference, to inquire into:
The aims and purposes of the curricula, and the methods and internal school organisation used to achieve them.
The organisation and scope of the school system, and the relationships between the post-primary schools and the university and other forms of further education.
The status of the teaching profession and its conditions of service, the recruitment and training of teachers (including in-service training), the staffing of schools and their physical facilities.
The distribution of public expenditure on education among the various objectives of educational policy.
The place of private contributions towards expenditure on education, whether by way of fees, subsidised contributions, gifts, or endowments.
The functions, powers, responsibilities, and inter-relationships of the Department of Education, education boards, school committees, post-primary school councils, and technical school boards, and the need, if any, for changes in the geographical areas of responsibility, the functions, constitutions, or powers of such bodies.
The desirability and practicability of greater use being made of school buildings and school facilities generally for community purposes.
The question of religious teaching in State schools.
Child welfare and delinquency so far as they have a bearing on the education system.
To consider also the question of financial assistance to private schools.
To report on these matters, and to make recommendations.
THE SCHOOL SYSTEM – Perhaps the best method of sketching the outline of the school system as it now stands is to trace the career of a child as he passes through the system. He may at the age of three enter a free kindergarten under the control of the Free Kindergarten Association. At the age of five he may enter, and at seven he must enter, either a primary school under one of the 10 education boards, or some other registered primary school, or, if living in an isolated area or physically handicapped, the primary department of the Education Department's Correspondence School. All State primary schools are co-educational. The child passes through the infant classes and Standards 1, 2, 3, and 4. This normally takes six years. The remaining two years of the primary course will be taken either in Forms I and II at the same primary school or, if there is one conveniently situated, at an intermediate school. The intermediate school is a comparatively recent development within the primary-school system, the first of these schools being established in 1922. It is a centrally situated school which pupils enter from the surrounding primary schools (called in these circumstances “contributing schools”) after they have completed the primary-school course as far as Standard 4. Because the intermediate school comprises a fairly large number of pupils (usually between 300 and 600) who are mainly between the ages of 11 and 13 years it is possible to classify them into groups of approximately equal ability, provide a good range of optional courses, and utilise specialist teachers and advanced equipment to the full. As at this point in his school career the pupil's social and intellectual interests have developed, he is ready to take full advantage of the varied and enriched courses provided. Where the number of pupils in an area is not sufficient to justify the establishment of a separate intermediate school an intermediate department may be attached to the local post-primary school, and thus utilise the special facilities available at the senior school. In some intermediate schools a third-year course (Form III) is provided to give a rounded-off education to pupils who do not intend to proceed to a post-primary school.
On completing a course in Form II or on reaching the age of 14 by 31 March of the first year in which he attends a post-primary school, the child becomes entitled to free post-primary education until the age of 19 is reached. The Education Amendment Act 1920 made provision for the raising of the school-leaving age from 14 to 15 years, but this change was not brought into operation until February 1944, and all children are now required to attend school until the new leaving age is reached. This means, in effect, that some period of secondary education is now compulsory for nearly all children. The only provision for exemption is inability to profit from the further period of education.
When a country child leaves the primary stage he may have no alternative but to enter Form III of a district high school (which is really a secondary top to a primary school and is under the same control), or enrol in the Correspondence School. In more thickly populated areas there will be either a secondary school or a technical high school available. In some towns a secondary school and a technical high school have been amalgamated to form a combined school. To those not understanding the peculiar character of the New Zealand technical high school this may seem a strange union, but the differences between schools of the two types are, except in the larger centres, relatively slight. The difference was further obscured when after 1944 secondary schools catered increasingly not only for “academic” pupils, but for those pupils as well who, after fulfilling the core requirements, specialise in the more practical subjects (technical, agricultural, domestic, commercial). A number of secondary departments of district high schools that had grown very large were made separate post-primary schools. The result of these developments is that post-primary schools are now all more or less multilateral.
The School Certificate Examination conducted by the Department of Education is now regarded as the accepted test of a completed post-primary education for the great bulk of the pupils who do not desire to proceed to university. The School Certificate Examination is taken at the end of the third or fourth year of the post-primary course. The subjects of the examination are English and such other subjects as are prescribed from time to time by the Minister of Education by notice in the Education Gazette. The School Certificate is awarded to pupils who pass the examination and, in other respects, have complied with the regulations governing the award of the certificate.
Provision is contained in the Education (Post-primary Instruction) Regulations 1954 for endorsement of School Certificates on satisfactory completion of an advanced course of instruction for one year. The regulations also provide for the award of Higher School Certificates. In general this certificate is awarded after a five years' course to pupils who have been awarded a School Certificate and satisfactorily completed an advanced course of two years; and to pupils who have been accredited for or have passed the University Entrance Examination and satisfactorily complete an advanced course of one year. A Higher School Certificate may also be awarded after a four years' course to pupils who have obtained a credit pass or better in the Entrance Scholarship Examination of the University of New Zealand.
The technical schools, combined schools, and a few of the secondary schools run evening classes, particularly in practical and vocational subjects, which an adolescent may attend after he leaves full-time day school. Apprentices in some trades are required to attend evening classes as a part of their trade training. In 1948 approval was given to the establishment of day classes for apprentices and the first of these was commenced in 1949. They now include classes in boilermaking and panel-beating, carpentry and joinery, cabinetmaking, electrical wiring, mechanical engineering, motor engineering, plumbing, aircraft engineering, radio servicing, refrigeration engineering, ship, yacht,and boat building, painting and decorating, signwriting, printing and photo-engraving, sheet-metal work, and moulding and casting. In some of the larger technical schools part-time students may take professional courses in engineering, architecture, and accountancy.
Apprentice classes are well established, as is the system of examinations provided for these students by the Trades Certification Board. In recent years there has developed a tendency towards regional consolidation and the substitution of “block” course for half-day-a-week attendance even though apprentices live within easy reach of a school. An important part in apprentice education is played by the Technical Correspondence School for about two in every five apprentices are on its roll. Its function is threefold: it fills the geographical gaps left by the other schools; it provides, on a national basis, technical education for some of the smaller trades and occupations; and it produces technical textbooks.
The development of courses for engineering technicians continues, and inquiries into the needs of other occupational groups for similar courses are in progress. In particular, details of courses for builders and chemical technicians are now being worked out.
The Central Technical College, Petone, was split into a Technical High School and a Senior Technical School or polytechnic – the first of its kind in New Zealand – from the beginning of 1960. The senior school, which specialises in block courses for apprentices and technicians, also includes the School of Pharmacy. A similar division of the Seddon Memorial Technical College in Auckland took place towards the end of 1960.
Prior to 1944 all pupils desiring to undertake a university course were required to sit and pass the University Entrance Examination conducted by the University of New Zealand. In 1944 a system of partial accrediting came into operation. Under this system pupils attending certain approved schools may be accredited for matriculation purposes provided they have completed a four years' post-primary-school course. The University Entrance Examination is still conducted by the University of New Zealand, and pupils not accredited for entrance to university may qualify in this manner. The standard of the present entrance examination is somewhat higher than that maintained prior to the introduction of the accrediting system.
Pupils who have been accredited for, or who have passed the University Entrance Examination may without further post-primary education receive half-tuition fees for part of their university course and then full fees for the rest of their course. Where pupils have obtained a Higher School Certificate, full tuition fees are payable plus an additional sum of £40 per annum where they are full-time university students. These pupils may also receive a boarding allowance of £50 per annum where they are obliged to live away from home to attend a full-time course. Although these bursaries are normally for four years, they may for certain courses be extended for a further year.
The University of New Zealand, whose controlling body is the University Senate, is constituted of the University of Auckland, the Victoria University of Wellington, the University of Canterbury, and the University of Otago. Massey and Canterbury Agricultural Colleges, associated with the University of New Zealand, are open to students specialising in agricultural studies. In 1960 there was established a new branch of the Victoria University of Wellington at Palmerston North, and a branch of the University of Auckland at Hamilton.
The seven teachers' training colleges, although they work in conjunction with the four universities, are organically related to them only through their boards of studies. The seventh teachers' training college was opened at Hamilton at the beginning of 1960. The education boards are the controlling authorities of the training colleges.
The State system also caters for the needs of certain special groups of children. Maori children may attend the public schools, but there are also public Maori schools provided for their primary education. There are also a few private church schools remaining from the pre-Maori War system established with the help of Government subsidies. For his post-primary education the Maori child may go free to any available public post-primary school or Maori district high school. If he lives in a rural area he may gain a Maori scholarship awarded by the Department of Education which will enable him to attend one of a number of full post-primary schools where boarding facilities are available. Of these, 11 are private church schools operated on a single-sex basis and providing full post-primary courses. Some of them are partly financed out of public endowments originally provided for the purpose of Maori education.
As mentioned earlier, children living in isolated areas or prevented in other ways from attending school may be enrolled in the Correspondence School for both primary and post-primary work.
For children with various types of handicap there are provided numerous special educational services. The mentally backward are grouped in 70 special classes attached to ordinary schools throughout the country and in two residential special schools. For children who are extremely backward mentally there are 14 special centres (occupation centres) in the main cities, and voluntary groups (occupational groups) which are given financial assistance by the Department have been formed in several smaller towns. Two residential schools cater for the needs of the deaf and those partially-deaf children who cannot profit from teaching in an ordinary primary school. In addition, two classes for severely deaf and one for partially deaf children are attached to ordinary schools. A national diagnostic and guidance service organised in association with the two schools for the deaf gives assistance to deaf babies and infants and their parents and advises teachers in ordinary schools who have children with a hearing loss in their classes. Children with speech defects attend regularly one of 60 speech clinics. In five of the largest cities there are seven remedial clinics to assist children suffering from serious educational retardation (mainly in reading). Two reading consultants have been appointed to assist teachers in ordinary schools in coping with backward readers. Classes have been established for partially sighted children in the four main cities, and blind children are catered for in a school for the blind attached to the Foundation for the Blind, Auckland. Six schools have been organised as separate units for cerebral-palsied children. Where a sufficient number of children in hospital justifies it, teachers are made available to conduct hospital classes which are attached to a local school. There are 42 classes of this type. There are four classes for physically handicapped or delicate children. Children who are admitted to one or other of the seven health camps for a period of six to 10 weeks attend the school associated with each health camp. Finally, there are special schools and homes to take care of children with the most serious and deep-seated problems of maladjustment or delinquency. These last-named institutions, also the schools for the deaf, and the two special schools for the mentally backward, are being administered for the Department by the Child Welfare Division, which, in educational matters, is under the control of the Minister of Education. All other special classes and centres are controlled by the education boards. The boards also employ 27 visiting teachers whose task it is to help children whose progress at school is causing concern, by acting as a link between the school, the home, and the community. The psychological service of the Department of Education is established in eight centres. It comprises 15 psychologists, all of whom are available for the psychological examining and educational testing of children with special problems, and six area organisers of special classes. The Department conducts special classes in five prisons for prisoners whose basic education is of a low standard.
In addition to the various State schools described, a parent may send his child to a private school, either primary or secondary, conducted by either religious bodies or private individuals. No Government free place is tenable at these schools,* but a secondary school bursary (referred to later) may be tenable at a private school, while assistance for transport by rail and road and a boarding allowance under certain conditions may also be given to pupils attending private schools, whether primary or post-primary. All private schools must be registered, and are subject to regular inspection by the Department's inspectors. The majority of the private schools are conducted by the Roman Catholic Church. Amongst the private schools are two endowed secondary schools modelled after the English public school.
To complete the above sketch it should be added that coeducation exists in all stages of the system. At the primary stage, all public, intermediate, and Maori schools and some private schools teach boys and girls together. At the teachers' training colleges and the universities, students of both sexes attend together. At the post-primary level all district high schools and technical colleges have both boys and girls on their rolls, whilst just over one-third of the secondary and combined schools and nearly all of the private secondary schools are single-sex schools. A comparison of the total enrolment of all post-primary schools (State as well as private) in 1959 with that over 20 years earlier shows that the ratio of pupils in single-sex to coeducational schools has changed from 51 to 49 in 1935 to 45 to 55 in 1959.
*Except for Maori “Government pupils” in the denominational secondary schools.
SCHOLARS AND STUDENTS - The numbers of scholars and students receiving instruction in educational institutions are shown in the following summary. The table refers to roll numbers at 1 July (except in the case of kindergartens, which are as at end of year).
| Class of Institution | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Pupils on roll at end of year. †There were also 1,844 students taking part-time courses. ‡ Includes 4,053 part-time students enrolled with Technical Correspondence School and 2,530 part-time students enrolled with Correspondence School. § There were also 1,345 “part-time students” who were full-time day pupils included under primary and post-primary education. ||Includes 515 students taking short courses. Students holding post-primary teacher studentships (1,161 in 1959) and bursaries (24 in 1959) are included under universities. | |||||
| Pre-school Education* | |||||
| Kindergartens (morning and afternoon sessions) | 11,596 | 12,810 | 13,368 | 13,928 | 14,807 |
| Primary Education | |||||
| Public (State) schools | 306,429 | 317,855 | 331,277 | 342,360 | 351,906 |
| Intermediate schools and departments | |||||
| Maori schools | 13,598 | 13,606 | 13,084 | 13,135 | 13,153 |
| Maori private church schools | 869 | 866 | 840 | 840 | 766 |
| Registered private primary schools | 43,105 | 45,294 | 46,982 | 47,470 | 50,670 |
| Lower departments of secondary schools | 112 | 101 | 131 | 108 | 113 |
| Correspondence classes (primary) | 1,210 | 1,169 | 1,176 | 1,087 | 1,150 |
| Chatham Islands schools | 116 | 111 | 116 | 112 | 117 |
| Totals, primary | 365,439 | 379,002 | 393,606 | 405,112 | 417,875 |
| Post-primary Education | |||||
| Secondary schools | 36,543 | 39,073 | 44,268 | 48,783 | 55,164 |
| Combined schools | 5,244 | 5,359 | 5,428 | 5,371 | 5,435 |
| Secondary departments of district high schools | 9,978 | 9,593 | 9,781 | 9,532 | 9,012 |
| Technical high schools | 20,144 | 21,198 | 19,231 | 18,984 | 19,869 |
| Maori secondary private (boarding) schools | 927 | 968 | 983 | 918 | 875 |
| Registered private and endowed schools | 14,043 | 14,855 | 15,282 | 16,066 | 16,788 |
| Correspondence classes (secondary) | 530 | 549 | 464 | 469 | 507† |
| Totals, post-primary | 87,409 | 91,595 | 95,437 | 100,123 | 107,650 |
| Technical Classes (excluding Technical High Schools and Technical Day Schools) | |||||
| Conducted by education, secondary school or high school boards | 13,210 | 14,750 | 14,898 | 17,008 | 24,819‡ |
| Conducted by technical school boards | 25,206 | 22,764 | 23,719 | 26,685 | 26,751 |
| Totals, technical | 38,416 | 37,514 | 38,617 | 43,693 | 51,570§ |
| Higher Education | |||||
| Universities | 9,487 | 9,669 | 10,197 | 11,155 | 12,455 |
| Canterbury and Massey Agricultural Colleges | 1,360 | 1,202 | 1,427 | 1,510 | 15350|| |
| Students exempt from lectures | 893 | 882 | 912 | 966 | 1,098 |
| Teachers' colleges | 2,847 | 2,963 | 3,218 | 3,602 | 3,753|| |
| Totals, higher | 14,587 | 14,716 | 15,754 | 17,233 | 18,656 |
| Totals, scholars and students | 517,447 | 535,637 | 556,782 | 580,089 | 610,558 |
The preceding table reveals the marked enrolment increases of between 20,000 and 30,000 in each of the last five years. The expansion of the education system began in 1945 when the enrolments of primary and post-primary full-time pupils rose by some 9,000, and by another 8,500 in the following year. In the 10-year period 1949 to 1959 the total increase in enrolments was 188,000 full-time pupils, and the number of part-time students at day and night classes increased by 32,000 in those 10 years. This development led in turn to proportionate increases in the recruitment of teachers, and in the provision of classrooms, of teaching equipment, and other facilities such as school transport.
The expansion was in the first instance due to the increase in the yearly number of births. This number was some 28,000 in 1936, but had risen to nearly 62,000 in 1959. The number of pupils and students at all educational institutions increased from 192 per 1,000 population in 1936 to 268 per 1,000 population in 1959. A second factor, accentuating the rate of expansion in the post-primary school sector, was the gradual increase in the number of students who stayed at school beyond the age of 15, and left school from a higher form. The effect of this second movement has been that the number of candidates for the School Certificate Examination increased by 146 per cent in the 10 years 1949 to 1959.
The school enrolment increases were felt first in the primer classes, then in the lower standards. They gradually spread to the upper primary classes, and are expected to reach peak figures at the post-primary school level in the next three years. With the increasing numbers of school leavers qualified for university entrance, a similar expansion at the level of higher education is to be expected, with a more rapid rate of enrolment increases expected between 1963 and 1968. Projections of school and university enrolment as far as 1972 were published in a statement by the Minister of Education (E. 2, 1959), which sets out in some detail the assumptions on which the projections were based.
The development since 1930 of the school enrolments is illustrated by the diagram below, which gives for the years 1960 to 1972 estimates based on the most recently revised enrolment projects.
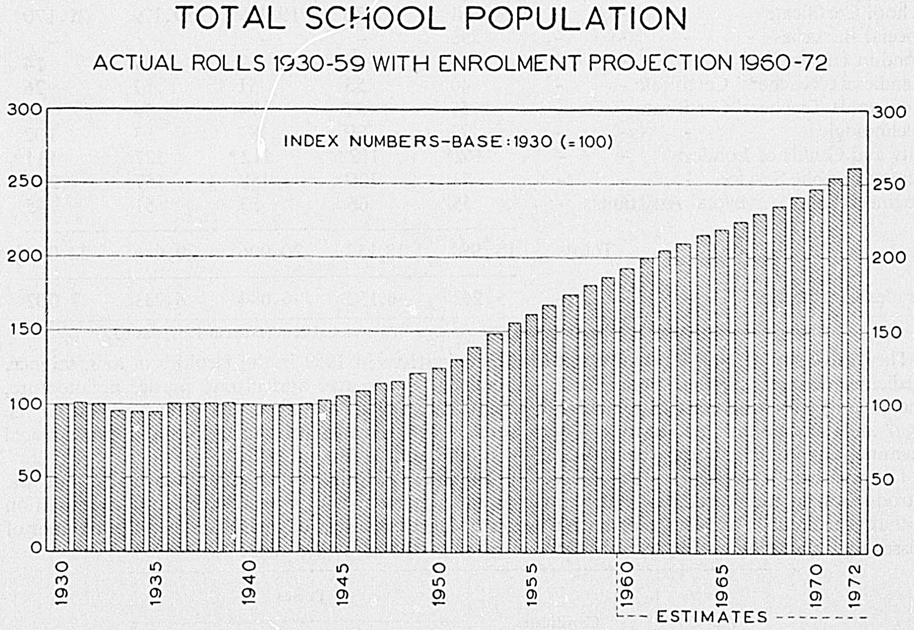
The changes in total enrolment were accompanied by changes in the yearly number of school leavers entering occupations. The first change was that less and less pupils leaving primary or intermediate school went directly to work, and more and more went on to some form of post-primary education; the latter proportion was 60 per cent in 1936, it rose to over 80 per cent in 1945, and has now reached over 95 per cent. The educational implications of this change for the kind of post-primary education, that now must cater for almost the whole of the country's child population, are obvious. The second change, which is now gradually taking effect, is that more and more of the pupils leaving post-primary school do so from higher forms than formerly. Finally, the total numbers of school leavers, have been increasing from an estimated 26,000 in 1951 to 35,000 in 1959; in 1962 more than 40,000 pupils are expected to leave school, and some 50,000 in 1969.
The number of part-time students attending day or evening classes also showed a steady increase in recent years. The total increase between 1949 and 1959 was 28,286, or 111 per cent, and is largely due to the development of apprentice classes and technical courses previously mentioned.
The enrolment at universities which reached a total of 14,911 in 1959 has almost trebled since 1939. From about 1956 onwards the age groups born after the depression years began to reach the institutions of higher education, and these had from then on to be ready to accommodate increasing numbers of students. The intake at the five teachers' training colleges was increased from 1948, when the fifth college was opened and the number of students admitted to Division A raised to 1,050, in order to meet the expected higher demand for certificated teachers. A sixth teachers' training college was opened at Palmerston North in February 1956. The total rolls at the training colleges were 2,684 in 1950, 2,704 in 1951, 2,710 in 1952, 2,769 in 1953, 2,744 in 1954 2,741 in 1955, 3,549 in 1956, 4,055 in 1957, 4,436 in 1958, and 4,915 in 1959; included in the latest figure are 1,161 post-primary teacher studentships. A seventh teachers' training college was opened at Hamilton at the beginning of 1960.
ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS - The number of candidates who actually presented themselves for the various examinations conducted by the Department of Education and also by the Trades Certification Board during the latest five years is given below.
| Examination | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *These numbers represent subjects taken. The number of individual candidates in 1959 was 65. | |||||
| Teachers' Certificate | 273 | 305 | 315 | 331 | 336 |
| School Certificate | 14,961 | 17,335 | 19,149 | 19,179 | 21,170 |
| Special Bursaries | 296 | - | - | - | - |
| London University | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 14 |
| Handicraft Teachers' Certificate | 40 | 53 | 51 | 67 | 76 |
| Homecraft Teachers' Certificate | 55 | 57 | 74 | 74 | - |
| Technological | 77 | 89 | 87 | 93 | 102 |
| City and Guilds of London | 162* | 112* | 112* | 127* | 111* |
| Samoan Public Service | 73 | 129 | 158 | 157 | 230 |
| Engineers' and Surveyors' Assistants | 55 | 66 | 53 | 51 | 45 |
| Totals | 15,998 | 18,152 | 20,006 | 20,086 | 22,084 |
| Trades Certification | 5,262 | 6,152 | 6,084 | 6,233 | 7,002 |
The University of New Zealand conducted examinations in 1959 in the faculties of arts, science, medicine, dentistry, home science, law, engineering, commerce, agriculture, music, architecture, and divinity; for diplomas in journalism, in banking, and in fine arts; and for admission to the legal and accountancy professions. There were 14,498 entrants for the degree and professional examinations in 1959, compared with 13,009 in 1958 and 11,701 in 1957.
The number of entries for the University Entrance Examination in 1943 was 5,152, but the introduction of the accrediting system in 1944 saw the number of candidates for the examination in that year reduced to 543. Comparative figures giving the number of candidates and the number of passes by accrediting and by examination are given in the following table.
| Year | Candidates | Passes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accredited | By Examination | ||
| 1955 | 4,638 | 2,522 | 506 |
| 1956 | 5,375 | 2,890 | 492 |
| 1957 | 6,588 | 3,605 | 692 |
| 1958 | 7,460 | 4,100 | 702 |
| 1959 | 7,340 | 3,949 | 774 |
TRADES EXAMINATIONS - The Trades Certification Act 1948 provides for the establishment of the New Zealand Trades Certification Board, consisting of the following members:
Three persons to be appointed on the recommendation of the Director of Education, one of the three to be appointed as chairman of the Board on the Director's recommendation.
Two persons to be nominated by the New Zealand Employers' Federation and two by the New Zealand Federation of Labour.
Two persons to be nominated by the New Zealand Technical School Teachers' Association and one by the Technical Education Association.
The person for the time being holding the office of Commissioner of Apprenticeship.
Three other persons, one of whom is to be nominated by the New Zealand Electrical Wire-men's Registration Board, one by the New Zealand Motor Trade Certification Board, and one by the Plumbers' Board of New Zealand.
Additional members of whom one shall be nominated by each other authority which conducts examinations and issues certificates for the whole of New Zealand in connection with a particular trade or trades, and which the Board recommends should be represented on the Board for the time being.
The members of the Board, other than the Commissioner of Apprenticeship, are appointed by the Minister of Education for a term of three years. Provision is made for reappointments, removals from office, etc.
The functions of the Board are to make provision for the examination of persons practising or intending to practise any trade who desire from time to time to present themselves for examination, and, secondly, to grant or issue, either independently or in conjunction with any other examining body, diplomas or certificates to any such persons in recognition of proficiency in any trade, or in any art, science, or matter relating to any trade.
The Board may also (a) co-opt if necessary any person or persons for advice in connection with any trade; (b) make representations to the appropriate New Zealand apprenticeship committee in regard to the prerequisite education for apprentices wishing to enter any industry, or in regard to other educational matters affecting apprentices; (c) appoint, with approval of the Minister, advisory or technical committees to advise the Board on such matters within the scope of its powers and functions as are referred to them by the Board, and appoint any person to be a member of such a committee even if he is not a member of the Board; and (d) charge fees for entry for any examination.
Payments incurred for the expenses of the Board and for administration generally are paid from the proceeds from fees and otherwise, and where the amounts from such sources are insufficient, the deficiency is met from the annual vote for the Department of Education.
PUBLIC EXPENDITURE ON EDUCATION - The following table shows the expenditure (after recoveries have been deducted) from public funds on each branch or service of education for the three years ended 31 March 1958, 1959, and 1960.
| Expenditure Year Ended 31 March | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Expenditure from vote, education | £ | £ | £ |
| General | 2,609,505 | 3,217,134 | 3,310,344 |
| Buildings, land, furniture, and equipment | 9,514,010 | 9,300,758 | 10,617,160 |
| Primary education | 10,779,398 | 11,442,184 | 12,140,565 |
| Post-primary education | 5,390,300 | 5,787,182 | 6,371,561 |
| Higher education | 1,975,491 | 2,066,639 | 2,188,257 |
| Training of teachers | 1,733,721 | 2,004,593 | 2,180,056 |
| Maori schools | 494,608 | 494,139 | 521,187 |
| Education of the blind | 99,427 | 74,252 | 181,338 |
| Special schools | 156,865 | 171,159 | 182,107 |
| Child welfare | 709,202 | 742,796 | 834,731 |
| Miscellaneous grants | 316,518 | 365,189 | 344,813 |
| National Library Service | 256,967 | 262,511 | 295,512 |
| Totals, vote Education | 34,036,012 | 35,928,536 | 39,167,631 |
The foregoing figures do not include revenue received by universities from endowments, fees, etc., which are available for educational purposes. By the Land Act 1948 all education reserves were declared Crown land, and the revenues received as from 1 April 1949 were paid into the Land Settlement Account. The reserves vested in post-primary schools were also declared by the Education Lands Act 1949 to be Crown land subject to the Land Act 1948.
The following figures show Government expenditure on education during the period 1949-50 to 1959-60.
| Year Ended 31 March | Expenditure from Public Funds | Expenditure as Percentage of National Income | Expenditure per Head of Mean Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||
| £(000) | per cent | £ | s. | |
| 1950 | 13,745 | 2.8 | 7 | 6 |
| 1951 | 15,030 | 2.5 | 7 | 17 |
| 1952 | 17,649 | 2.8 | 9 | 0 |
| 1953 | 21,338 | 3.2 | 10 | 12 |
| 1954 | 24,047 | 3.2 | 11 | 13 |
| 1955 | 25,409 | 3.1 | 12 | 1 |
| 1956 | 28,519 | 3.4 | 13 | 5 |
| 1957 | 31,636 | 3.6 | 14 | 8 |
| 1958 | 34,036 | 3.7 | 15 | 3 |
| 1959 | 35,929 | 3.7 | 15 | 2 |
| 1960 | 39,168 | 3.7* | 16 | 14 |
Education Buildings - The increases in school population have led to an expansion of the school building programme. The following numbers of classrooms were completed in recent years.
| Primary | Post-primary | |
|---|---|---|
| 1954 | 526 | 252 |
| 1955 | 548 | 259 |
| 1956 | 494 | 367 |
| 1957 | 593 | 360 |
| 1958 | 503 | 308 |
| 1959 | 539 | 341 |
The need to expand the school building programme has resulted in a number of measures being taken in recent years to increase the supply of classrooms.
An emergency measure introduced in 1946 was the provision of prefabricated buildings. Increasing use was made of these buildings until the year 1952, after which improved building resources allowed a gradual increase in the proportion of permanent building.
A further important step in the efforts to meet rapidly increasing rolls was the use of standard plans for both primary and post-primary schools. In 1951 a Dominion Basic Plan for primary schools was introduced, while, in the post-primary field, three standard designs were evolved; and a number of new schools were built to each of the plans over the period 1953 to 1956.
The year 1955 saw the application in New Zealand of new principles being followed overseas in the design of primary and post-primary schools. The resulting designs gave improved teaching facilities and amenities at a lower cost. The first primary schools planned on the “block” principle opened in 1955, and the first post-primary school in 1957. These planning principles are now being developed further in two-storied schools.
In view of the need for plans which meet more closely the particular needs of individual districts, a scheme has now been introduced in primary school building which aims at providing speed and economy in the erection of buildings while, at the same time, giving education boards increased responsibility in the planning and building of schools and an incentive to use local architectural and planning skill in the fullest possible way. Education boards are free under this scheme to plan and build within the limits or “white lines” imposed on the one hand by a building code which lays down minimum requirements for each type of building, and on the other by the ceiling placed by the Government on the amount of money which it is prepared to allocate to any particular project.
Pre-school Education - Children below the age of five years are not enrolled in the State primary schools. They may be enrolled, however, at free kindergartens controlled by local free kindergarten associations which are voluntary bodies formed for the purpose, or at nursery play centres controlled by nursery play centre associations.
Since 1942 the Government has made grants available to kindergarten students in training, and in 1949 accepted responsibility for the cost of sites and buildings for training centres. The salaries of kindergarten teachers and full-time training centre staff have, since 1948, been paid by the Department of Education, and grants are available towards the fees of part-time lecturers in the training centres. Subsidies of £2 for £1 on voluntary contributions raised for the purchase of land, buildings, and initial equipment are paid by the Government.
Nursery play centre associations receive from the Government a small annual maintenance grant in respect of nursery play centres which meet a required standard of equipment, and a small establishment grant towards initial costs is paid to new centres.
At the end of 1959 there were 14,807 children enrolled at 196 free kindergartens (7,716 for morning sessions and 7,091 for those held in the afternoon). In 1958 the corresponding figures were 13,928 and 192 respectively. In 1959 there were 128 recognised nursery play centres for 3,971 children.
PRIMARY SCHOOLS - The primary-school system at the end of 1959 consisted of 2,010 public schools (including district high schools and intermediate schools or departments), 156 Maori schools, 335 registered private primary schools (which included 12 Maori private church schools), and three lower departments of secondary schools. There were also 196 free kindergarten schools.
Lower departments of secondary schools may be run for pupils who have not passed Form II, provided that no part of the cost of instruction or of the maintenance of the department is met from public moneys. At the end of 1959 the total number of pupils in the three departments of secondary schools was 113 with four teachers.
The curriculum of the primary school, as set out in the syllabus of instruction, includes character training, English, arithmetic, geography and history, arts and crafts (including needlework), nature study, physical education (including swimming), health education, and music. Teachers are advised on the teaching of nature study, physical education, and arts and crafts by itinerant specialists. At the Forms I and II levels woodwork and metalwork instruction is given to boys at manual-training centres, and girls are taught domestic subjects, including cookery and hygiene.
The syllabus as a whole has been revised in recent years. Textbooks are issued free to pupils in all schools, both State and private. A series of basic primer readers and a considerable amount of equipment for primer classes are also provided by the Government.
Public (State) Schools - The figures tabulated below refer to pupils in public schools - i.e., all pupils in primary schools and intermediate schools and departments. Pupils in secondary departments of district high schools are not included.
| Year | Number of Schools (Including Intermediate Schools and Departments) | Pupils at End of Year | Average of Mean Weekly Roll | Average Attendance over Year | Average Attendance as Percentage of Weekly Roll |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1,938 | 321,405 | 309,935 | 284,982 | 91.9 |
| 1956 | 1,951 | 335,433 | 322,139 | 298,100 | 92.5 |
| 1957 | 1,964 | 348,940 | 334,357 | 311,523 | 93.2 |
| 1958 | 1,998 | 364,181 | 346,654 | 323,648 | 93.3 |
| 1959 | 2,010 | 373,807 | 356,877 | 330,313 | 92.6 |
While the number of schools has not increased greatly, mainly owing to the consolidation of small rural schools, the total rolls have increased by 111,000 since 1950. The changes which have taken place in the size of schools may be seen from the following table.
| Number of Public Schools | 1949 | 1959 | Increase (+) or Decrease (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roll 70 and under | 1,168 | 895 | -273 |
| Roll 71 to 350 | 503 | 710 | +207 |
| Roll 351 and over | 234 | 405 | +171 |
| Totals | 1,905 | 2,010 | +105 |
In each of the education districts are located inspectors of primary schools who form part of the staff of the Department of Education. The total number of primary-school inspectors at 31 March 1960 was 63, allocated as follows: Auckland, 15; South Auckland, 9; Hawke's Bay, 4; Taranaki, 4; Wanganui, 5; Wellington, 7; Nelson, 1; Canterbury, 11; Otago, 5; Southland, 2. These figures exclude one chief inspector and two inspectors in the Head Office of the Department.
The following table relates to pupils on the rolls of the public primary schools and Forms I and II only of intermediate schools at 1 July in each of the years shown.
| Age in Years | 1957: Total Pupils | 1958: Total Pupils | 1959 | Percentage of Total Pupils | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Total Pupils | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||
| 5 and under 6 | 41,397 | 41,828 | 22,239 | 21,029 | 43,268 | 12.6 | 12.2 | 12.3 |
| 6 “ 7 | 41,130 | 42,730 | 22,020 | 20,913 | 42,933 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.2 |
| 7 “ 8 | 41,563 | 41,552 | 22,085 | 20,596 | 42,681 | 12.6 | 12.1 | 12.1 |
| 8 “ 9 | 40,685 | 41,555 | 21,394 | 20,213 | 41,607 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 11.8 |
| 9 “ 10 | 41,388 | 41,067 | 21,231 | 20,281 | 41,512 | 12.5 | 12.0 | 11.8 |
| 10 “ 11 | 41,504 | 41,432 | 21,055 | 19,949 | 41,004 | 12.4 | 121 | 11.7 |
| 11 “ 12 | 34,316 | 41,073 | 20,954 | 19,844 | 40,798 | 10.3 | 12.0 | 11.6 |
| 12 “ 13 | 31,593 | 33,355 | 20,494 | 19,425 | 39,919 | 9.5 | 9.8 | 11.3 |
| 13 “ 14 | 14,060 | 14,714 | 8,855 | 6,480 | 15,335 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| 14 “ 15 | 3,143 | 2,761 | 1,632 | 943 | 2,575 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 15 “ 16 | 319 | 217 | 117 | 75 | 192 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 16 and over | 69 | 47 | 31 | 23 | 54 | -- | -- | -- |
| Totals | 331,167 | 342,331 | 182,107 | 169,771 | 351,878 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
In 1959 a total of 24,645 pupils (12,311 boys and 12,334 girls) left public primary schools as compared with 21,978 pupils (11,253 boys and 10,725 girls) in 1958. Of those leaving in 1959, 24,038, or 97.5 per cent, had completed a course in Form II. The effect of the raising of the school leaving age in 1944 is reflected in the numbers who proceeded to full-time post-primary schooling. Of those leaving in 1959, 97.9 per cent (boys, 97.5 per cent, girls 98.4 per cent) went on to post-primary schools, as compared with 76 per cent (boys, 74 per cent, girls, 78 per cent) in 1943. Of the pupils who left intermediate schools and departments in 1959, 98.5 per cent went on to post-primary schools.
The next table gives the number of public primary schools in each education district as at 30 September 1959, classified according to roll numbers. The number of intermediate schools and departments is also shown.
| Roll Numbers | Education Districts | Total Number of Schools, September 1959 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland | South Auckland | Taranaki | Wanganui | Hawke's Bay | Wellington | Nelson | Canterbury | Otago | Southland | ||
| 1-8 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 4 | - | - | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| 9- 24 | 23 | 17 | 14 | 45 | 39 | 37 | 14 | 51 | 21 | 23 | 284 |
| 25- 30 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 23 | 10 | 11 | 102 |
| 31- 35 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 15 | 7 | 7 | 68 |
| 36- 70 | 61 | 67 | 38 | 31 | 37 | 35 | 10 | 70 | 39 | 45 | 433 |
| 71- 80 | 8 | 11 | - | 4 | 1 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 49 |
| 81- 110 | 38 | 44 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 29 | 14 | 13 | 196 |
| 111- 120 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 2 | 1 | 26 |
| 121- 150 | 13 | 25 | 8 | 11 | 7 | 13 | - | 12 | 10 | 2 | 101 |
| 151- 160 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 3 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 34 |
| 161- 190 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 85 |
| 191- 200 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 29 |
| 201- 230 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | - | 5 | 7 | 2 | 51 |
| 231- 240 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| 241- 270 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 4 | - | 41 |
| 271- 280 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | - | - | 9 |
| 281- 310 | 9 | 11 | - | 4 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 42 |
| 311- 320 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 5 |
| 321- 350 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 34 |
| 351- 360 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | - | 2 | 1 | - | 14 |
| 361- 390 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | - | 3 | 1 | - | 36 |
| 391- 400 | 1 | 5 | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| 401- 430 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 32 |
| 431- 440 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 4 |
| 441- 470 | 11 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 4 | - | 38 | |
| 471- 480 | 3 | - | - | - | - | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 7 |
| 481- 510 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 26 |
| 511- 520 | 9 | 5 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | - | 24 |
| 521- 550 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 10 | - | 2 | 35 |
| 551- 560 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 11 |
| 561- 590 | 4 | 5 | - | 2 | 2 | 4 | - | 8 | 1 | - | 26 |
| 591- 600 | 3 | 1 | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7 |
| 601- 630 | 8 | 2 | - | 1 | - | 3 | - | 5 | 1 | 2 | 22 |
| 631- 640 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 641- 670 | 7 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 19 |
| 671- 680 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| 681- 710 | 1 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | 1 | - | - | 8 |
| 711- 720 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 3 |
| 721- 750 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 6 |
| 751- 760 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 761- 790 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | 6 |
| 871- 880 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 1,321-1,350 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Normal schools | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 6 |
| Intermediate schools and departments | 18 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 53 |
| Totals | 335 | 319 | 119 | 166 | 174 | 221 | 70 | 304 | 165 | 137 | 2,010 |
In addition there are three public schools in the Chatham Islands and 18 special schools for handicapped children.
Primary Schools for Maoris - 70 per cent of the Maori children in New Zealand are educated in the public schools. At 1 July 1959 there were 28,279 attending public schools out of a total of 40,342 Maori children receiving primary education in State schools. The long-term policy, endorsed by representatives of the Maori people themselves, is gradually to transfer the Maori schools now directly under the Department of Education to the control of the local education boards. However, transfers will take place only after full consultations with the local Maori people.
The language of instruction in the Maori schools is English, but the schools are not completely English in outlook, for Maori arts and crafts, songs, legend, and history are taught.
Methods of teaching are practical, and objectives closely related to the special needs of the Maori people. In many of the Maori schools, such equipment as woodwork rooms, cookery rooms, model cottages, baths, hot and cold showers, and laundries is supplied. Health education is featured in every Maori school.
The number of pupils on the rolls of the 156 Maori schools at 1 July 1959 was 13,153 (including 1,090 European children), while the total roll number of the 12 Maori private church schools was 766.
The following table gives the principal statistics of Maori schools during the latest five years.
| Year | Number of Schools at End of Year | Roll at 1 July | Average Attendance, Whole Year | Average Attendance as Percentage of Weekly Roll | Number of Teachers* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maori | European | Males | Females | ||||
| *Includes junior assistants (four males and 99 females in 1959). | |||||||
| 1955 | 166 | 12,351 | 1,247 | 11,333 | 88.3 | 222 | 293 |
| 1956 | 163 | 12,422 | 1,184 | 11,131 | 88.7 | 251 | 292 |
| 1957 | 160 | 11,990 | 1,094 | 10,930 | 88.4 | 251 | 294 |
| 1958 | 157 | 12,043 | 1,092 | 11,376 | 89.1 | 239 | 309 |
| 1959 | 156 | 12,063 | 1,090 | 11,547 | 86.0 | 240 | 309 |
Five inspectors of schools attached to the Department of Education are engaged in the inspection of Maori schools, private church schools, and secondary schools for Maoris.
Intermediate Schools - Pupils on the rolls of the 45 intermediate schools and 8 intermediate departments at the end of 1959 numbered 29,318. The progress that is being made with the establishment of this type of school may be gauged from the fact that 17 years earlier (1942) the number of pupils was 6,817. Of all children in Forms I and II of public (primary and intermediate) schools at 1 July 1959, 36 per cent were enrolled at the intermediate schools. The average attendance during the year was 27,436. The ages of pupils on the roll at 1 July of each of the latest three years were as follows.
| Age, in Years | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Total | Boys | Girls | Total | Boys | Girls | Total | |
| Under 11 - | 100 | 189 | 289 | 173 | 241 | 414 | 96 | 145 | 241 |
| 11 and under 12 | 3,318 | 3,514 | 6,832 | 4,147 | 4,685 | 8,832 | 4,209 | 4,702 | 8,911 |
| 12 “ 13 | 5,125 | 4,906 | 10,031 | 5,851 | 5,399 | 11,250 | 7,124 | 6,895 | 14,019 |
| 13 “ 14 | 2,543 | 1,815 | 4,358 | 2,864 | 2,091 | 4,955 | 3,144 | 2,165 | 5,309 |
| 14 “ 15 | 578 | 337 | 915 | 494 | 286 | 780 | 541 | 298 | 839 |
| 15 “ 16 | 62 | 34 | 96 | 48 | 23 | 71 | 53 | 33 | 86 |
| 16 and over - | 10 | 7 | 17 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 4 | 13 |
| Totals | 11,736 | 10,802 | 22,538 | 13,580 | 12,727 | 26,307 | 15,176 | 14,242 | 29,418 |
Private Schools - No private school may be established unless application is first made to the Department of Education for registration. Certain standards of efficiency and suitability of staff, premises, equipment, and curriculum have to be fulfilled.
The following table contains the principal statistics of private primary schools for each of the last five years. The figures include Maori private church schools which are also shown separately in the summary on page 218.
| Year | Number of Schools | Roll at End of Year | Average Yearly Attendance | Teachers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Total | Males | Females | Total | |||
| 1955 | 319 | 22,567 | 23,396 | 45,963 | 40,316 | 189 | 1,056 | 1,245 |
| 1956 | 318 | 23,817 | 24,617 | 48,434 | 43,035 | 161 | 1,070 | 1,231 |
| 1957 | 323 | 24,438 | 25,206 | 49,644 | 44,883 | 187 | 1,151 | 1,338 |
| 1958 | 324 | 25,074 | 25,989 | 51,063 | 47,032 | 180 | 1,136 | 1,316 |
| 1959 | 335 | 26,830 | 26,822 | 53,652 | 48,982 | 198 | 1,206 | 1,404 |
The majority of the schools included in the preceding table are Roman Catholic Church schools, of which there were 269 at the end of 1959 with 46,951 pupils (23,747 boys and 23,204 girls) and 1,114 teachers (100 males and 1,014 females). The average attendance was 42,877. The remaining private schools comprised 55 church schools of other denominations with 219 teachers and 5,685 pupils, and 11 undenominational schools with 71 teachers and 1,016 pupils.
POST-PRIMARY SCHOOLS - One of the most striking features in the development of New Zealand education - i.e., the marked increase in the proportion of pupils who proceed to some form of post-primary education at the conclusion of the primary course - has already been mentioned (page 224). The raising of the school leaving age to 15 years from 1944, which had been foreshadowed over 20 years earlier in the Education Amendment Act 1920, stimulated the movement towards secondary education for all. This movement began in 1901 when free places were introduced in district high schools. In 1903 it became obligatory on all State post-primary schools to provide some free places, and from 1914 every child who had passed the Proficiency Examination was entitled to free education for at least two years in any State post-primary school. In 1936 the Proficiency Examination was abolished, and every child gaining a Primary School Certificate or attaining the age of 14 years became entitled to free post-primary education until the year in which he reached the age of 19 years. Later, when the Primary School Certificate was in turn abolished, every child completing the work of Form II became entitled to free post-primary education. Extension of a free place beyond the age of 19 years is allowable in special cases approved by the Director of Education. In 1945, when it became clear that secondary education for all was no longer a programme but had become a reality, the post-primary syllabus was revised. The whole course was based on a common core, consisting of English, social studies, general science, elementary mathematics, music, arts and crafts, and physical education, to be followed by a degree of specialisation within a wide range of subjects that may be taken to the School Certificate stage. All types of post-primary schools are required by regulations made in 1945 (consolidated and amended in 1954) to give to all pupils during the first two years of their post-primary course a minimum number of units of instruction in the common core subjects.
Post-primary schools are either public (State) or private. The following table shows the number and types of post-primary schools in existence during each of the latest five years.
| Year | State Secondary Schools | Combined Schools | Secondary Departments of District High Schools | Technical High Schools | Maori Secondary Schools | Endowed and Private Secondary Schools | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 59 | 7 | 114 | 33 | 11 | 89 | 313 |
| 1956 | 66 | 7 | 113 | 36 | 11 | 91 | 324 |
| 1957 | 80 | 7 | 113 | 33 | 11 | 91 | 335 |
| 1958 | 89 | 7 | 111 | 34 | 11 | 93 | 345 |
| 1959 | 97 | 7 | 106 | 35 | 11 | 94 | 350 |
A combined school is an amalgamation of a secondary and a technical school under a single governing body. District high schools are public primary schools with a secondary “top” and the basic course is academic, as in the normal secondary school. Where staffing and equipment allow, special courses are provided in agriculture, commercial work, and domestic science. Technical schools are described later in this section.
Until 1904 secondary schools were established by special (local) Acts of the General Assembly, and until recently the majority of schools giving post-primary education had been established in this manner. At the present time the provisions of the Education Act 1914 allow the Minister of Education to establish such schools. State secondary schools and combined schools are controlled by boards of governors, and district high schools by the education boards.
The inspection of State post-primary schools is carried out by inspectors of post-primary schools attached to the Department of Education. Commencing in 1947, these inspectors took over the inspection of secondary departments of district high schools which were previously inspected by primary-school inspectors. There were (in 1960) 34 inspectors, one chief inspector of post-primary schools, and one superintendent and one assistant superintendent of technical education.
The number of pupils at the end of each of the latest five years is shown in the following table. No account is taken of lower departments of secondary schools, and in the case of district high schools only the secondary departments are included.
| Year | State Secondary Schools | Combined Schools | District High Schools | Technical High Schools | Maori Secondary Schools | Private Secondary Schools | Correspondence School | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 35,059 | 4,935 | 8,876 | 18,292 | 885 | 13,666 | 452 | 82,165 |
| 1956 | 37,170 | 5,090 | 8,618 | 19,069 | 832 | 14,553 | 442 | 85,774 |
| 1957 | 41,963 | 5,178 | 8,823 | 17,496 | 834 | 14,904 | 435 | 89,633 |
| 1958 | 46,364 | 5,109 | 8,720 | 17,406 | 755 | 15,802 | 439 | 94,595 |
| 1959 | 52,441 | 5,190 | 8,236 | 18,297 | 742 | 16,496 | 496 | 101,898 |
The foregoing table does not include part-time students attending technical classes (51,570 in July 1959), students receiving part-time tuition from the Correspondence School (2,530 in July 1959), and students receiving part-time instruction from the Technical Correspondence School (4,053 in July 1959).
The numbers of each sex attending post-primary schools at the end of 1959 were: State secondary schools, 27,014 boys and 25,427 girls; combined schools, 2,900 and 2,290; secondary departments of district high schools, 3,910 and 4,326; technical schools, 10,633 and 7,664; Maori secondary schools, 400 and 342; endowed and registered private secondary schools, 8,010 and 8,486; and full-time at Correspondence School, 218 and 278.
The following table shows the number of pupils at State secondary schools and combined schools taking the different courses available. (This table as at 1 July in each of the latest five years may be compared with the similar table for technical schools later.)
| Course | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | 4,493 | 4,745 | 6,030 | 6,996 | 8,134 |
| Commercial and general | 31,550 | 33,684 | 37,271 | 40,776 | 45,697 |
| Domestic | 3,986 | 4,084 | 4,421 | 4,493 | 4,698 |
| Agricultural | 1,579 | 1,642 | 1,791 | 1,743 | 1,803 |
| Fine arts | 179 | 277 | 183 | 146 | 267 |
| Totals | 41,787 | 44,432 | 49,696 | 54,154 | 60,599 |
Technical Schools - The technical schools fall roughly into two types: (a) those in the small centres, which provide for all the post-primary needs and are distinguishable from secondary schools only by having in general a rather more strongly developed practical side; and (b) the large technical schools in the main centres, in which there is less evidence of the generalised academic curriculum, since this is adequately provided by the city secondary schools.
However, even in the latter type most of the courses in the day schools are still designedly prevocational and not genuinely “technical” in character. Technical schools are normally controlled either by a board of managers or by the education board of the district acting in a similar capacity.
There were 35 technical schools in 1959. The following table shows the number of pupils taking the different courses available (as at 1 July in each of the latest five years).
| Course | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | 6,629 | 7,012 | 6,324 | 5,867 | 6,181 |
| Commercial and general | 9,236 | 9,803 | 8,955 | 9,421 | 9,892 |
| Domestic | 2,928 | 2,938 | 2,532 | 2,384 | 2,445 |
| Agricultural | 1,193 | 1,310 | 1,223 | 1,121 | 1,167 |
| Fine arts | 158 | 135 | 197 | 191 | 184 |
| Totals | 20,144 | 21,198 | 19,231 | 18,984 | 19,869 |
Technical Classes-The number of centres at which technical classes for part-time day and evening students are provided was 169 in 1959.
The total of individual students including apprentices attending day classes in 1959 was 51,570, made up as follows:
| Classes conducted by education or high school boards | 24,819 |
| Classes conducted by technical school boards or by managers | 26,751 |
Of the total of 51,570 students, 37,478 (15,352 males and 22,126 females) held free places.
The above figures include 6,583 part-time students at 1 July on the rolls of the Correspondence and Technical Correspondence Schools, but exclude 1,345 students who were also full-time day pupils at primary and secondary schools.
Technical Correspondence School - In July 1946 the Department took over the responsibility for the study courses previously conducted by the Army Educational and Welfare Service. A Technical Correspondence School was established in Wellington to develop these courses for men in the armed services, and also to provide correspondence instruction in vocational and technical subjects for apprentices and advanced students unable to attend technical schools or classes.
The number of students on the roll at 1 July 1959 was 4,053. There were 72 full-time teachers, besides the Principal, on the staff at 30 September 1959.
Probable Destination of Public Post-primary Pupils - An indication of the vocations intended to be followed by pupils leaving public post-primary schools during 1959 is contained in the next table. Of the totals, 7.6 per cent of boys and 3.3 per cent of girls intended to proceed to full-time university studies, while a further 1.9 per cent of boys and 7.5 per cent of girls stated their intention of entering the teaching profession. Clerical occupations (including typing) claimed 12.1 per cent of boys and 31.9 per cent of girls; shops and warehouses, 7.7 per cent and 14.2 per cent; manual trades, 28.3 per cent and 3.5 per cent; farming, 19.5 per cent and 0.8 per cent; 0.5 per cent and 11.5 per cent intended to stay at home; various other occupations claimed 15.7 per cent and 21.5 per cent while 6.7 per cent and 5.8 per cent of boys and girls respectively did not know their future vocations at the time.
| Occupation | Totals | Maoris Included in Totals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | |
| University | 1,109 | 441 | 11 | 5 |
| Teachers' college | 279 | 996 | 12 | 38 |
| Professional cadetship | 433 | 69 | 7 | 2 |
| Health services | 52 | 1,306 | 2 | 122 |
| Office work - | ||||
| (a) Government or local authority | 696 | 952 | 40 | 80 |
| (b) Industry and commerce | 1,074 | 3,307 | 14 | 63 |
| Shop and warehouse assistants | 1,126 | 1,895 | 34 | 70 |
| Skilled trades - | ||||
| (a) Government or local authority | 619 | 85 | 47 | 12 |
| (b) With private employers | 3,505 | 383 | 140 | 8 |
| Farming (including those engaged at their own home | 2,833 | 106 | 365 | 17 |
| Clothing workers | 24 | 574 | 7 | 50 |
| Factory operatives | 438 | 406 | 69 | 69 |
| Domestic work and at home | 71 | 1,533 | 29 | 437 |
| Armed forces (not included elsewhere) | 338 | 14 | 50 | 11 |
| Other occupations | 991 | 506 | 236 | 31 |
| Not known | 973 | 773 | 191 | 155 |
| Totals | 14,561 | 13,346 | 1,254 | 1,170 |
Duration of Stay at Public Post-primary School - The following table gives particulars of pupils who left public post-primary schools in 1959, classified according to years of attendance. The approximate average length of stay at the various types of school was: secondary school, 3 years 1 month; combined schools, 3 years 3 months; technical high and day schools, 2 years 8 months; secondary departments of district high schools, 2 years 5 months; all post-primary schools, 2 years 10 months.
| Year of Attendance | Secondary Schools | Combined Schools | Technical High and Day Schools | District High Schools | All Schools | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | |
| First | 1,121 | 6.99 | 74 | 4.68 | 788 | 10.76 | 482 | 16.25 | 2,465 | 8.83 |
| Second | 4,568 | 28.48 | 402 | 25.43 | 2,906 | 39.68 | 1,135 | 38.26 | 9,011 | 32.29 |
| Third | 4,832 | 30.13 | 450 | 28.46 | 2,286 | 31.21 | 947 | 31.93 | 8,515 | 30.51 |
| Fourth | 3,300 | 20.58 | 379 | 23.97 | 940 | 12.83 | 333 | 11.23 | 4,952 | 17.75 |
| Fifth | 2,020 | 12.60 | 249 | 15.75 | 372 | 5 08 | 64 | 216 | 2,705 | 9.69 |
| Sixth and over | 195 | 1.22 | 27 | 1.71 | 32 | 0.44 | 5 | 0.17 | 259 | 0.93 |
| Totals | 16,036 | 100.00 | 1,581 | 100.00 | 7,324 | 100.00 | 2,966 | 100.00 | 27,907 | 100.00 |
It has been mentioned earlier that, except in special circumstances, children are not permitted to leave school until they reach the age of 15 years, and it would appear that many pupils entering post-primary schools remain there only as long as they are required to, as approximately 41 per cent do not proceed beyond the second year of attendance. However, in 1948 the proportion not proceeding beyond the second year was approximately 50 per cent.
Secondary Schools for Maoris - At the end of 1959, 742 Maori pupils were receiving post-primary education at the 11 Maori secondary schools, 155 of the total being Government scholarship holders. In addition, there were 52 scholarship holders enrolled in public post-primary schools.
A further step forward in the provision of post-primary education for Maoris was the approval of the establishment of Maori district high schools. These schools, unlike the private denominational schools, are controlled by the Department of Education; they provide courses of a practical nature specially suited to the needs of the Maori pupils. There were 10 such schools at the end of 1959.
Secondary School Bursaries - Under regulations made in 1943, bursaries, of a maximum annual value of £40 and tenable for a period of up to two years, may be granted to pupils obliged to live away from home in order to take a Sixth Form course at a post-primary school (public or private) which is approved for accrediting purposes. In order to qualify, applicants must be under 18 years of age and must have passed either the School Certificate or the University Entrance Examinations or have been accredited for the latter.
Technical School Bursaries - Bursaries of a maximum value of £40 may be awarded to pupils who have completed at any post-primary school a two years' course preparatory to a specialised course in agriculture, fine arts, engineering, building construction, commerce, or home science which can be completed only at some technical school. The bursaries are tenable at post-primary schools approved for that purpose and may be held for a maximum of two years. Applicants must be under the age of 17 years at the commencement of the specialised course and must be obliged to live away from home in order to receive satisfactory instruction in the courses to be followed.
VOCATIONAL GUIDANCE - Since 1938 full responsibility for the work of vocational guidance of pupils at post-primary schools, which for some years had been carried on almost entirely by voluntary organisations, has been taken by the Government. Vocational guidance officers were appointed in each of the four chief centres, and educational guidance officers, known as “careers advisers”, were also selected at certain large post-primary schools to work in conjunction with the district vocational guidance officers. So far as the work of finding positions for children leaving school was concerned, the vocational guidance officers acted in collaboration during the war with the manpower officers of the National Service Department, and in each of the four main cities a “Youth Centre” was established where the work of guidance and placement was undertaken jointly by officers of the Education and National Service Departments.
The Department of Education assumed the full control of the youth centres in 1943, and the staffs of the centres (now called Vocational Guidance Centres) have been greatly strengthened and their activities expanded. Offices have been opened in the four main centres, and in Lower Hutt and Hamilton. The vocational guidance officers are, however, in close contact with the post-primary schools in other centres. The vocational guidance officers, acting in conjunction with headmasters and special careers teachers in the schools, offer their services at any point in the child's career where a choice has to be made, whether of school course or of vocation. When a child has made his choice career the vocational guidance officer will if requested find suitable employment for him and endeavour to follow up his progress until he is finally and satisfactorily settled in his line of work.
The centres are in frequent touch with a number of voluntary agencies such as “Heritage”, Crippled Children Society, and lay tuberculosis associations.
For the year ended 31 December 1959 the total callers at the centres numbered 22,960. In addition, 13,858 pupils were interviewed individually in post-primary schools. Group interviews were carried out with 666 groups of children (numbering in the aggregate several thousands) interested in discussing particular vocations. Other activities, apart from attention to numerous inquiries by letter and the preparation of information sheets covering over 100 occupations, included 1,392 visits to schools, addresses at 197 meetings, and 580 follow-up visits to persons placed in employment.
RURAL EDUCATION: Consolidation of Schools - In order to give children in country districts the advantage of special equipment and more specialised teaching in larger schools, the consolidation of the smaller rural schools has been undertaken wherever practicable. The extent of this consolidation will be evident from the fact that, whereas in 1934 there were 2,532 public primary (excluding intermediate) schools, the number in 1959, despite a considerable increase in the school population in the intervening period, was 1,957. The fall in numbers is also due in part to the exclusion since 1946 of part-time and side schools from the totals. There were approximately 80 such schools in 1934, and 40 in 1946.
Transport and Board - A natural consequence of consolidation was an increase in the numbers of pupils requiring some form of transport to enable them to attend school. In recent years school transport facilities have been steadily developed until now 18.8 per cent of the total school population receive assistance in one form or another. Most of these pupils are conveyed by buses under contract to education boards or operated by the Department of Education. Financial aid towards the cost of fares is given in some cases where the number of pupils is insufficient to warrant a special school bus service. In addition, free passes on the railway to the nearest public or private school are granted to eligible children living near a railway line but at some distance from a primary school, and the same privilege is enjoyed by pupils having to travel to attend secondary schools, combined schools, district high schools, and private secondary schools, as well as to part-time pupils travelling to attend technical schools or classes, and pupils attending manual-training centres.
In areas where there is no organised transport, capitation payments are made to parents for the conveyance of their children to school by car. Horseback allowances are also payable.
The expenditure on transport of pupils for the financial year 1959-60 was £1,698,928, as compared with £1,636,377 in 1958-59.
In certain cases, boarding allowances are granted to pupils living in areas where there are no available or convenient transport services to enable them to attend school. Boarding allowances are also granted to post-primary pupils to allow them to take, in other centres, certain specified courses not available at their local school.
The expenditure on boarding allowances of pupils attending schools for the last three years is given in the table below.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Public primary and intermediate | 7,474 | 7,372 | 6,814 |
| Private primary | 9,834 | 8,438 | 8,395 |
| State secondary | 78,827 | 70,715 | 71,735 |
| Maori | 7,110 | 7,517 | 8,112 |
| Private secondary | 51,404 | 50,874 | 50,528 |
| Totals | 154,649 | 144,916 | 145,584 |
The next table gives particulars of the number of children transported to school and the number in receipt of boarding allowances as at 1 July 1959, according to the type of school attended. Totals for the two preceding years are also shown.
| Type of School | Number of Pupils on Roll | Total Pupils Transported to School | Number Receiving Boarding Allowance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public primary schools | 322,488 | 53,786 | 334 |
| Intermediate schools and departments | 29,418 | 2,350 | 12 |
| Secondary departments of district high schools | 9,012 | 5,170 | 86 |
| Secondary schools | 55,164 | 13,417 | 1,715 |
| Combined schools | 5,435 | 802 | 577 |
| Technical schools | 19,869 | 6,143 | 332 |
| Maori schools | 13,153 | 4,392 | 41 |
| Chatham Islands schools | 117 | 84 | 5 |
| Private primary schools | 51,436 | 3,318 | 307 |
| Private post-primary schools | 17,663 | 1,927 | 2,013 |
| Totals, 1959 | 523,755 | 91,389 | 5,422 |
| Totals, 1958 | 503,571 | 94,760 | 5,134 |
| Totals, 1957 | 487,272 | 89,013 | 5,180 |
Correspondence School - Since 1922 correspondence classes have been conducted for the primary education of children in very remote areas and of those unable to attend school on account of lengthy illness or other causes. In 1929 courses were extended to cover post-primary education up to the stage of the University Entrance Examination. The usual subjects of the syllabus of instruction are taught at the school, and in addition pupils who require instruction which is usually available in a special class in a public school can receive instruction by correspondence. One of the features of the school is the provision of instruction in subjects involving practical work, such as needlework, woodwork, and the science subjects. A corporate school spirit is developed through the school badge and uniform, daily radio lessons, club activities, the publication of a school magazine,periodical exhibitions of work, and by parents' and ex-pupils' associations. The personal link between the pupil and the school is strengthened and the work of the school facilitated by a number of teachers from the school visiting pupils in their homes in the first term each year and, in two areas, by round-the-year visiting by resident teachers. Residential schools are held in November each year to give pupils the opportunity of taking part in group activities and of intensive tutorial work in subjects not readily dealt with by correspondence.
Young persons in employment, including uncertificated teachers of small public schools and junior assistants in Maori schools, inmates of Department of Justice institutions, pupils of post-primary schools who require examination subjects which their own schools cannot provide, officers of Government Departments, and others who are unable to attend evening classes at post-primary schools, also receive tuition as part-time students of the Correspondence School.
At the end of 1959 there were 3,503 pupils on the roll of the Correspondence School, 1,163 being in the primary division and 496 full-time and 1,844 part-time students in the post-primary division. The staff of the school consists of the headmaster, deputy head teacher, 84 post-primary and 34 primary assistant teachers.
Agricultural Clubs - More particularly in rural schools, practical interest in agriculture has been stimulated by the widespread formation of boys' and girls' agricultural clubs. The pupils undertake projects in livestock rearing and crop growing which are adjudged annually on the club field day, usually held at the school or local centre.
The agricultural instructors and nature study specialists employed by the education boards play an important part in the formation of the clubs, and by giving technical advice do much to assure the successful completion of the various projects. The clubs receive active support from parents, teachers, and the farmers' organisations.
HEALTH SERVICES - Information on the medical and dental inspection of school children and the dental-clinic system is given in Section 5A (Public Health) of this Yearbook.
Free Issue of Milk - The milk-in-schools scheme, for the free issue of a half-pint daily ration of milk to children, commenced on 1 March 1937.
TEACHING PROFESSION: Training of Teachers - In 1959 there were six teachers' training colleges (at Auckland, Ardmore, Palmerston North, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin) available to students who desired to enter the teaching profession, and at the end of 1959 there were 4,854 students in training. This number includes 1,169 holders of post-primary teacher studentships (Division U) who are full-time university students but at the same time are an integral part of the training colleges. Included in the remainder, were 3,050 “Division A” students undertaking training for primary teaching and 223 “Division C” students undertaking training for post-primary teaching. The minimum academic qualification for admission to Division A is the School Certificate, but approximately two-thirds of these students have an Endorsed School Certificate or University Entrance. Nearly all “Division C” students are university graduates at the time of admission.
The following table shows the number of students in these two groups in December of each of the years 1955-1959.
| Year | Division A | Division C | Totals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| 1955 | 675 | 1,585 | 93 | 92 | 2,445 |
| 1956 | 700 | 1,703 | 91 | 116 | 2,610 |
| 1957 | 700 | 1,896 | 105 | 127 | 2,828 |
| 1958 | 731 | 2,119 | 101 | 132 | 3,083 |
| 1959 | 775 | 2,275 | 104 | 119 | 3,273 |
The normal course of training for “Division A” students is a period of two years at a teachers' training college, followed by a further period of one year as a probationary assistant attached to a public school. Third-year studentships, which entitle holders to an extra year's training in lieu of a probationary year, are available to selected students who wish to specialise in nature study, music,physical education, or arts and crafts, or who wish to become speech therapists or teachers of the deaf. A limited number of selected students are permitted to spend most of the third year of training doing full-time study towards a university degree. For students of “Division C” the course is for one year. These students are university graduates who train for service in post-primary schools. To enable students to qualify to teach homecraft subjects, bursaries providing training at a teachers' training college and at a technical high school were instituted in 1943. There were 170 homecraft trainees in the Auckland and Dunedin Training Colleges in 1959. A further 39 trainees were being trained in 1959 as manual training instructors.
In order to meet future staffing requirements due to the rapidly increasing school population a special training scheme was started in September 1949 for selected trainees aged 21 years and over. The last of these courses opened in September 1959. In December 1959 the number of trainees taking the final special one-year course at two of the training colleges was 120. On completion of the special training-college course these trainees are required to serve for one year as probationary assistants before being granted trained teachers' certificates. These trainees are not included in the figures in the tabulation of students at training colleges shown earlier, nor are some fee-paying students (Division B) of whom there were 10 in 1959.
In 1948 a new post-primary teachers' bursary scheme was instituted to enable suitable students, who had reached a standard of education at least equivalent to University Entrance, to complete approved degree courses in preparation for entry into the post-primary teaching profession. Candidates were required to have reached 16 years of age by 31 December of the year of application for a bursary. The tenure was for a maximum period of four years. On completing their university courses students were required to attend a teachers' training college for one year as “Division C” students, and then to serve for a period of four or five years as teachers in post-primary schools.
A maximum of 20 physical education bursaries were also awarded annually to enable students to attend the School of Physical Education at the University of Otago for a three-year diploma course in physical education. The bursaries were of the same value as the post-primary teachers' bursaries, and the bursars were required, on the completion of the course, to undertake work for a period of three or four years either as teachers of physical education or in some other occupation approved by the Director of Education. The number of such bursars attending university in 1955 was 55. In 1956. holders of physical education bursaries elected to transfer to post-primary teacher studentships.
By 1955 it had been evident for some time that the value of these bursaries (£70 cash allowance plus payment of tuition fees, and £40 boarding allowance if the student was obliged to live away from home) was not attracting good students in sufficient numbers to supply the needs of the growing school population. Furthermore, there was a very high rate of loss during the years of study. During 1955 a new system of recruiting teachers for the post-primary service received Government approval and this was brought into operation in 1956. As a result, the post-primary teachers' bursaries and the physical education bursaries, although still awarded in some cases, have been largely replaced by the new post-primary teacher studentships. To be eligible for one of these awards an applicant must have reached the age of 16 years on 31 December of the year of application, and must at the time of application have qualified for entrance to the university, or hold some equivalent or higher qualification approved by the Director of Education. Students are attached to the training college in the appropriate university centre, and a newly created senior lecturer, appointed to each training college, supervises the work of the students and assists them towards the completion of their university courses. Each student on accepting the award, signs an agreement that he will satisfy the stated conditions. One important condition is that if he does not achieve reasonable success in his university studies he will transfer to the “Division A” course at training college and there complete his training as a teacher.
The allowances payable are -
For the first and second year of the studentship, £250;
For the third and fourth year of the studentship, £345;
For the graduate training year - First step on the teachers' basic scale (£640 for men, £555 for women).
Tuition fees are paid in addition to the above allowance. During the four years of the studentship a boarding allowance at the rate of £45 per annum is paid if the student is required to live away from home.
In 1959, 677 post-primary teacher studentships were awarded and 589 were taken up. In addition, 21 holders of post-primary teachers' bursaries in 1958 qualified in 1959 to transfer to post-primary teacher studentships.
There were 24 holders of post-primary teachers' bursaries and 1,169 holders of post-primary teacher studentships attending university institutions in 1959.
Public Primary-school Teachers - The following table shows the number of teachers in public primary schools in the various education districts as at 30 November 1959, together with totals for 1958, 1957, and 1940.
| Sole Teachers | Heads of Schools | Assistant Teachers | Probationary Assistants | Total Number of Teachers | Percentage of Male to Female Teachers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | M. | F. | |||
| Education district - | ||||||||||
| Auckland | 37 | 1 | 272 | 1 | 665 | 1,073 | 101 | 197 | 2,347 | 84.5 |
| South Auckland | 30 | - | 268 | 3 | 415 | 710 | 40 | 154 | 1,620 | 86.9 |
| Taranaki | 23 | - | 89 | 2 | 108 | 200 | 10 | 48 | 480 | 92.0 |
| Wanganui | 53 | 3 | 99 | 2 | 182 | 284 | 25 | 64 | 712 | 101.7 |
| Hawke's Bay | 52 | 3 | 106 | - | 185 | 299 | 28 | 49 | 722 | 105.7 |
| Wellington | 43 | 6 | 151 | 8 | 345 | 580 | 57 | 126 | 1,316 | 82.8 |
| Nelson | 17 | - | 46 | - | 86 | 113 | 9 | 28 | 299 | 112.0 |
| Canterbury | 76 | 3 | 208 | 4 | 421 | 679 | 58 | 114 | 1,563 | 95.4 |
| Otago | 33 | - | 118 | 3 | 226 | 281 | 25 | 58 | 744 | 117.5 |
| Southland | 37 | 4 | 92 | - | 136 | 168 | 9 | 32 | 478 | 134.3 |
| Intermediate schools and departments | - | - | 45 | - | 484 | 321 | 9 | 14 | 873 | 160.6 |
| Totals, 1959 | 401 | 20 | 1,494 | 23 | 3,253 | 4,708 | 371 | 884 | 11,154 | 97.9 |
| Totals, 1958 | 427 | 35 | 1,492 | 35 | 3,049 | 4,503 | 394 | 855 | 10,790 | 98.8 |
| Totals, 1957 | 448 | 42 | 1,429 | 52 | 2,876 | 4,392 | 304 | 696 | 10,239 | 97.6 |
| Totals, 1940 | 644 | 363 | 991 | 147 | 886 | 2,890 | 227 | 438 | 6,586 | 71.6 |
Between 1940 and 1959 the total number of teachers increased by 4,568, male teachers contributing 2,771 of this increase and female teachers 1,797. The average number of pupils per teacher (including probationary assistants) in all public primary schools was 30.0 in 1940, 32.3 in 1957, 31.7 in 1958, and 29.6 in 1959.
Post-primary-school Teachers - The following table indicates the number of full-time teachers employed in the post-primary schools mentioned. The principals are included except in the case of district high schools, the figures for which apply to assistants in the secondary department only.
| Year | Secondary Schools | District High Schools | Technical High Schools | Combined Schools | Grand Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| 1955 | 950 | 668 | 377 | 116 | 687 | 298 | 137 | 92 | 3,325 |
| 1956 | 1,032 | 708 | 352 | 116 | 758 | 295 | 140 | 89 | 3,490 |
| 1957 | 1,206 | 787 | 369 | 123 | 715 | 254 | 141 | 90 | 3,685 |
| 1958 | 1,334 | 846 | 358 | 110 | 730 | 238 | 147 | 93 | 3,856 |
| 1959 | 1,519 | 959 | 338 | 98 | 760 | 263 | 155 | 83 | 4,175 |
Male teachers employed in post-primary schools fell from 908 in 1940 to 707 in 1942, this decrease being almost entirely due to enlistment in the armed forces. The position was slightly improved in 1943, and each succeeding year has shown a further advance, the number in 1959 being 2,772, an increase of 1,864 as compared with 1940. The number of female teachers rose from 630 in 1940 to 838 in 1945, this increase being partially due to the employment of women during the war period in positions normally occupied by men. There was a fall to 795 in 1946, but the number at the end of 1959 (1,403) was 773 in excess of the number employed in 1940. Teachers employed in private post-primary schools and Maori secondary schools are not included in the figures. In 1959, 816 full-time teachers (399 male, 417 female) were employed in these schools.
FREE TEXTBOOKS IN SCHOOLS - Free textbooks were supplied to all primary and post-primary pupils in both State and private schools from the beginning of 1959. Under the free textbooks scheme, the books remain the property of the school controlling authorities and are issued on loan to pupils. The school authorities have a wide discretion in their choice of suitable books.
TEACHING AIDS - Regular broadcasting programmes for schools were initiated in 1931. A varied series of programmes linked with the curriculum are broadcast each school day from all main national stations. Special lessons are also broadcast each day for Correspondence School pupils.
Visual Aids - The National Film Library, a branch of the Department of Education, lends films and gramophone records free of charge to schools and to organisations having some educational purpose. Some 1,900 schools and 1,700 other organisations having some educational purpose have 16 mm sound projectors.
The Library contains more than 21,000 films with about 4,400 titles. Between 4,000 and 5,000 reels of film are issued each week, and of these 71 per cent go to schools or colleges.
Film strips are also available on free loan from the film-strip libraries in the offices of education boards. They can also be purchased for a nominal sum from the National Film Library. About two-thirds of the schools are equipped with film-strip projectors.
Museums - To assist schools to make the fullest use of the museums, an education officer is attached jointly to the museum and the teachers' training college in each of the four main centres. Cases of exhibits are circulated amongst schools where pupils are unable to make regular visits to a museum.
Publications - The School Journal, an illustrated paper, is published in four separate parts suitable for pupils in the various standard classes. Parts 1 and 2 are published six times in the year while Parts 3 and 4 for the senior classes appear four times a year. Five Primary School Bulletins, dealing with topics of New Zealand history, geography, and nature study, are published every year. These publications are prepared in the School Publications Branch of the Department of Education and issued free to all primary and intermediate schools, both State and private. Vernacular Journals are also issued to schools in Western Samoa, Cook, Niue, and Tokelau Islands.
Arithmetic textbooks for all classes in primary schools have been prepared and published over the last few years and a set of infant readers is in preparation.
The Post-Primary School Bulletin is published 10 times a year and issued free to all public and private post-primary schools. It provides background reading for subjects of the revised curriculum, particularly in social studies, science, and literature.
The Education Gazette is published by the Department twice a month. It is a medium for the dissemination of official information and for the advertisement of vacancies. Copies are distributed to educational authorities and to State schools throughout New Zealand, and private schools receive one copy free of charge.
Education, a magazine for teachers, is published 10 times a year.
HIGHER EDUCATION: New Zealand University - Control of higher education in New Zealand is vested in the New Zealand University, founded by the New Zealand University Acts of 1870, 1874, and 1875.
The University was formerly an examining, not a teaching, body with four teaching institutions affiliated to it - the Auckland University College, founded in 1882; Victoria University College, founded in 1897 at Wellington; Canterbury University College, founded in 1873 at Christchurch; and University of Otago, founded in 1869 at Dunedin. By the New Zealand University Amendment Act 1926 the constitution of the University was altered so that it consisted of the four University colleges. A further change was made in 1957 when legislation was passed to change the names of three of the constituent colleges without altering their powers or their relationships with the University of New Zealand. Auckland University College became the University of Auckland, Victoria University College became the Victoria University of Wellington, and Canterbury University College became the University of Canterbury. Each of the universities, besides offering courses in the faculties of arts, science, commerce, law, and music, specialises in certain fields. Otago University has medical and dental schools, a school of mining and metallurgical engineering, a school of home science, and a school of physical education; Canterbury University has a school of engineering (mechanical, electrical, civil, and chemical), and a school of fine arts; Auckland University has a school of architecture, a school of fine arts, a school of engineering (mechanical, electrical, and civil), and a post-graduate department of obstetrics and gynaecology; and Victoria University of Wellington has a school of public administration, and a school of social science. There are also two agricultural colleges - viz, Massey and Canterbury - associated with the University (see page 240).
In 1930 a New Zealand University Amendment Act was passed to enable the University to discharge its functions under the Law Practitioners Amendment Act 1930. For this purpose a Council of Legal Education was established to make recommendations to the Academic Board of the University with respect to any matter relating to legal education. Further, the Senate of the University in making or altering statutes concerning legal education must first consider any recommendations made by the Academic Board or the Council of Legal Education. The provisions of the New Zealand University Amendment Act 1930 were amended in 1956 to allow the Council of Legal Education to make representations directly to the Senate, instead of to the Academic Board. A copy of any such recommendation to the Senate must be sent to the Academic Board so that it may forward to the Senate its comments on the recommendation.
In 1948, by means of an amendment to its own statutes and with the consent of its constituent institutions and the agricultural colleges, the University set up a University Grants Committee, through which applications for grants were placed before the Government. Under the University Grants Committee Act 1960, however, the previous Grants Committee went out of office on 31 December 1960 and was replaced by a statutory body with the same title but with somewhat extended functions. The Committee has three academic and four lay members.
The New Zealand University Amendment Act 1954 provided for the establishment of a Curriculum Committee to which the Senate of the University might delegate certain powers of approving courses, and which might in its turn delegate certain powers to the colleges and universities; the effect of this Act was to make it possible for them to achieve a considerable degree of autonomy in academic matters. This autonomy was extended further by the New Zealand University Amendment Act 1959. The amendment validates the practice of the Senate of delegating its powers in respect of the conduct of examinations to the governing bodies of its constituent institutions and the agricultural colleges.
In 1959 there were 13,290 students actually in attendance at the four universities and the two agricultural colleges. Of these, 929 were graduates, 11,168 undergraduates, and 1,193 unmatriculated students. In addition, there were 1,098 students attached to the various universities, but exempt from lectures, and 515 students who were taking short courses at the agricultural colleges. Comparable figures for the five years quoted are given in the following table.
| Year | Students Attending Lectures | Exempt Students | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| 1955 | 8,202 | 2,647 | 779 | 114 | 11,742 |
| 1956 | 7,654 | 2,541 | 747 | 135 | 11,077 |
| 1957 | 8,232 | 2,617 | 770 | 142 | 11,761 |
| 1958 | 9,015 | 2,900 | 795 | 171 | 12,881 |
| 1959 | 9,942 | 3,348 | 921 | 177 | 14,388 |
The following table gives particulars of students who were taking definite courses during 1959 and each of the preceding two years.
| Course | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Agriculture - | |||||||||
| Intermediate | 71 | 2 | 73 | 71 | 4 | 75 | 63 | 2 | 65 |
| Degree | 105 | 1 | 106 | 172 | 6 | 178 | 237 | 3 | 240 |
| Diploma | 485 | 9 | 494 | 460 | 4 | 464 | 457 | 14 | 471 |
| Other | 95 | - | 95 | 71 | - | 71 | 86 | 4 | 90 |
| Architecture - | |||||||||
| Degree | 118 | 4 | 122 | 125 | 6 | 131 | 149 | 2 | 151 |
| Diploma | 37 | 1 | 38 | 55 | 2 | 57 | 66 | 5 | 71 |
| Other | 76 | 4 | 80 | 55 | 3 | 58 | 75 | 2 | 77 |
| Arts | 2,120 | 1,582 | 3,702 | 2,383 | 1,816 | 4,199 | 2,465 | 2,082 | 4,547 |
| Commerce | 1,659 | 81 | 1,740 | 1,821 | 92 | 1,913 | 1,995 | 86 | 2,081 |
| Dentistry: Intermediate | 68 | 1 | 69 | 72 | 2 | 74 | 63 | - | 63 |
| Dentistry | 166 | 3 | 169 | 167 | 1 | 168 | 163 | 1 | 164 |
| Divinity | 40 | - | 40 | 48 | 2 | 50 | 62 | 4 | 66 |
| Education: Diploma | 142 | 58 | 200 | 111 | 35 | 146 | 118 | 56 | 174 |
| Engineering: Intermediate | 378 | - | 378 | 446 | - | 446 | 481 | - | 481 |
| Engineering | 492 | - | 492 | 540 | - | 540 | 634 | - | 634 |
| Fine Arts: Diploma | 78 | 125 | 203 | 76 | 126 | 202 | 109 | 145 | 254 |
| Home Science - | |||||||||
| Intermediate | - | 16 | 16 | 4 | 16 | 20 | - | 15 | 15 |
| Degree | - | 20 | 20 | - | 28 | 28 | - | 34 | 34 |
| Diploma | - | 108 | 108 | - | 111 | 111 | - | 127 | 127 |
| Horticulture | 18 | 9 | 27 | 16 | 13 | 29 | 16 | 3 | 19 |
| Journalism: Diploma | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | - | 2 |
| Law | 876 | 33 | 909 | 896 | 37 | 933 | 914 | 38 | 952 |
| Medical Science | 5 | 1 | 6 | 4 | - | 4 | 5 | - | 5 |
| Medicine: Intermediate | 294 | 33 | 327 | 286 | 35 | 321 | 287 | 35 | 322 |
| Medicine | 475 | 44 | 519 | 481 | 46 | 527 | 497 | 53 | 550 |
| Mining: Diploma | 19 | - | 19 | 5 | - | 5 | 5 | - | 5 |
| Music | 81 | 92 | 173 | 68 | 112 | 180 | 73 | 106 | 179 |
| Physical Education: Diploma | 23 | 60 | 83 | 27 | 52 | 79 | 32 | 47 | 79 |
| Public Administration: Diploma | 9 | 1 | 10 | 8 | - | 8 | 8 | - | 8 |
| Science | 1,040 | 239 | 1,279 | 1,210 | 281 | 1,491 | 1,396 | 343 | 1,739 |
| Social Science: Diploma | 11 | 12 | 23 | 9 | 8 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 17 |
| Other courses | 21 | 60 | 81 | 53 | 66 | 119 | 29 | 61 | 90 |
| Totals | 9,003 | 2,600 | 11,603 | 9,743 | 2,905 | 12,648 | 10,497 | 3,275 | 13,772 |
Free University Education - Free university education was instituted in 1911 for all holders of University Scholarships and, in more recent years, increasing numbers of bursaries have been awarded. The most important awards for those entering the University were the 10 University Junior Scholarships awarded by the University of New Zealand, and the 25 University National Scholarships for which funds are provided by the Department of Education. By the New Zealand University Amendment Act 1957, the number of National Scholarships was increased to 30 in 1958, to 35 in 1959, and to 40 in 1960. Both forms of scholarships are tenable for four years and provide full tuition fees, a scholarship allowance of £100 (junior) and £80 (national) plus an additional allowance of £60 (junior) and £50 (national) for students who have to live away from home. These scholarships, together with the Taranaki Scholarships and certain privately endowed scholarships, are awarded on the results of the Entrance Scholarships Examination conducted by the University of New Zealand.
Scholarships awarded during the degree course are the University Senior (£120 per annum) and John Tinline Scholarships (£90 per annum). The various universities and agricultural colleges also have private scholarships for which their own students may compete. The scholarships awarded at the end of the university course, which are listed in full in the university calendars, include the Rhodes Scholarships, the 1851 Exhibition Scholarships, the Post-graduate Scholarships in Arts and Science, the Travelling Scholarships in Commerce, Law, Engineering, Architecture, Medicine, and Dentistry, the Macmillan Brown Agricultural Scholarship, the Shirtcliffe Scholarships, the Gordon Watson Scholarship, the Shell Post-graduate Scholarship, the Michael Hiatt Baker Scholarship, the Rutherford Scholarships, the Orford Studentship, and the National Research Scholarships. All these are tenable abroad. In addition there are post-graduate scholarships tenable in New Zealand. The University of New Zealand also awards Research Fellowships, the value of which is not fixed, but the normal grants have been approximately £300 per annum for a period of two years. Each university may also award one Research Scholarship, tenable in New Zealand.
The system of bursaries for students entering upon a university course which has been in operation for a number of years was radically changed as the result of a Government decision made at the end of 1955. The new system came into effect from the beginning of 1956. No further special bursaries, national boarding bursaries, or ordinary national bursaries will be awarded. Instead, the following kinds of bursaries are tenable for four years, except for students studying medicine, dentistry, architecture, and engineering, for whom payment for a fifth year is provided.
Entrance Bursaries are awarded to part-time or full-time students who have qualified for entrance to the university either by examination or accrediting. These bursaries provide for payment of half-fees until the student has passed the equivalent of three Stage I Arts units; thereafter full fees are payable for the balance of the term for which the bursary is awarded.
H.S.C. Part-time Bursaries are awarded to part-time students who are holders of the Higher School Certificate. These bursaries provide for payment of full tuition fees.
H.S.C. Full-time Bursaries are awarded to full-time students who hold the Higher School Certificate and who are living at home. In addition to full fees, bursars receive a bursary allowance of £40 a year.
H.S.C. Boarding Bursaries are available to full-time students who are similarly qualified but who are required to live away from home or their usual place of residence in order to attend a university or college affording tuition in the subjects appropriate to their course and year. The bursary provides for full fees, a bursary allowance of £40 a year, and a boarding allowance of £50 a year.
A Bursary Allowance for Special Merit to the value of £20 in addition to the allowances already mentioned is paid to each of not more than 150 bursars who are commencing the final year of their bursary and who are nominated by the University of New Zealand for the award.
All these bursaries are subject to strict rules as to suspension and cancellation. A student who in any year does not pass in a prescribed number of units will have his bursary suspended and it will not be reinstated unless in the following year he is credited with a prescribed number of passes. Only one such suspension is allowed and subsequent failure results in cancellation of the bursary.
Full details of the amounts payable and other qualifying conditions for the various classes of bursaries are available in a vocational guidance pamphlet entitled Next Year which is issued annually by the Department of Education.
The Government offers for competition annually two bursaries to students wishing to attend the School of Social Science at the Victoria University of Wellington. Preference is given to candidates nominated by non-State organisations engaged in social work. These bursaries provide for full fees, a bursary allowance of £80, and a boarding allowance of £50 where appropriate.
The total number of University National, Entrance, and Higher School Certificate bursaries current in 1959 was 5,203.
Bursaries, etc., are also awarded annually by other Government Departments and include medical, dental, physiotherapy, and dietetic bursaries (Department of Health), national research scholarships and national research fellowships (Department of Scientific and Industrial Research), rehabilitation bursaries (Rehabilitation Board), coal-mining bursaries (Mines Department). Study awards are made to selected public servants to enable them to undertake university study. The Department of Education has a very generous system of studentships available for those intending ultimately to qualify as post-primary teachers.
From the table given below will be seen the number of students, including those taking short courses at agricultural colleges, who received free university education during each of the last five years.
| Year | Junior University, University National, and Taranaki Scholarships | Senior University Scholarships | University National, Entrance, and H.S.C. Bursaries | Training College Studentships | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 126 | 19 | 3,899 | 542 | 1,169 | 5,755 |
| 1956 | 117 | 24 | 3,900 | 525 | 1,184 | 5,750 |
| 1957 | 126 | 21 | 4,161 | 542 | 1,422 | 6,272 |
| 1958 | 139 | 23 | 4,358 | 590 | 1,875 | 6,985 |
| 1959 | 156 | 29 | 5,203 | 756 | 2,032 | 8,176 |
Holders of rehabilitation bursaries numbered 37 in 1959, 34 in 1958, 40 in 1957, 47 in 1956, and 85 in 1955.
Agricultural Colleges - There are two agricultural colleges specialising in higher agricultural education - Massey Agricultural College, near Palmerston North, and Canterbury Agricultural College, near Christchurch. The colleges are separately governed, though both are attached to the University of New Zealand. The total number of students at Massey College in 1959 was 590 and at Canterbury 808. These numbers include 94 students at Massey and 421 at Canterbury Agricultural Colleges taking short courses.
Encouragement in the development of higher agricultural education is given through Government grants to the colleges, amounting to £239,750 in 1959-60. Various research projects at the colleges have been aided by expert assistance and grants from the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
COMMITTEE ON NEW ZEALAND UNIVERSITIES - In 1959 the Committee on New Zealand Universities was set up by the Government to make recommendations on the long-term pattern of development of the university system in New Zealand. The members of the Committee were: Sir David Hughes Parry, Q.C., of the University of London (chairman); Dean G. C. Andrew, of the University of British Columbia; and Dr. R. W. Harman, of Auckland. The Committee's report was completed in December 1959 and provided a basis for the consideration of the future needs of the university system. The salary rises for most academic staff as recommended by the Committee were approved in March 1960 and later in the year increases were approved for staffs at the Medical and Dental Schools, for those in Adult Education, and for non-academic staff in the universities. Substantial increases in the recurring grants, including an increase in the Research Grant, were also approved and special library grants were made. The reconstituted University Grants Committee took up its duties on 1 January 1961 and legislative action is proposed during the 1961 session of Parliament to make the universities autonomous institutions.
CHILD WELFARE - The Child Welfare Act 1925 provided for the creation of a special branch of the Department of Education now known as the Child Welfare Division. The Act was passed to make better provision with respect to the maintenance, care, and control of children who are placed specially under the protection of the State, and to provide generally for the protection and training of indigent, neglected, and delinquent children. The powers conferred by the principal Act were further defined and extended by the Child Welfare Amendment Act 1927. The meaning of the expression “delinquent” was extended by a 1954 amendment to the principal Act.
An important section of the Act provided for the establishment of Children's Courts, to be presided over by Stipendiary Magistrates or Justices specially authorised to exercise jurisdiction in these Courts. Provision was made for the appointment of child welfare officers with wide responsibilities connected with the welfare of children. There were 181 men and women child welfare officers employed at 31 March 1960. The Act also provided for the appointment of honorary child welfare officers. These officers are people of integrity and local standing in their communities who are appointed annually by the Minister in charge of the Division. At 31 March 1960 there were 150 men and women serving in an honorary capacity.
Very wide discretionary powers are given to Children's Courts. Wherever practicable the hearings are conducted in premises apart from the Magistrate's Court, and no newspaper is permitted to publish either the names of children appearing before these Courts or any particulars that are likely to identify a child.
A child was originally defined for purposes of the Act as one under 16 years of age. This age was raised to 17 in 1927.
Children's Courts deal with cases of children brought either (a) on a complaint under the Child Welfare Act that a child is neglected, indigent, delinquent, not under proper control, or living in a detrimental environment or (b) charged with an offence. After hearing the complaint or the charge and in the light of the child welfare officer's report, the Court may, according to the needs of the case, commit the child to the care of the Superintendent of Child Welfare, or place him under supervision of a child welfare officer for a period (usually one year or two years) or discharge him with an admonition and, on occasion, an order for restitution or a fine.
The numbers of children appearing before the Children's Courts in the latest three years (ended 31 March) were as follows.
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| On “complaints” (under the Child Welfare Act) | 456 | 473 | 528 |
| For offences (including offences against Acts, regulations, or bylaws) | 3,910 | 3,904 | 3,567 |
| Totals | 4,366 | 4,377 | 4,095 |
On the basis of the total juvenile population at the time, the incidence of appearances for offences is shown as follows.
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Number of cases per 10,000 of the population aged seven to 17 years. | |||
| Total Court appearances for offences | 3,910 | 3,904 | 3,567 |
| Rate* | 87 | 83 | 77 |
| Court appearances for all more serious offences (excluding offences against special Acts, regulations, or bylaws) | 2,425 | 2,404 | 2,300 |
| Rate* | 54 | 51 | 48 |
The decisions made in Children's Courts during the year ended 31 March 1960 are shown in the summary below.
| Decision | Year Ended 31 March 1960 |
|---|---|
| Committed to the care of the Child Welfare Superintendent | 589 |
| Placed under supervision of child welfare officers | 1,383 |
| Admonished and discharged with or without costs, restitution, or fine | 1,440 |
| All other decisions | 683 |
| Total | 4,095 |
Many of the children who are committed to the care of the Superintendent of Child Welfare and who are thereby under his guardianship are placed immediately in foster homes and either at school or in employment. Those who require special care and training which cannot be provided in the ordinary life of the community are placed in institutions administered by the Superintendent. Some few reside in private institutions and some are in boarding schools.
Of the total of 10,771 children under the control and supervision of the Child Welfare Superintendent and his officers at 31 March 1960, 3,314 were under the guardianship of the Superintendent. These 3,314 children were at that date placed as shown in the following summary.
| Number | Percentage of Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Residing in individual private homes (foster homes, employers' or relatives' homes) | 2,657 | 80.2 |
| In institutions administered by the Child Welfare Division (including those temporarily admitted) | 411 | 12.4 |
| In mental hospitals | 100 | 3.0 |
| In residential schools and colleges (including schools for handicapped children) | 86 | 2.6 |
| In hospitals, convalescent homes, etc. | 11 | 0.3 |
| In children's homes (including orphanages, etc.) | 44 | 1.3 |
| Attending university or teachers' training college | 5 | 0.2 |
For the children requiring institutional care and training the Child Welfare Division administers several different types of institution. The Girls' Training Centre at Burwood, Christchurch, and the Boys' Training Centre at Levin each provide for the more difficult or disturbed girls or boys. The centres are open institutions providing full educational facilities with qualified and trained teachers and also a wide range of vocational training. Another small institution at Featherston provides specially for Maori girls who, while not seriously difficult, require some training before placement in the community. Two small hostels for girls at Wellington and at Christchurch provide for those who, while in ordinary employment, require for the time being the conditions of supervision and care obtainable in a hostel. There are 11 receiving homes and boys' homes in the larger centres providing for temporary care and observation.
Children not requiring institutional care but presenting behaviour and personality problems beyond the capacity of most ordinary foster parents are provided for in “Family Homes”. These are private houses owned by the Division and occupied rent-free by specially selected married couples who agree to care for children on a long-term basis, as a condition of the tenancy. These homes are also used to provide transit accommodation in areas in which there is no receiving home or boys' home. There are 12 of these homes at present in operation throughout the country and more are planned.
Children placed by the Courts under supervision of child welfare officers are supervised in their own homes, except that in a few cases, with the approval of the parents or guardians, the child welfare officer arranges placement elsewhere - e.g., in employment. Magistrates have the authority to order that part or all of the period of supervision be spent in an institution. Most children placed under supervision respond well; where they do not they may appear before the Court again and be committed to the care of the Superintendent. There were 1,700 children under supervision at 31 March 1960.
Preventive cases, numbering 3,426 at 31 March 1960, consist of children who, without any Court appearance, are being supervised and assisted by child welfare officers under arrangements made voluntarily with the parents or guardians.
Child welfare officers undertake a wide variety of miscellaneous investigations and inquiries concerning the welfare of children. In the year ended 31 March 1960, 11,971 cases were handled. Cases may be referred by neighbours, police, teachers, employers, doctors, solicitors, etc., or by parents themselves who are seeking advice and guidance. Some of these cases will respond quickly to help. Others may need preventive oversight and guidance over several months or even two or three years. Financial help can be given in special cases. In a relatively small number of cases preventive help is not sufficient and Court action is the outcome of inquiries.
As provided for in the Child Welfare Act 1925, child welfare officers, on receiving from the Registrars notifications of ex-nuptial births, make confidential inquiries and assist the mother as necessary in making provision for her child.
Child welfare officers administer the provisions of the Infants Act 1908 by which children under six years of age living apart from their parents or guardians for more than seven consecutive days are required to be in licensed foster homes. At 31 March 1960, 809 such children were being supervised.
Under the Adoption Act 1955 a child welfare officer must give prior approval to the placement for adoption of a child under 15 years, or alternatively, the applicants must apply for an interim order of adoption from the Court. The Court is required to obtain a child welfare officer's report on such a placement before granting an order. A waiting period of at least six months is required, during which the placement is supervised by a child welfare officer, before a final order can be made.
The Division also has a measure of responsibility towards handicapped children generally, partly because of its role in assisting in the administration of residential schools for deaf children or for backward children. Child welfare officers, more especially in country areas, also assist in locating children who require special education, in advising parents or teachers concerning the facilities available, and in ensuring that the circumstances become known to appropriate agencies.
Inspection of children's homes operated by private organisations and administration of schemes of Government financial assistance to these homes is another important function of the Division. Financial assistance is given in the form of capitation payments for children in care and subsidies of up to 50 per cent on expenditure for extension or replacement of buildings or additions to facilities.
The Child Welfare Amendment Act 1958 provided for the making of regulations for the registration and licensing of “Child Care Centres” (e.g., day nurseries, creches, etc.). These regulations were made on 7 November 1960 and came into force on 1 March 1961.
COUNCIL FOR EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH - In 1933 the Carnegie Corporation of New York set up a committee to report on the proposal to found in New Zealand a Council for Educational Research. This committee called a conference of representative educationists to consider the proposal and approached educational authorities for their cooperation. In view of the unanimous support given to the proposal, the committee recommended the foundation of the Council, and in November 1933 the Carnegie Corporation appropriated a substantial grant for the purpose, payable in five-yearly instalments, beginning in 1933-34. In 1938 the corporation extended the grant to cover a second five-year period, from 1940 to 1944.
When the corporation grants ceased in 1944 the Government passed legislation giving statutory existence to the Council, and since 1945 has made an annual grant to it. In 1953 the Government grant was raised from £3,000 to £4,000, and again raised to £6,000 in 1959. The corporation has continued to show an interest in the work of the Council, and from time to time has made smaller grants for specific purposes.
The Council has concentrated on New Zealand problems, and many of its publications (39 research reports and 17 shorter studies in education) consist of critical surveys on various aspects of New Zealand education and of accounts of outstanding experiments in school practice. The work done under the auspices of the Council has been carried out not only by its own permanent staff but also by part-time investigators.
In addition to its activities as a research organisation, the Council acts as a clearing house for information on educational matters.
The Council's activities are under the control of a permanent officer (the director), who is assisted by a staff of three. There are local institutes for educational research in Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin.
ADULT EDUCATION: National Council of Adult Education - In 1938 an Education Amendment Act provided for the establishment of a Council of Adult Education to coordinate activities of adult education, to make recommendations to the Minister of Education concerning the amount and distribution of the annual grant, and to receive reports from the bodies to whom grants were made.
The Adult Education Act 1947, which followed largely the recommendations of a Consultative Committee reporting in the same year, abolished the Council and set up a National Council of Adult Education with much wider powers. The functions of the National Council are:
To promote and foster adult education and the cultivation of the arts; and
To make recommendations to the Minister of Education as to the amount of the annual grant to be made to the National Council of Adult Education out of moneys appropriated by Parliament for the purpose, and to receive, administer, and control the expenditure of such moneys granted.
The National Council has power to appoint staff and to impose conditions on grants made by it. The full-time executive officer of the Council, the National Secretary of Adult Education, is located in Wellington. The National Council comprises the Director of Education, the Director of Broadcasting, the Director of the National Library Service, or their representatives; one member appointed by the Senate of the University of New Zealand; two members appointed by each of the four universities; one member appointed by the Dominion Council of the Workers' Educational Association; one member appointed by the Minister of Education to represent the Maori race; and up to two members appointed by the Council itself.
Regional Councils of Adult Education - Staff for field work in adult education is employed by the Councils of the four constituent institutions of the University of New Zealand. Each University Council has the advice of a Regional Council of Adult Education, to which certain of the powers of the University Council are delegated. The four Regional Councils are differently constituted, but the 1947 Act requires that at least one-half of the members shall be persons appointed on the nomination of voluntary associations or organisations engaged or interested in adult education in the district. In each region the teaching staff consists of a director, “general purpose” tutors, and specialist tutors. The work supervised by the Regional Councils covers a wide range of interests - lecture courses, discussion courses, and various forms of assistance to specially organised groups or groups formed originally for other purposes, in both town and country. An important recent development has been the establishment of the Community Arts Service, which arranges for visits of exhibitions, musicians, and drama and ballet groups to country centres. The Regional Councils also organise short-term summer and winter schools in town and country.
Voluntary Agencies - The tutors, working under the direction of the Regional Councils of Adult Education, offer assistance to a large number of voluntary agencies such as parent-teacher associations, home and school societies, play centre associations, and groups concerned with drama, music, and art.
The Country Women's Coordinating Committee, representing both the Women's Division of Federated Farmers and the Women's Institutes, organises classes in rural areas and is supplied with tutors by the Regional Councils.
The Workers' Educational Association operates in conjunction with the universities and organises classes, mostly one-year classes, in the main cities and in a few of the larger towns. Tutors for these classes are provided by the Regional Councils of Adult Education. The Regional Councils also now conduct much of the country work formerly organised by the Workers' Educational Association. The Workers' Educational Association is financed by grants from the National Council of Adult Education and donations from local authorities, trade unions, and private individuals.
Education of New Settlers - The large number of new settlers who have come to New Zealand from European countries in recent years has led to the establishment of evening classes for teaching English and what may broadly be called civics. Several thousands of new settlers have now passed through these classes and many are now becoming naturalised New Zealand citizens. For those persons not in the position to attend classes, a correspondence course is provided. Special textbooks and other material have been prepared for use by teachers and students. The classes are normally held at technical colleges.
Community Centres - In 1938 an experimental community centre was established at Feilding under the supervision of two experienced educationists specially appointed to the staff of the Feilding Agricultural High School. Classes have been conducted in drama, child care, literature, art appreciation, and physical welfare, both at the centre and in outlying areas. In 1944 a community centre was opened in a suburb of Christchurch. Subsequently, experimental centres were opened in Westport, Wakari, Hawera, and in the coal-mining districts of the Buller. All these receive some assistance, directly or indirectly, from public funds. There are, however, many other community centre schemes supported by voluntary effort.
The Adult Education Act 1947 gave the Minister of Education power to establish or recognise community centres and to make grants to them.
NATIONAL LIBRARY SERVICE - The establishment of a National Library Service by the Minister of Education in 1945 followed a recommendation by the New Zealand Library Association. The National Library Service has four divisions - the Country Library Service, the School Library Service, the National Library Centre, and the Library School.
Country Library Service - The Country Library Service, founded in 1938 under the control of the Minister of Education, has been extended through district offices for closer contact with participating libraries. It assists library authorities in country districts and towns with a population of less than 15,000 by loans from book vans, request service, and subject loan collections. Libraries in towns with a greater population, excluding the four main centres, receive assistance under certain conditions. Free loans of books are made to libraries controlled by local authorities, both borough and county, which operate a free service locally and maintain it at a reasonable standard of efficiency. Subscription libraries in country districts - i.e., outside the area of boroughs and town districts - may hire books at the rate of £3 for 50. Seven specially equipped vans, each carrying 1,600-2,000 books covering a wide range, travel over the whole territory so that both free and subscription libraries can make their own exchanges every four months. In between visits books go by post from the headquarters and district offices to libraries requesting them. Hampers of books are sent to isolated groups of readers.
Free public libraries which extend their service to general hospitals in their area receive special collections of books for the use of patients. A library service is given to lighthouses, and a service to Ministry of Works, Electricity Department, and New Zealand Forest Service camps has been given since 1949. Tuberculosis patients in sanatoria and in tuberculosis wards of general hospitals are served from a special collection of books built up to meet their particular needs. Mental hospitals receive collections of books which are exchanged regularly. Prisons and borstal institutions receive books and change them on the four-monthly visits of the travelling book vans.
The number of libraries obtaining books from the Country Library Service on 31 March 1960 was as follows: free libraries, 118; subscription libraries, 881; groups, 32; Ministry of Works, Electricity Department, and New Zealand Forest Service camps, 54; tuberculosis sanatoria, 13; mental hospitals, 13; hospitals, 18; prisons and borstal institutions, 15.
School Library Service - The launching of the School Library Service, operating on a circulating basis, has been a most important development. This service, which is financed by the Department of Education and administered by the National Library Service, aims at giving children access to the best literature.
At 31 March 1960 regular exchanges of children's and young people's books were being sent to a number of public libraries and to 2,510 schools. The schools served are primary, both public and private, intermediate, and district high schools. Pupils of the Correspondence School also receive books regularly.
All schools, including post-primary schools, receive additional books on request. Some 443,518 requests were filled during the year ended 31 March 1960.
The total number of books circulated during the same period was 1,319,221.
National Library Centre - The National Library Centre is responsible for the professional work of the headquarters sections of the National Library Service, including the purchase of books and periodicals for Government Departments operating within the Public Account. It also undertakes various bibliographical projects such as the maintenance of the Union Catalogue of Non-fiction Books, the Union List of Serials, and a National Bibliography of New Zealand publications. The Centre's other main functions, developed in conjunction with the Book Resources Committee of the New Zealand Library Association, are concerned with the national system of inter-library loan and the necessary steps to ensure the availability through New Zealand libraries of at least one copy of all books of any consequence published in the English language. The headquarters collection of the service now amounts to about 155,000 volumes.
Library School - The Library School was established in 1946, and at the end of 1959, 248 students had taken the course.
The school offers professional training to those holding university degrees or with equivalent education. The course lasts from March to November.
Students receive allowances equal to those paid to students of teachers' training colleges.
Short courses for librarians of smaller libraries were held in 1947, 1948, 1950, 1957, and 1958. A short course for librarians of Government Departments was held in 1949, and the Library School has collaborated in holding short courses for teacher-librarians. Since 1952, Part Two of the New Zealand Library Association's General Training Course has been carried out by a five weeks' course at the school. Facilities for training are offered to students sponsored by UNESCO and by countries participating in the Colombo Plan.
PACIFIC ISLANDS EDUCATION - The Department of Education has always taken an active interest in education in the Pacific islands, but it was not until 1946 that a Division was set up in the Department to act as a liaison unit to the Department of Island Territories and to assist other administrations including those in Fiji, Tonga, the Gilbert and Ellice Islands, and Pitcairn Island with their educational problems.
As part of this assistance, the Department of Education recruits an average strength of 150 education officers and teachers, inspects them and protects their rights against their return to New Zealand. The Officer for Islands Education maintains a small staff including two inspectors, a scholarships officer, and two textbook writers to provide assistance in a large variety of ways. Apart from advisory visits to most of the islands, supplies of modern texts and apparatus are sent regularly by this Division. Several publications have been produced recently.
In addition, a very important function of the Division is to operate and supervise closely a scholarship system which enables 184 islands students to obtain in New Zealand schools, trade training centres, and universities, more advanced education than would otherwise be available to them. During the term of their scholarship these students are fully maintained by the Department of Island Territories. In 1959, approximately 230 other students from Fiji and Tonga, the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, and the Gilbert and Ellice Islands were supervised and assisted in obtaining the benefits of a more varied or advanced education than they could gain in the islands.
The following table shows the numbers of teachers and estimated numbers of pupils in the areas receiving some help from the Islands Education Division of the Department of Education for the year 1959.
| Territory | Teachers | Pupils | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | Local | Primary | Secondary | Total | |
| *Indicates areas where New Zealand assists but has no administrative authority. | |||||
| Fiji* | 68 | 2,457 | 76,182 | 5,439 | 81,621 |
| Western Samoa | 37 | 836 | 24,790 | 593 | 25,383 |
| Cook Islands | 28 | 230 | 4,760 | 190 | 4,950 |
| Niue | 10 | 79 | 1,217 | 56 | 1,273 |
| Tonga* | 9 | 681 | 14,811 | 3,482 | 18,293 |
| C.A.A., Nandi | 4 | - | 120 | - | 120 |
| Tokelau Islands | - | 21 | 530 | - | 530 |
| Totals | 156 | 4,304 | 122,410 | 9,760 | 132,170 |
LAW OF NEW ZEALAND - The law applied in the Courts of New Zealand has three principal sources - the common law of England, certain statutes of the United Kingdom Parliament enacted prior to 1947, and statutes of the New Zealand Parliament.
The initial law of New Zealand when it became a British colony was the law of England as it existed on 14 January 1840 - that is, the common law together with those statutes of the United Kingdom Parliament which were applicable to the circumstances of the colony at that date. Subsequent law consists of those enactments of the United Kingdom Parliament between 1840 and 1947 which extended expressly or by necessary implication to New Zealand, and the enactments of the New Zealand Legislature.
In interpreting the common law the Courts have been concerned to preserve uniformity with common law interpretation in England. This unity is ensured not only by the existence of the Privy Council as the final Court of appeal for New Zealand, but by the practice of the Judges of following English decisions even though they are in theory not bound by them.
The New Zealand Parliament is now the sole authority with inherent power to legislate for the country, and there are no constitutional restrictions on the law which it can pass. Before the adoption by New Zealand of the Statute of Westminster in 1947 the powers of Parliament were limited in two respects. First, there was a somewhat uncertain and ill defined incapacity to make laws having extra-territorial application, and, secondly, there was an incapacity to make laws conflicting with a statute of the United Kingdom Parliament extending to New Zealand. Since 1947, however, both these limitations have disappeared, although the United Kingdom Parliament still has the power to make laws extending to New Zealand at the request and with the consent of the New Zealand Legislature.
REVISION OF LAW - In any progressive society the law requires alteration from time to time if it is to reflect the life of the community and adequately give effect to the needs of the people. As in other countries in modern times legislation is by far the most important means by which the law of New Zealand is adapted to changing circumstances. The responsibility of bringing before Parliament proposals for the revision of the common law and that part of the statute law not administered by other Departments of State is in the hands of the Attorney-General and Minister of Justice. In formulating these proposals the Attorney-General is assisted by the Department of Justice and by the Law Revision Committee, an informal advisory body first set up in 1937. In addition to the Attorney-General, who is chairman, the Committee (at the beginning of 1960) comprised two representatives of the Parliamentary Opposition, the Permanent Heads of the principal legal Departments of State (the Solicitor-General, the Law Draftsman, and the Secretary for Justice), two representatives of the New Zealand Law Society, two representatives of the university faculties of law, and a former Solicitor-General.
The purpose of the Law Revision Committee is to bring into the work of reforming the law the principal groups, both inside and outside the ordinary Government machinery, which by their interest or expert knowledge can contribute in a special way to this task. The existence of the Law Revision Committee ensures that before proposals for the amendment of the law are put forward for Parliamentary approval they have been considered from many different points of view and have secured a substantial measure of informed support.
COURTS - The hierarchy of Courts in New Zealand comprises the Court of Appeal, the Supreme Court, and the Magistrates' Court.
The constitution of the Court of Appeal was completely altered by the Judicature Amendment Act 1957. Previously the Court of Appeal in New Zealand was not separate from the Supreme Court. The Court of Appeal as first established by the Court of Appeal Act 1862 consisted of all the Judges of the Supreme Court of whom two formed a quorum. Under the Judicature Act 1908 the Court of Appeal comprised two Divisions, each consisting of five or six Judges of the Supreme Court. The allocation of Judges to the two Divisions was made by the Governor-General in Council on the recommendation of the Chief Justice and two other Judges. While this system was well suited to the circumstances of the country in earlier years, the increasing population and complexity of society, and the increase in the business of the Courts to which this led, made desirable the establishment of a separate Court of Appeal such as exists in other Commonwealth countries.
As constituted by the Judicature Amendment Act 1957 the Court of Appeal consists of the Chief Justice by virtue of his office as head of the judiciary and of a President and two Judges of the Court of Appeal appointed by the Governor-General. An additional Judge or Judges of the Supreme Court may be nominated by the Chief Justice to sit on the Court of Appeal in any particular case where it is expedient. The Judges of the Court of Appeal are also Judges of the Supreme Court, but have seniority over all other Judges of that Court except the Chief Justice or the acting Chief Justice.
The Court of Appeal may from time to time appoint ordinary or special sittings and may make rules in respect of places and times for sittings and similar matters.
The Court of Appeal, unlike other Courts, exercises an appellate jurisdiction only. In addition to ordinary appeals from the Supreme Court, certain other proceedings in inferior Courts may, on an order from the Supreme Court, be removed into the Court of Appeal for argument. It may be noted that the Court of Appeal also determines criminal appeals under the Criminal Appeal Act 1945 which is discussed later in this section.
All decisions of the Court of Appeal are final unless leave is granted to appeal to the Privy Council. This leave may be granted either by the Court of Appeal or by the Privy Council itself. The Privy Council thus remains the final Court of appeal in all civil cases and also occasionally hears appeals in special criminal cases.
The Supreme Court, which was first established by the Supreme Court Ordinance 1841, is now constituted under the Judicature Act 1908. The Members of the Court are a Chief Justice and 14 other Judges, the number being fixed by statute. An amendment in 1953 provides, however, that an additional Judge or Judges may be appointed whenever the Governor-General deems it necessary by reason of absence or anticipated absence of any of the Judges on leave prior to retirement, each appointment being a permanent one from the time when it is made. The fixing of the number of Judges, together with the provision that the salary of a Judge shall not be diminished during his term of office, is an important safeguard for the principle of judicial independence. Judges, who retire at 72, are appointed to hold office during good behaviour and may be removed only by the Queen upon an Address by the House of Representatives. The Governor-General may suspend a Judge upon a like Address.
Magistrates' Courts are now set up under the Magistrates' Courts Act 1947 and possess an extensive jurisdiction in both civil and criminal cases. The jurisdiction of the Court is exercised by Stipendiary Magistrates, whose number is limited by statute to 40, there being 36 at present holding office. Justices of the Peace, however, still sit as a Magistrates' Court to hear a limited number of minor criminal charges.
Stipendiary Magistrates must have been qualified as barristers and solicitors of the Supreme Court for at least seven years. They are appointed by the Governor-General, and under the Magistrates' Courts Act 1947 may be removed by the Governor-General for inability or misbehaviour only. They retire at 68 years of age.
Apart from these Courts of general jurisdiction there are in New Zealand several Courts with specialist functions. These include the Court of Arbitration, which makes awards governing pay and working conditions in industry, and also makes general wage orders; the Compensation Court, which determines claims under the Workers' Compensation Act; the Land Valuation Court, which determines disputes over the valuation of land and hears claims for compensation when land is taken for public purposes; and the Maori Land Court and Maori Appellate Court, which have jurisdiction in respect of questions relating to Maori land.
JURIES - The institution of the jury is regulated in New Zealand by the Juries Act 1908. Subject to certain exceptions, every male British subject (other than a Maori) between 21 and 65 years resident within 15 miles of a Supreme Court centre is liable to serve on a jury. There is provision for Maoris to serve on juries in criminal cases where both the victim and the accused are Maoris and in civil cases where one of the parties is a Maori.
A new list of exempted persons was enacted by the Juries Amendment Act 1951, the principal change being the removal of most Government employees from the class of exempted persons.
The following is a summary of the persons now exempted from jury service:
Members of the Executive Council and of the House of Representatives; Judges of the Supreme Court and of the Compensation Court; Judges and Members of the Court of Arbitration and of the Land Valuation Court; Judges and Commissioners of the Maori Land Court; Magistrates; Visiting Prison Justices; Coroners; the Chairman of the Local Government Commission; the Chairman and Members of the Licensing Control Commission; Officers of Parliament; clergymen; persons wholly engaged in teaching and school inspectors; barristers and solicitors; medical practitioners and dentists; registered chemists; members of the armed forces; members of the Police Force and traffic officers; pilots, masters, and crews of vessels; members of fire brigades; and certain officers of the Department of Justice, including those engaged in Court or prison work.
Provision was made by the Women Jurors Act 1942 for women to serve on juries. Women between the ages of 25 and 60 who would be liable for jury service if they were men may have their names placed on the jury list, but there is no obligation for them to do so. In fact, very few women have volunteered for jury service.
Special juries are provided for in section 71 of the Juries Act. That section provides that in a civil action in the Supreme Court triable by jury either party may, by leave of the Court or a Judge thereof, procure trial by a special jury instead of a common jury. Except with the consent of all the parties, however, no action may be tried with a special jury unless in the opinion of the Court or a Judge difficult questions in relation to scientific, technical, business, or professional matters are likely to arise.
New Zealand still retains the Grand Jury as part of its legal system, although it has been abolished in most other countries outside the United States of America, where it performs a different function.
CIVIL JURISDICTION: Magistrates' Courts - From the beginning of settlement in New Zealand there has existed a speedy and inexpensive forum for determining everyday disputes between citizens. From 1846 to 1925 there were two types of Lower Court, as well as the Supreme Court. Resident Magistrates' Courts (from 1893 called Magistrates' Courts) dealt with the smallest claims, while larger minor claims were determined first by Courts of Requests, and from 1858 by District Courts.
The most important feature of this period was the gradual replacement of the three-tier structure by a two-tier structure as the jurisdiction of Magistrates' Courts became more extensive and the District Courts fell gradually into disuse. The jurisdiction of the Magistrates' Courts was considerably extended in 1893, but the main reason for the increasing importance of these Courts was the requirement, first introduced in 1913, that every Magistrate should be a qualified barrister and solicitor. In 1925 District Courts were formally abolished, leaving the Magistrates' Courts and the Supreme Court as the sole Courts with general jurisdiction.
Before 1947 the jurisdiction of Magistrates' Courts was limited (a) as to amount, the maximum sum which could be claimed being £300, and (b) as to remedies, which virtually limited jurisdiction to claims for debt or damages.
The Magistrates' Courts Act 1947 revised the whole framework of Magistrates' Courts procedure, which had been substantially unchanged for 80 years, and brought it into line with present-day jurisdiction and requirements. The jurisdiction of the Court was also widened. It may now hear all claims up to £500, but if the parties agree in writing that the Court shall hear their case it has jurisdiction whatever the amount claimed. In the exercise of this jurisdiction it may now grant the same remedies, legal and equitable, as the Supreme Court.
The following table shows the number of plaints entered, cases disposed of, amounts sued for, and amounts for which judgment was recorded in the Magistrates' Courts during the latest 11 years.
| Year | Plaints Entered | Cases Disposed of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Total Amount Sued for | Number | Total Amount Claimed | Total Amount for Which Judgment Entered | |
| £ | £ | £ | |||
| 1949 | 34,403 | 994,291 | 17,694 | 550,362 | 463,995 |
| 1950 | 35,747 | 1,209,988 | 18,090 | 553,021 | 460,910 |
| 1951 | 38,966 | 1,331,375 | 20,111 | 733,562 | 588,300 |
| 1952 | 46,836 | 1,701,963 | 24,753 | 880,840 | 743,680 |
| 1953 | 53,277 | 2,183,452 | 29,842 | 1,180,275 | 1,014,240 |
| 1954 | 58,156 | 2,496,388 | 32,932 | 1,288,545 | 1,064,327 |
| 1955 | 66,078 | 2,843,109 | 38,475 | 1,502,398 | 1,318,362 |
| 1956 | 72,746 | 3,066,946 | 43,872 | 1,859,033 | 1,599,585 |
| 1957 | 79,000 | 3,212,820 | 46,477 | 1,865,331 | 1,575,680 |
| 1958 | 82,493 | 3,182,053 | 50,094 | 1,819,169 | 1,575,016 |
| 1959 | 80,856 | 2,885,959 | 51,386 | 1,805,710 | 1,570,604 |
The average amount claimed in each plaint has risen from almost £29 in 1949 to over £35 in 1959.
Supreme Court—The jurisdiction of the Supreme Court is twofold, original and appellate. It has by statute a general jurisdiction to administer the laws of New Zealand. One important aspect of this original jurisdiction is an inherent power to control inferior Courts and judicial tribunals through the writs of certiorari and prohibition. This is essentially a power to determine the limits of jurisdiction of other Courts and is to be distinguished from its appellate function by which the Supreme Court reviews a case which was properly heard and determined by a lower Court. An appeal to the Supreme Court lies only where it is provided for by statute. With certain exceptions, all cases determined in the Magistrates' Court are subject to appeal to the Supreme Court.
The next table shows the number of actions commenced, cases tried, and judgments entered, together with the amounts for which judgments were recorded in the civil jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in the latest 11 years.
| Year | Number of Actions Commenced | Cases Tried | Judgments Recorded | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Jury | Without Jury | Number | Amount | ||
| £ | |||||
| 1949 | 1,208 | 108 | 293 | 241 | 158,202 |
| 1950 | 1,059 | 90 | 268 | 202 | 108,132 |
| 1951 | 1,135 | 91 | 224 | 218 | 169,440 |
| 1952 | 1,451 | 125 | 302 | 242 | 182,036 |
| 1953 | 1,435 | 106 | 282 | -- | 232,733 |
| 1954 | 1,527 | 130 | 237 | -- | 291,041 |
| 1955 | 1,614 | 137 | 198 | -- | 255,513 |
| 1956 | 1,735 | 146 | 199 | -- | 400,341 |
| 1957 | 1,817 | 144 | 206 | -- | 354,528 |
| 1958 | 1,931 | 153 | 242 | -- | 467,872 |
| 1959 | 2,136 | 138 | 240 | -- | 585,891 |
Court of Appeal—During the five years 1955 to 1959 there were 136 civil appeals, of which 47 were allowed, and also six cases removed to the Appeal Court, resulting in three judgments for the plaintiffs and three for the defendants.
CRIMINAL JURISDICTION: Magistrates' Courts—The criminal jurisdiction of Magistrates' Courts has gradually grown out of the general jurisdiction historically enjoyed in respect of minor offences by Justices of the Peace. The Court previously had power to deal with all summary cases — that is, cases where a statute provides that an offence shall be dealt with summarily — and with a few indictable offences. Since 1952, however, Magistrates have had jurisdiction, which is now given by the Summary Proceedings Act 1957, to deal with the majority of indictable offences. This Act gives a Magistrate jurisdiction over all crimes against property and all but the most grave of other crimes, such as treason, homicide, rape, and perjury. If the Magistrate deals summarily with an indictable offence, he may impose a sentence of imprisonment of up to three years or a fine of up to £200. A Magistrate may, however, decline to deal with an offence summarily, in which case the accused is committed for trial in the Supreme Court in the ordinary way. The accused person has, moreover, the right to claim jury trial if he is charged with any indictable offence punishable by imprisonment for more than three months.
Justices of the Peace now hear only a small number of summary cases where the statute creating the offence provides that one Justice or two or more Justices are to have power to deal with it, or where jurisdiction is expressly conferred on Justices in a particular case. This is provided for in the Summary Proceedings Act and is a departure from the previous law, under which Justices had jurisdiction in all summary cases unless otherwise provided. The tendency is to have all but the most trivial criminal cases dealt with by Stipendiary Magistrates, although the extent to which this is practicable varies from district to district.
The following table shows the number of criminal charges dealt with in Magistrates' Courts in the latest 11 years. These figures and all the figures relating to Magistrates' Courts, Supreme Court, and prisons include Maoris; Children's Court cases are excluded and will be found under the section relating to juvenile offences.
| Year | Number | Per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Against Males | Against Females | Total | Against Males | Against Females | Total | |
| 1949 | 54,768 | 2,883 | 57,651 | 58.35 | 3.09 | 30.80 |
| 1950 | 55,536 | 2,915 | 58,451 | 58.18 | 3.05 | 30.62 |
| 1951 | 60,106 | 3,002 | 63,108 | 61.46 | 3.09 | 32.40 |
| 1952 | 78,536 | 3,666 | 82,202 | 78.26 | 3.69 | 41.18 |
| 1953 | 85,895 | 4,606 | 90,501 | 83.38 | 4.52 | 44.17 |
| 1954 | 84,200 | 3,977 | 88,177 | 79.93 | 3.82 | 42.09 |
| 1955 | 82,218 | 4,317 | 86,535 | 76.41 | 4.06 | 40.46 |
| 1956 | 91,314 | 5,262 | 96,576 | 83.18 | 4.85 | 44.24 |
| 1957 | 104,142 | 5,655 | 109,797 | 92.77 | 5.09 | 49.18 |
| 1958 | 113,506 | 6,804 | 120,310 | 98.72 | 5.99 | 52.63 |
| 1959 | 106,360 | 6,622 | 112,982 | 90.59 | 5 71 | 48.39 |
The great majority of these charges are, as may be expected, for comparatively minor offences, particularly against the traffic laws. Traffic offences alone accounted for more than two-thirds of the convictions in the Magistrates' Courts in 1959; of the 101,655 convictions, 69,893 were for traffic offences, while 4,297 were for offences against the liquor laws, and 4,556 for drunkenness.
The following table classifies the convictions in Magistrates' Courts into more common offences or groups of offences for the latest five years. The figures refer to total charges, with the corresponding number of distinct cases following the totals in each year.
| Type of Offence | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Counting only the principal offence in cases where a person is charged simultaneously with two or more offences. | |||||
| Common assault | 760 | 889 | 870 | 956 | 843 |
| Sexual offences | 412 | 405 | 475 | 518 | 407 |
| Other offences against the person | 288 | 212 | 199 | 233 | 176 |
| Theft | 2,630 | 3,164 | 3,537 | 4,496 | 3,997 |
| Wilful damage | 536 | 568 | 832 | 908 | 734 |
| Other offences against property (including forgery) | 3,079 | 4,007 | 4,371 | 5,222 | 5,508 |
| Drunkenness (including drunk in charge, etc.) | 5,983 | 6,016 | 5,941 | 4,886 | 4,556 |
| Application for prohibition order | 1,012 | 970 | 1,005 | 818 | 696 |
| Offensive conduct or language, obstruction, etc., of police, and vagrancy | 1,573 | 1,938 | 2,411 | 2,167 | 2,164 |
| Minor traffic offences | 43,250 | 50,187 | 59,707 | 71,452 | 67,960 |
| Other offences against good order | 1,269 | 1,983 | 1,059 | 1,221 | 921 |
| Breach of probation | 201 | 323 | 298 | 345 | 356 |
| Unlawfully on licensed premises and other breaches of Licensing Act | 5,401 | 5,569 | 5,962 | 4,781 | 4,297 |
| Failing to furnish return and making false return of land and income | 4,147 | 3,271 | 4,013 | 2,253 | 1,763 |
| Failing to pay maintenance | 1,436 | 1,360 | 1,552 | 1,640 | 1,690 |
| Deserting merchant ships | 369 | 519 | 322 | 286 | 139 |
| Breaches of price control orders | 254 | 155 | 57 | 64 | 168 |
| Other offences | 5,206 | 5,858 | 6,036 | 6,545 | 5,280 |
| Totals | 77,806 | 87,394 | 98,647 | 108,791 | 101,655 |
| Distinct cases* | 63,569 | 71,802 | 79,741 | 87,745 | 82,307 |
The total convictions (101,655) for 1959 represent a rate of 43.54 per 1,000 of mean population.
Comparing 1959 with the previous year, the larger increases according to types of offence were as follows:
| Other offences against property (including forgery) | 286 |
| Breaches of price control orders | 104 |
| Major decreases according to types of offence were as follows: | |
| Common assault | 113 |
| Sexual offences | 111 |
| Theft | 499 |
| Wilful damage | 174 |
| Drunkenness | 330 |
| Applications for prohibition orders | 122 |
| Minor traffic offences | 3,492 |
| Other offences against good order | 300 |
| Unlawfully on licensed premises and other breaches of Licensing Act | 484 |
| Failing to furnish, and making false, return of land and income | 490 |
| Deserting merchant ships | 147 |
| Other offences | 1,265 |
The next table classifies the result of hearing and punishment inflicted on summary conviction for all cases during 1959.
| Result of Hearing | Offences Against the Person | Offences Against Property | Offences Against Good Order | Other Offences | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dismissed, withdrawn, or struck out | 464 | 1,569 | 4,013 | 4,624 | 10,670 |
| Committed for trial or sentence | 126 | 461 | 19 | 38 | 644 |
| Admonished and discharged | - | 5 | 7 | 1 | 13 |
| Imprisonment | 453 | 3,161 | 892 | 463 | 4,969 |
| Corrective training | 14 | 269 | 4 | 8 | 295 |
| Detention in borstal institution, etc. | 20 | 1,330 | 21 | 54 | 1,425 |
| Released on probation | 104 | 2,107 | 194 | 63 | 2,468 |
| Convicted and ordered to come up for sentence | 77 | 191 | 152 | 34 | 454 |
| Fined | 692 | 2,322 | 71,527 | 9,315 | 83,856 |
| Convicted and discharged (or pay costs) | 66 | 859 | 3,221 | 560 | 4,706 |
| Suspended imprisonment (maintenance cases) | - | - | - | 1,459 | 1,459 |
| Miscellaneous | - | - | 783 | 1,240 | 2,023 |
| Totals | 2,016 | 12,274 | 80,833 | 17,859 | 112,982 |
| Distinct cases | 1,639 | 5,657 | 69,635 | 13,580 | 90,511 |
Traffic Offences — Traffic offences form so large a proportion of summary convictions that a further analysis is of interest. The most frequent traffic offences are breaches of parking regulations and excessive speed.
The following table analyses all traffic convictions dealt with in Magistrates' Courts for the latest five years.
| Offence | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negligently driving motor vehicle causing death | 46 | 30 | 46 | 36 | 29 |
| Drunk in charge of motor vehicle causing death | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| Negligent driving causing injury | 34 | 29 | 24 | 33 | 30 |
| Drunk in charge of motor vehicle causing injury | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - |
| Failing to stop motor vehicle after accident involving bodily injury | 47 | 36 | 22 | 27 | 18 |
| Unlawfully converting vehicle to own use | 710 | 932 | 829 | 1,088 | 1,135 |
| Drunk in charge of motor vehicle | 933 | 875 | 957 | 786 | 711 |
| Drunk in charge of other vehicle | 18 | 18 | 12 | 14 | 10 |
| Excessive speed in motor vehicle | 8,540 | 10,422 | 11,616 | 15,963 | 16,590 |
| Negligent or dangerous driving of motor vehicle | 8,488 | 8,898 | 11,602 | 12,849 | 11,437 |
| Negligent or dangerous driving of other vehicle | 130 | 125 | 108 | 77 | 128 |
| Breaches of regulations for the lighting of vehicles | 2,274 | 2,438 | 2,627 | 2,782 | 3,092 |
| Offences relating to the registration, etc., of motor vehicles | 4,747 | 4,536 | 4,895 | 6,003 | 6,105 |
| Offences relating to driver's licence | 3,318 | 3,167 | 3,684 | 3,776 | 3,727 |
| Breaches of parking regulations | 10,121 | 14,788 | 16,854 | 20,563 | 18,027 |
| Other traffic offences | 5,632 | 5,814 | 8,323 | 9,439 | 8,854 |
| Totals | 45,039 | 52,108 | 61,601 | 73,437 | 69,893 |
| Convictions per 1,000 of mean population | 21.06 | 23.87 | 27.59 | 32.13 | 29.94 |
Convictions in 1959 for traffic offences showed, for the first time since 1955, a decrease from the previous year, being 3,544 or 4.8 per cent, below 1958. Of the 16 types of offence given in the preceding table, 10 show decreases compared with the previous year, five increases, while one remained as before. The largest decrease from the previous year was in the number of convictions for parking offences which were 2,536, or 12.3 per cent, less than in 1958. Other major decreases in convictions (with the percentage decreases in parentheses) were recorded for the following: negligent or dangerous driving of motor vehicles, 1,412 (10.2); other traffic offences, 585 (6.2); drunk in charge of motor vehicle, 75 (9.5); and offences relating to driver's licence, 49 (1.3). Major increases in convictions for 1959 over 1958 were recorded as follows: excessive speed in motor vehicle, 627 (3.9); breaches of lighting regulations, 310 (11.1); breaches relating to registration, 102 (1.7); negligent or dangerous driving of other vehicle, 51 (66.2); and unlawful conversion, 47 (4.3). It should be noted that the number of motor vehicles increased from 794,810 at 30 June 1958 to 825,163 at 30 June 1959.
The previous table excludes the more serious cases involving death or injury, which are sent forward to the Supreme Court for trial or sentence. In 1959, 17 such cases were sent forward and there were 14 sentences, comprising 9 for negligent or drunken driving causing death, and 4 for negligent or drunken driving causing injury, and 1 for failing to stop after accident involving injury.
Of the 69,893 convictions for traffic offences, 3,726 persons had their drivers' licences cancelled for varying lengths of time. These are given below:
| Period for which Licence Cancelled | Number |
|---|---|
| Under 3 months | 1,207 |
| 3 months and under 6 months | 704 |
| 6 months and under 1 year | 166 |
| 1 year and under 2 years | 857 |
| 2 years and under 3 years | 131 |
| 3 years and under 4 years | 558 |
| 4 years and under 5 years | 11 |
| 5 years and over | 92 |
| Total cancellations | 3,726 |
Drunkenness — The following table shows the number of convictions for drunkenness, together with the rate per 1,000 of mean population, for each of the latest five years.
| Year | Convictions for Drunkenness | Per 1,000 of Mean Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| 1955 | 5,777 | 206 | 5,983 | 5.38 | 0.19 | 2.80 |
| 1956 | 5,778 | 238 | 6,016 | 5.26 | 0.22 | 2.76 |
| 1957 | 5,738 | 203 | 5,941 | 5.11 | 0.18 | 2.66 |
| 1958 | 4,691 | 195 | 4,886 | 4.08 | 0.17 | 2.14 |
| 1959 | 4,402 | 154 | 4,556 | 3.75 | 0.13 | 1.95 |
Repeated charges against the same person are included in the totals shown in the preceding table, but the figures do not include cases of application for the issue of prohibition orders, of which there were 696 in 1959. After dropping to a record low rate of 1.54 convictions per 1,000 mean population in 1947, the convictions for drunkenness rose steadily each year until 1953, which showed a small decrease. Increases were recorded in 1954 and 1955, but the rate has declined in the last four years. The rate per 1,000 of mean population in 1895 was 6.52.
Supreme Court — Criminal cases in the Supreme Court are of two classes — those in which the accused person has pleaded guilty in the Lower Court and has been committed to the Supreme Court for sentence, and those actually tried in the Supreme Court.
The following table gives a summary of criminal cases dealt with in the Supreme Court during each of the latest five years. Frequently a series of charges is preferred against the one offender and this serves to explain the distinction between total cases and distinct persons.
| Year | Tried in Supreme Court | Sentences in Case of Committal for Sentence | Total Sentences | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indictments and Informations | Convictions | ||||||||
| M | F | M | F | M | F | M | F | Total | |
| (a) Total Cases | |||||||||
| 1955 | 423 | 35 | 172 | 23 | 181 | 1 | 353 | 24 | 377 |
| 1956 | 581 | 23 | 304 | 14 | 283 | - | 587 | 14 | 601 |
| 1957 | 506 | 25 | 260 | 16 | 276 | 15 | 536 | 31 | 567 |
| 1958 | 809 | 23 | 323 | 13 | 219 | 3 | 542 | 16 | 558 |
| 1959 | 578 | 40 | 274 | 14 | 302 | 5 | 576 | 19 | 595 |
| (b) Distinct Persons | |||||||||
| 1955 | 163 | 12 | 87 | 8 | 51 | 1 | 138 | 9 | 147 |
| 1956 | 193 | 13 | 125 | 9 | 70 | - | 195 | 9 | 204 |
| 1957 | 202 | 16 | 117 | 9 | 69 | 4 | 186 | 13 | 199 |
| 1958 | 257 | 12 | 147 | 7 | 50 | 2 | 197 | 9 | 206 |
| 1959 | 262 | 17 | 146 | 12 | 52 | 2 | 198 | 14 | 212 |
Of the 279 distinct person indicted during 1959, 158 were convicted and 106 acquitted, and “no bill” was returned or the prosecution was not otherwise proceeded with in the remaining 15 cases.
The next table summarises the offences of persons convicted and sentenced in the Supreme Court during each of the latest five years.
| Year | Total Convictions and Sentences | Distinct Persons Convicted and Sentenced | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offences Against the Person | Offences Against Property | Forgery and Offences Against the Currency | Other Offences | Total | Offences Against the Person | Offences Against Property | Forgery and Offences Against the Currency | Other Offences | Total | |
| 1955 | 104 | 237 | 21 | 15 | 377 | 74 | 56 | 7 | 10 | 147 |
| 1956 | 193 | 368 | 6 | 34 | 601 | 100 | 84 | 3 | 17 | 204 |
| 1957 | 186 | 349 | 1 | 31 | 567 | 90 | 98 | 1 | 199 | |
| 1958 | 203 | 312 | 17 | 26 | 558 | 90 | 94 | 6 | 16 | 206 |
| 1959 | 115 | 421 | 28 | 31 | 595 | 83 | 104 | 9 | 16 | 212 |
The table which follows shows the number of distinct persons sentenced in the Supreme Court during each of the latest five years classified according to the principal types of offences.
| Type of Offence | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes persons charged with murder but convicted of manslaughter. | |||||
| Murder | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Attempted murder | 2 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Manslaughter* | 3 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 8 |
| Traffic offences involving death or injury | 5 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 14 |
| Assaults and wounding | 14 | 21 | 10 | 17 | 22 |
| Sexual offences | 45 | 64 | 58 | 54 | 34 |
| Other offences against the person | 1 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| Robbery, burglary, and breaking and entering | 19 | 36 | 38 | 47 | 48 |
| Theft, receiving, and fraud | 35 | 44 | 52 | 41 | 48 |
| Other offences against property | 2 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 8 |
| Forgery and uttering | 7 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 9 |
| Other offences | 10 | 17 | 10 | 16 | 16 |
| Totals | 147 | 204 | 199 | 206 | 212 |
| Per 10,000 mean population | 0.69 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
Sentences imposed in the Supreme Court during each of the latest five years were as follows:
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Commuted to life imprisonment. | |||||
| Probation (under Criminal Justice Act) | 24 | 25 | 30 | 26 | 19 |
| Ordered to come up for sentence | 1 | - | 1 | 5 | 4 |
| Discharged | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Fined | 9 | 5 | 12 | 17 | 17 |
| Imprisoned | 78 | 116 | 118 | 127 | 137 |
| Corrective training | 8 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 5 |
| Borstal training | 7 | 19 | 2 | 9 | 10 |
| Preventive detention | 14 | 29 | 26 | 14 | 17 |
| Death | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1* | 2* |
| Totals | 147 | 204 | 199 | 206 | 212 |
In 1941 the death sentence for murder was abolished, life imprisonment with hard labour being substituted therefor, but was restored in 1950 by the Capital Punishment Act. On conviction for murder a sentence of death must be imposed, except in the case of an expectant mother, who is to be sentenced to imprisonment for life, and a person under 18, who is to be sentenced to detention during Her Majesty's pleasure.
Flogging and whipping were also abolished in 1941 and have not been restored.
CRIMINAL APPEALS — The law relating to criminal appeals was substantially changed by the Criminal Appeal Act 1945. Previously an appeal lay only on a point of law and was available both to the prosecution and to the accused. These provisions have been retained, but the Act for the first time gave a convicted person a general right of appeal to the Court of Appeal against conviction. The Act provides that any person convicted on indictment or committed for sentence may appeal to the Court —
Against his conviction on any ground involving a question of law.
With the leave of the Court or on the certificate of the Judge who tried the case, on any ground involving a question of fact or on any other ground deemed sufficient by the Court.
With the leave of the Court against the sentence passed unless it is one fixed by law.
The Court may quash the conviction, vary the sentence, or order the case to be retried in the Supreme Court.
The Act does not affect the Crown's prerogative of mercy, but contains a provision enabling the Governor-General to refer to the Court of Appeal any application for the exercise of the prerogative.
OFFENCES BY WOMEN — Of the 112,982 criminal charges dealt with in the Magistrates' Court in 1959, 6,622, or 5.9 per cent, were preferred against females. This figure showed a decrease on the 1958 total which was 6,804.
Most of the offences for which summary convictions are entered against women are of a trivial nature, such as minor breaches of traffic regulations.
Convictions for more serious offences during 1958 and 1959 included the following:
| 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|
| Attempted suicide | 4 | 3 |
| Common assault | 16 | 24 |
| Drunkenness | 180 | 143 |
| Theft | 522 | 469 |
| Fraud and false pretences | 172 | 110 |
| Offensive conduct or language | 41 | 61 |
| Vagrancy | 74 | 91 |
Supreme Court statistics also showed that women in general are of a law-abiding disposition; 14 females (6.6 per cent of the total) were sentenced in 1959 for criminal offences.
Women received into prison under sentence in 1959 numbered 112. The principal offences concerned were: theft, 33; fraud and false pretences, 9; other vagrancy, 23; breach of probation, 6; common assault, 4; cruelty to children, 4; soliciting prostitution, 4. The corresponding total in 1958 was 98, and the main offences were: theft, 31; vagrancy, 15; drunkenness, 6; breach of probation, 13; fraud and false pretences, 6; burglary, 5.
OFFENCES BY MAORIS — As previously mentioned, Maoris are included in the statistical tables presented elsewhere in this section, the data given here being for purposes of comparison. According to the population estimate of 31 December 1959, 5.14 per cent of the total population of New Zealand aged 15 and over were Maoris.
It is not possible to classify Maoris and non-Maoris in Magistrates' Court summons cases, but an accurate classification can be arrived at in the case of arrests, and the following summary shows total charges for arrest cases in 1959. Figures for Europeans are quoted for comparative purposes.
| Class of Offence | Total Charges for Arrest Cases | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Against the Person | Against Property | Against Good Order | Other Offences | |||||
| Drunkenness | Other | Males | Females | Total | ||||
| Maoris | 260 | 2,331 | 434 | 573 | 177 | 3,451 | 324 | 3,775 |
| Europeans | 1,005 | 7,304 | 3,288 | 2,880 | 662 | 14,409 | 730 | 15,139 |
| Totals | 1,265 | 9,635 | 3,722 | 3,453 | 839 | 17,860 | 1,054 | 18,914 |
Of the total number of arrests and convictions 20.0 per cent and 20.2 per cent respectively were Maoris.
The total number of Maoris convicted and sentenced in the Supreme Court during the five years 1955 to 1959 was 167, or 17.3 per cent of the total of 968. Of the 41 Maoris (including five females) sentenced during 1959, 10 were committed from Magistrates' Courts and 31 were tried and convicted in the Supreme Court. The following table shows the number of Maoris sentenced in the Supreme Court during each of the last five years, together with the percentage of Maori offenders to total persons sentenced in each case.
| Year | Offences Against the Person | Offences Against Property* | Total Offences† | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sexual Offences | Other | |||||||
| Maoris Sentenced | Percentage of Total Sentences | Maoris Sentenced | Percentage of Total Sentences | Maoris Sentenced | Percentage of Total Sentences | Maoris Sentenced | Percentage of Total Sentences | |
*Including forgery and uttering. †Includes other offences. | ||||||||
| 1955 | 5 | 111 | 3 | 10-3 | 8 | 12.7 | 16 | 10.9 |
| 1956 | 23 | 35.9 | 7 | 19.4 | 12 | 13.8 | 43 | 21.1 |
| 1957 | 15 | 25.9 | 10 | 31.2 | 9 | 9-1 | 36 | 18.1 |
| 1958 | 6 | 11.1 | 10 | 27.8 | 14 | 14.0 | 31 | 15.0 |
| 1959 | 6 | 17.6 | 10 | 20.4 | 24 | 21.2 | 41 | 19.3 |
During 1959, 777 Maoris (including 57 females) were received into prison under sentence, this being 26.3 per cent of the total committals. Of the 1,746 persons held in custody on 31 December 1959, 523, or 29.9 per cent, were Maoris. Corresponding figures for 1958 were: 737 received under sentence (including 47 females), 24.1 per cent of the total committals, and 1,695 held in custody on 31 December 1958, of which Maoris comprised 451, or 26.6 per cent of the total.
JUVENILE OFFENDERS — Children's Courts were established in New Zealand under Part IV of the Child Welfare Act 1925, and are expressly designed to separate youthful offenders and children in need of protection from the atmosphere and associations of the regular Courts. All offences, except murder or manslaughter, committed by children under 17 years are dealt with in Children's Courts, the procedure and rules of which differ widely from those of the ordinary Courts. In addition, when an offender between 17 and 18 years comes before a regular Court, the Court may order his case to be heard in the Children's Court.
To fulfil the object for which Children's Courts were set up, the legislation prescribes that as far as possible persons attending a Children's Court shall not be brought into contact with persons attending any other Court. Unless no other suitable room is available, sittings of the Children's Court are not held in a courtroom and, where a Children's Court is in the same building as any other Court, it does not sit when that other Court is in session. Proceedings in Children's Courts are not open to the public, and no report of them may be published except with the consent of the presiding Magistrate.
When a child was brought before a Children's Court and charged with any offence, the Court was formerly not required to hear the charge against him. The law was changed in 1948, and all charges must now be heard and determined. It is not necessary, however, to record a conviction even if the charge is proved, and in practice convictions are not entered. The Court has power without recording a conviction to impose any penalty or make any order as if a conviction had been recorded.
The following table shows the number of cases dealt with in the Children's Courts during each of the latest eleven years and the number of distinct cases — that is, excluding multiple charges against the same person.
| Year | Total Cases | Distinct Cases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| 1949 | 2,675 | 393 | 3,068 | 1,537 | 321 | 1,858 |
| 1950 | 3,185 | 477 | 3,662 | 1,772 | 364 | 2,136 |
| 1951 | 3,315 | 508 | 3,823 | 1,816 | 405 | 2,221 |
| 1952 | 3,910 | 453 | 4,363 | 2,118 | 345 | 2,463 |
| 1953 | 3,775 | 576 | 4,351 | 2,138 | 416 | 2,554 |
| 1954 | 4,851 | 571 | 5,422 | 2,409 | 422 | 2,831 |
| 1955 | 5,026 | 685 | 5,711 | 2,730 | 548 | 3,278 |
| 1956 | 5,420 | 593 | 6,013 | 2,949 | 495 | 3,444 |
| 1957 | 7,306 | 875 | 8,181 | 3,770 | 646 | 4,416 |
| 1958 | 8,084 | 1,089 | 9,173 | 4,358 | 745 | 5,103 |
| 1959 | 7,158 | 809 | 7,967 | 3,525 | 640 | 4,165 |
Detailed statistics for Children's Court cases during each of the latest five years are as follows. The figures shown refer to total cases.
| Type of Offence | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes forgery and uttering. | |||||
| Sexual offences | 97 | 83 | 95 | 143 | 116 |
| Assaults | 45 | 57 | 72 | 107 | 82 |
| Other offences against the person | 16 | 11 | 12 | 31 | 9 |
| Robbery, burglary, and breaking and entering | 677 | 704 | 1,162 | 1,198 | 1,336 |
| Theft, receiving, and fraud | 2,012 | 2,176 | 2,712 | 3,200 | 2,607 |
| Unlawful conversion of vehicles | 707 | 580 | 680 | 864 | 830 |
| Wilful damage | 414 | 419 | 600 | 668 | 457 |
| Other offences against property* | 40 | 27 | 133 | 73 | 56 |
| Offences against good order | 755 | 1,090 | 1,565 | 1,771 | 1,482 |
| Indigent or delinquent child | 476 | 579 | 853 | 785 | 824 |
| Other offences | 472 | 287 | 297 | 333 | 168 |
| Totals | 5,711 | 6,013 | 8,181 | 9,173 | 7,967 |
The cases heard during 1959 resulted as follows:
| Dismissed or withdrawn | 516 |
| Admonished and discharged | 1,529 |
| Committed to care of Child Welfare Division of the Department of Education | 1,395 |
| Placed under supervision | 2,587 |
| Committed to an institution | 313 |
| Fined | 940 |
| Otherwise dealt with | 687 |
| Total cases | 7,967 |
PROBATION — By passing the First Offenders' Probation Act in 1886 New Zealand introduced the second Probation Act in the world. Originally it was intended that probation should only be used for first offenders guilty of trivial offences, but its scope was gradually widened. The present legislation, Part I of the Criminal Justice Act 1954, applies to any offender guilty of an offence punishable by imprisonment either on indictment or summarily.
An offender may be released on probation for a period of not less than one year nor more than three years, and during this time he must observe certain statutory conditions governing his behaviour and must accept the supervision of a Probation Officer. The statutory conditions of probation relate to such matters as reporting to a Probation Officer, employment and residence, associates, and general behaviour. In addition, the Court may impose particular conditions designed to assist his rehabilitation and to prevent further crime. It may also impose a fine in addition to probation. At the end of his period of probation the offender is deemed to be a free man, but if at any time during the period he breaks any of the conditions on which probation has been granted to him, he may be brought back to Court and becomes liable to a term of imprisonment or to a fine. In addition, he may be sentenced for the original offence for which he was placed on probation.
The probation method has come to be accepted as an integral part of the penal system and is widely used in New Zealand. The following figures show the number of persons released on probation during each of the past 11 years.
| Year | Number Admitted to Probation |
|---|---|
| 1949 | 1,104 |
| 1950 | 1,098 |
| 1951 | 1,071 |
| 1952 | 1,176 |
| 1953 | 1,098 |
| 1954 | 1,278 |
| 1955 | 1,429 |
| 1956 | 1,692 |
| 1957 | 1,749 |
| 1958 | 1,870 |
| 1959 | 1,804 |
The next table gives the ages of offenders placed on probation during 1959, together with the period of their probation.
| Age, in Years | 1 Year | 15 Months | 18 Months | 2 Years | 3 Years | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes 3 offenders placed on probation for 30 months. | ||||||
| Under 20 | 164 | 4 | 106 | 530 | 152 | 956 |
| 20 and under 25 | 99 | 3 | 63 | 179 | 52 | 396 |
| 25 “ 30 | 42 | - | 15 | 78 | 19 | 154 |
| 30 “ 40 | 66 | - | 22 | 82 | 23 | 193 |
| 40 “ 50 | 36 | - | 7 | 17 | 7 | 67 |
| 50 “ 60 | 15 | - | 2 | 11 | 1 | 29 |
| 60 “ 70 | - | - | - | 5 | 2 | 7 |
| 70 and over | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| Totals | 422 | 7 | 215 | 904* | 256 | 1,804 |
Probation is a conditional suspension of imprisonment and provides the opportunity whereby the offender may, with the assistance and supervision of a Probation Officer, rehabilitate himself. The real purpose of probation is to prevent further offences, and it is more freely used in the case of first offenders and young offenders.
PRISONS: Historical Development — The historical development of prisons is summarised in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
Administration — The object of imprisonment is the protection of society, and this may be achieved by the processes of deterrence and reformation. It is the duty of the prisons administration to exert every effort to divert the young and malleable offender from further crime and to attempt reformation in any case offering any hope of success. It is also necessary to balance the demands is of reformative training and security. The interest of the community as well as of the offender demand that so far as possible the time spent in prison should be so used as to bring about the greatest likelihood that the prisoner will lead a law-abiding and socially purposeful life on his discharge.
The Criminal Justice Act 1954, which came into force on 1 January 1955, revised the penal system. The Act had a twofold purpose: the first, to provide every possible means of diverting the young or inexperienced offender from a life of crime, and the second, to protect the community against the hardened offender by keeping him away from society for a long period.
From the coming into force of the Act the sentences of detention which the courts may impose are as follows:
Borstal training, which means detention in a borstal institution for an indefinite period not exceeding three years. The offender must be at least 17 years (in special cases 15) but under 21 years. The time of his release is decided by the Parole Board, which must consider his case from time to time. After his release he is on probation for 12 months.
Detention in a detention centre, the term fixed by statute being three months. The offender must be at least 16 but under 23 years of age, and he may earn up to one month's remission of his sentence by good conduct. (The part of the Act relating to this type of punishment has not yet been brought into force.)
Corrective training, which means detention in prison for corrective training for an indefinite period not exceeding three years. The offender must be at least 21 but under 30 years of age (in exceptional cases 35) and he must qualify for this sentence by the gravity of his offence or by the number of his previous convictions and the type of his previous sentences. The time of his release is decided by the Parole Board, which must consider his case from time to time. After his release he is on probation for 12 months.
Imprisonment for a stated number of years or for life. If the sentence is for less than 12 months the Court may order that the offender be on probation for a period of up to 12 months from his release. If the sentence is for 12 months or more the offender will automatically be on probation on his release, the period of probation being for 12 months or for the unexpired term of his sentence, whichever is the greater. An offender sentenced to imprisonment may earn remission of his sentence up to one-quarter.
Preventive detention, which means detention in prison for an indefinite term to be decided by the Parole Board, but in any event not less than three years nor, except where the offender has qualified for preventive detention through sexual offences, more than 14 years. The offender must be 25 years of age or over and must have qualified for preventive detention by the number of his previous convictions and the type of his previous sentences. After serving three years of his sentence the offender may be released on probation on the recommendation of the Parole Board, provided the Board is of opinion that he is not likely to resume his criminal career. The period of probation in each case extends until the expiry of the full 14 years or for life, as the case may be.
Subject to the overall control of the Minister of Justice, the administration and general management of the prisons and the borstal institutions are the responsibility of the Secretary for Justice.
Classification — The key to successful prison work lies in understanding the individual prisoner, and in order to assist the prisons administration to this end Classification Boards have been established in the three main reception centres, Auckland Prison, Wellington Prison, and Paparua Prison, Christchurch.
Classification is still in an experimental stage, but it is intended that every man sentenced to imprisonment for a term of six months or more will come before a subcommittee of the Board — consisting of the superintendent, deputy superintendent, and welfare officer of the prison — which will determine whether or not it is necessary for the prisoner to be more fully examined. According to the circumstances of each case the subcommittee will either report finally to the administration or will call upon a psychologist, psychiatrist, vocational guidance officer, probation officer, or any other form of specialist service which may be of assistance in defining the offender's character and potential, and in advising upon the most hopeful form of treatment while he is in prison.
In New Zealand the total number of prisoners is not high. There is therefore little opportunity for special categories of prisons. The task of the Classification Board is to advise on the question of allocation of prisoners. Boards have no executive powers, but they furnish to the prisons administration a report on each prisoner whom they see and their recommendations are as far as possible carried out.
Measures Employed in Treatment — This section may conveniently be dealt with under five heads — vocational and non-vocational training; earnings; punishments; and after care.
Vocational Training — Every prisoner must assist by his labour to reduce the cost of his maintenance in custody; it is also necessary that he should develop the habit of hard and consistent work. In New Zealand all available prisoners are put to work on some form of constructive employment, whether it be industrial production in a secure institution or food production on a prison farm. In addition, and particularly for the younger offender, there are courses of trade training.
Non-vocational Training — If a prisoner is eventually to be released into the community, then it is important during his period of imprisonment to pay regard to every aspect of his life as a citizen. It is not enough merely to restrict his freedom and to train him to work; he must also be kept or made mentally and morally fit.
An increasing number and variety of evening activities are being introduced into the prisons, and the number of prisoners engaged on them is likewise increasing. Very real training benefit is derived from these activities, whether they be recreational, educational, cultural, individual, or collective.
There are full-time teachers in Auckland Prison and in Invercargill Borstal Institution, and part-time teachers in many other institutions. It is their task to seek to improve the general education of those prisoners who have been unable to reach the level of the present Form II or the old Standard VI, and also to assist those who are undertaking further education or technical courses through a Correspondence School. The interest shown in education is encouraging, since in many cases it fits a prisoner for better employment on his release and thereby helps to reduce the chances of his further offending.
Since 1945, when, as the Country Library Service, it made some provision for the Invercargill Borstal Institution, the National Library Service has year by year increased its assistance to prisons. At the present time all institutions receive at regular intervals a generous supply of well chosen books and, in addition, inmates are permitted a free use of the Library's Request Service.
Earnings — All prisoners are credited with earnings based on a system of marks assessed according to diligence and conduct. The present system has been in operation for several years and is proving beneficial. A portion of the earnings may be spent on tobacco, confectionery, and toilet necessities in a prison canteen, and this provides an incentive to good work and conduct. At the same time the loss of this privilege is a useful disciplinary measure.
Punishments — An inmate charged with one of the less serious offences against discipline appears before the Superintendent, who may impose a penalty or in his discretion refer the case to a Visiting Justice or to the Court. A Visiting Justice may deal with all cases of offences against discipline and must deal with those which are outside the jurisdiction of the Superintendent, unless he thinks they should be brought before the Court. His powers of punishment are wider than those of a Superintendent. The provisions as to offences and punishments are the same for both prisons and borstals.
After care — Offenders serving a sentence of borstal training, corrective training, preventive detention, or imprisonment for 12 months or more are released on probation. For a period of time they must be under the supervision of a Probation Officer, and, during any part of that period falling within the maximum period they could have been detained in an institution, are subject to recall if their behaviour on release is not satisfactory. This period of supervision has a dual purpose — it is the protection of the community against further offending and it is at the same time an aid to the prisoner to re-establish himself. The step from custody to freedom is a difficult one for prisoners, many of whom require assistance, advice, and discipline during this period.
An offender serving a sentence of imprisonment of less than 12 months is on probation after release if the sentencing Court so orders.
Parole Board — This Board was established in 1910 under the name of the Prisons Board and it formerly reviewed the cases of all persons undergoing a sentence in prison or borstal. Following the coming into force of the Criminal Justice Act 1954, cases of all offenders serving terms of borstal training, corrective training, preventive detention, or life imprisonment are reviewable from time to time by the Board, whose duty it is to recommend release on probation in any instance where it thinks the person under sentence is sufficiently reformed to warrant it. Offenders serving sentences of imprisonment other than life are able to earn remission of up to a quarter of the sentence, but may have their cases referred to the Board in special circumstances.
The Board, consists of a Judge of the Supreme Court, the Secretary for Justice, and at least one but not more than five other members, all except the Secretary for Justice being appointed by the Governor-General for three years and being eligible for reappointment.
Categories of persons whose cases were considered by the Parole Board during each of the years 1955 to 1959 were as follows.
| Year | Borstal Detention | Corrective Training | Imprisonment or Hard Labour | Habitual Criminals or Preventive Detention | Persons on Parole | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 347 | 322 | 59 | 60 | 7 | 795 |
| 1956 | 466 | 254 | 41 | 43 | 11 | 815 |
| 1957 | 610 | 195 | 36 | 29 | 12 | 882 |
| 1958 | 817 | 247 | 48 | 35 | 11 | 1,158 |
| 1959 | 1,075 | 198 | 40 | 67 | 4 | 1,384 |
It will be seen from the above table that, since the coming into force on 1 January 1955 of the Criminal Justice Act 1954, there has been, since the initial decrease of 1955, a steady increase each year in the number of cases to come before the Board. Of the cases considered in 1959, recommendations were made for release on probation in 354 instances. Two paroles were recommended for discharge, no recommendation was made in three cases, while the remaining 1,025 were deferred.
STATISTICS OF PRISONERS— There are 13 institutions serving as prisons or borstals in New Zealand, and 11 police gaols. Any person serving a sentence of not more than eight days may be detained at any police station, which is deemed to be a prison for that period.
The prison population during the year 1959 is shown in the following table.
| Males | Females | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persons in prison at 1 January 1959 | 1,625 | 70 | 1,695 |
| Receptions during the year (including multiple receptions of the same person, but excluding transfers) | 4,791 | 260 | 5,051 |
| Discharges during the year (including multiple discharges of the same person, but excluding transfers) | 4,759 | 241 | 5,000 |
| Persons in prison at 31 December 1959 | 1,657 | 89 | 1,746 |
| Daily average number of prisoners | 1,683 | 103 | 1,786 |
Not all prisoners received were actually persons undergoing sentence on conviction for criminal offences. In 1959, 327 debtors were released after being detained or imprisoned for non-payment of debt following a Court order, 17 were classed as mental defectives and transferred to mental hospitals, while 1,352 persons were not returned to prison after release for hearing of the charge, being acquitted, fined, placed on probation, etc.
The following table analyses the ages and offences of distinct persons received into prison under sentence during 1959.
| Age, in Years | Offences Against the Person | Burglary, Theft, and Fraud | Conversion, Wilful Damage, etc. | Vagrancy and Drunkenness | Other Offences | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sexual Offences | Assaults | Other | ||||||
| Under 21 | 29 | 21 | 4 | 300 | 91 | 25 | 114 | 584 |
| 21 and under 25 | 31 | 36 | 12 | 220 | 61 | 44 | 141 | 545 |
| 25 “ 30 | 21 | 36 | 12 | 163 | 29 | 60 | 121 | 442 |
| 30 “ 40 | 34 | 41 | 5 | 225 | 14 | 141 | 217 | 677 |
| 40 “ 50 | 27 | 17 | 10 | 131 | 8 | 121 | 143 | 457 |
| 50 “ 60 | 14 | 2 | 4 | 37 | 2 | 70 | 69 | 198 |
| 60 and over | 3 | 1 | - | 14 | - | 26 | 8 | 52 |
| Totals | 159 | 154 | 47 | 1,090 | 205 | 487 | 813 | 2,955 |
| Maoris (included above) | 47 | 59 | 9 | 295 | 91 | 83 | 193 | 777 |
The next table gives particulars of ages and length of sentence of distinct persons received into prison under sentence during 1959.
| Age, in Years | Length of Sentence | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 1 Month | 1 Month and Under 3 Months | 3 Months and Under 12 Months | 1 Year and Under 3 Years | 3 Years and Under 5 Years | Over 5 Years | Other Total | ||
| *Sentenced to death but commuted to life imprisonment. | ||||||||
| Under 21 | 70 | 110 | 73 | 12 | 318 | - | 1* | 584 |
| 21 and under 25 | 126 | 129 | 154 | 73 | 58 | 5 | - | 545 |
| 25 “ 30 | 113 | 111 | 122 | 65 | 25 | 6 | - | 442 |
| 30 “ 40 | 178 | 196 | 198 | 70 | 25 | 10 | - | 677 |
| 40 “ 50 | 134 | 110 | 144 | 51 | 12 | 6 | - | 457 |
| 50 “ 60 | 62 | 62 | 56 | 12 | 5 | 1 | - | 198 |
| 60 and over | 18 | 14 | 18 | 2 | - | - | - | 52 |
| Totals | 701 | 732 | 765 | 285 | 443 | 28 | 1* | 2,955 |
Of the total of distinct persons received into prison in 1959 no less than 73.3 per cent had been convicted for an offence on at least one previous occasion, and 30.6 per cent of these had been convicted more than six times.
Receptions of prisoners to undergo sentence (imposed during the year) for criminal offences numbered 3,375 in 1959, but, deducting multiple receptions of the same prisoner, the number of distinct persons was 2,955 (2,843 males and 112 females). Corresponding figures for 1958 were 3,056 distinct persons (2,958 males and 98 females).
An analysis is given below of distinct persons received into prison according to nature of sentence imposed in 1957, 1958, and 1959.
| Nature of Sentence | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imprisonment | 2,676 | 2,648 | 2,582 |
| Corrective training | 79 | 64 | 54 |
| Borstal training | 254 | 330 | 304 |
| Preventive detention | 26 | 13 | 13 |
| Death | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Totals | 3,037 | 3,056 | 2,955 |
The next table shows the number of persons in prison at 31 December in each of the latest 11 years.
| At 31 December | Persons in Gaol | Proportion per 10,000 of Population as at 31 December | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undergoing Sentence | On Remand and Awaiting Trial, etc. | Total | Undergoing Sentence | Total in Confinement | |
| 1949 | 941 | 50 | 991 | 4.97 | 5.24 |
| 1950 | 1,043 | 40 | 1,083 | 5.41 | 5.62 |
| 1951 | 1,040 | 36 | 1,076 | 5.28 | 5.46 |
| 1952 | 1,083 | 30 | 1,113 | 5.35 | 5.50 |
| 1953 | 1,088 | 27 | 1,115 | 5.24 | 5.37 |
| 1954 | 1,196 | 27 | 1,223 | 5.65 | 5.77 |
| 1955 | 1,117 | 37 | 1,154 | 5.16 | 5.33 |
| 1956 | 1,362 | 41 | 1,403 | 6.17 | 6.35 |
| 1957 | 1,469 | 44 | 1,513 | 6.49 | 6.69 |
| 1958 | 1,636 | 59 | 1,695 | 7.06 | 7.32 |
| 1959 | 1,702 | 44 | 1,746 | 7.29 | 7.48 |
The number of distinct persons received into prison under sentence of imprisonment during the latest 11 years, with the proportion per 10,000 of mean population, is given in the next table.
| Year | Number | Per 10,000 of Mean Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 1,788 | 9.55 |
| 1950 | 2,080 | 10.90 |
| 1951 | 1,975 | 10.14 |
| 1952 | 2,268 | 11.36 |
| 1953 | 2,354 | 11.49 |
| 1954 | 2,404 | 11.48 |
| 1955 | 2,531 | 11.83 |
| 1956 | 2,8S6 | 13.22 |
| 1957 | 3,037 | 13.60 |
| 1958 | 3,056 | 13.37 |
| 1959 | 2,955 | 12.83 |
POLICE — The Police in New Zealand are maintained wholly by the General Government. The law relating to the establishment and regulation of the Police is contained in the Police Act 1958, which consolidated and amended the Police Force Act 1947.
Organisation and Duties — A Commissioner and an Assistant Commissioner, with headquarters at Wellington, subject to the directions of the Minister of Police, have the general superintendence and control of the Police. New Zealand is divided into 15 districts, each under the charge of a Superintendent or Chief Inspector of Police, who is responsible for the maintenance of good order and the proper execution of police duty therein. Districts are divided into subdistricts under the charge of Chief Inspectors, Inspectors, senior sergeants, sergeants, or constables, and cities and towns, where regular beat duty is performed, are divided into beats, patrolled by constables under the supervision of sergeants, and supplemented by mobile patrols.
In addition to the enforcement of the criminal law and the provisions of the Police Offences and the Official Secrets Acts, there are several statutes of a regulatory nature which the members of the Police are called upon to administer, wholly or partly, such as the Arms Act, Licensing Act, Gaming Act, Dangerous Drugs Act, Transport Act, Pawnbrokers Act, Secondhand Dealers Act, etc. They also undertake certain types of inquiries and other duties on behalf of other Departments of the Government Service.
Police in country districts in some cases hold such additional appointments as Registrars and Bailiffs of Magistrates' Courts, Probation Officers, Inspectors of Sea Fishing, and Kauri-gum Rangers.
Recruiting — In general, male recruits for the Police must be between the ages of 19 and 35 years, be not less than 5 ft 8 1/2 in. in height, and female recruits must be between the ages of 23 and 33 years, with a height of not less than 5 ft 5 in. Recruits must be the holders of a School Certificate or possess educational qualifications of equal or higher standard or alternatively pass a departmental pre-entry test. They must be of British nationality, of good character, smart, active, intelligent, and be passed as medically fit. The selection of recruits is made after exhaustive inquiries into the character of antecedents, and qualifications of the applicants. On appointment they undergo a three months' course of training at the Police Training School, Trentham, where they are drilled and receive comprehensive training in their powers and responsibilities as police officers, fitting them to deal with the situations which may be faced on duty.
Appointments to vacancies in the higher ranks are made from those members of the next lower rank who have qualified by examination, efficiency, and seniority for such promotion.
Members who show an aptitude for detective duty are detailed for service in the Criminal Investigation Branch, which is attached to each district headquarters and undertakes the investigation and detection of the more serious crimes.
Strength — In addition to the Commissioner, the effective strength of the Police on 31 March 1960 was 2,453, there being an increase of 17 during the year. The total was made up as follows: Assistant Commissioner, 3 Chief Superintendents, 5 Superintendents, 19 Chief Inspectors, 24 Inspectors, 3 Temporary Inspectors, 94 senior sergeants, 252 sergeants, 12 acting sergeants, 12 temporary sergeants, 1,983 constables, and 44 policewomen. In addition to the above, there were also 74 police cadets, 50 police surgeons, 6 matrons, and 1 district constable.
Women Police — The first 10 appointees completed their training and commenced duty in October 1941. The present strength is 44, and these are stationed at Auckland, Hamilton, Napier, New Plymouth, Wanganui, Palmerston North, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill. Their duties consist mainly in investigating complaints in respect of women and children, patrol duties in uniform, and generally their work is confined largely to their own sex, but six are employed in the Criminal Investigation Branch.
Table of Contents
CONTROL AND COORDINATION OF DEFENCE — In New Zealand control and coordination of defence activities are obtained through the Defence Council, the appointment of one Minister of Defence in charge of the three Services, and through a series of inter-service committees. The comparative simplicity of defence problems in New Zealand has required neither the appointment of a Minister of Defence directing subordinate Ministers in charge of each Service nor the establishment of a Department of Defence superior to the Navy, Army, and Air Departments. Coordination is facilitated by the presence in the Prime Minister's Department of a Defence Secretariat serving the main policy-forming committees and performing some of the functions which in other countries are handled by Departments of Defence.
Defence Council — The Defence Council consists of the Prime Minister, the Minister of Defence, and other Ministers concerned with various aspects of national security. The Chiefs of the Naval, General, and Air Staffs, and the Secretaries of the Treasury and of External Affairs, attend meetings of the council in a consultative capacity. The purpose of the council is to keep defence policy and organisation constantly under review, including questions of cooperation on defence with other countries of the British Commonwealth and military questions arising as a result of New Zealand membership of the United Nations.
Military Adviser to Government — Since 1960 there has been a Military Adviser to Government responsible for advice on overseas military commitments and he is the military representative at meetings of Commonwealth and international organisations.
Chiefs of Staff Committee — The Chiefs of Staff Committee, comprising the Chiefs of the Naval, General, and Air Staffs and the Military Adviser, is responsible for advising the Government on defence policy and strategic questions. It is served by several inter-service committees dealing with various subjects such as strategic and operational plans, intelligence, and communications.
Principal Personnel Officers' Committee — This committee comprises the senior personnel officers of the three Services with a senior representative of the Treasury attending, by invitation, when matters having a financial implication are discussed. This committee is responsible for personnel matters such as manpower, conditions of service (including pay), medical services, education, and welfare.
Principal Administrative Officers' Committee — This committee consists of the senior supply officers of the three Services with a Treasury representative attending when appropriate. Their sphere of responsibility covers matters such as supply and maintenance, quartering, transportation, works, munitions, and equipment. This and the preceding committee are served by subordinate committees responsible for administrative planning, and in various specialist fields such as medical, recruiting, and the design and provisioning of clothing and other stores.
Cooperation With Other Countries — In order that contact might be maintained with other countries, New Zealand joint service liaison staffs are maintained in London, Canberra, and Washington. A New Zealand military liaison officer is on the staff of the Commissioner for New Zealand in Singapore and is accredited also to the High Commissioner for New Zealand in Malaya. The head and deputy head of the New Zealand Services Liaison Mission in Washington are accredited to the Canadian service authorities as military, naval, and air advisers to the High Commissioner for New Zealand in Ottawa. In 1957 a New Zealand military liaison officer was appointed to the Commonwealth Liaison Mission in Korea. The United Kingdom and Australia have service representatives in Wellington attached to the offices of their respective High Commissioners, and there is a military attaché on the staff of the United States Embassy in Wellington.
Industrial War Potential — Planning in respect of the demands which, in war or on the threat of war, the services would make on industry is the task of the Joint War Production Committee, on which is represented the Departments of Industries and Commerce, Scientific and Industrial Research, and the Services.
Defence Science — Defence science activities in New Zealand are guided by an executive committee, comprising the Chiefs of Staff and the Secretary of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, known as the Defence Science Policy Committee.
The Defence Science Policy Committee is served by appropriate technical subcommittees of service and scientific composition. It is aided by the Defence Science Advisory Committee consisting of non-Government scientists and experts. The Policy Committee with its supporting groups is known as the Defence Research Organisation.
Defence science activities are coordinated with Commonwealth requirements through the Commonwealth Advisory Committee on Defence Science or by direct negotiation with other Commonwealth Governments.
LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY FOR THE ARMED SERVICES — The principal statutes governing the armed services are as follows: Army, the New Zealand Army Act 1950 and its amendments, the Military Manoeuvres Act 1915; Navy, the Navy Act 1954 and its amendments, the Naval Discipline Act (U.K.), the Naval and Victualling Stores Act 1908; and Air Force, the Royal New Zealand Air Force Act 1950 and its amendments.
Two other Acts of general application, are the National Service Registration Act 1958 and the Courts-Martial Appeals Act 1953. The latter provides for the establishment of a special Court of Appeal for the Navy, Army, and Air Force, to which persons convicted by a court martial may appeal against conviction.
The Court is to consist of an uneven number of Judges (not fewer than three), of whom one is a Judge of the Supreme Court and the others either Judges, barristers, or former Judges of the Supreme Court.
The Courts Martial Appeal Court is empowered to allow an appeal if it thinks that the finding of the court martial is unreasonable, or cannot be supported having regard to the evidence, or involves a wrong decision on a question of law, or that on any other ground there was a miscarriage of justice. The Court may dismiss any appeal if it considers that no substantial miscarriage of justice has actually occurred. When the Court allows an appeal it may direct either an acquittal or a new trial.
The Court may also substitute what it regards as another lawful conviction for the conviction appealed from, and it is empowered to substitute when necessary an appropriate sentence for the sentence of the court martial without increasing the sentence.
The decision of the Court on any appeal is to be final unless the Attorney-General grants a certificate that a point of law of exceptional public importance is involved, and that another appeal is desirable in the public interest, in which case it may be made to the Court of Appeal.
National Service Registration Act 1958 — The National Service Registration Act 1958, which came into force on 1 April 1959, repealed the Military Training Act 1949. The Act preserves the existing liability for six years' service on the reserve, of persons who have received training with any of the armed forces under the Military Training Act 1949.
The National Service Registration Act 1958 provides that every male ordinarily resident in New Zealand is liable to register for National Service on attaining the age of 18 years on or after 1 July 1958. The Minister of Labour may from time to time, by notice in the Gazette, fix any age between 18 and 21 years as the age for registration. Any person subject to registration under this Act may be served with written notice requiring him to submit himself for medical examination at a specified time, date, and place.
In March 1961 the Government announced that registration and medical examination of youths aged 18 years was to cease immediately.
STRENGTH OF DEFENCE SERVICES — The following table gives the strengths of the regular forces of the three services together with any emergency force over the latest 11 years.
| As at 31 March | Navy | Army | Air Force | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2,511 | 3,096 | 3,495 | 9,102 |
| 1951 | 2,669 | 4,402 | 3,500 | 10,571 |
| 1952 | 2,525 | 5,995 | 3,985 | 12,505 |
| 1953 | 2,823 | 6,558 | 4,624 | 14,005 |
| 1954 | 2,915 | 5,970 | 4,691 | 13,576 |
| 1955 | 2,809 | 4,571 | 4,763 | 12,143 |
| 1956 | 2,832 | 4,380 | 4,701 | 11,913 |
| 1957 | 2,926 | 3,907 | 4,790 | 11,623 |
| 1958 | 2,998 | 4,400 | 4,769 | 12,167 |
| 1959 | 3,007 | 4,230 | 4,547 | 11,784 |
| 1960 | 2,919 | 5,342 | 4,510 | 12,771 |
THE ROYAL NEW ZEALAND NAVY — The Government in New Zealand has since the earliest days made provision for naval forces in its defence measures. Royal Naval vessels regularly visited New Zealand waters, but these were soon supplemented by a number of Government-owned vessels, the first of which was the Australia, a schooner purchased from India in 1842. In addition, in 1877 the New Zealand Government began regular financial contributions towards maintaining Royal Naval ships in New Zealand waters.
A Naval Defence Act was passed in 1913 to provide for the maintenance of a sea-going naval force and a training centre under the immediate control of the New Zealand Government. Unfortunately the First World War intervened, but in 1921 this policy was implemented and the naval forces became the New Zealand Division of the Royal Navy. In 1941 these forces became the Royal New Zealand Navy.
Command and Administration — The command and administration of the Royal New Zealand Navy is carried out by the Naval Board. The Naval Board consists of the Chairman (the Minister of Defence), Chief of the Naval Staff and First Naval Member (a Rear Admiral), Second Naval Member and Member for Personnel and Materiel (a Commodore), Third Naval Member and Member for Supply (a Commodore), and Navy Secretary and Member for Finance (a senior public servant).
Role of the Royal New Zealand Navy — Through the collective defence arrangements made by New Zealand, e.g., under UN, SEATO, and ANZUS agreements, and within the Commonwealth, the Royal New Zealand Navy provides forces capable of intergrating with the navies of friendly nations. These forces are also planned to provide a measure of defence for the home territories should the need arise.
One ship is permanently attached to the Commonwealth Far East Strategic Reserve and others could reinforce it at short notice. The normal peacetime duties are many and varied, and include flag-showing cruises to foreign ports and around New Zealand and its island territories; support for New Zealand Antarctic interests, surveying, fishery protection, and servicing weather stations. These are in addition to training both active service personnel and reserves for their wartime tasks.
State of the Navy — Her Majesty's New Zealand ships are at present:
| *In reserve. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cruisers | Royalist Black Prince* | At least one cruiser or frigate is maintained on the Far East Station if required. The remaining ships in commission are normally employed within the New Zealand Naval Station. |
| Frigate (Whitby Class) | Otago | |
| Frigates | Rotoiti | |
| Kaniere | ||
| Pukaki | ||
| Taupo* | ||
| Tutira* | ||
| Hawea* | ||
| Survey ship | Lachlan | |
| Ocean minesweepers | Stawell* | |
| Kiama* | ||
| Inverell* | ||
| Echuca* | ||
| Anti-submarine minesweeping vessel | Kiwi* | |
| Fleet auxiliary | Tui | Naval and oceanographic research. |
| Ex-netlayer | Endeavour | Antarctic support ship. |
| Motor launches | Twelve | Fishery protection. Training. Survey work. Harbour duties. RNZNVR Divisions. |
| Ship under construction: Whitby class frigate | Taranaki | Launched August 1959. |
Shore Establishments — Navy Office, Wellington, is the office of the New Zealand Naval Board and its associated naval and administrative staffs.
The Naval Base at Devonport, Auckland, consists of the office of the naval officer in charge, Auckland (a Commodore, RNZN), HMNZS Philomel (the naval barracks and training establishment), the Royal New Zealand Naval Hospital and the Dockyard.
The Dockyard which is administered by a Captain Superintendent and which includes the Naval Store Depot and the Naval Depot is capable of refitting ships up to light cruisers.
HMNZS Tamaki is the new entry training establishment for the Navy and is situated at Motuihe Island, Auckland. HMNZS Irirangi is the wireless station for the New Zealand Naval Station and is situated at Waiouru in the centre of the North Island.
Personnel — Entry into the Royal New Zealand Navy is open to young men through the following channels:
| Boys | Ages 15 years 3 months to 16 years 3 months. |
| Artificer apprentices | Ages 15 years to 17 years 6 months. |
| Youths | Ages 16 years 3 months to 17 years 6 months. |
| Adult entries | Ages 17 years 6 months to 25 years (28 years for tradesmen) |
With the exception of the artificer apprentices who carry out their initial training in Philomel before proceeding to the United Kingdom for trade training, all new entries receive their basic training in Tamaki. Technical and specialist training is, as far as possible, carried out in New Zealand, but where no facilities exist, ratings attend courses in naval establishments in Australia and the United Kingdom.
There are also two schemes for direct entry as officer cadets. Candidates between the ages of 15 years 6 months and 16 years 6 months are eligible for selection as cadet midshipmen; these cadets carry out three years' training at the Royal Australian Naval College, Jervis Bay, New South Wales, before proceeding to the United Kingdom for specialist technical training. To cater for the older age group, young men between the ages of 17 years 8 months and 19 years are eligible for selection as special entry cadets; these cadets proceed direct to the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth, for a period of up to two and a half years. On leaving Dartmouth, officers of both types of entry undergo specialist training as acting sub-lieutenants for periods varying from 18 months to three years, after which they take appointments as trained officers in the Royal New Zealand Navy.
Suitable ratings who qualify educationally and professionally are eligible for promotion to officer rank, dependent on age and experience.
Women's Royal New Zealand Naval Service — The Women's Royal New Zealand Naval Service was first formed in 1942 as a wartime service. In 1949 the WRNZNS became a permanent part of the Royal New Zealand Navy. Employment of members of the WRNZNS is varied and includes duties as cooks, stewards, writers, shorthand typists, chart correctors, motor-transport drivers, and teleprinter operators. These duties are supplemented or amended as necessary to meet the requirements of the Navy.
Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Reserve — There is a division of the Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Reserve in each of the four main centres — Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin. When the Military Training Act 1949 was introduced these divisions accepted the responsibility of training the Navy's compulsory naval reservists. In all they trained 1,992 men before it was decided in 1957 to cease compulsory training for the Navy. The divisions then reverted to their former purely volunteer role.
Strength of the Navy — The strength of the Navy as at 31 July 1960 is shown below:
| Officers | Ratings | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Forces (including WRNZNS) | 315 | 2,604 | 2,919 |
| Active reserves — | |||
| Royal New Zealand Naval Reserve | 14 | - | 14 |
| Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Reserve | 115 | 376 | 491 |
| Total (reserves) | 129 | 376 | 505 |
| Inactive reserves — | |||
| Royal New Zealand Naval Fleet Reserve | - | 1,348 | 1,348 |
| Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Supplementary Reserve | 311 | - | 311 |
| Royal New Zealand Naval Emergency Reserve | - | 544 | 544 |
| Royal New Zealand Naval Volunteer Emergency Reserve | - | 17 | 17 |
| Retired officers and pensioners | 234 | 149 | 383 |
| Compulsory naval reservists | 2 | 1,350 | 1,352 |
| Royal Naval Volunteer Supplementary Reserve | 19 | - | 19 |
| Royal Naval Special Reserve (National Service) | - | 6 | 6 |
| Totals (inactive reserves) | 566 | 3,414 | 3,980 |
Naval Expenditure — During the year ended 31 March 1960 the sum of £8,442,378 was expended on the Royal New Zealand Navy. Of this sum £4,325,924 was expended from vote “Navy”, £3,831,676 from the Defence Fund, and the sum of £284,778 from vote “Defence Construction and Maintenance — Subdivision I — Navy”. The total expenditure for the previous financial year was £7,766,287.
Activities in 1960 — Operations in areas ranging from the United Kingdom to the Antarctic occupied ships of the Royal New Zealand Navy during 1960. The Antarctic operations were those of HMNZS Endeavour which made her usual summer voyage to McMurdo Sound on 27 November 1959 with 120 tons of stores for Scott Base and the intention of conducting a series of extensive oceanographic cruises in the Southern Ocean. However, the weather was worse than for many years and ice conditions were so bad that she was forced to curtail much of her research programme. She finally returned to Bluff on 5 March 1960. In the United Kingdom, the fast frigate HMNZS Otago was commissioned on 21 June and reached New Zealand early in 1961.
Operations also included a wide variety of exercises. In February HMNZS Pukaki, which was then the New Zealand contribution to the Commonwealth Naval Strategic Reserve in the Far East, took part in “Jet 60”, an Indian Ocean training period attended by ships of seven Commonwealth navies. In March “Star Globe” was held in mid-Tasman. This was a maritime exercise to which Australia and New Zealand contributed ships and aircraft. In April HMNZS Rotoiti, which had succeeded HMNZS Pukaki in the Far East, joined “Sea Lion” the largest SEATO maritime exercise yet held. Finally, in September and October New Zealand ships and aircraft were active in “Auckex Four” a maritime exercise in the Hauraki Gulf area which was also attended by Royal Navy destroyers and a submarine.
Major personnel changes during 1960 included the formation of the first Naval Board in which all three Naval Members were officers of the Royal New Zealand Naval Board. This marked the completion of a plan by which New Zealand officers moved into progressively more senior naval appointments.
THE ARMY — The New Zealand Army is raised, maintained, and organised under the authority of the New Zealand Army Act 1950.
The Army consists of the Regular Force, the Territorial Force, the Army Reserve, the Cadet Corps, and military forces raised in time of war or other like emergency.
The New Zealand Army comprises the following Corps:
Royal Regiment of New Zealand Artillery.
Royal New Zealand Armoured Corps.
Corps of Royal New Zealand Engineers.
Royal New Zealand Corps of Signals.
Royal New Zealand Infantry Corps.
New Zealand Special Air Service.
Royal New Zealand Army Service Corps.
Royal New Zealand Army Medical Corps.
Royal New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps.
Corps of Royal New Zealand Electrical and Mechanical Engineers.
Royal New Zealand Dental Corps.
Royal New Zealand Chaplains Department.
New Zealand Army Pay Corps.
New Zealand Army Legal Service.
Royal New Zealand Provost Corp.
New Zealand Army Education Corps.
Royal New Zealand Nursing Corps.
New Zealand Women's Royal Army Corps.
New Zealand Cadet Corps.
The New Zealand Army Act as far as possible places the officers and soldiers of the Regular and Territorial Forces on the same footing.
Command and Organisation — The Army Board consists of —
The Minister of Defence, as President; The Chief of the General Staff (First Military Member); The Adjutant-General (Second Military Member); The Quartermaster-General (Third Military Member); The Army Secretary; and a Territorial Officer (Associate Member).
The board is charged with the administration and, through the officers appointed for that purpose, the command of the Army.
The Army in peace is so organised, trained, and equipped that, in the event of war, it can undertake rapidly and efficiently the tasks which will fall to it.
The Army consists basically of:
A static Regular Force.
An operational Regular Formation.
A volunteer Territorial Force.
The Static Regular Force — The static Regular Force commands, trains, and equips the Army as a whole, including the provision of cadres for the Territorial Force. The establishment of the static force is approximately 2,500 all ranks, augmented by certain dual-role service units of the operational Regular Formation.
The Operational Regular Formation — The operational Regular Force is designed to provide an infantry brigade group prepared for overseas service. A battalion of this formation is deployed with the British Commonwealth Far East Strategic Reserve. In addition this formation assists in the training of the Territorial Force and the Cadet Corps. It is organised on the lines of a standard British brigade group with an establishment of 5,619 all ranks.
The Territorial Force — The volunteer Territorial Force is designed to provide additional formations and certain theatre troops should additional forces be required. It will also provide reserves of trained officers and N.C.O.s as necessary to place the Army on a war footing.
The Territorial Force is organised as a division. Its volunteer strength as at 30 September 1960 was 7,296 all ranks.
In time of war or other like emergency the Governor-General may, by Proclamation, transfer the Army Reserve or any specified portion thereof to the Regular Force or to the Territorial Force, and declare the Territorial Force liable for continuous service within New Zealand or overseas during the continuance of such state of war or emergency.
The New Zealand Army Act also empowers the Governor-General to accept the offer of any officers or soldiers of the Territorial Force or the Army Reserve or of any other persons to render themselves liable, or to enlist in the Army, as the case may be, for service within or outside New Zealand.
From 1 April 1959 Territorial soldiers serve for a period of three years on the Active List without Reserve liability. On completion of this engagement annual extensions may be granted up to retiring age.
A gratuity of £60 is to be payable to volunteer Territorial Force personnel for each consecutive three years of efficient service completed from 1 April 1959.
Conditions of Service — Regular Force: All officers and soldiers of the Regular Force are liable for service within New Zealand and, with the exception of minors and the Home Service Section, overseas.
Enlistment in the Regular Force, which is voluntary, is until retiring age for officers, with provision for special short-term engagements, and for soldiers of the General Service Section as follows:
Men: Eight years, of which three, four, or five may be served on the Active List and the balance on the reserve. Re-engagement may be for a period to complete five, eight, or 12 years' service on the Active List or until retiring age. Reserve service after re-engagement will be for three years or until retiring age, whichever is the sooner.
Women: Three years, with re-engagement for one, two or three years or until retiring age.
Training — Regular Force: Except in the case of special entries and Quartermaster officers commissioned from the ranks all Regular officers are commissioned on graduation from the Royal Military Academy, Sandhurst, England, the Royal Military College, Duntroon, Australia, or from the Officer Cadet School, Portsea, Australia.
Post-graduate and specialist training is received either in New Zealand or at overseas training establishments. Candidates for Staff College must pass the same entrance examinations as British Regular officers except for military law, administration, and morale, upon which candidates are examined by Army Headquarters, Wellington.
Promotion to lieutenant, captain, and major is gained after two, six, and seven years' service respectively in the previous rank, provided that the prescribed promotion courses and examinations are passed.
Regular soldiers are trained at the Army Schools, Corps Depots, and in Regular units in New Zealand. In certain cases special training is received at overseas training establishments. Before promotion, qualification is required at a unit test for corporal, a district course for sergeant, written examinations set and marked by Army Headquarters for staff sergeant, and a course at Army Schools for warrant officer.
Territorial Force — Volunteer officers and soldiers are required to carry out annually a minimum of 26 and 20 days training respectively to be classified as efficient. Of this training a minimum of 14 days must be annual camp training.
The maximum number of days training, including attendance at courses, for which officers and soldiers can receive pay is: (a) commanding officers of units, 60 days; (b) other officers, 50 days; (c) non-commissioned officers, 50 days; and (d) privates, 40 days.
Before promotion to captain and major, officers are required to qualify at prescribed promotion courses and examinations, and before promotion to lieutenant-colonel at a promotion course.
Training Establishments — The Army Schools: Headquarters, The Army Schools, commands and administers a group of Army schools situated at the one centre, which provide courses for all ranks of the Regular Force as well as for officers and specialist non-commissioned officers of the Territorial Force and New Zealand Cadet Corps.
The group consists of the Tactical School, Regular Force Depot, School of Army Administration, School of Artillery, School of Signals, School of Infantry, Royal New Zealand Army Service Corps School, Royal New Zealand Electrical and Mechanical Engineering School, the Regular Force Cadet Unit, and the Regular Force Cadet School.
The Regular Force Depot provides basic recruit and instructor courses for all arms of the Regular Force, including Regular Force Cadets.
The Regular Force Cadet School provides academic training for cadets between the ages of 16 and 18 years. Trade training of cadets is carried out at the appropriate corps school or depot.
Other training establishments, the Armoured Corps Depot, School of Military Engineering, Medical Corps Depot, and the Army Ordnance School are situated apart from the central Army School organisation but fulfil similar functions. In addition, each military district from time to time holds courses for Territorial officers and soldiers, and for personnel of the New Zealand Cadet Corps.
New Zealand Army in Malaya — In accordance with New Zealand's undertaking to make a contribution to the British Commonwealth Strategic Reserve in Malaya, a small formation headquarters and an infantry battalion at lower establishment are at present serving in South-East Asia. The original force was replaced at the end of 1959 by a force which totalled approximately 39 officers and 686 other ranks.
New Zealand Cadet Corps — There are 182 secondary schools with cadet units. These units are designated by the name of the school. Service is voluntary, and annual training approximates 30 hours. All units are basically infantry, but provision is made in the larger units for such specialist activities as Sea Cadets, Artillery Troops, and Air Training Corps Flights. All units can take part in certain Empire shooting competitions, and have had marked success in this respect. Courses for officers and non-commissioned officers are held at district training camps, and units may hold camps or barracks annually.
Activities During 1959–60 — The requirement to train units and personnel of the Regular Brigade Group up to operational standards has necessitated more intensive training of Regular personnel in New Zealand. The training of volunteer Territorial soldiers, many of whom had no previous military experience, made greater demands on Territorial officers and N.C.O.s.
The policy of cooperation with New Zealand's closest geographic allies, Australia and the United States, was continued during the year. Selected officers and N.C.O.s attended both specialist corps and staff courses in the United Kingdom, United States of America, and Australia. Assistance to the Fiji Military Forces, including the provision of courses and other training, was continued.
Six Army officers were provided as United Nations observers in Palestine and a further three as United Nations observers in India/Pakistan. One of the officers in Palest was transferred for duty in the Congo during 1960.
The 2nd Battalion, New Zealand Regiment, relieved the 1st Battalion, New Zealand Regiment, in Malaya in November 1959.
Rifle Clubs and Associations — All rifle clubs and associations (including the parent body, the National Rifle Association of New Zealand) must be formally recognised by the Army Board. There are 172 rifle clubs and 18 rifle associations in New Zealand.
The planning, construction, and maintenance of rifle ranges, and safety precautions to be observed in conducting rifle practices and competitions, are governed by orders issued by the Army Board.
Army Expenditure — The following table shows Army expenditure for the financial years 1958–59 and 1959–60.
| 2958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|
| £(000 | £(000) | |
| Vote: Army | 5,943 | 6,585 |
| Vote: Defence Construction and Maintenance | 809 | 1,033 |
| Defence Fund | 1,464 | 1,875 |
| 8,216 | 9,493 |
Strength of the Army — The strength of the Army as at 30 September 1960 was as follows.
| Officers | Soldiers | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Force (including force in Malaya, women, and personnel seconded from the British and Australian Armies) | 569 | 4,336 | 4,905 |
| Territorial Force (Active) | 1,030 | 6,266 | 7,296 |
| Reserve of Officers (Regimental List) | 179 | - | 179 |
| Reserve of Officers (General List) | 1,005 | - | 1,005 |
| Class A Reserve (Territorial Force) | - | 54,643 | 54,643 |
| Class B Reserve (Regular Force) | - | 555 | 555 |
THE ROYAL NEW ZEALAND AIR FORCE — The Royal New Zealand Air Force had its inception in the New Zealand Permanent Air Force and the New Zealand Air Force (Territorial), established as part of the defence forces of the country in 1923. Permission to change the name of the NZPAF to Royal New Zealand Air Force was granted by His Majesty King George V in 1934. By the Air Force Act 1937, the RNZAF was constituted as a separate armed service, and its administration was vested in the newly formed Air Department. Until 1951 the administration of Air Force law was in accordance with RAF practice, but with the coming into force that year of the Royal New Zealand Air Force Act 1950 the provisions of the RAF code ceased to apply.
Command and Organisation — The force is raised, maintained, and organised under the Royal New Zealand Air Force Act 1950 and the amending Acts of 1954 and 1959, and consists of —
The Regular Air Force.
The Territorial Air Force.
The Air Force Reserve.
The Women's Royal New Zealand Air Force.
The Air Training Corps.
It is administered by the Air Board, which consists of the Minister of Defence, as President; the Chief of the Air Staff; the Air Member for Personnel; the Air Member for Supply; the Assistant Chief of the Air Staff; and the Air Secretary, who is also the permanent head of the Air Department.
Command of the RNZAF is exercised by the Air Officer Commanding, who also holds the appointment of Chief of the Air Staff. RNZAF Headquarters is located in Wellington. There are seven stations in New Zealand, including Headquarters Unit, and one in Fiji. A small headquarters is established in London and liaison staffs are in Washington and Melbourne. Two squadrons are serving with the Far East Air Force in Singapore.
Role — The role of the RNZAF is to provide forces for the defence of New Zealand and her island and trust territories, for the defence of sea and air communications, and for deployment overseas as necessary to support the United Nations and to meet obligations to, and defence arrangements with, the Commonwealth and allied countries. In order to meet these commitments the RNZAF is organised to provide an operational force immediately available in an emergency. In addition, the RNZAF provides support for the search and rescue organisation in New Zealand and the South Pacific area.
Administration:Regular Air Force — Candidates for commissions in the General Duties Branch are drawn mainly from civil life and appointed to short-service commissions. Permanent commissions in the General Duties Branch are granted to limited numbers of men who are selected for training at the RAF and RAAF colleges at Cranwell and Point Cook respectively, and also to selected officers serving on short-service commissions.
Candidates for commissions in branches other than General Duties are drawn largely from the ranks. Some, with higher educational and specialist qualifications, are commissioned on joining the service. Commissions are either permanent or short-service; the latter are of five years' duration and carry an obligation for service with the Air Force Reserve.
Retiring ages for officers holding permanent commissions in the General Duties Branch are: squadron leader and below, 45 years; wing commander, 48 years; group captain and above, 53 years; while those for other branches are 49, 51, and 53 years respectively.
Service for airmen in the Regular Air Force is mainly through initial engagements of up to eight years on the active list, according to trade, with a reserve liability of four years in each case. Twelve-year engagements are granted to men who are selected for apprentice training. This training was formerly carried out at the RAF apprentice schools at Halton and Locking, but from 1960 is being provided by the RAAF apprentice schools at Wagga, New South Wales, and Canterbury, Victoria. Opportunities exist for re-engagement. To qualify for superannuation, it is necessary to complete a minimum period of 20 years' service before attaining the age of 55 years. For women, the initial term of service is normally for three years with no reserve obligation. Opportunities exist for re-engagement, and airwomen may qualify for superannuation.
Non-regular Air Force — The non-regular forces of the RNZAF consist of:
(a) The Territorial Air Force, (b) the Active Reserve, and (c) the General Reserve.
The Territorial Air Force is manned in specialist branches only. Some members serve full time, some train annually. The Active Reserve is manned by personnel who either have reserve obligations following service in the Regular Air Force, or who volunteer subsequent to the expiry of those obligations. They have an annual training liability. The General Reserve has no training obligation in time of peace.
The Air Training Corps provides a valuable source of recruits for the Regular Air Force and fosters airmindedness throughout the youth of New Zealand. Annual flying scholarships provide training at the Central Flying School for selected cadets.
Recruitment — Recruiting is effected through three area recruiting offices located at Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch, and through the Air Training Corps Office in Dunedin.
Operational Units — Operational units comprise a light bomber squadron and a medium-range transport squadron serving with the RAF in Singapore, a maritime squadron stationed in Fiji, a long-range transport squadron at Whenuapai, and a light bomber squadron based at Ohakea. These squadrons are supported by operational conversion units and a transport support unit.
Training Establishments:Flying Training — The training of all aircrew is undertaken at the Flying Training School at Wigram.
Ground Training — Boy entrants undergo an educational, general service, and basic training course for 12 months at the Boy Entrant School, Woodbourne. During this period boy entrants enlisted in non-technical trades are trained to specialist level, while those enlisted in technical trades complete training to a basic engineering level. All other recruits, both airmen and airwomen, receive initial general-service training at Wigram. Airmen technical recruits then go to No. 1 T.T.S., Hobsonville, for basic engineering training and graduate to No. 2 T.T.S., Wigram; No. 4 T.T.S., Woodbourne, or to the Photographic Training School, Ohakea, for specialist trade training. Recruits in administrative trades receive their trade training at No. 3 T.T.S., Wigram. After a period of employment on units, ranging from 12 months to two years, airmen and airwomen are given further training to an advanced level. The training of N.C.O.s, provosts, and general service instructors is conducted at General Service Training School, Wigram.
Officer Training — Officer training, other than that carried out by aircrew trainees as part of the F.T.S. course, is given at the Command and Staff School, Whenuapai, which embraces initial, intermediate, and staff college training.
Activities During 1960 — No. 75 Squadron, in Singapore, continues to operate in the light bomber role with squadrons of the RAF and RAAF.
No. 41 Squadron, which moved from New Zealand to Singapore in May 1955, also forms part of the British Commonwealth Strategic Reserve in the Far East. It operates in the medium-range transport role and is engaged on transport and courier flights within the area. In addition it takes part in operations in support of the ground forces in Malaya.
No. 40 Squadron operates in the long-range transport role and provides communications between New Zealand, the Far East, and the United Kingdom.
No. 5 Squadron, in Fiji, continued throughout the year to train in the maritime role and to provide search and rescue services in the area. Aircraft are detached as required from time to time to take part in combined exercises in the South-East Asia theatre.
Of the home-based squadrons, No. 14 Squadron is equipped with Canberra aircraft, and is training in the light bomber role. The Bomber Operational Conversion United undertakes the training of pilots for jet aircraft and replacement crews for the light bomber squadrons.
No. 42 Squadron operates as an internal communications squadron and also undertakes flights between New Zealand, Australia, and the Pacific islands. In addition it carries out conversion training of pilots on to multi-engined aircraft.
An RNZAF Antarctic Flight has again been established and will continue to be deployed in support of the New Zealand Antarctic Expedition.
Strength of the Air Force — The strength of the RNZAF at 31 March 1960 was —
| Regular Air Force | 4,207 |
| WRNZAF | 287 |
| Territorial Air Force | 112 |
| Active Reserve | 1,143 |
| General Reserve | 8,916 |
Air Force Expenditure — The total expenditure of the Air Force for the year ended 31 March 1960 was £10,068,690. The comparable figure for 1958–59 was £9,987,009.
ARMED FORCES OVERSEAS — A brief summary of forces raised and employed overseas in the post-war period 1945–55 with the British Commonwealth Occupation in Japan, on service with the United Nations forces in Korea, and on garrison duties in Cyprus is given in the 1959 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
Malaya — The Prime Minister announced in early 1955 that it was intended to recruit an Army Special Air Service Squadron for jungle warfare in Malaya. This squadron left New Zealand in November 1955 and, after completing jungle and parachute training in the theatre, joined its parent unit early in 1956 in an operational role. Towards the end of 1957 this squadron was replaced by an infantry battalion. The New Zealand Unit is in addition to the Royal New Zealand Air Force contribution comprising No. 75 Bomber Squadron (which replaced No. 14 Squadron in 1958) and No. 41 Transport Squadron, together with occasional training visits by maritime reconnaissance aircraft. The Royal New Zealand Navy continues to maintain a frigate or a cruiser in the area.
10*
STRENGTHS OF THE ARMED SERVICES IN WAR: South African War — Approximately 6,500 troops from New Zealand served in the South African War.
First World War, 1914–18 — A total of 124,211 persons (including 91,941 volunteers) were called up for overseas and home service prior to 12 November 1918. Of these 100,444 proceeded overseas. This total comprised 98,950 troops serving with the New Zealand Expeditionary Forces in the European, Mediterranean, or Samoan areas; 550 nurses; and 944 others (including 211 British Army reservists, 541 naval personnel, and 192 Royal Flying Corps personnel). In addition, it was known that 3,370 (not included above) left New Zealand and enlisted in British and Australian forces, while others (exact numbers unknown) are known to have joined Canadian and South African forces.
At Armistice date in November 1918 New Zealand had over 56,000 troops overseas, and a further 10,000 were ready to embark or in training.
The troops provided for overseas service represented nearly 10 per cent of the total population of New Zealand in 1914 and over 40 per cent of the male population between the ages of 20 and 45 years. These percentages do not take into account New Zealanders who served in the British or Australian naval or military forces.
Second World War, 1939–45 — Approximately 60,000 men volunteered for service in the New Zealand forces in the Second World War before conscription was introduced in July 1940.
The net intake of men to the armed forces – i.e., exclusive of transfers between the services and of re-entries — was 194,000, equivalent to 67 per cent of the male population between the ages of 18 and 45 years. In addition, approximately 10,000 women served in the forces.
The following table shows the approximate strength of each of the services from the outbreak of war in September 1939 at yearly intervals until August 1945, when hostilities ceased. The figures at July 1942 are also shown, as that month marked the peak for mobilisation, there being 151,073 men in the armed forces at that time, representing approximately 43 per cent of the male population of military age.
| As at 31 March | Navy | Army | Air Force | All Services | Total | Female Personnel (Included in Previous Columns) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In New Zealand | Overseas | ||||||
| 1939 (September) | 1,320 | 18,000 | 1,486 | 20,392 | 414 | 20,806 | - |
| 1940 | 1,791 | 29,300 | 3,808 | 27,628 | 7,271 | 34,899 | 18 |
| 1941 | 3,579 | 75,148 | 10,213 | 54,997 | 33,943 | 88,940 | 202 |
| 1942 | 5,605 | 109,389 | 18,228 | 82,201 | 51,021 | 133,222 | 2,356 |
| 1942 (July) | 6,110 | 124,773 | 23,666 | 104,490 | 50,059 | 154,549 | 3,476 |
| 1943 | 7,657 | 104,087 | 33,777 | 82,740 | 62,781 | 145,521 | 7,302 |
| 1944 | 10,018 | 72,662 | 41,595 | 55,039 | 69,236 | 124,275 | 7,942 |
| 1945 | 10,412 | 46,698 | 35,004 | 42,731 | 49,383 | 92,114 | 5,609 |
| 1945 (August) | 10,466 | 40,942 | 31,578 | 36,962 | 46,024 | 82,986 | 4,632 |
The establishment of the Emergency Reserve Corps in August 1940, consisting of (1) the Home Guard, (2) the Emergency Precautions Services, and (3) the Women's War Service Auxiliary, provided for the effective utilisation of civilian personnel in the case of emergency. The Home Guard, which was constituted a part of the defence forces on 30 July 1941, reached its peak in April 1943 with a total strength of 124,194 men, while the total numbers involved in the Emergency Precautions Services at one stage reached 150,000. The New Zealand Naval Auxiliary Patrol Service commenced operations in December 1941, and attained its maximum strength of 463 ratings in August 1942. None of these figures is included in the table given.
CASUALTIES ON ACTIVE SERVICE — The following table gives particulars of casualties suffered on active service by members of the armed forces in the wars, etc., listed. For the Second World War the figures shown for Navy and Air Force include New Zealand personnel serving with the Royal Navy and Royal Air Force respectively. Deaths and injuries due to accidental causes while on active service are included in the figures of deaths and wounded respectively. The number shown as “missing” refers to the number so classified at the end of the period quoted.
| Deaths (Including Died as Prisoner of War) | Wounded and Injured | Prisoners of War | Wounded and Taken Prisoner of War | Interned | Missing | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *At 4 August 1919 this total comprised 16,688 deaths, 41,315 wounded, and 1 missing. | |||||||
| South African War, 1899–1902 | 228 | 166 | - | - | - | - | 394 |
| First World War, 1914–18 (up to 12 November 1918)— | |||||||
| 1 N.Z.E.F. | 16,302 | 41,262 | 356 | - | - | 84 | 58,004* |
| Samoa | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Nurses | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | 13 |
| Totals | 16,317 | 41,262 | 356 | - | - | 84 | 58,019 |
| Second World War, 1939–45 (up to 31 December 1946)— | |||||||
| Navy | 573 | 170 | 54 | - | 3 | - | 800 |
| Army | 6,793 | 15,324 | 6,644 | 1,219 | - | 46 | 30,026 |
| Air Force | 4,149 | 255 | 520 | 32 | 23 | - | 4,979 |
| Mercantile Marine | 110 | - | - | - | 123 | - | 233 |
| Totals | 11,625 | 15,749 | 7,218 | 1,251 | 149 | 46 | 36,038 |
| Jayforce (up to December 1948) | 11 | - | - | - | - | - | 11 |
| Korea (up to December 1954)— | |||||||
| Navy | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Army | 37 | 80 | 1 | - | - | - | 118 |
| Totals | 39 | 81 | 1 | - | - | - | 121 |
| Malaya (up to September 1960)— | |||||||
| Army | 10 | 21 | - | - | - | - | 31 |
| Air Force | 5 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 7 |
| Totals | 15 | 23 | - | - | - | - | 38 |
SUMMARY OF WARTIME ACTIVITIES OF ARMED FORCES — A condensed account of the wartime activities of the three armed services was given in the 1958 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY AND ADMINISTRATION — The Rehabilitation Act 1941 and its amendments made provision for the re-establishment in civil life of discharged servicemen. Under the Emergency Forces Rehabilitation Act 1953 regulations have been made for the rehabilitation and protection of servicemen and dependants of servicemen who served overseas in connection with any emergency under the United Nations Charter or otherwise.
A Rehabilitation Board and a National Rehabilitation Council were set up under the Rehabilitation Act 1941. The board consists of the Minister as Chairman, the Director of Rehabilitation, the Secretary to the Treasury, the Managing Director of the State Advances Corporation, the Director-General of Lands, the Secretary for Maori Affairs, the Commissioner of Works, and five other persons appointed by the Governor-General. The general functions of the board are to organise the establishment in civil life of discharged servicemen or servicemen's widows, and to coordinate and use the services available in Departments of State and elsewhere for the carrying out of its functions. The board also determines the nature and extent of the assistance that may be granted to any class or classes of servicemen, and approves the granting of such assistance.
The board has the assistance of District Rehabilitation Committees, which keep in touch with discharged servicemen and act in an advisory capacity concerning rehabilitation matters in their respective districts. The number of committees operating at 31 March 1960 was nine.
Future of Rehabilitation Assistance and of the Organisation — Since 1947 the Rehabilitation Board has closely watched the demand for rehabilitation assistance and, as this demand has lessened, steps have been taken to reduce and adjust the organisation accordingly. These adjustments have resulted in closing of all except three departmental district offices and the cessation of operations at the board's full-time training centres with a consequent reduction in staff.
Components of the organisation which have been retained are the portfolio of Rehabilitation, the Rehabilitation Board, and the Rehabilitation Council. The original Rehabilitation Committee organisation of 114 committees has been replaced by one consisting of a limited number of District Rehabilitation Committees comprised of representatives of towns or communities within the respective districts. Farming subcommittees of the Rehabilitation Board were absorbed into reconstituted Land Settlement Committees from 1 April 1954.
On 1 April 1954 the Rehabilitation Department ceased to function as a separate Department and became a division of the Department of Internal Affairs, in the form of a board secretariat with regional representation at Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch. From 1 January 1960 the Rehabilitation Division became part of the Social Security Department.
With the reduction in demand for rehabilitation benefits, the provision of initial rehabilitation assistance has been substantially completed in all fields except land settlement and housing, and decisions terminating the availability of various forms of assistance in so far as they apply to ex-servicemen of the Second World War have been made from time to time.
No time limits have been fixed in respect of the availability of any rehabilitation assistance for (a) children of deceased and totally incapacitated ex-servicemen, or (b) ex-servicemen whose rehabilitation may at any time be retarded or interrupted or become necessary from war disability. Appropriate forms of assistance for these groups will continue under such terms and conditions as may be considered appropriate by the Rehabilitation Board from time to time.
For other ex-servicemen of the Second World War the present position is as follows. Applications have already closed for (a) initial applications for farm settlement; (b) trade-training assistance; and (c) initial applications for educational assistance. Tools-of-trade loans are no longer available and the preferential quota of State rental houses was abolished as from 30 September 1956. Business loans, miscellaneous loans, and related assistance ceased to be available at 31 March 1958.
None of the above decisions has any force in respect of ex-servicemen eligible under the Emergency Forces Rehabilitation Regulations, but during 1956 time limits were fixed within which these ex-servicemen also must lodge their applications for certain forms of assistance. Those who required farm training or settlement, preferential allocation of a State rental house, for which purposes a quota of State rental houses has been retained, educational or trade training assistance, or tools-of-trade loan were required to make their applications within 12 months of the date of their discharge from the emergency forces, or their return to New Zealand, whichever was the earlier. Those who returned before 31 March 1957 had up to 31 March 1958 to lodge their applications. The types of assistance listed are those which ex-servicemen can usually be expected to seek within a short time of their discharge from the forces. Housing and furniture loans and loans for establishment in business are in a different category, and no time limit affecting these forms of assistance has been fixed in the meantime.
Special provisions exist to ensure that rehabilitation assistance will continue to be available to all ex-servicemen whose rehabilitation may at any time be interrupted or become necessary as a result of disability arising from service with emergency forces.
TRADE TRAINING — The “A” class training scheme provided in a number of the building trades full-time intensive theoretical and practical indoor classes, followed by full-time advanced practical work under the supervision of the board's instructors. The number of men who completed “A” class training from the inception of the scheme to its closing on 31 March 1954 was 7,346.
The “B” class scheme of training provides for contracts between employers and trainees and the board for engagement and training over suitable periods in the employer's own workshop. The wages are subsidised by the board at a gradually decreasing amount as the training progresses and the trainee's skill and productive value increases. With the closing down of the “A” class training centres, “B” class facilities are available to ex-servicemen not affected by time limits who wish to learn a skilled trade.
Certain trades such as boot repairing, watchmaking, jewellery manufacturing, etc., are particularly suited to the needs of disabled men, and, so far as is reasonably possible, training in such vocations is reserved for ex-servicemen suffering from major disabilities.
During the year ended 31 March 1960 “B” class training was completed by two ex-servicemen, and 15 were under training. The total trained under this scheme at 31 March 1960 was 4,306.
Arrangements similar to those in regard to trade training have been made for the training of ex-servicemen with suitable educational background as clerical workers, and in a number of professions such as law, accountancy, surveying, architecture, and journalism.
The “C” class training scheme caters for the resumption of apprenticeships interrupted by service.
DISABLED SERVICEMEN — Apart from the board's general forms of assistance which are available to these men, special training assistance continues to be provided on behalf of the board by the Disabled Servicemen's Re-establishment League and the Blinded Servicemen's Trust Board.
The league provides training in trades particularly suited to seriously disabled men, and the Rehabilitation Board is prepared to subsidise wages of any such disabled men whose disabilities make institutional treatment necessary or preferable to training within industry. This assistance is valuable for the ex-serviceman whose disability prevents him from following his normal occupation.
The league also provides employment under sheltered conditions for ex-servicemen whose disabilities make them unemployable in the ordinary industrial life of the community. Here again the Rehabilitation Board is prepared to assist by subsidising wages.
Since the league undertook this work on behalf of the Rehabilitation Board 529 men had completed their training by 31 March 1960. Eighteen men were receiving training at that date.
The Blinded Servicemen's Trust Board was constituted in 1945 to provide training facilities for the wholly or partially blinded ex-servicemen and to promote their welfare. Many men have attended the training centre, “St. Dunstan's”, for instruction in additional techniques and new methods. The bulk of training has now been accomplished, and the trust board's activity is mainly concentrated on after-care of some 60 men located throughout New Zealand and the coordination of assistance available through State and private channels.
FARM TRAINING AND SETTLEMENT — In its approach to the task of settling the servicemen on the land the Rehabilitation Board had the benefit of the experience gained from the operations of the Discharged Soldiers' Settlement Act 1915, and in framing its policy it has endeavoured, as far as possible, to avoid the pitfalls of the past.
The board decided that the following basic principles should be applied in its land-settlement scheme for ex-servicemen from the Second World War:
To make settlement facilities available only to fully experienced applicants.
To give adequate training to those eligible applicants who were not fully experienced.
To settle ex-servicemen on farms which should, under reasonable conditions, be capable of producing sufficient to maintain the property, provide a reasonable standard of living, and pay all other outgoings, including mortgage charges.
The Grading System — The board, in consequence of the above, decided that the qualifications of every farming applicant should be subjected to the closest scrutiny and that eligible applicants should be classified according to their ability.
Grade “A”: Experienced men qualified for immediate settlement on farms of their own.
Grade “B”: Partly experienced men in need of further training to fit them to take up and manage farms of their own.
Grade “C”: Inexperienced men considered suitable for training with the intention that they should ultimately be established on farms of their own.
Grade “D”: Not suitable for farm training or settlement.
The grading of applicants is the responsibility of Land Settlement Committees established under the Land Act 1948 and comprising the Commissioner of Crown Lands as Chairman and experienced private farmers and representatives of the State Advances Corporation or the Department of Maori Affairs. Twenty of these committees operate throughout the country and, in addition to their statutory functions, have taken over the functions previously exercised by farming subcommittees of the Rehabilitation Board.
Acceptance of Applications — Provision is made for discharged servicemen from the emergency forces who were engaged continuously in farm employment before service, but otherwise no new applications for farm grading have been accepted since 31 March 1951, except in special circumstances.
The following table shows the number of ex-servicemen settled and the number of ex-servicemen graded “A” awaiting settlement as at 31 March 1960.
| Class of Settlement | Number |
|---|---|
| Settled on single units by Rehabilitation Loans Committee | 8,685 |
| Settled on land settlement blocks by Rehabilitation Loans Committee | 3,188 |
| Settled on land settlement blocks, financial adjustments yet to be made | 152 |
| Employed by Department of Lands and Survey with promise of titles | - |
| Settled on single units and blocks through Maori Rehabilitation Finance Committee | 176 |
| Employed by Department of Maori Affairs on single units and blocks with promise of title | - |
| Settled without rehabilitation assistance on freehold, Crown, and private leasehold properties | 1,067 |
| Maori ex-servicemen assisted by Department of Maori Affairs under Maori Land Amendment Act | 89 |
| Total settled | 13,357 |
| Number of “A” grade ex-servicemen awaiting settlement | 385 |
The area of land acquired for the settlement of ex-servicemen up to 31 March 1960 was 2,417,387 acres. This area does not include particulars relating to those who have purchased established farms on their own account with rehabilitation assistance. Further particulars are contained in Section 10B. Particulars of financial assistance will be found under a later heading.
EDUCATION — Educational facilities are provided by the Rehabilitation Board for ex-servicemen in the way of bursaries, payment of fees, book allowance, etc.
It should be noted that these forms of assistance are granted in relation to career training only and not for purely cultural studies. In deciding the type of bursary and the period for which assistance will be granted, factors such as interruption to study through service, length and type of service in the armed forces, relation to pre-service career, and prospects upon qualification and suitability for the particular course of study, are all taken into account.
During the year ended 31 March 1960 assistance was given to 27 ex-servicemen. Facilities had been granted in 54,410 cases up to 31 March 1960.
Education and Career Assistance to Children of Deceased or Totally Incapacitated Servicemen — In conjunction with the War Pensions Office, the Rehabilitation Board is also concerned with the education of the children of deceased servicemen whose deaths have been the result of war injuries, and of the children of ex-servicemen who through war disability are totally incapacitated for work. The responsibility for the education of these children through the primary and post-primary school stages is undertaken by the War Pensions Office. Assistance for education and career training after post-primary schooling is completed may be granted by the Rehabilitation Board, the assistance taking the form of tuition and examination fees and a contribution towards the cost of books. Where full-time study is approved, a subsistence allowance is payable, varying from £3 15s. per week to £5 5s. per week at the age of 21 years, with married male bursars being granted the same rate as ex-servicemen.
So that due encouragement is given to any children wishing to train for a worth-while trade or career the board will, where necessary, consider a payment to bring their wages up to £5 net per week where required to live away from home or £3 15s. per week when living at home. Those 21 years of age and over, whether living at or away from home while engaged in career occupations not covered by apprenticeships, may be considered for a grant sufficient to bring their net wages up to £5 10s. per week.
FINANCIAL — The following is a summary of loan limits and net interest rates applicable to the various types of loan granted by the Rehabilitation Board.
| Type of Loan | Maximum Amount | Rate of Interest |
|---|---|---|
*Above these limits it is normal to ask the ex-serviceman to contribute on a pound-for-pound basis and, more recently, and in suitable cases, to ask for less than the pound-for-pound contribution. †This limit applies with up to two children. The limit increases with the number of children to a maximum of £2,650 where there are five or more. | ||
| £ | Per Cent | |
| (a) Tools of trade | 50 | Free |
| (b) Furniture | 100 | Free |
| (c) Business | 500 | 4 |
| (d) Farms— | ||
| Going concerns — | ||
| Dairy | 5,000* | 3 |
| Sheep | 6,250* | 3 |
| Stock and plant only — | ||
| Dairy | 1,500 | 4 |
| Sheep or mixed | 2,500 | 4 |
| (e) Houses — | ||
| New | 2,500† | 3 |
| Existing | 1,800 | 3 |
In the case of business, farm, and housing loans the interest rate for the first year is reduced to 2 per cent per annum. Supplementary and suspensory interest-free loans are available in the case of housing loans in appropriate cases. Both classes of loan are on a percentage basis. Supplementary loans, which are interest free and repayable only in the event of the sale of the security, amount to 5 per cent of the reasonable cost with a maximum of £100 in the case of new houses, and for existing dwellings are 5 per cent of the approved value with a maximum of £90. Suspensory loans, also interest free, relate to new houses only and are cancelled after a period of seven years provided the owner fulfils the required occupancy conditions. They are limited to 10 per cent of the approved cost with a maximum of £200.
Interest-free loans have also been made available in a number of farm loans, and the Land Amendment Act 1950 extended the suspensory loan principle to cases where ex-servicemen are settled, under the Rehabilitation Act, on Crown land after 1 November 1950. The suspensory loan in such cases is for an amount not exceeding the difference between the 1942 value and the current market value. Such a loan will not be enforceable as long as the purchaser resides personally on the land and farms it for his own use and benefit and fulfils the conditions of any prior mortgage to the Crown or to the State Advances Corporation. Provided the purchaser fulfils these conditions the loan is discharged at the end of 10 years. These suspensory loans were introduced consequent upon the passing of the Servicemen's Settlement Act 1950, which provided that the value of land for the purposes of that Act was to be the current market value instead of the 1942 value.
Particulars of the various classes of loan authorised during the year ended 31 March 1960, and the totals to 31 March 1960, are as follows.
| Class of Loan | Year Ended 31 March 1960 | Totals to 31 March 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | |
| £ | £ | |||
| Purchase of farms, etc. | 108 | 1,451,960 | 11,873 | 72,353,063 |
| Housing | 1,550 | 3,433,785 | 59,548 | 88,432,636 |
| Tools of trade | 1 | 50 | 1,482 | 48,964 |
| Furniture | 137 | 13,371 | 63,635 | 5,968,111 |
| Business | 7 | 10,220 | 11,523 | 7,529,011 |
| Miscellaneous | 2 | 250 | 670 | 132,057 |
| Totals | 1,805 | 4,909,636 | 148,731 | 174,463,842 |
Rehabilitation expenditure (including loan authorisations) for the year ended 31 March 1960, together with the totals to 31 March 1960, was as follows.
| Item | To 31 March 1959 From Outset | Year Ended 31 March 1960 | To 31 March 1960 From Outset |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Administration expenses, including advertising and publicity | 3,289,104 | 35,688 | 3,324,792 |
| Educational facilities, including books, tuition fees, and subsistence allowance | 1,774,721 | 11,190 | 1,785,911 |
| Trade training — | |||
| Grants and loans to Disabled Servicemen's Re-establishment League | 318,044 | 23,562 | 341,606 |
| Land and buildings for trade-training schemes, Disabled Servicemen's Re-establishment Leagues, etc. | 287,352 | 795 | 288,147 |
| Motor vehicles purchased for trade-training centres | 12,429 | - | 12,429 |
| Plant and equipment for hostels, etc. | 7,987 | - | 7,987 |
| Private firms and Disabled Servicemen's Re-establishment League (includes subsidies to employers and separation allowances) | 1,576,713 | 8,305 | 1,585,018 |
| Purchase and establishment of artificial-limb factories | 32,035 | - | 32,035 |
| Therapeutic employment for ex-servicemen | 25,302 | - | 25,302 |
| Tool store (cost of tools for resale to ex-servicemen tradesmen) | 156,971 | - | 156,971 |
| Trade-training centres operated by Rehabilitation Board (includes establishment and operational charges, trainees' wages, separation allowances and travelling expenses, tools, plant, and equipment) | 5,860,264 | - | 5,860,264 |
| Training of blinded ex-servicemen | 115,263 | 3,100 | 118,363 |
| 8,392,360 | 35,762 | 8,428,122 | |
| Farm training and settlement (excluding loans) — | |||
| Farm training, including fees and subsistence allowance at approved agricultural colleges and training farms, and subsidy to approved employers | 485,700 | - | 485,700 |
| Purchase of lands for settlement, development, and other expenses in connection therewith (excluding £25,617,487 recovered from Rehabilitation Loans Committee and shown under “Loans”) | 35,037,224 | 1,428,835 | 36,466,059 |
| 35,522,924 | 1,428,835 | 36,951,759 | |
| Loans — | |||
| Interest concessions | 8,623,950 | 749,897 | 9,373,847 |
| Loans authorised (Maori Rehabilitation Finance Committee) | 2,891,276 | 197,200 | 3,088,476 |
| Loans authorised (Rehabilitation Loans Committee) | 169,554,206 | 4,909,636 | 174,463,842 |
| Reserve Fund contributions | 2,279,374 | 54,783 | 2,334,157 |
| Small Farms Act leases; losses and interest concessions | 55,327 | - | 55,327 |
| Suspensory loans (Maori Rehabilitation Finance Committee) | 125,474 | 8,994 | 134,468 |
| Suspensory loans (Rehabilitation Loans Committee) | 4,769,385 | 144,115 | 4,913,500 |
| Earthquake damage insurance | 633 | - | 633 |
| 188,299,625 | 6,064,625 | 194,364,250 | |
| Grants — | |||
| Rehabilitation allowances | 431,885 | - | 431,885 |
| Special grants (including supplementary wage grants to children) | 107,917 | 169 | 108,086 |
| Special grants to Returned Services' Associations | 67,411 | 600 | 68,011 |
| Travelling expenses of ex-servicemen, including fares, furniture removals, and loss of earnings | 42,669 | - | 42,669 |
| 649,882 | 769 | 650,651 | |
| Other items | 9,709 | - | 9,709 |
| Totals | 237,938,325 | 7,576,869 | 245,515,194 |
Business Assistance for Ex-servicemen — In addition to the loan facilities available to assist ex-servicemen in purchasing existing businesses, or in establishing new businesses, special assistance has been given to ex-servicemen requiring licences for licensed industries and trades, and also in obtaining stock, plant, and equipment which may be in short supply or subject to control.
The following table shows the main classes of business for which loans have been granted up to 31 March 1960.
| Type | Number | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| £ | ||
| Butchery | 273 | 239,662 |
| Grocery, general store | 782 | 693,101 |
| Bakery, dairy, refreshment rooms | 484 | 341,708 |
| Milk rounds | 377 | 314,070 |
| Building trades | 1,031 | 544,876 |
| Mechanical trades | 543 | 375,190 |
| Manufacturing business | 343 | 227,274 |
| Stationery and fancy goods | 134 | 302,894 |
| Eggs and poultry | 44 | 27,673 |
| Professional equipment | 1,065 | 555,855 |
| Radio and electrical | 286 | 160,626 |
| Hotel and guest houses | 46 | 50,388 |
| Taxi, service car, and transport | 2,411 | 1,339,867 |
| Carriers and mail contractors | 1,420 | 1,076,096 |
| Hairdressers, tobacconists | 145 | 78,215 |
| Boot repairers | 71 | 58,724 |
| Painters and paperhangers | 365 | 136,294 |
| Fishing | 122 | 80,384 |
| Agricultural contractors | 453 | 326,536 |
| Chemists | 39 | 44,380 |
| Miscellaneous | 989 | 728,387 |
| Additional advances | 26,811 | |
| Totals | 11,523 | 7,529,011 |
Housing — During the prevailing housing shortage, the housing of ex-servicemen was one of the Rehabilitation Board's main problems. Assistance in this connection consists of a certain priority in the allocation of State rental houses, and provision of finance for the erection of new, and the purchase of existing dwellings.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, four State rental houses and flats were allocated to ex-servicemen, making a total allocation to 31 March 1960 of 18,325.
The number of loan authorisations for the erection of new homes during the year ended 31 March 1960 was 945, making a total of 28,291 to 31 March 1960.
Loans for the purchase of existing dwellings were authorised in 505 cases in 1959–60, while the total up to the end of that period was 31,157.
MAORI REHABILITATION — The following table gives particulars of assistance afforded to Maori ex-servicemen up to 31 March 1960. Maoris are entitled to the same assistance under the same general conditions as Europeans, although special measures have been provided to meet their particular needs. At 31 March 1960, 5,352 Maori ex-servicemen had been demobilised, of whom 3,951 had served overseas.
| Type of Assistance | Number of Ex-servicemen | Amount Authorised |
|---|---|---|
| Loans— | ||
| Farm | 227 | 1,424,423 |
| Housing | 1,297 | 2,110,278 |
| Furniture | 1,501 | 147,505 |
| Business | 243 | 106,983 |
| Tools of trade | 63 | 2,053 |
| Miscellaneous | 62 | 8,212 |
| Totals, loans | 3,393 | 3,799,454 |
| Educational assistance | 155 | - |
| Trade training— | ||
| “A” class | 673 | ... |
| “B” class | 65 | ... |
| “C” class | 8 | ... |
| “D” class | 76 | ... |
| “F” class | 3 | .... |
| Total, trade training | 825 | ... |
| Farm training | 277 | ... |
| Total number assisted | 4,650 | ... |
In addition, 89 ex-servicemen have been settled on farms under the Maori Land Amendment Act 1936 and 35 ex-servicemen have received housing assistance under the Maori Housing Act 1935.
DEMOBILISATION — Demobilisations as recorded by the Rehabilitation Division total, to date, 216,380.
Table of Contents
OCCUPATION OF LAND — The total area of New Zealand, excluding the island territories comprising Cook and associated islands and Tokelau Islands, and exclusive of Western Samoa, but inclusive of the minor islands since these form parts of land districts, is 66,390,700 acres. Of this total, 44,018,897 acres were assessed in 1960 as being in occupation, including reserves and Maori lands leased, but excluding areas within borough boundaries, holdings of less than 10 acres in extent, and Maori land held on the communal system.
The number of holdings and percentages of total holdings in occupation, grouped according to size, as returned in each of the years 1946, 1949, 1952, and 1957 are given below. For these years statistics were collected for areas under 10 acres.
| Area, in Acres | Number of Holdings | Percentage of Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | 1949 | 1952 | 1957 | 1946 | 1949 | 1952 | 1957 | |
| 1 and under 10 | 11,380 | 11,463 | 12,363 | 11,765 | 13.20 | 13.16 | 13.69 | 13.90 |
| 10 “ 50 | 14,014 | 13,611 | 13,716 | 10,396 | 16.25 | 15.63 | 15.19 | 12.29 |
| 50 “ 100 | 12,812 | 12,962 | 13,460 | 11,932 | 14.86 | 14.89 | 14.91 | 14.10 |
| 100 “ 200 | 16,699 | 17,250 | 18,104 | 17,949 | 19.36 | 19.81 | 20.05 | 21.22 |
| 200 “ 320 | 9,862 | 10,084 | 10,308 | 10,289 | 11.44 | 11.58 | 11.42 | 12.16 |
| 320 “ 640 | 10,392 | 10,653 | 11,083 | 11,184 | 12.05 | 12.23 | 12.27 | 13.22 |
| 640 “ 1,000 | 4,154 | 4,215 | 4,382 | 4,357 | 4.82 | 4.84 | 4.85 | 5.15 |
| 1,000 “ 5,000 | 5,882 | 5,827 | 5,866 | 5,745 | 6.82 | 6.69 | 6.50 | 6.79 |
| 5,000 “ 10,000 | 556 | 538 | 535 | 531 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.63 |
| 10,000 “ 20,000 | 287 | 278 | 276 | 261 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.31 |
| 20,000 “ 50,000 | 145 | 144 | 143 | 141 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| 50,000 and over | 56 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Totals | 86,239 | 87,076 | 90,288 | 84,604 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Although approximately 40 per cent of holdings in 1957 were less than 100 acres in extent, the total area of such holdings represented only a little under 3 per cent of the occupied land of New Zealand. A further 21 per cent of the holdings ranged between 100 and 200 acres, but the aggregate area of these amounted to less than 6 per cent of the total. At the other end of the scale it is found that 65 per cent of the occupied land was held in areas of 1,000 acres and upwards, although the number of such holdings was only a little under 8 per cent of the total. Holdings of 5,000 acres and upwards, of which there were 987 in 1957, accounted for 39 per cent of the total area of occupied land. The total acreage of holdings in each group is given in the following table.
| Area of Holdings, in Acres | 1946 | 1949 | 1952 | 1957 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| acres | ||||
| 1 and under 10 | 52,938 | 53,053 | 56,401 | 50,871 |
| 10 “ 50 | 356,797 | 344,548 | 346,400 | 265,188 |
| 50 “ 100 | 936,146 | 949,958 | 989,287 | 882,805 |
| 100 “ 200 | 2,338,315 | 2,417,342 | 2,536,230 | 2,521,234 |
| 200 “ 320 | 2,468,817 | 2,527,401 | 2,584,876 | 2,579,161 |
| 320 “ 640 | 4,697,290 | 4,823,068 | 5,011,073 | 5,061,457 |
| 640 “ 1,000 | 3,302,224 | 3,349,984 | 3,470,297 | 3,452,809 |
| 1,000 “ 5,000 | 11,498,507 | 11,377,539 | 11,367,370 | 11,125,375 |
| 5,000 “ 10,000 | 3,793,591 | 3,661,138 | 3,670,182 | 3,592,587 |
| 10,000 “ 20,000 | 4,012,385 | 3,891,586 | 3,870,948 | 3,704,443 |
| 20,000 “ 50,000 | 4,408,209 | 4,457,035 | 4,404,001 | 4,326,151 |
| 50,000 and over | 5,214,789 | 4,864,847 | 4,912,638 | 4,989,284 |
| Totals | 43,080,008 | 42,717,499 | 43,219,703 | 42,551,365 |
The following additional details not normally obtained in the annual farm production survey were collected under the special census of agriculture in 1950:
| Holdings at 31 January 1950 | Number | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Occupied by Maoris | 4,705 | 5.21 |
| Worked on share system | 2,678 | 2.97 |
| Lying entirely idle and unused | 2,339 | 2.59 |
A classification of all holdings in 1950 according to the status of the occupier showed the following position:
| Holdings at 31 January 1950 | Number | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Status of occupier— | ||
| Owner | 55,088 | 61.01 |
| Lessee | 17,844 | 19.77 |
| Manager | 2,532 | 2.80 |
| Partner | 1,242 | 1.38 |
| Shareworker | 2,303 | 2.55 |
| Part owner, part lessee | 11,281 | 12.49 |
| Totals | 90,290 | 100.00 |
Condition of Occupied Land — The land in occupation in New Zealand at 31 January 1960 was classified according to condition and use as follows.
| Acres | Percentage of Total | |
|---|---|---|
| *Includes areas also sown with grasses and clovers. | ||
| In principal cereal crops and crops for threshing* | 362,980 | 0.82 |
| In green, root, and other crops* | 806,337 | 1.83 |
| In fallow | 126,022 | 0.29 |
| In sown grasses and clovers — | ||
| Cut for hay, seed, or silage | 1,142,872 | 2.60 |
| Not cut for hay, seed, or silage | 17,200,636 | 39.08 |
| In orchards | 30,675 | 0.07 |
| In private gardens and grounds, etc. | 88,894 | 0.20 |
| In plantations | 944,065 | 2.14 |
| Total area in cultivation | 20,702,481 | 47.03 |
| Unimproved land | 23,316,416 | 52.97 |
| Total area in occupation | 44,018,897 | 100.00 |
Information collected in 1960 in conjunction with the World Census of Agriculture showed that 36 per cent of the total area in occupation was stated as being capable of cultivation by ploughs or discs.
Land in cultivation (under crop and in pasture) forms the subject matter of Section 14 — Farming. An indication of the condition and geographical distribution of unimproved land is afforded by the following table, which relates to the position at 31 January 1960.
| Land District | Phormium (New Zealand Flax) | Tussock and Naturally Established Native Grasses | Fern, Scrub, and Second Growth | Standing Native Bush | Barren and Unproductive Land | Total, Unimproved Occupied Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acres | ||||||
| North Auckland | 3,575 | 107,539 | 871,412 | 263,177 | 95,023 | 1,340,726 |
| South Auckland | 1,717 | 62,322 | 1,299,029 | 687,679 | 107,206 | 2,157,953 |
| Gisborne | 65 | 116,171 | 310,830 | 178,136 | 29,368 | 634,570 |
| Hawke's Bay | 55 | 286,719 | 341,212 | 69,538 | 42,198 | 739,722 |
| Taranaki | 61 | 4,295 | 150,328 | 193,136 | 17,863 | 365,683 |
| Wellington | 7,923 | 589,474 | 672,635 | 290,726 | 126,672 | 1,687,430 |
| North Island | 13,396 | 1,166,520 | 3,645,446 | 1,682,392 | 418,330 | 6,926,084 |
| Marlborough | 5,838 | 1,407,022 | 278,281 | 112,482 | 225,566 | 2,029,289 |
| Nelson | 2,089 | 200,676 | 380,029 | 190,723 | 41,938 | 815,455 |
| Westland | 4,323 | 43,758 | 207,166 | 214,841 | 126,146 | 596,234 |
| Canterbury | 4,897 | 3,931,458 | 242,723 | 113,033 | 539,795 | 4,831,906 |
| Otago | 2,031 | 5,054,486 | 614,061 | 250,702 | 439,049 | 6,360,329 |
| Southland | 6,956 | 1,231,629 | 303,981 | 147,452 | 67,201 | 1,757,219 |
| South Island | 26,134 | 11,869,029 | 2,026,241 | 1,029,233 | 1,439,695 | 16,390,332 |
| New Zealand | 39,530 | 13,035,549 | 5,671,687 | 2,711,625 | 1,858,025 | 23,316,416 |
Tenure of Occupied Lands — The area of land in occupation as at 31 January 1960, classified according to tenure, was as follows:
| Acres | |
|---|---|
| Crown land (including leases and licences) | 18,256,493 |
| Freehold (including all land held on deferred payment) | 22,335,285 |
| Leaded from private individuals (other than Maoris) | 1,368,505 |
| Leased from public bodies | 573,121 |
| Leased from Maoris | 1,485,493 |
| Total occupied area | 44,018,897 |
Lands in occupation are not strictly comparable with Crown lands alienated or in process of alienation, for certain lands which were never made waste lands of the Crown have passed into the hands of Europeans. It must also be remembered that not all of the freehold land is in occupation, while (as stated previously) holdings within boroughs or under 10 acres in extent are excluded from the annual statistics.
RESERVES, DOMAINS, AND SCENIC RESERVES — These are areas which have been:
Set apart by the Crown.
Purchased by the Crown or by local authorities.
Vested in the Crown or in local authorities by other Acts, such as the Land Subdivision in Counties Act 1946, Municipal Corporations Act 1954, etc.
The legislation governing these areas is the Reserves and Domains Act 1953, which provides for overall policy and management by the Minister of Lands with administration by the Department of Lands and Survey.
As a general rule the control and management of public reserves of a local nature, such as plantations and gravel reserves, are vested in the appropriate local authority, which may then use the area for the particular purpose for which it is set aside.
Day-to-day control of recreation reserves and domains is usually vested in locally elected boards of interested persons or in the local authority. Local interest is thereby sustained and the community encouraged to help itself with the development, control, and management of these areas so that they provide for the recreation needs of the district. There is ample provision in the legislation for sporting clubs and bodies to assist in development and control, with adequate safeguards for the protection of the rights of the general public to use and enjoy these areas. The legislation also allows suitable portions of these reserves to be set aside and developed for camping and similar purposes.
Scenic and historic reserves provide for the preservation of the more outstanding and attractive features of the natural landscape and sites of historic significance.
There is also provision for the creation of private scenic reserves and historic reserves. In these cases the owner retains ownership of the land, but the reservation ensures the conservation of the scenic and historic features. These reservations may be revoked at the owner's pleasure.
Provision is also made for the administration of bird sanctuaries, such as those established on Little Barrier Island in the Hauraki Gulf, Cape Kidnappers at the south-eastern point of Hawke's Bay, the white heron colony near Okarito in Westland, and Kapiti Island off Paraparaumu on the south-west coast of the Wellington district.
NATIONAL PARKS — The National Parks Act 1952 codified the law relating to the establishment and control of New Zealand's national parks. Provision was made for the establishment of the National Parks Authority, representative of governmental, scientific, recreational, and cultural interests. The Authority's general functions are to advocate and adopt schemes for the protection of national parks and for their development on a national basis; to recommend the enlargement of existing parks and the setting apart of new areas; and generally control in the national interest the administrative policy affecting all national parks throughout the country.
Local control of individual parks is vested in park boards which are appointed by the Minister of Lands and are representative of users of the parks and those interested in their conservation.
Urewera National Park, administered by the Commissioner of Crown Lands at Hamilton, and Westland National Park, administered by the Commissioner of Crown Lands at Hokitika, are the only parks not yet under board control.
Park boards administer the parks under their control, subject to the general policy and direction of the Authority, so as to secure to the public the fullest proper use and enjoyment of the parks consistent with the preservation of their natural features and the protection and well-being of their native flora and fauna. Boards have power to develop or authorise the development of parts of parks for specific recreation purposes; they may erect or authorise erection of mountain huts or ski tows; may erect or authorise the erection of hostels, accommodation houses, and other buildings and facilities; may develop or authorise the development of camping grounds and may charge or consent to charges for facilities provided. Provision is also made for the setting apart of wilderness areas, which are to be kept and maintained in a state of nature. No buildings or other development may take place in them, with the exception of construction of foot tracks where necessary and desirable.
At present there are nine national parks in New Zealand, these being (areas in acres in parentheses): Urewera (453,971), Tongariro (161,552), Egmont (81,236), Abel Tasman (43,061), Nelson Lakes (139,834), Arthur's Pass (239,152), Mount Cook (172,979), Westland (210,070), and Fiordland (2,923,153).
SUMMARY OF AREAS RESERVED — The following table of reservations may be of interest, the figures given relating to 31 March 1960.
| Type of Reservation | No. | Acres |
|---|---|---|
| Scenic and historic reserves | 980 | 667,308 |
| Public domains | 918 | 60,227 |
| National parks | 9 | 4,425,008 |
WILDLIFE SANCTUARIES — The Wildlife Act 1953 provides for the constitution of wildlife sanctuaries, these being areas devoted primarily as habitat areas for wildlife where the maximum degree of protection can be afforded. Restrictions are imposed on entry into the sanctuaries and certain prohibitions dealing with killing or disturbance of wildlife are imposed. The former game sanctuaries are now termed wildlife refuges. Occupiers of any land in wildlife refuges can be authorised to carry out certain operations necessary for the normal use of land.
REGISTRATION OF LAND OWNERS — Practically all title to privately owned land and interests in land in New Zealand is held under the land transfer system administered under the Land Transfer Act 1952. This system was introduced into New Zealand by the Land Transfer Act 1870. While that Act retained some of the provisions and innovations of the Land Transfer Act 1860 which it repealed and superseded, it was largely based on the revolutionary Torrens system of registration of title devised for South Australia.
Under this land transfer system, which with certain modifications has operated in New Zealand since 1870, the title to land is not secured or effected by the mere execution of deeds or documents. Registration of a valid title is the fundamental principle, and it is only by such registration that title to land or any interest therein may pass or be obtained. The District Land Registrar appointed in and for each of the land registration districts is responsible for the registration in his district, and any person named in the register as taking an interest under a registered instrument acquires a practically indefeasible title.
No instrument or dealing may be registered unless it is in accordance with statute or general law or if forbidden by positive law. An increasing number of statutes and regulations expressly impose upon the District Land Registrar the duty and responsibility of ensuring that no instrument is registered or no interests in land are acquired in contravention of the statutory provisions and requirements regulating the aggregation and subdivision of land, the alienation of Crown land, Maori land, or public reserves, the dedication or constitution of roads, streets, and access ways, and many other matters involving Government policy.
The land transfer and deeds systems operated side by side until 1924 when the Land Transfer (Compulsory Registration of Titles) Act 1924 was passed. This Act provided for Registrars to bring all the deeds system land in their districts under the provisions of the Land Transfer Act within a period of five years. Defects in title were accounted for by issuing “limited” titles which did not become State guaranteed until the defects had been remedied. In passing this legislation New Zealand moved ahead of all other countries using the Torrens system and is now in the fortunate position of being the only country which has a State-guaranteed system for virtually all of its privately owned land.
The land transfer system has proved so successful and has provided such a reliable record of dealings with land that over the last half century there has been an increasing tendency on the part of local authorities and other statutory bodies to use its facilities to give specific notice of obligations and restrictions attaching to land by virtue of their respective statutes. When national or district schemes of drainage, irrigation, water supply, or sewerage which result in improvement to land are undertaken today, statutory authority is customarily given to charge part of the cost against the land. These charges are recorded against the titles concerned. While entries of this nature on the register were not envisaged in the original land transfer system they do ensure that a prospective purchaser, by inspection of the Register, can acquaint himself with all matters affecting the property. The land transfer registration system is also used extensively to ensure that other statutory restrictions governing the acquisition and subdivision of land and dealings with land are not contravened.
Special procedures are necessary for the registration of dealings with Crown land and Maori land and these are contained in the Land Act 1948, the Maori Affairs Act 1953, and the various related Acts respectively.
The demand for land for housing development has resulted in adaptations to the system. The normal procedures relating to subdivision title and finance have been streamlined and, as in most forms of substantial purchase today, provision made for payment by instalment. The State-sponsored group building schemes, the Housing Act 1955, and the housing provisions in the Municipal Corporations Act 1954 and the Counties Act 1956 have met this situation. Agreements for sale and purchase and occupation licences are registered today in great numbers in the same way as the traditional forms of dealing with land.
The Joint Family Homes Act which was passed in 1950 provides for settlements of land as “joint family homes” and increasing use is made of this procedure year by year. (See Section 19.)
The table following shows transfers registered under the Land Transfer Act during each of the latest 11 years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Town and Suburban Properties | Country Properties | All Properties: Total Consideratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Area | Consideration | Freehold | Total Freehold and Leasehold | |||||
| Number | Area | Consideration | Number | Consideration | |||||
| acres | £(000) | acres (000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1950 | 33,182 | 10,822 | 27,629 | 5,336 | 1,269 | 12,289 | 5,876 | 13,034 | 40,663 |
| 1951 | 49,880 | 14,063 | 61,537 | 7,419 | 1,162 | 16,886 | 8,058 | 17,823 | 79,360 |
| 1952 | 46,145 | 12,084 | 73,165 | 9,655 | 1,514 | 34,010 | 10,464 | 35,965 | 109,129 |
| 1953 | 39,325 | 10,008 | 65,461 | 8,285 | 1,343 | 33,050 | 9,053 | 35,241 | 100,702 |
| 1954 | 43,427 | 10,925 | 75,503 | 8,442 | 1,371 | 36,596 | 9,188 | 38,915 | 114,419 |
| 1955 | 46,978 | 11,840 | 88,761 | 8,804 | 1,725 | 44,460 | 9,593 | 47,964 | 136,725 |
| 1956 | 41,378 | 10,363 | 80,684 | 7,112 | 1,237 | 37,366 | 7,722 | 40,256 | 120,940 |
| 1957 | 38,066 | 9,578 | 75,614 | 6,677 | 1,205 | 36,089 | 7,268 | 39,064 | 114,678 |
| 1958 | 42,183 | 10,391 | 89,641 | 7,703 | 1,440 | 46,113 | 8,390 | 50,060 | 139,701 |
| 1959 | 41,854 | 10,283 | 85,216 | 6,796 | 1,072 | 39,619 | 7,299 | 42,400 | 127,616 |
| 1960 | 45,125 | 10,999 | 94,866 | 7,204 | 1,263 | 44,576 | 7,730 | 47,859 | 142,725 |
Certificates of Title Issued - The following table shows the number of certificates issued for the latest eight years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Total |
|---|---|
| 1953 | 22,763 |
| 1954 | 26,907 |
| 1955 | 25,356 |
| 1956 | 24,069 |
| 1957 | 22,948 |
| 1958 | 23,590 |
| 1959 | 25,521 |
| 1960 | 26,953 |
The numbers of transfers shown in the table relate only to transfers of land on sale, i.e., they do not include transfers of land from trustees to beneficiaries or to new trustees, transfers of mortgages, easements, etc.
In 1950-51 transfers of town and suburban properties increased by 16,698 (50 per cent) and the amount of consideration by £33,908,000 (123 per cent) as compared with 1949-50. Country transfers increased by 2,182 (37 per cent) in number and by £4,789,000 (37 per cent) in the amount of consideration. The large increase in transfers in 1950-51 was contributed to by the exemption of town and suburban properties from land sales control from 23 February 1950 and by the relaxation of control on farm lands by the enactment of the Servicemen's Settlement Act 1950, which came into force on 1 November 1950.
Whereas the number of transfers registered during 1951-52 did not reach the high figure established in the previous year, the amount of consideration involved rose to £109,129,000. This figure represented an increase of 38 per cent on the total for 1950-51, and was 33 per cent greater than the previous highest figure of £81,790,000 recorded in 1921. Town and suburban transfers during 1951-52 showed decreases in both number registered and area, but a substantial increase of £11,628,000, or 19 per cent, in the amount of consideration involved. The 1951-52 year was the first complete one after the enactment of the Servicemen's Settlement Act 1950. The effect of the relaxation of control on farm lands brought about by this legislation is evidenced in the large increases in the number, area, and value of country transfers registered. The increases amounted to 2,406 in number, 390,896 acres in area, and £18,142,000 in consideration, representing percentage increases of 30 per cent, 27 per cent, and 102 per cent respectively.
This was followed in 1952-53 by decreases in all categories when compared with the previous year, very slight as far as the consideration for country properties is concerned, but amounting to £7,704,000, or 11 per cent, for town and suburban properties. Increases in number, area, and consideration were recorded for 1953-54 and 1954-55. The significant feature of the 1954-55 figures was the high value of the consideration for all properties of £136,725,000, there being marked increases in the value of town and suburban and country properties of £13,258,000 and £9,049,000 respectively.
Decreases were recorded in all categories during the year 1955-56, and the decline, though not as great as in the previous year, continued in 1956-57. Unlike the previous year, the decrease was more marked in town and suburban properties, where a drop of 3,312, or 8 per cent, occurred in number, than in rural properties. The total number of transactions was the lowest since 1949-50, a year that for the most part was under controls. The area and consideration dropped accordingly. The trend in land transfer business, in contrast with the decline shown in the two previous years, showed a marked expansion in 1957-58. Consideration for all properties rose to £139,701,000, an increase of £25,023,000, or 22 per cent, as compared with 1956-57.
In 1958-59 decreases were recorded in all categories. Consideration for all properties decreased by £12,085,000 (8.7 per cent) to £127,616,000. The number of urban transactions decreased by 329 to 41,854 and the number of rural transactions decreased by 1,091 to 7,299. Consideration for urban and rural properties decreased by £4,425,000, or 4.9 per cent, and £7,660,000, or 15.3 per cent, respectively.
Town and suburban properties transferred in 1959-60 totalled 45,125, an increase of 3,271 over the 1958-59 total, and the highest number recorded since 1954-55. The total consideration of £94,866,000 for 1959-60 was a record, this figure comparing with the previous record total of £89,641,000 in 1957-58.
Rural transactions also showed increases both in number and consideration. Consideration for all properties in 1959-60 increased by £15,109,000 (11.8 per cent) to a record total of £142,725,000; urban and rural properties increased by £9,650,000 (11.3 per cent) and £5,459,000 (12.9 per cent) respectively.
As all classes of properties are included, land transfer figures do not give a precise indication of any changes that may take place in property values. In the case of town and suburban properties, however, the numbers involved are probably sufficient to smooth out changes from year to year in the proportions of different classes of property included in the total. The average amount of consideration for town and suburban property increased each year for a decade but showed a drop in 1958-59. However, there was an increase of £66 in 1959-60. The averages were £1,234 in 1950-51, £1,586 in 1951-52, £1,665 in 1952-53, £1,739 in 1953-54, £1,889 in 1954-55, £1,950 in 1955-56, £1,986 in 1956-57, £2,125 in 1957-58, £2,036 in 1958-59, and £2,102 in 1959-60.
Data, covering the last five years, of average consideration per transaction of town and suburban properties are shown in the next table. As can be seen, there has been little change in the proportions in the various consideration groups during this period.
| Year Ended 31 March | Under £1,000 | £1,000-£9,999 | £10,000-£24,999 | £25,000 and Over | Totals | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Consideration | Average | Number | Consideration | Average | Number | Consideration | Average | Number | Consideration | Average | Number | Consideration | Average | |
| £ (000) | £ | £ (000) | £ | £ (000) | £ | £ (000) | £ | £ (000) | £ | ||||||
| 1956 | 18,384 | 7,501 | 408 | 22,650 | 66,004 | 2,914 | 280 | 3,980 | 14,214 | 64 | 3,200 | 49,998 | 41,378 | 80,684 | 1,950 |
| 1957 | 16,727 | 7,077 | 423 | 21,009 | 61,274 | 2,917 | 247 | 3,540 | 14,332 | 83 | 3,724 | 44,862 | 38,066 | 75,614 | 1,986 |
| 1958 | 17,512 | 7,775 | 444 | 24,267 | 72,808 | 3,000 | 303 | 4,232 | 13,966 | 101 | 4,826 | 47,785 | 42,183 | 89,641 | 2,125 |
| 1959 | 18,131 | 8,391 | 463 | 23,362 | 69,907 | 2,992 | 290 | 4,071 | 14,038 | 71 | 2,846 | 40,082 | 41,854 | 85,216 | 2,036 |
| 1960 | 19,554 | 9,661 | 494 | 25,144 | 76,600 | 3,046 | 345 | 4,779 | 13,853 | 82 | 3,825 | 46,648 | 45,125 | 94,866 | 2,102 |
The following analysis shows, for 1959-60, transfers of country freehold properties classified by area groups. The average consideration per acre is also given for the two earlier years.
| Size Group (Acres) | Number | Area | Consideration | Consideration per Acre | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959-60 | 1959-60 | 1959-60 | 1959-60 | 1958-59 | 1957-58 | |
| acres | £(000) | £ | £ | £ | ||
| Under 30 | 3,445 | 24,863 | 9,916 | 398.84 | 377.64 | 363.76 |
| 30 and under 50 | 429 | 16,874 | 1,945 | 115.28 | 108.57 | 111.43 |
| 50 “ 100 | 931 | 66,920 | 6,111 | 91.32 | 82.52 | 84.55 |
| 100 “ 250 | 1,258 | 196,698 | 11,086 | 56.36 | 54.60 | 55.06 |
| 250 “ 500 | 608 | 211,225 | 7,281 | 34.47 | 33.05 | 31.15 |
| 500 and over | 533 | 746,155 | 8,237 | 11.04 | 13.47 | 10.60 |
| Totals | 7,204 | 1,262,735 | 44,576 | 35.30 | 36.97 | 32.03 |
Further particulars relating to transfers of country freehold properties from the year 1949-50 onwards are contained in the next table. As indicated previously, very diverse types of property are included in the figures, and the averages should not be taken for more than they purport to show. This is particularly so in the case of country properties, where the number of transactions is comparatively small.
| Year Ended 31 March | Average Value per Transaction | Average Value per Acre |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1950 | 2,303 | 9.69 |
| 1951 | 2,276 | 14.53 |
| 1952 | 3,523 | 22.46 |
| 1953 | 3,989 | 24.61 |
| 1954 | 4,335 | 26.69 |
| 1955 | 5,050 | 25.77 |
| 1956 | 5,254 | 30.21 |
| 1957 | 5,405 | 29.94 |
| 1958 | 5,986 | 32.03 |
| 1959 | 5,830 | 36.97 |
| 1960 | 6,188 | 35.30 |
Monthly statistics of transfers on sale of land registered under the Land Transfer Act are published in the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
LEGISLATION CONCERNING LAND SETTLEMENT AND SALE OF LAND - Legislation governing this aspect is found in the Land Settlement Promotion Act 1952 and the Marginal Lands Act 1950.
Land Settlement Promotion Act 1952 - This Act has the objectives of providing for the closer settlement of farm land, for the acquisition of farm land that is, or when subdivided and developed will be, capable of substantially increased production, and to prevent the undue aggregation of farm land.
The Act as amended in 1959 provides that persons purchasing or leasing farm land between 7 October 1959 and 31 August 1962 are required to reside personally on the land and farm it for their own benefit for a period of three years. The Act prevents, without the consent of the Minister of Lands, the purchase of farm land by a trustee for any person under the age of 17 years, or the purchase by a company the members of which are less than 10 in number, and include persons under the age of 17 years or trustees for such persons.
Part I of the Act relates to the taking of farm land for settlement (including a lease or licence of Crown land or a lease of West Coast settlement land) and gives power to the Minister of Lands to do so if he is of the opinion that additional farm land is required for the settlement of landless discharged servicemen and others requiring land on which to establish themselves in farming, and that sufficient land cannot be acquired for that purpose by voluntary negotiation. The Minister in such a case may, on the recommendation of the Land Settlement Board, take any farm land that is, in his opinion, suitable for settlement, and is, or when subdivided and developed will be, capable of substantially increased production.
Land is not to be taken from any owner unless he owns farm land in fee simple or on lease perpetually renewable or on lease in perpetuity which, in the aggregate, amounts to three or more economic farms or could provide for these by subdivision.
The owner also has the right to retain an area of land which is the equivalent of two economic farms (or which could by subdivision provide these) and also is sufficient to provide (a) a separate economic farm for each child of the owner under 21 years of age at the time, and (b) at the Minister's discretion, for each child of the owner over the age of 21 years who, at the time, is in the Minister's opinion likely to follow farming as a career. In every case the owner shall be entitled if he so desires to retain his homestead.
Objections to the taking of land may be made, and provision is made for the hearing of the objection by the Land Valuation Committee or the Land Valuation Court, which may allow or disallow it either unconditionally or subject to such conditions as the Court thinks fit.
Provision is also made for the payment of compensation for any land or estate or interest in the land so taken. It the offer of compensation made by the Minister is not accepted the amount of compensation payable will be that prescribed by order of the Land Valuation Court, which shall be final as regards the amount awarded. Another provision deals with compensation in respect of mortgaged lands.
Part II deals with the control of sales and leases of farm land to prevent undue aggregation. The Act applies to sales of freehold farm land, to leases of farm land for terms of three years or more, to sales of the lessees' interest under leases granted under the West Coast Settlement Reserves Act 1892, and to transfers of Crown land which, under section 208 of the Land Act 1924, do not require the consent of the Land Settlement Board, as well as to options for such sales and leases.
The consent of the Land Valuation Court is required to such transactions unless the purchaser or lessee files a declaration with the District Land Registrar within one month of the date of the transaction to the effect that he owns no farm land, has no interest in any estate or trust owning farm land, has not since the passing of the Act transferred any farm land to any person as trustee for any person or created any trust in respect of any farm land, that he has entered into the transaction solely on his own behalf, and intends to reside personally on the land and farm it for his own benefit.
The matters to be considered by the Court or committee in determining whether undue aggregation would result include: (a) whether the farm land already owned, leased, held, or occupied in fee simple or under any tenure of more than one year's duration, by the purchaser or lessee, is sufficient to support him, his wife, and any dependent children in a reasonable manner and reasonable standard of comfort; (b) whether, having regard to land so held, etc., the acquisition of additional land could, judged by ordinary and reasonable standards, be considered excessive; (c) the nature of the use to which the purchaser proposes to devote the land and his ability to achieve that purpose; (d) whether the acquisition would be in or against the public interest; and (e) whether refusal of consent would result in unavoidable and substantial hardship to the vendor or lessor.
Marginal Lands Act 1950 - The objects of this Act, which came into force from 1 April 1951, are to assist farmers to restore, maintain, and increase production on marginal lands. The administration of the Act is the responsibility of the Minister of Lands and is carried out by the Department of Lands and Survey. Actual control is vested in the Marginal Lands Board. To assist it in the administration of the Act the Board has appointed Marginal Lands Committees in each land district. Each committee consists of three members - the Commissioner of Crown Lands for the land district, who is chairman, an officer of the Department of Agriculture, and one other person selected from a panel of farmers appointed for each committee. This panel is limited by the Act to five members, who are selected for their experience in the farming or management of marginal lands.
The Board is empowered to make loans for clearing, cultivation, grassing, fencing, drainage, irrigation, buildings, farm machinery, livestock, in fact for any purpose having for its object the successful development and farming of a property regarded as suitable for a loan.
It is the policy of the Board not to compete with existing lending institutions and before it will make an advance the applicant must satisfy the Board that finance cannot be obtained through normal business channels. The Board will not normally provide finance for the improvement of a property unless it is capable of being developed into an economic unit. The policy is to assist competent men to make their holdings economic rather than help farmers already substantially established to bring into production additional land which could be developed from their private resources or out of revenue.
Activity under the Act in the initial period was slow and farmers appeared cautious in availing themselves of the assistance offering, but as the operations and purposes of the Act became more widely known a greater number of applications for advances were received. The scheme has been successful in that the objective of increasing production from marginal country has been achieved. Although there have been a few mortgagors who have not produced the results expected, many farmers on difficult and unattractive properties have, with Marginal Lands assistance and with application and energy, established and maintained profitable production. Many have completed their development programmes and as a result have been able to convert their current account mortgages to instalment mortgages, repaying the advances over a term of years, while others have repaid their advances in full.
For the year ended 31 March 1960 the Board granted 52 loans totalling £283,375. In all, from the inception of the marginal lands scheme, 731 loans have been approved, amounting to £3,060,484. The present rates of interest payable on advances are:
| Current account first mortgage | 5 per cent. |
| Current account second and subsequent mortgages | 5 1/2 per cent. |
| Instalment mortgage, first | 5 1/2 per cent, reducible to 5 per cent. |
| Instalment mortgage, second and subsequent mortgages | 6 per cent, reducible to 5 1/2 per cent. |
SOIL CONSERVATION AND RIVERS CONTROL - The problem of exhausted soils on hill country, deteriorating pastures, widespread soil erosion, and increasing run-off, as well as mounting damage to the lowlands by flooding and river erosion, led to the passing of the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Act in 1941. This provided for the establishment of a Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council, which in turn was empowered to constitute catchment districts in problem areas. The Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council is responsible for promoting the wider adoption of soil conservation practices, and, by specialised surveys and the use of conservation techniques on demonstration farms, has succeeded in promoting substantial benefits and increased protection in many districts.
New Zealand's soil erosion and flooding problems have their origin on the hill country pastoral lands, especially where farming has forced grass to take over the protective functions of vigorous native forest, scrub, fern, and swamp vegetation. The drastic changes in the vegetation brought about by developing farm resources have been reflected in drastic changes in the soil in the hill country where soil erosion and flooding have their origin. The protective, stabilising, and water-controlling combination of vigorous native vegetation, litter, and spongy soil has given way to a shallow-rooted, less protective carpet of grass on compacted, impervious, and often exhausted soils. The problem is one of restoring an erosion-resistant and water-absorbent combination of soil and vegetation with a satisfactory capacity to control water, which causes most soil erosion. Successful techniques which have been developed include spelling, control of burning and of animal pests, oversowing, topdressing, strict grazing control, the wider use of cattle, subdivisional fencing, stock water ponds, gully-control contour ploughing, terraces, grassed waterways, and spaced and close tree planting for stability.
Catchment Boards and Catchment Commissions - A catchment board is established on the recommendation of the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council when endorsed by the Local Government Commission. Thirteen boards, each consisting of nine or 10 elected representatives of catchment districts and five representatives from Government Departments, have been established. Together they cover about three-fifths of the country. Most of the resources of the boards are devoted to river control, but vigorous efforts are also made to promote soil conservation practices and to improve drainage.
The Waikato Valley Authority was constituted by special Act in 1956, and in terms of the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Amendment Act 1959, the Council can declare any other part of New Zealand to be a catchment area, and appoint a catchment commission which, through delegation by the Council, can exercise the functions and powers of a catchment board in that catchment area.
To assist farmers directly to tackle their own problems subsidies are made on farmers' contributions. These are at the rate of £1 for £1 on tree planting for stability and wind breaks, on cost of materials for conservation fencing, contouring, or flood-control dams, and on gully-control planting and structures. The rate of subsidy for this last purpose may be increased up to £2 for £1. Major river works and flood-retention dams may be subsidised up to £3 to £1. It is hoped that the final objects of catchment control - the planned integration of the necessary conservation measures in the upper catchments with drainage and river control in the lower catchments - will soon pass from the demonstration phase to general application.
Land Capability and Catchment Control - Experience has proved that the American system of land classification for soil conservation purposes is very satisfactory. In this system an inventory is made of the physical factors of slope, soil type, climate, and soil erosion. Along with a knowledge of vegetation and farming experience a land capability map is prepared classifying the land into classes according to the way in which the land in each class can be used. The required soil conservation practices are also determined for each class.
From this basic classification of the land in a catchment more detailed surveys of individual farms provide the data necessary for detailed conservation farming plans. These plans are then discussed with the farmer and fitted into his capacity for implementing them over a period of years. Great care is taken to support the necessary special soil conservation practices with accepted good farm management practices. The conservation treatment and farm management practice can then be dovetailed with the river control and drainage plans for the lower catchment to provide the ultimate plan for catchment control. Allied operations of importance are soil conservation forestry, fire prevention, and animal pest destruction.
Plans have now been developed in this country to integrate farming practices with the physical limitations of the land in order to assure permanent production consistent with stability and permanence of the land and conservation of the rain that falls.
Agricultural Aviation and Conservation - The Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council has an advisory committee on agricultural aviation, which has since 1949-50 sponsored new developments in aviation for conservation purposes. The promotion of aerial topdressing, aerial oversowing with grasses and clovers, dropping of fencing materials, and spreading of rabbit poison is enabling millions of acres of denuded and eroded high country to receive conservation treatment progressively. These aerial aids to farming, coupled with the wider adoption of provident management practices on the land, provide a practical soil conservation approach with great potentialities on the dominantly hilly problem lands.
Staffing and Finance - The Ministry of Works and Department of Agriculture provide the technical and administrative services required by the Council. The Council and the catchment boards have built up a team of specialist engineers in river control and drainage work, which ensures that investigations, planning, supervision, and execution of works are carried out to high standards. Four mobile works units equipped with tractors and special equipment have been set up by the Council, and three catchment boards have developed their own works units.
An administrative rate of up to 1/12d. in the pound on capital value over the district provides for the services of catchment boards, but special rates struck on a classification according to the benefit accruing provide the local contribution for actual works. Over the past 10 years the appropriation for soil conservation and rivers control work has grown to £1,600,000 a year to provide for subsidies and services.
Works Completed - Soil conservation works completed in the period from 1952 to 1960 have included the planting of 3,705,000 trees, the terracing and grading of 268 miles of banks, and the erection of 376 miles of conservation fencing.
River and drainage works completed from 1948 to 1960 have included 3,901 miles of newly dug or reconstructed drains; 1,993 miles of river channel cleared; 113 miles of river diversion cuts; 651 miles of stopbanks erected; and 1,091 miles of banks protected.
The Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council has sponsored information services by way of publications, movie films, show displays, and radio broadcasts.
ADMINISTRATION - Crown land is administered under the authority of the Land Act 1948. The Minister of Lands is charged with the administration of the Land Act, and his executive officer is the Director-General of Lands, who is the Permanent Head of the Department of Lands and Survey.
New Zealand is divided into 12 land districts, the executive officer for each district being a Commissioner of Crown Lands. There is a central authority entitled the Land Settlement Board. This board consists of the Minister of Lands (Chairman), the Director-General of Lands (Deputy Chairman). the Secretary to the Treasury, the Director-General of Agriculture, the Valuer-General, a representative of the State Advances Corporation, the Director of Rehabilitation, the Assistant Director-General of Lands, the Fields Director of the Department of Lands and Survey, a representative of the New Zealand Returned Services' Association, and not more than two other persons to be appointed by the Governor-General.
The duties of the board are broadly defined in the Act as follows:
It shall be the duty of the board to carry out the provisions of this Act for the administration, management, development, alienation, settlement, protection, and care of Crown land; and to carry out all negotiations for the purchase of land by the Crown under this Act, and the performance and completion of all contracts of purchase so entered into by the Crown.
The Land Settlement Board is required to appoint one or more Land Settlement Committees for each land district, and 20 of these committees have been set up. Each committee consists of three members, including the Commissioner of Crown Lands for the land district as chairman. The board may also appoint as an associate member of any committee any person who in the opinion of the board possesses expert knowledge of advantage to the committee in the execution of its functions. The functions of these committees are not expressly set out in the Act, but the board has wide powers of delegating to committees any of its functions.
METHODS OF ACQUIRING CROWN LAND - Crown land is normally offered to the public at valuation and if necessary a ballot is conducted to decide the successful applicant, although in certain circumstances preferential allotment can be made. Under legislation introduced by the Land Amendment Act 1950 any urban or commercial or industrial land may be offered for disposal by tender at a minimum price or rental value or by public auction at an upset price. Every applicant must be of the age of 17 years or upwards, and must apply for Crown land solely for his own use or benefit. Two or more persons may make application to purchase or take on lease or licence as joint tenants or tenants in common.
Crown land may be acquired on the following tenures:
Farm land, urban land, commercial or industrial land - (a) On renewable lease; (b) for cash; (c) on deferred payments. A renewable lease is for a term of 33 years with a perpetual right of renewal for the same term and, except where otherwise provided for, with a right of acquiring the fee simple. The board may, however, determine that any specified land may be taken on renewable lease only, but without the right of acquiring the fee simple. The board may also determine that any specified commercial or industrial land may be taken on lease only, but without the right of acquiring the fee simple, for any term with or without a right of renewal, but so that the aggregate term, including renewals (if any), does not exceed 50 years.
Pastoral land - (a) On pastoral lease for a term of 33 years with a perpetual right of renewal for the same term, but with no right of acquiring the fee simple; (b) on pastoral occupation licence for a term not exceeding 21 years, with no right of renewal or of acquiring the fee simple.
Short tenancies for grazing or other purposes for a term not exceeding five years.
In some cases a holder of a lease or licence is required to effect within a certain specified period such improvements as the board determines. In most cases the lessee or licensee of any farm or pastoral land is required to commence to reside on the land within one year after the date of his licence.
LAND DEVELOPMENT - The Land Act empowers the Land Settlement Board to carry out such development works as may be required to improve the quality or condition of any Crown land or to make it fit for settlement. This includes the erection of buildings, and the board may carry on all usual farming activities on land developed or being developed until the time is appropriate for the disposal of the land on permanent tenure.
SELECTIONS - The following table shows details of the various freehold selections during the year 1959-60, together with totals for 1958-59.
| Freehold | Number of Selectors | Total Area Selected | Purchase Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crown lands | acres | £ | |
| Farm land | 244 | 6,006 | 36,755 |
| Urban land | 437 | 184 | 183,652 |
| Commercial or industrial land | 44 | 18 | 65,876 |
| Land freeholded: Land Subdivision in Counties Act | 46 | 13 | 21,270 |
| Totals, 1959-60 | 771 | 6,221 | 307,553 |
| Totals, 1958-59 | 797 | 9,795 | 288,810 |
Corresponding details concerning selections made under leasehold tenures are given for similar periods.
| Leases and Licences | Number of Selectors | Total Area Selected | Annual Rental | Annual Instalments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Areas and rentals not shown; licences on royalty basis only. | ||||
| Crown lands- | ||||
| Renewable lease | acres | £ | £ | |
| Farm | 91 | 54,283 | 10,114 | ... |
| Urban | 164 | 33 | 5,163 | 190 |
| Commercial or industrial | 2 | 5 | 35 | ... |
| Pastoral lease | 3 | 101,079 | 990 | ... |
| Pastoral occupation licence | 1 | 100 | 15 | ... |
| Deferred-payment licence- | ||||
| Farm | 49 | 9,383 | ... | 7,804 |
| Urban | 1,397 | 334 | ... | 63,090 |
| Commercial or industrial | 59 | 13 | ... | 8,515 |
| Land Subdivision in Counties Act | 191 | 45 | ... | 10,094 |
| Special leases under section 67, Land Act | 44 | 19,277 | 18,074 | 113 |
| Special leases under section 165, Land Act* | 26 | .. | .. | .. |
| Grazing and other tenancies, section 68, Land Act | 2,174 | 71,111 | 80,367 | 304 |
| Totals | 4,201 | 255,663 | 114,758 | 90,114 |
| Endowment lands- | ||||
| Westport Harbour Board endowments | 9 | 113 | 16 | ... |
| Leases under section 47, Land Act | 5 | 26 | 340 | ... |
| Leases under section 48, Land Act | 52 | 1,206 | 2,827 | ... |
| Sundry endowment leases | 58 | 25,743 | 1,193 | ... |
| Grand totals, 1959-60 | 4,325 | 282,751 | 119,134 | 90,114 |
| Grand totals, 1958-59 | 4,633 | 116,526 | 116,916 | 107,995 |
NOTE - Section numbers refer to Land Act 1948.
LEASES AND LICENCES CURRENT AT 31 MARCH 1960 - The following table shows the total number of leases and licences current at 31 March 1960. This table is in two parts, the first (a), dealing with leases and licences issued under the Land Act 1948, and the second (b), with those issued under Acts other than the Land Act 1948 and still current at 31 March 1960.
| Tenure | Number | Area | Annual Rent | Annual Instalment (Including Improvement Loading) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Areas and rentals not shown; licences on royalty basis only. | ||||
| (a) Tenures Under the Land Act 1948 | ||||
| Crown lands- | ||||
| Renewable leases | acres | £ | £ | |
| Farm | 4,621 | 2,461,691 | 404,984 | 10,533 |
| Urban | 2,724 | 913 | 50,479 | 454 |
| Commercial or industrial | 72 | 96 | 7,498 | 136 |
| Pastoral leases | 382 | 6,283,326 | 73,362 | 1,522 |
| Pastoral occupation licences | 42 | 258,136 | 2,063 | ... |
| Deferred-payment licences- | ||||
| Farm | 1,261 | 444,902 | ... | 131,512 |
| Urban | 8,491 | 2,186 | ... | 368,642 |
| Commercial or industrial | 275 | 2,001 | .... | 62,120 |
| Land Subdivision in Counties Act | 863 | 205 | ... | 36,189 |
| Special leases (section 67, Land Act)- | ||||
| Renewable- | ||||
| Farm | 149 | 44,407 | 4,983 | 817 |
| Urban | 115 | 28 | 539 | 160 |
| Commercial or industrial | 18 | 3,879 | 7,302 | 228 |
| Non-renewable- | ||||
| Farm | 50 | 12,749 | 2,833 | 117 |
| Urban | 14 | 12 | 121 | ... |
| Commercial or industrial | 7 | 82 | 19,901 | ... |
| Licences for removal of minerals* | 186 | .. | .. | .. |
| Flax leases | 7 | 1,246 | 98 | 415 |
| Communal grazing licences | 4 | 2,584 | 510 | 55 |
| Miscellaneous licences | 5,115 | 428,463 | 120,164 | ... |
| Totals, Crown lands | 24,396 | 9,946,906 | 694,837 | 612,900 |
| Endowment lands- | ||||
| Leases under section 169, Land Act | 24 | 2,795 | 377 | ... |
| Leases under section 48, Land Act | 249 | 5,121 | 14,581 | ... |
| Leases under section 47, Land Act | 8 | 87 | 392 | ... |
| Sundry tenures | 130 | 218,932 | 6,368 | ... |
| Totals, tenures under Land Act 1948 | 24,807 | 10,173,841 | 716,555 | 612,900 |
| (b) Tenures Under Acts Other Than the Land Act 1948 | ||||
| Renewable leases | 5,262 | 1,490,685 | 157,835 | 2,926 |
| Leases under section 5, Discharged Soldiers' Settlement Amendment Act 1921-22 | 29 | 7,564 | 1,864 | 34 |
| Special tenure leases | 404 | 144,887 | 19,056 | 307 |
| Leases in perpetuity | 6,425 | 1,309,774 | 153,256 | 67 |
| Perpetual leases | 42 | 2,532 | 278 | ... |
| Mining district land occupation leases | 94 | 1,127 | 215 | ... |
| Pastoral regulation licences (mining districts) | 65 | 11,109 | 326 | ... |
| Small grazing-run leases | 123 | 394,955 | 12,165 | ... |
| Pastoral-run licences | 181 | 1,919,956 | 19,850 | ... |
| Education reserves: Public Bodies' Leases Act | 402 | 44,482 | 7,363 | 80 |
| Deferred-payment licences | 760 | 166,017 | 29,868 | |
| Miscellaneous licences | 773 | 36,968 | 5,064 | ... |
| Small farm leases | 28 | 564 | 99 | ... |
| Leases under Education Lands Act- | ||||
| Leases | 143 | 24,195 | 11,763 | 189 |
| Temporary tenancies | 19 | 8 | 1,083 | ... |
| Agreements sale and purchase- | ||||
| Waikato Land Settlement Scheme | 5 | 606 | 799 | |
| Hanmer Crown leases | 105 | 279 | 534 | ... |
| Sundry leases | 15 | 265 | 144 | 47 |
| Subtotals, Crown lands | 14,875 | 5,555,973 | 390,895 | 34,317 |
| Endowment lands- | ||||
| Westport Harbour Board Endowment | 572 | 11,621 | 2,830 | ... |
| Thermal Springs licences | 61 | 33 | 255 | ... |
| Sundry other endowments | 99 | 41,238 | 3,459 | 19 |
| Totals, tenures under Acts other than Land Act 1948 | 15,607 | 5,608,865 | 397,439 | 34,336 |
| Grand totals, all tenures | 40,414 | 15,782,706 | 1,113,994 | 647,236 |
LEASES AND LICENCES FREEHOLDED - Over the past few years many Crown lessees have availed themselves of the provisions of the Land Act 1948 and have freeholded their leases, either for cash or on deferred-payment licence.
In 1959-60, 298 leases were freeholded, either for cash or on deferred payments. The area embraced by these leases was 39,970 acres, and the total purchase price £367,654, of which £244,109 was on deferred payments. These figures are a decrease on those for 1958-59, when 345 leases over 50,294 acres were freeholded for a total of £355,689.
| Leases and Licences Freeholded | Number | Area | Purchase Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| For cash | Acres | £ | |
| Crown lands | 145 | 12,312 | 116,684 |
| Endowment lands | 4 | 2 | 6,861 |
| On deferred payments- | |||
| Crown lands | 148 | 27,655 | 240,352 |
| Endowment lands | 1 | 1 | 3,757 |
| Totals | 298 | 39,970 | 367,654 |
PURCHASE OF LAND FOR SETTLEMENT - The Land Act 1948 authorises the Land Settlement Board to purchase private land or the interest of any lessee or licensee in any Crown land or Maori land for the purposes of settlement as farming, urban, commercial and industrial, or pastoral land. The Land Settlement Promotion Act 1952 gives power to the Minister of Lands, under certain conditions, to take any farm land suitable for settlement where additional farm land is required for settlement of landless discharged servicemen and others requiring land on which to establish themselves in farming (see p. 292).
LAND FOR DISCHARGED SERVICEMEN - Authority is contained in the Land Act 1948 for the granting of a lease or licence over Crown land to a discharged serviceman without competition. The Act also provides that where there are simultaneous applications for Crown land and, in the opinion of the Land Settlement Board, there are two or more applicants who are equally suitable to be allotted the land, an applicant who is a serviceman or a discharged serviceman or the wife or widow of a serviceman or discharged serviceman may have preference over all other classes of applicants.
Land is provided by the Crown for the purposes of settling ex-servicemen by the following methods:
By the purchase of privately owned properties:
By the use of unalienated Crown land:
By the resumption by the Crown of land already held under Crown lease or licence:
The following table contains particulars of land acquired for development and settlement during the year ended 31 March 1960, and from the commencement of the scheme to 31 March 1960; also shown are those areas made available for settlement and the balance on hand at the latter date. The figures do not include particulars relating to ex-servicemen who have been assisted by way of rehabilitation loans to purchase established farms on their own account. Further information concerning the settlement of ex-servicemen on the land will be found in Section 9B, Rehabilitation.
| Year Ended 31 March 1960 | From Inception to 31 March 1960 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Units | Area | Units | |
| *Tentative figures only. Final subdivision and utilisation is decided as development is approaching completion. | ||||
| ACQUISITIONS | ||||
| acres | acres | |||
| (a) Purchased by voluntary negotiation | 77,825 | 95* | 1,404,944 | .. |
| (b) Compulsorily acquired (Servicemen's Settlement and Land Sales Act 1943 and Servicemen's Settlement Act 1950) | - | -281,472 | .. | |
| (c) Properties where ex-servicemen substituted under section 31 (3) (b), Servicemen's Settlement Act 1950 | - | -17,390 | .. | |
| (d) Crown land made available | 20,460 | 17* | 730,971 | .. |
| Totals, acquisitions | 98,285 | 112* | 2,434,777 | 5,268 |
| DISPOSALS | ||||
| I To Grade “A” Ex-servicemen | ||||
| (a) Developed units (including substitutions) | 13,724 | 28 | 1,318,026 | 3,367 |
| (b) Partially developed units | - | - | 4,182 | 32 |
| (c) Unimproved units | - | - | 1,314 | 5 |
| (d) General land settlement scheme | - | - | 2,300 | 15 |
| 13,724 | 28 | 1,325,822 | 3,419 | |
| II To Non-graded Ex-servicemen and Civilians | ||||
| (a) Developed units | 20,184 | 39 | 32,109 | 69 |
| (b) Partially developed units | - | - | 6,225 | 28 |
| (c) Unimproved units | 1,094 | 3 | 33,727 | 79 |
| (d) General land settlement scheme | - | - | 9,347 | 22 |
| (e) Miscellaneous | - | - | 7,870 | 58 |
| 21,278 | 42 | 89,278 | 256 | |
| III Sundry Disposals | ||||
| (a) Transferred to Department of Maori Affairs for settlement of Maori ex-servicemen | - | -11,963 | 30 | |
| (b) Transferred to Department of Agriculture for experimental purposes | - | -2,447 | 8 | |
| (c) Workers' homes, adjacent owners, riverbank reserve, bush reserve, unsuitable for settlement, etc. | 2,390 | 1 | 111,120 | 5 |
| 2,390 | 1 | 125,530 | 43 | |
| Totals, disposals | 37,392 | 71 | 1,540,630 | 3,718 |
| Land on hand planned for development | - | - | 894,147 | 1,550* |
Rent under renewable lease is based on the unimproved value of the land at the date of the lease or renewal, and in the case of discharged servicemen is calculated at the rate of 2 per cent of such unimproved value for the first year and 3 per cent for the balance of the first term.
DEFINITION AND KINDS OF MAORI LANDS - Maori land is of two kinds, namely, customary land and Maori freehold land. Customary land is land which has never been the subject of a Crown grant and is held by Maoris under the customs and usages of the Maori people. It is land in respect of which the ancient customary Maori title as recognised by the appropriate provisions of the Maori Affairs Act 1953 has not yet been extinguished. Such land, since it has not been Crown-granted, remains vested in the Crown, subject, however, to the customary title of the Maoris, and to their right to have the customary title transformed into a freehold title by the Maori Land Court. There is little of this class of land now left in New Zealand. Maori freehold land is the land held by Maoris under an ordinary freehold title, deriving, mainly, from the orders made by the Court on the investigation of the customary title.
Whether land is Maori or European land depends upon the beneficial ownership of it, and not merely on the legal ownership. If land is held by a European in trust for a Maori, it is Maori land; if it is held in trust by a Maori for a European, it is European land. There are, however, four exceptions to this:
When land has once become European land it does not again become Maori land unless by special enactment, by being exchanged for Maori land, or in special circumstances by declaration by Order in Council.
Land purchased by a Maori from the Crown for a pecuniary consideration is not Maori land. This does not include an exchange of land, with or without a payment of money by way of equality of exchange.
Land held by a Maori in severalty may be declared to be European land by the Maori Appellate Court.
Under certain circumstances the Maori owner may have been declared a European.
Even though one of many Maori owners may sell, the land remains Maori land until all have disposed of their interest, or until the purchaser has had his interests partitioned off. The term “Maori” includes a half-caste, or a person intermediate in blood between a Maori and a half-caste.
Since 1954, by virtue of various provisions in the Maori Affairs Act 1953, emphasis has been placed on the need for the improvement of existing Maori land titles by the elimination of small fractional interests and the reduction in the number of owners. The idea behind this is to clear the way for the better use of the land in an attempt to keep Maori freehold land in the possession of the Maoris.
POWERS OF ALIENATION - The ordinary provisions as to alienation of Maori land do not affect the power to dispose of land by will, but a Maori cannot will to a European except it be a husband or wife or other relative of the person making the will. A Maori cannot dispose of customary land, whether by will or otherwise. No alienation of Maori land by a Maori has any effect until it is confirmed by the Maori Land Court.
The Court, before confirming an alienation, must satisfy itself, inter alia, that it is not contrary to the interests of the Maori alienating; that the consideration is adequate; that the purchase money or other consideration is paid or secured; and that the alienation is not otherwise prohibited by law. A lease of Maori land cannot be for a longer term than 50 years.
With regard to Maori freehold land, the Court during 1959-60 approved of new leases comprising 22,144 acres to Europeans and 16,386 acres to Maoris, the previous year's figures being 22,925 and 15,255 acres respectively. It confirmed transfers (apart from sales to the Crown) affecting 54,215 acres of freehold land to Europeans and 4,588 acres to Maoris in 1959-60, the corresponding 1958-59 figures being 11,460 and 3,632 acres respectively. During the year ended 31 March 1959 timber-cutting rights were confirmed by the Court in respect of 28,094 acres.
REMAINING LAND - The area of Maori land still held by Maoris in the North Island is estimated at 3,750,000 acres, and in the whole of New Zealand at 4,000,000 acres. In many cases the Maoris are utilising their land for pastoral and dairying purposes. Other lands are being farmed for them by the Maori Trustee. Extensive areas formerly managed for the Maori owners by the East Coast Commissioner, acting under statutory powers, have practically all been returned to the management of the owners, who are farming them under the system of incorporated owners provided by Part XXII of the Maori Affairs Act 1953.
BOARD OF MAORI AFFAIRS - The Board of Maori Affairs constituted under the Maori Affairs Act 1953 consists of the Minister of Maori Affairs, the Secretary for Maori Affairs, the Director-General of Lands, the Valuer-General, the Secretary to the Treasury, the Director-General of Agriculture, the member of the Executive Council representing the Maori race or, if there is no such member, any member of the Executive Council appointed by the Governor-General to be a member of the Board, and three other members appointed by the Governor-General.
The functions of the Board include, inter alia, the following:
The control of the development and settlement of Maori land or land owned or occupied by Maoris.
The approval of investment and advances, and of certain expenditure from the Maori Trustee funds.
The control of negotiations for the acquisition of Maori lands by the Crown.
The control of expenditure on housing operations under the Maori Housing Act 1935, as amended in 1938.
MAORI LAND COURT - The Maori Land Court consists of a Chief Judge and such other Judges as the Governor-General may think fit to appoint. All powers of the Court may be exercised by a single Judge, but there are certain important powers vested exclusively in the Chief Judge. Commissioners are appointed who exercise such jurisdiction of a Judge as the Governor-General authorises. The chief matters within the jurisdiction of the Court are:
The investigation of title to customary land, and transforming it into Maori freehold land.
The exclusive power of partitioning land among the owners.
The sanctioning of exchanges for other Maori land and European land.
Granting probates of wills and effecting succession to the estates of Maoris.
Making orders for the adoption of children.
Appointing trustees for Maoris who are minors or under other disability.
The incorporation of the owners of Maori land.
The determination of various claims as between Maoris.
To grant confirmation of alienation of Maori land.
The Maori Appellate Court consists of any two or more Judges of the Maori Land Court, provided that two Judges at least shall concur in every decision of the Court. With certain exceptions the Appellate Court determines appeals, whether on law or on fact, from all final orders of the Maori Land Court.
MAORI TRUSTEE - The Maori Trust Office was originally created to take over from the Public Trust Office the administration of certain Maori reserves and the administration of the estates of deceased Maoris and those under disability. The Maori Trust Office now forms part of the Department of Maori Affairs and is headed by the Maori Trustee, comparable in status and function with the Public Trustee. The control of most Maori Trustee activities has been decentralised by the delegation of wide powers to the District Officers of the Department of Maori Affairs, who deal primarily with all Maori Trustee matters in their districts. A detailed review of the functions and power of the Maori Trustee is contained in parliamentary paper G. 9 of 1954.
The Maori Trustee may be appointed executor of the will of a deceased Maori or administrator of an intestate Maori estate. He may also be appointed trustee to manage the property of Maoris who are minors or suffer from some other legal disability, and is statutory trustee of the estates of Maori mental patients. The Maori Trust Office Regulations 1954 prescribe the rates of commission and fees chargeable by the Maori Trustee and the rates of interest payable in respect of moneys held by him in his Common Fund.
In addition to the administration of Maori reserves, situated mainly in Taranaki, and in Nelson, Greymouth, and other South Island localities, the Maori Trustee has the responsibility for the administration of large areas of Maori land elsewhere. Most of these lands are, like the Maori reserves, vested in the Maori Trustee, who is responsible for leasing them and distributing the proceeds to the owners. The two principal statutes under which the Maori Trustee acts in relation to the control and leasing of land are the Maori Vested Lands Administration Act 1954 and the Maori Reserved Land Act 1955. Another function is the collection and distribution to owners of rents from most other Maori land leased under Part XXIII of the Maori Affairs Act 1953.
The Maori Trustee has extensive lending powers used principally for the settlement and improvement of Maori land, for the establishment of Maoris in business, and for housing purposes. Most advances are made on the security of Maori land.
The following table is a summary of the assets and liabilities of the Maori Trustee as at 31 March 1959 and 1960.
| As at 31 March | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| Assets | £ | £ |
| Cash | 212,660 | 112,428 |
| Investments- | ||
| Government securities | 2,254,601 | 2,404,476 |
| Local authority debentures | 123,532 | 142,410 |
| Mortgages, charges, and advances on overdraft | 1,068,104 | 1,174,238 |
| Land, buildings, and miscellaneous | 119,683 | 128,267 |
| Totals | 3,778,580 | 3,961,819 |
| Liabilities- | ||
| Amounts held for beneficiaries and sundry depositors | 2,909,712 | 2,995,665 |
| Reserves and Appropriation Account | 863,477 | 961,485 |
| Sundry creditors, etc. | 5,391 | 4,669 |
| Totals | 3,778,580 | 3,961,819 |
MAORI LAND DEVELOPMENT - Maori land development policy is directed to the settlement of Maori farmers on farms which will assure them of a reasonable standard of living based on today's costs and standards; to secure them the best possible tenure for the lands they farm; to assist them to develop the land and to teach them modern methods of farming. The means at the Department's disposal have permitted the development of approximately 10,000 acres of new land annually. In the year ended 30 June 1960 there were 17 farms settled.
The Lands and Survey Department has estimated that Maori land at 31 March 1955 totalled 4,072,398 acres. This total is broken down, very tentatively, by the Department of Maori Affairs into the following categories:
| Acres | ||
|---|---|---|
| Leased to Europeans | 750,000 | |
| Under control of the Department and the Maori Trustee (Part XXIV) | 445,230 | This includes: |
| 132,840 acres grassed but not settled | ||
| 78,850 acres suitable for development | ||
| 211,690 acres | ||
| Farmed by Maori trusts and incorporations | 1,477,770 | |
| Idle land suitable for development | 550,000 | |
| Idle land not suitable for development | 777,000 | |
| 4,000,000 |
The estimated area of Maori land suitable for settlement is thus limited to 760,000 acres (212,000 acres under departmental control and 550,000 acres of idle land).
Up to 30 June 1960 the Department had settled 2,214 Maoris on farms. If the use of the remaining 760,000 acres follows the usual pattern of one-third sheep farms and two-thirds dairy farms, only 3,910 more Maori farmers can be settled, i.e., 560 sheep farmers and 3,350 dairy farmers.
INTRODUCTORY - The surveys of Crown lands, Maori lands, land purchased under the former Settlements Acts and the Land Act 1948, lands acquired under the Land Settlement Promotion Act 1952, and lands acquired or taken for public works, are executed under the authority of the Minister of Lands, and are carried out by staff and contract surveyors registered by the Survey Board under the provisions of the Surveyors Act 1938. This Act provides that in order to undertake surveys all registered surveyors must hold annual practising certificates, issued by the secretary of the New Zealand Institute of Surveyors.
The surveys of private lands for the purpose of the Land Transfer Act 1952 are carried out by private surveyors similarly registered.
Statutory authority for the surveyor to enter upon any land and to place survey marks thereon is contained in several Acts, and the wilful destruction of these marks is subject to a severe penalty.
All surface surveys are made in accordance with regulations laid down and are subject to field check (if thought necessary) and to office examination prior to approval and deposit.
The standard of length is the chain of 22 Imperial yards divided into 100 links, and all linear measurements have to be expressed in terms thereof, and areas in acres, roods, and perches, with decimals of a perch. Standard comparison bands are available in each district office of the Department of Lands and Survey, as well as at the office of the Surveyor-General.
SURVEY SYSTEM - In the 1957 and earlier issues of the Yearbook there is described the survey system of minor triangulation adopted in 1876 to enable settlers to be given possession of definite pieces of land, with each section having for the purpose of record and title registration a complete identification by means of its number, the number of the block, and the name of the district.
In 1906 a geodetic triangulation to coordinate the local systems and to cover the whole country was commenced. This work was carried on intermittently over the years and the field work was eventually completed in 1946. Computations of the filed information were completed in 1949 when the Geodetic Datum 1949 was established.
Immediately on the outbreak of war the Army requested the Department of Lands and Survey to undertake the responsibility for the production of military maps. At the end of the war half of the country had been mapped for military purposes.
It was fortunate that the geodetic control was sufficiently advanced to enable the topographical maps produced during the war period 1939-45 to be coordinated in terms of an overall military grid. This grid was a provisional one and due to this factor and the various expediencies which had to be adopted to produce the topographical data the maps published were issued as a provisional series.
STANDARD SURVEYS - In order to more adequately correlate and redefine old boundary marks for land-title purposes and to provide a permanent standard of reference for future surveys in cities and boroughs where land values are high, and on highways and on main arterial roads where modern road surfaces have eliminated survey marks, a precise survey is carried out, all intersections being referenced with permanent standard marks, normally iron tubes in concrete blocks protected by an iron cover.
These surveys are of two classes - (1) those in the cities and boroughs, being of standard of accuracy of 2 inches to the mile, the cost of which is borne partly by the local authority concerned and partly by the Department of Lands and Survey and (2) those carried out on highways and arterial roads to a lesser standard of accuracy, for the purpose of referencing survey marks lost or obliterated by road works and surfaces.
These standard traverses will in the future be correlated with precise levelling traverses, thus providing a standard level datum for engineering works.
PRECISE LEVELLING - Approximately 1,271 miles of precise levelling have been carried out for the purpose of correlating the level data of irrigation and drainage and other engineering works. This type of levelling has been carried out in accordance with international standards of accuracy - namely, 0.012 feet or 0.144 inches per mile.
These levels are at mean sea-level datum determined from the tidal records of the principal tidal stations or of tide gauges established specially for that purpose. The traverses are referenced at approximately 10-mile intervals by fundamental bench marks and at approximately 1-mile intervals by standard bench marks.
This work is being further extended to meet the requirements of national drainage, irrigation, hydro-electric, and river-control development, where related and coordinated levels in terms of a fixed datum are essential.
AERIAL SURVEY AND TOPOGRAPHICAL MAPPING - Prior to the Army demand for military maps the Department of Lands and Survey had in 1936 set up a small photogrammetric unit equipped with two small stereo plotters capable of plotting topographic detail from vertical aerial photographs. An area had been photographed by the RNZAF in the Hawke's Bay district in 1935, and by 1939 the first topographical map of the national 1 mile to an inch series was produced. On the outbreak of the war an overall contract was entered into by the Army with a private operating company for a complete photographic coverage of New Zealand to be carried out in accordance with priorities fixed by the Department.
Gradually greater use was made of aerial photographs as a basis for topographical map production. The private company has continued to supply all the aerial photographic requirements of all Government Departments, orders for the supply of which are coordinated and issued by the Department of Lands and Survey. An up-to-date and well equipped photogrammetric branch is now capable of producing any type and scale of topographic map or plan including those used for road location and hydro design purposes.
The responsibility for the production of all aeronautical charts for RNZAF and civil aviation purposes is also a permanent function of the Department of Lands and Survey. Assistance is also given to the hydrographic branch of the Navy Department in the establishment of shore beacons for the control of the offshore hydrographic survey at present being carried out by the Navy Department.
There is an increasing demand for topographical maps of all scales for land development, forestry, engineering, geological and soil survey, and other governmental purposes. New cartographic techniques have revolutionised the production of better and more varied scales and types of maps. In consequence it can now be claimed that New Zealand has a mapping organisation that compares more than favourably with other overseas mapping agencies.
Extensive use is made of the aerial photographs for other than purely mapping purposes. All types of land and engineering development, investigations into geological resources, afforestation, and town and rural planning are now based on data extracted from the aerial photographs. The Department is responsible for the maintenance of a complete library of aerial photographs, which are made available for all national purposes. All orders for photography required by any Department of State are coordinated and priorities for such photography fixed by a coordinating committee. At present the North Island has been completely photographed while two-thirds of the South Island has been covered.
TIDAL SURVEY - The tidal work carried out by the Department at the commencement of the survey operations in New Zealand consisted of determinations of mean high-water mark (H.W.M.) for the purpose of defining the boundary of land abutting on tidal waters.
Later the adoption of mean sea level as the datum of reference for the heights shown on the maps of trigonometrical and precise levelling surveys led to a more accurate system of tidal observations being initiated; but it was not until 1909 that a complete tidal survey was inaugurated, at the request of the Admiralty, to include the predictions of the times and heights of high and low water of the ports of Auckland and Wellington in the Admiralty Tide Tables.
The tidal observations are made mainly by self-registering tide gauges, in which a curve is traced which shows the height of the water at any time above an arbitrary datum. This curve is decomposed, by a process devised by Lord Kelvin, and known as “harmonic analysis,” into its harmonic elements. These components are now computed for the ports of Auckland, New Plymouth, Wellington, Lyttelton, Dunedin, Bluff, and Westport, and from them the predicted times and heights of high and low water are obtained by means of the tide predictor at the Tidal Institute, University of Liverpool, and published in advance in the New Zealand Nautical Almanac, the Admiralty Tide Tables, and several of the maritime publications of foreign nations.
The seven ports for which tide tables are prepared serve as standards of reference on which to base, by means of tidal difference, the times and heights of high and low water of all the other ports in New Zealand.
GEOGRAPHIC BOARD - The New Zealand Geographic Board, constituted under the provisions of the New Zealand Geographic Board Act 1946, is the official place-names authority.
The main function of the board is to adjudicate on matters pertaining to place and feature names in New Zealand. The board has authority to assign new names for localities, geographical features, post offices, railway stations, etc., and to alter existing names subject to the right of appeal vested in the general public and to the rights of local authorities concerning names within the areas administered by such local authorities.
The board together with three co-opted members also acts as the Antarctic Place Names Committee. This committee is the official New Zealand authority for approval of names in the Antarctic. Its activities are confined mainly to the Ross Dependency but liaison is maintained with the place-name authorities of other countries.
The membership of the board comprises the Surveyor-General, two representatives of the Maori race, a representative of the New Zealand Geographical Society, a representative of the Federated Mountain Clubs of New Zealand, and two members appointed on the recommendation of the Minister of Lands.
MISCELLANEOUS - The Department, in addition to the activities outlined in the preceding paragraphs, carries out many miscellaneous functions, among which are the drawing of maps and diagrams for special publications, the periodic preparation of maps for census and electoral purposes, the copying of maps and plans by photostat process, the preparation of aerial photograph mosaics and enlargements for departmental purposes, compilation of maps and data for town and regional planning purposes, the control and administration of the subdivision of land in counties required for housing, the preparation of special topographical maps for land settlement, engineering and scientific development, the preparation of maps for air navigation requirements, the production of all maps for the armed services, and many other cognate duties requiring the services of the surveyor or the draughtsman.
PUBLICATIONS - Reports: An annual report of the departmental activities is published as a parliamentary paper, C. 1A. At intervals a publication called The Records of the Survey is issued, the latest volume being numbered five. The publication of professional papers is now discontinued, these being incorporated in the Records.
MAPS - Map sales agencies are maintained at each of the district offices except Wellington and at the Head Office of the Department of Lands and Survey. In addition about 233 private selling agents have been appointed throughout the country. All maps for sale are listed in the Catalogue of Maps published by the Department.
Maps are published and listed under the following headings:
GENERAL AND MISCELLANEOUS MAPS - General Maps of New Zealand are small-scale maps of New Zealand and larger scale maps which are not included in the cadastral and topographical section of the catalogue.
Pacific Islands Maps are of islands within the territories of New Zealand, of Western Samoa, and Norfolk Island.
Miscellaneous Maps are maps which have been prepared for special purposes, and in general include those of interest to mountaineers and tourists. A wide range of maps is included in the Descriptive Atlas of New Zealand.
CADASTRAL MAPS - The following series are published by the Department, these maps showing land title boundaries and land designations:
Survey District Series - 1 inch to 1 mile.
County Series - 1 inch to 1 mile.
Town Maps Series - At various scales from 1 inch to 2 chains, to 1 inch to 10 chains.
TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS - The following medium and large-scale maps are published:
1: 63,360 - 1 inch to 1 mile.
1: 25,000.
1: 15,840 - 1 inch to 20 chains.
1: 10,000 to 1: 20,000 - Street maps of towns.
1: 250,000.
1: 500,000.
The 1: 63,360 series now covers approximately 65 per cent of the country and embraces most of the settled areas. The 1: 25,000 series is as yet restricted to the closely settled areas at the main centres of population. The 1: 15,840 series is confined to certain areas of undeveloped lands which are being developed as farmlands.
MOSAIC MAPS - The sheet lines of the mosaic maps conform to the sheet lines of the 1: 25,000 topographic series. The mosaic maps are gridded and show place names and are published at scale 1: 15,840 (1 inch to 20 chains).
AERONAUTICAL CHARTS - Aeronautical charts published include-
Aerodrome approach and landing charts.
Plotting charts at scales 1: 1,000,000 and 1: 3,000,000.
Aeronautical charts 1: 500,000 and 1: 1,000,000.
GENERAL - The necessity for fixing equitable land values arises in many of the relations of the General Government and local governing authorities with the individual. In particular they are required in connection with the following:
The levying of land tax.
The apportionment of rating levies over contributory local authorities.
The levying of rates by local authorities.
The advancing of money on mortgage by Government Departments and by trustees under the Trustee Act.
The assessing of stamp, estate, and gift duties.
The fixing of prices payable by lessees to the Crown for acquiring the freehold of Crown lands.
In assessing the compensation payable where land is taken under the Public Works Act and certain other statutes.
In estimating the prices payable in alienations of Maori lands.
SYSTEM AND PROCEDURE - Prior to 1896 the valuing of land was not conducted on a uniform basis. Each State Department and local authority employed as valuers such persons whom it thought fit, and estimates of values by different authorities varied considerably. To bring about some order the Government Valuation of Land Act 1896 set up a separate Department of State charged with the duty of assessing the values of real estate for taxation and other purposes of the General Government and for local rating purposes. The present law relating to the valuation of land is contained in the Valuation of Land Act 1951, and in the Land Valuation Court Act 1948.
The work of the Valuation Department is directed by the Valuer-General, the actual work of valuing being done by district valuers and assistant valuers. The duty of a valuer is to examine each property and to estimate to the best of his ability (1) the unimproved value of the land contained therein, (2) the value of the buildings (if any) or other improvements (if any) upon such land, and (3) the capital value of the property.
Valuers are enjoined not to strain after high values, nor to accept special prices paid for land in exceptional circumstances, but to determine the value neither above nor below the fair selling value in view of the many and diverse purposes for which the values are used.
Generally, under the New Zealand law, the increased value attaching to any piece of land which is due to the successful working of other lands in the district, or to State or local authority expenditure on public works, or to the general prosperity and development of the country, forms portion of the “unimproved value”.
“Improvements” on land are defined, with certain provisos, as any work done or materials used on or for the benefit of the land by any owner or occupier resulting in an increase in the value of the land.
The “capital value” is the sum of the “unimproved value” plus the value of “improvements”.
THE VALUATION ROLL - The Valuation of Land Act 1951 directs the preparation of a valuation roll for each district over which a local authority has rating jurisdiction, setting forth in respect of each separate property the following particulars:
The name of the owner of the land, and the nature of his estate or interest therein, together with the name of the beneficial owner in the case of land held in trust:
The name of the occupier within the meaning of the Rating Act 1925:
The situation, description, and area of the land:
The nature and value of the improvements:
The unimproved value of the land:
The capital value of the land:
Such other particulars as are prescribed.
Revision of Rolls - District valuation rolls are revised by the Valuer-General at such dates as the Governor-General in Council from time to time directs. Previously there were no fixed periods between revisions. Since the necessity for revision depended upon the extent to which values had moved since the previous revision, the periods between revisions varied considerably between old-established and currently-developing districts. The considerable changes in land values over recent years have caused a wider realisation of the need for up-to-date valuations, and it is now provided that valuation rolls must be revised at intervals of not more than five years unless the Governor-General in Council directs otherwise.
There is provision that in the revaluation of a borough rating on the unimproved value the Governor-General in Council may direct that the revision is to be confined either to the unimproved values only or to the value of improvements only, with consequent adjustments of the capital values.
Equalisation of Values - Naturally it is not generally possible to revalue all the constituent districts of a special purpose rating authority such as a catchment board in one year, and with rising values, this sectional revaluation has led to some criticism that an unfair burden of the special purpose authority's rates was falling on the newly revalued districts.
In the long run very little injustice resulted because such anomalies tended to favour first the one district and then the other because of the unevenness in time of the movement in values. However, there was undoubtedly a short-run effect which needed dealing with, and as a result special legislation was enacted in 1957 - the Valuation Equalisation Act of that year.
The general purpose of this Act is to provide for an equitable adjustment of rates and of levies based on rateable values as between the several constituent districts comprising the district of an ad hoc local authority where those constituent districts have been revalued by the Valuer-General at different times.
Section 3 of the Act provides that the ad hoc local authority may of its own motion, and shall if so requested by the local authority of any constituent district, apply to the Valuer-General to make an adjusted valuation of all the rateable property in the several constituent districts comprising the district of the ad hoc local authority. On receipt of such an application the Valuer-General is to supply to the ad hoc local authority a certificate specifying the total amount of the rateable values of all the rateable property in the several constituent districts comprising the district of the ad hoc local authority, that valuation being calculated as at a date to be fixed by the Valuer-General which must be the date on which the valuation roll of one of the constituent districts came into force.
Section 4 provides that so long as a certificate of adjusted values issued by the Valuer-General remains in force:
All levies made by the ad hoc local authority on the local authorities of the constituent districts shall, so far as they are based on rateable values, be apportioned in proportion to the adjusted values instead of the current roll values.
Every rate made in each constituent district by or on behalf of the ad hoc local authority shall be so calculated that the proceeds of the rate will be equal to the proceeds that would be received from the rate that would have been required to be made if the total rateable value of all the rateable property in each constituent district had been equal to the adjusted value according to the Valuer-General's certificate.
Alterations During Currency of Rolls - At any time between the revisions of district rolls the Valuer-General may readjust, correct, or bring up to date the entries therein in consequence of:
Any improvements being added to or removed from the land:
Any change in the ownership or occupancy of the land:
Any new valuation being made on the requirement of the owner of the land:
Any land being omitted from the roll, or the name of the owner or the description or other particulars of the land being erroneously entered therein:
Any subdivision of the land:
Any lease or any other terminable charge or interest affecting the respective interests of the respective owners.
In new valuations as a consequence of (c) or (e), the aim is to preserve uniformity with the existing roll values of comparable parcels of land.
The Supplementary Roll - There is, in addition to the district valuation roll for each district, a supplementary roll for that district. The supplementary roll may be used for the same purposes as the district roll except that it may not be used for the assessment of land tax or local rates. Generally, all special valuations of land made during the currency of a district roll for particular purposes - e.g., the granting of loans by Government Departments or trustees on the security of lands, the assessment of stamp, gift, and estate duties - are entered on the supplementary roll, but not on the district roll. There is generally a right of objection to such special valuations procedurally similar to the objections discussed under the next heading.
Objections to Valuations - When a district valuation roll is revised the Valuer-General addresses to each owner, and also to the owner concerned when any particular valuation in that roll is altered, a notice showing the new valuation and naming a date before which all objections (in writing) to the values must be lodged. In the case of a revision of a district roll the Valuer-General, any local authority, or any owner whose name appears on the roll, may object to any valuation thereon. Where a particular property only is revalued, only the owner has a right of objection.
The Valuer-General refers any objections to his district valuers for reconsideration. He may then decide (1) of his own motion to refer the objection to the Land Valuation Court, (2) to alter the valuation to the extent claimed, (3) to alter the valuation to such extent as is agreed upon with the objector, or (4) to decline to alter the valuation. If his decision is either (2), (3), or (4), he serves notice of it on the objector, and on the owner if other than the objector. Either of these may notify the Valuer-General within 14 days that he desires the objection to be heard by the Land Valuation Court. If no such notice is received the Valuer-General's decision is deemed to be assented to, and the roll is amended, if necessary, to give effect to his decision.
LAND VALUATION COURT - The Land Valuation Court Act 1948 established the Land Valuation Court, which consists of three members appointed by the Governor-General in Council, one of whom is the Judge of the Court. In addition to its jurisdiction under the Valuation of Land Act the Court hears claims for compensation under the Public Works Act 1928 and determines values under the Land Settlement Promotion Act 1952.
The Act also established Land Valuation Committees which, in the exercise of their powers and functions, are subject to the general jurisdiction of the Court. A local authority may appoint a person, other than a member or paid officer of a local authority, to be an additional member of the Land Valuation Committee exercising its functions in the district of that local authority. This provision is limited to cases where objections to valuations of property situated in that local authority's district are being heard.
The Valuer-General files with a Registrar of the Land Valuation Court a list of objections, including those which of his own motion he has decided to refer to the Court and those which the objectors desired to be heard by the Court. Copies of the objections are filed with the list. The Registrar refers the objections to the appropriate district Land Valuation Committee for hearing, and the committee embodies its determination in each case in a formal order which, after a lapse of 14 days, is sealed by the Registrar and becomes an order of the Court. Within the period of 14 days, however, either the Crown representative, or any one affected by the order, may appeal to the Land Valuation Court, or the Court of its own motion may amend the order. Except that the Judge of the Court may on the application of any party to proceedings, or of his own motion, state a case for the opinion of the Court of Appeal on a question of law, the decisions of the Land Valuation Court (either decisions of the Court itself or orders of the committees sealed by the Registrar) are final.
In the case of an objection to a valuation being allowed, the new valuation dates back to the date at which the valuation objected to would have been effected had no objection been lodged.
If any owner who has objected to a valuation made at a revision of a district roll is not satisfied with the value of the land as fixed by the Land Valuation Court's order, he may, within 14 days of the sealing of the order, give notice to the Valuer-General that he requires the capital value to be reduced to the value which he (the owner) considers to be the fair selling value as specified in his notice (but not less than the aggregate amount owing on mortgages or other charges on the land), or the land to be acquired on behalf of Her Majesty, or sold, at that value. There is also provision that if the Valuer-General is of the opinion that the value has been fixed by the Court at less than the capital value, he may within 14 days after the sealing of the Court's order require the owner to consent to what he (the Valuer-General) considers is the fair capital value, and, failing such consent being given within 30 days after notice is delivered, he may, with the approval of the Governor-General in Council, acquire the property at that value on behalf of Her Majesty.
VALUATIONS IN RELATION TO RATING - The district valuation roll so long as it continues in force is by law the roll from which the valuation roll of every local authority rating on the capital or on the unimproved value is framed.
Owing to the heavy decline in values during the early nineteen-thirties, and the impracticability of a universal revaluation, the provision enabling new valuations to be made was availed of by many owners with the object of reducing their rate payments. In order to maintain rating equity the Valuation of Land Amendment Act 1933 authorised local authorities to levy rates upon a proportionate part (not being under 75 per cent) of values upon the roll. Where an individual owner had obtained a revaluation, the lower of either the new figure or the proportionate part of the previously existing figure was taken. Since 1945 the right of objection to such a new valuation is limited to the claim that uniformity has not been preserved with existing roll values of comparable parcels of land.
The Urban Farm Land Rating Act 1932 provides for rating relief for farm lands subject to rates levied by borough (or city) councils, independent town councils, and county councils in respect of county towns. The Act provides that these local authorities may assess valuations for rating purposes for such farm lands lower than the values for the same lands appearing on the district valuation rolls. There are rights of objection to such valuations, either to a specially constituted Assessment Court where the valuations are to appear on a farm-land roll, or to a Magistrate if special rateable values are being assessed for the ordinary rating roll. The values are generally revised at five-yearly intervals.
A heritage of the days of independent valuations by local authorities is the provision by which they can rate on the annual (rental) values of properties within their areas, these values being assessed by the local authorities' own valuers. The annual value is defined as the rent at which a property would let from year to year reduced by 20 per cent in the case of houses, buildings, and other perishable property, and by 10 per cent in the case of land, but it may not be less than 5 per cent of the value of the fee simple. A new valuation roll in this regard is prepared either annually or triennially.
CAPITAL AND UNIMPROVED VALUES OF LAND - General valuations of land for the whole of New Zealand were made periodically up to the year 1897-98. Since that year no general valuations for the whole country have been made, but portions are revalued from time to time. As previously mentioned, however, it is now provided that every revision of a district valuation roll shall be followed by a further revision within five years, unless such revision is postponed by the Governor-General in Council. The figures in the following table, showing valuations over a long period of years, therefore represent general valuations up to 1897 only, while for subsequent years the figures include the latest valuation available of each division.
GROSS CAPITAL AND UNIMPROVED VALUES
| At 31 March | Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) |
|---|---|---|
| £ (thousand) | ||
| 1878 | 99,567 | 62,574 |
| 1885 | 113,271 | .. |
| 1888 | 111,138 | 75,497 |
| 1891 | 122,225 | 75,832 |
| 1897 | 138,591 | 84,401 |
| 1902 | 154,816 | 94,848 |
| 1905 | 197,684 | 122,937 |
| 1907 | 236,645 | 149,683 |
| 1909 | 271,516 | 172,760 |
| 1911 | 293,117 | 184,063 |
| 1913 | 340,560 | 212,963 |
| 1915 | 371,077 | 230,705 |
| 1916 | 389,165 | 241,322 |
| 1917 | 405,466 | 251,088 |
| 1918 | 421,383 | 260,922 |
| 1919 | 445,533 | 275,988 |
| 1920 | 470,094 | 290,880 |
| 1921 | 518,584 | 317,631 |
| 1922 | 544,503 | 329,174 |
| 1923 | 553,404 | 330,791 |
| 1924 | 568,501 | 333,870 |
| 1925 | 587,350 | 339,310 |
| 1926 | 603,250 | 341,048 |
| 1927 | 618,264 | 341,519 |
| 1928 | 631,455 | 335,217 |
| 1929 | 655,907 | 344,758 |
| 1930 | 664,571 | 338,887 |
| 1931 | 667,911 | 331,635 |
| 1932 | 662,829 | 321,799 |
| 1933 | 653,708 | 314,556 |
| 1934 | 650,362 | 309,770 |
| 1935 | 637,604 | 301,138 |
| 1936 | 635,802 | 295,696 |
| 1937 | 632,230 | 287,845 |
| 1938 | 636,363 | 282,326 |
| 1939 | 652,899 | 282,806 |
| 1940 | 660,524 | 278,881 |
| 1941 | 673,118 | 277,542 |
| 1942 | 681,922 | 276,885 |
| 1943 | 684,181 | 276,881 |
| 1944 | 688,795 | 277,039 |
| 1945 | 697,366 | 277,495 |
| 1946 | 710,425 | 279,214 |
| 1947 | 746,412 | 284,274 |
| 1948 | 796,038 | 291,617 |
| 1949 | 889,268 | 307,152 |
| 1950 | 985,880 | 324,465 |
| 1951 | 1,112,747 | 349,160 |
| 1952 | 1,314,879 | 394,228 |
| 1953 | 1,532,358 | 449,814 |
| 1954 | 1,702,727 | 487,125 |
| 1955 | 2,068,313 | 579,128 |
| 1956 | 2,306,585 | 644,410 |
| 1957 | 2,496,337 | 697,540 |
| 1958 | 2,677,250 | 751,129 |
| 1959 | 2,832,252 | 805,299 |
| 1960 | 3,066,231 | 889,821 |
The table shows a continuous decrease in land values from 1929 to 1943. Probably the lowest point in real values was reached about 1934, and the decreases shown after that year merely indicate that the new valuations being made were still at levels lower than the existing pre-depression figures. After 1943 land values were stabilised through the operation of the Servicemen's Settlement and Land Sales Act 1943, and the increases shown to 1950 mainly reflect the writing into new valuations of increases which had occurred prior to 1943.
The lifting of land sales control on urban properties from 23 February 1950 was reflected in the 1951 general revaluations of boroughs and cities. County revaluations did not, however, reflect the transition to a free market basis until the 1952 revaluations, the effect of the higher basis having been postponed 12 months as provided for by section 38 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1950.
The fact that land valuations are not continuously up to date has the effect in the above table of delaying the appearance of other than the steepest movements and of reducing their apparent magnitudes. Consequently, the movements in the table cannot be regarded as indicative of the trends in land values at any given time. Rural land values are generally conditioned by the prices received for our exports of primary products. If it were not for the irregular periodicity of revisions of valuations, the movements in unimproved values in the preceding table could be expected to follow the trends of export prices shown in Section 23, though with less exaggerated movements and perhaps an upward bias due to improved efficiency in farming methods, growth of population, improved internal transport, and other facilities, etc.
Capital values are influenced not only by the prices of primary products (in so far as they affect the unimproved value included in the capital value and indirectly by their effect on price levels generally), but also by the amount of activity in the building and construction industry.
The values shown in the foregoing table and in that following are the gross values; they include the value not only of rateable properties, but also of churches, schools, unoccupied Crown lands, and other lands exempt from local rating.
GROSS VALUES
| As at 31 March | Number* | North Island | South Island | New Zealand | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | ||
| *As constituted on 1 April. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| Counties | |||||||
| 1956 | 125 | 651,197 | 189,604 | 305,943 | 110,951 | 957,140 | 300,555 |
| 1957 | 122 | 688,744 | 199,839 | 348,490 | 125,576 | 1,037,234 | 325,415 |
| 1958 | 121 | 748,843 | 216,519 | 382,137 | 139,113 | 1,130.980 | 355,632 |
| 1959 | 121 | 803,199 | 233,712 | 405,664 | I48,444 | 1,208,863 | 382,155 |
| 1960 | 121 | 854,809 | 245,950 | 427,397 | 154,998 | 1,282,206 | 400,949 |
| Boroughs | |||||||
| 1956 | 145 | 981,919 | 255,608 | 356,561 | 86,508 | 1,338,480 | 342,116 |
| 1957 | 143 | 1,054,113 | 275,633 | 395,280 | 94,995 | 1,449,394 | 370,629 |
| 1958 | 143 | 1,115,079 | 293,589 | 421,906 | 100,547 | 1,536,985 | 394,136 |
| 1959 | 143 | 1,167,280 | 314,657 | 446,487 | 107,092 | 1,613,767 | 421,749 |
| 1960 | 143 | 1,297,221 | 364,848 | 477,498 | 122,653 | 1,774,719 | 487,501 |
| Independent Town Districts | |||||||
| 1956 | 20 | 8,131 | 1,447 | 2,834 | 292 | 10,965 | 1,739 |
| 1957 | 17 | 7,441 | 1,307 | 2,269 | 189 | 9,710 | 1,496 |
| 1958 | 16 | 6,817 | 1,157 | 2,467 | 204 | 9,284 | 1,361 |
| 1959 | 16 | 7,093 | 1,190 | 2,529 | 205 | 9,622 | 1,395 |
| 1960 | 15 | 7,433 | 1,232 | 1,873 | 139 | 9,306 | 1,371 |
| Grand Totals | |||||||
| 1950 | 690,084 | 215,935 | 295,796 | 108,531 | 985,880 | 324,465 | |
| 1951 | 782,632 | 235,253 | 330,115 | 113,907 | 1,112,747 | 349,160 | |
| 1952 | 917,274 | 265,854 | 397,605 | 128,373 | 1,314,879 | 394,228 | |
| 1953 | 1,093,872 | 313,896 | 438,486 | 135,917 | 1,532,358 | 449,814 | |
| 1954 | 1,223,171 | 342,660 | 479,556 | 144,465 | 1,702,727 | 487,125 | |
| 1955 | 1,477,970 | 405,183 | 590,343 | 173,946 | 2,068,313 | 579,128 | |
| 1956 | 1,641,247 | 446,658 | 665,338 | 197,752 | 2,306,585 | 644,410 | |
| 1957 | 1,750,298 | 476,779 | 746,039 | 220,761 | 2,496,337 | 697,540 | |
| 1958 | 1,870,739 | 511,266 | 806,511 | 239,864 | 2,677,250 | 751,129 | |
| 1959 | 1,977,571 | 549,558 | 854,681 | 255,741 | 2,832,252 | 805,299 | |
| I960 | 2,159,464 | 612,030 | 906,767 | 277,790 | 3,066,231 | 889,821 | |
RATEABLE VALUES - The values quoted earlier in this section relate to gross values (i.e., the value of all property, whether exempt from local rating or not). The following summary indicates rateable values for counties, boroughs, and independent town districts as at 31 March 1960.
| North Island | South Island | New Zealand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | Capital Value (Land and Improvements) | Unimproved Value of Land (Included in Previous Column) | |
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| Counties | 769,922 | 232,375 | 396,060 | 149,070 | 1,165,981 | 381,444 |
| Boroughs | 1,158,782 | 329,794 | 425,467 | 111,582 | 1,584,244 | 441,377 |
| Town districts (independent) | 6,308 | 1,039 | 1,661 | 128 | 7,969 | 1,168 |
| Totals | 1,935,011 | 563,208 | 823,188 | 260,780 | 2,758,199 | 823,989 |
The next table shows the percentage distribution of area and population as at 1 April 1960, and of rateable property values between the different types of local authority districts as at 31 March 1960.
| Local Authority District | Area | Population | Rateable Property Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Value | Unimproved Value | Value of Improvements | |||
| Percentage Distribution | |||||
| Counties | 99.5 | 36.5 | 42.3 | 46.3 | 40.6 |
| Boroughs | 0.5 | 63.0 | 57.4 | 53.6 | 59.0 |
| Town districts (independent) | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
It will be observed that there is a closer correlation between value of improvements and population distribution than in the case of unimproved values and population distribution, with capital values consequently taking up an intermediate position.
Particulars of values for each county, borough, and independent town district in considerable detail are contained in the Local Authorities Handbook, where similar data are also given for dependent town districts and for road districts.
Table of Contents
GENERAL - The Bay of Islands was the first New Zealand port used by commercial shipping, but port development soon followed in other northern harbours such as Hokianga, Mangonui, and Auckland. Wellington came later, followed by New Plymouth. With settlements becoming established in the South Island, shipping was next recorded at Nelson, Akaroa, and Port Chalmers. By 1853, when statistics were first compiled for New Zealand as a whole, 11 ports were receiving shipping direct from overseas. The number of ports in use by overseas vessels increased during the gold-rush period, but later decreased to a number which has not changed greatly during the past 50 years.
The following table, which enumerates entrances of ships direct from overseas, illustrates the changing pattern of overseas shipping since 1853, and indicates the great increase in the size of vessels during these years.
| Year | Number of Ports Entered | Number of Vessels | Total Tonnage of Vessels | Average Tonnage of Vessels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | No. | tons | tons | |
| 1853 | 11 | 238 | 65,504 | 275 |
| 1860 | 14 | 398 | 140,276 | 352 |
| 1870 | 23 | 756 | 273,151 | 362 |
| 1880 | 19 | 730 | 395,675 | 542 |
| 1890 | 20 | 744 | 662,769 | 891 |
| 1900 | 15 | 616 | 854,632 | 1,387 |
| 1910 | 17 | 609 | 1,389,031 | 2,281 |
| 1920 | 17 | 744 | 2,062,370 | 2,772 |
| 1930 | 15 | 600 | 2,297,142 | 3,829 |
| 1940 | 15 | 601 | 2,834,499 | 4,716 |
| 1950 | 13 | 597 | 2,688,223 | 4,503 |
| 1960 | 12 | 818 | 3,800,255 | 4,646 |
The early development of coastal shipping is not easy to trace. Coastal movements of vessels were first recorded in the statistics in 1873, and no distinction was made between the movements of purely coastal vessels and the coastal movements of overseas vessels. This position obtained until 1921.
The following table includes all inward movements of ships, i.e., direct entrances from overseas, coastal movements of overseas ships, and entrances of coastal vessels. This gives some idea of the development of the activities of the ports over the period.
| Year | Ports Included in Records | Inward Movements of Vessels |
|---|---|---|
| *In these years data were collected from some minor ports which were later omitted from the records. | ||
| 1873 | 30 | 14,029 |
| 1880 | 30 | 17,615 |
| 1890 | 30 | 17,860 |
| 1900 | 30 | 21,478 |
| 1910 | 31 | 27,304 |
| 1920 | 34 | 20,156 |
| 1930 | 51* | 20,834 |
| 1940 | 46* | 18,343 |
| 1950 | 38 | 14,393 |
| 1960 | 35 | 13,373 |
The tonnage of total shipping at the ports is not available on a comparable basis over the whole period of this table.
The Customs Department records statistics of the number and tonnage of all vessels arriving in New Zealand ports direct from overseas, and of the departures of all vessels for overseas destinations. The Department of Statistics receives monthly from each port a statement of all shipping handled.
The figures given in this section include all registered merchant vessels trading at New Zealand ports: thus they exclude naval vessels when engaged in their normal duties, private launches, lighters engaged in loading or unloading vessels in roadsteads, trawlers, other fishing vessels, and pleasure craft.
OVERSEAS SHIPPING - In recording the statistics of overseas shipping only one entry and one clearance is counted for each voyage, viz, at the first port of call and at the port of final departure, regardless of the number of ports visited by the vessel while in New Zealand waters.
The following table gives the number and net tonnage of overseas vessels entering and clearing New Zealand ports during the last 11 years, distinguishing those entered and cleared “with cargo” (cargo manifest tonnages are also shown for these) from those “in ballast”.
| Year | With Cargo | In Ballast† | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vessels | Net Tonnage | Cargo Manifest Tonnage* | Vessels | Net Tonnage | Vessels | Net Tonnage | |
*Direct comparisons of import and export tonnages are invalid since the former contain a much higher proportion of goods recorded in “measurement” tons than do the latter. dagger;“In ballast” means (a) inwards - “having no cargo for discharge in New Zealand”; (b) outwards - “having no cargo loaded in New Zealand”. | |||||||
| Entered | |||||||
| 1950 | 549 | 2,464,093 | 3,492,032 | 48 | 224,130 | 597 | 2,688,223 |
| 1951 | 502 | 2,316,344 | 3,641,667 | 44 | 236,465 | 546 | 2,552,809 |
| 1952 | 652 | 2,759,949 | 4,400,254 | 52 | 268,081 | 704 | 3,028,030 |
| 1953 | 614 | 2,502,856 | 3,617,497 | 59 | 264,701 | 673 | 2,767,557 |
| 1954 | 687 | 2,882,310 | 4,453,506 | 64 | 277,822 | 751 | 3,160,132 |
| 1955 | 753 | 3,173,211 | 4,858,369 | 71 | 353,357 | 824 | 3,526,568 |
| 1956 | 720 | 3,022,713 | 4,422,905 | 60 | 341,835 | 780 | 3,364,548 |
| 1957 | 795 | 3,503,875 | 4,560,463 | 101 | 436,064 | 896 | 3,939,939 |
| 1958 | 794 | 3,445,543 | 4,536,110 | 135 | 608,225 | 929 | 4,053,768 |
| 1959 | 750 | 3,355,648 | 3,989,897 | 133 | 671,477 | 883 | 4,027,125 |
| 1960 | 818 | 3,800,255 | 4,636,376 | 154 | 700,637 | 972 | 4,500,892 |
| Cleared | |||||||
| 1950 | 363 | 1,713,242 | 1,163,934 | 212 | 911,647 | 575 | 2,624,889 |
| 1951 | 332 | 1,561,642 | 1,129,629 | 218 | 986,398 | 550 | 2,548,040 |
| 1952 | 388 | 1,774,658 | 1,173,577 | 338 | 1,365,638 | 726 | 3,140,296 |
| 1953 | 406 | 1,746,157 | 1,175,035 | 270 | 1,057,863 | 676 | 2,804,020 |
| 1954 | 427 | 1,800,305 | 1,224,978 | 308 | 1,332,629 | 735 | 3,132,934 |
| 1955 | 451 | 2,014,952 | 1,328,155 | 349 | 1,435,521 | 800 | 3,450,473 |
| 1956 | 464 | 2,017,829 | 1,476,096 | 321 | 1,346,892 | 785 | 3,364,721 |
| 1957 | 549 | 2,488,506 | 1,516,780 | 346 | 1,451,350 | 895 | 3,939,856 |
| 1958 | 554 | 2,495,808 | 1,531,033 | 357 | 1,478,484 | 911 | 3,974,292 |
| 1959 | 577 | 2,506,593 | 1,791,165 | 326 | 1,608,136 | 903 | 4,114,729 |
| 1960 | 610 | 2,643,682 | 1,747,897 | 351 | 1,764,743 | 961 | 4,408,425 |
Direction of Overseas Shipping - Particulars of the number and net tonnage of vessels entered and cleared between New Zealand and various countries during 1958 and 1959 are given in the following table.
| 1958 | 1959 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entered | Cleared | Entered | Cleared | |||||
| No. | Net Tonnage | No. | Net Tonnage | No. | Net Tonnage | No. | Net Tonnage | |
| United Kingdom | 144 | 955,345 | 149 | 1,016,060 | 130 | 881,554 | 144 | 966,890 |
| Aden | 1 | 15,017 | 1 | 4,934 | 3 | 16,367 | - | - |
| Hong Kong | 3 | 11,039 | 6 | 10,767 | 8 | 11,753 | 4 | 10,889 |
| Ceylon | 2 | 11,449 | 1 | 7,176 | 4 | 24,959 | 5 | 20,376 |
| Republic of India | 17 | 81,403 | 7 | 28,150 | 11 | 53,023 | 6 | 26,518 |
| Malaya | 2 | 12,053 | 2 | 12,639 | 3 | 18,143 | 5 | 21,519 |
| Singapore | 25 | 111,463 | 22 | 84,526 | 15 | 64,914 | 21 | 115,582 |
| Union of South Africa | 10 | 47,587 | 2 | 3,577 | 14 | 65,528 | - | - |
| Canada | 23 | 141,185 | 16 | 95,303 | 20 | 116,364 | 14 | 69,406 |
| Australia | 379 | 1,405,602 | 385 | 1,346,441 | 360 | 1,432,370 | 400 | 1,494,841 |
| Fiji | 51 | 158,041 | 39 | 96,798 | 26 | 70,665 | 30 | 85,156 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 8 | 35,854 | 5 | 23,630 | 8 | 37,139 | 10 | 49,978 |
| Nauru Island | 27 | 118,775 | 35 | 151,918 | 29 | 148,913 | 22 | 113,675 |
| Belgium | 7 | 32,901 | 1 | 6,251 | 2 | 7,793 | - | - |
| France | - | - | 9 | 36,985 | - | - | 13 | 55,503 |
| Sweden | 5 | 17,219 | - | - | 8 | 30,624 | 2 | 18,719 |
| Union of Soviet Socialist Republics | 1 | 3,942 | 27 | 18,964 | - | - | - | - |
| Bahrain | 1 | 4,926 | 4 | 26,437 | 3 | 16,540 | 1 | 6,538 |
| Iran | 9 | 49,248 | 9 | 51,427 | 15 | 85,294 | 12 | 75,878 |
| Indonesia | 8 | 43,327 | 14 | 85,832 | 8 | 42,348 | 8 | 50,147 |
| Japan | 46 | 103,515 | 49 | 129,123 | 53 | 120,286 | 66 | 148,566 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 12 | 77,050 | 13 | 81,512 | 17 | 108,323 | 10 | 60,408 |
| United States of America | 43 | 304,144 | 58 | 415,774 | 55 | 359,270 | 55 | 391,364 |
| Whale Fisheries (Foreign) | 31 | 32,305 | 2 | 1,183 | - | - | - | - |
| Other countries | 74 | 280,378 | 55 | 238,885 | 91 | 314,955 | 75 | 332,776 |
| Totals | 929 | 4,053,768 | 911 | 3,974,292 | 883 | 4,027,125 | 903 | 4,114,729 |
In earlier years the tonnage of shipping entering from and clearing for the United Kingdom was higher than that for any other individual country. In 1954, however, shipping to and from Australia exceeded that recorded for the United Kingdom, and this has been the case for subsequent years also. The year 1954 was the first in which over 1,000,000 tons of shipping left New Zealand for an individual country. Shipping to Australia has been over that figure each year since then, and in 1956 and 1958 over 1,000,000 tons departed for the United Kingdom also.
The next table shows the net tonnage of shipping between New Zealand and certain principal countries for the five years 1955-59.
| Year | Australia | United Kingdom | United States of America | Canada | Pacific Islands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Tons | |||||
| Entered | |||||
| 1955 | 1,046,282 | 1,035,251 | 199,666 | 140,951 | 342,638 |
| 1956 | 966,502 | 955,058 | 188,068 | 63,688 | 365,335 |
| 1957 | 1,150,046 | 1,028,742 | 578,088 | 31,865 | 305,383 |
| 1958 | 1,405,602 | 955,345 | 304,144 | 141,185 | 422,736 |
| 1959 | 1,432,370 | 881,554 | 359,270 | 116,364 | 381,656 |
| Cleared | |||||
| 1955 | 1,173,515 | 965,945 | 72,325 | 113,140 | 399,789 |
| 1956 | 1,089,037 | 1,061,118 | 152,661 | 65,430 | 357,224 |
| 1957 | 1,222,762 | 975,140 | 507,494 | 20,136 | 390,863 |
| 1958 | 1,346,441 | 1,016,060 | 415,774 | 95,303 | 358,363 |
| 1959 | 1,494,841 | 966,890 | 391,364 | 69,406 | 382,653 |
Ports of Arrival and Departure - The next table shows the extent to which various ports were made the first port of arrival or the last port of departure by overseas vessels during the last three years. The relative overseas trade of the various ports can be judged only by taking into account the coastwise visits of overseas vessels in the course of unloading and loading. This is shown in later tables.
| Port | Entered | Cleared | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Net Tons | ||||||
| Auckland | 2,200,604 | 2,398,796 | 2,414,215 | 1,677,449 | 1,592,093 | 1,652,183 |
| Tauranga | 1,909 | 12,052 | 43,946 | 167,548 | 258,098 | 316,384 |
| Gisborne | 321 | 321 | 745 | 20,931 | 16,996 | 17,222 |
| Napier | 59,067 | 55,451 | 64,783 | 164,960 | 137,916 | 206,532 |
| New Plymouth | 88,266 | 94,389 | 93,351 | 193,328 | 151,018 | 191,016 |
| Wanganui | 321 | 768 | 321 | 321 | 7,253 | 321 |
| Wellington | 1,083,552 | 983,507 | 865,301 | 895,132 | 959,931 | 874,792 |
| Picton | 4,117 | 1,896 | 20,162 | 655 | 378 | 189 |
| Nelson | 11,848 | 26,128 | 22,739 | 48,443 | 18,880 | 51,712 |
| Greymouth | 310 | 1,073 | 2,668 | 1,256 | 1,297 | 963 |
| Lyttelton | 314,351 | 322,649 | 351,265 | 260,287 | 251,705 | 302,917 |
| Timaru | 34,248 | 18,041 | 24,883 | 26,111 | 44,885 | 29,442 |
| Oamaru | - | - | 321 | 7,691 | 3,806 | - |
| Otago | 105,513 | 109,767 | 89,708 | 327,398 | 378,016 | 285,569 |
| Bluff | 35,512 | 28,930 | 32,717 | 148,346 | 152,020 | 185,487 |
| Total | 3,939,939 | 4,053,768 | 4,027,125 | 3,939,856 | 3,974,292 | 4,114,729 |
Outstanding in this table is the increase in tonnage of shipping making Tauranga the final port of departure. This port has been greatly improved to facilitate export of the output of the new pulp and paper industries, and of pine logs.
As will be seen, in 1959, 81 per cent of overseas vessels (on a tonnage basis) arriving in New Zealand made Auckland or Wellington their first port of entry, and 61 per cent used one of these two ports as the final departure point.
Nationality of Overseas Shipping - The table following shows the nationality of vessels arriving in New Zealand during the years 1955-59.
OVERSEAS SHIPPING INWARDS
| Country of Registry | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Tons (000) | |||||
| British Commonwealth- | |||||
| United Kingdom | 2,164 | 2,022 | 2,046 | 2,110 | 1,913 |
| New Zealand | 482 | 484 | 581 | 550 | 516 |
| Other British Commonwealth | 205 | 247 | 251 | 242 | 287 |
| With cargo | 2,557 | 2,443 | 2,550 | 2,479 | 2,337 |
| In ballast | 294 | 309 | 328 | 423 | 379 |
| Totals, British Commonwealth countries | 2,851 | 2,752 | 2,878 | 2,902 | 2,716 |
| Total | 81 | 82 | 73 | 72 | 67 |
| Other- | |||||
| Norway | 238 | 192 | 271 | 306 | 282 |
| Sweden | 69 | 61 | 47 | 41 | 88 |
| Netherlands | 63 | 54 | 142 | 116 | 205 |
| Panama | 98 | 84 | 88 | 104 | 102 |
| United States of America | 44 | 46 | 331 | 364 | 381 |
| Remaining countries | 164 | 175 | 183 | 220 | 253 |
| Cargo | 616 | 580 | 954 | 966 | 1,018 |
| Ballast | 60 | 32 | 108 | 185 | 293 |
| Totals, other countries | 676 | 612 | 1,062 | 1,151 | 1,311 |
| Total | 19 | 18 | 27 | 28 | 33 |
| Totals | 3,527 | 3,365 | 3,940 | 4,054 | 4,027 |
The following table shows the changes that have taken place in recent years in the proportions of cargo carried to and from New Zealand in ships of different countries of registry. United Kingdom ships still carry the bulk of our external trade although the proportion of both the inward and outward cargo carried in vessels of this country of registry has tended to decrease over the period shown.
| Country of Registry | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | |||||
| Cargo Inward from Overseas | |||||
| United Kingdom | 56.8 | 52.2 | 48.0 | 50.3 | 45.3 |
| New Zealand | 13.8 | 17.1 | 20.2 | 17.8 | 18.7 |
| Australia | 0.9 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 2.6 | 3.8 |
| United States of America | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | - | 0.3 |
| Norway | 11.3 | 10.1 | 13.2 | 15.0 | 13.7 |
| Panama | 4.5 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 5.4 |
| Denmark | 3.0 | 3.4 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| Netherlands | 1.9 | 2.8 | 4.6 | 3.8 | 3.0 |
| Sweden | 3.3 | 3.4 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 4.1 |
| Other countries | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Cargo Outward for Overseas | |||||
| United Kingdom | 81.7 | 75.5 | 71.6 | 71.8 | 65.7 |
| New Zealand | 12.8 | 16.0 | 16.6 | 16.5 | 15.7 |
| Australia | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.9 |
| Japan | 1.6 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 5.4 | 9.6 |
| Panama | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | - | - |
| Other countries | 2.1 | 4.1 | 5.9 | 4.9 | 7.1 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Passengers - The overseas passenger traffic is concentrated principally at Auckland and Wellington. Small numbers of overseas passengers, however, arrive at and leave from the other ports. The following table gives the numbers of passengers arriving at and departing from each port for the years 1955–59.
| Port | Passengers Arriving from Overseas | Passengers Departing for Overseas | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Bay of Islands | - | - | 4 | - | 4 | |||||
| Auckland | 18,164 | 17,638 | 20,646 | 21,140 | 20,622 | 15,382 | 13,762 | 15,818 | 17,756 | 20,865 |
| Tauranga | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | 13 | 18 | 15 |
| Gisborne | - | - | - | 4 | - | 28 | 37 | - | 19 | 7 |
| Napier | 24 | 51 | 22 | 61 | 48 | 69 | 59 | 119 | 86 | 91 |
| New Plymouth | 18 | 69 | 25 | 28 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 24 | 40 | 54 |
| Wanganui | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Wellington | 20,704 | 20,360 | 20,693 | 19,562 | 19,523 | 15,293 | 16,910 | 13,790 | 14,646 | 15,328 |
| Picton | - | - | - | - | 18 | - | - | 4 | ||
| Nelson | 5 | - | 26 | - | 22 | - | - | - | - | 10 |
| Greymouth | - | - | 5 | |||||||
| Lyttelton | 582 | 856 | 799 | 1,071 | 1,151 | 212 | 160 | 179 | 204 | 193 |
| Timaru | 10 | - | 12 | - | 27 | 2 | 4 | 6 | - | 16 |
| Oamaru | - | - | - | - | 2 | |||||
| Otago | 2 | 41 | 30 | 56 | 37 | 110 | 130 | 94 | 89 | 66 |
| Bluff | 14 | - | 5 | 12 | 11 | 37 | 40 | 45 | 27 | 43 |
| Totals | 39,523 | 39,015 | 42,267 | 41,935 | 41,470 | 31,134 | 31,104 | 30,092 | 32,885 | 36,689 |
TRADE OF PORTS - The following matters dealing with the trade of ports are now covered: shipping tonnages, cargo statistics, and transhipments.
Shipping Tonnages - This section deals with the tonnage recorded by the various ports in New Zealand and includes overseas and coastal shipping, irrespective of whether the former had been entered or cleared overseas or coastwise. Thus the coastal movements of overseas vessels are included, each overseas vessel being recorded as such at every port of call. In the earlier tables overseas vessels were recorded only at the first port of arrival and the final port of departure.
The movement of overseas and coastal vessels on the New Zealand coast is well illustrated in the following table, which gives the total number and tonnage of all calls made during each of the years 1950–60.
| Year | Overseas Vessels | Coastal Vessels | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Net Tonnage | Number | Net Tonnage | Number | Net Tonnage | |
| 1950 | 1,529 | 6,364,068 | 12,864 | 4,324,152 | 14,393 | 10,688,220 |
| 1951 | 1,397 | 6,131,367 | 11,422 | 3,806,253 | 12,819 | 9,937,620 |
| 1952 | 1,820 | 7,640,410 | 13,622 | 4,621,963 | 15,442 | 12,262,373 |
| 1953 | 1,841 | 7,257,775 | 13,696 | 4,451,465 | 15,537 | 11,709,240 |
| 1954 | 2,049 | 8,332,107 | 13,502 | 4,782,208 | 15,551 | 13,114,315 |
| 1955 | 2,200 | 9,189,066 | 13,239 | 4,740,267 | 15,439 | 13,929,333 |
| 1956 | 2,268 | 9,752,769 | 12,984 | 4,855,295 | 15,252 | 14,608,064 |
| 1957 | 2,443 | 10,304,913 | 12,927 | 4,827,719 | 15,370 | 15,132,632 |
| 1958 | 2,977 | 11,879,349 | 12,735 | 4,793,364 | 15,712 | 16,672,706 |
| 1959 | 2,875 | 12,699,652 | 10,999 | 4,972,529 | 13,874 | 17,672,181 |
| 1960 | 3,124 | 13,548,761 | 10,249 | 4,978,142 | 13,373 | 18,526,903 |
Figures for recent years show substantial increases in the numbers and net tonnages of overseas vessels recorded at ports. These figures, which also reflect the increased number of ports visited by ships while on the New Zealand coast, have doubled since 1951. The average number of coastal calls that each overseas vessel made was 2.7 in 1957, 3.2 in 1958, 3.3 in 1959, and 3.8 in 1960.
The movements of coastal vessels, on the other hand, have declined since 1953, though net tonnages have steadily increased.
The following table shows for the three years 1957–59 the number and net tonnage of overseas vessels arriving at New Zealand ports, either direct or coastwise.
| Port | 1957 | 1958 | 959 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Tonnage | Number | Tonnage | Number | Tonnage | |
| Bay of Islands | 4 | 19,873 | 23 | 102,268 | 32 | 120,897 |
| Whangarei | 19 | 57,459 | 20 | 66,475 | 21 | 74,673 |
| Auckland | 693 | 3,189,237 | 794 | 3,474,309 | 750 | 3,595,105 |
| Onehunga | 1 | 321 | 6 | 1,398 | 2 | 378 |
| Raglan | - | - | - | - | 1 | 321 |
| Tauranga | 94 | 204,214 | 125 | 348,884 | 170 | 478,067 |
| Tolaga Bay | - | - | 1 | 745 | ||
| Gisborne | 23 | 91,058 | 34 | 140,037 | 27 | 122,630 |
| Napier | 127 | 554,644 | 178 | 716,647 | 192 | 786,613 |
| New Plymouth | 109 | 512,567 | 129 | 562,058 | 151 | 720,049 |
| Wanganui | 2 | 642 | 4 | 768 | 3 | 971 |
| Wellington | 488 | 2,261,954 | 589 | 2,532,099 | 516 | 2,670,792 |
| Picton | 6 | 11,216 | 10 | 33,166 | 6 | 33,859 |
| Nelson | 42 | 135,944 | 56 | 139,636 | 66 | 172,433 |
| Westport | 2 | 388 | 6 | 4,473 | 6 | 2,371 |
| Grey mouth | 5 | 1,954 | 26 | 31,161 | 3 | 2,446 |
| Lyttelton | 359 | 1,434,120 | 418 | 1,609,102 | 406 | 1,706,060 |
| Timaru | 84 | 341,110 | 116 | 439,224 | 101 | 481,451 |
| Oamaru | 12 | 18,763 | 6 | 10,408 | 6 | 9,442 |
| Otago | 278 | 1,074,132 | 304 | 1,170,611 | 288 | 1,208,934 |
| Bluff | 95 | 395,317 | 132 | 495,873 | 128 | 512,160 |
| Totals | 2,443 | 10,304,913 | 2,977 | 11,879,342 | 2,875 | 12,699,652 |
Overseas vessels are shown to have called at 19 ports in 1957, 20 in 1958, and 20 in 1959. In the years 1936–38 approximately 24 New Zealand ports were visited by overseas vessels. The following table shows the percentages of inward overseas shipping tonnage recorded at the ports of Wellington, Auckland, and Lyttelton for the years 1955–59. In most years these three ports handle two-thirds of the total tonnage of overseas shipping.
| Port | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | |||||
| Auckland | 28.5 | 27.8 | 30.9 | 29.2 | 28.3 |
| Wellington | 24.8 | 22.4 | 22.0 | 21.3 | 21.0 |
| Other North Island | 12.9 | 14.7 | 14.0 | 16.4 | 18.2 |
| North Island | 66.2 | 64.9 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 67.5 |
| Lyttelton | 13.6 | 15.1 | 13.9 | 13.5 | 13.4 |
| Other South Island | 20.2 | 20.0 | 19.2 | 19.6 | 19.1 |
| South Island | 33.8 | 35.1 | 33.1 | 33.1 | 32.5 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
The following table shows for the years 1957–59 the total shipping traffic handled inwards at the various ports. Overseas and coastal vessels calling at more than one port in the course of a single voyage have been recorded as entered at every port visited.
| Port | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Tonnage | Number | Tonnage | Number | Tonnage | |
| Awanui | 163 | 11,354 | 159 | 11,108 | 133 | 9,206 |
| Mangonui | 56 | 4,268 | 54 | 4,513 | 55 | 3,942 |
| Whangaroa | 70 | 4,536 | 70 | 3,871 | 75 | 4,316 |
| Bay of Islands | 67 | 23,513 | 88 | 105,925 | 104 | 125,297 |
| Whangarei | 828 | 228,265 | 879 | 239,654 | 831 | 225,677 |
| Auckland | 5,655 | 3,584,204 | 5,605 | 3,824,568 | 3,615 | 3,913,417 |
| Onehunga | 83 | 24,919 | 97 | 30,830 | 125 | 37,468 |
| Raglan | 51 | 16,215 | 51 | 17,400 | 54 | 14,802 |
| Thames | 360 | 9,047 | 248 | 5,566 | 194 | 3,567 |
| Coromandel | 104 | 3,155 | 133 | 3,593 | 104 | 3,675 |
| Whitianga | 97 | 2,198 | 88 | 2,180 | 90 | 2,011 |
| Tauranga | 242 | 231,925 | 266 | 383,711 | 313 | 508,498 |
| Whakatane and Ohiwa | 82 | 8,579 | 75 | 8,311 | 48 | 5,484 |
| Kutarere | 35 | 2,815 | 34 | 3,679 | 29 | 3,004 |
| Opotiki | 24 | 2,056 | 9 | 916 | 5 | 522 |
| Tokomaru Bay | 22 | 6,677 | 21 | 6,668 | 15 | 4,808 |
| Tolaga Bay | 15 | 4,519 | 14 | 4,791 | 11 | 3,438 |
| Gisborne | 163 | 150,238 | 176 | 196,446 | 177 | 189,175 |
| Napier | 287 | 625,981 | 326 | 777,066 | 362 | 859,345 |
| New Plymouth | 207 | 549,467 | 235 | 610,296 | 270 | 772,674 |
| Patea | 88 | 9,262 | 88 | 9,333 | 53 | 5,467 |
| Wanganui | 318 | 103,903 | 296 | 90,528 | 303 | 96,717 |
| Wellington | 2,262 | 3,922,441 | 2,395 | 4,214,266 | 2,336 | 4,379,178 |
| Picton | 359 | 253,985 | 333 | 305,639 | 326 | 308,820 |
| Wairau | 53 | 4,664 | 64 | 5,632 | 67 | 5,695 |
| Nelson | 662 | 251,242 | 660 | 251,431 | 785 | 306,948 |
| Motueka | 220 | 31,413 | 207 | 25,657 | 224 | 31,823 |
| Collingwood | 10 | 1,034 | ||||
| Westport | 153 | 135,010 | 157 | 131,232 | 148 | 117,867 |
| Greymouth | 119 | 112,262 | 112 | 97,930 | 122 | 115,960 |
| Kaiapoi | - | - | - | - | 77 | 4,457 |
| Lyttelton | 1,139 | 2,685,986 | 1,271 | 2,887,427 | 1,290 | 3,017,909 |
| Timaru | 321 | 440,367 | 412 | 553,693 | 407 | 618,847 |
| Oamaru | 99 | 59,539 | 105 | 54,511 | 102 | 55,425 |
| Otago | 446 | 1,148,714 | 484 | 1,246,525 | 497 | 1,319,628 |
| Bluff | 391 | 459,307 | 382 | 537,598 | 396 | 572,257 |
| Half-moon Bay | 119 | 19,572 | 118 | 20,212 | 131 | 24,857 |
| Totals | 15,370 | 15,132,632 | 15,712 | 16,672,706 | 13,874 | 17,672,181 |
In 1959 Wellington ranked as the first port of New Zealand as regards aggregate tonnage of shipping entered, followed by Auckland, Lyttelton, Otago, Napier, New Plymouth, Timaru, Bluff, and Tauranga, in that order.
The most noteworthy changes in the tonnage of shipping handled during the last three years were at Tauranga, where extra port development has taken place for the handling of timber and logs and the output of the new pulp and paper industries of the district, and at Bay of Islands, where developments in 1957 enabled this port to be used by overseas vessels.
In the cases of Wellington, Lyttelton, and Picton, the figures are inflated by the recording of the regular inter-island steamer express services.
Cargo Statistics - The Department of Statistics collects from each port a monthly statement of the cargo handled. In this statement provision is made for analysis of the cargo under 38 commodity headings, for each of which is shown the quantity handled, both inwards and outwards, and the transhipments. Cargo statistics were first collected in 1922. The tables which follow are compiled from the data provided in these returns.
The following table gives a summary of the tonnage of cargo handled at all ports for the last eleven years.
| Year | Inwards* | Transhipments | Outwards* | Total Tonnage† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal | Overseas | Coastal | Overseas | |||
*Excluding transhipments. †Transhipments included twice. | ||||||
| Manifest Tons | ||||||
| 1950 | 1,923,221 | 3,504,616 | 225,464 | 1,901,224 | 1,203,203 | 8,983,192 |
| 1951 | 1,649,439 | 3,810,425 | 152,839 | 1,596,387 | 1,166,335 | 8,528,064 |
| 1952 | 1,971,925 | 4,811,147 | 207,218 | 1,846,616 | 1,328,218 | 10,372,342 |
| 1953 | 1,975,448 | 3,835,923 | 174,294 | 1,858,608 | 1,253,384 | 9,271,951 |
| 1954 | 2,120,786 | 4,529,665 | 170,855 | 1,948,195 | 1,277,572 | 10,217,928 |
| 1955 | 2,155,588 | 5,050,090 | 204,305 | 1,951,014 | 1,389,657 | 10,954,959 |
| 1956 | 2,148,733 | 4,947,327 | 190,172 | 1,943,784 | 1,555,598 | 10,975,786 |
| 1957 | 2,252,605 | 5,169,225 | 174,109 | 1,963,710 | 1,610,988 | 11,344,746 |
| 1958 | 2,259,487 | 4,865,187 | 148,282 | 2,018,076 | 1,664,984 | 11,104,298 |
| 1959 | 2,179,689 | 4,494,627 | 127,633 | 1,930,003 | 1,912,677 | 10,772,262 |
| 1960 | 2,282,968 | 5,059,083 | 109,963 | 1,995,578 | 1,932,786 | 11,490,341 |
The next table shows for each port the total cargo inwards and outwards in 1959. The high proportion of transhipments in the case of Wellington is due to the central position of the port and the fact that much overseas cargo is transhipped from Wellington to South Island ports.
| Port | Inwards* | Transhipments | Outwards* | Total Tonnage† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal | Overseas | Coastal | Overseas | |||
*Excluding transhipments. †Transhipments included twice. | ||||||
| Manifest Tons | ||||||
| Mangonui | 2,169 | - | - | 490 | - | 2,659 |
| Bay of Islands | 2,092 | 3,150 | - | 270 | 19,806 | 25,318 |
| Whangarei | 105,378 | 56,631 | - | 134,551 | 5,632 | 302,192 |
| Auckland | 561,159 | 1,700,164 | 33,209 | 206,807 | 557,197 | 3,091,745 |
| Onehunga | 61,652 | 1,412 | 14 | 59,084 | - | 122,176 |
| Raglan | 13,553 | 300 | - | 1,499 | - | 15,352 |
| Thames | 3,919 | - | - | 476 | - | 4,395 |
| Tauranga | 21,896 | 222,607 | - | 21,871 | 303,981 | 570,355 |
| Whakatane (including Ohiwa) | 3,245 | - | - | 4,650 | - | 7,895 |
| Kutarere | 1,544 | - | - | 2,467 | - | 4,011 |
| Opotiki | 226 | - | - | 717 | - | 943 |
| Tokomaru Bay | 508 | - | - | 992 | - | 1,500 |
| Tolaga Bay | 212 | - | - | 802 | - | 1,014 |
| Gisborne | 57,110 | 3,124 | 875 | 12,784 | 14,037 | 88,805 |
| Napier | 89,069 | 209,917 | 953 | 10,678 | 136,204 | 447,774 |
| New Plymouth | 59,272 | 258,629 | - | 5,766 | 128,362 | 452,029 |
| Patea | 270 | - | - | 8,236 | - | 8,506 |
| Wanganui | 117,685 | 1,014 | - | 11,606 | - | 130,305 |
| Wellington | 461,235 | 943,322 | 82,512 | 404,030 | 264,049 | 2,237,660 |
| Picton | 49,122 | 475 | - | 40,567 | 3,715 | 93,879 |
| Wairau | 6,161 | - | - | 3,633 | - | 9,794 |
| Nelson | 65,829 | 38,015 | 1,473 | 80,375 | 60,302 | 247,467 |
| Motueka | 4,831 | - | - | 31,080 | - | 35,911 |
| Westport | 4,881 | 2,912 | - | 199,132 | - | 206,925 |
| Greymouth | 8,216 | 175 | - | 192,062 | 7,138 | 207,591 |
| Kaiapoi | 5,959 | - | - | 8,209 | - | 14,168 |
| Lyttelton | 268,789 | 589,149 | 2,589 | 304,818 | 127,912 | 1,295,846 |
| Timaru | 36,160 | 25,689 | - | 73,577 | 83,153 | 218,579 |
| Oamaru | 14,001 | 6,551 | 22 | 21,802 | - | 42,398 |
| Otago | 107,534 | 275,649 | 5,986 | 64,326 | 86,506 | 545,987 |
| Bluff | 43,747 | 155,742 | - | 21,185 | 114,683 | 335,357 |
| Half-moon Bay | 2,265 | - | - | 1,461 | - | 3,726 |
| Totals | 2,179,689 | 4,494,627 | 127,633 | 1,930,003 | 1,912,677 | 10,772,262 |
In any consideration of these statistics it is advisable to note that the term “ton” does not invariably denote a weight of 2,240 lb. It is practicable to obtain the actual weights involved for only a portion of the goods handled. In other cases close approximations are made by applying uniform formulae as to the number of bales, cases, sacks, etc., to the ton. A considerable portion of trading goods, however, is recorded in measurement tons, 40 cubic feet of space being regarded as the equivalent of a ton. As the practice is uniform, comparisons from year to year are not appreciably affected, nor are comparisons between ports, unless there is a radical difference in the class of trade carried on, in which case recourse should be had to consideration of items of trade. Since a much larger proportion of imports are in measurement tons, thus artificially swelling the figures, direct comparison of import cargo tonnage with export is invalid.
In the Section dealing with the export trade it is pointed out that pastoral products make up over 90 per cent of New Zealand's exports. The following table shows how the various ports participated in the handling of the main pastoral produce items in the outward overseas cargo during 1959. Although pastoral products constitute the bulk of New Zealand's exports on a value basis, a number of other types of commodities constitute an important part of the total outward overseas cargo. The table also shows the extent to which exporting ports participated in the handling of the major remaining items.
| Port | Butter | Cheese | Other Milk Products | Frozen Meat | Hides and Skins | Tallow | Wool |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manifest Tons | |||||||
| Bay of Islands | 10,478 | - | 479 | 7,043 | 400 | 776 | 160 |
| Whangarei | |||||||
| Auckland | 163,275 | 16,354 | 117,519 | 85,749 | 16,952 | 15,502 | 43,964 |
| Tauranga | - | - | 282 | - | - | 176 | 3 |
| Gisborne | 468 | - | - | 6,984 | 602 | 1,230 | 4,305 |
| Napier | - | - | 416 | 42,810 | 4,134 | 5,252 | 41,869 |
| New Plymouth | 15,209 | 50,886 | 6,107 | 38,799 | 3,012 | 4,702 | 2,702 |
| Wellington | 17,490 | 6,655 | 17,003 | 66,360 | 11,489 | 7,569 | 51,599 |
| Picton | - | - | - | 1,114 | - | 344 | 239 |
| Nelson | 171 | 152 | - | 2,550 | 228 | 903 | 608 |
| Lyttelton | 298 | 671 | 807 | 46,479 | 8,688 | 8,772 | 30,842 |
| Timaru | - | 870 | - | 50,438 | 3,894 | 4,861 | 20,097 |
| Otago | 119 | 1,765 | 1,082 | 30,004 | 4,074 | 3,814 | 29,433 |
| Bluff | 146 | 5,177 | 1,806 | 61,102 | 4,894 | 7,003 | 31,231 |
| Totals | 207,654 | 82,530 | 145,501 | 439,432 | 58,367 | 60,904 | 257,052 |
| Port | Fruit, Fresh | Iron and Steel, etc. | Paper, Newsprint, etc. | Timber, Softwood | Wood Pulp | All Other Goods | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manifest Tons | |||||||
| Bay of Islands | - | - | - | - | - | 470 | 19,806 |
| Whangarei | - | - | - | - | - | 5,632 | 5,632 |
| Auckland | 3,345 | 22,856 | 1,215 | 12,784 | 4,953 | 52,729 | 557,197 |
| Tauranga | - | - | 55,791 | 170,777 | 73,078 | 3,874 | 303,981 |
| Gisborne | - | - | - | - | - | 448 | 14,037 |
| Napier | 15,213 | - | - | 9,017 | - | 17,493 | 136,204 |
| New Plymouth | - | - | - | - | - | 6,945 | 128,362 |
| Wellington | 4,167 | 12,253 | 12 | 4,858 | - | 64,594 | 264,049 |
| Picton | 752 | - | - | 760 | - | 506 | 3,715 |
| Nelson | 23,514 | - | - | 29,763 | - | 2,413 | 60,302 |
| Greymouth | - | - | - | - | - | 7,138 | 7,138 |
| Lyttelton | 9 | 6,227 | - | 1,431 | - | 23,688 | 127,912 |
| Timaru | - | - | - | 4 | - | 2,989 | 83,153 |
| Otago | 384 | - | 3 | 3,493 | - | 12,335 | 86,506 |
| Bluff | - | - | - | 27 | - | 3,297 | 114,683 |
| Totals | 47,384 | 41,336 | 57,021 | 232,914 | 78,031 | 204,551 | 1,912,677 |
Transhipments - Transhipments of cargo during 1959 totalled 127,633 tons, of which 82,512 tons were transhipped at Wellington. As was noted earlier, the central position of this port tends to increase the quantity of goods transhipped. Quantities of cargo are carried to Wellington coastwise for transhipment there to overseas ships, and quantities of inward overseas cargo are transhipped at Wellington for delivery to South Island ports. Two notable contributions to transhipment at Wellington are apples carried by coasters across from Nelson and until July 1959 cheese brought by coastal vessels from Patea for eventual export at Wellington.
Transhipments fall into the following four classes:
Coastal to Coastal - Cargo which has been loaded in a vessel at one New Zealand port and is transhipped to another vessel for discharge at another New Zealand port.
Coastal to Overseas - Cargo which has been loaded in a vessel at a New Zealand port and is transhipped to another vessel for discharge at a port outside New Zealand.
Overseas to Coastal - Cargo which has come from overseas and is transhipped to another vessel for discharge at a New Zealand port.
Overseas to Overseas - Cargo which has come from overseas and is transhipped to another vessel for discharge outside New Zealand.
The first class represents purely coastal trade while goods in the last class do not enter New Zealand, but each of the others may be added to the appropriate figures of overseas trade shown previously, to ascertain the total tonnage of goods arriving from or departing for overseas. Thus the total inward tonnage from overseas in 1959 was 4,558,535, and the total outward tonnage going overseas 1,962,785. Comparative figures for 1958 were 4,945,692 and 1,718,365 tons respectively.
The following table shows for 1958 and 1959 the transhipment trade of each port affected.
| Coastal to Coastal | Coastal to Overseas | Overseas to Coastal | Overseas to Overseas | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Manifest Tons | ||||||||||
| Auckland | 1,793 | 1,764 | 4,055 | 4,722 | 24,253 | 21,414 | 6,785 | 5,309 | 36,886 | 33,209 |
| Onehunga | - | 14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 14 |
| Gisborne | - | - | 111 | 875 | - | - | - | - | 111 | 875 |
| Napier | 78 | 95 | 740 | 712 | 1,125 | 146 | - | - | 1,943 | 953 |
| New Plymouth | - | - | - | - | 34 | - | - | - | 34 | - |
| Wellington | 2,159 | 4,135 | 48,294 | 43,572 | 44,973 | 34,805 | 3,100 | - | 98,526 | 82,512 |
| Nelson | 229 | 612 | 117 | 227 | 642 | 634 | - | - | 988 | 1,473 |
| Lyttelton | 54 | 1,303 | - | - | 1,109 | 1,284 | 53 | 2 | 1,216 | 2,589 |
| Timaru | - | - | - | - | 135 | - | - | - | 135 | - |
| Oamaru | - | - | - | - | - | 22 | - | - | - | 22 |
| Otago | 145 | 383 | 64 | - | 8,234 | 5,603 | - | - | 8,443 | 5,986 |
| Totals | 4,458 | 8,306 | 53,381 | 50,108 | 80,505 | 63,908 | 9,938 | 5,311 | 148,282 | 127,633 |
The next table shows the various items of merchandise, etc., which comprised the transhipment trade in 1959.
| Item | Coastal to Coastal | Coastal to Overseas | Overseas to Coastal | Overseas to Overseas | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manifest Tons | |||||
| Beans and peas | 15 | 213 | 88 | - | 316 |
| Butter | - | 37 | - | - | 37 |
| Cement | 652 | - | 2 | 417 | 1,071 |
| Cereal products | 70 | 10 | 36 | - | 116 |
| Chaff, hay, and straw | 26 | - | - | - | 26 |
| Cheese | - | 6,943 | - | - | 6,943 |
| Coke | 35 | - | - | - | 35 |
| Fish | 5 | 73 | - | - | 78 |
| Flour | 6 | - | - | 9 | 15 |
| Fruit, preserved | 6 | 28 | 1,052 | 7 | 1,093 |
| Fruit, fresh | 172 | 27,416 | 965 | 5 | 28,558 |
| Grain | 254 | - | 20 | - | 274 |
| Hemp, linen flax, and phormium | - | - | 178 | - | 178 |
| Hides, skins, and pelts | 10 | 570 | 1 | 5 | 586 |
| Iron and steel, pipes, etc. | 104 | - | 8,627 | 205 | 8,936 |
| Lime | 17 | - | - | 24 | 41 |
| Machinery | 75 | 13 | 1,470 | 37 | 1,595 |
| Manures | 22 | 164 | 1,759 | - | 1,945 |
| Meat, frozen | - | 3,620 | - | 132 | 3,752 |
| Meat, preserved | 6 | - | - | - | 6 |
| Milk products (other than butter and cheese) | 77 | 52 | - | - | 129 |
| Motor vehicles, parts, and tyres | 108 | 17 | 414 | 297 | 836 |
| Oil, other mineral | 304 | 203 | 7,596 | 27 | 8,130 |
| Paper, newsprint, etc. | 171 | 19 | 910 | - | 1,100 |
| Potatoes | 17 | 111 | - | - | 128 |
| Seeds | 59 | 33 | 38 | - | 130 |
| Sugar | 137 | - | - | - | 137 |
| Tallow | - | 769 | - | - | 769 |
| Timber, hardwoods | 16 | - | 2,615 | 12 | 2,643 |
| Timber, softwoods | 58 | - | 2,765 | - | 2,823 |
| Wine, spirits, ale, beer | 11 | - | 387 | 135 | 533 |
| Wood pulp | - | - | 522 | - | 522 |
| Wool | 42 | 8,236 | 1 | - | 8,279 |
| All other goods | 5,831 | 1,581 | 34,462 | 3,999 | 45,873 |
| Totals | 8,306 | 50,108 | 63,908 | 5,311 | 127,633 |
Shipping Between New Zealand and Island Dependencies - In the tables of overseas shipping no account is taken of ships moving between the main islands of New Zealand and the island dependencies of Cook Islands and Niue. These islands are constitutionally part of New Zealand, and shipping to or from them is not treated as overseas. The following table illustrates the extent of this shipping movement during the years 1955–59.
| Year | Entered New Zealand Ports from Cook Islands and Niue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Cargo | In Ballast | ||||
| Vessels | Net Tonnage | Cargo (Manifest Tonnage) | Vessels | Net Tonnage | |
| 1955 | 13 | 8,107 | 6,395 | 1 | 122 |
| 1956 | 13 | 10,596 | 11,494 | - | - |
| 1957 | 18 | 13,697 | 8,399 | 1 | 76 |
| 1958 | 16 | 20,680 | 15,654 | 3 | 10,152 |
| 1959 | 12 | 10,112 | 10,560 | 1 | 5,741 |
| Year | Cleared New Zealand Ports for Cook Islands and Niue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Cargo | In Ballast | ||||
| Vessels | Net Tonnage | Cargo (Manifest Tonnage) | Vessels | Net Tonnage | |
| 1955 | 14 | 12,037 | 7,274 | - | - |
| 1956 | 13 | 6,835 | 6,479 | - | - |
| 1957 | 17 | 9,323 | 9,501 | 1 | 76 |
| 1958 | 12 | 11,374 | 10,036 | 1 | 80 |
| 1959 | 9 | 5,679 | 6,005 | - | - |
In most years all the departures to the islands are from Auckland. The 12 vessels bringing cargo from the islands in 1959 were all of New Zealand registry.
Shipping on Inland Waters - Although New Zealand is well supplied with rivers, few can be used by shipping for other than short distances. There are no regular passenger or cargo services on any of the rivers. The only inland-water shipping of consequence is the service on Lake Wakatipu operated with the Earnslaw. This vessel is the property of the New Zealand Railways. Passengers and cargo are carried from Queenstown to other points on the shores of the lake. Farmers use this service for transporting livestock. The next table shows the operations of this service during the latest five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Passengers | Livestock | Timber | Other Goods | Revenue | Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | No. | super. ft. (000) | tons | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 31,576 | 5,812 | 302 | 4,529 | 19,761 | 29,147 |
| 1957 | 31,063 | 8,618 | 191 | 4,383 | 22,101 | 26,594 |
| 1958 | 29,602 | 10,205 | 326 | 4,787 | 22,699 | 27,173 |
| 1959 | 24,078 | 10,289 | 204 | 4,338 | 21,651 | 27,479 |
| 1960 | 33,430 | 10,921 | 306 | 3,824 | 21,838 | 28,994 |
Values of Exports and Imports by Ports - Tables showing the values of exports and imports through the various ports are included in Sections 22B and 22C respectively.
NEW ZEALAND SHIPPING REGISTER - The figures for vessels registered in New Zealand as at the end of each of the last 11 years are as follows.
| Year | Sailing Vessels | Steam and Motor Vessels | Totals | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | |
| 1950 | 44 | 4,066 | 3,525 | 455 | 241,477 | 124,538 | 499 | 245,543 | 128,063 |
| 1951 | 43 | 3,761 | 3,281 | 460 | 249,781 | 128,622 | 503 | 253,542 | 131,903 |
| 1952 | 43 | 2,920 | 2,492 | 462 | 246,819 | 127,758 | 505 | 249,739 | 130,250 |
| 1953 | 40 | 2,059 | 1,653 | 463 | 259,633 | 133,882 | 503 | 261,692 | 135,535 |
| 1954 | 39 | 2,042 | 1,643 | 465 | 253,387 | 130,648 | 504 | 255,429 | 132,291 |
| 1955 | 37 | 1,831 | 1,497 | 476 | 255,107 | 131,090 | 513 | 256,938 | 132,587 |
| 1956 | 37 | 1,831 | 1,497 | 481 | 258,924 | 132,547 | 518 | 260,755 | 134,044 |
| 1957 | 36 | 1,821 | 1,487 | 490 | 264,309 | 134,669 | 526 | 266,130 | 136,156 |
| 1958 | 36 | 1,821 | 1,487 | 495 | 271,179 | 137,660 | 531 | 273,000 | 139,147 |
| 1959 | 41 | 2,338 | 1,898 | 490 | 260,248 | 131,409 | 531 | 262,586 | 133,307 |
| 1960 | 42 | 2,471 | 2,031 | 491 | 243,008 | 122,631 | 533 | 245,479 | 124,662 |
In the table which follows, the vessels on the New Zealand register at 31 December 1959 are classified into sailing, steam, and motor, and are listed for the various ports of registry.
| Port of Registry | Sailing Vessels | Steam Vessels | Motor Vessels | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | Vessels | Gross Tonnage | Net Tonnage | |
| Auckland | 35 | 2,279 | 1,854 | 32 | 10,212 | 4,951 | 283 | 43,225 | 20,889 |
| Napier | - | - | - | 2 | 948 | 537 | 10 | 4,196 | 1,896 |
| Wellington | 6 | 59 | 44 | 29 | 81,209 | 40,876 | 62 | 80,953 | 42,969 |
| Nelson | - | - | - | - | - | - | 17 | 6,450 | 2,764 |
| Lyttelton | - | - | - | 6 | 2,798 | 1,021 | 13 | 3,233 | 1,563 |
| Timaru | - | - | - | 1 | 942 | 488 | - | - | - |
| Otago | - | - | - | 5 | 7,314 | 3,673 | 14 | 17,234 | 9,200 |
| Bluff | - | - | - | 3 | 1,056 | 428 | 13 | 478 | 154 |
| Totals | 41 | 2,338 | 1,898 | 78 | 104,479 | 51,974 | 412 | 155,769 | 79,435 |
Auckland is the port of registry of the majority of the vessels forming New Zealand's “mosquito” fleet, the average net tonnage of the 350 vessels on the Auckland register being only 79 tons.
In the next table vessels registered in New Zealand at the end of 1959 have been classified according to whether employed in the coastal or the foreign trade. The totals given therein do not agree with those shown above, as vessels employed exclusively within “restricted limits” and pleasure craft are not included. The total number of vessels engaged in trading was 152, of an aggregate net tonnage of 122,234.
| Size of Vessels | Employed in the Coastal Trade Only | Employed Partly in the Coastal and Partly in the Foreign Trade | Employed in the Foreign Trade Only | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Vessels | Net Tonnage | Number of Vessels | Net Tonnage | Number of Vessels | Net Tonnage | |
| Under 50 tons | 35 | 604 | - | - | - | - |
| 50 and under 100 tons | 16 | 1,104 | - | - | - | - |
| 100 “ 200 “ | 20 | 2,653 | - | - | - | - |
| 200 “ 300 “ | 5 | 1,217 | 1 | 219 | - | - |
| 300 “ 400 “ | 19 | 6,773 | - | - | - | - |
| 400 “ 600 “ | 4 | 1,925 | - | - | - | |
| 600 “ 800 “ | 1 | 762 | - | - | 1 | 632 |
| 800 “ 1,000 “ | 1 | 807 | 1 | 909 | 4 | 3,630 |
| 1,000 “ 1,200 “ | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 1,200 “ 1,500 “ | 3 | 3,960 | 1 | 1,297 | 8 | 10,539 |
| 1,500 “ 2,000 “ | 1 | 1,625 | 4 | 7,940 | 11 | 21,287 |
| 2,000 tons and over | 3 | 9,710 | - | - | 13 | 44,641 |
| Totals | 108 | 31,140 | 7 | 10,365 | 37 | 80,729 |
MARINE OFFICERS' CERTIFICATES - The examinations for masters, mates, and engineers serving in the Mercantile Marine are conducted by the Marine Department, the regulations relating to these examinations being based upon those of the United Kingdom Ministry of Transport with such modifications as are necessitated by local conditions. The Ministry of Transport recognises the following certificates only as of Commonwealth validity: extra master, master, first mate and second mate foreign-going ships, first- and second-class steam and motor engineers. It is a condition of such recognition that candidates must possess service qualifications and pass examinations similar and not inferior to those prescribed by the Ministry of Transport. Regulations provide for the examinations for masters and mates; in the year ended 31 December 1959 the total number of candidates examined for foreign-going certificates of Commonwealth validity was 103, of whom 37 obtained certificates. In addition, 97 candidates were examined for home-trade and local certificates, of whom 48 obtained certificates. Further regulations provide for the examinations for marine engineers. In the year ended 31 December 1959 the total number of candidates examined for foreign-going certificates (of Commonwealth validity), or parts thereof, was 189, of whom 46 gained certificates and 31 gained partial passes. A total of 172 candidates was examined for home-trade and local certificates, of whom 93 passed, while a further 38 candidates were examined for the engineering section for master of a restricted-limit motor ship not exceeding 10 register tons, of whom 32 passed.
SHIP SURVEY STATISTICS - The Marine Department carries out the survey of ships as required by the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952, and during the period 1 January 1959 to 31 December 1959 certificates of survey were issued to the following categories of New Zealand ships:
| Passenger ships engaged in international voyages | 6 |
| Cargo steamships engaged in international voyages | 7 |
| Cargo motorships engaged in international voyages | 34 |
| Home-trade steamships | 13 |
| Home-trade motorships | 76 |
| Restricted-limits steamships | 34 |
| Restricted-limits motorships | 306 |
| Total | 476 |
In addition to the certificates of survey required under the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952, the Department is required to issue certificates to vessels engaged in international voyages in accordance with the provisions of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea 1948, to which the New Zealand Government is a signatory. During the year ended 31 December 1959 there were 100 such certificates issued to New Zealand registered ships and 30 to overseas ships.
Special surveys additional to the above were made for seaworthiness after damage, for efficiency of equipment, and for tonnage measurement. These occasional surveys totalled 417.
LIGHTHOUSES - Along the New Zealand coast there are 87 coastal lights of various types. In 26 cases the lights are manually attended and the apparatus is classed as of the dioptric order - i.e., a central lamp sending its ray through a combination of surrounding lenses - while the remaining 61 coastal lights are automatic lights. The buildings housing the lights are of varying kinds, as necessitated by their respective situations.
Fog signals of the diaphone type are established on Tiritiri Matangi, at Pencarrow Head, Godley Head, and Taiaroa Head; while radio beacons have been established at Cape Reinga, East Cape, Portland Island, Cuvier Island, Mokohinau, Baring Head, Stephens Island, the Brothers Island, Cape Campbell, Godley Head, Taiaroa Head, Dog Island, and Puysegur Point.
The most powerful light is that of Stephens Island, which, placed some 600 ft above high water, is visible at a distance of 32 nautical miles. Next in order come Cape Reinga (altitude 542 ft), visibility 31 miles; East Cape (505 ft), visible at 30 miles; Cape Brett (altitude 490 ft), visible at 29 miles; Cuvier Island (altitude 390 ft) and Mokohinau (altitude 400 ft), both of which have a visibility of 26 miles; Godley Head (altitude 317 ft) and Portland Island (altitude 300 ft), both visible at 24 miles. Thirteen other lights have a range of 20 miles or over, being Centre Island, Baring Head, and Akaroa, of 23 miles; Cape Palliser, Brothers, and Nugget Point, of 22 miles; Cape Foulwind, of 21 miles; Tiritiri Matangi, Cape Saunders, Channel Island, Marotiri, Taiaroa Head, and Gibson Point, 20 miles each. The remaining lights have visibilities of under 20 miles.
All manually attended coastal lighthouses are equipped with signalling lamps, the keepers being competent to transmit messages by lamp, or receive messages by flags or lamp. In addition, 11 of the principal lighthouses are equipped with radiotelephone systems of communication. Coastal lights - i.e., those outside the bounds of the various harbour authorities - are maintained by the Marine Department.
WRECKS - In the case of any wreck or shipping casualty in New Zealand waters a Collector of Customs, Superintendent of Mercantile Marine, or other person empowered by the Minister of Marine, institutes an inquiry into the cause and circumstances of such casualty. If necessary, a formal investigation is held by a Magistrate, who has power to cancel or suspend the certificate of any officer from whose wrongful act or default damage has resulted.
Should any wreck occur on the coast, the Receiver of Wrecks for that district, usually an officer of the Customs, has the necessary authority to be used in the preservation of life and property.
The numbers of shipping casualties reported to the Marine Department during the year ended 31 December 1959 are shown in the following table. It should be noted that figures list all casualties, including small craft.
| Type of Ship | Miscellaneous and Berthing, Unberthing | Collision | Explosion | Fire | Foundering | Stranding | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 5 |
| Cargo | 8 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 14 | 31 |
| Fishing | 1 | - | - | - | 4 | 1 | 6 |
| Pleasure | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Totals | 12 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 17 | 44 |
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT - Railway history in New Zealand dates from the year 1860. In that year a contract was let for the construction of a line from Christchurch to Lyttelton, and the first portion of this line was opened on 1 December 1863. A line from Invercargill to Bluff Harbour was opened on 5 February 1867. The Provincial Council of Auckland in 1865 began the construction of a line from Auckland to Drury.
Although practically the whole of the railways are now State owned, some sections were built by private enterprise, notably the 83-mile line from Wellington to Longburn constructed by the Wellington and Manawatu Railway Co. Ltd. in 1882–86 and operated by the company until 1908.
By 31 March 1880, 1,182 miles of State-owned lines were open for traffic and by 31 March 1900 more than 2,100 route miles in 10 separate sections were in use. The 369-mile trunk line between Christchurch and Invercargill was completed for through traffic as early as 1879, but the 426-mile North Island main trunk railway between Auckland and Wellington was not completed until November 1908.
More recently, other main lines have been completed, linking up most of the hitherto isolated sections. Westland was connected with Canterbury via the 5 1/4-mile Otira Tunnel in 1923; Whangarei was connected to the main North Island system in 1924; Gisborne and Dargaville to the same system in 1942; and Westport was linked with the South Island system in 1943. In 1945 the Christchurch-Picton main line was completed.
The past decade has seen the building of new lines to serve the extensive man-made forests in the North Island. An 18-mile branch railway from Putaruru through Tokoroa to Kinleith was opened in 1952 and the 9-mile Kawerau branch and 36-mile Murupara branch were completed in 1957.
Vast improvements have been made to existing railways during the past 60 years and many sections have been reconstructed at considerable expense to ease gradients, shorten distances, and reduce curvature. The Auckland-Westfield deviation, opened in 1930; the Wellington-Tawa deviation, brought into full use in July 1937; and the Turakina-Okoia deviation, opened in December 1947, are typical examples. The most recent example is the Rimutaka deviation and its 5 1/2-mile tunnel between Upper Hutt and Featherston, which was opened in November 1955 to eliminate the 1-in-15 Rimutaka Incline used from 1878.
The total route milage of railways vested in the Railways Department and open for traffic at 31 March 1960 was 3,336 – 1,647 miles in the North Island and 1,689 in the South Island. In addition, traffic was being worked by the Railways Department over a further 6 miles of railways owned by other Government Departments. Double line was provided on 153 route miles of track.
The Otira - Arthur's Pass section of line, including the Otira Tunnel, was electrified in 1923, the Christchurch-Lyttelton section in 1929, the Wellington-Johnsonville line in 1938, and the Wellington-Paekakariki section in 1940. The first part of electrified services between Wellington and the Hutt Valley was brought into operation in 1953, and the last stage of this project was completed in July 1955.
The introduction of main-line diesel-electric locomotives in 1952 was the beginning of a radical change in motive power operation in New Zealand. By 31 March 1960, 107 of these locomotives were in use. In addition 86 diesel-mechanical and 18 diesel-electric shunting locomotives had been purchased. Between 1955 and 1959, 35 new articulated diesel railcars were placed in service. Diesel traction was responsible for handling 40 per cent of the traffic during the year 1959–60. The total fleet of 50 railcars ran approximately 46 per cent of the total passenger train milage.
Government railways in most instances have been constructed by the Ministry of Works and transferred to the Railways Department when completed. The gauge is 3 ft 6 in. Standard rails for heavy traffic main lines weigh 91 lb per lineal yard, and for secondary and branch lines 72 lb per yard. At present much of the track is laid to the standards adopted prior to 1950 - viz, 85 lb, 70 lb, and 55 lb rails. Sleepers, 2,400 to the mile, are principally of Australian hardwood, but substantial orders were placed in 1960 for pine sleepers from New Zealand mills.
Cook Strait Rail/Air Freight Service - An air freight service across Cook Strait was commenced in February 1947; information on its operation is given in Subsection 11D.
Cook Strait Passenger, Road, and Rail Ferry Service - A ferry to carry road, rail, and passenger traffic between Wellington and Picton is being constructed for the Railways Department with the aim of introducing this new service in 1962. The ferry will be of 4,300 tons and will hold 20 to 25 rail wagons plus 40 motorcars and accommodate 1,150 passengers.
ADMINISTRATION - In the year 1876 the railways that were operated by Provincial Governments passed into the control of the Public Works Department. In 1880 the opened lines were handed over to the Working Railways Department under a single management, but in 1889 a board of three Railway Commissioners was appointed. This was the form of management for five years, when a General Manager, responsible to the Minister of Railways, was appointed. Control by a General Manager continued until 1952, except for two short periods of board management, from 1925 to 1928, when a board of three members was appointed, and from 1931 to 1936, when the board consisted of five members.
Following a recommendation of a Royal Commission appointed on 3 March 1952 to inquire into and report upon all aspects of the New Zealand Government Railways, their future development, and sphere of operations, the Government established a Railways Commission. Five Directors were appointed from 12 January 1953. When the position of General Manager became vacant on 1 April 1955, the Government appointed a Director of the Railways Commission to the dual position of General Manager and Director. The Government Railways Amendment Act 1956 provided for the abolition of the Railways Commission on 1 April 1957, and reversion of control to the General Manager, who is responsible to the Minister of Railways.
COST OF CONSTRUCTION - The capital cost of State railways as at the end of each of the last five financial years is given below.
| 31 March 1956 | 31 March 1957 | 31 March 1958 | 31 March 1959 | 31 March 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Equal to £38,285 per mile of open line. Includes cost of rolling stock, buildings, and equipment as well as right of way and track. | |||||
| £ (thousand) | |||||
| Open for traffic - | |||||
| Railway | 101,418 | 111,674 | 115,746 | 123,583 | 127,718* |
| Lake Wakatipu steamer service | 23 | 23 | 23 | 24 | 24 |
| Subsidiary services | 7,108 | 8,405 | 9,703 | 10,336 | 10,729 |
| Totals | 108,548 | 120,101 | 125,472 | 133,943 | 138,472 |
| Works under construction | 9,704 | 3,117 | 299 | 298 | 298 |
| Totals | 118,253 | 123,218 | 125,771 | 134,242 | 138,770 |
So varied are the geographical features of New Zealand that a great disparity exists in the cost of constructing the individual sections of lines. Numerous mountain chains and rivers make railway construction in general both difficult and expensive. The Otira Tunnel is 5 miles 26 chains long, and the Rimutaka Tunnel is 5 miles 37 chains. The length of the longest bridge, over the Rakaia River, is 5,720 ft, and the largest viaduct, the Molaka, 887 ft long and 318 ft above water level.
ROLLING STOCK - Information as to the rolling stock in use on the State railways as at 31 March 1960 is given in the following table.
| *In addition there arc 5 diesel-electric shunting locomotives in use in workshops and 97 diesel and petrol shunting tractors, both road and rail type, in use at stations. | |
|---|---|
| Locomotives - | |
| Tender | 411 |
| Tank | 72 |
| Electric | 28 |
| Diesel-electric | 107 |
| Diesel-electric shunting | 18 |
| Diesel-mechanical shunting | 86 |
| Total | 722* |
| Passenger vehicles - | |
| Sleepers | 18 |
| First class | 100 |
| Second class | 685 |
| Composite | 8 |
| Railcars | 50 |
| Electric multiple units | 128 |
| Postal | 6 |
| Total | 995 |
| Wagons | Four Wheeled | Bogie |
|---|---|---|
| Horse boxes | 23 | 51 |
| Cattle | 1,007 | 43 |
| Sheep | 2,970 | 23 |
| Frozen and chilled meat | 659 | 787 |
| Cool, ventilated | 1,273 | - |
| Covered goods | 337 | 428 |
| High side | 19,950 | 266 |
| Low side | 1,408 | - |
| Platform | - | 1,166 |
| Brake vans | 10 | 431 |
| Other | 2,911 | 523 |
| 30,548 | 3,718 | |
| Total | 34,266 | |
From 1901 to 1939 most of the locomotives and rolling stock were built in the railway workshops. Some special types, however, such as multiple-unit electric coaches and a number of electric locomotives, were imported from England. In addition, many steam locomotives and goods wagons were imported after the First World War. Since the 1939–45 war, construction of steam locomotives and goods wagons has continued in New Zealand railway workshops, the annual output being dependent on the availability of staff and materials. It has been necessary to supplement this output with importations of locomotives, railcars, multiple-unit coaches, and goods wagons, mainly from England. Since 1945, more than 12,500 goods and livestock wagons of modern design have been placed in service, also 111 multiple-unit electric coaches, 35 diesel railcars, and many steam, diesel, and electric locomotives.
The last steam locomotives built in the North Island were completed at the Hutt Valley workshops in 1950. They were oil-fired 145-ton locomotives of the KA class. Sixteen 110-ton JA class oil-fired locomotives were imported from Scotland in 1952 for North Island service. In the South Island, the last of 35 coal-fired JA class steam locomotives was completed at the Hillside railway workshops in 1956. These will probably be the last steam locomotives ever built for New Zealand Railways.
Four 25-ton diesel-mechanical shunting locomotives were imported in 1949 and gave such good results that 82 more of different types, ranging in weight from 25 to 37 1/2 tons and in power from 204 to 260 h.p., were later ordered for distribution to shunting yards throughout the system. Several smaller diesel locomotives, of 15 and 20 tons weight, have also been acquired for light shunting duties at busy stations.
The first diesel-electric locomotives for main-line service in New Zealand were 51-ton (660 h.p.) machines imported from England in 1952 and placed in service at Auckland and Wellington. They were followed in 1954 by ten 108-ton (1,500 h.p.) locomotives. Forty 78-ton (1,425 h.p.) locomotives - 30 from North America in 1955 and 10 from Australia in 1957 - have since been put into service. All of these were for the North Island. The present diesel-electric locomotive fleet is completed by 42 (750 h.p.) locomotives placed in service between 1955 and 1957, 31 in the North Island and 11 in the South Island. These were imported from England. Eighteen 40-ton (400 h.p.) diesel-electric locomotives for heavy shunting duties in the Auckland district were built in England and delivered during 1959.
The latest diesel railcars, of which 35 were placed in service between 1955 and 1959, each weigh 56 tons unladen and seat 88 passengers. Designed for a top speed of 65 m.p.h. on level track, they are powered by two 210 h.p. diesel engines. With 15 railcars of earlier design, they provide fast passenger services covering a total of more than 7,000 miles daily spread over 12 main lines.
Standard main-line passenger cars are 56 ft in length, have chair seats, and are steam heated and electrically lit. They are steel sheathed and fitted with enclosed vestibules and gangways. Sleeping cars are provided with wash basins in each two-berth cabin, wall mirrors, reading lights, and plug-in sockets for electric razors.
Typical of the modern wagons now in use are steel high-side open wagons with a capacity of 15 tons; double-deck sheep wagons able to carry 80 sheep; covered goods wagons with capacity for 12 tons of goods; long 50-ft covered goods wagons for express goods trains; and high-capacity all-steel insulated wagons for frozen meat and chilled beef traffic. A new type of wagon, 42 1/2 ft long and 9 ft wide, for the Murupara-Kawerau log traffic, was specially designed for carrying a 26-ton bundle of logs loaded up to 12 ft above rail level. Deliveries of a new type of covered goods wagon designed for palletised goods traffic began in 1960.
The types of motive power handling New Zealand's railway traffic are illustrated in the following table. Diesel power has increased while steam power has decreased.
In these traffic figures, the weight of motive power is excluded - except in the case of diesel railcars and multiple-unit electric trains.
| 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Ton-miles (Million) | Per Cent | Gross Ton-miles (Million) | Per Cent | Gross Ton-miles (Million) | Per Cent | |
| Passenger trains - | ||||||
| Steam locomotives | 346.0 | 46.23 | 329.2 | 43.96 | 299.1 | 40.37 |
| Diesel locomotives | 40.4 | 5.40 | 46.9 | 6.26 | 46.1 | 6.22 |
| Diesel railcars | 143.6 | 19.19 | 152.5 | 20.37 | 170.4 | 23.00 |
| Electric locomotives | 50.2 | 6.70 | 50.6 | 6.76 | 50.3 | 6.79 |
| Electric multiple unit | 168.3 | 22.48 | 169.6 | 22.65 | 175.0 | 23.62 |
| Totals, passenger | 748.5 | 100.00 | 748.8 | 100.00 | 740.9 | 100.00 |
| Mixed and goods trains - | ||||||
| Steam | 1,937.4 | 59.64 | 1,823.9 | 55.86 | 1,810.2 | 54.62 |
| Diesel | 1,233.4 | 37.97 | 1,365.0 | 41.80 | 1,427.4 | 43.07 |
| Electric | 77.9 | 2.39 | 76.5 | 2.34 | 76.3 | 2.30 |
| Totals, mixed and goods | 3,248.7 | 100.00 | 3,265.4 | 100.00 | 3,313.9 | 100.00 |
| All trains - | ||||||
| Steam locomotives | 2,283.4 | 57.12 | 2,153.1 | 53.64 | 2,109.3 | 52.02 |
| Diesel locomotives | 1,273.8 | 31.87 | 1,411.9 | 35.17 | 1,473.5 | 36.34 |
| Diesel railcars | 143.6 | 3.59 | 152.5 | 3.80 | 170.4 | 4.20 |
| Electric locomotives | 128.1 | 3.20 | 127.1 | 3.17 | 126.6 | 3.12 |
| Electric multiple unit | 168.3 | 4.22 | 169.6 | 4.22 | 175.0 | 4.32 |
| Totals, gross ton-miles | 3,997.2 | 100.00 | 4,014.2 | 100.00 | 4,054.8 | 100.00 |
REVENUE AND EXPENDITURE - Gross revenue and expenditure on the railways (including subsidiary services) are shown in the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Gross Revenue | Expenditure | Net Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Loss recovered from General Reserve. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 32,262,916 | 30,829,399 | 1,433,517 |
| 1957 | 32,765,336 | 33,034,709 | —269,373* |
| 1958 | 34,442,769 | 35,588,196 | —1,145,427* |
| 1959 | 34,372,864 | 35,137,305 | —764,441* |
| 1960 | 34,936,914 | 35,500,047 | —563,133* |
The expenditure figures do not include interest on capital liability. With £5,389,827 interest added, the 1959–60 loss of £563,133 would become a loss of £5,952,960. The chief items of expenditure for 1959–60 were wages £20,828,228, locomotive fuel (including electricity) £2,030,024, stores and materials £4,508,314, depreciation and renewals £4,848,739, and miscellaneous £3,284,742.
A sum of £5,041,466 was set aside in 1959–60 for depreciation and track renewals, while expenditure from these funds amounted to £2,453,534. The amounts standing to the credit of the Depreciation and Renewals Accounts at 31 March 1960 were £13,867,571 and £194,153 respectively.
The revenue and expenditure for the last five years, distinguishing between railway operation and other items, are given in the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Gross Revenue | Expenditure | Net Revenue | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Railway Operation | Subsidiary Services, etc. | Railway Operation | Subsidiary Services, etc. | Railway Operation | Subsidiary Services, etc. | |
| *Net loss. | ||||||
| £ (thousand) | ||||||
| 1956 | 27,871 | 4,392 | 26,775 | 4,054 | 1,096 | 337 |
| 1957 | 28,507 | 4,258 | 28,694 | 4,340 | —187* | —82* |
| 1958 | 30,010 | 4,433 | 31,064 | 4,525 | —1,054* | —91* |
| 1959 | 29,823 | 4,550 | 30,505 | 4,632 | —682* | —82* |
| 1960 | 30,271 | 4,666 | 30,758 | 4,742 | —487* | —76* |
The respective Island figures of revenue and expenditure for railway operation only (i.e., omitting subsidiary services) are given below for the 1959–60 year.
| Section of Railway | Revenue | Expenditure | Net Revenue or Loss | Ratio of Expenditure to Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent | |
| North Island main line and branches | 20,380,292 | 19,183,341 | 1,196,951 | 94.13 |
| South Island main line and branches | 9,890,958 | 11,575,029 | -1,684,071 | 117.03 |
| Totals | 30,271,250 | 30,758,370 | -487,120 | 101.61 |
The various subsidiary services now conducted by the Railways Department, with the revenue and expenditure of each during the last two years, are shown below. Full working costs, including interest, are charged against these services, and the interest so charged is taken into miscellaneous receipts as revenue.
| Service | Revenue | Expenditure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
| £ (thousand) | ||||
| Lake Wakatipu steamers | 22 | 22 | 27 | 29 |
| Refreshment service | 370 | 356 | 397 | 398 |
| Bookstall service | 268 | 279 | 262 | 277 |
| Advertising service | 81 | 88 | 73 | 78 |
| Departmental dwellings | 363 | 379 | 1,046 | 1,037 |
| Leases of bookstalls, etc. | 121 | 125 | 113 | 125 |
| Road services - Passengers and goods | 2,684 | 2,748 | 2,713 | 2,797 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 642 | 669 | - | - |
| Totals | 4,550 | 4,666 | 4,632 | 4,742 |
Revenue - In the following table the railway operating revenue is classified according to the class of traffic, etc., from which it was derived. On 11 November 1956 fares were increased by 10 per cent and goods rates by an average of 8 per cent.
| Year Ended 31 March | Passenger Fares | Parcels, Luggage, and Mails | Goods and Livestock | Labour, Demurrage, etc. | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *As from April 1959 revenue from checked and left luggage was included with passenger revenue; parcels and mail revenue was included with freight revenue. | |||||
| £ (thousand) | |||||
| 1956 | 2,669 | 624 | 24,075 | 503 | 27,871 |
| 1957 | 2,789 | 646 | 24,431 | 642 | 28,507 |
| 1958 | 2,778 | 665 | 25,847 | 720 | 30,010 |
| 1959 | 2,769 | 652 | 25,710 | 692 | 29,823 |
| 1960 | 2,798 | * | 26,785 | 688 | 30,271 |
The revenue from passenger fares and luggage during the year 1959–60 represented an expenditure on railway travel of £1 3s. 10d. per head of mean population. The total railway operating revenue was equal to £12 18s. 1d. per head.
Expenditure - The operating expenditure under various heads is now given.
| Year Ended 31 March | Maintenance of Way and Works | Maintenance of Rolling Stock | Locomotive Transportation | Traffic Transportation | Head Office and General Charges* | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Including superannuation subsidy. | ||||||
| £ (thousand) | ||||||
| 1956 | 6,961 | 5,606 | 5,572 | 8,001 | 636 | 26,775 |
| 1957 | 7,453 | 6,356 | 5,673 | 8,509 | 702 | 28,694 |
| 1958 | 8,791 | 6,862 | 5,799 | 8,838 | 773 | 31,064 |
| 1959 | 8,617 | 6,792 | 5,586 | 8,739 | 771 | 30,505 |
| 1960 | 8,288 | 7,220 | 5,539 | 8,901 | 809 | 30,758 |
The increase in expenditure has been due chiefly to the greater milage run, an increased wages bill, mainly the result of higher rates of pay and improved conditions of employment, and to a general rise in the price of stores.
PASSENGER AND GOODS TRAFFIC - From about 1925 until 1933 there was a steady decline in the number of passenger journeys recorded. This was attributed to the development of motor competition and, after 1930, to the severe economic depression. As economic conditions improved from 1933 to 1939 there was an upward trend, and from 1939 to 1944 there was a sharp increase caused by the wartime movement of members of the armed forces, the curtailment of road services, and the restrictions placed on private motoring by rationing of petrol and shortage of rubber tyres.
In January 1944 train services had to be reduced drastically owing to shortage of coal. This fact, together with the large decline in armed forces traffic after the cessation of hostilities, caused the annual number of railway passenger journeys to recede considerably until the 1948–50 period, when restoration of a number of main line and suburban passenger train services became possible. Many branch-line and country main-line mixed-train services that had been discontinued were not restored, however, and the short-distance traffic that they carried was transferred permanently to road services.
Curtailment of main line and suburban services was again necessitated in 1951 because of shortage of coal arising from industrial disputes. Subsequent staff shortages prevented any large-scale restoration of services until more railcars could be introduced on main lines and until the Hutt Valley electrification scheme was nearing completion. Nevertheless, the number of passenger journeys per annum rose steadily from 1952 to 1957, reaching 25,377,170 in 1956–57. There was a decline to 24,816,639 in 1957–58, attributed partly to the continuing development of private-car competition and long-distance air services, and also to the exceptional series of floods and line blockages during the year, but an increase again in 1958–59 when the number of journeys rose to 25,437,083, and a further increase in 1959–60 to 26,134,480.
The quantity of goods traffic carried by New Zealand Railways increased steadily year by year until 1929–30, but declined considerably during the depression until 1933. Since 1933 there has been a steady upward trend, with only occasional and brief recessions reflecting fluctuations in economic activity, so that over the 27 years to 1960, the tonnage of goods carried has almost doubled (from 5,490,686 tons to 10,543,097 tons), and the ton-milage has more than trebled (from 363.4 million to 1,170.7 million).
Revenue-earning ton-miles in 1959–60 (1,170.7 million) reached a record figure, being an increase of 1.13 per cent compared with 1958–59 traffic. The average distance that each ton of goods was hauled rose from 66 miles in 1932–33 to 111 miles in 1959–60.
| Year Ended 31 March | Length Open Miles | Train Milage (Revenue) | Passengers | Season Tickets Issued | Tonnage of Goods and Livestock* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Including Season-ticket Holders | Excluding Season-ticket Holders | |||||
| *Livestock converted to equivalent tonnage. | ||||||
| 1956 | 3,422 | 14,883,724 | 25,075,242 | 7,975,196 | 1,504,220 | 10,677,923 |
| 1957 | 3,418 | 15,101,821 | 25,377,170 | 8,132,352 | 1,492,647 | 10,324,684 |
| 1958 | 3,466 | 14,825,110 | 24,816,639 | 7,768,579 | 1,461,141 | 10,331,948 |
| 1959 | 3,420 | 14,604,931 | 25,437,083 | 8,070,341 | 1,490,732 | 10,367,478 |
| 1960 | 3,336 | 14,480,209 | 26,134,480 | 8,245,190 | 1,516,296 | 10,543,097 |
Passenger train-miles run during 1959–60 totalled 5,717,600, and the total passenger revenue (including luggage) received represents 117.44d. per passenger train-mile, and £1,133 per mile of line operated by passenger services.
The number of ordinary passenger journeys in 1959–60 increased by 2.17 per cent, compared with the previous year. The tonnage of goods handled increased by 175,619 tons, or 1.69 per cent.
The numbers of livestock carried for the last two years were as follows.
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | Variation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||
| Cattle and horses | 882,175 | 806,767 | —75,408 | —8.55 |
| Calves | 640,961 | 574,927 | —66,034 | —10.30 |
| Sheep | 7,352,540 | 8,434,903 | +1,082,363 | +14.72 |
| Pigs | 453,706 | 440,928 | —12,778 | —2.82 |
| Totals | 9,329,382 | 10,257,525 | +928,143 | +9.95 |
| Equivalent tonnage | 642,865 | 657,121 | +14,256 | +2.22 |
| Revenue | £1,899,861 | £1,976,806 | +£76,945 | +4.05 |
Detailed figures showing the numbers of rail passengers carried and the numbers of season tickets issued during the last five years are given in the following table.
| 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard fare | 2,382,567 | 2,276,971 | 2,036,207 | 1,908,604 | 1,877,380 |
| Suburban | 4,638,794 | 4,981,360 | 4,944,302 | 5,327,221 | 5,556,295 |
| Other fares | 953,835 | 874,021 | 788,070 | 834,516 | 811,515 |
| Totals | 7,975,196 | 8,132,352 | 7,768,579 | 8,070,341 | 8,245,190 |
| Estimated number of journeys on season tickets | 17,100,040 | 17,244,818 | 17,048,060 | 17,366,742 | 17,889,290 |
| Number of season tickets issued - | |||||
| Suburban weekly | 557,390 | 564,462 | 563,044 | 574,585 | 596,364 |
| Weekly 10-trip | 31,785 | 28,003 | 27,005 | 28,245 | 26,617 |
| Bearer 12-trip | 81,626 | 93,144 | 97,482 | 100,857 | 106,166 |
| Bearer six-trip | 773,588 | 745,551 | 712,275 | 724,043 | 721,833 |
| School | 16,751 | 16,648 | 15,994 | 15,425 | 16,573 |
| Tourist | 36 | 25 | 13 | 29 | 34 |
| Travellers' annual | 52 | 54 | 40 | 38 | 28 |
| Other | 42,992 | 44,760 | 45,288 | 47,510 | 48,681 |
| Totals | 1,504,220 | 1,492,647 | 1,461,141 | 1,490,732 | 1,516,296 |
The importance of suburban passenger traffic is indicated in the following table showing the number of journeys.
| Year Ended 31 March | Non-suburban | Suburban | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 6,550,558 | 19,344,695 | 25,895,253 |
| 1958 | 3,177,241 | 21,639,398 | 24,816,639 |
| 1959 | 3,065,225 | 22,371,858 | 25,437,083 |
| 1960 | 2,985,941 | 23,148,539 | 26,134,480 |
In the year ended 31 March 1960 Wellington suburban journeys totalled 15,822,271, Auckland 3,929,801, Christchurch 1,755,619, Dunedin 1,552,638, and Invercargill 88,210.
The following table gives interesting information as to the constitution of the goods and livestock traffic and earnings for the year 1959–60.
| Commodity | Tonnage | Revenue | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tons Carried | Per Cent of Total | Tons 1 Mile | Average Haul | Total | Per Cent of Total | Per Ton | Per Ton-mile | |||
| Products of Agriculture | Per Cent | (000) | miles | £ | Per Cent | £ | s. | d. | d. | |
| Grain and seeds | 291,563 | 2.77 | 20,357 | 70 | 445,119 | 1.66 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 5.25 |
| Meal | 109,424 | 1.04 | 9,495 | 87 | 205,090 | 0.77 | 1 | 17 | 6 | 5.18 |
| Fruit and vegetables | 54,506 | 0.52 | 9,700 | 220 | 234,733 | 0.88 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4.02 |
| Root crops and fodder | 113,937 | 1.08 | 14,171 | 124 | 240,196 | 0.90 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4.07 |
| Totals | 569,430 | 5.41 | 53,723 | 94 | 1,125,138 | 4.21 | 1 | 19 | 6 | 5.03 |
| Animal and Other Products | ||||||||||
| Cattle, calves, and horses | 297,665 | 2.82 | 31,970 | 107 | 774,171 | 2.89 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 5.81 |
| Sheep and pigs | 359,456 | 3.41 | 40,940 | 114 | 1,202,635 | 4.49 | 3 | 6 | 11 | 7.05 |
| Meat, fresh and frozen | 464,667 | 4.41 | 18,524 | 40 | 1,030,413 | 3.85 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 13.35 |
| Butter | 189,400 | 1.80 | 17,849 | 94 | 509,555 | 1.90 | 2 | 13 | 10 | 6.85 |
| Cheese | 125,842 | 1.19 | 5,288 | 42 | 205,122 | 0.77 | 1 | 12 | 7 | 9.31 |
| Wool | 256,517 | 2.43 | 24,640 | 96 | 840,402 | 3.14 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 8.19 |
| Dairy by-products | 88,423 | 0.84 | 9,421 | 107 | 255,964 | 0.96 | 2 | 17 | 11 | 6.52 |
| Fat, hides, and skins | 77,364 | 0.73 | 5,306 | 69 | 214,729 | 0.80 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 9.71 |
| Fish | 7,822 | 0.07 | 1,438 | 184 | 36,423 | 0.14 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 6.08 |
| Totals | 1,867,156 | 17.70 | 155,376 | 83 | 5,069,414 | 18.94 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 7.83 |
| Products of Mines | ||||||||||
| Agricultural lime | 264,506 | 2.51 | 23,323 | 88 | 320,956 | 1.20 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3.30 |
| Coal, New Zealand hard | 602,194 | 5.71 | 47,354 | 79 | 722,013 | 2.70 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 3.66 |
| Coal, New Zealand brown | 1,207,689 | 11.46 | 164,769 | 136 | 2,196,465 | 8.20 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 3.20 |
| Road metal | 58,160 | 0.55 | 5,332 | 92 | 100,030 | 0.37 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 4.50 |
| Totals | 2,132,549 | 20.23 | 240,778 | 113 | 3,339,464 | 12.47 | 1 | 11 | 4 | 3.33 |
| Products of Forests | ||||||||||
| Timber, imported | 16,918 | 0.16 | 1,538 | 91 | 44,071 | 016 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 6.88 |
| Timber, New Zealand | 748,617 | 7.10 | 135,099 | 180 | 2,201,010 | 8.22 | 2 | 18 | 10 | 3.91 |
| Logs and poles, New Zealand | 804,273 | 7.63 | 35,626 | 44 | 453,116 | 1.69 | 11 | 3 | 3.05 | |
| Firewood, posts, etc. | 23,415 | 0.22 | 2,902 | 124 | 42,371 | 0.16 | 1 | 16 | 2 | 3.50 |
| Totals | 1,593,223 | 15.11 | 175,165 | 110 | 2,740,568 | 10.23 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 3.75 |
| Manufactures, etc. | ||||||||||
| Benzine, gasoline, kerosene | 325,073 | 3.08 | 34,136 | 105 | 962,102 | 3.59 | 2 | 19 | 2 | 6.76 |
| Cement | 276,059 | 2.62 | 48,781 | 177 | 817,372 | 3.05 | 2 | 19 | 2 | 4.02 |
| Manures, phosphates, etc. | 922,213 | 8.75 | 88,090 | 96 | 1,645,627 | 6.15 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 4.48 |
| Totals | 1,523,345 | 14.45 | 171,007 | 112 | 3,425,101 | 12.79 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 4.81 |
| Miscellaneous | 2,857,394 | 27.10 | 374,665 | 132 | 11,072,709 | 41.36 | 3 | 17 | 6 | 7.09 |
| Totals | 10,543,097 | 100.00 | 1,170,714 | 111 | 26,772,394 | 100.00 | 2 | 10 | 9 | 5.48 |
The next table shows the tonnage of goods carried, freight train-miles run, and net ton-miles run, together with the respective averages.
| Year Ended 31 March | Tonnage Carried | Freight Train-miles | Tons 1 Mile | Gross Revenue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Ton | Per Freight Train-mile | Per Ton-mile | ||||||||
| *Revenue now includes parcels traffic. | ||||||||||
| (000) | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | d. | |||
| 1956 | 10,677,923 | 9,635,949 | 1,148,330 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 5.03 |
| 1957 | 10,324,684 | 9,392,245 | 1,136,074 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 5.17 |
| 1958 | 10,331,948 | 9,092,635 | 1,150,543 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 16 | 10 | 5.36 |
| 1959 | 10,367,478 | 8,836,856 | 1,157,636 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 18 | 3 | 5.30 |
| 1960 | 10,543,097 | 8,762,609 | 1,170,714 | 2 | 10 | 9* | 3 | 1 | 2* | 5.48* |
The following diagram illustrates the growth in the tonnage of goods and livestock carried over the last 80 years.

A classification of goods traffic is now given.
| Year Ended 31 March | Agricultural and Pastoral Produce | Agricultural Lime and Manures | Timber and Firewood | Coal | Motor Spirits and Kerosene | Other | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Produce | Dairy Produce | Meat, Fish, and Livestock | Wool | |||||||
| Tons (thousand) | ||||||||||
| 1956 | 541 | 303 | 1,050 | 214 | 1,687 | 946 | 1,820 | 419 | 3,698 | 10,678 |
| 1957 | 525 | 346 | 1,058 | 219 | 1,471 | 1,173 | 1,833 | 390 | 3,310 | 10,325 |
| 1958 | 563 | 375 | 1,040 | 224 | 1,318 | 1,298 | 1,855 | 347 | 3,312 | 10,332 |
| 1959 | 621 | 372 | 1,063 | 244 | 1,099 | 1,499 | 1,881 | 324 | 3,264 | 10,367 |
| 1960 | 569 | 403 | 1,130 | 257 | 1,187 | 1,593 | 1,810 | 325 | 3,269 | 10,543 |
RAILWAY EMPLOYEES - The average number of persons employed by the State railways throughout the year ended 31 March 1960 was 25,519. The staff is divided into two divisions - namely, the salaried division, and the general division - and is further classed in a number of branches, as shown in the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Traffic | Way and Works | Locomotive Running | Workshops | Other Branches | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 7,703 | 5,941 | 3,416 | 4,787 | 2,794 | 24,641 |
| 1957 | 7,918 | 6,380 | 3,527 | 4,907 | 2,820 | 25,552 |
| 1958 | 8,025 | 6,804 | 3,601 | 5,068 | 2,833 | 26,331 |
| 1959 | 7,813 | 6,657 | 3,590 | 5,075 | 2,816 | 25,951 |
| 1960 | 7,571 | 6,495 | 3,613 | 5,046 | 2,794 | 25,519 |
A system of classification, first introduced in 1896 and revised at various times since, applies to railway employees. An Appeal Board is constituted to hear grievances of members dissatisfied with decisions in regard to promotion, loss of status, or breaches of discipline. The board consists of a Magistrate and two members of the Railways service, one appointed by the Minister of Railways and the other elected by the members of the Department. The Government Railways Amendment Act 1944 provided for the establishment of a tribunal of three members whose principal functions are to prescribe scales of salaries and rates of wages for railway employees; conditions in regard to hours of work, overtime, etc.; and terms and conditions in regard to leave of absence, railway travel concessions, etc. This tribunal, known as the Government Railways Industrial Tribunal, is deemed to be a Commission of Inquiry under the Commissions of Inquiry Act 1908. The members, who must not be members of the Railways Department or of any of the railway employees' organisations, are appointed for a term of three years.
A superannuation fund in connection with the Railways service was established in 1903, but was merged with other State superannuation funds as from 1 April 1948, all moneys standing to the credit of the fund being transferred to the newly created Government Superannuation Fund as from that date. Information concerning this is given in Section 6C.
Paid sick leave was introduced for employees in the general division in September 1956. Previously only salaried division employees had been entitled to paid sick leave.
RAILWAY ACCIDENTS - During the year ended 31 March 1960, 24 persons were killed and 428 injured in all kinds of accidents associated with train working and movements of rolling stock. Comparative figures for the previous year were 29 killed and 461 injured. These figures do not include employees who were killed or injured whilst engaged on other duties, e.g., railway workshops.
Of the 24 persons meeting with fatal accidents in 1959–60, two were passengers and four were employees; of the remainder who were neither passengers nor employees one was killed in an accident on the line and 17 at level crossings. Of those injured, 35 were passengers, 310 employees (chiefly in minor accidents), and 83 were neither passengers nor employees. Of the 83 other persons, 44 were injured in crossing accidents.
PRIVATE RAILWAYS - There are a number of short private railways in New Zealand, principally lines serving collieries and sawmills. The most important is the 7-mile line of the Ohai Railway Board, extending from Wairio (north-west of Invercargill) to coal mines at Ohai and carrying a substantial coal traffic. The Whakatane Board Mills Ltd. in the North Island operates logging trains over the 15-mile Matahina Tramway from Matahina to Edgecumbe, thence by running rights over the Government railways for 4 miles to Awakeri and finally over their 6 1/2-mile line from Awakeri to the mill at Whakatane. At Portland, near Whangarei, Wilsons Portland Cement Co. Ltd., operates an extensive private railway system serving its works.
ROADS AND BRIDGES - The total milage of formed roads in New Zealand at 31 March 1959 was 56,503, in addition to which there were 4,818 miles of bridle tracks and 15,774 miles of unformed legal roads. Details are given in the following table.
| Counties | Boroughs | Town Districts | Road Districts | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes 998 miles of pumice roads. | |||||
| Formed roads and streets | miles | ||||
| Sealed surfaces | 10,357 | 3,656 | 77 | 5 | 14,095 |
| Metal or gravel surfaces | 34,991 | 1,085 | 116 | 100 | 36,292 |
| Unmetalled surfaces | 5,946* | 126 | 28 | 16 | 6,116 |
| Totals, formed roads | 51,294 | 4,867 | 221 | 121 | 56,503 |
| Bridle tracks | 4,721 | 16 | 6 | 75 | 4,818 |
| Unformed legal roads | 15,404 | 330 | 21 | 19 | 15,774 |
| Totals, all roads | 71,419 | 5,213 | 248 | 215 | 77,095 |
The formation of roads in many parts has been attended with considerable expense and difficulties, arising from the configuration of the country and the abundance of rivers. As illustrating the latter aspect, the following table, showing the number and lengths of bridges incorporated in the roads system as at 31 March 1959, is of interest. Only bridges 25 ft or over in length have been taken into account, no official enumeration having been made of the innumerable culverts and short bridges. A perusal of the figures shown in this and the preceding table gives an average of 14 ft of bridging per mile of formed road.
| Materials of which Bridge Constructed | Counties | Boroughs | Town Districts | Road Districts | Totals | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Total Length | No. | Total Length | No. | Total Length | No. | Total Length | No. | Total Length | |
| ft | ft | ft | ft | ft | ||||||
| All concrete or stone | 2,140 | 218,931 | 161 | 16,940 | 7 | 383 | - | - | 2,308 | 236,254 |
| Steel and concrete | 704 | 76,774 | 76 | 12,379 | 5 | 255 | - | - | 785 | 89,408 |
| Steel, concrete, and timber | 686 | 57,701 | 23 | 2,247 | 2 | 71 | 3 | 105 | 714 | 60,124 |
| Steel and timber | 1,080 | 98,817 | 29 | 2,736 | 5 | 180 | - | - | 1,114 | 101,733 |
| Australian hardwood | 2,153 | 191,195 | 84 | 8,501 | 3 | 210 | - | - | 2,240 | 199,906 |
| Native timbers | 1,757 | 99,384 | 32 | 2,915 | 3 | 142 | 10 | 425 | 1,802 | 102,866 |
| Totals | 8,520 | 742,802 | 405 | 45,718 | 25 | 1,241 | 13 | 530 | 8,963 | 790,291 |
ROADS ADMINISTRATION - The main statutes covering roads administration in New Zealand are the Public Works Act 1928, the Counties Act 1956, and the National Roads Act 1953.
By the National Roads Act a National Roads Board was established from 1 April 1954, and its functions are defined as follows:
To administer the National Roads Fund in accordance with the provisions of the Act.
To provide an advisory service in respect of the whole roading system of counties, boroughs, and town districts throughout New Zealand, and to report to the Government from time to time on the progress being made in providing a roading system adequate for needs arising from current developments in motor traffic.
To advise the Government of any changes necessary in the legislation and regulations relating to the use of roads.
To act as the final authority in disputes relating to road classifications.
To advise the Government of changes necessary in the provision of finance for road construction and maintenance, particularly of changes considered advisable in the levying and collection of motor taxation, including exemptions therefrom.
To assist and advise local authorities generally on roading matters and any special roading problems arising from development of industries, etc.
To undertake at not more than five or less than three year intervals a comprehensive survey into the roading position in New Zealand, including standards, growth of traffic, adequacy, etc.
To give effect to any special matter of roading policy communicated to it by the Government.
To initiate and conduct research into roading problems in New Zealand.
To collect information on roading developments in other countries and make this available to roading authorities in New Zealand.
To undertake any other activity for the provision of a roading system adequate both for the needs of an efficient road transport system and for the benefit generally of motor-vehicle operators and the safety of the public in relation to motor traffic.
District roads councils are also established to function in their districts in relation to roading requirements and standards of the various local authorities. The National Roads Board, through the district councils and otherwise, has functions in relation to the maintenance of roads other than State highways in the districts of local authorities.
The 1953 Act provided that there would be automatic allocation of moneys to a National Roads Fund to be expended for roading purposes, but the 1955 amendment provided that the portion contributed from the Consolidated Fund would be appropriated annually by Parliament. Portion of the funds are allocated to local authorities for roading purposes.
The composition of the National Roads Board is: (a) one member, to be appointed Chairman of the Board (prior to the 1955 amending Act the Chairman was an officer of the Ministry of Works); (b) the person holding the appointment in the Ministry of Works as Director of Roading; (c) an officer of the Ministry of Works; (d) an officer of the Transport Department; (e) two nominees of the New Zealand Counties Association (Incorporated); (f) two nominees of the Municipal Association of New Zealand (Incorporated); (g) a representative of commercial road users; and (h) a representative of private motorists.
Roads Council Districts - New Zealand is divided into 21 roads districts, composed of local authorities grouped according to geographic situation and community interest.
For each roads district there is an advisory body, known as the District Roads Council, which is constituted to include the District Commissioner of Works, one representative of each constituent county and road district, one person to represent boroughs and independent town districts for each two members representing counties or road districts, a representative of commercial road users, a representative of private motorists, and a nominee of the Commissioner of Transport.
The principal functions of these councils include the making of recommendations to the Board each year as to which roads within the several districts should be declared State highways and the works which should be undertaken, together with estimates of the cost of works, their opinion of the roading needs of their districts as a whole, and their recommendations on other matters of interest to road users or affecting road safety.
Finance - The National Roads Act 1953 provided for a National Roads Fund to be established within the Public Account, the revenue of the Fund to be derived mainly from motor taxation together with an annual contribution from the Government. Expenditure from the Fund is for the purpose of developing State highways to modern standards and of subsidising the roading programmes of local authorities.
On the revenue side of the Fund's operations the Act reintroduced the principle of reserving motor taxation for roading purposes.
Details of the classes of revenue automatically paid into the Fund from 1 April 1954 arc as follows:
Fees and charges from registration and licensing of motor vehicles (section 34, Transport Act 1949), refer page 347 for present rates.
Heavy traffic licence fees (section 59, Transport Act 1949), less cost of collection not exceeding 5 per cent of the amount.
Motor spirits tax and milage tax (Part IV of Transport Act 1949).
Tyre tax (Customs Duties Tariff item 205 (b), Customs Acts Amendment Act 1934).
Receipts from any source in respect of the construction, maintenance, or control of any highway.
Receipts from transfers, sales, or hire of materials or plant or property of any kind or from executing works for other organisations.
Any other moneys credited to the Fund.
In addition, the former automatic payment of £1,000,000 annually from the Consolidated Fund was made subject to annual appropriation by the 1955 amendment to the principal Act. (The payment for 1959–60 was £1,200,000 to compensate for the reduction in roading revenue caused by the special additional petrol tax imposed from 27 June 1958.)
Since April 1954 a tax on motor spirits of 1s. 3d. per gallon has been paid into the National Roads Fund. (Additional tax of 1s. per gallon imposed from 27 June 1958, and reduced to 2d. in 1960, has been paid to the Consolidated Fund.)
Expenditure from the Fund may be made without appropriation as follows:
Payment of annual subsidies to local authorities for roading purposes.
Payments by the Crown in respect of the construction, maintenance, and control of State highways.
Compensation payable by the Crown for acquisition of land for a State highway.
Compensation and damages payable by the Crown for accidents and injuries in relation to works the cost of which is chargeable to the Fund.
Cost of purchase or hire of machinery or equipment.
Cost of survey and other preparatory work for State highways.
Cost of experimental work.
Cost of administration by the Ministry of Works.
Other expenses by the National Roads Board in exercise of its functions.
Prior to 1 April 1960 the highways system consisted of State highways (5,394 miles) and main highways (7,787 miles). From 1 April 1960 this system is replaced by a network of State highways totalling 7,196 miles. The figures of expenditure, etc., quoted herein refer to the highways system as it existed up to 31 March 1960.
Following is a statement of receipts and expenditure of the National Roads Fund for the years ended 31 March 1959 and 1960.
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|
| *Collection expenses deducted. | ||
| Receipts | £ | £ |
| Petrol tax (net) | 14,435,798* | 15,248,670 |
| Milage tax | 363,262* | 388,743 |
| Tyre tax | 29,678 | 28,900 |
| Fees and charges - | ||
| Registration and licence fees | 2,237,650* | 2,309,906 |
| Heavy traffic fees | 2,361,852* | 2,486,039 |
| Contribution from Consolidated Fund | 1,500,000 | 1,200,000 |
| Miscellaneous receipts - | ||
| Repayments of plant purchases | 73,865 | 60,222 |
| Repayments of advances to local authorities | 12,749 | 8,072 |
| Rents | 40,436 | 28,606 |
| Fees | 28 | 2,646 |
| Sales of land and buildings | 21,362 | 4,900 |
| Interest on plant purchases | 8,028 | 6,187 |
| Interest on advances to local authorities | 2,090 | 1,510 |
| Sale of bridging material | 1,155 | 186,586 |
| Bailey bridging hire | 20,626 | 21,525 |
| Interest on investments | 26,416 | 28,083 |
| Total receipts | 21,134,995 | 22,010,595 |
| Expenditure - | ||
| Highways maintenance | 4,901,642 | 5,554,659 |
| Highways construction | 8,782,976 | 10,513,076 |
| Payments to local authorities - | ||
| Subsidies on rates or population | 4,095,824 | 4,040,213 |
| Bridge renewal, flood damage, special and other grants | 1,399,521 | 1,526,142 |
| Maintenance of Government and county roads | 109,980 | 134,179 |
| Administration and general expenses - | ||
| Ministry of Works administration | 1,095,817 | 1,035,553 |
| Abolition of toll gates | 595 | 410 |
| Purchases of plant (local authority) | 43,112 | 6,490 |
| Fees and travelling expenses | 5,264 | 6,278 |
| Miscellaneous expenses | 139,037 | 61,228 |
| Advances to local authorities | - | 3,000 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | 425 | 1,308 |
| Total expenditure | 20,574,193 | 22,882,536 |
| Balance in Fund at end of year | 2,352,452 | 1,480,511 |
In the following table are shown the amounts which have been expended on highways construction, renewal, or maintenance during the last five years. Maintenance figures include the cost of flood damage restoration when applicable.
| Class of Expenditure | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Construction and improvement | 7,986,168 | 8,503,760 | 6,370,750 | 7,298,287 | 8,954,534 |
| Renewal of bridges | 1,533,895 | 1,857,490 | 1,569,777 | 1,484,689 | 1,558,542 |
| Maintenance, repairs, etc. | 4,178,864 | 4,801,435 | 4,681,921 | 4,901,642 | 5,554,659 |
| Totals | 13,698,927 | 15,162,685 | 12,622,448 | 13,684,618 | 16,067,735 |
An analysis of the actual expenditure on maintenance in each Island, as compared with the number of motor vehicles in each Island at 31 March of each of the last five years, appears in the following table, the percentages relating to New Zealand totals.
| 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of New Zealand Totals | |||||
| North Island - | |||||
| Maintenance expenditure | 65.68 | 67.78 | 66.41 | 65.41 | 69.04 |
| Motor vehicles | 67.06 | 67.19 | 67.41 | 67.37 | 67.46 |
| South Island - | |||||
| Maintenance expenditure | 34.32 | 32.22 | 33.59 | 34.59 | 30.96 |
| Motor vehicles | 32.94 | 32.81 | 32.59 | 32.63 | 32.54 |
The following table shows the milage of State and main highways in the North and South Islands at 31 March 1960, together with a classification as to the type of construction or surface.
| Length of Highways | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dustless Surface | Gravel or Macadam Surface | Total | |
| miles | |||
| North Island | 4,355 | 3,100 | 7,455 |
| South Island | 3,348 | 2,400 | 5,748 |
| Total | 7,703 | 5,500 | 13,203 |
Assistance to Local Authorities - On State highways the Board meets the whole cost of maintenance, construction, and reconstruction. On main highways (which existed up to 31 March 1960) a subsidy of not less than £3 for £1 was applicable to the cost of maintenance, construction, and reconstruction.
On State and main highways, a total amount of £16,067,735 was expended on maintenance and improvements by the National Roads Board during 1959–60.
Under the National Roads Amendment Act 1959 the National Roads Board pays from 1 April 1960 a subsidy at the rate of 15s. for each £1 that is spent by the local authority out of its own funds in the financial year on such programme of subsidised works as has been accepted for that financial year by the Board; the amount of subsidy is to be not less than 14 per cent of the Board's revenue in the case of boroughs and independent town districts, and not less than 30 per cent in the case of counties, dependent town districts, and road districts.
Prior to 1 April 1960 the Board also provided for local authorities: (a) annual subsidies for boroughs and independent town districts on a population basis, and for counties and road districts, based on general rates (other than those levied for other local authorities) and special rates for roading purposes collected by them; and (b) additional subsidies on the cost of renewing bridges, restoring flood damage on local authority roads and streets, extraordinary damage and maintenance caused by certain types of heavy traffic, plus special monetary assistance to local authorities whose financial position was such that they could not cope with their roading responsibilities from their own resources and the various forms of subsidy available from the National Roads Fund.
During the year 1959–60 the Board expended the following sums on the additional forms of assistance mentioned:
| £ | |
|---|---|
| Bridge renewals | 736,779 |
| Flood damage repair | 132,160 |
| Extraordinary damage or maintenance | 150,580 |
| Special financial grants | 448,415 |
| Subsidised highways | 25,352 |
| Municipal arterial roads | 32,856 |
| Total | 1,526,142 |
The payment shown earlier as “subsidised highways” was a contribution made to the Auckland Harbour Bridge Authority towards the cost of constructing the northern approach to the Auckland Harbour Bridge. This is under the authority of the National Roads Amendment Act 1956, which empowers the Board to subsidise roads which, although not controlled by a roading authority, will be available for public use.
Loan Assistance - In special circumstances the Board may advance money by way of loan to local authorities to provide for the proportion of cost payable by a local authority in respect of the construction or reconstruction of a highway. Such loans must be repaid by instalments extending over a period (not exceeding 10 years) to be agreed upon between the Board and the local authority, and interest is payable at a rate approved by the Minister of Finance.
The Board is also empowered to sell roadmaking machinery, plant, and equipment to local authorities on such terms as it thinks fit, including terms for the repayment of the purchase money by instalments extending over not more than four years, with interest on the unpaid balance at such rate as is fixed by the Board. Since this scheme was introduced by the Main Highways Board, plant, etc., has been purchased to the value of £1,093,533, of which sum £71,590 was outstanding at 31 March 1960. New advances made and repayments received during 1959–60 totalled £6,542 and £60,222 respectively.
State Highways - The National Roads Act provides for the declaration of roads as State highways with the approval of the Minister of Works.
The National Roads Board has the sole power of construction, maintenance, and control of all State highways. These powers may be delegated, for any State highway or portion thereof, to the local authority in whose district the road is situated. Any construction or maintenance work that is not delegated by the Board to a local authority is carried out by or through the agency of the Commissioner of Works and the cost borne by the Fund. The Board may also delegate to the Ministry of Works its duties in connection with design, supervision, construction, or maintenance, or the administration of any specified State highway. No new construction works are to be commenced by the Board, however, without the prior consent of the Minister of Works.
For State highways, the whole cost of construction is to be met from the National Roads Fund.
Highway Standards - In order to qualify for highway subsidies local authorities are required to carry out works to a standard approved by the National Roads Board. Subsidies are not payable unless the approved standard is observed, although work of a higher standard may be undertaken provided that the additional expenditure involved is found by the local authorities concerned. From time to time the Board's standards are revised to meet the latest developments in highway practice and engineering design and also to cater for the requirements of increasing traffic. Roadmaking materials used in highway works are subject to standard tests, and during recent years advances have been made in the direction of framing standard specifications which allow of a wider use of certain local materials which formerly were not accepted.
Motorways - Legislation by means of the Public Works Amendment Act 1947, as amended by section 44 of the Public Works Amendment Act 1948, makes provision for the declaration of limited-access highways or, more shortly, motorways. It is emphasised that motorways are not merely better all-purpose highways.
In addition to providing the most efficient and economic transport service, the main distinguishing features of a motorway are the control of access and the total elimination of ribbon development, both of which will go far to improve road safety and prevent obsolescence.
The total milage of motorways in use at 31 March 1960 was 31 miles 26 chains. During 1959–60, 5 motorway bridges, totalling 403 ft, were completed. Additional lengths are under construction at Auckland. The figures quoted for motorways' milages and bridging are additional to those shown under highways.
Activity During the Year Ended 31 March 1960 - During the year ended 31 March 1960, 364 miles of new sealing on highways were completed, giving an aggregate of 7,702 miles sealed, or 58 per cent of the total highway milage. In addition, improvements to existing sealed surfaces were effected on 1,040 miles of highways.
New bridging totalled 13,406 linear feet, compared with 13,546 linear feet in the previous year.
REGISTRATION AND LICENSING OF MOTOR VEHICLES - The following scale of fees is operative from 1 July 1961: Registration fees are £1 for any tractor, trailer, or power cycle, and £2 for any other motor vehicle. Annual licence fees are as follows: Power cycles, £1; motor cycles, £2; motorcars and private station wagons, £3; motor vehicles designed to carry more than nine passengers, £5; motor vehicles of which the manufacturer's gross laden weight exceeds two tons, £5; traction engines, £7 10s.; motor vehicles not otherwise specified, £4; trailers (two or more axles), £5; trailers (other), £1 10s. Other fees include drivers' licences. 5s.; changes of ownership, 10s.; and dealers' licences (motor cycles, £2; any other motor vehicles, £3). All such fees, except those for drivers' licences which are payable to the local authorities, are credited to the National Roads Fund.
The Transport Act 1949 provides that the annual licence may take the form of new registration plates or be in such other form as prescribed by regulation. The Motor Vehicles (Registration and Licensing) Regulations 1949, replacing earlier emergency regulations, authorise the permanent alternative of a licensed label system instead of an annual change of registration plates. The charge for licence stickers is 6d., for each set of two number plates, 3s. 6d., and 1s. 9d. for a single plate for a trailer or motor cycle.
The following table shows the numbers of the various types of motor vehicles licensed as at 31 March in each of the last five years.
| Type of Vehicle | Licensed as at 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| *Figures now include trailers formerly included under the heading “vehicles exempted from payment of annual licence fees”. | |||||
| Cars | 393,504 | 425,018 | 462,439 | 480,381 | 502,574 |
| Light trucks (i.e., 2 tons and under, laden) | 63,200 | 60,946 | 50,472 | 50,235 | 49,724 |
| Heavy trucks (i.e., over 2 tons laden) | 51,963 | 60,522 | 64,873 | 67,466 | 69,686 |
| Contract vehicles | 2,207 | 2,166 | 2,248 | 1,730 | 1,679 |
| Omnibuses | 2,055 | 2,174 | 2,193 | 2,268 | 2,317 |
| Taxis | 2,436 | 2,438 | 2,431 | 2,442 | 2,445 |
| Rental cars | 2,010 | 1,977 | 2,200 | 2,234 | 2,225 |
| Private-hire cars | 253 | 246 | 227 | 184 | 174 |
| Service cars | 733 | 733 | 708 | 673 | 628 |
| Trailers | 60,710 | 77,988* | 83,410* | 91,283* | 100,855* |
| Vehicles exempted from payment of annual licence fees (other than exempted Government-owned vehicles) | 50,685 | 48,459 | 50,815 | 52,852 | 57,224 |
| Government vehicles | 15,789 | 16,543 | 16,686 | 16,862 | 16,683 |
| Motor cycles | 24,592 | 25,389 | 26,084 | 26,624 | 26,874 |
| Power cycles | 4,180 | 5,781 | 7,813 | 9,544 | 9,937 |
| Totals | 674,317 | 730,380 | 772,599 | 804,778 | 843,025 |
| Dealers' cars | 2,875 | 3,079 | 3,275 | 3,221 | 3,054 |
| Dealers' motor cycles | 130 | 197 | 253 | 200 | 152 |
| Totals | 677,322 | 733,656 | 776,127 | 808,199 | 846,231 |
Motor vehicles exempted from the annual licence fee include a miscellaneous collection of machines such as farmers' motor vehicles used solely on the farm and only venturing on roads to proceed from one part of the farm to another, or from farm to garage for repair, etc., excavators, scoops, trench diggers, logging machinery, cranes, etc.
The rate of increase in the number of motor vehicles has exceeded the rate of increase in population. The following table shows the changes in relationship between the number of licensed vehicles and population as at 31 March in the latest 11 years.
| As at 31 March | Number of Persons in Population per Car | Number of Persons in Population per Motor Vehicle (Excluding Trailers) |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 8.1 | 5.0 |
| 1951 | 7.7 | 4.7 |
| 1952 | 7.0 | 4.2 |
| 1953 | 6.6 | 4.0 |
| 1954 | 6.4 | 3.8 |
| 1955 | 5.9 | 3.7 |
| 1956 | 5.5 | 3.5 |
| 1957 | 5.2 | 3.4 |
| 1958 | 4.8 | 3.2 |
| 1959 | 4.8 | 3.2 |
| 1960 | 4.7 | 3.2 |
The next table shows the estimated total consumption of motor spirits in New Zealand, together with the quantity consumed by motor vehicles, for each year during the period 1949 to 1960.
| Calendar Year | Consumption of Motor Spirits | |
|---|---|---|
| By Motor Vehicles | Total Consumption | |
| million gallons | ||
| 1949 | 111.5 | 132.6 |
| 1950 | 122.5 | 145.8 |
| 1951 | 139.4 | 165.9 |
| 1952 | 149.0 | 182.7 |
| 1953 | 160.5 | 196.7 |
| 1954 | 172.1 | 213.0 |
| 1955 | 185.0 | 228.5 |
| 1956 | 200.7 | 244.6 |
| 1957 | 207.0 | 252.4 |
| 1958 | 217.0 | 263.7 |
| 1959 | 218.5 | 261.0 |
| 1960 | 234.3 | 280.4 |
Consumption of motor spirits for civilian purposes reached its lowest level since the depression in 1942, successive increases occurring from then until 1948, when consumption was influenced by reversion to a modified form of the wartime rationing. The following years also recorded increases principally owing to the abolition of rationing in 1950 and to the greater number of vehicles on the roads in recent years.
The following diagram illustrates the movement that has taken place in the number of motor vehicles licensed, and in the consumption of motor spirits by motor vehicles since 1933. The low consumption of motor spirits during the depression period, the effects of rationing during the war years, the post-war recovery, and the subsequent increases paralleling the greater number of vehicles licensed in later years, are clearly demonstrated.
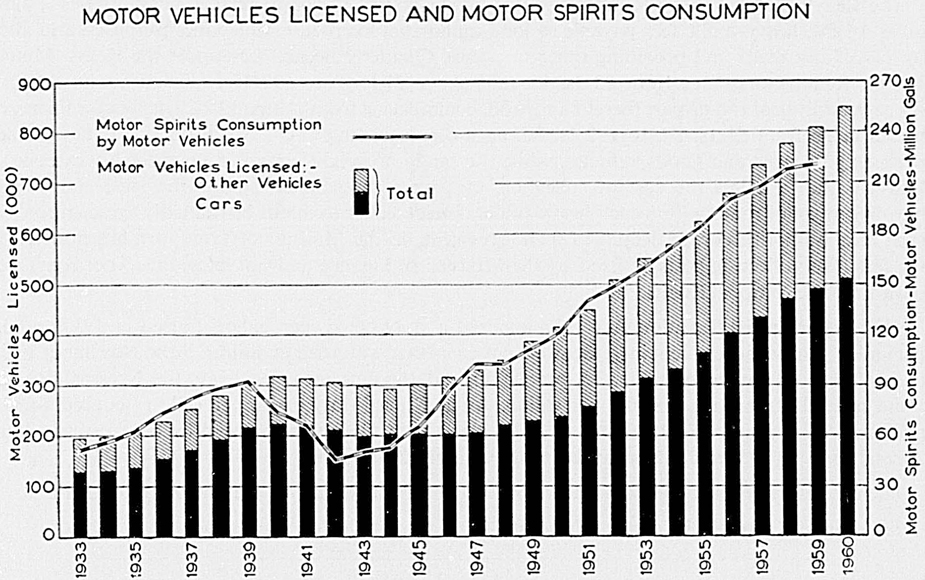
The following table gives particulars of the numbers of motor vehicles newly registered during each of the last five financial years. It should be noted that if a vehicle is again brought into use after its registration has been cancelled, it is treated as a new registration.
| Year Ended 31 March | Cars | Motor Cycles (Including Power Cycles) | Commercial Vehicles | Trailers | Total Registrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 45,116 | 3,710 | 21,096 | 12,423 | 82,345 |
| 1957 | 38,348 | 5,106 | 19,821 | 14,275 | 77,550 |
| 1958 | 41,178 | 7,682 | 17,957 | 15,771 | 82,588 |
| 1959 | 31,644 | 7,757 | 26,085 | 15,704 | 81,190 |
| 1960 | 30,932 | 5,980 | 24,291 | 16,667 | 77,870 |
Since 1 April 1958 registrations of new vehicles and those vehicles previously registered only in another country are available separately. These particulars (which exclude re-registrations) are as follows:
| Year Ended 31 March | Cars | Motor Cycles (Including Power Cycles) | Commercial Vehicles (Including Trailers) | Total Registrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 29,872 | 6,149 | 31,206 | 67,227 |
| 1960 | 28,338 | 3,464 | 27,620 | 59,422 |
ROAD TRANSPORT - The Transport Act 1949 is the main legislation governing road transport and the operations of the Transport Department. The Traffic Regulations 1956, made pursuant to the Transport Act, set out the rules of the road, the requirements as to motor vehicle equipment, and the obligations of motor drivers and owners and pedestrians.
The Heavy Motor Vehicle Regulations 1955 fix, in respect of commercial vehicles of over 2 tons gross weight, heavy-traffic fees payable to local authorities for road-maintenance purposes, and also for classifying roads and providing other measures. Quarterly licence fees under the Heavy Motor Vehicle Regulations range from £2 3s. 4d. (not above 2 1/2 tons) to £97 15s. (30 tons), with £3 10s. for each additional ton or part thereof above 30, commencing from 1 June 1955. The fees for farmers' trucks range from £1 1s. 8d. to £92 1s. 8d. on a corresponding basis. No distinction is now made between passenger and goods vehicles, while the range of weight classes is considerably extended. Heavy-traffic fees, less the cost of collection, etc., were apportioned among the local authorities having control of roads within each heavy-traffic district, either as might be mutually agreed upon by such local authorities or, in default of such agreement, by the Minister of Transport, but from 1954 the fees (less collection costs as fixed by the Minister of Finance and not exceeding 5 per cent) are payable to the National Roads Fund.
The Motor Spirits Taxation Act 1927 imposed a duty of 4d. per gallon (raised in 1930 to 6d. per gallon; further subsequent increases were not connected with road taxation). From November 1953 the full duty was increased to 1s. 3d. per gallon, and this amount is paid into the National Roads Fund instead of only the first 6d. per gallon. An additional duty of 1s. per gallon (reduced to 8d. and then 4d. per gallon in 1959 and to 2d. per gallon in 1960) was imposed by the Customs Acts Amendment Act 1958 and this is payable to the Consolidated Fund.
There is also a tyre tax collected under the Customs Act and paid to the National Roads Fund.
The estimated road use by motor vehicles in 1959 is given in the following table:
| Type of Vehicle | Petrol or Diesel Fuel Consumed | Vehicle Miles | Gross Ton Miles |
|---|---|---|---|
| per cent | |||
| Cars (including taxis and rental cars) | 51.4 | 67.5 | 39.9 |
| Trucks not exceeding 2 tons laden | 9.9 | 9.5 | 8.1 |
| Trucks exceeding 2 tons laden | 34.4 | 17.0 | 45.1 |
| Omnibuses and service cars | 3.5 | 1.7 | 6.5 |
| Motor cycles and power cycles | 0.8 | 4.3 | 0.4 |
| 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
TRANSPORT LICENSING - The Transport Act 1949 provides that any authority under the Act when dealing with an application or any other matter concerned with road transport or harbour-ferry services, is to have regard primarily to the public interest, the desirability of the service, and the needs of the district. More generally the authority is to have regard also to the following:
The provision of modern transport facilities best suited according to the nature of the service to meet the needs of national production and living standards and of national defence.
The fair and impartial regulation of all forms of public transport in order to develop and maintain transportation facilities adequate to meet the needs of New Zealand and of national and Commonwealth defence; and, for these purposes, to administer such facilities so as to recognise and preserve the inherent advantages of each form of transport; to promote safe, adequate, economic, and efficient service, and the fostering of sound economic conditions in transportation; to encourage the establishment and maintenance of reasonable transport charges without unjust discrimination, undue preference or advantage, or unfair or destructive practices; and to promote good working conditions for workers.
The constitution of transport, goods-service, and harbour-ferry-service districts is provided for in the Act, together with the establishment of a licensing authority for each district. For the four metropolitan transport districts, the licensing authorities appointed are the Auckland Transport Board and the Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin City Councils respectively. Goods-service districts may be identical with a transport district or be a part of the latter. The Governor-General may also declare any specified harbour or harbours or parts thereof to be a harbour-ferry-service district.
The licensing authority for any transport district may also be declared to be the licensing authority for the goods-service district. The Act provides for the appointment of a licensing authority for each harbour-ferry district instead of the former practice under which the licensing authority for the transport district to which the harbour is contiguous was to be the licensing authority for the harbour-ferry district. The Minister may authorise any specified licensing authority to exercise jurisdiction in respect of licences which would otherwise come within the jurisdiction of some other licensing authority.
The licensing authority, other than a metropolitan authority, is to consist of either one or three persons as the Minister may determine, who are appointed for a term of up to three years' duration. Members are also eligible for reappointment. The sole member or the chairman (where the authority consists of three members) has the authority and privileges of a Magistrate in respect of proceedings.
Passenger and goods services and harbour-ferry services are only to be carried on under licence. The position concerning the 50-mile and 30-mile limits and the term “available route” have been further clarified by the Transport Amendment Acts 1958 and 1959 and are covered by Transport Licensing Regulations.
A transport licence is not required for: (1) The carriage to and from school of school children and their teachers only; (2) the carriage by a contract vehicle or a harbour ferry of a private party on a special occasion; (3) carriage of workmen to and from work by the Government or a public body, where the vehicle is not designed principally for the carriage of persons and such service has been approved by the Minister for this purpose; (4) for carriage of newspapers, or in connection with funerals or repair and wreckage of vehicles which have met with mishap; (5) farmers carrying milk' cream, or whey to and from dairy factories for their neighbours where a licensed goods service is not available; (6) relieving or assisting inhabitants of a locality affected by flood, earthquake, or fire; (7) carriage of showman's goods, etc. by a vehicle owned by the showman; and (8) goods services otherwise exempted by Order in Council.
In considering applications for licences the licensing authority is to have regard to the extent to which any proposed service or improved service is necessary or desirable in the public interest, and the needs of the district concerned and the protection of public funds where the Minister of Railways holds a licence. If further consideration be then given, factors to be taken into account are existing services, financial ability of applicant to carry on the service, provision and maintenance of a reasonable standard of living and satisfactory working conditions in the transport industry, the manner in which a service has already been carried on, or the likelihood of satisfactorily carrying on a service, timetables and frequency of service, vehicles or ferries to be used, conditions of roads, routes and load restrictions, speeds, etc., and representations that may be made by various bodies, persons carrying on transport services and likely to be affected, and petitions of 25 or more adult persons of the locality concerned, etc.
Preference is to be given to applications by Government and local authority or other public body under certain conditions, chiefly where no existing services are available or where the proposal is for an extension of an existing service, or if the new service is wholly within the applicant's district in the case of a local authority, etc., or where there will be no competition with an existing service to the same locality by means of another route.
The licensing authority is to prescribe the terms and conditions of the licences such as class (continuous, seasonal, or temporary), commencement date, localities and routes, timetables, etc.
Additional requirements may be prescribed for taxicab licences to ensure the control of the service in the interests of efficiency and of the public - e.g., complying with roster of duties, joining an organisation for the purpose of obtaining telephone facilities, etc. There is no limitation on the period for which licences may be issued, and they may be transferred subject to certain conditions.
Certificates of fitness are required for each passenger service or goods-service vehicle and all trucks with gross laden weight exceeding two tons. Charges are to be fixed, in the case of a service owned by a public body, by that body itself, and in the case of any other service, by the Commissioner of Transport, there being a right of appeal to the Transport Charges Appeal Authority in either case.
The Transport Charges Appeal Authority, as in the case of the Transport Licensing Appeal Authority, also established under the Act, is to be either a Judge of the Supreme Court or the holder of any office under any Act who is entitled to the equivalent rights and tenure of office as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
Applications to fix road and harbour-ferry charges may be made by the holder of, or an applicant for, the licence; any other person whose interests are affected, being the holder of a licence, an applicant, the permanent head of a Government Department, a local authority, or a public body; any 25 or more adult residents of a locality in which the charges are or would be in force; all parties to a contract for the carriage of passengers or goods by any such services; and incorporated bodies whose members have a special interest in the type of transport concerned or whose principal objects are the protection of the interests of transport operators. The power to fix fares to be charged on any road passenger service carried on by the Minister of Railways to which Part III of the Government Railways Act 1949 applies, is expressly excluded from the jurisdiction of the charge-fixing bodies, but there is now right of appeal to the Charges Appeal Authority.
The principles to be observed in determining transport charges include: the promotion and maintenance of the economic stability of New Zealand; desirability of increasing national production by granting concessions on the carriage of producers' goods; desirability of providing special fares for all regular users of passenger services, and that children under four years be carried free, with children from the age of four years and under 15 years at half adult rates; desirability of maintaining a reasonable standard of living and satisfactory working conditions in the road-transport and harbour-ferry industries; and the maintenance of efficiency of the transport services to which the proceedings relate.
Included in the general provisions is one under which the owner of any motor vehicle licensed for passenger services or goods services and involved in an accident attended by serious injury to any person, or serious damage to the property of any person, shall notify the Commissioner of Transport within 48 hours of the occurrence.
Operations of Licensed Goods and Passenger Services - The following tables review the operations of licensed road transport services to which the preceding paragraphs relate. The first of these tables gives the estimated overall figures concerning licensed road goods services for each of the four latest years ended 31 March.
| Road Goods Services | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | £ | 31,217,000 | 33,623,000 | 36,054,000 | 37,000,000 |
| Capital | £ | 19,715,000 | 22,229,000 | 24,966,000 | 27,000,000 |
| Total vehicle-miles | 214,000,000 | 224,000,000 | 229,000,000 | 234,000,000 | |
| Number of goods service licences | 6,194 | 6,987 | 7,101 | 6,944 | |
| Average revenue per vehicle-mile | d. | 35.01 | 36.06 | 37.85 | 38.37 |
| Average number of miles per vehicle | 15,350 | 15,160 | 14,918 | 14,632 | |
The second table shows traffic data, revenue, and number of vehicles used by the road passenger services operating in New Zealand, and is inclusive of services in the four Metropolitan Transport Districts, for each of the latest four years ended 31 March.
| Road Passenger Services | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic statistics - | |||||
| Passengers carried | 153,809,946 | 153,219,147 | 149,786,871 | 154,570,063 | |
| Vehicle-miles | 68,518,699 | 68,558,880 | 70,588,393 | 70,031,641 | |
| Total revenue | £ | 8,289,683 | 8,506,153 | 8,990,027 | 9,134,800 |
| Total revenue, per mile | d. | 29.04 | 29.78 | 30.57 | 31.30 |
| Number of vehicles included | 3,314 | 3,467 | 3,703 | 3,694 | |
ROAD SAFETY - The New Zealand Road Safety Council, first set up in 1936 to advise the Government on matters of road safety, was reconstituted in 1947. Subcommittees have now been set up dealing with the following: the motor driver, motor vehicle, roads, traffic laws, traffic law enforcement, road accident statistics, road safety publicity, and child education in traffic. Since April 1953 local road safety committees have been formed to deal with local problems and make recommendations to the parent body. There are now 36 local organisations operating throughout New Zealand.
Publicity directed towards road safety is carried out per medium of the press, posters, screen slides, and radio, concentrating on simultaneous presentation, as far as possible, of specific aspects of the problem. Other means employed in furthering road safety consist of traffic instruction in schools, inspection of motor vehicles, and enforcement of traffic laws.
The Transport Act 1949, as amended in 1950 and 1955, contains several provisions designed to achieve greater safety on the roads. A maximum speed limit of 50 miles per hour is fixed, but lower limits are provided for special classes of vehicles - e.g., motor cycles with pillion riders, 40 miles per hour (30 miles per hour without safety helmets); heavy passenger vehicles, 40 miles per hour; vehicles drawing trailers, 40 miles per hour; and heavy goods vehicles, 30 miles per hour. A uniform speed limit of 30 miles an hour is fixed in boroughs, town districts, or other localities which have been declared to be closely populated localities by notice published by the Minister of Transport in the New Zealand Gazette. The Act also gives the Minister power to exempt any road in a particular borough or town district from the provisions of the maximum speed limit, and further exceptions are ambulances (fitted with a siren or bell) or police vehicles travelling on urgent duty, or fire engines proceeding to a fire. Limited-speed zones may now be defined and indicated by signs at the approaches to closely settled areas, and there a maximum speed-limit of 30 m.p.h. operates when adverse conditions prevail, such as poor visibility or heavy traffic.
Persons convicted on indictment of negligent or reckless driving, or driving while under the influence of drink or a drug to such an extent as to be incapable of having proper control of a motor vehicle, if injury or death to any person results from their actions, are liable to a maximum penalty of five years' imprisonment or a fine of £500. Where no person is injured or where the offence as above results in summary conviction, the maximum penalty is three months' imprisonment or a fine of £100. The terms of the compulsory disqualification for serious driving offences were materially extended by the Transport Amendment Act (No. 2) 1958. For driving while under the influence of drink to such an extent as to be incapable of having proper control of the vehicle the minimum disqualification from obtaining a licence, unless the Court thinks fit to order otherwise, is now three years for the first offence and 10 years for any subsequent offence. For negligent or reckless driving the minimum cancellation of licence is now one year. Application may be made to the Court to review the disqualification within six months except for intoxicated driving for which the period is 12 months and two years for a subsequent offence. The Act prescribes penalties for careless or inconsiderate driving, certain accident promoting offences (3 months' disqualification), the drinking of intoxicants in a public vehicle, and makes compulsory the reporting to the police of all motor-vehicle accidents involving injury.
Included in the Traffic Regulations 1956 are the requirements to which motor drivers must conform and which are designed to promote the safety of those using the roads.
The following table shows the nature of the offences resulting in convictions during the latest four years ended 31 March.
| Type of Offence | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes 470 motor cyclists exceeding 30 miles per hour without safety helmets. †Includes 632 motor cyclists exceeding 30 miles per hour without safety helmets. ‡Includes 689 motor cyclists exceeding 30 miles per hour without safety helmets. | ||||
| (a) Road traffic offences - | ||||
| Intoxicated in charge | 210 | 262 | 190 | 180 |
| Negligent driving | 12 | 27 | 33 | 38 |
| Dangerous manner | 194 | 273 | 252 | 175 |
| Dangerous speed | 143 | 152 | 154 | 118 |
| Careless or inconsiderate driving | 606 | 805 | 730 | 929 |
| Exceeding 30 m.p.h. | 2,838 | 3,164 | 4,029 | 4,738 |
| Overtaking offences | 168 | 191 | 294 | 355 |
| Failing to keep left | 310 | 406 | 450 | 443 |
| Failing to yield right of way | 263 | 308 | 342 | 314 |
| Driver's licence offences | 746 | 895 | 879 | 1,009 |
| Licensing and registration offences | 472 | 551 | 729 | 970 |
| Lighting offences | 854 | 822 | 1,043 | 1,120 |
| Defective brakes | 104 | 106 | 152 | 130 |
| No warrant of fitness | 1,231 | 1,375 | 1,695 | 2,204 |
| Loading offences | 93 | 134 | 88 | 116 |
| Exceeding 50 m.p.h. | 528 | 563 | 879 | 1,042 |
| Cycling offences | 302 | 418 | 394 | 859 |
| Failing to dip | 72 | 68 | 69 | 97 |
| Failing to give right of way to pedestrians | 66 | 96 | 110 | 97 |
| Exceeding 40 m.p.h. with pillion passenger | 212 | 239 | 260 | 293 |
| L plate offences | 356 | 354 | 410 | 401 |
| Crossing railway line | 51 | 46 | 54 | 70 |
| Compulsory stop | 439 | 621 | 759 | 865 |
| Parking | 2,953 | 4,388 | 5,621 | 5,079 |
| Miscellaneous | 530 | 1,143* | 1,581† | 1,946‡ |
| (b) Heavy motor-vehicle offences - | ||||
| Exceeding heavy-traffic licence | 405 | 398 | 610 | 568 |
| Exceeding axle load | 622 | 633 | 1,109 | 1,179 |
| No heavy-traffic licence | 585 | 497 | 543 | 550 |
| Speeding | 682 | 662 | 918 | 962 |
| Miscellaneous | 53 | 45 | 35 | 66 |
| (c) Transport licensing offences - | ||||
| Unlicensed goods service | 178 | 168 | 238 | 171 |
| Breach of goods service licence | 134 | 186 | 312 | 250 |
| Unlicensed passenger service | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
| Breach of passenger service licence | 4 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| No certificate of fitness | 223 | 201 | 230 | 201 |
| No vehicle authority | 38 | 37 | 46 | 26 |
| Drivers' hours breaches | 13 | 1 | 11 | 6 |
| Overloading | 37 | 18 | 88 | 65 |
| Rental vehicle offences | 41 | 45 | 59 | 75 |
| Miscellaneous transport offences | 31 | 29 | 26 | 62 |
| (b) Miscellaneous offences under miscellaneous | ||||
| Acts and regulations | 29 | 12 | 16 | 35 |
| Totals | 16,830 | 20,343 | 25,449 | 27,826 |
The above table covers only the offences reported by officers of the Transport Department.
TRAFFIC ACCIDENTS ON ROADS - Motor-vehicle accidents involving death or personal injury are required by law to be reported to the police. For the year ended 31 December 1959, 8,265 such accidents, resulting in 349 fatalities and in injuries to 11,703 other people, were reported. Comparative figures for 1958 and 1957 years were (1957 figures being given in parentheses): number of accidents, 8,194 (7,948); fatalities, 379 (384); persons injured, 11,408 (11,053). The increase in the traffic flow over the last few years, caused largely by the increased number of vehicles on the road, has been an important factor in the increase in motor accidents. New Zealand has one of the lowest motor accident death rates (based on deaths per 10,000 licensed motor vehicles), the figure for 1959 being 4.88. Details of the number and nature of road accidents for the latest five calendar years, which have been compiled by the Transport Department, are as follows.
| Nature of Accident | Number of Accidents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Collisions - | |||||
| Between two or more motor vehicles | 2,609 | 2,861 | 3,286 | 3,467 | 3,532 |
| Between motor vehicle and bicycle | 1,208 | 1,166 | 1,315 | 1,331 | 1,259 |
| Between motor vehicle and pedestrian | 1,120 | 1,165 | 1,236 | 1,294 | 1,310 |
| Between motor vehicle and fixed object | 406 | 503 | 660 | 654 | 642 |
| Between motor vehicle and animal or horse vehicle | 55 | 54 | 46 | 54 | 53 |
| Between motor vehicle and railway train | 45 | 55 | 40 | 49 | 56 |
| Between motor vehicle and tram | 16 | 19 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
| Multiple and other collisions | 288 | 240 | 234 | 188 | 221 |
| Totals, collisions | 5,747 | 6,063 | 6,827 | 7,045 | 7,081 |
| Non-collisions - | |||||
| Drove off road | 199 | 193 | 246 | 228 | 264 |
| Went over bank | 252 | 308 | 323 | 295 | 291 |
| Overturned on roadway | 353 | 359 | 401 | 461 | 475 |
| Person fell from vehicle | 97 | 90 | 122 | 132 | 116 |
| Other | 28 | 29 | 29 | 33 | 38 |
| Totals, non-collisions | 929 | 979 | 1,121 | 1,149 | 1,184 |
| Total accidents | 6,676 | 7,042 | 7,948 | 8,194 | 8,265 |
Particulars of fatal motor-vehicle accidents included in the foregoing table are now given. It should be noted that the figures relate to the number of accidents and not to the number of deaths, which, as stated above, numbered 349 in 1959.
| Nature of Accident | Number of Fatal Accidents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Collisions, motor vehicle with - | |||||
| Pedestrian | 79 | 80 | 89 | 87 | 90 |
| Motor vehicle | 73 | 74 | 99 | 93 | 77 |
| Train | 11 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| Bicycle | 26 | 20 | 41 | 37 | 26 |
| Horse vehicle or animal | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| Other | 37 | 40 | 45 | 47 | 47 |
| Otherwise | 75 | 80 | 71 | 72 | 63 |
| Totals | 304 | 306 | 355 | 346 | 313 |
Statistics of deaths resulting from motor-vehicle accidents are available for many years from vital statistics, these figures being discussed briefly in Section 4C.
The following table shows the distribution of motor accidents on the system of roads and streets during the calendar year 1959.
| Classification of Locality | Fatal Accidents | Injury Accidents | All Accidents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage of Total | Number | Percentage of Total | Number | Percentage of Total | |
| Four main cities | 51 | 16.3 | 2,462 | 31.0 | 2,513 | 30.5 |
| Secondary cities (11) | 26 | 8.3 | 1,085 | 13.6 | 1,111 | 13.4 |
| Boroughs 6,000 and over (32) | 32 | 10.2 | 1,269 | 15.9 | 1,301 | 15.7 |
| Small boroughs, town districts, and closely populated localities | 32 | 10.2 | 773 | 9.7 | 805 | 9.7 |
| Total in built-up areas | 141 | 45.0 | 5,589 | 70.2 | 5,730 | 69.3 |
| State highways | 99 | 31.7 | 1,341 | 16.9 | 1,440 | 17.4 |
| Main highways | 35 | 11.2 | 515 | 6.5 | 550 | 6.7 |
| Other rural roads | 38 | 12.1 | 507 | 6.4 | 545 | 6.6 |
| Total on rural roads | 172 | 55.0 | 2,363 | 29.8 | 2,535 | 30.7 |
| Total accidents | 313 | 100.0 | 7,952 | 100.0 | 8,265 | 100.0 |
The next table gives an analysis by percentages of the more important causes of accidents involving motor vehicles during the year ended 31 December 1959.
| Cause | Accidents Where Motorists Considered Responsible | Accidents Where Pedestrians Considered Responsible | Accidents Where Cyclists Considered Responsible | All Miscellaneous Causes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| per cent | ||||
| Failure to yield right of way | 25 | - | 14 | - |
| Failure to keep left | 7 | - | 7 | - |
| Driver/rider inattentive | 12 | - | 23 | - |
| Excessive speed | 10 | - | - | - |
| intoxicated | 3 | - | - | - |
| Overtaking faults | 6 | - | - | - |
| Pedestrian crossing roadway heedless of traffic | - | 49 | - | - |
| Pedestrian emerging from behind vehicle or object | - | 18 | - | - |
| Pedestrian stepping into roadway without due care | - | 14 | - | - |
| Pedestrian intoxicated | - | 6 | - | - |
| Pedestrian confused by traffic | - | 2 | - | - |
| Pedestrian failing to keep to side of road where no footpath | - | 3 | - | - |
| Turning suddenly | 3 | - | 10 | - |
| Failure to give proper signal | - | - | 4 | - |
| Reckless emergence from another road | - | - | 5 | - |
| Door opened in moving vehicle | - | - | - | 8 |
| Animals on roadway | - | - | - | 12 |
| Door of vehicle opened in path of other party | - | - | - | 10 |
| Road surface slippery from weather conditions | - | - | - | 12 |
| Excessive depth of loose metal | - | - | - | 9 |
| Weather conditions | - | - | - | 11 |
| Sundry causes | 34 | 8 | 37 | 38 |
| Totals | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
On week days, from Monday to Friday inclusive, the worst hourly period for motor accidents was from 5 p.m. to 6 p.m., on Saturdays from 6 p.m. to 7 p.m., and on Sundays from 5 p.m. to 6 p.m. More accidents occur on Saturday than on any other day of the week.
The following table shows motor accident death and injury rates in 1959 for New Zealand in comparison with other countries.
| Country | Persons Killed | Persons Injured | Killed per 10,000 Vehicles | Killed per 100,000 Population | Injured per 10,000 Vehicles | Injured per 100,000 Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | 349 | 11,703 | 4.88 | 14.95 | 164 | 501 |
| Australia | 2,224 | 54,465 | 8.59 | 22.39 | 210 | 548 |
| Great Britain | 6,520 | 326,933 | 7.97 | 12.93 | 399 | 648 |
| United States of America | 37,800 | 1,400,000 | 5.40 | 21.24 | 200 | 787 |
URBAN TRANSPORT OPERATED BY LOCAL AUTHORITIES - In recent years the use of motor-bus and trolley-bus services has increased and electric tramways have become a small sector of the urban passenger services. Only one electric tramway system serving a city area continues to run, this being in Wellington.
The data provided in this section cover the whole of the urban passenger transport services operated by local authorities in the respective periods. These consist of: (1) Motor-bus services only; (2) combined trolley-bus and motor-bus services; (3) combined tram, trolley-bus and motor-bus services.
No account is taken in this section of the various motor-bus services operated by the New Zealand Government Railways or by any private enterprise.
Systems Comprising Motor-bus Services Only - In the following tables information is given on the operations of those municipal services which consist entirely of motor-buses.
| Service | Year Ended 31 March | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Number of Passengers Carried | |||
| Gisborne | 795,007 | 816,547 | 784,065 |
| Palmerston North | 1,541,130 | 1,510,881 | 1,490,062 |
| Eastbourne | 1,233,016 | 1,275,260 | 1,240,079 |
| Christchurch | 20,461,853 | 20,861,514 | 21,425,460 |
| Timaru | 1,280,340 | 1,271,503 | 1,347,253 |
| Invercargill | 2,460,142 | 2,363,746 | 2,489,618 |
| Totals | 27,771,488 | 28,099,451 | 28,776,537 |
| Average Number of Passengers per Mile Run | |||
| Gisborne | 4.48 | 4.27 | 4.10 |
| Palmerston North | 4.44 | 4.45 | 4.56 |
| Eastbourne | 2.04 | 2.13 | 2.25 |
| Christchurch | 4.81 | 4.86 | 4.85 |
| Timaru | 5.79 | 5.85 | 5.23 |
| Invercargill | 4.98 | 4.85 | 5.02 |
| 4.55 | 4.59 | 4.61 | |
| Revenue | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Gisborne | 25,926 | 25,638 | 27,021 |
| Palmerston North | 33,843 | 35,306 | 37,012 |
| Eastbourne | 78,680 | 78,066 | 76,581 |
| Christchurch | 551,123 | 569,349 | 585,232 |
| Timaru | 32,140 | 32,150 | 36,030 |
| Invercargill | 47,940 | 47,223 | 50,559 |
| Totals | 769,652 | 787,732 | 812,435 |
| Expenditure | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Gisborne | 27,132 | 26,631 | 25,941 |
| Palmerston North | 53,108 | 50,555 | 43,658 |
| Eastbourne | 69,761 | 69,244 | 70,399 |
| Christchurch | 707,244 | 726,997 | 739,088 |
| Timaru | 37,059 | 39,010 | 40,209 |
| Invercargill | 67,688 | 72,158 | 69,491 |
| Totals | 961,992 | 984,595 | 988,786 |
| Number of Buses in Use | |||
| Gisborne | 10 | 10 | 9 |
| Palmerston North | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Eastbourne | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Christchurch | 168 | 167 | 155 |
| Timaru | 14 | 17 | 17 |
| Invercargill | 20 | 19 | 19 |
| Totals | 249 | 250 | 237 |
| Seating Capacity | |||
| Gisborne | 315 | 317 | 291 |
| Palmerston North | 536 | 518 | 467 |
| Eastbourne | 770 | 775 | 775 |
| Christchurch | 6,552 | 6,680 | 6,200 |
| Timaru | 531 | 641 | 647 |
| Invercargill | 726 | 708 | 707 |
| Totals | 9,430 | 9,639 | 9,087 |
| Miles Run During Year | |||
| Gisborne | 177,401 | 191,025 | 191,376 |
| Palmerston North | 346,833 | 339,858 | 327,065 |
| Eastbourne | 605,478 | 597,368 | 551,505 |
| Christchurch | 4,255,600 | 4,289,189 | 4,414,262 |
| Timaru | 221,205 | 217,282 | 257,745 |
| Invercargill | 494,443 | 487,384 | 496,001 |
| Totals | 6,100,960 | 6,122,106 | 6,237,954 |
| Service | Average Fare per Passenger | Revenue per Mile | Expenditure per Mile | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| d. | d. | d. | d. | d. | d. | d. | d. | d. | |
| Gisborne | 7.49 | 7.19 | 7.94 | 35.07 | 32.21 | 33.89 | 36.71 | 33.46 | 32.53 |
| Palmerston North | 5.00 | 5.34 | 5.68 | 23.42 | 24.93 | 27.16 | 36.75 | 35.70 | 32.04 |
| Eastbourne | 15.05 | 14.44 | 14.44 | 31.19 | 31.36 | 33.33 | 27.65 | 27.82 | 30.64 |
| Christchurch | 6.34 | 6.44 | 6.43 | 31.08 | 31.86 | 31.82 | 39.89 | 40.68 | 40.18 |
| Timaru | 5.38 | 5.89 | 6.18 | 34.87 | 35.51 | 33.55 | 40.21 | 43.09 | 37.44 |
| Invercargill | 4.53 | 4.69 | 4.76 | 23.27 | 23.25 | 24.46 | 32.86 | 35.53 | 33.62 |
| Totals | 6.48 | 6.59 | 6.62 | 30.28 | 30.88 | 31.26 | 37.84 | 38.60 | 38.04 |
Systems Comprising Combined Trolley-bus and Motor-bus Services - New Plymouth has operated a service of this type since disposing of electric trams in July 1954, Dunedin since the cessation of electric trams in March 1957, and Auckland since December 1956.
Route Milage - Lengths of routes in use at 31 March 1960 are given below.
| Service | Trolley-bus Routes | Motor-bus Routes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | ch | m | ch | |
| Auckland | 66 | 35 | 75 | 11 |
| New Plymouth | 3 | 29 | 19 | 39 |
| Dunedin | 25 | 20 | 42 | 35 |
The following tables set out details of the operations of these authorities during the last three years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Vehicles | Seating Capacity | Number of Miles Run | Total Passengers Carried | Passengers per Mile Run | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trolley Buses | Motor Buses | Trolley Buses | Motor Buses | Trolley Buses | Motor Buses | |||
| Auckland | ||||||||
| 1958 | 101 | 265 | 4,391 | 11,145 | 2,783,621 | 5,705,488 | 54,598,872 | 6.43 |
| 1959 | 115 | 249 | 4,895 | 10,694 | 2,745,050 | 5,537,893 | 53,473,481 | 6.46 |
| 1960 | 133 | 243 | 5,727 | 10,508 | 3,537,138 | 4,767,379 | 53,374,000 | 6.43 |
| New Plymouth | ||||||||
| 1958 | 4 | 17 | 168 | 647 | 85,355 | 421,310 | 3,231,324 | 6.38 |
| 1959 | 4 | 17 | 168 | 681 | 86,281 | 430,618 | 3,312,636 | 6.41 |
| 1960 | 4 | 17 | 168 | 681 | 87,142 | 449,905 | 3,415,381 | 6.36 |
| Dunedin | ||||||||
| 1958 | 72 | 44 | 2,880 | 1,475 | 1,635,845 | 975,502 | 20,456,260 | 7.83 |
| 1959 | 74 | 37 | 2,960 | 1,243 | 1,603,864 | 769,478 | 18,792,336 | 7.92 |
| 1960 | 75 | 40 | 3,000 | 1,377 | 1,464,439 | 776,481 | 18,555,949 | 8.28 |
| Totals | ||||||||
| 1958 | 177 | 326 | 7,439 | 13,267 | 4,504,821 | 7,102,300 | 78,286,456 | 6.74 |
| 1959 | 193 | 303 | 8,023 | 12,618 | 4,435,195 | 6,737,989 | 75,578,453 | 6.76 |
| 1960 | 212 | 300 | 8,895 | 12,566 | 5,088,719 | 5,993,765 | 75,345,330 | 6.80 |
| Year Ended 31 March | Revenue | Average Fare per Passenger | Revenue per Mile Run | Expenditure | Expenditure per Mile Run | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger Fares | Total (Including “Other”) | Operating Expenses | Capital Charges | Total (Including “Other”) | ||||
| £ | £ | d. | d. | £ | £ | £ | d. | |
| Auckland | ||||||||
| 1958 | 1,645,689 | 1,677,178 | 7.23 | 47.42 | 1,417,734 | 289,124 | 1,824,796 | 51.59 |
| 1959 | 1,655,303 | 1,677,707 | 7.43 | 48.61 | 1,364,598 | 308,437 | 1,773,921 | 51.40 |
| 1960 | 1,664,566 | 1,686,719 | 7.48 | 48.75 | 1,386,956 | 311,286 | 1,755,758 | 50.74 |
| New Plymouth | ||||||||
| 1958 | 61,046 | 66,567 | 4.54 | 31.53 | 69,299 | 77,587 | 36.75 | |
| 1959 | 63,904 | 65,568 | 4.63 | 30.44 | 64,598 | 72,923 | 33.86 | |
| 1960 | 65,476 | 69,397 | 4.60 | 31.01 | 73,076 | 81,207 | 36.29 | |
| Dunedin | ||||||||
| 1958 | 392,793 | 399,972 | 4.61 | 36.76 | 411,769 | 58,892 | 534,885 | 49.16 |
| 1959 | 410,001 | 417,685 | 5.24 | 42.24 | 377,982 | 53,188 | 487,094 | 49.26 |
| 1960 | 401,414 | 415,459 | 5.19 | 44.50 | 369,379 | 52,432 | 468,012 | 50.12 |
| Totals | ||||||||
| 1958 | 2,099,528 | 2,143,717 | 6.44 | 44.33 | 1,898,802 | 348,016 | 2,437,268 | 50.40 |
| 1959 | 2,129,208 | 2,160,960 | 6.76 | 46.42 | 1,807,178 | 361,625 | 2,333,938 | 50.13 |
| 1960 | 2,131,456 | 2,171,575 | 6.79 | 47.01 | 1,829,411 | 363,718 | 2,304,977 | 49.92 |
Systems Comprising Combined Electric Tramways, Trolley-bus and Motor-bus Services - Wellington has now the only electric tramway in New Zealand, and also the only cable tram service which runs from the centre of the city to Kelburn. Electric tramways reached the peak of milage of track in use in 1929 when 170 miles of line were operated by the various local authorities. A steady decline in the milage of track in use took place until 1950 when 158 miles of line were used. From that year onwards the change has been more rapid. At the same time there has been a steady expansion in the milage of the trolley-bus routes and a more rapid growth of motor-bus routes.
In Wellington there were at 31 March 1960, 15 miles 79 chains of tram route, 21 miles 16 chains of trolley-bus route, and 57 miles 18 chains of motor-bus route being operated.
The following is a summary of the operations of this service. Details cover the combined tramway, trolley-bus and motor-bus service in Wellington.
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| Passengers carried | No. | 37,203,399 | 37,563,073 | 37,101,174 |
| Passengers per mile run | No. | 9.33 | 8.55 | 8.29 |
| Passenger fares | £ | 863,129 | 871,271 | 967,727 |
| Average fare per passenger | d. | 5.57 | 5.57 | 6.26 |
| Total revenue | £ | 887,329 | 895,039 | 990,831 |
| Revenue per mile run | d. | 53.38 | 48.87 | 53.11 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 997,901 | 1,069,129 | 1,108,802 |
| Expenditure per mile run | d. | 60.04 | 58.38 | 59.43 |
| Number of vehicles - | ||||
| Tramcars and trailers | No. | 105 | 89 | 89 |
| Trolley buses | No. | 48 | 69 | 69 |
| Motor buses | No. | 106 | 112 | 112 |
| Seating capacity - | ||||
| Tramcars and trailers | No. | 3,583 | 3,077 | 3,077 |
| Trolley buses | No. | 2,016 | 2,898 | 2,898 |
| Motor buses | No. | 4,115 | 4,305 | 4,305 |
| Miles run - | ||||
| Tramcars and trailers | No. | 2,079,671 | 1,355,971 | 1,352,021 |
| Trolley buses | No. | 884,424 | 1,315,812 | 1,317,205 |
| Motor buses | No. | 1,025,149 | 1,723,294 | 1,808,492 |
The following is a summary of the operations of all local authority transport undertakings.
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passengers carried | No. | 143,261,343 | 141,240,977 | 141,223,041 |
| Miles run | No. | 21,697,325 | 21,690,367 | 21,798,156 |
| Average passengers per mile run | No. | 6.60 | 6.51 | 6.48 |
| Passenger fares | £ | 3,712,922 | 3,772,556 | 3,893,025 |
| Average fare per passenger | d. | 6.22 | 6.41 | 6.62 |
| Revenue | £ | 3,800,698 | 3,843,731 | 3,974,841 |
| Revenue per mile run | d. | 42.04 | 42.53 | 43.76 |
| Expenditure | £ | 4,397,161 | 4,387,662 | 4,402,565 |
| Expenditure per mile run | d. | 48.64 | 48.55 | 48.47 |
ADMINISTRATION - Civil aviation in New Zealand is administered by the Civil Aviation Administration of Air Department. The Air Department was constituted by the Air Department Act of 1937. Prior to that date the control of civil aviation, like its military counterpart, was vested in the Defence Department. The Civil Aviation Act of 1948 provides for the position of Director of Civil Aviation.
The organisational structure of the Civil Aviation Administration consists of a Directorate Staff, three technical divisions - viz, Operations, Airworthiness, and Airways - and an Administration Division. Principal functions of the four divisions include:
Examining and licensing of flight crews and aircraft maintenance engineers.
Operation of the airways communication and air traffic control systems.
The surveying of, and issuing certificates of airworthiness for, civil aircraft.
Collaboration with the Ministry of Works on airport projects.
Licensing of aerodromes.
The provision and maintenance of radio aids to air navigation.
Operational certification of commercial aircraft operators.
Dissemination of aeronautical and general aviation information.
Liaison with the Royal New Zealand Air Force on matters of common interest and with overseas organisations, particularly the International Civil Aviation Organisation.
FACILITIES PROVIDED - Various facilities for air navigation are provided by the Civil Aviation Administration. Radio navigational aids of different kinds are installed at the more important airfields in New Zealand and in the south-west Pacific, as well as en route aids at various points along the internal airways.
In addition, the Civil Aviation Administration has a number of aeradio stations in New Zealand providing air to ground, ground to air, and ground point-to-point communication facilities, plus communication centres located at Auckland, Christchurch, and Wellington.
The air traffic control system comprises control towers situated at the important aerodromes with area control centres situated at Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch. In addition, communication facilities are provided at aerodromes in the Cook Islands, Fiji, and Western Samoa. In Fiji an air traffic control service is also maintained by the Civil Aviation Administration.
As already mentioned, the Civil Aviation Administration is responsible for collaborating with the Ministry of Works on airport planning, with the Ministry undertaking the actual construction and maintenance. At the larger airports in New Zealand and in the south-west Pacific crash/fire facilities are provided by the Civil Aviation Administration.
The Civil Aviation Charges Regulations 1954 prescribe the rates of dues payable by operators for the use of airways and airport facilities provided or maintained by the Crown. Different rates are prescribed in respect of international and domestic operators, and a distinction is made in respect of air transport and other domestic operations. No charges, other than those prescribed by regulations, are to be made for the use of aerodromes or connected facilities without the approval of the Minister in Charge of Civil Aviation.
The administration of Raoul Island in the Kermadec Group and Campbell Island, on which weather-reporting stations arc located, is another responsibility of the Civil Aviation Administration.
GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE - The net Government expenditure on civil aviation in New Zealand and its island territories in 1959–60 was £2,174,743, compared with £2,563,155 in 1958–59.
Prior to 1 April 1957 New Zealand, as administering authority for the South Pacific Air Transport Council, provided for the establishment and maintenance costs of the International Airport at Nandi, Fiji. Approximately two-thirds of this expenditure was recoverable from other member Governments. From 1 April 1957, under revised accounting arrangements, the major member Governments (United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand) now make advance payments to a Pool Trust Account from which all costs are met. New Zealand now meets one-fifth of the cost and is no longer required to provide the initial finance.
AIR SERVICES LICENSING - Licensing of air services in New Zealand is vested in the Air Services Licensing Authority which was constituted by the Air Services Licensing Act of 1951. This Authority consists of one chairman and three members appointed by the Crown, and its principal functions are to hear and determine applications for the granting, renewal, or transfer of air service licences. An air service (including aerial topdressing) may not be commenced or carried on without a licence granted under the Act except that any aero club affiliated to the Royal New Zealand Aero Club (Inc.) may carry club members in club-owned or hired aircraft without such a licence.
For the year 1959–60, 50 applications were received in respect of air service licences, and the following table shows the decisions of the Authority.
| Category | Decision by Authority | Total Applications Received | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Licence Issued | Temporary Licence Issued | Existing Licence Amended | Application Declined | Application Withdrawn or Adjourned | ||
| Topdressing | 2 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 28 |
| Scheduled services | 1 | - | 2 | - | 1 | 4 |
| Non-scheduled services | 4 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 18 |
| Totals | 7 | 5 | 22 | 4 | 12 | 50 |
Provision also is made in the Air Services Licensing Act for the appointment of an Appeal Authority of one member. During the year no appeals were lodged against any of the Authority's decisions.
NEW ZEALAND NATIONAL AIRWAYS CORPORATION - The operation of the internal air services is no longer under the complete control of the National Airways Corporation, as provision was made for other operators to run services under the Air Services Licensing Act 1951 previously mentioned. However, the bulk of the internal scheduled services are still operated by the Corporation. Information concerning the establishment of the National Airways Corporation and its duties and functions may be found on pages 329–330 of the 1951–52 Yearbook.
The Corporation's operating revenue figures for the year ended 31 March 1960, together with those for the two preceding years, are as follows.
| 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Passenger fares | 2,679,693 | 2,944,269 | 3,500,575 |
| Excess baggage | 32,855 | 33,807 | 37,646 |
| Freight | 442,277 | 454,800 | 528,171 |
| 129,096 | 130,956 | 140,645 | |
| Charters | 63,151 | 62,737 | 65,606 |
| Incidental revenue | 62,692 | 70,869 | 75,966 |
| Totals | 3,409,764 | 3,697,438 | 4,348,609 |
Operating expenditure in 1959–60 totalled £4,185,636 (including depreciation on equipment), as compared with £3,480,694 in 1958–59 and £3,174,694 in 1957–58.
An operating profit of £162,637 for the year 1959–60 was recorded and, after adding interest on investments, deducting interest on capital loans, and allowing £44,716 as provision for taxation, a net profit of £23,179 remained. The corresponding net profit for 1958–59 was £60,976.
FLYING OPERATIONS: Domestic Scheduled Services - Scheduled air transport operations over specific routes were first commenced in New Zealand in December 1934, on the route Inch-bonnie - Hokitika - Franz Josef Glacier, on the West Coast of the South Island. Subsequent extensions of services up to the outbreak of war in September 1939 had covered almost the whole of New Zealand. During 1946 and 1947 the New Zealand National Airways Corporation absorbed all then existing scheduled commercial services, and by adding to the fleet of aircraft was able to commence new services.
In February 1953 a scheduled service between Christchurch and Oamaru via Ashburton and Timaru was commenced by South Island Airways Ltd., followed by a Christchurch to Nelson service during 1954. In April 1956 these services were taken over by a new company, Trans Island Airways Ltd. The Christchurch-Oamaru service ceased in June 1957 and the Christchurch-Nelson service ceased in March 1959. Bay of Plenty Airways Ltd. came into existence in July 1958, taking over the non-scheduled operations of Tauranga Air Services Ltd. Bay of Plenty Airways now operate the scheduled services set out below. Their Wellington service commenced in September 1959.
At 30 September 1960 domestic scheduled services were being operated on the following routes:
| Terminating Points of Routes | Intermediate Stops | Route Miles | Scheduled Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand National Airways Corporation | |||
| Weekday Services | |||
| Auckland-Christchurch | Wellington | 505 | 3 return flights daily and 1 flight north daily |
| Auckland-Christchurch | Nil | 479 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Wellington | Nil | 284 | 1 return flight daily |
| Wellington-Christchurch | NIL | 218 | 1 return flight daily and 1 flight north |
| Wellington-Dunedin | Nil | 386 | 2 return flights daily |
| Christchurch-Dunedin | Timaru | 202 | 1 return flight daily |
| Christchurch-Dunedin | Nil | 198 | 3 return flights daily and 1 flight north |
| Christchurch-Invercargill | Dunedin | 305 | 2 south flights daily |
| Invercargill-Dunedin | Nil | 107 | 1 return flight daily and 1 flight north |
| Invercargill-Christchurch | Nil | 289 | 1 flight north daily |
| Auckland-Wellington | Tauranga, Gisborne, Napier, Palmerston North | 483 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Wellington | Gisborne, Napier | 443 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Napier | Nil | 222 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland - Palmerston North | New Plymouth | 280 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Wellington | New Plymouth | 298 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Whangarei | Nil | 72 | 3 return flights daily, plus 2 return flights weekly |
| Auckland-Kaitaia | Kaikohe | 142 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland - Palmerston North | Nil | 251 | 1 return flight daily |
| Palmerston North - Wellington | Nil | 83 | 1 return flight daily |
| Christchurch-Wellington | Blenheim | 201 | 1 return flight daily |
| Auckland-Wellington | Hamilton, Palmerston North | 309 | 1 return flight daily |
| Hamilton-Wellington | Nil | 243 | 2 return flights daily |
| Christchurch - Palmerston North | Nil | 270 | 1 return flight daily |
| Wellington-Blenheim | Nil | 72 | 4 return flights daily |
| Wellington-Nelson | Nil | 96 | 7 return flights daily |
| Nelson-Westport | Nil | 95 | 1 return flight daily |
| Westport-Hokitika | Nil | 75 | 3 return flights weekly |
| Freight Services | |||
| Wellington-Christchurch | Nil | 218 | 3 return flights daily |
| Christchurch-Auckland | Wellington, Palmerston North, New Plymouth, Hamilton | 607 | 6 return flights weekly and others as required |
| Auckland-Christchurch | Gisborne, Napier, Wellington | 661 | 6 return flights weekly and others as required |
| Christchurch-Dunedin | Nil | 198 | 3 return flights weekly and others as required |
| Sunday Services | |||
| Auckland-Christchurch | Wellington | 505 | 3 return flights |
| Auckland-Christchurch | Nil | 479 | 1 return flight |
| Auckland-Wellington | Nil | 284 | 1 return flight |
| Wellington-Christchurch | Nil | 218 | 2 return flights |
| Wellington-Dunedin | Christchurch | 388 | 1 flight south |
| Christchurch-Dunedin | Nil | 198 | 1 return flight and 1 flight north |
| Christchurch-Invercargill | Dunedin | 305 | 1 return flight |
| Wellington-Blenheim | Nil | 72 | 3 return flights |
| Wellington-Nelson | Nil | 96 | 3 return flights |
| Auckland-Wellington | Tauranga, Gisborne, Napier | 478 | 1 return flight |
| Auckland-Wellington | New Plymouth, Palmerston North | 280 | 1 return flight |
| Wellington-Hamilton | Nil | 243 | 1 return flight |
| West Coast, Airways Ltd. | |||
| Hokitika-Haast | Franz Josef, Fox, as required | 125 | 5 return flights weekly |
| Straits Air Freight Express Ltd. | |||
| Wellington-Nelson (freight) | Nil | 96 | Daily as required |
| Wellington-Blenheim (freight) | Nil | 72 | |
| Bay of Plenty Airways Ltd. | |||
| Auckland-Tauranga | Nil | 104 | 9 return flights weekly |
| Auckland-Rotorua | Tauranga | 136 | 1 return flight daily and 1 flight south daily |
| Auckland-Rotorua | Nil | 125 | 1 flight north daily |
| Tauranga-Wellington | Rotorua | 235 | 3 return flights weekly |
| Tauranga-Rotorua | Nil | 32 | 1 flight south daily |
| Tauranga-Whakatane | Nil | 48 | 1 return flight daily |
The following table gives the summarised results of the operations of scheduled commercial air services during the last 10 years. Statistics for the New Zealand Railways Freight Service, operated by Straits Air Freight Express Ltd. since 1 April 1951, are excluded.
| Year Ended 31 March | Hours Flown | Miles Flown (000) | Passengers | Freight lb (000)* | Mail lb (000) | Passenger-miles (000) | Freight Ton-miles† (000) | Mail Ton-miles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes excess baggage. † Includes excess baggage ton-miles. | ||||||||
| 1951 | 34,066 | 4,369 | 238,405 | 5,724 | 917 | 59,745 | 659 | 175,923 |
| 1952 | 37,191 | 4,818 | 303,048 | 10,881 | 1,782 | 78,352 | 1,351 | 238,507 |
| 1953 | 37,049 | 4,740 | 312,309 | 7,835 | 1,124 | 79,512 | 1,010 | 146,457 |
| 1954 | 44,047 | 5,504 | 369,408 | 10,491 | 1,740 | 89,957 | 1,366 | 174,132 |
| 1955 | 46,946 | 5,831 | 387,365 | 15,595 | 1,024 | 93,890 | 1,977 | 183,686 |
| 1956 | 49,572 | 6,276 | 428,494 | 19,070 | 1,157 | 104,402 | 2,397 | 218,878 |
| 1957 | 53,016 | 6,815 | 476,779 | 19,017 | 1,229 | 118,659 | 2,419 | 250,218 |
| 1958 | 54,309 | 7,107 | 513,694 | 20,854 | 1,757 | 130,266 | 2,811 | 277,286 |
| 1959 | 55,356 | 7,481 | 556,545 | 21,329 | 1,808 | 146,392 | 2,990 | 278,639 |
| 1960 | 54,776 | 7,614 | 650,812 | 22,492 | 1,993 | 169,936 | 3,165 | 312,656 |
Aircraft used in the operation of services on these routes were:
| Aero Commander 680 | 1 |
| Bristol 170 | 4 |
| Cessna 180 | 1 |
| DH 89 Dominie | 4 |
| Douglas DC 3 | 22 |
| Douglas DC 3 (Freighter) | 4 |
| Vickers Viscount 807 | 3 |
| Total | 39 |
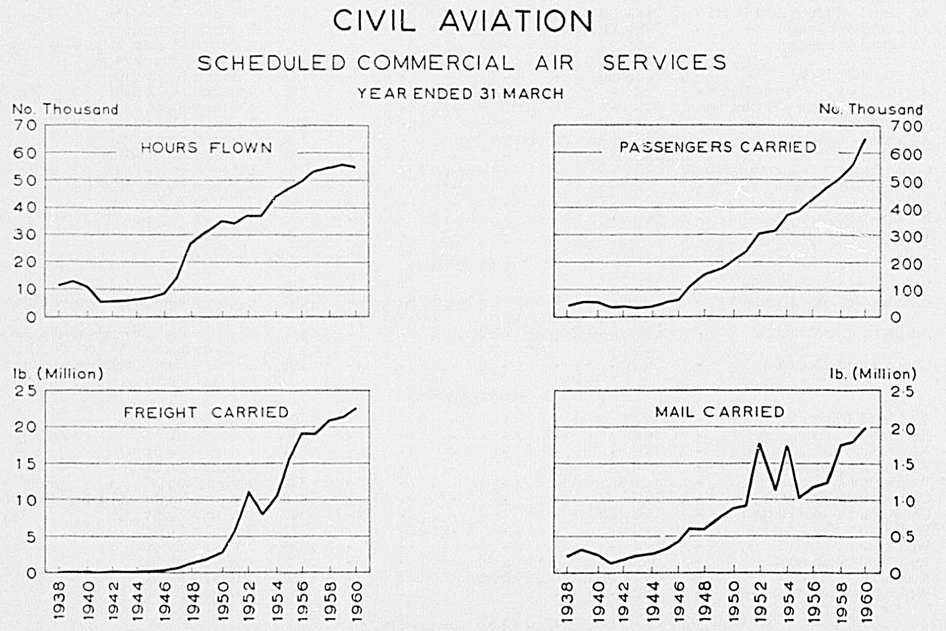
Cook Strait Rail/Air Freight Service - The New Zealand Railways Air Freight Service was commenced officially in February of 1947 following a number of special inter-island freight flights which had been carried out by the Royal New Zealand Air Force at the request of the Railways Department to meet a shipping emergency. With the introduction of the Cook Strait Rail/Air Freight Services, delays caused by lack of shipping space and industrial troubles were somewhat alleviated. The service was conducted by the RNZAF, operating Dakota aircraft, until June 1947, when the service was handed over to the New Zealand National Airways Corporation, which continued to operate with Dakotas.
In 1950 the Railways Department decided to allow private enterprise the opportunity of tendering for the contract to run the service, and the successful tenderer was Straits Air Freight Express Ltd., which took over on 1 April 1951. The service is at present being maintained by four Bristol Freighter aircraft on a daily basis, the number of trips varying according to the amount of cargo offering.
In recent years increasing numbers of passengers and motor vehicles have been carried on the car-ferry service operated by the company between Wellington on the one hand and Blenheim and Nelson on the other.
Traffic statistics for this freight service for the years 1950 to 1960 are as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Trips Flown | Hours Flown | Miles Flown | Freight lb (000) | Freight Ton-miles (000) | Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 3,018 | 1,949 | 232,042 | 21,790 | 746 | |
| 1951 | 4,297 | 2,781 | 320,514 | 31,293 | 1,046 | |
| 1952 | 4,541 | 2,461 | 335,714 | 49,671 | 1,644 | |
| 1953 | 2,913 | 1,412 | 213,459 | 33,879 | 1,106 | 113 |
| 1954 | 3,937 | 1,954 | 293,892 | 40,498 | 1,360 | 598 |
| 1955 | 4,885 | 2,487 | 364,076 | 50,145 | 1,668 | 858 |
| 1956 | 5,411 | 2,683 | 398,547 | 53,914 | 1,780 | 986 |
| 1957 | 6,107 | 3,033 | 453,912 | 54,364 | 1,797 | 1,308 |
| 1958 | 7,415 | 3,826 | 554,688 | 67,857 | 2,240 | 1,660 |
| 1959 | 8,563 | 4,365 | 642,666 | 76,280 | 2,527 | 1,437 |
| 1960 | 9,509 | 4,465 | 628,113 | 87,612 | 2,566 | 1,225 |
Non-scheduled Air Services - At 31 March 1960, 22 companies and 18 aero clubs were providing timetable, charter, taxi, scenic, and joyriding services. The RNZAF, using Sunderland flying boats, flew 11 flights to the Chatham Islands during the year. The following is a traffic summary of these services for the years ended 31 March 1959 and 31 March 1960.
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Companies | Aero Clubs | Total | Commercial Companies | Aero Clubs | Total | |
| Number of flights | 13,288 | 5,399 | 18,687 | 16,363 | 5,216 | 21,579 |
| Hours flown | 8,573 | 3,508 | 12,081 | 9,577 | 3,493 | 13,070 |
| Miles flown | 1,020,603 | 375,201 | 1,395,804 | 1,120,310 | 360,569 | 1,480,879 |
| Passengers carried | 30,518 | 9,993 | 40,511 | 39,770 | 10,562 | 50,332 |
| Freight carried (tons) | 4,607 | 28 | 4,635 | 3,670 | 27 | 3,697 |
Aerial Work Operations - The Royal New Zealand Air Force undertook extensive trials in the dropping of fertiliser from the air in 1948 at the request of the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council, which was interested in aerial topdressing as a means of improving hill pastures and checking and preventing soil erosion. The RNZAF experiments were successful and as a result the interest of the farming community was aroused and private firms began commercially operating in 1949.
The industry grew rapidly and is now an accepted feature of the national economy. More than half the fertiliser sown in the country is applied from the air and, in the year ended 30 September 1960, more than half a million tons of fertiliser was distributed in this way.
Aerial application of insecticides and weedkillers has developed rapidly during the last five years and over one and a half million gallons of spray was distributed by air in the year ended 31 March 1960.
Other aerial works include photography, seed sowing, and the dropping of rabbit and opossum poison, supplies, and fencing materials.
Progress of agricultural aviation in this country was shown at an International Agricultural Aviation Show held at Palmerston North in November 1956. This was the first show of its kind in the world and some 200 aircraft demonstrated the aerial farming techniques developed in New Zealand. It is possible that a similar show will be held in 1962.
At Wanganui in May 1959 an Agricultural Aviation Symposium was convened under the auspices of Civil Aviation Administration. The emphasis was on aerial spraying and the papers presented were of interest to both the aviation industry and to the farming community.
In June 1960 Civil Aviation Administration introduced the Chemical Rating, a technical qualification which is now mandatory for pilots engaged in the application of all agricultural chemicals except fertilisers. Many agricultural chemicals are highly toxic and the Chemical Rating ensures that pilots are familiar with their properties and the correct application techniques.
A summary of aerial work operations for the year ended 31 March 1960 follows:
| Topdressing - | |
| Hours flown | 60,228 |
| Fertiliser distributed (tons) | 474,528 |
| Area treated (acres) | 3,960,906 |
| Seed sowing - | |
| Hours flown | 985 |
| Seed sown (tons) | 755 |
| Area treated (acres) | 85,954 |
| Rabbit poisoning - | |
| Hours flown | 2,999 |
| Bait distributed (tons) | 4,387 |
| Fencing materials - | |
| Hours flown | 225 |
| Materials dropped (tons) | 538 |
| Spraying - | |
| Hours flown | 3,992 |
| Weedkiller and insecticide distributed (gallons) | 1,556,422 |
| Aerial photography and survey - | |
| Hours flown | 991 |
| Supply dropping - | |
| Hours flown | 248 |
| Materials dropped (tons) | 163 |
| Miscellaneous - | |
| Hours flown | 1,219 |
| Materials dropped (tons) | 450 |
| Number of aerial-work operators | 64 |
| Number of aerial-work aircraft owned | 248 |
International Services - In March-April 1954 broad proposals for the reorganisation of the Pacific air services were announced. Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. became owned equally by the New Zealand and Australian Governments, and was re-equipped with DC 6 pressurised land planes previously operated by British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines. The company's aircraft are based in New Zealand.
The services formerly carried out by British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines between Australia and North America were taken over by Australia and integrated with the Kangaroo services now operated by Qantas Empire Airways, which continues in partnership with British Overseas Airways Corporation on the Kangaroo route; New Zealand withdrew from the British Commonwealth Pacific Airlines, which was then wound up.
Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. - An air service from Australia to New Zealand across the Tasman Sea is the last stage of an air route from the United Kingdom to New Zealand. The first survey of this route was undertaken by Imperial Airways Ltd., of London, in 1937. Subsequently a company known as Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. was formed to operate a proposed trans-Tasman air service. The share capital was subscribed by the Governments of the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand, the share proportions being 20, 30, and 50 per cent respectively. Later it became equally owned by Australia and New Zealand, and then wholly by New Zealand from 1 April 1961.
On 30 April 1940 the Auckland-Sydney service commenced. In June 1950 the company took over from New Zealand National Airways Corporation the Auckland-Suva service. The Wellington-Sydney service was inaugurated on 3 October 1950 and the Christchurch-Melbourne service on 28 June 1951. With the withdrawal of the Short Solent flying boats from the trans-Tasman routes, the Wellington-Sydney service was discontinued in June 1954 and a new service from Christchurch to Sydney using the Douglas DC 6s was commenced in the following month. The same type of aircraft were also employed on the Auckland-Fiji route as from June 1954.
The first of the Lockheed Electra aircraft was brought into use on the trans-Tasman service in December 1959, and by March 1960 all TEAL services between Australia, New Zealand, and Fiji had been converted to Electras. A Melbourne-Auckland-Nandi service is carried out with Super Constellation aircraft chartered from Qantas Empire Airways. Recently two additional trans-Tasman services have been added to the TEAL trans-Tasman network. Auckland-Brisbane are now linked with a direct service on a seasonal basis, and Wellington-Sydney are now linked with a direct service using the new airport at Wellington as the eastern terminal.
The Coral Route to Tahiti via Suva and Aitutaki was inaugurated in December 1951 with a frequency of one return trip monthly. This was increased to one return trip fortnightly in May 1952. In October 1952 Apia in Western Samoa was added to the route, and in August 1953 a service to Tonga was inaugurated. This Suva-Tonga service was discontinued in June 1957. TEAL changed from flying boats to land planes on its Coral Route services late in 1960. Initially DC 6s and then, from March 1961, jet-prop Lockheed Electras have flown direct from Nandi in Fiji to Faa'a Airport at Papeete, Tahiti. The service to Norfolk Island, formerly conducted by the New Zealand National Airways Corporation, was taken over by Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. from 1 November 1955. Aircraft used are DC 4s chartered from Qantas Empire Airways Ltd.
The following routes were operating at 30 October 1960.
| Route No. | Route | Route Miles | Scheduled Frequency Up to: |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Auckland-Sydney | 1,333 | 8 return flights weekly |
| 2 | Auckland-Brisbane | 1,410 | 1 return flight weekly |
| 3 | Auckland-Melbourne | 1,665 | 2 return flights weekly |
| 4 | Auckland-Nandi | 1,326 | 5 return flights weekly |
| 5 | Auckland - Norfolk Island | 660 | 2 return flights monthly |
| 6 | Wellington-Sydney | 1,385 | 7 return flights weekly |
| 7 | Christchurch-Sydney | 1,325 | 3 return flights weekly |
| 8 | Christchurch-Melbourne | 1,516 | 1 return flight weekly |
| 9 | Christchurch-Nandi (via Auckland) | 1,803 | 1 return flight weekly |
| 10 | Nandi-Papeete (Tahiti) | 2,180 | 1 return flight weekly |
Revenue traffic statistics for the years ended 31 March 1959 and 31 March 1960 are given below.
| Item | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|
| Hours flown | 9,958 | 10,228 |
| Miles flown | 2,464,516 | 2,688,991 |
| Passengers | 69,721 | 83,435 |
| Passenger-miles | 94,826,738 | 114,104,286 |
| Available seat-miles | 125,550,140 | 150,871,651 |
| Passenger load factor (per cent) | 75.53 | 75.63 |
| Cargo - (lb) | ||
| Freight | 925,921 | 1,386,637 |
| Excess baggage | 110,370 | 116,993 |
| 908,634 | 1,050,985 | |
| Ton-miles flown - | ||
| Passenger | 8,632,678 | 11,550,876 |
| Excess baggage | 66,881 | 80,236 |
| Freight | 554,308 | 932,500 |
| 534,125 | 692,867 | |
| Total ton-miles | 9,787,992 | 13,256,479 |
| Available capacity ton-miles | 13,965,992 | 19,848,340 |
| Overall load factor (per cent) | 70.08 | 66.79 |
The following is a summary of traffic statistics for Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. for the latest five years, and includes services flown by other airlines under charter to the company.
| Year Ended 31 March | Hours Flown | Miles Flown (000) | Passengers | Freight* lb (000) | Mail lb (000) | Passenger-miles (000) | Freight Ton-miles† (000) | Mail Ton-miles (000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes excess baggage. †Includes excess baggage ton-miles. | ||||||||
| 1956 | 7,716 | 1,852 | 49,389 | 1,016 | 796 | 66,247 | 599 | 475 |
| 1957 | 8,396 | 2,044 | 62,168 | 1,131 | 843 | 83,609 | 659 | 506 |
| 1958 | 8,712 | 2,103 | 61,903 | 1,184 | 922 | 83,687 | 706 | 554 |
| 1959 | 9,958 | 2,465 | 69,721 | 1,036 | 909 | 94,827 | 621 | 534 |
| 1960 | 10,228 | 2,689 | 83,435 | 1,504 | 1,051 | 114,104 | 1,013 | 667 |
Pan American World Airways, Inc. - The service between San Francisco and Auckland via Honolulu, Kingman Reef, and Pago Pago was commenced by Pan American Airways after a survey flight from Honolulu to Auckland in December 1937, but was discontinued in December 1941 after the outbreak of hostilities with Japan.
This organisation recommenced services in the Pacific on 6 June 1946 over the route Auckland - San Francisco (via Fiji, Canton Island, and Honolulu). Aircraft employed at present between Auckland and Fiji are Boeing Stratocruisers, while Boeing 707s are used on the remainder of the route. The frequency is two return trips weekly.
Canadian Pacific Air Lines - Under the terms of the Air Transport Agreement of 1950 between New Zealand and Canada, Canadian Pacific Air Lines was selected as the Canadian airline to operate across the Pacific to New Zealand. The service was commenced in January 1952. The route at present followed is Vancouver - Honolulu - Nandi (Fiji) - Auckland. Canadian Pacific Air Lines use Douglas DC 6B aircraft on the route. The frequency is one return trip weekly.
Transports Aériens Intercontinentaux - This French company, operating DC 6B aircraft, commenced on 5 February 1957 a weekly service linking Noumea in the French Territory of New Caledonia with Auckland on a route beginning in Paris and serving Athens, Karachi, Saigon, Darwin, and Brisbane.
Total Traffic Statistics for Overseas Airlines (CPAL, PAWA, and TAI). - Total traffic statistics for Canadian Pacific Air Lines, Pan American World Airways, and Transports Aériens Inter-continentaux to and from New Zealand for the year ended 31 March 1960 are given below, together with the total for 1958–59.
| Year Ended March 1960 | Total 1959–60 | Total 1958–59 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPAL | PAWA | TAI | |||
| Traffic entering New Zealand - | |||||
| Passengers | 1,368 | 1,830 | 808 | 4,006 | 4,913 |
| Freight (lb) | 72,950 | 148,015 | 21,194 | 242,159 | 273,373 |
| Mail (lb) | 14,953 | 55,480 | 3,250 | 73,683 | 97,251 |
| Traffic leaving New Zealand - | |||||
| Passengers | 1,110 | 1,495 | 790 | 3,395 | 4,288 |
| Freight (lb) | 14,655 | 127,551 | 15,121 | 157,327 | 191,618 |
| Mail (lb) | 6,816 | 8,662 | 2,221 | 17,699 | 23,076 |
Entrances and Clearances of Aircraft in the Overseas Trade - The following figures supplied by the Customs Department give the number of aircraft entering New Zealand classified by the countries from which they arrived, and aircraft departing by the countries to which they departed, during the calendar years 1959 and 1960. Air freight carried is also shown for the same years.
| Country from Which Arrived or to Which Departed | Entrances | Clearances | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Air Freight (lb) | Number | Air Freight (lb) | |||||
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| United Kingdom | 1 | 1 | 1,060 | 42 | - | - | - | - |
| Hong Kong | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Canada | 53 | 64 | 63,296 | 121,869 | 53 | 59 | 19,187 | 13,695 |
| Enderbury - | ||||||||
| Canton Islands | 1 | - | 2,786 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fiji | 169 | 211 | 122,885 | 181,313 | 170 | 221 | 96,622 | 102,969 |
| Norfolk Island | 21 | 29 | 7,300 | 10,544 | 28 | 27 | 34,981 | 37,202 |
| Australia | 786 | 895 | 729,965 | 1,276,875 | 762 | 904 | 256,241 | 699,143 |
| Papua | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - |
| Czechoslovakia | 1 | - | 10,138 | - | - | - | - | - |
| France | 51 | 53 | 16,936 | 16,789 | 51 | 53 | 18,115 | 18,020 |
| Netherlands | 1 | 4 | - | 35 | - | 3 | - | - |
| United States of America | 116 | 94 | 176,319 | 154,326 | 118 | 89 | 131,878 | 124,229 |
| Totals | 1,200 | 1,352 | 1,130,685 | 1,761,793 | 1,183 | 1,356 | 557,024 | 995,258 |
AERO CLUBS - Practical interest in aviation was greatly stimulated by the first trans-Tasman flight of Kingsford-Smith and Ulm in 1928, and to this flight the aero-club movement largely owes its inception. The steady progress made by the movement has been in a great measure due to the scheme initiated by the Government of subsidising a limited number of light aeroplane clubs.
As from 1 April 1955 a new scheme of financial assistance to aero clubs has been in operation. This scheme was reviewed in 1957 and again in 1960 and now operates as follows: A student pilot can qualify for his private pilot licence at a cost of between £40 and £60 compared with a previous cost of between £80 and £120. In respect of pilots trained and qualifying for a private pilot licence, the Government refunds to the pilot himself one-half of the cost of the training up to an assessed standard rate of £3 per hour, with a maximum of £60. The club receives a subsidy of one-twelfth of the cost of training with a maximum of £10. In addition a payment of 2s. an hour flown on training and solo hire is made to clubs. During the year ended 31 March 1960 financial assistance to aero clubs and to pilots amounted to £23,640, compared with £37,276 in the previous year. At March 1960 there were 34 aero clubs affiliated to the Royal New Zealand Aero Club.
The next table gives a summary of the training activities of aero clubs for the latest five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Clubs Operating | Membership | Aircraft in Use | Hours Flown | Ab Initio Pupils Under Training | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associate | Flying | Dual | Solo | ||||
| 1956 | 26 | 3,196 | 3,362 | 108 | 9,095 | 20,864 | 894 |
| 1957 | 33 | 3,240 | 3,368 | 105 | 11,338 | 27,309 | 863 |
| 1958 | 35 | 3,369 | 3,758 | 109 | 10,769 | 30,497 | 720 |
| 1959 | 36 | 3,556 | 4,006 | 108 | 10,365 | 29,355 | 734 |
| 1960 | 36 | 3,518 | 4,107 | 106 | 11,490 | 27,713 | 844 |
LICENCES - A summary of licences and certificates current at 31 March 1960 is given below.
| Flight Crew (ICAO) Type | Number at 31 March 1960 |
|---|---|
| Pilot licences - | |
| Student Pilot | 1,029 |
| Private Pilot | 1,302 |
| Commercial Pilot | 490 |
| Airline Transport Pilot | 165 |
| Pilot Licence Ratings - | |
| Instructor | 179 |
| Instrument | 262 |
| Navigator Licences - | |
| Flight Navigator | 38 |
| Licences to Operate Radio Equipment in Aircraft - | |
| Flight Radio Operator | 8 |
| Flight Radiotelephone Operator | 931 |
| Flight Engineer Licences - | |
| Flight Engineer | 18 |
| Other Licences, Certificates, etc. - | |
| Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licences | 304 |
| Aircraft - | |
| Certificates of Registration | 654 |
| Certificates of Airworthiness | 605 |
| Aerodromes - | |
| Public Licences | 40 |
| Air Service Certificates | 43 |
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTORY - Post Office history in New Zealand began in 1831 when the Postmaster-General for New South Wales commissioned a resident of Kororareka in the Bay of Islands to make up and receive mails.
With the arrival of Governor Hobson in 1840 the first post office proper was set up at Kororareka (now Russell). The same year saw the establishment of offices at other settlements in the north and at Port Nicholson (Wellington), and the beginnings of overland mail routes.
By 1858 seventy-three post offices had been opened to provide communications services for the scattered settlers. In that year a Post Office Act was passed making the Post Office an independent Department of State. The Post Office had previously operated under the control of the Customs Department.
The system of communication by telegraph was inaugurated in the 1860s. A separate Department, the Telegraph Department, was created by Act of Parliament in 1865 to take the responsibility for erecting telegraph lines, the opening of morse telegraph offices, and the laying and maintaining of lines of communication under Cook Strait to connect the telegraph lines of the North and South Islands. This Act vested the control of communication by electric telegraph in the new Department.
During 1881 the first New Zealand telephone exchanges were opened at Christchurch and Auckland. An amendment to the Electric Telegraph Act of 1875 had been passed in September 1880 extending the power of the Government, through the Telegraph Department, to control all electric communication by telephone and making it unlawful for any but the approved authority to establish telephone lines without express permission.
The telegraph and postal services were amalgamated at the beginning of 1881. The Postmaster-General became Minister of Telegraphs, and the Post and Telegraph Department was created to replace the two previous authorities. Under the Post Office Act 1959, which came into operation on 1 January 1960, the name of the Department became the Post Office, and the Minister's title became Postmaster-General.
Through its control of electric communications the Post Office has extended its functions to include communications by radio. In addition to administering New Zealand's radio regulations, the Post Office transmitting and receiving stations bring New Zealand into the world radio communications network. The overseas radiotelephone service was inaugurated with the Australian link in 1930 and since then New Zealand has extended its radiotelephone communication to most countries in the world. A further development in radio communication brought a radio-photograph service with Australia and the United Kingdom in 1947.
POSTAL BUSINESS - At 31 March 1960 there were 1,440 post offices in New Zealand. In addition, there were 202 offices at which telephone business only was transacted.
The following table shows the numbers of articles posted in the latest five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Letters, Lettercards, and Postcards | Accounts, Circulars, Newspapers, Packets, etc. | Parcels | Total Articles Posted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| million | ||||
| 1956 | 187.5 | 213.7 | 6.8 | 408.0 |
| 1957 | 192.0 | 213.4 | 7.0 | 412.4 |
| 1958 | 202.3 | 229.4 | 6.9 | 438.6 |
| 1959 | 204.7 | 234.6 | 7.2 | 446.4 |
| 1960 | 210.3 | 246.6 | 7.4 | 464.3 |
Compared with the year ended 31 March 1959, letters, lettercards, and postcards posted during the year ended 31 March 1960 showed an increase of 5.6 million (2.7 per cent); and accounts, circulars, etc., an increase of 120 million (5.1 per cent). Parcel postings increased by 201,019 during the year.
The average numbers of letters, etc., posted in New Zealand per head of population during the year ended 31 March 1960 were: letters, lettercards, and postcards, 87.6; accounts, circulars, newspapers, packets, etc., 102.7; parcels, 3.1.
During the 1959–60 year, 663,543 lb of letters and 197,827 parcels were posted by inland air mails, and 247,844 lb of letters, 83,145 lb of newspapers and packets, etc., and 37,473 lb of parcels were posted by overseas air mail.
RURAL MAIL DELIVERY - The rural delivery system enables country residents to obtain postal notes, money orders, and stamps, to register correspondence, and to collect or post their mail in boxes at or near their gates. The deliveries are generally performed by contractors who handle the mail in conjunction with the carriage of goods, and thus the rural-mail delivery is in many areas the medium by which residents obtain their newspapers, bread, parcels, etc. The growth of this scheme can be gauged from the following figures: 1921, 8,700; 1940, 32,382; 1947, 40,689; and in March 1960, 71,880 boxholders.
AIR MAILS: Inland - On 16 March 1936 the first regular air-mail services linking up larger centres of population were established between Palmerston North and Dunedin, and between Nelson, Blenheim, and Wellington. As air services increased in frequency and extent the air-mail facilities were correspondingly expanded. The present network extends from Kaitaia to Invercargill.
From 1 September 1955 the rate of postage for inland air-mail correspondence has been 4d. for the first half-ounce and 2d. each additional half-ounce. For parcels up to 28 lb the rates range from 2s. 6d. to 15s.
The numbers of letters and parcels carried by air in New Zealand during the latest 11 years are shown hereunder.
| Year Ended 31 March | Letters | Parcels |
|---|---|---|
| *Abnormal increase due to interruption of surface connections owing to industrial dispute. | ||
| 1950 | 13,839,600 | 91,226 |
| 1951 | 14,206,000 | 99,575 |
| 1952 | 19,089,800* | 217,726* |
| 1953 | 14,577,960 | 150,680 |
| 1954 | 14,590,360 | 151,222 |
| 1955 | 18,981,400 | 168,521 |
| 1956 | 20,676,560 | 167,486 |
| 1957 | 22,357,000 | 161,599 |
| 1958 | 24,596,000 | 184,185 |
| 1959 | 24,592,000 | 185,100 |
| 1960 | 26,542,000 | 197,827 |
Overseas:Trans-Tasman Air Services - The first flight of the regular trans-Tasman service linking Auckland and Sydney took place on 30 April 1940, connection being made at Sydney with the Empire service to London. The existing service provides for flights from New Zealand (Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch) and Australia (Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane) with a frequency overall of at least one flight each day.
New Zealand - United Kingdom Air Service - This service is now operating daily between Sydney and London, the transit time New Zealand to the United Kingdom being normally three to five days.
Trans-Pacific Services - The trans-Pacific service operating between New Zealand and North America commenced on 20 July 1940. Air lines now operate six trips each week to San Francisco, and there is also a service between Auckland and Vancouver.
Regional Pacific Services - Services from New Zealand to Norfolk Island, Fiji, Tonga, Samoa, and the Cook Islands operated by the RNZAF in the immediate post-war period were placed under the control of the National Airways Corporation on 1 November 1947. Tasman Empire Airways subsequently took over the Auckland-Fiji service on 6 November 1950, and on 27 December 1951 extended this service to Aitutaki (Cook Islands) and Papeete (French Polynesia). On 14 October 1952 Tasman Empire Airways replaced the National Airways Corporation services to Apia (Samoa). From 1 March 1955 Tasman Empire Airways took over the service to Norfolk Island, thus finally replacing the National Airways Corporation overseas services to the Pacific and controlling all New Zealand operated overseas flights.
New Zealand - France Service - On 8 February 1957 a service New Zealand - France was commenced by a French airline. In 1960 the service was rerouted France - New Caledonia - Fiji - French Polynesia. A connection between New Caledonia and New Zealand is provided by a feeder service between Noumea and Auckland.
OVERSEAS PARCEL POST - Particulars of overseas parcels received and dispatched in each of the latest five years are contained in the following table.
| Year | Overseas Parcels Received | Overseas Parcels Dispatched | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Weight | Customs Duty | Number | Weight | |
| lb | £ | lb | |||
| 1956 | 479,841 | 4,318,569 | 1,082,136 | 147,165 | 1,144,636 |
| 1957 | 447,471 | 4,027,239 | 890,545 | 146,607 | 1,136,428 |
| 1958 | 464,700 | 4,182,300 | 812,495 | 158,700 | 1,428,300 |
| 1959 | 399,500 | 3,595,000 | 582,875 | 156,100 | 1,404,900 |
| 1960 | 410,456 | 3,694,100 | 492,388 | 160,797 | 1,447,200 |
NEWSPAPERS - In March 1960 there were 310 publications on the Post Office Register of Newspapers. Of these 44 are published daily, 12 being morning papers and 32 evening papers. Nine appear three times per week, 18 twice per week, 70 weekly, 26 fortnightly, 141 monthly, and two at irregular intervals; many of these are magazines rather than newspapers as popularly understood.
MONEY ORDER AND POSTAL NOTE SERVICES - Details of these services are now given.
Money Orders - New Zealand has reciprocal money-order agreements with all British Commonwealth countries and also with the United States of America, the Republic of Ireland, and Tonga. Money orders may also be issued in New Zealand for payment in any other country with which the United Kingdom has exchanges of money orders.
For payment within New Zealand the maximum amount for a single order is £100, but there is no limit to the amount which may be remitted. The commission is computed on each individual order. Commission on inland money orders is 7d. for the first £10 and 3d. for each additional £5 or part thereof. A money order may be transmitted by telegraph for the additional telegraph charge of 1s. 9d.
For money orders issued for payment overseas there is a limit for most countries of £40 for a single order, but for some countries the limit is £10. There are two special rates of commission, one rate applying to Australia (and countries advised through Australia), Fiji, Norfolk Island, and Tonga, and the other rate to all other countries.
During 1959, 1,403,933 money orders were issued in New Zealand for a total of £24,043,789, and of that total 53,562 orders of a value of £277,542 were issued for payment overseas. Money orders issued overseas for payment in New Zealand in 1959 numbered 22,819 and totalled in value £134,872.
The analysis of the overseas money-order business for 1959 is now given.
| Country of Issue or Payment | Orders Issued in New Zealand for Payment Overseas | Orders Issued Overseas for Payment in New Zealand | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | Number | Value | |
| *No service to New Zealand. | ||||
| £ | £ | |||
| United Kingdom | 22,895 | 179,271 | 5,502 | 55,712 |
| United Stales of America | 880 | 2,664 | 1,319 | 8,051 |
| Australia | 26,055 | 51,456 | 11,331 | 31,598 |
| Canada | 257 | 1,660 | 1,463 | 6,384 |
| Ceylon | 8 | 66 | 13 | 8 |
| Republic of Ireland | 1,000 | 10,950 | 110 | 878 |
| Fiji | 792 | 17,172 | 1,366 | 5,471 |
| Hong Kong | 74 | 794 | 8 | 23 |
| India | 907 | 7,864 | * | * |
| Norfolk Island | 68 | 129 | 68 | 480 |
| Tonga | 36 | 344 | 1,340 | 23,821 |
| Pakistan | 306 | 2,575 | * | * |
| South Africa | 284 | 2,597 | 299 | 2,446 |
| Totals | 53,562 | 277,542 | 22,819 | 134,872 |
The following table gives particulars of all money orders issued and paid during each of the years specified. The figures include overseas money-order business which is given in the preceding table.
| Year Ended 31 December | Number of Offices at End of Year | Money Orders Issued | Money Orders Paid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | Commission | Number | Value | ||
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1955 | 985 | 1,336,541 | 25,460,852 | 49,725 | 1,269,972 | 25,116,062 |
| 1956 | 991 | 1,382,633 | 26,300,387 | 51,847 | 1,325,579 | 26,061,638 |
| 1957 | 998 | 1,339,267 | 24,906,959 | 53,300 | 1,292,701 | 24,775,472 |
| 1958 | 1,020 | 1,352,509 | 25,039,096 | 54,461 | 1,316,277 | 24,897,000 |
| 1959 | 1,035 | 1,403,933 | 24,043,789 | 55,537 | 1,365,990 | 23,742,422 |
Postal Notes - Postal notes in 40 denominations ranging from 1s. to £1 and for £2 are issued in New Zealand for payment within New Zealand, Niue, the Cook Islands, and Western Samoa. The poundage payable is as follows: 1s. to 2s. 6d., 2d.; 3s. to 7s. 6d., 3d.; 8s. to 15s., 4d.; 15s. 6d. to £1, 5d.; and for £2, 6d.
Postal notes are negotiable, and their period of validity is unlimited. They are, therefore, a popular medium for making small inland remittances by post, and during the year ended 31 March 1960, 2,368,774 postal notes valued at £1,336,728 were purchased by the public.
Information regarding the issue and payment of postal notes is given below.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Offices at End of Year | Postal Notes Issued | Postal Notes Paid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value* | Commission | Number | Value | ||
| *Value figures are inclusive of commission shown in next column. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1956 | 1,115 | 2,333,998 | 1,122,645 | 35,871 | 2,322,736 | 1,086,215 |
| 1957 | 1,112 | 2,230,381 | 1,071,954 | 35,502 | 2,215,707 | 1,071,953 |
| 1958 | 1,114 | 2,175,775 | 1,135,580 | 37,569 | 2,208,930 | 1,132,981 |
| 1959 | 1,133 | 2,239,901 | 1,230,201 | 40,496 | 2,254,615 | 1,230,201 |
| 1960 | 1,152 | 2,368,774 | 1,336,728 | 44,005 | 2,378,976 | 1,323,481 |
British Postal Orders - These are both issued and paid in New Zealand. Denominations sold in this country are 6d., 1s., 1s. 6d., 2s., 2s. 6d., 3s., 5s., 10s., 15s., and 20s. The commission payable ranges from 2d. to 6d.
As these orders are payable in several British Commonwealth countries they are a popular medium for making small postal remittances to overseas countries, particularly the United Kingdom.
During the year ended 31 March 1960 the Post Office sold 912,590 British postal orders valued at £415,528, and paid 79,324 orders valued at £100,016.
POST OFFICE SAVINGS BANK - Details on the Post Office Savings Bank are given in Section 29. Banking and Currency.
TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE SERVICES - Up to 31 March 1960 a total sum of £67,819,432 had been expended on telegraph construction, including the construction of telephone exchanges. The amount expended during the financial year 1959–60 was £6,063,821.
Details of telegraph and telephone services for each of the last five financial years are now given.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Paid Telegrams and Toll Messages Forwarded During the Year | Revenue (Including Miscellaneous Receipts) | Total Value of Business | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telegraph and Toll | Telephone Exchange | |||
| million | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 44.7 | 5,314,651 | 6,538,800 | 11,853,451 |
| 1957 | 47.0 | 5,694,972 | 7,217,107 | 12,912,079 |
| 1958 | 50.0 | 6,205,858 | 8,166,093 | 14,371,951 |
| 1959 | 51.7 | 6,410,312 | 8,769,039 | 15,179,351 |
| 1960 | 55.5 | 6,951,096 | 9,780,109 | 16,731,205 |
The number of telegrams forwarded in 1959–60 was 8.0 million, while the number of toll communications at 47.5 million showed an increase of 3.6 million.
The charge for ordinary telegrams on weekdays is 1s. 2d. for six words or less, and 1d. for each additional word. The charge for letter-telegrams, which are delivered by post on the morning following the day of lodgment, is a flat rate of 1s. 6d. for 22 words, and 1d. for each additional two words. On Sundays and departmental holidays the rate for ordinary telegrams is 1s. 9d. for six words or less, and 1 1/2d. for each additional word, the total charge being taken to the next penny where necessary. An additional charge of 9d. is made for an urgent telegram, irrespective of the number of words contained in the message.
The delivery of telegrams, especially in the larger cities, continues to have its problems because of the difficulties in the recruitment of staff for this work. To meet these difficulties the telephoning of telegrams was resorted to some years ago. The system provides also for the phoning in of telegrams for dispatch. Approximately 50 per cent of telegrams are now handled by telephone.
Machine-printing telegraphs operating at 45 words per minute were introduced on 5 December 1921. In 1929 a teleprinter circuit, working at a speed of 66 words per minute, commenced operation.
The first voice-frequency telegraph system - of three high-speed channels between Wellington and Christchurch - was installed in 1938. Since then a network embracing all the larger provincial towns has been developed. At 31 March 1960 there were 690 channels and more are to be provided in the near future.
A leased teleprinter service for business organisations was begun in 1953. There are now 75 organisations leasing 40,743 miles of telegraph circuit. Annual revenue from this source is £230,000.
Until 1951 daily newspapers received their outside news over the public telegraph system but in that year their national organisation leased an extensive teleprinter network so that the news could be transmitted direct from Wellington into the various newspaper offices. Newspapers participating in this arrangement number 37.
TELEPHONE-EXCHANGE SERVICE - At 31 March 1960 there were 493 telephone exchanges in New Zealand serving a total of 686,021 connections. Of these exchanges 300 were manually operated, serving 196,793 connections, or 29 per cent of the total, and 193 were automatic, serving 489,228 connections, or 71 per cent of the total.
The following table indicates the growth of the New Zealand telephone-exchange service (the figures are as at 31 March of each year shown).
| 952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Represents separate instruments connected to main telephone system. | |||||||||
| Exchanges | 371 | 381 | 397 | 405 | 411 | 440 | 459 | 478 | 493 |
| Subscribers' main stations | 285,171 | 307,453 | 330,825 | 359,674 | 386,732 | 409,740 | 434,804 | 459,869 | 491,773 |
| Service stations | 3,533 | 3,596 | 3,755 | 3,687 | 3,713 | 3,858 | 3,948 | 4,073 | 4,281 |
| Toll stations | 1,719 | 1,691 | 1,659 | 1,633 | 1,605 | 1,567 | 1,531 | 1,507 | 1,490 |
| Public call stations | 2,085 | 2,223 | 2,341 | 2,450 | 2,545 | 2,675 | 2,803 | 2,912 | 3,058 |
| Extension stations | 98,239 | 106,591 | 114,193 | 125,463 | 136,658 | 147,872 | 159,646 | 170,777 | 183,399 |
| Private telephone lines | 3,819 | 3,632 | 3,516 | 3,386 | 3,248 | 2,627 | 2,492 | 2,204 | 2,020 |
| Totals* | 394,566 | 425,186 | 456,289 | 496,293 | 534,501 | 568,339 | 605,224 | 641,342 | 686,021 |
| Number installed during year | 26,536 | 33,560 | 36,155 | 42,738 | 41,011 | 40,152 | 43,744 | 45,366 | 53,603 |
| Number of waiting applicants | 58,348 | 54,946 | 43,303 | 33,344 | 33,862 | 35,330 | 34,501 | 32,087 | 28,711 |
The total number of telephone stations shows an increase of 291,455, or 74 per cent, during the period covered by the table, the net gain for each of the last five years being 38,208, 33,838, 36,885, 36,118, and 44,679 respectively. The increase in subscribers' main stations during the same period amounted to 206,602, or approximately 72 per cent, while extension stations show an increase of 85,160, or almost 87 per cent.
The “party” line system of telephone service is extensively used, particularly by those whose premises are situated at a distance from an exchange. In March 1960 the number of “party” lines was 54,610, serving a total of 181,068 stations.
According to the latest comparative data available (January 1959), compiled by the Chief Statistician of the American Telephone and Telegraph Co., New Zealand ranks fifth in the number of telephones per 100 of population, the leading countries being the United States of America (37.97), Sweden (34.00), Canada (29.64), Switzerland (28.31), New Zealand (27.57), and Denmark (21.53).
The first public call stations (coin-in-the-slot telephones) erected in New Zealand were installed at Wellington in August 1910, and 1,564 such instruments were in use at 31 March 1960. The revenue from local calls from slot telephones during the year ended 31 March 1960 was £171,448. In addition, there were 1,494 multi-coin slot telephones in use, the first of which was installed at Christchurch in October 1938. These instruments take penny, sixpenny, and shilling coins, and are used for effecting both local and toll calls and for telegrams.
The capital expenditure on the equipment, etc., of the telephone exchanges up to 31 March 1960 was £57,783,206.
The following table shows the classification of telephone exchanges and the annual rental rates for different classes of connection.
| Class of Exchange | Class of Connection | Annual Rate Within Base-rate Area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business | Residential | ||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Special (Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin) | Individual | 29 | 10 | 0 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
| 2-party | 22 | 15 | 0 | 13 | 2 | 6 | |
| 3-party | 20 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 5 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 17 | 10 | 0 | 11 | 10 | 0 | |
| Class I (Over 3,000 subscribers) (Typical exchanges are Gisborne, Hamilton, Napier, New Plymouth, and Invercargill) | Individual | 23 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 10 | 0 |
| 2-party | 17 | 12 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 0 | |
| 3-party | 16 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 15 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 0 | |
| 5-party | 12 | 5 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 6 | |
| 6–10 party | 11 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 6 | |
| Class II (2,001 to 3,000 subscribers) (Typical exchanges are Levin and Greymouth) | Individual | 19 | 17 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 0 |
| 2-party | 15 | 17 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 0 | |
| 3-party | 14 | 12 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 13 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 0 | |
| 5-party | 11 | 5 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 | |
| 6–10 party | 10 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 6 | |
| Class III (1,001 to 2,000 subscribers) (Typical exchanges are Taumarunui, Marton, and Waimate) | Individual | 18 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 2-party | 15 | 5 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 0 | |
| 3-party | 14 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 15 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 12 | 15 | 0 | 9 | 5 | 0 | |
| 5-party | 10 | 17 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 6 | |
| 6–10 party | 10 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 0 | |
| Class IV (201 to 1,000 subscribers with continuous attendance) (Typical exchanges are Piopio, Waipawa, Waverley, and Picton) | Individual | 17 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| 2-party | 14 | 15 | 0 | 9 | 15 | 0 | |
| 3-party | 13 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 5 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 12 | 5 | 0 | 8 | 15 | 0 | |
| 5-party | 10 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 15 | 0 | |
| 6–10 party | 9 | 17 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 0 | |
| Class V (Up to 1,000 subscribers with restricted attendance and automatic exchanges with less than 200 subscribers) (Typical exchanges are Kawhia, Te Akau, and Waitotara) | Individual | 14 | 12 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| 2-party | 12 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 10 | 0 | |
| 3-party | 11 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4-party | 10 | 17 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 0 | |
| 5-party | 9 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 6 | |
| 6–10 party | 8 | 12 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 6 | |
For stations located outside the boundary of the base-rate area of an exchange a milage rate is added to the general base-rate-area rental, depending on the distance by line measurement from the base-rate boundary to the respective subscriber's station. Rural line telephone service is provided at all exchanges except those in the special class. This service provides for a minimum of five subscribers and a maximum of 10 subscribers on any one line. In general, subscribers connected on rural lines reside beyond the boundary of the base-rate area.
TOLL SERVICE - Toll rates for distances up to 30 miles range from 4d. to 10d. for each three minutes or fraction. They are the same day and night. For distances over 30 miles, the rates range from 1s. 4d. to a maximum of 7s. 9d. for three minutes' conversation. These rates are increased by approximately one-third of the relative initial rate for each minute exceeding three. Between 6 p.m. and 8 a.m. on weekdays, and between midnight and 6 a.m. on Sundays and departmental holidays, the rates for calls over 40 miles are reduced and vary from 1s. 6d. to 5s. 10d. for three minutes' conversation, with a proportionate increase for each additional minute.
The charge for an urgent call is double the rate for an ordinary call.
OVERSEAS CABLE SERVICES - Telegraphic communication overseas was first established between New Zealand and Australia by means of the Eastern Extension Telegraph Company's cable from Wakapuaka (Nelson) to Sydney in 1876, this cable being duplicated in 1890. Subsequent developments were the opening in 1902 of the Pacific cable between Auckland and Canada via Norfolk Island, Suva, and Fanning Island, with a connection linking Norfolk Island to Brisbane; the laying of a cable direct between Auckland and Sydney in 1912; shifting of terminals from Wakapuaka to Wellington in 1917; laying a cable direct between Auckland and Suva in 1923, and duplicating the Suva-Canada cable in 1927. In 1929 a merger of British cable and wireless companies resulted in the overseas cable services being brought under the control of one authority (the private company of Cable and Wireless Ltd., with headquarters in London), following which one cable between Wellington and Sydney was abandoned, part of it being lifted for reuse, and the route of the other was altered to terminate at Auckland instead of Wellington. One of the two direct Auckland-Sydney cables later became faulty and has not been repaired, leaving only one direct cable link between Auckland and Sydney. Following upon a conference of representatives of Commonwealth Governments (including New Zealand) held in London in 1945, the Commonwealth's external telecommunications systems were brought under Government control and, in accordance with the Commonwealth Telegraphs Agreement 1948, the New Zealand Post Office purchased the assets of Cable and Wireless Ltd., in New Zealand, and took over the operation of the overseas cable services.
RADIO COMMUNICATION: Government Stations - The first wireless-telegraph station in New Zealand for communicating with ships at sea was opened at Wellington on 26 July 1911.
An event of major importance in the development of New Zealand's external telecommunication services was the opening of the Himatangi radio transmitting station in November 1953 thus providing for direct New Zealand - United Kingdom radiotelephone and radiotelegraph circuits. The receiving station complementary to the Himatangi transmitting station is Makara Radio.
The principal stations under the control of the New Zealand Government are at Awarua, Wellington, and Auckland on the New Zealand mainland, at Rarotonga and Niue in the Cook Islands, and at the Chatham Islands. Smaller stations are established at certain lighthouses on the New Zealand coast and also on a number of adjacent islands. Marine radio beacons are operated at the lighthouses at Cape Reinga, Cuvier Island, Mokohinau Island, East Cape, Portland Island, Stephens Island, Baring Head, Cape Campbell, The Brothers, Godley Head, Taiaroa Head, Dog Island, and Puysegur Point.
Communication is effected with outer islands in the Cook Group by Rarotonga Radio through small feeder stations at Aitutaki, Atiu, Mangaia, Manihiki, Manuae, Mauke, Mitiaro, Nassau, Palmerston, Penrhyn, Pukapuka, and Rakahanga. Small stations at Aleipata, Atafu, Fagamalo, Mulifanua, Sataua, Satupaitea, Fakaofo, Nukunono, Salailua, and Tuasivi communicate with Apia Radio. Niue communicates with Apia Radio, Rarotonga Radio, and Wellington Radio.
By means of the radio stations at Wellington, Apia, Rarotonga, and Niue, communication is maintained between New Zealand and the Pacific islands, the last three stations mentioned having direct communication with New Zealand. Direct communication is also available with Chatham Islands, Papeete (Tahiti), Nukualofa (Tonga), Noumea (New Caledonia), London, Sydney, and San Francisco.
Particulars of the radio business, exclusive of free (service) messages, transacted by the New Zealand coast stations during the latest five years are given in the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Forwarded | Received | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Messages | Words | Post Office Revenue | Messages | Words | Post Office Revenue | |
| £ | £ | |||||
| 1956 | 46,067 | 923,467 | 11,240 | 101,160 | 1,976,964 | 17,980 |
| 1957 | 45,725 | 960,197 | 12,016 | 102,175 | 2,033,231 | 20,820 |
| 1958 | 47,909 | 1,042,200 | 14,340 | 108,339 | 2,528,411 | 24,826 |
| 1959 | 47,970 | 1,007,849 | 13,801 | 108,144 | 2,400,230 | 24,937 |
| 1960 | 50,210 | 1,128,235 | 14,544 | 111,411 | 2,493,748 | 26,140 |
Facilities exist for the dispatch of radiotelegrams to vessels at sea, and special rates operate for vessels registered in New Zealand and Australia.
Other Radio Services - Telephone communication by radio is now available to 66 countries, as well as to Ross Dependency (Scott Base), Raoul Island, Chatham Islands, Campbell Island, and H.M. New Zealand and Australian warships in New Zealand waters and in the Tasman Sea. There has also been a remarkable expansion of the Post Office very-high-frequency radiotelephone service for mobile units first introduced in 1948. It is now operating in 22 centres for a total of 3,891 mobile units. Ambulance services, fire boards, traffic officers, taxi companies, veterinary services, and motor-transport companies are the principle users of the service. Radiotelephone services continue to provide essential service for isolated communities which cannot reasonably be reached by landline - e.g., isolated settlers, alpine huts, etc. There is also a free radio-medical service for ships at sea and for lighthouses on the New Zealand coast for use in emergency cases.
Private Stations - Private radio stations are governed by the New Zealand Radio Regulations 1953.
The licences for broadcast receiving stations (i.e., ordinary radio licences) authorise reception from broadcasting stations, and may be obtained at any savings bank office on payment of the prescribed fee. Further reference to these licences will be found in Section 12B, Radio and Television Broadcasting.
Licences for amateur stations are intended to provide facilities for experimental transmission to those interested in radio science, and are issued only to holders of amateur operators' certificates.
Eight radio firms and four educational institutions have been given authority to conduct experimental television transmissions for the purposes of studying the techniques involved and for investigating equipment developments in this new field of radio.
RECEIPTS AND PAYMENTS - The receipts and payments of the Post Office for the latest three financial years are now shown.
| Receipts | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Net figure - i.e., receipts less payments. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Postages | 5,710,964 | 5,980,016 | 6,157,058 |
| Money-order and postal-note commission | 89,490 | 92,754 | 98,249 |
| Private box and bag rents and rural-delivery fees | 147,086 | 139,688 | 170,300 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 2,930,203 | 2,945,504 | 3,236,449 |
| Telegrams | 988,307 | 970,075 | 990,532 |
| Tolls | 5,000,188 | 5,164,313 | 5,620,236 |
| Telephone-exchange rentals | 7,500,636 | 7,718,941 | 8,580,652 |
| Overseas telecommunications | 373,903* | 358,915* | 367,912* |
| Totals | £22,740,777 | £23,370,206 | £25,221,388 |
| Payments | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Salaries | 10,857,279 | 10,929,797 | 11,794,103 |
| Conveyance of mails by sea and air | 924,968 | 860,964 | 997,205 |
| Conveyance of mails by road | 578,905 | 627,976 | 669,349 |
| Conveyance of mails by railway | 367,097 | 365,217 | 372,759 |
| Maintenance and renewal of telecommunication system | 1,190,897 | 1,069,881 | 1,107,722 |
| Motor services and workshops | 1,237,456 | 1,200,965 | 1,190,348 |
| Miscellaneous | 5,400,965 | 5,504,523 | 5,843,398 |
| Interest on capital liability | 2,179,694 | 2,436,094 | 2,654,487 |
| Sick-benefit Fund | 29,189 | 37,308 | 34,894 |
| Post Office buildings | 438,808 | 480,133 | 577,492 |
| Superannuation Fund subsidy | 312,250 | 345,000 | 402,750 |
| 23,517,508 | 23,857,858 | 25,644,507 | |
| Less transfers to Vote - Telegraph Extension | 2,095,431 | 2,194,175 | 2,174,527 |
| Totals | £21,422,077 | £21,663,683 | £23,469,980 |
Receipts and payments for the latest 11 years are shown by the following figures:
| Year Ended 31 March | Receipts £ | Payments £ |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 9,647,950 | 10,491,851 |
| 1956 | 19,071,222 | 17,228,465 |
| 1951 | 11,324,137 | 11,186,126 |
| 1957 | 20,545,530 | 19,293,577 |
| 1952 | 13,081,276 | 13,850,574 |
| 1958 | 22,740,777 | 21,422,077 |
| 1953 | 13,705,433 | 14,766,186 |
| 1959 | 23,370,206 | 21,663,683 |
| 1954 | 15,991,908 | 15,578,311 |
| 1960 | 25,221,388 | 23,469,980 |
| 1955 | 17,995,308 | 16,252,648 |
WORK PERFORMED FOR OTHER DEPARTMENTS - In addition to its natural functions, the Post Office performs a large amount of work for other Government Departments, its widespread organisation being of inestimable value in this respect. Among the principal activities in this connection are the receipt and payment of moneys on behalf of the various Departments, the more important of which are enumerated below.
Receipts - For the following Departments: Social Security (arrears of social security charge on income), Agriculture (inspection fees, etc.), Education (child-welfare receipts and examination fees, etc.), Health, Inland Revenue (land tax and income tax, including social security income tax under PAYE system), Lands and Survey, National Roads Board (special milage tax on motor vehicles), Public Trust Office, State Advances Corporation (State rents, loan and interest repayments), Electricity (Southland, Waimea, and Buller electric-power receipts), Transport, Tourist and Publicity (Mamaku, Atiamuri, Reporoa, and Ngongotaha power receipts), Valuation, New Zealand Broadcasting Service (radio licence fees and subscriptions to New Zealand Listener), Customs (collection of Customs duty and sales tax), Treasury (Government Superannuation and National Provident Fund receipts).
Payments - Departments of Social Security (social security benefits and war pensions, etc.), Health (refunds of medical expenses), Army, Air, Education (boarding-out orders), Labour (subsidised wage payments and military training medical examination payments), Maori Affairs (Maori trust payments), National Roads Board (refunds of duty on motor spirits), Public Trust Office, Police (witness warrants), Treasury (Government Superannuation payments and miscellaneous payments for other Departments), Ministry of Works, and for Reserve Bank (interest warrants and coupons).
Other services performed by the Post Office are the control of the licensing of, and the issue of licences in respect of, motor vehicles and radio apparatus, provision of advice and service on radio matters to the Marine Department and the Civil Aviation Administration of the Air Department, and provision of a fleet of motor vehicles in the larger centres for hire by other Departments. In some of the smaller centres postmasters act as Registrars of Births, Deaths, and Marriages, Registrars of Electors, and agents for the State Advances Corporation.
Other activities, not strictly departmental, include the receipt of motor vehicles insurance (third-party risks) premiums under the Transport Act 1949, the issue of fishing and game licences on behalf of acclimatisation societies, organising and collecting investments in respect of national savings, organising and selling health stamps, and collecting revenue for such outside bodies as the New Zealand Poultry Board, the New Zealand Trade Certification Board, and the Armed Forces Canteen Council.
STAFF - The large volume and varied nature of the business of the Post Office entails the employment of a large staff. The Department is administered by the Postmaster-General, with the Director-General as executive head. The staff at 31 March 1960 was as follows: Permanent, 17,635, temporary, 5,690, non-classified, 390, total, 23,715. In addition there were 814 country postmasters and telephonists who acted as such in conjunction with other pursuits and did not rank as officers of the Department. There were also 39 officers of the Railways Department who acted as postmasters.
VEHICLES - The Post Office fleet consists of 2,567 vehicles - 1,880 trucks and vans, 679 cars, and eight motor scooters. Of this fleet, 371 vehicles are used for hire to other Departments, 1,675 for engineering construction work, and 521 on postal, telegram delivery, and other general work.
NEW ZEALAND BROADCASTING SERVICE - The Broadcasting Act of 1936 established the National Broadcasting Service as from 1 July 1936, and vested its control in a Minister of the Crown. All property, rights, liabilities, and engagements of the pre-existing controlling authority (the New Zealand Broadcasting Board) were transferred to the Crown. The administration of the National Broadcasting Service was placed in the hands of a Director of Broadcasting, appointed by the Governor-General in Council. Permanent officers in the employ of the board became officers of the Public Service as from 1 July 1936.
The Broadcasting Act 1936 also authorised the Minister of Broadcasting to establish and operate commercial broadcasting stations from which advertising matter might be broadcast. For every locality that is served by a commercial station the Minister is required to provide an alternative service from at least one non-commercial station. This obligation does not apply in respect of television stations.
The Broadcasting Amendment Act 1937 made legislative provision for the establishment of a National Commercial Broadcasting Service. The administration of the Commercial Service, which in 1938 operated five stations, was placed in the hands of a Controller. Thus in 1938 there were two separate broadcasting organisations in New Zealand - the National Broadcasting Service under a Director, and the National Commercial Broadcasting Service under a Controller. This provision was repealed by section 4 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1943, the position of Controller was abolished, and from 26 August 1943 the two services were combined under a Director of Broadcasting. The Commercial Service was thus absorbed into the National Broadcasting Service.
In 1946 the title of the Department was changed to the New Zealand Broadcasting Service to give effect to the complete amalgamation of the two pre-existing authorities, which had in fact commenced prior to 1943 with the amalgamation of all technical resources under a Chief Engineer. Thus since 1946 there has been only one broadcasting organisation, the New Zealand Broadcasting Service, controlling commercial and non-commercial broadcasting in New Zealand.
The Broadcasting Amendment Act 1960 provided for the establishment of a television service to be operated by the Minister in Charge of Broadcasting in association with the existing broadcasting service. Provision is made for the appointment of a Director of Television.
Stations and Programmes - On 31 March 1961 there were in New Zealand 34 medium-wave broadcasting stations and two short-wave transmitters of Radio New Zealand, the latter with 19 assigned frequencies. Two of the medium-wave stations (2XM and 4XD), are privately owned and operated with the assistance of a subsidy from the Broadcasting Account. Of those controlled by the New Zealand Broadcasting Service, nine are full-time national advertising stations, marked “(a)” in the following list, six are local stations carrying advertising for a maximum of 14 hours daily, listed as “(b)”, and four stations, marked “(c)”, are local stations carrying a limited number of advertisements each day. No advertising material is given on Sundays. The complete list of medium-wave stations follows.
MEDIUM-WAVE STATIONS
| Call Sign and Location of Studio | Radiated Power | Frequency | Normal Hours of Transmission per Week | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Operates during period when 2YA is broadcasting proceedings of the House of Representatives. | ||||
| kilowatts | kilocycles | h | min | |
| 1XN, Whangarei (b) | 2.00 | 970 | 113 | 30 |
| 1YA, Auckland | 10.00 | 760 | 121 | 20 |
| 1YC, Auckland | 10.00 | 880 | 42 | 0 |
| 1ZB, Auckland (a) | 10.00 | 1,070 | 126 | 0 |
| 1YD, Auckland (c) | 2.50 | 1,250 | 48 | 0 |
| 1XH, Hamilton (a) | 2.00 | 1,310 | 123 | 30 |
| 1ZD, Tauranga (a) | 10.00 | 1,000 | 35 | 0 |
| 1YZ, Rotorua | 10.00 | 800 | 108 | 30 |
| 1ZC, Rotorua (c) | 0.50 | 1,520 | 59 | 0 |
| 2XG, Gisborne (b) | 2.00 | 1,010 | 113 | 30 |
| 2XM, Gisborne | 0.09 | 1,180 | 16 | 30 |
| 2XP, New Plymouth (b) | 2.00 | 1,370 | 113 | 30 |
| 2YZ, Napier | 5.00 | 860 | 108 | 30 |
| 2ZC, Napier (a) | 2.50 | 1,280 | 123 | 30 |
| 2XA, Wanganui (b) | 2.00 | 1,200 | 113 | 30 |
| 2ZA, Palmerston North (a) | 2.00 | 940 | 123 | 30 |
| 2XB, Masterton (c) | 2.50 | 840 | 59 | 0 |
| 2YA, Wellington | 60.00 | 570 | 128 | 20 |
| 2YC, Wellington | 60.00 | 660 | 42 | 0 |
| 2YX, Wellington | 1.00 | 1,400 | * | |
| 2ZB, Wellington (a) | 10.00 | 980 | 126 | 0 |
| 2YD, Wellington (c) | 2.50 | 1,130 | 21 | 0 |
| 2XN, Nelson (b) | 2.00 | 1,340 | 113 | 30 |
| 3YZ, Greymouth | 10.00 | 920 | 108 | 30 |
| 3YA, Christchurch | 10.00 | 690 | 121 | 20 |
| 3YC, Christchurch | 10.00 | 960 | 42 | 0 |
| 3ZB, Christchurch (a) | 10.00 | 1,100 | 126 | 0 |
| 3XC, Timaru (b) | 2.00 | 1,160 | 113 | 30 |
| 4YA, Dunedin | 10.00 | 780 | 121 | 20 |
| 4YC, Dunedin | 10.00 | 900 | 42 | 0 |
| 4ZB, Dunedin (a) | 10.00 | 1,040 | 126 | 0 |
| 4XD, Dunedin | 0.06 | 1,430 | 12 | 0 |
| 4YZ, Invercargill | 5.00 | 720 | 114 | 20 |
| 4ZA, Invercargill (a) | 10.00 | 820 | 123 | 30 |
Each of the two short-wave transmitters employed by Radio New Zealand has a power of 7.50 kilowatts into the aerials, and frequencies used are in the 6, 9, 11, 15, and 17 megacycle bands. Frequencies are adjusted throughout the day and seasonally to give best reception in the target areas: of the various frequencies 15.28, 15.22, and 11.78 megacycles are commonly used for daily transmissions of the home service programme, and 9.54 and 6.08 megacycles for transmissions of special evening programmes to the Pacific islands and Australia. Broadcasting hours amount to 15 1/2 hours daily to the Pacific islands and 12 1/2 hours daily to Australia.
The total transmission time of all stations of the Service amounted during the year ended 31 March 1960 to 165,414 hours. Of this scheduled programme time, 26 hours were lost through technical faults.
All programmes to be transmitted from the private broadcasting stations are supervised, and the Minister has authority to prohibit the broadcasting of any programme or part of a programme which in his opinion is unsuitable for broadcasting.
Programmes of the various stations are published in the New Zealand Listener, a weekly paper controlled by the New Zealand Broadcasting Service, which was first issued on 30 June 1939.
Radio Coverage - The functions of medium-wave stations operated by the Broadcasting Service in the programme coverage of New Zealand are as follows:
Stations 1YA, 2YA, 3YA, 4YA, 1YZ, 2YZ, 3YZ, and 4YZ broadcast non-advertising programmes to listeners throughout the country.
Stations 1YC, 2YC, 3YC, 4YC, and 2YX provide alternative non-advertising programmes to those of the YA and YZ stations in (a) but with slightly less extensive coverage.
Stations 1ZB, 2ZB, 3ZB, 4ZB, 1XH, 2ZA, 2ZC, 4ZA, 1YD, 1ZC, 2XB, and 2YD present advertising programmes mainly of a light character, coverage being comparable with stations listed in (a).
Stations 1XN, 2XG, 2XP, 2XA, 2XN, and 3XC serve the immediate locality of the centres in which they operate and present advertising and non-advertising programmes during specified hours. Within their coverage range these stations give alternative programmes to those provided by stations listed in (a), (b), and (c).
Short-wave Service - Radio New Zealand broadcasts to the Pacific islands a daily home-service programme from 5 a.m. to 5.45 p.m. on one frequency and a special evening programme from 6 p.m. to 8.45 p.m. on two frequencies. Its transmission to Australia comprises a daily home-service programme from 8 a.m. to 5.45 p.m. on one frequency and a special evening programme from 9 p.m. to 11.45 p.m. on two frequencies. In addition to its large radio audience throughout Oceania, Radio New Zealand has listeners as far distant as the United Kingdom, Sweden, France, the United States, and Japan. Radio New Zealand programmes illustrate many different aspects of life in this country.
National (Non-commercial) Service - An analysis of the combined programmes of the national non-commercial stations for a sample week in June 1960 showed that of the total broadcasting hours, 16.75 per cent was devoted to serious music, 43.37 per cent to light music, 1.41 per cent to modern dance music, 3.25 per cent to broadcasting Parliament, 8.63 per cent to plays, sketches, short stories, and dramatic serials, 4.10 per cent to sports commentaries and results, 10.69 per cent to talks, documentaries, and children's educational programmes, 7.33 per cent to news and commentaries, 2.47 per cent to church and devotional services, and 2.00 per cent to children's programmes.
Programmes broadcast by national stations of the Service are designed and classified to suit the major divisions of public taste and the Broadcasting Service is continually concerned to provide adequately for all sections of the community in all parts of the country.
The best musical and other talent available is engaged by the Service and, throughout the year, a large number of singers and other soloists as well as bands, choral, and instrumental groups of varying composition and size are broadcast from its studios or by relay of public concerts.
The National Orchestra of the New Zealand Broadcasting Service, formed in 1946, is managed by the Concert Section which also arranges series of concerts and broadcast recitals in New Zealand by overseas celebrity artists. Distinguished soloists, often from other countries, and choral groups frequently appear with the National Orchestra in public concerts in the main centres as well as in studio broadcast performances. Free concerts for school children are an established feature of the National Orchestra's tour programme.
The Production Section is responsible for presenting plays, short stories, and other dramatic as well as documentary features. Local dramatic talent is employed and every encouragement given to New Zealand writers to submit material suitable for radio.
“Broadcasts to schools” sessions are given for three hours weekly. Sessions include singing, music and movement, music appreciation, literature, book reviews, current events, social studies, science and, during the first and second school terms, French language for post-primary scholars. The Department of Education Correspondence School broadcasts to its pupils a weekday morning programme of one and one-half hours duration weekly. A special programme, “Kindergarten of the Air”, is produced three times weekly for younger children.
All proceedings of the House of Representatives are broadcast from Station 2YA. During broadcasts of Parliament the scheduled programmes of Station 2YA are broadcast by Station 2YC, and those of Station 2YC transmitted by Station 2YX.
Time signals from the Seismological Observatory are broadcast every day from Station 2YA or 2YC. The signals take the form of a series of six “dots” at intervals of one second, the last “dot” being the exact minute. Fuller details of this time service may be obtained from the article published in Section 39 (Miscellaneous) of this Yearbook.
Commercial Service - Following the coming into operation of the Broadcasting Act in 1936 the Government purchased Station 1ZB Auckland, previously a privately-owned station independent of the Broadcasting Board, and commenced the broadcasting of programmes which included advertising matter. Commercial stations were subsequently established at Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin in 1937, and at Palmerston North in 1938. Station 1XH Hamilton was transferred to the status of a full-time commercial station on 2 November 1955. Station 4ZA Invercargill began transmission on 1 October 1956, Station 2ZC Napier on 1 October 1957, Station 2XB Masterton on 17 March 1958, and Station 1ZC Rotorua on 1 July 1959. Stations 1YD Auckland and 2YD Wellington, formerly non-commercial, from 1 October 1957 began to carry advertising for three hours each evening.
In January 1949 the first station to broadcast both commercial and non-commercial programmes was opened at Timaru. Similar stations now operate at Whangarei, Gisborne, New Plymouth, Wanganui, and Nelson.
The emphasis in commercial programmes is upon entertainment and, in addition to advertising matter which occupies a relatively small proportion of total broadcasting time, listeners may hear variety, dramatic, and comedy programmes of high standard as well as informative sessions, reviews, and a comprehensive announcements service.
Financial Statistics - The following tables show the financial results of the principal activities of the Service for the last four financial years.
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Net deficit. Note - Minus sign(—) indicates an excess of expenditure over revenue. | ||||
| Non-commercial Activities | ||||
| National stations | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Expenditure on programmes | 182,874 | 185,477 | 190,991 | 182,725 |
| General administrative and running expenses | 558,274 | 566,112 | 567,331 | 587,571 |
| Post Office charges for licence fee collection | 96,244 | 108,179 | 109,150 | 111,932 |
| Depreciation | 120,932 | 124,886 | 130,223 | 135,504 |
| 958,324 | 984,654 | 997,695 | 1,017,732 | |
| Less recovery from commercial stations for provision of technical facilities and services | 113,112 | 116,737 | 129,003 | 128,080 |
| Net expenditure | 845,212 | 867,917 | 868,692 | 889,652 |
| Revenue | 819,191 | 881,904 | 895,601 | 922,989 |
| Balance of revenue over expenditure | — 26,021 | 13,987 | 26,909 | 33,337 |
| National Orchestra and concert presentation | ||||
| Net expenditure | 127,513 | 127,085 | 129,306 | 160,541 |
| Less concert proceeds | 39,270 | 32,009 | 40,802 | 68,502 |
| Balance of expenditure | 88,243 | 95,076 | 88,504 | 92,039 |
| Experimental television - | ||||
| Net expenditure | - | - | 1,854 | 3,295 |
| Total deficit non-commercial activities | 114,264 | 81,089 | 63,449 | 61,997 |
| Commercial Activities | ||||
| Commercial stations - | ||||
| Expenditure on programmes | 80,625 | 126,177 | 147,656 | 141,616 |
| General administrative and running expenses | 664,207 | 779,239 | 848,456 | 928,850 |
| Charge from national for provision of technical facilities and services | 113,112 | 116,737 | 129,003 | 128,080 |
| Net expenditure | 857,944 | 1,022,153 | 1,125,115 | 1,198,546 |
| Revenue | 1,050,811 | 1,320,098 | 1,486,152 | 1,646,316 |
| Net surplus before tax | 192,867 | 297,945 | 361,037 | 447,770 |
| New Zealand Listener - | ||||
| Printing, publishing, and distribution costs | 74,675 | 80,347 | 75,476 | 73,823 |
| General administrative and running expenses | 38,315 | 39,269 | 38,175 | 38,168 |
| Net expenditure | 112,990 | 119,616 | 113,651 | 111,991 |
| Revenue | 125,372 | 123,545 | 116,793 | 118,207 |
| Net surplus before tax | 12,382 | 3,929 | 3,142 | 6,216 |
| Total net surplus before tax | 205,249 | 301,874 | 364,179 | 453,986 |
| Provision for taxation | 105,797 | 154,188 | 179,594 | 225,345 |
| Net surplus after tax | 99,452 | 147,686 | 184,585 | 228,641 |
| Summary | ||||
| Total net deficit non-commercial activities | 114,264 | 81,089 | 63,449 | 61,997 |
| Less commercial surplus | 99,452 | 147,686 | 184,585 | 228,641 |
| Net surplus for Service | —14,812* | 66,597 | 121,136 | 166,644 |
In the table for national stations the amount recovered from commercial activities on account of provision of technical services provides for Head Office engineering overhead and services, allowance for depreciation on assets in use commercially, and share of the costs of interference suppression and frequency measurement.
The Service has two principal sources of revenue, radio-licence fees and sales of station time (advertising). While licence fee revenue is credited to the accounts of the non-commercial stations and sales revenue to those of the commercial stations, in fact the Service operates a common fund, all revenue being available for the general purpose of broadcasting. However, the commercial surplus is subject to taxation without any set-off from the deficit arising from the non-commercial activities.
Revenue from radio-licence fees and from sale of nation time for the last four financial years is shown in the following table.
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Radio-licence fees | 765,177 | 828,439 | 835,949 | 857,053 |
| Sale of station time | 1,027,898 | 1,217,179 | 1,374,150 | 1,526,586 |
| Totals | 1,793,075 | 2,045,618 | 2,210,099 | 2,383,639 |
Statistics of Radio Licences - The growth in the number of radio-receiving licences is apparent from the following table. Free licences, which are referred to later, are included in the figures. The licence fee for a receiving station, which from 1 April 1935 had been £1 5s. a year, was increased to £1 10s. a year from 1 January 1954.
| At 31 March | Auckland | Wellington | Canterbury | Otago | New Zealand Totals | Licences per Hundred of Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 155,797 | 155,585 | 78,286 | 59,679 | 449,347 | 23.86 |
| 1951 | 160,743 | 160,973 | 80,795 | 60,907 | 463,418 | 23.89 |
| 1952 | 165,838 | 167,471 | 83,924 | 62,300 | 479,533 | 24.11 |
| 1953 | 173,008 | 169,918 | 85,415 | 63,515 | 491,856 | 24.14 |
| 1954 | 178,499 | 171,938 | 87,018 | 64,301 | 501,756 | 24.18 |
| 1955 | 183,812 | 173,836 | 87,753 | 63,542 | 508,943 | 23.88 |
| 1956 | 188,775 | 176,136 | 87,585 | 64,296 | 516,792 | 23.76 |
| 1957 | 191,138 | 175,638 | 88,177 | 64,825 | 519,778 | 23.40 |
| 1958 | 206,755 | 184,853 | 90,279 | 67,420 | 549,307 | 24.14 |
| 1959 | 215,242 | 189,163 | 93,682 | 69,077 | 567,164 | 24.38 |
| 1960 | 219,918 | 193,197 | 93,944 | 70,344 | 577,403 | 24.36 |
A summary of all radio licences in force in New Zealand at 31 March 1960 follows.
| District | Receiving Stations | Radio Dealers | Private Experimental | Other | Total Licences | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amateur | Research | |||||
| Auckland | 219,918 | 1,041 | 996 | 76 | 37 | 222,068 |
| Wellington | 193,197 | 942 | 1,054 | 58 | 24 | 195,275 |
| Canterbury | 93,944 | 386 | 472 | 15 | 20 | 94,837 |
| Otago | 70,344 | 363 | 285 | 23 | 19 | 71,034 |
| Totals | 577,403 | 2,732 | 2,807 | 172 | 100 | 583,214 |
A licence issued for a receiving station situated in a family residence is sufficient in respect of all stations in that residence other than stations owned and used by subtenants or lodgers occupying part of the premises in the residence.
Free licences arc issued to blind persons and institutions for the blind, as well as to public hospitals and orphan and other charitable institutions where radio receivers are used for the benefit of patients or inmates. Free licence privileges are also extended to the operation of radio sets in schools for educational broadcast purposes. The total number of free licences issued for each of the last five years, at 31 March, was: 1956, 2,804; 1957, 2,836; 1958, 2,874; 1959, 2,932; and 1960, 2,992.
A penalty is attached to the operating of unlicensed radio apparatus. Requirements with respect to licences are set out in the Radio Regulations 1953.
TELEVISION - The relatively high cost of establishing television in New Zealand has been the main reason for the delay in providing this service. Few countries of such a small population are so isolated and beyond the reach of the stimuli and assistance which arise from telecasts in a neighbouring country, with opportunities for sharing programmes, relays, and so on. In addition, the hilly terrain in some parts of the country presents difficulties in the attainment of a comprehensive coverage.
However, in August 1958 the Postmaster-General and the Minister of Broadcasting jointly announced that, on a recommendation of the Inter-departmental Committee on Television (established in 1949) and with the advice of the New Zealand Radio and Television Manufacturers Federation, it had been decided to establish the 625 line system as the standard for any television service in New Zealand.
In October 1958 approval was given to purchase equipment to enable technical investigations to be made on such matters as the likely coverage of TV transmitters, the determination of suitable transmitter sites, the provision of a TV coverage plan, and the relative suitability of different operating frequencies. Channel 2 Auckland (vision 55.25 megacycles per second, sound 60.75 megacycles per second), which was originally opened in 1959 as an experimental television station, began its regular programme service on 1 June 1960 with a weekly two-hour transmission. By November 1960 the hours of telecasting had increased to two and a half each evening, Monday to Friday. On 1 January 1961 telecasting on seven nights a week began, the hours from 1 April being: Monday to Saturday, 6.30 p.m. - 10.30 p.m.; and Sunday, 6 p.m. - 10 p.m.
Experimental television stations are expected to be established in Christchurch by 1 June 1961, in Wellington by 1 July 1961, and later in Dunedin.
At 31 March 1961 there were 4,598 television receiving licences in force and included in this total was one hirer's licence which covered 211 television sets actually out on hire. The licence fee is £6 10s. a year.
NEWSPAPERS - There are eight daily newspapers in the four main metropolitan areas with a total circulation of 647,000. In the smaller cities and provincial towns there are 34 daily newspapers with a total circulation of 256,000. Other-than-dailies increase the aggregate circulation per day to 1,090,000. In addition, there are three national weeklies circulating over 423,000 copies.
When circulation figures for daily newspapers are related to population figures, it is found that New Zealand has 387 copies per 1,000 inhabitants. The latest comparative figures for other countries include United Kingdom, 573; Australia, 381; Canada, 244; United States, 347; U.S.S.R., 107; Sweden, 462; Norway, 374; Denmark, 376; and France, 244. (Source: UNESCO Statistics of Newspapers and Other Periodicals 1959.)
Statistics compiled from various sources disclose that from 1840 to 1940 altogether 468 newspapers (of all categories) were established in New Zealand. The acceleration of motor transport had a speedy and decisive effect on the small-town press. Many local papers which, by publishing once, twice, or three times a week, had been serving adequately the needs of a district and backblocks were unable to survive when the city papers were able to reach remote settlements within a few hours of publication, offering to country dwellers such superior attractions as daily publication, full services of New Zealand and world news, sporting news, and attractive magazine features. Under the steady pressure of competition, mergers were effected in a number of provincial towns to reduce the quota of papers, generally to a single daily. (Reference: Newspapers in New Zealand by Dr Guy H. Scholefield.)
The circulation of all periodicals is not known, but for 111 periodicals (not including three national weeklies earlier classified as newspapers) the circulation is 1,563,000. (These statistics are compiled from information gathered by the Association of New Zealand Advertisers.)
The total number of magazines, reviews, journals, and periodicals published (but not necessarily all sold) in 1958–59 was 12,953,000.
Advertising - The advertising revenue of newspapers and periodicals is shown in the following table, along with the selling value at the factory door.
| Advertising Revenue | Selling Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Newspapers, daily | 6,996,868 | 7,202,236 | 2,430,819 | 2,531,548 |
| Newspapers other than daily | 666,160 | 636,493 | 869,689 | 949,708 |
| Magazines, reviews, journals, periodicals and periodicals | 165,435 | 175,789 | 313,691 | 338,578 |
LIBRARIES - New Zealand is fairly well served with libraries and the book stocks and circulation figures compare favourably with those of other English-speaking nations.
Under the auspices of the New Zealand Library Association Incorporated, a well developed system of interlibrary cooperation has been developed, particularly in the use of resources by means of interlibrary loans. A union catalogue, which records the holdings of major libraries in one combined file, was begun in 1941 and is maintained on behalf of the association by the National Library Centre of the National Library Service, which also maintains a union list of periodical holdings. The centre acts as a clearing house for requests from libraries in cases in which the location of a book or periodical is not known, and in the year ended 31 March 1959 handled 29,508 such requests. This work and various other bibliographical projects are carried out by the centre in close cooperation with the Library Association.
Public libraries outside the main centres, and groups of readers in country areas, receive assistance from the Country Library Service, a division of the National Library Service. Such assistance takes the form of bulk loans of books, renewed at regular intervals, special loans of collections of books, and a request service for individual titles. To supply serious requests for titles which are not in its own stock the Country Library Service uses the collection of the National Library Centre or, if the books are not available there, uses the machinery of interlibrary loan. It is therefore possible for a reader in the most isolated locality to have access to almost any book held by a New Zealand library. (Fuller information on the National Library Service is given in Section 7 - Education.)
Two complementary systems of training librarians exist. The New Zealand Library Association conducts a two-year correspondence course for assistants with a minimum educational standard of School Certificate, and awards its certificate to successful students. The Library School of the National Library Service admits university graduates to its professional course, which lasts for one academic year and leads to the award of the diploma of the school. The Library School course is a full-time one and students receive allowances based on those paid to students of teachers' training colleges. The possession of either qualification, followed by prescribed periods of suitable work in libraries, entitles librarians to apply for the Associateship of the New Zealand Library Association.
Census of Libraries, 1959 - The quinquennial census of libraries was taken for the year ended 31 March 1959. The census covered a total of 286 libraries comprising three national libraries, 21 university libraries (including the libraries of other institutions of higher education), 98 special libraries, and 164 public libraries. This census differed from the previous one taken in 1954 when only public libraries were included.
There is no comprehensive national library in New Zealand, but the three libraries listed as national libraries - the General Assembly Library, the Alexander Turnbull Library, and the National Library Service - perform most of the functions of a national library.
The university libraries (including other institutions of higher education) comprised the libraries of the four universities with six libraries in close association, the libraries of six teachers' training colleges, the libraries of the two agricultural colleges, together with one library closely associated, and the libraries of two theological colleges.
The special libraries were for the purpose of this census, divided into (a) libraries of learned societies, etc., and of commercial interests and (b) libraries of Government Departments. There were 22 libraries in the former category and 76 in the latter.
Public libraries (those controlled or largely supported by a local authority) showed an increase of 26 over the 1954 census - 164 as against 138.
The following are summarised tables of the results of the 1959 census. Full details have been published in a separate report dealing with this subject, prepared by the Department of Statistics.
NATIONAL, UNIVERSITY, AND SPECIAL LIBRARIES - BOOK STOCK AND CIRCULATION
| Number of Libraries | Book Stock at 31 March 1959 | Circulation During Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Books | Serials | Pamphlets | Total | Items Lent Outside the Library* | Items Lent to Other Libraries* | Items Borrowed From Other Libraries* | ||
*Items include books, serials, and pamphlets. †Total does not balance as in some instances information was incomplete. | ||||||||
| National libraries | 3 | 983,766 | 27,008 | 80,248 | 1,091,022 | 31,286 | 120,278 | 5,173 |
| University libraries | 21 | 406,972 | 91,926 | 91,403 | 818,189† | 296,509 | 5,275 | 5,418 |
| Special libraries - | ||||||||
| Learned societies, etc. | 22 | 113,695 | 52,514 | 25,872 | 225,943† | 32,881 | 1,219 | 1,175 |
| Government Departments | 76 | 361,162 | 321,774 | 424,193 | 1,110,004† | 348,958 | 6,974 | 17,801 |
| Totals, special libraries | 98 | 474,857 | 374,288 | 450,065 | 1,335,947† | 381,839 | 8,193 | 18,976 |
| Totals | 122 | 1,865,595 | 493,222 | 621,716 | 3,245,158† | 709,634 | 133,746 | 29,567 |
PUBLIC LIBRARIES - BOOK STOCK AT 31 MARCH 1959
| Public Libraries in Areas With a Population of | Number of Libraries | Own Stock | For Reference Only (Included in Own Stock) | Country Library Service Stock | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Junior | Adult | Junior | |||||||
| Pay Collection | Free Fiction | Free Non-fiction | Fiction | Non-fiction | Total | |||||
| *Total does not balance as one library gave total only. | ||||||||||
| 50,000 and over | 21 | 104,204 | 307,107 | 545,692 | 107,710 | 46,832 | 1,111,545 | 56,625 | 1,189 | 16,102 |
| 20,000 and under 50,000 | 11 | 39,014 | 107,712 | 180,611 | 54,842 | 20,472 | 402,651 | 22,305 | 5,783 | 10,516 |
| 10,000 “ 20,000 | 12 | 34,716 | 35,430 | 61,084 | 26,907 | 5,150 | 163,287 | 2,720 | 17,864 | 7,698 |
| 3,000 “ 10,000 | 50 | 109,846 | 91,828 | 57,647 | 35,524 | 5,860 | 311,705* | 3,578 | 28,676 | 10,652 |
| Under 3,000 | 70 | 81,665 | 90,340 | 35,347 | 17,477 | 3,322 | 228,151 | 2,860 | 31,025 | 8,300 |
| Totals | 164 | 369,445 | 632,417 | 880,381 | 242,460 | 81,636 | 2,217,339* | 88,088 | 84,537 | 53,268 |
PUBLIC LIBRARIES - BOOKS: CIRCULATION AND USE
| Public Libraries in Areas With a Population of | Number of Libraries | Own Stock | Country Library Service Stock | Inter-library Loans | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Junior | Total | Adult | Junior | Lent to Other Libraries | Borrowed From Other Libraries | |||||
| Pay Collection | Free Fiction | Free Non-fiction | Periodicals | ||||||||
| *Total does not balance as in some instances information was incomplete. | |||||||||||
| 50,000 and over | 21 | 1,748,568 | 1,466,614 | 1,137,945 | 422,498 | 1,265,976 | 6,041,601 | 4,890 | 115,264 | 1,976 | 5,196 |
| 20,000 and under 50,000 | 11 | 730,266 | 1,269,168 | 514,918 | 130,228 | 708,716 | 3,353,296 | 27,773 | 41,798 | 462 | 4,208 |
| 10,000 and over 20,000 | 12 | 666,002 | 436,404 | 358,676 | 86,178 | 400,307 | 1,947,567 | 60,849 | 39,357 | 23 | 6,584 |
| 3,000 and under 10,000 | 50 | 1,065,150 | 583,767 | 372,769 | 62,189 | 381,484 | 2,465,359 | 142,581 | 85,742 | 325 | 9,325 |
| Under 3,000 | 70 | 704,312 | 338,997 | 123,115 | 21,887 | 159,829 | 1,353,864* | 161,993 | 58,058 | 183 | 7,467 |
| Totals | 164 | 4,914,298 | 4,094,950 | 2,507,423 | 722,980 | 2,916,312 | 15,161,687* | 398,086 | 340,219 | 2,969 | 32,780 |
NATIONAL, UNIVERSITY, AND SPECIAL LIBRARIES - FINANCE FOR YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 1959
| Number of Libraries | Receipts | Expenditure | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grants from Controlling Authority | Other Receipts | Total Receipts | Salaries and Wages | Books and Periodicals | Other Library Material | Other Operating Expenses | Capital Expenses | Value by Gift and Exchange | Total Expenditure | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| National libraries | 3 | 158,651 | 1,482 | 160,136 | 112,092 | 56,498 | 1,644 | 8,097 | 8,330 | 186,661 | |
| University libraries | 21 | 71,264 | 9,005 | 80,269 | 69,648 | 54,660 | 2,054 | 12,122 | 29,899 | 8,990 | 177,373 |
| Special libraries - | |||||||||||
| Learned societies, etc. | 22 | 17,234 | 4,961 | 22,195 | 9,666 | 9,697 | 279 | 2,547 | 1,807 | 4,908 | 28,904 |
| Government Departments | 76 | 61,273 | 26,265 | 87,538 | 85,627 | 54,440 | 466 | 9,956 | 10,041 | 160,530 | |
| Totals, special libraries | 98 | 78,507 | 31,226 | 109,733 | 95,293 | 64,137 | 745 | 12,503 | 1,807 | 14,949 | 189,434 |
| Totals | 122 | 308,422 | 41,716 | 350,138 | 277,033 | 175,295 | 4,443 | 32,722 | 31,706 | 32,269 | 553,468 |
PUBLIC LIBRARIES - FINANCE FOR YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 1959
| Libraries in Areas With a Population of | Number of Libraries | Amount Levied for Library Purposes | Receipts | Expenditure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grants from Controlling Authority | Other Receipts | Total Receipts | Salaries and Wages | Books and Periodicals | Other Operating Expenses | Total Operating Expenses | Special Works and Capital Expenditure | Total Expenditure | |||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 50,000 and over | 21 | 282,679 | 291,661 | 78,180 | 369,841 | 172,382 | 80,301 | 90,353 | 343,036 | 25,614 | 368,650 |
| 20,000 and under 50,000 | 11 | 32,830 | 63,048 | 44,922 | 107,970 | 57,632 | 32,472 | 17,760 | 107,864 | 4,935 | 112,799 |
| 10,000 “ 20,000 | 12 | 31,712 | 43,773 | 19,802 | 63,575 | 31,358 | 19,016 | 12,760 | 63,134 | 3,075 | 66,209 |
| 3,000 “ 10,000 | 50 | 29,664 | 76,145 | 34,194 | 110,339 | 36,710 | 27,184 | 12,653 | 76,547 | 34,223 | 110,770 |
| Under 3,000 | 70 | 13,255 | 22,581 | 23,254 | 45,835 | 18,357 | 16,420 | 6,588 | 41,365 | 3,107 | 44,472 |
| Totals | 164 | 390,140 | 497,208 | 200,352 | 697,560 | 316,439 | 175,393 | 140,114 | 631,946 | 70,954 | 702,900 |
International Statistics on Libraries - The following tables compiled from published UNESCO statistics show New Zealand's position in relation to other English-speaking countries as regards library resources, borrowers and book circulation. (Source: Statistics on Libraries, UNESCO, 1959.)
NATIONAL, UNIVERSITY, AND SPECIAL LIBRARIES
| Country | Population (Million) | Year | Type of Data | Library Category | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | University | Special | ||||
*Estimated. †In 1949. ‡In 1955. ?Books and pamphlets only. This library's holdings total 35,332,000 documents. | ||||||
| New Zealand | 2.3 | 1959 | Libraries | 3 | 21 | 98 |
| Volumes (000) | 1,091 | 818 | 1,336 | |||
| Australia | 9.0 | 1954 | Libraries | 1 | 11 | 350* |
| Volumes (000) | 400 | 1,319 | ||||
| Canada | 14.8 | 1953 | Libraries | 1 | 268 | 332 |
| Volumes (000) | 7,630 | 4,232 | ||||
| Union of South Africa | 12.9 | 1952 | Libraries | 2 | 24 | |
| Volumes (000) | 598 | 975 † | ||||
| United Kingdom | 51.2 | 1956 | Libraries | 8 | 458 ‡ | 858* |
| Volumes (000) | 9,648 | 19,190 | 13,654* | |||
| United States of America | 168.2 | 1956 | Libraries | 1 | 1,832 | |
| Volumes (000) | 10,776? | 125,000 | ||||
PUBLIC LIBRARIES
| Country | Population (Million) | Year | Number of Libraries | Book Stock, Number of Volumes | Borrowers | Circulation, Number of Volumes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Estimated. †For 100 libraries only. †Number of public library systems operating 31,957 service points. | ||||||
| (000) | (000) | (000) | ||||
| New Zealand | 2.3 | 1959 | 164 | 2,217 | 492 | 15,162 |
| Australia | 90 | 1954 | 320* | 3,340* | 5,264† | |
| Canada | 14.8 | 1953 | 765 | 8,405 | 1,672 | |
| Union of South Africa | 12.9 | 1952 | 333 | 3,298 | 325 | 10,230 |
| United Kingdom | 51.2 | 1956 | 573 ‡ | 63,400 | 13,570 | 398,730 |
| United States of America | 168.2 | 1956 | 7,500 | 157,224 | 25,361 | 348,606 |
PICTURE THEATRES - Statistics relating to picture theatres are normally collected every alternate year. These statistics relate only to picture theatres, and do not purport to show employees, revenue, and expenditure of the motion-picture industry as a whole. In particular, the full revenue and expenditure in connection with screen advertising, and also head office expenses of controlling companies (including such items as interest on debentures and mortgage charges), unless recovered from exhibitors, are not recorded in the statistics. The item “Rent” under “Theatre expenditure” does not represent the rental value of all theatres, but only the rent paid where theatres were leased or rented.
The following statistics for the last three collections cover the operations of all classes of cinematograph theatres - viz, (a) those operating six days per week; (b) those operating on odd days per week; (c) circuit, or itinerant operators.
| 1953–54 | 1956–57 | 1958–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Theatres - | |||
| Screening six days per week | 195 | 206 | 206 |
| Screening odd days per week | 328 | 332 | 298 |
| Circuit | 59 | 40 | 43 |
| Totals | 582 | 578 | 547 |
| Theatres according to seating accommodation - | |||
| Other than circuit theatre - | |||
| Under 200 | 91 | 105 | 89 |
| 200 and under 500 | 220 | 215 | 206 |
| 500 and under 1,000 | 170 | 179 | 170 |
| 1,000 and under 1,500 | 32 | 29 | 28 |
| Over 1,500 | 10 | 10 | 11 |
| Circuit theatres | 59 | 40 | 43 |
| Totals | 582 | 578 | 547 |
| *1953–54 figures are approximations only. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seating accommodation (all theatres)* | 1953–54 | 1956–57 | 1958–59 | |
| Seats, under 2s. (excluding amusement tax) | No. | 102,962 | 70,846 | 63,867 |
| Seats, 2s. and under 3s. (excluding amusement tax) | No. | 145,181 | 149,281 | 144,656 |
| Seats, 3s. and under 4s. (excluding amusement tax) | No. | 16,759 | 32,247 | 34,195 |
| Seats, 4s. and over (excluding amusement tax) | No. | 12,051 | 14,965 | |
| Totals | No. | 264,902 | 264,425 | 257,683 |
| Number of paid admissions | No.(000) | 37,368 | 37,596 | 38,208 |
| Average admission charge (including amusement tax) | d. | 23.6 | 28.6 | 30.5 |
| Average attendance per head of population | No. | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.6 |
| Number of performances for year | No. | .. | 153,262 | 155.273 |
| Average attendance per performance | No. | .. | 245 | 246 |
| Average seating capacity per hall | No. | .. | 457 | 471 |
| Average number of screenings per week - | ||||
| Theatres - | ||||
| Screening six days per week | No. | .. | 10.7 | 11.0 |
| Screening odd days per week | No. | .. | 2.1 | 2.2 |
| Circuit | No. | .. | 0.9 | 1.3 |
| Persons engaged - | ||||
| Full time - Males | No. | 590 | 594 | 550 |
| Females | No. | 456 | 449 | 444 |
| Part time - Males | No. | 908 | 987 | 1,083 |
| Females | No. | 1,274 | 1,462 | 1,524 |
| Totals | No. | 3,228 | 3,492 | 3,601 |
| 1953–54 | 1956–57 | 1958–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | £(000) | ||
| Admission receipts (including amusement tax) | 3,680 | 4,483 | 4,850 |
| Screen advertising | 127 | 132 | 135 |
| Other receipts | 153 | 114 | 119 |
| Totals | 3,959 | 4,729 | 5,104 |
| Expenditure - | |||
| Salaries and wages | 840 | 1,009 | 1,081 |
| Film hire | 982 | 1,186 | 1,319 |
| Freight | 49 | 57 | 58 |
| Advertising | 253 | 273 | 324 |
| Amusement tax | 300 | 370 | 425 |
| Rent | 319 | 350 | 361 |
| Repairs and maintenance | 116 | 192 | 180 |
| Depreciation | 81 | 135 | 161 |
| Other expenses | 465 | 475 | 459 |
| Totals | 3,404 | 4,047 | 4,368 |
The number of theatres covered in this survey dropped from 578 in 1956–57 to 547 in the latest year, the decrease being entirely within the group of cinemas screening odd days in the week. Theatres screening six days or more a week, at 206, remained the same as at the census two years previously. Average admission charges at 30.5d. record a rise of 7 per cent over those of the previous year covered (1956–57) and although paid admissions increased to 38,208,000, over half a million more than 1956–57, the number of annual attendances per head of population fell from 17.1 to 16.6.
The following table gives figures of cinema attendances and takings from 1938–39 (the first year these statistics were collected) to the latest collection.
| Year | Admissions | Gross Admission Takings | Amusement Tax | Net Admission Takings | Average Admission Price | Admissions Per Head |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (000) | £ | £ | £ | d. | No. | |
| 1938–39 | 29,809 | 1,893,617 | 46,838 | 1,846,779 | 15.2 | 18.5 |
| 1939–40 | 31,171 | 2,009,662 | 53,783 | 1,955,879 | 15.5 | 19.1 |
| 1940–41 | 31,492 | 2,107,443 | 58,146 | 2,049,297 | 16.1 | 19.3 |
| 1941–42 | 31,218 | 2,133,523 | 69,799 | 2,063,724 | 16.4 | 19.1 |
| 1942–43 | 34,034 | 2,421,058 | 87,609 | 2,333,449 | 17.1 | 20.8 |
| 1943–44 | 38,257 | 2,803,086 | 121,169 | 2,681,917 | 17.6 | 23.4 |
| 1944–45 | 35,520 | 2,588,111 | 110,241 | 2,477,870 | 17.5 | 21.3 |
| 1945–46 | 36,966 | 2,817,646 | 131,199 | 2,686,447 | 18.3 | 21.6 |
| 1947–48 | 34,078 | 2,634,730 | 123,034 | 2,511,696 | 18.6 | 18.9 |
| 1949–50 | 36,353 | 2,789,696 | 135,684 | 2,654,012 | 18.4 | 19.3 |
| 1951–52 | 36,342 | 3,131,550 | 205,467 | 2,926,083 | 20.7 | 18.6 |
| 1953–54 | 37,368 | 3,679,540 | 300,444 | 3,379,096 | 23.6 | 18.1 |
| 1956–57 | 37,596 | 4,482,651 | 369,958 | 4,112,693 | 28.6 | 17.1 |
| 1958–59 | 38,208 | 4,850,483 | 425,434 | 4,425,049 | 30.5 | 16.6 |
Cinema Attendance in Principal Countries - The table below shows the number of admissions per head per year in those countries with the highest rates of attendance. These figures are taken from the United Nations Statistical Yearbook.
| Country | Year | Number of Admissions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (Million) | Per Head | ||
| Ireland | 1957 | 52 | 18.0 |
| New Zealand | 1958 | 38 | 16.6 |
| Austria | 1955 | 110 | 15.8 |
| Germany, Eastern | 1958 | 273 | 15.7 |
| Hong Kong | 1952 | 34 | 15.1 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 1957 | 3,063 | 15.1 |
| Italy | 1958 | 730 | 15.0 |
| Israel | 1957 | 28 | 14.7 |
| United Kingdom | 1958 | 754 | 14.6 |
| Australia | 1956 | 137 | 14.5 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1957 | 186 | 13.9 |
| Germany, Fed. Rep. of | 1958 | 753 | 13.8 |
| Hungary | 1958 | 131 | 13.3 |
| United States of America | 1958 | 2,200 | 12.6 |
| Japan | 1958 | 1,127 | 12.3 |
| Bulgaria | 1958 | 89 | 11.6 |
| Belgium | 1957 | 103 | 11.5 |
| Denmark | 1958 | 50 | 11.0 |
| Canada | 1957 | 177 | 10.7 |
| Spain | 1954 | 300 | 10.4 |
| Norway | 1958 | 35 | 9.8 |
| France | 1957 | 429 | 9.7 |
| Sweden | 1958 | 70 | 9.4 |
Classification by Provincial Districts - The following two tables show some of the principal statistics of cinemas for 1958–59 by provincial districts. It will be noticed that admissions in North Island districts are higher per person than in the South Island, with the notable exception of Westland. In total, attendances in the North Island represented 17.5 visits a year to the cinema for every member of the population as against 14.0 visits in the South Island. The popularity of the cinema is most pronounced on the West Coast. Average attendances per person in Westland Provincial District were 19.5, far exceeding those of other districts, and approximately 17 per cent higher than the average attendance for New Zealand.
| Provincial District | Population 1 April 1959 | Number of Theatres | Seating Accommodation | Paid Admissions | Average Admission Charge | Average Attendance per Person* | Gross Admission Takings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Based on mean population in this case. | |||||||
| No. | No. | No. of Seats | (000) | d. | No. | £ | |
| Auckland | 950,609 | 237 | 107,813 | 16,414 | 30.6 | 17.3 | 2,094,163 |
| Hawke's Bay | 108,800 | 29 | 12,690 | 1,853 | 28.9 | 17.0 | 222,918 |
| Taranaki | 98,700 | 31 | 13,414 | 1,521 | 27.8 | 15.4 | 176,302 |
| Wellington | 451,900 | 79 | 50,499 | 8,373 | 30.7 | 18.5 | 1,071,132 |
| Marlborough | 27,800 | 8 | 3,092 | 367 | 30.6 | 13.2 | 46,679 |
| Nelson | 73,400 | 25 | 8,992 | 941 | 26.3 | 12.8 | 103,277 |
| Westland | 18,700 | 10 | 3,366 | 364 | 28.0 | 19.5 | 42,452 |
| Canterbury | 329,920 | 60 | 28,228 | 4,815 | 32.6 | 14.6 | 654,337 |
| Otago - | |||||||
| Otago portion | 174,500 | 44 | 19,137 | 2,304 | 30.7 | 13.2 | 294,375 |
| outhland portion | 91,800 | 24 | 10,452 | 1,255 | 27.7 | 13.7 | 144,848 |
| Totals | 2,326,129 | 547 | 257,683 | 38,208 | 30.5 | 16.6* | 4,850,483 |
| Provincial District | Amusement Tax | Net Admission Takings | Film Hire | Film Hire as a Proportion of Net Admission Takings | Number of Performances for Year | Average Attendance per Performance | Average Seating Capacity per Hall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent | No. | No. | No. | |
| Auckland | 179,123 | 1,915,040 | 548,538 | 28.6 | 66,879 | 245 | 455 |
| Hawke's Bay | 19,299 | 203,619 | 65,253 | 32.0 | 8,038 | 231 | 437 |
| Taranaki | 15,118 | 161,184 | 45,077 | 28.0 | 6,860 | 222 | 432 |
| Wellington | 95,729 | 975,403 | 296,381 | 30.4 | 32,600 | 257 | 639 |
| Marlborough | 4,075 | 42,604 | 10,025 | 23.5 | 1,928 | 190 | 386 |
| Nelson | 8,873 | 94,404 | 29,144 | 30.9 | 4,672 | 202 | 359 |
| Westland | 3,586 | 38,866 | 10,521 | 27.1 | 1,660 | 220 | 336 |
| Canterbury | 61,307 | 593,030 | 184,607 | 31.1 | 18,053 | 267 | 470 |
| Otago - | |||||||
| Otago portion | 25,909 | 268,466 | 85,578 | 31.9 | 9,123 | 253 | 434 |
| Southland portion | 12,415 | 132,433 | 43,668 | 33.0 | 5,460 | 230 | 435 |
| Totals | 425,434 | 4,425,049 | 1,318,792 | 29.8 | 155,273 | 246 | 471 |
Classification by Urban Areas - Statistics have been prepared for the principal urban areas for the latest year and are shown in the next table. The Hutt urban area has been included with Wellington for the purposes of these statistics.
This table shows that the average attendance per person is nearly 30 per cent higher in Wellington and Auckland than the two South Island urban areas of Christchurch and Dunedin. On the other hand, average admission charges are higher in the South Island, as is the average attendance per performance.
Seating accommodation of cinemas as a proportion of population shows Wellington to be very well off, one cinema seat for each 8.1 persons. Auckland comes next with one seat for every 8.8 persons, then Dunedin with one seat for 10.2 persons, while Christchurch seems relatively low with only one seat for every 14.4 persons.
| Urban Areas | Population 1 April 1959 | Number of Theatres | Seating Accommodation | Paid Admissions | Admissions per Seat | Average Admission Charge | Average Attendance per Person | Gross Admission Takings | Amusement Tax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (000) | No. | No. of Seats | (000) | No. | d. | No. | £ | £ | |
| Auckland | 413.1 | 59 | 46,874 | 8,814 | 188.0 | 33.3 | 21.3 | 1,224,183 | 108,234 |
| Wellington (incl. Hutt) | 236.2 | 40 | 29,000 | 5,133 | 177.0 | 32.0 | 21.7 | 685,182 | 62,139 |
| Christchurch | 210.0 | 20 | 14,556 | 3,511 | 241.2 | 34.3 | 16.7 | 501,219 | 47,857 |
| Dunedin | 102.5 | 13 | 10,050 | 1,665 | 165.7 | 32.9 | 16.2 | 228,032 | 20,927 |
| Totals | 961.8 | 132 | 100,480 | 19,123 | 190.3 | 33.1 | 19.9 | 2,638,616 | 239,157 |
| Urban Areas | Net Admission Takings | Film Hire | Film Hire as Proportion of Net Admission Takings | Revenue | Expenditure | Number of Performances for Year | Average Attendance per Performance | Average Number of Seats Available per Performance | Proportion of Hall Capacity Filled per Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | Per Cent | £(000) | £(000) | No. | No. | No. | Per Cent | |
| Auckland | 1,115,949 | 331,941 | 29.7 | 1,292 | 1,085 | 31,558 | 279 | 978 | 28.6 |
| Wellington (incl. Hutt) | 623,043 | 187,452 | 30.1 | 710 | 614 | 19,279 | 266 | 902 | 29.5 |
| Christchurch | 453,362 | 146,028 | 32.2 | 524 | 467 | 10,800 | 325 | 882 | 36.9 |
| Dunedin | 207,105 | 70,096 | 33.8 | 238 | 215 | 5,373 | 310 | 1,040 | 29.8 |
| Totals | 2,399,459 | 735,517 | 30.7 | 2,763 | 2,383 | 67,010 | 285 | 946 | 30.2 |
Classification of Theatres - The following table shows the classification of theatres according to number of screening days per week and of circuit operators.
| Screening | Number of Theatres | Seating Accommodation | Paid Admissions | Admissions per Seat | Average Admission Charge | Gross Admission Takings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Thirteen circuits. | ||||||
| No. | No. of Seats | (000) | No. | d. | £ | |
| Six days per week | 206 | 169,112 | 33,177 | 196.2 | 31.5 | 4,352,088 |
| Odd days per week | 298 | 81,076 | 4,735 | 58.4 | 23.8 | 468,739 |
| Circuit | 43* | 7,495 | 295 | 39.4 | 24.1 | 29,656 |
| Totals | 547 | 257,683 | 3,208 | 148.3 | 30.5 | 4,850,483 |
| Screening | Amusement Tax | Net Admission Takings | Film Hire | Film Hire as a Proportion of Net Admission Takings | Revenue | Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent | £(000) | £(000) | |
| Six days per week | 390,775 | 3,961,313 | 1,185,646 | 29.9 | 4,557 | 3,863 |
| Odd days per week | 32,971 | 435,768 | 124,596 | 28.6 | 515 | 473 |
| Circuit | 1,688 | 27,968 | 8,550 | 30.6 | 32 | 31 |
| Totals | 425,434 | 4,425,049 | 1,318,792 | 29.8 | 5,104 | 4,368 |
| Screening | Persons Engaged | Number of Performances for Year | Average Attendance per Performance | Average Number of Seats Available per Performance | Proportion of Hall Capacity Filled per Performance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Time | Part Time | |||||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||||
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | Per Cent | |
| Six days per week | 512 | 429 | 476 | 1,207 | 118,282 | 280 | 892 | 31.5 |
| Odd days per week | 34 | 15 | 571 | 309 | 34,133 | 139 | 341 | 40.7 |
| Circuit | 4 | - | 36 | 8 | 2,858 | 103 | 191 | 54.1 |
| Totals | 550 | 444 | 1,083 | 1,524 | 155,273 | 246 | 758 | 32.5 |
Estimates of the value, and of movements in the volume, of physical production have been made in New Zealand for many years, considerably antedating the technique of national income estimates. The latter, of course, take into account the value of the tertiary services of transport, commerce, administration, social services, etc., as well as physical production; the earlier series were concerned only with the last named. The estimates of physical production in this section are based in the main on the production data which appear in the seven sections following.
GROSS FARMING INCOME - Farming occupies such an important position in the economic structure of New Zealand that statistical information relating to farm production is vested with special interest. Statistics of quantitative farm production and prices received by farmers constitute the basic data used in the computation of estimates of aggregate receipts from sales of farm produce. Such charges as sales commissions and producer boards' levies, forming part of the value of the finished products but not of returns to the farmers, are excluded. The figures do not purport to show the aggregate net income from farming after all expenses of farm operations have been met. They are intended to afford an indication of the income available to farmers as a whole to meet current expenses of farm operation, living costs, interest payments, and all other costs.
A series such as this periodically requires considerable revision of method to take advantage of new techniques of compilation, new sources of information becoming available, and because of other sources of information ceasing. A general revision was carried out prior to publication of the 1955 Yearbook and the series was reworked back to 1938–39 on the new basis. Figures for years before 1938–39, appearing in earlier issues of the Yearbook, have not been revised in this way, but these are still regarded as reasonably comparable with current figures. In addition to this general revision, minor amendments are made from time to time.
Except in the cases indicated in the next paragraph, no attempt has been made to exclude from the scope of the compilations that portion of marketable farm produce which may be consumed on the farm. Similarly, that portion of farm produce which is sold to other farmers as material for further farm production is in general included. For example, the value of production of grass seeds is included under the heading “Agricultural”, although - except for exports - almost the whole of this crop is used for the sowing or renewal of pasture lands. An exception, however, occurs in the case of inter-farm sales of livestock, whether the animals are for breeding or fattening, as no data are available on which to base an estimate of the aggregate annual value of such sales. With this exception, the totals shown for all farm produce thus represent the total income (including receipts from sales to other farmers), plus certain allowances for farm produce used on the farm. On the other hand, products of kitchen gardens and of other activities more intimately associated with the home than with the farm do not come within the ambit of this inquiry.
Production of green-fodder crops, turnips, and mangolds is not included. The view taken is that production of these crops is a normal and essential part of farm routine to be regarded more in the nature of a farm cost than as production of a salable commodity. Consequently, the unknown - but, it is believed, very small - proportion sold of the total production of this class of farm produce is omitted from the totals shown. It is arbitrarily assumed that 20 per cent both of grasses and clovers cut for hay, and of oats cut for chaff or hay, come within the scope of this inquiry, the remainder being omitted for reasons similar to those advanced in the case of green fodder, etc.
The division into the three groups - (1) Agricultural, (2) Pastoral, and (3) Dairying, Poultry, and Bees - has been made entirely on the basis of the nature of the produce. The values of all livestock slaughtered, including bobby calves, cull cows from dairy herds, and pigs, are included in the pastoral group.
The principal items included in the agricultural group are wheat, oats, and other grain crops, grass seeds, potatoes, onions, tobacco, linen flax, orchard produce, and produce of market gardens, nurseries, hop gardens, etc. The prices at which the various commodities are valued are, in general, the prices received by farmers in the early months of the year, when the crops are harvested. Transport charges from farm to market and commission on sales are excluded.
The items included in the pastoral group are wool production, livestock slaughterings, and changes in numbers of livestock on farms.
Shorn wool production is valued at the average prices realised at sales or appraisals held during each season, the aggregate arrived at representing the value of wool produced in each season at average sale or appraisal prices ruling during that season. No adjustments are made to cover the unknown increase or decrease in the total ultimate return from the season's production, arising from higher or lower prices realised for wool carried over and sold in a subsequent season. Deductions have been made to cover the cost of transport of wool to selling centres; the Wool Board levy; brokers' commissions and other charges for receiving into store, cataloguing etc.; and for such services as binning, reclassing, and skirting when performed by brokers.
The value of livestock slaughtered has been assessed on the basis of live values at freezing works, and as such includes the returns from wool on slaughtered animals and from by-products. Deductions are made to cover the cost of transport from farm to works, saleyards, etc., and of commission on sales of livestock. The value of store stock or young lambs sold by one farmer to another is counted only once - that is, when sold for slaughtering as fat stock. In the 1955 revisions, referred to earlier, slaughterings during years ended 30 June were substituted for the figures for years ended 31 March as used hitherto.
The largest individual item included in the dairying, etc., group is the payout to suppliers by butter, cheese, and dried milk, etc., factories during each of the dairy seasons shown. From 1938–39 onwards this is on a farm-gate basis, an estimated allowance for the cost of milk transport to cheese factories being deducted. An estimate of the value of human consumption of raw milk at farm-gate prices is also included, together with the value of butter produced on farms for home use or for sale. The available data permit of only a rough estimate of the value of poultry products, which, with bee products, are included in this group mainly for purposes of convenience.
The following table shows the figures of gross farming income (in £(N.Z.) million) for the past 11 production seasons and for 1938–39, which is as far back as the main series of recent revisions were carried. The total effect of the changes in method was not great in the earlier years of this period, so that comparisons between these figures and those for still earlier seasons given in previous issues of the Yearbook are by no means invalidated. The table also shows the relative contributions of the three groups in each year, in the form of percentages of the total of all farm production.
| Production Year | Agricultural | Pastoral | Dairying, Poultry, and Bees | All Farm Produce | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Per Cent | Value | Per Cent | Value | Per Cent | Value | Per Cent | |
*Revised from previous year. †Provisional. | ||||||||
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | |||||
| 1938–39 | 8.3 | 12 | 30.9 | 44 | 31.0 | 44 | 70.1 | 100 |
| 1949–50 | 20.8 | 11 | 99.5 | 54 | 63.9 | 35 | 184.3 | 100 |
| 1950–51 | 20.8 | 7 | 198.4 | 68 | 71.4 | 25 | 290.6 | 100 |
| 1951–52 | 23.5 | 11 | 112.9 | 51 | 82.5 | 38 | 218.9 | 100 |
| 1952–53 | 24.4 | 9 | 143.3 | 55 | 93.7 | 36 | 261.5 | 100 |
| 1953–54 | 27.0 | 10 | 153.9 | 56 | 92.0 | 34 | 272.9 | 100 |
| 1954–55 | 27.4 | 10 | 161.9 | 57 | 92.2 | 33 | 281.5 | 100 |
| 1955–56 | 27.4 | 10 | 153.5 | 55 | 96.8 | 35 | 277.7 | 100 |
| 1956–57 | 26.1 | 9 | 182.3 | 59 | 99.0 | 32 | 307.4 | 100 |
| 1957–58 | 25.9 | 9 | 169.4 | 57 | 102.0 | 34 | 297.3 | 100 |
| 1958–59 | 25.8* | 9 | 162.7 | 58 | 93.8* | 33 | 282.3* | 100 |
| 1959–60† | 27.7 | 9 | 187.5 | 59 | 101.3 | 32 | 316.6 | 100 |
The changes in gross farming income and its component groups are shown in the following diagram.
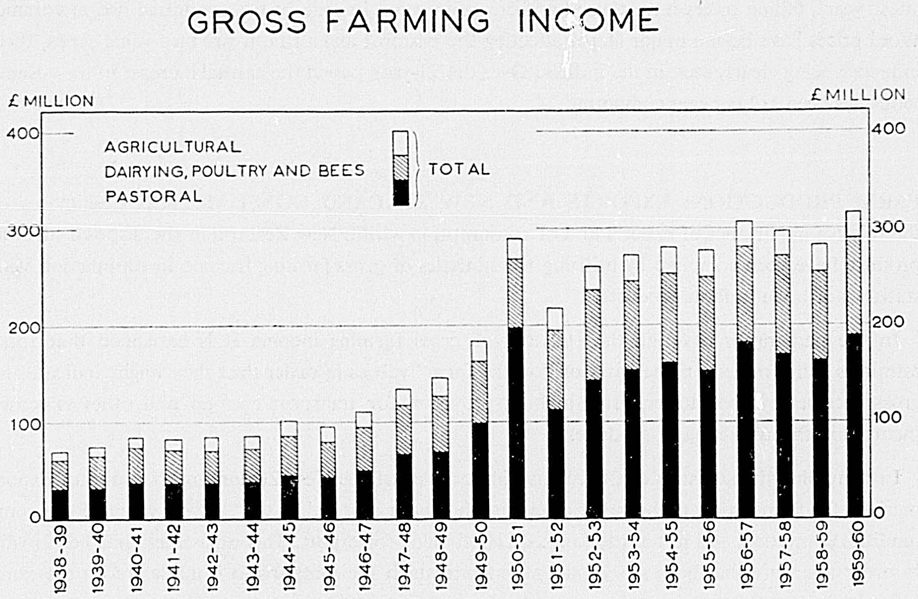
In the course of the compilation of the indices of the volume of total production given later in this section, index numbers have been compiled showing the movements in volume of farm production. For the compilation of these index numbers a computation has been made for each season showing what the aggregate annual value would have been had 1938–39 prices been constant throughout the period. From the resultant aggregates, index numbers have been compiled which measure the movements in the volume of production; for, since prices were assumed to be constant, volume is the only variable factor in the aggregates. The coverage of the pastoral production series includes allowances for changes in the numbers of livestock on farms.
In the following table index numbers of value and volume on the base: 1938–39 (= 100) are given, and these give a clearer idea of the extent of year-to-year changes.
| Production Year | Agricultural | Pastoral | Dairying, etc. | All Farm Produce | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Volume | Value | Volume | Value | Volume | Value | Volume | |
*Revised from previous year. †Provisional. | ||||||||
| 1938–39 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1949–50 | 251 | 150 | 322 | 123 | 206 | 117 | 263 | 123 |
| 1950–51 | 251 | 153 | 642 | 124 | 230 | 123 | 415 | 127 |
| 1951–52 | 283 | 148 | 365 | 124 | 266 | 123 | 312 | 126 |
| 1952–53 | 294 | 143 | 464 | 130 | 302 | 130 | 373 | 132 |
| 1953–54 | 325 | 155 | 498 | 136 | 297 | 123 | 389 | 132 |
| 1954–55 | 330 | 150 | 524 | 141 | 297 | 125 | 402 | 135 |
| 1955–56 | 330 | 148 | 497 | 143 | 312 | 130 | 396 | 138 |
| 1956–57 | 314 | 158 | 590 | 146 | 319 | 130 | 438* | 140 |
| 1957–58 | 312 | 153 | 548 | 160 | 329 | 138 | 424 | 149 |
| 1958–59 | 311* | 156* | 527 | 174 | 303* | 137 | 403 | 156 |
| 1959–60† | 334 | 162 | 607 | 180 | 327 | 136 | 452 | 158 |
Over most of the period reviewed in this table the general upward movement in prices has resulted in the value series outstripping the volume series. In some recent years, however (though not the latest year), falling prices have caused a decrease in value in spite of the continued rise in volume. Wool prices have been a major factor affecting the pastoral and all farm produce value series, their influence being clearly seen in the indices. Over the 21-year period the annual increase in the volume series has been 2.2 per cent compound.
FARM PRODUCTION: EXPORTS AND NEW ZEALAND CONSUMPTION - Estimates of the relative importance of exports and of consumption within New Zealand in the disposal of farm produce have been compiled by utilising the statistics of gross farming income in conjunction with statistics of trade in farm products.
In the paragraphs covering the statistics of gross farming income it is explained that these estimates were framed on the basis of “on the farm” values in order that they might indicate the gross receipts by the farmer, after making provision for transport charges and other expenses incurred in the marketing of produce.
In compiling the statistics of the relative importance of the New Zealand market and of export markets for farm products the value of exports has been assessed at the “farm” value of the commodities concerned, and not at the f.o.b. declared value for export. This adjustment has been made in order to ensure that both sets of statistics from which the comparison is made are on the same value basis. It will be realised, then, that the figures given in this statement indicate the proportions of total gross returns to farmers arising from farm products exported and from consumption of such products within New Zealand.
The figures of the return to farmers in respect of New Zealand consumption of farm produce have been obtained by deducting exports from total production. In these compilations exports of milk products have been converted to a butterfat equivalent, the returns to farmers being computed on the basis of butterfat payout; while the slaughterings represented by exports of meat products have been taken as the basis on which to estimate farmers' receipts from exports of meat. In instances where statistics of stocks are available adjustment has been made for the carryover from one season to another. It has been assumed that stocks of wool, frozen meat, and butter and cheese carried over are held for export, and that other stocks are subsequently consumed within New Zealand.
Since the estimates of New Zealand consumption are the residual element in the process of compilation, any lack of correspondence between the statistics of production and of trade will affect the accuracy of these estimates. Statistics of production relate to the production year for each commodity, or group of commodities, coming within the scope of this investigation. As the production years do not cover identical 12-monthly periods, the aggregate of production of farm produce includes statistics for a number of yearly periods ending in different months. Exports during any one year do not consist entirely of commodities produced within the same 12-monthly period to which the export statistics relate. The value of changes in number of livestock on farms is, on account of the complexities otherwise involved, wholly applied to the residual New Zealand consumption figure. The effect of these various factors is, however, minimised by taking averages for five seasons.
The following table shows for quinquennial periods, except for the latest period covering four years, the proportions of gross farming income arising from exports of farm produce and from consumption of such produce within New Zealand.
| Gross Farming Income | 1931–32 to 1935–36 | 1936–37 to 1940–41 | 1941–42 to 1945–46 | 1946–47 to 1950–51 | 1951–52 to 1955–56 | 1956–57 to 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural — | per cent | |||||
| From exports | 12 | 9 | 18 | 12 | 15 | 13 |
| From New Zealand consumption | 88 | 91 | 82 | 88 | 85 | 87 |
| Totals | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Pastoral - | ||||||
| From exports | 78 | 81 | 86 | 84 | 84 | 81 |
| From New Zealand consumption | 22 | 19 | 14 | 16 | 16 | 19 |
| Totals | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Dairying, poultry, and bees - | ||||||
| From exports | 72 | 68 | 65 | 69 | 64 | 59 |
| From New Zealand consumption | 28 | 32 | 35 | 31 | 36 | 41 |
| Totals | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| All farm produce - | ||||||
| From exports | 66 | 67 | 67 | 71 | 70 | 68 |
| From New Zealand consumption | 34 | 33 | 33 | 29 | 30 | 32 |
| Totals | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
VALUE OF PRODUCTION - Complete statistics covering all phases of production are not available, and in compiling the following statistics estimates of production have been made in several cases where direct data are not obtainable. Since statistical information as to production in each of the major productive activities is readily available, the items for which estimates must be made are, with the exception of one group of commodities, relatively unimportant. Although the value of products made in the home - e.g., home-made clothing, jams, kitchen-garden products, etc. - must, in the aggregate, account for a considerable annual value, it is impossible to estimate with any reasonable degree of accuracy the value of such production, which is, on this account, omitted from the statistics of the value of production.
It should be noted that production of material commodities only is taken into consideration in these statistics.
The general principle followed in assessing values has been to value products as near as possible to the actual point of production. For example, livestock is valued at “on the hoof” prices, while values at the factory are used in the case of factory products. In some few cases, however, reliable data as to values at or near the point of production cannot be obtained; and in these cases export valuations or wholesale-price quotations have been used in assessing values. Although absolute uniformity of treatment in the basis of valuation as between different commodities has not been possible, the basis of valuation gives comparable aggregate values for the period covered. The statistics thus afford a fairly accurate indication of fluctuations in the value of production from year to year, although the absolute figures for any individual year must be regarded as an approximation only.
Since the basis of valuation is, in general, at the point of production, transport costs are only partly represented in the values shown, while the accretions to the value of commodities caused by the services of retailers and other distributors of finished products are not included in the statistics. Commissions and levies forming part of the value of finished farm products, but not of the returns to the farmers, are excluded from the gross farming income series appearing on the preceding pages, but are not excluded from the value of production figures. It should perhaps be mentioned that butter and cheese are valued at the internal guaranteed price level, including any distributions of surpluses on realisations made by the Dairy Products Marketing Commission, not at overseas market realisation prices, while the values of livestock slaughtered for export include any deficiency payments made under the Meat Export Prices Act. Shorn wool is valued (as described under Gross Farming Income) at the average prices realised at sales for each season. This includes the value of wool purchased by the Wool Commission, as such purchases are included (once only and not when re-offered for sale by the Commission) in computing these average prices.
In classifying the value of production into the principal groups duplication has generally been avoided, products of one group which constitute the raw material of another group being counted once only. For example, the major portion of agricultural products, being animal fodder crops utilised in livestock production, are excluded, since livestock and livestock products are included in either the Pastoral or the Dairying, etc., group. However, no deductions have been made for some major inputs into the primary industry groups - e.g., of fertilisers into farming.
Products have been classified into the groups to which they most logically belong from a production point of view, butter and cheese, for example, being classified under Dairying, etc., and not as factory products. The figure shown under the heading “Factory” is the aggregate value added to materials by the process of manufacture, excluding industries which are already included in other groups (e.g., butter and cheese making, meat freezing, fish curing, and sawmilling). As a result of the inclusion of industries processing farm products in the appropriate farming subgroups as well as for reasons already stated, the values for these subgroups and for the farming group shown in this series naturally differ from the corresponding values in the gross farming income series. The total value of output of factory industries is included under “Factory” in cases where the materials are produced in New Zealand and are not already included as production in some other group.
The 1955 and later revisions in the Gross Farming Income series, mentioned earlier in this section, necessitated corresponding revisions in the farming groups in this series. These revised estimates (from 1938-39 onwards) are quoted in the following table, in terms of New Zealand currency. Since comparisons between the old and the revised series are of limited validity the figures for years prior to 1938-39 which appeared in the 1954 and earlier issues of the Yearbook are not reproduced here. It has not appeared worthwhile attempting to carry the revisions back any further, the old series up to 1937-38 being quite valid measures of movements up to that date. As mentioned in connection with Gross Farming Income, global estimates such as these, are, from their nature, subject to amendment from time to time as additional data on production become available and improvements are made in technique.
VALUE OF PRODUCTION
| Year | Agricultural | Pastoral | Dairying, Poultry, and Bees | Total, Farming Groups | Mining | Fisheries | Forestry | Factory* | Building and Miscellaneous | Totals (All Groups) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding factory industries included in other groups. †Revised from previous year. ‡Provisional. | ||||||||||
| £(million) | ||||||||||
| 1938-39 | 8.3 | 37.5 | 33.3 | 79.1 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 4.0 | 30.5 | 14.7 | 133.3 |
| 1939-40 | 9.6 | 38.8 | 36.3 | 84.7 | 4.9 | 0.6 | 4.4 | 33.5 | 15.4 | 143.5 |
| 1940-41 | 10.3 | 46.3 | 39.3 | 95.9 | 5.1 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 37.1 | 14.4 | 157.6 |
| 1941-42 | 11.4 | 45.9 | 37.9 | 95.2 | 5.4 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 41.2 | 14.8 | 161.7 |
| 1942-43 | 13.3 | 46.9 | 36.6 | 96.8 | 5.3 | 0.6 | 5.0 | 45.2 | 15.5 | 168.4 |
| 1943-44 | 14.4 | 48.1 | 36.2 | 98.7 | 5.7 | 0.7 | 5.3 | 49.4 | 15.9 | 175.7 |
| 1944-45 | 16.4 | 56.3 | 43.3 | 116.0 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 5.4 | 52.0 | 16.4 | 196.3 |
| 1945-46 | 15.9 | 55.0 | 39.8 | 110.7 | 6.0 | 0.9 | 6.1 | 55.6 | 19.0 | 198.3 |
| 1946-47 | 15.9 | 64.9 | 48.4 | 129.2 | 6.4 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 61.7 | 23.1 | 228.0 |
| 1947-48 | 17.4 | 81.1 | 55.9 | 154.4 | 6.3 | 11 | 8.7 | 70.8 | 24.4 | 265.7 |
| 1948-49 | 19.6 | 84.4 | 62.7 | 166.7 | 6.9 | 1.2 | 10.5 | 77.0 | 27.8 | 290.1 |
| 1949-50 | 20.8 | 118.0 | 68.9 | 207.7 | 8.2 | 1.4 | 10.9 | 84.5 | 31.1 | 343.8 |
| 1950-51 | 20.8 | 213.0 | 77.4 | 311.2 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 12.8 | 97.4 | 36.8 | 469.0 |
| 1951-52 | 23.5 | 136.8 | 90.9 | 251.2 | 9.3 | 1.5 | 15.5 | 112.3 | 41.4 | 431.2 |
| 1952-53 | 24.4 | 167.5 | 103.0 | 294.9 | 11.0 | 1.8 | 15.5 | 115.9 | 43.0 | 482.1 |
| 1953-54 | 27.0 | 180.0 | 101.1 | 308.1 | 11.0 | 2.1 | 17.3 | 131.2 | 48.9 | 518.6 |
| 1954-55 | 27.4 | 191.4 | 100.4 | 319.2 | 13.7 | 2.4 | 19.5 | 151.4 | 58.9 | 565.1 |
| 1955-56 | 27.5 | 185.6 | 105.4 | 318.5 | 16.6 | 2.7 | 21.0 | 163.5 | 59.3 | 581.6 |
| 1956-57 | 26.2 | 215.7† | 107.9† | 349.8 | 18.9 | 2.9 | 21.1 | 169.5 | 60.1 | 622.3 |
| 1957-58† | 26.0 | 203.0 | 111.7 | 340.7 | 18.6 | 2.9 | 22.8 | 188.2 | 67.3 | 640.5 |
| 1958-59† | 25.6 | 197.3 | 103.3 | 326.2 | 19.0 | 2.9 | 24.1 | 201.6 | 67.6 | 641.4 |
| 1959-60‡ | 367.0 | 367.0 | 49.0 | 214.0 | 70.0 | 704.0 | ||||
Taken together the farming groups outweigh all others so that the all groups aggregate reflects largely the movements in these groups. Prices of primary products, particularly of wool, have been major factors influencing movements in the all-groups aggregate in recent years. However, in spite of the falling prices for these products in 1957-58 and 1958-1959, the all-groups figure continued to rise, on account of the increases in factory production.
VOLUME OF PRODUCTION - The method of computation of the volume series is somewhat involved and is based on figures of physical volume of output where available (as for practically all farm, mining, forestry, and fishery production). Quantity figures - either of products or of materials used - are available for most factory industries and form the basis of the volume estimates. In cases where these are not available estimates of volume are assessed from the figures of added value, assuming price and cost movements similar to the measured movements in allied industries.
Information as to the number of houses erected, classified according to size, is available for certain years. From a consideration of these data, value figures for other classes of building activity for the same years have been converted into equivalent house or room units, and composite totals of actual and equivalent units used in computing the index number of volume of total production for these years. For other years, for which size classifications of houses erected are not available, the composite total for the last year in which the information was available has been projected forward by the movement in the total value of building permits issued, deflated by the movement in the average value of newly constructed State rental houses of similar size and type. The volume of Government civil construction is assessed from a consideration of the numbers of men engaged, with allowances for changes in working hours and increasing mechanisation.
Items not included in the computations, mainly factories too small for the regular annual collection of factory production statistics, and non-Government civil construction, are not considered to have a significant effect on year-to-year movements in total physical production.
The following table gives figures of value, and index numbers of value and volume of production, for the principal headings.
VALUE AND VOLUME OF PRODUCTION
| Base of index numbers: 1938-39 (= 100) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Farm | Factory* | Total (Including Other) | ||||||
| Value | Index of Volume | Value | Index of Volume | Value | Index of Volume | ||||
| Total | Index | Total | Index | Total | Index | ||||
*Excluding factory industries included in other groups. †Revised from previous year. ‡Provisional. | |||||||||
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 79.1 | 100 | 100 | 30.5 | 100 | 100 | 133.3 | 100 | 100 |
| 1939-40 | 84.7 | 107 | 104 | 33.5 | 110 | 110 | 143.5 | 108 | 106 |
| 1940-41 | 95.9 | 121 | 115 | 37.1 | 122 | 114 | 157.6 | 118 | 112 |
| 1941-42 | 95.2 | 120 | 111 | 41.2 | 135 | 117 | 161.7 | 121 | 110 |
| 1942-43 | 96.8 | 122 | 107 | 45.2 | 148 | 122 | 168.4 | 126 | 109 |
| 1943-44 | 98.7 | 125 | 106 | 49.4 | 162 | 129 | 175.7 | 132 | 109 |
| 1944-45 | 116.0 | 147 | 115 | 52.0 | 170 | 132 | 196.3 | 147 | 114 |
| 1945-46 | 110.7 | 140 | 107 | 55.6 | 182 | 136 | 198.3 | 149 | 112 |
| 1946-47 | 129.2 | 163 | 111 | 61.7 | 202 | 146 | 228.0 | 171 | 118 |
| 1947-48 | 154.4 | 195 | 114 | 70.8 | 232 | 159 | 265.7 | 199 | 123 |
| 1948-49 | 166.7 | 211 | 118 | 77.0 | 252 | 167 | 290.1 | 218 | 130 |
| 1949-50 | 207.7 | 263 | 123 | 84.5 | 277 | 174 | 343.8 | 248 | 137 |
| 1950-51 | 311.2 | 393 | 127 | 97.4 | 319 | 184 | 469.0 | 352 | 141 |
| 1951-52 | 251.2 | 318 | 126 | 112.3 | 368 | 196 | 431.2 | 323 | 144 |
| 1952-53 | 294.9 | 373 | 132 | 115.9 | 380 | 196 | 482.1 | 362 | 147 |
| 1953-54 | 308.1 | 390 | 132 | 131.2 | 430 | 211 | 518.6 | 389 | 152 |
| 1954-55 | 319.2 | 404 | 135 | 151.4 | 496 | 235 | 565.1 | 424 | 164 |
| 1955-56 | 318.5 | 403 | 138 | 163.5 | 536 | 250 | 581.6 | 436 | 169 |
| 1956-57 | 349.8 | 442 | 140 | 169.5 | 556 | 253 | 622.3 | 467 | 171 |
| 1957-58† | 340.7 | 431 | 149 | 188.2 | 617 | 273 | 640.5 | 480 | 183 |
| 1958-59† | 326.2 | 412 | 156 | 201.6 | 661 | 287 | 641.4 | 481 | 190 |
| 1959-60‡ | 367.0 | 464 | 158 | 214.0 | 702 | 301 | 704.0 | 528 | 198 |
A measure of relative national productivity is afforded by the next table, which gives figures and index numbers of value and volume of production in total and per head of population.
VALUE AND VOLUME OF PRODUCTION
| Year | Mean Population Year Ended 30 June | Value of Production | Volume of Production | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Per Head | Index Numbers 1938-39 (=100) | Index Numbers 1938-39 (=100) | ||||
| Total | Per Head | Total | Per Head | ||||
*Revised from previous year. †Provisional. | |||||||
| (000) | £(m) | £ | |||||
| 1938-39 | 1,617 | 133.3 | 82.4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1939-40 | 1,637 | 143.5 | 87.7 | 108 | 106 | 106 | 105 |
| 1940-41 | 1,634 | 157.6 | 96.5 | 118 | 117 | 112 | 111 |
| 1941-42 | 1,631 | 161.7 | 991 | 121 | 120 | 110 | 109 |
| 1942-43 | 1,639 | 168.4 | 102.7 | 126 | 125 | 109 | 108 |
| 1943-44 | 1,641 | 175.7 | 107.1 | 132 | 130 | 109 | 108 |
| 1944-45 | 1,673 | 196.3 | 117.3 | 147 | 142 | 114 | 111 |
| 1945-46 | 1,729 | 198.3 | 114.7 | 149 | 139 | 112 | 104 |
| 1946-47 | 1,779 | 228.0 | 128.2 | 171 | 156 | 118 | 107 |
| 1947-48 | 1,817 | 265.7 | 146.2 | 199 | 177 | 123 | 110 |
| 1948-49 | 1,853 | 290.1 | 156.6 | 218 | 190 | 130 | 113 |
| 1949-50 | 1,891 | 343.8 | 181.8 | 258 | 221 | 137 | 117 |
| 1950-51 | 1,927 | 469.0 | 243.4 | 352 | 295 | 141 | 118 |
| 1951-52 | 1,970 | 431.2 | 218.9 | 323 | 266 | 144 | 118 |
| 1952-53 | 2,023 | 482.1 | 238.3 | 362 | 289 | 147 | 118 |
| 1953-54 | 2,073 | 518.6 | 250.2 | 389 | 304 | 152 | 119 |
| 1954-55 | 2,117 | 565.1 | 266.9 | 424 | 324 | 164 | 125 |
| 1955-56 | 2,161 | 581.6 | 269.1 | 436 | 327 | 169 | 127 |
| 1956-57 | 2,206 | 622.3 | 282.1 | 467 | 342 | 171 | 125 |
| 1957-58* | 2,259 | 640.5 | 283.5 | 480 | 344 | 183 | 131 |
| 1958-59* | 2,311 | 641.4 | 277.4 | 481 | 337 | 190 | 133 |
| 1959-60† | 2,356 | 704.0 | 298.8 | 528 | 363 | 198 | 136 |
Table of Contents
SOILS AND LAND USE - Soil is the product of its environment - of the rock waste which is the parent material, of the climate under which it weathers, of the kind of topography upon which it is situated, of the vegetation under which it develops, and of the length of time during which it has been developing. In New Zealand, the wide variety of conditions under which the many kinds of rock are transformed into soil results in a complex pattern. Yet it is a complexity showing regularities and relationships that enable the soils to be grouped and classified. The conditions that control soil formation tend also to govern the kind of land use. Thus a close relationship between soils and land use arises in two ways - from characteristics inherent in the soils themselves and from environmental factors such as the climate and topography. Maps showing the pattern of soils and of land use are published in A Descriptive Atlas of New Zealand (1959). Soils are shown in two divisions: (a) zonal soils, and (b) intrazonal and azonal soils; and descriptions of the location, properties, and productive capacities of the different soil types in New Zealand are now given.
Zonal Soils - If the soils formed from unusual parent materials, e.g., volcanic ash, and those occupying special sites, such as steep slopes and swampy hollows, are set aside, a simple pattern of zonal soils is revealed. It consists of the brown-grey earths of the semi-arid areas where the rainfall is less than about 20 inches a year; the yellow-grey earths of subhumid areas where the rainfall is approximately 20-40 inches a year; the northern, central and southern, and high-country yellow-brown earths respectively of the humid regions where the rainfall is well distributed and is greater than approximately 40 inches a year; and the podzolised yellow-brown earths and podzols where an acid litter of decomposing vegetation and high rainfall result in excessive leaching. Zonal soils comprise 18 million of the country's 66 million acres.
The brown-grey earths (1 1/2 m; 1/2 m acres*) occupy the dry inter-montane basins of Central Otago and the Mackenzie Plains where rainfall is insufficient for plant requirements for most of the year. They are generally rich in plant nutrients and are weakly acid to alkaline, in places with salty patches. Many of them are stony. Their chief need is more water but irrigation must be practised with care to avoid waterlogging or spreading salts. They produce fine wool and store sheep and, where irrigated, fat lambs; lucerne is grown and, in favoured spots, stone fruits and brassica and other seed crops.
The yellow-grey earths (2 1/2 m; 3/4 m acres) are the seasonally dry soils of southern Otago, Canterbury, Wairarapa, Hawke's Bay, and Manawatu, where rainfall is inadequate for plant growth for a third to half of the year. They are moderately to weakly acid, and the older soils have a thick hard silt-pan in the subsoil. Fat-lamb farming is the principal use with mixed arable farming on the drier soils and some dairying on the moister soils. Stony soils related to the yellow-grey earths (1 1/2 m acres) cover much of Canterbury Plains; they are used for sheep farming including fat lambs; with irrigation, they carry over four ewes per acre and grow cereal and pasture seed crops.
The rainfall of the yellow-brown earths is usually adequate for plant growth for most of the year. The high-country yellow-brown earths (1/2 m; 1 m acres) of the cold upland basins east of the Southern Alps are developed under tussock at high elevations. They have yellow friable subsoils and are moderately acid and strongly leached. Where oversown with clovers they respond to molybdenised superphosphate and sulphur. They are used mostly for wool production and some store sheep. The southern and central yellow-brown earths (2 m; 4 1/2 m acres) of the cool and mild districts like Southland and Wellington were formed under forest and have nutty subsoils. When sown to pasture with lime and superphosphate (in places molybdenised), they are used for dairying and fat lambs on the rolling land, and for wool production, store stock, and some fat lambs on the more hilly slopes.
*Where two areas are given in parentheses after particular types of soil they refer to easy and hilly land respectively, and are usually expressed in millions of acres.
Cattle are also run to help control pasture growth and prevent its reversion to scrub and fern. The associated podzolised yellow-brown earths and podzols (140,000; 200,000 acres) are best developed in Southland. They are formed under rimu-kamahi forest and are very strongly leached with grey acid structureless topsoils and with iron pans in the subsoils in places. They are being brought into pasture to sheep and cattle grazing. Waterlogged counterparts of these soils, the gley podzols or “pakihi soils” (3/4 m; 100,000 acres) occur in Westland where the rainfall is 100 inches or so per year. They have structureless subsoils and their chief problem is one of drainage to remove the excess water. They are difficult to utilise once the forest has been removed. The northern yellow-brown earths (1/2 m; 3/4 m acres), formed under mixed forest in the warm moist climate of North Auckland, are mostly heavy clays. The more fertile soils are moderately acid but support good pastures when top-dressed with lime and phosphate, in places molybdenised; the rolling land is used for dairying and fat lambs, the hills for sheep and cattle grazing. The less fertile soils support fair pastures when top-dressed with lime and superphosphate; on the easier land many dairy- and fat-lamb farms are situated, but pastures on the hill country are less easy to maintain.
The northern podzolised yellow-brown earths and podzols (1/2 m; 300,000 acres) have thin grey structureless topsoils overlying a grey siliceous horizon, and are strongly acid and very low in plant nutrients. Where formed under kauri they are known as “gumlands”. In places, especially where the soils are sandy, farming should be approached with caution because subsoil pans of humus and iron impede drainage; otherwise with fertilisers the soils can be made to support good dairy pastures.
Intrazonal and Azonal Soils - The intrazonal soils include the soils from less common parent materials and those influenced by high ground water; and the azonal soils are youthful owing to recent renewal by sedimentation, volcanic eruptions, or erosion.
Rendzina and other lime-rich soils, mostly from limestones, occur both in subhumid areas (100,000 acres) such as near Oamaru, in North Canterbury, and in Hawke's Bay, and in the humid areas (1/4 m acres) particularly North Auckland. They are fertile, with deep, dark granular topsoils. In the drier areas, they are used for intensive arable farming and sheep farming and, near Oamaru, for poultry farming; in the humid areas, for dairying and fat lambs.
The yellow-brown sands (3/4 m acres), from coastal sand drifts of various ages, occur on sandhills which dry out excessively in summer and on sand plains where ground water approaches the surface in winter. The drier soils are used for grazing; the soils with moister subsoils, after fertilising with phosphate and potash, are used for sheep farming and dairying. Where the subsoils are loose, blowing is a problem.
The yellow-brown pumice soils (2 m; 2 m acres) of central North Island are formed mostly of two volcanic ash showers that fell 800 and 1,700 years ago. Their topsoils are mostly sands or sandy loams, and the subsoils pumice sands and gravels. Because the cattle and sheep became bush sick these areas were difficult to farm for many years and large areas were planted in exotic forests. However, the ailment is now overcome by topdressing with cobaltised superphosphate and, except where droughty, the soils can be converted into good farmland. In addition to phosphate they need consolidation and, after continued use, potash topdressing. The yellow-brown loams (4 m acres) are derived mostly from fine-textured ashes erupted by volcanoes in central North Island and by Mount Egmont and occur around the margin of the younger pumice soils. They are very friable loamy soils, respond well to superphosphate topdressing, and give slight to good responses to lime; potash responses are expected to increase with continued use. The soils are used mainly for dairying and fat-lamb production. The red and brown loams and brown granular clays (1 1/4 m acres) are formed from basalts and andesites and are rich in iron and aluminium. They are friable soils with strong structure and a marked power to fix phosphates. The younger, more fertile soils (1/2 m; 1/4 m acres) respond to superphosphate and lime, those from basalt also respond to potash; they are used for dairying, fat-lamb production, and sheep grazing, and in places for market gardens and orchards. The older soils have lower natural fertility and include the strongly acid granular soils and the moderately acid ironstone soils; they carry fair pastures when topdressed with lime, phosphate, and potash and, on the acid soils, with molybdenised superphosphate.
The organic soils (1/2 m acres) are peaty and occur mostly in the Auckland district. Where mellow and fertile they can be farmed satisfactorily, but the peats of acid bogs require special treatment. The gley soils (3/4 m acres) are formed under the influence of groundwater which causes the formation of grey subsoils commonly mottled with rust colours. They, too, occur mostly in the Auckland district, and when drained are used for dairying and fat-lamb production.
Recent soils from alluvium (1 1/2 m acres) are formed from flood sediments on river flats. For the most part they are fertile, deep loams, but some are gravelly with excessive drainage. They are used mainly for fat lambs and dairying; also, in drier areas, for cereals, pasture and vegetable seed crops, pulse crops for canning, pip and stone fruits, small fruits, and tobacco.
Recent soils from volcanic ash (1 3/4 m acres) occur mostly around the active volcanoes of Ngauruhoe and Ruapehu, and also around Mount Tarawera. Where they cover the pumice soils their cobalt content offsets the deficiency in the pumice.
Steepland soils occupy about half the area of New Zealand, being most extensive on the axial ranges, and in north-west Nelson and east Taranaki. Although showing characters related to the zone where they occur they are for the most part shallow and their subsoils vary widely in fertility according to the underlying rock. They are relatively unstable and are periodically renewed by erosion. When the plant cover is disturbed by man the erosion is accelerated and the results affect not only the hillsides but also the rivers and river flats. Areas occupied by these soils are: steepland brown-grey earths, 1/2 m acres; steepland yellow-grey earths, 1/2 m acres; high-country steepland yellow-brown earths, 4 1/2 m acres; other steepland yellow-brown earths, 14 m acres (including 2 m with high natural fertility); and podzolised steepland soils, 6 3/4 m acres. The podzolised steepland soils are largely in forest, and occur mainly in western Nelson, Westland, and western Southland, at altitudes from 5,000 ft in the north to 3,000 ft in the south. Above these levels there are 2 3/4 m acres of poor wet soils largely in subalpine scrub and tussock, and grading up to the alpine barrens (3 3/4 m acres) at elevations where vegetation is sparse or absent and much bare rock and ice are present.
New Approach to Land Use - The rapid increase in knowledge of the soils of New Zealand has brought about a change in approach to land use. In the early thirties the use of land was still guided by the art of judging its capabilities from external appearances and a general knowledge of farming and local conditions. This method had its successes but in places failed badly, for example, in parts of the country, pastures could not be maintained and farm land was abandoned. The need for solving such problems led to the improvement in ways of recognising and mapping the soils so that their properties and uses could be determined. Today, land use is guided for the most part by the capabilities of the soil type as revealed by investigation. The reliability of predictions made in this way has stimulated the rapid conversion of large areas of “problem” land into good farms and has raised land use to a new pitch of efficiency. It reflects the modern swing from farming as a traditional art to farming as an up-to-date science.
The broad grouping of land use for farm and other purposes is shown in the following table; more details on particular uses are given in this and subsequent subsections, and Section 10 on Land Tenure.
| Acres (million) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Occupied farm land | ||
| Improved grassland | 18.4 | |
| Tussock and other native grassland | 13.0 | |
| Total grassland | 31.4 | |
| Land in field crops, gardens, and orchards | 1.4 | |
| Plantations | 0.9 | |
| Land in fern, scrub, and second growth | 5.7 | |
| Standing bush | 2.7 | |
| Barren and unproductive land | 1.9 | |
| Total other occupied farm land | 12.6 | |
| Total occupied farm land | 44.0 | |
| Land in cities and boroughs | 0.4 | |
| National parks, reserves, and domains | 5.1 | |
| State forest land | 9.8 | |
| Other land, including waste land such as mountains, bare rock, water surfaces, roads, etc. | 7.1 | |
| Total land | 66.4 |
NATURE OF FARMING - The natural tussock grassland, which occurs mainly on the hilly and mountainous country to the east of the Main Divide of the South Island, is used for extensive pastoral farming, where the main product is wool and in some instances store sheep, while on the less steep country, particularly in the North Island where there is surface-sown grassland, both store sheep and cattle are additional products. The third type of grassland, that sown after ploughing, is found on the flat and gently undulating country of both Islands and is used mainly for the production of meat and dairy produce. Here farmers have exploited the use of certified strains of grasses and clovers, phosphatic fertilisers, lime and trace elements. However, with the advent of mechanisation, and, more particularly, the use of aircraft for topdressing hill pastures, considerable areas of surface-sown grassland have been topdressed in recent years. This treatment of country otherwise inaccessible to normal topdressing methods, coupled with oversowing of grass, is resulting in considerable improvement to hill pasture, with a consequent increase in carrying capacity and production.
Most farming districts have been reticulated with electricity, which is being put to a variety of uses on the farm, but by far the most important is that of providing power for milking machinery. For instance, in the dairying districts of the North Island there are approximately 83,000 electric motors over a quarter horsepower, which is 68 per cent of the total number used on farms in New Zealand. About 97 per cent of the dairy cows in New Zealand are machine milked.
The North Island - Many parts of the North Island have proved very suitable for dairying because of the temperate climate, a fairly high rainfall well distributed over the year, and land reasonably flat and of average to good quality. Approximately 87 per cent of the total dairy stock in the country are grazed on the flat and undulating land of North Auckland, South Auckland, Taranaki, and Wellington Land Districts. Pastures of high feeding value form the basis of the industry. The main winter supplementary feed is hay and silage made from the surplus spring and early summer growth of the pastures. The area saved for this purpose in these dairying districts comprises approximately 63 per cent of the total area saved in New Zealand. In most of the dairying areas fat-lamb raising is associated with dairying, particularly in the Waikato and the Bay of Plenty.
Various forms of sheep farming are carried on throughout the Island, but it is most concentrated on the eastern section from the Wairarapa, through Hawke's Bay, to the hill country north of Gisborne.
The South Island - Sheep farming is carried on in practically all parts of the Island. On the tussock grasslands, particularly on the higher parts, extensive sheep farming is practised. Merino and half-bred flocks predominate, with emphasis on the production of fine wool. Because of the comparatively severe climate - hot, dry summers and cold winters with occasional heavy snow-storms - there is a considerable risk of heavy sheep losses. On the easier hill country, in addition to returns from wool, a considerable portion of the revenue comes from the sale of store sheep, which are purchased by the farmers on the plains and undulating country for fattening and for flock-replacement purposes.
On the plains and downlands of Canterbury and in parts of Marlborough, Otago, and Southland, where the climate and soils are suitable, arable mixed farming is a feature. Approximately 89 per cent of New Zealand's wheat, oats, and barley acreage is in these districts. Associated with cereal production is fat-lamb raising, for sheep and lambs are fattened on the majority of these farms. Because of the dry summers and relatively severe winters considerable areas (approximately three-quarters of the New Zealand acreage) of rape, kale, turnips, and swedes are grown for summer and winter supplementary feed.
Dairying is very localised and is concentrated near the cities to cater for whole-milk requirements. Districts where herds are run for dairy-factory supply are the plains areas of Southland; parts of Nelson and Westland; and Banks Peninsula, in Canterbury.
CLASSIFICATION OF HOLDINGS BY PRINCIPAL FARMING ENTERPRISES - The collection of farm production statistics in 1950 was carried out as New Zealand's part of the World Census of Agriculture. Detailed information was published separately in the report on the New Zealand Census of Farm Production, 1949-50. Similarly a report is being prepared for publication on the New Zealand Census of Farm Production, 1959-60.
For purposes of fuller analysis of the New Zealand results than is customarily given in Land District tables, counties with some affinity as to farming types, etc., have been regrouped to form what have been designated “Regional Areas”, and certain tables given in Sections 14B and 14C of this volume are set out on this basis. The following sets out in detail the content of these regional areas -
| Regional Area | Counties Included (as at 1950) |
|---|---|
| Northland | Mangonui, Whangaroa, Hokianga, Bay of Islands, Whangarei, Hobson, Otamatea, Rodney, Waitemata, Eden. |
| South Auckland | Manukau, Franklin, Raglan. |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | Waikato, Waipa, Otorohanga, Hauraki Plains, Piako, Matamata. |
| Cape Colville | Great Barrier, Coromandel, Thames, Ohinemuri. |
| Central Plateau | Tauranga, Rotorua, Taupo, Whakatane. |
| Western Uplands | Kawhia, Waitomo, Taumarunui, Ohura, Whangamomona, Clifton, Kaitieke, Waimarino. |
| Taranaki | Taranaki, Inglewood, Egmont, Stratford, Eltham, Waimate West, Hawera. |
| East Cape | Opotiki, Matakaoa, Waiapu, Uawa, Waikohu, Cook. |
| Hawke's Bay | Wairoa, Hawke's Bay, Waipawa, Waipukurau, Patangata. |
| Rangitikei | Patea, Waitotara, Wanganui, Rangitikei, Kiwitea, Pohangina. |
| Manawatu | Dannevirke, Woodville, Oroua, Manawatu, Kairanga, Horowhenua, Pahiatua. |
| Castlepoint | Weber, Akitio, Castlepoint. |
| Wairarapa | Eketahuna, Mauriceville, Masterton, Wairarapa South. |
| Featherston | Hutt, Makara, Featherston. |
| Nelson | Waimea, Takaka, Collingwood, Buller, Murchison, Inangahua. |
| Marlborough | Sounds, Marlborough, Awatere, Kaikoura. |
| Westland | Grey, Westland. |
| North Canterbury | Amuri, Cheviot, Waipara. |
| Foothills | Ashley, Oxford, Tawera, Selwyn. |
| Canterbury Plains | Kowai, Rangiora, Eyre, Malvern, Paparua, Springs, Ellesmere. |
| Christchurch | Waimairi, Heathcote, Halswell. |
| Banks Peninsula | Mount Herbert, Akaroa, Wairewa. |
| Mackenzie | Mackenzie. |
| South Canterbury | Ashburton, Geraldine, Levels, Waimate, Waitaki. |
| Otago | Waihemo, Waikouaiti, Peninsula, Taieri, Tuapeka. |
| Central Otago | Maniatoto, Vincent, Lake. |
| Southern | Bruce, Clutha, Southland, Wallace. |
| Remainder | Chatham Islands, Stewart Island. |
Since 1950 there have been changes in county structure which have affected the boundaries of regional areas and these will be taken into account when the classification of holdings is revised; relevant changes are the absorption of Eden county into Auckland city, of Weber county into Dannevirke county, of Whangamomona county into Stratford county, of Castlepoint county into Masterton county, and the partition of Kawhia county between Otorohanga and Waitomo counties.
A type classification of farm holdings was also brought into use in 1949-50, and figures, as to the number of holdings of various principal types of farming enterprises, in the several regional areas (each Island separately) are here presented.
| Regional Area | Predominant Enterprise | Total | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep Farming | Dairy Farming | Beef Cattle Raising | Mixed Farming | Arable Cropping (Including Grass-seed Production) | Horticulture (Including Market Gardens) | Poultry Keeping | Grazing Areas | Residential | Other* and Unspecified | Idle and Unused | ||
*Including horse raising, 473; plantations, 272; pig raising, 217; timber cutting, 75; and phormium tenax (N.Z. flax), 22. †In regional area statements, 95 holdings in the Chatham Islands are excluded from the North Island totals but included in the South Island totals. | ||||||||||||
| Northland | 785 | 7,313 | 330 | 58 | 8 | 688 | 219 | 804 | 874 | 422 | 670 | 12,171 |
| South Auckland | 756 | 3,504 | 86 | 17 | 2 | 294 | 130 | 89 | 317 | 101 | 78 | 5,374 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | 877 | 6,936 | 82 | 37 | 1 | 75 | 28 | 293 | 165 | 113 | 68 | 8,675 |
| Cape Colville | 128 | 849 | 33 | 4 | - | 23 | 4 | 95 | 54 | 32 | 68 | 1,290 |
| Central Plateau | 284 | 2,266 | 44 | 19 | 9 | 211 | 36 | 93 | 113 | 114 | 120 | 3,309 |
| Western Uplands | 1,395 | 1,149 | 60 | 29 | 1 | 35 | 3 | 71 | 172 | 76 | 77 | 3,068 |
| Taranaki | 439 | 3,974 | 22 | 17 | - | 35 | 37 | 144 | 178 | 82 | 18 | 4,946 |
| East Cape | 945 | 1,108 | 25 | 107 | 93 | 128 | 81 | 106 | 354 | 56 | 53 | 3,056 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,987 | 739 | 35 | 58 | 96 | 654 | 71 | 199 | 418 | 61 | 50 | 4,368 |
| Rangitiki | 1,820 | 1,263 | 29 | 18 | 29 | 43 | 30 | 102 | 306 | 48 | 28 | 3,716 |
| Manawatu | 1,413 | 2,990 | 41 | 25 | 28 | 185 | 62 | 160 | 268 | 57 | 39 | 5,268 |
| Castlepoint | 274 | 23 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 17 | - | 8 | 326 |
| Wairarapa | 636 | 661 | 5 | 25 | 19 | 10 | 17 | 32 | 88 | 30 | 10 | 1,533 |
| Featherston | 354 | 489 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 41 | 43 | 50 | 101 | 29 | 50 | 1,183 |
| Totals, North Island† | 12,093 | 33,264 | 801 | 427 | 292 | 2,422 | 761 | 2,240 | 3,425 | 1,221 | 1,337 | 58,283 |
| Nelson | 529 | 1,014 | 75 | 77 | 51 | 806 | 36 | 192 | 368 | 211 | 216 | 3,575 |
| Marlborough | 740 | 393 | 9 | 73 | 176 | 96 | 31 | 37 | 164 | 56 | 52 | 1,827 |
| Westland | 137 | 408 | 159 | 7 | - | 13 | 7 | 50 | 111 | 73 | 149 | 1,114 |
| North Canterbury | 596 | 39 | 3 | 50 | 79 | 6 | 6 | 42 | 65 | 16 | 10 | 912 |
| Foothills | 338 | 83 | 1 | 58 | 89 | 31 | 36 | 40 | 84 | 21 | 22 | 803 |
| Canterbury Plains | 426 | 727 | 14 | 161 | 809 | 69 | 89 | 153 | 415 | 152 | 34 | 3,049 |
| Christchurch | 38 | 271 | 10 | 17 | 75 | 546 | 78 | 75 | 354 | 119 | 40 | 1,623 |
| Banks Peninsula | 271 | 193 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 25 | 5 | 52 | 44 | 9 | 5 | 622 |
| Mackenzie | 287 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 16 | 2 | - | 16 | 22 | 8 | 12 | 380 |
| South Canterbury | 2,232 | 885 | 31 | 542 | 948 | 213 | 277 | 378 | 744 | 166 | 66 | 6,482 |
| Otago | 938 | 558 | 34 | 76 | 29 | 180 | 76 | 144 | 227 | 102 | 86 | 2,450 |
| Central Otago | 661 | 83 | 3 | 18 | 66 | 168 | 7 | 118 | 91 | 28 | 68 | 1,311 |
| Southern | 3,908 | 1,836 | 84 | 221 | 151 | 37 | 43 | 436 | 577 | 186 | 186 | 7,665 |
| Remainder | 74 | 3 | 7 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 37 | 15 | 56 | 194 |
| Totals, South Island† | 11,175 | 6,506 | 440 | 1,307 | 2,494 | 2,193 | 691 | 1,734 | 3,303 | 1,162 | 1,002 | 32,007 |
| Totals, New Zealand | 23,268 | 39,770 | 1,241 | 1,734 | 2,786 | 4,615 | 1,452 | 3,974 | 6,728 | 2,383 | 2,339 | 90,290 |
DAIRY PRODUCTION - The total butterfat production “at the pail” during the 1959-60 dairy season is estimated to have amounted to 545.4 million lb, a decrease of 10.4 million lb, or 1.9 per cent, on the 1958-59 figure of 555.8 million lb.
The quantity of butterfat processed by dairy factories in 1959-60 is estimated at 478 million lb, compared with 489 million lb processed by factories during 1958-59.
Variations over the last 10 years in total butterfat production, including estimates for butterfat in milk and cream sold for human consumption, used and lost on farms, etc., are shown hereunder. The table also gives the number of dairy cows recorded as in milk, on farms of 1 acre or more outside borough boundaries, and estimates of the average butterfat production per cow “at the pail”, this estimate being based on data concerning tested herds.
| Year | Total Butterfat | Dairy Cows in Milk | Average Production per Cow |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Relates to holdings of 10 acres and over, whereas figures for earlier years relate to holdings of one acre and over. | |||
| Million lb | (000) | lb | |
| 1950-51 | 495 | 1,898 | 259 |
| 1951-52 | 502 | 1,906 | 262 |
| 1952-53 | 535 | 1,962 | 271 |
| 1953-54 | 496 | 1,999 | 247 |
| 1954-55 | 506 | 1,995 | 252 |
| 1955-56 | 529 | .. | 263 |
| 1956-57 | 523 | 1,998 | 261 |
| 1957-58 | 557 | 1,967 | 282 |
| 1958-59 | 556 | 1,931 | 287 |
| 1959-60 | 545 | 1,887* | 285 |
The next table shows the estimated production and utilisation of butterfat during each of the last five seasons.
| Utilisation | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes small quantities of creamery fat used in whey buttermaking. †Including residual fat in skim-milk from home separation. | |||||
| million lb | |||||
| Creamery buttermaking* | 370.5 | 367.2 | 397.5 | 403.5 | 384.6 |
| Cheesemaking | 86.3 | 84.1 | 85.6 | 76.9 | 83.1 |
| Whole-milk products | 6.6 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 8.3 |
| Total | 463.4 | 457.5 | 489.2 | 486.9 | 476.0 |
| Residual fat in skim-milk products | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| Total processed by dairy factories | 465.0 | 459.3 | 491.4 | 489.2 | 478.3 |
| Consumed as milk, cream, or ice cream | 45.6 | 46.3 | 47.7 | 48.9 | 49.6 |
| Farm butter | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Fed to stock† | 12.4 | 12.0 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 11.9 |
| Wastage | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.4 |
| Total production “at pail” | 528.5 | 523.0 | 556.7 | 555.8 | 545.4 |
Changes in the usage of butterfat in dairy factories over recent years are indicated by the percentages in the following table.
| Percentage of Total Butterfat | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
| Butterfat received into factories from farms and used for - | |||||
| Buttermaking | 80.0 | 80.3 | 81.3 | 82.9 | 80.8 |
| Cheesemaking | 18.6 | 18.4 | 17.5 | 15.8 | 17.5 |
| Whole milk products | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.7 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Creamery butter production during 1959-60 amounted to 207,912 tons, being a decrease of 10,684 tons, or 4.9 per cent, below the previous season's total of 218,596 tons. Whey butter manufacture amounted to 3,103 tons, an increase of 234 tons, or 8.2 per cent, above the previous season's total of 2,869 tons. Cheese manufacture amounted to 93,034 tons, an increase of 7,716 tons, or 9.0 per cent, above the previous season's total of 85,318 tons.
The production of condensed and powdered whole milk totalled 16,553 tons in 1959-60, 2,763 tons (20.0 per cent) more than the previous season. The output of buttermilk powder reached record levels at 16,621 tons, 152 tons or 0.9 per cent, more than the previous year. At 49,363 tons skim-milk powder production for 1959-60 was not far below the record figure of 50,600 tons in 1956-57. The total for the latest season was 8,800 tons, or 21.7 per cent, higher than 1958-59. Casein production for 1959-60 was 24,551 tons, 2,525 tons less than the record figure of the previous year - 27,076 tons. This was a consequence of the switch back to cheese manufacture during the season.
Production by dairy factories during the last five seasons is set out in the following table.
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tons (000) | |||||
| Creamery butter | 200.0 | 198.2 | 215.1 | 218.6 | 207.9 |
| Whey butter | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 3.1 |
| Cheese | 96.3 | 94.6 | 96.6 | 85.3 | 93.0 |
| Condensed and powdered whole milk | 14.7 | 15.5 | 13.6 | 13.8 | 16.6 |
| Skim-milk powder | 35.3 | 50.6 | 46.1 | 40.6 | 49.4 |
| Buttermilk powder | 12.5 | 14.1 | 15.8 | 16.5 | 16.6 |
| Casein | 14.6 | 13.8 | 22.5 | 27.1 | 24.6 |
The following diagram shows the progress of the dairy industry over a long period of years.
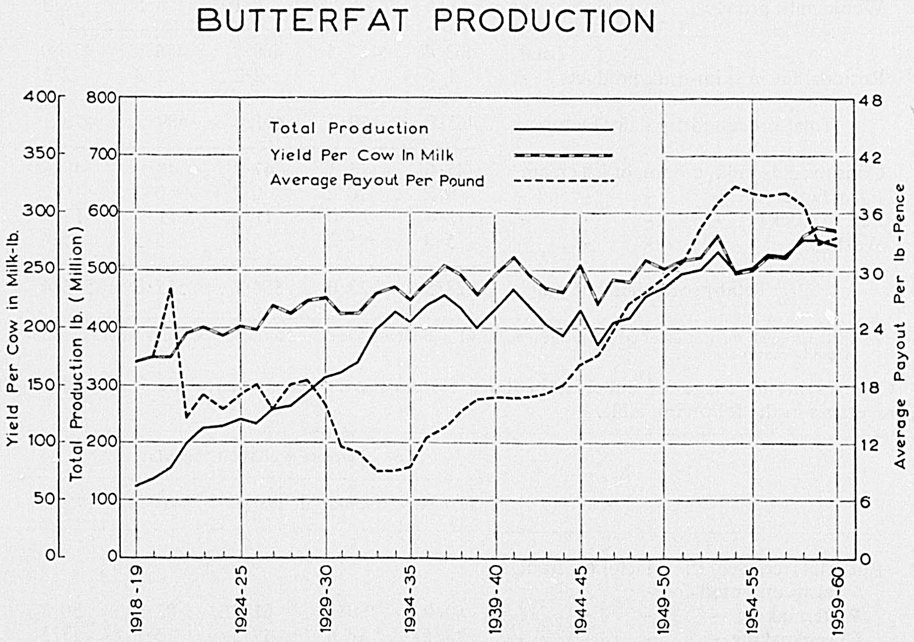
The New Zealand Dairy Board of eight members has had its principal functions defined in the Dairy Board Act 1953 in the following terms: “to promote and organise the orderly development of the dairy, bobby calf, and pig industries with a view to maintaining and improving the standard of quality of the stock or produce derived from those industries, and expanding production of that stock or produce, and generally for ensuring, as far as may be practicable, the adoption of measures and practices designed to promote greater efficiency in those industries, in furtherance of the interests and welfare of the persons engaged therein”.
The Board is financed by a levy on dairy produce. It shares with the Government the management and finance of the Dairy Research Institute, and, with the Government, the New Zealand Meat Producers Board, and the New Zealand Wool Board, the control of the Veterinary Services Council.
The Dairy Board is also represented on the Dairy Products Marketing Commission, the Dairy Industry Loans Council, the Meat Producers Board, the Pig Producers Council, the Bobby Calf Pools Central Executive, the Dairy Factory Managers Registration Board, and on a committee which examines improvements in manufacture.
The Dairy Industry Act 1908 with its amendments, regulates the production, collection, treatment, preparation, and manufacture, under proper sanitary conditions, of dairy produce - i.e., milk, cream, butter, cheese, and any other product of milk or cream - intended for sale for human consumption within New Zealand or for export.
Inspectors are empowered to inspect premises used for the production or manufacture of dairy produce. Any defects affecting the cleanliness and sanitation of the premises, or of the plant, machinery, and apparatus used in connection therewith, may be ordered to be remedied to the satisfaction of the inspector, and until so remedied their use in the production of dairy produce may be forbidden. Inspectors are authorised to condemn any dairy produce considered unfit for human consumption, and the sale of unwholesome milk or other dairy produce is prohibited.
Dairy produce intended for export must be sound and wholesome in all respects, and must comply with the requirements of the Act as to inspection, grading, and marking. The export of butter containing more than 16 per cent of water or less than 80 per cent of butterfat is prohibited. The export of cheese of which the water-free substance consists of less than 50 per cent of fats wholly derived from milk is also illegal.
The Cooperative Dairy Companies Act 1949 provides for the registration of cooperative dairy companies.
MEAT PRODUCTION AND DISPOSAL - Meat production for the seasons ended September 1958, 1959, and 1960 shows the total carcass weight of meat to be 687,700, 736,300, and 756,600 tons respectively. The following table shows in summary form production and disposal of meat for the years 1954-55 to 1958-59. Carcass meat is shown at bone-in weight.
| 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tons (thousand) | |||||
| Production | |||||
| Beef | 202.1 | 236.5 | 240.2 | 244.9 | 213.4 |
| Veal | 23.4 | 24.8 | 26.3 | 23.4 | 22.9 |
| Mutton | 137.9 | 141.0 | 125.7 | 121.4 | 168.4 |
| Lamb | 208.0 | 210.7 | 209.7 | 231.4 | 255.4 |
| Pig meat - | |||||
| Porker | 14.4 | 14.3 | 14.0 | 12.8 | 20.0 |
| Baconer | 21.9 | 23.3 | 20.6 | 23.1 | 20.5 |
| Chopper | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 3.0 |
| Total carcass meat | 610.2 | 653.4 | 639.1 | 659.1 | 703.6 |
| Edible offal | 27.0 | 28.4 | 30.8 | 28.6 | 32.7 |
| Total production | 637.2 | 681.7 | 669.9 | 687.7 | 736.3 |
| Disposal | |||||
| Exports to United Kingdom | 398.8 | 439.0 | 428.8 | 441.8 | 488.2 |
| Other exports | |||||
| Ships' stores | |||||
| For canning | 19.8 | 18.3 | 14.2 | 8.7 | 7.9 |
| Local consumption | 218.5 | 224.4 | 226.9 | 237.1 | 240.3 |
| Total production | 637.2 | 681.7 | 669.9 | 687.7 | 736.3 |
Meat consumed in New Zealand during 1958-59 represented approximately 32.6 per cent of total production. The total consumption per head at 231.1 lb, was an increase of 3.2 lb per head on the previous year. The figures in the next table give actual consumption during the years ended 30 September, by classes of meat.
| Total Consumption | Consumption per Head of Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | |
| tons (thousand) | lb | |||||
| Beef | 106.0 | 107.9 | 96.2 | 107.0 | 106.4 | 92.7 |
| Veal | 6.4 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 5.9 |
| Mutton | 67.7 | 67.5 | 79.8 | 68.4 | 66.5 | 76.9 |
| Lamb | 7.9 | 9.9 | 12.4 | 80 | 9.8 | 11.9 |
| Pig meat - | ||||||
| Porker | 10.0 | 10.4 | 14.5 | 10.1 | 10.3 | 14.0 |
| Baconer | 18.6 | 18.1 | 18.5 | 18.8 | 17.8 | 17.8 |
| Chopper | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.1 |
| Total carcass meat | 218.4 | 222.9 | 229.7 | 220.4 | 219.8 | 221.3 |
| Edible offal | 8.9 | 8.3 | 10.0 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 9.7 |
| Totals | 227.2 | 231.2 | 239.7 | 229.3 | 227.9 | 231.0 |
Details of sources of supply for local consumption in 1958-59 are given in the following table. Figures for meat export works include those for a few bacon works. In the case of local abattoirs and rural slaughterhouses, edible offal has been estimated at 4 per cent of total carcass weight excluding pig meats.
| Local Abattoirs | Meat Export Works | Rural Slaughter-houses | Farms | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tons | |||||
| Beef | 5 | 28,104 | 8,577 | 1,130 | 96,168 |
| Veal | 3, | 2,249 | 64 | 293 | 6,152 |
| Mutton | 33,053 | 27,229 | 4,346 | 15,156 | 79,784 |
| Lamb | 2,998 | 7,050 | 742 | 1,581 | 12,371 |
| Pig meat - | |||||
| Porker | 6,953 | 6,456 | 629 | 509 | 14,547 |
| Baconer | 2,385 | 16,112 | - | - | 18,497 |
| Chopper | 515 | 1,649 | - | - | 2,164 |
| Total carcass meat | 107,807 | 88,849 | 14,358 | 18,669 | 229,683 |
| Edible offal | 3,928 | 5,546 | 550 | - | 10,024 |
| Total | 111,735 | 94,395 | 14,908 | 18,669 | 239,707 |
The following table shows the numbers of the different classes of livestock slaughtered for food during each of the last 11 September years. The figures are for total killings - i.e., they include export works, abattoirs, rural slaughterhouses, and an allowance for killings on farms.
LIVESTOCK SLAUGHTERINGS
| Year Ended 30 September | Sheep | Lambs | Cattle | Calves | Pigs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcasses (000) | |||||
| 1950 | 5,000 | 12,795 | 693 | 1,275 | 677 |
| 1951 | 4,433 | 11,694 | 692 | 1,311 | 707 |
| 1952 | 5,929 | 12,415 | 743 | 1,311 | 685 |
| 1953 | 5,632 | 12,300 | 652 | 1,236 | 740 |
| 1954 | 5,467 | 13,324 | 780 | 1,330 | 760 |
| 1955 | 5,733 | 13,992 | 900 | 1,435 | 778 |
| 1956 | 5,886 | 14,807 | 1,000 | 1,406 | 816 |
| 1957 | 5,301 | 14,339 | 1,047 | 1,407 | 751 |
| 1958 | 5,081 | 15,883 | 1,106 | 1,314 | 768 |
| 1959 | 7,459 | 18,355 | 962 | 1,222 | 883 |
| 1960 | 7,356 | 19,283 | 956 | 1,234 | 863 |
Meat intended for export from New Zealand is slaughtered at meat export slaughterhouses, of which 37 are at present operating. They are licensed annually under the provisions of the Meat Act 1939 and regulations thereunder, which also authorise officers of the Department of Agriculture to carry out inspection of all meat whether for export or for local consumption.
The supervision of grading of meat for export is one of the responsibilities of the New Zealand Meat Producers Board. Grading at each freezing works is carried out, after slaughtering and dressing, by graders employed by the concern operating the freezing works. Supervising graders of the Meat Producers Board are allotted to each group of works to ensure uniformity of grading.
To supply meat for the larger urban centres there are at present 42 abattoirs operating, the larger ones being organised on the same lines as meat export works, and the supply is augmented by meat drawn from export works. At rural slaughterhouses meat is killed for consumption in small country towns and rural districts. Many farmers, particularly on sheep farms, kill their own meat.
To regulate and control the marketing of bobby calves, Bobby Calf Committees were established in 1938 and are now governed by the Bobby Calf Marketing Regulations 1955 under the control of the Dairy Board.
WOOL PRODUCTION - Although about fifth in order in actual size of flocks, New Zealand holds third place in the world as a producer of wool, and second place as an exporter. New Zealand specialises in the production and export of crossbred wool. With the exception of a small annual consumption by local mills the whole of the wool produced in New Zealand is exported. The quantity on a greasy basis used by local mills prior to the war was from 7,000,000 lb to 8,000,000 lb per annum, but this was greatly increased during the war period. By 1946-47 the wartime demand had eased and the quantity had fallen from 17,200,000 lb in 1943-44 to 13,100,000 lb. From then until 1957-58 local consumption ranged between 11,000,000 lb and 13,500,000 lb, rising to 14,500,000 lb in 1958-59 and 15,600,000 lb in 1959-60.
The following table shows the total wool production (greasy basis), the movement in the average price per pound of wool (greasy basis), and the estimated total value of wool production for the last 11 seasons.
| Season Ended 30 June | Total Wool Production (Greasy Basis) | Average Price per Pound (Greasy Basis) | Estimated Value of Total Wool Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| lb(m) | d. | £(m) | |
| 1950 | 390 | 37.98 | 61.7 |
| 1951 | 390 | 87.84 | 142.7 |
| 1952 | 407 | 40.19 | 68.2 |
| 1953 | 418 | 46.19 | 80.4 |
| 1954 | 426 | 50.25 | 89.2 |
| 1955 | 455 | 49.67 | 94.2 |
| 1956 | 462 | 46.19 | 88.9 |
| 1957 | 491 | 54.76 | 112.0 |
| 1958 | 496 | 41.16 | 85.1 |
| 1959 | 540 | 36.07 | 81.2 |
| 1960 | 577 | 44.65 | 107.3 |
On account of lack of information on changes in stocks of wool on farms, the above figures of production should not be taken as precise measures of actual production in each season.
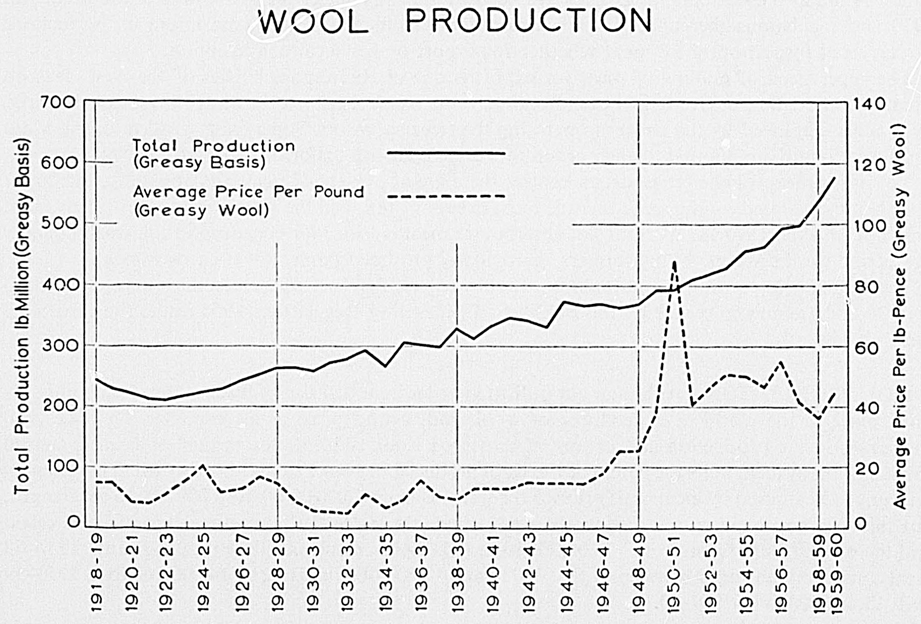
An analysis of wool sold at New Zealand auctions, according to quality groups, is given in the following table.
| Quality Group | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bales | Percentage of Total Sales | Bales | Percentage of Total Sales | Bales | Percentage of Total Sales | Bales | Percentage of Total Sales | Bales | Percentage of Total Sales | |
| 60-64's and up | 17,537 | 1.7 | 19,174 | 1.7 | 15,420 | 1.4 | 13,667 | 1.1 | 15,273 | 1.3 |
| 60's | 10,496 | 1.0 | 11,834 | 1.3 | 11,668 | 1.1 | 10,472 | 0.9 | 11,260 | 0.9 |
| 50-60's, 58's, and 56-58's | 96,457 | 9.5 | 101,797 | 9.5 | 95,385 | 8.7 | 89,269 | 7.4 | 95,270 | 7.8 |
| 50-56's and 56's | 127,422 | 12.7 | 131,041 | 12.5 | 125,350 | 11.4 | 116,583 | 9.7 | 123,831 | 10.2 |
| 52's | 68,221 | 6.8 | 73,607 | 7.0 | 65,168 | 5.9 | 50,203 | 4.2 | 55,659 | 4.6 |
| 50's | 145,710 | 14.5 | 158,769 | 15.0 | 145,357 | 13.2 | 147,959 | 12.3 | 155,342 | 12.7 |
| 48-50's | 174,376 | 17.3 | 167,431 | 16.0 | 151,700 | 13.8 | 187,049 | 15.6 | 176,425 | 14.5 |
| 46-50's and 48's | 268,599 | 26.7 | 289,883 | 27.5 | 326,258 | 29.7 | 377,687 | 31.5 | 387,322 | 31.8 |
| 46-48's | 79,808 | 7.9 | 82,708 | 7.8 | 111,241 | 10.1 | 150,538 | 12.6 | 143,602 | 11.8 |
| 46's and lower | 19,081 | 1.9 | 19,419 | 1.7 | 51,426 | 4.7 | 56,909 | 4.7 | 54,810 | 4.5 |
| Totals | 1,007,707 | 100.0 | 1,055,663 | 100.0 | 1,098,973 | 100.0 | 1,200,336 | 100.0 | 1,218,794 | 100.0 |
The Wool Industry Act 1944 provided for the establishment of the New Zealand Wool Board, replacing the New Zealand Wool Council established under the Wool Industry Promotion Act 1936. The Board's principal concern is the promotion of the wool industry, particularly in regard to markets, scientific and industrial research in relation to wool and sheep with a view to improvement in quality and quantity, and the discovery of new or improved methods of utilisation. Specific matters in relation to which the Board may be called upon to exercise certain functions are the production, handling, pooling, appraising, storage, distribution, marketing, and disposal of wool. The Board is empowered to act in combination or association with other bodies established outside New Zealand functioning on similar lines, such as the International Wool Secretariat and the Wool Bureau, and with the New Zealand Meat Producers Board and the New Zealand Dairy Board. It is also represented on the Wool Commission established by the Wool Commission Act 1951. To provide funds for the Board to carry out its functions the Wool Industry Act authorises a levy on all wool produced in New Zealand, the rate of the levy to be fixed each season by the Board. Under the Wool Commission Act, payment of this levy is at present suspended, the expenses of the Board and of the Commission being met, half from a charge imposed by regulation under that Act on all wool exported or used in New Zealand, and half from a special reserve account held by the Commission. The charge over the past few years has been 3s. per bale, with an equivalent amount being released from the reserve account, and was raised to 4s. per bale as from October 1959.
In December 1960 there was set up the Wool Research Organisation of New Zealand supported by the Wool Board and the Government (through the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research). The main object of the organisation is to promote and conduct research into the properties of wool, but it will also study problems of handling, storage, transport, marketing, and related matters.
References to the activities of the Wool Commission set up under the Wool Commission Act 1951 are to be found in Section 21.
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE - The Department of Agriculture has existed as a separate Department since 1892 and has been instrumental in building up farm production. The principal functions of the Department, as set out in the Department of Agriculture Act 1953, are - (a) to promote and encourage the development of all phases of the agricultural, pastoral, and horticultural industries in New Zealand, including the stock, poultry, fruit, vegetable, flax (Phormium tenax), tobacco, hops, and honey production industries, with a view to maintaining and improving the quality of the products derived from those industries and increasing the production of those products; (b) to promote and encourage the marketing and sale of those products.
Under the control of the Minister of Agriculture, the Department of Agriculture provides a service of which the main object is the advancement of the interests of primary production. Under a Director-General of Agriculture there are Divisional Directors of Animal Industry, Dairy, Farm Advisory, Horticulture, and Administration as well as the Directors of the Ruakura and Wallaceville Research Stations, since 1960 directly responsible to the Director-General.
While the service is primarily educative, the Department administers a number of Acts and regulations. Under the Animal Industry Division all meat killed at meat export slaughterhouses and abattoirs is inspected by qualified officers, and periodical inspections are carried out at registered rural slaughterhouses.
All meat intended for local consumption is graded by the inspection staff. The Division is responsible for the control of infectious diseases of livestock, and vaccination and testing are carried out to prevent and eradicate certain serious stock diseases. Special attention is given to herds supplying milk for human consumption. Livestock husbandry forms an essential part of the extension service provided by this Division.
All stock exported and imported is examined by the Division's veterinarians. Special instruction and advice are given in poultry keeping, swine husbandry, and wool growing and handling. Among other activities the Division is concerned with the control of noxious weeds and, with the Rabbit Destruction Council through district rabbit boards, in the eradication of rabbits. It also conducts a wool-testing service.
Work at Ruakura has been concerned to a large extent with animal nutrition under conditions of grassland farming, and Wallaceville with disease and diagnostic work. An additional diagnostic station is now being established at Taieri, near Dunedin. Associated with Ruakura are two substations, Whatawhata, near Hamilton, and Manutuke, near Gisborne.
Instruction in the manufacture of butter, cheese, milk powder, and casein is given by the Dairy Division. Dairy produce is inspected and graded before shipment and a close supervision is exercised over butter and cheese at all stages of manufacture. Dairy farm premises are inspected, and the Division is responsible for the registration of town milk supply premises. It also provides technical advice on the administration of market milk treatment. The Division has modern laboratories at Auckland and Wallaceville which provide a comprehensive examination of dairy products as a background to its controls of dairy produce quality. The Division is responsible for the registration and licensing of dairy factories, approval of their design, general suitability, and economic justification.
The Farm Advisory Division is concerned with research and advisory work in soil management, crop and pasture production, and farm management. A field staff of farm advisory officers acts as a link between the research stations and the farmers and also carries out cooperative field trials and demonstrations on farmers' properties. The Division has special sections devoted to seed certification and crops, field experimental work, pastures, soil conservation, farm management and economics, rural sociology and home economics, and farm engineering and machinery. Soil testing and assistance with farm drainage work are both undertaken on a fee-paying basis. The Division controls the following stations: Seed Testing Station, Palmerston North; Rukuhia Soil Research Station, Hamilton; Experimental Area, Marton; Phormium plantation, Moutoa; Flock House Farm of Instruction, Bulls; Winchmore Irrigation Station, Ashburton; and Invermay Agricultural Research Station, Mosgiel; and the following soil-conservation demonstration farms and areas: Waerenga-o-kuri, Tangoio, Makara, Cannock, Wither Hills, Moutere Hills, Adair, Tara Hills, Mid-Dome, Lake Cameron, and Wairakei.
The Horticulture Division provides an advisory service to fruitgrowers, market gardeners, nurserymen, flower growers, and beekeepers. Its officers inspect market gardens, nurseries, and apiaries for disease, and grade pip fruit for export and home consumption. The Division operates the plant quarantine service in New Zealand, which is designed to prevent the introduction of diseased plant material. At Te Kauwhata Experimental Station investigations are carried out into grape and wine production, and at Levin Research Station into berry fruit and vegetable production.
The Department's Editorial Section is responsible for the production each month of the Journal of Agriculture, which has a very wide circulation amongst farmers. In addition, a large number of bulletins on special subjects are produced, most of which are available free of charge.
In 1953 the former Marketing Department was absorbed by the Department and, although most of its functions have been assumed by statutory producer boards and authorities, the Department is concerned with many of the issues relating to the marketing of primary products, both overseas and within New Zealand, as well as with general economic problems affecting farming industries as a whole.
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH - Under the supervision of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research the Department devotes a large part of its activities to the promotion of agricultural research relating to most phases of agriculture.
The Soil Bureau has already made a survey of New Zealand soils which provides basic information on their most suitable use for agricultural and other purposes. It also undertakes research on the relationship of soil to problems of agriculture, horticulture, and forestry.
Microbiologists at the Bureau are making a survey of all soil micro-organisms and have isolated a fungus which has been found to be the cause of facial eczema disease in sheep. This discovery should not only facilitate control of this serious disease but also suggest a new method of approach to many animal nutrition and health problems.
The Crop Research Division is concerned with producing new and improved varieties of field and vegetable crops suited for local conditions. Special attention is given to the development of disease resistance.
The Hop and Tobacco Research Stations, both of which are subsidised by the industry, investigate problems relating to the growing of these two crops, while the Fruit Research Division performs a similar function for the whole fruit industry.
The work of the Grasslands Division is directed towards improving the productivity of our pastures by breeding improved varieties of grasses and clovers and investigating the factors affecting their growth.
Closely associated with the Grasslands Division is the Plant Chemistry Division, which undertakes research on plant nutrition and metabolism with special reference to the relationship between pasture quality and animal health and nutrition. Particular attention has been given to investigating the causes and control of bloat.
Farmers, fruitgrowers, and gardeners are assisted by the Plant Diseases Division, which investigates all types of plant diseases, with the object of bringing them under control. The Entomology Division studies New Zealand insects with special reference to those, such as grass grub, which attack agricultural crops. The Animal Ecology Section investigates the ecology of introduced mammals, such as the rabbit, with the object of discovering more effective methods of control.
The Wheat Research Institute, which like the Tobacco and Hop Research Stations is subsidised by industry, aims at improving the milling and baking qualities of the wheats produced in this country. A moisture-testing service helps farmers to determine when wheat crops are ready for harvesting.
The work of the Botany Division and the Applied Mathematics Laboratory has only an indirect bearing on agriculture. The Botany Division's function is to study all plant life in New Zealand, and in doing so it provides basic information of use to other divisions of the Department. The Applied Mathematics Laboratory assists other divisions by advising on the design of experiments so that these yield the maximum information.
Closely associated with the Department are a number of research associations and institutes which undertake research work of importance to agriculture. The Fertilizer Manufacturers' Research Association concerns itself with problems relating to the production, distribution, and use of fertilisers, the Wool Industries' Research Institute studies all aspects of wool manufacture, the Meat Research Institute studies problems affecting the meat industry, while the Dairy Research Institute investigates the production of milk in relation to feeding, breeding, and management of dairy animals and the manufacture of dairy products. It also investigates the building, design, and efficiency of dairy machinery.
The Value of Agricultural Research - The value of research to agriculture, which is not easy to assess in monetary terms, is reflected in the development of improved and higher yielding varieties of plants, in their more effective handling, and in the control of pests and diseases.
A soil survey of the whole of New Zealand has been completed, and the problems of mineral deficiency diseases such as bush sickness and dopiness have been solved. Tobacco research has resulted in the area devoted to this crop being doubled, simultaneously with the doubling of the yield per acre, and the industry has become one of the most prosperous of the rural industries. The Hop Research Station has recently developed two new hop varieties of improved quality and good yield, and with effective resistance to the serious disease, root rot. Effective control has been secured over a wide range of plant diseases. Ball smut and loose smut of cereals have almost disappeared, dry rot of brassicas has materially lessened, and blast of stone fruit has been controlled. A system of certifying spray materials effective against a wide range of diseases of horticultural and garden crops has been devised. A most effective culture to promote lucerne growth has been found and maintained. Numerous serious insect pests have been brought under control, and the diamond-back moth, white butterfly, and codling moth are not the menace they formerly were; subterranean caterpillar also has been checked and, more recently, grass grub, the most costly insect of all, has capitulated to the newer chemical insecticides.
The work of the Grasslands and Crop Research Divisions has resulted in the development and expansion of a profitable farm-seeds industry. Research into the breeding of new strains of pasture plants, and into the utilisation and management of pastures, has done much to enable New Zealand to lead the world in grassland farming, and raise its per-acre yield of meat and dairy produce. Research leading to successful pasture establishment on pumice soils of the central North Island has greatly increased production in this area. Rape and turnip seed, hitherto imported from overseas, are now produced locally and exported, as the result of breeding and selection work done by the Crop Research Division, which in addition, has improved the quality of oats, barley, lupins, carrots, and lucerne.
Of particular interest are two new high-yielding varieties of potato - Tahi and Rua - developed by the Division to withstand wind, drought, and competition from weeds.
Two new hop varieties - First Choice and Calycross - bred by the Hop Research Station are resistant to the serious disease, root rot, which has in the past few years greatly reduced yields from the most commonly used varieties.
The Wheat Research Institute, in collaboration with the Crop Research Division, has been responsible for improvement in wheat, flour, and bread quality by breeding several new varieties of wheat specially suited for local conditions. The latest variety developed, Aotea, has shown an increase in yield of more than 20 per cent over Cross 7, which was itself an improved variety developed 20 years previously. This advance in yield has been achieved without loss of baking quality. The Institute has also devised methods of utilising sprouted wheat and of controlling the vitamin B content of flour.
Corky pit of apples and other deficiency diseases of fruit have been overcome, and investigations in transport have vastly improved the quality of fruit arriving in the United Kingdom.
PASTURE GRASSES - Researches and experiments in regard to pasture grasses are regular features of the activities of both the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research. These experiments, which extend right on to individual farms throughout New Zealand, and are conducted in cooperation with the farmers themselves, are wide in their application, and cover all the major phases of pasture management, dealing in particular with such items as pasture mixtures, suitability as to soil types, methods of establishment and management, the efficient use of fertilisers, etc. The results are made available per medium of the Journal of Agriculture and such allied publications, as well as by special pamphlets which are distributed without charge. The farmer is thus enabled to avail himself of, and profit by, highly specialised knowledge and experience. In addition, a constant endeavour is being made not only to improve existing strains by such measures as seed certification and the provision of pedigree seed, but also to evolve new strains. At the beginning of the year 1960 there were 18,549,787 acres under artificially sown grasses (including 1,142,872 acres cut for seed, hay, or silage during the season), and in addition 13,035,549 acres of occupied land still remained in tussock or naturally established native grasses, making a total of 31,585,336 acres of grassland being farmed.
The following table shows the respective areas occupied by artificially sown grasses and by tussock and other naturally established native grasses during the five years specified.
| Year | Artificially Sown Pasture Grasses | Tussock and Other Naturally Established Native Grasses | Total Area Under Grass* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cut for Seed, Hay, or Silage | Not Cut for Seed, Hay, or Silage† | |||
*Includes lucerne. †Includes approximately 220,000 acres also sown with crops. | ||||
| acres | ||||
| 1954-55 | 974,807 | 16,799,187 | 13,391,857 | 31,165,851 |
| 1956-57 | 1,332,892 | 16,559,486 | 13,253,571 | 31,145,949 |
| 1957-58 | 1,220,483 | 16,782,347 | 13,206,701 | 31,209,531 |
| 1958-59 | 1,201,620 | 16,833,871 | 13,186,261 | 31,221,752 |
| 1959-60 | 1,142,872 | 17,406,915 | 13,035,549 | 31,585,336 |
TOPDRESSING (PASTURE LANDS) - An important characteristic of grassland farming is the use of an annual or semi-annual topdressing of artificial fertilisers. The chief fertiliser is superphosphate, which is manufactured in New Zealand from imported materials. Agricultural lime, produced locally, is also used in considerable quantities.
Farm production, particularly of pastoral products, is of such importance to the national economy that, whenever necessary, the Government has encouraged farmers to increase their use of fertilisers and lime. A direct subsidy on the price of superphosphate was paid from 1932 until 1947, but then it was discontinued and there are at present no subsidies on artificial fertilisers. Lime transport has been subsidised since 1898, originally under a system of free railage for 100 miles, but since 1947 by a Lime Transport Assistance Scheme, funds for which were until 1959 contributed by the New Zealand Meat Producers Board (70 per cent), the New Zealand Dairy Board (15 per cent), and the Consolidated Fund (15 per cent). The Boards are not now contributing to this scheme which is being continued on a modified basis by the Government.
The farmer is protected in the buying of his fertilisers by the Fertilisers Act 1927. In the registering of a fertiliser the name, the brand under which it is sold, the percentage of fertiliser ingredients, and the analysis have all to be stated.
Topdressing in New Zealand is carried out mainly on sheep- and cattle-grazing areas, including, of course, dairy farms; the North Island, which contains 88 per cent of the total cattle, accounted in 1959-60 for 74 per cent of the area topdressed.
The following table gives particulars of areas of grassland topdressed during the latest five years.
| Year | Grassland Area Topdressed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Artificial Fertiliser Only | With Lime Only | With Both Artificial Fertiliser and Lime | Total Grassland Topdressed | |
| *1959-60 figures relate to holdings of 10 acres and over, whereas figures for earlier years relate to holdings of 1 acre and over. | ||||
| acres | ||||
| 1955-56 | 8,932,515 | |||
| 1956-57 | 7,191,188 | 520,951 | 1,457,813 | 9,169,952 |
| 1957-58 | 7,309,985 | 514,341 | 1,433,338 | 9,257,664 |
| 1958-59 | 7,174,256 | 450,591 | 1,177,103 | 8,801,950 |
| 1959-60* | 7,140,228 | 421,908 | 1,335,171 | 8,897,307 |
The productive capacity of fertiliser manufacturers has been increased in recent years with the establishment of four new works. The fall in the use of fertilisers in 1958-59 was attributable to a reduction in farm incomes. Ruling prices for certain items of farm produce have since improved and the demand for fertiliser is again increasing.
The activities of the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research in the treatment of experimental plots from the various aspects of soil and crop requirements, and the subsequent data published thereon, have been an important factor in conveying to the farmer the many advantages to be derived from the scientific treatment of pastures.
While topdressing in the past was practically confined to sown grasses on the flat and gently undulating country, the application of fertilisers to the surface-sown hill-country pastures in increasing quantities from aircraft has followed from the development of commercial aerial topdressing operations since 1949. Further information in this connection is contained in Section 11D.
SUBSIDIES, GRANTS, ETC. - For many years a number of grants and subsidies have been paid to the farming industry from public funds. In addition, agricultural and pastoral production is assisted financially by grants to the agricultural colleges.
Subsidies reached their peak during the war and immediate post-war years, details of which are available in earlier issues of the Yearbook. In more recent years there has been a considerable curtailment of this type of assistance to farmers.
The following table shows the payments during the latest three years.
| Subsidy, Grant, etc. | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Refer text of following paragraph. | |||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Carriage of lime | 401,112* | 325,306* | 327,210* |
| Stock Act: compensation | 117,914 | 127,113 | 300,433 |
| Compensation for loss of production, ex gratia payments for hardship from compulsory tuberculosis test | 64,981 | 67,854 | 61,319 |
| Meat Act: compensation | 16,283 | 15,556 | 14,776 |
| Subsidies to rabbit boards | 528,391 | 508,496 | 498,444 |
| Grants to rabbit boards | 250,000 | 180,000 | 140,000 |
| Cow-testing organisations | 35,461 | 26,583 | 26,426 |
| Destruction of kea | 333 | 105 | 238 |
| Veterinary Services Council | 50,000 | 50,000 | 50,000 |
| Nassella Tussock Act: subsidies to boards | 23,592 | 69,174 | 68,599 |
| Noxious Weeds Act: subsidies to county councils and road boards | 26,714 | 37,912 | 37,997 |
| Compensation for scrapie disease | 10,824 | 5,000 | 3,000 |
| Emergency expenditure to assist primary producers | - | 23,827 | 31,438 |
In regard to the carriage of lime there was an agreement between the farmers' organisations and the Government that certain proportions of the subsidy paid could be recovered from the various stabilisation or reserve accounts of the farming industry. The total amount recovered in each of the three (July) years was £387,729 in 1957-58, £311,203 in 1958-59, and £166,205 in 1959-60. Approximately £7,000 still remains to be recovered in respect of this scheme.
Comment on some of the more important items is necessary to explain their origin and significance.
Fertiliser and Lime Subsidies - The transport of lime has been subsidised for many years to encourage its wider use.
Lime usage reached a peak of 1,535,000 tons in 1954, but receded to 1,174,000 tons in 1957, 1,046,000 tons in 1958, and 1,011,879 tons in 1959 (calendar years). Factors in the decline include the growing use of the trace element molybdenum in partial substitution for heavy liming in some areas as a means of facilitating availability of phosphate to plants, the ready availability of phosphate fertilisers at reasonable prices and a more judicious usage of lime according to proved soil needs.
The cost of the lime transport assistance scheme was £401,112 in 1957-58, £325,306 in 1958-59, and £327,210 in 1959-60. The cost was borne by the Meat Industry Account (70 per cent), Dairy Industry Account (15 per cent), and Consolidated Fund (15 per cent), being apportioned between the export and locally consumed portions of farm produce. As a result, however, of the exhaustion of the Dairy Industry Account no recovery was made from the Dairy Industry Account for its 15 per cent share of 1957-58 and 1958-59 costs, the Government paying both its share and the Dairy Board's share. In 1959 the Dairy Board and the Meat Producers Board informed the Government that they were discontinuing their contributions to the subsidy. The system which had operated from 1947 therefore ceased on 30 November 1959.
Since 30 November 1959 a subsidy on lime transport has been paid to farmers applying lime to newly developed land which is lime responsive, has not previously been limed, and which is cultivated and sown for the first time; or, if it cannot be cultivated, which receives its first dressing of lime. Farmers meet full transport costs and are entitled to claim a refund from the Department of Agriculture, at the same rates as applied up to 30 November 1959.
For a time there were subsidies on imported phosphatic fertilisers such as basic slag. These were designed to encourage imports when local manufacture of superphosphate was inadequate to meet the demand. For a time also there were payments from the Consolidated Fund to assist in the transport of superphosphate. This arose through the inability of the railway system to handle all the goods offering during the autumn peak season. To relieve the pressure, road and water services were utilised for fairly long hauls, and the difference in cost to the farmers between the service thus utilised, and the normal railage charge, was met by the Government. Both these types of payment have now been discontinued and are not likely to be reintroduced.
Rabbit Boards - In the post-war years a determined effort has been made to rid the country of rabbits which were lowering the carrying capacity of farmland and causing a loss of production running into many million pounds in value annually. Rabbit-infested areas were brought under rabbit board control. In 1948 there were 47 boards in the South Island and 61 in the North Island covering 18 million acres. By 1960 there were 148 South Island and 62 North Island boards covering 37 million acres. Rabbit board rates paid by some 40,000 farms are subsidised by the Government, which also makes grants to rabbit boards. Good progress has been made towards the eradication of the rabbit and this goal is now in sight in many areas.
Other Items - Most of the remaining subsidies represent attempts to deal with specific problems of disease and pest control which are of importance to the whole community but the handling of which would impose a serious burden on individuals or small groups. Under this heading come such items as compensation for diseased stock under the Meat Act and the Stock Act, and destruction of kea, etc. Subsidies of this nature are mostly charges against the vote of the Department of Agriculture. They are not recoverable except in the case of compensation paid for diseased stock under the Stock Act, where a partial recovery is obtained by the sale of by-products from condemned stock in certain cases.
FARM MACHINERY - The results of a full census of farm machinery taken in 1950 have been published in earlier volumes of the Yearbook.
The following table gives details of farm machinery for those items where a comparison is available for the years 1947, 1950, 1952, 1956, 1957, and 1960. The 1960 figures relate to holdings of 10 acres and over, whereas figures for earlier years relate to holdings of 1 acre and over.
| 1947 | 1950 | 1952 | 1956 | 1957 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*This item covers only those machines actually used for threshing wheat or oats during the year specified. †Estimates, 1953, 52,495; 1954, 55,623; 1955, 62,137; 1958, 73,499; 1959, 75,291. ‡Stationary shearing machine plants only. §Electric motors of over one-quarter horsepower only. | ||||||
| Milking machines | 32,596 | 36,368 | 37,563 | .. | 38,764 | 36,721 |
| Cream separators | 48,194 | 54,421 | .. | .. | .. | 30,608 |
| Shearing machines- | ||||||
| Plants | 14,564 | 18,791 | 20,810 | .. | 26,592 | 28,922§ |
| Stands | 33,907 | 40,536 | 44,472 | .. | .. | 61,637 |
| Agricultural tractors† | 21,156 | 34,918 | 45,734 | 66,478 | 71,456 | 78,415 |
| Rotary hoes and garden tractors | 1,646 | 3,093 | 4,380 | 10,459 | .. | .. |
| Electric motors | 82,721 | 10,683 | 123,439 | .. | 139,080 | 122,758‡ |
| Internal-combustion engines | 23,109 | 29,926 | 29,052 | .. | .. | .. |
| Threshing machines* | 1,641 | 1,900 | 1,965 | .. | .. | .. |
The figures show a continuation of the trend towards more intensive mechanisation of farm work that has been in evidence over a considerable period.
Milking Machines - Information concerning milking machines on farms was first collected in 1919, in which year there were 7,577 plants recorded. Since that year the use of milking machines has expanded rapidly. Of the 1,905,534 cows in milk on 31 January 1952, 1,799,375, or 94 per cent, were on holdings employing milking machines. In 1951 the corresponding percentage was 94 and in 1942, 87.
Agricultural Tractors - During the 15 years from 1942 to 1957 the number of agricultural tractors employed on holdings of 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries rose from 13,967 to 71,456. These figures do not include rotary hoes or garden tractors, which showed an increase from 813 in 1942 to 4,380 in 1952.
The number of holdings on which tractors were located in 1952 was 38,434 out of a total of 90,288. The 6,046 cases in 1952, in which there were more than one tractor on the farm, were made up as follows: two tractors, 5,110; three, 720; four, 157; five or more, 59.
As at 31 January 1960, there were 78,415 tractors on farm holdings of 10 acres and over outside borough boundaries. These were made up as follows.
| Diesel oil - Crawler | Number | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|
| 20 h.p. and over | 6,612 | 8.43 |
| Under 20 h.p | 203 | 0.26 |
| Wheel- | ||
| 20 h.p. and over | 12,892 | 16.44 |
| Under 20 h.p | 723 | 0.92 |
| Total, diesel oil | 20,430 | 26.05 |
| Petrol or kerosene - Crawler- | ||
| 20 h.p. and over | 4,738 | 6.04 |
| Under 20 h.p | 1,696 | 2.16 |
| Wheel- | ||
| 20 h.p. and over | 39,785 | 50.74 |
| Under 20 h.p. | 11,766 | 15.01 |
| Total, petrol or kerosene | 57,985 | 73.95 |
| Total, tractors | 78,415 | 100.00 |
Header Harvesters - There has been a rapid expansion in the use of header harvesters since their introduction to New Zealand in 1930. By 1952 most of the threshing mills had disappeared, the figures being 1,852 header harvesters, 62 threshing mills, and 51 tin mills on farm holdings of 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries. The number of header harvesters on holdings of 10 acres and over outside borough boundaries as at 31 January 1960 was 4,746.
GENERAL - Crops grown in New Zealand are in general able to meet domestic needs for agricultural products, apart from tropical and subtropical products such as tea, sugar, cotton, etc., though a substantial proportion of wheat requirements is imported.
Local requirements of all the important fruits and berries grown in temperate zones are met by New Zealand orchard production. Citrus fruits are grown in the subtropical northern portion of the North Island, and grapes are also cultivated in certain localities with a favourable climate. In addition to meeting local demand, there is a substantial export trade in apples and pears.
Home gardens supply a considerable proportion of family requirements of vegetables, but there is a substantial area planted in market gardens, both inside and outside borough boundaries, to meet the needs of a growing population. Potato production is normally adequate but has occasionally to be supplemented by imports. The production of onions has been more than sufficient for local requirements of recent years.
Animals can be grazed in open pasture for the full 12 months of the year, but the winter growth of grass, except in certain favoured localities, requires to be supplemented in order to keep stock in good condition during the colder months, and in some districts supplementary fodders are necessary in the drier summer months. The supply of supplementary fodders is adequate both in quantity and in quality, so that New Zealand imports stock food to a very minor extent only.
Hay and silage crops are grown almost exclusively on the farms where they are consumed, though some districts specialise in the growing of certain other supplementary fodder crops. The bulk of the supplementary fodders other than grass and clover hay, and silage, is grown in the South Island, since the colder climate necessitates more extensive supplementary feeding than in the North Island.
The renewal and extension of pastures require the annual supply of very considerable quantities of grass seeds, which are now grown almost entirely in New Zealand. There is a small import of certain classes of seeds, but this is almost negligible in relation to requirements; on the other hand, an appreciable export trade in some species of grass seeds has been developed.
GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION - Grain growing is localised to a considerable extent, the Canterbury Land District, with its fertile plains, supplying in 1959-60, 63 per cent of New Zealand's wheat yield, 41 per cent of the oats threshed, and 72 per cent of the barley yield. Maize growing is largely confined to certain portions of the Gisborne and South Auckland districts. The growing of peas for threshing is carried out extensively in Canterbury, and to a lesser extent in Marlborough, Wellington, and Otago, Canterbury alone producing over half of the total yield. In the season 1959-60, 60 per cent of the area closed off for production of grass seed was in Canterbury district.
The Canterbury district also produces a large proportion of the commercial potato crop, followed by Wellington, while the growing of potatoes for the early market is of importance in a few relatively frost-free areas, particularly Pukekohe, near Auckland. The Pukekohe district also provides that city with a considerable portion of its vegetable requirements as well as being the main onion-growing area of the Island. Wellington draws most of its vegetable supplies from the Otaki and Levin districts, while Ohakune, in the centre of the North Island, with climate and soils suitable for the production of cabbages and broccoli, supplies both cities with these vegetables. Further large areas are utilised for these purposes in the Hastings district of Hawke's Bay, which is also the largest contributor of canned or processed vegetables.
In the South Island market gardening is carried on near the cities, and on the rich soils near Christchurch some 2,000 acres are devoted to this purpose; also to the immediate south of Oamaru and on the Taieri Plains just south of Dunedin there are other areas aggregating 1,000 acres. Nelson also produces considerable quantities of fresh and processed vegetables, most of which are marketed in Wellington.
Commercial orchards in New Zealand are largely confined to certain areas suited by climatic and soil conditions. The Nelson and Hawke's Bay districts are famed for their apple and pear orchards, a high percentage of the crops from these districts normally being exported. Central Otago is well suited to the growing of stone fruits, notably apricots. Hawke's Bay and Nelson are also noted for their peach production. In certain particularly warm areas of the North Island with suitable soils citrus fruits are grown, the principal areas being Kerikeri, in Northland; Tauranga, in the Bay of Plenty; and Gisborne.
Grape growing is of importance in Auckland and Hawke's Bay, and to a lesser extent in South Auckland. Tobacco growing is confined to the Nelson district, hop growing also being concentrated in this area.
A detailed analysis of arable cropping farms in 1949-50 was undertaken as part of the World Census of Agriculture. The following table, compiled from the results of this analysis, shows the number of arable cropping farms in each regional area. The dominance of the South Island, with 90 per cent of the farms of this type, is clearly shown.
| Regional Area* | Principally Arable Cropping | Arable Cropping | Special Cropping Units | Grass Seed Production | Other Arable Holdings | Total Number of Arable Holdings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Sheep | With Dairying | With Beef | With Horse Raising | With Poultry | With Horticulture | With Mixed Farming | ||||||
| *For details of counties included see page 407. | ||||||||||||
| North Island | ||||||||||||
| North Island | 7 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8 |
| South Auckland | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Cape Colville | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Central Plateau | 6 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 9 |
| Western Uplands | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Taranaki | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| East Cape | 68 | 7 | 3 | - | - | 6 | - | 5 | - | 4 | - | 93 |
| Hawke's Bay | 62 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 20 | 5 | 96 |
| Rangitikei | 11 | 9 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 3 | 3 | 1 | - | 29 |
| Manawatu | 16 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 28 |
| Castlepoint | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Wairarapa | 11 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 3 | - | 19 |
| Featherston | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Totals | 186 | 23 | 17 | 1 | - | 6 | 1 | 13 | 8 | 30 | 7 | 292 |
| South Island | ||||||||||||
| Nelson | 24 | 3 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 5 | - | 12 | 5 | 51 |
| Marlborough | 58 | 40 | 7 | 3 | - | - | 2 | 23 | - | 30 | 13 | 176 |
| Westland | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| North Canterbury | 13 | 50 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | - | 7 | 4 | 79 |
| Foothills | 26 | 31 | 7 | - | - | - | - | 12 | - | 11 | 2 | 89 |
| Canterbury Plains | 317 | 281 | 58 | - | 2 | 6 | - | 90 | 8 | 15 | 32 | 809 |
| Christchurch | 52 | 4 | 6 | - | - | - | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 75 |
| Banks Peninsula | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 5 |
| Mackenzie | 3 | 7 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 4 | - | 16 |
| South Canterbury | 249 | 451 | 56 | - | 1 | 3 | - | 115 | 4 | 42 | 27 | 948 |
| Otago | 12 | 8 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 29 |
| Central Otago | 21 | 31 | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 8 | 4 | 66 |
| Southern | 24 | 25 | 4 | 2 | - | - | - | 4 | - | 84 | 8 | 151 |
| Totals | 801 | 932 | 142 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 5 | 264 | 15 | 219 | 99 | 2,494 |
| Totals | 987 | 955 | 159 | 6 | 3 | 15 | 6 | 277 | 23 | 249 | 106 | 2,786 |
The area devoted to each of the principal crops in the 1959-60 season and the percentage area in each land district are given in the following table.
| Name of Crop | Area (New Zealand) | Land District Percentages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Auckland | South Auckland | Gisborne | Hawkes Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | North Island | ||
| For threshing | acres | |||||||
| Wheat | 163,158 | - | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.9 | - | 4.9 | 7.0 |
| Oats | 33,524 | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | 0.8 | - | 1.3 | 2.3 |
| Barley | 62,497 | - | 0.5 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 0.1 | 12.3 | 17.4 |
| Maize | 8,338 | 5.1 | 10.4 | 80.0 | 3.9 | - | 0.1 | 99.5 |
| Peas | 28,370 | 0.2 | - | 0.3 | 3.0 | - | 9.4 | 12.9 |
| For chaff, hay, or silage- | ||||||||
| Oats (incl. oats for green fodder) | 47,039 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 4.4 | 10.8 |
| Grasses, clovers | 870,098 | 12.0 | 38.7 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 11.2 | 8.8 | 74.6 |
| Lucerne | 139,258 | 0.5 | 8.2 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 0.8 | 2.2 | 15.4 |
| Green fodder- | ||||||||
| Rape | 147,400 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 4.8 | - | 3.4 | 9.8 |
| Chou moellier, kale | 149,917 | 2.3 | 10.3 | 0.4 | 15.7 | 3.4 | 26.4 | 58.5 |
| Wheat, barley, and maize for chaff, hay, silage, or green fodder | 20,054 | 6.9 | 16.2 | 3.4 | 5.7 | 2.3 | 11.5 | 46.0 |
| Root crops- | ||||||||
| Swedes | 182,828 | 0.8 | 14.0 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 24.6 |
| Turnips | 213,143 | 3.4 | 11.3 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 6.2 | 25.8 |
| Turnips and rape | 40,767 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 6.9 |
| Potatoes | 21,410 | 14.1 | 4.6 | 1.6 | 5.3 | 0.7 | 18.8 | 45.1 |
| Grasses, clovers, and lucerne for seed | 133,516 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 7.2 | 0.2 | 3.5 | 13.0 |
| Orchards, market gardens, nurseries | 30,675 | 22.5 | 7.1 | 2.7 | 16.2 | 1.1 | 8.1 | 57.7 |
| Vegetable crops for processing | 10,924 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 8.8 | 50.3 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 75.2 |
| Name of Crop | Area (New Zealand) | Land District Percentages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Southland | South Island | ||
| For threshing- | ares | |||||||
| Wheat | 163,158 | 3.1 | 0.2 | - | 66.4 | 13.9 | 9.4 | 93.0 |
| Oats | 33,524 | 2.7 | 0.3 | - | 50.1 | 13.8 | 30.8 | 97.7 |
| Barley | 62,497 | 3.7 | 3.7 | - | 69.0 | 5.8 | 0.4 | 82.6 |
| Maize | 8,338 | - | 0.1 | - | 0.4 | - | - | 0.5 |
| Peas | 28,370 | 16.6 | 0.4 | - | 62.6 | 5.7 | 1.8 | 87.1 |
| For chaff, hay, or silage- | ||||||||
| Oats (incl. oats for green fodder) | 47,039 | 5.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 44.8 | 22.2 | 13.5 | 89.2 |
| Grasses, clovers | 870,098 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 8.8 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 25.4 |
| Lucerne | 139,258 | 3.9 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 51.1 | 21.3 | 7.2 | 84.6 |
| Green fodder- | ||||||||
| Rape | 147,400 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 50.3 | 25.0 | 11.1 | 90.2 |
| Chou moellier, kale | 149,917 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 15.6 | 10.9 | 12.7 | 41.5 |
| Wheat, barley, and maize for chaff, hay, silage, or green fodder | 20,054 | 7.6 | 1.6 | - | 24.1 | 16.4 | 4.3 | 54.0 |
| Root crops- | ||||||||
| Swedes | 182,828 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 14.7 | 20.4 | 37.8 | 75.4 |
| Turnips | 213,143 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 44.0 | 14.1 | 11.5 | 74.2 |
| Turnips and rape | 40,767 | 1.3 | 1.1 | - | 29.7 | 18.7 | 42.3 | 93.1 |
| Potatoes | 21,410 | 1.1 | 3.3 | - | 40.0 | 6.5 | 4.0 | 54.9 |
| Grasses, clovers, and lucerne for seed | 133,516 | 4.5 | 1.1 | - | 60.3 | 8.6 | 12.5 | 87.0 |
| Orchards, market gardens, nurseries | 30,675 | 2.3 | 16.7 | - | 8.4 | 14.7 | 0.2 | 42.3 |
| Vegetable crops for processing | 10,924 | 3.2 | 13.6 | - | 6.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 24.8 |
STATISTICS - Detailed statistics of crops are contained in the Report on the Farm Production Statistics of New Zealand issued annually by the Department of Statistics. It should be noted that, unless otherwise stated, the statistics quoted in this subsection relate to holdings of 1 acre and over situated outside borough boundaries up to the year 1958-59. Commencing with the year 1959-60 a change was made in the coverage so that it included only holdings of 10 acres and over situated outside borough boundaries.
BUSHEL WEIGHTS - For statistical and other purposes it is at times necessary to convert bushel units to a weight basis. For New Zealand produce and fruit, conversion is effected by using the following weights per bushel for the commodities mentioned.
| Produce | Weight of Bushel | Fruit | Weight of Bushel |
|---|---|---|---|
| lb | lb | ||
| Wheat | 60 | Apples | 40 |
| Oats | 40 | Pears | 38 |
| Barley | 50 | Quinces | 40 |
| Maize | 56 | Peaches | 42 |
| Peas | 60 | Nectarines | 42 |
| Ryecorn | 56 | Apricots | 42 |
| Beans | 65 | Plums | 42 |
| Grass seed | 20 | Cherries | 42 |
| Oranges | 42-43 | ||
| Lemons (uncured) | 42 |
AREA UNDER CULTIVATION - A general summary of the areas under cultivation during each of the last 11 years is given in the following table. The statistics quoted in this and other tables in this subsection relate to holdings of 1 acre or upwards outside borough boundaries up to the year 1958-59. From 1959-60 the coverage was changed to holdings of 10 acres and upwards outside borough boundaries. (The effect of this change on comparability is not great. In 1956-57 although some 13 per cent of holdings outside boroughs were 1 and under 10 acres in nearly all items the percentage in this group was less than 1 per cent. Exceptions were market gardens, orchards, nurseries, and potato and onion cropping.
| Year | Pasture Land* | Field Crops | Plantations | Orchards | Lying Fallow | Other Cultivated Land | Total Cultivated Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding areas of grasses and clovers cut for seed, hay, or silage, which have been included in field crops. †Includes market gardens and nurseries (previously in “Other Cultivated Land”). | |||||||
| acres | |||||||
| 1949-50 | 17,164,957 | 1,931,393 | 908,360 | 18,853 | 90,819 | 114,448 | 20,228,830 |
| 1950-51 | 17,042,347 | 2,061,429 | 902,164 | 19,722 | 114,536 | 111,032 | 20,251,230 |
| 1951-52 | 16,797,344 | 2,062,910 | 915,835 | 19,973 | 143,367 | 109,598 | 20,049,027 |
| 1952-53 | 16,574,439 | 2,131,170 | 949,533 | 21,464 | 173,626 | 111,364 | 19,961,596 |
| 1953-54 | 16,573,004 | 2,060,678 | 967,666 | 21,246 | 144,328 | 111,986 | 19,878,908 |
| 1954-55 | 16,557,819 | 2,141,623 | 962,592 | 21,998 | 161,201 | 116,136 | 19,961,369 |
| 1955-56 | |||||||
| 1956-57 | 16,346,749 | 2,427,189 | 915,132 | 19,944 | 163,604 | 97,017 | 19,969,635 |
| 1957-58 | 16,561,688 | 2,296,429 | 906,219 | 20,518 | 173,378 | 100,086 | 20,058,318 |
| 1958-59 | 16,614,071 | 2,344,175 | 921,864 | 20,292 | 138,054 | 99,123 | 20,137,579 |
| 1959-60 | 17,200,636 | 2,312,189 | 944,065 | 30,675† | 126,022 | 88,894 | 20,702,481 |
In the following pages statistics of the principal crops are quoted with explanatory comment. In addition to summary tables, covering in each instance a range of related items, important individual crops are discussed under separate headings.
PRINCIPAL FIELD CROPS - The following table shows the areas under each of the principal field crops for the years 1954-55 to 1959-60.
| Crop | 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Including turnips and rape mixed. †Excluding wheat, oats, barley, maize, and peas fed off. ‡Included under “other crops”. §Rape, kale, and chou moellier only. | ||||||
| acres | ||||||
| Wheat | 108,617 | .. | 68,315 | 86,254 | 135,583 | 166,317 |
| Oats | 101,742 | .. | 136,319 | 87,260 | 93,595 | 80,563 |
| Barley | 52,291 | .. | 69,206 | 75,342 | 63,587 | 73,061 |
| Maize | 8,267 | .. | 10,439 | 11,398 | 12,134 | 14,669 |
| Peas for threshing | 29,506 | 25,239 | 24,759 | 31,876 | 26,080 | 28,370 |
| Linseed | 7,741 | .. | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ |
| Linen flax | 304 | 555 | 685 | 774 | 761 | 699 |
| Potatoes | 21,373 | 17,665 | 22,519 | 24,047 | 23,796 | 21,410 |
| Turnips and swedes* | 504,728 | .. | 443,952 | 429,386 | 444,210 | 436,738 |
| Mangolds | 2,052 | .. | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ |
| Onions | 1,616 | 1,442 | 1,363 | 1,399 | 1,305 | 1,275 |
| Tobacco | 3,104 | .. | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ | ‡ |
| Green fodder† | 306,258 | .. | 269,919? | 277,748? | 288,311? | 297,317? |
| Grasses, clovers, and lucerne for seed | 189,187 | .. | 274,643 | 209,669 | 173,438 | 133,516 |
| Grasses and clovers for hay or silage | 691,662 | 1,001,371 | 920,341 | 865,699 | 891,634 | 870,098 |
| Lucerne for hay or silage | 93,958 | 137,908 | 145,115 | 136,548 | 139,258 | |
| Other crops | 19,217 | .. | 46,821 | 50,462 | 53,193 | 48,898 |
| Totals | 2,141,623 | .. | 2,427,189 | 2,296,429 | 2,344,175 | 2,312,189 |
The figures quoted in the foregoing table in respect of wheat, oats, barley, maize, and peas relate to the total areas under these crops for grain or fodder. A considerable portion of the area under cereal crops, particularly oats, is cut for chaff, hay, or silage, or is fed off. In regard to peas it should be noted that additional areas of this crop for domestic consumption in the form of green peas are included under market gardens and crops for processing.
GRAIN AND SEED CROPS - Details of areas for threshing, total yields, and yields per acre of the principal grain and seed crops during recent years are set out in the following table.
| Year | Wheat | Oats | Barley | Maize | Peas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Estimated. | |||||
| Areas for Threshing | |||||
| acres | acres | acres | acres | acres | |
| 1951-52 | 89,955 | 45,561 | 46,064 | 6,449 | 24,379 |
| 1952-53 | 127,225 | 49,087 | 55,334 | 5,973 | 27,265 |
| 1953-54 | 113,813 | 20,529 | 68,479 | 4,062 | 30,889 |
| 1954-55 | 103,989 | 31,164 | 41,674 | 3,154 | 29,506 |
| 1955-56 | 68,479 | 42,168 | 49,195 | .. | 25,239 |
| 1956-57 | 65,743 | 56,496 | 59,776 | 5,486 | 24,759 |
| 1957-58 | 83,936 | 29,981 | 65,881 | 6,346 | 31,876 |
| 1958-59 | 132,913 | 34,011 | 53,620 | 6,612 | 26,080 |
| 1959-60 | 163,158 | 33,524 | 62,497 | 8,338 | 28,370 |
| 1960-61* | 165,000 | 39,000 | 62,000 | 8,000 | 26,000 |
| Total Yields | |||||
| bushels | bushels | bushels | bushels | bushels | |
| 1951-52 | 3,890,167 | 2,469,530 | 2,182,175 | 381,835 | 730,288 |
| 1952-53 | 4,525,298 | 2,385,129 | 2,139,886 | 349,194 | 614,417 |
| 1953-54 | 4,783,227 | 945,386 | 3,335,399 | 259,248 | 953,749 |
| 1954-55 | 4,113,444 | 1,602,058 | 1,991,875 | 201,913 | 885,432 |
| 1955-56 | 2,658,428 | 1,947,404 | 2,031,526 | 634,846 | |
| 1956-57 | 2,950,273 | 2,888,310 | 2,854,592 | 313,486 | 845,644 |
| 1957-58 | 3,727,117 | 1,460,149 | 3,552,229 | 302,618 | 1,046,847 |
| 1958-59 | 6,038,822 | 1,575,755 | 2,661,090 | 378,908 | 829,852 |
| 1959-60 | 8,700,199 | 1,825,104 | 3,136,837 | 702,668 | 923,810 |
| 1960-61* | 8,250,000 | 2,028,000 | 3,286,000 | .. | .. |
| Yields per Acre | |||||
| bushels | bushels | bushels | bushels | bushels | |
| 1951-52 | 43.25 | 54.20 | 47.37 | 59.21 | 29.96 |
| 1952-53 | 35.57 | 48.59 | 38.67 | 58.46 | 22.54 |
| 1953-54 | 42.03 | 46.05 | 48.71 | 63.82 | 30.88 |
| 1954-55 | 39.56 | 51.41 | 47.80 | 64.02 | 30.01 |
| 1955-56 | 38.82 | 46.18 | 41.30 | .. | 25.15 |
| 1956-57 | 44.88 | 51.12 | 47.75 | 57.14 | 34.16 |
| 1957-58 | 44.40 | 48.70 | 53.92 | 47.69 | 32.84 |
| 1958-59 | 45.43 | 46.33 | 49.63 | 57.31 | 31.82 |
| 1959-60 | 53.32 | 54.44 | 50.19 | 84.27 | 32.56 |
| 1960-61* | 50.00 | 52.00 | 53.00 | .. | .. |
WHEAT - With a view to reducing imports of Grade A wheat necessary for mixing purposes, the Wheat Research Institute has been endeavouring to encourage the growing in New Zealand of better-quality varieties which do not require blending with imported wheat. New varieties developed by the institute have included Cross 7, Hilgendorf, Yielder, Arawa, and Aotea. Tests of flour from commercial crops confirmed the outstanding baking quality of Hilgendorf wheat. In an endeavour to encourage the growing of this variety, and so help to bring about an improvement in flour and bread quality, a premium of 1s. per bushel was payable to farmers on all crops of Hilgendorf wheat handled by the Wheat Committee. The premium was further increased to 2s. per bushel from the 1957-58 season.
Wheat production dropped away between 1955 and 1958. With an immediate target of 150,000 acres the Government increased the price of wheat grown in the South Island by 2s. a bushel and in the North Island by 6d. a bushel from the 1958-59 season. Current prices are 13s. 6d. a bushel in the South Island and 14s. 6 1/2d. in the North Island. The introduction of these prices was an attempt to reduce the steadily increasing wheat imports which over the three years ended 1958 averaged 10,080,000 bushels annually.
As a result of the increase in the overall price of wheat, combined with the release of Arawa and later Aotea varieties, and also the drop in the fat-lamb prices, the acreage threshed increased from 83,936 acres in 1957-58 to 132,913 acres in 1958-59, then to 163,158 acres in 1959-60. It is estimated that 165,000 acres were threshed in the 1960-61 season.
The following diagram shows the fluctuations that have occurred in the area sown in wheat during the last 32 seasons, together with the total yield and the average yield per acre.
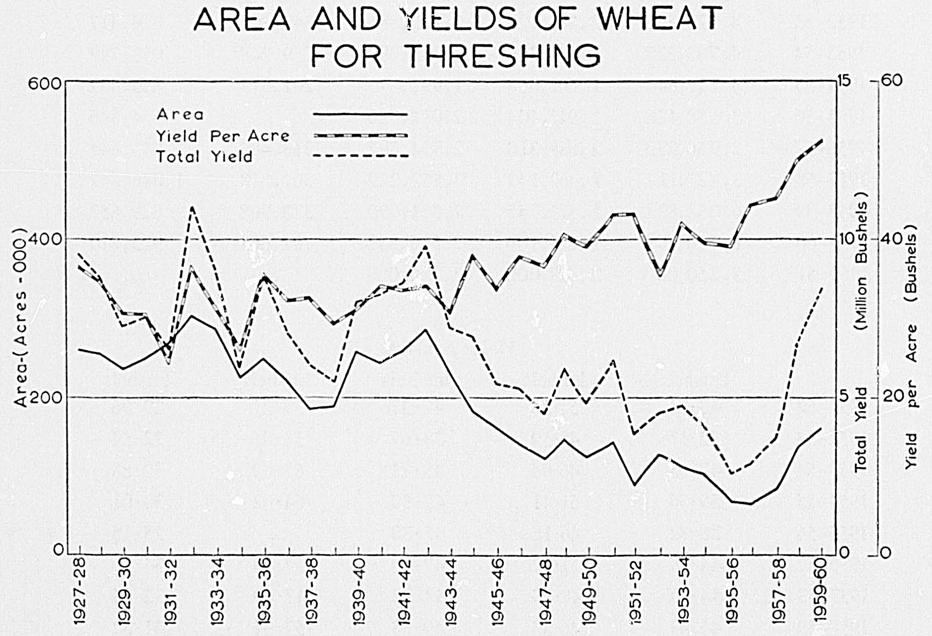
Wheat Committee - Control of the importation of wheat and flour and of the distribution of both imported and locally produced wheat rests with the Wheat Committee. The operations of this Committee, which consists of representatives of flourmillers, wheat growers, and bakers, with the Minister of Industries and Commerce as Chairman, and his nominee from the Department of Industries and Commerce as Deputy Chairman, are governed by the Board of Trade (Wheat and Flour) Regulations.
All New Zealand milling wheat is purchased from farmers by the Wheat Committee through the agency of the grain merchants acting as brokers for the Committee. The Committee is responsible for the importation of any wheat and flour and the distribution of imported poultry wheat in the North Island; in the South Island poultry wheat is not controlled. Its functions also include arrangements for the processing of wheat and the sale of flour to merchants, bakers, pastrycooks, grocers, and others.
The annual consumption of wheat in New Zealand approximates 14 million bushels - some 9 million bushels being required for flour, and the balance for poultry food and seed. Over the five seasons ending with 1959-60 the annual local production of wheat has averaged 4,814,968 bushels, while imports over the five years ended 1960 averaged 8,850,000 bushels annually.
Varieties of Wheat-The choice of wheat varieties for sowing is influenced by their suitability to local conditions of climate, soil type, etc. Wheat growers receive valuable guidance regarding suitable varieties as the result of research work and field trials undertaken by the Wheat Research Institute and the Department of Agriculture. A survey of varieties of wheat grown for threshing was carried out in 1960. This survey related to wheat sown in 1959 and harvested in 1960 and showed the following results.
| Variety | Area (Acres) | Yield | Average Yield per Acre (Bushels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushels | Percentage of Total Production | |||
| *Area of wheat threshed in survey by varieties; total area threshed was 163, 158 acres. | ||||
| Aotea | 118,660 | 6,404,891 | 79.01 | 53.98 |
| Arawa | 14,961 | 808,837 | 9.98 | 54.07 |
| Cross 7 | 5,585 | 283,811 | 3.50 | 50.82 |
| Gabo | 3,507 | 177,702 | 2.19 | 50.67 |
| Hilgendorf | 2,721 | 93,030 | 1.15 | 34.19 |
| Tainui | 2,311 | 107,505 | 1.33 | 46.52 |
| Other varieties | 4,748 | 230,415 | 2.84 | 48.53 |
| Totals | 152,493* | 8,106,191 | 100.00 | 53.16 |
OATS - The area under oats declined steadily after the Second World War, the greatest decrease being in oats for chaff, hay, and silage. This decline resulted largely from the replacement of horses by tractors. During the five years 1944-45 to 1948-49 the average area under oats for all purposes was 192,834 acres, and of this figure the proportion for chaff, etc., was 41.5 per cent, whereas for the five years 1950-51 to 1954-55 the comparable figures were 111,598 acres and 29.4 per cent. Taking the same two 5-yearly periods the average area under oats for chaff, etc., has declined by 59 per cent.
It is estimated that some 39,000 acres will yield an expected 2,028,000 bushels for 1960-61 based on a pre-harvest estimated yield of 52 bushels per acre.
Varieties of Oats Threshed - A survey covering the season 1959-60 gave the following results:
| Variety | Area (Acres) | Yield | Average Yield per Acre (Bushels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushels | Percentage of Total Production | |||
| *Area of oats threshed in survey by varieties; total area threshed was 33,524 acres. | ||||
| Onward | 14,142 | 909,148 | 57.76 | 64.29 |
| Algerian | 3,835 | 143,469 | 9.11 | 37.41 |
| Grey Winter | 3,703 | 138,969 | 8.83 | 37.53 |
| Dun | 1,651 | 58,725 | 3.73 | 35.57 |
| Black | 1,419 | 72,453 | 4.60 | 51.06 |
| Abundance | 582 | 24,995 | 1.59 | 42.95 |
| Milford | 480 | 32,227 | 2.05 | 67.14 |
| Achilles | 375 | 16,799 | 1.07 | 44.80 |
| Other varieties | 3,125 | 177,306 | 11.26 | 56.74 |
| Totals | 29,312* | 1,574,091 | 100.00 | 53.70 |
BARLEY - Prior to 1945 considerable quantities of barley were imported, mainly for use as stock food, but the quantities imported since then have declined considerably. Outstanding increases in the area planted were recorded in each of the four years up to 1947-48, the area threshed in that year (63,398 acres) and the yield of grain (2,087,900 bushels) exceeding all previous figures. Since then harvestings have fluctuated considerably from year to year. New records were established in the 1953-54 season, when 68,479 acres were grown for threshing, and a record average yield of 48.71 bushels per acre gave a total production of 3,335,399 bushels. This was followed by a sharp fall in the 1954-55 season, when 41,674 acres were threshed for a yield of 1,991,875 bushels. However, the area threshed continued to build up again up to 1957-58, some 49,195 acres being harvested in 1955-56, 59,776 acres in 1956-57, and 65,881 acres in 1957-58 with a fall to 53,620 acres in 1958-59 and a rise again to 62,497 acres in 1959-60.
Varieties grown in the 1959-60 season were as set out below.
| Variety | Area (Acres) | Yield | Average Yield per Acre (Bushels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushels | Percentage of Total Production | |||
| *Area of barley threshed in survey by varieties; total area threshed was 62,497 acres. | ||||
| Research | 28,504 | 1,444,460 | 51.45 | 50.68 |
| Kenia | 21,801 | 1,103,953 | 39.33 | 50.64 |
| Other varieties | 5,252 | 258,711 | 9.22 | 49.26 |
| Totals | 55,557* | 2,807,124 | 100.00 | 50.53 |
Of the total area grown, 86 per cent was threshed for grain in 1960, the remaining 14 per cent being used for stock fodder (mostly feeding off). Malting varieties normally account for over 80 per cent of the area sown in barley.
The area for threshing in 1960-61 is estimated at 62,000 acres, and, if pre-harvest yield estimates are realised, some 3,286,000 bushels can be expected.
PEAS - The area of peas for threshing has fallen considerably since the peak of 50,000 acres averaged over the three seasons 1946-47 to 1948-49, the average area for the five years 1955-56 to 1959-60 being 27,265 acres. There have been fluctuations in the export figures for this commodity. In 1949 nearly 850,000 bushels were exported, whereas by 1953 the amount had fallen to approximately 370,000 bushels. Over the five years 1955 to 1959 exports averaged 498,000 bushels annually.
Varieties of peas grown in the 1959-60 season were as under.
| Variety | Area (Acres) | Yield | Average Yield per Acre (Bushels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bushels | Percentage of Total Production | |||
| *Area of peas threshed in survey by varieties; total area threshed was 28,370 acres. | ||||
| Garden varieties | 11,147 | 355,516 | 43.54 | 31.89 |
| Field varieties- | ||||
| Blue Boiling | 1,225 | 37,497 | 4.59 | 30.61 |
| Maple | 11,188 | 381,819 | 46.76 | 34.13 |
| White | 1,474 | 41,761 | 5.11 | 28.33 |
| Total | 25,034* | 816,593 | 100.00 | 32.62 |
The foregoing figures exclude green peas grown for market or processing (e.g., canning and quick freeze). There has been an increasing use of quick-frozen peas since they were introduced to the New Zealand market a few years ago, and apart from a large local consumption of these and canned peas New Zealand also exports large quantities of both commodities. A peak quantity of 9,685,000 lb of canned peas was exported in 1956, the bulk of which went to the United Kingdom. There has since been a decline in the exports of this commodity, the figures for the last three years being: 1958, 6,209,000 lb; 1959, 3,530,000 lb; and 1960, 2,287,000 lb. Also 27,961 cwt of frozen peas were exported in 1960 and 30,000 cwt in 1959. No earlier export figures for frozen peas are available.
POTATOES - The production of potatoes is usually adequate to meet the home market.
Under the Potato Growing Industry Act 1950 a Potato Board was established consisting of seven members, three of whom are representative of the growers on an elective basis, three nominated by the New Zealand Grain, Seed, and Produce Merchants' Association (Incorporated), and one an officer of the Public Service acting in an advisory capacity.
The principal functions of the Board are to ensure that adequate supplies of main-crop potatoes are available for consumption in New Zealand, and for that purpose to enter into contracts with growers for the growing of main-crop potatoes. The Act provides that the Board may impose a levy not exceeding 30s. per ton on main-crop potatoes sold by growers, the proceeds of which are to be applied by the Board in payment of charges, etc., for which it may become liable in the exercise of its functions.
The Board undertakes to compensate contract growers for any declared unsold number one grade contract produce held by growers at the end of the season. For the 1960-61 season the rate involved varies according to varieties from £12 to £15 per ton in the South Island and £14 to £17 per ton in the North Island.
Figures for area and yield of potatoes for the latest five years are as follows.
| Year | Area | Total Yield | Yield per Acre |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Not strictly comparable with previous years due to a change in coverage from 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries to 10 acres and over outside borough boundaries. (In 1956-57 potato areas and yields in the 1 and under 10 acre group represented 4 per cent of the total.) | |||
| acres | tons | tons | |
| 1955-56 | 17,665 | 100,677 | 5.70 |
| 1956-57 | 22,519 | 145,247 | 6.45 |
| 1957-58 | 24,047 | 157,105 | 6.53 |
| 1958-59 | 23,796 | 149,926 | 6.30 |
| 1959-60* | 21,410 | 156,807 | 7.32 |
The estimated area for 1960-61 is placed at 20,000 acres. No advance estimates of yield are attempted.
ONIONS - Areas in, and yields of, onions for the latest five years are as follows.
| Year | Area | Total Yield | Yield per Acre |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Not strictly comparable with previous years due to a change in coverage from 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries to 10 acres and over outside borough boundaries. (In 1956-57 areas in onions in the 1 and under 10 acre group represented 9 per cent of the total.) | |||
| acres | tons | tons | |
| 1955-56 | 1,442 | 13,416 | 9.30 |
| 1956-57 | 1,363 | 13,573 | 9.96 |
| 1957-58 | 1,399 | 13,363 | 9.55 |
| 1958-59 | 1,305 | 11,959 | 9.16 |
| 1959-60* | 1,275 | 15,242 | 11.95 |
In earlier years the production of onions was rarely sufficient to supply domestic requirements. As onions are a semiperishable commodity it was found convenient to export in the flush of the New Zealand season, and to obtain supplies from overseas later in the year. However, a considerable improvement has been effected in the keeping qualities of the varieties grown, and insignificant quantities of onions have been imported into New Zealand for some years, while over the five years 1955 to 1959 exports averaged over 2,500 tons annually.
LINSEED - The area under this crop has fluctuated considerably over a long period. The highest level of 24,437 acres was reached in 1951-52. Reduced world prices, among other factors, led to a sharp contraction in the area planted in the 1953-54 season, only 2,822 acres being sown. This area gave a yield of 29,022 cwt of seed at an average of 10.28 cwt per acre. There was a partial recovery in the 1954-55 season, when 7,741 acres were harvested for a total yield of 77,588 cwt. Because of falling overseas prices the sole processing plant for linseed oil at Dunedin closed down at the end of 1954, but reopened again in 1957 in order to conserve overseas funds. A quantity of linseed is also used in stock feed mixtures.
SUPPLEMENTARY FODDER CROPS - Although grass is the main crop of the farmer in New Zealand, at certain periods during the year the pastures need supplementing in order to maintain stock in a satisfactory condition. In mid winter the grass is at a low stage of productivity generally, while under dry summer conditions it loses part of its nutritive value. During these periods it is necessary that some extra feed should be provided, and this is usually done either by cutting the grass for hay or silage when there is an ample surplus on the pastures during the flush of the growing season, or by the provision of green fodder or root crops.
The following table gives detailed figures of the areas of the supplementary fodder crops available during the years 1952-53 to 1959-60.
| Year | Chaff, Hay, or Silage | Green Fodder | Root and Other Crops for Feeding to Stock | Total Area of Fodder Crops | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereal Crops | Grasses and Clovers, Including Lucerne | Cereal Crops | Other Crops | |||
*Separate figures not available; these two items totalled 97,704 acres in 1952-53, 96,778 acres in 1956-57, 74,110 acres in 1957-58, 77,743 acres in 1958-59, and 67,093 acres in 1959-60. † Rape, kale, and chou moellier only. ‡ Swedes, turnips, and turnips and rape only. § Excludes small areas of other minor fodder crops. | ||||||
| acres | ||||||
| 1952-53 | * | 877,140 | * | 277,012 | 429,205 | 1,681,061 |
| 1953-54 | 23,089 | 769,620 | 45,181 | 309,643 | 478,382 | 1,625,915 |
| 1954-55 | 34,126 | 785,620 | 56,810 | 306,258 | 508,603 | 1,691,417 |
| 1955-56 | .. | 1,001,371 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1956-57 | * | 1,058,249 | * | 269,919† | 443,952‡ | 1,868,898§ |
| 1957-58 | * | 1,010,814 | * | 277,748† | 429,386‡ | 1,792,058§ |
| 1958-59 | * | 1,028,182 | * | 288,311† | 444,210‡ | 1,838,446§ |
| 1959-60 | * | 1,009,356 | * | 297,317† | 436,738‡ | 1,810,504§ |
In 1959-60 grasses and clovers cut for hay or silage totalled 870,098 acres and lucerne 139,258 acres. Oats was the only cereal crop utilised in any quantity for this purpose. Oats also was the principal cereal crop fed off to stock. The area of oats cut for chaff, hay, or silage or fed off amounted to 47,039 acres. The principal green-fodder crops apart from oats are rape (147,400 acres) and chou moellier including kale (149,917 acres). Swedes and turnips are the principal root crops grown in New Zealand, the total area sown in these crops in 1959-60 being 436,738 acres (including 40,767 acres of turnips and rape mixed).
GRASS SEED - The total area of grasses, clovers, and lucerne cut for seed during the 1959-60 season was 133,516 acres, as against 173,438 acres in 1958-59. Canterbury, Otago, and Southland Land Districts between them provided 81 per cent of the area cut for seed.
The areas of grass, clover, and lucerne crops harvested for seed, distinguishing the principal varieties, during each of the last five years for which figures are available, are given in the table following. (1955-56 and 1959-60 figures are not available.)
| Crop | 1953-54 | 1954-55 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryegrass | |||||
| acres | |||||
| Perennial | 33,681 | 50,804 | 79,766 | 41,960 | 40,651 |
| Italian | 5,261 | 8,120 | 9,230 | 6,010 | 6,635 |
| Short rotation (H1) | 16,898 | 21,617 | 25,118 | 15,707 | 17,532 |
| Cocksfoot | 6,279 | 7,145 | 7,923 | 9,139 | 10,826 |
| Chewings fescue | 8,587 | 9,988 | 5,928 | 3,931 | 3,693 |
| Crested dogstail | 4,540 | 6,439 | 11,146 | 8,457 | 6,631 |
| Red clover (including cowgrass) | 17,118 | 20,197 | 27,796 | 27,380 | 19,281 |
| White clover | 45,069 | 49,486 | 84,466 | 65,897 | 44,061 |
| Other grasses and clovers | 16,477 | 15,391 | 23,270 | 31,188 | 24,128 |
Quantities (in dressed weights) of grass and clover seeds treated by machine dressing plants for the last three years are given below.
| Type of Seed | Unit | Quantity (Year Ended 31 October) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| Ryegrass — | ||||
| Perennial | bush | 513,746 | 739,318 | 1,008,817 |
| Short rotation (H1) | bush | 231,612 | 303,857 | 319,230 |
| Italian (including W. Wolths) | bush | 81,719 | 79,647 | 80,815 |
| Cocksfoot | lb | 1,430,055 | 1,097,080 | 1,430,150 |
| Chewings fescue | lb | 315,146 | 313,818 | 243,072 |
| Crested dogstail | lb | 977,019 | 643,552 | 1,000,794 |
| Brown top | lb | 746,685 | 235,608 | 201,811 |
| Timothy | lb | 583,497 | 747,182 | 1,178,085 |
| White clover | lb | 6,899,177 | 2,992,945 | 4,576,066 |
| Suckling clover | lb | 345,979 | 116,367 | 157,101 |
| Suckling white mixture | lb | 742,960 | 177,472 | 327,848 |
| Cowgrass (including broad red clover) | lb | 1,482,161 | 1,449,802 | 793,661 |
| Montgomery red clover | lb | 775,897 | 843,535 | 1,197,605 |
| Lucerne | lb | 531,084 | 382,022 | 524,090 |
| Other grasses and clovers | lb | 115,635 | 47,174 | 107,267 |
Large quantities of grass and clover seed have been exported during recent years, especially to the United Kingdom, Australia, and the United States of America. Details of the volume and value of exports during recent years will be found in Section 22B of this issue.
HORTICULTURE — In 1949–50 a special farming type classification as part of the World Census of Agriculture showed the following breakup by regional areas of those farms where 75 per cent or more of the farm enterprise was devoted to horticulture or, if a mixed farm, where 50 per cent or more was given to horticultural production. Although the North Island had 52 per cent of these enterprises the South Island predominated on an acreage basis with 74 per cent.
The following table shows the number of horticultural enterprises by regional areas in 1949–50.
| Orchards | Vineyards | Principally Market Gardens | Small Fruits | Nurseries | Apiculture | Other Horticultural Holdings | Total Horticultural Enterprises* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excluding boroughs. | ||||||||
| Northland | 371 | 38 | 75 | 14 | 33 | 10 | 147 | 688 |
| South Auckland | 9 | 7 | 224 | 2 | 24 | 3 | 25 | 294 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | 16 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 16 | 18 | 75 |
| Cape Colville | 10 | - | 5 | - | 2 | 2 | 4 | 23 |
| Central Plateau | 123 | 2 | 29 | - | 4 | 8 | 45 | 211 |
| Western Uplands | 2 | - | 22 | - | 2 | 5 | 4 | 35 |
| Taranaki | - | - | 7 | 1 | 22 | 3 | 2 | 35 |
| East Cape | 25 | 7 | 49 | - | 1 | 8 | 38 | 128 |
| Hawke's Bay | 314 | 12 | 208 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 87 | 654 |
| Rangitikei | 8 | - | 17 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 3 | 43 |
| Manawatu | 5 | 1 | 138 | 3 | 21 | 2 | 15 | 185 |
| Wairarapa | 1 | - | 6 | 1 | - | - | 2 | 10 |
| Featherston | 2 | - | 21 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 41 |
| Nelson | 224 | 2 | 75 | 32 | 11 | 1 | 461 | 806 |
| Marlborough | 23 | - | 27 | 4 | 5 | - | 37 | 96 |
| Westland | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 10 | - | 13 |
| North Canterbury | - | - | 3 | - | - | 3 | - | 6 |
| Foothills | 28 | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 31 |
| Canterbury Plains | 9 | - | 34 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 69 |
| Christchurch | 47 | - | 362 | 27 | 35 | - | 75 | 546 |
| Banks Peninsula | 8 | - | 12 | - | 1 | - | 4 | 25 |
| Mackenzie | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | 2 |
| South Canterbury | 16 | - | 75 | 51 | 12 | 12 | 47 | 213 |
| Otago | 88 | - | 32 | 15 | 13 | 4 | 28 | 180 |
| Central Otago | 118 | - | 12 | 6 | - | 4 | 28 | 168 |
| Southern | 1 | - | 7 | 2 | 9 | 16 | 2 | 37 |
| Remainder | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Totals | 1,449 | 77 | 1,450 | 183 | 236 | 132 | 1,088 | 4,615 |
GARDENS AND PLANTATIONS — The acreages for market gardens, plantations, etc., for the last five years are given below. Forest Service plantations are covered by these figures. It should be noted that the statistics relate only to holdings of 1 acre or more outside boroughs up to and including 1958–59 and holdings of 10 acres and over outside boroughs from 1959–60. In the case of market gardens, nurseries, and private gardens the 1959–60 figures are not comparable with earlier years for this reason. In 1956–57 the area of market gardens in the 1 and under 10 acre group represented 19 per cent of the total acreage; in the case of nurseries the percentage was 21 per cent and for private gardens 5 per cent. Plantations were scarcely affected, being well under 1 per cent. Figures include berry-fruit gardens. The table has been compiled from farm production statistics. Figures for 1955–56 are not available.
| Year | Market Gardens* | Nurseries | Private Gardens, etc. | Plantations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding crops for processing. †Separate figure not available; market gardens, nurseries, and orchards, 30,675 acres. | ||||
| acres | ||||
| 1954-55 | 17,795 | 1,522 | 94,727 | 962,592 |
| 1956-57 | 13,529 | 2,805 | 80,683 | 915,132 |
| 1957-58 | 13,565 | 2,909 | 83,612 | 906,219 |
| 1958-59 | 13,328 | 2,984 | 82,811 | 921,864 |
| 1959-60 | † | † | 88,894 | 944,065 |
Market Gardens — The Vegetables Levy Act 1957 provides for the collection of a levy from vegetable growers in respect of the sale of certain vegetables in order to provide funds for the benefit generally of vegetable growers. The following vegetables are covered by the Act: asparagus, beans, beetroot, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower (including broccoli), celery, cucumber, leek, lettuce, marrow, melon (musk, rock, or water), parsnip, peas (excluding any crop harvested for marketing as dried peas), pumpkin, radish, rhubarb, silver beet, spinach, squash, sweet corn, tomatoes. Previously market gardens were registered under the Commercial Gardens Registration Act but with the revocation of the Act only estimates can now be made (including gardens within boroughs). The Department of Agriculture estimates that 2,676 growers were gardening an area of 31,381 acres in 1960. Processing firms are estimated to have used produce from approximately half the total acreage to meet the mounting local and export demand for processed vegetable products.
The total area of berry fruits according to figures estimated by the Department of Agriculture as at 31 March 1960 was 947 acres. Raspberries, the major crop, occupied 528 acres; strawberries, 264 acres; gooseberries, 50 acres; black currants, 59 acres; loganberries, 16 acres; and boysenberries, 30 acres. These estimates include those grown in borough areas. The only berry fruit under control is raspberry, for which local marketing committees have been established in Nelson (since 1940) and in Canterbury and Otago (since 1950), while a Central Council of Raspberry Growers was created by the Raspberry Marketing Regulations 1950. The 1959–60 season produced a crop of 827 tons of raspberries, while strawberries were estimated at 741 tons, black currants 74 tons, gooseberries 176 tons, boysenberries 46 tons and loganberries at 22 tons. In 1959–60 season there were 475 growers of berry fruits, some of these growers producing two or more types of fruits; 227 of these growers grew strawberries; 222, raspberries; 36, gooseberries; 33, black currants; 27, boysenberries; and 14, loganberries.
Nurseries — Since 1939, owners or occupiers of nurseries raising for sale certain specific trees, shrubs, and plants have been required to register their nurseries before being permitted to sell trees or plants. The number of nurseries so registered at 31 December 1959 totalled 489 and these covered 1,495 acres.
The 1,587 acres recorded under nurseries on holdings of 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries in 1950 were divided into the following categories: flowers and ornamental shrubs, 812 acres; forest-tree seedlings, 352 acres; seedling fruit trees, 255 acres; and vegetable seedlings, 168 acres.
Home Garden Production — Home garden production, on which a question was asked for the first time at the 1956 Census, is dealt with in the next table.
| Proportion of Requirements | Potatoes Grown | Other Vegetables Grown | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Households | Per Cent of Total Specified | Number of Households | Per Cent of Total Specified | |
| All | 48,084 | 8.73 | 45,498 | 8.27 |
| Three-quarter | 24,293 | 4.41 | 54,395 | 9.88 |
| One-half | 46,251 | 8.40 | 69,901 | 12.70 |
| One-quarter | 56,866 | 10.33 | 56,604 | 10.29 |
| Under one-quarter | 101,288 | 18.40 | 107,329 | 19.50 |
| Nil | 273,811 | 49.73 | 216,630 | 39.36 |
| Not specified | 12,459 | - | 12,695 | - |
| Totals | 563,052 | 100.00 | 563,052 | 100.00 |
Of the specified cases 49.73 per cent of householders did not grow potatoes and 39.36 per cent did not grow other types of vegetables.
Of the total households where a return was made 62 per cent kept a garden and 38 per cent had no garden. Where only 37 per cent of dwellings with one occupant returned “yes”, this rose sharply to 59 per cent of households with two occupants. The proportions answering “yes” to this question increased continuously from two to six occupants, and declined from seven occupants onwards.
ORCHARDS AND THE FRUIT INDUSTRY — Because of New Zealand's geographic position the climate is varied, and favours the production of a wide variety of fruits. The climate in most parts of Northland, Auckland, Bay of Plenty, and Gisborne is sufficiently mild for the production of citrus and other subtropical fruit such as passion fruit, tree tomatoes, and Chinese gooseberries. Central Otago, with its hot summers and severe winters, produces the greater part of the English plums, apricots, and cherries. The main apple- and pear-growing areas are in Nelson, Hawke's Bay, Central Otago, and near Auckland. Peach and plum orchards are similarly distributed.
The area in holdings of 1 acre and over outside borough boundaries returned as under fruit trees was given as 20,292 acres at 31 January 1959.
The Orchard Levy Act 1953 provides for the levying in each year by the New Zealand Fruitgrowers' Federation of an amount not exceeding £2 10s. on occupiers of orchards containing no fewer than 120 fruit trees. This levy (at present £1 10s.) is used as required in assisting and developing the industry.
During 1958 the Department of Agriculture made the second comprehensive field survey of fruit trees in commercial orchards. (It is proposed to continue to carry out similar surveys every five years.) This survey covered all orchards with 100 or more deciduous fruit trees, over 50 citrus trees, or over half an acre in berry fruits, grapes, subtropical fruits, and mixed orchards of half an acre and over. The Horticulture Division of the Department of Agriculture has supplied the following numbers of fruit trees of principal kinds in commercial orchards based on 1958 survey figures: apple, 1,087,116; pear, 144,701; quince, 6,073; peach, 306,902; nectarine, 32,235; apricot, 121,426; plum, 104,744; cherry, 19,091; lemon, 41,235; orange, 40,616; grapefruit, 48,651; mandarin, 13,213; tangelos, 1,037.
The growing of outdoor grapes is chiefly confined to the districts situated between the North Cape and Hawke's Bay. The vineyard area in wine grapes in 1959 was estimated at 899 acres in full bearing and 130 acres in young non-bearing vines. A further 98 acres were established in dessert varieties, while glasshouse vineries occupied about 436,200 square feet. In 1940 the quantity of wine produced was 185,000 gallons from a licensed vineyard area of 469 acres. The figures for 1959 show wine production at 829,822 gallons made by 154 licensed wine makers.
Apples and Pears — A summary of the activities of the New Zealand Apple and Pear Board appears in Section 21.
Quantities of apples and pears marketed in New Zealand by the Board in the last five seasons are given below. These figures exclude direct sales from fruitgrowers to the public.
| Season | Apples | Pears | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| bushel cases | |||
| 1956 | 1,482,853 | 359,134 | 1,841,987 |
| 1957 | 1,388,478 | 349,119 | 1,737,597 |
| 1958 | 1,605,086 | 365,845 | 1,970,931 |
| 1959 | 1,525,400 | 447,600 | 1,973,000 |
| 1960 | 1,461,100 | 356,600 | 1,817,700 |
The following table shows the quantities of the main varieties of apples and pears marketed in New Zealand by the Apple and Pear Marketing Board and exported to the United Kingdom and elsewhere during the 1959–60 season, together with the total estimated production of each variety. Factories are given authority to purchase fruit for processing direct from the growers.
| Variety | Marketed in New Zealand by the Apple and Pear Board | Exported to United Kingdom | Exported to Other Countries | Estimated Total Production* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Estimated by Horticulture Division, Department of Agriculture. | ||||
| bushel cases | ||||
| Apples — | ||||
| Sturmer Pippin | 269,600 | 234,235 | 247,444 | 867,000 |
| Delicious | 239,600 | 95,542 | 207,003 | 606,000 |
| Jonathan | 132,000 | 162,117 | 125,767 | 450,000 |
| Granny Smith | 213,500 | 75,539 | 92,349 | 477,000 |
| Cox's Orange Pippin | 84,500 | 158,919 | 156 | 303,000 |
| Ballarat Seedling | 50,400 | 70,540 | 15,106 | 206,000 |
| Golden Delicious | 66,500 | 63,409 | 67,718 | 223,000 |
| Gravenstein | 109,900 | - | - | 133,000 |
| Dougherty | 38,400 | 74,541 | 10,842 | 144,000 |
| Rome Beauty | 51,200 | 7,924 | 25,157 | 90,000 |
| Others | 205,500 | 107,932 | 59,210 | 457,000 |
| Totals, apples | 1,461,100 | 1,050,698 | 850,752 | 3,956,000 |
| Pears — | ||||
| William's Bon Chretien | 58,500 | - | - | 181,000 |
| Winter Cole | 127,200 | 703 | 1,763 | 140,000 |
| Winter Nelis | 78,900 | - | 425 | 89,000 |
| Others | 92,000 | 21,666 | 522 | 169,000 |
| Totals, pears | 356,600 | 22,369 | 2,710 | 579,000 |
Citrus Fruits — Estimated quantities of citrus fruits marketed in New Zealand by the Citrus Marketing Authority, together with direct sales to the public by citrus growers, are given in the following table.
| Year | Grapefruit | Lemons* | Sweet Oranges | Mandarins and Other Citrus Fruits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Figures for lemons relate to packed 3/4 bushel cases. †Provisional. | ||||
| bushels | ||||
| 1956 | 124,700 | 101,800 | 17,300 | 2,000 |
| 1957 | 92,000 | 105,600 | 12,900 | 3,600 |
| 1958 | 130,500 | 89,000 | 14,800 | 3,400 |
| 1959 | 138,900 | 119,200 | 13,900 | 4,500 |
| 1960† | 151,200 | 113,900 | 17,400 | 5,700 |
Reference to the Citrus Marketing Authority is to be found in Section 21.
Subtropical Fruits - Although there is no district in New Zealand where the climate is purely subtropical, parts of the Auckland district are warm enough for a number of subtropical fruits to flourish, and several are produced commercially. Notable among these are tree tomatoes, Chinese gooseberries, passion fruit, and feijoas. Estimated production figures for 1959 are: tree tomatoes, 865 tons; passion fruit, 90 tons; Chinese gooseberries, 548 tons. Feijoas are not an important crop in New Zealand and annual estimates of the production of these fruits have been discontinued. The estimate for 1958 for this crop was 39 tons. The Bay of Plenty, Kerikeri, and Auckland (in that order) are the chief producing districts for subtropical fruits.
HOPS - Practically the whole of the hop gardens are located in Waimea county. Production per acre usually ranges between 1,200 lb and 1,500 lb, and the aggregate crop is usually sufficient to satisfy local requirements as well as to provide a surplus for export. Production in the 1959–60 season was 898,600 lb, compared with 1,090,239 lb in the previous year. The 1959–60 yield met all requirements and 49,543 lb were exported, compared with 332 lb in 1958–59.
The hop area at the end of 1960 was estimated at 590 acres, 77 acres less than the previous year. Though small extensions had been made in some gardens, a number of gardens had been reduced through the removal of areas which had become uneconomic on account of root-rot disease which is still a major limiting factor in hop production.
A Hop Marketing Committee of six members (one Government and five producer) was established by the Hop Marketing Regulations 1939 to regulate and control the marketing either locally or overseas of all hops produced in New Zealand and to assist the industry generally.
TOBACCO - After the establishment of the Tobacco Board in 1936 production rose from 1,197,161 lb in 1935–36 to 5,436,314 lb in 1950–51. Reduced plantings since then have been largely offset by higher yields. Commercial tobacco growing is confined to those to whom licences are issued by the Tobacco Board established under the Tobacco Growing Industry Act 1935 to control the industry. Most of the tobacco produced is flue-cured, producing a yellow-leaf tobacco which is largely used for the manufacture of cigarettes, the balance, air-cured, being used mainly in the manufacture of smoking mixtures and pipe tobacco. Some 7,542,982 lb of raw tobacco leaf was imported for the calendar year 1959.
The following particulars relating to tobacco production have been taken from the annual report of the New Zealand Tobacco Board. It should be noted that the figures relate to the total commercial tobacco production and not merely to holdings of 10 acres or over situated outside borough boundaries.
| Season | Number of Growers | Area Planted | Production | Estimated Value of Crop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| acres | lb | £(000) | ||
| 1955–56 | 418 | 3,137 | 4,733,086 | 979 |
| 1956–57 | 416 | 3,138 | 4,463,976 | 922 |
| 1957–58 | 411 | 3,265 | 4,650,711 | 962 |
| 1958–59 | 469 | 3,534 | 5,606,951 | 1,156 |
| 1959–60 | 468 | 3,750 | 7,075,577 | 1,537 |
The production figures represent the weight of the leaf purchased from growers before redrying. Flue-cured leaf accounted for 97.26 per cent and air-dried leaf for 2.74 per cent of the 1959–60 crop.
Mechanisation of the industry on the growing side continues to increase. Picking and tying, however, are still done by hand, although a tobacco-harvesting machine imported from the United States of America has been highly successful.
PHORMIUM TENAX - Certain areas in various parts of New Zealand are covered by natural stands of Phormium tenax (New Zealand flax), once used by the Maoris for many purposes and one of the earliest of this country's exports. Only a small proportion of the natural area is millable but this, together with an estimated planted area of about 3,000 acres, produces some 5,000 tons of fibre and tow. The industry provides at least one-third of the local requirements of woolpacks while large supplies of rope were produced during the war. Prior to the war the export trade diminished on account of competition from Manila hemp and Mexican sisal, and has been discontinued in recent years.
LINEN FLAX — Investigations into the growing of linen flax in New Zealand were first instituted in 1936. Though 403 acres of linen flax were grown in 1939–40, the industry was not established on a commercial basis till the 1940–41 season, when 13,118 acres were grown under contract to the Crown in response to a request received from the United Kingdom Ministry of Supply. This area was increased to 21,067 acres by 1942–43, but with the end of the war fell to approximately 4,500 acres and further decreases occurred, the area recorded in 1953–54 being only 1,886 acres.
In 1955 the Linen Flax Corporation decided to concentrate operations in the Geraldine district and much smaller acreages have been grown in the last five seasons: 1955–56, 555 acres; 1956–57, 685 acres; 1957–58, 774 acres; 1958–59, 761 acres; and 1959–60, 699 acres.
The 1959 harvest yielded 2,063 tons of straw. The crop from the 761 acres was very good, though the average yield of fibre was slightly lower, being 10.2 per cent, compared with 10.4 per cent for the preceding season.
The Linen Flax Corporation of New Zealand reported that production from the single factory still operating was as under.
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| tons | |||
| Straw processed | 553 | 1,233 | 1,526 |
| Scutched fibre | 54 | 128 | 156 |
| Seed | 49 | 131 | 169 |
| Tow | 26 | 57 | 54 |
| Linmeal | 37 | 88 | 105 |
With the 1959 harvest the production of fibre reached the objective of 150 tons annually which had been set in 1955 when the industry was concentrated around Geraldine.
There is a strong demand for all linen fibre produced in New Zealand from a local manufacturer of twine who uses this kind of fibre in the making of bag- and bale-closing twine, meat- and ham-rolling twine, and for other purposes which require a twine made from a strong durable fibre.
SEED CERTIFICATION — Commencing with the certification of seed potatoes and seed wheat in 1928, the Department of Agriculture has extended its activities in this direction to include such crops as perennial ryegrass, Italian ryegrass, short rotation (H1) ryegrass, cocksfoot, timothy, browntop, Phalaris tuberosa, white clover, cowgrass (broad red clover), Montgomery red clover, subterranean clover, oats, barley, ryecorn, sweet blue lupins, onions, chou moellier, rape, kale, turnip, and swede seeds. The scheme was introduced to provide the buyer of certified seeds with a guarantee that the produce of such seeds would be true to type and free from seed-borne diseases. Selected strains are multiplied under the Department's certification scheme through the stages of certified “Pedigree” seed and certified “Mother” seed to certified “Standard” or “Permanent Pasture” seed. These seeds are sold through the usual commercial channels.
SUMMARY OF LIVESTOCK — Detailed statistics of livestock are contained in the Report on the Farm Production Statistics of New Zealand issued annually by the Department of Statistics. This publication also contains the summary tables appearing in parliamentary paper H. 23, which is devoted exclusively to a statistical analysis of the annual sheep returns. It should be noted that, unless otherwise stated, the statistics quoted in the tables in this subsection relate to holdings of 1 acre and over situated outside borough boundaries up to the year 1958–59. Commencing with the year 1959–60 a change was made in the coverage to holdings of 10 acres and over situated outside borough boundaries.
From the 1952–53 to the 1954–55 seasons farming statistics were based on a sample survey (ratio 1 : 7). In 1956 the opportunity was taken to collect the 1955–56 statistics in conjunction with the population census conducted on 17 April 1956. The 1956 farm census was designed to give information on certain major items only from a very abbreviated questionnaire and also to provide the basis for a change in the type of sample to that of an area-unit sample. The area-unit sample was selected for farms of under 2,000 acres, and all farms of 2,000 acres and over were automatically added to the sample. Certain of the data usually published are not available in such detail for 1955–56, but major items are given wherever possible, followed by full statistics for 1956–57, 1957–58, 1958–59, and 1959–60. The 1959–60 statistics, which were gathered as part of the World Census of Agriculture, were collected from occupiers of all holdings of 10 acres and over situated outside borough boundaries.
The numbers of livestock of various kinds at each of the last five annual enumerations were as shown in the following table, while figures over a longer period are shown in the Statistical Summary at the back of the Yearbook. Horses, dairy cows in milk, total cattle, sows, and total pigs are as at 31 January; sheep shorn, lambs shorn, and lambs tailed are for the season ending in the year stated; breeding ewes and total sheep are as at 30 June.
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes those in boroughs and on holdings under 1 acre. | |||||
| Horses | 139,114 | 129,309 | 123,261 | 122,957 | 104,995 |
| Dairy cows in milk | .. | 1,997,819 | 1,966,547 | 1,931,112 | 1,886,672 |
| Cattle (including dairy cows) | .. | 5,808,635 | 5,885,584 | 5,973,352 | 5,991,938 |
| Sheep shorn during season | .. | 37,868,868 | 39,769,523 | 42,106,637 | 44,010,09 |
| Lambs shorn during season | .. | 9,022,424 | 9,873,472 | 10,795,836 | 11,179,887 |
| Lambs tailed during season | 24,921,464 | 25,496,275 | 27,798,981 | 30,574,832 | 31,116,535 |
| Sheep (including lambs)* | 40,255,488 | 42,382,008 | 46,025,930 | 46,876,222 | 47,133,557 |
| Breeding ewes* | 27,015,612 | 28,899,470 | 30,875,704 | 31,816,093 | 32,632,784 |
| Pigs (total) | .. | 602,469 | 627,812 | 691,568 | 660,261 |
| Breeding sows | 85,463 | 83,905 | 87,925 | 92,970 | 87,824 |
In the following table figures for livestock other than sheep are given for each land district and Island for the 1959–60 season.
| Land District | Horses | Dairy Cows in Milk | Total Cattle | Breeding Sows | Total Pigs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Auckland | 14,358 | 422,884 | 1,000,949 | 23,174 | 174,202 |
| South Auckland | 21,223 | 757,394 | 1,874,579 | 30,750 | 225,675 |
| Gisborne | 10,108 | 35,979 | 394,054 | 2,076 | 14,391 |
| Hawke's Bay | 9,843 | 41,593 | 540,966 | 1,943 | 13,812 |
| Taranaki | 4,855 | 256,719 | 479,323 | 8,595 | 71,438 |
| Wellington | 17,379 | 204,905 | 973,693 | 11,205 | 79,536 |
| North Island | 77,766 | 1,719,474 | 5,263,564 | 77,743 | 579,054 |
| Marlborough | 1,709 | 11,908 | 63,286 | 978 | 7,691 |
| Nelson | 1,531 | 33,304 | 85,027 | 2,525 | 21,371 |
| Westland | 765 | 14,395 | 53,732 | 930 | 8,467 |
| Canterbury | 10,716 | 55,553 | 239,758 | 3,809 | 29,943 |
| Otago | 7,239 | 23,892 | 139,889 | 1,007 | 7,347 |
| Southland | 5,269 | 28,146 | 146,682 | 832 | 6,388 |
| South Island | 27,229 | 167,198 | 728,374 | 10,081 | 81,207 |
| New Zealand | 104,995 | 1,886,672 | 5,991,938 | 87,824 | 660,261 |
The corresponding figures for sheep are now given.
| Land District | Sheep Shorn | Lambs Shorn | Lambs Tailed | Breeding Ewes* | Total Sheep* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *As at 30 June 1960—includes sheep in boroughs. | |||||
| North Auckland | 2,130,198 | 762,863 | 1,319,895 | 1,573,046 | 2,256,422 |
| South Auckland | 5,764,523 | 2,288,280 | 4,052,081 | 4,553,766 | 6,399,116 |
| Gisborne | 2,086,966 | 927,004 | 1,105,550 | 1,404,820 | 2,341,377 |
| Hawke's Bay | 5,140,311 | 2,106,321 | 3,465,116 | 3,842,296 | 5,800,320 |
| Taranaki | 1,018,572 | 418,350 | 734,531 | 784,780 | 1,081,913 |
| Wellington | 7,765,012 | 3,158,580 | 5,194,798 | 5,545,032 | 8,385,049 |
| North Island | 23,905,582 | 9,661,398 | 15,871,971 | 17,703,740 | 26,264,197 |
| Marlborough | 1,168,352 | 141,131 | 632,467 | 777,021 | 1,249,903 |
| Nelson | 525,373 | 78,316 | 302,431 | 367,538 | 580,135 |
| Westland | 124,263 | 22,084 | 101,302 | 113,466 | 143,493 |
| Canterbury | 7,524,189 | 562,715 | 5,860,803 | 5,744,497 | 7,862,399 |
| Otago | 5,366,252 | 298,299 | 3,668,042 | 3,778,104 | 5,584,658 |
| Southland | 5,396,081 | 415,944 | 4,679,519 | 4,148,418 | 5,448,772 |
| South Island | 20,104,510 | 1,518,489 | 15,244,564 | 14,929,044 | 20,869,360 |
| New Zealand | 44,010,092 | 11,179,887 | 31,116,535 | 32,632,784 | 47,133,557 |
The next table shows the percentage distribution of the various kinds of livestock in each land district and Island. The figures reveal that the dairying and beef-production industries are both largely concentrated in the North Island, which has 88 per cent of the total cattle and 91 per cent of the dairy stock. Localising the dairying industry still further, it is found that over half the milking cows of New Zealand are in the area comprised of the land districts of North and South Auckland. Taranaki and Wellington are practically equally important as regards the number of cows in milk; between them they account for nearly one-quarter of the total.
Taking the number of beef breeding cows two years' old and over as a guide to beef production, South Auckland and Wellington Land Districts easily lead with two-fifths of the New Zealand total between them. Hawke's Bay is next, followed by Gisborne and North Auckland in that order. These five districts together depasture 82 per cent of breeding cows reserved for beef production.
Pig farming is largely an adjunct of dairy farming, and consequently the distribution closely follows that of dairy cattle. Thus North and South Auckland Land Districts account for 61 per cent of the pig population and Wellington for 12 per cent. Taranaki, however, which is mainly a cheese-producing district, has 13.6 per cent of New Zealand's milking cows, but only 10.8 per cent of the pigs, while Nelson, Westland, and Canterbury, which together have only 5.5 per cent of the cows in milk, have 9.1 per cent of the pig population.
Sheep farming is more evenly distributed between the North and South Islands. The land districts of major importance are Wellington, Canterbury, South Auckland, Hawke's Bay, Otago, and Southland, in that order, these six districts accounting for 84 per cent of the total sheep population in 1960.
| Land District | Dairy Cows, Two Years Old and Over (in Milk) | Beef Breeding Cows, Two Years Old and Over | Total Cattle | Breeding Sows | Total Pigs | Total Horses | Sheep Shorn* | Lambs Shorn* | Lambs Tailed* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Sheep shorn, lambs shorn, and lambs tailed during 1959–60, remaining particulars for stock at 31 January 1960. | |||||||||
| per cent | |||||||||
| North Auckland | 22.41 | 11.12 | 16.70 | 26.39 | 26.38 | 13.68 | 4.84 | 6.83 | 4.24 |
| South Auckland | 40.14 | 22.77 | 31.28 | 35.01 | 34.18 | 20.21 | 13.10 | 20.47 | 13.02 |
| Gisborne | 1.91 | 13.17 | 6.58 | 2.36 | 2.18 | 9.63 | 4.74 | 8.29 | 3.55 |
| Hawke's Bay | 2.21 | 15.98 | 9.03 | 2.21 | 2.09 | 9.38 | 11.68 | 18.84 | 11.14 |
| Taranaki | 13.61 | 2.54 | 8.00 | 9.79 | 10.82 | 4.62 | 2.31 | 3.74 | 2.36 |
| Wellington | 10.86 | 19.29 | 16.25 | 12.76 | 12.05 | 16.55 | 17.65 | 28.25 | 16.70 |
| North Island | 91.14 | 84.87 | 87.84 | 88.52 | 87.70 | 74.07 | 54.32 | 86.42 | 51.01 |
| Marlborough | 0.63 | 1.56 | 1.06 | 1.11 | 1.16 | 1.63 | 2.66 | 1.26 | 2.03 |
| Nelson | 1.77 | 1.02 | 1.42 | 2.87 | 3.24 | 1.46 | 1.19 | 0.70 | 0.97 |
| Westland | 0.76 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 1.06 | 1.28 | 0.73 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.33 |
| Canterbury | 2.94 | 4.82 | 4.00 | 4.34 | 4.54 | 10.20 | 17.10 | 5.03 | 18.83 |
| Otago | 1.27 | 3.46 | 2.33 | 1.15 | 1.11 | 6.89 | 12.19 | 2.67 | 11.79 |
| Southland | 1.49 | 3.35 | 2.45 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 5.02 | 12.26 | 3.72 | 15.04 |
| South Island | 8.86 | 15.13 | 12.16 | 11.48 | 12.30 | 25.93 | 45.68 | 13.58 | 48.99 |
SHEEP — In each successive year since 1951 new record levels have been reached for both the number of breeding ewes and total sheep.
At 30 June 1960 the number of breeding ewes was 32,632,784 and of total sheep 47,133,557, both these totals setting new record peaks. The increase of 816,691 breeding ewes was slightly less than the previous year's increase. Although there was an increase in the total sheep, the increase was a small one when compared with other recent years, amounting to only 0.55 per cent.
It is interesting to note the increasing proportion of breeding ewes to total sheep. Forty years ago 49 per cent of the total flock numbers were breeding ewes. This proportion had risen to 61.75 per cent by 1937, and to 63.47 per cent by 1947. The proportions as at 30 June 1958, 1959, and 1960, were 67.08 per cent, 67.87 per cent and 69.23 per cent respectively. These changes in the composition of flocks provide the basis of the greatly increased sheep numbers now being recorded.
The special farming type classification made in 1949–50 as part of the World Census of Agriculture shows the following break up by regional areas of those farms where 50 per cent or more of the farm enterprise was given over to sheep. Of all the farm types this classification shows the most equal balance between the North and South Islands, though the diversification of sheep farming with other agricultural pursuits is very evident in the South Island.
The following table shows the number of sheep farms in 1949–50 by regional areas.
| Regional Area* | Principally Sheep | Sheep | Other Sheep Holdings | Total Sheep Farms | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Beef Stock | With Dry Dairy Stock | With Dairy Stock | With Cropping | With Poultry | With Horticulture | With Mixed Farming | No. | Area | |||
| *For list of counties included see page 407. | |||||||||||
| acres | |||||||||||
| Northland | 442 | 282 | 12 | 34 | - | 1 | - | 14 | - | 785 | 699,643 |
| South Auckland | 542 | 130 | 23 | 50 | - | - | - | 10 | 1 | 756 | 464,330 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | 648 | 97 | 70 | 42 | - | 1 | 1 | 13 | 5 | 877 | 399,398 |
| Cape Colville | 85 | 15 | 18 | 5 | - | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 128 | 117,496 |
| Central Plateau | 166 | 59 | 34 | 13 | - | - | - | 11 | 1 | 284 | 265,071 |
| Western Uplands | 980 | 297 | 48 | 57 | 1 | - | - | 11 | 1 | 1,395 | 1,442,304 |
| Taranaki | 265 | 27 | 79 | 30 | 1 | 4 | - | 31 | 2 | 439 | 234,952 |
| East Cape | 582 | 272 | 11 | 36 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 27 | 5 | 945 | 1,751,473 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,619 | 157 | 18 | 87 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 49 | 33 | 1,987 | 2,098,902 |
| Rangitikei | 1,528 | 78 | 22 | 114 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 42 | 4 | 1,820 | 1,616,668 |
| Manawatu | 1,149 | 39 | 47 | 119 | 17 | - | 2 | 35 | 5 | 1,413 | 709,578 |
| Castlepoint | 256 | 8 | - | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | 274 | 396,046 |
| Wairarapa | 530 | 22 | 3 | 39 | 4 | - | - | 33 | 5 | 636 | 628,843 |
| Featherston | 293 | 14 | 11 | 23 | - | - | - | 11 | 2 | 354 | 515,160 |
| Nelson | 404 | 34 | 2 | 57 | 8 | - | 7 | 13 | 4 | 529 | 446,117 |
| Marlborough | 568 | 18 | 4 | 23 | 73 | - | 1 | 30 | 23 | 740 | 1,785,507 |
| Westland | 65 | 64 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 4 | 1 | 137 | 197,646 |
| North Canterbury | 405 | 4 | - | 10 | 93 | - | - | 64 | 20 | 596 | 1,323,947 |
| Foothills | 231 | 2 | 2 | 16 | 38 | 1 | - | 33 | 15 | 338 | 1,045,148 |
| Canterbury Plains | 222 | 3 | 5 | 17 | 129 | 2 | - | 32 | 16 | 426 | 268,438 |
| Christchurch | 31 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | - | - | 3 | - | 38 | 22,422 |
| Banks Peninsula | 216 | 18 | 2 | 18 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 271 | 178,298 |
| Mackenzie | 230 | 4 | - | 5 | 23 | - | 1 | 14 | 10 | 287 | 1,476,035 |
| South Canterbury | 1,242 | 8 | 3 | 127 | 559 | 21 | 4 | 212 | 56 | 2,232 | 3,350,892 |
| Otago | 696 | S | 4 | 80 | 36 | 4 | 3 | 73 | 34 | 938 | 1,640,281 |
| Central Otago | 565 | - | 1 | 15 | 40 | 3 | 4 | 23 | 10 | 661 | 3,789,679 |
| Southern | 2,853 | 70 | 8 | 309 | 160 | 3 | 1 | 352 | 152 | 3,908 | 3,368,001 |
| Remainder | 74 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 74 | 177,371 |
| Totals, Number | 16,887 | 1,731 | 428 | 1,339 | 1,245 | 49 | 29 | 1,151 | 409 | 23,268 | - |
| Acreage (000) | 24,621 | 2,981 | 151 | 493 | 741 | 20 | 24 | 1,080 | 298 | - | 30,410 |
In the following table total sheep distribution is shown by Islands, the figures including sheep in boroughs.
| Year | North Island | South Island | Total Sheep at 30 June | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Per Cent of Total | Number | Per Cent of Total | Number | |
| 1956 | 22,131,688 | 54.98 | 18,123,800 | 45.02 | 40,255,488 |
| 1957 | 23,094,709 | 54.49 | 19,287,299 | 45.51 | 42,382,008 |
| 1958 | 25,047,815 | 54.42 | 20,978,115 | 45.58 | 46,025,930 |
| 1959 | 25,885,746 | 55.22 | 20,990,476 | 44.78 | 46,876,222 |
| 1960 | 26,264,197 | 55.72 | 20,869,360 | 44.28 | 47,133,557 |
A similar table showing breeding ewe distribution by Islands is now given.
| Year | North Island | South Island | Total Breeding Ewes at 30 June | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Per Cent of Total | Number | Per Cent of Total | Number | |
| 1956 | 14,607,606 | 54.07 | 12,408,006 | 45.93 | 27,015,612 |
| 1957 | 15,484,109 | 53.57 | 13,415,361 | 46.43 | 28,899,470 |
| 1958 | 16,421,132 | 53.18 | 14,454,572 | 46.82 | 30,875,704 |
| 1959 | 17,168,067 | 53.96 | 14,648,026 | 46.04 | 31,816,093 |
| 1960 | 17,703,740 | 54.25 | 14,929,044 | 45.75 | 32,632,784 |
The following table shows the number of rams, wethers, breeding ewes, dry ewes, and ram, wether, and ewe hoggets in New Zealand for the last nine years, together with a broad classification into stud and other groups for the years 1952 and 1957. Figures are at 30 June. The statistics of breeds of sheep are now being collected at five-yearly intervals.
| Year | Rams | Wethers | Breeding Ewes | Dry Ewes | Hoggets | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ram | Wether | Ewe | ||||||
| *Change in classification. | ||||||||
| Totals | ||||||||
| 1952 | 632,086 | 2,979,156 | 22,963,340 | 450,734 | 167,402 | 2,589,937 | 5,601,615 | 35,384,270 |
| 1953 | 639,550 | 2,660,768 | 23,781,376 | 444,624 | 176,086 | 2,690,420 | 5,800,111 | 36,192,935 |
| 1954 | 669,096 | 2,719,589 | 24,850,530 | 428,757 | 192,947 | 2,815,107 | 6,334,928 | 38,010,954 |
| 1955 | 702,306 | 2,558,621 | 26,186,358 | 479,130 | 199,960 | 2,562,828 | 6,428,097 | 39,117,300 |
| 1956 | 729,165 | 2,495,284 | 27,015,612 | 477,271 | 206,694 | 2,712,850 | 6,618,612 | 40,255,488 |
| 1957 | 770,739 | 2,261,994 | 28,899,470 | 430,539 | 234,296 | 2,786,005 | 6,998,965 | 42,382,008 |
| 1958 | 805,461 | 2,600,580 | 30,875,704 | 445,850 | 269,379 | 3,092,948 | 7,936,008 | 46,025,930 |
| 1959 | 836,561 | 2,438,099 | 31,816,093 | 494,574 | 278,132 | 2,880,217 | 8,132,546 | 46,876,222 |
| 1960 | 860,461 | 2,324,064 | 32,632,784 | 508,518 | 270,459 | 2,545,047 | 7,992,224 | 47,133,557 |
| Stud Sheep (Entered in Flock Book) | ||||||||
| 1952 | 12,828 | - | 331,180 | 5,937 | 118,675 | - | 129,810 | 598,430 |
| 1957 | 17,045 | - | 440,662 | 5,503 | 153,037 | - | 167,532 | 783,779 |
| Sheep of a Distinctive Breed but Not Entered in Flock Book | ||||||||
| 1952* | 587,545 | 2,393,105 | 17,804,304 | 356,554 | 42,407 | 1,997,031 | 4,482,900 | 27,663,846 |
| 1957 | 720,330 | 1,969,954 | 24,698,756 | 352,036 | 72,164 | 2,336,020 | 6,095,523 | 36,244,783 |
| Crossbred Sheep | ||||||||
| 1952* | 31,713 | 586,051 | 4,827,856 | 88,243 | 6,320 | 592,906 | 988,905 | 7,121,994 |
| 1957 | 33,364 | 292,040 | 3,760,052 | 73,000 | 9,095 | 449,985 | 735,910 | 5,353,446 |
The 1957 classification of breeds shows that of the 42,382,008 sheep in New Zealand 30,264,335 (71.41 per cent) were Romneys and 5,353,446 (12.63 per cent) were crossbreds. The remainder were principally half bred 2,577,090, Corriedale 2,128,832, Merino 1,021,159, and Southdown 786,040.
The average size of the flocks was 1,055 in 1956, 1,092 in 1957, 1,148 in 1958, 1,141 in 1959, and 1,140 in 1960. There has been little change in average flock size over the past three years. A classification according to size for the last five years shows the following position.
| Size of Flocks | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 and under 100 | 4,239 | 4,180 | 4,071 | 4,568 | 4,753 |
| 100 “ 200 | 3,059 | 2,940 | 2,888 | 3,050 | 3,079 |
| 200 “ 500 | 6,832 | 6,600 | 6,651 | 6,669 | 6,602 |
| 500 “ 1,000 | 9,182 | 9,136 | 8,934 | 9,023 | 8,965 |
| 1,000 “ 1,500 | 6,674 | 7,034 | 7,383 | 7,422 | 7,555 |
| 1,500 “ 2,000 | 3,538 | 3,840 | 4,355 | 4,438 | 4,457 |
| 2,000 “ 2,500 | 1,767 | 1,996 | 2,264 | 2,297 | 2,252 |
| 2,500 “ 5,000 | 2,282 | 2,442 | 2,849 | 2,920 | 2,973 |
| 5,000 “ 7,500 | 375 | 396 | 451 | 463 | 429 |
| 7,500 “ 10,000 | 111 | 110 | 128 | 121 | 140 |
| 10,000 “ 20,000 | 100 | 107 | 110 | 111 | 116 |
| 20,000 and over | 13 | 13 | 14 | 19 | 19 |
| Total flocks | 38,172 | 38,794 | 40,098 | 41,101 | 41,340 |
CATTLE — The total number of cattle in 1960 was calculated to be 5,991,938 as against 5,973,352 in 1959.
| Dairy stock— | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|
| Cows and heifers, two years old and over — | ||
| Cows in milk during season | 1,931,112 | 1,886,672 |
| Heifers not yet in milk | 65,779 | 71,342 |
| Cows not in milk during season, but intended to be used again for dairying | 34,587 | 30,739 |
| Heifers — | ||
| One and under two years old | 411,300 | 413,547 |
| Under one year old | 455,744 | 477,088 |
| Bulls and bull calves intended for dairy breeding | 105,179 | 93,388 |
| Totals, dairy stock | 3,003,701 | 2,972,776 |
| Beef stock — | ||
| Breeding cows and heifers, two years old and over | 1,084,699 | 1,143,925 |
| Cows, two years old and over, not used for breeding | 86,082 | 84,258 |
| Heifers — | ||
| One and under two years old | 312,824 | 313,610 |
| Under one year old | 348,425 | 388,548 |
| Steers and bulls of all ages | 1,137,621 | 1,088,821 |
| Totals, beef stock | 2,969,651 | 3,019,162 |
| Totals, cattle | 5,973,352 | 5,991,938 |
The following table shows the number of holdings with dairy cows in milk, grouped according to size of herd in milk, for the three last five-yearly intervals for which such information is available. The figures relate to holdings of 1 acre and over situated outside borough boundaries.
| Year | Number of Cows in Milk | Total Holdings With 10 or more Cows in Milk | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-19 | 10-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70-79 | 80-89 | 90-99 | 100 and Over | ||
| 1947 | 5,135 | 5,499 | 5,947 | 4,876 | 3,522 | 2,76? | 1,946 | 1,314 | 814 | 1,891 | 33,306 |
| 1952 | 4,368 | 4,536 | 5,527 | 5,245 | 4,438 | 3,665 | 2,512 | 1,726 | 1,105 | 2,532 | 35,654 |
| 1957 | 3,477 | 3,563 | 4,549 | 4,835 | 4,589 | 4,305 | 3,071 | 2,023 | 1,351 | 3,094 | 34,857 |
Analysing those farm holdings where 50 per cent or more of the enterprise is devoted to dairying, the North Island predominates with 84 per cent of dairy farms. The following table shows the number of dairy farms in 1949–50 by regional areas.
| Regional Area | Principally Dairying | Dairying | Dry Dairy Cows and Heifers Only | Other Dairy Holdings | Total Dairy Farms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Sheep | With Cropping | With Beef Stock | With Poultry | With Pigs | With Bees | With Horticulture | With Mixed Farming | No. | Area | ||||
| acres | |||||||||||||
| Northland | 6,815 | 154 | - | 23 | 58 | 14 | 2 | 37 | 55 | 148 | 7 | 7,313 | 1,485,711 |
| South Auckland | 3,165 | 112 | 1 | 4 | 33 | 5 | - | 19 | 26 | 131 | 8 | 3,504 | 395,319 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | 6,544 | 193 | - | 4 | 7 | 20 | - | 7 | 39 | 118 | 4 | 6,936 | 967,162 |
| Cape Colville | 787 | 27 | - | 1 | 4 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 26 | - | 849 | 192,907 |
| Central Plateau | 2,065 | 65 | 1 | - | 18 | 11 | 1 | 23 | 40 | 39 | 3 | 2,266 | 439,416 |
| Western Uplands | 907 | 184 | - | 2 | - | 5 | - | 5 | 30 | 13 | 3 | 1,149 | 284,159 |
| Taranaki | 3,713 | 77 | - | 1 | 17 | 15 | - | 1 | 23 | 123 | 4 | 3,974 | 514,993 |
| East Cape | 915 | 65 | 13 | - | 44 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 38 | 18 | 2 | 1,108 | 150,572 |
| Hawke's Bay | 594 | 78 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 11 | 21 | 8 | 9 | 739 | 87,371 |
| Rangitikei | 1,024 | 187 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 3 | - | 4 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 1,263 | 181,504 |
| Manawatu | 2,716 | 178 | 6 | - | 11 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 19 | 36 | 4 | 2,990 | 335,070 |
| Castlepoint | 15 | 7 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 23 | 5,403 |
| Wairarapa | 556 | 72 | - | - | 5 | 7 | 1 | - | 11 | 6 | 3 | 661 | 117,093 |
| Featherston | 422 | 41 | - | - | 5 | 5 | - | 1 | 3 | 12 | - | 489 | 131,792 |
| Nelson | 817 | 99 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 | - | 30 | 35 | 11 | 2 | 1,014 | 277,251 |
| Marlborough | 324 | 30 | 5 | - | 1 | 3 | - | - | 19 | 5 | 6 | 393 | 75,858 |
| Westland | 345 | 19 | - | 9 | 1 | 6 | 3 | - | 17 | 8 | - | 408 | 177,268 |
| North Canterbury | 32 | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 39 | 2,625 |
| Foothills | 50 | 12 | 6 | - | 6 | - | 1 | - | 4 | 3 | 1 | 83 | 13,908 |
| Canterbury Plains | 526 | 19 | 91 | - | 12 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 51 | 11 | 3 | 727 | 75,155 |
| Christchurch | 223 | 5 | 19 | 1 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 271 | 20,697 |
| Banks Peninsula | 145 | 36 | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | - | - | 4 | 1 | 3 | 193 | 36,125 |
| Mackenzie | 8 | 3 | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 1,612 |
| South Canterbury | 635 | 75 | 57 | 2 | 39 | 14 | 4 | 2 | 39 | 8 | 10 | 885 | 72,107 |
| Otago | 439 | 58 | 10 | 1 | 12 | 1 | - | 2 | 17 | 9 | 9 | 558 | 70,880 |
| Central Otago | 68 | 8 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 4 | 1 | - | 83 | 11,777 |
| Southern | 1,295 | 423 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 11 | 1 | 2 | 70 | 11 | 5 | 1,836 | 295,814 |
| Remainder | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 138 |
| Totals, Number | 35,148 | 2,230 | 228 | 59 | 309 | 165 | 18 | 168 | 588 | 764 | 93 | 39,770 | |
| Acreage (000) | 5,190 | 805 | 24 | 28 | 21 | 23 | 1 | 12 | 224 | 74 | 18 | 6,420 | |
A similar analysis for beef-cattle farms shows that the North Island contributed 65 per cent of the New Zealand total for this type of farming. The following table shows the number of beef-cattle farms in 1949–50 by regional areas.
| Regional Area | Principally Beef Cattle | Beef Cattle | Other Beef-cattle Holdings | Total Beer-cattle Farms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Sheep | With Dairying | With Arable Cropping | With Mixed Farming | Number | Area | |||
| *Not available separately. Areas are included in the total. | ||||||||
| acres | ||||||||
| Northland | 245 | 67 | 3 | - | 4 | 11 | 330 | 184,825 |
| South Auckland | 69 | 10 | 2 | - | 1 | 4 | 86 | 22,133 |
| Waikato and Hauraki Lowlands | 71 | 6 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 82 | 20,956 |
| Cape Colville | 24 | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 33 | 20,249 |
| Central Plateau | 30 | 11 | 1 | - | - | 2 | 44 | 61,313 |
| Western Uplands | 44 | 13 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 60 | 27,844 |
| Taranaki | 16 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 22 | 2,287 |
| East Cape | 15 | 9 | 1 | - | - | - | 25 | 28,458 |
| Hawke's Bay | 28 | 7 | - | - | - | - | 35 | 20,483 |
| Rangitikei | 22 | 4 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 29 | 11,599 |
| Manawatu | 36 | 3 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 41 | 11,181 |
| Castlepoint | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | * |
| Wairarapa | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 2,352 |
| Featherston | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | 3,692 |
| Nelson | 63 | 8 | - | - | - | 4 | 75 | 39,130 |
| Marlborough | 8 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 9 | 462,507 |
| Westland | 108 | 44 | 3 | - | 4 | - | 159 | 398,477 |
| North Canterbury | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 212,855 |
| Foothills | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | * |
| Canterbury Plains | 14 | - | - | - | - | - | 14 | 3,676 |
| Christchurch | 9 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 10 | 1,294 |
| Banks Peninsula | 7 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 9 | 4,569 |
| Mackenzie | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | * |
| South Canterbury | 29 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 31 | 5,946 |
| Otago | 27 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 34 | 16,663 |
| Central Otago | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 3 | 106,677 |
| Southland | 59 | 20 | 2 | - | 2 | 1 | 84 | 31,688 |
| Remainder | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | 7 | 539 |
| Totals, Number | 952 | 215 | 17 | 2 | 18 | 37 | 1,241 | |
| Acreage | 1,389,252 | 286,158 | 6,153 | 374 | 12,802 | 10,565 | 1,705,304 | |
Most of the leading breeds of the cattle of Great Britain are represented in New Zealand by herds bred on sound lines. Provision was made in the 1950 Census of Agriculture for the collection of breeds of cattle. Details of breeds were given on pages 488 and 489 of the 1954 issue of the Yearbook. Dairy stock in New Zealand in 1950 was predominantly of Jersey breed (84.7 per cent), while the beef stock breeds were mainly Polled Angus (66.7 per cent), Hereford (21.9 per cent), and Shorthorn (7.1 per cent).
PIGS — The 1960 figure of 660,261 pigs showed a decline of 4.5 per cent compared with the 1959 figure and 17.6 per cent compared with the peak figure of 800,802 in 1936. It was, however, 5.2 per cent higher than the 1958 figure.
| At 31 January | Pigs Under Six Months' Old | Pigs Six Months and Under One Year Old | Boars One Year Old and Over | Sows One Year Old and Over | Total Pigs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1954 | 417,992 | 129,031 | 14,775 | 87,104 | 648,902 |
| 1955 | 434,400 | 142,246 | 15,744 | 88,969 | 681,359 |
| 1956 | .. | .. | .. | 85,463 | .. |
| 1957 | 518,564 | 83,905 | 602,469 | ||
| 1958 | 539,887 | 87,925 | 627,812 | ||
| 1959 | 598,598 | 92,970 | 691,568 | ||
| 1960 | 572,437 | 87,824 | 660,261 | ||
Particulars as to pig breeds collected in 1950 showed that the principal distinctive breeds were Berkshire (6.6 per cent) and Tamworth (5.5 per cent), but over 80 per cent of the pigs in New Zealand were classified as crossbreds.
HORSES — The following table includes the latest information available of the number of horses in each class shown, excluding horses in boroughs.
| 1951 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Not collected separately. | |||||
| Draught and three-quarter draught | 65,901 | 32,463 | 28,758 | 28,469 | * |
| Spring cart (including half-draught) | 22,541 | ||||
| Hacks and light working horses | 75,318 | 72,964 | 70,878 | 71,440 | * |
| Thoroughbred and other horses | 20,212 | 23,882 | 23,625 | 23,048 | * |
| Total horses | 183,972 | 129,309 | 123,261 | 122,957 | 104,995 |
Since 1911, when the peak number of 404,000 was recorded, there has been a steady decline in the number of horses in New Zealand. The greater part of the decrease has occurred in horses of the heavy type and has been accompanied by a marked increase in the use of mechanical traction for farm work, the number of agricultural tractors on farms in 1952 being 46,000 as compared with 14,000 in 1942. By 1959 the number of heavy-type horses had fallen to 28,500 while tractors had increased to 75,300. Hacks and light working horses have decreased to a much lesser extent over the period.
DOGS — A count of dogs registered during the 1960 registration year showed that there were 199,926 dogs registered in counties, of which 123,279 were in the North Island and 76,647 in the South Island. The total number of dogs registered in boroughs was 38,533, in town districts 898, and in road districts 252. Unregistered dogs and those up to six months old are not included in these figures.
POULTRY — The following table shows the numbers recorded at the censuses 1921–56. All references to fowls, ducks, etc., are intended to cover both male and female birds.
| Census | Number of Households Keeping Fowls, Ducks, Geese, or Turkeys | Total Number of Fowls, Ducks, Geese, or Turkeys | Fowls | Ducks | Geese | Turkeys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding Maori flocks. †Including Maori flocks (107,361 birds in 1936). | ||||||
| April 1921* | 145,993 | 3,991,009 | 3,491,567 | 379,988 | 46,234 | 73,220 |
| April 1926* | 158,856 | 3,781,145 | 3,308,384 | 352,030 | 43,879 | 76,852 |
| March 1936† | 166,354 | 4,019,076 | 3,488,516 | 377,791 | 66,667 | 86,102 |
| September 1945† | 159,333 | 4,470,366 | 4,070,683 | 319,918 | 41,903 | 37,862 |
| April 1951† | 180,723 | 4,199,590 | 3,829,481 | 260,659 | 58,474 | 50,976 |
| April 1956† | 192,736 | 4,485,571 | 4,160,424 | 210,718 | 60,938 | 53,491 |
The comparability of the foregoing figures is affected by two important considerations, the first being that the 1951 and 1956 figures include only birds aged four months or over, while the 1945 figures cover birds of all ages. At earlier censuses the question was for the number of birds — no reference being made to age. The second factor is that the census of 1945 was taken in the spring, whereas the other censuses were taken in the autumn.
Number and Size of Flocks — Although poultry farming is regarded as a definite branch of the farming industry, a classification as to sizes of flocks indicates that poultry keeping is generally carried on merely as a sideline. The 192,736 households recorded as keeping poultry at the 1956 census showed an increase of 6.6 per cent as compared with the 1951 census. Taking only fowls into consideration, it is found that 173,802, or 91.4 per cent, of the households keeping poultry had less than 25 birds, the corresponding percentage in 1951 being 89.5. In 12,858 cases in 1956 the number of birds ranged from 25 to 99, making a total of 186,660 cases, or 98.2 per cent, in which the flocks consisted of less than 100 birds. The total number of flocks of fowls was 190,072 in 1956.
Of 521 flocks in which the number of birds was 1,000 or over, 402 ranged from 1,000 to 1,999, 79 from 2,000 to 2,999, 25 from 3,000 to 3,999, and 15 exceeded 4,000. In 1951 the number of flocks of 1,000 or over amounted to 366. The average flock in rural districts was 27.3, in urban districts 14.8, and in New Zealand as a whole 21.9 birds.
Poultry farming is confined almost entirely to egg production, but recently greater attention has been paid to table poultry. Most table birds, however, are still by-products of commercial egg production. Commercial poultry farms are distributed over both Islands, the largest numbers being concentrated around Auckland, Christchurch, and Oamaru. Duck-egg farming is carried on only to a limited extent and is centred mainly around Auckland. The poultry industry does not cater for overseas markets, though limited quantities of frozen egg pulp, surplus to local requirements, are exported. Egg production has been steadily increasing, sales through licensed distributors rising from 15,990,090 dozen in 1958–59 to 18,431,847 dozen in 1959–60. It is estimated that approximately one-third of the total egg production passes through these channels.
Until recent years the most popular breed for egg production was the White Leghorn, still much favoured in the South Island. During the last few years, however, there has been a marked increase in the number of Australorps kept and an ever-growing tendency to cross the White Leghorn with the Australorp. These latter crossbred pullets are responsible for a high percentage of the eggs produced at present. Interest is also being shown in Rhode Island Reds. Khaki Campbell and Runner ducks are mainly used for egg production, while Khaki Campbell, Muscovy, and some Pekin ducks are marketed as table birds. There is little organised turkey production but one or two commercial turkey farms have come into being since the war.
In 1945 the poultry industry, assisted by the Department of Agriculture, established the New Zealand Poultry Flock Improvement Plan, which operates on a voluntary basis. The number of flocks accredited under this plan in 1960 was 177, covering some 183,900 female birds. The Department of Agriculture provides a diagnostic service available to all poultry producers and also operates a poultry demonstration plant where progeny testing and other trials are carried out.
Poultry Control — The Poultry Act 1924 provides for the regulating of poultry keeping and of the sale and export of poultry and eggs. Provision is made for the appointment of inspectors, on whom certain powers of entry are conferred for purposes of inspection of poultry or of eggs intended for sale or export. Poultry are required to be kept under sanitary conditions, and cruelty to poultry is made an offence. Every owner of poultry is required to notify an inspector of any outbreak of disease among his flock and to comply with the inspector's directions. It is an offence to sell diseased poultry. The Governor-General in Council is empowered to declare diseases, to appoint ports of export, and to appoint grading stores.
In order to provide finance for the organisation and development of the poultry industry, the Poultry-runs Registration Act was passed in 1933 and a Poultry Board constituted of two Government and four producer members. The Act makes compulsory the annual registration of every poultry run, which is defined as land used for the keeping of not less than 25 head of poultry (hens and ducks not less than six months' old) and the production of eggs for sale. The fee payable annually for registration is 2s. 6d. if the flock is in excess of 24 but does not exceed 100 head. For each additional hundred (or part thereof) an additional 2s. 6d. is payable. Figures supplied by the board show that the number of poultry runs registered at 31 May 1959 was 6,340, covering an aggregate of 1,906,507 birds. Although the number of registered flocks fell to 6,193 at 31 May 1960 the aggregate number of birds increased to 2,080,136.
Reference to the field covered by the Egg Marketing Authority is given in Section 21 of this Yearbook.
BEES — The rich pasture lands of New Zealand and some bush areas are particularly favourable for apiculture and the production of high-grade honey for the local and export markets.
Production for the year ended 31 March 1960 was estimated at 5,800 tons of honey and 203,000 1b of commercial beeswax, approximately 2,000 tons of honey and 70,500 1b of beeswax more than the previous season.
Over the past five seasons the annual export of honey has averaged 1,919,176 1b.
Registrations under the Apiaries Act show that at 31 May 1959 there were 4,974 beekeepers with a total of 11,536 apiaries and 176,350 established hives. Sixty-six per cent of hives and 63 per cent of apiaries were in the North Island. Following is a summary of these registrations showing beekeepers in groups according to the number of hives kept.
| Group | 1–5 Hives | 6–29 Hives | 30–250 Hives | 251 Hives and Over |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beekeepers | 3,403 | 962 | 366 | 243 |
| Apiaries | 3,490 | 1,219 | 1,661 | 5,166 |
| Hives established | 7,609 | 10,868 | 28,913 | 128,960 |
Under the Apiaries Act 1927 stringent regulations have been enacted in order to control foulbrood, bee moths, and other diseases of bees. Beekeepers are required to register all apiaries of one or more hives, and it is an offence to keep bees in an unregistered apiary. Only frame hives may be used, box hives being prohibited.
The introduction into New Zealand of bees, and used appliances for the keeping of bees and the harvesting of their products, is prohibited save with the prior consent of the Minister of Agriculture. The consent of the Minister in regard to used appliances is restricted to such appliances as are necessary to serve as containers for bees so introduced.
In view of the greatly increased amount of crop spraying for weed and pest control it has been necessary to bring down regulations prohibiting the application to cruciferous and leguminous field crops of sprays and dusts that are toxic to bees at any time during the period between 1 September in any year and 31 March in the following year when the crop is in flower, except with a permit issued by the Department of Agriculture.
Exports of honey for the latest five years ended 31 December are given below.
| Quantity | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| *Provisional | ||
| Year | 1b | I |
| 1956 | 2,092,032 | 130,513 |
| 1957 | 2,085,374 | 133,368 |
| 1958 | 2,980,069 | 173,734 |
| 1959 | 1,493,439 | 80,594 |
| 1960* | 944,964 | 54,003 |
Reference to the activities of the Honey Marketing Authority is given in Section 21 of this issue.
HISTORICAL INTRODUCTION — New Zealand, except in certain limited areas*, possesses a climate favourable to forest growth, and in ancient times land was almost entirely forest clad. Volcanic action in the central North Island, decreasing rainfall in the east of both islands, and cultivation and use of fire by the Maoris substantially reduced the forest area; nevertheless, the first white settlers found a land which may have been two-thirds covered by dense forest.
In the early days of settlement the demand for timber was met by exploitation of the kauri forests of the far north. These forests were almost completely destroyed by logging and subsequent burning of the cut-over areas. Wide areas of podocarp-broadleaf forest in both islands were cleared, often without extraction of timber, to make way for farms. Although Acts of Parliament passed in the 1870s and 1880s made provision for the setting aside of forest reserves, there was little interest in conservation, and land-clearing operations extended well beyond the limits now considered desirable in the public interest. Towards the end of the century the need to conserve the forests of the high mountain watersheds was recognised. National parks, scenic and “climatic” reserves amounting to about 2 million acres, in all constituting 3.1 per cent of the land area of New Zealand, had been set aside as “permanent forest” by the early 1900s.
In 1909, in addition to this “permanent forest”, there were more than 7 million acres of privately owned forest (including forest on Maori land) and nearly 8 million acres of Crown-owned forest. The whole of these latter areas was open to exploitation and the forest was being rapidly destroyed in the production of the annual cut of some 400 million board feet of timber. Although some “State forests” had been proclaimed, the name did not, as now, imply forest preservation, and the State forests were subject to the same lifting of reservations and the same destruction as other forests on Crown land. Milled areas were either sold for settlement or replanted with exotics.
It was at that time universally believed that the indigenous timber trees were too slow growing to have any place in schemes of forest management for continuous yield, that New Zealand's millable indigenous forests would be exhausted some time in the 1940s, and that future timber supplies must come from imports and from the exotic plantations which the State had been steadily establishing since 1898. In 1913 a Royal Commission on Forestry recommended extension of the permanent forests of the mountainous regions by nearly 2 million acres. However, it sanctioned the continued destruction of the indigenous milling forest on the ground that no land should be permitted to remain under forest if it could be “occupied and resided upon in reasonably limited areas”. The Commission recommended greatly increased State plantings of exotics (especially radiata pine and eucalypts) to provide for future needs, but the rate of planting remained the same (about 2,000 acres a year) until the 1920s.
The First World War brought a timber famine and high prices. Awakened public opinion, alarmed at the prospect of the exhaustion of indigenous timber supplies within a generation, demanded a new approach to the question of forestry. The full impact of the recommendations made by overseas professional foresters who had from time to time reported on the forests at the request of the Government was at last felt. In 1919 the Commissioner of State Forests formulated a policy of permanent dedication to forest management of all Crown forested lands valuable chiefly for forestry and timber production, and of extended State planting to provide supplementary timber supplies.
In 1920 a new administrative agency, the State Forest Service, was created to carry out this policy. At its head, as Director of Forestry, was placed a highly trained and experienced forester. Professional forestry officers were appointed, and henceforward the forests were to be managed on scientific principles.
In the period 1923–36 State planting was greatly expanded, 376,500 acres being planted with exotics. In the same period afforestation companies created 297,000 acres of exotic forest. This activity was designed to provide exotic forests whose produce would offset the forthcoming acute shortage of native timber. The resulting forests are characterised by lack of variety in age and species (88 per cent of commercial plantings were radiata pine), by large areas which are poorly stocked, owing to unsuitable siting and the use of inferior strains, and by lack of silvicultural tending. Although these characteristics render them extremely susceptible to insect and fungal attack, New Zealand's exotic forests have not been devastated by epidemics; but as the trees mature the danger increases. The Forest Service recognises these facts, and the policy since 1937 has been to plant at a slower rate (several thousand acres each year), to establish a wider range of species, to use the best seed, and to pay attention to correct siting and tending. A Forest Biology Survey has been established to operate a sentinel service for the detection of incipient insect or fungal epidemics.
*The exceptions are: land above 4,000–5,000 ft (North Island), above 3,500–4,500 ft (South Island), and above 1,000–1,500 ft (Stewart Island), and parts of the eastern South Island.
Owing to the ever-present threat of disease in the exotic plantations, the Forest Service is preserving, as a safeguard, as much as possible of the indigenous forests which, by reason of their adaptation to the country and their tremendously varied composition, are much less vulnerable.
The indigenous forests are still, despite the greatly increased use of exotic timber, being depleted at the rate of some 30,000 acres a year to provide some 300,000,000 board feet of timber annually. However, as public acceptance of exotic timbers becomes more complete, it will be possible to reduce the output of indigenous timber to a level at which cutting is more in line with conservation policy.
NATIONAL FOREST POLICY — The aim of the Forest Service is to manage the national forest estate in such a way that it will provide the greatest possible economic and social benefits for the people of New Zealand. These benefits include the production of timber, paper pulp, and other forest products; the prevention of erosion and the regulation of stream flow; and the provision of scenic and recreational resources.
The national forest policy requires (a) the conservation of the indigenous forests for perpetual (though of necessity limited) timber production, for soil protection, and for recreation; and (b) the extension of the exotic forests to maintain the pulp and paper industry, and to make possible, by providing additional timber supplies, the conservation of the indigenous forests.
The rapid expansion of the pulp and paper industry and the declining cut of indigenous timber will result in much wider utilisation based on exotic forests. It is inevitable that the yield of these forests will be fully taken up much sooner than has formerly been calculated. It is also certain that forest products, particularly pulp and paper, will form a substantial part of the country's overseas trade. More use will have to be made of suitable tree-growing country, and the exotic forests, both State and private must be expanded considerably. The Forest Service aims to plant a million acres by the end of the century and a further million by the year 2025, and it is hoped that private owners and farmers will plant another million acres.
FOREST RESOURCES: Forest Produce Supplies — The salient features of the supply situation are:
The National Forest Survey has shown that of the remaining indigenous forest some 2,000,000 acres contain timber merchantable by today's standards. It has been estimated that the amount is 3,200 million cubic feet, representing 20,500 million board feet of sawn timber. In addition, there are about 945,000 acres of exotic forests.
The indigenous forests, from which 20 years ago 86 per cent of rough-sawn timber supplies were obtained, at present supply approximately 50 per cent. In 20 years' time they are expected to provide about 14 per cent. In the distant future the amount of produce obtained from them will depend upon the successful introduction of management practices.
It can be expected that a high proportion of the exotic forests will be worked on a sustained-yield basis. Besides supplying 50 per cent of the rough-sawn timber cut at present, they yield in addition 43 million cubic feet of pulp logs, veneer logs and smallwood.
Imports of timber have varied from 30 to 60 million board feet during the past 10 years. They are composed of special-purpose timbers — large-dimension Oregon pine for structural use, joinery timbers, and Australian hardwood poles and sleepers.
While supplies of produce from indigenous forests will decrease in the future, the area in exotic forests and the produce from them will increase. Timbers from exotic species could also in time largely replace imported timber and, provided the increase in forest area is sufficient, will provide a substantial amount of produce for export.
Extent of Forested Land — All readily accessible native forests have now been cleared, and forested land is reduced to about a quarter of the total land area. Nevertheless, this portion represents a very large area as the following table of land categories shows.
| Type of Land | Area, in Acres | Percentage of Total Land Area |
|---|---|---|
| Forested land | 15,396,00 | 23.2 |
| Non-forested land | 50,103,000 | 75.3 |
| Minor islands | 205,000 | 0.3 |
| Water area | 687,000 | 1.0 |
| Total land area (including water surfaces) | 66,391,000 | 100.0 |
The best use of the 15,400,000 acres of forested land will be decided, within the framework of the forest policy already outlined, by the location, tenure, and economic value of its component parts. It falls into three descriptive classes.
Classification of Forests — More than three-quarters is not merchantable forest and is termed “other land classed as forest”. This is mainly Crown-owned, indigenous forest, and, because it covers much of the remoter mountainous and high-rainfall country, its primary function is that of soil protection and water regulation. Nevertheless, it includes considerable areas of potentially productive forest land which could, in the distant future, be placed under production management. Such management would always be subordinate to the protective functions of this class of forest.
Some 5 per cent of the forested area may be classed as “potentially merchantable” forest — forest which, owing to inaccessibility, has not yet been exploited but would be merchantable if such factors as demand and transport become favourable. “Potentially merchantable” forests also lie mainly on Crown land, and are entirely indigenous.
“Fully merchantable” forests are more diverse in tenure and composition than either of the other two classes already mentioned because they include almost all the planted (exotic) forests, of which nearly half are owned privately or by local authorities. Fully merchantable indigenous forests have receded well in advance of close settlement, and the largest areas are now on Crown lands and Maori lands in regions (especially on the West Coast of the South Island) little suited to other forms of land use. The distribution of merchantable exotic forests has been influenced mainly by the availability of cheap, undeveloped land in the period (1900 to 1935) when most of these forests were established. Hence there is a preponderance of exotic forest (State owned and private) on the volcanic plateau of the North Island.
The distribution by area of these three classes of forested land in 1955 is shown by the following table.
| Class of Forest | State Forest | Communal Forest | Private Forest | Total Forest | Percentage of Total Forest Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acres (thousand) | |||||
| (a) Merchantable— | |||||
| Indigenous | 1,534 | - | 579 | 2,113 | 13.8 |
| Exotic | 465 | 37 | 412 | 914 | 5.9 |
| Totals | 1,999 | 37 | 991 | 3,027 | 19.7 |
| (b) Potentially merchantable— | |||||
| Indigenous | 700 | - | 101 | 801 | 5.2 |
| Exotic | - | - | - | - | |
| Totals | 700 | - | 101 | 801 | 5.2 |
| (c) Other land classed as forest— | |||||
| Indigenous | 8,906 | - | 2,650 | 11,556 | 75.0 |
| Exotic | 12 | - | - | 12 | 0.1 |
| Totals | 8,918 | - | 2,650 | 11,568 | 75.1 |
| (d) Grand totals— | |||||
| Indigenous | 11,140 | - | 3,330 | 14,470 | 94.0 |
| Exotic | 447 | 37 | 412 | 926 | 6.0 |
| Total forest area | 11,617 | 37 | 3,742 | 15,396 | 100.0 |
| NOTES | |||||
| 1. State forest includes all forest under the control of the State through the New Zealand Forest Service or other Government Departments. | |||||
| 2. Communal forest includes all forest under the control of local (i.e., public) authorities other than the State. | |||||
| 3. Maori forest is included under private forest. | |||||
| 4. Areas of communal and private forests are approximate only. | |||||
Botanical Composition of Forests — The indigenous forests of New Zealand may be grouped very broadly into two main formations, mixed temperate evergreen forest and southern-beech forest. The former is a mixed community of many species of broad-leaved trees and conifers, and the latter a pure community of one or more of the species of southern beech (Nothofagus).
In general terms, the mixed temperate evergreen forests are the forests of the north and of the warm, wet lowlands and lower mountain slopes. Their upper altitudinal limit becomes gradually lower from north to south. The beech forests are the forests of the south, of the high mountains and of the drier lowlands. But the beech species are absent from many localities, e.g., Stewart Island and Mt. Egmont, where their presence might be expected. There are also extensive areas, especially in the north-west and south-west of the South Island, and on the mountain ranges of the North Island, where the two types mingle to form forests of very varied composition.
Most of the mixed forest has been cut over for timber and cleared for farming purposes, whereas the southern-beech forest, because of the difficult topography and the poor soils on which it most frequently grows, is largely intact. The following description gives in more detail the distribution and the present state of the main forest communities.
Kauri forest (mixed temperate evergreen forest in which kauri is the dominant species) once occupied much of the area north of a line joining Port Waikato to Tauranga, but, except for limited reservations and small pockets, it has disappeared. The main secondary tree species are taraire and tawa. Mixed podocarp forest (the principal podocarp is rimu; the important secondary ones, totara, matai, and miro) was found at all latitudes in the three main islands. The heaviest commercial stands were on flat or near-flat sites; in steeper country timber trees thinned out and secondary species became more plentiful. The remaining forest of this type consists of pockets which will be worked for a few decades to come, some large areas on steep country, such as the Urewera, which can be classed mainly as protection forest, and fairly extensive forests in the centre of the North Island and on the West Coast of the South Island which contain most of the remaining indigenous-softwood supplies. The main species of broad-leaved trees in these forests are kamahi, tawa, and rata. Kahikatea forest occupied low-lying swampy river silts, but this has almost disappeared to make way for farming.
Bog forests, whose dominant trees are smaller podocarps of the silver-pine group, occupy limited areas mainly in the central North Island and on the West Coast of the South Island. They have largely been cut over, at least once, for posts and sleepers.
Although most southern-beech forests can be classified as protection forests, there remain large areas in more accessible regions which have been cut over and are regenerating, or which have not yet been cut over and will be reserved for sustained-yield management. Where southern-beech forest is present in the more accessible areas of the North Island and northern Marlborough-Nelson, the species are hard beech (Nothofagus truncata) and black beech (N. solandri). Red beech (N. fused) abounds in the less accessible upper areas, where it is usually accompanied by the silver beech (N. menziesii), the main tree at high altitudes. In rather dry places mountain beech (N. cliffortioides) replaces silver beech. On the eastern slopes of the Southern Alps there was once a belt of mountain-beech forest, but all except pockets of this has been burnt. On the western side of the Alps, beech forest is absent from the Taramakau River southwards for one hundred miles. In western Otago and western Southland silver beech is the main forest tree, with fair areas of mountain beech and small pockets of red beech. At the lower elevations silver beech is extensively milled and much of the forest has disappeared.
Important forest trees at high elevations, not already mentioned, are kaikawaka (Libocedrus bidwillii) and thin-bark totara (Podocarpus hallii).
In the undisturbed indigenous vegetation there were limited transition areas between tussock grassland and forest proper that carried manuka (Leptospermum scoparium and L. ericoides), and sometimes bracken fern (Pteridium esculentum). With the destruction of much tussock grassland and forest, these belts have extended, and manuka has even occupied extensive areas of destroyed forest remote from any original manuka stands. These stands are important because they are often a stage in succession back to mature forest. Manuka is also a very useful fuel.
Much land now classified as forest consists of a second growth of broad-leaved shrubs and trees which have come in after milling operations or on abandoned farm land.
Exotic plantations over 10 acres in extent now total some 930,000 acres, besides which there is a large total acreage of smaller farm woodlots and shelter belts. These areas of exotic species already provide nearly half of the country's timber requirements, and before many more years have passed must supply most of it. In some poorly forested districts shelter belts now provide a large part of the local timber supply.
Most of the larger exotic plantations are in the central North Island region. They were established with radiata pine (Pinus radiata) between the years 1925 and 1935. Other plantations are scattered throughout the country, although there are still some timberless districts with few plantations, notably Taranaki, Poverty Bay and the east coast, and South Canterbury.
NATIONAL FOREST ADMINISTRATION: Forest Authority — The administration of State forests and afforestation activities was for many years under the control of the Department of Lands and Survey. But in 1918 the office of Commissioner of State Forests was separated from that of Minister of Lands, and in 1919 a forestry sub department was formed. In 1920 the State Forest Service was established as a separate Department of State, which was given statutory recognition and administration authority by the Forests Act 1921–22. The Forests Act 1949 consolidated previous legislation and changed the title of the Minister from Commissioner of State Forests to Minister of Forests, and that of the State Forest Service to the New Zealand Forest Service. The Act provides for the appointment of a Minister of Forests, a Director-General of Forests, Conservators of Forests, and other officers. The Minister may delegate such of his powers as he thinks fit. The Act prescribes that the Forest Service shall have under the direction of the Minister exclusive responsibility in carrying out all matters of forest policy affecting State forest land and shall have exclusive control and management of:
All State forest land, whether for the production of timber or other forest produce, or for the protection of the land with a view to water conservation or soil stabilisation, or for ensuring the balanced use of the land, or for scientific purposes, or for recreational or amenity purposes not prejudicial to forestry;
The establishment, culture, and maintenance of forests on State forest land, and the harvesting, utilisation, transport, sale, or other disposal of forest produce from State forest land;
The granting of licences, leases, permits, and other rights and authorities under the Act;
The enforcement of the conditions of licences, leases, permits, and other rights and authorities granted under the Act or any enactment repealed;
The collection and recovery of all purchase moneys, rents, fees, royalties, charges, and revenues of the Service; and
Generally the exercise of all powers, authorities, and duties conferred or imposed on the Minister or the Forest Service by the Act.
Central control of the Forest Service is exercised by the Director-General of Forests from the head office in Wellington. A Conservator of Forests, who is the local representative of the Director-General, controls each of the seven conservancies into which New Zealand is divided. Forest Rangers, responsible to the Conservators, have charge of districts, which are subdivisions of the conservancies. Each district contains one or more managed forests. The central administration of forest policy is carried out by seven divisions, each under an Inspector in Charge.
State Forests — State forests are administered under the authority of the Forests Act 1949. The powers conferred by this Act to deal with forest produce are subject to the provisions of the Coal Mines Act 1925, the Mining Act 1926, and the Petroleum Act 1937. Section 23 of the Mining Amendment Act 1934 provides for the payment to the Crown of compensation for damage resulting from mining operations to any land vested in the Crown. Such compensation in respect of State forests may be claimed by the Minister of Forests from time to time as damage is caused.
The Minister of Forests also administers the Waitangi Endowment under powers set out in the Waitangi Endowment Act 1932–33.
Mining Privileges and Coal-mining Rights — Under the Coal Mines Act 1925 and the Mining Act 1926 a mining privilege or coal-mining right over State forest land may not be granted except with the consent in writing of the Minister of Forests and subject to such conditions as he may impose. Notwithstanding anything in the Mining Act 1926 or in any licence, lease, title, right, privilege, or other authority under those Acts granted after the Forests Act 1949 came into force, no person may cut or remove any timber or other forest produce on or from State forest land except in accordance with the provisions of the Forests Act 1949.
Regulations — The Forests Act 1949 authorises the appointment by regulation of committees to advise the Minister of Forests on specified matters. Regulations issued under this authority are the Timber Production Advisory Committee Regulations 1949, the Sirex Advisory Committee Regulations 1950, the Forest and Fire Publicity Committee Regulations 1952, and the Waipoua Forest Sanctuary Advisory Committee Regulations 1952.
Other regulations in force are the Sawmill Registration Regulations 1952, the Timber Regulations 1948, the Forest Service Fees and Charges Regulations 1953, and the Forest Produce Import and Export Regulations 1956.
Noxious Animals Act 1956 — This Act transfers to the Forest Service the responsibility for controlling and eradicating noxious wild animals, and confers on the Minister of Forests the appropriate powers. These activities were formerly carried out by the Wildlife Branch of the Department of Internal Affairs under the Wildlife Act 1953; but the Forest Service, being responsible for the welfare of the forests and having a greater knowledge of their needs, is now considered to be the more appropriate authority.
The Opossum Regulations 1953 continue in force as if they had been made under the Noxious Animals Act 1956, and are now administered by the Forest Service.
Fire Prevention and Control — The Forest and Rural Fires Act 1955 and the Fire Services Act 1949 provide for fire prevention and control throughout New Zealand.
The Forest and Rural Fires Act 1955 makes each county council a fire authority for the county area under its control, and provides for the setting up of rural fire districts each administered by a committee, or by the Minister of Forests, as fire authority. The Minister of Forests is the fire authority also for almost all unoccupied Crown-owned land outside rural fire districts, while the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council is the fire authority for soil-conservation districts. Rural fire districts, soil-conservation districts, most unoccupied Crown-owned land, and urban fire districts are excluded from the control of county councils. Regulations in force under this Act are the Rural Fire Committee Regulations 1949 and the Forest and Rural Fires Regulations 1956, which replace the regulations of 1951.
The Fire Services Act 1949 provides for the protection of urban districts.
FOREST MANAGEMENT: Objectives — In the field of production forestry, as distinct from protection forestry, the management activities of the Forest Service are directed towards two ends:
To protect, conserve, and, if possible, perpetuate the remaining indigenous forests of the country.
To create an exotic estate large enough and sufficiently diverse to supply the future needs of New Zealand in timber and other forest produce, and to provide an exportable surplus.
Indigenous-forest Management — Conservation measures in indigenous production forests involve regulation and restriction of the permissible annual cut, protection against fire, a careful watch for trespass and the prosecution of offenders caught, rigid insistence on close utilisation, both of forests and forest products, and finally block sales of carefully measured and appraised standing timber. Of these measures the last one is particularly important. The system of block sales introduced by the Forest Service in 1921 is in sharp contrast to the previous method of “royalty payment off the saw”. The present system encourages close utilisation since the sawmiller is required to pay for all timber measured; the previous one encouraged unnecessary waste both in the forests themselves and in the subsequent milling processes. It is estimated that through this administrative reform the Forest Service has succeeded in conserving some 700,000,000 board feet of timber which would otherwise have been left to rot in the forests or been thrown away in slab heaps. A large part of the indigenous-forest officers' work is in the routine administration of the block sale system, i.e., in the careful measurement and appraisal of trees for sale and in the periodic and equally careful inspection of milling operations to ensure that waste is not taking place.
Of equal importance to this policy of “conservation through close utilisation” is that of rationing the cut of indigenous timbers so that the remaining supplies, particularly of high-quality wood, are spread out over as long a period as possible instead of being used up in a very short time. To this end the Forest Service formulates working plans for all major State forests and through them regulates, both by individual forests and by districts, the amount of timber that may be cut annually. So far as may be practicable, consideration is given to the essential timber requirements of a district and to the extent to which these requirements can be met by the substitution of exotic timbers.
At the same time the possibility of ultimately regenerating podocarp forests and bringing them into a productive state is far from being overlooked. Research into the ecology of the natural forest associations and into the silvicultural characteristics of the individual species is being pursued. Past work has shown the importance of preserving a forest climate, which means that clear felling, or any condition that allows exposure and desiccation, must be avoided. In consequence, felling in narrow strips has been introduced in commercial logging in Westland, and trials by the Forest Service of other forms of partial felling are planned. Protection from fire and grazing after logging are standard measures which encourage development of natural second-growth associations which should in time act as nurse crops for podocarp seedlings.
Parallel to the policy of rationing the cut is that of making long-term log and timber sales. This has the effect of giving stability to sawmilling industries and to the communities dependent upon them. In one or two places further stability is being sought by the practice of interplanting logged areas with exotic species (mainly Douglas fir and western red cedar), combined where possible with the planting of adjacent areas of open country. By this means a sustained yield, part exotic and part indigenous, can be achieved, and the sawmilling industries and communities can look forward to a life in perpetuity.
The kauri forests, now only remnants of the vast forests from which timber was first felled in quantity in New Zealand, are owned principally by the State. The remaining kauri stands show promise of being amenable to sound forestry management. Bleeding for gum, which damaged many trees in the past, is forbidden. The annual cut is strictly rationed. Wherever kauri is felled a portion of the growing stock in young vigorous trees is left as a reserve. Young pole stands are silviculturally treated to free them from competition and improve growth. Natural regeneration is assisted and encouraged, and planting extends the species on to lands which have not held kauri for generations. A small but regular cut of this valuable species is assured, and forests for the future are being established and cultivated.
The prospects of improving and perpetuating the beech forests of New Zealand on a sustained-yield basis are good. Both the major species, red and silver beech, when given the right conditions, will regenerate freely; both grow sufficiently rapidly to grow on a medium-length rotation (100–130 years); and both show their optimum development on sites that are unsuitable for agriculture. There are many large areas of virgin forest still intact, and, in the case of red beech, extensive stands of pole forest which have originated as a result of fire, wind throw, or mining activities. Against these favourable circumstances must be set the presence in many localities of red deer, whose browsing may check or even prevent effective regeneration.
Recreation in Forests — As the population increases and as the cleared land becomes more firmly occupied by agricultural interests, so does the call on the recreational resources of the forests become greater. Weekend hunters head for the forest to shoot deer and pigs; fishermen frequent the streams; trampers wander along the many tracks; and alpinists climb through the forest to the heights above. The Forest Service caters for this demand in popular forests by establishing regular patrols, clearing and maintaining tracks, making camping sites and fireplaces, and (with the help of tramping and alpine clubs) building and maintaining huts and erecting bridges.
Exotic-forest Management — The establishment of State exotic forests dates from 1896 when an Afforestation Branch of the Lands Department was formed and forest-tree nurseries were established at Tapanui and Eweburn in the South Island and at Rotorua in the North Island. Planting commenced in 1898, and proceeded at a slow rate until 1922, by which time 47,000 acres had been established. The formation of the New Zealand Forest Service as a separate Department of State in the early twenties coincided approximately with an afforestation boom, and in the period 1923–36 no less than 376,000 acres were planted. Since then plantings have again been on a modest scale and over the last few years have averaged only some 7,000 acres a year.
In the earlier years the areas selected for planting were often chosen with little consideration for the suitability of the site for tree growing or for the proximity of the forests to existing and future markets. As a result there have been some partial or complete failures, and the geographical distribution of the forests leaves much to be desired. These faults are now being corrected by the establishment of new forests in timber-hungry districts and by the careful selection of areas where the climate, soil, and topography are all favourable to tree growth.
The original plantations contained a great variety of species, most of the common timber trees of Europe being represented as well as many from America and Australia, particularly eucalypts and North American conifers. In general, except locally and on very good sites, the European hardwoods such as ash, oak, and sycamore were failures; and of the multitude of eucalypts tried, only a few proved suited to New Zealand conditions. The standard European softwood, Scots pine, was a complete failure, as were many of the American pines, firs, and spruces. Norway spruce promised well for some years, but was finally wiped out by insect attack. Austrian pine was planted extensively in the earlier years and developed into very poor stands; much later, similar results were obtained from extensive plantings of the scopulorum variety of ponderosa pine, and even worse results from the wide-scale and indiscriminate attempts to establish Californian redwood. The successes, however, were no less numerous than the failures, and before long it became fairly obvious which would be the most suitable and profitable species. Pride of place went to radiata pine, which showed the ability to grow rapidly on a wide range of sites and to produce fine stands of timber. It became, and still is, the major exotic conifer of New Zealand. Other major species, planted according to site, are Douglas fir, Corsican pine, and ponderosa pine. Of recent years the southern pines — loblolly, slash, and long-leaf pines — have found a place in the more northerly forests. Minor species planted on a restricted scale are larch, lodgepole, strobus, and patula pines, Japanese cedar, Lawson cypress, macrocarpa, and western red cedar.
The estimated species distribution in State and private plantations at 31 March 1960 was:
| Species | Acres (000) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Radiata pine | 554 | 59 |
| Ponderosa pine | 80 | 8 |
| Corsican pine | 84 | 9 |
| Douglas fir | 54 | 6 |
| Others and mixtures | 173 | 18 |
| Totals | 945 | 100 |
In spite of failures New Zealand now has a large and valuable exotic-forest estate which is providing approximately one-half of the annual sawn-wood requirements and, in addition, is supporting a large and growing pulp and paper industry. Qualitatively the forests leave much to be desired. Their various shortcomings, due largely to past mistakes, now present problems which will tax the ingenuity of the forestry profession to the utmost. Specifically, management of the State exotic forests is rendered difficult and complex by reason of:
The Bad Age-class Distribution: Sixty-five per cent of the total radiata pine area was planted in one 10-year period. In the absence of tending this will result in a corresponding peak in production of mature timber, leading to utilisation difficulties. The position is much the same with the other major species.
The High Proportion of Radiata Pine: Some 44 per cent of the total area is in radiata pine, but the proportion in some individual forests and in some districts is much higher. A greater diversity of species would enable a wider range of forest products to be supplied and would lessen the risk of insect or fungal attack on an epidemic scale.
The Considerable Areas of Low Productivity: The maximum value from the soil is not being obtained in areas which are occupied by poor species such as P. ponderosa var. scopulorum, Austrian pine, some races of lodgepole pine, eucalypts, etc. Their replacement by more valuable species must be undertaken.
The Low Stocking of Many Areas: Two causes are responsible — the practice during the boom afforestation period of planting at a wide initial spacing, and the failure during the same period to plant up gaps in the original establishment. The resultant trees are often open grown and branchy, and are producing firewood and pulping material rather than sawlogs.
Lack of Tending: Large areas formed before the Second World War have received little treatment since planting. Low pruning has been carried out over several thousand acres, but thinning has been badly neglected. As a result, the final-crop trees of many forests are failing to produce the quantity and the quality of wood they are capable of.
For these reasons management activities in State exotic forests are directed towards getting a better distribution of age classes in the next rotation, which entails felling some stands before they are mature and leaving others to be carried on to over-maturity, towards converting areas of low productivity to well stocked stands of more valuable species, and above all towards catching up with arrears of thinning. At the same time all these activities must be integrated with utilisation projects so that the demand for forest products can be met and forest industries can have continuity of supply; and they must be so planned as to fit into long-term schemes for sustained-yield operation. Working plans, which when approved have ministerial authority, are prepared for all exotic forests, with the object of coordinating all these operations for a term of five to 10 years. They also embody long-term plans of 20 to 30 years or even longer.
Large-scale clear felling in State exotic forests began in 1939 and has been confined almost entirely to radiata pine. Natural regeneration has frequently followed logging, and second-rotation crops have been established.
Production from State exotic forests is now over 38,000,000 cubic feet annually and is increasing rapidly. Sawlogs account for the greater part of this yield, but many other types of forest produce are included, notably pulpwood, posts, poles, mining timber, fencing materials, and firewood. This diversity of produce permits the utilisation of trees of widely varying dimensions, a very necessary condition in operations designed to improve the quality of maturing timber stands. In particular the growing sales of small logs to the Tasman Pulp and Paper Co. for the production of chemical and groundwood pulp permits the clearing of much produce previously wasted as unsalable.
Soil Conservation and Water Regulation — Through its ownership and control of some 6,000,000 acres of protection forest the Forest Service is deeply involved in the vital national question of conserving soil and water resources. Ever since its inception the Forest Service has insisted that maintenance of an adequate vegetative cover on steep country is the only means of preventing accelerated soil erosion and one of the main means of regulating stream flow. Engineering work in the lower reaches of rivers is essential to reclaim swamps and to prevent flooding of alluvial flats, but these must be protected by adequate measures in the headwaters and catchments of rivers. Soil erosion, which both denudes the catchments and aggrades the rivers, can be prevented only by a continuous cover of vegetation.
Guided by these convictions, the policy of the Forest Service in soil-conservation measures is clear cut. It is simply to initiate or encourage any action which would conserve or improve the existing cover, and to prevent or discourage any action which would have the reverse effect. This policy dictates the management activities of all State forests where soil erosion is an important consideration; it is advocated by the Forest Service as the correct policy for all types of eroded land, irrespective of land tenure.
The forest-management activities undertaken in protection forests are protection from fire, prohibition and control of grazing, limitation of sawmilling activities, reservation of secondary species in some logging operations, control of animal pests, and, in some cases, artificial reestablishment. Of these, the most important are fire prevention and suppression and the control of introduced animal pests.
Forest-protection work is coordinated through the Department's representation on the Soil Conservation Council and on the 13 catchment boards now operating throughout the country, through the secondment of a professional forest officer to the staff of the Soil Conservation Council, and through the activities of the local land-use committees (representing the Departments of Agriculture and Lands and Survey and the Forest Service) which recommend the optimum land-use policy for marginal or doubtful areas.
Stabilisation of Sand Dunes — Sand-dune fixation is under the joint control of the Department of Lands and Survey and the New Zealand Forest Service. The objective is twofold: the stabilisation of dunes for the protection of agricultural and pastoral land, and the establishment of production forests. The Forest Service plants marram grass, sows lupin, and later establishes trees on certain protective zones and on areas that have no agricultural or pastoral potential. Four schemes are in operation — at Woodhill, Waiuku, Waitarere, and Santoft — the total gross area of which is 46,338 acres. About 12,000 acres of trees have been planted. Much of the area permanently fixed with trees will become productive forest in years to come.
Protection of Forests and Timber:Protection Against Fire — The fire-protection policy of the Forest Service follows from the premise that fire is the greatest single menace to forests and protection vegetation in New Zealand; within a few hours fire can undo the work of decades in building up a soil and vegetation balance.
The fire risk in New Zealand cannot be measured by comparing the generally adequate and well distributed rainfall experienced in most districts with conditions in countries where droughts are frequent and severe and the summers normally hotter and drier. New Zealand is a mountainous country and the characteristic high winds and strong sunshine will dry out the forest vegetation on exposed situations even in the heavy rainfall areas in a remarkably short time.
Although widespread dangerous fire conditions occur only infrequently there are few seasons during which there are not dry spells or near droughts in some part or other of the country, and very high fire hazards develop. The year 1946 brought the great fires of the central plateau of the North Island, and in 1949 conditions were severe enough in the Auckland provincial district to cause mortality from drought in a number of native forest species. During 1950 there were numerous forest fires on the West Coast of the South Island, and there was a long continued dry spell in the summer-rainfall districts of the extreme south. In 1955 a serious fire occurred in late spring in an exotic forest in Canterbury.
The peculiar feature of many New Zealand forest species in being extremely exacting in their requirements for regeneration to take place is of special significance. Forest fires in most countries mean the loss of a crop; in New Zealand a severely burnt forest usually means a destroyed forest. Even the beech species, which will regenerate freely under favourable conditions, can only do so after a severe fire under circumstances which are often quite fortuitous in character. Virgin mixed temperate forests admittedly do not burn readily during normal seasons, but the greater proportion of the remaining forests of this type have been logged for the commercial species. As cut-over forests they are very inflammable, and when burnt become waste lands.
The consequences of the relatively small fires which occur all over the country every normal season are as serious in the long run as the spectacularly large fires common in some countries. The losses are cumulative because most of our forest species lack the powers to recuperate from fire damage.
The existing areas of protective vegetation on the headwaters of the main rivers are inadequate for the purposes of soil and water conservation. Unless these protective areas are themselves protected and allowed to extend, abnormal flooding with costly river-control schemes will continue to be a heavy drain on the resources of the country.
The fire-protection organisation of the Forest Service operates over the whole of New Zealand, covering State forests, forests on other Crown lands, scenic reserves, and national parks. The organisation has also the responsibility of securing coordination and uniformity in the administration of the Forest and Rural Fires Act by other fire authorities.
An efficient fire-fighting service is maintained wherever the Department has fire-fighting responsibilities, according to the needs of each district. This reaches its highest level of organisation in the larger exotic forests, where standard Forest Service lookout cabins equipped with fire finders, radio, and telephones are located. Trained fire-fighting crews with modern equipment can be brought into action at a minute's notice and controlled through a radio network. Aerial patrols operate during each fire season in the important Rotorua area.
The provision of a fire-hazard prediction and warning service is an essential function of the fire-protection organisation. A nation-wide network of fire-weather and radio stations is maintained, and the fire-hazard situation in any part of the country is known at the Head Office of the Forest Service in Wellington each day during the fire season (October to April) within an hour of the weather observations being taken at the stations. This enables appropriate action, such as advice to fire authorities and broadcasting of warnings, to be taken.
The legislative provisions for fire protection are outlined earlier.
Protection Against Noxious Animals — The Division of Protection Forestry is concerned with the provisions of the Noxious Animals Act 1956 and is responsible for the control of deer, goats, opossums, wallabies, chamois, pigs, thar, and other introduced wild animals on all lands where the damage they cause significantly affects the economic welfare of the country.
The widespread populations of many of these animals have a serious effect on the regeneration of forest trees and of ground-cover vegetation both in forests and on the alpine meadows above the mountain forests. The natural forest floor of ferns, mosses, and shrubs has been extensively damaged by such ground-browsing animals as deer and goats, while simultaneously the upper storey is being adversely affected by the canopy-feeding opossum. These changes have led to a much accelerated water run-off with consequent soil erosion, root exposure, river-bed aggradation, and flooding. Damage resulting from the impact of noxious animals on protection forest and in contiguous alpine areas, while not as devastating as that from fire, is continuous and much more widespread.
Damage by deer and opossums in commercial exotic forests over the past few years has made it necessary to extend control measures into these forests.
Though hundreds of thousands of noxious animals are destroyed each year and though modern facilities, such as the dropping of supplies by parachute to field parties in remote and mountainous regions, are made use of, the task of control is arduous and dangerous, and overall progress is slow.
Noxious-animal advisory committees have been established to assist in coordinating various public interests and to encourage the sportsman and private hunter to take a more active part in the control of noxious animals. Mass-killing methods more effective than killing with the rifle are necessary and the possibilities of employing these are being investigated.
Small field-investigation teams of the Development Division are concerned with the development of improved techniques of control. When the latter pass out of the experimental stage they are applied on a large scale by the Division of Protection Forestry.
Control of Insects and Fungi — Sound silvicultural practices are the first line of defence, rendering trees less vulnerable to attack.
Biological control over insect pests is exerted by their natural enemies, insect or fungal parasites. Introduced species frequently come into the country without their natural enemies; part of the work of the biologist is to breed and liberate the latter.
Chemical control is an emergency measure to deal with outbreaks. It includes spraying of affected forests from aeroplanes, chemical treatment of nursery soils, and the dipping of timber to prevent attack by bark beetles and fungi.
Observers of the Forest Biology Survey maintain a constant watch on the exotic forests and on woodlots and shelter belts, and it is planned to extend this surveillance to the indigenous forests. The observers send thousands of representative collections of insects and fungi to the Biology Survey laboratory at the Forest Research Institute, Rotorua, where the material is identified and studied. Thus any incipient epidemics can be detected in time for effective control measures to be taken; and much information is accumulated which helps to elucidate the relationships between the organisms and the forests.
Timber Inspection and Quarantine — In keeping with current world trends, the Forest Service has developed an efficient quarantine service which covers all timber entering or leaving New Zealand.
In the past, this country has enjoyed comparative freedom from introduced insect pests, but the ever increasing tempo of international trade has multiplied the chances of accidental importation of harmful insects. Timber quarantine as practised in New Zealand embraces all imported timbers (including sawn, hewn, and natural-round produce), ship's dunnage, and imported cases and crates. These are inspected, and if necessary are treated to destroy harmful insects.
The same care is given to export timber, which must be completely free of insect attack before export is permitted.
RESEARCH AND TRAINING — The complexity of the many indigenous-forest and exotic-forest problems requires the maintenance of an organisation to ensure the continuity and coordination of research effort. Since 1947 all forestry and forest-products research (including research on noxious animals) administered by the Forest Service has been undertaken or coordinated by the Forest Research Institute, Rotorua. In addition, the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, the universities, and private industrial organisations undertake research into certain aspects of forestry and forest products.
The scope of present research by the Forest Research Institute is outlined below.
Silviculture — (a) Intensive study of the ecology of beech, kauri, and podocarp forests leading to the development of systems of silviculture which will provide the basis of sustained-yield management.
(b) Establishment of a series of permanent sample plots in commercial exotic forests to study the response to various grades of thinning and to obtain data on growth and yield throughout the rotation.
(c) Research on the origin and quality of seed, applied to the breeding of improved strains of trees, and on the vegetative propagation of desirable parent stock. Forest-soils investigations (in collaboration with the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research), with particular reference to the long-term changes in pumice soils, and to the effect of chemical treatments on soils associated with poor tree growth.
(d) Development of national arboreta in geographically representative localities, and a central herbarium of forest vegetation.
Mensuration — The compilation of volume tables for both standing forests and logs, in respect of both indigenous and exotic species. Yield tables for exotic species, increment studies, research on timber conversion factors and log scaling, and form-class investigations applicable to chief exotic conifers.
Forest Pathology — All matters concerning the health of forest trees are investigated, in particular the effects of various insects and fungi. Most of the work is concentrated on radiata pine and beech forests.
Indigenous Ecology — The manner in which the different kinds of indigenous forests are changing (especially under the impact of animal populations), and the rates of change, are being investigated so that those changes important in forest management may be predicted.
Forest and Range Experiment Station — Headquarters are at Rangiora, with a substation at Napier. It conducts research into the present condition of, and trends in, the protection forests and the mountain-range country associated with them (subalpine scrub, alpine meadows, etc.).
Animal Research — The various aspects of forest/animal interactions are being studied, so that a sound knowledge of ecology may form the basis of animal-population control. It is hoped that this work will assist in maintaining or, where necessary, improving the protective vegetation. (See also Protection Against Noxious Animals earlier.)
Forest Products — Current research is centred upon evaluation of the inherent properties of those timbers, both indigenous and exotic, which must gradually replace the widely used indigenous softwoods and imported timbers and other forest products. Parallel with the basic studies are those relating to the establishment of grading rules, to air seasoning and kiln drying, and to wood preservation and wood use generally. The research data are used also in the preparation of standard specifications and codes of practice, for instance, in revision of the building code for timber construction, which has been a major task during recent years. Work is undertaken by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research on wood chemistry, paints and other coatings, and wood preservatives, especially in relation to timber-boring insects. Larger companies engaged in utilisation of exotic-forest softwoods are building up technical and research staff whose contributions are more especially in the pulp, paper, and timber-utilisation fields.
Training in Forestry — The Forest Service recruits its forest rangers and professional officers as technical trainees at the age of 17 to 19 years. They work for one year in the forests, after which future forest rangers attend a ranger school for two years. A few are chosen as professional trainees and are assisted to obtain a B.Sc. degree (or a degree in arts or commerce for an administration career); after graduation the former are eligible for selection to attend a school of forestry overseas.
To build up a permanent and efficient skilled-labour force, the Forest Service now recruits each year about 80 youths 15 to 17 years of age. These junior woodsmen undergo a four-year course of training in practical forestry at one of the two woodsman schools which are situated at Kaingaroa and Golden Downs. In 1959 a scheme for the training of hunters for the control of noxious animals was inaugurated. Those selected attend a course at hunter-training schools in the Nelson Conservancy followed by field training under experienced hunters. The Forestry Training Centre at Rotorua regularly offers the timber industry courses in timber grading, timber inspection, and other forestry operations. A continuous series of courses is provided for Forest Service staff on all phases of Forest Service activity.
The Government also offers bursaries to help science graduates not in its employ to qualify at recognised overseas forestry schools. Other scholarships for study or for research are available from a private fund.
PRIVATE FORESTRY:Extension Services — Private planting commenced as early as 1855 and for some years afterwards was encouraged by grants of land or money. In 1916 the State commenced selling trees to private planters at very cheap rates and then assisted further by appointing extension-forestry officers. In 1931, after strong representations from the Horticultural Trades Association, the sale of trees was discontinued and extension-forestry work became part of the duties of Forest Service field staff. Recently, discussions with the association resulted in a plan of cooperation between the State and the trade for the supply of planting stock in bulk lots. The sale of cheap trees, coupled with a revival of interest through the activities of farm-forestry associations newly established throughout the country, has resulted in an increase in extension-forestry work.
Forest Taxation — Since 1949 some measure of tax relief has been afforded to farmers who own plantations. Expenditure incurred in planting, protecting, and maintaining shelter belts and woodlots has since that year been allowed to be charged against income for tax purposes. At the same time income from the intermittent sale of farm trees could, on application to the Commissioner of Taxes, be spread over a period of five years in order to mitigate the effects of the higher graduated tax. In 1960 the timber value of trees growing on a deceased's estate was exempted from death duties. This exemption removes the fear of a crippling burden on the estate and the possibility of the forced sale of a perhaps immature plantation.
Private Forest Estate — Forest holdings other than State have been reported to aggregate, in 1957, 462,000 acres in the following ownership categories: afforestation companies, 311,000 acres; local authorities, 30,000 acres; and private persons (mostly farmers); 121,000 acres.
It is doubtful whether the plantings since 1957 have done much more than replace the acres of mature timber felled each year for utilisation purposes, so that the present acreage is probably not much higher than that quoted above.
Afforestation companies boomed in the 1923–30 period, when huge areas, mostly of radiata pine, were planted. Utilisation, which has been in operation for some time now, is endeavouring to bring this short-period establishment into a normal series of age gradations and the area cut over is already being regenerated.
FINANCE OF STATE ACTIVITIES — Indigenous forests from which timber is sold are revenue producing. Exotic forests become revenue producing as they come to maturity and, indeed, a few of the older exotic forests have already reached this stage. Overall, at present more money is being spent on the establishment and tending of forests than is obtained in revenue.
Expenditure by way of general administration of forestry as distinct from the development of State forests for subsequent management is met in full from the Consolidated Fund.
The excess of expenditure over forest revenue in connection with forest and allied development has been financed as follows during the latest five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Excess of Expenditure over Forest Revenue | Excess Financed from: | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loans | Consolidated Fund | ||
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 2,014,000 | 1,156,000 | 858,000 |
| 1957 | 2,268,000 | 897,000 | 1,371,000 |
| 1958 | 1,998,000 | 513,000 | 1,485,000 |
| 1959 | 1,505,000 Cr. | 11,000 | 1,516,000 |
| 1960 | 1,639,000 | 136,000 | 1,503,000 |
The following table provides a summary of receipts and payments from all sources for the latest five financial years.
| Item | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts | |||||
| Indigenous forests — | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Sales of standing timber | 360,081 | 374,067 | 377,882 | 458,885 | 416,764 |
| Log sales from managed forests | 202,203 | 192,911 | 193,393 | 195,632 | 254,652 |
| Miscellaneous | 76,601 | 57,989 | 56,445 | 43,866 | 29,215 |
| Exotic forests: log sales, poles, posts, firewood, etc. | 727,032 | 875,099 | 913, 906 | 939,617 | 965,691 |
| Sawmills, etc.— | |||||
| Sawn timber | 894,757 | 556,968 | 739,935 | 819,655 | 1,020,462 |
| Treated products | 265,869 | 305,986 | 242,368 | 340,116 | 362,495 |
| Box shooks | 201,384 | 152,419 | 93,587 | 54,900 | 25,008 |
| Miscellaneous | 25,537 | 34,513 | 31,894 | 32,603 | 44,384 |
| Miscellaneous credits | 43,616 | 115,866 | 106,310 | 125,533 | 172,977 |
| Totals | 2,797,080 | 2,665,818 | 2,755,720 | 3,010,807 | 3,291,648 |
| Payments | |||||
| Allocation of revenue— | |||||
| Local authorities | 61,198 | 71,067 | 63,963 | 68,533 | 79,258 |
| General management charges— | |||||
| Salaries | 749,396 | 881,533 | 1,043,771 | 1,100,854 | 1,207,252 |
| General expenses | 252,714 | 559,949 | 552,182 | 548,240 | 645,496 |
| Land purchase | 21,832 | 41,463 | 17,511 | 40,554 | 25,782 |
| Forestry projects under development and management— | |||||
| Exotic | 1,292,340 | 1,557,254 | 1,455,703 | 1,367,274 | 1,677,355 |
| Indigenous | 223,391 | 216,260 | 211,611 | 293,672 | 248,416 |
| Sawmills, etc.— | |||||
| Operating expenses | 1,135,142 | 924,635 | 942,802 | 1,030,593 | 1,020,872 |
| Capital extensions | 225,689 | 156,073 | 56,066 | 32,342 | 26,253 |
| Murupara pulp, paper, and saw-milling project — equipment, roading, etc. | 849,102 | 526,136 | 410,663 | 34,635 | - |
| Totals | 4,810,804 | 4,934,370 | 4,754,272 | 4,516,697 | 4,930,684 |
The revenue from indigenous forests is used to reduce loan moneys required to finance forest activities under the Public Works Account, and statutory allocations of receipts to local authorities are a charge on the Consolidated Fund.
FOREST UTILISATION: Production of Sawn Timber — Sawn timber is produced from two entirely distinct but nevertheless complementary resources — the indigenous forests and the exotic forests. From the days of the first European settlement the indigenous forests have been subjected to destructive cutting, and, because of the long cycle of reproduction, must from a commercial viewpoint be regarded as largely a wasting asset. Consequently, as far as the indigenous forest is concerned, the sawmilling industry has had to follow a constantly receding forest edge — with the inevitable result that the industry has never been able to achieve any real measure of stability. Thus the production of indigenous timber has been based traditionally on rather primitive mills with poor living conditions for the workers; the forest could not be worked on a continuous cycle that would permit a sawmill to operate successfully on a permanent basis; hence there was no incentive to undertake more than the minimum of capital expenditure.
Up to about 1935 almost the whole output of sawn timber was produced in this way. The usual sawing equipment was a circular breaking-down saw for flitching the logs and a breast-bench circular resaw. The characteristics of the product may be summed up by saying that, although the quality of the timber itself was probably equal to any in the world, the sawing was inaccurate. The mills in general had a low cutting capacity and the annual sawn output per mill seldom exceeded 2,000,000 board feet. Up to the Second World War the total yearly production of sawn timber in normal years fluctuated around the level of 300,000,000 board feet.
In the 1930s significant changes began to develop. On the one hand the easy abundance of indigenous timber had gone, while on the other hand certain forests of exotic species which had been established about the beginning of the century had reached an age when cutting could commence. These exotic forests put on rapid growth, and the primary and original aim has been their management for sustained yield to provide permanency in forest industries and stability for modern communities based on them. In 1930 the production of exotic species was only 10,000,000 board feet, but by 1939 it had risen to 42,000,000 board feet. However, almost all of this production came from farm shelter belts and woodlots and was sawn in the same type of primitive mill as that characteristic of the indigenous forest. The product was used almost entirely for rough temporary work and box making, as there was still ample indigenous timber for all more demanding needs.
At the end of the 1930s the first great step was taken to change sawmilling from a primitive, shiftless industry to a stable industry based on permanent, well constructed capital installations with modern equipment and good living and working conditions. The Forest Service established a modern sawmill of Swedish design at Waipa, near Rotorua, and subsequently established another mill of this type at Conical Hill, near Tapanui (Southland). These mills were designed to serve as demonstration units and to enable the Forest Service to pioneer sawing, seasoning, grading, and merchandising techniques for the logs and timber yielded by the exotic forests. While such mills involve a large capital investment, they are permanent, have a high output with low unit costs, and yield accurately sawn timber. Several mills similar in type, with high-speed gang frames and large bandsaws, have been constructed since the Second World War by private enterprise.
The production of exotic timber is expanding rapidly, and it is being increasingly accepted for general building purposes, especially framing, and for a wide range of other uses. By far the most important of the exotic timber species is radiata pine, which accounts for about 95 per cent of the total cut of exotics; larch, eucalypts, Douglas fir, and a few other species are produced only on a minor scale. Only about half the country's timber requirements now come from the indigenous forests, and this proportion must inevitably fall as cutting is gradually reduced to the point where a small sustained yield of indigenous timber can be maintained. In connection with even the indigenous forests, however, it should be noted that the policy of the Forest Service, wherever possible, is to arrange sales on such a basis as to give mills an operating life long enough to warrant the installation of modern plants, and the provision of a good standard of housing and amenities.
Logging methods, too, have been changing from the traditional use of steam haulers and bush tramways, linking bush with mill, to tractor logging and motor-truck haulage of logs. The latter method permits the working of scattered and lightly stocked stands of indigenous timber. Roads, too, are an essential feature of exotic forests for fire protection and forest management as well as for log haulage, and tractors are favoured for their dual role of roading and extraction.
The table below gives the production of rough-sawn timber from 1921 onwards.
| Year Ended 31 March | Softwoods | Hardwoods | Grand Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indigenous | Exotic | Total | Indigenous | Exotic | Total | ||
| board feet (million) | |||||||
| 1921 | 290 | 10 | 300 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 308 |
| 1926 | 335 | 7 | 342 | 10 | 1 | 11 | 353 |
| 1931 | 208 | 13 | 221 | 9 | - | 9 | 230 |
| 1936 | 249 | 34 | 283 | 10 | - | 10 | 293 |
| 1941 | 277 | 54 | 331 | 11 | - | 12 | 343 |
| 1946 | 226 | 97 | 323 | 19 | 3 | 22 | 345 |
| 1951 | 301 | 190 | 492 | 32 | 4 | 36 | 528 |
| 1956 | 275 | 305 | 580 | 43 | 3 | 46 | 626 |
| 1957 | 274 | 281 | 556 | 38 | 3 | 41 | 597 |
| 1958 | 283 | 278 | 561 | 32 | 4 | 36 | 597 |
| 1959 | 287 | 314 | 601 | 32 | 4 | 36 | 637 |
| 1960 | 303 | 351 | 654 | 36 | 4 | 40 | 694 |
NOTE — Quantities have been rounded to the nearest million board feet. In some cases this rounding off results in a total disagreeing slightly with the total individual items shown in the table.
The growth of exotic-timber production compared with the relatively steady production of indigenous timber is shown in the following diagram.
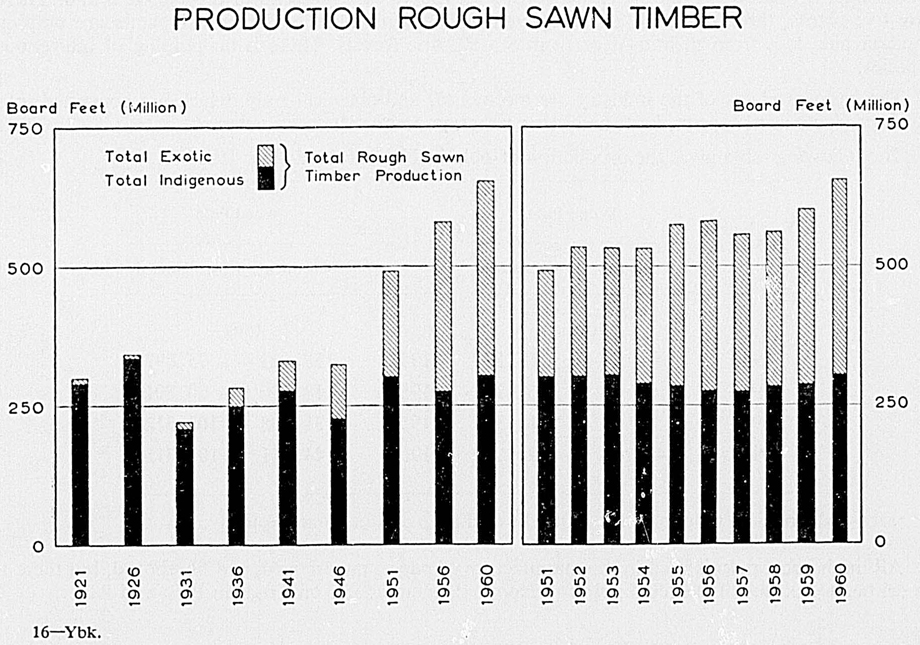
The following table gives details of timber production by species for the past five years; quantities are quoted in board feet (i.e., units of 12 in. by 12 in. by 1 in.).
| Species | Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| board feet (million) | |||||
| Rimu and miro | 208 | 212 | 219 | 220 | 232 |
| Matai | 35 | 33 | 33 | 35 | 36 |
| Totara | 12 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| Kahikatea | 18 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 20 |
| Tawa | 18 | 16 | 13 | 15 | 19 |
| Beech | 20 | 19 | 15 | 14 | 14 |
| Other indigenous | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| Totals, indigenous | 318 | 312 | 314 | 319 | 339 |
| Exotic pines | 297 | 273 | 268 | 303 | 334 |
| Douglas fir | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 13 |
| Eucalypts | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Other exotic | 6 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| Totals, exotic | 308 | 285 | 282 | 318 | 355 |
| Totals (all species) | 626 | 597 | 597 | 637 | 694 |
The Pulp and Paper Industry - The New Zealand pulp and paper industry is now equipped for the substantial utilisation of the big exotic forests on the volcanic plateau of the North Island. There are five plants, three of which are integrated with sawmilling. The integrated plants are pulping radiata pine logs from their own or from State exotic forests. There is no pulping of indigenous species.
The basic products of the industry are mechanical and chemical pulp, which are converted into such products as newsprint, kraft and other paper, paperboard, and fibreboard.
The following table gives the production of pulp in New Zealand since 1939–40.
| Year Ended 31 March | Wood Pulp | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Mechanical | |
| tons | ||
| 1940 | - | 217 |
| 1945 | - | 15,434 |
| 1950 | - | 21,438 |
| 1955 | 43,204 | 29,568 |
| 1957 | 115,423 | 75,897 |
| 1958 | 118,636 | 90,801 |
| 1959 | 131,708 | 103,512 |
| 1960 | 144,741 | 102,715 |
| NOTE – Mechanical pulp includes ground-wood pulp and defibrated pulp. | ||
All mechanical pulp is used in the manufacture of paper, paperboard, and fibreboard, but there is a deliberate surplus of chemical pulp for export. (See table later on Trade in Pulp and Paper.)
Production figures of pulp products in New Zealand since 1939–40 are as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Newsprint | Other Paper | Paperboard | Fibreboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tons | ||||
| 1940 | - | 6,253 | 6,620 | - |
| 1945 | - | 6,335 | 14,284 | 6,862 |
| 1950 | - | 7,111 | 14,676 | 13,526 |
| 1955 | - | 22,494 | 17,779 | 20,591 |
| 1956 | 9,000 | 28,154 | 20,225 | 21,340 |
| 1957 | 52,700 | 30,838 | 24,732 | 21,415 |
| 1958 | 64,700 | 37,998 | 28,282 | 21,000 |
| 1959 | 75,300 | 43,864 | 32,484 | 23,030 |
| 1960 | 76,100 | 49,168 | 36,417 | 24,830 |
The rise of production of pulp and pulp products is clearly shown in the following diagram.
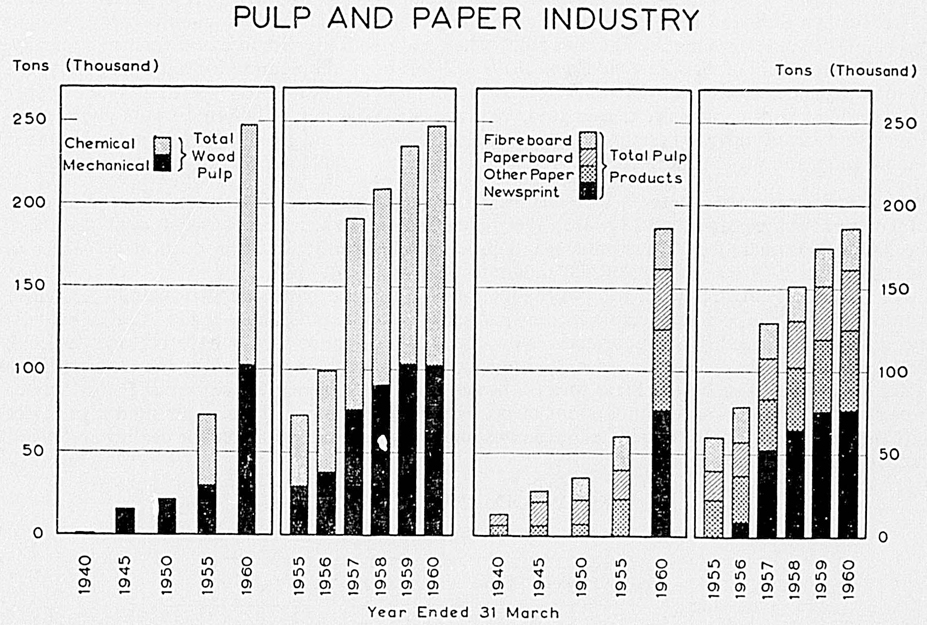
Tasman Pulp and Paper Co. – This company was formed in 1952 to utilise timber from the Kaingaroa State Forest. Practical encouragement and financial backing were given by the New Zealand Government, which is represented on the board of directors. The company's plant is at Kawerau, Bay of Plenty. The pulp and paper mill came into operation late in 1955 and the sawmill early in 1956. The annual rated capacity of the sawmill is 36 million board feet of sawn timber in one shift, while the capacity of the pulp and paper plant is 90,000 tons of newsprint, 60,000 tons of chemical pulp, and 65,000 tons of mechanical pulp. In September 1959 the company announced a further expansion with the installation of a second paper machine and ancillary plant as soon as possible to increase the annual newsprint capacity to 180,000 tons.
A subsidiary, the Kaingaroa Logging Co., whose headquarters is at Murupara, was formed to handle the log supply for the Tasman mills. Its directorate represents both Government and Tasman interests.
For details of the history of the Murupara scheme see the 1958 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
16*
New Zealand Forest Products Ltd. – This public company is already utilising over 30,000,000 cubic feet of timber a year from its own 176,000 acres of radiata pine forest. Plant capacity is 38,500 tons of kraft paper, 91,000 tons of kraft pulp, and 80,000,000 board feet of sawn timber per annum. In addition, the company is equipped to convert 10,000,000 board feet of timber into wooden cases and to produce 50,000,000 square feet of veneer, 33,000 tons of fibre board, and 25,000,000 multi-wall paper bags. Approximately half the annual increment of the company's forest is at present being utilised, and a programme of vigorous expansion is taking place, including the installation of a third paper machine and a second fibreboard mill. The integrated pulp mill, kraft-paper mill, and sawmill is located at Kinleith, near Tokoroa, while the fibreboard, multiwall paper bags, and wooden cases are manufactured in Auckland.
Whakatane Board Mills Ltd. now operates two paperboard machines, with an annual production capacity of 38,000 tons. The company manufactures its own mechanical and semi-chemical pulp, and is self-sufficient for more than 90 per cent of its raw materials.
Butter-box board is manufactured in Auckland by a company financed jointly by New Zealand Forest Products Ltd. and Whakatane Board Mills Ltd.
The company owns its own radiata-pine forest at Matahina and hauls the logs 23 miles to the mill over its private railway line. An associated company, Whakatane Timber Mills Ltd., has its modern sawmill located near the board mill to take the larger logs from the forest.
Caxton Paper Mills Ltd., owns a mill making tissue and various lightweight papers adjacent to the Tasman Pulp and Paper Co's plant at Kawerau. The mill has a production of between eight and nine thousand tons annually. It draws pulp, water, and steam supplies from the Tasman company.
The Mataura mill of New Zealand Paper Mills Ltd. has been in operation for more than 80 years. Its three machines produce a wide range of papers from fine tissues to heavy krafts, as well as paper felt, pressings, and manilas for special trade requirements. The mill is powered by its own hydroelectric and steam-turbo generating plants, and uses New Zealand made sulphate pulp, imported sulphite pulp, and waste paper. Annual production capacity is 8,000 tons of kraft and other papers.
Plywood and Veneer Manufacture – Five factories are engaged in the manufacture of plywood, and the total output for the year ended 31 March 1960, when reduced to a uniform basis of 3/16 in. thickness, was 43,100,000 square feet. Three other plants produce veneer only. Total production of veneer in the industry in 1959–60 was 169,200,000 square feet (1/16 in. basis).
For the most part logs from the indigenous forests form the basis of the plywood and veneer industry, though the peeling of exotic species, particularly radiata pine, shows a good deal of promise and is increasing steadily in importance. Now that the indigenous forests have become depleted, the production of peeler logs for veneer and plywood manufacture is regarded by the Forest Service as having a first claim on the State forests; hence in its own logging activities the Forest Service aims at producing the maximum amount of peeler logs, and has recently also adopted a policy of requiring sawmillers purchasing State indigenous forest to reserve logs suitable for peeling and divert them to the veneer factories.
PLYWOOD AND VENEER
| (a) Production | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Ended 31 March | Plywood (3/16 in.) | Veneer (1/16 in.)* | ||
| 1,000 Square Feet | Value | 1,000 Square Feet | Value | |
| *Veneer produced for sale commercially as such. | ||||
| £ | £ | |||
| 1956 | 35,660 | 1,003,241 | 40,438 | 205,735 |
| 1957 | 37,831 | 1,129,429 | 49,986 | 199,813 |
| 1958 | 38,769 | 1,219,776 | 50,763 | 217,253 |
| 1959 | 39,960 | 1,347,159 | 64,283 | 274,905 |
| 1960 | 43,089 | .. | 56,514 | 203,679 |
NOTE – Quantities are shown on a common thickness basis.
(b) Volume of Logs Used
| Year Ended 31 March | Species | Total | Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rimu | Matai | Kahikatea | Radiata Pine | Other | |||
| cubic feet (thousand) | £ | ||||||
| 1956 | 856 | 107 | 167 | 341 | 33 | 1,504 | 328,951 |
| 1957 | 885 | 96 | 163 | 488 | 89 | 1,721 | 380,062 |
| 1958 | 989 | 99 | 121 | 477 | 61 | 1,747 | 412,557 |
| 1959 | 973 | 95 | 117 | 511 | 103 | 1,799 | 468,376 |
| 1960 | 1,055 | 89 | 168 | 560 | 113 | 1,996 | 513,208 |
Production of Round and Split Produce – Considerable quantities of native timbers have been required in the past to meet the needs for mining, fencing timbers, and firewood, and for a proportion of sleeper, pole, and bridge-timber requirements. Thinnings and small-diameter logs from exotic forests are now making useful contributions towards satisfying those needs, and ensure the operation of preservative-treating plants.
Wood Preservation – Apart from plants treating round produce, for ground-contact use, with creosote and oil-soluble preservatives, the more recent establishment of plants for treatment of sawn timber with water-soluble preservatives has permitted far greater use in buildings of the non-durable grades and species from both indigenous and exotic forests.
On a per-head basis New Zealand is now by far the world's largest producer of preservative-treated timber for building purposes. House construction has traditionally been based on the use of heartwood of the indigenous softwoods, this having excellent durability, strength, and stability. Where sapwood of these timbers was used extensively, insect borers have been troublesome. Peculiar emphasis on the significance of borer attack led to the progressive adoption of preservative treatment of such wood, as its use became more general owing to the depletion of indigenous resources. The further diminution in supply of both heartwood and sapwood indigenous softwoods has in turn stimulated the use of exotic conifers for which preservative treatment against both decay and insect attack is justifiable and technically easy.
Much controversy arose regarding the effectiveness of various preservatives and types of treatment and the extent to which treated timbers should be used in a building. This controversy retarded development in new methods of timber preservation and, in order to resolve the conflicting opinions, the Government in September 1955 issued the Timber Preservation Regulations, under which was set up the Timber Preservation Authority. The main functions of this Authority are to decide what shall be authorised preservative treatments and to establish and administer such inspectorial and advisory service as is necessary to ensure that treatments are in accordance with its authorisations. Eleven organisations, including five Government Departments, are represented on the Authority and the inspection is done on behalf of the Authority by the New Zealand Forest Service. The Authority has adjudicated on and approved of a number of specifications and methods for timber preservation. New methods of wood preservation are continually being investigated and approvals issued of satisfactory formulations and processes.
Collection of statistics on wood preservation was introduced in 1955 and the following table shows the importance of this industry.
| Year | Open Tank | Diffusion Impregnation* | Pressure Impregnation | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Mainly boron. | ||||
| board feet (thousand) | ||||
| 1954–55 | 53 | 6,984 | 61,484 | 68,520 |
| 1955–56 | - | 7,307 | 81,967 | 89,274 |
| 1956–57 | - | 8,829 | 83,792 | 92,621 |
| 1957–58 | 5 | 21,637 | 83,522 | 105,163 |
| 1958–59 | - | 47,187 | 96,584 | 143,770 |
| 1959–60 | 30 | 70,889 | 105,837 | 176,756 |
In addition to the above, 1,853,000 cubic feet of roundwood, such as poles and fencing materials, was treated by the open-tank method, by diffusion, and by pressure impregnation.
Employment Statistics – The following table shows the number of employees in the forest industries at 15 October in the years stated. (Source: Labour and Employment Gazette, Department of Labour.)
| At 15 October | Forestry | Logging | Sawmilling | Pulp and Paper Industry | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Included in Other. | ||||||
| 1946 | 1,807 | 1,760 | * | 1,868 | 15,049 | 20,484 |
| 1950 | 2,133 | 2,202 | * | 2,222 | 18,074 | 24,631 |
| 1955 | 2,207 | 2,842 | 6,328 | 3,573 | 13,679 | 28,629 |
| 1956 | 2,490 | 2,854 | 6,236 | 4,138 | 13,529 | 29,247 |
| 1957 | 2,446 | 2,680 | 5,934 | 4,129 | 13,633 | 28,822 |
| 1958 | 2,564 | 2,738 | 6,221 | 4,520 | 14,124 | 30,167 |
| 1959 | 2,886 | 2,702 | 6,139 | 4,803 | 14,369 | 30,899 |
| NOTES | ||||||
| 1. “Forestry” includes silviculture, nurseries, etc. | ||||||
| 2. “Logging” includes felling, cutting, and haulage. | ||||||
| 3. “Pulp and Paper Industry” includes manufacture of pulp and conversion of pulp into paper, paperboard, fibreboard, and paper products (excluding stationery). | ||||||
| 4. “Other” includes plywood and veneer manufacture, timber merchanting, and other wood-using industries. | ||||||
OVERSEAS TRADE–New Zealand is self-sufficient in timber resources as far as quantity is concerned, but has always found it necessary to import strong, hard, and durable Australian hardwoods for railway sleepers, poles, cross-arms, wharf, bridge, and constructional timbers, etc. In addition there has been a traditional demand for Douglas fir, redwood, and western red cedar from North America for structural uses and exterior joinery. Other imports are normally limited to Japanese oak for the furniture trade and to small quantities of other species for specie specialty purposes.
While exports of indigenous timbers in recent years have virtually ceased owing to the conservation of these timbers for home consumption, there is a growing trade with Australia in radiata pine. The potential surplus of exotic pine available for export is approximately 150 million board feet annually, but the attainment of this level is dependent on overseas markets. Trade with Japan in pine logs is a recent development. In 1958, 1.5 million cubic feet of logs were exported, and in 1959, 5.0 million cubic feet.
Tables giving details of the external trade in timber now follow. The value of imports is the current domestic value in the country of origin; the value of exports is free on board at the port of shipment.
TIMBER IMPORTS
| Calendar Year | Sawn Timber | Sleepers | Logs and Poles | Total, All Timber | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australian Hardwoods | North American Softwoods* | Oak | Other | Total | ||||
| *Douglas fir, redwood and cedar. | ||||||||
| board feet (million) | ||||||||
| 1955 | 8.8 | 22.0 | 3.0 | 4.7 | 38.5 | 7.8 | 4.2 | 50.5 |
| 1956 | 8.0 | 13.1 | 1.6 | 6.0 | 28.7 | 12.2 | 5.7 | 46.5 |
| 1957 | 10.7 | 19.5 | 1.6 | 7.0 | 38.7 | 19.5 | 5.4 | 63.6 |
| 1958 | 10.0 | 14.9 | 3.1 | 5.0 | 32.9 | 12.1 | 4.9 | 49.8 |
| 1959 | 6.2 | 13.3 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 24.7 | 5.5 | 3.4 | 33.6 |
| NOTE – Figures have been adjusted to include items not given in board feet in published statistics. | ||||||||
IMPORTS OF TIMBER: COUNTRIES OF ORIGIN
| Calendar Year | Australia | Canada | United States of America | Japan | Other Countries | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| board feet (million) | ||||||
| 1955 | 20.7 | 16.5 | 5.6 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 50.5 |
| 1956 | 25.8 | 10.4 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 5.7 | 46.5 |
| 1957 | 35.3 | 17.1 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 7.1 | 63.6 |
| 1958 | 26.2 | 9.0 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 5.5 | 49.8 |
| 1959 | 14.4 | 5.1 | 8.2 | 1.7 | 4.2 | 33.6 |
| £ (thousand) | ||||||
| 1955 | 928 | 663 | 247 | 281 | 185 | 2,305 |
| 1956 | 1,258 | 456 | 134 | 148 | 237 | 2,233 |
| 1957 | 1,934 | 729 | 154 | 113 | 249 | 3,180 |
| 1958 | 1,292 | 377 | 249 | 219 | 209 | 2,346 |
| 1959 | 657 | 253 | 328 | 113 | 132 | 1,483 |
TIMBER EXPORTS
| Calendar Year | Indigenous Timber | Radiata Pine | Other Exotics | Total Exotics | Total, All Sawn Timber | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sawn | Cases | |||||
| board feet (million) | ||||||
| 1955 | 0.1 | 38.5 | 4.2 | - | 42.7 | 42.8 |
| 1956 | - | 30.9 | 3.6 | 0.1 | 34.6 | 34.7 |
| 1957 | - | 27.2 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 29.9 | 29.9 |
| 1958 | 0.4 | 33.4 | 4.9 | 1.3 | 39.6 | 40.1 |
| 1959 | 0.3 | 41.3 | 4.5 | 4.9 | 50.8 | 51.0 |
| NOTE – Small quantities of roundwood are included in the exports. | ||||||
EXPORTS OF TIMBER: DESTINATION
| Calendar Year | Australia | Pacific Islands | Other Countries | Totals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| bd. ft. | bd. ft. | bd. ft. | bd. ft. | |||||
| (million) | £(000) | (million) | £(000) | (million) | £(000) | (million) | £(000) | |
| 1955 | 39.6 | 1,096 | 3.2 | 164 | - | - | 42.8 | 1,261 |
| 1956 | 32.5 | 947 | 2.1 | 113 | - | - | 34.7 | 1,059 |
| 1957 | 28.5 | 821 | 1.4 | 74 | - | - | 29.9 | 896 |
| 1958 | 35.7 | 1,057 | 4.4 | 246 | - | 1 | 40.1 | 1,305 |
| 1959 | 46.9 | 1,445 | 4.0 | 221 | - | 2 | 51.0 | 1,668 |
Total production of the pulp and paper industry will almost fully meet New Zealand's requirements, limit imports of these products, and leave a considerable surplus for export of some of the major products such as newsprint and sulphate pulp.
The following tables give New Zealand's external trade in pulp and paper for the latest five years.
EXTERNAL TRADE IN PULP AND PAPER
| Calendar Year | Wood Pulp | Fibreboard | Paper and Paperboard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Newsprint | Paperboard | Other Paper† | Total | |||
*In 1,000 square feet. †Includes all other paper exported, but not manufactures of paper and paperboard; values include items for which no quantities are given. Basis for valuation: free on board at port of shipment. | ||||||
| Imports | ||||||
| tons | ||||||
| 1955 | 5,462 | 9,869* | 45,926 | 8,696 | 33,563 | 88,185 |
| 1956 | 3,637 | 7,186* | 39,876 | 3,868 | 25,322 | 69,066 |
| 1957 | 6,835 | 5,775* | 32,759 | 4,368 | 25,939 | 63,066 |
| 1958 | 8,546 | 1,195* | 24,152 | 3,350 | 30,368 | 57,870 |
| 1959 | 8,789 | 55* | 19,571 | 3,251 | 31,856 | 54,678 |
| Value £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955 | 256 | 226 | 2,451 | 718 | 3,970 | 7,139 |
| 1956 | 195 | 107 | 1,823 | 433 | 3,427 | 5,683 |
| 1957 | 316 | 87 | 1,913 | 448 | 3,668 | 6,029 |
| 1958 | 381 | 15 | 1,381 | 429 | 4,370 | 6,180 |
| 1959 | 327 | 1 | 1,114 | 380 | 4,247 | 5,741 |
| Exports | ||||||
| tons | ||||||
| 1955 | 27,341 | 1,616* | 360 | 294 | 15 | 669 |
| 1956 | 47,355 | 2,010* | 25,740 | 2,211 | 103 | 28,054 |
| 1957 | 64,994 | 737* | 35,907 | 1,869 | 1,183 | 38,959 |
| 1958 | 68,963 | 1,133* | 41,737 | 1,096 | 1,601 | 44,434 |
| 1959 | 76,826 | 1,955* | 43,662 | 1,901 | 2,338 | 47,901 |
| Value £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955 | 1,131 | 28 | 21 | 21 | 3 | 45 |
| 1956 | 2,002 | 38 | 1,545 | 138 | 12 | 1,695 |
| 1957 | 2,626 | 13 | 2,170 | 135 | 135 | 2,439 |
| 1958 | 2,725 | 19 | 2,632 | 81 | 173 | 2,885 |
| 1959 | 2,921 | 32 | 2,716 | 118 | 245 | 3,080 |
PRINCIPAL FOREST TREES – A brief description of the chief forest trees with their distribution and the uses and strength of their timber was given on pages 577–585 of the 1957 Yearbook, and in earlier issues. Detailed information is contained in publications of the New Zealand Forest Service, including Forest Trees and Timbers of New Zealand (Entrican, Hinds, and Reid); Exotic Forest Trees in New Zealand (Weston); The National Forest Survey of New Zealand, 1955, Vol. I: The Indigenous Forest Resources of New Zealand (Masters, Holloway, and McKelvey); The Physical and Mechanical Properties of the Principal Indigenous Woods of New Zealand (Entrican, Ward, and Reid); New Zealand Building Timbers (Reid); and the annual reports of the Forest Service and Forest Research Institute. See also the list of works on flora of New Zealand, page 16.
GENERAL – The principal characteristics of New Zealand's fisheries are the great length of the coastline, extensive natural harbours, numerous sheltered bays, and narrow continental shelf. Off its more northerly coasts, which come within the influence of the south equatorial current, a rich variety of subtropical fish is found, as exemplified by such species as the flying fish, the sunfish, the swordfish, and several shark species. On the other hand, its southern coasts, washed by the Antarctic drift, are the natural haunt of the fur-bearing seal, and yield varieties of fish which are characteristic of cold-water conditions.
Of the many kinds of excellent edible fishes the most important are the snapper (Pagrosomus auratus), which is the principal species in the catch (mainly by trawl) in the north-western part of the South Island, the west coast of the North Island, and the east coast of the North Island to just south of East Cape; next in importance is tarakihi (Dactylopagrus macropterus), which is taken mainly by trawlers working off the east coast of the North Island and in smaller quantities off the coasts of the South Island. The groper or hapuku (Polyprion oxygeneios) is caught on lines in the deeper water from North Cape to Stewart Island, but principally in Cook Strait and on the rocky parts of the east coast of the South Island, while the blue cod (Parapercis colias) is the staple line-caught product of the southern line fisheries, particularly about Foveaux Strait, Stewart Island, and at Chatham Islands.
The flounder and sole (Pleuronectidae) occur in the more shallow and sheltered waters.
The most productive grounds are in relatively shallow water, and, except for groper and ling fished for by means of deep long lines, most of the fishing is carried on at depths of less than 40 fathoms. Depths of over 100 fathoms occur at a comparatively short distance from the coast, and up to the present it is not known to what extent these deeper waters may be productive of marketable fishes. The principal methods of fishing are long-lining for groper (hapuku), ling, “hake” or “kingfish”, and snapper; hand-lining for blue cod; trawling and Danish seining, by which flounders, snapper, tarakihi, gurnard, John Dory, and a variety of other fish are taken. In bays and estuaries set-nets are used for flounders, snapper, and mullet, and seines are also employed principally for the capture of flat fish and snapper.
The fishing industry – that is, “the taking of fish and shell fish for sale” – came wholly under the control of the Marine Department by virtue of the Fisheries Amendment Act 1945, which provides that any boat used in fishing for purposes of sale must be registered, and that the owner of such a boat must be the holder of a licence authorising the boat to be so used.
The principal regulations dealing with fisheries are set out hereunder. Two comprehensive series are the Fisheries (General) Regulations 1950 and the Fresh Water Fisheries Regulations 1951. Under the latter are issued a number of modification notices which deal with particular aspects – e.g., permissible length of different classes of fish to be taken – while the various acclimatisation societies' rules are issued under the authority of these regulations. The Sea Fisheries (Boats and Licences) Regulations 1951, the Oyster Fishing Regulations 1946, and the Whitebait Fishing Regulations 1951 are directly relevant to the fishing industry. Other regulations include the Seal Fisheries Regulations 1946, the Quinnat Salmon Regulations 1940, the Fish-pass Regulations 1947 and the Toheroa Regulations 1955.
STATISTICS OF FISHERIES – As at 31 December 1959 there were 1,376 licensed fishing boats. Of these boats 682 earned more than £500, 158 earned more than £200 but less than £500, and 536 earned less than £200 during the 12 months ended 31 December 1959.
The estimated total quantity and value of the principal classes of fishery products marketed in the years 1958 and 1959 were as follows.
| Unit | Quantity | Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | ||
| £ | £ | ||||
| Wet fish | cwt | 494,173 | 519,917 | 1,586,300 | 1,543,021 |
| Whitebait (West Coast, South Island only) | cwt | 2,266 | 2,766 | 101,517 | 113,590 |
| Oysters (dredged) | sacks | 83,255 | 99,488 | 166,510 | 198,976 |
| Oysters (rock) | sacks | 3,957 | 4,541 | 12,226 | 15,589 |
| Mussels | sacks | 38,740 | 36,247 | 18,522 | 26,422 |
| Crayfish | cwt | 87,351 | 78,925 | 728,637 | 665,166 |
| Whale oil | tons | 1,373 | 2,730 | 68,650 | 159,750 |
| Fish livers | lb | 348,638 | 308,130 | 26,765 | 23,952 |
| Total value | 2,709,127 | 2,746,466 | |||
In the most important group, “wet fish” (i.e., all the ordinary fishes caught by all the methods of fishing), the annual totals for the successive years were as follows.
| Year | Total Quantity | Total Value |
|---|---|---|
| cwt | £ | |
| 1942–43 | 311,971 | 442,976 |
| 1943–44 | 294,445 | 489,268 |
| 1944 | 308,237 | 522,954 |
| 1945 | 331,773 | 558,404 |
| 1946 | 380,321 | 660,096 |
| 1947 | 438,300 | 802,496 |
| 1948 | 446,265 | 838,334 |
| 1949 | 449,903 | 864,332 |
| 1950 | 440,179 | 918,051 |
| 1951 | 408,365 | 949,551 |
| 1952 | 408,858 | 1,079,099 |
| 1953 | 435,497 | 1,200,038 |
| 1954 | 414,122 | 1,195,568 |
| 1955 | 435,335 | 1,299,494 |
| 1956 | 450,890 | 1,356,556 |
| 1957 | 498,302 | 1,503,914 |
| 1958 | 494,173 | 1,586,300 |
| 1959 | 517,917 | 1,543,021 |
Kind or Class of Wet Fish Caught – The following table shows the quantity and value of each kind of “wet fish” caught during 1958 and 1959.
Snapper was again the principal “wet fish” taken in 1959 and exceeded tarakihi by 34,522 cwt. The snapper catch was 8,425 cwt and tarakihi 16,934 cwt above the 1958 catch. Tarakihi and snapper comprised 53.53 per cent of the total “wet fish” landed in 1959.
| Kinds or Class of Fish | Quantity | Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| cwt | per cent | £ | per cent | |||||
| Snapper | 147,435 | 155,860 | 29.83 | 30.10 | 388,228 | 404,734 | 24.48 | 26.24 |
| Tarakihi | 104,404 | 121,338 | 21.12 | 23.43 | 284,882 | 303,947 | 17.97 | 19.68 |
| Gurnard | 39,476 | 36,136 | 7.99 | 6.98 | 80,890 | 53,552 | 5.11 | 3.47 |
| Blue cod | 30,869 | 34,974 | 6.25 | 6.76 | 89,153 | 87,712 | 5.62 | 5.81 |
| Trevally | 28,786 | 31,258 | 5.84 | 603 | 38,218 | 40,170 | 2.41 | 2.60 |
| Hapuku | 30,148 | 25,795 | 6.10 | 4.98 | 185,239 | 152,965 | 11.67 | 9.91 |
| Elephant fish | 24,381 | 22,595 | 4.95 | 4.36 | 104,758 | 91,243 | 6.61 | 5.91 |
| Flounder | 16,494 | 17,133 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 145,084 | 147,764 | 9.16 | 9.57 |
| Sole | 17,200 | 17,081 | 3.48 | 3.29 | 128,835 | 119,267 | 8.12 | 7.73 |
| Pioke | 8,224 | 8,748 | 1.67 | 1.71 | 20,132 | 21,328 | 1.27 | 1.38 |
| Shark | 6,374 | 5,987 | 1.29 | 1.16 | 10,414 | 9,557 | 0.66 | 0.61 |
| Moki | 7,332 | 5,674 | 1.48 | 1.09 | 18,300 | 13,162 | 1.15 | 0.85 |
| John Dory | 4,457 | 5,335 | 0.90 | 103 | 13,117 | 15,599 | 0.83 | 1.02 |
| Mullet | 5,166 | 4,799 | 1.05 | 0.93 | 15,454 | 14,066 | 0.98 | 0.91 |
| Ling | 5,200 | 4,662 | 1.05 | 0.90 | 18,149 | 14,931 | 1.14 | 0.96 |
| Barracouta | 4,706 | 4,461 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 7,306 | 5,393 | 0.46 | 0.35 |
| Warehou | 2,193 | 2,740 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 5,176 | 6,301 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
| Red cod | 1,931 | 2,631 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 4,832 | 5,268 | 0.30 | 0.34 |
| Hake | 1,680 | 2,424 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 6,726 | 10,173 | 0.42 | 0.65 |
| Butterfish | 1,458 | 1,980 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 8,212 | 11,084 | 0.52 | 0.71 |
| Whiptail | 912 | 1,510 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 1,307 | 2,056 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| Kahawai | 1,135 | 933 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 1,414 | 1,202 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Monkfish | 862 | 837 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 1,995 | 1,943 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Kingfish | 325 | 600 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 685 | 1,870 | 0.04 | 0.11 |
| Mixed rounds | 751 | 594 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 1,264 | 1,300 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Brill | 404 | 505 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 3,075 | 3,385 | 0.19 | 0.22 |
| Herring | 456 | 462 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 1,031 | 1,057 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Parore | 457 | 268 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 521 | 335 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Skate | 383 | 216 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 494 | 209 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Sardine | 163 | 128 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 456 | 550 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Garfish | 37 | 85 | - | 0.02 | 180 | 380 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Mackerel | 181 | 55 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 174 | 61 | 0.01 | - |
| Trumpeter | 67 | 55 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 277 | 279 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Perch | 16 | 19 | - | - | 23 | 37 | - | - |
| Maomao | 21 | 17 | - | - | 74 | 105 | - | - |
| Conger eel | 83 | 11 | 0.02 | - | 214 | 16 | 0.01 | - |
| Creamfish | 3 | 7 | - | - | 2 | 9 | - | - |
| Whiting | 1 | 3 | - | - | 2 | 10 | - | - |
| Bonita | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||||
| Frostfish | 1 | - | - | 3 | - | - | ||
| Totals | 494,173 | 517,917 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 1,586,300 | 1,543,021 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Methods of Capture – A table showing the total quantity of “wet fish” caught in 1959 by each of the common methods of fishing is shown below, with the figures for 1958 included for comparison.
| Method of Fishing | Quantity | Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| cwt | per cent | £ | per cent | |||||
| Trawl | 342,164 | 363,083 | 69.24 | 70.10 | 1,035,674 | 1,000,188 | 65.29 | 64.82 |
| Danish seine | 27,743 | 31,755 | 5.61 | 6.13 | 63,551 | 73,140 | 4.01 | 4.74 |
| Long and hand lines | 89,476 | 89,269 | 18.11 | 17.24 | 341,872 | 311,320 | 21.55 | 20.18 |
| Set and drag nets | 34,790 | 33,810 | 7.04 | 6.53 | 145,203 | 158,373 | 9.15 | 10.26 |
| Totals | 494,173 | 517,917 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 1,586,300 | 1,543,021 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
The steam trawlers landed a total catch of 17,555 cwt (3.38 per cent), while motor trawlers landed 345,528 cwt (66.71 per cent.)
Landings at Ports – Ports where the total landed catch was in excess of 10,000 cwt are shown in order of importance in the table below. The percentage of the grand total is also included.
| Port | Quantity | Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| cwt | per cent | £ | per cent | |||||
| Auckland | 115,183 | 131,546 | 23.31 | 25.39 | 256,222 | 287,253 | 16.15 | 18.61 |
| Wellington | 45,301 | 44,638 | 9.17 | 8.61 | 163,968 | 152,175 | 10.34 | 9.84 |
| Timaru | 40,994 | 43,821 | 8.30 | 8.46 | 180,679 | 158,126 | 11.39 | 10.23 |
| Gisborne | 24,657 | 31,217 | 4.99 | 6.02 | 56,463 | 68,161 | 3.56 | 4.41 |
| Napier | 28,961 | 28,988 | 5.86 | 5.59 | 81,989 | 79,006 | 5.16 | 5.11 |
| Tauranga | 17,122 | 25,313 | 3.46 | 4.88 | 45,808 | 60,369 | 2.89 | 3.91 |
| Manukau | 24,692 | 24,902 | 5.00 | 4.80 | 52,573 | 53,344 | 3.31 | 3.45 |
| Chatham Islands | 18,157 | 23,866 | 3.67 | 4.60 | 26,927 | 35,987 | 1.70 | 2.32 |
| Lyttelton | 26,942 | 19,417 | 5.45 | 3.74 | 107,888 | 68,277 | 6.80 | 4.41 |
| Nelson | 19,756 | 16,785 | 4.00 | 3.23 | 61,087 | 56,424 | 3.85 | 3.65 |
| Thames | 14,454 | 14,218 | 2.93 | 2.74 | 42,695 | 48,062 | 2.69 | 3.10 |
| Port Chalmers | 14,030 | 12,435 | 2.84 | 2.40 | 69,693 | 60,328 | 4.39 | 3.90 |
| Bluff | 10,750 | 10,573 | 2.18 | 2.04 | 50,051 | 42,879 | 3.16 | 2.77 |
The total quantity of fish landed at these ports was 427,719 cwt, which was 82.58 per cent of the grand total.
EXPORTS – The total value of fish and shellfish exported during 1959 was £1,252,512.
A table showing the principal classes of fishery products exported during each of the latest three years is set out below.
| Unit | Quantity | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||
| £ | £ | £ | |||||
| Oysters, frozen | cwt | 23 | - | - | 665 | - | - |
| Mussels, etc. | cwt | 45 | 96 | 97 | 542 | 1,180 | 1,160 |
| Fish, frozen | cwt | 65,517 | 47,157 | 58,235 | 553,580 | 428,600 | 493,309 |
| Crayfish, frozen, including craytails | cwt | 38,981 | 23,301 | 21,200 | 1,345,980 | 811,195 | 739,547 |
| Fish, smoked, dried, etc. | cwt | 277 | 226 | 361 | 3,032 | 2,437 | 4,091 |
| Fish and shellfish, canned | lb | 66,054 | 58,611 | 30,156 | 12,257 | 15,282 | 14,405 |
| Total values | ... | ... | ... | ... | 1,916,056 | 1,258,694 | 1,252,512 |
Fish-liver Oil – The quantity of fish livers processed during 1959 was 308,130 lb, 40,508 lb less than in 1958. The total oil produced was 16,762 gallons, a decrease of 1,541 gallons from the 1958 production.
The production of synthetic vitamins overseas at competitive prices is a factor which limits the kinds of livers it is economical to process. The 1959 exports of oil were 6,452 gallons, compared with 15,661 gallons in 1958.
The total weight of livers processed and the quantity of oil produced in each of the latest five years were as follows.
| Year | Weight of Livers Treated lb | Quantity of Oil Produced gallons |
|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 636,764 | 31,696 |
| 1956 | 370,920 | 20,409 |
| 1957 | 258,073 | 14,485 |
| 1958 | 348,638 | 18,303 |
| 1959 | 308,130 | 16,762 |
OYSTER BEDS – The principal oyster beds around the coast of New Zealand are those situated in Foveaux Strait, between South and Stewart Islands, and the rock-oyster beds on the east and west coasts of the Auckland peninsula.
In South Island waters a close season is observed from 1 October to 14 February, and in North Island waters from 1 November to 30 April in each year. The taking of oysters is governed by the Oyster-fishing Regulations 1946, and vessels operating commercially are subject to the Sea-fisheries (Boats and Licences) Regulations 1951. During the 1959 season 99,488 sacks of oysters were dredged from Foveaux Strait, compared with 83,225 in 1958.
The rock-oyster beds of Auckland were worked for many years under a variety of systems, but, owing to stripping of the beds, close seasons had frequently to be proclaimed. From 1908 the picking and wholesale marketing of rock oysters from the North Island beds was undertaken by the State, private picking being prohibited. In 1958 a change was made in the marketing procedure, and sales to the public through the oyster depot were discontinued. The total supply of oysters is now allocated direct to the trade in an endeavour to achieve wider distribution through the retail fish shops.
Oyster-cultivation work is being systematically carried on by the Marine Department in the Hauraki Gulf, in the Bay of Islands, and in the Kaipara district.
Rock oysters picked by the State in 1959 totalled 4,541 sacks, compared with 3,957 sacks in 1958.
CRAYFISH – Marine crayfish occur off many parts of the New Zealand coast. Part of the catch of crayfish is sold in local markets for domestic consumption, part is exported as frozen crayfish tails and whole crays, while a small quantity is canned.
With the development of the export of frozen crayfish tails to the United States of America and the high price received for this product, the increase in the catch of crayfish has been phenomenal, but already some grounds are showing a reduced return for the gear worked. The catch of crayfish over the latest five years is as follows.
| Year | Quantity cwt | Value £ |
|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 116,670 | 782,269 |
| 1956 | 128,609 | 964,134 |
| 1957 | 99,178 | 800,638 |
| 1958 | 87,351 | 728,637 |
| 1959 | 78,925 | 665,166 |
WHALING – The 1959 total catch was 320 whales, 318 being humpbacks and 2 sei whales. Both the Cook Strait and Hauraki Gulf stations were in operation. In the Cook Strait area the season started on 21 May and closed on 13 October. The Hauraki Gulf season was from 3 June to 31 October.
The total yield for the season was 2,730 tons of whale oil, 440 tons of whale meat, 10 tons of whale liver, and 120 tons of bone dust. Both stations had favourable weather during the season and the catch was the highest on record.
SEALS – The taking of seals in New Zealand waters has been on a restricted scale during the last 50 years, these animals being placed on the protected list in 1894. No sealing was then allowed until 1913, when there was an open season, but with certain restrictions. From 1916 a close season was observed until 1922, when the taking of seals was again permitted, but only till 1924, since when a close season was observed until 1946.
A short restricted open season was permitted during 1946 by the Seal Fisheries Regulations 1946, but a close season is again being observed.
BIG-GAME FISHING – Swordfish (striped and black marlin, and occasionally broadbill), mako shark, and other big-game fish occur principally off the east coast of the Auckland Provincial District, and attract both New Zealand and visiting big-game fishermen. The principal centres for this sport are Whangaroa, Russell (Bay of Islands), Whitianga (Mercury Bay), and Tauranga, where specially designed and equipped launches in charge of experienced men may be hired. The season lasts from December to May, the best months usually being February and March. The world's record black marlin swordfish (976 lb) was caught off the Bay of Islands in February 1926.
To preserve this very important fishery the Fisheries (General) Regulations 1947, superseded by the regulations of similar title issued in 1950, were gazetted prohibiting the taking of these fish by other than rod and line, and stipulating that the line was not to be heavier than No. 39 linen thread line. In addition, a limit bag of not more than four fish per boat per day has been imposed.
In the 1959 season (from November 1958 to June 1959), big-game fish caught included 12 black marlin, 375 striped marlin, 1 blue marlin, 206 mako shark, and 49 other species. Figures for the 1958 season recorded 9 black marlin, 541 striped marlin, 3 blue marlin, 249 mako shark, and 109 other species.
WHITEBAIT – A fishery that is peculiar to New Zealand with regard both to the product and to the methods of operation, and carried on from July to November in the tidal reaches of many rivers, is the whitebait fishery. The most productive fishing grounds are near the mouths of the rivers of the West Coast of the South Island and in the lower reaches of the Waikato River. Normally the whitebait fishery gives employment to over 300 regular fishermen, and a greater number of part-time fishers, and, over a period of years, produced an average of approximately 3,000 cwt of whitebait. As a result of reasonably good seasons over a period of years, and with improved transport from the more remote rivers, in which aeroplanes have played an important part, a substantial whitebait industry has been developed, particularly on the West Coast of the South Island, where 2,766 cwt were caught in 1959.
FRESH-WATER FISHERIES – Descriptions of native and acclimatised fishes have been given in the 1957 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
With the exception of the Rotorua Acclimatisation District in the thermal lakes region and the Southern Lakes District in the South Island, which are under the control of the Department of Internal Affairs, the local administration and management of fresh-water fisheries are in the hands of acclimatisation societies.
The Freshwater Fisheries Regulations 1951 contain provisions of general application with regard to limit bag, size limit, baits and lures, duration of season, etc. Such general regulations apply unless modification notices for particular districts are issued varying these limits.
A fishing licence, for which the fee for the season (opens 1 October and continues for seven months) is £2, enables the holder to fish for acclimatised fish in any part of New Zealand except the Rotorua Acclimatisation District (which includes the Taupo Trout Fishing District) and the Southern Lakes Acclimatisation District. For fishing in the Rotorua area and the Southern Lakes District the local licence fees are £2 10s. and £1 10s. respectively for all male adults, but in the Taupo area of the Rotorua Acclimatisation District, which is the most popular of all New Zealand angling resorts, the licence fees for each season arc £3 10s. for male adults and £2 for females and males under 17 years, weekly licences are 15s. and 7s. 6d. respectively, and daily licences 5s. in all cases. For all acclimatisation districts there is a reduced scale of licence fees for female and juvenile anglers. Monthly, weekly, and daily licences are also available, while half-season, weekend, and single-river licences are optional in some districts. The open season for Taupo waters extends from 1 July to 30 June (a 12-month season).
The Fisheries Amendment Act 1953 provides for the establishment of fisheries experimental waters by Order in Council. In such cases the fresh-water regulations applicable may be declared not to apply or to apply, subject to modifications. Under this authority, Lake Waingata was declared a fisheries experimental water during 1956, and Lake Opouri in 1957.
The same amendment also enables the Governor-General under certain conditions to dispense with a close season for trout and salmon in any one or more years or to fix a close season of less than five months' duration for all or part of the waters of the district concerned. Special regulations providing for winter fishing at Lake Tutira, Hawke's Bay; Lake Ratapiko, Taranaki; and Lakes Pauri, Kowhata, and Wiritoa, Wanganui, were issued in 1960.
MINERAL PRODUCTION – New Zealand's mineral resources are limited, particularly as regards metallic ores.
For many years following the first discovery of gold at Coromandel in 1852, and later in the South Island, gold mining was of great importance to New Zealand's economy. From an output of 10,437 oz in 1857, gold production reached a peak of 735,376 oz in 1866, then valued at £2,844,157. Since then a steady decline has resulted in gold production amounting to only 36,758 oz in 1959.
Coal has for many years been New Zealand's most important mineral, the value of production being £7,910,000 in 1959.
With New Zealand's increasing agricultural and industrial needs, quarrying has grown in importance over the past 20 years, production in 1959 being valued at over £9 million. By far the largest contributor to non-metallic production is sand, rock, gravel, and aggregate for building purposes and road making, while limestone-quarrying is also an important industry.
The following table shows the production of metals and minerals during 1958 and 1959 from mines and quarries.
| Mineral | 1958 | 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| Fuels | £ | £ | ||
| Coal | 2,720,034 tons | 7,820,000 | 2,809,594 tons | 7,910,000 |
| Petroleum (crude) | 192,000 gal | 8,000 | 189,000 gal | 7,800 |
| Natural gas | 5,431,800 cu. ft. | 1,494 | 5,457,300 cu. ft. | 1,498 |
| Metals | ||||
| Gold | 24,981 oz | 313,068 | 36,758 oz | 460,308 |
| Silver | 2,339 oz | 87 | 4,873 oz | 1,539 |
| Iron ore | 1,533 ton | 7,25 | 1,505 tons | 7,449 |
| Manganese ore | 103 ton | 798 | 101 tons | 783 |
| Tungsten ore | 3 ton | 577 | 9 tons | 4,475 |
| Non-metallics | ||||
| tons | tons | |||
| Asbestos | 405 | 20,069 | 572 | 27,480 |
| Bentonite | 1,801 | 24,266 | 2,149 | 29,242 |
| Clay for bricks, tiles, etc. | 296,257 | 158,360 | 279,988 | 141,806 |
| Clay for pottery, fillers, etc. | 7,790 | 17,715 | 6,684 | 23,488 |
| Diatomite | 5,657 | 39,489 | 7,278 | 72,777 |
| Dimension stone for building | 23,773 | 65,088 | 9,972 | 46,216 |
| Dolomite | 3,052 | 17,702 | 3,165 | 18,990 |
| Limestone for agriculture | 1,046,837 | 1,040,031 | 1,011,879 | 1,046,916 |
| Limestone for industry | 47,162 | 55,844 | 53,063 | 46,033 |
| Limestone, marl, silica sand, etc., for cement | 1,083,373 | 342,322 | 1,111,872 | 337,492 |
| Magnesite | 1,200 | 1,855 | - | - |
| Perlite (manufactured value) | 360 | 10,000 | 378 | 9,600 |
| Pumice | 23,082 | 18,295 | 28,395 | 13,250 |
| Quartzite | 371 | 2,041 | - | - |
| Rock for harbour work | 1,234,873 | 608,541 | 1,242,903 | 534,469 |
| Salt | 7,650 | 107,100 | 20,300 | 275,300 |
| Sand, rock, gravel, etc., for building aggregate | 2,717,311 | 1,915,924 | 2,831,762 | 2,090,695 |
| Sand, rock, gravel, etc., for road and ballast | 10,503,020 | 5,228,954 | 10,618,664 | 5,050,512 |
| Sand for industry | 104,715 | 70,621 | 95,299 | 55,571 |
| Serpentine | 98,121 | 209,431 | 107,063 | 146,759 |
| Silica sand | 23,082 | 93,452 | 46,637 | 96,267 |
| ... | 18,199,449 | ... | 18,456,715 | |
COAL – Coal in New Zealand has for many years been mined in certain well defined areas, beyond which no coal is known to exist in any significant quantities. The major coalfields, with the class of coal found in each, are -
Bituminous Coal (Coking): Greymouth, Westport (Buller Coalfield), Reefton (Garvey Creek).
Sub-bituminous Coal (Non-coking): Waikato (including North Taranaki), Otago (Kaitangata), Southland (Ohai), Reefton.
Lignite (Non-coking Low Grade): Southland (Mataura).
Minor coalfields from which coal is being mined, but which cannot be expected to provide an important contribution to our coal resources, are –
Sub-bituminous Coal: Nelson (Puponga, Westhaven), Murchison.
Lignite: Canterbury (numerous small deposits), Otago, Charleston (Westport).
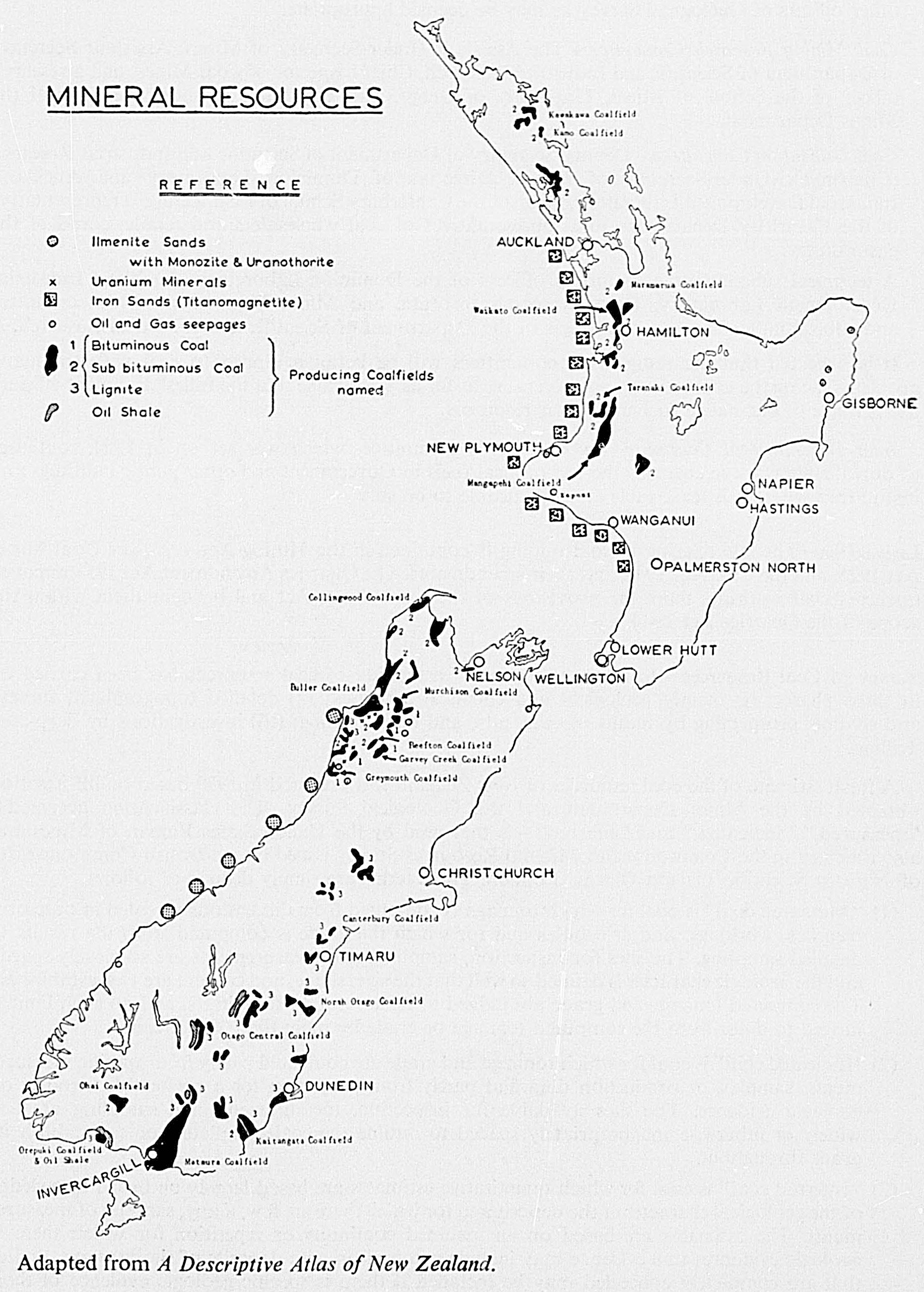
Coal Utilisation and Research – Coal utilisation and research is guided by three committees. They are:
Coal Resources Committee – Two officers of the Mines Department with the Director and such other officers of Geological Survey as may be deemed appropriate.
Coal Mining Research Committee – The Assistant Under-Secretary of Mines, Assistant Secretary of Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Chief Inspector of Coal Mines, and a research officer of the School of Mines, University of Otago. This committee is under the aegis of the Mines Department.
Coal Utilisation Committee – Deputy Secretary of Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (Chairman), Under-Secretary of Mines, Directors of Dominion Laboratory and Auckland Industrial Development Laboratory, Dean of the Canterbury School of Engineering, a representative of the Electricity Department, and representatives of coal wholesalers and retailers, and of the gas industry.
A technical subcommittee comprises officers of the Dominion Laboratory, Auckland Industrial Development Laboratory, Dairy Research Institute, and Mines Department. This committee and subcommittee are under the aegis of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
It is expected that the reorganised committees will be better equipped to deal with the many problems facing the coal industry and to ensure as far as practicable that the fullest and most efficient use is made of our native fuel and power resources.
Inter-Departmental Committee on Fuel – This committee, which was set up in 1954, continues to do valuable work in ensuring the use of local fuels in Government and other public buildings and institutions where it is reasonable and practicable to do so.
Legislation – The law relating to coal mining is contained in the Mining Act 1926, the Coal Mines Act 1925, and the Coal Act 1948, and their amendments. The Quarries Amendment Act 1951 removed opencast coal workings from the provisions of the Coal Mines Act and brought them within the scope of the Quarries Act 1944.
Survey of Coal Resources – In recent years the investigation of coal resources has been carried on in three phases: (i) mainly geological and chemical activities; (ii) detailed topographical surveys and shallow prospecting by means of cuts, pits, and hand drilling; (iii) investigations by deep-core drilling.
A fresh estimate of the coal resources of New Zealand was prepared in 1959 based on information obtained by the Mines Department and the Geological Survey. The classification accepted – “measured,” “indicated,” and “inferred” – is that used by the United States Bureau of Mines and also accepted in the Commonwealth Mineral Resources Survey issued by the British Commonwealth of Nations Scientific Liaison Offices, London. These terms are simply defined as follows.
“Measured coal” is coal for which tonnage is computed from dimensions revealed in outcrops, trenches, workings, and drill holes and for which the grade is computed from the results of detailed sampling. The sites for inspection, sampling, and measurements are so closely spaced and the geologic character is defined so well that the size, shape, and content are well established. The computed tonnage and grade are judged to be accurate within limits, and no such limit is judged to differ from the computed tonnage or grade by more than 20 per cent.
“Indicated coal” is coal for which tonnage and grade are computed partly from specific measurements, samples, or production data and partly from projection for a reasonable distance on geologic evidence. The sites available for inspection, measurement, and sampling are too widely or otherwise inappropriately spaced to outline the coal completely or to establish its grade throughout.
“Inferred coal” is coal for which quantitative estimates are based largely on broad knowledge of the geological character of the deposit and for which there are few, if any, samples of measurements. The estimates are based on an assumed continuity or repetition for which there is geologic evidence; this evidence may include comparison with deposits of similar type. Bodies that are completely concealed may be included if there is specific geologic evidence of their presence.
These clearly and specifically defined terms have wide international acceptance. The table below sets out the estimated coal resources of New Zealand.
| Measured | Indicated | Inferred | |
|---|---|---|---|
| tons | |||
| Bituminous | |||
| Buller | 29,600,000 | 18,800,000 | 15,000,000 |
| Murchison | 110,000 | 660,000 | 1,300,000 |
| Garvey Creek | 175,000 | 3,000,000 | 5,000,000 |
| Greymouth | 11,000,000 | 15,000,000 | 30,000,000 |
| 40,885,000 | 37,460,000 | 51,300,000 | |
| Sub-bituminous | |||
| Northland | 100,000 | 500,000 | 3,000,000 |
| Maramarua | 19,000,000 | 36,000,000 | 24,000,000 |
| Huntly | 25,800,000 | 99,170,000 | 72,000,000 |
| Kawhia | 260,000 | 470,000 | 6,000,000 |
| Mangapehi | 1,800,000 | 600,000 | 3,300,000 |
| Tatu (including Ohura] | 3,400,000 | 1,100,000 | 12,000,000 |
| Waitewhena | 400,000 | 900,000 | 11,000,000 |
| Mokau | - | - | 60,000,000 |
| Nelson | 60,000 | 130,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Buller Gorge | 100,000 | 2,000,000 | 8,000,000 |
| Reefton | 1,670,000 | 3,940,000 | 8,000,000 |
| Fletcher Creek | - | - | 3,000,000 |
| Punakaiki | - | - | 2,000,000 |
| Kaitangata | 1,920,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| Ohai | 7,720,000 | 8,400,000 | 90,000,000 |
| Orepuki | - | - | 1,000,000 |
| 62,230,000 | 153,710,000 | 304,800,000 | |
| Lignite | |||
| Charleston | 6,000,000 | 2,000,000 | 8,000,000 |
| Canterbury | 250,000 | - | 20,000,000 |
| North Otago | 250,000 | - | 2,000,000 |
| Central Otago | 250,000 | - | 15,000,000 |
| Green Island | 250,000 | - | 3,000,000 |
| Kaitangata | 3,300,000 | 20,900,000 | 75,000,000 |
| Pomahaka | - | - | 60,000,000 |
| Mataura Valley | 5,400,000 | 20,200,000 | 216,000,000 |
| 15,700,000 | 43,100,000 | 399,000,000 | |
| Summary: Measured | 118,815,000 tons | ||
| Indicated | 234,270,000 tons | ||
| Inferred | 755,100,000 tons | ||
| Grand total | 1,108,185,000 tons |
Since 1954 many estimates have been revised in the light of information gained from drilling, prospecting, and surveying. While 1959 aggregate figures do not differ materially from those adopted in 1954, there has been some alteration in classification as the result of closer examination in the several areas concerned. This, of course, must be a continuing process.
Summary of Operations – The following table summarises coal-mining operations.
| Year | Output (tons) | Persons Ordinarily Employed | Lives Lost by Accidents In or About Collieries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Underground | Totals | Per Million Tons Produced | Per Thousand Persons Employed | Lives Lost | ||
| Prior to 1955 | 133,186,026 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 598 |
| 1955 | 2,556,653 | 1,494 | 3,035 | 4,529 | 1.57 | 0.89 | 4 |
| 1956 | 2,627,716 | 1,514 | 3,034 | 4,548 | 1.52 | 0.88 | 4 |
| 1957 | 2,612,463 | 1,641 | 3,016 | 4,657 | 0.76 | 0.43 | 2 |
| 1958 | 2,720,034 | 1,662 | 3,084 | 4,746 | 4.40 | 2.52 | 12 |
| 1959 | 2,809,594 | 1,617 | 2,922 | 4,539 | 1.42 | 0.90 | 4 |
| Totals | 146,512,486 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 624 |
Underground Mines – The following table gives particulars of the operations of underground mining during the last five years.
| Calendar Year | Output (tons) | Men Employed Underground | Tons per Man Underground | Men Employed on Surface | Tons per Man on Pay Roll |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1,789,347 | 3,035 | 590 | 1,152 | 427 |
| 1956 | 1,830,726 | 3,034 | 603 | 1,194 | 433 |
| 1957 | 1,875,041 | 3,016 | 621 | 1,236 | 440 |
| 1958 | 1,930,301 | 3,084 | 626 | 1,168 | 454 |
| 1959 | 1,921,376 | 2,922 | 658 | 1,102 | 477 |
Of late years the output per hewer shift has risen, and there has been an appreciable overall increase in output per man on pay roll.
There were 116 underground mines in operation in 1959, and of these 24 operated by the State produced 1,280,751 tons of coal. Production from individual State mines is set out in the Mines Statement, parliamentary paper C. 2.
Opencast Mines – Production of coal from opencast mines in 1959 amounted to 888,218 tons, which was 98,485 tons more than the production in 1958. The proportion of the total production of coal obtained from opencast mines amounted to 31.61 per cent.
There were 50 opencast mines in operation in 1959, and of these 13 operated by the State produced 310,432 tons. All of these State mines have come into production since the beginning of 1944. The progress of opencast mining during the last five years is illustrated by the following table.
| Year | Output (tons) | Men Employed | Tons per Man Employed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 767,306 | 342 | 2,243 |
| 1956 | 796,990 | 320 | 2,490 |
| 1957 | 737,422 | 405 | 1,820 |
| 1958 | 789,733 | 494 | 1,599 |
| 1959 | 888,218 | 515 | 1,725 |
Derived Products – Low-temperature carbonisation works, using the Lurgi process, established at Rotowaro, 70 miles south of Auckland, in 1931, produced during 1959, 15,755 tons of carbonettes, 281,670 gallons of tar and oil, and 2,315 tons of char from 31,223 tons of slack coal, which was part of the output of a group of local mines.
The Sockburn plant, near Christchurch, produced 27,231 gallons of tar and 5,757 tons of coke during 1959.
Coal Consumption – The approximate distribution of coal consumption during each of the five years 1955–59 is shown in the following table. The total quantity is based on actual production in each year plus imports and minus exports (including bunker coal for overseas vessels). Where the information is available, adjustments have been made for stocks on hand at the beginning and end of the year.
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes hospitals, hotels, etc. | |||||
| tons | |||||
| Railways | 371,000 | 311,000 | 269,000 | 238,000 | 227,000 |
| Coastal shipping | 29,000 | 32,000 | 28,000 | 25,000 | 14,000 |
| Gasworks | 268,000 | 261,000 | 256,000 | 271,000 | 276,000 |
| Factories* | 1,383,000 | 1,493,000 | 1,519,000 | 1,633,000 | 1,767,000 |
| Households | 520,000 | 540,000 | 550,000 | 550,000 | 540,000 |
| Total consumption | 2,571,000 | 2,637,000 | 2,622,000 | 2,717,000 | 2,824,000 |
Mercer Power Station – Of the greatest importance to the coal industry has been the building of the coal-fired steam-generating station at Mercer. This station, of 180,000 kW capacity, will require 600,000 to 800,000 tons of coal per annum. One-third of the coal requirements is being provided from the Huntly coalfield from existing mines plus some additional opencast development.
The remaining two-thirds is being provided from the Maramarua coalfield about 7 miles distant from the station. Initially it is expected that most of the Maramarua quota will, of necessity, be supplied from opencast development, but it should be possible within 10 years to mine 25 per cent of this quota from underground sources to conserve opencast coal in this district.
These proportions will ensure continuity of production and employment at Huntly, and at the same time ensure that the better-quality Huntly coals are not used up at a greatly accelerated rate for the one power undertaking.
State Coal Mines – The purchase of coal mines by the State in 1940, together with subsequent purchases, left only three large private mines in production. A proposal to purchase all coal in the ground, including unworked coal, by the Coal Act 1948, was reversed by a change of Government, when the Act was repealed.
During 1959 there were 37 State coal mines in operation and the average number of persons employed was 3,374.
Financial – Sales of coal, etc., through the medium of the depots totalled 1,403,839 tons (value £6,127,438) for the year ended 31 December 1959. This compares with 1,518,722 tons (value £6,588,241) for the year ended 31 December 1958.
The operating loss for the year was £870,531, and with interest of £378,211 on loan capital the total loss was £1,248,742.
As interest could not be paid it was remitted under section 15 of the New Zealand Loans Act 1953.
Reserves were increased by £41,717 and now stand at £728,159. Accumulated losses however are now £1,224,038, so that in effect the reserves have been used up.
Capital expenditure for the year was £358,259. Depreciation was £414,109 and with the £250,000 grant from Consolidated Fund used to write down new development, fixed assets were reduced by £305,850 to £5,895,275.
Accidents – The number of compensatable accidents at State coal mines for the year ended 31 December 1959 was 1,910, compared with 1,854 the previous year.
Coal Mining Districts' Welfare and Research Fund – This fund, into which is paid a levy at the rate of 9d. per ton on coal other than lignite and 71/2d. per ton on lignite, is used for coal-miners' relief, provision of amenities, establishment and maintenance of rescue stations, research, and generally for the benefit of the industry.
Information concerning monetary benefits for miners incapacitated by miner's phthisis or any other occupational disease or heart disease contracted while working as a miner in New Zealand appears in Section 6A – Social Security.
IRON ORES – The two main sources of iron available in New Zealand are the iron-ore deposits of the Onekaka region, Golden Bay, in the Nelson Provincial District, and the ironsands which are largely concentrated on the beaches of Taranaki, though not limited to that district.
As a result of a systematic prospecting programme of tunnelling and boring carried out by the State during the years 1938 to 1942, the ore reserves of the Onekaka deposits are estimated at 9,500,000 tons, assaying 40 per cent iron.
Although the whole of New Zealand's iron-bearing sands have not been surveyed, there is no doubt that the total quantity is enormous. As a result of prospecting operations by the State the titaniferous ironsands in the vicinity of Patea have been estimated as amounting to 45,500,000 tons, assaying 21 per cent soluble iron, which, by magnetic separation, would yield 14,500,000 tons of concentrates assaying 53 per cent soluble iron. Preliminary investigations at Wanganui and at Waitara have shown great quantities of sand but of lower iron content, while deposits at Mokau, Awakino, and Manukau still await investigation.
Many attempts have been made to smelt Taranaki ironsand, but commercial success has not so far attended any of these efforts. Difficulty has been experienced owing to the fineness of the sand and also to the presence of titanic acid. In 1949 large-scale tests on the smelting of ironsands by means of an electric furnace and the use of char obtained from sub-bituminous coal were carried out at Onekaka under the supervision of overseas experts. The tests showed that pig iron suitable for conversion to steel could be obtained from Taranaki ironsands by these means. There has recently been developed a laboratory process of smelting that promises to lead to the establishment of an economic method of smelting, and the Government is proceeding with the investigational work envisaged with the passing of the Iron and Steel Industry Act 1959.
There has been a small annual production of iron ore from the Onekaka deposits and certain small deposits in the North Auckland district, for use in gas purification, the preparation of stock licks, and in the brickmaking industry.
Production in 1959 was 1,505 tons.
URANIUM AND THORIUM – While the existence in minute amount of uranium- and thorium-bearing minerals in beach sands and alluvial deposits had been known for some years, it was not until 1955 that their occurrence in solid formation was discovered. The first discovery was made in a lode traversing the Hawk Crag Breccia at Batty Creek in the Buller Gorge. Following on this discovery prospecting of an area of Hawk Crag Breccia on the north side of the Buller River has revealed the presence of bedded mineralised horizons in the breccia containing uranium-bearing minerals and these horizons have been traced over considerable distances, the horizons proved to underlie extensive areas and the deposits to be of potential value. These deposits occur in steep, broken country which is heavily covered with bush, the area is subject to heavy rainfall and access is difficult, all of which was combined to make investigation work difficult until an access road was completed. Prospecting work, however, has been disappointing and ore has not been found rich enough to be worked economically at present price levels. Similar mineralised horizons have been found to exist in Hawk Crag Breccia situated in the headwaters of Bullock Creek and of the Porarari River in the Punakaiki area. Other areas containing Hawk Crag Breccia, particularly the area south of the Buller River, are known to contain similar mineralisation. Float boulders containing thorium minerals were located near the Haast River, South Westland, in 1955, but have not been traced to their source.
The Atomic Energy Amendment Act 1957 amended the Atomic Energy Act 1945 by adding several new provisions designed to encourage the search for and production of uranium or other substances which may be used for the production of atomic energy. Rewards may be granted by the Minister of Mines for the discovery of uranium, thorium, plutonium, neptunium, or other prescribed substances. Prospectors must obtain a miner's right or a mineral prospecting warrant. No mining for any of the minerals is permissible except under a mineral licence.
GOLD – The gold-mining industry, which in its early stages contributed greatly to the progress and settlement of New Zealand, declined in importance with the exhaustion of the more accessible alluvial-gold deposits and of ore from the zones of enrichment. Annual production is now almost confined to dredging.
The following table gives particulars of the estimated gold content of gold/silver/bullion production for the last three years.
| Quantity | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| oz. | oz. | oz. | £ | £ | £ | |
| Quartz mining | 90 | 258 | 953 | 1,042 | 3,109 | 11,388 |
| Alluvial mining | 745 | 825 | 700 | 8,849 | 10,047 | 8,375 |
| Dredge mining | 29,360 | 23,898 | 35,105 | 366,332 | 299,912 | 440,545 |
| Totals | 30,195 | 24,981 | 36,758 | 376,223 | 313,068 | 460,308 |
SILVER – Nearly the whole of the locally produced silver exported from New Zealand was obtained from the refinement of bullion from the quartz mines of the Hauraki goldfields, where gold and silver were found alloyed. A small quantity of silver is won in the process of gold dredging.
TUNGSTEN – The principal ore of tungsten in New Zealand is scheelite, though a little wolfram is found in Otago and Stewart Island, but not in economic quantities.
The scheelite-bearing quartz-veins are generally small and broken, while the scheelite is most erratically distributed in the veins, with the greatest concentration of scheelite situated close to the surface or at shallow depth. Access and transport present difficulties, and production costs are relatively high. Owing to the price of tungsten ores continuing at a low level, scheelite mining was on a much reduced scale during 1959.
In 1959, 9 tons of scheelite were produced as compared with 31/4 tons in 1958. Production was confined to the Glenorchy field in Otago.
COPPER – Ores of copper are found in New Zealand in no fewer than 32 known localities, but during the last 70 years attempts at their successful exploitation have been unprofitable.
It is estimated that the total production of copper to the end of 1952 amounted to 6,404 tons, valued at £124,302. There has been no production of copper ore in New Zealand since 1952.
MANGANESE – Manganese ores are found in many localities, chiefly in the older sedimentary rocks. Of recent years there has been some production from deposits at Bombay, Moumoukai, and Otau, all in the Auckland district. Deposits are, however, generally small and shallow and capable of producing only limited tonnages of ore. Production from Otau in 1959 totalled 101 tons, compared with 103 tons in 1958.
MERCURY – Cinnabar, the principal ore of mercury, is widely distributed in New Zealand, but only in a few localities is it found in quantities of economic importance. The most promising deposits of mercury ore in New Zealand are those of the Puhipuhi district, where for many years efforts were made to place the production of the metal on a commercial basis. During the war these efforts were revived and production recommenced, the ore being obtained by opencast mining and the mercury recovered in a modern treatment plant with a capacity of 50 tons of ore per day. Owing to the drastic slump in the price and the need for additional earth-moving equipment, operations were discontinued in 1945.
ANTIMONY – Small quantities of antimony ore have been won from deposits in the South Island, but there has been no production since 1953.
TIN – Cassiterite in the form of “stream tin” occurs in small deposits near Port Pegasus, Stewart Island, and these have been worked to some extent.
PLATINUM – Platinum occurs in several places, associated generally with gold in gravel, but quantities produced have been insignificant, and production has now ceased.
PETROLEUM – Indications of the presence of petroleum are found on the surface in North Auckland, at Moturoa near New Plymouth and elsewhere in Taranaki, over wide areas on the eastern coast of the North Island, and in the South Island at Kotuku, near Murchison, and in the Cheviot district. After the passing of the Petroleum Act 1937 considerable interest was displayed by some of the major oil organisations, and practically all the potential oil-bearing lands in New Zealand were held under petroleum-prospecting licences.
Under the Petroleum Act 1937 there are 159 petroleum prospecting and mining licences, covering an area of 24,128 square miles, current in New Zealand. These licences are distributed as follows:
| District | No. of Licences | Area Square Miles |
|---|---|---|
| Auckland | 10 | 656 |
| Taranaki-Wellington | 33 | 5,722 |
| Gisborne - Hawke's Bay - Wellington | 77 | 13,198 |
| Marlborough | 6 | 655 |
| Nelson-Westland | 8 | 557 |
| Canterbury | 17 | 2,786 |
| Otago | 4 | 227 |
| Southland | 4 | 327 |
| Totals | 159 | 24,128 |
Although there are a number of licence holders, only two large concerns are operating – in Taranaki and in the Gisborne - Hawke's Bay area. These concerns, operating in areas prospected between 1937 and 1944, have carried out extensive geological and geophysical programmes.
As a result of these investigations, drilling was decided upon. One well was drilled to a depth of 13,040 ft at Kapuni in Taranaki, and wet gas was encountered in the structure explored by the well. The full significance of the gas has not yet been assessed, and it is proposed to continue with further geophysical work and the drilling of another well.
A drilling site was selected in the Gisborne district and drilling operations commenced in May 1960.
Although other licensees have not carried out the extensive geological and geophysical programmes conducted in Taranaki and on the East Coast, a considerable amount of prospecting work has been done and some wells drilled.
For many years small quantities of petroleum have been produced at New Plymouth. The company operating in this area is currently producing approximately 200,000 gallons of crude oil from four wells at Moturoa. In addition, about 600,000 cubic feet of natural gas, chiefly methane, is supplied to the New Plymouth Gas Co. for domestic and industrial use.
Production for 1959 was 189,000 gallons of crude oil, from which was obtained:
| Gallons | |
|---|---|
| Motor spirit | 40,525 |
| Distillate | 10,775 |
| Power kerosene | 38,060 |
| Diesel oil | 38,030 |
| Residual oil | 52,160 |
| Total | 179,550 |
By the Petroleum Amendment Act 1955, the Minister is required to specify at the time of the grant of the prospecting licence, the conditions on which a mining licence will be granted in exchange for a prospecting licence, and the conditions to which both will be subject; at the time of exchange the licensee has the right to specify the land desired to be in the mining licence. After consultation with the licensee, the Minister is empowered to direct the latter to refine the oil products in New Zealand, provided it can be done economically, and that the products are required in New Zealand.
The total production of crude petroleum to 31 December 1959 is estimated at 6,255,083 gallons.
BENTONITE – The most promising deposits of this mineral occur at Porangahau, in the Hawke's Bay district, and at Mangatu, near Gisborne. Bentonite is mainly used in the preparation of foundry moulding-sands and drilling muds, but the mineral has many other uses. The quantity of bentonite produced in 1959 was 2,149 tons of a value of £29,242.
PERLITE – During 1959, 378 tons of perlite were obtained from deposits at Atiamuri and processed at Wellington. The estimated value was £9,600.
ASBESTOS – Chrysotile asbestos occurs at several points in the massive serpentines of Nelson and Otago, but the only deposits of importance so far located are those of Upper Takaka in the Nelson district. In 1955 production of asbestos was resumed after a temporary cessation. The quantity of asbestos produced in 1959 was 572 tons valued at £27,480.
KAURI GUM – Production of kauri gum has been at a comparatively low level in recent years. During 1959, 81 tons of kauri gum, valued at £13,085, were exported.
PHOSPHATE – The occurrence of phosphate has been reported from many localities in New Zealand, but so far the deposits of Clarendon and Milburn have proved to be the only ones of economic importance but the more favourable sections of the deposits have been exhausted.
SERPENTINE – Serpentine, which in the South Island forms vast rock masses in Nelson and Otago, and which occurs in smaller amounts in the North Island, is now of value to the fertiliser industry in the preparation of serpentine superphosphate. Production at first was mainly confined to the smaller occurrences in North Auckland owing to ease of access and transport, but production is now made from much larger deposits at Piopio, near Te Kuiti, in the North Island, and near Mossburn, in the South Island. To the end of 1959, 1,237,887 tons of serpentine had been mined, including 107,063 tons in 1959.
GREENSTONE – The mineral nephrite, the “pounamu” of the Maori, a deep-green semi-transparent mineral with dark opaque patches, more popularly known as one of the varieties of “greenstone”, occurs as rounded segregations in the talc or talc-serpentine rocks of the Griffin Range of north Westland. The principal supply was obtained from the gravels of the Arahura and Taramakau Rivers, and from gold-sluicing claims of the Kumara district. Some of this has been cut and polished in New Zealand for personal and other small ornaments; the remainder has been exported. With the decline in sluicing operations this mineral has been in short supply.
SALT – At Lake Grassmere, in Marlborough, salt is being produced by the solar evaporation of sea water. The low rainfall, long hours of sunlight, and the wind conditions make this locality the most suitable one in New Zealand for this purpose. Salt harvested in 1952 totalled 700 tons valued at £8,750. Owing to unfavourable weather conditions there was no production in 1953, but in 1954, 1,500 tons valued at £18,750 were produced. In 1955 the harvest was 3,000 tons valued at £45,900, in 1956 it was 10,400 tons valued at £135,200, in 1957 it was 11,200 tons valued at £151,200, in 1958 it was 7,650 tons valued at £107,100, in 1959 it was 20,300 tons valued at £275,300, and in 1960 it was 17,020 tons valued at £256,500.
BUILDING AND ORNAMENTAL STONES – New Zealand possesses a great variety of handsome and durable building stones scattered throughout both Islands. Their distribution is described in the 1958 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
STATE AID TO MINING – State aid to mining in New Zealand is given in several forms–viz, (1) geological survey and bulletins; (2) financial aid to prospecting; (3) schools of mines; (4) subsidised roads to mining fields; (5) research by the Dominion Laboratory.
Geological Survey – Imperative to long-term assessment of New Zealand's mineral resources is an understanding of the country's geology. In New Zealand almost all Government geological work is carried out by the New Zealand Geological Survey, a scientific institution founded in 1865, which since 1927 has been a branch of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research. Mines, Works, and other Government Departments consult the Geological Survey on geological problems, and do not themselves maintain a geological staff.
The Survey's principal work is to prepare geological maps of New Zealand and to determine the country's geological structure and geological history. Along with this, the Survey studies and helps assess the country's mineral deposits and underground water resources, and gives advice on geological problems encountered in State and private civil engineering projects such as the construction of hydro-electric dams, bridges, tunnels, roads, and building foundations.
The Geological Survey has in the past done most of its regional geological mapping on a scale of 2 miles to the inch, about one-third of the country so far being covered by maps on this scale. Most of these maps have been issued in groups with a text describing the geology and mineral resources of the regions concerned. Paleontological bulletins are also issued. To speed the geological mapping of the country, the Survey in 1956 embarked on a programme to map the whole country on a less detailed scale by 1963. These new maps (scale of 1: 250,000) are known informally as the “Four Mile” series. They each carry about 3,000 words of descriptive text in their margins; there will be 28 of them altogether. The first two were published in 1959, and three in 1960. One-mile maps and bulletins will continue to be issued at intervals for areas of special economic or scientific importance. Geological mapping has also been carried out in New Zealand's island territories and in the Ross Dependency.
Mineral Resources Surveys – As well as its systematic geological exploration of the country, the Geological Survey makes detailed study of areas with mineral deposits of present or potential economic value. Field studies are made by the geologists, and laboratory examination of ores by the petrology specialists. Chemical analysis is usually done by the Dominion Laboratory, Department of Scientific and Industrial Research. The Petrology Section makes free identifications of rocks and minerals forwarded by Mines Department, prospectors, and others.
Metallic Minerals – In earlier years when gold was of major importance the Survey reported on most of the goldfields, several bulletins being published. Deposits of ores of iron, copper, tungsten, manganese, chrome, and other metals have also been investigated over the years. Much field and laboratory work has been done since 1955 on the uranium deposits of the Buller Gorge and other West Coast districts (see 1959 Yearbook, pages 583–4, for details).
Coal – Coal is still New Zealand's most important mineral, and mapping the coalfields in detail has been one of the Survey's major undertakings in economic geology. Preliminary assessment of the geology and coal quantities of some coalfields was made by the Survey earlier this century, but in 1936, after the setting up of a coal survey committee, intensive study was made of all New Zealand coalfields. Work has proceeded in cooperation with Mines Department and with the Dominion Laboratory, Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, where thousands of analyses of New Zealand coals have been made. Detailed maps and bulletins on Greymouth, Reefton, and Kaitangata coalfields have been published, while those for the Waikato and Ohai fields will be the next to be issued. Although the mapping of the coalfields is largely complete, Survey geologists continue to help with a large number of day-to-day problems in the coalfields.
Oil – The Government does not undertake oil exploration. Oil companies however draw on Survey maps and bulletins for basic information about the country's stratigraphy and geological structure which enables them to narrow down areas deserving more detailed examination. Close and mutually beneficial cooperation has usually developed between Survey geologists and paleontologists and those of oil companies. Copies of oil company reports and maps are deposited with the Government at the close of operations.
Other Non-metallic Minerals and Rock Products – So far as is possible with the staff available, the Survey advises Ministry of Works and local authority engineers, contractors, and other users on where rock materials for road metal, aggregate, building stone, sand, etc., can be obtained. Marl, limestone, and pozzolana for cement manufacture, perlite, bentonite, clays, talc, mica, magnesite are other non-metallic minerals in whose utilisation the Survey has played a part.
Limestone suitable for agricultural use is abundant in some parts of New Zealand and scarce in others. Limestone investigations are an important part of the Survey's mineral work. North Island supplies of serpentine rock for the manufacture of serpentine superphosphate are nearly exhausted, and Survey officers have assisted mining companies by reporting on the quantities of serpentine and dunite in certain South Island deposits. A search for phosphate minerals has recently been made in the Chatham and Cook Islands and in Western Samoa, Niue Island, and Tonga, in conjunction with the Commonwealth Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Canberra, Australia.
HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT – The function of the early manufacturing industries in New Zealand was to supply locally the immediate needs of the small scattered communities for food, clothing, building materials, and home furnishings and to provide shipping with ropes, spars, and repairs. These handicraft activities grew into factories as the settlements expanded and as there developed more opportunities for the organisation and specialisation of labour, and for the more complex processing of domestic or imported raw materials. Flour mills, flax mills, ropewalks, and sawmills appeared in the early eighteen forties followed by breweries, brick kilns, cooperages in the mid forties and, later in that decade, lime kilns, ship and boat yards, soap and candle works, and tanneries.
By 1867, the first year in which statistics of factory production were collected in conjunction with the population census, manufacturing establishments included grain mills, breweries, biscuit factories, a bone-manure works, brick and tile yards and potteries, candle and soap works, coach-building workshops, fellmongeries, tanneries, wool-scouring works, flax works, aerated water and cordial factories, iron and brass foundries, lime kilns, malt kilns, engineering workshops, a patent slip, a petroleum works, rope and cordage works, sawmills, sash and door factories, ship and boat yards, and a woollen mill. The factories of this period were still primarily concerned with the satisfaction of the needs of the limited local markets.
The development boom of the eighteen seventies, the rapid rise in population, and the better communications between internal markets encouraged further factory expansion. There was to some extent a natural protection from overseas competition in the high freight rates on imports. Other factors which assisted in this expansion were the admission of certain raw materials free of duty, the imposition of a tariff on some finished goods, and the granting of bounties by central and provincial governments for new factories. These were followed by protection by way of a tariff in 1888 as a specific policy when the home market was shrinking and capital and labour were beginning to leave the colony. Footwear and clothing factories, machinery makers, and metal workers were protected by this tariff. A wider protective Customs tariff was imposed in 1895. During the depressed years of the eighteen eighties low wage costs enabled some New Zealand manufacturers to export their products, but this was partly attributable also to the special suitability of some New Zealand products, such as farm implements, to the needs of other developing communities overseas.
The first shipment of refrigerated meat in 1882 opened the way for the establishment and growth of the meat-freezing and butter and cheese industries. Ten years after this first shipment, 21 meat-freezing works and 104 butter and cheese factories had been established.
The recovery from the long depression, the resumption of large-scale immigration at the beginning of the present century, the spectacular development of meat-freezing and dairy factories, and the breaking in of new land, especially in the North Island, all contributed to the revival of a strong internal demand which stimulated manufacturing growth.
Auckland early established itself as the predominant manufacturing province in New Zealand, but in the general prosperity following the gold boom of the sixties there was a spectacular increase in manufacturing activity in Otago, which led Auckland until the nineties. Canterbury was the next most important manufacturing province. Today, Auckland, Wellington, and Canterbury are ahead of Otago.
With the rising population and increased export income during the first decade of this century, manufacturing continued to expand at a steady rate. The growth continued to be concentrated on industries processing farm products for export and those supplying the more simple goods, housing materials and equipment, repairs and supplies for farmers. In this period the electrical, wire-work, sheet-metal, and motor-vehicle industries had their beginnings.
Developments in the nineteen twenties included the expansion of the vehicle industry (particularly motor and cycle works), the sawmills, and the metal-working, furnishings, and apparel industries. These developments carried forward the tendency for industries processing farm products to be less dominating in value of production and employment to other types of industry.
During the depression of the nineteen thirties the volume of output of factories as a whole declined with the contraction of New Zealand's export income and the drop in internal demand. While prices fell the output of factories processing farm products rose, but not sufficiently to offset the loss in volume from other industry. The rapid drop in purchasing power caused the farmer to produce more but its impact on the factories processing “non-farm” materials meant a heavy reduction in the output of consumer goods, building materials, and agricultural and dairy machinery and implements. By 1934–35, however, the volume of factory production had been restored to the 1929–30 level.
Industry emerged from the depression in much the same pattern as before – apart from the metal-working and vehicle factories which had improved their position significantly.
The recovery of manufacturing after the depression was primarily the result of better export prices, more public development, and an expansionist monetary policy, all of which resulted in the re-engagement of most of the unemployed.
There had been little time for any protective effect of exchange control and import selection to stimulate industrial expansion between the date they were introduced (December 1938) and the outbreak of war in September 1939. It was the war and its shortages which changed the manufacturing pattern and gave great impetus to industrial development. The engineering and apparel industries, which contributed so much to war needs, made the greatest progress.
The factories expanded in response to the need to replace imports that the United Kingdom and other countries could no longer supply; to make uniforms, weapons, and equipment for the armed forces and to supply New Zealand and allied troops with preserved foodstuffs and many other kinds of provisions and ordnance.
In the immediate post-war years also the supply shortages and the requests by the United Kingdom not to spend to the full New Zealand's overseas earnings meant that if New Zealand did not produce the scarce goods it would go without.
One protective effect of the war and post-war periods and their associated import controls was that domestic industry was often enabled to attain its optimum (New Zealand) output quickly without a difficult competitive struggle with imports.
The pattern of New Zealand industry changed again from 1949–50 with the exemption from import control of many items. Industrial production as a whole continued to increase but this was a time of readjustment and, within this general rising trend, some firms closed down or ceased production of certain lines, others sustained a fall in production or did not expand to the extent they otherwise would have done. As a whole, factory expansion was sustained by a high level of internal demand, by a widening of the range of products and, to some extent, by the restriction of imports for a short period of exchange control. In this period the food group increased its volume relatively slowly (its output depending largely on the level of farm production), the leather industry production fell (as a result of competition from imports and synthetics), while footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods also increased slowly, more or less in line with population growth. Spectacular increases in production came from new developments in the pulp and paper and the rubber industries. But it was the engineering factories that contributed most (as in past years) to the growth of manufacturing since 1949–50. The expansion in this field was stimulated especially by mechanisation on farms, the high level of investment in New Zealand, the demand for consumer durables, and the increased imports of motor vehicles.
The growth in production has been assisted by increases in manpower engaged and capital used. Since the end of the Second World War there has been a considerable amount of factory building and new machinery installed – for new industries as well as for the extension and improvement of existing industries. A measure of the increase in capital employed is that the value of land and buildings, plant, and machinery at the end of the production year for each person engaged was £436 in 1945–46, £633 in 1950–51, rising to £1,149 in 1956–57, £1,161 in 1957–58, and £1,220 in 1958–59.
The greater use of machinery for manufacturing during the last 20 years is illustrated also by the continuing rise in the average horsepower for each person engaged in manufacturing. In 1935–36 the average was 2.86; in 1945–46, 2.97; in 1955–56, 4.42; and in 1958–59, 4.65. This expansion has been helped by the growth in electric power generation and by the greater use of the individual drive technique. In the production year 1958–59 the use of electric motors in factories accounted for 93 per cent of the total rated horsepower for all types of engines employed in factories. The number and horsepower of steam, petrol, oil, and other non-electrical engines has declined absolutely as well as relatively.
Industrial progress has been rapid, but manufacturing in New Zealand is still organised on a relatively small scale. In 1958–59, 62 per cent of the factories employed 10 persons or less, a reflection of the fact that, partly as a result of geographical configuration, many factories still supply small local markets. Although these small factories are numerous, they accounted for only 13 per cent of the total value of factory output. There were only 115 factories (about 1.3 per cent of the total) in 1958-59 where the number of persons engaged exceeded 200, but these factories accounted for nearly 33 per cent of total value of output. They were engaged in processing goods for export (30 were meat-freezing works) or supplying the national market.
Manufacturing plays a vital part in employment. In April 1960 about 25 per cent of the total labour force was employed in manufacturing industries. Of these, females comprised 23 per cent of the persons so engaged.
The Industrial Efficiency Act of 1936 was passed “to promote the economic welfare of New Zealand by providing for the promotion of new industries in the most economic form and by so regulating the general organisation, development, and operation of industries that a greater measure of industrial efficiency will be secured”. The provisions of the Act were used more especially to rationalise some of the distributive industries, and to prevent redundancy in some manufacturing industries, where the size of the market for their products would not permit the economic operation of more than a few units. This Act was repealed in 1956, but the licensing of certain industries was continued under the Industries and Commerce Act 1956 and the Licensed Industries Regulations 1957. The industries concerned were the manufacture of pulp, paper, and board, and multi-walled paper bags; paua shell for sale; and pneumatic rubber tyres and tubes for motor vehicles, but the regulations were revoked in July 1960, and these industries are now no longer subject to industrial licensing.
In the latter part of 1957 and in early 1958 the terms of trade changed substantially to New Zealand's disadvantage and a serious depletion of overseas reserves resulted from the effects of heavy importing in 1957 and the fall in price of our main export commodities. To reduce overseas expenditure and arrest this drain on the reserves New Zealand reintroduced comprehensive import controls, which became effective on 1 January 1958.
Because of the present and future importance of manufacturing industries in the employment of a rapidly increasing labour force and the necessity for these industries to expand their output of goods and to produce new goods in substitution of imports, imported materials for industry received considerable priority. However, this necessary expansion of manufacturing was threatened by the shortage of overseas funds which, in turn, was accentuated because of New Zealand's heavy reliance on imported raw materials for manufacturing. Thus, it is estimated that materials and plant and equipment for manufacturing comprise directly about 51 per cent of total imports. It therefore seems desirable for manufacturing output to expand in depth as well as in breadth by increasing the New Zealand content of a range of manufactured goods. This would involve manufacturing in a number of industries being taken back to more basic stages rather than being, for example, the mere assembly of imported components; making greater use of New Zealand's already available raw materials, such as wool and timber; developing if possible any potential raw materials hitherto unexploited, such as iron ore.
Manufacturing industries responded admirably to the twin spurs of necessity and Government encouragement. Despite reduced imports and reduced internal demand in 1958, the volume of production rose by 5.5 per cent between 1957–58 and 1958–59. In addition to significant increases in output by existing industries such as woollen mills, clothing and footwear factories, the pulp and paper industry, rubber factories, and electrical machinery and appliances factories, a number of new industries have been established and many new products made. These include the manufacture of steel drums, fork-lift trucks, water jet engines, forage harvesters and other agricultural machinery, launderers' washing machines and tumbler dryers, axminster carpets, wallpapers, kerosene heaters, household electric appliances, motor-vehicle components, soluble coffee, and glucose and dextrose.
In 1959–60 another rise of 4.4 per cent in the volume of production took place. Some significant increases took place in the textile, pulp and paper, leather, and timber industries.
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT CONFERENCE – The Industrial Development Conference held in June 1960 was a forum to obtain the views of representatives from all sections of New Zealand's economic life on the question of development. Representatives from manufacturing, farming, commerce, the employers, trade unions, and many other organisations were present at the conference. Many aspects of development were considered, more especially external economic influences, the better use of resources – both natural and human – and the problem of raising productivity.
The conference concluded by making a series of recommendations which, it considered, would help to create a more favourable climate for development. During the subsequent two months the Government was able to carry out 15 of the recommendations, including delicensing of industry, the stepping up of assisted immigration of skilled workers, the extension of export services, power concessions to industry, improving transport facilities, extending education and research facilities, and raising the margins paid for skill in the Public Service. A number of recommendations were put into effect through the Budget, including changes in depreciation allowances, capital issues controls, revision of the tariff, amendments to the excess retention tax, increased insurance allowances, incentives to stimulate saving, bank advances for industrial equipment, incentives for forestry development, and encouragement of the arts.
DEVELOPMENTS PLANNED – There are plans for a number of “heavy” industries which, when established, will greatly affect the pattern of manufacture in New Zealand. These are now set out.
Oil Refinery – In May 1959 the Shell Co. of New Zealand Ltd. announced its plans to build an oil refinery in New Zealand. Capital cost will be about £20 million, of which 40 per cent will be subscribed in New Zealand, the balance being invested by the Shell Co. and the other five oil companies operating in New Zealand. It is expected that production will begin in 1964 and that the output will be 1.88 million tons a year.
Because of the unusual pattern of demand for petroleum products in New Zealand – almost 50 per cent being for motor spirits and aviation gasoline – it is proposed to import enriched crude oil instead of the normal crude oil. This will enable the pattern of demand to be met at a lower initial capital cost than would otherwise be the case. The refinery will, however, be sufficiently flexible to use various types of crude oil and will be capable of expansion. Labour required will be about 350 persons. The company has announced that the refinery will be built at Marsden Point, Whangarei.
Merchant Bar Mill – Final plans have been announced by two New Zealand companies for the joint establishment in Auckland of a mill to make steel products from steel scrap collected in New Zealand. The mill will have an output of 50,000 tons a year on a one-shift basis and of 120,000 tons a year on a three-shift basis. A range of merchant bar products – rounds, angles, flats, and squares – will be produced and production will begin about the end of 1961.
Capital required is £3.6 million and about 60 per cent of the equity capital will be held in New Zealand. Some 250 people will be employed.
Aluminium Fabricating Industry – A United Kingdom subsidiary of a major Canadian aluminium-producing company is to establish an aluminium-fabricating plant in New Zealand to make various aluminium products from imported ingots. Employing about 250 skilled men, the plant will have an initial production capacity of 5,000 tons a year of aluminium sheet and foil products and 2,000 tons of aluminium wire and cable for electrical transmission lines. The capital cost will be approximately £2 million. Exchange savings are estimated at about £400,000 a year. The company commenced production of corrugated aluminium sheet from imported aluminium strip in temporary premises early in 1960 and hopes to have its main plant operating in mid 1961.
Aluminium Smelting – On 19 November 1960 it was announced that Consolidated Zinc Co. Pty. Ltd. had decided to proceed with the establishment of an aluminium-smelting works based on the power potential of the Lake Manapouri – Te Anau area. This vast industrial undertaking to produce for world markets is planned to come into operation in 1966. The capital cost of the industry, which will provide employment for 6,000 people, will be between £100 million and £200 million. Kaiser Aluminium and Chemical Corporation has joined with Consolidated Zinc Co. Pty. Ltd. as an equal partner in the venture.
Iron and Steel Industry – The Government announced in May 1959 its intention to set up a company to investigate the feasibility of an iron and steel industry using New Zealand ironsands as its raw material. It was estimated that the sum of £250,000 would be required to carry out the necessary investigations and it was proposed that the Government would hold 51 per cent of the shares in the investigating company and that private interests would hold the remaining 49 per cent.
In June 1960 the Government announced that it would proceed alone with the formation of the investigating company. As a result of this decision the New Zealand Steel Investigating Co. Ltd. was registered on 3 October 1960. The Minister of Industries and Commerce holds all but six of the 250,000 one-pound shares in the company. Each of the six directors of the company – three prominent business men and three public servants – holds one share.
Ironsands prospecting commenced with drilling at Raglan in November 1960 and the company is proceeding with investigations into other material resources – such as coal and electricity – and with investigations into the economic aspect of an iron and steel industry.
Copper Fabricating – By late 1961 a New Zealand company owned by two overseas concerns expects to have established a copper and brass rolling mill involving capital of £2 million. (There will be provision for New Zealand participation to the extent of at least one-quarter of the capital at a later stage.) The company will produce nearly all New Zealand's requirements of copper and brass tube, plate, sheet, and strip, and will save £700,000 annually in overseas exchange. The factory will employ about 250 persons. Together with the steel rolling mill and the aluminium-fabricating plant, the concern will help to fill a gap in the country's metal-processing industry.
Wire Rope – A wire rope manufacturing plant is to be established at Auckland by a United Kingdom company and its New Zealand subsidiary. Capital will total nearly £1 million. Production is to commence during 1961 and will cover almost all New Zealand's requirements of wire rope. Roping wire will be imported until such wire is made in New Zealand. The project is expected to save £300,000 in overseas funds a year, and the factory will employ about 100 men.
Cotton Mill – By early 1962 a cotton mill will be established at Nelson to produce a wide range of cotton-type materials, starting with such products as denims, cotton wool, and surgical dressings, and later developing the production of more finished lines such as sheeting, pillow casings, and shirtings. This £5 million project will have the most modern spinning, weaving, and finishing equipment and will operate on a 24-hour three shift basis. The principal shareholder in the new company will be a United Kingdom concern.
Window Glass – A New Zealand company is to establish a window glass manufacturing industry at Whangarei to produce most of the country's requirements of such glass. Technical assistance is being obtained from overseas. The project will involve capital of £500,000, and there will be an annual saving in overseas funds of about £400,000. The raw materials will come from domestic sources. The factory's staff will number approximately 130 and production is expected to commence late in 1961.
Pulp and Paper – There is increasing production of pulp and paper products. One manufacturer has installed a second papermaking machine and plans the installation of a third machine. A second newsprint machine is to be installed by another company. Other companies arc expanding their production of paper, building board, and packaging materials. Manufacture of wallpaper is also being increased substantially. Capital involved in recent and projected development of paper and allied production exceeds £14 million.
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH FOR INDUSTRY – There is a growing recognition in this country of the importance of scientific research in industry. In the major manufacturing countries some of the larger concerns are able to undertake their own research, but the stage of development of manufacturing in New Zealand is such that some form of assistance from Government research organisations is necessary.
A number of branches of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research carry out research and a limited amount of service work for manufacturing industry.
The Dominion Laboratory, in addition to doing testing work for other Government Departments, undertakes research on natural products and minerals. Typical examples are the pozzolanic materials, pumicite and diatomite, which have proved suitable for replacement of cement in big concrete works such as hydro dams. One of the projects of great value to industry was the design of an automatic gravity-feed stoker which handles non-coking coals much more efficiently than do ordinary underfeed stokers.
The Dominion Physical Laboratory does research and investigational work on physical and engineering problems. One of the laboratory's recent projects of interest to the building industry and particularly to structural engineers has been the development of an analogue computer which will enable an assessment to be made of the forces to which proposed buildings are likely to be subjected by earthquakes. In the development of electric power from geothermal steam these two laboratories worked in close collaboration with the Geological Survey and the Geophysics Division in providing the Ministry of Works with basic information required in the construction of the power station at Wairakei. Work by geologists and geophysicists indicated where boreholes should be dug, physicists advised on how to measure and control the pressure of the steam, while chemists showed how to clean the steam and prevent it from rusting the pipes. This station is today providing electric power for both primary and secondary industries in the North Island.
In all the branches of the Department already mentioned assistance to secondary industry constitutes only part of the work, but there is one branch, the Auckland Industrial Development Laboratories (AIDL), which was specifically set up to provide a research service for industry. The policy of AIDL is to undertake only such work as industry cannot do, and it is the aim to assist manufacturers themselves to obtain the facilities to carry out such work.
In Christchurch a somewhat similar organisation, which originated as a branch of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, now operates as the Canterbury University Industrial Development Department.
RESEARCH ASSOCIATIONS – Working in close collaboration with the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research are a number of cooperative research associations in which contributions from a particular industry are subsidised by the Government on a pound-for-pound basis. The idea of cooperative research was introduced in the United Kingdom towards the end of the First World War, and considerable success followed the formation of numerous research associations, which were encouraged and supported financially by the Government in the interests of national welfare. The same need existed in New Zealand during the Second World War. Industries were expanding through the war effort and the Manufacturers Research Committee was set up in 1944 for the purpose of promoting research in New Zealand's manufacturing industries. Provision was also made for certain existing units of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research to be formed into incorporated research associations. Of the seven associations now operating as autonomous bodies, three are concerned with the problems of primary industry and four with those of secondary industry.
The New Zealand Leather and Shoe Research Association (Inc.) undertakes research problems on behalf of fellmongers, hide processors, tanners, and shoe manufacturers.
The New Zealand Pottery and Ceramics Research Association, originally set up in 1945 to assist the development of the whitewares section of the clay industry, was in 1951 extended to cover the whole field of clay industries by including manufacturers of heavy clay products such as bricks, roofing tiles, field tiles, and refractories.
The Research Institute of Launderers, Drycleaners, and Dyers of New Zealand was established in 1947 to cater for commercial concerns engaged in laundering, drycleaning, and dyeing, manufacturers of laundry and drycleaning machinery and materials, and manufacturers, importers, and distributors of textiles.
The New Zealand Wool Industries Research Institute, established in 1937 as a unit of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and incorporated in 1945, is now concerned with research relating to all aspects of wool manufacturing from the raw wool to finished cloth.
The Manufacturers Research Committee encourages the application of science in the development, extension, and modernisation of existing industries, and the establishment of further research associations. Industries too small to justify the formation of such associations may form an industrial research group. Under this scheme, firms in an industry cooperate on a programme of research carried out by a scientist in an appropriate Government laboratory.
SCOPE OF STATISTICS – Statistics of factory production were collected in New Zealand from 1867 to 1916 in conjunction with the population census; but, commencing with the year 1918–19, the collection became an annual one, the results being published in the Statistical Report on Industrial (previously Factory) Production.
Since the year 1951–52 factories have been classified according to the New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification, and as a result some of the individual industry statistics will not now compare with previously published figures. However, where possible, information for individual industries has been reclassified for the two previous years, and grand totals have been brought into line with the new classification from the beginning of the series. Apart from transfers within the framework of this series of factory production statistics, the adoption of the New Zealand Standard Classification has meant the elimination from the series altogether of three important industries. These relate to the logging operations of sawmillers, previously included in sawmilling, and the generation and supply of gas and electricity, accounting in all for the activities of approximately 10,000 persons. Information on the generation and supply of gas and electricity is still the subject of an annual inquiry, but the results are no longer included in the series on factory production. Separate and detailed statistics for these industries are recorded in Section 20 of this Yearbook.
The statistics of factory production collected annually by the Department of Statistics embrace the activities of factories coming within the Manufacturing Division of the New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification of all Economic Activities, which is an adaptation of the United Nations International Standard Industrial Classification. The classification covers registered factories employing at least two hands (including the working proprietor) engaged in the manufacture, repair, or treatment of articles. Important factories not covered in this survey which, however, come within this section of the Standard Classification are: 1. Bakeries. 2. Cake and pastry kitchens. 3. Boot repairers. 4. Watch repairers. 5. Bespoke tailors, dressmakers, milliners. 6. Abattoirs. 7. Railway and tramway workshops. 8. Naval dockyard. 9. All one-man factories.
The exclusion of the foregoing from the scope of the statistical inquiry, and also of all persons engaged in factories in a purely distributive capacity reduces the total manufacturing labour force from that quoted by the Department of Labour (214,000 – average of October 1958 and April 1959 surveys) to the figure recorded in these statistics for 1958–59 – 168,742. However, the proportion of factory production covered in this inquiry is much greater than the ratio implied by the above-mentioned totals, in that practically all of the establishments of any considerable size are included.
The year covered by these statistics is generally the year ending 31 March, but concerns are permitted to furnish returns covering their financial year most closely corresponding to this period. In the case of the important semi-primary industries – butter, cheese, and other milk products, and meat freezing and preserving – the years correspond with the production seasons ending in June and September respectively.
GENERAL SUMMARY – The statistics in the following table illustrate the growth of New Zealand's factory production to its present standing. Where figures are not available, leaders have been inserted. Throughout this table the logging industry and gas and electricity supply are excluded.
| Year | Number of Establishments | Persons* Engaged | Salaries* and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials | Other Expenses of Production | Value of Output | Added Value | Value of Land and Buildings, Plant and Machinery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*For the year 1915–16 and earlier years, figures refer to productive employees only. †Estimates based on results of sample survey carried out during that year. ‡Revised. | ||||||||
| No. | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| 1877–78 | 1,093 | 10,604 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,382 |
| 1880–81 | 1,430 | 13,922 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,701 |
| 1885–86 | 1,833 | 19,653 | .. | .. | .. | 6,458 | .. | 4,069 |
| 1890–91 | 2,152 | 23,761 | ?657 | .. | .. | 8,558 | .. | 4,335 |
| 1895–96 | 2,361 | 25,397 | 1,748 | 3,562 | .. | 9,264 | 5,703 | 4,777 |
| 1900–01 | 3,059 | 38,651 | 2,811 | 7,716 | .. | 16,485 | 8,769 | 6,546 |
| 1905–06 | 3,381 | 45,198 | 3,593 | 13,290 | .. | 21,610 | 8,320 | 9,537 |
| 1910–11 | 3,421 | 42,142 | 4,353 | 18,738 | .. | 28,569 | 9,831 | 11,989 |
| 1915–16 | 3,657 | 44,673 | 5,317 | 29,850 | .. | 41,924 | 12,073 | 15,799 |
| 1918–19 | 3,385 | 53,062 | 7,646 | 38,291 | .. | 53,806 | 15,515 | 19,144 |
| 1920-21 | 3,894 | 62,972 | 11,753 | 53,009 | .. | 75,489 | 22,479 | 25,696 |
| 1925–26 | 4,643 | 70,212 | 14,149 | 51,303 | 7,262 | 78,468 | 27,165 | 32,420 |
| 1930–31 | 5,047 | 70,625 | 13,885 | 45,314 | 8,448 | 71,721 | 26,407 | 34,496 |
| 1932–33 | 4,847 | 62,583 | 10,674 | 38,945 | 7,519 | 60,159 | 21,214 | 32,945 |
| 1933–34 | 4,883 | 65,961 | 10,729 | 43,513 | 7,538 | 65,908 | 22,395 | 31,965 |
| 1934–35 | 5,126 | 72,095 | 11,694 | 48,835 | 8,163 | 73,320 | 24,485 | 32,415 |
| 1935–36 | 5,391 | 78,701 | 13,091 | 56,859 | 8,665 | 83,766 | 26,907 | 33,175 |
| 1936–37 | 5,584 | 87,822 | 16,296 | 67,496 | 9,778 | 99,379 | 31,883 | 34,386 |
| 1937–38 | 5,780 | 93,534 | 18,703 | 71,750 | 9,808 | 106,502 | 34,752 | 36,308 |
| 1938–39 | 6,002 | 93,638 | 19,927 | 71,173 | 9,316 | 106,608 | 35,435 | 38,597 |
| 1939–40 | 6,198 | 99,349 | 21,893 | 80,210 | 10,345 | 120,324 | 40,114 | 41,020 |
| 1940–41 | 6,252 | 104,784 | 24,306 | 93,013 | 11,203 | 137,399 | 44,386 | 42,165 |
| 1941–42 | 6,225 | 108,275 | 26,813 | 96,482 | 12,047 | 145,608 | 49,126 | 43,752 |
| 1942–43 | 5,985 | 106,179 | 29,427 | 101,900 | 12,541 | 155,779 | 53,879 | 44,674 |
| 1943–44 | 6,062 | 109,221 | 31,398 | 107,027 | 13,626 | 164,837 | 57,810 | 45,984 |
| 1944–45 | 6,340 | 113,534 | 34,197 | 116,476 | 14,556 | 178,586 | 62,110 | 48,765 |
| 1945–46 | 6,847 | 118,886 | 37,910 | 117,059 | 15,312 | 183,542 | 66,483 | 51,781 |
| 1946–47 | 7,498 | 124,925 | 41,488 | 131,348 | 17,279 | 205,649 | 74,301 | 55,775 |
| 1947–48 | 7,822 | 130,504 | 47,940 | 174,845 | 20,077 | 259,181 | 84,336 | 63,316 |
| 1948–49† | 7,852 | 132,427 | 51,402 | 195,053 | 21,955 | 286,396 | 91,343 | 73,585 |
| 1949–50 | 7,815 | 133,245 | 56,231 | 215,009 | 24,140 | 317,343 | 102,334 | 77,993 |
| 1950–51 | 8,113 | 138,435 | 65,005 | 266,885 | 28,867 | 380,200 | 113,316 | 87,617 |
| 1951–52‡ | 8,546 | 144,352 | 75,029 | 290,731 | 31,940 | 430,984 | 140,252 | 97,522 |
| 1952–53‡ | 8,511 | 143,164 | 78,483 | 318,949 | 35,258 | 463,940 | 144,912 | 109,100 |
| 1953–54‡ | 8,377 | 146,488 | 86,621 | 332,825 | 40,263 | 495,213 | 162,389 | 122,269 |
| 1954–55‡ | 8,366 | 153,575 | 98,413 | 365,299 | 47,853 | 550,618 | 185,318 | 138,274 |
| 1955–56‡ | 8,515 | 158,238 | 107,939 | 384,794 | 56,541 | 585,942 | 201,148 | 168,573 |
| 1956–57‡ | 8,488 | 156,752 | 110,948 | 394,988 | 59,902 | 602,041 | 207,053 | 180,123 |
| 1957–58‡ | 8,529 | 162,985 | 119,989 | 417,918 | 66,052 | 644,929 | 227,011 | 189,287 |
| 1958–59‡ | 8,565 | 168,742 | 128,278 | 418,647 | 70,321 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 205,886 |
| 1959–60‡ | 8,550 | 172,106 | 136,176 | 439,088 | 72,963 | 705,617 | 266,529 | 223,727 |
| NOTE – Further figures for the year 1959–60 are given in the Latest Statistical Information Section at the back of this Yearbook. | ||||||||
Production totals for the 1958–59 year rose by 5.5 per cent in volume of output over the previous year. The annual increases in volume of output for the two previous years were 0.6 per cent in 1956–57 and 7.2 per cent in 1957–8. Production of two groups of industries dropped in volume in 1958–59, namely, beverages (–5.3 per cent) and chemicals and chemical products (–0.6 per cent). Although indexes are not available for all groups of industries, employment and added value figures indicate further declines in the furniture and fittings and transport equipment groups. In three groups the volume index rose by over 10 per cent compared with the previous year – textiles, 15.6 per cent; leather and leather products, 15.5 per cent; and electrical machinery and appliances, 12.1 per cent. In the several groups without individual volume indexes, employment and added value figures indicate a substantial increase in volume for the miscellaneous group in which plastic manufactures feature predominantly. Using the same indicators, two other groups also had worth-while increases in volume of production – petroleum and coal products and basic metal manufactures.
In the 8,565 establishments recorded in 1958–59 the number of persons engaged was 168,742, an increase of 5,757, or 3.5 per cent over the 8,529 establishments from which returns were obtained in 1957–58. The amount of salaries and wages paid increased by £8.3 million, or by 6.9 per cent, and wage earners worked 21,724,241 hours of overtime, an increase of 1,292,432 hours, or 6.3 per cent. Cost of materials used rose by £0.7 million, or by 0.2 per cent; value of output increased by £14.5 million, or by 2.3 per cent; and added value increased by £13.8 million, or by 6.1 per cent.
The following table gives the main statistics by provincial districts for the year 1958–59.
| Provincial District | Number of Establishments | Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials | Value of Output | Added Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Percentage of Total | ||||||
| No. | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Auckland | 3,446 | 71,134 | 54,239 | 186,635 | 294,452 | 107,817 | 44.77 |
| Hawke's Bay | 383 | 6,239 | 4,744 | 17,476 | 25,702 | 8,226 | 3.42 |
| Taranaki | 361 | 5,485 | 4,434 | 23,876 | 31,607 | 7,731 | 3.21 |
| Wellington | 1,803 | 35,624 | 27,656 | 87,717 | 138,929 | 51,211 | 21.27 |
| Marlborough | 96 | 1,041 | 775 | 2,044 | 3,118 | 1,074 | 0.45 |
| Nelson | 253 | 2,738 | 1,984 | 5,039 | 9,299 | 4,261 | 1.77 |
| Westland | 95 | 1,017 | 736 | 1,555 | 2,907 | 1,352 | 0.56 |
| Canterbury | 1,234 | 27,909 | 20,514 | 53,495 | 89,232 | 35,737 | 14.84 |
| Otago – | |||||||
| Otago portion | 550 | 12,586 | 8,967 | 24,517 | 41,191 | 16,674 | 6.92 |
| Southland portion | 344 | 4,969 | 4,229 | 16,293 | 23,018 | 6,725 | 2.79 |
| Totals | 8,565 | 168,742 | 128,278 | 418,647 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 100.00 |
Further analyses by industrial groups of the figures shown in this table will be found in the appropriate contexts in the following pages.
In the next table the statistics for the year 1958–59 are reclassified by employment districts of the Department of Labour, which provide a more comprehensive locality classification of manufacturing strength. The fairest guide to actual volume of production is the last column in the table on “Added Value”. This shows Auckland district's dominance in the manufacturing field; its production now being more than the total for the South Island.
| Employment District | Number of Factories | Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials | Value of Output | Added Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males* | Females | Males* | Females | Total | Percentage of Total | ||||
| *Revised. | |||||||||
| No. | No. | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Whangarei | 237 | 2,570 | 227 | 2,047 | 94 | 12,837 | 17.886 | 5,049 | 2.10 |
| Auckland | 2,132 | 34,682 | 16,372 | 30,653 | 7,496 | 112,717 | 182,257 | 69,540 | 28.88 |
| Hamilton | 532 | 6,181 | 868 | 5,160 | 369 | 28,534 | 39,177 | 10,643 | 4.42 |
| Paeroa | 123 | 1,462 | 328 | 1,185 | 127 | 11,057 | 13,625 | 2,567 | 1.07 |
| Tauranga | 115 | 1,048 | 209 | 799 | 79 | 4,402 | 6,140 | 1,738 | 0.72 |
| Rotorua | 207 | 5,283 | 392 | 4,994 | 179 | 13,648 | 30,016 | 16,369 | 6.80 |
| Gisborne | 115 | 1,387 | 367 | 1,089 | 154 | 3,746 | 5,971 | 2,225 | 0.92 |
| Napier | 159 | 1,661 | 410 | 1,334 | 179 | 4,813 | 7,747 | 2,934 | 1.22 |
| Hastings | 164 | 3,159 | 617 | 2,661 | 288 | 11,297 | 16,111 | 4,814 | 2.00 |
| New Plymouth | 346 | 4,033 | 775 | 3,398 | 317 | 20,698 | 27,315 | 6,617 | 2.75 |
| Wanganui | 238 | 2,787 | 926 | 2,451 | 372 | 10,298 | 15,028 | 4,730 | 1.96 |
| Palmerston North | 438 | 4,729 | 1,548 | 3,954 | 684 | 18,798 | 27,025 | 8,227 | 3.42 |
| Masterton | 145 | 1,678 | 332 | 1,393 | 135 | 7,247 | 9,835 | 2,588 | 1.07 |
| Lower Hutt | 320 | 7,737 | 2,759 | 7,502 | 1,380 | 34,686 | 52,866 | 18,180 | 7.55 |
| Wellington | 722 | 9,040 | 4,915 | 8,245 | 2,355 | 20,927 | 39,691 | 18,763 | 7.79 |
| Totals, North Island | 5,993 | 87,437 | 31,045 | 76,864 | 14,208 | 315,704 | 490,689 | 174,985 | 72.67 |
| Blenheim | 96 | 867 | 174 | 696 | 79 | 2,044 | 3,118 | 1,074 | 0.45 |
| Nelson | 180 | 1,881 | 358 | 1,459 | 150 | 4,240 | 7,821 | 3,581 | 1.49 |
| Greymouth | 160 | 1,243 | 226 | 986 | 94 | 2,311 | 4,284 | 1,974 | 0.82 |
| Christchurch | 1,005 | 17,163 | 6,990 | 14,411 | 3,110 | 42,047 | 73,088 | 31,041 | 12.89 |
| Ashburton | 68 | 943 | 207 | 816 | 98 | 2,944 | 4,494 | 1,550 | 0.64 |
| Timaru | 169 | 2,252 | 401 | 1,928 | 183 | 8,548 | 11,752 | 3,204 | 1.33 |
| Oamaru | 57 | 933 | 187 | 733 | 75 | 3,557 | 4,864 | 1,308 | 0.54 |
| Dunedin | 493 | 8,367 | 3,099 | 6,838 | 1,321 | 20,961 | 36,327 | 15,366 | 6.38 |
| Invercargill | 344 | 4,528 | 441 | 4,046 | 183 | 16,293 | 23,018 | 6,725 | 2.79 |
| Totals, South Island | 2,572 | 38,177 | 12,083 | 31,913 | 5,294 | 102,944 | 168,766 | 65,822 | 27.33 |
| Totals, New Zealand | 8,565 | 125,614 | 43,128 | 108,777 | 19,501 | 418,647 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 100.00 |
A further summary of the operations of factories is given below for the three latest years. Attention is drawn to the fact that figures previously published have been revised in this table.
| 1956–57* | 1957–58* | 1958–59* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Revised. | ||||
| Number of establishments | 8,488 | 8,529 | 8,565 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 156,752 | 162,985 | 168,742 |
| Production costs– | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 110,947,524 | 119,989,253 | 128,278,259 |
| Materials | £ | 394,987,942 | 417,918,274 | 418,647,288 |
| Other expenses | £ | 59,902,151 | 66,052,015 | 70,320,610 |
| Totals | £ | 565,837,617 | 603,959,542 | 617,246,157 |
| Value of output | £ | 602,041,358 | 644,928,872 | 659,454,543 |
| Manufacturers' surplus | £ | 36,203,741 | 40,969,330 | 42,208,386 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 207,053,416 | 227,010,598 | 240,807,255 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | hrs. | 19,243,074 | 20,431,809 | 21,724,241 |
| Volume index for industry: Base 1956–57 (= 1000) | 1000 | 1072 | 1130 | |
| Premises and plant - | ||||
| Value at end of year – | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 104,637,510 | 112,758,584 | 123,629,077 |
| Plant and machinery | £ | 75,485,934 | 76,528,492 | 82,257,290 |
| Capital expenditure during year – | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 9,573,848 | 9,420,308 | 11,184,624 |
| Plant and machinery | -£ | 14,769,535 | 13,801,687 | 16,653,921 |
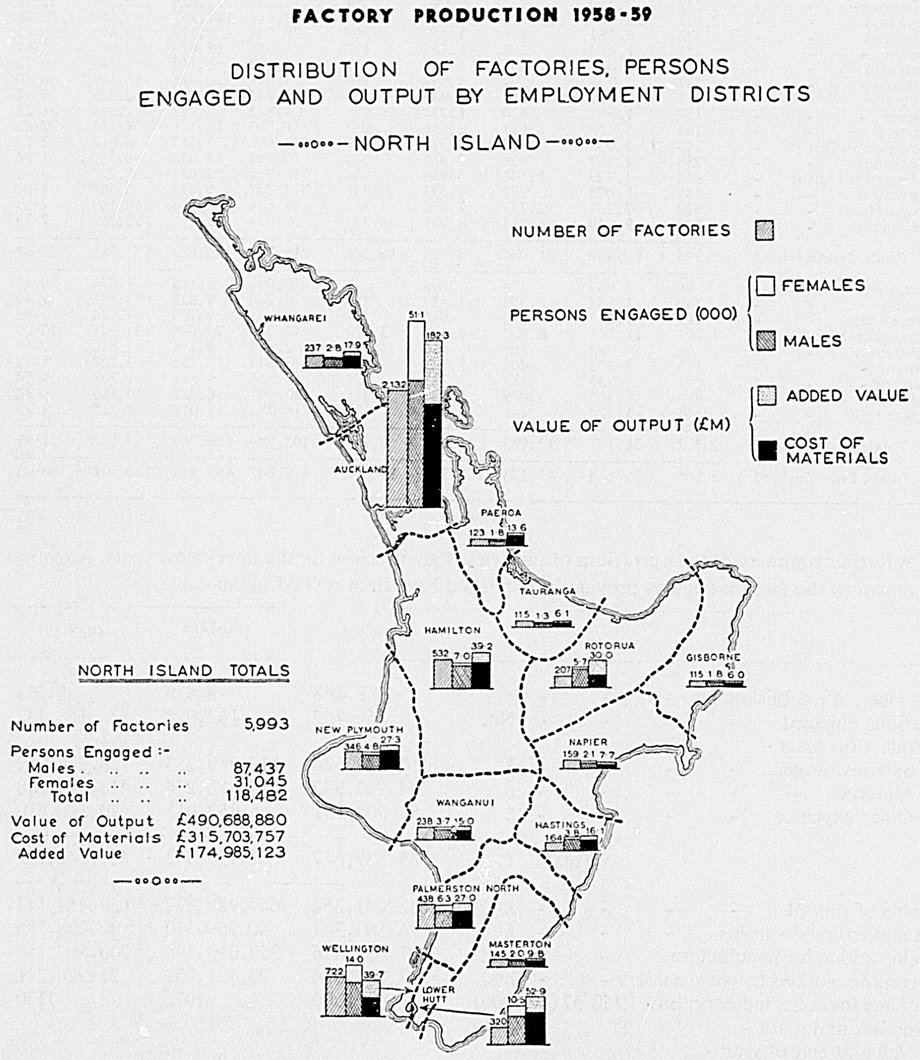
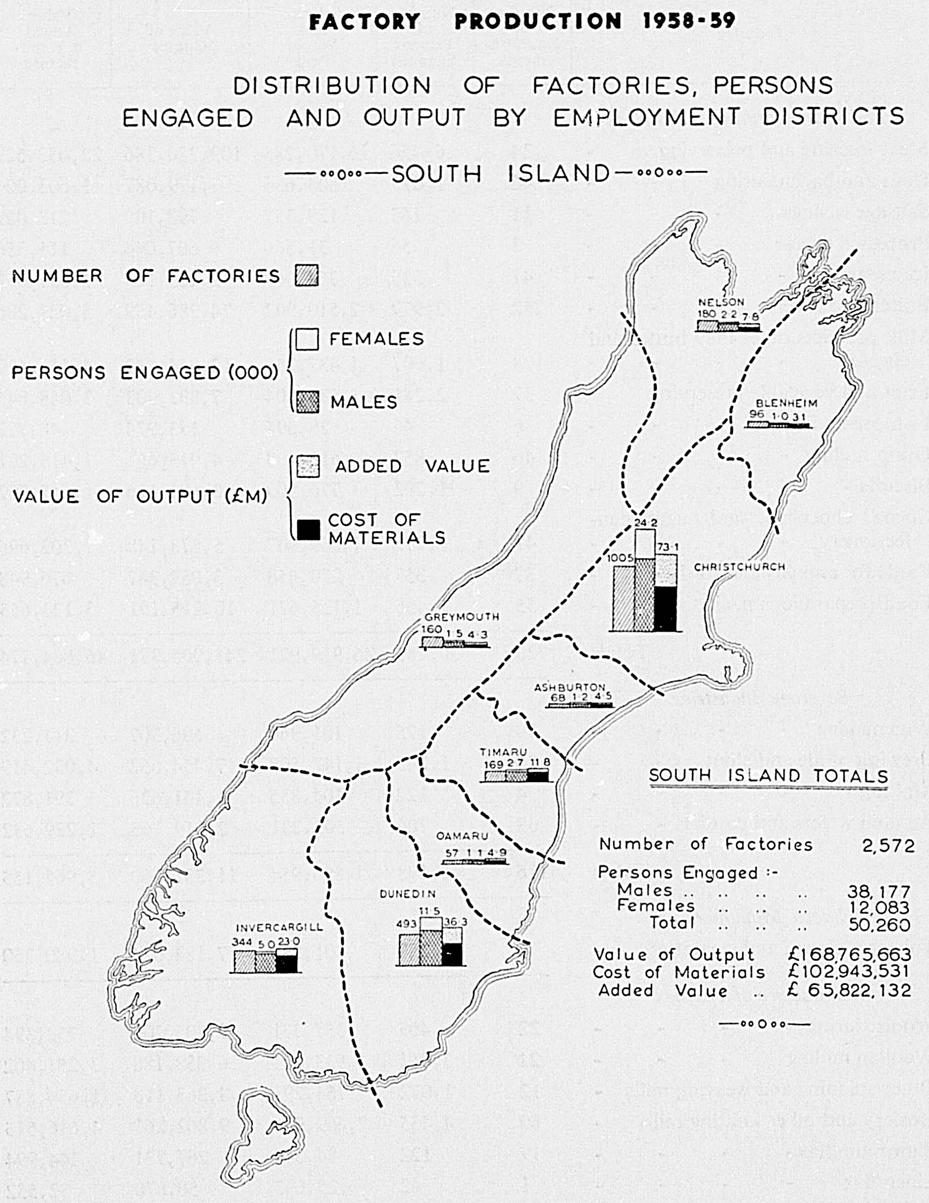
The following table gives a summary of some of the principal production statistics for the year 1958–59 classified by individual industries. Totals for the industrial groups to which these industries belong are also shown.
| Industry | Number of Establishments | Number of Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Value of Output | Value Added in Manufacture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Manufacturing Industries | £ | £ | £ | ||
| Meat freezing and preserving | 34 | 16,456 | 16,170,285 | 109,380,386 | 22,453,529 |
| Ham and bacon curing | 46 | 1,015 | 804,636 | 7,179,087 | 1,603,004 |
| Sausage casings | 11 | 165 | 129,357 | 798,109 | 213,089 |
| Processed cheese | 3 | 56 | 31,566 | 607,044 | 111,556 |
| Ice cream | 41 | 538 | 364,369 | 2,155,164 | 1,097,052 |
| Butter and cheese | 252 | 2,979 | 2,510,902 | 74,286,459 | 5,021,206 |
| Milk products other than butter and cheese | 108 | 1,607 | 1,437,255 | 12,064,132 | 4,113,499 |
| Fruit and vegetable preserving | 37 | 2,281 | 1,585,204 | 7,893,903 | 3,048,845 |
| Fish preserving | 6 | 46 | 28,394 | 173,974 | 48,722 |
| Grain milling | 46 | 852 | 615,408 | 4,915,661 | 1,416,271 |
| Biscuits | 9 | 1,202 | 776,509 | 3,601,126 | 1,647,702 |
| Cocoa, chocolate, and sugar confectionery | 41 | 1,779 | 1,069,907 | 5,578,148 | 2,309,696 |
| Feeds for animals and fowls | 37 | 353 | 270,458 | 3,057,387 | 676,948 |
| Food preparations n.e.i. | 55 | 1,456 | 1,125,671 | 10,215,191 | 3,123,655 |
| Totals | 726 | 30,785 | 26,919,921 | 241,905,771 | 46,884,774 |
| Beverage Industries | |||||
| Winemaking | 20 | 125 | 101,360 | 606,307 | 311,232 |
| Brewing of ale and stout | 24 | 1,245 | 1,147,508 | 7,454,652 | 4,032,419 |
| Malting | 4 | 122 | 104,855 | 1,151,636 | 391,872 |
| Aerated waters and cordials | 68 | 706 | 503,231 | 2,019,165 | 1,229,632 |
| Totals | 116 | 2,198 | 1,856,954 | 11,231,760 | 5,965,155 |
| Tobacco Manufactures | |||||
| Tobacco, cigars, and cigarettes | 6 | 1,280 | 801,250 | 7,184,024 | 1,980,760 |
| Manufacture of Textiles | |||||
| Woolscouring | 22 | 409 | 357,371 | 9,705,200 | 732,394 |
| Woollen milling | 21 | 3,051 | 1,933,371 | 6,338,188 | 3,251,402 |
| Other spinning and weaving mills | 12 | 1,072 | 764,291 | 3,363,118 | 1,630,887 |
| Hosiery and other knitting mills | 89 | 4,435 | 2,669,956 | 9,862,261 | 4,616,515 |
| Phormium flax | 17 | 122 | 84,544 | 267,731 | 144,994 |
| Linen flax | 1 | 42 | 25,693 | 50,870 | 32,552 |
| Textiles n.e.i. | 22 | 426 | 388,752 | 2,086,067 | 969,306 |
| Totals | 184 | 9,557 | 6,223,978 | 31,673,435 | 11,378,050 |
| Industry | Number of Establishments | Number of Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Value of Output | Value Added in Manufacture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacture of Footwear, Other Wearing Apparel, and Made-up Textiles | £ | £ | £ | ||
| Leather gloves and apparel | 10 | 129 | 68,871 | 235,458 | 113,156 |
| Men's and boys' outerwear | 171 | 4,372 | 2,348,994 | 7,612,727 | 3,030,336 |
| Women's and girls' outerwear | 331 | 5,553 | 2,792,297 | 8,597,766 | 3,988,124 |
| Underclothing | 42 | 1,662 | 834,911 | 3,531,991 | 1,234,548 |
| Hats, caps, and millinery | 55 | 1,044 | 543,307 | 1,528,409 | 777,283 |
| Corsetry | 24 | 1,089 | 563,556 | 1,675,746 | 880,702 |
| Neckties | 8 | 194 | 107,665 | 448,106 | 191,338 |
| Shirts and pyjamas | 52 | 1,785 | 874,758 | 3,234,972 | 1,347,694 |
| Wearing apparel n.e.i. | 117 | 4,007 | 2,010,719 | 7,283,372 | 2,861,865 |
| Fur coats and necklets | 29 | 179 | 117,183 | 338,425 | 181,751 |
| Footwear (other than rubber) | 128 | 4,937 | 3,251,827 | 9,221,167 | 4,716,984 |
| Canvas goods | 43 | 444 | 273,344 | 998,847 | 438,938 |
| Made-up textiles (other than wearing apparel) | 59 | 632 | 346,848 | 1,864,902 | 731,233 |
| Totals | 1,069 | 26,027 | 14,134,280 | 46,571,888 | 20,493,952 |
| Manufactures of Wood and Cork (Except Manufacture of Furniture) | |||||
| Sawmills | 486 | 5,984 | 4,953,909 | 18,895,492 | 10,291,395 |
| Planing mills | 151 | 1,810 | 1,361,793 | 8,368,218 | 2,634,651 |
| Joinery | 377 | 3,404 | 2,729,053 | 9,160,852 | 4,324,185 |
| Wooden containers | 45 | 631 | 506,876 | 2,506,350 | 848,017 |
| Plywood and veneer | 8 | 567 | 471,483 | 1,881,969 | 1,031,644 |
| Wood products n.e.i. | 47 | 389 | 288,350 | 910,626 | 501,056 |
| Totals | 1,114 | 12,785 | 10,311,464 | 41,723,507 | 19,630,948 |
| Manufacture of Furniture and Fixtures | |||||
| Furniture | 452 | 4,196 | 3,127,028 | 8,923,773 | 4,481,285 |
| Mattress manufacture | 34 | 558 | 406,866 | 2,039,688 | 788,151 |
| Venetian blinds | 24 | 230 | 179,631 | 923,919 | 316,201 |
| Totals | 510 | 4,984 | 3,713,525 | 11,887,380 | 5,585,637 |
| Manufacture of Paper and Paper Products | |||||
| Pulp, paper, and paperboard | 7 | 2,091 | 2,205,435 | 16,004,814 | 11,092,930 |
| Cardboard boxes, cartons, and paper bags | 51 | 1,908 | 1,334,317 | 8,148,291 | 2,667,424 |
| Paper products n.e.i. | 42 | 1,192 | 822,688 | 5,403,336 | 1,870,315 |
| Totals | 100 | 5,191 | 4,362,440 | 29,556,441 | 15,630,669 |
| Printing, Publishing, and Allied Inds. | |||||
| Printing and publishing | 95 | 5,270 | 4,392,317 | 13,491,795 | 8,852,708 |
| Job and general printing | 276 | 4,664 | 3,509,646 | 9,649,865 | 5,873,428 |
| Service industries for printing trade | 38 | 474 | 414,302 | 809,610 | 644,885 |
| Totals | 409 | 10,408 | 8,316,265 | 23,951,270 | 15,371,021 |
| Industry | Number of Establishments | Number of Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Value of Output | Value Added in Manufacture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacture of Leather and Leather Products (Except Footwear) | £ | £ | £ | ||
| Tanning | 12 | 689 | 559,567 | 2,495,180 | 892,343 |
| Fellmongery | 6 | 78 | 56,747 | 583,686 | 136,852 |
| Leather goods | 76 | 844 | 512,110 | 1,557,400 | 803,788 |
| Totals | 94 | 1,611 | 1,128,424 | 4,636,266 | 1,832,983 |
| Manufacture of Rubber Products | |||||
| Motor tyres and tubes | 3 | 860 | 974,892 | 5,137,502 | 2,557,525 |
| Rubber goods (other than motor tyres and tubes) | 25 | 1,479 | 1,202,769 | 4,235,727 | 2,283,224 |
| Vulcanising and tyre retreading | 61 | 572 | 494,617 | 2,096,659 | 1,152,674 |
| Totals | 89 | 2,911 | 2,672,278 | 11,469,888 | 5,993,423 |
| Manufacture of Chemicals and Chemical Products | |||||
| Chemical fertilisers | 11 | 1,240 | 1,071,144 | 9,051,620 | 2,866,682 |
| Vegetable and animal oils and fats | 41 | 422 | 356,393 | 2,159,200 | 958,541 |
| Ink | 8 | 105 | 80,472 | 414,908 | 204,580 |
| Soap and candle | 14 | 467 | 375,712 | 2,761,300 | 1,172,246 |
| Paint and varnish | 28 | 916 | 768,396 | 5,847,606 | 1,890,514 |
| Pharmaceuticals, toilet goods, and cosmetics | 40 | 782 | 478,754 | 3,193,923 | 1,241,326 |
| Chemical products n.e.i. | 76 | 1,290 | 994,522 | 6,393,655 | 2,532,917 |
| Totals | 218 | 5,222 | 4,125,393 | 29,822,212 | 10,866,806 |
| Manufacture of Products of Petroleum and Coal | |||||
| Petroleum and coal products | 12 | 184 | 163,173 | 1,711,292 | 404,042 |
| Bituminous paving and roofing materials | 30 | 220 | 186,531 | 1,536,531 | 552,979 |
| Totals | 42 | 404 | 349,704 | 3,247,823 | 957,021 |
| Manufacture of Non-metallic Mineral Products (Except Products of Petroleum and Coal) | |||||
| Structural clay products | 48 | 1,035 | 866,570 | 2,166,847 | 1,982,035 |
| Pottery, china, and earthenware | 7, | 607 | 385,868 | 835,513 | 699,338 |
| Cement | 6 | 734 | 697,717 | 5,022,561 | 3,960,575 |
| Glass and glass products | 50 | 1,133 | 898,052 | 2,992,690 | 1,837,066 |
| Concrete products | 272 | 2,127 | 1,725,351 | 6,074,571 | 3,350,755 |
| Lime | 81 | 353 | 272,763 | 1,162,115 | 809,781 |
| Fibrous plaster | 67 | 386 | 300,422 | 828,098 | 429,581 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 8 | 450 | 402,668 | 2,450,213 | 939,967 |
| Totals | 539 | 6,825 | 5,549,411 | 21,532,608 | 14,009,097 |
| Industry | Number of Establishments | Number of Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Value of Output | Value Added in Manufacture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Metal Industries | £ | £ | £ | ||
| Basic metal industries | 80 | 924 | 808,072 | 3,633,537 | 1,599,807 |
| Manufacture of Metal Products (Except Machinery and Transport Equipment) | |||||
| Sheet-metal working | 151 | 3,733 | 3,052,108 | 11,364,968 | 5,346,776 |
| Wire working | 32 | 478 | 407,563 | 2,017,133 | 805,721 |
| Nail making | 6 | 134 | 111,447 | 1,119,223 | 217,699 |
| Electroplating and metal polishing | 46 | 416 | 369,247 | 742,115 | 582,352 |
| Metal products n.e.i. | 168 | 3,545 | 3,026,087 | 10,704,567 | 5,264,851 |
| Totals | 403 | 8,306 | 6,966,452 | 25,948,006 | 12,217,399 |
| Manufacture, Assembly, and Repair of Machinery (Except Electrical Machinery) | |||||
| Agricultural and pastoral machinery | 73 | 868 | 655,682 | 3,271,820 | 1,063,488 |
| Machinery n.e.i. | 422 | 8,546 | 7,173,381 | 23,387,296 | 11,508,379 |
| Totals | 495 | 9,414 | 7,829,063 | 26,659,116 | 12,571,867 |
| Manufacture of Electrical Machinery, Apparatus, Appliances, and Supplies | |||||
| Range making | 7 | 1,048 | 760,503 | 2,265,974 | 1,212,887 |
| Radio assembly and manufacture | 22 | 1,132 | 767,639 | 3,946,443 | 1,228,204 |
| Electrical machinery, appliances n.e.i. | 106 | 2,241 | 1,660,931 | 8,144,775 | 3,565,459 |
| Totals | 135 | 4,421 | 3,189,073 | 14,357,192 | 6,006,550 |
| Manufacture of Transport Equipment | |||||
| Boat building and ship repairing | 54 | 1,144 | 942,912 | 1,955,964 | 1,275,334 |
| Motor-vehicle assembly | 13 | 2,503 | 2,279,848 | 23,892,233 | 5,276,796 |
| Motor-body building | 77 | 1,163 | 880,022 | 2,284,458 | 1,267,374 |
| Repairs to motor vehicles | 1,808 | 14,931 | 10,609,487 | 30,754,803 | 16,350,622 |
| Aircraft maintenance and repair | 17 | 1,548 | 1,319,795 | 2,817,204 | 2,073,337 |
| Perambulators | 13 | 169 | 115,071 | 312,551 | 166,175 |
| Transport equipment n.e.i. | 23 | 587 | 473,631 | 1,375,231 | 823,468 |
| Totals | 2,005 | 22,045 | 16,620,766 | 63,392,444 | 27,233,106 |
| Miscellaneous Manufacturing Industries | |||||
| Optical, surgical, and dental, etc., equipment | 26 | 172 | 128,013 | 357,351 | 193,606 |
| Jewellery | 56 | 511 | 349,818 | 873,416 | 508,414 |
| Brushes and brooms | 13 | 431 | 278,130 | 1,017,299 | 482,926 |
| Toys and sports goods | 23 | 452 | 288,374 | 1,048,326 | 502,579 |
| Manufacturing industries n.e.i. | 113 | 1,878 | 1,355,211 | 5,773,583 | 2,910,705 |
| Totals | 231 | 3,444 | 2,399,546 | 9,069,975 | 4,598,230 |
| Grand totals | 8,565 | 168,772 | 128,318,259 | 659,454,543 | 240,807,255 |
ESTABLISHMENTS AND EMPLOYEES – The increases in the number of factories in the immediate post-war years were the highest recorded annually and compare with the percentage increases recorded after the First World War. The same factors operated after both wars, viz, the re-establishment of businesses closed down during the war period and the opening of new businesses by returned servicemen. In more recent years the shortage of labour in the principal centres has resulted in branch factories and workrooms being opened in secondary towns to tap the labour resources in those areas. The peak was reached in 1951–52 when 8,547 factories were included in the survey. This number after a slight contraction in 1953–54 and 1954–55 has remained fairly stable and stands at 8,565 in 1958–59. Employment on the other hand has increased by 17 per cent since 1951–52, at an annual average increase of approximately 3,500 persons.
The following table shows the number of factories in each provincial district for the three latest years.
| Provincial District | Number of Factories | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| Auckland | 3,331 | 3,382 | 3,446 |
| Hawke's Bay | 363 | 375 | 383 |
| Taranaki | 371 | 371 | 361 |
| Wellington | 1,816 | 1,819 | 1,803 |
| Marlborough | 99 | 100 | 96 |
| Nelson | 256 | 256 | 253 |
| Westland | 97 | 95 | 95 |
| Canterbury | 1,235 | 1,233 | 1,234 |
| Otago – | |||
| Otago portion | 572 | 562 | 550 |
| Southland portion | 348 | 336 | 344 |
| Totals | 8,488 | 8,529 | 8,565 |
An analysis of the 1958–59 totals by industrial groups appears in the next table.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| Number of Factories 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| Food | 239 | 30 | 116 | 121 | 13 | 21 | 4 | 93 | 50 | 39 | 726 |
| Beverages | 41 | 13 | 7 | 22 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 12 | 8 | 2 | 116 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 2 | 1 | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Textiles | 60 | 8 | 1 | 49 | 1 | 7 | - | 32 | 19 | 7 | 184 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 492 | 22 | 19 | 277 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 170 | 66 | 13 | 1,069 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 431 | 63 | 50 | 159 | 20 | 80 | 43 | 147 | 65 | 56 | 1,114 |
| Furniture and fittings | 203 | 27 | 11 | 122 | 6 | 15 | 3 | 84 | 24 | 15 | 510 |
| Paper and paper products | 48 | 1 | - | 26 | - | - | - | 15 | 7 | 3 | 100 |
| Printing and publishing, etc. | 153 | 14 | 9 | 119 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 61 | 29 | 9 | 409 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 44 | 3 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 1 | - | 19 | 4 | 4 | 94 |
| Rubber products | 41 | 2 | 3 | 19 | 1 | 2 | - | 15 | 4 | 2 | 89 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 84 | 6 | 6 | 66 | 2 | 4 | - | 31 | 17 | 2 | 218 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 15 | 1 | 3 | 11 | - | - | - | 8 | 4 | - | 42 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 187 | 40 | 18 | 96 | 7 | 16 | 6 | 89 | 37 | 43 | 539 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 35 | - | 2 | 18 | - | 1 | - | 17 | 5 | 2 | 80 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 195 | 11 | 6 | 89 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 57 | 26 | 13 | 403 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 203 | 23 | 17 | 102 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 78 | 25 | 27 | 495 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 50 | 6 | - | 44 | - | - | - | 28 | 7 | - | 135 |
| Transport equipment | 825 | 111 | 89 | 371 | 27 | 75 | 23 | 238 | 140 | 106 | 2,005 |
| Miscellaneous products | 98 | 1 | 3 | 72 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 40 | 13 | 1 | 231 |
| Totals | 3,446 | 383 | 361 | 1,803 | 96 | 253 | 95 | 1,234 | 550 | 344 | 8,565 |
The number of factories and persons engaged are shown together in the following table, classified by industrial groups. Persons engaged include proprietors actively participating in their own businesses but exclude all persons engaged in selling and distribution. Figures for persons engaged refer to the average number over the whole year.
| Industry Group | Number of Factories | Number of Persons Engaged | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| Food | 752 | 749 | 726 | 28,656 | 29,835 | 30,785 |
| Beverages | 126 | 120 | 116 | 2,239 | 2,322 | 2,198 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 7 | 7 | 6 | 1,109 | 1,184 | 1,280 |
| Textiles | 177 | 179 | 184 | 8,273 | 8,671 | 9,557 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 1,066 | 1,058 | 1,069 | 24,279 | 25,474 | 26,027 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 1,125 | 1,110 | 1,114 | 12,451 | 12,401 | 12,785 |
| Furniture and fittings | 530 | 524 | 510 | 4,944 | 5,112 | 4,984 |
| Paper and paper products | 98 | 103 | 100 | 4,615 | 4,858 | 5,191 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 398 | 405 | 409 | 9,684 | 10,102 | 10,408 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 97 | 93 | 94 | 1,494 | 1,465 | 1,611 |
| Rubber products | 85 | 85 | 89 | 2,833 | 2,805 | 2,911 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 214 | 216 | 218 | 4,971 | 5,076 | 5,222 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 39 | 42 | 42 | 320 | 375 | 404 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 549 | 547 | 539 | 6,186 | 6,541 | 6,825 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 87 | 64 | 80 | 841 | 850 | 924 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 395 | 389 | 403 | 7,453 | 7,902 | 8,306 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 497 | 505 | 495 | 8,733 | 8,963 | 9,414 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 131 | 135 | 135 | 3,851 | 4,081 | 4,421 |
| Transport equipment | 1,900 | 1,954 | 2,005 | 21,053 | 21,994 | 22,045 |
| Miscellaneous products | 215 | 224 | 231 | 2,767 | 2,974 | 3,444 |
| Totals | 8,488 | 8,529 | 8,565 | 156,752 | 162,985 | 168,742 |
Persons engaged are shown in the table below for the year 1958–59 classified into working proprietors, managerial and clerical staff, and wage earners.
| Industry Group | Working Proprietors, Managers, Clerical Staff | Wage-earning Employees | All Persons Engaged | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | Total | |
| Persons Engaged 1958–59 | |||||||
| Food | 3,116 | 1,062 | 23,006 | 3,601 | 26,122 | 4,663 | 30,785 |
| Beverages | 315 | 129 | 1,643 | 111 | 1,958 | 240 | 2,198 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 80 | 47 | 381 | 772 | 461 | 819 | 1,280 |
| Textiles | 555 | 299 | 4,244 | 4,459 | 4,799 | 4,758 | 9,557 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 1,467 | 1,093 | 4,572 | 18,895 | 6,039 | 19,988 | 26,027 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 1,806 | 289 | 10,554 | 136 | 12,360 | 425 | 12,785 |
| Furniture and fittings | 708 | 176 | 3,704 | 396 | 4,412 | 572 | 4,984 |
| Paper and paper products | 518 | 192 | 3,199 | 1,282 | 3,717 | 1,474 | 5,191 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 1,310 | 814 | 6,738 | 1,546 | 8,048 | 2,360 | 10,408 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 179 | 52 | 909 | 471 | 1,088 | 523 | 1,611 |
| Rubber products | 324 | 122 | 2,040 | 425 | 2,364 | 547 | 2,911 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 821 | 387 | 3,174 | 870 | 3,965 | 1,257 | 5,222 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 79 | 20 | 288 | 17 | 367 | 37 | 404 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 881 | 187 | 5,413 | 344 | 6,294 | 531 | 6,825 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 151 | 36 | 726 | 11 | 877 | 47 | 924 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,015 | 306 | 6,375 | 610 | 7,390 | 916 | 8,306 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 1,448 | 404 | 7,463 | 99 | 8,911 | 503 | 9,414 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 421 | 184 | 2,912 | 904 | 3,333 | 1,088 | 4,421 |
| Transport equipment | 3,577 | 955 | 17,304 | 209 | 20,881 | 1,164 | 22,045 |
| Miscellaneous products | 365 | 167 | 1,863 | 1,049 | 2,228 | 1,216 | 3,444 |
| Totals | 19,136 | 6,921 | 106,508 | 36,207 | 125,614 | 43,128 | 168,742 |
Further information is given in the following table on persons engaged in 1958–59. Totals in each industrial group are shown by provincial districts.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| Number of Persons Engaged 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| Food | 11,684 | 2,571 | 2,267 | 4,372 | 282 | 709 | 31 | 4,477 | 2,530 | 1,862 | 30,785 |
| Beverages | 1,002 | 114 | 60 | 373 | 9 | 59 | 24 | 314 | 213 | 30 | 2,198 |
| Tobacco manufacturers | 106 | 124 | - | 1,050 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1,280 |
| Textiles | 2,471 | 169 | 36 | 2,104 | 4 | 51 | - | 2,818 | 1,799 | 105 | 9,557 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 12,524 | 378 | 614 | 5,853 | 144 | 69 | 167 | 4,695 | 1,436 | 147 | 26,027 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 6,641 | 427 | 544 | 1,526 | 79 | 621 | 405 | 1,333 | 604 | 605 | 12,785 |
| Furniture and fittings | 2,266 | 275 | 72 | 969 | 27 | 70 | 15 | 844 | 332 | 114 | 4,984 |
| Paper and paper products | 3,523 | 15 | - | 929 | - | - | - | 272 | 226 | 226 | 5,191 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 3,693 | 380 | 253 | 3,169 | 58 | 156 | 71 | 1,536 | 847 | 245 | 10,408 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 814 | 17 | 6 | 162 | 2 | 2 | - | 372 | 188 | 48 | 1,611 |
| Rubber products | 828 | 22 | 22 | 576 | 5 | 7 | - | 1,420 | 25 | 6 | 2,911 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 1,871 | 158 | 211 | 1,797 | 37 | 35 | - | 632 | 464 | 17 | 5,222 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 211 | 6 | 10 | 111 | - | - | - | 43 | 23 | - | 404 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 3,278 | 210 | 86 | 829 | 37 | 196 | 44 | 1,324 | 512 | 309 | 6,825 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 337 | - | 140 | 180 | - | 2 | - | 193 | 64 | 8 | 924 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 4,307 | 83 | 43 | 1,797 | 5 | 51 | 4 | 1,174 | 733 | 109 | 8,306 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 4,050 | 329 | 390 | 2,093 | 88 | 46 | 62 | 1,519 | 573 | 264 | 9,414 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 1,369 | 94 | - | 1,428 | - | - | - | 1,069 | 461 | - | 4,421 |
| Transport equipment | 8,534 | 839 | 690 | 5,304 | 227 | 661 | 185 | 3,334 | 1,400 | 871 | 22,045 |
| Miscellaneous products | 1,625 | 28 | 41 | 1,002 | 37 | 3 | 9 | 540 | 156 | 3 | 3,444 |
| Totals | 71,134 | 6,239 | 5,485 | 35,624 | 1,041 | 2,738 | 1,017 | 27,909 | 12,586 | 4,969 | 168,742 |
The distribution of the sexes among the persons engaged shows a considerable preponderance of males. In the five years prior to the Second World War the proportion of female employees in factories was steady at approximately 25 per cent. After rising rapidly to a peak of 31.5 per cent in 1942–43 as a result of additional women being recruited for factory work and men being called for military service, the proportion then fell equally rapidly back to the pre-war figure. At present this percentage is 25.6.
In the smaller districts there are few industries employing female labour to any great extent; but the male preponderance is considerably smaller in the four main districts, where female labour is in great demand mainly on account of the importance of the clothing and textile industries. The greater number of females in manufacturing industries are engaged in four classes: food; footwear and other wearing apparel; textiles; and printing, publishing, etc. In 1958–59 these classes accounted for 74 per cent of all females in factories. In two classes only did the number of females exceed the number of males – viz, tobacco manufactures, where there were 178 females to every 100 males, and footwear and other wearing apparel, etc., where there were 331 females per 100 males. The lower table on the previous page shows the average number of males and females engaged according to industry groups for the year 1958–59.
Further information is available in the table below on the extent to which females were engaged in factories in New Zealand for 1958–59. This table gives by provincial districts the number of males per 100 females engaged, and the total persons engaged per 1,000 of population.
| Provincial District | Males | Females | Total | Number of Males per 100 Females | Total Population at 1 April 1959 | Total Persons Engaged per 1,000 of Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland | 52,371 | 18,763 | 71,134 | 279 | 950,609 | 75 |
| Hawke's Bay | 5,120 | 1,119 | 6,239 | 458 | 108,800 | 57 |
| Taranaki | 4,691 | 794 | 5,485 | 591 | 98,700 | 56 |
| Wellington | 25,255 | 10,369 | 35,624 | 244 | 451,900 | 79 |
| Marlborough | 867 | 174 | 1,041 | 498 | 27,800 | 37 |
| Nelson | 2,329 | 409 | 2,738 | 569 | 73,400 | 37 |
| Westland | 836 | 181 | 1,017 | 462 | 18,700 | 54 |
| Canterbury | 20,317 | 7,592 | 27,909 | 268 | 329,920 | 85 |
| Otago – | ||||||
| Otago portion | 9,300 | 3,286 | 12,586 | 283 | 174,500 | 72 |
| Southland portion | 4,528 | 441 | 4,969 | 1,027 | 91,800 | 54 |
| Totals | 125,614 | 43,128 | 168,742 | 291 | 2,326,129 | 73 |
A classification of the establishments, according to the number of persons engaged, is given at five-yearly intervals from 1929–30 onwards. Figures for the two latest years are added. Since 1951–52 the series no longer includes certain sectors of production previously included – principal omissions being the logging activities of sawmills and the operations of gas and electric supply stations.
| Year | Factories With Persons Engaged Numbering – | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 or Under | 11–20 | 21–50 | 51–100 | Over 100 | ||
| Number of Factories | ||||||
| 1929–30 | 3,476 | 800 | 591 | 164 | 137 | 5,168 |
| 1934–35 | 3,725 | 764 | 496 | 143 | 142 | 5,270 |
| 1939–40 | 4,218 | 957 | 772 | 212 | 183 | 6,342 |
| 1944–45 | 4,139 | 1,046 | 833 | 270 | 197 | 6,485 |
| 1949–50 | 4,993 | 1,409 | 1,106 | 312 | 207 | 8,027 |
| 1954–55 | 5,350 | 1,473 | 1,020 | 310 | 213 | 8,366 |
| 1957–58 | 5,361 | 1,557 | 1,076 | 303 | 232 | 8,529 |
| 1958–59 | 5,316 | 1,603 | 1,089 | 313 | 244 | 8,565 |
| Number of Persons Engaged | ||||||
| 1929–30 | 15,474 | 11,785 | 17,977 | 11,658 | 25,967 | 82,861 |
| 1934–35 | 14,901 | 11,321 | 15,309 | 9,716 | 28,111 | 79,358 |
| 1939–40 | 17,212 | 14,048 | 23,316 | 14,737 | 39,409 | 108,722 |
| 1944–45 | 18,382 | 15,547 | 25,787 | 18,809 | 43,889 | 122,414 |
| 1949–50 | 24,481 | 20,608 | 34,386 | 21,304 | 43,530 | 144,309 |
| 1954–55 | 27,206 | 21,432 | 31,650 | 21,808 | 51,479 | 153,575 |
| 1957–58 | 27,242 | 22,651 | 33,341 | 21,346 | 58,405 | 162,985 |
| 1958–59 | 27,355 | 23,501 | 33,819 | 22,095 | 61,972 | 168,742 |
The classification according to the number of persons engaged shows clearly that, judged by the standards of highly industrialised communities, the average size of the industrial unit in New Zealand is small. Factories employing 10 persons or under accounted for 62.1 per cent of the total number of factories in 1958–59.
A further break-up by employment groups, this time by industrial classes, is shown in the following table, which gives both the number of establishments and persons engaged in each industrial group for the year 1958–59.
| Industry Group | Establishments (E) Persons (P) | Factories With Persons Engaged Numbering – | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 6 | 6 to 10 | 11 to 20 | 21 to 50 | 51 to 100 | 101 to 200 | Over 200 | |||
| Food | E | 189 | 173 | 178 | 105 | 29 | 14 | 38 | 726 |
| P | 657 | 1,334 | 2,574 | 3,325 | 2,069 | 2,217 | 18,609 | 30,785 | |
| Beverages | E | 39 | 31 | 24 | 11 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 116 |
| P | 128 | 244 | 351 | 325 | 610 | 234 | 306 | 2,198 | |
| Tobacco manufactures | E | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| P | - | - | –25 | 160 | 124 | 971 | 1,280 | ||
| Textiles | E | 30 | 27 | 43 | 43 | 16 | 10 | 15 | 184 |
| P | 104 | 214 | 642 | 1,381 | 1,145 | 1,331 | 4,740 | 9,557 | |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | E | 184 | 214 | 289 | 271 | 78 | 24 | 9 | 1,069 |
| P | 657 | 1,695 | 4,392 | 8,486 | 5,421 | 3,109 | 2,267 | 26,027 | |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | E | 418 | 336 | 239 | 104 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 1,114 |
| P | 1,417 | 2,524 | 3,509 | 3,144 | 612 | 635 | 944 | 12,785 | |
| Furniture and fittings | E | 253 | 124 | 75 | 47 | 11 | - | - | 510 |
| P | 803 | 962 | 1,126 | 1,367 | 726 | - | - | 4,984 | |
| Paper and pulp products | E | 16 | 18 | 14 | 30 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 100 |
| P | 65 | 133 | 211 | 995 | 706 | 1,152 | 1,929 | 5,191 | |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | E | 131 | 95 | 83 | 57 | 28 | 5 | 10 | 409 |
| P | 445 | 740 | 1,215 | 1,753 | 2,064 | 631 | 3,560 | 10,408 | |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | E | 41 | 15 | 18 | 11 | 6 | 3 | - | 94 |
| P | 137 | 116 | 256 | 328 | 428 | 346 | - | 1,611 | |
| Rubber products | E | 32 | 26 | 14 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 89 |
| P | 116 | 202 | 197 | 247 | 119 | 389 | 1,641 | 2,911 | |
| Chemicals and chemical products | E | 68 | 49 | 34 | 42 | 12 | 13 | - | 218 |
| P | 229 | 398 | 501 | 1,355 | 848 | 1,891 | - | 5,222 | |
| Petroleum and coal products | E | 19 | 9 | 8 | 6 | - | - | - | 42 |
| P | 56 | 65 | 113 | 170 | - | - | - | 404 | |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | E | 289 | 116 | 73 | 45 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 539 |
| P | 877 | 879 | 1,049 | 1,336 | 417 | 730 | 1,537 | 6,825 | |
| Basic metal manufacturers | E | 26 | 29 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | 80 |
| P | 95 | 240 | 237 | 165 | 57 | 130 | - | 924 | |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | E | 137 | 97 | 73 | 59 | 23 | 10 | 4 | 403 |
| P | 503 | 761 | 1,025 | 1,926 | 1,654 | 1,381 | 1,056 | 8,306 | |
| Machinery (except electrical) | E | 195 | 115 | 83 | 67 | 19 | 8 | 8 | 495 |
| P | 697 | 866 | 1,215 | 2,068 | 1,318 | 1,159 | 2,091 | 9,414 | |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | E | 35 | 26 | 22 | 26 | 15 | 8 | 3 | 135 |
| P | 118 | 184 | 329 | 797 | 1,082 | 1,133 | 778 | 4,421 | |
| Transport equipment | E | 942 | 611 | 292 | 118 | 29 | 5 | 8 | 2,005 |
| P | 3,329 | 4,617 | 4,190 | 3,630 | 2,016 | 738 | 3,525 | 22,045 | |
| Miscellaneous products | E | 115 | 46 | 24 | 32 | 9 | 5 | - | 231 |
| P | 395 | 353 | 369 | 996 | 643 | 688 | - | 3,444 | |
| Totals | E | 3,159 | 2,157 | 1,603 | 1,089 | 313 | 129 | 115 | 8,565 |
| P | 10,828 | 16,527 | 23,501 | 33,819 | 22,095 | 18,018 | 43,954 | 168,742 | |
SALARIES AND WAGES – The figures relating to the amounts paid as salaries and wages include amounts paid as bonuses and for overtime, also amounts drawn in lieu of salary by working proprietors. The amounts received by male and female employees (inclusive of all groups – executive, clerical, and wage earning), and the average amount received per employee of each sex, as recorded in the last five collections, are set out below. A number of the figures are revised.
| Year | Males | Females | Both Sexes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Average | Total | Average | Total | Average | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1954–55 | 83,436,537 | 730 | 14,976,908 | 382 | 98,413,445 | 641 |
| 1955–56 | 91,851,515 | 777 | 16,087,203 | 402 | 107,938,718 | 682 |
| 1956–57 | 94,765,088 | 804 | 16,182,436 | 416 | 110,947,524 | 708 |
| 1957–58 | 102,240,304 | 839 | 17,748,949 | 431 | 119,989,253 | 736 |
| 1958–59 | 108,776,937 | 866 | 19,501,322 | 452 | 128,278,259 | 760 |
The averages shown relate to all persons engaged, irrespective of age, industry, status, and personal occupation, and year-to-year comparisons may also be affected by changes in any of these factors. The figures do, however, give an indication of the increased earnings of factory workers in recent years, the average for males having risen by 46.5 per cent and for females by 42.6 per cent since 1951–52.
The amount of salaries and wages paid in each industrial group and in all industries during the last three years is given hereunder.
| Industry Group | Salaries and Wages Paid | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| £(000) | |||
| Food | 22,922 | 24,971 | 26,920 |
| Beverages | 1,814 | 1,882 | 1,857 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 643 | 736 | 801 |
| Textiles | 4,978 | 5,414 | 6,224 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 12,164 | 13,115 | 14,134 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 9,297 | 9,636 | 10,311 |
| Furniture and fittings | 3,330 | 3,675 | 3,714 |
| Paper and pulp products | 3,524 | 4,077 | 4,362 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 7,193 | 7,886 | 8,316 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 976 | 990 | 1,128 |
| Rubber products | 2,421 | 2,548 | 2,672 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 3,724 | 3,912 | 4,125 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 271 | 320 | 350 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 4,768 | 5,202 | 5,549 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 700 | 724 | 808 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 5,797 | 6,377 | 6,966 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 6,760 | 7,208 | 7,829 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 2,614 | 2,848 | 3,189 |
| Transport equipment | 15,315 | 16,491 | 16,621 |
| Miscellaneous products | 1,733 | 1,980 | 2,400 |
| Totals | 110,948 | 119,989 | 128,278 |
In the following table an analysis is made of the 1958–59 totals according to provincial districts in which the industries were carried on.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| *To avoid disclosure of details of individual establishments, figures have been included in those for Miscellaneous products. | |||||||||||
| Salaries and Wages Paid 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| £(000) | |||||||||||
| Food | 9,870 | 2.080 | 2,218 | 3,931 | 254 | 494 | 23 | 4,116 | 2,005 | 1,928 | 26,920 |
| Beverages | 857 | 98 | 39 | 331 | * | 46 | 19 | 264 | 171 | * | 1,857 |
| Tobacco manufactures | * | * | - | * | - | - | - | - | - | - | 801 |
| Textiles | 1,607 | 137 | * | 1,477 | * | 25 | * | 1,779 | 1,103 | 72 | 6,224 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 6,855 | 188 | 296 | 3,239 | 76 | 28 | * | 2,568 | 740 | 67 | 14,134 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 5,536 | 333 | 390 | 1,214 | 52 | 473 | 334 | 1,036 | 461 | 482 | 10,311 |
| Furniture and fittings | 1,763 | 198 | 52 | 742 | 19 | 46 | 10 | 598 | 211 | 75 | 3,714 |
| Paper and paper products | 3,200 | * | - | 701 | - | - | - | 174 | 123 | 152 | 4,362 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 2,927 | 269 | 205 | 2,711 | 48 | 118 | 57 | 1,136 | 654 | 190 | 8,316 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 565 | 13 | * | 108 | * | * | - | 254 | 155 | 27 | 1,128 |
| Rubber products | 787 | * | 18 | 584 | * | * | - | 1,228 | 24 | * | 2,672 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 1,439 | 146 | 171 | 1,452 | * | 28 | - | 483 | 365 | * | 4,125 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 180 | * | 7 | 104 | - | - | 38 | 15 | - | 350 | |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 2,682 | 175 | 66 | 701 | 30 | 183 | 39 | 991 | 422 | 262 | 5,549 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 306 | - | * | 160 | - | * | - | 157 | 54 | * | 808 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 3,697 | 72 | 33 | 1,445 | - | 39 | * | 978 | 600 | 94 | 6,966 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 3,452 | 267 | 306 | 1,862 | 67 | 33 | 37 | 1,151 | 440 | 215 | 7,829 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 959 | 72 | - | 1,092 | - | - | - | 739 | 326 | - | 3,189 |
| Transport equipment | 6,375 | 560 | 460 | 4,407 | 162 | 459 | 129 | 2,460 | 998 | 611 | 16,621 |
| Miscellaneous products | 1,184 | 135 | 172 | 1,395 | 68 | 11 | 89 | 363 | 100 | 54 | 2,400 |
| Totals | 54,239 | 4,744 | 4,434 | 27,656 | 775 | 1,984 | 736 | 20,514 | 8,967 | 4,229 | 128,278 |
A further analysis of salaries and wages paid is given in the table below for 1958–59, and shows the amounts paid to working proprietors, managers, clerical staff, and those paid to other employees, i.e., wage earners. As mentioned earlier, drawings in lieu of salaries are included for proprietors actively engaged in the business. Males and females are distinguished throughout.
| Industry Group | Working Proprietors, Managers, Clerical Staff | Wage-earning Employees | All Persons Engaged | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | Total | |
| Salaries and Wages Paid 1958–59 | |||||||
| £(000) | |||||||
| Food | 3,388 | 513 | 21,437 | 1,583 | 24,825 | 2,095 | 26,920 |
| Beverages | 342 | 65 | 1,394 | 57 | 1,735 | 122 | 1,857 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 105 | 26 | 304 | 366 | 409 | 393 | 801 |
| Textiles | 691 | 162 | 3,330 | 2,041 | 4,021 | 2,203 | 6,224 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 1,747 | 653 | 3,598 | 8,136 | 5,345 | 8,789 | 14,134 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 1,926 | 134 | 8,190 | 62 | 10,116 | 196 | 10,311 |
| Furniture and fittings | 769 | 86 | 2,687 | 172 | 3,456 | 258 | 3,714 |
| Paper and paper products | 697 | 104 | 2,988 | 573 | 3,686 | 677 | 4,362 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 1,478 | 399 | 5,763 | 676 | 7,241 | 1,076 | 8,316 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 202 | 27 | 679 | 220 | 881 | 247 | 1,128 |
| Rubber products | 417 | 63 | 1,982 | 211 | 2,398 | 274 | 2,672 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 961 | 208 | 2,588 | 368 | 3,550 | 576 | 4,125 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 93 | 11 | 239 | 7 | 331 | 19 | 350 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 963 | 91 | 4,350 | 145 | 5,314 | 236 | 5,549 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 193 | 19 | 591 | 5 | 784 | 24 | 808 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,224 | 159 | 5,284 | 300 | 6,508 | 458 | 6,966 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 1,702 | 190 | 5,880 | 58 | 7,582 | 247 | 7,829 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 474 | 101 | 2,210 | 404 | 2,684 | 505 | 3,189 |
| Transport equipment | 3,552 | 450 | 12,506 | 113 | 16,058 | 563 | 16,621 |
| Miscellaneous products | 457 | 86 | 1,396 | 460 | 1,853 | 546 | 2,400 |
| Totals | 21,382 | 3,546 | 87,395 | 15,955 | 108,777 | 19,501 | 128,278 |
The following statement shows the average earnings of males and females for the past 10 years and, although the basis of the calculations changed in the year 1951–52 the figures shown below should compare reasonably well.
| Year | Proprietors Actively Engaged | Managers, Overseers | Accountants, Clerks | Wage-earning Employees | Totals | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | |
| Average Salary or Wage | ||||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1949–50 | 491 | 346 | 730 | 463 | 460 | 266 | 460 | 248 | 481 | 253 |
| 1950–51 | 531 | 399 | 797 | 499 | 511 | 296 | 514 | 281 | 535 | 286 |
| 1951–52 | 596 | 459 | 871 | 525 | 576 | 330 | 566 | 311 | 591 | 317 |
| 1952–53 | 628 | 436 | 922 | 568 | 626 | 354 | 593 | 324 | 621 | 331 |
| 1953–54 | 746 | 497 | 995 | 590 | 688 | 388 | 640 | 344 | 672 | 353 |
| 1954–55 | 799 | 543 | 1,072 | 655 | 733 | 411 | 697 | 373 | 730 | 382 |
| 1955–56 | 840 | 597 | 1,127 | 683 | 794 | 436 | 741 | 392 | 777 | 402 |
| 1956–57 | 891 | 562 | 1,179 | 723 | 822 | 457 | 764 | 404 | 804 | 416 |
| 1957–58 | 919 | 621 | 1,241 | 744 | 848 | 477 | 797 | 419 | 839 | 431 |
| 1958–59 | 955 | 669 | 1,298 | 752 | 880 | 491 | 821 | 441 | 866 | 452 |
MOTIVE POWER – A supply of cheap motive power is a material element in industrial development. New Zealand industries were formerly handicapped in this respect, long railway hauls and, in some instances, sea carriage being involved in the transport of coal from the mines to the factories. The development of the country's electric power resources (as described in Section 20A) has been a potent factor in industrial growth, especially as the rates compare very favourably with those in other more highly industrialised countries. (The overall price for a unit retailed in 1958–59 was 1.39d. with much lower rates for industrial supply in the urban areas.) Despite the fact that since the outbreak of the Second World War shortage of electricity generating capacity has from time to time led to restrictions on the use of electric current, manufacturing production has not been materially affected. These restrictions have been lifted since July 1956 in the South Island and since the end of 1958 in the North Island.
The following table shows the number and aggregate horsepower of each class of engine used in factories in 1927–28, 1937–38, 1947–48, and the last two years available.
| Class of Engine | 1927–28 | 1937–38 | 1947–48 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric | No. | 12,428 | 25,626 | 70,274 | 149,819 | 157,571 |
| h.p. | 111,942 | 181,757 | 342,408 | 688,987 | 727,275 | |
| Steam | No. | 1,869 | 1,470 | 1,001 | 518 | 455 |
| h.p. | 63,930 | 50,736 | 34,788 | 21,174 | 20,106 | |
| Petrol and light oil | No. | 297 | 511 | 1,015 | 712 | 770 |
| h.p. | 25,302 | 14,214 | 15,266 | |||
| Heavy oil | No. | 3,769 | 12,333 | 411 | 315 | 293 |
| h.p. | 20,267 | 18,771 | 17,856 | |||
| Other | No. | 530 | 255 | 87 | 102 | 125 |
| h.p. | 16,367 | 6,059 | 2,885 | 3,498 | 3,426 | |
| Totals | No. | 15,124 | 27,862 | 72,788 | 151,466 | 159,214 |
| h.p. | 196,008 | 250,885 | 425,650 | 746,644 | 783,929 | |
The figures relating to horsepower represent the rated horsepower of engines ordinarily in use for driving factory plant. Steam boilers and engines for generating electric power in own works are excluded.
The following table shows the types and rated horsepower of engines ordinarily in use in the various industries during 1958–59.
| Industry Group | Rated Horsepower of Engines in Use | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric | Steam | Petrol and Light Oil | Heavy Oil | Other | Total | |
| Food | 173,112 | 9,328 | 1,329 | 2,136 | 267 | 186,172 |
| Beverages | 12,315 | 315 | 170 | 109 | - | 12,909 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 1,366 | - | - | - | 14 | 1,380 |
| Textiles | 30,331 | 799 | 36 | 264 | - | 31,430 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 15,193 | 315 | 182 | 215 | 7 | 15,912 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 113,476 | 7,724 | 7,379 | 10,704 | 1,378 | 140,661 |
| Furniture and fittings | 15,569 | 4 | 5 | - | - | 15,578 |
| Paper and paper products | 99,718 | 320 | 260 | 15 | - | 100,313 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 17,451 | 6 | 24 | 928 | 783 | 19,192 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 6,201 | 110 | 262 | - | 28 | 6,601 |
| Rubber products | 22,063 | - | 17 | - | 3 | 22,083 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 37,114 | 453 | 366 | 203 | 334 | 38,470 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 2,962 | 51 | 312 | - | 4 | 3,329 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 70,942 | 590 | 1,377 | 2,430 | 428 | 75,767 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 5,619 | - | 23 | 34 | - | 5,676 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 25,686 | 23 | 579 | 208 | 81 | 26,577 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 31,760 | 6 | 1,234 | 461 | 24 | 33,485 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 8,767 | - | 9 | - | 47 | 8,823 |
| Transport equipment | 29,581 | 52 | 1,675 | 149 | 27 | 31,484 |
| Miscellaneous products | 8,049 | 10 | 27 | - | 1 | 8,087 |
| Totals | 727,275 | 20,106 | 15,266 | 17,856 | 3,426 | 783,929 |
CONSUMPTION OF COAL – During the year 1958–59, 1,070,670 tons of New Zealand coal were used in industries covered by the statistics of factory production. Comparable figures for the two previous years were: 1957–58, 1,053,204 tons, and 1956–57, 1,031,980 tons. It is important to note that the new series of factory production statistics no longer includes the activities of the gas-making industry and electric generation and supply stations. These two industries for the year 1958–59 used 271,005 tons and 265,745 tons of coal respectively.
The following table shows for the year 1958–59 the consumption of coal by industrial groups.
| Industry Group | Tons of Coal Used |
|---|---|
| Food | 532,969 |
| Beverages | 20,564 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 275 |
| Textiles | 49,266 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 2,112 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 945 |
| Furniture and fittings | 138 |
| Paper and paper products | 124,471 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 254 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 7,088 |
| Rubber products | 19,442 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 25,746 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 41,319 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 239,347 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 111 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,799 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 952 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 2,327 |
| Transport equipment | 778 |
| Miscellaneous products | 767 |
| Total | 1,070,670 |
Approximately 83.8 per cent of the amount of coal used is accounted for in three groups: food, paper and paper products, and non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. Individual industries using more than 10,000 tons of coal in 1958–59 are as follows.
| Industry | Tons |
|---|---|
| Milk products other than butter and cheese | 204,452 |
| Cement | 176,398 |
| Meat freezing and preserving | 170,755 |
| Pulp, paper and paperboard | 124,347 |
| Butter and cheese | 103,608 |
| Structural clay products | 45,288 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 40,768 |
| Food preparations n.e.i. | 28,484 |
| Woollen milling | 26,223 |
| Brewing of ale and stout | 17,091 |
| Vegetable and animal oils and fats | 12,171 |
| Hosiery and knitting mills | 11,149 |
| Lime | 10,301 |
| Fruit and vegetable preserving | 10,220 |
| Rubber goods other than tyres and tubes | 10,214 |
MATERIALS – The value of materials used does not afford a very satisfactory basis of comparison as between one industry or industrial group and another, for the reason that the changes wrought during the process of manufacture vary considerably in degree. An example of the wide differences which may occur in the ratio of cost of materials to value of goods produced will be seen in the food group and the wood and cork products (except furniture) group. The values shown for materials used include the cost of containers and packing but exclude fuel costs.
Totals for the latest year show that the cost of materials used in food manufacture was £195,020,997, and the goods produced were valued at £241,905,771, while the materials used in the manufacture of wood and cork products cost £22,092,559 and finished goods produced were valued at £41,723,507.
The cost of materials used in each industrial group and in all industries for each of the latest three years is given hereunder.
| Industry Group | Cost of Materials Used | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| £(000) | |||
| Food | 192,873 | 200,619 | 195,021 |
| Beverages | 5,403 | 5,622 | 5,267 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 4,399 | 4,905 | 5,203 |
| Textiles | 21,652 | 20,220 | 20,295 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 22,303 | 24,070 | 26,078 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 19,115 | 20,055 | 22,093 |
| Furniture and fittings | 5,396 | 6,318 | 6,302 |
| Paper and paper products | 10,377 | 12,243 | 13,926 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 7,564 | 8,170 | 8,580 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 2,582 | 2,545 | 2,803 |
| Rubber products | 5,535 | 5,425 | 5,476 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 17,544 | 18,761 | 18,955 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 1,662 | 2,091 | 2,291 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 6,527 | 7,232 | 7,524 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 2,053 | 1,925 | 2,034 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 10,729 | 12,587 | 13,731 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 14,968 | 16,063 | 14,087 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 6,162 | 7,254 | 8,351 |
| Transport equipment | 35,224 | 38,238 | 36,159 |
| Miscellaneous products | 2,921 | 3,575 | 4,472 |
| Totals | 394,988 | 417,918 | 418,647 |
An analysis by provincial districts of the cost of materials used for the year 1958–59 is given below.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| *To avoid disclosure of details of individual establishments, figures have been included in those for Miscellaneous products. | |||||||||||
| Cost of Materials Used 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| £(000) | |||||||||||
| Food | 89,922 | 10,399 | 19,410 | 26,203 | 1,365 | 2,596 | 401 | 21,291 | 11,473 | 11,961 | 195,021 |
| Beverages | 2,673 | 200 | 71 | 586 | * | 83 | 29 | 1,141 | 453 | * | 5,267 |
| Tobacco manufactures | * | - | * | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5,203 |
| Textiles | 5,855 | 1,942 | * | 4,230 | * | 47 | - | 5,031 | 2,540 | 627 | 20,295 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 12,425 | 349 | 664 | 6,174 | 177 | 49 | * | 4,707 | 1,229 | 122 | 26,078 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 12,244 | 786 | 698 | 2,941 | 98 | 1,021 | 656 | 1,868 | 910 | 871 | 22,093 |
| Furniture and fittings | 3,085 | 258 | 71 | 1,264 | 18 | 55 | 10 | 999 | 423 | 118 | 6,302 |
| Paper and paper products | 9,980 | * | - | 2,290 | - | - | - | 638 | 326 | 513 | 13,926 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 3,448 | 209 | 139 | 2,476 | 28 | 67 | 22 | 1,326 | 715 | 150 | 8,580 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1,328 | 67 | * | 177 | * | * | - | 533 | 462 | 228 | 2,803 |
| Rubber products | 1,663 | * | 33 | 1,178 | * | * | - | 2,489 | 52 | * | 5,476 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 7,015 | 782 | 1,134 | 6,520 | * | 174 | - | 1,522 | 1,732 | * | 18,955 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 1,118 | * | 21 | 862 | - | - | - | 207 | 51 | - | 2,291 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 4,055 | 211 | 104 | 913 | 33 | 269 | 33 | 1,011 | 616 | 279 | 7,524 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1,100 | - | * | 342 | - | * | - | 159 | 42 | * | 2,034 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 7,277 | 116 | 92 | 3,220 | * | 49 | * | 1,711 | 1,088 | 171 | 13,731 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 6,742 | 504 | 452 | 3,424 | 59 | 42 | 32 | 1,861 | 707 | 262 | 14,087 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 2,860 | 125 | - | 2,839 | - | - | - | 2,149 | 378 | - | 8,351 |
| Transport equipment | 11,203 | 737 | 550 | 16,433 | 203 | 567 | 185 | 4,188 | 1,185 | 908 | 36,159 |
| Miscellaneous products | 2,642 | 792 | 437 | 5,646 | 64 | 18 | 187 | 664 | 137 | 84 | 4,472 |
| Totals | 186,635 | 17,476 | 23,876 | 87,717 | 2,044 | 5,039 | 1,555 | 53,495 | 24,517 | 16,293 | 418,647 |
A large proportion of the total cost of materials is accounted for by the food group, which includes the semi-primary industries dealing with meat freezing and preserving and the manufacture of butter, cheese, and other milk products. In the latest year, for example, the cost of materials used by this group, £195,020,997, represented 47 per cent of the total cost of materials used by all industries, £418,647,288. For this reason, variations in the prices received for primary produce have a very marked effect on this total, and it should be remembered that, due to the operation of the different primary produce price stabilisation schemes, the price levels within the country for these products may not be identical with the price levels on overseas markets.
PRODUCTS – The value of products is based upon the valuation of goods at the factory door. It is the selling value at the factory to customers of all goods made or processed during the year after deducting all costs of selling and distribution.
In making use of the gross value of products it must be borne in mind that the figures include the value of raw materials operated upon, which value normally constitutes approximately two-thirds of the value of products. Where the products of one industry – for example, sawmilling – are treated again in other industries, such as furniture making, joinery, etc., part of the value of the timber shown as products of the former industry appears again as the materials of the latter industry and enters into the value of furniture and joinery made. Duplication of this kind is found in many industries.
The following tables show the gross value of products for each industrial group and for all industries for the last three years available.
| Industry Group | Products | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| £(000) | |||
| Food | 236,124 | 246,190 | 241,906 |
| Beverages | 10,366 | 11,149 | 11,232 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 6,073 | 6,730 | 7,184 |
| Textiles | 30,239 | 30,022 | 31,673 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 39,473 | 42,724 | 46,572 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 36,498 | 38,648 | 41,724 |
| Furniture and fittings | 10,371 | 11,823 | 11,887 |
| Paper and paper products | 22,323 | 27,054 | 29,556 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 20,873 | 22,895 | 23,951 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 4,090 | 4,110 | 4,636 |
| Rubber products | 10,565 | 10,900 | 11,470 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 27,026 | 28,914 | 29,822 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 2,413 | 2,936 | 3,248 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 18,528 | 20,678 | 21,533 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 3,380 | 3,299 | 3,634 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 20,888 | 23,752 | 25,948 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 26,102 | 28,179 | 26,659 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 10,693 | 12,556 | 14,357 |
| Transport equipment | 60,092 | 65,265 | 63,392 |
| Miscellaneous products | 5,926 | 7,104 | 9,070 |
| Totals | 602,041 | 644,929 | 659,455 |
A similar analysis by provincial districts, but limited to the year 1958–59, is now given.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| *To avoid disclosure of details of individual establishments, figures have been included in those for Miscellaneous products. | |||||||||||
| Products 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| £(000) | |||||||||||
| Food | 109,236 | 13,733 | 23,048 | 32,876 | 1,588 | 3,605 | 446 | 27,816 | 15,231 | 14,327 | 241,906 |
| Beverages | 5,087 | 478 | 165 | 1,749 | * | 199 | 77 | 2,306 | 1,069 | * | 11,232 |
| Tobacco manufactures | * | * | - | * | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7,184 |
| Textiles | 8,978 | 2,175 | * | 7,053 | * | 94 | - | 8,095 | 4,442 | 756 | 31,673 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 22,408 | 612 | 1,154 | 10,888 | 283 | 85 | * | 8,398 | 2,225 | 218 | 46,572 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 23,372 | 1,430 | 1,358 | 5,001 | 196 | 1,895 | 1,329 | 3,634 | 1,750 | 1,759 | 41,724 |
| Furniture and fittings | 5,693 | 555 | 146 | 2,424 | 39 | 120 | 23 | 1,891 | 764 | 233 | 11,887 |
| Paper and paper products | 23,262 | * | - | 3,579 | - | - | - | 1,029 | 587 | 863 | 29,556 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 8,852 | 734 | 480 | 7,355 | 128 | 268 | 108 | 3,452 | 1,966 | 609 | 23,951 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 2,270 | 90 | * | 349 | * | * | - | 890 | 723 | 297 | 4,636 |
| Rubber products | 3,374 | * | 76 | 2,433 | * | * | - | 5,341 | 108 | * | 11,470 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 10,694 | 1,195 | 1,712 | 10,459 | * | 302 | - | 2,607 | 2,676 | * | 29,822 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 1,628 | * | 33 | 1,152 | - | - | - | 299 | 89 | - | 3,248 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 11,000 | 546 | 225 | 2,320 | 86 | 1,231 | 122 | 2,970 | 2,068 | 966 | 21,533 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1,732 | - | * | 656 | - | * | - | 429 | 125 | * | 3,634 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 13,599 | 232 | 148 | 6,116 | * | 113 | * | 3,315 | 2,075 | 329 | 25,948 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 12,380 | 949 | 954 | 6,468 | 137 | 91 | 95 | 3,558 | 1,402 | 624 | 26,659 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 4,578 | 216 | - | 4,881 | - | - | - | 3,776 | 907 | - | 14,357 |
| Transport equipment | 21,144 | 1,636 | 1,297 | 24,521 | 459 | 1,255 | 390 | 8,150 | 2,701 | 1,838 | 63,392 |
| Miscellaneous products | 5,165 | 1,121 | 811 | 8,648 | 202 | 41 | 317 | 1,276 | 282 | 199 | 9,070 |
| Totals | 294,452 | 25,702 | 31,607 | 138,929 | 3,118 | 9,299 | 2,907 | 89,232 | 41,191 | 23,018 | 659,455 |
ADDED VALUE – As indicated under the heading of “Products“, the value of products is not always a satisfactory measure of either the absolute or the relative importance of a given industry, for the reason that only part of this value is actually created by the manufacturing processes carried on in the industry itself. In many cases by far the larger portion of the value of products represents the value of the materials used. From a manufacturing standpoint, the best measure of the importance of an industry is the value created by the manufacturing operations carried on within the industry. This value is obtained in New Zealand by deducting the cost of materials used from the gross value of the products, and is referred to as the “added value”.
The tables given herewith show the added value for each industrial group and for all industries for each of the last three years available, with an analysis of the 1958–59 totals according to the provincial districts in which the industries were carried on.
| Industry Group | Added Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| £(000) | |||
| Food | 43,251 | 45,571 | 46,885 |
| Beverages | 4,963 | 5,527 | 5,965 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 1,673 | 1,825 | 1,981 |
| Textiles | 8,586 | 9,802 | 11,378 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 17,170 | 18,654 | 20,494 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 17,383 | 18,593 | 19,631 |
| Furniture and fittings | 4,975 | 5,505 | 5,586 |
| Paper and paper products | 11,946 | 14,812 | 15,631 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 13,309 | 14,726 | 15,371 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1,508 | 1,565 | 1,833 |
| Rubber products | 5,029 | 5,475 | 5,993 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 9,482 | 10,153 | 10,867 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 751 | 845 | 957 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 12,001 | 13,446 | 14,009 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1,327 | 1,374 | 1,600 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 10,159 | 11,165 | 12,217 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 11,134 | 12,116 | 12,572 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 4,531 | 5,302 | 6,007 |
| Transport equipment | 24,869 | 27,027 | 27,233 |
| Miscellaneous products | 3,004 | 3,529 | 4,598 |
| Totals | 207,053 | 227,011 | 240,807 |
The analysis for 1958–59 by provincial districts now follows.
| Industry Group | Auckland | Hawke's Bay | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otago Portion | Southland Portion | ||||||||||
| *To avoid disclosure of details of individual establishments, figures have been included in Miscellaneous products. | |||||||||||
| Added Value 1958–59 | |||||||||||
| £(000) | |||||||||||
| Food | 19,314 | 3,334 | 3,638 | 6,673 | 223 | 1,010 | 45 | 6,525 | 3,758 | 2,366 | 46,885 |
| Beverages | 2,414 | 278 | 93 | 1,163 | * | 116 | 48 | 1,165 | 615 | * | 5,965 |
| Tobacco manufactures | * | * | - | * | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1,981 |
| Textiles | 3,123 | 233 | * | 2,823 | * | 47 | - | 3,064 | 1,903 | 130 | 11,378 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 9,983 | 263 | 490 | 4,714 | 107 | 37 | * | 3,691 | 996 | 96 | 20,494 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 11,128 | 644 | 660 | 2,060 | 98 | 874 | 673 | 1,765 | 840 | 888 | 19,631 |
| Furniture and fittings | 2,608 | 297 | 75 | 1,160 | 21 | 64 | 13 | 892 | 341 | 115 | 5,586 |
| Paper and paper products | 13,281 | * | - | 1,289 | - | - | - | 391 | 262 | 350 | 15,631 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 5,404 | 525 | 341 | 4,879 | 101 | 200 | 86 | 2,125 | 1,251 | 459 | 15,371 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 943 | 22 | * | 172 | * | * | - | 357 | 261 | 69 | 1,833 |
| Rubber products | 1,711 | * | 43 | 1,255 | * | * | - | 2,852 | 57 | * | 5,993 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 3,679 | 413 | 578 | 3,939 | * | 127 | - | 1,086 | 945 | * | 10,867 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 510 | * | 12 | 290 | - | - | - | 91 | 38 | - | 957 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 6,945 | 335 | 121 | 1,407 | 52 | 962 | 89 | 1,959 | 1,452 | 687 | 14,009 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 632 | - | * | 314 | - | * | - | 270 | 83 | * | 1,600 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 6,322 | 117 | 56 | 2,896 | * | 64 | * | 1,604 | 987 | 158 | 12,217 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 5,638 | 445 | 502 | 3,044 | 78 | 48 | 63 | 1,697 | 695 | 362 | 12,572 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 1,718 | 91 | - | 2,042 | - | - | - | 1,627 | 529 | - | 6,007 |
| Transport equipment | 9,941 | 899 | 747 | 8,088 | 257 | 688 | 205 | 3,962 | 1,516 | 929 | 27,233 |
| Miscellaneous products | 2,523 | 329 | 374 | 3,003 | 138 | 23 | 130 | 611 | 146 | 115 | 4,598 |
| Totals | 107,817 | 8,226 | 7,731 | 51,211 | 1,074 | 4,261 | 1,352 | 35,737 | 16,674 | 6,725 | 240,807 |
A further table is shown below giving details of added value by industry groups and the main employment districts of the Department of Labour. This compilation is a comparatively new one in the factory production series and serves to pinpoint the main areas of manufacture far better than does the classification by provincial districts shown in the previous table. (The first table on page 499 also gives information by employment districts.)
| Industry Group | Auckland | Lower Hutt | Wellington | Other North Island Districts | Christ-church | Dunedin | Other South Island Districts | Total for New Zealand | Percentage of Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Included in Miscellaneous. | |||||||||
| Added Value 1958–59 | |||||||||
| £(000) | |||||||||
| Food | 12,137 | 1,576 | 1,060 | 18,186 | 4,756 | 3,345 | 5,825 | 46,885 | 19.47 |
| Beverages | 1,792 | 135 | 590 | 1,431 | 1,054 | 615 | 348 | 5,965 | 2.48 |
| Tobacco manufactures | * | * | * | * | - | - | - | 1,981 | 0.82 |
| Textiles | 2,893 | 879 | 623 | 1,836 | 2,099 | 1,623 | 1,426 | 11,378 | 4.73 |
| Footwear, clothing | 9,153 | 753 | 2,733 | 2,811 | 3,653 | 988 | 402 | 20,494 | 8.51 |
| Wood manufactures | 2,672 | 419 | 414 | 10,987 | 1,502 | 751 | 2,886 | 19,631 | 8.15 |
| Furniture and fittings | 2,385 | 415 | 384 | 956 | 845 | 339 | 262 | 5,586 | 2.32 |
| Paper and paper products – | 3,630 | 443 | 527 | 10,027 | 384 | 262 | 358 | 15,631 | 6.49 |
| Printing, publishing – | 4,356 | 185 | 3,968 | 2,640 | 1,904 | 1,208 | 1,111 | 15,371 | 6.38 |
| Leather and products | 931 | 38 | 98 | 75 | 350 | 261 | 79 | 1,833 | 0.76 |
| Rubber products | 1,472 | 1,032 | 72 | 474 | 2,847 | 57 | 41 | 5,993 | 2.49 |
| Chemicals and products | 3,183 | 2,079 | 1,375 | 1,972 | 1,060 | 922 | 275 | 10,867 | 4.51 |
| Petroleum, coal products – | 377 | 75 | 208 | 168 | 90 | 38 | 1 | 957 | 0.40 |
| Non-metallic mineral products | 3,576 | 492 | 308 | 4,433 | 1,541 | 1,332 | 2,328 | 14,009 | 5.82 |
| Basic metal products | 569 | 146 | 104 | 415 | 248 | 83 | 36 | 1,600 | 0.67 |
| Metal products | 6,082 | 1,175 | 1,163 | 972 | 1,564 | 979 | 283 | 12,217 | 5.07 |
| Machinery | 4,378 | 1,240 | 925 | 3,085 | 1,524 | 591 | 827 | 12,572 | 5.22 |
| Electrical products | 1,522 | 524 | 1,467 | 338 | 1,627 | 529 | 6,007 | 2.49 | |
| Transport | 6,099 | 4,627 | 1,792 | 7,158 | 3,388 | 1,296 | 2,873 | 27,233 | 11.31 |
| Miscellaneous | 2,332 | 1,952 | 952 | 537 | 605 | 146 | 56 | 4,598 | 1.91 |
| Totals, added value | 69,540 | 18,180 | 18,763 | 68,501 | 31,041 | 15,366 | 19,415 | 240,807 | 100.00 |
| Percentage of New Zealand Total | 28.88 | 7.55 | 7.79 | 28.45 | 12.89 | 6.38 | 8.06 | 100.00 | - |
A final table on added value has been compiled which classifies factories into several added value groupings, giving a general picture of size distribution.
| Added Value Groups | Establishments | Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials used | Value of Output | Added Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Per Person Engaged | ||||||
| £ | Number | Number | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £ |
| Under 5,000 | 2,314 | 7,675 | 5,114 | 8,677 | 16,170 | 7,494 | 976 |
| 5,000–9,999 | 2,292 | 15,259 | 10,628 | 21,858 | 38,457 | 16,599 | 1,088 |
| 10,000–19,999 | 1,848 | 22,700 | 15,866 | 40,139 | 66,359 | 26,220 | 1,155 |
| 20,000–49,999 | 1,312 | 32,115 | 22,488 | 74,104 | 114,267 | 40,163 | 1,251 |
| 50,000–99,999 | 436 | 20,964 | 15,260 | 65,305 | 95,491 | 30,186 | 1,440 |
| 100,000–499,999 | 300 | 40,136 | 30,606 | 91,136 | 151,745 | 60,609 | 1,510 |
| 500,000 and over | 63 | 29,893 | 28,316 | 117,429 | 176,967 | 59,537 | 1,990 |
| Totals | 8,565 | 168,742 | 128,278 | 418,647 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 1,427 |
The development of factory production in New Zealand from 1930–31 onward is clearly portrayed in the following diagram, which also shows the relationship between cost of materials, added value and value of output.
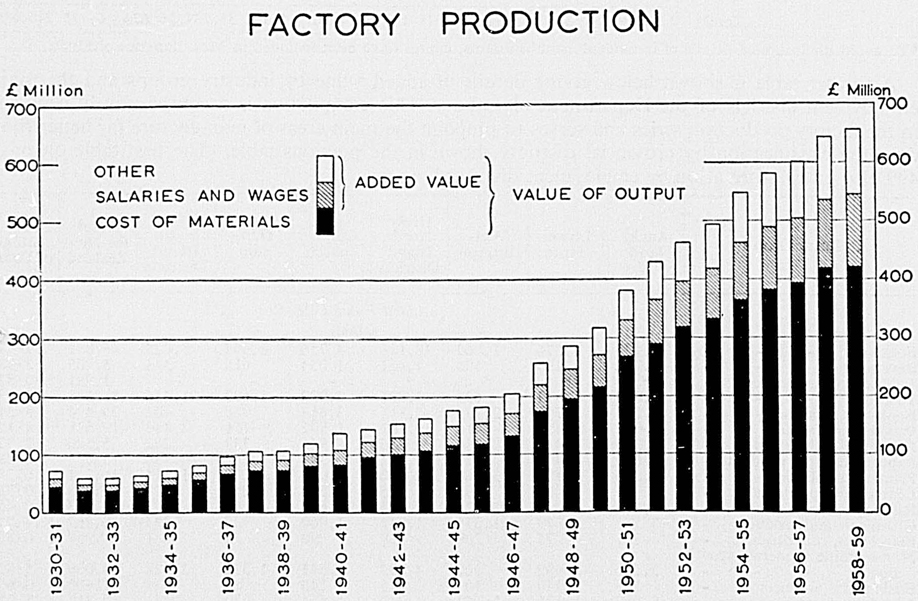
EXPENSES OF OPERATION – Total operating costs of factory production for the year 1958–59 amounted to £617,286,157, of which salaries and wages accounted for £128,318,259, cost of materials for £418,647,288, and other expenses for £70,320,610, while value of output totalled £659,454,543.
The table below shows the principal items comprised in the figure for expenses of operation, other than salaries and wages and cost of materials, by industry groups for the year 1958–59.
| Industry Group | Coal | Electricity | Coke, Gas, Oils, etc. | Insurance | Interest on Loans, etc. | Depreciation | Rent | Repairs and Maintenance | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(000) | ||||||||||
| Food | 2,447 | 1,543 | 333 | 727 | 524 | 3,626 | 164 | 3,012 | 3,386 | 15,761 |
| Beverages | 107 | 90 | 61 | 69 | 113 | 556 | 55 | 345 | 713 | 2,110 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 2 | 9 | 13 | 24 | 36 | 113 | 10 | 48 | 342 | 597 |
| Textiles | 228 | 199 | 62 | 148 | 162 | 711 | 75 | 714 | 927 | 3,224 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 13 | 207 | 52 | 148 | 198 | 516 | 563 | 437 | 1,477 | 3,612 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 5 | 402 | 141 | 487 | 330 | 1,313 | 111 | 1,232 | 2,060 | 6,082 |
| Furniture and fittings | 1 | 74 | 5 | 98 | 65 | 151 | 108 | 110 | 357 | 970 |
| Paper and paper products | 496 | 897 | 272 | 222 | 740 | 2,590 | 83 | 768 | 1,981 | 8,049 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 2 | 144 | 49 | 133 | 130 | 889 | 151 | 361 | 1,906 | 3,766 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 29 | 28 | 5 | 31 | 15 | 62 | 31 | 79 | 102 | 381 |
| Rubber products | 94 | 144 | 72 | 78 | 26 | 433 | 31 | 220 | 610 | 1,708 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 121 | 198 | 98 | 175 | 169 | 1,172 | 71 | 630 | 1,058 | 3,691 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 3 | 21 | 42 | 17 | 7 | 72 | 8 | 60 | 103 | 334 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 1,296 | 482 | 436 | 174 | 156 | 1,090 | 56 | 1,186 | 957 | 5,834 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1 | 39 | 53 | 20 | 25 | 65 | 15 | 56 | 132 | 405 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 8 | 171 | 95 | 147 | 161 | 488 | 159 | 380 | 1,048 | 2,658 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 7 | 164 | 121 | 184 | 188 | 462 | 147 | 322 | 1,215 | 2,810 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 11 | 113 | 59 | 69 | 58 | 207 | 49 | 168 | 677 | 1,412 |
| Transport equipment | 5 | 319 | 105 | 367 | 230 | 989 | 487 | 654 | 2,670 | 5,825 |
| Miscellaneous products | 5 | 83 | 20 | 58 | 43 | 232 | 92 | 167 | 394 | 1,093 |
| Totals | 4,879 | 5,327 | 2,095 | 3,376 | 3,377 | 15,736 | 2,466 | 10,948 | 22,116 | 70,321 |
CAPITAL INVESTED AND ASSETS – Information as to the amount of capital invested in manufacturing industries was collected for some years, but the figures obtained were found to be unsatisfactory. The chief factors militating against the collection of reliable information have been the methods of accounting in use in many of the smaller establishments, and the difficulty of apportioning capital where an establishment is only partly manufacturing.
A more satisfactory indication of the capital investment in a manufacturing industry is obtained from figures of manufacturers' fixed assets. Not only are the figures more reliable than those for capital invested, but they do not suffer from the understatement of capital (from the economic viewpoint) which occurs in those cases where the factory premises, or, in some few cases, even the plant, is not owned by the manufacturer, but is rented. In these cases an estimate of the value of the rented asset has been obtained by capitalising the annual rental shown. Approximations in the figures for fixed assets are also made where one building houses two or more factories carrying on different industries, necessitating an apportionment as between the industries. In most instances, too, fixed assets are stated at their book value, and this may be an overstatement due to insufficient allowance having been made for depreciation, obsolescence, etc., or an understatement owing to appreciated site value, excessive allowance for depreciation, or currency depreciation resulting in the assets being understated in terms of their present earning capacity or replacement cost. It is necessary to bear in mind these limitations to the accuracy of the figures of fixed assets appearing in the following table, which shows the values of these assets for each of the last three years together with an analysis by principal industries for 1958–59. For the year 1958–59 information is also shown by industry groups of the amounts expended during the year by way of capital additions and alterations, together with totals for all industries for the two previous years.
| Industry Group | Capital Additions and Alterations During the Year | Value at End of Year (Including Estimated Value of Rented Assets) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land and Buildings | Plant and Machinery | Total | Land and Buildings | Plant and Machinery | Total | |
| *Revised. | ||||||
| Totals – | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| 1956–57 | 9,573,848 | 14,769,535 | 24,343,383 | 104,637,510 | 75,485,934 | 180,123,444 |
| 1957–58 | 9,420,308 | 13,801,687 | 23,221,995 | 112,758,584 | 76,528,492 | 189,287,076 |
| 1958–59 – | ||||||
| Food | 2,302,325 | 3,872,753 | 6,175,078 | 29,229,746 | 20,735,169 | 49,964,915 |
| Beverages | 894,047 | 1,046,553 | 1,940,600 | 4,547,491 | 3,613,227 | 8,160,718 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 42,737 | 197,530 | 240,267 | 722,359 | 612,894 | 1,335,253 |
| Textiles | 181,850 | 894,320 | 1,076,170 | 4,250,646 | 3,603,330 | 7,853,976 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 513,523 | 621,187 | 1,134,710 | 9,755,503 | 3,382,488 | 13,137,991 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 798,451 | 880,376 | 1,678,827 | 7,939,766 | 6,997,958 | 14,937,724 |
| Furniture and fittings | 201,257 | 191,347 | 392,604 | 2,961,183 | 958,740 | 3,919,923 |
| Paper and paper products | 599,895 | 1,661,184 | 2,261,079 | 7,089,631 | 10,476,181 | 17,565,812 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 982,453 | 1,229,334 | 2,211,787 | 6,979,088 | 5,647,499 | 12,626,587 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 60,539 | 68,500 | 129,039 | 738,698 | 329,708 | 1,068,406 |
| Rubber products | 114,980 | 308,006 | 422,986 | 1,876,675 | 1,625,413 | 3,502,088 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 881,723 | 1,262,232 | 2,143,955 | 6,971,521 | 4,512,367 | 11,483,888 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 27,684 | 106,888 | 134,572 | 439,051 | 367,010 | 806,061 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 810,772 | 1,526,872 | 2,337,644 | 6,540,447 | 6,961,273 | 13,501,720 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 88,966 | 95,999 | 184,965 | 770,613 | 479,540 | 1,250,153 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 609,548 | 642,764 | 1,252,312 | 5,576,053 | 2,763,732 | 8,339,785 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 454,773 | 577,849 | 1,032,622 | 5,407,374 | 2,797,924 | 8,205,298 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 374,699 | 362,335 | 737,034 | 2,401,616 | 1,016,546 | 3,418,162 |
| Transport equipment | 1,128,265 | 841,468 | 1,969,733 | 17,200,667 | 4,304,247 | 21,504,914 |
| Miscellaneous products | 116,137 | 266,424 | 382,561 | 2,230,949 | 1,072,044 | 3,302,993 |
| Totals, 1958–59 | 11,184,624 | 16,653,921 | 27,838,545 | 123,629,077* | 82,257,290* | 205,886,367* |
MANUFACTURERS' STOCKS – A quarterly survey of manufacturers' stocks has been conducted by the Department of Statistics since 1957. The survey is carried out on a sample basis, the selection representing approximately 10 per cent of all the factories covered by the annual census of factory production. The number of establishments included in the sample is approximately 900 and their combined stocks as returned in the annual survey at March 1957 represented 67 per cent by value of total manufacturers' stocks.
The following table compares in summary form the results of the quarterly surveys from 31 March 1958 to 31 March 1960. In presenting the results, the chief seasonal industries – meat processing and dairy products manufacture – have been segregated to assist in the interpretation of movements in stock holdings. The heading “Materials” wherever shown includes work in progress, fuel, and miscellaneous supplies.
| Total Stocks | Movement in Stocks at Annual Intervals | Percentage Movement in Stocks at Annual Intervals | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finished Goods | Materials | Total | Finished Goods | Materials | Total | Finished Goods | Materials | Total | |
| Including Primary Produce Processing Industries | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | per cent | per cent | per cent |
| 31 March 1958 | 46,278 | 74,682 | 120,960 | – 95 | + 3,434 | + 3,339 | – 0.21 | + 4.82 | + 2.84 |
| 30 June 1958 | 46,376 | 77,073 | 123,449 | + 5,663 | +3,129 | +8,791 | +13.91 | +4.23 | +7.67 |
| 30 September 1958 | 41,735 | 77,283 | 119,018 | + 750 | + 2,971 | + 3,721 | + 1.83 | +4.00 | + 3.23 |
| 31 December 1958 | 45,223 | 78,427 | 123,651 | + 456 | + 5,067 | + 5,523 | + 1.02 | + 6.91 | +4.68 |
| 31 March 1959 | 45,259 | 81,430 | 126,689 | –1,019 | + 6,748 | + 5,729 | – 2.20 | + 9.04 | +4.74 |
| 30 June 1959 | 49,725 | 78,495 | 128,220 | + 3,350 | + 1,421 | +4,771 | + 7.22 | + 1.84 | + 3.86 |
| 30 September 1959 | 46,032 | 77,804 | 123,836 | +4,297 | + 521 | +4,818 | + 10.30 | + 0.67 | +4.05 |
| 31 December 1959 | 48,274 | 76,288 | 124,563 | + 3,051 | –2,139 | + 912 | + 6.75 | –2.73 | + 0.74 |
| 31 March 1960 | 52,206 | 82,133 | 134,339 | + 6,947 | + 703 | + 7,650 | + 15.35 | + 0.86 | + 6.04 |
| Excluding Primary Produce Processing Industries | |||||||||
| 31 March 1958 | 23,546 | 69,995 | 93,541 | + 1,718 | + 3,327 | + 5,046 | + 7.87 | +4.99 | + 5.70 |
| 30 June 1958 | 24,637 | 72,671 | 97,308 | + 1,786 | + 3,137 | + 4,923 | + 7.81 | + 4.51 | + 5.33 |
| 30 September 1958 | 26,193 | 72,152 | 98,346 | + 1,559 | + 2,626 | +4,185 | + 6.33 | + 3.78 | +4.44 |
| 31 December 1958 | 24,467 | 73,536 | 98,003 | + 602 | +4,982 | + 5,585 | + 2.52 | + 7.27 | + 6.04 |
| 31 March 1959 | 24,188 | 76,529 | 100,718 | + 642 | + 6,534 | +7,177 | + 2.73 | +9.33 | +7.67 |
| 30 June 1959 | 26,760 | 74,115 | 100,875 | + 2,123 | + 1,443 | + 3,567 | + 8.62 | + 1.99 | + 3.67 |
| 30 September 1959 | 28,134 | 73,074 | 101,208 | + 1,941 | + 921 | +2,862 | + 7.41 | + 1.28 | + 2.91 |
| 31 December 1959 | 26,802 | 71,482 | 98,285 | + 2,335 | –2,053 | + 282 | + 9.54 | –2.79 | +0.29 |
| 31 March 1960 | 26,767 | 76,635 | 103,402 | + 2,579 | + 106 | + 2,685 | + 10.66 | +0.14 | + 2.67 |
More detailed information on stocks is given in the next table showing by industry groups comparative stock figures at the end of March for the years 1959 and 1960.
| Industry Group | Stocks at 31 March | Increase or Decrease in Stocks, March 1959 to March 1960 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | ||||||||
| Finished Goods | Materials | Total | Finished Goods | Materials | Total | Finished Goods | Materials | Total | |
| Primary Produce Processing Industries | £(000) | ||||||||
| Meat freezing, ham, bacon, and casings | 14,954 | 3,438 | 18,392 | 18,668 | 3,789 | 22,457 | + 3,714 | + 351 | +4,065 |
| Dairy | 6,117 | 1,462 | 7,580 | 6,771 | 1,709 | 8,480 | + 654 | + 246 | + 900 |
| Totals | 21,071 | 4,901 | 25,972 | 25,439 | 5,498 | 30,937 | +4,368 | + 597 | +4,965 |
| Other food | 4,139 | 6,579 | 10,718 | 4,404 | 7,433 | 11,837 | + 265 | +854 | + 1,119 |
| Beverages | 1,055 | 1,688 | 2,742 | 1,356 | 1,474 | 2,830 | + 301 | –214 | + 87 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 6,018 | 6,018 | 5,723 | 5,723 | –295 | – 295 | |||
| Textiles | 1,615 | 5,405 | 7,020 | 2,087 | 5,311 | 7,397 | + 472 | – 94 | + 378 |
| Footwear, clothing | 2,365 | 7,630 | 9,995 | 2,662 | 7,275 | 9,937 | + 297 | –355 | – 58 |
| Wood manufactures | 2,793 | 3,655 | 6,447 | 3,093 | 4,004 | 7,097 | + 300 | + 350 | + 649 |
| Furniture and fittings | 458 | 1,811 | 2,268 | 402 | 2,078 | 2,480 | - 56 | + 267 | + 211 |
| Paper and products | 1,070 | 4,419 | 5,489 | 1,606 | 4,424 | 6,030 | + 536 | + 5 | + 541 |
| Printing, publishing | 234 | 4,650 | 4,883 | 292 | 4,396 | 4,688 | + 59 | –254 | – 195 |
| Leather and products | 252 | 735 | 988 | 247 | 704 | 950 | – 6 | – 32 | – 37 |
| Rubber products | 1,048 | 1,764 | 2,812 | 1,037 | 1,869 | 2,905 | – 11 | + 105 | + 94 |
| Chemicals and products | 2,772 | 5,462 | 8,234 | 2,993 | 5,703 | 8,696 | + 221 | +241 | + 462 |
| Petroleum, coal products | 71 | 335 | 407 | 79 | 324 | 403 | + 7 | – 11 | – 4 |
| Non-metallic mineral products | 1,287 | 2,786 | 4,073 | 1,324 | 2,798 | 4,122 | + 37 | + 13 | + 49 |
| Basic metal products | 88 | 567 | 655 | 87 | 693 | 780 | – 1 | + 126 | + 125 |
| Metal products | 823 | 5,234 | 6,057 | 936 | 4,854 | 5,789 | + 113 | -381 | – 268 |
| Machinery | 1,596 | 6,149 | 7,745 | 1,564 | 5,653 | 7,217 | – 32 | –496 | – 527 |
| Electrical products | 811 | 3,896 | 4,707 | 880 | 3,996 | 4,876 | + 69 | + 100 | + 169 |
| Transport | 1,007 | 5,780 | 6,788 | 956 | 6,271 | 7,227 | – 51 | +491 | + 440 |
| Miscellaneous | 705 | 1,967 | 2,673 | 764 | 1,653 | 2,418 | + 59 | –314 | – 255 |
| Totals | 24,188 | 76,529 | 100,718 | 26,767 | 76,635 | 103,402 | + 2,579 | + 106 | + 2,685 |
| Totals, all factory industries | 45,259 | 81,430 | 126,689 | 52,206 | 82,133 | 134,339 | + 6,947 | + 703 | + 7,650 |
ORGANISATION OF INDUSTRY – New Zealand's industrial progress has been fairly rapid, but industry is as yet organised on a relatively small scale.
The law in New Zealand restricts the membership of a partnership to not more than 25 persons, a private company to not fewer than two or more than 25 persons, and a public company to not fewer than seven persons. Cooperation is characteristic of certain industries engaged in the processing of primary products, mainly butter and cheese manufacturing.
Information as to the character of organisation of the establishments engaged in factory production during 1958–59 is given in the following table.
| Character of Organisation | Number of Establishments | Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials Used or Operated Upon | Value of Manufactures or Products Total | Added Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Per Establishment | ||||||
| Number | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £ | ||
| Individual | 954 | 4,538 | 2,989 | 4,782 | 9,444 | 4,662 | 4,887 |
| Private firm or partnership | 504 | 2,773 | 1,937 | 3,292 | 6,447 | 3,155 | 6,260 |
| Public registered company | 843 | 55,452 | 44,595 | 137,208 | 228,265 | 91,057 | 108,015 |
| Private registered company | 5,779 | 98,524 | 72,594 | 194,624 | 324,284 | 129,660 | 22,436 |
| Municipal and Government | 101 | 2,717 | 2,178 | 1,971 | 5,319 | 3,349 | 33,156 |
| Cooperative and miscellaneous | 384 | 4,738 | 3,984 | 76,770 | 85,695 | 8,925 | 23,243 |
| Totals | 8,565 | 168,742 | 128,278 | 418,647 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 28,115 |
As would be expected, the average size of establishments operated by public registered companies is larger than in any other type of industrial organisation, the added value per unit being nearly five times as high as that for private registered companies. Private companies, however, occupy a very high place, both numerically and in the share they contribute to the total added value created in New Zealand factories (53.8 per cent in 1958–59, as compared with 37.8 per cent in the case of public companies).
Since 1951–52, the first years of the new series, private and public registered companies have increased their combined share of added value from 87.8 per cent to 91.7 per cent. The separate share of public companies increased from 34.7 per cent to 37.8 per cent, and that of private companies from 53.1 per cent of 53.8 per cent. All other types of organisations listed recorded declines in their share of added value over this period.
VALUE AND VOLUME INDICES OF FACTORY PRODUCTION – Below is a table giving index numbers of added value, value of output, and volume of production based on the year 1938–39. This table commences with the year 1928–29 and runs through to 1950–51, at which stage a new series was commenced.
| Production Year | Index Numbers of – | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Added in Manufacture | Value of Output | Volume of Production | |
| Base: 1938–39 (=100) | |||
| 1928–29 | 80 | 79 | 71 |
| 1929–30 | 83 | 79 | 74 |
| 1930–31 | 75 | 68 | 69 |
| 1931–32 | 62 | 58 | 60 |
| 1932–33 | 60 | 58 | 63 |
| 1933–34 | 64 | 63 | 65 |
| 1934–35 | 70 | 69 | 74 |
| 1935–36 | 77 | 79 | 81 |
| 1936–37 | 90 | 93 | 92 |
| 1937–38 | 99 | 99 | 97 |
| 1938–39 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1939–40 | 113 | 113 | 110 |
| 1940–41 | 125 | 129 | 114 |
| 1941–42 | 137 | 136 | 116 |
| 1942–43 | 151 | 145 | 120 |
| 1943–44 | 162 | 154 | 125 |
| 1944–45 | 173 | 166 | 129 |
| 1945–46 | 185 | 171 | 131 |
| 1946–47 | 205 | 191 | 140 |
| 1947–48 | 233 | 238 | 151 |
| 1948–49 | 252 | 263 | 155 |
| 1949–50 | 285 | 290 | 164 |
| 1950–51 | 311 | 345 | 172 |
With the reclassification in 1951–52 a new series of index numbers was commenced and these are shown below. It should be realised in comparing the two series of index numbers that the latter excludes the activities of three important industries. These relate to the logging operations of sawmillers, previously included in the sawmilling industry, and the generation and supply of gas and electricity, accounting in all for the activities of approximately 10,000 persons. However, the effect of the exclusion of these industries entirely from the new series is not great, as the two series in the overlapping period record very similar movements.
| Production Year | Index Numbers of – | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Added in Manufacture | Value of Output | Volume of Production | |
| Base: 1956–57 (= 100) | |||
| 1950–51 | 55 | 63 | 75 |
| 1951–52 | 68 | 72 | 81 |
| 1952–53 | 70 | 77 | 80 |
| 1953–54 | 78 | 82 | 85 |
| 1954–55 | 90 | 92 | 94 |
| 1955–56 | 97 | 97 | 99 |
| 1956–57 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1057–58 | 110 | 107 | 107 |
| 1958–59 | 116 | 110 | 113 |
The table which follows sets out, by industry groups, index numbers of value of output, added value, and volume of output for the three latest yeast. It is not possible to arrive at volume of production index numbers for all the groups, for technical reasons, and consequently some have been omitted, but the total index number for the year is calculated in such a way as to include the groups which cannot be assessed separately.
INDEX NUMBERS OF VALUE AND VOLUME OF FACTORY PRODUCTION
| Base: 1956–57 (= 1000) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry Group | Value of Output | Value Added in Manufacture | Volume of Production | ||||||
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| *Indices not available for the groups, but allowed for in compiling total index. | |||||||||
| Food | 1000 | 1043 | 1024 | 1000 | 1054 | 1087 | 1000 | 1061 | 1121 |
| Beverages | 1000 | 1076 | 1084 | 1000 | 1114 | 1202 | 1000 | 1048 | 993 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 1000 | 1108 | 1183 | 1000 | 1091 | 1184 | 1000 | 1108 | 1148 |
| Textiles | 1000 | 993 | 1047 | 1000 | 1142 | 1325 | 1000 | 1114 | 1287 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 1000 | 1082 | 1180 | 1000 | 1086 | 1194 | 1000 | 1053 | 1148 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 1000 | 1059 | 1143 | 1000 | 1070 | 1129 | 1000 | 987 | 1053 |
| Furniture and fittings | 1000 | 1140 | 1146 | 1000 | 1107 | 1123 | * | * | * |
| Paper and paper products | 1000 | 1212 | 1324 | 1000 | 1240 | 1308 | 1000 | 1220 | 1306 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 1000 | 1097 | 1147 | 1000 | 1106 | 1155 | 1000 | 1057 | 1093 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1000 | 1005 | 1133 | 1000 | 1038 | 1216 | 1000 | 1015 | 1172 |
| Rubber products | 1000 | 1032 | 1086 | 1000 | 1089 | 1192 | 1000 | 1098 | 1144 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 1000 | 1070 | 1103 | 1000 | 1109 | 1146 | 1000 | 1047 | 1040 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 1000 | 1217 | 1346 | 1000 | 1125 | 1274 | * | * | * |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 1000 | 1116 | 1162 | 1000 | 1120 | 1167 | 1000 | 1078 | 1121 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1000 | 970 | 1075 | 1000 | 1035 | 1206 | * | * | * |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1000 | 1137 | 1242 | 1000 | 1099 | 1203 | * | * | * |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 1000 | 1080 | 1021 | 1000 | 1088 | 1129 | * | * | * |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 1000 | 1174 | 1343 | 1000 | 1170 | 1326 | 1000 | 1153 | 1293 |
| Transport equipment | 1000 | 1086 | 1055 | 1000 | 1087 | 1095 | * | * | * |
| Miscellaneous products | 1000 | 1199 | 1531 | 1000 | 1175 | 1531 | * | * | * |
| Totals | 1000 | 1071 | 1095 | 1000 | 1096 | 1163 | 1000 | 1072 | 1130 |
OVERTIME – Details of overtime worked in factories by wage-earning employees are summarised in the tables given, which show, by industry groups, the hours worked during the latest three years. The averages given are calculated on the basis of the total number of wage earners engaged irrespective of the number who actually worked overtime.
| Industry Group | Total Overtime Hours Worked by Wage Earners (Both Male and Female) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | |
| Food | 6,204,712 | 6,385,230 | 7,243,656 |
| Beverages | 537,356 | 531,347 | 496,345 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 173,437 | 202,765 | 182,433 |
| Textiles | 588,208 | 717,444 | 934,840 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 639,628 | 740,032 | 796,343 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | -1,262,582 | 1,418,209 | 1,434,388 |
| Furniture and fittings | 375,282 | 476,858 | 490,997 |
| Paper and paper products | 542,517 | 709,348 | 845,942 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 708,399 | 816,120 | 890,270 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 124,519 | 124,576 | 166,025 |
| Rubber products | 425,006 | 426,446 | 395,908 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 828,321 | 803,396 | 763,275 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 40,640 | 39,182 | 42,385 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 1,396,409 | 1,399,719 | 1,330,693 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 138,090 | 134,154 | 172,052 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,331,443 | 1,382,243 | 1,478,352 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 1,159,237 | 1,335,509 | 1,447,889 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 385,541 | 453,324 | 464,190 |
| Transport equipment | 2,177,665 | 2,114,280 | 1,830,898 |
| Miscellaneous products | 204,082 | 221,627 | 317,360 |
| Totals | 19,243,074 | 20,431,809 | 21,724,241 |
The next table shows, by industry groups, the hours of overtime worked during 1958–59 by males and females separately.
| Industry Group | Total Overtime Hours Worked by Wage Earners | Average Overtime Hours Worked by All Wage Earners | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | |
| Food | 6,752,892 | 490,764 | 293.53 | 136.29 |
| Beverages | 488,900 | 7,445 | 297.57 | 67.07 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 97,834 | 84,599 | 256.78 | 109.58 |
| Textiles | 734,112 | 200,728 | 172.98 | 45.02 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 378,807 | 417,536 | 82.85 | 22.10 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 1,430,210 | 4,178 | 135.51 | 30.72 |
| Furniture and fittings | 475,456 | 15,541 | 128.36 | 39.24 |
| Paper and paper products | 767,871 | 78,071 | 240.03 | 60.90 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 791,169 | 99,101 | 117.42 | 64.10 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 144,648 | 21,377 | 159.13 | 45.39 |
| Rubber products | 381,016 | 14,892 | 186.77 | 35.04 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 726,411 | 36,864 | 228.86 | 42.37 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 42,025 | 360 | 145.92 | 21.18 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 1,301,710 | 28,983 | 240.48 | 84.25 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 171,146 | 906 | 235.74 | 82.36 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,418,545 | 59,807 | 222.52 | 98.04 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 1,435,105 | 12,784 | 192.30 | 129.13 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 418,131 | 46,059 | 143.59 | 50.95 |
| Transport equipment | 1,812,642 | 18,256 | 104.75 | 87.35 |
| Miscellaneous products | 270,663 | 46,697 | 145.28 | 44.52 |
| Totals | 20,039,293 | 1,684,948 | 188.15 | 46.54 |
SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS – The following table, by assembling data from previous pages, affords an analysis of production costs in 1958–59, together with the value of products for each industry group and for all industries. In addition, by virtue of the complete details collected annually of the cost structure of goods produced in manufacturing industries, it is possible to give information on the surplus available to manufacturers prior to payment of dividends, taxation, and other appropriations. The only exception occurs in the case of cooperative dairy companies, which do not purchase milk and cream in the way that other manufacturers purchase raw materials. They collect the milk and cream from their shareholders, process it, and pay out to these shareholders the whole of the profits of the sales of the products, less amounts paid to reserves. Manufacturing surplus shown by these companies is therefore confined to the amount of these transfers to reserves and any undistributed profits.
In quite a number of cases, articles produced are transferred at cost to separate selling departments and warehouses, or to retail stores run by the same company or establishment. Where this is apparent, the company concerned is asked to substitute a commercial value for its production. The same procedure holds where a company controls more than one factory, and transfers the products of one to the other for further processing. It must be recognised that estimated values have to be accepted in many transactions of this type.
| Industry Group | Production Costs | Value of Products | Manufacturing Surplus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salaries and Wages | Cost of All Materials Used | Other Expenses of Operation | Total | |||
| £(000) | ||||||
| Food | 26,920 | 195,021 | 15,761 | 237,702 | 241,906 | 4,204 |
| Beverages | 1,857 | 5,267 | 2,110 | 9,234 | 11,232 | 1,998 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 801 | 5,203 | 597 | 6,602 | 7,184 | 582 |
| Textiles | 6,224 | 20,295 | 3,224 | 29,744 | 31,673 | 1,930 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 14,134 | 26,078 | 3,612 | 43,824 | 46,572 | 2,747 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 10,311 | 22,093 | 6,082 | 38,486 | 41,724 | 3,238 |
| Furniture and fittings | 3,714 | 6,302 | 970 | 10,985 | 11,887 | 902 |
| Paper and paper products | 4,362 | 13,926 | 8,049 | 26,337 | 29,556 | 3,220 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 8,316 | 8,580 | 3,766 | 20,663 | 23,951 | 3,288 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1,128 | 2,803 | 381 | 4,312 | 4,636 | 324 |
| Rubber products | 2,672 | 5,476 | 1,708 | 9,856 | 11,470 | 1,613 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 4,125 | 18,955 | 3,691 | 26,772 | 29,822 | 3,050 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 350 | 2,291 | 334 | 2,974 | 3,248 | 273 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 5,549 | 7,524 | 5,834 | 18,907 | 21,533 | 2,626 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 808 | 2,034 | 405 | 3,246 | 3,634 | 387 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 6,966 | 13,731 | 2,658 | 23,355 | 25,948 | 2,593 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 7,829 | 14,087 | 2,810 | 24,726 | 26,659 | 1,933 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 3,189 | 8,351 | 1,412 | 12,952 | 14,357 | 1,405 |
| Transport equipment | 16,621 | 36,159 | 5,825 | 58,605 | 63,392 | 4,788 |
| Miscellaneous products | 2,400 | 4,472 | 1,093 | 7,964 | 9,070 | 1,106 |
| Totals | 128,278 | 418,647 | 70,321 | 617,246 | 659,455 | 42,208 |
LIST OF CERTAIN COMMODITIES PRODUCED IN RECENT YEARS – The following is a list of certain commodities produced in New Zealand during the years 1956–57 to 1959–60.
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toasters | No. | 33,784 | 28,559 | 33,640 | 31,592 |
| Irons | No. | 19,945 | 8,939 | 19,872 | 34,774 |
| Jugs and kettles | No. | 47,131 | 55,744 | 47,169 | 53,122 |
| Radiators | No. | 24,477 | 35,129 | 51,117 | 47,245 |
| Vacuum cleaners | No. | 28,449 | 34,784 | 38,210 | 37,280 |
| Washing machines | No. | 33,746 | 36,597 | 35,866 | 38,080 |
| Refrigerators (home and commercial and freezers) | No. | 58,809 | 63,025 | 50,918 | 49,624 |
| Electric ranges | No. | 26,028 | 29,130 | 34,806 | 32,969 |
| Electric rangettes | No. | 4,058 | 4,379 | 4,286 | 3,756 |
| Radios | No. | 97,870 | 106,304 | 127,632 | 120,867 |
| Women's fully fashioned nylon hose | doz. prs. | 406,930 | 453,332 | 444,931 | 418,992 |
| Men's half hose | doz. prs. | 227,722 | 256,928 | 316,083 | 314,311 |
| Blankets | Pairs | 154,006 | 151,872 | 167,827 | 190,247 |
| Floor coverings (textile top coverings) | sq. yd. | 1,526,215 | 1,827,735 | 2,343,823 | 2,564,135 |
| Mattresses – | |||||
| Innerspring – | |||||
| Single | No. | 26,266 | 33,596 | 37,964 | 48,142 |
| Double | No. | 20,398 | 24,167 | 25,116 | 24,192 |
| Soft filled – | |||||
| Single | No. | 82,637 | 84,672 | 73,428 | 73,739 |
| Double | No. | 23,781 | 23,497 | 21,896 | 16,963 |
| Infants | No. | 17,964 | 16,410 | 14,937 | 11,848 |
| Venetian blinds | sq. ft. | 4,331,542 | 4,172,770 | 3,661,819 | 3,628,555 |
| Newspapers produced – | |||||
| Dailies | thousand | 276,514 | 282,133 | 290,052 | 290,462 |
| Other than dailies | thousand | 45,736 | 45,497 | 46,474 | 50,539 |
| Hot-water bottles | No. | 193,319 | 194,191 | 292,897 | 354,632 |
| Soap – | |||||
| Toilet | ton | 3,314 | 2,880 | 3,297 | 3,345 |
| Bar | ton | 4,788 | 5,180 | 5,065 | 5,197 |
| Powder and flake | ton | 10,040 | 10,990 | 12,689 | 14,361 |
| Paints – | |||||
| Ready mixed – | |||||
| Oil and alkyd-vehicle type | gal | 1,813,890 | 1,824,787 | 1,860,555 | 1,907,762 |
| Enamels | gal | 680,975 | 721,587 | 738,757 | 788,730 |
| Toothpaste | cwt | 8,805 | 8,741 | 9,340 | 8,917 |
| Furniture and floor polish | cwt | 25,355 | 24,712 | 22,221 | 20,618 |
| Shoe polishes and cleaners | cwt | 3,878 | 3,788 | 3,385 | 3,441 |
| Water heaters – | |||||
| Under 10 gallons | No. | 12,095 | 15,569 | 12,820 | 11,687 |
| 10 gallons and over | No. | 36,682 | 36,344 | 35,725 | 37,635 |
| Sinks: stainless steel | No. | 23,602 | 30,873 | 45,368 | 38,622 |
| Sink tops: stainless steel | No. | 14,616 | 16,934 | 16,352 | 19,815 |
| Wheelbarrows | No. | 7,086 | 14,119 | 13,256 | 15,340 |
| Lawnmowers (hand and power) | No. | 62,934 | 65,498 | 59,889 | 53,845 |
| Prams, pushchairs, strollers – | |||||
| Cane (inc. dolls') | No. | 10,267 | 12,908 | 9,653 | 8,595 |
| Other than cane | No. | 21,385 | 22,509 | 24,456 | 29,756 |
| Toothbrushes | No. | 1,838,724 | 1,914,624 | 2,082,960 | 1,863,216 |
DETAILS OF CERTAIN PRINCIPAL INDUSTRIES – The principal statistics regarding leading factory industries for the last three years available are set out in the following pages. Fuller details are given in the annual Report on the Industrial Production Statistics.
| 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Revised. †Includes products of establishments classified in other industries. *Includes production by establishments classified in other industries. †In addition, in 1956–57, 104,589 gallons; in 1957–58, 99,256 gallons; and in 1958–59, 72,556 gallons were recorded by establishments classified in other industries. *Revised. *Principal products shown for this industry include the production of establishments classified in other industries. * Revised. *Revised. *Principal products shown for these industries include the production of establishments classified in other industries. † Revised. | ||||
| Meat Freezing and Preserving | ||||
| Number of establishments | 36 | 35 | 34 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 14,690 | 15,641 | 16,456 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 13,292,872 | 14,699,559 | 16,170,285 |
| Materials | £ | 82,936,023 | 86,068,481 | 86,926,857 |
| Other expenses | £ | 5,564,693 | 5,994,101 | 6,447,642 |
| Totals | £ | 101,793,588 | 106,762,141 | 109,544,784 |
| Value of output | £ | 104,843,412 | 108,188,448 | 109,380,386 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 21,907,389 | 22,119,967 | 22,453,529 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 3,800,885 | 3,916,662 | 4,667,402 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Meat – | ||||
| Lamb carcasses | No. | 13,925,976 | 15,479,240 | 17,835,448 |
| cwt | 4,034,261 | 4,533,697 | 4,967,544 | |
| Mutton carcasses | No. | 2,912,730 | 2,773,694 | 4,233,053 |
| cwt | 1,379,508 | 1,240,109 | 1,929,826 | |
| Boned mutton | cwt | 73,090 | 65,741 | 165,575 |
| Mutton and lamb pieces | cwt | 35,418 | 28,627 | 55,517 |
| Beef quarters, shipped bone in | cwt | 1,996,225 | 1,173,910 | 1,022,127 |
| Beef quarters, without bone | cwt | 63,759 | 40,497 | 69,891 |
| Boneless beef | cwt | 793,240 | 1,345,345 | 1,152,869 |
| Bobby veal | cwt | 197,109 | 184,434 | 167,275 |
| Other veal | cwt | 96,265 | 65,011 | 82,163 |
| Pork | cwt | 435,383 | 424,495 | 472,762 |
| Edible offals | cwt | 514,994 | 507,585 | 559,994 |
| By-products – | ||||
| Runners (not processed) | No. | 3,998,369 | 4,493,209 | 4,551,199 |
| Casings | bundles | 3,395,593 | 3,927,454 | 4,669,953 |
| Woolly sheepskins | No. | 166,815 | 166,448 | 181,246 |
| Pelts | No. | 18,343,945 | 19,200,868 | 23,318,676 |
| Cow hides | No. | 469,370 | 560,518 | 488,072 |
| Ox and bull hides | No. | 306,437 | 276,178 | 245,185 |
| Bobby calf hides | No. | 1,330,134 | 1,225,247 | 1,124,648 |
| Other calf hides | No. | 59,610 | 45,600 | 54,319 |
| Wool | lb | 47,657,387 | 52,897,378 | 61,741,664 |
| Boiling-down products – | ||||
| Tallow | cwt | 876,784 | 1,048,375 | 1,145,798 |
| Neatsfoot oil | gal | 111,375 | 115,808 | 137,346 |
| Manures | cwt | 642,571 | 712,564 | 740,545 |
| Livermeal | cwt | 19,177 | 40,996 | 29,838 |
| Meatmeal | cwt | 318,184 | 335,691 | 398,011 |
| Canned and other preserved meats, pastes, extracts, and miscellaneous cannings | cwt | 145,499 | 109,305 | 98,833 |
| Ham and Bacon Curing | ||||
| Number of establishments | 43 | 44 | 46 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 937 | 977 | 1,015 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 721,554 | 776,098 | 804,636 |
| Materials | £ | 4,989,140 | 5,352,739 | 5,576,083 |
| Other expenses | £ | 336,571 | 355,640 | 377,134 |
| Totals | £ | 6,047,265 | 6,484,477 | 6,757,853 |
| Value of output | £ | 6,419,083 | 6,906,964 | 7,179,087 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,429,943 | 1,554,225 | 1,603,004 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 162,194 | 154,421 | 182,071 |
| Pigs dealt with – | ||||
| Carcasses | No. | 400,214 | 407,338 | 431,487 |
| Cost | £ | 4,118,463 | 4,127,482 | 4,066,190 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Ham and bacon | cwt | 307,555 | 303,011 | 325,491 |
| Frozen pork | cwt | 32,027 | 28,179 | 32,583 |
| Small goods | cwt | 169,744 | 174,408 | 176,083 |
| Lard (edible) | cwt | 12,359 | 12,875 | 12,695 |
| Butter, Cheese, and Other Milk Products | ||||
| Number of establishments – | ||||
| Butter and cheese | No. | 285 | 277 | 252 |
| Other milk products | No. | 90 | 104 | 108 |
| Persons engaged | No. | 4,680 | 4,817 | 4,586 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 3,658,418 | 3,856,485 | 3,948,157 |
| Materials | £ | 81,891,312 | 83,920,452 | 77,215,886 |
| Other expenses | £ | 4,576,032 | 4,834,740 | 4,784,355 |
| Totals | £ | 90,125,762 | 92,611,677 | 85,948,398 |
| Value of output | £ | 90,526,811 | 93,502,318 | 86,350,591 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 8,635,499 | 9,581,866 | 9,134,705 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 885,167 | 842,112 | 810,606 |
| Butterfat used – | ||||
| For creamery butter | lb(000) | 367,231 | 397,689 | 403,660 |
| For cheesemaking | lb(000) | 83,924 | 85,670 | 79,423 |
| For whey butter making – | ||||
| Recoveries from own whey | lb(000) | 3,046 | 3,016 | 3,175 |
| Whey fat purchased | lb(000) | 2,450 | 2,461 | 1,996 |
| Second grade creamery butterfat | lb(000) | 153 | 127 | 91 |
| Total for whey butter | lb(000) | 5,649 | 5,604 | 5,262 |
| For other manufacturing or for separation for cream sales | lb(000) | 6,862 | 7,355 | 6,946 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Creamery butter | ton | 199,096 | 214,930 | 218,322 |
| Whey butter | ton | 3,055 | 3,025 | 2,861 |
| Cheese | ton | 94,141 | 96,483 | 85,264 |
| Condensed and powdered whole milk | ton | 15,290 | 13,466 | 13,824 |
| Skim-milk powder | ton | 51,184 | 46,214 | 40,551 |
| Buttermilk powder | ton | 13,418 | 15,870 | 16,529 |
| Casein | ton | 13,898 | 22,924 | 27,255 |
| Ice Cream | ||||
| Number of establishments | 43 | 43 | 41 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 543 | 525 | 538 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 340,340 | 352,958 | 364,369 |
| Materials | £ | 1,124,251 | 982,380 | 1,058,112 |
| Other expenses | £ | 371,300 | 399,271 | 386,869 |
| Totals | £ | 1,835,891 | 1,734,609 | 1,809,350 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,161,684 | 2,011,640 | 2,155,164 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,037,433 | 1,029,260 | 1,097,052 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 42,453 | 34,744 | 35,865 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Milk | gal | 569,643 | 505,589 | 571,477 |
| Cream | gal | 34,892 | 37,677 | 56,572 |
| Ice-cream mixture | cwt | 60,485 | 50,969 | 56,851 |
| Butter | lb | 1,286,544 | 1,250,480 | 1,400,896 |
| Skim-milk powder | lb | 1,607,536 | 1,529,024 | 1,488,368 |
| Sugar | cwt | 32,450 | 27,162 | 29,417 |
| Products – | ||||
| Bulk ice-cream | gal | 2,431,679 | 2,231,663 | 2,411,185 |
| Ice cream, cartoned, wrapped, chocolate-coated, etc. | gal | 1,805,831 | 1,896,894 | 2,073,540 |
| Iced lollies | gal | 565,359 | 472,882 | 562,665 |
| Grain Milling | ||||
| Number of establishments | 45 | 45 | 46 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 804 | 805 | 852 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 569,923 | 587,826 | 615,408 |
| Materials | £ | 3,284,160 | 3,380,470 | 3,499,390 |
| Other expenses | £ | 415,462 | 452,800 | 521,909 |
| Totals | £ | 4,269,545 | 4,421,096 | 4,636,707 |
| Value of output | £ | 4,539,234 | 4,680,780 | 4,915,661 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,255,074 | 1,300,310 | 1,416,271 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 100,505 | 97,890 | 107,063 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Wheat | bushel | 8,462,560 | 8,748,292 | 9,046,096 |
| Oats | bushel | 617,313 | 588,384 | 506,479 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Flour | short ton | 184,623 | 191,397 | 200,386 |
| Wholemeal, wheatmeal | short ton | 9,404 | 8,557 | 9,223 |
| Bran and pollard | short ton | 53,152 | 54,995 | 57,795 |
| Prepared cereals for human consumption – | ||||
| Oatmeal, rolled oats | short ton | 6,411 | 5,969 | 5,540 |
| Other (including cereals in biscuit and flake form)† | short ton | 6,408 | 7,187* | 7,825 |
| Biscuits | ||||
| Number of establishments | 10 | 9 | 9 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,294 | 1,223 | 1,202 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 730,139 | 761,489 | 776,509 |
| Materials | £ | 1,789,588 | 1,869,892 | 1,953,424 |
| Other expenses | £ | 555,580 | 529,132 | 509,676 |
| Totals | £ | 3,075,307 | 3,160,513 | 3,239,609 |
| Value of output | £ | 3,288,498 | 3,462,507 | 3,601,126 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,498,910 | 1,592,615 | 1,647,702 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 164,712 | 216,766 | 241,537 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Flour | short ton | 3,786 | 3,545 | 4,037 |
| Sugar | ton | 10,975 | 10,695 | 10,792 |
| Chocolate | cwt | 6,407 | 5,303 | 5,395 |
| Margarine, lard, confectionery fat | cwt | 51,388 | 53,645 | 56,765 |
| Biscuits manufactured | ton | 15,889 | 16,289 | 16,659 |
| Cocoa, Chocolate, and Sugar Confectionery | ||||
| Number of establishments | 46 | 42 | 41 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,821 | 1,811 | 1,779 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,000,802 | 1,050,032 | 1,069,907 |
| Materials | £ | 3,022,568 | 3,146,845 | 3,268,452 |
| Other expenses | £ | 555,698 | 630,576 | 610,269 |
| Totals | £ | 4,579,068 | 4,827,453 | 4,948,628 |
| Value of output | £ | 4,911,446 | 5,265,147 | 5,578,148 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,888,878 | 2,118,302 | 2,309,696 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 169,265 | 162,993 | 165,303 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Sugar | ton | 9,000 | 9,561 | 9,890 |
| Cocoa beans | cwt | 43,179 | 42,040 | 44,695 |
| Cocoa butter | cwt | 8,041 | 8,837 | 8,174 |
| Glucose | cwt | 61,349 | 63,634 | 63,854 |
| Confectionery manufactured – | ||||
| Chocolate and chocolate-coated | ton | 6,586 | 6,900 | 6,969 |
| Sugar | ton | 9,665 | 9,855 | 9,889 |
| Fruit and Vegetable Preserving | ||||
| Number of establishments | 38 | 38 | 37 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,864 | 2,024 | 2,281 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,183,889 | 1,390,815 | 1,585,204 |
| Materials | £ | 3,572,152 | 4,501,585 | 4,845,058 |
| Other expenses | £ | 701,965 | 963,741 | 1,127,617 |
| Totals | £ | 5,458,006 | 6,856,141 | 7,557,879 |
| Value of output | £ | 5,844,014 | 7,236,909 | 7,893,903 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 2,271,862 | 2,735,324 | 3,048,845 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 621,758 | 682,586 | 770,865 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Fruit | ton | 8,876 | 11,930 | 12,401 |
| Vegetables and tomatoes | ton | 27,285 | 34,130 | 40,103 |
| Sugar | ton | 3,677 | 4,873 | 5,218 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Canned fruit | cwt | 77,946 | 103,907 | 123,225 |
| Canned beans in sauce | cwt | 47,538 | 47,518 | 52,978 |
| Canned peas | cwt | 102,463 | 170,374 | 138,155 |
| Canned green beans | cwt | 24,703 | 36,125 | 32,106 |
| Other canned vegetables (not tomatoes) | cwt | 46,808 | 46,744 | 53,339 |
| Tomato soup | gal | 349,456 | 374,650 | 370,744 |
| Pickles and sauces* | gal | 544,384 | 651,585 | 696,741 |
| Jams, jellies, and conserves | cwt | 63,205 | 81,671 | 81,397 |
| Canned spaghetti in sauce | cwt | 51,580 | 58,411 | 59,544 |
| Canned tomatoes (whole and halves) | cwt | 13,229 | 11,729 | 16,806 |
| Quick-frozen vegetables – | ||||
| Peas | cwt | 111,948 | 140,012 | 126,387 |
| Beans | cwt | 23,252 | 23,716 | 34,846 |
| Other | cwt | 11,917 | 22,457 | 19,142 |
| Breweries | ||||
| Number of establishments | 26 | 25 | 24 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,335 | 1,359 | 1,245 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,178,746 | 1,185,759 | 1,147,508 |
| Materials | £ | 3,723,031 | 3,852,187 | 3,422,233 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,227,634 | 1,338,561 | 1,443,146 |
| Totals | £ | 6,129,411 | 6,376,507 | 6,012,887 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,074,865 | 7,550,935 | 7,454,652 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,351,834 | 3,698,748 | 4,032,419 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 450,671 | 433,553 | 399,261 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Malt | bushel | 1,420,913 | 1,468,288 | 1,325,492 |
| Hops | cwt | 6,852 | 7,062 | 6,648 |
| Sugar | cwt | 83,779 | 89,815 | 89,041 |
| Beer produced for sale | gal | 48,216,418 | 50,772,729 | 47,484,151 |
| Stout produced for sale | gal | 435,632 | 482,639 | 310,766 |
| Aerated Waters and Cordials | ||||
| Number of establishments | 72 | 71 | 68 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 666 | 707 | 706 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 441,329 | 484,978 | 503,231 |
| Materials | £ | 675,072 | 757,821 | 789,533 |
| Other expenses | £ | 284,622 | 346,128 | 382,771 |
| Totals | £ | 1,401,023 | 1,588,927 | 1,675,535 |
| Value of output | £ | 1,689,017 | 1,956,858 | 2,019,165 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,013,945 | 1,199,037 | 1,229,632 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 32,572 | 42,999 | 58,214 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Sugar | ton | 4,268 | 4,762 | 4,823 |
| Essential oils and essences | lb | 132,485 | 163,212 | 304,899 |
| Fruit extracts and juices | gal | 77,673 | 76,642 | 64,343 |
| Aerated waters made | gal | 6,601,000 | 7,121,693 | 7,039,908 |
| Cordials made† | gal | 411,343 | 417,922 | 409,000 |
| Tobacco, Cigars, and Cigarettes | ||||
| Number of establishments | 7 | 7 | 6 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,109 | 1,184 | 1,280 |
| Production costs– | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 643,374 | 736,006 | 801,250 |
| Materials | £ | 4,399,131 | 4,905,042 | 5,203,264 |
| Other expenses | £ | 458,164 | 505,072 | 597,417 |
| Totals | £ | 5,500,669 | 6,146,120 | 6,601,931 |
| Value of output | £ | 6,072,607 | 6,729,820 | 7,184,024 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,673,476 | 1,824,778 | 1,980,760 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 173,437 | 202,765 | 182,433 |
| Tobacco leaf used in manufacture | lb | 9,780,458 | 10,618,608 | 10,951,043 |
| Cigarettes made | million | 1,929 | 2,150 | 2,428 |
| Tobacco made | lb | 4,945,071 | 5,024,114 | 5,019,933 |
| Woollen Milling | ||||
| Number of establishments | 20 | 20 | 21 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,569 | 2,627 | 3,051 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,509,767 | 1,608,393 | 1,933,371 |
| Materials | £ | 2,260,791 | 2,654,523 | 3,086,786 |
| Other expenses | £ | 705,875 | 804,147 | 928,140 |
| Totals | £ | 4,476,433 | 5,067,063 | 5,948,297 |
| Value of output | £ | 4,489,867 | 5,365,748 | 6,338,188 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 2,229,076 | 2,711,225 | 3,251,402 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 194,370 | 258,789 | 388,056 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Wool fibres – | ||||
| Greasy and slipe wool | lb | 6,830,474 | 7,347,152 | 8,956,011 |
| Scoured wool | lb | 539,203 | 441,419 | 331,666 |
| Tops, noils | lb | 511,316 | 816,778 | 1,045,998 |
| Woollen and worsted yarn | lb | 114,243 | 114,180 | 207,871 |
| Non-wool fibres – | ||||
| Artificial and synthetic | lb | 232,505 | 568,107 | 441,217 |
| Other | lb | 1,458 | 2,802 | 12,090 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Woollen cloth | -yd, 54 in. | 838,785 | 1,002,728 | 1,286,663 |
| Worsted cloth | -yd, 54 in. | 921,291 | 1,050,381 | 1,320,436 |
| Flannel | -yd, 54 in. | 282,161 | 284,959 | 290,021 |
| Blankets | - pairs | 154,006 | 151,872 | 167,827 |
| Rugs | No. | 55,323 | 49,762 | 55,685 |
| Yarn produced for sale or transfer – | ||||
| Fingering | lb | 314,945 | 401,289 | 536,930 |
| Machine knitting | lb | 1,650,672 | 1,739,313 | 2,319,174 |
| Hosiery and Other Knitting Mills | ||||
| Number of establishments | 87 | 86 | 89 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 3,743 | 4,085 | 4,435 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,094,470 | 2,321,509 | 2,669,956 |
| Materials | £ | 3,763,000 | 4,464,757 | 5,245,746 |
| Other expenses | £ | 977,470 | 1,116,318 | 1,145,641 |
| Totals | £ | 6,834,940 | 7,902,584 | 9,061,343 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,242,653 | 8,513,054 | 9,862,261 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,479,653 | 4,048,297 | 4,616,515 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 131,070 | 179,940 | 213,582 |
| Clothing | ||||
| Number of establishments | 788 | 788 | 800 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 18,296 | 19,365 | 19,706 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 8,701,987 | 9,428,198 | 10,076,207 |
| Materials | £ | 16,760,956 | 18,229,442 | 19,601,199 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,992,364 | 2,233,724 | 2,453,246 |
| Totals | £ | 27,455,307 | 29,891,364 | 32,130,652 |
| Value of output | £ | 28,951,046 | 31,453,617 | 33,913,089 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 12,190,090 | 13,224,175 | 14,311,890 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 358,066 | 403,883 | 413,345 |
| Footwear | ||||
| Number of establishments | 121 | 121 | 128 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 4,645 | 4,773 | 4,937 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,719,720 | 2,916,577 | 3,251,827 |
| Materials | £ | 3,734,346 | 3,953,972 | 4,504,183 |
| Other expenses | £ | 710,082 | 796,485 | 901,085 |
| Totals | £ | 7,164,148 | 7,667,034 | 8,657,095 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,451,079 | 8,047,127 | 9,221,167 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,716,733 | 4,093,155 | 4,716,984 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 235,831 | 280,262 | 331,008 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Upper leather | sq. ft. | 8,476,725 | 8,865,564 | 9,281,731 |
| Sole leather | lb | 3,891,900 | 3,703,186 | 3,229,242 |
| Felt | sq. yd. | 134,650 | 128,910 | 87,711 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Men's and boys' boots and shoes | pair | 916,376 | 924,043 | 1,030,443 |
| Women's and girls' shoes | pair | 1,766,865 | 2,096,093 | 2,288,967 |
| Sandals (all kinds) | pair | 759,769 | 768,604 | 1,032,512 |
| Slippers, leather and felt, etc. | pair | 1,400,421 | 1,471,581 | 1,606,553 |
| Sawmills | ||||
| Number of establishments | 522 | 501 | 486 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 5,786 | 5,883 | 5,984 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 4,397,231 | 4,645,759 | 4,953,909 |
| Materials | £ | 7,505,898 | 7,900,340 | 8,604,097 |
| Other expenses | £ | 3,612,620 | 3,950,920 | 4,015,685 |
| Totals | £ | 15,515,749 | 16,497,019 | 17,573,691 |
| Value of output | £ | 16,421,665 | 17,739,724 | 18,895,492 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 8,915,767 | 9,839,384 | 10,291,395 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 440,059 | 592,621 | 614,704 |
| Rough-sawn timber produced | thousand ft b.m. | 584,710 | 593,628 | 632,584 |
| Planing Mills | ||||
| Number of establishments | 140 | 146 | 151 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,867 | 1,798 | 1,810 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,328,639 | 1,309,997 | 1,361,793 |
| Materials | £ | 5,193,320 | 5,479,422 | 5,733,567 |
| Other expenses | £ | 640,904 | 654,012 | 681,309 |
| Totals | £ | 7,162,863 | 7,443,431 | 7,776,669 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,817,040 | 8,101,597 | 8,368,218 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 2,623,720 | 2,622,175 | 2,634,651 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 220,677 | 202,936 | 192,203 |
| Rough-sawn timber used in manufacture | thousand ft b.m. | 116,726 | 115,161 | 124,033 |
| Dressed timber produced – | ||||
| Floorboards | thousand ft b.m. | 33,380 | 31,283 | 28,779 |
| Weatherboards | -thousand ft b.m. | 21,778 | 20,571 | 24,126 |
| Other | thousand ft b.m. | 42,544 | 49,026 | 50,124 |
| Joinery work done | £ | 1,157,127 | 1,236,371 | 1,273,407 |
| Joinery | ||||
| Number of establishments | 353 | 360 | 377 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 3,239 | 3,237 | 3,404 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,424,933 | 2,539,471 | 2,729,053 |
| Materials | £ | 4,025,555 | 4,142,909 | 4,836,667 |
| Other expenses | £ | 650,883 | 674,134 | 750,340 |
| Totals | £ | 7,101,371 | 7,356,514 | 8,316,060 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,852,250 | 8,144,729 | 9,160,852 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,826,695 | 4,001,820 | 4,324,185 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 438,399 | 444,915 | 441,675 |
| Timber used in manufacture | thousand ft b.m. | 57,927 | 55,636 | 62,243 |
| Dressed timber produced – | ||||
| Floorboards | thousand ft b.m. | 3,210 | 3,611 | 3,845 |
| Weatherboards | thousand ft b.m. | 1,927 | 1,685 | 2,370 |
| Other | thousand ft b.m. | 3,835 | 4,097 | 4,027 |
| Joinery and other woodwork | £ | 7,350,120 | 7,597,879 | 8,513,109 |
| Furniture | ||||
| Number of establishments | 463 | 461 | 452 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 4,143 | 4,286 | 4,196 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,786,837 | 3,087,352 | 3,127,028 |
| Materials | £ | 3,604,653 | 4,319,073 | 4,442,488 |
| Other expenses | £ | 605,107 | 670,296 | 729,245 |
| Totals | £ | 6,996,597 | 8,076,721 | 8,298,761 |
| Value of output | £ | 7,526,092 | 8,762,081 | 8,923,773 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,921,439 | 4,443,008 | 4,481,285 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 324,853 | 413,813 | 419,514 |
| Pulp, Paper, and Paperboard | ||||
| Number of establishments | 6 | 6 | 7 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,994 | 2,077 | 2,091 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,879,102 | 2,233,653 | 2,205,435 |
| Materials | £ | 3,987,873 | 4,572,751 | 4,911.884 |
| Other expenses | £ | 6,441,753 | 6,989,108 | 6,998,486 |
| Totals | £ | 12,308,728 | 13,795,512 | 14,115,805 |
| Value of output | £ | 12,397,557 | 15,378,084 | 16,004,814 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 8,409,684 | 10,805,333 | 11,092,930 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 283,788 | 399,953 | 406,788 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Newsprint | ton | 60,339 | 74,711 | 72,567 |
| Other paper | ton | 30,927 | 38,872 | 43,857 |
| Paperboard | ton | 25,808 | 30,918 | 33,244 |
| Fibreboard | sq. yd. (000) | 7,352 | 7,536 | 7,802 |
| Wood pulp for sale | ton | 69,095 | 79,846 | 83,894 |
| Cardboard Boxes, Cartons, and Paper Bags | ||||
| Number of establishments | 46 | 51 | 51 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,532 | 1,638 | 1,908 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 940,617 | 1,086,920 | 1,334,317 |
| Materials | £ | 3,722,223 | 4,537,613 | 5,480,867 |
| Other expenses | £ | 513,267 | 603,510 | 662,759 |
| Totals | £ | 5,176,107 | 6,228,043 | 7,477,943 |
| Value of output | £ | 5,721,842 | 6,813,021 | 8,148,291 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,999,619 | 2,275,408 | 2,667,424 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 155,795 | 195,915 | 330,881 |
| Paper used in manufacture | ton | 7,667 | 8,786 | 9,512 |
| Cardboard used in manufacture | ton | 27,222 | 34,619 | 41,046 |
| Cardboard boxes, cartons, made | £ | 4,231,559 | 4,985,793 | 6,150,244 |
| Paper bags, made | £ | 1,159,280 | 1,326,227 | 1,409,399 |
| Printing and Publishing | ||||
| Number of establishments | 96 | 95 | 95 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 4,950 | 5,146 | 5,270 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 3,855,581 | 4,160,985 | 4,392,317 |
| Materials | £ | 4,215,573 | 4,492,229 | 4,639,087 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,968,111 | 2,123,645 | 2,251,832 |
| Totals | £ | 10,039,265 | 10,776,859 | 11,283,236 |
| Value of output | £ | 12,034,518 | 13,139,349 | 13,491,795 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 7,818,945 | 8,647,120 | 8,852,708 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 277,112 | 308,848 | 354,734 |
| Newsprint used | ton | 48,991 | 50,882 | 51,609 |
| Other paper used | ton | 3,147 | 3,048 | 3,273 |
| Job and General Printing | ||||
| Number of establishments | 269 | 275 | 276 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 4,340 | 4,518 | 4,664 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 3,010,954 | 3,353,235 | 3,509,646 |
| Materials | £ | 3,223,898 | 3,536,278 | 3,776,437 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,138,859 | 1,291,676 | 1,389,887 |
| Totals | £ | 7,373,711 | 8,181,189 | 8,675,970 |
| Value of output | £ | 8,198,919 | 9,026,686 | 9,649,865 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 4,975,021 | 5,490,408 | 5,873,428 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 392,231 | 464,623 | 487,311 |
| Newsprint used | ton | 735 | 940 | 1,076 |
| Other paper used | ton | 12,051 | 12,555 | 13,666 |
| Cardboard used | ton | 3,649 | 4,093 | 3,745 |
| Tanning | ||||
| Number of establishments | 14 | 12 | 12 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 666 | 651 | 689 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 497,129 | 496,201 | 559,567 |
| Materials | £ | 1,361,818 | 1,317,379 | 1,602,837 |
| Other expenses | £ | 194,933 | 204,911 | 212,543 |
| Totals | £ | 2,053,880 | 2,018,491 | 2,374,947 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,115,717 | 2,123,601 | 2,495,180 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 753,899 | 806,222 | 892,343 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 86,624 | 86,053 | 113,038 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Cattle hides | No. | 278,044 | 289,924 | 273,009 |
| Yearling and calf hides | No. | 96,539 | 96,062 | 240,259 |
| Pelts | No. | 354,933 | 219,587 | 432,240 |
| Sheepskins | No. | 28,600 | 35,059 | 33,500 |
| Crust-tanned skins | No. | 236,581 | 254,773 | 333,352 |
| Goat skins | No. | 143,751 | ||
| Principal products – | ||||
| Leather – | ||||
| Hides – | ||||
| Bends | lb | 2,191,468 | 2,047,361 | 1,884,288 |
| Shoulders | lb | 1,189,082 | 1,002,361 | 964,772 |
| Bellies | lb | 1,324,960 | 1,079,094 | 970,071 |
| Chrome and other sides | sq.ft. | 6,507,082 | 7,194,752 | 7,324,308 |
| Yearling | sq. ft. | 730,635 | 833,628 | 1,933,280 |
| Calf | Sq. ft. | 466,737 | 459,357 | |
| Sheep – | ||||
| Basils | sq. ft. | 119,099 | 116,207 | 85,409 |
| Roans | sq.ft. | 726,477 | 564,770 | 771,640 |
| Chamois | doz | 20,642 | 6,949 | 9,010 |
| Woolly skins | sq. ft. | 166,349 | 158,230 | 200,185 |
| Persians | sq.ft. | 939,121 | 856,600 | 1,192,741 |
| Goat skins | sq. ft. | 337,999 | 544,212 | 639,553 |
| Rubberware | ||||
| Number of establishments | 27 | 26 | 28 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,268 | 2,227 | 2,339 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,969,769 | 2,089,420 | 2,177,661 |
| Materials | £ | 4,623,193 | 4,463,530 | 4,532,480 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,192,040 | 1,260,451 | 1,374,275 |
| Totals | £ | 7,785,002 | 7,813,401 | 8,084,416 |
| Value of output | £ | 8,682,632 | 8,874,484 | 9,373,229 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 4,059,439 | 4,410,954 | 4,840,749 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 356,275 | 355,262 | 321,516 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Natural rubber | lb(000) | 13,696 | 11,982 | 12,309 |
| Synthetic rubber | lb(000) | 2,266 | 4,126 | 4,719 |
| Latex | gal | 305,269 | 432,712 | 355,548 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Motor tyres | No. | 622,306 | 692,022 | 662,293 |
| Motor tubes | No. | 390,165 | 349,885 | 451,571 |
| Camelback | lb | 3,571,953 | 3,819,721 | 4,490,296 |
| Milking rubberware | £ | 1,013,131 | 1,138,370 | 1,213,102 |
| Bicycle tyres and tubes | ||||
| Battery containers | ||||
| Rubber and canvas footwear | ||||
| Chemical Fertilisers | ||||
| Number of establishments | 9 | 9 | 11 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,248 | 1,231 | 1,240 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,064,854 | 1,078,002 | 1,071,144 |
| Materials | £ | 7,254,659 | 7,244,359 | 6,184,938 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,021,035 | 1,138,551 | 1,421,013 |
| Totals | £ | 9,340,548 | 9,460,912 | 8,677,095 |
| Value of output | £ | 10,031,804 | 10,108,457 | 9,051,620 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 2,777,145 | 2,864,098 | 2,866,682 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 434,397 | 410,749 | 338,933 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Rock phosphate | ton | 549,633 | 507,841 | 455,163 |
| Serpentine rock | ton | 81,670 | 98,312 | 89,319 |
| Sulphur | ton | 103,775 | 98,973 | 91,468 |
| Carbonate of lime | ton | 16,852 | 11,319 | 12,586 |
| Nitrate of soda | ton | 4,411 | 3,888 | 2,915 |
| Potash | ton | 22,110 | 27,899 | 31,773 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Serpentine superphosphate and mixtures | ton | 302,983 | 370,598* | 231,122 |
| Basic and reverted superphosphate and mixtures | ton | 49,274 | 36,536 | 30,763 |
| Straight super and mixtures | ton | 662,697 | 568,833* | 466,184 |
| Aerial super and mixtures | ton | 147,175 | ||
| Other (including ground rock) | ton | 6,280 | ||
| Superphosphate content of above | ton | 898,645 | 843,139 | 767,197 |
| Soap and Candle Manufacture | ||||
| Number of establishments | 14 | 14 | 14 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 472 | 474 | 467 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 354,244 | 369,966 | 375,712 |
| Materials | £ | 1,362,654 | 1,444,148 | 1,589,054 |
| Other expenses | £ | 324,433 | 341,786 | 366,398 |
| Totals | £ | 2,041,331 | 2,155,900 | 2,331,164 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,313,303 | 2,453,054 | 2,761,300 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 950,649 | 1,008,906 | 1,172,246 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 57,590 | 51,292 | 64,105 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| Tallow | ton | 10,089 | 10,491 | 11,468 |
| Other oils | ton | 989 | 1,055 | 1,137 |
| Caustic soda | ton | 1,659 | 1,725 | 2,021 |
| Soda ash | ton | 2,300 | 2,730 | 2,973 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Soap – | ||||
| Toilet | ton | 3,314 | 2,880 | 3,297 |
| Bar | ton | 4,788 | 5,180 | 5,065 |
| Powder and flakes | ton | 10,040 | 10,990 | 12,689 |
| Candles | ton | 427 | 165* | 284 |
| Sandsoap | ton | 526 | 572 | 466 |
| Paint and Varnish | ||||
| Number of establishments | 27 | 27 | 28 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 829 | 885 | 916 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 622,803 | 688,535 | 768,396 |
| Materials | £ | 3,593,031 | 3,799,025 | 3,957,092 |
| Other expenses | £ | 456,006 | 453,431 | 486,896 |
| Totals | £ | 4,671,840 | 4,940,991 | 5,212,384 |
| Value of output | £ | 5,147,027 | 5,398,311 | 5,847,606 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,553,996 | 1,599,286 | 1,890,514 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 126,351 | 118,993 | 122,618 |
| Main materials used – | ||||
| White lead | cwt | 20,268 | 20,873 | 18,213 |
| Other pigments and extenders | cwt | 179,036 | 184,914 | 192,542 |
| Linseed oil | gal | 480,196 | 493,591 | 503,955 |
| Solvents | gal | 1,583,913 | 1,561,441 | 1,673,690 |
| Gums and resins | cwt | 67,980 | 71,883 | 73,514 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Ready mixed paints | gal(000) | 1,969 | 2,041 | 2,153 |
| Varnishes (for sale) | gal(000) | 110 | 140 | 133 |
| Enamels, lacquers | gal(000) | 854 | 933 | 956 |
| Pharmaceuticals, Toilet Goods, and Cosmetics* | ||||
| Number of establishments | 42 | 41 | 40 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 733 | 729 | 782 |
| Production costs– | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 426,396 | 434,219 | 478,754 |
| Materials | £ | 1,609,433 | 1,741,134 | 1,952,597 |
| Other expenses | £ | 241,827 | 264,060 | 236,734 |
| Totals | £ | 2,277,656 | 2,439,413 | 2,668,085 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,776,361 | 3,014,375 | 3,193,923 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,166,928 | 1,273,241 | 1,241,326 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 18,799 | 22,683 | 22,438 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Pharmaceutical products | £ | 1,354,973 | 1,520,097 | 1,671,243 |
| Toilet preparations and cosmetics – | ||||
| Dentifrices | £ | 305,616 | 353,152 | 359,015 |
| Cosmetic creams and lotions | £ | 153,870 | 152,698 | 162,059 |
| Hair dressings | £ | 374,871 | 398,405 | 419,863 |
| Powder, face and talcum | £ | 191,882 | 192,085 | 200,399 |
| Lipstick | £ | 64,724 | 65,565 | 86,938 |
| Structural Clay Products | ||||
| Number of establishments | 48 | 48 | 48 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,005 | 1,028 | 1,035 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 784,987 | 816,461 | 866,570 |
| Materials | £ | 167,005 | 158,973 | 184,812 |
| Other expenses | £ | 757,008 | 823,269 | 899,504 |
| Totals | £ | 1,709,000 | 1,798,703 | 1,950,886 |
| Value of output | £ | 1,867,920 | 2,033,242 | 2,166,847 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,700,915 | 1,874,269 | 1,982,035 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 248,972 | 231,182 | 242,749 |
| Clay used– | ||||
| Purchased | ton | 21,034 | 13,444 | 17,439 |
| From own quarry | ton | 235,695 | 288,137 | 319,086 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Firebricks | No. | 2,458,758* | 3,029,135* | 3,205,117 |
| Building bricks | No. | 43,834,661 | 49,294,429 | 52,176,885 |
| Roofing tiles | No. | 1,766,000 | 1,047,900 | 1,195,000 |
| Salt-glazed pipes – | ||||
| Above 6 in. | No. | 11,472 | 14,839 | 9,475 |
| 6 in. and below | No. | 2,394,964 | 2,352,371 | 2,280,910 |
| Pottery, China, and Earthenware | ||||
| Number of establishments | 6 | 6 | 7 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 389 | 455 | 607 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 239,616 | 296,379 | 385,868 |
| Materials | £ | 99,931 | 114,781 | 136,175 |
| Other expenses | £ | 174,730 | 208,234 | 248,887 |
| Totals | £ | 514,277 | 619,394 | 770,930 |
| Value of output | £ | 556,165 | 665,363 | 835,513 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 456,234 | 550,582 | 699,338 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 39,739 | 66,106 | 71,241 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Insulators and refractory insulator elements | £ | 184,893 | 224,836 | 255,584 |
| Crockery, artware and novelties, stoneware | £ | 245,254 | 250,516 | 374,759 |
| Other earthenware including sanitaryware | £ | 123,104 | 148,761 | 154,486 |
| Cement | ||||
| Number of establishments | 3 | 5 | 6 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 589 | 704 | 734 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 526,608 | 679,584 | 697,717 |
| Materials | £ | 955,679 | 1,150,967 | 1,061,987 |
| Other expenses | £ | 1,923,695 | 2,377,399 | 2,375,211 |
| Totals | £ | 3,405,982 | 4,207,950 | 4,134,915 |
| Value of output | £ | 4,311,129 | 5,170,912 | 5,022,561 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,355,450 | 4,019,945 | 3,960,574 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 299,054 | 419,421 | 298,933 |
| Principal materials – | ||||
| Limestone | ton | 324,541 | 375,663 | 377,677 |
| Clay, marl, cement rock | ton | 554,577 | 666,994 | 679,606 |
| Gypsum | ton | 14,958 | 19,215 | 20,444 |
| Cement made | ton | 472,090 | 543,967 | 542,110 |
| Concrete Products | ||||
| Number of establishments | 290 | 288 | 272 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,062 | 2,183 | 2,127 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 1,588,133 | 1,715,801 | 1,725,351 |
| Materials | £ | 2,566,772 | 2,840,229 | 2,723,816 |
| Other expenses | £ | 673,688 | 775,527 | 821,885 |
| Totals | £ | 4,828,593 | 5,331,557 | 5,271,052 |
| Value of output | £ | 5,579,358 | 6,190,291 | 6,074,571 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 3,012,586 | 3,350,062 | 3,350,755 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 347,635 | 306,955 | 356,574 |
| Materials used – | ||||
| Portland cement | ton | 77,203 | 83,932 | 83,389 |
| Sand, shingle | yd | 327,300 | 355,591 | 379,486 |
| Reinforcing | ton | 11,196 | 12,703 | 10,850 |
| Pumice | yd | 29,682 | 30,611 | 28,794 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Roofing tiles | No. | 10,235,718 | 9,546,265 | 9,354,999 |
| Fencing posts | No. | 2,973,699 | 3,201,563 | 2,528,092 |
| Housing bricks and blocks | No. | 6,177,850 | 7,289,467 | 8,923,984 |
| Coppers, boilers | No. | 7,229 | 5,812 | 3,697 |
| Pipes | ton | 92,100 | 106,916* | 112,011 |
| Plywood and Veneer | ||||
| Number of establishments | 9 | 8 | 8 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 570 | 538 | 567 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 429,763 | 427,475 | 471,483 |
| Materials | £ | 660,600 | 704,244 | 850,325 |
| Other expenses | £ | 244,708 | 270,332 | 324,218 |
| Totals | £ | 1,335,071 | 1,402,051 | 1,646,026 |
| Value of output | £ | 1,469,987 | 1,566,611 | 1,881,969 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 809,387 | 862,367 | 1,031,644 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 60,420 | 47,997 | 59,327 |
| Species of logs used – | ||||
| Rimu | ft (H. Dahl) | 8,337,891 | 9,318,884 | 9,175,634 |
| Matai | ft (H. Dahl) | 905,347 | 932,818 | 897,612 |
| Kahikatea | ft (H. Dahl) | 1,541,750 | 1,142,206 | 1,098,657 |
| Radiata pine | ft (H. Dahl) | 4,598,195 | 4,498,732 | 4,817,690 |
| Other | ft (H. Dahl) | 839,336 | 571,400 | 1,032,037 |
| Plywood made (3/16 in. basis) | sq. ft. | 37,830,760 | 38,769,091 | 39,960,414 |
| Range Making* | ||||
| Number of establishments | 7 | 7 | 7 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 900 | 912 | 1,048 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 617,799 | 639,975 | 760,503 |
| Materials | £ | 729,951 | 891,117 | 1,053,087 |
| Other expenses | £ | 237,439 | 239,179 | 280,070 |
| Totals | £ | 1,585,189 | 1,770,271 | 2,093,660 |
| Value of output | £ | 1,592,608 | 1,904,411 | 2,265,974 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 862,657 | 1,013,294 | 1,212,887 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 103,681 | 107,629 | 111,867 |
| Iron and steel used | ton | 3,994 | 4,366 | 5,120 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Domestic electric ranges | No. | 26,028 | 29,130 | 34,806 |
| Domestic electric rangettes | No. | 4,058 | 4,379 | 4,286 |
| Domestic coal ranges | No. | 3,240 | 3,624 | 667 |
| Radio Assembly and Manufacture* | ||||
| Number of establishments | 19 | 22 | 22 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 905 | 1,032 | 1,132 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 576,035 | 677,291 | 767,639 |
| Materials | £ | 1,726,973 | 2,136,804 | 2,718,239 |
| Other expenses | £ | 200,972 | 224,399 | 258,402 |
| Totals | £ | 2,503,980 | 3,038,494 | 3,744,280 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,680,382 | 3,248,622 | 3,946,443 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 953,409 | 1,111,818 | 1,228,204 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 57,736 | 97,861 | 92,657 |
| Principal products – | ||||
| Radios – | ||||
| Car | No. | 20,417 | 21,256 | 20,428 |
| Portable | No. | 9,184 | 10,922 | 22,760 |
| Table | No. | 42,347 | 41,662 | 49,617 |
| Console | No. | 381 | 174 | - |
| Radiograms – | ||||
| Portable | No. | 6,138 | 3,855 | 1,1680 |
| Table | No. | 1,152 | ||
| Console | No. | 19,209 | 28,435 | 27,000 |
| Recorder-gram | No. | 4,625 | ||
| Motor-vehicle Assembly | ||||
| Number of establishments | 12 | 13 | 13 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,921 | 3,206 | 2,503 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,548,917 | 2,910,580 | 2,279,848 |
| Materials | £ | 20,237,439 | 22,607,065 | 18,615,437 |
| Other expenses | £ | 928,094 | 1,018,097 | 938,143 |
| Totals | £ | 23,714,450 | 26,535,742 | 21,833,428 |
| Value of output | £ | 25,942,076 | 28,975,263 | 23,892,233 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 5,704,637 | 6,368,198 | 5,276,796 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 18,983 | 729,162 | 427,839 |
| Vehicles assembled – | ||||
| Cars | No. | 32,117 | 36,168 | 26,103 |
| Buses | No. | 119 | 117 | 152 |
| Vans | No. | 1,325 | 1,380 | 2,557 |
| Trucks | No. | 5,967 | 5,291† | 5,493 |
| Motor-body Building | ||||
| Number of establishments | 81 | 74 | 77 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,190 | 1,163 | 1,163 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 881,026 | 869,685 | 880,022 |
| Materials | £ | 970,172 | 941,974 | 1,017,084 |
| Other expenses | £ | 224,644 | 227,740 | 228,078 |
| Totals | £ | 2,075,842 | 2,039,399 | 2,125,184 |
| Value of output | £ | 2,319,844 | 2,204,795 | 2,284,458 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,349,672 | 1,262,821 | 1,267,374 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 122,025 | 101,766 | 120,401 |
| Main materials – | ||||
| Timber | ft. b.m. | 1,349,253 | 1,275,031 | 1,062,631 |
| Plywood | sq. ft. | 315,376 | 346,651 | 324,860 |
| Paints and oils | gal | 27,577 | 27,974 | 26,167 |
| Motor bodies built – | ||||
| Buses | No. | 197 | 185 | 162 |
| Vans | No. | 436 | 213 | 265 |
| Trucks – | ||||
| Cabs | No. | 533 | 511 | 390 |
| Trays | No. | 1,227 | 1,038 | 721 |
| Motor Repairs | ||||
| Number of establishments | 1,695 | 1,755 | 1,808 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 13,712 | 14,344 | 14,931 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 9,319,577 | 10,076,107 | 10,609,487 |
| Materials | £ | 11,904,270 | 12,683,687 | 14,404,181 |
| Other expenses | £ | 2,934,587 | 3,293,627 | 3,604,457 |
| Totals | £ | 24,158,434 | 26,053,421 | 28,618,125 |
| Value of output | £ | 26,054,742 | 28,251,684 | 30,754,803 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 14,150,472 | 15,567,997 | 16,350,622 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 729,456 | 749,025 | 725,477 |
| Sheet-metal Working | ||||
| Number of establishments | 164 | 155 | 151 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 3,462 | 3,531 | 3,733 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 2,642,223 | 2,817,097 | 3,052,108 |
| Materials | £ | 4,759,571 | 5,371,622 | 6,018,192 |
| Other expenses | £ | 998,350 | 1,144,567 | 1,214,308 |
| Totals | £ | 8,400,144 | 9,333,286 | 10,284,608 |
| Value of output | £ | 9,373,985 | 10,276,053 | 11,364,968 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 4,614,414 | 4,904,431 | 5,346,776 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 633,488 | 612,266 | 594,639 |
| Metal Products n.e.i. | ||||
| Number of establishments | 153 | 152 | 168 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 3,135 | 3,382 | 3,545 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries and wages | £ | 2,478,310 | 2,751,830 | 3,026,087 |
| Materials | £ | 4,378,525 | 5,080,178 | 5,439,716 |
| Other expenses | £ | 979,686 | 1,043,583 | 1,077,141 |
| Totals | £ | 7,836,521 | 8,875,591 | 9,542,944 |
| Value of output | £ | 8,703,828 | 9,878,367 | 10,704,567 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 4,325,303 | 4,798,189 | 5,264,851 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 542,487 | 566,401 | 669,600 |
| Agricultural and Pastoral Machinery | ||||
| Number of establishments | 89 | 86 | 73 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,131 | 1,038 | 868 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 797,281 | 763,508 | 655,682 |
| Materials | £ | 3,855,268 | 4,322,155 | 2,208,332 |
| Other expenses | £ | 242,315 | 272,779 | 226,824 |
| Totals | £ | 4,894,864 | 5,358,442 | 3,090,838 |
| Value of output | £ | 5,253,816 | 5,739,297 | 3,271,820 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 1,398,548 | 1,417,142 | 1,063,488 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 95,176 | 85,296 | 71,572 |
| Machinery n.e.i. | ||||
| Number of establishments | 408 | 419 | 422 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 7,602 | 7,925 | 8,546 |
| Production costs – | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 5,963,032 | 6,444,211 | 7,173,381 |
| Materials | £ | 11,113,023 | 11,741,060 | 11,878,917 |
| Other expenses | £ | 2,137,475 | 2,390,064 | 2,583,223 |
| Totals | £ | 19,213,530 | 20,575,335 | 21,635,521 |
| Value of output | £ | 20,848,431 | 22,439,682 | 23,387,296 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 9,735,408 | 10,698,622 | 11,508,379 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 1,064,061 | 1,250,213 | 1,376,317 |
INTRODUCTORY – An interesting feature of building and housing construction activity in New Zealand is the absence of a marked seasonal decline in the winter months, since winters are not sufficiently severe, except in a few districts, to interfere materially with the building of houses and flats or other construction work.
The increasing housing needs of a growing population have been reflected in a steady long-term increase in the building of houses and flats. The increase in trade and industry, with the resultant growth of the towns, has been accompanied by extensive construction of factories, shops, offices, warehouses, etc. The diversification of factory industries in recent years has involved extensive building operations while modernisation of factory equipment and of shop and office accommodation has been responsible for a further appreciable proportion of building activity.
Private building suffered severely during the depression, but later revived substantially to reach its pre-war peak in 1938–39. The cumulative effect of the war may be gauged from the record low level of building permits for urban districts in 1942–43, their value being £2.7 million, compared with the 1938–39 figure of £12.1 million. Thereafter, with the completion of the major portion of defence programmes, a distinct revival of civil building took place, the improvement being progressively maintained despite the hampering effects of shortages of skilled labour and many essential building materials. By 1944–45 the annual value had exceeded the highest pre-war figure, although it would appear that much of the increase over earlier years was a reflection of higher costs. If the number of permits for new houses and flats can be safely used as a guide, then by the 1946–47 year, building activity both in volume and value had by far exceeded pre-war figures. Since then building activity continued at higher levels in each successive year until 1954–55, since when there were two slight annual decreases, until 1957–58 when a large increase was recorded. A small increase was recorded in 1958–59 with a substantial increase in 1959–60.
The total value of permits for New Zealand in 1959–60 was £114.0 million, which is an increase of £12.51 million on the 1958–59 year.
Building controls introduced as wartime emergency regulations to conserve materials and manpower were finally removed in December 1956. It is significant that 1957–58, which was the first full financial year after the complete removal of building controls, should see a record level reached in the value of building permits, this level being almost maintained in 1958–59, and exceeded very substantially in 1959–60.
Statistics of the Nature of Building Activity – The results of a collection of building statistics taken in 1952 were given on pages 609–613 of the 1954 issue of the Yearbook which showed, largely in tabular form, the operations of persons and establishments regularly engaged in the building trade and the types of construction; a statement summarising the activities of owner-builders was given separately.
Trends in Average Costs of Some Representative Lines – The following table is of interest in that it illustrates trends in the cost of representative lines of building activity over a period with general characteristics of rising costs.
| Cost in Year Stated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | 1945 | End of 1950 | End of 1955 | End of 1960 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| State rental house (976 square feet) | 1,061 | 1,479 | 2,172 | 2,582 | 2,764 |
| Buildings (reinforced concrete): For similar size and type | 10,000 | 15,700 | 25,100 | 28,800 | 32,100 |
Building Materials – Most materials are manufactured in New Zealand with current production meeting demand. With the reintroduction of import licensing in 1958 supplies of imported materials were restricted but building operations have been only mildly hampered.
The expansion in the quantity and range of materials and fittings manufactured in New Zealand is still continuing.
The following materials called for special comment at the end of 1960:
Portland Cement – Adequate supplies of cement were available to all areas from domestic production. Four manufacturers were producing an early strength rapid-hardening Portland cement, which offers advantages in speeding up construction work.
Bricks – Overall supplies were adequate, though local shortages of particular types still persisted. The industry was manufacturing a wider variety of shapes and sizes than formerly.
Ceramic Tiles – Domestic production was limited in range, and ceased for several months because of fire damage to the manufacturing plant. Substantial imports were necessary for 1960 to ensure adequate supplies, and will also be required in 1961.
Sanitary Earthenware – Imports during 1960 were on a higher level than in 1959 to meet the increased building activity during the year. Domestic manufacture could meet only a portion of the demand. Heavy fireclay ware is no longer manufactured in New Zealand.
Plaster of Paris – A second factory will commence production in 1961 at Christchurch. Production from this factory will reduce the dependence on imported supplies to supplement domestic production. The other factory is in Auckland.
Plaster Coreboard – A new factory is to commence production in Christchurch during 1961. Plaster coreboard will now be produced in three factories, situated at Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch.
Vinyl Tiles – A new factory which had recently begun production of these tiles in Auckland was expected to meet a large part of the demand for this type of flooring.
Timber – While the production of timber was increasing, imports were necessary for some purposes for which New Zealand timbers were not suitable, or were not in sufficient supply, e.g., hardwoods and joinery, weatherboard, and furniture timbers.
Plywood – Although production had increased, demand remained high and it was necessary to import specialty plywoods, e.g., for the manufacture of radio cabinets. Peeler logs were being imported to supplement the range and quantity available from New Zealand forests.
Veneers – Most veneers produced in New Zealand were being used in plywood manufacture. Domestic supplies of veneers marketed as such were being supplemented by imports of fancy grades.
Steel, Including Galvanised Corrugated Iron – Deliveries from overseas had been irregular and there were local shortages of some types from time to time. Alternative roofing materials had been freely available.
Availability of Principal Building Materials – The following tables show the availability of the principal building materials in the years quoted.
The first of the two tables relates to the production of principal building materials.
PRODUCTION OF PRINCIPAL BUILDING MATERIALS
| Year Ended 31 March | Rough-sawn Timber | Dressed Timber (from Rough-sawn) | Building Sheet* | Plywood | Wall-board† | Paints, etc. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paints | Varnishes | Enamels, Lacquers | ||||||
* Asbestos-cement and cement sheet. † Includes fibrous plasterboard. | ||||||||
| ft. b.m. (million) | sq. ft. (million) | gal (thousand) | ||||||
| 1950 | 478.4 | 76.2 | 18.6 | 26.0 | 85.5 | 1,048 | 182 | 586 |
| 1951 | 527.6 | 92.2 | 23.2 | 31.1 | 88.7 | 1,208 | 179 | 688 |
| 1952 | 575.2 | 112.6 | 23.8 | 32.9 | 102.5 | 1,203 | 174 | 807 |
| 1953 | 573.0 | 104.5 | 25.0 | 30.8 | 106.1 | 1,093 | 151 | 800 |
| 1954 | 572.2 | 113.7 | 26.5 | 30.9 | 121.8 | 1,316 | 162 | 861 |
| 1955 | 616.0 | 119.4 | 31.2 | 32.7 | 124.5 | 1,620 | 132 | 990 |
| 1956 | 625.8 | 121.1 | 28.4 | 35.7 | 132.0 | 1,677 | 115 | 1,098 |
| 1957 | 596.9 | 110.1 | 26.2 | 37.8 | 125.1 | 1,969 | 110 | 854 |
| 1958 | 596.8 | 105.7 | 28.1 | 38.8 | 125.5 | 2,041 | 140 | 933 |
| 1959 | 636.8 | 119.3 | 28.7 | 40.0 | 141.2 | 2,153 | 128 | 956 |
| 1960 | 693.8 | 128.4 | 31.6 | 43.1 | 153.1 | 2,244 | 118 | 1,045 |
| Year Ended 31 March | Roofing Tiles | Bricks and Blocks | Drainpipes, Salt Glazed, 6 in. and Below | Cement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Concrete | Building Bricks, Clay | Concrete | ||||
| Bricks | Blocks | ||||||
| No. (million) | tons (000) | ||||||
| 1950 | 4.3 | 15.1 | 34.3 | .. | .. | .. | 245.6 |
| 1951 | 3.5 | 14.9 | 38.1 | .. | .. | .. | 204.4 |
| 1952 | 2.6 | 14.9 | 37.2 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.83 | 238.6 |
| 1953 | 2.8 | 16.4 | 40.6 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 1.87 | 274.6 |
| 1954 | 2.7 | 13.3 | 41.6 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 2.05 | 288.2 |
| 1955 | 2.4 | 13.6 | 48.0 | 0.4 | 4.0 | 2.20 | 361.8 |
| 1956 | 2.2 | 12.4 | 48.1 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 2.37 | 422.7 |
| 1957 | 1.8 | 10.2 | 43.8 | 0.5 | 5.7 | 2.39 | 472.1 |
| 1958 | 1.0 | 9.5 | 49.3 | 0.6 | 6.7 | 2.35 | 544.0 |
| 1959 | 1.2 | 9.4 | 52.2 | 0.6 | 8.4 | 2.28 | 542.1 |
| 1960 | - | 11.4 | 50.9 | 0.5 | 10.1 | 2.76 | 575.4 |
To complete the review, the second table deals with imports of these materials.
IMPORTS OF PRINCIPAL BUILDING MATERIALS
| Year Ended 31 December | Timber, Sawn | Building Sheet* | Plywood | Wallboard | Linseed Oil | Common Window Glass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Asbestos-cement and cement sheet. | ||||||
| ft (b.m.) (million) | sq. ft. (000) | sq. ft. (000) | sq. ft. (000) | gal (000) | sq. ft. (000) | |
| 1950 | 19.5 | 4,109 | 828 | 8,203 | 188 | 6,933 |
| 1951 | 21.3 | 9,324 | 1,576 | 11,839 | 637 | 7,427 |
| 1952 | 38.8 | 5,903 | 2,317 | 20,301 | 380 | 12,779 |
| 1953 | 20.4 | 410 | 420 | 1,910 | 34 | 9,278 |
| 1954 | 28.2 | 317 | 918 | 2,346 | 553 | 10,138 |
| 1955 | 38.5 | 621 | 4,886 | 15,957 | 961 | 12,616 |
| 1956 | 28.7 | 233 | 4,094 | 16,442 | 668 | 13,903 |
| 1957 | 38.7 | 278 | 3,847 | 13,507 | 673 | 9,752 |
| 1958 | 32.9 | 66 | 849 | 4,403 | 537 | 12,727 |
| 1959 | 23.9 | 1 | 735 | 171 | 329 | 13,110 |
| 1960 | 31.5 | 55 | 1,873 | 435 | 242 | 14,700 |
| Year Ended 31 December | Plaster of Paris | Gypsum | Asbestos Crude | Cement | Galvanised-iron Sheet | Aluminium Sheet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrugated | Flat | ||||||
| cwt(000) | |||||||
| 1950 | 168.5 | 566.2 | 75.7 | 1,424.9 | 102 | 117 | 70 |
| 1951 | 141.2 | 304.3 | 47.0 | 2,868.1 | 131 | 122 | 50 |
| 1952 | 365.2 | 702.0 | 94.9 | 2,466.3 | 217 | 163 | 76 |
| 1953 | 222.0 | 610.2 | 36.5 | 3,863.8 | 404 | 145 | 15 |
| 1954 | 330.8 | 788.3 | 69.0 | 3,727.1 | 645 | 293 | 19 |
| 1955 | 425.9 | 781.2 | 81.2 | 2,695.0 | 799 | 254 | 33 |
| 1956 | 354.4 | 714.0 | 55.7 | 926.1 | 509 | 229 | 26 |
| 1957 | 334.8 | 948.3 | 25.5 | 74.0 | 938 | 242 | 32 |
| 1958 | 292.1 | 1,171.9 | 78.3 | 60.8 | 636 | 347 | 47 |
| 1959 | 220.1 | 1,153.2 | 84.0 | 39.7 | 661 | 232 | 43 |
| 1960 | 290.8 | 1,307.3 | 90.2 | 64.0 | 655 | 224 | 58 |
THE HOUSING SITUATION – The number of new houses and flats constructed each year has doubled since the pre-war period. A peak of 21,600 was reached in the year ended 31 March 1960. This rate of house building in relation to population is higher than in most countries. Over 88 per cent of the houses built at present are for private home ownership.
There was a fairly rapid expansion in house building from 1945 to 1951, when there was a noticeable levelling-off at just over 16,000 houses each year. In August 1953 the Government convened a National Housing Conference for the purpose of surveying the general housing situation in New Zealand and investigating ways and means of implementing the Government's housing policy of promoting the building of more houses at a reasonable cost. The conference was attended by builders and others directly associated with the building industry, and also by employers, workers, welfare organisations, local bodies, organisations interested in housing finance, and other sections of the public. Every aspect of housing was discussed, and action taken on the resolutions adopted by the conference helped to effect a further expansion in house building to the present level. The conference assessed the extent of the housing shortage and set a number of 206,000 houses in 10 years as a target to overcome the shortage and provide for the increase in population expected from both natural increase and immigration. This target represented an increase of 25 per cent in the building rate. A National Housing Council was also set up.
The most noteworthy development in house building which has resulted has been the group building scheme. This scheme has been designed to give builders continuity of work, to reduce non-productive time between the finishing of one house and the starting of the next, and to assist builders in administration and supervision by enabling them to build houses for sale in groups. Plans and specifications are checked by the State Advances Corporation, which also inspects the work and, on behalf of the Government, gives an undertaking to take over at approved prices a specified number of any unsold houses. At 31 March 1960 there were 500 builders participating in the scheme, and 14,903 houses had been programmed; of these 12,411 had been completed and sold, and 688 were under construction.
Among other policy changes made in September 1953, a mortgage guarantee scheme was provided whereby the State Advances Corporation guaranteed financial institutions repayment by the borrower of the difference between the normal housing loan and 90 per cent of the valuation, the maximum loan under this scheme being £2,500. (See Section 30b.) Withdrawals could also be made at any time from national savings accounts for the acquisition of homes.
In July 1957 the Government announced the commencement of a home lay-by scheme in the Post Office Savings Bank. A subsidy, known as a suspensory free deposit, of £5 per £100 up to a limit of £50 is credited to each home lay-by account when the money is used to acquire a home to be occupied by the depositor. There is no limit to the amount which can be deposited but the maximum amount in any one year on which the subsidy can be credited is £250. The effect of the scheme is that a person who deposits £250 each year in a home lay-by account for four years will qualify for the maximum subsidy of £50, in addition to the normal savings bank interest. Deposits of £100 a year for 10 years can also earn the maximum subsidy.
An increase in the maximum housing loans to be advanced by the State Advances Corporation was announced by the Minister of Housing in September 1957. The maximum loan on the normal two-thirds lending basis was increased from £2,250 to £2,500, while the maximum for special loans in excess of the two-thirds lending margin was increased from £2,000 to £2,400 according to the size of family. These loans were inclusive of any loans granted under the suspensory loan scheme which was instituted in December 1949. The Corporation had been providing mortgage finance for 35 per cent of all houses constructed, and the higher loan limits caused an upsurge in applications for housing loans, and also an increase in building permits issued.
In February 1958 the Minister announced the introduction by the State Advances Corporation of building loans at 3 per cent interest for families whose income is not more than £1,000 a year, plus £50 for each dependent child, but excluding family benefit, war disability pension, and any income of the wife or children. The amount of the loan is determined by the circumstances of the applicant. Normal and special loans as mentioned in the previous paragraph continue to be granted at 43/4 per cent interest to those not eligible for the reduced rate. The availability of loans at 3 per cent interest from the State Advances Corporation has attracted large numbers of borrowers. The ruling rate of interest for first mortgages charged by private lending institutions averages about 51/2 per cent. For the year ended 31 March 1960 the Corporation authorised loans valued at £29.5 million, of which £22.8 million was at the 3 per cent rate. For the same period of the previous year the total of all new housing loans granted by the State Advances Corporation was £23.2 million.
The Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act 1958 provides for payment in a lump sum of the social security family benefit, the capitalised benefit to be applied towards the provision of a family home or for essential alterations or for repayment of encumbrances on a family home. The scheme became operative on 1 April 1959 for approved cases. Benefits in respect of any number of children may be capitalised, provided the aggregate advance does not exceed £1,000. Family benefit capitalisation advances totalling £5,684,074 were authorised from 1 April 1959 to 31 March 1960 by the State Advances Corporation to applicants holding eligibility certificates issued by the Social Security Commission.
Since 1937 the State, using the services of private contractors, has been building rental dwellings. At 31 March 1960 over 56,100 of these houses and flats had been built and, since 1950, 15,585 of them had been sold to the occupiers. About 2,000 of these dwellings are now built each year and let to applicants in difficult housing circumstances with an income of not more than £805 a year. Some 500 houses are also built by the State each year for the accommodation of Government employees.
It has been the policy of the National Housing Council to encourage the holding of Homes Weeks or Parades of Homes in all major centres throughout the country. Since 1954 forty Parades of Homes have been held, and these exhibitions have proved very popular. The principal objects of a Parade of Homes are to show the latest developments in low- and moderate-cost housing, to encourage home ownership and stimulate public interest in the building of houses, and to permit builders, manufacturers, and others concerned in house building to display their products. The scheme is probably unique to New Zealand, offering as it does an opportunity to the public of inspecting a group of new houses erected by local builders in open competition.
The building of flats to achieve higher density housing has been developed through the introduction of a system of company ownership of flats. An individual can buy a block of shares, the ownership of which entitles him to permanent occupation of a particular flat in a block of flats.
The achievement of a smoothly operated housing policy depends upon the help of many sections of the community, such as builders, lending institutions, and local authorities. The Minister of Housing has arranged the issue of a number of publications, including a manual for local authorities,Housing the Citizen, two editions of Your Own Home – How ? and their successor Home Ownership – How to Achieve it, as well as leaflets on Staff Housing, Plans for Flats, Land Development for Local Authorities, and sets of notes on the operation of the Group Building Scheme, the operation of the Rural Housing Act, and the organisation of a Parade of Homes.
Reference to the provisions made for the governmental financing of home building on behalf of private owners is contained in the section of this Yearbook dealing with State Advances (Section 30B). The Housing Act 1955 consolidated and amended the Housing Act 1919 and subsequent amendments. Part I of the 1955 Act relates to State houses, the acquisition of land therefor, the general programmes of development, the adjustment of State house rentals, and the sale, lease, or tenancy of State housing land. There is much incidental legislation, as in the Coal Mines Act and the Government Railways Act, where provision is made for the suitable housing of employees.
Role of Local Authorities – In addition to the activities briefly outlined earlier, the housing policy of the Government includes the provision of loans to local authorities at 31/2 per cent per annum to enable them to undertake the erection of accommodation for pensioners or persons in comparable circumstances. Since 1950 there has been a generous Government subsidy for pensioners' housing, and it now is half the net capital cost, with a maximum of £850 for a two-person unit and £700 for a one-person unit. At 31 March 1960 Government subsidies of £962,343 had been granted to local authorities and also loans of £1,047,090. Local authorities were providing accommodation for 1,944 elderly persons. (These subsidies are separate from those granted to religious and relief organisations – see Section 5B.)
The Rural Housing Act 1939, and subsequent amendments thereto, provide facilities for the granting of financial assistance to farmers requiring new houses for themselves or their employees, or desiring to improve their existing houses. The county councils have been charged with the duty of investigating the loan applications, and provided they are satisfied with the security, etc., they have authority to approve a loan. Loans arc made by the State Advances Corporation to local authorities bearing interest at 4 per cent (rate charged by the county to the farmer borrowers is 41/2 per cent), and are repayable on the amortisation system over terms of up to 35 years. The amount that may be advanced for the erection of a house under this scheme has been raised from £2,000 to £2,500, and the suspensory loan benefits described in Section 30B are available to applicants who comply with the conditions laid down. At 31 March 1960, £1,372,338 (in respect of 927 houses) had been uplifted by county councils.
Borough councils are authorised under the Municipal Corporations Act to provide loans for housing purposes up to a limit of £2,525; to subdivide for such purposes any land vested in a council and not held by it in trust for any particular purpose other than housing; and to sell or lease allotments for housing purposes. Local authorities may also apply to the Local Authorities Loans Board for blanket authorities for the purchase of land for subdivision for housing purposes. Local authorities are being encouraged to play a more prominent part in the housing of their citizens.
Housing regulations are contained in the Municipal Corporations Act, where definite measurements are laid down to prevent overcrowding, and provision is made for the appointment of inspectors to reduce fire risk and other dangers. Similarly the Health Act 1956 provides for medical inspection and for sanitation minima; an owner may be ordered to cleanse or demolish his building, or to close it till certain alterations are made. Under the Town and Country Planning Act 1953 the aim is to develop and reconstruct areas in such a way as to promote their healthfulness and convenience.
Further provision with respect to the improvement of housing conditions is contained in the Housing Improvement Act 1945. The Act authorises the making of regulations prescribing the standard of fitness of houses, and gives local authorities certain powers of enforcing the regulations or of assisting owners to comply with them. When a notice is given under the Act by a local authority requiring the owner to demolish a house which cannot be made to comply with the regulations, the Act makes it clear that alternative accommodation must be provided only for the persons residing in the house at the time of the service of the notice, and it is an offence for any other persons to commence to occupy the house after the notice has been served. In default of action by the local authority the Minister of Works is given power to act, or he may act under agreement with the local authority. Provision is also made for regulations requiring local authorities to keep a register of houses and to acquire land where a house is unfit for habitation or an area is below the minimum standard. The Act also deals with the reclamation of overcrowded areas, and gives power to local authorities with regard to the proclamation of reclamation areas and the re subdivision and improvement of such areas.
STATISTICS OF THE 1956 CENSUS – All figures in the following tables include dwellings occupied by Maoris. The first table gives a full distribution according to the nature of the dwelling, while the remaining tables relate only to inhabited permanent private dwellings. Where available, comparative figures for the 1951 census are shown.
Nature of Dwelling – The following table shows the nature of dwellings at the two censuses.
| Nature of Dwelling | Numbers | Percentage of Total Inhabited | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 1956 | 1951 | 1956 | |
| A. Inhabited dwellings – | ||||
| Permanent private dwellings – | ||||
| Private house, not partly sublet | 437,078 | 495,632 | 86.56 | 86.53 |
| Private house, partly sublet | 1,225 | 3,684 | 0.24 | 0.64 |
| Flat | 35,021 | 41,669 | 6.94 | 7.28 |
| Combined shop and dwelling, rooms attached to offices, etc. | 8,040 | 7,686 | 1.59 | 1.34 |
| Bach, hut | 12,393 | 14,340 | 2.45 | 2.50 |
| Other | 255 | 41 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Totals | 494,012 | 563,052 | 97.83 | 98.30 |
| Temporary dwellings – | ||||
| Mobile residences | 1,675 | 1,580 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| Other | 833 | 344 | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| Totals | 2,508 | 1,924 | 0.49 | 0.34 |
| Non-private dwellings– | ||||
| Hotels, boardinghouses, etc. | 6,354 | 6,071 | 1.26 | 1.06 |
| Public and private hospitals | 515 | 490 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| Camps | 550 | 567 | 0.11 | 0.10 |
| Other (including not specified) | 1,048 | 655 | 0.21 | 0.11 |
| Totals | 8,467 | 7,783 | 1.68 | 1.36 |
| Totals, inhabited dwellings | 504,987 | 572,759 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| B. Uninhabited dwellings – | ||||
| Occupants temporarily away | 9,307 | 10,944 | ... | ... |
| Untenanted dwellings | 7,747 | 12,614 | ... | ... |
| Baches (weekend or summer dwellings) | 15,615 | 19,899 | ... | ... |
| Totals | 32,669 | 43,457 | ... | ... |
| C. Building– | ||||
| Dwellings in course of erection | 9,597 | 10,462 | ... | ... |
Between 1951 and 1956 the number of inhabited permanent private dwellings increased by 69,040, or 14 per cent, while the population increased by 12.1 per cent, and there were also substantially more uninhabited dwellings in 1956. The average number of occupants per dwelling was 3.61 in 1951 and 3.58 in 1956.
Tenure of Dwelling – The following table classifies the inhabited permanent private dwellings according to tenure.
| Tenure | 1951 | 1956 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | Per Cent of Total Specified | Numbers | Per Cent of Total Specified | |
| Renting or leasing | 148,679 | 30.25 | 144,721 | 25.80 |
| Free dwelling provided with job | 31,502 | 6.41 | 34,270 | 6.11 |
| Loaned without payment | 9,122 | 1.86 | 9,224 | 1.65 |
| Buying on time payment or with table mortgage | 94,625 | 19.25 | 130,947 | 23.35 |
| With flat mortgage | 56,296 | 11.45 | 72,760 | 12.97 |
| Unspecified mortgage cases | 279 | 0.06 | 553 | 0.10 |
| Owned without mortgage | 150,985 | 30.72 | 168,383 | 30.02 |
| Not specified | 2,524 | ... | 2,194 | ... |
| Total | 494,012 | 100.00 | 563,052 | 100.00 |
The proportion of “owned” dwellings to the total specified cases increased by almost 5 per cent between 1951 and 1956, the greater part of this increase (4.1 per cent) being in those classified as “buying on time payment or with table mortgage”. The proportion of “rented” dwellings decreased by 4.45 per cent.
Amenities of Dwellings – The next two tables present the various amenities in permanent private dwellings in 1956 and show whether they were used solely by the occupants of a dwelling or shared by occupants of other dwellings.
| Amenity | Not Shared | Shared | Nil | Not Specified | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piped water | 472,569 | 8,672 | 78,180 | 3,631 | 563,052 |
| Hot water service | 487,676 | 9,291 | 65,206 | 879 | 563,052 |
| Bath or shower | 517,019 | 13,494 | 31,646 | 893 | 563,052 |
| Flush toilet | 442,065 | 13,456 | 106,698 | 833 | 563,052 |
| Refrigerator | 301,565 | 3,281 | 256,650 | 1,556 | 563,052 |
| Washing machine | 316,511 | 5,356 | 239,367 | 1,818 | 563,052 |
Of the specified cases, 54.3 per cent of houses had the sole or shared use of refrigerators and 57.3 per cent had the sole or shared use of washing machines. Almost 14 per cent of dwellings did not have piped water.
| Means of Cooking | Number | Per Cent of Total Specified |
|---|---|---|
| Electric range, stove | 318,810 | 56.88 |
| Electric cooker, stovette, rangette, plate, ring, etc. | 2,831 | 0.51 |
| Gas range, stove | 88,818 | 15.85 |
| Gas cooker, stovette, ring, etc. | 411 | 0.07 |
| Coal, wood, coke, range | 108,291 | 19.32 |
| Oil range, stove | 591 | 0.10 |
| Oil, other, including primus stove | 236 | 0.04 |
| Electric range and gas range | 4,523 | 0.81 |
| Electric range and coal, wood, coke, range | 25,460 | 4.54 |
| Gas range and coal, wood, coke range | 8,296 | 1.48 |
| Other, including open fire, primus (not stove), camp oven, etc. | 2,246 | 0.40 |
| Not specified | 2,539 | ... |
| Total | 563,052 | 100.00 |
Considering only cases where one means of cooking is used, the electric range held pride of place, being used in 56.88 per cent of inhabited dwellings; the next place being held by the coal, wood, or coke range which was used in 19.32 per cent of inhabited dwellings. Including cases where alternatives are also installed, it will be noted that 62.23 per cent of the dwellings in New Zealand were equipped with an electric range. When this question was first asked (1945 census), the position was that in 37.66 per cent of the dwellings a coal, wood, or coke range was used and in 29.95 per cent an electric range. It should be remembered that the 1945 figures do not include Maori dwellings.
Materials of Outer Walls – The following table gives an analysis showing the materials of which the outer walls of inhabited permanent private dwellings were constructed.
| Material of Outer Walls | Number of Dwellings | |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 1956 | |
| Wood | 374,566 | 411,370 |
| Stone | 1,086 | 1,121 |
| Concrete, including concrete blocks | 14,465 | 17,869 |
| Concrete and wood | 1,375 | 1,087 |
| Brick, including hollow brick | 34,561 | 47,420 |
| Brick and wood | 3,680 | 3,332 |
| Brick and other material | 2,939 | 3,401 |
| Wood and iron | 5,270 | 3,721 |
| Wood and proprietary wallboard | 2,407 | 2,369 |
| Iron | 5,357 | 3,862 |
| Asbestos | 1,543 | 2,011 |
| Proprietary wallboards of asbestos type | 19,002 | 26,250 |
| Roughcast on wood lath and plaster | 5,313 | 23,999 |
| Roughcast not otherwise defined | 8,209 | 3,945 |
| Other materials | 5,432 | 3,922 |
| Not specified | 8,807 | 7,373 |
| Totals | 494,012 | 563,052 |
Although the number of houses with outer walls of wood increased by almost 37,000 between the 1951 and 1956 censuses, as a percentage of all inhabited permanent private dwellings they decreased from 75.8 to 73.1.
Houses with outer walls constructed of concrete, brick, proprietary wallboards of asbestos type, and roughcast increased both in number and as a percentage of the total, thus continuing the trend established between the 1945 and 1951 censuses.
GOVERNMENT CAPITAL ASSISTANCE ON NEW HOUSING – The following table gives the Government's total capital assistance on new housing in the year ended 31 March 1960, and includes both direct expenditure by Government Departments and money advanced by way of mortgages and loans by State lending institutions. Expenditure on new housing by hospital boards, education boards, etc., is not included.
| £ | |
|---|---|
| Land purchase and development, State house construction, etc. | 11,015,882 |
| Expenditure by Housing Division for other Departments | 1,141,745 |
| Department of Maori Affairs | 1,722,000 |
| Department of Lands and Survey | 275,830 |
| Ministry of Works construction workers' houses | 20,000 |
| State Advances and rehabilitation loans paid out for new urban houses including suspensory loans | 24,283,341 |
| State Advances and rehabilitation loans paid out for new rural houses, including suspensory loans | 310,055 |
| State Advances loans paid to local authorities for rural housing, pensioners' housing, etc. | 424,985 |
| Department of Health subsidies paid to local authorities for pensioners' flats | 203,008 |
| Total, year ended 31 March 1960 | 39,396,846 |
MAORI HOUSING – Financial assistance towards the erection of houses, including the purchase of building sites, additions, repairs to existing dwellings, and for the purchase of houses, is available to Maoris under the Maori Housing Act 1935, the lending authority being the Board of Maori Affairs. Section 18 of the Maori Housing Amendment Act 1938 provided for the Special Housing Fund to be set up. The use of this fund as a reserve enables the Board of Maori Affairs to cater for families who are unable to meet the full repayments normally required.
In addition to providing loans, the Department, through its building organisation, arranges for construction of the houses in many cases. Private building contractors are used where the applicant is able to arrange for construction by these means. The Department has available a comprehensive plan service covering varying bedroom types to meet the special needs of the Maori people. In determining its building programme the Department endeavours to ensure that the most needy cases are given priority.
The extended loan limits, 3 per cent interest rate, and capitalisation of family benefit are available to Maoris on similar conditions as apply to Europeans. Where the applicant does not qualify for the special interest concession, loans are granted at an interest rate of 47/8 per cent, suspensory interest-free loans also being available in such cases, subject to usual conditions.
Special “pools” of State rental houses are established in some of the larger towns and cities to help meet the housing needs of Maori families. The quota of houses available to these special “pools” is based on the number of urgent Maori applications held in relation to European applications, and allocations to eligible Maori families are made by special allocation committees which have been set up.
The following summary shows the number of new houses built, the number of houses purchased, and the number of renovations and additions to houses, etc., from inception of the building organisation of the Department to 31 March 1958, 1959, and 1960.
| Total to 31 March | |||
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Houses erected | 6,313 | 6,888 | 7,511 |
| Houses purchased | 460 | 465 | 468 |
| Other building work (including erection of other buildings, renovations, and additions to houses and other buildings) | 4,316 | 4,472 | 4,650 |
In addition to the above, there were 161 houses in course of erection at 31 March 1960.
STATE HOUSE CONSTRUCTION – A programme of building State rental houses and flats was commenced in March 1937. These are for letting (and subsequent purchase if the occupier wishes) to people in the moderate income group according to need. Since 1950 there has been an income bar (at present £805 per annum) on applicants for tenancies of State rental units, increased slightly in respect of special classes of accommodation.
A Housing Construction Branch of the State Advances Corporation was set up in September 1936. In 1944 this branch was merged with the Public Works Department and became the Housing Division of what is now the Ministry of Works. The Housing Division acquires and develops sites for houses and flats and arranges contracts for their construction. These activities are covered by the Housing Act 1955.
Completed housing units are handed over to the State Advances Corporation for letting and subsequent administration. The total numbers handed over by housing districts from the inception of the scheme to 31 March 1960 are as follows.
| Housing District | 1959–60 | Previous Total | Total to 31 March 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland | 457 | 16,470 | 16,927 |
| Hamilton | 195 | 5,443 | 5,638 |
| Napier | 275 | 3,323 | 3,598 |
| Palmerston North | 235 | 5,292 | 5,527 |
| Wellington | 583 | 12,030 | 12,613 |
| Christchurch | 217 | 7,789 | 8,006 |
| Dunedin | 166 | 3,704 | 3,870 |
| Totals | 2,128 | 54,051 | 56,179 |
The totals of State rental units completed and handed over for occupation year by year since 1948–49 are shown in the following table.
| Year | Number of Units | Cumulative Total |
|---|---|---|
| 1948–49 | 3,414 | 28,879 |
| 1949–50 | 3,388 | 32,267 |
| 1950–51 | 3,365 | 35,632 |
| 1951–52 | 2,118 | 37,750 |
| 1952–53 | 2,124 | 39,874 |
| 1953–54 | 2,781 | 42,655 |
| 1954–55 | 2,892 | 45,547 |
| 1955–56 | 2,258 | 47,805 |
| 1956–57 | 2,746 | 50,551 |
| 1957–58 | 1,853 | 52,404 |
| 1958–59 | 1,647 | 54,051 |
| 1959–60 | 2,128 | 56,179 |
Special Types of Accommodation – Included in the 2,128 units handed over in 1959–60 were 10 houses built for occupancy by casual farm labourers and by employees of rabbit boards.
Flats and Multi-unit Dwellings – In compliance with Government policy, aiming at higher density housing in the interests of conserving land and at the same time arresting urban sprawl, the State has continued to build increasing numbers of multi-unit dwellings, mainly two and four units, also a number of three-storey blocks of flats each comprising 12 units. The following table sets out the number of multi units in relation to single units built by the Housing Division up to 31 March 1960.
| Class | State Rentals | State Services | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single units | 42,513 | 7,849 | 50,362 |
| Two units | 9,938 | 160 | 10,098 |
| Three units | 225 | - | 225 |
| Four- to eight-unit blocks | 1,628 | 103 | 1,732 |
| Totals | 54,304 | 8,112 | 62,416 |
| Plus: | |||
| Multi-storey flats | 844 | - | 844 |
| Pensioners' flats | 1,031 | - | 1,031 |
| Totals | 56,179 | 8,112 | 64,291 |
State Services Housing – The State services houses referred to in the previous table are houses built for Government Departments and the Armed Forces. The total number of such houses erected by the Division to 31 March 1960 was 8,112. This includes houses built at the site of major construction jobs such as electric power schemes.
Finance – The cost of the State housing programme, including the acquisition and development of land, is financed from the Housing Construction “vote” in the Public Works Account, i.e., out of national development loan moneys.
The following table shows the annual expenditure from the Housing Construction “vote”.
| Year Ended 31 March | State Housing | State Services | Land Purchase and Development | Administration and General | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ (thousand) | |||||
| 1950 | 7,171 | 1,643 | 1,359 | 535 | 10,709 |
| 1951 | 6,591 | 1,567 | 1,234 | 462 | 9,854 |
| 1952 | 4,385 | 1,035 | 1,152 | 440 | 7,012 |
| 1953 | 6,528 | 1,126 | 1,639 | 461 | 9,754 |
| 1954 | 7,574 | 776 | 1,744 | 514 | 10,608 |
| 1955 | 6,117 | 746 | 1,951 | 536 | 9,351 |
| 1956 | 5,808 | 1,044 | 3,026 | 522 | 10,399 |
| 1957 | 6,552 | 61 | 2,786 | 555 | 9,955 |
| 1958 | 4,816 | 56 | 2,695 | 570 | 8,138 |
| 1959 | 4,865 | 26 | 3,113 | 599 | 8,602 |
| 1960 | 7,186 | 30 | 3,201 | 598 | 11,016 |
The next table shows the annual total expenditure by the Housing Division in the last four years.
| Year | Vote, “Housing Construction” | Vote, “Murupara Development” | On Behalf of Other Departments (Charged Direct) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction, Land Purchase and Development, Administration | Land Development, Murupara* | On Behalf of Other Departments† | Total | ||||
*Previously charged to vote, “Murupara Development”. †Expenditure on behalf of other Departments charged meantime to vote, “Housing Construction”. | |||||||
| £ (thousand) | |||||||
| 1956–57 | 9,894 | - | 61 | 9,955 | 549 | 1,329 | 11,832 |
| 1957–58 | 8,082 | - | 56 | 8,138 | 142 | 1,191 | 9,471 |
| 1958–59 | 8,558 | 18 | 26 | 8,602 | - | 1,503 | 10,105 |
| 1959–60 | 10,974 | 12 | 30 | 11,016 | - | 1,142 | 12,158 |
Room Content of Units (State Houses and State Services Housing) – The types of units according to the number of bedrooms in units built during 1959–60 as compared with the previous year, also the totals to date, are shown in the following table.
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | Totals to Date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Units | Percentage of Total | Number of Units | Percentage of Total | Number of Units | Percentage of Total | |
| One bedroom or bed-sitting room | 26 | 1.3 | 87 | 3.6 | 3,748 | 5.8 |
| Two bedrooms | 328 | 15.7 | 215 | 8.9 | 21,157 | 32.9 |
| Three bedrooms | 1,540 | 73.8 | 1,903 | 78.8 | 35,180 | 54.7 |
| Four or more bedrooms | 192 | 9.2 | 210 | 8.7 | 4,206 | 6.6 |
| Totals | 2,086 | 100.0 | 2,415 | 100.0 | 64,291 | 100.0 |
Sheathing Materials Used (State Houses and State Services Housing) – The sheathing materials used in the units built during 1959–60 as compared with the previous year, also the total to date, is as follows.
| Material | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | Total to Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weatherboard | 929 | 1,248 | 37,829 |
| Brick | 317 | 227 | 11,935 |
| Concrete | 284 | 204 | 3,489 |
| Other sheathing | 556 | 736 | 11,038 |
| Totals | 2,086 | 2,415 | 64,291 |
Land Acquisition – During 1959–60 a total of 1,000 developed unit sites was purchased as a charge against the Housing Construction “vote”, also some 707 acres of undeveloped land estimated ultimately to yield 2,627 unit sites. About three-fifths of these sections are intended for State rental units and two-fifths for the group building scheme sponsored by the Government.
State Rental Housing Tender Prices – The following table shows typical tender prices being accepted in the four main centres at the end of each financial year since 1949–50 for similar types of three-bedroom State rental houses of equivalent floor space. In each case the house is a typical single unit on a flat section, built in weatherboards with a tiled roof. The price includes drainage, fencing, paths, toolshed, revolving clothes line, and letterbox. The cost of the section is not included. The figures in parentheses represent the cost per square foot.
| Year | Auckland | Wellington | Christchurch | Dunedin | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1949–50 | 2,192 | (43 | 0) | 2,169 | (40 | 5) | 2,095 | (38 | 8) | 2,188 | (41 | 0) |
| 1950–51 | 2,490 | (47 | 2) | 2,357 | (46 | 2) | 2,170 | (42 | 8) | 2,388 | (44 | 6) |
| 1951–52 | 2,705 | (50 | 1) | 2,613 | (48 | 2) | 2,324 | (44 | 10) | 2,482 | (47 | 10) |
| 1952–53 | 2,762 | (51 | 9) | 2,618 | (49 | 10) | 2,348 | (45 | 0) | 2,570 | (50 | 1) |
| 1953–54 | 2,809 | (53 | 9) | 2,762 | (50 | 1) | 2,406 | (47 | 4) | 2,576 | (50 | 2) |
| 1954–55 | 2,890 | (55 | 4) | 2,896 | (53 | 0) | 2,600 | (48 | 4) | 2,634 | (48 | 0) |
| 1955–56 | 3,062 | (58 | 4) | 2,964 | (56 | 8) | 2,710 | (51 | 7) | 3,001 | (57 | 2) |
| 1956–57 | 3,085 | (58 | 9) | 3,007 | (57 | 3) | 2,557 | (48 | 8) | 3,054 | (58 | 2) |
| 1957–58 | 3,051 | (58 | 2) | 3,002 | (57 | 2) | 2,545 | (48 | 6) | 3,031 | (57 | 9) |
| 1958–59 | 3,009 | (57 | 4) | 3,022 | (57 | 7) | 2,538 | (48 | 4) | 2,952 | (56 | 3) |
| 1959–60 | 3,109 | (59 | 2) | 3,034 | (57 | 9) | 2,681 | (51 | 1) | 3,067 | (58 | 5) |
BUILDING PERMITS: Annual Statistics – Building permit statistics for cities, boroughs, and town districts have been compiled since 1921–22, while the scope of the collection was extended in 1937–38 so that all local authorities in New Zealand, including rural counties, were included. The annual statistics are compiled from returns from local authorities, Government Departments, hospital and education boards.
The returns from local authorities that operate a building-permit system cover all private and local authority building subject to permit, and to enable a complete picture of building activity to be shown construction by Government Departments, hospital and education boards is included, even though permits are not actually taken out.
In using these figures as a guide to short-period fluctuations in building activity, it should be noted that the value shown represents in the majority of instances, the total contract price or estimated cost of the building. A permit for a large building may involve work spread over several years, whereas in the permit statistics the value is shown entirely for the year or month in which the permit is issued. This qualification applies with greater force to the monthly than the annual statistics, and applies more particularly to large buildings, other than houses and flats.
A further point worth considering, is that the value placed on a building is usually less than the actual cost. This applies particularly to large new buildings which take a considerable time to complete. In these cases the final cost, owing to wage increases, rising costs of materials, etc., may be greater than originally estimated. This increase is not reflected in building permit figures and should be borne in mind when use is being made of these statistics.
Building Permits in Urban and Rural Districts Combined – The following table gives a summary for New Zealand of building permits (including State building operations) for the years ended 31 March 1959 and 1960.
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Houses and Flats: Number | New Houses and Flats: Value | Total, All Buildings: Value | New Houses and Flats: Number | New Houses and Flats: Value | Total, All Buildings: Value | |
| £ (000) | £ (000) | £ (000) | £ (000) | |||
| Urban districts | 15,590 | 44,501 | 80,309 | 18,437 | 53,197 | 93,031 |
| Rural districts | 4,978 | 12,513 | 21,157 | 5,141 | 13,142 | 20,981 |
| Totals, New Zealand | 20,568 | 57,014 | 101,466 | 23,578 | 66,339 | 114,013 |
Although statistics of building activity have been collected since 1921–22 for urban districts, as stated above, the collection of rural statistics was not commenced until 1937–38. In many cases, in earlier years, for rural districts estimates only were supplied, while in some instances no data whatever could be obtained. From 1947–48 to 1955–56, however, the Building Controller's authorisations were used where counties could not supply information. This source is no longer available following the abolition of building controls, but in the few cases where counties do not now issue building permits, the local authorities make an estimate.
The following table shows a summary of New Zealand building activity since 1949–50.
| Year Ended 31 March | Permits Issued for New Houses and Flats | Total Value, All New Houses and Flats | Total Value, All Buildings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private | Government | Total | |||
| £ (000) | £ (000) | ||||
| 1950 | 12,262 | 5,395 | 17,657 | 28,999 | 42,477 |
| 1951 | 14,551 | 3,298 | 17,849 | 32,728 | 48,770 |
| 1952 | 14,297 | 2,814 | 17,111 | 36,457 | 59,243 |
| 1953 | 12,607 | 3,610 | 16,217 | 37,278 | 61,128 |
| 1954 | 14,025 | 3,432 | 17,457 | 41,736 | 69,500 |
| 1955 | 17,420 | 3,443 | 20,863 | 52,767 | 93,405 |
| 1956 | 16,234 | 3,270 | 19,504 | 51,486 | 90,173 |
| 1957 | 15,694 | 2,660 | 18,354 | 49,214 | 89,388 |
| 1958 | 16,985 | 1,970 | 18,955 | 52,504 | 101,767 |
| 1959 | 18,121 | 2,447 | 20,568 | 57,014 | 101,466 |
| 1960 | 20,527 | 3,051 | 23,578 | 66,339 | 114,013 |
The following diagram illustrates building-permit figures relating to New Zealand totals since 1938–39.
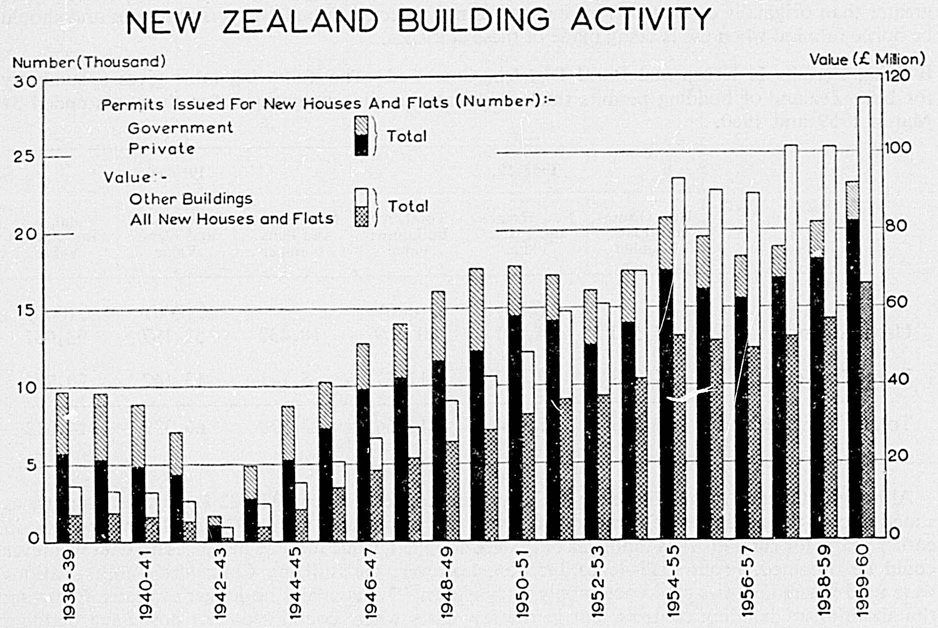
Building Permits in Urban Districts – In the next table, figures are given under two headings, one showing the totals for all urban districts covered in the particular year, and the second showing the totals for only cities, boroughs, and town districts. Data in respect of rural building will be found later in this section.
| Year Ended 31 March | All Urban Districts Covered | Cities, Boroughs, and Town Districts | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of New Private Houses and Flats | Value of New Houses and Flats | Value of Other New Buildings | Total Value, All Buildings (Including Alterations and Additions) | Number of New Private Houses and Flats | Value of New Houses and Flats | Value of Other New Buildings | Total Value, All Buildings (Including Alterations and Additions) | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| 1950 | 11,530 | 20,822 | 3,397 | 30,366 | 9,613 | 17,540 | 3,181 | 26,514 |
| 1951 | 11,379 | 22,991 | 4,689 | 35,031 | 9,510 | 19,355 | 4,435 | 30,660 |
| 1952 | 12,443 | 27,763 | 8,856 | 46,279 | 9,188 | 21,457 | 7,964 | 38,118 |
| 1953 | 11,700 | 28,045 | 9,037 | 47,180 | 8,836 | 22,036 | 8,044 | 39,341 |
| 1954 | 12,596 | 31,524 | 10,981 | 53,973 | 9,594 | 24,803 | 10,223 | 45,476 |
| 1955 | 15,443 | 40,242 | 20,485 | 74,590 | 12,064 | 32,199 | 18,894 | 63,870 |
| 1956 | 14,162 | 38,512 | 16,382 | 70,157 | 10,767 | 30,084 | 14,985 | 59,166 |
| 1957 | 13,445 | 37,171 | 17,062 | 69,009 | 10,102 | 28,437 | 15,240 | 57,278 |
| 1958 | 13,772 | 39,254 | 23,190 | 79,438 | 10,113 | 29,310 | 21,014 | 66,103 |
| 1959 | 15,590 | 44,501 | 17,978 | 80,309 | 11,278 | 32,645 | 16,424 | 64,968 |
| 1960 | 18,437 | 53,197 | 19,344 | 93,031 | 13,863 | 40,136 | 16,839 | 75,462 |







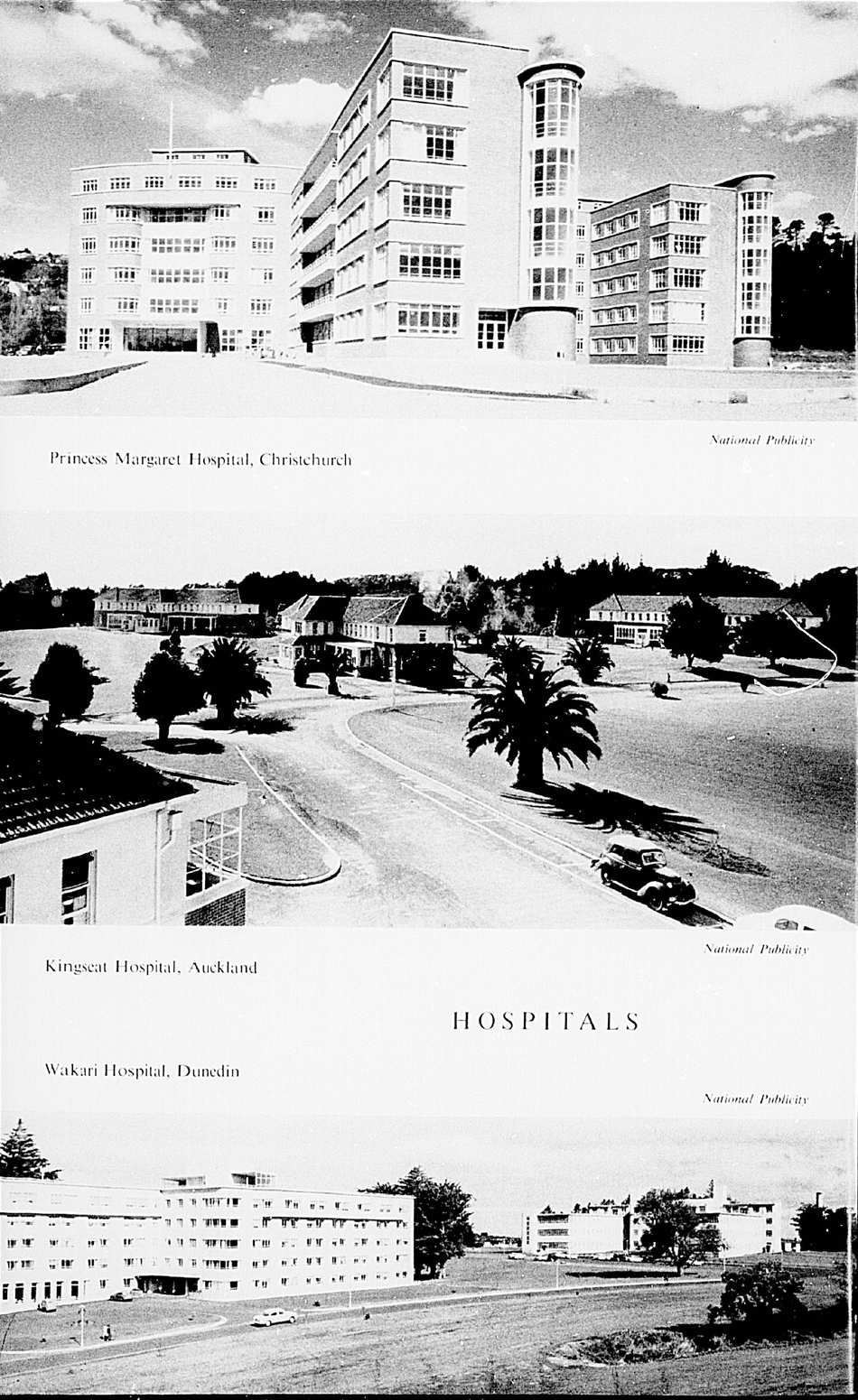


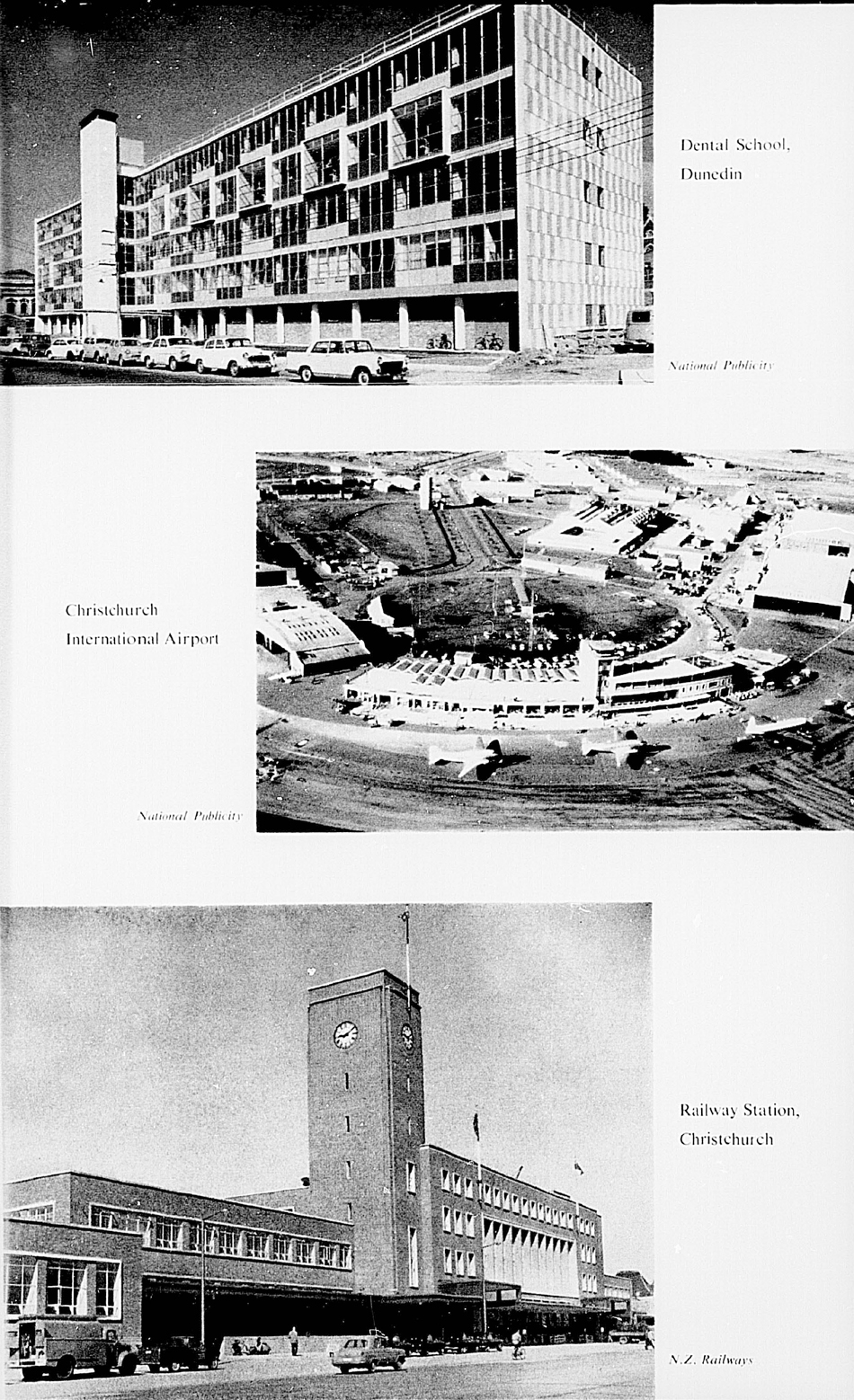





The figures shown for “cities, boroughs, and town districts” cover the districts existing in the year to which the statistics refer. Since these statistics were inaugurated, however, several new boroughs and town districts have been created and are accordingly included, while a few town districts and boroughs have been excluded consequent on their abolition and merger into counties. The net result has, however, been a gradual accession which has tended to raise slightly the figures for later years.
Statistics relating to new private houses and flats include units in transit camps run by State or local authorities where these are in effect of a semi-permanent nature. However, “workmen's huts”, etc., as in railways or works camps, are not included.
Statistics of houses and flats treat each flat as one unit. During the year ended 31 March 1960 370 blocks of flats, totalling 1,395 individual units, were commenced in urban districts.
The following table shows details for the last 10 years of blocks of flats included in the numbers of permits for houses and flats issued for cities, boroughs, and town districts.
| Year Ended 31 March | Cities, Boroughs, and Town Districts | |
|---|---|---|
| Blocks | Number of Flats | |
| 1951 | 51 | 141 |
| 1952 | 64 | 223 |
| 1953 | 54 | 207 |
| 1954 | 73 | 189 |
| 1955 | 141 | 615 |
| 1956 | 118 | 515 |
| 1957 | 167 | 558 |
| 1958 | 278 | 953 |
| 1959 | 262 | 929 |
| 1960 | 357 | 1,365 |
These figures cover only buildings erected as new blocks of flats. Where flats have been created by conversion of existing buildings, the values of such conversions are included in alterations and additions. However, as this class of work has become more prevalent in recent years it was decided to collect information on the number of flats being created in such a manner, the first data being for the year ended 31 March 1955 for urban districts.
The following table shows the numbers of permits for the last five years for flats to be created by conversion of existing buildings.
| Year Ended 31 March | New Zealand Total | All Urban Districts | Cities, Boroughs, and Town Districts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 532 | 518 | 505 |
| 1957 | 682 | 655 | 651 |
| 1958 | 711 | 700 | 685 |
| 1959 | 810 | 792 | 778 |
| 1960 | 899 | 883 | 862 |
The statistics quoted in the preceding paragraphs relate only to the main types of building activity. More detailed statistics are included in the annual report on Population, Migration, and Buildings Statistics compiled by the Department of Statistics.
In 1959–60 the number of permits for houses and flats in urban districts showed a substantial increase of 2,847 or 18.26 per cent, over 1958–59.
The value of permits for houses and flats in 1959–60 rose by £8,696,278, or 19.5 per cent, over the preceding year. The average permit value in 1959–60 was £2,885, as against £2,854 in 1958–59 and £2,850 in 1957–58.
For new buildings other than houses or flats, together with alterations and additions, the value of permits issued showed an increase of £4,026,271, or 11 per cent, on the 1958–59 figure.
The following table arranges urban local authorities with building values of over £500,000 in 1959–60 in descending order.
| £(000) | |
| Auckland city | 6,668 |
| Christchurch city | 6,455 |
| Wellington city | 5,185 |
| Waitemata county | 4,911 |
| Manukau county | 3,734 |
| Dunedin city | 3,311 |
| Lower Hutt city | 2,949 |
| Waimairi county | 2,836 |
| Hutt county | 2,449 |
| Hamilton city | 2,306 |
| Palmerston North city | 2,174 |
| Makara county | 2,083 |
| Wanganui city | 1,962 |
| New Plymouth city | 1,617 |
| Invercargill city | 1,611 |
| Manurewa borough | 1,583 |
| One Tree Hill borough | 1,465 |
| Hastings city | 1,432 |
| Napier city | 1,432 |
| Mount Roskill | 1,344 |
| Rotorua borough | 1,295 |
| Nelson city | 1,212 |
| Gisborne city | 1,097 |
| Masterton borough | 1,062 |
| Tawa borough | 1,042 |
| Mount Wellington borough | 991 |
| Paparua county | 940 |
| Takapuna borough | 925 |
| Timaru city | 924 |
| Upper Hutt borough | 820 |
| Tauranga borough | 710 |
| Papakura borough | 687 |
| Papatoetoe borough | 682 |
| Whangarei borough | 676 |
| Ashburton borough | 602 |
| Oamaru borough | 577 |
| New Lynn borough | 575 |
| Howick borough | 556 |
| Mosgiel borough | 517 |
| Blenheim borough | 507 |
| Hawera borough | 500 |
Building Permits in Rural Districts – The collection of data from counties was inaugurated in the year ended 31 March 1938. For some years building statistics had been obtained from the counties of Hutt, Makara, Waimairi, and Heathcote, and the road district of Eden County, and these were included in urban building statistics. As from 1 April 1951 the counties of Waitemata, Manukau, Paparua, Peninsula, and Taieri, previously included in rural districts, were added to the urban building statistics. The great majority of the population in these counties is urban, and they were included in order to obtain more complete statistics of building activity for the urban areas of Auckland, Hutt, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin.
The tabulation for rural districts was therefore confined to the remaining counties and Waiheke Island. Most rural districts were able to supply the information required. Previously this was limited in scope, but since 1955–56 this has been returned in full the same as for urban districts. In the few instances where counties do not operate a building-permit system estimates of building activity have been accepted.
Data are available for all Government building in rural districts and have been included in the total for rural building.
Excluding the nine counties which are included in urban districts, the total value of rural building in 1959–60 amounted to £20,981,310, a decrease of £175,939 as compared with the 1958–59 figures for the same districts. The number of new dwellings was 5,141, an increase of 163 on the preceding year.
The following table arranges rural local authorities with building values of over £500,000 in 1959–60 in descending order.
| County | £(000) |
|---|---|
| Southland | 1,477 |
| Waipa | 1,081 |
| Rotorua | 1,059 |
| Matamata | 938 |
| Waikato | 919 |
| Hawke's Bay | 800 |
| Taranaki | 772 |
| Tauranga | 735 |
| Horowhenua | 597 |
The total value of building for the nine counties included in the total for urban districts in 1959–60 was £17,569,600, and the number of new houses and flats 4,574. The comparable value for 1958–59 was £15,340,572, and the number of new houses and flats 4,312.
Government Building of Houses and Flats – The erection of houses by the Housing Division of the Ministry of Works was commenced in March 1937. Details of houses and flats commenced for the last 10 years are as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Urban Districts | Rural Districts |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 2,020 | 734 |
| 1952 | 1,914 | 386 |
| 1953 | 2,880 | 435 |
| 1954 | 2,572 | 615 |
| 1955 | 2,871 | 438 |
| 1956 | 2,610 | 438 |
| 1957 | 2,250 | 232 |
| 1958 | 1,567 | 253 |
| 1959 | 2,107 | 212 |
| 1960 | 2,722 | 201 |
Most of these are State rental units and departmental houses, but a few are houses and flats built for sale.
Houses are also erected by the Department of Maori Affairs, under its various development schemes, particulars of which will be found earlier in this section. As these houses are for individual Maori ownership they are not included in Government building figures.
In addition, houses and flats are erected by the Ministry of Works, Department of Lands and Survey, Department of Justice, etc.
In all, there were 3,051 Government houses and fiats (2,728 in urban and 323 in rural districts) commenced in 1959–60 compared with 2,447 (2,120 in urban and 327 in rural districts) in 1958–59. The value of the houses and flats commenced in 1959–60 was £9,155,132 as against £7,257,000 in 1958–59.
The following table shows urban local authorities in which 20 or more houses and flats were commenced during the year ended 31 March 1960, together with the comparable number commenced for the year ended 31 March 1959 by the various Government Departments concerned.
| New Houses and Flats | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
| Cities and boroughs – | ||
| Whangarei | 3 | 25 |
| Northcote | 40 | 52 |
| Auckland city | 145 | 321 |
| Mount Roskill | 76 | 30 |
| Mount Wellington | 12 | 23 |
| Huntly | 6 | 21 |
| Hamilton city | 119 | 134 |
| Gisborne city | 59 | 54 |
| Napier city | 73 | 93 |
| Hastings city | 81 | 80 |
| New Plymouth city | 58 | 72 |
| Wanganui city | 33 | 60 |
| Palmerston North city | 92 | 102 |
| Levin | 12 | 20 |
| Lower Hutt city | 54 | 207 |
| Petone | 1 | 24 |
| Tawa | 98 | 87 |
| Masterton | 22 | 35 |
| Blenheim | 9 | 20 |
| Christchurch city | 104 | 101 |
| Timaru city | 54 | 46 |
| Oamaru | 13 | 30 |
| Dunedin city | 10 | 103 |
| Mosgiel | 73 | 36 |
| Invercargill city | 67 | 77 |
| Others | 305 | 292 |
| Totals | 1,619 | 2,145 |
| Counties and road districts– | ||
| Waitemata | 1 | 42 |
| Manukau | 152 | 102 |
| Makara | 302 | 386 |
| Waimairi | 16 | 31 |
| Others | 13 | 15 |
| Totals | 484 | 576 |
| Independent town districts | 17 | 7 |
| Dependent town districts – | - | - |
| Totals, urban districts | 2,120 | 2,728 |
Rural districts (counties) in which the number of houses and flats was 20 or more in 1959–60, with comparable figures for the previous year shown in parentheses, were: Otorohanga 20 (16); Rotorua 58 (51); Taupo 30 (85); Rangitikei 21 (1); Malvern 25 (nil).
Other Government Building Operations – In 1959–60 Government building commenced, other than houses and flats, totalled £6,233,465 in value. The comparable figure for 1958–59 was £4,134,176. Buildings erected by or for hospital or education boards are not included in these figures but are included in the total building statistics quoted previously. For the year ended 31 March 1960 the value of building commenced for hospital boards amounted to £2,982,433, while that commenced for education boards was valued at £4,040,161. The comparable figures for 1958–59 were: hospital boards £3,536,088; education boards £3,414,182.
Monthly Permit Statistics – While the annual statistics of building permits issued afford an indication of year-to-year changes in the value and volume of building activity, short-period movements in building activity are of considerable interest, particularly in times of rapid economic change. With the purpose of providing information as to current changes in building activity, monthly statistics of building permits are collected from the larger centres.
While these returns cover 62 per cent of the total population, they represent 81 per cent of the total New Zealand building activity.
BUILDING PERMITS IN LARGER CENTRES
| Month | New Buildings | Alterations to Existing Buildings | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Houses and Flats | Total | No. | Value | No. | Value | |||
| No. | Value | No. | Value | |||||
| 1959 | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| January | 811 | 2,392 | 897 | 3,730 | 1,227 | 1,048 | 2,124 | 4,778 |
| February | 1,172 | 3,409 | 1,273 | 3,929 | 1,841 | 1,060 | 3,114 | 4,989 |
| March | 1,201 | 3,343 | 1,315 | 5,290 | 2,190 | 2,142 | 3,505 | 7,432 |
| April | 1,263 | 3,698 | 1,384 | 4,814 | 2,457 | 1,056 | 3,841 | 5,870 |
| May | 1,180 | 3,358 | 1,283 | 4,582 | 2,175 | 1,153 | 3,458 | 5,736 |
| June | 1,188 | 3,443 | 1,314 | 4,289 | 2,334 | 1,819 | 3,648 | 6,109 |
| July | 1,436 | 4,204 | 1,564 | 5,670 | 2,219 | 1,188 | 3,783 | 6,858 |
| August | 1,405 | 4,065 | 1,528 | 5,407 | 2,127 | 1,520 | 3,655 | 6,927 |
| September | 1,462 | 4,252 | 1,612 | 5,933 | 2,272 | 1,894 | 3,884 | 7,826 |
| October | 1,454 | 4,172 | 1,593 | 5,293 | 2,207 | 1,877 | 3,800 | 7,170 |
| November | 1,499 | 4,327 | 1,644 | 5,139 | 2,219 | 1,298 | 3,863 | 6,437 |
| December | 1,077 | 3,206 | 1,214 | 5,699 | 2,013 | 1,359 | 3,227 | 7,058 |
| 1960 | ||||||||
| January | 1,024 | 3,012 | 1,104 | 4,804 | 1,494 | 1,234 | 2,598 | 6,038 |
| February | 1,426 | 4,131 | 1,541 | 5,132 | 2,063 | 1,196 | 3,604 | 6,328 |
| March | 1,763 | 5,174 | 1,941 | 7,525 | 2,823 | 2,889 | 4,764 | 10,414 |
| April | 1,216 | 3,627 | 1,333 | 5,015 | 2,329 | 1,223 | 3,662 | 6,238 |
| May | 1,683 | 4,868 | 1,766 | 6,395 | 2,910 | 2,380 | 4,676 | 8,775 |
| June | 1,317 | 3,947 | 1,388 | 4,901 | 2,556 | 2,687 | 3,944 | 7,588 |
| July | 1,388 | 4,057 | 1,480 | 4,984 | 2,446 | 3,625 | 3,926 | 8,609 |
| August | 1,620 | 4,842 | 1,728 | 7,083 | 2,707 | 2,687 | 4,435 | 9,770 |
| September | 1,589 | 4,821 | 1,691 | 5,658 | 2,556 | 2,615 | 4,227 | 8,272 |
| October | 1,376 | 4,171 | 1,472 | 8,044 | 2,405 | 2,213 | 3,877 | 10,256 |
| November | 1,553 | 4,715 | 1,663 | 6,866 | 2,562 | 2,015 | 4,225 | 8,881 |
| December | 1,103 | 3,433 | 1,188 | 4,274 | 2,105 | 1,976 | 3,293 | 6,250 |
HOUSES AND FLATS COMPLETED – Local authorities which supply building-permit figures also give particulars of new houses and flats which were completed in their districts.
Statistics of completed houses and flats include any new flats which are created by the conversion of existing buildings, details of which are shown previously. Some difficulty is encountered in obtaining accurate figures for completions from a few local authorities, and in some cases estimates have been made, either by the local authorities concerned, or by the Department of Statistics. While it is therefore believed these figures are reasonably accurate, and enable a comparison to be made of year-to-year changes, it is the practice of the Department to round completed figures to the nearest hundred. All houses and flats completed by the Government are included.
The results of this collection of statistics for the latest five years are given in the following table.
| District | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban districts | 14,200 | 14,300 | 13,700 | 14,800 | 16,900 |
| Rural districts | 5,000 | 4,900 | 4,900 | 4,800 | 4,700 |
| Totals | 19,200 | 19,200 | 18,600 | 19,600 | 21,600 |
The number of houses and flats completed in 1959–60 was the highest recorded since the inception of this collection in 1948–49, being 2,000 higher than the previous record figure of 19,600 in 1958–59.
JOINT FAMILY HOMES – The Joint Family Homes Act 1950, including amendments, aims at promoting a sense of dual ownership under which the family home will belong not to the husband or wife separately, but to both of them jointly so as to pass to the survivor on the death of one of them. The Act makes it possible for a husband and his wife, or either of them, being solvent and owning land, whether freehold or leasehold, to settle the land on the husband and wife as a joint family home, provided they actually reside and have their home in a dwellinghouse erected on the land, and use it exclusively or principally as a home for themselves and the members of their household. No one can register more than one home as a family home. Registration is cancelled when the land is sold or when both husband and wife have died or have ceased permanently to reside and have their home on the land. The benefits of registration are considerable. Once the home is registered the husband and wife have equal rights in connection with ownership and possession while they are both living. On the death of either of them the joint family home becomes the property of the survivor. To encourage the adoption of the scheme provision is made that the settled home shall be protected against the claims of creditors to the extent of £2,000, and an amount of £3,000 will not come into the calculation made for the purpose of the assessment of death and succession duties when it passes on the death of one joint tenant to the survivor. The settled home is also protected from gift duty and stamp duty on the creation of the settlement.
Joint family homes under the Joint Family Homes Act 1950 registered for the latest seven years are shown in the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Homes Settled |
|---|---|
| 1954 | 4,808 |
| 1955 | 4,477 |
| 1956 | 5,363 |
| 1957 | 5,655 |
| 1958 | 6,262 |
| 1959 | 7,052 |
| 1960 | 11,195 |
Recent increases up till 1959 were due largely to the gradual relaxing of restrictions on settlement which originally applied. The Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act passed in 1959 caused a very substantial increase due mainly to the condition attaching to capitalisation of the benefits that the home, if not in the sole name of the beneficiary, be settled as a joint family home.
TENANCY – The Tenancy Act 1955 is the enactment at present governing tenancy and rents. This Act is administered by the Department of Labour. Earlier the Tenancy Act 1948 had replaced the considerable body of fair rents legislation passed during the period 1936 to 1947. (This legislation was summarised on pages 1076–77 of the 1958 issue of the Yearbook and in earlier volumes).
Up to the passing of the Tenancy Act 1955, rent for dwellinghouses erected prior to 1942 was based on their value as at 1942 increased by 15 per cent. The 1955 Act provided for a further increase of 20 per cent on the basis of valuation (i.e., a rent based on a value exceeding the 1953 fair rent value by 20 per cent and by the cost of improvements made after 1 September 1942 and including an allowance to cover outgoings). For dwellinghouses built since 1942, or purchased after February 1950 and let after December 1951, and after the date of purchase, the rent may be based on the capital cost to the landlord when built or purchased, increased by the cost of improvements made and an allowance to cover outgoings, or on the same basis as dwellings erected prior to 1942, whichever is the greater. The maximum interest rate which may be applied to the value of the premises in assigning the fair rent has been fixed by the Tenancy Regulations 1956 at 5 per cent. Where, however, there is a mortgage on the premises at a higher rate of interest, such rate of interest may be applied to as much of the value of the premises as is represented by the mortgage.
A landlord or a tenant is enabled to apply to the Court to fix the fair rent, or the parties may agree on a rent and submit this for the approval of a Rents Officer.
A landlord or a tenant may apply to a Rents Officer to assess the fair rent. Notice of his assessment is given to both parties, stating that it will become the fair rent as if fixed by the Court unless application is made within 21 days by either party to the Court to fix the fair rent. This procedure enables either party to have the fair rent assessed without cost.
The rent of commercial properties may be based on the present-day values; the 1955 Act did not alter the law in this respect.
The provisions as to rent restriction of tenancies (inclusive of subtenancies) relates to dwelling-houses and to properties, except that the definition of the term “property” excludes farm lands and licensed hotels and camp sites (let for periods not exceeding six weeks). The definition of the term “rent” includes money's worth. The Court for fixing the fair rent is the Magistrate's Court, with a right of appeal to the Supreme Court where the fair rent exceeds an annual rental of £525.
The following exemptions from the operation of the Act are contained in the Tenancy Act 1955: all new dwellinghouses and properties erected after the date of commencement of the Act (21 October 1955), as well as the existing exemptions of blocks of flats and buildings converted into self-contained flats after 12 November 1953; new tenancies of dwellinghouses not let during the three months prior to the date of commencement of the Act; dwellinghouses let for periods of six weeks or less; and properties let after October 1955 for terms of not less than four years.
A section extends to all premises the provision which prevents the basic rent from being affected by including furniture in the tenancy. As far as a “fair rent” is concerned, the Court can fix the fair rent payable by the landlord where he is himself a tenant. A fair rent fixed for a dwellinghouse or property continues in force until a subsequent order takes effect.
A section relating to fines, premiums, etc., prohibits a landlord or outgoing tenant from receiving from a new tenant any consideration other than:
In the case of a dwellinghouse, the rent:
In the case of either a dwellinghouse or property, the price of any chattels not exceeding the fair selling value, or the replacement cost of stock in trade.
The time within which excess payments of rents may be recovered from the landlord by the tenant or deducted from current rent is 12 months.
Exemption from the restrictions on recovery of possession from a tenant is provided for where, in the case of the letting of any dwellinghouse or property, the landlord and the tenant by agreement in writing dated not earlier than 1 March 1950, and incorporating the terms and conditions of the tenancy, have agreed that Part IV and sections 45, 46, and 47 of the Tenancy Act or the corresponding portions of the former 1948 Act shall not apply. The agreement has to be approved in writing by a Rents Officer, and a copy of the agreement deposited with the latter before the date of commencement of the tenancy. In the following cases also those provisions containing the restrictions on recovery of possession cease to apply – namely, a dwellinghouse let to a worker by his employer; a dwellinghouse or urban property let on behalf of a mental patient; where a tenant has sublet the whole of the dwellinghouse, provided that the subletting is not due to the temporary absence of the tenant for not more than a year; and to a tenancy of any urban property transferred either directly or by subtenancies, after the expiration of six months from the. date of the transfer of the tenancy unless the landlord consents or the Court orders that those provisions shall continue. The Act also includes in the list of exemptions leases of properties for more than five years.
The Act provides for recovery of possession on the following grounds:
Failure to pay rent or to comply with other conditions of the tenancy:
Failure to take reasonable care of premises or the tenant has committed waste:
Tenant is guilty of conduct that is a nuisance or annoyance to adjoining or neighbouring occupiers. Where application on this ground has not been successful, the Court may order the cessation of restrictions after six months, unless the landlord's conduct has contributed to the circumstances complained of. The order may be revoked within five months on the ground that the circumstances had been improved:
and
For a dwelling or a property, that the premises are reasonably required by the landlord or joint landlords for his or their own occupation:
and
For a dwelling or a property, that the landlord is a trustee, and the premises are required by the beneficiaries under the trust for their own occupation:
and
For a dwelling or a property, that an agreement for its sale has been made and that the premises are required by the purchaser for his occupation:
For a dwelling forming part of the same building as the one occupied by the landlord, that the premises are reasonably required for the aged parents of the landlord or, where the landlord is an aged parent, for the son or daughter to live with the landlord:
For a dwelling, that the premises are required for occupation by any person in (or intended to be in) the regular employment of the landlord:
The tenant, by subletting the premises, or part thereof, is making a profit which, compared with the rent paid, is unreasonable:
For a property, that possession is required only of a part of the premises in excess of the reasonable requirements of the tenant:
For a dwelling, that the premises are not reasonably required for occupation as such by the tenant:
That the estate or interest of the landlord in the premises will have expired or been determined not later than three months after the date of the application for the order:
That the premises are required for demolition or reconstruction or for removal to another site:
That the landlord is an administrator of the estate of the deceased former landlord, and the premises are required for sale for the purpose of distributing the estate:
That suitable alternative accommodation is available for the tenant or will be available for him when the order takes effect.
Suitable alternative accommodation has to be provided or greater hardship established before orders can be made in respect of applications on grounds (d), (e), (f), (g), (k), (o), listed above. Suitable alternative accommodation is also required for grounds (h), (i), (p), or (q).
In any Court proceedings on ground (r) the onus of proving that the accommodation offered is suitable is placed on the applicant for the order. In any proceedings except on ground (r), where the Court is satisfied that any alternative accommodation is or will be available for the tenant, that accommodation shall be deemed to be suitable unless the Court is satisfied that it is inadequate for the needs of the tenant, or is of unreasonably low standard, or is for any special reason unsuitable for the tenant.
Neither alternative accommodation nor greater hardship provisions apply, although relative hardship is taken into account, for cases (i) where the landlord of a dwelling has been such for a period of three years prior to application date, or if in receipt of an age benefit and has also been a landlord for two years, (ii) where the landlord of property has given one year's notice, and has been such for two years prior to the notice, although the Court may adjourn proceedings for up to six months if it considers that it is just and equitable to do so.
Relative hardship is still taken into account for the remaining grounds, with the following exceptions: The alternative accommodation, greater hardship, or relative hardship requirements do not apply where a dwelling is required by the landlord for his own occupation if (i) he is 60 years of age, or if a woman, she is 55 years, (ii) he has given six months' notice, (iii) he has been the landlord for three years immediately prior to the notice, and (iv) he did not have adequate and suitable living accommodation in premises owned by him. Relative hardship is not required to be established for applications on ground (q) listed earlier.
The Act also provides that the landlord or other person represented as requiring possession of premises for his own occupation is restricted from letting or selling the premises for a period of two years, unless an authoring order is obtained from the Magistrate's Court.
Other conditions of the Act give the landlord of a dwellinghouse or property a right to apply for an order for the recovery of excess land for building purposes, or for sale for that purpose or for the purposes of his business, or for an order authorising him to convert a dwellinghouse into flats, one to be let to the existing tenant with appropriate adjustment of rent payable and subject to the Act to the same extent as the old tenancy, and also make it an offence for a landlord to evict a tenant without an order of a Court or the tenant's consent; extend protection of tenancy in case of death to members of the deceased's family; preserve a tenancy for the wife or husband of the tenant in cases of separation or desertion; prescribe conditions implied in tenancies; require receipts to be given for rent payments; make it an offence for a landlord to deprive a tenant of his amenities, as by cutting off electric power, gas, or water; and deal with the case of unauthorised occupiers.
The Destitute Persons Amendment Acts 1951 and 1953 contain provisions relating to the power of a Magistrate, in making a separation or guardianship order, to vest the tenancy of a dwelling-house in any person, either complainant or defendant, and giving the landlord the right to apply for cancellation or variation of such a vesting order.
Regulations made under the Emergency Forces Rehabilitation Act 1953, replacing earlier legislation, govern the protection against eviction granted to servicemen who serve in any of the forces raised to meet an emergency arising out of the obligation undertaken by New Zealand in the Charter of the United Nations.
GENERAL – Electric power distributed for public use in New Zealand has been generated principally by water power, most of the fuel plants in operation previously having been maintained for standby purposes and to meet peak loads. This is not the case with Wairakei geothermal steam station and Meremere coal-fired steam station, both of which commenced generating late in 1958, for both these will operate at a high-load factor. During the year ended 31 March 1960 a total of 6,349,086,000 kWh was generated by public utilities, of which 5,483,166,000 kWh (86 per cent) was generated by water power, 876,302,000 kWh by steam engines, and 1,214,000 kWh by oil engines. A further 11,596,000 kWh was purchased by public supply authorities from generating stations operated by industrial establishments and fed into the supply system, making a total of 6,360,682,000 kWh available for distribution. By far the major portion of the generation is undertaken by Government-owned plants, which, in the period under review, generated 5,185,338,000 kWh by the use of water power, 864,707,000 kWh by use of steam power, and 20,700 kWh by use of oil engines.
During and following the Second World War the quantity of power was not sufficient to satisfy requirements and restrictions on the use of power were necessary, but by the end of 1958 it was possible to lift all restrictions.
The following table shows the annual and daily average quantities of electricity generated for public supply over the latest 11 years. Index numbers are on base 1954 (= 100).
| Year Ended 31 March | North Island | South Island | New Zealand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Quantity | Daily Average | Index No. | Total Quantity | Daily Average | Index No. | Total Quantity | Daily Average | Index No. | |
| (000) kWh | (000) kWh | (000) kWh | |||||||
| 1950 | 2,024,571 | 5,547 | 73 | 1,011,200 | 2,770 | 80 | 3,035,771 | 8,317 | 75 |
| 1951 | 2,054,696 | 5,629 | 74 | 1,042,000 | 2,855 | 82 | 3,096,696 | 8,484 | 77 |
| 1952 | 2,335,702 | 6,382 | 84 | 1,126,600 | 3,078 | 88 | 3,462,302 | 9,460 | 86 |
| 1953 | 2,391,827 | 6,553 | 87 | 1,187,200 | 3,253 | 93 | 3,579,027 | 9,806 | 89 |
| 1954 | 2,758,132 | 7,557 | 100 | 1,271,359 | 3,483 | 100 | 4,029,491 | 11,040 | 100 |
| 1955 | 3,066,970 | 8,403 | 111 | 1,316,255 | 3,606 | 104 | 4,383,225 | 12,009 | 109 |
| 1956 | 3,323,888 | 9,082 | 120 | 1,424,446 | 3,892 | 112 | 4,748,334 | 12,974 | 118 |
| 1957 | 3,540,088 | 9,699 | 128 | 1,427,274 | 3,910 | 112 | 4,967,362 | 13,609 | 123 |
| 1958 | 3,955,782 | 10,838 | 143 | 1,688,367 | 4,626 | 133 | 5,644,149 | 15,463 | 140 |
| 1959 | 3,892,377 | 10,664 | 141 | 1,785,035 | 4,891 | 140 | 5,677,412 | 15,555 | 141 |
| 1960 | 4,419,558 | 12,075 | 160 | 1,941,124 | 5,304 | 152 | 6,360,682 | 17,379 | 157 |
LEGISLATIVE BACKGROUND – The provisions of earlier Acts were consolidated in 1928 in the Public Works Act, placing all hydro-electric development under the control of the Public Works Department, and authorising that Department, in certain circumstances, to delegate the right to use water power for the generation of electricity. Amended regulations concerning delegation of this right were published in 1934, and in 1945 the Electricity Act was passed, creating the State Hydroelectric Department, which under this Act took over the control of hydro-electric development previously exercised by the Public Works Department. With the passing of the Electricity Amendment Act 1958 the official name of the Department became New Zealand Electricity Department as from 23 September 1958, and the Minister in charge became the holder of the major portfolio of Minister of Electricity.
The Electric Power Boards Amendment Act 1952 was passed with the object of maintaining existing gas supplies as far as possible in order to reduce added demands for electric power. In 1955 the Electricity and Gas Coordination Committee was set up, by an Act of the same name, and, following its report, all but three of the 34 gas undertakings then operating were declared essential in the national interest. The report was tabled in Parliament, and as a result there was passed the Electricity and Gas Coordination Act 1956, which empowered electrical supply authorities to acquire essential gas undertakings. In 1958 the Gas Industry Act, which revoked the 1956 Act, set up the New Zealand Gas Council which administers the Gas Industry Account from which subsidies and grants are paid. The Council advises the Government on matters relating to the preservation and expansion of the gas industry.
DEVELOPMENT OF WATER POWER: North Island – The Waihi Gold Mining Co. Ltd. constructed the first large hydro-electric scheme at Horahora, which supplied power for the operation of a quartz battery at Waikino and the mine at Waihi, supply commencing in 1913. This station was purchased by the Government in 1919, and its capacity of 6,300 kW was increased to 10,300 kW in 1925, work being commenced on the Arapuni station (also on the Waikato River) at about the same time. These two stations were linked when Arapuni came into operation (with one unit) in 1929, but Arapuni was closed down between 1930 and 1932 as a result of damage caused by an earth movement. By 1946 Arapuni had eight units operating, while construction work was in progress at Karapiro (commenced 1940) and Maraetai (commenced 1945). Karapiro station came into operation in 1947–48 with three units, each of 30,000 kW, the Horahora station ceasing generation prior to its site being submerged by the newly formed Karapiro lake. This artificial lake is 14 miles long and extends up river to Arapuni. Late in 1952 the Maraetai station was brought into operation and by the end of June 1953 three machines were producing 108,000 kW. The fourth machine was commissioned in January 1954 and the fifth machine in May 1954, bringing Maraetai to its full rating of 180,000 kW. Construction on Whakamaru commenced in 1949; the station was commissioned with two machines in May 1956 and completed in December 1956 with four machines rated at 100,000 kW. Atiamuri station was begun in 1953 and the first machine was commissioned in November 1958, reaching its originally planned capacity of 63,000 kW from three machines in May 1959. The station will now have installed an additional machine for peak-load purposes.
Arapuni, Karapiro, Maraetai, Whakamaru, and Atiamuri power stations have been constructed on the Waikato River. Two other stations are in the course of construction – namely, Waipapa and Ohakuri (scheduled for first operation in 1961). A station to be built at Aratiatia is scheduled for completion in 1964 with a capacity of 90,000 kW. Government has also approved the duplication of Maraetai powerhouse with two 36,000 kW machines to be installed initially. These stations will make use of the greater part of the fall of the Waikato River from Lake Taupo to Cambridge. This river constitutes the principal power source in the North Island, having, in its course of 200 miles from Lake Taupo, a total fall of 1,170 ft and a final discharge of over 10,000 cusecs. The rate of flow from Lake Taupo is controlled by works constructed in 1941 to conserve the water previously lost in the heavy spring and summer run-off.
The Mangahao station, of 19,200 kW capacity, was actually the first station constructed in the North Island by the Government. It is situated in the Tararua Ranges, and commenced supply to the surrounding area at the end of 1924.
After the Mangahao station was completed a commencement was made in 1926 on the development of the Waikaremoana scheme, which consists of three stations, Kaitawa, Tuai, and Piripaua. The first station completed, Tuai, commenced supply in 1929 with a capacity of 32,000 kW, increased in 1939 to 52,000 kW; Piripaua station (40,000 kW) was completed in 1943; and Kaitawa station (32,000 kW) in 1948. The three stations are within a distance of 5 miles, and the power generated by each is collected and transmitted from Tuai, the centre station.
The Waikato, Mangahao, and Waikaremoana stations are linked and operate as one system. Connections also exist with all the larger non-Government generating stations (steam and hydro) and steam plants maintained by the Government. To transmit power for distribution from the new stations on the Waikato, a 220,000-volt system has been added to the existing network of 110,000-and 50,000-volt transmission lines and interconnected substations. From Whakamaru collecting station, electricity is now transmitted to the new major substations at Otahuhu in the north and Bunnythorpe and Haywards in the south.
South Island – The Lake Coleridge station was commenced in the year following the passing of the Aid to Water Power Works Act 1910 and completed in 1915. This was the first station wholly designed and constructed by the Government. Its initial capacity was 4,500 kW, but by 1930 this was increased to 34,500 kW. The next station, Waitaki, commenced in 1928, came into use in 1935, and with the commissioning of its fifth machine in March 1949 was developed to its originally designed capacity of 75,000 kW. This was later increased by the addition of two further units which came into operation in May and June 1954. With a total capacity of 105,000 kW Waitaki is the next largest station to Roxburgh operating in the South Island. Further use of the Waitaki River at Black Jack's Point is to be made, where Benmore station of at least 540,000 kW capacity is in the initial stages of construction. Control works were built at Lakes Pukaki and Tekapo, to ensure an adequate water supply to Waitaki stations during the winter, and a single unit of 25,200 kW, incorporated in the control works at Lake Tekapo, was commissioned in May 1951. Another single unit, also of 25,200 kW, was installed in 1945 at Highbank to make use of the surplus water available in winter from the Rangitata irrigation race.
In 1936 the Government took over the Southland Electric Power Board's system, including the generating station at Lake Monowai, and in 1938 acquired from the Grey Electric Power Board the Arnold station at Kaimata.
Construction of the Cobb River station, with a capacity of 12,000 kW, was commenced by a private company, but the project was taken over and completed by the Government. Supply from this station, which has now been expanded in capacity to 32,000 kW, commenced in 1944.
The Roxburgh station on the Clutha River will ultimately have a capacity of 320,000 kW. First operation of this station was in July 1956, and by December 1956 four machines with a capacity of 160,000 kW were commissioned. Preliminary work has begun on the installation of the other four machines. Investigation and access roading work was carried on at Lake Rotoroa in connection with the proposed Braeburn scheme of about 60,000 kW capacity. The Government, however, announced in 1955 that instead of building Braeburn in the meantime it would go ahead with 220 kV transmission from Islington to provide further supply to the Nelson-Marlborough area.
A grid system similar to that in the North Island was established in 1939, when the Lake Monowai, Arnold, Lake Coleridge, and Waitaki stations were linked. A 220,000-volt line was constructed from Roxburgh to a major substation at Islington to bring the power from Roxburgh. From Islington a 220,000-volt line was extended to Kikiwa in the Nelson Provincial District and completed in 1958. This linked the Nelson-Marlborough area with the main South Island network.
THERMAL STATIONS – In the North Island a steam station at King's Wharf, Auckland, and one at Evans Bay, Wellington, with a combined capacity of 49,000 kW are now used only for peak-load and emergency purposes. Two small diesel plants in the South Island with a total capacity of 8,110 kW are now rarely used. In order to provide additional power in the North Island, a coal-fired steam station has been constructed near Mercer, on the Waikato River. Meremere station, as it is called, was commenced in 1956 and first commissioned with two machines in August 1958 and completed in 1960 with six machines rated at 180,000 kW. Coal to feed the boilers is being obtained from Huntly mines and is also being brought by aerial cableway across the swamps from opencast mines at Maramarua.
GEOTHERMAL STEAM – At Wairakei station, a few miles north of Taupo, geothermal steam is being harnessed for the generation of electricity and the first machine in the initial 69,000 kW development commenced generating in November 1958. Bores which are 4, 6, or 8 in. in diameter have been drilled to depths varying between 570 ft and 4,000 ft. With closed bores, well-head pressures vary between 50 and 500 lb per sq. in. High-pressure valves are required to control the output from the bores. The quantity of steam discharged from the bores varies considerably, and a large quantity of water is ejected with the steam. The steam contains a trace of gas, mostly carbon dioxide; and in the water about three parts in a thousand are dissolved solids.
Steam is collected from a number of wells after being separated from the water that is ejected with it and piped to the power station through steel mains. From the mains the steam passes through high-pressure, intermediate-pressure, and low-pressure turbo-alternators, after which it is condensed to water and discharged into the Waikato River. The initial development of 69,000 kW from seven turbo-alternators is known as Stage I, and all the plant is housed in a building known as Station A. Stage II development was authorised by Government in September 1957 and will bring the station capacity up to 151,400 kW. Some of the plant for Stage II will be housed in space left for the purpose in Station A, but most of it will be located in a new building to be known as Station B. This building will also provide space for a projected further development, which could bring the total capacity up to 250,000–280,000 kW.
With Stage II an experimental pilot plant for converting some of the hot water from the wells into steam at a lower pressure will be installed. The steam will be produced by piping the hot water to the station at a high pressure and spraying it into “flash” tanks where, due to a drop in pressure, it will be “flashed” into steam and fed into the low-pressure steam mains and thence to the turbines.
COOK STRAIT SUBMARINE POWER CABLE – The Government announced in March 1956 that it had been decided to proceed immediately with a detailed investigation into the practicability of linking the power systems of the North and South Islands by a submarine cable across Cook Strait. The interconnection by a direct-current cable designed for 600,000 kW capacity was investigated and a trial length of cable which was laid in Cook Strait in May 1958 was lifted in March 1960 and returned to the manufacturers in England for inspection. An overseas firm of consultants furnished an independent report in 1959 for Government consideration. The report stated that the installation of submarine power cables across Cook Strait would be difficult but the project was feasible. In March 1961 the Government decided to install cables across Cook Strait.
BASIS OF FORWARD PLANNING – In March 1957 a Combined Committee, consisting of two members of the State Hydro-electric Department (now the Electricity Department), two members of Ministry of Works, and six members from engineers actively serving with the electrical supply authorities, reported to the Government advising how the increasing demand could be met. In June 1957 the Government announced that the report was approved in principle as a basic plan for the comprehensive and orderly development of a power system to meet the full needs of the country, the programme being estimated to cost some £235 million in the 13 years from 1958 onwards. The committee's report was published. In August 1958 a statement was presented to Parliament reviewing the position and introducing modifications to the plan, and it was then announced that a permanent departmental committee was to be set up to report annually on the whole matter of power planning, and that another committee with representatives of the New Zealand Electricity Department, the Government Statistician, and of electrical supply authorities would be appointed to report annually on future power requirements; the first reports of these committees were presented to Parliament in September 1959. The committee to review power requirement's considered estimates from the supply authorities and estimates from the Government Statistician before recommending schedules for the use of the Planning Committee. The Planning Committee, under the Chairmanship of the Minister of Electricity, with representatives of the New Zealand Electricity Department, Ministry of Works, and Treasury accepted the schedules from the power needs committee and recommended that, in addition to the works in hand, the Matahina scheme on the Rangitaiki River should be approved as preferable to the Kaituna scheme. Further planning for the future could not be completed in the absence of the consultant's report on the inter-Island connection by submarine cable, and it was stated the committee would meet again as soon as that report was available to give urgent consideration to the steps to be taken to cope with the North Island problem from 1965 onwards. Up to that date the power supply in both Islands should be satisfactory.
In December 1960 the Planning Committee was reconstituted along the lines of the previous Combined Committee, but with only three engineering representatives of the supply authorities, and this Committee reported in March 1961 on future power needs. Following consideration of this report the Government decided to adopt a seven-year programme of electricity generation at an estimated cost of £45 million. This involves the construction of an inter-connecting transmission system between the North and South Island power systems to come into operation in 1965, the construction of Aviemore power station (200,000 kW) on the Waitaki River to come into service in 1968, and the construction of Kopuriki power station on the Rangitaiki River to come into service in 1968.
To finance the huge outlay involved in electricity development the New Zealand Electricity Department drew up a plan which involved decreasing dependence on loan moneys, thus reducing the interest bill as well as stabilising the price. Legislation was passed in 1957 which made the Department no longer liable for income tax, provided that interest formerly capitalised be charged to revenue, and allows for revenue to provide a direct contribution towards capital requirements. This last provision has been deferred meanwhile until 1961.
GOVERNMENT STATIONS – The following table covers all Government plants in operation and those under construction or for which contracts for machinery have been let, and shows the installed capacity and ultimate installed capacity, together with the static head.
| Name of Station | Installed Capacity at 31 March 1961 | Ultimate Installed Capacity | Static Head (ft) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Units | kW | kVA | Number of Units | kW | kVA | ||
| *Under construction. | |||||||
| Hydro | |||||||
| Arapuni | 8 | 157,800 | 180,000 | 8 | 157,800 | 180,000 | 175 |
| Karapiro | 3 | 90,000 | 100,000 | 3 | 90,000 | 100,000 | 100 |
| Maraetai | 5 | 180,000 | 200,000 | 10 | 360,000 | 400,000 | 200 |
| Whakamaru | 4 | 100,000 | 111,000 | 4 | 100,000 | 111,000 | 124 |
| Atiamuri | 3 | 63,000 | 70,000 | 4 | 84,000 | 93,333 | 82 |
| Waipapa* | .. | .. | ... | 3 | 51,000 | 56,667 | 54 |
| Ohakuri | 2 | 56,000 | 62,222 | 4 | 112,000 | 124,444 | 115 |
| Aratiatia* | ... | ... | ... | 3 | 90,000 | 100,000 | 109 |
| Matahina* | ... | ... | ... | 2 | 70,000 | 77,778 | 195 |
| Mangahao | 5 | 19,200 | 24,000 | 5 | 19,200 | 24,000 | 896 |
| Waikaremoana – | |||||||
| Kaitawa | 2 | 32,000 | 38,000 | 2 | 32,000 | 38,000 | 443 |
| Tuai | 3 | 52,000 | 62,200 | 3 | 52,000 | 62,200 | 676 |
| Piripaua | 2 | 40,000 | 44,400 | 2 | 40,000 | 44,400 | 370 |
| Cobb River | 6 | 32,000 | 37,222 | 6 | 32,000 | 37,222 | 1,876 |
| Arnold | 2 | 3,060 | 3,600 | 2 | 3,060 | 3,600 | 42 |
| Lake Coleridge | 9 | 34,500 | 40,640 | 9 | 34,500 | 40,640 | 490 |
| Highbank | 1 | 25,200 | 28,000 | 1 | 25,200 | 28,000 | 330 |
| Waitaki | 7 | 105,000 | 116,666 | 7 | 105,000 | 116,666 | 70 |
| Benmore* | 6 | 540,000 | 675,000 | 305 | |||
| Lake Tekapo | 1 | 25,200 | 28,000 | 1 | 25,200 | 28,000 | 80–105 |
| Roxburgh | 4 | 160,000 | 177,777 | 8 | 320,000 | 355,555 | 150 |
| Monowai | 3 | 6,000 | 7,050 | 3 | 6,000 | 7,050 | 154 |
| Thermal | |||||||
| Meremere | 6 | 180,000 | 211,764 | 6 | 180,000 | 211,764 | - |
| Evans Bay | 4 | 22,000 | 27,500 | ... | ... | ... | - |
| King's Wharf | 4 | 27,000 | 33,800 | ... | ... | ... | - |
| Stoke | 6 | 2,350 | 2,937 | 6 | 2,350 | 2,937 | - |
| Dobson | 4 | 5,760 | 7,200 | 4 | 5,760 | 7,200 | - |
| Geothermal | |||||||
| Wairakei | 8 | 80,070 | 89,000 | ||||
| Totals | 102 | 1,498,140 | 1,702,978 | ||||
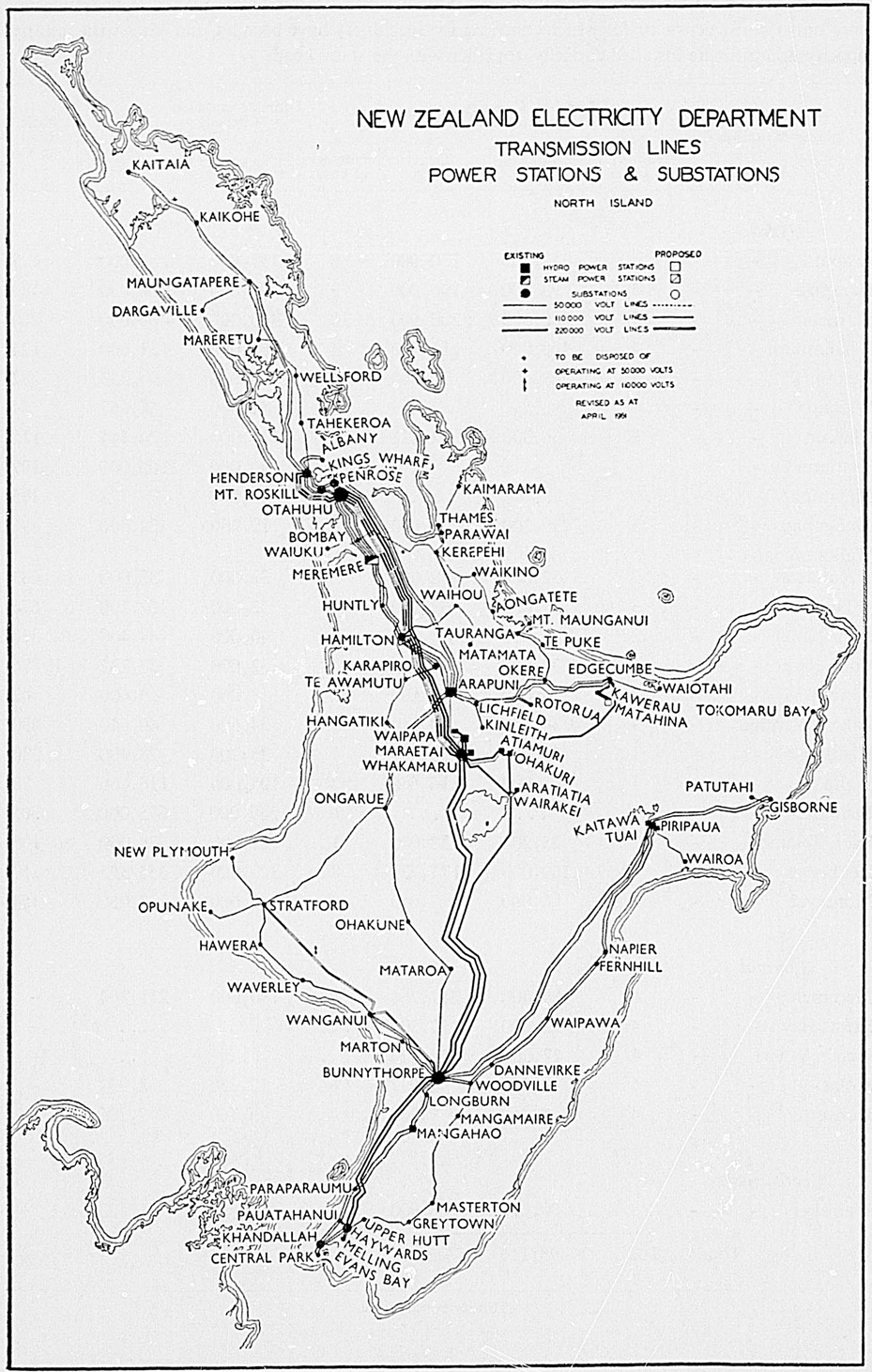
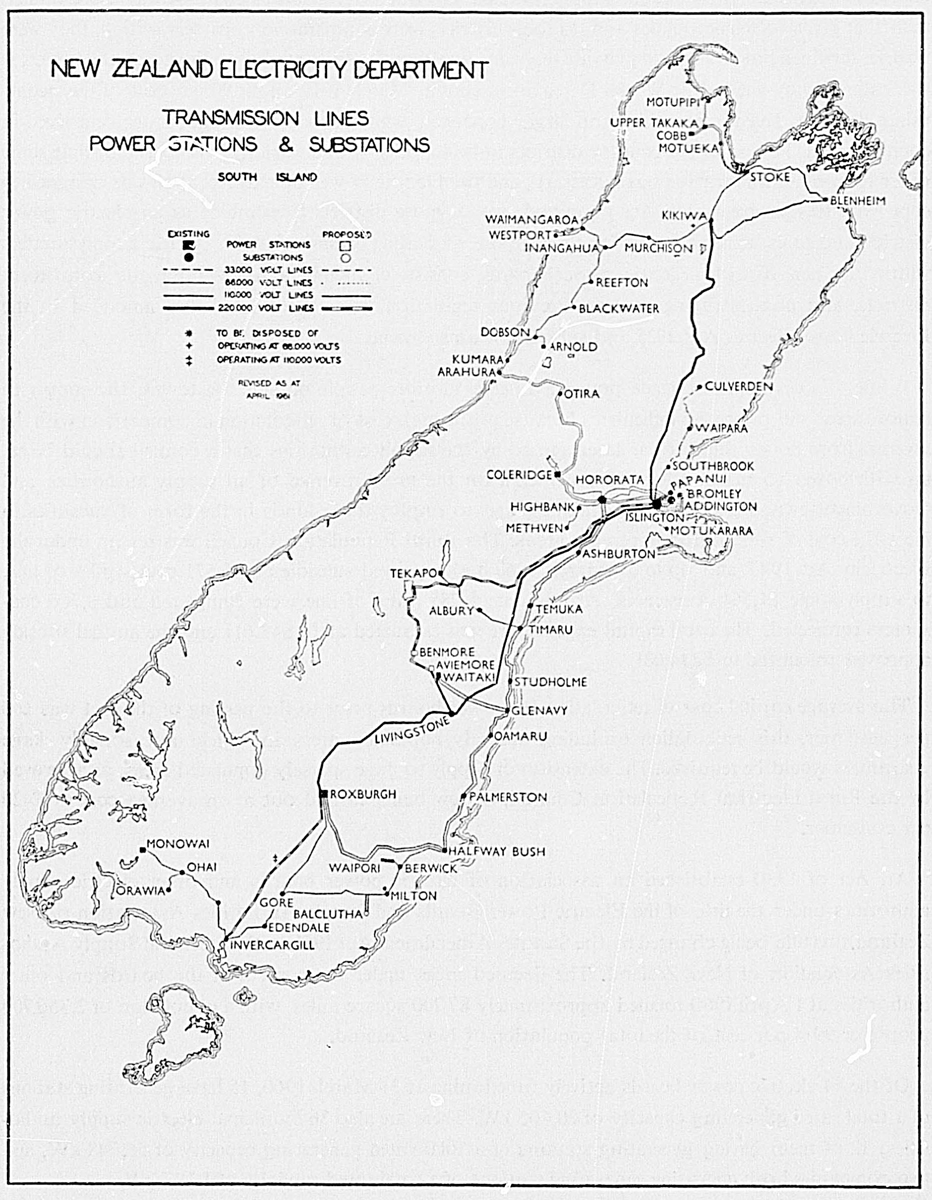
ELECTRIC POWER BOARDS – The Counties Act and Municipal Corporations Act passed in 1886 empowered county authorities and municipal corporations to arrange for the supply of electricity in the areas under their control, and until 1918 no provision was made for the constitution of bodies to attend solely to electric supply matters. The authority given to counties was more limited than that given to municipalities and, as their districts were comparatively sparsely settled, they were unable, for financial reasons, to provide the same electrical facilities as those enjoyed by the towns. It was estimated by the Public Works Department that in March 1919 about 90 per cent of the people using electricity lived in the cities and larger boroughs, while probably less than 1 per cent lived in country areas. To enable the country districts to be supplied with electricity it was evident that some other form of administration was necessary, and the Electric Power Boards Act 1918 was designed to cope with this problem. The Act permitted two or more districts to combine as an electric power district, and to establish a board for the purpose of dealing exclusively with electric supply matters within the new district. Electric power boards consist of members representing the constituent districts, and possess rating powers. Previous legislation was consolidated and amended in the Electric Power Boards Act 1925 and subsequent amendments.
While this development made power available to more people outside the towns, the supply to remote areas still presented difficulties because of the high cost of reticulation in comparison with the revenue from power sold. It was later agreed by the supply authorities that a council should be set up with power to make a levy of 1/4 per cent on the gross revenue of all supply authorities and Government-owned electrical undertakings, and to employ these funds in the form of subsidies to meet the cost of reticulation in remote areas. The Rural Reticulation Council was set up under the Electricity Act 1945, and up to 31 March 1960 had approved subsidies on 6,571 route-miles of line, to supply some 11,564 consumers. At this date 5,285 miles of line were completed and 8,766 consumers connected. The total capital expenditure was estimated at £4,843,611 and the annual subsidy approved amounted to £214,081.
The average capital cost of reticulation by power boards prior to the passing of the Act was £60 per customer, this reticulation excluding sparsely populated areas in which unreasonably large guarantees would be required. The extension of supply to these sparsely populated areas, as approved by the Rural Electrical Reticulation Council, is now being carried out at an average cost of £420 per consumer.
An Act of 1930 established an association of electric power boards and other electric supply authorities under the title of the Electric Power Boards and Supply Authorities Association of New Zealand, this title being changed by the Statutes Amendment Act 1951 to the Electrical Supply Authorities Association of New Zealand. The licensed areas under the control of the boards and other authorities at 1 April 1960 totalled approximately 87,700 square miles, with a population of 2,356,700 people or 99.4 per cent of the total population of New Zealand.
Of the 44 electric power boards actively functioning at 31 March 1960, 15 have generating stations of a total rated generating capacity of 20,465 kW. There arc also 36 municipal electric supply authorities, 12 of them having generating stations of a total rated generating capacity of 56,748 kW, and two companies both operating generating stations of a total rated capacity of 1,197 kW.
In February 1959 a Commission of Inquiry was appointed to inquire into the organisation and efficiency of the distribution of electricity, the retail charges therefor, and other relevant matters, and reported in December 1959. The report is obtainable from the Government Printer.
REVIEW OF OPERATIONS: Government Establishments – The following table gives details of the operations of Government establishments generating and distributing electricity during the years 1957–58, 1958–59, and 1959–60. It includes Southland electric power supply, operated by the New Zealand Electricity Department.
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| Establishments | No. | 18 | 19 | 21 |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,269 | 2,505 | 2,747 |
| Salaries and wages paid | £ | 2,007,583 | 2,160,538 | 2,470,577 |
| Consumers | No. | 19,171 | 19,924 | 20,653 |
| Prime movers – | ||||
| Hydro | b.h.p. | 1,504,900 | 1,564,900 | 1,594,900 |
| Thermal | b.h.p. | 81,139 | 245,139 | 417,499 |
| Totals | b.h.p. | 1,586,039 | 1,810,039 | 2,012,399 |
| Generators (capacity) – | ||||
| A.C. | kW | 1,119,070 | 1,281,070 | 1,430,965 |
| kVA | 1,269,992 | 1,457,658 | 1,628,456 | |
| Revenue – | ||||
| Sales of power – | ||||
| Retail | £ | 1,005,155 | 1,462,643 | 1,529,887 |
| Bulk and interchange | £ | 9,704,025 | 13,863,931 | 15,476,057 |
| Other | £ | 95,538 | 114,057 | 119,978 |
| Total revenue | £ | 10,804,718 | 15,440,631 | 17,125,922 |
| Expenditure – | ||||
| Power purchased (including interchange) | £ | 194,053 | 231,230 | 220,252 |
| Generating costs | £ | 2,301,369 | 2,422,989 | 2,496,953 |
| Transmission and distribution costs | £ | 1,088,160 | 1,318,566 | 1,232,018 |
| Management and general | £ | 952,624 | 1,005,371 | 1,072,414 |
| Capital charges | £ | 6,293,229 | 9,638,783 | 10,945,230 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 10,829,435 | 14,616,939 | 15,966,867 |
| Capital outlay – | ||||
| Total expenditure to date | £ | 164,505,001 | 181,941,695 | 199,433,353 |
| Expenditure during year | £ | 21,421,533 | 17,436,694 | 17,491,658 |
| Generation – | ||||
| Hydro | (000) kWh | 5,086,259 | 4,971,895 | 5,185,338 |
| Steam | (000) kWh | 247,970 | 391,090 | 864,707 |
| Oil | (000) kWh | 324 | 68 | 21 |
| Totals | (000) kWh | 5,334,553 | 5,363,053 | 6,050,066 |
| Retail sales | (000) kWh | 288,246 | 306,077 | 317,231 |
Electric Power Boards – This table gives similar information concerning generation and distribution by electric power boards.
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| Establishments | No. | 43 | 43 | 44 |
| Persons engaged | No. | 2,900 | 3,060 | 3,418 |
| Salaries and wages paid | £ | 2,378,630 | 2,616,691 | 3,019,164 |
| Consumers | No. | 483,634 | 503,060 | 522,296 |
| Prime movers – | ||||
| Hydro | b.h.p. | 24,633 | 22,398 | 25,268 |
| Thermal | b.h.p. | 4,890 | 4,690 | 4,930 |
| Totals | b.h.p. | 29,523 | 27,088 | 30,198 |
| Generators (capacity) – | ||||
| A.C. | kW | 20,274 | 18,765 | 20,465 |
| kVA | 24,286 | 22,770 | 24,895 | |
| Revenue – | ||||
| Sales of power – | ||||
| Retail | £ | 14,132,885 | 17,590,137 | 19,503,237 |
| Bulk and interchange | £ | 676,117 | 1,029,139 | 1,118,832 |
| Other (including rates) | £ | 383,847 | 317,979 | 346,925 |
| Total revenue | £ | 15,192,849 | 18,937,255 | 20,968,994 |
| Expenditure – | ||||
| Power purchased (including interchange) | £ | 7,187,955 | 10,285,212 | 11,553,082 |
| Generating costs | £ | 60,414 | 46,386 | 49,459 |
| Transmission and distribution costs | £ | 2,068,372 | 2,197,397 | 2,391,482 |
| Management and general | £ | 1,353,015 | 1,433,178 | 1,524,467 |
| Capital charges | £ | 2,950,875 | 3,265,195 | 3,435,878 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 13,620,631 | 17,227,568 | 18,954,368 |
| Capital outlay – | ||||
| Total expenditure to date | £ | 47,189,173 | 50,649,331 | 57,309,726 |
| Expenditure during year | £ | 3,611,636 | 3,460,158 | 6,660,395 |
| Generation – | ||||
| Hydro | (000) kWh | 84,788 | 90,778 | 92,096 |
| Oil | (000) kWh | 54 | 74 | 56 |
| Totals | (000) kWh | 84,842 | 90,852 | 92,152 |
| Retail sales | (000) kWh | 2,907,343 | 2,939,878 | 3,340,271 |
All Establishments – The next table sets out the same information in respect of all establishments engaged in the generation and distribution of power. These consisted at 31 March 1960 of 21 Government establishments, 2 limited liability companies, 44 electric power boards, 10 city councils, 20 borough councils, 4 county councils, and 2 town boards.
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| Establishments | No. | 101 | 102 | 103 |
| Persons engaged | No. | 6,785 | 7,064 | 7,784 |
| Salaries and wages paid | £ | 5,736,867 | 6,004,971 | 6,854,606 |
| Consumers | No. | 751,363 | 777,462 | 802,927 |
| Prime movers – | ||||
| Hydro | b.h.p. | 1,613,188 | 1,670,798 | 1,699,008 |
| Thermal | b.h.p. | 93,510 | 255,065 | 426,695 |
| Totals | b.h.p. | 1,706,698 | 1,925,863 | 2,125,703 |
| Generators (capacity) – | ||||
| A.C. | kW | 1,201,035 | 1,359,976 | 1,509,375 |
| kVA | 1,369,902 | 1,554,112 | 1,724,499 | |
| Revenue – | ||||
| Sales of power – | ||||
| Retail | £ | 21,602,797 | 27,317,304 | 30,031,508 |
| Bulk and interchange | £ | 10,523,441 | 14,972,611 | 16,666,165 |
| Other (including rates) | £ | 519,116 | 571,400 | 581,242 |
| Total revenue | £ | 32,645,354 | 42,861,315 | 47,278,915 |
| Expenditure – | ||||
| Power purchased (including interchange) | £ | 10,543,677 | 15,029,713 | 16,731,743 |
| Generating costs | £ | 2,476,963 | 2,587,124 | 2,701,015 |
| Transmission and distribution costs | £ | 4,232,919 | 4,704,208 | 4,854,887 |
| Management and general | £ | 2,787,322 | 3,028,163 | 3.150,572 |
| Capital charges | £ | 10,170,617 | 13,919,846 | 15,456,443 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 30,211,498 | 39,269,054 | 42,894,660 |
| Capital outlay – | ||||
| Total expenditure to date | £ | 229,340,654 | 251,703,892 | 278,454,554 |
| Expenditure during year | £ | 26,252,842 | 22,363,240 | 26,750,662 |
| Generation – | ||||
| Hydro | (000) kWh | 5,382,282 | 5,273,611 | 5,483,166 |
| Steam | (000) kWh | 260,135 | 401,770 | 876,302 |
| Oil | (000) kWh | 1,732 | 2,031 | 1,214 |
| Totals | (000) kWh | 5,644,149 | 5,677,412 | 6,360,682 |
| Generation per head of mean population | kWh | 2,499 | 2,465 | 2,712 |
| Retail sales | (000) kWh | 4,653,002 | 4,702,100 | 5,273,932 |
Employment – The foregoing tables include only those employees whose salaries and wages are paid directly out of revenue from the sale of electric power. Further details concerning the number of these employees and the salaries and wages paid to them are given in the following table covering the year ended 31 March 1960.
| Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | To Males | To Females | Total | |
| No. | No. | No. | £ | £ | £ | |
| Administrative, engineering, and clerical staff | 1,817 | 625 | 2,442 | 1,944,146 | 324,166 | 2,268,312 |
| Employees engaged in operation and maintenance | 5,242 | 100 | 5,342 | 4,537,680 | 48,614 | 4,586,294 |
| Totals | 7,059 | 725 | 7,784 | 6,481,826 | 372,780 | 6,854,606 |
Capital Expenditure – The following table gives capital expenditure during 1959–60 and total capital outlay to 31 March 1960.
| Expenditure During Year | Total Capital Outlay to 31 March 1960 | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Generating system – | ||
| Head works, pipelines, etc. | 6,870,311 | 85,483,227 |
| Powerhouse, buildings, cottages, etc. | 3,365,665 | 21,132,014 |
| Generating plant and machinery, etc. | 4,443,214 | 33,271,995 |
| Transmission and distribution lines, substations, land and houses | 7,482,606 | 102,257,640 |
| Street lighting | 203,061 | 1,398,197 |
| Office and store buildings, workshops, garages, houses, service buildings | 519,708 | 6,593,008 |
| Loose tools, meters, instruments, furniture, trucks, motorcars, equipment | 1,825,886 | 7,561,942 |
| Miscellaneous (cost of raising loans, loan conversion premiums, surveys, preliminary expenses, interest during construction) | 224,233 | 13,184,815 |
| Stock and materials (including trading department stocks) | 1,774,104 | 7,347,483 |
| Other items not capable of inclusion above | 41,874 | 224,233 |
| Total capital outlay | 26,750,662 | 278,454,554 |
Additions to the capital value of all electrical systems during 1959–60 totalled £27,010,716, while deductions, i.e. sales and amounts written off amounted to £260,054. The previous table shows for each item the net expenditure only during the year.
General Balance Sheet as at 31 March 1960 – The next table summarises the balance sheet at 31 March 1960 for all establishments.
| Liabilities | ||
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Capital raised – | ||
| Original amount of current | ||
| loans | 229,833,689 | |
| Less amounts repaid | 20,340,006 | |
| Balance owing on 31 March 1960 | 209,493,683 | |
| Temporary loans | 461,667 | |
| Sundry creditors — | ||
| Bank overdraft | 383,883 | |
| Other | 6,815,424 | |
| Reserves — | ||
| Loan repayment reserve | 30,776,270 | |
| Capital expenditure out of revenue | 15,802,741 | |
| Sinking fund reserve | 1,692,799 | |
| Depreciation reserve | 25,134,335 | |
| Renewal fund reserve | 1,143,160 | |
| General and other reserves | 7,894,201 | |
| Surplus in Appropriation Account | 4,956,004 | |
| Total | 304,554,167 | |
| Assets | ||
| £ | ||
| Total capital outlay | 278,454,554 | |
| Sundry debtors | 8,145,675 | |
| Other assets – | ||
| Cash and trading bank balances | 3,587,260 | |
| State Advances stock, balances at POSB, National Savings | 87,003 | |
| New Zealand Government stock | 6,694,020 | |
| Local authority stock | 582,653 | |
| Public Trust and National Provident Fund | 4,216,927 | |
| Overseas investments | 206,630 | |
| Other | 2,579,445 | |
| Total | 304,554,167 | |
Power – The following table sets out the number of units generated and their disposal. The excess generation of certain local factories, which is bought in “for public supply, is given in the column “Other Sources”.
| Year Ended 31 March | Generated for Public Supply | Sold Retail | Non-productive | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N.Z. Electricity Department | Supply Authorities | Other Sources | Total | |||
| thousand kWh | ||||||
| 1956 | 4,375,803 | 358,366 | 14,165 | 4,748,334 | 3,876,311 | 872,023 |
| 1957 | 4,693,153 | 258,449 | 15,760 | 4,967,362 | 4,064,292 | 903,070 |
| 1958 | 5,334,553 | 297,430 | 12,166 | 5,644,149 | 4,653,002 | 991,147 |
| 1959 | 5,363,053 | 303,679 | 10,680 | 5,677,412 | 4,702,100 | 975,312 |
| 1960 | 6,050,066 | 299,020 | 11,596 | 6,360,682 | 5,273,932 | 1,086,750 |
Analysis of Units Retailed – The following table gives a classification of power retailed according to the various purposes for which it was sold. In this table “Domestic” includes domestic water-heating units, and “Commercial” both commercial and dairy water-heating units.
| Year Ended 31 March | Domestic | Commercial and Industrial | Street Lighting | Tramways | Electric Railways | Other Purposes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| thousand kWh | |||||||
| 1956 | 2,314,666 | 1,476,531 | 23,795 | 28,865 | 21,885 | 10,569 | 3,876,311 |
| 1957 | 2,366,707 | 1,624,567 | 25,513 | 24,469 | 22,893 | 143 | 4,064,292 |
| 1958 | 2,750,433 | 1,827,742 | 29,367 | 22,042 | 23,202 | 216 | 4,653,002 |
| 1959 | 2,741,070 | 1,884,590 | 32,009 | 20,952 | 22,970 | 509 | 4,702,100 |
| 1960 | 3,122,173 | 2,066,783 | 39,054 | 22,376 | 23,294 | 252 | 5,273,932 |
The following diagram portrays the growth in the use of electric power, and shows also the principal purposes for which the power was employed.
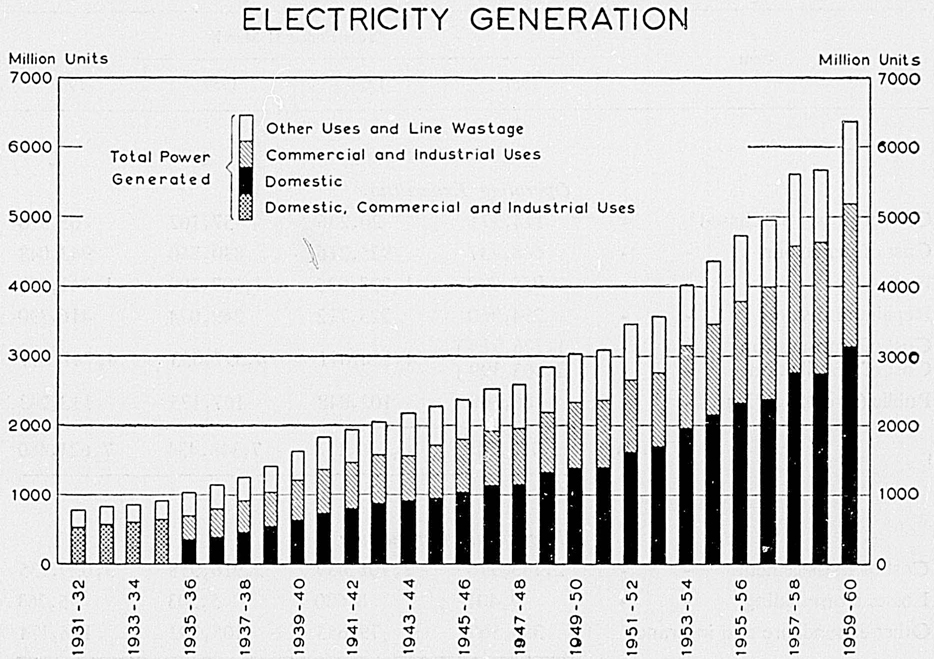
Revenue – Revenue is derived chiefly from the sale of power, and in 1959–60 this source was 97.6 per cent of the total. The following table sets out the revenue from all sources (excluding bulk sales) for the years 1955–56 to 1959–60.
| Year Ended 31 March | Sale of Power (Retail) | Profits from Trading | Miscellaneous | Interest | Total* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding revenue from interchange of power. †1958 miscellaneous figure includes interest. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 18,112,682 | 109,207 | 479,980 | 15,354 | 18,717,223 |
| 1957 | 19,034,919 | 90,638 | 513,688 | 25,476 | 19,664,721 |
| 1958 | 21,602,797 | 109,850 | 541,331† | ... | 22,253,978 |
| 1959 | 27,317,304 | 118,007 | 617,183 | ... | 28,052,494 |
| 1960 | 30,031,508 | 121,337 | 617,337 | ... | 30,770,182 |
Expenditure – Of the total expenditure of £ 26,228,495 (excluding cost of interchange of power in bulk) recorded in the year ended 31 March 1960, 70.9 per cent represented overhead costs (comprising management expenses and capital charges), while operating expenses of prime costs stood at 29.1 per cent.
Power may be sold more than once in bulk before reaching the retailing authority, and in these tables the revenue from such interchange of power between authorities is set off against the cost, the net figure for cost of power purchased representing the cost to the industry of purchases from outside sources. In this connection mention may be made of certain contracts existing between the Government and some local authorities, whereby the latter are required to maintain their plants and to operate them, whenever called upon, to supplement the State electricity supply. The units so generated, often by fuel plants, are purchased by the Government and resold, in most cases to the generating authority, for distribution.
The table following gives an analysis of expenditure.
| Item | Year Ended 31 March | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| *Does not include the interchange of power between supply authorities. | ||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Operating Expenditure | ||||
| Cost of power purchased* | 114,371 | 20,236 | 57,102 | 65,578 |
| Cost of generation | 648,737 | 925,216 | 830,760 | 943,048 |
| Fuel | 958,098 | 1,328,035 | 1,507,290 | 1,341,577 |
| Repairs and stores | 294,860 | 223,712 | 249,074 | 416,390 |
| Cost of transmission | 1,176,915 | 4,130,071 | 4,597,033 | 4,741,644 |
| Cost of distribution | 2,503,399 | |||
| Public (street) lighting | 86,360 | 102,848 | 107,175 | 113,243 |
| Totals | 5,782,740 | 6,730,118 | 7,348,434 | 7,621,480 |
| Miscellaneous Expenditure | ||||
| Cost of management | 2,133,378 | 2,701,039 | 2,916,958 | 3,029,135 |
| Losses from trading | 9,401 | 6,630 | 5,503 | 5,263 |
| Other expenditure and insurance | 380,567 | 79,653 | 105,702 | 116,174 |
| Totals | 2,523,346 | 2,787,322 | 3,028,163 | 3,150,572 |
| Capital Charges (Including Taxation) | ||||
| Interest | 5,084,968 | 5,648,491 | 7,688,107 | 8,392,687 |
| Sinking fund | 420,017 | 435,432 | 1,425,340 | 438,511 |
| Renewals | 563,281 | 651,043 | 769,439 | 762,920 |
| Depreciation | 2,075,428 | 2,129,722 | 2,577,883 | 3,188,766 |
| Loan repayment | 1,142,983 | 1,305,929 | 1,459,077 | 2,673,559 |
| Totals | 9,286,677 | 10,170,617 | 13,919,846 | 15,456,443 |
| Grand totals | 17,592,763 | 19,688,057 | 24,296,443 | 26,228,495 |
The distribution of the expenditure per unit sold retail is given hereunder.
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| d. | d. | d. | d. | |
| Operating expenses | 0.341 | 0.347 | 0.375 | 0.347 |
| Miscellaneous expenses | 0.149 | 0.144 | 0.155 | 0.143 |
| Capital charges | 0.549 | 0.525 | 0.710 | 0.704 |
| Totals | 1.039 | 1.016 | 1.240 | 1.194 |
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT – The gas industry was amongst the first industrial enterprises founded in New Zealand. The first gasworks was erected in the year 1862 at Auckland when the European population of that town was about 25,000, and the total European population of New Zealand was only some 100,000 persons; the Christchurch and Dunedin works commenced supply in 1863; with the addition of the Wellington establishment in 1869 there was then a gasworks in each of the four main centres. Subsequent growth of the industry was rapid, and in 1916 there were 56 establishments engaged in generation and supply of gas to the public. This was the peak year so far as the number of establishments is concerned.
Since this date the number of works in use has declined steadily, although the output of gas actually increased for the next 30 years and a much larger number of consumers is supplied now than in the year 1916. Electricity first came into general use for lighting; it gradually supplanted gas for this purpose from 1919 onwards, and, as new appliances were introduced, continued successfully to compete with gas in heating and cooking. Plants in the larger towns and cities have been able to carry on successfully, but the works serving smaller towns have found it increasingly hard to cope with rising costs and to meet competition from electricity, so much so that a number have either sold out or closed down, leaving 33 works still operating in 1960.
As a part of the general stabilisation policy during the war, the Government instituted a system of subsidies to gasworks to enable them to meet rising costs without unduly increasing the price of gas to the consumer. These subsidies were paid from 1943 onwards to individual works as required, each case being considered separately. The subsidies were withdrawn in 1950, the price of gas to consumers being raised to meet the additional cost of gas making consequent on this withdrawal. Further increases in operating costs, wages, and coal prices in 1951 led to a restoration of subsidies to the gas industry in the form of a subsidy to all gasworks of 2s. per 1,000 cu. ft. of gas sold. Financial assistance in the form of loans was also offered to works for the purpose of carrying out work necessary to restore the efficiency of gas making and storage plant, and it was considered that at the end of two years the industry would be in a strong enough position for the subsidy to be withdrawn. This has not proved to be the case, and the subsidy is still in force. From October 1959 this subsidy was reduced to 1s. 8d., except for works on the West Coast and the oil plant at Hastings. In addition, a new subsidy covering freight charges on coal was given to 19 undertakings. The annual average prices of gas in the four main centres during the period 1910–11 to 1959–60 are shown in the following table.
AVERAGE PRICE OF GAS TO CONSUMER PER 1,000 CUBIC FEET
| Year | Auckland | Wellington | Christchurch | Dunedin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | |
| 1910–11 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 10 |
| 1929–30 | 7 | 0 | 6 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 6 | 3 |
| 1939–40 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 11 |
| 1949–50 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 2 |
| 1957–58 | 13 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 7 | 5 |
| 1958–59 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 5 |
| 1959–60 | 13 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 5 |
The decline of the gas industry was viewed with concern by the Government and the authorities which are required to supply the country with electric power, because of the additional demand for electricity which must follow any reduction of the gas supply. In order to conserve the contribution by the gasworks to the national sources of power, an Electricity and Gas Coordination Committee was set up in 1955 and commenced its work in January 1956, at which time 34 gas undertakings were in operation. The Committee considered that all but three smaller undertakings were essential in the national interest. On 5 September 1956 the Committee reported to the Minister making recommendations concerning the future operation of essential undertakings and in respect of the acquisition of such undertakings by the local electricity supply authority.
The Electricity and Gas Coordination Act 1956 established an Electricity and Gas Coordination Board to advise the Minister on the coordination of the electricity and gas industries. Following a report from the Board regarding the difficulties to be overcome in effecting local mergers, legislation was passed in 1958 setting up a Gas Council in place of the Board. The main functions of the new Council are to advise the Government and the industry regarding the preservation and expansion of gas supplies, and to operate the Gas Industry Account, from which subsidies, grants, and loans may be made to assist the industry.
Prior to the year 1918–19 statistical information concerning gasworks was collected in conjunction with the population census at five-yearly intervals, but since that date information has been supplied annually. The very early returns naturally did not give much detailed information, but that which is available since 1867 is given in the following historical table which shows certain main items, generally at five-yearly intervals, up to the present time.
STATISTICAL SUMMARY, 1867–1960
| Year | Works in Operation | Persons Engaged* | Value of Land and Buildings | Value of Machinery and Plant | Gas Produced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excludes administrative and distributing staff up to 1915–16. A comparable total for 1920–21 was 966 persons. † Includes revaluation in certain cases. | |||||
| cu. ft. | |||||
| No. | No. | £(000) | £(000) | (000,000) | |
| 1867 | 3 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1874 | 8 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1878 | 12 | 145 | .. | .. | .. |
| 1880–81 | 17 | 188 | 178 | 314 | 247 |
| 1885–86 | 20 | 344 | 208 | 448 | 403 |
| 1890–91 | 27 | 249 | 111 | 619 | 427 |
| 1895–96 | 27 | 293 | 121 | 646 | 532 |
| 1900–01 | 30 | 572 | 154 | 817 | 787 |
| 1905–06 | 38 | 954 | 268 | 1,107 | 1,275 |
| 1910–11 | 48 | 757 | 326 | 753 | 2,075 |
| 1915–16 | 56 | 598 | 351 | 1,031 | 2,776 |
| 1920–21 | 50 | 1,856 | 593 | 2,696 | 3,401 |
| 1925–26 | 48 | 2,053 | 554 | 3,720 | 3,870 |
| 1930–31 | 46 | 1,778 | 619 | 4,412 | 4,230 |
| 1935–36 | 46 | 1,779 | 654 | 3,715 | 3,885 |
| 1940–41 | 44 | 1,873 | 625 | 3,489 | 4,480 |
| 1945–46 | 44 | 1,830 | 512 | 3,484 | 5,241 |
| 1950–51 | 44 | 1,711 | 550 | 4,264 | 5,446 |
| 1955–56 | 35 | 1,583 | 643 | 4,859 | 5,222 |
| 1957–58 | 33 | 1,560 | 914† | 5,238 | 5,311 |
| 1958–59 | 33 | 1,560 | 866† | 5,350 | 5,520 |
| 1959–60 | 33 | 1,557 | l,113† | 5,535 | 5,664 |
LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY – The Gas Supply Act 1908, requires, amongst other things, that a gas undertaking should give, and continue to give, if required, a supply of gas to any premises situated within 100 yd of a gas main or connected to a gas main, the gas supplier to bear the cost of not more than 50 ft of any service pipe laid for this purpose outside the property of the consumer; authorises the supplier to require security and fixes the manner in which security should be given; fixes the liability of an incoming tenant for arrears of gas rent; and empowers gas companies to erect gasometers and lay and service gas mains. The Board of Trade (Gas) Regulations 1924 and amendments set standards of calorific value, purity, and pressure of gas which are required to be observed by scheduled gas undertakings.
The Electricity and Gas Coordination Act 1956 empowered a supply authority to acquire and carry on a gas undertaking and required each supply authority which controlled an essential gas undertaking to carry on the undertaking in such manner as to ensure that, as far as practicable, the supply of gas was maintained and that available supplies of electricity were conserved by the encouragement of the use of gas for the generation of heat and power. The Gas Industry Act 1958 repealed the 1956 Act, but any gas undertakings taken over under that Act may be carried on as if the Act had not been repealed.
Under the Gas Industry Act 1958 there has been set up the New Zealand Gas Council of 10 members with the Minister of Electricity as chairman. The main functions of the Council are to advise on the preservation and expansion of the gas industry and to operate the Gas Industry Account. As from 1 April 1959 money may be paid from the Consolidated Fund into this account, from which the Council may pay subsidies and make grants and loans available to assist the industry.
RECENT STATISTICS – Statistics for the years 1957–58 to 1959–60 are set out in the table which follows.
| 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes revaluation in certain cases. † Including natural gas. | ||||
| Works | No. | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| Value of land and buildings | £ | 914,337* | 865,907* | 1,113,348* |
| Value of plant (generating and distributing) | £ | 5,238,206 | 5,349,794 | 5,534,857 |
| Persons engaged | No. | 1,560 | 1,560 | 1,557 |
| Salaries and wages paid | £ | 1,230,194 | 1,262,370 | 1,322,251 |
| Coal used– | ||||
| Quantity | tons | 255,822 | 271,005 | 276,045 |
| Cost | £ | 1,570,020 | 1,620,784 | 1,663,017 |
| Cost of purifying and other materials | £ | 79,583 | 77,055 | 82,317 |
| Other expenses (other than salaries and wages and materials) | £ | 874,958 | 938,193 | 1,086,890 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 3,754,755 | 3,898,402 | 4,154,475 |
| Total revenue | £ | 3,741,318 | 3,892,782 | 4,101,688 |
| Consumers | No. | 175,910 | 170,995 | 168,737 |
| Gas generated† | cu. ft. (000) | 5,310,757 | 5,520,377 | 5,663,943 |
| Gas sold retail – | ||||
| Quantity | cu. ft. (000) | 4,241,398 | 4,379,893 | 4,540,448 |
| Value | £ | 2,870,703 | 2,981,011 | 3,076,018 |
| Average price of gas to consumer per 1,000 cu. ft. | - | 11s. 6d. | 11s. 7d. | 11s. 7d. |
A further analysis of the 1959–60 statistics is given below, these being dissected by locality of gasworks (North and South Island) and character of organisation. It will be seen that 67.35 per cent of the total quantity of gas was generated in the North Island and 32.65 per cent in the South Island, while proportions generated by registered companies and municipal authorities were 70.76 per cent and 29.24 per cent respectively.
| Registered Companies | Municipal Authorities | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Depreciated values. † Undepreciated. Depreciation funds amounted to £38,557. ‡ Including natural gas. | ||||
| North Island | ||||
| Works | No. | 8 | 10 | 18 |
| Value of land and buildings | £ | 742,295* | 104,537† | 846,832 |
| Value of machinery and plant | £ | 2,030,585* | 1,557,305† | 3,587,890 |
| Capital additions during year– | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 5,877 | 4,109 | 9,986 |
| Machinery and plant | £ | 213,414 | 31,790 | 245,204 |
| Persons engaged — | ||||
| Males | No. | 793 | 222 | 1,015 |
| Females | No. | 68 | 12 | 80 |
| Totals | No. | 861 | 234 | 1,095 |
| Salaries and wages paid – | ||||
| To males | £ | 683,882 | 203,419 | 887,301 |
| To females | £ | 34,432 | 4,993 | 39,425 |
| Totals | £ | 718,314 | 208,412 | 926,726 |
| Motive power – | ||||
| Engines in use | No. | 177 | 95 | 272 |
| Total horsepower | h.p. | 3,168 | 533 | 3,701 |
| Materials used – | ||||
| Coal | tons | 140,703 | 42,798 | 183,501 |
| £ | 851,183 | 288,688 | 1,139,871 | |
| Oil | gal | 923,751 | 18,373 | 942,124 |
| £ | 49,947 | 1,570 | 51,517 | |
| Products – | ||||
| Gas generated‡ | cu. ft. (000) | 3,117,544 | 697,063 | 3,814,607 |
| Gas sold retail | cu. ft. (000) | 2,405,053 | 587,093 | 2,992,146 |
| £ | 1,720,523 | 454,694 | 2,175,217 | |
| Coke | tons | 26,839 | 9,698 | 36,537 |
| £ | 247,228 | 91,163 | 338,391 | |
| Tar | gal | 1,250,845 | 339,685 | 1,590,530 |
| £ | 149,419 | 31,735 | 181,154 | |
| Other residuals | £ | 39,696 | 6,195 | 45,891 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 2,226,464 | 698,879 | 2,925,343 |
| Total revenue | £ | 2,243,038 | 604,813 | 2,847,851 |
| Consumers | No. | 85,218 | 25,928 | 111,146 |
| Registered Companies | Municipal Authorities | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Depreciated values. †Undepreciated. Depreciation funds amounted to £340,611. | ||||
| South Island | ||||
| Works | No. | 3 | 12 | 15 |
| Value of land and buildings | £ | 89,032* | 177,484† | 266,516 |
| Value of machinery and plant | £ | 700,566* | 1,246,401† | 1,946,967 |
| Capital additions during year – | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 1,557 | 572 | 2,129 |
| Machinery and plant | £ | 31,870 | 62,256 | 94,126 |
| Persons engaged – | ||||
| Males | No. | 201 | 233 | 434 |
| Females | No. | 19 | 9 | 28 |
| Totals | No. | 220 | 242 | 462 |
| Salaries and wages paid – | ||||
| To males | £ | 170,610 | 211,700 | 382,310 |
| To females | £ | 8,532 | 4,683 | 13,215 |
| Totals | £ | 179,142 | 216,383 | 395,525 |
| Motive power – | ||||
| Engines in use | No. | 72 | 163 | 235 |
| Total horsepower | h.p. | 915 | 982 | 1,897 |
| Materials used – | ||||
| Coal | tons | 46,029 | 46,515 | 92,544 |
| £ | 234,751 | 288,395 | 523,146 | |
| Oil | gal | - | 370,869 | 370,869 |
| £ | - | 26,456 | 26,456 | |
| Products – | ||||
| Gas generated | cu. ft. (000) | 890,093 | 959,243 | 1,849,336 |
| Gas sold retail | cu. ft. (000) | 775,515 | 772,787 | 1,548,302 |
| £ | 424,126 | 476,675 | 900,801 | |
| Coke | tons | 21,786 | 13,693 | 35,479 |
| £ | 115,567 | 97,981 | 213,548 | |
| Tar | gal | 469,913 | 483,559 | 953,472 |
| £ | 45,547 | 45,235 | 90,782 | |
| 0ther residuals | £ | 8,901 | 1,891 | 10,792 |
| Total expenditure | £ | 528,476 | 700,656 | 1,229,132 |
| Total revenue | £ | 606,760 | 647,077 | 1,253,837 |
| Consumers | No. | 20,197 | 37,394 | 57,591 |
Table of Contents
GENERAL MARKETING SITUATION: Meat – Most meat produced in the world is used for domestic consumption, and only about 6 per cent of world output enters into international trade. About three-quarters of all meat exports come from five countries. In order of importance these are Argentina, New Zealand, Denmark, Australia, and the Netherlands. The import trade is dominated by the United Kingdom, which takes about two-thirds of the total exports. Next in importance as importers are the United States of America, and the Western European countries such as Italy, Western Germany, and France.
The principal class of meat in the world trade is beef and veal, which trade is continuing to expand rapidly. Mutton and lamb imports on the other hand have not tended to increase very greatly in recent years. New Zealand faces a problem of disposing of a rapidly increasing quantity of sheep meats in world markets where an increasing proportion of the present demand is for beef. The United Kingdom has been a sheep-rearing country for centuries, and her people have developed a taste for mutton and lamb. In other likely markets the taste must to some extent be cultivated.
The population of the United Kingdom is increasing only slowly, and although there has been increased consumption per head in recent years it seems that the capacity of the country to consume greater quantities of meat is slowing down. At the same time the United Kingdom Government is encouraging home production by a system of guaranteed agricultural prices.
Though the United Kingdom is traditionally New Zealand's export market for meat and must remain so in the foreseeable future, there has been for some years a growing realisation of the need for supplementary markets. Efforts made during the past few years to develop alternative markets have had a good deal of success.
In the past the main markets outside the United Kingdom for New Zealand's meat have been the countries of Western Europe, but in recent years exports to these areas have declined, as these countries have intensified protection of their agricultural industries. Market opportunities may also be affected by the formation of the European Economic Community, comprising Belgium, France, Italy, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, and Western Germany, and also by the European Free Trade Area of the Seven, comprising United Kingdom, Austria, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, and Switzerland.
Canada and the United States of America have been developed into important supplementary markets for lamb, and sales of mutton to Japan, Greece, and other markets outside the United Kingdom have increased substantially.
A reduction in size of beef herds in the United States of America following a drought and low prices in 1955–56 led to a demand for imported beef by that country. In 1958 New Zealand became a leading exporter of beef to the United States with shipments totalling about 91,000 tons, mostly boneless. In 1958 Canada also bought 4,100 tons of New Zealand beef and veal, with the result that 76 per cent of New Zealand's 1957–58 beef exports went to North American markets. In 1958–59, however, there was a drop in shipments to both the United States and Canada, partly because there was less beef for export and partly from competition from a greater supply of Australian beef following an amendment to the United Kingdom – Australian long-term agreement on meat which permitted Australia to divert a larger proportion of her production to markets outside the United Kingdom. Shipments of beef to the United States declined by 15,000 tons in 1959–60 but increased sales were made to other markets which took New Zealand beef in the years before the American boom in beef prices developed.
Cattle numbers in the United States have been building up since 1958 and at 1 January 1961 reached an all-time peak. Pig and sheep numbers have also been steady. A rise in domestic production of meat in the United States can be expected and this could slightly affect the demand for imported beef, but substantial exports of New Zealand meat to that country can be expected to continue with the trade contacts that have been developed, and the availability of refrigerated shipping. In recent years packers have modernised their plants and trained staff to prepare the beef, inspect it, and pack it in heavy cardboard cartons lined with polythene.
The following table shows the main destination of exports of frozen and chilled beef and veal for the four latest years.
| Country (of Import) | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||||||
| tons | £(000) | tons | £(000) | tons | £(000) | tons | £(000) | |
| United Kingdom | 52,709 | 6,276 | 12,870 | 1,689 | 7,358 | 1,182 | 20,373 | 3,217 |
| United States | 22,469 | 3,969 | 84,030 | 20,923 | 68,529 | 18,072 | 56,322 | 14,543 |
| Japan | 14,932 | 1,966 | 2,771 | 308 | 1,307 | 210 | 3,582 | 560 |
| Other countries | 25,438 | 3,463 | 16,099 | 3,148 | 11,659 | 2,719 | 18,395 | 1,161 |
| Totals | 115,548 | 15,674 | 115,770 | 26,068 | 88,853 | 22,183 | 98,672 | 19,481 |
Wool – New Zealand is one of the largest exporters of wool in the world but marketing presents no difficulties. Most of the wool is auctioned in New Zealand and buyers come from interested countries to make their purchases of wool. A small percentage of wool produced is shipped to England for sale on the London market. Prices fluctuate according to the demand for wool, but the present market requirements are such that the Wool Commission has not had to buy in very much wool under its minimum price scheme, and even then has had to hold it only temporarily. The threat of competition from synthetic materials is such that the International Wool Secretariat is actively promoting advertising, merchandising, and research. World wool production and wool utilisation have in recent years been approximately in balance and there has been no pressure on supplies. Destocking movements by manufacturers have contributed to an easing of prices.
Dairy Produce – For the sale of dairy products New Zealand is very largely dependent on the United Kingdom market, which is practically the only open market of any size for butter and cheese. In 1958 the total production of butter by 30 of the main producing countries of the world amounted to 3.9 million tons. In the same year world exports by 20 of the leading exporters amounted to about 550,000 tons, that is, only about 14 per cent of world production entered into international trade. Of this quantity, 410,000 tons (75 per cent) came on to the United Kingdom market. These figures show that relatively small changes in demand-supply relationships in individual countries can have a most disturbing effect on the United Kingdom market.
Some countries have adopted agricultural income and price support policies to maintain and stabilise farming incomes. Only industrialised countries with a relatively low proportion of their national income derived from agriculture can continue support measures on a large scale. International trade is adversely affected in several ways. To maintain prices at support levels many countries have restricted imports of agricultural products, so that entry into markets, in which New Zealand's exports could effectively compete, has often been denied. High support prices and consequent high domestic prices discourage consumption and often lead to the accumulation of supplies which are surplus to domestic requirements. Surpluses generated in this manner are frequently disposed of in other markets at prices well below the cost of production. New Zealand's position in the United Kingdom market was adversely affected in 1958 when some European countries dumped on the market such quantities that there were serious falls in prices.
Since 1958 price reductions in some European countries have to some extent stimulated consumption in them, and increasing effort is being directed towards the elimination or reduction of subsidised dairy production that led to dumping. It is essential for New Zealand to maintain strong and consistent pressure in international councils so that these measures are furthered. There were indications in 1960 that O.E.E.C. countries were prepared to exercise restraints to ensure a normal flow of supplies to the United Kingdom market, but dumping by a number of countries led to a serious fall in prices early in 1961.
The United States of America for a time followed a policy under her commodity disposal programmes which embarrassed other exporters of certain kinds of dairy produce. Although the United States of America reduced the quantities of butter and cheese for surplus disposal, she continued to ship milk powder abroad at uneconomic prices. Canada was also for a time disposing of skim milk powder at uneconomic prices.
New Zealand is moving towards the development of more supplementary markets for dairy produce, although quantities that can be disposed of in them are relatively small compared with the United Kingdom, New Zealand's long-standing market. Major industrial countries where income levels and food-consumption habits could provide important markets have adopted trading policies aimed at restricting imports of foodstuffs to protect their agriculture. The extent of these restrictions is partly dependent upon seasonal conditions, e.g., if seasonal conditions are favourable the restrictions are tightened.
TRADE AGREEMENTS – The United Kingdom has always been New Zealand's main export market for primary produce. New Zealand's trading relations with the United Kingdom are governed by a number of formal commitments. Under the Ottawa Agreement of 1932 New Zealand undertook to maintain a preferential tariff on imports from the United Kingdom, while the United Kingdom for its part was obliged to grant duty-free entry for practically all New Zealand products and maintain specified duties on some foreign products of interest to New Zealand. The United Kingdom also undertook to place quota restrictions on foreign meats.
On butter the foreign tariff rate, and therefore the margin of preference, fixed in 1932 was 15s. a hundredweight (at which comparatively low rate it still remains); on cheese the tariff preference is 15 per cent; on meat there is no preference on mutton and lamb, and a negligible tariff preference exists on beef coupled with a foreign quota on meat which was designed to ensure an expanding share of the United Kingdom's market; while on wool there has never been a preference.
During the trade talks in the United Kingdom in April-May 1957 the question of a review of the Ottawa Agreement was raised, and following discussions which took place in New Zealand early in 1958 on the occasion of the visit of the United Kingdom Prime Minister it was agreed desirable to review the provisions of the Ottawa Agreement which had remained substantially unaltered since 1932. Negotiations were opened by a New Zealand official delegation in London on 17 April 1958, and the new agreement came into force on 25 November 1958.
The agreement gave new flexibility to New Zealand's international trading and negotiating position. The levels of preferences in favour of the United Kingdom of the 1932 Agreement could be modified but the basic principle was retained to ensure that the close and mutually beneficial economic partnership between the United Kingdom and New Zealand would continue. Recognising that, because of changed conditions, the balance of advantage under the 1932 Trade Agreement had moved against New Zealand, the United Kingdom Government agreed to New Zealand having the right to reduce the 20-per-cent margin of preference on British goods. (See Section 22D – Customs Tariff and Revenue.)
The greater flexibility which will result will assist in reducing the cost of imports, and also enable other markets for an increasing volume of exports to be maintained and developed. New Zealand must be able to produce exports at competitive prices and to do this it is essential that plant and raw material used in production be imported on the most favourable basis. Provision has also been made for New Zealand to resort to a limited measure of bilateral trading with third countries, without causing serious harm to the trade of the United Kingdom.
In the new agreement all existing rights and preferences for New Zealand goods entering the United Kingdom market are preserved. These include the 1957 supplementary agreement providing for annual consultations on the agricultural production and marketing policies of the two countries, as well as the 10-year right of entry to the United Kingdom market, without restriction as to quantity, of butter, cheese, skim and buttermilk powders, casein, and chilled and frozen pork. The 15-year right of entry for New Zealand meat, agreed to in 1952 outside the 1932 pact, remains in force.
Under the agreement the United Kingdom and New Zealand Governments recognise that each other's trade may be materially injured by competition from dumped or subsidised exports from third countries. If, after consultation, it is established that such injury is being caused or threatened, each Government will consider remedial action consistent with its own laws and its international obligations.
A revised trade agreement had earlier been negotiated between the United Kingdom and Australia.
A treaty establishing the European Economic Community entered into force on 1 January 1958. Under the terms of this treaty, the six member countries, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands will, over a transitional period of 12 to 15 years, eliminate tariffs and other restrictions to trade within the Community. At the same time the tariffs on goods entering each member country from outside the Community will be adjusted until all the six countries have a common external tariff. If the Community adopts a common agricultural policy aimed at self sufficiency in foodstuffs, New Zealand's limited access to the agricultural markets of the Six could be even more restricted.
The establishment of the European Economic Community was followed by revived negotiations concerning a European free trade area embracing 17 countries, including the Six. The proposals for a free trade area involved the gradual abolition of tariffs and other restrictions on trade within the area, but each member would retain its own individual tariff on imports from outside the area. Negotiations broke down for a Free Trade Area of the 17 nations but there has now been formed a Free Trade Area of the Seven (United Kingdom, Austria, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, and Switzerland). One of the primary objectives of this smaller Free Trade Area is to link in some way its activities with the Six. The Free Trade Area of the Seven will have special rules regarding agricultural products.
UNITED KINGDOM MARKET: Dairy Produce – New Zealand's important position in the supply of butter, cheese, and milk powder to the United Kingdom market is illustrated in the following table, showing imports into the United Kingdom, by country of export. In the case of butter, domestic production in the United Kingdom is relatively small in comparison with total supplies, amounting to only 14,000 tons in 1959. Domestic cheese supplies, on the other hand, are comparatively large, the total for 1959 being 88,000 tons, while domestic output of milk powder in 1959 was 57,000 tons. (Source: Commonwealth Economic Committee.)
| Country (of Export) | Butter | Cheese | Milk, Preserved | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1938 | 1958 | 1959 | 1938 | 1958 | 1959 | 1938 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| tons (thousand) | |||||||||
| New Zealand | 130 | 170 | 163 | 82 | 81 | 76 | 7 | 31 | 47 |
| Australia | 90 | 49 | 64 | 12 | 7 | 13 | 2 | 11 | 25 |
| Canada | 2 | - | 6 | 34 | 7 | 9 | - | - | 1 |
| Denmark | 118 | 95 | 95 | 1 | 10 | 10 | - | 2 | 2 |
| Netherlands | 36 | 30 | 14 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 5 | 6 | 16 |
| Other countries | 100 | 79 | 59 | 7 | 5 | 14 | 4 | 7 | 13 |
| Total imports | 476 | 423 | 401 | 146 | 119 | 136 | 18 | 57 | 104 |
| United Kingdom production | 20 | 30 | 14 | 43 | 95 | 88 | .. | .. | .. |
For the 1958–59 season 93 per cent of New Zealand's total exports of butter went to the United Kingdom, while 94 per cent of the total exports of cheese went to the United Kingdom.
The following table shows the comparative figures for consumption of butter and margarine in the United Kingdom.
| 1938 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lb per head | |||||
| Butter | 24.1 | 15.6 | 17.5 | 20.2 | 18.5 |
| Margarine | 10.0 | 16.9 | 15.1 | 13.4 | 15.0 |
Meat - The following table shows the imports of meat into the United Kingdom from the principal countries, by country of export. (Source: Commonwealth Economic Committee.)
| Country (of Export) | Mutton and Lamb | Beef and Veal | All Meats* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1938 | 1958 | 1959 | 1938 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Including bacon and ham. | ||||||||
| tons (thousand) | ||||||||
| New Zealand | 184 | 257 | 295 | 52 | 14 | 7 | 296 | 322 |
| Australia | 95 | 45 | 36 | 115 | 125 | 110 | 240 | 163 |
| Argentina | 45 | 26 | 24 | 354 | 256 | 211 | 364 | 258 |
| Denmark | - | - | - | - | - | - | 261 | 257 |
| Other countries | 22 | 12 | 10 | 68 | 7 | 28 | 203 | 357 |
| Totals | 346 | 341 | 365 | 589 | 402 | 356 | 1,364 | 1,357 |
| United Kingdom production | 211 | 190 | 246 | 604 | 813 | 718 | 1,784 | 1,744 |
The important part played by New Zealand in the supply of meat to the United Kingdom is shown in the above table, this country being one of the leading suppliers, accounting in 1959 for 81 per cent of the mutton and lamb and 24 per cent of total meat products. Corresponding figures for 1958 were 75 per cent and 21 per cent respectively.
It should be noted that over half of the meat consumed in the United Kingdom is now obtained from domestic supplies, the production figures for 1959 being: Beef and veal, 718,000 tons; mutton and lamb, 246,000 tons; all meats, excluding bacon and ham, 1,534,700 tons.
As the United Kingdom takes the great bulk of the mutton and lamb exported from New Zealand it is interesting to note the extent to which New Zealand contributes to this market in comparison with other countries. In the calendar year 1938 New Zealand supplied 63 per cent of the total frozen mutton imported into the United Kingdom and 50 per cent of the total imports of frozen lamb. Australia, the next largest supplier in 1938, contributed 23 per cent of mutton imports and 29 per cent of lamb imports, while Argentina, which ranked third on the list, supplied 6 per cent and 15 per cent respectively. That New Zealand has more than maintained her position in this connection in the post-war years is evidenced by the figures for 1959, when New Zealand supplied 81 per cent of frozen mutton and lamb imported into the United Kingdom, whereas the proportions supplied by other countries were: Australia 10 and Argentina 7 per cent respectively.
New Zealand's frozen beef competes under difficulties with chilled and fresh beef from countries nearer the United Kingdom, with the consequence that the New Zealand share of the United Kingdom's beef imports has been relatively small; in addition in recent years a market for boneless packaged beef has been developed in North America, particularly in the United States, and supplies have been diverted there. In 1959 New Zealand supplied approximately 2 per cent of the United Kingdom's total imports of beef, as compared with 7 per cent in 1938.
New Zealand pork is shipped almost exclusively to the United Kingdom, but the quantity is relatively small.
In international trade, exports of bacon far exceed those of other pig products, with the United Kingdom normally absorbing most of the exports of other countries. Although New Zealand supplies a substantial proportion of the imports of frozen and chilled pork into the United Kingdom, her contributions of bacon are negligible.
THE ORGANISATION OF MARKETING - In a country such as New Zealand which is very dependent upon overseas trade, the efficient organisation of marketing of primary produce takes on a special importance. Since the gradual abandonment of the principles of laissez faire from the First World War onwards, great changes have taken place, and developments have been described in detail in earlier issues of the Yearbook.
The Primary Products Marketing Act 1936 established the Marketing Department, which was empowered to acquire and market primary products. The Department confined its pre-war operations to dairy produce.
Broadly speaking, the policy of controlled marketing of primary products has exhibited four phases:
The normal tendency was for the State to trade directly, buying products outright, bearing losses and retaining profits.
This was followed, after the outbreak of the Second World War and the establishment of bulk purchase, by the formation of financial pool accounts for each industry, the profits, subject to the general policy of stabilisation, being paid out to the suppliers, and any reserves held for the benefit of the industry. During the war the United Kingdom Government was the sole purchaser of imported foodstuffs, and the Marketing Department the authority in New Zealand responsible for the bulk purchase and shipment of dairy produce, meat, wool, and tallow.
The third phase was the direction of policy by boards and committees with the assumption of executive and not, as previously, merely advisory powers. Each body continued to use the marketing organisation for assembly, storage, transport, distribution, and accounting which the Marketing Department had built up, these services being made available at cost.
The fourth phase has been the progressive transfer to various boards or authorities representative of the industry concerned (with Government representation to protect consumer interests) of the responsibility and authority for the effective marketing of their own products, or the return to private enterprise with the boards assuming mainly their former pre-war functions.
Marketing Authorities, Specific and General - Progressively from 1947 onwards primary producer organisations have assumed control of the marketing of their produce. The major statutes under which specific marketing authorities operate are the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Act 1947, the Meat Export Control Act 1921-22 and the Amendment Act of 1956 (for the Meat Producers Board), and the Meat Export Prices Act 1955, the Wool Commission Act 1951, the Milk Act 1944, the Potato Growing Industry Act 1950, the Apple and Pear Marketing Act 1948, and the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment Acts 1956 and 1958.
In addition to the specific statutes authorising the industry body concerned to carry out marketing functions for certain major commodities - e.g., dairy produce, meat, potatoes, apples and pears, milk - an Act passed in 1953, entitled the Primary Products Marketing Act 1953, authorised the setting up of other marketing authorities by Orders in Council on the recommendation of the Minister of Agriculture. The Minister was required to be satisfied that a large majority of the producers in the industry concerned desired to have an authority established, and provision was made for the protection of consumer interests by the appointment of experienced Government representatives to such authorities. Other protection measures included provision for consultation between the Minister and the various boards or authorities, empowering the Minister to give directions on matters of Government trade policy, the presentation of annual reports to Parliament by each body, and Government audit of their accounts.
Orders in Council have been gazetted entitled the Citrus Marketing Regulations 1953, the Egg Marketing Regulations 1953, and the Honey Marketing Regulations 1953, all three being confirmed and validated by the Primary Products Marketing Confirmation Act 1953.
Summary of Present Position - The present position may be summarised as follows.
Dairy Produce - By the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Act 1947 the functions of the Marketing Department as regards butter and cheese for export (later extended to cover the control of all dairy produce for export) were transferred to the New Zealand Dairy Products Marketing Commission. By the same Act the control and regulation of butter and cheese for local consumption was also transferred to the Commission. The Commission was given the task of determining the guaranteed price to be paid out to producers, while the general conditions to be taken into account in its determination were also specified, but the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment Act 1956 transferred this latter function to the Dairy Products Prices Authority, which was established from 1 August 1957.
The Dairy Products Marketing Commission acquires and markets all New Zealand butter and cheese intended for export, controls the export of other dairy products, and regulates the marketing of butter and cheese in New Zealand. In selling the industry's exportable surplus of milk powder and casein, the Commission is guided by an advisory committee for each product. The Commission owns in the United Kingdom a company, Milk Products (N.Z.) Ltd., through which all New Zealand milk powder sold in the United Kingdom is distributed. It also owns Empire Dairies Ltd., which acts as one of the 17 first-hand agents through which New Zealand butter and cheese are distributed in Britain. The Commission carries out extensive advertising and publicity of New Zealand produce in the United Kingdom.
Meat - By arrangement with the Government in early 1948, the Meat Producers Board (which was formed in 1922 under the Meat Export Control Act 1921-22) resumed the regulation of shipping and physical handling of meat and became responsible for the purchase of meat for export and the payment to the freezing companies for such meat. In negotiation of prices, etc., for the sale of meat and meat products overseas the representatives of the Board acted as advisers in association with the representatives of the New Zealand Government, and for the 1953-54 season's prices the Meat Producers Board was authorised to conduct the price negotiations with the United Kingdom Ministry of Food. The United Kingdom Government agreed to this procedure subject to the New Zealand Government vouching for the accuracy of any cost statistics used by the Board's representatives. Meat destined for local consumption is not dealt with by the Meat Producers Board. With the end of the bulk purchase agreements in September 1954, the export trade in meat reverted to a trader-to-trader basis. Provision was made by the Meat Export Prices Act 1955, however, for the determination annually by the Meat Export Prices Committee of minimum prices for meat exported from New Zealand. If necessary, the Committee fixes each week a schedule of deficiency payments which may be made to producers, the deficiency being the difference between the minimum price for that class of meat shown in the annual table and the f.o.b. value in the week to which the schedule relates. These deficiency payments are met from the Meat Industry Reserve Account, and the Meat Board is responsible for arranging payment. The farmer sells his stock to a works and is paid by the works or exporters, who in turn are reimbursed by the Meat Board.
Under the Meat Export Control Amendment Act 1959 the Meat Board may purchase meat for sale outside New Zealand to promote the sale of meat in other countries, provided such action establishes new markets.
To encourage the further exploitation of new markets, a company was formed in 1960 on the initiative of the Meat Board. The capital is provided by the New Zealand owned freezing companies, but these companies and the Meat Board appoint an equal number of directors. The company will ensure that new markets are adequately supplied and that reasonable pricing policies are followed.
Wool - The minimum-price system created by the Joint Organisation for the disposal of war surplus stocks of wool was operated in New Zealand by the Wool Disposal Commission, which was prepared to buy, at minimum reserve prices, wool from current clips offered at public auction but in respect of which prices failed to reach the reserve fixed. By the Wool Commission Act 1951 the Wool Disposal Commission was abolished and a Wool Commission authorised, with the principal function of assuring minimum prices for greasy, scoured, and growers' slipe wool in accordance with the table of minimum prices (effective only after agreement with the Minister), for New Zealand wool sold in New Zealand or the United Kingdom at auction sales approved by the Commission. The Wool Disposal Account was abolished and its moneys, together with those standing to the credit of the Wool Industry Deposit Account, were transferred to the Wool Commission Account which was established by the Act. The marketing of wool is carried out by public auction. The Wool Commission Act authorises a charge on all wool sold or exported to be used to cover administration costs of the Commission and in substitution for the levy, at present in abeyance, which may be imposed under the Wool Industry Act 1944 for the purposes of the Wool Board. In recent seasons a charge under the Wool Commission Act of 4s. a bale has been made on all wool exported from New Zealand or delivered to a wool manufacturer for use in New Zealand. This charge is being increased from 1 October 1961.
Apples and Pears - Apples and pears are purchased from growers by the New Zealand Apple and Pear Marketing Board. This Board was set up in 1948, in terms of the Apple and Pear Marketing Act 1948, to take over direction of the acquisition and marketing of the apple and pear harvest. It administers a guaranteed price scheme based on the cost of production of apples and pears. This price is a New Zealand average, and within it prices to growers vary for the different varieties, grades, and sizes. In this case the Board does not itself declare the average price to be paid for apples and pears, its powers being limited in this respect to making recommendations to the Minister of Agriculture, who declares the cost of production. This cost of production has, since the passing of an amending Act in 1954, become the average price to be paid for apples and pears for the season concerned. The Board is charged with the duty of recovering from the market these prices together with the costs of marketing. It determines the wholesale prices at which fruit is sold by authorised wholesalers to retailers. If in any season the total receipts from sales of fruit by the Board exceed the amount which the Board is required to pay to growers in accordance with the declared average price, the surplus, after deduction of costs and expenses incurred by the Board, is apportioned between a reserve fund and the growers. Until the reserve fund reached £1,000,000 the whole of the annual profit was paid into it. From then until the fund reached £1,250,000 the profit was distributed in the proportion of 25 per cent to the growers and 75 per cent to the fund. This amount having been reached, the profit is now allocated equally between the two. If sales in any season realise less than the amount the Board is required to pay, the deficiency is met from the reserve fund. All apples and pears are not purchased by the Board, the Act making provision for certain private sales by growers in accordance with regulations issued thereunder. The Board was able to declare a bonus to fruitgrowers for five seasons from 1953-54, the average amounts paid out per case being for 1954, 4.09d.; for 1955, 2.37d.; for 1956, 3.98d.; for 1957, 14.07d.; and for 1958, 4.92d. In 1959 a loss of £433,963 was incurred by the Board, and in 1960, though a profit of £304,443 was made by the Board, it was agreed with the growers that no bonus would be paid.
The Apple and Pear Board at first did not employ its own staff, except for secretarial and investigational duties, the physical functions in assembly, distribution, and marketing being carried out by the Marketing Department as the agent of the Board. However the Board set up its own marketing organisation and took over direct control as from 1 December 1953.
With the exceptions listed below, all fruit must be offered to the Board, and accepted by it if it comes within the scope of the New Zealand Grown Fruit Regulations 1952, which set standard grades with which the packed fruit must conform.
Officers of the Department of Agriculture inspect the fruit, and if it complies with the required standards the fruit becomes the property of the Board.
The exceptions under which fruit is not required to be offered to the Board are:
Growers, with permission of the Board, may sell direct to consumers in lots of not more than two cases, or to retailers in specified localities. In the latter case the Board may prescribe conditions as to quantities, varieties, standards, etc., of fruit sold:
Manufacturers may be licensed by the Board to purchase their requirements direct from growers (although in some cases the Board itself purchases fruit and resells it to the factory). In such cases, also, the Board may make conditions as above:
Growers may also be permitted by the Board to sell at municipal markets established under the Municipal Corporations Act 1954. The Board is not obliged to accept fruit from a grower while he holds a permit to sell at such a market.
The Board decides what proportion of the fruit is to remain in New Zealand and what proportion is to be exported, and arranges for the storage and release of varieties according to their condition and keeping capacity, in order to make fruit available for as long a period as possible during the year. As at 1 December 1953 the Board purchased from the Government the greater part of the facilities then in use for the handling of the crop. They included cool stores and ancillary equipment. Since then, however, the reserve fund, which has been built up from profits derived almost solely from exports, has been invested in a chain of modern cool stores and mechanical equipment designed for the improved handling of fruit.
Potatoes - Commencing during the war period, the Marketing Department let contracts to ensure an adequate supply of main-crop potatoes for local consumption. The last such contracts were let for the 1950-51 season.
The Potato Board, with equal representation of growers and merchants, was established by the Potato Growing Industry Act 1950. Its principal function is to ensure that an adequate supply of main-crop potatoes shall be available for consumption. Its powers include the making of contracts between growers and the Board, and the appointment of wholesalers authorised to purchase from growers and to sell potatoes in respect of which contracts have been made with the Board. The Board replaced the Potato Advisory Committee of the Marketing Department from November 1950. In June 1956 the Government announced that it would guarantee the overdraft of the Potato Board to enable the Board to guarantee a certain schedule of minimum prices to contract growers for any potatoes unsold at the end of the season. The purpose is to encourage the growing of an adequate supply of potatoes.
Milk - The Milk Act 1944 set up a Central Milk Council under whose general direction were established local milk authorities of various types according to conditions. The Marketing Department, and later the Department of Agriculture, acted as the administrative agent of the Council. It also administered the National Milk Scheme under which local supply associations of farmers contracted to supply the requirements in given areas at prices fixed from time to time by agreement between the industry representatives and the Government. The scheme controlled prices and allowances for processing and distribution at all stages from the farm gate to the consumer. The Milk Amendment Act 1953, however, further implemented the policy of divorcing marketing of primary products from direct Government control. It provided for the setting up of the New Zealand Milk Board to replace the Central Milk Council, with powers considerably greater than those of the Council, and for this reason one extra Government member was appointed to the Board. The Board has its own officers and operates the National Milk Scheme and treatment stations owned by the Crown, and engages in other activities for the purpose of ensuring an adequate supply and efficient distribution of milk.
The Central Milk Council Account was also replaced by the Milk Industry Account. While subsidies are payable from the Consolidated Fund, the Board may make a levy on milk for the purpose of providing for its operations if the Minister of Agriculture approves.
Retail prices are fixed by Price Order. The price for the milk to the producer is fixed by the Government after consultation with the Milk Board. Intermediate margins, such as those for chilling and bottling milk and to vendors for its delivery, are fixed by the Government on the recommendation of the Board. The total cost at the present time exceeds the amount paid by the consumers, the balance being met by subsidy. It is the function of the Milk Board to administer the whole town milk scheme on behalf of the Government which, however, retains a direct interest by virtue of the substantial sum still paid in subsidy.
Eggs - The marketing of eggs and egg products was formerly controlled by the National Egg Marketing Committee, set up under regulations issued in 1951 and amended in 1952. Private firms in various towns and cities were licensed by the Minister of Marketing to receive and sell eggs on commission and to manufacture and sell egg pulp. The prices paid to the poultrykeepers were those fixed from time to time by the Minister on the Committee's recommendation, while the wholesale and retail selling prices to the public were fixed by price order. It was the responsibility of the Committee to obtain from the market the average cost of production for the producer. It operated by adjusting prices, by deciding the proportion of eggs for pulping, and by instituting economies in marketing; it also administered funds collected from the producers by means of levies on feed and eggs, applying these towards meeting administrative costs and marketing expenses.
The Egg Marketing Authority Regulations 1953 transferred to the Egg Marketing Authority the power to regulate and control the marketing and distribution of eggs and egg pulp in substantially the same manner and extent as those powers were exercisable by the Minister and the Department of Agriculture under the Egg Marketing Regulations 1951.
The Egg Marketing Authority consists of seven members - four producer members of the New Zealand Poultry Board and three Government representatives.
The principal function of the Authority is to regulate and control the marketing and distribution of eggs and egg pulp in New Zealand and elsewhere in accordance with the regulations, to ensure as far as possible sufficient supplies of eggs and their equitable distribution in the general interests of producers and consumers.
The New Zealand Egg Marketing Authority as the successor with autonomous powers to the National Egg Marketing Committee, operates principally through licensed distributors in the various districts who, on commission, receive and resell eggs, or, as directed by the Authority, manufacture egg pulp for the use of bakers and pastrycooks. The poultry industry does not enjoy a full guaranteed price from the Government, but, within limits fixed by the assessed costs of production, is free to recover these costs from the market. A subsidy, at present at the rate of 4d. per dozen, is paid by the Government in respect of eggs received at authorised egg floors (as the licensed distributors are known).
Imported Citrus Fruits and Bananas - The control and distribution of bananas and imported citrus fruits were placed in the hands of the Internal Marketing Division in 1938, pineapples being added in 1940. Since the beginning of 1951, however, the importation and marketing of imported citrus fruits, bananas, and pineapples have been taken over by a registered company, Fruit Distributors Ltd., representing trade interests.
New Zealand Lemons and Oranges - The Citrus Marketing Authority Regulations 1953 provided the Citrus Marketing Authority with the principal task of selling fresh lemons, either directly or through agents, throughout New Zealand at prices related to cost of production, and to process unmarketable but otherwise sound fruit into by-products, such as fruit juice and lemon peel. The Authority has a membership of five, four of whom are nominees of the New Zealand Citrus Council and represent the producers, and one appointed by the Minister of Agriculture representing the consumers.
The Citrus Marketing Authority is now empowered to control the assembly and distribution of New Zealand lemons, including the variety known as the Meyer lemon which was hitherto exempt from regulation, and also New Zealand grown sweet oranges. The entire output of packed lemons, which now comes under the jurisdiction of the Authority, is sold at agreed prices to Fruit Distributors Ltd. The Authority has taken over the processing and packing facilities at Kerikeri, Auckland, and Tauranga, and most of the staff previously associated with this work.
Honey - A Honey Export Control Board was set up in 1924, the powers of which were assumed by the Minister of Marketing in 1938. In the same year regulations were made to provide for a levy at the rate of 1/2d. per pound on honey sold by beekeepers within New Zealand, subject to certain small exceptions. At a later date regulations under the Marketing Acts set up the Honey Marketing Committee which at first was advisory in nature, but some years later was given virtually executive powers. The Honey Marketing Authority Regulations 1953, made under the Primary Products Marketing Act 1953, amalgamated all the foregoing provisions and provided for a Honey Marketing Authority, which undertakes the task of packing and marketing honey within New Zealand and for export, and operates the blending plant in Auckland. The levy referred to was continued at the rate of 1d. per pound on all honey sold locally and the funds paid into the Honey Industry Account, which is administered by the authority for the benefit of the industry in general. The greater part of the funds hitherto obtained from this levy has been applied to equalising the return received by those whose honey has been exported by the Authority with the return from honey sold on the local market.
The Authority comprises four members elected by beekeepers, and one member appointed by the Government to watch the interests of the consumer.
PRICES OF PRIMARY PRODUCTS: Wool - Statistics of greasy wool sold at auction in New Zealand (compiled from information supplied by the New Zealand Wool Commission) are given below in two sections. The first table gives total quantities and values as recorded at sales, no attempt being made to allow for variations in quality or in the relative quantities of the various types of wool sold from season to season. Besides price movements, therefore, the average value per pound of wool sold shown in this table includes variations on account of these additional factors. Under the Wool Commission Act 1951 the Wool Commission is authorised to prepare a table of minimum prices for various classes of wool, which becomes effective by agreement with the Minister of Agriculture. Where wool is sold at less than the minimum price at an approved sale, the Commission may supplement the sale price so as to increase it to the minimum price, or, alternatively, may buy such wool at a price not greater than the minimum price.
WEIGHT, SALE VALUE, AND AVERAGE VALUE PER POUND OF GREASY WOOL SOLD AT AUCTION
| Season | Weight of Greasy Wool Sold | Sale Value | Value per Pound | Average Minimum Floor Price per Pound of Greasy Wool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Reserve price. †See latest statistical information. | ||||
| 1b (000) | £(000) | d. | d. | |
| 1948-49 | 287,211 | 30,882 | 25.81 | 16.98* |
| 1949-50 | 297,886 | 47,138 | 37.98 | 16.98* |
| 1950-51 | 293,737 | 107,509 | 87.84 | 19.10* |
| 1951-52 | 314,896 | 52,734 | 40.19 | 24.00 |
| 1952-53 | 311,902 | 60,022 | 46.19 | 24.00 |
| 1953-54 | 317,093 | 66,392 | 50.25 | 26.00 |
| 1954-55 | 338,608 | 70,084 | 49.67 | 26.00 |
| 1955-56 | 341,576 | 65,735 | 46.19 | 30.00 |
| 1956-57 | 356,237 | 81,283 | 54.76 | 30.00 |
| 1957-58 | 370,407 | 63,520 | 41.16 | 33.00 |
| 1958-59 | 406,261 | 61,064 | 36.07 | 33.00 |
| 1959-60 | 409,199 | 76,121 | 44.65 | 33.00 |
| 1960-61 | † | † | † | 33.00 |
In the next table details of a wool price index on base 1949-50 (= 1000) are given. This index has been compiled in an attempt to eliminate all but the price factor in movements of average wool values. A description of the make-up of this index is given in the March 1952 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
| Season | Price per Pound on Floor, Greasy* | Index Numbers† Base: 1949-50 (= 1000) |
|---|---|---|
*Average of selected types. †Based on price on floor, clean. ‡See latest statistical information. | ||
| d. | ||
| 1949-50 | 37.98 | 1000 |
| 1950-51 | 87.47 | 2299 |
| 1951-52 | 41.59 | 1088 |
| 1952-53 | 47.07 | 1219 |
| 1953-54 | 50.83 | 1310 |
| 1954-55 | 49.98 | 1286 |
| 1955-56 | 46.98 | 1208 |
| 1956-57 | 56.15 | 1430 |
| 1957-58 | 42.72 | 1089 |
| 1958-59 | 37.59 | 962 |
| 1959-60 | 46.05 | 1179 |
| 1960-61 | ‡ | ‡ |
Dairy Produce - A contributory factor to the drop in dairy produce realisations in the United Kingdom for the 1956-57 and 1957-58 seasons was the dumping of large quantities of butter on the British market by Finland, Sweden, the Republic of Ireland, and Argentina. These countries charged their own people very high prices, dumped their surplus on the British market and subsidised their dairy farmers. For 1957 the total imports into the United Kingdom were 365,300 tons, of which 61,100 tons came from the countries which were found to be indulging in export subsidisation. Dumped butter had the effect of depressing the market, and the price received for New Zealand butter was considerably less than the amount required to meet the guaranteed price.
In February 1958 representations were made by the New Zealand Government to the United Kingdom Government because it was considered that the serious fall in butter and cheese prices during the previous nine months which had contributed to the deterioration in the position of New Zealand's balance of payments was largely attributable to the unfair trading practices adopted by a number of countries. A formal request was made to the Board of Trade in London to impose antidumping or countervailing duties under the Customs Duties (Dumping and Subsidies) Act 1957 on butter imported into the United Kingdom from Finland, the Republic of Ireland, Sweden, and Argentina. In May 1958 the President of the Board of Trade announced that the Government agreed that exports from the four countries were subsidised and that there had been material injury to the New Zealand dairy industry. It had therefore asked Finland and Sweden to eliminate the practice of subsidisation or to keep their exports within agreed limits. In the event of non-compliance the United Kingdom Government stated its intention to impose countervailing duties. Finland and Sweden agreed to limit their exports. The United Kingdom considered that the position in respect of the Republic of Ireland would be satisfactory and that the level of imports from Argentina in 1958 would not be sufficiently large as to justify action in the meantime.
In announcing the United Kingdom Government's decision, the President of the Board of Trade stated that it had been decided that imports of butter from Poland should also be limited and that the open licence for imports of butter from Eastern Europe generally and from Belgium was being withdrawn.
The measures introduced by the United Kingdom Government were, no doubt, an important factor contributing to the improvement in the price of butter which took place in the second half of 1958.
In December 1958, however, the United Kingdom Government decided to uplift the quota restrictions previously imposed and withdrew its requests to Sweden and Finland to limit their exports and informed the Republic of Ireland that arrangements with it could lapse. The United Kingdom Government stated that if at any future time the imports of dumped or subsidised butter from any country should assume such proportions as to cause or threaten material injury to the New Zealand producers, application could again be made by New Zealand under the Customs Duties (Dumping and Subsidies) Act, and an assurance was given that any application would be dealt with expeditiously.
Largely as a result of an exceptionally dry summer in Europe in 1959, which reduced dairy production and resulted in depleted stocks in the United Kingdom, the price of New Zealand butter rose remarkably during the year to reach a peak of 410s. per hundredweight in October 1959. Early in 1960 the price dropped quickly following a loss of some trade to margarine and greater shipments from Europe due to a good production season.
There were indications in 1960 that European countries had adopted some change of outlook so far as the flooding of the United Kingdom market with surplus butter was concerned, and would tend to encourage greater sales on their home markets, but disposals of surpluses in 1961 again upset the market.
Cheese supplies on the United Kingdom market were short at the same time, and the price of cheese reached the relatively high level of 300s. per hundredweight in October 1959. Prices for cheese also dropped early in 1960.
The following table shows the average weekly sterling price for New Zealand butter ex-store for each month in the past four years, along with the average weekly sales on the London market during the same period. (Source: Dairy Products Marketing Commission.)
| Month | Butter | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Finest and First Grades) Average Price per Cwt | (All Grades) Weekly Averages Sales | |||||||||
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | |
| s. | s. | s. | s. | s | tons | tons | tons | tons | tons | |
| January | 261 | 256 | 290 | 403 | 269 | 2,578 | 2,169 | 2,726 | 2,611 | 2,294 |
| February | 254 | 241 | 290 | 354 | 258 | 4,224 | 2,675 | 2,792 | 2,552 | 3,181 |
| March | 257 | 233 | 290 | 334 | 250 | 1,481 | 2,649 | 3,679 | 2,424 | 3,693 |
| April | 256 | 207 | 290 | 292 | 250 | 4,176 | 4,469 | 3,955 | 2,984 | 3,517 |
| May | 291 | 206 | 300 | 290 | .. | 3,095 | 3,425 | 3,471 | 2,570 | .. |
| June | 317 | 207 | 328 | 292 | .. | 1,455 | 3,644 | 3,145 | 3,159 | .. |
| July | 312 | 220 | 352 | 310 | .. | 2,645 | 4,272 | 2,946 | 2,598 | .. |
| August | 310 | 235 | 373 | 304 | .. | 3,643 | 3,547 | 3,011 | 1,924 | .. |
| September | 310 | 235 | 392 | 282 | .. | 1,308 | 3,280 | 3,095 | 2,634 | ... |
| October | 296 | 241 | 399 | 290 | .. | 2,165 | 4,196 | 3,115 | 2,212 | .. |
| November | 271 | 266 | 410 | 287 | .. | 2,669 | 5,125 | 3,442 | 2,093 | .. |
| December | 260 | 283 | 410 | 280 | .. | 2,568 | 3,865 | 2,848 | 2,731 | .. |
| Annual average | 280 | 231 | 343 | 307 | .. | 2,597 | 3,656 | 3,199 | 2,505 | .. |
The next table gives similar information for the London sales of New Zealand cheese. (Source: Dairy Products Marketing Commission.)
| Month | Cheese | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Finest and First Grades, White) Average Price per Cwt (Crated) | (All Grades) Weekly Average Sales | |||||||||
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | |
| s. | s. | s. | s. | s. | tons | tons | tons | tons | tons | |
| January | 245 | 130 | 290 | 290 | 230 | 1,461 | 2,229 | 1,559 | 1,064 | 1,309 |
| February | 238 | 136 | 290 | 251 | 230 | 1,560 | 2,829 | 1,505 | 1,387 | 1,687 |
| March | 231 | 151 | 290 | 230 | 230 | 1,134 | 1,280 | 1,154 | 1,584 | 1,351 |
| April | 202 | 149 | 290 | 230 | 230 | 1,133 | 2,203 | 2,307 | 1,814 | 1,760 |
| May | 191 | 150 | 290 | 230 | .. | 2,841 | 1,826 | 1,488 | 1,585 | .. |
| June | 195 | 159 | 290 | 230 | .. | 747 | 2,295 | 1,523 | 2,230 | .. |
| July | 181 | 180 | 290 | 230 | .. | 1,187 | 2,268 | 1,249 | 1,287 | .. |
| August | 178 | 184 | 290 | 230 | .. | 1,295 | 1,091 | 1,410 | 1,094 | .. |
| September | 167 | 185 | 290 | 230 | .. | 1,553 | 2,679 | 1,159 | 1,905 | .. |
| October | 143 | 207 | 295 | 230 | .. | 1,621 | 1,751 | 1,044 | 1,440 | .. |
| November | 129 | 290 | 300 | 230 | .. | 2,631 | 1,196 | 885 | 1,090 | .. |
| December | 129 | 290 | 300 | 230 | .. | 1,052 | 1,090 | 1,235 | 1,310 | .. |
| Annual average | 179 | 177 | 294 | 237 | .. | 1,505 | 1,853 | 1,409 | 1,505 | .. |
The next table gives the comparative f.o.b. and ex-store London prices in relation to the basic or guaranteed price.
| Year | Product | Basic Price d. per lb | F.o.b.* Equivalent s. per cwt | Price Equivalent Ex-store London† s. per cwt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*F.o.b. = free on board, i.e., loaded at a New Zealand port. †The ex-store price includes insurance and freight to London, unloading and storing charges, and commission on sales. | ||||
| 1957-58 | Butter | 36.25 | 310 | 345 |
| Cheese | 39.25 | 173 | 209 | |
| 1958-59 | Butter | 32 | 277 | 315 |
| Cheese | 35 | 159 | 194 | |
| 1959-60 | Butter | 32 | 279 | 313 |
| Cheese | 38 | 171 | 205 | |
| 1960-61 | Butter | 32 | 277 | 312 |
| Cheese | 38 | 171 | 210 | |
The movements in prices and sales of butter on the United Kingdom market are shown in the following diagram.
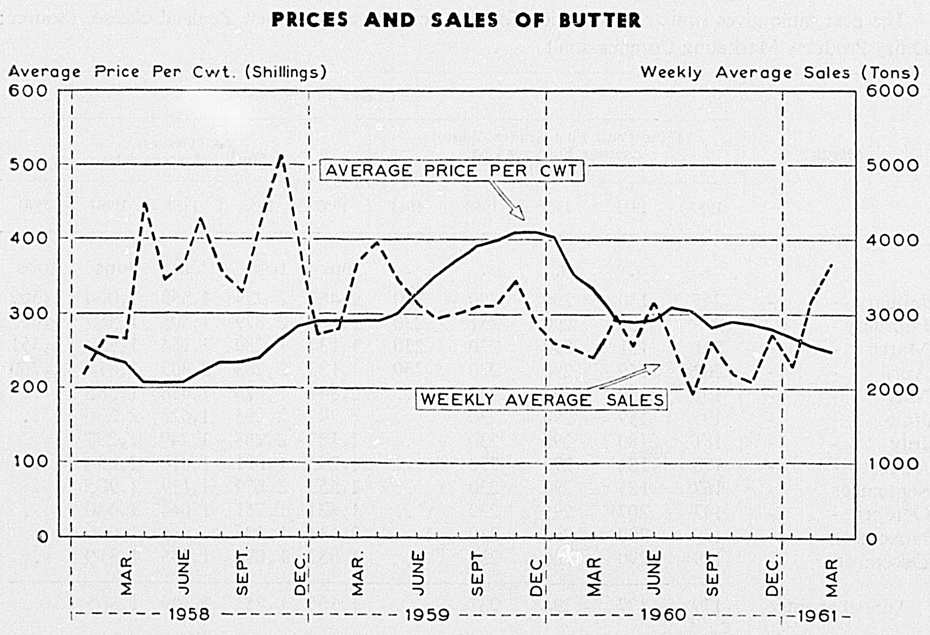
The movements in prices and sales of cheese on the United Kingdom market are shown in the following diagram.
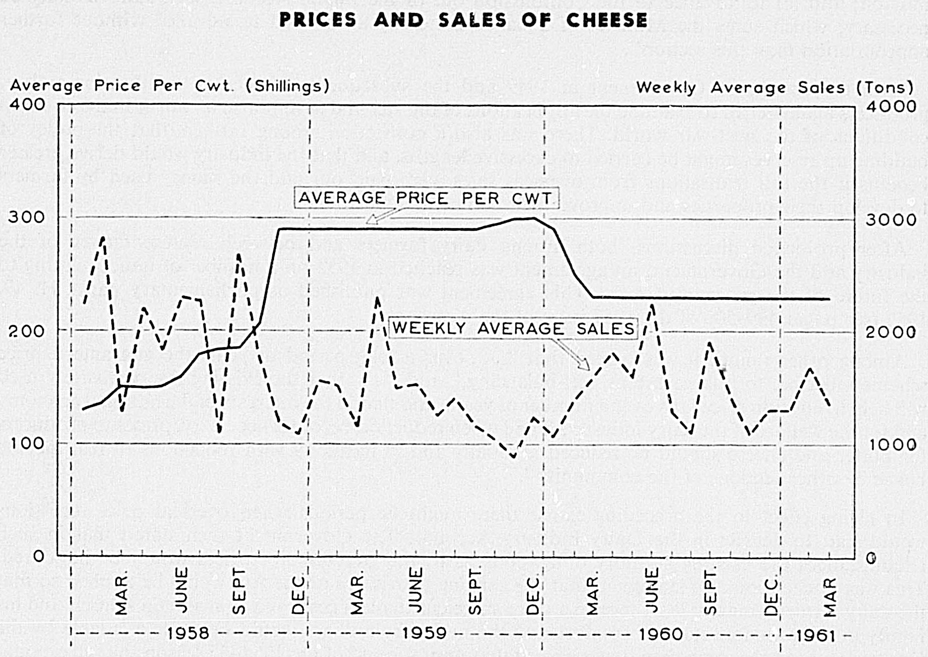
Guaranteed Prices for Dairy Produce - Guaranteed prices for butter and cheese were introduced by the Government on 1 August 1936 to give stability to the dairy industry, and the Primary Products Marketing Act 1936 set out the principles which underlay the fixing of the prices, namely: (a) The necessity in the public interest of maintaining the stability and efficiency of the dairy industry; (b) the costs involved in the efficient production of dairy produce; (c) the general standard of living of persons engaged in the dairy industry in comparison with the general standard of living throughout New Zealand; and (d) the estimated cost to the Marketing Department of the dairy produce concerned and also the cost of the general administration of the Act.
Due regard having been paid to these matters, prices were to be “. . . such that any efficient producer engaged in the dairy industry under usual conditions and in normal circumstances, should be assured of sufficient net return from his business to enable him to maintain himself and his family in a reasonable state of comfort”.
The preamble to the Act described the need to protect producers against the effects of market fluctuations and went on to add that “. . . it is thought that the most effective and appropriate way of affording such production, so far as it relates to primary products intended for export, is to provide that the Government, on behalf of the Crown, shall acquire the ownership of such products at prices to be fixed and promulgated from time to time . . .”
With the transfer by Act, in 1947, to the Dairy Products Marketing Commission of authority to fix the guaranteed price, a fresh statement of the Government's responsibility to underwrite the price was required. The 1947 Act added an extra principle to those that were to be considered in fixing the price - namely, the promotion of the general economic stability of New Zealand. The Government's responsibilities were set forth in clause 23, and were as follows:
“(1) The prices which the Commission fixes . . . shall be duly paid as required by this Act. (2) The Minister of Finance is hereby empowered, for the purpose of giving effect to the last preceding subsection, (a) to consent in writing . . . to the amount of the overdraft with the Reserve Bank of New Zealand being increased beyond the limit therein prescribed; (b) to consent to the borrowing of such sums as may be necessary and the mortgaging or charging of any of the property of the Commission; and (c) to advance to the Commission out of the Public Account such sums as may be necessary, which sums the Minister of Finance is hereby authorised to advance without further appropriation than this section”.
With the change of Government in 1949 and the subsequent changes in stabilisation policy, producers again began to examine the implications of the Act and to appraise its worth in the changed conditions of the post-war world. There was also a conviction among farmers that the policy of building up reserves might be carried to excessive lengths, and that the industry would derive greater benefits if the full realisations from overseas sales were paid out and the money used by farmers to develop their properties and improve their competitive position.
After prolonged discussions, both among dairy farmers and between representatives of the industry and the Government, an agreement was reached in 1952 on a number of issues relating to the future of the guaranteed price. This agreement was published as parliamentary paper H. 49, 1952 (see pages 499-500 of the 1957 issue of the Yearbook).
Among other things, it was agreed that “. . . over a long period of years the guaranteed price scheme must be, to a large extent, self-balancing,” and “. . . that the existing reserves wisely used will help to cushion price falls over a number of years, and that in the interests of the national economy and for the welfare of the dairy industry, if and when reduction becomes necessary, prices to producers for butter and cheese should be reduced gradually and in harmony with reductions in real income borne by other sections of the community”.
In giving effect to the preceding clause there might be periods when overseas price recessions would lead to deficits in the Dairy Industry Account. The Government then stated that in such circumstances the existing statutory obligations as to the guarantee of prices would be honoured. This was understood as a statement that the existing provisions of the Act would be applied so that the dairy farmer would at least receive a price sufficient to meet costs and to maintain himself and his family in a reasonable state of comfort and the necessary moneys would be made available by the Government. At the same time it was agreed that until the end of the 1954-55 season the full amount of overseas realisations would be paid out.
With the end to bulk purchase in 1954 and a return to competitive trading, it became apparent that the market for dairy produce might experience a good many fluctuations and that some of the assumptions made when the 1952 agreement was concluded might require closer examination.
In 1955 the Dairy Board appointed a committee of inquiry to investigate a number of problems facing the industry, including the marketing of its products and the fixing of the guaranteed price. Subsequently three senior Government officers were added to the committee, though it was made plain at the time that they were acting as individuals and that the Government was not bound to any decisions to which they were a party. In its report in March 1956 the committee recommended that a separate authority be set up to fix prices for butter and cheese, account to be taken of costs of production and overseas realisations, but the price for one season to be not less than 95 per cent of the floor price for the previous season. It was also recommended that the functions of the Dairy Board and of the Dairy Products Marketing Commission be to some extent amalgamated, though the separate entity of the Commission would be preserved. These proposals were widely discussed by dairy farmers in subsequent months, the Government having already indicated that it would give legislative effect to such proposals that had the full support of those engaged in the industry. This was done in October 1956 when the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment Act was passed.
This Act, which came into force on 1 August 1957, made miscellaneous amendments to the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Act 1947. It reconstituted the Dairy Products Marketing Commission, established a Dairy Products Prices Authority and a Dairy Industry Loans Council, and provided for the disposal of any annual surplus received from the sale of butter and cheese.
The Commission consists of three members appointed as Government representatives, two members of the Dairy Board, and two members not members of the Dairy Board, but nominated at the annual conference of the Dairy Board. The Chairman is elected annually by the members of the Commission.
The Dairy Industry Loans Council consists of three members of the Dairy Commission, three members of the Dairy Board, the Secretary to the Treasury, and the Director-General of Agriculture. The functions of the Council are to approve loans from the Dairy Industry Account to cooperative dairy companies and for other purposes in the interests of any primary industry. In practice these loans are for improvements to plant and buildings.
The Dairy Products Prices Authority consists of a chairman who is appointed by the Government and approved by the Dairy Board, one member representing the Government, and all seven members of the Commission. The principal functions of the Authority are to fix the prices of butter and cheese acquired by the Commission and to authorise payments from any annual surplus obtained from the sale of butter and cheese. The Authority determines the cost of production at the commencement of each season, and takes this into account in fixing the prices to be paid for butter and cheese. The price fixed for the first season had to be not less than 95 per cent of the cost of production, and in subsequent seasons was to be not less than 95 per cent of the maximum price for the preceding season.
In fixing prices for butter, regard must be paid to the necessity of maintaining the stability and efficiency of the dairy industry, the cost of production, the amount being realised for butter and cheese, the ruling level of prices for farm products other than dairy produce, the estimated cost of marketing, any recommendations made by the Dairy Board, and other relevant matters. The price for cheese is fixed by the Authority after considering the cost of the production of cheese as compared with the cost of production of butter, and the desirability of ensuring that dairy produce will be produced in such quantity and in such proportions as will be of the greatest benefit to the dairy industry.
The 1956 amendment to the principal Act made a number of significant changes, the most important being the reduced emphasis on costs of production, the deletion of all reference to the dairy farmer's standard of living, and the inclusion of the provision that the price for any one season shall not be less than 95 per cent of the maximum for the previous season. No change was made in the sections of the 1947 Act which lay down the Government's responsibility to underwrite the price. The 1956 amendment includes provision for the further building up of industry reserves. Section 12 lays down that, if the season's operations result in the accumulation of a surplus, the first call upon this surplus will, unless the Dairy Board agrees otherwise, be a payment to suppliers to bring the pay out up to the level of the assessed costs of production. Provision is made in the same section for the building up of reserves, after this has been done. It is stated that after the price of butter and cheese has been equalised with the costs of production, “If the amount of the excess . . . has not been expended . . . the balance remaining, or so much of that balance as the authority thinks fit shall be expended or used for the benefit of the dairy industry in such manner as the Authority, after consultation with the Dairy Board, thinks fit, having regard to - (a) any recommendations made by the Dairy Board, and (b) the amount, if any, standing to the credit of the Dairy Industry Account”.
At the beginning of the 1957-58 season agreement was reached by the Minister of Agriculture and the Dairy Board as to the basic cost of production of butterfat, the figure being 38.25d. The Authority later fixed the price of butterfat for the year at 36.25d., this being 95 per cent of the former figure in terms of the price for butter.
The dairy industry reserve funds were exhausted during the 1957-58 season principally because the general world oversupply of butter and the dumping of large quantities by European countries on the United Kingdom market resulted in realisations being far below the basic price. In April 1958 the London price for finest butter was as low as 206s. a hundredweight, whereas the guaranteed price equivalent was 345s. a hundredweight. By July 1958, following action taken by the United Kingdom Government against the practice of dumping, the price had recovered to only 235s. a hundredweight (2s. 1d. per pound) although it was considered that the price might reach 2s. 9d. per pound by the end of the year.
In these circumstances the legislative restriction limiting any reduction in the guaranteed price to 5 per cent of that of the previous season became impractical. Following discussions between representatives of the industry and the Government it was announced at the end of August that sufficient assistance would be provided to enable dairy farmers producing butterfat for butter to receive a price of approximately 32d. per pound of butterfat. Assistance would take the form of a loan to the industry and would be repaid as soon as market realisations allowed this to be done. The fixed price for butter at 29.6895d. per pound represented a reduction of 10.4 per cent on the previous season's price. The Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment Act 1958 provided the necessary authority for this change by suspending for the 1958-59 season the application of the section in the 1956 Act which laid down the criteria to be observed in fixing the price including the provision that it must be not less than 95 per cent of that fixed for the previous season. The Dairy Products Prices Authority later fixed the basic price for butterfat for butter at 32d. per pound, and for butterfat for cheese at 35d. per pound.
For the 1959-60 season the basic price for butterfat for butter remained at 32d. per pound, but the basic price of butterfat for cheese was increased to 38d. per pound.
In his Budget statement at the end of June 1958 the Minister of Finance announced that up to £5 million would be provided by way of loan for assistance to the dairy industry, as a deficit for the season of up to £12 million was expected at the time.
Of the amount of £5 million, an advance of £0.2 million was made, and then £4.8 million was paid to the credit of the Dairy Industry Account by the Government in March 1959. At that time butter was still being sold in London below the basic price equivalent in New Zealand and the overseas market situation was still uncertain and a further addition to the deficit could have been incurred.
With the marked improvement in overseas prices after this date there was a surplus in the 1958-59 trading, and the £5 million advance was not required to finance that year's operations. It was repaid in April 1960.
When a surplus is achieved in any one trading year the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Act 1947, as amended in 1956, provides that it shall, unless the Dairy Board otherwise agrees, be paid out to producers up to the assessed cost of production for that year (the trading period is defined by the Act as the 12 months ending 31 May). As early as July 1959 it had become clear that the industry's account for the year ending 31 May 1960 was likely to show a surplus. An understanding was reached between the industry and the Government that half of any such surplus would be paid to the producers and half would be retained in the Dairy Industry Account.
In July 1960 it was announced that, after negotiations between a committee representing the Dairy Board and the Dairy Products Marketing Commission and the Government, agreement had been reached on a number of questions relating to future marketing and price policy. The main questions on which agreement was reached are as follows:
1. The Board and the Commission would be amalgamated into one body comprised of 11 producer and two Government members.
2. Price fixing will be carried out by an authority of seven members, three of which will be nominated by the industry, three by the Government, and a chairman will be appointed by the Government with the approval of the industry.
3. In a normal trading year 50 per cent of any surplus will be distributed to dairy companies and 50 per cent placed in reserve. (If the existing deficit in the account is greater than the trading surplus the amount distributed to dairy companies may not exceed 25 per cent of the trading surplus.)
Prices for butter and cheese will be fixed by the Authority after taking into account the following criteria:
The necessity in the public interest of maintaining the stability and efficiency of the dairy industry.
The amount which butter and cheese acquired by the Commission is realising and the market prospects for the coming year.
The state of the Dairy Industry Account.
Any submissions made by the new body.
Any other matters deemed relevant.
It was also agreed that the annual movement in the basic price of butterfat should not be up or down by more than 5 per cent of the previous season's basic price and that the Authority should consult the Minister before fixing the price. The Government, for its part, has agreed to incorporate the above changes in legislation to be introduced during 1961.
The fixed prices in pence per pound of butter and cheese for export paid to dairy factories are now given.
| Season Ended 31 July | Creamery Butter (Finest Grade 93-93 1/2 pt) | Whey Butter (First Grade) | Cheese (First Grade 92-92 1/2 pt) |
|---|---|---|---|
*Equivalent, on a product basis, of additional amounts paid to dairy companies. For details refer to appropriate annual reports of New Zealand Dairy Products Marketing Commission. †These additional amounts are surplus payments, as authorised by the Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment Act 1956. | |||
| pence per lb | (net weight) | ||
| 1936-37 | 12.5625 | 11.5625 | 7.0625 |
| 1937-38 | 13.6600 | 12.6600 | 7.7500 |
| 1938-39 | 14.8900 | 13.8900 | 8.4200 |
| 1939-40 | 14.8900 | 13.8900 | 8.42O0 |
| 1940-41 | 14.8900 | 13.8900 | 8.4200 |
| 1941-42 | 14.8900 | 13.8900 | 8.4200 |
| 1942-43 | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 1943-44 | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 0.8690* | 0.2390* | 0.4661* | |
| 1944-45 | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 2.6702* | 0.2990* | 1.4743* | |
| 1945-46 | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 3.5441* | 0.3376* | 1.8976* | |
| 1946-47 | |||
| 1 August - 31 October | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 4.6374* | 0.3786* | 2.5020* | |
| 1 November - 31 July | 15.3900 | 13.8900 | 8.7300 |
| 6.0468* | 0.3786* | 3.2024* | |
| 1947-48 | 23.8520 | 22.8520 | 13.0620 |
| 1948-49 | |||
| 1 August - 31 May | 24.5980 | 23.5980 | 13.5260 |
| 1 June - 31 July | 25.7437 | 24.7437 | 14.0486 |
| 1949-50 | |||
| 1 August - 30 April | 25.8694 | 24.8694 | 14.2457 |
| 1 May - 31 July | 26.4674 | 25.4674 | 14.5265 |
| 1950-51 | |||
| 1 August - 14 February | 27.1589 | 26.1589 | 14.9522 |
| 15 February - 31 July | 28.5791 | 26.1589 | 15.6580 |
| 1951-52 | 30.8066 | 29.2521 | 17.0000 |
| 0.6160* | 0.3061* | ||
| 1952-53 | 32.5372 | 31.6181 | 18.1000 |
| 1.1294* | 0.5612* | ||
| 1953-54 | |||
| 1 August - 14 September | 32.5372 | 31.6181 | 18.1747 |
| 1.1294* | 0.5612* | ||
| 15 September - 31 July | 34.3532 | 32.9086 | 19.1380 |
| 1.1294* | 0.5612* | ||
| 1954-55 | |||
| 1 August - 30 November | 33.9425 | 32.4979 | 18.7437 |
| 1 December - 31 July | 34.4969 | 32.4979 | 19.0204 |
| 1955-56 | 33.2649 | 31.2649 | 18.3600 |
| 0.5749*† | 0.2857*† | ||
| 0.8163* | |||
| 1956-57 | 34.1355 | 32.1355 | 19.2673 (gross weight) |
| 1957-58 | 33.1491 | 31.1491 | 18.5335 |
| 1958-59 | 29.6895 | 27.6895 | 16.9622 |
| 1959-60 | 29.7950 | 27.7950 | 18.3196 |
| 3.6225*† | 1.7598*† | ||
| 1960-61 | 29.729 | 27.729 | 18.308 |
Produce of other grades incurs differential premiums or penalties according to grading points. Differentials used since the introduction of guaranteed purchase prices are as follows.
CREAMERY BUTTER
| 1936-37 to 1957-58 | 1958-59 and 1959-60 | 1960-61 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pence per lb | |||
| Finest 94 points and over | +0.125 | +0.1875 | +0.2 |
| Finest 93-93 1/2 points (basic) | - | - | - |
| First 92-92 1/2 points | -O.0625 | -0.1875 | -0.2 |
| First 90-91 1/2 points | -0.25 | -0.5625 | -0.75 |
| Second grade | -0.75 | -2.0 | -2.0 |
| Third grade (from 1955-56) | -6.0 | -6.0 | -6.0 |
CHEESE
| 1936-37 to 1950-51 | 1951-52 to 1954-55 | 1955-56 to 1959-60 | 1960-61 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pence per lb | ||||
| Finest 94 points and over | +0.15625 | +0.3125 | +0.3125 | +1.25 |
| Finest 93-93 1/2 points | +0.125 | +0.215 | +0.215 | +1.0 |
| First 92-92 1/2 (basic) | - | - | - | - |
| First 91-91 1/2 points | -0.0625 | -0.0625 | -0.0625 | -0.25 |
| Second 88-90 1/2 points | -0.25 | -0.725 | -1.075 | -1.25 |
| Second 87 and under | -1.2 | -3.75 | -3.75 | |
The prices quoted in the table on page 605 were designed to enable efficient dairy companies to pay to suppliers the following amounts in pence per pound of butterfat used for butter or cheese manufacture. Also given is the average payout per pound of butterfat supplied for seasons up to 1948-49, and average net revenue for later seasons.
| Season | Price per Pound of Butterfat Used for- | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butter-making (Basic Price) | Cheese-making (Basic Price) | Butter-making (Average Payout or Net Revenue) | Cheese-making (Average Payout or Net Revenue) | |
| *An additional 2d. per pound of butterfat was paid in 1955-56 to factories on all butterfat used for cheesemaking during the season. | ||||
| pence per lb | ||||
| 1946-47 | 23.391 | 25.391 | 23.691 | 25.753 |
| 1947-48 | 25.907 | 27.907 | 26.229 | 27.945 |
| 1948-49- | ||||
| August 1948 to May 1949 | 26.751 | 28.751 | 27.369 | 29.190 |
| June 1949 and July 1949 | 28.146 | 30.146 | ||
| 1949-50- | ||||
| August 1949 to April 1950 | 28.244 | 30.244 | 28.720 | 30.785 |
| May 1950 to July 1950 | 28.972 | 30.972 | ||
| 1950-51- | ||||
| August 1950 to 14 February 1951 | 29.678 | 31.678 | 30.568 | 32.425 |
| 15 February 1951 to July 1951 | 31.407 | 33.407 | ||
| 1951-52 | 33.655 | 36.155 | 34.106 | 36.764 |
| 1952-53 | 35.670 | 38.670 | 35.916 | 38.958 |
| 1953-54- | ||||
| August 1953 to 14 September 1953 | 35.834 | 38.334 | 37.610 | 40.554 |
| 15 September 1953 to July 1954 | 37.984 | 40.984 | ||
| 1954-55- | ||||
| August 1954 to 30 November 1954 | 37.349 | 39.831 | 37.732 | 40.133 |
| 1 December 1954 to July 1955 | 37.961 | 40.240 | ||
| 1955-56 | 36.459 | 38.459* | 36.547 | 38.730 |
| 1956-57 | 37.548 | 40.548 | 37.479 | 40.887 |
| 1957-58 | 36.250 | 39.250 | 36.322 | 39.822 |
| 1958-59 | 32.000 | 35.000 | 32.352 | 35.271 |
| 1959-60 | 32.000 | 38.000 | 32.346 | 38.259 |
| 1960-61 | 32.000 | 38.000 | ||
In addition to the basic price payments, payouts were made from realisations of the sale of butter and cheese in the 1951-52, 1952-53, and 1953-54 seasons, in accordance with the agreement by which the full proceeds received from the sale of these commodities up to the end of the 1954-55 season were to be used for the benefit of suppliers and/or dairy companies.
There was no surplus distribution in 1954-55, the Commission in fact incurring a loss of £2,000,000. In 1955-56 payments were made to cheese companies, thus increasing the differential as mentioned later. At the end of the 1955-56 season an additional payment of 0.7d. per pound of butterfat was made.
With the decline in butter prices during 1956 and the heavy falls for both butter and cheese during 1957 and into 1958, the funds in the Dairy Industry Account, amounting to £27 million at the start of the 1956-57 season, were exhausted during 1958. After the completion of sales of butter and cheese produced in the 1957-58 season the account was in debit to an amount of £7,349,485, but the sales of the 1958-59 production at higher prices brought about a recovery in the account. A surplus payment of 4.3995d. per pound of butterfat received and used in the manufacture of butter and cheese for the period 1 August 1959 to 31 May 1960 was made to dairy companies in August 1960.
The price differential of butterfat for manufacture of cheese over that for manufacture of butter was 2d. a pound during 1937-38 to 1950-51, 2 1/2d. for 1951-52, 3d. for 1952-53 and 1953-54, 2 1/2d. for 1954-55, and, as shown in the previous table, was first fixed at 2d. for 1955-56. By subsequent announcements during the season this was increased to 4d., the additional 2d. being distributed, not by increasing the basic price for cheese, but by paying to factories 2d. per pound on all butterfat used by them in the manufacture of cheese during the season. For 1956-57, 1957-58 and 1958-59 the price differential was 3d., but for 1959-60 it was increased to 6d. to maintain the volume of cheese production and remained at this figure for 1960-61.
There is an assumption implicit in the basic price scheme that the payout to butter factory suppliers is for cream at the farm and the payout to cheese factory suppliers is for whole milk delivered to the factory. Where a factory receives whole milk and makes butter, the residual skim milk can be manufactured into any of several products, the main ones being skim-milk powders and casein. The only possible products of a cheese factory additional to those covered by the guaranteed price for cheese are products of separated whey and are of relatively insignificant value. Because of the existence of the price differential of butterfat for manufacture of cheese over that for manufacture of butter, factories with the necessary equipment generally make butter and skim-milk powder or butter and casein only where the combined returns are likely to be at least equal to the return from cheese.
Meat - With the cessation of contract prices, the only overseas information at present available consists of ruling wholesale prices for representative qualities of meat sold during the particular week. The Imported Meat Trade Association in the United Kingdom compiles weekly London wholesale meat prices. The basis of quotation for frozen meat was altered from the beginning of March 1958 from “ex-store London” to “ex-hooks to retailers at Smithfield market”, this change resulting in the comparative prices quoted since then being approximately 1/2d. per pound higher than on the old basis. The next table gives prices at the end of the last week in the month from March 1958. Two-thirds of the value of all exports of frozen and chilled meat are generally accounted for by lamb, and the two first-quality weight grades quoted in the table usually account for approximately 5 per cent and 45 to 50 per cent respectively of all lamb carcasses exported. Beef accounts for one-fifth of the total exports of frozen and chilled meat (by value), but mutton comprises only 7 or 8 per cent of the total value of frozen-meat exports. With the reduction of regular supplies of quarter beef to the United Kingdom, price quotations have been infrequent since the beginning of 1958. There was a substantial drop in the London prices for mutton and lamb during 1959. The principal cause of the fall in prices was the heavy increase in production of mutton and lamb from United Kingdom farms, the home output being some 25 per cent greater than the previous year.
The increase in domestic production was based on a rise of breeding ewe population, under the stimulus of a substantial Government subsidy, but was added to by an inrush of domestic supply in August and September following the extremely dry summer in the United Kingdom. An additional factor contributing to over-supply of the market was an increase in imports, including additional lamb carcasses from New Zealand as a result of the steady rise in sheep population.
| Lamb (First Quality) | Mutton | Beef | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wether | Ewe | Chilled Ox | Frozen Ox (First Quality) | |||||||
| 28 lb and under | 29 to 36 lb | 49 to 56 lb | 57 to 64 lb | 49 to 56 lb | 57 to 64 lb | Hinds | Fores | Hinds | Fores | |
| All Weights | 161 to 210 lb | 145 to 210 lb | ||||||||
*Nominal; figures so marked have, in the absence of actual quotes, been carried forward from earlier weeks in the same month, or derived from movements in the prices of supplies from other sources, e.g., Argentinian chilled beef and Australian frozen beef, assuming the normal price margins. †Basis of quotation for frozen meats altered - see Notes of the Month in Monthly Abstract of Statistics, April 1958. ‡4 July 1958. §19 December 1958. | ||||||||||
| pence per lb | ||||||||||
| End of last week in- | ||||||||||
| 1958—March† | 24 1/2–25 | 21 1/2–22 | 14 1/2 | 13 | 12 | 10 1/2 | 19–21 | 15–16 | 20* | 15* |
| June† | 27-27 1/2 | 24 1/2–26 | 17–17 1/2 | 15 | 12 | 10 1/2 | 21 | 15 | .. | .. |
| September | 29 1/2 | 27–27 1/2 | 17 1/2 | 15 1/2 | 12 1/2 | 11 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| December? | 28 1/2 | 25 1/2–26 1/2 | 13 1/2–14 | 12 | 10–11 | 10 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1959—March | 22 1/2 | 21–22 | 12 | 10 1/2–11 | 10 | 9 1/2–10 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| June | 20 1/2–21 | 20 1/2–21 | 13 | 12 1/2 | 8 | 7 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| September | 19 1/2–20 | 18–18 1/2 | 11 1/2–12 | 11–11 1/2 | 9 1/2 | 9 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| December | 27 | 25–26 | 10–10 1/2 | 9 1/2–10 | 8–8 1/2 | 7 1/2 | .. | .. | 22–22 1/2 | 17 1/2–18 |
| 1960—January28– | 28 1/2 | 26–27 1/2 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 8 | .. | .. | 22 1/2–23 | 18–18 1/2 |
| February | 27 | 23 1/2–25 | 13–13 1/2 | 11 1/2 | 9 1/2–10 | 8 1/2 | .. | .. | 23 1/2 | 19 1/2* |
| March | 24–25 | 22–23 | 14 1/2* | 13* | 11–11 1/2 | 10 | .. | .. | 25 | 20–20 1/2 |
| April | 25–26 | 24 1/2–25 1/2 | 13 | 11 1/2 | 33 1/2–34 1/2 | 22 1/2–23 | 27–28* | 20 1/2–21* | ||
| May | 24–24 1/2 | 24–24 1/2 | 15 1/2–16 | 14 1/2 | 10 1/2–11 | 9–9 1/2 | 27–28* | .. | 22–24* | 19–19 1/2* |
| June | 28 1/2–29 | 27 1/2–28 | 15 1/2 | 14 1/2 | 9 1/2–10 | 8–8 1/2 | 25–27 1/2 | 14–15 | 23–24 | .. |
| July | 28–28 1/2 | 26–26 1/2 | 15–15 1/2 | 14 | 9 | 7 1/2–8 | 24–27* | .. | 23–24* | .. |
| August | 29–29 1/2 | 26–26 1/2 | 15 1/2 | 14 | 10 1/2 | 8 1/2–9 | 29* | 15–15 1/2* | 24–25* | 16 1/2–17 |
| September | 27 | 24 1/2–25 1/2 | 15 1/2 | 14 | 11 1/2 | 10 | .. | .. | 25–26 | 18–18 1/2 |
| October | 26–26 1/2 | 24 1/2–25 1/2 | 15–15 1/2 | 13 1/2 | 12 | 11 | .. | .. | 25–25 1/2* | .. |
| November | 23–24 | 21 1/2–22 1/2 | 14 1/2–15 | 13–13 1/2 | 11 | 9–9 1/2 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| December | 23 1/2–24 | 22–23 1/2 | 14–14 1/2 | 13–13 1/2 | 11 1/2–12 | 10 1/2 | .. | .. | 21–21 1/2 | .. |
| 1961—January | 22–22 1/2 | 21–22 1/2 | 12–13 | 11 1/2–12 | 11 1/2–12 | 10–10 1/2 | .. | .. | 20–21 | .. |
| February | 19 1/2–20 1/2 | 19–20 | 11 1/2–12 | 11 | 10 1/2–11 | 9 1/2–10 | .. | .. | 19 1/2 | 15–15 1/2 |
| March | 22 1/2–23 | 21 1/2–22 | 12 1/2 | 12 | 12–13 | 11–11 1/2 | .. | .. | 21–22 | 15 1/2–16 1/2 |
Opening Schedule Prices - Under the stabilised prices and costs procedures operative up to the 1947-48 season, the fat stock schedule prices at which meat operators purchased from producers were fixed. In the two seasons following, while the opening schedules for each season were fixed in consultations between the Government, the Meat Producers Board, and the meat operators, subsequent movements during each season due to wool growth and fluctuations in prices of by-products were the responsibility of the meat operators. Since the beginning of the 1950-51 season the fixing of the schedule prices has been wholly in the control of the operators. The Meat Producers Board keeps a close watch on the prices being received for the meat and all by-products and on processing costs to ensure that the schedule prices give a just and equitable return to producers.
The opening schedules for the 1951-52 to 1960-61 seasons are given below.
| Item | Season | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1951-52 | 1952-53 | 1953-54 | 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1960-61 | |||||||||||
*From 1951-52 to 1952-53 price is given for 720 lb and under, for 1953-54 the average price relates to carcasses of up to 880 lb, and from 1954-55 to 1957-58 the price refers to carcasses of up to 800 lb. †1/2d. per pound less paid for weight 49 lb-56 lb. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Price of Lamb, Wether, and Ewe Mutton, in Pence per Pound | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lambs - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Downs (29-36 lb) | 16 | 18 3/4 | 19 3/4 | 27 | 24 | 23 | 26 | 20 | 13 1/2 | 20 1/2 | ||||||||||
| Canterbury (29-36 lb) | 16 3/4 | 19 1/2 | 20 1/4 | 13 | 20 | |||||||||||||||
| Crossbred (29-36 lb) | 16 1/2 | 19 | 19 1/2 | 13 1/2 | 20 1/2 | |||||||||||||||
| Seconds (29-36 lb) (N.I.) | 15 | 18 1/4 | 19 | 26 | 23 1/2 | 22 | 25 | 19 | 12 1/2 | 19 1/2 | ||||||||||
| Wethers- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Primes (48 lb and under) - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| North Island | 10 | 11 | 12 1/2 | 14 3/4 | 16 1/4 | 15 3/4 | 14 | 11 3/4 | 6 | 11 1/2 | ||||||||||
| South Island | 9 | 10 1/2 | 11 5/8 | 14 1/2 | 15 1/2 | 15 | 13 1/4 | 11 | 5 1/4 | 10 3/4 | ||||||||||
| Seconds (48 lb and under) - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| North Island | 9 | 9 1/8 | 10 3/8 | 11 3/4 | 13 1/4 | 12 3/4 | 11 3/4 | 9 3/4 | 5 1/2† | 10 1/2 | ||||||||||
| South Island | 8 | 8 5/8 | 9 1/2 | 11 1/2 | 12 1/2 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 4 3/4 | 9 3/4 | ||||||||||
| Ewes (48 lb and under) (N.I.) | 6 1/2 | 5 3/4 | 7 1/2 | 6 1/4 | 8 3/4 | 8 5/8 | 6 | 7 3/4 | 4 | 6 1/4 | ||||||||||
| Price in Shillings and Pence, per 100 lb of Beef (N.I.) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter beef, North Island - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ox, chiller beef (680 lb and under | 127 | 0 | 140 | 0 | 120 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 95 | 0 | 130 | 0 | 135 | 0 | 140 | 0 | ||||
| Ox- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| G.A.Q. (680 lb and under)* | 91 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 104 | 0 | 124 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 130 | 0 | 135 | 0 | 140 | 0 |
| F.A.Q. (all weights) | 67 | 0 | 88 | 6 | 92 | 0 | 107 | 6 | 100 | 0 | 55 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 117 | 6 | 117 | 6 | 122 | 6 |
| Heifer- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| G.A.Q. (680 lb and under)* | 91 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 104 | 0 | 124 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 55 | 0 | 72 | 6 | 122 | 6 | 127 | 6 | 132 | 6 |
| F.A.Q. (600 lb and under) | 67 | 0 | 88 | 6 | 92 | 0 | 107 | 6 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 70 | 0 | 117 | 6 | 117 | 6 | 115 | 0 |
| Cow, G.A.Q. (all weights) | 64 | 6 | 75 | 0 | 73 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 65 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 110 | 0 |
| Boner beef (cow) | 50 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 85 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 70 | 0 | 82 | 6 | 140 | 0 | 120 | 0 | 110 | 0 |
Minimum Prices for Export Meat - The institution of a system of minimum prices for meat exported from New Zealand was provided for by the Meat Export Prices Act 1955. A Meat Export Prices Committee was established, and consists of two members of the Meat Board, the Secretary to the Treasury, the Director-General of Agriculture, and a Chairman nominated by agreement between the Government and the producers. A schedule of minimum prices is fixed at the beginning of the season. Regard must be paid by the Committee to the average of the prices received for each class of meat during the preceding three seasons, the ruling level of minimum prices, and the Committee may have regard to the market trend and future prospects for the sale of meat, prices ruling for other farm products, and the general level of costs, prices, and wages in New Zealand. The following table gives the minimum prices which apply for the year ending 30 September 1961.
| Class of Meat | Grade of Meat | Minimum Price per Pound f.o.b. |
|---|---|---|
| d. | ||
| Lamb | Prime down cross 29-36 lb | 15 1/2 |
| Wether mutton | Prime 49-56 lb | 8 3/4 |
| Ewe mutton | Prime 49-56 lb | 5 3/8 |
| Chilled beef | Ox 680 lb and under | 14 3/4 |
| Ox and heifer quarter beef | G.A.Q.: 680 lb and under | 12 |
| Quarter cow beef | G.A.Q.: 600 lb and under | 9 3/8 |
| Boner cow, ox, and heifer | All weights, boned-out value | 11 1/2 |
| Boner bull | 12 | |
| Veal (sides or quarters) | Under 280 lb | 10 |
| Porkers | Prime 60-80 lb | 15 1/2 |
| Baconers | Prime 111-160 lb | 14 |
Deficiency Payments - Payments are made from the Meat Industry Reserve Account when the f.o.b. equivalents of the prices paid to farmers fall below the minimum price determined for any class of meat in the week to which the schedule relates. For the season ended 30 September 1956, deficiency payments were declared for beef from the end of March onwards, expenditure amounting to £367,169 at an average of 1.1d. per pound of killings in that period; no payments were necessary in other classes of meat. Deficiency payments continued into the succeeding production season but at diminishing rates until early in February 1957, when prices for all classes of meat were above the minimum levels, and the payments in the 1956-57 season amounted to only £111,975. In the 1957-58 season there were no payments under the scheme. Some payments were made in the 1958-59 season and the amount involved was £79,000. For the 1959-60 season the total amount involved in deficiency payments was £930,000, of which £380,000 was paid on lambs. No deficiency payments were necessary during the first six months of the 1960-61 season.
FARM INDUSTRY RESERVES - Although the details of wartime bulk-purchase agreements are now of historical interest only, it was during the period of bulk purchase that the present farm industry reserves were built up. Following the introduction of the Government stabilisation scheme in December 1942, agreement was reached between the Government and farmers' organisations in May 1943 regarding the stabilisation of meat and dairy prices. It was agreed that other than those increases necessary to meet higher costs of production, all increases in overseas realisations would be paid into a special fund which would be used in subsequent years for the benefit of the industry concerned. A meat pool account was already in existence, having been created to assist those producers who were injured by restrictions imposed on the export of particular classes of meat as a result of the shipping shortage. Subsidies designed to keep down farm production costs were also paid out of these funds. The wool reserve account was created in a somewhat different fashion arising in the main from the profits derived from the sale of wartime surplus stocks, and in part from a levy on all wool sold at auctions.
The following table shows the balances remaining in the various farm industry reserves during the period quoted.
| Balances as at 31 July | Dairy Industry Stabilisation Account | Meat Industry Reserve Account* | Wool Capital Account† | Wool Contributory Charge‡ | Wool Retention Moneys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*As at 30 September from 1948. †Profits from disposal of wool stocks taken over by Wool Disposal Commission at the end of the war. ‡This was a levy on all wool sold at auction. §No balance remained in wool retention accounts after 31 January 1957. ||This amount was reduced by the payment to dairy companies of £6,951,000 shortly after the end of the season under the agreement that half the surplus earned during the trading year ended 31 May 1960 would be paid out to producers. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1942 | - | 750 | - | - | - |
| 1943 | - | 1,884 | - | - | - |
| 1944 | 4,075 | 4,317 | - | - | - |
| 1945 | 4,841 | 9,159 | - | - | - |
| 1946 | 4,896 | 12,202 | - | - | - |
| 1947 | 6,832 | 18,222 | 5,046 Dr. | 1,165 | - |
| 1948 | 12,663 | 25,629 | 1,047 Dr. | 2,593 | - |
| 1949 | 15,331 | 29,536 | 5,182 Cr. | 4,205 | - |
| 1950 | 18,450 | 35,337 | 12,933 Cr. | 5,563 | - |
| 1951 | 23,037 | 37,256 | 19,608 Cr. | 6,167 | 32,755 |
| Wool Commission Account (30 June) | |||||
| 1952 | 24,557 | 40,429 | 26,673 | 28,093 | |
| 1953 | 25,528 | 40,450 | 27,630 | 21,801 | |
| 1954 | 25,127 | 39,551 | 28,388 | 16,174 | |
| 1955 | 24,530 | 40,277 | 28,230 | 10,226 | |
| 1956 | 27,146 | 40,681 | 28,991 | 3,798§ | |
| 1957 | 13,913 | 41,292 | 29,751 | - | |
| 1958 | - 7,349 | 42,228 | 30,523 | - | |
| 1959 | 2,132 | 43,218 | 31,268 | - | |
| 1960 | 8,670|| | 43,444 | 32,507 | - | |
INTRODUCTORY - Statistics of domestic trade in New Zealand commenced with the Census of Distribution in 1953. This census was followed by a continuing sample survey covering retail trading, commencing in March 1954. The field covered by distribution statistics was extended in October 1955 by the inauguration of a restricted survey covering quarterly statistics of consumer credit. A further Census of Distribution was taken in 1958, which, in the main, closely followed the lines of the first census of this nature. Detailed tables were later published in a volume entitled Census of Distribution 1958.
With the completion of the 1958 Census of Distribution, a new quarterly sample survey of retail trading was commenced in June 1959. A continuing quarterly survey of wholesale trading was commenced in September 1960.
Census of Distribution 1958 - For the second Census of Distribution taken in 1958, the period for which the information was requested, and to which most of it related, was the year ended 31 March 1958.
In general the 1958 census followed the same plan as that of the earlier census. In 1958, however, milk vendors and chartered clubs (the latter in respect of sales of liquor and tobacco and cigarettes) were included. Some revised classifications were also introduced so that (for instance) some firms coded as general stores in 1953 were classed as grocers in 1958 where the store had 60 per cent or more of its annual turnover in groceries. In 1953 stock and station agents (so stated) were classified as wholesale, but in 1958 such stores were classified according to the dominant method of selling as specified by the firm concerned.
In 1958 the method of selling was obtained under six headings, cash, charge account, hire-purchase, budget account (limited credit account, store currency account, etc.), cash-order coupons, and other instalment (including layby). Two questions, those relating to capital invested and periodicity of stocktaking, were excluded from the 1958 inquiry, which, however, included one completely new question - on the use of “self-service” units - applied exclusively to those businesses handling groceries.
The following tables give results of the Census of Distribution 1958 in a summarised form.
Retail Establishments - Of the 26,876 retail stores covered by the census, 18,502, or 68.8 per cent, were situated in the North Island, and 8,374, or 31.2 per cent, in the South Island.
The following table shows details by provincial districts. The figures quoted in parentheses are in each case the percentage of total.
| Provincial District | Population at 31 March 1958 | Number of Stores | Purchases During 1957-58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957-58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Auckland | 921.9 | 10,804 | 180,048 | 231,808 | 36,352 |
| (40.6) | (40.2) | (38.5) | (38.7) | (37.4) | |
| Hawke's Bay | 106.4 | 1,333 | 23,869 | 30,156 | 5,071 |
| (4.7) | (5 0) | (5.1 | (5.0) | (5.2) | |
| Taranaki | 97.0 | 1,104 | 20,961 | 26,141 | 4,243 |
| (4.3) | (4.1) | (4.5) | (4.4) | (4.4) | |
| Wellington | 442.0 | 5,261 | 95,249 | 122,872 | 20,502 |
| (19.5) | (19.6) | (20.4) | (20.5) | (21.1) | |
| Marlborough | 27.3 | 314 | 5,071 | 6,441 | 1,105 |
| (1.2) | (1.2) | (1.1) | (1.1) | (1.1) | |
| Nelson | 72.7 | 885 | 12,958 | 16,545 | 2,667 |
| (3.2) | (3.3) | (2.8) | (2.7) | (2.7) | |
| Westland | 18.7 | 324 | 4,093 | 5,268 | 866 |
| (0.8) | (1.2) | (0.9) | (0.9) | (0.9) | |
| Canterbury | 322.5 | 3,644 | 67,004 | 86,041 | 14,152 |
| (14.2) | (13.5) | (14.3) | (14.4) | (14.6) | |
| Otago - | |||||
| Otago portion | 172.1 | 2,176 | 35,678 | 45,392 | 7,549 |
| (7.6) | (8.1) | (7.6) | (7.6) | (7.8) | |
| Southland portion | 89.8 | 1,031 | 22,487 | 28,114 | 4,647 |
| (3.9) | (3.8) | (4.8) | (4.7) | (4.8) | |
| Totals | 2,270.4 | 26,876 | 467,418 | 598,778 | 97,154 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.O) | (100.0) | (100.0) | |
The principal centres of population (urban areas) include 55.2 per cent of New Zealand's people, but contained 60.8 per cent of all retail stores, with 65.8 per cent of total sales or turnover.
The following table shows details by urban and rural areas. The figures in parentheses are in each case the percentage of total.
| Location Group | Population at 31 March 1958 | Number of Stores | Sales or Turnover During 1957-58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Main urban areas (including Hutt Urban Area) | 940.5 (41.4) | 11,795 (43.9) | 274,696 (45.9) | 43,158 (44.4) |
| Secondary urban areas (excluding Hutt Urban Area) | 313.7 (13.8) | 4,540 (16.9) | 119,462 (20.0) | 20,221 (20.8) |
| Smaller centres | 164.5 (7.3) | 3,323 (12.4) | 82,252 (13.7) | 14,394 (14.8) |
| Other urban | 159.7 (7.0) | 3,564 (13.2) | 67,039 (11.2) | 11,620 (12.0) |
| Rural | 692.0 (30.5) | 3,654 (13.6) | 55,329 (9.2) | 7,761 (8.0) |
| Totals | 2,270.4 | 26,876 | 598,778 | 97,154 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
The information in the preceding table is presented graphically in the following diagram.
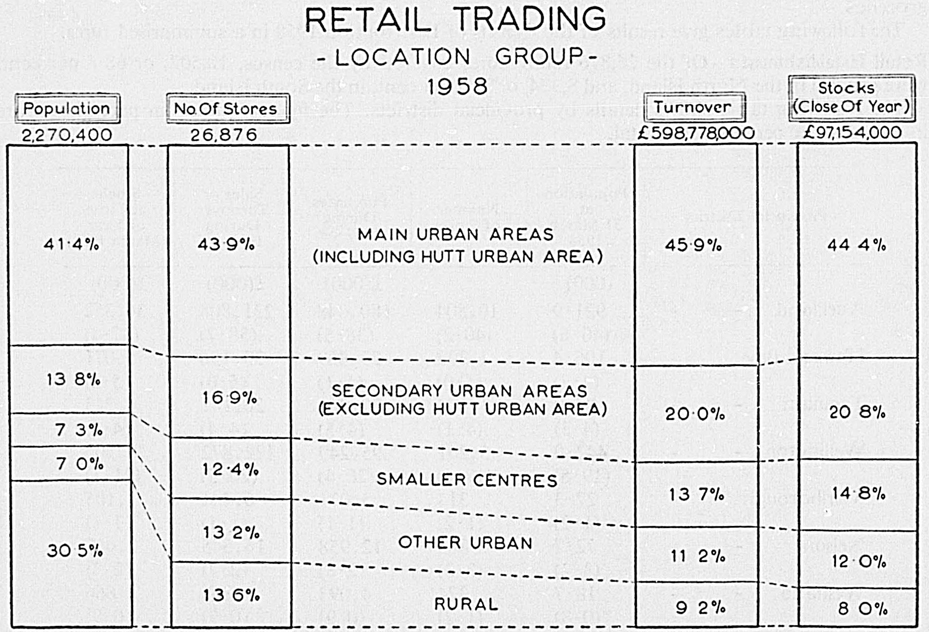
Just over half the total number of retail stores were in the food and drink group - grocers, butchers, dairies, hotels, etc. This group accounted for only 34 per cent of the turnover, however, the average turnover per store being £15,000. As against this, the automotive group, which accounts for only 4 per cent of all retail stores, handled 11 per cent of the turnover, with an average turnover of £61,200 per store.
The following table shows details by store-type groups.
| Store-type Group | Number of Stores | Number of Paid Employees on 15 April 1958 | Total Labour Force on 15 April 1958 | Average Labour Force per Store | Salaries and Wages Paid During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Average Sales or Turnover per Unit of Labour Force | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | ||||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £ | £(000) | |||||||
| Food and drink | 13,464 | 15,901 | 10,823 | 26,724 | 45,053 | 3.3 | 15,366 | 201,771 | 4,479 | 12,189 |
| Apparel | 3,851 | 3,563 | 7,678 | 11,241 | 14,998 | 3.9 | 6,146 | 65,396 | 4,360 | 21,215 |
| Furniture | 1,339 | 4,344 | 1,655 | 5,999 | 7,117 | 5.3 | 4,117 | 38,684 | 5,435 | 8,979 |
| Automotive | 1,032 | 4,539 | 745 | 5,284 | 6,197 | 6.0 | 3,716 | 63,116 | 10,185 | 7,376 |
| Hardware | 774 | 2,801 | 989 | 3,790 | 4,488 | 5.8 | 2,713 | 30,574 | 6,812 | 6,726 |
| Chemicals (chemist, etc.) | 886 | 1,273 | 1,133 | 2,406 | 3,181 | 3.6 | 1,477 | 12,497 | 3,929 | 2,714 |
| Department, variety, and general stores | 689 | 5,487 | 8,980 | 14,467 | 15,018 | 21.8 | 7,592 | 69,756 | 4,645 | 14,047 |
| Miscellaneous | 4,841 | 10,399 | 5,474 | 15,873 | 20,637 | 4.3 | 10,382 | 116,984 | 5,669 | 23,908 |
| Totals, all retail stores | 26,876 | 48,307 | 37,477 | 85,784 | 116,689 | 4.3 | 51,509 | 598,778 | 5,131 | 97,154 |
The following table shows details by turnover size groups.
| Amount of Total Turnover | Number of Stores | Number of Paid Employees on 15 April 1958 | Total Labour Force on 15 April 1958 | Salaries and Wages Paid During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |||||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| Under 5,000 | 5,225 | 608 | 1,534 | 2,142 | 8,795 | 778 | 15,913 | 3,121 | |
| 5,000– | 9,999 | 7,165 | 2,789 | 4,307 | 7,096 | 16,530 | 3,209 | 52,676 | 7,874 |
| 10,000– | 19,999 | 7,770 | 7,336 | 7,984 | 15,320 | 24,912 | 8,293 | 110,344 | 16,590 |
| 20,000– | 49,999 | 4,787 | 12,941 | 8,119 | 21,060 | 25,446 | 13,358 | 141,564 | 22,154 |
| 50,000– | 99,999 | 1,099 | 7,549 | 3,661 | 11,210 | 11,796 | 7,466 | 75,666 | 12,472 |
| 100,000– | 249,999 | 615 | 7,772 | 4,345 | 12,117 | 12,333 | 8,093 | 91,970 | 16,304 |
| 250,000– | 499,999 | 152 | 4,372 | 2,378 | 6,750 | 6,778 | 4,347 | 51,476 | 8,621 |
| 500,000 and over | 63 | 4,940 | 5,149 | 10,089 | 10,099 | 5,965 | 59,169 | 10,018 | |
| Totals, all retail stores | 26,876 | 48,307 | 37,477 | 85,784 | 116,689 | 51,509 | 598,778 | 97,154 | |
Just under 44 per cent of retail stores were returned as being under individual ownership, while 35 per cent were shown as operated by private registered companies, 15 per cent by partnerships, and 4 per cent by public registered companies.
The following table shows details by type of organisation. The figures quoted in parentheses are in each case the percentage of total.
| Type of Organisation | Number of Stores | Turnover During 1957–58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) |
|---|---|---|---|
| £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Private registered companies | 9,486 (35.3) | 300,519 (50.2) | 55,828 (57.5) |
| Public registered companies | 1,099 (4.1) | 116,541 (19.5) | 20,503 (21.1) |
| Individual ownership | 11,759 (43.8) | 109,516 (18.3) | 12,470 (12.8) |
| Partnership | 4,042 (15.0) | 51,222 (8.5) | 5,467 (5.6) |
| Other | 490 (1.8) | 20,980 (3.5) | 2,886 (3.0) |
| Totals | 26,876 | 598,778 | 97,154 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) |
The number of multiple stores engaged in retail trading represented only 10 per cent of the total stores, but accounted for 28 per cent of the total turnover. A multiple store was so termed where the store was one of a group of four or more under common ownership.
| Store-type Group | Number of Stores | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Stocks at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start of Year (April 1957) | Close of Year (March 1958) | |||
| Multiple Stores | ||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Food and drink | 1,098 | 31,113 | 1,634 | 1,707 |
| Apparel | 339 | 10,285 | 2,829 | 3,082 |
| Furniture | 167 | 8,017 | 1,320 | 1,468 |
| Automotive | 35 | 6,874 | 833 | 1,047 |
| Hardware | 71 | 9,692 | 1,684 | 1,748 |
| Chemicals (chemist, etc.) | 23 | 687 | 130 | 137 |
| Department, variety, and general stores | 220 | 38,247 | 6,923 | 7,013 |
| Miscellaneous | 764 | 64,921 | 12,138 | 12,795 |
| Totals | 2,717 | 169,836 | 27,491 | 28,997 |
| Other Stores | ||||
| Food and drink | 12,366 | 170,658 | 9,250 | 10,482 |
| Apparel | 3,512 | 55,111 | 17,004 | 18,133 |
| Furniture | 1,172 | 30,667 | 6,596 | 7,511 |
| Automotive | 997 | 56,242 | 5,573 | 6,329 |
| Hardware | 703 | 20,882 | 4,647 | 4,978 |
| Chemicals (chemist, etc.) | 863 | 11,810 | 2,217 | 2,577 |
| Department, variety, and general stores | 469 | 31,509 | 6,300 | 7,034 |
| Miscellaneous | 4,077 | 52,063 | 10,547 | 11,113 |
| Totals | 24,159 | 428,942 | 62,134 | 68,157 |
The following table shows the disposition of the different methods of selling by store-type group and by location group. The figures quoted in parentheses are in each case the percentage of total.
| Turnover (1957–58) in the Form of- | Total Sales or Turnover (1957–58) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | Charge Account | Hire Purchase | Budget Store Credit, etc. | Cash-order Coupons | Other Instalments | ||
| Store-type Groups £(000) | |||||||
| Food and drink | 167,990 | 33,777 | 4 | 201,771 | |||
| (47.9) | (16.2) | (0.1) | (33.7) | ||||
| Apparel | 53,897 | 9,131 | 200 | 377 | 148 | 1,643 | 65,396 |
| (15.4) | (4.4) | (0.6) | (32.0) | (63.8) | (54.4) | (10.9) | |
| Furniture | 12,075 | 15,688 | 10,505 | 89 | 11 | 316 | 38,684 |
| (3.4) | (7.5) | (30.2) | (7.5) | (4.7) | (10.5) | (6.5) | |
| Automotive | 25,685 | 23,981 | 13,366 | 2 | 82 | 63,116 | |
| (7.3) | (11.5) | (38.4) | (0.9) | (2.7) | (10.5) | ||
| Hardware | 7,829 | 22,526 | 198 | 1 | 20 | 30,574 | |
| (2.2) | (10.8) | (0.6) | (0.4) | (0.7) | (5.1) | ||
| Chemicals (chemist, etc.) | 10,411 | 2,048 | 26 | 1 | 11 | 12,497 | |
| (3.0) | (1.0) | (0.1) | (0.1) | (0.4) | (2.1) | ||
| Department, variety, and general stores | 34,765 | 29,676 | 3,826 | 600 | 51 | 838 | 69,756 |
| (9.9) | (14.2) | (11.0) | (50.9) | (22.0) | (27.7) | (11.7) | |
| Miscellaneous | 38,199 | 71,892 | 6,656 | 112 | 19 | 106 | 116,984 |
| (10.9) | (34.4) | (19.1) | (9.5) | (8.2) | (3.5) | (19.5) | |
| Totals, all retail stores | 350,851 | 208,719 | 34,777 | 1,179 | 232 | 3,020 | 598,778 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | |
| Location Groups £(000) | |||||||
| Main urban areas (including Hutt Urban Area) | 176,236 | 74,335 | 20,749 | 851 | 220 | 2,305 | 274,696 |
| (50.2) | (35.6) | (59.6) | (72.2) | (94.8) | (76.3) | (45.9) | |
| Secondary urban areas (excluding Hutt Urban Area) | 65,646 | 45,780 | 7,479 | 162 | 9 | 386 | 119,462 |
| (18.7) | (21.9) | (21.5) | (13.7) | (3.9) | (12.8) | (20.0) | |
| Smaller centres | 43,002 | 34,716 | 4,300 | 44 | 1 | 189 | 82,252 |
| (12.3) | (16.6) | (12.4) | (3.7) | (0.4) | (6.3) | (13.7) | |
| Other urban | 35,954 | 29,142 | 1,730 | 89 | 2 | 122 | 67,039 |
| (14.0) | (10.2) | (5.0) | (7.6) | (0.9) | (4.0) | (11.2) | |
| Rural | 30,013 | 24,746 | 519 | 33 | 18 | 55,329 | |
| (8.6) | (11.9) | (1.5) | (2.8) | (0.6) | (9.2) | ||
| Totals, all retail stores | 350,851 | 208,719 | 34,777 | 1,179 | 232 | 3,020 | 598,778 |
| (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | (100.0) | |
The following table shows, by the store-type group, average turnover and average labour force per establishment, turnover per unit of labour force and per head of population, and the approximate number of times stock was turned over per annum.
| Store-type Group | Average Sales or Turnover per Establishment | Average Labour Force per Establishment | Sales or Turnover per Unit of Labour Force | Sales or Turnover per Head of Population | Number of Times Stock Turned Over per Annum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |||
| Food and drink | 14,986 | 3.3 | 4,479 | 88.87 | 16.6 |
| Apparel | 16,982 | 3.9 | 4,360 | 28.80 | 3.1 |
| Furniture | 28,890 | 5.3 | 5,435 | 17.04 | 4.3 |
| Automotive | 61,159 | 6.0 | 10,185 | 27.80 | 8.6 |
| Hardware | 39,501 | 5.8 | 6,812 | 13.47 | 4.5 |
| Chemicals | 14,105 | 3.6 | 3,929 | 5.50 | 4.6 |
| Miscellaneous | 33,769 | 6.4 | 5,237 | 82.25 | 4.9 |
| Totals, all retail stores | 22,279 | 4.3 | 5,131 | 263.73 | 6.2 |
The 1958 Census of Distribution schedule included a question directed exclusively to those businesses handling groceries, inquiring whether or not the business was conducted as a self-service unit, using a check-out point. The following table shows the results of this inquiry by turnover-size groups. It will be noted that the percentage of self-service units rose progressively with the increase in turnover size until in the highest group, that comprising stores with an annual turnover of £50,000 or over, 72.2 per cent of stores handling groceries operated self-service units.
| Turnover Size | With Self-service Units | Without Self-service Units | Percentage of Self-service Units to Total Stores | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stores | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Value of Stocks | Number of Stores | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Value of Stocks | |||||
| Start of Year | Close of Year | Start of Year | Close of Year | |||||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Under 5,000 | 25 | 79 | 11 | 20 | 272 | 924 | 110 | 132 | 8.4 | |
| 5,000 to | 9,999 | 100 | 794 | 71 | 92 | 737 | 5,669 | 557 | 609 | 11.9 |
| 10,000 ,, | 19,999 | 430 | 6,502 | 571 | 646 | 1,490 | 21,468 | 1,932 | 2,138 | 22.4 |
| 20,000 ,, | 29,999 | 267 | 6,597 | 524 | 582 | 539 | 12,921 | 1,187 | 1,290 | 33.1 |
| 30,000 ,, | 39,999 | 121 | 4,099 | 308 | 350 | 143 | 4,836 | 421 | 478 | 45.8 |
| 40,000 ,, | 49,999 | 60 | 2,652 | 175 | 210 | 35 | 1,503 | 172 | 187 | 63.2 |
| 50,000 and over | 52 | 3,638 | 343 | 379 | 20 | 1,627 | 165 | 190 | 72.2 | |
| Totals | 1,055 | 24,361 | 2,003 | 2,279 | 3,236 | 48,948 | 4,544 | 5,024 | 24.6 | |
Wholesale Establishments - The total of 2,595 wholesale stores included in the tables accounted for a turnover of £433,296,000, or an average turnover of £167,000 per store.
The principal centres of population (urban areas) contained 87.4 per cent of wholesale stores with 94.5 per cent of total turnover. Auckland and Wellington (including Hutt) urban areas together accounted for 46.9 per cent of stores and 60.7 per cent of turnover.
The following table shows the distribution of wholesale trading by provincial districts and by main location groups. The figures in parentheses are in each case the percentage of total.
| Population at 31 March 1958 | Number of Stores | Purchases During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Provincial Districts | |||||
| Auckland | 921.9 (40.6) | 979 (37.7) | 130,751 (36.3) | 157,205 (36.3) | 23,199 (36.3) |
| Hawke's Bay | 106.4 (4.7) | 101 (3.9) | 8,114 (2.3) | 9,648 (2.2) | 1,380 (2.2) |
| Taranaki | 97.0 (4.3) | 63 (2.4) | 5,272 (1.5) | 6,368 (1.5) | 854 (1.3) |
| Wellington | 442.0 (19.5) | 650 (25.1) | 123,665 (34.3) | 146,995 (33.9) | 21,834 (34.1) |
| Marlborough | 27.3 (1.2) | 22 (0.8) | 1,894 (0.5) | 2,099 (0.5) | 297 (0.5) |
| Nelson | 72.7 (3.2) | 50 (1.9) | 3,261 (0.9) | 4,278 (1.0) | 484 (0.7) |
| Westland | 18.7 (0.8) | 17 (0.7) | 1,165 (0.3) | 1,404 (0.3) | 129 (0.2) |
| Canterbury | 322.5 (14.2) | 440 (17.0) | 54,502 (15.1) | 66,446 (15.4) | 10,348 (16.2) |
| Otago - | |||||
| Otago portion | 172.1 (7.6) | 193 (7.4) | 23,600 (6.5) | 29,181 (6.7) | 4,242 (6.6) |
| Southland portion | 89.8 (3.9) | 80 (3.1) | 8,145 (2.3) | 9,672 (2.2) | 1,216 (1.9) |
| Totals, all wholesale stores | 2,270.4 (100.0) | 2,595 (100.0) | 360,369 (100.0) | 433,296 (100.0) | 63,983 (100.0) |
| Location Groups | |||||
| Main urban areas (including Hutt Urban Area) | 940.5 (41.4) | 1,771 (68.2) | 291,287 (80.8) | 351,715 (81.2) | 54,261 (84.8) |
| Secondary urban areas (excluding Hutt Urban Area) | 313.7 (13.8) | 497 (19.2) | 48,525 (13.5) | 57,655 (13.3) | 7,126 (11.1) |
| Smaller centres, other urban and rural | 1,016.2 (44.8) | 327 (12.6) | 20,557 (5.7) | 23,926 (5.5) | 2,596 (4.1) |
| Totals, all wholesale stores | 2,270.4 (100.0) | 2,595 (100.0) | 360,369 (100.0) | 433,296 (100.0) | 63,983 (100.0) |
The following tables show details of wholesale establishments by store-type groups.
| Store-type Group | Number of Stores | Number of Paid Employees on 15 April 1958 | Total Labour Force on 15 April 1958 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |||
| Food and drink | 622 | 6,463 | 1,871 | 8,334 | 8,803 |
| Apparel | 289 | 1,629 | 1,955 | 3,584 | 3,774 |
| Furniture | 146 | 965 | 261 | 1,226 | 1,322 |
| Automotive | 194 | 3,040 | 709 | 3,749 | 3,801 |
| Hardware | 288 | 3,407 | 781 | 4,188 | 4,276 |
| General merchants | 202 | 4,240 | 1,320 | 5,560 | 5,619 |
| Miscellaneous | 854 | 7,625 | 2,883 | 10,508 | 10,888 |
| Totals, all wholesale stores | 2,595 | 27,369 | 9,780 | 37,149 | 38,483 |
| Store-type Group | Average Labour Force per Store | Salaries and Wages Paid During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Average Sales or Turnover per Unit of Labour Force | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(000) | £(000) | £ | £(000) | ||
| Food and drink | 14.2 | 6,060 | 104,838 | 11,909 | 6,851 |
| Apparel | 13.1 | 2,279 | 29,467 | 7,808 | 6,470 |
| Furniture | 91 | 909 | 15,045 | 11,380 | 2,142 |
| Automotive | 19.6 | 2,843 | 58,530 | 15,399 | 7,558 |
| Hardware | 14.8 | 3,051 | 38,351 | 8,969 | 9,159 |
| General merchants | 27.8 | 4,059 | 70,567 | 12,559 | 9,517 |
| Miscellaneous | 12.7 | 7,853 | 116,498 | 10,700 | 22,286 |
| Totals, all wholesale stores | 14.8 | 27,054 | 433,296 | 11,259 | 63,983 |
A classification by size of turnover shows that stores with under £20,000 turnover numbered 680 (26.2 per cent), but accounted for only £6,661,000, or 1.5 per cent of turnover. At the other end of the scale a total turnover of £216,203,000 (49.9 per cent) was accounted for by only 183 stores (7.1 per cent) which had a turnover of £500,000 or more.
| Amount of Total Turnover | Number of Stores | Number of Paid Employees on 15 April 1958 | Total Labour Force on 15 April 1958 | Salaries and Wages Paid During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | Stocks at Close of Year (March 1958) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | |||||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| Under 5,000 | 160 | 65 | 80 | 145 | 324 | 62 | 476 | 102 | |
| 5,000– | 9,999 | 212 | 284 | 185 | 469 | 713 | 266 | 1,586 | 307 |
| 10,000– | 19,999 | 308 | 743 | 500 | 1,243 | 1,479 | 737 | 4,599 | 794 |
| 20,000– | 49,999 | 557 | 2,400 | 1,102 | 3,502 | 3,818 | 2,445 | 18,602 | 3,654 |
| 50,000– | 99,999 | 460 | 3,018 | 978 | 3,996 | 4,161 | 3,017 | 32,733 | 6,525 |
| 100,000– | 249,999 | 465 | 5,523 | 1,695 | 7,218 | 7,352 | 5,445 | 72,900 | 12,649 |
| 250,000– | 299,999 | 87 | 1,361 | 429 | 1,790 | 1,814 | 1,322 | 23,737 | 3,499 |
| 300,000– | 399,999 | 97 | 2,001 | 762 | 2,763 | 2,767 | 2,073 | 33,107 | 5,055 |
| 400,000– | 499,999 | 66 | 2,063 | 537 | 2,600 | 2,611 | 1,915 | 29,353 | 4,390 |
| 500,000 and over | 183 | 9,911 | 3,512 | 13,423 | 13,444 | 9,772 | 216,203 | 27,008 | |
| Totals, all wholesale stores | 2,595 | 27,369 | 9,780 | 37,149 | 38,483 | 27,054 | 433,296 | 63,983 | |
Service Establishments - Only a selected group of services was included in the Census of Distribution 1958. These were grouped in three broad divisions, personal, business and community, and other services.
Nine-tenths of service establishments provided services only while in the remainder some secondary form of trading was carried on.
Services covered by the census totalled 2,702 establishments of which 1,888, or 69.9 per cent, were in the North Island and 814, or 30.1 per cent, in the South Island.
The principal centres of population (urban areas) contained 67.3 per cent of service establishments, with 83.5 per cent of the total turnover of such establishments.
The following table gives details of numbers and location of those services covered by the census.
| Personal Services | Business and Community Services | Other Services | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of establishments | No. | 1,640 | 353 | 709 | 2,702 |
| Sales or turnover during 1957–58 | £(000) | 9,088 | 6,336 | 2,577 | 18,001 |
| Location of establishments - | |||||
| Main urban areas (including Hutt Urban Area) | No. | 759 | 222 | 325 | 1,306 |
| Secondary urban areas (excluding Hutt Urban Area) | No. | 326 | 64 | 123 | 513 |
| Smaller centres | No. | 233 | 44 | 89 | 366 |
| Other urban | No. | 242 | 17 | 104 | 363 |
| Rural | No. | 80 | 6 | 68 | 154 |
| Paid employees on 15 April 1958 - | |||||
| Males | No. | 2,536 | 638 | 541 | 3,715 |
| Females | No. | 4,605 | 467 | 66 | 5,138 |
| Totals | No. | 7,141 | 1,105 | 607 | 8,853 |
| Total labour force on 15 April 1958 | No. | 8,903 | 1,453 | 1,381 | 11,737 |
| Salaries and wages paid during 1957–58 | £(000) | 3,466 | 948 | 392 | 4,806 |
Service establishments are further analysed in the following table.
| Amount of Total Turnover | Number of Establishments | Number of Paid Employees on 15 April 1958 | Total Labour Force 15 April 1958 | Salaries and Wages During 1957–58 | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | ||||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| Under 1,000 | 591 | 9 | 52 | 61 | 698 | 15 | 370 | |
| 1,000– | 2,999 | 1,057 | 140 | 620 | 760 | 1,966 | 265 | 1,902 |
| 3,000– | 4,999 | 388 | 249 | 472 | 721 | 1,150 | 330 | 1,482 |
| 5,000– | 9,999 | 342 | 576 | 630 | 1,206 | 1,583 | 635 | 2,361 |
| 10,000– | 19,999 | 183 | 690 | 627 | 1,317 | 1,472 | 797 | 2,487 |
| 20,000– | 49,999 | 91 | 904 | 1,300 | 2,204 | 2,255 | 1,115 | 2,800 |
| 50,000– | 99,999 | 30 | 466 | 495 | 961 | 988 | 572 | 2,093 |
| 100,000 and over | 20 | 681 | 942 | 1,623 | 1,625 | 1,077 | 4,506 | |
| Totals | 2,702 | 3,715 | 5,138 | 8,853 | 11,737 | 4,806 | 18,001 | |
Special Analyses - Special analyses were taken out to show total retail trading by retail and service establishments and, at the same time, details were also obtained of total services provided.
The following table shows details of retail trading as above by commodity groups.
| Commodity Group | Sales Of Turnover During 1957–58 | |
|---|---|---|
| Amount | Per Cent of Total | |
| £(000) | ||
| Groceries and small goods (including butter, bacon, etc.) | 78,723 | 13.2 |
| Meat and fish (uncooked) | 33,367 | 5.6 |
| Fruit and vegetables | 17,711 | 3.0 |
| Other foods (baked and cooked foods, meals, etc.) | 17,969 | 3.0 |
| Milk, ice-cream, confectionery, soft drinks | 24,790 | 4.2 |
| Beer, wine, and spirits | 36,689 | 6.2 |
| Tobacco, cigarettes, and tobacconists' sundries | 16,633 | 2.8 |
| Chemists' goods, toiletries, cosmetics (including dispensing) | 14,298 | 2.4 |
| Clothing, drapery, dress piece goods | 76,594 | 12.9 |
| Footwear | 13,128 | 2.2 |
| Furniture, bedding, floor coverings, soft furnishings and household textiles | 29,387 | 4.9 |
| Musical instruments (including radios) | 7,689 | 1.3 |
| Household appliances and electrical goods | 20,008 | 3.4 |
| Domestic hardware, china, and glassware | 14,674 | 2.5 |
| Builders' hardware and materials (excluding timber, bricks, and roofing tiles) | 26,183 | 4.4 |
| Books, stationery, and newspapers | 14,624 | 2.4 |
| Motor vehicles, parts, accessories (excluding petrol and oil) | 64,499 | 10.8 |
| Bicycles, parts and accessories | 1,915 | 0.3 |
| Coal, coke, and firewood | 3,922 | 0.6 |
| Fertilisers and manures | 11,510 | 1.9 |
| Florists' goods | 875 | 0.1 |
| Grain, seed, and fodder | 12,403 | 2.1 |
| Jewellery (including watches, clocks, and precious stones) | 4,527 | 0.8 |
| Leather, luggage, and harness | 1,582 | 0.3 |
| Agricultural machinery | 13,030 | 2.2 |
| Office machinery | 3,846 | 0.6 |
| Other machinery | 8,035 | 1.3 |
| Paint, glass, and wallpaper | 5,282 | 0.9 |
| Photographic supplies and equipment | 1,249 | 0.2 |
| Plumbing equipment and piping | 968 | 0.2 |
| Professional and scientific equipment | 2,367 | 0.4 |
| Rubber goods | 579 | 0.1 |
| Sewing machines and accessories | 1,570 | 0.3 |
| Sports goods (including toys and games) | 4,167 | 0.7 |
| Seeds, plants, and garden supplies | 2,186 | 0.4 |
| Other goods | 8,303 | 1.4 |
| Totals, retail commodities | 595,282 | 100.0 |
The following table shows details of total services provided by retail and service establishments.
| Type of Service | Number of Establishments Handling Service Specified | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 |
|---|---|---|
| Personal service provided by establishments classified as | £(000) | |
| Service establishments | 1,640 | 8,882 |
| Retail stores | 826 | 1,160 |
| Totals, personal services | 2,466 | 10,042 |
| Community and business services provided by establishments classified as - | ||
| Service establishments | 353 | 6,301 |
| Retail stores | 116 | 91 |
| Totals, community and business services | 469 | 6,392 |
| Other services provided by establishments classified as - | ||
| Service establishments | 709 | 2,197 |
| Retail stores | 1,412 | 2,866 |
| Totals, other services | 2,121 | 5,063 |
| Grand totals, all services | 5,056 | 21,497 |
The following table shows a commodity analysis of wholesale trading.
| Commodity Group | Sales or Turnover During 1957–58 | |
|---|---|---|
| Amount | Per Cent of Total | |
| £(000) | ||
| Groceries and small goods (including butter, bacon, etc.) | 64,340 | 14.8 |
| Meat and fish (uncooked) | 8,529 | 2.0 |
| Fruit and vegetables | 21,982 | 5.1 |
| Other food (bread, cakes, pastry, etc.) | 6,146 | 1.4 |
| Milk, ice cream, confectionery, soft drinks | 13,630 | 3.1 |
| Beer, wine, and spirits | 17,475 | 4.0 |
| Tobacco, cigarettes, and tobacconists' sundries | 26,291 | 6.1 |
| Chemists' goods, toiletries, cosmetics | 15,184 | 3.5 |
| Clothing, drapery, and piece goods | 31,677 | 7.3 |
| Footwear | 4,710 | 1.1 |
| Furniture, bedding, floor coverings, soft furnishings, and household textiles | 11,472 | 2.6 |
| Musical instruments (including radios) | 3,263 | 0.8 |
| Household appliances and electrical goods | 21,991 | 5.1 |
| Domestic hardware, china, and glassware | 9,089 | 2.1 |
| Builders' hardware and materials (excluding timber, bricks, and roofing tiles) | 17,748 | 4.1 |
| Books, stationery, and newspapers | 6,290 | 1.4 |
| Motor vehicles, parts, accessories (excluding petrol and oil) | 58,820 | 13.6 |
| Coal, coke, and firewood | 4,485 | 1.0 |
| Fertilisers, manures, grain, seed, and fodder | 13,731 | 3.2 |
| Jewellery (including watches, clocks, and precious stones) | 2,460 | 0.6 |
| Leather, luggage, and harness | 2,670 | 0.6 |
| Agricultural machinery | 5,925 | 1.4 |
| Other machinery | 20,142 | 4.6 |
| Paint, glass, and wallpaper | 6,517 | 1.5 |
| Photographic supplies and equipment | 2,618 | 0.6 |
| Plumbing equipment and piping | 5,931 | 1.4 |
| Rubber goods (excluding tyres and tubes) | 1,573 | 0.4 |
| Seeds, plants, and garden supplies | 1,354 | 0.3 |
| Sports goods (including toys and games) | 3,487 | 0.8 |
| Other | 23,766 | 5.5 |
| Totals, wholesale commodities | 433,296 | 100.0 |
QUARTERLY SURVEY OF RETAIL TRADING - Following the Census of Distribution in 1953 a continuing quarterly sample survey of retail trade was inaugurated, the results of the census forming a framework from which a random sample of firms, stratified by broad geographical divisions and size of turnover, was drawn. The first inquiry related to trade during the three-monthly period ended 31 March 1954, and the survey was continued at three-monthly intervals up to and including the quarter ended 31 March 1959.
Commencing with the quarter ended 30 June 1959, quarterly retail trade statistics have been compiled using a sample that comprises stores selected on account of their location and of a type known as an area-unit cluster sample. The 1958 Census of Distribution provided a base for this sample, a detailed description of which was given in a supplement to the November 1959 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
The sample excludes certain types of retail stores which were included in the Census of Distribution 1958; these store types are hotels, chartered clubs, wine and spirit merchants, milk vendors, and the complete automotive group. Besides the above exclusions, for purposes of the sample survey some changes in the grouping of store types were made. In the following table comparable census figures are given together with the estimates of turnover, based on sample results, for the quarters ended 30 September 1960 and 31 December 1960. The composition of the store-type groups can be readily seen.
| Store Type and Grouping | Sales or Turnover | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Ended 31 March 1958 (Census Figures) | Quarter Ended | |||
| 30 September 1960 | 31 December 1960 | |||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | 31,959 | 9,139 | 9,262 | |
| Grocer | 73,309 | 21,517 | 23,317 | |
| Other food and drink - | ||||
| Baker, pastrycook', etc. | 7,919 | |||
| Confectioner | 1,436 | |||
| Dairy, milk bar | 16,004 | |||
| Fish, fish and chip shop | 2,883 | |||
| Fruiterer, greengrocer | 14,142 | |||
| Restaurant, cafeteria, tearoom | 8,139 | |||
| Other food and drink | 442 | |||
| Total, other food and drink | 50,965 | 15,616 | 17,195 | |
| Footwear | 10,056 | 2,840 | 3,651 | |
| Other apparel - | ||||
| Draper, etc. | 41,700 | |||
| Men's and boys' clothier | 12,396 | |||
| Other apparel | 1,244 | |||
| Total, other apparel | 55,340 | 14,160 | 17,899 | |
| Furniture and soft furnishings | 22,071 | 6,510 | 7,630 | |
| Household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. - | ||||
| Household appliances, radios, etc. | 16,613 | |||
| Electrical goods | 2,529 | |||
| Music store | 3,370 | |||
| Sewing machine dealer | 1,580 | |||
| Total, household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. | 24,092 | 6,452 | 7,167 | |
| Hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. - | ||||
| Hardware, builders' hardware, etc. | 23,980 | |||
| Paints and varnishes | 4,997 | |||
| Other hardware | 1,597 | |||
| Total, hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. | 30,574 | 8,234 | 9,036 | |
| Chemist | 12,190 | 3,849 | 4,446 | |
| General, department, and variety | 69,756 | 18,877 | 23,917 | |
| Other - | ||||
| Bookseller, newsagent, stationer | 12,330 | |||
| Coal and wood merchant | 3,499 | |||
| Florist | 837 | |||
| Jeweller | 4,747 | |||
| Pawnbroker, secondhand dealer | 1,609 | |||
| Seedsman, nurseryman | 4,081 | |||
| Tobacconist | 6,026 | |||
| Toys, novelties, etc. | 1,238 | |||
| Other chemicals | 307 | |||
| Stock and station agents | 42,021 | |||
| Miscellaneous | 33,117 | |||
| Total, other | 109,812 | 31,093 | 36,249 | |
| Totals, New Zealand | 490,124 | 138,287 | 159,769 | |
Information for later quarters will be found in the section on Latest Statistical Information.
It will be noticed that total turnover for retail stores for the year ended 31 March 1958, as shown above, £490,124,000, differs from the figure, £598,778,000, in respect of all retail trading as quoted on a preceding page. The sample does not purport to cover all aspects of retail trading, but covers all store types with the exception of the exclusions already specified.
The sample survey from which quarterly estimates are obtained is designed to provide satisfactory accuracy in store-type figures at national level and in regional figures at the all-store-type level. To obtain the same accuracy in regional figures for each store type it would be necessary to make the sample very much larger and a great deal of the saving in trouble and cost which the sample gives would be lost. Of the regional figures for each store type it can be said that, in general, they give quite a good indication of the value of trading, but that in this case successive quarterly figures are unreliable as an indication of trends.
The following table gives details of value of sales or turnover by store-type groups for each of six geographical regions for the quarters ended 30 June, 30 September, and 31 December 1960.
VALUE OF SALES OR TURNOVER
| Store-type Group | North Island | South Island | Totals, New Zealand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland Urban Area | Wellington and Hutt Urban Areas | Remainder of North Island | Totals, North Island | Christ-church Urban Area | Dunedin Urban Area | Remainder of South Island | Totals, South Island | ||
| £ (thousand) | |||||||||
| Quarter Ended 30 June 1960 | |||||||||
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | 1,994 | 1,119 | 2,902 | 6,015 | 782 | 474 | 1,349 | 2,605 | 8,620 |
| Grocer | 3,792 | 2,473 | 7,677 | 13,942 | 2,030 | 995 | 3,448 | 6,473 | 20,415 |
| Other food and drink | 3,835 | 1,887 | 5,200 | 10,922 | 1,457 | 587 | 1,917 | 3,961 | 14,883 |
| Footwear | 632 | 409 | 1,229 | 2,270 | 351 | 133 | 457 | 941 | 3,211 |
| Other apparel | 3,092 | 1,957 | 6,377 | 11,426 | 1,274 | 867 | 2,671 | 4,812 | 16,238 |
| Furniture and soft furnishings | 1,543 | 979 | 1,947 | 4,469 | 623 | 273 | 907 | 1,803 | 6,272 |
| Household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. | 825 | 980 | 2,169 | 3,974 | 665 | 220 | 819 | 1,704 | 5,678 |
| Hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. | 1,132 | 1,097 | 3,246 | 5,475 | 853 | 371 | 1,009 | 2,233 | 7,708 |
| Chemist | 788 | 397 | 1,395 | 2,580 | 326 | 158 | 487 | 971 | 3,551 |
| General, department, and variety | 4,305 | 1,965 | 6,962 | 13,232 | 2,517 | 890 | 2,928 | 6,335 | 19,567 |
| Other | 4,302 | 2,812 | 13,284 | 20,398 | 2,543 | 1,584 | 5,294 | 9,421 | 29,819 |
| Totals | 26,240 | 16,075 | 52,388 | 94,703 | 13,421 | 6,552 | 21,286 | 41,259 | 135,962 |
| Quarter Ended 30 September 1960 | |||||||||
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | 2,127 | 1,158 | 3,130 | 6,415 | 860 | 534 | 1,330 | 2,724 | 9,139 |
| Grocer | 4,035 | 2,554 | 8,144 | 14,733 | 2,161 | 1,057 | 3,566 | 6,784 | 21,517 |
| Other food and drink | 4,104 | 1,921 | 5,422 | 11,447 | 1,570 | 593 | 2,006 | 4,169 | 15,616 |
| Footwear | 562 | 372 | 1,016 | 1,950 | 373 | 138 | 379 | 890 | 2,840 |
| Other apparel | 2,657 | 1,853 | 5,574 | 10,084 | 1,215 | 701 | 2,160 | 4,076 | 14,160 |
| Furniture and soft furnishings | 1,541 | 896 | 2,176 | 4,613 | 657 | 321 | 919 | 1,897 | 6,510 |
| Household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. | 1,017 | 1,010 | 2,421 | 4,448 | 825 | 215 | 964 | 2,004 | 6,452 |
| Hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. | 1,124 | 1,283 | 3,375 | 5,782 | 946 | 374 | 1,132 | 2,452 | 8,234 |
| Chemist | 871 | 435 | 1,515 | 2,821 | 351 | 171 | 506 | 1,028 | 3,849 |
| General, department, and variety | 3,991 | 1,879 | 6,838 | 12,708 | 2,334 | 925 | 2,910 | 6,169 | 18,877 |
| Other | 4,394 | 3,273 | 13,277 | 20,894 | 2,388 | 1,864 | 5,947 | 10,199 | 31,093 |
| Totals | 26,423 | 16,584 | 52,888 | 95,895 | 13,680 | 6,893 | 21,819 | 42,392 | 138,287 |
| Quarter Ended 31 December 1960 | |||||||||
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | 2,106 | 1,183 | 3,309 | 6,598 | 832 | 503 | 1,329 | 2,664 | 9,262 |
| Grocer | 4,331 | 2,790 | 8,946 | 16,067 | 2,359 | 1,134 | 3,757 | 7,250 | 23,317 |
| Other food and drink | 4,417 | 2,073 | 6,081 | 12,571 | 1,684 | 654 | 2,286 | 4,624 | 17,195 |
| Footwear | 707 | 494 | 1,337 | 2,538 | 466 | 159 | 488 | 1,113 | 3,651 |
| Other apparel | 3,415 | 2,285 | 7,004 | 12,704 | 1,507 | 790 | 2,898 | 5,195 | 17,899 |
| Furniture and soft furnishings | 1,642 | 1,020 | 2,688 | 5,350 | 814 | 352 | 1,114 | 2,280 | 7,630 |
| Household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. | 1,074 | 1,027 | 2,919 | 5,020 | 719 | 237 | 1,191 | 2,147 | 7,167 |
| Hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. | 1,281 | 1,355 | 3,732 | 6,368 | 1,011 | 397 | 1,260 | 2,668 | 9,036 |
| Chemist | 979 | 511 | 1,740 | 3,230 | 425 | 195 | 596 | 1,216 | 4,446 |
| General, department, and variety | 5,171 | 2,517 | 8,365 | 16,053 | 3,109 | 1,196 | 3,559 | 7,864 | 23,917 |
| Other | 5,353 | 3,968 | 15,294 | 24,615 | 2,828 | 2,034 | 6,772 | 11,634 | 36,249 |
| Totals | 30,476 | 19,223 | 61,415 | 111,114 | 15,754 | 7,651 | 25,250 | 48,655 | 159,769 |
The information in the preceding table has been regrouped in the fallowing table to give estimates of commodity sales.
COMMODITY SALES OR TURNOVER
| Commodity Group | Quarter Ended | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 June 1960 | 30 September 1960 | 31 December 1960 | |
| £ (thousand) | |||
| Groceries and small goods (including butter, bacon, etc.) | 22,298 | 23,563 | 25,676 |
| Meat, fish, fruit, and vegetables | 14,227 | 15,349 | 16,392 |
| Other foods (baked and cooked foods, meals, etc.) | 5,431 | 5,638 | 5,774 |
| Milk, ice cream, confectionery, soft drinks, etc. | 4,806 | 4,845 | 5,622 |
| Tobacco, cigarettes, and tobacconists' sundries | 5,590 | 5,789 | 6,319 |
| Chemists' goods, toiletries, cosmetics (including dispensing) | 4,219 | 4,541 | 5,477 |
| Clothing, drapery, dress piece goods | 23,552 | 20,688 | 26,360 |
| Footwear | 4,237 | 3,733 | 4,817 |
| Furniture, bedding, floor coverings, soft furnishings, and household textiles | 8,103 | 8,104 | 9,168 |
| Musical instruments (including radios) | 2,323 | 2,589 | 2,621 |
| Household appliances and electrical goods | 4,926 | 5,562 | 6,918 |
| Domestic hardware, china and glassware | 3,723 | 3,852 | 5,090 |
| Builders' hardware and materials (excluding timber, bricks, and roofing tiles) | 6,238 | 6,575 | 6,398 |
| Books, stationery, etc. | 3,496 | 3,700 | 4,870 |
| Other commodities | 22,793 | 23,759 | 28,267 |
| Total sales or turnover | 135,962 | 138,287 | 159,769 |
Retail Stocks - The following table shows stock values as at 30 June, 30 September, and 31 December 1959 and 1960.
| Store-type Group | Value of Stocks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As at 30 June | As at 30 September | As at 31 December | ||||
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £ (thousand) | ||||||
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | 397 | 388 | 423 | 361 | 347 | 327 |
| Grocer | 7,686 | 8,374 | 7,731 | 8,425 | 7,902 | 8,417 |
| Other food and drink | 1,955 | 2,288 | 2,055 | 2,301 | 2,177 | 2,406 |
| Footwear | 4,017 | 4,454 | 4,242 | 4,483 | 3,995 | 4,420 |
| Other apparel | 19,848 | 20,706 | 20,799 | 21,925 | 19,935 | 21,191 |
| Furniture and soft furnishings | 5,541 | 5,969 | 5,601 | 6,182 | 5,444 | 6,166 |
| Household appliances, electrical goods, radios, etc. | 4,931 | 5,108 | 4,915 | 5,606 | 4,782 | 5,519 |
| Hardware, builders' hardware, paints, etc. | 6,972 | 6,907 | 6,895 | 7,054 | 6,819 | 7,205 |
| Chemist | 2,687 | 2,938 | 2,703 | 2,901 | 2,726 | 2,885 |
| General, department, and variety | 15,588 | 15,650 | 16,943 | 17,123 | 15,829 | 17,358 |
| Other | 24,352 | 24,985 | 25,137 | 26,164 | 25,060 | 25,923 |
| Totals | 93,974 | 97,767 | 97,444 | 102,525 | 95,016 | 101,817 |
Revision of Statistics for Earlier Quarters - The growth in the number of stores causes considerable difficulty in the field of statistical collection if the retail trading of such new stores is to be adequately allowed for in the quarterly surveys. Whereas the compilation procedures used in conjunction with the area-unit sample automatically allow for the retail trade of new stores, the old sample failed to do this. The old sample, therefore, yielded statistics which accurately described the retail trade of established stores but understated that for new stores.
A number of alterations in the grouping and coverage of store types in the survey, of which details have already been given, were also made with the introduction of the new sample. For this reason, together with the understatement of turnover of new stores in the old survey, there was a need for revised statistics of sales turnover with which the statistics for the new sample could be directly related. Such revised statistics extending back to the March 1954 quarter are given in the next table.
QUARTERLY SALES OR TURNOVER - STORE-TYPE GROUPS
| Quarter Ended | Revised Turnover for Store-type Group | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butcher, poulterer, etc. | Grocer | Other Food and Drink | Footwear | Other Apparel | Furniture and Soft Furnishings | Household Appliances, Electrical Goods, Radios, etc. | Hardware, Builders' Hardware, Paints, etc. | Chemist | General, Department, and Variety | Other | All Groups | |
| £ (thousand) | ||||||||||||
| 1954- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 6,216 | 14,923 | 10,918 | 1,753 | 10,125 | 3,868 | 4,142 | 5,752 | 1,987 | 13,350 | 20,710 | 93,744 |
| Jun | 6,793 | 14,982 | 10,625 | 2,189 | 12,948 | 4,708 | 4,764 | 6,909 | 2,031 | 14,982 | 21,960 | 102,891 |
| Sep | 7,013 | 15,574 | 10,543 | 1,869 | 11,496 | 4,809 | 4,950 | 6,951 | 2,132 | 14,373 | 22,595 | 102,305 |
| Dec | 7,232 | 17,219 | 11,864 | 2,490 | 14,434 | 5,354 | 6,191 | 7,662 | 2,477 | 18,103 | 27,130 | 120,156 |
| 1955- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 6,856 | 15,278 | 11,093 | 1,873 | 10,776 | 4,079 | 4,953 | 6,470 | 2,103 | 14,494 | 22,831 | 100,806 |
| Jun | 7,135 | 15,509 | 10,988 | 2,269 | 13,330 | 4,916 | 5,169 | 7,410 | 2,257 | 15,444 | 23,637 | 108,064 |
| Sep | 7,512 | 16,262 | 11,508 | 1,961 | 12,242 | 4,813 | 5,212 | 7,352 | 2,468 | 15,594 | 23,240 | 108,164 |
| Dec | 7,479 | 17,462 | 12,670 | 2,534 | 14,990 | 5,230 | 6,564 | 7,570 | 2,823 | 18,357 | 28,210 | 123,889 |
| 1956- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 7,040 | 16,242 | 11,784 | 1,999 | 11,540 | 4,134 | 4,964 | 6,887 | 2,394 | 14,785 | 23,083 | 104,852 |
| Jun | 7,350 | 16,639 | 11,804 | 2,341 | 13,553 | 4,939 | 4,652 | 7,104 | 2,528 | 15,896 | 24,359 | 111,165 |
| Sep | 7,434 | 17,054 | 12,210 | 2,028 | 11,897 | 5,076 | 4,996 | 7,096 | 2,501 | 15,271 | 24,567 | 110,139 |
| Dec | 7,659 | 18,657 | 13,384 | 2,654 | 14,778 | 5,639 | 7,081 | 7,583 | 2,888 | 18,780 | 29,594 | 128,697 |
| 1957- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 7,234 | 16,895 | 12,321 | 2,092 | 11,276 | 4,247 | 5,502 | 6,901 | 2,605 | 15,322 | 25,309 | 109,704 |
| Jun | 7,820 | 17,654 | 12,259 | 2,603 | 14,876 | 5,348 | 5,014 | 7,414 | 2,879 | 16,851 | 25,557 | 118,275 |
| Sep | 8,121 | 18,018 | 12,273 | 2,190 | 12,475 | 5,558 | 5,495 | 7,642 | 2,939 | 16,188 | 26,386 | 117,285 |
| Dec | 8,447 | 19,394 | 13,712 | 2,845 | 15,553 | 6,214 | 7,672 | 7,936 | 3,425 | 20,071 | 31,469 | 136,738 |
| 1958- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 7,571 | 18,243 | 12,721 | 2,418 | 12,436 | 4,951 | 5,911 | 7,582 | 2,947 | 16,646 | 26,400 | 117,826 |
| Jun | 8,191 | 18,536 | 12,485 | 2,685 | 15,647 | 6,055 | 5,918 | 8,190 | 2,984 | 18,460 | 27,997 | 127,148 |
| Sep | 8,386 | 18,536 | 12,712 | 2,304 | 12,949 | 5,393 | 5,091 | 8,019 | 2,968 | 16,873 | 26,840 | 120,071 |
| Dec | 8,455 | 20,333 | 13,857 | 2,868 | 15,340 | 5,777 | 6,298 | 8,812 | 3,479 | 20,310 | 30,189 | 135,709 |
| 1959- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 7,552 | 18,321 | 12,657 | 2,290 | 11,453 | 4,409 | 4,518 | 6,963 | 2,910 | 15,733 | 24,000 | 110,806 |
| Jun | 8,433 | 18,981 | 13,111 | 2,777 | 14,898 | 5,146 | 4,970 | 7,339 | 3,189 | 18,155 | 26,619 | 123,618 |
| Sep | 8,725 | 19,456 | 13,734 | 2,346 | 12,648 | 5,402 | 5,291 | 7,302 | 3,267 | 17,414 | 27,729 | 123,314 |
| Dec | 8,968 | 21,468 | 15,151 | 3,064 | 15,930 | 6,434 | 6,598 | 8,423 | 3,920 | 22,220 | 32,880 | 145,056 |
| 1960- | ||||||||||||
| Mar | 8,149 | 19,788 | 14,854 | 2,515 | 12,942 | 5,207 | 5,382 | 7,390 | 3,396 | 17,729 | 32,078 | 129,430 |
| Jun | 8,620 | 20,415 | 14,883 | 3,211 | 16,238 | 6,272 | 5,678 | 7,708 | 3,551 | 19,567 | 29,819 | 135,962 |
| Sep | 9,139 | 21,517 | 15,616 | 2,840 | 14,160 | 6,510 | 6,452 | 8,234 | 3,849 | 18,877 | 31,093 | 138,287 |
| Dec | 9,262 | 23,317 | 17,195 | 3,651 | 17,899 | 7,630 | 7,167 | 9,036 | 4,446 | 23,917 | 36,249 | 159,769 |
The information in the preceding table has been regrouped in the following table to give estimates of commodity sales.
QUARTERLY SALES OR TURNOVER - COMMODITY GROUPS
| Quarter Ended | Groceries and Small Goods (Including Butter, Bacon, etc.) | Meat, Fish, Fruit, and Vegetables | Other Foods (Baked and Cooked Foods, Meals, etc.) | Milk, Ice Cream, Confectionery, Soft Drinks, etc. | Tobacco, Cigarettes, and Tobacconists' Sundries | Chemists' Goods, Toiletries, Cosmetics (Including Dispensing) | Clothing, Drapery, Dress Piece Goods | Footwear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ (million) | ||||||||
| 1954 - Mar | 16.2 | 10.0 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 13.8 | 2.3 |
| Jun | 16.2 | 10.7 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 17.8 | 2.9 |
| Sep | 16.9 | 11.1 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 2.6 | 15.8 | 2.4 |
| Dec | 18.8 | 11.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 2.9 | 19.8 | 3.2 |
| 1955 - Mar | 16.3 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 15.2 | 2.4 |
| Jun | 16.5 | 11.0 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 18.4 | 2.9 |
| Sep | 17.3 | 11.6 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 16.8 | 2.5 |
| Dec | 18.9 | 12.1 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 3.4 | 20.5 | 3.3 |
| 1956 - Mar | 17.3 | 11.0 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 16.0 | 2.6 |
| Jun | 17.8 | 11.6 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 3.0 | 18.7 | 3.0 |
| Sep | 18.5 | 12.0 | 4.3 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 16.5 | 2.6 |
| Dec | 20.2 | 12.6 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 20.3 | 3.5 |
| 1957 - Mar | 18.1 | 11.7 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 3.5 | 3.1 | 15.6 | 2.7 |
| Jun | 18.9 | 12.3 | 4.5 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 20.4 | 3.4 |
| Sep | 19.4 | 12.8 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 17.2 | 2.9 |
| Dec | 21.1 | 13.7 | 4.8 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 4.0 | 21.5 | 3.7 |
| 1958 - Mar | 19.3 | 12.3 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 17.4 | 3.2 |
| Jun | 19.6 | 12.9 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 21.5 | 3.5 |
| Sep | 19.8 | 13.5 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 17.8 | 3.0 |
| Dec | 21.8 | 14.2 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 21.0 | 3.8 |
| 1959 - Mar | 19.0 | 12.3 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 15.9 | 3.0 |
| Jun | 20.9 | 13.5 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 22.0 | 3.7 |
| Sep | 22.0 | 14.2 | 4.9 | 4.3 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 18.7 | 3.1 |
| Dec | 24.1 | 15.3 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 4.9 | 23.8 | 4.1 |
| 1960 - Mar | 22.0 | 13.9 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 4.0 | 19.1 | 3.4 |
| Jun | 22.3 | 14.2 | 5.4 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 4.2 | 23.6 | 4.2 |
| Sep | 23.6 | 15.3 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 5.8 | 4.5 | 20.7 | 3.7 |
| Dec | 25.7 | 16.4 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 5.5 | 26.4 | 4.8 |
| Quarter Ended | Furniture, Bedding, Floor Coverings, Soft Furnishings, and Household Textiles | Musical Instruments (Including Radios) | Household Appliances and Electrical Goods | Domestic Hardware, China, and Glassware | Builders' Hardware and Materials (Excluding Timber, Bricks, and Roofing Tiles) | Books, Stationery, etc. | Other Commodities | Total Sales or Turnover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (million) | ||||||||
| 1954 - Mar | 5.2 | 1.1 | 3.6 | 2.6 | 5.0 | 3.1 | 17.6 | 93.7 |
| Jun | 6.2 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 18.3 | 102.9 |
| Sep | 6.4 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 5.9 | 2.8 | 18.6 | 102.3 |
| Dec | 7.1 | 1.6 | 5.5 | 3.7 | 6.4 | 3.9 | 23.7 | 120.2 |
| 1955 - Mar | 5.6 | 1.3 | 4.2 | 2.9 | 5.5 | 3.2 | 19.7 | 100.8 |
| Jun | 6.3 | 1.5 | 4.4 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 2.9 | 20.6 | 108.1 |
| Sep | 6.6 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 6.3 | 2.8 | 20.4 | 108.2 |
| Dec | 6.8 | 1.7 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 6.3 | 3.8 | 25.0 | 123.9 |
| 1956 - Mar | 5.6 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 3.1 | 5.9 | 3.4 | 19.8 | 104.9 |
| Jun | 6.5 | 1.6 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 6.2 | 3.1 | 20.8 | 111.2 |
| Sep | 6.7 | 1.7 | 4.2 | 3.1 | 5.6 | 3.1 | 21.4 | 110.1 |
| Dec | 7.3 | 1.9 | 6.0 | 3.9 | 6.3 | 4.1 | 26.2 | 128.7 |
| 1957 - Mar | 5.7 | 1.5 | 4.5 | 3.1 | 5.9 | 3.6 | 22.1 | 109.7 |
| Jun | 7.1 | 1.9 | 4.2 | 3.3 | 6.5 | 3.3 | 21.6 | 118.3 |
| Sep | 7.4 | 1.8 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 3.3 | 22.6 | 117.3 |
| Dec | 8.1 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 4.2 | 6.6 | 4.2 | 28.0 | 136.7 |
| 1958 - Mar | 6.7 | 1.7 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 6.4 | 3.8 | 22.5 | 117.8 |
| Jun | 8.2 | 2.1 | 5.0 | 3.9 | 7.2 | 3.4 | 24.0 | 127.1 |
| Sep | 7.3 | 1.7 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 23.0 | 120.1 |
| Dec | 7.6 | 1.8 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 7.3 | 4.4 | 26.9 | 135.7 |
| 1959 - Mar | 5.9 | 1.3 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 5.8 | 3.6 | 21.0 | 110.8 |
| Jun | 7.0 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 19.3 | 123.6 |
| Sep | 7.1 | 2.0 | 4.6 | 3.4 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 20.5 | 123.3 |
| Dec | 8.0 | 2.7 | 6.4 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 4.6 | 24.1 | 145.1 |
| 1960 - Mar | 6.7 | 2.1 | 4.9 | 3.5 | 5.8 | 3.6 | 24.9 | 129.4 |
| Jun | 8.1 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 6.2 | 3.5 | 22.8 | 136.0 |
| Sep | 8.1 | 2.6 | 5.6 | 3.9 | 6.6 | 3.7 | 23.8 | 138.3 |
| Dec | 9.2 | 2.6 | 6.9 | 5.1 | 6.4 | 4.9 | 28.3 | 159.8 |
Retail Trading Statistics Corrected for Seasonal Fluctuations and for Price and Population Changes - In common with other economic time series, statistics of retail trading reflect the effects of a variety of influences. It is sometimes helpful in analysis if the actual figures are first adjusted to remove the effects of certain known factors, thereby making clearer the effects of other influences.
To facilitate direct comparisons between any or all quarterly figures seasonally corrected values of retail trade turnover have been prepared. To do this the actual figure for each quarter was expressed as a ratio to the estimated trend value for that quarter (the trend values being calculated as appropriately centred moving averages). Several ratios were thus obtained for each calendar quarter, of which the median was taken as the typical one. After adjusting the four typical quarterly ratios so that their annual product was unity the adjusted ratios were divided into the actual figures for the appropriate quarters to obtain a seasonally corrected series.
Over the period covered by the retail trade survey there has been a rise in the general price level so that part of the increase in the survey figures has been the result purely of this price change and does not represent an increase in the real volume of sales. A special price index has been prepared for the purpose of deflating the retail sales figures to give a series in pounds of constant purchasing power - i.e., the adjusted series shows the changes in the real volume of retail sales. The principal source of the prices used for this index are the commodity prices used in the Consumers' Price Index. The prices have been appropriately weighted and the whole index expressed on the base: year ended 31 March 1958 (= 1000), so that application of the index to the original figures, both before and after seasonal correction, gives series in constant 1957–58 pounds.
Finally, a further adjustment has been made to express the series in terms of turnover per head of population in recognition of the fact that part of the expansion of retail turnover is due to population growth.
The results of these calculations and adjustments are shown in the following table.
QUARTERLY SALES OR TURNOVER - ALL STORE TYPES
| Quarter Ended | Total Sales or Turnover | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Current £s | In Constant 1957–58 £s | |||||
| As Recorded | Seasonally Corrected | Before Seasonal Correction | Seasonally Corrected | |||
| Value | Index Number* | Value | Index Number* | |||
| *Base: Average quarterly values during the year ended March 1958 (= 1000). | ||||||
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | |||
| 1954 - March | 93.7 | 100.2 | 819 | 99.6 | 106.5 | 871 |
| June | 102.9 | 103.9 | 850 | 107.2 | 108.2 | 885 |
| September | 102.3 | 105.6 | 863 | 107.1 | 110.6 | 904 |
| December | 120.2 | 107.9 | 882 | 125.4 | 112.7 | 922 |
| 1955 - March | 100.8 | 107.7 | 881 | 105.0 | 112.2 | 917 |
| June | 108.1 | 109.1 | 892 | 111.7 | 112.8 | 922 |
| September | 108.2 | 111.6 | 913 | 111.3 | 114.9 | 939 |
| December | 123.9 | 111.3 | 910 | 128.1 | 115.1 | 941 |
| 1956 - March | 104.9 | 112.0 | 916 | 108.1 | 115.5 | 944 |
| June | 111.2 | 112.2 | 917 | 113.6 | 114.7 | 938 |
| September | 110.1 | 113.7 | 930 | 110.7 | 114.2 | 934 |
| December | 128.7 | 115.6 | 945 | 129.7 | 116.5 | 953 |
| 1957 - March | 109.7 | 117.2 | 958 | 112.1 | 119.8 | 980 |
| June | 118.3 | 119.4 | 976 | 119.3 | 120.5 | 985 |
| September | 117.3 | 121.1 | 990 | 117.4 | 121.2 | 991 |
| December | 136.7 | 122.8 | 1004 | 136.3 | 122.5 | 1002 |
| 1958 - March | 117.8 | 125.9 | 1029 | 117.0 | 125.0 | 1022 |
| June | 127.1 | 128.4 | 1050 | 125.4 | 126.6 | 1035 |
| September | 120.1 | 123.9 | 1013 | 116.0 | 119.7 | 979 |
| December | 135.7 | 121.9 | 997 | 130.3 | 117.0 | 957 |
| 1959 - March | 110.8 | 118.4 | 968 | 106.5 | 113.8 | 930 |
| June | 123.6 | 124.8 | 1020 | 118.8 | 119.9 | 980 |
| September | 123.3 | 127.3 | 1041 | 117.6 | 121.4 | 993 |
| December | 145.1 | 130.3 | 1065 | 138.5 | 124.4 | 1017 |
| 1960 - March | 129.4 | 138.3 | 1131 | 123.5 | 131.9 | 1078 |
| June | 136.0 | 137.3 | 1123 | 129.4 | 130.7 | 1069 |
| September | 138.3 | 142.7 | 1167 | 130.5 | 134.7 | 1101 |
| December | 159.8 | 143.5 | 1173 | 149.7 | 134.5 | 1100 |
| Quarter Ended | Total per Head of Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Current £s | In Constant 1957–58 £s | |||||
| As Recorded | Seasonally Corrected | Before Seasonal Correction | Seasonally Corrected | |||
| Value | Index Number* | Value | Index Number* | |||
| *Base: Average quarterly values during the year ended March 1958 (= 1000). | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |||
| 1954 - March | 45.0 | 48.1 | 883 | 47.9 | 51.2 | 940 |
| June | 49.2 | 49.7 | 913 | 51.3 | 51.8 | 951 |
| September | 48.8 | 50.3 | 924 | 51.1 | 52.7 | 968 |
| December | 56.9 | 51.1 | 938 | 59.4 | 53.4 | 981 |
| 1955 - March | 47.4 | 50.7 | 931 | 49.4 | 52.8 | 970 |
| June | 50.7 | 51.1 | 938 | 52.4 | 52.9 | 972 |
| September | 50.5 | 52.1 | 957 | 52.0 | 53.6 | 984 |
| December | 57.5 | 51.6 | 948 | 59.4 | 53.4 | 981 |
| 1956 - March | 48.3 | 51.6 | 948 | 49.8 | 53.2 | 977 |
| June | 51.1 | 51.6 | 948 | 52.2 | 52.7 | 968 |
| September | 50.4 | 52.0 | 955 | 50.7 | 52.3 | 961 |
| December | 58.5 | 52.6 | 966 | 59.0 | 53.0 | 973 |
| 1957 - March | 49.5 | 52.9 | 972 | 50.6 | 54.1 | 994 |
| June | 53.2 | 53.7 | 986 | 53.6 | 54.1 | 994 |
| September | 52.4 | 54.1 | 994 | 52.5 | 54.2 | 995 |
| December | 60.7 | 54.5 | 1001 | 60.5 | 54.4 | 999 |
| 1958 - March | 51.9 | 55.5 | 1019 | 51.6 | 55.1 | 1012 |
| June | 55.8 | 56.3 | 1034 | 55.0 | 55.6 | 1021 |
| September | 52.5 | 54.1 | 994 | 50.7 | 52.3 | 961 |
| December | 58.8 | 52.9 | 972 | 56.5 | 50.7 | 931 |
| 1959 - March | 47.7 | 51.0 | 937 | 45.9 | 49.0 | 900 |
| June | 53.1 | 53.6 | 984 | 51.0 | 51.5 | 946 |
| September | 52.8 | 54.5 | 1001 | 50.3 | 52.0 | 955 |
| December | 61.7 | 55.4 | 1017 | 58.9 | 52.9 | 972 |
| 1960 - March | 54.7 | 58.5 | 1074 | 52.2 | 55.8 | 1025 |
| June | 57.3 | 57.9 | 1063 | 54.6 | 55.1 | 1012 |
| September | 58.2 | 60.0 | 1102 | 54.9 | 56.7 | 1041 |
| December | 66.7 | 60.0 | 1102 | 62.5 | 56.2 | 1032 |
SURVEY OF CONSUMER CREDIT - A restricted survey covering consumer credit transactions was commenced in October 1955. The totals recorded in this restricted survey are of course incomplete on account of the limited coverage, and care has been exercised to avoid duplication on account of the transfer or assignment of business to finance corporations. Despite, the limitations in coverage and the resultant considerable understatement, it is considered that the statistics record accurately trends, etc., associated with trading over the period reviewed.
Turnover - The following analysis of turnover comprises the statistics for 49 firms.
| Period | Cash | Cash Order | Charge Accounts | Instalment or Layby | Hire Purchase | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ (thousand) | ||||||
| Calendar year - | ||||||
| 1953 | 16,736 | 77 | 13,121 | 831 | 10,142 | 40,907 |
| 1954 | 19,351 | 60 | 15,011 | 1,067 | 12,624 | 48,113 |
| 1955 | 20,177 | 54 | 16,795 | 1,043 | 12,148 | 50,217 |
| 1956 | 19,776 | 47 | 17,259 | 1,182 | 12,174 | 50,438 |
| 1957 | 21,301 | 38 | 18,258 | 1,346 | 13,516 | 54,459 |
| 1958 | 20,412 | 33 | 18,596 | 1,592 | 13,322 | 53,955 |
| 1959 | 18,989 | 30 | 17,008 | 1,587 | 13,133 | 50,747 |
| 1960 | 22,953 | 28 | 21,820 | 1,390 | 16,102 | 62,293 |
| Quarter ended - | ||||||
| 1959–31 Dec | 5,642 | 9 | 5,031 | 419 | 4,488 | 15,589 |
| 1960–31 Mar | 5,233 | 6 | 4,989 | 395 | 3,424 | 14,047 |
| 30 Jun | 5,638 | 8 | 5,378 | 321 | 3,972 | 15,317 |
| 30 Sep | 5,378 | 5 | 5,040 | 326 | 3,789 | 14,538 |
| 31 Dec | 6,704 | 9 | 6,413 | 348 | 4,917 | 18,391 |
An analysis of turnover in 1937–38 gave the following proportionate distribution under the main headings - cash 38 per cent, charge accounts 29 per cent, and hire purchase 32 per cent. Similar proportions for the calendar year 1960 were 37 per cent, 35 per cent, and 26 per cent respectively.
The high proportion of hire-purchase trading in relation to total turnover in the financial year 1937–38 was due to the predominance of motor vehicle sales financed in this way.
An analysis of the method of selling for the 26,876 retail stores included in the Census of Distribution for the year ended 31 March 1958 gave the following proportionate distribution - cash 59 per cent, charge accounts 35 per cent, and hire purchase 6 per cent.
Hire-purchase Trading - Not all firms in the restricted survey were able to segregate their hire-purchase trading from their overall debtors' accounts, but a comparison based on the available figures is presented next.
Sales of plant and machinery under hire-purchase arrangements are very small in the aggregate and are confined to relatively few firms. Separate figures are not at present being published covering this type of business.
Regulations covering hire-purchase trading specifying, inter alia, minimum deposits, maximum loan values, and maximum periods of credit, were gazetted on 22 July 1955. These were replaced on 14 October 1955 by new regulations containing certain modifications. An amendment to these regulations, dated 11 April 1956, provided for a much smaller deposit and correspondingly increased loan value in respect of certain specific items of household goods. New regulations which came into force on 1 August 1957 exempted all goods (other than motor vehicles) from hire-purchase regulation, but from June 1958 a minimum deposit of 10 per cent was required, and the maximum credit period was 18 months. A further amendment on 23 December 1958 reduced the minimum deposit required on certain household goods to 7 1/2 per cent and increased the maximum credit period to two years. On 10 July 1959 hire-purchase controls were removed from all goods other than motorcars and motor cycles. For new motorcars, the minimum deposit of 50 per cent and the maximum repayment period of 18 months was retained. For motorcars which had travelled more than 5,000 miles, the minimum deposit was reduced to 33 1/3 per cent and the maximum period of credit extended to 24 months. This latter provision also applied to motor cycles, whether new or secondhand. On 17 April 1961 amended regulations increased the minimum deposit on new motorcars to 66 2/3 per cent, and reduced the maximum repayment period to 12 months, while the minimum deposit for secondhand cars was increased to 50 per cent and the maximum repayment period reduced to 18 months; a minimum deposit of 5 per cent was required on furniture and furnishings and of 10 per cent on other consumer goods, the maximum period of credit being 18 months.
The effects of the original regulations and variations from time to time made in these regulations are reflected in the following table. This table shows, for those firms in the restricted survey which were able to supply the necessary background data, the percentage of the cash payments to the total value of goods sold.
| Period | Total Value of Goods | Details of Purchase | Percentage in Cash to Total Value of Goods Sold | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Payments | Amount Financed Under Hire-purchase Agreements | |||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Motor Vehicles | ||||
| Financial year 1937–38 | 2,465 | 927 | 1,538 | 37.6 |
| Calendar year - | ||||
| 1953 | 2,331 | 990 | 1,341 | 42.5 |
| 1954 | 2,951 | 1,285 | 1,666 | 43.5 |
| 1955 | 3,563 | 1,770 | 1,793 | 49.7 |
| 1956 | 3,445 | 1,777 | 1,668 | 51.6 |
| 1957 | 3,639 | 1,830 | 1,809 | 50.3 |
| 1958 | 3,153 | 1,595 | 1,558 | 50.6 |
| 1959 | 3,181 | 1,589 | 1,592 | 50.0 |
| 1960 | 4,166 | 1,841 | 2,325 | 44.2 |
| Quarter ended - | ||||
| 1959–31 December | 862 | 411 | 451 | 47.7 |
| 1960–31 March | 897 | 403 | 494 | 44.9 |
| 30 June | 1,141 | 520 | 621 | 45.7 |
| 30 September | 954 | 429 | 525 | 45.0 |
| 31 December | 1,174 | 489 | 685 | 41.7 |
| Household and Personal Goods | ||||
| Financial year 1937–38 | 811 | 92 | 719 | 11.3 |
| Calendar year - | ||||
| 1953 | 3,048 | 414 | 2,634 | 13.6 |
| 1954 | 3,691 | 512 | 3,179 | 13.9 |
| 1955 | 3,773 | 605 | 3,168 | 16.0 |
| 1956 | 3,855 | 698 | 3,157 | 18.1 |
| 1957 | 4,476 | 624 | 3,852 | 13.9 |
| 1958 | 4,383 | 600 | 3,783 | 13.7 |
| 1959 | 4,785 | 551 | 4,234 | 11.5 |
| 1960 | 5,616 | 579 | 5,037 | 10.3 |
| Quarter ended - | ||||
| 1959–31 December | 1,646 | 144 | 1,502 | 8.7 |
| 1960–31 March | 1,127 | 117 | 1,010 | 10.4 |
| 30 June | 1,347 | 144 | 1,203 | 10.7 |
| 30 September | 1,382 | 155 | 1,227 | 11.2 |
| 31 December | 1,760 | 163 | 1,597 | 9.3 |
NOTE - The values quoted in the above tables are exclusive of insurance and hiring charges.
The amounts owing under hire-purchase agreements with firms covered by this restricted survey, totalled £14,827,000 at 31 December 1960. A comparison covering the operations of 49 firms shows the following amounts owing at the respective dates: the final column shows the percentage of payments overdue.
| As at | Amount Owing Under Hire-purchase Agreements | Percentage of Payments Overdue |
|---|---|---|
| *Estimated. | ||
| £(000) | ||
| End of financial year 1937–38 | 4,560* | 5.08 |
| 1953 – 31 December | 7,796 | 4.14 |
| 1954 – 31 December | 9,964 | 3.80 |
| 1955 – 31 December | 9,663 | 3.70 |
| 1956 – 31 December | 9,600 | 3.76 |
| 1957 – 31 December | 11,264 | 4.23 |
| 1958 – 31 December | 10,830 | 4.48 |
| 1959 – 31 December | 11,780 | 4.32 |
| 1960 – 31 March | 12,174 | 3.74 |
| 30 June | 12,646 | 3.81 |
| 30 September | 13,106 | 3.70 |
| 31 December | 14,827 | 3.80 |
The preceding information is based on a restricted survey which is confined to the larger retail firms and institutions financing hire purchase and similar trading.
GENERAL - Throughout its short history New Zealand has been dependent on overseas trade for its development and progress. Early trade was principally with Australia. In the 1840s the foundations of the agricultural industries were laid. Sheep had already been introduced and the first shipment of wool was exported to Hobart in 1839. Dairying was established, grain and potatoes were cultivated, and kauri gum was dug from the ground in the far north. In 1853, when the population of New Zealand, exclusive of Maoris, was only 32,000, trade data were first compiled for New Zealand as a whole. The values of the main exports were: timber, £93,000, wool, £67,000; potatoes, £30,000; whale oil, £22,000; kauri gum, £16,000; and grain, £19,000. At this time Australia was settling into its “gold rush” period, and the demands of the rapidly increasing Australian population created an opportunity for increased exports from New Zealand, and quantities of butter and cheese were shipped across the Tasman. A rapid change then took place in the pattern of the trade. In 1855 the principal items were wool (25 per cent of total value), grain (22 per cent), and potatoes (25 per cent). By 1860 wool accounted for 76 per cent of total exports, and with the opening of the goldfields in 1861 wool and gold together accounted for 93 per cent of exports in that year.
During this period the imports far exceeded exports, being about double in value, and consisted mainly of capital goods for the development of new industries, together with clothing and foodstuffs to sustain the growing numbers of new settlers. The borrowing policy initiated by Vogel in 1870 for an extensive public works programme had the immediate effect of increasing imports and later gave an indirect impetus to exports.
The introduction of refrigeration in 1882 further changed the pattern of the export trade, making possible the shipment of perishable foodstuffs to more distant markets. This had a marked effect on New Zealand's trade with the United Kingdom. In 1870 only 52 per cent of the exports went to the United Kingdom; by 1880 the proportion had increased to 75 per cent. Australia, which had been New Zealand's main trading partner in the early years, was receiving only 21 per cent of the exports by 1880 and 15 per cent by 1890.
In more recent years Australia has received a greatly diminished share of exports and the proportion marketed in the United Kingdom has also dropped.
There has been some reduction in the proportion of total imports over the last 100 years coming from the United Kingdom and from Australia. However, in the more recent years there has not been any great variation in the proportions coming from these two countries, although the share of imports from the United Kingdom has tended to decrease.
Any analysis of the direction of New Zealand's external trade illustrates the importance of the United Kingdom both as a source supplier for import requirements and as the main market for our major exports.
The following table shows the changing pattern of external trade.
| Year | United Kingdom | Australia | United States of America | Other Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||
| Exports | ||||
| 1860 | 70 | 27 | - | 3 |
| 1870 | 52 | 46 | - | 2 |
| 1880 | 75 | 21 | 2 | 2 |
| 1890 | 75 | 15 | 6 | 4 |
| 1900 | 77 | 14 | 6 | 3 |
| 1910 | 84 | 9 | 3 | 4 |
| 1920 | 74 | 5 | 16 | 5 |
| 1930 | 80 | 3 | 5 | 12 |
| 1940 | 88 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1950 | 66 | 3 | 10 | 21 |
| 1959 | 56 | 4 | 15 | 25 |
| Year | United Kingdom | Australia | United States of America | Other Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||
| Imports | ||||
| 1860 | 56 | 42 | 1 | 1 |
| 1870 | 58 | 36 | 1 | 5 |
| 1880 | 56 | 31 | 4 | 9 |
| 1890 | 67 | 17 | 6 | 10 |
| 1900 | 61 | 17 | 10 | 12 |
| 1910 | 62 | 14 | 8 | 16 |
| 1920 | 48 | 17 | 18 | 17 |
| 1930 | 47 | 8 | 18 | 27 |
| 1940 | 47 | 16 | 12 | 25 |
| 1950 | 60 | 12 | 7 | 21 |
| 1959 | 47 | 18 | 8 | 27 |
So far as our export markets are concerned New Zealand has unrestricted access to the United Kingdom, but increased competition is being met from United Kingdom producers and other supplying countries. Perhaps the most important development in recent years has bean the expansion of British agriculture fostered by Government subsidies. Consequently, New Zealand's chief competitor in the supply of some primary products is the United Kingdom farmer. The move toward economic integration in Europe has also had some adverse effect on the United Kingdom market for our primary produce. In addition however, to this competition on the United Kingdom market from other primary producing countries and from home production, New Zealand butter has had to face competition from blended butter and margarine.
As a result, New Zealand has found it necessary in recent years to develop supplementary markets, but in doing so has had to face the quantitative restrictions which these potential markets have imposed on agricultural products. Nevertheless, there has been a marked expansion of New Zealand's overseas markets in recent years notably in the United States, France, Western Germany, and Japan.
Since the Second World War New Zealand's external trade has expanded considerably and its importance to the New Zealand economy can be appreciated when it is realised that in the last eight years exports f.o.b. have averaged 26.4 per cent and imports c.i.f. 25.8 per cent of the gross national product. Moreover, the value per head of New Zealand's overseas trade is one of the highest for any country in the world, particularly if re-exports are excluded.
Except for the growth of trade in pulp and paper products, which have assumed importance in recent years, the composition of New Zealand's exports today does not vary greatly from that of pre-war years. About 90 per cent of the total value of exports is still derived from wool, meat, and dairy produce. Except for a period during the Second World War, wool has always been competed for at auction by a number of countries. New markets have been developed for meat; and since the end of bulk purchase by the United Kingdom there has been a considerable switch of meat to markets outside the United Kingdom; in fact in 1959 meat went to nearly 60 countries. The main market for beef is now the United States of America, where imports in boneless packaged form have increased in recent years.
Good export prospects are held for the products of the rapidly expanding exotic timber industry. The industry is paying careful attention to the requirements of the Australian market in the way of quality, grading, and packaging of timber, principally radiata pine. Associated with the timber trade is the recent production of pulp and paper. Paper products - particularly newsprint, kraft paper, and pulp - have been added to the range of New Zealand's exports, the main market being Australia. Other traditional items such as hides and skins, tallow, sausage casings, seeds, fresh fruit, and fish have, in general, retained their relative position over recent years.
Attention is being given to the development of exports of New Zealand manufactured goods, and, although the trade is still small, there has been some expansion. Trade missions have surveyed market prospects for a variety of goods of a kind which are, or could be, made in New Zealand.
The distribution of New Zealand's overseas trade by broad groupings during the last 11 years is given in the following table.
| Year | United Kingdom | Other Commonwealth Countries | European Countries | Other Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||
| Proportions of Export Trade | ||||
| 1949 | 73.38 | 6.05 | 15.23 | 5.34 |
| 1950 | 66.44 | 6.27 | 15.70 | 11.59 |
| 1951 | 57.57 | 7.40 | 20.79 | 14.24 |
| 1952 | 65.33 | 6.72 | 12.70 | 15.25 |
| 1953 | 67.21 | 6.09 | 16.18 | 10.52 |
| 1954 | 66.98 | 6.83 | 18.15 | 8.04 |
| 1955 | 65.59 | 7.22 | 19.50 | 7.69 |
| 1956 | 64.58 | 7.37 | 19.03 | 9.02 |
| 1957 | 58.79 | 7.98 | 21.35 | 11.88 |
| 1958 | 55.78 | 8.79 | 16.88 | 18.55 |
| 1959 | 56.41 | 7.91 | 16.32 | 19.36 |
| Proportions of Import Trade | ||||
| 1949 | 55.13 | 26.00 | 4.17 | 14.70 |
| 1950 | 60.06 | 22.54 | 4.06 | 13.34 |
| 1951 | 53.59 | 24.73 | 6.84 | 14.84 |
| 1952 | 54.91 | 21.26 | 9.41 | 14.42 |
| 1953 | 56.45 | 24.92 | 7.88 | 10.75 |
| 1954 | 56.63 | 23.93 | 7.71 | 11.73 |
| 1955 | 54.99 | 23.71 | 8.57 | 12.73 |
| 1956 | 53.73 | 25.07 | 8.47 | 12.73 |
| 1957 | 51.38 | 26.99 | 8.72 | 12.91 |
| 1958 | 52.53 | 27.08 | 8.99 | 11.40 |
| 1959 | 47.28 | 28.64 | 9.35 | 14.73 |
The direction of external trade is shown graphically in the following diagram.
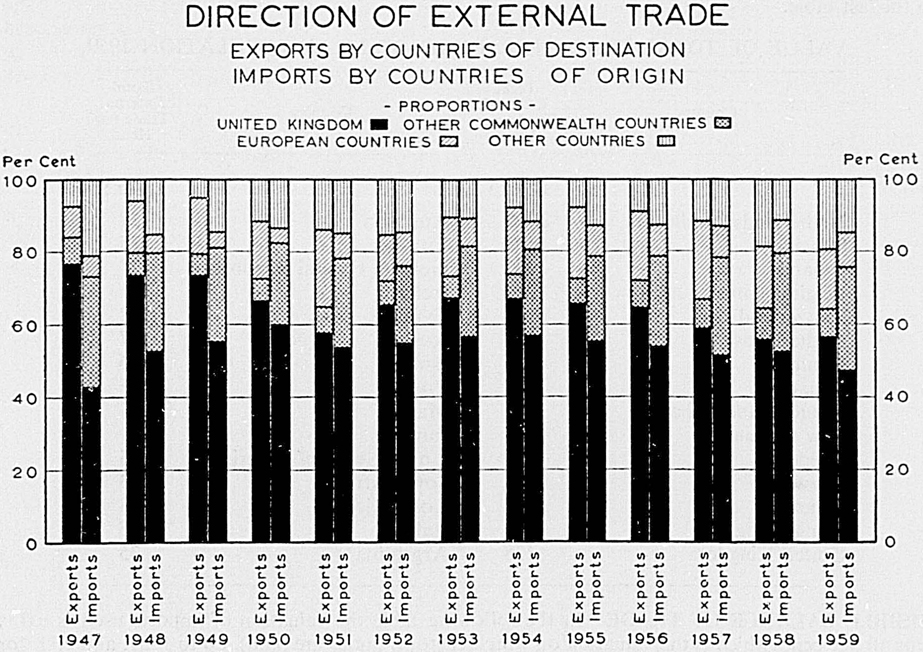
TRADE PER HEAD - The next table shows the value of exports, imports, and total trade per head of mean population. Values are expressed in terms of New Zealand currency.
| Year | Exports | Imports | Total Trade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1939 | 35 | 12 | 11 | 27 | 11 | 4 | 63 | 4 | 3 |
| 1940 | 45 | 0 | 9 | 27 | 4 | 1 | 72 | 4 | 10 |
| 1941 | 41 | 7 | 6 | 27 | 8 | 2 | 68 | 15 | 8 |
| 1942 | 49 | 11 | 6 | 29 | 17 | 2 | 79 | 8 | 8 |
| 1943 | 43 | 18 | 9 | 52 | 18 | 10 | 96 | 17 | 7 |
| 1944 | 46 | 19 | 7 | 47 | 8 | 9 | 94 | 8 | 4 |
| 1945 | 48 | 3 | 5 | 29 | 11 | 1 | 77 | 14 | 6 |
| 1946 | 57 | 11 | 6 | 36 | 19 | 7 | 94 | 11 | 1 |
| 1947 | 71 | 19 | 5 | 65 | 0 | 8 | 137 | 0 | 1 |
| 1948 | 80 | 11 | 5 | 63 | 13 | 9 | 144 | 5 | 2 |
| 1949 | 78 | 13 | 9 | 58 | 6 | 0 | 136 | 19 | 9 |
| 1950 | 96 | 5 | 0 | 75 | 3 | 4 | 171 | 8 | 4 |
| 1951 | 127 | 8 | 1 | 96 | 8 | 4 | 223 | 16 | 5 |
| 1952 | 120 | 10 | 3 | 114 | 18 | 11 | 235 | 9 | 2 |
| 1953 | 115 | 2 | 5 | 79 | 17 | 2 | 194 | 19 | 7 |
| 1954 | 116 | 13 | 11 | 101 | 15 | 0 | 218 | 8 | 11 |
| 1955 | 121 | 4 | 5 | 117 | 3 | 9 | 238 | 8 | 2 |
| 1956 | 127 | 2 | 5 | 107 | 11 | 2 | 234 | 13 | 7 |
| 1957 | 123 | 17 | 7 | 117 | 4 | 8 | 241 | 2 | 3 |
| 1958 | 109 | 8 | 11 | 110 | 11 | 11 | 220 | 0 | 10 |
| 1959 | 125 | 15 | 8 | 87 | 16 | 10 | 213 | 12 | 6 |
| 1960 | 127 | 5 | 4 | 105 | 18 | 9 | 233 | 4 | 1 |
When compared with the value of trade per head of population in other countries, the New Zealand figures take a leading place. There are difficulties in the way of making precise comparisons with the values of trade in other countries, mainly on account of differing methods of valuation used. In the following table, however, New Zealand's position is shown in comparison with some of the main trading countries. The source, in respect of data for other countries, is a United Nations publication providing data on trade values using the c.i.f. basis for the valuation of imports. For comparative purposes the c.i.f. basis has been used to value New Zealand imports, and therefore the figure given below as a value for New Zealand trade per head of population exceeds that given in the last table.
VALUE OF TOTAL TRADE PER HEAD OF MEAN POPULATION 1959
| Country | Total External Trade per Head |
|---|---|
| £(Stg.) | |
| Netherlands Antilles | 2,725 |
| Singapore | 543 |
| Iceland | 332 |
| Belgium-Luxemburg | 255 |
| Switzerland | 246 |
| Netherlands | 238 |
| Denmark | 236 |
| Canada | 228 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 225 |
| New Zealand | 225 |
| Sweden | 221 |
| Norway | 214 |
| Venezuela | 207 |
| Hong Kong | 180 |
| United Kingdom | 138 |
| Australia | 137 |
| Finland | 135 |
| German Federal Republic | 124 |
| Ireland | 121 |
| Cyprus | 108 |
| Austria | 107 |
| Israel | 106 |
| France | 85 |
| Malaya | 73 |
| Jamaica | 69 |
| United States of America | 65 |
| South Africa | 63 |
| Costa Rica | 58 |
| Italy | 45 |
| Argentina | 35 |
VISIBLE BALANCE OF TRADE - In the following table the valuation of imports used is c.d.v. plus 10 per cent (which is the valuation on which customs duties are paid), up to 1951, and c.i.f. for the subsequent years.
| Year | Visible Excess of Exports |
|---|---|
*Excess of imports. †Provisional. | |
| £(000) | |
| 1949 | 27,247 |
| 1950 | 25,809 |
| 1951 | 41,594 |
| 1952 | -35,655* |
| 1953 | 43,680 |
| 1954 | -1,354* |
| 1955 | -27,845* |
| 1956 | 9,068 |
| 1957 | -20,529* |
| 1958 | -34,904* |
| 1959 | 62,241 |
| 1960† | 21,744 |
Visible trade is not the only factor to be taken into account in considering the balance of payments between countries. Debt services, capital transfers, charitable and other personal remittances, freight payments, insurances, tourist expenditure, and the like, are vitally important factors which frequently reverse a credit visible balance of trade into a debit balance of payments (see Section 25B). A statement of New Zealand's overseas exchange transactions is given later in this section.
TRADE STATISTICS - The statistics of the external trade of New Zealand given in this section (comprising the three subsections) do not include the Cook Islands and Niue, which, though constitutionally part of New Zealand, are treated separately for trade statistics purposes, nor do they include Western Samoa. More detailed data relative to the external trade of the territories comprising the New Zealand currency area are given in the following publications: Statistical Report on the External Trade of New Zealand, in two volumes Exports and Imports published annually by the Customs Department.
Report on and Analysis of the External Trade Statistics of New Zealand, published annually by the Department of Statistics.
Reports on the Cook, Niue, and Tokelau Islands, New Zealand parliamentary paper A. 3.
Report on Western Samoa, New Zealand parliamentary paper A. 4.
Some information is also included in Section 38 of this Yearbook dealing with Island Territories.
New Zealand adopted the Standard International Trade Classification as from 1 January 1955, and from the same date this classification was put into effect for recording the external trade of the Cook Islands and Niue.
In the subsections dealing with exports and imports, information is given regarding the nature of the transactions which are included in the trade statistics, there being particular inclusions and exclusions which require to be considered when using the figures.
Of considerable consequence in the use of external trade statistics are the methods used in valuing the commodities comprising the trade. In New Zealand it has always been the practice to record exports at free-on-board (f.o.b.) values, except during the Second World War when a departure from this procedure was effected in respect of wool exports. Wool was valued for export at the appraisal prices and, as the prices later realised were higher than the appraisal prices, and New Zealand shared in this profit, export values for the years concerned were understated.
Up to the end of 1951 imports were recorded on the basis of their value for Customs purposes, this being their current domestic value (c.d.v.) in the country of export at the time of shipment, plus 10 per cent. For several years the limitations of this basis of valuation for economic studies, particularly those relating to balances of trade and of payments, had been apparent. There was a tendency generally to regard the Customs value of imports as being equivalent to at least a conventional c.i.f. value (cost including freight and insurance). In fact the Customs value of some imports probably fell short of the actual c.i.f. cost by varying amounts ranging up to 15 per cent. The domestic and export price levels in the exporting country may differ on account of price controls, subsidies, etc., while external packing, railway freights, etc., generally tend to raise the f.o.b. cost of goods above the current domestic price. For some few types of commodities the 10 per cent allowance is more than adequate to cover insurance and freight charges. For a larger proportion of imports, particularly those where the value relative to weight or bulk is low, the allowance is inadequate to cover these costs.
As from 1 January 1952 a change was made in that imports were recorded in the trade statistics without the additional 10 per cent required for duty purposes, i.e., at current domestic value, generally, as indicated above, equivalent to but not identical with the f.o.b. cost. Provision was also made to record statistical class totals and the grand total of imports on the c.i.f. basis. Since the introduction of the Standard International Trade Classification in 1955, division totals have replaced class totals for presentation on the c.i.f. basis. A description of the changed classification appears later in this Section.
The proportional difference between the two figures of valuation now made available - viz., c.d.v. and c.i.f. - will vary from period to period depending on (1) the make-up of imports in the different periods, (2) differential changes in import prices and in freight rates, (3) differences between domestic and export prices in the exporting countries, and (4) price fluctuations between dates of purchase and of shipping. The relatively high freight rates and insurance charges in wartime resulted in c.i.f. costs rising considerably above Customs values. The high charter freights of 1951-52 had a similar effect. In all the tables imports are now shown at c.d.v., unless otherwise specified in respect of particular tables.
Monthly summaries of the principal items of exports and imports are prepared and passed to the Department of Statistics, which publishes this information in the Monthly Abstract of Statistics. The exports recorded relate to goods on vessels which have cleared their final port of call in New Zealand during the period, save that, to facilitate the flow of work through the Customs Department's accounting machines, the figures for each month are in fact closed off before the end of the calendar month. Although what is published as a calendar month's transactions is not precisely the month's operations, the omissions at the end of the month are balanced by the amount carried forward from the end of the previous month. As the whole of the holiday period at Christmas and New Year is included in the January accounting period the figures for that month are usually low. As the goods loaded on a vessel for export are not recorded as exported until the vessel actually departs from New Zealand, it is possible for portions of the cargo which have been loaded at ports along the coast to have been on board the vessel for some time before actually being recorded as exports.
The trade figures for imports are compiled from the import entries, either for home consumption or into bonded warehouse, passed by the Customs Department. Under the system in use it is possible for an importer to pay the duty involved, if any, and have the import entry passed very shortly after he receives the shipping documents; this enables him to take delivery of the goods on arrival. Thus the import may be recorded before the carrying vessel has reached New Zealand. Generally, however, the import entries are not passed until the goods are available for discharge from the wharf. On the other hand, it may sometimes occur that goods may have been unloaded and in the custody of a harbour board for some time before the importer has the entry passed (and the import is recorded) and takes delivery.
New Zealand trade statistics are compiled on a calendar year basis. Special tables are, however, prepared to show the values of trade during years ended 31 March and 30 June. The Government financial year ends on 31 March, and external trade tables drawn up for that period show the relationship between the trade transactions and the public accounts for the year. In New Zealand the farm production year fits reasonably well to the year ended 30 June, and trade statistics compiled for years ended 30 June accordingly include the export values of approximately a whole season's production from the pastoral and agricultural industries.
In the following table are given the values of the export and import trade for years ending 31 December, 31 March, and 30 June. The movement of specie is not included in these figures.
| Year | Exports f.o.b. | Imports | |
|---|---|---|---|
| c.d.v. | c.i.f. | ||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Year Ended 31 December | |||
| 1949 | 147,281 | 109,121 | .. |
| 1950 | 183,752 | 143,585 | .. |
| 1951 | 248,127 | 187,758 | .. |
| 1952 | 240,561 | 229,447 | 276,215 |
| 1953 | 235,860 | 163,613 | 192,180 |
| 1954 | 244,466 | 213,155 | 245,820 |
| 1955 | 259,289 | 250,661 | 287,134 |
| 1956 | 277,483 | 234,779 | 268,415 |
| 1957 | 276,569 | 261,738 | 297,098 |
| 1958 | 250,173 | 252,800 | 285,077 |
| 1959 | 293,659 | 205,076 | 231,417 |
| 1960 | 302,508 | 250,207 | 278,923 |
| Year Ended 31 March | |||
| 1949 | 148,288 | 108,577 | .. |
| 1950 | 154,603 | 122,569 | .. |
| 1951 | 197,173 | 138,508 | .. |
| 1952 | 248,820 | 224,456 | .. |
| 1953 | 238,413 | 198,713 | 240,725 |
| 1954 | 242,817 | 173,308 | 201,915 |
| 1955 | 235,008 | 226,769 | 259,773 |
| 1956 | 278,776 | 245,692 | 281,455 |
| 1957 | 275,634 | 236,875 | 270,374 |
| 1958 | 275,452 | 267,034 | 303,438 |
| 1959 | 250,179 | 233,454 | 263,087 |
| 1960 | 313,755 | 216,787 | 243,909 |
| Year Ended 30 June | |||
| 1949 | 149,069 | 100,447 | .. |
| 1950 | 162,040 | 127,953 | .. |
| 1951 | 207,708 | 149,911 | .. |
| 1952 | 254,000 | 247,548 | .. |
| 1953 | 244,123 | 171,592 | 208,224 |
| 1954 | 241,829 | 182,080 | 210,130 |
| 1955 | 239,747 | 241,639 | 277,211 |
| 1956 | 270,663 | 241,782 | 276,848 |
| 1957 | 277,603 | 243,229 | 276,681 |
| 1958 | 272,023 | 268,280 | 305,203 |
| 1959 | 260,734 | 217,262 | 244,640 |
| 1960 | 314,768 | 227,206 | 254,585 |
The following table shows for the year 1959 the values of merchandise exports to, and imports from, each of the principal countries trading with New Zealand. Exports are valued f.o.b. New Zealand ports, and imports at current domestic value in country of shipment and in country of origin. The New Zealand trade statistics will yield different results, in respect of its trade with any given country, from those obtained from the trade statistics of that country, since in the latter New Zealand's exports will in most cases be valued c.i.f. in the given country and New Zealand's imports f.o.b. in that country.
These systems, however, are not universally used, and the methods of valuation in any particular country with whose trade statistics any comparison is attempted must be considered separately.
TRADE BY COUNTRIES, 1959
| Country | Exports | Imports | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand Produce | Total | By Country of Origin | By Country of Purchase | |
| Commonwealth Countries- | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||
| United Kingdom | 165,073 | 165,657 | 96,971 | 97,705 |
| Cyprus | 3 | 3 | 69 | 68 |
| Aden | 13 | 13 | 383 | 385 |
| Bahrain | - | -979 | 979 | |
| North Borneo | 1 | 2 | 24 | 23 |
| Brunei | 1 | 1 | - | 2 |
| Ceylon | 284 | 284 | 2,206 | 2,204 |
| Malaya | 331 | 335 | 1,791 | 1,767 |
| Singapore | 423 | 455 | 869 | 999 |
| Hong Kong | 382 | 390 | 806 | 878 |
| India | 686 | 687 | 4,308 | 4,256 |
| Kuwait | - | - | 153 | 153 |
| Pakistan | 45 | 45 | 148 | 147 |
| Sarawak | 2 | 2 | 23 | 19 |
| Ghana | 1 | 1 | 535 | 460 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 39 | 40 | 363 | 353 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 138 | 138 | 99 | 95 |
| Mauritius | 47 | 47 | 8 | 8 |
| Seychelles | - | - | - | - |
| Tanganyika | 1 | 1 | 204 | 210 |
| Union of South Africa | 919 | 922 | 1,078 | 1,040 |
| Bahamas | 133 | 133 | - | - |
| Barbados | 279 | 279 | - | 2 |
| Bermuda | 213 | 213 | - | - |
| British Guiana | 110 | 110 | 8 | 5 |
| Canada | 3,030 | 3,054 | 4,802 | 4,769 |
| Jamaica | 1,589 | 1,589 | 110 | 101 |
| Leeward and Windward Islands | 58 | 58 | 3 | 2 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 1,181 | 1,181 | 111 | 110 |
| Australia | 10,377 | 10,944 | 37,104 | 37,776 |
| Fiji | 919 | 1,150 | 988 | 1,022 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 11 | 14 | 159 | 159 |
| Nauru | 44 | 53 | 515 | 516 |
| Papua | 2 | 4 | 39 | 20 |
| Tonga | 208 | 223 | 65 | 65 |
| Western Samoa | 765 | 823 | 668 | 670 |
| Other Commonwealth countries | 17 | 20 | 107 | 109 |
| Totals, Commonwealth count | 187,325 | 188,871 | 155,696 | 157,077 |
| Foreign Countries– | ||||
| Republic of Ireland | 145 | 145 | 122 | 121 |
| Austria | 32 | 32 | 329 | 305 |
| Belgium-Luxemburg | 5,200 | 5,204 | 1,513 | 1,459 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1,367 | 1,367 | 264 | 256 |
| Bulgaria | 140 | 140 | ||
| Denmark | 394 | 396 | 305 | 296 |
| Finland | 176 | 176 | 98 | 81 |
| France | 17,241 | 17,243 | 1,304 | 1,250 |
| German Federal Republic | 9,649 | 9,693 | 6,194 | 6,057 |
| German Democratic Republic | 3 | 3 | 95 | 92 |
| Greece | 322 | 322 | 3 | 3 |
| Italy | 6,004 | 6,008 | 1,466 | 1,422 |
| Netherlands | 4,134 | 4,179 | 2,432 | 2,442 |
| Norway | 159 | 159 | 686 | 663 |
| Poland | 1,264 | 1,264 | 11 | 10 |
| Portugal | 382 | 382 | 159 | 156 |
| Rumania | - | - | ||
| Spain | 81 | 81 | 138 | 110 |
| Sweden | 692 | 697 | 2,326 | 2,278 |
| Switzerland | 37 | 40 | 1,630 | 1,533 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 152 | 152 | 44 | 6 |
| Turkey | 2 | 2 | 49 | 33 |
| Yugoslavia | 239 | 239 | 2 | 1 |
| Burma | 107 | 107 | 1 | |
| China | 2,490 | 2,490 | 419 | 241 |
| Indonesia | 3 | 3 | 2,135 | 2,049 |
| Iran | - | - | 1,673 | 1,652 |
| Iraq | - | 74 | 70 | |
| Israel | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Japan | 6,681 | 6,685 | 3,584 | 3,560 |
| Philippines | 269 | 273 | 57 | 57 |
| Saudi Arabia | 1,356 | 1,356 | ||
| Thailand | 38 | 38 | 41 | 40 |
| Algeria | 8 | 8 | 20 | 20 |
| Ethiopia | - | - | 27 | 25 |
| Egypt | 173 | 173 | 2 | 1 |
| Morocco | - | - | 3 | |
| Mozambique | 41 | 41 | ||
| Brazil | 1 | 1 | 55 | 25 |
| Chile | 16 | 16 | 27 | 27 |
| Haiti | 22 | 22 | - | - |
| Mexico | 117 | 117 | 212 | 210 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 271 | 271 | 3,024 | 3,029 |
| Panama Canal Zone | 75 | 75 | - | |
| Panama Republic | 273 | 273 | - | 5 |
| Peru | 730 | 730 | 300 | 299 |
| United States of America | 42,938 | 43,057 | 16,739 | 16,329 |
| Venezuela | 201 | 201 | 167 | 124 |
| American Samoa | 145 | 145 | - | - |
| Guam | 65 | 65 | - | - |
| Hawaii | 912 | 913 | 8 | 8 |
| French Oceania | 1 | 1 | 208 | 208 |
| Society Islands | 144 | 170 | 9 | 9 |
| Antarctic Regions | - | 161 | - | - |
| Remaining countries | 47 | 49 | 68 | 80 |
| Totals, foreign countries | 103,585 | 104,011 | 49,380 | 47,999 |
| Ships' stores | 88 | 776 | - | - |
| Grand totals | 290,998 | 293,659 | 205,076 | 205,076 |
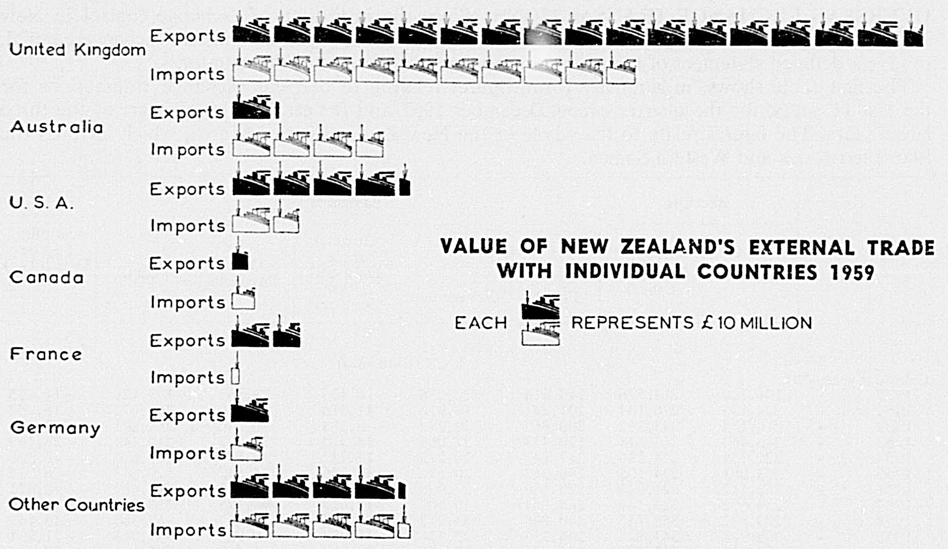
Attention is drawn here to changes made in the list of countries used in the recording of New Zealand trade statistics in 1955 concurrently with the introduction of the Standard International Trade Classification. Major changes consisted of breaking down several country titles used in the past to their several constituent parts - e.g., British West Africa is now treated under the separate headings of Gambia and Sierra Leone, Ghana, and Nigeria; British West Indies is now treated under the headings of Bahamas, Barbados, Jamaica, Leeward and Windward Islands, Trinidad and Tobago; British Borneo is now treated under the headings of Brunei, Sarawak, and North Borneo. It is accordingly not possible in all cases to make comparisons between country trade data for 1955 and subsequent years with those for earlier years. In the cases of the countries mentioned above it is necessary to add together the figures for the separate units for 1955 or subsequent years to make a comparison with 1954, and no data are available to give an earlier comparison with the trade of a separate unit contained in one of the older headings used. From 1957 onwards separate records have been maintained for the Federation of Malaya and for Singapore.
The next table shows the values of New Zealand's trade with several groupings of countries during the last six years.
| Year | Exports (Excluding Ships' Stores) | Imports | Exports (Excluding Ships' Stores) | Imports | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| According to Country of Origin | According to Country of Purchase | According to Country of Origin | According to Country of Purchase | |||
*Belgium, Luxemburg, France, German Federal Republic, Italy, and Netherlands. †United Kingdom, Austria, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, and Switzerland. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| Sterling Area | Dollar Area | |||||
| 1955 | 184,348 | 189,051 | 192,081 | 20,362 | 29,720 | 28,651 |
| 1956 | 195,372 | 178,870 | 181,533 | 24,440 | 24,217 | 23,734 |
| 1957 | 179,963 | 198,648 | 200,929 | 27,647 | 27,321 | 26,658 |
| 1958 | 157,239 | 195,444 | 197,645 | 42,072 | 23,330 | 22,554 |
| 1959 | 186,065 | 151,017 | 152,429 | 48,206 | 22,003 | 21,536 |
| 1960 | 183,850 | 176,528 | 45,067 | 35,973 | ||
| EEC Countries* | EFTA Countries† | |||||
| 1955 | 41,863 | 14,777 | 14,109 | 171,116 | 143,740 | 146,202 |
| 1956 | 44,166 | 14,217 | 13,751 | 180,197 | 131,068 | 133,977 |
| 1957 | 50,578 | 15,648 | 15,153 | 163,562 | 140,760 | 142,145 |
| 1958 | 35,422 | 16,020 | 15,746 | 140,842 | 138,436 | 139,064 |
| 1959 | 42,327 | 12,909 | 12,629 | 167,364 | 102,406 | 102,936 |
| 1960 | 50,358 | 17,368 | 162,260 | 115,562 | ||
OVERSEAS EXCHANGE TRANSACTIONS - Since the institution of exchange control in New Zealand it is possible through the records of the Reserve Bank, which administers exchange control, to give a detailed statement of the overseas exchange transactions of the country.
The first table shows, in summary form, figures relating to overseas exchange transactions for the last 11 years, for the quarter ended December 1957 and for each of the quarters of the three latest years. The figures relate to the whole of the New Zealand currency area, which includes the island territories and Western Samoa.
| Receipts | Payments | Surplus (+) or Deficit (-) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exports | Total (Including Other) | Imports | Government Debt and Other Services | Other Payments | Total | |||
| Private | Government | |||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||||
| Calendar year - | ||||||||
| 1950 | 194,786 | 213,576 | 140,816 | 22,038 | 6,406 | 29,861 | 199,121 | +14,455 |
| 1951 | 254,135 | 276,134 | 201,293 | 18,916 | 11,078 | 28,790 | 260,077 | +16,057 |
| 1952 | 216,133 | 245,362 | 200,060 | 30,290 | 8,213 | 30,240 | 268,803 | -23,441 |
| 1953 | 243,469 | 266,318 | 170,473 | 27,064 | 14,315 | 28,297 | 240,149 | +26,169 |
| 1954 | 221,154 | 271,284 | 217,647 | 20,212 | 17,222 | 32,800 | 287,880 | -16,596 |
| 1955 | 253,081 | 294,105 | 246,362 | 20,682 | 17,786 | 35.S12 | 320,642 | -26,537 |
| 1956 | 282,112 | 324,333 | 229,680 | 27,098 | 12,856 | 45,827 | 315,462 | +8,871 |
| 1957 | 284,592 | 328,584 | 268,068 | 30,507 | 18,012 | 44,175 | 360,762 | -32,178 |
| 1958 | 273,822 | 358,717 | 240,046 | 34,277 | 20,558 | 50,687 | 345,568 | +13,149 |
| 1959 | 305,948 | 343,825 | 206,236 | 22,736 | 31,988 | 60,983 | 321,943 | +21,881 |
| 1960 | 299,939 | 345,656 | 255,846 | 22,958 | 28,810 | 65,490 | 373,104 | -27,448 |
| Quarter ended- | ||||||||
| 1957—Dec | 52,145 | 63,003 | 75,378 | 7,486 | 6,135 | 12,351 | 101,351 | -38,348 |
| 1958-Mar | 75,477 | 87,296 | 57,996 | 9,999 | 3,297 | 10,839 | 82,132 | +5,164 |
| Jun | 72,126 | 94,217 | 64,209 | 7,929 | 5,469 | 15,054 | 92,662 | +1,554 |
| Sep | 64,256 | 80,999 | 56,480 | 7,156 | 3,668 | 12,161 | 79,464 | +1,535 |
| Dec | 61,963 | 96,206 | 61,361 | 9,193 | 8,124 | 12,633 | 91,310 | +4,895 |
| 1959-Mar | 75,241 | 84,045 | 44,861 | 4,633 | 4,643 | 11,494 | 65,631 | +18,414 |
| Jun | 88,447 | 98,078 | 48,811 | 6,275 | 4,446 | 22,352 | 81,884 | +16,194 |
| Sep | 71,080 | 80,952 | 51,123 | 6,437 | 8,754 | 13,110 | 79,424 | +1,527 |
| Dec | 71,180 | 80,751 | 61,441 | 5,391 | 14,145 | 14,028 | 95,004 | 14,253 |
| 1960-Mar | 83,512 | 93,292 | 55,732 | 6,130 | 9,346 | 13,800 | 85,008 | +8,284 |
| Jun | 95,308 | 104,509 | 58,920 | 4,446 | 4,096 | 17,633 | 85,095 | +19,414 |
| Sep | 63,063 | 74,105 | 66,893 | 4,998 | 5,215 | 16,604 | 93,710 | -19,605 |
| Dec | 58,056 | 73,750 | 74,301 | 7,384 | 10,153 | 17,453 | 109,291 | -35,541 |
The next table, also drawn from Reserve Bank statistics, gives summarised overseas exchange transactions with the United Kingdom and with the principal currency areas for recent periods.
| Transactions With | 1959 | 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six Months Jan-Jun | Six Months Jul-Dec | Six Months Jan-Jun | Six Months Jul-Dec | |
| United Kingdom- | ||||
| £N.Z.(million) | ||||
| Receipts– | ||||
| Exports | 92.8 | 80.7 | 90.6 | 68.8 |
| Total | 101.2 | 91.4 | 100.8 | 83.0 |
| Payments– | ||||
| Imports | 69.8 | 76.4 | 74.9 | 86.6 |
| Total | 90.6 | 100.9 | 99.1 | 115.8 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (-)– | ||||
| On current transactions | +10.1 | -6.7 | +0.2 | -33.4 |
| On all transactions | +10.6 | -9.5 | +1.6 | -32.9 |
| Sterling area (including United Kingdom)– | ||||
| Receipts– | ||||
| Exports | 101.1 | 91.1 | 100.9 | 77.4 |
| Total | 117.6 | 107.6 | 117.5 | 100.8 |
| Payments– | ||||
| Imports | 87.7 | 99.7 | 97.0 | 114.0 |
| Total | 124.8 | 133.7 | 131.6 | 154.6 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (-)– | ||||
| On current transactions | +16.9 | -44.0 | -14.8 | -53.8 |
| On all transactions | -7.2 | -26.1 | -14.2 | -53.8 |
| Dollar area– | ||||
| Receipts– | ||||
| Exports | 29.1 | 22.9 | 29.4 | 20.5 |
| Total | 30.6 | 25.4 | 31.4 | 23.3 |
| Payments– | ||||
| Imports | 9.6 | 15.7 | 18.3 | 25.5 |
| Total | 14.3 | 30.3 | 26.9 | 32.0 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (.-) on all transactions | +16.3 | -4.9 | +4.4 | -8.8 |
| Non-Sterling European Payments Union countries and possessions– | ||||
| Receipts– | ||||
| Exports | 26.1 | 19.3 | 35.5 | 16.8 |
| Total | 26.4 | 19.3 | 35.8 | 17.1 |
| Payments– | ||||
| Imports | 5.9 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 9.6 |
| Total | 6.7 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 11.2 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (-) on all transactions | +19.7 | +12.1 | +27.5 | +6.0 |
| Grand totals (including other foreign countries) | ||||
| Receipts– | ||||
| Exports | 163.7 | 142.3 | 178.8 | 121.2 |
| Total | 182.1 | 161.7 | 197.8 | 147.9 |
| Payments– | ||||
| Imports | 104.9 | 124.4 | 125.2 | 154.6 |
| Total | 147.5 | 174.4 | 170.1 | 203.0 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (-) on all transactions | +34.6 | -12.7 | +27.7 | -55.2 |
The figures for export receipts and import payments recorded in these tables differ from the corresponding external trade figures as a result of (1) the different territorial coverage of the two sets of figures, (2) the lack of uniformity in the basis of valuation, particularly in imports, (3) the inclusion in the trade figures of “no-remittance” imports and similar movements of goods with no corresponding monetary transactions, and (4) the actual movements of goods and the corresponding monetary transactions occurring in different recording periods.
The figures on page 642 show the fluctuations that have occurred during the past 11 years in the value of imports. They bring out, too, New Zealand's heavy annual deficit on transactions (particularly “invisibles”) with the sterling area, mainly United Kingdom and Australia, which is offset by a surplus on transactions with other currency areas. The nature of the “invisibles” is apparent in the next table giving detailed figures for the 1959 and 1960 calendar years.
21*
| Item | Year Ended 31 December | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |||
| Receipts | Payments | Receipts | Payments | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||
| Merchandise– | ||||
| Exports | 305,980 | 300,038 | ||
| Licensed imports | 199,223 | 237,933 | ||
| Decontrolled imports | 4,114 | 13,632 | ||
| Government imports | 22,736 | 22,958 | ||
| Other imports | 3,098 | 4,447 | ||
| Totals, merchandise | 305,980 | 229,171 | 300,038 | 278,970 |
| Transport – | ||||
| Freights, fares, ships' charters | 4,412 | 12,137 | 5,911 | 13,411 |
| Travel – | ||||
| Private and business (exclusive of fares) | 3,083 | 8,364 | 3,589 | 12,900 |
| Insurance – | ||||
| Insurance, reinsurance, other transfers | 944 | 2,424 | 1,650 | 2,880 |
| International investment income – | ||||
| Interest, dividends, and other private investment income | 4,887 | 9,291 | 6,640 | 10,689 |
| Interest on Government and local authority loans | 5,744 | 5,417 | ||
| Totals, international investment income | 4,887 | 15,035 | 6,640 | 16,107 |
| Government transactions – | ||||
| Current expenditure by New Zealand Government overseas | 8,003 | 9,659 | ||
| Current receipts by New Zealand Government and expenditure by other Governments in New Zealand | 2,194 | 2,663 | ||
| Totals, Government transactions | 2,194 | 8,003 | 2,663 | 9,659 |
| Miscellaneous current transactions – | ||||
| Commissions, royalties, rebates, etc. | 1,029 | 3,013 | 1,327 | 3,092 |
| Films and entertainments | 1,136 | 1,220 | ||
| Unilateral transfers (migrants' transfers, personal remittances, charitable, legacies, etc.) | 7,421 | 9,653 | 7,738 | 10,921 |
| Expenses of business firms | 794 | 3,989 | 1,055 | 4,808 |
| Other current transactions | 681 | 1,639 | 841 | 1,368 |
| Totals miscellaneous current transactions | 9,925 | 19,430 | 10,961 | 21,408 |
| Totals, current transactions | 331,425 | 294,563 | 331,451 | 355,334 |
| Capital transfers – | ||||
| Private | 12,166 | 2,863 | 8,445 | 4,711 |
| Government | 101 | 16,153 | 5,664 | 12,420 |
| Local authority | 910 | 639 | ||
| Drawings Australian bank credit | 51 | 7,455 | - | - |
| Totals, capital transfers | 12,318 | 27,380 | 14,109 | 17,770 |
| Totals, capital transactions | 12,318 | 27,380 | 14,109 | 17,770 |
| Unidentified | 82 | 96 | ||
| Grand totals | 343,825 | 321,943 | 345,656 | 373,104 |
INDEX NUMBERS OF VOLUME OF EXTERNAL TRADE - Index numbers of volume of external trade are now published on the base: 1952 (= 100). The figures given in the following table refer only to calendar years, but quarterly figures are published in the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
The series for exports of New Zealand produce are linked chain series. Up to the year 1949 the exports of each year were revalued at the unit values of the immediately preceding year and the aggregate so obtained (after imputing to the 2 per cent of items, for which quantities and consequently unit values were not available, price movements similar to the priced items) was compared with the recorded value in that (preceding) year. Each year's index was, therefore, a Laspeyre type index on base previous year. From 1950 on, aggregates were also calculated for immediately preceding years at the unit values of the latest year, which, compared with the recorded value in the latest year, gave a Paasche type index. The final index for the year was then obtained as the geometric mean of these two - i.e., a Fisher “Ideal” index - and in the table the successive annual movements are linked. The quarterly indices are similarly calculated on base previous year, but only a limited number of the more important commodity headings are used in the calculation. When the final indices for the year become available the quarterly indices are adjusted to accord with these; consequently, the indices for quarters are provisional.
The series for total exports includes an allowance for re-exports of imported goods. Since these are normally approximately 1 per cent of total exports and only became significant during the war years, the approximate volume movements were obtained by “deflating” the recorded values by the import price index as the best indicator available of price movements for these commodities. The two indices, exports of New Zealand produce and re-exports, were then combined by weighting by their relative values in the base period. This was a change from the method previously used and resulted in some slight alterations in the indices from those published in issues of the Yearbook prior to 1954.
The import volume index up to 1946 was calculated by revaluing each year's imports at 1937 unit values, assuming comparable price movements in the unpriced items as in the priced items. Thereafter a change was made to the calculation of each year on base previous year and the linking of these annual movements. Anterior year weights were used up to 1949 to give a Laspeyre type index. From 1950 on, a Fisher “Ideal” index has been obtained as the geometric mean of both anterior year and current year weighted indices. The quarterly indices, too, are calculated on base previous year, and, like the export series, are provisional until the calculation of the annual index. Currently, the items for which quantities are recorded (and consequently unit values obtained) represent approximately two-thirds of the total value of imports. Price movements are imputed to the remaining third on the basis of the price movements of items in the same statistical class.
The total exports and imports series are combined into the total trade series by weighting by their relative values in the base period.
VOLUME INDEX NUMBERS OF EXTERNAL TRADE Base: 1952 (= 100)
| Calendar Year | Exports | Imports | Total Trade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand Produce | Total Exports | ||||||
| Dairy Produce | Meat | Wool | Total | ||||
| 1949 | 82 | 85 | 99 | 90 | 89 | 67 | 78 |
| 1950 | 81 | 83 | 90 | 86 | 86 | 80 | 83 |
| 1951 | 86 | 72 | 72 | 76 | 76 | 89 | 83 |
| 1952 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1953 | 92 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 90 | 76 | 83 |
| 1954 | 78 | 99 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 99 | 95 |
| 1955 | 85 | 99 | 96 | 94 | 94 | 118 | 106 |
| 1956 | 93 | 105 | 97 | 100 | 100 | 107 | 104 |
| 1957 | 85 | 98 | 100 | 99 | 100 | 116 | 108 |
| 1958 | 94 | 105 | 106 | 106 | 106 | 112 | 109 |
| 1959 | 103 | 108 | 122 | 116 | 116 | 93 | 104 |
IMPORT AND EXPORT PRICES AND TERMS OF TRADE - Descriptions of the index numbers of export and import prices compiled in New Zealand and of the terms of trade are given in Section 23, together with the index numbers.
MOVEMENT OF SPECIE - There is no mint in New Zealand and all new coin is imported from the Royal Mint in England. In Section 29 dealing with Banking and Currency is a description of the coinage in use in New Zealand. The movement of specie to and from New Zealand is recorded in the trade statistics, but the value is not included in the totals of merchandise exports and imports. All records of specie are at face value.
The following table shows exports and imports of specie stated at face value for each of the 11 years 1949-59.
| Year | Specie Imported | Specie Exported | Excess of Specie Imports (+) or Exports (–) |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1949 | 1,040,725 | 570,220 | +470,505 |
| 1950 | 169,823 | 514,455 | -344,632 |
| 1951 | 250,108 | 280,150 | -30,042 |
| 1952 | 84,567 | 26,943 | +57,624 |
| 1953 | 107,106 | 7,929 | +99,177 |
| 1954 | 21,360 | 7,573 | +13,787 |
| 1955 | 43,726 | 13,255 | +30,471 |
| 1956 | 12,027 | 2,463 | +9,564 |
| 1957 | 48,931 | 15,026 | +33,905 |
| 1958 | 97,577 | 161,547 | -63,970 |
| 1959 | 54,864 | 38,823 | +16,041 |
IMPORT AND EXPORT CONTROL AND EXCHANGE ALLOCATION - A decline in overseas assets commenced during 1936-37 and continued steadily until 28 November 1938, when the net overseas assets of the New Zealand banking system stood at under £(N.Z.)8 million. This figure compared with an average of £(N.Z.)29 million in 1936.
To ensure that overseas debt services would be met and sufficient funds be available for essential imports, the Import Control Regulations 1938 and the Export Licences Regulations 1938 were issued by Orders in Council dated 5 December 1938. The Import Control Regulations were confirmed as valid by the Customs Acts Amendment Act 1939. The Import Control Regulations prohibited the import of goods except under a licence or an exemption (e.g., Government imports). The Export Licences Regulations provided (with minor exceptions) that an export licence, must be obtained before goods could be exported. In addition the requirement of an export permit was introduced by the Export Prohibition Emergency Regulations 1939, which have since been replaced by the Export Prohibition Regulations 1953.
Export Control - Three classes of export licences are provided for, viz, particular, general, and purchaser's. The particular licence applies to an occasional shipment, the general licence is issued to exporters who make regular or frequent shipments, while the purchaser's licence applies to those cases where goods have been purchased in New Zealand for export and credits have been established from overseas funds (e.g., wool purchases). A condition of the issue of any export licence is that the overseas exchange earned must be sold to a New Zealand bank for New Zealand currency.
Whereas the purpose of the Export Licences Regulations is to ensure that all foreign exchange earned is sold to the New Zealand banking system, the aim of the Export Prohibition Regulations 1953 is to control the export of essential goods in short supply, of goods on which subsidies have been granted, and of goods shipped to strategic destinations.
Import Selection - The administration of the Import Control Regulations of 1938 is carried out by means of Import Licensing Schedules. The first four Schedules were for six-monthly periods and the first three were confidential to Government Departments. Since 1941 the Schedules have been issued for calendar years, with occasional extensions into the following year.
The items in the Import Licensing Schedules were originally divided into: basic items for which licences were allocated according to the applicant's import history in a base year; items subject to individual consideration (C); and items for which no licences were available (D). In the case of basic items there were differentiations between the sources of supply, with emphasis on sterling area countries, and several hard-currency countries were excluded from the allocation of basic licences.
Import licences are issued by the Customs Department which is advised by the Department of Industries and Commerce on the import of materials and machinery for existing or planned New Zealand manufacturing industries and on the import of goods of a kind made in New Zealand.
In the 1949 Schedule provision was made for token licences to allow old-established business connections with United Kingdom exporters to be maintained on a small scale in cases where no allocation for such items had been made. The amount of token licences was a percentage of 1938 imports from the United Kingdom.
In May 1950 the Government set up an Import Advisory Committee for the purpose of examining the import licensing system and recommending improvements in its administration. The activities of the committee resulted in the extension of import licences on sterling area countries to all non-scheduled countries commencing with the 1951 Schedule. Scheduled countries are those countries enumerated in the annual Import Licensing Schedule for which only individual licences, limited to the specific country, are issued.
The list of scheduled countries incorporated in the Import Licensing Schedule was reduced from time to time until by 1956 it comprised only the countries in the dollar area, Japan, and Korea.
Apart from the scheduled countries there was full equity from the import licensing point of view between all countries, thus enabling traders to buy from the best source within the non-scheduled countries.
The Import Advisory Committee, which was constituted the Board of Trade under the Board of Trade Act 1950 as from 1 December 1950, recommended to the Government a number of new departures from the usual set-up of the Import Schedule. The innovations were: the freeing of a large number of items from licensing if the goods were imported from non-scheduled countries; the introduction of world exemption items (“EE”); and the introduction of two categories of modified “D” items. These two categories were “SD” items which provided for licences for goods of a specific kind not made in New Zealand although similar and possibly competitive kinds may be manufactured in New Zealand; and “OD” items (opened “D”) which provided for limited imports of goods (especially clothing) of a kind manufactured in New Zealand to give the consumer a greater variety of goods and to introduce some overseas competition in price and quality in fields previously reserved for domestic industries.
In May 1950, as a further liberalisation of import licensing, the Government made provision for the issue of no-remittance licences which could be financed out of the applicant's own overseas funds. As no limit was placed on the nature or extent of imports that could be made, nor of the funds to be used, abuses soon became apparent and it was necessary to amend the scheme. A limitation was placed on the type of overseas funds which could be used and the amended scheme applied in general only to imports required by private individuals for their own use and not for purposes of resale.
The import of motor vehicles, which had been freed from import licensing, was brought back under control in March 1952. Since that date it has been usual to make a separate yearly announcement for motor vehicle imports. A few other items were also brought back under control, the most important being certain kinds of paper for particular uses; jams, jellies, and preserves; and woollen piece goods.
A relaxation of New Zealand's import policy towards Japan was introduced in 1954 and this was continued in subsequent years until in 1958 a trade agreement was completed removing Japan from the list of scheduled countries.
As the sterling area's gold and dollar reserves improved the policy for imports from the dollar area was relaxed. The dollar countries also benefited from the increase in the number of exemption items.
The 1958 Import Licensing Schedule was initially released in August 1957 but, because of New Zealand's balance of payments crisis, the Government found it necessary to withdraw this Schedule and issue a new one which restored import control on virtually all private imports, the main exceptions being passengers' effects and official supplies for diplomatic representatives. The new 1958 Schedule operated from 1 January 1958. Provision was made for goods that had been ordered under items previously exempt and shipped from the country of export to New Zealand not later than 31 December 1957. However, all licences for 1958 imports issued up to that time were revoked and licences were issued in accordance with the new Schedule. Any goods imported against the old 1958 licence and shipped to New Zealand from the country of export not later than 31 December 1957 were a charge against the new licences. All goods ordered overseas but not shipped before 1 January 1958, whether formerly exempt or not, were subject to the new 1958 allocation and importers were required to ensure that provision for them was made under their new licences.
An important change in the new Schedule was that it included all tariff items. The allocations for items were based on 1956 imports but some items were given a “B” category (or “B” plus percentage classification) and these allocations were related to the old 1958 Schedule provision. Other categories were the “C” (individual consideration) and “D” (no allocation), but the “E” (exempt) and “EE” (world exempt) categories were cancelled. It was also necessary to withdraw the scheme for token imports. However, a new category “A” was introduced under which licences were granted for imports from non-scheduled countries up to the full value sought.
Because of the further deterioration of New Zealand's balance of payments, the 1959 Schedule provided for lower imports than in 1958. One feature of the Schedule was the reintroduction of “global” licences, which can be used for imports from any source, for all items except a limited number designated “M”. Licences for “M” items were available for non-scheduled countries only. However, it was later decided to issue licences for scheduled countries on the same basis as that which applied to the same goods from other countries.
Towards the end of 1958 there was a considerable improvement in the overseas prices received for New Zealand's exports. This rise continued in 1959 and enabled the Government to make additional funds available for imports. Two major relaxations in April 1959 and June 1959 greatly extended the 1959 provision for imports.
The improvement in New Zealand's overseas reserves was reflected in the 1960 Import Licensing Schedule. The 1960 Schedule provided for a much higher value of imports than in 1959 and introduced several new features in licensing procedures. These new departures were aimed at giving the maximum flexibility to importers while retaining those minimum restrictions which were necessary for the effective protection of the balance of payments.
The 1960 Schedule had an increased number of basic allocations, a total of 401 items being in this category. The basis was mainly the value of 1959 licences, although in several cases other bases were used. Many items which were previously considered individual were made basic to let the importer know his entitlement as soon as possible, so eliminating delays in dealing with applications for licences.
The exemption of items from import licensing was reintroduced. Although the number of items is not large, their import value amounts to a considerable sum. The items are: raw sugar, crude oil, motor spirits, certain bulk oils (kerosene and lubricating oils), explosives, crude sulphur in bulk, and manures. These items were particularly suited for exemption as they are essential, of major value, and are imported by relatively few firms so that actual and likely expenditure can be readily ascertained.
The token licence provision which had been cancelled because of the critical circumstances at the beginning of 1958 was reintroduced in a new form. Over a wide range of items, for which no other allocation had been made, token licences were available for imports from any source to the extent of 10 per cent of the value of imports of the same goods from any source in 1956. For a few items which were severely restricted in 1956 the basis was 100 per cent of the value of 1956 licences. The token licence procedure permits overseas suppliers and their New Zealand customers to maintain trading contact; it also introduces variety and keeps overseas standards before manufacturers and consumers.
The most important new features of the Schedule were the replacement licence (“R”) scheme and the industry group scheme. The replacement scheme permits an importer to obtain his genuine import needs of an item. (In 1960 an importer was entitled to an initial licence representing 50 per cent of the value of his normal 1959 licence for the “R” items. Further licences were issued up to the ceiling of 150 per cent in replacement of the value of actual imports made under his 1960 licence.) The replacement licence may be issued for each shipment as it arrives or for several shipments, according to the importer's desire and to suit the nature of his business. The “R” system applies also to new importers. Any firm or person wishing to receive a new importer's entitlement must apply in writing to the Collector of Customs providing such information as may be necessary to establish that he has the facilities to engage in the business of importing those goods. The applicant will be told of the licence entitlement available under the “R” items for which he has applied, but an actual licence will not be issued until there has been produced evidence of firm orders placed overseas and confirmation of a financial commitment entered into for the purchase of the goods.
The provision for “industry groups” was made with the object of allowing interested licence holders greater flexibility in the use of their total available licence value. There are 15 industry groups. An importer who has a licence entitlement to any of the items in a group may, if he so elects, apply for a licence for the group rather than for the individual items.
The application of “global” licences introduced in the 1959 Schedule was extended in 1960 so that the only goods remaining subject to the “M” limitation are motor vehicles (excluding spare parts). For this item the allocation for “scheduled” countries is the same as for “non-scheduled” countries.
The restoration of import control for all private imports and the selection of 1956 as the base year gave rise to a number of anomalies. Anomalies arose particularly in those cases in which for some specific and valid reason an established importer had abnormally low imports in the base year, compared with previous and subsequent years. Some of these anomalies were eliminated by the liberal provisions of the 1960 Schedule, especially where the licence entitlements were no longer dependent on base-year imports. Where importers still felt that they were placed at a real disadvantage they were invited to make application to the Customs Department which examined each case on its merits with a view to establishing a normal pattern of imports.
With the intensification of import restrictions in January 1958 ordinary licences carry the right to exchange, but excess licences had to be referred to the Reserve Bank for individual consideration. The necessary exchange was finally made available before 31 March 1959 where payment had not already been authorised or made.
The 1961 Import Licensing Schedule, released in September 1960, provided for another easing of the import licensing allocations. The number of “Replacement” (“R”) and “A” items - that is, items for which licences are issued as applied for (a category reintroduced in March 1960) - was increased and the initial entitlement to “R” licences raised from 50 to 100 per cent. The number of “R” items stood now at 206 and that of “A” items at 63. It was estimated that 55 per cent of private imports was either exempt from import licensing or subject to the “R” or “A” allocations which make licences available to regular or prospective new importers. In May 1961 it was announced that the Government had decided to make import licences issued for the 1961 calendar year last for 15 months.
For imports exempt from licensing (raw sugar, crude oil, motor spirits, certain bulk oils, explosives, crude sulphur in bulk, and manure) trading banks do not have to refer to the Reserve Bank for an exchange allocation.
Section 29 on Banking and Currency contains detailed information on the exchange allocation system.
BOARD OF TRADE - In May 1950 an Import Advisory Committee was established to examine questions relating to import control and associated matters and to make recommendations thereon to the Minister of Customs. The committee comprised a chairman and three members. As a result of the committee's recommendations, many items were exempted from import licensing on non-scheduled countries and a number of reforms were made in the import licensing system.
In December 1950 the Board of Trade Act 1950 was passed. This Act provided for the establishment of a Board of Trade to consist of not more than four members. From 1950 until November 1957 the membership of the Board comprised a chairman and two other members, each of whom had been a member of the Import Advisory Committee. A fourth member was appointed to the Board in November 1957. Since July 1959, however, the Board has consisted of a chairman and two members. Members are appointed by the Governor-General on the recommendation of the Minister of Customs for a term of three years and may from time to time be reappointed. The Board has the powers of a Commission of Inquiry under the Commissions of Inquiry Act 1908, and may hold public inquiries and summon persons to give evidence.
The Board's principal function is to make recommendations, within the scope of the legislation, to the Minister of Customs, but it may also, when requested by the Minister of Customs, make recommendations to other Ministers. The advisory functions of the Board include the economic aspects of such matters as the rates of customs duties and the general effect of the operation of the Tariff; the maintenance and expansion of existing industries and the development of new industries; the administration of the licensing of imports and the licensing of exports (except in relation to agricultural or pastoral products) and applications and appeals relating thereto; international trade agreements and conferences; and the marketing and distribution of products and the obtaining of raw materials and other goods for use in industry, except as may be specially provided in any other Act in respect of any particular industry or product.
As a result of the Board's recommendations, many additional items, covering a wide field, were removed from import licensing, and control was also relaxed on some other items. Prior to making its recommendations, the Board considered whether additional tariff protection was required and in some cases the tariff was increased.
An important part of the functions of the Import Advisory Committee, and then of the Board of Trade in relation to import licensing, concerned motor vehicles.
On 21 March 1956 Government informed the Board that it should undertake a general review of the Customs Tariff in place of the individual industry-by-industry inquiries and that, until completed, this would be the Board's major work. For the duration of the review, the then Comptroller of Customs would be associated with the Board. The terms of reference for the general review were as follows: “To inquire into the Customs Tariff of New Zealand and to recommend for consideration of the Government any alterations therein having regard to existing trade agreements to which New Zealand is a party; to the general financial, economic, and industrial conditions in, and requirements of, New Zealand; and to the interests of the primary and manufacturing industries, and of consumers.” Government also asked the Board to report particularly on the desirability of (i) changing the basis of value for duty from current domestic value plus 10 per cent to current domestic value or f.o.b. price, whichever is higher, and the abolition of the 10 per cent by a corresponding increase in the rates of duty; (ii) abolishing primage duty and surtax; and (iii) bringing the Tariff more into line with the Brussels Tariff Nomenclature.
The Board was occupied principally on the review throughout the remainder of 1956 and 1957.
Changes in the Customs Tariff made by Government in July 1960 were based, in many instances, on recommendations made by the Board following the completion of the review.
In July 1958 the Board, on the request of Government, undertook an investigation into the supply of building materials used in New Zealand, with a view principally to reducing the quantity and value of imports of these materials, to encouraging the use of locally produced materials, and to reducing the costs of building.
From 1958 to 1960, following appropriate inquiries, the Board has made recommendations to the Minister of Customs upon a number of Tariff matters, the availability of supplies of motor vehicle spare parts, and upon the practicability of instituting a system of recording forward commitments of exchange for imports. In addition the Board has examined and made recommendations on import licensing appeals and on certain import licensing allocations which have been referred to it by the Minister of Customs.
TRADE COMMISSIONER SERVICE - Facilities for the promotion of overseas trade are provided by the Department of Industries and Commerce through the service of Trade Commissioners, who are stationed in 13 posts - Sydney, Melbourne, Singapore, Kuala Lumpur, Hong Kong, Tokyo, New Delhi, London, New York, Washington, San Francisco, Montreal, and Trinidad. While this representation is modest in comparison with other countries, it reflects the country's growing interest in the desirability of diversifying export markets. This is further exemplified by the fact that six posts have been established in the last five years: New York and Singapore in 1956, Trinidad in 1958, San Francisco and Kuala Lumpur in 1959, and Hong Kong in 1960. In most instances Trade Commissioners have appropriate diplomatic or consular status in the countries to which they are accredited.
While the selling of goods in overseas markets is basically the responsibility of New Zealand exporters, the Trade Commissioner can be of considerable help in conducting market surveys and supplying information on import and exchange restrictions, Customs duty, sales tax, normal sources of supply (local production and imported), marketing methods, freight rates, statutory or customary requirements for packing, labelling, etc., and reliable importers in his territory. He may also assist New Zealand importers to locate new sources of supply of essential commodities. New Zealand businessmen travelling overseas may be saved much time and trouble by enlisting the services of the Trade Commissioner, whose knowledge of local conditions and whose connections with businessmen and Government officials in his territory enable him to give valuable advice. His task is made easier if he is given adequate notice of the visit.
The Trade Commissioner keeps a careful watch on the pattern of New Zealand trade with his territory and reports on significant changes. Where imports from New Zealand are affected, for example, by a new interpretation of an agricultural inspection regulation, or by the imposition of import restrictions, the Trade Commissioner is often called upon to make representations at the official level.
Trade Commissioners are also engaged in numerous other activities, some of which are: representing New Zealand at international conferences, reporting on economic and industrial developments in their territories, acting on behalf of Government Departments in the procurement of stores, payment of accounts, etc., and maintaining liaison where they are stationed with business and Government circles.
Business men may write for information direct to the New Zealand Trade Commissioner in the country concerned but, where convenient, it is preferred that requests be made through the Secretary, Department of Industries and Commerce, Wellington, who is often able to give preliminary advice and assistance.
Overseas representatives are listed in Section 40, Official.
GENERAL - In New Zealand the Customs Department requires for every package exported a declared statement of the contents, value, and destination, and the export statistics are compiled from the analysis and totals of these statements.
Exports are valued in New Zealand currency “free on board at the port of shipment”, except re-exports ex bonded warehouse or under drawback of duty, which are recorded at the original import values. Where goods are not sold till arrival at their destination, values are assessed at current prices at time of shipment. Meat and dairy-produce exports are valued like other commodities, on the basis of overseas realisation, not on the basis of the prices payable to producers under the internal purchasing procedures. Wool acquired under the wartime appraisal scheme and subsequently exported to be auctioned overseas was valued on export at appraisal prices, not ruling prices at the time of export.
The ultimate destination of the goods is distinguished as far as practicable, but it is impossible to discover what proportion of the exports is intended for home consumption in the country of destination. The trade records distinguish between exports of New Zealand produce and re-exports of imported goods.
CLASSIFICATION OF EXPORTS - The table following gives merchandise exports (i.e., excluding specie) for the latest 11 years for the four main commodity groups.
| Year | Dairy Produce | Meat | Wool | Hides, Skins, and Pelts | Total Merchandise Exports* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Including other commodities, among them uncoined gold and silver. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1949 | 51,867 | 30,439 | 46,554 | 6,679 | 147,281 |
| 1950 | 54,612 | 32,302 | 74,653 | 9,996 | 183,752 |
| 1951 | 63,324 | 31,302 | 128,176 | 12,862 | 248,127 |
| 1952 | 79,856 | 50,445 | 81,998 | 9,949 | 240,561 |
| 1953 | 77,684 | 47,826 | 84,598 | 10,692 | 235,860 |
| 1954 | 66,798 | 59,556 | 88,437 | 10,449 | 244,466 |
| 1955 | 70,423 | 68,190 | 93,887 | 9,223 | 259,289 |
| 1956 | 82,223 | 71,079 | 91,532 | 10,606 | 277,483 |
| 1957 | 66,292 | 70,706 | 105,959 | 10,117 | 276,569 |
| 1958 | 58,502 | 79,518 | 80,037 | 8,317 | 250,173 |
| 1959 | 88,514 | 76,869 | 89,643 | 13,254 | 293,659 |
The commodity groups shown above normally account for more than 90 per cent of the total value of merchandise exports.
The relative importance of dairy produce, meat, and wool as the main individual constituents of New Zealand's export trade has varied considerably, as is seen from the figures in the preceding table. In the preceding subsection is set out a table of volume index numbers for these commodities. A table showing the export price index numbers and terms of trade is given in Section 23, Prices.
New Zealand's reliance upon grassland farming for her exports is brought out by the figures in the next table showing total exports of pastoral products and the percentage which they represent of the total exports of New Zealand produce.
EXPORTS OF PASTORAL PRODUCTS
| Year | Value | Percentage* |
|---|---|---|
| *Of total exports of New Zealand produce. | ||
| £(000) | ||
| 1938 | 54,299 | 93.9 |
| 1939 | 53,744 | 93.6 |
| 1940 | 69,057 | 94.6 |
| 1941 | 62,238 | 93.0 |
| 1942 | 74,361 | 92.3 |
| 1943 | 61,029 | 86.9 |
| 1944 | 58,948 | 82.2 |
| 1945 | 68,112 | 87.0 |
| 1946 | 89,582 | 89.3 |
| 1947 | 120,342 | 94.2 |
| 1948 | 137,750 | 94.0 |
| 1949 | 138,702 | 95.0 |
| 1950 | 174,399 | 95.7 |
| 1951 | 239,137 | 97.1 |
| 1952 | 228,179 | 95.7 |
| 1953 | 223,746 | 95.8 |
| 1954 | 229,204 | 94.6 |
| 1955 | 246,093 | 95.7 |
| 1956 | 259,667 | 94.4 |
| 1957 | 257,676 | 93.9 |
| 1958 | 231,283 | 93.3 |
| 1959 | 273,271 | 93.9 |
Of exports other than pastoral the principal ones of economic significance are: frozen fish and crayfish tails and fish-liver oils; timber, mainly of exotic species, both sawn and in logs, and timber manufactures such as wood pulp and paper; fresh apples, canned and frozen vegetables, peas, and grass and clover seed. The export of scrap metal, which has been of importance in recent years, has been prohibited since January 1961.
Quantity figures of exports of the principal items of New Zealand produce are next given for the years 1957 to 1959, while the Statistical Summary, towards the end of the book, shows the figures for some of the more important commodities for the last 50 years. For some purposes, especially for comparisons between recent and more remote years, quantities are preferable to values, since the latter are affected by price variations.
| Commodity (New Zealand Produce) | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mining products – | ||||
| Coal | (ton) | 2,902 | 580 | 7,140 |
| Pumice | (cwt) | 31,382 | 21,632 | 22,968 |
| Gold | (oz) | 26,769 | 19,392 | 30,333 |
| Scheelite | (ton) | 15 | 11 | 14 |
| Cement | (cwt) | 2,390 | 140 | 1,355 |
| Fishery products – | ||||
| Fish, fresh and frozen | (cwt) | 65,466 | 47,084 | 58,235 |
| Fish, other | (cwt) | 415 | 597 | 729 |
| Crayfish | (cwt) | 38,981 | 23,301 | 21,200 |
| Whale oil | (gal) | 348,845 | 445,725 | 264,892 |
| Fish oils and fish-liver oils | (gal) | 13,270 | 10,437 | 7,763 |
| Forest products – | ||||
| Kauri gum | (ton) | 197 | 180 | 81 |
| Timber – | ||||
| Sawn | (sup. ft.) | 27,811,622 | 35,194,070 | 46,542,864 |
| For cases in shooks | (sup. ft.) | 2,112,391 | 4,881,496 | 4,540,241 |
| Wood pulp | (ton) | 64,994 | 68,963 | 76,826 |
| Newsprint | (cwt) | 718,134 | 834,743 | 873,244 |
| Building board | (sq. ft.) | 736,805 | 1,133,000 | 1,952,162 |
| Plywood | (sq.ft.) | 8,078 | 17,453 | 35,985 |
| Logs, radiata pine | (cu. ft.) | 1,137,712 | 5,012,715 | |
| Pastoral products – | ||||
| Butter | (cwt) | 2,901,499 | 3,507,844 | 3,859,564 |
| Casein | (cwt) | 282,567 | 401,286 | 583,603 |
| Cheese | (cwt) | 1,769,529 | 1,788,554 | 1,669,044 |
| Milk, dried and condensed | (cwt) | 1,354,217 | 1,060,610 | 1,407,588 |
| Sugar of milk | (cwt) | 87,275 | 59,838 | 93,439 |
| Eggs – | ||||
| In shell | (doz) | 35,738 | 48,646 | 55,834 |
| Not in shell | (lb) | 418,282 | 3,072 | 385,745 |
| Honey | (lb) | 2,085,374 | 2,980,069 | 1,493,439 |
| Meat, frozen and dulled | (cwt) | 7,768,919 | 8,108,010 | 8,694,780 |
| Meat, canned | (cwt) | 102,851 | 68,864 | 63,991 |
| Meat extract | (lb) | 415,735 | 369,233 | 312,335 |
| Other preserved meat | (cwt) | 14,264 | 14,040 | 14,576 |
| Sausage casings | (lb) | 6,981,205 | 7,371,644 | 9,094,268 |
| Liver meal | (cwt) | 33,044 | 34,682 | 38,783 |
| Cattle hides | (number) | 905,523 | 904,102 | 880,424 |
| Horse hides | (number) | 10,563 | 9,669 | 9,294 |
| Calfskins | (number) | 1,280,316 | 1,015,100 | 963,122 |
| Deer skins | (number) | 62,451 | 53,683 | 59,046 |
| Opossum skins | (number) | 334,144 | 291,290 | 321,047 |
| Rabbit skins | (number) | 68,690 | - | - |
| Sheep skins and pelts | (number) | 19,811,369 | 20,593,518 | 25,867,922 |
| Hair | (cwt) | 792 | 768 | 594 |
| Wool | (lb) | 431,529,366 | 456,927,692 | 528,664,167 |
| Inedible offals (including dried blood) | (cwt) | 117,220 | 130,571 | 142,844 |
| Lard | (cwt) | 12,201 | 14,137 | 17,102 |
| Edible tallow | (cwt) | 186,137 | 225,801 | 227,894 |
| Edible Stearine | (cwt) | 15,597 | 13,678 | 11,551 |
| Inedible tallow | (ton) | 36,900 | 39,970 | 42,164 |
| Neatsfoot oil | (gal) | 124,869 | 90,986 | 127,228 |
| Live cattle | (number) | 179 | 1,462 | 1,025 |
| Live sheep | (number) | 5,401 | 834 | 1,366 |
| Live horses | (number) | 362 | 354 | 451 |
| Agricultural products – | ||||
| Apples | (lb) | 56,006,800 | 68,992,960 | 70,483,880 |
| Pears | (lb) | 1,382,230 | 4,144,495 | 6,270,360 |
| Hops | (lb) | 320,864 | 90,121 | 332 |
| Potatoes | (ton) | 2,010 | 2,786 | 2,700 |
| Onions | (ton) | 1,416 | 1,969 | 3,038 |
| Canned vegetables | (lb) | 8,070,958 | 6,619,705 | 4,379,671 |
| Frozen vegetables | (cwt) | 34,921 | 37,178 | 41,902 |
| Peas, food | (cental) | 111,048 | 142,851 | 149,731 |
| Peas, seed | (cental) | 190,024 | 177,337 | 151,700 |
| Seeds, grass and clover | (cwt) | 162,552 | 148,230 | 91,221 |
| Linen flax | (cwt) | - | 133 | 418 |
| Miscellaneous – | ||||
| Biscuits | (cwt) | 3,393 | 3,040 | 1,601 |
| Ale, beer, stout | (gal) | 209,367 | 256,553 | 170,682 |
| Sugar | (cwt) | 6,313 | 3,123 | 2,046 |
| Cigarettes | (lb) | 12,172 | 16,616 | 17,906 |
| Cut tobacco | (lb) | 203,655 | 212,048 | 252,224 |
| Textile waste | (lb) | 2,146,521 | 1,983,731 | 2,415,686 |
| Soaps | (lb) | 1,219,766 | 1,416,642 | 1,425,017 |
| Scrap metal | (ton) | 92,885 | 64,749 | 55,899 |
| Chamois leather | (sq ft) | 315,015 | 221,938 | 227,016 |
The values of the principal exports are given in the following table.
| Commodity (New Zealand Produce) | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining products – | £ | £ | £ |
| Coal | 10,474 | 3,511 | 28,326 |
| Pumice | 16,100 | 11,698 | 12,242 |
| Gold | 310,951 | 232,364 | 364,479 |
| Scheelite | 7,736 | 2,761 | 3,129 |
| Cement | 1,588 | 106 | 925 |
| Fishery products – | |||
| Fish, fresh and frozen | 553,518 | 428,097 | 493,309 |
| Fish, other | 11,354 | 16,454 | 19,682 |
| Fish soups and other products | 2,522 | 1,163 | 937 |
| Crayfish | 1,345,980 | 811,195 | 739,533 |
| Whale oil | 106,966 | 110,047 | 63,942 |
| Fish oils and fish-liver oils | 27,843 | 42,418 | 44,382 |
| Forest products – | |||
| Kauri gum | 28,196 | 20,885 | 13,085 |
| Timber – | |||
| Sawn | 787,930 | 1,032,131 | 1,424,110 |
| For cases in shooks | 107,589 | 272,636 | 245,653 |
| Wood pulp | 2,625,772 | 2,725,019 | 2,920,728 |
| Newsprint | 2,169,542 | 2,631,855 | 2,716,489 |
| Other paper and paper board | 269,644 | 253,298 | 363,475 |
| Building board | 12,731 | 19,119 | 32,489 |
| Plywood | 629 | 1,071 | 2,059 |
| Logs, radiata pine | 133,462 | 535,450 | |
| Pastoral products – | |||
| Butter | 38,455,960 | 38,850,362 | 55,807,901 |
| Casein | 2,236,996 | 3,109,633 | 4,402,830 |
| Cheese | 17,922,774 | 12,401,609 | 22,103,108 |
| Milk, dried and condensed | 5,741,428 | 3,806,182 | 5,728,978 |
| Sugar of milk | 436,535 | 322,467 | 457,891 |
| Other dairy produce | 1,408,685 | 11,466 | 13,538 |
| Eggs – | |||
| In shell | 8,403 | 12,001 | 11,672 |
| Not in shell | 41,272 | 500 | 35,339 |
| Honey | 133,368 | 173,734 | 80,594 |
| Meat, frozen and chilled | 64,077,636 | 73,489,818 | 71,250,496 |
| Meat, canned | 1,643,038 | 1,257,925 | 1,248,294 |
| Meat extract | 162,597 | 114,999 | 63,125 |
| Other preserved meat | 170,544 | 173,424 | 174,912 |
| Sausage casings | 4,652,295 | 4,481,649 | 4,131,924 |
| Liver meal | 86,129 | 83,297 | 132,156 |
| Cattle hides | 2,283,223 | 2,148,850 | 3,162,771 |
| Horse hides | 20,032 | 17,808 | 25,490 |
| Calfskins | 957,437 | 843,603 | 1,304,829 |
| Deer skins | 69,539 | 45,534 | 61,699 |
| Opossum skins | 100,143 | 94,474 | 117,767 |
| Rabbit skins | 1,734 | - | - |
| Sheep skins and pelts | 6,620,865 | 5,085,450 | 8,457,271 |
| Hair | 23,142 | 20,366 | 13,620 |
| Wool | 105,958,787 | 80,036,777 | 89,643,287 |
| Inedible offals (including dried blood) | 518,924 | 417,408 | 556,625 |
| Lard | 76,759 | 84,407 | 98,251 |
| Edible tallow | 647,565 | 784,579 | 790,922 |
| Edible stearine | 62,856 | 54,424 | 45,953 |
| Inedible tallow | 2,385,613 | 2,628,925 | 2,492,144 |
| Neatsfoot oil | 46,378 | 32,837 | 50,629 |
| Live cattle | 29,238 | 108,701 | 32,838 |
| Live sheep | 176,137 | 49,586 | 25,677 |
| Live horses | 243,028 | 273,856 | 301,953 |
| Agricultural products – | |||
| Apples | 1,758,670 | 2,159,091 | 2,204,556 |
| Pears | 42,851 | 130,249 | 196,424 |
| Hops | 76,812 | 22,607 | 112 |
| Potatoes | 65,454 | 62,970 | 66,909 |
| Onions | 47,489 | 47,430 | 99,890 |
| Canned vegetables | 387,320 | 315,335 | 216,385 |
| Frozen vegetables | 307,697 | 311,533 | 399,600 |
| Peas, food | 263,574 | 301,712 | 306,030 |
| Peas, seed | 625,812 | 525,793 | 426,409 |
| Seeds, grass and clover | 1,189,605 | 1,517,710 | 988,271 |
| Other seeds | 45,907 | 44,944 | 45,792 |
| Linen flax | 660 | 2,087 | |
| Miscellaneous – | |||
| Biscuits | 24,904 | 29,658 | 19,738 |
| Ale, beer, stout | 65,019 | 82,370 | 60,673 |
| Sugar | 20,580 | 10,843 | 6,874 |
| Soups | 341 | 826 | 947 |
| Infant and invalid food (cereal) | 68,538 | 27,439 | 19,146 |
| Cigarettes | 10,207 | 17,184 | 17,760 |
| Cut tobacco | 54,087 | 57,313 | 90,528 |
| Textile waste | 186,664 | 139,109 | 178,888 |
| Soaps | 48,094 | 51,941 | 53,288 |
| Scrap metal | 1,860,721 | 897,738 | 695,025 |
| Dairy machinery | 93,211 | 71,438 | 88,894 |
| Chamois leather | 28,818 | 23,732 | 28,792 |
| Vitamins and concentrates | 21,011 | 30,140 | 19,185 |
| Washing machines | 19,146 | 25,980 | 8,147 |
| Other New Zealand produce | 1,196,530 | 1,312,531 | 1,908,809 |
| Totals, New Zealand produce | 274,305,187 | 247,984,217 | 290,998,067 |
In the two preceding tables commodities are grouped according to the sector of origin. However, for general statistical purposes New Zealand has, since 1955, used the Standard International Trade Classification when classifying the import and export trade of New Zealand. In the following tables the export trade is classified into the sections and divisions of this international classification.
The next table gives such information for the years 1957-59.
| Exports - Section and Division | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 0. Food | |||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Div. 00 Live animals chiefly for food | 208 | 160 | 61 |
| Div. 01 Meat and meat preparations | 70,706 | 79,519 | 76,869 |
| Div. 02 Dairy produce, eggs, and honey | 63,713 | 55,257 | 83,782 |
| Div. 03 Fish and fish preparations | 1,919 | 1,260 | 1,256 |
| Div. 04 Cereals and cereal preparations | 114 | 65 | 47 |
| Div. 05 Fruits and vegetables | 2,993 | 3,401 | 3,530 |
| Div. 06 Sugar and sugar preparations | 462 | 340 | 472 |
| Div. 07 Coffee, tea, cocoa, spices, and manufactures thereof | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| Div. 08 Feeding stuff for animals (not including unmilled cereals) | 215 | 197 | 350 |
| Div. 09 Miscellaneous food preparations | 785 | 935 | 929 |
| Totals, Section 0 | 141,120 | 141,138 | 167,297 |
| Section 1. Beverages and Tobacco | |||
| Div. 11 Beverages | 96 | 109 | 88 |
| Div. 12 Tobacco and tobacco manufactures | 98 | 100 | 134 |
| Totals, Section 1 | 194 | 209 | 222 |
| Section 2. Crude Materials, Inedible, Except Fuels | |||
| Div. 21 Hides, skins, and fur skins, undressed | 10,117 | 8,318 | 13,254 |
| Div. 22 Oil seeds, oil nuts, and kernels | - | - | 13 |
| Div. 23 Crude rubber, including synthetic and reclaimed | - | - | |
| Div. 24 Wood, lumber, and cork | 791 | 1,166 | 1,960 |
| Div. 25 Pulp and waste paper | 2,635 | 2,735 | 2,943 |
| Div. 26 Textile fibres (not manufactured into yarn, thread, or fabrics and waste) | 106,254 | 80,227 | 89,926 |
| Div. 27 Crude fertilisers and crude minerals, excluding coal, petroleum, and precious stones | 76 | 80 | 97 |
| Div. 28 Metalliferous ores and metal scrap | 1,873 | 900 | 698 |
| Div. 29 Animal and vegetable crude materials, inedible, n.e.i. | 2,518 | 2,646 | 2,076 |
| Totals, Section 2 | 124,265 | 96,072 | 110,967 |
| Section 3. Mineral Fuels, Lubricants, and Related Materials | |||
| Div. 31 Mineral fuels, lubricants, and related materials | 670 | 821 | 840 |
| Totals, Section 3 | 670 | 821 | 840 |
| Section 4. Animal and Vegetable Oils and Fats | |||
| Div. 41 Animal and vegetable oils (not essential oils), fats, greases, and derivatives | 2,657 | 2,887 | 2,720 |
| Totals, Section 4 | 2,657 | 2,887 | 2,720 |
| Section 5. Chemicals | |||
| Div. 51 Chemical elements and compounds | 41 | 53 | 84 |
| Div. 52 Mineral tar and crude chemicals from coal, petroleum, and natural gas | - | ||
| Div. 53 Dyeing, tanning, and colouring materials | 42 | 30 | 35 |
| Div. 54 Medicinal and pharmaceutical products | 92 | 95 | 94 |
| Div. 55 Essential oils and perfume materials, toilet, polishing, and cleansing preparations | 60 | 61 | 64 |
| Div. 56 Fertilisers, manufactured | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Div. 59 Explosives and miscellaneous chemical materials and products | 2,327 | 3,251 | 4,603 |
| Totals, Section 5 | 2,565 | 3,494 | 4,881 |
| Section 6. Manufactured Goods Classified Chiefly by Material | |||
| Div. 61 Leather, leather manufactures n.e.i., and dressed furs | 76 | 48 | 98 |
| Div. 62 Rubber manufactures n.e.i. | 53 | 91 | 123 |
| Div. 63 Wood and cork manufactures (excluding furniture) | 135 | 305 | 294 |
| Div. 64 Paper, paperboard, and manufactures thereof | 2,536 | 2,992 | 3,212 |
| Div. 65 Textile yarn, fabrics, made-up articles, and related products | 118 | 65 | 81 |
| Div. 66 Non-metallic mineral manufactures n.e.i. | 41 | 25 | 33 |
| Div. 67 Silver, platinum, gems, and jewellery | 41 | 6 | 15 |
| Div. 68 Base metals | 63 | 52 | 179 |
| Div. 69 Manufactures of metal | 328 | 416 | 583 |
| Totals, Section 6 | 3,390 | 3,999 | 4,619 |
| Section 7. Machinery and Transport Equipment | |||
| Div. 71 Machinery other than electric | 498 | 416 | 591 |
| Div. 72 Electric machinery, apparatus, and appliances | 136 | 138 | 174 |
| Div. 73 Transport equipment | 231 | 230 | 372 |
| Totals, Section 7 | 865 | 783 | 1,136 |
| Section 8. Miscellaneous Manufactured Articles | |||
| Div. 81 Prefabricated buildings, sanitary, plumbing, heating and lighting fixtures, and fittings | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| Div. 82 Furniture and fixtures | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Div. 83 Travel goods, handbags, and similar articles | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Div. 84 Clothing | 9 | 7 | 25 |
| Div. 85 Footwear | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Div. 86 Professional, scientific, and controlling instruments; photographic and optical goods, watches, and clocks | 62 | 55 | 58 |
| Div. 89 Miscellaneous manufactured articles n.e.i. | 135 | 103 | 123 |
| Totals, Section 8 | 226 | 188 | 232 |
| Section 9. Miscellaneous Transactions and Commodities n.e.i. | |||
| Div. 92 Live animals, not for food | 247 | 278 | 307 |
| Div. 93 Returned goods and special transactions | 2 | 7 | 3 |
| Div. 95 Unclassified goods under £10 in value | 59 | 63 | 70 |
| Div 99 Gold | 311 | 233 | 365 |
| Totals, Section 9 | 618 | 582 | 744 |
| Grand totals, merchandise exports | 276,569 | 250,173 | 293,659 |
DESTINATION OF NEW ZEALAND EXPORTS - Since the 1850s the United Kingdom has been New Zealand's principal trading partner, replacing Australia, which took the bulk of the trade in the early days of settlement. The proportion of our exports going to the United Kingdom market in the years prior to the Second World War was between 70 and 80 per cent of the total value of all exports. With the growing diversification of our markets in recent years the proportion of New Zealand's exports going to this market has fallen and by 1959 represented only 57 per cent of the total value of all exports.
Trade with the Commonwealth countries has always greatly exceeded that with foreign countries. During recent years, however, there has been a decline in the proportion of the export trade going to Commonwealth countries, occasioned mainly by the export of wool to European countries and meat to the United States of America. In 1948 Commonwealth countries took 80 per cent of the total exports. By 1959 this proportion had fallen to 64 per cent.
In recent years trade has been recorded with over 100 countries each year.
The principal destinations of New Zealand's exports of merchandise (including re-exports) during the last 21 years are given in the table below. The nomenclature used in this and subsequent tables in regard to the countries of destination refers generally to status and territories in the years indicated and not necessarily to the present position.
| Year | United Kingdom | Canada | Australia | France | Germany* | United States of America | Other Countries† | Total Merchandise Exports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Figures for post-war years represent German Federal Republic only. † Including ships' stores. | ||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1939 | 46,689 | 964 | 2,256 | 1,579 | 390 | 2,847 | 3,324 | 58,049 |
| 1940 | 64,129 | 1,709 | 2,159 | 717 | - | 2,826 | 2,201 | 73,741 |
| 1941 | 52,396 | 2,822 | 2,400 | - | - | 5,191 | 4,671 | 67,479 |
| 1942 | 60,471 | 3,617 | 2,718 | - | - | 5,990 | 8,489 | 81,285 |
| 1943 | 46,368 | 4,535 | 2,849 | - | - | 6,385 | 11,725 | 71,863 |
| 1944 | 55,427 | 1,940 | 3,093 | - | - | 5,063 | 12,265 | 77,787 |
| 1945 | 58,643 | 2,251 | 4,195 | 47 | - | 7,985 | 8,510 | 81,631 |
| 1946 | 70,924 | 2,803 | 3,631 | 3,465 | 1,639 | 9,716 | 9,124 | 101,302 |
| 1947 | 98,698 | 3,060 | 4,096 | 4,447 | 78 | 8,174 | 10,866 | 129,420 |
| 1948 | 107,915 | 2,991 | 3,954 | 8,308 | 2,725 | 7,273 | 14,655 | 147,821 |
| 1949 | 107,706 | 2,196 | 3,748 | 7,658 | 2,994 | 5,492 | 17,488 | 147,281 |
| 1950 | 121,685 | 3,557 | 4,779 | 8,077 | 5,939 | 18,387 | 21,327 | 183,752 |
| 1951 | 142,362 | 8,565 | 5,113 | 17,854 | 8,836 | 28,859 | 36,538 | 248,127 |
| 1952 | 156,485 | 5,212 | 3,930 | 10,559 | 5,227 | 27,267 | 31,880 | 240,561 |
| 1953 | 158,047 | 2,958 | 4,655 | 15,684 | 6,084 | 18,379 | 30,053 | 235,860 |
| 1954 | 163,300 | 2,997 | 6,445 | 14,675 | 10,491 | 13,896 | 32,663 | 244,466 |
| 1955 | 169,657 | 4,230 | 6,692 | 15,287 | 12,688 | 15,100 | 35,635 | 259,289 |
| 1956 | 178,756 | 4,026 | 8,431 | 16,761 | 10,403 | 19,508 | 39,598 | 277,483 |
| 1957 | 162,131 | 4,435 | 10,113 | 21,697 | 12,260 | 21,730 | 44,203 | 276,569 |
| 1958 | 139,105 | 4,066 | 10,266 | 14,680 | 7,028 | 36,449 | 38,579 | 250,173 |
| 1959 | 165,657 | 3,054 | 10,944 | 17,243 | 9,693 | 43,057 | 44,011 | 293,659 |
The statistics quoted in the foregoing table indicate the destination of New Zealand exports as recorded by the Customs Department. In some instances the ultimate destination of exports is not known at the time of export, such goods being entered as exported to the country to which they are being shipped. This applies more particularly to wool, considerable quantities of which are shipped to the United Kingdom, and, in normal times subsequently re-exported to the Continent. It should be observed, however, that in all instances where the final destination is known at the time of export, the exports are credited to that destination in the New Zealand trade statistics. It is possible, of course, that the destination of goods may be changed while in transit; and this, in fact, happens occasionally. In such cases the actual destination will be different from that to which the goods have been credited in the statistics; however it is quite impossible to keep a record of all movements of this nature.
A further point of some importance is the fact that an appreciable quantity of wool is exported on an “optional” basis - United Kingdom, option Continent. In these cases, however, subsequent information is received by the Customs Department as to the actual destination of the goods, and the entries are amended.
It will be realised, therefore, that the actual final destinations of New Zealand exports may vary appreciably from the classification shown in the table. For these reasons it is probable that exports to Continental countries are normally somewhat higher than the figures indicate; conversely, exports to the United Kingdom for retention in that country are lower than the totals quoted in the table.
In the following table figures are given for the value of New Zealand's export trade to European countries during the period 1955-59, together with figures to show the importance of wool as the chief commodity in the trade.
| Country | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Austria | 26,053 | 16,703 | 48,930 | 7,922 | 32,433 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 4,635,280 | 5,726,036 | 6,317,641 | 4,501,704 | 5,203,885 |
| Bulgaria | 54 | 163,186 | 13,531 | 166,106 | 139,842 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1,664,781 | 1,775,771 | 972,666 | 987,774 | 1,366,757 |
| Denmark | 386,410 | 438,685 | 536,852 | 526,152 | 396,216 |
| Finland | 48,530 | 126,703 | 62,648 | 66,189 | 175,639 |
| France | 15,286,920 | 16,761,132 | 21,696,762 | 14,679,704 | 17,243,003 |
| German Federal Republic | 12,687,693 | 10,403,379 | 12,259,675 | 7,027,607 | 9,692,779 |
| German Democratic | |||||
| Republic | 914 | 162 | - | - | 3,435 |
| Greece | 454,300 | 757,872 | 225,701 | 389,818 | 322,340 |
| Hungary | 240 | 491 | 11,354 | 100 | 94 |
| Italy | 4,736,938 | 6,657,812 | 6,217,755 | 6,230,525 | 6,007,571 |
| Netherlands | 4,516,066 | 4,617,445 | 4,086,487 | 2,982,440 | 4,179,432 |
| Norway | 111,620 | 51,991 | 53,307 | 60,947 | 158,781 |
| Poland | 2,702,123 | 2,209,695 | 2,988,984 | 2,527,526 | 1,263,988 |
| Portugal | 44,784 | 77,344 | 203,778 | 384,668 | 382,056 |
| Rumania | 332 | 93,106 | - | 22,528 | - |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 2,166,134 | 2,048,688 | 2,680,694 | 687,816 | 152,279 |
| Spain | 170,362 | 21,181 | 7,678 | 6,756 | 80,532 |
| Sweden | 462,981 | 708,206 | 511,182 | 700,996 | 697,393 |
| Switzerland | 427,436 | 147,965 | 77,031 | 55,924 | 40,092 |
| Turkey | 36 | 25 | - | 137,939 | 2,462 |
| Yugoslavia | 20,107 | 10,926 | 68,783 | 81,334 | 239,423 |
| Totals | 50,550,094 | 52,814,484 | 59,041,439 | 42,232,475 | 47,780,432 |
| Per Cent | |||||
| Percentage of total New Zealand exports taken by European countries (value basis) | 19.50 | 19.03 | 21.35 | 16.88 | 16.27 |
| Value (£) | |||||
| Value of wool exported to European countries | 37,477,865 | 39,152,907 | 49,875,455 | 34,815,615 | 36,388,916 |
| Per Cent | |||||
| Percentage of wool exports to total exports to European countries (value basis) | 74.14 | 74.13 | 84.48 | 82.44 | 76.16 |
| Percentage of total New Zealand wool exports taken by European countries (value basis) | 39.92 | 42.78 | 47.07 | 43.50 | 40.59 |
22*
The table which follows shows for each of the last 11 years the percentage of total exports (excluding specie and ships' stores) taken by each of the principal countries trading with New Zealand.
| Country | 1949 | 1950 | 1951 | 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | |||||||||||
| British Commonwealth – | |||||||||||
| United Kingdom | 73.38 | 66.44 | 57.57 | 65.33 | 67.21 | 66.98 | 65.59 | 64.58 | 58.79 | 55.78 | 56.56 |
| India | 0.60 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.63 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.30 | 0.23 |
| Pakistan | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Canada | 1.50 | 1.94 | 3.50 | 2.18 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 1.64 | 1.45 | 1.61 | 1.63 | 1.04 |
| Australia | 2.56 | 2.61 | 2.07 | 1.64 | 1.98 | 2.64 | 2.59 | 3.05 | 3.67 | 4.12 | 3.74 |
| Other | 1.34 | 1.19 | 1.38 | 2.19 | 2.25 | 2.42 | 2.24 | 2.32 | 2.09 | 2.73 | 2.90 |
| Totals | 79.43 | 72.71 | 64.97 | 72.05 | 73.30 | 73.81 | 72.81 | 71.95 | 66.77 | 64.57 | 64.49 |
| European Economic Community – | |||||||||||
| Netherlands | 1.66 | 1.87 | 1.32 | 0.85 | 1.04 | 1.67 | 1.75 | 1.67 | 1.48 | 1.20 | 1.43 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 1.24 | 1.61 | 2.12 | 1.25 | 1.48 | 1.40 | 1.79 | 2.07 | 2.29 | 1.81 | 1.78 |
| France | 5.22 | 4.41 | 7.22 | 4.41 | 6.67 | 6.02 | 5.91 | 6.06 | 7.87 | 5.89 | 5.89 |
| German Federal Republic | 2.04 | 3.24 | 3.57 | 2.18 | 2.59 | 4.30 | 4.91 | 3.76 | 4.45 | 2.82 | 3.31 |
| Italy | 0.98 | 1.04 | 1.56 | 1.82 | 2.10 | 1.75 | 1.83 | 2.41 | 2.25 | 2.50 | 2.05 |
| Totals | 11.14 | 12.17 | 15.79 | 10.51 | 13.88 | 15.14 | 16.19 | 15.97 | 18.34 | 14.22 | 14.46 |
| Other countries – | |||||||||||
| Poland | 0.82 | 0.85 | 2.96 | 1.24 | 1.54 | 0.93 | 1.04 | 0.80 | 1.08 | 1.01 | 0.43 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 1.98 | 0.56 | 0.50 | - | - | 1.21 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.97 | 0.28 | 0.05 |
| Egypt | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.06 |
| Japan | 0.53 | 0.54 | 1.55 | 1.46 | 1.33 | 0.52 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 2.84 | 2.21 | 2.28 |
| United States or America | 3.75 | 10.04 | 11.67 | 11.38 | 7.82 | 5.70 | 5.84 | 7.05 | 7.88 | 14.61 | 14.70 |
| Remaining countries | 2.18 | 3.05 | 2.42 | 3.30 | 2.07 | 2.63 | 2.37 | 2.28 | 2.09 | 2.97 | 3.53 |
| Totals | 9.43 | 15.12 | 19.24 | 17.44 | 12.82 | 11.05 | 11.00 | 12.08 | 14.89 | 21.21 | 21 05 |
Exports to Each Country, 1957-59 – The table following shows exports (including re-exports, but excluding specie) according to the countries of destination. Reference should be made to remarks made earlier regarding re-exports of New Zealand produce from the United Kingdom.
| Country | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| British Commonwealth Countries, Protected Slates, and Trust Territories | £ | £ | £ |
| Europe – | |||
| United Kingdom | 162,130,837 | 139,105,325 | 165,657,255 |
| Cyprus | 6,417 | 4,836 | 2,777 |
| Gibraltar | - | 1,763 | - |
| Malta | 48 | 44 | 225 |
| Totals | 162,137,302 | 139,111,968 | 165,660,257 |
| Asia – | |||
| Aden | 3,649 | 5,595 | 12,775 |
| Bahrain | 6,734 | 10,340 | |
| North Borneo | 1,745 | 2,155 | 1,723 |
| Ceylon | 74,080 | 177,036 | 284,027 |
| Hong Kong | 161,090 | 205,111 | 390,368 |
| India | 1,612,579 | 736,202 | 686,694 |
| Malaya | 235,002 | 319,280 | 334,999 |
| Pakistan | 70,246 | 35,977 | 45,158 |
| Singapore | 442,061 | 356,815 | 454,972 |
| Other | 195 | 688 | 3,411 |
| Totals | 2,607,381 | 1,849,199 | 2,214,127 |
| Africa – | |||
| Gambia and Sierra Leone | 858 | - | - |
| Ghana | 18,833 | 1,548 | 1,153 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 18,784 | 22,999 | 40,082 |
| Mauritius | 20,611 | 34,309 | 47,065 |
| Nigeria | 12,097 | 1,664 | 540 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 68,301 | 257,996 | 137,589 |
| Union of South Africa | 283,761 | 676,743 | 922,426 |
| Other | 1,606 | 1,540 | 2,408 |
| Totals | 424,851 | 996,799 | 1,151,263 |
| America – | |||
| Bahamas | 76,268 | 74,556 | 132,819 |
| Barbados | 236,476 | 276,429 | 279,303 |
| Bermuda | 154,919 | 147,764 | 213,033 |
| British Guiana | 76,744 | 75,800 | 110,374 |
| British Honduras | 3,082 | 4,877 | 5,326 |
| Canada | 4,434,594 | 4,065,957 | 3,054,191 |
| Falkland Islands | 68 | 346 | 421 |
| Jamaica | 1,102,048 | 1,232,177 | 1,588,588 |
| Leeward and Windward Islands | 48,597 | 67,375 | 57,527 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 774,815 | 766,201 | 1,180,654 |
| Totals | 6,907,611 | 6,711,482 | 6,622,236 |
| Pacific – | |||
| Australia | 10,112,912 | 10,266,097 | 10,944,003 |
| Fiji | 1,039,266 | 1,039,917 | 1,149,666 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 52,663 | 43,936 | 14,430 |
| Nauru Island | 69,672 | 39,590 | 52,961 |
| New Hebrides | 10,819 | 4,264 | 4,375 |
| Norfolk Island | 12,415 | 13,180 | 4,545 |
| Papua and New Guinea | 6,243 | 2,099 | 3,780 |
| Pitcairn Island | 1,013 | 1,536 | 1,813 |
| Solomon Islands | 3,582 | 2,331 | 1,217 |
| Tonga | 300,161 | 190,238 | 222,788 |
| Western Samoa | 462,157 | 755,274 | 823,145 |
| Other | 2,189 | 2,016 | 542 |
| Totals | 12,073,092 | 12,360,478 | 13,223,265 |
| Antarctic – | |||
| Ross Dependency | 6,039 | - | |
| Totals, British Commonwealth countries etc. | 184,150,237 | 161,035,965 | 188,871,148 |
| Other Countries | |||
| Europe – | |||
| Austria | 48,930 | 7,922 | 32,433 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 6,317,641 | 4,501,704 | 5,203,885 |
| Bulgaria | 13,531 | 166,106 | 139,842 |
| Czechoslovakia | 972,666 | 987,774 | 1,366,757 |
| Denmark | 536,852 | 526,152 | 396,216 |
| Finland | 62,648 | 66,189 | 175,639 |
| France and Monaco | 21,696,762 | 14,679,704 | 17,243,003 |
| German Democratic Republic | - | - | 3,435 |
| German Federal Republic | 12,259,675 | 7,027,607 | 9,692,779 |
| Greece | 225,701 | 389,818 | 322,340 |
| Hungary | 11,354 | 100 | 94 |
| Ireland, Republic of | 132,850 | 166,724 | 144,770 |
| Italy and San Marino | 6,217,755 | 6,230,525 | 6,007,571 |
| Netherlands | 4,086,487 | 2,982,440 | 4,179,432 |
| Norway | 53,307 | 60,947 | 158,781 |
| Poland | 2,988,984 | 2,527,526 | 1,263,988 |
| Portugal | 203,778 | 384,668 | 382,056 |
| Rumania | - | 22,528 | |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 2,680,694 | 687,816 | 152,279 |
| Spain | 7,678 | 6,756 | 80,532 |
| Sweden | 511,182 | 700,996 | 697,393 |
| Switzerland and Liechtenstein | 77,031 | 55,924 | 40,092 |
| Turkey | - | 137,939 | 2,462 |
| Yugoslavia | 68,783 | 81,334 | 239,423 |
| Totals | 59,174,289 | 42,399,199 | 47,925,202 |
| Asia – | |||
| Burma | 123,461 | 104,624 | 107,124 |
| China | 595,356 | 977,984 | 2,489,906 |
| Formosa | 12,076 | 2,835 | 5,550 |
| Indonesia | 1,376 | 50,940 | 3,033 |
| Iraq | 1,839 | 1,665 | 100 |
| Israel | 2,902 | 151,827 | 1,927 |
| Japan | 7,825,531 | 5,513,926 | 6,685,041 |
| Korea, Republic of | 12,863 | - | 2,302 |
| Lebanon | 217 | 2,338 | 4,242 |
| Philippines | 483,849 | 212,163 | 273,137 |
| Saudi Arabia | 13,404 | 10,844 | 415 |
| Syria | 5,311 | 9,229 | 8,296 |
| Thailand | 8,898 | 32,123 | 38,239 |
| Other | 715 | - | 582 |
| Totals | 9,087,798 | 7,070,498 | 9,619,894 |
| Africa – | |||
| Algeria | 5,915 | 1,642 | 7,509 |
| Belgian Congo | 84,000 | 532 | 1,514 |
| Egypt | 71,823 | 322,475 | 172,888 |
| Liberia | 676 | 1,506 | - |
| Morocco | 14,883 | 68,785 | - |
| Mozambique | 11,175 | 51,724 | 41,313 |
| Sudan | - | 10,105 | 5,378 |
| Other | 63 | - | - |
| Totals | 188,535 | 456,769 | 228,602 |
| America – | |||
| Argentina | 4,934 | 2,483 | 271 |
| Brazil | 43,480 | - | 1,000 |
| Chile | 4,919 | 9,460 | 15,500 |
| Colombia | 50,330 | 4,595 | 5,015 |
| Haiti | 9,449 | 21,813 | |
| Mexico | 177,922 | 110,592 | 116,878 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 234,625 | 290,120 | 271,489 |
| Panama Republic | 261,794 | 224,972 | 272,545 |
| Panama Canal Zone | 11,311 | 118,158 | 75,405 |
| Peru | 19,647 | 94,940 | 730,182 |
| United States of America | 21,730,408 | 36,448,948 | 43,057,378 |
| Uruguay | 17,197 | 1,602 | 6,881 |
| Venezuela | 14,545 | 201,040 | |
| Other | 1,671 | 1,290 | 4,660 |
| Totals | 22,558,238 | 37,331,154 | 44,780,057 |
| Pacific – | |||
| Guam | - | 18,109 | 65,276 |
| Hawaii | 366,099 | 720,465 | 912,825 |
| New Caledonia | 15,391 | 1,237 | 2,546 |
| Society Islands | 112,409 | 96,926 | 169,702 |
| French Oceania | 777 | 9,196 | 792 |
| American Samoa | 128,786 | 121,007 | 145,489 |
| Totals | 623,462 | 966,940 | 1,296,630 |
| Antarctic – | |||
| Foreign Antarctica | - | 141,242 | 161,047 |
| Totals, other countries | 91,632,322 | 88,365,802 | 104,011,432 |
| Ships' stores | 786,449 | 771,038 | 776,074 |
| Totals, all merchandise exports | 276,569,008 | 250,172,805 | 293,658,654 |
Destination of Main Exports – The table which follows shows quantities and values of the principal exports of New Zealand produce sent to various destinations during the years 1958 and 1959. Details for each country to which goods are exported are shown in all cases where the trade was £10,000 or more in either of the two years included in the table.
| Country to Which Exported | 1958 | 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| Wool (Greasy, Slipe, and Scoured) | ||||
| lb | £ | lb | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 171,115,375 | 30,130,615 | 178,675,889 | 30,718,006 |
| Union of South Africa | 714,714 | 147,900 | 860,964 | 187,644 |
| India | 1,377,879 | 276,778 | 769,621 | 152,024 |
| Canada | 3,065,008 | 626,083 | 3,654,903 | 668,788 |
| Australia | 4,744,744 | 795,918 | 4,922,673 | 846,320 |
| Republic of Ireland | 203,235 | 34,964 | 335,336 | 56,002 |
| Belgium | 25,093,356 | 3,905,044 | 27,651,461 | 4,352,053 |
| Bulgaria | 778,254 | 166,106 | 788,219 | 139,842 |
| Rumania | 91,062 | 22,528 | - | - |
| Norway | 156,800 | 38,587 | 84,494 | 18,876 |
| Denmark | 2,077,205 | 463,327 | 1,517,748 | 327,971 |
| Finland | 112,846 | 22,506 | 208,221 | 40,062 |
| Poland | 11,412,626 | 2,527,526 | 5,739,067 | 1,081,715 |
| Portugal | 2,165,756 | 368,080 | 2,219,055 | 364,241 |
| German Federal Republic | 26,838,758 | 5,110,281 | 34,615,722 | 6,111,435 |
| Netherlands | 10,110,789 | 1,703,656 | 12,732,130 | 2,153,916 |
| France | 84,767,532 | 14,128,512 | 93,330,393 | 15,457,811 |
| Sweden | 2,389,970 | 579,048 | 2,433,548 | 526,418 |
| Switzerland | 129,085 | 30,430 | 116,596 | 22,537 |
| Italy | 21,851,191 | 3,871,478 | 25,829,882 | 4,238,817 |
| Czechoslovakia | 5,109,085 | 987,643 | 7,367,323 | 1,337,843 |
| Greece | 863,447 | 196,031 | 299,442 | 58,240 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 3,313,151 | 687,816 | 737,665 | 152,279 |
| Egypt | 1,189,949 | 271,263 | 669,646 | 136,624 |
| Morocco | 75,448 | 13,373 | - | - |
| Japan | 15,883,668 | 3,056,984 | 19,920,351 | 3,380,110 |
| China | 4,796,848 | 929,741 | 11,967,526 | 2,246,921 |
| Mexico | 576,852 | 110,592 | 567,811 | 115,128 |
| United States of America | 55,803,038 | 8,813,264 | 90,578,144 | 14,735,062 |
| Other countries | 120,021 | 20,703 | 70,337 | 16,602 |
| Totals | 456,927,692 | 80,036,777 | 528,664,167 | 89,643,287 |
| Frozen and Chilled Beef and Veal | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 257,395 | 1,689,380 | 147,150 | 1,182,035 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 1,719 | 17,156 | 36 | 656 |
| Bermuda | 1,754 | 32,916 | 1,518 | 35,390 |
| Bahamas | 4,529 | 51,019 | 5,881 | 74,005 |
| Barbados | 21,204 | 160,401 | 10,860 | 93,202 |
| Jamaica | 19,018 | 142,454 | 13,148 | 122,130 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 21,434 | 223,672 | 17,190 | 187,993 |
| Canada | 81,959 | 863,928 | 67,903 | 760,656 |
| Fiji | 1,296 | 20,525 | 1,012 | 17,301 |
| Tonga | 903 | 9,961 | 833 | 10,062 |
| Western Samoa | 1,619 | 16,288 | 2,669 | 29,882 |
| Belgium | 1,811 | 14,306 | 1,003 | 9,115 |
| France | 2,044 | 13,060 | 258 | 2,228 |
| German Federal Republic | 8,050 | 60,753 | 15,684 | 130,971 |
| Greece | 5,072 | 33,302 | 1,729 | 13,441 |
| Italy | 35,482 | 299,126 | 2,718 | 24,363 |
| Netherlands | 7,710 | 57,828 | 4,837 | 51,840 |
| Panama Canal Zone | 8,322 | 74,211 | 5,349 | 54,946 |
| Israel | 23,945 | 145,439 | - | - |
| Philippines | 9,231 | 93,526 | 2,656 | 26,514 |
| Japan | 55,422 | 307,787 | 26,133 | 209,875 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 20,143 | 206,296 | 13,641 | 163,139 |
| United States of America | 1,680,597 | 20,922,941 | 1,370,575 | 18,071,881 |
| Venezuela | - | - | 11,973 | 148,950 |
| Guam | 1,625 | 15,207 | 5,569 | 56,136 |
| Hawaii | 38,468 | 542,853 | 39,305 | 606,700 |
| Society Islands | 1 | 13 | 2,212 | 27,571 |
| American Samoa | 2,109 | 22,842 | 3,442 | 43,589 |
| Other countries | 2,529 | 30,588 | 1,777 | 28,851 |
| Totals | 2,315,391 | 26,067,778 | 1,777,061 | 22,183,422 |
| Frozen Lamb and Mutton | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 5,045,144 | 40,380,984 | 5,974,620 | 41,161,316 |
| Singapore | 716 | 7,003 | 2,961 | 21,771 |
| Barbados | 1,215 | 11,531 | 841 | 6,465 |
| Jamaica | 3,204 | 22,517 | 4,395 | 25,612 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 5,112 | 40,212 | 8,777 | 57,454 |
| Bermuda | 3,251 | 45,139 | 2,612 | 32,393 |
| Canada | 141,367 | 1,146,383 | 55,557 | 373,371 |
| Fiji | 8,996 | 50,575 | 10,518 | 53,526 |
| Western Samoa | 3,551 | 22,527 | 5,293 | 29,679 |
| Belgium | 1,517 | 5,309 | 4,458 | 14,341 |
| Czechoslovakia | - | -9,844 | 28,668 | |
| Greece | 44,160 | 157,616 | 97,346 | 241,451 |
| Netherlands | 8,324 | 26,434 | 9,298 | 24,988 |
| German Federal Republic | 2,007 | 7,759 | 24,923 | 76,584 |
| Sweden | 5,606 | 33,545 | - | - |
| Turkey | 37,174 | 137,939 | - | - |
| Japan | 209 | 1,647 | 65,208 | 220,735 |
| Saudi Arabia | 618 | 10,844 | 40 | 411 |
| Peru | - | - | 29,249 | 87,091 |
| United States of America | 67,987 | 539,685 | 110,837 | 899,286 |
| Hawaii | 3,910 | 38,103 | 4,253 | 42,458 |
| Other countries | 7,605 | 58,024 | 11,930 | 77,439 |
| Totals | 5,391,673 | 42,743,776 | 6,432,960 | 43,475,039 |
| Frozen Pork | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 57,000 | 561,574 | 80,791 | 742,911 |
| Aden | 569 | 5,589 | 1,170 | 12,716 |
| Hong Kong | 1,403 | 15,241 | 5,647 | 60,011 |
| Singapore | 2,600 | 28,305 | 5,898 | 63,653 |
| Canada | 1,321 | 18,199 | - | - |
| Jamaica | 2,389 | 25,053 | 2,417 | 22,207 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 7,614 | 84,936 | 13,149 | 138,175 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 548 | 5,943 | 1,355 | 15,172 |
| Australia | 794 | 10,383 | 6,065 | 75,347 |
| Hawaii | 611 | 7,328 | 1,319. | 14,767 |
| Fiji | 1,057 | 11,308 | 1,270 | 14,306 |
| Belgium | 6,306 | 68,204 | 6,207 | 60,397 |
| Other countries | 967 | 11,435 | 1,503 | 16,614 |
| Totals | 83,179 | 853,498 | 126,791 | 1,236,276 |
| Other Frozen Meat | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 265,471 | 3,475,478 | 291,210 | 3,863,499 |
| Singapore | 1,562 | 13,100 | 847 | 9,572 |
| Fiji | 2,695 | 31,816 | 2,692 | 31,706 |
| Canada | 666 | 7,288 | 570 | 13,022 |
| Jamaica | 8,313 | 53,780 | 12,470 | 94,417 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 5,761 | 42,381 | 7,014 | 52,047 |
| German Federal Republic | 3,011 | 16,217 | 3,954 | 25,476 |
| Australia | 2,758 | 27,664 | 1,084 | 8,107 |
| Western Samoa | 2,622 | 16,144 | 3,018 | 22,024 |
| Italy | 9,010 | 25,667 | 7,963 | 20,642 |
| Netherlands | 1,239 | 12,908 | 8,976 | 58,761 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 1,541 | 15,086 | 1,835 | 18,061 |
| Japan | 5,040 | 24,555 | 1,710 | 8,825 |
| Peru | - | - | 3,659 | 10,404 |
| United States of America | 2,349 | 18,424 | 3,188 | 58,688 |
| Hawaii | 1,576 | 14,335 | 1,354 | 14,733 |
| Other countries | 4,153 | 29,923 | 6,424 | 45,775 |
| Totals | 317,767 | 3,824,766 | 357,968 | 4,355,759 |
| Canned Meat | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 39,528 | 769,698 | 37,979 | 767,668 |
| Jamaica | 6,999 | 92,464 | 4,494 | 69,185 |
| Fiji | 4,760 | 85,773 | 3,870 | 71,840 |
| Tonga | 2,428 | 43,122 | 2,963 | 53,041 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 1,797 | 29,300 | 172 | 3,900 |
| Nauru | 847 | 14,257 | 1,617 | 33,247 |
| Western Samoa | 5,239 | 96,770 | 5,188 | 106,678 |
| German Federal Republic | 2,120 | 35,996 | ||
| Society Islands | 3,389 | 57,781 | 3,281 | 58,018 |
| American Samoa | 2,140 | 40,666 | 1,456 | 31,352 |
| Other countries | 1,737 | 28,094 | 851 | 17,369 |
| Totals | 68,864 | 1,257,925 | 63,991 | 1,248,294 |
| Butter | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 3,356,488 | 36,777,921 | 3,506,981 | 50,012,894 |
| Hong Kong | 10,749 | 127,946 | 11,517 | 162,878 |
| Ceylon | 3,289 | 41,067 | 6,647 | 96,378 |
| Singapore | 5,004 | 60,662 | 6,518 | 99,413 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 4,657 | 61,020 | 4 | 66 |
| South Africa | - | - | 35,000 | 489,190 |
| British Guiana | 1,509 | 18,656 | 1,709 | 27,329 |
| Bermuda | 4,259 | 51,132 | 7,477 | 115,633 |
| Bahamas | 946 | 10,816 | 3,040 | 46,430 |
| Barbados | 1,648 | 23,282 | 3,210 | 52,077 |
| Jamaica | 31,127 | 423,316 | 44,722 | 754,471 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 12,547 | 148,169 | 16,128 | 251,112 |
| Leeward and Windward Islands | 1,426 | 17,131 | 752 | 12,274 |
| Fiji | 5,396 | 83,862 | 6,670 | 115,935 |
| Tonga | 906 | 13,768 | 1,019 | 15,849 |
| Western Samoa | 1,498 | 22,653 | 1,854 | 28,950 |
| France | - | - | 59,997 | 1,153,443 |
| German Federal Republic | - | - | 65,879 | 1,013,329 |
| Italy | 21,059 | 274,191 | 140 | 2,032 |
| Philippines | 3,382 | 41,022 | 6,872 | 99,806 |
| Haiti | 789 | 9,362 | 1,379 | 21,709 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 4,116 | 54,327 | 3,859 | 63,748 |
| Panama Canal Zone | 2,323 | 32,803 | 893 | 14,856 |
| Panama Republic | 15,650 | 218,316 | 16,299 | 257,537 |
| Peru | 3,859 | 63,688 | 32,247 | 517,609 |
| United States of America | 9,327 | 172,637 | 7,563 | 160,455 |
| Hawaii | 2,518 | 54,505 | 7,676 | 164,322 |
| Other countries | 3,372 | 48,110 | 3,512 | 58,176 |
| Totals | 3,507,844 | 38,850,362 | 3,859,564 | 55,807,901 |
| Cheese | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 1,671,459 | 11,308,321 | 1,561,550 | 20,859,799 |
| Union of South Africa | 9,215 | 65,607 | 2,325 | 30,231 |
| British Guiana | 4,174 | 32,055 | 3,058 | 36,859 |
| Barbados | 4,811 | 44,309 | 6,112 | 74,272 |
| Bermuda | 679 | 6,698 | 820 | 11,282 |
| Jamaica | 15,748 | 183,383 | 16,866 | 221,712 |
| Leeward and Windward Islands | 2,422 | 27,779 | 2,444 | 30,380 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 12,864 | 112,347 | 17,036 | 215,794 |
| Australia | 4,038 | 61,033 | 3,872 | 67,454 |
| German Federal Republic | 26,274 | 225,826 | 12,133 | 147,580 |
| Japan | 451 | 3,651 | 1,237 | 13,203 |
| United States of America | 32,184 | 287,251 | 38,507 | 355,461 |
| Other countries | 4,235 | 43,349 | 3,084 | 39,081 |
| Totals | 1,788,554 | 12,401,609 | 1,669,044 | 22,103,108 |
| Milk (Dried, Condensed, etc.) | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 743,029 | 2,448,155 | 1,027,694 | 3,905,497 |
| Ceylon | 5,102 | 33,596 | 14,636 | 94,458 |
| India | 58,607 | 226,824 | 67,672 | 311,522 |
| Singapore | 34,950 | 165,403 | 29,445 | 126,760 |
| Malaya | 38,401 | 248,465 | 26,521 | 200,258 |
| Hong Kong | 826 | 4,847 | 1,716 | 12,880 |
| Pakistan | 5,445 | 19,673 | 9,240 | 38,844 |
| Union of South Africa | 5,291 | 18,661 | 1,380 | 4,493 |
| Mauritius | 8,934 | 32,403 | 8,672 | 36,153 |
| Barbados | 1,897 | 7,957 | 3,600 | 14,355 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 11,407 | 49,792 | 26,404 | 184,963 |
| Jamaica | 32,436 | 118,224 | 54,307 | 193,569 |
| Fiji | 9,180 | 66,011 | 9,279 | 68,917 |
| Western Samoa | 2,326 | 18,396 | 3,202 | 25,445 |
| German Federal Republic | 2,000 | 7,020 | 39,365 | 149,644 |
| Netherlands | 39,399 | 131,814 | 12,000 | 47,162 |
| Japan | 22,660 | 63,206 | 1,000 | 4,000 |
| Philippines | 3,741 | 11,351 | 11,575 | 65,546 |
| Peru | 3,907 | 12,523 | 28,449 | 101,380 |
| United States of America | 15,568 | 45,638 | 9,108 | 28,328 |
| Hawaii | 4,375 | 13,441 | 5,225 | 17,094 |
| Society Islands | 2,775 | 17,686 | 3,123 | 19,468 |
| Other countries | 8,354 | 45,096 | 13,975 | 78,242 |
| Totals | 1,060,610 | 3,806,182 | 1,407,588 | 5,728,978 |
| Edible Tallow | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 83,111 | 275,493 | 158,303 | 545,768 |
| India | 39,794 | 132,387 | 38,973 | 134,419 |
| Singapore | 3,563 | 13,169 | 5,032 | 17,960 |
| Australia | 72,338 | 268,720 | - | - |
| Netherlands | 5,278 | 17,479 | 4,844 | 16,559 |
| Burma | 2,718 | 9,964 | 3,588 | 12,508 |
| Egypt | 5,591 | 20,360 | 8,261 | 32,015 |
| Japan | 5,515 | 19,491 | 2,133 | 7,898 |
| Other countries | 7,893 | 27,516 | 6,760 | 23,795 |
| Totals | 225,801 | 784,579 | 227,894 | 790,922 |
| Inedible Tallow | ||||
| tons | £ | tons | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 13,936 | 894,272 | 20,936 | 1,206,477 |
| Ceylon | 1,316 | 93,040 | 998 | 68,143 |
| India | 441 | 31,253 | 410 | 29,300 |
| Singapore | 245 | 14,901 | 455 | 25,686 |
| Malaya | 679 | 46,447 | 480 | 27,719 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 241 | 14,236 | 220 | 12,691 |
| Pakistan | 197 | 13,764 | 15 | 1,074 |
| Union of South Africa | 6,131 | 392,047 | 3,005 | 158,414 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 2,847 | 183,625 | 2,090 | 118,822 |
| British Guiana | 129 | 8,967 | 494 | 35,828 |
| Jamaica | 1,650 | 113,915 | 654 | 42,510 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 822 | 49,850 | 1,550 | 84,634 |
| Australia | 712 | 49,078 | - | - |
| Fiji | 323 | 22,331 | 342 | 21,598 |
| Finland | 326 | 22,106 | 269 | 16,314 |
| Italy | 357 | 24,474 | - | - |
| Netherlands | 559 | 30,242 | 27 | 1,092 |
| Mozambique | 710 | 43,572 | 613 | 35,267 |
| Burma | 1,343 | 92,640 | 1,238 | 82,954 |
| China | 190 | 13,242 | 3,626 | 213,303 |
| Japan | 6,205 | 433,791 | 4,049 | 265,489 |
| Thailand | 388 | 25,552 | 392 | 25,323 |
| Sudan | 145 | 10,105 | 78 | 5,378 |
| Other countries | 78 | 5,475 | 223 | 14,128 |
| Totals | 39,970 | 2,628,925 | 42,164 | 2,492,144 |
| Cattle Hides | ||||
| No. | £ | No. | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 97,355 | 248,171 | 95,887 | 385,759 |
| Canada | 6,004 | 12,386 | 9,237 | 23,627 |
| Australia | 12,485 | 33,989 | 8,816 | 34,295 |
| Finland | 3,402 | 9,664 | 7,526 | 31,646 |
| German Federal Republic | 324,525 | 779,145 | 206,048 | 730,718 |
| Italy | 267,524 | 581,459 | 133,044 | 463,114 |
| Netherlands | 42,999 | 100,924 | 50,065 | 181,114 |
| Norway | 8,250 | 22,132 | 29,871 | 132,148 |
| Poland | - | - | 56,652 | 182,273 |
| Portugal | 5,828 | 12,269 | 2,000 | 4,140 |
| Yugoslavia | 30,178 | 76.684 | 55,941 | 238,276 |
| Japan | 74,026 | 198,659 | 206,243 | 694,582 |
| Morocco | 20,915 | 47,754 | - | - |
| United States of America | 2,617 | 5,809 | 6,457 | 17,635 |
| Venezuela | - | - | 5,000 | 21,431 |
| Other countries | 7,994 | 19,805 | 7,637 | 22,013 |
| Totals | 904,102 | 2,148,850 | 880,424 | 3,162,771 |
| Calf Skins | ||||
| No. | £ | No. | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 101,609 | 78,955 | 61,643 | 77,651 |
| Canada | 10,000 | 11,000 | 32,000 | 42,756 |
| Belgium | 57,081 | 45,696 | - | - |
| France | 39,398 | 32,042 | 40,630 | 57,490 |
| German Federal Republic | 146,158 | 119,016 | 97,328 | 123,618 |
| Netherlands | 225,143 | 185,771 | 317,788 | 441,800 |
| Italy | 324,096 | 273,730 | 180,533 | 268,863 |
| United States of America | 105,715 | 92,236 | 225,860 | 283,017 |
| Other countries | 5,900 | 5,157 | 7,340 | 9,634 |
| Totals | 1,015,100 | 843,603 | 963,122 | 1,304,829 |
| Sheep Skins (With Wool) | ||||
| No. | £ | No. | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 152,900 | 116,567 | 147,954 | 126,300 |
| Belgium | 35,179 | 43,201 | 81,617 | 97,858 |
| France | 542,160 | 329,777 | 753,310 | 423,840 |
| Italy | 131,080 | 84,803 | 134,436 | 84,851 |
| Netherlands | 47,860 | 22,294 | 51,623 | 24,149 |
| Portugal | 4,124 | 4,108 | 9,932 | 13,554 |
| Spain | - | - | 68,845 | 80,522 |
| Other countries | 1,211 | 679 | 2,251 | 1,673 |
| Totals | 914,514 | 601,429 | 1,249,968 | 852,747 |
| Sheep Skins (Without Wool) | ||||
| No. | £ | No. | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 3,691,923 | 993,821 | 3,432,028 | 1,281,178 |
| Canada | 48,000 | 9,075 | 86,784 | 19,600 |
| Australia | 160,859 | 31,464 | 816 | 366 |
| Belgium | 759,532 | 259,204 | 1,168,265 | 476,632 |
| Denmark | 90,756 | 17,623 | - | - |
| Finland | 62,616 | 10,978 | 59,934 | 16,916 |
| France | 145,680 | 28,782 | 154,868 | 36,974 |
| German Federal Republic | 216,403 | 67,791 | 366,690 | 141,889 |
| Italy | 143,369 | 46,292 | 260,948 | 87,910 |
| Netherlands | 1,219,439 | 373,263 | 1,340,609 | 534,257 |
| Sweden | 192,404 | 41,728 | 239,190 | 66,852 |
| United States of America | 12,942,161 | 2,602,829 | 17,494,022 | 4,937,942 |
| Other countries | 5,862 | 1,171 | 13,800 | 4,008 |
| Totals | 19,679,004 | 4,484,021 | 24,617,954 | 7,604,524 |
| Sausage Casings | ||||
| lb | £ | lb | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 3,803,607 | 2,605,958 | 4,951,760 | 2,445,074 |
| Canada | 1,475,970 | 1,209,793 | 1,604,499 | 1,009,668 |
| Australia | 41,661 | 13,882 | 5,814 | 2,462 |
| Denmark | 20,125 | 18,094 | 22,977 | 15,869 |
| German Federal Republic | 302,353 | 71,495 | 488,431 | 102,043 |
| United States of America | 1,711,242 | 559,509 | 2,011,936 | 551,278 |
| Other countries | 16,686 | 2,918 | 8,851 | 5,530 |
| Totals | 7,371,644 | 4,481,649 | 9,094,268 | 4,131,924 |
| Casein | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 113,475 | 881,723 | 123,619 | 934,011 |
| India | 3,802 | 29,434 | 2,143 | 15,882 |
| Canada | 8,000 | 61,900 | 2,800 | 19,700 |
| German Federal Republic | 12,899 | 94,314 | 54,311 | 401,250 |
| Italy | 74,836 | 559,858 | 92,089 | 703,730 |
| Netherlands | 11,811 | 76,683 | 37,683 | 273,135 |
| Japan | 47,981 | 410,385 | 67,379 | 512,630 |
| United States of America | 127,544 | 987,744 | 200,714 | 1,520,434 |
| Other countries | 938 | 7,592 | 2,865 | 22,058 |
| Totals | 401,286 | 3,109,633 | 583,603 | 4,402,830 |
| Apples (Fresh) | ||||
| lb | £ | lb | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 54,651,520 | 1,707,852 | 46,590,600 | 1,455,668 |
| Malaya | 362,720 | 11,335 | 457,000 | 14,282 |
| Canada | 6,400 | 201 | 1,036,720 | 32,398 |
| Belgium | 2,648,440 | 82,675 | 4,386,400 | 137,076 |
| Finland | - | - | 2,262,360 | 70,699 |
| France | 1,225,000 | 38,281 | - | - |
| German Federal Republic | 5,811,560 | 181,572 | 6,235,520 | 194,877 |
| Netherlands | 1,592,200 | 49,757 | 3,592,000 | 112,251 |
| Sweden | 805,120 | 25,160 | 2,387,400 | 74,606 |
| United States of America | 136,000 | 4,250 | 1,245,120 | 38,911 |
| Venezuela | 405,000 | 12,500 | 700,000 | 21,875 |
| Hawaii | 573,400 | 17,919 | 629,560 | 19,674 |
| Other countries | 775,600 | 27,589 | 961,200 | 32,239 |
| Totals | 68,992,960 | 2,159,091 | 70,483,880 | 2,204,556 |
| Seeds (Grass and Clover) | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 57,770 | 674,660 | 35,224 | 429,808 |
| Canada | 3,154 | 54,817 | 919 | 16,037 |
| Australia | 46,688 | 402,923 | 32,009 | 309,868 |
| Republic of Ireland | 10,536 | 101,270 | 5,996 | 62,602 |
| Belgium | 2,002 | 21,182 | 406 | 6,475 |
| France | 10,082 | 71,726 | 4,678 | 55,930 |
| German Federal Republic | 4,190 | 73,194 | 556 | 8,052 |
| Italy | 1,686 | 14,422 | 1,206 | 14,865 |
| Netherlands | 1,971 | 27,284 | 1,965 | 16,269 |
| Chile | 477 | 9,441 | 641 | 10,707 |
| United States of America | 8,672 | 54,426 | 6,093 | 42,745 |
| Other countries | 1,002 | 12,371 | 1,528 | 14,913 |
| Totals | 148,230 | 1,517,716 | 91,221 | 988,271 |
| Peas (Food) | ||||
| cental | £ | cental | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 121,171 | 256,261 | 126,426 | 258,265 |
| Belgium | 8,184 | 16,703 | 4,214 | 8,925 |
| United States of America | 7,868 | 17,575 | 8,272 | 17,481 |
| Other countries | 5,628 | 11,173 | 10,819 | 21,359 |
| Totals | 142,851 | 301,712 | 149,731 | 306,030 |
| Peas (Seed) | ||||
| lb | £ | lb | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 10,336,197 | 294,292 | 8,117,991 | 224,195 |
| Australia | 6,714,434 | 212,218 | 6,703,427 | 191,574 |
| Other countries | 683,105 | 19,283 | 348,612 | 10,640 |
| Totals | 17,733,736 | 525,793 | 15,170,030 | 426,409 |
| Wood Pulp | ||||
| tons | £ | tons | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 17,817 | 593,495 | 15,162 | 463,440 |
| India | 54 | 2,066 | - | - |
| Australia | 48,366 | 2,036,899 | 60,325 | 2,423,095 |
| China | 1,041 | 32,913 | - | - |
| Philippines | 1,506 | 54,225 | 1,339 | 34,193 |
| Other countries | 179 | 5,421 | - | - |
| Totals | 68,963 | 2,725,019 | 76,826 | 2,920,728 |
| Timber (Sawn and Hewn) | ||||
| sup. ft. | £ | sup. ft. | £ | |
| Australia | 35,137,615 | 1,029,482 | 46,372,528 | 1,417,687 |
| Other countries | 56,455 | 2,649 | 170,336 | 6,423 |
| Totals | 35,194,070 | 1,032,131 | 46,542,864 | 1,424,110 |
| Timber (for Cases, in Shooks) | ||||
| sup. ft. | £ | sup. ft. | £ | |
| Australia | 547,420 | 27,845 | 534,785 | 26,947 |
| Tonga | 56,806 | 2,500 | - | - |
| Western Samoa | 4,230,050 | 239,574 | 3,851,724 | 211,303 |
| Other countries | 47,220 | 2,717 | 153,732 | 7,403 |
| Totals | 4,881,496 | 272,636 | 4,540,241 | 245,653 |
| Fish (Other than Canned) | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| Australia | 46,192 | 424,004 | 55,461 | 482,961 |
| United States of America | 22,831 | 793,153 | 20,668 | 717,949 |
| Hawaii | 389 | 15,524 | 377 | 15,668 |
| Other countries | 1,292 | 10,137 | 3,389 | 21,541 |
| Totals | 70,704 | 1,242,818 | 79,895 | 1,238,119 |
| Newsprint | ||||
| cwt | £ | cwt | £ | |
| Malaya | 400 | 1,059 | 18,045 | 48,529 |
| Australia | 833,651 | 2,627,944 | 851,897 | 2,658,471 |
| Other countries | 692 | 2,852 | 3,302 | 9,489 |
| Totals | 834,743 | 2,631,855 | 873,244 | 2,716,489 |
EXPORTS BY PORTS - The following table shows for the years 1954-59 the value of total exports according to the ports at which they were actually placed on board the overseas vessels.
While, in the case of imports, goods received through parcels post are allocated according to ports of entry, similar treatment is not possible in the case of exports. The total of goods exported by parcels post is accordingly shown under the heading “Parcels Post” until 1956 but outward postal parcels are not now recorded in the export statistics.
| Port | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Parcels post has not been included in New Zealand export statistics after 1956. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Auckland | 76,196,678 | 89,281,668 | 89,810,883 | 80,495,985 | 76,976,535 | 105,005,868 |
| Tauranga | 1,331,339 | 1,613,978 | 3,874,869 | 5,273,918 | 6,217,902 | 7,724,847 |
| Gisborne | 3,545,793 | 3,334,395 | 2,883,018 | 3,187,225 | 3,158,703 | 2,902,219 |
| Napier | 22,214,543 | 25,991,469 | 24,685,202 | 23,999,743 | 21,475,235 | 23,716,523 |
| New Plymouth | 13,362,420 | 14,599,264 | 16,996,722 | 16,366,481 | 16,265,400 | 24,416,885 |
| Wanganui | 442 | 297 | 564 | 1,335 | 673 | 100 |
| Wellington | 54,434,532 | 45,320,404 | 55,158,851 | 55,739,849 | 47,855,494 | 45,975,878 |
| Picton | 21,930 | 61,806 | 68,071 | 23,178 | 90,321 | 249,166 |
| Nelson | 906,455 | 1,157,429 | 1,591,925 | 1,832,128 | 1,909,218 | 1,824,458 |
| Greymouth | 145,434 | 176,405 | 204,168 | 250,376 | 192,814 | 344,107 |
| Lyttelton | 22,751,855 | 21,832,937 | 24,833,212 | 26,893,220 | 22,744,022 | 23,175,616 |
| Timaru | 13,095,200 | 14,422,418 | 15,674,917 | 16,245,821 | 15,213,945 | 15,717,367 |
| Oamaru | 9,034 | 6,855 | - | 228 | 10,060 | - |
| Dunedin | 15,034,177 | 18,102,586 | 17,269,453 | 19,330,245 | 15,290,217 | 18,724,527 |
| Bluff | 21,281,948 | 23,259,813 | 24,271,870 | 26,929,276 | 22,772,266 | 23,881,093 |
| Parcels post* | 134,426 | 127,000 | 159,105 | - | - | - |
| Totals | 244,466,206 | 259,288,724 | 277,482,830 | 276,569,008 | 250,172,805 | 293,658,654 |
Auckland occupies a commanding position in the export trade of New Zealand, usually about one-third of all exports being dispatched from that port. Wellington occupies second place, usually with approximately one-fifth of the trade. As will be seen from the above table, the order of the other ports varies from year to year. The steady increase in the value of exports through Tauranga is attributed to the pulp, paper, and timber industries of the district.
EXPORTS FOR YEARS ENDED 30 JUNE – As indicated elsewhere in this section (page 633), farm products account for an extremely high proportion of exports from New Zealand. The farm-production export season fits much more closely to a June year than to a calendar year. The flush of the dairy-production season is spread over the months of October to March, while the whole harvest season, and most of the wool-selling season, occur in the early months of the calendar year. By 30 June in normal times the great bulk of the season's farm produce destined for export is shipped, except held-over wool and a certain amount of dairy produce and frozen meat kept in cool store to equalise shipments. It is desirable, therefore, for some purposes to tabulate New Zealand exports for the years ending in June instead of December.
QUANTITIES OF PRINCIPAL ITEMS OF NEW ZEALAND PRODUCE EXPORTED FOR YEARS ENDED 30 JUNE 1958-60
| Commodity | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mining products – | ||||
| Coal | (ton) | 2,901 | 7,718 | 3,744 |
| Gold | (oz) | 23,286 | 19,714 | 31,434 |
| Fishery products – | ||||
| Fish | (cwt) | 93,719 | 73,109 | 90,736 |
| Forest products – | ||||
| Kauri gum | (ton) | 182 | 114 | 115 |
| Timber, sawn | (sup. ft.) | 31,556,971 | 37,971,164 | 49,474,174 |
| Timber, for cases, in shooks | (sup. ft.) | 3,294,614 | 4,495,633 | 4,584,263 |
| Logs, radiata pine | (cu. ft.) | 353,380 | 2,279,511 | 6,146,480 |
| Wood pulp | (ton) | 69,150 | 73,451 | 75,613 |
| Newsprint | (cwt) | 777,771. | 812,544 | 965,030 |
| Pastoral products – | ||||
| Butter | (cwt) | 3,449,321 | 3,455,768 | 3,611,635 |
| Casein | (cwt) | 337,725 | 535,901 | 543,517 |
| Cheese | (cwt) | 1,825,525 | 1,635,674 | 1,776,675 |
| Milk, dried | (cwt) | 1,196,953 | 1,139,901 | 1,207,013 |
| Milk, preserved | (cwt) | 54,729 | 35,783 | 40,044 |
| Sugar of milk | (cwt) | 71,154 | 79,615 | 92,311 |
| Eggs, not in shell | (lb) | 143,372 | 2,490 | 875,661 |
| Honey | (lb) | 3,167,587 | 1,994,470 | 1,115,259 |
| Beef, chilled | (cwt) | 144,911 | 10,952 | 18,872 |
| Beef frozen | (cwt) | 1,988,046 | 1,891,816 | 1,691,657 |
| Lamb, frozen (whole carcasses) | (cwt) | 4,178,176 | 4,658,641 | 4,951,266 |
| Mutton, frozen (whole carcasses) | (cwt) | 844,486 | 1,116,863 | 1,434,325 |
| Pork, frozen | (cwt) | 60,723 | 115,859 | 93,816 |
| Veal, frozen | (cwt) | 213,274 | 185,746 | 179,875 |
| Other frozen meat | (cwt) | 369,655 | 456,404 | 513,841 |
| Meat, canned | (cwt) | 99,687 | 53,325 | 73,428 |
| Meat extract | (lb) | 464,205 | 349,384 | 233,554 |
| Sausage casings | (lb) | 7,661,305 | 8,270,217 | 9,584,046 |
| Liver meal | (cwt) | 39,286 | 43,313 | 19,796 |
| Inedible offals | (cwt) | 122,187 | 138,841 | 166,314 |
| Calfskins | (number) | 1,222,583 | 965,816 | 955,543 |
| Cattle hides | (number) | 969,916 | 905,454 | 853,387 |
| Opossum skins | (number) | 289,968 | 300,843 | 345,740 |
| Sheep skins, with wool | (number) | 1,095,571 | 1,069,162 | 1,297,664 |
| Sheep skins, without wool | (number) | 20,646,385 | 23,561,660 | 24,954,216 |
| Wool | lb (000) | 458,782 | 515,582 | 527,766 |
| Edible tallow | (cwt) | 220,567 | 240,287 | 209,373 |
| Inedible tallow | (ton) | 38,654 | 41,825 | 45,020 |
| Agricultural products – | ||||
| Apples | (lb) | 71,846,152 | 72,298,728 | 81,614,080 |
| Hops | (lb) | 221,846 | 90,133 | 240 |
| Potatoes | (ton) | 2,291 | 2,839 | 3,204 |
| Onions | (ton) | 1,791 | 3,309 | 2,668 |
| Canned vegetables | (lb) | 6,635,073 | 4,092,813 | 3,199,436 |
| Frozen vegetables | (cwt) | 33,495 | 49,846 | 31,784 |
| Peas | (cental) | 340,260 | 337,444 | 298,221 |
| Seeds, grass and clover | (cwt) | 176,015 | 114,736 | 114,771 |
| Linen flax and tow | (cwt) | - | 551 | - |
VALUES OF PRINCIPAL ITEMS OF NEW ZEALAND PRODUCE EXPORTED YEARS ENDED 30 JUNE 1958-60
| Commodity | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining products | £ | £ | £ |
| Coal | 10,471 | 31,814 | 16,303 |
| Gold | 279,396 | 236,496 | 377,886 |
| Fishery products – | |||
| Fish | 1,700,805 | 1,315,879 | 1,290,115 |
| Forest products – | |||
| Kauri gum | 23,951 | 14,421 | 16,736 |
| Timber, sawn | 904,170 | 1,134,371 | 1,520,419 |
| Timber, for cases, in shooks | 179,064 | 248,821 | 245,095 |
| Logs, radiata pine | 37,930 | 253,197 | 660,831 |
| Wood pulp | 2,731,592 | 2,846,729 | 2,924,823 |
| Newsprint | 2,404,922 | 2,546,634 | 3,012,877 |
| Pastoral products – | |||
| Butter | 44,588,940 | 38,699,171 | 61,339,915 |
| Casein | 2,736,831 | 4,047,089 | 4,200,946 |
| Cheese | 13,158,514 | 17,124,432 | 23,342,198 |
| Milk, dried | 4,538,677 | 4,050,226 | 5,463,747 |
| Milk, preserved | 349,387 | 209,010 | 239,341 |
| Sugar of milk | 376,846 | 404,458 | 452,591 |
| Other dairy products | 84,262 | 12,063 | 16,305 |
| Eggs, not in shell | 14,414 | 411 | 77,439 |
| Honey | 197,134 | 108,228 | 63,044 |
| Beef, chilled | 972,724 | 116,634 | 186,659 |
| Beef, frozen | 17,902,372 | 23,339,280 | 19,501,180 |
| Lamb, frozen (whole carcasses) | 38,826,909 | 39,299,057 | 37,752,592 |
| Mutton, frozen (whole carcasses) | 3,173,887 | 4,030,921 | 3,766,070 |
| Pork, frozen | 650,705 | 1,155,989 | 937,236 |
| Veal, frozen | 1,929,999 | 2,355,151 | 2,187,814 |
| Other frozen meat | 4,031,508 | 5,135,038 | 5,309,625 |
| Meat, canned | 1,648,114 | 1,030,535 | 1,365,748 |
| Meat extract | 167,548 | 85,612 | 53,611 |
| Sausage casings | 4,898,841 | 4,343,452 | 3,765,063 |
| Liver meal | 98,859 | 127,136 | 63,640 |
| Inedible offals | 444,560 | 472,978 | 640,126 |
| Calfskins | 925,199 | 868,375 | 1,318,874 |
| Cattle hides | 2,439,452 | 2,269,190 | 3,240,736 |
| Opossum skins | 101,536 | 94,762 | 133,222 |
| Sheep skins, with wool | 1,034,822 | 595,915 | 1,029,620 |
| Sheep skins, without wool | 5,225,158 | 6,521,623 | 8,545,648 |
| Other hides and skins | 127,304 | 155,504 | 248,081 |
| Wool | 97,171,793 | 80,281,366 | 103,771,636 |
| Edible tallow | 765,173 | 845,434 | 638,212 |
| Inedible tallow | 2,572,217 | 2,680,965 | 2,259,129 |
| Agricultural products – | |||
| Apples | 2,246,843 | 2,260,924 | 2,551,757 |
| Hops | 56,127 | 22,611 | 83 |
| Potatoes | 60,500 | 66,654 | 77,405 |
| Onions | 55,369 | 88,499 | 97,695 |
| Canned vegetables | 321,733 | 204,418 | 154,299 |
| Frozen vegetables | 283,959 | 478,489 | 241,226 |
| Peas | 941,916 | 846,203 | 700,373 |
| Linen flax and tow | - | 2,747 | - |
| Seeds, grass and clover | 1,292,592 | 1,345,959 | 1,248,078 |
| Other New Zealand produce | 4,740,006 | 4,059,405 | 7,721,667 |
| Totals, New Zealand produce | 269,425,031 | 258,464,276 | 314,767,716 |
RE-EXPORTS - Until recent years the forwarding trade of New Zealand has never been of great significance. In most years, ships' and international aircraft stores, in which aviation spirit and bunker and lubricating oils loom largely, make up between a quarter and a third of the total re-exports. The balance is made up principally of miscellaneous stores sent to the Pacific Islands and goods returned to the United Kingdom and Australia. Munitions and war stores comprised the bulk of the large totals for the later war years.
Particulars of re-exports over a period of 21 years are contained in the next table. Specie is not included in the figures.
| £ | £ | £ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | 601,286 | 1946 | 994,612 | 1953 | 2,386,391 |
| 1940 | 767,597 | 1947 | 1,703,235 | 1954 | 2,093,328 |
| 1941 | 532,477 | 1948 | 1,354,856 | 1955 | 2,138,869 |
| 1942 | 739,063 | 1949 | 1,194,463 | 1956 | 2,383,620 |
| 1943 | 1,627,900 | 1950 | 1,420,140 | 1957 | 2,263,821 |
| 1944 | 6,105,148 | 1951 | 1,732,955 | 1958 | 2,188,588 |
| 1945 | 3,114,747 | 1952 | 2,141,980 | 1959 | 2,660,587 |
The destination of this re-export trade for the latest three years is shown in the following table.
| Country | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| United Kingdom | 411,760 | 335,812 | 584,323 |
| Hong Kong | 8,358 | 5,402 | 7,907 |
| India | 6,657 | 3,864 | 1,073 |
| Malaya | 3,669 | 446 | 3,945 |
| Singapore | 3,050 | 7,452 | 31,488 |
| Union of South Africa | 7,588 | 6,312 | 3,762 |
| Canada | 14,578 | 5,614 | 24,277 |
| Australia | 607,842 | 523,064 | 566,511 |
| Fiji | 174,240 | 170,358 | 230,219 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 15,474 | 4,548 | 3,361 |
| Nauru Island | 20,727 | 15,350 | 9,108 |
| Norfolk Island | 5,783 | 8,290 | 1,137 |
| Papua and New Guinea | 5,341 | 372 | 1,531 |
| Solomon Islands | 779 | 565 | 165 |
| Tonga | 26,923 | 18,442 | 14,863 |
| Western Samoa | 44,133 | 60,703 | 58,618 |
| German Federal Republic | 19,805 | 28,746 | 43,717 |
| Belgium | 2,429 | 588 | 4,011 |
| France | 2,088 | 2,348 | 2,384 |
| Sweden | 2,851 | 925 | 5,624 |
| Switzerland | 4,037 | 1,156 | 2,642 |
| Netherlands | 43,455 | 14,080 | 45,708 |
| Indonesia | 165 | 47,832 | 200 |
| Japan | 5,404 | 534 | 4,131 |
| United States of America | 88,132 | 93,944 | 119,833 |
| Society Islands | 849 | 532 | 25,555 |
| Foreign Antarctic regions | 141,242 | 161,047 | |
| Other countries | 24,480 | 15,268 | 15,461 |
| Ships' stores | 713,224 | 674,799 | 687,986 |
| Totals (excluding specie) | 2,263,821 | 2,188,588 | 2,660,587 |
GOODS SHIPPED TO COOK ISLANDS AND NIUE – Trade with the Cook and associated Pacific Islands is not regarded as external to New Zealand, but merely as interchange between different parts of the country, and it is therefore not included in the account of the external trade. The trade of these islands with other countries is also omitted from New Zealand trade statistics. Separate returns are made of the transactions between New Zealand and these islands, and the values of goods shipped to the islands are summarised below.
| Year | Exports | Year | Exports |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | ||
| 1948 | 291,227 | 1954 | 559,775 |
| 1949 | 278,471 | 1955 | 587,650 |
| 1950 | 210,066 | 1956 | 565,936 |
| 1951 | 525,100 | 1957 | 656,516 |
| 1952 | 478,290 | 1958 | 750,673 |
| 1953 | 490,440 | 1959 | 648,959 |
Further particulars regarding the trade of the islands will be found in Section 38, Island Territories.
GENERAL - Statistics of imports arc compiled from entries passed at the Customs. The basis of valuation is usually c.d.v. (current domestic value in the country of export at time of shipment). However in certain tables the value c.i.f. (cost including insurance and freight) is also given. Import values are expressed in terms of New Zealand currency, and import totals are exclusive of specie, except where the contrary is expressly stated.
Reference should be made to Section 22A for details of the systems of valuation of imports as now used in these tables. Section 22A also gives a summary of import totals for recent years and index numbers of the volume of import trade.
IMPORT CONTROL - Reference to import control is made in Section 22A.
CLASSIFICATION OF IMPORTS - The table following, classifying imports by broad divisions, is based on a grouping of the divisions given in the subsequent table. It illustrates the great variety of imports which New Zealand receives in exchange for its few basic exports.
| Calendar Year | Imports (c.d.v.) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food, Beverages, and Tobacco | Mineral Fuels | Chemicals, Including Manufactured Fertilisers | Base Metals and Manufactures of Metal | Machinery and Transport Equipment | Textiles, Clothing, and Footwear | Total* | |
| * Including divisions not listed. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| 1950 | 17,538 | 10,214 | 7,740 | 16,772 | 36,400 | 30,956 | 143,585 |
| 1951 | 21,439 | 10,743 | 10,151 | 20,086 | 46,226 | 43,607 | 187,758 |
| 1952 | 23,715 | 15,074 | 12,166 | 34,155 | 66,672 | 35,157 | 229,447 |
| 1953 | 19,741 | 13,067 | 8,097 | 22,871 | 47,007 | 23,573 | 163,613 |
| 1954 | 24,829 | 14,964 | 13,237 | 27,135 | 61,489 | 35,272 | 213,155 |
| 1955 | 26,226 | 16,551 | 15,801 | 35,165 | 75,456 | 37,299 | 250,661 |
| 1956 | 25,237 | 18,969 | 15,516 | 32,583 | 67,275 | 33,518 | 234,779 |
| 1957 | 27,555 | 21,879 | 17,521 | 38,637 | 74,642 | 37,638 | 261,738 |
| 1958 | 24,769 | 19,952 | 20,703 | 38,588 | 71,238 | 36,786 | 252,800 |
| 1959 | 19,289 | 18,499 | 16,725 | 32,367 | 54,967 | 28,168 | 205,076 |
In Section 22A is a description of the change made in the classification of New Zealand trade for statistical purposes as from 1 January 1955, when the Standard International Trade Classification was brought into use. Figures for several years prior to 1955 were rearranged to show the values for the sections and divisions of the SITC as they would have appeared had that classification been in use during the period, and these were published in the 1954 issue of the Report on and Analysis of External Trade Statistics.
The following table shows the values of import trade for the years 1958 and 1959 according to the sections and divisions of the Standard International Trade Classification. Both c.d.v. and c.i.f. bases of valuation are shown.
| Section and Division | 1958 | 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.d.v. | c.i.f. | c.d.v. | c.i.f. | |
| Sect. 0. Food– | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Div. 00 Live animals chiefly for food | 66 | 83 | 27 | 34 |
| ” 01 Meat and meat preparations | 366 | 375 | 306 | 313 |
| ” 02 Dairy produce, eggs, and honey | 64 | 53 | 12 | 15 |
| ” 03 Fish and fish preparations | 841 | 922 | 516 | 558 |
| ” 04 Cereals and cereal preparations | 6,405 | 7,708 | 4,725 | 5,704 |
| ” 05 Fruits and vegetables | 4,144 | 5,517 | 3,409 | 5,083 |
| ” 06 Sugar and sugar preparations | 4,001 | 4,761 | 3,041 | 3,451 |
| ” 07 Coffee, tea, cocoa, spices, and manufactures thereof | 4,156 | 5,360 | 3,704 | 4,928 |
| ” 08 Feeding stuff for animals (not including un-milled cereals) | 46 | 59 | 69 | 95 |
| ” 09 Miscellaneous food preparations | 156 | 170 | 72 | 76 |
| Totals, Section 0 | 20,246 | 25,008 | 15,881 | 20,257 |
| Sect. 1. Beverages and Tobacco – | ||||
| Div. 11 Beverages | 1,923 | 2,232 | 1,398 | 1,641 |
| ” 12 Tobacco and tobacco manufactures | 2,601 | 2,824 | 2,011 | 2,297 |
| Totals, Section 1 | 4,524 | 5,056 | 3,409 | 3,938 |
| Sect. 2. Crude Materials, Inedible, Except Fuels – | ||||
| Div. 21 Hides, skins, and fur skins, undressed | 64 | 66 | 54 | 58 |
| ” 22 Oil seeds, oil nuts, and kernels | 247 | 285 | 438 | 477 |
| ” 23 Crude rubber, including synthetic and reclaimed | 1,868 | 2,071 | 1,750 | 1,974 |
| ” 24 Wood, lumber, and cork | 2,355 | 3,434 | 1,493 | 2,238 |
| ” 25 Pulp and waste paper | 381 | 479 | 326 | 441 |
| ” 26 Textile fibres (not manufactured into yarn, thread, or fabrics, and waste) | 1,210 | 1,361 | 1,099 | 1,228 |
| ” 27 Crude fertilisers and crude minerals, excluding coal, petroleum, and precious stones | 2,754 | 5,804 | 2,793 | 5,424 |
| ” 28 Metalliferous ores and metal scrap | 8 | 9 | 12 | 14 |
| ” 29 Animal and vegetable crude materials, inedible, n.e.i. | 1,022 | 1,127 | 704 | 785 |
| Totals, Section 2 | 9,908 | 14,635 | 8,669 | 12,639 |
| Sect. 3. Mineral Fuels, Lubricants, and Related Materials – | ||||
| Div. 31 Mineral fuels, lubricants, and related materials | 19,952 | 25,209 | 18,499 | 23,696 |
| Totals, Section 3 | 19,952 | 25,209 | 18,499 | 23,696 |
| Sect. 4. Animal and Vegetable Oils and Fats – | ||||
| ” 41 Animal and vegetable oils (not essential oils), fats, greases, and derivatives | 910 | 1,026 | 622 | 702 |
| Totals, Section 4 | 910 | 1,026 | 622 | 702 |
| Sect. 5. Chemicals – | ||||
| Div. 51 Chemical elements and compounds | 5,283 | 6,033 | 4,371 | 4,998 |
| ” 52 Mineral tar and crude chemicals from coal, petroleum, and natural gas | 147 | 290 | 93 | 179 |
| ” 53 Dyeing, tanning, and colouring materials | 1,776 | 1,949 | 1,243 | 1,328 |
| ” 54 Medicinal and pharmaceutical products | 3,796 | 3,727 | 3,764 | 3,671 |
| ” 55 Essential oils and perfume materials, toilet, polishing, and cleansing preparations | 866 | 896 | 414 | 419 |
| ” 56 Fertilisers, manufactured | 1,204 | 1,839 | 1,225 | 1,697 |
| ” 59 Explosives and miscellaneous chemical materials and products | 7,632 | 7,889 | 5,615 | 5,849 |
| Totals, Section 5 | 20,703 | 22,623 | 16,725 | 18,141 |
| Sect. 6. Manufactured Goods Classified Chiefly by Material – | ||||
| Div. 61 Leather, leather manufactures n.e.i., and dressed furs | 1,009 | 1,049 | 817 | 805 |
| ” 62 Rubber manufactures n.e.i. | 1,690 | 1,615 | 1,593 | 1,510 |
| ” 63 Wood and cork manufactures (excluding furniture) | 649 | 835 | 431 | 546 |
| ” 64 Paper, paperboard, and manufactures thereof | 6,698 | 7,682 | 6,146 | 7,045 |
| ” 65 Textile yarn, fabrics, made-up articles, and related products | 33,487 | 36,396 | 26,811 | 29,216 |
| ” 66 Non-metallic mineral manufactures n.e.i. | 4,114 | 4,838 | 3,505 | 4,006 |
| ” 67 Silver, platinum, gems, and jewellery | 670 | 697 | 417 | 424 |
| ” 68 Base metals | 27,936 | 31,991 | 22,439 | 25,109 |
| ” 69 Manufactures of metal | 10,653 | 11,368 | 9,928 | 10,543 |
| Totals, Section 6 | 86,905 | 96,471 | 72,089 | 79,204 |
| Sect. 7. Machinery and Transport Equipment – | ||||
| Div. 71 Machinery other than electric | 32,264 | 33,764 | 25,196 | 26,198 |
| ” 72 Electric machinery, apparatus, and appliances | 17,428 | 18,131 | 13,614 | 13,948 |
| ” 73 Transport equipment | 21,545 | 23,914 | 16,158 | 18,123 |
| Totals, Section 7 | 71,238 | 75,809 | 54,968 | 58,269 |
| Sect. 8. Miscellaneous Manufactured Articles – | ||||
| Div. 81 Prefabricated buildings, sanitary, plumbing, heating and lighting fixtures, and fittings | 715 | 797 | 474 | 526 |
| ” 82 Furniture and fixtures | 236 | 278 | 68 | 73 |
| ” 83 Travel goods, handbags, and similar articles | 56 | 62 | 3 | 3 |
| ” 84 Clothing | 2,310 | 2,517 | 1,047 | 1,129 |
| ” 85 Footwear | 989 | 1,080 | 311 | 343 |
| ” 86 Professional, scientific, and controlling instruments; photographic and optical goods, watches, and clocks | 4,668 | 4,438 | 4,083 | 3,711 |
| ” 89 Miscellaneous manufactured articles n.e.i. | 8,876 | 9,516 | 7,115 | 7,607 |
| Totals, Section 8 | 17,851 | 18,687 | 13,101 | 13,392 |
| Sect. 9. Miscellaneous Transactions and Commodities n.e.i. – | ||||
| Div. 92 Live animals, not for food | 65 | 33 | 66 | 30 |
| ” 93 Returned goods and special transactions | 104 | 89 | 85 | 81 |
| ” 95 Unclassified goods under £10 in value | 344 | 379 | .. | .. |
| Unclassified goods under £20 in value | .. | .. | 913 | 1,018 |
| ” 99 Gold | 52 | 52 | 51 | 50 |
| Totals, Section 9 | 564 | 553 | 1,115 | 1,179 |
| Grand totals, merchandise imports | 252,800 | 285,077 | 205,076 | 231,417 |
The next classification presented is that according to the purpose or use of commodities, particulars being given for the years 1947, 1957, 1958, and 1959. It should be mentioned that the absence of essential information in regard to actual purpose or use of a number of commodities has created certain difficulties, necessitating the employment of arbitrary decisions in some instances. Where certain commodities are used for more than one purpose it has not been possible to segregate the portion applicable to each, in such cases the whole import has been assessed according to the principal use of the article or commodity in New Zealand. The basis of valuation is c.d.v.
| Class of Merchandise | 1947 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Producers' materials – | ||||
| Building and construction | 5,013 | 11,725 | 9,399 | 7,713 |
| Farm | 2,519 | 4,691 | 4,376 | 4,044 |
| Manufacturing – | ||||
| Food | 7,122 | 12,750 | 11,965 | 9,237 |
| Beverages | 239 | 590 | 1,111 | 981 |
| Tobacco | 1,109 | 1,681 | 2,108 | 1,978 |
| Textiles (apparel or household goods) | 20,346 | 22,999 | 24,793 | 20,610 |
| Other | 20,438 | 57,966 | 64,738 | 53,938 |
| Fuels and lubricants | 6,421 | 21,002 | 19,220 | 17,790 |
| Auxiliary aids to production | 3,473 | 4,278 | 4,124 | 3,484 |
| Producers' equipment – | ||||
| Farm | 2,140 | 7,640 | 6,130 | 3,702 |
| Commerce and industry | 16,602 | 40,489 | 41,141 | 33,371 |
| Transport equipment — | ||||
| Railway | 1,426 | 4,964 | 5,655 | 2,472 |
| Road | 12,799 | 20,645 | 16,752 | 13,040 |
| Other | 286 | 1,473 | 1,182 | 1,778 |
| Consumers' goods— | ||||
| Food | 2,552 | 6,805 | 5,406 | 4,207 |
| Beverages | 3,068 | 5,766 | 4,580 | 3,764 |
| Tobacco | 1,980 | 1,032 | 539 | 61 |
| Clothing and accessories | 4,717 | 5,202 | 4,111 | 1,845 |
| Household equipment | 6,835 | 11,841 | 9,428 | 5,771 |
| Other | 8,291 | 16,426 | 14,119 | 12,126 |
| Unclassified | 1,264 | 1,773 | 1,924 | 3,165 |
| Totals, merchandise imports | 128,641 | 261,738 | 252,800 | 205,076 |
In the next table particulars are given of New Zealand's import trade for the years 1947, 1957, 1958, and 1959, according to the stage of production or degree of manufacture of commodities, the divisions used being “crude”, “simply transformed”, and “more elaborately transformed”. The basis of valuation is c.d.v.
| — | 1947 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Including unclassified items. | ||||
| Producers' materials – | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Crude | 8,929 | 15,512 | 16,205 | 14,517 |
| Simply transformed | 12,897 | 38,208 | 38,953 | 32,089 |
| More elaborately transformed | 34,960 | 58,683 | 63,333 | 51,895 |
| Fuels and lubricants – | ||||
| Crude | 1,814 | 50 | 1 | 2 |
| Simply transformed | 4,607 | 20,952 | 19,219 | 17,788 |
| More elaborately transformed | - | - | - | - |
| Auxiliary aids to production – | ||||
| Crude | - | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | 88 | 710 | 889 | 553 |
| More elaborately transformed | 3,473 | 4,278 | 4,124 | 3,484 |
| Producers' equipment – | ||||
| Crude | 89 | 40 | 66 | 29 |
| Simply transformed | 88 | 710 | 889 | 553 |
| More elaborately transformed | 18,566 | 47,379 | 46,316 | 36,491 |
| Transport equipment – | ||||
| Crude | - | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | 576 | 2,697 | 2,306 | 1,112 |
| More elaborately transformed | 13,935 | 24,386 | 21,282 | 16,177 |
| Consumers' goods – | ||||
| Crude | 3,832 | 6,093 | 5,743 | 5,218 |
| Simply transformed | 250 | 588 | 456 | 274 |
| More elaborately transformed | 24,625 | 40,391 | 31,984 | 22,281 |
| Total merchandise imports *– | ||||
| Crude | 14,664 | 21,695 | 22,018 | 19,768 |
| Simply transformed | 18,418 | 63,155 | 61,823 | 51,816 |
| More elaborately transformed | 95,559 | 176,888 | 168,960 | 133,491 |
| Totals, all merchandise* | 128,641 | 261,738 | 252,800 | 205,076 |
An indication of the changes that have occurred during the same period is contained in the next table, which gives the figures for each of the divisions as percentages of total imports.
| 1947 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Including unclassified items. | ||||
| Producers' materials – | Per Cent | |||
| Crude | 6.9 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 7.1 |
| Simply transformed | 10.0 | 14.6 | 15.4 | 15.6 |
| More elaborately transformed | 27.2 | 22.4 | 25.1 | 25.3 |
| Fuels and lubricants – | ||||
| Crude | 1.4 | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | 3.6 | 8.0 | 7.6 | 8.7 |
| More elaborately transformed | - | - | - | - |
| Auxiliary aids to production – | ||||
| Crude | - | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | - | - | - | - |
| More elaborately transformed | 2.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| Producers' equipment – | ||||
| Crude | - | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | - | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| More elaborately transformed | 14.4 | 18.1 | 18.3 | 17.8 |
| Transport equipment | ||||
| Crude | - | - | - | - |
| Simply transformed | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| More elaborately transformed | 10.8 | 9.3 | 8.4 | 7.9 |
| Consumers' goods – | ||||
| Crude | 3.0 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Simply transformed | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| More elaborately transformed | 19.1 | 15.4 | 12.7 | 10.9 |
| Total merchandise imports –* | ||||
| Crude | 11.4 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9.6 |
| Simply transformed | 14.3 | 24.1 | 24.5 | 25.3 |
| More elaborately transformed | 74.3 | 67.6 | 66.8 | 65.1 |
| Totals, all merchandise* | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
While there has been no marked change in the proportions of various classes of goods imported in the last few years, the above percentages indicate a tendency for proportions of “crude” and “simply transformed” to increase at the expense of “more elaborately transformed”.
DIRECTION OF IMPORT TRADE – The United Kingdom has been the chief supplier of New Zealand imports since the eighties of last century. Prior to that the main supply was from Australia. In the years following the Second World War, the proportion of the import trade received from the United Kingdom rose from 47.8 per cent in 1946 to a maximum of 60.1 per cent in 1950. Since 1950 there has been an overall decline, and in 1959 only 47.3 per cent of imports came from that source. The trade with Australia in most of the recent years has been between 10 and 14 per cent of the total. In 1957 and 1958, however, it rose to 17.3 percent, and in 1959 to 18.1 per cent.
The principal changes in the direction of the import trade are illustrated in the table in Section 22A giving the percentages received from the United Kingdom, other Commonwealth countries, European, and other countries. It will be seen that European countries are now playing a greater part in providing New Zealand's import requirements.
The table which follows shows imports (valuation c.d.v.) during the latest 11 years from the United Kingdom, other British Commonwealth countries, and other countries.
| Year | Country where Purchased | Country of Origin | Total Merchandise Imports | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Other British Commonwealth Countries | Other Countries | United Kingdom | Other British Commonwealth Countries | Other Countries | ||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| 1949 | 60,517 | 29,507 | 19,098 | 59,976 | 28,510 | 20,635 | 109,121 |
| 1950 | 87,583 | 33,254 | 22,747 | 86,241 | 32,353 | 24,990 | 143,584 |
| 1951 | 102,804 | 47,946 | 37,007 | 100,620 | 46,430 | 40,709 | 187,758 |
| 1952 | 129,213 | 50,856 | 49,378 | 125,991 | 48,734 | 54,722 | 229,447 |
| 1953 | 93,496 | 41,621 | 28,496 | 92,352 | 40,768 | 30,493 | 163,613 |
| 1954 | 122,010 | 52,027 | 39,118 | 120,714 | 51,002 | 41,439 | 213,155 |
| 1955 | 140,540 | 59,787 | 50,335 | 137,831 | 59,453 | 53,377 | 250,661 |
| 1956 | 129,226 | 58,490 | 47,063 | 126,144 | 58,858 | 49,777 | 234,779 |
| 1957 | 136,623 | 70,759 | 54,357 | 134,488 | 70,640 | 56,610 | 261,738 |
| 1958 | 133,685 | 69,661 | 49,455 | 132,804 | 68,454 | 51,543 | 252,800 |
| 1959 | 97,705 | 59,372 | 47,999 | 96,971 | 58,725 | 49,380 | 205,076 |
The next table shows in more detail the principal countries from which New Zealand draws its imports, figures on the basis of country of origin being given for the years 1957 to 1959 on a c.d.v. basis of valuations.
| Country | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| British Commonwealth Countries, Protected States, and Trust Territories | |||
| Europe – | £ | £ | £ |
| United Kingdom | 134,487,755 | 132,803,804 | 96,970,987 |
| Cyprus | 828 | 59,946 | 68,740 |
| Malta | 23,186 | 14,710 | 13,217 |
| Asia – | |||
| Aden Colony and Aden Protectorate | 720,766 | 80,021 | 383,143 |
| Bahrain | 903,872 | 939,751 | 978,697 |
| North Borneo | 18,935 | 31,229 | 23,528 |
| Sarawak | 33,291 | 45,056 | 23,259 |
| Ceylon | 2,577,999 | 2,202,991 | 2,206,440 |
| Malaya | 1,897,971 | 1,823,941 | 1,791,296 |
| Hong Kong | 961,736 | 956,972 | 806,045 |
| India | 4,976,535 | 5,985,880 | 4,307,784 |
| Kuwait | - | - | 152,614 |
| Pakistan | 60,454 | 72,115 | 147,619 |
| Singapore | 1,323,477 | 1,152,244 | 869,033 |
| Africa – | |||
| Seychelles | 28 | 69,169 | 15 |
| Gambia and Sierra Leone | - | - | 757 |
| Ghana | 286,427 | 513,192 | 535,001 |
| Nigeria | 4,476 | 8,102 | 8,395 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 183,076 | 365,738 | 363,092 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 29,596 | 109,248 | 98,622 |
| Mauritius | 33,464 | 26,535 | 8,293 |
| Swaziland, Bechuanaland, Basutoland | 103 | 525 | - |
| Tanganyika Territory | 256,791 | 307,641 | 204,161 |
| Union of South Africa | 1,200,938 | 1,175,232 | 1,077,966 |
| Zanzibar | 3,122 | 4,764 | 1,729 |
| Other | - | 30 | 46 |
| America - | |||
| Bermuda | - | 11,553 | - |
| British Guiana | 29,881 | 7,487 | 7,502 |
| Jamaica | 257,811 | 226,680 | 109,929 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 344,186 | 136,118 | 111,067 |
| Canada | 6,633,627 | 5,925,179 | 4,801,648 |
| Other | 1,139 | 2,849 | 2,999 |
| Pacific – | |||
| Australia | 45,184,800 | 43,679,697 | 37,103,578 |
| Fiji | 1,436,919 | 1,217,700 | 987,693 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 174,128 | 90,731 | 159,291 |
| Nauru Island | 623,845 | 538,497 | 514,761 |
| New Zealand (re-imports) | 58,313 | 82,225 | 85,496 |
| Tonga | 52,263 | 28,982 | 64,700 |
| Western Samoa | 336,747 | 550,527 | 667,807 |
| Other | 9,707 | 10,286 | 38,712 |
| Totals, British Commonwealth countries | 205,128,192 | 201,257,347 | 155,695,662 |
| Other Countries | |||
| Europe – | |||
| Austria | 438,687 | 429,695 | 328,913 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 2,012,876 | 1,939,159 | 1,513,147 |
| Czechoslovakia | 437,286 | 446,254 | 263,910 |
| Denmark | 481,907 | 369,778 | 305,168 |
| Finland | 68,738 | 110,129 | 98,184 |
| France | 1,768,767 | 1,825,914 | 1,303,689 |
| German Federal Republic | 7,815,859 | 7,612,967 | 6,194,304 |
| German Democratic Republic | 99,063 | 125,778 | 95,069 |
| Greece | 18,316 | 19,266 | 2,815 |
| Republic of Ireland | 33,712 | 42,676 | 122,347 |
| Italy | 1,599,884 | 1,502,333 | 1,465,956 |
| Netherlands | 2,450,328 | 3,139,872 | 2,431,656 |
| Norway | 742,392 | 832,065 | 685,969 |
| Poland | 6,528 | 13,970 | 10,524 |
| Portugal | 218,722 | 261,175 | 159,185 |
| Russia (U.S.S.R.) | 41,555 | 64,375 | 43,746 |
| Spain | 171,940 | 215,973 | 138,367 |
| Sweden | 2,540,859 | 1,982,727 | 2,325,574 |
| Switzerland | 1,849,199 | 1,756,412 | 1,629,919 |
| Turkey | 67,874 | 57,601 | 49,259 |
| Yugoslavia | 6,852 | 11,323 | 1,673 |
| Other | 4,260 | 8,350 | 7,906 |
| Asia – | |||
| Burma | 1,893 | 4,789 | 713 |
| China | 340,764 | 437,697 | 418,586 |
| Formosa | 12,072 | 13,384 | 9,765 |
| Indonesia | 5,703,950 | 3,094,213 | 2,134,788 |
| Iran | 1,412,983 | 1,347,278 | 1,673,120 |
| Iraq | 117,811 | 106,221 | 73,625 |
| Japan | 2,236,328 | 2,832,152 | 3,584,121 |
| Philippines | 29,581 | 62,888 | 57,173 |
| Saudi Arabia | 650,107 | 663,253 | 1,356,061 |
| Thailand | 40,584 | 29,675 | 40,797 |
| Other | 16,355 | 9,486 | 6,702 |
| Africa – | |||
| Algeria | 2,067 | 4,792 | 19,788 |
| Belgian Congo | 4,554 | 5,379 | 2,668 |
| Ethiopia | 35,966 | 41,201 | 27,204 |
| Egypt | 1,595 | 1,329 | 2,411 |
| Tunisia | 8,177 | - | 123 |
| Sudan | 11,277 | 24,321 | 18,251 |
| Other | 6,553 | 14,188 | 7,937 |
| America – | |||
| Argentina | 23,480 | 8,647 | 2,892 |
| Brazil | 56,629 | 60,295 | 54,602 |
| Chile | 55,524 | 64,387 | 26,837 |
| Ecuador | 23,029 | 5,141 | 2,408 |
| Mexico | 55,925 | 48,335 | 212,390 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 1,643,485 | 1,996,253 | 3,024,370 |
| Peru | 544,817 | 319,528 | 299,521 |
| United States of America | 20,543,180 | 17,173,171 | 16,739,228 |
| Venezuela | 33,852 | 110,841 | 166,612 |
| Other | 1,735 | 2,384 | 15,501 |
| Pacific Islands – | |||
| French Oceania | 108,760 | 281,154 | 207,820 |
| Other | 11,318 | 12,904 | 17,152 |
| Totals, other countries | 56,609,955 | 51,543,078 | 49,380,446 |
| Totals, all countries | 261,738,147 | 252,800,425 | 205,076,108 |
The following table shows for the last 11 years the percentage of the value on basis of the country of origin of total imports (excluding specie) received into New Zealand.
| Country | 1949 | 1950 | 1951 | 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | |||||||||||
| United Kingdom | 55.13 | 60.06 | 53.59 | 54.91 | 56.45 | 56.63 | 54.99 | 53.73 | 51.38 | 52.53 | 47.29 |
| Bahrain | 1.26 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 1.17 | 1.77 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.36 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.48 |
| Ceylon | 1.41 | 1.26 | 1.84 | 0.59 | 1.19 | 1.24 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 1.08 |
| India | 2.55 | 1.41 | 3.21 | 1.02 | 1.10 | 1.28 | 1.29 | 1.47 | 1.90 | 2.37 | 2.10 |
| Pakistan | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 0.75 | 0.93 | 1.97 | 0.78 | 1.87 | 2.26 | 1.77 | 1.35 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.30 |
| Union of South Africa | 0.40 | 0.62 | 0.83 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.53 |
| Canada | 3.87 | 2.26 | 2.98 | 3.52 | 1.40 | 2.06 | 3.34 | 2.67 | 2.53 | 2.34 | 2.34 |
| Australia | 12.79 | 12.05 | 10.29 | 10.62 | 14.45 | 12.90 | 12.16 | 14.19 | 17.26 | 17.28 | 18.09 |
| Fiji | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 1.02 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.48 |
| Other British Commonwealth countries | 2.19 | 2.21 | 2.03 | 1.96 | 1.62 | 1.59 | 1.93 | 1.99 | 1.71 | 1.71 | 216 |
| Totals, British Commonwealth countries | 81.13 | 82.60 | 78.32 | 76.15 | 81.37 | 80.56 | 78.71 | 78.80 | 78.37 | 79.61 | 75.92 |
| Belgium | 1.64 | 0.74 | 1.46 | 2.09 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.74 |
| France | 0.34 | 0.77 | 113 | 1.58 | 1.20 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.64 |
| German Federal Republic | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 2.05 | 2.74 | 2.81 | 2.99 | 3.01 | 3.02 |
| Netherlands | 0.21 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 0.70 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 1.24 | 1.19 |
| Italy | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.71 |
| Sweden | 0.56 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 1.36 | 1.21 | 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 0.78 | 1.13 |
| Switzerland | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.79 |
| Iran | 1.49 | 2.31 | 1.27 | 0.09 | -- | -- | 0.35 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.82 |
| Japan | 0.30 | 0.30 | 1.18 | 1.64 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 1.01 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 1.12 | 1.75 |
| Indonesia | 1.93 | 2.13 | 1.95 | 2.13 | 1.68 | 1.14 | 1.85 | 2.69 | 2.18 | 1.22 | 1.04 |
| Netherlands Antilles | -- | -- | 0.13 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 1.09 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 1.47 |
| United States of America | 9.62 | 7.29 | 9.38 | 9.26 | 7.42 | 8.20 | 8.50 | 7.58 | 7.85 | 6.79 | 8.16 |
| Other countries | 2.05 | 2.14 | 2.04 | 2.07 | 2.91 | 1.78 | 1.78 | 1.64 | 1.91 | 2.14 | 2.62 |
| Totals, other countries | 18.87 | 17.40 | 21.68 | 23.85 | 18.63 | 19.44 | 21.29 | 21.20 | 21.63 | 20.39 | 24.08 |
Origin of Principal Imports - The table which follows shows details of commodity imports, by country of origin, where the trade with any country is of the value of £10,000 or over for any of the years 1957 to 1959. C.d.v. basis of valuation is used.
| Country of Origin | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canned Fish | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 99 | 65 | 61 |
| Union of South Africa | 14 | 9 | 3 |
| Canada | 619 | 387 | 245 |
| Norway | 133 | 122 | 71 |
| Japan | 93 | 89 | 53 |
| Other countries | 12 | 10 | 11 |
| Totals | 970 | 682 | 444 |
| Canned Fruit | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 22 | 18 | 2 |
| Ceylon | 28 | 6 | 3 |
| Malaya | 153 | 127 | 117 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 28 | 30 | 11 |
| Union of South Africa | 285 | 295 | 89 |
| Australia | 479 | 149 | 204 |
| Other countries | 9 | 20 | 7 |
| Totals | 1,014 | 645 | 433 |
| Dried Fruits | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Union of South Africa | 38 | 51 | 11 |
| Australia | 904 | 1,044 | 880 |
| Iran | 25 | 62 | 49 |
| Iraq | 116 | 106 | 74 |
| Spain | 9 | 29 | 2 |
| Turkey | 19 | 21 | 25 |
| United States of America | 253 | 227 | 125 |
| Other countries | 6 | 2 | 1 |
| Totals | 1,370 | 1,542 | 1,166 |
| Bananas | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Fiji | 139 | 94 | 23 |
| Tonga | 42 | 18 | 52 |
| Western Samoa | 100 | 274 | 303 |
| Ecuador | 17 | - | - |
| Other countries | - | 1 | - |
| Totals | 298 | 387 | 377 |
| Oranges | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Cyprus | - | 56 | 66. |
| Union of South Africa | 60 | 31 | 41 |
| Jamaica | 145 | 124 | 72 |
| Australia | 521 | 442 | 411 |
| United States of America | 51 | 19 | 117 |
| Totals | 777 | 672 | 707 |
| Peanuts | |||
| -£(000) | |||
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 6 | 11 | 5 |
| Tanganyika | 12 | 23 | 21 |
| Union of South Africa | 147 | 125 | 94 |
| China | 29 | 17 | 6 |
| India | - | - | 38 |
| Indonesia | 13 | 4 | 1 |
| Other countries | 16 | 6 | 1 |
| Totals | 223 | 186 | 167 |
| Wheat | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Australia | 6,059 | 5,816 | 4,347 |
| Raw Sugar | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Australia | 2,883 | 2,654 | 1,897 |
| Fiji | 1,239 | 910 | 884 |
| Indonesia | 143 | - | - |
| Totals | 4,266 | 3,564 | 2,781 |
| Cocoa Beans (Raw) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Ghana | 256 | 467 | 495 |
| Western Samoa | 30 | 227 | 99 |
| Other countries | 4 | - | - |
| Totals | 290 | 695 | 594 |
| Coffee Beans (Raw) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| India | 9 | 16 | 3 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 130 | 210 | 195 |
| Tanganyika | 36 | 53 | 54 |
| Papua | 6 | 9 | 38 |
| Indonesia | 21 | 26 | 3 |
| Ethiopia | 11 | 17 | 13 |
| Brazil | 4 | 10 | 10 |
| Costa Rica | - | - | 11 |
| Other countries | 13 | 17 | 14 |
| Totals | 230 | 358 | 339 |
| Tea | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Ceylon | 2,385 | 2,055 | 2,018 |
| India | 304 | 282 | 217 |
| Indonesia | 28 | 56 | 25 |
| Other countries | 17 | 12 | 4 |
| Totals | 2,734 | 2,405 | 2,264 |
| Beverage Spirits | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,862 | 1,437 | 1,101 |
| Jamaica | 46 | 33 | 13 |
| Australia | 38 | 60 | 33 |
| France | 235 | 168 | 92 |
| Netherlands | 36 | 22 | 24 |
| Other countries | 39 | 19 | 12 |
| Totals | 2,256 | 1,739 | 1,275 |
| Cigarettes | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 785 | 305 | 30 |
| Australia | 71 | 127 | |
| Switzerland | 16 | 8 | - |
| Other countries | 6 | 4 | 1 |
| Totals | 878 | 444 | 30 |
| Tobacco | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 20 | 9 | 2 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 5 | 85 | 86 |
| Canada | 6 | 19 | 24 |
| Netherlands | 11 | 10 | - |
| United States of America | 1,663 | 1,998 | 1,846 |
| Other countries | 11 | 7 | 23 |
| Totals | 1,716 | 2,128 | 1,980 |
| Wool | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 115 | 97 | 79 |
| Australia | 418 | 405 | 396 |
| Other countries | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Totals | 538 | 504 | 477 |
| Kapok | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Ceylon | 7 | 12 | 1 |
| India | 24 | 26 | 10 |
| China | - | 25 | 13 |
| Indonesia | 127 | 89 | 41 |
| Thailand | 4 | 9 | 13 |
| Other countries | 6 | 8 | 7 |
| Totals | 169 | 169 | 84 |
| Hat Hoods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 92 | 106 | 83 |
| Australia | 15 | 13 | 8 |
| Czechoslovakia | 41 | 45 | 21 |
| France | 18 | 37 | 23 |
| Italy | 101 | 111 | 75 |
| China | 19 | 25 | 24 |
| Formosa | 9 | 11 | 8 |
| Japan | 18 | 6 | 6 |
| Other countries | 31 | 29 | 16 |
| Totals | 344 | 383 | 264 |
| Hosiery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 425 | 200 | 20 |
| Other countries | 13 | 4 | - |
| Totals | 438 | 205 | 21 |
| Cloves | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 132 | 113 | 65 |
| Malta | 19 | 14 | 13 |
| Hong Kong | 54 | 48 | 34 |
| France | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| German Federal Republic | 75 | 79 | 54 |
| Other countries | 20 | 16 | 7 |
| Totals | 310 | 275 | 177 |
| Infants' Wear | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 439 | 475 | 314 |
| Hong Kong | 74 | 51 | 35 |
| Other countries | 13 | 8 | 7 |
| Totals | 526 | 534 | 356 |
| Footwear | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 880 | 845 | 255 |
| Hong Kong | 25 | 44 | 7 |
| India | 26 | 20 | 13 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 22 | 26 | 10 |
| Australia | 10 | 5 | 12 |
| Italy | 19 | 8 | 2 |
| Netherlands | 35 | 30 | 9 |
| Other countries | 7 | 11 | 3 |
| Totals | 1,024 | 989 | 311 |
| Made-up Sheets, Tablecloths, Table Napkins, and Towels | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,107 | 877 | 785 |
| Hong Kong | 48 | 40 | 27 |
| India | 75 | 49 | 55 |
| Canada | 17 | - | 6 |
| Czechoslovakia | 40 | 49 | 28 |
| German Federal Republic | 22 | 15 | 17 |
| Netherlands | 21 | 15 | 9 |
| Japan | 41 | 29 | 124 |
| Other countries | 29 | 34 | 29 |
| Totals | 1,400 | 1,108 | 1,079 |
| Cheese Bandages and Meat Wraps | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 944 | 734 | 740 |
| Hong Kong | 37 | 60 | 108 |
| India | 31 | 74 | 53 |
| Other countries | 1 | ||
| Totals | 1,012 | 869 | 902 |
| Woven Cotton Piece Goods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 5,522 | 5,593 | 4,127 |
| Hong Kong | 101 | 226 | 249 |
| India | 922 | 736 | 930 |
| Canada | 18 | 27 | 13 |
| Australia | 48 | 48 | 62 |
| Austria | 35 | 42 | 48 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 139 | 147 | 158 |
| Czechoslovakia | 75 | 89 | 103 |
| France | 76 | 61 | 82 |
| German Federal Republic | 250 | 459 | 315 |
| Italy | 70 | 54 | 77 |
| Netherlands | 84 | 137 | 189 |
| Spain | 13 | 26 | 27 |
| Sweden | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| Switzerland | 194 | 216 | 173 |
| China | - | 14 | 34 |
| Japan | 775 | 1,274 | 1,472 |
| United States of America | 527 | 253 | 225 |
| Other countries | 10 | 9 | 10 |
| Totals | 8,865 | 9,419 | 8,307 |
| Rayon Piece Goods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,890 | 1,888 | 1,204 |
| Australia | 24 | 38 | 29 |
| Austria | 7 | 12 | 10 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 22 | 14 | 8 |
| France | 82 | 88 | 62 |
| German Federal Republic | 414 | 313 | 242 |
| German Democratic Republic | 21 | 19 | 36 |
| Italy | 81 | 93 | 98 |
| Netherlands | 112 | 97 | 92 |
| Spain | 2 | 5 | 12 |
| Switzerland | 65 | 89 | 51 |
| Japan | 365 | 286 | 366 |
| United States of America | 347 | 365 | 345 |
| Other countries | 14 | 15 | 11 |
| Totals | 3,446 | 3,323 | 2,566 |
| Nylon Piece Goods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 511 | 481 | 267 |
| Australia | 15 | 21 | 24 |
| Austria | 17 | 12 | 18 |
| France | 47 | 16 | 15 |
| German Federal Republic | 9 | 16 | 8 |
| Italy | 37 | 81 | 74 |
| Switzerland | 29 | 44 | 44 |
| Japan | 80 | 34 | 75 |
| United States of America | 173 | 84 | 78 |
| Other countries | 19 | 12 | 1 |
| Totals | 937 | 802 | 605 |
| Woollen Piece Goods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 2,901 | 2,841 | 1,881 |
| Australia | 68 | 41 | 36 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 28 | 64 | 52 |
| German Federal Republic | 21 | 18 | 10 |
| Italy | 41 | 30 | 24 |
| Japan | - | - | 16 |
| Other countries | 17 | 11 | 20 |
| Totals | 3,076 | 3,006 | 2,039 |
| Jute and Hessian Piece Goods | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 123 | 98 | 42 |
| India | 561 | 438 | 401 |
| Other countries | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| Totals | 686 | 539 | 453 |
| Bags, Sacks, and Woolpacks | |||
| £(000) | |||
| India | 1,488 | 1,330 | 1,031 |
| Pakistan | - | - | 80 |
| Other countries | 19 | 5 | 5 |
| Totals | 1,507 | 1,335 | 1,116 |
| Woollen Carpets (Rolls, Squares, and Rugs) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,877 | 1,634 | 318 |
| India | 36 | 40 | 6 |
| Australia | 11 | 11 | 1 |
| Czechoslovakia | 4 | 10 | 1 |
| Other countries | 16 | 8 | 2 |
| Totals | 1,944 | 1,703 | 328 |
| Linoleum and Congoleum | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 946 | 612 | 753 |
| Australia | 19 | 7 | 6 |
| India | 19 | 2 | 1 |
| Other countries | 10 | 1 | 11 |
| Totals | 994 | 622 | 772 |
| Cotton Threads | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 613 | 683 | 685 |
| Australia | 27 | 42 | 37 |
| United States of America | 2 | 4 | 31 |
| Other countries | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Totals | 643 | 729 | 756 |
| Cotton Yarn | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 533 | 694 | 607 |
| Hong Kong | - | 17 | 117 |
| Australia | 47 | 52 | 23 |
| Other countries | 3 | 6 | 8 |
| Totals | 583 | 770 | 755 |
| Synthetic Yarn | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 579 | 1,051 | 889 |
| France | 11 | 14 | 6 |
| German Federal Republic | 4 | 13 | 6 |
| Netherlands | 41 | 57 | 49 |
| Norway | 4 | 18 | 44 |
| Switzerland | 1 | 12 | 11 |
| United States of America | 50 | 42 | 49 |
| Other countries | 4 | 12 | 19 |
| Totals | 695 | 1,220 | 1,073 |
| Wool Yarn | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,510 | 1,621 | 1,213 |
| Australia | 52 | 73 | 37 |
| Other countries | - | - | 2 |
| Totals | 1,562 | 1,693 | 1,251 |
| Motor and Aviation Spirit | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Aden | 635 | 80 | 338 |
| Bahrain | 743 | 780 | 716 |
| India | 998 | 2,381 | 1,076 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 949 | 731 | 636 |
| Australia | 1,207 | 3,217 | 2,175 |
| Indonesia | 3,600 | 1,660 | 1,176 |
| Iran | 1,132 | 713 | 836 |
| Saudi Arabia | 557 | 294 | 538 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 1,435 | 1,627 | 2,612 |
| Peru | - | 24 | 133 |
| Venezuela | - | - | 123 |
| United States of America | 572 | 120 | 39 |
| Totals | 11,829 | 11,629 | 10,398 |
| Kerosene | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Bahrain | 16 | 43 | 17 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 31 | 12 | 77 |
| Indonesia | 293 | 227 | 302 |
| Iran | 53 | 72 | 12 |
| Saudi Arabia | - | 34 | - |
| Netherlands Antilles | - | 22 | 18 |
| Australia | - | - | 25 |
| Other countries | - | 7 | - |
| Totals | 394 | 417 | 452 |
| Diesel and Fuel Oils | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Aden | 66 | - | 45 |
| Bahrain | 145 | 112 | 228 |
| India | 15 | - | - |
| Kuwait | - | - | 153 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 245 | 251 | 47 |
| Australia | 4,207 | 2,958 | 2,539 |
| Indonesia | 1,157 | 728 | 293 |
| Iran | 190 | 419 | 753 |
| Saudi Arabia | 93 | 335 | 818 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 204 | 334 | 231 |
| Peru | 543 | 294 | 163 |
| Venezuela | - | 83 | - |
| Other countries | - | 1 | - |
| Totals | 6,866 | 5,515 | 5,270 |
| Lubricating Oils | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 529 | 628 | 676 |
| Canada | 11 | 138 | 55 |
| Australia | 8 | 16 | 28 |
| United States of America | 1,043 | 693 | 632 |
| Venezuela | 34 | 27 | 43 |
| Other countries | 13 | 17 | 10 |
| Totals | 1,639 | 1,519 | 1,444 |
| Linseed Oil | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 254 | 205 | 164 |
| India | 19 | 10 | 10 |
| Canada | - | 11 | 4 |
| Australia | 23 | 13 | 5 |
| Netherlands | 34 | 17 | 12 |
| Argentina | 23 | 2 | 2 |
| Other countries | 3 | 1 | - |
| Totals | 356 | 259 | 196 |
| Gypsum | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Australia | 66 | 95 | 112 |
| Other countries | 1 | 2 | - |
| Totals | 67 | 97 | 112 |
| Cement | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 34 | 35 | 23 |
| United States of America | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| Other countries | 4 | 6 | 5 |
| Totals | 48 | 42 | 34 |
| Iron and Steel - Pipes, Tubes, and Fittings | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,634 | 1,832 | 1,420 |
| Union of South Africa | 22 | 14 | 14 |
| Canada | 48 | 15 | 6 |
| Australia | 387 | 458 | 614 |
| Belgium | 2 | 7 | 32 |
| France | 13 | 6 | - |
| German Federal Republic | 106 | 53 | 35 |
| Netherlands | 28 | 10 | 1 |
| Sweden | 16 | 5 | 4 |
| United States of America | 65 | 45 | 122 |
| Other countries | 9 | 11 | 13 |
| Totals | 2,330 | 2,457 | 2,260 |
| Iron and Steel - Plate, Sheet, Hoop, and Strip | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 4,079 | 4,420 | 3,616 |
| Canada | 170 | 170 | 145 |
| Australia | 4,848 | 4,199 | 4,029 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 49 | 50 | 33 |
| France | 29 | 16 | 8 |
| German Federal Republic | 13 | 1 | 47 |
| United States of America | 174 | 158 | 70 |
| Other countries | 1 | 2 | 10 |
| Totals | 9,364 | 9,015 | 7,956 |
| Iron and Steel - Wire (excepting Barbed Wire) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,326 | 1,598 | 653 |
| Australia | 852 | 1,444 | 1,288 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 47 | 199 | 82 |
| France | 2 | 18 | 7 |
| German Federal Republic | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| United States of America | 13 | 2 | - |
| Other countries | - | 2 | 2 |
| Totals | 2,257 | 3,266 | 2,035 |
| Iron and Steel - Bars, Rods, Billets, Bloom, and Pig | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 2,669 | 2,136 | 865 |
| Hong Kong | - | 37 | 22 |
| Canada | 68 | 53 | 28 |
| Australia | 567 | 1,227 | 1,439 |
| Union of South Africa | 2 | - | 59 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 161 | 185 | 63 |
| France | 64 | 40 | 21 |
| German Federal Republic | 89 | 23 | 41 |
| Republic of Ireland | 17 | 8 | 90 |
| Netherlands | 12 | 1 | - |
| United States of America | 81 | 9 | 2 |
| Other countries | 12 | 12 | 6 |
| Totals | 3,743 | 3,732 | 2,637 |
| Iron and Steel - Angles, Tees, Girders, and Channels | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,086 | 1,287 | 553 |
| Australia | 323 | 448 | 613 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 133 | 29 | 3 |
| France | 23 | 6 | 2 |
| German Federal Republic | 21 | 15 | 1 |
| Netherlands | 20 | 18 | - |
| United States of America | 22 | 27 | 5 |
| Other countries | 4 | 5 | - |
| Totals | 1,631 | 1,830 | 1,177 |
| Aluminium and its Alloys | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 959 1 | ,386 | 1,279 |
| Canada | 153 | 221 | 132 |
| Australia | 52 | 74 | 89 |
| Belgium | - | - | 11 |
| German Federal Republic | 7 | 29 | 40 |
| Netherlands | 26 | 26 | 72 |
| United States of America | 65 | 57 | 9 |
| Other countries | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| Totals | 1,270 | 1,799 | 1,635 |
| Copper | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,763 | 1,681 | 1,775 |
| Canada | 188 | 312 | 250 |
| Australia | 505 | 609 | 388 |
| France | - | - | 63 |
| Other countries | 7 | 4 | 4 |
| Totals | 2,462 2 | ,606 | 2,482 |
| Tin | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 20 | 31 | 47 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 238 | 242 | 233 |
| Australia | 24 | 15 | 11 |
| Other countries | 3 | - | 4 |
| Totals | 285 | 288 | 295 |
| Artificers Tools | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 794 | 542 | 632 |
| Canada | 224 | 184 | 167 |
| Australia | 142 | 82 | 143 |
| German Federal Republic | 161 | 117 | 136 |
| Italy | 3 | 7 | 12 |
| Sweden | 31 | 32 | 40 |
| United States of America | 331 | 194 | 216 |
| Japan | 4 | 3 | 18 |
| Other countries | 14 | 14 | 19 |
| Totals | 1,705 | 1,175 | 1,383 |
| Ball and Similar Bearings | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 286 | 452 | 350 |
| Canada | 11 | 12 | 6 |
| Austria | 8 | 11 | 17 |
| German Federal Republic | 9 | 24 | 22 |
| Italy | 3 | 15 | 10 |
| Sweden | 59 | 71 | 51 |
| United States of America | 114 | 111 | 81 |
| Other countries | 7 | 13 | 21 |
| Totals | 497 | 709 | 558 |
| Electric Motors and Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 867 | 1,057 | 926 |
| Canada | 11 | 10 | 11 |
| Australia | 39 | 40 | 27 |
| German Federal Republic | 9 | 20 | 13 |
| Sweden | 35 | 38 | 34 |
| United States of America | 5 | 15 | 18 |
| Other countries | 1 | 4 | 13 |
| Totals | 966 | 1,185 | 1,042 |
| Insulated Cable and Wire | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 2,499 | 2,387 | 1,246 |
| Union of South Africa | 12 | 51 | 143 |
| Australia | 112 | 341 | 127 |
| Republic of Ireland | - | 8 | 15 |
| Netherlands | 59 | 220 | 128 |
| Sweden | 88 | 5 | 3 |
| United States of America | 11 | 2 | 1 |
| Other countries | 9 | - | 3 |
| Totals | 2,790 | 3,014 | 1,666 |
| Telegraphy and Telephony Apparatus | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 2,042 | 2,748 | 2,252 |
| Australia | 112 | 66 | 34 |
| Netherlands | 18 | 4 | 7 |
| Sweden | 81 | 18 | 6 |
| Switzerland | - | 2 | 14 |
| United States of America | 32 | 35 | 49 |
| Other countries | 18 | 29 | 22 |
| Totals | 2,303 | 2,902 | 2,835 |
| Radio and Radar Apparatus | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 457 | 406 | 596 |
| Australia | 138 | 86 | 155 |
| German Federal Republic | 43 | 46 | 48 |
| Netherlands | 152 | 211 | 220 |
| Japan | 3 | 5 | 63 |
| United States of America | 165 | 90 | 69 |
| Other countries | 12 | 17 | 13 |
| Totals | 971 | 860 | 1,163 |
| Transformers and Converters | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 498 | 723 | 345 |
| Canada | - | 1 | 114 |
| Australia | 9 | 11 | 34 |
| Austria | 41 | - | - |
| German Federal Republic | 49 | 169 | 2 |
| Italy | 13 | 17 | 155 |
| Sweden | 27 | 129 | 37 |
| Switzerland | 67 | 25 | 25 |
| Other countries | 3 | 11 | 7 |
| Totals | 708 | 1,087 | 719 |
| Tractors and Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 3,397 | 3,024 | 1,707 |
| Australia | 42 | 48 | 50 |
| German Federal Republic | 35 | 27 | 25 |
| Italy | 4 | 41 | 30 |
| United States of America | 2,332 | 1,328 | 1,152 |
| Other countries | 11 | 16 | 3 |
| Totals | 5,821 | 4,484 | 2,968 |
| Domestic Baths | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 196 | 79 | 38 |
| Other countries | - | - | - |
| Totals | 196 | 79 | 38 |
| Sewing Machines | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 364 | 275 | 152 |
| German Federal Republic | 57 | 97 | 26 |
| Italy | 101 | 42 | 54 |
| Sweden | 119 | 56 | 36 |
| Switzerland | 179 | 166 | 100 |
| Japan | 39 | 169 | 47 |
| United States of America | 104 | 81 | 62 |
| Other countries | 5 | 8 | 4 |
| Totals | 969 | 893 | 482 |
| Raw, Synthetic, and Reclaimed Rubber | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 38 | 35 | 67 |
| Ceylon | 11 | 25 | 23 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 1,297 | 1,349 | 1,385 |
| Western Samoa | 11 | 4 | - |
| Canada | 73 | 91 | 101 |
| United States of America | 192 | 364 | 167 |
| Other countries | 5 | - | 6 |
| Totals | 1,626 | 1,868 | 1,750 |
| Sawn Timber | |||
| £(000) | |||
| North Borneo | 6 | 9 | 11 |
| Malaya and Singapore | 150 | 109 | 57 |
| Hong Kong | 13 | 3 | - |
| Ghana | 26 | 44 | 38 |
| Canada | 728 | 377 | 253 |
| Australia | 575 | 507 | 283 |
| British Guiana | 21 | - | I |
| Japan | 113 | 219 | 113 |
| United States of America | 155 | 249 | 329 |
| Other countries | 22 | 31 | 14 |
| Totals | 1,810 | 1,548 | 1,096 |
| Plate and Sheet Glass | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 478 | 600 | 538 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 252 | 329 | 364 |
| France | 20 | 22 | 20 |
| German Federal Republic | 12 | 32 | 66 |
| United States of America | 15 | 6 | 9 |
| Other countries | 15 | 24 | 28 |
| Totals | 794 | 1,014 | 1,025 |
| Table Chinaware | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 757 | 713 | 486 |
| Australia | 15 | 14 | 8 |
| German Federal Republic | 42 | 33 | 26 |
| Japan | 2 | 7 | 72 |
| Other countries | 30 | 25 | 16 |
| Totals | 846 | 792 | 608 |
| Table Glassware and Tumblers | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 122 | 47 | 47 |
| Belgium | 11 | 4 | 2 |
| Czechoslovakia | 23 | 26 | 9 |
| German Federal Republic | 25 | 14 | 11 |
| Japan | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| Other countries | 18 | 12 | 17 |
| Totals | 203 | 105 | 94 |
| Newsprint | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,060 | 699 | 680 |
| Canada | 830 | 666 | 417 |
| Norway | 17 | 4 | 9 |
| Other countries | 6 | 11 | 8 |
| Totals | 1,913 | 1,381 | 1,114 |
| Other Priming Paper | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 810 | 997 | 984 |
| Canada | 122 | 115 | 106 |
| Australia | 154 | 293 | 278 |
| Austria | 11 | 26 | 18 |
| Finland | 12 | 17 | 6 |
| German Federal Republic | 13 | 15 | 20 |
| Netherlands | 18 | 15 | 14 |
| Norway | 144 | 164 | 189 |
| Sweden | 125 | 206 | 198 |
| United States of America | 32 | 25 | 33 |
| Other countries | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| Totals | 1,443 | 1,877 | 1,851 |
| Writing Paper | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 219 | 201 | 233 |
| Canada | 14 | 7 | 5 |
| Australia | 139 | 82 | 125 |
| Norway | 26 | 34 | 38 |
| Sweden | 13 | 9 | 5 |
| Other countries | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Totals | 417 | 335 | 409 |
| Books, Magazines, Newspapers, and Music | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,972 | 2,139 | 1,999 |
| Australia | 1,090 | 887 | 1,000 |
| German Federal Republic | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| Netherlands | 20 | 13 | 22 |
| Japan | 22 | 26 | 37 |
| United States of America | 312 | 263 | 349 |
| Other countries | 39 | 40 | 29 |
| Totals | 3,464 | 3,378 | 3,447 |
| Timepieces and Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 145 | 110 | 96 |
| German Federal Republic | 273 | 176 | 145 |
| Switzerland | 423 | 261 | 201 |
| Other countries | 14 | 13 | 10 |
| Totals | 855 | 559 | 452 |
| Common Salt | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 282 | 299 | 256 |
| Australia | 62 | 90 | 100 |
| Other countries | 4 | 4 | 11 |
| Totals | 348 | 394 | 366 |
| Crude Sulphur | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Mexico | 50 | 39 | 199 |
| United States of America | 870 | 593 | 623 |
| Other countries | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Totals | 923 | 634 | 824 |
| Rock Phosphate | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 174 | 91 | 159 |
| Nauru Island | 624 | 538 | 515 |
| French Oceania | 109 | 281 | 208 |
| Totals | 907 | 910 | 882 |
| Basic Slag | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 300 | 315 | 192 |
| Japan | 71 | - | - |
| Other countries | - | 1 | - |
| Totals | 371 | 316 | 192 |
| Chloride (Muriate) of Potash | |||
| £(000) | |||
| France | 177 | 337 | 208 |
| German Federal Republic | 56 | 105 | 225 |
| German Democratic Republic | 12 | 1 | 2 |
| United States of America | 170 | 104 | 300 |
| Other countries | - | 2 | - |
| Totals | 415 | 549 | 735 |
| Aircraft and Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 188 | 186 | 195 |
| Australia | 15 | 10 | 38 |
| United States of America | 583 | 420 | 735 |
| Other countries | 8 | 3 | 14 |
| Totals | 793 | 620 | 982 |
| Bicycles | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 327 | 247 | 242 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1 | 10 | 1 |
| Other countries | 1 | - | 1 |
| Totals | 329 | 257 | 244 |
| Motor Cycles | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 86 | 82 | 36 |
| Austria | 21 | 26 | 4 |
| Czechoslovakia | 4 | 11 | 1 |
| German Federal Republic | 12 | 15 | 7 |
| Other countries | 7 | 1 | 5 |
| Totals | 130 | 135 | 52 |
| Motorcars | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 10,878 | 8,177 | 6,832 |
| Canada | 747 | 664 | 415 |
| Australia | 1,661 | 686 | 745 |
| Czechoslovakia | 57 | 31 | 8 |
| France | 175 | 168 | 21 |
| German Federal Republic | 643 | 414 | 305 |
| Italy | 67 | 50 | 13 |
| United States of America | 136 | 136 | 9 |
| Totals | 14,366 | 10,325 | 8,348 |
| Buses, Lorries, Trucks, and Vans | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 3,121 | 3,244 | 2,519 |
| Australia | 360 | 414 | 261 |
| German Federal Republic | 120 | 219 | 58 |
| United States of America | 79 | 50 | 34 |
| Other countries | - | 3 | 1 |
| Totals | 3,680 | 3,930 | 2,873 |
| Motor-vehicle Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,906 | 1,707 | 1,581 |
| Canada | 93 | 87 | 58 |
| Australia | 246 | 262 | 238 |
| France | 11 | 12 | 7 |
| German Federal Republic | 91 | 94 | 67 |
| United States of America | 239 | 168 | 154 |
| Other countries | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| Totals | 2,591 | 2,337 | 2,112 |
| Railway and Tramway Vehicles and Parts | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,175 | 2,069 | 947 |
| Australia | 725 | 628 | 82 |
| Italy | - | 53 | 3 |
| Switzerland | 10 | - | - |
| United States of America | 44 | 130 | 47 |
| Other countries | 2 | 6 | 5 |
| Totals | 1,957 | 2,885 | 1,083 |
| Railway and Tramway Rails and Rail Accessories | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,276 | 1,395 | 576 |
| Australia | 69 | 273 | 234 |
| Belgium | 8 | - | 12 |
| Italy | - | 13 | 31 |
| United States of America | 286 | 2 | 5 |
| Other countries | 1 | - | 1 |
| Totals | 1,640 | 1,683 | 859 |
| Pneumatic Tyres and Tubes (over 1 3/4 in. Diameter) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 368 | 394 | 351 |
| Union of South Africa | 13 | 37 | 35 |
| Canada | 61 | 41 | 76 |
| Australia | 14 | 29 | 38 |
| German Federal Republic | 18 | 29 | 37 |
| United States of America | 124 | 122 | 101 |
| Other countries | 7 | 9 | 5 |
| Totals | 606 | 662 | 643 |
| Musical Instruments, Parts, and Gramophone Records | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,215 | 1,019 | 470 |
| Australia | 221 | 67 | 21 |
| Austria | 6 | 13 | 2 |
| Czechoslovakia | 12 | 8 | 5 |
| France | 15 | 14 | 3 |
| German Federal Republic | 124 | 84 | 49 |
| Italy | 92 | 64 | 19 |
| Netherlands | 81 | 295 | 40 |
| Norway | 5 | 12 | |
| Japan | 15 | 8 | 10 |
| United States of America | 25 | 25 | 26 |
| Other countries | 20 | 12 | 7 |
| Totals | 1,831 | 1,621 | 652 |
| Thermosetting and Thermoplastic Resins | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 890 | 1,815 | 803 |
| Canada | 40 | 26 | 21 |
| Australia | 97 | 121 | 129 |
| German Federal Republic | 153 | 174 | 168 |
| Netherlands | 44 | 69 | 47 |
| United States of America | 489 | 741 | 501 |
| Other countries | 4 | 6 | 15 |
| Totals | 1,718 | 2,953 | 1,683 |
| Agricultural Machinery (Cultivating) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 182 | 159 | 98 |
| Canada | 11 | 5 | 1 |
| Australia | 127 | 106 | 71 |
| Other countries | 11 | 7 | 11 |
| Totals | 331 | 277 | 181 |
| Agricultural Machinery (Harvesting, Threshing, etc.) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 792 | 554 | 244 |
| Canada | 55 | 4 | 5 |
| Australia | 55 | 82 | 36 |
| German Federal Republic | 172 | 123 | 100 |
| France | 11 | 10 | 36 |
| Netherlands | 66 | 45 | 2 |
| Sweden | 68 | 41 | 37 |
| United States of America | 567 | 328 | 300 |
| Other countries | - | 5 | 8 |
| Totals | 1,785 | 1,193 | 767 |
| Agricultural Machinery (Dairying) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 52 | 55 | 46 |
| Australia | 26 | 23 | 4 |
| Denmark | 5 | 1 | 25 |
| German Federal Republic | 43 | 10 | 6 |
| France | 10 | 27 | 4 |
| Sweden | 31 | 49 | 40 |
| United States of America | 15 | 10 | 3 |
| Other countries | - | 3 | 1 |
| Totals | 180 | 177 | 129 |
| Builders' Hardware | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 446 | 411 | 319 |
| Australia | 162 | 96 | 71 |
| United States of America | 8 | 11 | 5 |
| Other countries | 13 | 8 | 6 |
| Totals | 629 | 525 | 401 |
| -working Machinery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,102 | 766 | 858 |
| Canada | 8 | 6 | 17 |
| Australia | 351 | 375 | 405 |
| Austria | 1 | 3 | 11 |
| Denmark | 10 | 6 | 11 |
| France | 12 | 4 | 2 |
| German Federal Republic | 158 | 132 | 123 |
| Italy | 4 | 4 | 13 |
| Sweden | 34 | 30 | 28 |
| Switzerland | 8 | 5 | 11 |
| United States of America | 165 | 147 | 186 |
| Other countries | 15 | 9 | 11 |
| Totals | 1,868 | 1,487 | 1,677 |
| Woodworking Machinery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 208 | 193 | 172 |
| Canada | 239 | 171 | 172 |
| Australia | 41 | 15 | 19 |
| German Federal Republic | 64 | 42 | 37 |
| Sweden | 32 | 16 | 32 |
| Switzerland | 14 | 18 | 1 |
| United States of America | 302 | 178 | 282 |
| Other countries | 18 | 7 | 13 |
| Totals | 918 | 640 | 727 |
| Paper-mill and Pulp-mill Machinery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 257 | 275 | 655 |
| Canada | 15 | 30 | 24 |
| Sweden | 15 | 12 | 11 |
| Norway | 9 | 4 | 12 |
| Netherlands | - | - | 112 |
| United States of America | 23 | 51 | 116 |
| Other countries | 3 | 3 | 14 |
| Totals | 322 | 375 | 945 |
| Earth-moving and Road-making Machinery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,408 | 1,302 | 733 |
| Union of South Africa | 2 | 11 | 14 |
| Australia | 199 | 92 | 77 |
| Belgium | 261 | 1 | 40 |
| German Federal Republic | 18 | 12 | 6 |
| United States of America | 772 | 540 | 364 |
| Other countries | 14 | 5 | 20 |
| Totals | 2,673 | 1,962 | 1,254 |
| Antiseptics | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 228 | 379 | 132 |
| Hong Kong | 10 | 13 | 3 |
| Australia | 41 | 63 | 151 |
| Switzerland | 41 | 38 | 29 |
| United States of America | 32 | 27 | 49 |
| Other countries | 6 | 17 | 21 |
| Totals | 358 | 538 | 386 |
| Inorganic Colours | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 559 | 841 | 552 |
| Australia | 44 | 94 | 51 |
| German Federal Republic | 76 | 147 | 96 |
| Japan | 16 | 22 | 38 |
| United States of America | 11 | 6 | 8 |
| Other countries | 6 | 12 | 13 |
| Totals | 711 | 1,122 | 758 |
| Medicinal Preparations | |||
| (Including Proprietary Medicines) | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 1,053 | 1,075 | 965 |
| Union of South Africa | 16 | 22 | 22 |
| Australia | 173 | 319 | 340 |
| German Federal Republic | 15 | 32 | 28 |
| Netherlands | 16 | 14 | 16 |
| Switzerland | 55 | 95 | 99 |
| United States of America | 32 | 24 | 50 |
| Other countries | 12 | 14 | 9 |
| Totals | 1,372 | 1,595 | 1,530 |
| Weedkillers and Scrubkillers | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 86 | 121 | 74 |
| Australia | 348 | 161 | 76 |
| Belgium | 2 | 11 | - |
| German Federal Republic | 178 | 133 | 188 |
| Switzerland | - | - | 25 |
| China | - | - | 61 |
| United States of America | 46 | 104 | 68 |
| Other countries | - | 6 | 17 |
| Totals | 660 | 538 | 509 |
| Photographic Films | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 324 | 218 | 209 |
| Australia | 395 | 553 | 656 |
| Belgium | 39 | 43 | 40 |
| German Federal Republic | 55 | 97 | 70 |
| Italy | 16 | 14 | 15 |
| United States of America | 20 | 23 | 19 |
| Other countries | 8 | 15 | 10 |
| Totals | 857 | 963 | 1,018 |
| Jewellery and Imitation Jewellery | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 196 | 96 | 33 |
| Hong Kong | 17 | 4 | 2 |
| Australia | 45 | 15 | 4 |
| Austria | 63 | 42 | 10 |
| Czechoslovakia | 21 | 17 | 8 |
| German Federal Republic | 210 | 108 | 23 |
| Other countries | 22 | 17 | 11 |
| Totals | 573 | 299 | 90 |
| Railway Sleepers | |||
| £(000) | |||
| Australia | 1,057 | 623 | 253 |
| Totals | 1,057 | 623 | 253 |
| Sports Goods and Materials for their Manufacture | |||
| £(000) | |||
| United Kingdom | 346 | 283 | 269 |
| Pakistan | 26 | 14 | 12 |
| Australia | 80 | 60 | 61 |
| France | 22 | 18 | 16 |
| German Federal Republic | 59 | 42 | 35 |
| Italy | 11 | 9 | 8 |
| Norway | 12 | 10 | 7 |
| Sweden | 12 | 11 | 6 |
| Japan | 36 | 19 | 31 |
| United States of America | 24 | 22 | 13 |
| Other countries | 30 | 26 | 22 |
| Totals | 659 | 514 | 481 |
QUANTITIES OF PRINCIPAL ITEMS IMPORTED - The following table shows the quantity imported, during each of the years 1957 to 1959, of a large number of the principal items.
| Item | Unit of Quantity | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canned fish | lb (000) | 6,327 | 4,690 | 3,096 |
| Fruit – | ||||
| Canned | ,, | 18,095 | 12,292 | 8,364 |
| Dried | ,, | 21,923 | 24,111 | 17,673 |
| Fresh – | ||||
| Bananas | ,, | 50,719 | 72,020 | 71,153 |
| Oranges | ,, | 30,390 | 25,648 | 27,056 |
| Grain and pulse – | ||||
| Wheat | bush (000) | 10,541 | 9,992 | 8,087 |
| Maizena and cornflour | lb (000) | 4,098 | 3,842 | 2,137 |
| Rice (other than rice flour and ground rice) | cwt (000) | 51.6 | 66.5 | 57.7 |
| Nuts, edible | lb (000) | 1,652 | 1,417 | 991 |
| Desiccated coconut | ,, | 3,082 | 2,086 | 3,179 |
| Jams, jellies, and preserves | ,, | 781 | 326 | - |
| Confectionery | ,, | 2,347 | 981 | 165 |
| Sugar | cwt (000) | 2,186 | 2,845 | 2,294 |
| Tea | lb (000) | 17,493 | 16,426 | 15,395 |
| Coffee, raw | ,, | 1,655 | 2,505 | 2,668 |
| Cocoa beans, raw | ,, | 4,824 | 5,100 | 6,236 |
| Cigarettes | ,, | 1,663 | 741 | 44 |
| Tobacco | ,, | 6,223 | 7,480 | 7,546 |
| Spirits (beverages) | liq. gal. (000) | 1,332 | 1,097 | 810 |
| Wine | ,, | 275 | 149 | 135 |
| Cotton and linen piece goods – | ||||
| Cheese bandages and meat wraps | lb (000) | 3,578 | 3,330 | 3,622 |
| Knitted | ,, | 130 | 143 | 121 |
| Woven | sq. yd. (000) | 60,146 | 67,259 | 63,974 |
| Woollen piece goods | ,, | 5,453 | 5,351 | 3,741 |
| Silk, and artificial and synthetic fibre piece goods – | ||||
| Woven | ,, | 19,072 | 18,981 | 17,242 |
| Knitted | lb (000) | 719 | 787 | 376 |
| Yarns – | ||||
| Cotton | ,, | 2,040 | 2,833 | 3,108 |
| Silk and artificial silk | ,, | 1,603 | 2,560 | 2,595 |
| Woollen | ,, | 2,375 | 2,272 | 2,023 |
| Bags, sacks, wool packs | doz (000) | 1,314 | 1,539 | 1,704 |
| Footwear – | ||||
| Children's | doz pairs (000) | 76.7 | 113.5 | 53.9 |
| Adults' | ,, | 29.7 | 22.9 | 3.4 |
| Hosiery – | ||||
| Full length | ,, | 90.7 | 33.5 | 7.4 |
| Half and three-quarter hose | ,, | 40.9 | 24.6 | 0.4 |
| Gloves | ,, | 123.1 | 103.1 | 72.7 |
| Hat hoods, felt, unblocked | doz (000) | 93.3 | 104.8 | 77.1 |
| Mowers and harvesters | No. | 4,980 | 3,526 | 2,321 |
| Cream separators | ,, | 514 | 879 | 517 |
| Electrical – | ||||
| Storage batteries | ,, | 15,471 | 13,649 | 8,025 |
| Wireless valves | No. (000) | 1,117 | 1,062 | 1,003 |
| Electric motors – | ||||
| Under 1 b.h.p. | No. | 90,414 | 133,336 | 132,934 |
| 1 b.h.p. and over | ,, | 19,938 | 15,222 | 12,551 |
| Sparking plugs | No. | 1,799 | 2,174 | 1,440 |
| Typewriters | ,, | 9,423 | 8,754 | 7,730 |
| Sewing machines, domestic | ,, | 28,053 | 34,814 | 18,793 |
| Iron and steel – | ||||
| Bar, rod, billet, bloom, Pig | cwt (000) | 1,712 | 1,819 | 1,361 |
| Angle, tee, channel, girder | ,, | 756 | 856 | 592 |
| Plate and sheet | ,, | 2,726 | 2,509 | 2,242 |
| Pipes, tubes, and fittings | ,, | 564 | 597 | 572 |
| Wire | ,, | 831 | 1,216 | 768 |
| Copper | ,, | 134.4 | 174.3 | 156.1 |
| Brass and muntz | ,, | 13.8 | 18.1 | 13.6 |
| Lead | ,, | 92.4 | 104.5 | 67.0 |
| Tin | ,, | 7.9 | 8.1 | 7.6 |
| Cordage of metal | ,, | 76.1 | 102.6 | 76.2 |
| Bicycles | -No. | 37,401 | 30,108 | 28,598 |
| Motor cycles | ,, | 1,479 | 1,432 | 557 |
| Motor cars | ,, | 41,452 | 29,058 | 26,307 |
| Lorries, trucks, etc.” | ,, | 6,675 | 8,451 | 6,677 |
| Tractors | ,, | 10,375 | 6,414 | 3,535 |
| Tyres (excluding bicycle) | No. (000) | 48 | 67 | 62 |
| Mineral oils – | ||||
| Motor spirits | gal (000) | 259,261 | 243,925 | 248,611 |
| Lubricating oil | ,, | 8,330 | 8,282 | 8,505 |
| Kerosene | ,, | 8,704 | 10,025 | 10,155 |
| Crude petroleum, fuel oils, etc. | ,, | 173,996 | 164,488 | 150,448 |
| Chemicals – | ||||
| Acids | cwt (000) | 28.6 | 30.0 | 20.8 |
| Calcium carbide | ,, | 48.6 | 50.1 | 50.5 |
| Sulphur | tons | 92,270 | 65,195 | 88,182 |
| Salt | cwt (000) | 957 | 961 | 930 |
| Caustic soda | ,, | 66.6 | 75.9 | 67.5 |
| Carbonate of soda | ,, | 188.9 | 251.6 | 249.7 |
| Manures – | ||||
| Nitrate of soda | tons | 2,911 | 2,995 | 1,829 |
| Phosphatic | ,, | 590,926 | 530,300 | 495,117 |
| Potash | ,, | 41,635 | 55,234 | 75,817 |
| Sulphate of ammonia | ,, | 5,234 | 5,341 | 5,822 |
| Timber, sawn | sup. ft. (000) | 38,715 | 32,876 | 23,935 |
| Glass, plate and sheet | sq. ft. (000) | 12,694 | 16,252 | 16,259 |
| Linseed oil | gal (000) | 673 | 537 | 329 |
| Plaster-of-paris | cwt (000) | 334.8 | 292.1 | 220.1 |
| Gypsum | ,, | 948.3 | 1,171.9 | 1,153.2 |
| Asbestos, crude | ,, | 25.5 | 78.3 | 84.0 |
| Cement | ,, | 74.0 | 60.8 | 39.9 |
| Pulp and paper building board | sq. ft. (000) | 5,775 | 1,196 | 55 |
| Printing paper | cwt (000) | 878.8 | 776.4 | 689.4 |
| Other paper | ,, | 116.3 | 106.3 | 138.4 |
| Cardboard, etc. | ,, | 87.1 | 67.0 | 60.3 |
| Rubber | ,, | 180.5 | 209.9 | 165.1 |
| Paraffin wax | lb (000) | 4,434 | 3,289 | 3,418 |
| Wood and paper pulp | tons | 6,835 | 8,546 | 8,788 |
| Plywood | sq. ft. (000) | 4,221 | 1,381 | 848 |
Imports by Ports - New Zealand has 15 ports of entry for Customs purposes - seven in the North Island and eight in the South Island. The following table gives the total value of imports of merchandise for the several ports of entry during each of the latest five years. The value of overseas cargo landed at other ports is included with the appropriate port of entry. Basis of valuation is c.d.v.
| Port | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ (thousand) | |||||
| Auckland | 100,180 | 91,391 | 105,184 | 101,727 | 82,714 |
| Tauranga | 131 | 195 | 1,106 | 1,407 | 1,967 |
| Gisborne | 449 | 403 | 470 | 402 | 323 |
| Napier | 3,578 | 3,312 | 3,244 | 3,917 | 2,984 |
| New Plymouth | 3,114 | 3,131 | 4,114 | 3,448 | 2,883 |
| Wanganui | 691 | 638 | 696 | 639 | 1,638 |
| Wellington | 85,753 | 80,547 | 85,802 | 82,379 | 65,589 |
| Picton | 144 | 146 | 145 | 130 | 83 |
| Nelson | 802 | 887 | 1,270 | 1,381 | 1,050 |
| Greymouth | 157 | 263 | 555 | 585 | 308 |
| Lyttelton | 34,325 | 34,064 | 37,876 | 36,605 | 29,266 |
| Timaru | 1,464 | 1,511 | 1,978 | 1,286 | 1,208 |
| Oamaru | 122 | 114 | 235 | 227 | 221 |
| Dunedin | 16,518 | 14,816 | 15,060 | 14,182 | 11,344 |
| Bluff | 3,233 | 3,360 | 4,004 | 4,485 | 3,489 |
| Totals | 250,661 | 234,779 | 261,738 | 252,800 | 205,076 |
Three-quarters of the total imports usually come in by way of Auckland or Wellington. Lyttelton and Dunedin occupy third and fourth places in importance. Following these, however, the relative importance of the ports varies from year to year.
It should be mentioned that imports by air have been credited to the port in whose district the airport is located. Thus goods which came in through Whenuapai were included in the Auckland figures, imports through Wellington Airport and Ohakea in the Wellington figures, and through Harewood in the Lyttelton figures.
GOODS SHIPPED FROM COOK AND ASSOCIATED ISLANDS - Trade with the Cook and associated islands is not included in the export and import totals for New Zealand, but is shown separately in official publications. These islands are constitutionally part of New Zealand and the carriage of goods between them and the main islands of New Zealand is not really external trade, but is merely the transport of goods from one part of the country to another. The following table shows the movement of goods from these islands to the main islands of New Zealand. Particulars of the trade of the islands with other countries will be found in the section dealing with Island Territories.
| Year | Value of Goods from Cook Islands |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1948 | 168,553 |
| 1949 | 171,314 |
| 1950 | 161,705 |
| 1951 | 192,398 |
| 1952 | 245,883 |
| 1953 | 287,002 |
| 1954 | 286,418 |
| 1955 | 283,443 |
| 1956 | 298,273 |
| 1957 | 289,545 |
| 1958 | 297,071 |
| 1959 | 343,007 |
The principal goods brought to New Zealand from the Cook and associated islands and their values in recent years are as follows.
| Item | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Fruits, fresh – | ||||
| Oranges | 44,357 | 64,637 | 74,377 | 109,509 |
| Tomatoes | 54,564 | 54,786 | 36,870 | 44,023 |
| Mandarins | 9,836 | 6,544 | 10,753 | 16,100 |
| Bananas | 1,506 | 2,771 | 485 | 259 |
| Other | 21,937 | 12,079 | 11,385 | 8,957 |
| Copra, coconut oil and meal | 137,609 | 100,518 | 97,434 | 99,584 |
| Apparel | 23,934 | 40,028 | 43,649 | 44,697 |
| Vegetables | 1,758 | 2,995 | 8,143 | 10,931 |
| Wickerware | 852 | 1,000 | 2,873 | 2,601 |
| All other items | 1,920 | 4,187 | 11,102 | 6,346 |
| Totals | 298,273 | 289,545 | 297,071 | 343,007 |
THE TARIFF - Briefly the Customs tariff, apart from the obtaining of revenue, has for its objects the following:
The development of New Zealand industries.
The maintenance and extension of markets for New Zealand produce.
The encouragement of intra-Commonwealth trade.
When New Zealand's first Customs Ordinance was proclaimed in 1841 the intention was to raise revenue and to some extent to give preference to goods of British origin. The tariff changes of 1851 and 1864 widened the scope of the tariff but retained its revenue aspects, though at this time the duties were mainly specific rather than ad valorem. In 1888 ad valorem rates became more general and the rate of duty was raised to 20 per cent, which was double the amount charged in earlier years.
The prevailing economic philosophy was, of course, that of free trade, and in New Zealand's case it was underlined by the fact that Parliament predominantly represented the farming community. Even so, the depression of the eighties had so affected some of New Zealand's manufacturing industries that protection by tariffs became practical politics in 1888. The tariff revision of 1895 was aimed at protecting a small range of industries, and at the same time it eliminated the duties on many items which entered into the cost of living of those residing in urban areas. These tendencies were continued in 1900 and 1907 and 1921, with British preferences becoming more evident.
In 1921 provision was made for an extra rate of duty on goods from countries with a depreciated rate of exchange. This was the first occasion when the legislature tried to cope with twentieth century economic conditions which threatened to cut across tariffs designed to give protection to industries which were supposed to develop in a manner normal to the nineteenth century. The 1921 tariff also made provision for anti-dumping duties - another attempt to meet so-called abnormal practices. The depreciated currency duties ranged from 2 1/2 to 20 per cent; the dumping duty was not to exceed the difference between the sale price and the current domestic value.
The 1927 tariff revision extended further British preferences and increased the number of duties imposed for protection purposes. Further important items, if of British origin, were also placed on the free list. In 1930 surtaxes on dutiable goods were imposed for revenue purposes and the general tariff rate was increased by about 5 per cent. In 1931 a primage of 3 per cent was charged on imports (except in specified cases) which were otherwise free of duty.
In the meantime there had been a change in United Kingdom trade policy, which had tended to become one of protection rather than one of free trade.
As a result of the changing conditions the Ottawa Conference was called. The outcome of this conference was the Ottawa Agreement of 1932, the effect of which was to give further preference to British goods and to inhibit the use of the tariff by New Zealand for purely protective purposes.
In 1934 a Tariff Commission submitted a report which in the main adhered to the already established principle of British preference, and actually reduced the protection for New Zealand industries in more cases than it provided protection. The adoption of this report by the Customs Acts Amendment Act 1934 resulted in a wide range of items being made dutiable for revenue purposes, while a small group of items with a low to moderate duty gave limited protection against goods of British origin. Thus New Zealand's tariff remained an expression of the fact that New Zealand placed its economic emphasis on primary production, the market for which was mainly in the United Kingdom.
This tariff remained practically unchanged until 1960, although extended in its scope by subsequent trade agreements. In 1960 some amendments were made, and a new tariff is planned for 1962.
An agreement signed in Wellington in August 1959 between New Zealand and the United Kingdom made provision for the minimum margin of preference of 20 per cent accorded to British goods under the Ottawa Agreement to be reduced.
In recent years a number of changes in the tariff have resulted from public inquiries conducted by the Board of Trade, and the Board in November 1957 completed a comprehensive review of the whole structure and incidence of the tariff and reported to Government.
A summarised historical account of the Customs tariff of New Zealand, setting forth the principal developments and changes up to 1930, will be found in the 1931 issue of the Yearbook. Reference should also be made in this connection to the annual reports of the Customs Department (parliamentary paper H. 25).
The basis of Customs taxation is principally ad valorem, but specific duties are applied to some lines, including several of the principal revenue items such as alcoholic beverages, tobacco, tea, sugar, and motor spirits.
The rates of Customs and excise duty in force in New Zealand are set out in the publication entitled The Customs Tariff of New Zealand, available from the Government Printer, Wellington.
As the rates of duty on goods vary according to their country of origin as well as their classification, the tariff is printed in “multi-column” form listing rates of duty under the British preferential tariff, agreements with certain Commonwealth countries, the most-favoured-nation tariff (under which goods from countries adhering to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade are admitted), and the general tariff.
The following is a list of the principal items which, regardless of their country of origin, are entirely free of duty or subject to primage only under the present tariff:
Live animals; barley (if to be used as stock food); bran; pollard; seeds; vegetable butters or fats; currants; dates; figs; prunes; glucose and caramel; nuts, except walnuts; rice; certain acids; inorganic salts of metallic elements, and many other drugs and chemicals; certain surgical appliances; bags and sacks of jute, etc.; woolpacks; raw cotton; buttons; needles and pins; wadding; cotton piece goods for meat wraps and cheese bandages; umbrella-makers' materials; upholsterers' materials; coir, flax, and jute yarns; patent leathers; bricks, other than firebricks; eyes, artificial; glass cloches; plaster of pans; marble in the rough; grindstones and whetstones; cinema films (subject, however, to film-hire tax); bookbinders' materials; maps, charts, plans; filter paper and filter pulp; parchment and greaseproof paper; printed books, papers, and music; beekeepers' apparatus; percussion caps, detonators, and explosives; hay rakes, reapers and binders, mowers, and certain other agricultural implements; certain dairying machinery; sewing machines; iron and other metal in ingots, pigs, or billets; fish and vegetable (other than linseed and coconut) oils in bulk; kerosene and other refined mineral oils not exceeding in specific gravity 0.860 at 60° F (other than motor spirits); waxes; red lead; cork; engine packing; crude tanning materials; manures; skins and hides (undressed).
The following are entirely free or subject only to primage duty if British, but dutiable at varying rates if of foreign origin: Food for animals; mixed bird seed; chaff; tea in bulk; bananas; oranges, mandarins, and grapefruit; raisins; dried apricots; infants' and invalids' foods; mustard; salt; raw cocoa beans; raw coffee; sago and tapioca; cornflour; macaroni; acetic acid; cream of tartar; sheep dip; chloroform and other anaesthetics; antiseptics; manufactured dyes; most surgical, dental, optical, and scientific instruments and materials; vitamins; cotton, linen, and canvas piece goods; silk; leather cloth; oil baize; sewing, etc., cottons and threads; elastics; plain tape; tailors' lining materials; plain tablecloths, towels, and similar plain articles; belting (other than leather); children's boots, shoes, sizes 0-8 1/2 inclusive, and gumboots, sizes 0-6 inclusive; sheet glass; lenses; watch glasses; pianos and certain other musical instruments; gramophone records; artists' materials; paperhangings; sensitised surfaces; paper (other than wrapping) in large sheets or rolls; ball bearings; rivets; buckles; chains; fire engines, and certain other fire-extinguishing appliances; typewriters; accounting machines; rabbit traps; some electrical apparatus; measuring, testing, etc., appliances; sheep-shearing machines; tractors; many artificers', etc., tools; machinery peculiar to industrial processes; iron and other metal in bars or sheets; wire and wire netting (other than certain sizes of plain non-ferrous wire); metal cordage (other than certain sizes of non-ferrous metal cordage); rails for railways and tramways; asphalt and bitumen; bicycles and tricycles (other than power-operated).
Tariff proposals announced in the 1960 Budget comprised the following major features: (1) Provision of greater protection of New Zealand's rubber goods industry; (2) Protection for the plastic goods industry; (3) Expansion of the electrical goods section to provide protection for local production; (4) Changes in existing tariff procedure.
CUSTOMS DUTIES - It is impossible to give here an account of the range of duties payable on all of the numerous tariff items, but the duties as at the beginning of August 1960 on some of the principal commodities in general use are mentioned hereunder. It should be noted that surtax or primage may be payable.
Tea - On and after 26 July 1948 a duty of 4d. per pound was imposed on tea in bulk imported from most-favoured nations, and from the same date all tea imported under the British preferential tariff was exempted from surtax. On 3 September 1951 tea in bulk of British origin was exempted from all duty and the rates on foreign tea became most-favoured-nation, 1d., general tariff, 2d. per pound.
Sugar - Since 9 February 1933 the duty on refined sugar has been 1 1/4d. per pound and on raw sugar 1d. per pound. Raw sugar imported for refining at Auckland enters free of duty under bond, an excise duty of 1d. per pound being levied on the refined products.
Tobacco - Customs duties on tobacco are at the following rates (August 1960): Cigarettes not exceeding 2 1/2 lb per 1,000: British countries 76s. per 1,000; general countries, 45s. 6d. per 1,000 plus surtax, plus 36s. 6d. per 1,000. Cigarettes exceeding 2 1/2 lb per 1,000: British countries, 30s. 8d. per pound; general countries, 18s. 6d. per pound plus surtax, plus 12s. 2d. per pound. Cigars: British countries, 22s. per pound plus surtax and 10 per cent surtax plus 6s. per pound; general countries, 26s. per pound plus surtax and 10 per cent surtax plus 6s. per pound. Snuff: All countries, 20s. per pound surtax plus 6s. per pound. Tobacco (cut): All countries, 14s. per pound plus surtax plus 8s. 7d. per pound. Tobacco (plug): All countries, 13s. 10d. per pound plus surtax plus 8s. 9d. per pound.
Note - Surtax is one-twentieth of the duty in each case. In respect of British countries, surtax relates only to goods being the produce or manufacture of Canada, Pakistan, Union of South Africa, India, and the Republic of Ireland.
A duty of 1/2d. (plus surtax at a rate of nine-fortieths of the duty) British preferential tariff or 3/4d. (plus surtax at the rate of nine-fortieths of the duty) general tariff is levied on each 60 cigarette tubes or papers or the equivalent thereof. The excise duties on tobacco, etc., made in New Zealand are shown later under “Excise Duties”.
Alcoholic Beverages - Prior to the imposition in 1939 of special taxation for war purposes the rate of duty payable on most spirituous beverages was 40s. per proof gallon, except rum of foreign origin, which was dutiable at 44s. per proof gallon. Sparkling wine was liable to a duty of 10s. per gallon under the British preferential tariff, 9s. 6d. under the trade agreement with the Union of South Africa, and 13s. or 15s. under the most-favoured-nation and general tariff respectively. Australian and South African still wines were liable to a duty of 5s. 6d. per gallon, the duty under the British preferential tariff was 4s. and under the general tariff, 6s. The duty on imported beer was 1s. 9d. per gallon under the British preferential tariff, and 3s. under the general tariff. In order to assist in financing the expenses of the war further duties, in addition to those set out above, and equal to 15 per cent of the duties, were levied as from 27 September 1939; these were increased to 50 per cent as from 1 May 1942, except in the case of beer, on which the additional duty was 1s. 3d. per gallon.
On 26 July 1948 rum, brandy, and gin imported from British Commonwealth countries and most-favoured nations were exempted from surtax and a special most-favoured-nation rate of 15s. per gallon (including the additional 1942 duty) was established for champagne. The excise duty on beer produced in New Zealand is given under “Excise Duties”.
From 27 June 1958 the duties on alcoholic beverages were increased by the following amounts: ale, beer, etc., 3s. per gallon; spirits, 60s. per gallon.
Apparel - Most apparel, except that made to the order or measurement of a New Zealand resident, which is liable to duty at the rate of 40 per cent under the British preferential tariff, pays duty at the rate of 20 per cent, 25 per cent or 271 per cent under the British preferential tariff, and 65 per cent under the general tariff. The duties on apparel of Canadian and Australian origin vary from the British preferential rates to 40 per cent, 45 per cent, and 55 per cent.
Timber - There is a miscellaneous range of duties for the different categories of imported timber. The duties on coniferous timbers, other than dressed, were suspended from 9 November 1951, but the suspension expired at the end of December 1957 and the duty was again levied.
Textiles - Some changes to the Tariff items for textiles were made with effect from 22 July 1960. Woven piece goods of cotton, silk, and vegetable fibres and also moquettes, tapestries, and tickings, other than of wool, were generally not affected and these continue to be admitted either free or subject to primage duty only from British sources, and subject to 15 per cent ad valorem from foreign countries. While the normal rates of duty on knitted or lockstitched piece goods, composed wholly or principally of silk or man-made fibres, remains unchanged at 3 per cent under the British preferential tariff and 25 per cent under the general tariff, provision was made for the Minister of Customs to make determinations imposing substantial duties on certain types where protection for local manufacturers was considered warranted. The rates which may be imposed are 25 per cent or 3s. per pound (whichever rate returns the higher duty) under the British preferential tariff, and 40 per cent or 3s. per pound plus 15 per cent ad valorem under the general tariff. Knitted piece goods composed wholly or principally of cotton are liable to duty at the rate of 3s. per pound from British sources and 3s. per pound plus 15 per cent ad valorem from foreign countries, but there is provision for certain types which are not made locally to be admitted by the Minister at the former rates of duty, viz, 3 per cent from British sources and 15 per cent from foreign countries. Piece goods containing in any proportion man-made discontinuous fibres, but not containing wool or hair, and weighing not less than 6 oz per square yard, are dutiable at the rate of 20 per cent under the British preferential tariff, 35 per cent under the most-favoured-nation tariff, and 55 per cent under the general tariff. The Minister is empowered, however, to approve the admission of particular fabrics, subject to duty of only 3 per cent from British sources, and 15 per cent from elsewhere, when it is considered the fabrics are not competitive with wool. Dress, curtain, and similar nets are dutiable at 15 per cent under the British preferential tariff, 35 per cent under the most-favoured-ration tariff, and 45 per cent under the general tariff, as also are moquettes and tapestries of wool or containing wool, except that the general tariff rate is 40 per cent. For other piece goods of wool or containing wool the rates are 20 per cent under the British preferential tariff, 30 per cent under the Australian agreement, 40 per cent under the most-favoured-nation tariff, and 45 per cent under the general tariff.
Motor Vehicles - Motor vehicles imported in an unassembled or completely knocked-down condition are dutiable at 5 per cent under the British preferential tariff, 40 per cent under the most-favoured-nation tariff, and 50 per cent under the general tariff. Assembled motor vehicles are subject to a duty of 15 per cent if admissible under the British preferential tariff, 50 per cent under the most-favoured-nation tariff, and 60 per cent if liable to the general tariff. Rates intermediate between the British preferential and the most-favoured-nation tariffs apply to vehicles of substantially Canadian origin.
Tyres for Motor Vehicles - Since 22 July 1960 there has been provision for the Minister of Customs to approve of pneumatic rubber tyres and tubes being admitted free of duty from British sources, or subject to duty at the rate of 7d. per pound from foreign countries when the tyres or tubes are of sizes or types which he is satisfied do not compete with those locally produced. However, the normal rates of duty, which became effective from the same date, are as follows:
Tyres weighing not more than 2 1/2 lb and inner tubes weighing not more than 1 lb, 2s. per pound from British sources, 2s. per pound plus 20 per cent ad valorem from most-favoured-nation countries, and 2s. per pound plus 40 per cent ad valorem from foreign countries.
Tyres weighing more than 2 1/2 lb and inner tubes weighing more than 1 lb, 1s. per pound from British sources and 1s. 7d. per pound from foreign countries.
Solid rubber tyres not exceeding 1 3/4 in. in diameter, 20 per cent under the British preferential tariff, 40 per cent under the most-favoured-nation tariff, and 45 per cent under the foreign tariff.
Solid rubber tyres exceeding 1 3/4 in. in diameter, 20 per cent from British sources, and 20 per cent plus 4d. per pound from foreign countries.
Motor Spirits - Towards the end of 1927 the Motor Spirits Taxation Act of that year imposed a duty of 4d. per gallon (increased in 1930 to 6d.) on motor spirits. The proceeds of this tax were devoted to roading purposes. In 1931 and 1933 an increase in duty of 2d. per gallon in each year was made, and an additional 4d. per gallon duty was imposed as from 2 August 1939. The total duty on motor spirits remained at 1s. 2d. per gallon (plus a surtax of one-twentieth of the duty if of foreign origin) until 3 September 1951, when it was reduced by 2d. per gallon. On 4 December 1951 the surtax was made payable also on motor spirits of British origin. The tax on motor spirits was raised to 1s. 3d. per gallon from 26 November 1953, all of which was devoted to roading purposes from 1 April 1954. From 27 June 1958 the duty on motor spirits was increased by 1s. per gallon, this additional taxation going to the Consolidated Fund; this additional duty was reduced to 8d. per gallon on 4 November 1959, to 4d. per gallon on 22 December 1959, and then to 2d. per gallon on 22 July 1960.
PROHIBITED AND RESTRICTED IMPORTS - Full particulars of the goods which are prohibited or restricted from being imported into New Zealand are contained in the publication entitled The Customs Tariff of New Zealand.
The Import Control Regulations 1938 prohibited the importation of any goods except in pursuance of a licence under the regulations or under an exemption granted by the Minister of Customs. A considerable number of items were exempted from import licensing from 1950, and of approximately 1,000 items in the earlier import licensing schedules only 269 remained in the 1957 schedule. The restoration of import licensing on virtually all private imports from 1 January 1958 is explained on page 647.
EXCISE DUTIES:Beer - As from 22 August 1947 the excise duty on beer became 3s. per gallon where the specific gravity of the worts used did not exceed 1,036, increased by 1d. for every unit of specific gravity above 1,036. From 27 June 1958 the excise duty on beer was increased to 6s. a gallon where the specific gravity does not exceed 1,036, advancing by 2d. for every unit of specific gravity above 1,036. The specific gravity of distilled water at 60°F is taken as 1,000, and the specific gravity of the worts is determined in relation thereto.
Tobacco - From 27 June 1958 the excise duty on tobacco was increased to the following amounts: tobacco, cut, 22s. 9d. per pound; tobacco, plug, 22s. 9d. per pound; cigars and snuff, 12s. per pound; cigarettes not exceeding 2 1/2 lb weight for 1,000, 70s. per 1,000; cigarettes exceeding 2 1/2 lb per 1,000, 28s. per pound. From 22 July 1960 the duty was reduced, on both cut and plug tobaccos, by 2s. 6d. per pound, on cigarettes not exceeding 2 1/2 lb weight for 1,000, by 6s. per 1,000, and on other cigarettes, by 2s. 4d. per pound. An excise duty of 1/2d. is levied on each 60 cigarette tubes or papers or the equivalent thereof.
Sugar - There is an excise duty of 1d. per pound on sugar manufactured in New Zealand.
Alcohol - Excise duties were formerly levied direct on certain manufactures the preparation of which involved the use of a considerable proportion of spirits. In lieu of excise duty on the finished manufactured article, however, a special schedule of duties has been provided since 1921 on imported alcohol used in manufacturing these articles in licensed warehouses. The present rates are: on alcohol used in the manufacture of: perfumed spirits, 36s. per proof gallon; toilet preparations, 34s.; culinary and flavouring essences, 20s.; medicinal preparations containing more than 50 per cent of proof spirit, 4s. 6d. per proof gallon. In similar medicinal preparations containing not more than 50 per cent, the alcohol used is duty free.
EXPORT DUTIES:Timber - The Timber Export Duty Revocation Order 1960, which became effective on 29 July 1960, revoked the export duty previously payable on certain classes of logs and flitches of white pine and kauri timber. No export duty is now payable in respect of any class or species of timber.
Wool - The Wool Industry Act 1944 provides for a levy on all wool exported or delivered to a wool manufacturer for use in New Zealand, and the proceeds, less cost of collection, etc., are payable to the New Zealand Wool Board established under the Act to enable it to carry out its functions (see also Section 21).
Meat - Under section 13 of the Meat Export Control Act 1921-22 provision is made for a levy on all meat exported from New Zealand. The section further provides that the net amounts, after deduction of the cost of collection, shall be paid to the New Zealand Meat Producers Board and shall form part of its funds. The levy has been increased, with effect as at 1 October 1960, from 1/20 to 3/50d. per pound on lamb, mutton, beef, veal, bobby veal, and pig meat.
CUSTOMS REVENUE - In the earlier years of New Zealand's history the revenue derived from Customs and excise duties represented a greater proportion of the total revenue from taxation than it has in recent years when it has generally been less than one-fifth of total taxation. The figures for the last 11 years are as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Total Taxation | Customs and Excise Duties | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Percentage of Total Taxation | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | per cent | |
| 1950 | 135,556 | 26,297 | 19.40 |
| 1951 | 157,947 | 28,636 | 18.13 |
| 1952 | 200,550 | 37,873 | 18.88 |
| 1953 | 199,771 | 32,740 | 16.39 |
| 1954 | 206,802 | 32,177 | 15.56 |
| 1955 | 234,766 | 34,177 | 14.56 |
| 1956 | 244,829 | 36,633 | 14.96 |
| 1957 | 252,852 | 35,691 | 14.12 |
| 1958 | 244,882 | 39,003 | 15.93 |
| 1959 | 305,243 | 51,290 | 16.80 |
| 1960 | 297,288 | 56,790 | 19.10 |
The figures for Customs and excise duties are exclusive of tyre tax and the highways proportion (6d. per gallon) of the motor-spirits tax up to and including 1953-54, two classes of taxes collected through the Customs and paid to the Consolidated Fund in the years quoted. From 1954-55 to 1957-58 all these receipts were paid into the National Roads Fund, and were therefore excluded from Customs duties. Such taxation is, however, included in total taxation. From 27 June 1958 the increased duty on motor spirits was paid into the Consolidated Fund and this portion of the motor-spirits tax collected is included in the 1959 and 1960 totals of Customs and excise duties as well as being included in the total taxation figures.
The Customs and excise duties received during the latest four financial years available are shown in more detail in the next table. The figures have been rounded off to the nearest thousand. Primage duties and surtax are included. Tyre tax and a portion (approximately 1s. 3 3/4d. per gallon) of the motor-spirits taxation, although levied on imports and collected through the Customs, have been excluded because they are credited to the National Roads Fund. The balance of the motor-spirits taxation is included in the 1958-59 and 1959-60 figures.
| 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customs duties | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||||||
| Wines and spirits | 3,194 | 3,798 | 3,688 | 4,514 | ||||||||
| Cigars, cigarettes, snuff, and tobacco | 2,599 | 2,392 | 1,725 | 1,316 | ||||||||
| Other duties, including primage and surtax | 15,988 | 18,060 | 22,693 | 22,122 | ||||||||
| Totals, Customs duties | 21,781 | 24,250 | 28,106 | 27,952 | ||||||||
| Excise duties – | ||||||||||||
| Alcohol used in perfumed spirit, etc., in New Zealand | 48 | 42 | 40 | 47 | ||||||||
| Cigarette papers and tubes | 79 | 80 | 79 | 83 | ||||||||
| Tobacco, cigars, cigarettes, snuff, New Zealand manufactured | 6,157 | 6,685 | 10,842 | 14,348 | ||||||||
| Beer, New Zealand | 6,753 | 7,020 | 11,258 | 13,351 | ||||||||
| Sugar | 873 | 926 | 965 | 1,009 | ||||||||
| Totals, excise duties | 13,910 | 14,753 | 23,184 | 28,838 | ||||||||
| Grand totals, Customs and excise duties | 35,691 | 39,003 | 51,290 | 56,790 | ||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| Revenue per head of population – | ||||||||||||
| From Customs duties | 9 | 18 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 18 | 4 |
| From excise duties | 6 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 12 | 5 | 10 |
| Totals | 16 | 5 | 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 22 | 6 | 4 | 24 | 4 | 2 |
PREFERENCE AND RECIPROCITY - The following are the classes of goods which are deemed to be the produce or manufacture of countries which are entitled to be entered for duty at British preferential rates:
Goods wholly the produce of such countries.
Goods wholly manufactured in such countries from unmanufactured raw material and/or from one or more of the imported partly manufactured raw materials which are enumerated in the regulations.
Goods partially manufactured in such countries, provided that the final process of manufacture has been performed in such countries, and also that the expenditure in material produced in such countries and/or labour performed within such countries in each and every article is not less than one-half of the factory or works cost of such article in its finished state.
The conditions applying to British Commonwealth countries, the products of which are admissible under the British preferential tariff pursuant to agreements made by New Zealand with such countries, may be varied to suit the provisions of such agreements.
In the calculation of the proportion of produce or labour none of the following items is to be included or considered:
Manufacturer's profit, or the profit or remuneration of any trader, agent, broker, or other person dealing in the article in its finished condition.
Royalties payable in respect of the finished goods.
The cost of outside packages or any cost of packing the goods thereinto.
Administrative and general office expenses.
Any cost of conveying, insuring, or shipping the goods subsequent to their manufacture.
Any other charges incurred subsequent to the completion of the manufacture of the goods.
Tea to be free of duty must have been grown in some part of the British Commonwealth, and the final process of manufacture must also have been performed in some country of the British Commonwealth.
Under the reciprocal trade agreements with Australia and Canada discussed hereunder, the duties on certain items are sometimes higher than the corresponding duties under the British preferential tariff and in a few cases lower.
Reciprocity With United Kingdom - Under the Ottawa Agreement New Zealand undertook to preserve the existing margins of preference on United Kingdom goods where the margin of preference did not exceed 20 per cent, and where the margin exceeded that figure not to reduce it below 20 per cent without the consent of the Government of the United Kingdom.
In 1958 New Zealand sought new arrangements with the United Kingdom and on 25 November 1958 the two Governments signed Heads of Agreement. This provided the basis for a new agreement to give New Zealand the right to reduce the margins of preference applied to United Kingdom goods entering New Zealand to 5 per cent on certain imports essential for industry, to 7 1/2 per cent on an extensive list of welfare and producer goods, and to 10 per cent on all other goods. The formal text of the new New Zealand - United Kingdom Trade Agreement was signed in Wellington on 12 August 1959.
The following table shows the merchandise trade with the United Kingdom for the latest five years.
| Year | Merchandise Imports | Merchandise Exports to United Kingdom | |
|---|---|---|---|
| From United Kingdom | Of United Kingdom Origin | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| 1955 | 140,540 | 137,831 | 169,657 |
| 1956 | 129,226 | 126,144 | 178,756 |
| 1957 | 136,023 | 134,488 | 162,131 |
| 1958 | 133,685 | 132,804 | 139,105 |
| 1959 | 97,775 | 97,041 | 165,610 |
Reciprocity With the Union of South Africa - There was inaugurated in 1907 a reciprocal arrangement with the Union of South Africa whereby products of that country, when imported direct, were admitted into New Zealand at reduced rates of duty, in return for similar concessions granted by South Africa in respect of New Zealand products. This agreement was revised in 1922 and subsequently further amended.
The items specially provided for in the agreement were feathers, fish, fresh fruit, dried fruit, tea, and wine; while in the case of all other dutiable goods, with the exception of spirits and tobacco, a reduction of 3 per cent of the duty payable was made.
The legislation giving effect to the arrangement with the Union of South Africa was revoked by the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade Act 1948, although that Act provides for the continuation of most of the concessions previously granted, an exception being the reduction of 3 per cent of the duty formerly granted. The British preferential tariff will not apply to other goods after 31 May 1961.
The following table shows the merchandise trade with the Union of South Africa for the five years.
| Year | Merchandise Imports | Merchandise Exports to Union of South Africa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| From Union of South Africa | Of Union of South Africa Origin | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| 1955 | 881 | 956 | 450 |
| 1956 | 989 | 1,011 | 373 |
| 1957 | 1,180 | 1,201 | 284 |
| 1958 | 1,148 | 1,175 | 677 |
| 1959 | 1,038 | 1,076 | 922 |
Reciprocity With Australia - An agreement, completed in April 1933 and confirmed by the Trade Agreement (New Zealand and Australia) Ratification Act of that year, came into operation on 1 December 1933, and remains in force until terminated by either party.
Under the agreement each country grants to the goods of the other the benefits of its British preferential tariff, except with regard to certain classes of goods, enumerated in the Schedules to the agreement, on which special rates are fixed.
The agreement provides for lower duties than those prescribed under Australia's British preferential tariff on many classes of New Zealand products entering Australia, including fresh and frozen fish and fish pastes; dried peas; fresh, smoked, and preserved meats; onions; lucerne seed; wine; furs; hats; caps; floor rugs; various agricultural and dairying implements; whale oil; casein; sugar of milk; and timber.
Minor modifications have been made to the Schedules of the agreement from time to time, but they remain substantially the same as originally negotiated.
Merchandise trade between New Zealand and Australia during the latest five years has been as follows.
| Year | Merchandise Imports | Merchandise Exports to Australia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| From Australia | Of Australian Origin | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| 1955 | 31,421 | 30,478 | 6,692 |
| 1956 | 33,765 | 33,305 | 8,431 |
| 1957 | 45,653 | 45,185 | 10,113 |
| 1958 | 44,342 | 43,680 | 10,266 |
| 1959 | 37,812 | 37,140 | 10,952 |
The setting up of an Australian - New Zealand Consultative Committee on Trade was agreed on by the Australian and New Zealand Governments in August 1960.
Reciprocity With Canada - Reciprocal trade arrangements between Canada and New Zealand are governed by an agreement negotiated in 1932, and this agreement remains in force until terminated by either party.
Under the terms of the agreement sausage casings, hides and skins, wool, apples, seeds, kauri gum, and phormium fibre are amongst the New Zealand products admitted free of duty. Certain other items such as butter, cheese, mutton, and lamb are admitted at rates of duty lower than the British preferential tariff.
Merchandise trade with Canada (including Newfoundland) during the latest five years is shown in the following table.
| Year | Merchandise Imports | Merchandise Exports to Canada | |
|---|---|---|---|
| From Canada | Of Canadian Origin | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| 1955 | 8,368 | 8,360 | 4,230 |
| 1956 | 6,298 | 6,258 | 4,026 |
| 1957 | 6,590 | 6,634 | 4,435 |
| 1958 | 5,848 | 5,925 | 4,066 |
| 1959 | 4,706 | 4,738 | 3,053 |
Reciprocity With the Federation of Malaya - A trade agreement between the Federation of Malaya and New Zealand was signed in February 1961 by which each country will accord preferential rates of duty to the other for an initial period of three years. Both countries agreed to guarantee minimum margins of tariff preference which apply to certain important items in each other's trade.
Other Trade Arrangements - New Zealand is also a party to certain commercial treaties, conventions, or arrangements with countries outside the Commonwealth. In some earlier cases New Zealand automatically became a party to arrangements concluded by the United Kingdom; in others she became a party by signifying her willingness to adhere to such arrangements. Other arrangements again resulted from direct negotiations between New Zealand and the countries concerned. In practice many of these arrangements (which generally provided for reciprocal most-favoured-nation tariff treatment) are superseded by New Zealand's accession to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade. However, some remain separately in force, and, in addition to those countries which are contracting parties to the General Agreement, New Zealand grants most-favoured-nation tariff treatment to Argentina, China, Egypt, Israel, Liberia, Spain, Yugoslavia, and Somalia.
Most-favoured-nation tariff treatment on certain items is extended to Switzerland as a result of a trade arrangement between Switzerland and New Zealand dating from 1938, under which New Zealand receives general most-favoured-nation tariff treatment and a guaranteed import quota for apples and pears. Since 1957 the arrangement has been extended also to Liechtenstein.
A trade agreement with Japan came into force on 9 September 1958 and remains in force for a period of three years. The agreement provides for reciprocal most-favoured-nation. tariff treatment. Japan was removed from the list of scheduled countries for import licensing purposes and New Zealand is given the opportunity to compete for the Japanese allocation of exchange for imports of major interest to New Zealand. The agreement also includes a clause safeguarding New Zealand industry from serious injury caused or threatened to be caused by excessive imports from Japan.
An exchange of letters between Israel and New Zealand was completed in January 1959. The arrangement provided for imports from each country to receive most-favoured-nation tariff treatment in the other. A quota for imports of New Zealand beef into Israel was also provided. The arrangement was for one year. At present there is reciprocal most-favoured-nation tariff treatment under an interim arrangement pending Israel's accession to GATT.
The Federal Republic of Germany and New Zealand concluded a trade agreement in April 1959. The agreement is designed to facilitate as far as possible the exchange of goods and services between the two countries. New Zealand is granted quotas on certain primary products while for some others New Zealand will be considered as a source of supply for imports into Germany under the import programme. The agreement was concluded following international discussions under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade on problems arising out of the Federal Republic's import restrictions. The circumstances under which the negotiations with the Federal Republic were initiated were thus somewhat different from the usual, and because of this New Zealand is not required under the agreement to make any special arrangements regarding German exports. As contracting parties to the General Agreement the two countries already granted each other most-favoured-nation tariff treatment.
GENERAL AGREEMENT ON TARIFFS AND TRADE (GATT) - Tariff negotiations took place in Geneva in 1947, and the concessions given by each participating country were embodied in schedules to a General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade. The tariff negotiations themselves were bilateral but all the concessions were applied multilaterally, so that New Zealand receives the benefit of reductions made by all participants, and, conversely, New Zealand's concessions apply to all the other countries which took part. Concessions are of two kinds - actual reductions of duties and bindings of duties against increase. The Agreement, which provides for concessions under both the British preferential and most-favoured-nation tariffs, was applied provisionally by New Zealand on 26 July 1948.
The foreign countries to whose products the concessional rates (i.e., the most-favoured-nation rates) of duty apply by virtue of their membership in GATT are: Austria, Burma, Belgium (including overseas territories), Brazil, Chile, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Dominican Republic, German Federal Republic, Finland, France (including overseas territories), Greece, Haiti, Italy, Luxemburg, Netherlands (including overseas territories), Nicaragua, Norway, Peru, Republic of the United States of Indonesia, Sweden, Turkey, United States of America, Uruguay, Union of South Africa.
The following Commonwealth countries are members of GATT: Australia, Canada, Ceylon, Ghana, India, Malaya, Pakistan, Rhodesia and Nyasaland.
While the reduction of tariffs and other barriers to trade has been the principal aim of the General Agreement it has also provided an internationally accepted code of rules in world trade, and its regular sessions have been useful as a forum for the discussion and settlement of international trade problems and disputes.
Developments have tended to whittle away most of the trading advantages which countries relying heavily on agricultural exports reasonably expected to get from GATT membership. There has been a growing disparity between the benefits accruing under GATT to the industrialised countries and the far less tangible advantages it provides for primary producing countries like New Zealand. This has been due primarily to the growing use of quantitative restrictions on agricultural products by most of the large industrialised countries as an aspect of their policies of agricultural protectionism.
INTERNATIONAL WHEAT AGREEMENT - The first International Wheat Agreement was negotiated in March 1949 and, with minor amendments, was renewed in 1953 and 1956. Following conferences from January to March 1959 the 1956 Agreement, which was due to expire on 31 July 1959, was replaced by a new agreement which differs on some major points from its predecessors.
The objectives of the International Wheat Agreement are to assure supplies of wheat to importing countries and markets for wheat to exporting countries at equitable and stable prices. Under the terms of the 1956 Agreement New Zealand guaranteed to import 160,000 metric tons (5,878,994 bushels) of wheat annually. The guarantee to purchase became operative only when the price was at the minimum laid down in the agreement, and a similar guarantee to sell by exporters operated only when the price reached the maximum under the agreement. The maximum and minimum prices were $2.00 and SI.50 based on Manitoba, Northern No. 1 wheat, in bulk, in store, Fort William/Port Arthur.
In the new agreement, which came into force on 1 August 1959, New Zealand, as a signatory, has a contractual obligation to purchase 90 per cent of its imports under the agreement while the price is between the maximum and minimum prices. The maximum price for the basic wheat has been reduced to $1.90 but the minimum remains at $1.50. At the maximum price importers are released from their obligation to purchase, while exporters are required to supply the average of each importer's purchases over the first five of the previous six years.
INTERNATIONAL SUGAR AGREEMENT - A new International Sugar Agreement, replacing the agreement negotiated in 1953, came into effect on 1 January 1959. The 1953 Agreement had marked the end of several unsuccessful attempts over a long period from before 1939 to secure international collaboration in sugar matters.
The main objectives of the new agreement, which differs little from the previous one, are similar to those of the International Wheat Agreement - to assure supplies of sugar to importing countries and markets for sugar to exporting countries at equitable and stable prices.
Unlike the International Wheat Agreement, participating importing countries do not undertake to purchase a specified percentage of sugar from the participating exporting countries, but they are restricted in the quantities they may purchase from non-participating exporting countries. Exporting countries are restricted in the quantities they may offer on the “free market” and are allocated specific quantities or “basic export tonnages”.
The agreement contains detailed formulae for maintaining world prices of sugar by the increase or decrease of the “basic export tonnages” for individual exporting countries. When world prices range between 3.45 and 3.75 cents a pound F.A.S. Cuba (in United States currency) the full export quotas provided in the agreement apply. Outside this price range the formulae for adjusting export quotas become affective.
The new agreement was negotiated at conferences held at Geneva in October 1958 under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations Organisation. It terminates on 31 December 1963, although there is provision for a review of the price range and of basic export tonnages after three years.
New Zealand acceded to this agreement in November 1960. New Zealand's annual requirements of raw sugar are approximately 115,000 tons, imported in recent years mainly from Australia and Fiji. Of this quantity, 75,000 tons are purchased annually from Commonwealth sources under a special arrangement.
PRICE TRIBUNAL - The Control of Prices Act 1947 consolidated the powers and functions formerly exercised mainly under Emergency Regulations issued during the course of the Second World War. It defined the general duties and functions of the Price Tribunal as the fixing of prices for goods and services, the investigation of complaints with respect to prices, maintenance of a survey of the prices of goods or services, the institution of legal proceedings for offences in relation to prices, and the taking of such other steps as in its opinion might be necessary to prevent profiteering or the exploitation of the public. It provided that, except in special circumstances, the sittings of the Tribunal should be open to the public. The Price Tribunal has power to:
Make price orders fixing, in such manner as it thinks fit, the actual or the maximum or the minimum price for any goods sold in a specified market and under specified conditions. Price orders are published in the New Zealand Gazette, and must generally be displayed in any shop where the goods to which they relate are sold.
Authorise selling prices, which may be of general or special application.
Since the passing of the Act the Tribunal has, in the case of many commodities, issued price orders which prescribe that maximum prices are to be calculated by adding specified percentages to costs. In other cases, where there has been a general cost increase resulting from the reduction or removal of subsidies, the raising of freight charges, or a wage increase prescribed by a general order of the Court of Arbitration, the position has sometimes been met by the issue of general price adjustment orders under which most manufacturers have been permitted to recover by means of price increases the whole or a specified part of such increased costs.
Since 1948 a policy of progressive decontrol has been followed: lists of items freed from direct price fixation (although remaining subject to profiteering and other provisions of the Act) were published from time to time, but all goods and services not specifically exempted in this manner remained subject to control. However, in accordance with powers provided under the 1953 amendment to the Act, a noteworthy change in the system of control became effective on the gazetting of the Control of Prices (Positive List) Notice 1955 on 14 March 1955. The system of general control with specified exemptions was thereby replaced by the control of specified items only - all goods or services not on the Positive List being decontrolled. The many additional items subsequently decontrolled outdated the Positive List issued on 14 March 1955, and it was replaced by a new Positive List gazetted on 14 March 1957. Since then further items have been exempted and two, namely, honey and meat, have been placed under control again.
The Control of Prices Amendment Act 1953 also made provision for the delegation of pricing powers to the Secretary of Industries and Commerce, subject to a right of appeal to the Tribunal.
A further amendment to the Act in October 1956 transferred from the Price Tribunal to the Minister the function of exempting goods or services from price fixation.
Towards the end of 1951 an Advisory Committee, consisting of representatives of the business community meeting under the chairmanship of the Director of Price Control, was set up to advise on matters of procedure and administration, and to promote mutual confidence and understanding. Other Advisory Committees have since been established to deal with the pricing problems of particular industries, and representatives of the business groups concerned meet under the chairmanship of a senior officer of the Department of Industries and Commerce.
It should be observed that certain prices controlled under other legislation do not come within the scope of the Control of Prices Act 1947. For example, the maximum price of motor spirits is fixed by Order in Council (on the recommendation of the Minister of Industries and Commerce) under the Motor Spirits (Regulation of Prices) Act 1933; while, in certain circumstances, the Tenancy Act 1955 provides for the fixation, on application, of rents by a Magistrate's Court or by a Rents Officer of the Department of Labour. As a further illustration the Transport Amendment Act 1950 provides for the fixation of passenger fares and freight charges on services, other than those operated by local authorities, by the Commissioner of Transport, subject to a right of appeal to a Transport Charges Appeal Authority.
Although the earlier legislation providing for an Economic Stabilisation Commission was repeated in the Economic Stabilisation Act of 1948, there have been no appointed members of the Commission since 1950, following a steady trend since 1947 towards loosening the restraints which had been accepted as part of the fuller wartime stabilisation programme. Fuller references to stabilisation measures are contained in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
Marketing of Major Primary Commodities - Certain fields of price fixation are intimately connected with the functions of the marketing authorities (and formerly of the Marketing Department), although the relevant price orders are generally issued by the Price Tribunal.
TRADE PRACTICES ACT 1958 - The Trade Practices Act 1958 provides machinery for the registration and investigation of certain trade practices and provides means whereby trade practices found to be contrary to the public interest may be regulated. A Trade Practices and Prices Commission was established in terms of section 3 of the Act, which provides for members of the Price Tribunal automatically to become members of the Commission, for the president of the Price Tribunal to become chairman of the Commission, and for the Governor-General, on the recommendation of the Minister of Industries and Commerce, from time to time to appoint additional members to the Commission who will automatically become members of the Price Tribunal also. A Commissioner of Trade Practices and Prices was also appointed. The functions of the Commission are to inquire into trade practices for the purpose of ascertaining whether any such practices are contrary to the public interest and to make orders requiring the amendment, discontinuance, or prohibiting the repetition of any such practices which it finds to be contrary to the public interest. There is a right of appeal to a Trade Practices Appeal Authority.
Agreements or arrangements must be registered where they come within the categories listed in section 19 (2) of the Trade Practices Act. This subsection contains some 16 clauses and aims at covering a wide range of trading agreements which, by reason of price maintenance, limitation of sales outlets, zoning, ring tendering, or through any of the other means mentioned, may operate in a manner inimical to public interest.
The Act came into force on 3 October 1958, and agreements or arrangements then in existence were required to be registered within three months of that date. Subsequent agreements must be registered within three months of the date on which they are made, whilst variations to or determinations of agreements which have been registered are themselves required to be registered within one month. Further amplification of the requirements in regard to registration is given in the Trade Practices Regulations 1958.
The number of agreements which had been registered at 31 March 1961 was 818. A substantial number of additional agreements which have been submitted will be registered when they have been examined.
The Trade Practices and Prices Commission has held eight public hearings. The goods and services covered were glazing contracts, wire mattresses, phonograph records, aerated waters, wire netting, hairdressing charges, pricing by master grocers' organisations, and refusal by a trade association to admit a new member.
The result of each of the first four inquiries was that the trade practice under examination ceased. Some agreements were terminated prior to hearings, but in other cases it was necessary for the Commission to make an order.
Orders were also made in reference to wire netting, hairdressing charges, and grocery prices, but these were the subject of appeals to the Trade Practices Appeal Authority. The Appeal Authority in effect dismissed the appeal on hairdressing charges, disallowed the appeal on grocery prices in regard to the New Zealand Master Grocers' Federation and two of the four associations (allowing the appeal in regard to the other two associations), and referred the wire netting appeal back to the Commission for further inquiry.
The Commission declined to make an order in regard to the refusal by the trade association to admit a new member.
CONSUMER COUNCIL - A Consumer Council, whose functions are to protect and promote the interest of consumers of goods and services, was established under section 8 of the Finance Act 1959. The chairman and members of the Council were appointed by the Minister of Industries and Commerce, who also approved the membership of four district consumer committees on a regional basis corresponding with New Zealand's four university districts. The district committees work in close liaison with the parent body, the Consumer Council.
A conference was held in September 1959 to enlist the support of those organisations interested in consumer welfare. Citizens may become associate members of Consumer Service on payment of a fee of 10s. a year, which entitles them to receive copies of a quarterly magazine, information broadsheets, newsletters, and other assistance from the organisation. By October 1960, over 13,000 persons had joined Consumer Service. It is hoped to build Consumer Service into a strong, self-reliant, and valuable organisation. Those associate members who wish to take a more active part in the work of the Service may become members of local consumers' associations which have been formed in several centres.
PRICE STATISTICS - Actual prices of many goods and services at various levels are collected periodically by the Department of Statistics. The fields covered are retail prices, wholesale prices, export prices, import prices, share prices, and wool prices. In the case of retail and wholesale prices, direct inquiry is made, export and import prices (or strictly, unit values) being mainly derived from trade statistics, share prices from records of the stock exchanges, and wool prices from the New Zealand Wool Commission. In addition, average prices of many materials and products of manufacture are available from the statistics of industrial production. Some retail prices are given in the following table, and a wider coverage is published in the annual Report on Prices, Wages, and Labour Statistics: the chief use made of the prices collected, however, is in the compilation of price index numbers. These are, fundamentally, weighted averages of price ratios, the weighting being so arranged that the index numbers give a general indication of price movements in the field covered. The usual technique employs fixed weights with, however, provision for revision of the weighting pattern at suitable intervals.
Retail Prices - New Zealand retail prices (weighted average prices over 21 towns) at 15 November 1960 of a number of the commodities which enter into the Consumers' Price Index are shown hereunder.
| Item | Unit | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | ||
| Milk, fresh, delivered | pint | 4 3/4 | |
| Butter | lb | 2 | 0 |
| Cheese, mild | lb | 2 | 1 |
| Bread | 28 oz loaf | 7 1/2 | |
| Flour | 25 lb bag | 6 | 6 1/2 |
| Oatmeal | 5 lb bag | 5 | 0 1/4 |
| Rice | lb | 10 1/4 | |
| Sugar | 6 1b | 3 | 11 1/2 |
| Honey | 1 lb carton | 2 | 3 3/4 |
| Eggs (in carton) | dozen | 4 | 4 |
| Tea | lb | 6 | 7 3/4 |
| Cocoa | 1/2 lb packet | 2 | 9 |
| Coffee, pure, ground, loose | lb | 8 | 2 3/4 |
| Jam, raspberry | 28 oz tin | 5 | 5 3/4 |
| Salt | 5 lb bag | 2 | 2 1/2 |
| Baked beans | 16 oz tin | 1 | 9 1/2 |
| Tomato sauce | 10 oz bottle | 2 | 2 1/4 |
| Tomato soup | 11 oz tin | 1 | 2 |
| Milk powder, full cream | 2 1/2 lb tin | 7 | 9 1/2 |
| Aerated water | 10 oz bottle | 71/2 | |
| Chocolate | 3 oz tablet | 1 | 3 |
| Ice cream | pint block | 1 | 10 1/4 |
| Apples | lb | 1 | 2 1/4 |
| Oranges | lb | 1 | 3 |
| Cabbage | lb | 11 1/4 | |
| Carrots | lb | 11 1/4 | |
| Peaches, canned | 30 oz tin | 4 | 1 3/4 |
| Peas, fresh, frozen | 10 oz packet | 2 | 3 1/4 |
| Onions | lb | 8 1/2 | |
| Potatoes, main crop | lb | 7 3/4 | |
| Beef – | |||
| Sirloin | lb | 3 | 6 3/4 |
| Prime ribs | lb | 3 | 0 1/4 |
| Rump steak | lb | 4 | 6 |
| Blade steak | lb | 3 | 3 |
| Mince | lb | 2 | 9 3/4 |
| Corned silverside | lb | 3 | 3 1/4 |
| Mutton – | |||
| Leg, shank end | lb | 2 | 7 |
| Forequarter | lb | 1 | 5 |
| Chops, middle loin | lb | 2 | 4 1/2 |
| Pork – | |||
| Leg | lb | 3 | 4 |
| Loin chops | lb | 3 | 6 1/2 |
| Tripe | lb | 1 | 1 3/4 |
| Sheep's liver | lb | 2 | 11 3/4 |
| Sheep's tongue | each | 6 1/4 | |
| Sausages, beef | lb | 1 | 10 |
| Ham, cooked, sliced | lb | 7 | 10 1/4 |
| Bacon, side | lb | 4 | 7 1/2 |
| Fish – | |||
| Tarakihi, fillets | lb | 3 | 0 3/4 |
| Groper (hapuku), pieces | lb | 3 | 2 1/4 |
| Sole or flounder, gutted | lb | 3 | 1 |
| Smoked fish | lb | 2 | 11 1/4 |
| Herrings, canned | 14 oz tin | 2 | 4 1/2 |
| Men's – | |||
| Suit, ready made | each | 420 | 2 |
| Sports coat, ready made | each | 232 | 9 |
| Overcoat, woollen gabardine | each | 282 | 7 |
| Overcoat, oilskin | each | 181 | 8 |
| Trousers, working | pair | 25 | 1 |
| Trousers, sports | pair | 107 | 2 |
| Shirt, negligee | each | 37 | 7 |
| Shirt, working | each | 20 | 2 |
| Singlet, all wool | each | 33 | 0 |
| Singlet, cotton, athletic | each | 7 | 7 |
| Pullover, all wool | each | 32 | 11 |
| Pyjamas, flannelette | pan | 30 | 7 |
| Socks, wool and nylon | pair | 10 | 4 1/4 |
| Hat, fur felt | each | 53 | 7 |
| Bathing costume, all wool | each | 35 | 0 |
| Handkerchief | each | 2 | 6 |
| Boys' – | |||
| Sports coat, ready made | each | 95 | 2 |
| Trousers, shorts, tweed | pair | 28 | 8 |
| Raincoat, proofed cotton | each | 94 | 5 |
| Shirt, grey flannel | each | 26 | 2 |
| Pullover, all wool | each | 35 | 7 |
| 3/4 hose, school | pair | 9 | 10 1/3 |
| School cap | each | 15 | 3 3/4 |
| Women's – | |||
| Costume coat and skirt, ready made | each | 362 | 0 |
| Raincoat, woollen gabardine | each | 304 | 11 |
| Skirt, worsted | each | 113 | 11 |
| Cardigan, all wool | each | 74 | 3 |
| Smock, cotton print | each | 39 | 2 |
| Women's – | |||
| Stockings, fully fashioned nylon | pair | 10 | 7 3/4 |
| Stockings, fully fashioned pure silk, heavyweight | pair | 15 | 2 1/2 |
| Underslip, nylon | each | 51 | 3 |
| Vest, silk and wool | each | 13 | 8 |
| Panties, interlock | pair | 8 | 8 1/4 |
| Nightdress, locknit | each | 33 | 11 |
| Nightdress, winceyette | each | 33 | 4 |
| Corset | each | 83 | 11 |
| Brassiere | each | 25 | 0 |
| Girls' – | |||
| Gym frock, serge | each | 75 | 1 |
| Blazer, all wool | each | 63 | 8 |
| Blouse, cotton, long sleeves | each | 19 | 10 |
| Pyjamas, winceyette | pair | 24 | 11 |
| Bloomers, interlock | pair | 6 | 3 |
| Stockings, lisle | pair | 12 | 2 3/4 |
| Sockettes, stretch nylon | pair | 6 | 10 1/4 |
| Beret, school | each | 8 | 4 |
| Infants' – | |||
| Nursery squares | dozen | 50 | 9 |
| Baby wool | 1 oz | 2 | 8 |
| Piece goods – | |||
| Wool-cotton mixture | yard | 9 | 3 |
| Velour coating | yard | 30 | 3 |
| Figure print | yard | 7 | 7 1/4 |
| Opaque nylon | yard | 12 | 11 1/4 |
| Rayon | yard | 7 | 11 1/2 |
| Wool, hand knitting | 1 oz | 2 | 6 |
| Drapery – | |||
| Blankets, single | pair | 146 | 9 |
| Sheets, single | pair | 46 | 9 |
| Towel, turkish | each | 9 | 3 1/2 |
| Tea towel, linen | each | 4 | 11 |
| Men's – | |||
| Boots, heavy | pair | 83 | 3 |
| Shoes, heavy | pair | 66 | 8 |
| Shoes, light | pair | 92 | 5 |
| Sandshoes | pair | 13 | 4 1/2 |
| Slippers, leather | pair | 41 | 6 |
| Shoe repairs | pair | 20 | 5 |
| Boys' – | |||
| Football boots | pair | 53 | 6 |
| Shoes, heavy | pair | 52 | 2 |
| Sandals | pair | 31 | 0 |
| Gumboots | pair | 33 | 9 |
| Shoe repairs | pair | 15 | 9 1/2 |
| Women's – | |||
| Shoes, heavy | pair | 81 | 7 |
| Shoes, light | pair | 85 | 7 |
| Slippers, felt | pair | 23 | 3 |
| Shoe repairs | pair | 14 | 5 |
| Girls' – | |||
| Shoes, school | pair | 42 | 3 |
| Shoes, light | pair | 45 | 7 |
| Shoe repairs | pair | 11 | 1 3/4 |
| Infants' – | |||
| Shoes, glace kid | pair | 22 | 11 |
| Bedstead and rails, 4 ft. 6 in. | each | 168 | 10 |
| Tallboy, four-drawer | each | 218 | 5 |
| Mattress, 4 ft. 6 in. wire | each | 116 | 1 |
| Mattress, 4 ft. 6 in. kapok | each | 233 | 4 |
| Mattress, 4 ft. 6 in. foam rubber | each | 530 | 10 |
| Pillow, 2 lb kapok | each | 16 | 0 1/4 |
| Child's cot | each | 167 | 8 |
| Dining table, drawleaf | each | 290 | 0 |
| Dining chair | each | 82 | 11 |
| Sideboard, leadlight | each | 491 | 0 |
| Kitchen table | each | 82 | 1 |
| Kitchen chair | each | 32 | 1 |
| Suite, upholstered | each | 1,194 | 9 |
| Linoleum, inlaid | yard | 32 | 1 |
| Carpet, Axminster, 27 in. | yard | 49 | 6 |
| Feltex, marbled, 5 ft. | yard | 49 | 0 |
| Hammer, carpenter's | each | 29 | 0 |
| Spade, garden | each | 37 | 7 |
| Fork | each | 28 | 6 |
| Axe, 4 lb | each | 36 | 10 |
| Broom, hair and fibre | each | 18 | 11 1/4 |
| Mop, white cotton | each | 8 | 10 3/4 |
| Scrubbing brush | each | 4 | 2 1/4 |
| Bucket, galvanised, 12 in. | each | 9 | 9 3/4 |
| Electric-light bulb, 60 watt | each | 1 | 9 |
| Pressure cooker, 10 1/4 pint | each | 155 | 4 |
| Saucepan, aluminium, 8 in | each | 22 | 7 |
| Pie dish, enamel, 11 in. | each | 8 | 0 1/4 |
| Cup and saucer, tea size | 1/2 dozen | 22 | 10 |
| Plate, 10 in. | 1/2 dozen | 22 | 10 |
| Preserving jars, glass, quart size | dozen | 15 | 3 |
| Knives, table, stainless | 1/2 dozen | 43 | 3 |
| Forks, table, E.P.N.S. A1 | 1/2 dozen | 39 | 2 |
| Doormat, coir | each | 12 | 11 1/4 |
| Soap, laundry | 2.8 lb bar | 3 | 6 |
| Soap powder | standard packet | 2 | 0 |
| Detergent | packet | 1 | 8 1/4 |
| Starch | 1 lb packet | 2 | 1 |
| Kerosene | 26 oz bottle | 1 | 3 3/4 |
| Boot polish | medium tin | 1 | 1 1/2 |
| Household cleaning paste | tin | 2 | 6 |
| Toilet paper | roll | 1 | 0 |
| Lunch wrap | 75 ft in container | 2 | 3 |
| Torch battery, dry cell | each | 11 1/2 | |
| Coal, domestic | 1/4 ton | 42 | 10 |
| Coke | cwt | 12 | 4 |
| Firewood (pine) | bag | 5 | 7 1/2 |
| Electric current (excluding water heating) | 1st 140 kWh | 15 | 2 |
| Electric current (including water heating) | 1st 380 kWh | 31 | 2 |
| Gas (cooking) | 1,600 cu. ft. | 22 | 3 |
| Refrigerator | each | 1,990 | 0 |
| Washing machine | each | 1,287 | 2 |
| Vacuum cleaner | each | 497 | 6 |
| Radio receiving set | each | 395 | 8 |
| Electric radiator | each | 119 | 6 |
| Electric jug | each | 59 | 6 |
| Electric toaster | each | 76 | 11 |
| Electric iron | each | 99 | 6 |
| Electric razor | each | 197 | 6 |
| Lawnmower, hand type | each | 151 | 6 |
| Sewing machine | each | 1,110 | 0 |
| Bicycle, men's sports roadster | each | 495 | 7 |
| Bicycle tyre | each | 18 | 0 |
| Bicycle tube | each | 8 | 6 |
| Perambulator | each | 383 | 8 |
| Paint, lead, final coat | gallon tin | 57 | 2 |
| Wallpaper, English | roll | 10 | 8 1/4 |
| Tennis racquet | each | 58 | 9 |
| Tennis balls | pair | 6 | 5 1/4 |
| Meccano set | each | 42 | 0 |
| Teddy bear | each | 45 | 9 |
| Attache case, fibre | each | 16 | 5 1/4 |
| Watch, wristlet, men's | each | 172 | 10 |
| Watch, repair fee | each | 30 | 3 |
| Alarm clock | each | 31 | 3 |
| Leather satchel | each | 39 | 0 |
| Cinema admission | seat | 3 | 0 |
| Football admission | seat | 1 | 10 1/4 |
| Football subscription | each | 13 | 6 1/4 |
| Golf green fees | each | 3 | 9 1/4 |
| Library subscription | per book | 8 | |
| Radio licence | each | 30 | 0 |
| Drycleaning, men's suit | per suit | 10 | 2 |
| Laundering, sheet | each | 10 | |
| Hair cut, men | each | 3 | 6 |
| Hair cut, women | each | 4 | 0 |
| Hair set | each | 7 | 6 |
| Permanent wave | each | 35 | 0 |
| Optical lenses | pair | 110 | 4 |
| Dental extraction | each | 19 | 5 1/2 |
| Dental filling | each | 13 | 1 |
| Dentures | set | 500 | 4 |
| Medical (excess over Social Security) – | |||
| Consultation fee | 7 | 6 | |
| Specialist's fee | 13 | 6 | |
| Private general hospital | per day | 32 | 2 |
| Union dues (annual subscription) | per member | 34 | 9 |
| Face powder, block type | each | 3 | 6 |
| Vanishing cream | 2 oz jar | 3 | 11 |
| Lipstick | each | 4 | 6 |
| Baby talcum powder | tin | 2 | 3 |
| Bobby pins | card of 10 | 6 | |
| Toothbrush | each | 2 | 0 |
| Toothpaste | large tube | 2 | 9 |
| Toilet soap | small cake | 8 | |
| Hair cream | jar | 3 | 11 |
| Razor blades | packet of 10 | 3 | 4 |
| Aspirin | packet of 25 | 1 | 9 |
| Antiseptic healing cream | tin | 3 | 0 |
| Disinfectant | bottle | 2 | 9 |
| Popular book | each | 3 | 6 |
| Dictionary | each | 6 | 6 |
| Writing pad | each | 1 | 6 |
| Envelopes | packet of 18 | 10 | |
| Camera film | each | 2 | 9 |
| Developing and printing film | per film | 4 | 8 |
| Tobacco | 2 oz | 4 | 6 |
| Cigarettes | packet of 10 | 1 | 3 |
| Petrol | gallon | 3 | 4 1/4 |
International Comparisons - The two tables next following provide comparisons of retail and wholesale prices respectively between New Zealand and certain other countries. All the prices, which relate generally to the month of September 1960, have been converted into New Zealand currency. In the first table prices shown for the United States of America are exclusive of sales tax.
| COMPARISON OF RETAIL PRICES OF BASIC FOODSTUFFS | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Unit | New Zealand (Average 21 Towns) September 1960 | Australia (Sydney) September 1960 | South Africa (Cape Town) September 1960 | Great Britain (London) September 1960 | Canada (Dominion Average) September 1960 | United States of America (Average 46 Large Cities) September 1960 | ||||||
* 1 3/4 lb. † At price for 3 lb lots. ‡ Loose. § September Quarter, 1960. || Sirloin. ¶ Cooking quality. | |||||||||||||
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| Bread | 2 lb | 0 | 7 1/2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 1/2* | 2 | 3+ | 2 | 11 1/4 |
| Flour | 25 lb | 6 | 6 1/2 | 15 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 12 | 1 3/4 † | 16 | 1 1/4 | 19 | 9 |
| Tea | lb | 6 | 6 | 4 | 11 1/2 | 7 | 9 3/4 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 8 3/4 | .. | .. |
| Coffee | lb | 8 | 2 1/2 ‡ | .. | .. | 7 | 7 3/4 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 4 1/2 | 5 | 4 |
| Sugar | lb | 0 | 8 | 0 | 8 3/4 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 73/4 | 0 | 8 1/2 | 0 | 10 1/4 |
| Milk (fresh) | quart | 0 | 9 1/4 | 1 | 6 1/2 | 1 | 1 1/2 | 1 | 3 1/2 | 1 | 8 3/4 | 2 | 3 |
| Butter | lb | 2 | 0 | 3 | 10 1/2 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 1/4 |
| Cheese | lb | 2 | 0 1/4 | 2 | 11 1/2 | 2 | 11 1/2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 9 1/4 | 4 | 10 3/4 |
| Bacon | lb | 4 | 6 1/4 | 5 | 9 3/4 | 4 | 2 1/2 | 4 | 3 1/2 | 6 | 0 1/4 | 4 | 11 |
| Prunes | lb | 2 | 11 | .. | .. | 2 | 8 1/2 | 2 | 3 | .. | .. | 2 | 10 |
| Canned peaches | 30 oz tin | 4 | 1 3/4 | 2 | 7 1/4 | 2 | 7 1/4 | 2 | 6 3/4 | 3 | 6 1/4 | 2 | 4 3/4 |
| Beef, rib roast | lb | 2 | 10 1/4 | 3 | 2 1/2§ | 2 | 7 1/4|| | 3 | 4 | 6 | 4 3/4 | 5 | 9 1/2 |
| Mutton, leg | lb | 2 | 6 | 1 | 9 3/4 | 2 | 11 3/4 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 2 3/4 |
| Pork – | |||||||||||||
| Leg | lb | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4§ | 3 | 2 1/2 | 4 | 0 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Chops | lb | 3 | 6 1/2 | 4 | 4 3/4§ | 3 | 4 1/2 | 4 | 10 | 5 | 5 1/2 | 6 | 5 1/4 |
| Margarine | lb | 1 | 7 1/2 ¶ | 2 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 3 1/4 | 1 | 11 |
Source:
Australia: Commonwealth Statistician.
South Africa: Bureau of Census and Statistics.
Great Britain: New Zealand High Commissioner.
Canada: Dominion Bureau of Statistics.
U.S.A.: Monthly Labor Review.
COMPARISON OF WHOLESALE PRICES OF CERTAIN COMMODITIES
| Item | Unit | New Zealand, August 1960* | South Africa, September 1960 | Great Britain, September 1960 | Canada, September 1960 | United States of America, September 1960 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Priced once each quarter. † Price excluding tax (including tax the price ranges from 1s. 8d. to 2s. 0 3/4d. according to the State). | ||||||||||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | ||
| Wheat | bushel | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 16 | 7 1/2 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 8 3/4 | 0 | 15 | 4 |
| Oats | bushel | 0 | 8 | 6 | .. | .. | .. | 0 | 7 | 3 3/4 | 0 | 7 | 5 3/4 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
| Flour | ton | 13 | 18 | 1 | 35 | 6 | 4 | 35 | 3 | 7 | 47 | 5 | 0 3/4 | 37 | 17 | 2 |
| Sugar | cwt | 3 | 5 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 19 | 11 | 3 | 12 | 0 |
| Butter | lb | 0 | 1 | 10 1/2 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 8 1/4 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
| Cheese | lb | 0 | 1 | 7 1/2 | 0 | 2 | 6 1/2 | 0 | 2 | 0 3/4 | .. | .. | .. | 0 | 3 | 0 3/4 |
| Motor spirits | gallon | 0 | 3 | 0 1/4 | 0 | 3 | 0 3/4 | 0 | 3 | 10 | .. | .. | .. | 0 | 1 | 0 3/4† |
Source:
South Africa: Monthly Bulletin of Statistics.
Great Britain: The Economist – Intelligence Unit.
Canada: Prices and Price Indexes - Dominion Bureau of Statistics.
U.S.A.: Survey of Current Business.
RETAIL PRICES INDEX NUMBERS - An historical survey of retail prices in New Zealand will be found on pages 1007-1016 of the 1947-49 Yearbook, including an account of the various series of official index numbers of retail prices in New Zealand which had been current up to 1949, while pages 998-1003 of the same volume provide a brief description of the original Consumers' Price Index initiated in that year. For fuller details, however, reference should be made to the Special Supplement to the October-November 1949 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics entitled “Retail Prices in New Zealand with Special Reference to the Consumers' Price Index”. This index was completely revised in 1955-56 and a full description of the revision was published as a special supplement to the November 1956 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics under the title “Consumers' Price Index, 1955 Revision”. Extracts from that publication were also reprinted as an appendix to the 1957 Yearbook (pages 1214-37). For the complete regimen however (i.e., the schedule of items included along with comparative weights) as well as for a continuation up to 1955 of the historical survey of retail prices, direct reference should be made to the 1956 special supplement.
Consumers' Price Index - A brief summary of the salient features of the index is as follows:
The basic formula used is that of Laspeyres in its aggregative form.
The index relates primarily to urban dwellers living as families.
About 85 per cent of personal expenditure is covered.
The number of items regularly priced is 375.
The base is: 1952-53 consumption costed at 1955 prices.
Sources of group and commodity weights were (1) the Census of Distribution 1952-53; (2) an analysis of household budgets collected privately in 1952-53; and (3) an extension of regularly compiled statistics of consumable goods. Where considered desirable the base weight assigned to selected items is broadened to allow for expenditure on kindred items not selected for pricing.
Prices are collected by field officers in 23 towns, including two combined areas.
A scientific sample of rented houses and flats has been selected.
Special techniques are employed for costs of owner-occupiers, for prices of seasonal fruits and vegetables, and for transport charges.
Index numbers are compiled for all food and its subgroups at monthly intervals, and for all other groups and subgroups at quarterly intervals.
Individual town index numbers are published for 21 towns, showing each town both on a common base and on its own base.
To provide a continuous series the prerevision all-groups index has been recalculated on a 1955 base.
Costs of the following items are, for various reasons, outside the scope of the index: hotel accommodation, licensed and private; long-distance rail and bus transport; all sea and air transport; legal fees, commissions on sales, etc.; gambling; church and charitable donations; private and boarding school fees; music, elocution, dancing, etc., tuition fees; instalment credit interest and similar financial charges; personal accident insurance; funeral directors' charges; photographers' charges; wages of domestic servants, jobbing gardeners, etc.; fees to chiropractors, herbalists, chiropodists, etc.; sundry licences (marriage, dog, etc.); direct taxation; savings, including amortisations of capital debts, investments, and life insurance; spirits and wine; jewellery and florists' goods; durable goods other than replacements; private holiday transport; cost of removal to another locality.
In general the index assumes a constant pattern of expenditure for all towns, whether large cities or provincial centres, whether with warm or cool climates, etc. In. transportation, however, the index compromises by setting up a constant base expenditure on transport for all towns, but allowing a varying dissection between the various modes of transport from town to town, according to local circumstances. Consequently there are no true “each on all” indices for transportation, but “each on each” indices can be used to produce “all on all” indices. (“Each on all” means an index for an individual town which uses as base the average for all towns, etc.)
The table immediately following provides a long-term linked series of retail price (all groups) index numbers combining the present Consumers' Price Index with its predecessors back to 1907, the whole being placed on a uniform base, i.e., the calendar year 1955.
LONG-TERM LINKED SERIES
| Base: Calendar year 1955 (= 1000) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Index Number |
| 1907 | 308 |
| 1908 | 309 |
| 1909 | 305 |
| 1910 | 308 |
| 1911 | 306 |
| 1912 | 315 |
| 1913 | 322 |
| 1914 | 332 |
| 1915 | 357 |
| 1916 | 382 |
| 1917 | 415 |
| 1918 | 449 |
| 1919 | 482 |
| 1920 | 538 |
| 1921 | 546 |
| 1922 | 503 |
| 1923 | 507 |
| 1924 | 520 |
| 1925 | 530 |
| 1926 | 533 |
| 1927 | 529 |
| 1928 | 531 |
| 1929 | 530 |
| 1930 | 518 |
| 1931 | 479 |
| 1932 | 443 |
| 1933 | 420 |
| 1934 | 427 |
| 1935 | 442 |
| 1936 | 456 |
| 1937 | 488 |
| 1938 | 502 |
| 1939 | 523 |
| 1940 | 547 |
| 1941 | 567 |
| 1942 | 586 |
| 1943 | 599 |
| 1944 | 610 |
| 1945 | 618 |
| 1946 | 623 |
| 1947 | 643 |
| 1948 | 694 |
| 1949 | 706 |
| 1950 | 745 |
| 1951 | 828 |
| 1952 | 892 |
| 1953 | 933 |
| 1954 | 976 |
| 1955 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 1035 |
| 1957 | 1057 |
| 1958 | 1104 |
| 1959 | 1146 |
| 1960 | 1154 |
The following diagram shows the movement in retail prices index numbers over the period 1907-60, the data being drawn from the figures given in the preceding table (long-term linked series).
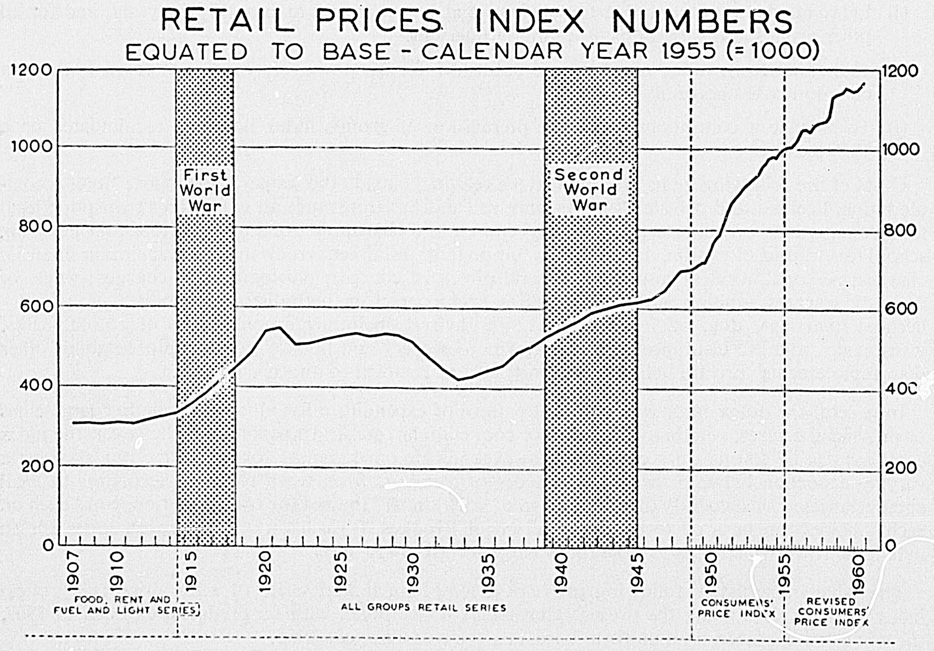
Consumers' Price Index Numbers - The tables which now follow relate to the current Consumers' Price Index only.
The first table supplies all-groups index numbers and index numbers of individual groups and subgroups for 21 towns combined in respect of the calendar years 1955-60 and for each of the four quarters of the years 1956-60. The group and subgroup weights are also shown as percentages of the base expenditure.
TWENTY-ONE TOWNS COMBINED
| Base: Weighted average twenty-one towns, 1955 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Housing | Household Operation | Apparel | Transportation | Miscellaneous | All Groups | |
| Groups— | |||||||
| Percentages of base expenditure | 32.26 | 15.40 | 10.60 | 15.43 | 8.76 | 17.55 | 100.00 |
| Calendar year— | |||||||
| 1955 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 1057 | 1055 | 1013 | 999 | 1016 | 1030 | 1035 |
| 1957 | 1054 | 1118 | 1038 | 1005 | 1076 | 1055 | 1057 |
| 1958 | 1071 | 1179 | 1074 | 1022 | 1160 | 1160 | 1104 |
| 1959 | 1077 | 1236 | 1094 | 1041 | 1240 | 1273 | 1146 |
| 1960 | 1092 | 1286 | 1107 | 1063 | 1213 | 1232 | 1154 |
| Quarter ended— | |||||||
| 1956—31 March | 1015 | 1032 | 1007 | 1001 | 1009 | 1009 | 1013 |
| 30 June | 1043 | 1048 | 1011 | 998 | 1015 | 1023 | 1027 |
| 30 September | 1092 | 1061 | 1016 | 1000 | 1015 | 1042 | 1049 |
| 31 December | 1078 | 1079 | 1018 | 998 | 1026 | 1046 | 1049 |
| 1957—31 March | 1025 | 1098 | 1033 | 998 | 1069 | 1047 | 1041 |
| 30 June | 1057 | 1112 | 1035 | 1001 | 1077 | 1056 | 1056 |
| 30 September | 1066 | 1124 | 1038 | 1009 | 1076 | 1058 | 1063 |
| 31 December | 1069 | 1138 | 1044 | 1011 | 1083 | 1061 | 1068 |
| 1958—31 March | 1057 | 1155 | 1049 | 1012 | 1095 | 1063 | 1069 |
| 30 June | 1069 | 1169 | 1074 | 1019 | 1114 | 1065 | 1080 |
| 30 September | 1072 | 1189 | 1086 | 1025 | 1206 | 1264 | 1130 |
| 31 December | 1085 | 1203 | 1088 | 1031 | 1226 | 1250 | 1137 |
| 1959—31 March | 1075 | 1220 | 1090 | 1030 | 1234 | 1263 | 1139 |
| 30 June | 1070 | 1231 | 1090 | 1038 | 1239 | 1274 | 1142 |
| 30 September | 1078 | 1241 | 1097 | 1045 | 1244 | 1304 | 1154 |
| 31 December | 1086 | 1251 | 1101 | 1050 | 1244 | 1250 | 1150 |
| 1960—31 March | 1071 | 1266 | 11,088 | 1056 | 1223 | 1237 | 1145 |
| 30 June | 1068 | 1281 | 1107 | 1061 | 1223 | 1239 | 1147 |
| 30 September | 1102 | 1292 | 1105 | 1064 | 1205 | 1226 | 1157 |
| 31 December | 1128 | 1304 | 1107 | 1069 | 1202 | 1228 | 1168 |
| Food | Housing | Household Operation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat and Fish | Fruits, Vegetables, and Eggs | Other Foods | Rent | Home Ownership | Fuel and Light | Home Furnishings | Domestic Supplies and Services | |
| Subgroups— | ||||||||
| Percentages of base expenditure | 8.24 | 8.03 | 15.99 | 4.66 | 10.74 | 3.20 | 4.70 | 2.70 |
| Calendar year— | ||||||||
| 1955 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 995 | 1231 | 1002 | 1048 | 1058 | 1015 | 1010 | 1016 |
| 1957 | 1054 | 1105 | 1029 | 1098 | 1126 | 1042 | 1022 | 1059 |
| 1958 | 1152 | 1067 | 1030 | 1143 | 1195 | 1104 | 1055 | 1073 |
| 1959 | 1171 | 1073 | 1031 | 1197 | 1253 | 1129 | 1073 | 1091 |
| 1960 | 1176 | 1109 | 1041 | 1232 | 1309 | 1128 | 1088 | 1114 |
| Quarter ended— | ||||||||
| 1956— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1008 | 1045 | 1004 | 1024 | 1036 | 1010 | 1003 | 1012 |
| 30 June | 986 | 1191 | 997 | 1045 | 1050 | 1012 | 1008 | 1014 |
| 30 September | 989 | 1375 | 1002 | 1051 | 1065 | 1017 | 1014 | 1017 |
| 31 December | 995 | 1312 | 1003 | 1073 | 1082 | 1022 | 1015 | 1020 |
| 1957— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 992 | 1091 | 1010 | 1089 | 1101 | 1039 | 1015 | 1056 |
| 30 June | 1028 | 1141 | 1029 | 1097 | 1118 | 1043 | 1016 | 1057 |
| 30 September | 1080 | 1098 | 1042 | 1103 | 1133 | 1043 | 1023 | 1059 |
| 31 December | 1115 | 1088 | 1035 | 1103 | 1153 | 1044 | 1033 | 1065 |
| 1958— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1101 | 1066 | 1029 | 1116 | 1172 | 1044 | 1042 | 1067 |
| 30 June | 1151 | 1061 | 1030 | 1125 | 1187 | 1108 | 1052 | 1071 |
| 30 September | 1173 | 1047 | 1032 | 1162 | 1202 | 1132 | 1060 | 1076 |
| 31 December | 1183 | 1094 | 1030 | 1167 | 1218 | 1133 | 1064 | 1079 |
| 1959— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1181 | 1059 | 1029 | 1186 | 1235 | 1134 | 1066 | 1079 |
| 30 June | 1160 | 1058 | 1029 | 1196 | 1247 | 1133 | 1066 | 1083 |
| 30 September | 1163 | 1083 | 1031 | 1202 | 1258 | 1128 | 1077 | 1093 |
| 31 December | 1181 | 1091 | 1034 | 1203 | 1272 | 1120 | 1083 | 1109 |
| 1960— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1167 | 1042 | 1037 | 1214 | 1289 | 1133 | 1088 | 1113 |
| 30 June | 1144 | 1045 | 1040 | 1230 | 1303 | 1130 | 1089 | 1114 |
| 30 September | 1175 | 1149 | 1041 | 1242 | 1314 | 1124 | 1086 | 1114 |
| 31 December | 1220 | 1201 | 1044 | 1242 | 1331 | 1124 | 1091 | 1114 |
CONSUMERS' PRICE INDEX - QUARTERLY INDEX NUMBERS (ALL GROUPS)
| Apparel | Transportation | Miscellaneous | All Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clothing | Footwear | Public Transport | Private Transport | Tobacco and Alcohol | Other Supplies | Other Services | ||
| Subgroups— | ||||||||
| Percentages of base expenditure | 13.06 | 2.37 | 2.48 | 6.28 | 8.53 | 4.90 | 4.12 | 100.00 |
| Calendar year | ||||||||
| 1955 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 992 | 1039 | 1007 | 1020 | 1010 | 1035 | 1066 | 1035 |
| 1957 | 992 | 1078 | 1122 | 1058 | 1014 | 1064 | 1131 | 1057 |
| 1958 | 1005 | 1115 | 1140 | 1168 | 1196 | 1083 | 1180 | 1104 |
| 1959 | 1018 | 1164 | 1175 | 1266 | 1396 | 1106 | 1216 | 1146 |
| 1960 | 1030 | 1242 | 1203 | 1217 | 1285 | 1130 | 1245 | 1154 |
| Quarter ended— | ||||||||
| 1956— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 996 | 1010 | 999 | 1013 | 1000 | 1018 | 1016 | 1013 |
| 30 June | 991 | 1039 | 1008 | 1017 | 1013 | 1031 | 1034 | 1027 |
| 30 September | 993 | 1039 | 1008 | 1018 | 1013 | 1039 | 1104 | 1049 |
| 31 December | 989 | 1048 | 1013 | 1031 | 1013 | 1051 | 1108 | 1049 |
| 1957— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 988 | 1054 | 1113 | 1052 | 1013 | 1051 | 1110 | 1041 |
| 30 June | 988 | 1076 | 1113 | 1063 | 1014 | 1064 | 1132 | 1056 |
| 30 September | 995 | 1090 | 1122 | 1058 | 1014 | 1070 | 1136 | 1063 |
| 31 December | 996 | 1092 | 1140 | 1060 | 1014 | 1071 | 1147 | 1068 |
| 1958— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 996 | 1099 | 1140 | 1077 | 1014 | 1077 | 1147 | 1069 |
| 30 June | 1003 | 1108 | 1140 | 1103 | 1014 | 1079 | 1154 | 1080' |
| 30 September | 1007 | 1123 | 1140 | 1232 | 1394 | 1085 | 1208 | 1130 |
| 31 December | 1013 | 1130 | 1142 | 1259 | 1361 | 1089 | 1212 | 1137 |
| 1959— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1012 | 1129 | 1143 | 1270 | 1384 | 1093 | 1215 | 1139 |
| 30 June | 1019 | 1141 | 1171 | 1266 | 1406 | 1106 | 1202 | 1142 |
| 30 September | 1019 | 1183 | 1186 | 1267 | 1458 | 1110 | 1214 | 1154 |
| 31 December | 1023 | 1203 | 1199 | 1261 | 1335 | 1116 | 1235 | 1150 |
| 1960— | ||||||||
| 31 March | 1027 | 1215 | 1201 | 1231 | 1298 | 1123 | 1245 | 1145 |
| 30 June | 1028 | 1243 | 1201 | 1231 | 1298 | 1130 | 1245 | 1147 |
| 30 September | 1030 | 1251 | 1206 | 1205 | 1272 | 1130 | 1246 | 1157 |
| 31 December | 1034 | 1260 | 1204 | 1201 | 1272 | 1138 | 1245 | 1168 |
In the table which follows, annual figures are shown for all index towns combined in respect to the years 1955-60 and each of the fifteen months ended December 1960.
CONSUMERS' PRICE INDEX - MONTHLY INDEX NUMBERS (FOOD), TWENTY-ONE TOWNS COMBINED
| Base: Weighted average twenty-one towns, 1955 (= 1000) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat and Fish | Fruits, Vegetables, and Eggs | Other Foods | All Food | |
| Calendar Year | ||||
| 1955 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 955 | 1231 | 1002 | 1057 |
| 1957 | 1054 | 1105 | 1029 | 1054 |
| 1958 | 1152 | 1067 | 1030 | 1071 |
| 1959 | 1171 | 1073 | 1031 | 1077 |
| 1960 | 1176 | 1109 | 1041 | 1092 |
| Month— | ||||
| 1959—October | 1183 | 1096 | 1034 | 1088 |
| November | 1186 | 1066 | 1034 | 1081 |
| December | 1174 | 1111 | 1034 | 1089 |
| 1960—January | 1181 | 1070 | 1035 | 1081 |
| February | 1184 | 1021 | 1038 | 1071 |
| March | 1135 | 1034 | 1039 | 1062 |
| April | 1134 | 1037 | 1039 | 1063 |
| May | 1146 | 1040 | 1039 | 1066 |
| June | 1153 | 1059 | 1042 | 1075 |
| July | 1160 | 1126 | 1040 | 1092 |
| August | 1175 | 1179 | 1040 | 1109 |
| September | 1189 | 1144 | 1042 | 1105 |
| October | 1215 | 1169 | 1043 | 1118 |
| November | 1230 | 1250 | 1045 | 1144 |
| December | 1216 | 1184 | 1044 | 1123 |
The following tables distinguish individual towns and groupings of towns, but the subgroup indices are omitted; the periods covered are the calendar years 1955, 1959, and 1960 and the separate quarters of 1960. Attention is called, however, to the two-fold method of presentation: in the first place current prices in each town are compared with prices in the same town during the base period; in the second, current prices in each town are compared with average prices over all the 21 towns in the base period.
CONSUMERS' PRICE INDEX - GROUP INDEX NUMBERS FOR INDIVIDUAL TOWNS AND GROUPINGS OF TOWNS
| Base: Weighted average each town, and grouping, separately, 1955 (= 1000) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Housing | |||||||||||||
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| Auckland | 1000 | 1070 | 1064 | 1074 | 1115 | 1161 | 1103 | 1000 | 1231 | 1257 | 1269 | 1281 | 1292 | 1275 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1000 | 1088 | 1069 | 1062 | 1100 | 1121 | 1088 | 1000 | 1249 | 1280 | 1289 | 1297 | 1313 | 1295 |
| Christchurch | 1000 | 1104 | 1105 | 1091 | 1119 | 1134 | 1112 | 1000 | 1220 | 1255 | 1295 | 1303 | 1318 | 1293 |
| Dunedin | 1000 | 1084 | 1088 | 1072 | 1093 | 1097 | 1088 | 1000 | 1214 | 1250 | 1265 | 1280 | 1286 | 1271 |
| Four chief centres | 1000 | 1083 | 1076 | 1074 | 1110 | 1138 | 1099 | 1000 | 1232 | 1262 | 1279 | 1289 | 1302 | 1283 |
| Hamilton | 1000 | 1045 | 1036 | 1039 | 1075 | 1101 | 1063 | 1000 | 1267 | 1294 | 1308 | 1337 | 1338 | 1319 |
| Gisborne | 1000 | 1075 | 1061 | 1053 | 1108 | 1131 | 1088 | 1000 | 1263 | 1289 | 1305 | 1322 | 1337 | 1314 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1000 | 1076 | 1050 | 1065 | 1092 | 1111 | 1079 | 1000 | 1227 | 1260 | 1269 | 1283 | 1290 | 1275 |
| New Plymouth | 1000 | 1081 | 1072 | 1047 | 1077 | 1109 | 1076 | 1000 | 1269 | 1292 | 1301 | 1310 | 1314 | 1304 |
| Wanganui | 1000 | 1050 | 1051 | 1059 | 1096 | 1112 | 1079 | 1000 | 1256 | 1295 | 1292 | 1298 | 1315 | 1300 |
| Palmerston North | 1000 | 1045 | 1038 | 1044 | 1081 | 1099 | 1065 | 1000 | 1239 | 1260 | 1281 | 1291 | 1305 | 1284 |
| Nelson | 1000 | 1086 | 1079 | 1068 | 1093 | 1128 | 1092 | 1000 | 1221 | 1249 | 1264 | 1273 | 1286 | 1268 |
| Timaru | 1000 | 1077 | 1094 | 1072 | 1111 | 1120 | 1099 | 1000 | 1276 | 1311 | 1323 | 1333 | 1321 | 1322 |
| Invercargill | 1000 | 1082 | 1114 | 1088 | 1104 | 1104 | 1102 | 1000 | 1212 | 1250 | 1256 | 1262 | 1273 | 1260 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1000 | 1065 | 1061 | 1057 | 1089 | 1109 | 1079 | 1000 | 1247 | 1277 | 1288 | 1301 | 1309 | 1294 |
| Whangarei | 1000 | 1066 | 1047 | 1047 | 1088 | 1130 | 1078 | 1000 | 1231 | 1263 | 1282 | 1307 | 1325 | 1294 |
| Tauranga | 1000 | 1076 | 1075 | 1056 | 1094 | 1138 | 1091 | 1000 | 1258 | 1305 | 1300 | 1320 | 1373 | 1325 |
| Rotorua | 1000 | 1066 | 1062 | 1047 | 1078 | 1109 | 1074 | 1000 | 1244 | 1271 | 1267 | 1276 | 1285 | 1275 |
| Masterton | 1000 | 1081 | 1060 | 1056 | 1089 | 1108 | 1078 | 1000 | 1216 | 1258 | 1269 | 1280 | 1286 | 1273 |
| Blenheim | 1000 | 1085 | 1083 | 1069 | 1101 | 1121 | 1093 | 1000 | 1276 | 1313 | 1324 | 1332 | 1354 | 1331 |
| Greymouth | 1000 | 1074 | 1076 | 1065 | 1089 | 1112 | 1085 | 1000 | 1192 | 1220 | 1233 | 1241 | 1243 | 1234 |
| Ashburton | 1000 | 1074 | 1074 | 1069 | 1093 | 1108 | 1086 | 1000 | 1253 | 1291 | 1304 | 1335 | 1317 | 1312 |
| Oamaru | 1000 | 1075 | 1097 | 1075 | 1091 | 1091 | 1088 | 1000 | 1233 | 1255 | 1265 | 1268 | 1292 | 1270 |
| Eight other towns | 1000 | 1073 | 1069 | 1058 | 1089 | 1116 | 1083 | 1000 | 1233 | 1267 | 1275 | 1289 | 1304 | 1284 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1077 | 1071 | 1068 | 1102 | 1128 | 1092 | 1000 | 1236 | 1266 | 1281 | 1292 | 1304 | 1286 |
| Household Operation | Apparel | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| Auckland | 1000 | 1093 | 1112 | 1104 | 1098 | 1095 | 1102 | 1000 | 1024 | 1036 | 1040 | 1042 | 1048 | 1042 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1000 | 1091 | 1111 | 1113 | 1113 | 1122 | 1115 | 1000 | 1047 | 1059 | 1060 | 1065 | 1078 | 1065 |
| Christchurch | 1000 | 1093 | 1103 | 1103 | 1100 | 1107 | 1103 | 1000 | 1049 | 1069 | 1079 | 1076 | 1079 | 1076 |
| Dunedin | 1000 | 1107 | 1123 | 1132 | 1125 | 1131 | 1128 | 1000 | 1055 | 1081 | 1087 | 1091 | 1093 | 1088 |
| Four chief centres | 1000 | 1094 | 1111 | 1109 | 1106 | 1108 | 1108 | 1000 | 1038 | 1053 | 1058 | 1060 | 1067 | 1059 |
| Hamilton | 1000 | 1107 | 1106 | 1108 | 1104 | 1103 | 1105 | 1000 | 1062 | 1071 | 1080 | 1090 | 1092 | 1083 |
| Gisborne | 1000 | 1111 | 1123 | 1122 | 1122 | 1112 | 1120 | 1000 | 1053 | 1073 | 1079 | 1088 | 1087 | 1682 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1000 | 1119 | 1116 | 1115 | 1112 | 1115 | 1114 | 1000 | 1032 | 1040 | 1050 | 1055 | 1056 | 1050 |
| New Plymouth | 1000 | 1096 | 1112 | 1113 | 1113 | 1115 | 1113 | 1000 | 1057 | 1065 | 1071 | 1071 | 1073 | 1070 |
| Wanganui | 1000 | 1078 | 1071 | 1073 | 1073 | 1077 | 1073 | 1000 | 1055 | 1082 | 1091 | 1091 | 1094 | 1089 |
| Palmerston North | 1000 | 1094 | 1104 | 1102 | 1103 | 1108 | 1104 | 1000 | 1034 | 1070 | 1078 | 1079 | 1082 | 1077 |
| Nelson | 1000 | 1083 | 1095 | 1098 | 1099 | 1102 | 1098 | 1000 | 1044 | 1044 | 1059 | 1061 | 1061 | 1056 |
| Timaru | 1000 | 1095 | 1104 | 1130 | 1128 | 1134 | 1124 | 1000 | 1029 | 1043 | 1044 | 1043 | 1050 | 1045 |
| Invercargill | 1000 | 1085 | 1099 | 1102 | 1098 | 1093 | 1098 | 1000 | 1034 | 1051 | 1054 | 1062 | 1063 | 1058 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1000 | 1098 | 1104 | 1107 | 1105 | 1106 | 1105 | 1000 | 1045 | 1060 | 1068 | 1072 | 1074 | 1069 |
| Whangarei | 1000 | 1072 | 1086 | 1086 | 1083 | 1085 | 1085 | 1000 | 1024 | 1032 | 1049 | 1050 | 1050 | 1045 |
| Tauranga | 1000 | 1070 | 1089 | 1088 | 1084 | 1086 | 1087 | 1000 | 1062 | 1077 | 1095 | 1097 | 1093 | 1090 |
| Rotorua | 1000 | 1109 | 1119 | 1126 | 1129 | 1125 | 1125 | 1000 | 1062 | 1080 | 1080 | 1091 | 1104 | 1089 |
| Masterton | 1000 | 1089 | 1102 | 1098 | 1099 | 1104 | 1101 | 1000 | 1047 | 1058 | 1065 | 1071 | 1074 | 1067 |
| Blenheim | 1000 | 1059 | 1066 | 1068 | 1068 | 1071 | 1068 | 1000 | 1044 | 1047 | 1053 | 1055 | 1056 | 1053 |
| Greymouth | 1000 | 1100 | 1111 | 1115 | 1118 | 1116 | 1115 | 1000 | 1048 | 1059 | 1055 | 1058 | 1057 | 1057 |
| Ashburton | 1000 | 1062 | 1086 | 1087 | 1080 | 1084 | 1084 | 1000 | 1029 | 1036 | 1039 | 1040 | 1042 | 1039 |
| Oamaru | 1000 | 1096 | 1103 | 1107 | 1104 | 1104 | 1105 | 1000 | 1055 | 1080 | 1086 | 1083 | 1088 | 1084 |
| Eight other towns | 1000 | 1085 | 1098 | 1100 | 1099 | 1100 | 1099 | 1000 | 1047 | 1059 | 1066 | 1069 | 1072 | 1066 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1094 | 1108 | 1107 | 1105 | 1107 | 1107 | 1000 | 1041 | 1056 | 1061 | 1064 | 1069 | 1063 |
| Base: Weighted average each town, and grouping, separately, 1955 (= 1000) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Miscellaneous | |||||||||||||
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| Auckland | 1000 | 1248 | 1236 | 1236 | 1221 | 1221 | 1229 | 1000 | 1269 | 1236 | 1238 | 1225 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1000 | 1240 | 1241 | 1241 | 1225 | 1222 | 1233 | 1000 | 1274 | 1237 | 1237 | 1224 | 1226 | 1231 |
| Christchurch | 1000 | 1226 | 1199 | 1199 | 1182 | 1178 | 1190 | 1000 | 1263 | 1224 | 1231 | 1219 | 1219 | 1223 |
| Dunedin | 1000 | 1239 | 1217 | 1217 | 1201 | 1199 | 1208 | 1000 | 1281 | 1249 | 1251 | 1239 | 1242 | 1245 |
| Four chief centres | 1000 | 1241 | 1228 | 1228 | 1212 | 1211 | 1220 | 1000 | 1270 | 1235 | 1238 | 1225 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Hamilton | 1000 | 1245 | 1217 | 1217 | 1197 | 1195 | 1206 | 1000 | 1273 | 1236 | 1238 | 1225 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Gisborne | 1000 | 1236 | 1208 | 1208 | 1186 | 1183 | 1196 | 1000 | 1270 | 1232 | 1232 | 1218 | 1221 | 1226 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1000 | 1235 | 1213 | 1211 | 1182 | 1178 | 1196 | 1000 | 1284 | 1233 | 1232 | 1219 | 1222 | 1226 |
| New Plymouth | 1000 | 1241 | 1212 | 1211 | 1195 | 1192 | 1203 | 1000 | 1279 | 1242 | 1241 | 1228 | 1231 | 1236 |
| Wanganui | 1000 | 1245 | 1216 | 1216 | 1195 | 1191 | 1204 | 1000 | 1278 | 1242 | 1241 | 1228 | 1221 | 1235 |
| Palmerston North | 1000 | 1241 | 1219 | 1219 | 1223 | 1199 | 1215 | 1000 | 1280 | 1242 | 1241 | 1228 | 1231 | 1235 |
| Nelson | 1000 | 1246 | 1218 | 1222 | 1199 | 1195 | 1208 | 1000 | 1274 | 1233 | 1239 | 1227 | 1228 | 1232 |
| Timaru | 1000 | 1247 | 1223 | 1223 | 1201 | 1197 | 1211 | 1000 | 1272 | 1235 | 1241 | 1229 | 1230 | 1234 |
| Invercargill | 1000 | 1235 | 1205 | 1203 | 1178 | 1176 | 1191 | 1000 | 1279 | 1249 | 1251 | 1239 | 1242 | 1246 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1000 | 1241 | 1215 | 1215 | 1196 | 1190 | 1204 | 1000 | 1277 | 1238 | 1239 | 1227 | 1229 | 1233 |
| Whangarei | 1000 | 1229 | 1224 | 1222 | 1198 | 1196 | 1210 | 1000 | 1278 | 1244 | 1247 | 1233 | 1235 | 1240 |
| Tauranga | 1000 | 1255 | 1225 | 1223 | 1196 | 1193 | 1209 | 1000 | 1273 | 1240 | 1242 | 1229 | 1231 | 1235 |
| Rotorua | 1000 | 1220 | 1194 | 1193 | 1171 | 1169 | 1182 | 1000 | 1278 | 1245 | 1247 | 1234 | 1236 | 1240 |
| Masterton | 1000 | 1249 | 1216 | 1216 | 1193 | 1188 | 1203 | 1000 | 1282 | 1246 | 1246 | 1233 | 1231 | 1239 |
| Blenheim | 1000 | 1231 | 1204 | 1202 | 1178 | 1174 | 1190 | 1000 | 1277 | 1238 | 1244 | 1232 | 1233 | 1237 |
| Greymouth | 1000 | 1208 | 1183 | 1183 | 1164 | 1161 | 1173 | 1000 | 1271 | 1233 | 1240 | 1228 | 1228 | 1232 |
| Ashburton | 1000 | 1260 | 1226 | 1226 | 1202 | 1197 | 1213 | 1000 | 1267 | 1233 | 1240 | 1228 | 1229 | 1232 |
| Oamaru | 1000 | 1268 | 1236 | 1236 | 1212 | 1209 | 1223 | 1000 | 1281 | 1249 | 1251 | 1239 | 1241 | 1245 |
| Eight other towns | 1000 | 1236 | 1211 | 1210 | 1187 | 1183 | 1198 | 1000 | 1276 | 1241 | 1244 | 1232 | 1233 | 1237 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1240 | 1223 | 1223 | 1205 | 1202 | 1213 | 1000 | 1273 | 1237 | 1239 | 1226 | 1228 | 1232 |
| Base: Weighted average twenty-one towns, 1955 (= 1000)* | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Housing | |||||||||||||
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| *To give better inter-town comparisons pricing is now carried out in all 21 towns. Index numbers for each individual town have been revised back to 1955, but the 21 towns index numbers are not affected. | ||||||||||||||
| Auckland | 998 | 1068 | 1062 | 1072 | 1113 | 1159 | 1102 | 1618 | 1253 | 1280 | 1292 | 1304 | 1315 | 1298 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1012 | 1102 | 1082 | 1075 | 1114 | 1135 | 1102 | 1047 | 1307 | 1339 | 1349 | 1357 | 1374 | 1355 |
| Christchurch | 990 | 1093 | 1094 | 1080 | 1108 | 1123 | 1101 | 1000 | 1220 | 1255 | 1295 | 1303 | 1318 | 1293 |
| Dunedin | 977 | 1060 | 1064 | 1048 | 1068 | 1072 | 1063 | 984 | 1195 | 1231 | 1245 | 1260 | 1266 | 1251 |
| Four chief centres | 998 | 1080 | 1074 | 1072 | 1107 | 1136 | 1097 | 1018 | 1253 | 1284 | 1301 | 1312 | 1325 | 1306 |
| Hamilton | 1023 | 1069 | 1060 | 1063 | 1100 | 1127 | 1088 | 958 | 1213 | 1239 | 1253 | 1280 | 1281 | 1264 |
| Gisborne | 997 | 1072 | 1058 | 1050 | 1105 | 1127 | 1085 | 952 | 1202 | 1227 | 1242 | 1258 | 1273 | 1250 |
| Napier-Hastings | 958 | 1030 | 1006 | 1020 | 1046 | 1064 | 1034 | 940 | 1153 | 1184 | 1192 | 1206 | 1212 | 1198 |
| New Plymouth | 987 | 1067 | 1058 | 1034 | 1064 | 1095 | 1063 | 972 | 1234 | 1256 | 1265 | 1274 | 1278 | 1268 |
| Wanganui | 1014 | 1065 | 1065 | 1074 | 1111 | 1127 | 1094 | 932 | 1171 | 1207 | 1204 | 1210 | 1225 | 1211 |
| Palmerston North | 1019 | 1064 | 1057 | 1063 | 1101 | 1119 | 1085 | 984 | 1219 | 1239 | 1260 | 1270 | 1284 | 1263 |
| Nelson | 985 | 1070 | 1062 | 1051 | 1076 | 1110 | 1075 | 997 | 1218 | 1245 | 1260 | 1269 | 1282 | 1264 |
| Timaru | 987 | 1063 | 1080 | 1058 | 1096 | 1105 | 1085 | 970 | 1238 | 1271 | 1283 | 1293 | 1281 | 1282 |
| Invercargill | 1013 | 1096 | 1128 | 1102 | 1117 | 1118 | 1116 | 1006 | 1220 | 1258 | 1264 | 1270 | 1281 | 1268 |
| Nine provincial towns | 999 | 1064 | 1060 | 1056 | 1089 | 1109 | 1078 | 966 | 1205 | 1234 | 1245 | 1258 | 1265 | 1250 |
| Whangarei | 1044 | 1113 | 1093 | 1093 | 1135 | 1180 | 1125 | 98 | 1207 | 1239 | 1257 | 1282 | 1299 | 1269 |
| Tauranga | 1028 | 1106 | 1106 | 1086 | 1125 | 1170 | 1122 | 1014 | 1276 | 1323 | 1318 | 1339 | 1392 | 1343 |
| Rotorua | 1043 | 1112 | 1108 | 1093 | 1124 | 1157 | 1120 | 982 | 1221 | 1247 | 1244 | 1253 | 1261 | 1251 |
| Masterton | 1005 | 1087 | 1065 | 1062 | 1095 | 1114 | 1084 | 981 | H93 | 1234 | 1245 | 1255 | 1262 | 1249 |
| Blenheim | 974 | 1057 | 1055 | 1041 | 1072 | 1092 | 1065 | 966 | 1232 | 1267 | 1279 | 1286 | 1307 | 1285 |
| Greymouth | 1007 | 1082 | 1084 | 1072 | 1097 | 1120 | 1093 | 975 | 1162 | 1189 | 1202 | 1209 | 1212 | 1203 |
| Ashburton | 1004 | 1078 | 1079 | 1073 | 1097 | 1113 | 1091 | 944 | 1183 | 1219 | 1231 | 1260 | 1243 | 1238 |
| Oamaru | 983 | 1057 | 1079 | 1057 | 1073 | 1073 | 1070 | 940 | 1158 | 1179 | 1189 | 1191 | 1214 | 1193 |
| Eight other towns | 1017 | 1091 | 1087 | 1076 | 1107 | 1135 | 1101 | 977 | 1204 | 1238 | 1245 | 1259 | 1274 | 1254 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1077 | 1071 | 1068 | 1102 | 1128 | 1092 | 1000 | 1236 | 1266 | 1281 | 1292 | 1304 | 1286 |
| Base: Weighted average twenty-one town, and grouping, separately, 1955 (= 1000)* | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household Operation | Apparel | |||||||||||||
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| *To give better inter-town comparisons pricing is now carried out in all 21 towns. Index numbers for each individual town have been revised back to 1955, but the 21 towns index numbers arc not affected. | ||||||||||||||
| Auckland | 1005 | 1099 | 1118 | 1110 | 1104 | 1101 | 1108 | 1032 | 1057 | 1069 | 1073 | 1075 | 1081 | 1075 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 994 | 1084 | 1104 | 1106 | 1106 | 1115 | 1108 | 985 | 1031 | 1043 | 1044 | 1049 | 1062 | 1049 |
| Christchurch | 988 | 1080 | 1090 | 1090 | 1094 | 1094 | 1091 | 971 | 1018 | 1038 | 1048 | 1045 | 1047 | 1044 |
| Dunedin | 937 | 1037 | 1052 | 1060 | 1054 | 1060 | 1056 | 999 | 1054 | 1081 | 1086 | 1090 | 1092 | 1087 |
| Four chief centres | 991 | 1084 | 1101 | 1099 | 1096 | 1098 | 1099 | 1004 | 1042 | 1058 | 1062 | 1064 | 1071 | 1064 |
| Hamilton | 975 | 1079 | 1079 | 1081 | 1077 | 1075 | 1078 | 975 | 1035 | 1044 | 1053 | 1063 | 1065 | 1056 |
| Gisborne | 1114 | 1239 | 1251 | 1251 | 1250 | 1239 | 1248 | 998 | 1051 | 1071 | 1077 | 1085 | 1084 | 1079 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1049 | 1174 | 1171 | 1169 | 1167 | 1170 | 1169 | 997 | 1028 | 1037 | 1046 | 1051 | 1052 | 1047 |
| New Plymouth | 1005 | 1101 | 1117 | 1118 | 1118 | 1120 | 1118 | 989 | 1045 | 1053 | 1059 | 1059 | 1061 | 1058 |
| Wanganui | 1022 | 1101 | 1094 | 1096 | 1097 | 1100 | 1097 | 993 | 1048 | 1075 | 1083 | 1084 | 1086 | 1082 |
| Palmerston North | 1021 | 1117 | 1127 | 1125 | 1126 | 1131 | 1127 | 997 | 1032 | 1068 | 1075 | 1077 | 1080 | 1075 |
| Nelson | 1006 | 1090 | 1102 | 1106 | 1106 | 1109 | 1106 | 985 | 1028 | 1027 | 1042 | 1045 | 1045 | 1040 |
| Timaru | 973 | 1066 | 1074 | 1100 | 1098 | 1104 | 1094 | 1016 | 1045 | 1059 | 1061 | 1060 | 1067 | 1062 |
| Invercargill | 1028 | 1116 | 1130 | 1134 | 1130 | 1124 | 1129 | 1011 | 1046 | 1063 | 1066 | 1074 | 1075 | 1070 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1017 | 1117 | 1123 | 1125 | 1124 | 1125 | 1124 | 994 | 1038 | 1054 | 1062 | 1066 | 1068 | 1062 |
| Whangarei | 1020 | 1093 | 1108 | 1108 | 1104 | 1107 | 1107 | 1009 | 1034 | 1042 | 1059 | 1060 | 1060 | 1055 |
| Tauranga | 925 | 989 | 1006 | 1006 | 1002 | 1004 | 1005 | 993 | 1054 | 1069 | 1087 | 1089 | 1086 | 1083 |
| Rotorua | 1033 | 1145 | 1155 | 1163 | 1166 | 1161 | 1161 | 946 | 1004 | 1021 | 1022 | 1032 | 1044 | 1030 |
| Masterton | 1036 | 1128 | 1142 | 1138 | 1139 | 1144 | 1141 | 1000 | 1046 | 1058 | 1064 | 1071 | 1073 | 1067 |
| Blenheim | 1035 | 1096 | 1103 | 1105 | 1106 | 1109 | 1106 | 1060 | 1107 | 1110 | 1116 | 1118 | 1119 | 1116 |
| Greymouth | 976 | 1074 | 1085 | 1088 | 1091 | 1090 | 1089 | 988 | 1035 | 1046 | 1042 | 1046 | 1044 | 1045 |
| Ashburton | 1070 | 1136 | 1162 | 1163 | 1156 | 1160 | 1160 | 984 | 1012 | 1019 | 1022 | 1023 | 1024 | 1022 |
| Oamaru | 1047 | 1148 | 1155 | 1159 | 1156 | 1157 | 1157 | 972 | 1025 | 1050 | 1056 | 1053 | 1058 | 1054 |
| Eight other towns | 1011 | 1098 | 1111 | 1113 | 1112 | 1113 | 1112 | 990 | 1036 | 1049 | 1055 | 1059 | 1061 | 1056 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1094 | 1108 | 1107 | 1105 | 1107 | 1107 | 1000 | 1041 | 1056 | 1061 | 1064 | 1069 | 1063 |
| Transportation | Miscellaneous | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| Auckland | 1000 | 1248 | 1236 | 1236 | 1221 | 1221 | 1229 | 1002 | 1271 | 1238 | 1240 | 1227 | 1229 | 1234 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1000 | 1240 | 1241 | 1241 | 1225 | 1222 | 1233 | 998 | 1272 | 1235 | 1234 | 1221 | 1224 | 1229 |
| Christchurch | 1000 | 1226 | 1199 | 1199 | 1182 | 1178 | 1190 | 1006 | 1271 | 1232 | 1238 | 1226 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Dunedin | 1000 | 1239 | 1217 | 1217 | 1201 | 1199 | 1208 | 988 | 1266 | 1234 | 1236 | 1225 | 1227 | 1230 |
| Four chief centres | 1000 | 1241 | 1228 | 1228 | 1212 | 1211 | 1220 | 1000 | 1271 | 1236 | 1238 | 1225 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Hamilton | 1000 | 1245 | 1217 | 1217 | 1197 | 1195 | 1206 | 1002 | 1275 | 1238 | 1240 | 1227 | 1229 | 1234 |
| Gisborne | 1000 | 1236 | 1208 | 1208 | 1186 | 1183 | 1196 | 998 | 1268 | 1230 | 1229 | 1216 | 1219 | 1224 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1000 | 1235 | 1213 | 1211 | 1182 | 1178 | 1196 | 998 | 1282 | 1230 | 1230 | 1217 | 1219 | 1224 |
| New Plymouth | 1000 | 1241 | 1212 | 1211 | 1195 | 1192 | 1203 | 999 | 1278 | 1240 | 1239 | 1227 | 1229 | 1234 |
| Wanganui | 1000 | 1245 | 1216 | 1216 | 1195 | 1191 | 1204 | 998 | 1276 | 1239 | 1239 | 1226 | 1229 | 1233 |
| Palmerston North | 1000 | 1241 | 1219 | 1219 | 1223 | 1199 | 1215 | 998 | 1278 | 1239 | 1238 | 1226 | 1228 | 1233 |
| Nelson | 1000 | 1246 | 1218 | 1222 | 1199 | 1195 | 1208 | 1006 | 1281 | 1241 | 1247 | 1235 | 1236 | 1240 |
| Timaru | 1000 | 1247 | 1223 | 1223 | 1201 | 1197 | 1211 | 1004 | 1277 | 1240 | 1246 | 1234 | 1235 | 1239 |
| Invercargill | 1000 | 1235 | 1205 | 1203 | 1178 | 1176 | 1191 | 988 | 1264 | 1234 | 1237 | 1225 | 1227 | 1231 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1000 | 1241 | 1215 | 1215 | 1196 | 1190 | 1204 | 999 | 1276 | 1237 | 1238 | 1225 | 1228 | 1232 |
| Whangarei | 1000 | 1229 | 1224 | 1222 | 1198 | 1196 | 1210 | 1002 | 1280 | 1247 | 1249 | 1236 | 1238 | 1243 |
| Tauranga | 1000 | 1255 | 1225 | 1223 | 1196 | 1193 | 1209 | 1002 | 1276 | 1243 | 1245 | 1231 | 1233 | 1238 |
| Rotorua | 1000 | 1220 | 1194 | 1193 | 1171 | 1169 | 1182 | 1002 | 1280 | 1247 | 1249 | 1236 | 1238 | 1243 |
| Masterton | 1000 | 1249 | 1216 | 1216 | 1193 | 1188 | 1203 | 998 | 1279 | 1244 | 1243 | 1230 | 1229 | 1237 |
| Blenheim | 1000 | 1231 | 1204 | 1202 | 1178 | 1)74 | 1190 | 1006 | 1284 | 1245 | 1251 | 1239 | 1240 | 1244 |
| Greymouth | 1000 | 1208 | 1183 | 1183 | 1164 | 1161 | 1173 | 1006 | 1279 | 1241 | 1247 | 1235 | 1236 | 1240 |
| Ashburton | 1000 | 1260 | 1226 | 1226 | 1202 | 1197 | 1213 | 1006 | 1275 | 1241 | 1247 | 1235 | 1236 | 1240 |
| Oamaru | 1000 | 1268 | 1236 | 1236 | 1212 | 1209 | 1223 | 988 | 1266 | 1234 | 1236 | 1224 | 1226 | 1230 |
| Eight other towns | 1000 | 1236 | 1211 | 1210 | 1187 | 1183 | 1198 | 1002 | 1278 | 1243 | 1246 | 1234 | 1235 | 1240 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1240 | 1223 | 1223 | 1205 | 1202 | 1213 | 1000 | 1273 | 1237 | 1239 | 1226 | 1228 | 1232 |
| All Groups | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base: Weighted Average Each Town, and Grouping, Separately, 1955 (= 1000) | Base: Weighted Average Twenty-one Towns Base 1955 (= 1000)* | |||||||||||||
| Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | Annual | Annual | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Annual | |
| 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1955 | 1959 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 | |
| *To give better inter-town comparisons pricing is now carried out in all 21 towns. Index numbers for each individual town have been revised back to 1955, but the 21 towns index numbers are not affected. | ||||||||||||||
| Auckland | 1000 | 1140 | 1139 | 1145 | 1156 | 1173 | 1153 | 1008 | 1149 | 1149 | 1154 | 1165 | 1183 | 1163 |
| Wellington-Hutt | 1000 | 1153 | 1150 | 1149 | 1160 | 1173 | 1158 | 1008 | 1162 | 1159 | 1158 | 1169 | 1182 | 1167 |
| Christchurch | 1000 | 1151 | 1152 | 1157 | 1162 | 1170 | 1160 | 992 | 1143 | 1143 | 1148 | 1152 | 1161 | 1151 |
| Dunedin | 1000 | 1151 | 1156 | 1155 | 1160 | 1164 | 1159 | 981 | 1129 | 1134 | 1133 | 1139 | 1142 | 1137 |
| Four chief centres | 1000 | 1147 | 1146 | 1149 | 1159 | 1171 | 1156 | 1002 | 1149 | 1148 | 1151 | 1161 | 1174 | 1159 |
| Hamilton | 1000 | 1144 | 1138 | 1143 | 1156 | 1165 | 1151 | 995 | 1139 | 1132 | 1137 | 1150 | 1160 | 1145 |
| Gisborne | 1000 | 152 | 1146 | 1147 | 1164 | 1172 | 1157 | 1003 | 1155 | 1150 | 1150 | 1168 | 1176 | 1161 |
| Napier-Hastings | 1000 | 1147 | 1134 | 1141 | 1147 | 1155 | 1144 | 981 | 1126 | 1113 | 1120 | 1126 | 1134 | 1123 |
| New Plymouth | 1000 | 1157 | 1151 | 1145 | 1152 | 1164 | 1153 | 990 | 1145 | 1140 | 1134 | 1141 | 1153 | 1142 |
| Wanganui | 1000 | 1141 | 1141 | 1145 | 1154 | 1162 | 1151 | 995 | 1135 | 1135 | 1139 | 1148 | 1157 | 1145 |
| Palmerston North | 1000 | 1136 | 1135 | 1141 | 1153 | 1160 | 1147 | 1005 | 1142 | 1140 | 1146 | 1158 | 1166 | 1153 |
| Nelson | 1000 | 1148 | 1141 | 1144 | 1150 | 1163 | 1149 | 994 | 1141 | 1134 | 1137 | 1143 | 1156 | 1143 |
| Timaru | 1000 | 1151 | 1156 | 1155 | 1164 | 1167 | 1161 | 991 | 1141 | 1146 | 1145 | 1154 | 1157 | 1151 |
| Invercargill | 5000 | 1142 | 1155 | 1148 | 1151 | 1152 | 1152 | 1008 | 1151 | 1164 | 1157 | 1160 | 1161 | 1160 |
| Nine provincial towns | 1000 | 1146 | 1143 | 1145 | 1154 | 1162 | 1151 | 995 | 1140 | 1137 | 1139 | 1148 | 1156 | 1145 |
| Whangarei | 1000 | 1135 | 1130 | 1136 | 1149 | 1166 | 1145 | 1015 | 1152 | 1147 | 1153 | 1166 | 1184 | 1163 |
| Tauranga | 1000 | 1152 | 1155 | 1151 | 1162 | 1184 | 1163 | 1002 | 1155 | 1158 | 1153 | 1164 | 1187 | 1166 |
| Rotorua | 1000 | 1147 | 1146 | 1141 | 1151 | 1164 | 1150 | 1006 | 1155 | 1153 | 1149 | 1158 | 1171 | 1158 |
| Masterton | 1000 | 1147 | 1140 | 1141 | 1150 | 1158 | 1147 | 1002 | 1149 | 1143 | 1144 | 1153 | 1160 | 1150 |
| Blenheim | 1000 | 1152 | 1148 | 1148 | 1155 | 1165 | 1154 | 999 | 1151 | 1148 | 1147 | 1154 | 1164 | 1153 |
| Greymouth | 1000 | 1138 | 1137 | 1136 | 1142 | 1149 | 1141 | 995 | 1132 | 1131 | 1130 | 1136 | 1143 | 1135 |
| Ashburton | 1000 | 1142 | 1142 | 1144 | 1151 | 1154 | 1148 | 990 | 1141 | 1141 | 1143 | 1150 | 1153 | 1147 |
| Oamaru | 1000 | 1151 | 1157 | 1153 | 1154 | 1158 | 1156 | 984 | 1133 | 1139 | 1135 | 1136 | 1140 | 1137 |
| Eight other towns | 1000 | 1144 | 1143 | 1142 | 1151 | 1162 | 1150 | 1002 | 1146 | 1145 | 1144 | 1153 | 1164 | 1152 |
| Twenty-one towns combined | 1000 | 1146 | 1145 | 1147 | 1157 | 1168 | 1154 | 1000 | 1146 | 1145 | 1147 | 1157 | 1168 | 1154 |
WHOLESALE PRICES - Wholesale Prices Index numbers have been available in New Zealand since 1920, when index numbers covering prices of a range of commodities for the years 1891 to 1919 were published on a base equating the average of the five years 1909-13 to 1000. This series was revised in 1925, the revision being carried back to 1913, and again in 1937, when the base was changed to 1926-30 (= 1000). In this latter index commodities were classified by their physical characteristics and priced, as far as possible, in their least processed state.
Revision of Wholesale Prices Index - In 1959 a full-scale revision of the Wholesale Prices Index was completed, a description of this revision being published as a special supplement to the October 1959 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics under the title “Index Numbers of Wholesale Prices”. A brief summary of the salient features of this revision appears in the 1960 Yearbook (pages 992-994).
The index is not a single wholesale prices index, but a series of price index numbers related to broad groupings of the inter-industry transactions distinguished in the Department's input-output tables for the New Zealand economy.* Thus each of the index numbers relates to a group of commodity transactions occurring at certain price-levels between defined sectors in the economy. Capital goods as well as goods for current consumption or usage are represented in the various commodity flows.
Wholesale Prices Index Numbers - The table which follows is divided into two parts; the first covers “input” prices and the second “output” prices. Within the first part of the table there is a break-up into goods for industrial use (analysed by sector destinations), for consumption, and for export. In each flow imported goods are distinguished from locally produced goods. In this part of the table all prices are inclusive of sales tax and excise duties and net of subsidies; the prices for exports are overseas market prices brought to an f.o.b. basis, i.e., their “input” prices to other countries.
*See Report on the Inter-industry Study of the New Zealand Economy for the Year 1954-55, Department of Statistics, Wellington, 1959.
In the second part of the table the broad producing sectors are distinguished. Here the prices of their outputs are used. They are taken before the addition of sales tax and excise duties or the deduction of subsidies. The prices for export meat and dairy products are those payable to producers under the different stabilisation and minimum export-meat-prices schemes.
The primary produce processing industries group comprises the two major industries, meat export works and dairy factories, processing farm products mainly for export.
The expression base for the index is the calendar year 1958, and the table shows the index numbers in respect of the calendar years 1958-60 and each of the four quarters of 1959 and 1960.
WHOLESALE PRICES INDEX
| Base: 1958 (= 1000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index Numbers of Commodity Prices by Sectors of Destination* | |||||||||||||
| Prices Paid for Commodities Used by - | All Commodities | ||||||||||||
| Domestic Industry | Consumers | Domestic Industry and Consumers | Other Countries (Exported) | ||||||||||
| Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | ||
*The prices used in this part of the table arc those payable by the using or consuming sectors, i.e., including indirect taxation and net after subsidies; the export prices are f.o.b. equivalent of overseas market prices. †Provisional. Subject to possible amendment to incorporate extra payments that may be made after close of production year to primary producers under schemes to stabilise returns. | |||||||||||||
| Calendar year – | |||||||||||||
| 1958 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 1015 | 998 | 1004 | 1055 | 1034 | 1039 | 1025 | 1011 | 1015 | 1141 | 1025 | 1039 | 1035 |
| 1960 | 1008 | 1018† | 1015† | 1019 | 1028 | 1026 | 1010 | 1022† | 1018† | 1139 | 1010 | 1047† | 1038† |
| Quarter ended – | |||||||||||||
| 1959 - 31 March | 1013 | 987 | 995 | 1059 | 1032 | 1038 | 1024 | 1002 | 1009 | 1079 | 1024 | 1019 | 1020 |
| 30 June | 1018 | 989 | 998 | 1059 | 1022 | 1031 | 1028 | 1000 | 1008 | 1106 | 1028 | 1023 | 1024 |
| 30 September | 1016 | 1020 | 1019 | 1061 | 1047 | 1050 | 1027 | 1029 | 1029 | 1197 | 1027 | 1065 | 1056 |
| 31 December | 1012 | 998 | 1002 | 1043 | 1037 | 1038 | 1020 | 1011 | 1014 | 1183 | 1020 | 1048 | 1041 |
| 1960 - 31 March | 1005 | 1014 | 1011 | 1027 | 1018 | 1020 | 1010 | 1015 | 1014 | 1216 | 1010 | 1059 | 1047 |
| 30 June | 1008 | 1025 | 1020 | 1024 | 1017 | 1019 | 1012 | 1023 | 1019 | 1146 | 1012 | 1049 | 1040 |
| 30 September | 1008 | 1016† | 1013† | 1010 | 1030 | 1026 | 1008 | 1021† | 1017† | 1124 | 1008 | 1043† | 1034† |
| 31 December | 1009 | 1018† | 1015† | 1016 | 1047 | 1040 | 1011 | 1028† | 1023† | 1070 | 1011 | 1037† | 1030† |
| Prices Paid for Commodities Used by Domestic Industry | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Industries | Primary Produce Processing Industries | Other Manufacturing Industries | |||||||||
| Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | |||
| Farming | All Other Industries | Other Manufacturing Industries | All Other Industries | ||||||||
| Calendar year – | |||||||||||
| 1958 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 996 | 927 | 1010 | 972 | 1021 | 978 | 980 | 1008 | 1013 | 1030 | 1014 |
| 1960 | 986 | 958 | 1014 | 985 | 1007 | 1005† | 1005† | 1006 | 1024 | 1066 | 1025 |
| Quarter ended – | |||||||||||
| 1959-31 March | 1009 | 947 | 1011 | 983 | 1039 | 955 | 958 | 1001 | 997 | 993 | 998 |
| 30 June | 1003 | 944 | 1011 | 981 | 1028 | 951 | 953 | 1012 | 1017 | 1000 | 1011 |
| 30 September | 993 | 915 | 1010 | 966 | 1015 | 1035 | 1034 | 1010 | 1016 | 1085 | 1029 |
| 31 December | 978 | 903 | 1009 | 958 | 1002 | 973 | 974 | 1006 | 1022 | 1040 | 1018 |
| 1960-31 March | 968 | 921 | 1017 | 966 | 967 | 1013 | 1012 | 1005 | 1022 | 1053 | 1021 |
| 30 June | 972 | 937 | 1015 | 973 | 1013 | 1037 | 1036 | 1009 | 1027 | 1067 | 1027 |
| 30 September | 996 | 980 | 1013 | 996 | 993 | 981† | 981† | 1006 | 1023 | 1081 | 1028 |
| 31 December | 1009 | 996 | 1011 | 1004 | 1054 | 988† | 990† | 1003 | 1023 | 1065 | 1023 |
24*
| Prices Paid for Commodities Used by Domestic Industry | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building and Construction | Transport and Communication | Other Industries‡ | |||||||
| Imported | Home Produced | Total | Imported | home Produced | Total | Imported | Home Produced | Total | |
*The prices used in this part of the table are those payable by the using or consuming sectors, i.e., including indirect taxation and net after subsidies; the export prices are f.o.b. equivalent of overseas market prices. †Provisional Subject to possible amendment to incorporate extra payments that may be made after close of production year to primary producers under schemes to stabilise returns. ‡ Includes wholesale and retail trade, banking and finance, public utilities, and services. § The prices used in this part of the table are those receivable by producers, i.e., before addition of indirect taxation or deduction of consumer or user subsidies; prices for dairy produce and meat are those payable to producers under the schemes to stabilise returns from year to year. || Comprises the outputs of the five sectors mentioned in this part of the table. | |||||||||
| Calendar year – | |||||||||
| 1958 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 1032 | 1015 | 1921 | 1038 | 1039 | 1039 | 1016 | 1017 | 1017 |
| 1960 | 1042 | 1030 | 1034 | 987 | 1042 | 1002 | 1003 | 1027 | 1020 |
| Quarter ended – | |||||||||
| 1959-31 March | 1033 | 1012 | 1020 | 1040 | 1031 | 1038 | 1015 | 1020 | 1019 |
| 30 June | 1026 | 1014 | 1018 | 1042 | 1031 | 1039 | 1017 | 1016 | 1017 |
| 30 September | 1030 | 1014 | 1019 | 1043 | 1046 | 1044 | 1016 | 1017 | 1017 |
| 31 December | 1038 | 1022 | 1028 | 1029 | 1048 | 1034 | 1014 | 1015 | 1015 |
| 1960-31 March | 1038 | 1025 | 1030 | 992 | 1051 | 1008 | 1005 | 1018 | 1015 |
| 30 June | 1037 | 1027 | 1031 | 989 | 1051 | 1006 | 1003 | 1023 | 1018 |
| 30 September | 1045 | 1031 | 1036 | 985 | 1032 | 998 | 999 | 1031 | 1023 |
| 31 December | 1047 | 1034 | 1039 | 981 | 1034 | 995 | 1005 | 1034 | 1026 |
| Index Numbers of Commodity Prices by Sector of Origin§ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prices Received for Commodities Produced in New Zealand | ||||||||
| Output of | Used by | |||||||
| Farming | Other Primary Industries | Primary Produce Processing Industries | Other Manufacturing Industries | Public Utilities | All Domestic Industry|| | Industry and Consumers | Other Countries (Exported) | |
| Calendar year – | ||||||||
| 1958 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 1010 | 1005 | 1000 | 1010 | 1041 | 1009 | 1001 | 1036 |
| 1960 | 1043† | 1052 | 1037† | 1025 | 1035 | 1034† | 1020† | 1079† |
| Quarter ended – | ||||||||
| 1959 - 31 March | 966 | 996 | 989 | 1002 | 1045 | 990 | 990 | 990 |
| 30 June | 980 | 1008 | 972 | 1005 | 1045 | 992 | 988 | 1009 |
| 30 September | 1069 | 1007 | 1024 | 1017 | 1039 | 1035 | 1019 | 1087 |
| 31 December | 1025 | 1011 | 1014 | 1018 | 1035 | 1020 | 1008 | 1058 |
| 1960-31 March | 1047 | 1024 | 1073 | 1022 | 1037 | 1040 | 1013 | 1129 |
| 30 June | 1053 | 1059 | 1065 | 1024 | 1036 | 1042 | 1021 | 1113 |
| 30 September | 1034† | 1059 | 1024† | 1026 | 1034 | 1029† | 1020† | 1059† |
| 31 December | 1037† | 1066 | 988† | 1028 | 1033 | 1025† | 1027† | 1016† |
Long-termed Linked Series - Since the index incorporates a major change in construction method, linking to obtain a long-term series is not very satisfactory. Nevertheless, some such link will be required occasionally in making longer-term surveys of price movements. Accordingly, in the table which follows, the previous index, converted to base 1958 (= 1000), has been linked to the component “Commodities used by Domestic Industry and Consumers”. The subdivisions “Imported” and “Home Produced” commodities have similarly been linked. When using these linked series it should be borne in mind that the price sources and weighting pattern of the current index are quite different from its predecessors.
WHOLESALE PRICES INDEX NUMBERS - LONG-TERM LINKED SERIES
| Base: Calendar year 1958 (= 1000) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Imported | Home Produced | Total |
| *Provisional Subject to possible amendment to incorporate extra payments that may be made after close of production year to primary producers under schemes to stabilise returns. | |||
| 1913 | 268 | 254 | 263 |
| 1914 | 270 | 274 | 271 |
| 1915 | 274 | 319 | 292 |
| 1916 | 312 | 331 | 320 |
| 1917 | 379 | 360 | 372 |
| 1918 | 481 | 389 | 444 |
| 1919 | 504 | 407 | 465 |
| 1920 | 626 | 455 | 557 |
| 1921 | 555 | 463 | 518 |
| 1922 | 461 | 392 | 433 |
| 1923 | 412 | 393 | 405 |
| 1924 | 406 | 407 | 406 |
| 1925 | 400 | 410 | 404 |
| 1926 | 375 | 393 | 382 |
| 1927 | 352 | 380 | 363 |
| 1928 | 344 | 385 | 361 |
| 1929 | 341 | 385 | 358 |
| 1930 | 335 | 370 | 349 |
| 1931 | 328 | 326 | 327 |
| 1932 | 326 | 307 | 319 |
| 1933 | 345 | 301 | 327 |
| 1934 | 341 | 310 | 329 |
| 1935 | 342 | 335 | 340 |
| 1936 | 342 | 344 | 343 |
| 1937 | 371 | 370 | 371 |
| 1938 | 375 | 378 | 376 |
| 1939 | 379 | 403 | 389 |
| 1940 | 448 | 412 | 434 |
| 1941 | 503 | 436 | 476 |
| 1942 | 552 | 456 | 514 |
| 1943 | 609 | 461 | 549 |
| 1944 | 629 | 472 | 565 |
| 1945 | 638 | 481 | 575 |
| 1946 | 636 | 489 | 577 |
| 1947 | 650 | 523 | 598 |
| 1948 | 730 | 574 | 667 |
| 1949 | 714 | 586 | 662 |
| 1950 | 758 | 667 | 721 |
| 1951 | 883 | 777 | 840 |
| 1952 | 996 | 842 | 933 |
| 1953 | 947 | 891 | 924 |
| 1954 | 904 | 932 | 915 |
| 1955 | 920 | 935 | 926 |
| 1956 | 944 | 985 | 960 |
| 1957 | 968 | 977 | 972 |
| 1958 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 1025 | 1011 | 1015 |
| 1960 | 1010 | 1022* | 1018* |
EXPORT PRICES - Quarterly and annual index numbers of export prices are compiled, based chiefly on the declared export values of the principal commodities of New Zealand produce exported.
The first indices of export prices compiled in New Zealand were all of the Paasche type, being calculated from comparisons of current export values with values obtained as the products of current quantities at prices ruling in some earlier base period. The prices so-called were in fact unit values obtained from the export trade statistics.
The index currently in use is a fixed-weight index with an integrated set of destination and commodity weights. The base year, both for calculation and expression, is 1952.
This index superseded an earlier index published on the expression base of 1909-13, which had intra-group five-year moving average quantitative weights, and initially five-year moving average group value weights. But as this method led to some bias, the group weights were later revised back by deflating each by its group price index number.
A fuller description of these indices may be found in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
In the following tables are given export price index numbers for the calendar years 1950-60 and for years ended 30 June from 1950 to 1960.
EXPORT PRICES-INDEX NUMBERS
| Base: Export prices during 1952 (= 100) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Butter | Cheese | All Dairy Produce | Meat | Wool | Meat, Wool, and Byproducts | All Pastoral and Dairy Produce |
| Calendar year— | |||||||
| 1950 | 86 | 86 | 86 | 77 | 147 | 119 | 107 |
| 1951 | 94 | 92 | 93 | 86 | 178 | 144 | 125 |
| 1952 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1953 | 106 | 108 | 106 | 109 | 120 | 115 | 112 |
| 1954 | 108 | 105 | 106 | 117 | 112 | 118 | 114 |
| 1955 | 111 | 111 | 108 | 133 | 121 | 122 | 117 |
| 1956 | 91 | 143 | 102 | 130 | 120 | 121 | 114 |
| 1957 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 135 | 132 | 129 | 112 |
| 1958 | 72 | 101 | 79 | 129 | 93 | 104 | 95 |
| 1959 | 106 | 145 | 113 | 120 | 100 | 107 | 109 |
| Year ended 30 June— | |||||||
| 1950 | 83 | 84 | 83 | 74 | 95 | 88 | 86 |
| 1951 | 92 | 89 | 91 | 80 | 218 | 160 | 134 |
| 1952 | 97 | 95 | 97 | 94 | 103 | 103 | 100 |
| 1953 | 104 | 105 | 104 | 104 | 116 | 110 | 108 |
| 1954 | 108 | 109 | 107 | 112 | 124 | 118 | 114 |
| 1955 | 105 | 96 | 100 | 128 | 122 | 121 | 113 |
| 1956 | 108 | 134 | 111 | 132 | 115 | 119 | 115 |
| 1957 | 87 | 119 | 94 | 130 | 136 | 129 | 116 |
| 1958 | 70 | 77 | 73 | 131 | 104 | 111 | 97 |
| 1959 | 85 | 138 | 97 | 127 | 92 | 103 | 101 |
| 1960 | 105 | 131 | 109 | 118 | 112 | 113 | 112 |
| Period | All Foods | All Non-foods | All Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| To United Kingdom | To Other Countries | To All Countries | |||
| Calendar year— | |||||
| 1950 | 82 | 140 | 97 | 125 | 105.9 |
| 1951 | 90 | 173 | 112 | 149 | 124.3 |
| 1952 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1000 |
| 1953 | 106 | 118 | 110 | 113 | 111.2 |
| 1954 | 109 | 119 | 114 | 112 | 113.3 |
| 1955 | 116 | 117 | 120 | 108 | 116.4 |
| 1956 | 112 | 116 | 116 | 109 | 113.5 |
| 1957 | 103 | 125 | 111 | 114 | 111.8 |
| 1958 | 98 | 92 | 98 | 89 | 95.2 |
| 1959 | 115 | 101 | 114 | 99 | 108.8 |
| Year ended 30 June— | |||||
| 1950 | 79 | 95 | 83 | 91 | 85.8 |
| 1951 | 86 | 200 | 118 | 165 | 133.1 |
| 1952 | 95 | 108 | 98 | 106 | 100.5 |
| 1953 | 104 | 113 | 107 | 109 | 107.6 |
| 1954 | 108 | 122 | 113 | 115 | 113.8 |
| 1955 | 110 | 118 | 115 | 109 | 113.1 |
| 1956 | 118 | 112 | 120 | 106 | 115.4 |
| 1957 | 107 | 128 | 115 | 117 | 115.6 |
| 1958 | 94 | 101 | 97 | 97 | 96.8 |
| 1959 | 108 | 92 | 106 | 90 | 100.9 |
| 1960 | 111 | 111 | 113 | 108 | 111.3 |
The fact that the calendar year does not coincide with the farm production year is especially significant in New Zealand, since the great bulk of export goods is farm produce. For a number of purposes the portion of the foregoing tables relative to years ended 30 June is the more important, in that the figures relate to the farming year.
The next table shows export prices index numbers for all pastoral and dairy produce groups and for all groups combined in respect of each year from 1914 to 1960.
| Base: 1952 (= 100) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Index Numbers | |
| All Pastoral and Dairy Produce | All Groups Combined | |
| 1914 | 30 | 30 |
| 1915 | 34 | 34 |
| 1916 | 41 | 40 |
| 1917 | 46 | 45 |
| 1918 | 46 | 46 |
| 1919 | 49 | 49 |
| 1920 | 50 | 50 |
| 1921 | 48 | 47 |
| 1922 | 37 | 37 |
| 1923 | 44 | 44 |
| 1924 | 49 | 49 |
| 1925 | 52 | 51 |
| 1926 | 42 | 42 |
| 1927 | 42 | 42 |
| 1928 | 46 | 46 |
| 1929 | 45 | 44 |
| 1930 | 35 | 35 |
| 1931 | 26 | 27 |
| 1932 | 24 | 24 |
| 1933 | 23 | 24 |
| 1934 | 29 | 30 |
| 1935 | 28 | 29 |
| 1936 | 33 | 33 |
| 1937 | 39 | 39 |
| 1938 | 36 | 36 |
| 1939 | 35 | 35 |
| 1940 | 40 | 41 |
| 1941 | 41 | 42 |
| 1942 | 42 | 43 |
| 1943 | 44 | 45 |
| 1944 | 47 | 47 |
| 1945 | 50 | 51 |
| 1946 | 55 | 56 |
| 1947 | 70 | 70 |
| 1948 | 77 | 78 |
| 1949 | 75 | 75 |
| 1950 | 107 | 106 |
| 1951 | 125 | 124 |
| 1952 | 100 | 100 |
| 1953 | 112 | 111 |
| 1954 | 114 | 113 |
| 1955 | 117 | 116 |
| 1956 | 114 | 114 |
| 1957 | 112 | 112 |
| 1958 | 95 | 95 |
| 1959 | 109 | 109 |
During the post-war period the index rose rapidly until 1951, partly by reason of advances in prices under long-term contracts with the United Kingdom Government, but more particularly as a result of the brisk demand for New Zealand wool displayed since the resumption of auction sales in September 1946, and greatly heightened during 1950 and the early part of 1951, when the whole index was dominated by spectacular advances in wool prices. In spite of continued increases in export prices of dairy produce and meat, a recession in the latter part of 1951 from the inflated wool values of the previous season, combined with some other less significant price decreases (mainly in skins), brought about a fall in the all-groups export prices index number for 1952 of almost 20 per cent as compared with 1951. The 1952 figure still, however, substantially exceeded that for every year prior to 1950, while the 1955 index was the second highest on record. In the years 1956 and 1957, however, slight fails were recorded, while in 1958 the figure dropped back below that, for 1950 under the influence of low prices for butter and wool. It should be noted that the general upward trend in export prices was marked in 1949 by the appreciation in August 1948 of the New Zealand pound to parity with sterling.
IMPORT PRICES - A series of import prices index numbers based on the year 1926 (= 100), and weighted in accordance with average quantities imported during the years 1926-30, was instituted in 1933. While the basic data were deficient in many respects, nevertheless the index served a very useful purpose. With the passage of time, however, certain inherent weaknesses in this series became apparent, while information previously lacking in some cases became available.
Accordingly, a revised series of index numbers was computed, based in the case of individual items on average quantities imported during the three years 1936-38. Group weights were instituted in the new series, to accord to the various groups their relative importance, and these were based on the average total value for the respective groups during the three years 1936-38. The difficulty, inherent in an index number of imports, of obtaining sufficient coverage to provide a reliable indication of changes in prices for any one group, was overcome in the revised series by the utilisation of figures of exports to New Zealand, obtained in detail from the published trade figures of certain overseas countries.
A new and much more detailed statistical classification of imports was adopted by the Customs Department from 1 January 1949. The index of import prices for 1950 was constructed using the items of the more detailed classification and based on a composite weighting pattern of the two years 1949 and 1950, utilising group weights, and linked to the old index. The index for 1951 was similarly based on the composite 1950-51 weighting pattern and linked on. The index for each subsequent year has been similarly calculated on the base of the previous year in each case, using a composite weighting pattern of the two years, the resultant index number being linked on to the old series.
When the Standard International Trade Classification was brought into use in 1955 it became necessary to draw up a revised list of items for use in computing the index. Various items in the classification previously in use could not be precisely matched with items in the Standard International Trade Classification. The revised series of items now used, however, represents approximately the same proportion of the total imports.
In order to avoid any possible confusion between the import prices index number and the wholesale prices index number for imported commodities, it seems desirable to draw attention to the fact that the price quotations on which the Import Prices Index is based are declared values of commodities for import expressed in terms of New Zealand currency.
Owing to different proportional changes over the years between domestic commodity prices in exporting countries, the costs of these same commodities delivered f.o.b. for export, and marine insurance and freight rates, the Import Prices Index can only be regarded as the best available approximate indicator of changes in the cost of imports delivered c.i.f. New Zealand ports. For instance, the large increase in marine transport, costs during the war years, to the extent that it exceeded the rise in commodity prices, was not reflected in the index. There is reason to believe that, for recent periods compared with pre-war, the rises in f.o.b. costs of commodities and in marine freight and insurance rates may have exceeded the rises in domestic prices in exporting countries recorded in the index.
IMPORT PRICES - INDEX NUMBERS
| Base: 1936-38 (= 100) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Index Number |
| 1926 | 125 |
| 1927 | 119 |
| 1928 | 113 |
| 1929 | 111 |
| 1930 | 110 |
| 1931 | 102 |
| 1932 | 97 |
| 1933 | 99 |
| 1934 | 98 |
| 1935 | 96 |
| 1936 | 96 |
| 1937 | 102 |
| 1938 | 102 |
| 1939 | 102 |
| 1940 | 118 |
| 1941 | 131 |
| 1942 | 144 |
| 1943 | 159 |
| 1944 | 167 |
| 1945 | 170 |
| 1946 | 190 |
| 1947 | 226 |
| 1948 | 230 |
| 1949 | 210 |
| 1950 | 230 |
| 1951 | 269 |
| 1952 | 293 |
| 1953 | 277 |
| 1954 | 274 |
| 1955 | 273 |
| 1956 | 279 |
| 1957 | 289 |
| 1958 | 288 |
| 1959 | 281 |
TERMS OF TRADE - The table below shows, for the years 1950 to 1960, index numbers of import prices and of export prices and terms of trade for major commodity groups and total exports. The terms of trade is the expression of the ratio of export prices to import prices, i.e., an index of the purchasing power (in units of imports) of a fixed quantity of exports. In the table that follows terms of trade are expressed on base 1957 (= 100). However, an index above or below 100 means only that terms of trade are more or less favourable than in 1957. The choice of 100 is made for arithmetical convenience, not to indicate that 1957 was a normal or standard year. For the purposes of this table both import prices and export prices indices have also been converted to a 1957 base.
INDEX NUMBERS OF IMPORT AND EXPORT PRICES AND TERMS OF TRADE
| All Countries - Base: 1957 (= 100) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Import Prices | Butter | Cheese | Meat | Wool | All Exports | |||||
| Export Price | Terms of Trade | Export Price | Terms of Trade | Export Price | Terms of Trade | Export Price | Terms of Trade | Export Price | Terms of Trade | ||
| 1950 | 78 | 103 | 132 | 102 | 131 | 57 | 73 | 111 | 142 | 95 | 122 |
| 1951 | 91 | 112 | 123 | 109 | 120 | 63 | 69 | 135 | 148 | 111 | 122 |
| 1952 | 99 | 119 | 120 | 119 | 120 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 89 | 90 |
| 1953 | 94 | 127 | 135 | 129 | 137 | 80 | 85 | 91 | 97 | 99 | 105 |
| 1954 | 92 | 129 | 140 | 125 | 136 | 87 | 95 | 92 | 100 | 101 | 110 |
| 1955 | 94 | 133 | 141 | 132 | 140 | 98 | 104 | 92 | 98 | 104 | 111 |
| 1956 | 97 | 108 | 111 | 171 | 176 | 96 | 99 | 91 | 94 | 102 | 105 |
| 1957 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1958 | 100 | 86 | 86 | 120 | 120 | 95 | 95 | 71 | 71 | 85 | 85 |
| 1959 | 97 | 127 | 131 | 173 | 178 | 88 | 91 | 76 | 78 | 97 | 100 |
SHARE PRICES - Changes in the market value of shares listed on the Stock Exchange give a very sensitive indication of changes in business conditions generally. A series of index numbers of share prices on base: 1926 (= 1000), and instituted in 1932, was published by the Department of Statistics for some considerable time, but the present revised series of index numbers is based on the year 1938. The market prices-as on the last trading day in each month-of shares of 43 representative companies, with shares listed on the New Zealand Stock Exchanges, form the basis on which the indices have been computed. With one or two exceptions, only companies whose business is conducted largely or wholly in New Zealand are included. The index numbers are for ordinary shares.
The market prices on which the index numbers are based have been extracted from Stock Exchange lists of individual exchanges prior to September 1929, and from the list of share prices included in the Stock Exchange Gazette and its successor, the Official Record of the Stock Exchanges of New Zealand, since that date. The prices quoted relate to the last trading day in each month; so that the “monthly” index numbers compiled from these data relate to that day only, while the annual averages represent the averages of the monthly index numbers. Each individual share price, and each group, is weighted in accordance with the number and value of shares held in New Zealand. The index numbers of New Zealand share prices give an indication of changes in share values as compared with the base year. In particular, they are intended to indicate the changes in value of a parcel of representative ordinary shares as compared with their 1938 value. The base adopted in this revised series is the average price ruling during the year 1938 (= 1000).
Shares in industrial companies and in finance, etc., companies have been computed separately and the annual index numbers from 1926 to 1959 on base: 1938 (= 1000) are as follows.
| Year | Industrial Groups | Finance, etc., Groups | All Groups |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1926 | 909 | 1271 | 1108 |
| 1927 | 851 | 1254 | 1073 |
| 1928 | 879 | 1301 | 1111 |
| 1929 | 960 | 1330 | 1163 |
| 1930 | 835 | 1147 | 1007 |
| 1931 | 674 | 921 | 810 |
| 1932 | 667 | 852 | 769 |
| 1933 | 804 | 972 | 897 |
| 1934 | 996 | 1097 | 1051 |
| 1935 | 1102 | 1120 | 1112 |
| 1936 | 1075 | 1043 | 1057 |
| 1937 | 1073 | 1067 | 1069 |
| 1938 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1939 | 959 | 945 | 952 |
| 1940 | 1024 | 978 | 999 |
| 1941 | 1021 | 984 | 1001 |
| 1942 | 1005 | 1014 | 1010 |
| 1943 | 1156 | 1188 | 1174 |
| 1944 | 1249 | 1304 | 1279 |
| 1945 | 1285 | 1400 | 1346 |
| 1946 | 1372 | 1601 | 1486 |
| 1947 | 1444 | 1697 | 1570 |
| 1948 | 1430 | 1609 | 1520 |
| 1949 | 1368 | 1566 | 1467 |
| 1950 | 1499 | 1795 | 1647 |
| 1951 | 1566 | 2027 | 1796 |
| 1952 | 1273 | 1697 | 1485 |
| 1953 | 1216 | 1747 | 1482 |
| 1954 | 1358 | 2049 | 1703 |
| 1955 | 1449 | 2166 | 1807 |
| 1956 | 1470 | 2261 | 1865 |
| 1957 | 1646 | 2421 | 2034 |
| 1958 | 1593 | 2252 | 1923 |
| 1959 | 1812 | 2544 | 2178 |
| 1960 | 2419 | 3144 | 2782 |
The fluctuations in share prices since 1926 are clearly shown in the accompanying diagram, which is based on the foregoing index numbers.
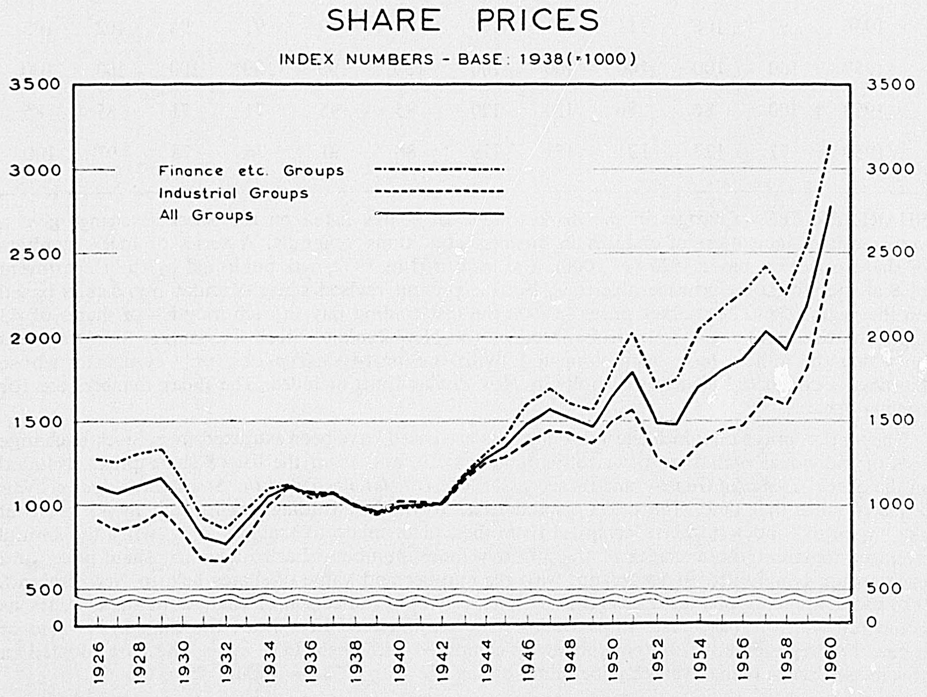
An indication of movements in the index numbers for individual groups may be gauged from the following tables, the first of which is confined to the industrial groups.
SHARE PRICES - INDEX NUMBERS BY GROUPS
| Base: Average for each group, 1938 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calendar Year | Frozen Meat | Woollens | Gas | Timber | Minerals | Miscellaneous (Industrial) | All Industrial Groups |
| 1950 | 2125 | 1933 | 934 | 1792 | 1400 | 1463 | 1499 |
| 1951 | 2311 | 1973 | 818 | 2210 | 1476 | 1504 | 1566 |
| 1952 | 1726 | 1665 | 666 | 1694 | 1254 | 1248 | 1273 |
| 1953 | 1864 | 1634 | 624 | 1387 | 1135 | 1196 | 1216 |
| 1954 | 2227 | 1943 | 598 | 1488 | 1286 | 1319 | 1358 |
| 1955 | 2500 | 2035 | 693 | 1810 | 1287 | 1462 | 1449 |
| 1956 | 2809 | 1671 | 964 | 1648 | 1182 | 1431 | 1470 |
| 1957 | 3856 | 1605 | 914 | 1632 | 1269 | 1470 | 1646 |
| 1958 | 3785 | 1744 | 712 | 1459 | 1290 | 1436 | 1593 |
| 1959 | 4378 | 2067 | 699 | 1454 | 1252 | 1736 | 1812 |
| 1960 | 5177 | 2973 | 694 | 1515 | 1560 | 2609 | 2419 |
| Calendar Year | All Industrial Groups | Banks | Insurance | Loan and Agency | Miscellaneous (Other) | All Finance, etc., Groups | All Groups Combined |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1499 | 1220 | 2012 | 2174 | 2032 | 1795 | 1647 |
| 1951 | 1566 | 1251 | 2350 | 2587 | 2263 | 2027 | 1796 |
| 1952 | 1273 | 1029 | 1972 | 2058 | 1967 | 1697 | 1485 |
| 1953 | 1216 | 1039 | 2080 | 2091 | 1971 | 1747 | 1482 |
| 1954 | 1358 | 1252 | 2383 | 2682 | 2258 | 2049 | 1703 |
| 1955 | 1449 | 1223 | 2569 | 2964 | 2373 | 2166 | 1807 |
| 1956 | 1470 | 1185 | 2994 | 2843 | 2116 | 2261 | 1865 |
| 1957 | 1646 | 1345 | 3189 | 3241 | 2091 | 2421 | 2034 |
| 1958 | 1593 | 1322 | 2823 | 2956 | 2156 | 2252 | 1923 |
| 1959 | 1812 | 1637 | 3009 | 3421 | 2536 | 2544 | 2178 |
| 1960 | 2419 | 1680 | 3831 | 4348 | 3365 | 3144 | 2782 |
NOTE - Index numbers in these tables are comparable vertically but not horizontally.
Monthly index numbers of share prices for the latest three years are given in the following table, the base being 1938 (= 1000).
| Industrial Groups | Finance, etc., Groups | All Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| *Interpolated. | |||||||||
| January | 1718 | 1573 | 2152 | 2398 | 2264 | 3084 | 2058 | 1919 | 2618 |
| February | 1730 | 1608 | 2142 | 2391 | 2304 | 3017 | 2060 | 1956 | 2579 |
| March | 1641 | 1635 | 2144 | 2313 | 2251 | 2962 | 1977 | 1943 | 2553 |
| April | 1585 | 1665 | 2191 | 2260 | 2294 | 3007 | 1922 | 1979 | 2599 |
| May | 1547 | 1689 | 2423 | 2271 | 2330 | 3067 | 1909 | 2009 | 2745 |
| June | 1555 | 1764 | 2496 | 2209 | 2387 | 3159 | 1882 | 2075 | 2827 |
| July | 1551 | 1860 | 2597 | 2192 | 2552 | 3133 | 1872 | 2206 | 2866 |
| August | 1569 | 1925 | 2636 | 2227 | 2684 | 3306 | 1898 | 2305 | 2971 |
| September | 1562 | 1940 | 2620 | 2208 | 2622 | 3396 | 1885 | 2281 | 3008 |
| October | 1558 | 1957 | 2610 | 2188 | 2842 | 3292 | 1873 | 2400 | 2951 |
| November | 1543 | 2032 | 2495 | 2171 | 2969 | 3165 | 1857 | 2501 | 2830 |
| December* | 1558 | 2092 | 2524 | 2200 | 3026 | 3136 | 1879 | 2559 | 2830 |
SUMMARY OF PRICE MOVEMENTS - A comparative table of index numbers of various related prices series from the year 1926 onward is as follows. All index numbers are quoted on a New Zealand currency basis, and on the base: 1955 (= 1000), with the exception of those of import and export prices which are on the base: 1955 (= 100).
| Year | Base: 1955 (= 100) | Base: 1955 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Import Prices | Export Prices | Wholesale Prices | Retail Prices | Share Prices (All Groups) | |||||
| Pastoral and Dairy Produce | All Groups | Imported | Home Produced | Total | Food | All Groups | |||
| *Provisional. | |||||||||
| 1926 | 46 | 36 | 36 | 407 | 421 | 413 | 455 | 533 | 613 |
| 1927 | 44 | 36 | 36 | 383 | 406 | 392 | 435 | 529 | 594 |
| 1928 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 374 | 412 | 390 | 445 | 531 | 615 |
| 1929 | 41 | 38 | 38 | 370 | 412 | 387 | 449 | 530 | 644 |
| 1930 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 364 | 396 | 377 | 432 | 518 | 557 |
| 1931 | 37 | 22 | 23 | 356 | 349 | 353 | 375 | 479 | 448 |
| 1932 | 35 | 20 | 21 | 354 | 328 | 344 | 344 | 443 | 426 |
| 1933 | 36 | 20 | 21 | 374 | 323 | 354 | 325 | 420 | 496 |
| 1934 | 36 | 25 | 26 | 371 | 332 | 356 | 343 | 427 | 582 |
| 1935 | 35 | 24 | 25 | 372 | 359 | 367 | 370 | 442 | 615 |
| 1936 | 35 | 28 | 29 | 372 | 368 | 370 | 386 | 456 | 585 |
| 1937 | 37 | 33 | 34 | 403 | 396 | 401 | 424 | 488 | 592 |
| 1938 | 37 | 30 | 31 | 407 | 404 | 406 | 439 | 502 | 553 |
| 1939 | 38 | 30 | 30 | 412 | 431 | 420 | 466 | 523 | 527 |
| 1940 | 43 | 35 | 35 | 487 | 441 | 468 | 477 | 547 | 553 |
| 1941 | 48 | 35 | 36 | 547 | 466 | 514 | 489 | 567 | 554 |
| 1942 | 53 | 36 | 37 | 600 | 488 | 553 | 500 | 586 | 559 |
| 1943 | 58 | 38 | 38 | 662 | 493 | 593 | 503 | 599 | 650 |
| 1944 | 61 | 40 | 40 | 684 | 505 | 611 | 511 | 610 | 708 |
| 1945 | 62 | 43 | 44 | 694 | 515 | 621 | 510 | 618 | 745 |
| 1946 | 70 | 47 | 48 | 692 | 523 | 623 | 511 | 623 | 822 |
| 1947 | 83 | 60 | 60 | 706 | 560 | 646 | 543 | 643 | 869 |
| 1948 | 84 | 66 | 67 | 793 | 614 | 720 | 613 | 694 | 841 |
| 1949 | 77 | 64 | 64 | 776 | 627 | 715 | 630 | 706 | 812 |
| 1950 | 84 | 92 | 91 | 823 | 714 | 779 | 692 | 745 | 911 |
| 1951 | 99 | 107 | 107 | 960 | 831 | 907 | 796 | 828 | 994 |
| 1952 | 108 | 86 | 86 | 1082 | 901 | 1008 | 876 | 892 | 822 |
| 1953 | 102 | 96 | 96 | 1029 | 953 | 998 | 929 | 933 | 820 |
| 1954 | 100 | 97 | 97 | 983 | 998 | 989 | 977 | 976 | 942 |
| 1955 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 102 | 98 | 98 | 1026 | 1054 | 1038 | 1057 | 1035 | 1032 |
| 1957 | 106 | 96 | 96 | 1052 | 1046 | 1050 | 1054 | 1057 | 1126 |
| 1958 | 106 | 82 | 82 | 1087 | 1070 | 1080 | 1071 | 1104 | 1064 |
| 1959 | 103 | 93 | 93 | 1114 | 1082 | 1097 | 1077 | 1146 | 1205 |
| 1960 | 1098 | 1094* | 1100* | 1092 | 1154 | 1540 | |||
A further comparative table, of various price and wage rates index numbers from the year 1937 onwards, is presented below. Both March year and June year index numbers are included.
| Year | Base: Calendar Year 1955 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wholesale Prices | Retail Prices | Wage Rates | Share Prices (All Groups) | |||||
| Imported | Home Produced | Total | Food | All Groups | Nominal | Effective | ||
| *Provisional. | ||||||||
| Year Ended 31 March | ||||||||
| 1937 | 375 | 375 | 376 | 395 | 462 | 381 | 825 | 581 |
| 1938 | 409 | 401 | 406 | 432 | 493 | 409 | 830 | 588 |
| 1939 | 406 | 408 | 407 | 443 | 505 | 426 | 844 | 541 |
| 1940 | 423 | 436 | 428 | 472 | 528 | 432 | 818 | 537 |
| 1941 | 508 | 444 | 483 | 478 | 550 | 449 | 816 | 549 |
| 1942 | 553 | 475 | 522 | 493 | 570 | 460 | 807 | 551 |
| 1943 | 618 | 490 | 566 | 501 | 589 | 485 | 823 | 581 |
| 1944 | 671 | 500 | 602 | 505 | 602 | 496 | 824 | 669 |
| 1945 | 686 | 505 | 612 | 510 | 612 | 502 | 820 | 712 |
| 1946 | 697 | 514 | 623 | 511 | 620 | 550 | 887 | 766 |
| 1947 | 685 | 532 | 623 | 513 | 624 | 566 | 907 | 838 |
| 1948 | 732 | 576 | 668 | 565 | 659 | 590 | 895 | 867 |
| 1949 | 792 | 620 | 722 | 617 | 698 | 624 | 894 | 831 |
| 1950 | 780 | 634 | 721 | 635 | 709 | 669 | 944 | 827 |
| 1951 | 848 | 754 | 809 | 718 | 763 | 721 | 945 | 946 |
| 1952 | 1005 | 856 | 944 | 822 | 851 | 813 | 955 | 954 |
| 1953 | 1077 | 908 | 1008 | 889 | 901 | 852 | 946 | 803 |
| 1954 | 1013 | 968 | 995 | 944 | 945 | 922 | 976 | 847 |
| 1955 | 983 | 1005 | 993 | 985 | 988 | 973 | 990 | 966 |
| 1956 | 1006 | 998 | 1004 | 1007 | 1005 | 1002 | 997 | 1011 |
| 1957 | 1035 | 1052 | 1042 | 1059 | 1042 | 1033 | 991 | 1040 |
| 1958 | 1054 | 1057 | 1056 | 1063 | 1064 | 1070 | 1006 | 1143 |
| 1959 | 1102 | 1081 | 1092 | 1075 | 1122 | 1081 | 963 | 1051 |
| 1960 | 1110 | 1085 | 1098 | 1076 | 1148 | 1109 | 966 | 1294 |
| 1961 | 1099 | 1092* | 1100* | 1099 | 1159 | 1157* | 998* | 1578 |
| Year Ended 30 June | ||||||||
| 1937 | 384 | 383 | 383 | 404 | 471 | 394 | 837 | 581 |
| 1938 | 410 | 404 | 407 | 437 | 497 | 413 | 831 | 580 |
| 1939 | 405 | 413 | 408 | 447 | 509 | 428 | 841 | 531 |
| 1940 | 440 | 440 | 441 | 476 | 533 | 433 | 812 | 545 |
| 1941 | 525 | 448 | 494 | 481 | 556 | 455 | 818 | 544 |
| 1942 | 566 | 481 | 532 | 494 | 574 | 463 | 807 | 552 |
| 1943 | 635 | 493 | 577 | 501 | 593 | 491 | 828 | 607 |
| 1944 | 677 | 502 | 606 | 508 | 605 | 497 | 821 | 686 |
| 1945 | 688 | 506 | 615 | 511 | 615 | 510 | 829 | 718 |
| 1946 | 699 | 517 | 626 | 511 | 621 | 556 | 895 | 789 |
| 1947 | 682 | 538 | 623 | 515 | 625 | 569 | 910 | 855 |
| 1948 | 758 | 594 | 691 | 589 | 675 | 602 | 892 | 857 |
| 1949 | 789 | 621 | 720 | 619 | 700 | 631 | 901 | 820 |
| 1950 | 790 | 653 | 734 | 648 | 717 | 680 | 948 | 850 |
| 1951 | 881 | 781 | 841 | 744 | 784 | 747 | 953 | 973 |
| 1952 | 1038 | 873 | 971 | 845 | 869 | 821 | 945 | 909 |
| 1953 | 1064 | 921 | 1006 | 899 | 910 | 862 | 947 | 796 |
| 1954 | 1000 | 983 | 993 | 962 | 958 | 945 | 986 | 879 |
| 1955 | 988 | 1006 | 996 | 991 | 988 | 984 | 996 | 982 |
| 1956 | 1011 | 1009 | 1011 | 1016 | 1012 | 1006 | 994 | 1022 |
| 1957 | 1043 | 1056 | 1048 | 1063 | 1049 | 1046 | 997 | 1063 |
| 1958 | 1055 | 1056 | 1056 | 1066 | 1070 | 1073 | 1003 | 1125 |
| 1959 | 1116 | 1084 | 1099 | 1075 | 1137 | 1083 | 953 | 1068 |
| 1960 | 1105 | 1091 | 1101 | 1076 | 1149 | 1125 | 979 | 1391 |
Statistics of consumption cannot be compiled with absolute accuracy, owing to the impossibility of obtaining exact comparability in component statistics of production, exports, and imports. There are several deficiencies in the statistical data at present available, the most serious being occasioned by the lack of statistics illustrating the distribution among individuals of the annual flow of commodities entering into consumption. Nevertheless, a sufficient degree of comparability can normally be attained to permit of the compilation of statistics of overall consumption with a reasonable approach to accuracy.
VALUE OF GOODS AVAILABLE FOR USE - Statistics of the value of production, of exports, and of imports have been compiled regularly for many years. From these statistics an estimate of the annual value of goods, including both capital and consumption goods, available for use in New Zealand can be made, the value of exports being deducted from that of production, and the value of imports added to the residuum. The result of this computation gives a close approach to the value of all goods available for use in the country. Following revisions and corrections in the value of production estimates consequent corrections are made in this series.
The following descriptive notes under the respective headings will serve to indicate the nature and scope of the figures of production, exports, and imports used in this section.
Production - The series of value and volume of production figures as quoted in Section 13 of this Yearbook form the basis of the tables which follow. The figures relate to the production year, which, in most cases, approximates closely to the year ended 30 June.
Exports - The official export figures (f.o.b.) for the years ended 30 June have been adjusted to exclude charges incurred between the stages of production and export.
Since the value of production figures is on the basis of prices received by producers, adjustments have necessarily been made to the export value figures (which are based on overseas realisations) for credits to, or drawings from, the primary produce stabilisation accounts.
Adjustments have also been made for changes in stocks awaiting shipment, so that the export figures quoted in this section represent the segment of production in any year exported, or ultimately destined for export. This applies to the volume as well as the value series.
Various adjustments were also made to the figures for the war years to ensure the exclusion from the domestic market supplies of goods supplied to the New Zealand and allied forces, etc.
Imports - For the period up to 1948-49 the official import figures (Customs values) for the years ended 30 June, excluding ordnance, have been adjusted to take into account additional freight and insurance charges above the nominal 10 per cent allowed in the official figures. For the years 1949-50 to 1951-52 some information on actual c.i.f. (cost including insurance and freight) values of imports was available to help in making assessments of value on this basis. From 1952-53 onwards the official Customs c.i.f. values have been used.
Further adjustments have been made for the realisation on certain war assets.
Unfortunately, comprehensive statistics of merchandise stocks are not available, so that the figures illustrate goods available for use and not necessarily goods actually used during each of the years.
The following table gives the position in regard to value of goods, but care should be exercised in interpreting the table in view of the substantial upward trend in unit values that has taken place over the period covered by the table. Some overstatement of the value of goods available for use in 1948-49 may have occurred through the adjustment of the value of the New Zealand pound to parity with sterling as from 20 August 1948. Figures are given for the year 1938-39 and for each of the latest 11 years.
| Year Ended 30 June | Produced in New Zealand | Imported | All Goods Available for Use in New Zealand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Exported | Available for Use in New Zealand | Total | Per Head | |||
| Total | Per Head | ||||||
*Revised from figures shown in previous years. †Provisional. | |||||||
| VALUES | |||||||
| £(m.) | £(m.) | £(m.) | £ | £(m.) | £(m.) | £ | |
| 1939 | 133.3 | 58.0 | 75.3 | 46.6 | 59.1 | 134.4 | 83.1 |
| 1949 | 290.1 | 120.9 | 169.2 | 91.3 | 116.5 | 285.7 | 154.2 |
| 1950 | 343.8 | 137.2 | 206.6 | 109.3 | 149.4 | 356.0 | 188.3 |
| 1951 | 469.0 | 233.3 | 235.7 | 122.3 | 174.8 | 410.5 | 213.0 |
| 1952 | 431.2 | 194.9 | 236.3 | 119.9 | 293.3 | 529.6 | 268.8 |
| 1953 | 482.1 | 231.0 | 251.1 | 124.1 | 208.2 | 459.3 | 227.1 |
| 1954 | 518.6 | 229.2 | 289.4 | 139.6 | 210.1 | 499.5 | 240.9 |
| 1955 | 565.1 | 240.7 | 324.4 | 153.3 | 277.2 | 601.6 | 284.2 |
| 1956 | 581.6 | 264.1 | 317.5 | 146.9 | 276.8 | 594.3 | 275.0 |
| 1957 | 622.3 | 276.8* | 345.5* | 156.6 | 277.7 | 623.2* | 282.5 |
| 1958 | 640.5* | 286.6* | 353.9* | 156.6* | 305.2 | 659.1* | 291.7* |
| 1959† | 641.4 | 241.3 | 400.1 | 173.1 | 244.6 | 644.7 | 278.9 |
| VALUE INDEX NUMBERS: BASE 1938.39 (= 100) | |||||||
| 1939 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1949 | 218 | 208 | 225 | 196 | 197 | 213 | 186 |
| 1950 | 258 | 237 | 274 | 235 | 253 | 265 | 227 |
| 1951 | 352 | 402 | 313 | 262 | 296 | 305 | 256 |
| 1952 | 323 | 336 | 314 | 257 | 496 | 394 | 323 |
| 1953 | 362 | 398 | 333 | 266 | 352 | 342 | 273 |
| 1954 | 389 | 395 | 384 | 300 | 355 | 372 | 290 |
| 1955 | 424 | 415 | 431 | 329 | 469 | 448 | 342 |
| 1956 | 436 | 455 | 422 | 315 | 468 | 442 | 331 |
| 1957 | 467 | 477 | 459 | 336 | 470 | 464 | 340 |
| 1958 | 480* | 494* | 470* | 336* | 516 | 490 | 351 |
| 1959† | 481 | 416 | 531 | 371 | 414 | 480 | 336 |
AGGREGATE VOLUME OF GOODS AVAILABLE FOR USE - Index numbers of volume of total production, based in most cases on figures of actual physical production, and index numbers of volume of exports and of imports, form the basis on which figures indicating the volume of goods available for New Zealand use are estimated. Attention is drawn to the notes on adjustments, etc., applied under the various headings and explained under the preceding title. Quarterly index numbers of volume of exports, easily assembled into June year aggregates, have been compiled since 1951. For earlier years the quantitative figures of exports, readily available from the official statistics and confined to a relatively small number of items, made it a comparatively simple matter to compile index numbers of volume for years ending with the month of June. For many years a similar position did not hold in the case of imports, as they are far more diversified in nature, and import volume index numbers were available only for calendar years. Using quarterly import price index numbers obtained by interpolation from the annual series, quarterly figures of values of imports up to and including 1948 have been deflated to pounds of constant value and then expressed as index numbers and reconciled with the calendar year volume index numbers. These quarterly figures, together with the quarterly volume of imports index numbers compiled regularly since 1949, have been readily aggregated into years ending 30 June. By the use of quantitative figures of production, exports, and imports, reasonably accurate figures of movements in volume may be ascertained, and figures arrived at indicating the volume of goods available for New Zealand use. The aggregates used in the process are based on unit values ruling in 1938-39 and are shown in the table following for the same years as in the preceding table.
| (On basis of unit values ruling in 1938.39) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Ended 30 June | Produced | Exports | Imports | Available for Use |
*Revised from figures shown in previous years. †Provisional. | ||||
| £(million) | ||||
| 1939 | 133.3 | 58.0 | 59.1 | 134.4 |
| 1949 | 173.0 | 70.2 | 59.3 | 162.1 |
| 1950 | 182.5 | 68.7 | 72.1 | 185.9 |
| 1951 | 187.8 | 66.5 | 76.3 | 197.6 |
| 1952 | 192.2 | 72.6 | 106.9 | 226.5 |
| 1953 | 196.2 | 78.1 | 74.1 | 192.2 |
| 1954 | 203.3 | 73.2 | 82.0 | 212.1 |
| 1955 | 218.5 | 74.5 | 109.7 | 253.7 |
| 1956 | 225.5 | 83.1 | 107.4 | 249.8 |
| 1957 | 228.1 | 81.8 | 105.8 | 252.1 |
| 1958 | 243.9 | 89.9* | 115.9* | 269.9* |
| 1959† | 253.8 | 91.8 | 93.9 | 255.9 |
The next table gives volume index numbers corresponding to these values.
INDEX NUMBERS OF VOLUME OF GOODS: BASE 1938-39 (= 100)
| Year Ended 30 June | Produced in New Zealand | Imported | All Goods Available for Use in New Zealand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Exported | Available for Use in New Zealand | Total | Per Head | |||
| Total | Per Head | ||||||
*Revised from figures shown in previous years. †Provisional. | |||||||
| 1939 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1949 | 130 | 121 | 137 | 119 | 100 | 121 | 105 |
| 1950 | 137 | 118 | 151 | 129 | 122 | 138 | 118 |
| 1951 | 141 | 114 | 161 | 135 | 129 | 147 | 123 |
| 1952 | 144 | 125 | 159 | 131* | 181 | 169 | 138 |
| 1953 | 147 | 134 | 157 | 126* | 125 | 143 | 114 |
| 1954 | 152 | 126 | 173 | 135 | 139 | 158 | 123 |
| 1955 | 164 | 128 | 191 | 146 | 186 | 189 | 144 |
| 1956 | 169 | 143 | 189 | 141 | 182 | 186 | 139 |
| 1957 | 171 | 141 | 194 | 142 | 179 | 188 | 138 |
| 1958 | 183 | 155 | 205 | 146 | 196* | 201 | 144 |
| 1959† | 190 | 158 | 215 | 150 | 159 | 190 | 133 |
It should, perhaps, be emphasised that the tables cover capital as well as consumer goods; consequently the headings “available for use in New Zealand” include not only commodities entering into current consumption, but also such items as additions to merchandise stocks, to factory plant and buildings, to farm capital stock, etc.
Following the low levels of the war years the volume of goods available for use began to rise from 1945-46, the level of 1938-39 being passed by total goods available in 1946-47, and by goods available per head in 1947-48. The rising trend has continued since those dates, with interruptions for a few individual years, including the latest year shown. Year-to-year fluctuations have tended to reflect variations in volume of imports rather than of retained domestic production.
In conjunction with the previous table, it is interesting to consider the proportions of New Zealand produced goods and of imported goods in the total quantum of goods entering into use. Over the period for which the break-up is available, locally produced goods supplied 61 per cent and imported goods 39 per cent of the total.
Comparisons in this respect for individual years are given hereunder.
| Year | Locally Produced | Imported |
|---|---|---|
| per cent | per cent | |
| 1938-39 | 56 | 44 |
| 1939-40 | 65 | 35 |
| 1940-41 | 71 | 29 |
| 1941-42 | 72 | 28 |
| 1942-43 | 71 | 29 |
| 1943-44 | 64 | 36 |
| 1944-45 | 66 | 34 |
| 1945-46 | 70 | 30 |
| 1946-47 | 66 | 34 |
| 1947-48 | 59 | 41 |
| 1948-49 | 63 | 37 |
| 1949-50 | 61 | 39 |
| 1950-51 | 61 | 39 |
| 1951-52 | 53 | 47 |
| 1952-53 | 61 | 39 |
| 1953-54 | 61 | 39 |
| 1954-55 | 57 | 43 |
| 1955-56 | 57 | 43 |
| 1956-57 | 58 | 42 |
| 1957-58 | 57 | 43 |
| 1958-59 | 63 | 37 |
While strict accuracy cannot be claimed for these figures - particularly in respect of single years - they afford a useful indication of trends. The policy of import restriction introduced in December 1938, and the dictates of a war economy, were responsible for the relatively low proportion of imported goods to total goods available evident from 1939-40 to 1946-47. The percentages for imports clearly reflect the progressive lifting of import controls from 1950 onwards, the introduction of exchange control in 1952, its abolition at the end of 1954, and the reimposition of import restrictions in 1958.
CONSUMPTION OF NEW ZEALAND PRODUCE - While the statistical data discussed in the foregoing pages afford an indication of movements in the aggregate value and volume of consumption, considerable interest attaches to the statistics for individual commodities of importance. Estimates of the consumption of a selection of individual commodities are given in the following paragraphs. No indication of the distribution of consumption of these commodities among individual classes of consumers is available; but with full employment and the absence of real poverty in New Zealand it is beyond question that the per head rates of consumption of various commodities shown later are truly representative of general living standards.
The proportion of the total production that is consumed in New Zealand and the proportion which is exported, of the main food products in which an export trade is maintained, are shown in the next table, giving aggregate percentages over the three-year period 1957-60.
| Consumed in New Zealand | Exported | |
|---|---|---|
| per cent | per cent | |
| Butter | 20.5 | 79.5 |
| Cheese | 7.2 | 92.8 |
| Beef and veal | 43.3 | 56.7 |
| Mutton | 50.8 | 49.2 |
| Lamb | 4.9 | 95.1 |
| Pig meat | 83.2 | 16.8 |
Local (New Zealand) consumption of all meats combined, during this same three-year period, amounted to 33 per cent of total meat production.
PER HEAD QUANTITIES OF PRINCIPAL FOODSTUFFS AVAILABLE FOR CONSUMPTION - Estimates of annual consumption per head of population have been made for the principal items of foodstuffs for recent years and for a pre-war period, mostly the average of 1934-38. Basic statistical data are rather scanty in the case of some items, particularly fresh vegetables, and the estimates may be subject to correction as further information becomes available.
Dairy Produce - Measured in terms of butterfat content, it is estimated that 26.3 per cent of total dairy production in 1959-60 was used for local human consumption. A further 3.1 per cent was accounted for by stock feeding, wastage, changes in stocks, etc., leaving 70.6 per cent for export in the form of butter, cheese, processed milk and casein. Estimated figures of annual consumption levels for individual items of dairy produce, pre-war and for recent periods, are given below.
| Pre-war | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole milk (pint) | 220.0 | 321.1 | 324.2 | 328.0 |
| Cream (pint) | 6.9 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.0 |
| Ice cream (pint) | 3.2 | 14.7 | 15.6 | 16.8 |
| Cheese (lb) | 4.5 | 6.3 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| Butter (lb) | 41.2 | 42.4 | 43.2 | 43.3 |
| Processed milk (lb) | 4.7 | 131 | 14.7 | 16.8 |
In the following comparison of butter and cheese consumption in various countries the figures for countries other than New Zealand have been taken from the publication Dairy Produce, issued by the Intelligence Branch of the Commonwealth Economic Committee.
BUTTER AND CHEESE CONSUMPTION PER HEAD
| Butter | Cheese | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1938 or 1938-39 | 1958 or 1959 | 1938 or 1938-39 | 1958 or 1959 | |
| lb | lb | lb | lb | |
| United Kingdom | 24.1 | 20.2 | 8.9 | 9.9 |
| Sweden | 24.1 | 21.6 | 12.8 | 13.9 |
| Denmark | 18.3 | 29.8 | 14.1 | 16.3 |
| Netherlands | 12.3 | 10.8 | 17.0 | 17.6 |
| United States of America | 16.6 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 8.5 |
| Canada | 31.9 | 19.1 | 3.6 | 6.8 |
| Republic of Ireland | 32.2 | 39.9 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Australia (1958-59) | 32.6 | 25.9 | 4.3 | 5.2 |
| New Zealand (1959-60) | 42.8 | 43.3 | 4.5 | 6.6 |
In considering New Zealand's relatively high consumption of butter it should be noted that the use of margarine as a spread, common in some countries, is unknown in New Zealand.
Meats - In estimating the average annual consumption of meats an allowance has been made in the case of each item for killings on farms and for condemnations. The consumption levels for the various items are as follows, the weights in each case being on a bone-in dressed-carcass basis.
| Pre-war | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef (lb) | 112.0 | 92.7 | 91.4 |
| Veal (lb) | 7.5 | 5.9 | 6.2 |
| Mutton (lb) | 60.0 | 76.9 | 81.4 |
| Lamb (lb). | 6.5 | 11.9 | 14.3 |
| Pork, including chopper meat (lb) | 9.0 | 16.1 | 16.2 |
| Ham and bacon (lb) | 17.0 | 17.8 | 17.3 |
| Edible offal (lb) | 9.0 | 9.7 | 10.5 |
Vegetables and Fruits - Estimates under this heading have been made, particularly in the case of vegetables, with considerable difficulty owing to a number of factors, not the least being the fact that domestic garden production must of necessity be taken into account. Where there is no evidence as to changes in consumption habits, the estimates for both pre-war and the later years shown have been treated as on an equality. The estimates include, at fresh weights, New Zealand produced fruits and vegetables canned for local consumption; imports of canned produce are excluded. Consumption levels for individual items are estimated as follows.
| Pre-war | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potatoes (lb) | 120 | 121 | 113 |
| Kumeras (lb) | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Cabbages and leaf greens (lb) | 30-35 | 30-35 | 30-35 |
| Carrots (lb) | 10-15 | 10-15 | 10-15 |
| Tomatoes (lb) | 20 | 21 | 21 |
| Apples (lb) | 45 | 39 | 39 |
| Pears and quinces (lb) | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Stone fruits (lb) | 10 | 22 | 21 |
| Citrus fruits (lb) | 23 | 16 | 18 |
| Bananas (lb) | 21 | 30 | 29 |
| Pineapples (lb) | 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Canned Fruit and Vegetables - Total consumption of canned fruits and vegetables per head is estimated as:
| Pre-war | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canned fruit (lb) | 10 to 11 | 10.9 | 9.6 |
| Canned tomatoes, including sauces and soups (lb) | Not available | 4.7 | 4.8 |
| Canned vegetables (lb) | 1.6 | 13.9 | 9.4 |
These figures are inclusive of New Zealand produced canned fruit and vegetables already accounted for as fresh fruit under the preceding heading. Consumptions of (net) imports of these commodities are estimated as:
| Pre-war | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canned fruit (lb) | 7.6 | 5.3 | 3.6 |
| Canned tomatoes, including sauces and soups (lb) | .. | 0.6 | 0.3 |
Before the war approximately 70 to 80 per cent of canned fruit requirements were imported and consisted mainly of pineapples, peaches, and apricots. The war considerably upset this trade, but there was a marked recovery from 1947. There has also been some progress in the local canning of fruit, but consumption per head of all canned fruit is still only at about pre-war level.
The consumption of canned vegetables, owing in some measure to the striking wartime expansion of the industry, is now at a high level. Before the war there were some imports of peas and beans, but most requirements are now met from local production. The largest development has been in the production of canned green peas, of which about one-third are exported.
Quick-frozen Fruit and Vegetables - There has been a remarkable development in the quick-frozen foods industry in recent years. Consumption per head in New Zealand for the latest three years for which figures are available is estimated as:
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits (lb) | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Vegetables (lb)– | |||
| Peas | 4.7 | 6.2 | 4.7 |
| Beans | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.7 |
| Other | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
Other Foodstuffs - Estimated annual consumption levels for other items of foodstuffs are given hereunder.
| Pre-war | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poultry (lb) | 3.9 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Fish - edible portion, excluding processed imports (lb) | 11.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 |
| Shellfish - edible portion (lb) | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| Eggs (dozen) | 20.0 | 23.0 | 24.0 |
| Honey (lb) | 2.1 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Refined sugar (lb) | 104.0 | 92.0 | 93.0 |
| Dried peas and beans (lb) | 1.6 | 2.9 | 3.0 |
| Flour, wheaten (lb) | 185.0 | 179.0 | 181.0 |
| Oatmeal, oaten products (lb) | 10.5 | 4.9 | 5.1 |
| Rice (lb) | 5.3 | 3.2 | 2.8 |
| Tea (lb) | 6.8 | 6.7 | 6.5 |
| Cocoa (lb) | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
Beer, Wine, Spirits, and Tobacco - As the consumption of these items is particularly susceptible to economic conditions, the depression and immediate post-depression years have been avoided in ascertaining pre-war consumption. In interpreting the big increase in beer consumption from pre-war years it should not be overlooked that as a war measure the alcoholic strength of beer was, in 1942, reduced by about one-quarter, and it is possible that, on account of this, consumption was higher than it would otherwise have been. Although this restriction was removed at the end of 1948 the additional duty on beer exceeding the reduced strength has had much the same effect as the former restriction in limiting the production of stronger beers.
Domestic wine production has increased during recent years and now accounts for the greater part of total consumption.
| Pre-war | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | |||
| Beer (gallons) | 10.8 | 21.1 | 19.7 |
| Grape wine (gallons) | 0.20 | 0.41 | 0.41* |
| Spirits (proof gallons) | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.27* |
| Tobacco (lb) | 3.9 | 4.9 | 4.7 |
Comparison With Other Countries - In considering the question of supplies of foodstuffs in various countries the food balance sheets prepared at the instigation of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation present information on a comparable basis. The table which follows presents in summarised form statistics appearing in the Organisation's Production Yearbook, and in the United Nations Statistical Yearbook. The data quoted are expressed in kilogrammes per person per year, except that for each country a total figure is given showing calories per person per day, and the percentage thereof derived from livestock products (meat, poultry, eggs, fish, milk, butter, cheese, slaughter fats, marine oils). The total calories figure includes also foodstuffs not specifically mentioned in the table.
A table such as this necessarily includes data of an approximate nature, but is of value as an overall picture of food consumption and availability in the various countries.
| Country | Cereals | Potatoes, etc. | Sugar | Pulses and Nuts | Meat | Milk and Milk Products* | Fats† and Oils | Calories | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | Protein | Per Day | Percentage of Animal Origin | ||||||||
*Excluding butter. †Including butter. ‡Negligible. § Percentages for earlier post-war years in these cases. ||Includes present territory of Pakistan. | |||||||||||
| Kilogrammes per Person per Year | |||||||||||
| Australia | Pre-war | 101 | 49 | 53 | 2 | 120 | 6 | 5 | 16 | 3,300 | 40 |
| 1957-58 | 87 | 55 | 51 | 4 | 113 | 7 | 6 | 16 | 3,200 | 42 | |
| Canada | Pre-war | 93 | 60 | 43 | 6 | 62 | 8 | 7 | 19 | 3,020 | 39 |
| 1958-59 | 70 | 66 | 44 | 5 | 75 | 8 | 9 | 19 | 3,110 | 43§ | |
| New Zealand | Pre-war | 87 | 50 | 48 | 3 | 109 | 8 | 8 | 17 | 3,260 | 48 |
| 1958 | 86 | 59 | 42 | 4 | 105 | 11 | 10 | 20 | 3,440 | 51 | |
| United Kingdom | Pre-war | 95 | 82 | 42 | 5 | 67 | 5 | 5 | 21 | 3,110 | 38 |
| 1958-59 | 84 | 93 | 50 | 6 | 68 | 7 | 7 | 22 | 3,260 | 38§ | |
| Union of South Africa | Pre-war | 156 | 16 | 21 | 2 | 38 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2,340 | 19 |
| 1957 | 148 | 16 | 43 | 4 | 45 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 2,660 | 22 | |
| United States of America | Pre-war | 91 | 67 | 44 | 7 | 72 | 8 | 7 | 21 | 3,280 | 38 |
| 1958 | 67 | 47 | 41 | 7 | 90 | 8 | 9 | 21 | 3,100 | 41 | |
| Argentina | Pre-war | 106 | 66 | 27 | 2 | 107 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 2,780 | 36 |
| 1957 | 105 | 94 | 32 | 2 | 122 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 3,100 | 35§ | |
| Denmark | Pre-war | 94 | 120 | 50 | 5 | 75 | 8 | 8 | 27 | 3,450 | 35 |
| 1958-59 | 78 | 128 | 48 | 5 | 71 | 9 | 8 | ,26 | 3,350 | 41§ | |
| France | Pre-war | 124 | 143 | 24 | 8 | 55 | 4 | 5 | 16 | 2,880 | |
| 1958-59 | 113 | 100 | 30 | 6 | 68 | 6 | 7 | 17 | 2,950 | ||
| Netherlands | Pre-war | 107 | 116 | .29 | 5 | 38 | 7 | 8 | 21 | 2,840 | 32 |
| 1958-59 | 87 | 89 | 40 | 4 | 43 | 8 | 8 | 25 | 2,940 | 29§ | |
| Sweden | Pre-war | 95 | 122 | 44 | 3 | 49 | 11 | 10 | 18 | 3,120 | 38 |
| 1958-59 | 74 | 100 | 40 | 4 | 52 | 9 | 9 | 20 | 2,890 | 41§ | |
| India | Pre-war|| | 139 | 8 | 13 | 22 | 3 | 3† | 2 | 2* | 1,950 | 8 |
| 1957-58 | 124 | 11 | 14 | 26 | 2 | 3† | 2 | 4* | 1,800 | 6§ | |
| Japan | Pre-war | 158 | 46 | 13 | 33 | 3 | ‡ | ‡ | 1 | 2,050 | 5 |
| 1957-58 | 157 | 68 | 12 | 32 | 5 | ‡ | ‡ | 3 | 2,220 | 7 | |
SUBSIDIES - During the war and post-war period the Government implemented a policy of stabilising internal price levels at the level of those prevailing in December 1942. For the effective operation of this policy a system of Government subsidies was essential. An account of the use and extent of subsidies paid in 1942-43 and from 1947-48 to 1951-52 was given in parliamentary paper B.5 of 1952.
The table following shows the total cost of the foregoing subsidies and in addition the cost of the subsidy paid on the transport of citrus fruit, for the five latest financial years.
| Subsidy Items | Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | |
| *Subsidy ceased 1 April 1959. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| Butter, milk, and eggs | 8,880 | 8,849 | 7,971 | 7,661 | 10,761 |
| Bread and flour | 3,003 | 3,600 | 4,500 | 4,500 | 4,000 |
| Gas | 465 | 479 | 466 | 440 | 590 |
| Transport of citrus fruit | 3 | 2 | 3 | * | * |
| Total subsidies | 12,351 | 12,930 | 12,940 | 12,601 | 15,351 |
The general position is that stabilisation subsidies increased up to 1947 as import prices and wages rose. The full increase in costs above basic level (mainly 15 December 1942) was not always covered by subsidy. In most cases a part of the increased cost had to be borne by the industry concerned, either at the source of the increased cost or at some later stage in the distribution of the goods and services.
In 1947 the Government decided to review the position. The number of commodities on which subsidy was paid had grown too large for administrative ease. Also to have continued subsidies at the previous rate would have raised the estimated expenditure to £19.6 million, which would have imposed a severe strain on the public finances. Further, a great many of the costs met by subsidy were permanent. Accordingly many farm subsidies, which on an annual basis cost approximately £4.2 million, were removed, and compensating adjustments were made in the prices of farm products. Of the other subsidies, all the smaller and less important ones were abolished, in part or in full. There were also increases in the price of shipping and railway freights and fares, tea, sugar, and many other commodities. On an annual basis these subsidies would have cost about £8 million.
In spite of the removal in 1947 of total subsidies of over £12 million a year, the cost of the remaining subsidies had risen to a level of over £17 million a year by 1950. The Government therefore removed subsidies in May 1950 amounting to £12 million a year. The subsidies on coal and tea were discontinued (apart from certain social payments), and subsidies on flour, bread, milk, butter, and eggs were reduced substantially. In addition, rail freights and fares were again increased. In September 1951 the retail prices of butter, bread, flour, and gas were substantially reduced, the subsidies on these commodities being adjusted accordingly. By mid-1952 subsidy expenditure was running at the annual rate of £17.5 million. Following upon the general wage order of November 1953 the position was again reviewed. It was decided that the maintenance by subsidy of price levels previously subsisting would have entailed too great a burden on the public funds, and accordingly the prices of subsidised items, particularly bread, butter, and milk, were allowed to rise. Nevertheless these items still carry heavy subsidies, as is indicated in the following table, which shows the amount of subsidy paid on the main commodities in April 1961.
| s. | d. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Butter | 8 | per lb | |
| Milk | 4.25 | per quart | |
| Bread | 3.9 | per 2 lb loaf | |
| Flour | 4 | 3.25 | per 25 lb bag |
| Gas | 1 | 11 | per 1,000 cubic feet sold |
| Eggs | 4 | per dozen |
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTORY - The estimates of National Income and Expenditure shown on the following pages follow the same pattern, both in method of estimation and presentation, as those published in previous issues of the Yearbook.
The principal of these aggregates is that of “National Income”, which, in general terms, measures the total value of all incomes (before deduction of taxation) earned by the residents of New Zealand in producing the current output of goods and services.
Income can be earned in a variety of ways and accrues to individuals according to the manner in which they participate in current production. Salary and wage payments represent the return to labour for services rendered, and include in this concept supplementary income in kind such as board and keep provided by the employer. The item pay and allowances of armed forces, while analogous to salary and wage payments, does not necessarily fit in with this concept, when the civilian occupation of the serviceman is considered. This fact must be taken into account in comparing the distributive shares of the various groups in the national income over the war period. Clothing, food, accommodation, and other income in kind supplied to members of the armed forces are included under this heading, as are also deferred-pay, mufti-allowances, and war-gratuity payments.
Rental value of owner-occupied houses is a non-monetary item representing the imputed net rent (before payment of rates, but after deductions for depreciation, mortgage interest, insurance, and repairs and maintenance) of all owner-occupied houses (except farm houses).
Other personal income (excluding company dividends) represents the aggregate income of professional men, farmers, and individual traders, as well as income other than salary and wages received by salary and wage earners - e.g., rent, interest, etc. Included under this heading as current income are changes in balances of primary-produce stabilisation accounts, and moneys retained under authority of the Wool Proceeds Retention Act 1950.
Company income represents the total income (distributed and undistributed) of companies. This means that dividends distributed to individuals are included under this heading, and not as personal income.
Apart from these incomes which result from current productive activities on the part of individuals receiving them, there are other incomes of a “non-productive” nature in the form of social security benefits, pensions, and interest on public debt. These transfer incomes, as they are called, do not arise from the current production of goods and services and must therefore be excluded from the national income. They do, however, form part of the intermediate concept of private income, which represents the aggregate of earned incomes and unearned transfer incomes received by or accruing to persons. Private income includes as income accruing, but not actually received, undistributed incomes of companies. The deduction of direct taxation gives the concept of private disposable income. Capital receipts - e.g., from deceased persons' estates, repayment of debt, etc. - are, however, excluded both from private income and national income.
In general, only incomes arising from the production of goods and services destined for the market form part of the national income; it follows, therefore, that the services of housewives, or the produce of home gardens are excluded. On the other hand, farm produce cons on farms is part of the national income.
The addition to private income of Government and local-authority trading profits and the deduction of transfer incomes, as detailed above, gives the concept of net national income at factor cost or, more briefly, national income. This may be defined as the income (before tax) earned by or accruing to the factors of production, in or only temporarily absent from New Zealand, in producing the current output of goods and services of all kinds. The further addition of indirect taxes (net of subsidies) is necessary to bring the net national income to market price valuation.
Gross national product is obtained by adding depreciation allowances to net national income at market prices, and represents the value of current output before deduction of allowances for depreciation and obsolescence, and is equal on the expenditure side to gross national expenditure.
The following table shows the principal of the above aggregates and the manner in which they are derived one from the other for the years 1938-39 to 1959-60.
PRINCIPAL INCOME AGGREGATES
| Year Ended 31 March | (26) Private Income | Plus | Less Transfer Incomes | (9) Net National Income at Factor Cost | (10) Plus Indirect Taxation | (11) Less Subsidies | (12) Net National Income at Market Prices | (13) Plus Depreciation Allowances | (14) Gross National Product | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (6) Government Trading Income | (7) Lump Sum Payments from United Kingdom Government | (22) Social Security Benefits and Pensions | (8) Interest on Public Debt Paid in New Zealand | ||||||||
| *Provisional. | |||||||||||
| £(million) | |||||||||||
| 1938-39 | 200.2 | 8.8 | - | -7.5 | -7.0 | 194.5 | 20.6 | -0.6 | 214.5 | 17.0 | 231.5 |
| 1939-40 | 215.7 | 10.5 | 3.0 | -11.2 | -7.5 | 210.5 | 21.0 | 0.5 | 231.0 | 18.0 | 249.0 |
| 1940-41 | 235.0 | 12.0 | 3.0 | -12.3 | -7.8 | 229.9 | 22.3 | -1.6 | 250.6 | 18.0 | 268.6 |
| 1941-42 | 256.6 | 13.6 | 3.0 | -12.7 | -8.4 | 252.1 | 23.2 | -2.7 | 272.6 | 18.0 | 290.6 |
| 1942-43 | 294.9 | 16.7 | 3.0 | -14.0 | -9.4 | 291.2 | 28.0 | -3.3 | 315.9 | 19.0 | 334.9 |
| 1943-44 | 331.8 | 17.9 | 3.0 | -15.5 | -11.3 | 325.9 | 31.8 | -3.1 | 354.6 | 20.0 | 374.6 |
| 1944-45 | 339.5 | 14.7 | 5.0 | -17.2 | -12.9 | 329.1 | 34.0 | -4.6 | 358.5 | 21.0 | 379.5 |
| 1945-46 | 360.5 | 15.6 | 5.0 | -20.6 | -13.3 | 346.7 | 37.3 | -6.6 | 377.4 | 22.0 | 399.4 |
| 1946-47 | 397.3 | 15.0 | 5.0 | -34.4 | -15.1 | 367.8 | 43.0 | -11.8 | 399.0 | 26.0 | 425.0 |
| 1947-48 | 446.4 | 13.9 | 5.0 | -.7.2 | -15.3 | 412.8 | 53.0 | -13.6 | 452.2 | 29.0 | 481.2 |
| 1948-49 | 464.5 | 12.9 | - | -39.0 | -15.5 | 422.9 | 46.1 | -11.5 | 457.5 | 32.0 | 489.5 |
| 1949-50 | 526.2 | 14.6 | - | -42.2 | -16.2 | 482.4 | 49.8 | -14.6 | 517.6 | 35.0 | 552.6 |
| 1950-51 | 659.5 | 16.8 | - | -47.1 | -17.0 | 612.2 | 55.6 | -9.4 | 658.4 | 39.0 | 697.4 |
| 1951-52 | 675.6 | 20.1 | - | -53.0 | -17.4 | 625.3 | 71.0 | -16.1 | 680.2 | 43.0 | 723.2 |
| 1952-53 | 709.8 | 19.3 | - | -53.7 | -17.2 | 658.2 | 67.0 | -15.0 | 710.2 | 48.0 | 758.2 |
| 1953-54 | 786.5 | 24.8 | - | -57.7 | -18.3 | 735.3 | 67.5 | -15.5 | 787.3 | 51.0 | 838.3 |
| 1954-55 | 853.5 | 30.0 | - | -61.3 | -20.2 | 802.0 | 80.7 | -13 | 4.869.3 | 60.0 | 929.3 |
| 1955-56 | 897.1 | 31.9 | - | -64.4 | -20.9 | 843.7 | 85.3 | -12.3 | 916.7 | 65.0 | 981.7 |
| 1956-57 | 945.1 | 30.5 | - | -66.3 | -23.3 | 886.0 | 84.1 | -13.3 | 956.8 | 72.0 | 1,028.8 |
| 1957-58 | 993.5 | 32.7 | - | -70.0 | -26.3 | 929.9 | 91.2 | -13.6 | 1,007.5 | 78.0 | 1,085.5 |
| 1958-59 | 1,035.8 | 37.2 | - | -80.1 | -28.4 | 964.5 | 104.1 | -13.5 | 1,055.1 | 86.0 | 1,141.1 |
| 1959-60* | 1,132.1 | 41.4 | - | -99.0 | -29.6 | 1,044.9 | 108.3 | -12.9 | 1,140.3 | 93.0 | 1,233.3 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-752.
Estimates of gross national product from 1932-33 to 1937-38 are as follows:
| 1932-33 | 1933-34 | 1934-35 | 1935-36 | 1936-37 | 1937-38 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross national product-£ (million) | 113.7 | 127.0 | 135.6 | 155.4 | 192.3 | 211.9 |
These estimates are based upon former computations of aggregate private income, with suitable adjustments to bring them into line with present-day concepts.
From 1938-39 to 1957-58, inclusive, the main source of information for estimating national income was the social security charge levied under the Social Security Act 1938. For later years, however, information from this source was no longer available owing to alterations in taxation procedure; some changes have therefore had to be made in the manner of estimating certain items.
The various aggregates are conventionally measured in New Zealand over periods of one year, ending 31 March. Monetary values in all cases are given in New Zealand currency without adjustment for price changes between individual years. Full details of the methods used and a description of the items in the following tables are given in the Report on the Official Estimates of National Income and Expenditure for the Year 1959-60, obtainable from the Government Printer, Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch.
NATIONAL INCOME AND EXPENDITURE - It is necessary to point out that the estimates of national expenditure should be used with some caution, owing to the fact that not all of the items of expenditure can be estimated directly. On the other hand it is well to realise that, whatever inherent error there may exist in the absolute values of individual expenditure items, year-to-year changes are likely to be much more accurate, simply because the method of estimation remains the same.
The method adopted by necessity does not permit a check to be made on the present national income aggregates, in which no allowances have been made for any possible understatement of incomes shown in the taxation returns on which the estimates are based. Neither do these aggregates take into account “negative” incomes nor losses of previous years allowed as a set-off against current profits for taxation purposes. Any understatement of the gross product total arising from these omissions will therefore be reflected in a similar understatement of personal consumption which is shown as a residual item in the break up of national expenditure (refer table on page 748, item 15). Direct estimates are made of expenditure on Government-provided goods and services, gross capital formation in New Zealand by private and Government sectors, and the balance of overseas payments on current account (sometimes termed net overseas investment or net lending abroad).
After ascertaining personal consumption in the manner outlined above, it becomes possible to make an estimate of private savings. By deducting personal expenditure and direct taxation from aggregate private income, another residual is obtained - viz, private savings (refer table on page 750). Being a residual item it will, of course, contain certain minor errors of estimation inherent in the aggregates from which it is derived. It will be free, however, from the major apparent error which is caused by the understatement of incomes through tax evasion; this is due to the fact that the underestimate is cancelled out by being included both in the minuend and subtrahend, and the residual is consequently not affected.
The various tables are given and their derivation and composition discussed later, but before presenting this detail it is of interest to examine the relationships existing between some of the more important aggregates. The following table gives the principal of these.
PRINCIPAL AGGREGATES AND THEIR RELATIONSHIPS
| 1938-39 | 1943-44 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||||||
| National income (9) | £m. | 195 | 326 | 844 | 886 | 930 | 965 | 1,045 |
| Gross national product (14) | £m. | 232 | 375 | 982 | 1,029 | 1,086 | 1,141 | 1,233 |
| Personal expenditure on consumer goods and services (15) | £m. | 162 | 179 | 645 | 672 | 728 | 752 | 773 |
| As percentage of gross national product | 70 | 48 | 66 | 65 | 67 | 66 | 63 | |
| Gross capital formation in New Zealand (17) | £m. | 44 | 39 | 240 | 235 | 261 | 258 | 258 |
| As percentage of gross national product | 19 | 10 | 24 | 23 | 24 | 23 | 21 | |
| Cost of Government-provided goods and services (16) | £m. | 32 | 161 | 128 | 140 | 148 | 155 | 165 |
| As percentage of gross national product | 14 | 43 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | |
| Private income (26) | £m. | 200 | 332 | 897 | 945 | 994 | 1036 | 1132 |
| Private savings (29) | £m. | 14 | 77 | 78 | 88 | 93 | 63 | 149 |
| As percentage of private income | 7 | 23 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 13 | |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-752.
In the financial year ended March 1960 New Zealand's national income increased by a further £80 million to reach £1,045 million and gross national product increased by £92 million to £1,233 million. Expressed as percentages the increases are 8.3 and 8.1 per cent respectively.
The most important highlights of the 1959-60 national accounts are the first reversal in six years of continuing balance of payments deficits and a sharp and significant increase in private savings. The two are not, of course, entirely unconnected because the finance of an external surplus requires domestic savings of some kind and in this particular instance it was the private sector which supplied them.
Starting from an estimated external deficit of £24 million in the preceding year, the balance of payments improved by £61 million to achieve a current surplus of £37 million. This is a record level exceeding even the year 1950-51 surplus of £30 million. Restraint on current and capital expenditure in both the private and public sectors of the economy within a general setting of increased production and improved terms of trade and a lower rate of stock accumulation freed sufficient resources to achieve this surplus. But there was also another notable shift in the formation of savings as between the public and the private sector. Although public current and capital expenditure declined somewhat in terms of gross national product (from 22.9 to 22.2 per cent), direct tax revenue of General Government declined even further in relative terms as well as absolutely. In consequence the General Government's savings declined from £68 to £35 million in 1959-60, whereas private savings increased from £63 to £149 million. The relative decline in personal consumption, coupled with a reduction of tax withdrawals from the private sector, and therefore leaving a larger portion of savings in the private sector is best illustrated in the following short table which expresses private outlay in terms of total private income.
| In Percentages of Private Income | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | Average of All Post-war Years | |
| Personal expenditure on goods and services | 73.2 | 72.6 | 68.3 | 69.7 |
| Direct taxation | 17.4 | 21.3 | 18.6 | 19.3 |
| Private savings | 9.4 | 6.1 | 13.2 | 11.0 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Personal savings, which are total private savings less undistributed profits of companies, increased threefold from £40 to £120 million. Undistributed profits of companies are estimated to have risen from £23 to £29 million.
As already mentioned, the 1959-60 economic picture can be characterised by a restraint in all forms of domestic expenditure. Personal expenditure on goods and services, although increasing absolutely from £752 to £773 million, fell from 65.9 to 62.7 per cent of gross national product. The same trends are evident in public consumption (Cost of goods and services provided by General and local Government) and private and public capital formation. Showing the preceding year's values (1958-59) in parentheses, the cost of Government provided goods and services increased to £129 million (£121 million) and that of local authorities to £36 million (£33 million) or, for the public sector combined, to £165 million (£155 million). This is equivalent to 13.4 per cent (13.6 per cent) of gross national product against a post-war average of 13.2 per cent. Private capital formation at £142 million (£136 million) is now 11.5 per cent of gross national product (11.9 per cent) against a post-war average of 11.9 per cent. Public capital formation at £109 million (£106 million) also shows a proportionate decline from 9.3 to 8.8 per cent, the latter value being equal to its post-war average. In general, the estimates appear to indicate a declining trend in the share of gross national product devoted to capital formation from 1954-55 onward, the private sector being more affected than the public sector.
Considering the distribution of factor shares, salary and wage payments increased by 6.1 per cent (£560 to £594 million), company profits before dividend distribution by 7.3 per cent (from £110 to £118 million) and other income of persons - largely the net income of non-corporate business, farmers, interest, and net rents - by 13.4 per cent (from £247 to £280 million). The latter group of incomes includes the surpluses of primary-produce stabilisation accounts and producer boards (£8 million) operating within the confines of the farming industry which means that the “cash” incomes of farmers are reduced by an equal amount. The uneven rates of growth in individual income groups have the obvious result of altering the pattern of income distribution. With previous year's values in parentheses, salary and wage payments amounted to 56.8 per cent (58.1), company incomes 11 11.3 per cent (11.4), and other incomes of persons 26.8 per cent (25.6). For all post-war years, the distribution pattern of the three main income groups is as follows: salary and wage payments 53.8, company profits 11.7, and other personal income 29.2 per cent.
The four tables on pages 748-752 give the complete details of the various aggregates already mentioned and the manner in which they are derived from the accounts covering the different sectors of the economy.
National Income and Expenditure - This table gives the composition of the gross national product and the manner in which it has been expended - i.e., gross national expenditure. As mentioned previously, personal expenditure on consumer goods and services is obtained as a residual item in this table, all other aggregates being obtained by direct assessment.
Private Income and Outlay - This table gives in detail the break-up of private income into the various factor incomes and, on the expenditure side, the manner in which these incomes are spent on personal expenditure on consumer goods and services, paid in direct taxation, or saved. A break-up of other personal income is given for each of the years shown except 1943-44, when this detail was not available. The total of personal consumption derived from the preceding table is carried forward to this table, and this time private savings are obtained as a residual item. The limitations of these two residual items have already been mentioned, and for the reasons given care should be taken in their use.
General Government and Local Authority Revenue Account - The Government sector is discussed in more detail later in this Section, but this table gives a consolidated statement of General Government and local authority revenue and expenditure, showing as a balance that portion of the revenue which was utilised for capital investment in the case of a surplus, or the call on private savings made necessary by a deficit.
Combined Capital Account - This account indicates the manner in which finance for capital formation has been made available - (a) from private savings, (b) from revenue surpluses of Government, and (c) from amounts set aside as depreciation allowances from income. Gross capital formation represents the construction in New Zealand or purchase from overseas of durable capital assets by the private, General Government, and local authority sectors, plus net investment in stocks by trading concerns. The net change in overseas assets is the same as the item net overseas investment shown in the table on page 748 and is an estimate of the change in our overseas investment consequent on the movement in the balance of payments on current account.
These four tables, then, give a comprehensive picture in broad terms of the changing pattern of New Zealand's economy over a period of 21 years which has included the dislocating effects of a major war. One important point to consider when examining the tables, however, is that all the figures are at prices current during the period and consequently are inflated to a greater or less extent by price movements over the period.
The following are the four tables mentioned.
NATIONAL INCOME AND EXPENDITURE
| March Year | Salary and Wage Payments | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces | Rental Value, Owner-occupied Houses | Other Personal Income | Company Income | Government and Local Authority Trading Income | Lump Sum Payments from United Kingdom Government | Less Public Debt Interest Paid in New Zealand | Net National Income at Factor Cost | Plus Indirect Taxation | Less Subsidies | Net National Income at Market Prices | Plus Depreciation Allowances | Gross National Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | |
| INCOME £(million) | ||||||||||||||
| 1938-39 | 111 | 1 | 6 | 55 | 20 | 9 | - | -7 | 195 | 21 | -1 | 215 | 17 | 232 |
| 1943-44 | 141 | 58 | 9 | 72 | 36 | 18 | 3 | -11 | 326 | 32 | -3 | 355 | 20 | 375 |
| 1946-47 | 187 | 8 | 10 | 110 | 48 | 15 | 5 | -15 | 368 | 43 | -12 | 399 | 26 | 425 |
| 1947-48 | 210 | 6 | 11 | 129 | 53 | 14 | 5 | -15 | 413 | 53 | -14 | 452 | 29 | 481 |
| 1948-49 | 227 | 5 | 12 | 134 | 48 | 13 | - | -16 | 423 | 46 | -12 | 458 | 32 | 490 |
| 1949-50 | 250 | 5 | 13 | 159 | 58 | 15 | - | -16 | 482 | 50 | -15 | 518 | 35 | 553 |
| 1950-51 | 279 | 6 | 14 | 243 | 71 | 17 | - | -17 | 612 | 56 | -9 | 658 | 39 | 697 |
| 1951-52 | 328 | 8 | 15 | 192 | 80 | 20 | - | -17 | 625 | 71 | -16 | 680 | 43 | 723 |
| 1952-53 | 348 | 11 | 16 | 204 | 78 | 19 | - | -17 | 658 | 67 | -15 | 710 | 48 | 758 |
| 1953-54 | 384 | 12 | 18 | 224 | 90 | 25 | - | -18 | 735 | 68 | -16 | 787 | 51 | 838 |
| 1954-55 | 431 | 12 | 20 | 232 | 97 | 30 | - | -20 | 802 | 81 | -13 | 869 | 60 | 929 |
| 1955-56 | 468 | 12 | 22 | 236 | 94 | 32 | - | -21 | 844 | 85 | -12 | 917 | 65 | 982 |
| 1956-57 | 495 | 12 | 24 | 250 | 98 | 31 | - | -23 | 886 | 84 | -13 | 957 | 72 | 1,029 |
| 1957-58 | 534 | 13 | 25 | 246 | 106 | 33 | - | -26 | 930 | 91 | -14 | 1,008 | 78 | 1,086 |
| 1958-59 | 560 | 12 | 27 | 247 | 110 | 37 | - | -28 | 965 | 104 | -14 | 1,055 | 86 | 1,141 |
| 1959-60* | 594 | 13 | 28 | 280 | 118 | 41 | - | -30 | 1,045 | 108 | -13 | 1,140 | 93 | 1,233 |
| March Year | Personal Expenditure on Consumer Goods and Services (15) | Cost of Government-provided Goods and Services (16) | Gross Capital Formation in New Zealand (17) | Net Investment Overseas (18) | Gross National Expenditure (19) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private (a) | Government (b) | Changes in Stocks (c) | |||||
| *Provisional. | |||||||
| EXPENDITURE £(million) | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 162 | 32 | 17 | 22 | 5 | -6 | 232 |
| 1943-44 | 179 | 161 | 13 | 14 | 12 | -4 | 375 |
| 1946-47 | 257 | 54 | 37 | 27 | 21 | 29 | 425 |
| 1947-48 | 292 | 63 | 43 | 33 | 56 | -6 | 481 |
| 1948-49 | 351 | 65 | 48 | 40 | -19 | 5 | 490 |
| 1949-50 | 358 | 72 | 57 | 48 | 14 | 4 | 553 |
| 1950-51 | 415 | 78 | 74 | 51 | 49 | 30 | 697 |
| 1951-52 | 476 | 96 | 91 | 53 | 37 | -30 | 723 |
| 1952-53 | 471 | 108 | 98 | 73 | 13 | -5 | 758 |
| 1953-54 | 533 | 116 | 104 | 78 | -21 | 28 | 838 |
| 1954-55 | 610 | 117 | 130 | 82 | 29 | -39 | 929 |
| 1955-56 | 645 | 128 | 129 | 92 | 19 | -31 | 982 |
| 1956-57 | 672 | 140 | 122 | 103 | 10 | -18 | 1,029 |
| 1957-58 | 728 | 148 | 138 | 107 | 16 | -51 | 1,086 |
| 1958-59 | 752 | 155 | 136 | 106 | 16 | -24 | 1,141 |
| 1959-60* | 773 | 165 | 142 | 109 | 7 | 37 | 1,233 |
The graph which follows demonstrates the use to which resources available in New Zealand were put during selected years. The numerical values for this graph are derived from the expenditure part of the preceding account, and total resources available in New Zealand are equivalent to gross national product plus deficit or minus surplus on current balance of payments accounts.
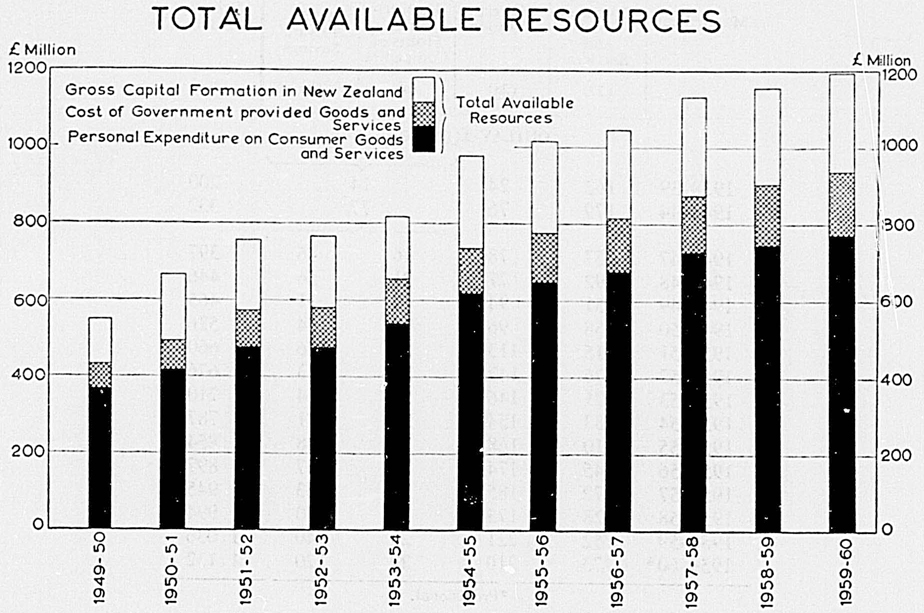
PRIVATE INCOME AND OUTLAY
| March Year | Salary and Wage Payments | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces | Social Security Benefits and Pensions | Rental Value of Owner-occupied Houses | (24) Other Personal Income | Company Income Before Distribution | Private Income (Before Tax) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professional Occupations | Commerce, Trade or Business | Farming | Change in Balances of Primary-produce Stabilisation Accounts | Change in Balances in Wool Retention Moneys | Interest, Rent, etc. | Other | |||||||
| (20) | (21) | (22) | (23) | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | (25) | (26) | |
| *Provisional. | |||||||||||||
| INCOME £(million) | |||||||||||||
| 1938-39 | 111 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 26 | -2 | - | 15 | 2 | 20 | 200 | |
| 1943-44 | 141 | 58 | 16 | 9 | 72 | 36 | 332 | ||||||
| 1946-47 | 187 | 8 | 34 | 10 | 9 | 21 | 47 | 12 | - | 16 | 5 | 48 | 397 |
| 1947-48 | 210 | 6 | 37 | 11 | 11 | 24 | 60 | 12 | - | 16 | 6 | 53 | 446 |
| 1948-49 | 227 | 5 | 39 | 12 | 12 | 25 | 64 | 11 | – | 16 | 6 | 48 | 465 |
| 1949-50 | 250 | 5 | 42 | 13 | 14 | 27 | 84 | 11 | – | 16 | 7 | 58 | 526 |
| 1950-51 | 279 | 6 | 47 | 14 | 16 | 33 | 118 | 17 | 33 | 18 | 8 | 71 | 660 |
| 1951-52 | 328 | 8 | 53 | 15 | 18 | 38 | 105 | 6 | -3 | 18 | 10 | 80 | 676 |
| 1952-53 | 348 | 11 | 54 | 16 | 19 | 41 | 116 | 4 | -6 | 19 | 11 | 78 | 710 |
| 1953-54 | 384 | 12 | 58 | 18 | 21 | 46 | 130 | 1 | -6 | 20 | 12 | 90 | 787 |
| 1954-55 | 431 | 12 | 61 | 20 | 22 | 51 | 132 | 1 | -6 | 20 | 12 | 97 | 854 |
| 1955-56 | 468 | 12 | 64 | 22 | 23 | 53 | 128 | 5 | -6 | 20 | 13 | 94 | 897 |
| 1956-57 | 495 | 12 | 66 | 24 | 24 | 58 | 144 | -5 | -6 | 21 | 14 | 98 | 945 |
| 1957-58 | 534 | 13 | 70 | 25 | 25 | 62 | 142 | -19 | - | 21 | 15 | 106 | 994 |
| 1958-59 | 560 | 12 | 80 | 27 | 25 | 61 | 124 | - | 22 | 15 | 110 | 1,036 | |
| 1959-60* | 594 | 13 | 99 | 28 | 26 | 64 | 143 | 8 | - | 23 | 16 | 118 | 1,132 |
| March Year | Personal Expenditure on Consumer Goods and Services (27) | Direct Taxation (28) | Private Savings (29) | Private Outlay (30) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undistributed Profits of Companies (a) | Other Private Savings (b) | ||||
| *Provisional. | |||||
| OUTLAY £(million_ | |||||
| 1938-39 | 162 | 24 | 14 | 200 | |
| 1943-44 | 179 | 76 | 77 | 332 | |
| 1946-47 | 257 | 78 | 16 | 46 | 397 |
| 1947-48 | 292 | 77 | 21 | 56 | 446 |
| 1948-49 | 351 | 94 | 9 | 11 | 465 |
| 1949-50 | 358 | 96 | 18 | 54 | 526 |
| 1950-51 | 415 | 113 | 26 | 106 | 660 |
| 1951-52 | 476 | 142 | 25 | 33 | 676 |
| 1952-53 | 471 | 146 | 19 | 74 | 710 |
| 1953-54 | 533 | 154 | 29 | 71 | 787 |
| 1954-55 | 610 | 168 | 28 | 48 | 854 |
| 1955-56 | 645 | 174 | 21 | 57 | 897 |
| 1956-57 | 672 | 185 | 25 | 63 | 945 |
| 1957-58 | 728 | 173 | 23 | 70 | 994 |
| 1958-59 | 752 | 221 | 23 | 40 | 1,036 |
| 1959-60* | 773 | 210 | 29 | 120 | 1,132 |
The following diagram presents the distribution of private outlay (shown in the second part of the preceding table) in graphical form.
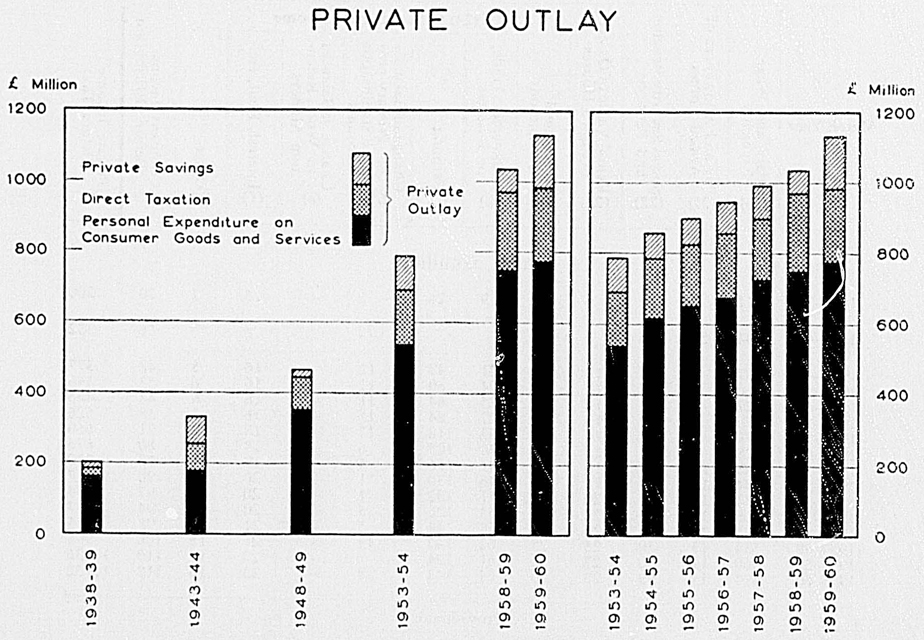
GENERAL GOVERNMENT AND LOCAL AUTHORITIES - REVENUEACCOUNT
| March Year | Taxation (31) | Trading Income (32) | Less Direct Taxes Paid by Government Trading Undertakings (33) | Lump Sum Payments From United Kingdom Government (34) | Total Revenue (35) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct (a) | Indirect (b) | |||||
| REVENUE £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 24 | 21 | 9 | - | 53 | |
| 1943-44 | 77 | 32 | 18 | -1 | 3 | 128 |
| 1946-47 | 79 | 43 | 15 | -1 | 5 | 141 |
| 1947-48 | 79 | 53 | 14 | -1 | 5 | 149 |
| 1948-49 | 95 | 46 | 13 | -1 | - | 153 |
| 1949-59 | 97 | 50 | 15 | -2 | - | 160 |
| 1950-51 | 115 | 56 | 17 | -2 | - | 186 |
| 1951-52 | 144 | 71 | 20 | -2 | - | 233 |
| 1952-53 | 148 | 67 | 19 | -2 | - | 232 |
| 1953-54 | 156 | 68 | 25 | -2 | - | 246 |
| 1954-55 | 171 | 81 | 30 | -3 | - | 279 |
| 1955-56 | 177 | 85 | 32 | -3 | - | 291 |
| 1956-57 | 188 | 84 | 31 | -3 | - | 300 |
| 1957-58 | 175 | 91 | 33 | -2 | - | 297 |
| 1958-59 | 224 | 104 | 37 | -3 | - | 362 |
| 1959-60* | 213 | 108 | 41 | -3 | - | 360 |
| March Year | Cost of Provision of Goods and Services (36) | Transfer Income | Subsidies (39) | Balance of Revenue Over Expenditure (40) | Total Expenditure Plus or Minus Revenue Balances (41) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Security Benefits and Pensions (37) | Interest on Public Debt Paid in New Zealand (38) | |||||
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| EXPENDITURE £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 32 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 53 |
| 1943-44 | 161 | 16 | 11 | 3 | -63 | 128 |
| 1946-47 | 54 | 34 | 25 | 12 | 26 | 141 |
| 1947-48 | 63 | 37 | 15 | 14 | 20 | 149 |
| 1948-49 | 65 | 39 | 16 | 12 | 22 | 153 |
| 1949-50 | 72 | 42 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 160 |
| 1950-51 | 78 | 47 | 17 | 9 | 34 | 186 |
| 3951-52 | 96 | 53 | 17 | 16 | 51 | 233 |
| 1952-53 | 108 | 54 | 17 | 15 | 38 | 232 |
| 1953-54 | 116 | 58 | 18 | 16 | 39 | 246 |
| 1954-55 | 117 | 61 | 20 | 13 | 68 | 279 |
| 1955-56 | 128 | 64 | 21 | 12 | 66 | 291 |
| 1956-57 | 140 | 66 | 23 | 13 | 57 | 300 |
| 1957-58 | 148 | 70 | 26 | 14 | 39 | 297 |
| 1958-59 | 155 | 80 | 28 | 14 | 86 | 362 |
| 1959-60* | 165 | 99 | 30 | 13 | 53 | 360 |
COMBINED CAPITAL ACCOUNT
| March Year | Private Savings (42) | Revenue Balances General Government and Local Authorities (43) | Depreciation Allowances (44) | Total Savings (45) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAVINGS £(million) | ||||
| 1938-39 | 14 | 6 | 17 | 38 |
| 1943-44 | 77 | -63 | 20 | 35 |
| 1946-47 | 62 | 26 | 26 | 114 |
| 1947-48 | 77 | 20 | 29 | 126 |
| 1948-49 | 20 | 22 | 32 | 74 |
| 1949-50 | 72 | 16 | 35 | 123 |
| 1950-51 | 132 | 34 | 39 | 204 |
| 1951-52 | 58 | 51 | 43 | 152 |
| 1952-53 | 93 | 38 | 48 | 179 |
| 1953-54 | 100 | 39 | 51 | 189 |
| 1954-55 | 76 | 68 | 60 | 203 |
| 1955-56 | 78 | 66 | 65 | 209 |
| 1956-57 | 88 | 57 | 72 | 217 |
| 1957-58 | 93 | 39 | 78 | 210 |
| 1958-59 | 63 | 86 | 86 | 235 |
| 1959-60* | 149 | 53 | 93 | 295 |
| March Year | Gross Capital Formation in New Zealand (46) | Net Investment Overseas (47) | Total Investments (48) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private (a) | General Government (b) | Local Authorities (c) | Changes in Stocks (d) | |||
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| INVESTMENTS £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 17 | 16 | 6 | 5 | -6 | 38 |
| 1943-44 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 12 | -4 | 35 |
| 1946-47 | 37 | 21 | 6 | 21 | 29 | 114 |
| 1947-48 | 43 | 26 | 7 | 56 | -6 | 126 |
| 1948-49 | 48 | 32 | 8 | -19 | 5 | 74 |
| 1949-50 | 57 | 39 | 9 | 14 | 4 | 123 |
| 1950-51 | 74 | 41 | 10 | 49 | 30 | 204 |
| 1951-52 | 91 | 41 | 12 | 37 | -30 | 152 |
| 1952-53 | 98 | 55 | 18 | 13 | -5 | 179 |
| 1953-54 | 104 | 57 | 21 | -21 | 28 | 189 |
| 1954-55 | 130 | 59 | 23 | 29 | -39 | 203 |
| 1955-56 | 129 | 66 | 26 | 19 | -31 | 209 |
| 1956-57 | 122 | 72 | 31 | 10 | -18 | 217 |
| 1957-58 | 138 | 72 | 35 | 16 | -51 | 210 |
| 1958-59 | 136 | 70 | 36 | 16 | -24 | 235 |
| 1959-60* | 142 | 72 | 37 | 7 | 37 | 295 |
THE GOVERNMENT SECTOR - The Revenue account of General Government and local authorities shown on page 751 is a consolidation and simplification of a separate and more detailed General Government Revenue Account on pages 754 and 755 and the local authorities Revenue Account on page 756. The Consolidated Account eliminates all transfers between the two levels of Government and aggregates the respective totals of economically significant flows.
The publication The Accounts of the Government Sector 1956-57 to 1959-60 contains an integrated Government account which will ultimately replace the account presented herein. There are certain differences between the two which are due to differences in coverage, concepts employed in analysis, and improved methods. The new account is a preferable description of Government transactions, being more complete and exact. In the meantime, it cannot be used here for several important reasons. The new account is available for only four years and it was not possible to revise earlier years. Furthermore, the national accounting concepts employed in the new Government account have not been extended to the rest of the national accounts and its introduction into the present system would cause incompatibilities in the various flows between the Government and private sector. Finally, the organisational work of obtaining primary information for the new account - it should be remembered that some Departments had to reorganise their own reporting systems in order to make the necessary information available - has not improved sufficiently to obtain the data in time for inclusion in national income and expenditure estimates.
It is for these reasons that the existing presentation has been retained for the time being. Although the account on pages 754-755 is incomplete, its present advantage is that it can be speedily compiled.
General Government - The Revenue Account of the General Government has been obtained by an analysis of the various accounts within the Public Account. In the case of trading Department operations, which are treated separately, profits only are brought into the main account as a revenue item. Expenditure has been taken “net” in all cases, sundry departmental receipts being set off against departmental expenditure. The account covers only current revenue items and therefore excludes capital receipts and payments of all kinds, thus accounting in part for the differences between the details given here and those given in the published statement of the Public Accounts in parliamentary paper B. 1. [Pt. I]. In order that the difference between these two sets of figures may be appreciated a reconciliation statement is given at the end of this section.
The cost of Government-provided goods and services (item 6, page 755, and part of item 16, page 748) has increased from £23.2 million in the last pre-war year to £44.8 million in the first postwar year and to £121.4 million in 1958-59; the latest figure is £129 million. Attention has, however, already been drawn to the fact that expenditures expressed in money terms do not afford a meaningful basis of comparison. Expressed in ratios to gross national expenditure - of which the cost of Government-provided goods and services is a part - percentages of 10.0, 10.5, 10.6 and 10.5 are obtained. For the 14 post-war years the average percentage is 10.4 per cent. It is thus that the more than five-fold increase in the money cost of Government services is put into its proper perspective.
Although all the other forms of Government expenditure such as transfer payments - social security cash benefits, interest on public debt, and subsidies - and transfers to local authorities are also paid from taxation and trading revenue of General Government, they do not form part of Government final expenditures but only become final expenditures when consumption takes place in the hands of recipients. For this reason their effect can only be measured by a comparison with national income from which they are met.
Social security cash benefits were £7.5 million in 1938-39 and £34.4 million in 1946-47, after which they advanced to £80.1 million and £99.0 million in the last two years. In percentages of national income the four years above are represented by 3.9, 9.4, 8.3, and 9.5 per cent. The 1959-60 figure of 9.5 per cent is the peak figure of this particular series. The relative importance of social security monetary benefits and pensions steadily declined from 1946-47 onwards until the rise shown in the last two years brought them back to slightly above the 1946-47 level.
Subsidies are of a much lesser importance than social security cash benefits, both relatively and absolutely. In 1938-39, £0.6 million was paid in subsidies against £12.9 million in 1959-60; expressed in percentages of national income it is 0.3 and 1.2 per cent respectively. Interest on the public debt, although its importance has been steadily growing over the past five years or so, represented only 2.2 per cent of national income in 1959-60 against 2.4 per cent before the war, in spite of its value increase from £4.7 million to £23.2 million.
Transfers to local authorities is a flow which can be usefully measured against current General Government revenue. Although these payments have been increasing in an almost uninterrupted fashion over the 22 years shown in the accounts, rising from £5.3 million in 1938-39 to £25.8 million in 1959-60, yet in percentages of current Government revenue they are only 7.9 per cent today as against 12.3 per cent before the war.
Over the period of years covered, the Government interest in economic affairs had a marked effect on the development and application of fiscal policies. Not only are individual types of Government transactions (direct and indirect taxation, profits of Government trading undertakings, transfer payments or current consumption expenditure) used to provide expansion or contraction in individual sectors in the economy with a view to achieving specific aims, but the change in the size of the current surplus itself (i.e., the balance of revenue over expenditure) is another facet of the same development. Whereas in the last pre-war year the surplus amounted to 4.0 per cent of total revenue, levels as high as 21.6 per cent (1954-55) and 20.7 per cent (1958-59) were reached; in the latest year the figure stood at 10.7 per cent, a relatively low level for the post-war period. Although these rates are bound to vary abruptly from year to year in conformity with specific policies, it is evident that the increased reliance by Government on the financing of the Capital Account from current revenue (as compared with the pre-war period) has also an influence over the economy in general.
As mentioned in the previous paragraph the balance of revenue over expenditure represents the surplus after net expenditure on normal current Government activities has been allowed for. This balance is utilised for the carrying out of necessary capital works and purchase of equipment, or for net lending and repayment of debt. Where there is an excess of expenditure over revenue, as was the case in 1943-44, the deficit must be met by a call on private savings in New Zealand or overseas. It is equally true, of course, that if total Government expenditure in any one year, including expenditure on capital works, exceeds revenue for that year, this overall deficit must be met in a similar way.
GENERAL GOVERNMENT -REVENUE ACCOUNT
| 1938-39 | 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Includes social security income tax and also £2.4 million received as social security charge on 1957-58 income. *Provisional. †Includes contribution under Colombo Plan in each year. | |||||||
| 1. Taxation - | |||||||
| (a) Direct - | REVENUE £(million) | ||||||
| Income tax | 9.3 | 88.3 | 90.7 | 98.1 | 77.8 | 109.4 | 175.9† |
| Social security taxation | 5.5 | 56.2 | 59.9 | 61.6 | 66.3 | 80.6 | |
| Land tax | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Death duties | 1.8 | 9.4 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 9.0 | 10.4 | 12.3 |
| Other | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Totals | 17.8 | 154.8 | 160.3 | 169.4 | 154.4 | 201.9 | 189.8 |
| (b)Indirect - | |||||||
| Sales tax | 3.6 | 22.6 | 23.4 | 22.3 | 24.2 | 25.8 | 24.2 |
| Customs and excise duties | 11.7 | 34.2 | 36.6 | 35.7 | 390 | 41.6 | 46.6 |
| Motor vehicles taxation | 3.1 | 16.1 | 17.5 | 18.4 | 19.7 | 28.7 | 28.9 |
| Other | 1.7 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.8 |
| Totals | 20.0 | 79.9 | 84.5 | 83.583.4 | 90.5 | 103.4 | 107.5 |
| 2. Totals, all taxation | 37.8 | 234.8 | 244.8 | 252.9 | 244.9 | 305.2 | 297.3 |
| 3. Trading income | 5.4 | 23.0 | 24.2 | 23.0 | 23.9 | 27.1 | 30.1 |
| 4. Less direct taxation paid by trading Departments | -0.2 | -2.6 | -3.0 | -3.0 | -2.2 | -2.5 | -2.8 |
| Totals | 5.2 | 20.4 | 21.2 | 20.0 | 21.7 | 24.6 | 27.3 |
| 5. TOTAL REVENUE | 43.0 | 255.2 | 266.0 | 272.9 | 266.6 | 329.8 | 324.6 |
| 6. Cost of Provision of Goods and Services- | |||||||
| EXPENDITURE £(million) | |||||||
| (a) General administration | 2.2 | 15.0† | 15.2† | 15.6† | 16.4† | 17.7† | 18.0† |
| (b) Interest on General Government debt paid overseas | 6.8 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 4.6 | 5.6 |
| (c) Law and order | 0.8 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 3.4 |
| (d) Development of primary and secondary industries Social services | 0.7 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 9.1 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 10.2 |
| (e) Health | 0.8 | 4.9 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 6.6 | 7.0 | 7.7 |
| (f) Education | 4.2 | 19.2 | 21.2 | 23.1 | 25.7 | 27.9 | 29.9 |
| (g) Non-monetary social security benefits | 12.6 | 15.5 | 16.8 | 17.1 | 18.7 | 19.9 | |
| (h) Other social services | 3.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| (i) Defence | 2.1 | 23.6 | 25.0 | 26.1 | 24.9 | 25.7 | 27.8 |
| (j) Rehabilitation | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| (k) Maintenance of public works and services | 2.3 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 3.9 |
| Totals | 23.2 | 91.9 | 100.7 | 109.4 | 114.2 | 121.4 | 129.0 |
| Transfer Income – | |||||||
| 7. (a) Monetary social security benefits and pensions | 7.5 | 61.3 | 64.4 | 66.3 | 70.0 | 80.1 | 95.1 |
| (b) Family benefit advances | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.9 |
| 8. Interest on General Government debt paid in New Zealand | 4.7 | 17.2 | 17.7 | 19.4 | 21.6 | 22.7 | 23.2 |
| Totals | 12.2 | 78.5 | 82.1 | 85.6 | 91.6 | 102.8 | 122.2 |
| 9. Transfers to Local Authorities – | |||||||
| (a) Hospital boards | 0.9 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 12.9 | 15.4 | 15.8 | 17.2 |
| (b) Other | 4.4 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.6 |
| Totals | 5.3 | 16.3 | 16.9 | 19.9 | 22.8 | 23.7 | 25.8 |
| 10. Subsidies | |||||||
| (a) Primary production | 0.4 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| (b) Essential clothing and food stuffs | 0.2 | 11.9 | 10.9 | 12.4 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.2 |
| (c) Miscellaneous | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | |
| (d) Housing suspensory loans | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.5 | ||
| Totals | 0.6 | 13.4 | 12.4 | 13.3 | 13.6 | 13.5 | 12.9 |
| 11. TOTAL EXPENDITURE | 41.3 | 200.1 | 212.1 | 228.2 | 242.2 | 261.4 | 289.9 |
| 12. Balance of revenue over expenditure | 1.7 | 55.1 | 53.9 | 44.7 | 24.4 | 68.4 | 34.7 |
| 13. TOTAL EXPENDITURE PLUS REVENUE BALANCES | 43.0 | 255.2 | 266.0 | 272.9 | 266.6 | 329.8 | 324.6 |
(b) Local Authorities - The Revenue Account of local authorities is in all respects similar to that of the General Government and has been obtained by an analysis of the accounts of all local authorities, including hospital boards. The limitations in the scope of local government activities as compared with those of the General Government do not call for a detailed analysis of expenditure items and therefore current expenditure on the provision of goods and services by local authorities is shown as a single total.
LOCAL AUTHORITIES - revenue account
| 1938-39 | 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | |||||||
| 14. Taxation | |||||||
| REVENUE £(million) | |||||||
| (a) Direct: Rates | 6.2 | 16.2 | 16.7 | 18.6 | 20.4 | 21.7 | 23.4 |
| (b) Indirect: Licence fees | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Totals | 6.8 | 17.0 | 17.4 | 19.3 | 21.1 | 22.4 | 24.2 |
| 15. Trading income | 3.4 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 10.1 | 11.2 |
| 16. Grants from General Government | 5.3 | 16.3 | 16.9 | 19.9 | 22.8 | 23.7 | 25.8 |
| 17. TOTAL REVENUE | 15.5 | 40.4 | 42.1 | 46.8 | 52.7 | 56.2 | 61.2 |
| EXPENDITURE £(million) | |||||||
| 18. Cost of provision of goods and services | 8.5 | 24.7 | 26.9 | 30.8 | 33.9 | 33.4 | 36.2 |
| 19. Interest on local authority debt paid in New Zealand | 2.3 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 5.7 | 6.4 |
| 20. TOTAL EXPENDITURE | 10.8 | 27.7 | 30.1 | 34.8 | 38.6 | 39.1 | 42.6 |
| 21. Balance of revenue over expenditure | 4.7 | 12.7 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 14.1 | 17.1 | 18.6 |
| 22. TOTAL EXPENDITURE PLUS REVENUE BALANCES | 15.5 | 40.4 | 42.1 | 46.8 | 52.7 | 56.2 | 61.2 |
(c) Reconciliation Statement - The reconciliation given below indicates the fundamental differences between the analysis of the public accounts made for national-income purposes and that published in parliamentary paper B. 1 [Pt. I].
RECONCILIATION BETWEEN BALANCE OF REVENUE OVER EXPENDITURE PER NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTS, AND COMBINED SURPLUS CONSOLIDATED FUND, SOCIAL SECURITY FUND,AND NATIONAL ROADS FUND, 1959-60 (PROVISIONAL)
| £(m.) | |
| 23. Balance of revenue over current expenditure, per National Income Accounts (table on page 755) | 34.7 |
| Less | |
| 24. Amortisation of debt charged to Consolidated Fund | 9.3 |
| 25. Transfers to other accounts | -1.0 |
| 26. Capital expenditure charged to Consolidated Fund and National Roads Fund | -27.8 |
| Plus – | |
| 27. Current expenditure charged to Defence Fund Adjustment for Trading Income | 9.6 |
| 28. Profits of trading Departments | -30.1 |
| 29. Plus transfers of profits to Consolidated Fund | 21.1 |
| Total | -2.8 |
| 30. Consolidated Fund surplus 1959-60 | -0.6 |
| 31. Social Security Fund deficit 1959-60 | 0.9 |
| 32. National Roads Fund deficit 1959-60 | -2.5 |
| Total deficit of Consolidated Fund, Social Security Fund, and National Roads Fund as shown in the Public Accounts B. 1 [Pt. I] 1959-60 | -2.8 |
For the reconciliation for earlier years between the balances of revenue over expenditure and the Budget surpluses (or deficits), reference should be made to the previous issues of the Yearbook.
The preceding reconciliation provides an illustration of the differences between the balance (surpluses or deficits) arrived at in official publications of Government accounts, such as parliamentary paper B. 1 [Pt. I] and the revenue balance used for national accounts, which is the expression of Government saving and by the same token the value of the Government's contribution to the capital account of the economy. This latter idea is expressed by the introduction of the Government revenue balance into the savings and investment account of the economy as a whole as shown on page 752.
The principal difference between the two accounts is in the treatment of capital items, transfers, and trading profits and this is apparent from the reconciliation steps described on page 756. The main accounts in the Public Account do not segregate capital expenditures, debt repayments, and transfers, from other current transactions; profits of various trading undertakings are entered only to the extent that they are transferred, and whether the total or only a part of profits is transferred, the transfer usually takes place in the following year and not in the year when profits are earned. The Government revenue account as shown on page 754 does, however, segregate capital and current expenditure and takes in profits at the time of accrual rather than at time of transfer. No allowance is made for depreciation of physical assets other than those used in activities of an enterprise character and the account does not include imputations for the net rental value of buildings and land used.
THE DISTRIBUTION OF PRIVATE INCOME - A detailed survey of private income and outlay has already been given (refer table on pages 749-750) for the years 1938-39, 1943-44, and 1946-47 to 1959-60. An analysis of private income, in less comprehensive form, is given below for the years 1938-39 to 1959-60. Group totals are shown in value form, as percentages of private income, and as index numbers on base 1938-39 (=100).
PRIVATE INCOME
| Year | Salary and Wage Payments (1) | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces (2) | Social Security Benefits and Pensions (22) | Rental Value, Owner-occupied Houses (3) | Other Personal Income† (Excluding Company Dividends) (4) | Company Income (Before Distribution) (5) | Private Income (26) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Includes changes in primary-produce stabilisation accounts and wool retention moneys. | |||||||
| £(million) | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 111.3 | 0.9 | 7.5 | 6.4 | 54.5 | 19.6 | 200.2 |
| 1939-40 | 110.8 | 2.9 | 11.2 | 6.7 | 59.4 | 24.7 | 215.7 |
| 1940-41 | 117.8 | 15.6 | 12.3 | 7.4 | 58.3 | 23.6 | 235.0 |
| 1941-42 | 120.8 | 25.5 | 12.7 | 7.7 | 62.3 | 27.6 | 256.6 |
| 1942-43 | 126.8 | 46.0 | 14.0 | 8.1 | 67.2 | 32.8 | 294.9 |
| 1943-44 | 140.6 | 58.3 | 15.5 | 8.6 | 72.4 | 36.4 | 331.8 |
| 1944-45 | 147.1 | 48.5 | 17.2 | 8.9 | 79.9 | 37.9 | 339.5 |
| 1945-46 | 162.0 | 39.4 | 20.6 | 9.4 | 87.4 | 41.7 | 360.5 |
| 1946-47 | 186.5 | 8.2 | 34.4 | 10.1 | 110.2 | 47.9 | 397.3 |
| 1947-48 | 210.1 | 6.4 | 37.2 | 10.9 | 129.1 | 52.7 | 446.4 |
| 1948-49 | 227.2 | 4.5 | 39.0 | 11.6 | 133.9 | 48.3 | 464.5 |
| 1949-50 | 250.1 | 4.6 | 42.2 | 12.7 | 158.8 | 57.8 | 526.2 |
| 1950-51 | 278.5 | 5.9 | 47.1 | 13.6 | 243.3 | 71.1 | 659.5 |
| 1951-52 | 327.8 | 8.4 | 53.0 | 14.8 | 191.5 | 80.1 | 675.6 |
| 1952-53 | 348.0 | 10.6 | 53.7 | 16.3 | 203.6 | 77.6 | 709.8 |
| 1953-54 | 384.4 | 11.9 | 57.7 | 18.4 | 223.7 | 90.4 | 786.5 |
| 1954-55 | 431.1 | 12.1 | 61.3 | 19.8 | 231.8 | 97.4 | 853.5 |
| 1955-56 | 468.4 | 12.0 | 64.4 | 21.7 | 236.4 | 94.2 | 897.1 |
| 1956-57 | 495.1 | 12.1 | 66.3 | 23.7 | 249.5 | 98.4 | 945.1 |
| 1957-58 | 534.1 | 12.9 | 70.0 | 25.2 | 245.6 | 105.7 | 993.5 |
| 1958-59 | 560.0 | 12.2 | 80.1 | 26.6 | 246.6 | 110.3 | 1,035.8 |
| 1959-60* | 593.6 | 13.0 | 99.0 | 27.9 | 280.2 | 118.4 | 1,132.1 |
| As Percentage of Private Income | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 55.6 | 0.4 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 27.2 | 9.8 | 100.0 |
| 1939-40 | 51.4 | 1.3 | 5.2 | 3.1 | 27.5 | 11.5 | 100.1 |
| 1940-41 | 50.1 | 6.6 | 5.2 | 3.1 | 24.8 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 1941-42 | 47.1 | 9.9 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 24.3 | 10.8 | 100.0 |
| 1942-43 | 43.0 | 15.6 | 4.7 | 2.7 | 22.8 | 11.1 | 100.0 |
| 1943-44 | 42.4 | 17.6 | 4.7 | 2.6 | 21.8 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| 1944-45 | 43.3 | 14.3 | 5.1 | 2.6 | 23.5 | 11.2 | 100.0 |
| 1945-46 | 44.9 | 10.9 | 5.7 | 2.6 | 24.2 | 11.6 | 100.0 |
| 1946-47 | 46.9 | 2.1 | 8.7 | 2.5 | 27.7 | 12.1 | 100.0 |
| 1947-48 | 47.1 | 1.4 | 8.3 | 2.4 | 28.9 | 11.8 | 100.0 |
| 1948-49 | 48.9 | 1.0 | 8.4 | 2.5 | 28.8 | 10.4 | 100.0 |
| 1949-50 | 47.5 | 0.9 | 8.0 | 2.4 | 30.2 | 11.0 | 100.0 |
| 1950-51 | 42.2 | 0.9 | 7.1 | 2.1 | 36.9 | 10.8 | 100.0 |
| 1951-52 | 48.5 | 1.2 | 7.8 | 2.2 | 28.3 | 11.9 | 100.0 |
| 1952-53 | 49.0 | 1.5 | 7.6 | 2.3 | 28.7 | 10.9 | 100.0 |
| 1953-54 | 48.9 | 1.5 | 7.3 | 2.3 | 28.4 | 11.5 | 100.0 |
| 1954-55 | 50.5 | 1.4 | 7.2 | 2.3 | 27.2 | 11.4 | 100.0 |
| 1955-56 | 52.2 | 1.3 | 7.2 | 2.4 | 26.4 | 10.5 | 100.0 |
| 1956-57 | 52.4 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 26.4 | 10.4 | 100.0 |
| 1957-58 | 53.8 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 2.5 | 24.7 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
| 1958-59 | 54.1 | 1.1 | 8.7 | 2.5 | 24.8 | 10.5 | 100.0 |
| 1959-60 | 52.4 | 1.1 | 8.7 | 2.5 | 24.8 | 10.5 | 100.0 |
| As Index Numbers (1938-39 = 100) | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 100 | ... | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1939-40 | 100 | ... | 149 | 105 | 109 | 126 | 108 |
| 1940-41 | 106 | ... | 164 | 116 | 107 | 120 | 117 |
| 1941-42 | 109 | ... | 169 | 120 | 114 | 141 | 128 |
| 1942-43 | 114 | ... | 187 | 127 | 123 | 167 | 147 |
| 1943-44 | 126 | ... | 207 | 134 | 133 | 186 | 166 |
| 1944-45 | 132 | ... | 229 | 139 | 147 | 193 | 170 |
| 1945-46 | 146 | ... | 275 | 147 | 160 | 213 | 180 |
| 1946-47 | 168 | ... | 459 | 158 | 202 | 244 | 198 |
| 1947-48 | 189 | ... | 496 | 170 | 237 | 269 | 223 |
| 1948-49 | 204 | ... | 520 | 181 | 246 | 246 | 232 |
| 1949-50 | 225 | ... | 563 | 198 | 291 | 295 | 263 |
| 1950-51 | 250 | ... | 628 | 213 | 446 | 363 | 329 |
| 1951-52 | 295 | ... | 707 | 231 | 351 | 409 | 337 |
| 1952-53 | 313 | ... | 716 | 255 | 374 | 396 | 355 |
| 1953-54 | 345 | ... | 769 | 288 | 410 | 461 | 393 |
| 1954-55 | 387 | ... | 817 | 309 | 425 | 497 | 426 |
| 1955-56 | 421 | ... | 859 | 339 | 434 | 481 | 448 |
| 1956-57 | 445 | ... | 884 | 370 | 458 | 502 | 472 |
| 1957-58 | 480 | ... | 933 | 394 | 451 | 539 | 496 |
| 1958-59 | 503 | ... | 1068 | 416 | 452 | 563 | 517 |
| 1959-60* | 533 | ... | 1320 | 436 | 514 | 604 | 565 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-749.
The following tables are presented for the purpose of showing various relationships between direct and indirect taxation on one hand and private income 0n the other. The tables on this and following pages give a tabular description of the incidence of direct taxation on various classes of income and the relationships of disposable (after tax) incomes to each other and their changes over time.
PRIVATE INCOME AND TOTAL TAXATION
| March Year | Private Income (26) | Direct Taxation† (28) | Indirect Taxation (10) | Less Subsidies (11) | Total Taxation Less Subsidies† | Total Taxation Less Subsidies as a Percentage of Private Income |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Excluding direct taxes paid by Government trading Departments. | ||||||
| £(million) | per cent | |||||
| 1938-39 | 200.2 | 23.8 | 20.6 | -0.6 | 43.8 | 21.9 |
| 1939-40 | 215.7 | 30.5 | 21.0 | -0.5 | 51.0 | 23.6 |
| 1940-41 | 235.0 | 45.6 | 22.3 | -1.6 | 66.3 | 28.2 |
| 1941-42 | 256.6 | 51.4 | 23.2 | -2.7 | 71.9 | 28.0 |
| 1942-43 | 294.9 | 66.4 | 28.0 | -3.3 | 91.1 | 30.9 |
| 1943-44 | 331.8 | 75.5 | 31.8 | -3.1 | 104.2 | 31.4 |
| 1944-45 | 339.5 | 81.2 | 34.0 | -4.6 | 110.6 | 32.6 |
| 1945-46 | 360.5 | 84.9 | 37.3 | -6.6 | 115.6 | 32.1 |
| 1946-47 | 397.3 | 78.2 | 43.0 | -11.8 | 109.4 | 27.5 |
| 1947-48 | 446.4 | 77.4 | 53.0 | -13.6 | 116.8 | 26.2 |
| 1948-49 | 464.5 | 93.5 | 46.1 | -11.5 | 128.1 | 27.6 |
| 1949-50 | 526.2 | 95.6 | 49.8 | -14.6 | 130.8 | 24.9 |
| 1950-51 | 659.5 | 113.1 | 55.6 | - 9.4 | 159.3 | 24.2 |
| 1951-52 | 675.6 | 142.0 | 71.0 | -16.1 | 196.9 | 29.1 |
| 1952-53 | 709.8 | 145.7 | 67.0 | -15.0 | 197.7 | 27.9 |
| 1953-54 | 786.5 | 153.6 | 67.5 | -15.5 | 205.6 | 26.1 |
| 1954-55 | 853.5 | 168.4 | 80.7 | -13.4 | 235.7 | 27.6 |
| 1955-56 | 897.1 | 174.0 | 85.3 | -12.3 | 247.0 | 27.5 |
| 1956-57 | 945.1 | 185.0 | 84.1 | -13.3 | 255.8 | 27.1 |
| 1957-58 | 993.5 | 172.6 | 91.2 | -13.6 | 250.2 | 25.2 |
| 1958-59 | 1,035.8 | 221.5 | 104.1 | 13.5 | 312.1 | 30.1 |
| 1959-60* | 1,132.1 | 210.4 | 108.3 | 12.9 | 305.8 | 27.0 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-750.
PRIVATE INCOME AND TOTAL TAXATION (EXCLUDING TRANSFER INCOMES AND PAYMENTS)
| March Year | Private Income Before Tax (26) | Less Transfer Payments (8 + 22) | Private Income (Excluding Transfer Payments) | Total Taxation (Less Subsidies) | Less Transfer Payments | Non monetary Social Security Benefits† | Total Taxation (Excluding Transfer Payments and Subsidies) | Total Taxation as a Percentage of Private Income (Excluding Transfer Payments) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Excluding mental hospital benefits. | ||||||||
| £(million) | per cent | |||||||
| 1938-39 | 200.2 | -14.5 | 185.7 | 43.8 | -14.5 | - | 29.3 | 15.8 |
| 1939-40 | 215.7 | -18.7 | 197.0 | 51.0 | -18.7 | -0.9 | 31.4 | 15.9 |
| 1940-41 | 235.0 | -20.1 | 214.9 | 66.3 | -20.1 | -1.6 | 44.6 | 20.8 |
| 1941-42 | 256.6 | -21.1 | 235.5 | 71.9 | -21.1 | -2.3 | 48.5 | 20.6 |
| 1942-43 | 294.9 | -23.4 | 271.5 | 91.1 | -23.4 | -3.5 | 64.2 | 23.6 |
| 1943-44 | 331.8 | -26.8 | 305.0 | 104.2 | -26.8 | -4.5 | 72.9 | 23.9 |
| 1944-45 | 339.5 | -30.1 | 309.4 | 110.6 | -30.1 | -5.0 | 75.5 | 24.4 |
| 1945-46 | 360.5 | -34.4 | 326.1 | 115.6 | -34.4 | -5.6 | 75.6 | 23.2 |
| 1946-47 | 397.3 | -49.5 | 347.8 | 109.4 | -49.5 | -6.2 | 53.7 | 15.4 |
| 1947-48 | 446.4 | -52.5 | 393.9 | 116.8 | -52.5 | -7.0 | 57.3 | 14.5 |
| 1948-49 | 464.5 | -54.5 | 410.0 | 128.1 | -54.5 | -7.9 | 65.7 | 16.0 |
| 1949-50 | 526.2 | -58.4 | 467.8 | 130.8 | -58.4 | -8.5 | 63.9 | 13.7 |
| 1950-51 | 659.5 | -64.1 | 595.4 | 159.3 | -64.1 | -8.7 | 86.5 | 14.5 |
| 1951-52 | 675.6 | -70.4 | 605.2 | 196.9 | -70.4 | -9.4 | 117.1 | 19.3 |
| 1952-53 | 709.8 | -70.8 | 639.0 | 197.7 | -70.8 | -10.4 | 116.5 | 18.2 |
| 1953-54 | 786.5 | -76.0 | 710.5 | 205.6 | -76.0 | -10.6 | 119.0 | 16.7 |
| 1954-55 | 853.5 | -81.5 | 772.0 | 235.7 | -81.5 | -12.6 | 141.6 | 18.3 |
| 1955-56 | 897.1 | -85.3 | 811.8 | 246.9 | -85.3 | -15.5 | 146.1 | 18.0 |
| 1956-57 | 945.1 | -89.7 | 855.4 | 255.8 | -89.7 | -16.8 | 149.3 | 17.5 |
| 1957-58 | 993.5 | -96.3 | 897.2 | 250.2 | -96.3 | -17.1 | 136.8 | 15.2 |
| 1958-59 | 1,035.8 | -108.5 | 927-3 | 311.7 | -108.5 | -18.7 | 184.5 | 19.9 |
| 1959-60* | 1,132.1 | -128.6 | 1,003.5 | 305.8 | -128.6 | -19.9 | 157.3 | 15.7 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-749.
PRIVATE INCOME AND INCIDENCE OF DIRECT TAXATION
| March Year | Salary and Wage Payments (1) | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces (2) | Social Security Benefits and Pensions (22) | Other Personal Income (Including Rental Value of Owner-occupied Houses) (3 + 4) | Company Income (Before Distribution) (5) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Excludes direct taxes on Government trading profits. | ||||||
| PRIVATE INCOME £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 111.3 | 0.9 | 7.5 | 60.9 | 19.6 | 200.2 |
| 1939-40 | 110.8 | 2.9 | 11.2 | 66.1 | 24.7 | 215.7 |
| 1940-41 | 117.8 | 15.6 | 12.3 | 65.7 | 23.6 | 235.0 |
| 1941-42 | 120.8 | 25.5 | 12.7 | 70.0 | 27.6 | 256.6 |
| 1942-43 | 126.8 | 46.0 | 14.0 | 75.3 | 32.8 | 294.9 |
| 1943-44 | 140.6 | 58.3 | 15.5 | 81.0 | 36.4 | 331.8 |
| 1944-45 | 147.1 | 48.5 | 17.2 | 88.8 | 37.9 | 339.5 |
| 1945-46 | 162.0 | 39.4 | 20.6 | 96.8 | 41.7 | 360.5 |
| 1946-47 | 186.5 | 8.2 | 34.4 | 120.3 | 47.9 | 397.3 |
| 1947-48 | 210.1 | 6.4 | 37.2 | 140.0 | 52.7 | 446.4 |
| 1948-49 | 227.2 | 4.5 | 39.0 | 145.5 | 48.3 | 464.5 |
| 1949-50 | 250.1 | 4.6 | 42.2 | 171.5 | 57.8 | 526.2 |
| 1950-51 | 278.5 | 5.9 | 47.1 | 256.9 | 71.1 | 659.5 |
| 1951-52 | 327.8 | 8.4 | 53.0 | 206.3 | 80.1 | 675.6 |
| 1952-53 | 348.0 | 10.6 | 53.7 | 219.9 | 77.6 | 709.8 |
| 1953-54 | 384.4 | 11.9 | 57.7 | 242.1 | 90.4 | 786.5 |
| 1954-55 | 431.1 | 12.1 | 61.3 | 251.6 | 97.4 | 853.5 |
| 1955-56 | 468.4 | 12.0 | 64.4 | 258.1 | 94.2 | 897.1 |
| 1956-57 | 495.1 | 12.1 | 66.3 | 273.2 | 98.4 | 945.1 |
| 1957-58 | 534.1 | 12.9 | 70.270 | 8 | 1050.7 | 993.5 |
| 1958-59 | 560.0 | 12.2 | 80.1 | 273.2 | 110.3 | 1,035.8 |
| 1959-60* | 593.6 | 13.0 | 99.0 | 308.1 | 118.4 | 1,132.1 |
| DIRECT TAXES† £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 4.9 | ... | ... | 11.9 | 7.0 | 23.8 |
| 1939-40 | 8.0 | ... | ... | 13.3 | 9.2 | 30.5 |
| 1940-41 | 12.5 | 0.8 | ... | 18.8 | 13.5 | 45.6 |
| 1941-42 | 15.6 | 1.1 | ... | 20.7 | 14.0 | 51.4 |
| 1942-43 | 19.5 | 3.2 | ... | 24.1 | 19.6 | 66.4 |
| 1943-44 | 23.4 | 3.5 | ... | 25.9 | 22.7 | 75.5 |
| 1944-45 | 24.3 | 3.8 | ... | 26.4 | 26.7 | 81.2 |
| 1945-46 | 26.6 | 3.3 | ... | 29.6 | 25.4 | 84.9 |
| 1946-47 | 23.8 | 1.2 | ... | 29.2 | 24.0 | 78.2 |
| 1947-48 | 23.6 | 0.4 | ... | 30.8 | 22.6 | 77.4 |
| 1948-49 | 24.7 | 0.5 | ... | 37.8 | 30.5 | 93.5 |
| 1949-50 | 26.5 | 0.5 | ... | 39.5 | 29.1 | 95.6 |
| 1950-51 | 32.5 | 0.05 | ... | 48.0 | 32.1 | 113.1 |
| 1951-52 | 36.0 | 0.6 | ... | 65.9 | 39.5 | 142.0 |
| 1952-53 | 43.9 | 0.8 | ... | 60.1 | 40.9 | 145.7 |
| 1953-54 | 46.4 | 0.8 | ... | 65.5 | 40.9 | 153.6 |
| 1954-55 | 49.9 | 1.0 | ... | 71.5 | 46.0 | 168.4 |
| 1955-56 | 52.2 | 1.0 | ... | 70.8 | 50.0 | 174.0 |
| 1956-57 | 61.5 | 1.0 | ... | 72.0 | 50.5 | 185.0 |
| 1957-58 | 46.7 | 1.1 | ... | 73.7 | 51.1 | 172.6 |
| 1958-59 | 66.8 | 1.3 | ... | 100.1 | 52.9 | 221.1 |
| 1959-60* | 71.4 | 1.3 | ... | 84.7 | 53.0 | 210.4 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-749.
PRIVATE INCOME AND INCIDENCE OF DIRECT TAXATION-con
| March Year | Salary and Wage Payments (1) | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces (2) | Social Security Benefits and Pensions (22) | Other Personal Income (Including Rental Value of Owner-occupied Houses) (3 + 4) | Company Income (Before Distribution) (5) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| DISPOSABLE INCOME £(million) | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 106.4 | 0.9 | 7.5 | 49.0 | 12.6 | 176.4 |
| 1939-40 | 102.8 | 2.9 | 11.2 | 52.8 | 15.5 | 185.2 |
| 1940-41 | 105.3 | 14.8 | 12.3 | 46.9 | 10.1 | 189.4 |
| 1941-42 | 105.2 | 24.4 | 12.7 | 49.3 | 13.6 | 205.2 |
| 1942-43 | 107.3 | 42.8 | 14.0 | 51.2 | 13.2 | 228.5 |
| 1943-44 | 117.2 | 54.8 | 15.5 | 55.1 | 13.7 | 256.3 |
| 1944-45 | 122.8 | 44.7 | 17.2 | 62.4 | 11.2 | 258.3 |
| 1945-46 | 135.4 | 36.1 | 20.6 | 67.2 | 16.3 | 275.6 |
| 1946-47 | 162.7 | 7.0 | 34.4 | 91.1 | 23.9 | 319.1 |
| 1947-48 | 186.5 | 6.0 | 37.2 | 109.2 | 30.1 | 369.0 |
| 1948-49 | 202.5 | 4.0 | 39.0 | 107.7 | 17.8 | 371.0 |
| 1949-50 | 223.6 | 4.1 | 42.2 | 132.0 | 28.7 | 430.6 |
| 1950-51 | 246.0 | 5.4 | 47.1 | 208.9 | 39.0 | 546.4 |
| 1951-52 | 291.8 | 7.8 | 53.0 | 140.4 | 40.6 | 533.6 |
| 1952-53 | 304.1 | 9.8 | 53.7 | 159.8 | 36.7 | 564.1 |
| 1953-54 | 338.0 | 11.1 | 57.7 | 176.6 | 49.5 | 632.9 |
| 1954-55 | 381.2 | 11.1 | 61.3 | 180.1 | 51.4 | 685.1 |
| 1955-56 | 416.2 | 11.0 | 64.4 | 187.3 | 44.2 | 723.1 |
| 1956-57 | 433.6 | 11.1 | 66.3 | 201.2 | 47.9 | 760.1 |
| 1957-58 | 487.4 | 11.8 | 70.0 | 197.1 | 54.6 | 820.9 |
| 1958-59 | 493.2 | 10.9 | 80.1 | 173.1 | 57.4 | 814.7 |
| 1959-60* | 522.2 | 11.7 | 99.0 | 223.4 | 65.4 | 921.7 |
NOTE - The numbers in parentheses after the items refer to items in the tables given on pages 748-749.
PRIVATE DISPOSABLE INCOME
| March Year | Salary and Wage Payments | Pay and Allowances of Armed Forces | Social Security Benefits and Pensions | Other Personal Income (Including Rental Value of Owner-occupied Houses) | Company Income (Before Distribution) | Private Disposable Income |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| AS PERCENTAGE OF PRIVATE DISPOSABLE INCOME | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 60.3 | 0.5 | 4.3 | 27.8 | 7.1 | 100.0 |
| 1939-40 | 55.5 | 1.6 | 6.0 | 28.5 | 8.4 | 100.0 |
| 1940-41 | 55.6 | 7.8 | 6.5 | 24.8 | 5.3 | 100.0 |
| 1941-42 | 51.3 | 11.9 | 6.2 | 2.40 | 6.6 | 100.0 |
| 1942-43 | 47.0 | 18.7 | 6.1 | 22.4 | 5.8 | 100.0 |
| 1943-44 | 45.7 | 21.4 | 6.1 | 21.5 | 5.3 | 100.0 |
| 1944-45 | 47.5 | 17.3 | 6.7 | 24.2 | 4.3 | 100.0 |
| 1945-46 | 49.1 | 13.1 | 7.5 | 24.4 | 5.9 | 100.0 |
| 1946-47 | 51.0 | 2.2 | 10.8 | 28.5 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| 1947-48 | 50.5 | 1.6 | 10.1 | 29.6 | 8.2 | 100.0 |
| 1948-49 | 54.6 | 1.1 | 10.5 | 29.0 | 4.8 | 100.0 |
| 1949-50 | 51.9 | 0.9 | 9.8 | 30.7 | 6.7 | 100.0 |
| 1950-51 | 45.0 | 1.0 | 8.6 | 38.2 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| 1951-52 | 54.7 | 1.5 | 9.9 | 26.3 | 7.6 | 100.0 |
| 1952-53 | 53.9 | 1.7 | 9.6 | 28.3 | 6.5 | 100.0 |
| 1953-54 | 53.4 | 1.8 | 9.1 | 27.9 | 7.8 | 100.0 |
| 1954-55 | 55.6 | 1.6 | 9.0 | 26.3 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| 1955-56 | 57.6 | 1.5 | 8.9 | 25.9 | 6.1 | 100.0 |
| 1956-57 | 57.0 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 26.5 | 6.3 | 100.0 |
| 1957-58 | 59.4 | 1.4 | 8.5 | 24.0 | 6.7 | 100.0 |
| 1958-59 | 60.5 | 1.3 | 9.8 | 21.3 | 7.1 | 100.0 |
| 1959-60* | 56.7 | 1.3 | 10.7 | 24.2 | 7.1 | 100.0 |
| AS INDEX NUMBERS (1938-39 = 1000 | ||||||
| 1938-39 | 100 | ... | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 1939-40 | 97 | ... | 149 | 108 | 123 | 105 |
| 1940-41 | 99 | ... | 164 | 96 | 80 | 107 |
| 1941-42 | 99 | ... | 169 | 101 | 108 | 116 |
| 1942-43 | 101 | ... | 187 | 104 | 105 | 130 |
| 1943-44 | 110 | ... | 207 | 112 | 109 | 145 |
| 1944-45 | 115 | ... | 229 | 127 | 89 | 146 |
| 1945-46 | 127 | ... | 275 | 137 | 129 | 156 |
| 1946-47 | 153 | ... | 459 | 186 | 190 | 181 |
| 1947-48 | 175 | ... | 496 | 223 | 239 | 209 |
| 1948-49 | 190 | ... | 520 | 220 | 141 | 210 |
| 1949-50 | 210 | ... | 563 | 269 | 228 | 244 |
| 1950-51 | 231 | ... | 628 | 426 | 310 | 310 |
| 1951-52 | 274 | ... | 707 | 287 | 322 | 302 |
| 1952-53 | 286 | ... | 716 | 326 | 291 | 320 |
| 1953-54 | 318 | ... | 769 | 360 | 393 | 359 |
| 1954-55 | 358 | ... | 817 | 368 | 408 | 388 |
| 1955-56 | 391 | ... | 859 | 382 | 351 | 410 |
| 1956-57 | 408 | ... | 884 | 411 | 380 | 431 |
| 1957-58 | 458 | ... | 933 | 402 | 433 | 465 |
| 1958-59 | 464 | ... | 1068 | 353 | 456 | 462 |
| 1959-60* | 491 | ... | 1320 | 456 | 519 | 523 |
THE ACCOUNTS OF THE GOVERNMENT SECTOR - The accounts of the Government sector, as set out in preceding pages 754-755, have now been complemented by the publication The Accounts of the Government Sector 1956-57 to 1959-60 issued as a special supplement to the report on the Official Estimates of National Income and Expenditure for the Year 1959-60 and available from the Government Printer. The publication of these new accounts is the first stage in a major revision of the national accounts, but until this revision is completed it will not be possible to integrate the new accounts of the Government sector into the overall national accounting structure.
The accounts of the Government sector present the first comprehensive and consistently classified statement of all central Government transactions. In preparing these accounts coverage has been extended to all Government accounting units, and all transactions have been classified according to a consistent economic analysis of receipts and payments. As it stands, the new system of accounts is a valuable addition to the material available to the public and to the policy maker on Government finance. The bulk of Government accounting material hitherto available has been of a detailed nature designed to permit parliamentary and audit control of various departmental expenditures. Although this detailed presentation is essential for these purposes, it has had the undesirable effect of obscuring the broad pattern of Government operations.
The assumption by Governments of overall responsibility for the health of the national economy has created a need for a presentation of Government accounts in a form which reveals the broad types of financial flows through which the Government can influence the growth and stability of the economy. Although most of the main items included in such flows as direct taxation, subsidies, and Government transfer payments are easily obtainable by any person familiar with the public accounts, it has not been possible to obtain total figures for any of these flows. The accounts of the Government sector enable such a view to be obtained.
In addition to providing improved measures of the current account transactions as recorded in the General Government - Revenue Account, the new accounts include a full analysis of the Government's capital transactions. Details of Government lending and borrowing are classified according to changes in claims on, and in liabilities to, local authorities, the private sector, and the rest of the world.
A major problem encountered in the preparation of the new accounts has been the elimination of numerous transfers between the many separate Government accounting units. The existence of these interaccount transfers has made it difficult for the public to understand the net effect of Government transactions. For example, public attention is frequently drawn to changes in the public debt, which is usually regarded as measuring changes in Government borrowing from nongovernment sources. In fact the Government is one of the main holders of New Zealand Government securities and what appear as changes in the public debt may in fact reflect no more than the transfer of Government money from one Government account to another.
It is hoped that the new Government accounts by eliminating all such internal transactions and by classifying transactions in a consistent manner will, in addition to assisting those concerned with policy, improve general understanding of the nature of Government transactions.
INTRODUCTORY - The link between external economic transactions and the domestic economy is given by the net balance between all credits (exports and other current receipts) and all debits (imports and other current payments) and is called the balance of payments on current account. Irrespective of whether this balance is a surplus or a deficit, it evokes a corresponding movement in the country's claims on or liabilities to residents of all other countries; a deficit on current account will increase this country's liabilities and decrease its claims on overseas residents, and a surplus will have the opposite effect. These capital movements can be summarised under the term of “net overseas disinvestment” and “net overseas investment”, which are due to a deficit or surplus on current account respectively.
It is this net capital balance, net overseas investment (denoted with a minus sign in the case of a current deficit or capital disinvestment), which appears in the aggregative national income estimates (Section 25A, page 748). A current surplus or net overseas investment means in this context that a certain portion of the gross national product has been expended on or disposed of - in the same way as other portions of the gross national product are expended on private consumption, Government consumption, or the formation of new physical capital assets - to create a financial claim on nonresidents. It should be noted that in this instance only the net balance is integrated into a system of national accounts.
Apart from its place within the framework of national accounting, a balance of payments account, as a record of economic transactions with other countries, is an important set of economic statistics on its own merits. As an independent presentation it shows in detail various types of payments and receipts, it concerns itself with transactions by currency areas, presents its capital account on a gross basis in order that various classes of capital movements can be studied in isolation, and so forth.
The present series of balance of payments estimates is based on the principles adopted by successive manuals published by the International Monetary Fund, and is in conformity with the methods used in most overseas countries. The statement is divided into a current account and capital account, which are described below. It will be seen that the balances on both accounts are, by definition, of the same magnitude; the capital account shows how the surplus or deficit on current account was financed. For a more detailed description of statistical concepts and methods used in preparing balance of payments estimates, refer to the Report on the Official Estimates of Balance of Payments for the Year 1959-60 obtainable from the Government Printer.
Current Account - In very general terms, the current account shows the results of the year's trading with other countries when services as well as goods are included; and a credit balance in this account indicates that more has been sold to other countries than has been bought from them, thus increasing their indebtedness to New Zealand or reducing New Zealand indebtedness to them.
More strictly defined, the current account records all transactions other than those representing changes in the international creditor-debtor position. Every attempt is made to record transactions on a gross credit-debit basis rather than on the basis of net settlements. The current account includes both credits and debits in respect of merchandise, services (invisibles), as well as unilateral transfers (donations), and movements in non-monetary gold which, in essence, represent net additions to gold reserves. The difference between current credits and current debits is the balance of payments surplus (deficit) on current account; it is the measure of the extent to which a country does or does not live within its current income. It is the most significant datum emerging from a balance of payments compilation.
Capital Account - The capital account records all known changes in claims on, or liabilities to, the rest of the world. Of the items comprising the capital account, the category of net overseas assets - the overseas exchange holdings of New Zealand's banking system - is most widely known and appreciated. Its importance lies in the fact that it records changes in overseas liquid resources which by their nature can be made immediately available for purposes of imports, public debt repayments, capital investments, etc. But within the confines of the balance of payments capital account the movement in net overseas assets is only one of several other capital movements with which it forms an integral part; it is the combination of all these capital changes which must be studied in order to understand the financing of the current surplus or deficit.
Attention is drawn to the item “Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions”, which is a balancing residual in the capital account. Apart from certain inevitable errors of estimation and omissions due to incomplete information available, the above-mentioned item gives a valuable pointer to year-to-year changes in “leads and lags” of short-term commercial credit (rime extensions or restrictions in credit facilities to New Zealand exporters or importers by overseas buyers or sellers) and other capital movements not explained elsewhere.
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS AND EXCHANGE RECORD - There are several very important differences between a balance of payments statement and the statistics of overseas receipts and payments which are included in an exchange record, e.g.:
The former attempts to show all economic transactions between residents of one country and residents of other countries, whereas the exchange record shows only transactions involving remittances.
The import and export figures in the balance of payments are based on trade (Customs) statistics, which enable goods to be valued at a definite and uniform valuation boundary-viz., f.o.b. country of export; the exchange record, on the other hand, records remittances for imports and exports whenever these are made and without adhering to any valuation boundary (f.o.b. or c.i.f.). The result is a difference both in timing and valuation between the two statements.
Whereas exchange statistics record net settlements resulting from a number of possible contra-entries or offsets, the balance of payments shows these transactions as far as possible on a gross basis.
Other differences arise from the fact that the balance of payments is constructed on a basis of country of purchase for imports and country of destination for exports, country of residence of remittor or remittee, and nationality in the case of shipping companies, whereas the record of exchange transactions is based on the country of monetary settlement.
GENERAL - The balance of payments is a record of economic transactions between residents and non-residents.
Residents are all persons living permanently in New Zealand (or for a period exceeding 12 months), subsidiaries and branches of overseas companies being treated as residents, while subsidiaries and branches of New Zealand companies operating overseas are regarded as residents of the country of their business.
In order to simplify the rather complex operations of overseas shipping companies, the shipping transactions of their branches in New Zealand (such as their receipts of freights, port disbursements, administrative expenses in New Zealand) are regarded as transactions of non-residents, by way of exception to the general rule stated above; on the other hand, their investment activity is included in the data on New Zealand blanches of overseas companies (page 786) and conforms to the general rule.
GEOGRAPHICAL DIVISION - The regional break-up of the balance of payments is on a geographical, as distinct from a currency basis. This means that it is not the currency in which any economic transaction is settled but the residence of New Zealand's immediate partner in the transaction which determines in which regional column the transaction is recorded. Any exception to this rule is due to statistical necessity - insufficiency of basic data, etc. - rather than choice.
The New Zealand figures include transactions of New Zealand's dependent island territories and the Trust Territory of Western Samoa.
The following geographical division of other areas has been chosen in order to group together countries whose currencies are of particular economic interest.
Other Sterling Countries - Other Commonwealth countries (excluding Canada and Newfoundland) and their trustee and dependent territories; the colonies, protectorates, and trustee territories, etc. of the United Kingdom; the Republic of Ireland, Burma, and Iceland.
Dollar Countries - The United States of America, Canada, all the Central American republics, Cuba, Haiti, Dominican Republic, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, the Philippine Islands, and Liberia.
EEC Countries - These are the six members of the European Economic Community which formed a common market in 1958-Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxemburg, France, Italy, and the Federal German Republic, together with their dependent overseas territories.
Other OEEC Countries - The remaining members of the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation - Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Switzerland, Portugal, Spain, Austria, Greece, and Turkey, together with any dependent overseas territories.
Other Countries - All countries not included in any other group.
ACCOUNTING PERIOD - All estimates are for financial years ending 31 March.
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS 1959-60 - The results of the 1959-60 balance of payments estimates are now given.
Current Account - This account may be discussed under several headings.
Merchandise Transactions - New Zealand's overseas transactions on current account in the year ended 31 March 1960 resulted in a balance of payments surplus of £36.1 million. This was an improvement of £60.6 million on the previous year's deficit of £24.5 million.
This surplus was higher than that of £28.1 million recorded in 1953-54, and even higher than that of £30.5 million in 1950-51, so far the highest on record.
The principal factor in the improvement of the balance of payments was the surplus on account of merchandise trade to the extent of £92.0 million, compared with the preceding year's surplus of £27.7 million. In 1959-60 exports at £310.1 million were 15 per cent higher than the year before (£261.6 million), while imports at £218.1 million declined from the preceding year's total of £233.9 million. In all cases imports and exports are recorded at f.o.b. valuations and imports exclude freight and insurance which is entered separately in the “invisibles” section of the balance of payments account.
The main contribution to the rise in the total value of exports in 1959-60 came from wool, the exports of which exceeded the 1958-59 figure by approximately £25 million, and to a smaller degree from exports of dairy produce.
There was a decline in imports in spite of progressive relaxation of import controls during the year ended 31 March 1960; time has probably not yet permitted full advantage to be taken of the relaxation of import controls.
Invisible Transactions - Over 60 per cent of the surplus in merchandise transactions was offset by the deficit of £55.9 million on “invisibles” transactions, compared with the 1958-59 deficit of £52.2 million. This deficit on invisibles is more or less a minimum figure in view of low imports. Had these been larger, the deficit on “transportation” of £13.5 million would have been greater, thus increasing the deficit on invisibles. In fact, the transportation deficit declined by £4.1 million from the level of 1958-59.
Transactions with Trade Areas - An analysis is now made of the balance of payments by trade areas; the previous year's figures are shown in parentheses, New Zealand had a surplus of £37.3 million with the United Kingdom (deficit of £1.4 million), a surplus with OEEC countries of £24.7 million (£10.1 million), a surplus with the dollar area of £16.1 million (£17.5 million), and with other countries a surplus of £6.7 million (£0.1 million). The traditional balance of payments deficit with other sterling countries-in which Australia plays by far the greatest role-was £48.7 million, a slight decline from the previous deficit of £50.8 million. As already mentioned, information is available now on the European Economic Community group of countries (hereafter described as EEC countries), which was previously shown as part of the wider group of countries associated with the Organisation of European Economic Cooperation; the surplus with the EEC was £31.1 million but no comparative figure is available for the preceding year. With countries other than the EEC, but part of the OEEC grouping, New Zealand had a deficit of £6.4 million. It appears that the new area analysis will show the “Other OEEC Countries” to be another area of chronic balance of payments deficits, as far as New Zealand is concerned.
The following short table for 1959-60 shows the effect of invisible transactions on the gains or losses resulting from trade transactions with the various areas.
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(million) | ||||||
| Merchandise trade (f.o.b.) | 65.9 | -36.7 | 24.4 | 33.7 | -3.0 | 7.6 |
| Balance of payments on current account | 37.3 | -48.7 | 16.1 | 31.1 | -6.4 | 6.7 |
| Loss on invisibles | -28.6 | -12.0 | -8.3 | -2.6 | -3.4 | -0.9 |
Travel is another constituent item of the invisibles bill which deserves special attention. The deficit on this item in 1959-60 reached £6.4 million, an increase of £1.5 million above the deficit of 1958-59. The figures for receipts and payments respectively were as follows: £3.0 million and £7.8 million in 1958-59 and £3.3 million and £9.7 million in 1959-60.lt can be seen that the considerable increase in payments was not matched by the smaller increase in receipts. This development is not unexpected and not entirely dissimilar to past years. It should be pointed out that for technical and conceptual reasons fares paid in New Zealand are included under “transportation”. It is worthy of notice that the increase of expenditure on this item has persisted despite measures to restrict travel funds available for non-business purposes to a limit of £750 per person.
Payments for servicing direct private overseas investment in New Zealand increased from £11.9 million in 1958-59 to £12.7 million, while total payments on account of profits, dividends, and private and public interest were £21.3 million, i.e., £2.4 million greater than in the preceding year. Receipts under the same heading were £7.2 million against £5.9 million in 1958-59. Thus the net international investment income bill was approximately £14.1 million, i.e., £1.1 million higher than in the preceding year.
Gross investment income of Government and official institutions has increased by £1.0 million, reaching a figure of £3.5 million, mainly as a consequence of acquisition of new investments in the United Kingdom.
Government expenditure increased from £7.1 million in the preceding year to £9.8 million. This was reduced by Government receipts of £1.3 million, resulting in a net expenditure figure of £8.5 million in 1959-60, compared with £6.0 million in the previous year.
Foreign Government expenditure doubled from 1958-59, giving a figure of £1.2 million, the highest on record to date.
No special analysis is necessary for this year's distribution of the merchandise transactions between the areas, as it can be ascertained from the tables on pages 773-774. The relatively sharp decline in this year's imports from the United Kingdom - on an absolute and percentage basis - is perhaps the most noticeable though not unexpected feature if one considers the general decline in imports and the United Kingdom's position as New Zealand's largest supplier.
The Capital Account - This account shows how the surplus on current account was reflected in changes of external liabilities or assets. In 1959-60 capital exports amounted to £51.7 million while imports of capital were only £15.6 million.
Overseas direct private investment in New Zealand, which was £11.8 million in 1958-59, declined to £6.0 million in the latest year. Its composition is interesting. Increases in both paid-up capital and reserves of subsidiaries of overseas companies amounted to £4.1 million. The reduction to £6.0 million occurred as a result of the decrease in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness. This is the reverse of the 1958-59 situation when the increase in direct investment was mainly due to increases in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness, these accounting for two-thirds of its value.
The £5.8 million decline from the 1958-59 figure was mainly shared by the United Kingdom (£5.6 million) and by the dollar countries (£1.2 million). The decline in direct investment from these two areas was modified by an increase in investment from “Other Sterling Countries”, while a decline in the figures for other areas accounted for the final result.
It is a remarkable feature of the capital account that overseas private direct investment and the balance of payments surpluses or deficits are inversely correlated to a great degree. As can be seen from the diagram following they tended to rise or fall in directions opposite to each other in all years except one for which information is available.
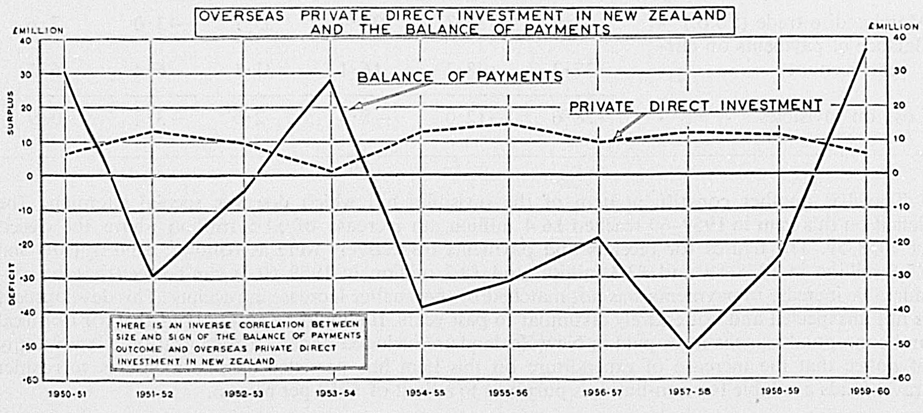
New Zealand direct investment overseas has risen considerably, reaching a record figure of £2.4 million in 1959-60. However, the general level of these flows is still fairly low.
Other long-term capital movements into New Zealand reached £8.1 million, compared with the 1958-59 level of £4.0 million; this was mainly the consequence of loans in excess of £3.0 million raised in the United States by private firms for the purchase of capital equipment. Government investments increased by £12.4 million, the principal factors being the purchase of £10.1 million United States Treasury bonds to be ultimately applied to the redemption of a three-year loan maturing late in 1961. In the United Kingdom the Government purchased securities valued at £2.2 million towards redemption of several other loans reaching maturity in the next few years.
The General Government debt decreased by £5.1 million as a result of repayment of loans to United States (£4.6 million) and a transfer of securities from the London to the New Zealand register (£0.5 million).
The decrease in local authority debt was £0.5 million. The corresponding figure for last year was £1.1 million.
Short-term Government investment increased but the resources for this were largely made available from the drawing down of Government cash balances held abroad. An amount of £3.9 million was invested in the United Kingdom, the purpose being the same as for long-term Government investments.
Liquid exchange reserves increased by £22.7 million, compared with a rise of £25.1 million in 1958-59.
SUMMARY TABLES, CURRENT AND CAPITAL ACCOUNTS - The following table summarises current transactions with all countries. The figures shown in the credit, debit, and net balance columns are the same as those appearing in the “Total, all Countries” columns in the current account tables on pages 771-780.
| Current Account | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||
| Credits | |||||
| Exports f.o.b. | 261,100 | 272,900 | 268,550 | 261,550 | 310,050 |
| Non-monetary gold | — | — | — | — | — |
| Transportation | 11,550 | 9,800 | 11,400 | 11,050 | 12,100 |
| Travel | 2,450 | 3,150 | 3,550 | 2,950 | 3,250 |
| Insurance | 150 | 400 | 1,050 | 200 | 300 |
| International investment income | 6,900 | 7,550 | 6,800 | 5,900 | 7,150 |
| Income from direct investment | 1,900 | 1,800 | 1,450 | 1,450 | 2,100 |
| Other private investment | 1,800 | 1,950 | 2,050 | 1,950 | 1,550 |
| Government and official institutions | 3,200 | 3,800 | 3,300 | 2,500 | 3,500 |
| Government transactions | 1,400 | 1,750 | 2,550 | 1,550 | 2,500 |
| Foreign Government expenditure | 600 | 800 | 700 | 600 | 1,200 |
| New Zealand Government receipts | 800 | 950 | 1,850 | 950 | 1,300 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 4,000 | 4,850 | 6,000 | 5,050 | 5,200 |
| Unilateral transfers | 7,150 | 7,850 | 8,650 | 7,350 | 7,650 |
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 3,700 | 3,800 | 3,900 | 3,800 | 4,050 |
| Migrants' funds | 2,150 | 2,400 | 3,350 | 2,450 | 2,250 |
| Legacies | 1,300 | 1,650 | 1,400 | 1,100 | 1,350 |
| Total credits | 294,700 | 308,250 | 308,550 | 295,600 | 348,200 |
| Current Account | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | t 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||
| Debits | |||||
| Imports f.o.b. | 249,450 | 244,250 | 273,200 | 233,900 | 218,100 |
| Non-monetary gold | — | — | – | — | — |
| Transportation | 29,300 | 29,800 | 31,800 | 28,600 | 25,550 |
| Travel | 6,600 | 6,700 | 6,850 | 7,800 | 9,650 |
| Insurance | 800 | 900 | 1,000 | 1,200 | 1,450 |
| International investment income | 15,350 | 17,800 | 16,850 | 18,900 | 21,300 |
| Income from direct investment | 11,100 | 11,650 | 11,000 | 11,850 | 12,650 |
| Other private investment | 700 | 2,550 | 2,000 | 2,300 | 2,950 |
| Government and official institutions | 3,250 | 3,400 | 3,700 | 4,600 | 5,550 |
| Local authority interest | 300 | 200 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| Government transactions | 6,750 | 6,100 | 9,550 | 7,050 | 9,800 |
| New Zealand Government expenditure | 6,750 | 6,100 | 9,550 | 7,050 | 9,800 |
| Miscellaneous payments | 7,550 | 10,700 | 10,750 | 11,550 | 13,200 |
| Films | 1,000 | 900 | 900 | 1,100 | 1,150 |
| Unilateral transfers | 8,950 | 9,150 | 9,250 | 10,000 | 11,900 |
| Government contribution to Colombo Plan | 7,000 | 1,000 | 750 | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 3,400 | 3,850 | 3,850 | 3,650 | 5,450 |
| Migrants' funds | 3,200 | 2,900 | 3,000 | 4,050 | 3,600 |
| Legacies | 1,350 | 1,400 | 1,650 | 1,300 | 1,850 |
| Total debits | 325,750 | 326,300 | 360,150 | 320,100 | 312,100 |
| Net Balance | |||||
| Merchandise transactions f.o.b. | 11,650 | 28,650 | -4,650 | 27,650 | 91,950 |
| Non-monetary gold | — | — | — | — | — |
| Transportation | -17,750 | -20,000 | -20,400 | -17,550 | -13,450 |
| Travel | 4,150 | -3,550 | -3,300 | -4,850 | -6,400 |
| Insurance | -650 | -500 | 50 | -1,000 | -1,150 |
| International investment income | -8,450 | -10,250 | -10,050 | -13,000 | -14,150 |
| Government transactions | -5,350 | -4,350 | -7,000 | -5,500 | -7,300 |
| Miscellaneous receipts and payments | -3,550 | -5,850 | -4,750 | -6,500 | -8,000 |
| Films | -1,000 | -900 | -900 | -1,100 | -1,150 |
| Unilateral transfers | -1,800 | -1,300 | -600 | -2,650 | -4,250 |
| Balance on current account | -31,050 | -18,050 | -51,600 | -24,500 | +36,100 |
Minus sign - denotes excess of imports over exports or payments over receipts.
The next table repeats the balance of payments current account on a net basis (by offsetting credits against debits in respect of corresponding groups of items) and by countries or currency regions.
| Current Account (Net) | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||||
| 1955-56 | |||||||
| Merchandise transactions | 29,900 | -37,850 | -6,100 | 22,250 | 3,500 | 11,650 | |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - | |
| Transportation | -14,450 | 50 | -800 | -1.650 | -900 | -17,750 | |
| Travel | -3,550 | -400 | 50 | -100 | 50 | -4,150 | |
| Insurance | -600 | 50 | 50 | 50 | -650 | ||
| International investment income | -5,850 | -200 | -2,500 | 100 | -8,450 | ||
| Government transactions | -2,650 | -2,400 | -200 | 50 | 150 | -5,350 | |
| Miscellaneous | -1,100 | -650 | -1,200 | -550 | -50 | -3,550 | |
| Films | -150 | -150 | -700 | - | 1,000 | ||
| Unilateral transfers | 1,250 | -2,550 | 100 | -250 | -350 | -1,800 | |
| Balance on current account | 2,800 | -44,100 | -11,500 | 19,850 | 1,950 | -31,050 | |
| 1956-57 | |||||||
| Merchandise transactions | 34,350 | -39,800 | 100 | 33,650 | 300 | 28,650 | |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - | |
| Transportation | -15,200 | -750 | -1,000 | -2,050 | -1,000 | -20,000 | |
| Travel | -3,000 | -450 | 50 | -100 | 50 | -3,500 | |
| Insurance | -300 | -200 | - | - | -500 | ||
| International investment income | -7,350 | -350 | -2,800 | 200 | 50 | -10,250 | |
| Government transactions | -2,650 | -1,850 | 300 | 100 | -250 | -4,350 | |
| Miscellaneous | -2,500 | -850 | -2,000 | -450 | 50 | -5,850 | |
| Films | 150 | -150 | -600 | -900 | |||
| Unilateral transfers | 1,550 | -2,100 | 100 | -450 | -400 | -1,300 | |
| Balance on current account | 4,750 | -46,500 | -5,850 | 30,900 | -1,400 | -18,050 | |
| 1957-58 | |||||||
| Merchandise transactions | 7,750 | -43,800 | 1,600 | 25,400 | 4,350 | -4,650 | |
| Non-monetary gold | — | ||||||
| Transportation | -17,200 | 900 | -900 | -1,900 | -1,300 | -20,400 | |
| Travel | -3,000 | -200 | 50 | -100 | 50 | -3,300 | |
| Insurance | 200 | 300 | 50 | 50 | |||
| International investment income | -5,950 | -450 | -3,850 | 50 | 150 | -10,050 | |
| Government transactions | -4,800 | -1,950 | -150 | 100 | -200 | -7,000 | |
| Miscellaneous | -2,050 | -900 | -1,400 | -350 | 50 | -4,750 | |
| Films | 150 | -100 | -650 | -900 | |||
| Unilateral transfers | 1,700 | -1,600 | 50 | -400 | -350 | -600 | |
| Balance on current account | -23,900 | -47,800 | -5,300 | 22,800 | 2,550 | -51,600 | |
| 1958-59 | |||||||
| Merchandise transactions | -29,400 | -42,400 | 25,050 | 14,200 | 1,400 | 27,650 | |
| Non-monetary gold | |||||||
| Transportation | -14,000 | -850 | -900 | -2,900 | -600 | -17,550 | |
| Travel | -3,400 | -1,200 | 50 | 150 | 50 | -4,850 | |
| Insurance | -800 | -150 | -100 | 50 | -1,000 | ||
| International investment income | -7,550 | -1,300 | -4,050 | -200 | 50 | -13,000 | |
| Government transactions | -1,900 | -3,100 | -200 | 50 | -350 | -5,500 | |
| Miscellaneous | -3,450 | -700 | -1,750 | -550 | 50 | -6,500 | |
| Films | 250 | -150 | -700 | ... | -1,100 | ||
| Unilateral transfers | 550 | -2,650 | 150 | -400 | -300 | -2,650 | |
| Balance on current account | -1,400 | -50,800 | 17,450 | 10,100 | 100 | -24,500 | |
| 1959-60 | |||||||
| Merchandise transactions | 65,850 | -36,650 | 24,400 | 33,700 | -3,000 | 7,550 | 91,950 |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - |
| Transportation | -9,000 | 1,000 | -1,400 | -1,500 | -2,500 | 50 | -13,450 |
| Travel | -4,200 | -1,750 | -100 | 150- | 100 | 100 | -6,400 |
| Insurance | 800 | -250 | -50 | ... | ... | ... | -1,150 |
| International investment income | -7,750 | -2,050 | -4,150 | 50- | 200 | 50 | -14,150 |
| Government transactions | -3,550 | -3,050 | 50 | -100- | 250 | -400 | -7,300 |
| Miscellaneous | -3,150 | -2,150 | -1,850 | -700- | 150 | -8,000 | |
| Films | 250 | -100 | -800 | -1,150 | |||
| Unilateral transfers | 100 | -3,650 | 50 | -100- | 200 | -350 | -4,250 |
| Balance on current account | 37,250 | -48,650 | 16,050 | 31,100 | -6,400 | 6,700 | +36,100 |
Minus sign (–) denotes excess of imports over exports or payments over receipts.
The consolidated capital account shown below summarises capital transactions with all countries; it consists of the “Total, All Countries” column of the capital account tables on pages 777-781, but some of the items are presented in simplified form (by adding or offsetting capital movements where these have occurred in respect of equally defined items).
| Capital Account | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||
| Increase in Assets | |||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | |||||
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | 800 | 1,550 | 1,250 | 750 | 2,350 |
| Other long-term capital movements | - | -1,050 | -2,550 | - | - |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | |||||
| Government investments | 1,300 | -800 | 300 | 100 | 12,350 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | |||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 150 |
| Wool credit to France | - | -1,250 | -3,750 | - | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | |||||
| Government cash balances | -5,400 | - | 300 | -350 | -1,250 |
| Other | - | 1,700 | - | 3,200 | 3,600 |
| Short-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | |||||
| Net overseas assets | -9,450 | 4,650 | -39,600 | 25,050 | 22,700 |
| Monetary gold | - | - | - | - | - |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions | 50 | - | 3,150 | - | 4,500 |
| Total increase in assets | -12,600 | 4,900 | -40,800 | 28,S50 | 44,400 |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||
| Increase in Liabilities | |||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | |||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | 15,100 | 9,850 | 12,650 | 11,750 | 5,950 |
| Other long-term capital movements | 4,700 | - | - | 4,000 | 8,100 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | |||||
| Public debt | -1,850 | 9,350 | -1,100 | 38,200 | -5,100 |
| Local authority debt | - | - | -500 | -1,100 | -500 |
| Other | -50 | -200 | -200 | -150 | -150 |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | |||||
| Other than cash balances | 550 | - | -50 | - | - |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions | - | 3,950 | 650 | - | |
| Total increase in liabilities | 18,450 | 22,950 | 10,800 | 53,350 | 8,300 |
| Net Balance | |||||
| Balance on capital account | -31,050 | -18,050 | -51,600 | -24,500 | +36,100 |
Minus sign(–) denotes a decrease in assets or liabilities.
MERCHANDISE TRANSACTIONS: Exports-The source of the export tables is Customs information on total exports (exclusive of ships' stores) at f.o.b. valuation; exports from New Zealand to Western Samoa have been excluded from Customs figures, but exports from Western Samoa and Cook Islands to other countries have been added to New Zealand totals. The remaining adjustments are for items which are either entirely omitted from Customs statistics (relief supplies, ships and aircraft sold and leaving under their own power), items where the valuation requires correction, e.g., parcel post, or items which are accounted for elsewhere in the balance of payments export of gold).
| Exports | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||||
| 1957-58 | |||||||
| Exports f.o.b. (excluding ships' stores and exports to Western Samoa) | 152,300 | 18,200 | 27,800 | 50,100 | 15,800 | 264,200 | |
| Plus adjustment for parcel post | 200 | 150 | 50 | .. | .. | 400 | |
| Plus adjustment for relief supplies | .. | 300 | .. | 300 | 200 | 800 | |
| Plus exports from Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 1,000 | 100 | 250 | 100 | .. | 1,450 | |
| Plus exports of ships' stores and bunkers | 1,200 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 1,450 | |
| Plus sale of vessels and aircraft | 50 | 200 | .. | .. | 250 | ||
| Exports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 154,750 | 19,000 | 28,150 | 50,600 | 16,050 | 268,550 | |
| 1958-59 | |||||||
| Exports f.o.b. (excluding ships' stores and exports to Western Samoa) | 147,450 | 17,600 | 46,050 | 36,100 | 9,950 | 257,150 | |
| Plus adjustment for parcel post | 200 | 250 | 50 | .. | 550 | ||
| Plus adjustment for relief supplies | 100 | 350 | .. | 250 | 250 | 900 | |
| Plus exports from Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 1,300 | 100 | 250 | 50 | .. | 1,700 | |
| Plus exports of ships' stores and bunkers | 1,050 | 50 | .. | 50 | 50 | 1,150 | |
| Plus sale of vessels and aircraft | - | 100 | .. | 100 | |||
| Exports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 150,100 | 18,450 | 46,350 | 36,450 | 10,250 | 261,550 | |
| 1959-60 | |||||||
| Exports f.o.b.; excluding ships' stores and exports to Western Samoa) | 166,750 | 20,650 | 48,150 | 49,300 | 2,550 | 17,900 | 305,250 |
| Plus adjustment for parcel post | 200 | 250 | 100 | .. | .. | .. | 550 |
| Plus adjustment for relief supplies | 100 | 300 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 900 | |
| Plus exports from Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 1,150 | 100 | 250 | 150 | 150 | 100 | 1,950 |
| Plus exports of ships' stores and bunkers | 1,050 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | .. | 1,250 |
| Plus sale of vessels and aircraft | .. | 100 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 150 |
| Exports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 169,250 | 21,450 | 48,550 | 49,600 | 2,850 | 18,250 | 310,050 |
Imports - The basic figures in the import tables also originate in Customs statistics. New Zealand imports from Western Samoa have been excluded from the Customs figures, but imports into Cook Islands and Western Samoa from other countries have been added. Besides additions for aircraft and ships arriving in New Zealand under their own power, there is a deduction for the notional import values of commercial films; remittances of film rentals which express more exactly the cost of films to this country are substituted for the latter.
It is necessary to comment here on the valuation method adopted for imports. Balance of payments accounts treat freight and marine insurance payments on imports - as far as they are made to nonresidents - as invisible payments. As a result, merchandise transactions are shown on a f.o.b. valuation basis for imports and exports alike. This method of treatment has many advantages, and international comparability of merchandise movements is one of them.
There is, however, no provision in New Zealand statistics for a f.o.b. valuation of imports; all imports - as distinct from exports which have always been valued f.o.b. - are valued either on the basis of “current domestic value” or c.i.f. Evidence suggests that f.o.b. values are, on the average, higher than current domestic values as defined by the Customs Department. Packing and transport charges from warehouse to port in exporting countries and buying commissions would account for the greater portion of the difference. This difference has been estimated from all the data at present available and added to c.d.v. Customs figures.
| Imports | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OKEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z. (thousand) | |||||||
| 1957-58 | |||||||
| Imports f.o.b. (excluding imports from Western Samoa) | 144,400 | 62,200 | 26,200 | 24,950 | 11,550 | 269,250 | |
| Plus imports of vessels and aircraft | 2,200 | - | 100 | 200 | - | 2,500 | |
| Plus imports into Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 400 | 600 | 250 | 50 | 150 | 1,450 | |
| Imports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 147,000 | 62,800 | 26,550 | 25,200 | 11,700 | 273,200 | |
| 1958-59 | |||||||
| Imports f.o.b. (excluding imports from Western Samoa) | 117,300 | 59,450 | 21,000 | 22,000 | 8,650 | 228,400 | |
| Plus imports of vessels and aircraft | 3,000 | 700 | 50 | 150 | 3,900 | ||
| Plus imports into Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 400 | 700 | 250 | 100 | 200 | 1,600 | |
| Imports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 120,700 | 60,850 | 21,300 | 22,250 | 8,850 | 233,900 | |
| 1959-60 | |||||||
| Imports f.o.b. (excluding imports from Western Samoa) | 101,050 | 57,200 | 23,750 | 15,700 | 5,800 | 10,500 | 214,000 |
| Plus imports of vessels and aircraft | 1,900 | - | - | 150 | - | - | 2,050 |
| Plus imports into Cook Islands and Western Samoa | 450 | 900 | 400 | 50 | 50 | 200 | 2,050 |
| Imports (adjusted) f.o.b. | 103,400 | 58,100 | 24,150 | 15,900 | 5,850 | 10,700 | 218,100 |
DIRECTION OF TRADE - The following table showing exports and imports by areas as percentages of the total reveals the direction of New Zealand's trade for financial years.
| Year | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | |||||||
| Exports f.o.b. | |||||||
| 1950-51 | 64.5 | 3.6 | 12.5 | 14.1 | 5.3 | 100.0 | |
| 1951-52 | 57.7 | 4.6 | 17.2 | 16.3 | 4.2 | 100.0 | |
| 1952-53 | 68.6 | 4.6 | 12.2 | 11.5 | 31 | 100.0 | |
| 1953-54 | 67.3 | 1.4 | 8.6 | 15.0 | 3.7 | 100.0 | |
| 1954-55 | 66.4 | 5.9 | 7.8 | 16.2 | 3.7 | 100.0 | |
| 1955-56 | 64.6 | 5.7 | 8.9 | 16.4 | 4.4 | 100.0 | |
| 1956-57 | 61.6 | 6.2 | 8.8 | 19.5 | 3.9 | 100.0 | |
| 1957-58 | 57.6 | 7.1 | 10.5 | 18.8 | 6.0 | 100.0 | |
| 1958-59 | 57.4 | 7.1 | 17.7 | 13.9 | 3.9 | 100.0 | |
| 1959-60 | 54.6 | 6.9 | 15.7 | 16.0 | 0.9 | 5.9 | 100.0 |
| Imports f.o.b. | |||||||
| 1950.51 | 60.0 | 20.6 | 9.9 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 100.0 | |
| 1951-52 | 54.6 | 19.9 | 12.7 | 8.2 | 4.7 | 100.0 | |
| 1952-53 | 54.1 | 19.6 | 12.9 | 9.0 | 4.4 | 100.0 | |
| 1953-54 | 57.9 | 23 1 | 81 | 6.9 | 30 | 100.0 | |
| 1954-55 | 58.1 | 20.5 | 9.7 | 8.9 | 2.8 | 100.0 | |
| 1955-56 | 55.6 | 21.2 | 11.8 | 8.2 | 3.2 | 100.0 | |
| 1956-57 | 54.8 | 23.2 | 9.8 | 80 | 4.2 | 100.0 | |
| 1957-58 | 53.8 | 23 0 | 9.7 | 9.2 | 4.3 | 100.0 | |
| 1958-59 | 51.6 | 26.0 | 9.1 | 9.5 | 3.8 | 100.0 | |
| 1959-60 | 47.4 | 26.6 | 11.1 | 7.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 100.0 |
REGIONAL ACCOUNTS - The tables on the following pages give detailed figures relating to the overall current and capital accounts in the balance of payments as well as particulars for each of the main countries and currency regions. The accounts are presented for the financial years 1957-58 to 1959-60, and each year's account is divided into current credits (gross), current debits (gross), and the capital account.
Current Credits - The item non-monetary gold represents the purchase by the Reserve Bank of gold produced in this country. Transportation represents mainly port disbursements (exclusive of bunkers and provedoring) of overseas shipping companies operating in New Zealand; their establishment expenses, however, are included in miscellaneous receipts. The regional break-up of travel receipts is subject to revision; at present it is still shown on the basis of currency received rather than residence (nationality) of traveller. The all countries total is, however, not affected. International investment income consists of net (after overseas taxes) earnings of New Zealand companies operating overseas, irrespective of whether these have been remitted to New Zealand or reinvested overseas.
Current Debits - Transportation consists mainly of freight and marine insurance on imports paid to non-resident shipping companies and port disbursements by New Zealand companies overseas and charters. Travel is exclusive of fares paid in New Zealand, which are included in the transportation account. International investment income is based on total earnings of overseas companies operating in New Zealand, irrespective of whether these are remitted or re-invested in New Zealand. (Refer also to table on page 783 Summary of Overseas Direct Investment in New Zealand.) The item “Films” represents film rentals of commercial films exhibited in New Zealand. Unilateral transfers is the general term for donations or transactions where there is no quid pro quo, as would be the case with merchandise transactions or the rendering of services; the item in the tables consists both of monetary payments as shown in the exchange record and Government and private supplies in kind, such as the estimated value of gift parcels, relief supplies, etc. Migrants' funds and legacies are included in the same group because, from a country's point of view, there is no “consideration” in the ordinary meaning of the word.
Capital Account - As mentioned in the introductory notes, it is the purpose of the capital account to explain how the current surplus or deficit has been financed or, in other words, what changes have occurred to various overseas assets and liabilities (long term, short term, gold reserves) to account for the balance on current account. The tables are largely self-explanatory, but one or two points require mention. The item “Net overseas assets” (of official and banking institutions) is shown in the column of the United Kingdom, although this is not strictly correct. Gross overseas assets and gross overseas liabilities of the Reserve Bank and trading banks arising out of New Zealand business are to a small extent owned or due in currencies other than sterling. At present it has been found impossible to separate movements in other than net sterling assets, but the resulting error is believed to be not very significant. There is another point in connection with this item which should be explained: Net overseas assets are shown here under the description of “Short-term capital and monetary gold - official and banking institutions”. It is well known, of course, that a portion of what is commonly known as sterling exchange is held in the form of investments in United Kingdom stock or short-dated United Kingdom Government paper; these are purchased or sold according to whether there is need for liquidity or not. It is largely a matter of interpretation whether these investments should be treated as short term or long term. The treatment accorded to the item in the table is largely one of convenience.
Attention is drawn to the items “Other short-term capital movements (including errors and omissions)” and “Multilateral transfers”. At the present stage it is impossible to separate the two items on an area-by-area basis, and they are bracketed together. They are shown in one figure in the regional columns, and are merely the residual between the balance on capital account for each area and the capital items which are estimated and shown separately in the same area column.
In the way in which these are shown in the regional columns, they represent (a) short-term capital movements between each respective area and New Zealand, (b) multilateral transfers, i.e., the differences between current account transactions between New Zealand residents and the residents of the respective areas and the movement of financial assets or liabilities in the same area. To give an example, a difference of this kind would arise in the following instance: New Zealand imports of oil from, say, Indonesia may be settled by a remittance to the United Kingdom. While the current account between New Zealand and Indonesia (included in the regional column “Other countries”) would show a debit in that column, the decrease in our overseas assets (from which the payment is made) is shown in the column for the United Kingdom. The purpose of the multilateral transfer entry is to credit the capital account of the United Kingdom, and debit the capital account of the “Other countries” column, in order to compensate the divergent movement in the current and capital accounts.
Because all multilateral transfers, as included in the area column, necessarily cancel each other out, the entry for multilateral transfers in the “Total, All Countries” column is nil; the amount shown in this column represents other short-term capital movements (including errors and omissions) only. Although this entry is a residual balancing item, it is believed to be a fair indicator of movements in short-term commercial credit such as would be caused by timing changes in payments for exports and imports (a shift towards shorter-dated or longer-dated bills or any other change in credit facilities in respect of imports or exports).
REGIONAL BALANCE OF PAYMENTS 1957-58
| A. CURRENT ACCOUNT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | |
| £N.Z. (thousand) | ||||||
| Credits | ||||||
| Exports f.o.b. | 154,750 | 19,000 | 28,150 | 50,600 | 16,050 | 268,550 |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Transportation | 8,550 | 2,050 | 600 | 100 | 100 | 11,400 |
| Travel | 1,000 | 1,950 | 550 | 50 | .. | 3,550 |
| Insurance | 650 | 400 | .. | .. | .. | 1,050 |
| International investment income - | ||||||
| Income from direct investment | 500 | 1,300 | -500 | 50 | 150 | 1,450 |
| Other private investment income | 700 | 1,250 | 100 | .. | .. | 2,050 |
| Interest on investments of Government and official institutions | 3,200 | - | - | 100 | - | 3,300 |
| Government transactions - | ||||||
| Expenditure by foreign governments in New Zealand | 100 | 200 | 100 | 150 | 150 | 700 |
| New Zealand Government current receipts from overseas | 1,050 | 550 | 250 | .. | .. | 1,850 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 3,500 | 1,200 | 550 | 700 | 50 | 6,000 |
| Unilateral transfers - | ||||||
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 2,300 | 1,100 | 400 | 100 | .. | 3,900 |
| Immigrants' fund | 2,250 | 900 | 100 | 100 | .. | 3,350 |
| Legacies | 950 | 400 | 50 | .. | .. | 1,400 |
| Total debits | 179,500 | 30,300 | 30,350 | 51,950 | 16,500 | 308,550 |
| Debits | ||||||
| Imports f.o.b. | 147,000 | 62,800 | 26,550 | 25,200 | 11,700 | 273,200 |
| Transportation | 25,750 | 1,150 | 1,500 | 2,000 | 1,400 | 31,800 |
| Travel | 4,000 | 2,150 | 500 | 150 | 50 | 6,850 |
| Insurance | 850 | 100 | 50 | .. | .. | 1,000 |
| International investment income - | ||||||
| Income from direct investment in New Zealand | 5,200 | 2,700 | 3,050 | 100 | .. | 11,000 |
| Other private investment income | 1,500 | 300 | 200 | .. | .. | 2,000 |
| Interest on Government debt | 3,500 | .. | 200 | .. | .. | 3,700 |
| Interest on local authority debt | 150 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 150 |
| Government transactions - | ||||||
| Current Government expenditure | 5,950 | 2,700 | 500 | 50 | 350 | 9,550 |
| Miscellaneous payments | 5,550 | 2,100 | 1,950 | 1,050 | 100 | 10,750 |
| Films | 150 | 100 | 650 | 900 | ||
| Unilateral transfers - | ||||||
| Government contribution to Colombo Plan | 750 | 750 | ||||
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 1,550 | 1,440 | 100 | 450 | 350 | 3,850 |
| Emigrants' funds | 1,350 | 1,200 | 350 | 100 | 3,000 | |
| Legacies | 900 | 650 | 50 | 50 | 1,650 | |
| Total debits | 203,400 | 78,100 | 35,650 | 29,150 | 13,950 | 360,150 |
| Balance on current account (surplus +; deficit -) | -23,900 | -47,800 | -5,300 | +22,800 | +2,550 | -51,600 |
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | ||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Long-term capital (private) – | ||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 9,550 | ... | 1,800 | ... | -900 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | -100 | 1,300 | ... | -100 | ... | |
| Other long-term capital movements | -1,350 | -250 | -200 | 50 | -250 | 900 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government investments | -1,250 | - | 1,550 | - | - | - |
| Public debt | ... | -850 | ... | 250 | ... | -500 |
| Local authority debt | ... | 500 | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | 200 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | 100 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Wool credit to France | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government cash balances | 250 | - | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Other | -400 | - | - | -450 | -- | -- |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| Net overseas assets | -39,600 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Other short-term capital movements, in eluding errors and omissions | 26,400 | - | - | 48,800 | - | 5,650 |
| Multilateral transfers | ||||||
| Balance on capital account | -23,900 | -47,800 | -5,300 | |||
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
| OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | ||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Long-term capital (private) – | ||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 2,200 | ... | - | ... | 12,650 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | ... | ... | 100 | ... | 1,250 | ... |
| Other long-term capital movements | -50 | ... | .. | .. | -1,850 | 700 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government investments | - | - | - | - | 300 | - |
| Public debt | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | -1,100 |
| Local authority debt | - | - | - | - | - | -500 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | -200 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) – | ||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | - | - | - | - | 100 | - |
| Wool credit to France | -3,750 | - | - | - | 3,750 | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) – | ||||||
| Government cash balances | - | - | - | - | 300 | - |
| Other | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 50 |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| Net overseas assets | ... | ... | ... | ... | -39,600 | - |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions | 28,800 | - | 2,450 | - | 3,150 | - |
| Multilateral transfers | - | - | ||||
| Balance on capital account | +22,800 | +2,550 | -51,600 | |||
REGIONAL BALANCE OF PAYMENTS 1958-59
| A. CURRENT ACCOUNT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Credits | ||||||
| Exports f.o.b. | 150,100 | 18,450 | 46,350 | 36,450 | 10,250 | 261,550 |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | .. |
| Transportation | 8,350 | 2,400 | 100 | .. | 200 | 11,050 |
| Travel | 1,000 | 1,500 | 450 | .. | .. | 2,950 |
| Insurance | 150 | .. | .. | 50 | .. | 200 |
| International investment income - | ||||||
| Income from direct investment | 400 | 1,450 | -500 | ... | 50 | 1,450 |
| Other private investment income | 800 | 1,150 | ... | ... | ... | 1,950 |
| Interest on investments of Government and official institutions | 2,500 | - | - | - | - | 2,500 |
| Government transactions - | ||||||
| Expenditure by foreign governments in New Zealand | 50 | 200 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 600 |
| New Zealand Government current receipts from overseas | 200 | 650 | 100 | .. | .. | 950 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 2,900 | 1,500 | 500 | 150 | .. | 5,050 |
| Unilateral transfers - | ||||||
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 2,300 | 950 | 450 | 100 | .. | 3,800 |
| Immigrants' funds | 1,550 | 700 | 150 | 50 | .. | 2,450 |
| Legacies | 700 | 300 | 100 | - | 1,100 | |
| Total credits | 171,000 | 29,250 | 47,900 | 36,900 | 10,550 | 295,600 |
| Debits | ||||||
| Imports f.o.b. | 120,700 | 60,850 | 21,300 | 22,250 | 8,850 | 233,900 |
| Transportation | 22,350 | 1,550 | 1,000 | 2,900 | 800 | 28,600 |
| Travel | 4,400 | 2,700 | 500 | 150 | 50 | 7,800 |
| Insurance | 950 | 150 | 100 | .. | - | 1,200 |
| International investment income - | ||||||
| Income from direct investment in New Zealand | 5,050 | 3,600 | 3,100 | 100 | - | 11,850 |
| Other private investment income | 1,750 | 300 | 150 | 100 | - | 2,300 |
| Interest on Government debt | 4,300 | - | 300 | - | - | 4,600 |
| Interest on local authority debt | 150 | - | - | - | 150 | |
| Government transactions - | ||||||
| Current Government expenditure | 2,150 | 3,950 | 500 | 50 | 400 | 7,050 |
| Miscellaneous payments | 6,350 | 2,200 | 2,250 | 700 | 50 | 11,550 |
| Films | 250 | 150 | 700 | .. | .. | 1,100 |
| Unilateral transfers - | ||||||
| Government contribution to Colombo Plan | - | 1,000 | - | - | .. | 1,000 |
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 1,450 | 1,400 | 100 | 400 | 300 | 3,650 |
| Emigrants' funds | 1,800 | 1,700 | 400 | 150 | .. | 4,050 |
| Legacies | 750 | 500 | 50 | .. | .. | 1,300 |
| Total debits | 172,400 | 80,050 | 30,450 | 26,800 | 10,450 | 320,100 |
| Balance on current account (surplus + ; deficit -) | -1,400 | -50,800 | +17,450 | +10,100 | +100 | -24,500 |
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | ||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | ||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 7,650 | ... | 3,100 | ... | 500 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | -200 | ... | 950 | ... | 50 | |
| Other long-term capital movements | -1,650 | -350 | 250 | 2,450 | -100 | 350 |
| Long-term capital (Government) – | ||||||
| Government investments | .... | 100 | ... | - | ... | |
| Public debt | ... | 18,700 | .... | - | ... | 19,600 |
| Local authority debt | ... | -1,100 | ... | - | ... | - |
| Other | ... | - | ... | - | ... | -150 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | 100 | - | – | - | - | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government cash balances | -2,350 | – | -200 | - | 2,200 | - |
| Other | 3,200 | - | ... | - | ... | - |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| Net overseas assets | 25,050 | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Other short-term capital movements, in eluding errors and omissions | - | 650 | - | 46,350 | 35,700 | - |
| Multilateral transfers | ||||||
| Balance on capital account | 1 ,400 | -50,800 | +17,450 | |||
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
| OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | ||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z. [thousand) | ||||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | ||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 500 | ... | ... | ... | 11,750 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | ... | ... | 50 | ... | 750 | ... |
| Other long-term capital movements | 50 | - | - | - | -1,550 | 2,450 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government investments | - | - | - | - | 100 | – |
| Public debt | ... | - | ... | - | ... | -38,200 |
| Local authority debt | ... | - | ... | - | ... | 1,100 |
| Other | ... | - | ... | - | ... | 150 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | - | - | - | - | 100 | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government cash balances | - | ... | - | - | -350 | ... |
| Other | - | - | - | - | 3,200 | - |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| Net overseas assets | ... | ... | ... | ... | 25,050 | - |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions | 10,650 | - | 50 | - | ... | 650 |
| Multilateral transfers | - | |||||
| Balance on capital account | +10,000 | +100 | -24,500 | |||
REGIONAL BALANCE OF PAYMENTS 1959-60
| A. CURRENT ACCOUNT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||||
| Credits | |||||||
| Exports f.o.b. | 169,250 | 21,450 | 48,550 | 49,600 | 2,850 | 18,250 | 310,050 |
| Non-monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | |
| Transportation | 8,850 | 2,600 | 300 | 50 | 50 | 250 | 12,100 |
| Travel | 1,000 | 1,600 | 600 | 50 | ... | ... | 3,250 |
| Insurance | 350 | -50 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 300 |
| International investment income - | |||||||
| Income from direct investment overseas | 500 | 1,750 | -200 | .. | - | 50 | 2,100 |
| Other private investment income | 550 | 850 | 150 | .. | .. | .. | 1,550 |
| Interest on investments of Government and official institutions | 3,500 | .. | .. | - | - | - | 3,500 |
| Government transactions - | |||||||
| Expenditure by foreign governments in New Zealand | 150 | 350 | 550 | 100 | .. | 50 | 1,200 |
| New Zealand Government current receipts from overseas | 300 | 800 | 200 | .. | .. | .. | 1,300 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 3,050 | 1,150 | 700 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 5,200 |
| Unilateral transfers - | |||||||
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 2,500 | 1,000 | 450 | 100 | .. | .. | 4,050 |
| Immigrants' funds | 1,300 | 750 | 150 | 50 | .. | .. | 2,250 |
| Legacies | 900 | 250 | 100 | 50 | 50 | - | 1,350 |
| Total credits | 192,200 | 32,500 | 51,550 | 50,100 | 3,050 | 18,700 | 348,200 |
| Debits | |||||||
| Imports f.o.b. | 103,400 | 58,100 | 24,150 | 15,900 | 5,850 | 10,700 | 218,100 |
| Transportation | 17,850 | 1,600 | 1,700 | 1,550 | 2,550 | 300 | 25,550 |
| Travel | 5,200 | 3,350 | 700 | 200 | 100 | 100 | 9,650 |
| Insurance | 1,150 | 200 | 50 | .. | .. | .. | 1,450 |
| International investment income - | |||||||
| Income from direct investment in New Zealand | 5,750 | 3,800 | 2,900 | 50 | 150 | .. | 12,650 |
| Other private investment income | 1,800 | 850 | 250 | .. | 50 | .. | 2,950 |
| Interest on Government debt | 4,600 | - | 950 | - | - | - | 5,550 |
| Interest on local authority debt | 150 | .. | - | - | - | - | 150 |
| Government transactions - | |||||||
| Current Government expenditure | 4,000 | 4,200 | 700 | 200 | 250 | 450 | 9,800 |
| Miscellaneous payments | 6,200 | 3,300 | 2,550 | 800 | 250 | 100 | 13,200 |
| Films | 250 | 100 | 800 | .. | .. | .. | 1,150 |
| Unilateral transfers - | |||||||
| Government contribution to Colombo Plan | .. | 1,000 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 1,000 |
| Personal remittances and other donations and transfers | 2,800 | 1,850 | 50 | 200 | 200 | 350 | 5,450 |
| Emigrants' funds | 800 | 2,200 | 450 | 100 | 50 | .. | 3,600 |
| Legacies | 1,000 | 600 | 250 | .. | .. | .. | 1,850 |
| Total debits | 154,950 | 81,150 | 35,500 | 19,000 | 9,450 | 12,000 | 312,100 |
| Balance on current account (surplus +; deficit –) | + 37,250 | -48,650 | + 16,050 | +31,100 | -6,400 | +6,700 | +36,100 |
| B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | ||||
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | ||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | ||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 2,050 | ... | 4,200 | ... | -650 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | 1,150 | ... | 1,200 | ... | 50 | ... |
| Other long-term capital movements | -2,000 | 1,550 | -300 | 250 | 150 | 3,800 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government investments | 2,200 | - | 50 | - | 10,100 | - |
| Public Debt | ... | -500 | ... | - | ... | -4,600 |
| Local authority debt | ... | -500 | ... | - | ... | - |
| Other | ... | – | ... | - | – | -150 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | 150 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | ||||||
| Government cash balances | -600 | - | -50 | - | -600 | - |
| Other | 3,850 | - | - | 250 | - | - |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||
| Net overseas assets | 22,700 | - | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and omissions | 12,400 | - | - | 44,850 | 5,150 | - |
| Multilateral transfers | ||||||
| Balance on capital account | + 37,250 | -48 ,650 | + 16,050 | |||
| EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | Increase in | |||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||||
| Long-term capital (private) - | ||||||||
| Overseas direct investment in New Zealand | ... | 300 | ... | 50 | ... | 50 | ... | 5,950 |
| New Zealand direct investment overseas | ... | ... | - | ... | 50 | ... | 2,350 | ... |
| Other long-term capital movements | - | 50 | - | - | - | - | -2,450 | 5,650 |
| Long-term capital (Government) - | ||||||||
| Government investments | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12,350 | - |
| Public debt | ... | - | ... | – | ... | - | ... | -5,100 |
| Local authority debt | ... | - | ... | - | ... | - | ... | -500 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | - | ... | -150 |
| Long-term capital (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||||
| New Zealand Wool Commission | - | - | - | - | - | - | -150 | - |
| Short-term capital (Government) - | ||||||||
| Government cash balances | ... | - | ... | - | ... | - | -1,250 | ... |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3,850 | 250 |
| Short-term capital and monetary gold (official and banking institutions) - | ||||||||
| Net overseas assets | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 22,700 | - |
| Monetary gold | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | - | |
| Other short-term capital movements, including errors and 1 omissions | 31,450 | - | - | -6,350 | 6,700 | - | -4,500 | - |
| Multilateral transfers | - | - | ||||||
| Balance on capital account | +31,100 | -6,400 | +6,700 | +36,100 | ||||
The following diagram shows New Zealand's balance of payments by monetary areas for the five years 1955-56 to 1959-60.
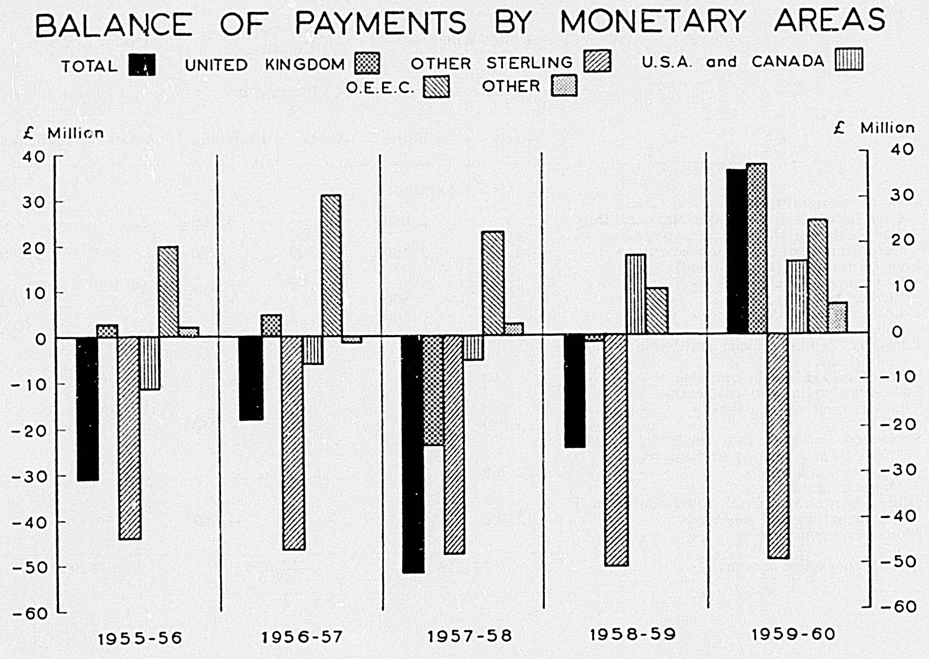
SURVEY OF COMPANIES WITH OVERSEAS AFFILIATIONS - The picture of international capital movements would be incomplete without the consideration of investment flows originating with private commercial firms. While such investment takes place in response to usual economic motivations, its effect on a country's balance of payments differs in no respect from other capital movements, such as Government lending or borrowing abroad, investment or repatriation of assets from abroad by private individuals, etc.
The type of investment referred to here is that defined as direct private investment. Subsidiaries under control of an overseas company, branches of overseas companies, companies where the majority of shareholders reside overseas, or any other companies where overseas shareholders exercise a controlling interest, fall under this category. The question of control is decided in some cases on the strength of the parent company's holdings (a 25 per cent holding of the subsidiary's ordinary share capital is deemed as the qualifying minimum), in others on the actual circumstances of the case. The same criteria apply for direct investment by New Zealand companies and residents overseas.
Direct investment flows assume various forms: they may be by remittances of cash, the provision of plant, machinery, or goods without corresponding payments, charging up of services rendered by the parent company, the reinvestment in New Zealand of undistributed profits, or the partial remittance only of declared dividends and branch earnings. The inclusion of undistributed profits may require some explanation: the non-remittance abroad of the whole of the current year's earnings, or any portion of them involves, where no statutory constraints exist on remittances of current profits, a decision to invest which is in every respect equal to a decision to bring additional investment capital into the country. By treating, as already mentioned previously, total New Zealand earnings of subsidiaries and branches as a current account debit or payment to the rest of the world, the un-remitted portions of such earnings are treated as an inflow of investment capital which, together with other forms of investment capital (cash, goods, services), make up the total of the private direct investment item in the capital account (see tables on pages 777-781).
The information tabulated in the following tables is based on an annual survey of companies with overseas affiliations in which the companies report on the distribution of paid-up capital and its changes, dividends and dividend remittances, intercompany accounts with the parent company or affiliated company, and head office accounts in the case of branches.
It should be noted that investment figures given in the following three tables are in terms of annual changes at current prices. The total worth of direct investment assets is extremely difficult to establish in view of the fact that book values may bear little relationship to what such investments would realise on sale; annual changes on the other hand are capable of precise expression, and define exactly their relationship to other capital movements.
Overseas Private Direct Investment in New Zealand - Data on overall private direct investment in New Zealand are shown in the following table. The figures are totals reflecting investment changes in firms resident in New Zealand and controlled from overseas irrespective of their legal organisation. They include therefore subsidiaries incorporated in New Zealand, companies incorporated in New Zealand which have a majority of shareholders resident overseas or are controlled by overseas residents, and New Zealand branches of overseas companies.
The figures shown in the, country or regional area columns refer to the country of incorporation of the New Zealand firm's parent company, head office, or associate company from which the investment flow originates, or the country of residence of individual shareholders who either individually or collectively hold a majority interest in the New Zealand company or who exercise de facto control.
| Total Investment Increase | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Total, All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Includes a small increase in holdings by companies of “other countries”. | ||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955-56 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in paid-up capital | 2,650 | 350 | 280 | - | 3,280 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness | 7,480 | -310 | 200 | -140 | 7,230 | |
| Increase in reserves | 2,400 | 1,140 | 1,020 | 30 | 4,590 | |
| Total increase in investment | 12,530 | 1,180 | 1,500 | -110 | 15,100 | |
| 1956-57 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in paid-up capital | 3,080 | 590 | 50 | 140 | 3,860 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness | -950 | 1,930 | 450 | 730 | 2,160 | |
| Increase in reserves | 2,390 | 1,030 | 340 | 80 | 3,840 | |
| Total increase in investment | 4,520 | 3,550 | 840 | 950 | 9,860 | |
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| 1957-58 | ||||||
| Increase in paid-up capital | 1,650 | 50 | 230 | 1,930 | ||
| Increase in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness | 7,270 | 680 | -1,460 | 2,170 | 8,660 | |
| Increase in reserves | 610 | 1,070 | 340 | 20 | 2,040 | |
| Total increase in investment | 9,530 | 1,800 | - 890 | 2,190 | 12,630 | |
| 1958-59 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in paid-up capital | 870 | 680 | 30 | 30 | 1,610 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness | 5,940 | 1,310 | 230 | 430 | 7,910 | |
| Increase in reserves | 860 | 1,100 | 260 | 10 | 2,230 | |
| Total increase in investment | 7,670 | 3,090 | 520 | 470 | 11,750 | |
| 1959-60* | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in paid-up capital | 2,030 | 1,260 | 740 | 10 | 20 | 4,100† |
| Increase in net branch assets and intercompany indebtedness | -2,490 | 1,830 | -1,790 | 260 | -50 | -2,250 |
| Increase in reserves | 2,500 | 1,100 | 400 | 20 | 80 | 4,100 |
| Total increase in investment | 2,040 | 4,190 | -650 | 290 | 50 | 5,950 |
The graph now presented shows changes in the overseas direct investment in New Zealand for the five years 1955-56 to 1959-60.
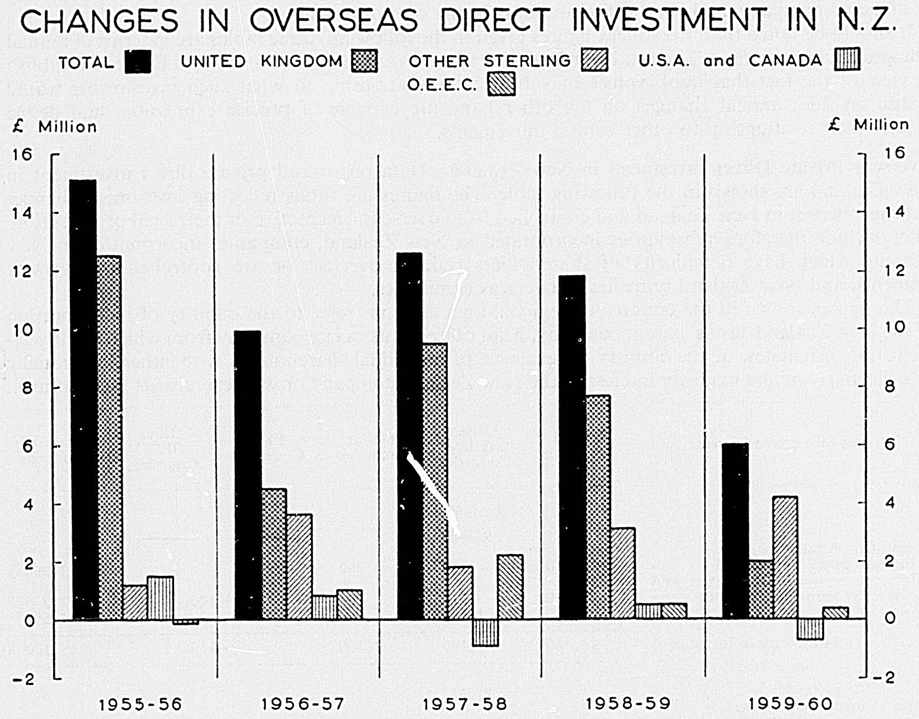
Investment in New Zealand Subsidiaries of Overseas Companies - The table below provides information on subsidiaries only; the figures shown here form part of the totals in the preceding table. The parent company's or associate company's country of incorporation or residence determines the country or regional area column.
| Investment Increase in New Zealand Subsidiaries | United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Total, All Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Provisional. †Includes a small increase in holdings by companies of “other countries”. | ||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955-56 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in holdings of paid-up capital | 2,650 | 350 | 280 | - | 3,280 | |
| Increase in intercompany indebtedness | 1,240 | 220 | 40 | 130 | 1,630 | |
| Increase in reserves | 2,400 | 1,140 | 1,020 | 30 | 4,590 | |
| Total increase in investment | 6,290 | 1,710 | 1,340 | 160 | 9,500 | |
| 1956-57 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in holdings of paid-up capital | 3,080 | 590 | 50 | 140 | 3,860 | |
| Increase in intercompany indebtedness | -2,710 | 340 | 400 | 170 | -1,800 | |
| Increase in reserves | 2,390 | 1,030 | 340 | 80 | 3,840 | |
| Total increase in investment | 2,760 | 1,960 | 790 | 390 | 5,900 | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| 1957-58 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in holdings of paid-up capital | 1,650 | 50 | 230 | 1,930 | ||
| Increase in intercompany indebtedness | 3,980 | 630 | -1,190 | -40 | 3,380 | |
| Increase in reserves | 610 | 1,070 | 340 | 20 | 2,040 | |
| Total increase in investment | 6,240 | 1,750 | -620 | -20 | 7,350 | |
| 1958-59 | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in holdings of paid-up capital | 870 | 680 | 30 | 30 | 1,610 | |
| Increase in intercompany indebtedness | 2,930 | -360 | -90 | 90 | 2,570 | |
| Increase in reserves | 860 | 1,100 | 260 | 10 | 2,230 | |
| Total increase in investment | 4,660 | 1,420 | 200 | 130 | 6,410 | |
| 1959-60* | ||||||
| Form of investment increase - | ||||||
| Increase in holdings of paid-up capital | 2,030 | 1,260 | 740 | 10 | 20 | 4,100† |
| Increase in intercompany indebtedness | -690 | 530 | 1,120 | 130 | -30 | -1,190 |
| Increase in reserves | 2,500 | 1,100 | 400 | 20 | 80 | 4,100 |
| Total increase in investment | 3,840 | 2,890 | 20 | 160 | 70 | 7,010 |
New Zealand Subsidiaries of Overseas Companies: Dividends - The table gives an account of dividend appropriations (dividends declared) and remittances of dividends to overseas shareholders. Dividends declared are part of the item “Income from direct investment in New Zealand” on the debit side of each year's balance of payments account where, together with undistributed profits, they account for all subsidiary profits accruing to overseas shareholders. The difference between dividends declared and dividends remitted forms part of the increase in intercompany indebtedness shown in the tables on pages 783-785, from which it is ultimately transferred into the capital account of the balance of payments.
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Total, All Countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Dividends Declared | ||||||
| 1951-52 | 350 | 270 | 530 | 30 | 1,180 | |
| 1952-53 | 370 | 440 | 720 | 10 | 1,540 | |
| 1953-54 | 780 | 390 | 1,170 | 50 | 2,390 | |
| 1954-55 | 540 | 370 | 1,240 | 10 | 2,160 | |
| 1955-56 | 690 | 460 | 1,880 | 10 | 3,040 | |
| 1956-57 | 1,250 | 500 | 2,280 | 20 | 4,050 | |
| 1957-58 | 1,440 | 520 | 2,610 | 40 | 4,610 | |
| 1958-59 | 1,610 | 810 | 2,450 | 80 | 4,50 | |
| 1959-60 | 1,560 | 1,040 | 2,320 | 10 | 60 | 4,990 |
| Totals, 1951-52 to 1959-60 | 8,590 | 4,800 | 15,200 | 320 | 28,910 | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| Dividends Remitted | ||||||
| 1951-52 | 250 | 250 | 540 | 30 | 1,070 | |
| 1952-53 | 290 | 370 | 710 | 1,370 | ||
| 1953-54 | 670 | 330 | 920 | 40 | 1,960 | |
| 1954-55 | 530 | 290 | 1,140 | 10 | 1,970 | |
| 1955-56 | 560 | 280 | 1,880 | 2,720 | ||
| 1956-57 | 910 | 370 | 2,270 | 10 | 3,560 | |
| 1957-58 | 980 | 480 | 2,580 | 30 | 4,070 | |
| 1958-59 | 1,180 | 730 | 2,260 | 50 | 4,220 | |
| 1959-60 | 1,330 | 860 | 1,850 | 10 | 10 | 4,100 |
| Totals, 1951-52 to 1959-60 | 6,700 | 3,960 | 14,150 | 230 | 25,040 | |
New Zealand Branches of Overseas Companies - Net (after tax) earnings and remittances of such earnings and annual increases in investments by overseas companies in their New Zealand branches are described in the table which follows. Net branch earnings, together with dividends declared and undistributed profits of subsidiaries, account for the whole of “Income from direct investment in New Zealand” as shown amongst the debit items of the current balance of payments. The difference between net (after tax) earnings and remittances of such earnings is part of the third item in the following table (increase in net branch assets and other investments) and is a capital item; it is again repeated in the table on page 783 and finally transferred from there to the balance of payments capital account.
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Total, All Countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955-56 | ||||||
| Net earnings of branches (after tax) | 2,570 | 830 | 70 | 10 | 3,480 | |
| Net earnings remitted | 1,400 | 690 | 70 | 10 | 2,170 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and other investments | 6,240 | -530 | 160 | -270 | 5,600 | |
| 1956-57 | ||||||
| Net earnings of branches (after tax) | 3,000 | 740 | 30 | 10 | 3,780 | |
| Net earnings remitted | 1,200 | 380 | 90 | 10 | 1,680 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and other investments | 1,760 | 1,590 | 50 | 560 | 3,960 | |
| 1957-58 | ||||||
| Net earnings of branches (after tax) | 3,150 | 1,100 | 90 | 20 | 4,360 | |
| Net earnings remitted | 1,280 | 620 | 110 | 10 | 2,020 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and other investments | 3,290 | 50 | -270 | 2,210 | 5,280 | |
| 1958-59 | ||||||
| Net earnings of branches (after tax) | 2,600 | 1,670 | 390 | 10 | 4,670 | |
| Net earnings remitted | 1,300 | 980 | 170 | 10 | 2,460 | |
| Increase in net branch assets and other investments | 3,010 | 1,670 | 320 | 340 | 5,340 | |
| 1959-60* | ||||||
| Net earnings of branches (after tax) | 1,670 | 1,660 | 190 | - | 20 | 3,540 |
| Net earnings remitted | 1,030 | 870 | 120 | - | 10 | 2,030 |
| Increase in net branch assets and other investments | -1,800 | 1,300 | -570 | 130 | -20 | -1,060 |
Investment by New Zealand Companies Overseas - The following table presents the converse picture of those immediately preceding, viz, direct investment income and capital investment by New Zealand companies in their overseas subsidiaries and branches. The net earnings (after overseas taxation) series is again repeated in the item “Income from direct investment overseas” on the credit side of the current balance of payments account, and the combined figure for investment in subsidiaries and branches is transferred to each country (regional) area column in the capital account (item “New Zealand direct investment overseas”).
| United Kingdom | Other Sterling Countries | Dollar Countries | EEC Countries | Other OEEC Countries | Other Countries | Total, All Countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Provisional. | |||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||||||
| 1955-56 | |||||||
| Net earnings (after overseas taxation) | 530 | 1,160 | 210 | - | - | 1,900 | |
| Investment – | |||||||
| Subsidiaries | -240 | 40 | -30 | .. | - | 230 | |
| Branches | 290 | 330 | 390 | - | 30 | 1,040 | |
| Total increase in investment | 50 | 370 | 360 | - | 30 | 810 | |
| 1956-57 | |||||||
| Net earnings (after overseas taxation) | 460 | 1,280 | -40 | 40 | 50 | 1,790 | |
| Investment – | |||||||
| Subsidiaries | 450 | -30 | -20 | 40 | - | 440 | |
| Branches | 430 | 520 | 40 | - | 110 | 1,100 | |
| Total increase in investment | 880 | 490 | 20 | 40 | 110 | 1,540 | |
| 1957-58 | |||||||
| Net earnings (after overseas taxation) | 480 | 1,310 | -500 | 40 | 130 | 1,460 | |
| Investment – | |||||||
| Subsidiaries | -30 | 120 | -50 | .. | - | 40 | |
| Branches | -70 | 1,200 | -30 | - | 120 | 1,220 | |
| Total increase in investment | -100 | 1,320 | -80 | .. | 120 | 1,260 | |
| 1958-59 | |||||||
| Net earnings (after overseas taxation) | 400 | 1,470 | -480 | 20 | 30 | -1,440 | |
| Investment – | |||||||
| Subsidiaries | -30 | 20 | -30 | .. | - | -40 | |
| Branches | -170 | 910 | - | - | 60 | 800 | |
| Total increase in investment | -200 | 930 | -30 | .. | 60 | 760 | |
| 1959-60* | |||||||
| Net earnings (after overseas taxation) | 480 | 1,750 | -200 | .. | - | 50 | 2,080 |
| Investment – | |||||||
| Subsidiaries | 370 | -130 | -40 | .. | - | - | 200 |
| Branches | 770 | 1,340 | 10 | - | - | 40 | 2,160 |
| Total increase in investment | 1,140 | 1,210 | -30 | .. | - | 40 | 2,360 |
In recent years two inter-industry studies of the New Zealand economy for the years 1952-53 and 1954-55 have been completed. Details of the 1954-55 study together with amended figures for 1952-53 were given in the 1959 and 1960 Yearbooks. Readers interested in the technical details of this particular aspect of social accounts are referred to the Report on the Inter-Industry Study of the New Zealand Economy in 1952-53 a special supplement to the February 1957 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics, and the Report on the Inter-Industry Study of the New Zealand Economy for the year 1954-55 issued as a separate volume in 1959.
Table of Contents
GENERAL - The legislation relating to the custody, administration, and audit of the public moneys and securities is contained in the Public Revenues Act 1953. All public moneys are paid into or are payable to either one account at the Reserve Bank called the “Public Account” or to certain other accounts which are outside the Public Account (refer to text following).
The statistical material presented in the ensuing pages relates solely to those accounts or funds included within the framework of the Public Account. (However, a consolidated review of Government receipts and expenditure on current account appears in the section on National Income and Expenditure. This review has accordingly taken into consideration the net surpluses or deficits of trading and other accounts not within the Public Account. This analysis has now been supplemented for the years 1956-57 to 1959-60 by a more comprehensive economic classification of the accounts of the Government Sector, copies of which are available from the Government Printer.)
Financial Year - The financial year commences on 1 April and ends on 31 March. The receipts of any financial year represent the money received into the Public Account at the bank at Wellington within the year, together with that received into the Public Account at London, of which advice is received in time for inclusion in the accounts for the year. The payments represent the money paid (a) at the Treasury within the year, (b) by imprestees, of which accounts are received at the Treasury within the year, and (c) at London, of which advice is received in time for inclusion. The Public Account, formerly held at the Bank of New Zealand, was taken over by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand from 1 August 1934.
At the end of each financial year the Appropriation Act of that year lapses, but the Minister of Finance is authorised for a period of three months from the commencement of the next financial year to pay money in respect of any service, provided that the amount does not exceed the unexpended balance voted for that purpose in the previous year, together with an amount equal to one-fourth of such vote.
The normal practice has been for Parliament to meet at the end of June in each year and to vote supplies from month to month until the estimated expenditure for the year has been approved and the annual Appropriation Act is passed. Where a later session of Parliament is foreseen, a temporary amendment to the provisions set out in the preceding paragraph is made. In the event of a mid-session adjournment, supplies in anticipation of the Appropriation Act may be voted for more than one month.
Where provision has been made for expenditure in the nature of a grant or for a purpose that does not normally recur, but the expenditure cannot be made during the financial year, the Minister of Finance may direct that the unexpended balance shall be transferred to a separate fund or account. In such a case the amount is held there until payment is required, when the amount may be expended without further appropriation.
Audit of Expenditure - In the audit of expenditure both the pre-audit and post-audit systems are in operation. Pre-audit is applied to vouchers in respect of payments on account of officers claiming more than one month's salary at any time; interest, loan transactions, and return of deposits; unauthorised expenditure; or expenditure chargeable against the accounts of local authorities. Post-audit is applied to all other payments.
Vouchers must be certified as correct by the proper officer, and forwarded by him to the head of his Department for approval. Vouchers subject to pre-audit arc then forwarded to the Audit Office, and on being found correct are sent on to the Treasury to be entered on requisitions for payment. Vouchers subject to post-audit are transmitted by the head of the Department direct to the Treasury. Payment is made by the Treasury, and the claim is afterwards submitted for audit.
Section 20 of the Public Revenues Act 1953 enables the Controller and Auditor-General to determine, within reasonable limits, the extent of the audit of the Public Accounts.
Income and Expenditure - A number of departmental balance sheets and statements of accounts showing the cost of the various Departments and services on a commercial basis, as distinct from cash payments out of appropriations, referred to at the beginning of this subsection, are published annually in either the annual report of the Department concerned or parliamentary' paper B. 1 (Pt. IV).
ACCOUNTS AND FUNDS OUTSIDE THE PUBLIC ACCOUNT - In addition to those moneys payable into the Public Account, money paid into the following accounts is also deemed to be public money - Broadcasting Account, Government Accident Insurance Account, Government Insurance Account, Government Superannuation Fund Account, Housing Account, Maori Trustee's Account, Meat Industry Account, Post Office Account, National Provident Fund Account, Public Trustee's Account, State Fire Insurance Account, and such other accounts as from time to time are declared to be such by Order in Council.
Transactions in connection with the majority of these accounts are given in the various sections of the Yearbook dealing with the relevant activity.
ACCOUNTS AND FUNDS WITHIN THE PUBLIC ACCOUNT - The records of the Public Account in the books of the Treasury consist of a number of ledger accounts for the special subsidiary funds or accounts, and a number of other accounts established by statute or kept by Treasury under authority of the Public Revenues Act. In these accounts are recorded for each separate fund or account the receipts, payments, and cash balance so that the bank balance in the Public Account is apportioned among the funds and accounts, and balanced itemised statements of the receipts and payments for each of the funds or accounts are prepared for publication.
The use of the terms “fund” and “account” implying some significant distinction is hardly justified. The use of the term “Social Security Fund,” for example, does not imply any technical accounting distinction between the Social Security Fund and the Public Works Account or the other accounts within the Public Account.
The following accounts and funds were included in the Public Account at 1 April 1960: Consolidated Fund, Public Works Account, Social Security Fund, Defence Fund, Deposits Account, Earthquake and War Damage Fund, Electric Supply Account, Land Settlement Account, Loans Redemption Account, National Development Loans Account, Reserve Fund, State Coal Mines Account, Working Railways Account, National Roads Fund, and Gas Industry Account.
Particulars of some of the more important accounts are contained in the following pages, while others are dealt with in the appropriate sections of this volume. The Deposits Account represents only lodgements or withdrawals of (mainly) non-Government moneys. The Loans Redemption Account is dealt with in the subsection on indebtedness.
The figures shown under the various headings of this subsection are on the basis of receipts and payments. In some sections devoted to the operations of various Departments and activities, the figures are given on an income and expenditure basis and accordingly differ to some extent from those appearing here.
SUMMARY OF PUBLIC ACCOUNT FOR 1958-59 AND 1959-60 - The source of the following table is parliamentary paper B. 6, 1960.
Explanatory Note
1. In previous years the “net purchase of miscellaneous investments” has been shown as a single total and included with other items of works and capital expenditure. Because of the substantial increase in this item, due mainly to the investment in 1959-60 of £16 million in New York and London, the item has been shown separately in the following table and analysed to show annual changes in Public Account holdings of miscellaneous investments both in New Zealand and overseas. All other investment transactions are indicated by footnote.
2. The items at the foot of the expenditure side of the table which were previously described as the “overall cash surplus or deficit” have been shown in the table under the heading “Balancing Items”. These show how the total receipts and payments of the Public Account have been balanced each year either by change in cash balances or in debt to the banking system. No other items are included. In 1959-60 Public Account indebtedness to the banking system increased by £34.3 million, but after allowing for the £16 million invested overseas, the net or effective deficit amounted to £18.3 million.
3. Minor modifications to the table include the analysis of receipts of the National Roads Fund and the grouping of the transfer entries together on the receipts side of the table to facilitate interpretation.
| Receipts | Year Ended 31 March | |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
*Includes transfers made under other expenditure headings. † Investment transactions. ‡Includes £16-0 million invested in New York and London offset by realisation of investments totalling £0.5 million, §Includes £16.5 million repaid to Reserve Bank from proceeds short-term overseas borrowing. | ||
| £(million) | ||
| Consolidated Fund and Social Security Fund | ||
| Taxation receipts - | ||
| Income tax | 109.4 | 175.9 |
| Social security tax | 80.6 | |
| Customs duty | 40.0 | 43.4 |
| Beer duty | 11.3 | 13.3 |
| Sales tax | 25.8 | 24.2 |
| Stamp, racing, and estate duties | 17.4 | 19.8 |
| Other taxation | 1.7 | 1.9 |
| Totals | 286.2 | 278.5 |
| Other receipts- | ||
| Interest | 13.8 | 15.0 |
| Profits from trading undertaking | 3.7 | 3.4 |
| Departmental receipts | 18.4 | 20.5 |
| Total Consolidated Fund and Social Security Fund receipts | 322.1 | 317.4 |
| Expenditure | Year Ended 31 March | |
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| Expenditure - | ||
| Social services | 159.9 | 185.8 |
| Defence | 17.8 | 19.2 |
| Administration, etc. | 27.8 | 31.1 |
| Stabilisation | 12.9 | 12.6 |
| Maintenance of works, etc. | 11.5 | 12.3 |
| Development of industry | 22.9 | 18.6 |
| Interest and management of public debt | 28.6 | 29.1 |
| Totals | 281.4 | 308.7 |
| Transfer from Consolidated Fund to - | ||
| Loans Redemption Account | 8.8 | 9.3 |
| Public Works Account | 5.0 | - |
| Defence Fund | 9.0 | - |
| National Roads Fund | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Total Consolidated Fund and Social Security Fund expenditure | 305.7 | 319.2 |
| Other Accounts Within the Public Account | ||
| Transfers from Consolidated Fund to -* | ||
| Loans Redemption Account | 8.8 | 9.3 |
| Public Works Account | 5.3 | 0.5 |
| Defence Fund | 9.0 | - |
| National Roads Fund | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Totals | 24.6 | 11.0 |
| Miscellaneous receipts - | ||
| Highways taxation | 19.8 | 20.8 |
| Sinking Fund contributions, etc. | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| Miscellaneous capital receipts | 3.9 | 4.6 |
| Excess receipts of trading accounts, etc., within the Public Account | 4.3 | 10.7 |
| Totals | 31.7 | 40.5 |
| Receipts from borrowing and sale of investments- | ||
| Borrowing in New Zealand — | ||
| Public and departmental | 24.6 | 31.0 |
| Post Office Savings Bank† | 6.5 | 20.0 |
| Borrowing overseas - | ||
| United Kingdom | 20.0 | - |
| United States of America | 20.1 | - |
| Totals | 71.2 | 51.0 |
| Totals | 449.6 | 419.9 |
| Miscellaneous expenditure - | ||
| National Roads Fund | 21.2 | 23.5 |
| Defence Fund | 8.8 | 9.6 |
| Charges and expenses of repaying loans | 0.2 | - |
| Totals | 30.2 | 33.1 |
| Works and other capital expenditure - | ||
| Expenditure from Public Works Account for - | ||
| Housing | 8.6 | 11.0 |
| Forest development | 1.8 | 2.0 |
| Public buildings | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Transfers from National Development Loans Account for - | ||
| Electric supply | 17.0 | 16.0 |
| Land settlement | 3.0 | 3.2 |
| State coal mines | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Railways | 5.6 | 4.5 |
| Post Office | 5.0 | 6.0 |
| Other | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| State Advances Corporation† | 15.0 | 16.0 |
| Totals | 61.0 | 63.8 |
| Repayment of loans - | ||
| In New Zealand | 11.3 | 15.1 |
| Overseas | 0.5 | 4.6 |
| Totals | 11.8 | 19.7 |
| Net purchase of miscellaneous investments - † | ||
| In New Zealand | 6.4 | 2.9 |
| Overseas | 2.6 | 15.5‡ |
| Totals | 9.0 | 18.4 |
| Balancing items - | ||
| Reserve Bank: Purchase (+) or sale (–) of Government securities | +16.5 | -15.0 |
| Increase (+) or decrease (–) in cash balances in the Public Account | +15.4 | -19.3 |
| Totals | +31.9§ | -34.3 |
| Totals | 449.6 | 419.9 |
ESTIMATES OF RECEIPTS AND EXPENDITURE FOR 1960-61 - The following table supplies a composite account embracing the Consolidated Fund and the Social Security Fund, showing the estimated receipts and payments for 1960-61.
| Estimated Receipts | 1960-61 |
|---|---|
| Consolidated Fund £(million) | |
| Taxation - | |
| Customs duties | 40.0 |
| Beer duty | 14.0 |
| Sales tax | 21.5 |
| Estate and racing duties | 21.5 |
| Income tax | 116.7 |
| other taxation | 2.0 |
| 215.7 | |
| Other receipts - | |
| Interest | 16.2 |
| Profits from trading undertakings | 4.7 |
| Departmental receipts | 25.5 |
| Total | 262.1 |
| Interest and debt repayment | 39.6 |
| Other permanent appropriations | 6.9 |
| Annual appropriations - | |
| Stabilisation | 15.0 |
| Defence | 20.7 |
| Development of primary and secondary industries - | 19.5 |
| Social services (excluding transfer to Social Security Fund) | 86.4 |
| Other votes | 72.9 |
| Supplementary estimates | 1.0 |
| Total | 262.0 |
| Social Security Fund £(million) | |
| Social security income tax | 75.8 |
| Miscellaneous receipts and interest | 0.3 |
| Transfer from Consolidated Fund | 34.7 |
| Administration expenses and emergency benefits | 3.1 |
| Medical, hospital, etc., benefits | 21.2 |
| Monetary benefits - | |
| Age | 27.3 |
| Family | 30.9 |
| Universal superannuation | 19.9 |
| Other | 8.4 |
| Total | 11.8 |
THE CONSOLIDATED FUND - The Consolidated Fund, the principal account in the Public Account, covers the ordinary revenue and expenditure of the General Government - i.e., apart from capital items, commercial and special undertakings, advances, etc. In earlier years its operations afforded an excellent comparison of State revenue and expenditure from year to year, but successive changes in system have largely destroyed the comparability of the figures. All tax receipts are shown here with the exception of the social security tax* and, from April 1954, National Roads Fund taxation. Taxation receipts as a whole are the subject of the succeeding subsection. In addition, the Consolidated Fund is the focal point of the earnings of a number of State-owned undertakings as it records the receipts of interest, profits, and dividends from them.
Figures of receipts and payments of the Consolidated Fund over a long period of years will be found in the Statistical Summary near the end of this volume. For the years prior to 1937-38 they are there presented on the old or net basis - i.e., certain interest and other payments, since treated as receipts, were treated as credits in reduction of expenditure. For later years the figures are on a gross basis.
*In 1959-60 this is included in the Consolidated Fund under “Income tax”, and Social Security Fund receipts are derived wholly by way of transfer.
A summary of receipts, payments, current surpluses, and net balance carried forward is contained in the following table, together with the amounts utilised in each year from the surplus of the preceding year.
| Year Ended 31 March | Receipts | Payments | Surplus | Net Balance Carried Forward at End of Year | Transfers of Previous Year's Surplus to Other Accounts During Year Quoted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*To War Emergency Account. †To Public Works Account. ‡Utilised for payment of family bonus. §To National Development Loans Account. ||Deficit. ¶Excludes £933,000 in 1958-59 and £2,326,000 in 1959-60 of duty on motor spirits refunded under the Transport Amendment Act 1958; this comprises refunds to persons entitled to exemption from the additional payment of Customs duty from 27 June 1958. **Includes social security income tax and also £2,420,000 social security charge on 1957-58 income. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1950 | 124,997 | 120,689 | 4,308 | 11,448 | - |
| 1951 | 143,757 | 135,504 | 8,253 | 15,394 | 4,308† |
| 1952 | 180,788 | 168,153 | 12,636 | 19,776 | 3,079‡ |
| 5,174* | |||||
| 1953 | 177,822 | 174,515 | 3,307 | 10,448 | 4,000§ |
| 8,636† | |||||
| 1954 | 182,319 | 180,516 | 1,803 | 8,944 | 3,307† |
| 1955 | 191,216 | 184,376 | 6,840 | 13,981 | 1,803† |
| 1956 | 197,433 | 193,282 | 4,151 | 11,292 | 6,840 |
| 1957 | 206,276 | 202,951 | 3,326 | 10,466 | 4,151† |
| 1958 | 193,580 | 193,736 | -155|| | 6,986 | 3,326† |
| 1959 | 240,377¶ | 239,955¶ | 422 | 7,407 | - |
| 1960 | 314,8481¶** | 314,217¶ | 631 | 8,038 | - |
Receipts - Details of receipts of the Consolidated Fund are given in the next table. Taxation receipts represent only those amounts paid into the Consolidated Fund. In addition substantial amounts of special taxation arc paid to the National Roads Fund. Up to 31 March 1959 social security taxation was paid into the Social Security Fund, but for 1959-60 social security taxation was credited to the Consolidated Fund and the amount necessary for administering the Social Security Act was appropriated out of the Consolidated Fund. Full details of taxation receipts are contained in Section 26b.
| Source | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
*See footnote ¶ above. † Includes social security income tax and also £2,420,000 social security charge on 1957-58 income. | |||
| Taxation | £(thousand) | ||
| Customs | 31,982 | 39,099* | 41,090* |
| Beer duty | 7,020 | 11,258 | 13,350 |
| Sales tax | 24,222 | 25,751 | 24,241 |
| Film-hire tax | 150 | 169 | 166 |
| Milage tax | - | 82 | 190 |
| Stamp duties and racing taxation | 7,451 | 7,193 | 7,625 |
| Death (including gift) duties | 9,003 | 10,426 | 12,335 |
| Land tax | 1,308 | 1,448 | 1,526 |
| Income tax | 77,787 | 109,406 | 175,923† |
| Interest on capital liability - | |||
| Electric supply | 5,240 | 6,030 | 6,559 |
| Housing account | 1,435 | 1,477 | 1,540 |
| Housing construction | 121 | 139 | 157 |
| Post Office | 2,180 | 2,436 | 2,654 |
| Land settlement | 1,650 | 1,700 | 1,700 |
| Maori land development, etc. | 341 | 387 | 431 |
| National Airways Corporation | 102 | 74 | 95 |
| Interest on other public moneys | 1,323 | 1,542 | 1,840 |
| Profits on trading undertakings | 4,820 | 3,748 | 3,355 |
| Departmental receipts | 17,443 | 18,014 | 20,070 |
| Totals | 193,580 | 240,377* | 314,848*† |
Payments - Payments from the Consolidated Fund are divided into two main groups, according to whether they are made under permanent or under annual appropriation. The latter heading covers the payments under the various departmental votes, while the former covers interest on and amortisation of the public debt, and payments under numerous special Acts.
Payments under the main heads of permanent appropriation and each head of annual appropriation were as follows.
| Head | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
*See footnote ¶ on page 792. *See footnote ¶ on page 792. | |||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Permanent appropriations - | |||
| Civil List | 187 | 176 | 194 |
| Debt services - | |||
| Interest | 25,316 | 27,277 | 28,759 |
| Amortisation | 8,410 | 8,844 | 9,343 |
| Administration and management | 345 | 1,299 | 333 |
| Superannuation (subsidy and contribution) | 4,620 | 4,852 | 4,971 |
| Miscellaneous | 579 | 575* | 952* |
| Totals, permanent appropriations | 39,455 | 43,025* | 44,553* |
| Annual appropriations - | |||
| Legislative | 280 | 265 | 269 |
| Prime Minister's Office | 24 | 22 | 24 |
| External Affairs | 1,983 | 2,293 | 2,665 |
| Finance - | |||
| Treasury | 396 | 398 | 524 |
| Stabilisation | 12,930 | 12,940 | 12,601 |
| Customs | 559 | 621 | 643 |
| Inland Revenue | 1,759 | 1,824 | 1,992 |
| Audit | 228 | 233 | 251 |
| Totals, finance | 15,872 | 16,015 | 16,012 |
| General administration - | |||
| Public Service Commission | 138 | 137 | 152 |
| Internal Affairs | 2,887 | 2,714 | 2,204 |
| Island Territories | 1,025 | 952 | 1,534 |
| Printing and Stationery | 1,436 | 1,409 | 1,609 |
| Marine | 708 | 664 | 748 |
| Labour | 2,342 | 2,021 | 1,819 |
| Maori Affairs | 962 | 992 | 1,054 |
| Valuation | 424 | 424 | 432 |
| Statistics | 224 | 227 | 226 |
| Rehabilitation | 988 | 960 | 917 |
| Totals, general administration | 11,133 | 10,501 | 10,695 |
| Law and order - | |||
| Justice | 2,106 | 1,976 | 2,224 |
| Crown Law | 30 | 30 | 39 |
| Police | 2,885 | 3,031 | 3,298 |
| Totals, law and order | 5,021 | 5,036 | 5,562 |
| Defence | £(thousand) | ||
| Navy | 5,448 | 3,920 | 4,326 |
| Army | 7,052 | 5,943 | 6,585 |
| Air | 8,487 | 6,140 | 6,214 |
| Defence construction and maintenance | 2,454 | 1,790 | 2,097 |
| Totals, defence | 23,441 | 17,793 | 19,222 |
| Maintenance - | |||
| Public works and services | 10,768 | 10,694 | 11,509 |
| Roads | 1,930 | 2,309 | 2,026 |
| Development of primary and secondary industries - | |||
| Lands and Survey | 2,053 | 2,041 | 2,114 |
| Forest Service | 2,602 | 2,747 | 2,951 |
| Agriculture | 5,528 | 10,274 | 5,661 |
| Industries and Commerce | 484 | 494 | 528 |
| Tourist and Publicity | 1,042 | 1,068 | 1,162 |
| Scientific and Industry search | 1,535 | 1,658 | 1,812 |
| Mines | 280 | 197 | 130 |
| Transport | 669 | 706 | 751 |
| Civil Aviation and Meteorological Services | 3,007 | 3,678 | 3,441 |
| Totals, development of primary and secondary industries | 17,200 | 22,864 | 18,550 |
| Social services - | |||
| Health | 7,109 | 7,586 | 8,335 |
| Public hospitals | 15,390 | 15,774 | 17,205 |
| Education | 34,257 | 36,145 | 39,445 |
| War and other pensions | 9,805 | 10,962 | 11,576 |
| Contribution to Social Security Fund | 24,600 | 106,500 | |
| Totals, social services | 66,561 | 95,067 | 183,060 |
| Totals, annual appropriations | 154,213 | 182,858 | 269,594 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | 67 | 72 | 70 |
| Transfer to Defence Fund | - | 9,000 | – |
| Transfer to Public Works Account | - | 5,000 | - |
| Grand totals | 193,736 | 239,955* | 314,217* |
In a number of cases the expenditure incurred on various related services appears partly in each of two or more places in the accounts. Typical instances occur where capital expenditure out of the Public Works Account or money paid under permanent appropriations are not associated with departmental votes (refer parliamentary paper B. 1 [Pt. II], 1960).
PUBLIC WORKS - The Public Works Account, once the major construction account, now covers only those development works relating to forestry, State housing construction, and provision of public buildings.
Receipts - A summary of receipts of the Public Works Account is contained in the following table.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
*Includes amounts transferred from Consolidated Fund: Public buildings, £250,000 in 1957-58, 1958-59, and 1959-60 (from vote “Public Works and Services”); and Forest development, £100,000 in 1957-58, 1958-59, and 1959-60 (from vote “Forest Service”). †From vote “External Affairs”. | |||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Forest development | 1,638* | 1,780* | 1,844* |
| Housing construction | 1,383 | 1,267 | 1,064 |
| Transfer from Deposits Accounts - | |||
| New Zealand Government Building, London | - | - | 604 |
| Public buildings | 391* | 292* | 254* |
| Transfers from National Development Loans Account | 3,000 | 7,000 | 14,000 |
| Transfers from Consolidated Fund | - | 5,000 | 100† |
| Surplus from previous year | 3,326 | - | - |
| Repayment of loans of capital advances, and recoveries of capital moneys (various) | 5 | 65 | 80 |
| Miscellaneous | 152 | 65 | 76 |
| Totals | 9,895 | 15,470 | 18,021 |
Payments - Particulars of payments from the account are now given.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Remainder of expenditure met from votes “Public Works and Services”, “Housing Construction”, “Forest Development” and “Working Railways”. | |||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Forest development | 1,742 | 1,769 | 1,980 |
| Housing construction | 8,138 | 8,602 | 11,016 |
| Public buildings | 3,116 | 2,969 | 2,987 |
| Murupara development | 1,003 | * | - |
| Unauthorised expenditure | - | - | 1 |
| Totals | 13,999 | 13,340 | 15,984 |
For the three years concerned, balances at the end of the year were: 1957-58, £67,000; 1958-59 £2,197,000; and 1959-60, £4,235,000.
NATIONAL ROADS FUND - The National Roads Act 1953 established a National Roads Fund within the Public Account, the revenue of the Fund being derived mainly from motor taxation together with an annual contribution from the Government. Expenditure from the Fund is for the purpose of developing State and main highways to modern standards and of subsidising the roading programmes of local authorities.
Receipts and payments of the National Roads Fund were as follows.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Highways revenue | 19,701 | 19,798 | 20,842 |
| Contribution from Consolidated Fund | 1,000 | 1,500 | 1,200 |
| Miscellaneous | 426 | 449 | 569 |
| Interest | 18 | 26 | 28 |
| Totals | 21,144 | 21,774 | 22,639 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Highways maintenance | 4,819 | 4,989 | 5,557 |
| Highways construction | 8,035 | 8,632 | 10,268 |
| Payments to local authorities | 5,348 | 5,795 | 6,045 |
| Administration and general expenses | 1,870 | 1,797 | 1,640 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | 2 | 1 | |
| Totals | 20,074 | 21,213 | 23,511 |
The balance of this account at the end of March 1958 was £1,792,000, at the end of March 1959, £2,352,000, and at the end of March 1960, £1,481,000.
TRADING ACCOUNTS - Several important trading operations of the Government are outside the scope of the Public Account, while certain others are included in the Consolidated Fund, notably the Working Railways Account and the State Coal Mines Account. The Working Railways Account records the revenue from, and operating costs of, the services under the control of the Railways Department, also the cost of capital improvements (including new rolling stock).
Working Railways Account - Receipts and payments of the Working Railways Account were as follows.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Railway revenue | 34,012 | 33,645 | 34,198 |
| Transfer from National Development Loans Account | 5,300 | 5,550 | 4,500 |
| Interest | 103 | 123 | 122 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 798 | 977 | 1,019 |
| Total | 40,213 | 40,295 | 39,839 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Annual appropriations - | |||
| Working Railways | 41,890 | 38,979 | 36,157 |
| Subsidy to Government Superannuation Fund | 387 | 286 | 552 |
| Totals | 42,277 | 39,265 | 36,710 |
At the end of each year the following balances remained in the account: 1957-58, £5,149,000; 1958-59, £6,179,000; and 1959-60, £9,308,000.
State Coal Mines Account - A statement of receipts and payments of the State Coal Mines Account is now presented.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Sales of coal and miscellaneous receipts | 7,584 | 7,463 | 7,147 |
| Transfer from National Development Loans Account | 1,250 | 1,050 | 1,000 |
| Totals | 8,834 | 8,513 | 8,147 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Annual appropriations - | |||
| State Coal Mines | 8,767 | 8,483 | 7,752 |
| Transfer to Loans Redemption Account for redemption of securities | 87 | - | - |
| Subsidy to Government Superannuation Fund | 11 | 8 | 13 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | 19 | 16 | - |
| Totals | 8,884 | 8,508 | 7,765 |
Balances at the end of March for years 1957-58 to 1959-60 amounted to £12,000, £17,000, and £399,000 respectively.
Electric Supply Account - This account reflects the cash transactions of the Government in the supply of bulk electricity to local distributive organisations such as power boards and municipalities. The principal item of outgo comprises capital expenditure on new power stations (about two-thirds) and on the main trunk transmission system, and operating costs. Receipts and payments were as follows.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Transfer from National Development Loans Account | 19,500 | 17,000 | 16,000 |
| Sales of electrical energy and miscellaneous receipts | 11,191 | 14,813 | 17,521 |
| Interest on investments | - | - | 5 |
| Totals | 30,691 | 31,813 | 33,525 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Development and generation of electric power | 25,531 | 23,146 | 23,291 |
| Interest on capital liability | 5,240 | 6,030 | 6,559 |
| Debt redemption | - | - | 1,000 |
| Subsidy to Government Superannuation Fund | 49 | 52 | 63 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | - | - | |
| Totals | 30,820 | 29,227 | 30,914 |
The balances in the account at the end of each of the three years were: 1957-58, £278,000; 1958-59, £2,865,000; and 1959-60, £5,476,000.
Land Settlement Account - Though this account covers numerous and diverse activities in connection with land settlement, four are dominant: the development of Crown land for farming, the development and settlement for farming of Maori land, provision of houses for Maoris, and purchase of housing sections for resale or lease. Advances for the purchase of farm units from developed Crown land are made by the State Advances Corporation.
The principal advances accounts, those relating to State Advances to settlers, workers, etc., are, as stated earlier in this subsection, outside the Public Account and are not included here (refer Section 30b).
A statement of receipts and payments of the Land Settlement Account is now given.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Transfer from National Development Loans Account | 2,500 | 3,000 | 3,250 |
| Department of Lands and Survey - | |||
| Capital receipts | 1,406 | 1,162 | 1,453 |
| Rents, interest, royalties, etc. | 1,316 | 1,388 | 1,449 |
| Land development | 4,589 | 3,479 | 3,673 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 29 | 30 | 35 |
| Transfer from Consolidated Fund | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| Department of Maori Affairs - | |||
| Receipts from land development schemes | 1,563 | 1,579 | 1,551 |
| Repayment of advances under Maori Housing Act | 625 | 659 | 859 |
| Receipts from rehabilitation of Maori ex-servicemen | 237 | 224 | 244 |
| Receipts from other activities | 36 | 9 | 11 |
| Transfer from Consolidated Fund | 210 | 215 | 146 |
| Interest on investments | 1 | ||
| Totals | 12,961 | 12,194 | 13,121 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Crown lands | 6,002 | 5,783 | 5,518 |
| Maori land settlement | 3,436 | 3,401 | 3,642 |
| Interest on loans and capital liability | 1,991 | 2,087 | 2,131 |
| Payment in respect of land and improvements acquired for disposal under Land Act 1948 | 1,261 | 1,225 | 942 |
| Other | 86 | 106 | 104 |
| Totals | 12,777 | 12,601 | 12,337 |
The balances in the account for each of the three years were: 1957-58, £567,000; 1958-59, £160,000; and 1959-60, £944,000.
SOCIAL SECURITY FUND - The Social Security Fund was established as from 1 April 1939 under the authority of the Social Security Act of 1938. Receipts and payments of the Fund were as follows.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Social security charge | 66,256 | - | - |
| Social security charge 1957-58 income | - | 10,366 | 2,420 |
| Social security income tax | - | 70,249 | - |
| Contribution from Consolidated Fund | - | 24,600 | 104,080 |
| Interest | 83 | -- | 21 |
| Deserted wives' maintenance (recoveries) | 104 | 116 | 131 |
| Recoveries on account reciprocity arrangements | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Miscellaneous receipts | 58 | 62 | 73 |
| Totals | 66,510 | 105,400 | 106,733 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||
| Administration expenses and emergency benefits | 2,436 | 2,467 | 2,773 |
| Medical, hospital, etc., benefits | 17,058 | 18,655 | 19,892 |
| Monetary benefits | 59,397 | 68,332 | 82,639 |
| Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act 1958 - Advances under section 4 (1) | - | - | 3,880 |
| Balance of maintenance moneys | -- | -- | -- |
| Reciprocity benefits | 10 | 9 | 11 |
| Totals | 78,901 | 89,463 | 109,194 |
The balances remaining in this account for the three years were as follows: 1957-58, £4,665,000; 1958-59, £20,601,000; and 1959-60, £18,140,000.
More detailed information concerning payments under the various headings is given in Section 6A of this Yearbook.
NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT LOANS ACCOUNT - Since the inauguration of the National Development Loans Account in April 1942 all loan moneys raised for public works and other capital purposes are first paid into this account and then transferred to the various accounts covering the activities for which the moneys are required.
Particulars of receipts and payments of the National Development Loans Account were as follows.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-50 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||
| Stock issued | 35,119 | 46,091 | 47,603 |
| Advance subscriptions | 40 | 1,580 | 4 |
| Totals | 35,159 | 47,671 | 47,607 |
| Expenditure £(thousand) | |||
| Public Works Account | 3,000 | 7,000 | 14,000 |
| Electric Supply Account | 19,500 | 17,000 | 16,000 |
| Land Settlement Account | 2,500 | 3,000 | 3,250 |
| State Coal Mines Account | 1,250 | 1,050 | 1,000 |
| Working Railways Account | 5,300 | 5,500 | 4,500 |
| Post Office Account | 5,000 | 5,000 | 6,000 |
| Advances to National Airways Corporation | 600 | 500 | 450 |
| Contribution on transfer of Christmas Island to Australian administration | 1,167 | - | - |
| Advances to Tourist Hotel Corporation | 265 | 402 | 100 |
| Advance subscriptions from previous year allocated | 359 | 40 | 1,580 |
| Totals | 38,941 | 39,542 | 46,880 |
The balance in the account at the end of each year was as follows: 1957-58, £366,000; 1958-59, £8,494,000; and 1959-60, £9,222,000.
EARTHQUAKE AND WAR DAMAGE FUND - The Earthquake and War Damage Fund, which replaced the War Damage Fund created by the War Damage Act 1941, was set up under the provisions of the Earthquake and War Damage Act 1944. Premiums paid into the Fund during the three years 1957-58 to 1959-60 amounted to £1,535,000, £1,640,000, and £1,754,000, respectively. Interest on investments amounted to £514,000, £603,000, and £689,000. Payments during the same years amounted to £194,000, £445,000, and £279,000, leaving balances of £17,648,000, £19,446,000, and £21,611,000 in the Fund at 31 March 1958, 1959, and 1960, respectively.
A description of the provisions of the Act and further details of the Fund will be found in Section 31d.
DEFENCE FUND - In order to provide moneys for the purchase of modern equipment for the Royal New Zealand Air Force, an Air Defence Fund was created in June 1948. This Fund has since been extended to cover the three Services, and the title has been changed to the Defence Fund. The Fund may be expended for any purpose connected with the defence of New Zealand or directly or indirectly with any war or threat of war faced by New Zealand. If not required for its original purposes, money in the Fund may be transferred to the Reserve Fund or to the Loans Redemption Account. The amounts paid into the Defence Fund were £1,600,000 in 1948 49, £1,300,000 in 1949-50, £3,950,000 in 1950-51, £6,300,000 in 1951-52, £140,000 in 1952-53, £3,500,000 in 1953-54, £3,770,000 in 1954-55, and £9,000,000 in 1958-59, together with interest on investments totalling £5,602,000 to 31 March 1960, and a transfer of £12,079,000, being the balance in the former War Expenses Account. After expenditure of £26,136,000, consisting of £4,491,000 on service expenditure in Korea, £1,000,000 in 1955-56 as an advance payment on a naval vessel, £1,851,000 on service expenditure in Malaya in 1957-58, £400,000 on the purchase, construction, etc., of naval vessels in 1957-58, £8,825,000 overseas expenditure on staff, stores, and equipment, etc., and £7,000 other expenditure in 1958-59, and £9,562,000 overseas expenditure on staff, stores, and equipment, etc. in 1959-60, a balance of £21,106,000 was left in the Fund at 31 March 1960.
TOTAL TAXATION - A summary of taxation revenue during the last 11 March years is given in the following table. In addition to total taxation the amounts received from direct taxes on income are also shown.
| Year Ended 31 March | Direct Taxes on Income (i.e., Income Tax and Social Security Taxation on Income) | Total Taxation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Percentage of Total Taxation (All Sources) | Amount | |||||
| Total | Per Head of Mean Population | Total | Per Head of Mean Population | ||||
| *Excludes £933,000 in 1958.59 and £2,326,000 in 1959-60 of duty on motor spirits refunded under the Transport Amendment Act 1958; this comprises refunds to persons entitled to exemption from the additional payment of Customs duty from 27 June 1958. | |||||||
| £(000) | £ | s. | £(000) | £ | s. | ||
| 1950 | 80,186 | 42 | 12 | 59.2 | 135,556 | 72 | 1 |
| 1951 | 95,208 | 49 | 13 | 60.3 | 157,947 | 82 | 7 |
| 1952 | 121,714 | 62 | 3 | 60.7 | 200,550 | 102 | 8 |
| 1953 | 124,209 | 61 | 16 | 62.2 | 199,770 | 99 | 8 |
| 1954 | 130,517 | 63 | 6 | 63.4 | 206,802 | 100 | 6 |
| 1955 | 144,492 | 68 | 12 | 61.5 | 234,766 | 111 | 10 |
| 1956 | 150,609 | 70 | 1 | 61.5 | 244,829 | 113 | 17 |
| 1957 | 159,753 | 72 | 16 | 63.2 | 252,852 | 115 | 5 |
| 1958 | 144,043 | 64 | 3 | 58.8 | 244,882 | 109 | 1 |
| 1959 | 190,021 | 82 | 13 | 62.1 | 305,243* | 132 | 16 |
| 1960 | 175,923 | 75 | 0 | 59.2 | 297,288* | 126 | 15 |
The following table shows receipts, under the various heads, of taxation during the last five years.
| Head | Revenue for Year Ended 31 March | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||||||
*Excludes £933,000 in 1958-59 and £2,326,000 in 1959-60 of duty on motor spirits refunded under the Transport Amendment Act 1958; this comprises refunds to persons entitled to exemption from the additional payment of Customs duty from 27 June 1958. †Includes social security income tax and also £2,420,000 received as social security charge on 1957-58 income. | ||||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||||
| Consolidated Fund - | ||||||||||
| Customs revenue | 30,066 | 28,938 | 31,982 | 39,099* | 41,090* | |||||
| Beer duty | 6,567 | 6,754 | 7,020 | 11,258 | 13,350 | |||||
| Milage tax | - | - | - | 82 | 190 | |||||
| Land tax | 1,228 | 1,400 | 1,308 | 1,448 | 1,526 | |||||
| Income tax (ordinary) | 90,698 | 98,118 | 77,787 | 109,406 | 175,923† | |||||
| Sales tax | 23,443 | 22,281 | 24,222 | 25,751 | 24,241 | |||||
| Estate duties | 7,751 | 7,625 | 8,188 | 9,165 | 10,593 | |||||
| Gift duties | 733 | 643 | 815 | 1,260 | 1,742 | |||||
| Racing taxation | 4,065 | 4,128 | 4,267 | 4,135 | 4,155 | |||||
| Duty on instruments | 1,522 | 1,497 | 1,800 | 1,674 | 2,010 | |||||
| Amusement tax | 440 | 463 | 502 | 519 | 560 | |||||
| Adhesive stamps | 60 | 45 | 60 | - | - | |||||
| Impressed stamps | 520 | 543 | 571 | 610 | 633 | |||||
| Other stamps taxation | 184 | 214 | 252 | 255 | 267 | |||||
| Film-hire tax | 142 | 147 | 150 | 169 | 166 | |||||
| Totals | 167,419 | 172,795 | 158,925 | 204,830* | 276,446* | |||||
| Social security taxation - | ||||||||||
| Social security charge | 59,911 | 61,635 | 66,256 | - | - | |||||
| Social security charge - 1957-58 income | - | - | - | 10,366 | - | |||||
| Social security income tax | - | - | - | 70,249 | - | |||||
| Totals | 59,911 | 61,635 | 66,256 | 80,615 | - | |||||
| National Roads Fund - | ||||||||||
| Highways revenue (less rebates) | 17,499 | 18,422 | 19,701 | 19,798 | 20,842 | |||||
| Total taxation receipts | 244,829 | 252,852 | 244,882 | 305,243* | 297,288* | |||||
| Taxation receipts per head population - | ||||||||||
| £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | |
| Ordinary (Consolidated Fund) | 77 | 17 | 78 | 15 | 70 | 15 | 89 | 2 | 117 | 17 |
| Social security | 27 | 17 | 28 | 2 | 29 | 10 | 35 | 1 | - | |
| National Roads Fund | 8 | 3 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 15 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 18 |
| Totals | 113 | 17 | 115 | 5 | 109 | 1 | 132 | 16 | 126 | 15 |
On a comparable basis (i.e., an amalgamation of the amounts paid into the Consolidated, Social Security, and National Roads Funds in 1958-59, and the Consolidated and National Roads Funds in 1959-60) total taxation receipts decreased by £7,955,334, or 2.6 per cent, in 1959-60 compared with those for the previous 12 months.
Items of taxation showing significant increases and the amount of the increases were as follows: beer duty, £2,100,000; Customs revenue, £2,000,000; and death duties, £1,900,000.
It should be noted that for the year 1958-59 social security receipts from taxation were augmented by the receipt of social security tax on income other than salary or wages derived in the year ended 31 March 1958. The Land and Income Tax Amendment Act 1958 provided for the payment within three years of this social security income tax; taxpayers had the option of paying the whole of this tax by 7 December 1958, in which case a rebate of 5 per cent of the total amount was allowed. In 1959-60 all receipts of tax on incomes were paid into the Consolidated Fund first, and an appropriate transfer made to the Social Security Fund. This applied also to the social security charge received in respect of 1957-58 income.
The Social Security Act 1938 provided that, in addition to the special taxation for the purposes of the Fund, payment might be made to the Fund of such other moneys as might be appropriated by Parliament from time to time, and a substantial amount was transferred from the Consolidated Fund each year up to and including 1956-57, and again in 1958-59. In 1959-60 social security taxation was credited to the Consolidated Fund and the amount necessary for administering the Social Security Act was transferred from the Consolidated Fund. The following table shows for each of the last 11 years the taxation receipts of the Consolidated Fund, the amounts transferred to other accounts, and the taxation receipts of the Social Security Fund plus the amounts of transfers to that Fund.
| Year Ended 31 March | Consolidated Fund | Social Security Taxation Plus Transfers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxation Receipts | Transfers to - | ||||
| Social Security Fund | Public Works Account | Other Accounts | |||
*War Emergency Account. †National Development Loans Account. ‡Defence Fund. §Defence Fund, £1,000,000; National Development Loans Account, £3,500,000. ||No transfer in this year. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1950 | 103,853 | 12,000 | - | - | 43,703 |
| 1951 | 122,181 | 14,000 | - | - | 49,766 |
| 1952 | 156,937 | 14,000 | - | 11,774* | 57,613 |
| 1953 | 154,262 | 14,000 | 14,636 | 4,000† | 59,508 |
| 1954 | 156,196 | 14,000 | 3,307 | 3,500‡ | 63,717 |
| 1955 | 162,509 | 14,000 | 3,803 | 4,500§ | 70,175 |
| 1956 | 167,419 | 14,000 | 14,340 | - | 73,911 |
| 1957 | 172,795 | 14,000 | 4,151 | - | 75,635 |
| 1958 | 158,925 | - | 3,326 | - | 66,256|| |
| 1959 | 204,830 | 24,600 | 5,000 | 9,000‡ | 105,215 |
| 1960 | 276,446 | 106,500 | - | - | 106,500 |
A comparison of taxation revenue and total private income and national income is afforded by the following table, which also shows taxation as a percentage of private income and national income.
| Year | Total Private Income | National Income at Factor Cost | Taxation Revenue | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | As a Percentage of- | ||||
| Private Income | National Income | ||||
| *Provisional. | |||||
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | per cent | per cent | |
| 1949-50 | 526.2 | 482.4 | 135.6 | 25.8 | 28.1 |
| 1950-51 | 659.5 | 612.2 | 157.9 | 23.9 | 25.8 |
| 1951-52 | 675.6 | 625.3 | 200.5 | 29.7 | 32.1 |
| 1952-53 | 709.8 | 658.2 | 199.8 | 28.1 | 30.4 |
| 1953-54 | 786.5 | 735.3 | 206.8 | 26.3 | 28.1 |
| 1954-55 | 853.5 | 802.0 | 234.8 | 27.5 | 29.3 |
| 1955-56 | 897.1 | 843.7 | 244.8 | 27.3 | 29.0 |
| 1956-57 | 945.1 | 886.0 | 252.9 | 26.8 | 28.5 |
| 1957-58 | 993.5 | 929.9 | 244.9 | 24.7 | 26.3 |
| 1958-59 | 1,035.8 | 964.5 | 305.2 | 29.5 | 31.6 |
| 1959-60 | 1,132.1* | 1,044.9* | 297.3 | 26.3 | 28.5 |
The following diagram shows the extent to which taxation receipts have increased since the year 1931-32, and also the extent to which social security taxation has contributed towards this increase.
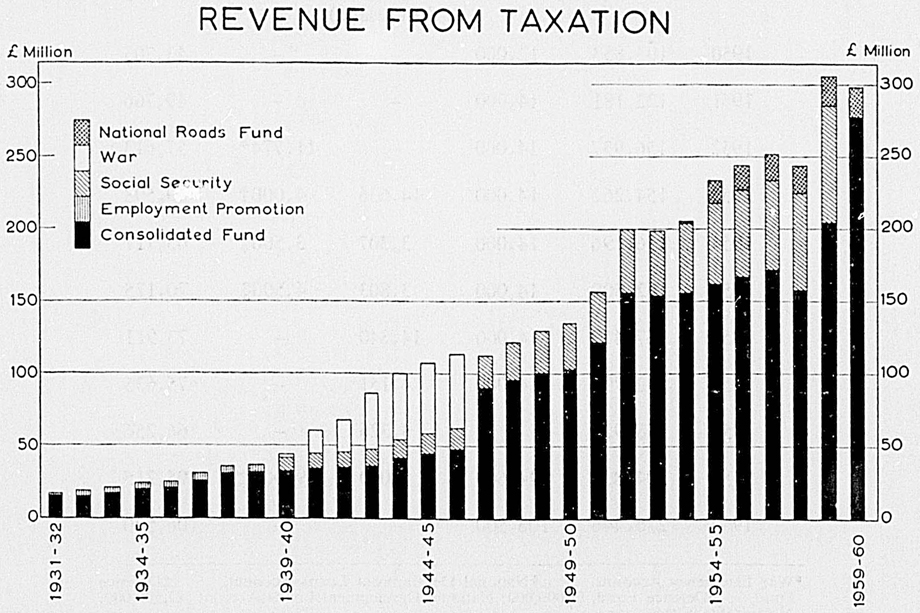
CUSTOMS AND EXCISE TAXATION - Revenue included under the heading of Customs is exclusive of receipts from tyre tax and from motor spirits tax. Sales tax receipts are not counted as ordinary Customs revenue, although collected by the Customs Department. The following figures show Customs and excise revenue, for ordinary revenue purposes, for the last five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Customs Duties* | Beer Duty | Total Customs and Excise Duties | Proportion of Total Taxation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excise duties other than beer duty are here included with Customs duties. | ||||
| £(thousand) | per cent | |||
| 1956 | 30,066 | 6,567 | 36,633 | 15.0 |
| 1957 | 28,938 | 6,754 | 35,691 | 14.1 |
| 1958 | 31,982 | 7,020 | 39,003 | 15.9 |
| 1959 | 39,099 | 11,258 | 50,356 | 16.5 |
| 1960 | 41,090 | 13,350 | 54,440 | 18.3 |
Information in regard to Customs and excise duties generally is contained in Section 22D - Customs Tariff and Revenue.
ROADS TAXATION - The National Roads Act 1953 provided for the establishment of the National Roads Board with power to administer a national roading system.
The National Roads Fund, also established by the 1953 Act, derives its revenues from a tax on motor spirits (at present 1s. 3d. per gallon for this purpose), registration and licence fees of motor vehicles, heavy traffic licence fees, a milage tax on vehicles not using motor spirits, and a tax on imported tyres (details of the origin of these are also given in earlier Yearbooks); other revenues of the Fund, which are not classed as taxation, consist of a Government contribution, interest earned, and miscellaneous receipts - e.g., from the sale of materials, etc.
Taxation receipts for roads purposes have been as follows during the latest five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Registration and Licence Fees, etc., Under Transport Act 1949 | Tyre Tax | Motor Spirits Taxation | Milage Tax | Heavy Traffic Fees | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1956 | 2,077 | 28 | 13,014 | 207 | 2,173 | 17,499 |
| 1957 | 2,217 | 22 | 13,642 | 265 | 2,275 | 18,422 |
| 1958 | 2,344 | 31 | 14,596 | 310 | 2,421 | 19,701 |
| 1959 | 2,429 | 30 | 14,501 | 365 | 2,474 | 19,798 |
| 1960 | 2,528 | 29 | 15,305 | 391 | 2,588 | 20,842 |
Taxation receipts for 1954-55 to 1958-59 are not directly comparable with those for previous years, as the full amount of tax (less collection costs and refunds in certain cases) was credited to the National Roads Fund; in earlier years, only a proportion of the tyre, milage, and motor spirits taxation was regarded as highways taxation, the remainder being ordinary Customs revenue in those years. Heavy traffic fees were also formerly retained by local authorities. Although it does not affect the table it should be noted that from 27 June 1958 an additional 1s. a gallon tax (reduced to 8d. a gallon on 4 November 1959, to 4d. a gallon on 22 December 1959, and to 2d. a gallon on 22 July 1960) was imposed on motor spirits, and this is credited not to the National Roads Fund but to the Consolidated Fund for general revenue purposes.
LAND AND INCOME TAX - The Land and Income Tax Act 1954 consolidated all existing legislation into one enactment. A brief review of the various changes in the rates of, and the law relating to, land and income tax between 1940 and 1954 appeared in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook. A similar history of changes between 1915 and 1939 appeared for the last time in the 1940 Yearbook. Major amendments since the consolidating Act of 1954 are briefly discussed in the following notes.
The 1955 Land and Income Tax Amendment Act added to the list of incomes exempted from income tax the incomes of milk treatment corporations, veterinary clubs, and herd improvement associations.
In general, this list of exempted incomes refers to cases where no part of the income or funds is available for the private pecuniary profit of any proprietor, shareholder, or member. Included are the incomes of non-trading Government Departments, local authorities, building societies, trustees for superannuation funds, societies or associations established for charitable purposes or to promote any amateur sport (other than horse racing or trotting), and similar bodies.
Income derived from war pensions, workers' compensation payments, social security benefits (except the superannuation benefit), educational bursaries, and some other specified types of income are also exempt.
This 1955 amending Act also provided for the apportionment over three years of income derived by land dealers from the disposition of land to the Crown and limited the proprietary company provisions to shareholders that were companies.
A rebate of 20 per cent from the basic rates of tax, with a maximum of £75, was introduced by the 1955 annual taxing Act. The basic rates of tax were brought into operation in 1940 and remained unaltered until an amendment in 1954 increased each rate by 6d. in the pound. Taxation is adjusted to revenue requirements by fixing each year a percentage increase or decrease on these basic rates. This was the first rebate since 1940, and applied to individuals and not to companies.
The special exemption for dependent relatives may, since 31 March 1956, be claimed where the relative is receiving a monetary benefit from the Social Security Fund. The 1956 Land and Income Tax Amendment Act also provided that, where a farmer was obliged to sell livestock because his lease had expired or his farm had been acquired by the Crown, the excess income represented by the difference between standard and selling values of livestock might be carried forward for the next one or two income years and offset by the writing down of substituted livestock to a new standard value. In 1959 this was extended to include events declared to be disasters (e.g., fire, flood, drought, disease among livestock, etc.). The penalty for tax remaining unpaid after due date was increased from 5 to 10 per cent, subject to a remission of one-half of the additional tax if paid within three months after due date. (Penalties for late payment of land tax and social security charge were also amended to make the late payment penalty identical for all three forms of taxation.) The Commissioner is not now to issue a taxation clearance certificate to any person adjudged bankrupt within the last three years, unless he has been discharged from bankruptcy or certain other conditions have been satisfied.
The rebate from the basic rates of tax was reduced to 10 per cent (maximum £40) for the income year 1955-56.
The 1957 amending Act extended the definition of a superannuation fund to include a fund established for the benefit of contributors who are “self employed”.
The normal maximum insurance exemption, which includes superannuation payments, of £175 was increased to a maximum of £250 in cases where self-employed superannuation contributions were involved. (This additional exemption allowance was withdrawn by the 1960 Act, which raised the maximum insurance exemption to £250 in all cases.)
Premiums on pure endowment insurance policies now qualify for the special exemption, provided that the taxpayer is unable to obtain a normal policy on account of ill health or physical disabilities. There are restrictions regarding term and maturity date of such policies.
Other provisions of the 1967 Land and Income Tax Amendment Acts included the exemption of the Electric Supply Account and approved research societies and associations from tax, and the exemption of income received as benefits under personal sickness or accident policies of insurance unless the benefits are calculated according to loss of earnings or profits.
During 1957 there was an extensive review of the schedule of depreciation allowances and a substantial number of increased allowances were granted.
For the income year 1956-57 there was a rebate of £100 to each taxpayer (individuals only) or a rebate equal to the amount of tax assessed if less than £100.
A new feature in New Zealand income tax law was introduced by the 1958 Amendment Act. This is the taxation of company dividends in the hands of individual (but not company) shareholders, and the imposition of an excess retention tax on companies which applies if the amount of dividends is less than 40 per cent of the income after taxation.
Dividends received by individual shareholders are included as part of their assessable income. After deduction of any exemptions to which the taxpayer is entitled, he pays ordinary income tax at normal rates on the total taxable income. The dividend income is not liable for social security income tax, and ordinary income tax on the dividends is limited to an average rate of 7s. in the pound. The total taxation payable by the company and by the shareholder on the dividends therefore does not exceed an overall rate of 13s. 6d. in the pound of company income. This is the same as the maximum rate for individuals. Dividends, whether in cash or in the form of bonus share issues, are exempted if made from capital profits or the writing up of capital assets.
The excess retention tax on insufficient dividend distributions (i.e., where the dividends paid are less than 40 per cent of the company's income after taxation) is at the flat rate of 7s. in the pound on the amount by which the dividend distribution falls short of the required 40 per cent.
Companies have a period of 10 months after balance date in which dividends may be declared. Certain types of companies are exempt from the excess retention fax. These include cooperative dairy companies, industrial and provident societies, life insurance companies, the New Zealand branches of companies incorporated overseas, and New Zealand subsidiary companies of overseas parent companies if all the ordinary shares are held by overseas companies.
The Land and Income Tax Amendment Act 1959 provided that fully or partly paid bonus shares are non-assessable income of the shareholders where the income from which the bonus share dividend is declared was derived by the company before 31 March 1957. It also made provision for an adjustment of tax on an insufficient distribution where the required percentage dividend distribution is exceeded in any of the six subsequent years.
The 1958 Amendment Act altered the amounts of the personal and wife's exemptions. The former was reduced from £375 to £338 for the 1958-59 income year and to £300 for subsequent years. The latter was increased from £125 to £162 for 1958-59 and to £200 thereafter. These amendments brought provisional taxpayers on to the same effective basis as taxpayers whose PAYE tax deductions at source were final. The latter retained the previous exemption for the first six months of the income year and received the new exemptions (£300 personal and £200 wife) as from 1 October 1958.
Bona fide payments incurred in the production of the assessable income by a husband to his wife (or vice versa) for services rendered by the wife may now be claimed as a deduction, but services in or in connection with the home are excluded.
Where salary and wage payments made by a private company to a shareholder-employee are irregular, or less than two-thirds of the total income derived as an employee of the company, such payments are generally not liable to deduction at source and are treated as income subject to provisional tax.
In addition to the exemption from the social security charge of the first £100 of the 1957-58 income from other than salary and wages, a rebate equal to 1s. 6d. in the pound on two-thirds of such income for 1930-31 and one-third of the 1931-32 income was allowed. Ordinary income tax on 1957-58 incomes was remitted in full in the case of individuals. The tax on 1958-59 incomes of individuals was at basic rates less a rebate of 12 1/2 per cent with a maximum of £37 10s.
The 1959 Land and Income Tax Amendment Act limited the income tax payable by a nonresident investment company on income from investments or assets which are used wholly or principally for developing New Zealand. The New Zealand income tax is not to exceed the tax which the company would pay in the country in which it is resident. Incomes of visitors, other than public entertainers, who were in New Zealand for not more than 92 days (the period is 183 days for a resident of a country with which there is a double taxation agreement) and whose employers were not resident in New Zealand, were exempted from income taxation.
The incomes of both husband and wife were to be £650 before the aggregation of incomes provisions applied. Profits on the sale of depreciated assets may be allowed against the cost of replacement assets, and in some circumstances the purchaser of depreciated property may not be allowed a larger depreciation deduction than that which would have been allowed to the vendor.
This Amendment Act also amended the PAYE legislation by repealing the provisions relating to partial pay-period taxpayers. It provided that where the rates of tax are altered, the altered tax deduction applies to the whole of a then current pay period if it does not exceed one month. Pay-period taxpayers may claim an adjustment of tax deductions based on an averaged weekly income, and the same method is used to determine the tax payable by provisional taxpayers whose incomes do not exceed £1,040. The averaged weekly income adjustment is discussed more fully later in this section.
There was also a No. 2 Amending Act in 1959 which generally came into force on 1 April 1960. The special exemptions were altered to: personal, £468; dependent wife (or housekeeper), £156; and each dependent child or relative, £78. The notional exemption of £25 for life insurance premiums where the income of the taxpayer did not exceed £1,040 was withdrawn. The basic rates of ordinary income tax were altered to 3s. in every pound where the taxable income does not exceed £500. The rate increases by 6d. in every pound for each increase of £100 in taxable income until £900 of taxable income is reached. Above £900 of taxable income, the increase is 3d. in every pound for each increase of £100 of taxable income, the maximum rate of 12s. being reached at £3,600. Individuals were granted a rebate of 10 per cent (maximum £30) in respect of 1959-60 incomes.
Provisional tax on provisional income became payable in two instalments (in August and in February) instead of three instalments.
In 1960 an amendment to the Inland Revenue Department Act provided for the establishment of one or more Boards of Review. Members of a board are to be appointed by the Governor-General and are to consist of a chairman who is to be a barrister or solicitor of the Supreme Court of not less than seven years' practice, and two other members. The functions of a board are to sit as a judicial authority for hearing and determining such objections to assessments of tax or duty or to decisions or determinations of the Commissioner as are authorised by the Inland Revenue Acts. A determination of a board is final as to any question of fact, but subject to appeal to the Supreme Court on any question of law. A Board of Review was constituted in December 1960.
The Land and Income Tax Amendment Act 1960 provides for the right of objection to the amount of penal tax charged. This Act increased the exemption for life insurance premiums to 20 per cent of the assessable income with a maximum of £250 but it dropped the increased exemption allowed for contributions by self-employed persons to a superannuation fund. The income from interest which is exempted from income tax was increased from £12 to £30, but it now applies only to interest derived from Government securities or deposits in a trustee savings bank, a National Savings account, or a Post Office Savings Bank account. In general, aggregation of the incomes of husband and wife was restricted to instances where the Commissioner considers that some scheme has been devised for the purpose of diverting income from one spouse to the other. Special depreciation allowances for plant and machinery (motorcars excepted) were re-introduced, and a total additional allowance of 20 per cent of the cost is to be spread over five years. Interest on convertible notes offered by a company after 8 September 1960 is not allowed as a deduction from the company's assessable income and is treated as a dividend in the hands of the holder. Unit trusts are to be treated as companies, and income and other payments to unit holders are to be treated as dividends. Excess retention tax will not be payable if the Commissioner is satisfied that the income retained is required for essential development of buildings, plant, or machinery. Companies will be given three years in which to expend or definitely commit such retained income.
A summary of the changes in the principal special exemptions and in the rates of ordinary income tax for the 10 years ended 31 March 1960 appears in the table which follows. These changes applied only to individuals. The tax on 1957-58 incomes was remitted in full.
| Income Year Ended 31 March | Special Exemptions | Ordinary Income Tax | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal | Wife | Child | Insurance (Maximum) | Basic Rates Employed | Rebate | ||
| Rate | Maximum | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |||
| 1951 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 150 | 1940 | £15 | 15 |
| 1952 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 150 | 1940 | £15 | 15 |
| 1953 | 230 | 100 | 65 | 175 | 1940 | £15 | 15 |
| 1954 | 375 | 125 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | - | - |
| 1955 | 375 | 125 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | 20% | 75 |
| 1956 | 375 | 125 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | 10% | 40 |
| 1957 | 375 | 125 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | £100 | 100 |
| 1958 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1959 | 338 | 162 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | 12 1/2% | 37 |
| 1960 | 300 | 200 | 75 | 175 | 1954 | 10% | 30 |
The following points should be noted.
Basic Rates - The 1940 rates were 2s. 6d. in the pound on the first £100 of taxable income, plus 3d. in the pound for each additional £100 of taxable income. The 1954 rates commenced at 3s. in the pound, but were otherwise similar.
Rebate - The basic rates were increased by 10 per cent in 1951, 5 per cent in 1952, and 2 1/2 per cent in 1953 before application of the rebate.
Insurance - In 1959 and 1960 the maximum was £250 where contributions to superannuation funds for self-employed were included.
Persons Over 65 Years - From 1951 to 1953 inclusive an additional rebate was allowed. Thereafter there was an additional personal exemption of £45.
Pay As You Earn Income Tax - A feature of the 1957 income tax legislation was the passing of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1957 to provide for the payment of income tax on a “pay as you earn” basis. Income tax now consists of two parts, namely, ordinary income tax and social security income tax, thus incorporating the social security charge previously payable under the Social Security Act 1938.
The Act came into operation as from 1 April 1958. It applies to salary and wage earners, to self-employed individuals, to other incomes of individuals, and to estates. It does not apply to companies, unless incorporated after 25 July 1957, or unless the company voluntarily elects to come within the provisions of the Act.
The main features of the scheme, as subsequently amended, are:
Income tax and social security income tax became one combined tax on income.
The combined tax on salary and wages is deducted by the employer. In the main, for taxpayers earning less than £1,040 of salary and wages during the year, the tax deductions made by the employer are final. The taxpayer is not required to furnish an annual return of income and in such cases there is no “end of year” adjustment of tax by the Commissioner. The taxpayer, however, may furnish a return of income in order to take advantage of provisions for determining tax deductions on the basis of an “averaged” weekly income.
All other individuals (including self-employed), estates, and companies within the scheme, pay provisional tax in two instalments on a provisional declaration of the then current year's income. There is a final adjustment at the end of the year when the return of income is furnished.
The change from payment of income tax on the previous year's income to tax on the current year's income involved the payment of income tax for two year's income in one income year, and the Act provided for the remission of income tax (but not social security charge) on income for the year ended 31 March 1958, subject to safeguards to ensure that the income for the year of remission was a normal income.
Employees fall into two classes: pay-period taxpayers, and others.
Pay-period Taxpayers - An employee is a pay-period taxpayer where the total income is less than £1,040 for the year and the only income received consists of salary or wages, non-assessable income, and exempted income from interest. Up to £30 of interest income is exempted provided that it is derived from Government securities or from trustee savings banks, National Savings or Post Office Savings Bank deposits.
This class of taxpayer is not required to furnish an annual return of income. The tax deductions by the employer are final, and there is no “end of year” adjustment of tax by the Commissioner. The taxpayer may, however, in certain circumstances obtain an adjustment, for example, where he is entitled to claim for excess life insurance premiums paid.
A pay-period taxpayer may furnish a return of income and thereby claim an adjustment of the tax deductions on the basis of the weekly average of the annual income. The adjustment is calculated as follows:
The average weekly wage is obtained (total wages for year divided by 52).
The tax deduction on the average weekly wage is ascertained from the tax deduction table. Where tax rates, etc., have changed during the year the average of the two or more tax deduction amounts is used.
The tax code used is that which applies to the taxpayer on the last day of the income year.
The weekly tax deduction is multiplied by 52. The amount of tax then becomes the smaller of:
The total of the tax deductions originally made.
The amount of tax as calculated above.
Other Employees - Where the taxpayer does not qualify as a pay-period taxpayer the tax deductions made by the employer are not final. An annual return of income is to be furnished to the Commissioner, who will assess the tax payable on the income and allow a credit equal to the amount of the tax deductions made by the employer.
Tax Code Declarations - Employees are required to deliver a tax code declaration to the employer each year before 1 April. The tax code declaration specifies whether or not the taxpayer has a dependent wife, and the number of other dependants.
There is no obligation on the employer to check the accuracy of the tax code declaration. Except for cases where the employee ends and commences employment during the week, the employee must not have more than one tax code declaration current during the pay period. There is, however, provision for secondary tax code declarations where the employee has two or more employers at the same time.
If the employee does not wish to deliver the tax code declaration to the employer, he may deliver it to the Commissioner. The Commissioner may, on application by the employee, issue to the employer a tax code certificate which specifies the employee's tax code as determined on the basis that some or all of the employee's dependants are omitted. In such cases the Commissioner will make an appropriate tax adjustment at the end of the year. There are other circumstances such as, for example, where the employer is not the principal employer, where the Commissioner may issue a tax code certificate specifying the tax code or tax deduction rate applicable to the employee.
At the end of the year the employer completes the tax code declaration by entering the amount of wages and salary paid and the amount of tax deductions made, hands one copy to the employee, and sends the other copy to the Commissioner.
Alteration of Tax Code Declaration During Year - When the employee changes employment during the year, he must deliver a declaration to the new employer. If the declaration is delivered before the end of the first pay period, it applies from and including the first pay.
Employees who become entitled to claim allowances for new dependants during the year may deliver a new tax code declaration immediately the event occurs (e.g., marriage or the birth of a child). The new tax code applies to the pay period commencing after the pay period in which the declaration was delivered.
When it becomes apparent that a dependent wife's income will exceed £156 for the year, the employee must deliver a new tax code declaration immediately and the new code applies to the pay period following that in which it was delivered.
In other cases where a dependant ceases to be a dependant during the year - i.e., where a dependent wife dies or a child dies or reaches the age of 18 years - the employee is entitled to retain the tax code including them as dependants until the following 31 March. This applies even when the employee delivers a new tax code declaration on a change of employment.
Tax Deduction Tables: Principal Tables - The tax code declaration bears a code (M, if the taxpayer is entitled to a wife's exemption; S, if not so entitled; and a number which represents the number of other dependants) and the tax deduction tables specify for each code and number the amount of tax to be deducted from the salary or wage payment for the period.
The following principles have been observed in the calculation of the amounts of tax shown in the deduction tables which came into force on 1 April 1960.
That part of the weekly income which corresponds to the amount of the exemptions allowances is taxed at the rate for social security income tax (1s. 6d. in the pound). The annual exemptions (personal, wife, dependants) to which the taxpayer is entitled have been converted into proportionate weekly parts.
The residue of the weekly income attracts both ordinary income tax and social security income tax. The tax deduction tables are based on proportionate weekly parts of the annual ordinary income tax basic rates.
Amounts paid by an employee to a superannuation fund are deducted from the gross salary for the period. The amount of the tax deduction is then the table deduction appropriate to the net payment to the employee, plus the social security income tax on the amount of the superannuation contribution.
In previous tables the first £2 of weekly income were exempted from the social security income tax. One of the objects of this concession was to provide a means of preventing, as far as possible. the pay-period taxation from exceeding that which would have been paid if the total income for the year had been taxed on an annual basis. This could have happened, for example, when the employee received a fluctuating weekly income through the working of irregular overtime. Pay-period taxpayers may now claim adjustment on the basis of the averaged weekly earnings, and in consequence the exemption has been withdrawn. Where this withdrawal would have caused the new tax deduction amount to exceed that provided in the previous table, the earlier tax deduction amount has been retained.
When there is no tax code declaration or tax code certificate, the tax deduction is at the “no declaration” rate shown in the tables. This deduction is at the flat rate of 5s. 6d. in the pound.
Special Tables - Special tables are provided for shearers and for casual agricultural employees. These are tables of deductions from daily earnings. There is also a table of deductions at a flat rate of 4s. 6d. per £1. This applies to payments of extra emoluments and to secondary employment unless a special tax code is issued by the Commission.
Extra emoluments - e.g., end-of-year bonuses and retrospective wage increases - are treated as separate payments. Secondary employment exists where the taxpayer has two or more employers at the same time. The secondary employers deduct tax according to the flat rate table, while the principal employer uses the normal table.
Employer's Duties - The employer is required to keep a record for each employee showing the amount of the source deduction payment and the amount of tax deducted. Not later than 20 April each year he is to deliver to each employee a signed certificate showing the total amounts of payments and tax deductions for the year (or period of employment if less than one year). A similar certificate is to be given to the employee within seven days from the cessation of employment.
The aggregate amount of all tax deductions is to be remitted to the Commissioner each month. Not later than 15 May each year the employer is to deliver to the Commissioner a reconciliation statement showing the total amount of tax deductions paid to the Commissioner in respect of deductions made during the year, and the total amount of tax deductions shown in the employee's certificates, together with an explanation if the two totals do not agree. The reconciliation statement is accompanied by signed copies of all tax deduction certificates, and all tax code declarations and certificates.
Withholding Payments - These are payments made for services rendered, but in circumstances where there is no real employer-employee relationship. Instances are company director's fees, agricultural contract work, fees for free-lance journalists, etc. Tax is to be deducted from the gross amounts of such payments at flat rates which vary from 1s. 6d. to 5s. in the pound according to the nature of the work.
The Commissioner may determine from time to time that a proportion of the withholding payment to specified classes is to be regarded as expenditure incurred in the production of the income. In such cases, tax would be deducted from the balance of the payment.
An exemption certificate may be issued by the Commissioner to any person specifying that no tax deduction is to be made from payments to that person. The income so exempted will later be included in the recipient's annual return of income.
Provisional Taxpayers - Provisional taxpayers are individuals who derive assessable income from sources other than salary or wages. However, the first £30 of interest from Government securities, trustee savings banks, and National Savings or Post Office Savings Bank deposits is exempted from income tax, and is therefore not assessable income. Estates, trusts, and companies incorporated after 25 July 1957, are also provisional taxpayers. Existing companies may voluntarily elect to become provisional taxpayers.
Salary and wage earners who receive more than £1,040 for the year are provisional taxpayers Employers make the normal tax deductions and such taxpayers pay provisional tax only on other income, if any.
Tax on provisional incomes is payable in two instalments during the year - on 7 August and on 7 February. Normally the provisional income is an amount equal to the taxpayer's income for the preceding year. When the taxpayer anticipates that the income will be less than that of the preceding year, he may make an estimate of the provisional income and pay provisional tax on the estimated income. If he does this and underestimates the actual final tax or the normal provisional tax (whichever is the smaller) by more than 20 per cent, he may be liable to pay an additional 10 per cent on the amount of tax underestimated.
The taxpayer may at any time make voluntary payments of additional provisional tax.
Provisional taxpayers are required to furnish returns of income, irrespective of the amount of income. The Commissioner makes an assessment of tax, and any difference between that assessment and the amounts of tax deducted at source or paid as provisional tax is payable by the taxpayer or credited or refunded to him.
Where the total income of the provisional taxpayer is over £1,040 for the year, the final assessment of tax is according to the main provisions of the Land and Income Tax Act. If the total income is under £1,040, the final assessment procedure is that which applies to a pay-period taxpayer who has claimed an adjustment based on the average weekly earnings. This adjustment procedure has been previously mentioned in these notes.
Remission of Tax in Transitional Year - Both salary and wage earners and provisional taxpayers had the income tax on the income for the transitional year, which was the 1957-58 income year, remitted in full. This did not apply to companies, whether provisional taxpayers or not. In other respects the 1957-58 income year was treated as a normal income year for ordinary income tax purposes; losses made were carried forward, etc. Salary and wage earners already had social security income tax on salary or wages for 1957-58 deducted at the source. Provisional taxpayers received a remission of the first £7 10s. from the social security income tax on the 1957-58 income, and also a rebate equal to 1s. 6d. in the pound on two-thirds of income other than salary and wages derived in 1930-31, and on one-third of the same income for 1931-32. The balance was payable by instalments spread over three years.
The Act contained a number of clauses designed to prevent the inflation of 1957-58 incomes at the expense of those of other years. When the 1957-58 income was, in the opinion of the Commissioner, greater than the normal income, the Commissioner determined the amount of the normal income. Any excess income was added to the assessable or non-assessable income for 1958-59.
In determining the amount of the normal income the Commissioner was required to take into account the income of the three preceding years, and, among other things, whether any income had been included in the transitional year which normally would have been included in another income year, or any normal expenditure diverted from the transitional year to another year. In general the Commissioner was empowered to take into account any matters which were relevant to the ascertainment of the normal income. Final determination of the normal income may be deferred until the nature or amount of the income for the next two succeeding years is known.
A Transitional Income Tax Appeal Authority has been set up to hear and determine any objections to the amount of the normal 1957-58 income as determined by the Commissioner.
Statistics relating to the incidence of income tax are given in Section 28 of this volume.
Income Tax - Individuals pay tax on the amount of taxable income (i.e., the assessable income less any special exemptions to which the taxpayer is entitled).
These special exemptions for the income year which commenced on 1 April 1960 were:
A personal exemption of £468.
A wife's (or husband's) exemption of £156, diminished £1 for each £1 of the wife's (or husband's) income in excess of £156.
An exemption, not exceeding £156, for payments to a housekeeper who is employed by a widowed, divorced, or unmarried person to have the care and control of children.
An exemption, of £78, for each dependent child. The exemption is normally allowed for children up to the age of 18 years.
An exemption, not exceeding £78 of contributions towards the support of a dependent relative. A relative is a person related to the taxpayer by blood, marriage, or adoption. The term includes a former wife or a foster child.
An exemption, not exceeding 20 per cent of the assessable income with a maximum of £250, for life-insurance premiums, contributions to superannuation funds, etc.
Absentees are only entitled to the personal exemption.
Equivalent exemption allowances for wife and for dependent children are written into the tax deduction tables under the PAYE system.
Any expenditure or loss exclusively incurred in the production of the assessable income may be deducted from the total income derived. Depreciation is allowed. On premises, the allowable depreciation rates vary from 2 1/2 per cent on cost price for wooden-walled and framed buildings to 1 per cent on cost price for buildings of reinforced concrete. There are higher rates for buildings used as cool stores, chemical works, etc. Various rates of depreciation allowances have been fixed by the Commissioner of Inland Revenue for different classes of plant, machinery, and equipment. These are normally expressed as percentages of the diminishing value of the asset.
Companies pay tax on their assessable incomes (i.e., there are no special exemptions to be deducted as in the case of individuals) before the distribution of dividends. Companies are also liable for excess retention tax where dividend distributions are less than 40 per cent of the income after normal taxation.
Certain specified incomes and types of income are exempt from income tax. The incomes of local and public authorities (excepting for certain Government trading departments) building societies, cooperative dairy and milk treatment companies, trustees of superannuation funds, friendly societies, charitable societies, and others of similar character are exempt from income tax. The general principle is where any society or association carries on business exclusively for the purposes for which it was established and does not operate for the private pecuniary profit of any individual, the income is exempt from income tax. Monetary benefits from the Social Security Fund (excepting the universal superannuation benefit), sick benefits from friendly societies, workers' compensation payments, war pensions, etc., are exempt income.
The rates of ordinary income tax for the year which commenced on 1 April 1960 were as follows.
Debentures Issued by Companies and Local Public Authorities - Where the income has been derived from debentures issued by a company on terms providing for the payment of income tax by the company, the rate of tax is 8s. 6d. per £1.
Maori Authorities - On all undistributed income assessable to a Maori authority, the basic rate of tax for every £1 of taxable income is 2s. 6d.
Companies and Public Authorities - On income not already specified, the rate of income tax for every £1 of taxable income in the case of companies and public authorities is: (i) where the taxable income does not exceed £6,300 2s. 6d., increased by 1/100 for every £1 of taxable income; (ii) where the taxable income exceeds £6,300 7s. 9d., increased by 1/150 for every £1 of the taxable income in excess of £6,300, but so as not to exceed in any case the rate of 8s. 6d. per £1.
Other Taxpayers - On all income not included earlier, the basic rates of income tax are as follows: On so much of the taxable income as docs not exceed £500, the rate of tax per £1 is 3s. For each succeeding £100 or part thereof the rate of tax increases by 6d. until the taxable income reaches £900. From this point the rate of tax increases by 3d. in the pound for each additional £100 (or part thereof) of taxable income. The maximum rate of 12s. 0d. applies where the taxable income exceeds £3,600.
Excess Retention Tax - The basic rate is 7s. for every pound of the insufficient distribution of dividends by a company.
Social Security Income Tax - All taxpayers pay 1s. 6d. for every pound of assessable income.
PAYE Tax Deductions - The tax rates for the purposes of PA YE tax deductions at source are actually the amounts shown in the tax deduction tables. These deductions are fixed according to the current amount of exemptions and tax rates. Some examples of these tax deductions are given in the tables which follow. These are the weekly tables, and social security income tax and ordinary income tax are combined to form one deduction. Tax rates or exemption allowances, or both, have been changed on four occasions since the inception of PAYE on 1 April 1958 and the four tables therefore give the history of the tax deductions since that date.
| Weekly Earnings | Not Entitled to Wife's Exemption | Entitled to Wife's Exemption | Entitled to Exemption for Wife and for- | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One Child | Two Children | Three Children | |||||||||||||
| Operative from 1 April 1958 | |||||||||||||||
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| 5 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 8 | 0 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 |
| 10 | 0 | 18 | 2 | 0 | 12 | 10 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 |
| 12 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 13 | 1 | 9 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 17 | 7 | 0 | 16 | 6 |
| 14 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 18 | 1 |
| 15 | 1 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| 16 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 17 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 9 | 3 |
| 18 | 2 | 12 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 16 | 9 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| 19 | 2 | 17 | 8 | 2 | 8 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 17 | 1 |
| 20 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 13 | 6 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 25 | 4 | 11 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 4 |
| 30 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 17 | 8 | 4 | 12 | 2 |
| 35 | 7 | 16 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 19 | 6 |
| 40 | 9 | 15 | 3 | 8 | 18 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 8 |
| 45 | 12 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 1 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 8 |
| 50 | 14 | 8 | 2 | 13 | 8 | 3 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 5 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 4 |
| Operative from 1 October 1958 | |||||||||||||||
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| 5 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 8 | 0 | 15 | 5 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 |
| 10 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| 11 | 1 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 |
| 12 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 17 | 8 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 13 | 1 | 19 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 11 | 0 | 16 | 6 |
| 14 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 2 |
| 15 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 16 | 2 | 15 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 10 |
| 17 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 5 |
| 18 | 3 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 16 | 1 |
| 19 | 3 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 16 | 8 | 2 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| 20 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 16 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 11 | 2 | 5 | 9 |
| 25 | 5 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 17 | 1 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 17 | 3 |
| 30 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 9 | 5 | 15 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 11 |
| 35 | 9 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 18 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 10 |
| 40 | 11 | 14 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 17 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 19 | 1 |
| 45 | 14 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 10 | 19 | 6 |
| 50 | 16 | 9 | 3 | 14 | 17 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 3 | 13 | 3 | 2 |
| Operative from 7 October 1959 | |||||||||||||||
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| 5 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 8 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 12 | 11 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| 11 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 16 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 |
| 12 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 17 | 2 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 13 | 1 | 14 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 17 | 8 | 0 | 16 | 6 |
| 14 | 1 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 18 | 1 |
| 15 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 9 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 11 |
| 16 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 8 |
| 17 | 2 | 14 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 17 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 1 | 9 | 8 |
| 18 | 2 | 19 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 13 | 8 |
| 19 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 17 | 10 |
| 20 | 3 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 25 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 19 | 8 | 3 | 14 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 3 |
| 30 | 6 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 13 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 15 | 4 |
| 35 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 19 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 40 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 15 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 18 | 9 |
| 45 | 12 | 17 | 3 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 16 | 11 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 16 | 5 |
| 50 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 13 | 14 | 0 | 13 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 1 |
| Operative from 1 April 1960 | |||||||||||||||
| £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| 5 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 |
| 6 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 6 |
| 8 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 10 | 6 |
| 10 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 7 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| 11 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 6 |
| 12 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 11 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 13 | 1 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 19 | 6 | 0 | 17 | 4 | 0 | 16 | 6 |
| 14 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| 15 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 16 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| 17 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| 18 | 2 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 11 | 6 |
| 19 | 2 | 18 | 8 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 16 | 0 |
| 20 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| 25 | 4 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 18 | 11 | 3 | 12 | 11 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 30 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 15 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 5 |
| 35 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 16 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 3 |
| 40 | 10 | 3 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 15 | 9 |
| 45 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 14 | 6 |
| 50 | 14 | 14 | 6 | 13 | 10 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 10 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 7 |
It should be noted that in the first three tables when the normal wage was less than £20 for the week, but overtime brought the amount to over £20, a different tax deduction table was used. From 1 April 1960 deductions from all overtime payments are in accordance with the principal table.
The preceding tables may be regarded as giving either the immediate deduction from a particular week's earnings, or the net weekly tax on the average weekly earnings where the taxpayer has exercised the right to claim an adjustment. The net weekly tax referred to is in effect the immediate tax deduction less the weekly value of the refund.
Where the income of a provisional taxpayer is less than £1,040 for the year the amount of tax deductions provided in the tables arc applied. The final tax payable is the annual equivalent of a weekly deduction on the average weekly earnings. Where more than one tax deduction table has been in operation during the year the different weekly tax deductions are averaged.
In interpreting the tables as an indication of the incidence of social security and ordinary income taxation in New Zealand it should be noted that under the provisions of the Social Security Act a family benefit of £26 per annum up to 1 October 1958 and £39 per annum since that date is paid in respect of each child under 16 years of age, irrespective of the income of the parents. The family benefit is normally paid to the mother, but with her concurrence may be used as an offset against income tax due.
Land Tax - Land tax is assessed on the unimproved value of land after deductions provided for by statute have been made by way of special exemption. The ordinary exemption, which was formerly £3,000, was increased by the Land and Income Tax Amendment Act 1957 to £6,000, reducible by £1 for each £1 of the excess of the unimproved value over £6,000. The exemption thus disappears at £12,000.
Where the land is subject to registered mortgage an alternative scale of exemption is provided - viz, £10,000 in cases where the unimproved value does not exceed £10,000, the exemption of £10,000 being diminished by £1 for every £1 above the margin of £10,000 of unimproved value, and disappearing altogether at £20,000. Where the capital value of the mortgage is less than the amount of deduction provided, such capital value is deducted instead.
The taxpayer receives whichever is the greater of the ordinary exemption or the mortgage exemption.
No special exemption is allowed in the case of land not situated in a borough when such land has been owned by a person for three years and not improved to the extent of £1 per acre or equal to one-third of the improved value if, in the opinion of the Commissioner, it should have been so improved. In the case of such land also, the rate of land tax is 50 per cent more than the ordinary rate.
In lieu of the special exemptions set out above, the Commissioner has discretionary powers to grant relief in certain specified cases of hardship. Subject to deductions provided, life tenants are liable to tax, and joint owners are assessed jointly as regards the land held in conjunction, and are liable severally in respect of each owner's interest in such land and any other land. This liability for joint assessment also applies to companies owning land if half of the paid-up capital or half (in nominal value) of the allotted shares of each company is held by or on behalf of shareholders in the other.
In case of default by a taxpayer in respect of land tax the amount of tax may be demanded from his successor in title, from a tenant of the taxpayer or his successor, or from a mortgagee of the estate or interest concerned. Land tax constitutes a charge on the land, and, notwithstanding any disposition of it, such land continues to be liable in the hands of a purchaser or other holder thereof for the payment of the tax so long as the charge remains in force. Registration of the charge is required, and no disposition of the land or of any interest in it may be registered while the charge remains in force. Provision is made for relief in cases of hardship.
Where the unimproved value on which land tax is payable does not exceed £10,000 the rate of land tax is 1d. in the pound. This rate is increased on a “step” system as follows:
| Taxable Value | Tax Rate for Every £1 | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 10,001 | -15,000 | 2d. |
| 15,001 | -20,000 | 3d. |
| 20,001 and over | 4d. | |
ESTATE AND GIFT DUTIES - The legislation dealing with estate duty and gift duty is contained in the Estate and Gift Duties Act 1955 and its amendments.
Where the final balance of the dutiable estate of a deceased person exceeds £1,000, estate duty is levied on the amount thereof. Exemptions are provided for the successions of a wife, husband, or infant child of a deceased person, the final balance of whose estate does not exceed £60,000. (For this purpose an infant child is widely defined to include not only an infant adopted child but also an infant stepchild or infant dependant of the deceased.) These exemptions are subject to the following limitations and operate by way of a deduction from the duty of so much as is attributable to the exempted succession or exempted portion of the succession. In the case of a wife, the exemption applies to the value of her succession or £7,500, whichever is the less; in the case of a husband, to the value of his succession or £1,000, whichever is the less; and in the case of an infant child, to the value of the child's succession or £500, whichever is the less. However, the value of the succession to which the exemption applies (or if more than one, the aggregate of such values) must where necessary be reduced so as not to exceed one-quarter of the difference between the amount of the final balance and £60,000. For example, where the amount of the final balance is £40,000, the maximum extent of the widow's succession which is given exemption is not £7,500 but £5,000 (being one-quarter of the difference between the final balance of £40,000 and £60,000).
There are also various exemptions which operate by way of the exclusion of certain property in computing the amount of the final balance of the estate, as, for example, for an interest in a home settled under the Joint Family Homes Act 1950 which passes to the surviving spouse; the property in an outright gift made before death to a charity; certain superannuation allowances for widows and infant children; and the wood value of growing trees on any land, a proprietary interest in which forms part of the dutiable estate.
Relief is provided for quick successions where estate duty is payable twice on the same property by reason of the two deaths occurring within a short period. The duty is reduced in the second estate according to the interval between the two deaths as follows: second death within four months, 75 per cent reduction; within eight months, 60 per cent reduction; within one year, 50 per cent reduction; within two years, 40 per cent reduction; within three years, 30 per cent reduction; within four years, 20 per cent reduction; within five years, 10 per cent reduction.
Ordinary income tax and social security income tax in respect of a deceased person up to the date of death are treated as a debt of the deceased in all cases.
Estate duty is due and payable to the Commissioner of Inland Revenue (Duties Division) on assessment, an additional 5 per cent penalty being payable if duty is not paid within three months after notice. Interest is charged on all duty unpaid within four months after death, at the rate of 4 per cent on duty paid within 15 months after death and at the rate of 5 per cent on all duty unpaid within 15 months (though this period may be extended in certain cases).
The Estate and Gift Duties Amendment Act 1960 introduced a scheme for prepayments towards estate duty. The scheme in general provides for the payment by any person of £10 or any multiple of £10, which on his death does not form part of his dutiable estate, but is applied in payment of estate duty on his estate. If he dies within 12 months after making the payment, the prepayment is discounted by 10 per cent. Any such payment may not be recovered by the payer or any other person. If the person making the payment dies within seven days, the amount of the payment is to form part of his dutiable estate and, to the extent that it is not applied in satisfaction of the estate duty payable in his estate, is to be refunded.
There is a right of appeal to the Board of Review, constituted under the Inland Revenue Department Amendment Act 1960, against decisions of the Commissioner in the exercise of his discretion under certain sections of the Act. There is also a right of appeal on points of law or of fact by way of a case stated to the Supreme Court.
The following table gives the scale of rates of estate duty which applies to estates of persons dying on or after 27 June 1958.
| Final Balance of Estate | Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1,001- | 2,000 | 4 per cent of excess of final balance over £1,000 |
| 2,001- | 3,000 | 2 per cent of £2,000 (£40) plus 5 per cent of excess |
| 3,001- | 4,000 | 3 per cent of £3,000 (£90) plus 7 per cent of excess |
| 4,001- | 5,000 | 4 per cent of £4,000 (£160) plus 9 per cent of excess |
| 5,001- | 6,000 | 5 per cent of £5,000 (£250) plus 11 per cent of excess |
| 6,001- | 7,000 | 6 per cent of £6,000 (£360) plus 13 per cent of excess |
| 7,001- | 8,000 | 7 per cent of £7,000 (£490) plus 15 per cent of excess |
| 8,001- | 9,000 | 8 per cent of £8,000 (£460) plus 17 per cent of excess |
| 9,001- | 10,000 | 9 per cent of £9,000 (£810) plus 19 per cent of excess |
| 10,001- | 1,000 | 10 per cent of £10,000 (£1,000) plus 21 per cent of excess |
| 11,001- | 12,000 | 11 per cent of £11,000 (£1,210) plus 23 per cent of excess |
| 12,001- | 13,000 | 12 per cent of £12,000 (£1,440) plus 25 per cent of excess |
| 13,001- | 14,000 | 13 per cent of £13,000 (£1,690) plus 27 per cent of excess |
| 14,001- | 15,000 | 14 per cent of £14,000 (£1,960) plus 29 per cent of excess |
| 15,001- | 16,000 | 15 per cent of £15,000 (£2,250) plus 31 percent of excess |
| 16,001- | 17,000 | 16 per cent of £16,000 (£2,560) plus 33 per cent of excess |
| 17,001- | 18,000 | 17 per cent of £17,000 (£2,890) plus 35 per cent of excess |
| 18,001- | 19,000 | 18 per cent of £18,000 (£3,240) plus 37 per cent of excess |
| 19,001- | 20,000 | 19 per cent of £19,000 (£3,610) plus 39 per cent of excess |
| 20,001- | 21,000 | 20 per cent of £20,000 (£4,000) plus 41 per cent of excess |
| 21,001- | 22,000 | 21 per cent of £21,000 (£4,410) plus 43 per cent of excess |
| 22,001- | 23,000 | 22 per cent of £22,000 (£4,840) plus 45 per cent of excess |
| 23,001- | 24,000 | 23 per cent of £23,000 (£5,290) plus 47 per cent of excess |
| 24,001- | 25,000 | 24 per cent of £24,000 (£5,760) plus 49 per cent of excess |
| 25,001- | 26,000 | 25 per cent of £25,000 (£6,250) plus 51 per cent of excess |
| 26,001- | 27,000 | 26 per cent of £26,000 (£6,760) plus 53 per cent of excess |
| 27,001- | 28,000 | 27 per cent of £27,000 (£7,290) plus 55 per cent of excess |
| 28,001- | 29,000 | 28 per cent of £28,000 (£7,840) plus 57 per cent of excess |
| 29,001- | 30,000 | 29 per cent of £29,000 (£8,410) plus 59 per cent of excess |
| Over £30,000 | 30 per cent of £30,000 (£9,000) plus 60 per cent of excess | |
Gift Duty - A gift means any disposition of property (situate in New Zealand at the time of the gift) which is made otherwise than by will, whether with or without an instrument in writing, without fully adequate consideration in money or its equivalent. There is provision for a deduction from the value of the gift of money payments adequately secured to the donor which were fixed or ascertainable at the date of the gift. No duty is payable on a gift which, together with the value of all other gifts (not exempt from duty by reason of their nature) made at the same time or within 12 months previously or subsequently by the same donor to the same or any other beneficiary does not exceed the value of £500. Gifts up to £50 in any year to the same person are not taken into account for gift duty (or estate duty) if made as part of the donor's normal expenditure. Various other exemptions, including gifts to any charitable trust, are contained in the Act.
The amount of the gift duty is payable by either the donor or the beneficiary, but the beneficiary is entitled to be indemnified by the donor unless the terms of the gift provide otherwise. Particulars of any gift made exceeding £500 (or the value of which when aggregated with the value of all gifts made by the donor within 12 months previously exceeds £500) are required to be furnished for assessment of duty within one month of the date of the gift, and if not paid within one year of making of the gift a 10 per cent penalty is imposed. Where duty is payable, the rate is based on the following scale.
| Value of Gift (Together With Value of All Aggregated Gifts) | Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 501- | 1,000 | 10 per cent of excess over £500 |
| 1,001- | 1,500 | 5 per cent of £1,000 (£50) plus 8 per cent of excess |
| 1,501- | 2,000 | 6 per cent of £1,500 (£90) plus 10 per cent of excess |
| 2,001- | 2,500 | 7 per cent of £2,000 (£140) plus 12 per cent of excess |
| 2,501- | 3,000 | 8 per cent of £2,500 (£200) plus 14 per cent of excess |
| 3,001- | 3,500 | 9 per cent of £3,000 (£270) plus 16 per cent of excess |
| 3,501- | 4,000 | 10 per cent of £3,500 (£350) plus 18 per cent of excess |
| 4,001- | 4,500 | 11 per cent of £4,000 (£440) plus 20 per cent of excess |
| 4,501- | 5,000 | 12 per cent of £4,500 (£540) plus 22 per cent of excess |
| 5,001- | 6,000 | 13 per cent of £5,000 (£650) plus 19 per cent of excess |
| 6,001- | 7,000 | 14 per cent of £6,000 (£840) plus 21 per cent of excess |
| 7,001- | 8,000 | 15 per cent of £7,000 (£1,050) plus 23 per cent of excess |
| 8,001- | 9,000 | 16 per cent of £8,000 (£1,280) plus 25 per cent of excess |
| 9,001- | 10,000 | 17 per cent of £9,000 (£1,530) plus 27 per cent of excess |
| 10,001- | 11,000 | 18 per cent of £10,000 (£1,800) plus 29 per cent of excess |
| 11,001- | 12,000 | 19 percent of £11,000 (£2,090) plus 31 per cent of excess |
| 12,001- | 12,000 | 20 per cent of £12,000 (£2,400) plus 33 per cent of excess |
| 13,001- | 14,000 | 21 per cent of £13,000 (£2,730) plus 35 per cent of excess |
| 14,001- | 15,000 | 22 per cent of £14,000 (£3,080) plus 37 per cent of excess |
| 15,001- | 16,000 | 23 per cent of £15,000 (£3,450) plus 39 per cent of excess |
| 16,001- | 18,000 | 24 per cent of £16,000 (£3,840) plus 33 per cent of excess |
| 18,001- | 20,000 | 25 per cent of £18,000 (£4,500) plus 35 per cent of excess |
| 20,001- | 25,000 | 26 per cent of £20,000 (£5,200) plus 31 per cent of excess |
| 25,001- | 30,000 | 27 per cent of £25,000 (£6,750) plus 33 per cent of excess |
| 30,001- | 35,000 | 28 per cent of £30,000 (£8,400) plus 35 per cent of excess |
| 35,001- | 40,000 | 29 per cent of £35,000 (£10,150) plus 37 per cent of excess |
| Over £40,000 | 30 per cent of the value of the gift | |
The net revenue received from estate duty and gift duty during each of the latest five years together with succession duty, which was abolished by the Act of 1955, is given below.
| Year Ended 31 March | Estate Duty | Succession Duty | Gift Duty | Total Estate, Succession, and Gift Duties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 6,243,931 | 1,507,054 | 732,824 | 8,483,809 |
| 1957 | 7,624,901 | - | 643,464 | 8,268,365 |
| 1958 | 8,188,007 | - | 815,438 | 9,003,445 |
| 1959 | 9,165,299 | - | 1,260,310 | 10,425,609 |
| 1960 | 10,592,638 | - | 1,741,899 | 12,334,537 |
ESTATES PASSED FOR DEATH DUTY - Particulars of deceased persons' estates certified during the calendar year 1959 are given in the tables following. Comparative totals for the previous four years are appended. Estates of Maoris, in value a negligible proportion of the total, are included, other than hereditary interests in Maori land.
| Size of Estate (Net Value) | Number of Estates | Aggregate Net Value of Estates | Estate Duties Assessed | Duties as Per Cent of Net Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Total | Males | Total | ||||
| Estates Passed for Duty 1959 | |||||||
| £(000 | £(000) | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Under | 1 | 1,338 | 2,658 | 755,465 | 1,492,608 | 386 | 003 |
| 1 and under | 2 | 1,240 | 2,310 | 1,856,724 | 3,447,283 | 28,993 | 0.84 |
| 2“ | 3 | 1,030 | 1,810 | 2,542,369 | 4,454,789 | 73,363 | 1.65 |
| 3“ | 4 | 690 | 1,125 | 2,392,240 | 3,894,337 | 84,929 | 2.18 |
| 4“ | 5 | 436 | 684 | 1,939,460 | 3,042,124 | 82,215 | 2.70 |
| 5“ | 6 | 295 | 481 | 1,621,241 | 2,638,904 | 90,911 | 3.45 |
| 6“ | 7 | 203 | 345 | 1,325,097 | 2,240,721 | 94,534 | 4.22 |
| 7“ | 8 | 185 | 276 | 1,382,616 | 2,064,146 | 108,061 | 5.24 |
| 8“ | 9 | 123 | 211 | 1,043,879 | 1,783,907 | 111,818 | 6.27 |
| 9“ | 10 | 131 | 192 | 1,241,864 | 1,818,896 | 133,262 | 7.33 |
| 10“ | 11 | 80 | 131 | 837,497 | 1,371,494 | 122,024 | 8.90 |
| 11“ | 12 | 97 | 151 | 1,116,610 | 1,738,512 | 182,408 | 10.49 |
| 12“ | 15 | 222 | 325 | 2,972,212 | 4,347,798 | 529,821 | 12.19 |
| 15“ | 20 | 233 | 327 | 4,043,096 | 5,656,394 | 883,219 | 15.61 |
| 20“ | 25 | 162 | 208 | 3,594,728 | 4,616,304 | 923,925 | 20.01 |
| 25“ | 30 | 103 | 124 | 2,828,509 | 3,400,790 | 851,651 | 25.04 |
| 30“ | 35 | 76 | 93 | 2,456,587 | 3,010,867 | 905,886 | 30.09 |
| 35“ | 40 | 39 | 49 | 1,450,897 | 1,823,470 | 600,884 | 32.95 |
| 40“ | 45 | 35 | 45 | 1,488,957 | 1,909,172 | 706,492 | 37.01 |
| 45“ | 50 | 25 | 27 | 1,183,183 | 1,278,291 | 499,338 | 39.06 |
| 50“ | 60 | 40 | 47 | 2,151,669 | 2,533,807 | 1,066,231 | 42.08 |
| 60“ | 70 | 15 | 20 | 974,619 | 1,296,356 | 557,668 | 43.02 |
| 70“ | 80 | 9 | 11 | 680,236 | 827,071 | 379,538 | 45.89 |
| 80“ | 90 | 8 | 9 | 664,653 | 745,700 | 365,270 | 48.98 |
| 90“ | 100 | 3 | 4 | 282,717 | 379,018 | 187,337 | 49.43 |
| 100 and over | 12 | 12 | 1,801,568 | 1,801,568 | 928,666 | 51.55 | |
| Totals, 1959 | 6,830 | 11,675 | 44,628,693 | 63,614,327 | 10,498,830 | 16.50 | |
| Totals, 1958 | 6,890 | 11,840 | 45,105,526 | 64,241,431 | 10,005,233 | 15.57 | |
| Totals, 1957 | 7,047 | 11,977 | 41,076,812 | 58,465,881 | 7,597,986 | 13.00 | |
| Totals, 1956 | 6,814 | 11,572 | 41,119,571 | 57,386,197 | 7,917,189 | 13.79 | |
| Totals, 1955 | 6,503 | 11,156 | 34,617,713 | 49,833,615 | 7,477,421 | 15.00 | |
The average net value per estate certified in 1959 was £5,449 (males £6,534; females, £3,919), inclusive of a small number of “nil” estates. Duty on male estates amounted to £8,220,353 and on female estates £2,278,477.
The fall in percentage of duty assessed from 1955 to 1957 follows the far-reaching changes in the law relating to death duties introduced by the Estate and Gift Duties Act 1955, which applied to the estates of all persons dying on or after 21 July 1955. By this Act, to which more detailed reference is made in Section 26B (Taxation), estate and succession duties were replaced by a single duty scale of estate duties, involving a marked reduction in estimated tax yield. An amendment to the Act, passed in 1958, provided for a graduated increase in duties on estates of a net value of over £12,000. The 1958 provisions are reflected in the figures for 1959.
The table of averages and percentages given below illustrates the increase in the amount of duty assessed in proportion to the final net value of the estate.
| Size of Estate (Net Value) | Average Duty Assessed per Estate | Average Duty as Percentage of Average Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | £ | £ | £ | per cent | per cent | per cent |
| Under | 1 | -- | -- | -- | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| 1 and under | 2 | 9 | 17 | 13 | 0.60 | 1.14 | 0.87 |
| 2 “ | 3 | 28 | 57 | 41 | 1.13 | 2.32 | 1.67 |
| 3 “ | 4 | 51 | 114 | 75 | 1.47 | 3.30 | 2.17 |
| 4 “ | 5 | 84 | 183 | 120 | 1.89 | 4.12 | 2.70 |
| 5 “ | 6 | 131 | 280 | 189 | 2.38 | 5.12 | 3.45 |
| 6 “ | 7 | 187 | 398 | 274 | 2.86 | 6.17 | 4.22 |
| 7 “ | 8 | 321 | 534 | 392 | 4.29 | 7.13 | 5.24 |
| 8 “ | 9 | 436 | 661 | 530 | 5.14 | 7.86 | 6.27 |
| 9 “ | 10 | 616 | 863 | 694 | 6.50 | 9.12 | 7.33 |
| 10 “ | 11 | 861 | 1,043 | 931 | 8.22 | 9.96 | 8.89 |
| 11 “ | 12 | 1,180 | 1,259 | 1,208 | 10.25 | 10.93 | 10.49 |
| 12 “ | 15 | 1,579 | 1,740 | 1,630 | 11.79 | 13.03 | 1218 |
| 15 “ | 20 | 2,655 | 2,815 | 2,701 | 15.30 | 16.40 | 15.61 |
| 20 “ | 25 | 4,356 | 4,745 | 4,442 | 19.63 | 21.37 | 20.01 |
| 25 “ | 30 | 6,833 | 7,041 | 6,868 | 24.88 | 25.84 | 25.04 |
| 30 “ | 35 | 9,604 | 10,354 | 9,741 | 29.71 | 31.76 | 30.09 |
| 35 “ | 40 | 12,367 | 11,857 | 12,263 | 32.24 | 31.82 | 32.95 |
| 40 “ | 45 | 15,786 | 15,399 | 15,700 | 37.11 | 36.65 | 37.01 |
| 45 “ | 50 | 18,513 | 18,255 | 18,494 | 39.12 | 38.39 | 39.06 |
| 50 “ | 60 | 22,548 | 23,474 | 22,686 | 41.92 | 43.00 | 42.08 |
| 60 “ | 70 | 29,569 | 22,826 | 27,883 | 45.51 | 35.47 | 43.02 |
| 70 “ | 80 | 34,420 | 34,880 | 34,503 | 45.54 | 47.51 | 45.89 |
| 80 “ | 90 | 40,705 | 39,628 | 40,586 | 48.99 | 48.90 | 48.98 |
| 90 “ | 100 | 46,208 | 48,713 | 46,834 | 49.03 | 50.58 | 48.43 |
| 100 and over | - | 7,389 | - | 77,389 | 51.55 | - | 51.55 |
| All estates, 1959 | 1,204 | 470 | 899 | 18.43 | 11.99 | 16.50 | |
| All estates, 1958 | 1,135 | 441 | 845 | 17.34 | 11.41 | 15.57 | |
| All estates, 1957 | 837 | 344 | 634 | 14.37 | 9.76 | 13.00 | |
| All estates, 1956 | 929 | 334 | 684 | 15.39 | 9.77 | 13.79 | |
| All estates, 1955 | 844 | 335 | 670 | 15.86 | 10.24 | 15.00 | |
A summary showing gross assets, notional estate, and debts and charges, classified in broad groups according to size of estate, is now given. As the figures for assets are taken from the administrators' statements in many cases, prior to checking and adjustment, the residual value (total assets less debts and charges) does not agree with the figure for aggregate net value of estates given in the preceding table, the difference amounting to almost £444,000. This may be accounted for by the fact that under rather than over valuation is more common in the statement of gross assets, and that subsequent investigation sometimes discloses the existence of unstated assets.
ESTATES PASSED FOR DUTY 1959
| Size of Estate (Net Value) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under £5,000 | £5,000 and Under £10,000 | £10,000 and Under £20,000 | £20,000 and Under £50,000 | £50,000 and Under £100,000 | £100,006 and Over | All Estates | ||
| Gross assets - | ||||||||
| New Zealand property - | ||||||||
| Cash | £(000) | 4,067 | 2,169 | 2,000 | 1,802 | 592 | 178 | 10,809 |
| Average per estate | £ | 474 | 1,441 | 2,142 | 3,300 | 6,508 | 14,857 | 926 |
| Furniture, effects, etc. | £(000) | 1,253 | 474 | 403 | 350 | 84 | 24 | 2,587 |
| Average per estate | £ | 146 | 310 | 431 | 641 | 922 | 1,964 | 222 |
| Farm, stock, implements, etc. | £(000) | 151 | 287 | 443 | 917 | 374 | 60 | 2,234 |
| Average per estate | £ | 18 | 191 | 475 | 1,680 | 4,115 | 5,005 | 191 |
| Private business interests | £(000) | 142 | 267 | 469 | 624 | 127 | 33 | 1,662 |
| Average per estate | £ | 16 | 178 | 502 | 1,143 | 1,398 | 2,758 | 142 |
| Assurance policies | £(000) | 986 | 675 | 654 | 909 | 225 | 95 | 3,545 |
| Average per estate | £ | 115 | 449 | 700 | 1,665 | 2,475 | 7,911 | 304 |
| Loans | £(000) | 985 | 1,131 | 1,868 | 2,002 | 536 | 116 | 6,638 |
| Average per estate | £ | 115 | 751 | 2,000 | 3,668 | 5,887 | 9,671 | 569 |
| Shares, stocks, etc. | £(000) | 885 | 1,488 | 2,599 | 3,430 | 1,727 | 848 | 10,976 |
| Average per estate | £ | 103 | 988 | 2,783 | 6,281 | 18,980 | 7,656 | 940 |
| Real property | £(000) | 7,969 | 3,706 | 4,031 | 4,888 | 1,424 | 232 | 22,251 |
| Average per estate | £ | 928 | 2,462 | 4,316 | 8,953 | 15,653 | 19,295 | 1,906 |
| Interest, estates, and trusts | £(000) | 251 | 222 | 282 | 325 | 123 | 8 | 1,211 |
| Average per estate | £ | 29 | 148 | 302 | 595 | 1,348 | 652 | 104 |
| Other property | £(000) | 546 | 313 | 318 | 376 | 94 | 46 | 1,693 |
| Average per estate | £ | 64 | 208 | 340 | 690 | 1,031 | 3,829 | 145 |
| Foreign property | £(000) | 97 | 129 | 234 | 434 | 328 | 108 | 1,330 |
| Average per estate | £ | 11 | 86 | 250 | 796 | 3,600 | 9,016 | 114 |
| Notional estate | £(000) | 795 | 491 | 551 | 842 | 369 | 143 | 3,191 |
| Average per estate | £ | 93 | 326 | 590 | 1,543 | 4,054 | 11,899 | 273 |
| Debts - | ||||||||
| Unsecured - New Zealand | £(000) | 856 | 372 | 398 | 454 | 142 | 59 | 2,281 |
| Secured - New Zealand | £(000) | 1,071 | 525 | 455 | 468 | 84 | 32 | 2,636 |
| Total (including foreign) | £(000) | 1,952 | 902 | 858 | 927 | 227 | 90 | 4,956 |
| Average per estate | £ | 227 | 599 | 919 | 1,698 | 2,492 | 7,521 | 424 |
The number of estates in each age group for 1959 are classified below according to net value of estate.
| Age Group, in Years | Under £500 | £500 to £999 | £1,000 to £1,999 | £2,000 to £2,999 | 3,000 to £3,999 | £4,000 to £4,999 | £5,000 to £5,999 | £10,000 to £14,999 | £15,000 to £19,999 | £20,000 to £20,999 | £30,000 to £30,999 | £40,000 to £40,999 | £50,000 to £50,999 | £100,000 and over | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | Years | |||||||||||||||
| Under 20 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 32 | |
| 20 and under | 25 | 12 | 22 | 32 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 85 |
| 25 “ | 30 | 6 | 14 | 18 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 72 |
| 30 “ | 35 | 9 | 10 | 20 | 11 | 8 | 5 | 15 | 3 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 82 |
| 35 “ | 40 | 11 | 23 | 30 | 21 | 9 | 8 | 22 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 134 |
| 40 “ | 45 | 17 | 36 | 29 | 27 | 16 | 9 | 31 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 3 | - | - | - | 185 |
| 45 “ | 50 | 30 | 44 | 53 | 56 | 38 | 16 | 63 | 13 | 10 | 12 | 2 | 3 | - | - | 340 |
| 50 “ | 55 | 40 | 66 | 90 | 68 | 59 | 34 | 69 | 25 | 12 | 14 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 489 |
| 55 “ | 60 | 54 | 86 | 152 | 100 | 56 | 37 | 97 | 37 | 22 | 23 | 10 | 3 | 3 | - | 680 |
| 60 “ | 65 | 92 | 133 | 192 | 143 | 87 | 48 | 143 | 52 | 21 | 24 | 17 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 969 |
| 65 “ | 70 | 123 | 168 | 248 | 202 | 124 | 95 | 160 | 75 | 37 | 45 | 27 | 8 | 13 | 2 | 1,327 |
| 70 “ | 75 | 182 | 198 | 370 | 280 | 167 | 109 | 232 | 113 | 66 | 61 | 18 | 9 | 11 | - | 1,816 |
| 75 “ | 80 | 218 | 227 | 404 | 338 | 215 | 129 | 255 | 114 | 54 | 64 | 20 | 20 | 16 | 4 | 2,078 |
| 80 “ | 85 | 154 | 232 | 350 | 313 | 172 | 100 | 211 | 91 | 58 | 50 | 21 | 6 | 18 | 4 | 1,780 |
| 85 “ | 90 | 112 | 149 | 217 | 168 | 105 | 51 | 120 | 50 | 19 | 21 | 12 | 8 | 10 | - | 1,042 |
| 90 “ | 95 | 43 | 59 | 70 | 38 | 43 | 25 | 51 | 12 | 8 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 4 | - | 369 |
| 95 and over | 9 | 14 | 12 | 15 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 1 | 2 | - | 81 | |
| Unspecified | 32 | 20 | 13 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | - | 114 | |
| Totals | 1,150 | 1,508 | 2,310 | 1,810 | 1,125 | 684 | 1,505 | 607 | 327 | 332 | 142 | 72 | 91 | 12 | 11,675 | |
| Per cent | 9.85 | 12.92 | 19.78 | 15.50 | 9.64 | 5.86 | 2.89 | 5.20 | 2.80 | 2.84 | 1.22 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.10 | 100.00 | |
OTHER DUTIES - These cover a miscellany of items of taxation imposed by the legislation such as the Stamp Duties Act 1954 and the Amusement Tax Act 1955.
In the next table the receipts for the last five years are shown under the various heads; receipts under agreement on sales of overseas lottery tickets in New Zealand have been added to the revenue items handled by the Duties Division of the Inland Revenue Department.
| Year Ended 31 March | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Adhesive stamps | 59,764 | 44,903 | 59,929 | - | - |
| Duty on instruments | 1,522,358 | 1,496,533 | 1,800,453 | 1,673,867 | 2,009,628 |
| Fines and penalties | 12,035 | 2,679 | 2,848 | 1,931 | 5,990 |
| Impressed stamps | 519,842 | 543,171 | 570,556 | 610,090 | 633,409 |
| Racing taxation | 4,065,155 | 4,127,636 | 4,266,608 | 4.135,237 | 4,154,628 |
| Amusement tax | 440,229 | 462,996 | 501,561 | 518,827 | 560,198 |
| Lottery duty | 66,850 | 65,754 | 61,106 | 64,054 | 64,051 |
| Overseas lottery duty | 104,940 | 145,717 | 188,436 | 189,325 | 196,694 |
| Totals | 6,791,173 | 6,889,389 | 7,451,497 | 7,193,331 | 7,624,598 |
Some of the more important items included in the foregoing table are dealt with in more detail under subsequent headings.
RACING TAXATION - The Government taxation on totalisator (pari mutuel) turnover is, under the Finance Act 1951, 2 1/2 per cent on the first £20,000 of gross turnover received by a club in any year and 5 per cent on the balance in excess of £20,000. There is also a tax of 1 per cent on the total value of all stakes. In addition there is a dividend tax of 5 per cent on the total amount available for dividends after the following deductions have been made: (a) totalisator tax; (b) club's commission of 7 1/2 per cent; (c) 1/2 per cent levy as provided by the Gaming Amendment Act 1953. Where the latter levy is deducted by a racing or hunt club it is paid to the New Zealand Racing Conference and where it is deducted by a trotting club it is paid to the New Zealand Trotting Conference. Each conference is to pay the moneys received by it into a separate account, which is to be applied solely for the purpose of assisting clubs to provide, maintain, and replace amenities for the public and course improvements on their racecourses. The proceeds of the levy and the amounts paid to clubs are not subject to taxation. The Gaming Amendment Act 1960 provides that the levy is to cease on 1 November 1965.
The Totalisator Agency Board, established by the Gaming Amendment Act 1949 to conduct off-course betting, receives 7 1/2 per cent of the turnover made through the totalisator agencies. This amount forms part of the general funds of the Board, but the Board distributes to racing and trotting clubs surplus funds not required for its own operations.
The Gaming Act 1908 and amendments provide for the Minister of Internal Affairs to grant totalisator licences for not more than 380 days in any racing year. Of these 380 days, 259 are allocated to racing and hunt clubs and 121 to trotting clubs. In 1957-58 and in 1958-59 an additional racing day was authorised, in the former year for a Royal Meeting and in the latter year for the Hawke's Bay Centennial celebrations. In 1959-60, two additional days were granted for Marlborough Centennial celebrations and one additional day for the Westland Centennial celebrations.
The following figures relate to the racing year, which ends on 31 July.
| Year Ended 31 July | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
*The Totalisator Agency Board commenced operations in April 1951. † Retained by the clubs. ‡Includes extra day on account of Royal Meeting of Wellington Racing Club. §Includes extra day on account of Hawke's Bay Centennial celebrations. ||Includes two extra days on account of Marlborough Centennial celebrations, and one for the Westland Centennial celebrations. | |||||
| Number of racing days | 369 | 374 | 381‡ | 381§ | 383|| |
| Number of races | 2,952 | 3,005 | 3,064 | 3,065 | 3,080 |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| Amount of stakes | 1,615 | 1,599 | 1,601 | 1,555 | 1,551 |
| Totalisator turnover - | |||||
| On course | 22,782 | 22,563 | 23,591 | 21,679 | 22,888 |
| With TAB* | 21,275 | 21,909 | 22,839 | 21,995 | 24,430 |
| Totals | 44,056 | 44,471 | 46,430 | 43,674 | 47,318 |
| Amount paid in dividends | 36,292 | 36,635 | 38,253 | 35,992 | 38,999 |
| Government taxes - | |||||
| Totalisator turnover | 2,140 | 2,160 | 2,257 | 2,118 | 2,300 |
| On dividends | 1,916 | 1,934 | 2,020 | 1,900 | 2,058 |
| On stakes | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Totals | 4,073 | 4,110 | 4,292 | 4,033 | 4,374 |
| Amount (7 1/2 per cent) of totalisator turnover retained by clubs and TAB | 3,359 | 3,399 | 3,547 | 3,342 | 3,615 |
| Unpaid fractions † | 121 | 121 | 122 | 104 | 109 |
| Levy of 1/2 per cent | 220 | 222 | 232 | 218 | 237 |
For the financial year ended 31 March 1960 Government receipts from racing taxation amounted to £4.16 million, as compared with £4.14 million in 1958-59.
The rising tendency in recent years in the volume of betting as measured by totalisator turnover, which was halted during the racing year ended 31 July 1959 continued again in the 1959-60 year. For this period an amount of £47,318,000 was handled by totalisators, as compared with £43,674,000 in 1958-59.
The greater part of this increase occurred in the volume of turnover handled by the Totalisator Agency Board which rose by £2,435,000 to £24,430,000 during the 1959-60 racing year. There was also an increase of £1,208,000 in on-course betting.
It will be noted that the turnover handled by the Totalisator Agency Board during the racing year exceeded the turnover in respect of on-course betting.
Of the amount placed on the totalisators in 1959-60, 82.4 per cent was returned to bettors by way of dividends. Government taxes absorbed 9.2 per cent, 7.9 per cent was retained by the racing clubs, and the special levy described in an earlier paragraph amounted to 0.5 per cent.
Of the 383 racing days in the 1959-60 racing year, 260 were devoted to racing (galloping) meetings and 123 to trotting meetings. It should be mentioned, however, that a number of racing clubs include trotting events in their programmes, but there are no trotting clubs which cater in a similar manner for gallopers. Of the total amount placed on the totalisator during the year, £36,522,000 was on racing meetings and £10,796,000 on trotting meetings, giving an average of £140,468 per day for racing clubs and £87,773 per day for trotting clubs. Stakes paid at racing meetings totalled £1,096,000, the average amount per race being £523, while at trotting meetings the total was £456,000, and the average amount per race £462.
Doubles totalisator turnover increased from £13,801,000 in 1958-59 to £15,698,000 in 1959-60. This is an increase of £1,897,000, or 13.7 per cent of the total doubles turnover; £13,070,000 was placed at racing meetings and £2,628,000 at trotting meetings.
AMUSEMENT TAX - Amusement tax is levied on payments for admission to certain entertainments. The present authority is the Amusement Tax Act 1960. Entertainments taxable are horse-race meetings and exhibitions of cinematograph films, but not lectures illustrated by motion pictures. Amusement tax is not charged on payments for admission to an entertainment where the whole of the takings is devoted to charitable purposes - without any charge on the takings for any expenses of the entertainment. The Commissioner of Inland Revenue may refund tax where the net proceeds of an entertainment are donated for charitable purposes and the whole of the expenses of the entertainment does not exceed 50 per cent of the total takings.
The following net amounts have been collected during the latest 11 years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Amount Collected |
|---|---|
| £ | |
| 1950 | 256,716 |
| 1951 | 236,373 |
| 1952 | 308,976 |
| 1953 | 396,306 |
| 1954 | 401,704 |
| 1955 | 416,797 |
| 1956 | 440,229 |
| 1957 | 462,996 |
| 1958 | 501,561 |
| 1959 | 518,827 |
| 1960 | 560,198 |
FILM-HIRE TAX - Part V of the Finance Act 1930 imposed, as from 1 July 1930, a film-hire tax, which is payable monthly by holders of renters' licences under Part IV of the Cinematograph Films Act 1928.
The film-hire tax payable is assessed on the net monthly receipts derived by the renter from renting sound-picture films. On British Commonwealth films the tax is 10 per cent and on foreign films 25 per cent of the net receipts. Films made wholly in New Zealand are exempt from the tax. The film-hire tax yielded a revenue of £142,020 in 1955-56, £147,218 in 1956-57, £150,081 in 1957-58, £168,873 in 1958-59, and £166,094 in 1959-60.
SOCIAL SECURITY TAXATION - The Social Security Act 1938 provided for the establishment of a Social Security Fund with special taxation (as from 1 April 1939) superseding employment promotion taxation. The Finance Act (No. 2) 1945 increased the social security charge to 1 1/2d. for every 1s. 8d., the new rate applying to all salaries and wages in respect of any period after 12 May 1946, and in the case of income other than salaries and wages to all such income derived during the year ended 31 March 1946 and subsequent years. The income of companies has been liable for social security taxation since the inception of the scheme.
Under the Income Tax Assessment Act 1957, which introduced PAYE taxation from 1 April 1958, social security income tax is combined with ordinary income tax as one tax on income. By the Social Security Amendment Act 1958 all income tax, including social security income tax, was payable into the Consolidated Fund in 1958-59 and 1959-60, and the amount necessary for administering the Social Security Act was appropriated out of that Fund. The Finance Act 1959 provided for the payment into the Social Security Fund, from 1 April 1960, of an amount computed at the rate of 1s. 6d. for each pound of the total national private income for the preceding year, as estimated by the Government Statistician.
SALES TAX - Sales tax is collected under the authority of the Sales Tax Act 1932-33 and its amendments. Numerous classes of goods were originally exempt from the tax, these being, in the main, commodities of primary production, articles used in the primary industries, machinery for use in manufacture, and the more important foodstuffs for household consumption. Goods exported from New Zealand were exempt, as were also certain commodities (e.g., motor spirits) which were subject to special taxation. In the post-war years a wide range of goods has been exempted from sales tax. The Sales Tax Exemption Order 1955 consolidated in one list all the then existing exemptions from sales tax. Beer and manufactured tobacco were exempted from sales tax on 4 November 1959. The rate of tax is normally 20 per cent, but it was increased to 40 per cent for motor vehicles in June 1958 and then reduced to 33 1/3 per cent for motor vehicles on 22 July 1960. The tax is not a turnover tax, being payable only once and, as far as possible, at the point where the goods pass to the retailer. The Sales Tax Act is administered by the Customs Department. The net amount yielded by the sales tax during each of the last five March years has been: 1955-56, £23,443,000; 1956-57, £22,281,000; 1957-58, £24,222,000; 1958-59, £25,751,000; and 1959-60, £24,241,000.
Monthly figures of sales tax collected during recent calendar years have been as follows.
| Month | Total Sales Tax Receipts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £(thousand) | |||||
| January | 2,141 | 2,534 | 2,531 | 2,555 | 1,888 |
| February | 1,557 | 791 | 946 | 604 | 1,133 |
| March | 1,756 | 2,315 | 2,665 | 2,609 | 2,022 |
| April | 1,578 | 1,999 | 2,167 | 2,385 | 1,833 |
| May | 2,061 | 1,849 | 2,049 | 2,072 | 1,959 |
| June | 1,717 | 986 | 1,800 | 2,003 | 1,972 |
| July | 1,861 | 2,863 | 2,519 | 2,009 | 1,782 |
| August | 1,824 | 2,001 | 2,100 | 1,077 | 1,339 |
| September | 785 | 1,460 | 2,203 | 2,224 | 2,317 |
| October | 2,947 | 2,501 | 2,283 | 2,187 | 1,928 |
| November | 1,981 | 2,186 | 1,324 | 1,908 | 2,148 |
| December | 1,818 | 2,188 | 3,481 | 2,307 | 2,305 |
The collections during a month relate in general to sales during the preceding month. Sales tax for any one month must be paid by the twenty-eighth of the following month to secure the discount. When the twenty-eighth falls on a Friday in a thirty-day month last-minute payments posted on the Friday are actually received in the succeeding month, e.g., sales tax on January sales posted on 28 February (when this is the last day of the month) is credited in March receipts.
The following table of receipts from the sales tax gives some indication of comparative trading operations in the principal centres. These figures and those in the preceding table are compiled from monthly departmental returns and in most cases differ slightly from the final Treasury figures shown earlier.
| Year Ended 31 March | Auckland | Wellington | Rest of North Island | Christchurch | Dunedin | Rest of South Island | Total* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes receipts through the Post Office. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| 1956 | 6,598 | 11,748 | 986 | 2,520 | 1,235 | 724 | 23,869 |
| 1957 | 6,310 | 10,705 | 971 | 2,367 | 1,172 | 638 | 22,210 |
| 1958 | 7,101 | 11,530 | 1,066 | 2,481 | 1,244 | 716 | 24,182 |
| 1959 | 7,115 | 12,854 | 1,103 | 2,654 | 1,254 | 689 | 25,694 |
| 1960 | 6,344 | 12,734 | 926 | 2,498 | 1,107 | 580 | 24,215 |
LOCAL TAXATION - Local governing authorities have power under various Acts of the Legislature to impose taxes for general or special purposes, as set out in Section 27 of this Yearbook. The amount of revenue collected by local authorities during the latest five March years was as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Rates | Licences and Other Taxes | Total | Per Head of Mean Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | £ | s. | |||
| 1955 | 18,259 | 763 | 19,022 | 8 | 17 |
| 1956 | 18,883 | 747 | 19,631 | 9 | 3 |
| 1957 | 20,659 | 661 | 21,320 | 9 | 14 |
| 1958 | 22,707 | 699 | 23,407 | 10 | 8 |
| 1959 | 24,392 | 731 | 25,123 | 10 | 19 |
The figures are exclusive of wharfage dues, tolls, etc., received by harbour boards, such receipts being regarded as charges for services.
GENERAL - The principal legislative measure which is concerned with public indebtedness is the New Zealand Loans Act 1953.
There was established within the Public Account, as from 1 April 1942, a National Development Loans Account into which all moneys, principally by way of loans for national development, are paid. The amounts raised by loans since the inception of this account to 31 March 1960 totalled £491,993,964, of which £47,602,709 was raised in 1959-60. Moneys are transferred from this account as required, the amounts transferred during the last three years being given in Section 26a. The balance in the account at 31 March 1960 was £9,221,861.
The Minister of Finance may raise loans, when authorised by Parliament so to do, by the issue of debentures, or scrip, or stock, in New Zealand or elsewhere at his discretion. When raising a loan the Minister may prescribe the mode and conditions of repayment, the rates of interest (not exceeding the maximum rate fixed by the authorising Act), and the times and places of payment of principal and interest respectively. Power is given to convert debentures or scrip into stock, and the Minister may specify the terms of conversion at the time when a loan is raised, or arrange that terms shall be subsequently agreed upon. For the purpose of paying off or renewing at maturity any debenture, scrip, or other security, new debentures or other securities may be issued and disposed of if necessary. Authority also exists for the conversion of loan money which has not yet matured, as well as for the redemption and cancellation of securities before maturity. The management of the public debt was transferred to the Reserve Bank of New Zealand as from 1 October 1936.
The money composing the public debt has been borrowed on the security of the public revenues of New Zealand. Apart from portion of the gold holding of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand deposited in connection with the loan raised from a group of United States banks (see page 832), no portion of the public estate is pledged for payment of either principal or interest.
National Savings - The National Savings Act 1940 provides that investments made in accordance therewith shall be applied in like manner to receipts from the sale of the Post Office investment certificates - i.e., available for the purposes of any loan authorised by Parliament - the immediate object was to assist in financing the Second World War. Two forms of investment were provided: (a) deposits in National Savings accounts with the Post Office and certain authorised trustee savings banks, and (b) purchase of National Savings bonds. These investments are approved trustee securities, the interest rate being 3 per cent a year from the inception of the scheme to 30 June 1956, thereafter 3 1/2 per cent a year.
Deposits in National Savings accounts cannot be withdrawn at will, but are invested for a definite period. Moneys deposited up to 30 June 1943 were repayable on 30 June 1945, and each subsequent investment period is for a term of two years - i.e., deposits made during the year ended 30 June 1960 are repayable on 30 June 1962, and so on. National Savings bonds were issued in three denominations - £1, £10, and £100 - for a term of five years, but the sale of these was discontinued as from 1 May 1956.
Recording of Public Debt - At the commencement of the financial year 1943-44 a change in practice was effected in regard to the treatment of exchange on overseas transactions. As from that date the cost of exchange has been treated as a part of the payment from which it arose, and not accounted for in the public accounts under the one heading of “Exchange”, as was the previous practice.
It was further decided that Government funds and investments held in the United Kingdom as at 1 April 1943 and all subsequent overseas transactions were to be converted into pounds New Zealand at a fixed exchange rate of 25 per cent and brought into the public accounts at the increased figure. Previously pounds New Zealand and pounds sterling were treated as if they were of the same value, despite the fact that New Zealand currency for many years had been at a discount on sterling.
In keeping with the foregoing decisions, that portion of the public debt domiciled in the United Kingdom, which was previously shown only at the sterling figure, was converted to pounds New Zealand, and the whole of the debt was shown in the debt tables in New Zealand currency in addition to the nominal amounts. The nominal increase resulting from the adjustment at 1 April 1943 was £39,569,000.
With the adjustment of the exchange rate as from 20 August 1948 New Zealand currency again became on a par with sterling. To facilitate comparison over a period on a common basis the public debt tables in this section have, in general, been so shown that either nominal amounts or the amounts in New Zealand currency can be readily ascertained during the period of divergence.
The Finance Act (No. 2) 1952 in redefining the term “public debt” excluded from the debt those loans funded by agreement with the United Kingdom Government under the authority of section 8 of the Finance Act 1922. The public debt figures throughout this section have therefore been adjusted to be on a comparable basis and exclude the amount of £24,100,000 (£(N.Z.)30,125,000 for years 1932-48, i.e., the years in which the New Zealand pound was at a discount of 25 per cent on sterling) funded in terms of the 1922 Act, and in respect of which interest payments have been suspended by agreement with the United Kingdom Government since 1931. This amount originally formed part of the First World War debt.
An amount of £2,090,909 (£(N.Z.)2,613,639 for years 1932-48) raised for State Advances purposes but on which interest payments have also been suspended since 1931 is also excluded from the figures.
GROSS INDEBTEDNESS - On only five* occasions in the history of New Zealand has a reduction in the gross public debt been effected during the financial year. The first occasion was in 1891-92, when the debt was reduced by £117,000; and the second in 1922-23, when another slight reduction (£101,000) was recorded. The third occasion was in 1934-35, when the floating debt of £22,857,000 - comprising outstanding Treasury revenue bills amounting to £3,452,000 and Treasury bills for £19,405,000 in respect of the Banks Indemnity (Exchange) Act, was entirely paid off. The fourth occasion was in 1947-48, the debt being reduced by £3,137,000 in New Zealand currency (having regard to exchange rate relationships existing prior to 20 August 1948), or £302,000 if nominal amounts only are taken into account. The fifth occasion was in 1951-52, the debt being reduced by £13,571,000 by the sale of State Advances stock, held by Treasury, to the Post Office Savings Bank, and an equivalent amount of Government stock, held by the Savings Bank, being redeemed.
The gross indebtedness of the General Government and the rate of indebtedness per head of population for each of the last 21 years are given in the following table.
*See, however, page 603 of 1940Yearbook.
The figures are given in two series, the first showing the debt at the nominal amount throughout the period 1940-60, and the second, covering the same period, with the debt shown in New Zealand currency. In the latter case the amount of overseas debt has been converted to New Zealand currency at the rate of exchange ruling during the period.
| At 31 March | Amount | Per Head of Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A - Nominal Amounts | |||
| £(000) | £ | s. | |
| 1940 | 296,716 | 180 | 17 |
| 1941 | 323,236 | 197 | 11 |
| 1942 | 359,207 | 219 | 16 |
| 1943 | 437,634 | 267 | 16 |
| 1944 | 500,526 | 304 | 9 |
| 1945 | 537,227 | 319 | 16 |
| 1946 | 568,140 | 323 | 8 |
| 1947 | 578,380 | 323 | 4 |
| 1948 | 578,078 | 316 | 5 |
| 1949 | 614,986 | 329 | 17 |
| 1950 | 643,880 | 338 | 7 |
| 1951 | 667,233 | 344 | 6 |
| 1952 | 653,662 | 329 | 7 |
| 1953 | 667,688 | 327 | 14 |
| 1954 | 704,371 | 337 | 8 |
| 1955 | 728,593 | 341 | 18 |
| 1956 | 735,201 | 337 | 19 |
| 1957 | 757,120 | 340 | 17 |
| 1958 | 782,111 | 343 | 14 |
| 1959 | 816,552 | 351 | 1 |
| 1960 | 844,516 | 356 | 6 |
| B - In New Zealand Currency | |||
| £(000) | £ | s. | |
| 1940 | 329,634 | 200 | 18 |
| 1941 | 356,282 | 217 | 15 |
| 1942 | 391,098 | 239 | 6 |
| 1943 | 470,655 | 288 | 0 |
| 1944 | 533,755 | 324 | 14 |
| 1945 | 570,500 | 339 | 12 |
| 1946 | 591,773 | 336 | 17 |
| 1947 | 602,013 | 336 | 8 |
| 1948 | 598,875 | 327 | 12 |
| 1949 | 614,986 | 329 | 17 |
| 1950 | 643,880 | 338 | 7 |
| 1951 | 667,233 | 344 | 6 |
| 1952 | 653,662 | 329 | 7 |
| 1953 | 667,688 | 327 | 14 |
| 1954 | 704,371 | 337 | 8 |
| 1955 | 728,593 | 341 | 18 |
| 1956 | 735,201 | 337 | 19 |
| 1957 | 757,120 | 340 | 17 |
| 1958 | 782,111 | 343 | 14 |
| 1959 | 816,552 | 351 | 1 |
| 1960 | 844,516 | 356 | 6 |
It should be noted that the figures in the foregoing table are exclusive of £26,191,000 (£(N.Z.)32,739,000 up to 1948) in respect of which interest payments have been suspended by agreement with the United Kingdom Government since 1931. This amount consists of £24,100,000 advances from the United Kingdom Government funded in terms of the Finance Act 1922, and £2,091,000 raised for State Advances purposes.
An outstanding advance of £125,268 to the Government Insurance Account by way of overdraft is not included in the public debt at 31 March 1960.
State guarantees cover such items as the guarantee to policyholders of the Government Insurance Department under the Government Life Insurance Act 1953; the guarantee to the Reserve Bank under the Finance Act 1934 in respect of sterling exchange (which was exercised in the case of the adjustment of the New Zealand currency exchange rate to parity with sterling as from 20 August 1948); the guarantee under the Finance Act (No. 2) 1946 to the Reserve Bank in respect of moneys advanced to Governments of other countries to finance the purchase of New Zealand produce; guarantees to certain undertakings under the State Advances Corporation Act and certain local authority loans. There are also certain contingent State liabilities in respect of the Government Superannuation Fund and in respect of £26,191,000 funded debt referred to earlier.
At 31 March 1960 the amount of contingent loans outstanding in respect of State Advances Corporation stock and debentures, the major portion of which is at present held by the State in consideration of the transfer of property securities from the State to the Corporation, was £176,222,000; and in addition there was a further amount of £1,378,000 in respect of loans to industries by the Corporation.
Other contingent liabilities covering the guarantee of overdrafts were: Apple and Pear Marketing Board, £500,000; Dairy Products Marketing Commission, £3,950,000; Linseed Growers Ltd., £250,000; Tourist Hotel Corporation, £30,000; and Wellington Gas Co. Ltd. and A.M.P. Society, £400,000.
CLASSIFICATION OF PUBLIC DEBT - A broad classification of the public debt according to nature or purpose is contained in the following table, the distinction being made on the basis of whether raised for ordinary purposes, war purposes, or housing. It should be noted that the debt is expressed in terms of nominal amounts, these differing from figures in terms of New Zealand currency for the 1940 year only.
| Class | Gross Debt at 31 March | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| *Includes debt due to United Kingdom Government (see p. 828). | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| Ordinary | 121,082 | 197,600 | 245,217 | 358,267 | 552,896 | 585,414 |
| Housing | - | - | 11,559 | 57,331 | 111,064 | 119,829 |
| War loans (1914-18) | 80,089* | 69,784* | 36,854 | 26,757 | - | - |
| War expenses (1939-45) | - | - | 3,086 | 201,526 | 152,592 | 139,273 |
| Totals | 201,171 | 267,383 | 296,716 | 643,880 | 816,552 | 844,516 |
The amount per head of population for each class as at 31 March 1960 was as follows: ordinary, £247; housing, £50 11s.; war expenses, 1939-45, £58 15s.
A more detailed allocation of the public debt as at 31 March 1960 is now given.
| £(thousand) | ||
| (a) Earning full interest - | ||
| Electric power | 176,987 | |
| Post Office | 71,340 | |
| Bank of New Zealand shares | 7,202 | |
| Land Settlement | 44,417 | |
| New Zealand National Airways Corporation | 2,750 | |
| Tasman Pulp and Paper Co. Ltd. | 8,968 | 311,664 |
| (b) Earning interest but not at full rate - | ||
| Housing | 107,104 | |
| Housing under construction | 12,725 | 119,829 |
| (c) Not earning interest though represented by permanent assets - | ||
| Education buildings | 13,882 | |
| Forests (State) | 13,545 | |
| Roads and highways | 56,352 | |
| General Public Works | 12,079 | |
| Railways | 138,472 | |
| State coal mines | 10,203 | 244,533 |
| (d) Non-productive debt - | ||
| War Loans, 1939-45 | 139,273 | |
| Reserve Bank exchange adjustment | 20,000 | |
| New loan moneys on hand | 9,217 | |
| 168,490 | ||
| Total | £844,516 | |
MOVEMENT IN PUBLIC DEBT DURING 1959-60 - A summary of transactions in connection with the public debt during the year ended 31 March 1960 is as follows.
| Amount Outstanding a | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 31 March 1959 | 31 March 1960 | + Increase - Decrease | |
| £(thousand) | |||
| External debt: London | 118,277 | 117,764 | -512 |
| United States of America | 23,548 | 18,965 | -4,583 |
| Internal debt - | |||
| Long-term debt | 634,067 | 699,587 | +65,520 |
| Floating debt | 40,661 | 8,200 | -32,461 |
| Totals | 816,552 | 844,516 | + 27,964 |
A more detailed statement which shows also the main purposes for which loan moneys were raised during the year 1959-60 is now given.
| External debt | £ | £ | £ |
| London - | |||
| Decreases - | |||
| Transfers to New Zealand Register | 513,000 | ||
| United States of America - | |||
| Decreases - | |||
| Repayments from Loans Redemption Account - | |||
| From revenue | 4,583,000 | ||
| Decrease in external debt | 5,095,000 | ||
| Internal debt | |||
| Increases - | |||
| New issues - | |||
| National Development Loans Account | 47,603,000 | ||
| Loans Redemption Account | 69,517,000 | ||
| Transfers from London Register | 513,000 | ||
| 117,632,000 | |||
| Decreases - | |||
| Repayments from Loans Redemption Account - | |||
| From revenue | 15,073,000 | ||
| New issues in New Zealand | 69,500,000 | ||
| 84,573,000 | |||
| Increase in internal debt | 33,059,000 | ||
| Total increase in public debt | £27,964,000 | ||
PUBLIC DEBT CONVERSION SCHEMES AND NEW LOANS - A scheme of conversion of practically the whole of the locally domiciled debt bearing interest higher than 4 per cent was successfully carried out in the early part of 1933. Holders had the option of dissenting, but interest on the dissented portion was made subject to an interest tax of 33 1/3 per cent. Holders who signified neither assent nor dissent were regarded as having assented.
Details of this conversion and of other conversions during the period up to 31 March 1945, together with a schedule of war loans over the period 1940-45, were given on pages 503-504 of the 1950 issue of the Yearbook, while conversions and loans in the subsequent period up to 31 March 1950 were given on pages 819-820 of the 1957 issue of the Yearbook. Conversions in the further period up to 31 March 1958 were given on pages 812-813 of the 1958 issue, and loans for this further period up to 31 March 1958 were given on pages 828-829 of the 1960 issue.
Three conversion loans were offered during 1958, the first in May in conversion of a loan of £7.7 million raised in 1939 maturing 31 May 1958, the second in July in conversion of a short-term loan of £4.2 million raised in 1955 maturing 15 August 1958, and in November a conversion offer was made in respect of £6.7 million raised in 1941 maturing 15 January 1959. Stock offered was in each case the same as that of the 1958 Works Loan, except that in the first conversion offer the middle-term stock maturing 1963-64 was not available. Nearly £6.2 million of the May maturity, £3.6 million of the August maturity, and £5.8 million of the January 1959 maturity stock was converted.
Three conversion loans were offered during 1959, the first in March in conversion of a loan of £18 million raised in 1945 maturing 15 April 1959, the second in May in conversion of a short-term loan of £7.9 million raised in 1956 maturing 15 June 1959, and in July a conversion offer was made in respect of £13.5 million raised in 1954-55 maturing 15 September 1959. Stock offered was in each case the same as the 1959 Works Loan, £14.6 million of the April maturity, £5.1 million of the June maturity, and £8.8 million of the September maturity stock being converted.
Four conversion loans were offered during 1960, the first in April in conversion of a £265,000 3 1/2 per cent stock maturing 22 May 1960 and £10.7 million of 3 3/4 per cent stock maturing 15 June 1960, the second in July in conversion of £15.3 million 4 1/2 per cent stock maturing 15 August 1960 and £16.4 million 3 1/4 per cent stock maturing 15 September 1960. Stock offered in conversion was 4 3/8 per cent maturing 15 July 1963, 4 5/8 per cent maturing 15 July 1965-66, or 4 3/4 per cent maturing 15 July 1970-72; the third in October in conversion of £7.2 million 3 per cent stock maturing 15 November 1960. Stock offered to holders of this stock was 4 3/8 per cent 15 November 1963, 4 5/8 per cent 15 November 1965-66, 4 3/4 per cent repayable 15 November 1970-72, £9.9 million of the April offer, £23.2 million of the July offer, and £4 million of the October offer being converted. The fourth in December was for the conversion of £(A)5 million 5 per cent stock maturing 15 December 1960; stock offered in conversion was 5 per cent maturing 15 December 1973.
A loan of £20,000,000 was raised in London in April 1958. It consisted of New Zealand Government 6 per cent stock issued at £99 per cent and maturing in 1976-80.
An agreement under which the New Zealand Government obtained a loan of $34,500,000 and a credit of 811,500,000 from a group of banks in the United States of America was signed on 30 September 1958. The loan bears interest at 3 1/2 per cent and matures on 30 September 1961, while the credit, which bore interest at 4 1/2 per cent, was repaid on 30 September 1959. Thirteen per cent of the loan was left on deposit with the contributing banks. In connection with the loan, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand deposited with the Federal Reserve Bank of New York gold valued at S31,500,000 as security. An amount of £10,000,000 has been invested in New York to enable repayment of the loan in September 1961.
For the first time New Zealand raised a public loan in the United States of America in December 1958. An amount of $10,000,000 bearing interest at 5 1/2 per cent and maturing in 1970 was raised in New York. The issue price was S99 per cent. The bond issue has a sinking fund designed to retire $395,000 of the debt annually, beginning 1 June 1961. By this means 75 per cent of the debt will be repaid by maturity.
Within New Zealand the 1958 Works Loan of £15,000,000 was opened in June. Stock, at par, was offered with either of three maturity dates, 4 1/2 per cent maturing 15 July 1961 or 4 3/4 per cent maturing either 15 July 1963-64 or 15 July 1968-70. The loan, which had the usual option regarding death duty stock, was oversubscribed, £15,200,000 being raised.
The 1959 Works Loan of £15,000,000 was opened in May. Stock, at par, was offered with either of two maturity dates, 4 1/2 per cent maturing 15 October 1962, 4 3/4 per cent maturing 15 October 1971-73. The loan, which had the usual option regarding death duty stock, was under subscribed, £14,226,680 being raised.
In January 1960 a Government loan was opened with no specific total sought and no closing date. Stock, at par, was offered with either of two maturity dates, 4 3/8 per cent maturing 15 October 1963, or 4 3/4 per cent maturing 15 October 1971-73. The loan was closed on 31 March 1960, by which time £14,485,000 had been subscribed.
In May 1960 a Government cash loan of £15,000,000 was opened; three-year stock was offered at 4 3/8 per cent, six year stock at 4 5/8 per cent, and 12-year stock at 4 3/4 per cent. Stock issued totalled £15,103,760.
In February 1961 a Government cash loan of £10,000,000 was opened; stock at par was offered as follows: 4 3/8 per cent maturing 15 November 1963, 4 5/8 per cent maturing 15 November 1965-66; and stock was also issued at £99 per cent with an interest rate of 4 3/4 per cent and maturing 15 November 1970-72. An amount of £13,665,000 was subscribed by 7,400 applicants.
DOMICILE OF DEBT - The table following shows, for each of the last 11 years ended 31 March the amount of New Zealand's public debt domiciled in London, United States of America, Australia, and New Zealand. All amounts shown are exclusive of the contingent liability due to the United Kingdom Government to which reference has been made elsewhere in this subsection.
| At 31 March | Amount | Percentage of Total on New Zealand Currency Basis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| London | United States of America | Australia | New Zealand | London | United States of America | Australia | New Zealand | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | per cent | |||||||
| 1950 | 78,140 | - | 628 | 565,112 | 12.13 | - | 0.10 | 87.77 |
| 1951 | 77,808 | - | - | 589,425 | 11.66 | - | - | 88.34 |
| 1952 | 77,808 | - | 575,855 | 11.90 | - | - | 88.10 | |
| 1953 | 77,790 | - | - | 589,898 | 11.65 | - | - | 88.35 |
| 1954 | 87,790 | - | - | 616,581 | 12.46 | - | - | 87.54 |
| 1955 | 97,789 | - | - | 630,804 | 13.42 | - | - | 86.58 |
| 1956 | 95,804 | - | - | 639,397 | 13.03 | - | - | 86.97 |
| 1957 | 100,425 | 4,429 | - | 652,265 | 13.26 | 0.59 | - | 86.15 |
| 1958 | 99,576 | 3,963 | - | 678,572 | 12.73 | 0.51 | - | 86.76 |
| 1959 | 118,277 | 23,548 | - | 674,728 | 14.49 | 2.88 | - | 82.63 |
| 1960 | 117,764 | 18,965 | - | 707,787 | 13.94 | 2.25 | - | 83.81 |
MATURITY YEARS OF DEBT - The maturity years of the debt outstanding at 31 March 1960 are shown in the following statement, which distinguishes between the various countries of domicile. All amounts shown may be regarded as being either in New Zealand pounds or in nominal amounts.
| Loans Maturing in Financial Year Ending 31 March* | Due in | Total Debt (Nominal Amount) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S.A. (in New Zealand Currency) | London (in New Zealand Currency) | New Zealand | |||
| Public | Departmental and Other | ||||
*In respect of many of the loans the Government has the option to redeem the securities at an earlier date. †Excludes United Kingdom Government advance of £26,191,000. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| Treasury bills | - | - | - | 8,200 | 8,200 |
| Promissory notes, various (from 15 May 1960 to 15 May 1966) | 3,031 | - | - | - | 3,031 |
| 1961 | - | 6,290 | 37,468 | 16,689 | 60,447 |
| 1962 | 12,350 | - | 40,690 | 16,159 | 69,199 |
| 1963 | - | - | 34,127 | 30,160 | 64,287 |
| 1964 | - | 7,337 | 37,972 | 19,616 | 64,925 |
| 1965 | - | - | 23,543 | 13,420 | 36,963 |
| 1966 | - | 17,047 | 24,461 | 23,744 | 65,252 |
| 1967 | - | 6,696 | 13,054 | 13,817 | 33,567 |
| 1968 | - | - | 11,824 | 10,974 | 22,798 |
| 1969 | - | 15,627 | 1,636 | 75,500 | 92,763 |
| 1970 | - | - | 7,470 | 8,629 | 16,099 |
| 1971 | 3,584 | - | 5,244 | 5,858 | 14,686 |
| 1972 | - | 4,969 | 31 | - | 5,000 |
| 1973 | - | - | 680 | 19,416 | 20,096 |
| 1974 | - | 9,975 | 8,053 | 42,024 | 60,052 |
| 1975 | - | - | 2,545 | 40,358 | 42,903 |
| 1976 | - | - | - | 33,948 | 33,948 |
| 1977 | - | - | - | 50,800 | 50,800 |
| 1978 | - | 6,956 | 44 | 27,500 | 34,500 |
| 1979 | - | 9,944 | 56 | - | 10,000 |
| 1980 | - | 18,290 | 1,710 | - | 20,000 |
| 1983 | - | 5,000 | - | - | 5,000 |
| 1985 | - | 9,633 | 367 | - | 10,000 |
| Totals | 18,965 | 117,764† | 250,975 | 456,812 | 844,516 |
DEPARTMENTAL INVESTMENTS - As shown in the preceding table, £456,812,000 of the public debt outstanding at 31 March 1960 was held by various Government Departments and quasi-Government organisations. A summary of these investments for the last two years is as follows.
| At 31 March | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| £(thousand) | ||
| Investments held by accounts within the Public Account | 53,970 | 54,814 |
| Government Life Insurance | 7,539 | 7,535 |
| Government Superannuation Board | 27,353 | 30,653 |
| Maori Trustee | 2,289 | 2,440 |
| National Provident Fund | 8,499 | 16,327 |
| New Zealand Broadcasting Service | 1,550 | 1,750 |
| Post Office | 134,282 | 135,782 |
| Post Office: National Savings | 56,900 | 61,137 |
| Public Trustee | 4,075 | 4,066 |
| Reserve Bank | 56,321 | 71,321 |
| State Advances Corporation | 2,553 | 2,953 |
| State Fire Insurance Office - | ||
| Accident Branch | 1,502 | 1,552 |
| Fire Branch | 1,363 | 1,637 |
| Meat Industry Account | 37,804 | 35,904 |
| Wool Commission Account | 24,672 | 28,941 |
| Totals | 420,672 | 456,812 |
PRICES OF NEW ZEALAND STOCKS - The following table gives the quotations in London for the principal new stocks (excluding accrued interest) in December of each of the years 1949-57 and at quarterly intervals from March 1958 to December 1960.
| Date | 3 1/4 Per Cent, 1962-65 | 3 1/2 Per Cent, 1960-64 | 4 1/4 Per Cent, 1970-73 | 5 Per Cent, 1956-71 | 6 Per Cent, 1976-80 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1949 - 29 Dec | 98 | 15 | 0 | 100 | 18 | 9 | - | 110 | 16 | 3 | - | ||||
| 1950 - 1 Dec | 100 | 0 | 0 | 102 | 2 | 6 | - | 110 | 12 | 6 | - | ||||
| 1951 - 6 Dec | 93 | 3 | 9 | 95 | 16 | 101/2 | - | 104 | 0 | 0 | - | ||||
| 1952 - 4 Dec | 91 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 94 | 16 | 10 1/2 | - | 102 | 16 | 3 | - | ||||
| 1953 - 3 Dec | 94 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 97 | 6 | 10 1/2 | - | 103 | 1 | 3 | - | ||||
| 1954 - 3 Dec | 98 | 0 | 7 1/2 | 99 | 16 | 10 1/2 | - | 102 | 18 | 9 | - | ||||
| 1955 - 9 Dec | 87 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 6 | 3 | 92 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 98 | 7 | 8 1/2 | - | ||
| 1956 - 7 Dec | 81 | 12 | 6 | 85 | 16 | 3 | 85 | 6 | 3 | 93 | 2 | 6 | - | ||
| 1957 - 6 Dec | 82 | 13 | 1 1/2 | 86 | 16 | 3 | 83 | 13 | 9 | 91 | 3 | 1 1/2 | - | ||
| 1958 - 7 Mar | 83 | 8 | 9 | 87 | 8 | 9 | 85 | 5 | 0 | 91 | 18 | 1 1/2 | - | ||
| 6 Jun | 84 | 0 | 0 | 88 | 9 | 4 1/2 | 84 | 6 | 3 | 91 | 12 | 6 | 101 | 1 | 3 |
| 5 Sep | 85 | 11 | 10 1/2 | 90 | 16 | 10 1/2 | 85 | 19 | 4 1/2 | 91 | 15 | 0 | 103 | 10 | 0 |
| 5 Dec | 85 | 8 | 1 1/2 | 92 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 87 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 94 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 102 | 5 | 0 |
| 1959 - 6 Mar | 89 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 94 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 89 | 10 | 0 | 95 | 18 | 1 1/2 | 104 | 18 | 1 1/2 |
| 5 Jun | 87 | 18 | 1 1/2 | 93 | 9 | 4 1/2 | 88 | 16 | 10 1/2 | 95 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 104 | 3 | 1 1/2 |
| 4 Sep | 88 | 9 | 4 1/2 | 94 | 1 | 10 1/2 | 89 | 5 | 0 | 96 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 104 | 7 | 6 |
| 4 Dec | 89 | 15 | 7 1/2 | 95 | 1 | 10 1/2 | 89 | 9 | 4 1/2 | 99 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 106 | 0 | 0 |
| 1960 - 3 Mar | 89 | 19 | 4 1/2 | 94 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 87 | 13 | 1 1/2 | 96 | 17 | 6 | 103 | 15 | 7 1/2 |
| 1 Jun | 89 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 93 | 13 | 1 1/2 | 87 | 9 | 4 1/2 | 95 | 11 | 3 | 102 | 3 | 9 |
| 1 Sep | 88 | 5 | 0 | 92 | 0 | 0 | 84 | 5 | 1 1/2 | 91 | 8 | 9 | 99 | 10 | 7 1/2 |
| 1 Dec | 89 | 1 | 3 | 93 | 1 | 3 | 84 | 16 | 3 | 91 | 16 | 3 | 99 | 15 | 7 1/2 |
INTEREST—Of the public debt outstanding at 31 March 1932, approximately 30 per cent only of the total bore interest at a rate of 4 per cent or lower. Following on conversion operations and a general decline in interest rates for new money in the succeeding years until recent times, the amount of debt bearing interest at a rate of 4 per cent or under at 31 March 1960 was £618.8 million, or 73 per cent of the total debt (excluding the contingent liability on which interest payments have been suspended since 1931 by agreement with the United Kingdom Government), while on £283.2 million, or approximately 34 per cent, the rate did not exceed 3 per cent. Of the debt domiciled in New Zealand at 31 March 1960, 37 per cent was at rates of 3 per cent or under, the remainder (or 63 per cent) being at rates which did not exceed 6 per cent. A classification of the public debt as at 31 March 1960, according to the rates of interest payable and domicile, is contained in the following table, the values being in terms of New Zealand currency.
| Rate of Interest (per cent) | Debt Maturing in - | Total | Gross Annual Interest Charge | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| London | United States of America | New Zealand | |||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1 | - | - | 83,700 | 83,700 | 719 |
| 2 1/2 | - | - | 9,080 | 9,080 | 227 |
| 3 | 22,582 | - | 167,843 | 190,425 | 5,713 |
| 3 1/4 | 23,743 | - | 16,796 | 40,540 | 1,050 |
| 23,260 | 12,350 | 95,740 | 131,350 | 4,594 | |
| 3 3/4 | - | - | 74,430 | 74,430 | 2,591 |
| 4 | 9,944 | - | 79,374 | 89,318 | 3,573 |
| 4 1/4 | 9,975 | - | 25 | 10,000 | 425 |
| 4 3/8 | - | - | 6,071 | 6,071 | 266 |
| 4 1/2 | - | - | 67,196 | 67,196 | 2,679 |
| 4 5/8 | - | - | 22,798 | 22,798 | 1,054 |
| 4 3/4 | - | 3,031 | 78,185 | 81,215 | 3,852 |
| 5 | 4,969 | - | 4,840 | 9,809 | 491 |
| 5 1/4 | 5,000 | - | - | 5,000 | 263 |
| 5 1/2 | - | 3,584 | - | 3,584 | 197 |
| 6 | 18,291 | - | 1,710 | 20,000 | 1,200 |
| Totals | 117,764 | 18,965 | 707,787 | 844,516 | 28,894 |
The total amount of interest payable on the public debt - i.e., excluding the contingent liability on which interest payments have been suspended by agreement with the United Kingdom Government- as at 31 March 1960 was £28,894,000, which gives an average rate of £3 8s. 5d. per cent.
The amount of interest and the average rate per cent payable on the debt domiciled in the respective markets were—
| Amount of Interest | Average Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | s. | d. | |
| London | 4,708,222 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| United States of America | 937,771 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| New Zealand | 23,113,234 | 3 | 7 | 4 |
The total interest payments from the Consolidated Fund during the year ended 31 March 1960 was £28,759,000. Of this amount £4,614,000 was paid in London and £94,000 in New Zealand on account of debt domiciled in London, £938,000 was paid on account of debt domiciled in the United States of America, while the remaining £23,113,000 was paid in New Zealand in respect of internal debt.
The total amount of interest credited to the Consolidated Fund on account of capital liability of various enterprises during 1959-60 was £13,137,000, the contributing accounts being Post Office, £2,654,000; Electric Supply, £6,559,000; Housing Account, £1,540,000; Housing Construction, £157,000; Land Settlement Account, £1,506,000; under section 31 (3) of Land Act 1948, £625,000; and New Zealand National Airways Corporation, £95,000. Interest is also received from the investment of other public moneys, the total under this heading being £1,840,000, including £106,000 from the State Advances Corporation, £750,000 from the Public Account Cash Balance Investment Account, £142,000 from the Christmas Island Phosphate Commission, £22,000 from the British Phosphate Commission, £133,000 from the Deposits Accounts, £231,000 from the Loans Redemption Account, and £315,000 from the Tasman Pulp and Paper Co. Ltd. The total interest receipts of the Consolidated Fund were thus £14,977,000, leaving the net interest charges for the year £13,782,000, as compared with £13,492,000 in 1958-59.
The following table shows the gross payments of interest together with the net interest charges for the last eleven financial years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Gross Payments | Receipts | Gross Payments, Less Receipts |
|---|---|---|---|
| £N.Z.(thousand) | |||
| 1950 | 16,737 | 5,886 | 10,850 |
| 1951 | 17,264 | 6,566 | 10,698 |
| 1952 | 17,713 | 7,337 | 10,376 |
| 1953 | 17,321 | 6,894 | 10,427 |
| 1954 | 18,128 | 7,746 | 10,382 |
| 1955 | 20,014 | 8,378 | 11,636 |
| 1956 | 21,001 | 9,147 | 11,854 |
| 1957 | 22,729 | 11,554 | 11,174 |
| 1958 | 25,316 | 12,392 | 12,924 |
| 1959 | 27,277 | 13,785 | 13,492 |
| 1960 | 28,759 | 14,977 | 13,782 |
Administration and management charges in respect of debt services amounted to £333,000 in 1959-60, as compared with £1,299,000 in 1958-59.
AMORTISATION OF DEBT: Public Debt Repayment - With certain exceptions, the repayment of the public debt is now subject to the provisions of the New Zealand Loans Act 1953. For this purpose there is issued annually out of the Consolidated Fund:(a) a sum equal to 1/2 per cent of the total amount of the public debt outstanding at the end of the preceding financial year;(b) £2,865,000, being 4 per cent of the redemptions effected from 1 April 1925 up to 1 January 1954;(c) a sum equal to 4 per cent of the total amounts paid under section 59 of the Act between the commencement of the Act (1 January 1954) and the end of the preceding financial year: Provided that if the Minister of Finance so directs, any amount required to be paid under this section may be reduced by the amount paid into the Loans Redemption Account under paragraph (c) of section 57 of the Act, but the amount payable under paragraph (c) of this section in any subsequent year shall be computed as if no such reduction had been made. The bulk of the savings in interest on debt paid off is thus applied to further repayments of debt. In brief, provision is made to repay the debt in approximately 60 years from the date of the inception of the scheme (1925) or from the date of raising subsequent loans.
The annual contribution from the Consolidated Fund paid to the Loans Redemption Account is utilised to redeem such securities as the Public Debt Commission determines, which are a charge upon the public revenues of New Zealand. All other moneys raised or available for the purpose of repayment of any loan forming a charge on public revenues are similarly paid into the Loans Redemption Account and utilised for the redemption of such securities charged upon the public revenues as the Minister of Finance from time to time determines.
Transactions involving merely the exchange of one class of securities for another of the same rate of interest and term, or where the only variation is an extension of the term by not more than two years, are not recorded in the Loans Redemption Account.
The repayment scheme provided for under the New Zealand Loans Act 1953 does not apply to the whole of the public debt, moneys borrowed on the security of Treasury bills issued under section 41 of the Public Revenues Act 1953 being excluded. The funded debt and a contingent liability linked with it are not part of the debt nor are they covered by the repayment provisions.
Amounts devoted to the repayment or redemption of the public debt during each of the last five years are set out below, together with a brief statement of the class of debt affected by redemption operations.
| Year Ended 31 March | Repayments Section 58 (a) of 1953 Act | Amounts Utilised for Redemption | Class of Debts Affected by Redemption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section 58 (b) of 1953 Act | Section 58 (c) of 1953 Act | Total Amount Utilised | Item | Amount | ||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1956 | 25,588 | 4,452 | 8,706 | 13,157 | War expenses | 11,267 |
| 0ther debt | 1,891 | |||||
| 1957 | 241,208 | 4,899 | 9,060 | 13,959 | War expenses | 12,721 |
| Other debt | 1,238 | |||||
| 1958 | 34,447 | 8,178 | 1,975 | 10,153 | War expenses | 7,774 |
| Other debt | 2,378 | |||||
| 1959 | 56,751 | 2,762 | 9,061 | 11,823 | War expenses | 3,961 |
| Other debt | 7,861 | |||||
| 1960 | 69,500 | 13,108 | 6,548 | 19,656 | War expenses | 13,319 |
| Other debt | 6,337 | |||||
The following table shows the amounts available for redemption for each of the last five years under the repayment scheme provided for by the New Zealand Loans Amendment Act 1953, the amounts utilised, and the nominal value of securities redeemed and cancelled to date.
| Year Ended 31 March | Balance of Amortisation Contributions Unspent at Beginning of Year | Transfers from Consolidated Fund | Utilised to Redeem and Cancel Securities | Nominal Value of Securities Redeemed and Cancelled from 1 April 1925 to 31 March 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 Per Cent of Public Debt Outstanding at Beginning of Year | 4 Per Cent of Total Amount of Public Debt Redeemed or Repaid to Beginning of Year | Total | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1956 | 3,052 | 3,653 | 3,379 | 7,033 | 4,452 | 85,851 |
| 1957 | 5,633 | 3,676 | 3,661 | 7,337 | 4,899 | 90,750 |
| 1958 | 8,071 | 3,786 | 3,954 | 7,740 | 8,178 | 98,928 |
| 1959 | 7,632 | 3,911 | 4,264 | 8,174 | 2,762 | 101,690 |
| 1960 | 13,045 | 4,083 | 4,590 | 8,673 | 13,108 | 114,798 |
NET INDEBTEDNESS - While the sinking funds were annually increasing it was customary to regard the net indebtedness figures as giving the best comparison of indebtedness between one year and another. The initiation of the present system of amortisation, however, destroyed the comparison on this basis, and the gross figures (as shown at the beginning of this subsection) now afford a better and more comparable index. The net indebtedness figures for the last two years are: 1958-59, £799,269,000 (£343 12s. per head of population); 1959-60, £833,128,000 (£351 10s. per head of population).
The net indebtedness quoted is merely the balance left after deducting from the amount of debentures and stock in circulation, the net balance of the Loans Redemption Account. No allowance is made for the fact that a portion of the debt is actually held by the Government itself. In the course of the year's financial transactions securities are bought and sold by Treasury accounts, and the investments held as at 31 March in each year, while forming part of the debt, do not represent amounts due directly or indirectly to the public. New Zealand Government investments held by Treasury accounts as at 31 March of the last five years have been: 1956, £47,784,000; 1957, £50,605,000; 1958, £52,388,000; 1959, £72,027,000; 1960, £71,461,000.
In addition to the above, Government investments in corporations, etc., held at 31 March 1960 (shown in the return required by the Public Revenues Act 1953 and published in parliamentary paper B. 1 [Pt I]) are given in the following table.
| Investment | Amount at 31 March 1960 |
|---|---|
| £(000) | |
| Bank of New Zealand | 12,018 |
| Bay of Plenty Fertiliser Works Ltd. | 110 |
| British Phosphate Commission | 532 |
| Christmas Island Phosphate Commission | 3,384 |
| Dominion Salt Ltd. | 150 |
| East Coast Farmers' Fertiliser Co. Ltd. | 45 |
| Kaingaroa Logging Co. Ltd. | 50 |
| Linen Flax Corporation | 200 |
| Maramarua Coalfields Ltd. | 75 |
| New Zealand National Airways Corporation | 2,750 |
| New Zealand Woolpack and Textiles Ltd. | 150 |
| Reserve Bank of New Zealand | 1,500 |
| State Advances Corporation | 3,753 |
| Tasman Empire Airways Ltd. | 811 |
| Tasman Pulp and Paper Co. Ltd. | 2,000 |
| Tourist Hotel Corporation of New Zealand | 2,275 |
| Miscellaneous | 132 |
| Total | £29,936 |
GENERAL AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT DEBT - The statistics given throughout this subsection refer to the indebtedness of the General Government only, and do not include the debt of local-governing authorities, which is dealt with in the section of this volume relating to local government.
Local-governing authorities had at 31 March 1960 a gross indebtedness equivalent to £168,659,408 and if this amount be added to the gross debt of the General Government at 31 March 1960 (£844,516,000) the aggregate becomes £1,013,175,408. This latter total is exclusive of £26,191,000 contingent liability due to the United Kingdom. Allowing for duplication on account of outstanding loans to local authorities from the State Advances Corporation, the Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council, and the Fire Services Council, the total is reduced to approximately £1,010,572,643.
The figures relating to local authorities' indebtedness in the foregoing paragraph are inclusive of hospital boards, and to this extent differ from those generally given in the section on local government. Hospital board gross indebtedness at 31 March 1960 totalled £25,102,838.
GENERAL - The constitution and franchise of local authorities are now described in Section 2, “History, Constitution, and Government”.
Detailed statistics relating to each local authority, other than hospital boards, are contained in the Local Authorities Handbook, an annual publication of the Department of Statistics. Hospital boards, which supply their returns to the Department of Health, are omitted from most of the statistics contained in this section, a special note is made where they are included, but summarised data relating to them will be found in Section 5B.
The local authority year now uniformly ends on 31 March, except in the case of most harbour boards and the Hutt Valley Drainage Board. In certain cases where the harbour is administered by a county or borough council the year ends on 31 March, but in all other cases on 30 September.
BORROWING - Under the Local Authorities Loans Act 1956 all loan proposals of local authorities, except in regard to money borrowed in anticipation of revenue, require the sanction of the Local Authorities Loans Board. The board consists of the Secretary to the Treasury, the Commissioner of Works, and five other members appointed by the Governor-General. In cases where a poll of ratepayers is necessary preparatory to raising a loan, the board's consent must be obtained before the poll is held. In no case may the board sanction any application unless provision is made to its satisfaction for repayment of the loan within such period as it deems reasonable, having regard to the probable duration and continuing utility of the works on which the loan moneys are to be expended.
A local authority is empowered to raise a special loan for the construction of any public work, for the purchase of land or buildings, or for the purpose of engaging in any undertaking into which it may lawfully enter. As a general rule local authorities may raise a loan by special order and without a poll of ratepayers, but, in the case of a local authority that is a rating body, a poll of ratepayers is to be taken if—
The Local Authorities Loans Board requires a poll to be taken; or
Before the date fixed for the meeting of the local authority to confirm the resolution to raise the loan not less than 5 per cent of the ratepayers demand a poll; or
The local authority itself decides to take a poll.
A poll cannot be required in cases such as renewal loans, loans raised for emergency expenditure by reason of flood, storm, earthquake, etc., or loans for work of national and local importance and carried out by an agreement between the Government and a local authority.
Where a poll is required it shall be deemed to be carried if a bare majority of the valid votes recorded is in favour of the proposal. The properties and revenue of the local authority may be pledged as security for the repayment of any principal sum or interest thereon, or a special rate may be levied for the same purpose.
The borrowing activities of certain types of local authority are subject to special provisions. Under the Hospitals Act 1957 a hospital board must first obtain the approval of the Minister of Health before exercising its power to borrow; under the Fire Services Act 1949 the boards of urban fire authorities must obtain the prior consent of the Fire Service Council. Harbour boards derive their authority to borrow for harbour works from special empowering legislation, and similar authority is given for the capital works of certain other local authorities.
RATING - Local authorities are largely dependent on revenue from rates to carry out their activities, and even loans raised for special purposes are, except where the assets purchased provide revenue to meet the loan charges, ultimately liquidated by rate revenues - known then as special rates. Three broad classes of rates are distinguished:
General, for general purposes.
Separate rates levied for the construction of public works, for the acquisition of land or buildings, or for the benefit of the whole or part of a local district.
Special rates imposed to secure the repayment of loan money, being sufficient to produce interest and sinking fund, or interest and instalment of principal, as the case may be. Special rates can be levied only by resolution gazetted, and, unlike general and separate rates, are not subject to any statutory limit.
There are three main systems of rating: (1) capital (land and improvements) value, (2) annual value, and (3) unimproved value. Rating on an acreage basis is applied mainly by rabbit boards which also, in two districts, rate according to the number of sheep and/or cattle owned.
The Rating Act 1925 provides that the local authority of any district (other than a district wherein the system of rating on the unimproved value is in force) may from time to time by resolution determine whether the system of rating on the annual value or on the capital value shall be in force in the district. In the case of rating on the capital value the rating roll is based on the district valuation roll prepared by the Valuation Department. Where the rating is on the annual value the local authority generally prepares its valuation roll on the basis of valuations made by its own valuers. There is, however, provision that annual values may be prepared on the basis of the annual value being equal to £6 per cent of the capital value, and also that a rate of 1s. in the pound on the annual value is equivalent to 3/4d. in the pound on the capital value. The Rating Amendment Act 1954 further provides that the Valuer-General may act as a local authority's valuer where an annual value roll is to be prepared. (See also Section 10E on valuation of land.)
Under the Rating Act 1925 it is entirely at the option of the ratepayers of local districts to decide the system of rating. The poll is taken in the same manner as in the case of a loan poll required under the Local Authorities Loans Act 1956. The question of adoption or otherwise is decided by a bare majority of the valid votes recorded, irrespective of the number of ratepayers who have voted.
A rescinding proposal can be carried at a poll by the same means as one for adoption, but not until after three years have elapsed; and, vice versa, rejection of a proposal bars its being brought forward for a similar period.
Under the authority of the Counties Act 1956 the ratepayers within a county town may require the county council to take a poll within the town on a proposal to adopt a system of rating which differs from that in force in the county.
A town district, borough, or another county formed from part of a county automatically rates on the system in force in the county at the time of the constitution of the new district; also two boroughs amalgamating adopt the system in force in the district with the greater population, unless their councils agree to the contrary.
Distribution of Rating Systems in Force - A table is given of rating systems in force during the financial year 1958-59 in those districts which levy rates.
| System of Rating | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unimproved Value | Capital Value | Annual Value | Acreage Basis | On Stock | ||
*Includes Chatham Islands county, for which import and export dues are charged in lieu of rates on land. †Includes one board with the powers of a drainage board which also rates on an acreage basis. | ||||||
| Counties | 66 | 52 | - | - | - | 119* |
| Boroughs | 113 | 16 | 14 | - | - | 143 |
| Town districts | 16 | 12 | 2 | - | - | 30 |
| Road districts | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 3 |
| River districts | 4t | 5 | - | 3 | - | 12 |
| Catchment districts | - | 13 | - | - | - | 13 |
| Land-drainage districts | 28 | 13 | - | 1 | - | 42 |
| Water-supply district | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Rabbit districts | - | 2 | - | 199 | 2 | 203 |
| Totals | 228† | 115 | 16 | 204 | 2 | 566* |
The position in regard to the four major classes of local authorities at 1 April 1959 (i.e., the beginning of the 1959-60 financial year) is set out in the following table. The figures in parentheses are proportions per cent of the total.
| Rating on | Total for Zealand | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unimproved Value | Capital Value | Annual Value | ||||||
| No. | Population | No. | Population | No. | Population | No. | Population* | |
*Estimated population at 1 April 1959, exclusive of persons on shipboard, etc. †Includes Sounds and Fiord counties in which the Counties Act is not wholly in force, and Chatham Islands county for which export and import dues are charged in lieu of rates on land. | ||||||||
| Counties (excluding town districts) | 67 | 519,630 | 51 | 320,310 | - | - | 121† | 841,500† |
| (55.4) | (61.8) | (42.1) | (38.1) | (-) | (-) | |||
| Cities and boroughs | 115 | 1,149,950 | 15 | 59,710 | 13 | 247,860 | 143 | 1,457,520 |
| (80.4) | (78.9) | (10.5) | (4.1) | (9.1) | (17.0) | |||
| Independent town districts | 10 | 8,440 | 5 | 3,660 | 1 | 610 | 16 | 12,710 |
| (62.5) | (66.4) | (31.2) | (28.8) | (6.3) | (4.8) | |||
| Dependent town districts | 8 | 3.770 | 5 | 2,430 | I | 600 | 14 | 6,800 |
| (57.1) | (55.5) | (35.7) | (35.7) | (7.2) | (8.8) | |||
| Totals | 200 | 1,681,790 | 76 | 386,110 | 15 | 249,070 | 294† | 2,318,530† |
| (68.0) | (72.5) | (25.9) | (16.7) | (5.1) | (10.7) | |||
For the purposes of the foregoing tables a district is deemed to rate on the unimproved value where the general rate is levied on an unimproved-value basis. In a number of instances, in particular of boroughs, certain of the subsidiary rates are levied on other systems.
The following table shows the amounts levied under the various systems of rating and by annual fees or charges by counties, boroughs, and town, and road districts for the year ended 31 March 1959. Amounts levied on behalf of other local authorities are included.
| System of Rating | Uniform Fees and Charges | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unimproved Value | Capital Value | Annual Value | |||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 4,710,255 | 2,713,316 | 31,384 | 61,405 | 7,516,360 |
| Boroughs | 10,187,466 | 989,172 | 3,302,585 | 1,429,494 | 15,908,717 |
| Town districts | 41,925 | 20,115 | 4,295 | 14,035 | 80,370 |
| Road districts | 24,049 | 2,626 | - | - | 26,675 |
| Totals | 14,963,695 | 3,725,229 | 3,338,264 | 1,504,934 | 23,532,122 |
RECEIPTS - The sources from which the various classes of local authorities secure the moneys necessary to exercise their functions vary greatly, according to the nature of the statutory duties of the local authority concerned. Generally, however, receipts fall under one of four main classes—viz, rates; revenue from public utilities, licences, rents, etc.; revenue receipts from the General Government; and receipts such as loan money and special grant, and subsidies from the Government which cannot properly be regarded as revenue.
The receipts of local authorities, divided into the various groups mentioned, are given for each of the latest 11 years. As stated earlier, the figures quoted here and elsewhere in this section (unless specifically stated to this effect) do not cover the operations of hospital boards.
| Year Ended 31 March | Revenue From | Total Revenue | Receipts Not Revenue | Total Receipts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rates | Public Utilities, Licences, Rents, etc. | Government | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1949 | 10,797 | 19,077 | 680 | 30,554 | 5,458 | 36,012 |
| 1950 | 11,645 | 20,327 | 752 | 32,724 | 7,367 | 40,091 |
| 1951 | 12,577 | 21,716 | 910 | 35,203 | 7,461 | 42,664 |
| 1952 | 14,514 | 24,051 | 1,104 | 39,669 | 9,543 | 49,212 |
| 1953 | 15,354 | 27,588 | 1,128 | 44,071 | 14,615 | 58,685 |
| 1954 | 16,421 | 32,322 | 1,200 | 49,943 | 19,307 | 69,250 |
| 1955 | 18,259 | 35,314 | 3,766 | 57,338 | 17,280 | 74,618 |
| 1956 | 18,883 | 38,396 | 3,999 | 61,278 | 21,424 | 82,702 |
| 1957 | 20,659 | 39,565 | 4,310 | 64,534 | 26,058 | 90,592 |
| 1958 | 22,707 | 42,343 | 4,516 | 69,567 | 31,051 | 100,618 |
| 1959 | 24,392 | 48,903 | 4,935 | 78,236 | 29,874 | 108,105 |
Local authorities received by the way of rates in the financial year 1958-59 a total amount of £24,392,264, and the sum of £731,174 was raised by licences, making £25,123,438 altogether from taxation, which is equivalent to £10 18s. 2d. per head of the total mean population.
During 1958-59 rates formed 31.2 per cent of the revenue proper; public utilities, licences, rents, and other sources yielded 62.5 per cent; and 6.3 per cent came from the General Government.
Revenue proper in 1958-59 was £8,663,813 greater than in 1957-58, while receipts other than revenue decreased by £1,776,566. Rates accounted for £1,684,808 of the revenue increase, and public utilities, licences, rents, etc., for £6,559,989.
Of the revenue proper of counties, which amounted to £11,567,889 in 1958-59, no less a sum than £6,791,851, or 58.7 per cent, was raised by way of rates. Town districts, road districts, river districts, catchment districts, land-drainage districts, urban drainage districts, and the water-supply district also rely on taxation for the greater part of their income. In the case of boroughs and harbour boards, on the other hand, rates supply a considerably smaller proportion of the total revenue. During 1958-59 this source of income accounted for 42.1 per cent of the total revenue of boroughs and 10 8 per cent of that of harbour boards. Rates collected for, or to meet levies by, fire boards are included as revenue from rates by the levying authorities. Electric power districts did not rate during 1958-59.
The next table shows the receipts for 1958-59 (classified as in the preceding table) for each type of local authority.
| Revenue From | Receipts not Revenue | Total Receipts | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rates | Public Utilities, Licences, Rents, etc. | Government | |||
*Levy on milk. †Including contributions from authorities levying rates. ‡Harbour improvement ate, £373,465, and rates on land in harbour rating area, £359,604. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 6,791,851 | 2,169,533 | 2,606,505 | 6,653,456 | 18,221,345 |
| Boroughs | 13,819,638 | 17,364,627 | 1,652,910 | 9,799,551 | 42,636,726 |
| Town districts | 103,488 | 69,967 | 21,310 | 21,332 | 216,097 |
| Road districts | 27,246 | 4,539 | 9,575 | 7,324 | 48,684 |
| River districts | 55,831 | 34,394 | - | 17,387 | 107,612 |
| Catchment districts | 583,436 | 331,621 | - | 1,035,135 | 1,950,192 |
| Land-drainage districts | 144,665 | 36,795 | - | 69,793 | 251,253 |
| Electric power districts | - | 18,937,255 | - | 3,099,845 | 22,037,100 |
| Water-supply district | 7,693 | 100 | - | 10 | 7,803 |
| Urban drainage districts | 1,236,135 | 23,594 | - | 3,540,549 | 4,800,278 |
| Urban transport districts | 365,804 | 2,247,056 | - | 243,310 | 2,856,170 |
| Local railway district | - | 33,726 | - | 10,000 | 43,726 |
| Gas districts | - | 174,437 | - | 2,368 | 176,805 |
| Milk districts | 9,129* | 56,462 | - | 16,744 | 82,335 |
| Valley authority | 12,000 | 9,639 | - | 5,100 | 26,739 |
| Nassella tussock districts | 9,317 | 76,916 | - | 8,170 | 94,403 |
| Harbour bridge authority | - | - | - | 2,093,830 | 2,093,830 |
| Plantation board | - | 19,271 | - | 2,607 | 21,878 |
| Underground water authorities | - | 451 | - | - | 451 |
| Rabbit districts | 492,962 | 92,267 | 504,431 | 216,609 | 1,306,269 |
| Fire districts | - | 1,023,696† | 106,750 | 281,205 | 1,411,651 |
| Harbour boards | 733,069‡ | 6,197,036 | 33,526 | 2,750,172 | 9,713,803 |
| Totals | 24,392,264 | 48,903,382 | 4,935,007 | 29,874,497 | 108,105,150 |
Of the total rates £24,392,264 collected during 1958-59 general rates levied brought in £17,052,884 and other rates (including penalty on overdue rates) £7,339,380. Of the latter, £6,062,292 was received by boroughs and £765,787 by counties. The whole of the rates collected by harbour boards £733,069 were classed as general rates.
It is of interest to note that for the year 1958-59 the total of all rates collected by counties was equal to £6.57 per £1,000 of rateable capital value (land and improvements) at the beginning of the year. The corresponding figure for boroughs' was £9.99, for independent town districts £9.82 and for dependent town districts £572 (excluding rates levied by county councils).
Sections in successive Finance Acts from 1930 to 1936 authorised the remission or postponement in whole or in part of the 10 per cent penalty on unpaid rates. This authority then lapsed, but was reinstated on a permanent basis and made retrospective by the Statutes Amendment Act 1938.
Public Utilities, Licences, Rents, etc. — As indicated earlier, rates are not the only form of local taxation. Local authorities derive a certain amount of revenue from publicans' licences, motor-drivers licences, drivers' (other vehicles) licences, auctioneers' and hawkers' licences, building permit, dog taxes, pound taxes, etc. Sources of revenue not classed as taxation are rents, fines and penalties, sales of material, sales of light and power from gasworks and electric-supply works, transport receipts, interest on deposits, wharf dues, etc.
Of the total revenue of £17,364,627 accruing to boroughs under this head in 1958-59, £1,648,069 represented transport receipts, £8,108,079 sales of electric light and power, and £1,127,330 sales of gas. Comparable figures for 1957-58 were £15,607,614, £1,678,729, £6,465,891, and £1,092,015 respectively.
Receipts from General Government - A statement of revenue receipts by local authorities from the General Government during the five financial years ended 31 March 1955-59 is given in the next table.
| Year Ended 31 March | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Amount carried over from 1953-54. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Rates on Crown lands | 19,875 | 25,495 | 27,587 | 23,224 | 22,181 |
| Fire Service Council | 83,386 | 85,408 | 93,013 | 101,798 | 106,750 |
| Timber and flax royalties | 54,300 | 61,696 | 68,986 | 60,364 | 76,087 |
| Goldfields revenue and gold duty | 9,763 | 9,065 | 11,906 | 13,599 | 8,275 |
| Fees and fines | 39,972 | 43,386 | 57,477 | 71,185 | 81,618 |
| Subsidies— | |||||
| National Roads Board— | |||||
| On rates | 1,636,509 | 1,860,831 | 2,047,209 | 2,232,274 | 2,510,026 |
| On population | 1,403,530 | 1,432,260 | 1,418,610 | 1,452,723 | 1,586,420 |
| Rabbit Destruction Council | 416,598 | 421,146 | 509,199 | 518,533 | 504,431 |
| Motor-spirits tax | 94,615* | - | - | - | - |
| Other revenue receipts | 7,019 | 59,545 | 75,969 | 42,291 | 39,219 |
| Totals, Revenue Account | 3,765,567 | 3,998,832 | 4,309,956 | 4,515,991 | 4,935,007 |
| Loans from State Advances Corporation (Housing Account only) | 155,051 | 182,215 | 311,205 | 348,290 | 340,897 |
| Loans from Treasury | 25,036 | 9,371 | 4,000 | - | - |
| Advances from National Roads Board | 2,800 | 39,000 | 2,500 | - | - |
| Advances from Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council | 23,600 | 19,535 | 10,055 | 10,500 | - |
| Advances from Fire Service Council | 3,829 | 15,630 | 14,650 | 19,913 | - |
| Grants for special works, etc., from— | |||||
| Department of Labour | 32,501 | 29,367 | 24,827 | 19,808 | 17,647 |
| National Roads Board | 2,309,265 | 3,788,693 | 4,829,089 | 4,846,239 | 4,709,675 |
| Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council | 514,423 | 691,517 | 870,805 | 980,135 | 948,505 |
| Ministry of Works | 757,586 | 974,975 | 656,041 | 677,837 | 741,458 |
| Other Departments | 1,036,606 | 875,514 | 859,117 | 931,424 | 934,412 |
| Total receipts from Government | 8,726,264 | 10,624,649 | 11,892,245 | 12,350,137 | 12,627,601 |
EXPENDITURE - The expenditure of local authorities during each of the latest 11 years has been as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Works and Utilities (Construction and Maintenance) | Hospital Board Levies | Administration | Interest on Loans and Overdraft | Other | Total Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1949 | 25,623 | 1,415 | 2,315 | 2,332 | 4,128 | 35,812 |
| 1950 | 29,099 | 1,506 | 2,412 | 2,284 | 4,363 | 39,664 |
| 1951 | 32,130 | 1,669 | 2,897 | 2,221 | 4,325 | 43,242 |
| 1952 | 36,989 | 1,855 | 3,222 | 2,219 | 4,561 | 48,346 |
| 1953 | 45,061 | 1,748 | 3,437 | 2,329 | 5,763 | 58,337 |
| 1954 | 53,664 | 1,660 | 4,056 | 2,595 | 6,314 | 68,289 |
| 1955 | 58,094 | 1,455 | 4,583 | 2,874 | 6,974 | 73,981 |
| 1956 | 66,418 | 1,080 | 4,857 | 3,157 | 8,047 | 83,559 |
| 1957 | 72,751 | 660 | 5,428 | 3,659 | 8,241 | 90,740 |
| 1958 | 79,619 | ... | 5,857 | 4,225 | 8,587 | 98,288 |
| 1959 | 85,868 | ... | 6,191 | 5,133 | 9,407 | 106,599 |
Included in the total of other payments for 1958-59 is an amount of £6,237,551 in respect of amortisation of debt, which compares with the figure of £5,842,616 in 1957-58.
The main items of expenditure of the various classes of local authorities during 1958-59 are shown below.
| Works and Utilities (Construction and Maintenance) | Administration | Interest on Loans and Overdraft | Amortisation of Debt | Other Payments | Total Expenditure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 14,989,622 | 1,469,330 | 338,234 | 534,839 | 545,416 | 17,877,441 |
| Boroughs | 34,536,624 | 1,947,433 | 2,222,640 | 2,740,590 | 855,295 | 42,302,582 |
| Town districts | 159,540 | 21,623 | 6,917 | 11,223 | 5,611 | 204,914 |
| Road districts | 37,297 | 7,034 | 652 | 2,662 | 643 | 48,288 |
| River districts | 69,962 | 14,094 | 4,770 | 5,648 | 180 | 94,654 |
| Catchment districts | 1,441,480 | 299,777 | 31,002 | 65,485 | 26,133 | 1,863,877 |
| Land-drainage districts | 191,259 | 21,320 | 11,214 | 13,668 | 2,167 | 239,628 |
| Electric power districts | 16,327,481 | 1,433,178 | 932,104 | 1,576,322 | 756,769 | 21,025,854 |
| Water supply | 5,290 | 1,463 | 25 | 172 | 10 | 6,960 |
| Urban drainage districts | 4,027,395 | 149,125 | 454,415 | 256,373 | 30,156 | 4,917,464 |
| Urban transport districts | 2,077,652 | 139,024 | 179,855 | 289,701 | 11,727 | 2,697,959 |
| Road tunnel authority | - | 229 | - | - | - | 229 |
| Local railway district | 38,897 | 2,851 | 1,088 | - | - | 42,836 |
| Gas districts | 171,838 | 14,705 | 8,927 | 13,861 | 1,300 | 210,631 |
| Milk districts | 52,363 | 17,732 | 38 | 895 | 18,878 | 89,906 |
| Valley authority | 12,282 | 14,552 | 102 | 42 | - | 26,978 |
| Nassella tussock districts | 77,192 | 5,799 | - | - | 351 | 83,342 |
| Harbour bridge authority | 1,979,145 | 13,040 | 198,370 | - | - | 2,190,555 |
| Plantation board | 16,157 | 5,197 | - | - | - | 21,354 |
| Underground water authorities | 402 | - | - | - | - | 402 |
| Rabbit districts | 1,114,513 | 101,633 | 5,809 | 17,788 | 4,041 | 1,243,784 |
| Fire districts | 1,156,725 | 33,364 | 68,875 | 89,753 | 105,065 | 1,453,782 |
| Harbour boards | 7,385,504 | 478,819 | 667,580 | 618,529 | 805,558 | 9,955,990 |
| Totals | 85,868,620 | 6,191,322 | 5,132,617 | 6,237,551 | 3,169,300 | 106,599,410 |
The next table shows for some of the more important classes of local authorities the proportions per cent that the main items of expenditure bear to the totals. These percentages are based on the figures shown in the preceding table.
| Works and Utilities (Construction and Maintenance) | Administration | Interest on Loans and Overdraft | Amortization of Debt | Other Payments | Total Expenditure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes districts not listed. | ||||||
| Per Cent | ||||||
| Counties | 83.9 | 8.2 | 1.9 | 30 | 30 | 100.0 |
| Boroughs | 81.6 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Town districts | 77.9 | 10.5 | 3.4 | 5.5 | 2.7 | 100.0 |
| Catchment districts | 77.3 | 161 | 1.7 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 100.0 |
| Electric power districts | 77.7 | 6.8 | 4.4 | 7.5 | 3.6 | 100.0 |
| Urban drainage districts | 81.9 | 30 | 9.3 | 5.2 | 0.6 | 100.0 |
| Urban transport districts | 77.0 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 10.7 | 0.4 | 100.0 |
| Rabbit districts | 89.6 | 8.2 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 100.0 |
| Fire districts | 79.6 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 6.2 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| Harbour boards | 74.2 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 6.2 | 8.1 | 100.0 |
| Totals, all districts* | 80.5 | 5.8 | 4.8 | 5.9 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
The table following gives, in respect of boroughs only, the expenditure on new works out of loan money during the latest 11 years, classified under various heads.
| Year Ended 31 March | Roads, Streets, and Bridges | Drainage and Sewerage | Water Supply | Houses, Workers' Dwellings, etc. | Parks Gardens Town Halls, Libraries, Art Galleries, and Places of Public Recreation | Gasworks and Electrical Works | Other Public Works | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1949 | 192 | 101 | 350 | 97 | 97 | 154 | 116 | 1,106 |
| 1950 | 262 | 158 | 443 | 76 | 78 | 322 | 181 | 1,521 |
| 1951 | 281 | 201 | 502 | 83 | 57 | 480 | 246 | 1,849 |
| 1952 | 370 | 255 | 683 | 77 | 92 | 386 | 438 | 2,300 |
| 1953 | 791 | 382 | 1,146 | 136 | 163 | 463 | 437 | 3,516 |
| 1954 | 1,005 | 428 | 1,310 | 252 | 244 | 906 | 611 | 4,755 |
| 1955 | 1,300 | 587 | 1,637 | 246 | 442 | 451 | 572 | 5,236 |
| 1956 | 1,319 | 852 | 1,802 | 299 | 687 | 366 | 546 | 5,872 |
| 1957 | 1,703 | 813 | 2,009 | 438 | 727 | 341 | 822 | 6,853 |
| 1958 | 1,828 | 772 | 3,358 | 588 | 621 | 541 | 1,313 | 9,021 |
| 1959 | 1,803 | 986 | 1,523 | 616 | 704 | 728 | 1,520 | 7,880 |
ASSETS AND LIABILITIES - The assets and liabilities of local authorities at the end of the financial year 1958-59 were as shown in the table following.
| Assets | Liabilities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Assets | Other Assets (as Estimated in Published Balance Sheets) | Debentures and Other Securities: Net Indebtedness | Other Liabilities | Total Net Liabilities | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 4,964,493 | 15,487,882 | 7,074,786 | 1,575,249 | 8,650,035 |
| Boroughs | 14,349,408 | 103,724,816 | 52,246,232 | 3,649,989 | 55,896,221 |
| Town districts | 118,112 | 742,474 | 153,462 | 14,970 | 168,432 |
| Road districts | 15,499 | 67,197 | 15,347 | 4,485 | 19,832 |
| River districts | 94,155 | 107,806 | 99,531 | 6,930 | 106,461 |
| Catchment districts | 584,570 | 2,327,320 | 667,141 | 130,329 | 797,470 |
| Land-drainage districts | 102,135 | 237,086 | 205,277 | 9,955 | 215,232 |
| Electric power districts | 8,540,798 | 53,367,060 | 21,714,021 | 3,786,896 | 25,500,917 |
| Water-supply district | 1,652 | 3,560 | 46 | 124 | 170 |
| Urban drainage districts | 1,240,038 | 9,975,000 | 11,180,685 | 564,976 | 11,745,661 |
| Urban transport districts | 759,893 | 6,241,220 | 3,738,439 | 204,975 | 3,943,414 |
| Road tunnel authority | - | - | - | 886 | 886 |
| Local railway district | 5,357 | 216,488 | - | 28,067 | 28,067 |
| Gas districts | - | 480,555 | 163,386 | 80,500 | 243,886 |
| Milk districts | 104,769 | 9,535 | 317 | 4,000 | 4,317 |
| Valley authority | 6,765 | 15,078 | 4,058 | 634 | 4,692 |
| Nassella tussock districts | 20,285 | 39,448 | 570 | 570 | |
| Harbour bridge authority | 517,493 | 5,771,459 | 5,149,400 | 1,139,551 | 6,288,951 |
| Plantation board | 63,573 | 117,366 | - | 845 | 845 |
| Underground water authorities | 345 | - | - | 5 | 5 |
| Rabbit districts | 648,923 | 1,171,738 | 102,416 | 59,054 | 161,470 |
| Fire districts | 437,884 | 4,005,084 | 1,629,775 | 141,468 | 1,771,243 |
| Harbour boards | 7,674,971 | 31,140,675 | 16,350,218 | 506,210 | 16,856,428 |
| Totals | 40,251,118 | 235,248,847 | 120,494,537 | 11,910,668 | 132,405,205 |
The figures shown in the column “Other Assets” are taken from the respective balance sheets, but are far from complete, inasmuch as no valuations are made for certain items. This applies particularly to roads, which, although representing considerable wealth to the community, do not figure at all in the assets. The greater part of the expenditure of counties and road districts is made in this direction. For boroughs, although the proportion is very much less, 20.37 per cent of the loan-money expenditure during the last 10 years was on roads, streets, and bridges. Assets of local authorities as returned for the latest available eleven years arc as under.
| As at 31 March | Cash Assets | Other Assets (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| £(000) | £(000) | |
| 1949 | 19,154 | 98,730 |
| 1955 | 29,436 | 155,478 |
| 1950 | 19,970 | 99,713 |
| 1956 | 29,925 | 172,770 |
| 1951 | 20,339 | 104,741 |
| 1957 | 32,205 | 191,494 |
| 1952 | 21,403 | 112,495 |
| 1958 | 37,101 | 213,686 |
| 1953 | 22,812 | 126,782 |
| 1959 | 40,251 | 235,249 |
| 1954 | 27,295 | 140,310 |
Cash assets are made up chiefly of loan balances, reserve investments, and cash in hand. Sinking funds, which amounted to £7,475,816 at 31 March 1959, do not appear in the foregoing table, but are shown as a deduction from the gross loan indebtedness of local authorities. Other assets are composed mainly of fixed assets and of stocks of stores and materials.
Boroughs are responsible for 42.9 per cent of the total assets, electric power districts for 22.5 per cent, and harbour boards for 14.1 per cent. Counties show the comparatively low percentage of 7.4 but this is due to the fact that practically the whole of county expenditure is made on roads, bridges, etc., for which no valuation is available.
Hospital boards, which are not included in the foregoing figures, had assets (excluding outstanding fees and subsidies) amounting to £40,553,081 at 31 March 1959 bringing the total (excluding sinking funds) for all local authorities to approximately £316,053,046.
REGISTERED STOCK - The Local Authorities Amendment Act 1955 authorised local authorities to issue registered stock and nominated the Reserve Bank as Registrar. Prior to 1955 securities given by local authorities for loan moneys were in bearer form, being either debentures for a fixed term with interest coupons attached or table debentures providing for periodic repayments of principal and interest. Lenders, many of whom were presumably already the holders of Government stock and were accustomed to registered securities, have apparently found local authorities stock a satisfactory form of investment, and the following table indicates the growth in this form of security. (Source: Reserve Bank of New Zealand.)
| Date | Amount | Total Gross Debt of Local Authorities at 31 March* | Registered Stock as a Percentage of Gross Debt |
|---|---|---|---|
*Includes hospital boards. †Estimated. | |||
| £(000) | £(000) | Per Cent | |
| March 1956 | 48 | 100,882 | 005 |
| March 1957 | 6,114 | 114,667 | 5.34 |
| March 1958 | 18,239 | 132,033 | 13.81 |
| March 1959 | 34,342 | 147,259 | 23.32 |
| March 1960 | 54,926 | 168,259† | 32.64 |
INDEBTEDNESS - The total gross debt of local authorities at 31 March 1959 amounted to £127,970,353, while net indebtedness (i.e., after deducting accumulated sinking funds from debentures and other securities) was £120,494,537.
It is necessary to observe that figures of local authority debt given herein are not quoted in uniform currency terms. Debt held in New Zealand (the great majority of the total) is expressed in New Zealand currency; that held in Australia is expressed in Australian currency; and that held in the United Kingdom is expressed in sterling. The total is ascertained by adding the three currencies together without conversion to a common basis. If the amount domiciled overseas is converted to New Zealand currency, the total gross debt at 31 March 1959, at the then rate of exchange, was £127,915,422.
The total gross debt of local authorities including hospital boards, at 31 March 1959, was £147,259,026. From 1939-40 to 1947-48 there was a progressive decline in the debt aggregating £9,494,504. Between 1947-48 and 1949-50 there was a decrease of £244,299, while in 1950-51 the debt increased by the comparatively small sum of £126,648, which showed a fairly stable position for those four years. The substantial increases of £7,598,020, £11,843,155, £7,311,003, £9,948,217, £13,784,291, £17,366,015, and £15,226,344 which took place over the years 1952-53 to 1958-59, show the effect of the large loan amounts sanctioned during those years.
Included in the gross indebtedness figure in the previous paragraph are amounts owing by local authorities to Government Departments, and the amounts of the securities held at 31 March for the last five years are shown in the following table. The percentages to the total gross debt are given at the foot of the table.
| Department | As at 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| New Zealand Government Insurance Office | 5,743,837 | 5,675,956 | 6,200,431 | 7,308,224 | 8,031,355 |
| National Provident Fund Board | 9,508,115 | 13,402,683 | 15,762,352 | 18,161,756 | 19,378,373 |
| Public Trustee | 3,161,765 | 2,838,871 | 3,058,818 | 3,477,764 | 3,598,485 |
| State Advances Corporation - | |||||
| Trading | 5,179,685 | 7,097,569 | 7,037,447 | 7,184,575 | 7,727,437 |
| Housing Account | 948,673 | 980,578 | 1,116,769 | 1,184,147 | 1,267,212 |
| Rural Housing Act 1939 | 261,601 | 338,770 | 467,220 | 607,276 | 777,388 |
| Other | 2,082,749 | 2,274,333 | 4,006,796 | 3,962,056 | 4,094,293 |
| Totals | 26,886,425 | 32,608,760 | 37,649,833 | 41,885,798 | 44,874,543 |
| Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | |
| Ratio per cent to total gross indebtedness | 29.6 | 32.3 | 32.8 | 31.7 | 30.5 |
The outstanding loans of local authorities (other than hospital boards) at the end of each of the latest 11 years are shown in the following table.
| At 31 March | Debentures and Other Securities | Inscribed Debt | Total Debt | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Debt | Net Debt (i.e., Less Accumulated Sinking Funds) | Gross Debt | Present Indebtedness (Actuarially Computed) | Gross Debt | Net Debt | |
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1949 | 56,182 | 48,171 | 424 | 27 | 56,605 | 48,198 |
| 1950 | 56,043 | 43,395 | 259 | 12 | 56,302 | 48,407 |
| 1951 | 55,998 | 48,799 | 89 | 4 | 56,087 | 48,803 |
| 1952 | 57,853 | 50,384 | 16 | 1 | 57,869 | 50,385 |
| 1953 | 64,422 | 56,704 | 5 | -- | 64,427 | 56,704 |
| 1954 | 73,445 | 65,808 | 1 | -- | 73,446 | 65,808 |
| 1955 | 79,320 | 72,075 | - | - | 79,320 | 72,075 |
| 1956 | 87,984 | 80,525 | - | - | 87,984 | 80,525 |
| 1957 | 99,088 | 91,670 | - | - | 99,088 | 91,670 |
| 1958 | 114,675 | 107,239 | - | - | 114,675 | 107,239 |
| 1959 | 127,970 | 120,495 | - | - | 127,970 | 120,495 |
Of the total net indebtedness of £120,494,537 at 31 March 1959 boroughs were responsible for £52,246,232, which represents 3.6 per cent of their rateable capital value at 31 March 1959. For counties, which have a much lower expenditure per head on works, etc., the aggregate net indebtedness was £7,074,786, and the percentage of rateable capital value at 31 March 1959 only 0.6.
The following table shows, per head of the population, the gross debt of local authorities and the annual charge thereon for the latest 11 years.
| At 31 March | Population | Gross Debt | Annual Loan Charge | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Rate per Head | Amount | Rate per Head | ||||
| £ | £ | s. | £ | £ | s. | ||
| 1949 | 1,864,560 | 56,605,024 | 30 | 7 | 5,133,722 | 2 | 15 |
| 1950 | 1,902,883 | 56,302,066 | 29 | 12 | 5,287,589 | 2 | 16 |
| 1951 | 1,938,032 | 56,086,596 | 28 | 19 | 5,498,866 | 2 | 17 |
| 1952 | 1,984,730 | 57,869,169 | 29 | 3 | 5,805,138 | 2 | 19 |
| 1953 | 2,037,553 | 64,427,185 | 31 | 12 | 6,293,612 | 3 | 2 |
| 1954 | 2,087,740 | 73,445,570 | 35 | 4 | 6,996,154 | 3 | 7 |
| 1955 | 2,130,927 | 79,320,054 | 37 | 5 | 7,721,730 | 3 | 13 |
| 1956 | 2,175,373 | 87,983,747 | 40 | 9 | 8,977,546 | 4 | 3 |
| 1957 | 2,221,169 | 99,087,670 | 44 | 12 | 9,723,557 | 4 | 8 |
| 1958 | 2,275,515 | 114,675,190 | 50 | 8 | 10,811,021 | 4 | 15 |
| 1959 | 2,326,129 | 127,970,353 | 55 | 0 | 12,047,271 | 5 | 4 |
It should be noted that the debt of electric power districts shown in the following table does not represent the complete local authority debt on account of electric power activities, since a considerable portion of the borough debt, and a small part of the county and town district debt also, was incurred for that purpose.
| At 31 March | Counties and Road Districts | Boroughs and Town Districts | Urban Drainage Districts | Urban Transport Districts | Electric Power Districts | Harbour Boards | Other Districts | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1949 | 4,914 | 26,405 | 2,612 | 1,534 | 11,580 | 8,046 | 1,514 | 56,605 |
| 1950 | 4,660 | 26,482 | 2,590 | 1,200 | 11,997 | 7,785 | 1,588 | 56,302 |
| 1951 | 4,419 | 26,579 | 2,579 | 1,033 | 12,462 | 7,382 | 1,633 | 56,087 |
| 1952 | 4,352 | 27,517 | 2,704 | 1,151 | 13,004 | 7,496 | 1,645 | 57,869 |
| 1953 | 4,347 | 30,137 | 3,152 | 1,645 | 14,422 | 8,886 | 1,839 | 64,427 |
| 1954 | 4,333 | 34,208 | 3,571 | 2,820 | 15,970 | 10,362 | 2,181 | 73,446 |
| 1955 | 4,596 | 36,816 | 3,961 | 3,082 | 17,213 | 10,812 | 2,841 | 79,320 |
| 1956 | 5,136 | 40,251 | 4,933 | 3,376 | 18,827 | 11,619 | 3,842 | 87,984 |
| 1957 | 5,950 | 44,833 | 6,725 | 3,747 | 19,789 | 13,060 | 4,983 | 99,088 |
| 1958 | 6,790 | 51,581 | 8,988 | 4,149 | 21,300 | 15,689 | 6,178 | 114,675 |
| 1959 | 7,429 | 55,909 | 12,127 | 3,908 | 22,930 | 17,562 | 8,104 | 127,970 |
The debt of road districts at 31 March 1959, which is included with that of counties, was £15,347; the town district debt at the same date was £158,043. The debt of “other districts” at 31 March 1959 was mainly that of river districts (£102,827), catchment districts (£685,718), land-drainage districts (£243,503), gas districts (£163,386), fire districts (£1,652,385) and a harbour bridge authority (£5,149,400).
The following table shows the amount of indebtedness, at 31 March 1959, classified according to the purpose for which the loans were raised.
| Local Districts | Roads, Streets, Footways and Bridges | Drainage, Sewerage, and Water Supply | Tramways and Omnibuses | Electric Supply and Lighting | Harbour Works | Other and Unspecified | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Counties | 2,897,102 | 1,793,960 | - | 156,963 | 746 | 2,564,676 | 7,413,447 |
| Boroughs | 13,384,962 | 20,796,585 | 3,265,188 | 4,836,613 | 86,380 | 13,381,412 | 55,751,140 |
| Electric power districts | - | - | - | 22,496,766 | - | 433,688 | 22,930,454 |
| Urban drainage districts | - | 12,108,312 | - | - | - | 18,882 | 12,127,194 |
| Urban transport districts | - | - | 3,908,451 | - | - | - | 3,908,451 |
| Harbour boards | - | - | - | - | 17,523,784 | 38,437 | 17,562,221 |
| Other | 5,177,118 | 66,974 | - | 9,285 | 2,175 | 3,021,894 | 8,277,446 |
| Totals | 21,459,182 | 34,765,831 | 7,173,639 | 27,499,627 | 17,613,085 | 19,458,989 | 127,970,353 |
The debt owing on electric supply and lighting is .5 per cent of the total, showing that heavy borrowing is necessary to finance this utility, while the percentage for drainage, sewerage, and water system is 27.2.
Domicile of Debt - A five-year summary of the domicile of loans outstanding, is given hereunder.
| At 31 March | Amount | Percentage of Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | United Kingdom | Australia | New Zealand | United Kingdom | Australia | |
| £ | £ | £ | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | |
| 1955 | 75,404,819 | 3,612,000 | 303,235 | 95.07 | 4.55 | 0.38 |
| 1956 | 84,069,898 | 3,612,000 | 301,849 | 95.55 | 4.11 | 0.34 |
| 1957 | 95,340,143 | 3,470,000 | 277,527 | 96.22 | 3.50 | 0.28 |
| 1958 | 111,434,663 | 2,963,000 | 277,527 | 97.18 | 2.58 | 0.24 |
| 1959 | 125,812,700 | 1,883,000 | 274,653 | 98.31 | 1.47 | 0.22 |
During 1958-59 the amount domiciled in New Zealand increased by £14,378,037, while the amount domiciled in the United Kingdom decreased by £1,080,000.
Debt Charges - Particulars of the annual loan charge of local authorities during each of the latest 11 years are as follows.
| At 31 March | On Debentures and Other Securities | On Inscribed Debt | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1949 | 5,118,969 | 14,753 | 5,133,722 |
| 1950 | 5,278,382 | 9,207 | 5,287,589 |
| 1951 | 5,495,768 | 3,098 | 5,498,866 |
| 1952 | 5,804,578 | 560 | 5,805,138 |
| 1953 | 6,293,442 | 170 | 6,293,612 |
| 1954 | 6,996,118 | 36 | 6,996,154 |
| 1955 | 7,721,730 | - | 7,721,730 |
| 1956 | 8,977,546 | - | 8,977,546 |
| 1957 | 9,723,557 | - | 9,723,557 |
| 1958 | 10,811,021 | - | 10,811,021 |
| 1959 | 12,047,271 | - | 12,047,271 |
Amortisation charges are included in the above, the amount payable during 1959-60 on debt at 31 March 1959 being £6,470,318. Interest charges payable during 1959-60 on the debt outstanding at 31 March 1959 aggregated £5,576,953, payable according to countries of domicile, as follows: New Zealand, £5,467,011; Australia, £14,498 (on face value); United Kingdom, £95,444.
The loans outstanding, at 31 March 1959, are classified below according to domicile, and also according to rate of interest. Reference should be made to observations on page 848 in regard to the currencies in which local authority debts are expressed.
| Rate of Interest Per Cent | Domiciled in New Zealand | Domiciled in United Kingdom | Domiciled in Australia | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Free of interest | 169,659 | - | - | 169,659 |
| 3 | 1,200,500 | - | 9,900 | 1,210,400 |
| 3 1/8 | 4,471,570 | - | - | 4,471,570 |
| 3 1/4 | 17,774,700 | - | 17,774,700 | |
| 3 5/16 | 1,067 | - | - | 1,067 |
| 3 3/8 | 420,155 | - | - | 420,155 |
| 3 1/2 | 2,376,478 | - | - | 2,376,478 |
| 3 5/8 | 17,092 | - | - | 17,092 |
| 3 7/10 | 17,840 | - | - | 17,840 |
| 3 3/4 | 250,779 | - | - | 250,779 |
| 3 7/8 | 102,380 | - | - | 102,380 |
| 4 | 32,026,743 | - | - | 32,026,743 |
| 4 1/8 | 103,519 | - | - | 103,519 |
| 4 1/4 | 13,066,601 | - | - | 13,066,601 |
| 4 2/6 | 9,694 | - | - | 9,694 |
| 4 1/2 | 157,147 | 87,000 | - | 244,147 |
| 4 3/5 | 67,726 | - | - | 67,726 |
| 4 5/8 | 1,875,639 | - | - | 1,875,639 |
| 4 3/4 | 14,745,521 | - | - | 14,745,521 |
| 4 4/5 | 276,596 | - | - | 276,596 |
| 4 7/8 | 6,448,152 | - | - | 6,448,152 |
| 5 | 30,220,774 | 550,000 | - | 30,770,774 |
| 51 | 1,000 | - | - | 1,000 |
| 5 1/4 | 515 | 749,700 | - | 750,215 |
| 5 1/2 | 10,203 | 496,300 | 16,768 | 523,271 |
| 5 3/4 | - | - | 247,985 | 247,985 |
| 6 | 650 | - | - | 650 |
| Totals | 125,812,700 | 1,883,000 | 274,653 | 127,970,353 |
The average rates of interest work out as follows: New Zealand, 4.26 per cent; United Kingdom, 5.23 per cent; Australia, 5.63 per cent; total 4.28 per cent.
The interest rates quoted are those applicable to the amount of debt outstanding. They have not been adjusted to the prices at which the respective loans were raised - e.g., where a loan was issued below par the rate of interest on the sum actually received (omitting the question of flotation expenses) would be higher than the rates quoted above.
Loan Maturities - The following table classifies loans outstanding at 31 March 1959 according to years of maturity and countries of domicile.
| Years of Maturity | Domiciled in New Zealand | Domiciled in United Kingdom | Domiciled in Australia | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1959-63 | 29,211,921 | 1,468,000 | 31,230 | 30,711,151 |
| 1964-68 | 45,204,634 | 415,000 | 9,423 | 45,629,057 |
| 1969-73 | 17,003,375 | - | 234,000 | 17,237,375 |
| 1974-78 | 18,667,854 | - | - | 18,667,854 |
| 1979-83 | 6,934,801 | - | - | 6,934,801 |
| 1984-88 | 2,188,537 | - | - | 2,188,537 |
| 1989-93 | 3,238,722 | - | - | 3,238,722 |
| 1994-2009 | 3,362,856 | - | - | 3,362,856 |
| Totals | 125,812,700 | 1,883,000 | 274,653 | 127,970,353 |
In the case of table loans the year of maturity is taken as that in which the final instalment is payable. Practically the whole of the debt domiciled abroad is composed of loans with one fixed date of maturity.
Loans Sanctioned, Authorised, Raised, and Uplifted - Consents to borrowing by local authorities have been much higher during the latest 11 years than for any earlier period, while there were particularly large amounts approved during the last nine years. The reduction in the two years 1955-56 and 1956-57 was caused by the restriction of loan sanctions to essential works as an anti-inflationary measure. That local authorities themselves cooperated in achieving greater stability is indicated by the reduced total amount of applications made for loan sanctions in those two years. Total applications in 1958-59 showed a reduction of 0.4 million on the previous year, but increased again by £11.3 million for 1959-60.
The following summary of the operations of the Local Authorities Loans Board during the last 11 years shows concisely the trend of local authority borrowing during that period. Hospital boards are included in this instance.
| Year | Total Applications | Sanctioned | |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Works | Redemption Loans | ||
| £(thousand) | |||
| 1949-50 | 8,063 | 6,602 | 762 |
| 1950-51 | 10,825 | 9,243 | 486 |
| 1951-52 | 15,093 | 13,891 | 1,029 |
| 1952-53 | 29,130 | 17,854 | 196 |
| 1953-54 | 24,908 | 23,983 | 300 |
| 1954-55 | 28,587 | 25,819 | 449 |
| 1955-56 | 22,504 | 15,462 | 437 |
| 1956-57 | 20,951 | 17,233 | 30 |
| 1957-58 | 31,934 | 25,800 | 850 |
| 1958-59 | 21,510 | 20,538 | 542 |
| 1959-60 | 32,848 | 28,973 | 237 |
From statistics of borrowing, which local authorities are required to furnish quarterly, it is possible to ascertain the amount of loan authorisations granted and exercised. The tables below show summaries of borrowing at 31 March 1960 by each class of local authority.
LOANS AUTHORISED DURING YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 1959 - WITH AMOUNTS RAISED AND UPLIFTED TO 31 MARCH 1960
| Local Authority | Amounts Authorised* | Up to 31 March 1959 | During Year Ended 31 March 1960 | Balance Unexercised at 31 March 1960 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amounts Raised | Amounts Uplifted† | Amounts Raised | Amounts Uplifted† | |||
*Adjusted for amounts revoked or lapsed. †For the authorisations listed. ‡Original amount £25,429,470. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| County councils | 1,320 | 599 | 450 | 431 | 552 | 291 |
| Borough councils | 6,775 | 3,310 | 3,082 | 2,933 | 3,111 | 533 |
| Town councils | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - |
| Catchment boards | 127 | 75 | 74 | 47 | 48 | 5 |
| Land-drainage boards | 13 | 11 | 8 | - | 3 | 3 |
| Electric power and gas boards | 2,952 | 1,412 | 1,346 | 1,372 | 1,408 | 168 |
| Urban drainage boards | 5,960 | 1,623 | 1,587 | 2,660 | 2,696 | 1,678 |
| Urban transport boards | 225 | 72 | 72 | 87 | 87 | 67 |
| Rabbit boards | 8 | 4 | 4 | - | - | 5 |
| Fire boards | 158 | 82 | 3t | 61 | 98 | 15 |
| Harbour boards | 3,821 | 1,728 | 1,454 | 1,797 | 1,784 | 297 |
| Hospital boards | 3,896 | 1,403 | 1,276 | 2,359 | 2,400 | 134 |
| Other totally uplifted at 31 March 1959 | 100 | 100 | 100 | - | - | - |
| Totals | 25,361‡ | 10,420 | 9,484 | 11,749 | 12,190 | 3,192 |
LOANS AUTHORISED DURING YEAR ENDED 31 MARCH 1960, WITH AMOUNTS RAISED AND UPLIFTED
| Local Authority | Amounts Authorised During Year* | Amounts Raised During Year | Balance Unexercised at End of Year | Amounts Uplifted During Year† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
*Adjusted for amounts revoked or lapsed. †For authorisations listed. ‡Original amount £25,035,727. | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||
| County councils | 1,487 | 528 | 959 | 483 |
| Borough councils | 8,750 | 4,734 | 4,016 | 4,441 |
| Town councils | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Catchment boards | 144 | 82 | 62 | 75 |
| Electric power and gas boards | 2,477 | 1,315 | 1,162 | 1,276 |
| Urban drainage boards | 743 | 646 | 97 | 646 |
| Urban transport boards | 200 | 132 | 68 | 132 |
| Harbour bridge authority | 500 | 15 | 485 | 15 |
| Rabbit boards | 9 | 7 | 2 | 6 |
| Fire boards | 206 | 73 | 133 | 68 |
| Harbour boards | 4,185 | 1,924 | 2,261 | 1,695 |
| Hospital boards | 6,331 | 4,399 | 1,932 | 4,120 |
| Totals | 25,035‡ | 13,855 | 11,180 | 12,960 |
Statistics of the amounts authorised are available from the 1952-53 financial year, and the following table shows comparative debt figures.
| Year Ended 31 March | Amounts Sanctioned by Loans Board | Amounts Authorised by Orders in Council | Gross Indebtedness at Beginning of Year | Amount Uplifted | Principal Repaid | Gross Indebtedness at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Estimated | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1953 | 18,050 | 10,844 | 64,182 | 11,641 | 4,043 | 71,780 |
| 1954 | 24,283 | 12,122 | 71,780 | 16,622 | 4,779 | 83,623 |
| 1955 | 26,268 | 23,912 | 83,623 | 12,804 | 5,493 | 90,934 |
| 1956 | 15,900 | 18,341 | 90,934 | 15,086 | 5,138 | 100,882 |
| 1957 | 17,263 | 19,638 | 100,882 | 20,389 | 6,604 | 114,667 |
| 1958 | 26,650 | 25,717 | 114,667 | 24,429 | 7,063 | 132,033 |
| 1959 | 21,080 | 25,429 | 132,033 | 22,653 | 7,426 | 147,259 |
| 1960 | 29,210 | 25,035 | 147,259 | 29,948 | 8,548 | 168,659 |
| 1961 | 35,123 | 29,967 | 168,659 | 27,000* | 8,500* | 187,159* |
Interest Rates - The Local Authorities Interest Reduction and Loans Conversion Amendment Act 1934 limited borrowings to an interest rate not exceeding 3 1/2 per cent, with provision, however, for varying the rate by Order in Council under the Local Government Loans Board Act 1926. In May 1939 the maximum was raised to 4 1/4 per cent, but during the period 1941 to 1947 market conditions were responsible for a reduction to 3 1/4 per cent. In 1952 the rate was raised again to a maximum of 4 per cent. The Local Government Loans Board Amendment Act 1954 placed the determining of rates of interest in the hands of the board, subject to the approval of the Minister of Finance. In October 1955 the maximum rate was raised to 4 1/4 per cent, and a further increase to 4 3/4 per cent was made in March 1956. In June 1956 a scheme of graduated rates was introduced providing for the terms of five, eight, and 12 years the maxima of 4 5/8, 4 3/4, and 4 7/8 per cent respectively. This scheme continued until July 1957, when the rates were again altered to 4 3/4 per cent for terms of up to five years, and 5 per cent for longer periods. Consequent on the presentation by the Minister of Finance of the 1960 Budget the Loans Board determined the following revised terms for local authority borrowing. The maximum rate of interest shall be 4 7/8 per cent per annum. The maximum rate of interest for terms not exceeding five years shall be 4 5/8 per cent per annum except where any amount so borrowed is portion of a sum borrowed from a single lender and partly repayable over a period longer than five years.
EMPLOYMENT BY LOCAL AUTHORITIES - Employment by local authorities comprises principally the construction and maintenance of roads and streets, and the operation and maintenance of public-utility industries (gas, electric supply, and tramways), and social services.
Particulars relating to wage-earning employees employed by the various classes of local authorities during the five-year period 1954-55 to 1958-59 are presented in the next table. The figures shown are averages of the numbers employed at the fifteenth (or nearest representative day) of each month. The statistics do not cover hospital boards or electric power boards. Employees of electric power boards arc included in the figures in Section 20A (Electric Power) (their average number during 1958-59 was 2,769), while employees of hospital boards are shown in a subsequent table.
| Class of Local District | Number of Wage Earners (Average of 12 Months Ended March) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Counties | 3,605 | 3,781 | 3,979 | 4,051 | 4,049 |
| Boroughs | 9,295 | 9,477 | 9,713 | 9,895 | 10,044 |
| Town districts | 67 | 61 | 60 | 54 | 49 |
| Road districts | 14 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| River districts | 38 | 49 | 46 | 28 | 24 |
| Catchment districts | 343 | 330 | 351 | 377 | 374 |
| Land-drainage districts | 46 | 37 | 38 | 59 | 61 |
| Water-supply districts | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Urban drainage districts | 251 | 267 | 314 | 355 | 361 |
| Urban transport districts | 1,845 | 1,659 | 1,552 | 1,517 | 1,440 |
| Road tunnel authority | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Local railway district | 15 | 14 | 14 | 16 | 13 |
| Gas districts | 35 | 35 | 42 | 48 | 46 |
| Milk districts | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Valley authority | - | - | - | 1 | 2 |
| Nassella tussock districts | 18 | 21 | 21 | 32 | 47 |
| Joint transit-housing committee | 2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| Harbour bridge authority | - | - | 1 | 10 | 4 |
| Plantation board | 11 | 13 | 12 | 17 | 17 |
| Rabbit districts | 907 | 884 | 850 | 856 | 815 |
| Fire districts | 467 | 450 | 491 | 523 | 535 |
| Harbour boards | 3,001 | 3,072 | 3,225 | 3,363 | 3,403 |
| All districts | 19,968 | 20,171 | 20,731 | 21,223 | 21,305 |
The institutional staff of public hospitals and charitable institutions under the control of hospital boards was as follows for each of the latest five years ended 31 March.
| Nature of Staff | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stipendiary medical | 1,122 | 1,165 | 1,173 | 1,208 | 1,246 |
| Other professional and technical | 1,143 | 1,224 | 1,299 | 1,396 | 1,475 |
| Nursing | 8,307 | 8,470 | 9,053 | 9,431 | 9,869 |
| Maintenance and ground | 764 | 846 | 880 | 939 | 981 |
| Other institutional | 6,399 | 6,475 | 6,700 | 6,903 | 7,180 |
| Totals | 17,735 | 18,180 | 19,105 | 19,877 | 20,751 |
The numbers of visiting medical staff of hospital boards for the last five years ended 31 March are as follows: 1955, 597; 1956, 676; 1957, 691; 1958, 686; and 1959, 716.
STATISTICS OF INCOMES AND INCOME TAX - Statistics of incomes and income tax are compiled annually by the Department of Statistics. In the case of individuals, these statistics are in normal years substantially based on a 10 per cent sample, but the statistical data for the 1957-58 income year were affected by the introduction of a system of PAYE income tax on 1 April 1958. Further information concerning this system will be found in Section 26B of this volume. One important effect of the PAYE system on these statistics was that individuals who received income from salary and wages only and whose total income was less than £1,040 were not required to furnish an annual return of income for the 1957-58 income year. Consequently, while the 1957-58 statistics were estimates based on the normal 10 per cent sample collection as far as non-salary and wage incomes are concerned, the figures for purely salary and wage incomes of less than £1,040 were estimates based on projections of the data in the statistics for previous years.
Formerly the coverage of the principal statistics commenced at an income of £375. For 1957-58 this coverage was extended downwards to include incomes of over £12 if the income was derived solely from interest, and all incomes, irrespective of amount and expecting only salary and wages, from any other source. However, as there was no information available for previous years, it was not practicable to extend the projections of salary and wage income to those of less than £375.
A summary of the situation relating to the 1957-58 statistics therefore is:
Total Income of Under £375 - The statistics included only incomes principally derived from investments and from self-employment. Individuals who were principally salary and wage earners were not included.
Total Income Between £375 and £1,040 - The statistics were estimates based on the normal sample collection, but included figures for purely salary and wage earners which were projections of the data of previous years.
Total Income of £1,040 and Over - Estimates which were based on the usual sample collection, plus a complete enumeration of all incomes of £4,000 and over.
The 1957-58 statistics also differ from those of previous years in that the first £12 of income from interest was exempted from income tax and was therefore omitted from the statistics.
The use of the sampling method explains the “rounded-off” figures which are shown for the statistics in the tables which follow. In some cases this process of rounding off results in the total figure given disagreeing slightly with the aggregate of the component items.
The figures arc given to the nearest 10 for numbers of assessments, etc., and to the nearest 10,000 for the amounts columns. These units were adopted to lessen the difficulties associated with the rounding off of the figures. It is not intended to imply that the estimates are regarded as having a degree of accuracy as high as the units in which the results are expressed.
CLASSES OF TAXPAYERS - “Individuals” comprise all assessments for individual persons. Partnership returns are ignored in the compilation, as the individual shares of partnership income are included in the individual tax assessments. The incomes of deceased persons' estates are not included, as the greater part of these are transferred to the assessments of the beneficiaries.
The term “companies” not only covers companies incorporated under the Companies Act and other Acts relating to the formation of companies, but also includes local and public authorities, associations (incorporated or unincorporated), and aggregations of individuals (other than partnerships) which form separate and distinct entities for income tax purposes. Government Departments which are liable to pay income tax are included, but local and public authorities are generally not taxable even in respect of their trading operations, and consequently are not included in these statistics.
Apart from the next two tables, statistics of the incomes of individuals and of companies are presented as two distinct parts of this section.
SUMMARY OF INCOMES, EXEMPTIONS, AND TAX - The following tables briefly summarise the main items of information for each of the last five income years available. Individuals and companies are given in separate tables.
INDIVIDUALS
| Year | Number of Returns | Number of Taxpayers | Assessable Income | Total Income | Exemptions | Taxable Income | Ordinary Income Tax Assessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| 1953-54 | 660,550 | 522,960 | 540,760 | 555,170 | 338,930 | 201,830 | 48,090 |
| 1954-55 | 648,860 | 576,000 | 577,520 | 594,640 | 343,500 | 234,010 | 46,740 |
| 1955-56 | 663,500 | 606,810 | 604,570 | 621,350 | 354,440 | 250,120 | 51,590 |
| 1956-57 | 688,620 | 131,990 | 657,770 | 676,180 | 371,220 | 286,560 | 32,250 |
| 1957-58 | 814,450 | - | 702,750 | 723,930 | 417,660 | 311,240 | - |
COMPANIES
| Year | Number of Returns | Number of Taxpayers | Assessable Income* | Returnable Income | Taxable Income* | Income Tax Assessed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary | Social Security | ||||||
| *Assessable income and taxable income are identical, as “exemptions” are normally nil. | |||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| 1953-54 | 22,007 | 17,916 | 96,924 | 101,211 | 96,924 | 37,390 | 7,086 |
| 1954-55 | 24,129 | 19,598 | 107,786 | 113,856 | 107,786 | 41,382 | 7,834 |
| 1955-56 | 25,949 | 20,865 | 105,254 | 112,730 | 105,254 | 40,059 | 7,630 |
| 1956-57 | 28,450 | 22,522 | 110,024 | 117,701 | 110,024 | 41,575 | 7,982 |
| 1957-58 | 31,108 | 24,005 | 117,784 | 124,420 | 117,784 | 43,943 | 8,404 |
A strict comparison of the figures for one year with those of another is not possible, as changes in compilation practice and numerous amendments in income tax law have affected the comparability of the figures.
Two events which had major repercussions on the number of taxpayers and the amounts of tax paid by individuals were the granting of a rebate of £100 from the gross tax assessed in 1956-57 and the remission of tax on 1957-58 incomes as a result of the introduction of the PAYE system on 1 April 1958.
AMOUNT OF INCOME - The broad principle adopted in calculating the assessable income is that any expenditure or loss exclusively incurred in the production of assessable income for any year may be deducted from the total income from any assessable source far that year. Depreciation is allowed, varying rates for different classes of assets being fixed. The assessable income is approximately equivalent to the net profit as determined by the normal commercial accounting systems. It is, on the whole, rather higher than the commercial net profit, since certain types of expenditure which are regarded as a revenue charge in commercial accounts are not permissible deductions from income for income tax purposes.
Where the operations of a source of income which would be assessable for income tax have resulted in a loss for the year, the loss may be set off against assessable profits from other sources (if any) or, in default thereof, may be set off against assessable profits in the six following years.
Capital profits are not assessable and capital losses are not deductible.
In these statistics the incomes given for individuals are the net incomes after deducting losses from the same source which have been carried forward from previous years. Losses for the current year which have been set off against income from some other source are recorded in the tables in this volume as the difference between the total of the component income items and the given total income.
For companies, losses carried forward from previous years are shown in a separate column and the assessable and returnable incomes given are those after the deduction of such losses. Losses during the current year from any source are deducted from the income from any other source.
INCOMES OF INDIVIDUALS: PROVISIONAL ESTIMATES - The data required for this statistical compilation do not become available for a lengthy period after the end of the income year. This, coupled with the necessary time taken by the statistical processing, means an unduly long time lag before the first results of the compilation are available.
In an endeavour to have the most important data available at an earlier date, a small sample of returns is selected from those which are furnished within a short period after the close of the income year. Each case included in the sample shows the income for the recently completed income year and the two previous income years. The income trends disclosed by this sample are applied to the statistical data of the normal sample collection which are then available for the first of the three income years in question.
The income distributions for the first income year shown in returns for the provisional estimates are compared with the income distributions for the final estimates for the same year, and allowances are made for over and under representation in the sample for provisional estimates. Industrial and occupational representations are similarly compared and corrected. Despite these representation corrections and allowances, the trends shown by the sample may be incorrect. For example, the early closing date means that business returns with balance dates later than March cannot be included in the sample. But for otherwise identical business units one with a December balance date may have a very different net income to one with a June balance date.
Past experience has shown that provisional estimates similar to those given in the following tables have normally been sufficiently accurate for most practical uses. However, it is emphasised that the data in the provisional estimates are definitely provisional and are liable to be revised substantially at a later date.
Although figures for three income years are given to afford a convenient comparison of the results for each year, only the two later years have been estimated from the restricted sample.
The next table gives data for the principal sources of incomes of individuals.
| Source of Total Income | Income Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | ||||
| Number of Returns | Income | Number of Returns | Income | Number of Returns | Income | |
| *Self-employed and investment incomes only. | ||||||
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | ||||
| Sheep farming | 21,740 | 46.2 | 22,000 | 33.1 | 22,300 | 42.6 |
| Dairy farming | 35,870 | 39.8 | 36,200 | 38.6 | 36,600 | 41.8 |
| Other farming | 23,390 | 31.6 | 23,600 | 29.2 | 23,700 | 32.8 |
| Totals | 81,000 | 117.6 | 81,800 | 100.9 | 82,600 | 117.2 |
| Manufacturing | 6,040 | 6.7 | 6,100 | 6.4 | 6,100 | 6.7 |
| Construction | 14,920 | 17.4 | 15,100 | 16.1 | 15,200 | 17.1 |
| Commerce | 17,590 | 19.2 | 17,900 | 18.9 | 18,100 | 20.3 |
| Transport | 5,100 | 6.1 | 5,200 | 5.8 | 5,400 | 6.4 |
| Services - | ||||||
| Professional | 8,300 | 19.9 | 8,400 | 18.3 | 8,400 | 20.5 |
| Other | 10,270 | 8.8 | 10,600 | 8.5 | 10,800 | 9.2 |
| Miscellaneous (forestry, mining, etc.) | 2,440 | 3.5 | 2,500 | 3.3 | 2,600 | 3.6 |
| Totals | 145,660 | 199.2 | 147,500 | 178.2 | 149,200 | 201.1 |
| Salary and wages | 569,740 | 499.1 | ||||
| Investment income | 99,050 | 25.6 | 102,300 | 26.0 | 106,410 | 28.4 |
| Totals | 814,450 | 723.9 | 249,800* | 204.2* | 255,610* | 229.5* |
From and including 1957.58 it has not been generally necessary for individuals receiving salary or wages only of less than £1,040 to make an annual return of income. Consequently it was not practicable to include salary and wage earners in the latest series of provisional income estimates.
In the past the provisional estimate has referred to the assessable income. In the preceding table and the two immediately subsequent tables “total” incomes have been estimated. The figures given for each of the three latest years in these provisional estimates tables are, however, fully comparable.
It will be noticed that farming incomes dropped sharply in 1958.59 and then regained the 1957.58 position in 1959.60. Low wool prices in 1958.59 were mainly responsible. However, economic conditions were generally less buoyant in 1958.59 and the incomes of other self-employed individuals also fell, although to a much smaller extent than farming incomes.
It will be noticed that these estimates provide for only comparatively small increases in the numbers for some of the sources of income in the above table. The principal reason is that in recent years the numbers of companies have risen substantially, with corresponding deductions from the numbers of individuals operating as sole traders or as partnerships.
This practice of changing to company ownership has reached dimensions which are large enough to have some effect on the income trends disclosed in these statistics of individuals. There is a greater tendency for the higher income units to adopt company ownership.
The next table provides an analysis of the incomes of self-employed individuals by the amount of total income.
| Amount of Total Income | Income Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |||||
| Number of Returns | Income | Number of Returns | Income | Number of Returns | Income | ||
| £ | £ | £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | |||
| Losses | 1,040 | 1,300 | 1,100 | - | |||
| 0- | 99 | 3,920 | 0.2 | 4,000 | 0.2 | 3,200 | 0.2 |
| 100- | 199 | 4,720 | 0.8 | 4,800 | 0.8 | 4,000 | 0.6 |
| 200- | 299 | 5,010 | .5 | 5,300 | 1.3 | 4,600 | 1.2 |
| 300- | 399 | 6,670 | 2.6 | 6,500 | 2.3 | 5,900 | 2.1 |
| 400- | 499 | 7,590 | 3.9 | 7,300 | 3.3 | 6,600 | 3.0 |
| 500- | 599 | 8,740 | 5.3 | 8,300 | 4.5 | 7,700 | 4.2 |
| 600- | 699 | 9,220 | 6.5 | 8,900 | 5.8 | 8,300 | 5.4 |
| 700- | 799 | 8,500 | 7.0 | 9,800 | 7.4 | 9,300 | 7.0 |
| 800- | 899 | 8,820 | 7.9 | 9,400 | 8.0 | 9,200 | 7.8 |
| 900- | 999 | 7,890 | 7.9 | 8,000 | 7.6 | 8,200 | 7.8 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 15,700 | 17.9 | 16,600 | 18.2 | 16,200 | 17.8 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 11,930 | 16.1 | 13,400 | 17.4 | 13,300 | 17.3 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 9,600 | 150 | 10,000 | 150 | 10,700 | 16.1 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 6,810 | 12.1 | 7,000 | 11.9 | 7,600 | 12.9 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 5,490 | 10.9 | 5,400 | 10.2 | 5,600 | 10.7 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 14,120 | 35.7 | 13,900 | 33.3 | 17,100 | 41.1 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 5,440 | 19.6 | 4,800 | 16.2 | 6,300 | 21 5 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 2,044 | 9.7 | 1,400 | 6.1 | 2,000 | 8.7 |
| 5,000 and over | 2,406 | 18.6 | 1,400 | 8.7 | 2,300 | 15.7 | |
| Totals | 145,660 | 199.2 | 147,500 | 178.2 | 149,200 | 201.1 | |
Sheep farmers are heavily represented in the top income groups, particularly the £5,000 and over group. Lower sheep farming earnings in 1958-59 were the cause of most of the fall in the numbers of individuals in that group in 1958.59.
The next table gives corresponding data for individuals whose incomes were principally derived from interest, rents and royalties, “estate” income, and also company dividends if there was no other major source of income.
| Amount of Total Income | Income | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |||||
| Number of Returns | Total Income | Number of Returns | Total Income | Number of Returns | Total Income | ||
| £ | £ | £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | |||
| Losses | 360 | 400 | 350 | ||||
| 0- | 99 | 59,590 | 1.7 | 60,700 | 1.8 | 62,000 | 1.9 |
| 100- | 199 | 12,310 | 1.7 | 13,000 | 1.8 | 13,500 | 1.9 |
| 200- | 299 | 5,730 | 1.4 | 6,000 | 1.4 | 6,200 | 1.5 |
| 300- | 399 | 3,710 | 1.3 | 3,900 | 1.3 | 4,100 | 1.4 |
| 400- | 499 | 3,040 | 1.4 | 3,340 | 1.5 | 3,600 | 1.6 |
| 500- | 599 | 2,730 | 1.5 | 3,030 | 1.7 | 3,350 | 1.8 |
| 600- | 699 | 1,890 | 1.2 | 2,000 | 1.3 | 2,200 | 1.4 |
| 700- | 799 | 1,560 | 1.2 | 1,700 | 1.3 | 1,900 | 1.4 |
| 800- | 899 | 1,230 | 1.0 | 1,400 | 1.2 | 1,650 | 1.4 |
| 900- | 999 | 930 | 0.9 | 1,030 | 1.0 | 1,100 | 1.0 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 1,420 | 1.5 | 1,320 | 1.5 | 1,520 | 1.7 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 1,130 | 1.5 | 1,050 | 1.4 | 1,150 | 1.5 |
| l,400- | 1,599 | 760 | 11 | 840 | 1.3 | 920 | 1.4 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 570 | 1.0 | 520 | 0.9 | 650 | 1.1 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 360 | 0.7 | 340 | 0.6 | 400 | 0.8 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 970 | 2.4 | 1,050 | 2.5 | 1,050 | 2.5 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 330 | 1.1 | 300 | 1.0 | 350 | 1.2 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 154 | 0.7 | 140 | 0.6 | 150 | 0.7 |
| 5,000 and over | 272 | 2.3 | 250 | 1.9 | 280 | 2.2 | |
| Totals | 99,050 | 25.6 | 102,300 | 26.0 | 106,410 | 28.4 | |
It will be noticed that more than one half of the total number of individuals so classed have incomes of less than £100. The majority of these have a small income from interest on savings bank deposits. The first £12 of interest income is exempted from taxation and a large proportion of persons included in this table have incomes £12 larger than that shown. This applies also to higher income groups but in that case the exempted amount is a much smaller proportion of the total income.
The previous table completes the data coming under the heading of provisional estimates. The further data which are given in the following pages are based, in the case of individuals, on the normal 10 per cent sample collection and the results are not provisional.
NUMBERS OF RETURNS AND AMOUNTS OF INCOME - The numbers of returns and the amounts of total income for 1957-58 and the two previous years are shown in the table hereunder.
| Amount of Total Income | Number of Returns | Total Income | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | ||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Losses | .. | .. | 1,400 | .. | .. | - | |
| 0- | 99 | .. | .. | 63,250 | .. | .. | 1,950 |
| 100- | 199 | .. | .. | 16,430 | .. | .. | 2,320 |
| 200- | 299 | .. | .. | 10,010 | .. | .. | 2,420 |
| 300- | 374 | .. | .. | 7,680 | .. | .. | 2,560 |
| 375- | 399 | 14,260 | 13,920 | 11,860 | 5,490 | 5,360 | 4,610 |
| 400- | 499 | 67,620 | 67,360 | 66,160 | 30,360 | 30,190 | 29,810 |
| 500- | 599 | 72,520 | 67,210 | 70,650 | 39,820 | 36,930 | 38,750 |
| 600- | 699 | 91,690 | 83,480 | 82,490 | 59,610 | 54,320 | 53,640 |
| 700- | 799 | 101,380 | 98,960 | 91,230 | 75,890 | 74,160 | 68,380 |
| 800- | 899 | 87,900 | 90,350 | 91,150 | 74,450 | 76,560 | 77,020 |
| 900- | 999 | 62,030 | 67,520 | 74,050 | 58,630 | 63,940 | 70,060 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 70,530 | 81,740 | 97,370 | 76,420 | 88,630 | 105,170 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 29,060 | 36,680 | 44,350 | 37,400 | 47,160 | 57,040 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 16,500 | 20,510 | 23,320 | 24,600 | 30,550 | 34,800 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 10,510 | 13,240 | 13,830 | 17,780 | 22,400 | 23,360 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 7,530 | 9,010 | 9,400 | 14,260 | 17,040 | 17,760 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 18,770 | 23,030 | 23,790 | 44,990 | 55,230 | 57,350 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 7,270 | 8,640 | 8,540 | 24,860 | 29,510 | 29,180 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 2,727 | 3,200 | 3,105 | 12,117 | 14,229 | 13,831 |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 1,337 | 1,577 | 1,788 | 7,285 | 8,581 | 9,739 |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 669 | 816 | 909 | 4,302 | 5,264 | 5,862 |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 401 | 436 | 504 | 2,985 | 3,252 | 3,754 |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 226 | 236 | 320 | 1,906 | 1,993 | 2,706 |
| 9,000- | 9,999 | 144 | 162 | 219 | 1,362 | 1,534 | 2,078 |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 359 | 457 | 539 | 4,688 | 5,895 | 6,900 |
| 20,000- | 29,999 | 38 | 56 | 71 | 943 | 1,346 | 1,712 |
| 30,000- | 39,999 | 12 | 19 | 16 | 424 | 662 | 565 |
| 40,000- | 49,999 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 181 | 219 | 131 |
| 50,000 and over | 9 | 15 | 8 | 596 | 1,229 | 467 | |
| Totals | 663,500 | 688,620 | 814,450 | 621,350 | 676,180 | 723,930 | |
The much higher grand totals for 1957-58 are due to the extension of the statistical coverage to incomes of less than £375. There is an explanation on page 856 of this volume concerning the extent of the increased coverage and the methods adopted to estimate the figures given in the table.
There were 620,200 males and 194,250 females included in the 1957-58 income year statistics. The respective numbers of these for each total income group appear in the next table, which also gives comparisons with the two immediately preceding years.
| Amount of Total Income | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| £ | £ | ||||||
| Losses | 840 | 550 | |||||
| 0- | 99 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 12,790 | 50,460 |
| 100- | 199 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5,480 | 10,940 |
| 200- | 299 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4,290 | 5,720 |
| 300- | 374 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 3,730 | 3,950 |
| 375- | 399 | 5,050 | 9,210 | 5,320 | 8,600 | 4,300 | 7,560 |
| 400- | 499 | 30,290 | 37,330 | 28,480 | 38,880 | 27,660 | 38,500 |
| 500- | 599 | 47,680 | 24,840 | 39,310 | 27,900 | 39,930 | 30,720 |
| 600- | 699 | 78,260 | 13,430 | 67,900 | 15,580 | 64,490 | 18,000 |
| 700- | 799 | 95,030 | 6,350 | 91,090 | 7,870 | 82,590 | 8,640 |
| 800- | 899 | 84,080 | 3,820 | 86,010 | 4,340 | 86,220 | 4,920 |
| 900- | 999 | 59,420 | 2,610 | 64,800 | 2,720 | 71,290 | 2,770 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 67,830 | 2,700 | 78,140 | 3,600 | 93,200 | 4,170 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 27,640 | 1,420 | 34,860 | 1,820 | 41,890 | 2,460 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 15,670 | 830 | 19,340 | 1,170 | 22,030 | 1,300 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 10,020 | 490 | 12,500 | 740 | 13,040 | 790 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 7,090 | 440 | 8,460 | 550 | 8,910 | 500 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 17,670 | 1,100 | 21,730 | 1,300 | 22,430 | 1,370 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 6,790 | 480 | 8,110 | 530 | 8,080 | 460 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 2,577 | 150 | 2,987 | 213 | 2,910 | 195 |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 1,250 | 87 | 1,480 | 97 | 1,684 | 104 |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 614 | 55 | 751 | 65 | 852 | 57 |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 363 | 38 | 400 | 36 | 478 | 26 |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 204 | 22 | 214 | 22 | 298 | 22 |
| 9,000- | 9,999 | 131 | 13 | 149 | 13 | 200 | 19 |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 333 | 26 | 409 | 48 | 495 | 44 |
| 20,000- | 29,999 | 33 | 5 | 49 | 7 | 64 | 7 |
| 30,000- | 39,999 | 12 | 19 | 16 | - | ||
| 40,000- | 49,999 | 4 | 5 | 3 | - | ||
| 50,000 and over | 9 | 15 | 8 | - | |||
| Totals | 558,050 | 105,450 | 572,520 | 116,100 | 620,200 | 194,250 | |
It should be noted that, as has been previously mentioned, the data for incomes of under £375 did not include salary and wage incomes and this to some extent distorts the picture. The preponderance of females in the lower income groups was very evident in 1957-58. By far the largest number of females in any one income group appeared in the £0-£99 total income class. The vast majority of these females received a small income from interest earned. It should be remembered that in such cases the true income range was from £13 to £112 as the first £12 of interest was exempted. One-third of the total number of females received incomes between £400 and £599 and it appears that the earning capacity of most female salary and wage earners was still within this range in 1957-58. The high proportion of young salary and wage earners in the pre-marriage ages would help to swell the number of females in this income range. However, the number of women in the £600-£699 group increased significantly in the three years covered by the table. Males exceeded females from the income group £600-£699 upwards. For males, the modal income group shifted from £700-£799 in 1955-56 to £800-£899 in 1957-58.
Total Income - The term “total” income corresponds in concept with the “returnable” income which was used in previous Yearbooks. Total income is used in the sense that it is the total of the various component items of income. It does not include income which is exempt from income tax such as social security benefits (except for universal superannuation), the first £12 of income from interest, war pensions, workers' compensation payments, and certain other types of income.
Broad trends in total income movements over the three latest available income years appear in the percentages which are given in the following table.
| Amount of Total Income | Number of Returns | Total Income | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | ||
| £ | £ | Per Cent | |||||
| 375- | 599 | 23.03 | 21.56 | 20.77 | 12.03 | 10.72 | 10.24 |
| 600- | 999 | 51.86 | 49.42 | 47.36 | 43.30 | 39.78 | 37.65 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 20.28 | 23.41 | 26-31 | 27.48 | 30.43 | 33.32 |
| 2,000- | 4,999 | 4.35 | 506 | 4.95 | 13.21 | 14.64 | 14.04 |
| 5,000 and over | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 3.98 | 4.43 | 4.75 | |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
Incomes of £375 and over only were taken into account in the table. Average total incomes were £936 in 1955-56, £982 in 1956-57, and £999 in the latest year. As would be expected from these averages, incomes of £1,000 upwards were expanding rapidly in numbers as more and more salary and wage earners in particular passed this milestone. In 1957-58, individuals with incomes of £1,000 and over shared between them slightly over one-half of the aggregate total income.
Self-employed individuals predominate in income groups from £1,600 upwards. The main subdivision into incomes derived principally from self-employment, from investments, and from salary and wages by amount of total income forms the subject of the next table, which relates to the income year 1957-58.
| Amount of Total Income | Number of Returns | Total Income | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-employed | Investments | Salary and Wage Earners | Self-employed | Investments | Salary and Wage Earners | ||
| £ | £ | Per Cent | |||||
| 375- | 599 | 12.39 | 36.21 | 22.16 | 3.98 | 16.00 | 12.46 |
| 600- | 999 | 26.46 | 30.92 | 52.57 | 13.68 | 21.56 | 47.70 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 40.37 | 23.36 | 23.25 | 36.51 | 29.36 | 32.22 |
| 2,000- | 4,999 | 18.44 | 8.01 | 1.82 | 34.55 | 21.19 | 5.72 |
| 5,000 and over | 2.34 | 1.50 | 0.20 | 11.28, | 11.89 | 1.90 | |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
Only 2 per cent of salary and wage earners received £2,000 or over, compared with 21 per cent for self-employed individuals and 10 per cent for those with incomes principally derived from investments. It should be noted that the percentages in the above table related to individuals who were so classified because they obtained the largest part of their assessable income from that source. They did not refer to amounts of income actually derived from those sources.
The 1957-58 data relating to the source of income are given in the next table.
| Number of Returns | Taxed at Source | Not Taxed at Source | Non-Assessable | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-employed | Other | |||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Self-employed | 145,660 | 4,490 | 187,640 | 4,610 | 2,540 | 199,250 |
| Investments | 99,050 | 5,730 | 490 | 13,920 | 5,570 | 25,580 |
| Salary and wage earners | 569,740 | 472,220 | 3,570 | 10,440 | 13,060 | 499,100 |
| Totals | 814,450 | 482,450 | 191,700 | 28,970 | 21,180 | 723,930 |
As the terms used in this table were adopted as a consequence of the introduction of PAYE taxation, the meanings attached to them are:Income Taxed at Source - This is essentially salary and wages, including bonuses, taxable allowances, and the like. Also included are withholding payments, which arc substantially salary and wage payments made in circumstances where no true employer-employee relationship exists (e.g., company directors' fees, fees for contributions to newspapers, jurors' fees) and some “estate” income.
Income Not Taxed at Source - The principal component is income derived from self-employment, which is given separately in the table. Subdivisions of “other” such income for which statistics are available were net rents and royalties (total £6,410,000) and social security universal superannuation (total £3,280,000). The balance is mainly income from interest, but it includes a substantial proportion of income derived by beneficiaries from “estates” and salaries of shareholder-employees of companies. In certain circumstances, such salaries are not subject to tax deduction at source.
Non-assessable Income - Primarily this is either overseas income or dividends from companies. The latter are now generally assessable income, but the former classification was retained in the 1957-58 statistics.
As has been previously mentioned, in the preceding table, as in the other statistical tables relating to individuals, the aggregate of the component income items may be greater than the given totals. This is due to the fact that “losses” for particular income sources are deducted in order to arrive at the total income. Negative incomes are, however, ignored in the totalling of incomes from any particular source.
These same data about sources of income are in the following table analysed by amount of total income.
| Amount of Total Income | Number of Returns | Taxed at Source | Not Taxed at Source | Non-Assessable | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Employed | other | ||||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| Losses | 1,400 | 10 | - | 40 | 10 | - | |
| 0- | 99 | 63,250 | 40 | 200 | 1,690 | 30 | 1,950 |
| 100- | 199 | 16,430 | 70 | 580 | 1,620 | 50 | 2,320 |
| 200- | 299 | 10,010 | 120 | 990 | 1,240 | 70 | 2,420 |
| 300- | 374 | 7,680 | 130 | 1,510 | 840 | 90 | 2,560 |
| 375- | 399 | 11,860 | 3,860 | 440 | 290 | 30 | 4,610 |
| 400- | 499 | 66,160 | 25,410 | 2,780 | 1,440 | 210 | 29,810 |
| 500- | 599 | 70,650 | 32,640 | 4,310 | 1,590 | 240 | 38,750 |
| 600- | 699 | 82,490 | 46,570 | 5,400 | 1,420 | 260 | 53,640 |
| 700- | 799 | 91,230 | 60,610 | 6,060 | 1,420 | 290 | 68,380 |
| 800- | 899 | 91,150 | 67,950 | 7,350 | 1,420 | 320 | 77,020 |
| 900- | 999 | 74,050 | 60,940 | 7,470 | 1,350 | 300 | 70,060 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 97,370 | 84,900 | 17,350 | 2,230 | 730 | 105,170 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 44,350 | 38,170 | 15,920 | 1,980 | 1,010 | 57,040 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 23,320 | 17,770 | 14,490 | 1,670 | 880 | 34,800 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 13,830 | 9,330 | 12,040 | 1,090 | 900 | 23,360 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 9,400 | 6,000 | 10,210 | 880 | 720 | 17,760 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 23,790 | 15,030 | 35,020 | 3,280 | 4,030 | 57,350 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 8,540 | 5,420 | 19,940 | 1,480 | 2,360 | 29,180 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 3,105 | 2,288 | 9,421 | 611 | 1,522 | 13,831 |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 1,788 | 1,651 | 6,383 | 440 | 1,268 | 9,739 |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 909 | 939 | 3,771 | 276 | 880 | 5,862 |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 504 | 539 | 2,483 | 127 | 607 | 3,754 |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 320 | 400 | 1,746 | 118 | 443 | 2,706 |
| 9,000- | 9,99 | 219 | 318 | 1,191 | 79 | 492 | 2,078 |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 539 | 932 | 3,803 | 231 | 1,937 | 6,900 |
| 20,000 and over | 98 | 423 | 847 | 109 | 1,497 | 2,875 | |
| Totals | 814,450 | 482,450 | 191,700 | 28,970 | 21,180 | 723,930 | |
Individuals with total incomes of £2,000 or more were 4.9 per cent of the total number and they received 18.5 per cent of the total income. An interesting feature is that non-assessable income is largely concentrated in the hands of these individuals, as they received as much as 71.0 per cent of the total non-assessable income. They also shared 44.1 per cent of the income from self-employment.
Industrial Classification of Incomes - Incomes of individuals who were classified as mainly deriving income from self-employment in 1957-58 are in the next table analysed by industrial affiliation. For the sake of completeness, the table also includes the totals for salary and wage earners and for individuals deriving income from investments, but there is no information available concerning the industrial classification of these two classes of individuals.
| Number of Returns | Taxed at Source | Not Taxed at Source | Non-Assessable | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Employed | Other | |||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| Agricultural and livestock production | ||||||
| Sheep farming | 21,740 | 860 | 43,140 | 1,430 | 770 | 46,210 |
| Dairy farming | 35,870 | 730 | 38,200 | 720 | 130 | 39,770 |
| Other | 23,390 | 750 | 29,840 | 750 | 250 | 31,600 |
| Totals | 81,000 | 2,340 | 111,180 | 2,900 | 1,150 | 117,580 |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 1,150 | 40 | 1,200 | 20 | 10 | 1,270 |
| Mining and quarrying | 380 | 10 | 630 | - | 10 | 650 |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||
| Food, drink, and tobacco | 750 | 20 | 900 | 20 | 10 | 950 |
| Apparel, textiles, and footwear | 1,650 | 10 | 1,180 | 60 | 20 | 1,270 |
| Metals and metal products | 1,590 | 30 | 1,900 | 50 | 20 | 1,990 |
| Other | 2,050 | 60 | 2,310 | 50 | 70 | 2,490 |
| Construction | 14,920 | 400 | 16,570 | 260 | 150 | 17,370 |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Commerce - | ||||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 17,590 | 480 | 18,050 | 450 | 280 | 19,250 |
| Other | 910 | 70 | 1,360 | 80 | 60 | 1,570 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 5,100 | 150 | 5,800 | 60 | 50 | 6,060 |
| Services, community - | ||||||
| Professional | 8,300 | 630 | 18,270 | 440 | 630 | 19,950 |
| Other | 10,270 | 260 | 8,290 | 220 | 90 | 8,850 |
| Totals | 145,660 | 4,490 | 187,640 | 4,610 | 2,540 | 199,250 |
| Salary or wages | 569,740 | 472,220 | 3,570 | 10,440 | 13,060 | 499,100 |
| Investment income | 99,050 | 5,730 | 490 | 13,920 | 5,570 | 25,580 |
| Grand totals | 814,450 | 482,450 | 191,700 | 28,970 | 21,180 | 723,930 |
As the table gives the amounts received from each major source of income, it will be appreciated that the classification is based on the source of the largest component item of total income. The United Nations' “enterprise” concept has been adopted for classification purposes. Under this concept, if an individual receives income from two or more of the separately classifiable industries, the whole of the income is classed as if derived from the industry which provided the largest amount of income, and no attempt is made to allocate the component portions of the income to the different industries from which derived. These statistics are therefore not exactly comparable with most other types of statistics where the “establishment” concept is generally used. This provides for the. subdivision of the “enterprise” where more than one separately classifiable industry is carried on and each subdivision is then appropriately classified.
Aggregation of Incomes: Husband and Wife - Tables in previous issues of the Yearbook have given statistics of the incomes of husbands and wives whose incomes were aggregated for taxation purposes. Data concerning aggregated incomes were not available for the income year 1957-58. A recent amendment to the Land and Income Tax Act has, to a very large extent, abolished such aggregation.
Exemptions - In the case of individuals certain statutory deductions are made from the assessable income, and income tax is paid on the balance. Absentees are not usually entitled to the benefit of exemptions other than the personal exemption. The exemptions which have been recorded in these statistics for 1957-58 were, strictly, those which applied to the assessments of provisional tax for the year 1958-59. Assessments of tax on 1957-58 incomes were not prepared as the tax was remitted in full. These exemptions were:
A personal exemption of £338 (or £383 if 65 years of age or over).
An exemption of £162 in respect of a dependent; wife (or husband) whose personal income did not exceed £113. The exemption was diminished by £1 for every £1 of the wife's income in excess of £113.
An exemption not exceeding £162 in respect of a housekeeper employed by a widow, widower, or divorced person to have the care and control of any child or children. This is included with the wife's exemption in the statistics.
An exemption for contributions not exceeding £75 towards the support of a relative by blood, marriage, or adoption, who was dependent on the taxpayer. Children of the taxpayer were included in this definition.
Life assurance premiums, National Provident Fund, superannuation, and similar contributions. An exemption was allowed up to a maximum of 15 per cent of assessable income or £175, whichever amount was the lesser. The maximum was increased to £250 where contributions to superannuation funds for self-employed persons were included.
The exemptions given above have since been substantially altered. Details of the later exemptions are given in Section 26B.
In past years the amounts of exemptions recorded in these statistics were the effective exemptions. In cases when the exemptions exceeded the assessable income the potentially available exemptions were reduced accordingly. The next table which shows the amounts of the insurance, total and excess exemptions for the income year 1957-58, classified by size of total income, departs from the former procedure. Potential exemptions have been recorded and the “excess” column gives the amounts by which the exemptions exceed the assessable income (excluding from that term company dividends, which are now assessable income).
| Amount of Total Income | Insurance | Total | Excess | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) |
| Losses | 50 | 690 | 690 | |
| 0- | 99 | 1,570 | 13,440 | 11,510 |
| 100- | 199 | 420 | 6,460 | 4,190 |
| 200- | 299 | 260 | 4,160 | 1,810 |
| 300- | 374 | 210 | 3,360 | 890 |
| 375- | 399 | 310 | 4,630 | 290 |
| 400- | 499 | 1,820 | 26,330 | 1,480 |
| 500- | 599 | 2,010 | 30,190 | 1,690 |
| 600- | 699 | 2,510 | 39,430 | 1,540 |
| 700- | 799 | 2,930 | 48,100 | 1,050 |
| 800- | 899 | 3,160 | 51,710 | 510 |
| 900- | 999 | 3,140 | 44,360 | 150 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 4,420 | 59,850 | 80 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 2,250 | 27,740 | 60 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 1,440 | 15,040 | 20 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 950 | 8,990 | 40 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 700 | 6,130 | 20 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 2,040 | 16,030 | 90 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 920 | 5,890 | 10 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 357 | 2,150 | 6 |
| 5,000 and over | 543 | 2,976 | 15 | |
| Totals | 32,010 | 417,660 | 26,150 | |
The numbers of individuals who were entitled to a wife's (or husband's) exemption in 1957-58 appear in the following table. The table distinguishes, for each category of total income, between those who were entitled to the full exemption of £162, those who received only a partial exemption because the wife's income exceeded £113, and those who were not entitled to any exemption.
| Amount of Total Income | Numbers of Exemptions for Wife | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | Partial | Nil | Total | ||
| £ | £ | ||||
| Losses | 550 | - | 850 | 1,400 | |
| 0- | 99 | 1,480 | 80 | 61,700 | 63,250 |
| 100- | 199 | 1,380 | 80 | 14,960 | 16,430 |
| 200- | 299 | 1,780 | 70 | 8,160 | 10,010 |
| 300- | 374 | 1,650 | 70 | 5,950 | 7,680 |
| 375- | 399 | 730 | 50 | 11,090 | 11,860 |
| 400- | 499 | 6,520 | 420 | 59,220 | 66,160 |
| 500- | 599 | 12,800 | 740 | 57,100 | 70,650 |
| 600- | 699 | 28,170 | 1,630 | 52,690 | 82,490 |
| 700- | 799 | 43,910 | 2,660 | 44,650 | 91,230 |
| 800- | 899 | 52,260 | 3,010 | 35,870 | 91,150 |
| 900- | 999 | 46,830 | 2,780 | 24,450 | 74,050 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 66,140 | 1,730 | 29,490 | 97,370 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 32,090 | 810 | 11,450 | 44,350 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 17,430 | 650 | 5,240 | 23,320 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 10,080 | 340 | 3,400 | 13,830 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 6,770 | 340 | 2,290 | 9,400 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 17,380 | 630 | 5,790 | 23,790 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 6,160 | 270 | 2,120 | 8,540 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 2,063 | 102 | 940 | 3,105 |
| 5,000 and over | 2,574 | 181 | 1,622 | 4,377 | |
| Totals | 358,750 | 16,650 | 439,040 | 814,450 | |
Numbers of persons with and without a wife's exemption were approximately equal in the £700-799 income group. The percentage of individuals with this exemption fell sharply in each lower income group. The converse was evident in the income groups which immediately followed the £700-799 group, but once an income of £1,200 was reached there was a fairly stable relation between numbers with a wife's exemption and those without the exemption.
The data in the table hereunder are concerned with instances where there were claims for exemptions for one or more dependent children or relatives in 1957-58.
| Amount of Total Income | Numbers of Exemptions for Children or Dependent Relatives (Classified by Number of Children or Dependent Relatives) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 and Over | Total | ||
| £ | £ | ||||||||||
| Losses | 120 | 150 | 90 | 40 | 10 | - | - | 10 | - | 420 | |
| 0- | 99 | 220 | 160 | 190 | 70 | 30 | - | - | - | 10 | 680 |
| 100- | 199 | 240 | 180 | 150 | 80 | 50 | - | 10 | - | 10 | 730 |
| 200- | 299 | 260 | 280 | 250 | 100 | 80 | 70 | 10 | 10 | 40 | 1,100 |
| 300- | 374 | 350 | 330 | 220 | 110 | 70 | 50 | 20 | 10 | - | 1,160 |
| 375- | 399 | 270 | 170 | 130 | 120 | 40 | 20 | 20 | - | 10 | 780 |
| 400- | 499 | 2,310 | 1,750 | 930 | 390 | 170 | 100 | 40 | 10 | - | 5,700 |
| 500- | 599 | 4,410 | 3,180 | 2,000 | 1,030 | 450 | 250 | 110 | 50 | 60 | 11,540 |
| 600- | 699 | 8,980 | 7,020 | 4,150 | 2,260 | 840 | 580 | 200 | 150 | 70 | 24,250 |
| 700- | 799 | 12,310 | 12,220 | 7,730 | 3,300 | 1,700 | 780 | 320 | 200 | 100 | 38,670 |
| 800- | 899 | 14,490 | 15,900 | 10,240 | 4,890 | 2,240 | 830 | 390 | 240 | 100 | 49,330 |
| 900- | 999 | 11,810 | 14,640 | 9,780 | 4,840 | 2,220 | 840 | 330 | 130 | 60 | 44,660 |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 17,700 | 20,310 | 13,770 | 6,100 | 3,640 | 1,480 | 590 | 230 | 120 | 63,950 |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 8,260 | 9,120 | 6,410 | 3,090 | 1,120 | 360 | 170 | 70 | 50 | 28,660 |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 4,160 | 4,870 | 3,430 | 1,670 | 630 | 290 | 100 | - | 40 | 15,190 |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 2,460 | 2,940 | 2,200 | 960 | 360 | 150 | 40 | 20 | 10 | 9,140 |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 1,770 | 1,850 | 1,300 | 760 | 240 | 70 | 50 | 20 | - | 6,050 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 4,110 | 4,650 | 3,980 | 2,150 | 680 | 130 | 180 | 10 | 20 | 15,900 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 1,680 | 1,480 | 1,390 | 610 | 290 | 70 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 5,570 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 547 | 611 | 481 | 276 | 97 | 32 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 2,056 |
| 5,000 and over | 813 | 762 | 618 | 333 | 128 | 43 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 2,716 | |
| Totals | 97,280 | 102,580 | 69,440 | 33,180 | 15,090 | 6,150 | 2,600 | 1,190 | 730 | 328,250 | |
A total of 790,120 exemptions for either children or dependent relatives were claimed in this income year.
Taxable Income and Tax Assessed - After all exemptions have been deducted the balance of income (if any) is taxed in accordance with the basic rates. The next table gives statistics of these data for the income year 1957-58 and the two previous years.
As exemptions for 1956-57 were the same as in 1955-56, taxable incomes for 1956-57 were influenced only by increased numbers of returns and higher incomes. Exemptions were altered for the 1957-58 income year; the personal exemption was decreased and a dependent wife's exemption was increased by a similar amount. A notional insurance exemption was also allowed where the total income was under £1,040. To a very large extent these changes in the exemptions appeared to neutralise each other. Again, income changes and increased numbers mainly determined the level of taxable income.
| Amount of Total Income | Taxable Income | Ordinary Income Tax | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | ||
| £ | £ | £(thousand) | |||||
| Under 400 | 150 | 150 | 230 | 20 | - | - | |
| 400- | 499 | 3,800 | 3,690 | 4,750 | 520 | - | - |
| 500- | 599 | 8,810 | 8,320 | 10,010 | 1,240 | - | - |
| 600- | 699 | 15,380 | 14,650 | 15,490 | 2,210 | - | - |
| 700- | 799 | 21,610 | 21,830 | 21,040 | 3,170 | - | - |
| 800- | 899 | 23,760 | 24,650 | 25,490 | 3,560 | - | - |
| 900- | 999 | 21,230 | 23,130 | 25,560 | 3,260 | 60 | - |
| 1,000- | 1,199 | 31,870 | 37,390 | 44,680 | 5,080 | 530 | - |
| 1,200- | 1,399 | 18,300 | 23,230 | 28,350 | 3,100 | 1,020 | - |
| 1,400- | 1,599 | 13,150 | 16,590 | 18,900 | 2,350 | 1,330 | - |
| 1,600- | 1,799 | 10,320 | 13,170 | 13,510 | 1,970 | 1,500 | - |
| 1,800- | 1,999 | 8,750 | 10,290 | 10,930 | 1,770 | 1,420 | - |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 29,660 | 36,570 | 37,370 | 7,010 | 7,130 | - |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 17,710 | 21,280 | 20,940 | 5,370 | 5,920 | - |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 9,098 | 10,634 | 10,165 | 3,312 | 3,737 | - |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 5,450 | 6,518 | 7,242 | 2,267 | 2,624 | - |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 3,183 | 4,056 | 4,367 | 1,425 | 1,771 | - |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 2,153 | 2,530 | 2,802 | 1,011 | 1,167 | - |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 1,350 | 1,481 | 2,048 | 649 | 711 | - |
| 9,000- | 9,999 | 933 | 1,176 | 1,442 | 465 | 576 | - |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 2,770 | 3,994 | 4,610 | 1,448 | 2,080 | - |
| 20,000 and over | 685 | 1,224 | 1,316 | 389 | 681 | - | |
| Totals | 250,120 | 286,560 | 311,240 | 51,590 | 32,250 | - | |
Rates of Ordinary Income Tax: Individuals - The basic rates of tax, which have since been altered, were not changed in any of these three income years. The basic rate commenced at 3s. in the £1 on so much of the taxable income as did not exceed £100. For each succeeding £100 or part thereof, the rate of tax on that income increased by 3d. in the £1, until the maximum rate of 12s. was reached at £3,600. These rates were normally subject to a percentage increase or decrease each year in accordance with the provisions of the Land and Income Tax (Annual) Act fixing rates for that year. The rebate was 10 per cent in 1955-56, with a maximum of £40. There was a rebate of £100 in 1956-57. This was substituted for, and was not in addition to, a percentage rebate. As a result of the introduction of the PAYE system ordinary income tax on 1957-58 incomes was remitted in full.
Ordinary income tax is payable on the amount of the taxable balance, but non-assessable income is included for purposes of determining the actual rate of tax.
COMPANY INCOMES - It is perhaps desirable to draw attention to the fact that the term “companies” as it is used in connection with these statistics has been given a wider meaning than that which is commonly assigned to it. A definition of the term will be found on page 856.
The New Zealand Electricity Department was exempted from income taxation as from the income year 1957-58. The exclusion of this Government Department from the statistics has appreciably affected comparisons between 1957-58 and earlier years in a number of the statistical tables in this section.
The various statutory exemptions which are granted to individuals do not apply in the case of companies. The amounts of assessable income and taxable income are identical in the case of companies.
With the exceptions of the table which gives provisional estimates of assessable incomes for 1958-59 and 1959-60 and also the “assets” data which appear at the end of this section, these statistics for companies have been compiled from returns for all companies, and are not estimates based on a sample survey.
The following table gives particulars of the number of companies and their aggregate assessable incomes for 1957-58 and the two preceding income years.
| Amount of Assessable Income | Number of Returns | Assessable Income | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | ||
| £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 0-99 | 2,589 | 2,832 | 3,448 | 88 | 92 | 115 | |
| 100-199 | 1,283 | 1,479 | 1,574 | 187 | 217 | 227 | |
| 200-299 | 1,079 | 1,233 | 1,351 | 267 | 304 | 334 | |
| 300-399 | 1,078 | 1,092 | 1,198 | 375 | 381 | 417 | |
| 400-499 | 913 | 1,015 | 1,053 | 408 | 456 | 472 | |
| 500-599 | 910 | 1,001 | 1,030 | 498 | 547 | 563 | |
| 600-699 | 857 | 902 | 929 | 557 | 584 | 603 | |
| 700-799 | 688 | 801 | 826 | 514 | 600 | 618 | |
| 800-899 | 681 | 764 | 727 | 577 | 648 | 616 | |
| 900-999 | 593 | 584 | 583 | 561 | 554 | 552 | |
| 1,000-1,999 | 3,785 | 4,150 | 4,227 | 5,385 | 5,934 | 6,090 | |
| 2,000-2,999 | 1,824 | 1,989 | 2,053 | 4,462 | 4,863 | 5,016 | |
| 3,000-3,999 | 1,073 | 1,119 | 1,227 | 3,707 | 3,854 | 4,243 | |
| 4,000-4,999 | 699 | 687 | 735 | 3,120 | 3,071 | 3,279 | |
| 5,000-5,999 | 439 | 468 | 488 | 2,389 | 2,564 | 2,671 | |
| 6,000-6,999 | 306 | 310 | 324 | 1,988 | 1,996 | 2,102 | |
| 7,000-7,999 | 231 | 227 | 264 | 1,727 | 1,692 | 1,972 | |
| 8,000-8,999 | 187 | 182 | 232 | 1,587 | 1,542 | 1,967 | |
| 9,000-9,999 | 157 | 151 | 144 | 1,494 | 1,433 | 1,367 | |
| 10,000-19,999 | 765 | 785 | 795 | 10,565 | 10,773 | 11,003 | |
| 20,000-29,999 | 244 | 255 | 262 | 5,911 | 6,252 | 6,375 | |
| 30,000-39,999 | 111 | 125 | 124 | 3,838 | 4,301 | 4,291 | |
| 40,000-49,999 | 81 | 66 | 83 | 3,602 | 2,960 | 3,739 | |
| 50,000-99,999 | 149 | 163 | 159 | 10,244 | 11,586 | 10,898 | |
| 100,000-199,999 | 78 | 71 | 84 | 10,781 | 10,351 | 11,590 | |
| 200,000-299,999 | 24 | 27 | 38 | 6,004 | 6,434 | 8,989 | |
| 300,000-399,999 | 15 | 11 | 14 | 5,100 | 3,862 | 4,737 | |
| 400,000-499,999 | 4 | 11 | 11 | 1,796 | 5,007 | 4,846 | |
| 500,000 and over | 18 | 19 | 21 | 17,523 | 17,168 | 18,094 | |
| Current net loss | 3,924 | 4,640 | 5,590 | ... | ... | ... | |
| Assessable income before losses | 1,164 | 1,291 | 1,514 | ... | ... | ... | |
| Totals | 25,949 | 28,450 | 31,108 | 105,254 | 110,024 | 117,784 | |
The provisional estimates of assessable income, in the next table, are calculations based on the income trends revealed by a small sample of returns. The sample is confined to those income returns which are available at an early date. Companies with balance dates later than 30 June would be almost completely unrepresented in the sample.
The estimates are given with the warning that the figures are subject to a possible considerable margin of error and should therefore be used with caution.
| Industry Group | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Returns | Assessable Income | Number of Returns | Assessable Income | Number of Returns | Assessable Income | |
| £(m) | £(m) | £(m) | ||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 1,841 | 2.6 | 2,200 | 2.5 | 2,500 | 3.6 |
| Manufacturing | 6,524 | 40.4 | 6,750 | 43.9 | 6,943 | 44.8 |
| Construction | 2,414 | 6.2 | 2,626 | 5.9 | 2,807 | 6.7 |
| Commerce - | ||||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 11,004 | 42.5 | 11,692 | 43.8 | 12,550 | 46.7 |
| Other | 4,768 | 16.6 | 5,260 | 17.9 | 5,710 | 19.8 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 1,553 | 4.3 | 1,627 | 3.6 | 1,650 | 3.9 |
| Services, community | 2,544 | 4.1 | 2,770 | 4.6 | 2,950 | 4.6 |
| Miscellaneous | 460 | 1.1 | 475 | 1.3 | 490 | 1.4 |
| Totals | 31,108 | 117.8 | 33,400 | 123.5 | 35,600 | 131.5 |
It is expected that 1958-59 company incomes will increase by approximately £6,000,000 and that in 1959-60 they will increase by another £8,000,000. In 1958-59, however, a large part of the increased income was concentrated in the manufacturing group while in 1959-60 the incomes of wholesale and retail trading companies showed the largest rise.
The item “assessable income before losses”, which appears in a preceding table and also in subsequent tables, requires a little further explanation. Companies, and also individuals, are permitted to offset losses from one particular source of assessable income against the profits from any other source of assessable income during the same income year. The remainder of the loss, if any, can be carried forward and offset against the assessable profits of the next six income years. This item represents the number of companies whose assessable incomes for the current year have been reduced to “nil” by the offsetting of losses incurred in previous income years.
In the following table, which is also classified by the amount of assessable income, more complete data for the 1957-58 income year only are presented.
| Amount of Assessable Income | Number of Returns | Assessable Income Before Losses* | Assessable Income | Returnable Income | Current Net Loss | Income Tax Assessed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary | Social Security | |||||||
| *This column represents assessable income plus losses which have been carried forward from previous years. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | £(thousand) | ||||||
| 0- | 99 | 3,448 | 176 | 115 | 1,797 | - | 25 | 8 |
| 100- | 199 | 1,574 | 274 | 227 | 390 | 25 | 33 | 16 |
| 200- | 299 | 1,351 | 360 | 334 | 677 | - | 46 | 24 |
| 300- | 399 | 1,198 | 460 | 417 | 499 | - | 59 | 31 |
| 400- | 499 | 1,053 | 510 | 472 | 498 | - | 68 | 35 |
| 500- | 599 | 1,030 | 602 | 563 | 587 | 2 | 83 | 41 |
| 600- | 699 | 929 | 637 | 603 | 664 | - | 93 | 45 |
| 700- | 799 | 826 | 640 | 618 | 628 | - | 97 | 46 |
| 800- | 899 | 727 | 643 | 616 | 646 | 89 | 100 | 46 |
| 900- | 999 | 583 | 568 | 552 | 908 | 62 | 92 | 41 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 4,227 | 6,234 | 6,090 | 6,448 | 104 | 1,153 | 452 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 2,053 | 5,057 | 5,016 | 5,202 | - | 1,160 | 374 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 1,227 | 4,255 | 4,243 | 4,314 | - | 1,163 | 316 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 735 | 3,299 | 3,279 | 3,301 | - | 1,028 | 246 |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 488 | 2,687 | 2,671 | 2,730 | - | 957 | 200 |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 324 | 2,102 | 2,102 | 2,142 | - | 829 | 156 |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 264 | 1,975 | 1,972 | 2,013 | - | 824 | 148 |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 232 | 2,071 | 1,967 | 1,991 | - | 832 | 146 |
| 9,000- | 9,999 | 144 | 1,376 | 1,367 | 1,400 | - | 585 | 102 |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 795 | 11,061 | 11,003 | 11,670 | 10 | 4,679 | 819 |
| 20,000- | 29,999 | 262 | 6,478 | 6,375 | 6,543 | - | 2,704 | 473 |
| 30,000- | 39,999 | 124 | 4,327 | 4,291 | 4,534 | - | 1,820 | 319 |
| 40,000- | 49,999 | 83 | 3,770 | 3,739 | 3,970 | - | 1,597 | 280 |
| 50,000- | 99,999 | 159 | 10,900 | 10,898 | 11,091 | - | 4,640 | 817 |
| 100,000- | 199,999 | 84 | 11,594 | 11,590 | 11,925 | - | 4,794 | 832 |
| 200,000- | 299,999 | 38 | 8,989 | 8,989 | 9,291 | - | 3,768 | 657 |
| 300,000- | 399,999 | 14 | 4,737 | 4,737 | 4,829 | - | 1,932 | 326 |
| 400,000- | 499,999 | 11 | 4,846 | 4,846 | 4,889 | 5 | 1,851 | 296 |
| 500,000 and over | 21 | 18,094 | 18,094 | 18,566 | - | 6,931 | 1,112 | |
| Net loss | 5,590 | - | - | 162 | 6,880 | - | - | |
| Assessable income before losses | 1,514 | 1,638 | - | 116 | - | - | - | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 31,108 | 120,359 | 117,784 | 124,420 | 7,177 | 43,943 | 8,404 |
| 1956-57 | 28,450 | 111,992 | 110,024 | 117,701 | 6,757 | 41,575 | 7,982 | |
| 1955-56 | 25,949 | 107,017 | 105,254 | 112,730 | 4,755 | 40,059 | 7,630 | |
Companies are classified by industry, the classification being identical with that used for individuals, with the minor exception that community services - professional - do not form a separate group. Attention is drawn to the remarks on page 866 regarding the difference between the enterprise and the establishment concepts. These statistics are based on the enterprise concept, i.e., the whole of the company's activities are classified according to the predominant activity. The figures in the next table give the results of this classification for the income year 1957-58.
| Industry Group | Number of Returns | Assessable Income Before Losses* | Assessable Income | Returnable Income | Current Net Loss | Income Tax Assessed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary | Social Security | |||||||
| *This column represents assessable income plus losses which have been carried forward from previous years. | ||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 1,841 | 2,745 | 2,603 | 2,655 | 693 | 824 | 195 | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 134 | 293 | 282 | 290 | 47 | 100 | 21 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 251 | 592 | 571 | 574 | 87 | 201 | 43 | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 931 | 10,939 | 10,658 | 10,896 | 460 | 4,396 | 798 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 884 | 4,447 | 4,272 | 4,337 | 303 | 1,679 | 320 | |
| Metals and metal products | 2,174 | 8,044 | 7,890 | 8,099 | 428 | 2,967 | 590 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 2,535 | 17,750 | 17,522 | 17,820 | 1,715 | 7,011 | 1,313 | |
| Construction | 2,414 | 6,406 | 6,233 | 6,303 | 424 | 2,219 | 466 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 18 | 171 | 169 | 169 | 18 | 70 | 13 | |
| Commerce - | ||||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 11,004 | 43,237 | 42,483 | 43,701 | 1,711 | 16,308 | 3,181 | |
| Other | 4,768 | 16,791 | 16,609 | 20,787 | 628 | 5,126 | 833 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 1,553 | 4,642 | 4,297 | 4,331 | 271 | 1,565 | 321 | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 2,544 | 4,235 | 4,130 | 4,392 | 382 | 1,455 | 306 | |
| Unknown or not stated | 57 | 67 | 64 | 65 | 11 | 22 | 5 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 31,108 | 120,359 | 117,784 | 124,420 | 7,177 | 43,943 | 8,404 |
| 1956-57 | 28,450 | 111,992 | 110,024 | 117,701 | 6,757 | 41,575 | 7,982 | |
| 1955-56 | 25,949 | 107,017 | 105,254 | 112,730 | 4,755 | 40,059 | 7,630 | |
Rates of Tax: Companies - For incomes received during the income year 1957-58 the rate of ordinary income tax payable by a company was 2s. 6d., increased by 1/100 d. for every £1 of taxable income up to £6,300. Above £6,300 the rate was 7s. 9d., increased by 1/150d. for every £1 of taxable income in excess of £6,300, with a maximum of 8s. 6d. in the £1. Social security income tax was levied at the rate of 1s. 6d. per £1 of income. Not all companies were liable to pay this charge. Further information concerning rates of taxation will be found on page 813.
The next table shows some additional data concerning companies which relate to the income year 1957-58.
| Industry Group | Stocks at End of Period | Income | Expenditure | Gross Profit | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales and Services | Interest and Gross Rents | Purchases | Salaries and Wages | Interest | Rent | Depreciation | ||||
| *Gross profit not normally available. | ||||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 7,232 | 19,971 | 168 | 5,901 | 5,226 | 518 | 430 | 1,306 | 11,249 | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 203 | 2,735 | 95 | .. | 871 | 70 | 42 | 227 | 817 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 414 | 11,145 | 81 | .. | 5,189 | 334 | 174 | 726 | * | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 37,802 | 342,103 | 740 | 250,902 | 35,176 | 1,146 | 705 | 5,414 | 44,938 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 18,942 | 77,059 | 316 | 42,419 | 20,155 | 481 | 930 | 1,387 | 15,477 | |
| Metal and metal products | 24,624 | 120,201 | 417 | 73,088 | 26,258 | 651 | 879 | 2,108 | 23,707 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 39,895 | 207,211 | 967 | 106,710 | 45,202 | 2,002 | 1,913 | 9,411 | 47,708 | |
| Construction | 13,703 | 99,099 | 330 | 48,488 | 26,225 | 431 | 353 | 2,664 | 18,477 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 588 | 2,682 | 21 | 1,078 | 633 | 78 | 4 | 223 | 1,001 | |
| Commerce - | ||||||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 168,365 | 1,006,563 | 4,418 | 803,012 | 84,396 | 3,578 | 5,998 | 8,825 | 158,395 | |
| Other | 643 | 58,210 | 36,985 | 1,906 | 18,363 | 9,037 | 656 | 2,155 | * | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 739 | 49,855 | 309 | 5,445 | 17,712 | 374 | 378 | 3,952 | * | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 2,303 | 53,118 | 1,101 | 18,665 | 15,032 | 450 | 1,452 | 1,648 | 9,957 | |
| Unknown or not stated | 113 | 1,345 | 7 | 1,054 | 96 | 6 | 20 | 15 | 248 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 315,565 | 2,051,296 | 45,954 | 1,358,667 | 300,535 | 19,155 | 13,934 | 40,061 | 331,973 |
| 1956-57 | 287,733 | 1,880,690 | 41,552 | 1,228,768 | 279,850 | 20,893 | 12,105 | 35,969 | 307,192 | |
| 1955-56 | 279,850 | 1,770,802 | 36,495 | 260,412 | 17,800 | 11,078 | 31,161 | 284,067 | ||
Trading stocks at the end of 1957-58 were £27,830,000 larger than at the end of 1956-57. The increase in that year was, however, smaller than was normal, and the 1957-58 figure evidently represents, in part, a return to a normal stock level from a “run-down” total for 1956-57. Sales of goods and services rose by £171 million, compared with an increase of £110 million in 1956-57. Purchases were also larger, but gross profit improved by £25 million.
One point which should be noted is that the purchases figures have not been given for the forestry and mining industry groups. It was found that there was a considerable lack of uniformity in such data for these two groups, which was probably connected with differing treatments of royalty and equivalent payments.
The amount of gross profit shown in the accounts is used in these statistics, despite the wide variations in the conception of gross profit. No attempt has been made to secure uniformity of calculation for individual companies, but of course the total gross profit for each industry should correspond with that industry's average conception of gross profit. In some industries, such as the transport industry, it is not normal practice to calculate gross profit, and in such cases the gross profit is recorded in these statistics as nil. Estimates of the amount of gross profit were, however, made when any company did not calculate the gross profit, and it was the custom of the industry concerned to show this figure.
The abridged version of the full industry classification for which data are given in this publication does not reveal the individual industries where the gross profit is not generally calculated. Apart from “Mining and Quarrying”, “Commerce, other” and “Transport, etc.”, there are a number of industries included in “Services, community” which do not show gross profit.
The paid-up capital and shareholders' funds for 1957-58 are given in the two following tables.
| Industry Group | Number of Returns | Assessable Income | Dividends Paid | Shareholders' Funds | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Paid-up Capital | |||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 1,841 | 2,603 | 1,175 | 27,654 | 15,511 | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 134 | 282 | 138 | 4,537 | 2,706 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 251 | 571 | 208 | 5,322 | 3,014 | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 931 | 10,658 | 2,521 | 80,094 | 37,760 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 884 | 4,272 | 1,605 | 27,706 | 14,617 | |
| Metals and metal products | 2,174 | 7,890 | 2,926 | 40,407 | 19,580 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 2,535 | 17,522 | 6,120 | 102,466 | 64,653 | |
| Construction | 2,414 | 6,233 | 2,571 | 24,787 | 10,880 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 18 | 169 | 68 | 2,349 | 1,591 | |
| Commerce - | ||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 11,004 | 42,483 | 15,808 | 232,175 | 109,574 | |
| Other | 4,768 | 16,609 | 6,382 | 160,978 | 81,615 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 1,553 | 4,297 | 1,330 | 32,160 | 15,085 | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 2,544 | 4,130 | 1,752 | 28,431 | 10,312 | |
| Unknown or not stated | 57 | 64 | 15 | 218 | 162 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 31,108 | 117,784 | 42,618 | 769,283 | 387,059 |
| 1956-57 | 28,450 | 110,024 | 35,874 | 713,453 | 360,945 | |
| 1955-56 | 25,949 | 105,254 | 32,872 | 643,487 | 329,718 | |
For the purposes of these statistics, the shareholders' funds of a company are defined, briefly, as the amount which would be available to shareholders if the assets were realised and the liabilities discharged at the net values shown in the balance sheet. In the case of New Zealand branches of overseas companies, either the paid-up capital and the shareholders' funds are apportioned on some equitable basis, or the balance of the branch's head office account is taken. The capital loan liabilities of those Government Departments which are included in these statistics have been omitted from both paid-up capital and shareholders' funds. Advances from shareholders have been added to shareholders' funds and advances to shareholders deducted.
An analysis of companies by amount of paid-up capital for 1957-58 discloses the position shown in the next table. Those with no paid-up capital are mostly industrial and provident societies, clubs, associations, and similar incorporated bodies.
| Amount of Paid-up Capital | Number of Returns | Paid-up Capital | Shareholders' Funds | Dividends Paid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |
| Nil | 1,992 | - | 25,077 | 553 | |
| 0- | 499 | 1,761 | 369 | 7,722 | 624 |
| 500- | 999 | 2,394 | 1,514 | 8,642 | 773 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 5,748 | 7,079 | 26,064 | 2,285 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 4,200 | 9,267 | 26,475 | 2,179 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 2,868 | 9,104 | 20,757 | 1,669 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 1,831 | 7,686 | 16,498 | 1,214 |
| 5,000- | 5,999 | 1,974 | 10,059 | 22,897 | 1,984 |
| 6,000- | 6,999 | 1,226 | 7,541 | 15,452 | 1,084 |
| 7,000- | 7,999 | 755 | 5,486 | 10,422 | 650 |
| 8,000- | 8,999 | 588 | 4,807 | 8,583 | 603 |
| 9,000- | 9,999 | 423 | 3,915 | 7,138 | 388 |
| 10,000- | 19,999 | 2,836 | 34,959 | 71,639 | 4,300 |
| 20,000- | 29,999 | 961 | 21,769 | 38,256 | 2,309 |
| 30,000- | 39,999 | 405 | 13,200 | 23,779 | 1,498 |
| 40,000- | 49,999 | 196 | 8,331 | 14,356 | 720 |
| 50,000- | 59,999 | 174 | 9,051 | 19,402 | 1,302 |
| 60,000- | 69,999 | 96 | 6,008 | 10,626 | 609 |
| 70,000- | 79,999 | 78 | 5,713 | 9,796 | 630 |
| 80,000- | 89,999 | 51 | 4,235 | 9,379 | 327 |
| 90,000- | 99,999 | 33 | 3,122 | 5,800 | 226 |
| 100,000- | 199,999 | 236 | 30,532 | 57,581 | 3,416 |
| 200,000- | 299,999 | 95 | 21,765 | 39,085 | 1,961 |
| 300,000- | 399,999 | 56 | 18,906 | 30,771 | 1,636 |
| 400,000- | 499,999 | 21 | 8,876 | 13,750 | 1,875 |
| 500,000- | 599,999 | 24 | 12,292 | 22,556 | 833 |
| 600,000- | 699,999 | 14 | 8,998 | 16,052 | 572 |
| 700,000- | 799,999 | 13 | 9,678 | 15,646 | 617 |
| 800,000- | 899,999 | 6 | 4,911 | 7,089 | 102 |
| 900,000- | 999,999 | 7 | 6,601 | 13,484 | 596 |
| 1,000,000 and over | 46 | 91,283 | 154,509 | 5,083 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 31,108 | 387,059 | 769,283 | 42,618 |
| 1956-57 | 28,450 | 360,945 | 713,453 | 35,874 | |
| 1955-56 | 25,949 | 329,718 | 643,487 | 32,872 | |
In 1957-58 there were 518 companies with paid-up capital of £100,000 and over, compared with 498 for a year earlier. These companies had 55.2 per cent of the total paid-up capital and 482 per cent of the total shareholders' funds.
The rate of company formation continued at a high level. In 1957-58 the number of companies increased by 9.3 per cent and paid-up capital for all companies rose by 7.2 per cent.
Company formation in the farming sector still continued at high levels in 1957-58, as the number of companies rose from 1,447 in 1956-57 to 1,841 in 1957-58. This is the largest absolute increase so far recorded, but in percentage terms the 1957-58 increase over the previous year was 272 per cent, compared with 31.2 per cent in 1956-57.
Dividends paid by companies in 1957-58 were £6,744,000 larger than in 1956-57. This was well in excess of the increase in the income after taxation, and it is obvious that the approaching liability of dividends to taxation in the hands of shareholders and the imposition of an excess retention tax were factors which played a major part in determining the 1957-58 dividend level.
An analysis by the type of company - i.e., private, public, overseas, etc. - is given in the three following tables, which present some of the principal data for the year 1957-58.
| Industry Group | Number of Returns | Assessable Income | Ordinary and Social Security Income Tax | Net Business Less | Shareholders' Funds | Dividends Paid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paid-up Capital | Total | |||||||
| New Zealand Private Companies | ||||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 1,821 | 2,513 | 975 | 692 | 14,829 | 26,549 | 1,150 | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 118 | 221 | 92 | 27 | 779 | 2,284 | 107 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 226 | 438 | 179 | 75 | 1,419 | 2,967 | 172 | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 610 | 4,258 | 2,019 | 263 | 12,025 | 25,727 | 1,156 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 833 | 2,401 | 1,061 | 236 | 6,380 | 13,528 | 979 | |
| Metals and metal products | 2,103 | 6,061 | 2,649 | 369 | 13,717 | 29,452 | 2,381 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 2,298 | 9,079 | 4,115 | 415 | 20,649 | 42,827 | 3,350 | |
| Construction | 2,391 | 5,859 | 2,500 | 402 | 9,719 | 22,975 | 2,538 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 5 | 14 | 6 | - | 37 | 82 | 3 | |
| Commerce - | ||||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 10,397 | 27,761 | 12,163 | 1,500 | 66,983 | 144,772 | 11,938 | |
| Other | 4,165 | 3,419 | 1,136 | 238 | 34,067 | 58,329 | 3,417 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 1,412 | 2,920 | 1,210 | 244 | 7,941 | 15,972 | 1,083 | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 1,651 | 2,759 | 1,129 | 238 | 8,089 | 15,136 | 1,575 | |
| Unknown or not stated | 54 | 28 | 9 | 11 | 162 | 218 | 15 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 28,084 | 67,733 | 29,244 | 4,712 | 196,795 | 400,818 | 29,863 |
| 1956-57 | 25,476 | 62,064 | 26,912 | 3,824 | 181,366 | 365,185 | 25,246 | |
| 1955-56 | 23,084 | 59,102 | 25,762 | 3,846 | 162,541 | 323,455 | 21,418 | |
| New Zealand Public Companies | ||||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 14 | 61 | 29 | 232 | 453 | 25 | ||
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 16 | 61 | 29 | 20 | 1,928 | 2,252 | 31 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 25 | 133 | 64 | 12 | 1,595 | 2,355 | 36 | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 302 | 5,871 | 2,913 | 25 | 20,263 | 47,369 | 1,347 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 48 | 1,870 | 937 | 57 | 8,166 | 14,041 | 626 | |
| Metals and metal products | 58 | 1,536 | 766 | 43 | 4,880 | 8,892 | 513 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 201 | 7,833 | 3,908 | 1,274 | 42,100 | 55,870 | 2,707 | |
| Construction | 10 | 162 | 80 | 2 | 492 | 771 | 33 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 13 | 155 | 77 | 18 | 1,554 | 2,267 | 65 | |
| Commerce | ||||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 272 | 10,407 | 5,203 | 60 | 36,271 | 67,596 | 2,851 | |
| Other | 319 | 5,757 | 2,496 | 115 | 35,066 | 71,180 | 2,954 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 118 | 1,232 | 606 | 26 | 7,073 | 15,461 | 247 | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 68 | 810 | 397 | 53 | 2,192 | 5,804 | 165 | |
| Unknown or not stated | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 1,464 | 35,887 | 17,505 | 1,704 | 161,811 | 294,313 | 11,600 |
| 1956-57 | 1,470 | 33,729 | 16,894 | 2,562 | 152,700 | 279,355 | 9,560 | |
| 1955-56 | 1,467 | 33,057 | 16,558 | 563 | 144,321 | 258,094 | 10,286 | |
| Remainder of Companies (Overseas, Industrial, and Provident Societies, etc.) | ||||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 6 | 29 | 15 | 1 | 450 | 652 | - | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Mining and quarrying | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 19 | 529 | 262 | 172 | 5,471 | 6,998 | 18 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 3 | 1 | 10 | 71 | 137 | - | ||
| Metals and metal products | 13 | 292 | 143 | 15 | 982 | 2,063 | 32 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 36 | 609 | 300 | 26 | 1,904 | 3,769 | 63 | |
| Construction | 13 | 212 | 105 | 19 | 669 | 1,040 | - | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Commerce - | ||||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 335 | 4,316 | 2,124 | 150 | 6,321 | 19,806 | 1,019 | |
| Other | 284 | 7,433 | 2,326 | 276 | 12,481 | 31,468 | 10 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 23 | 145 | 71 | 1 | 72 | 727 | - | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 825 | 561 | 234 | 91 | 31 | 7,492 | 12 | |
| Unknown or not stated | 3 | 36 | 18 | - | - | - | - | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 1,560 | 14,163 | 5,597 | 762 | 28,452 | 74,152 | 1,155 |
| 1956-57 | 1,504 | 14,230 | 5,752 | 372 | 26,879 | 68,913 | 1,068 | |
| 1955-56 | 1,398 | 13,095 | 5,369 | 346 | 22,856 | 61,938 | 1,168 | |
Government Departments which are liable for income tax have been classified as New Zealand public companies. In a small percentage of cases, precise information concerning the type of company was not available and there consequently may be a few instances of incorrect classifications.
It will be noticed that the total of public companies has been almost stationary in the last three years. Practically the whole of the increase in numbers has been in private companies. On average, private companies are much smaller than are public companies, but in the aggregate they employ a larger amount of paid-up capital. Their shareholders' funds are also a rather higher percentage of the paid-up capital (204 per cent against 182 per cent for public companies). However, as shareholders' funds include advances from shareholders (£61,461,000), the bulk of which relate to private companies, it is evident that the relation of retained income to paid-up capital is nearly identical for both types of companies. The earning power per unit of shareholders' funds employed is considerably higher in the case of private companies, since their assessable incomes total £67,733,000 against the £35,887,000 for public companies. This earning power is also reflected in the amount of dividends paid, which is two and one-half times that paid by public companies.
While on the subject of dividends paid, it should be pointed out that the disposable profits of the New Zealand branches of overseas companies are remitted to their overseas head offices and that these disposable profits are not included as dividends paid in New Zealand. Where the overseas company operates through a New Zealand subsidiary company, the New Zealand company is classified as either public or private and any dividends paid will be included in the statistics.
ASSETS OF COMPANIES - Information on assets is collected for a sample group of companies. The sample comprises a random selection of 10 per cent of the number of companies, plus a complete coverage of those which are deemed to fall into a “large company” category.
The estimates for the various classes of assets are given in the table which now follows, and which relates to the income year 1957.58. At present these estimates should be regarded as being only approximately correct. The figures show the position at the close of the income year. Estimates of the assets of clubs, associations, etc., which form part of the “community services” group, and the assets of the “other or undefined” group have not been included.
| Industry Group | Land and Buildings | Other Fixed Assets | Investments | Closing Stocks | Other Current Assets | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(million) | |||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 22.36 | 5.13 | 2.40 | 7.23 | 4.28 | 41.40 | |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 1.19 | 3.19 | - | 0.20 | 1.15 | 5.73 | |
| Mining and quarrying | 2.03 | 8.18 | 0.90 | 0.41 | 5.76 | 17.28 | |
| Manufacturing - | |||||||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 36.31 | 27.54 | 10.00 | 37.80 | 29.08 | 140.73 | |
| Textiles, wearing apparel, and made-up textiles | 6.72 | 6.66 | 2.33 | 18.94 | 11.52 | 46.17 | |
| Metals and metal products | 12.95 | 11.04 | 2.28 | 24.63 | 17.66 | 68.56 | |
| Wood, paper, and chemical products (including miscellaneous) | 34.79 | 46.30 | 12.23 | 39.89 | 35.46 | 168.67 | |
| Construction | 5.20 | 11.45 | 3.66 | 13.70 | 13.74 | 46.75 | |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 0.97 | 5.30 | 0.24 | 0.59 | 0.43 | 7.53 | |
| Commerce - | |||||||
| Wholesale and retail | 59.22 | 40.99 | 26.76 | 168.36 | 149.39 | 444.72 | |
| Other | 57.13 | 2.66 | 498.86 | 0.64 | 317.85 | 877.14 | |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 6.55 | 25.35 | 2.74 | 0.74 | 12.73 | 48.11 | |
| Services, community and business, and recreation | 13.50 | 8.44 | 5.59 | 2.21 | 9.79 | 39.53 | |
| Totals - | 1957-58 | 258.92 | 202.23 | 566.99 | 315.34 | 608.84 | 1,952.32 |
| 1956-57 | 239.72 | 319.37 | 536.27 | 287.63 | 579.21 | 1,962.20 | |
| 1955-56 | 204.28 | 283.04 | 502.80 | 279.62 | 553.32 | 1,823.06 | |
Total assets rose by £121 million during 1957-58. The net investment in land, buildings, and other fixed assets accounted for £30 million, the balance being spread between investments, stocks, and current assets. Shareholders provided £62 million of the required funds, either from retained profits or by additional investment. The extra £59 million came from a rise in “provisions” (reserves for specific purposes which are not deducted from an asset) and external liabilities. The figures which have been quoted exclude the “electricity, gas, etc.” industry group, where comparison has been affected by the exemption from income taxation, from 1957-58 onwards, of a large Government Department.
Several points about the classification adopted should be noted. “Other current assets” was used to some extent as a residual class. It includes assets such as goodwill, establishment accounts, etc. Other nominal assets, such as accumulated losses and similar accounts, were excluded from the assets and deducted from shareholders' funds.
Where the balance sheet did not distinguish between land and buildings and other fixed assets, the whole amount was included in the class deemed the greatest part in value of the assets.
Loans secured by mortgages of property were treated as investments. Loans and advances by banks on overdraft, by finance companies for hire purchase credit, etc., and others of a like nature were classed as “other current assets”. This is particularly important in the “commerce - other” industry group, which includes banks, insurance companies, holding companies, Government lending institutions, etc.
It has been previously mentioned that the term “companies” includes Government Departments which are liable to pay income tax, and that the capital loan liabilities of these Departments are not included in either paid-up capital or shareholders' funds. These capital loan liabilities are, however, represented by investments which appear in the assets. This should be remembered if the ratios of shareholders' funds to total assets are being examined.
CENSUS 1956: INCOMES OF INDIVIDUALS - The following statistics on incomes were compiled from the population census taken on 17 April 1956.
The table divides into income groups the persons actively engaged, and also the total population, including those not actively engaged in employment.
The questionnaire on the schedule asked for income for the year ended 31 March 1956 from all sources without deduction of taxes, superannuation, life insurance, rates, etc. Social security benefits (age, family, etc.) and war pensions were not included.
| Income Group | Persons Actively Engaged | Total Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | ||
| £ | £ | ||||||
| Nil | 5,572 | 5,791 | 11,363 | 428,462 | 792,070 | 1,220,532 | |
| 1- | 49 | 4,134 | 5,394 | 9,528 | 13,776 | 36,532 | 50,308 |
| 50- | 99 | 4,634 | 6,904 | 11,538 | 10,968 | 23,329 | 34,297 |
| 100- | 299 | 34,351 | 53,546 | 87,897 | 44,629 | 82,439 | 127,068 |
| 300- | 499 | 65,424 | 78,717 | 144,141 | 73,377 | 90,449 | 163,826 |
| 500- | 699 | 168,922 | 30,632 | 199,554 | 173,662 | 35,153 | 208,815 |
| 700- | 899 | 162,481 | 6.556 | 169,037 | 164,984 | 8,462 | 173,446 |
| 900- | 1,099 | 74,595 | 2,129 | 76,724 | 75,929 | 3,142 | 79,071 |
| 1,100- | 1,299 | 32,327 | 831 | 33,158 | 33,253 | 1,430 | 34,683 |
| 1,300- | 1,499 | 15,186 | 429 | 15,615 | 15,729 | 773 | 16,502 |
| 1,500 and over | 51,524 | 1,538 | 53,062 | 53,449 | 2,915 | 56,364 | |
| Not specified | 3,608 | 1,627 | 5,235 | 4,993 | 4,157 | 9,150 | |
| Totals | 622,758 | 194,094 | 816,852 | 1,093,211 | 1,080,851 | 2,174,062 | |
Included in the “nil” income group for actively engaged persons are those people who entered the labour force between 1 and 17 April 1956, and thus did not have income for the year ended 31 March 1956.
There would also be, in the smaller income group, considerable numbers of people who began work towards the end of the year 1955-56.
The largest income group for males actively engaged was the £500 to £699 group, with 168,922, or 27.1 per cent of those males actively engaged. This was followed closely by the £700 to £899 group with 162,481, or 26.1 per cent. The actively engaged males with incomes of £1,500 and over numbered 51,524, or 8.3 per cent.
The largest income group for actively engaged females was the £300 to £499 group with 78,717, representing 40.6 per cent of all actively engaged females. There were only 1,538, or 0.79 per cent, of actively engaged females with incomes of £1.500 and over.
GENERAL - Banking institutions operating in New Zealand may be enumerated as follows:
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand.
Five trading banks.
The Post Office Savings Bank.
Six trustee savings banks.
In addition, a number of trading companies, investment societies, etc., perform quasi-banking functions, accepting deposits and granting credits (short-term and long-term) to clients. In some instances deposits are repayable to the client's order at call - virtually a system of cheque issuing.
Until the establishment of the Reserve Bank, which commenced to function on 1 August 1934, each of the six trading banks then functioning held the right of note issue, but this right is now vested solely in the Reserve Bank.
A full description of banking practice in New Zealand is beyond the scope of a Yearbook section, but those desiring information on this subject may usefully refer to the report of the Parliamentary Monetary Committee, parliamentary paper B.3 (1934), and to its minutes of evidence, published as an appendix; also to the report of the Royal Commission on Monetary, Banking, and Credit Systems, published as parliamentary paper B.3 (1956). For details of legislation governing banking a publication entitled Banking Legislation in New Zealand, published in 1948, may be obtained from the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, Wellington. In the March and April 1960 issues of the Reserve Bank Bulletin there are articles on Central Banking Practice in New Zealand.
The Government in March 1955 announced the membership and order of reference of the Royal Commission on Monetary, Banking, and Credit Systems. The order of reference was as follows: “With a view to fostering a greater degree of stability in prices, maintaining full employment of labour, ensuring the healthy development of natural resources, and promoting generally the economic, financial, and social welfare of the people of New Zealand, the Commission shall receive, inquire into, and report upon representations regarding any monetary, banking, and credit proposals that may be suggested as suitable for application in New Zealand; the present monetary, banking, and credit system of New Zealand and the advisability or otherwise of any changes in the system; and any associated matters which should be deemed by the Commission to be relevant to the genera objects of the inquiry.”
The report of the Royal Commission was released in April 1956, and is available as parliamentary paper B.3 (1956) from the Government Printer. A summary of the report (reprinted from the April 1956 Reserve Bank of New Zealand Bulletin) was given as Appendix (d) of the 1956 Yearbook.
THE RESERVE BANK - The Reserve Bank was constituted by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933 (amended in minor respects by the Finance Act 1934) with the primary object of exercising control, within defined limits, over monetary circulation and credit in New Zealand. As originally constituted, the Bank had a share capital of £500,000, composed of 100,000 publicly subscribed shares of £5, bearing a cumulative dividend of 5 per cent. Very important changes in the constitution of the Bank were made by the Reserve Bank Amendment Act 1936, which, among other things, abolished the subscribed share capital of the Bank, with provision for the repayment to shareholders (either in cash or in Government stock, at the option of the shareholder) of the value of shares held and accrued dividends. The General Reserve Fund of the Bank is maintained at £1,500,000, made up of a contribution of £1,000,000 by the Government at the passing of the original Act, and £500,000 to replace share capital after the passing of the 1936 Amendment Act. It will be seen that the whole of the reserve fund is contributed by the State - the Bank thus being State-owned. Additional powers were conferred on the Reserve Bank by the Finance Act (No. 2) 1936, and further important changes were made by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Amendment Acts of 1939, 1950, and 1960.
Prior to the passing of the 1960 Amendment Act the general function of the Bank, as defined in section 10 (1) of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Amendment Act 1936 and as amended in 1950, read as follows: “It shall be the general function of the Reserve Bank, within the limits of its powers, to give effect as far as may be to the monetary policy of the Government as communicated to it from time to time by the Minister of Finance. For this purpose, and to the end that the economic and social welfare of New Zealand may be promoted and maintained, the Bank shall regulate and control credit and currency in New Zealand, the transfer of moneys to or from New Zealand, and the disposal of moneys that are derived from the sale of any New Zealand products and for the time being are held overseas, and shall do all such things within the limits of its powers as it deems necessary or desirable to promote and safeguard a stable internal price level and the highest degree of production, trade, and employment that can be achieved by monetary action.”
The provisions of section 10 (1) of the 1936 Amendment Act were amplified by section 2 of the amending Act of 1939, which read as follows: “In the exercise of their functions and powers under the principal Act, the Governor and Board of Directors shall have regard to any representations that may be made by the Minister of Finance in respect of any functions or business of the Reserve Bank, and shall give effect to any decision of the Government in relation thereto conveyed to the Governor in writing by the Minister of Finance.” Section 2 of the 1939 amending Act was, however, repealed by the 1950 amendment, and the following section substituted: “In the exercise of their functions and powers under the principal Act, the Governor and the Board of Directors shall give effect to any resolution of the House of Representatives in respect of any functions or business of the Reserve Bank.” This section was subordinate to section 10 (1) of the 1936 Amendment Act as further amended in 1950 and its practical effect was that, if the Reserve Bank was not in agreement with the policy as communicated by the Minister of Finance, the matter could be referred to Parliament, which, by resolution in the House of Representatives, could direct a certain course of action.
By the 1960 Amendment Act, the then existing general function and the 1950 section providing for resolutions of Parliament, set out earlier, were repealed. New sections were enacted declaring the right of the Crown to regulate currency and credit, recasting the general function, re-enacting the 1939 provisions (see earlier), broadening both the general and particular regulatory powers of the Bank and introducing a statutory right for the Minister of Finance (after consultation with the Governor of the Bank) to determine the relationship between New Zealand currency and sterling.
The criteria for monetary policy - the maintenance of economic and social welfare, the promotion of production, trade, and employment, and the maintenance of a stable internal price level - which the legislation previously laid down as objectives for the Reserve Bank are now expressed as standards for Government monetary policy, the general function of the Bank being to give effect to this policy, as communicated to it from time to time by the Minister of Finance.
The following extracts show the main provisions of the 1960 Amendment Act:
Section 2 inserted a new section 12 in the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933, as follows:
“Right of Crown to Control Currency and Credit
“12 (1) It is hereby declared that it is the sovereign right of the Crown to control currency and credit.
“(2) For the purpose of giving effect to the provisions of subsection (1) of this section, but without limiting the generality of that subsection, the Minister of Finance may from time to time communicate to the Reserve Bank the monetary policy of the Government, which shall be directed to the maintenance and promotion of economic and social welfare in New Zealand having regard to the desirability of promoting the highest degree of production, trade, and employment and of maintaining a stable internal price level.”
Section 3 restated the general functions of the Bank in a new section 12A inserted in the 1933 Act, as follows:
General Functions of Reserve Bank
“12A (1) It shall be the general function of the Reserve Bank, within the limits of its powers, to give effect to the monetary policy of the Government, as communicated to the Bank from time to time by the Minister of Finance.
“(2) The Bank may, on behalf of the Government, regulate and control -
”(a) Money, banking, credit, and currency:
“(b) Rates of interest in respect of such classes of transactions as may from time to time be prescribed:
“(c) The transfer of money to or from New Zealand, and the disposal of money that is derived from the sale of any New Zealand products and is for the time being held overseas. “(3) It shall be the duty of the Bank -
“(a) To advise the Government on matters relating to monetary policy, banking, and exchange:
“(b) To keep the Government informed with regard to the measures adopted or proposed to be adopted by the Bank to give effect to the monetary policy of the Government:
“(c) To have regard to any representations that may be made by the Minister of Finance in respect of any functions or business of the Bank, and to give effect to any decision of the Government in relation thereto conveyed to the Governor in writing by the Minister of Finance.
“(4) For the purpose of enabling the Reserve Bank to fulfil its functions the Governor-General may from time to time by Order in Council make all such regulations, not inconsistent with this Act, as he considers necessary, and may prescribe therein such penalties as he thinks fit for the breach of any such regulations, not exceeding in any case a fine of one thousand pounds for any offence, or in the case of a continuing offence, not exceeding a fine of five hundred pounds for every day on which the offence is committed or has continued.
“(5) All regulations made under the authority of this section shall be laid before Parliament.”
Section 4 amended subsection (3) of section 16 of the 1933 Act to read as follows:
“(3) When the Bank gives sterling in exchange for its notes, or gives notes in exchange for sterling or gold, the rate at which the exchange is affected shall be fixed by the Bank:
“Provided that the relationship between New Zealand currency and sterling for immediate delivery in London may from time to time be determined by the Minister of Finance after consultation with the Governor of the Bank.”
The section also makes consequential amendments to section 4 of the Finance Act 1934 (see page 884) to preserve existing provisions whereby any profits or losses made by the Reserve Bank as a result of a change in the relationship between New Zealand currency and sterling are paid to or met by the Consolidated Fund.
Section 5 inserted a new section 45A as follows:
“Control of Bank Credit and Interest Rates
“45A(1) Where the Bank is satisfied that it is necessary or expedient in the public interest to do so, it may from time to time give directions to other banks for the time being carrying on business in New Zealand as to the policy to be followed in relation to advances, discounts, and investments and in relation to rates of interest payable to or by such banks, and, without limiting the generality of the foregoing provisions of this subsection, as to -
“(a) The aggregate amounts of advances, discounts, and investments for the time being deemed appropriate:
“(b) The classes of advances and discounts that should be encouraged or restricted or rejected, and the classes of investments that should be made or held: “(c) The rates of discount chargeable by such banks:
“(d) The rates of interest to be paid to or by such banks - and it shall be the duty of every such bank to comply with every such direction.
“(2) Nothing in this section shall —
“(a) Authorise the Bank to require any other bank to disclose the identity of any particular customer:
“(b) Affect the validity or enforceability, as between any bank and any other person, of any transaction.”
In addition to the general powers and functions contained in section 12A, shown earlier, the legislation gives the Bank, or the Governor of the Bank, the following particular powers and functions:
Make and issue bank notes (see heading in “Coinage and Currency”, later).
Buy and sell gold and silver coin and bullion.
Accept money on deposit or on current account.
Discount, rediscount, buy, and sell: (a) bills, notes, etc., whether commercial or agricultural, maturing within 120 days from date of document or 90 days after sight; (b) agricultural bills, notes, etc., maturing within six months of acquisition; (c) Treasury bills of any Government, or bills of any local authority in any British Commonwealth country, all such bills to be maturing within three months of acquisition.
Grant advances, up to three months, against: (a) gold coin or bullion or relative shipping documents thereof; (b) Government, local authority, or other approved securities readily marketable in New Zealand; (c) bills, etc., as referred to above; (d) promissory notes of banks in New Zealand.
Grant accommodation by way of overdraft (a) to the Government of New Zealand; (b) to any Department of State or statutory authority having power to carry on any business or to borrow moneys on overdraft; (c) to any board or other authority having statutory powers in relation to the marketing of any New Zealand produce, for the purpose of financing and marketing of any such produce.
Advance moneys to the Government of any other country in respect of the purchase of any New Zealand produce for export to that country, or guarantee any such advance that may be made by another bank. The amount outstanding in respect of any advances or guarantees in this respect shall not at any time exceed in the aggregate the sum of £10,000,000, and any loss suffered in respect of any such transaction is to be borne by the Consolidated Fund.
Buy and sell securities of the New Zealand or United Kingdom Governments, or securities guaranteed by the Government of New Zealand or by the Government of the United Kingdom.
Buy and sell currencies of other countries.
By authority of the Governor-General in Council, underwrite any loan proposed to be raised by the New Zealand Government, or by the State Advances Corporation of New Zealand.
Issue and manage loans for the Government or any local authority or public body in New Zealand.
Borrow money, establish credits, and give guarantees, whether in New Zealand or elsewhere, in any currency, and on terms providing for repayment or payment in the same or any other currency.
Charge, pledge, or deposit by way of security, any part of its assets for any purpose mentioned in paragraph 12 or for any other purpose whatsoever which may be approved in writing by the Minister of Finance.
Organise a clearing system.
Act as a correspondent for overseas banks or as agent of other reserve banks.
Do any other banking business not prohibited by the Act.
Vary the required minimum balances other banks are required to hold with the Reserve Bank (see page 885).
Control bank credit and interest rates by giving directions, from time to time, to other banks (see section 45A on the previous page).
It is the duty of the Government to entrust to the Bank, and of the Bank to undertake, all the money, remittance, exchange, and banking transactions of the Government. The duty of the Bank in respect of reserves is set out later.
The Bank administers the Exchange Control Regulations on behalf of the Government.
The following gives a summary of restrictions upon the conduct of business by the Bank as stated in the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933 and in later amendments. Except with the authority of the Governor-General in Council, it may not issue bank notes of a denomination less than 10s.; engage in trade or otherwise have a direct interest in any commercial, industrial, or similar undertaking; purchase the shares of any other bank in New Zealand or elsewhere (except shares of the Bank of International Settlements) or grant loans on the security of any shares that the Bank is prohibited from purchasing; make unsecured loans or advances; purchase or make advances on the security of real property, except so far as may be required to enable the Bank to conduct its business; pay interest on any moneys deposited with the Reserve Bank by any other bank or pay interest on any other moneys placed on deposit or on current account with the Bank, except that it may pay interest to the New Zealand Government on Government funds held by the Bank outside New Zealand; allow the renewal of maturing bills of exchange, promissory notes, or other similar documents purchased or discounted by or pledged to the Bank; draw or accept bills payable otherwise than on demand; and it may not grant accommodation to any State Department, local authority, or public body in excess of certain limits.
On the commencement of business on 1 August 1934 the Public Account was transferred to the Reserve Bank, and the management of the public debt was taken over from the Treasury by the Reserve Bank as from 1 October 1936.
The, net profits of the Bank are paid to the Consolidated Fund, provided that the Bank's General Reserve Fund is not less than £1,000,000. If the Reserve Fund falls below that level, part of the profits must be credited to the Reserve Fund. The net profits for the year ended 31 March 1960, which were subsequently paid to the Consolidated Fund, amounted to £3,497,000, as compared with £2,196,000 for the previous year.
Under section 4 of the Finance Act 1934, any appreciation or depreciation of assets due to alteration in the exchange rate is to be credited to or borne by the Consolidated Fund. In accordance with this provision, the Reserve Bank was credited with the sum of £20,576,000 from the Consolidated Fund in early 1949 by the Government as a result of the alteration of the exchange rate to parity with sterling as from 20 August 1948.
Details of the liabilities and assets of the Bank at the end of June for the years 1956-60, and weekly averages for the calendar years 1950-60, are shown in the following tables.
LIABILITIES OF RESERVE BANK
| Year | Bank Notes | Demand Liabilities | Other Liabilities* | Total Liabilities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Marketing | Banks | Other | ||||
*Includes General Reserve Fund of £1,500,000 throughout the period. †Included in these figures are the weekly averages in Wool Retention Accounts: 1950, £117,000; 1951, £4,204,400; and 1952, £6,000. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| Weekly Average for Calendar Year | |||||||
| 1950 | 55,126 | 15.446 | 74,239 | 1,232† | 6,290 | 152,333 | |
| 1951 | 60,361 | 18,844 | 69,326 | 4,929† | 6,765 | 160,224 | |
| 1952 | 62,252 | 14,962 | 48,557 | 490† | 7,387 | 133,648 | |
| 1953 | 64,035 | 6,154 | 3,621 | 90,741 | 1,368 | 8,249 | 174,167 |
| 1954 | 69,233 | 9,294 | 1,769 | 78,328 | 1,915 | 8,917 | 169,456 |
| 1955 | 70,087 | 14,180 | 2,093 | 55,751 | 1,070 | 9,095 | 152,277 |
| 1956 | 70,904 | 12,557 | 1,963 | 60,032 | 1,646 | 9,886 | 156,989 |
| 1957 | 74,263 | 11,440 | 1,228 | 62,374 | 1,435 | 10,489 | 161,229 |
| 1958 | 76,230 | 12,077 | 675 | 57,508 | 1,080 | 11,533 | 159,104 |
| 1959 | 77,031 | 11,609 | 484 | 62,255 | 1,216 | 12,118 | 164,713 |
| 1960 | 81,500 | 11,090 | 778 | 87,951 | 1,320 | 10,676 | 193,315 |
| At End of June | |||||||
| 1956 | 69,431 | 10,115 | 2,081 | 72,326 | 4,120 | 8,585 | 166,657 |
| 1957 | 72,712 | 9,171 | 1,351 | 69,287 | 1,488 | 12,263 | 166,272 |
| 1958 | 73,882 | 9,908 | 424 | 62,555 | 764 | 8,168 | 155,703 |
| 1959 | 75,038 | 9,853 | 413 | 67,908 | 1,664 | 8,756 | 163,632 |
| 1960 | 78,614 | 12,174 | 647 | 94,848 | 528 | 9,080 | 195,891 |
ASSETS OF RESERVE BANK
| Year | Reserve | Subsidiary Coin | Advances | Investments | Other Assets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | Sterling Exchange | Other Exchange | State | Marketing Organisations | Other Advances and Discounts | Overseas | In New Zealand | |||
*An increase in investments in New Zealand and a matching decrease in advances to the State follow from a change in the Government's method of borrowing from the Reserve Bank; holdings of 1 per cent three-month Treasury bills have been exchanged for 1 per cent Government stock. †Major portion of gold now shown in “Other Assets” as it was pledged against overseas loans and is therefore no longer within the official definition of “Reserves”. | ||||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||||
| Weekly Average for Calendar Year | ||||||||||
| 1950 | 4,269 | 51,319 | 256 | 180 | 52,245 | 5,096 | 5,378 | 4,463 | 26,850 | 2,277 |
| 1951 | 5,139 | 62,557 | 383 | 473 | 51,134 | 3,379 | 6,829 | 9,988 | 17,119 | 3,224 |
| 1952 | 5,856 | 23,416 | 1,235 | 601 | 50,795 | 2,290 | 6,125 | 30,244 | 11,325 | 1,761 |
| 1953 | 6,023 | 58,487 | 588 | 626 | 53,225 | 4,761 | 6,020 | 22,975 | 20,511 | 952 |
| 1954 | 6,150 | 74,481 | 428 | 599 | 38,418 | 6,692 | 8,938 | 23,557 | 9,279 | 913 |
| 1955 | 6,163 | 46,710 | 424 | 571 | 35,581 | 17,388 | 10,939 | 22,954 | 10,666 | 882 |
| 1956 | 6,162 | 39,751 | 535 | 586 | 41,231 | 15,818 | 12,364 | 26,959 | 12,503 | 1,081 |
| 1957 | 6,162 | 38,982 | 496 | 585 | 39,922 | 27,768 | 3,752 | 28,292 | 14,95 | 1,075 |
| 1958 | 4,618 | 25,224 | 659 | 563 | 48,115 | 36,832 | 2,533 | 14,066 | 23,837 | 2,656 |
| 1959 | 315† | 59,962 | 495 | 647 | 31,448 | 25,485 | 872 | 13,630 | 24,923 | 6,937† |
| 1960 | 315 | 54,325 | 447 | 571 | 25,161 | 18,967 | 1,663 | 23,177 | 61,683 | 7,005 |
| At End of June | ||||||||||
| 1956 | 6,162 | 51,715 | 413 | 597 | 36,612 | 17,252 | 14,859 | 27,786 | 10,387 | 875 |
| 1957 | 6,162 | 54,989 | 318 | 608 | 30,108 | 31,226 | 3,764 | 27,736 | 10,388 | 973 |
| 1958 | 6,163 | 22,685 | 738 | 562 | 44,069 | 41,623 | 2,370 | 13,569 | 22,808 | 1,116 |
| 1959 | 315 | 62,842 | 267 | 632 | 25,133 | 30,530 | 540 | 13,569 | 22,808 | 6,995 |
| 1960 | 315 | 67,140 | 319 | 567 | 2,708* | 19,341 | 160 | 26,390 | 71,308* | 7,643 |
NOTE - Total assets are equal to total liabilities.
The fall in the Reserve Bank's holding of sterling exchange in 1952 was due partly to the abnormally large volume of imports and partly to the conversion of liquid funds into sterling investments. Normally the Reserve Bank's sterling exchange is held in the form of British Treasury bills (short-term rate of interest), but as a matter of policy it was decided to invest a part of these funds in short- and medium-term British Government securities, which arc included in the Reserve Bank's investments.
TRADING BANKS - The Banking Act 1908, which is the law of New Zealand relating to the general business of banking in this country, provides that the incorporation of banks by Royal Charter shall be as effectual within New Zealand as Acts of the General Assembly. The number of directors is prescribed by the Act, and authority is given to any bank to increase its capital on a resolution of the shareholders. Transfers of shares on which there is any liability must be approved by the directors or their duly appointed attorney or attorneys. A sworn copy of an entry in the books of a bank shall in all legal proceedings be evidence of such entry, and a bank is not required in any legal proceedings to which it is not a party to produce its books before a Court, unless ordered by a Judge for special cause. Provision is made for the destruction of cheques, drafts, bills of exchange, or promissory notes after the expiration of 10 years from the date thereof in the case of documents payable on demand, or from the due date in the case of other documents.
Part II of the Bills of Exchange Act 1908 and the Cheques Act 1960 arc the law relating to cheques on a bank.
The provisions of sections 127 and 128 of the Companies Act 1955 (relating to branch registers) apply to banks incorporated in New Zealand; and those of sections 407 to 412 (imposing restrictions on the sale of shares and debentures) apply to companies incorporated outside New Zealand for the purpose of carrying on banking in New Zealand or elsewhere; the provisions of Part XV of the Act (which relate to annual licences) shall as far as they are applicable apply to banks; and also the provisions of section 464 (2) (which relate to the production and inspection of books where an offence is suspected); otherwise the Companies Act does not apply to banks.
With the establishment of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, which commenced to function on 1 August 1934, there was inaugurated an entirely new era in banking practice in New Zealand. The function of note issue was transferred from the trading banks to the Reserve Bank, while all gold coin or bullion held by trading banks for their own account was required by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933 to be transferred to the Reserve Bank in exchange for equivalent notes of the Reserve Bank or for credit with that Bank. The basis of payment was £3 17s. 10 1/2d. per ounce of standard - i.e., eleven-twelfths fine - gold content, which was the price at which such gold (in actual fact, coin only) had originally been acquired by the trading banks. Any profit derived from the sale or revaluation of this gold by the Reserve Bank accrues to the State and not to the Reserve Bank.
While the regulation of currency exchange is now a function of the Reserve Bank, commercial exchange transactions arc still carried out through the medium of the trading banks.
Each trading bank is required to maintain with the Reserve Bank a balance comprising a proportion of its demand liabilities in New Zealand, and of its time liabilities in New Zealand. These requirements may be varied by the Governor of the Reserve Bank, acting with the authority of the Minister of Finance, but not so as to be less than 7 and 3 per cent respectively. For a summary of the changes in these proportions refer to page 893.
There are five banks trading in New Zealand, two of these institutions - the Bank of New Zealand and the National Bank of New Zealand - being incorporated by special Acts of the General Assembly of New Zealand. The other three banks - the Australia and New Zealand Bank, the Bank of New South Wales, and the Commercial Bank of Australia - which are predominantly Australian institutions, have in the aggregate much greater capital resources, etc., than the two New Zealand banks. The close Australian affiliations of the Australian banks operating in New Zealand resulted in the past in an interlocking between the Australian and New Zealand financial structures, the separation of New Zealand business being one of the major motives leading up to the founding of the Reserve Bank.
Bank of New Zealand - On the passing of the Bank of New Zealand Act 1945, which came into operation on 1 November 1945, the Bank of New Zealand became a State trading bank. Prior to the passing of the Act the bank was partly State-owned, the New Zealand Government holding preference and certain long-term mortgage shares to the aggregate value of £2,109,000 out of a total paid-up capital of £6,328,000. The Act provided for the acquisition by the Crown of the whole of the remaining shares registered in New Zealand, and also made provision for the purchase by the Crown of shares registered in the United Kingdom or Australia.
The gross profit of the bank for the year ended 31 March 1960 was £5,203,000, while expenses amounted to £4,698,000, leaving a net profit of £505,000. Comparable figures for the previous year were £5,168,000, £4,633,000, and £535,000 respectively. The total assets at 31 March 1960 amounted to £161,466,000, the principal items comprising this total being: coin, Reserve Bank notes, and deposits with bankers, £26,928,000; money at call and short notice, Government securities and other securities in London, £12,709,000; securities of, or guaranteed by, New Zealand Government, £11,428,000; and advances, etc., £75,329,000. The principal item of liabilities was deposits (£138,710,000), while bills payable, etc., amounted to £9,310,000. The reserve fund, which is invested in United Kingdom Government securities, amounted to £4,000,000, and provision for taxation to £957,000. The paid-up capital of the bank remained unaltered at £6,328,000.
Liabilities and Assets of Trading Banks - Statements of liabilities and assets of the trading banks were gazetted quarterly up to 1934. Since the Reserve Bank commenced operations the trading banks have been required to submit at monthly intervals a return of certain liabilities and assets in respect of New Zealand business. Monthly averages for calendar years 1950-60, and figures as at the last Wednesday in June for the years 1956-60, are given in the next table.
LIABILITIES OF TRADING BANKS
| Year | Demand Liabilities | Time Liabilities | Total Liabilities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In New Zealand | Outside New Zealand | In New Zealand | Outside New Zealand | ||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| Monthly Average for Calendar Year | |||||
| 1950 | 167,526 | 7,039 | 39,787 | 428 | 214,781 |
| 1951 | 196,663 | 7,676 | 59,405 | 2,378 | 266,122 |
| 1952 | 187,478 | 8,552 | 67,985 | 1,034 | 265,048 |
| 1953 | 210,236 | 4,523 | 58,147 | 816 | 273,722 |
| 1954 | 233,609 | 5,316 | 55,040 | 963 | 294,928 |
| 1955 | 236,876 | 5,911 | 52,116 | 1,041 | 295,943 |
| 1956 | 236,485 | 5,860 | 42,269 | 857 | 285,471 |
| 1957 | 246,670 | 5,707 | 36,613 | 1,001 | 289,992 |
| 1958 | 242,595 | 7,937 | 42,056 | 1,240 | 293,828 |
| 1959 | 244,863 | 6,498 | 43,611 | 665 | 295,637 |
| 1960 | 280,529 | 5,964 | 50,838 | 737 | 338,069 |
| At End of June | |||||
| 1956 | 240,759 | 5,100 | 43,937 | 815 | 290,611 |
| 1957 | 255,186 | 4,426 | 35,783 | 1,044 | 296,439 |
| 1958 | 250,618 | 8,226 | 39,807 | 1,099 | 299,749 |
| 1959 | 252,484 | 5,291 | 41,992 | 764 | 300,530 |
| 1960 | 282,825 | 5,245 | 49,078 | 722 | 337,870 |
ASSETS OF TRADING BANKS
| Year | Coin and Bullion | Reserve Bank Notes | Balances Held in Reserve Bank | Overseas Assets | Securities Held | Advances and Discounts | Land, Buildings, etc. | Total Assets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| Monthly Average for Calendar Year | ||||||||
| 1950 | 1,681 | 9,813 | 75,180 | 24,830 | 13,407 | 94,065 | 2,557 | 221,533 |
| 1951 | 1,528 | 11,476 | 70,274 | 37,330 | 13,243 | 133,079 | 3,085 | 270,016 |
| 1952 | 1,473 | 11,108 | 51,149 | 26,571 | 13,036 | 166,560 | 3,583 | 273,481 |
| 1953 | 1,533 | 10,625 | 93,093 | 25,584 | 14,037 | 134,455 | 4,059 | 283,385 |
| 1954 | 1,447 | J 1,089 | 79,361 | 25,991 | 25,153 | 154,787 | 4,510 | 302,338 |
| 1955 | 1,371 | 10,228 | 56,947 | 25,647 | 25,171 | 180,047 | 5,315 | 304,728 |
| 1956 | 1,326 | 10,765 | 60,266 | 25,837 | 23,783 | 167,385 | 6,157 | 295,517 |
| 1957 | 1,311 | 12,747 | 63,826 | 26,234 | 23,650 | 162,806 | 6,868 | 297,442 |
| 1958 | 1,399 | 14,018 | 60,569 | 22,383 | 23,531 | 171,890 | 7,273 | 301,062 |
| 1959 | 1,449 | 14,254 | 64,820 | 25,596 | 23,477 | 166,380 | 7,947 | 303,924 |
| 1960 | 1,431 | 15,822 | 89,018 | 26,959 | 23,405 | 175,983 | 8,633 | 341,252 |
| At End of June | ||||||||
| 1956 | 1,315 | 9,936 | 72,216 | 25,591 | 23,793 | 164,681 | 6,104 | 303,636 |
| 1957 | 1,298 | 12,050 | 69,196 | 35,358 | 23,656 | 156,805 | 6,761 | 305,124 |
| 1958 | 1,387 | 13,258 | 62,295 | 25,016 | 23,536 | 173,014 | 7,065 | 305,571 |
| 1959 | 1,490 | 13,121 | 67,865 | 29,913 | 23,436 | 164,699 | 7,843 | 308,366 |
| 1960 | 1,403 | 13,939 | 94,660 | 30,808 | 23,398 | 173,536 | 8,528 | 346,271 |
Deposits and Advances - The weekly averages of total deposits (together with the amount per head of mean population), and of total advances, and the ratio of advances to deposits for each of the last 11 calendar years, are given in the following table.
| Year | Deposits | Advances† | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Bearing Interest (Free) | Bearing Interest (Fixed) | Ratio of Free to Fixed | Total* | Per Head of Mean Population | Total Amount | Ratio Deposits | ||
*Including Government deposits. †Exclusive of transfers by the Bank of New Zealand to its Long-term Mortgage Department. ‡Includes certain current accounts, operated by non-profit organisations, for which interest is payable on monthly minimum balances; these accounts were previously included in “deposits not bearing interest” column. | ||||||||
| £(000) | per cent | £(000) | £ | s. | £(000) | per cent | ||
| 1950 | 157,571 | 42,201 | 373 | 202,200 | 105 | 18 | 94,715 | 46.8 |
| 1951 | 205,336 | 42,500 | 483 | 250,723 | 128 | 15 | 132,917 | 53.0 |
| 1952 | 207,044 | 42,436 | 488 | 252,968 | 126 | 15 | 169,841 | 67.1 |
| 1953 | 222,077 | 39,832 | 558 | 265,269 | 129 | 10 | 136,827 | 51.6 |
| 1954 | 236,546 | 40,721 | 581 | 281,750 | 134 | 10 | 156,973 | 55.7 |
| 1955 | 233,363 | 39,414 | 592 | 279,855 | 130 | 17 | 182,929 | 65.4 |
| 1956 | 229,365 | 35,245 | 651 | 268,734 | 123 | 2 | 170,648 | 63.5 |
| 1957 | 235,822 | 38,697 | 609 | 278,858 | 124 | 18 | 164,877 | 59.1 |
| 1958 | 232,409 | 42,163 | 551 | 279,030 | 122 | 2 | 175,417 | 62.9 |
| 1959 | 224,878 | 53,459‡ | 421 | 283,364 | 121 | 8 | 170,076 | 60.0 |
| 1960 | 252,938 | 64,877‡ | 390 | 323,921 | 136 | 5 | 177,745 | 54.9 |
It will be noticed that whereas free deposits rose markedly between 1950 and 1954, since then they have remained relatively stable, the fall in free deposits between 1958 and 1959 being caused by the transfer of non-profit making organisations' deposits mentioned in the footnote above. The marked increase during 1960 was mainly due to an increase in trading bank advances and the deficit in the public accounts. Fixed deposits have remained fairly stable over the 10 year period, except for a fall in 1956 and the transfer in 1959. Advances rose steadily until 1955 apart from the effect of the import boom in 1952. Since 1955 credit restraint policies have tended to reduce advances, although in 1958 lower export prices, an increased level of stocks (through higher imports), and an increased use of credit in New Zealand to finance meat exports combined to expand average advances by £10.5 million. In 1959 the demand for advances fell as a result of slack economic conditions and this, in conjunction with higher farm incomes and the reversal of the above-mentioned trend in meat export financing, caused the average of advances to fall by over £5 million. In 1960 advances rose again, the main factor being inflationary economic conditions with a general expansion of expenditures, coupled with a high rate of importing and some increase in meat export finance.
The following diagram illustrates the movements that have occurred in deposits and advances from 1930 onwards, the figures used, as in the foregoing table, being the weekly averages for calendar years.
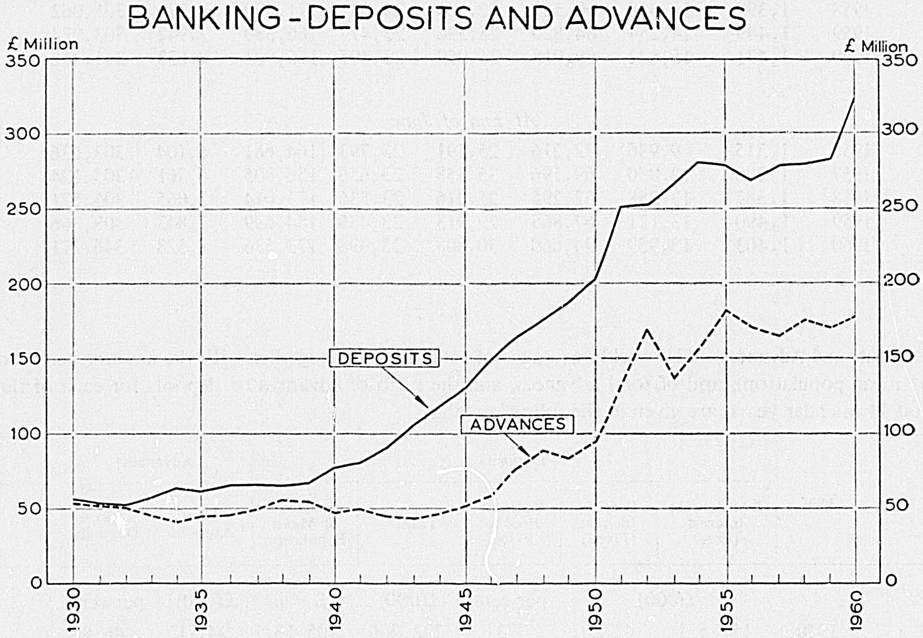
The average amount on deposit during each of the quarter months since March 1956 is shown in the next table.
| Month | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| March | 277,912 | 279,871 | 288,157 | 273,683 | 311,954 |
| June | 274,724 | 290,852 | 287,190 | 283,770 | 328,210 |
| September | 258,595 | 270,457 | 271,310 | 283,365 | 329,259 |
| December | 269,268 | 274,268 | 269,463 | 292,606 | 326,454 |
The average amount of advances outstanding (exclusive of transfers by the Bank of New Zealand to its Long-term Mortgage Department) during each of the quarter months since March 1956 is next shown.
| Month | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| March | 182,101 | 159,576 | 173,824 | 170,986 | 168,825 |
| June | 169,403 | 162,502 | 182,380 | 175,402 | 178,819 |
| September | 166,338 | 165,418 | 174,583 | 166,953 | 175,785 |
| December | 161,442 | 173,118 | 170,879 | 167,040 | 188,370 |
The following table shows the movement in advances, Government and other securities held, and deposits, the amounts being the averages of the figures for the last Wednesday of each month.
| Year | Advances (Including Discounts) | Securities Held | Total Advances and Securities | Total Deposits | Ratio of Advances (Plus Securities) to Total Deposits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Other | |||||
| £(thousand) | per cent | |||||
| 1950 | 94,065 | 11,730 | 1,677 | 107,472 | 205,295 | 52.4 |
| 1951 | 133,079 | 11,716 | 1,527 | 146,323 | 253,918 | 57.6 |
| 1952 | 166,560 | 11,701 | 1,335 | 179,596 | 253,528 | 70.8 |
| 1953 | 134,455 | 11,688 | 2,348 | 148,492 | 266,989 | 55.6 |
| 1954 | 154,787 | 12,002 | 13,151 | 179,940 | 283,907 | 63.4 |
| 1955 | 180,047 | 11,618 | 13,552 | 205,218 | 282,096 | 72.8 |
| 1956 | 167,385 | 11,376 | 12,406 | 191,167 | 269,847 | 70.8 |
| 1957 | 162,806 | 11,379 | 12,271 | 186,456 | 279,876 | 66.6 |
| 1958 | 171,890 | 11,374 | 12,157 | 195,421 | 279,230 | 70.0 |
| 1959 | 166,380 | 11,400 | 12,078 | 189,858 | 285,434 | 66.5 |
| 1960 | 175,983 | 11,469 | 11,936 | 199,390 | 327,071 | 61.0 |
The increase in other securities from 1954 reflects the sales of State Advances Corporation securities totalling £12 million to the trading banks in December 1953 and March 1954.
An analysis of advances of the New Zealand trading banks is published by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, and the classification is given in the following table.
| 13 March 1957 | 12 March 1958 | 11 March 1959 | 9 March 1960 | 8 March 1961 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| BUSINESS AND FARMING ADVANCES | |||||
| 1. Farming, forestry, hunting, and fishing - | |||||
| (a) Mainly dairy farming | 10,579 | 10,616 | 11,052 | 11,224 | 12,678 |
| (b) Mainly sheep farming | 9,066 | 10,769 | 13,652 | 12,288 | 13,877 |
| (c) Other farming | 3,955 | 4,045 | 4,237 | 4,249 | 4,635 |
| (d) Farm services | 532 | 866 | 957 | 829 | 928 |
| (e) Foresty, hunting, and fishing | 551 | 570 | 576 | 759 | 628 |
| Subtotals | 24,684 | 26,866 | 30,474 | 29,349 | 32,746 |
| 2. Mining and Quarrying | 401 | 699 | 634 | 568 | 433 |
| 3. Manufacturing - | |||||
| (a) Dairy companies, factories, etc. | 3,175 | 2,685 | 2,248 | 1,863 | 1,285 |
| (b) Freezing works, meat companies, etc. | 18,550 | 20,149 | 15,703 | 21,107 | 23,878 |
| (c) Other food, beverages, and tobacco | 4,682 | 4,677 | 6,097 | 5,033 | 5,320 |
| (d) Textiles, footwear, and clothing | 5,863 | 7,166 | 6,823 | 6,789 | 8,608 |
| (e) Pulp and paper and paper products | 2,596 | 2,215 | 1,279 | 1,008 | 1,887 |
| (f) Metal products, machinery and engineering | 6,736 | 6,028 | 7,036 | 6,109 | 8,013 |
| (g) Transport equipment | 2,801 | 4,077 | 3,519 | 3,327 | 3,521 |
| (h) Other manufacturing | 11,314 | 10,418 | 10,526 | 9,545 | 12,015 |
| Subtotals | 55,717 | 57,416 | 53,230 | 54,781 | 64,526 |
| 4. Construction | 7,399 | 7,758 | 8,531 | 8,421 | 10,156 |
| 5. Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 1,342 | 1,091 | 1,085 | 924 | 958 |
| 6. Transport, storage, and communication | 3,151 | 3,291 | 3,576 | 2,801 | 3,349 |
| 7. Commerce, trade, and finance - | |||||
| (a) Wholesalers, mainly importers | 13,236 | 14,793 | 11,567 | 11,539 | 14,576 |
| (b) Wholesalers, other | 4,601 | 4,832 | 4,341 | 3,551 | 5,400 |
| (c) Retailers | 13,793 | 15,643 | 15,019 | 13,723 | 18,468 |
| (d) Woolbuyers | 10,288 | 8,361 | 8,140 | 8,422 | 8,023 |
| (e) Stock and station agents | 3,383 | 6,435 | 9,814 | 3,210 | 6,614 |
| (f) Finance companies (mainly hire purchase) | 1,803 | 1,985 | 1,721 | 1,986 | 2,455 |
| (g) Other financial institutions | 1,758 | 2,139 | 2,492 | 2,451 | 4,300 |
| Subtotals | 48,862 | 54,188 | 53,094 | 44,882 | 59,836 |
| 8. Local authorities | 857 | 731 | 772 | 690 | 929 |
| 9. Services | 7,082 | 7,430 | 7,909 | 7,998 | 9,129 |
| PERSONAL ADVANCES | |||||
| 10. (a) For housing purposes | 7,552 | 8,068 | 7,864 | 8,549 | 9,596 |
| (b) Other personal advances | 9,433 | 10,382 | 11,276 | 11,894 | 13,993 |
| Subtotals | 16,985 | 18,450 | 19,140 | 20,443 | 23,589 |
| Total advances | 166,480 | 177,919 | 178,444 | 170,856 | 205,651 |
The following diagram illustrates the level of trading bank, advances in March of the last three years.
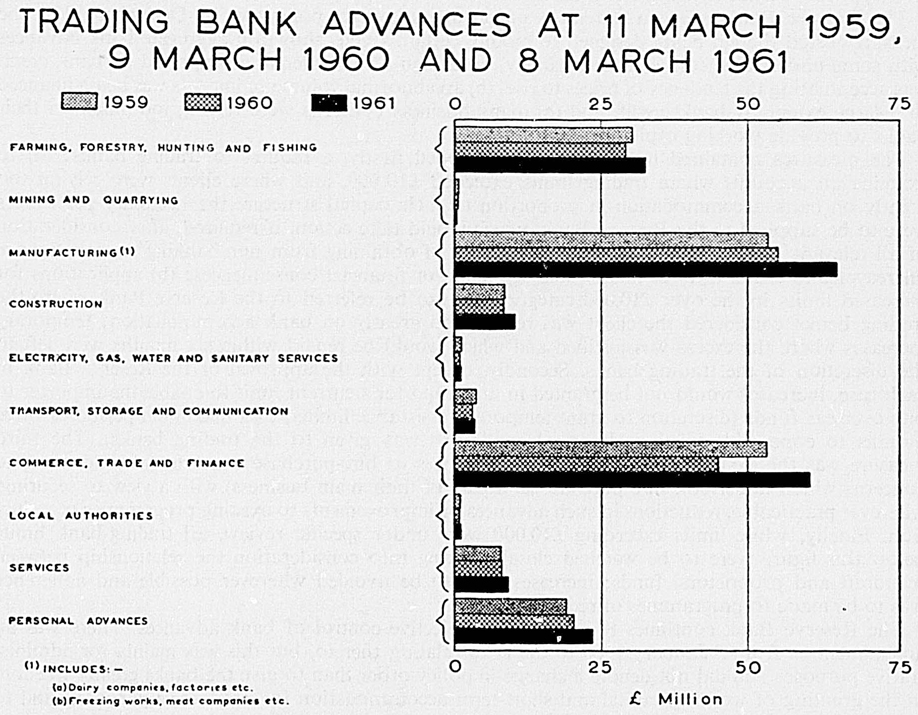
Advance Control Policy - Qualitative: As part of the Government policy designed to combat inflationary tendencies during wartime, from 1943 onwards the trading banks were precluded from increasing their holdings of securities, and existing holdings of Government stock were repaid as they matured. Reinvestment has, however, been permitted since 1949. An earlier measure, from January 1942, was the selective control of trading-bank advances by the Reserve Bank in cooperation with the trading banks. The general aim was to prevent the expansion of bank credit for speculative and other purposes considered inimical to the war effort. The necessity for such controls was also a feature of the immediate post-war years. The Reserve Bank issued statements in 1947 and 1948 outlining the existing policy in this respect, and indicating the inclusion in the restricted categories of advances for purely investment purposes, capital expenditure for business, industrial, and commercial purposes, building, purchasing or refinance of dwellings, in addition to those speculative and other classes previously covered.
Marginal cases and others involving special circumstances were referred to the Reserve Bank, the trading banks from time to time being given more discretion in dealing with such cases.
In March 1950 this discretion was extended so that marginal applications need only be referred to the Reserve Bank in cases where the term of the proposed advance exceeded two years and where the amount was also in excess of £2,000.
A major relaxation in the policy became effective from 24 May 1950. Advances for amounts up to £2,000 from each applicant were exempted from control, while the discretionary limit was raised to an amount not greater than £4,000, the latter being in order to allow for the new situation in which the first £2,000 was freed from control.
The number of restricted classes was reduced. In 1947 temporary finance for one year for the building of dwellings, and again in August 1949, advances to enable primary producers to purchase essential farm equipment and machinery up to the limit of £1,500, provided repayment was made within two years, were taken out of the restricted categories. As from 24 May 1950 advances for the following classes of purchase were excluded from control, irrespective of the amount concerned: (a) livestock needed for primary production; (b) farm machinery, farm vehicles, and farm implements; and (c) tools of trade (exclusive of industrial machinery).
The Reserve Bank issued a statement on advances control policy on 17 December 1951, the measures listed therein being designed to modify certain trends shown in aggregate bank advances with some undesirable consequences, namely, (a) a high level of demand supported by bank credit was accentuating the tendency of prices to rise, (b) an abnormal volume of imports was being financed to a large extent by bank credit, and (c) many business concerns were relying too much on their banks to provide working capital.
The measures contained in the statement included firstly, a request to trading banks: (a) to examine all accounts where trading limits exceeded £10,000, and where clients were relying too greatly on bank accommodation in proportion to their capital structure the necessary particulars were to be supplied to the Reserve Bank, which would take action, if required, after consideration of all relevant factors, including the practicability of obtaining from non-banking sources finance on reasonable terms without undesirable economic or financial consequences; (b) applications for increased limits in the, over £10,000 category were to be referred to the Reserve Bank where the trading banks considered the client was relying too greatly on bank accommodation; temporary increases where the excess was justified and which would be repaid within six months were left to the discretion of the trading banks. Secondly, except with the approval of the Reserve Bank in each case, increases would not be granted in any importer's current limit to enable the importer to buy overseas funds; (discretion to grant temporary assistance limited to a maximum period of three months to cope with existing abnormal conditions was given to the trading banks). The third measure was the examination of all existing advances to hire-purchase concerns (also advances to concerns which undertook hire purchase as a part of their main business) with a view to securing, wherever practicable, reductions in such advances or improvements to existing programmes of reduction. Finally, while limits exceeding £10,000 were under specific review, all trading-bank limits below this figure were to be watched closely, taking into consideration the relationship between overdraft and proprietors' funds; increases were to be avoided wherever possible and adherence was to be made to programmes of reduction.
The Reserve Bank continues to maintain the selective control of bank advances. There was an amendment as from 5 January 1960 to the rules relating thereto, but this was mainly for administrative purposes and did not denote a change in policy other than to give the banks greater freedom in the granting of working capital and short-term accommodation for productive purposes, and to provide for the needs of small businesses.
The qualitative controls over bank investments and advances have been and still are operated by arrangement. The new section 45A added to the Reserve Bank legislation in 1960 gave a statutory authority for such controls. This statutory power has not yet been invoked.
Quantitative - The advance control policy outlined above was supplemented in 1952 by the quantitative control of advances provided for in section 45 of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act and reliance is now placed mainly on the quantitative method of control through the reserve ratio procedure and discount rate policy. Section 45 authorises the Governor of the Bank, with the consent of the Minister of Finance, to vary the statutory reserve ratios of the trading banks, but not so as to be less than 7 per cent of their demand liabilities and 3 per cent of their time liabilities.
Commencing in 1952, by progressive increases in these ratios, the minimum balances the trading banks are required to maintain at the Reserve Bank were adjusted so as to reduce the margin of free cash (balances in excess of the minimum required) held by the trading banks. The Reserve Bank stated, in announcing the May 1953 increase, that the actual balances held by the trading banks at the Reserve Bank had been considerably in excess of the statutory minimum, and that this excess was a potential basis for an expansion of bank credit which would be inflationary in its effect and add to the difficulty of maintaining the external balance of payments. By the second half of 1954 this margin had been substantially reduced and some banks had to borrow from the Reserve Bank to comply with the ratio requirements. During 1954 the Reserve Bank's discount rate (the rate charged on advances to the trading banks) was raised in two steps from 1 1/2 per cent (effective since 1941) to 4 per cent. During 1955-56 and 1956-57 the ratios were kept at high levels and the discount rate was raised during 1955 in three further steps to 7 per cent, at which rate the banks were required at times to borrow substantially from the Reserve Bank. The changes made in the discount rate are listed on page 914, where discount rate policy is fully covered. Since 1957 a flexible policy of control has been followed. Following firm pressure on the trading banks in the 1958-59 financial year, from May 1959 the aim was to achieve stability in the volume of bank advances and not to induce a further contraction in bank lending. In recognition of the more favourable situation which developed towards the end of 1959, the Reserve Bank's discount rate was reduced to 6 per cent in October 1959. Since November 1960 the policy of restraint has been resumed, and the discount rate was raised to 7 per cent in March 1961.
The following table shows the changes that have taken place in the reserve ratios since 1 June 1956. On 31 May 1956 the Reserve Bank announced changes in the method of calculating the minimum balances which the trading banks must hold at the Reserve Bank. The main change made was that banks' holdings of Reserve Bank notes would for the purposes of reserve ratio requirements count as though they were deposits at the Reserve Bank standing to the credit of the trading banks, provided that the minimum balance maintained at the Reserve Bank, way still 7 per cent of demand liabilities and 3 per cent of time liabilities as laid down in the Reserve Bank Act. Alterations in the ratios from 1934 to 31 May 1956 are shown on page 855 of the 1958 Yearbook. These will not be comparable with figures after 1 June 1956 because of the inclusion in the minimum cash requirements since this date of Reserve Bank notes held.
| Date of Change | Percentage of New Zealand Liabilities Required to be Maintained by Trading Banks as Minimum Deposits with Reserve Bank or in the Form of Reserve Bank Notes Held by the Trading Banks | |
|---|---|---|
| Demand | Time | |
| 1 June 1956 | 32 | 10 |
| 13 July 1956 | 30 | 10 |
| 27 July 1956 | 27 | 10 |
| 14 September 1956 | 30 | 10 |
| 1 October 1956 | 34 | 12 1/2 |
| 9 November 1956 | 29 | 10 |
| 21 December 1956 | 31 | 10 |
| 1 March 1957 | 15 | 10 |
| 12 April 1957 | 22 1/2 | 10 |
| 3 May 1957 | 26 1/2 | 10 |
| 25 October 1957 | 28 | 15 |
| 28 February 1958 | 10 | 5 |
| 28 April 1958 | 26 | 10 |
| 30 July 1958 | 28 1/2 | 10 |
| 9 March 1959 | 20 | 10 |
| 10 April 1959 | 25 | 10 |
| 23 April 1959 | 28 1/2 | 10 |
| 21 September 1959 | 30 | 10 |
| 22 December 1959 | 34 | 10 |
| 15 March 1960 | 22 | 10 |
| 29 April 1960 | 29 | 10 |
| 23 May 1960 | 32 | 10 |
| 8 July 1960 | 35 | 10 |
| 15 August 1960 | 38 | 10 |
| 9 September 1960 | 34 | 10 |
| 7 November 1960 | 36 | 10 |
| 6 March 1961 | 20 | 10 |
| 30 March 1961 | 15 | 10 |
| 14 April 1961 | 21 | 10 |
| 21 April 1961 | 23 | 10 |
| 28 April 1961 | 25 | 10 |
In 1956, as shown in the paragraphs on overdraft and discount rates on page 914, the trading banks were permitted to increase the interest rate on overdrafts as part of the policy of credit restraint with flexibility.
Debits - The following table shows weekly averages of bank debits.
| Year | Debits Other Than Government | Government Debits |
|---|---|---|
| £(000) | ||
| 1950 | 56,242 | 7,120 |
| 1956 | 91,976 | 11,172 |
| 1951 | 70,234 | 8,496 |
| 1957 | 100,922 | 11,868 |
| 1952 | 70,554 | 9,951 |
| 1958 | 103,837 | 13,331 |
| 1953 | 73,996 | 10,063 |
| 1959 | 105,078 | 14,518 |
| 1954 | 84,625 | 10,792 |
| 1960 | 120,818 | 15,998 |
| 1955 | 90,317 | 10,809 |
Debits represent the total amount debited to customers' accounts at all branches. These figures, which have been compiled from the weekly returns furnished by the trading banks to the Government Statistician, give a reasonable indication of changes in the volume of business. Government debits with trading banks fell to comparatively small proportions as a consequence of the opening of the Reserve Bank, but the upward movement in evidence since 1936 has been more marked over recent years
Averages of debits (other than Government) for the four or five weeks ending on the last Wednesday of each of the quarter months from March 1956 onwards are now given.
| Month | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| March | 119,408 | 120,273 | 130,150 | 124,654 | 140,154 |
| June | 86,510 | 99,834 | 101,554 | 103,843 | 123,951 |
| September | 82,134 | 90,326 | 89,740 | 100,998 | 118,516 |
| December | 101,500 | 113,291 | 120,175 | 126,131 | 142,535 |
Unexercised Overdraft Authorities - Particulars of aggregate unexercised overdraft authorities of trading banks are available from April 1936. Following are the averages for calendar years and the amount at the end of June.
| Year | Average for Calendar Year | At End of June | Year | Average for Calendar Year | At End of June |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1950 | 64,178 | 63,116 | 1956 | 94,567 | 95,035 |
| 1951 | 72,230 | 76,425 | 1957 | 103,743 | 106,228 |
| 1952 | 69,888 | 68,825 | 1958 | 105,714 | 102,759 |
| 1953 | 93,464 | 93,095 | 1959 | 117,278 | 116,692 |
| 1954 | 110,298 | 111,653 | 1960 | 131,298 | 130,987 |
| 1955 | 100,819 | 100,087 | |||
NOTES IN CIRCULATION - As indicated elsewhere, the Reserve Bank assumed the note-issuing function on 1 August 1934. As from 10 January 1935 the notes of the trading banks ceased to be legal tender, while on 1 August 1936 the liability for the remaining outstanding trading-bank notes was taken over by the Reserve Bank, thus completing the process of the transfer of the note issue to the Reserve Bank. The following table shows the weekly average note circulation for the calendar years 1950-60, and the position as at the last Wednesday in June for the years 1956-60.
| Year | Total Note Issue | Notes Held by Trading Banks | Net Note Circulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||
| Weekly Average for Calendar Year | |||
| 1950 | 55,126 | 9,898 | 45,228 |
| 1951 | 60,361 | 11,391 | 48,970 |
| 1952 | 62,252 | 11,273 | 50,978 |
| 1953 | 64,035 | 10,648 | 53,387 |
| 1954 | 69,233 | 11,541 | 57,692 |
| 1955 | 70,087 | 10,631 | 59,456 |
| 1956 | 70,904 | 10,917 | 59,987 |
| 1957 | 74,263 | 13,047 | 61,216 |
| 1958 | 76,230 | 14,135 | 62,095 |
| 1959 | 77,031 | 14,339 | 62,692 |
| 1960 | 81,500 | 15,870 | 65,630 |
| At End of June | |||
| 1556 | 69,431 | 9,936 | 59,495 |
| 1957 | 72,712 | 12,050 | 60,662 |
| 1958 | 73,882 | 13,258 | 60,624 |
| 1959 | 75,038 | 13,121 | 61,917 |
| 1960 | 78,614 | 13,939 | 64,675 |
The following diagram of notes in circulation based on weekly averages illustrates the expansion in the note issue since the year 1910.
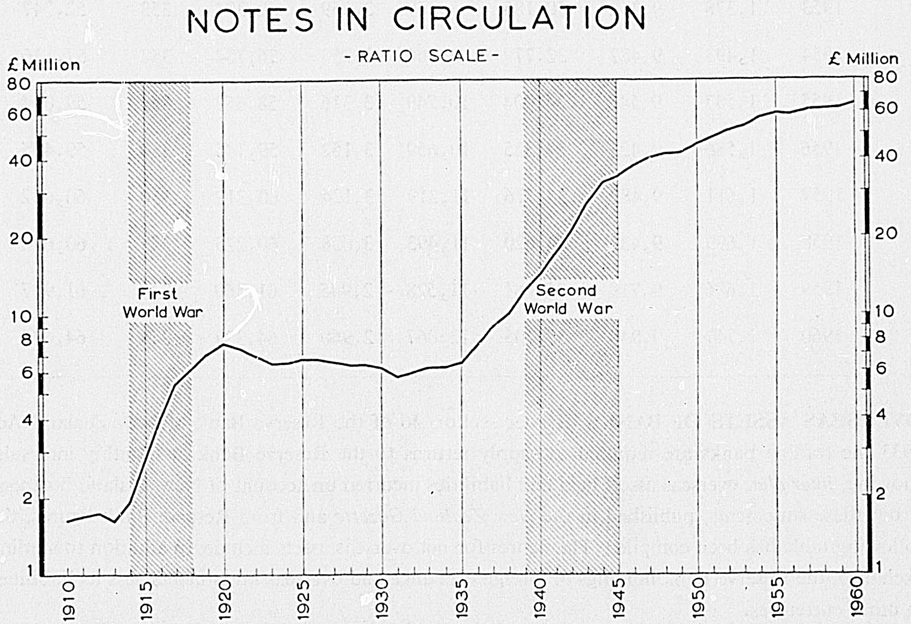
The year 1935 witnessed the commencement of an almost continuous upward movement in the note circulation, owing to more favourable economic conditions in association with such factors as the restoration of wage and salary cuts, higher wage rates, greater activity on public works and housing, increased pensions, etc. Following the outbreak of war, the increase in the note circulation quickened, expansion in 1942 and 1943 being particularly marked. The upward movement has since continued, but at a considerably lesser rate.
The following reasons have been given by the Reserve Bank for the increase in the net note circulation noted over recent years. The basic fact is the increase in incomes and in the total volume of money (coin, notes, bank demand deposits), the proportion of notes to the total volume of money remaining at a level of approximately 20 per cent. Other reasons include a rise in the number of cash transactions and in price levels.
An analysis of the net bank-note circulation, as at the last balance day in June, is compiled by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, and the figures are contained in the following table.
| Last Balance Day in June | Reserve Bank Note Issue (Excluding Trading Bank Holdings) | Total Reserve Bank Issue in Circulation | Trading Banks' Notes Outstanding | Total Net Note Circulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10s. | £1 | £5 | £10 | £50 | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1950 | 1,285 | 9,328 | 25,868 | 5,773 | 2,406 | 44,660 | 357 | 45,017 |
| 1951 | 1,281 | 9,412 | 27,833 | 6,865 | 2,697 | 48,088 | 356 | 48,443 |
| 1952 | 1,334 | 9,284 | 28,787 | 7,571 | 2,810 | 49,787 | 355 | 50,142 |
| 1953 | 1,378 | 9,312 | 30,185 | 8,459 | 3,059 | 52,394 | 353 | 52,747 |
| 1954 | 1,493 | 9,487 | 32,779 | 9,766 | 3,259 | 56,784 | 352 | 57,136 |
| 1955 | 1,537 | 9,546 | 34,004 | 10,249 | 3,316 | 58,653 | 351 | 59,004 |
| 1956 | 1,586 | 9,423 | 34,325 | 10,659 | 3,152 | 59,145 | 350 | 59,495 |
| 1957 | 1,611 | 9,482 | 34,776 | 11,319 | 3,124 | 60,312 | 350 | 60,662 |
| 1958 | 1,699 | 9,436 | 34,620 | 11,493 | 3,028 | 60,275 | 349 | 60,624 |
| 1959 | 1,696 | 9,719 | 35,681 | 11,528 | 2,945 | 61,569 | 348 | 61,917 |
| 1960 | 1,747 | 9,848 | 37,705 | 12,067 | 2,960 | 64,327 | 348 | 64,675 |
OVERSEAS ASSETS OF BANKS - Under section 46 of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933 the trading banks are required to supply returns to the Reserve Bank at monthly intervals, showing, inter alia, overseas assets held and liabilities incurred on account of New Zealand business. From these statements, published in the New Zealand Gazette and from Reserve Bank figures, the following table has been compiled The figures for net overseas assets include, in addition to sterling exchange, the Reserve Bank holdings of foreign exchange and overseas investments, less its liabilities in other currencies.
| Year | Trading Banks' Overseas Assets | Reserve Bank's Overseas Assets | Gross Overseas Assets | Overseas Liabilities of | Net Overseas Assets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In London | Elsewhere | Sterling Exchange | Other Overseas Assets | Trading Banks | Reserve Bank | |||
| *Included in the item “Other Overseas Assets” after 1951 are sterling investments. These amounted to £26,390,000 at the end of June 1960, and the weekly average for the calendar year 1960 was £23,176,000. Prior to 15 August 1951 the corresponding amounts were shown under the “Sterling Exchange” heading. | ||||||||
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||||
| Monthly Average for Calendar Year | ||||||||
| 1950 | 20,525 | 4,304 | 51,206 | 6,613 | 82,648 | 7,468 | 41 | 75,139 |
| 1951 | 32,064 | 5,266 | 61,537 | 15,259 | 114,126 | 10,054 | 50 | 104,022 |
| 1952 | 19,904 | 6,667 | 23,744* | 31,954* | 82,268 | 9,586 | 50 | 72,633 |
| 1953 | 21,711 | 3,872 | 59,414 | 23,948 | 108,946 | 5,339 | 43 | 103,564 |
| 1954 | 21,338 | 4,646 | 74,113 | 24,236 | 124,332 | 6,241 | 86 | 118,005 |
| 1955 | 20,210 | 5,437 | 46,036 | 23,613 | 95,296 | 6,952 | 42 | 88,302 |
| 1956 | 20,143 | 5,870 | 39,043 | 27,602 | 92,657 | 6,702 | 70 | 85,886 |
| 1957 | 19,909 | 6,474 | 38,229 | 28,660 | 93,271 | 6,718 | 63 | 86,490 |
| 1958 | 15,043 | 7,340 | 26,429 | 14,387 | 63,199 | 9,177 | 1,943 | 52,079 |
| 1959 | 19,180 | 6,416 | 59,103 | 14,306 | 99,004 | 7,163 | 1,902 | 89,940 |
| 1960 | 21,017 | 6,152 | 52,437 | 24,548 | 104,155 | 6,565 | 52 | 97,538 |
| At End of June | ||||||||
| 1950 | 23,014 | 4,426 | 58,652 | 9,793 | 95,885 | 8,835 | 33 | 87,016 |
| 1951 | 41,774 | 5,192 | 78,120 | 5,820 | 130,905 | 7,473 | 116 | 123,316 |
| 1952 | 23,977 | 6,762 | 20,741* | 34,411* | 85,892 | 11,213 | 90 | 74,588 |
| 1953 | 28,110 | 3,580 | 65,898 | 24,856 | 122,444 | 4,789 | 100 | 117,555 |
| 1954 | 23,688 | 4,478 | 93,519 | 24,363 | 146,043 | 6,831 | 39 | 139,173 |
| 1955 | 25,471 | 5,775 | 54,340 | 23,594 | 109,179 | 5,418 | 120 | 103,642 |
| 1956 | 19,557 | 6,034 | 51,715 | 28,318 | 105,624 | 5,915 | 42 | 99,667 |
| 1957 | 29,119 | 6,239 | 54,989 | 28,229 | 118,576 | 5,470 | 34 | 113,071 |
| 1958 | 15,929 | 9,088 | 22,685 | 14,533 | 62,235 | 9,324 | 25 | 52,885 |
| 1959 | 23,066 | 6,847 | 62,842 | 14,143 | 106,898 | 6,055 | 134 | 100,709 |
| 1960 | 25,500 | 5,308 | 67,140 | 26,910 | 124,858 | 5,967 | 159 | 118,732 |
The overseas assets of the banking system rose during the war years and reached a peak of £102.6 million in 1947. Figures from 1948 to 1950 showed successive declines to an average of £76.6 million. The fall in these years was principally due to the financing of a greater volume of imports at higher prices, the repayment of debt domiciled overseas, and to the alteration in the exchange rate in 194S mentioned elsewhere in this section. The 1951 totals showed a marked improvement and reflex the high prices ruling for primary produce, notably wool, during the earlier part of the year, while 1952 figures reflect the heavy payments made to finance the excess of import payments over export receipts during that year. The effects of the exchange allocation scheme resulting in smaller payments on account of imports, together with the higher export receipts, were largely instrumental in increasing net overseas assets in 1953 and 1954. Largely on account of the greater volume of imports there was a marked fall in overseas assets in 1955, and the same factor, associated with reduced export prices for dairy produce, caused a further fall in the latter part of 1957, the December 1957 figure being the lowest December figure since 1942.
The overseas assets were supplemented in 1958 by Government borrowing overseas totalling £45 million. The volume of imports was reduced by over 3 per cent at prices comparable with 1957, whilst the volume of exports increased by 6 per cent but at prices 15 per cent lower than in 1957. There was thus a fall of 15 per cent in New Zealand's terms of trade. A substantial improvement in the terms of trade occurred in 1959, as well as another significant increase in the volume of exports. There was also a marked fall in the volume of imports as a result of import control and reduced domestic demand. These factors were the main causes of a 73 per cent rise in the overseas assets of the banking system. The rise would have been greater had not the Government repaid £3.6 million in respect of one of the short-term loans raised in 1958, and invested £11.9 million (net) overseas. In 1960 higher payments for private imports and a slight decrease in export receipts resulted in overseas assets dropping from £88 million at the end of 1959 to £66 million at the end of 1960.
The following diagram shows the movement in the net amount of overseas assets from 1938 onwards, the first portion showing the figures as at the end of December and the second portion as at the end of June in each year quoted.
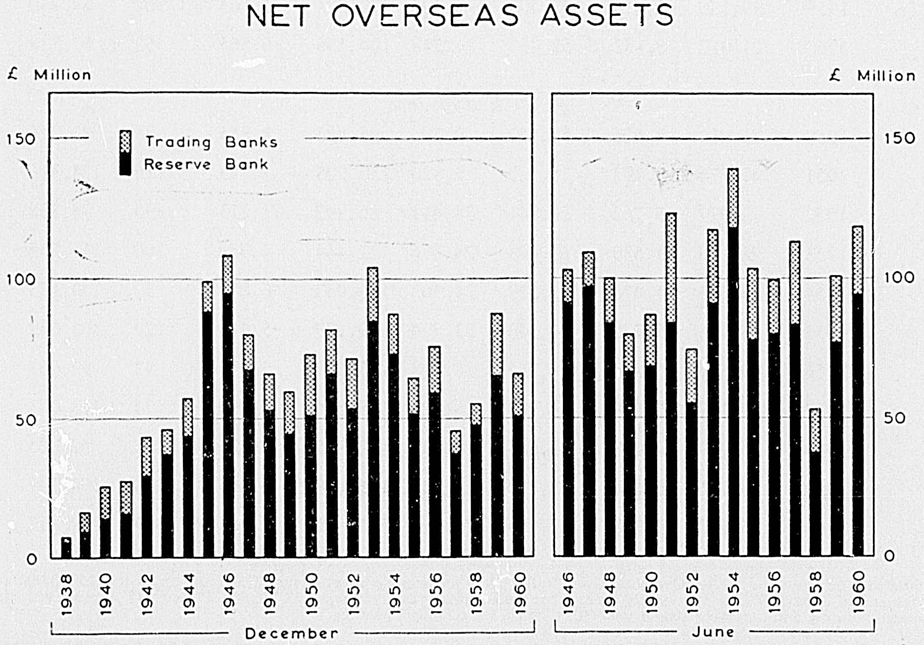
OVERSEAS EXCHANGE TRANSACTIONS - Since 1938 the Reserve Bank has been able to compile statements of New Zealand's overseas exchange transactions. In 1949 the method of compilation and the classification schedules were revised, and the statistics now include both transactions through the banking system and through the Government's overseas accounts. A full classification of overseas exchange transactions for the calendar years 1959 and 1960, showing details for the sterling area, dollar area, and other countries separately, in addition to the overall figures, is given below; figures for 1950 to 1958 are given in preceding issues of the Yearbook.
| Item | 1959 | 1960 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterling Area | Dollar Area | Other Countries | Total | Sterling Area | Dollar Area | Other Countries | Total | |
| £N.Z.(thousand) | ||||||||
| Receipts | ||||||||
| Current items - | ||||||||
| Exports - | ||||||||
| Butter | 56,980 | 443 | 2,951 | 60,373 | 41,792 | 510 | 2,403 | 44,705 |
| Cheese | 21,391 | 308 | 215 | 21,913 | 17,954 | 652 | 86 | 18,693 |
| Meat | 48,205 | 23,568 | 1,883 | 73,655 | 51,625 | 22,160 | 3,764 | 77,549 |
| Wool | 36,125 | 17,346 | 45,014 | 98,486 | 34,590 | 16,263 | 53,680 | 104,534 |
| Other | 29,488 | 10,343 | 11,690 | 51,521 | 32,369 | 10,359 | 11,803 | 54,531 |
| Totals, export receipts | 192,188 | 52,008 | 61,752 | 305,948 | 178,331 | 49,945 | 71,735 | 300,011 |
| Transport | 4,103 | 266 | 44 | 4,412 | 5,731 | 116 | 65 | 5,911 |
| Insurance | 819 | 58 | 944 | 1,585 | 14 | 50 | 1,550 | |
| Travel (excluding fares) | 2,497 | 544 | 42 | 3,083 | 2,813 | 746 | 30 | 3,589 |
| International investment income - | ||||||||
| Interest and dividends | 4,337 | 47 | 4 | 4,388 | 5,657 | 307 | 7 | 5,972 |
| Other investment income | 478 | 17 | 3 | 499 | 459 | 198 | 11 | 668 |
| New Zealand Government receipts, and expenditure by other Governments in New Zealand | 1,512 | 523 | 160 | 2,194 | 1,687 | 724 | 252 | 2,663 |
| Miscellaneous - | ||||||||
| Commissions, royalties | 787 | 196 | 46 | 1,029 | 933 | 320 | 74 | 1,327 |
| Expenses of business firms | 679 | 61 | 54 | 794 | 764 | 252 | 40 | 1,056 |
| Personal receipts, legacies, and immigrants' transfers | 6,492 | 707 | 222 | 7,420 | 6,750 | 767 | 221 | 7,738 |
| Other current transactions | 473 | 136 | 72 | 681 | 579 | 220 | 43 | 841 |
| Totals, current | 214,363 | 54,563 | 62,466 | 331,393 | 205,290 | 53,608 | 72,527 | 331,425 |
| Capital transfers - | ||||||||
| Private | 10,593 | 1,415 | 159 | 12,166 | 7,229 | 1,034 | 183 | 8,445 |
| Government | 101 | - | - | 101 | 5,664 | - | - | 5,664 |
| Drawings, Australian bank credit | 51 | - | - | 51 | - | - | - | - |
| Totals, capital | 10,744 | 1,415 | 159 | 12,318 | 12,892 | 1,034 | 183 | 14,109 |
| Cook Islands exports | 5 | 15 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 5 | 11 | 26 |
| Unidentified | 77 | 5 | - | 82 | 60 | 27 | 8 | 96 |
| Grand totals, receipts | 225,189 | 55,997 | 62,637 | 343,825 | 218,252 | 54,674 | 72,729 | 345,656 |
| Payments | ||||||||
| Current items - | ||||||||
| Imports - | ||||||||
| Private | 165,842 | 24,171 | 16,222 | 206,236 | 191,220 | 40,734 | 23,892 | 255,846 |
| Government | 21,513 | 1,096 | 127 | 22,736 | 19,700 | 3,023 | 235 | 22,958 |
| Totals, import payments | 187,355 | 25,267 | 16,349 | 228,972 | 210,920 | 43,757 | 24,126 | 278,804 |
| Transport | 10,802 | 1,037 | 297 | 12,137 | 11,791 | 994 | 626 | 13,411 |
| Insurance - | ||||||||
| Premiums | 351 | 10 | 5 | 367 | 441 | 7 | 6 | 455 |
| Claims | 192 | 11 | 2 | 205 | 148 | 9 | - | 158 |
| Other transfers | 1,794 | 53 | 5 | 1,852 | 2,219 | 44 | 4 | 2,267 |
| Travel (excluding fares) | 7,406 | 645 | 313 | 8,364 | 11,276 | 1,098 | 526 | 12,900 |
| International investment income - | ||||||||
| Interest and dividends | 4,009 | 2,017 | 102 | 6,128 | 4,682 | 2,053 | 90 | 6,824 |
| Other investment income | 2,797 | 336 | 30 | 3,163 | 2,994 | 729 | 144 | 3,868 |
| Government interest | 4,652 | 957 | - | 5,609 | 4,560 | 771 | - | 5,331 |
| Local authority interest | 135 | - | - | 135 | 83 | - | - | 83 |
| Government expenditure overseas | 6,930 | 569 | 504 | 8,003 | 8,620 | 512 | 527 | 9,659 |
| Miscellaneous - | ||||||||
| Commissions, royalties, and rebates | 1,594 | 907 | 512 | 3,014 | 1,401 | 857 | 836 | 3,092 |
| Expenses of business firms | 3,256 | 621 | 112 | 3,989 | 3,771 | 964 | 74 | 4,808 |
| Film hire and entertainment | 339 | 776 | 21 | 1,136 | 342 | 862 | 16 | 1,220 |
| Religious and charitable | 1,681 | 17 | 94 | 1,793 | 1,306 | 25 | 312 | 1,643 |
| Personal remittances, legacies, and emigrants' transfers | 4,748 | 453 | 228 | 5,429 | 6,052 | 449 | 247 | 6,747 |
| Transfers by temporary residents | 2,069 | 259 | 103 | 2,431 | 2,235 | 197 | 99 | 2,531 |
| Other current transactions | 1,320 | 239 | 80 | 1,639 | 1,033 | 238 | 96 | 1,368 |
| Totals, current | 241,430 | 34,176 | 18,758 | 294,365 | 273,875 | 53,565 | 27,728 | 355,169 |
| Capital transfers - | ||||||||
| Private | 2,620 | 189 | 53 | 2,862 | 3,987 | 546 | 178 | 4,711 |
| Government | 5,904 | 10,249 | - | 16,153 | 7,570 | 4,850 | - | 12,421 |
| Local authority | 910 | - | - | 910 | 639 | - | - | 639 |
| Repayment Australian Bank Advance | 7,455 | - | - | 7,455 | - | - | - | - |
| Totals, capital | 16,890 | 10,438 | 53 | 27,380 | 12,195 | 5,397 | 178 | 17,770 |
| Cook Islands imports | 148 | 30 | 21 | 199 | 127 | 26 | 12 | 165 |
| Grand totals, payments | 258,468 | 44,643 | 18,832 | 321,943 | 286,197 | 58,988 | 27,919 | 373,104 |
| Surplus of receipts over payments | -33,279 | + 11,354 | +43,805 | + 21,881 | -67,945 | -4,314 | +44,811 | -27,448 |
NOTE - Minus sign (-) denotes a deficit.
The next table gives overseas exchange transactions in summary form for a number of June years, which fit more closely to the farm-production export season than do calendar years. Information for calendar years over a similar period is in the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
| Year Ended 30 June | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £N.Z.(million) | |||||||||
| Receipts | |||||||||
| Exports - | |||||||||
| Butter | 50.1 | 49.6 | 46.2 | 36.4 | 52.3 | 39.6 | 37.5 | 51.9 | 59.9 |
| Cheese | 16.1 | 17.4 | 20.6 | 9.7 | 22.8 | 17.1 | 13.9 | 22.7 | 19.2 |
| Meat | 35.3 | 48.3 | 54.6 | 46.6 | 71.6 | 74.4 | 71.9 | 79.6 | 74.7 |
| Wool | 96.2 | 80.5 | 90.2 | 93.1 | 94.1 | 106.6 | 87-3 | 86.9 | 111.5 |
| Other | 390 | 38.7 | 33.3 | 34.2 | 40.4 | 48.5 | 46.0 | 48.7 | 55.9 |
| Other than exports | 28.7 | 23.5 | 36.5 | 53.8 | 38.3 | 44.6 | 55.3 | 69.4 | 38.4 |
| Totals | 265.4 | 258.1 | 281.3 | 273.7 | 319.6 | 330.9 | 311.9 | 359.3 | 359.5 |
| Payments | |||||||||
| Government imports | 25.0 | 28.1 | 24.2 | 19.8 | 24.5 | 28.7 | 32.6 | 27.3 | 22.4 |
| Government other payments | 11.6 | 12.0 | 14.6 | 18.9 | 13.0 | 15.2 | 19.3 | 20.9 | 36.3 |
| Private imports | 249.4 | 154.9 | 187.3 | 242.4 | 238.6 | 238.3 | 270.5 | 211.5 | 227.2 |
| Private other payments | 30.7 | 28.5 | 300 | 35.1 | 48.8 | 41.9 | 49.2 | 58.6 | 58.6 |
| Totals | 316.6 | 223.4 | 256.1 | 316.1 | 324.8 | 324.0 | 371.6 | 318.3 | 344.5 |
| Surplus (+) or deficit (—) | -51.3 | +34.7 | +25.2 | -42.3 | -5.2 | +6.9 | -59.7 | +41.0 | +15.0 |
Overseas Travel Allowances - On 4 December 1959 the Reserve Bank announced that funds allocated to New Zealand residents for overseas travel, whether for business or non-business purposes, would be available for use in any country of the world.
Prior to this, limits had been placed on the amounts which could be spent in the dollar countries, in Scandinavia, and on the Continent of Europe.
During the severe exchange crisis of 1958 the amount of travel funds made available for non-business purposes was limited to a maximum of £750 per person a year. In July 1960 the limit was raised by £500 for travellers who had not received an allocation for pleasure travel during the previous three years, but in April 1961 the figure of £1,250 was reduced to £1,000 and the qualifying term extended from three to five years.
Exchange Allocation Scheme - In order to assist in measures for strengthening the sterling area reserves and the balance of payments generally, the Government of New Zealand in March 1952 made certain decisions designed to ensure an increased surplus in New Zealand's overall balance of payments with non-sterling countries from an estimated £5 million for 1952 to £25 million on an annual basis (June year 1952-53). Measures listed covered the cancellation of licences issued for imports from all “scheduled” countries (the United States of America, Canada, and Japan were the countries with which New Zealand was principally concerned); new licences were required for all subsequent imports from these countries; the importation of motor vehicles from all countries was brought under import licensing control; there was no general imposition of import licensing in respect of sterling area countries; endeavours were made to expand primary production for export by providing alternative sources of supplies of agricultural fertiliser on a larger scale; and the Murupara pulp and paper project for the production of newsprint and pulp for export was pressed forward.
Except with the approval of the Reserve Bank, trading banks were advised not to sell to any importer during 1952 more than 80 per cent of the 1950 amount of exchange sold to him. This amount was the importer's basic allocation, and where foreign exchange in excess of this basic allocation was required application was to be made to the Reserve Bank.
This was followed in August 1952 by a decision to retain the existing exchange allocation scheme, with modifications, in 1953. With the high level of demand for exchange still continuing and the need to maintain reserves to provide a reasonable margin for contingencies in view of the 1952 deficit in overseas receipts over payments, the Reserve Bank was not prepared to draw further on reserves. Accordingly, except with the approval of the Reserve Bank, trading banks were advised not to sell to any importer during the whole of 1953 more than 40 per cent of the amount of exchange sold in 1950 to that importer for non-Government imports other than motor vehicles, and goods paid for under third-party certificates received from other licensed imports. This procedure provided, as formerly, for the basic allocations of exchange, and where importers required more than this quota they could make application to the Reserve Bank.
In July 1953 the Reserve Bank announced that, because of the high level of demand for overseas exchange to pay for imports, the exchange allocation scheme inaugurated in April 1952 would be continued in 1954. An important modification of the scheme was the announcement of a list of goods, payment for which would not require the authority of an exchange allocation. The trading banks were advised that, without the approval of the Reserve Bank and excepting payment for goods classed as “released items”, they were not to sell to any importer in 1954 more than 50 per cent (increased in November 1953 to 75 per cent) of the exchange sold in 1950 to that importer for non-Government imports other than motor vehicles, goods paid for under third-party certificates received, and goods which in 1954 would be classed as “released items”. This procedure provided, as formerly, for basic allocations of exchange, and where importers required more than this quota they could make application to the Reserve Bank.
The Prime Minister announced on 22 July 1954 that the exchange allocation system introduced in August 1952 was to be terminated as from 1 January 1955. Following this statement, the Reserve Bank made certain relaxations for the remainder of the 1954 year (e.g., additional allocations already granted could be used to pay for any items mentioned in the application instead of only those items specifically detailed in the approval, and could be used at any time during the rest of 1954), while allocations made up to termination date would not be linked to tariff items.
The Prime Minister announced on 1 January 1958 that a policy of overall import licensing would be instituted immediately. The new measures were designed to meet the deterioration in overseas reserves, which fell to £45.5 million on 25 December 1957. Under the new policy overseas funds would be allocated to meet all basic needs for imported foodstuffs and as far as possible factories would get raw materials to the full amount required.
On 2 January 1958 the Minister of Customs gave details of the new policy and stated that, as from 1 January 1958, all imports, apart from a few necessary exceptions, would require licences. The former Import Licensing Schedule for 1958, released in August 1957, was withdrawn and a new schedule made available in its place. Goods which were previously exempt from licensing and which were shipped by a vessel leaving a final port of departure by 31 December 1957 were to be admitted without a licence. Licences issued under normal allocations in the new 1958 Licensing Schedule would be automatically eligible for overseas funds, whilst an importer who had already placed orders in excess of the amount of such allocations could apply for “excess” licences. Such excess licences would not be eligible for overseas funds without the prior consent of the Reserve Bank obtained by application through the importer's own bank. Goods shipped before 1 January 1958 on a 1958 import licence issued under the old schedule were to be admitted, but their value was to be deducted from any new 1958 entitlement. Goods ordered as at 1 January 1958, but not shipped by that date, would be charged against 1958 licences. Where the amount exceeded the ordinary entitlement, excess licences had to be applied for.
The Prime Minister stated on 2 January that bona fide importing contracts already entered into would be honoured but that, where licences for 1958 were exceeded, the balance would be charged against 1959 licences.
On 10 February 1958 the Prime Minister stated that the Government was to review all applications for excess import licences because the Government was disturbed by the accumulated evidence of excessive ordering by importers toward the end of 1957. The normal pattern of importing was not to be interfered with.
The position regarding excess licences was clarified when the Reserve Bank of New Zealand stated on 20 February that where excess licences had been granted by the Customs Department, and there was no evidence of overordering, remittances would be approved for goods already imported into New Zealand, or for goods which were covered by an “on board” bill of lading dated prior to 20 February 1958. Excess licences in respect of goods covered by an “on board” bill of lading dated on or after 20 February 1958 were to be dealt with by the Reserve Bank in the light of the exchange position, but to the extent that the excess licences were supported by a certificate from the Customs Department that the importer was entitled to a normal allocation (in lieu of the excess licence) for the goods for the time being covered by the excess licence, the Reserve Bank would authorise remittances in the normal course. On 29 December 1958 the Minister of Finance announced that the Reserve Bank was in a position to allocate exchange in payment for goods landed in New Zealand during 1958 under excess licences. Exchange was made available from 1 January 1959 to the extent that payment had not been made overseas from any source whatever.
Administrative details on import and export control and exchange allocation are set out in Section 22A.
POST OFFICE SAVINGS BANK: Establishment – The establishment of the Post Office Savings Bank was authorised by the Post Office Savings Bank Act 1865, but actual business did not commence until 1 February 1867, when branches were established at Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Hokitika. The present authority is contained in the Post Office Act 1959.
Branches – There are now 1,038 branches of the bank throughout New Zealand. Deposits may be made at any of these branches. A full demand withdrawal service is provided at 179 branches which have ledgers, and a limited demand service is provided at the remaining non-ledger offices (see page 904 – withdrawal services).
Accounts Available – To meet the savings requirements of all sections of the community, the bank offers the following types of accounts: Ordinary Post Office Savings Bank; Thrift Club; Home Lay-by; Investment; National Savings; School Savings Bank. Descriptions of the several types of accounts are given later under appropriate headings.
Deposits, etc. – Any sum of 1s. or more, may be deposited to ordinary, Thrift Club, Home Lay-by, and School Savings Bank accounts.
The conditions concerning deposits to Investment accounts and National Savings accounts are mentioned later.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, deposits to ordinary Savings Bank accounts, Thrift Club accounts, Home Lay-by accounts, and Investment accounts totalled £158,152,504 and withdrawals £146,657,828, which represented an increase in the value of deposits of £16,315,573 and an increase in the value of withdrawals of £2,954,577 over the previous year.
The number of deposits made was 6,676,778 and the number of withdrawals 3,872,730. The figures for the previous year were 6,389,445 and 3,668,380 respectively. The total number of accounts open increased by 47,611 to reach 1,826,037 and the total amount at credit of depositors' accounts at £282,933,764 was £19,020,659 greater than the previous year. Interest (including Investment account interest) credited to depositors for the year amounted to £7,525,983. The average amount at credit of each account was £155.
The following table covering the activities of the Post Office Savings Bank since 1950 includes Savings Bank, Thrift Club, Home Lay-by, and Investment accounts, but does not include either School Savings Bank accounts, or National Savings Investment accounts, which are referred to later.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Depositors at End of March | Total Amount of Deposits | Interest | Total Amount of Withdrawals* | Excess of Deposits, Plus Interest, Over Withdrawals | Total Amount to Credit of Depositors at End of March |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*From January 1958 includes interest paid out on investment accounts. †Refer to note below. | ||||||
| (000) | £(thousand) | |||||
| 1950† | 1,373 | 11,448 | 3,821 | 3,793 | 7,655 | 170,982 |
| 77,963 | 73,306 | 8,478 | ||||
| 1951 | 1,407 | 86,395 | 3,915 | 85,190 | 5,120 | 176,103 |
| 1952 | 1,450 | 98,206 | 4,080 | 93,749 | 8,537 | 184,639 |
| 1953 | 1,486 | 99,126 | 4,208 | 96,700 | 6,634 | 191,274 |
| 1954 | 1,521 | 109,340 | 4,443 | 99,135 | 14,648 | 205,922 |
| 1955 | 1,555 | 117,881 | 4,711 | 112,842 | 9,749 | 215,671 |
| 1956 | 1,585 | 118,312 | 4,854 | 118,657 | 4,509 | 220,180 |
| 1957 | 1,650 | 131,444 | 6,301 | 121,319 | 16,425 | 236,606 |
| 1958 | 1,720 | 149,024 | 6,869 | 133,994 | 21,900 | 258,505 |
| 1959 | 1,778 | 141,837 | 7,274 | 143,703 | 5,408 | 263,913 |
| 1960 | 1,826 | 158,153 | 7,526 | 146,658 | 19,021 | 282,934 |
| 1961 | 1,884 | 182,130 | 7,988 | 166,785 | 23,332 | 306,266 |
NOTE – Under the War Service Gratuity Regulations 1945, war gratuity savings bank accounts, which matured on 31 March 1949, were deemed to be Post Office Savings Bank accounts on that date, and the total balance of the war gratuity accounts was amalgamated with the ordinary savings bank figures as at 31 March 1949. The amount so transferred was £11,447,754, of which £7,654,908, at the option of the holders, was left in the Savings Bank and £3,792,846 withdrawn. A total of £1,843,071 of the amount withdrawn was deposited in National Savings Investment accounts. These transactions are shown separately in the above table in italicised form.
The securities standing in the name of the Postmaster-General on account of the Post Office Savings Bank Fund on 31 March 1960 represented a nominal value of £284,392,746. A summary of the investments is as follows.
| £ | |
|---|---|
| New Zealand Government securities | 282,132,250 |
| Securities held in London | 2,260,496 |
| Total | £284,392,746 |
Post Office Savings Bank Accounts Classified by Amount Groups – The following is a classification of the balances in Post Office Savings Bank accounts, Thrift Club accounts, Home Lay-by accounts, and Investment accounts, shown by amount groups and percentage of accounts within each group.
| Amount Group | At 31 March 1958* | At 31 March 1959 | At 31 March 1960 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | |
| *Does not include Investment accounts or Home Lay-by accounts. | ||||||
| £ | ||||||
| Under 1 | 341,147 | 19.89 | 359,093 | 20.19 | 359,551 | 19.69 |
| 1 and under 10 | 438,681 | 25.58 | 455,409 | 25.67 | 457,129 | 25.03 |
| 10 “ 50 | 341,154 | 19.89 | 359,532 | 20.22 | 376,050 | 20.59 |
| 50 “ 100 | 141,538 | 8.25 | 147,746 | 8.30 | 153,506 | 8.41 |
| 100 “ 200 | 138,064 | 8.05 | 139,620 | 7.85 | 145,630 | 7.97 |
| 200 “ 300 | 75,230 | 4.39 | 78,484 | 4.41 | 82,007 | 4.49 |
| 300 “ 400 | 51,556 | 3.0 | 51,180 | 2.89 | 52,984 | 2.90 |
| 400 “ 500 | 39,141 | 2.28 | 38,833 | 2.18 | 40,506 | 2.22 |
| 500 “ 600 | 30,031 | 1.75 | 29,617 | 1.66 | 30,771 | 1.68 |
| 600 “ 700 | 19,340 | 1.13 | 18,939 | 1.06 | 20,635 | 1.13 |
| 700 “ 800 | 14,663 | 0.85 | 14,802 | 0.83 | 16,510 | 0.99 |
| 800 “ 900 | 12,150 | 0.71 | 12,070 | 0.67 | 12,702 | 0.66 |
| 900 “ 1,000 | 10,280 | 0.60 | 10,470 | 0.58 | 11,030 | 0.57 |
| 1,000 “ 1,500 | 30,336 | 1.77 | 31,444 | 1.76 | 33,617 | 1.84 |
| 1,500 “ 2,000 | 13,574 | 0.79 | 12,873 | 0.72 | 13,385 | 0.73 |
| 2,000 “ 3,000 | 11,932 | 0.70 | 11,641 | 0.65 | 12,125 | 0.64 |
| 3,000 “ 4,000 | 3,549 | 0.21 | 3,782 | 0.21 | 4,353 | 0.24 |
| 4,000 “ 5,000 | 1,640 | 0.09 | 1,710 | 0.09 | 1,862 | 0.10 |
| 5,000 and Over | 1,009 | 0.06 | 1,181 | 0.06 | 1,684 | 0.10 |
| Total number of accounts | 1,715,015 | 100.00 | 1,778,426 | 100.00 | 1,826,037 | 100.00 |
Withdrawal Services:Demand Withdrawals – When application is made at the ledger office where the account is held, a depositor may make a withdrawal on demand to the full extent of his account balance. Demand withdrawals may also be made at any other of the 1,038 Savings Bank offices, but the amount which may be obtained is limited. If the depositor's specimen signature is on file at the office of application he may withdraw on demand up to £100 in any week. Alternatively, if a specimen signature is not on file he may withdraw on demand up to £20 in any week, provided he can establish his identity. A depositor may have his specimen signature placed on file at any number of offices and because of this provision he may obtain funds without notice while travelling any where in New Zealand.
Other Means of Making Withdrawals – Either the postal or telegraph service may be used where the amount required is more than the limit authorised by the demand withdrawal system. Postal applications are forwarded to the office where the account is held and payment is made later at the accepting office. If desired the depositor can request that the amount be telegraphed to the accepting office. Alternatively, the application may be telegraphed both ways. No charge is made for telegraph withdrawals payable at Savings Bank offices within the same postal district as the ledger office. For withdrawals outside the postal district a charge of 1s. is made if the application is forwarded by post and the reply telegraphed. For telegraph service both ways a charge of 2s. is made.
Ordinary Savings Bank Accounts – These form the bulk of Post Office Savings Bank accounts. An account may be opened individually, jointly with another person, or as a trustee or beneficiary in a trust account. Club, societies, sports bodies, and any other non-mercantile body may also have these accounts, and organisations of this type have been able to operate under a cheque system since 1 March 1959.
Thrift Club Accounts – These accounts are designed to meet the needs of salary and wage earners who wish to save something each pay day to provide for annual recurring charges. Thrift Club accounts may be opened by any group of persons. In most cases, employees have a nominated amount deducted from their salary or wages each pay day for crediting to a Thrift Club account in their own name. Where this system does not operate the persons may themselves appoint an agent to collect from members and make the deposits. A passbook is issued to each depositor who may operate on the account in the same way as an ordinary account.
At 31 March 1960 there were 108,642 accounts open, the amount at credit being £5,057,581.
Home Lay-by Accounts – These accounts were introduced on 1 July 1957. Their main feature is a suspensory free deposit of £5 for every £100 saved with a maximum of £50. These accounts may be operated on in the same way as ordinary accounts and they earn the same rates of interest, in addition to the suspensory free deposit. The free deposit does not become payable until evidence is furnished that the funds are being used for the purchase or building of a home for the depositor's own occupancy. The first free deposits under this system became payable on 1 July 1959.
At 31 March 1960 there were 2,736 accounts open, the amount at credit being £767,385.
Investment Accounts – These accounts were introduced on 1 October 1957. They are a type of fixed deposit and accounts may be opened by any person or any organisation, including business concerns. The minimum deposit is £100 and deposits above £100 must be in multiples of £10. Any number of deposits may be made, but they must not exceed £10,000 in the aggregate in any year commencing on 1 October. The minimum term of investment is one year and deposits not withdrawn are automatically reinvested. Withdrawals are permitted at any time, but if any are required in the first year one week's notice in writing is required except in the case of business concerns. The interest rates are:
For every complete year and any part of a year after the first two – 31/2 per cent per year.
On amounts withdrawn in the first three months of the first year – 1 per cent per year.
On amounts withdrawn after three months in the first year – 2 per cent per year.
On amounts withdrawn during the second year (the full rate being received for the completed year) – 21/2 per cent per year.
On 31 March 1960, 6,218 Investment accounts were open with a total credit balance of £7,847,558.
Letters of Credit – This system has been superseded to a large extent by the demand-withdrawal system introduced in December 1956 and the demand is declining each year. The letter of credit (like the demand withdrawal) avoids the necessity of carrying large amounts in cash, and is there-fore, popular with people travelling, particularly at holiday times. The depositor completes an application for a withdrawal from his account and instead of cash receives a letter of credit, the maximum amount for each being £50, but more than one letter of credit may be obtained if desired. The fee payable is 7d. for the first £10 and 3d. for each additional £5 or part thereof.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, 480 letters of credit were issued, the value of these being £18,034. These figures represent a decrease of 351 in number and £11,575 in value on the 1959 issues.
Estates – The Postmaster-General may pay deposits to a maximum of £200 from any type of account to the legal representative of a deceased depositor without requiring him to take out letters of administration or to prove the will. Where there is more than one type of account the aggregate balances must not exceed £200, except in the case of a National Savings account, for which a separate maximum of £200 is permitted. This provision, together with another whereby a depositor may nominate one or more persons to receive part or all of the amount at credit of a Post Office Savings Bank, Thrift Club, or a Home Lay-by account after the depositor's death, enables the next-of-kin to obtain possession of perhaps much-needed funds without delay or cost.
School Savings Bank – The School Savings Bank scheme was introduced in 1934 with the object of encouraging thrift amongst young people. The aim of the scheme is to promote the habit of regular banking every week, so that upon commencing work the depositor will transfer his account to the Post Office Savings Bank and continue his weekly bankings out of his wages or salary.
Each depositor has a passbook, and the lodgement of deposits is made to teachers at the school, the cash and deposits slips being handed in later at the Post Office. Separate accounts for each depositor are held at the savings bank ledger office nearest to the school, and depositors may make withdrawals at their ledger office or by savings bank money order. Interest is payable at ordinary Post Office Savings Bank rates.
During the calendar year 1960 there were 2,627,329 deposits totalling £478,985. Since the inception of the scheme more than 140,000 children have transferred their School Savings Bank Accounts to the Post Office Savings Bank to form the nucleus of adult savings accounts.
A table showing the transactions in School Savings Bank accounts during the last 11 years is appended.
| Year Ended 31 December | Number of Schools Operating at End of Year | Total Number of Deposit Transactions During Year | Total Amount of Deposits During Year | Total Number of Withdrawal Transactions During Year | Total Amount of Withdrawals During Year* | Excess of Deposits Over Withdrawals | Interest Credited | Total Amount to Credit of Depositors at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes amounts transferred to Post Office Savings Bank. | ||||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||
| 1950 | 1,300 | 793,494 | 142,314 | 20,765 | 100,125 | 42,189 | 7,594 | 351,745 |
| 1951 | 1,395 | 881,768 | 168,247 | 18,341 | 107,996 | 60,251 | 8,862 | 420,858 |
| 1952 | 1,510 | 1,026,433 | 187,224 | 18,850 | 123,671 | 63,553 | 10,529 | 494,940 |
| 1953 | 1,625 | 1,210,671 | 218,551 | 21,906 | 135,375 | 83,176 | 12,593 | 590,709 |
| 1954 | 1,690 | 1,356,836 | 254,840 | 26,220 | 180,546 | 74,294 | 14,749 | 679,752 |
| 1955 | 1,749 | 1,423,153 | 264,874 | 27,448 | 201,890 | 62,984 | 16,490 | 759,226 |
| 1956 | 1,832 | 1,482,049 | 284,555 | 30,265 | 212,945 | 71,610 | 20,763 | 851,600 |
| 1957 | 1,983 | 1,966,880 | 366,068 | 32,282 | 231,671 | 134,397 | 25,501 | 1,011,499 |
| 1958 | 2,102 | 2,258,474 | 409,042 | 38,625 | 289,842 | 119,200 | 29,877 | 1,160,575 |
| 1959 | 2,136 | 2,407,448 | 431,560 | 49,814 | 422,339 | 9,221 | 33,479 | 1,203,276 |
| 1960 | 2,202 | 2,627,329 | 478,985 | 49,106 | 396,706 | 82,279 | 35,831 | 1,321,385 |
On 31 December 1960 there were 205,367 School Savings Bank accounts open.
TRUSTEE SAVINGS BANKS – The trustee savings bank movement is generally regarded as having originated in Scotland in 1810. The movement spread quickly, and the first such New Zealand Bank was established in Wellington in 1846, 20 years before the New Zealand Post Office Savings Bank commenced business. By 1870 nine trustee banks were in existence, but four, namely Lyttelton, Wellington, Napier, and Nelson did not survive the turn of the century. The five remaining banks – Auckland (1847), New Plymouth (1850), Dunedin (1864), Invercargill (1864), and Hokitika (1866) – have grown in strength and their activities have become an important factor in New Zealand's economic structure. An Order in Council of 22 January 1959 authorised the establishment of a further trustee savings bank, to be known as the Waikato Savings Bank, with a head office at Hamilton. The bank opened for business on 29 June 1959, and by the end of the first year of operations the amount to the credit of depositors had reached £1 million, a target which it had been anticipated would take three years to reach.
The legislation dealing with trustee savings banks is contained chiefly in the Trustee Savings Banks Act 1948, a consolidation of previous enactments. The Act prohibited the formation of new trustee banks and also laid down that no branch office or agency was to be established more than 25 miles from the head office. This prohibition was modified by an amending Act of 1957, by which provision was made for the establishment of new trustee savings banks by Order in Council, subject to such terms and conditions as may be specified, and it was under such an Order in Council that the new savings bank was established at Hamilton. Not less than 50 per cent of investments must be held in the form of Government stock, and at least 5 per cent of depositors' balances are to be kept as cash in hand or on current account. Repayment of deposits is guaranteed by the State.
In addition to ordinary deposits, recent legislation empowers trustee savings banks to accept investments similarly to the Post Office Savings Bank, by way of deposits in Home Lay-by or Investment accounts. The maximum rates of interest payable on deposits are fixed by Order in Council. Maximum rates payable on these and other deposits are given on page 916.
The total amount to credit of depositors at 31 March 1960 was £65,045,000.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number of Depositors at End of Year | Total Amount of Deposits During Year | Total Amount of Withdrawals During Year | Excess of Deposits Over Withdrawals | Interest Credited | Total Amount to Credit of Depositors at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excess of withdrawals over deposits. | ||||||
| No. | £(thousand) | |||||
| 1950 | 354,879 | 17,616 | 16,234 | 1,381 | 791 | 34,943 |
| 1951 | 359,780 | 20,720 | 19,610 | 1,110 | 839 | 36,893 |
| 1952 | 365,701 | 22,937 | 22,373 | 564 | 877 | 38,334 |
| 1953 | 371,404 | 22,645 | 23,012 | —367* | 886 | 38,854 |
| 1954 | 376,427 | 24,321 | 22,958 | 1,362 | 915 | 41,132 |
| 1955 | 382,357 | 26,924 | 26,188 | 737 | 958 | 42,826 |
| 1956 | 389,257 | 29,208 | 28,265 | 943 | 1,016 | 44,785 |
| 1957 | 400,395 | 33,431 | 30,408 | 3,024 | 1,299 | 49,108 |
| 1958 | 412,491 | 40,322 | 34,973 | 5,349 | 1,480 | 55,937 |
| 1959 | 424,175 | 39,341 | 38,389 | 952 | 1,604 | 58,493 |
| 1960 | 441,703 | 45,548 | 40,712 | 4,836 | 1,717 | 65,045 |
NOTE – This statement does not include national savings investment accounts.
The following table shows the results of the transactions, exclusive of National Savings investment accounts, of each of the trustee savings banks during the 12 months ended 31 March 1960.
| Bank | Number of Depositors at End of Year | Total Amount of Deposits During Year | Total Amount of Withdrawals During Year | Excess of Deposits Over Withdrawals | Interest Credited | Total Amount to Credit of Depositors at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excess of withdrawals over deposits. | ||||||
| No. | £(thousand) | |||||
| Auckland | 295,454 | 25,944 | 23,574 | 2,370 | 1,081 | 40,405 |
| Waikato | 3,669 | 1,097 | 321 | 776 | 12 | 787 |
| New Plymouth | 34,679 | 3,530 | 3,091 | 439 | 159 | 5,944 |
| Hokitika | 3,042 | 174 | 179 | —5* | 16 | 570 |
| Dunedin | 63,141 | 4,780 | 4,499 | 280 | 228 | 8,314 |
| Invercargill | 41,718 | 10,023 | 9,049 | 974 | 221 | 9,024 |
| Totals | 441,703 | 45,548 | 40,712 | 4,835 | 1,717 | 65,045 |
Following is a summary of trustee savings banks' assets at 31 March 1960. The total assets include an amount of £5,786,420 securing National Savings deposits, of which £5,777,848 is invested in New Zealand Government securities and £8,572 held in cash. Under the Trustee Savings Banks Act, however, National Savings deposits are not regarded as assets of the Trustee Savings Banks, and for this reason are shown separately.
| Bank | Mortgages | New Zealand Government Securities | Local Authority Debentures | Cash in Hand and on Call at Bank | Total Assets (Includes Other Assets but not National Savings Deposits) | National Savings Deposits | Total Held Including National Savings Deposits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes £25,000 deposits with banks on call and treated as cash at banks. †Includes £113,332 deposits with banks on call and treated as cash at banks. †Includes £200,000 deposits with banks on call and treated as cash at banks. §Includes £650,000 deposits with banks on call and treated as cash at banks. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| Auckland | 12,143 | 22,566 | 5,973 | 1,546 | 43,139 | 3,416 | 46,555 |
| Waikato | 707 | 37 | 37* | 794 | - | 794 | |
| New Plymouth | 2,537 | 2,886 | 120 | 514† | 6,259 | 763 | 7,022 |
| Hokitika | 254 | 305 | 31 | 50 | 646 | 646 | |
| Dunedin | 3,281 | 4,259 | 677 | 470‡ | 8,855 | 1,293 | 10,147 |
| Invercargill | 1,905 | 4,409 | 2,012 | 918§ | 9,406 | 315 | 9,721 |
| Totals | 20,121 | 35,131 | 8,851 | 3,535 | 69,099 | 5,786 | 74,885 |
NATIONAL SAVINGS – The National Savings Act 1940 made provision for the issue of savings bonds and the opening of special savings accounts with the Post Office and the Auckland, New Plymouth, Dunedin, and Invercargill Trustee Savings banks. These investments bear interest at the rate of 31/2 per cent per year. The sale of National Savings bonds was discontinued as from 1 May 1956.
Deposits to National Savings accounts are accepted up to £10,000 in any one year commencing on 1 July and are invested for a two- to three-year period according to the date of deposit. Interest on amounts withdrawn before the term of investment has expired is credited at Post Office Savings Bank rates. Interest may be withdrawn from 1 July to end of December each year, but if not withdrawn it is compounded and becomes part of the principal.
The following table gives particulars of deposits, withdrawals, etc., in regard to National Savings accounts for the latest 11 years and the cumulative totals from the inception of the scheme.
| Year Ended 31 March | Deposits | Withdrawals | Interest to 30 June Previous Year | Amount to Credit of Depositors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||
| 1950 | 10,577 | 4,282 | 1,179 | 47,671 |
| 1951 | 9,469 | 5,311 | 1,386 | 53,214 |
| 1952 | 10,974 | 6,511 | 1,542 | 59,218 |
| 1953 | 10,419 | 8,427 | 1,720 | 62,930 |
| 1954 | 10,329 | 9,630 | 1,839 | 65,469 |
| 1955 | 11,128 | 10,282 | 1,912 | 68,228 |
| 1956 | 10,240 | 11,014 | 1,998 | 69,451 |
| 1957 | 8,836 | 13,005 | 2,040 | 67,322 |
| 1958 | 7,509 | 12,940 | 2,331 | 64,222 |
| 1959 | 5,843 | 11,191 | 2,228 | 61,102 |
| 1960 | 5,560 | 9,878 | 2,124 | 58,908 |
| Totals, 1940–60 | 149,128 | 114,383 | 24,163 | ... |
The next table gives particulars of National Savings bonds sold and redeemed during the same period.
| Year Ended 31 March | Value of Bonds Sold* | Value of Bonds Redeemed |
|---|---|---|
| *Sales discontinued from 1 May 1956. | ||
| £(000) | ||
| 1950 | 458 | 2,421 |
| 1951 | 499 | 1,644 |
| 1952 | 537 | 619 |
| 1953 | 219 | 712 |
| 1954 | 360 | 555 |
| 1955 | 339 | 550 |
| 1956 | 201 | 595 |
| 1957 | 42 | 646 |
| 1958 | ... | 272 |
| 1959 | ... | 372 |
| 1960 | ... | 398 |
| Totals, 1940–60 | 15,838 | 17,500 |
SMALL SAVINGS – The following table shows the total amounts of transactions in small savings accounts, including accounts in the Post Office Savings Bank and trustee savings banks, also National Saving accounts, but excluding national savings bonds and School Savings Bank accounts.
| Year Ended 31 March | Total Amount of Deposits | Interest | Total Amount of Withdrawals* | Excess of Deposits Plus Interest Over Withdrawals | Total Amount to Credit or Depositors at End of March |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *From January 1958 includes interest paid out on Investment accounts. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1951 | 116,584 | 6,140 | 110,111 | 12,613 | 266,210 |
| 1952 | 132,117 | 6,499 | 122,633 | 15,982 | 282,191 |
| 1953 | 132,190 | 6,814 | 128,138 | 10,866 | 293,058 |
| 1954 | 143,990 | 7,197 | 131,723 | 19,464 | 312,522 |
| 1955 | 155,934 | 7,581 | 149,312 | 14,203 | 326,725 |
| 1956 | 157,759 | 7,868 | 157,935 | 7,692 | 334,417 |
| 1957 | 173,711 | 9,640 | 164,733 | 18,618 | 353,035 |
| 1958 | 196,856 | 10,680 | 181,907 | 25,629 | 378,665 |
| 1959 | 187,021 | 11,105 | 193,283 | 4,844 | 383,506 |
| 1960 | 209,260 | 11,366 | 197,248 | 23,378 | 406,887 |
| 1961 | 243,927 | 11,974 | 225,111 | 30,790 | 437,677 |
DEPOSITS, ADVANCES, ETC.: STOCK AND STATION AGENCIES – Financial data as at 30 June 1960 (with totals for the previous year) are given in two tables of deposits, advances, etc., for stock and station agencies operating in New Zealand. The statistics refer to the whole of the companies' trading operations including, in some cases, activities additional to normal stock and station transactions, such as retail trading in consumer goods.
The deposit figures include only moneys received for an agreed term and rate of interest and exclude amounts secured by mortgage or debenture, and amounts in credit on current account. Secured advances to customers include those made on mortgage or chattel security. The figure for merchandise and commodity stocks includes all types of trading stock which are regarded as current assets, but excludes livestock, goods held on consignment, or motor vehicles used by the company. Returns were collected from 30 agencies.
DEPOSITS HELD (ORIGINAL TERM)
| Rate of Interest | Call and Under 3 Months | 3 Months and Under 6 Months | 6 Months and Under 12 Months | 12 Months and Under 2 Years | 2 Years and Over | Totals, 30 June 1960 | Totals, 30 June 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| per cent | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| 11/4 | 388 | - | - | - | - | 388 | - |
| 11/2 | 433,807 | - | - | - | - | 433,807 | 468,736 |
| 13/4 | 534 | - | - | - | - | 534 | - |
| 2 | 71,178 | 21,940 | - | - | 2,000 | 95,118 | 37,305 |
| 21/2 | 332,416 | 82,000 | 83,619 | 500 | 500 | 499,035 | 304,257 |
| 23/4 | - | - | 17,756 | 2,400 | 20,156 | 11,001 | |
| 3 | 369,946 | - | 44,850 | 8,192 | 98,540 | 521,528 | 348,060 |
| 31/4 | - | - | - | 1,000 | 1,500 | 2,500 | 2,250 |
| 31/2 | 227,655 | 46,507 | 55,087 | 55,995 | 175,270 | 560,514 | 385,083 |
| 33/4 | 7,981 | 45,000 | 74,489 | 54,715 | 182,185 | 182,206 | |
| 4 | 607,115 | 5,654 | 58,900 | 44,809 | 578,257 | 1,294,735 | 903,096 |
| 41/4 | - | - | - | - | 139,174 | 139,174 | 129,727 |
| 41/2 | 14,503 | - | 46,932 | 37,500 | 266,863 | 365,798 | 214,299 |
| 43/4 | - | - | - | - | 24,509 | 24,509 | 15,209 |
| 5 | 9,443 | - | - | 6,000 | 635,657 | 651,100 | 332,326 |
| 51/4 | - | - | - | - | 1,761 | 1,761 | 1,761 |
| 51/2 | - | - | - | - | 59,590 | 59,590 | 46,790 |
| 7 | 3,275 | - | - | - | - | 3,275 | 1,408 |
| Totals, 1960 | 2,078,241 | 156,101 | 334,388 | 246,241 | 2,040,736 | 4,855,707 | 3,383,514 |
| Totals, 1959 | 1,219,351 | 34,455 | 207,961 | 230,202 | 1,691,545 | 3,383,514 | - |
| Totals, 1958 | 539,890 | 20,283 | 112,930 | 255,618 | 1,676,266 | 2,604,987 | - |
| Totals, 1957 | 1,072,647 | 15,265 | 108,107 | 68,441 | 1,089,056 | 2,353,516 | - |
A slight continued upward trend in interest rates is evidenced in the figures given above. At mid-1959, 65.4 per cent of the total deposits were at rates in excess of 3 per cent; a year later the proportion had increased to 67.7 per cent.
A summary of the liquid position of stock and station agencies is given below.
| At 30 June | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Customers' credit balances on current account | 18,887 | 15,706 | 14,374 | 17,843 |
| Advances to customers – | ||||
| (a) On current account (unsecured) | 16,554 | 17,185 | 17,365 | 17,753 |
| (b) Other advances (secured) | 9,119 | 15,843 | 16,449 | 17,569 |
| Investments – | ||||
| (a) Government securities | 2,939 | 2,077 | 1,853 | 2,278 |
| (b) Fixed deposits | 4,290 | 1,396 | 833 | 3,384 |
| (c) Other investments | 891 | 1,674 | 1,497 | 2,491 |
| Cash balances (in hand and at bank) | 3,945 | 904 | 1,798 | 3,389 |
| Merchandise and commodity stocks | 9,985 | 11,582 | 12,379 | 11,553 |
Although secured advances to customers have again increased in the latest year, an improvement in liquidity is shown by the 1960 figures as against 1959.
DEPOSITS WITH COMPANIES, ETC. – A summary of deposits with societies, finance companies, firms, and businesses as at 31 March 1960 (with totals for the previous year) is now given. The figures refer to interest-bearing deposits held for an agreed term, and exclude moneys received on mortgage or debenture security, or in the course of a mercantile current account. The figures of deposits with stock and station agents, given previously, are not included in the following table.
For this survey the coverage is believed to include nearly all companies, etc. accepting deposit moneys as defined.
| Rate of Interest per Annum (Per Cent) | Call and Under 3 Months | 3 Months and Under 6 Months | 6 Months and Under 12 Months | 12 Months and Under 2 Years | 2 Years and Over | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1 | 2,230 | - | - | - | - | 2,230 |
| 1 1/2 | 266,932 | - | - | - | - | 266,932 |
| 1 3/4 | 17 | - | - | - | - | 17 |
| 2 | 185,461 | - | - | 11 | 80 | 185,552 |
| 2 1/4 | 200,144 | 2,362 | 32,700 | 28 | 235,234 | |
| 2 1/2 | 168,567 | 56,228 | 15,686 | 28,512 | 8,294 | 277,287 |
| 2 3/4 | 104,200 | 4,406 | - | 5,045 | 2,010 | 115,661 |
| 3 | 2,864,939 | 47,559 | 431,620 | 19,304 | 47,030 | 3,410,452 |
| 3 1/4 | 115,563 | 6,425 | 53,538 | 30,466 | 5,844 | 211,836 |
| 3 1/2 | 269,455 | 45,898 | 65,753 | 447,451 | 359,191 | 1,187,748 |
| 3 3/4 | 19,350 | 100,000 | - | 32,329 | 342,787 | 494,466 |
| 4 | 725,800 | 10,498 | 20,569 | - | 2,753,893 | 3,510,760 |
| 4 1/4 | - | - | 4,000 | - | 178,827 | 182,827 |
| 4 1/2 | 118,155 | 4,635 | - | 44,454 | 1,102,968 | 1,270,212 |
| 4 3/4 | - | - | - | - | 256,237 | 256,237 |
| 4 7/8 | - | - | - | - | 5,600 | 5,600 |
| 5 | 397,608 | 59,608 | 23,676 | 55,170 | 4,007,234 | 4,543,296 |
| 5 1/4 | - | - | 1,965 | - | 73,398 | 75,363 |
| 5 1/2 | 10,850 | 2,885 | 500 | 1,500 | 74,878 | 90,613 |
| 5 3/4 | - | - | - | - | 1,680 | 1,680 |
| 6 | 455,402 | 121,539 | 20,938 | 73,484 | 122,435 | 793,798 |
| 6 1/2 | 8,475 | 2,500 | 3,150 | - | 22,240 | 36,365 |
| 6 3/4 | - | - | - | - | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| 7 | 165,854 | 46,464 | 22,639 | 16,900 | 39,593 | 291,450 |
| 71/4 | - | - | - | - | 1,500 | 1,500 |
| 71/2 | 48,185 | 6,750 | 9,721 | 100 | 14,643 | 79,399 |
| 8 | 160,944 | 12,425 | 11,427 | 90,756 | 62,656 | 338,208 |
| 81/2 | 9,300 | - | - | - | 5,300 | 14,600 |
| 9 | 11,160 | - | - | - | 59,758 | 70,918 |
| 10 | 79,072 | 3,805 | 24,843 | 12,054 | 85,161 | 204,935 |
| 15 | - | 1,000 | 100 | 11,150 | - | 12,250 |
| Totals, Mar 1960 | 6,387,663 | 534,987 | 742,825 | 868,714 | 9,634,237 | 18,168,426 |
| Totals, Mar 1959 | 5,579,918 | 370,780 | 626,311 | 858,146 | 8,382,648 | 15,817,803 |
| Totals, Mar 1958 | 5,513,139 | 485,252 | 834,528 | 648,896 | 7,898,840 | 15,380,655 |
| Totals, Mar 1957 | 3,273,546 | 147,859 | 986,786 | 453,977 | 2,919,339 | 7,781,507 |
The table above showing figures for March 1960 is not comparable with that published for earlier years owing to the extension of coverage through new companies, etc., being added each year.
However, the following summary table showing interest-bearing deposits held as at 31 March 1959 and 31 March 1960 relates only to those companies in the 1959 collection from which statistics were obtained again, and can be used for purposes of comparability.
| Period of Deposit | Amount as at 31 March | |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| £(000) | ||
| Call and under 3 months | 5,580 | 6,030 |
| 3 months and under 6 months | 371 | 477 |
| 6 months and under 12 months | 626 | 719 |
| 12 months and under 2 years | 858 | 819 |
| 2 years and over | 8,383 | 9,384 |
| Totals | 15,818 | 17,428 |
An interesting point is that new companies included for the first time in the 1959–60 collection, most of which were companies newly created and commencing operations during the year, show higher interest rates for deposits than older-established companies, etc.
Of the deposits held by companies, etc., included for the first time, 67.2 per cent were returning over 5 per cent interest, as against 8.7 per cent of the deposits held by companies included previously.
SUMMARY OF BANK DEPOSITS – In the preceding paragraphs statistics of deposits with various classes of banking institutions are shown. It is of interest to show the position in summary form in respect of all classes of deposits (other than Government deposits and trading bank deposits with the Reserve Bank).
| As at End of March 1960 | |
|---|---|
| *Includes approximately £3,000,000 of ordinary deposits from trustee savings banks. | |
| £(000) | |
| Deposits with Reserve Bank (excluding Government and trading banks' deposits) | 2,363 |
| Deposits with trading banks (excluding Government) | 311,025* |
| Deposits with Post Office Savings Bank | 282,934 |
| Deposits with school savings bank accounts | 1,191 |
| Deposits with trustee savings banks | 65,045 |
| Deposits in National Savings accounts | 58,908 |
| Total | 721,466 |
| Per head of population | £304 |
The above deposits are bank deposits only. It should be noted also that other classes of deposits exist, e.g., the Common Fund of the Public Trust Office, deposits with building and investment societies, and with trading companies.
VOLUME OF MONEY IN CIRCULATION – The following information, which has been published by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, sets out in detail the changes that have occurred in the amount of money in circulation in the form of coin, notes, and demand deposits of the Reserve Bank and of the trading banks. The first table shows the volume of such money as at the last balance day in January of each of the years given, the figures quoted being in £(N.Z.) million.
| 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Government and other demand deposits at Reserve Bank, excluding trading banks' balances at Reserve Bank. †Trading banks' total demand liabilities in New Zealand. | |||||||||
| £(million) | |||||||||
| Coin (estimated) | 3.7 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.2 |
| Notes held by public | 52.8 | 56.4 | 58.0 | 59.5 | 60.6 | 62.2 | 62.0 | 64.3 | 67.6 |
| Demand deposits at – | |||||||||
| Reserve Bank* | 8.9 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 12.0 | 12.8 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 12.1 | 11.5 |
| Trading banks† | 195.2 | 229.2 | 242.3 | 242.3 | 252.0 | 252.0 | 231.2 | 261.3 | 296.3 |
| Totals | 260.7 | 301.3 | 316.9 | 318.1 | 329.8 | 329.1 | 308.8 | 342.7 | 380.6 |
| Change during year | —0.9 | +40.7 | +15.6 | + 1.2 | +11.7 | — 0.7 | —20.3 | +33.9 | +37.9 |
The cumulative effect of the changes in the volume of money during the last 10 years is contained in the following summary.
| 1951–61 (10 Years) | |
|---|---|
*Government and other demand deposits at Reserve Bank, excluding trading banks' balances at Reserve Bank. †Trading banks' total demand liabilities in New Zealand. | |
| £(m.) | |
| Coin (estimated) | + 1.7 |
| Notes held by public | + 20.2 |
| Demand deposits at – | |
| Reserve Bank* | – 6.8 |
| Trading Banks† | +101.6 |
| Total | +116.7 |
The next table shows the causes of the changes in the volume of money that occurred during the period.
| 1951–61 (10 Years) | Movement During Each of Last Three Years | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958–59 | 1959–60 | 1960–61 | ||
*As shown by changes in the Reserve Bank's sterling exchange, plus overseas investments and trading bank's assets overseas in respect of New Zealand business, less overseas liabilities. †Minus sign indicates shift from demand to time liabilities. | ||||
| £(million) | ||||
| Overseas transactions* | –34.9 | +17.1 | +24.7 | –28.5 |
| Bank credit – | ||||
| Reserve Bank – | ||||
| Advances to State for general purposes | + 15.8 | –26.7 | +37.1 | +19.9 |
| Marketing and other advances | + 27.0 | – 3.5 | –20.0 | +16.9 |
| Trading banks – | ||||
| Advances and discounts | + 77.6 | – 1.9 | – 3.4 | +27.5 |
| Investments in New Zealand | + 10.0 | – 0.1 | - | – 0.1 |
| Shift from time to demand liabilities of trading banks† | + 12.5 | – 4.3 | – 5.4 | – 6.3 |
| Other items | + 8.7 | – 1.0 | + 0.9 | + 8.5 |
| Change during period | +116.7 | –20.4 | +33.9 | +37.9 |
OVERDRAFT AND DISCOUNT RATES – The trading banks' minimum overdraft rates and rates of discount, which had for many years been at 61/2 or 7 per cent, were reduced to 6 per cent as from 1 September 1932. This was followed by further reductions to 5 per cent from 1 May 1933, to 41/2 per cent from 30 November 1934, and to 4 per cent from 1 August 1941.
The Minister of Finance announced on 8 February 1956 that more flexibility was to be introduced into the control on interest charged by trading banks for loans on overdraft.
The former system, operative since 1941, was an arrangement whereby the trading banks adhered to a minimum rate of 4 per cent and a maximum rate of 5 per cent. Recently it had also been arranged that the average rate over all overdrafts would not exceed 43/4 per cent. The new system achieves flexibility by the abolition of the minimum and maximum rates but retains the feature of an average rate, which at first was not to exceed 5 per cent, but now approximates 51/2 per cent.
The object of the change is to permit the banks to use higher rates to discourage and deter excessive use of bank overdrafts for relatively non-essential purposes and to provide an additional incentive to borrowers with such overdrafts to reduce these as quickly as they could reasonably do so.
Section 45A of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act, which was added in 1960 (see page 882), now gives the Reserve Bank statutory power to control interest rates paid to or by banks.
The Reserve Bank's minimum discount or rediscount rate for New Zealand bills was originally 4 per cent, but was reduced to 31/2 per cent from 29 July 1935, to 21/2 per cent from 2 March 1936, and to 2 per cent from 29 June 1936. The rate was restored to the original 4 per cent on 19 November 1938, but was reduced to 3 per cent from 6 September 1939, to 2 per cent from 27 May 1940, and to 11/2 per cent from 26 July 1941. The rate was increased, however, to 31/2 per cent from 13 April 1954, to 4 per cent on 26 November 1954, to 5 per cent from 1 July 1955, to 6 per cent from 5 September 1955, and to 7 per cent from 19 October 1955. The rate was reduced to 6 per cent on 19 October 1959, but was raised again to 7 per cent on 23 March 1961.
The successive increases in the discount rate in 1954 and 1955 were in support of the reserve ratio system and of the Reserve Bank's general policy of credit restraint in recent years. The reduction of the rate to 6 per cent in October 1959 did not denote a change in credit policy but was intended as a reflection of the improvement in economic conditions during 1959. The increase in 1961 was allied to an intensified use of the reserve ratios, since advances had been increasing rapidly.
In effect, the discount rate is the minimum rate at which trading banks may borrow from the Reserve Bank if they need to do so in order to maintain the statutory minimum balances which they are required to deposit with the Reserve Bank.
The statutory minimum balances are calculated as a certain percentage of the trading banks' demand liabilities, plus a percentage of their time liabilities. These percentages are called the reserve ratios. For further details see page 892.
Discount rate policy is as follows: the Reserve Bank is required by law to publish a rate at which it will discount approved bills of exchange. It does this in its capacity as a “lender of last resort”, so that potential borrowers will know the minimum rate which will be charged for Reserve Bank credit. The bank has three kinds of lending operations to which the “bank rate” applies:
It may discount, rediscount, buy and sell bills of exchange arising out of commercial transactions, bearing two good signatures and maturing within specified short periods.
It may grant advances for fixed periods not exceeding three months against specified collateral security.
It may discount, rediscount, buy, and sell Treasury bills.
No restrictions are imposed on the Bank as to who may borrow from it, but in practice no transactions of the above types have taken place with the public, for the following reasons:
Bills of exchange are not used to any great extent to finance internal transactions, nor are Treasury bills held by the public.
It is not the Reserve Bank's function to compete with the trading banks for ordinary banking business. The trading banks would normally discount bills of exchange offered them which may be eligible for rediscount with the Reserve Bank.
So far the Reserve Bank's discount rate has applied only to transactions with the trading banks. The discount rate therefore is a supplement to the reserve ratio system as an aid to regulating bank credit. For when a trading bank is short of cash – that is, when its balance at the Reserve Bank is approaching or below the statutory minimum – it may borrow from another bank either in New Zealand or London, or it may sell sterling to the Reserve Bank. The most likely and normal procedure, however, is to borrow from the Reserve Bank. For this money it pays a rate of interest related to the bank's discount rate (3 per cent or a minimum based on bank rate, whichever is the higher). If the trading banks have a safe margin of free cash there would be no need for them to borrow from the Reserve Bank and the discount rate would then be a formality (though it has some psychological impact); but when this margin is small the discount rate acquires a much greater significance.
Advances to the State and to marketing organisations have been at 1 per cent from 22 February 1946. Advances to the State may be in the form of Treasury bills, overdrafts, or 1 per cent Government stock. During the financial year 1959–60 the Bank's holdings of Treasury bills was exchanged for 1 per cent stock and it is intended that, in future, short-term borrowing will be by overdraft or Treasury bills and longer-term borrowing by 1 per cent stock.
DEPOSIT AND INTEREST RATES: Trading Banks – The following is a schedule (since June 1912) of the rates paid by the Associated Banks in New Zealand for moneys lodged on fixed deposit.
| Date Operative From | 3 Months and Under 6 Months | 6 Months and Under 12 Months | 12 Months and Under 24 Months | 24 Months and Upwards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||
| 1 June 1912 | - | 2 | 31/2 | 4 |
| 20 January 1921 | 3 | 31/2 | 4 | 41/2 |
| 20 June 1921 | 31/2 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/2 |
| 11 December 1926 | 33/4 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/2 |
| 9 May 1927 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/2 | 5 |
| 9 July 1928 | 33/4 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/2 |
| 1 February 1930 | 33/4 | 33/4 | 41/4 | 5 |
| 22 April 1930 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/4 | 5 |
| 1 August 1931 | 31/2 | 33/4 | 4 | 41/2 |
| 1 June 1932 | 3 | 31/4 | 31/2 | 4 |
| 2 December 1932 | 21/2 | 23/4 | 3 | 31/4 |
| 11 July 1933 | 2 | 21/2 | 23/4 | 3 |
| 5 July 1934 | 11/2 | 2 | 21/2 | 23/4 |
| 2 November 1934 | 11/4 | 13/4 | 21/4 | 21/2 |
| 18 September 1940 | 3/4 | 11/4 | 21/4 | 21/2 |
| 17 July 1941 | 3/4 | 11/4 | 13/4 | 2 |
| 16 February 1956 | 11/2 | 13/4 | 21/4 | 21/2 |
| 14 June 1956 | 2 | 21/4 | 23/4 | 3 |
| 1 October 1957 | 2 | 21/2 | 31/4 | 31/2 |
The new section 45A mentioned earlier in this Section gives the Reserve Bank a statutory power to control deposit rates paid by banks.
Post Office Savings Bank – The Post Office Savings Bank pays interest on all deposits. The present rates on ordinary, Thrift Club, Home Lay-by, and School Savings Bank deposits are 3 per cent per year on deposits of up to £1,000 and 21/2 per cent for any balance up to a total of £10,000.
Interest is calculated on each complete £1 at credit for a calendar month subject to the following provisions:
Deposits made on the 1st, 2nd, or 3rd of a month bear interest for that month, but if the Post Office Savings Bank is closed on all of those three days, deposits made on the first business day bear interest for that month.
Withdrawals: No deduction of interest for the current month is made for amounts withdrawn on the last business day of that month. When a deposit and a withdrawal are made on the same day the deposit is deemed to precede the withdrawal.
The rate of interest on National Savings accounts is 31/2 per cent per year but if withdrawals are made before maturity date of the deposits, interest on the amount withdrawn is credited at Savings Bank rates.
The rates of interest on Investment accounts are shown in the description of these accounts on page 905.
Following is a table of interest rates payable in respect of Post Office Savings Bank deposits since 1921.
| Date Operative From | Amount of Deposit | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £1–£300 | £301–£500 | £501–£1,000 | £1,001–£2,000 | £2,001–£5,000 | £5,001–£7,500 | £7,501–£10,000 | |
| Per Cent | |||||||
| 1 January 1921 | 4 | 4 | 31/4 | 31/4 | 31/4 | Nil | Nil |
| 1 April 1928 | 4 | 4 | 31/4 | 31/4 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 August 1931 | 33/4 | 33/4 | 31/4 | 31/4 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 April 1933 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 August 1933 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 23/4 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 August 1934 | 3 | 3 | 21/2 | 21/2 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 August 1941 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 June 1942 | 21/2 | 21/2 | 2 | 2 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| 1 September 1952 | 21/2 | 21/2 | 2 | 2 | 11/2 | Nil | Nil |
| 1 May 1956 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 21/2 | 21/2 | Nil | Nil |
| 1 August 1957 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 21/2 | 21/2 | 21/2 | Nil |
| 1 August 1959 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 21/2 | 21/2 | 21/2 | 21/2 |
In May 1956 the interest rate was raised to 21/2 per cent on amounts £1,001 to £5,000, the rate for amounts £1 to £1,000 becoming 3 per cent. As from 1 August 1957 interest at the 21/2 per cent rate was extended to amounts from £5,000 to £7,500, and on 1 August 1959 the 21/2 per cent rate was extended from £7,500 to £10,000.
Trustee Savings Banks – The Trustee Savings Banks Act 1948 gives power to the Governor-General to fix the rates of interest to be paid on deposits. Changes in rates from 1908 onwards were given in the 1959 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
From 1 April 1955 maximum interest rates payable by trustee savings banks were 21/2 per cent up to £500 and 2 per cent for amounts over £500 and up to £750, while from 1 May 1956 the allowable maximum rate on all deposits was increased to 3 per cent on amounts up to £750, this limit being raised to £1,000 from 26 October 1956.
Company, etc., Deposits – Authority was taken in the National Expenditure Adjustment Act 1932 to fix by Order in Council the maximum rates of interest payable on deposits with stock and station agents, trading companies, and building and investment societies. Changes made in the maximum rates of interest from 1932 have been given in the 1959 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
As from 1 August 1957 interest rates on deposits with companies, etc., were freed from control, with the exception of deposits in the savings bank departments of building and investment societies, the maximum allowable rate for this class remaining at 3 per cent.
However on 22 July 1960, an Interest on Deposits Order became effective. This order fixed the maximum rates of interest payable for deposits held by companies, firms, building societies, etc. The rates ranged from 2 per cent for deposits at call and under 3 months up to 5 per cent for deposits for not less than seven years.
Other Deposit and Interest Rates – It is of service at this stage to mention briefly the interest rates payable in respect of certain other classes of deposits. The highest rate of interest payable on moneys in the Common Fund of the Public Trust Office (see Section 39) was fixed at 4 per cent from 1 January 1958. Reductions were made from 51/4 per cent in 1928 to 43/4 per cent in 1931, to 4 per cent in 1932, to 31/2 per cent in 1933, to 31/4 per cent in 1945, and to 3 per cent in 1949. There was an increase to 31/4 per cent in 1953, to 31/2 per cent on 1 January 1955, to 33/4 per cent on 1 April 1956, and to 4 per cent on 1 January 1958.
Local authorities may also accept deposits (in practice, only for short periods). The restrictions previously applying to maximum rates of interest were abolished from 24 October 1957 by Order in Council.
References to rates of interest on mortgages will be found in Section 30A (Mortgages), while interest on Government debt is referred to in Section 26C (State Indebtedness), and interest on local authority debt in Section 27 (Local Government Finance).
COINAGE AND CURRENCY: New Zealand Coin – Section 8 of the Finance Act (No. 2) 1932–33 authorised the Minister of Finance to arrange with the Master of the Royal Mint (in England) for a special issue of silver and bronze coinage of distinctive design for use in New Zealand. Any coins minted in accordance with this arrangement would conform to the standard Mint requirements of weight, fineness, etc., and were given status as legal tender in New Zealand.
The Coinage Act 1933, which came into operation on 1 December 1933, repealed section 8 of the Finance Act (No. 2) 1932–33, and made necessary provisions in respect of silver and of bronze or cupro-nickel coins. The Act contains no provision for the issue of New Zealand gold coins. Section 5 (4) of the Act authorised Proclamations declaring that British coins (other than gold coins) should not be legal tender in New Zealand, and a Proclamation was issued declaring British silver coins not legal tender in New Zealand on and after 1 February 1935.
Arrangements were made under which the Royal Mint agreed to remint free of charge the British and Australian silver coin circulating in New Zealand, replacing it with the New Zealand coin referred to above, and to allow the New Zealand Government the bullion value of the coin not used in making such replacement.
The profit which accrued to the New Zealand Government from the recoinage on this basis arose from the fact that the Australian coinage and a proportion of the British coinage then in circulation in New Zealand contained a larger proportion of silver than the new coin under the standard set out in the Schedule to the Coinage Act 1933, which was also the standard governing the production of British silver coin. In addition, the Commonwealth Government agreed to the repatriation at face value of a proportion of Australian coin circulating in New Zealand.
Up to 31 December 1960 New Zealand coins of a total face value of £9,064,606 have been minted by the Royal Mint in London. Statistics of the face values of the various denominations of coin minted to 31 December 1960, and the value of New Zealand coin in circulation at 31 December 1960, are as follows.
| Total Minted to 31 December 1960 | In Circulation | |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| Crown | 112,696 | 110,958 |
| Halfcrown | 2,465,100 | 1,284,482 |
| Florin | 2,427,000 | 1,325,936 |
| Shilling | 1,147,000 | 791,341 |
| Sixpence | 1,108,500 | 805,553 |
| Threepence | 1,297,500 | 1,070,414 |
| Penny | 434,550 | 390,293 |
| Halfpenny | 72,260 |
In 1947 cupro-nickel coins were issued in place of silver coins, many of which were withdrawn from circulation as they were received by the banks.
Withdrawals of silver coinage to 31 December 1960 totalled £1,674,257.
New Zealand silver coinage first came into circulation in 1933, and New Zealand bronze coins were first released for circulation in December 1939.
Restrictions on Import and Export of Currency – A prohibition placed on the importation of coin in 1941 has been revoked, as also has the Customs Import Prohibition (Bank Notes) Order 1956, which prohibited the importation of bank notes of the Bank of England and of bank notes issued by banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland.
The Customs Export Prohibition Order prohibits the exportation of all coin (other than silver coin which is more than 100 years old) of whatever metal and wherever and whenever minted and whether or not it is legal currency in New Zealand or elsewhere. Persons leaving New Zealand are permitted to take silver coin not exceeding £2; or, if the journey is by direct route (without transhipment) to Great Britain or Ireland, silver coin to the value of £5 may be taken. In addition to the above, the Finance Emergency Regulations 1940 prohibited the taking or sending of any money out of New Zealand except with the consent of the Minister, or except in the case of certain transactions especially exempted.
The Reserve Bank, which administers exchange control, has authority to grant permission to take or send money out of New Zealand. It has prohibited the export of New Zealand notes except that travellers proceeding to the United Kingdom may take up to £10, and if to any other destination, £5. These may be in denominations of £1 or 10s. only. In addition, notes may be taken in place of silver coin to the value of £5 or £2 as noted above.
In the cases of both the Export and the Import Prohibition Orders power is vested in the Minister to authorise in writing the variation of the provisions mentioned. Prohibitions mentioned in both orders have effect in addition to, and not in substitution for, any other prohibition in force relating or applicable to the importation or exportation of any of the items enumerated in the orders or in any other enactment.
Legal Tender and Issue of Notes – The Coinage Act 1933 provides that a tender or payment of money, if made in New Zealand coins of current weight, shall be a legal tender to the following extent:
Gold, to any amount.
Silver and cupro-nickel for amounts not exceeding £2.
Bronze for amounts not exceeding 1s.
The position in respect of the bank-note issue in New Zealand was radically altered by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 1933. Section 15 enacted that on and after a date fixed by Proclamation – the Proclamation was signed on 26 January 1934 and fixed the date as 1 August 1934 – the Reserve Bank had the sole right to issue bank notes in New Zealand; and thereupon the authority of every other bank to issue or reissue bank notes was terminated, and such banks were required to redeem their outstanding notes in Reserve Bank notes or subsidiary coin to the extent to which the latter was legal tender. On 1 August 1936 every other bank carrying on business in New Zealand was required to pay over to the Reserve Bank an amount equal to the value of its then outstanding notes issued or payable in New Zealand, and its liability in respect of such notes to the holders (estimated at £347,166 in January 1960) was assumed by the Reserve Bank. Bank notes not presented for payment within 40 years, from 1 April after the date of issue in the case of Reserve Bank notes, or 40 years after assumption of liability (as above) in other cases, are deemed not to be in circulation, and an amount equal to the value thereof must be paid into the Consolidated Fund as if unclaimed moneys. The Unclaimed Moneys Act 1908 provides for the payment to the rightful owner of any moneys paid into the Consolidated Fund under the provisions of the Act.
Reserve Bank notes are constituted legal tender up to any amount. There is a provision in the existing legislation which requires the Bank, on presentation at its head office in Wellington of notes to any amount not less than £1,000, to give in exchange sterling for immediate delivery in London. This requirement may be suspended at the discretion of the Minister of Finance, and actually has been suspended since December 1938. On similar presentation of gold or of sterling for immediate delivery in London, in either case to an amount of £1,000 or more, the Bank must give its notes in exchange therefor. The rate of exchange for the above transactions is fixed by the Bank, subject to a right of the Minister of Finance, after consultation with the Governor, to determine the relationship with sterling.
The principal Act required the Bank to maintain a minimum reserve of not less than 25 per cent of the aggregate amount of its notes in circulation and other demand liabilities; but the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Amendment Act 1939 empowered the Minister of Finance to vary or suspend this requirement. Both of these provisions were repealed by the Reserve Bank Amendment Act 1950, and the following provision substituted: “It shall be the duty of the Bank to maintain reserves which, in the opinion of the Board of Directors, will provide a reasonable margin for contingencies, after taking into account prospective receipts and disbursements of overseas funds, and having regard to the economic position within New Zealand.” The definition of the term “reserve” has been amended and now includes:
Gold coin and bullion in the unrestricted ownership of the Bank.
Sterling exchange, comprising (1) deposits at the Bank of England, (2) British Treasury bills of not more than three months unexpired currency, (3) bills of exchange bearing at least two good signatures and of not more than three months unexpired currency.
Net gold exchange, as defined in section 17 (c) of the Act of 1933.
Other exchange, i.e., balances standing to the credit of the Bank at the central bank of any country the currency of which is freely convertible into sterling.
For the purpose of ascertaining the net reserve, the amount of the Bank's liabilities in currencies other than New Zealand is deducted from the total of the “reserve”.
The gold coin and bullion holdings of the Reserve Bank are shown in the Bank's books at cost value to the bank. The amending legislation of 1939 permits the Minister of Finance to make a revaluation up to the market value of the fine gold contained in the reserve, the premium resulting from such revaluation to be credited to a special reserve to be held on behalf of the Crown. This special reserve is to be used in such manner as the Minister of Finance may from time to time determine; but up to the present no such revaluation has been made.
The Reserve Bank may not issue bank notes of a less denomination than 10s., except with the authority of the Governor-General in Council. The present issue of notes consists of the following denominations: 10s., £1, £5, £10, and £50.
Notes are issued solely in response to the demands of the public. In assessing likely requirements there are seasonal factors to be considered, as well as basic economic conditions, such as national income, the levels of salaries and wages, changes in price levels generally, and in the total volume of money. In addition, methods and frequency of payments affect the amount to be issued.
Currency Other Than Legal Tender – Neither Australian nor other overseas paper money circulates in New Zealand.
No consideration of the amount of credit currency in use at any moment can overlook the very large proportion of payments made by cheque, mainly upon the trading banks, but also upon one of the trustee savings banks, upon certain types of accounts in the Post Office Savings Bank, and upon various stock and station agencies which act in this respect for their customers in the capacity of banker. Such cheques usually go direct from the payee to the collecting bank, but occasionally they pass from hand to hand.
Government postal notes (issued in 39 denominations of from 1s. to £1) sometimes enjoy a certain length of life in the form of currency.
EXCHANGE RATES – Although the movement of gold, whether internally or externally, was unrestricted in years prior to the First World War, certain of the conditions usually considered essential in the full operation of the gold standard were never effective in New Zealand. More correctly, New Zealand was, and still is, upon a sterling-exchange standard. The explanation is that the New Zealand banking system is not self-contained, in that the banks normally hold a large amount of funds in London. In fact, these London balances are the real regulative factor and the key to the whole New Zealand banking system. The inter-relation between these balances and import control and exchange control is of interest in this respect.
While New Zealand currency was at parity with sterling, except for minor fluctuations above or below parity, no necessity existed for distinction between sterling and New Zealand currency. The latter is entitled to be considered as one of the sterling currencies; but, adopting the convenience of a growing usage, sterling is used herein to refer solely to the currency of Great Britain.
The unusual significance of the exchange rate in the case of New Zealand depends chiefly upon the country's position in regard to overseas trade and to overseas borrowings. The course of development of New Zealand has not reached a stage where the country is fully self-contained, and the external trade per head is greater than that of most countries of the world. Most of this external trade is with the United Kingdom, while the function of London as an international clearing house is also of importance in this connection. New Zealand's borrowings from the London financial market have also been, until the last two decades, upon a high scale, requiring, as noted elsewhere (see State Indebtedness and Local Government Finance), considerable annual payments in London.
The regulation of currency exchange and exchange rates is a function of the Reserve Bank, as noted previously. The Finance Act 1934 provides that any appreciation or depreciation of the assets of the Reserve Bank (expressed in the currency of New Zealand) owing to any alteration that may subsequently be made in the exchange rate, while the value of the local currency is not fixed by statute in terms of sterling, shall be credited to or be borne by the Consolidated Fund. In this respect, as already noted, the Consolidated Fund bore those losses incurred as a result of the 1948 adjustment of the exchange rate.
New Zealand and Sterling Exchange – The relationship of New Zealand currency to sterling gained added significance from December 1929. Prior to that date the New Zealand currency was at virtual parity with British currency, only slight deviations occurring from time to time, but then commenced to depreciate gradually, reaching, in January of 1931, a level of approximately £110 New Zealand = £100 London for telegraphic transfers. At that level it remained fairly stationary until January 1933, when as a result of Government intervention it was abruptly depreciated to a further degree. The relationship existing from 20 January 1933 until the establishment of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand on 1 August 1934, was £125 (selling) and £124 10s. (buying) New Zealand = £100 London for telegraphic transfers.
From 1 August 1934 Reserve Bank quotations for £100 sterling for immediate delivery in London were: buying rate, £124; selling rate, £125. It was intimated that the policy of the Bank would aim at retaining these rates unchanged for a long period unless there occurred marked changes in existing conditions. While prepared to fulfil its statutory obligations, the Reserve Bank did not desire to compete for exchange business, provided adequate facilities were available elsewhere.
Following the statement of the Reserve Bank's policy, the trading banks adopted as from 1 August 1934 a scale of rates representing a reduction of 10s. per £100 on the rates ruling from 20 January 1933 to 31 July 1934. The rates were slightly changed on 21 October 1938, and further changes were made in the selling rate as from 1 December and in the buying rate as from 6 November 1940. During the year 1945–46 the Reserve Bank agreed to certain alterations in the trading banks' on-demand and usance rates.
The position was very materially altered as from 20 August 1948, following on the announcement by the Government on the previous night of the appreciation of New Zealand currency to parity with sterling. The Reserve Bank quotations from 20 August 1948 for £100 sterling for immediate delivery in London were: buying rate, £100; selling rate, £101. Consequential adjustments to the scale of rates of trading banks in New Zealand were also made. The quotations current for New Zealand on London at beginning of March 1961 are given in the following table. On-demand and usance buying rates change with changes in the Bank of England discount rate.
| Category | Buying (on Basis of £(Stg.)100) | Selling (on Basis of £(Stg.)100) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telegraphic transfers (cable) | £(N.Z.)100 7s. 6d. | £(N.Z.)101 0s. 0d. | |
| Sterling notes | £(N.Z.) 97 13s. 3d. | £(N.Z.)101 0s. 0d. | |
| Air Mail | Sea Mail | Air and Sea Mail | |
| Bills, cheques, and drafts payable on demand | £(N.Z.)99 18s. 3d. | £(N.Z.)99 8s. 0d. | £(N.Z.)101 0s. 0d. |
| Bills or drafts 3 days sight | £(N.Z.)99 16s. 9d. | £(N.Z.)99 6s. 3d. | No quotation |
| Bills or drafts 30 days sight | £(N.Z.)99 8s. 3d. | £(N.Z.)98 18s. 0d. | £(N.Z.)100 19s. 3d. |
| Bills or drafts 60 days sight | £(N.Z.)99 0s. 0d. | £(N.Z.)98 9s. 9d. | £(N.Z.)100 18s. 6d. |
| Bills or drafts 90 days sight | £(N.Z.)98 11s. 9d. | £(N.Z.)98 1s. 6d. | £(N.Z.)100 17s. 6d. |
| Bills or drafts 120 days sight | £(N.Z.)98 3s. 6d. | £(N.Z.)97 13s. 3d. | No quotation |
On the occasion of the devaluation of sterling in terms of gold and the United States of America dollar in September 1949 it was decided that New Zealand should maintain the value of its currency at parity with sterling.
As most of the export credits in normal times are utilised for financing imports it is advisable to note that the full exchange rate is not operative in respect of dutiable goods. This arises from the fact that, although Customs duties are assessed in sterling, payment of Customs duties is accepted in New Zealand currency without addition of exchange.
New Zealand Exchange Rates with Other Currencies – The change in the sterling-dollar parity was followed by a change in the dollar value of a large number of currencies. Some countries maintained the sterling value of their currencies, others maintained the dollar value, and others again altered the exchange value of their currencies in relation to both sterling and the United States of America dollar. In the latter cases there was a consequent alteration in the rate at which New Zealand currency was exchangeable for the currency of the country concerned.
The following table shows exchange rates (since 17 December 1951 the exchange rates have been free to fluctuate within certain limits) for telegraphic transfers quoted by the New Zealand trading banks for various currencies.
| New Zealand on | At 31 March 1960 | At 30 March 1961 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buying | Selling | Buying | Selling | |
| United States of America (dollars per £(N.Z.)) | 2.8026 | 2.7707 | 2.7930 | 2.7614 |
| Canada (dollars per £(N.Z.)) | 2.6741 | 2.6393 | 2.7647 | 2.7288 |
| France (francs per £(N.Z.)) | 13.87 | 13.49 | 13.81 | 13.42 |
| Belgium (francs per £(N.Z.)) | 141.93 | 137.40 | 141.52 | 137.00 |
| Switzerland (francs per £(N.Z.)) | 12.19 | 11.95 | 12.09 | 11.85 |
| Pakistan (N.Z. pence per rupee) | 17.9063 | 18.3438 | 17.9063 | 18.3438 |
The rates applicable for telegraphic transfer to Australia in February 1961 were £(A)124 10s. 9d. buying and £(A)124 selling per £(N.Z.)100.
FINANCE EMERGENCY REGULATIONS AFFECTING BANKING AND CURRENCY – The Finance Emergency Regulations 1940 (No. 2) followed similar legislation passed in the United Kingdom shortly before the New Zealand measures came into force.
The regulations have been amended a number of times and were reprinted in 1953. The present position as regards banking and currency may be summarised as follows. Every person ordinarily resident in New Zealand who holds or acquires any non-sterling currency or a right to receive non-sterling currency is required to offer it for sale to the Reserve Bank of New Zealand. This rule applies to bank notes or other currency, postal notes, promissory notes, and free bank deposits. Fixed deposits have to be reported to the Reserve Bank but not offered for sale. Any non-sterling currency or fixed deposit to which the regulations apply must not be disposed of (other than by way of repatriation through a New Zealand Bank) except with the permission of the Reserve Bank. Prior to 9 March 1950 this provision applied also to sterling-area currencies. Now “invisible” receipts and private holdings of sterling area currency are free from control.
The regulations also provide that non-sterling securities owned by persons ordinarily resident in New Zealand are to be declared to the Reserve Bank by their owners, and are not to be sold or transferred without the prior consent of the Reserve Bank. Prior to 9 March 1950 this applied also to sterling-area securities, but these are now free from control.
It should be noted that the proceeds from the sale of exports under licence must still be sold to a bank in New Zealand. Information concerning import and export control is contained in Section 22A. It is also an offence to engage in transactions involving the conversion of New Zealand currency into the currency of any other country at other than the official rate of exchange.
Capital Issues Control – During the war period fairly intensive control was maintained over the issue of new capital, but in the post-war period such control was progressively eased. However, the heavy demand for capital moneys and the tendency for interest yields to increase in late 1951 and early 1952 caused the Government to decide to apply the existing powers of control over capital issues given by the Finance Emergency Regulations (No. 2) 1940 more fully. A Capital Issues Committee was therefore set up in 1952 to deal with applications for capital issues, including shares, debentures, mortgages, and deposits, and affecting mainly companies – not private individuals or partnerships. In March 1959 the regulations were amended to include partnerships where any partner was a company. Consent was required if the total raised exceeded £10,000 in any period of 12 months. Approval was more likely to be given to cases (a) where no recourse to new finance was involved, e.g., bonus issues, amalgamations, etc.; (b) where a substantial increase of exports or saving of imports were expected to result, whether directly or indirectly; and (c) where substantial shortages of essential goods were to be met.
In the 1960 Budget it was announced that a general consent to any issue of capital would be given by the Capital Issues Committee, with certain exceptions. These exceptions are:
Where the proposed interest rates exceed those fixed by the committee.
Where an overseas company desires to commence business in New Zealand.
For New Zealand companies desiring to obtain capital overseas, and overseas companies desiring to obtain capital in New Zealand.
For any issue of capital in excess of £10,000 which is to be used for the financing or discounting of hire purchase or credit sale agreements.
The Committee is still to be advised of any prospective issues of capital.
The following table shows the total approvals made in recent years.
| Year | Share Issues | Mortgages and Debentures | Total* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Companies | Existing Companies | |||||||
| No. | Value | No. | Value | No. | Value | No. | Value | |
| *In some cases a company is granted a share issue and mortgage, resulting in the individual items not adding to the total. | ||||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| 1956 | 256 | 6,799 | 200 | 20,222 | 350 | 9,458 | 679 | 36,479 |
| 1957 | 341 | 6,170 | 235 | 14,982 | 560 | 19,634 | 899 | 40,786 |
| 1958 | 243 | 5,197 | 192 | 11,286 | 514 | 16,303 | 772 | 32,786 |
| 1959 | 224 | 8,011 | 252 | 25,568 | 488 | 22,251 | 896 | 55,830 |
| 1960 | 275 | 11,397 | 486 | 43,105 | 532 | 18,124 | 1,237 | 72,626 |
MORTGAGE LAW - Under the Property Law Act 1952 a “mortgage” is defined as including a charge on any property for securing money or money's worth; and “mortgage money” means money or money's worth secured by a mortgage. Under the Land Transfer Act 1952 “mortgage” means and includes any charge on land created under the provisions of that Act for securing:
The repayment of a loan or satisfaction of an existing debt.
The repayment of future advances, or payment or satisfaction of any future or unascertained debt or liability, contingent or otherwise.
The payment to the holders for the time being of any bonds, debentures, promissory notes, or other securities, negotiable or otherwise, made or issued by the mortgagor before or after the creation of such charge.
The payment to any person or persons by yearly or periodical payments or otherwise of an annuity, rent charge, or sum of money other than a debt.
Where the ownership of land is registered under the Land Transfer Act (as, see Section 10A, the great majority of land titles now are) mortgages on that land are granted by virtue of the provisions of that Act; they take effect as securities and do not operate as transfers of the estate or interest charged. In the case of other land or property a mortgage is granted under what is known as the deeds or deeds-registration system; the mortgage in this instance operating as a conveyance or assignment of the land or property mortgaged, for the mortgagee becomes the registered proprietor of the land, subject to the right of the mortgagor to have the property reregistered in his name on the discharge of his obligations under the mortgage. Although in form a mortgage under the deeds system is a conveyance, in equity it is treated as merely a charge on the land.
Property That May be Mortgaged - Any land covered by the definitions of “land” in the Property Law Act 1952 and the Land Transfer Act 1952 may be mortgaged. Where, however, property is subject to restrictions upon alienation, these restrictions usually apply to prevent such property being mortgaged. The following are the main instances in which mortgage of property is forbidden by law:
Family homes registered under the Family Protection Act 1908, unless with prior approval of the Supreme Court.
Maintenance moneys under the Family Protection Act 1908.
Inalienable life annuities (Inalienable Life Annuities Act 1910).
Pensions under the War Pensions Act 1954.
Monetary benefits under the Social Security Act 1938.
Property subject to restraint upon anticipation, unless by consent of the Supreme Court.
Property subject to restraint upon alienation in accordance with section 33 of the Property Law Act 1952.
An infant's property, by the infant (Infants Act 1908, sections 12 and 13), unless the approval of the Magistrate's Court under the Statutes Amendment Act 1951 is obtained.
Redemption - A memorandum of discharge vacates the mortgage debt and operates as a deed of reconveyance of the estate and interest of the mortgagee in the mortgaged property “to the person for the time being entitled to the equity of redemption”; but the mortgagee may execute a deed of reconveyance “if he thinks fit and the mortgagor requires it”. The Public Trustee is empowered to receive mortgage moneys on account of absentee mortgagees, and in the case of a deed of mortgage to execute the necessary memorandum of discharge. Alternatively, application may be made to the Supreme Court, and the production of a certificate from the Registrar of the Supreme Court shall operate, upon registration, as a discharge of the land from the mortgage debt. A mortgagor may redeem in the following cases:
Before the due date, on payment of interest for the unexpired term of the mortgage. A special provision in the Mortgagors and Lessees Rehabilitation Act extends the powers of a mortgagor to redeem in certain cases before the due date.
At the due date, in accordance with the provisions of the mortgage.
After the due date, upon giving three months' notice in writing or paying three months' interest in lieu of notice, except where the mortgagee is or has been in possession or has taken steps to enforce his security, in which case the mortgagor may redeem at any time upon payment of all moneys due.
After default and before sale by the mortgagee. If the mortgagee has entered into possession of mortgaged land or part of it not held under the provisions of the Land Transfer Act 1952, the mortgagor loses his right of redemption after 12 years from the date of the mortgagee's entering into possession, or after 12 years from the last written acknowledgment of the mortgagor's title or of his right to redeem.
Earlier legislation abolished what was formerly known as the doctrine of consolidation of mortgages. Where a mortgagor is liable under more than one mortgage he may now pay off one mortgage without being called on to pay off any mortgage or mortgages on property not comprised in the mortgage he is paying off.
Rights of Mortgagee - Under New Zealand law a mortgagee has no power of foreclosure in respect of realty. The following represent his principal rights:
He is entitled to the custody of the title deeds of the property mortgaged.
He may sue on the personal covenant contained in the mortgage deed.
He may enter and take possession. This right is exercisable either by actually entering upon the land or a part of it or by bringing an action for possession. At least one month's notice of the intention to exercise the right must be served on the owner for the time being of the land subject to the mortgage. If there is a tenant whose rights are binding on the mortgagee, the latter can give notice to the tenant to pay the rent to him, and this will be equivalent to taking possession.
He may assign his interest, either absolutely or by way of submortgage.
He may sell, either under the express powers (if any) in the mortgage deed, or under powers implied by statute, if these have not been negatived in the deed.
Instead of selling, as above, a mortgagee entitled to exercise his power of sale may apply to the Registrar of the Supreme Court to conduct the sale. The mortgagee must state in his application the estimated value of the land, and the date of the sale must be not less than one month and not more than three months from the date of the application. He may bid at the sale and become the purchaser of the land, but in such case the amount paid for the land shall be not less than the value of the land as estimated. If it is, the mortgagor must be allowed in account the full amount of the estimate. As in the case of the right to enter and take possession, no power of sale shall become exercisable unless at least one month's notice of the contemplated action has been served on the owner of the land.
SUMMARY OF MORTGAGES REGISTERED AND DISCHARGED - A table is given showing the net numbers and amounts represented by mortgages registered and discharged during each of the last 21 years. The average rate of interest on new mortgages is also given.
| Year Ended 31 March | Mortgages Registered | Average Rate of Interest on New Mortgages Registered | Mortgages Discharged | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | ||
| £(000) | percent | £(000) | |||
| 1940 | 22,632 | 17,621 | 4.69 | 20,694 | 14,101 |
| 1941 | 21,660 | 16,267 | 4.69 | 22,897 | 15,934 |
| 1942 | 20,667 | 14,550 | 4.73 | 22,577 | 15,099 |
| 1943 | 17,075 | 12,141 | 4.72 | 23,708 | 16,680 |
| 1944 | 19,928 | 15,597 | 4.63 | 27,161 | 20,030 |
| 1945 | 21,212 | 18,100 | 4.51 | 27,414 | 21,012 |
| 1946 | 24,516 | 22,519 | 4.10 | 29,174 | 23,314 |
| 1947 | 29,882 | 31,089 | 3.85 | 32,234 | 25,947 |
| 1948 | 29,893 | 32,041 | 3.90 | 29,002 | 25,396 |
| 1949 | 29,578 | 35,299 | 3.98 | 26,642 | 23,375 |
| 1950 | 30,352 | 36,006 | 3.99 | 26,093 | 23,101 |
| 1951 | 43,875 | 45,820 | 4.09 | 35,503 | 32,266 |
| 1952 | 49,840 | 67,961 | 4.15 | 37,926 | 37,264 |
| 1953 | 50,633 | 73,713 | 4.29 | 34,160 | 31,401 |
| 1954 | 52,807 | 70,378 | 4.49 | 36,728 | 36,012 |
| 1955 | 57,992 | 84,599 | 4.69 | 37,931 | 41,155 |
| 1956 | 55,544 | 96,258 | 4.76 | 34,078 | 35,367 |
| 1957 | 51,230 | 91,211 | 5.09 | 32,663 | 37,680 |
| 1958 | 55,437 | 99,534 | 5.24 | 37,441 | 46,079 |
| 1959 | 56,195 | 108,546 | 5.15 | 36,920 | 44,394 |
| 1960 | 57,834 | 119,520 | 5.01 | 39,931 | 51,131 |
The figures given in the preceding table have been adjusted to exclude duplicate registrations, i.e., cases in which a mortgage has been registered in more than one district. It should also be noted that the figures include collateral mortgages and guarantee mortgages not representing money indebtedness. On the other hand, no amount is shown as secured in a proportion of cases where a mortgage is given in anticipation of advances, etc. In addition there are numbers of privately arranged advances which are not registered, and stock and crop liens, bills of sale, and instruments under the Chattels Transfer Act are not included in the statistics.
Many discharges are not registered, particularly in the case of leaseholds and also of second or other further mortgages when the power of sale has been exercised by the first mortgagee. The figures for discharges are further affected by the high proportion of table mortgages. This is particularly so in cases where the mortgage is approaching maturity, since the whole amount remains on the register until finally discharged, despite the fact that the original amount of indebtedness has been considerably reduced.
MORTGAGES REGISTERED: Value by Districts - The total amount for which mortgages were registered, under the Land Transfer Act, in each registration district during the last five financial years is given in the next table.
| District | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| North Auckland | 24,359 | 22,862 | 24,599 | 28,281 | 31,601 |
| South Auckland | 14,662 | 12,987 | 14,574 | 15,498 | 17,312 |
| Gisborne | 1,534 | 1,437 | 1,678 | 1,563 | 1,857 |
| Hawke's Bay | 5,875 | 4,959 | 5,195 | 6,039 | 6,415 |
| Taranaki | 3,667 | 3,803 | 4,187 | 3,722 | 4,368 |
| Wellington | 18,533 | 17,231 | 17,822 | 21,384 | 23,435 |
| Marlborough | 1,101 | 963 | 1,394 | 1,111 | 1,407 |
| Nelson | 2,111 | 1,750 | 2,212 | 1,920 | 2,714 |
| Westland | 396 | 446 | 477 | 501 | 545 |
| Canterbury | 13,405 | 13,425 | 14,823 | 15,555 | 17,011 |
| Otago | 7,505 | 6,714 | 7,811 | 8,487 | 8,655 |
| Southland | 4,999 | 4,785 | 6,084 | 5,128 | 5,687 |
| Totals | 98,144 | 91,361 | 100,855 | 109,187 | 121,006 |
| Duplications | 1,886 | 151 | 1,321 | 641 | 1,486 |
| Totals | 96,258 | 91,211 | 99,534 | 108,546 | 119,520 |
Classification by Amount-Of the gross total of £121,006,000 represented by mortgages registered during the financial year 1959-60, mortgages under £500 in value represented 1.7 percent of the total; from £500 to £999, 3.6 per cent; £1,000 to £1,999, 12.9 per cent; £2,000 to £2,999, 35.0 per cent; £3,000 to £3,999, 8.2 per cent; £4,000 to £4,999, 4.6 per cent; £5,000 to £7,499, 8.7 per cent; and from £7,500 and over, 25.3 per cent. The following table gives the number and amount for town and suburban and country properties according to sum secured.
| Amount Group | Town and Suburban | Country | All Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | Number | Amount | ||
| £ | £ | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Under | 500 | 7,241 | 1,888 | 596 | 165 | 7,837 | 2,052 |
| 500- | 999 | 5,736 | 3,840 | 767 | 516 | 6,503 | 4,356 |
| 1,000- | 1,999 | 9,670 | 13,559 | 1,550 | 2,092 | 11,220 | 15,651 |
| 2,000- | 2,999 | 16,386 | 39,182 | 1,392 | 3,224 | 17,778 | 42,406 |
| 3,000- | 3,999 | 2,124 | 6,894 | 913 | 2,975 | 3,037 | 9,869 |
| 4,000- | 4,999 | 661 | 2,797 | 650 | 2,775 | 1,311 | 5,572 |
| 5,000- | 7,*99 | 519 | 2,937 | 1,276 | 7,587 | 1,795 | 10,524 |
| 7,500 and over | 433 | 8,373 | 1,623 | 22,204 | 2,056 | 30,576 | |
| Unspecified | 4,472 | 1,858 | 6,330 | ||||
| Gross totals | 47,242 | 79,468 | 10,625 | 41,538 | 57,867 | 121,006 | |
| Duplications | 24 | 940 | 9 | 545 | 33 | 1,486 | |
| Net totals | 47,218 | 78,528 | 10,616 | 40,992 | 57,834 | 119,520 | |
Excluding mortgages for which no amounts were shown, the average amount for each mortgage registered in 1959-60 was £2,321, as compared with £2,113 in 1958-59.
Mortgages on Urban and Rural Securities - Figures are available in the case of mortgage registrations showing for each registration district the amounts advanced on urban and on rural properties. The distinction is between “town and suburban” and “country” holdings, but sufficient information to permit of a strictly accurate classification on that basis is not always available. Generally, however, mortgages are regarded as town and suburban if secured on properties situated within cities or boroughs or on small holdings in the nature of building allotments which are not definitely distinguishable as country properties. Mortgages classified as town and suburban in 1959-60 were secured on areas averaging just under one-quarter of an acre in extent, as compared with an average area of some 280 acres in the case of “country” securities.
Town and suburban securities accounted for 82 per cent of the number and 66 per cent of the aggregate value of mortgages in 1959-60 as compared with 18 per cent and 34 per cent respectively in the case of country properties.
The following table gives mortgages registered in the various districts during the year 1959-60.
| District | Town and Suburban | Country | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Area | Amount Secured | Number | Area | Amount Secured | |
| acres | £(000) | acres | £(000) | |||
| North Auckland | 14,200 | 3,584 | 24,711 | 2,252 | 320,021 | 6,890 |
| South Auckland | 4,828 | 1,358 | 8,693 | 2,105 | 492,860 | 8,619 |
| Gisborne | 589 | 197 | 1,013 | 194 | 115,843 | 844 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,936 | 505 | 3,061 | 638 | 218,743 | 3,354 |
| Taranaki | 1,331 | 439 | 2,182 | 533 | 133,783 | 2,186 |
| Wellington | 9,838 | 2,130 | 17,513 | 1,380 | 420,054 | 5,922 |
| Marlborough | 407 | 126 | 711 | 159 | 95,706 | 696 |
| Nelson | 1,119 | 284 | 1,518 | 388 | 68,336 | 1,196 |
| Westland | 278 | 73 | 341 | 96 | 34,355 | 203 |
| Canterbury | 6,897 | 1,570 | 11,156 | 1,364 | 485,768 | 5,854 |
| Otago | 4,253 | 881 | 5,875 | 807 | 349,992 | 2,779 |
| Southland | 1,566 | 379 | 2,693 | 709 | 240,095 | 2,994 |
| Totals | 47,242 | 11,526 | 79,468 | 10,625 | 2,975,556 | 41,538 |
During the past 11 years the trend in mortgage registrations has passed through several distinct stages. Prior to the lifting of controls on land sales there was a steady increase in the number of mortgage agreements due in large measure to the resettlement of ex-servicemen. Restrictions were removed from the sale of all lands other than farm lands in February 1950, and farm lands were released in November 1950. Following this change there was a marked increase in activity during the next two years, and since 1953-54 the level of mortgage business has remained high, and though there has been considerable fluctuation from year to year the general trend has been upward.
In 1950-51, the first full year following the release of urban properties from controls, the value of new urban mortgages was £32,030,000, compared with £22,631,000 in the previous year. The following year, 1951-52, new urban mortgages showed a further large increase to reach £46,751,000. For the next two years slight drops were recorded in the amount secured, but in 1954-55 the total for new urban mortgages increased by £10,609,000 to £52,874,000, and in 1955-56 rose markedly to £64,421,000. The statistics for the next two years were slightly below those for 1955-56, but in the two latest years, 1958-59 and 1959-60, small increases in the number of urban mortgages registered and significant increases in the amounts secured were recorded.
The movement in new rural mortgages does not always follow the same pattern as that of urban mortgages. In 1951-52, which was the first full year after the release of rural property from controls, the value of new mortgage transactions increased from £14,023,000 to £26,425,000. Since that time the total rural mortgage consideration has fluctuated from year to year but not to the extent that has been shown by urban mortgages. There was a marked increase of £5,828,000 or 18 per cent, in the value of new rural mortgages in 1957-58, a year in which the value of new urban mortgages increased by only about 6 per cent, and in 1958-59 rural mortgages registered decreased in value by £2,451,000, or 6 per cent, at a time when the new urban mortgages increased by 17 per cent in value. In the latest year an increase of £5,440,000, or 15 per cent, was recorded in the value of new rural mortgages, while new urban mortgages increased by only 9 per cent.
| Year Ended 31 March | Number | Area | Amount Secured | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Town and Suburban | Country | Total | Town and Suburban | Country | Total | ||
| acres | acres | acres | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| 1950 | 30,353 | 7,607 | 2,397,545 | 2,405,152 | 22,631 | 13,413 | 36,043 |
| 1951 | 43,884 | 9,373 | 2,429,844 | 2,439,217 | 32,030 | 14,023 | 46,053 |
| 1952 | 49,886 | 10,021 | 2,563,240 | 2,573,261 | 46,751 | 26,425 | 73,175 |
| 1953 | 50,658 | 9,966 | 2,808,605 | 2,818,571 | 45,159 | 29,574 | 74,732 |
| 1954 | 52,833 | 10,396 | 3,258,771 | 3,269,167 | 42,266 | 28,645 | 70,910 |
| 1955 | 58,028 | 11,654 | 3,560,915 | 3,572,569 | 52,874 | 32,375 | 85,249 |
| 1956 | 55,586 | 11,261 | 3,148,978 | 3,160,239 | 64,421 | 33,723 | 98,144 |
| 1957 | 51,257 | 10,401 | 2,640,129 | 2,650,530 | 58,640 | 32,721 | 91,361 |
| 1958 | 55,468 | 11,251 | 3,194,280 | 3,205,531 | 62,306 | 38,549 | 100,855 |
| 1959 | 56,218 | 11,876 | 2,739,511 | 2,751,387 | 73,089 | 36,098 | 109,187 |
| 1960 | 57,867 | 11,526 | 2,975,556 | 2,987,082 | 79,468 | 41,538 | 121,006 |
Note-These figures exclude certain miscellaneous registrations, but have not been adjusted to exclude duplications.
Rates of Interest - The following table gives a classification of mortgages registered according to the various rates of interest, and includes duplicate registrations (to the extent of £640,813 in 1958-59 and £1,485,919 in 1959-60).
| Rate percent Cent | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | |
| 1/2 | 27,800 | 6,304 |
| 3/4 | 2,080 | - |
| 1 | 69,839 | 113,753 |
| 1 1/2 | 4,836 | 8,200 |
| 1 4/5 | - | 1,000 |
| 2 | 138,681 | 178,771 |
| 2 1/8 | 410 | - |
| 2 1/2 | 76,707 | 107,874 |
| 3 | 13,788,295 | 20,728,729 |
| 3 1/8 | 34,444 | 567,249 |
| 3 1/4 | 7,600 | 45,438 |
| 3 1/3 | 27,000 | - |
| 3 1/2 | 218,463 | 149,493 |
| 3 3/4 | 3,547 | 8,912 |
| 3 4/5 | - | 3,000 |
| 3 9/10 | 325 | - |
| 4 | 1,191,625 | 1,594,027 |
| 4 1/20 | 2,000 | - |
| 4 1/8 | 963,570 | 799,499 |
| 4 1/5 | 7,000 | - |
| 4 1/4 | 418,166 | 405,883 |
| 4 1/3 | 110 | 500 |
| 4 3/8 | 8,530 | 2,700 |
| 4 1/2 | 682,760 | 674,196 |
| 4 3/5 | 200 | - |
| 4 5/8 | 31,607 | 30,654 |
| 4 2/3 | 515 | - |
| 4 7/10 | - | 2,340 |
| 4 3/4 | 10,472,738 | 6,354,108 |
| 4 7/8 | 1,310,188 | 932,145 |
| 5 | 12,388,291 | 13,408,365 |
| 5 1/10 | 6,000 | 2,700 |
| 5 1/8 | 12,180 | 24,500 |
| 5 1/5 | 5,000 | 716 |
| 5 1/4 | 317,431 | 152,928 |
| 5 3/10 | - | 1,700 |
| 5 1/2 | 34,368,556 | 38,420,175 |
| 5 5/8 | 2,000 | - |
| 5 3/4 | 318,104 | 522,704 |
| 5 7/8 | 12,725 | - |
| 6 | 11,165,867 | 13,388,355 |
| 6 1/10 | 800 | - |
| 6 1/8 | - | 5,500 |
| 6 1/4 | 88,050 | 53,500 |
| 6 3/8 | - | 11,000 |
| 6 1/2 | 3,701,093 | 3,027,972 |
| 6 3/4 | 17,190 | 17,600 |
| 6 4/5 | 600 | - |
| 7 | 1,772,727 | 1,635,465 |
| 7 1/10 | 3,500 | - |
| 7 1/4 | 4,100 | 7,200 |
| 7 1/2 | 931,924 | 473,610 |
| 7 2/3 | - | 750 |
| 7 3/4 | 5,697 | 7,380 |
| 8 | 1,358,477 | 1,201,197 |
| 8 3/20 | 347 | - |
| 8 1/5 | 2,750 | - |
| 8 1/4 | 40 | - |
| 8 1/2 | 183,678 | 47,777 |
| 8 2/3 | 1,581 | - |
| 8 3/4 | - | 350 |
| 9 | 115,233 | 103,277 |
| 9 1/2 | 24,145 | 2,325 |
| 10 | 552,419 | 595,726 |
| 10 1/2 | 2,100 | - |
| 11 | - | 3,150 |
| 12 | 3,700 | 4,525 |
| 12 1/2 | 31,435 | 14,020 |
| 14 | - | 4,695 |
| 15 | 12,887 | 8,351 |
| 16 | 9,950 | - |
| 18 | 5,800 | 519 |
| 19 | 205 | - |
| 19 1/2 | - | 318 |
| 20 | 29,820 | 287 |
| 22 | - | 600 |
| 24 | - | 1,000 |
| 30 | 2,355 | - |
| 33 | - | 2,420 |
| 48 | 50 | - |
| Unspecified | 12,239,156 | 15,138,318 |
| Totals | 109,186,999 | 121,005,749 |
A further classification of the 1959-60 figures in the preceding table is now given, showing the various rates of interest for town and suburban and country properties.
| 1959–60 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rate Per Cent | Town and Suburban | Country |
| £ | £ | |
| 1/2 | 4,024 | 2,280 |
| 1 | 24,856 | 88,897 |
| 1 1/2 | 3,040 | 5,160 |
| 1 4/5 | 1,000 | - |
| 2 | 74,499 | 104,272 |
| 2 1/2 | 23,927 | 83,947 |
| 3 | 18,701,766 | 2,026,963 |
| 3 1/8 | 539,646 | 27,603 |
| 3 1/4 | 39,438 | 6,000 |
| 3 1/2 | 76,685 | 72,808 |
| 3 3/4 | 8,912 | - |
| 3 4/5 | 3,000 | - |
| 4 | 384,743 | 1,209,284 |
| 4 1/8 | 147,205 | 652,294 |
| 4 1/4 | 205,248 | 200,635 |
| 4 1/3 | 500 | - |
| 4 3/8 | 2,700 | - |
| 4 1/2 | 198,244 | 475,952 |
| 4 5/8 | 2,574 | 28,080 |
| 4 7/10 | 2,340 | - |
| 4 3/4 | 5,832,119 | 521,989 |
| 4 7/8 | 534,095 | 398,050 |
| 5 | 5,148,151 | 8,260,214 |
| 5 1/10 | - | 2,700 |
| 5 1/8 | 6,000 | 18,500 |
| 5 1/5 | 216 | 500 |
| 5 1/4 | 25,096 | 127,832 |
| 5 3/10 | 1,700 | - |
| 5 1/2 | 23,724,754 | 14,695,421 |
| 5 3/4 | 297,996 | 224,708 |
| 6 | 8,975,913 | 4,412,442 |
| 6 1/8 | 5,500 | - |
| 6 1/4 | 40,000 | 13,500 |
| 6 3/8 | - | 11,000 |
| 6 1/2 | 2,375,084 | 652,888 |
| 6 3/4 | 17,500 | 100 |
| 7 | 1,219,038 | 416,427 |
| 7 1/4 | 7,200 | - |
| 7 1/2 | 304,983 | 168,627 |
| 7 2/3 | 750 | - |
| 7 3/4 | 2,380 | 5,000 |
| 8 | 971,641 | 229,556 |
| 8 1/2 | 46,867 | 910 |
| 8 3/4 | 350 | - |
| 9 | 77,501 | 25,776 |
| 9 1/2 | 975 | 1,350 |
| 10 | 364,300 | 231,426 |
| 11 | 3,150 | - |
| 12 | 4,525 | - |
| 12 1/2 | 9,020 | 5,000 |
| 14 | 4,695 | - |
| 15 | 5,401 | 2,950 |
| 18 | 519 | - |
| 19 1/2 | 318 | - |
| 20 | 287 | - |
| 22 | 600 | - |
| 24 | 1,000 | - |
| 33 | 2,420 | - |
| Unspecified | 9,011,815 | 6,126,502 |
| Totals | 79,468,206 | 41,537,543 |
The average rate of interest on new mortgages was maintained at over 6 per cent per annum from 1922 to 1932, but with the advent of the depression period and the effect of the mortgage relief legislation, subsequent years showed decreases. The inclusion of State Advances mortgages from the year 1935-36 onwards has no doubt also had the effect of reducing the average rate, and in addition the advent of rehabilitation mortgages to ex-servicemen in the earlier post-war years and their gradual diminution in later years affected the rate. The average rate has been showing a rising trend during the last decade but a drop was recorded in 1958-59 and again in 1959-60, largely as a result of the State Advances Corporation 3 per cent home-building loans which were introduced in February 1958. The average rate of interest for town and suburban properties for 1959-60 was 4.89 per cent, as compared with 5.25 per cent for country properties. The comparative figures for 1958-59 were 5.11 and 5.25 respectively.
Averages for recent years for all properties have been as follows.
| Year Ended 31 March | Average Rate Per Cent | Year Ended 31 March | Average Rate Per Cent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 3.98 | 1955 | 4.69 |
| 1950 | 3.99 | 1956 | 4.76 |
| 1951 | 4.09 | 1957 | 5.09 |
| 1952 | 4.15 | 1958 | 5.24 |
| 1953 | 4.29 | 1959 | 5.15 |
| 1954 | 4.49 | 1960 | 5.01 |
The average rate of interests, excluding mortgages at 3 per cent, was 5.51 per cent in 1958-59 and 5.50 per cent in 1959-60.
The following table shows interest rates of first mortgages on town and rural properties for the years ended 31 March 1956-60. It should be noted that mortgages registered with no specified rate of interest are excluded from the calculations of average rates.
| Year Ended 31 March | Class of Mortgage | Total Town and Suburban and Country | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Town and Suburban | Country | ||||||
| First Flat | First Table | Total (Including Other) | First Flat | First Table | Total (Including Other) | ||
| per cent | |||||||
| 1956 | 5.14 | 4.56 | 4.78 | 4.90 | 4.58 | 4.72 | 4.76 |
| 1957 | 5.50 | 4.83 | 5.11 | 5.28 | 4.86 | 5.07 | 5.09 |
| 1958 | 5.62 | 5.00 | 5.27 | 5.43 | 5.01 | 5.20 | 5.24 |
| 1959 | 5.77 | 4.77 | 5.11 | 5.47 | 5.13 | 5.25 | 5.15 |
| 1960 | 5.64 | 4.57 | 4.89 | 5.43 | 5.17 | 5.25 | 5.01 |
The table shows that there had been a rising trend in interest rates in all classes of mortgages until the years 1958-59 and 1959-60, when the State Advances Corporation home-building loans at 3 per cent had the effect of reducing the rate for first table town and suburban mortgages and the averages for total town and suburban and all property mortgages. In 1959-60 there were reductions in the average rate of interest for first flat mortgages on both town and suburban and country properties.
The next table gives the amount of mortgage money and interest rate of each class of mortgage for the three years ended 31 March 1958-60.
| Class of Mortgage | Amount Year Ended 31 March | Average Rate of Interest Year Ended 31 March | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| £(thousand) | Per cent | |||||
| First flat town | 15,578 | 14,610 | 12,423 | 5.62 | 5.77 | 5.64 |
| First table town | 34,614 | 45,211 | 52,157 | 5.00 | 4.77 | 4.57 |
| Totals, town (including other) | 55,636 | 65,252 | 70,456 | 5.27 | 5.11 | 4.89 |
| First flat rural | 13,542 | 9,518 | 9,685 | 5.43 | 5.47 | 5.43 |
| First table rural | 15,796 | 17,360 | 20,032 | 5.01 | 5.13 | 5.17 |
| Totals, rural (including other) | 34,872 | 31,696 | 35,411 | 5.20 | 5.25 | 5.25 |
| Totals, town and rural | 90,508 | 96,948 | 105,867 | 5.24 | 5.15 | 5.01 |
The average rate of interest on mortgages registered was 4.51 per cent in 1944-45. Sharp falls to 4.10 per cent in 1945-46 and to 3.85 per cent in 1946-47 were mainly due to rehabilitation loans advanced to ex-servicemen by the State Advances Corporation. The rate of interest charged on rehabilitation loans for residential and farm properties is 3 per cent, and of the gross amount of mortgages registered during the years 1947-48 to 1957-58 no less than 36.7, 30.2, 28.0, 22.4, 16.8, 16.2, 12.9, 9.3, 7.7, 6.5, and 5.8 per cent respectively were at this rate, as compared with only 2.0 per cent in 1944-45. The proportion of 3 per cent loans for 1958-59 rose to 14.2 per cent and in 1959-60 increased to 19.6 per cent. These increases have resulted from the introduction by the State Advances Corporation of 3 per cent home-building loans. The average rate of interest, excluding mortgages at 3 per cent, was 5.51 per cent in 1958-59 and 5.50 per cent in 1959-60. It is of interest to note that in 1931-32 only 10.2 per cent of the specified amount was at rates not exceeding 5 per cent, while no less than 43.3 per cent was at rates exceeding 6 per cent. The corresponding figures for 1959-60 were 43.6 and 6.8 respectively.
A further analysis showing amounts classified by interest rate groups is given below. This table shows that the proportion of new mortgages registered in the higher range of interest rates rose appreciably in the last five years.
| Year Ended 31 March | Not Exceeding 3 Per Cent | Over 3 Per Cent to 4 Per Cent | Over 4 1/2 Per Cent to 4 1/2 Per Cent | Over 4 1/2 Per Cent to 4 3/4 Per Cent | Over 4 3/4 Per Cent to 5 Per Cent | Over 5 Per Cent to 5 1/2 Per Cent | Over 5 1/2 Per Cent to 6 Per Cent | Exceeding 6 Per Cent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1950 | 10,302 | 5,525 | 12,748 | 258 | 2,440 | 277 | 380 | 569 |
| 1951 | 10,558 | 6,904 | 18,984 | 314 | 3,466 | 321 | 477 | 880 |
| 1952 | 12,635 | 9,838 | 34,621 | 387 | 4,722 | 990 | 652 | 1,113 |
| 1953 | 12,534 | 4,709 | 34,807 | 1,143 | 11,813 | 1,101 | 1,217 | 1,516 |
| 1954 | 9,512 | 3,607 | 21,984 | 940 | 21,776 | 1,643 | 2,225 | 1,651 |
| 1955 | 8,431 | 3,547 | 21,507 | 863 | 32,344 | 2,897 | 5,457 | 2,441 |
| 1956 | 8,137 | 2,708 | 21,488 | 2,100 | 43,683 | 4,510 | 5,109 | 2,861 |
| 1957 | 6,304 | 1,690 | 9,947 | 6,872 | 21,544 | 24,273 | 7,805 | 4,768 |
| 1958 | 6,233 | 1,801 | 2,810 | 11,917 | 16,932 | 33,951 | 11,003 | 5,863 |
| 1959 | 14,109 | 1,483 | 2,082 | 10,505 | 13,698 | 34,709 | 11,499 | 8,863 |
| 1960 | 21,145 | 2,368 | 1,883 | 6,387 | 14,341 | 38,603 | 13,911 | 7,231 |
| Percentage of Total | ||||||||
| 1950 | 31.7 | 17.0 | 39.2 | 0.8 | 7.5 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| 1951 | 25.2 | 16.5 | 45.3 | 0.7 | 8.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 2.1 |
| 1952 | 19.5 | 15.1 | 53.3 | 0.6 | 7.3 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.7 |
| 1953 | 18.2 | 6.8 | 50.6 | 1.7 | 17.2 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.2 |
| 1954 | 15.0 | 5.7 | 34.7 | 1.5 | 34.4 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 1955 | 10.9 | 4.6 | 27.8 | 1.1 | 41.7 | 3.7 | 7.0 | 3.1 |
| 1956 | 9.0 | 3.0 | 23.7 | 2.3 | 48.2 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 3.2 |
| 1957 | 7.6 | 2.0 | 12.0 | 8.3 | 25.9 | 29.2 | 9.4 | 5.7 |
| 1958 | 6.9 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 13.2 | 18.7 | 37.5 | 12.2 | 6.5 |
| 1959 | 14.6 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 10.8 | 14.1 | 35.8 | 11.9 | 9.1 |
| 1960 | 20.0 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 6.0 | 13.6 | 36.5 | 13.1 | 6.8 |
The trend in interest rates is further illustrated in the following diagram, which shows also the movement in mortgage registrations. The total amounts indicated in the diagram and in the two immediately preceding tables do not represent the total registrations in the respective years, as mortgages on which the rate of interest was not specified have been excluded.
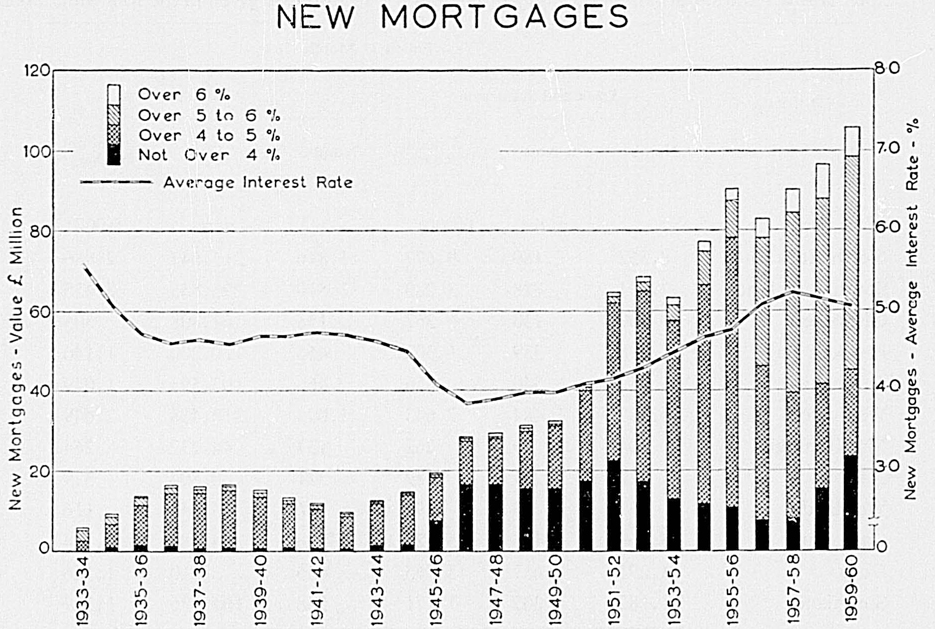
MORTGAGES DISCHARGED- The value of mortgages registered normally exceeds the value of mortgages released, although discharges exceeded registrations for a period of five years commencing with the year 1933-34, and again from 1941-42 to 1945-46. Registrations exceeded discharges by £53,456,000 in 1957-58, £64,152,000 in 1958-59, and £68,389,000 in 1959-60.
The amount released during 1955-56, at £35,367,000 was the lowest since 1952-53, but an increase to £37,680,000 occurred in 1956-57, and a large increase to reach £46,100,000 followed in 1957-58. The value of discharges in 1958-59 decreased by £1,685,000, but in 1959-60 there was an increase of £6,737,000 to a record figure of £51,131,000.
The total amount of mortgages discharged, including mortgages under the deeds-registration system, for the last four years is as follows.
| District | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | Number | Amount | Number | Amount | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| North Auckland | 8,219 | 9,243 | 9,396 | 10,439 | 9,331 | 10,676 | 10,168 | 12,563 |
| South Auckland | 3,227 | 3,990 | 4,005 | 5,521 | 3,802 | 5,389 | 4,441 | 6,735 |
| Gisborne | 518 | 716 | 597 | 857 | 524 | 611 | 558 | 672 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,545 | 1,923 | 1,627 | 2,363 | 1,658 | 2,148 | 1,753 | 2,447 |
| Taranaki | 1,186 | 1,605 | 1,373 | 1,895 | 1,240 | 1,634 | 1,318 | 1,905 |
| Wellington | 6,311 | 7,313 | 7,322 | 9,150 | 7,544 | 9,457 | 7,976 | 10,292 |
| Marlborough | 354 | 489 | 405 | 518 | 431 | 549 | 441 | 526 |
| Nelson | 923 | 834 | 1,000 | 979 | 1,046 | 1,030 | 1,143 | 1,068 |
| Westland | 266 | 169 | 344 | 272 | 292 | 229 | 335 | 313 |
| Canterbury | 5,056 | 6,158 | 5,560 | 7,064 | 5,657 | 6,726 | 6,106 | 8,307 |
| Otago | 3,547 | 3,256 | 4,006 | 4,238 | 3,860 | 3,896 | 3,946 | 4,530 |
| Southland | 1,514 | 1,992 | 1,811 | 2,792 | 1,540 | 2,071 | 1,750 | 2,399 |
| Totals | 32,666 | 37,689 | 37,446 | 46,088 | 36,925 | 44,418 | 39,935 | 51,758 |
| Duplications | 3 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 24 | 4 | 627 |
| Totals | 32,663 | 37,680 | 37,441 | 46,079 | 36,920 | 44,394 | 39,931 | 51,131 |
Details of town and suburban and country discharges for 1959-60 are given in the following table.
| District | Year Ended 31 March 1960 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Town and Suburban | Country | |||||
| Number | Area | Amount Discharged | Number | Area | Amount Discharged | |
| acres | £(000) | acres | £(000) | |||
| North Auckland | 8,352 | 2,189 | 9,677 | 1,816 | 215,642 | 2,886 |
| South Auckland | 2,931 | 828 | 3,280 | 1,510 | 295,855 | 3,455 |
| Gisborne | 400 | 130 | 367 | 158 | 61,808 | 305 |
| Hawke's Bay | 1,298 | 339 | 1,302 | 455 | 120,200 | 1,146 |
| Taranaki | 852 | 340 | 856 | 466 | 103,593 | 1,049 |
| Wellington | 6,882 | 1,484 | 7,643 | 1,094 | 310,488 | 2,649 |
| Marlborough | 304 | 99 | 262 | 137 | 44,232 | 264 |
| Nelson | 822 | 201 | 689 | 321 | 60,804 | 379 |
| Westland | 259 | 63 | 197 | 76 | 25,342 | 116 |
| Canterbury | 4,968 | 1,165 | 5,123 | 1,138 | 364,484 | 3,184 |
| Otago | 3,291 | 657 | 3,365 | 655 | 273,710 | 1,166 |
| Southland | 1,182 | 307 | 1,171 | 568 | 165,126 | 1,229 |
| Gross totals | 31,541 | 7,802 | 33,932 | 8,394 | 2,041,284 | 17,827 |
| Duplications | 2 | ... | 1 | 2 | 626 | |
| Net totals | 31,539 | 7,802 | 33,931 | 8,392 | 2,041,284 | 17,201 |
As early as 1892 the Government commenced the purchase of lands for cutting up for sale or lease to private individuals, and two years later the passing of the Government Advances to Settlers Act 1894 marked the inauguration of a series of schemes for lending money to settlers, workers, etc., for the purchase of homes, the improvement of farms, and the development of resources and of industries. The schemes varied considerably in detail, but all lay in one of two main classes - those in which the money was advanced on security, and those in which the expenditure was incurred by the Government itself in the first place and recouped from sales or leases. Advances to settlers, workers, and ex-servicemen are the principal examples of the former class, and the purchase of land for settlement (including the settlement of ex-servicemen) is the principal example of the latter.
STATE ADVANCES CORPORATION - The Mortgage Corporation of New Zealand Act 1934-35 authorised the creation of a Corporation under a board composed of directors appointed partly by the State and partly by the shareholders of the Corporation
By the State Advances Corporation Act 1936 the private capital invested in the Mortgage Corporation was cancelled, provision being made for buying out shareholders in respect of shares held in the Corporation. The capital of the Corporation was maintained at £1,000,000, however, by an investment from the Consolidated Fund, while all securities issued by the Corporation carry a State guarantee. The management of the Corporation is vested in a board of directors consisting of a managing director appointed by the Governor-General in Council, one or more other directors similarly appointed, and an ex officio director, being such officer of the Treasury as the Minister of Finance may approve from time to time. In the exercise of its powers, the board is enjoined to have regard to any representations that may be made by the Minister of Finance. Every direction in writing given by the Minister is binding on the board.
The change in administration and the institution of a State guarantee on securities issued by the Corporation represented the major alterations to the pre-existing law. All the functions of the Mortgage Corporation were transferred to the new body, while certain extensions of function were made e.g., the administration of the Housing Act.
In view of the heavy call on its financial resources and the need to overtake the housing shortage, the Corporation has for some years been concentrating its residential lending on the provision of loans for the erection of houses or the acquisition of houses which have not previously been occupied. Applicants are expected to contribute as fully as reasonably possible from their own resources. The Corporation's aim is to assist home seekers to acquire moderately-priced new homes of a good standard and provide reasonable accommodation for the applicant and his family.
Advances may be made on the security of a first mortgage of land and, under what is known as its “ordinary” lending operations, the Corporation entertains loans up to two-thirds of the assessed value of the land and house, with a maximum not generally in excess of £2,500.
Where a loan on a two-thirds margin is insufficient to enable the applicant to achieve his objective, “special” loans are entertained. Whilst no specific maximum loan is laid down for “special” loans, factors such as family commitments, capital resources and cost of house and land are taken into account. Each applicant is expected to make a reasonable contribution himself and, as already stated, is also expected to contribute as much as reasonably possible from his available assets. In general each case is considered on its merits.
Early in 1958 a scheme was introduced whereby loans with the interest rebated to 3 per cent were made available to borrowers who had not owned a property within a period of five years prior to the date of application, and where the income of the breadwinner did not exceed £1,000 per annum (increased by £50 for each dependent child), including overtime and bonuses, but without taking into account family benefit or war pensions. In the period from 12 February 1958 to 31 March 1960 there had been approved under this latter provision 16,362 loans of a total value of £39,862,685, the figures for the year ended 31 March 1960 being 9,176 loans involving £22,791,115.
Where an applicant does not qualify for 3 per cent interest any loan granted is at the Corporation's normal lending rate which is at present 4 3/4 per cent.
In cases where the normal lending margin is exceeded with the approval of the Government, the Corporation is guaranteed against any loss attributable to the granting of advances in excess of two-thirds of the value of the security.
Approximately 10 years ago the Government introduced a suspensory loan scheme which is still in operation. In effect an applicant having a house erected for himself can qualify for an additional subsidy up to 10 per cent of the cost of the house (with a maximum of £200). The suspensory loan is reduced by £1 for each £2 by which the cost exceeds £2,300, up to a total cost of £2,600. If, however, the applicant has three children the limit of £2,300 is increased to £2,450, for four children to £2,600, and for five or more children to £2,750. Applicants who are granted 3 per cent loans do not also qualify for suspensory loans. The number of loans of this type approved during the year ended 31 March 1960 was 421, involving £65,285, and the total to 31 March 1960 was £3,914,232 in respect of 24,194 loans.
In addition to the above suspensory loan scheme there is a further class of suspensory loan granted to rehabilitation farm applicants, the object of which is to settle the men on a basis comparable with that under the conditions which existed while the Servicemen's Settlement and Land Sales Act 1943 remained in force. During the 1959-60 year 73 suspensory loans of this type were granted involving advances of £122,275. Since the scheme was put into operation a total of 3,093 such suspensory loans have been authorised, the aggregate amount involved being £3,723,769. The funds required to meet urban and rural suspensory loans are provided by the Treasury out of the Consolidated Fund, and lump-sum payments are made by the Treasury to the Corporation to meet requirements from time to time.
The large majority of the loans granted by the board are secured by table mortgages for terms varying from 10 to 30 years, but the board also has power to make advances on flat mortgage on certain conditions.
When loans are granted in excess of normal lending margins, mortgagors may be required to offer some form of collateral security (e.g., mortgage of life policy). A mortgagor may not give any subsequent mortgage or any other charge over land subject to any mortgage to the Corporation except with the written authority of the board, unless the further mortgage or other charge is in favour of the Corporation.
All mortgagors who receive from the Corporation a loan secured by a mortgage of land are required to pay as a contribution to the General Reserve Fund an amount equal to 2 per cent of the amount of the loan. These amounts, which may be borrowed as an addition to the principal sum if so desired, together with the surplus profits referred to below, and certain past payments on account of mortgages transferred to the Corporation, form the General Reserve Fund.
The board is required from time to time to fix the rates of interest to be paid under mortgages to the Corporation, so as to make adequate provision to cover the costs of administration and for all other matters incidental to the proper functioning of the Corporation. After such provision as the Minister of Finance thinks proper has been made for the depreciation of securities or other assets, and for such other matters as in his opinion are necessary for the efficient conduct of the business of the Corporation, the surplus for each financial year is to be paid into the Public Account unless the Minister, in his discretion, authorises the board to credit it, in whole or in part, to the General Reserve Fund of the Corporation.
In addition to its primary function of providing cheap long-term finance in the form of first mortgage on property, the Corporation has been authorised to make loans to local authorities for the purpose of erecting pensioner and approved community housing schemes and farm dwellings, and also advances to individuals for the development of existing industries or the establishment of new industries.
The Corporation is also authorised to act as agent for other Departments of State, more particularly in respect of the inspection and supervision of properties and the collection of moneys payable to such Departments.
A further scheme of housing finance administered by the Corporation is that established by the Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act 1958, which came into operation on 1 April 1959, the moneys for which are provided by the Social Security Department and paid out by the Corporation. Applications for advances under this Act are received only from applicants who have already been declared eligible by the Social Security Commission. For the year ended 31 March 1960, 9,342 advances, totalling £5,684,074, were authorised by the Corporation under this agency.
The Corporation acts as the agent of the Rehabilitation Board in obtaining valuations and preparing reports in respect of farm and residential property for submission to the Rehabilitation Loans Committee (or to District Loans Committees acting under delegated authority from the Rehabilitation Loans Committee), which has been appointed to consider and approve of loan applications lodged by ex-servicemen who are eligible for assistance under the Rehabilitation Act 1941. The administration of such loans, when granted, is the subsequent responsibility of the Corporation. The classes of loans granted and the terms and conditions applicable thereto are set out in Section 9B (Rehabilitation). The securities taken in respect of rehabilitation loans for farms or houses are similar to mortgages taken for the purpose of securing advances made under the Corporation's ordinary lending activities, except that the Reserve Fund contribution on advances within the respective loan limits is paid by the Consolidated Fund, which also meets the difference between the Corporation's normal interest rate and the reduced interest rate charged to ex-servicemen.
A mortgage guarantee scheme was provided for by the State Advances Corporation Amendment Act 1953. This amendment enables the Corporation to guarantee financial institutions repayment by the borrower of the difference between their normal housing loan and 90 per cent of the valuation.
Reference to the Government's housing scheme under the Housing Act 1955, together with particulars of the numbers of houses erected, financial operations, etc., are contained in Section 19 (Building and Housing Construction; and Tenancy).
Summary of Activities - As already indicated, the Corporation, in addition to its normal lending functions, administers a number of other State activities, and a general summary of the business under administration as at 31 March 1960 is as follows.
| Classification | Number of Accounts | Capital Investment |
|---|---|---|
| State Advances Corporation - | ||
| Mortgage investments - | ||
| Urban | 89,295 | 125,990,878 |
| Rural | 23,329 | 54,752,977 |
| Loans to industries under section 29 | 34 | 1,269,930 |
| Net principal not due | 182,013,785 | |
| Seasonal current account debit balances | 356 | 615,162 |
| Government and local authority securities | 776 | 11,764,970 |
| Housing Account- | ||
| Dwellings let (less depreciation) | 42,081 | 90,992,458 |
| Shops, halls and communal garages less depreciation) | 188 | |
| Dwellings sold | 15,375 | 29,086,718 |
| Loans to local authorities | 141 | 1,390,503 |
| Loans to employers | 21 | 99,967 |
| Rural Housing Act: loans to local authorities | 90 | 951,706 |
| Advances under Rehabilitation Act 1941 | ||
| Furniture, tools of trade, business, and miscellaneous | 913 | 130,069 |
| Interest-free supplementary loans | 1,489,221 | |
| Other agencies - | ||
| Department of Health | 98 | 944,323 |
| Licensing Control Commission | 3 | 31,069 |
| Agriculture Emergency Powers Act 1934 | 1 | 1,625 |
| Gas companies | 4 | 202,913 |
| Suspensory loans (rural and urban) | 18,206 | 5,947,079 |
| Timber workers' housing - | ||
| Levies accounts | 6 | 275,700 |
| Rental accounts | 108 | |
| Miscellaneous rentals, etc. | 657 | ... |
| Totals | 191,682 | £325,937,268 |
Farm loans and residential loans to ex-servicemen under the Rehabilitation Act 1941 are included with “Mortgage investments” above. Particulars of all rehabilitation loan authorisations will be found in Section 9B (Rehabilitation).
Financial - Balance-sheet figures show that at 31 March 1960 the authorised capital was £1,000,000, while stock and debentures outstanding were £176,221,890, an increase of £16,600,000 in the case of the latter compared with 31 March 1959.
The General Reserve Fund at March 1960 amounted to £11,316,265, and, in addition, there were specific reserves amounting to £3,332,081, making a total of £14,648,346, as compared with £13,658,701 at 31 March 1959.
Mortgages and accrued interest at 31 March 1960 totalled £181,248,305, an increase of £17,691,196 as compared with 31 March 1959, while Government and local authority securities and accrued interest at £11,880,921 were greater by £1,317,910.
The disposition and appropriation of profits in respect of operations during each of the last three financial years are given in the following table.
| Disposition and Appropriation of Profits | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Gross income | 6,482,276 | 7,100,090 | 7,699,480 |
| Less interest on General Reserve Fund investments | 337,587 | 381,393 | 429,257 |
| Gross income (mortgage and temporary investments) | 6,144,689 | 6,718,697 | 7,270,223 |
| Interest on stock and debentures | 4,660,971 | 5,103,281 | 5,666,677 |
| Gross profit | 1,483,718 | 1,615,416 | 1,603,546 |
| Management expenses | 706,727 | 702,416 | 682,418 |
| Net profit | 776,991 | 913,000 | 921,128 |
| Less reserve for taxes | 600,000 | 675,000 | 725,000 |
| Less reserve for losses | 80,817 | 102,628 | 102,226 |
| Surplus payable to Crown | 96,174 | 135,372 | 93,902 |
The gross income of £7,699,480 in 1959-60 included £6,514,385 interest on mortgages and current accounts, £433,725 interest on Government and local authority securities and temporary investments, and £751,370 recovery from the Rehabilitation Division on account of interest concessions to ex-servicemen on rehabilitation advances. Corresponding figures for 1958-59 were £5,940,587, £383,988, and £775,515 respectively.
New Business- A summary of loan operations (new business) for the last two financial years is given in the following table.
| Loans Authorised | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | Number | Value | |
*Includes 18 loans covering 89 flats and houses. †Includes 20 loans covering 104 flats and houses. ‡Excludes the number of supplementary and suspensory loans. | ||||
| Urban securities - | £ | £ | ||
| Erection of dwelling | 9,861* | 23,182,990 | 11,931† | 29,486,590 |
| Purchase, refinance, and other purposes | 1,525 | 1,769,455 | 1,214 | 1,619,200 |
| Supplementary | (242) | 15,535 | (153) | 9,940 |
| Suspensory | (800) | 123,605 | (406) | 62,760 |
| Totals, urban | 11,386‡ | 25,091,585 | 13,145‡ | 31,178,490 |
| Rural securities- | ||||
| Purchase, refinance, and other purposes | 1,018 | 4,161,526 | 1,320 | 5,703,331 |
| Supplementary | (1) | 400 | ||
| Suspensory | (138) | 173,120 | (88) | 124,800 |
| Totals, rural | 1,018‡ | 4,335,046 | 1,320‡ | 5,828,131 |
| Loans to industry | 3 | 213,500 | 2 | 105,000 |
| Local authorities | 17 | 264,960 | 2 | 1,005,000 |
| Grand totals | 12,424 | 29,905,091 | 14,469 | 38,116,621 |
NOTE- In addition to the above the following loans were authorised to group builders: 19 loans amounting to £244,880 in 1958-59 and 34 loans amounting to £303,000 in 1959-60.
The preceding figures include rehabilitation loans in respect of farms and houses. Other rehabilitation loans granted by the Rehabilitation Loans Committee and administered by the Corporation were as follows.
| Loans Authorised | Year Ended 31 March 1959 | Year Ended 31 March 1960 | Total to 31 March 1960 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | Number | Value | Number | Value | |
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Business | 21 | 19,525 | 7 | 10,220 | 11,523 | 7,502,200 |
| Furniture | 292 | 27,796 | 137 | 13,371 | 63,635 | 5,942,584 |
| Tools of trade | - | - | 1 | 50 | 1,482 | 48,964 |
| Miscellaneous | 2 | 100 | 2 | 250 | 670 | 132,057 |
| Additional advances | 9 | 308 | - | - | 624 | 52,338 |
| Totals | 324 | 47,729 | 147 | 23,891 | 77,934 | 13,678,143 |
A statement is given below of the aggregate number and amount of loans approved by the Board of Management since the Corporation commenced business in 1935.
| Number | £ | |
|---|---|---|
| Farm (including supplementary) | 25,813 | 99,009,685 |
| Residential (including supplementary) | 141,325 | 224,474,991 |
| Local authorities | 1,129 | 18,927,713 |
| Industries | 63 | 3,335,048 |
| Totals | 168,330 | 345,747,437 |
The lending rate of the Corporation was maintained until the end of 1953 at 4 1/8 per cent. Where first establishment is involved, rehabilitation loans to ex-servicemen for houses and farms are, however, at 3 per cent, reducible to 2 per cent for the first year and for business loans at 4 per cent, reducible to 2 per cent for the first year. The amount involved in interest concessions of this kind is now recouped from the Consolidated Fund. Loans granted under the Corporation's normal lending business are in general secured by table mortgages for varying periods.
The State Advances Corporation increased interest rates from 1 January 1954 on loans for the purchase of approved urban and rural properties from 4 7/8 per cent to 4 7/8 per cent and, from 1 April 1956, to 5 per cent. The interest rate applicable to loans for the building of new houses was increased from 4 1/8 per cent to 4 3/4 per cent as from 1 April 1956.
The following summary shows the annual cost-i.e., interest and principal payments - per £100 borrowed on table mortgage at 3 per cent, 4 3/4 per cent, and 5 per cent for the various periods.
| Term | Annual Amount Payable Per £100 Borrowed | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Per Cent | 4 3/4 Per Cent | 5 Per Cent | |||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 10 Years | 11 | 13 | 0 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 8 |
| 15 Years | 8 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 0 | 9 | 11 | 2 |
| 20 Years | 6 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 16 | 0 | 7 | 19 | 4 |
| 25 Years | 5 | 14 | 4 | 6 | 17 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 0 |
| 30 Years | 5 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 9 | 4 |
Special plans prepared by leading architects are available in book form, and assistance in calling tenders and in the erection of the houses is available from the Corporation's technical officers.
RURAL INTERMEDIATE CREDIT - The Rural Intermediate Credit Board, appointed in terms of the Rural Intermediate Credit Act 1927, provided a source from which farmers could obtain loan finance on favourable terms for such purposes as the purchase of stock and plant and farm improvements.
Pursuant to the provisions of Part VI of the State Advances Corporation Act 1936, the former Rural Intermediate Credit Board went out of office on 1 July 1937, and was replaced by the Board of Management of the State Advances Corporation, whose members became the Rural Intermediate Credit Board.
In terms of the Rural Intermediate Credit Amendment Act 1946 the business of the Rural Intermediate Credit Board was, as from 1 October 1946, absorbed by the State Advances Corporation, the board being abolished as from that date.
Under the Act farmers may obtain assistance in the following manner:
By borrowing through cooperative rural intermediate credit associations whose formation (with not less than 20 members and with certain defined objects) is provided for by the Act. The application for the loan is received and considered by the association concerned, which, on approving it, applies to the Corporation for its confirmation and for an advance to cover the loan. These loans are repayable on demand, but it has been the policy to arrange for the borrower to repay the amounts advanced over a period of up to five years. Extensions beyond that period may be approved in suitable cases. An association may, with the approval of the Corporation, arrange with a bank or other approved financial institution for a loan in cases where the term is not more than six months.
Persons engaged in farming on their own account, trustees, executors, or administrators carrying on farming operations, may obtain loans direct from the Corporation, the conditions being similar to (a) above.
At 31 March 1960 there were six cooperative rural intermediate credit associations in operation. The loans authorised through this channel during the year 1959–60 amounted to £121,920, and there were 267 loans current at the end of the year for an aggregate amount of £197,012.
The interest fixed for advances other than to cooperative rural intermediate credit associations is 5 per cent per annum, except in the case of ex-servicemen eligible for rehabilitation assistance, where the interest rate is 4 per cent per annum (rebated to 2 per cent for the first year provided the loan conditions are fulfilled). In the case of loans to cooperative rural intermediate credit associations the rate charged is 4 per cent, so that associations may be in a position to make advances to their members at 5 per cent.
HOUSING ACT – In addition to its lending activities the State Advances Corporation has the important function of administering the Housing Act 1955 on behalf of the Crown. Under the Housing Act 1955 the Corporation administers State houses and flats which become available for letting or for sale to tenants, as well as loans to local authorities granted under the provisions of this Act.
The following are the main operations:
Applications for State tenancies.
The subsequent administration of these tenancies.
The sale of State houses to tenants desiring to purchase.
Housing loans to local authorities for projects within defined Government policy.
The number of additional dwelling units handed over to the Corporation during the year ended 31 March 1960 totalled 2,128. New State houses under administration on a tenancy basis at 1 April 1959 were 38,361. After adding the new units taken over and allowing for sales and repurchases, there was a net total of 40,234 for the year ended 31 March 1960, an increase of 1,873 over the previous year. In addition to these houses the Corporation also administers a group of older houses acquired for rental purposes, the number being 1,742 at 31 March 1960.
Substantial responsibilities are involved in the administration of the 42,081 tenancies which were current at 31 March 1960. The number of tenants in arrears during the year ended 31 March 1960 averaged 1.8 per cent, which is the same as the figure for the previous year. The maintenance of State houses is in itself a major undertaking.
Sale Of State Houses – Should they desire to own their own homes, State house tenants are given the opportunity of buying the houses they occupy.
In the case of tenants occupying State rental houses on or before 31 July 1950 the main sale terms are:
A minimum deposit of 5 per cent of the sale price.
A suspensory amount assessed at 10 per cent of the sale price, with a maximum of £200.
A repayment period up to 40 years for the balance of the purchase money, together with interest, on an instalment-table basis.
An interest charge of 5 per cent, reduced to 3 per cent while the conditions of sale are complied with.
Discount of 5 per cent for payments of purchase money in excess of the required principal instalments, or in excess of the minimum deposit.
Repayment insurance benefits applicable to all cases where the wage earner in the purchaser's family is under 60 years at the time of purchase.
If the purchaser wishes to resell the State house within seven years it must first be offered for sale back to the Crown.
The purchase terms available to tenants first occupying State rental houses after 31 July 1950 are more related to the loan terms for persons erecting new houses (see pp. 933–937). They include:
Suspensory amounts where purchasing tenant is first occupier.
A minimum deposit of 10 per cent of the gross purchase price or the amount of the purchase money in excess of £2,000, whichever is the greater. Where, however, the financial position of the purchaser warrants, the Board of Management of the Corporation may accept a reduced deposit in such a case.
The balance of the purchase money, together with interest, payable over a period of years on an instalment-table basis.
Interest at 5 per cent reducible to 4 1/8 per cent while conditions of sale are complied with.
Provision for the property to be offered for sale to the Crown in the event of the purchaser wishing to resell within seven years.
From the inception of the sale of State rental houses up to 31 March 1960 the number sold to the tenants was 16,495, for a total sale price of £38,761,190. These figures allow for repurchases by the Crown during the same period.
STATUTORY PROVISIONS – The law relating to building societies incorporated in New Zealand is in the main contained in the Building Societies Act 1908. Building societies are afforded all the powers and rights of an ordinary mortgagee, a description of which is contained in Section 30A – Mortgages. No reconveyance is needed to discharge a mortgage made under the Act, a receipt endorsed being a sufficient discharge for this purpose.
Authority was taken in the National Expenditure Adjustment Act 1932 to fix by Order in Council the maximum rates of interest payable (according to term of deposit) on deposits lodged with building societies. The rates were varied from time to time by subsequent orders and the restrictions were removed from 1 August 1957, except for deposits in the societies' savings banks, the rates for this class being the same as for Post Office Savings Bank deposits. However, on 22 July 1960 new rates of interest payable on deposits were provided for by the Interest on Deposits Order 1960. The maximum rates payable range from 2 per cent, for deposits at call and under three months, to 5 per cent on deposits for not less than seven years. Rates payable for short-term deposits are therefore now less than those paid by the Post Office Savings Bank.
Returns of each society's operations are furnished annually to the Department of Statistics.
CONSTITUTION AND FUNCTIONS – A distinction is made between permanent and terminating societies. A permanent society is statutorily defined as one which has not by its rules any fixed date or specified result at which it shall terminate, and a terminating society as one which by its rules is to terminate at a fixed date, or when a result specified in its rules is attained. In practice a terminating society, or a group thereof, closes when every member so desiring has obtained a loan. There is a considerable difference between the two types of societies, the terminating society being a purely cooperative institution belonging to and managed by the members, proprietary interests being discouraged by placing a limit to the number of shares (usually 10) that any member may hold in any one group. There is, however, nothing to prevent a member from holding the maximum number of shares in more than one group. In a typical terminating society contributions are at the rate of 1S. per week per share, each share entitling a member in due course to £200 of loan, with a maximum, until recent years, of £1,200. As £1,200 is not sufficient to meet the needs of the average prospective house owner on present-day costs, there is a tendency for the limit to be raised. In some groups of the terminating societies the loan maximum is now £4,000. It is these contributions, together with premiums on loans mentioned later, which make up the funds from which loans are made. Loans are made to members both by ballot and by auction, the latter going for the highest premium offered. Security is required for the loans, which are repaid, free of interest, in periods varying from 10 to 20 years. The weekly payment of 1S. per share is continued, usually till the end of the group, but sometimes only until the total contributions paid in, plus profits, credited to the shareholder, equal the amount owing on the loan. The shareholder's credit balance is then transferred to extinguish the loan. The profit of the society is derived from premiums on loans sold by auction.
Permanent societies are more in the nature of finance companies, and, while both investors and borrowers must be members, the borrower is frequently merely a nominal member. Investments in a permanent society may be made in either large or small amounts. Capital may be raised by shares with a fixed rate of interest, or subject to dividends varying according to profits. As will be observed from the statistics which follow, terminating societies do not issue capital shares. Bonds, debentures, deposits, and overdraft are other methods of financing. The principal object of a permanent society is to lend money at a profit on land and buildings, either freehold or leasehold. Table mortgages are normally adopted, the usual term of repayment being up to 20 years. The statistics refer generally to years ending on 31 March.
NUMBER OF SOCIETIES AND SHARES – The number of societies functioning in 1959–60 was 73, of which 55 were permanent and 18 terminating. The number of societies has shown little variation in recent years.
Permanent Societies – The following table shows for each of the latest five years particulars of permanent societies, including data on number and value of investing and capital shares.
| 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of societies | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 55 |
| Investing Shares | |||||
| Number of shares | 678,553 | 727,814 | 817,800 | 876,557 | 906,335 |
| Members holding | 26,751 | 26,834 | 27,739 | 28,042 | 27,671 |
| Aggregate value | £7,381,598 | £7,750,980 | £8,525,253 | £9,059,485 | £10,431,647 |
| Capital Shares | |||||
| Number of shares | 795,382 | 918,839 | 1,015,174 | 1,154,585 | 1,247,682 |
| Members holding | 5,644 | 5,868 | 6,001 | 6,083 | 6,087 |
| Aggregate value | £2,136,231 | £2,261,774 | £2,373,418 | £2,456,112 | £2,531,663 |
At March 1960 the average value of each investing share was £11 10S., and the average value of such shares held by each member was £377. The comparative figures for capital shares were £2 1S. and £416.
Terminating Societies – Although the number of terminating societies fell for some years, the total membership and value of shares continue to grow. Measured by these criteria, the size of the average existing society has therefore increased greatly. As stated earlier, one person may hold shares in several groups of a terminating society. The next table shows the progress of terminating societies during the latest five years. It should be noted that the information pertaining to shares relates to investing or contributory shares, there being no capital shares in a terminating society.
| Year | Societies | Groups | Members Holding Shares | Investing Shares | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | ||||
| £ | |||||
| 1955–56 | 17 | 366 | 158,732 | 1,071,560 | 12,623,470 |
| 1956–57 | 18 | 395 | 183,520 | 1,286,115 | 14,853,317 |
| 1957–58 | 18 | 418 | 204,480 | 1,472,960 | 17,371,301 |
| 1958–59 | 18 | 440 | 217,121 | 1,657,908 | 20,420,720 |
| 1959–60 | 18 | 468 | 229,278 | 1,908,800 | 23,204,508 |
The average value per share in 1959–60 was £12 3S., and the average value of shares held per member was £101 4S. The figures for 1955–56 were, respectively, £11 16S. and £79 10S.
RECEIPTS AND PAYMENTS – Following is a summary of receipts and payments for all societies during each of the latest five years.
| Item | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts £(thousand) | |||||
| Investors' subscriptions and capital shares | 3,750 | 4,132 | 5,000 | 5,261 | 5,883 |
| Advances repaid | 3,546 | 3,888 | 4,371 | 4,838 | 5,494 |
| Deposits | 2,696 | 2,557 | 3,132 | 3,640 | 3,980 |
| Interest | 740 | 791 | 903 | 1,004 | 1,127 |
| Other receipts | 603 | 679 | 660 | 1,001 | 825 |
| Total receipts | 11,334 | 12,047 | 14,067 | 15,743 | 17,308 |
| Payments £(thousand) | |||||
| Withdrawals | 948 | 1,149 | 1,364 | 1,484 | 1,827 |
| Advances | 6,187 | 6,256 | 7,470 | 8,421 | 9,323 |
| Expenses of management | 273 | 337 | 385 | 432 | 496 |
| Dividends paid | 127 | 130 | 140 | 145 | 156 |
| Deposits repaid | 2,636 | 2,662 | 2,952 | 3,016 | 3,252 |
| Interest paid | 252 | 269 | 301 | 352 | 428 |
| Other payments | 822 | 1,323 | 1,408 | 1,892 | 1,795 |
| Total payments | 11,245 | 12,127 | 14,021 | 15,742 | 17,277 |
The lifting of interest rate restrictions between 1 August 1957 and 22 July 1960 possibly contributed towards the increase in deposit receipts and loans advanced. The ratio of loan repayments to advances was 62.1 per cent in 1956–57, 58.5 per cent in 1957–58, 57.4 per cent in 1958–59, and 58.9 per cent in 1959–60.
LOANS – The number of borrowers and amount of loans outstanding at the end of each of the five years quoted were as follows. Advances on shares are excluded.
| Year | Permanent Societies | Terminating Societies | Totals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount* | Number | Amount | |
| *Includes balance owing on premiums on loans. | ||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1955–56 | 14,973 | 15,759 | 18,006 | 14,125 | 32,979 | 29,885 |
| 1956–57 | 15,087 | 16,283 | 22,046 | 16,349 | 37,133 | 32,631 |
| 1957–58 | 15,063 | 17,410 | 23,777 | 18,613 | 38,840 | 36,023 |
| 1958–59 | 15,295 | 18,673 | 25,613 | 20,997 | 40,908 | 39,670 |
| 1959–60 | 15,411 | 20,175 | 28,017 | 21,126 | 43,428 | 41,302 |
The average amount owing by each borrower at the end of each of the five years is given below.
| Class | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Permanent societies | 1,053 | 1,079 | 1,156 | 1,221 | 1,309 |
| Terminating societies | 784 | 742 | 783 | 820 | 754 |
| All societies | 906 | 879 | 927 | 970 | 951 |
Particulars of loans granted during each of the latest five years follow.
| Year | Permanent Societies | Terminating Societies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Ballot | By Auction | ||||||
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | Number | Amount | Premiums | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1955–56 | 2,416 | 2,745 | 1,049 | 1,230 | 1,438 | 2,026 | 843 |
| 1956–57 | 2,157 | 2,460 | 944 | 1,139 | 1,674 | 2,445 | 1,089 |
| 1957–58 | 2,511 | 3,255 | 1,164 | 1,531 | 1,791 | 2,596 | 1,201 |
| 1958–59 | 2,432 | 3,215 | 1,248 | 1,831 | 1,861 | 2,966 | 1,383 |
| 1959–60 | 2,642 | 3,746 | 1,213 | 1,926 | 1,964 | 3,104 | 1,315 |
The totals for loans in the above table represent loans granted and differ slightly from the figures shown as advances in the table relating to receipts and payments, where the amounts refer to payments actually made in respect of loans. The average loan granted by permanent societies amounted to £1,418, and by terminating societies (ballot) £1,588 and (auction) £1,580. The average premium on auctioned loans, representing total interest payments over the period of the loan, was £670.
For the five years prior to 1959–60 a pronounced rise in premium rates seemed to reflect the hardening of interest rates generally. However, in 1959–60 a drop in the premium rate occurred.
Premium rates on auctioned loans during the last five years have been: 1955–56, £41.6 per cent; 1956–57, £44.6 per cent; 1957–58, £46.3 per cent; 1958–59, £46.6 per cent; and 1959–60, £42.4 per cent.
It is possible that in 1959–60 capitalisation of the family benefit for housing purposes and 3 per cent interest-rate provisions by the Government for housing purposes, contributed to this fall by lessening demand pressure.
Commencing with the year 1937–38, statistics of building societies were extended to include a classification of loans into (1) loans granted to finance the erection of new dwellings, and (2) loans granted to finance the purchase of dwellings already built. For the purposes of the statistics new dwellings are deemed to include those which have been built by the borrower during the 12 months preceding the granting of the loan. Particulars for 1959–60, with totals for earlier years, are given in the following table.
| To Finance the Erection of New Dwellings | To Finance the Purchase of Dwellings Already Built | For Other and Unspecified Purposes | Totals | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Amount | No. | Amount | No. | Amount | No. | Amount | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| Permanent societies | 386 | 772 | 1,293 | 2,032 | 963 | 942 | 2,642 | 3,746 |
| Terminating societies – | ||||||||
| By ballot | 198 | 322 | 744 | 1,299 | 271 | 305 | 1,213 | 1,926 |
| By auction | 341 | 509 | 1,325 | 2,175 | 298 | 419 | 1,964 | 3,104 |
| Totals all societies – | ||||||||
| 1959–60 | 925 | 1,604 | 3,362 | 5,507 | 1,532 | 1,666 | 5,819 | 8,777 |
| 1958–59 | 1,105 | 1,778 | 3,101 | 4,997 | 1,335 | 1,237 | 5,541 | 8,012 |
| 1957–58 | 1,058 | 1,690 | 3,085 | 4,498 | 1,323 | 1,195 | 5,466 | 7,382 |
| 1956–57 | 939 | 1,485 | 2,774 | 3,769 | 1,062 | 790 | 4,775 | 6,044 |
| 1955–56 | 1,064 | 1,726 | 2,654 | 3,413 | 1,185 | 863 | 4,903 | 6,001 |
Loan authorisations again increased in 1959–60, most of the increased activity over the past three years being directed towards the purchase of existing dwellings.
The considerable number of loans shown for other and unspecified purposes is partly due to the fact that some societies are unable to give the necessary classification, so that it may be taken that the foregoing table understates the number of loans actually granted for the erection or purchase of dwellings.
LIABILITIES AND ASSETS – The liabilities and assets of building societies for each of the latest five years are given in the next table.
| LIABILITIES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | To Shareholders (Including Reserve Funds and Undivided profits | Deposits | Appropriations Not Taken Up, or in Trust | To Bankers and Other Creditors | Total Liabilities |
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1955–56 | 25,271 | 4,755 | 1,464 | 1,233 | 32,724 |
| 1956–57 | 28,498 | 4,684 | 1,603 | 1,398 | 36,183 |
| 1957–58 | 32,417 | 4,887 | 1,777 | 1,242 | 40,323 |
| 1958–59 | 36,493 | 5,795 | 1,788 | 1,119 | 45,195 |
| 1959–60 | 40,707 | 6,874 | 1,742 | 1,170 | 50,493 |
| ASSETS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Advances on Mortgage* | Advances on Shares | Other Investments and Assets | Cash in Hand and at Bank | Total Assets |
| *Includes balance owing on premiums on loans. | |||||
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1955–56 | 30,035 | 319 | 2,133 | 237 | 32,724 |
| 1956–57 | 32,869 | 410 | 2,689 | 214 | 36,183 |
| 1957–58 | 36,412 | 498 | 3,147 | 266 | 40,323 |
| 1958–59 | 40,514 | 616 | 3,813 | 252 | 45,195 |
| 1959–60 | 45,003 | 733 | 4,507 | 250 | 50,493 |
The ratio of advances on mortgage to total assets has been maintained at a high level during the last few years, the figure for 1959–60 being 89.1 per cent
GENERAL – The method of carrying on business by companies is now a proved system, a system for the incorporation of persons into a separate entity for trading purposes and providing a convenient method for the investment of capital and for the limitation of liability of the people associated in the company. The incorporation of a company with limited liability provides the framework of commercial and industrial life, and, particularly in the field of private companies, is becoming increasingly the form of business organisation for the small trader.
LEGISLATION – Comprehensive legislation relating to companies is contained in the Companies Act 1955, which came into force on 1 January 1957. This Act was substantially modelled on the United Kingdom Companies Act 1948, as far as that might properly be done having regard to New Zealand requirements and conditions. An important principle in the legislation is the protection of share-holders, creditors, and the general public by the requirement that there must be the fullest practicable disclosure of information concerning the activities of companies. The annual financial statements must exhibit a true and complete account of a company's affairs and transactions. A prescribed form of presentation is required and comparative figures for the previous year must be shown. A prospectus must be deposited with the Registrar of Companies before it is issued.
Any number of persons from two to 25 may form a private company; a public company must have at least seven members. A private company of not less than seven members may, under certain conditions, be reregistered as a public company.
NEW COMPANIES REGISTERED – The following table shows for the last 11 years the number and aggregate nominal capital of new private companies registered.
A notable feature is the increase in numbers and aggregate nominal capital during the last five years when compared with those for the previous five-year period.
During 1955–59 years inclusive, 14,920 new private companies were registered, with an aggregate nominal capital of £66 million, whereas in the period 1950–54 the comparable figures were 10,386 and £53 million.
Public companies, however, showed a decline in the aggregate nominal capital, which fell from £13.6 million in the 1950–54 period to £8 million in the 1955–59 period.
| Year | Private Companies | Public Companies | Overseas Companies | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Nominal Capital | Number | Nominal Capital | Number | Nominal Capital | |
*Of this number one company was limited (as to capital) by guarantee. † Of this number one company was created under special overseas Government charter and no capital information is available. | ||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1949 | 2,123 | 6,626 | 24 | 832 | 10 | 524 |
| 1950 | 2,047 | 8,226 | 15 | 366 | 12 | 1,586 |
| 1951 | 1,978 | 9,206 | 28 | 2,825 | 14 | 777 |
| 1952 | 1,704 | 9,307 | 28 | 8,393 | 12 | 15,708 |
| 1953 | 2,010 | 10,720 | 12 | 477 | 21* | 31,837 |
| 1954 | 2,647 | 15,831 | 19* | 1,513 | 17 | 10,402 |
| 1955 | 2,564 | 12,200 | 19* | 4,542 | 12 | 1,605 |
| 1956 | 3,214 | 13,733 | 20 | 1,492 | 21 | 20,368 |
| 1957 | 3,462 | 14,111 | 25 | 1,444 | 26* | 64,927 |
| 1958 | 2,995* | 12,259 | 12 | 428 | 27 | 16,658 |
| 1959 | 2,685* | 14,004 | 24* | 409 | 28† | 32,690 |
In comparing one year with another, as in the preceding table, it should not be overlooked that reregistrations, on account of reconstruction of companies or for other reasons, are included. Such reregistrations of large companies may have a considerable effect on the year's total, so far as capital is concerned.
The table following gives a classification of new companies registered in 1959 according to the amount of nominal capital.
| Amount of Nominal Capital | Private Companies | Public Companies | Overseas Companies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Nominal Capital | Number | Nominal Capital | Number | Nominal Capital | ||
| *Includes one company created under special overseas Government charter - no capital available. | |||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||||
| Under £1,000 | 630 | 216 | 2 | - | - | - | |
| £1,000 and under | £2,000 | 665 | 763 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| £2,000 | £3,000 | 443 | 945 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| £3,000 | £4,000 | 244 | 763 | 1 | 3 | - | - |
| £4,000 | £5,000 | 122 | 502 | 1 | 4 | - | - |
| £5,000 | £6,000 | 151 | 762 | 3 | 15 | 1 | 5 |
| £6,000 | £7,000 | 63 | 386 | - | - | - | - |
| £7,000 | £8,000 | 38 | 277 | - | - | - | - |
| £8,000 | £9,000 | 26 | 212 | - | - | - | - |
| £9,000 | £10,000 | 27 | 251 | - | - | - | - |
| £10,000 | £15,000 | 182 | 1,878 | 9 | 90 | 4 | 40 |
| £15,000 | £20,000 | 24 | 397 | 1 | 15 | - | - |
| £20,000 | £50,000 | 48 | 1,286 | 2 | 54 | 2 | 55 |
| £50,000 and over | 21 | 5,365 | 2 | 225 | 17 | 32,586 | |
| Limited by guarantee | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | |
| Totals | 2,685 | 14,004 | 24 | 409 | 28* | 32,690 | |
The nominal capital shown for overseas companies is the total nominal capital of these companies and, of course, bears no relationship to their capital resources employed in New Zealand. It is shown merely as some indication of the relative size of overseas companies commencing business in this country.
The total nominal value for March years of capital resources employed in New Zealand by branches of overseas companies is available on request to the Department of Statistics.
While the number of new registrations of private companies decreased in 1959, being 310 lower than the comparable 1958 figure, nominal capital of new registrations in 1959 increased by £1.7 million.
The average amount of authorised capital per company thus increased from £4,095 in 1958, to £5,218 in 1959. This increase was due to a substantial rise in the nominal capital of companies in excess of £100,000. Whereas in 1958 seven such private companies were registered, having a total nominal capital of £1.1 million, in 1959 10 such companies had a total nominal capital of £4.7 million.
The extent of changes in the number and nominal capital of new registrations of private companies between 1949 and 1959, expressed as percentages of the totals, is shown in the following table.
| Amount of Nominal Capital | Number | Amount of Capital | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 1959 | 1949 | 1959 | |
| percent | ||||
| Under £1,000 | 24.0 | 23.5 | 3.8 | 1.5 |
| £1,000 and under £5,000 | 59.4 | 54.9 | 38.6 | 21.2 |
| £5,000 and under £10,000 | 11.0 | 11.4 | 21.0 | 13.5 |
| £10,000 and over | 5.6 | 10.2 | 36.6 | 63.8 |
| Totals | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Compiled from published sources, the following summary gives the stated objects of all new companies registered during 1957-1959. Because of possible inaccuracies in the source data, and the difficulty of precise classification by industrial group from the information available, the figures should be regarded as approximate only.
| Industry Group | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture and livestock production | 499 | 408 | 331 |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 12 | 14 | 22 |
| Mining and quarrying | 30 | 32 | 22 |
| Manufacturing— | |||
| Food, beverages, and tobacco | 65 | 65 | 41 |
| Textile, footwear, and apparel | 116 | 114 | 57 |
| Woodwork and furniture | 78 | 60 | 28 |
| Machinery | 143 | 108 | 76 |
| Transport equipment | 152 | 125 | 58 |
| Other | 200 | 202 | 180 |
| Construction | 358 | 331 | 220 |
| Commerce— | |||
| Wholesale and retail | 966 | 763 | 858 |
| Banks and other financial institutions | 177 | 175 | 229 |
| Real estate | 239 | 241 | 321 |
| Other | 6 | — | 1 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 140 | 130 | 77 |
| Services— | |||
| Community and business | 50 | 27 | 35 |
| Personal | 221 | 169 | 152 |
| Other | 25 | 28 | 13 |
| Miscellaneous or not known | 36 | 42 | 16 |
| Totals | 3,513 | 3,034 | 2,737 |
Companies Carrying on Business — Statistics of companies carrying on business were compiled on four occasions, for the years 1926, 1932, 1938, and 1947.
For detailed tables in connection with the 1947 inquiry into registered companies the 1950 Yearbook should be consulted, while a summary only of the principal information for the four enumerations was given in the subsequent issues up to 1958.
Companies on Register, March 1960 and 1961 — The number of public companies on the register at 31 March 1960 was 1,571, and the number of private companies 36,906. At 31 March 1961 public companies numbered 1,613 and private companies 39,273. These figures were supplied by the Registrar of Companies, no further particulars being available.
ANALYSIS OF PUBLIC COMPANY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — The following article was contributed by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand. This article, which is a continuation of similar material published in the 1960 Yearbook on pages 923–928, is based on published balance sheets obtained from a number of New Zealand public companies.
Glossary — Current assets: Cash plus those assets which are held for realisation in the ordinary course of business, normally within 12 months. Current liabilities: Those liabilities which are normally met within 12 months. Funds available: Net increases in liabilities and net decreases in assets between annual balance dates. Funds used: Net increases in assets and net decreases in liabilities between annual balance dates. Liquidity ratio: Current assets minus stock divided by current liabilities minus bank overdraft.
Coverage — The survey in 1960 was considerably expanded to cover 307 companies compared with the 208 companies surveyed in 1959. The number of public companies on the register as at 31 March 1960 was 1,571. However, of these, only 250 were listed by the New Zealand Stock Exchange. Companies earning income outside New Zealand were excluded from the survey, e.g., insurance companies, some stock and station agents and transport companies. Other companies were excluded for various reasons: the late receipt of annual accounts; a change of balance date so that no comparable figures were available or an accounting period of more than a year. It is thought that the statistics give a good coverage of public company operations in New Zealand, as all major listed companies are included.
The tables cover the operations of companies balancing during the year ended March 1960. Thus the coverage is almost a two-year period, as companies balancing on, say, 30 April 1959 (which are included in the survey) represent the period 1 May 1958 to 30 April 1959. The next table shows the numbers and percentages of companies included in the survey balancing during each month of the year.
COMPANY BALANCE DATES
| Month | Number | Per Cent |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | ||
| April | 13 | 4 |
| May | 7 | 2 |
| June | 57 | 19 |
| July | 35 | 11 |
| August | 21 | 7 |
| September | 25 | 8 |
| October | 18 | 6 |
| November | 3 | 1 |
| December | 6 | 2 |
| 1960 | ||
| January | 15 | 5 |
| February | 19 | 6 |
| March | 88 | 29 |
| Total | 307 | 100 |
Company Size - The table on page 954 analyses the size of the various companies on the basis of total shareholders' funds. Company size may also be analysed with reference to total sales, but this information is not available in all cases. The groups mentioned - small, medium, and large - include:
| £(000) | |
|---|---|
| Small | Under 50 to 249 |
| Medium | 250 to 999 |
| Large | 1,000 and over |
A subgroup of the main table gives a further break-up of the major group, i.e., companies with shareholders' funds between £50,000 and £249,000. The arithmetic average of shareholders' funds of the 307 companies surveyed was £576,000.
The four largest companies (shareholders' funds of £5 million or over), were well spread throughout the various classes, i.e., beverages, forestry and wood, construction, and stock and station agents. In the “other food” group, the predominance lay in the small firm, as was the case also with clothing manufacturers, other manufacturing, mainly wholesale, financial, building societies, and transport. The clothing manufacturers, electrical machinery and appliances, gas, and the financial firms included in the survey were in the small or medium group. Stock and station agents were spread almost equally between the large and medium groups. The large firms did not outnumber the small and medium combined groups in any categories, the highest proportions of large business being in stock and station agents (one-half), meat processing and beverages (one-third), and departmental stores and woollen mills (one-quarter).
Liquidity - Various short-term liquidity ratios are shown in the second table on page 952. All the overall ratios show a stronger liquid position for the first time for two years, the exceptions for those two years being the ratio of bank overdraft to current assets. The overall liquidity ratio, still over 100 per cent, has remained relatively stable. In the balance sheet analysis earlier, mention was made of the overdrafts of the meat processing and stock and station agents groups. The movement of overdrafts there is reflected in the changes in the ratio of bank overdraft to current assets in the table.
Balance Sheets - The amalgamated balance sheets of the companies for 1959 and 1960 are set out in the table on page 950 in summary form. The total figures, contrary to the movement between 1958 and 1959, show a reduction in bank overdrafts, whilst cash and bank balances remained about the same. This trend was not followed in all groups. For example, meat processing companies' overdrafts between 1959 and 1960 more than doubled from £0.9 million to £2 million, whilst their cash and bank balances were reduced from £1.3 to £0.3 million. In the previous article it was mentioned that bank accommodation to stock and station agents had increased considerably. The figures currently published show a contraction from £4.0 to £2.2 million.
Stocks, as a whole, increased by a small amount, the result of two opposite movements. The manufacturing sectors, other than clothing manufacturers, increased their stocks, whilst the distributive and selling sectors reduced stocks.
Sundry debtors and bills receivable showed a slightly smaller increase than during 1959, which was spread over all groups, with the exception of “mainly wholesale” where there was a small reduction. The main contributors to the increase in land and buildings of £7.8 million were beverages, £3.1 million, and stock and station agents, £1.3 million.
On the liabilities side, the upward movement in creditors was not large, and was, in general, in the same direction as the movement in stocks, i.e., increasing in the manufacturing sector and decreasing in the non-manufacturing sector.
Mortgages and debentures again increased. During 1960 mortgages rose by £1.2 million and debentures by £0.6 million, whereas during 1959 the increases were mortgages, £0.7 million, and debentures, £1.2 million. Half the increase in mortgage financing during 1960 was attributable to beverages and “mainly retail groups”.
The totals of all the items included in shareholders' funds rose. All the increase in share capital, both ordinary and preference, did not, however, mean an equivalent demand for funds from the capital market, as there were numerous issues of capital to shareholders from accumulated reserves during the year, resulting in a reduction in reserves and an increase in paid-up share capital.
Source and Use of Funds - The sources and use of funds for the year 1959–60 is shown in the tables on pages 951–952. A further rise to 60 per cent in the proportion of total funds provided from tax-paid profits (retained profits and depreciation) was shown, which continued the trend indicated since the beginning of the series. For comparison, previous years' figures are shown below:
| per cent | |
|---|---|
| 1953–54 | 35.9 |
| 1954–55 | 37.1 |
| 1955–56 | 40.2 |
| 1956–57 | 50.6 |
| 1957–58 | 56.3 |
| 1958–59 | 57.3 |
| 1959–60 | 60.3 |
After remaining unchanged for two years, the relationship between retained profits and depreciation moved towards a larger proportion of profits. In the year under review retained profits were 33 per cent, and depreciation 67 per cent, compared with both the 1959 and 1958 percentages of 26 and 74 per cent respectively. In 1957 the shares were about equal.
The relation of long-term funds as a share of total funds rose to 92 per cent during 1960, after remaining fairly constant for three years at about 86 per cent.
Share capital rose from 14 to almost 18 per cent of the total source of funds, a level somewhat higher than for the preceding few years, with the exception of 1958, whereas mortgages and debentures were a less important source of funds than last year.
Although funds were used to reduce overdrafts and to increase by a small amount cash and bank balances, this trend was not followed by all groups. The notable exception was the meat processing group, which drew on cash and bank balances and increased overdrafts to the amount of £2 million (50 per cent of their source of funds). During 1958–59 this group used 7 per cent of their funds to repay bank overdrafts. In the case of stock and station agents, the position is reversed. During 1960 almost 40 per cent of their funds were used to reduce overdrafts and increase cash and bank balances, whereas during 1959 over 50 per cent of their funds came from these two sources.
During 1960 businesses obtained more funds from an increase in their creditors, both absolutely and as a percentage. The table shows that over £1.5 million was obtained in this manner, representing 5 per cent of the source of funds.
There was a considerable change in the use of funds during 1960 between short- and long-term purposes. In the year under review only 17 per cent of the funds received were used for short-term purposes, compared with almost 33 per cent during 1959, and 28 per cent during 1958. All classes did not follow this change, the two larger exceptions being clothing manufacturers (where the short-term use of funds more than doubled during 1960), and metals and machinery. The movement is also reflected in the share of funds used to finance stocks, which declined from 10 to 2 per cent of the total use of funds between 1959 and 1960. As mentioned below there was a build-up of stocks in the manufacturing sectors and a reduction in the selling and distributive sectors. This movement is clearly shown by the stock items on both sides of the source and uses of funds table.
In line with the reduced use of funds for short-term purposes, the percentage used to finance debtors declined from a peak of 22 per cent during 1959 to 6 per cent for 1960, the lowest figure since the series began in 1954, with the exception of 1957. Contributing most to this reduction was the stock and station agents group, which in 1959 used 45 per cent of their funds to finance higher debtors, whereas in 1960 they reduced debtors by a small proportion.
Total funds employed for long-term purposes increased to 83 per cent of all funds used. Of these long-term funds, additions to property and plant and depreciation absorbed the greatest part, 76 per cent of the total funds being employed in this way compared with 60 per cent during 1959 and 55 per cent in 1958. Major contributors to the increase were the beverages, other food, and printing and publishing groups.
Net Profits - Net profits after tax showed, in total, a reduction of 0.9 per cent. If, however, the losses in the meat processing group are excluded, the result is an overall improvement of 8.4 per cent. The meat processing group in the survey experienced lower profits for three successive years, including an overall loss in 1960. Moreover, the survey indicated that the number of groups having smaller profits is greater than for some years. Substantial improvements in the change in net profits are in the beverages, printing and publishing (a reduction last year), and construction groups.
The ratio of net profit to shareholders' funds has not, in total, moved appreciably over the two years, although there are wider movements in individual categories.
The table below, which gives the appropriation of income for both 1959 and 1960, is self-explanatory.
APPROPRIATION OF INCOME
| Account for year | 1959 | 1960 |
| Number of companies | 307 | 307 |
| £(000) | £(000) | |
| Trading profit | 38,793 | 38,720 |
| Less provision for depreciation | 12,129 | 11,795 |
| Trading profit, less provisions | 26,664 | 26,925 |
| Plus investment income | 907 | 1,023 |
| Other non-trading income | 211 | 306 |
| Less interest on fixed liabilities | 1,920 | 2,150 |
| Income to be appropriated | 25,862 | 26,104 |
| Less tax on current year's income | 12,983 | 13,337 |
| Net profit after tax | 12,879 | 12,767 |
| Plus prior year adjustments - | ||
| Tax | 171 | 92 |
| Other | 57 | 190 |
| Less dividends - | ||
| Preference | 659 | 670 |
| Ordinary | 6,762 | 7,495 |
| Less share due to minority interests | 70 | 77 |
| Transfer to reserves (net) | 3,908 | 3,400 |
| Goodwill, etc., written off | 68 | 42 |
| Balance carried forward | 1,640 | 1,365 |
AMALGAMATED BALANCE SHEETS (MARCH YEARS) OF 307 NEW ZEALAND PUBLIC COMPANIES
| Total Food | Manufacturing Other Than Food | Total Manufacturing | Total Other Than Manufacturing | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Companies | 43 | 131 | 174 | 133 | 307 | |||||
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Assets | £(million) | |||||||||
| Current assets - | ||||||||||
| Cash and bank | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 5.4 | 5.4 |
| Stock | 10.0 | 11.0 | 36.2 | 37.7 | 46.2 | 48.7 | 34.6 | 32.8 | 80.8 | 81.4 |
| Sundry debtors and bills receivable | 5.5 | 5.9 | 17.8 | 18.7 | 23.3 | 24.7 | 21.7 | 22.5 | 45.0 | 47.2 |
| Sundry (including deposits, subsidiary, current accounts, etc.) | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 14.7 | 14.3 | 15.9 | 16.0 |
| Total current assets | 17.5 | 18.3 | 56.9 | 60.5 | 74.4 | 78.8 | 72.6 | 71.2 | 147.0 | 150.1 |
| Fixed investments and loans - | ||||||||||
| Government and local body (where specified) | 1.5 | 1.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 7.3 | 7.4 |
| Other investments and loans | 3.7 | 3.8 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 19.7 | 21.3 | 25.7 | 27.7 |
| Total fixed investments and loans | 5.2 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 11.4 | 12.0 | 21.6 | 23.1 | 33.0 | 35.1 |
| Fixed assets - | ||||||||||
| Land and buildings | 15.1 | 19.0 | 30.5 | 31.8 | 45.5 | 50.8 | 24.9 | 27.3 | 70.4 | 78.2 |
| Plant, machinery, and other | 10.3 | 11.3 | 37.3 | 38.2 | 47.5 | 49.5 | 12.2 | 12.8 | 59.7 | 62.4 |
| Total fixed assets | 25.3 | 30.3 | 67.7 | 70.0 | 93.1 | 100.3 | 37.1 | 40.2 | 130.1 | 140.5 |
| Total assets | 48.0 | 54.2 | 130.8 | 137.0 | 178.9 | 91.2 | 131.2 | 134.5 | 310.1 | 325.7 |
| Liabilities | ||||||||||
| Current liabilities - | ||||||||||
| Bank overdraft | 3.1 | 4.2 | 9.3 | 9.5 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 14.5 | 11.1 | 26.8 | 24.9 |
| Sundry creditors and bills payable | 5.9 | 6.5 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 16.4 | 17.6 | 22.9 | 22.6 | 39.3 | 40.2 |
| Current tax provisions | 2.5 | 2.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 13.0 | 13.3 |
| Sundry (including deposits, subsidiary accounts, dividend provisions, etc.) | 2.5 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 12.9 | 14.0 |
| Total current liabilities | 14.0 | 15.6 | 29.2 | 31.3 | 43.3 | 47.0 | 48.8 | 45.4 | 92.1 | 92.4 |
| Long-term liabilities - | ||||||||||
| Fixed charges - | ||||||||||
| Mortgages | 1.8 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 12.9 | 14.1 |
| Debentures | 0.3 | 0.5 | 20.9 | 20.7 | 21.2 | 21.2 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 24.8 | 25.4 |
| Fixed deposits and other fixed charges | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 8.9 | 10.0 | 10.2 | 11.4 |
| Other provisions and minority interests | 2.4 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 5.6 |
| Total long-term liabilities | 4.7 | 6.4 | 27.9 | 28.1 | 32.7 | 34.5 | 19.6 | 22.0 | 52.3 | 56.5 |
| Shareholders' funds - | ||||||||||
| Paid-up capital - | ||||||||||
| Preference | 1.3 | 1.2 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 14.0 | 14.3 |
| Ordinary | 13.7 | 16.2 | 43.2 | 44.0 | 56.9 | 60.3 | 29.0 | 30.5 | 85.9 | 90.8 |
| Capital reserves | 2.7 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 7.3 | 8.7 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 12.1 | 14.3 |
| Revenue reserves | 9.0 | 9.2 | 17.1 | 19.0 | 26.1 | 28.3 | 16.6 | 17.7 | 42.7 | 46.0 |
| Profit and loss appropriation account | 2.6 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 11.0 | 11.4 |
| Total shareholders' funds | 29.3 | 32.1 | 73.7 | 77.6 | 103.0 | 109.7 | 62.8 | 67.1 | 165.7 | 176.8 |
| Total liabilities | 48.0 | 54.2 | 130.8 | 137.0 | 178.9 | 191.2 | 131.2 | 134.5 | 310.1 | 325.7 |
STATISTICAL TABLES
| Statement of Sources and Use of Funds During Year Ended 31 March 1960 for 307 New Zealand Public Companies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources Being Net Increases in Liabilities and Net Decreases in Assets | Total Net Change for Food | Total Net Change for Manufacturing Other Than Food | Total Net Change for all Manufacturing | Total Net Change for Total Other Than Manufacturing | Total Net Change According to Items |
| Number of companies | 43 | 131 | 174 | 133 | 307 |
| Short Term | |||||
| Per Cent | |||||
| Increases in - | |||||
| Bank overdraft | 11.8 | 1.9 | 6.5 | - | - |
| Creditors | 8.3 | 7.8 | 8.5 | - | 5.2 |
| Tax provision | - | 5.5 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Advances by subsidiary and associated companies | - | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Deposits (short term) | - | - | - | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| Decreases in - | |||||
| Cash and bank | 8.0 | - | 0.3 | - | - |
| Stock | - | - | - | 15.5 | - |
| Total short-term sources of funds | 28.1 | 16.5 | 18.1 | 17.2 | 7.7 |
| Long Term | |||||
| Long-term retained profits | 3.7 | 22.2 | 15.1 | 22.7 | 20.1 |
| Depreciation | 24.1 | 50.1 | 41.2 | 25.9 | 40.2 |
| Total funds from profits | 27.8 | 72.3 | 56.3 | 48.6 | 60.3 |
| Increases in - | |||||
| Deposits (long term) | - | - | - | 9.5 | 3.7 |
| Mortgages | 4.4 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 4.8 | 4.1 |
| Debentures | 1.9 | - | - | 5.8 | 2.2 |
| Other liabilities (long term) | 11.2 | 1.1 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 4.3 |
| Ordinary paid-up capital | 26.3 | 6.6 | 15.9 | 13.3 | 16.8 |
| Preference paid-up capital | - | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| Decreases in - | |||||
| Investment in subsidiaries | 0.3 | ||||
| Total long-term sources of funds | 71.9 | 83.5 | 81.9 | 82.8 | 92.3 |
| Total funds from all sources | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Short Term | |||||
| Decreases in - | |||||
| Bank overdraft | - | - | - | 28.4 | 6.7 |
| Creditors | - | - | - | 2.2 | - |
| Tax provision | 2.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Advances by subsidiary and associated companies | 0.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Deposits (short term) | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | - | - |
| Increases in - | |||||
| Cash and bank | - | 5.4 | - | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Debtors | 6.1 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 6.1 |
| Stock | 10.1 | 11.9 | 11.7 | - | 2.2 |
| Current investment | 0.2 | 3.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 1.9 |
| Total short-term use of funds | 19.7 | 27.9 | 21.2 | 35.0 | 17.1 |
| Use Being Net Increases in Assets and Net Decreases in Liabilities | Total Net Change for Food | Total Net Change for Manufacturing Other Than Food | Total Net Change Tor all Manufacturing | Total Net Change for Total Other Than Manufacturing | Total Net Change According to Items |
| Long Term | Per Cent | ||||
| Decreases in - | |||||
| Debentures | - | 1.7 | 0.2 | ||
| Mortgages and debentures (no break-up given) | - | 0.1 | - | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Other liabilities (long term) | 0.1 | - | - | - | - |
| Increases in - | |||||
| Investment in subsidiaries | - | 0.5 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.7 |
| Other investment (long term) | 4.0 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 11.1 | 6.5 |
| Property and plant and depreciation | 76.2 | 68.0 | 75.6 | 52.3 | 75.6 |
| Total long-term use of funds | 80.3 | 72.1 | 78.8 | 65.0 | 82.9 |
| Total use of funds | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Trends in Various Ratios for 307 New Zealand Public Companies for Year Ended 31 March 1960
| Class | Current Ratio (Current Assets to Current Liabilities) | Ratio of Bank Overdraft to Current Assets | Ratio of Stock to Net Working Capital | Liquidity Ratio | Net Profit to Shareholders' Funds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Per Cent | ||||||||||
| Manufacturing — | ||||||||||
| Meat processing | 110.9 | 91.5 | 14.0 | 33.0 | 589.8 | 55.3 | 45.8 | 8.1 | ||
| Beverages | 120.9 | 118.4 | 18.2 | 15.2 | 237.9 | 312.4 | 91.2 | 74.3 | 6.9 | 7.6 |
| Other food | 146.5 | 152.4 | 20.7 | 19.7 | 213.2 | 183.3 | 67.9 | 80.4 | 8.1 | 8.4 |
| All food | 124.7 | 117.1 | 17.6 | 23.0 | 288.0 | 213.8 | 68.6 | 64.3 | 7.6 | 4.6 |
| Woollen mills | 268.1 | 261.2 | 15.2 | 13.7 | 115.6 | 117.5 | 124.5 | 111.7 | 6.5 | 8.0 |
| Clothing manufacturers | 188.4 | 206.7 | 21.2 | 19.8 | 151.3 | 129.2 | 90.9 | 116.6 | 9.0 | 5.6 |
| Forestry and wood | 146.5 | 158.0 | 16.3 | 12.3 | 192.6 | 157.3 | 74.8 | 82.8 | 7.9 | 7.9 |
| Printing and publishing | 166.3 | 154.0 | 20.9 | 23.7 | 137.4 | 147.3 | 115.3 | 117.3 | 9.2 | 10.1 |
| Drugs and chemicals | 260.5 | 275.8 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 84.8 | 84.3 | 141.6 | 149.1 | 7.6 | 8.7 |
| Non-metallic minerals | 156.5 | 150.5 | 9.5 | 8.0 | 123.2 | 134.3 | 102.2 | 93.9 | 9.9 | 9.7 |
| Metals and machinery | 180.7 | 175.3 | 25.2 | 24.8 | 147.3 | 153.7 | 113.6 | 105.4 | 7.8 | 8.0 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 205.4 | 193.9 | 17.3 | 22.7 | 142.3 | 150.1 | 86.1 | 94.7 | 9.3 | 7.2 |
| Other manufacturing food | 234.1 | 224.2 | 9.1 | 8.8 | 122.2 | 119.4 | 89.2 | 94.5 | 8.4 | 9.1 |
| Manufacturing other than | 194.8 | 193.2 | 16.3 | 15.7 | 130.6 | 129.2 | 104.0 | 104.5 | 8.1 | 8.4 |
| All manufacturing | 172.1 | 167.8 | 16.6 | 17.4 | 148.1 | 137.7 | 91.4 | 90.7 | 8.0 | 7.3 |
| Other - | ||||||||||
| Construction | 136.3 | 131.3 | 37.9 | 37.5 | 313.3 | 352.5 | 84.0 | 84.5 | 6.0 | 6.7 |
| Gas | 103.7 | 98.8 | 51.7 | 58.5 | - | - | 86.4 | 95.9 | 4.4 | 3.9 |
| Mainly wholesale | 157.8 | 168.6 | 26.2 | 20.9 | 152.5 | 137.9 | 118.8 | 114.3 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| Mainly retail | 163.9 | 175.9 | 21.5 | 18.5 | 161.3 | 141.0 | 82.8 | 91.2 | 9.2 | 8.1 |
| Department stores | 182.3 | 189.4 | 14.8 | 10.4 | 147.3 | 137.2 | 83.7 | 83.2 | 8.4 | 7.6 |
| Stock and station agents | 156.8 | 174.1 | 13.0 | 7.4 | 89.9 | 72.5 | 133.0 | 138.1 | 7.2 | 6.8 |
| Financial | 128.3 | 125.1 | 10.3 | 8.7 | - | - | 147.8 | 140.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Building societies | 5.6 | 5.4 | 132.4 | 128.9 | - | - | 6.1 | 5.9 | 5.1 | 5.2 |
| Transport | 81.3 | 79.0 | 33.2 | 36.1 | - | - | 89.2 | 88.2 | 9.2 | 7.3 |
| Totals, other | 148.6 | 156.9 | 20.0 | 15.6 | 145.7 | 126.8 | 110.6 | 112.3 | 7.4 | 7.1 |
| Grand totals | 159.6 | 162.5 | 18.3 | 16.6 | 147.1 | 132.8 | 101.5 | 101.7 | 7.8 | 7.2 |
Net Profits (After Tax) of 307 New Zealand Public Companies
| Class | Changes in Net Profit 1959–60 | Distributed as Dividends | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |||
| *Due to net losses by meat processing group, totals figures are not comparable. | ||||
| £(000) | per cent | per cent | per cent | |
| Manufacturing - | ||||
| Meat processing | —1,132 | —148.2 | 54.7 | - |
| Beverages | 265 | 36.1 | 68.2 | 60.2 |
| Other food | 116 | 15.7 | 46.7 | 50.4 |
| All food | — 750 | — 33.5 | 56.5 | -* |
| Woollen mills | 175 | 29.5 | 69.8 | 55.2 |
| Clothing manufacturers | — 98 | — 37.8 | 69.5 | 103.1 |
| Forestry and wood | 103 | 6.5 | 45.5 | 54.1 |
| Printing and publishing | 130 | 17.9 | 42.7 | 41.6 |
| Drugs and chemicals | 102 | 17.3 | 61.5 | 58.0 |
| Non-metallic minerals | 23 | 3.3 | 49.7 | 51.6 |
| Metals and machinery | 81 | 9.7 | 65.2 | 78.5 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | — 46 | — 20.3 | 49.8 | 55.2 |
| Other manufacturing | 64 | 13.2 | 56.1 | 55.7 |
| Manufacturing other than food | 535 | 8.9 | 54.4 | 57.5 |
| All manufacturing | — 215 | — 2.6 | 55.0 | -* |
| Other - | ||||
| Construction | 47 | 12.7 | 91.6 | 83.0 |
| Gas | — 6 | — 6.1 | 77.6 | 75.0 |
| Mainly wholesale | 77 | 7.1 | 55.1 | 50.7 |
| Mainly retail | — 51 | — 7.1 | 61.8 | 72.0 |
| Department stores | — 18 | — 3.6 | 58.8 | 63.8 |
| Stock and station agents | 54 | 4.2 | 50.7 | 54.0 |
| Financial | 8 | 8.2 | 49.0 | 47.2 |
| Building societies | 16 | 4.8 | 86.1 | 86.1 |
| Transport | — 22 | — 13.1 | 97.0 | 61.6 |
| Totals, other | 103 | 2.2 | 62.3 | 62.1 |
| Grand totals | — 112 | — 0.9 | 57.6 | -* |
| Totals, excluding meat processing | + 1,020 | + 8.4 | 57.8 | 58.9 |
Company Size on Basis of Shareholders' Funds
| Class | Under £50,000 | £50,000 to £99,000 | £100,000 to £199,000 | £200,000 to £249,000 | £250,000 to £449,000 | £500,000 to £749,000 | £750,000 to £999,000 | £1m. and over | Total Number of Companies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing - | |||||||||
| Meat processing | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 3 | 9 |
| Beverages | 1 | - | 4 | - | - | 1 | - | 3 | 9 |
| Other food | 6 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 25 |
| All food | 7 | 4 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 9 | 43 |
| Woollen mills | - | - | 2 | - | 5 | - | 2 | 3 | 12 |
| Clothing manufacturers | 1 | 1 | 4 | - | 1 | 3 | - | - | 10 |
| Forestry and wood | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 18 |
| Printing and publishing | 5 | 3 | - | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 17 |
| Drugs and chemicals | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 13 |
| Non-metallic minerals | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 14 |
| Metals and machinery | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2 | - | 4 | 23 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | - | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 8 |
| Other manufacturing | 3 | 1 | 6 | - | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 16 |
| Manufacturing other than food | 15 | 13 | 23 | 11 | 27 | 13 | 8 | 21 | 131 |
| All manufacturing | 22 | 17 | 33 | 13 | 31 | 18 | 10 | 30 | 174 |
| Other - | |||||||||
| Construction | - | - | 2 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Gas | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | 5 |
| Mainly wholesale | 4 | 3 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 37 |
| Mainly retail | - | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 15 |
| Department stores | - | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| Stock and station agents | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 16 |
| Financial | 6 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 17 |
| Building societies | 2 | 3 | 7 | - | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 16 |
| Transport | - | 9 | 1 | - | 3 | - | - | - | 13 |
| Totals, other | 13 | 27 | 26 | 11 | 18 | 13 | 9 | 16 | 133 |
| Grand totals | 35 | 44 | 59 | 24 | 49 | 31 | 19 | 46 | 307 |
Table of Contents
CENTRAL - The statutory provisions affecting life assurance in New Zealand are in th main contained in the Life Insurance Act 1908; the Inalienable Life Annuities Act 1910; and the Government Life Insurance Act 1953. Any association other than a friendly society which issues policies or grants annuities on human life in New Zealand comes within the scope of the enactments. Every life company must deposit with the Public Trustee cash or approved securities to a value related to the total amount assured by its New Zealand policies, the maximum deposit being £50,000. The aggregate value of such deposits at 31 March 1960 was £803,630.
In the case of composite offices, provision is made for the receipts of life and annuity business to be treated as a separate fund, and the Act safeguards the interest of the policyholder by making these funds available only for liabilities arising from such business.
Annual returns of life assurance in the form required by statute are furnished to the Minister of Finance, and it is from copies of these returns that the statistical matter contained in this subsection has been compiled. The balance dates of the offices furnishing returns vary between June and March of the following year, the financial year of the majority ending in December.
Eighteen life-assurance offices conduct business in New Zealand, and of these, four only are purely New Zealand institutions - namely, the Government Life Insurance Office, the Provident Life Assurance Co., the Dominion Life Assurance Office of New Zealand Ltd., and the F.A.M.E. Insurance Co. Ltd.
The statistics here given relate exclusively to business transacted in New Zealand.
LIFE ASSURANCE: Ordinary and Industrial - The progress of life assurance in New Zealand is illustrated by the following diagram, which shows the amount of new business transacted at intervals over a period of 54 years.
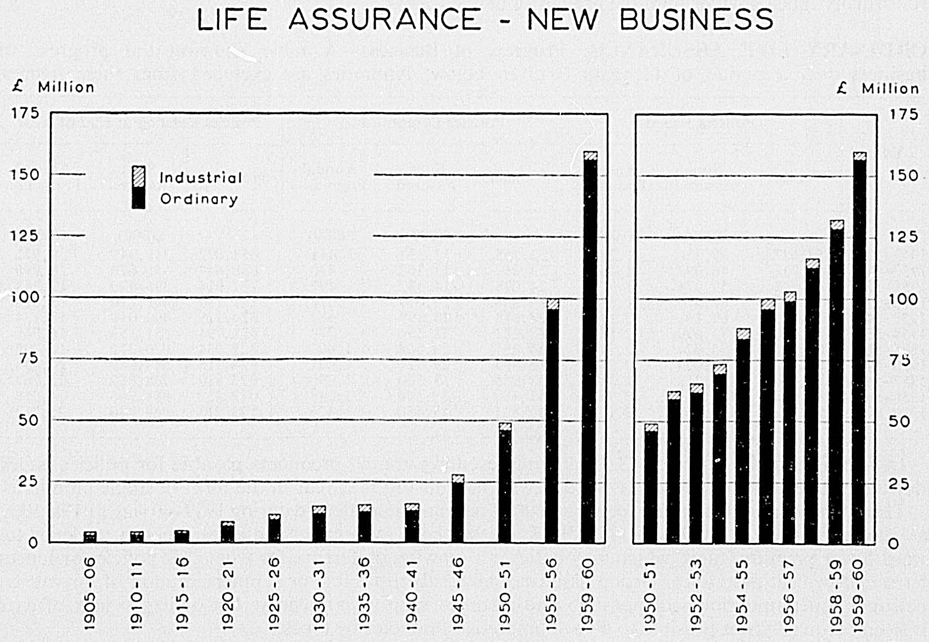
Eleven years' figures for value of new business, discontinuances, and policies in force for the combined departments (ordinary and industrial) are given in the table following.
| Year | Policies Issued | Policies Discontinued | Policies Existing at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||
| 1949–50 | 43,243 | 14,730 | 353,453 |
| 1950–51 | 49,343 | 15,580 | 387,216 |
| 1951–52 | 62,320 | 16,524 | 433,012 |
| 1952–53 | 65,214 | 19,150 | 479,077 |
| 1953–54 | 73,161 | 23,137 | 529,100 |
| 1954–55 | 88,163 | 25,473 | 591,790 |
| 1955–56 | 100,042 | 29,679 | 662,153 |
| 1956–57 | 103,127 | 33,102 | 732,177 |
| 1957–58 | 116,646 | 37,125 | 811,698 |
| 1958–59 | 132,229 | 41,979 | 901,948 |
| 1959–60 | 159,875 | 48,969 | 1,012,854 |
While the upward trend shown in the figures has been influenced both by the rate of monetary depreciation and the normal growth of population, the course of life-assurance business, particularly during the past decade, has been one of steady progress. From 1949–50 to 1959–60 the face value of new business written has more than trebled, and the amount of cover in force has risen by 187 per cent. This expansion has probably been assisted by the rise in the number of young people commencing work (in line with the rising birthrate in earlier years), and the growth in public favour of such types of policies as group insurance and mortgage repayment. A further point is the concession, for income-tax purposes, allowed by the deduction from assessable income of premiums to a certain maximum value.
As the total discontinuances include surrenders and lapses, the general tendency is for discontinuances to follow the same trend as new business, although there is naturally a time lag of, normally, about two years. This trend is plainly apparent, although the increase in discontinuances is normally much smaller than the growth of new business.
ORDINARY LIFE ASSURANCE: Progress of Business - A table showing the progress of business over a period of 11 years is given below. Annuities are excluded from these figures.
| Year | Policies Issued | Policies Discontinued | Policies Existing at End of Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1949–50 | 58,687 | 39,936 | 1,290 | 22,755 | 12,337 | 441 | 651,072 | 318,947 | 9,941 |
| 1950–51 | 60,731 | 46,093 | 1,464 | 23,359 | 13,362 | 470 | 688,444 | 351,678 | 10,936 |
| 1951–52 | 67,548 | 59,074 | 1,929 | 24,078 | 14,332 | 497 | 731,914 | 396,420 | 12,368 |
| 1952–53 | 70,770 | 61,470 | 1,882 | 25,504 | 16,679 | 576 | 777,180 | 441,210 | 13,674 |
| 1953–54 | 75,823 | 69,198 | 2,146 | 28,878 | 20,399 | 687 | 824,125 | 490,010 | 15,134 |
| 1954–55 | 83,920 | 83,699 | 2,580 | 29,251 | 22,556 | 773 | 878,794 | 551,153 | 16,941 |
| 1955–56 | 83,391 | 95,624 | 2,771 | 34,251 | 26,404 | 1,006 | 927,934 | 620,372 | 18,707 |
| 1956–57 | 81,575 | 99,024 | 2,702 | 35,394 | 29,726 | 1,001 | 974,115 | 689,669 | 20,408 |
| 1957–58 | 86,950 | 112,710 | 2,949 | 37,255 | 33,560 | 1,090 | 1,023,810 | 768,819 | 22,267 |
| 1958–59 | 89,822 | 128,652 | 2,997 | 41,180 | 28,504 | 1,248 | 1,072,452 | 858,966 | 24,016 |
| 1959–60 | 96,582 | 156,560 | 3,120 | 45,821 | 45,580 | 1,425 | 1,123,213 | 969,946 | 25,712 |
In addition to the figure of £3,119,917 representing annual premiums payable for policies issued during 1959–60, an amount of £1,145,216 was paid during that year in the form of single premiums.
The average annual premium for each £100 of new business effected during 1959–60 was £1 19s. 10d., as compared with £2 6s. 7d. in 1958–59. There has been evident for some years past a tendency toward lower premium rates, which may indicate a growing preference for whole life policies or longer term endowment assurance. Group assurance as a substitute for, or supplementation of, private or national superannuation schemes, has also assumed relative popularity, but owing to lack of data it is unfortunately not possible to give an analysis of policies by types.
Annuity policies issued during 1959–60 (excluded from these tables) numbered 228, as against 220 in 1958–59. The corresponding annual amounts were £475,193 and £401,900. There were 2,411 annuities in force at the end of the year assuring an annual amount of £2,511,807. The large decrease in annuities in force was the result of an abnormally large number of discontinuances by one company.
A prominent feature of new insurances of recent years has been, with the exception of 1952–53, the increase in the average amount of the sum assured per policy. Average amounts per new policy and the increases over the preceding year were as follows.
| Year | Average Amount | Increase |
|---|---|---|
| *Decrease. | ||
| £ | £ | |
| 1948–49 | 636 | 19 |
| 1949–50 | 680 | 44 |
| 1950–51 | 759 | 79 |
| 1951–52 | 875 | 116 |
| 1952–53 | 869 | -6* |
| 1953–54 | 913 | 44 |
| 1954–55 | 997 | 84 |
| 1955–56 | 1,147 | 150 |
| 1956–57 | 1,214 | 67 |
| 1957–58 | 1,297 | 83 |
| 1958–59 | 1,432 | 135 |
| 1959–60 | 1,621 | 189 |
The growth in the average amount of the sum assured per policy shown in the above table is due to several factors, including the changing types of policies being issued, and the increasing numbers of such policies which have a high cover, for example, cover for staff superannuation purposes by business concerns, temporary insurance with a high death-risk cover, multiple death benefit and family benefit policies having a high initial cover, and “unit” policies whereby a single premium provides a high initial death cover.
The average face value of discontinued policies during 1959–60 was £995, while the average of policies in force at the end of the year was £864.
The total amount written off during each year represents just over 5 per cent of the amount in force at the end of the year immediately preceding.
Particulars of Policies Discontinued - The causes of discontinuances during each of the latest five years are contained in the next table.
| Year | Death | Maturity | Surrender | Lapse | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Policies | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 4,048 | 9,061 | 11,235 | 7,027 | 2,880 | 34,251 |
| 1956–57 | 4,379 | 9,829 | 12,740 | 7,018 | 1,428 | 35,394 |
| 1957–58 | 4,574 | 10,390 | 13,831 | 7,208 | 1,252 | 37,255 |
| 1958–59 | 5,085 | 11,038 | 15,269 | 7,808 | 1,980 | 41,180 |
| 1959–60 | 5,092 | 12,592 | 17,631 | 8,952 | 1,554 | 45,821 |
| Sum Assured (£000) | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 2,492 | 2,661 | 11,881 | 6,498 | 2,872 | 26,404 |
| 1956–57 | 2,656 | 2,909 | 13,328 | 7,302 | 3,531 | 29,726 |
| 1957–58 | 2,746 | 3,336 | 14,437 | 8,759 | 4,283 | 33,560 |
| 1958–59 | 3,244 | 3,427 | 16,751 | 9,817 | 5,264 | 38,504 |
| 1959–60 | 3,283 | 3,902 | 18,908 | 12,935 | 6,553 | 45,580 |
During 1955–56 two large group policies were changed from an individual to a collective basis, resulting in the cancellation of over 2,000 small single policies. This explains the high number of discontinuances from other causes, the sum assured under this head not being affected to any great extent.
Reducing the sums assured in the previous table to a percentage basis, the results are as follows.
| Year | Death | Maturity | Surrender | Lapse | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 9.4 | 10.1 | 45.0 | 24.6 | 10.9 | 100.0 |
| 1956–57 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 44.8 | 24.6 | 11.9 | 100.0 |
| 1957–58 | 8.2 | 9.9 | 43.0 | 26.1 | 12.8 | 100.0 |
| 1958–59 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 43.5 | 25.5 | 13.7 | 100.0 |
| 1959–60 | 7.2 | 8.5 | 41.5 | 28.4 | 14.4 | 100.0 |
Revenue and Expenditure - A statement of revenue and expenditure under the various heads illustrates the course of ordinary life-assurance business in New Zealand during the past five years. Transfers between head offices and branches are excluded. The ratios of management expenses to premium income and to total revenue are also given.
| Item | 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| New and renewal premiums | 18,968,220 | 20,761,382 | 22,526,000 | 24,639,699 | 26,552,598 |
| Consideration for annuities | 119,613 | 103,879 | 124,045 | 117,463 | 329,770 |
| Interest, rents, etc. | 5,988,229 | 6,836,243 | 7,791,656 | 9,008,258 | 10,380,832 |
| Transfers | 991,684 | 454,731 | 1,005,053 | 2,708,399 | 2,287,383 |
| Other revenue | 54,941 | 1,586 | 2,714 | 8,679 | 219,068 |
| Totals, revenue | 26,122,687 | 28,157,821 | 31,449,468 | 36,482,498 | 39,769,651 |
| Expenditure | |||||
| Claims by death and maturity | 6,302,898 | 6,851,632 | 7,476,365 | 8,102,030 | 8,848,090 |
| Annuities | 138,384 | 141,664 | 142,338 | 144,183 | 152,676 |
| Surrenders | 1,355,230 | 1,614,531 | 1,787,182 | 2,201,259 | 2,719,396 |
| Cash bonuses | 26,245 | 44,198 | 36,928 | 42,710 | 55,324 |
| Commissions | 1,510,026 | 1,558,763 | 1,704,462 | 1,809,737 | 1,825,920 |
| Other management | 1,458,994 | 1,601,639 | 1,765,111 | 1,921,760 | 2,138,232 |
| Rates and taxes | 671,927 | 815,296 | 877,440 | 955,397 | 1,090,459 |
| Transfers | 344,162 | 365,302 | 923,398 | 150,832 | 90,562 |
| Other expenditure | 96,106 | 179,137 | 97,247 | 112,964 | 269,001 |
| Totals, expenditure | 11,903,972 | 13,172,162 | 14,810,471 | 15,440,872 | 17,189,660 |
| Ratios | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent |
| Management expenses to premium income | 15.65 | 15.22 | 15.40 | 15.14 | 14.93 |
| Management expenses to total revenue | 11.37 | 11.22 | 11.03 | 10.23 | 9.97 |
Of the excess of revenue as shown in the above statements a large proportion is transferred annually to reserves to meet future payments under policies.
INDUSTRIAL ASSURANCE: Progress of Business - In this class of insurance the premiums are payable at shorter intervals than three months, and provision is made for its control by regulation. Companies are required to deposit with the Minister of Finance forms of policy tables, rates of premiums, and other documents, and policies must contain only such conditions as have been approved by the Governor-General in Council. Restrictions are placed on the forfeiture of policies in default of payments or other requirements. There has been a long-term decline in the demand for industrial issues relative to ordinary policies, as the following figures exemplify. During the last decade particularly, the demand for ordinary life assurance has not been ***shared to any extent by the industrial department, the number of policies issued in 1959–60 being only 64.6 per cent of the 1949–50 total. Of the 18 life offices, five also engage in industrial business.
A summary of the course of industrial-assurance business from 1949–50 to 1959–60 is given in the following table.
| Year | Policies Issued | Policies Discontinued | Policies Existing at End of Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1949–50 | 33,815 | 3,307 | 153 | 36,153 | 2,393 | 132 | 574,636 | 34,506 | 1,839 |
| 1950–51 | 31,714 | 3,250 | 150 | 33,740 | 2,211 | 124 | 572,610 | 35,544 | 1,865 |
| 951–52 | 29,879 | 3,246 | 150 | 33,058 | 2,198 | 124 | 569,431 | 36,593 | 1,892 |
| 952–53 | 31,573 | 3,751 | 174 | 36,586 | 2,470 | 138 | 564,418 | 37,873 | 1,927 |
| 1953–54 | 31,953 | 3,963 | 184 | 39,983 | 2,738 | 151 | 556,388 | 39,098 | 1,961 |
| 1954–55 | 33,013 | 4,456 | 206 | 41,663 | 2,916 | 160 | 547,738 | 40,638 | 2,007 |
| 1955–56 | 29,885 | 4,418 | 205 | 42,435 | 3,275 | 176 | 535,188 | 41,781 | 2,035 |
| 1956–57 | 27,410 | 4,103 | 191 | 42,085 | 3,376 | 178 | 520,513 | 42,508 | 2,048 |
| 1957–58 | 26,506 | 3,937 | 184 | 42,734 | 3,565 | 188 | 504,285 | 42,879 | 2,044 |
| 1958–59 | 23,676 | 3,578 | 169 | 39,329 | 3,475 | 181 | 488,632 | 42,982 | 2,033 |
| 1959–60 | 21,848 | 3,315 | 157 | 35,312 | 3,388 | 180 | 475,168 | 42,908 | 2,010 |
The average sum assured under each policy of new business effected in 1959–60 amounted to £152 with an average annual premium of £7 4s. 0d. Corresponding averages for 1949–50 were £102 and £4 15s. 3d.
Particulars of Policies Discontinued - A summary of the number of industrial policies and the corresponding assurances discontinued according to the several causes is now given in the form of a five-year table.
| Year | Death | Maturity | Surrender | Lapse | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Policies | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 2,382 | 27,270 | 4,680 | 7,991 | 112 | 42,435 |
| 1956–57 | 2,051 | 27,067 | 4,978 | 7,945 | 44 | 42,085 |
| 1957–58 | 2,118 | 27,250 | 5,028 | 8,257 | 81 | 42,734 |
| 1958–59 | 1,892 | 24,243 | 5,376 | 7,767 | 51 | 39,329 |
| 1959–60 | 1,837 | 22,041 | 6,282 | 5,102 | 50 | 35,312 |
| Sum Assured (£) | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 127,780 | 1,255,676 | 618,401 | 1,263,773 | 9,238 | 3,274,868 |
| 1956–57 | 112,974 | 1,296,895 | 691,850 | 1,267,910 | 6,520 | 3,376,149 |
| 1957–58 | 120,546 | 1,398,173 | 777,896 | 1,256,575 | 11,842 | 3,565,032 |
| 1958–59 | 116,198 | 1,277,097 | 839,416 | 1,233,405 | 9,209 | 3,475,325 |
| 1959–60 | 117,707 | 1,175,714 | 922,960 | 1,161,360 | 10,644 | 3,388,385 |
The amount written off in each year is proportionately greater in the industrial than in the ordinary branch. Of the assurance in force at the end of the previous year, 5.3 per cent of the ordinary became void in 1959–60, as compared with 7.9 of the industrial.
In the following table the sums assured for the various classes of discontinuances are expressed as percentages of the total discontinuances.
| Year | Death | Maturity | Surrender | Lapse | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Cent | ||||||
| 1955–56 | 3.9 | 38.3 | 18.9 | 38.6 | 0.3 | 100.0 |
| 1956–57 | 3.3 | 38.4 | 20.5 | 37.6 | 0.2 | 100.0 |
| 1957–58 | 3.4 | 39.2 | 21.8 | 35.3 | 0.3 | 100.0 |
| 1958–59 | 3.3 | 36.7 | 24.2 | 35.5 | 0.3 | 100.0 |
| 1959–60 | 3.5 | 34.7 | 27.2 | 34.3 | 0.3 | 100.0 |
Discontinuances by death are relatively lower in industrial than in ordinary business, while the proportion of policies reaching maturity is much higher. The explanation probably lies in the comparatively short terms for which industrial policies are issued, and the fact that premiums are usually collected personally by agents.
Revenue and Expenditure - The several items of revenue and expenditure in industrial business are shown in the following five-yearly table, together with the ratios of management expenses to premium income and to total revenue. Transfers between head offices and branches are again excluded.
| Item | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Premiums | 2,002,025 | 2,029,561 | 2,031,878 | 2,017,410 | 1,992,439 |
| Interest, rents, etc. | 639,395 | 675,592 | 723,194 | 758,289 | 835,022 |
| Other revenue | 34,211 | 2,204 | 1,246 | 1,415 | 49,344 |
| Totals, revenue | 2,675,631 | 2,707,357 | 2,756,318 | 2,777,114 | 2,876,805 |
| Expenditure | |||||
| Claims by death and maturity | 1,540,988 | 1,592,822 | 1,712,188 | 1,575,628 | 1,441,962 |
| Surrenders | 106,022 | 122,991 | 130,018 | 146,159 | 169,723 |
| Commissions | 280,782 | 285,981 | 276,494 | 262,259 | 248,721 |
| Other management | 357,812 | 367,820 | 360,616 | 357,703 | 360,499 |
| Rates and taxes | 51,985 | 58,443 | 74,832 | 71,431 | 74,746 |
| Other expenditure | 30,767 | 9,235 | 21,678 | 12,250 | 55,637 |
| Totals, expenditure | 2,368,356 | 2,437,292 | 2,575,826 | 2,425,430 | 2,351,288 |
| Ratios | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent |
| Management expenses to premium income | 31.90 | 32.21 | 31.36 | 30.73 | 30.58 |
| Management expenses to total revenue | 24.17 | 24.15 | 23.11 | 22.32 | 21.18 |
The higher ratio of management expenses to premium income in the industrial branch is largely accounted for by the cost of renewal commissions on collection of premiums and the greater amount of office work involved in relation to the amount assured. In the ordinary branch, commission (new and renewal) in 1959-60 was equivalent to 6.9 per cent of the premium income, and in the industrial branch to 12.5 per cent. Excluding commission, the ratio of management expenses to premium income was 18.1 per cent in the industrial branch, as against 8.1 per cent in the ordinary.
LIFE-ASSURANCE DEATH RATES - The following table shows for the period 1949-50 to 1959-60 the death rate per thousand policies exposed to risk in each year. In computing these rates all policies which were in force for any portion of the year have been taken into account. The much lower death rate among policyholders, compared with that for the general population (9.05), points to a lower average age in the insured group, a normal consequence of rapid growth in the life-assurance field.
| Year | Death Rate per 1,000 Policies | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Life Assurance | Industrial Life Assurance | Ordinary and Industrial Combined | |
| 1949-50 | 4.70 | 4.40 | 4.56 |
| 1950-51 | 4.44 | 4.24 | 4.35 |
| 1951-52 | 4.61 | 4.23 | 4.44 |
| 1952-53 | 4.61 | 4.31 | 4.48 |
| 1953-54 | 4.53 | 3.77 | 4.22 |
| 1954-55 | 4.66 | 3.78 | 4.31 |
| 1955-56 | 4.21 | 4.12 | 4.18 |
| 1956-57 | 4.34 | 3.65 | 4.09 |
| 1957-58 | 4.31 | 3.87 | 4.16 |
| 1958-59 | 4.57 | 3.58 | 4.25 |
| 1959-60 | 4.36 | 3.60 | 4.13 |
LIABILITIES AND ASSETS - The principal items in the balance sheets of life-assurance companies are summarised below for the three latest years. Both classes of assurance are represented in the figures, which, as in the previous tables, relate to New Zealand business only. In the case of some companies other branches of insurance business are included.
Aggregate liabilities are first shown.
| Liabilities | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| Paid-up share capital | 204,045 | 203,495 | 207,445 |
| Life assurance and annuity funds | 196,852,727 | 218,256,413 | 240,759,347 |
| Depreciation, reserve, and other special funds | 2,874,642 | 3,119,157 | 3,882,787 |
| Claims admitted but not paid | 1,236,355 | 1,348,922 | 1,533,874 |
| Other liabilities | 2,233,993 | 2,384,610 | 2,963,302 |
| Totals | 203,401,762 | 225,312,597 | 249,346,755 |
The assets of the New Zealand branches at the end of each of the three latest years were as follows.
| Assets | Amount | Proportion to Totals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
| £ | £ | £ | per cent | per cent | per cent | |
| Mortgages on property | 90,644,788 | 101,502,541 | 113,357,746 | 44.56 | 45.05 | 45.46 |
| Loans on policies | 6,054,586 | 6,838,414 | 7,778,575 | 2.98 | 3.04 | 3.12 |
| New Zealand Government securities | 46,695,062 | 50,876,687 | 56,342,662 | 22.96 | 22.58 | 22.60 |
| Securities of other Governments | 370,224 | 370,725 | 371,157 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.15 |
| Local authority securities | 37,647,288 | 39,670,852 | 40,620,866 | 18.51 | 17.61 | 16.29 |
| Landed and house property | 6,109,877 | 7,236,599 | 9,780,532 | 3.00 | 3.21 | 3.92 |
| Other investments | 11,371,771 | 13,275,686 | 15,695,030 | 5.59 | 5.89 | 6.29 |
| Outstanding premiums | 1,339,154 | 1,537,392 | 1,594,768 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.64 |
| Interest accrued, etc. | 1,597,657 | 1,948,220 | 2,220,321 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.89 |
| Cash | 615,087 | 816,532 | 315,119 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.13 |
| Other assets | 956,268 | 1,238,949 | 1,269,979 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.51 |
| Totals | 203,401,762 | 225,312,597 | 249,346,755 | 100–00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
As a form of investment, mortgage securities have steadily gained in favour during the past decade, the proportion of assets held in this form rising from 21.7 per cent in 1949-50 to 45.5 per cent in 1959-60. This movement has been chiefly at the expense of the Government and local authority securities, the proportion of the former declining from 42.4 per cent to 22.7 during the same period. Other investments (chiefly company shares and debentures), although small in relation to the total, are gaining in popularity.
For 1959-60 the average rate of interest earned on the life funds of both departments was £5 2s. 8d. per cent, compared with £4 16s. 5d. during 1958-59. This rate was calculated by taking the arithmetic mean of funds at the beginning and end of the year less half the amount of interest, etc., earned.
The following diagram illustrates the expansion that has taken place since 1939-40 in the assets of the New Zealand branches of life-assurance companies. This, of course, is a natural consequence of the huge increase in the amount of business. As stated previously, receipts of life assurance and annuity business must be treated as a separate fund, and the interests of the policyholders are safeguarded by the fact that these funds are available only for liabilities arising from such business.
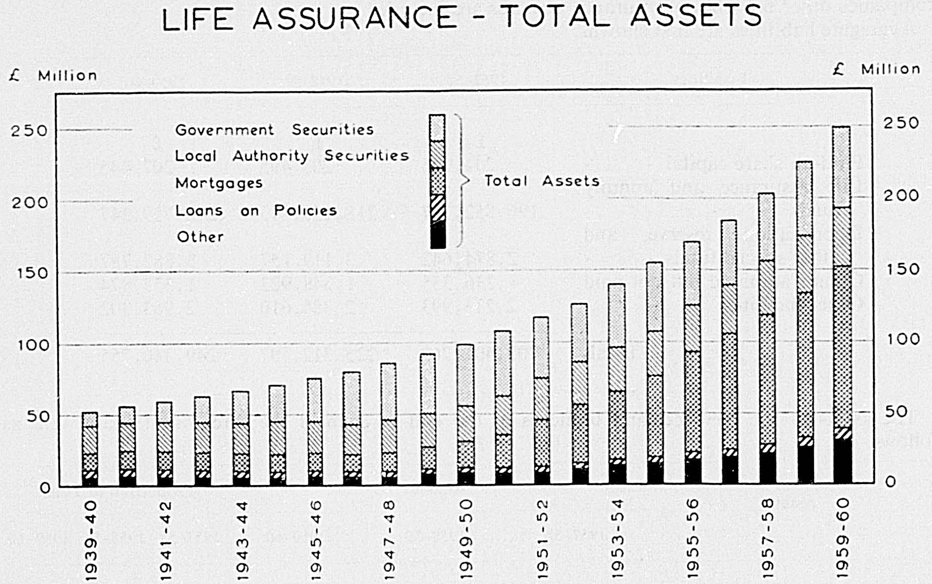
The diagram also shows the trend in the class of security in which the funds have been invested. The most significant change since 1949-50, referred to above, has been the preference for mortgage investment, the proportion rising almost fourfold during the 10-year period.
GENERAL - In terms of the Accident Insurance Companies Act 1908, accident insurance policies may be issued by any association, whether incorporated or not, provided such association is not established under any Act relating to friendly societies. The principal classes of accident insurance transacted in New Zealand are as follows:
Personal accident, covering accident, sickness, etc.
Employers' liability under statutory or common law.
Motor-vehicle insurance, comprehensive and compulsory third-party risks cover.
Other important classes of accident insurance policies are in respect of plate-glass insurance and fidelity-guarantee insurance.
The Workers' Compensation Amendment Act 1947 provided for the compulsory insurance with the Government Accident Insurance Branch of the State Fire Insurance Office of all employers' liability insurances as from 1 April 1949. However, insurances with certain specified mutual insurance companies were exempted from the operation of the Act. Further reference to this transfer will be found in Sections 31D and 37A. An amending Act of 1950, however, restored the right of insurance companies to undertake employers' liability insurance as from 1 April 1951.
Information relating to deposits required from companies transacting accident insurance business is contained in the next subsection, which deals with the cognate subject of fire insurance.
REVENUE AND EXPENDITURE - The number of accident insurance offices represented in the statistics for 1959-60 is 76, the head offices of the companies concerned being domiciled as follows: Great Britain, 27; Australia, 17; United States of America, 2; Hong Kong, 2; and New Zealand, 28.
Of the New Zealand offices only 13, including the State Accident Insurance Office, may be stated to be competitive in the ordinary sense of the term, the remainder having been formed by trade associations, etc., on a more or less cooperative basis. In the main an office of this latter type conducts one class of accident insurance business only, according to the nature of the association with which it is connected.
The following table shows, for the years quoted, the principal items of revenue and expenditure. Premiums and claims are net, i.e., reinsurance transactions, whether effected locally or overseas, are taken into account.
| Year | Number of Offices | Revenue | Expenditure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premiums | Other Revenue | Total* | Claims | Commission | Salaries | Other Expenses | Total* | ||
| * Excluding unexpired risks reserves provisions. | |||||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||||
| 1949-50 | 61 | 4,902 | 152 | 5,054 | 2,972 | 326 | 530 | 667 | 4,495 |
| 1950-51 | 62 | 5,817 | 171 | 5,987 | 3,466 | 369 | 594 | 782 | 5,211 |
| 1951-52 | 62 | 6,625 | 206 | 6,830 | 3,956 | 500 | 745 | 859 | 6,060 |
| 1952-53 | 61 | 7,965 | 221 | 8,187 | 4,886 | 617 | 815 | 885 | 7,203 |
| 1953-54 | 64 | 8,954 | 229 | 9,183 | 5,313 | 689 | 970 | 1,059 | 8,031 |
| 1954-55 | 67 | 9,918 | 304 | 10,222 | 6,072 | 779 | 1,116 | 1,091 | 9,057 |
| 1955-56 | 67 | 11,022 | 356 | 11,378 | 7,071 | 883 | 1,236 | 1,198 | 10,387 |
| 1956-57 | 67 | 12,400 | 415 | 12,815 | 8,213 | 1,025 | 1,395 | 1,213 | 11,846 |
| 1957-58 | 67 | 13,688 | 480 | 14,168 | 9,196 | 1,144 | 1,559 | 1,326 | 13,225 |
| 1958-59 | 71 | 14,821 | 550 | 15,370 | 9,954 | 1,228 | 1,647 | 1,518 | 14,347 |
| 1959-60 | 76 | 16,079 | 602 | 16,681 | 10,583 | 1,341 | 1,754 | 1,586 | 15,263 |
Premium receipts in 1959-60 were 8.5 per cent above the 1958-59 figure, while claims rose by 6.3 per cent.
Employers' liability insurance accounted for the largest single part of the premium increase (£436,000). To some extent this could be due to an increase of 20 per cent in the premium rates of this class of insurance as from 31 March 1960, although this rise would only have affected certain companies whose returns were for the year ending later than 31 March. The full effect will be reflected in next year's figures. Motor vehicle comprehensive insurance accounted for the next largest increase (£358,000).
Claims for employers' liability insurance which in 1958-59 had risen sharply by £498,000 again rose in 1959-60 by £210,000. However motor vehicle comprehensive insurance claims showed a larger increase of £268,000 in 1959-60, the increase in the previous year being only £61,000. Expenses other than claims totalled £4,680,000, of which taxation amounted to £414,000.
A review of the expenses incurred in transacting accident insurance is contained in the table following. The fluctuations over a period of five years are shown in the form of percentages of revenue to expenditure under various heads. The claims experience since 1955-56 has been slightly less favourable than the average of previous years, although 1959-60 claims experience showed an improvement on 1958-59.
| Year | Claims to Premiums | Commission to Premiums | Salaries to Premiums | Other Expenses to Premiums | Total Expenses (Other Than Claims) to Premiums | Total Expenditure to Premiums | Total Expenditure to Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| per cent | |||||||
| 1955-56 | 64.15 | 8.01 | 11.21 | 10.87 | 30.09 | 94.24 | 91.29 |
| 1956-57 | 66.23 | 8.27 | 11.25 | 9.78 | 29.30 | 95.53 | 92.44 |
| 1957-58 | 67.18 | 8.35 | 11.39 | 9.69 | 29.43 | 96.61 | 93.34 |
| 1958-59 | 67.16 | 8.29 | 11.11 | 10.24 | 29.64 | 96.80 | 93.33 |
| 1959.60 | 65.82 | 8.34 | 10.91 | 9.86 | 29.11 | 94.92 | 91.50 |
Working expenses (excluding taxation) amounted to £3,704,265 in 1957-58, £3,984,296 in 1958-59, and £4,266,609 in 1959-60. The ratios of working expenses to premium income for each of the three years were respectively 27.06, 26.88, and 26.54 per cent.
ANALYSIS OF PREMIUMS AND CLAIMS - In the next table particulars of premiums and claims for the three main classes of accident insurance are given for the last five years. Reinsurances effected outside New Zealand are not taken into account in the figures presented below.
| Year | Employers' Liability | Personal Accident | Motor Vehicle Comprehensive | Motor Vehicle Third-party Risks | Other Forms | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| Premiums | ||||||
| 1955-56 | 2,762 | 868 | 5,210 | 1,429 | 1,185 | 11,453 |
| 1956-57 | 3,276 | 977 | 5,756 | 1,534 | 1,344 | 12,886 |
| 1957-58 | 3,411 | 1,133 | 6,648 | 1,586 | 1,474 | 14,252 |
| 1958-59 | 3,374 | 1,266 | 7,426 | 1,660 | 1,774 | 15,500 |
| 1959-60 | 3,810 | 1,403 | 7,784 | 1,716 | 1,937 | 16,650 |
| Claims | ||||||
| 1955-56 | 1,969 | 301 | 3,651 | 824 | 477 | 7,222 |
| 1956-57 | 2,058 | 380 | 4,338 | 877 | 497 | 8,150 |
| 1957-58 | 2,387 | 429 | 4,680 | 1,093 | 579 | 9,167 |
| 1958-59 | 2,885 | 497 | 4,740 | 1,130 | 683 | 9,935 |
| 1959-60 | 3,095 | 596 | 5,008 | 1,265 | 728 | 10,692 |
Premiums and claims for motor vehicle third-party risks insurance relate to the years ended 30 June.
Reducing the figures of each class for the years 1957-58 to 1959-60 to a percentage basis, the following results are obtained.
| Class of Insurance | Claims to Premiums | Premiums to Total Premiums | Claims to Total Claims | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
| per cent | |||||||||
| Employers' liability | 69.96 | 85.51 | 81.23 | 23.94 | 21.77 | 22.88 | 26.03 | 29.04 | 28.94 |
| Personal accident and sickness | 37.86 | 39.29 | 42.47 | 7.95 | 8.16 | 8.43 | 4.68 | 5.01 | 5.57 |
| Motor vehicle comprehensive | 70.40 | 63.83 | 64.33 | 46.64 | 47.91 | 46.75 | 51.05 | 47.71 | 46.84 |
| Motor vehicle third-party risks | 68.91 | 68.06 | 73.74 | 11.13 | 10.71 | 10.31 | 11.93 | 11.37 | 11.84 |
| Other | 39.26 | 38.48 | 37.58 | 10.34 | 11.45 | 11.63 | 6.31 | 6.87 | 6.81 |
| All classes | 64.32 | 64.10 | 64.21 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
MOTOR VEHICLES INSURANCE (THIRD-PARTY RISKS) - The Transport Act 1949 requires owners of motor vehicles to insure against their liability, through their negligence, to pay damages on account of the death of or bodily injury to another person. The payment of the insurance premiums is made annually to Deputy Registrars of Motor Vehicles at the same time as the annual licence fee is paid. Owners of motor vehicles are required to nominate each year the insurance company with which the contract of insurance is to be made, and the contract is deemed to be complete on the payment of the premium.
Premium receipts and claims actually paid have been shown in the earlier tables, but the claims figures given later also show amounts on account of the estimated liability for claims still outstanding at 30 June 1960, which are necessarily subject to revision.
With the spectacular increase in road usage, the claims figures have steadily mounted, resulting in progressively higher premium rates until the last four years, during which period premium rates have remained relatively constant over all. The table following gives the premium rates for the various classes of motor vehicles over the last four years, together with a comparison of rates in 1949-50. The minimum rates for omnibuses, service cars, and contract motor vehicles are subject to increases according to seating capacity.
| Class of Motor Vehicle | 1949-50 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 1960-61 | 1961-62 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | £ | s. | |
| Motor cycles | 16 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 18 | |
| Power cycles | ... | ... | 15 | 15 | 12 1/2 | 10 | ||||
| Tractors and traction engines | 3 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |||||
| Private cars and station wagons | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Dealers' and business cars | 1 | 15 | 2 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Goods-service vehicles | 1 | 15 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 10 |
| Fire-brigade vehicles | 10 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | |
| Public taxicabs | 15 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 17 | 10 | 17 | 10 | 17 | 10 |
| Private taxicabs | 5 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 0 |
| Omnibuses (minimum) | 8 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 27 | 0 |
| Service cars (minimum) | 4 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Contract motor vehicles (minimum) | 3 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Trailers | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| Hearses and ambulances | 10 | 2 | 15 | 2 | 15 | 2 | 15 | 2 | 10 | |
| Rental car | 4 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
A sum of 2s. 6d. for every contract of insurance is deducted for administration expenses, and the balance paid to the insurance company concerned.
The liability of the company does not extend to indemnify the owner against any claim made in respect of the death of (or injury to) (a) his own passenger (other than a fare-paying passenger in a vehicle plying for hire); (b) any relative of the owner within the third degree of relationship (except in certain cases of school children travelling to or from school); (c) any employee, except where the accident occurs otherwise than in the course of employment.
The liability of any insurance company under any contract under the Act is limited to £7,500 (increased from £5,000 from 23 October 1959) in respect of any passenger in the motor vehicle concerned, and to £75,000 (£50,000 prior to 23 October 1959) for all claims made by or in respect of passengers carried for hire. Otherwise there is no limit as to amount.
The following particulars give the experience of the last five years, with a summary covering the 10 years to 30 June 1960. It should be noted that the liability for outstanding claims is usually overestimated, and that the total claims for any particular year when finally settled may be expected to be somewhat smaller than the amounts now given. For instance, taking a period of five years 1950-51 to 1954-55 inclusive, for which virtually all claims had been settled by 30 June 1960, it is found that premiums received totalled £5,020,712, while total claims paid up to 30 June 1960 in respect of accidents during the five year period quoted totalled £3,728,682, a ratio of claims to premiums of 74.27 per cent. The actual claims payments during the five years totalled £3,157,979, of which a proportion was on account of accidents occurring prior to 1949-50. From this explanation it follows that the ratios given below are also likely to be reduced in course of time, particularly those for the most recent years.
| Registration Year Ended 30 June | Total for Ten Years to 30 June 1960 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| *Total claims outstanding from 1953-54 - all previous years' claims having been settled. | ||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Premiums received | 1,428,847 | 1,533,555 | 1,586,394 | 1,660,399 | 1,715,983 | 12,945,890 |
| Claims actually paid to 30 June 1960 | 1,163,067 | 1,178,780 | 1,031,103 | 570,338 | 128,785 | 7,800,755 |
| Estimated liability for claims still outstanding at 30 June 1960 | 38,980 | 156,573 | 657,899 | 1,186,372 | 1,850,833 | 3,910,057* |
| Ratio per cent of claims paid and outstanding to premiums | 84.1 | 87.1 | 106.5 | 105.8 | 115.4 | 90.5 |
A summary showing the experience over the last four registration years for each of the principal classes of motor vehicle is given in the table following.
| Class of Motor Vehicle | Net Premiums Received | Claims Paid | Estimated Claims Outstanding | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arising During Year | Arising During Previous Year | Arising During Year | Arising During Previous Year | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956-57 | |||||
| Motor cycles | 48,759 | 1,985 | 21,650 | 32,793 | 84,215 |
| Private cars | 729,334 | 58,667 | 395,907 | 597,878 | 505,099 |
| Business cars | 154,326 | 12,793 | 55,976 | 138,371 | 134,719 |
| Goods-service vehicles | 404,047 | 32,512 | 197,422 | 326,942 | 308,068 |
| Public taxicabs | 59,423 | 5,361 | 30,388 | 36,399 | 47,300 |
| Public omnibuses | 60,803 | 3,260 | 18,050 | 50,855 | 37,840 |
| Other classes | 76,863 | 3,076 | 40,062 | 53,250 | 66,827 |
| Totals | 1,533,555 | 117,654 | 759,455 | 1,236,488 | 1,184,068 |
| 1957-58 | |||||
| Motor cycles | 41,099 | 2,037 | 32,741 | 33,862 | 52,351 |
| Private cars | 779,342 | 74,740 | 498,627 | 708,460 | 644,244 |
| Business cars | 176,837 | 20,381 | 104,257 | 179,003 | 204,183 |
| Goods-service vehicles | 398,855 | 24,845 | 221,237 | 332,389 | 457,850 |
| Public taxicabs | 51,091 | 3,450 | 24,701 | 33,890 | 58,314 |
| Public omnibuses | 61,661 | 13,677 | 26,648 | 49,645 | 28,950 |
| Other classes | 77,509 | 3,006 | 42,887 | 38,764 | 103,825 |
| Totals | 1,586,394 | 142,136 | 951,098 | 1,376,013 | 1,549,717 |
| 1958-59 | |||||
| Motor cycles | 47,177 | 710 | 20,376 | 21,896 | 69,796 |
| Private cars | 812,067 | 40,519 | 540,358 | 748,782 | 791,710 |
| Business cars | 188,879 | 19,764 | 141,822 | 231,095 | 210,598 |
| Goods-service vehicles | 411,787 | 35,393 | 229,460 | 442,682 | 480,187 |
| Public taxicabs | 46,578 | 2,478 | 31,624 | 35,509 | 70,960 |
| Public omnibuses | 62,370 | 4,298 | 17,207 | 54,440 | 45,115 |
| Other classes | 91,541 | 2,828 | 43,260 | 59,150 | 59,460 |
| Totals | 1,660,399 | 105,990 | 1,024,107 | 1,593,554 | 1,727,826 |
| 1959-60 | |||||
| Motor cycles | 47,273 | 2,365 | 24,191 | 31,556 | 49,060 |
| Private cars | 836,125 | 73,733 | 598,664 | 1,005,611 | 952,229 |
| Business cars | 222,371 | 16,249 | 138,137 | 210,221 | 311,635 |
| Goods-service vehicles | 414,346 | 24,303 | 302,766 | 450,410 | 533,805 |
| Public taxicabs | 44,973 | 2,190 | 28,070 | 46,000 | 75,200 |
| Public omnibuses | 61,481 | 3,957 | 21,949 | 67,785 | 50,305 |
| Other classes | 89,414 | 5,988 | 22,809 | 39,250 | 86,990 |
| Totals | 1,715,983 | 128,785 | 1,136,586 | 1,850,833 | 2,059,224 |
GENERAL - In the legislation dealing with insurance, four separate classes of fire insurance offices are distinguished, namely: (1) local insurance companies established within the limits of New Zealand; (2) foreign insurance companies established beyond New Zealand; (3) United Kingdom offices similarly established; and (4) mutual insurance associations. To these may be added the State Fire Insurance Office, established under a separate Act of Parliament.
Part XIV of the Companies Act 1933 required a minimum paid-up capital of £50,000 intact in the case of limited companies undertaking insurance business (other than life insurance) in New Zealand. A later provision, contained in the Finance Act (No. 3) 1934, allowed overseas companies limited by guarantee which were carrying on insurance business in New Zealand at 31 March 1934 to continue in such business if a sum of not less than £50,000 (including deposits required by law in respect of such business) was kept deposited with the Public Trustee. Part XIII of the Companies Act 1955, which came into force on 1 January 1957, re-enacted the provisions concerning local companies, but the authorisation to engage in insurance business was extended to overseas companies limited by shares and regardless of date of commencement. Part II of the Insurance Companies Act 1940 provides that, in the case of an insurance company of doubtful solvency, inspectors may be appointed to investigate and report on the affairs of the company. Mutual associations are referred to specifically at a later stage in this subsection.
DEPOSITS - The law regarding deposit requirements to be made with the Public Trustee for companies carrying on the business of insurance, except life assurance, marine insurance, and insurance against earthquake damage, is governed by the Insurance Companies Act 1953. For any New Zealand company commencing business the amounts of deposit required are: fire insurance, £22,500; employers' liability insurance, £22,500; motor vehicles third-party risks insurance, £10,000; all other kinds of insurance, except life, marine, and earthquake insurance, £5,000. These provisions date from 1940 legislation. In the original legislation and in the Consolidating Act of 1953 special requirements are laid down for New Zealand companies which were already carrying on business when the original legislation was introduced in 1940.
Details of deposits for other classes of company, such as British companies, agents of British companies, and foreign companies, are shown in the 1959 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
Life and marine businesses are not affected by the provisions mentioned in the preceding paragraphs. Deposits required from life assurance companies are dealt with under Section 31A.
The capital amount of deposits held by the Public Trustee at 31 March 1960, under the Insurance Companies' Deposits Act and amendments, on behalf of 81 companies and three associations, was £3,127,002, as compared with £2,995,000 at 31 March 1959.
Statistics of fire insurance are compiled annually by the Department of Statistics from returns furnished by the insurance companies for the financial year most closely approximating to the calendar year, and these in some cases extend up to the following June. For 1959-60 information was obtained from 60 offices conducting business in New Zealand. The head offices of these were distributed as follows: Great Britain, 28; New Zealand, 16; Australia, 12; Hong Kong, 2; United States of America, 2.
LIABILITIES AND ASSETS - The following table indicates generally the extent to which fire insurance offices have funds available to meet losses and liabilities. The figures refer to all departments of business underwritten. Funds of life departments are added for completeness, but by the Life Insurance Act 1908 (which follows the provisions of the United Kingdom statute on the subject) life funds must be accounted for separately, and form a security for life-policy holders which is not available for other classes of insurance transacted. Of the 60 fire offices, 20 also engage in life assurance business, but only four of these conduct such business in New Zealand. The amount of funds (other than life) in New Zealand and elsewhere is, it will be seen, approximately £1,845 million.
| 1959-60 | 1958-59 (Total) | 1957-58 (Total) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overseas Companies | Local Companies | Total | |||
| £(million) | |||||
| Paid-up capital | 114.6 | 7.5 | 122.1 | 97.2 | 92.1 |
| Reserves | 1,001.5 | 22.6 | 1,024.1 | 931.4 | 852.0 |
| Other liabilities | 680.7 | 17.8 | 698.4 | 618.5 | 569.5 |
| Totals | 1,796.8 | 47.9 | 1.844.6 | 1.647.1 | 1,513.6 |
| Life funds | 2,364.8 | 0.1 | 2,364.9 | 2,172-5 | 2,001.0 |
| Total liabilities (and assets) | 4,161.6 | 47.9 | 4,209.5 | 3,819.6 | 3,514.6 |
The following table gives the amount of assets in New Zealand as at the end of each of the last three years classified under various heads. The figures given include all investments in New Zealand securities and do not relate merely to the assets held by the New Zealand branches of the companies concerned. The assets of other departments - accident, life, marine, etc. - are also included.
| Assets in New Zealand | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| House and landed property | 3,892,897 | 4,346,685 | 4,842,632 |
| New Zealand Government securities | 11,888,415 | 12,947,087 | 12,353,108 |
| New Zealand local authority securities | 2,153,501 | 2,423,884 | 2,577,031 |
| Company stocks and shares | 2,874,829 | 3,251,568 | 3,897,870 |
| Mortgages, etc. | 2,354,200 | 2,726,640 | 3,273,753 |
| Outstanding premiums | 2,411,536 | 2,549,173 | 2,648,752 |
| Cash and other assets in New Zealand | 5,517,131 | 6,353,850 | 6,673,635 |
| Total New Zealand assets | 31,092,509 | 34,598,887 | 36,266,781 |
SUMMARY OF BUSINESS - The increase in extent and value of property over the years is reflected in the statistics of policies issued and business underwritten given in this subsection. The figure for new and renewal business for 1959-60 shows an increase of £890 million, or 36.4 per cent, compared with five years earlier.
The average premium rate per £100 of insurance cover fell from 11s. 11d. in 1920 to 9s. 2d. in 1930 and 7s. in 1940. The present rate of 4s. 9d. (the same as in 1958-59) is the lowest recorded, and points to the highly competitive nature of fire insurance business. This average is influenced not only by movements in premium rates, but also by the varying proportions of insurance risks which are rated at higher or lower premiums than the average. It should be explained that the figures in the table which follows relate to the business conducted with the insuring public. Reinsurance transactions are not taken into account.
| 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amounts Underwritten | |||
| Gross amount of insurance cover in force in New Zealand on 31 December | £2,714,151,875 | £2,990,574,293 | £3,198,640,082 |
| Number of policies representing the foregoing | 1,363,297 | 1,418,782 | 1,477,009 |
| Gross amount of new and renewal business underwritten during year | £3,040,463,090 | £3,370,464,020 | £3,597,866,096 |
| Number of policies representing the foregoing | 1,490,701 | 1,552,167 | 1,609,342 |
| Premiums | |||
| Total gross premiums charged on business (new and renewal) underwritten during year | £7,373,284 | £7,969,865 | £8,552,067 |
| Percentage of gross premiums to total amount of business underwritten | 4s. 10d. | 4s. 9d. | 4s. 9d. |
| Total premiums (as shown above), less premiums refunded to insured other than to other offices | £6,614,392 | £7,147,207 | £7,656,848 |
| Losses | |||
| Total number of separate fire losses with which offices were concerned | 27,155 | 29,438 | 30,374 |
| Gross losses | £3,468,720 | £3,159,621 | £2,676,393 |
| Percentage of gross loss to amount under-written (new and renewal) during year (as shown above) | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Percentage of gross loss to total premiums less refunds to insured (as shown above) | 52.27 | 44.08 | 34.95 |
| Average loss | £128 | £107 | £88 |
The next table shows the position of premium income and fire claims during the period 1949-50 to 1959-60. The figures shown correspond to those given in the previous table and refer to direct insurances only. The mounting costs of replacements are evident in the general upward trend in both premium income and claims paid. In addition, exceptionally severe losses were experienced in certain years, notably in wool-store fires. In 1958-59, however, the percentage of claims to premium income was lower by approximately 8 per cent, and was again lower by approximately 9 per cent in 1959-60, owing to the lesser number of large fire-loss payments incurred in each of these periods.
| Year | Premium Income | Fire Claims | Percentage of Claims to Premium Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | per cent | |
| 1949-50 | 3,603,568 | 981,697 | 27.2 |
| 1950-51 | 4,018,760 | 1,114.534 | 27.7 |
| 1951-52 | 4.672,914 | 1,244,467 | 26.6 |
| 1952-53 | 5,200,231 | 2,058.549 | 39.6 |
| 1953-54 | 5,561.964 | 1.996,302 | 35.9 |
| 1954-55 | 5,878,463 | 1,745,961 | 29.7 |
| 1955-56 | 6,241,319 | 2,077,756 | 33.3 |
| 1956-57 | 6,396,843 | 2,174,127 | 34.0 |
| 1957-58 | 6,614,392 | 3,468,720 | 52.4 |
| 1958-59 | 7,147,207 | 3,159,621 | 44.2 |
| 1959-60 | 7,656,848 | 2,676,393 | 35.0 |
REVENUE AND EXPENDITURE - A statement of the total revenue and expenditure, both gross and net, of all offices is now given in respect of New Zealand business. The gross figures include reinsurance business accepted, while the net figures comprise insurances with the public, plus reinsurances accepted, and less amounts reinsured with other offices.
It is insurance practice at the closing date of the accounts of a fire insurance company to transfer to a reserve a proportion of the income received during the year, to allow for policies whose currency extends into the following accounting year. This amount constitutes the unexpired risks reserve shown in the following table.
A change in the method of treating unexpired risks reserve was decided upon after consultation with insurance organisations, such a change to take place for the first time in the presentation of the 1959-60 statistics.
Previously the unexpired risks reserve shown as revenue comprised the amount of premiums collected in the previous year and set aside as reserve for use in the current year, while the unexpired risks reserve shown as expenditure comprised the amount of premiums collected in the current year but set aside for reserve for use in the following year.
This method of treatment has now been changed and the entry under unexpired risks reserve now shown represents the difference between the amount of reserves set aside for the previous and for the current year. In future years the entry will be entitled “Net effect of reserve provisions”.
Thus, if the amount transferred to reserve this year is larger than was transferred at the end of last year, the net effect is equivalent to an increase in this year's expenditure and the difference is therefore shown as expenditure. Similarly, if the amount transferred this year is less than last year, then the difference will be shown as revenue.
The revised method of treating unexpired risks reserve changes the basis of comparison with earlier years. So that some degree of comparability would be retained in this first year of changed treatment, figures were also compiled on the previous basis used for unexpired risks reserve and these figures are also shown in the following table.
The gross reserve for unexpired risks, it should be noted, is calculated on the assumption that it bears the same proportion to gross premium income as does the actual net reserve to the net premium income.
| 1958-59 | 1959-60* | 1959-60† | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross | Net | Gross | Net | Gross | Net | |
*Previous method of treating unexpired risks reserve. †Revised method of treating unexpired risks reserve. | ||||||
| Revenue | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ |
| Reserve to meet unexpired risks as at beginning of year | 3,220,000 | 1,752,280 | 3,437,000* | 1,882,224* | 25,000† | 13,779† |
| Amount of fire premiums receivable during year | 8,615,667 | 4,708,690 | 9,258,590 | 5,226,544 | 9,258,590 | 5,226,544 |
| Interest and dividends on stock, mortgages, etc. | 194,145 | 194,145 | 208,467 | 208,467 | 208,467 | 208,467 |
| Rents | 99,250 | 99,250 | 128,138 | 128,138 | 128,138 | 128,138 |
| Other revenue | 9,986 | 9,986 | 11,000 | 11,000 | 11,000 | 11,000 |
| Totals | 12,139,048 | 6,764,351 | 13,043,195* | 7,456,373* | 9,631,195† | 5,587,928† |
| Expenditure | ||||||
| Amount of fire claims incurred during year, including adjustment and other expenses of settlement but less salvage | 3,935,435 | 1,601,225 | 3,108,458 | 1,742,954 | 3,108,458 | 1,742,954 |
| Fire authority levies | 501,319 | 353,890 | 529,626 | 381,458 | 529,626 | 381,458 |
| New Zealand Government taxes | 416,454 | 398,463 | 294,786 | 317,018 | 294,786 | 317,018 |
| Rents | 74,613 | 72,588 | 82,647 | 80,923 | 82,647 | 80,923 |
| Depreciation | 48,194 | 48,027 | 53,384 | 53,086 | 53,384 | 53,086 |
| Allowances and commissions on premiums to agents, subagents, and others | 919,230 | 299,365 | 997,289 | 341,352 | 997,289 | 341,352 |
| Salaries and wages, including commissions on profits or bonuses | 1,064,991 | 1,006,211 | 1,111,872 | 1,046,385 | 1,111,872 | 1,046,385 |
| Other expenses of management | 441,548 | 427,313 | 482,965 | 461,314 | 482,965 | 461,314 |
| Reserve to meet unexpired risks as at the end of the year | 3,437,000 | 1,883,657 | 3,640,000* | 2,055,009* | 330,000† | 186,564† |
| Totals | 10,838,784 | 6,090,739 | 10,301,027* | 6,479,499* | 6,991,027† | 4,611,054† |
The principal items of net revenue and expenditure for 1959-60 of the two classes of offices operating in New Zealand are contained in the next table.
| Net Revenue | Net Expenditure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premiums | Total* | Claims | Salaries and Commissions | Total* | |
| *Excluding reserves to meet unexpired risks. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Overseas companies | 2,846,687 | 2,946,263 | 1,059,952 | 695,337 | 2,453,845 |
| Local companies | 2,379,857 | 2,627,886 | 683,002 | 692,400 | 1,970,645 |
| Totals | 5,226,544 | 5,574,149 | 1,742,954 | 1,387,737 | 4,424,490 |
Excluding unexpired risks reserves, the excess of net revenue over net expenditure for 1959-60 of £1,149,659 compares with surpluses of £804,989 and £619,229 for 1958-59 and 1957-58 respectively.
The following table shows the percentage ratio of working expenses to premium income for the years 1955-56 to 1959-60. It is sometimes contended that contributions to the fire-prevention authority are not a working expense, but should be added to the total of fire losses. While this view is not subscribed to in the compilation of the statistics, there is a definite relationship between the items, and this table shows the ratio both inclusive and exclusive of such levies.
| Item | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| per cent | |||||
| Net working expenses (excluding taxes) to net premium income | 48.14 | 47.09 | 47.69 | 46.88 | 45.24 |
| Net working expenses (excluding taxes and fire-service levies) to net premium income | 40.92 | 39.33 | 39.76 | 39.36 | 37.94 |
| Gross working expenses (excluding taxes) to gross premium income (including reinsurances from other offices) | 36.81 | 35.55 | 35.71 | 35.40 | 35.19 |
| Gross working expenses (excluding taxes and fire-service levies) to gross premium income (including reinsurances from other offices) | 31.20 | 29.65 | 29.56 | 29.58 | 29.47 |
FIRES AND LOSSES - In the following tables particulars are given of fire losses according to the causes of fires, extent of loss, etc., for the year 1959, the figures for earlier years being generally given for purposes of comparison. Payments or recoveries on account of reinsurance are excluded. The data, which cover insured losses only, refer to fires which occurred during the respective calendar years, and in respect of which payments were made by the insurance company concerned not later than 31 March of the following year. These figures are therefore not comparable with the fire claims data given previously, which relate to the accounting years of the various offices.
From and including 1955, the number of separate fires given in previous years has been replaced by the number of fire-loss payments, which includes an unknown number of multiple payments by insurance companies relating to the same outbreak. Experience has shown that the latter figure is greater by some 15 per cent than the actual number of fires.
A summary of losses over the 11-year period 1949-59 is given below. The growth of population and the rise in property values are reflected in the upward trend shown in the table. In addition, the figures have been augmented from time to time by heavy losses involved in the destruction of valuable buildings, plant, and stocks, such as the disastrous wool-store fires of 1951 and 1955. Major insured losses during 1958 included an extensive industrial plant at Gracefield, Lower Hutt, and hotel premises at Lake Wanaka, Otago. In 1959 a Dunedin departmental store fire and a large woodware and joinery fire caused major insured loss.
The uninsured loss is assessed by the fire-prevention authorities at a further 15 per cent of the figures given.
| Year | Separate Fires | Gross Cover* | Gross Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
*On buildings, etc., affected. †Fire-loss payments. | |||
| £ | £ | ||
| 1949 | 9,268 | 21,346,440 | 856,177 |
| 1950 | 10,178 | 22,195,869 | 1,029,945 |
| 1951 | 11,663 | 27,415,024 | 1,517,992 |
| 1952 | 12,602 | 37,033,938 | 1,716,450 |
| 1953 | 14,246 | 39,936,036 | 1,650,390 |
| 1954 | 16,568 | 49,175,580 | 1,525,866 |
| 1955 | 20,600† | 50,048,648 | 2,058,067 |
| 1956 | 22,199† | 58,277,042 | 1,980,647 |
| 1957 | 25,790† | 93,879,209 | 3,025,407 |
| 1958 | 27,428† | 73,108,676 | 2,708,090 |
| 1959 | 28,459† | 77,742,523 | 2,611,074 |
The average insurance claim paid for material fire damage per head of total population was £1 6s. 9d. in 1957, £1 3s. 8d. in 1958, and £1 2s. 4d. in 1959.
The total fire wastage is, of course, greater than the foregoing figures reveal, to the extent of the uninsured loss. This unknown figure is normally assessed by the fire authorities at 15 per cent of the insured loss, and on this assumption the 1959 property loss in New Zealand through fire would have amounted to £3,002,735.
The classification by fire districts which follows is based on the schedules to the Fire Services Act 1949, which set out in full the districts (and their status) originally constituted under the Act. Additions, deletions, and alterations in status are periodically gazetted. The administrative authority appointed by the Act is the Fire Service Council, responsible to the Minister of Internal Affairs.
| Type of Fire District | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Gross Amount of Insurance Cover on Risks Affected | Gross Amount of Loss Paid on Risks Affected | Percentage of Loss Paid to Amount at Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | ||||
| £ | £ | per cent | ||
| United urban fire districts | 10,855 | 35,514,662 | 993,969 | 2.80 |
| Urban fire districts | 12,258 | 30,747,044 | 988,666 | 3.22 |
| Secondary urban fire district | 2,182 | 4,180,943 | 191,577 | 4.58 |
| Remainder of New Zealand (including floating risks) | 3,164 | 7,299,874 | 436,862 | 5.98 |
| Totals | 28,459 | 77,742,523 | 2,611,074 | 3.36 |
The relationship between the number of payments and loss incurred is fairly closely sustained for the main types of district: 81.2 per cent of payments relating to fires which occurred in urban (including united urban) fire districts, the loss amounting to 75–9 per cent of the total.
Causes of Fires - Particulars regarding causes of fires are contained in the following table which covers the years 1957 to 1959.
| Cause of Fire | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | |
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Electricity | 6,668 | 256,652 | 6,693 | 198,186 | 7,348 | 235,328 |
| Gas | 443 | 27,726 | 482 | 8,046 | 508 | 12,282 |
| Chimneys and flues | 713 | 56,683 | 789 | 138,700 | 773 | 80,239 |
| Fireplaces and stoves | 8,846 | 318,956 | 9,711 | 192,424 | 9,896 | 216,518 |
| Smoking and matches | 4,570 | 100,107 | 4,969 | 140,219 | 5,037 | 172,128 |
| Inflammable spirits and materials | 543 | 72,669 | 758 | 64,056 | 745 | 68,924 |
| Outside causes | 775 | 75,339 | 934 | 89,949 | 966 | 128,435 |
| Arson and incendiarism | 64 | 22,204 | 56 | 14,079 | 76 | 22,490 |
| Other specified causes | 646 | 163,097 | 639 | 88,095 | 646 | 42,900 |
| Unknown causes | 2,522 | 1,931,974 | 2,397 | 1,774,336 | 2,464 | 1,631,830 |
| Totals | 25,790 | 3,025,407 | 27,428 | 2,708,090 | 28,459 | 2,611,074 |
The actual cause of many fires is not easily ascertainable, especially in cases of total, or near-total loss, where evidence as to origin is obliterated. This accounts for the high proportion of loss due to unknown causes and for the fact that the average loss payment is much greater in these instances. During 1958 the average payment for specified causes was £38, while the average for the unspecified group amounted to £662. As most major fires result from unknown causes this accounts for the large difference between the averages.
The Fire Services Amendment Act 1952 provides that the Minister of Internal Affairs may appoint any person to hold an inquiry into any fire and the steps taken to deal with it, whether the fire occurred before or after the commencement of the empowering section. Statutory authority had previously existed for coronial inquiries into fires of suspicious origin until the passing of the Coroners Act 1951.
Extent of Loss - The next table gives particulars of fire losses during the years 1957 to 1959, classified according to the amount of loss. The vast majority of fires cause only minor damage. During 1959 payments of less than £10 accounted for 66.1 per cent of the total number, but only 2.9 per cent of the total loss sustained. On the other hand, payments of £10,000 or over, numbering only 24, represented 32.8 per cent of the insured loss.
| Loss Category | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |||
| Under | 10 | 16,891 | 69,038 | 18,012 | 74,543 | 18,810 | 76,720 |
| 10 and under | 25 | 4,881 | 72,901 | 5,220 | 77,091 | 5,318 | 79,335 |
| 25 “ | 100 | 2,218 | 102,283 | 2,397 | 111,074 | 2,519 | 115,288 |
| 100 “ | 1,000 | 1,312 | 454,296 | 1,365 | 446,070 | 1,326 | 462,701 |
| 1,000 “ | 2,000 | 238 | 319,868 | 236 | 321,042 | 276 | 370,842 |
| 2,000 “ | 5,000 | 161 | 461,144 | 127 | 382,262 | 157 | 447,608 |
| 5,000 “ | 20,000 | 67 | 651,538 | 56 | 545,484 | 42 | 368,879 |
| 20,000 and over | 22 | 894,339 | 15 | 750,524 | 11 | 689,701 | |
| Totals | 25,790 | 3,025,407 | 27,428 | 2,708,090 | 28,459 | 2,611,074 | |
Class Groups - Losses have been classified in broad groups according to the nature of the risk, the figures for the years 1957-59 being presented in the next table. Fires in private dwellings accounted for 86.5 per cent of the total payments during 1959, but the proportion of loss sustained was only 35.1 per cent. It should be noted that the “contents”, where insured, are included in the various class groups. Consequently the total for the houses and flats group is swollen by the numerous small claims on account of damage to personal effects, etc., the actual building not being affected by the fire in many instances. The miscellaneous risks group also includes those cases where a fire has affected two or more buildings, which individually are classifiable into more than one of the other groups shown in the table, or, in some instances, single buildings housing occupiers of different occupational groupings.
| Class Group | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | Number of Fire-loss Payments | Amount of Loss | |
| £ | £ | £ | ||||
| Private houses and flats, boarding-houses, etc. | 21,799 | 798,092 | 23,639 | 829,431 | 24,611 | 916,505 |
| Hotels and restaurants | 633 | 81,447 | 657 | 262,311 | 611 | 158,592 |
| Offices and public buildings | 468 | 140,080 | 397 | 54,281 | 409 | 74,361 |
| Theatres and entertainment places | 107 | 53,594 | 91 | 46,131 | 110 | 99,930 |
| Bulk stores and warehouses | 146 | 312,741 | 137 | 342,033 | 124 | 61,378 |
| Shops | 662 | 193,217 | 614 | 210,220 | 776 | 725,929 |
| Factories and industrial risks | 980 | 1,269,459 | 913 | 844,004 | 852 | 487,469 |
| Farm risks (other than dwellings) | 279 | 72,999 | 295 | 67,946 | 303 | 57,819 |
| Miscellaneous (including unclassified) | 159 | 79,220 | 132 | 32,676 | 151 | 14,232 |
| Floating and travelling risks | 557 | 24,558 | 553 | 19,057 | 512 | 14,859 |
| Totals | 25,790 | 3,025,407 | 27,428 | 2,708,090 | 28,459 | 2,611,074 |
MUTUAL INSURANCE ASSOCIATIONS - Mutual associations are governed by the Mutual Insurance Act 1955, which allows 200 or more owners or occupiers of isolated or farm properties to subscribe to a declaration, and form themselves into a mutual association to insure against loss to an amount in the aggregate of not less than £200,000. The Act permits these associations to conduct accident business in addition to fire insurance. Such associations effect insurance on the premium note principle, and accept premium notes to be assessed for losses in the proportion of the total amount of such notes. The amount of a member's premium notes limits his liability. As stated in the section relating to deposits, mutual insurance associations carrying on employers' liability insurance business are now required to deposit approved securities to a specified value with the Public Trustee.
The Mutual Insurance Regulations, gazetted in 1956, permit these associations to carry on additional types of insurance (other than life assurance).
Summarised figures for the three associations formed under the Act appear below.
| Year Ended 31 March | Net Premium Income | Total Net Income | Net Claims | Reserves and Funds | Assets* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fire | Accident | Fire | Accident | ||||
*Including premium notes. †Previous method of treating unexpired risks reserve. ‡Revised method of treating unexpired risks reserve. | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1956 | 90,442 | 99,517 | 201,747 | 26,129 | 52,231 | 218,062 | 1,790,941 |
| 1957 | 98,312 | 116,526 | 288,709 | 21,450 | 49,685 | 243,620 | 1,202,561 |
| 1958 | 105,240 | 133,097 | 328,858 | 21,821 | 65,872 | 270,689 | 654,310 |
| 1959 | 113,192 | 139,066 | 365,427 | 28,918 | 77,749 | 231,488 | 693,883 |
| 1960† | 116,051 | 165,303 | 404,008† | 27,224 | 92,882 | 247,080 | 741,797 |
| 1960‡ | 116,051 | 165,303 | 304,443‡ | 27,224 | 92,882 | 247,080 | 741,797 |
FIRE BRIGADES - At 31 March 1961 there were 270 fire brigades under the administrative authority of the Fire Service Council. Of these, 22 were staffed with full-time personnel numbering 165 officers and 403 men, as well as 210 auxiliaries; while 213 brigades, together with 35 auxiliary units, were manned by 4,260 volunteers.
STATE LIFE ASSURANCE - The New Zealand Government Life Insurance Office was founded in 1869 at a time when New Zealanders had comparatively poor facilities in regard to life assurance. Payment of all policies with the Office is guaranteed by the Government. The administration of the Office is regulated by the Government Life Insurance Act 1953.
The total income of the Office for 1959 was £6,884,156, of which premium income amounted to £4,929,331, annuity purchase money £8,064, and interest, rents, etc. (net) £1,946,761.
During the year 1959 payments were made under the following heads: matured policies (including bonuses additions), £830,902; claims by death (including bonuses), £519,298; annuities, £75,549, surrendered policies and bonuses cashed, £577,593, commission, £351,964; other management expenses, £299,251; rates and taxes £125,142; and other expenditure, £56,269.
Income and expenditure figures of the Government Life Insurance Office are now given for each of the latest five years.
| Year | Premium Income (Including Purchase of Annuities) | Total Income | Management Expenses | Total Expenditure | Ratio of Management Expenses to Total Income | Ratio of Management Expenses to Premium Income |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | per cent | per cent | ||||
| 1955 | 3,599 | 4,693 | 517 | 2,033 | 11.02 | 14.36 |
| 1956 | 3,877 | 5,129 | 536 | 2,255 | 10.45 | 13.82 |
| 1957 | 4,122 | 5,570 | 599 | 2,364 | 10.76 | 14.54 |
| 1958 | 4,580 | 6,276 | 626 | 2,572 | 9.97 | 13.66 |
| 1959 | 4,937 | 6,884 | 651 | 2,836 | 9.46 | 13.19 |
Figures showing the progress of the Office are contained in the next table. Annuities are excluded.
| Year | New Business | Policies Discontinued | Policies in Force at End of Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Policies | Sum Assured | Annual* Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | Number | Sum Assured | Annual Premiums | |
| *Excludes single premiums. | |||||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| 1955 | 22,494 | 22,161 | 469 | 6,688 | 4,937 | 121 | 218,514 | 138,839 | 3,155 |
| 1956 | 22,629 | 22,673 | 483 | 7,222 | 5,569 | 134 | 233,921 | 155,943 | 3,504 |
| 1957 | 23,112 | 23,230 | 544 | 8,078 | 6,397 | 155 | 248,955 | 172,775 | 3,894 |
| 1958 | 23,652 | 26,030 | 541 | 9,029 | 7,428 | 181 | 263,578 | 191,377 | 4,253 |
| 1959 | 23,685 | 27,538 | 554 | 9,853 | 8,456 | 202 | 277,410 | 210,460 | 4,605 |
During 1959 there was an increase of 5.8 per cent over the previous year in the value of new policies written and an increase of 2.4 per cent in the amount of annual premiums represented. The average sum assured per policy was £1,005 in 1957, £1,101 in 1958, and £1,163 in 1959. In addition to the total sum assured at the end of the year, accrued reversionary bonuses amounted to £10,227,534. Immediate, deferred, and contingent annuities totalled £1,497,538, representing 540 policies. Single premium income for the years 1957 to 1959 was £348,686, £437,506, and £446,758 respectively.
The Office's balance sheet as at 31 December 1959 showed that the total assets amounted to £42,968,466, and were invested as shown in the following statement, which also gives the distribution of the assets at the end of the two preceding years for purposes of comparison.
| Class of Investment | Amount | Proportion to Totals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| *Mainly due and overdue premiums and interest, interest accrued, and company stocks, shares, and debentures. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | per cent | per cent | per cent | |||
| Mortgages on freehold property | 15,767 | 17,775 | 20,062 | 45.32 | 45.97 | 46.69 |
| Loans on policies | 1,254 | 1,445 | 1,670 | 3.60 | 3.74 | 3.89 |
| Government securities | 8,015 | 8,165 | 8,161 | 23.04 | 21.12 | 18.99 |
| Local authority securities | 7,179 | 7,813 | 8,691 | 20.64 | 20.20 | 20.23 |
| Landed and house property | 1,013 | 1,100 | 1,457 | 2.91 | 2.84 | 3.39 |
| Miscellaneous assets* | 1,563 | 2,371 | 2,928 | 4.49 | 6.13 | 6.81 |
| Totals | 34,791 | 38,669 | 42,968 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Assurance, annuity, and endowment funds, apart from special reserves of £948,387, amounted to £41,406,230, an increase (the largest ever recorded) of £4,048,188 over the corresponding figure at the end of the previous year.
STATE ACCIDENT INSURANCE - In the year 1901 the Government Life Insurance Office opened an Accident Branch. On 1 January 1925 the accident business was transferred to the control of the State Fire Insurance Office. General accident business was undertaken, but the branch was opened more especially to conduct insurance under the Workers' Compensation Act. In recent years other forms of accident insurance have contributed on an increasing scale to the premium income of the Office. The main classes transacted are employers' liability, personal accident, public risk, motor comprehensive, third-party risks, plate glass, and fidelity guarantee.
General Business - A summary of revenue and expenditure during the last five years is contained in the following table.
| Year | Revenue* | Expenditure* | Ratio of Claims to Earned Premiums | Total Assets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premiums | Total | Claims† | Working Expenses | Total | |||
*Excluding reserves for unearned premiums. †Including unadjusted losses. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | per cent | £(000) | |||||
| 1955 | 1,344 | 1,417 | 971 | 279 | 1,357 | 75.3 | 2,427 |
| 1956 | 1,518 | 1,598 | 1,066 | 330 | 1,456 | 73.6 | 2,586 |
| 1957 | 1,631 | 1,720 | 1,155 | 346 | 1,598 | 73.3 | 2,909 |
| 1958 | 1,799 | 1,896 | 1,377 | 319 | 1,761 | 80.8 | 3,103 |
| 1959 | 1,909 | 2,017 | 1,469 | 356 | 1,919 | 78.8 | 3,453 |
The ratio of working expenses to earned premiums in 1959 was 18.7 per cent compared with 17.7 per cent in the previous year. Working expenses increased by 11.8 per cent and claims by 6.7 per cent.
The total assets at 31 December 1959 included £1,473,832 invested in Government securities and £772,721 in local authorities securities. Reserves and funds totalled £1,879,361.
Employers' Liability Insurance Account - The Workers' Compensation Amendment Act 1943 made it obligatory for an employer to insure against his liability to pay compensation under the principal Act. From 1 April 1949 to 1 April 1951 all employers' liability insurances were required to be placed with the Government Accident Insurance Office. Statements of the experiences of the account during the period of operation have been given in some detail in previous issues of the Yearbook. Approximately 95,000 employers were insured under the fund in 1950. The Workers' Compensation Amendment Act 1950 restored the right of insurance companies to participate in this class of insurance.
STATE FIRE INSURANCE - The New Zealand State Fire Office was the first competitive State fire-insurance office in the world, and opened for business on 4 January 1905. Marine insurance has been undertaken since 1947. Premium-rate reductions and bonus rebates have reduced the cost of insurance.
Premium income advanced by £164,484 during 1959, while losses decreased by £14,266.
The apportionment for taxes was £115,649, while the net surplus rose from £91,146 in 1958 to £188,016 in 1959.
| Year | Net Premium Income | Total Net Income* | Claims† | Total Net Expenditure* | Accumulated Funds | Total Assets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excluding reserve for unearned premiums. †Including unadjusted losses. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1955 | 571 | 662 | 173 | 602 | 1,956 | 2,330 |
| 1956 | 630 | 720 | 185 | 618 | 2,089 | 2,339 |
| 1957 | 668 | 763 | 229 | 663 | 2,189 | 2,651 |
| 1958 | 796 | 909 | 275 | 753 | 2,344 | 2,797 |
| 1959 | 961 | 1,093 | 261 | 823 | 2,614 | 3,254 |
The percentages of various classes of expenditure to earned premiums and total income are given below.
| Item | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio of claims to earned premiums | 35.2 | 37.6 | 29.7 |
| Ratio of working expenses to earned premiums | 43.3 | 41.5 | 39.9 |
| Ratio of Fire Service Council levies to earned premiums | 10.5 | 10.0 | 8.8 |
| Ratio of underwriting surplus to earned premiums before providing for taxation | 11.0 | 10.9 | 21.5 |
EARTHQUAKE AND WAR DAMAGE INSURANCE - Under the Earthquake and War Damage Act 1944 there exists the Earthquake and War Damage Fund, which is administered by a Commission. All property insured against fire is deemed to be insured to the extent of the indemnity value against earthquake and war damage. Premiums at the rate of 1s. for each £100 of insurance cover are collected by the insurance companies and paid into the Fund (less commission of 2 1/2 per cent).
The Act provides for both compulsory and voluntary insurance against earthquake and war damage. Under the compulsory provisions of the original Act all property insured to any amount under any contract of fire insurance with an insurance company is deemed to be insured to the same amount against earthquake damage and war damage. An amending Act passed in 1951, however, provides that where the contract of fire insurance provides for the settlement of the claim upon the basis of the replacement value, the compulsory earthquake and war damage insurance will be for the amount of the indemnity or present value only. If the present value is certified by a registered architect or a registered valuer, the earthquake and war damage premium will be charged on the amount so certified. Under the voluntary provisions of the Act any person having an insurable interest in any property may make application to the Commission for earthquake or war damage insurance, and a contract may be made for the insurance of any property that is not insured under the compulsory section of the Act, or for the insurance to an additional amount of any property that is so insured.
Advances may be made from the Consolidated Fund if at any time the amount in the Earthquake and War Damage Fund is not sufficient to meet the claims thereon.
“Earthquake damage” is defined as damage occurring as the direct result of earthquake or of fire occasioned by or in consequence of earthquake. It also includes damage occurring as the direct result of measures taken under proper authority to avoid the spreading of, or otherwise to mitigate the consequence of, any such damage. In addition to damage occurring as a direct result of action by the enemy, “war damage” included damage occurring as the direct result of measures taken in combating the enemy or precautionary or preparatory measures taken under proper authority with a view to preventing or hindering any enemy or anticipated enemy action. It also includes accidental damage occurring as the direct result of any explosion or fire which involves any explosives or munitions, etc., required for war purposes.
During the financial year 1949-50 an extension of the scheme was instituted to provide some measure of protection to the insured against storm and flood of an abnormal or widespread nature. Finance is provided by crediting 10 per cent of the premiums compulsorily collected under the Act to a special Disaster Fund, without further liability on the Earthquake and War Damage Fund.
On 1 November 1954 the definition of disaster damage was extended to include volcanic eruption, and authority was given to the Commission to accept insurance against landslip. This latter type of cover does not apply automatically.
The Earthquake and War Damage Regulations 1956, came into force on 1 June 1956. The amount of the franchise (proportion of loss to be borne by the insured) was fixed for all cases as 1 per cent of the loss but not less than £10 where the loss is less than £5,000, and £50 where the loss exceeds £5,000. The franchise may be fixed at a higher rate where the property is more than normally susceptible to damage. Cover under the disaster provisions was widened by the deletion of the word “widespread” from the definition.
The following is a comparative statement for the last six years of the financial operations under the Earthquake and War Damage Act, together with a statement showing the position from the inception of the Fund to 31 March 1960.
| 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | 19 Dec. 1941 to 31 Mar. 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*At end of each period. †From Commencement in November 1949. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| Income | |||||||
| Premiums - | |||||||
| Earthquake and war damage | 1,065 | 1,173 | 1,297 | 1,383 | 1,509 | 1,580 | 17,799 |
| Storm and flood | 118 | 129 | 143 | 153 | 166 | 177 | 1,265 |
| Interest | 360 | 417 | 465 | 546 | 621 | 716 | 4,917 |
| Totals | 1,543 | 1,719 | 1,905 | 2,081 | 2,296 | 2,474 | 23,982 |
| Outgo - | |||||||
| Claims - | |||||||
| Earthquake and war damage | 2 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 37 | 129 |
| Storm and flood | 28 | 21 | 140 | 383 | 191 | 86 | 918 |
| Salaries and expenses of management | 6 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 102 |
| Discount to insurance offices | 30 | 32 | 36 | 38 | 41 | 44 | 377 |
| Exchange adjustment | 340 | ||||||
| Totals | 66 | 64 | 194 | 438 | 246 | 177 | 1,865 |
| Surplus | 1,476 | 1,655 | 1,711 | 1,643 | 2,051 | 2,297 | 22,117 |
| Earthquake and war damage fund* | 12,354 | 13,892 | 15,593 | 17,459 | 19,536 | 21,742 | 21,742 |
| Disaster Fund*† | 406 | 523 | 533 | 310 | 284 | 375 | 375 |
The item “exchange adjustment” of £339,525 was the depreciation in the New Zealand value of the Commission's overseas funds as the result of the alteration in the exchange rate to parity with sterling which came into operation during 1948.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, 624 earthquake and 1,301 storm and flood claims were lodged, compared with 140 and 1,887 for the previous year. The large increase in earthquake claims in 1959-60 was the result of an earthquake on 22 May 1959 which affected principally the Picton area and produced 461 claims. In the year 1959-60 there was a surplus in the Disaster Fund of £90,663 following an underwriting loss in the previous two years.
GENERAL - A short history of labour laws was given on pages 1009–1016 of the 1960 Yearbook and in earlier issues.
A considerable proportion of the persons comprising the labour force of New Zealand have their working conditions determined either directly or indirectly by virtue of the provisions of the Factories Act 1946, the Coal Mines Act 1925, the Shops and Offices Act 1955, the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952, the Agricultural Workers' Act 1936, the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954, and the Construction Act 1959. Legislative authority covering the working conditions of substantially the greater portion of the remaining participants in the labour force is contained in the Public Service Act 1912 and the Government Service Tribunal Act 1948, the Government Railways Act 1949, the Post Office Act 1959, the Police Act 1958, the Education Act 1914, the Hospitals Act 1957 and the Hospital Employment Regulations 1957, and the Waterfront Industry Act 1953.
In the following pages a survey is made first of the Court of Arbitration and then of the working and other conditions laid down by legislation.
COURT OF ARBITRATION - The Court of Arbitration, which dates from 1894 and whose jurisdiction is set out in the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954, consists of three members appointed by the Governor-General, one of whom is the Judge of the Court. No one may be appointed as the Judge unless he is a barrister or solicitor of not less than seven years' standing. One of the two other members is appointed on the recommendation of the industrial unions of employers and the other on the recommendation of the industrial unions of workers. Although the members other than the Judge are appointed for a term of three years only, in practice it has been found that they have usually served much longer terms on the Court.
The work of the Court may be divided into two sections - the making of laws through the promulgation of awards, apprenticeship orders, etc, and the interpretation and enforcement of industrial laws, including industrial agreements and certain statutes. The second function is similar to the functions of other Courts, but in making industrial law the Court of Arbitration has a unique role. In addition the Court has wide powers and responsibilities associated with the making of general wage orders (see Section 33 of the Yearbook).
Jurisdiction of Court - The following is a general account of the present jurisdiction, powers, and functions of the Court of Arbitration, some of which are legislative in character and others judicial.
Under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954:
The principal function of the Court is to settle any matters which are outstanding after the representatives of workers, unions and employers in any industry have failed under the procedure laid down in the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act to reach complete agreement in conciliation upon the minimum rates of wages and conditions of work which are to govern employment in the industry for a limited future period. This function of the Court is really legislative in character, for Parliament in effect has delegated authority to the Court to make law in a restricted field but its awards must not be inconsistent with any statute. For a large proportion (approximately one-half) of the labour force, the determining factor in minimum rates of wages and working conditions is the series of awards issued by the Court of Arbitration, and industrial agreements made by representatives of employers and workers. The number of awards and agreements in force is quite large - 608 at 31 March 1960 - and each is subject to individual negotiation by the unions or associations concerned during its formulation.
Included in the respective awards and agreements are provisions covering minimum rates of remuneration, the hours of work, overtime, holidays, safety, health, and welfare. Initiated by the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Amendment Act 1936 a 40-hour week is now prescribed in almost all awards and industrial agreements.
The Court does not settle strikes or lockouts. If there is a strike or lockout in an industry, access to the Court is not usually available to the parties unless and until work is resumed.
The provisions of awards and industrial agreements are enforced through Magistrate's Courts and the Court of Arbitration. There are limited rights of appeal against the judgments of Magistrates to the Court of Arbitration the determination of which is final. Inspectors of Awards who are officers of the Department of Labour may proceed directly in the Court of Arbitration for the recovery of penalties. In the Magistrate's Court actions for penalties may be brought at the suit of an Inspector of Awards or at the suit of any party to the award or industrial agreement.
The Court has power to impose penalties for a number of offences against special provisions of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act; for example, being a party to a strike or lockout when bound by an award or industrial agreement, combining to defeat an award, contempt of Court, obstruction of a conciliation council or the Court, failure to comply with a summons to give evidence, victimisation, and so forth.
Actions to recover moneys due to workers under awards and industrial agreements may be brought by Inspectors of Awards in the Court of Arbitration.
The Court of Arbitration upon application of Inspectors of Awards or upon applications of parties, joint or otherwise, may give its opinion upon any question connected with the construction of any award or industrial agreement or upon any particular determination or direction of the Court or upon the construction of any statute relating to matters within the jurisdiction of the Court. This function is largely availed of and enables many legal disputes to be settled with a minimum of friction and at a minimum cost.
The Court of Arbitration is vested with a jurisdiction to hear appeals from decisions of disputes committees set up to consider differences arising between parties to awards and industrial agreements as to any matter arising out of or connected with an award or agreement but not specifically dealt with therein.
The Court has a special jurisdiction to conduct inquiries into allegations of irregularities in connection with election of the officers of any industrial union and to make and enforce orders relating to such matters.
Under the Economic Stabilisation Act 1948 and regulations made thereunder.
The Court of Arbitration has power to make general orders amending the rates of remuneration in all awards and industrial agreements either of its own motion or on the application of any industrial union or association of workers or employers. For this purpose, the expression “rates of remuneration” has a very wide connotation.
Under the Shops and Offices Act 1955:
The Court has power when making an award in any trade to fix the opening and closing hours of all shops in the particular trade in that locality and also to provide that such shops shall not be open for business on one working day in each week or on any award holiday.
Under the Annual Holidays Act 1944:
The Court has power to impose penalties for offences against the provisions of the Act.
Under the Apprentices Act 1948:
The Court has power to make apprenticeship orders, in respect of any industry or branch thereof to which the Act applies, prescribing the wages, hours, and other conditions of employment to be incorporated in contracts of apprenticeship, the period of apprenticeship in any industry and the minimum age at which a person may commence to serve as an apprentice in any industry, and pre-requisite education.
The Court on the application of certain parties may give its opinion upon any question connected with the construction of any apprenticeship order or with any determination or direction of the Court under the Act.
The Court may hear appeals from decisions of apprenticeship committees and district commissioners of apprenticeship, and its decisions are final and conclusive.
The Court has jurisdiction to decide actions in respect of alleged breaches of any contract of apprenticeship order of the Court or requirement of the Apprentices Act.
Under the Agricultural Workers Act 1936:
Matters in dispute between certain classes of agricultural workers and their employers may be referred to the Court of Arbitration for the purpose of making a recommendation to the Minister of Labour as to how matters in dispute should be settled.
General - The Court of Arbitration early in its history expanded beyond the limited function originally conceived for it. It has been the major force in the formulation of industrial codes. In its evolution and in its task of establishing uniform wage rates, the Court has risen to a commanding position in the economic life of the country. Apart from occasional legislation to meet special economic conditions, or as in 1936 to introduce the 40-hour week, no attempt has been made by Parliament to express in law the social and economic policy to be followed by the Court. There is no right of appeal from the decisions of the Court on any matters coming within its exclusive jurisdiction.
HOURS OF WORK - The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Amendment Act 1936 contained inter alia, provisions aimed at the establishment of a 40-hour week, without reduction in the weekly wage rate. The Court of Arbitration might fix longer hours, but was required to state its reasons for so doing. The Factories Amendment Act 1936 required the fixing of a 40-hour week in factories. The Shops and Offices Amendment Act 1936 reduced the working hours in shops from 48 to 44 per week, and a further reduction to 40 hours was made by later amendments passed in 1945 and 1946. The Shipping and Seamen Amendment Act 1946 reduced seamen's hours to 40 per week. Employees in wood and coal yards, motor and horse drivers, and restaurant workers also obtained a 40-hour week in the same year. From 5 April 1948 a seven-hour day was, by decision of the Coal Mines Council, introduced for all underground workers in coal mines. By section 6 of the Mining Amendment Act 1948 this provision was extended as from 1 January 1949 to underground workers in other mines.
ANNUAL HOLIDAYS ACT - The Annual Holidays Act 1944 provides for an annual holiday of two weeks' duration on full pay for all workers, whether permanently or casually employed, who are not otherwise provided for in this respect. The holiday is to be given within six months after it becomes due, but if the employment is terminated before it has been taken the employer is required to pay the amount of holiday pay due. If any special holiday for which the worker is entitled to payment under any Act, award, or agreement, or under his contract of service, occurs during the period of the annual holiday, the length of the annual holiday is increased by one day in respect thereof. An amendment passed in 1945 provided that not less than seven days' notice must be given by the employer of the day on which the annual holiday is to commence, unless an agreement has been made to the contrary.
Where a worker has been employed for less than one year, on termination of employment he is entitled to payment equal to one twenty-fifth of his ordinary pay for the period of employment. An employer is required to keep a record (holiday book) containing particulars of employment, annual holidays, and amounts paid in respect of each worker in his employment.
ANZAC DAY ACT - The Anzac Day Act 1949 provides that the 25th day of April in each year shall be known as Anzac Day, and shall be observed throughout New Zealand in all respects as if Anzac Day were a Sunday. The Act prohibits the transfer of a holiday, observance of certain hours of labour, or payment at certain rates of wages on Anzac Day to any other day instead of Anzac Day, although an employer may grant a holiday on any other day instead of Anzac Day, where the worker is required to work on Anzac Day at ordinary rates of wages.
FACTORIES ACT - Under the Factories Act 1946, the definition of factory was varied to read “any building, office, or place in which two or more persons are engaged or in which one or more persons are employed . . . directly or indirectly, in any handicraft, or in preparing or manufacturing goods for trade or sale . . .”, thus excluding places (with certain specified exceptions) where one self-employed person was engaged. The 1946 Act also brought Government-owned factories within the scope of the legislation.
Hours of Work and Overtime - Since 1945 a 40-hour week has applied to all factories.
No boy or girl under 16 years of age is permitted to work overtime. No woman shall work more than three hours' overtime in one day (excluding time worked before noon on Saturday), and not more than nine hours in any week, nor 90 hours in any year. Thirty hours (above the 90) may be authorised by an Inspector of Factories, and a further 80 upon the consent of the Minister of Labour.
There are special provisions in regard to work for industries where raw materials which, in the opinion of the inspector are subject to rapid deterioration, are processed for sale as foodstuffs or where, in the opinion of the inspector, extended hours are necessary in order to meet a public demand.
Holiday Provisions - Whole holidays are prescribed for eight statutory holidays (apart from the annual holiday described earlier). Payment for each whole holiday mentioned in the Factories Act was made to apply to all persons employed at any time in the fortnight ending on the day on which the holiday occurs. Special provisions have been made requiring extra payment to be made for work done on Sundays or holidays. Generally speaking, treble time is counted for work done on statutory whole holidays (where the worker would be paid ordinary time if not working), double time on Sundays, and time and one-half on half-holidays. In connection with holidays, reference should also be made to the Annual Holidays Act 1944, the provisions of which have been outlined earlier.
It should be noted also that the Public Holidays Act 1955 gives rules which shall be applicable to the pro***visions of any Act, award, or industrial agreement when Christmas Day and New Year's Day fall on a Friday, Saturday, or Sunday. The effect of the Act is broadly to provide that provisions regarding the granting of a holiday or observance of certain hours of labour or payment of certain specified rates of wages are carried over from Saturday and Sunday to Monday (or Tuesday). In a similar way, where an anniversary day of any province falls on a Friday, Saturday, or Sunday, the provisions governing a holiday, pay, etc, on anniversary day apply on the next succeeding Monday; if it falls on a Tuesday, Wednesday, or Thursday, the provisions apply to the immediately preceding Monday as if it were the anniversary day. Labour Day is deemed to be the fourth Monday in October.
Section 15 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1948 made special provision in regard to holiday work for newspaper printing and publishing. A “day” for holiday and overtime purposes is defined as from noon on one day to noon on the following day in the case of newspaper offices and works.
Restrictions on Employment - No boy or girl under 15 years of age may be employed in any factory. No boy or girl under 16 years of age may be employed in any factory unless a certificate of fitness is issued by an Inspector of Factories, and no such certificate may be granted unless the proposed employer obtains at his own expense a medical certificate of fitness from a Medical Officer of Health, or from a registered medical practitioner nominated by a Medical Officer of Health.
Minimum Rates of Pay - Under the Factories Act 1946 the minimum rate of pay is 22s. 6d. per week with half-yearly increments of not less than 5s. per week, until a weekly rate of £2 12s. 6d. is reached. These rates would apply only in the case of juveniles not covered by an award or industrial agreement fixing a higher minimum. Minimum adult rates are prescribed under the Minimum Wage Act 1945 in those cases where a higher adult minimum is not fixed by award or industrial agreement or wage order.
Safety, Health, and Welfare - The safety measures have reference to machinery, dangerous liquids, means of access and safety of places of employment, and means of escape in case of fire, etc. The employer is required to keep a register of all accidents of which he has any knowledge, and first-aid appliances must be provided and maintained. The health and welfare provisions are very extensive and include reference to such matters as air space, cleanliness, ventilation, canteens, the care of employees, amenities and other things to be supplied by the employer to secure employees' health or welfare, and to the making of regulations laying down standards as to what may be regarded as adequate, effective, sufficient, or suitable health and welfare requirements.
Other Provisions - The Factories Act 1946 specifically states that the Act shall bind the Crown. It also includes the normal provisions relating to powers of inspection, registration, maintenance of records and exhibition of notices, requisitions by inspectors, and the prescription of offences, penalties, and procedure. Finally, it provides for awards and industrial agreements to be read subject to the provisions of the Factories Act.
SHOPS AND OFFICES ACT - Under the Shops and Offices Act 1955, a “shop” is defined as any building or place in which goods are kept, exposed, or offered for sale, or in which any part of the business of a shop is conducted, and includes an hotel, a restaurant, a hairdressing saloon, an auction market, and an automatic vending machine, but does not include a warehouse or a private hotel or boardinghouse; special provisions are contained relating to hotels and restaurants as well as to chemists, fruiterers, tobacconists, and other particular shops.
An “office” covers any building in which any person is employed, directly or indirectly, to do any clerical work in connection with any business carried on by the occupier, but does not include any building in which the clerical work of a factory or shop is carried on if situated within the factory or shop.
The definition of the term “shop assistant” includes those employed in the general management or control of a shop, subject to a wage qualification.
Hours of Work and Overtime - A 40-hour week for all shop assistants has applied since 1945. Hours must be worked continuously - i.e, not exceeding eight per day, but up to 11 on one day in the week - except for meal times and breaks for refreshments. If the meal time exceeds an hour, the extra time over this is to be regarded as time worked. Provision is made for two free days for each shop assistant in each week, thus providing for a normal working week of five days.
Limited overtime (to be paid for at time and half rates) may be worked for stocktaking and on special occasions. A break of not less than three-quarters of an hour for rest and refreshment must be allowed after four and one-quarter hours' continuous overtime work.
For shop assistants the hour of commencing work for persons under 16 years must not be earlier than 7 a.m., except that newspapers may be delivered from 6 a.m. by persons aged 12 years and under 16, and milk by persons aged 14 years and under 16 from the same hour. Boys under 18 or females may not be employed after 10.30 p.m. The Act provides that female assistants and boys under 18 cannot be employed in restaurants before 5 a.m. or after 10.30 p.m. However, it is not unlawful to employ female assistants over the age of 18 up to 11.30 p.m. or to midnight in connection with social functions (or if over 21 years, between midnight and 5.30 a.m.), if satisfactory provision for conveying these assistants to their homes be made. There is no limit under the Act to the time at which adult male hotel and restaurant employees may be required to commence or cease work.
There are no provisions as to hours of employment in offices or as to the times when they may be open. In practice, a five-day week is worked in most offices. Employment in excess of 40 hours in offices is permitted, payment for overtime at the rate of time and a half being mandatory in respect of such overtime.
Opening and Closing Hours of Shops - The Court of Arbitration has power when making an award in any trade to fix the opening and closing hours on Sundays as well as weekdays of any shops substantially (i.e., at least 20 per cent of turnover) carrying on the particular trade in that industrial district, and also to provide that such shops shall not be open for business on one working day in each week or on any award holiday. Before the Court exercises any of these powers, however, it is required to have regard to all relevant considerations. The Court is empowered (with the prior consent of the Minister of Labour except in the case of chemists' shops) to fix the times during which shops may be open on Sundays. Any organisations are entitled to be heard by the Court when dealing with these matters if in the opinion of the Judge they may be affected by the result of the proceedings. The Court is not to make an award without a hearing unless the Judge so directs. Applications for exemption may be made to the Shops and Offices Exemptions Tribunal.
The occupier of every shop, whether employing assistants or not, is deemed to be an employer within the meaning of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, and therefore bound by an award relating to shop assistants for the purpose of bringing his premises within the closing provisions fixed in an award.
Sunday Trading - Sunday trading is prohibited except (a) if provision is made in an award, the prior consent of the Minister being required to such inclusion, (b) for sale of exempted goods listed later, (c) if individual shops are granted exemption by the Shops and Offices Exemptions Tribunal to permit them to open on Sunday. This is designed to enable shops in motor camps and other holiday resorts to cater for the needs of the travelling public.
The term “exempted goods” means (a) tobacco, cigarettes, cigarette papers, cigars, and matches; (b) confectionery and sweetmeats; (c) milk, cream, eggs, butter, and cheese; (d) motor spirits, petrol, and oil; (e) motor accessories urgently and necessarily required for the functioning of a motor vehicle; (f) fruit, vegetables, and flowers, if for sale by the grower on the premises where grown; (g) goods of a class exempted from the provisions of the Act relating to the closing of shops by Order in Council. A specific list of exempted goods was given in the Shops and Offices Exempted Goods Order 1955. This list of exempted goods was extended in June 1957 and further reviewed in September 1959.
Non-exempted goods must be properly locked away from the view of the public.
Holiday Provisions - These are governed by the provisions of awards or industrial agreements. Employees are entitled to the benefits of the Annual Holidays Act 1944. The provisions of the Public Holidays Act 1955 also apply.
Minimum Rates of Pay - Wage rates are fixed by awards and industrial agreements. The provisions of the Minimum Wage Act 1945, and orders made under it, also apply.
Safety, Health, and Welfare Provisions - The Act also makes provision for the welfare, health, and safety of assistants. Particular matters that are covered relate to dangerous liquids and noxious gases, limitation of loads, safe means of access, construction and maintenance of floors, passages, stairs, fire precautions, lighting, cleanliness, ventilation, drinking water, drainage, washing facilities, clothing accommodation, seating and first-aid facilities, rest rooms for women, sanitary conveniences, temperature and heating appliances, accommodation for meals, etc.
AGRICULTURAL WORKERS ACT - The primary purpose of the Agricultural Workers Act 1936 was to make better provision for the accommodation of agricultural workers, and to make special provisions for the remuneration of workers on dairy farms and for the conditions of their employment. The Act also includes provision for the extension of these special provisions to other classes of agricultural workers, and Orders in Council have been issued under this provision. The orders do not apply to workers covered by awards or agreements under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act. Section 4 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1945 provides that where proposals for the extension to any specified class of agricultural workers have been submitted as required by the principal Act, and the parties are unable to agree, the matters in dispute may be referred to the Court of Arbitration for a recommendation to the Minister. The administration of the Act is carried out by the Department of Labour.
Another important measure dealing with farm workers is the Sharemilking Agreements Act 1937, which defines the respective responsibilities of employers and sharemilkers in farm management and control of stock, and prescribes the minimum percentages of returns to sharemilkers. The Act contains provision for terms and conditions to be altered by Order in Council, the current order being the Sharemilking Agreements Order 1951, which came into operation on 26 September 1951.
Holiday Provisions - Workers employed on dairy farms are to be allowed a holiday on full pay plus an amount equal to the full allowance for board and lodging. The duration of the holiday is to be not less than seven days in the aggregate for every 12 weeks of employment. If a regular weekly half-holiday commencing at noon is allowed, a holiday of 14 days a year (or proportionate duration for a lesser period of employment) will be regarded as sufficient compliance with the Act. Specific conditions pertain in respect of workers on farms and stations used for the commercial production of wool, meat, or grain (including seed).
Minimum Rates of Pay - Under the Agricultural Workers Act minimum weekly rates of pay are prescribed for workers on dairy farms. Rates of pay are fixed by Orders in Council. In fixing such rates the basic prices paid in respect of primary produce are taken into account, but later rates are not to be lower than those fixed by the Act. The minimum rate is £10 5s. 6d. per week, increased by £2 2s. 6d per week if the worker is not provided with board and lodgings by the employer. This rate is taken to include allowance for work done at weekends and on holidays as part of the normal week's work. Minimum rates of pay for casual workers are contained in all the extension orders made so far. At present (May 1961) the minimum rate for workers in casual employment and for permanent adult male workers on tobacco farms is 5s. 7 1/4d. per hour, with lesser rates for male and female workers according to specified ages; and for harvesters on farms, and stations 5s. 4d. per hour with rations. In the case of workers on farms and stations for whom the hours of work are not definitely laid down, the rates applicable are given in the Agricultural Workers (Farms and Stations) Extension Order 1952, Amendment No. 4, the minimum weekly rate for an adult male worker being £8 8s. 3d., increased by £2 2s. 6d. per week if the worker is not provided with board and lodging by the employer, or by £1 12s. 6d. per week if provided with only lodging or free house. The minimum rate of wages for adult males permanently employed in orchards is prescribed in the Agricultural Workers (Orchardists) Extension Order 1958, Amendment No. 1, at £11 13s. 3d. weekly. The corresponding rate for workers in market gardens provided for in the 1960 extension order is £11 6s. 7d.
Restrictions on Employment - No child under the age of 15 years may be employed for hire on a dairy farm or in market gardens except for the harvesting of peas, beans, tomatoes, and soft fruits.
Health and Welfare Provisions - The sections of the Act in relation to the accommodation of agricultural workers lay down definite requirements for the comfort of such workers, and Inspectors of Factories have power to inspect the accommodation and to require that improvements be made where necessary. In the various extension orders made under the authority of the principal Act, regulations are made dealing explicitly with questions of accommodation, sanitation, ventilation, etc. A number of orders also prohibit the lifting of excess weights by females.
CONSTRUCTION ACT 1959 - This is an Act to promote the safety, health, and welfare of workmen engaged on construction work. It widens the field and extends the scope of the former Scaffolding and Excavation Act of 1922 which it replaced.
Construction Work - Construction work is defined as meaning any work in connection with the construction, erection, installation, repair, maintenance, cleaning, painting, renewal, removal, alteration, dismantling, or demolition of a large range of building and engineering works. These involve buildings, structure, earth works, drainage undertakings, bridges, harbour and river works, power stations, transmission lines, and railways, and include site preparation and all work in connection with these undertakings.
Responsibility for Safety - The responsibility for safety is on the employer who is defined as the person liable for payment of wages of the workmen or who would be so liable if the men were so employed.
Safety of Other Persons - The safety provisions also apply to the safety of other persons, including the public, who are legally or lawfully in the vicinity of the work.
Application - The Act applies to all types of construction work, whether large or small, which is carried out by way of trade or business or in the exercise of the employer's functions for the purpose of any industrial or commercial undertaking.
Notifiable Work - Certain types of work which are considered more dangerous to workmen are classed as “notifiable works”. On these works the employer must have a representative in charge to ensure that safety measures are carried out and that the requirements of the Act and regulations are observed. This person is given the designation under the Act of “safety supervisor” and considerable details are laid down in regard to his duties and functions. Any notifiable work must be notified to the nearest office of the Department of Labour at least 24 hours before the work is commenced. Such notification must contain particulars as to the time and place of work and of the name of the safety supervisor.
Safety Supervisor - The safety supervisor must be experienced in the work being carried out and shall not be assigned such other duties as will prevent him from discharging with reasonable efficiency the duties required of him as safety supervisor. His name must be made known by the employer to the workmen on the job. The liability of an employer is not affected by the failure of a safety supervisor to exercise his proper functions. It is permissible for two or more employers to appoint jointly the same supervisor on any single construction work. Where, in the opinion of an inspector, a safety supervisor is considered incompetent or negligent in the performance of his duties, the inspector may require the employer to appoint another safety supervisor in his place.
General Safety Provisions - These require the employer to exercise such supervision on the work as will ensure that the provisions of the Act are complied with. He is required to take all reasonable precautions to ensure the safety of workmen employed on the work and to see that all temporary work is constructed of suitable material and is of adequate strength for the purpose intended. All apparatus, plant, and gear used in connection with the work must be operated only by competent workmen. Where work is being carried out on roads or public places, notices and warning devices as may be necessary must be installed and also such barricades, screens, or other devices as may be necessary to prevent workmen from being injured and to reduce the danger hazard to road users.
Other Safety Provisions - Special provisions are made for the safety of excavations, scaffolding, mechanical plant, use of plant, tools and gear, and explosives.
Health and Welfare - The Act prescribes in general terms that adequate provision must be made for drinking water, accommodation for meals and clothing, sanitary conveniences, first-aid and washing facilities, provision for drying clothes, lighting and ventilation, safe access and egress, fire protection, dewatering, and also for protective clothing and for protection from harmful effects arising from the work. These will be covered in more detail in regulations.
Administration - The Act is administered by the Department of Labour and provides for safety inspectors who have full rights of entry and power to issue direction orders or cease-work orders if there is a danger to workmen.
Accidents - Accidents of a serious nature to any person must be reported to the inspector, and serious injury is defined as requiring absence from work for 48 hours or more. Provision also exists for a magisterial inquiry into any accident if so directed by the Minister of Labour.
Appeals - Provision is made for an appeal within 14 days to a Magistrate from an inspector's direction or order, or from an inspector's decision concerning replacement of a safety supervisor.
Liabilities of Workmen - Any workman who fails to comply with any requirement under the Act or wilfully does anything likely to injure himself or others or negligently disregards any instruction given to him for the purpose of securing observance of the Construction Act, commits an offence. He may be charged either with the employer or separately.
Regulations - Notifiable works and much of the detail relating to safety are covered by the Construction Regulations 1961.
MINING LEGISLATION - The present law relating to mining and quarrying will be found for the most part in the Coal Mines Act 1925 and subsequent amendments, the Mining Act 1926 and amendments, and the Quarries Act 1944 and its amendments. A noteworthy feature of such Acts is the appointment of inspectors with wide powers.
Application of Mining Acts - A “mine” under the Mining Act means generally any mine other than a coal mine, while by the Quarries Act 1944 a quarry is defined as any place in which persons work in excavating any kind of material from the earth, including an opencast coal quarry, and includes an excavation for the purposes of the construction of any work for the generation of electricity, or for the purposes of the construction of a dam for the supply of water for the use of the public, and a tunnel. A quarry does not include any place (other than an opencast coal quarry) in which mining or searching for coal, gold, scheelite, or petroleum is carried on; any road cutting or railway cutting; or any tunnel in the construction of which explosives are not used and which is less than 50 ft long or any shaft less than 15 ft deep.
Working Conditions - In common with the practice pertaining for many other industrial groups of workers the current working conditions for quarry men generally are set out in awards made by the Court of Arbitration. In the coal-mining industry working conditions are usually determined by direct negotiation between the coal-mine owners and the workers' organisations. Both principal mining Acts prohibit employment in or about mines on Sundays unless the previous authority of an Inspector of Mines has been obtained.
Since 1948 an underground shift of seven hours has applied in the mining industry in lieu of the former eight-hour limit.
Restriction on Employment - No male under the age of 16 years may be employed underground in any coal mine, or in any alluvial mine, or on or about any dredge; while the minimum age in respect of underground work in a quartz mine is 19 years. No youth may be employed in a mine for more than eight hours per day or 48 hours per week except in cases of emergency.
Safety, Health, and Welfare Provisions - In general the provisions of the Coal Mines Act 1925 are similar to those of the Mining Act 1926 in so far as safety, etc, is concerned, although, of course, to combat the special risks of coal mining additional regulation is necessary. The appropriate provisions are considered under Occupational Safety in Section 37c.
SHIPPING AND SEAMEN LEGISLATION - The Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 states that the general superintendence of matters relating to merchant ships and seamen in New Zealand is with the Marine Department.
Hours of Work, Overtime, and Holiday Provisions - Under the Shipping and Seamen Act the normal hours of work of seamen, whether at sea or in port, are restricted to eight per day or 40 per week. Seamen may be required to work hours in excess of these, but shall be recompensed for the excess (by payment at a higher rate or by the allowance of time off on pay).
Holiday provisions are negotiated in the construction of the award applicable, while the benefits of the Annual Holidays Act 1944 operate as the minimum permissible limit.
Competence, Safety, Health, and Welfare Provisions - In the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 adequate provision is made to ensure competence on the part of the controlling officers of ships. Home-trade steamships of 60 tons register and upwards, and home-trade sailing ships of 100 tons register, must carry certificated mates, and such ships of 100 tons register and upwards trading more than 300 miles between terminal ports must have second mates. A foreign-going ship is required to carry two certificated mates. Foreign-going certificated mates are entitled to ship as mates in the home trade. Provision is made for issuing certificates of competency to second mates of home-trade ships, and for recognising as valid in New Zealand certificates of masters, mates, and engineers granted in any part of the British Commonwealth.
Further sections dealing with the safety of the ship require the adjustment of compasses to be carried out under regulations, while power is given to the Minister to define restricted trading limits for steamers and for vessels propelled by oil, gas, etc. The Governor-General in Council is empowered to make regulations as to the loading and stowage of ballast and the loading of grain cargo in bulk. It is an offence to ship wool, flax, tow, or skins in such a condition as to be liable to spontaneous combustion.
The following rules and regulations are all concerned with the subject-matter under consideration: Shipping Rules - Shipping Casualty 1937; Dangerous Goods 1953; Grain 1953; Load Line 1953; Closing of Openings in Hulls and Watertight Bulkheads 1954; Construction 1954; Direction Finders 1954; Lifesaving Appliances 1960; Musters 1954; Navigation Warnings 1954; Pilot Ladders 1954; Radio 1954; Signals of Distress 1954; and Fire Appliances 1958. Regulations - Ballast 1937; Ships Compass 1947; Deck Cargo 1950; Transport of Radioactive Substances 1951; Masters and Mates Examination 1952; Shipping (Accepted Safety Convention) 1953; Collisions Regulations Order 1953; Timber Cargo 1953; Crew Accommodation 1954; Certificates of Competency as A.B. 1954 (These certificates have reciprocity with United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland certificates); Load Line (Particulars of Depth of Loading) 1954; and Marine Engineers Examination 1957.
Since 1909 there has been a gradual extension of the type of ship required by law to be equipped with radio installations. The regulations now define the nature of the installations and service, and the number and grade of operators in different classes of vessels, and provide for inspection thereof.
The provisions regarding working conditions on vessels require, inter alia, proper sanitary, hospital, and lavatory accommodation, including bathrooms, to be provided for the crew, together with an adequate supply of hot water for those employed in connection with the engines, while a prescribed minimum of space for the seamen's quarters is also laid down.
Commonwealth ships where the agreement with the crew is first made in New Zealand, in addition to home-trade ships, are liable to pay the wages, maintenance, and medical expenses of seamen left on shore in New Zealand, by reason of illness or accident in the service of the ship, for a period of three months. The illness or accident which entitles a man to the benefits provided for is one which requires medical treatment for 14 days.
Fines not exceeding £100 in any case are prescribed for a breach of any safety rules made expressly for those small craft not subject to the provisions of the principal Act relating to survey, etc..
In 1959 the authority of Superintendents of Mercantile Marine to deal with matters in dispute was greatly increased. Previously they possessed authority to decide certain matters relating to wages. In 1959 by agreement between the parties concerned authority was given Superintendents to deal with other matters in dispute.
LEGISLATION GOVERNING WORKING CONDITIONS IN THE VARIOUS BRANCHES OF THE GOVERNMENT SERVICE - The principal measures which are concerned with the majority of persons employed either directly or indirectly by the State and which have reference to their working conditions are given in the succeeding paragraphs.
Members of the Public Service are governed by the Public Service Act 1912. The 1946 amendment provided for the control of the Public Service by a Commission as from 1 November 1946. Included in the functions of the Commission are the control of recruitment, maintenance of discipline and of a fair and efficient system of promotion, and also the regulation of a variety of points connected with personnel control - e.g., leave, hours of work, payment of allowances, etc.
The Government Service Tribunal Act 1948 provided for the establishment of a tribunal with functions, in relation to the remuneration and conditions of service of employees, of making (a) principal and other orders, and (b) recommendations to the Prime Minister on any matters other than those contained in the principal orders.
The Government Railways Act 1949, a consolidation measure, furnishes the legislative framework for determination of the working conditions of railway employees. In 1944 there was established the Government Railways Industrial Tribunal, the principal functions of which are to prescribe scales of salaries and rates of wages; conditions in regard to hours of work, overtime, etc.; and terms and conditions in respect of leave of absence, railway travel concessions, etc. The Government Railways (Staff) Regulations 1953 are also of relevance in this connection.
Working conditions for Post Office employees are determined by the administrative authority, the Postmaster-General, with the Director-General as executive head. Power is vested in the Minister by virtue of the Post Office Act 1959. There is a Post Office Staff Tribunal whose function it is to make recommendations to the Minister on such matters as may be referred to it by the Minister, the Director-General, or the New Zealand Post Office Association (Incorporated).
There are other legislative enactments which apply to the relevant sections of General Government employees. Members of the Police are governed by the Police Act 1958; the Police Regulations 1959 have been issued pursuant to the Police Act 1958. The three fighting services are controlled at present by the Army Act 1950, the Navy Act 1954, and the Royal New Zealand Air Force Act 1950.
The Education Act 1914 and amendments provide the legislative background authorising, either by regulation or through the agency of education boards, the determination of the conditions of employment, pay, leave of absence, etc, for the members of the teaching profession.
LEGISLATIVE PROVISION FOR CERTAIN OTHER GROUPS - The provisions relating to working conditions of hospital board employees, such as nurses, etc., will be found in the Hospitals Act 1957 while the Hospital Employment Regulations 1957 bear directly on these matters.
The legislation at present governing waterside work is contained in the Waterfront Industry Act 1953, which defines waterside work as “the loading and unloading of ships, barges, lighters, and other vessels; and, in relation to any port where the harbour board acts as wharfinger, includes the work of receiving and delivering cargo customarily performed by waterside workers at that port”. The functions of government are shared between two types of bodies - one legislative and judicial, the other administrative only.
The legislative and judicial body is the Waterfront Industry Tribunal which consists of a Chairman and two other members appointed by the Governor-General on the recommendation of the Minister of Labour. The Tribunal is appointed for a term of three years and is a Commission of Inquiry under the Commissions of Inquiry Act 1908. The functions of the Tribunal are, firstly, to prescribe the terms and conditions of employment for waterside work, and here the Tribunal's procedure is similar to that followed by the Government Service Tribunal. To assist with this function, the Act also provides for the setting up by the Minister of Labour of National Conciliation Committees consisting of eight employer and eight worker representatives, with an independent Chairman, to conduct conciliation proceedings on any application to the Tribunal which concerns two or more ports. Secondly, the Tribunal is required to settle any disputes that arise in relation to waterside work, and for this function has the assistance of Port Conciliation Committees which consist of an equal number of employers' and workers' representatives with an independent Chairman. These committees, also, are appointed by the Minister of Labour, but are subject to the control and direction of the Tribunal, and are responsible for conciliation proceedings on any matter concerning their port of appointment. In addition these committees have duties in relation to fixing the rules for the supply and discipline of waterside labour, and generally to act at a port in relation to local disputes or interpretations of terms and conditions of employment. Thirdly, the Tribunal is a general Appeal Court from decisions of Port Conciliation Committees (with certain limitations), National Amenities Committees, and orders of the Waterfront Industry Commission imposing levies or charges.
The Waterfront Industry Commission, which is the administrative body, consists of one Commissioner appointed for a term of five years by the Governor-General on the recommendation of the Minister of Labour. The functions of the Commission are, firstly, to carry out all administrative work in connection with the engagement and employment of, and payment of wages to, waterside workers, including administrative work in connection with guaranteed minimum payments, annual and statutory holiday payments and systems of payment by results for waterside workers. In this connection the Commission also administers and enforces the rules for the supply and discipline of waterside workers as fixed by Port Conciliation Committees or the Waterfront Industry Tribunal, and maintains statistical records in relation to the various aspects of waterside work. Secondly, the Commission is responsible for the provision of amenities for waterside workers (subject to the direction of the National Amenities Committee) and for the equipping, operation, and management of these amenities which include waiting rooms or assembly halls, restaurants, canteens, and first-aid rooms. The National Amenities Committee, which is associated with the Commission in the function of provision of amenities, consists of seven nominated representatives of employers, workers, and harbour boards and the Waterfront Industry Commissioner as Chairman, and is appointed by the Minister of Labour. This committee acts in an advisory capacity in authorising the Commission to provide amenities costing not more than £1,000 each at any port, in approving schemes for the provision by harbour boards of amenities costing more than £1,000 each at any port, in fixing the rates and methods of repayments to harbour boards for amenities provided for waterside workers and to arrange for the caretaking and cleaning of all waterside amenities. The National Amenities Committee may also appoint for any port a Port Amenities Committee consisting of a chairman (usually the Commission's local administrative officer) and representatives of interested parties, with duties to prepare port schemes for the provision of amenities and generally to assist the National Amenities Committee in carrying out its functions at that port.
To carry out its administrative functions the Waterfront Industry Commission maintains an office and permanent staff at all main and secondary ports, and has appointed local shipping companies as agents at some minor ports. In addition to actual administrative work the Commission is responsible for the provision of funds to meet costs of guarantee and holiday payments and costs of provision, operation, and maintenance of amenities. Finance is provided mainly by a national administration fund levy, based on paid labour hours, from all employers of waterside workers, but a proportion of administrative costs is recovered from profits under payments-by-results schemes, and a token grant to cover costs of Tribunal and other legislative and judicial functions is made by Government from the Consolidated Fund. Details of the Commission's annual statement of accounts and statistical tables are included as Appendices to the Annual Report (parliamentary paper H. 45) presented to the House of Representatives pursuant to section 53 of the Waterfront Industry Act 1953.
The organisation of “registered” waterside workers is on the basis of separate port unions with two associations or federations of unions, one of South Island and one of North Island port unions. There is also a joint committee of the executive officers of the two associations. Registration of the port unions and of the two associations is under the provisions of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954 - that is, through the Registrar of Industrial Unions in the Department of Labour. The provisions of the Act relating to strikes and lockouts and the taking of secret ballots in connection therewith, the cancellation by the Minister of Labour of the registration of a union or association, following on any discontinuance of employment and the enforcement of awards and agreements apply also to all waterside employers and unions of waterside workers and any associations of these employers or unions. In addition, where a discontinuance of employment in the waterfront industry causes or is likely to cause serious loss or inconvenience through the action of any union or association of unions, the Minister of Labour has power to suspend in whole or in part any order, direction or decision of the Tribunal, Commission, or any committee appointed under the Act as applies to all or any of the ports.
GENERAL - About half of New Zealand's wage and salary earners are subject to awards and industrial agreements made under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954 (a re-enactment of a measure which was originally enacted in 1894). The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act enables wage rates to be determined, industry by industry, by agreement between organisations of employers and workers concerned or, failing such agreement, by awards made by the Court of Arbitration after hearing the parties. The great majority of Government employees are subject to orders made by the Government Service Tribunal in the case of the Public Service and by similar tribunals for Railways and Post Office employees. Waterside workers are subject to orders of the Waterfront Industry Tribunal. Workers in certain branches of agriculture are subject to orders made under the Agricultural Workers Act 1936. Apprentices are subject to apprenticeship orders made under the Apprentices Act 1948. There are considerable numbers of employees in supervisory and executive grades whose wage rates or salaries are determined by individual contracts of service and there are some relatively small groups whose wage rates or salaries are determined under other legislation.
GENERAL WAGE ORDERS - In addition to its original jurisdiction, the Court of Arbitration is vested with the power to make general wage orders from time to time which have the effect of simultaneously increasing or reducing the rates of remuneration prescribed in all awards and industrial agreements in operation. The Court also has the power to exclude any class or section of workers from the operation of a general order, and to make such special provision as it considers just and equitable for that class or section.
General orders may be made by the Court of its own accord or on the application of any industrial union or industrial association of employers or workers.
The authority to make general orders is not derived from the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, but from regulations made under the Economic Stabilisation Act 1948.
Stabilisation as an explicitly stated object of policy came to the forefront early in the Second World War. It had long been realised that in wartime the normal supply or flow of goods would be restricted, particularly so in the case of imports, but also in some degree in the field of local production. It was recognised that this factor, reinforced by others such as the progressive withdrawal of elements of the labour force for service with the armed forces, changes in the extent and character of industrial activity and in the labour force generally, would inevitably exert an upward pressure on the wage and price structures of the country. It was equally necessary to limit or confine upward movements in these structures as far as possible. Measures to this effect were authorised, evolving into a fairly comprehensive system of regulations covering the general fields of price control, wages stabilisation, rent stabilisation, direction of manpower, subsidies, etc. After the close of the war some of these measures were dispensed with, while others were retained and relieved of their emergency status by further legislation.
The present jurisdiction to make general orders was introduced in 1940 as a war measure. Pursuant to the Emergency Regulations Act 1939, the Rates of Wages Emergency Regulations 1940 were promulgated, and during the following years were amended on many occasions.
In 1948 some of the provisions of the wartime regulations were incorporated into the permanent legislation of the country in the form of the Economic Stabilisation Act. Under the authority of that Act the Economic Stabilisation Regulations have been made, and frequently amended, and the Court of Arbitration operates under them today.
In making a general order the Court is directed by the regulations to take into account the following matters:
Any rise or fall in retail prices as indicated by any index published by the Government Statistician.
The economic conditions affecting finance, trade, and industry in New Zealand.
Any increase or decrease in productivity and in the volume and value of production in primary and secondary industries of New Zealand.
Relative movements in the incomes of different sections of the community.
Any other considerations that the Court deems relevant.
During the past 20 years 13 major cases under the Rates of Wages Emergency Regulations and the Economic Stabilisation Regulations have been heard. As a result eight general orders have been made. Four applications were followed by standard wage pronouncements (described elsewhere in this section), while in one instance an application for a general order was declined.
In dealing with such applications the Court is required to afford such opportunity to be heard as it thinks proper to representatives appointed by the parties bound by awards and industrial agreements or by orders of certain tribunals, namely, the Government Service Tribunal, the Government Railways Industrial Tribunal, and the Waterfront Industry Tribunal. The Court's normal jurisdiction does not extend to employees of the State or to workers employed on waterside work but, as the result of certain statutory provisions, decisions of the Court by way of general orders and standard wage pronouncements are taken into account by these Tribunals in determining rates of wages within the scope of their respective jurisdictions; consequently, provision was made to permit parties bound by orders of the Tribunals to appear when applications for general orders are before the Court, although the parties themselves cannot initiate applications. In practice the major burden of conducting the cases has been accepted by the New Zealand Federation of Labour and the New Zealand Employers Federation.
All the main aspects of the economy of the country are examined in considerable detail, and expert evidence is usually called in support of the submissions or to assist the Court in its task. For example, such persons as the Governor of the Reserve Bank, the Secretary of the Treasury, and the Government Statistician have frequently given evidence. The Court itself has no research staff. For basic information it relies for the most part on the comprehensive statistics published by the Government Statistician, the reports of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, official economic and other surveys, and reports of Government Departments, such as the Treasury, Department of Labour, Department of Agriculture, and the Department of Industries and Commerce. The advocates for the parties are invariably persons with long experience in the industrial arena. No professional lawyer has ever been engaged on the hearing of an application for a general order during the past 20 years. The applications have varied in nature and magnitude from time to time and have involved claims for annual increases in wages and salaries up to as much as 17 per cent of the gross national product.
The last general order was made on 18 September 1959 after the most extended hearing in the history of the Court.
The Economic Stabilisation Regulations 1953 had been amended in April 1959, principally for the purpose of authorising the Court to make a pronouncement that it would, if thought fit, incorporate in new awards the effect of general or other orders made under the regulations. An immediate application was then lodged for a general order increasing rates of remuneration and for a pronouncement on incorporation in terms of the authority contained in the amended regulations. A general order, effective from 12 October 1959, and revoking the general order of 1956, was made by the Court on 18 September 1959. This order increased the rates of remuneration prescribed by all awards and industrial agreements to which it applied by 24 per cent (instead of 18 per cent as hitherto and therefore increasing minimum rates of wages by a little over 5 per cent) on amounts up to and including £13 per week for adult males and certain adult female workers employed under awards and industrial agreements requiring them to be paid adult male rates, and £9 15s. and £7 10s. per week for other adult females and junior workers respectively. The effect of the order was to provide maximum increases of 15s. 7.2d. per week for those to whom the £13 limit applied and 11s. 8.4d. and 9s. per week respectively for those to whom the limits of £9 15s. and £7 10s. applied. For varying reasons 127 awards and industrial agreements were excluded from the operation of the order, it being open to any party to any excluded awards or agreements to apply to the Court for a subsequent order amending the rates of remuneration prescribed in such awards or agreements. The Court simultaneously made a pronouncement “that, when making any award to supersede, in whole or in part, any award or industrial agreement to which any general or other order applies, or to which it is specifically applied by any provision in that award or industrial agreement, the Court will incorporate in such rates of remuneration as the Court thinks just and equitable, as an integral part of those rates, the effect of the general or other order”. An amendment in May 1960 to the Economic Stabilisation Regulations 1953 gave the parties to awards and agreements the right to apply to the Court of Arbitration for incorporation immediately.
Theoretically, as a result of the general order effective from 12 October 1959, the present effective standard hourly rates are: skilled workers, 6s. 2.4d.,; semi-skilled workers 5s. 5.72d. to 5s. 9.44d.; and unskilled workers, 5s. 3.86d.
STANDARD WAGE PRONOUNCEMENTS - Before the Second World War it was the practice of the Court on intermittent occasions to make standard wage pronouncements and it has always possessed inherent powers to issue them, the object of doing so being to give parties to industrial disputes an indication of the manner in which the Court would be likely to adjust rates of wages when dealing with industrial disputes during the period following the pronouncement.
An extremely simple skeleton scale has usually been adopted, standard casual hourly rates being fixed for adult male workers of three classes - skilled workers, semi-skilled workers, and unskilled workers. Such pronouncements had no operative effect, but when awards were made after a pronouncement, the rates of wages were brought into approximately the same relative position, compared with the new standard rates, as they previously occupied in relation to the former standard rates. This procedure meant that, before all workers could benefit from the review of the standard rates, any period up to two years might elapse, because of the necessity for awaiting the expiry of current awards before adjusting the rates in accordance with the new standards. It also meant that some groups of workers received the benefit of their new rates appreciably earlier than other groups.
Special steps were taken under the wartime emergency legislation to eliminate the variable waiting period. At different times during the past 20 years the Court has been vested with special powers to make individual amendments simultaneously and immediately to every award and industrial agreement in the country, in order to enable the rates of wages prescribed therein to conform to any new pronouncement of standard wage rates. The last occasion on which the Court was granted such powers was in February 1952, and it was then enjoined in making amendments to have due regard to any increases in the rates of remuneration granted to the workers concerned since the date of the last preceding wage pronouncement dated 12 April 1949.
The object of this provision was to enable the Court, if it thought fit, to restore a proper balance between the minimum rates of wages prescribed for different classes of workers in the various industries. Some workers' unions have stronger bargaining power than others and some industries enjoy temporary periods of high prosperity. These circumstances, combined with the fact that in the post-war years there have been many more positions in New Zealand than workers to fill them, have tended to introduce unjustifiable disparities in the prescribed minimum rates of wages. The making of a general order increasing wages by a fixed percentage tends to aggravate the disparities. On the other hand, if a general order prescribes a flat increase, existing margins or differentials for skill and responsibility are detrimentally affected.
The technique of amending awards and agreements to give effect to a pronouncement while at the same time having regard to the increases gained in the previous three years enabled the Court to iron out disparities to some extent following the making of a pronouncement in July 1952. The Court's decisions on that occasion, however, were strongly criticised by workers' organisations. One factor which caused irritation was that some of the increases gained by workers in conciliation had in the course of bargaining been associated with the abandonment of certain restrictive provisions to the advantage of employers. The Court, in applying its pronouncement, was not in the position to take such matters into account, and some workers' unions felt they had been unfairly treated. The special powers to amend awards and agreements concurrently and immediately following a pronouncement were revoked by amending regulations in May 1953 and have not since been re-enacted.
The history and effects on wages of the standard wage pronouncements and general orders made since 1919 were given in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.
MINIMUM WAGE - Enforceable minimum wage rates are determined under various statutes, the most universally applicable being the Minimum Wage Act 1945. This Act provides that workers of the age of 21 years and upwards must receive not less than the rates prescribed under the Act. In the great majority of cases, however, workers are subject to wage orders, awards, or industrial agreements relating to the particular industries in which they are employed and which provide somewhat higher enforceable minimum rates.
The minimum wage prescribed in the Act or by Order in Council under the Act may be amended from time to time as fresh pronouncements of standard rates or general orders are made, if it is desired to preserve a balance between statutory minimum wages and such rates of wages. In this reference it will be noted that the minimum wage for males is set at a rate which is lower than the standard rate for unskilled labour.
The minima prescribed by the Minimum Wage Order 1959, and operating from 21 October 1959, are given below, while those in force during the earlier periods are also shown.
| Category | 1 Dec 1947 to 31 Aug 1949 | 1 Sep 1949 to 31 Aug 1950 | 1 Sep 1950 to 31 Jul 1951 | 1 Aug 1951 to 30 Sep 1952 | 1 Oct 1952 to 14 Dec 1953 | 15 Dec 1953 to 14 Dec 1954 | 15 Dec 1954 to 4 Dec 1956 | 5 Dec 1956 to 20 Oct 1959 | 21 Oct 1959 Onwards | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. |
| Paid by hour or by piece work | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 7 1/4 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| Paid by day | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 8 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Other (per week) | 5 | 15 | 0 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 6 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 7 | 18 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 17 | 6 |
| Females - | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paid by hour or piece work | 0 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 1/2 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| Paid by day | 0 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 17 | 4 | 0 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 4 |
| Other (per week) | 3 | 13 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 16 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 13 | 0 |
BASIC WAGE - There is now no “basic wage” in New Zealand; nor is there any formula for determining such a wage. In 1936 an amendment of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act required the Court to determine a basic wage for adult males and for adult females and directed that the basic wage for adult males should be sufficient to maintain a man, his wife, and three children in a fair and reasonable standard of comfort. The basic wage rates so determined by the Court, being below the prevailing minimum adult rates in awards and industrial agreements, were of little practical effect and were never revised. The relevant provisions were dropped from the Act in 1954.
SPECIAL PROVISIONS COVERING WAGES OF CERTAIN GROUPS OF WORKERS - Certain groups of workers have their wages fixed by special authorities. Minimum rates for agricultural workers are prescribed by the Agricultural Workers Act 1936 and the various extension orders made pursuant to section 20 of that Act. Rates of remuneration for waterside work are fixed by the Waterfront Industry Tribunal, constituted now under the Waterfront Industry Act 1953. Determination of wages in coal mines lies within the scope of the Coal Mines Council, established under the Coal Mines Council Emergency Regulations 1940. Rates of pay for workmen engaged on public-works construction have been determined from 1949 by the Government Service Tribunal and issued in the form of principal and other orders by that Tribunal.
Salaries and wages in the railways are, by the Government Railways Act 1949, prescribed by the Government Railways Industrial Tribunal. The legislative authority covering rates of remuneration for employees of the Post Office is contained in the Post Office Act 1959, while certain questions may be referred to the Post Office Staff Tribunal.
In 1948 the Government Service Tribunal Act was passed vesting the Tribunal with powers of making principal and other orders in relation to remuneration of public servants.
Pay and allowances for the Armed Services at present are prescribed in regulations under the Army Act 1950, the Navy Act 1954, and the Royal New Zealand Air Force Act 1950. Salary and wage rates for hospital board employees not under awards and agreements are covered by the Hospitals Act 1957 and the Hospital Employment Regulations 1957. Two other groups of employees may also be mentioned; members of the Police coming under the Police Act 1958, and finally members of the teaching profession, whose rates of remuneration are generally determined by authority of the Education Act 1914 and amendments.
Rates of pay for shearers and other wool-shed hands are adjusted proportionately with the movements of an index number prepared by the Government Statistician based on average prices realised at New Zealand sales for greasy wool (calculated for June years).
In referring to the general question of wage rates it is relevant to draw attention to the supplementary income which is provided by benefits available under the Social Security Act in certain cases, while the War Pensions Act is of significance also in this connection (see Section 6).
PROTECTION OF WAGES - Workers' wages were first safeguarded by the Truck Act of 1891, and are now protected by the Wages Protection and Contractors' Liens Act 1939.
Some of the salient provisions of the present law are now set out.
In the absence of any written agreement to the contrary, wages of manual workers are to be paid at intervals of not more than a week, and of other workers at intervals of not more than a month. The attachment of workers' wages for debt is prohibited except in the case of any surplus over an amount specified in the Act or when specific provision is made in any other Act for attachments on a lower minimum. Exceptions are made by the Child Welfare Act 1925 and the Destitute Persons Act 1910. The Coal Mines Amendment Act 1941 provides for deduction from wages, with the written consent of the employee, of sums towards repayment of principal or payment of interest, etc., in respect of advances by the mine owner to the worker for the purpose of acquiring a home. Section 210 of the Land and Income Tax Act 1954 provides for deduction of due amounts from the salary or wages of a taxpayer who has made default in the payment of income tax.
The Wages Protection and Contractors' Liens Act prohibits payment of wages being made in goods (truck) or in any other way than in money or by approved cheque, and also prohibits any stipulation as to how the wages money is to be expended. The truck provisions do not, however, apply where the employer supplies house accommodation, board and lodging, fuel, medical assistance, materials, tools and the like required for the work, nor to seamen or farm workers.
No deduction from workers' wages may be made for purposes of insurance against compensation for accident arising out of and in the course of employment.
Wages are further safeguarded by certain sections of the Bankruptcy Act, which give priority of payment for wages or salaries of workers (with certain limitations as to amount and period) in preference to certain other debts, and since the passing of the Bankruptcy Amendment Act 1927 wages take precedence over rents. Similarly, under the Companies Act, wages (with the same limitations as under the Bankruptcy Act) are a first claim on the assets of a company being wound up. Under the Bankruptcy Amendment Act 1956, compensation payments rank with wages as a priority charge on the assets of a bankrupt.
Various individual labour laws contain provisions with the special intent of protecting the payment of wages of the workers to whom such legislation applies.
STATISTICS
WAGE RATES - Wage rates are to be distinguished from rates of earnings which include additions by way of overtime and bonus payments. Wage rates themselves may be either minimum rates or actual rates and on either basis may be calculated as weekly rates or hourly rates. An age-sex classification shows rates for adult males, adult females, juvenile males, and juvenile females separately. Statistics are now given for nominal weekly wage rates for each of the age-sex classes mentioned, together with nominal minimum hourly wage rates for adult males and effective minimum weekly wage rates for adult males and adult females, all in the form of index numbers; then for selected minimum wage rates in shillings and pence weekly for each age-sex group; then for rates of earnings; and finally for index numbers of average weekly hours of labour for adult males and adult females. There is no complete coverage of actual wage rates.
Minimum Wage Rates - The material used by the Department of Statistics in the compilation of statistics of wage rates in New Zealand is taken from the awards made by, and the industrial agreements filed in, the Court of Arbitration, and decisions of other wage-fixing tribunals. The rates specified in these awards and orders are minimum rates; they take into account neither overtime nor ruling rates which may be above the prescribed minima. Nevertheless, for the purpose of tracing the movement in wage rates over any considerable space of time, the award rates form a more reliable basis than any other information at present available.
The award rates for the four principal districts - Northern, Wellington, Canterbury, and Otago and Southland - are in general taken as being representative of minimum wages throughout New Zealand. For such industries as are carried on in the towns these rates are quite satisfactory; in cases where the important centre of an industry is situated outside the geographical boundaries of the four principal districts, the award rates for that centre are used. For instance, the rates used for sawmilling in the Canterbury District are those prescribed by the awards for the Westland Industrial District.
Nominal Wage Rate Index - The current series of index numbers has the calendar year 1954 as the expression base and the average wage rates for this period were equated to 1000. This series superseded the one based on the five years 1926-30.
As far as possible the weighting pattern has been based on information obtained from the Census of 1951, but supplementary data were obtained from the statistics of Industrial Production, the half-yearly surveys of employment published by the Department of Labour in the Labour and Employment Gazette, figures of union membership published in the parliamentary paper (H. 11), the Census of Distribution 1953, and other special material and surveys.
There are 14 industrial groups in the series. The series are predominantly indices of wage rates of manual workers, such occupations as clerical and office workers, professional, technical, and related workers, managers, officials, and administrators, and most service workers being excluded. Besides all primary and secondary industries the following distributive trades and services are, however, included:
1. Retailing of meat, groceries, soft goods, and coal and firewood.
2. Provision of accommodation, meals, and personal services.
3. Transport industries.
Four series of wage-rates index numbers are compiled; these comprise indices for adult males, adult females, juvenile males, and juvenile females. The adult male index alone covers the 14 industrial groups and the weights for these industrial groups are as follows:
| Industrial Group | Group Weight |
|---|---|
| Provision of - | |
| Food, drink, etc. | 1,244 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 439 |
| Building and construction | 1,629 |
| Power, heat, and light | 241 |
| Transport by water and air | 611 |
| Transport by land | 927 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 354 |
| Working in or on - | |
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 818 |
| Metal | 1,255 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 358 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 220 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 63 |
| Mines and quarries | 274 |
| The land | 1,567 |
| All groups | 10,000 |
These group weights represent the sum of the weights assigned to the occupations within each of the industries which form the industrial group as listed.
A full description of this series, together with details of the weighting, can be found in the appendix to the Report on Prices, Wages, and Labour Statistics for the year 1954.
Wage Rates of Adult Male Workers - Index numbers of annual averages of nominal weekly wage rates of adult males over the period 1914-60 are given in the following table. This “long-term linked series” has been obtained by combining the successive series and converting the whole to the base of the new index, which is the weighted average of weekly wage rates for adult males in 1954 (= 1000).
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES), ALL INDUSTRIAL GROUPS
| Base: 1954 (= 1000) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Index Number |
| 1914 | 253 |
| 1915 | 263 |
| 1916 | 273 |
| 1917 | 289 |
| 1918 | 303 |
| 1919 | 329 |
| 1920 | 371 |
| 1921 | 402 |
| 1922 | 389 |
| 1923 | 375 |
| 1924 | 378 |
| 1925 | 387 |
| 1926 | 393 |
| 1927 | 401 |
| 1928 | 413 |
| 1929 | 414 |
| 1930 | 414 |
| 1931 | 383 |
| 1932 | 351 |
| 1933 | 339 |
| 1934 | 341 |
| 1935 | 349 |
| 1936 | 386 |
| 1937 | 421 |
| 1938 | 440 |
| 1939 | 447 |
| 1940 | 460 |
| 1941 | 476 |
| 1942 | 497 |
| 1943 | 513 |
| 1944 | 518 |
| 1945 | 562 |
| 1946 | 583 |
| 1947 | 606 |
| 1948 | 646 |
| 1949 | 682 |
| 1950 | 729 |
| 1951 | 829 |
| 1952 | 871 |
| 1953 | 929 |
| 1954 | 1000 |
| 1955 | 1035 |
| 1956 | 1055 |
| 1957 | 1104 |
| 1958 | 1116 |
| 1959 | 1136 |
| 1960 | 1193 |
The wage rates on which the foregoing index numbers are based are gross rates, no account having been taken of the fact that from August 1931 wages have been subject to certain forms of taxation not previously in operation. A summary of these taxes on wages since their introduction is as follows.
| Date from Which Effective | Rate per Pound | Class of Tax | |
|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | ||
| 1 August 1931 | 0 | 3 | Emergency unemployment charge. |
| 1 May 1932 | 1 | 0 | “ |
| 1 October 1934 | 0 | 10 | Employment promotion tax. |
| 1 October 1935 | 0 | 8 | “ |
| 1 April 1939 | 1 | 0 | Social security tax. |
| 21 July 1940 | 2 | 0 | Social security tax (1s. in pound). |
| National security tax (1s. in pound). | |||
| 11 May 1942 | 2 | 6 | Social security tax (1s. in pound). |
| National security tax (1s. 6d. in pound). | |||
| 13 May 1946 | 2 | 0 | Social security tax (1s. 6d. in pound). |
| National security tax (6d. in pound). | |||
| 21 April 1947 | 1 | 6 | Social security tax. |
Since 1 April 1958, under the PAYE tax system, income tax (ordinary income tax and social security income tax) has been deducted from wages at the rates set out in the relevant taxation tables - refer to Section 26B, Taxation, for further information.
The next table shows the index numbers of nominal weekly wage raise of adult males for each industrial group and for all groups combined for the years 1958-60. The base in this instance is the New Zealand weighted average wage rate for all groups combined, 1954 (= 1000).
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES)
| Base: All groups combined, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | Calendar Year | 1960 | |||||
| 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 31 Mar | 30 Jun | 30 Sep | 31 Dec | |
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 1187 | 1212 | 1272 | 1269 | 1272 | 1273 | 1278 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 1102 | 1125 | 1182 | 1173 | 1173 | 1191 | 1196 |
| Building and construction | 1070 | 1093 | 1149 | 1147 | 1155 | 1155 | 1157 |
| Power, heat, and light | 1046 | 1062 | 1120 | 1105 | 1108 | 1141 | 1145 |
| Transport by water and air | 1305 | 1340 | 1407 | 1405 | 1406 | 1406 | 1418 |
| Transport by land | 1122 | 1147 | 1213 | 1195 | 1224 | 1224 | 1224 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 1084 | 1098 | 1157 | 1150 | 1150 | 1169 | 1169 |
| Working in or on - | |||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 1131 | 1158 | 1221 | 1210 | 1227 | 1227 | 1227 |
| Metal | 1184 | 1204 | 1267 | 1261 | 1270 | 1271 | 1271 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 1065 | 1087 | 1135 | 1130 | 1136 | 1137 | 1151 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 1209 | 1227 | 1294 | 1295 | 1295 | 1298 | 1298 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 1065 | 1079 | 1142 | 1133 | 1147 | 1151 | 1151 |
| Mines and quarries | 1130 | 1144 | 1201 | 1196 | 1196 | 1206 | 1207 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 989 | 994 | 1029 | 1025 | 1025 | 1038 | 1038 |
| All groups combined | 1116 | 1136 | 1193 | 1187 | 1194 | 1199 | 1202 |
NOTE - The index numbers in this table are comparable both vertically and horizontally.
In the groups “accommodation, meals, and personal service”, and “transport by water and air”, the estimated value of board and lodging, and in the “working on the land” group, the value of rations as well as the estimated value of board and lodging are, where applicable, added to the money wage rate in order to make a legitimate comparison with other industries. Also included in the wages for workers in the “transport by water and air” group is a sea-going allowance where applicable. In the case of waterside workers (an important subgroup of the “water and air transport” group) these allowances are not, of course, applicable.
Movement in Individual Groups - The index numbers in the preceding table being on a national all-groups base, comparisons between movements in individual groups cannot readily be made; an increase in a group in which the index numbers are consistently low being considerably smaller numerically than would be an increase of the same percentage in one where the index numbers are higher. The following table brings out the movements in the various groups more clearly. The respective bases are the New Zealand average weekly wage rates for each industrial group, 1954 (= 1000), the heavily ruled vertical line indicating the commencement of the new series.
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES)
| Base: Each group separately, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1914 | 1939 | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 257 | 488 | 1000 | 1126 | 1146 | 1169 | 1227 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 246 | 454 | 1000 | 1104 | 1114 | 1137 | 1195 |
| Building and construction | 274 | 472 | 1000 | 1099 | 1112 | 1136 | 1194 |
| Power, heat, and light | 266 | 483 | 1000 | 1115 | 1128 | 1146 | 1208 |
| Transport by water and air | 237 | 440 | 1000 | 1118 | 1120 | 1150 | 1208 |
| Transport by land | 256 | 463 | 1000 | 1116 | 1132 | 1158 | 1224 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 282 | 460 | 1000 | 1094 | 1127 | 1142 | 1203 |
| Working in or on - | |||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 253 | 470 | 1000 | 1105 | 1115 | 1141 | 1203 |
| Metal | 274 | 475 | 1000 | 1104 | 1119 | 1138 | 1197 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 252 | 486 | 1000 | 1113 | 1129 | 1152 | 1203 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 287 | 472 | 1000 | 1117 | 1136 | 1153 | 1216 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 262 | 487 | 1000 | 1090 | 1100 | 1115 | 1180 |
| Mines and quarries | 268 | 450 | 1000 | 1155 | 1156 | 1171 | 1228 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 226 | 373 | 1000 | 1066 | 1065 | 1070 | 1107 |
| All groups combined | 253 | 447 | 1000 | 1104 | 1116 | 1136 | 1193 |
Care must be exercised in drawing inferences from this table, for, while horizontal comparisons are quite valid, the vertical comparison between the various groups is valid only in so far as it shows in which groups the greater or the smaller movements have occurred.
Indices of Hourly Wage Rates - The indices which follow (as is also the case in respect of the indices of standard weekly hours of labour) cover 13 only out of the 14 industrial groups commonly adopted, since working hours on farms (which would be essential to the fourteenth group) cannot for this purpose be satisfactorily treated statistically. The base of the first table is the New Zealand average hourly wage rate (computed as described after the two following tables) for all groups combined, 1954 (= 1000).
NOMINAL HOURLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES)
| Base: All groups combined, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| Provision of - | |||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 1024 | 1153 | 1173 | 1197 | 1256 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 977 | 1078 | 1088 | 1111 | 1167 |
| Building and construction | 950 | 1044 | 1057 | 1079 | 1135 |
| Power, heat, and light | 916 | 1020 | 1033 | 1049 | 1106 |
| Transport by water and air | 1108 | 1238 | 1241 | 1273 | 1338 |
| Transport by land | 979 | 1093 | 1108 | 1133 | 1198 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 950 | 1038 | 1070 | 1084 | 1143 |
| Working in or on - | |||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 1002 | 1107 | 1117 | 1143 | 1205 |
| Metal | 1045 | 1153 | 1169 | 1189 | 1251 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 932 | 1036 | 1052 | 1073 | 1121 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 1051 | 1174 | 1194 | 1212 | 1278 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 956 | 1042 | 1052 | 1066 | 1128 |
| Mines and quarries | 1038 | 1200 | 1200 | 1215 | 1275 |
| All groups combined | 1000 | 1111 | 1125 | 1148 | 1208 |
The next table shows the movement in individual groups. The base is the New Zealand average hourly wage rate for each group individually, 1954 (= 1000), the heavily ruled vertical line indicating the commencement of the new series.
NOMINAL HOURLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES)
| Base: Each group separately, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1914 | 1939 | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 196 | 448 | 1000 | 1126 | 1146 | 1169 | 1227 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 213 | 443 | 1000 | 1104 | 1114 | 1137 | 1195 |
| Building and construction | 241 | 473 | 1000 | 1099 | 1113 | 1136 | 1194 |
| Power, heat, and light | 221 | 481 | 1000 | 1114 | 1128 | 1146 | 1208 |
| Transport by water and air | 188 | 418 | 1000 | 1118 | 1120 | 1150 | 1208 |
| Transport by land | 213 | 443 | 1000 | 1117 | 1132 | 1158 | 1224 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 185 | 447 | 1000 | 1093 | 1127 | 1142 | 1203 |
| Working in or on - | |||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 220 | 471 | 1000 | 1105 | 1114 | 1141 | 1203 |
| Metal | 236 | 475 | 1000 | 1103 | 1119 | 1138 | 1197 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 212 | 483 | 1000 | 1112 | 1129 | 1152 | 1203 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 261 | 473 | 1000 | 1117 | 1136 | 1153 | 1216 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 218 | 468 | 1000 | 1090 | 1100 | 1115 | 1180 |
| Mines and quarries | 218 | 415 | 1000 | 1156 | 1156 | 1171 | 1228 |
| All groups combined | 217 | 455 | 1000 | 1111 | 1125 | 1148 | 1208 |
The figures shown in the last two tables are derived from average hourly rates calculated in every case by dividing the corresponding average weekly rate by the standard number of hours worked in the week.
Wage Rates of Adult Female Workers - Index numbers showing movements in wage rates of women workers are compiled, using the award rates of the Court of Arbitration; a much smaller list of occupations is used than is the case in computing index numbers of wage movements for male workers. Although only 21 occupations are taken into consideration in the case of women workers, these occupations normally cover a large proportion of the total women in industry - more than sufficient to constitute a representative sample for measuring movements in wages.
The following table shows index numbers of women's wage rates on base: New Zealand all-groups weighted average, 1954 (= 1000), divided into the principal industries in which women workers are normally engaged. In the compilation of these indices, the value of such perquisites as board and lodging in the case of hotel workers has been added to the money wage rates.
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT FEMALES)
| Base: All groups combined, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| Provision of - | |||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 909 | 998 | 1016 | 1028 | 1082 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 981 | 1088 | 1100 | 1118 | 1178 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 1083 | 1190 | 1233 | 1254 | 1326 |
| Working in paper, printing, etc. | 919 | 1045 | 1072 | 1090 | 1164 |
| All groups combined | 1000 | 1106 | 1128 | 1146 | 1210 |
Movements in Individual Groups - Movements within the various groups are brought out more clearly in the next table, the base in this case being the New Zealand weighted average weekly rate of each group, 1954 (= 1000), the heavily ruled vertical line indicating the commencement of the new series. As with the similar table relating to male wage rates (p. 997), horizontal comparisons are valid, but vertical comparisons merely show in which groups the greater or smaller movements have occurred.
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT FEMALES)
| Base: Each group separately, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1914 | 1939 | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 153 | 375 | 1000 | 1099 | 1118 | 1131 | 1191 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 192 | 372 | 1000 | 1109 | 1121 | 1140 | 1201 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 275 | 441 | 1000 | 1098 | 1138 | 1157 | 1224 |
| Working in paper, printing, etc. | 199 | 376 | 1000 | 1137 | 1166 | 1186 | 1267 |
| All groups combined | 213 | 390 | 1000 | 1106 | 1128 | 1146 | 1210 |
Weekly Wage Rates: All Adult Workers - A series of index numbers has been computed on the base, 1954 (= 1000) for all adult workers. In general this has followed the index for adult males, although for some years after 1945 female wage rates made on the whole relatively greater gains than male rates. Index numbers for the last 15 years are as follows.
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (ADULT MALES AND FEMALES COMBINED), ALL INDUSTRIAL GROUPS
| Base: 1954 (= 1000) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Index |
| 1946 | 579 |
| 1947 | 602 |
| 1948 | 644 |
| 1949 | 682 |
| 1950 | 729 |
| 1951 | 828 |
| 1952 | 869 |
| 1953 | 929 |
| 1954 | 1000 |
| 1955 | 1036 |
| 1956 | 1055 |
| 1957 | 1105 |
| 1958 | 1123 |
| 1959 | 1137 |
| 1960 | 1194 |
Wage Rates of Juvenile Workers - Index numbers of wage rates of juveniles, male and female, are compiled for each calendar year. Owing to the fact that a number of industries utilise juvenile labour to a limited extent only, or not at all, it has not been possible to cover a very wide field, but 36 occupations representing 12 out of the 14 industrial groups are included in the case of juvenile males, and five occupations representing three industrial groups in the case of juvenile females.
Wherever possible the weekly wage rate adopted in the compilation of the indices is that provided for a worker having attained the age of 18 years or having completed three years' service, according, to the terms of the award.
In the table which follows the respective bases are the New Zealand average weekly wage rates for each industrial group, 1954 (= 1000), the heavily ruled vertical line indicating the commencement of the new series.
NOMINAL WEEKLY WAGE-RATES INDEX NUMBERS (JUVENILE WORKERS)
| Base: Each group and each sex separately, 1954 (= 1000) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Group | 1914 | 1939 | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
| *No provision made in awards for juvenile females. | |||||||
| Juvenile Males | |||||||
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 215 | 407 | 1000 | 1147 | 1197 | 1234 | 1308 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 173 | 329 | 1000 | 1112 | 1162 | 1198 | 1260 |
| Building and construction | 177 | 321 | 1000 | 1115 | 1180 | 1203 | 1271 |
| Transport by land and air | 255 | 485 | 1000 | 1125 | 1136 | 1163 | 1236 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 168 | 339 | 1000 | 1111 | 1239 | 1255 | 1331 |
| Working in or on - | |||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 176 | 361 | 1000 | 1120 | 1163 | 1194 | 1268 |
| Metal | 146 | 361 | 1000 | 1115 | 1182 | 1197 | 1273 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 192 | 487 | 1000 | 1172 | 1200 | 1228 | 1319 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 184 | 295 | 1000 | 1117 | 1189 | 1206 | 1279 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 266 | 431 | 1000 | 1123 | 1157 | 1169 | 1287 |
| Mines and quarries | 264 | 468 | 1000 | 1265 | 1265 | 1281 | 1346 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 190 | 340 | 1000 | 1050 | 1053 | 1059 | 1122 |
| All industrial groups | 184 | 354 | 1000 | 1099 | 1134 | 1152 | 1221 |
| Juvenile Females | |||||||
| Provision of - | |||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 144 | 374 | 1000 | 1095 | 1121 | 1134 | 1199 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 182 | 386 | 1000 | 1116 | 1126 | 1148 | 1240 |
| Working in paper, printing, etc. | * | 395 | 1000 | 1179 | 1209 | 1226 | 1326 |
| All industrial groups | 180 | 385 | 1000 | 1118 | 1130 | 1151 | 1241 |
In recent years juvenile wages have been largely governed by the Apprentices Act 1948, under which the scale of wages in apprenticeship orders is based on a percentage of the ruling minimum rates for journeymen in the industry concerned. Consequently, the wage-rates index numbers for juvenile males now tend to move in sympathy with the index numbers of male adult wage rates. In the preceding table horizontal comparisons are valid, but vertical comparisons merely show in which groups the greater or smaller movements have occurred.
EFFECTIVE WEEKLY WAGE RATES — The index numbers quoted in the foregoing paragraphs relate to nominal weekly wage rates only — that is, they are based on actual or equivalent money rates without any allowance being made for changes during the period under review in the prices of those goods and services which are purchased out of wages earned. It is obvious that this factor is of considerable importance, for a rise in wage rates may be offset by a fall in the purchasing power of the monetary unit, while, on the other hand, a fall in money wages may be offset by a rise in the purchasing power of money. Index numbers of effective (or “real”) wage rates are arrived at by dividing the index numbers of nominal wage rates by the corresponding all-groups index numbers of retail prices (both series of index numbers having first been set on a common base) and multiplying the result by the base value of 1000.
The following table accordingly shows a comparison of nominal and effective weekly wage rates of adult male and female workers in each of the years 1950–60. The base of the index numbers is in each case the calendar year 1954 (= 1000).
| Year | Retail Prices (All Groups) | Nominal Weekly Wage Rates | Effective Weekly Wage Rates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| 1950 | 764 | 729 | 727 | 954 | 952 |
| 1951 | 848 | 829 | 817 | 978 | 963 |
| 1952 | 914 | 871 | 852 | 953 | 932 |
| 1953 | 956 | 929 | 924 | 972 | 967 |
| 1954 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1955 | 1024 | 1035 | 1039 | 1011 | 1015 |
| 1956 | 1061 | 1055 | 1056 | 994 | 995 |
| 1957 | 1083 | 1104 | 1106 | 1019 | 1021 |
| 1958 | 1132 | 1116 | 1128 | 986 | 996 |
| 1959 | 1175 | 1136 | 1146 | 967 | 975 |
| 1960 | 1183 | 1193 | 1210 | 1008 | 1023 |
The continuous series of retail prices index numbers required for the foregoing table has been obtained by linking the revised consumers' price index to the earlier series and converting the whole to the base: calendar year 1954 (= 1000).
In making use of these results it should not be overlooked that the index numbers of nominal wage rates apply only to full-time employment at award rates of pay. They do not take into account either on the one hand above-award rates or overtime earnings, or on the other, short-time deductions or wages tax imposed (a summary of the rates of wages tax in force during different periods will be found on page 996). Nor do the retail prices index numbers take cognisance of all classes of household expenditure; income tax, charitable and other gifts, sea and air travel, domestic help, etc., being omitted. Having regard to opportunities for spare-time gainful occupation, a comparison with movements in the index numbers of hours of labour shown later in this section is also relevant.
To the extent that female wages are not normally devoted to purchasing the full range of household requirements the results of employing the all-groups retail prices index to determine effective wages for females are subject to certain limitations.
AVERAGE RATES OF WAGES — The following table shows the New Zealand minimum weekly wage rates in various occupations for the years 1914, 1939, 1954, and 1957–60. The figures given are simple averages for the four principal industrial districts as at 31 March in the years indicated. The adult male wage rates on the same basis as at 31 March 1961 will be found in the Latest Statistical Information at the back of this volume. The rates shown throughout this table are money rates, and do not include any allowance for the value of board and lodging, which is a usual perquisite of the employment of some workers, e.g., seamen and hotel employees. Further information on this latter point is available in the note given at the end of the table.
| Occupation | Average Wage (Four Principal Districts) at 31 March | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1914 | 1939 | 1954 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | ||||||||
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | |
| Adult Males | ||||||||||||||
| Bakers — | ||||||||||||||
| Journeymen | 55 | 0 | 115 | 0 | 225 | 10 | 248 | 2 | 254 | 3 | 254 | 3 | 267 | 3 |
| Labourers | 48 | 0 | 95 | 0 | 190 | 10 | 210 | 8 | 214 | 9 | 214 | 9 | 225 | 8 |
| Butchers — | ||||||||||||||
| First shopmen | 72 | 6 | 123 | 2 | 241 | 1 | 264 | 6 | 268 | 5 | 268 | 5 | 284 | 8 |
| Second shopmen | 62 | 6 | 110 | 8 | 224 | 5 | 246 | 5 | 250 | 2 | 250 | 2 | 265 | 5 |
| Butter-factory employees — Churning and buttermaking: Others | 45 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 192 | 10 | 230 | 6 | 230 | 6 | 242 | 4 | 254 | 8 |
| Flourmilling — | ||||||||||||||
| Kilnmen | 48 | 0 | 99 | 4 | 218 | 9 | 240 | 4 | 240 | 4 | 246 | 3 | 258 | 7 |
| Assistant smuttermen | 48 | 0 | 91 | 4 | 208 | 8 | 229 | 6 | 229 | 6 | 233 | 5 | 245 | 2 |
| Rollermen | 56 | 0 | 103 | 4 | 235 | 3 | 258 | 0 | 258 | 0 | 269 | 10 | 283 | 5 |
| Meat freezing — | ||||||||||||||
| Slaughtermen, per 100 sheep | 27 | 6 | 45 | 0 | 98 | 3 | 111 | 7 | 113 | 1 | 113 | 1 | 118 | 4 |
| Workers not otherwise specified | 54 | 0 | 113 | 8 | 231 | 0 | 257 | 8 | 259 | 7 | 259 | 7 | 277 | 0 |
| Meat preserving — | ||||||||||||||
| Boners | 62 | 0 | 132 | 0 | 274 | 0 | 304 | 10 | 311 | 10 | 311 | 10 | 330 | 9 |
| Others | 59 | 6 | 110 | 0 | 231 | 0 | 259 | 7 | 267 | 6 | 267 | 6 | 285 | 3 |
| Sausage-casing making: Workers not otherwise specified | 58 | 8 | 117 | 4 | 238 | 4 | 265 | 6 | 273 | 4 | 273 | 4 | 295 | 7 |
| Aerated water and cordial making — | ||||||||||||||
| Cordial makers | 58 | 9 | 96 | 10 | 201 | 5 | 224 | 4 | 224 | 4 | 224 | 4 | 238 | 1 |
| Others | 45 | 0 | 88 | 3 | 191 | 11 | 214 | 7 | 214 | 7 | 214 | 7 | 227 | 11 |
| Brewing: Others | 47 | 7 | 94 | 5 | 209 | 0 | 238 | 11 | 238 | 11 | 245 | 7 | 260 | 5 |
| Tailors — | ||||||||||||||
| Journeymen | 53 | 9 | 101 | 2 | 220 | 0 | 239 | 11 | 244 | 10 | 244 | 10 | 257 | 4 |
| Stock cutters (factory) | 55 | 0 | 92 | 6 | 220 | 0 | 239 | 11 | 244 | 10 | 244 | 10 | 257 | 4 |
| Footwear manufacturing workers | 52 | 6 | 91 | 8 | 220 | 0 | 244 | 10 | 247 | 10 | 249 | 3 | 260 | 5 |
| Woollen mills — | ||||||||||||||
| Spinners | 51 | 0 | 103 | 4 | 223 | 8 | 245 | 10 | 248 | 9 | 248 | 9 | 268 | 8 |
| Others | 46 | 6 | 93 | 4 | 199 | 10 | 220 | 3 | 223 | 2 | 223 | 2 | 241 | 10 |
| Building — | ||||||||||||||
| Bricklayers | 68 | 5 | 115 | 0 | 233 | 5 | 251 | 8 | 256 | 9 | 256 | 9 | 270 | 0 |
| Carpenters and joiners | 64 | 3 | 112 | 6 | 226 | 8 | 248 | 1 | 253 | 0 | 253 | 0 | 73 | 4 |
| Plasterers | 67 | 9 | 114 | 7 | 230 | 3 | 255 | 5 | 256 | 5 | 261 | 3 | 275 | 6 |
| Plumbers | 66 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 231 | 5 | 259 | 5 | 259 | 5 | 265 | 3 | 285 | 0 |
| Builders' labourers | 52 | 6 | 93 | 4 | 207 | 9 | 224 | 8 | 226 | 11 | 229 | 10 | 241 | 7 |
| General labourers | 52 | 6 | 93 | 4 | 188 | 9 | 207 | 4 | 209 | 5 | 212 | 5 | 223 | 3 |
| Sawmilling — | ||||||||||||||
| Sawyers | 53 | 0 | 112 | 6 | 236 | 1 | 263 | 9 | 264 | 0 | 268 | 6 | 283 | 9 |
| Tailers-cut | 43 | 9 | 96 | 8 | 215 | 0 | 241 | 2 | 241 | 5 | 245 | 10 | 259 | 11 |
| Yardmen, head | 55 | 8 | 110 | 0 | 231 | 0 | 258 | 4 | 258 | 7 | 263 | 0 | 278 | 0 |
| Workers not specified | 51 | 0 | 95 | 0 | 210 | 10 | 236 | 9 | 237 | 0 | 241 | 5 | 255 | 3 |
| Boatbuilding: Shipwrights | 62 | 8 | 126 | 6 | 233 | 1 | 255 | 10 | 255 | 10 | 263 | 0 | 276 | 0 |
| Metal works, etc — | ||||||||||||||
| Boilermakers, journeymen | 62 | 8 | 110 | 0 | 224 | 7 | 247 | 10 | 253 | 8 | 253 | 8 | 266 | 8 |
| Iron and brass moulders | 64 | 7 | 110 | 0 | 226 | 6 | 250 | 9 | 250 | 9 | 256 | 8 | 269 | 8 |
| Tinsmiths, journeymen | 62 | 8 | 110 | 0 | 224 | 7 | 253 | 3 | 253 | 3 | 259 | 2 | 278 | 4 |
| Engineering fitters, etc. | 64 | 7 | 110 | 0 | 227 | 1 | 254 | 1 | 260 | 10 | 260 | 10 | 280 | 0 |
| Electrical wiremen | 61 | 10 | 110 | 5 | 229 | 2 | 258 | 5 | 258 | 5 | 264 | 4 | 277 | 5 |
| Motor mechanics | 64 | 8 | 110 | 0 | 232 | 11 | 259 | 11 | 259 | 11 | 260 | 10 | 273 | 11 |
| Printing — | ||||||||||||||
| Linotype (day) | 74 | O | 115 | 0 | 236 | 6 | 263 | 6 | 269 | 5 | 269 | 5 | 289 | 4 |
| Letterpress machinist (day) | 65 | O | 107 | 6 | 227 | 4 | 253 | 8 | 259 | 7 | 259 | 7 | 279 | 0 |
| Skin and leather workers — | ||||||||||||||
| Curriers | 58 | O | 105 | 0 | 213 | 7 | 235 | 0 | 238 | 11 | 238 | 11 | 255 | 0 |
| All other workers | 49 | 6 | 90 | 0 | 188 | 10 | 208 | 10 | 212 | 9 | 212 | 9 | 227 | 9 |
| Mineral and stone workers — | ||||||||||||||
| Flanger and moulder | 53 | 11 | 108 | 4 | 214 | 6 | 238 | 1 | 241 | 10 | 244 | 6 | 257 | 11 |
| All other workers | 46 | 9 | 95 | 0 | 194 | 4 | 216 | 6 | 219 | 11 | 222 | 1 | 234 | 6 |
| Mining (coal) — | ||||||||||||||
| Surface: Tippers | 53 | 7 | 91 | 3 | 217 | 9 | 267 | 6 | 267 | 6 | 267 | 6 | 283 | 1 |
| Miners (on day wages, per shift) | 11 | 4 | 20 | 10 | 46 | 6 | 53 | 3 | 53 | 3 | 53 | 3 | 56 | 5 |
| Truckers | 55 | 11 | 97 | 6 | 211 | 4 | 240 | 0 | 240 | 0 | 240 | 0 | 254 | 5 |
| Quarrymen | 52 | 8 | 94 | 2 | 195 | 1 | 210 | 9 | 211 | 2 | 214 | 1 | 225 | 0 |
| Agricultural and pastoral workers — | ||||||||||||||
| General farm workers | 26 | 4 | 45 | 0 | 152 | 0 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 168 | 3 |
| Threshing mill: Other workers, per hour | 1 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 5 | 7 1/2 | 5 | 11 |
| Ploughmen | 30 | 4 | 46 | 3 | 152 | 0 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 168 | 3 |
| Shearers (per 100 sheep shorn) | 20 | O | 28 | 6 | 68 | 0 | 68 | 0 | 77 | 0 | 68 | 0 | 62 | 6 |
| Shepherds | 31 | 2 | 52 | 6 | 152 | 0 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 161 | 6 | 168 | 3 |
| Wool pressers | 30 | O | 84 | 6 | 245 | 8 | 245 | 8 | 278 | 8 | 271 | 4 | 251 | 2 |
| Dairy-farm workers | 23 | O | 52 | 6 | 185 | 0 | 190 | 0 | 190 | 0 | 190 | 0 | 205 | 6 |
| Railways — | ||||||||||||||
| Enginedrivers, average third and sixth years | 75 | O | 120 | 0 | 244 | 4 | 283 | 9 | 283 | 9 | 292 | 1 | 307 | 1 |
| Firemen, average second and ninth years | 60 | O | 102 | 11 | 221 | 10 | 252 | 11 | 252 | 11 | 261 | 3 | 275 | 0 |
| Guards, average first and third years | 63 | O | 113 | 9 | 237 | 0 | 271 | 3 | 271 | 3 | 279 | 7 | 293 | 9 |
| Tramways — | ||||||||||||||
| Drivers | 53 | 6 | 101 | 3 | 211 | 9 | 236 | 0 | 243 | 10 | 243 | 10 | 262 | 6 |
| Conductors (after six months) | 47 | 7 | 95 | 7 | 203 | 6 | 227 | 2 | 235 | 0 | 235 | 0 | 253 | 2 |
| Shipping and cargo working — | ||||||||||||||
| Assistant stewards, first grade | 25 | 8 | 72 | 4 | 204 | 3 | 231 | 0 | 231 | 0 | 231 | 0 | 243 | 5 |
| Assistant stewards, second grade | 18 | 8 | 70 | 0 | 200 | 7 | 227 | 1 | 227 | 1 | 227 | 1 | 239 | 4 |
| Chief cooks | 60 | 8 | 106 | 10 | 252 | 2 | 282 | 6 | 282 | 6 | 282 | 6 | 297 | 6 |
| Second cooks | 37 | 4 | 88 | 2 | 227 | 2 | 255 | 7 | 255 | 7 | 255 | 7 | 269 | 5 |
| Able seamen | 37 | 4 | 89 | 1 | 219 | 11 | 247 | 11 | 247 | 11 | 247 | 11 | 261 | 4 |
| Ordinary seamen: 18 years or over | 28 | O | 60 | 10 | 170 | 1 | 190 | 8 | 190 | 8 | 190 | 8 | 199 | 2 |
| Waterside workers: Ordinary cargo | 62 | 4 | 106 | 8 | 231 | 8 | 259 | 7 | 259 | 7 | 259 | 7 | 283 | 4 |
| Hotel workers — | ||||||||||||||
| First cooks | 90 | 0 | 112 | 0 | 216 | 10 | 238 | 6 | 243 | 2 | 243 | 2 | 255 | 7 |
| Waiters | 31 | 1 | 65 | 0 | 153 | 0 | 170 | 0 | 174 | 9 | 174 | 9 | 183 | 8 |
| Miscellaneous — | ||||||||||||||
| Retailing of apparel — Shop assistants | 55 | 0 | 102 | 6 | 214 | 10 | 236 | 0 | 238 | 11 | 239 | 11 | 257 | 4 |
| Grocers' assistants | 50 | 0 | 102 | 6 | 205 | 10 | 225 | 8 | 236 | 0 | 236 | 0 | 249 | 1 |
| Warehouse storemen | 48 | 9 | 90 | 0 | 205 | 4 | 226 | 2 | 226 | 2 | 231 | 1 | 244 | 2 |
| Adult Females | ||||||||||||||
| Biscuit and confectionery factory workers | 20 | 0 | 49 | 0 | 130 | 0 | 143 | 0 | 145 | 11 | 145 | 11 | 157 | 6 |
| Tailoresses (factory): Journey-women | 27 | 6 | 50 | 0 | 140 | 10 | 155 | 4 | 158 | 4 | 158 | 4 | 166 | 5 |
| Footwear manufacturing workers | 27 | 6 | 50 | 10 | 139 | 8 | 155 | 9 | 158 | 4 | 159 | 4 | 170 | 7 |
| Woollen-mill workers | 25 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 141 | 2 | 155 | 4 | 159 | 1 | 159 | 1 | 17 | 6 |
| Hotel workers — | ||||||||||||||
| Cooks | 29 | 5 | 58 | 0 | 156 | 1 | 173 | 4 | 178 | 1 | 178 | 1 | 187 | 2 |
| Housemaids | 17 | 2 | 36 | 6 | 106 | 8 | 117 | 5 | 122 | 2 | 122 | 2 | 128 | 5 |
| Waitresses | 22 | 5 | 36 | 6 | 106 | 8 | 117 | 5 | 122 | 2 | 122 | 2 | 128 | 5 |
| Restaurant workers — | ||||||||||||||
| Cooks | 42 | 6 | 87 | 0 | 172 | 4 | 190 | 9 | 190 | 9 | 197 | 4 | 207 | 5 |
| Waitresses | 31 | 1 | 48 | 6 | 121 | 9 | 136 | 6 | 136 | 6 | 142 | 5 | 149 | 8 |
| Pantrymaids | 29 | 2 | 48 | 6 | 121 | 9 | 136 | 6 | 136 | 6 | 142 | 5 | 149 | 8 |
| Printing workers | 58 | 6 | 132 | 0 | 150 | 5 | 155 | 2 | 155 | 2 | 170 | 0 | ||
| Retailing of apparel: Shop assistants | 27 | 6 | 57 | 6 | 143 | 10 | 157 | 4 | 160 | 7 | 161 | 8 | 173 | 3 |
| Juvenile Males | ||||||||||||||
| Bakers' apprentice: After three years' service | 27 | 6 | 65 | 0 | 146 | 10 | 161 | 4 | 170 | 4 | 170 | 4 | 179 | 0 |
| Butchers' assistant: 18 years of age | 30 | 10 | 49 | 5 | 115 | 11 | 133 | 4 | 136 | 9 | 136 | 9 | 145 | 0 |
| Butter and cheese factory: Youth, 18 years of age | 30 | 0 | 52 | 6 | 123 | 9 | 154 | 5 | 154 | 5 | 160 | 4 | 168 | 6 |
| Flour-mill: Youth, after three years' service | 27 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 115 | 0 | 127 | 0 | 127 | 0 | 131 | 0 | 137 | 6 |
| Meat freezing and preserving: Youth, 18 years of age | 25 | 6 | 55 | 0 | 125 | 2 | 144 | 0 | 149 | 10 | 149 | 10 | 161 | 3 |
| Aerated water and cordial manufacture: Youth, 18 years of age | 25 | 0 | 46 | 7 | 99 | 8 | 125 | 10 | 125 | 10 | 125 | 10 | 133 | 6 |
| Tailoring, etc.: Apprentice, after three years' service | 19 | 2 | 40 | 0 | 129 | 10 | 141 | 7 | 151 | 10 | 151 | 10 | 159 | 7 |
| Footwear manufacturing: Apprentice, after three years' service | 25 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 129 | 10 | 144 | 5 | 153 | 7 | 154 | 6 | 161 | 6 |
| Woollen-mill: Youth, 18 years of age | 22 | 6 | 46 | 8 | 124 | 8 | 137 | 8 | 141 | 4 | 141 | 4 | 161 | 2 |
| Bricklayers' apprentice: After three years' service | 24 | 2 | 42 | 6 | 139 | 1 | 149 | 10 | 160 | 6 | 160 | 6 | 168 | 7 |
| Carpenters' apprentice: After three years' service | 24 | 6 | 43 | 2 | 136 | 6 | 149 | 1 | 159 | 4 | 159 | 4 | 172 | 0 |
| Plasterers' apprentice: After three years' service | 24 | 0 | 42 | 6 | 136 | 11 | 152 | 5 | 160 | 7 | 163 | 8 | 172 | 9 |
| Plumbers' apprentice. After three years' service | 19 | 5 | 40 | 0 | 138 | 7 | 155 | 9 | 172 | 2 | 175 | 11 | 186 | 9 |
| Sawmill: Youth, 18 years of age | 25 | 6 | 48 | 9 | 108 | 8 | 124 | 5 | 124 | 5 | 130 | 4 | 136 | 11 |
| Engineering: Apprentice, after three years' service | 20 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 135 | 0 | 151 | 3 | 163 | 3 | 163 | 3 | 175 | 2 |
| Brick, tile, etc., works: Youth, 18 years of age | 21 | 0 | 53 | 5 | 107 | 9 | 126 | 9 | 130 | 6 | 132 | 4 | 140 | 2 |
| Tannery: Youth, 18 years of age | 33 | 4 | 51 | 3 | 108 | 1 | 125 | 1 | 129 | 0 | 129 | 0 | 139 | 2 |
| Coalmining: Trucker, 18 years of age | 46 | 5 | 82 | 9 | 177 | 4 | 225 | 0 | 225 | 0 | 225 | 0 | 238 | 6 |
| Agriculture and dairying (mixed farms): Youth, 18 years of age | 31 | 0 | 111 | 6 | 114 | 6 | 114 | 6 | 114 | 6 | 122 | 9 | ||
| Retailing of apparel: Shop assistant, after three years' service | 20 | 0 | 45 | 0 | 125 | 7 | 138 | 2 | 140 | 5 | 147 | 4 | 158 | 5 |
| Grocers' assistant: After three years' service | 25 | 0 | 42 | 6 | 123 | 9 | 135 | 8 | 152 | 10 | 152 | 10 | 167 | 11 |
| Juvenile Females | ||||||||||||||
| Biscuit and confectionery factory: Assistant, after three years' service | 16 | 0 | 41 | 6 | 110 | 6 | 121 | 5 | 124 | 5 | 124 | 5 | 133 | 10 |
| Footwear manufacturing: Assistant, after three years' service | 19 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 101 | 2 | 120 | 4 | 120 | 4 | 121 | 4 | 130 | 4 |
| Woollen mill: Worker, after three years' service | 22 | 6 | 41 | 0 | 112 | 2 | 123 | 4 | 126 | 3 | 126 | 3 | 142 | 0 |
| Clothing factory: Improver, after three years' service | 19 | 2 | 43 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 120 | 11 | 123 | 11 | 123 | 11 | 130 | 3 |
| Printing trade: Worker, after three years' service | 44 | 6 | 112 | 2 | 132 | 9 | 136 | 7 | 136 | 7 | 150 | 0 | ||
NOTE — The following perquisites (as assessed for statistical purposes) as at 31 March 1960 should be added to the listed occupations: dairy-farm workers, 42s. 6d. per week for board and lodging; general farm workers, ploughmen, shepherds, and youths (18 years of age) employed on agricultural and dairy (mixed) farms, 42s. 6d. per week for board and lodging; shearers and wool pressers, 8s. per day for rations; assistant stewards (first and second grade), chief and second cooks, able seamen and ordinary seamen (first class), 54s. 5d. per week as value of board and lodging; and hotel first cooks and waiters, female cooks, housemaids, and waitresses, 54s. 6d. per week as value of board and lodging. Varying amounts in this connection would also be added to the occupations affected for earlier years.
EARNINGS AND HOURS WORKED IN INDUSTRY — The following pages supply information extracted from the half-yearly surveys conducted by the Department of Labour (see page 1014), the particulars relating to a sample week at the end of each half-year.
Up to April 1957, one result of the half-yearly survey was to show the average weekly payout per person. This was obtained by dividing the aggregate payout for one week by the number of full-time employees in the same week.
From and including the April 1957 survey some important changes were made in the information cards filled in by employers. From that date the Department of Labour has published average hourly rates for all workers covered by the half-yearly survey. In calculating these rates the Department has included part-time as well as full-time employees. To provide a long-term series, average weekly wage payouts per person, on this same basis, have been computed for all periods covered by the half-yearly surveys. Also, to provide a link with the previous series of average wage payouts per person, computations using full-time employees have continued to be made.
In the following table, which gives the average weekly payout per person, all ages, both sexes, and all occupations within industry are included in the one figure.
| Date of Survey | Weekly Wage Payout per Person (Including Overtime, Bonus Earnings, etc.)Aggregate Payout for One Week Divided by — | Nominal Minimum Weekly Wage for Adult Males as Prescribed in Awards and Industrial Agreements as at End of Preceding Month | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-time Employees | Full-time and Part-time Employees | ||||||||
| *Does not include retrospective payments arising from the general order of the Court of Arbitration of 19 November 1953. | |||||||||
| £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1949 — April | 7 | 14 | 8 | 7 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 0 |
| October | 8 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 16 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 3 |
| 1950 — April | 8 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 19 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 6 |
| October | 8 | 15 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 8 | 0 | 10 |
| 1951 — April | 9 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 19 | 8 |
| October | 10 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 16 | 1 | 9 | 3 | 11 |
| 1952 — April | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 6 | 0 |
| October | 10 | 13 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 14 | 6 |
| 1953 — April | 11 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 11 |
| October | 11 | 2 | 1* | 10 | 13 | 11* | 10 | 14 | 10 |
| 1954 — April | 12 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 13 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 0 |
| October | 12 | 7 | 0 | 11 | 17 | 1 | 10 | 16 | 4 |
| 1955 — April | 12 | 15 | 2 | 12 | 4 | 8 | 11 | 4 | 7 |
| October | 1 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 9 |
| 1956 — April | 13 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 4 |
| October | 13 | 10 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 1 | 11 | 9 | 1 |
| 1957 — April | 14 | 3 | 0 | 13 | 9 | 9 | 11 | 19 | 8 |
| October | 14 | 4 | 6 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 7 |
| 1958 — April | 14 | 8 | 6 | 13 | 13 | 10 | 12 | 2 | 7 |
| October | 14 | 10 | 6 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 12 | 3 | 2 |
| 1959 — April | 14 | 15 | 2 | 13 | 19 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 11 |
| October | 14 | 18 | 10 | 14 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 4 | 9 |
| 1960 — April | 15 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 17 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 3 |
| October | 15 | 18 | 8 | 14 | 18 | 11 | 13 | 1 | 1 |
The table shown next commences from April 1957 and continues at half-yearly intervals. It exhibits: (a) average minimum hourly wage rates as prescribed in awards and agreements for adult male workers in 13 industrial groups (excluding farming); (b) average hourly earnings in ordinary time for all workers covered by the half-yearly survey; (c) average hourly earnings in overtime for the same workers; (d) overall average hourly earnings for the same workers (ordinary time and overtime combined); (e) estimated average weekly ordinary-time hours worked by full-time employees covered by the half-yearly survey; (f) estimated average weekly overtime hours worked by the same workers; and (g) average total weekly hours worked by all employees covered by the survey. The totals from which these averages are derived are published in the Labour and Employment Gazette, where also the basis of each of the items (e) and (f) is explained (see pages 29–30 of the August 1957 Gazette). For item (e), aggregate ordinary-time hours worked during one week have been divided by the sum of full-time employees plus half only of the part-time employees. For item (f), the aggregate overtime hours worked during one week have been divided by the full-time employees only. If there are any parttime workers the sum of items (e) and (f) will not be equal to item (g).
| Average Minimum Hourly Rates as Prescribed in Awards and Industrial Agreements for Adult Males in 13 Industrial Groups (Excluding Farming) as at End of Preceding Month | Average Hourly Earnings for All Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | Average Weekly Hours Worked by Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Time | Overtime | Ordinary Time and Overtime Combined | Ordinary Time (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Overtime (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Ordinary Time and Overtime Worked by Full-time and Part-time Employees Combined | ||||||
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | hours | hours | hours | |
| April 1957 | 6 | 1.3 | 6 | 8.5 | 9 | 10.8 | 6 | 10.8 | 37.7 | 2.4 | 39.1 |
| October 1957 | 6 | 1.5 | 6 | 9.1 | 10 | 0.7 | 6 | 11.3 | 37.7 | 2.3 | 39.0 |
| April 1958 | 6 | 2.2 | 6 | 9.7 | 10 | 1.7 | 7 | 0.1 | 37.7 | 2.5 | 39.1 |
| October 1958 | 6 | 2.5 | 6 | 10.4 | 10 | 0.1 | 7 | 0.6 | 37.8 | 2.4 | 39.1 |
| April 1959 | 6 | 3.1 | 6 | 11.4 | 10 | 2.9 | 7 | 1.8 | 37.7 | 2.5 | 39.1 |
| October 1959 | 6 | 3.2 | 7 | 0.7 | 10 | 3.6 | 7 | 2.9 | 37.8 | 2.3 | 39.0 |
| April 1960 | 6 | 7.4 | 7 | 3.7 | 10 | 10.4 | 7 | 6.5 | 37.9 | 2.7 | 39.4 |
| October 1960 | 6 | 8.2 | 7 | 4.8 | 11 | 0.3 | 7 | 7.6 | 37.9 | 2.6 | 39.2 |
The preceding table combines all industries. A dissection by industrial groups of the last line of that table — relating to October 1960 — is now provided. Minimum hourly rates are omitted.
| Industrial Group | Average Hourly Earnings for All Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | Average Weekly Hours Worked by Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Time | Overtime | Ordinary Time and Overtime Combined | Ordinary Time (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Overtime (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Ordinary Time and Overtime Worked by Full-time and Part-time Employees Combined | ||||
| s. | d | s. | d. | s. | d. | hours | hours | hours | |
| Forestry, logging, mining, and quarrying — | |||||||||
| Forestry | 7 | 6.1 | 10 | 11.8 | 7 | 6.6 | 38.0 | 0.5 | 38.3 |
| Logging | 8 | 10.1 | 11 | 11.5 | 9 | 2.1 | 38.6 | 4.6 | 43.0 |
| Coalmining | 11 | 4.0 | 11 | 5.6 | 11 | 4.1 | 34.2 | 2.6 | 36.8 |
| Other mining | 8 | 2.2 | 11 | 10.6 | 8 | 9.0 | 38.2 | 7.0 | 44.9 |
| Quarrying (not lime, cement) | 7 | 6.0 | 10 | 10.9 | 8 | 0.5 | 38.7 | 7.4 | 45.8 |
| Totals | 9 | 1.8 | 11 | 5.6 | 9 | 4.0 | 36.8 | 3.2 | 39.8 |
| Seasonal manufacturing — | |||||||||
| Meat processing, etc. | 8 | 6.8 | 11 | 8.7 | 8 | 10.4 | 35.3 | 3.8 | 39.0 |
| Fruit and vegetable preserving | 6 | 7.8 | 10 | 8.7 | 6 | 11.1 | 35.7 | 2.7 | 38.2 |
| Dairy factories | 7 | 10.7 | 11 | 8.2 | 8 | 5.9 | 39.4 | 7.5 | 46.6 |
| Totals | 8 | 2.7 | 11 | 7.9 | 8 | 7.4 | 36.4 | 4.7 | 40.9 |
| Food, drink and tobacco (other than seasonal) — | |||||||||
| Grain milling | 7 | 6.6 | 9 | 9.8 | 7 | 8.1 | 38.0 | 2.4 | 39.9 |
| Bread bakeries | 7 | 4.3 | 12 | 3.9 | 7 | 10.6 | 37.5 | 4.7 | 39.5 |
| Biscuit making | 6 | 4.8 | 9 | 5.3 | 6 | 9.5 | 36.1 | 5.6 | 39.6 |
| Cake and pastry making | 5 | 10.4 | 10 | 10.0 | 6 | 0.4 | 37.8 | 1.5 | 35.2 |
| Sugar and confectionery | 6 | 7.1 | 10 | 3.9 | 6 | 11.2 | 36.0 | 3.9 | 37.7 |
| Other food | 7 | 0.2 | 11 | 3.7 | 7 | 4.9 | 37.3 | 3.8 | 40.1 |
| Beverages | 7 | 7.8 | 11 | 8.7 | 8 | 2.0 | 38.4 | 5.6 | 43.5 |
| Tobacco manufacture | 6 | 6.2 | 11 | 0.7 | 7 | 2.3 | 35.2 | 6.2 | 40.9 |
| Totals | 6 | 10.9 | 11 | 1.5 | 7 | 4.0 | 37.2 | 4.3 | 39.5 |
| Industrial Group | Average Hourly Earnings for All Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | Average Weekly Hours Worked by Workers Covered by Half-yearly Survey | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Time | Overtime | Ordinary Time and Overtime Combined | Ordinary Time (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Overtime (Estimated) Worked by Full-time Employees | Ordinary Time and Overtime Worked by Full-time and Part-time Employees Combined | ||||
| s. | d. | s. | d. | s. | d. | hours | hours | hours | |
| Textiles, clothing and leather — | |||||||||
| Tanneries | 7 | 9.3 | 10 | 2.5 | 8 | 0.0 | 38.1 | 4.0 | 42.0 |
| Fur dressing and manufacture | 6 | 11.8 | 14 | 1.8 | 7 | 0.4 | 35.9 | 0.3 | 33.5 |
| Leather goods | 6 | 0.9 | 9 | 0.6 | 6 | 2.7 | 36.9 | 2.1 | 37.5 |
| Knitted wear and hosiery | 6 | 7.8 | 9 | 3.4 | 6 | 9.2 | 37.9 | 1.7 | 38.9 |
| Flax, rope and twine | 7 | 8.6 | 9 | 6.2 | 7 | 9.6 | 38.7 | 1.9 | 40.2 |
| Woollen mills | 6 | 6.7 | 9 | 4.0 | 6 | 10.0 | 35.7 | 3.9 | 38.7 |
| Other textile production | 7 | 8.0 | 10 | 9.9 | 7 | 11.8 | 37.3 | 4.2 | 41.2 |
| Clothing manufacture | 5 | 9.2 | 7 | 10.0 | 5 | 9.9 | 36.6 | 1.0 | 36.4 |
| Footwear manufacture | 6 | 11.2 | 9 | 3.6 | 7 | 0.9 | 36.4 | 2.3 | 38.1 |
| Footwear repair | 6 | 3.0 | 8 | 7.0 | 6 | 3.6 | 39.4 | 0.9 | 38.9 |
| Other textile goods | 6 | 4.1 | 10 | 6.8 | 6 | 7.4 | 36.1 | 2.6 | 37.2 |
| Totals | 6 | 4.0 | 9 | 2.9 | 6 | 5.6 | 36.7 | 1.9 | 37.6 |
| Building materials and furnishings — | |||||||||
| Sawmilling, plywood, etc. | 8 | 0.1 | 11 | 8.2 | 8 | 4.0 | 38.0 | 3.7 | 41.4 |
| Builders' woodwork | 7 | 3.2 | 10 | 6.7 | 7 | 7.4 | 38.6 | 4.7 | 42.7 |
| Furniture and cabinets | 6 | 10.7 | 10 | 4.5 | 7 | 2.2 | 38.5 | 3.6 | 41.2 |
| Other wood manufacture | 6 | 8.0 | 10 | 4.2 | 6 | 10.5 | 37.8 | 2.4 | 39.0 |
| Structural clay products | 8 | 3.3 | 10 | 6.2 | 8 | 7.2 | 36.4 | 6.2 | 42.2 |
| Pottery and glass | 7 | 0.9 | 12 | 1.2 | 7 | 6.6 | 38.7 | 4.0 | 42.4 |
| Lime, cement, etc. | 7 | 9.4 | 11 | 6.1 | 8 | 3.3 | 37.5 | 5.9 | 42.8 |
| Totals | 7 | 6.8 | 11 | 2.7 | 7 | 11.2 | 38.0 | 4.3 | 41.9 |
| Engineering and metalworking — | |||||||||
| Engineering and machinery | 7 | 7.8 | 11 | 2.7 | 8 | 0.5 | 38.2 | 4.7 | 42.3 |
| Electrical manufacture | 7 | 2.8 | 10 | 7.6 | 7 | 5.6 | 37.6 | 2.7 | 39.8 |
| Ships, locomotives, etc. | 7 | 4.8 | 10 | 9.6 | 7 | 8.2 | 38.1 | 3.4 | 41.5 |
| Vehicle and cycle manufacture | 7 | 11.0 | 12 | 2.5 | 8 | 5.0 | 37.8 | 5.0 | 42.5 |
| Vehicle repair and aircraft | 7 | 0.8 | 10 | 6.9 | 7 | 2.7 | 38.7 | 1.9 | 39.8 |
| Totals | 7 | 5.0 | 11 | 1.5 | 7 | 8.6 | 38.3 | 3.5 | 41.2 |
| Miscellaneous manufacturing — | |||||||||
| Chemicals and by-products | 8 | 1.5 | 11 | 4.1 | 8 | 4.9 | 37.7 | 3.7 | 40.7 |
| Rubber manufacture | 9 | 0.2 | 10 | 4.3 | 9 | 1.4 | 37.9 | 3.2 | 40.7 |
| Paper and paper products | 8 | 7.1 | 13 | 0.3 | 9 | 0.8 | 36.9 | 4.5 | 40.9 |
| Printing, publishing and allied | 7 | 9.2 | 11 | 8.9 | 8 | 0.4 | 38.1 | 2.8 | 39.5 |
| Instruments, clocks, jewellery | 6 | 8.6 | 11 | 1.0 | 6 | 10.5 | 38.6 | 1.5 | 38.8 |
| Other manufacturing | 6 | 10.9 | 10 | 5.0 | 7 | 2.7 | 37.0 | 3.8 | 39.4 |
| Totals | 7 | 11.7 | 11 | 7.2 | 8 | 3.2 | 37.7 | 3.4 | 40.1 |
| Totals, manufacturing industries (including seasonal) | 7 | 4.3 | 11 | 1.1 | 7 | 8.1 | 37.6 | 3.5 | 40.3 |
| Power, water and sanitary services | 7 | 11.8 | 11 | 10.9 | 8 | 3.2 | 38.5 | 3.1 | 41.3 |
| Building and construction | 7 | 4.9 | 10 | 8.4 | 7 | 9.4 | 38.7 | 5.0 | 43.7 |
| Transport and communication — | |||||||||
| Rail transport | 7 | 7.8 | 12 | 2.8 | 8 | 3.1 | 39.1 | 6.0 | 45.1 |
| Road transport | 7 | 5.0 | 10 | 11.2 | 7 | 9.6 | 38.8 | 4.9 | 42.6 |
| Water transport (not waterfront work) | 8 | .9 | 12 | 5.9 | 9 | 0.1 | 38.2 | 4.9 | 42.9 |
| Air transport | 9 | 9.6 | 12 | 5.8 | 9 | 11.4 | 38.5 | 2.2 | 40.5 |
| Post Office | 7 | 1.1 | 12 | 0.6 | 7 | 4.4 | 38.5 | 2.3 | 40.4 |
| Totals | 7 | 6.6 | 11 | 10.4 | 7 | 11.6 | 38.8 | 4.2 | 42.5 |
| Distribution and finance — | |||||||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 6 | 11.6 | 10 | 5.6 | 7 | 0.5 | 38.9 | 0.9 | 38.1 |
| Storage | 7 | 10.5 | 11 | 1.6 | 8 | 0.2 | 38.7 | 1.8 | 39.5 |
| Finance | 8 | 7.6 | 11 | 7.3 | 8 | 7.8 | 37.1 | 0.3 | 37.0 |
| Insurance | 8 | 3.1 | 10 | 7.2 | 8 | 3.3 | 37.3 | 0.3 | 37.1 |
| Real estate | 8 | 6.2 | 10 | 8.1 | 8 | 6.6 | 38.1 | 0.7 | 36.8 |
| Totals | 7 | 2.6 | 10 | 6.2 | 7 | 3.4 | 38.6 | 0.8 | 37.9 |
| Wool and grain stores (seasonal) | 7 | 6.8 | 12 | 2.1 | 7 | 9.2 | 36.8 | 1.7 | 38.3 |
| Sub-totals (including wool and grain stores) | 7 | 2.7 | 10 | 7.0 | 7 | 3.5 | 38.6 | 0.8 | 37.9 |
| Domestic and personal services — | |||||||||
| Provision of lodging, food, etc. | 6 | 2.4 | 10 | 3.2 | 6 | 3.9 | 36.8 | 1.3 | 33.5 |
| Portrait and photo studios | 6 | 3.6 | 12 | 0.2 | 6 | 4.7 | 38.1 | 0.7 | 36.3 |
| Laundries, cleaning, etc. | 5 | 10.9 | 8 | 7.4 | 6 | 0.3 | 36.7 | 2.0 | 32.0 |
| Barbers, beauty shops, etc. | 4 | 4.1 | 5 | 10.6 | 4 | 4.2 | 38.6 | 0.3 | 37.5 |
| Recreation, sports, etc. | 7 | 9.6 | 10 | 7.4 | 7 | 10.5 | 31.0 | 1.3 | 24.9 |
| Undertaking, etc. | 7 | 6.3 | 11 | 0.8 | 7 | 8.4 | 38.7 | 2.0 | 39.7 |
| Totals | 6 | 4.0 | 9 | 10.7 | 6 | 5.3 | 35.7 | 1.3 | 31.6 |
| Administration and professional — | |||||||||
| Hospitals | 5 | 10.9 | 8 | 0.4 | 6 | 0.3 | 38.7 | 2.3 | 38.9 |
| Medical and allied services | 6 | 8.6 | 15 | 1.0 | 6 | 9.0 | 36.7 | 0.1 | 35.7 |
| Education and instruction | 8 | 9.1 | 16 | 9.5 | 8 | 9.5 | 35.7 | 0.2 | 33.6 |
| Arts, sciences, and religion | 8 | 4.5 | 12 | 9.7 | 8 | 5.0 | 37.9 | 0.4 | 37.1 |
| Government (n.e.i.) | 8 | 6.9 | 10 | 11.3 | 8 | 7.4 | 37.7 | 0.7 | 37.5 |
| Local authorities (n.e.i.) | 7 | 9.5 | 10 | 10.3 | 7 | 11.5 | 38.6 | 2.3 | 39.8 |
| Miscellaneous services and agencies | 6 | 11.6 | 10 | 0.5 | 6 | 11.9 | 36.7 | 0.3 | 35.5 |
| Totals | 7 | 7.5 | 9 | 7.0 | 7 | 8.1 | 37.3 | 1.1 | 36.6 |
| Grand totals, all industries (including seasonal) | 7 | 4.8 | 11 | 0.3 | 7 | 7.6 | 37.9 | 2.6 | 39.2 |
SUMMARY OF INDEX NUMBERS — The following table gives a summary for the years 1950–60 of the movements in index numbers covering both wage rates and standard hours of labour.
WEEKLY WAGE RATES, HOURLY WAGE RATES, AND STANDARD HOURS OF LABOUR: ALL INDUSTRIAL GROUPS COMBINED
| Base: 1954 (= 1000) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Nominal Weekly Wage Rates | Nominal Hourly* Wage Rates: Males, Adult | Standard Weekly Hours of Labour | |||||
| Adults | Juveniles | |||||||
| Males | Females | Combined | Males | Females | Males* | Females | ||
| *Excluding the agricultural and pastoral group. | ||||||||
| 1950 | 729 | 727 | 729 | 732 | 748 | 729 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1951 | 829 | 817 | 828 | 821 | 852 | 828 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1952 | 871 | 852 | 869 | 866 | 880 | 861 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1953 | 929 | 924 | 929 | 932 | 933 | 927 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1954 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1955 | 1035 | 1039 | 1036 | 1032 | 1039 | 1037 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1956 | 1055 | 1056 | 1055 | 1051 | 1061 | 1060 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1957 | 1104 | 1106 | 1105 | 1099 | 1118 | 1111 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1958 | 1116 | 1128 | 1123 | 1134 | 1130 | 1125 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1959 | 1136 | 1146 | 1137 | 1152 | 1151 | 1148 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 1960 | 1193 | 1210 | 1195 | 1221 | 1241 | 1208 | 1000 | 1000 |
PROMOTION OF EMPLOYMENT: National Employment Service — As from 1 April 1946 a National Employment Service was established under the Employment Act 1945 with the principal function of promoting and maintaining full employment in New Zealand. In fact, provision for Government Employment Bureaus had been made as early as 1891. From 1930 to 1936, the period of the operations of the Unemployment Board, the bureaus functioned rather as unemployment registration offices than as placement services. In 1936 the activities of the Unemployment Board were transferred to the Employment Division of the Department of Labour and the bureaus replaced by a State Placement Service, which operated a widely used system of local labour exchanges. From 1942 to the end of March 1946 this became merged in the Industrial Manpower Division of the National Service Department, and, with an augmented staff, carried out the wider and more complex functions of manpower direction and control. In this work the Industrial Manpower Division placed a much greater emphasis on the collection and use of employment and other economic data, on the research and planning aspects of employment, and on the coordination of industrial activities with manpower resources. The National Employment Service was built upon these foundations. After 12 months' activity as a separate Department the National Employment Service was, however, on 1 April 1947, amalgamated with the Department of Labour.
The functions and duties of the Department are set out in the Labour Department Act 1954. On the employment side the duties include: the provision of a complete employment service for the purpose of placing workers in employment, assisting employers to provide employment, helping persons to find better or more suitable employment, and aiding persons who require occupational readjustment or training; the collection and publication of information relating to employment and unemployment; the making of surveys and forecasts of the classes of employment required or available; the promotion of voluntary placing of suitable persons in such employment; and in general the promotion and maintenance of full employment. In particular the Department may operate hostels for workers, provide a home-aid service, and arrange for the selection, transport, and accommodation of immigrants.
Accordingly the Department seeks to maintain a policy of full employment at the highest productive level, operates 24 district employment offices, provides through a home-aid service domestic help for families in urgent circumstances, and administers employment schemes, subsidised where necessary, for those unfit to compete in the ordinary labour market.
The 15 camps and hostels operated by or for the Department at 31 March 1960 — comprising industrial workers' camps and hostels, immigration hostels, Public Service hostels, miners' hostels, and Maori youth hostels — provided accommodation for 1,803 workers.
Immigration matters, including the maintenance of immigration hostels, are, as already indicated, handled by the Department. Reference to assisted immigration has been made on pages 65–66 of this volume. To advise the Minister of Immigration on immigration matters and to aid the Department in the implementing of the immigration policy, an Immigration Advisory Council was established in April 1947 and continues to operate under the Act of 1954. Throughout the country there are also immigration welfare committees whose function is to coordinate welfare activities in respect of new settlers.
Of recent years special attention has been directed to the problem of Maori employment. Outstanding features of the Maori population are its rate of growth and the fact that the Maori people are largely resident in localities remote from the main centres of industrial activity. Practical measures for ensuring the continuing absorption of the Maori race into full employment have included the fostering of Maori apprenticeships and the establishment of Maori youth hostels.
In the post-war years the labour situation was characterised by overfull employment and a high number of vacancies in industry. The employment position is still one of great buoyancy with the demand for labour exceeding the supply and practically no unemployment.
One employment-promotion measure which has been in operation for some years is Scheme 13, under which 49 men were employed at 31 March 1961, compared with 57 on 31 March 1960. Most of these men are fit for light work only and are located in districts where employment opportunities are limited. Everything possible is done to place them in suitable private employment when the opportunity arises. They are allocated to local authorities and their wages are subsidised to an extent which brings their earnings up to the award rate for the type of work performed.
Information concerning the measures in operation for the rehabilitation of ex-servicemen will be found in Section 9B.
Vocational Guidance — Since 1938 full responsibility for the work of vocational guidance of pupils at post-primary schools, which for some years previously had been carried on almost entirely by voluntary organisations, has been taken by the Department of Education. A youth centre was established in each of the four main centres, and the work of guidance and placement was undertaken jointly by officers of the Education and National Service Departments. The Department of Education assumed full control of these youth centres (now called Vocational Guidance Centres) in 1943. At present six centres, including Lower Hutt and Hamilton, are in operation.
The numbers of those enrolled who were placed in employment during each of the last eight calendar years were as follows.
| Year Ended 31 December | Number Placed by Centres | Number Self-placed | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Number replaced in employment | |||
| 1953 | 1,409 | 525 | 1,934 |
| 1954 | 1,282 | 403 | 1,685 |
| 1955 | 1,203 | 520 | 1,723 |
| 1956 | 1,252 | 499 | 1,751 |
| 1957 | 1,171 | 461 | 1,632 |
| 1958 | 1,478 | 177* | 1,655 |
| 1959 | 1,372 | 151* | 1,523 |
| 1960 | 1,238 | 108* | 1,346 |
Apprenticeships — The Apprentices Act 1948 provides for orders governing apprenticeships to be made by the Court of Arbitration, which consists of a Judge, a workers' member, and an employers' member. Orders are made on the recommendations of New Zealand Apprenticeship Committees, which consist of three (or four) representatives of employers, three (or four) representatives of workers, a person conversant with technical education, and the Commissioner of Apprenticeship, who is ex officio chairman of each committee. The New Zealand Committees are in effect policy-making committees. There are 30 committees, which normally meet once or twice a year.
Day-to-day administration of the Apprentices Act and the apprenticeship orders is carried on by local apprenticeship committees, of which there are 206. They consist of three representatives of employers, three representatives of workers, a person conversant with technical education, and the District Commissioner of Apprenticeship, who is ex officio chairman of all committees for the district for which he is appointed. District Commissioners delegate chairmanship to other officers of the Department of Labour when necessary.
The methods of training followed are on the lines of the traditional apprenticeship system. The apprentice learns by doing tasks under supervision. Provision is made in a number of apprenticeship orders for a specific list of operations and skills to be taught apprentices by their employers. Both employers and apprentices are thus helped to define the scope of training, and apprenticeship committees, when called on to do so, are enabled to judge whether or not training is adequate.
As no employer may engage an apprentice without the prior consent of the appropriate local committee, the facilities for training are known to the committee in each case. When an employer who has not previously had an apprentice applies for permission to engage one, arrangements are made for an inspection of his workshop by two members of the local committee. On their report the full committee makes the appropriate decision. Every apprentice has a contract of apprenticeship, which is registered by the District Commissioner.
Local committees deal with complaints from apprentices and employers, with applications to transfer apprentices to other employers, and applications to discharge apprentices for misconduct. Their decisions, which are of a semi-judicial nature, are subject to review by way of appeal to the Court of Arbitration.
In the major industries there are provisions in apprenticeship orders for the attendance of apprentices at technical classes, both during working hours and in the evening. In the 40-hour week four hours are spent at day classes, with usually an equivalent amount of time at evening classes. In some industries technical training is concentrated into an annual course of three or four weeks' duration. The classes are operated by technical and other post-primary schools, as an adjunct to the post-primary education provided for school pupils.
Although technical schools are semi-autonomous bodies, the general policy regarding apprentice education is determined by the Department of Education. That Department itself operates a Technical Correspondence School, which provides courses of instruction for those apprentices who live too far from any school to allow them to attend evening classes.
A statutory body, the New Zealand Trades Certification Board, conducts examinations for apprentices (see Section 7 — Education). The examinations are voluntary and, except in the electrical trade and in plumbing, no examination test is required for the practice of a trade. There is very close liaison between New Zealand Apprenticeship Committees and the Board, the Commissioner of Apprenticeship being ex officio a member of the Board. The Commissioner is also ex officio a member of the New Zealand Council for Technical Education (see p. 221).
The number of apprenticeship contracts registered during the year, completed during the year, and in force at the end of the year are indicated in the following table for each of the years ended 31 March 1959 and 31 March 1960.
| Trade | Apprenticeship Contracts | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered During Year Ended 31 March | Completed During Year Ended 31 March | In Force at 31 March | ||||
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | |
| Aircraft | 42 | 30 | 26 | 29 | 188 | 185 |
| Baking | 54 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 130 | 128 |
| Boilermaking | 51 | 66 | 17 | 19 | 159 | 178 |
| Bricklaying | 43 | 58 | 15 | 38 | 171 | 177 |
| Carpentry | 1,090 | 1,271 | 887 | 1,056 | 4,912 | 4,914 |
| Clothing | 47 | 60 | 22 | 32 | 185 | 188 |
| Coachbuilding | 275 | 255 | 155 | 132 | 1,008 | 1,039 |
| Coopering | — | — | 1 | — | — | — |
| Dentistry | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 24 | 27 |
| Electrical | 299 | 284 | 234 | 247 | 1,296 | 1,276 |
| Engineering | 406 | 386 | 246 | 295 | 1,495 | 1,510 |
| Footwear making and repairing | 26 | 14 | 11 | 7 | 67 | 67 |
| Footwear manufacturing | 72 | 56 | 38 | 30 | 209 | 206 |
| Furniture | 215 | 218 | 155 | 177 | 889 | 849 |
| Gardening | 18 | 29 | 14 | 10 | 74 | 86 |
| Hairdressing | 35 | 34 | 20 | 23 | 125 | 124 |
| Jewellery | 30 | 33 | 28 | 26 | 138 | 131 |
| Lead burning | 1 | — | 1 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
| Masonry | 3 | 2 | 1 | — | 5 | 7 |
| Motor trades | 788 | 868 | 563 | 626 | 3,688 | 3,683 |
| Moulding | 19 | 14 | 6 | 33 | 35 | |
| Painting | 157 | 188 | 85 | 96 | 567 | 598 |
| Photo-engraving | 34 | 41 | 18 | 19 | 111 | 122 |
| Piano repairing and tuning | 7 | 8 | — | 3 | 13 | 12 |
| Plastering | 90 | 94 | 54 | 48 | 300 | 302 |
| Plumbing | 201 | 213 | 176 | 184 | 1,150 | 1,130 |
| Printing | 219 | 238 | 102 | 139 | 806 | 872 |
| Radio | 52 | 64 | 27 | 36 | 206 | 219 |
| Refrigeration servicing | 18 | 26 | 20 | 32 | 109 | 97 |
| Saddlery, leather, and canvas goods | 12 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 46 | 39 |
| Sheet-metal working | 66 | 50 | 23 | 32 | 189 | 188 |
| Shipbuilding | 22 | 22 | 14 | 14 | 96 | 97 |
| Terrazzo work | — | 2 | — | — | 1 | 3 |
| Timber industry | 15 | 20 | 1 | 5 | 37 | 41 |
| Others | 38 | 50 | 11 | 20 | 138 | 147 |
| Total | 4,449 | 4,744 | 3,009 | 3,412 | 18,570 | 18,681 |
DISTRIBUTION OF LABOUR FORCE — The table which follows shows the estimated distribution of the labour force (including Maoris) by broad industrial groups in April of each year from 1950 to 1960. The figures include estimates for industries (e.g., farming) and persons (in “one-man” businesses) not covered by the half-yearly surveys.
The figures have been adjusted into line with the 1956 census data.
| Year | Industry Group | Armed Forces | Unemployed | Totals, Labour Force | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Industry | Manufacturing Industry | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Building and Construction | Transport and Communication | Distribution and Finance | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Totals | ||||
| thousand | ||||||||||||
| Males | ||||||||||||
| 1950 | 136.1 | 139.1 | 9.4 | 53.2 | 67.5 | 79.7 | 18.3 | 50.1 | 553.4 | 8.2 | – | 561.6 |
| 1951 | 135.9 | 141.2 | 9.7 | 52.8 | 66.2 | 81.4 | 18.3 | 50.8 | 556.3 | 10.0 | – | 566.3 |
| 1952 | 134.8 | 142.4 | 9.8 | 57.2 | 68.9 | 83.0 | 18.2 | 51.3 | 565.6 | 10.0 | – | 575.6 |
| 1953 | 134.3 | 144.9 | 10.8 | 62.7 | 68.9 | 84.3 | 18.6 | 52.5 | 577.0 | 11.1 | – | 588.1 |
| 1954 | 133.9 | 149.1 | 10.8 | 68.0 | 69.1 | 87.0 | 19.2 | 53.7 | 590.8 | 10.9 | 0.1 | 601.8 |
| 1955 | 133.4 | 151.9 | 11.0 | 72.2 | 69.0 | 89.0 | 19.1 | 53.9 | 599.5 | 9.7 | – | 609.2 |
| 1956 | 133.5 | 154.1 | 11.1 | 74.4 | 70.9 | 91.3 | 19.1 | 56.1 | 610.5 | 8.9 | 0.1 | 619.5 |
| 1957 | 134.0 | 156.3 | 11.3 | 74.9 | 72.7 | 94.5 | 19.8 | 58.4 | 621.9 | 9.2 | 0.4 | 631.5 |
| 1958 | 134.1 | 160.9 | 11.4 | 77.6 | 74.3 | 96.6 | 20.2 | 61.2 | 636.3 | 8.9 | 0.4 | 645.6 |
| 1959 | 133.8 | 167.3 | 11.7 | 79.8 | 74.3 | 96.8 | 20.0 | 63.6 | 647.3 | 8.7 | 1.1 | 657.1 |
| 1960 | 133.4 | 171.6 | 11.8 | 81.5 | 74.5 | 98.7 | 20.3 | 66.0 | 657.8 | 10.0 | 0.6 | 668.4 |
| Females | ||||||||||||
| 1950 | 12.2 | 43.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 7.3 | 34.8 | 26.3 | 44.3 | 169.6 | 0.7 | – | 170.3 |
| 1951 | 12.2 | 44.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 7.6 | 36.4 | 25.8 | 45.2 | 173.3 | 0.8 | – | 174.1 |
| 1952 | 11.9 | 43.9 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 8.2 | 37.9 | 25.0 | 46.6 | 175.2 | 0.8 | – | 176.0 |
| 1953 | 11.5 | 42.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 8.5 | 39.3 | 25.4 | 48.7 | 177.6 | 1.0 | – | 178.6 |
| 1954 | 11.1 | 45.2 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 8.6 | 41.7 | 25.1 | 50.7 | 184.4 | 0.8 | – | 185.2 |
| 1955 | 11.2 | 47.0 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 8.8 | 44.2 | 24.8 | 52.2 | 190.3 | 0.8 | – | 191.1 |
| 1956 | 10.8 | 46.1 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 9.6 | 46.3 | 24.6 | 54.1 | 193.7 | 0.7 | – | 194.4 |
| 1957 | 10.9 | 46.6 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 10.0 | 47.7 | 25.0 | 56.6 | 199.0 | 0.7 | – | 199.7 |
| 1958 | 10.9 | 49.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 10.2 | 48.7 | 25.2 | 57.7 | 204.3 | 0.6 | – | 204.9 |
| 1959 | 10.9 | 50.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 10.3 | 48.8 | 25.0 | 60.2 | 208.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 208.7 |
| 1960 | 10.9 | 51.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 10.1 | 49.4 | 25.4 | 61.9 | 211.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 212.1 |
| Totals | ||||||||||||
| 1950 | 148.3 | 182.2 | 10.1 | 54.1 | 74.8 | 114.5 | 44.6 | 94.4 | 723.0 | 8.9 | – | 731.9 |
| 1951 | 148.1 | 185.6 | 10.4 | 53.8 | 73.8 | 117.8 | 44.1 | 96.0 | 729.6 | 10.8 | – | 740.4 |
| 1952 | 146.7 | 186.3 | 10.5 | 58.2 | 77.1 | 120.9 | 43.2 | 97.9 | 740.8 | 10.8 | – | 751.6 |
| 1953 | 145.8 | 187.2 | 11.6 | 63.8 | 77.4 | 123.6 | 44.0 | 101.2 | 754.6 | 12.1 | – | 766.7 |
| 1954 | 145.0 | 194.3 | 11.6 | 69.2 | 77.7 | 128.7 | 44.3 | 104.4 | 775.2 | 11.7 | 0.1 | 787.0 |
| 1955 | 144.6 | 198.9 | 11.8 | 73.5 | 77.8 | 133.2 | 43.9 | 106.1 | 789.8 | 10.5 | – | 800.3 |
| 1956 | 144.3 | 200.2 | 11.9 | 75.8 | 80.5 | 137.6 | 43.7 | 110.2 | 804.2 | 9.6 | 0.1 | 813.9 |
| 1957 | 144.9 | 202.9 | 12.1 | 76.3 | 82.7 | 142.2 | 44.8 | 115.0 | 820.9 | 9.9 | 0.4 | 831.2 |
| 1958 | 145.0 | 210.2 | 12.2 | 79.1 | 84.5 | 145.3 | 45.4 | 118.9 | 840.6 | 9.5 | 0.4 | 850.5 |
| 1959 | 144.7 | 217.7 | 12.6 | 81.3 | 84.6 | 145.6 | 45.0 | 123.8 | 855.3 | 9.3 | 1.2 | 865.8 |
| 1960 | 144.3 | 223.1 | 12.6 | 83.0 | 84.6 | 148.1 | 45.7 | 127.9 | 869.3 | 10.5 | 0.7 | 880.5 |
LABOUR FORCE PROJECTIONS — Accompanying the expected future growth of New Zealand's population, as shown by the population projections set out on pages 45–47, will be a substantial rise in the size of the labour force. Projections of the labour force based on these population projections have been made by the Department of Statistics and are displayed in the next table. The projections cover the period 1962–80 and assume that 1956 census labour force participation rates, adjusted to April 1960, for each quinquennial age group in the three population categories, males, not-married females, and married females, will continue. Reference should be made to the section on population projections for comment on the meaning and limitation of statistical projections.
Labour force projections for each year from 1962 to 1980 are set out in the following table.
| Year | Projected Labour Force Assuming Net Inward Migration of | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 per Annum | 10,000 per Annum | |||||
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| thousand | ||||||
| 1962 | 692 | 221 | 913 | 695 | 222 | 917 |
| 1963 | 704 | 227 | 931 | 710 | 228 | 938 |
| 1964 | 718 | 232 | 950 | 725 | 234 | 959 |
| 1965 | 731 | 238 | 969 | 741 | 240 | 981 |
| 1966 | 745 | 243 | 988 | 757 | 245 | 1,002 |
| 1967 | 759 | 248 | 1,007 | 773 | 250 | 1,023 |
| 1968 | 773 | 253 | 1,026 | 789 | 255 | 1,044 |
| 1969 | 787 | 257 | 1,044 | 805 | 260 | 1,065 |
| 1970 | 801 | 262 | 1,063 | 822 | 266 | 1,088 |
| 1971 | 815 | 266 | 1,081 | 839 | 271 | 1,110 |
| 1972 | 830 | 270 | 1,100 | 856 | 276 | 1,132 |
| 1973 | 845 | 274 | 1,119 | 874 | 281 | 1,155 |
| 1974 | 861 | 278 | 1,139 | 892 | 286 | 1,178 |
| 1975 | 877 | 282 | 1,159 | 910 | 290 | 1,200 |
| 1976 | 893 | 286 | 1,179 | 928 | 295 | 1,223 |
| 1977 | 909 | 290 | 1,199 | 946 | 300 | 1,246 |
| 1978 | 925 | 294 | 1,219 | 965 | 305 | 1,270 |
| 1979 | 942 | 298 | 1,240 | 985 | 309 | 1,294 |
| 1980 | 959 | 303 | 1,262 | 1,005 | 314 | 1,319 |
STATISTICS OF EMPLOYMENT: Half-yearly Surveys — Commencing in 1946 the Department of Labour has carried out at half-yearly intervals a general survey of employment in New Zealand. These surveys are conducted by means of inquiries sent out to employers of labour, the results being published in the Labour and Employment Gazette. Returns are required from all establishments in which at least two persons (including working proprietors) are engaged. Government and local authority employment is included. Each return covers six consecutive months, the initial survey (apart from a pilot survey taken for April 1946) relating to the period May to October 1946. Particulars of working proprietors, number of establishments, reported vacancies, and hours of work and earnings are available at half-yearly intervals only. Employers in farming, hunting, trapping, fishing, waterfront work, and private domestic service are not required to submit half-yearly returns. The following tables, which are based on these surveys, have been extracted from the Labour and Employment Gazette, and show the figures for April of each year from 1950 to 1960 and for October 1960. Separate tables are given for males and females (except for part-time employees by industrial groups), working proprietors are in general distinguished from employees, and the numbers of vacancies reported and of establishments covered are appended.
Since the introduction of half-yearly employment surveys there have been several changes in the industrial classification of units to bring the New Zealand classification into line with the United Nations Standard Industrial Classification. In respect of working proprietors and employees the effects of the various reclassifications have been carried back to 1946, and the figures in the following tables are on the revised basis.
Since April 1953 the industry of threshing and chaff cutting has been treated as a branch of farming and hence omitted from the inquiry, and the following tables exclude threshing and chaff cutting throughout.
A summary of the tables referred to is first provided.
| Full-time Employees and Working Proprietors | Vacancies | Part-time Workers | Half-yearly Percentage Rate of Labour Turnover* | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | |
| *The relationship between the number of terminations over the previous half-year and the average number of employees during the same period. | |||||||||||
| April— | Per Cent | Per Cent | |||||||||
| 1950 | 355,864 | 131,531 | 487,395 | 20,801 | 13,080 | 33,881 | 5,225 | 8,766 | 13,991 | 19 | 30 |
| 1951 | 356,233 | 134,917 | 491,150 | 21,404 | 11,392 | 32,796 | 6,178 | 10,006 | 16,184 | 20 | 32 |
| 1952 | 366,344 | 136,668 | 503,012 | 21,607 | 8,510 | 30,117 | 6,542 | 9,911 | 16,453 | 21 | 32 |
| 1953 | 376,743 | 138,282 | 515,025 | 14,197 | 6,217 | 20,414 | 7,204 | 10,017 | 17,221 | 18 | 28 |
| 1954 | 390,320 | 144,807 | 535,127 | 15,233 | 7,496 | 22,729 | 7,638 | 11,539 | 19,177 | 19 | 30 |
| 1955 | 399,992 | 150,784 | 550,776 | 18,983 | 8,545 | 27,528 | 9,048 | 13,058 | 22,106 | 21 | 32 |
| 1956 | 412,676 | 154,915 | 567,591 | 15,951 | 6,534 | 22,485 | 9,665 | 14,669 | 24,334 | 20 | 32 |
| 1957 | 423,720 | 159,606 | 583,326 | 11,983 | 5,562 | 17,545 | 11,221 | 15,408 | 26,629 | 19 | 31 |
| 1958 | 436,062 | 164,498 | 600,560 | 10,669 | 5,280 | 15,949 | 12,397 | 17,437 | 29,834 | 18 | 32 |
| 1959 | 447,003 | 167,802 | 614,805 | 8,490 | 4,026 | 12,516 | 12,855 | 18,401 | 31,256 | 18 | 32 |
| 1960 | 456,816 | 171,605 | 628,421 | 9,910 | 6,004 | 15,914 | 14,139 | 20,290 | 34,429 | 19 | 32 |
| October — | |||||||||||
| 1960 | 454,979 | 174,096 | 629,075 | 14,056 | 8,275 | 22,331 | 15,145 | 23,441 | 38,586 | 18 | 30 |
Employment in industry on 15 April of the years 1950–60, and on 15 October 1960, is given in the following table. No industrial dissection of part-time employment is available prior to April 1957.
| Primary Industry (Other Than Farming, Fishing, and Hunting) | Manufacturing Industry | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Building and Construction | Transport and Communication (Other Than Waterfront Work) | Distribution and Finance | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Totals, All Industries Covered | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Not included in any other figures in this table. | |||||||||
| Male Employees | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 11,529 | 120,437 | 9,213 | 35,857 | 49,241 | 57,574 | 10,739 | 37,941 | 332,531 |
| 1951 | 11,243 | 121,028 | 9,508 | 35,121 | 47,883 | 59,256 | 10,801 | 38,595 | 333,435 |
| 1952 | 10,963 | 125,098 | 9,619 | 38,011 | 49,422 | 60,745 | 10,760 | 39,186 | 343,804 |
| 1953 | 10,619 | 127,641 | 10,372 | 41,306 | 50,711 | 61,942 | 11,058 | 40,523 | 354,172 |
| 1954 | 10,428 | 131,182 | 10,810 | 44,579 | 50,596 | 63,303 | 11,237 | 41,066 | 363,201 |
| 1955 | 10,234 | 134,655 | 10,955 | 47,590 | 50,448 | 65,318 | 11,223 | 41,439 | 371,862 |
| 1956 | 10,339 | 137,805 | 11,022 | 49,197 | 51,755 | 67,785 | 11,251 | 43,957 | 383,111 |
| 1957 | 10,705 | 139,011 | 11,303 | 49,331 | 53,746 | 69,749 | 11,496 | 45,887 | 391,228 |
| 1958 | 10,754 | 143,061 | 11,415 | 51,188 | 54,846 | 71,104 | 11,666 | 48,373 | 402,407 |
| 1959 | 10,617 | 148,923 | 11,727 | 52,718 | 54,752 | 71,436 | 11,474 | 50,262 | 411,909 |
| 1960 | 10,637 | 152,939 | 11,784 | 53,743 | 55,188 | 72,543 | 11,726 | 52,216 | 420,776 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 10,738 | 149,164 | 11,834 | 54,046 | 55,232 | 73,214 | 11,747 | 52,526 | 418,501 |
| Male Working Proprietors | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 359 | 7,830 | 7 | 3,748 | 1,589 | 6,763 | 2,623 | 414 | 23,333 |
| 1951 | 330 | 7,349 | 7 | 3,922 | 1,535 | 6,697 | 2,562 | 396 | 22,798 |
| 1952 | 348 | 7,174 | 8 | 4,025 | 1,505 | 6,622 | 2,445 | 413 | 22,540 |
| 1953 | 330 | 7,269 | 4 | 3,971 | 1,419 | 6,676 | 2,535 | 367 | 22,571 |
| 1954 | 350 | 8,300 | 6 | 5,032 | 1,647 | 8,313 | 2,840 | 631 | 27,119 |
| 1955 | 304 | 8,489 | 3 | 5,465 | 1,630 | 8,810 | 2,936 | 491 | 28,130 |
| 1956 | 351 | 8,821 | 9 | 6,038 | 1,756 | 9,124 | 2,970 | 496 | 29,565 |
| 1957 | 456 | 9,776 | 9 | 6,344 | 1,969 | 10,105 | 3,260 | 573 | 32,492 |
| 1958 | 443 | 10,093 | 8 | 6,482 | 2,084 | 10,634 | 3,420 | 491 | 33,655 |
| 1959 | 483 | 10,263 | 8 | 7,049 | 2,267 | 10,972 | 3,515 | 537 | 35,094 |
| 1960 | 481 | 10,396 | 11 | 7,317 | 2,252 | 11,418 | 3,617 | 548 | 36,040 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 455 | 10,475 | 9 | 7,152 | 2,295 | 11,790 | 3,683 | 619 | 36,478 |
| Female Employees | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 212 | 39,343 | 658 | 847 | 6,737 | 30,101 | 13,858 | 35,358 | 127,114 |
| 1951 | 185 | 40,631 | 677 | 898 | 6,996 | 31,377 | 13,437 | 36,222 | 130,423 |
| 1952 | 206 | 40,120 | 695 | 909 | 7,464 | 32,119 | 13,224 | 37,414 | 132,151 |
| 1953 | 215 | 38,654 | 716 | 964 | 7,728 | 32,889 | 13,414 | 39,128 | 133,708 |
| 1954 | 205 | 41,151 | 774 | 1,048 | 7,810 | 34,211 | 13,546 | 40,496 | 139,241 |
| 1955 | 226 | 43,080 | 788 | 1,127 | 7,989 | 36,140 | 13,628 | 41,733 | 144,711 |
| 1956 | 237 | 42,353 | 809 | 1,203 | 8,575 | 37,887 | 13,966 | 43,571 | 148,601 |
| 1957 | 257 | 42,764 | 792 | 1,194 | 8,985 | 38,747 | 14,159 | 45,673 | 152,571 |
| 1958 | 295 | 45,375 | 819 | 1,257 | 9,233 | 39,390 | 14,258 | 46,599 | 157,226 |
| 1959 | 288 | 46,337 | 834 | 1,310 | 9,279 | 39,182 | 14,020 | 48,709 | 159,959 |
| 1960 | 292 | 47,265 | 839 | 1,283 | 9,332 | 39,850 | 14,296 | 50,195 | 163,352 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 293 | 48,691 | 843 | 1,282 | 9,304 | 40,448 | 14,291 | 50,394 | 165,546 |
| Female Working Proprietors | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 2 | 1,127 | — | — | 31 | 1,477 | 1,573 | 207 | 4,417 |
| 1951 | 3 | 1,129 | — | — | 38 | 1,554 | 1,579 | 191 | 4,494 |
| 1952 | 3 | 1,087 | — | 1 | 45 | 1,706 | 1,510 | 165 | 4,517 |
| 1953 | 1 | 1,058 | — | 1 | 34 | 1,744 | 1,577 | 159 | 4,574 |
| 1954 | 1 | 1,192 | — | 4 | 39 | 2,429 | 1,719 | 182 | 5,566 |
| 1955 | — | 1,204 | — | 3 | 35 | 2,805 | 1,825 | 201 | 6,073 |
| 1956 | — | 1,210 | — | 1 | 49 | 2,979 | 1,901 | 174 | 6,314 |
| 1957 | 2 | 1,278 | — | — | 70 | 3,426 | 2,070 | 189 | 7,035 |
| 1958 | 2 | 1,290 | — | — | 84 | 3,593 | 2,114 | 189 | 7,272 |
| 1959 | 2 | 1,369 | — | — | 99 | 3,900 | 2,264 | 209 | 7,843 |
| 1960 | 8 | 1,378 | — | — | 107 | 4,205 | 2,345 | 210 | 8,253 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 5 | 1,418 | — | — | 116 | 4,374 | 2,417 | 220 | 8,550 |
| Part-time Employees — Males and Females Combined* | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1957 | 81 | 5,111 | 103 | 1 | 1,152 | 6,031 | 7,416 | 6,734 | 26,629 |
| 1958 | 82 | 5,346 | 121 | — | 1,160 | 6,691 | 8,457 | 7,977 | 29,834 |
| 1959 | 81 | 5,484 | 110 | — | 1,161 | 7,192 | 9,200 | 8,028 | 31,256 |
| 1960 | 87 | 5,999 | 105 | — | 1,245 | 8,086 | 9,784 | 9,123 | 34,429 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 68 | 7,314 | 132 | — | 1,320 | 9,142 | 10,362 | 10,248 | 38,586 |
A dissection of the manufacturing industry column shown in the preceding table is now given over the same period.
| Seasonal Manufacturing | Food, Drink, and Tobacco (Other Than Seasonal) | Textiles, Clothing, and Leather | Building Materials and Furnishings | Engineering and Metal Working | Miscellaneous Manufacturing | Total Manufacturing Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Not included in any other figures in this table. | |||||||
| Male Employees | |||||||
| April — | |||||||
| 1950 | 19,012 | 8,976 | 12,882 | 22,169 | 41,953 | 15,445 | 120,437 |
| 1951 | 17,808 | 8,868 | 13,044 | 22,618 | 42,773 | 15,917 | 121,028 |
| 1952 | 20,237 | 8,905 | 12,487 | 23,411 | 44,403 | 15,655 | 125,098 |
| 1953 | 21,286 | 9,010 | 12,063 | 23,421 | 46,061 | 15,800 | 127,641 |
| 1954 | 20,678 | 9,070 | 12,446 | 24,249 | 48,021 | 16,718 | 131,182 |
| 1955 | 20,511 | 8,884 | 12,277 | 24,580 | 50,782 | 17,621 | 134,655 |
| 1956 | 21,548 | 8,897 | 11,866 | 24,993 | 51,347 | 19,154 | 137,805 |
| 1957 | 21,998 | 9,068 | 11,588 | 24,310 | 52,313 | 19,734 | 139,011 |
| 1958 | 23,144 | 9,111 | 12,100 | 24,546 | 53,701 | 20,459 | 143,061 |
| 1959 | 25,433 | 9,210 | 12,659 | 25,792 | 54,442 | 21,387 | 148,923 |
| 1960 | 25,801 | 9,265 | 12,739 | 26,305 | 56,313 | 22,516 | 152,939 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 13,214 | 9,494 | 13,297 | 27,032 | 57,930 | 23,197 | 149,164 |
| Male Working Proprietors | |||||||
| April — | |||||||
| 1950 | 62 | 1,157 | 1,011 | 1,616 | 3,162 | 822 | 7,830 |
| 1951 | 57 | 1,077 | 958 | 1,476 | 3,002 | 779 | 7,349 |
| 1952 | 60 | 960 | 914 | 1,466 | 3,027 | 747 | 7,174 |
| 1953 | 52 | 958 | 870 | 1,547 | 3,116 | 726 | 7,269 |
| 1954 | 66 | 1,035 | 981 | 1,716 | 3,661 | 841 | 8,300 |
| 1955 | 62 | 987 | 997 | 1,797 | 3,764 | 882 | 8,489 |
| 1956 | 64 | 1,001 | 1,027 | 1,891 | 3,922 | 916 | 8,821 |
| 1957 | 83 | 1,049 | 1,159 | 2,053 | 4,410 | 1,022 | 9,776 |
| 1958 | 99 | 1,053 | 1,178 | 2,066 | 4,653 | 1,044 | 10,093 |
| 1959 | 95 | 1,051 | 1,200 | 2,028 | 4,863 | 1,026 | 10,263 |
| 1960 | 95 | 1,040 | 1,197 | 2,010 | 4,939 | 1,115 | 10,396 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 96 | 1,048 | 1,187 | 2,031 | 5,015 | 1,098 | 10,475 |
| Female Employees | |||||||
| April — | |||||||
| 1950 | 1,477 | 4,897 | 22,309 | 1,154 | 3,684 | 5,822 | 39,343 |
| 1951 | 1,555 | 4,530 | 23,573 | 1,203 | 3,871 | 5,899 | 40,631 |
| 1952 | 1,636 | 4,580 | 22,528 | 1,276 | 4,225 | 5,875 | 40,120 |
| 1953 | 1,823 | 4,805 | 20,839 | 1,227 | 4,311 | 5,649 | 38,654 |
| 1954 | 1,777 | 4,763 | 22,662 | 1,321 | 4,614 | 6,014 | 41,151 |
| 1955 | 1,661 | 4,910 | 23,539 | 1,444 | 5,177 | 6,349 | 43,080 |
| 1956 | 1,748 | 4,764 | 22,763 | 1,506 | 5,059 | 6,513 | 42,353 |
| 1957 | 1,960 | 4,976 | 22,546 | 1,453 | 5,127 | 6,702 | 42,764 |
| 1958 | 2,179 | 5,064 | 24,079 | 1,531 | 5,420 | 7,102 | 45,375 |
| 1959 | 2,179 | 4,879 | 24,470 | 1,708 | 5,527 | 7,574 | 46,337 |
| 1960 | 2,256 | 5,028 | 24,015 | 1,867 | 5,978 | 8,121 | 47,265 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 1,915 | 5,211 | 24,767 | 1,928 | 6,460 | 8,410 | 48,691 |
| Female Working Proprietors | |||||||
| April — | |||||||
| 1950 | 5 | 461 | 528 | 16 | 41 | 76 | 1,127 |
| 1951 | 4 | 452 | 533 | 13 | 60 | 67 | 1,129 |
| 1952 | 4 | 411 | 535 | 19 | 50 | 68 | 1,087 |
| 1953 | 4 | 437 | 498 | 20 | 39 | 60 | 1,058 |
| 1954 | 7 | 455 | 556 | 25 | 73 | 76 | 1,192 |
| 1955 | 8 | 460 | 543 | 31 | 74 | 88 | 1,204 |
| 1956 | 7 | 451 | 555 | 27 | 78 | 92 | 1,210 |
| 1957 | 9 | 452 | 552 | 36 | 124 | 105 | 1,278 |
| 1958 | 9 | 451 | 540 | 37 | 144 | 109 | 1,290 |
| 1959 | 5 | 467 | 556 | 57 | 177 | 107 | 1,369 |
| 1960 | 5 | 457 | 531 | 46 | 215 | 124 | 1,378 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 4 | 473 | 529 | 56 | 229 | 127 | 1,418 |
| Part-time Employees—Males and Females Combined* | |||||||
| April — | |||||||
| 1957 | 171 | 919 | 1,439 | 493 | 1,102 | 987 | 5,111 |
| 1958 | 146 | 939 | 1,440 | 538 | 1,249 | 1,034 | 5,346 |
| 1959 | 160 | 952 | 1,447 | 544 | 1,319 | 1,062 | 5,484 |
| 1960 | 152 | 1,026 | 1,555 | 610 | 1,436 | 1,220 | 5,999 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 163 | 1,358 | 1,938 | 666 | 1,690 | 1,499 | 7,314 |
The following table shows the number of vacancies reported by employers in the half-yearly surveys. Figures on the basis of the revised industrial classification are not available for the years prior to 1953.
| Primary Industry (Other Than Farming, Fishing, and Hunting) | Manufacturing Industry* | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Building and Construction | Transport and Communication (Other Than Waterfront Work) | Distribution and Finance | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Totals, All Industries Covered* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excluding seasonal manufacturing. | |||||||||
| Males | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 643 | 8,549 | 482 | 2,739 | 4,016 | 2,237 | 318 | 1,87 | 20,801 |
| 1951 | 579 | 8,430 | 472 | 2,609 | 5,126 | 2,024 | 312 | 1,852 | 21,404 |
| 1952 | 806 | 7,857 | 562 | 3,021 | 5,259 | 2,085 | 285 | 1,732 | 21,607 |
| (Revised basis) | |||||||||
| 1953 | 333 | 5,080 | 351 | 1,904 | 3,803 | 1,417 | 173 | 1,136 | 14,197 |
| 1954 | 202 | 5,302 | 384 | 2,490 | 3,781 | 1,692 | 155 | 1,227 | 15,233 |
| 1955 | 409 | 6,867 | 388 | 2,971 | 4,249 | 2,231 | 272 | 1,596 | 18,983 |
| 1956 | 303 | 5,307 | 530 | 2,323 | 3,920 | 1,777 | 259 | 1,532 | 15,951 |
| 1957 | 133 | 4,018 | 316 | 1,528 | 3,204 | 1,399 | 224 | 1,161 | 11,983 |
| 1958 | 109 | 3,755 | 275 | 1,753 | 2,390 | 1,081 | 184 | 1,122 | 10,669 |
| 1959 | 53 | 2,955 | 153 | 957 | 2,221 | 824 | 149 | 1,178 | 8,490 |
| 1960 | 100 | 3,368 | 187 | 1,958 | 1,410 | 1,306 | 197 | 1,384 | 9,910 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 168 | 4,961 | 324 | 2,774 | 1,961 | 1,749 | 350 | 1,769 | 14,056 |
| Females | |||||||||
| April — | |||||||||
| 1950 | 15 | 7,894 | 31 | — | 243 | 1,668 | 721 | 2,508 | 13,080 |
| 1951 | 27 | 6,492 | 41 | — | 409 | 1,651 | 568 | 2,204 | 11,392 |
| 1952 | 24 | 3,824 | 35 | — | 416 | 1,511 | 446 | 2,254 | 8,510 |
| (Revised basis) | |||||||||
| 1953 | 11 | 2,728 | 59 | 1 | 323 | 886 | 289 | 1,920 | 6,217 |
| 1954 | 8 | 3,734 | 13 | — | 354 | 1,154 | 308 | 1,925 | 7,496 |
| 1955 | 11 | 4,160 | 24 | 1 | 337 | 1,496 | 463 | 2,053 | 8,545 |
| 1956 | 7 | 2,680 | 27 | 1 | 228 | 1,170 | 393 | 2,028 | 6,534 |
| 1957 | 12 | 2,204 | 21 | — | 184 | 979 | 417 | 1,745 | 5,562 |
| 1958 | 5 | ,372 | 10 | — | 181 | 854 | 371 | 1,487 | 5,280 |
| 1959 | 2 | 1,404 | 5 | — | 177 | 695 | 279 | 1,464 | 4,026 |
| 1960 | 5 | 2,332 | 10 | — | 196 | 968 | 414 | 2,079 | 6,004 |
| October — | |||||||||
| 1960 | 8 | 3,311 | 14 | — | 302 | 1,559 | 730 | 2,351 | 8,275 |
Reported vacancies in manufacturing industry included in the previous table are now shown separately.
| Food, Drink, and Tobacco (Other Than Seasonal) | Textiles, Cloth, and Leather | Building Materials and Furnishings | Engineering and Metal Working | Miscellaneous Manufacturing | Totals, Manufacturing Industry* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excluding seasonal manufacturing. | ||||||
| April — | Males | |||||
| 1950 | 386 | 1,373 | 1,432 | 4,249 | 1,109 | 8,549 |
| 1951 | 313 | 1,186 | 1,413 | 4,556 | 962 | 8,430 |
| 1952 | 332 | 772 | 1,228 | 4,616 | 909 | 7,857 |
| (Revised basis) | ||||||
| 1953 | 145 | 575 | 897 | 3,000 | 463 | 5,080 |
| 1954 | 130 | 678 | 948 | 2,887 | 659 | 5,302 |
| 1955 | 310 | 759 | 1,324 | 3,664 | 810 | 6,867 |
| 1956 | 160 | 392 | 975 | 3,080 | 700 | 5,307 |
| 1957 | 135 | 354 | 799 | 2,286 | 444 | 4,018 |
| 1958 | 129 | 330 | 822 | 2,102 | 372 | 3,755 |
| 1959 | 85 | 199 | 450 | 1,925 | 296 | 2,955 |
| 1960 | 107 | 300 | 700 | 1,822 | 439 | 3,368 |
| 1960 (October) | 241 | 430 | 1,079 | 2,607 | 604 | 4,961 |
| April — | Females | |||||
| 1950 | 495 | 5,993 | 56 | 408 | 942 | 7,894 |
| 1951 | 292 | 5,118 | 75 | 326 | 681 | 6,492 |
| 1952 | 394 | 2,654 | 47 | 234 | 495 | 3,824 |
| (Revised basis) | ||||||
| 1953 | 149 | 2,243 | 31 | 99 | 206 | 2,728 |
| 1954 | 175 | 2,934 | 65 | 205 | 355 | 3,734 |
| 1955 | 296 | 3,201 | 62 | 244 | 357 | 4,160 |
| 1956 | 137 | 2,075 | 33 | 156 | 279 | 2,680 |
| 1957 | 111 | 1,783 | 19 | 106 | 185 | 2,204 |
| 1958 | 116 | 1,881 | 62 | 121 | 192 | 2,372 |
| 1959 | 102 | 1,045 | 20 | 104 | 133 | 1,404 |
| 1960 | 171 | 1,685 | 36 | 213 | 227 | 2,332 |
| 1960 (October) | 365 | 2,266 | 45 | 267 | 368 | 3,311 |
The number of establishments covered by the half-yearly surveys is now shown, the second part of the table giving an analysis of the manufacturing industry column contained in the first part. Figures on the basis of the revised industrial classification are not available for the years prior to 1953.
| Primary Industry (Other Than Farming, Fishing, and Hunting) | Manufacturing Industry | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Building and Construction | Transport and Communication (Other Than Waterfront Work) | Distribution and Finance | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Totals, All Industries Covered | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April— | |||||||||
| 1950 | 767 | 11,052 | 225 | 3,488 | 2,181 | 12,307 | 3,861 | 2,900 | 36,781 |
| 1951 | 753 | 11,104 | 224 | 3,626 | 2,260 | 12,677 | 3,824 | 2,932 | 37,400 |
| 1952 | 776 | 11,147 | 224 | 3,895 | 2,378 | 13,006 | 3,707 | 2,882 | 38,015 |
| (Revised basis) | |||||||||
| 1953 | 592 | 11,740 | 244 | ,896 | 2,359 | 12,468 | 4,064 | 3,409 | 38,772 |
| 1954 | 611 | 12,095 | 241 | 4,716 | 2,457 | 13,459 | 4,278 | 3,540 | 41,397 |
| 1955 | 603 | 12,375 | 243 | 5,187 | 2,485 | 14,153 | 4,401 | 3,635 | 43,082 |
| 1956 | 625 | 12,599 | 247 | 5,675 | 2,513 | 14,720 | 4,445 | 3,724 | 44,548 |
| 1957 | 632 | 12,544 | 242 | 5,899 | 2,543 | 15,143 | 4,501 | 3,739 | 45,243 |
| 1958 | 621 | 12,611 | 251 | 6,057 | 2,605 | 15,604 | 4,626 | 3,822 | 46,197 |
| 1959 | 634 | 12,656 | 257 | 6,609 | 2,688 | 15,950 | 4,736 | 3,884 | 47,414 |
| 1960 | 634 | 12,708 | 267 | 6,507 | 2,684 | 16,384 | 4,841 | 4,008 | 48,033 |
| October - | |||||||||
| 1960 | 614 | 12,796 | 265 | 6,588 | 2,719 | 16,733 | 4,938 | 4,025 | 48,678 |
| Seasonal Manufacturing | Food, Drink, and Tobacco (Other Than Seasonal) | Textiles, Clothing, and Leather | Building Materials and Furnishings | Engineering and Metal Working | Miscellaneous Manufacturing | Total Manufacturing Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April — | |||||||
| 1950 | 554 | 1,532 | 1,991 | 1,748 | 4,040 | 1,187 | 11,052 |
| 1951 | 550 | 1,474 | 2,018 | 1,774 | 4,088 | 1,200 | 11,104 |
| 1952 | 546 | 1,387 | 2,004 | 1,819 | 4,206 | 1,185 | 11,147 |
| (Revised basis) | |||||||
| 1953 | 540 | 1,376 | 1,963 | 2,470 | 4,103 | 1,288 | 11,740 |
| 1954 | 540 | 1,369 | 1,949 | 2,553 | 4,347 | 1,337 | 12,095 |
| 1955 | 535 | 1,333 | 1,980 | 2,600 | 4,567 | 1,360 | 12,375 |
| 1956 | 527 | 1,315 | 1,975 | 2,661 | 4,735 | 1,386 | 12,599 |
| 1957 | 529 | 1,285 | 1,875 | 2,599 | 4,866 | 1,390 | 12,544 |
| 1958 | 518 | 1,254 | 1,861 | 2,588 | 4,973 | 1,417 | 12,611 |
| 1959 | 504 | 1,249 | 1,850 | 2,555 | 5,098 | 1,400 | 12,656 |
| 1960 | 495 | 1,222 | 1,832 | 2,528 | 5,176 | 1,455 | 12,708 |
| October — | |||||||
| 1960 | 477 | 1,230 | 1,833 | 2,552 | 5,245 | 1,459 | 12,796 |
The table now following shows the half-yearly survey totals of full-time employment in industry, under a more detailed industrial classification, as at 15 April 1959 and 1960; employment by the General Government, by local authorities, and by private employers being distinguished at the same time in the 1960 figures.
| Industry | Number of Persons* in Industry at 15 April 1959 | Number of Persons* in Industry at 15 April 1960 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | |||||||
| Males | Females | Government | Local Authorities | Private* | Government | Local Authorities | Private* | |
| *These figures are inclusive of working proprietors. | ||||||||
| Primary industry (other than farming, fishing, and hunting) — | ||||||||
| Forestry | 2,413 | 177 | 2,331 | — | 197 | 182 | — | 4 |
| Logging | 2,691 | 33 | 146 | — | 2,483 | 3 | — | 34 |
| Coal mining | 4,498 | 53 | 3,263 | — | 1,048 | 45 | — | 7 |
| Other mining | 209 | 7 | — | — | 268 | — | — | 8 |
| Quarrying (n.e.i.) | 1,289 | 20 | 108 | 1,274 | — | 2 | 15 | |
| Seasonal manufacturing — | ||||||||
| Meat processing, etc. | 19,974 | 758 | — | 247 | 20,299 | — | 1 | 882 |
| Fruit and vegetable preserving | 1,221 | 1,029 | — | — | 1,099 | — | — | 945 |
| Dairy factories | 4,333 | 397 | — | — | 4,251 | — | — | 433 |
| Food, drink, and tobacco (other than seasonal) | ||||||||
| Grain milling | 781 | 77 | — | — | 773 | — | — | 79 |
| Bread bakeries | 2,160 | 555 | — | — | 2,153 | — | — | 550 |
| Biscuit making | 651 | 615 | — | — | 660 | — | — | 641 |
| Cake and pastry making | 1,128 | 1,366 | — | — | 1,127 | — | — | 1,339 |
| Sugar and confectionery | 1,346 | 990 | — | — | 1,299 | — | — | 1,093 |
| Other food | 1,209 | 705 | — | — | 1,332 | — | — | 748 |
| Beverages | 2,499 | 336 | 17 | — | 2,449 | 2 | — | 317 |
| Tobacco manufacture | 487 | 702 | — | — | 495 | — | — | 716 |
| Textiles, clothing, and leather — | ||||||||
| Tanneries | 1,189 | 145 | — | — | 1,194 | — | — | 116 |
| Fur dressing and manufacture | 83 | 111 | — | — | 77 | — | — | 112 |
| Leather goods | 519 | 450 | — | — | 502 | — | — | 471 |
| Knitted wear and hosiery | 1,607 | 3,124 | — | — | 1,676 | — | — | 3,050 |
| Flax, rope, and twine | 391 | 52 | — | — | 425 | — | — | 65 |
| Woollen mills | 1,873 | 1,499 | — | — | 1,872 | — | — | 1,532 |
| Other textile production | 1,052 | 421 | — | — | 1,188 | — | — | 544 |
| Clothing manufacture | 3,477 | 16,184 | — | — | 3,374 | — | — | 15,516 |
| Footwear manufacture | 2,622 | 2,240 | — | — | 2,560 | — | — | 2,252 |
| Footwear repair | 315 | 33 | — | — | 318 | — | — | 35 |
| Other textile articles | 731 | 767 | — | — | 750 | — | — | 853 |
| Building materials and furnishings — | ||||||||
| Sawmilling, plywoods, etc. | 9,533 | 348 | 582 | — | 9,237 | 25 | — | 331 |
| Builders' woodwork | 4,615 | 147 | — | 35 | 4,635 | — | — | 162 |
| Furniture and cabinets | 4,244 | 382 | — | — | 4,199 | — | — | 401 |
| Other wood manufacture | 999 | 193 | — | — | 996 | — | — | 210 |
| Structural clay products | 1,181 | 34 | — | — | 1,149 | — | — | 43 |
| Pottery and glass | 1,645 | 443 | — | — | 1,751 | — | — | 522 |
| Lime, cement, etc. | 5,603 | 218 | — | 12 | 5,719 | — | — | 219 |
| Engineering and metal working — | ||||||||
| Engineering and machinery | 22,353 | 2,209 | 2 | 23,355 | — | — | 2,451 | |
| Electrical manufacture | 4,468 | 1,305 | — | — | 4,680 | — | — | 1,413 |
| Ships, locomotives, etc. | 6,817 | 64 | 5,880 | — | 1,015 | 48 | — | 18 |
| Vehicle and cycle manufacture | 3,748 | 339 | — | — | 4,181 | — | — | 419 |
| Vehicle repair and aircraft | 21,919 | 1,787 | — | 1,098 | 21,041 | — | 26 | 1,818 |
| Miscellaneous manufacturing — | ||||||||
| Chemicals and by-products | 4,714 | 1,614 | — | 3 | 4,829 | — | — | 1,714 |
| Rubber manufacture | 2,619 | 647 | — | — | 2,765 | — | — | 672 |
| Paper and paper products | 3,522 | 1,065 | — | — | 3,806 | — | — | 1,132 |
| Printing, publishing, and allied | 8,764 | 2,786 | 573 | — | 8,559 | 188 | — | 2,793 |
| Instruments, clocks, jewellery | 1,027 | 445 | — | — | 1,112 | — | — | 462 |
| Other manufacturing (n.e.i.) | 1,767 | 1,124 | — | — | 1,984 | — | — | 1,284 |
| Power, water, and sanitary services | 11,735 | 834 | 3,174 | 7,616 | 1,005 | 161 | 591 | 87 |
| Building and construction | 59,767 | 1,310 | 12,656 | 2,554 | 45,850 | 449 | 63 | 771 |
| Transport and communication — | ||||||||
| Rail transport | 17,877 | 1,119 | 17,646 | 13 | — | 1,080 | 2 | — |
| Road transport | 16,379 | 991 | 1,455 | 1,883 | 13,317 | 49 | 98 | 879 |
| Water transport (not waterfront) | 4,882 | 463 | 162 | 2,955 | 1,510 | 3 | 91 | 384 |
| Air transport | 1,777 | 422 | 680 | — | 1,263 | 74 | — | 382 |
| Post Office | 16,104 | 6,383 | 16,556 | — | — | 6,397 | — | — |
| Distribution and finance — | ||||||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 66,928 | 35,743 | 43 | 207 | 68,179 | 20 | 5 | 36,405 |
| Storage | 731 | 105 | — | — | 702 | — | — | 111 |
| Finance | 7,268 | 4,208 | 1,225 | — | 6,156 | 749 | — | 3,708 |
| Insurance | 3,636 | 2,569 | 659 | — | 3,073 | 411 | — | 2,177 |
| Real estate | 1,161 | 424 | — | — | 1,196 | — | — | 436 |
| Wool and grain stores (seasonal) | 2,684 | 33 | — | — | 2,521 | — | — | 33 |
| Domestic and personal services — | ||||||||
| Provision of lodging, food, etc. | 7,640 | 10,365 | 31 | 1 | 7,927 | 89 | 31 | 10,320 |
| Portrait and photo studios | 466 | 531 | — | — | 478 | — | — | 535 |
| Laundries, cleaning, etc. | 1,932 | 2,516 | — | — | 1,964 | — | — | 2,544 |
| Barbers, beauty shops, etc. | 847 | 1,518 | — | — | 838 | — | — | 1,731 |
| Recreation, sport, etc. | 3,710 | 1,315 | 988 | 948 | 1,785 | 420 | 47 | 879 |
| Undertaking | 394 | 39 | — | 153 | 230 | — | 3 | 42 |
| Administration and professional — | ||||||||
| Hospitals | 6,930 | 19,152 | 1,782 | 5,180 | 159 | 1,707 | 15,591 | 2,244 |
| Medical and allied services | 601 | 2,070 | 72 | — | 496 | 1,311 | — | 803 |
| Education and instruction | 14,487 | 14,999 | 1,850 | 12,013 | 1,622 | 1,357 | 12,147 | 2,126 |
| Arts, sciences, and religion | 1,547 | 538 | 739 | — | 904 | 186 | — | 365 |
| Government (n.e.i.) | 13,985 | 5,090 | 14,395 | — | — | 5,247 | — | — |
| Local authorities (n.e.i.) | 8,553 | 1,063 | — | 8,575 | — | — | 1,109 | — |
| Miscellaneous services and agencies | 4,696 | 6,006 | 226 | — | 4,751 | 140 | — | 6,072 |
| Totals | 87,131 | 43,603 | 326,082 | 20,343 | 29,807 | 121,455 | ||
| 447,003 | 167,802 | 456,816 | 171,605 | |||||
NOTE—The preceding table does not include armed forces personnel, numbering 9,300 in April 1959 and 10,500 in April 1960, or persons engaged in farming, fishing, hunting, waterfront work, one-man business units, etc., estimated to total 240,500 in April 1959 and 240,900 in April 1960.
An effective correlation of the figures shown in the preceding tables with those of employment in factories found in Section 18 of this volume is precluded by the differing definitions of “manufacturing industry”; furthermore, the tabulations of half-yearly surveys differ from factory-production statistics in including managers and foremen, clerical workers, and distributing staff attached to manufacturing establishments in one figure with factory operatives.
VACANCIES, PLACEMENTS, AND DISENGAGED PERSONS — In addition to the half-yearly surveys of the employment position as a whole, the Department of Labour maintains a month-to-month record of vacancies, placements, and disengaged persons seeking work. The following tables are derived from this record and hence relate only to the Department's operations as a labour exchange.
Notified Vacancies — For some years past insufficient labour has been available to satisfy the demands of industry; though diminished in intensity since 1950 this shortage still persists. Its extent and distribution may be measured to some degree by the number of unsatisfied vacancies at the end of each month. Particulars of such vacancies at the end of each month from December 1959 to December 1960 (together with monthly averages for the calendar years 1950–60 inclusive) are shown by district groupings in the following table. This table does not necessarily cover the same establishments as the preceding tables derived from half-yearly surveys; on the one hand it does not exclude vacancies on farms, in seasonal manufacturing industry, and in domestic service; but on the other hand it includes only those vacancies which have been notified to a district office of the Department of Labour in its capacity as a placement service.
| Auckland | Wellington and Lower Hutt | Other North Island | Christ-church | Dunedin | Other South Island | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly Average For Calendar Years | |||||||
| 1950 | 3,288 | 7,175 | 3,918 | 2,791 | 3,311 | 1,962 | 22,445 |
| 1951 | 3,090 | 6,607 | 4,445 | 2,948 | 2,623 | 2,255 | 21,968 |
| 1952 | 2,554 | 5,193 | 3,539 | 2,398 | 1,832 | 2,131 | 17,647 |
| 1953 | 1,648 | 3,521 | 2,761 | 1,266 | 945 | 1,258 | 11,399 |
| 1954 | 2,255 | 4,096 | 2,814 | 1,225 | 877 | 1,265 | 12,532 |
| 1955 | 2,255 | 5,692 | 3,115 | 1,555 | 753 | 1,484 | 14,854 |
| 1956 | 1,727 | 5,261 | 2,397 | 1,352 | 914 | 1,335 | 12,986 |
| 1957 | 1,472 | 3,276 | 1,757 | 734 | 652 | 1,035 | 8,926 |
| 1958 | 1,372 | 2,459 | 1,331 | 551 | 604 | 818 | 7,135 |
| 1959 | 992 | 2,068 | 834 | 540 | 348 | 518 | 5,300 |
| 1960 | 1,229 | 2,460 | 1,045 | 965 | 362 | 703 | 6,764 |
| Monthly Totals | |||||||
| 1959 — | |||||||
| December | 991 | 2,124 | 793 | 701 | 294 | 514 | 5,417 |
| 1960 — | |||||||
| January | 1,032 | 2,143 | 917 | 735 | 293 | 602 | 5,722 |
| February | 1,033 | 2,237 | 1,006 | 738 | 342 | 683 | 6,039 |
| March | 938 | 2,308 | 942 | 871 | 342 | 712 | 6,113 |
| April | 958 | 2,237 | 994 | 972 | 319 | 666 | 6,146 |
| May | 1,033 | 2,212 | 978 | 971 | 359 | 683 | 6,236 |
| June | 1,096 | 2,190 | 1,018 | 964 | 322 | 677 | 6,267 |
| July | 1,027 | 2,310 | 986 | 893 | 358 | 720 | 6,294 |
| August | 1,125 | 2,317 | 1,022 | 893 | 383 | 671 | 6,411 |
| September | 1,217 | 2,573 | 1,111 | 914 | 419 | 670 | 6,904 |
| October | 1,327 | 2,795 | 1,148 | 1,126 | 424 | 689 | 7,509 |
| November | 2,076 | 3,061 | 1,232 | 1,163 | 404 | 824 | 8,760 |
| December | 1,890 | 3,132 | 1,182 | 1,335 | 389 | 841 | 8,769 |
Placements — An industrial analysis of placements by the Department of Labour during the years 1956 to 1960 follows; not all these placements were, however, of disengaged persons.
| Primary Industry | Manufacturing Industry | Building and Construction | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Transport and Communication | Distribution and Finance, etc. | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Totals | |||||||||
| 1956 | 3,563 | 3,677 | 2,461 | 252 | 940 | 1,536 | 1,198 | 1,533 | 15,160 |
| 1957 | 3,433 | 4,274 | 2,440 | 226 | 1,162 | 1,869 | 1,313 | 1,706 | 16,423 |
| 1958 | 3,352 | 3,929 | 2,566 | 223 | 907 | 1,977 | 1,159 | 1,444 | 15,557 |
| 1959 | 3,959 | 4,125 | 3,263 | 187 | 1,090 | 1,635 | 1,301 | 1,404 | 16,964 |
| 1960 | 3,544 | 3,316 | 2,192 | 86 | 648 | 1,622 | 906 | 1,156 | 13,470 |
A classification of these placements by district grouping is contained in the next table.
| Auckland | Wellington and Lower Hutt | Other North Island | Christ-church | Dunedin | Other South Island | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Totals | |||||||
| 1956 | 1,675 | 2,979 | 3,308 | 1,280 | 1,944 | 3,974 | 15,160 |
| 1957 | 1,720 | 3,838 | 3,778 | 1,334 | 1,984 | 3,769 | 16,423 |
| 1958 | 1,893 | 3,265 | 3,803 | 1,259 | 1,70 | 3,628 | 15,557 |
| 1959 | 1,985 | 2,717 | 4,898 | 2,272 | 1,509 | 3,583 | 16,964 |
| 1960 | 1,494 | 2,329 | 3,810 | 1,598 | 980 | 3,259 | 13,470 |
Summary — The following table contains a summary of the numbers of notified vacancies, placements, and disengaged persons as recorded by the Department of Labour for each month from December 1959 to December 1960, together with monthly averages for the calendar years 1950–60 inclusive.
| Vacancies at End of Month | Placements During Month | Disengaged Persons at End of Month | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Monthly Average For Calendar Years | |||||||||
| 1950 | 13,165 | 9,280 | 22,445 | 1,320 | 495 | 1,815 | 34 | 4 | 38 |
| 1951 | 13,690 | 8,278 | 21,968 | 1,390 | 524 | 1,914 | 29 | 9 | 38 |
| 1952 | 11,733 | 5,914 | 17,647 | 1,470 | 535 | 2,005 | 33 | 14 | 47 |
| 1953 | 7,944 | 3,455 | 11,399 | 1,361 | 530 | 1,891 | 67 | 18 | 85 |
| 1954 | 8,404 | 4,128 | 12,532 | 997 | 422 | 1,419 | 48 | 10 | 58 |
| 1955 | 10,153 | 4,701 | 14,854 | 901 | 390 | 1,291 | 44 | 12 | 56 |
| 1956 | 8,958 | 4,028 | 12,986 | 866 | 397 | 1,263 | 240 | 19 | 259 |
| 1957 | 5,864 | 3,062 | 8,926 | 941 | 428 | 1,369 | 368 | 26 | 394 |
| 1958 | 4,407 | 2,728 | 7,135 | 890 | 406 | 1,26 | 733 | 52 | 785 |
| 1959 | 3,046 | 2,254 | 5,300 | 1,025 | 389 | 1,414 | 1,096 | 92 | 1,188 |
| 1960 | 4,076 | 2,688 | 6,764 | 793 | 329 | 1,122 | 569 | 64 | 633 |
| Monthly Totals | |||||||||
| 1959 — | |||||||||
| December | 3,223 | 2,194 | 5,417 | 499 | 236 | 735 | 803 | 89 | 892 |
| 1960 — | |||||||||
| January | 3,525 | 2,197 | 5,722 | 918 | 544 | 1,462 | 845 | 93 | 938 |
| February | 3,724 | 2,315 | 6,039 | 1,101 | 935 | 2,036 | 610 | 87 | 697 |
| March | 3,653 | 2,460 | 6,113 | 929 | 438 | 1,367 | 590 | 85 | 675 |
| April | 3,658 | 2,488 | 6,146 | 697 | 305 | 1,002 | 580 | 64 | 644 |
| May | 3,693 | 2,543 | 6,236 | 812 | 257 | 1,069 | 685 | 77 | 762 |
| June | 3,719 | 2,548 | 6,267 | 905 | 230 | 1,135 | 900 | 81 | 981 |
| July | 3,709 | 2,585 | 6,294 | 1,126 | 213 | 1,339 | 721 | 75 | 796 |
| August | 3,831 | 2,580 | 6,411 | 865 | 212 | 1,077 | 565 | 53 | 618 |
| September | 4,084 | 2,820 | 6,904 | 642 | 222 | 864 | 499 | 42 | 541 |
| October | 4,505 | 3,004 | 7,509 | 605 | 156 | 761 | 335 | 37 | 372 |
| November | 5,399 | 3,361 | 8,760 | 621 | 248 | 869 | 244 | 32 | 276 |
| December | 5,417 | 3,352 | 8,769 | 299 | 190 | 489 | 252 | 44 | 296 |
The number of disengaged persons enrolled for placement by the Department of Labour reached its lowest level (12) at the end of March 1951. The lowest figure recorded during 1960 was 276 in November of that year.
UNEMPLOYMENT — Except for occasional returns relating to State unemployment relief which were presented to Parliament from time to time, practically no direct statistical evidence as to the extent of unemployment in New Zealand prior to 1892 is extant. Such information is, however, available from the census (since 1896) and from the records of the Department of Labour (since 1892). In addition, statistics of unemployment among trade unionists were collected from trade union secretaries by the Department of Statistics from 1925 to 1930. A table showing figures of unemployment from June 1931 to March 1939 will be found on page 854 of the 1940 Yearbook.
Census Data on Unemployment — The great disadvantage of the census inquiry as an indicator of the trend of unemployment is that it provides data at quinquennial intervals only up to April 1926, since when only five censuses have taken place, one on 24 March 1936, one on 25 September 1945, one on 17 April 1951, one on 17 April 1956, and one on 18 April 1961. The unemployment figures from the 1956 census were 5,558 males and 2,378 females.
The following table gives relevant census data on unemployment from 1896 to 1956.
| Census | Number of Males Unemployed | Proportion per 1,000 Male Wage and Salary Earners |
|---|---|---|
| *Including Maoris. | ||
| 12 April 1896 | 14,759 | 100 |
| 31 March 1901 | 8,467 | 48 |
| 12 April 1906 | 8,189 | 39 |
| 2 April 1911 | 7,152 | 30 |
| 15 October 1916 | 5,920 | 26 |
| 17 April 1921 | 11,061 | 39 |
| 20 April 1926 | 10,694 | 34 |
| 24 March 1936 | 35,774 | 96 |
| 25 September 1945 | 5,823 | 16 |
| 17 April 1951* | 7,902 | 18 |
| 17 April 1956* | 5,558 | 12 |
The 1936 figure includes men on rationed relief work, but excludes men (16,222) partly unemployed but not on relief work. The 1945 figure includes ex-servicemen recently returned from overseas who had not then resumed work. At the time of the 1951 census the waterfront strike was in progress and it was estimated that approximately 15,000 workers in that and other industries were on strike. Evidently many of these were not returned as unemployed; it is likely that a number changed to other industries, while some may not have considered themselves to be unemployed.
Unemployment Benefit — In the years immediately preceding 1939 two forms of unemployment relief were available: the provision of work for unemployed under various employment promotion schemes, and the payment of sustenance without work (refer 1942 and earlier issues of the Yearbook). Measures for the promotion of employment are still in operation, but the payment of sustenance without work was discontinued on the introduction of a system of unemployment benefits under the Social Security Act 1938. These benefits came into force on 1 April 1939, and monthly figures of the number of benefits current have been published in previous editions of the Yearbook. The number in force at the end of March 1956 was only five, but since then the number of benefits has increased, there being 137 in force at the end of March 1961.
Subject to the conditions set out on page 184, the unemployment benefit may be claimed as of right from the Social Security Fund, to which all workers contribute indirectly through PAYE taxation. Registration at a district office of the Department of Labour is a compulsory prerequisite to eligibility for the benefit. Hence it is considered that the great majority of workers becoming involuntarily unemployed would register for employment in order to validate a claim for the benefit.
Close liaison is maintained between the Social Security Department and the Department of Labour to prevent the payment of benefit where work is available. In addition to the requirement that a benefit applicant must register for work at an employment office, all unemployment beneficiaries must report once weekly at the employment office.
INDUSTRIAL DISTRIBUTION, OCCUPATIONS, AND OCCUPATIONAL STATUS — Statistics on industrial distribution, occupations, and occupational status compiled from the population census taken on 17 April 1956 are given in the following tables. The tables illustrate the extent to which the population directly participated in the economic life of the country, according to industry and occupation, and show the nature of their activities, i.e., employer, wage or salary earner, etc.
Excluded from the tables are members of the Armed Services overseas at census dates, numbering 1,894 in 1951 and 2,162 in 1956. Maoris are included in all tables.
The next table shows the numbers and percentages actively engaged or otherwise.
| 1951 Census | 1956 Census | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Numbers | ||||||
| Actively engaged | 568,963 | 171,533 | 740,496 | 622,758 | 194,094 | 816,852 |
| Not actively engaged | 405,005 | 793,971 | 1,198,976 | 470,453 | 886,757 | 1,357,210 |
| Totals | 973,968 | 965,504 | 1,939,472 | 1,093,211 | 1,080,851 | 2,174,062 |
| percentages | ||||||
| Actively engaged | 58.42 | 17.77 | 38.18 | 56.97 | 17.96 | 37.57 |
| Not actively engaged | 41.58 | 82.23 | 61.82 | 43.03 | 82.04 | 62.43 |
| Totals | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
The percentage of actively engaged males to total male population dropped from 58.42 to 56.97 between 1951 and 1956. This is a reflection of the large increase recorded in the under 15 years age group between 1951 and 1956, as compared with the increase in the working age group of 15 to 64 years.
This would, in normal circumstances, have meant a similar drop in the proportion per cent of actively engaged females, but, owing mainly to the substantial increase in numbers of married women working, the percentage for females has increased from 17.77 to 17.96.
Occupational Status 1956 — The following table shows the distribution of the population according to the character of participation or non-participation in industry.
| Occupational Status | 1951 Census | 1956 Census | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Employer | 63,570 | 5,933 | 69,503 | 66,864 | 5,983 | 72,847 |
| Own account | 71,235 | 7,683 | 78,918 | 72,239 | 7,856 | 80,095 |
| Wage or salary earner | 423,174 | 154,520 | 577,694 | 476,637 | 176,721 | 653,358 |
| Unemployed | 7,902 | 1,726 | 9,628 | 5,558 | 2,378 | 7,936 |
| Relative assisting, unpaid | 1,966 | 1,248 | 3,214 | 1,208 | 1,038 | 2,246 |
| Not specified | 1,116 | 423 | 1,539 | 252 | 118 | 370 |
| Totals, actively engaged | 568,963 | 171,533 | 740,496 | 622,758 | 194,094 | 816,852 |
| Not actively engaged | 405,005 | 793,971 | 1,198,976 | 470,453 | 886,757 | 1,357,210 |
| Grand totals | 973,968 | 965,504 | 1,939,472 | 1,093,211 | 1,080,851 | 2,174,062 |
The total number actively engaged increased by 76,356, or 10.31 per cent, between 1951 and 1956. In the wage or salary earner group the increase was 75,664, or 13.1 per cent.
Female wage or salary earners increased by 22,201, or 14.37 per cent; a substantial increase in the number of married females working boosted the increase in this particular group.
The number of males unemployed in 1951 was inflated owing to industrial disturbances at that time.
Industrial Distribution 1956: Divisions — The industrial distribution of the population by the principal divisions of industry at the 1956 census is now given. (A more detailed classification by major groups was given in the 1960 and earlier issues of the Yearbook.)
| Division | Numbers | Proportion Per Cent of Actively Engaged | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| Agriculture, forestry, hunting, and fishing | 122,795 | 9,132 | 131,927 | 19.72 | 4.70 | 16.15 |
| Mining and quarrying | 7,272 | 112 | 7,384 | 1.17 | 0.06 | 0.90 |
| Manufacturing | 149,978 | 43,681 | 193,659 | 24.08 | 22.51 | 23.71 |
| Construction | 79,656 | 1,425 | 81,081 | 12.79 | 0.73 | 9.93 |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services | 9,388 | 733 | 10,121 | 1.51 | 0.38 | 1.24 |
| Commerce | 96,208 | 48,821 | 145,029 | 15.45 | 25.15 | 17.75 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 73,755 | 9,801 | 83,556 | 11.84 | 5.05 | 10.23 |
| Services | 80,492 | 79,424 | 159,916 | 12.92 | 40.92 | 19.58 |
| Activities not adequately described | 3,214 | 965 | 4,179 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.51 |
| Totals, actively engaged | 622,758 | 194,094 | 816,852 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Not actively engaged | 470,453 | 886,757 | 1,357,210 | ... | ... | ... |
| Grand totals | 1,093,211 | 1,080,851 | 2,174,062 | ... | ... | ... |
EMPLOYMENT ON FARMS — The omission of farm employment from the Department of Labour statistics shown on pages 1015–1020 is partly made good by figures derived from the collection of farm production statistics undertaken by the Department of Statistics.
A table giving special detailed statistics of farm workers and farm population at 31 January 1950, covering persons actually residing on holdings of 1 acre and over situated outside borough boundaries, was published on page 979 of the 1954 Yearbook.
SEASONAL FLUCTUATIONS IN EMPLOYMENT — The adoption of the maintenance of full employment as a desideratum in many countries has prompted research into various employment problems, including that of the fluctuation or periodicity of employment. Information on the annual cycle of employment in New Zealand is available for those industries which are covered by the half-yearly survey. The following table shows the month-to-month variations in male employment in seasonal industries for the period of 13 months from April 1959 to April 1960. The seasonal changes in female employment are less marked, such fluctuations as are evident originating mainly in the fruit- and vegetable-preserving industry.
| Meat Processing, etc. | Fruit and Vegetable Preserving | Dairy Factories | Wool and Grain Stores | Total, Seasonal Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | |||||
| April | 19,900 | 1,202 | 4,331 | 2,682 | 28,115 |
| May | 18,948 | 997 | 4,002 | 2,117 | 26,064 |
| June | 17,842 | 996 | 3,857 | 1,674 | 24,369 |
| July | 14,761 | 982 | 3,844 | 1,596 | 21,183 |
| August | 13,357 | 965 | 4,301 | 1,808 | 20,431 |
| September | 12,547 | 948 | 4,750 | 2,010 | 20,255 |
| October | 12,078 | 928 | 4,922 | 2,377 | 20,305 |
| November | 14,437 | 1,021 | 5,061 | 3,478 | 23,997 |
| December | 21,102 | 1,694 | 5,089 | 3,710 | 31,595 |
| 1960 | |||||
| January | 21,992 | 1,637 | 4,928 | 3,657 | 32,214 |
| February | 21,889 | 1,534 | 4,687 | 3,134 | 31,244 |
| March | 21,125 | 1,421 | 4,452 | 2,744 | 29,742 |
| April | 20,472 | 1,080 | 4,249 | 2,519 | 28,320 |
PUBLIC WORKS — Figures are available which include not only the number of workers in the direct employ of the Ministry of Works and the New Zealand Electricity Department, but also those employed by contractors for public works, and those employed by local authorities on works which are financed wholly or partly by the Ministry of Works, National Roads Board, and Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Council. In the next table figures on this basis are given for the years 1950 to 1960 and at quarterly intervals from December 1959 to December 1960. Departmental and contractors' workmen on Housing Division work are included.
PERSONS ENGAGED ON PUBLIC WORKS (INCLUDING ELECTRICITY WORKS AND HOUSING)
| Electricity Works | Roads | Irrigation | Soil Conservation and Rivers Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity Department | Ministry of Works | ||||
| Average for calendar year — | |||||
| 1950 | 1,945 | 2,465 | 4,472 | 148 | 336 |
| 1951 | 2,303 | 2,515 | 4,361 | 133 | 354 |
| 1952 | 2,501 | 2,825 | 4,659 | 102 | 338 |
| 1953 | 2,725 | 3,483 | 4,276 | 100 | 259 |
| 1954 | 2,845 | 3,036 | 4,373 | 126 | 291 |
| 1955 | 2,863 | 3,007 | 4,958 | 133 | 288 |
| 1956 | 2,845 | 2,798 | 5,582 | 118 | 257 |
| 1957 | 2,734 | 3,394 | 5,157 | 186 | 350 |
| 1958 | 2,708 | 3,953 | 4,917 | 174 | 363 |
| 1959 | 2,808 | 3,644 | 5,025 | 173 | 393 |
| 1960 | 2,909 | 3,124 | 5,417 | 140 | 380 |
| Month — | |||||
| 1959 — December | 2,861 | 3,206 | 5,107 | 167 | 379 |
| 1960 — March | 2,918 | 3,184 | 5,540 | 136 | 400 |
| June | 2,901 | 3,083 | 5,330 | 142 | 389 |
| September | 2,924 | 3,084 | 5,523 | 132 | 365 |
| December | 2,921 | 3,081 | 5,441 | 135 | 354 |
| Buildings | Aerodromes | Railways | Other Works | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average for calendar year — | |||||
| 1950 | 6,902 | 436 | 333 | 1,849 | 18,886 |
| 1951 | 4,961 | 377 | 336 | 1,766 | 17,106 |
| 1952 | 4,968 | 386 | 551 | 1,772 | 18,102 |
| 1953 | 5,833 | 390 | 660 | 1,908 | 19,634 |
| 1954 | 5,157 | 331 | 434 | 1,850 | 18,443 |
| 1955 | 5,309 | 345 | 142 | 1,860 | 18,905 |
| 1956 | 5,540 | 471 | 33 | 2,014 | 19,658 |
| 1957 | 4,451 | 229 | 118 | 2,639 | 19,258 |
| 1958 | 4,025 | 166 | 171 | 2,354 | 18,831 |
| 1959 | 4,676 | 156 | 101 | 2,484 | 19,460 |
| 1960 | 4,627 | 95 | 154 | 2,675 | 19,521 |
| Month — | |||||
| 1959 — December | 4,796 | 94 | 105 | 2,703 | 19,418 |
| 1960 — March | 4,929 | 82 | 114 | 2,660 | 19,963 |
| June | 4,638 | 80 | 166 | 2,769 | 19,498 |
| September | 4,398 | 98 | 206 | 2,608 | 19,338 |
| December | 4,296 | 148 | 155 | 2,620 | 19,151 |
The figures shown in this table and also those in the table following on local authority employment are included in the national employment tables already presented.
LOCAL AUTHORITIES — The following table shows employment by local authorities as at 31 March for the latest five years. Employees of electric power boards and fire boards are included here, but not those of hospital boards.
NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES*
| As at 31 March | Administrative, Professional, and Clerical | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Whether permanent, temporary, or part-time, and whether paid out of revenue, loan money, or Government subsidy or grant. | |||
| 1956 | 6,502 | 22,562 | 29,064 |
| 1957 | 6,712 | 23,189 | 29,901 |
| 1958 | 7,138 | 23,783 | 30,921 |
| 1959 | 7,546 | 23,806 | 31,352 |
| 1960 | 7,721 | 24,287 | 32,008 |
WORKING LIFE EXPECTANCIES — Precise statistics on the pattern of working life for New Zealand's population first became available with the compilation by the Department of Statistics in 1957 of Tables of Working Life based on the year 1951. These tables display the manner in which labour force rates of participation, entry, and withdrawal vary with age for both males and females. Also included are expectancies of future working life and retirement life for members of the labour force, assuming that 1951 experience continues. The main applications of these tables are to economic and social studies relating to large groups of people. Individuals frequently do not conform to group patterns and, therefore, applications of the expectancies and other statistics contained in the tables must be made with caution. An abridgement of the detailed tables is presented below. For an explanation of the contents of the Table of Working Life and a detailed analysis of the pattern of working life, male and female, in New Zealand, reference should be made to a Supplement to the February 1957 issue of the Monthly Abstract of Statistics.
ABRIDGED TABLES OF WORKING LIFE, 1951
| Exact Age (Years) | Percentage of Population in Labour Force | Number in Labour Force, per 100,000 Live Births | Changes in the Labour Force in the Following 5 Years of Age, per 100,000 Live Births | Expectation of Work Life of Person in Labour Force (Years) | Expectation of Retirement Life of Person in Labour Force (Years) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Entries | Total Withdrawals | |||||
*Entries of females into the labour force below the horizontal line are secondary entries by those who withdrew at younger ages for reasons connected with marriage. †The working life expectancies for females allow for the possibility of a second spell of labour force membership after a period of non-membership due to marriage. ‡Difference between life expectancy and working life expectancy. | ||||||
| Males | ||||||
| 15 | — | — | 88,331 | 555 | 46.7 | 8.6 |
| 20 | 92.7 | 87,776 | 4,304 | 913 | 42.0 | 8.7 |
| 25 | 97.3 | 91,167 | 382 | 864 | 37.5 | 8.7 |
| 30 | 97.6 | 90,685 | 187 | 1,007 | 32.8 | 8.8 |
| 35 | 97.7 | 89,865 | — | 1,337 | 28.1 | 8.9 |
| 40 | 97.5 | 88,528 | — | 1,806 | 23.5 | 8.9 |
| 45 | 97.1 | 86,722 | — | 3,638 | 18.9 | 9.0 |
| 50 | 95.7 | 83,084 | — | 8,389 | 14.6 | 9.1 |
| 55 | 90.3 | 74,695 | — | 12,304 | 11.0 | 8.7 |
| 60 | 81.6 | 62,391 | — | 26,000 | 7.6 | 8.5 |
| 65 | 53.8 | 36,391 | — | 16,088 | 6.7 | 6.1 |
| 70 | 36.4 | 20,303 | — | 11,770 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 75 | 20.5 | 8,533 | — | 5,972 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| 80 | 9.8 | 2,561 | — | 2,281 | 2.4 | 3.1 |
| 85 | 2.2 | 280 | — | 277 | 1.3 | 2.6 |
| 90 | 0.1 | 3 | — | 3 | 0.7 | 1.9 |
| Females | ||||||
| 15 | — | — | 81,805 | 8,473 | 16.2 | 42.7 |
| 20 | 76.5 | 73,332 | 1,129 | 42,407 | 12.4 | 41.8 |
| 25 | 33.6 | 32,054 | 1,136 | 14,064 | 16.7 | 32.7 |
| 30 | 20.2 | 19,126 | 4,031 | 5,030 | 20.3 | 24.4 |
| 35 | 19.2 | 18,127 | 4,228 | 3,062 | 19.9 | 20.1 |
| 40 | 20.7 | 19,293 | 3,014 | 1,803 | 17.5 | 17.9 |
| 45 | 22.3 | 20,504 | 1,297 | 2,651 | 13.6 | 17.2 |
| 50 | 21.3 | 19,150 | 775 | 4,676 | 9.9 | 16.6 |
| 55 | 17.6 | 15,249 | 351 | 5,449 | 7.2 | 15.2 |
| 60 | 12.3 | 10,151 | — | 6,414 | 4.6 | 13.8 |
| 65 | 4.9 | 3,737 | — | 2,592 | 3.8 | 11.0 |
| 70 | 1.7 | 1,145 | — | 1,014 | 2.5 | 8.9 |
| 75 | 0.2 | 131 | — | 131 | 1.1 | 7.4 |
INTRODUCTORY: Legislative Authority — In New Zealand dual provision for the registration and protection of unions of workers and of employers exists in the Trade Unions Act 1908 and the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954.
The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act requires certain provisions to be included in the rules of industrial unions, especially that elections of officials are to be made by secret ballot of financial members or by such other democratic method as may be approved by the Registrar of Industrial Unions. The Registrar may refuse any unreasonable or oppressive rule, subject to a right of appeal by the union to the Court of Arbitration. He may also, on application by at least 10 financial members, refer to the Court for inquiry a disputed election of union officials. Secret ballots are required to validate subscriptions in excess of 2s. weekly and levies on union members. Penalties are prescribed in the case of a strike or lockout, and these are heavier where an affirmative decision on the issue has not been made by a pre-strike or pre-lockout secret ballot of members concerned.
Provision is made under section 79 of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954 for the furnishing of an annual return showing the number and membership as at 31 December of unions registered under the Act. It is from this return (see parliamentary paper H. 11) that the tables in this section have been compiled. The number of unions registered under the Trade Unions Act as at the end of 1959 was two only. Unions registered under the Trade Unions Act may also be registered under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act.
General — The following paragraphs give a brief outline of the constitution, government, objects, and powers of industrial unions.
Constitution — An industrial union is constituted in accordance with the provisions of the statute under which it has been registered. Its membership consists of workers or employers in a specified industry or group of related industries, while its territorial scope is defined with reference to localities, industrial districts, the North or South Island, or the country as a whole. Industrial districts are provided for by section 6 of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954, and eight such districts have been gazetted (see Statutory Regulations 1954/221). Minimum membership requirements in the case of a union of employers are as follows: jurisdiction in one district only, not less than three members; two or more districts or in North or South Island, all the employers in the North Island or in the South Island, or a branch of not less than three members in each of at least two districts; and in New Zealand as a whole, all the employers in New Zealand, or a branch of not less than three members in each of at least four districts. For a union of workers the corresponding requirements are: jurisdiction in one district only, a society of 15 workers in the industry (if less than 15, then not less than one-quarter of the number engaged, with a minimum of five); in two or more districts or in the North or South Island, a branch having 15 members (or one-quarter of the number engaged, but not less than five) in each of at least two districts; and in New Zealand as a whole, a branch having 15 members (or one-quarter of the number engaged, but not less than five) in each of at least four districts. There are two exceptions to these requirements, namely, an incorporated company if an employer of labour, which can be registered individually, and certain organisations of Government railway employees, special statutory provisions applying to these.
Government — The method of government and the objects of a union are provided for in the rules recorded when the union is registered, any amendments becoming effective only after having been also recorded. A committee of management, either appointed or elected according to the rules, provides the executive aspect of the union. Government is exercised by regular meetings of the union where this is possible, together with half-yearly or annual general meetings. With larger unions having a wider coverage, to preserve the democratic aspect of each member having a right to participate in control, the practice is to establish branches (or sub-branches) where the membership warrants it, each branch having its own management committee, elected by the members, with power to conduct its business. In these cases, in lieu of annual general meetings, conferences attended by delegates elected by the various branches are held as required, normally annually, while provision is sometimes made in the rules or by statute for the determination of certain questions by secret postal or other ballot of all financial members, or for the ratification of conference decisions upon specified matters by a majority of the branches. In some unions a council, comprising the officers of the union together with an elected representative from each of several groups of branches, is set up to meet quarterly or as deemed necessary for the transaction of important business, with a subsidiary committee (usually called the executive), comprising the officers and a specified number of other elected members resident in reasonable proximity, to deal with day-to-day matters.
Objects — The primary object of an industrial union is to protect or promote the interests of either employers or workers in a specified industry or related industries in New Zealand or in a specified locality, the interests being purely industrial and relating exclusively to wages, hours, and conditions of employment. Ancillary objects are as follows:
To enter into industrial agreements relating to conditions of employment and, where necessary, to refer industrial disputes to Councils of Conciliation (upon which the union is entitled to be represented by its chairman or secretary or by a specified number of persons appointed in writing or in such other manner as its rules prescribe);
To affiliate with or be a member of any industrial association in the industry or any organisation formed for the purpose of protecting or promoting the interests of employers or workers throughout New Zealand;
To take or empower such legal and other lawful proceedings as may be necessary for the conduct of the union's business;
To invest the funds; and
To exercise such other rights and powers as may be conferred by law upon industrial unions registered under the Act.
Powers — The powers of a union are limited to those authorised by statute, and the manner in which such powers may be exercised, where not specifically mentioned in the statute, must be set out in the rules. It cannot use its funds for any purpose foreign to the purposes for which it is established, nor can it commence any project nor use its funds in any manner not contemplated by the Act under which it is registered. Under the Political Disabilities Removal Act 1960, a union may apply its funds in furtherance of political objects if a resolution is passed on a ballot of the members, taken in accordance with its rules. A resolution shall be deemed to have been passed in a ballot of the members if a majority of the total valid votes recorded at the ballot is in favour. The Act provides that, where any levy to be applied in the furtherance of political objects becomes lawfully payable, a member shall be exempt from payment of the levy by giving notice of objection in writing.
INDUSTRIAL UNIONS OF EMPLOYERS — The numbers and membership of industrial unions of employers registered under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act as at the end of each of the years 1955–59 are shown in the following table according to industrial groups.
NUMBER OF UNIONS AND MEMBERSHIP* AS AT 31 DECEMBER
| Industrial Group | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | |
| *In the few cases where current membership figures are not known the latest known figures are included. | ||||||||||
| Provision of — | ||||||||||
| Food and drink | 60 | 4,628 | 59 | 4,698 | 59 | 4,689 | 60 | 4,731 | 59 | 4,738 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 11 | 3,462 | 11 | 462 | 11 | 3,443 | 11 | 3,459 | 11 | 3,444 |
| Building and construction | 50 | 3,934 | 50 | 4,043 | 51 | 4,095 | 51 | 4,057 | 50 | 4,122 |
| Power, heat, and light | 11 | 728 | 1 | 709 | 11 | 635 | 11 | 646 | 11 | 641 |
| Transport by water and air | 14 | 108 | 14 | 111 | 14 | 105 | 14 | 111 | 14 | 110 |
| Transport by land | 11 | 457 | 11 | 443 | 11 | 421 | 11 | 512 | 11 | 475 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 34 | 2,277 | 32 | 2,225 | 33 | 2,350 | 33 | 2,488 | 33 | 2,617 |
| Working in or on — | ||||||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 9 | 436 | 9 | 575 | 9 | 540 | 9 | 527 | 9 | 518 |
| Metal | 13 | 846 | 13 | 882 | 12 | 812 | 12 | 829 | 12 | 852 |
| Stone, clay, glass, and chemicals | 7 | 692 | 8 | 699 | 8 | 698 | 8 | 700 | 8 | 703 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 19 | 398 | 18 | 404 | 18 | 430 | 18 | 421 | 18 | 434 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 6 | 26 | 6 | 27 | 6 | 26 | 6 | 26 | 6 | 25 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 10 | 2,602 | 10 | 2,628 | 10 | 2,628 | 10 | 3,180 | 10 | 3,299 |
| Miscellaneous | 8 | 387 | 8 | 468 | 8 | 467 | 7 | 465 | 7 | 465 |
| Totals | 263 | 21,031 | 260 | 21,374 | 261 | 21,339 | 261 | 22,152 | 259 | 22,443 |
The number of unions of employers and their membership rose gradually to 149 unions, with 5,819 members, in 1914, the year following that of the prolonged waterside workers' strike. From that year until the passing of the 1936 Act membership figures remained fairly constant. The effects of the 1936 amending Act may be judge the fact that the 1945 figure of membership showed an increase of approximately 290 per cent over the 1935 total. Further increases subsequently took place, and the 1959 figure of 22,443 was the highest yet recorded. A certain amount of duplication, however, exists in employers' union membership, many employers belonging to two or more unions.
INDUSTRIAL UNIONS OF WORKERS — The following table shows membership only of industrial unions of workers for each year from 1900 to 1959. The outstanding feature is the large increase consequent upon the 1936 Amendment to the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, which made union membership compulsory whenever an award or industrial agreement existed; on the other hand the effect of both world wars, of the economic depression of the 1930s, and of the waterfront strike of 1951 (which incidentally was responsible for an incomplete coverage in the 1950 statistics) are clearly discernible. For every year since 1950 an increased membership has been recorded. The figure for December 1960 is 332,362.
MEMBERSHIP OF INDUSTRIAL UNIONS OF WORKERS
| 1900 | 17,989 |
| 1901 | 23,768 |
| 1902 | 23,816 |
| 1903 | 27,640 |
| 1904 | 30,271 |
| 1905 | 29,869 |
| 1906 | 34,978 |
| 1907 | 45,614 |
| 1908 | 49,347 |
| 1909 | 54,519 |
| 1910 | 57,091 |
| 1911 | 55,629 |
| 1912 | 60,622 |
| 1913 | 71,544 |
| 1914 | 73,991 |
| 1915 | 67,661 |
| 1916 | 71,587 |
| 1917 | 72,873 |
| 1918 | 71,447 |
| 1919 | 82,553 |
| 1920 | 96,350 |
| 1921 | 97,719 |
| 1922 | 96,838 |
| 1923 | 94,438 |
| 1924 | 96,822 |
| 1925 | 100,540 |
| 1926 | 99,567 |
| 1927 | 101,071 |
| 1928 | 103,980 |
| 1929 | 102,646 |
| 1930 | 101,526 |
| 1931 | 90,526 |
| 1932 | 79,283 |
| 1933 | 71,888 |
| 1934 | 74,391 |
| 1935 | 80,929 |
| 1936 | 185,527 |
| 1937 | 232,986 |
| 1938 | 249,231 |
| 1939 | 254,690 |
| 1940 | 248,081 |
| 1941 | 231,049 |
| 1942 | 218,398 |
| 1943 | 214,628 |
| 1944 | 223,027 |
| 1945 | 229,103 |
| 1946 | 247,498 |
| 1947 | 260,379 |
| 1948 | 271,100 |
| 1949 | 275,977 |
| 1950 | 267,225 |
| 1951 | 272,957 |
| 1952 | 283,496 |
| 1953 | 290,149 |
| 1954 | 299,254 |
| 1955 | 304,520 |
| 1956 | 308,031 |
| 1957 | 317,137 |
| 1958 | 324,438 |
| 1959 | 327,495 |
The same information is now depicted graphically at yearly intervals from 1900 in the diagram below.
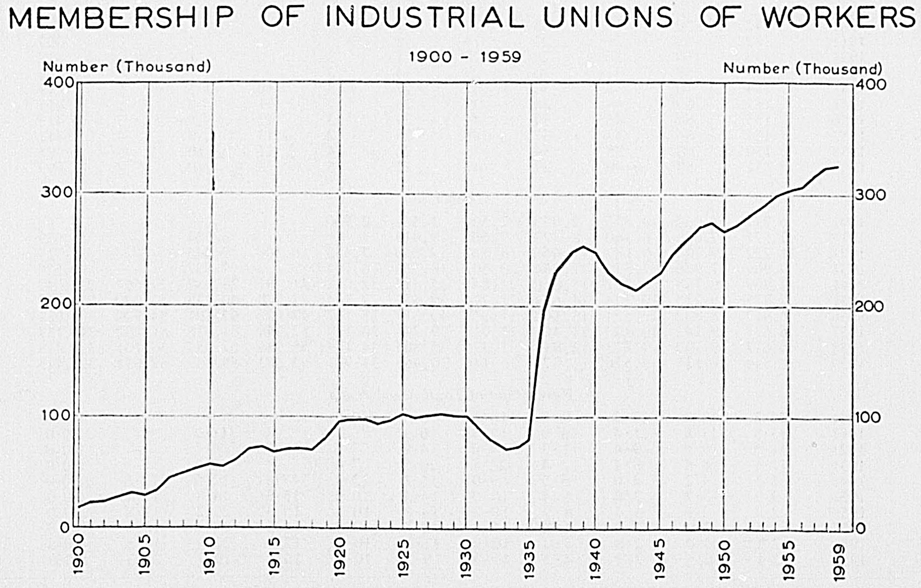
The next table shows both numbers of workers' unions and their membership as at the end of each of the five years 1955 to 1959 according to industrial groups.
NUMBER OF UNIONS AND MEMBERSHIP* AS AT 31 DECEMBER
| Industrial Group | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | Unions | Members | |
| *In the few cases where current membership figures are not known, the latest known figures are included. | ||||||||||
| Provision of — | ||||||||||
| Food and drink | 72 | 33,515 | 77 | 34,195 | 77 | 34,158 | 74 | 35,517 | 70 | 35,610 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 17 | 21,283 | 17 | 20,639 | 18 | 20,569 | 17 | 21,879 | 17 | 22,808 |
| Building and construction | 39 | 29,076 | 39 | 30,951 | 37 | 31,177 | 37 | 31,309 | 36 | 31,505 |
| Power, heat, and light | 5 | 732 | 5 | 708 | 5 | 727 | 5 | 735 | 5 | 735 |
| Transport by water and air | 47 | 12,795 | 47 | 13,420 | 47 | 13,815 | 47 | 13,615 | 47 | 13,463 |
| Transport by land | 22 | 34,507 | 21 | 34,395 | 21 | 37,135 | 21 | 38,267 | 21 | 38,042 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 26 | 24,200 | 26 | 25,128 | 26 | 26,346 | 26 | 27,016 | 26 | 27,978 |
| Working in or on — | ||||||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 17 | 13,599 | 17 | 13,723 | 17 | 13,670 | 17 | 13,667 | 17 | 13,873 |
| Metal | 25 | 35,188 | 25 | 34,296 | 25 | 36,011 | 25 | 36,291 | 24 | 35,613 |
| Stone, clay, glass, and chemicals | 20 | 3,408 | 20 | 3,132 | 21 | 3,090 | 20 | 3,242 | 21 | 3,874 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 3 | 5,958 | 3 | 6,220 | 3 | 6,308 | 3 | 6,511 | 3 | 6,944 |
| Skin, leather, etc. | 7 | 1,357 | 7 | 1,269 | 7 | 1,248 | 7 | 1,321 | 7 | 1,403 |
| Mines and quarries | 16 | 1,548 | 16 | 1,578 | 16 | 1,543 | 15 | 1,733 | 14 | 1,605 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 4 | 16,412 | 4 | 17,252 | 4 | 17,315 | 4 | 16,266 | 4 | 16,468 |
| Miscellaneous | 90 | 70,942 | 89 | 71,125 | 87 | 74,025 | 87 | 77,069 | 87 | 77,574 |
| Totals | 410 | 304,520 | 413 | 308,031 | 411 | 317,137 | 405 | 324,438 | 399 | 327,495 |
In the following table industrial unions of workers are classified according to membership. Unions for which no membership figures were available have been classified according to the latest known figures.
| Year | Under 100 | 100 and Under 200 | 200 and Under 300 | 300 and Under 500 | 500 and Under 1,000 | 1,000 and Under 2,000 | 2,000 and Under 3,000 | 3,000 and Under 5,000 | 5,000 and Under 10,000 | 10,000 and Over | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Unions | |||||||||||
| 1901 | 142 | 30 | 19 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | — | — | — | 202 |
| 1911 | 182 | 53 | 26 | 23 | 14 | 8 | — | — | 1 | — | 307 |
| 1921 | 239 | 70 | 36 | 28 | 28 | 11 | 3 | 2 | 1 | — | 418 |
| 1931 | 239 | 58 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 14 | 3 | — | 1 | — | 405 |
| 1941 | 184 | 70 | 38 | 38 | 32 | 27 | 13 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 419 |
| 1951 | 165 | 69 | 44 | 38 | 39 | 28 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 415 |
| 1956 | 155 | 64 | 45 | 39 | 44 | 29 | 13 | 12 | 9 | 3 | 413 |
| 1957 | 154 | 66 | 43 | 37 | 46 | 28 | 12 | 13 | 9 | 3 | 411 |
| 1958 | 150 | 68 | 38 | 34 | 48 | 26 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 3 | 405 |
| 1959 | 151 | 58 | 40 | 37 | 49 | 22 | 15 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 399 |
| Membership | |||||||||||
| 1901 | 5,777 | 4,032 | 4,815 | 2,073 | 2,520 | 1,651 | 2,900 | — | — | — | 23,768 |
| 1911 | 7,521 | 7,686 | 6,360 | 8,879 | 9,685 | 9,414 | — | — | 6,084 | — | 55,629 |
| 1921 | 11,222 | 9,708 | 9,182 | 11,066 | 18,527 | 14,580 | 7,433 | 6,506 | 9,495 | — | 97,719 |
| 1931 | 9,969 | 7,966 | 7,578 | 11,244 | 20,602 | 18,566 | 6,744 | — | 7,857 | — | 90,526 |
| 1941 | 7,909 | 9,768 | 9,207 | 15,060 | 22,841 | 35,417 | 31,012 | 41,191 | 28,987 | 29,657 | 231,049 |
| 1951 | 7,875 | 10,225 | 10,394 | 14,671 | 27,274 | 39,658 | 27,364 | 43,218 | 40,278 | 52,000 | 272,957 |
| 1956 | 6,947 | 8,802 | 10,554 | 15,164 | 31,354 | 40,019 | 31,167 | 47,023 | 62,101 | 54,900 | 308,031 |
| 1957 | 6,693 | 9,142 | 10,403 | 13,401 | 34,910 | 39,744 | 30,179 | 52,348 | 63,035 | 57,282 | 317,137 |
| 1958 | 6,677 | 9,700 | 9,213 | 12,815 | 35,396 | 35,805 | 34,193 | 55,984 | 67,954 | 56,701 | 324 438 |
| 1959 | 6,844 | 8,131 | 9,526 | 13,879 | 36,146 | 30,469 | 34,977 | 52,583 | 65,309 | 69,631 | 327,495 |
| Percentage of Total Membership | |||||||||||
| 1901 | 24.3 | 17.0 | 20.3 | 8.7 | 10.6 | 6.9 | 12.2 | — | — | — | 100.0 |
| 1911 | 13.5 | 13.8 | 11.4 | 16.0 | 17.4 | 16.9 | — | — | 11.0 | — | 100.0 |
| 1921 | 11.5 | 9.9 | 9.4 | 11.3 | 19.0 | 14.9 | 7.6 | 6.7 | 9.7 | — | 100.0 |
| 1931 | 11.1 | 8.8 | 8.4 | 12.4 | 22.8 | 20.5 | 7.4 | — | 8.6 | — | 100.0 |
| 1941 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 4.0 | 6.5 | 9.9 | 15.3 | 13.4 | 17.8 | 12.6 | 12.8 | 100.0 |
| 1951 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 10.0 | 14.5 | 10.0 | 15.8 | 14.8 | 19.1 | 100.0 |
| 1956 | 2.2 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 10.2 | 13.0 | 10.1 | 15.3 | 20.2 | 17.8 | 100.0 |
| 1957 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 4.2 | 11.0 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 16.5 | 19.9 | 18.1 | 100.0 |
| 1958 | 2.1 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 10.9 | 11.0 | 10.5 | 17.3 | 20.9 | 17.5 | 100.0 |
| 1959 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 4.2 | 11.0 | 9.3 | 10.7 | 16.1 | 19.9 | 21.3 | 100.0 |
There has been a more or less steady growth in the average size of workers' unions, the trend being to a certain extent obscured at times by the cancellation of registration by some large unions. An average membership of 118 in 1901 increased in 1921 to 234, in 1941 to 551, and in 1956 to 746. The average membership of the 399 workers' unions registered in 1959 was 821.
INDUSTRIAL ASSOCIATIONS — At 31 December 1959 there were 18 industrial associations of employers and 41 of workers, the former having 133 affiliated unions and the latter 219. The following summary shows the number of industrial associations of employers and workers in each industrial group, with the number of affiliated unions in each case. In most cases the associations cover the entire country.
| Industrial Group | Employers | Workers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associations | Affiliated Unions | Associations | Affiliated Unions | |||||
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| Provision of — | ||||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 5 | 5 | 37 | 36 | 5 | 5 | 26 | 23 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | — | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | 11 | 11 |
| Building and construction | 3 | 3 | 41 | 40 | 3 | 3 | 26 | 26 |
| Power, heat, and light | — | — | — | —1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Transport by water | 1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 31 | 31 |
| Transport by land | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 2 | 2 | 20 | 21 | 3 | 3 | 18 | 18 |
| Working in or on — | ||||||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 7 |
| Metal | — | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | 10 | 10 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 9 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 2 | 2 | 11 | 10 | — | — | — | — |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Mines and quarries | — | — | — | — | 2 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| The land (farming pursuits) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Miscellaneous | — | — | — | — | 8 | 8 | 60 | 59 |
| Totals | 18 | 18 | 135 | 133 | 41 | 41 | 225 | 219 |
PROPORTION OF UNIONISTS — The following table, showing the proportion of workers belonging to unions registered under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act to the total number of wage earners in the country, is of interest as manifesting the movement in and the extent of unionism during the period under review. The figures for total wage earners are derived from census enumerations and include professional, business, and other classes in which unionism prior to the passing of the amending Act of 1936 did not exist, and agricultural and pastoral occupations where it was practically non-existent. In addition, females are included in both sets of figures, although the proportion of women unionised prior to 1936 was negligible.
| Census Year | Total Wage Earners | End of Year Nearest to Census Date | Numbers of Workers on Rolls of Registered Unions | Percentage of Wage Earners on Rolls of Registered Unions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *1950 figures incomplete. | ||||
| 1901 (March) | 224,346 | 1900 | 17,989 | 8 |
| 1906 (April) | 269,039 | 1905 | 29,869 | 11 |
| 1911 (April) | 304,272 | 1910 | 57,091 | 19 |
| 1916 (October) | 302,161 | 1916 | 71,587 | 24 |
| 1921 (April) | 370,692 | 1920 | 96,350 | 26 |
| 1926 (April) | 414,673 | 1925 | 100,540 | 24 |
| 1936 (March) | 496,563 | 1935 | 80,929 | 16 |
| 1945 (September) | 473,684 | 1945 | 229,103 | 48 |
| 1951 (April) | 577,694 | 1950 | 267,225* | 46 |
| 1956 (April) | 653,358 | 1955 | 304,520 | 47 |
GENERAL — New Zealand's first legislation in industrial relations was the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act of 1894. This Act was almost revolutionary in its conception and aroused world-wide interest in its provisions for the compulsory reference of industrial disputes to arbitration. The Act was designed to promote the formation and registration of both employers' and workers' unions and provide regulation of conditions of employment by industrial agreements. It aimed at prevention of industrial disturbances by providing that disputes be referred to Boards of Conciliation. In the event of disagreement, either party could request that the dispute be referred to the Court of Arbitration. Findings of the Court were to be recorded in an award enforceable at law. It is of interest to note that the system has survived, despite the crises of depression and war, and has remained one against which, over a period of more than 60 years, no serious criticism on grounds of efficiency has been voiced.
The Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954 is the present statute governing most industrial disputes. The Act applies only where the workers in any industry have registered as an industrial union. Thereupon the union and the employers in the industry and locality may enter into an industrial agreement fixing the minimum wages, and other conditions of employment. In lieu of such agreement either side may bring a dispute before a Council of Conciliation with subsequent recourse to the Court of Arbitration for an award. Both industrial agreements and awards are enforceable in the Courts by parties thereto or by officers of the Department of Labour.
The term “dispute” is used in its widest sense and is intended to refer to the whole field of wage fixation and conditions of employment, as well as to the settlement of strikes and lockouts. New Zealand's approach to this problem is different from that adopted in most other countries in that it has preferred to follow a system of conciliation and compulsory arbitration, rather than to adopt the more normal system of collective bargaining with the unrestricted right to “strike” or “lockout”. It is, however, incorrect to say that unions in New Zealand must submit to compulsory arbitration. It is entirely in their own hands to decide whether they wish to follow that method or to remain outside the scope of the Act, and to settle their disputes by collective bargaining under the procedure laid down in the Labour Disputes Investigation Act 1913.
The principle which has been written into the Act is that if unions elect to register under the Act they forfeit the right to strike and elect to have their differences settled by conciliation and arbitration. Most unions have seen fit to register under the Act and thereby have forfeited their right to strike.
All industrial disputes must be referred to a Council of Conciliation before reference to the Court of Arbitration. The Conciliation Council consists of a Conciliation Commissioner, who is chairman, and not more than four assessors from each side. In the case of a dispute extending over two or more industrial districts, up to seven assessors from each side may be appointed. The proceedings are quite informal. It is the duty of the council to endeavour to bring about a settlement of the dispute between the parties. (The Conciliation Commissioner has no vote.)
If a settlement of a dispute is brought about by the council, the terms of settlement are reduced to writing and, when signed, the document operates as if it were an industrial agreement signed by all the parties to the dispute; but any party to the dispute may apply to the Court of Arbitration for exemption. In most cases the parties prefer an award and it is usual for the parties to apply to the Court to have the terms of settlement embodied in an award. This may be done by the Court without a hearing. If the council cannot bring about a settlement the dispute is automatically referred to the Court for settlement.
INDUSTRIAL CONCILIATION AND ARBITRATION ACT — The administration of the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act is in the hands of the Department of Labour. The Registrar of Industrial Unions is responsible for registration of industrial unions, recording of rules, and other administrative functions. Inspectors of Factories are charged with the duty of seeing that the provisions of awards and agreements are carried out. The following paragraphs indicate the procedure followed in regard to industrial disputes under the Act:
An industrial union (or association of unions) of workers registered under the Act may cite a union or association of unions of employers, or an employer, or a number of employers, before a Council of Conciliation for the hearing of an industrial dispute before a Commissioner and assessors appointed from either side.
An industrial union (or association of unions) of employers registered under the Act, or an individual employer, or employers, may cite a union of workers in a similar manner. The workers may compel any of their employers to come under the Act, but the employers cannot compel their workers to come under it unless the latter have registered as an industrial union or association thereunder; registration is voluntary.
If a settlement of a dispute is arrived at by the parties in the course of an inquiry held before a Council of Conciliation, the terms of the settlement are set forth as an industrial agreement. Applications for exemption from the terms of the agreement must be made within one month after it has been filed. The Court is empowered to grant or to refuse such applications. Where an agreement applies to the employers employing the majority of workers in the industry to which it relates, the agreement may be made binding on all employers, whether parties or not.
Every such agreement must be executed on behalf of the parties by the assessors representing the parties. If settlement cannot be arrived at before the Conciliation Council the matter is referred to the Court. The Council may at the same time submit a recommendation for the settlement of the dispute; whereupon the parties are notified of such recommendation, and, if acceptable to them, the recommendation is made an industrial agreement; failing agreement the matter is referred to the Court.
If a dispute comes before the Court, argument is heard upon the matters in debate, and the Court then makes its award, which becomes binding upon the employers specified in the award, upon any employers commencing business in the district subsequently to the date of the award, and upon all persons working for such employers. In all cases where an industrial agreement or accepted recommendation or award is filed, it becomes binding on all the parties. When an award or industrial agreement has been filed, a strike or lockout becomes unlawful. Unless the parties otherwise agree, rates of wages specified in an award shall have effect from two months after the date first appointed for the hearing by the Conciliation Council, or where two or more districts are affected, four months after this date, or as from the date of the making of the award, whichever is the earlier, or as from such other date as the Court in its discretion thinks fit after taking into consideration all relevant matters.
No industrial dispute shall be referred for settlement to a Council of Conciliation by an industrial union (or association of unions) unless the proposed reference has been approved by resolution by the committee of management of the union or of each of the unions concerned, as the case may be.
Where an application has been made to a Conciliation Commissioner for the hearing of an industrial dispute by a Council of Conciliation the claims made by the applicant may be amended or withdrawn at any time, whether before or during the hearing. Where any industrial dispute has been referred to the Court for settlement, or any application has been made to the Court under the principal Act, the reference or application may be withdrawn by the applicants at any time, whether before or during the hearing.
The Minister of Labour is empowered, if he is satisfied that any discontinuance of employment brought about wholly or partly by any industrial union of employers or of workers has caused, or is likely to cause, serious loss or inconvenience, to cancel the registration of the union concerned or to cancel any award or industrial agreement so far as this relates to it.
In 1951 provision was made that any award or industrial agreement may include provisions to the effect that any party to a dispute on a matter arising out of the award or agreement but not specifically dealt with therein may require the appointment of a local disputes committee, which will have power to decide the dispute or to refer it to a Conciliation Commissioner. The latter in his discretion can refer the dispute either to a national disputes committee, which may be appointed where any award relates to two or more industrial districts or parts thereof, or to the Court of Arbitration. Appeals against the decisions of the disputes committees may be made to the Court of Arbitration.
Where a majority of the workers affected by any industrial dispute under the principal Act are hospital board employees, the Director-General of Health is to be a party to the dispute and is to recommend assessors for the employers in the conciliation proceedings. Other sections provide that an award is not to be made affecting hospital employees now affected by regulations unless a majority votes in favour of an award, and for the concurrence of the Minister of Health with industrial agreements in similar circumstances.
Definitions of the terms “strike” and “lockout” are given in the Act (which apply also for the purposes of the Labour Disputes Investigation Act 1913). A strike means the act of any number of workers who are or have been in the employment of the same or of different employers:
In discontinuing that employment, whether wholly or partially; or
In breaking their contracts of service; or
In refusing or failing after any such discontinuance to resume or return to their employment; or
In refusing or failing to accept engagement for any work in which they are usually employed; or
In reducing their normal output or their normal rate of work —the act being due to any combination, agreement, common understanding, or concerted action, whether express or implied, made or entered into by any workers;
With intent to compel or induce any such employer to agree to terms of employment or comply with any demands made by the said or any other workers; or
With intent to cause loss or inconvenience to any such employer in the conduct of his business; or
With intent to incite, aid, abet, instigate, or procure any other strike; or
With intent to assist workers in the employment of any other employer to compel or induce that employer to agree to terms of employment or comply with any demands upon him by any workers.
A lockout means the act of an employer:
In closing his place of business, or suspending or discontinuing his business in any branch thereof; or
In discontinuing the employment of any workers, whether wholly or partially; or
In breaking his contracts of service; or
In refusing or failing to engage workers for any work for which he usually employs workers — with intent;
To compel or induce any workers to agree to terms of employment or comply with any demands made upon them by the said or any other employer; or
To cause loss or inconvenience to the workers employed by him or to any of them; or
To incite, aid, abet, instigate, or procure any other lockout; or
To assist any other employer to compel or induce any workers to agree to terms of employment or comply with any demands made by him.
An industrial dispute is a strike if it comes within the definition of a strike which is quoted above. It is in addition an unlawful strike if either:
The union or the workers taking part in it are for the time being bound by an award or industrial agreement under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954, or by a duly filed agreement under the Labour Disputes Investigation Act 1913, or by any principal order under the Waterfront Industry Act 1953; or
In the case of a dispute relating to conditions of employment between a society of workers to which the Labour Disputes Investigation Act 1913 applies, but who are not bound by any duly filed agreement under the Act, they have failed to give notice of the dispute to the Minister of Labour as required by section 4 of that Act, or if the strike occurs before the expiration of seven days after the publication of the result of a secret ballot of the workers directly concerned taken in pursuance of the Act.
Further, a strike which would not be unlawful for any of these reasons may be or become unlawful by the operation of regulations to that effect made under the Public Safety Conservation Act 1932, during a state of emergency declared by proclamation of the Governor-General in accordance with the provisions of that Act.
Maximum penalties and fines for being a party to or inciting, instigating, or aiding an unlawful strike or lockout are also provided for — namely, (a) for a worker, £50 or (in the case of certain essential industries) £75; (b) for a union official, £250 or £350; (c) for a union or association or employer, £500 or £750. The maximum penalty for impeding or interfering with a secret ballot on the question of a strike or lockout is imprisonment for 12 months or a fine of £100, or both.
The law relating to the taking of secret ballots by members of industrial unions of workers or of employers on questions relating to strikes and lockouts has been supplemented by making the union liable as having instigated any strike or lockout that takes place without a secret ballot having first been taken. The penalty in such a case is a fine not exceeding £100 for every member of the union taking part in a strike, and for every official of the union a fine of £500 unless he proves that he had no means of knowing the imminence of the strike or that he took every step possible to ensure compliance with the provision and to prevent the strike. Corresponding maximum penalties in respect of a lockout are £1,000 for a member of the union and £500 for an official.
Section 196 of the Act provides special penalties in certain circumstances for strikes in specified essential industries.
LABOUR DISPUTES INVESTIGATION ACT — Machinery for dealing with all disputes to which the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act does not relate is contained in the Labour Disputes Investigation Act 1913.
Under this Act, if a dispute concerning wages or other conditions of employment arises between a society (or societies) of workers, whether registered or not, that is not bound by any award or industrial agreement and its employers, the society must, before it may strike, give to the Minister of Labour formal notice of the dispute, setting forth the names of the parties to the dispute and the claims made by the society. The Minister then refers the dispute to a Conciliation Commissioner to call a conference, or to a labour disputes committee for investigation and recommendation. Such a committee consists of from one to three members chosen from each side, with an independent chairman. In the event of no settlement being arrived at, a secret ballot is taken by the Registrar of Industrial Unions among the members of the society as to whether, in the case of no recommendation having been made, a strike should eventuate; or, in the case of a recommendation having been made, as to whether the recommendation should be adopted. Seven days' notice must be given to the employers should a strike be decided upon.
Similar provisions apply with reference to the filing of a dispute and to a lockout by the employers.
In the event of an agreement being arrived at, it may be filed with the Clerk of Awards. It is then enforceable in the same manner as an industrial agreement under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act.
By this Act the principle of settlement of industrial disputes by conciliation and arbitration is extended to workers outside the scope of the Court of Arbitration, so that definite restrictions on the right to strike or to lockout exist over the whole field of industry in New Zealand. The powers under this Act are not, of course, as far reaching as those under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, its main object being that workers or employers should take time for consideration of the points at issue and not precipitate themselves into industrial strife.
INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS ACT 1949 — This measure contains a section enabling a Conciliation Commissioner or a person nominated by the Minister to call a compulsory conference of parties where there is reason to believe that a matter not provided for in the award or industrial agreement governing the industry is causing or is likely to cause industrial unrest.
STATISTICS OF INDUSTRIAL STOPPAGES — In the tabulations which follow only those disputes are included which resulted in a strike or lockout, or where organised “go slow” or other passive-resistance methods were clearly manifested. Many disputes are, of course, settled without recourse to such measures; these are not recorded for statistical purposes. To avoid confusion with the term “dispute” as used in the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act, these statistics have been called “industrial stoppages”.
The compilation of statistics regarding industrial stoppages was first undertaken by the Department of Statistics at the beginning of the year 1920. Returns furnished by Inspectors of Factories from inquiries made in each district form the main source from which information is obtained. It is considered that the statistics based on these reports are less liable to bias than would be the case if parties to the stoppage or other private persons were relied on to furnish the information. It is the duty of an inspector, during the course of a stoppage in his industrial district, to collect all available particulars relating to it. The inspectors have power to make the necessary inquiries, and thus are able to obtain complete information.
It occasionally happens that there are strikes in different centres with the same or similar objects, and occurring at or about the same time; in such cases the several disturbances are treated as one if the available evidence is sufficient to justify such a course, and the duration is taken as the maximum duration in any centre. While the stoppage itself may be tabulated under a single industrial district, the actual number of workers involved may be distributed over more than one of the districts.
In the tables following no distinction is drawn between strikes which were lawful and those which were unlawful. Detailed figures for the period 1921–60 are as follows:
| Year | Total Industrial Stoppages* | Firms Affected | Total Duration (Days) | Average Duration (Days) | Workers Involved† | Working Days Lost† | Average Days Lost per Worker Involved† | Estimated Loss in Wages† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*The number of lockouts included in total industrial stoppages were: 1925, 2; 1928, 2; 1929, 1; 1931, 1; 1940, 1; and 1944, 1. † Includes workers indirectly involved. | ||||||||
| £ | ||||||||
| 1921 | 77 | 112 | 769 | 9.99 | 10,433 | 119,208 | 11.43 | 90,477 |
| 1922 | 58 | 67 | 851 | 14.68 | 6,414 | 93,456 | 14.57 | 60,782 |
| 1923 | 49 | 79 | 603 | 12.31 | 7,162 | 201,812 | 28.18 | 114,074 |
| 1924 | 34 | 58 | 134 | 3.94 | 14,815 | 89,105 | 6.01 | 62,732 |
| 1925 | 83 | 93 | 598 | 7.20 | 9,905 | 74,552 | 7.53 | 49,149 |
| 1926 | 59 | 67 | 314 | 5.32 | 6,264 | 47,811 | 7.63 | 32,355 |
| 1927 | 38 | 40 | 83 | 2.18 | 4,476 | 12,485 | 2.79 | 11,819 |
| 1928 | 39 | 56 | 253 | 6.49 | 9,258 | 21,997 | 2.38 | 22,304 |
| 1929 | 47 | 60 | 342 | 7.28 | 7,151 | 25,889 | 3.62 | 26,940 |
| 1930 | 38 | 44 | 392 | 10.32 | 5,467 | 31,669 | 5.79 | 37,299 |
| 1931 | 24 | 37 | 262 | 10.92 | 6,356 | 48,486 | 7.63 | 44,544 |
| 1932 | 23 | 67 | 313 | 13.61 | 9,355 | 108,605 | 11.61 | 105,715 |
| 1933 | 15 | 43 | 205 | 13.67 | 3,558 | 65,099 | 18.30 | 59,334 |
| 1934 | 24 | 37 | 120 | 5.00 | 3,773 | 10,393 | 2.75 | 7,121 |
| 1935 | 12 | 65 | 88 | 7.33 | 2,323 | 18,563 | 7.99 | 15,266 |
| 1936 | 43 | 128 | 221 | 5.14 | 7,354 | 16,980 | 2.31 | 12,886 |
| 1937 | 52 | 72 | 320 | 6.15 | 11,411 | 29,916 | 2.62 | 32,129 |
| 1938 | 72 | 103 | 287 | 3.99 | 11,388 | 35,456 | 3.11 | 42,104 |
| 1939 | 66 | 636 | 416 | 6.30 | 15,682 | 53,801 | 3.43 | 60,394 |
| 1940 | 57 | 99 | 435 | 7.63 | 10,475 | 28,097 | 2.68 | 28,062 |
| 1941 | 89 | 97 | 233 | 2.62 | 15,261 | 26,237 | 1.72 | 34,552 |
| 1942 | 65 | 78 | 143 | 2.20 | 14,345 | 51,189 | 3.57 | 63,179 |
| 1943 | 69 | 114 | 122 | 1.77 | 10,915 | 14,687 | 1.35 | 20,179 |
| 1944 | 149 | 269 | 281 | 1.89 | 29,766 | 52,602 | 1.77 | 74,012 |
| 1945 | 154 | 1,255 | 379 | 2.46 | 39,418 | 66,629 | 1.69 | 92,546 |
| 1946 | 96 | 122 | 259 | 2.70 | 15,696 | 30,393 | 1.94 | 40,112 |
| 1947 | 134 | 234 | 834 | 6.2 | 26,970 | 102,725 | 3.81 | 187,669 |
| 1948 | 101 | 885 | 608 | 6.02 | 28,494 | 93,464 | 3.28 | 195,985 |
| 1949 | 123 | 1,315 | 672 | 5.46 | 61,536 | 218,172 | 3.55 | 390,773 |
| 1950 | 129 | 1,189 | 567 | 4.40 | 91,492 | 271,475 | 2.97 | 514,236 |
| 1951 | 109 | 354 | 3,464 | 31.78 | 36,878 | 1,157,390 | 31.38 | 3,111,307 |
| 1952 | 50 | 177 | 108 | 2.16 | 16,297 | 28,123 | 1.73 | 69,371 |
| 1953 | 73 | 880 | 145 | 1.99 | 22,175 | 19,291 | 0.87 | 48,433 |
| 1954 | 61 | 447 | 136 | 2.23 | 16,153 | 20,474 | 1.27 | 66,366 |
| 1955 | 65 | 114 | 211 | 3.25 | 20,224 | 52,043 | 2.57 | 185,287 |
| 1956 | 50 | 426 | 390 | 7.80 | 13,579 | 23,870 | 1.76 | 84,206 |
| 1957 | 51 | 88 | 165 | 3.24 | 15,545 | 28,186 | 1.81 | 83,023 |
| 1958 | 49 | 83 | 152 | 3.10 | 13,709 | 18,788 | 1.37 | 64,232 |
| 1959 | 73 | 119 | 229 | 3.14 | 18,762 | 29,651 | 1.58 | 107,461 |
| 1960 | 60 | 81 | 344 | 5.73 | 14,305 | 35,683 | 2.49 | 116,412 |
The following table shows figures of incidence rates of stoppages for the period 1947–60.
| Year | Number of Wage and Salary Earners* | Workers Involved as Percentage of Wage and Salary Earners | Working Days Lost per 1,000 of Wage and Salary Earners |
|---|---|---|---|
| *October estimates. | |||
| (000) | |||
| 1947 | 545.5 | 4.94 | 188.31 |
| 1948 | 556.3 | 5.12 | 168.01 |
| 1949 | 568.1 | 10.83 | 384.04 |
| 1950 | 574.9 | 15.91 | 472.21 |
| 1951 | 583.0 | 6.33 | 1,985.23 |
| 1952 | 591.4 | 2.76 | 47.55 |
| 1953 | 608.7 | 3.64 | 31.69 |
| 1954 | 623.7 | 2.59 | 32.83 |
| 1955 | 639.3 | 3.16* | 81.41 |
| 1956 | 652.5 | 2.08 | 36.58 |
| 1957 | 668.2 | 2.33 | 42.18 |
| 1958 | 688.1 | 1.99 | 27.30 |
| 1959 | 693.8 | 2.70 | 42.74 |
| 1960 | 714.0 | 2.00 | 49.98 |
The figures for stoppages include details of stop-work meetings unless, as on the waterfront, provision is made for these in the relevant award or agreement. In all cases unauthorised stop-work meetings are included, also unauthorised delays in resuming work after recognised stop-work meetings. A single stoppage may include or may consist of one stop-work meeting or several stop-work meetings; if several such meetings are included, these may be held at different times or different places, provided all relate to the same issue. This class of stoppage has assumed considerable importance recently, the number of such cases in the five years 1956–60 being 37 (44 stop-work meetings) involving 16,595 workers, and the loss of 8,619 working days and of £33,452 in wages.
In the table shown later recording methods of settlement, all such interruptions of labour, including periods of deliberate absence from work by way of a protest against an alleged injustice, are classified under the heading “voluntary return to work”. In 1956 these cases comprised 17 out of 50 stoppages; in 1957, 18 out of 51; in 1958, 19 out of 49; in 1959, 29 out of 73; and in 1960, 21 out of 60.
In calculating the number of working days lost it is assumed that work would have been continuous if no stoppage had taken place. No allowance is made for loss of work from unemployment or other causes which might have occurred even if there had been no stoppage, nor is the possibility taken into account of strikers being replaced with non-union labour. In some cases, such as shearing, there is a definite amount of work to be done, and a stoppage of work does not decrease the total amount of it, but only postpones its completion. In those cases the figures are perhaps more or less fictitious, but in the great majority of cases they represent a real loss.
From the preceding tables it will be seen that prior to 1951 the greatest time lost by stoppages in any one calendar year was in 1950, when several serious disturbances occurred, including a general railways strike, three separate waterfront disputes, a coal-mines stoppage, and a subsidy-removal protest involving workers in some 10 industries. The next highest figure of man-days lost was that for 1949, when the Auckland carpenters' strike and also a general waterfront stoppage occurred. Next in order — in point of lost time — came 1923 when serious stoppages occurred in the coal-mining and shipping industries, 1921 (marked by strikes of waterside workers), 1932 (chiefly strikes of waterside workers and coal miners), 1947 (stoppages among waterside workers, freezing workers, and coal miners), and 1948 (disturbances in coal mining, waterfront, and building and construction industries).
The year 1951 was marked by a prolonged waterfront strike, lasting from 9 February to 17 July, and constituting the most serious industrial disturbance which has ever occurred in New Zealand. During its course other essential industries, notably coal mining, shipping, and meat freezing, became involved. Since 1951 there has been comparative peace in industry; this is emphasised by the low incidence rates in these years compared with the rates recorded annually over the period 1947 to 1951 (inclusive).
The only serious dispute which occurred during 1952 was a disagreement as to wages between tradesmen in freezing works and their employers. Of the total of 28,123 days lost through all stoppages in that year, 13,933 days, or almost 50 per cent, were on account of this single strike. The year 1953 was marked by frequent minor stoppages of which, however, no single disturbance merits special mention. Time lost during 1954 included 6,300 working days in respect of a strike at the Roxburgh hydro-electric construction works, which was the only disturbance of any gravity during that year. Two stoppages accounted for over 50 per cent of the working days lost in 1955; a strike at the Roxburgh hydro-electric construction works involved the loss of 17,178 working days, and a stoppage over employment conditions in the building and construction industry resulted in the loss of 9,179 days. In 1956 two industrial groups — meat industry, and building and construction — accounted for about two-thirds of the number of working days lost and estimated loss in wages. During 1957 the majority of the time lost was in the building and construction, meat-freezing and, coal-mining industries, a number of comparatively minor stoppages having occurred in each of these fields. In 1958 the building and construction industry accounted for almost 45 per cent of the working days lost, the majority of the remaining time lost being due to strikes in the meat-freezing, coal-mining, and waterfront industries. During 1959 the meat-freezing industry was responsible for more than 43 per cent of the working days lost; the coal-mining, building and construction, and paper and pulp industries accounted for the major part of the remaining time lost. Of the working days lost in 1960 the meat freezing industry accounted for 18,924, or more than half, the second in order being the pulp and paper industry with 6,363 working days lost, or almost one-fifth of the total. The balance of the working time lost was shared fairly equally by the other industrial groups.
Nature and Duration — The next table shows the nature of the stoppages and the number of workers involved during the years 1950–60.
| Year | Nature of Stoppage | Number of Workers Involved | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Strike | Sympathetic Strike | Partial Strike* | Total | Direct Strike | Sympathetic Strike | Partial Strike* | Total | |
| *i.e., where no actual cessation of work, but a “go slow” or other policy of protest adopted. | ||||||||
| 1950 | 129 | — | — | 129 | 91,492 | — | — | 91,492 |
| 1951 | 58 | 48 | 3 | 109 | 22,427 | 13,878 | 573 | 36,878 |
| 1952 | 50 | — | — | 50 | 16,297 | — | — | 16,297 |
| 1953 | 73 | — | — | 73 | 22,175 | — | — | 22,175 |
| 1954 | 61 | — | — | 61 | 16,153 | — | — | 16,153 |
| 1955 | 62 | 2 | 1 | 65 | 20,044 | 123 | 57 | 20,224 |
| 1956 | 50 | — | — | 50 | 13,579 | — | — | 13,579 |
| 1957 | 51 | — | — | 51 | 15,545 | — | — | 15,545 |
| 1958 | 49 | — | — | 49 | 13,709 | — | — | 13,709 |
| 1959 | 71 | 2 | — | 73 | 16,176 | 2,586 | — | 18,762 |
| 1960 | 56 | 4 | — | 60 | 13,923 | 382 | — | 14,305 |
The table following illustrates the duration of stoppages during 1960.
| Duration | Number of Stoppages | Number of Firms Affected | Number of Workers Involved | Number of Working Days Lost | Estimated Loss in Wages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | |||||
| 1 day and less | 26 | 26 | 5,762 | 4,132 | 16,759 |
| Over 1 day but not over 2 days | 7 | 7 | 1,159 | 1,659 | 5,997 |
| Over 2 days but not over 3 days | 6 | 15 | 2,796 | 3,908 | 16,534 |
| Over 3 days but less than 1 week | 9 | 11 | 1,369 | 4,138 | 11,864 |
| 1 week but less than 2 weeks | 5 | 9 | 2,337 | 13,695 | 37,578 |
| 2 weeks but less than 4 weeks | 6 | 12 | 867 | 6,981 | 24,755 |
| 4 weeks but less than 8 weeks | — | — | — | — | — |
| 8 weeks and over | 1 | 1 | 15 | 1,170 | 2,925 |
| Totals | 60 | 81 | 14,305 | 35,683 | 116,412 |
Geographical Distribution — The following table shows the number of stoppages in each industrial district for the years 1956–60 and also the number of workers involved. In 1960 the Northern District had the greatest number of stoppages and the Otago and Southland District the greatest number of workers involved; the meat freezing and fertiliser industries accounted for all the workers involved in the latter district.
| Year | Northern | Taranaki | Wellington | Marlborough | Nelson | Westland | Canterbury | Otago and Southland | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stoppages | |||||||||
| 1956 | 19 | — | 4 | — | — | 7 | 14 | 6 | 50 |
| 1957 | 33 | — | 5 | — | — | 5 | 2 | 6 | 51 |
| 1958 | 26 | — | 8 | — | 2 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 49 |
| 1959 | 31 | 1 | 8 | — | — | 15 | 14 | 4 | 73 |
| 1960 | 26 | — | 7 | — | — | 12 | 3 | 12 | 60 |
| Number of Workers Involved | |||||||||
| 1956 | 2,529 | — | 1,773 | — | — | 1,466 | 4,775 | 3,036 | 13,579 |
| 1957 | 10,319 | — | 726 | — | — | 3,150 | 616 | 734 | 15,545 |
| 1958 | 10,133 | — | 613 | — | 631 | 1,175 | 835 | 322 | 13,709 |
| 1959 | 5,691 | 529 | 1,613 | — | — | 3,426 | 6,938 | 565 | 18,762 |
| 1960 | 3,212 | — | 2,329 | — | — | 3,640 | 462 | 4,662 | 14,305 |
A stoppage extending into more than one industrial district is, in the table “Number of stoppages”, allocated to that district which includes the greatest number of the workers involved. The actual (or occasionally estimated) numbers of workers in the several districts are, however, correctly distributed.
Industrial Distribution — In the following table industrial stoppages are classified according to the industrial groups in which they took place, this grouping being similar to that used in the compilation of wage and industrial-union statistics.
| Industrial Group | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | Totals 1956–60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stoppages | ||||||
| Provision of — | ||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 17 | 14 | 15 | 29 | 24 | 99 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 |
| Building and construction | 6 | 22 | 18 | 14 | 5 | 65 |
| Power, heat, and light | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 |
| Transport by water and air | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 21 |
| Transport by land | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 | 4 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Working in or on — | ||||||
| Wood, etc. | 1 | — | — | 1 | — | 2 |
| Metal | 1 | — | 1 | 4 | 3 | 9 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 8 | 1 | — | — | 4 | 13 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Mines and quarries — | ||||||
| Coal mines | 7 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 11 | 48 |
| Miscellaneous | 2 | 2 | — | — | — | 4 |
| Totals | 50 | 51 | 49 | 73 | 60 | 283 |
| Number of Workers Involved | ||||||
| Provision of — | ||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 5,434 | 2,122 | 2,984 | 8,897 | 6,418 | 25,855 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | — | — | — | 299 | — | 299 |
| Building and construction | 1,551 | 4,238 | 4,250 | 1,169 | 215 | 11,423 |
| Power, heat, and light | — | — | — | 40 | — | 40 |
| Transport by water and air | 2,438 | 4,903 | 3,757 | 4,040 | 1,326 | 16,464 |
| Transport by land | 103 | 20 | — | — | 889 | 1,012 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | — | — | — | — | 15 | 15 |
| Working in or on — | ||||||
| Wood, etc. | 150 | — | — | 17 | — | 167 |
| Metal | 137 | — | 62 | 165 | 627 | 991 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 1,317 | 72 | — | — | 383 | 1,772 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 938 | 430 | 850 | 709 | 1,188 | 4,115 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Mines and quarries — | ||||||
| Coal mines | 1,466 | 3,150 | 1,806 | 3,426 | 3,244 | 13,092 |
| Miscellaneous | 45 | 610 | — | — | — | 655 |
| Totals | 13,579 | 15,545 | 13,709 | 18,762 | 14,305 | 75,900 |
A more detailed analysis of stoppages occurring during 1960 is given below.
| Industrial Group | Number of Stoppages | Number of Firms Affected | Number of Workers Involved | Number of Working Days Lost | Estimated Loss in Wages | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directly | Indirectly | Total | |||||
| Provision of — | £ | ||||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 24 | 26 | 5,650 | 768 | 6,418 | 18,928 | 55,815 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Building and construction | 5 | 5 | 215 | — | 215 | 317 | 1,160 |
| Power, heat, and light | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Transport by water and air | 5 | 14 | 1,297 | 29 | 1,326 | 1,295 | 7,765 |
| Transport by land | 2 | 2 | 889 | — | 889 | 1,373 | 2,749 |
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 1 | 1 | 15 | — | 15 | 1,170 | 2,925 |
| Working in or on — | |||||||
| Wood, etc. | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Metal | 3 | 7 | 627 | — | 627 | 1,856 | 5,197 |
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 4 | 4 | 383 | — | 383 | 1,032 | 2,841 |
| Paper, printing, etc. | 5 | 11 | 1,188 | — | 1,188 | 6,363 | 21,080 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Mines and quarries — | |||||||
| Coal mines | 11 | 11 | 3,244 | — | 3,244 | 3,349 | 16,880 |
| Miscellaneous | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Totals | 60 | 81 | 13,508 | 797 | 14,305 | 35,683 | 116,412 |
Causes — In the next table the causes of stoppages which occurred during the years 1956–60 are shown. Under the heading “Wages” are included stoppages concerning wages, overtime, or rates for piece work.
Stoppages concerning the employment or non-employment of certain classes of persons are included under the heading “Employment”. This question usually arises in connection with industrial union affairs, such as, for instance, the dismissal of a worker on allegedly insufficient grounds, or formerly the employment of non-unionists. Since 1936, however, all adult workers who are subject to any award or industrial agreement have been required, unless specially exempted, to be members of a union, and, except when there are no unionists available, an employer may not employ a non-unionist.
“Other working conditions” are of diverse nature, but some may be mentioned as follows: distribution of work in coal mines and on wharves, conveyance to and from work, atmospheric conditions in coal mines, accommodation on ships, numbers of men to be allocated to certain duties, supply of food, method of handling cargo.
Under the heading “Sympathy” are included all stoppages caused by workers striking not on account of a grievance arising out of their own wages or conditions, but in sympathy with the demands of other workers.
| Cause | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stoppages | |||||
| Wages | 19 | 14 | 17 | 25 | 18 |
| Hours | 1 | — | 1 | — | 2 |
| Employment | 17 | 20 | 16 | 31 | 23 |
| Other working conditions | 5 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 9 |
| Sympathy | — | — | — | 2 | 4 |
| Other causes | 8 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 4 |
| Totals | 50 | 51 | 49 | 73 | 60 |
| Number of Workers Involved | |||||
| Wages | 6,882 | 3,920 | 2,833 | 6,875 | 4,209 |
| Hours | 135 | — | 194 | — | 514 |
| Employment | 2,518 | 5,453 | 4,218 | 5,549 | 5,349 |
| Other working conditions | 964 | 3,648 | 5,622 | 2,636 | 2,812 |
| Sympathy | — | — | — | 2,586 | 382 |
| Other causes | 3,080 | 2,524 | 842 | 1,116 | 1,039 |
| Totals | 13,579 | 15,545 | 13,709 | 18,762 | 14,305 |
A further analysis by causes for the year 1960 will be found on page 1046.
Methods of Settlement — Following is a table showing the methods of settlement of disputes causing stoppages during the years 1956–60. Negotiations supposedly under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act and the Labour Disputes Investigation Act are treated as “Intervention of third party.” “Voluntary return to work” includes such cases as “Protest” absence and stop-work meetings. Other headings are self-explanatory.
| Method of Settlement | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stoppages | |||||
| Private negotiations between parties | 24 | 18 | 15 | 27 | 18 |
| Intervention of third party | 9 | 15 | 11 | 17 | 20 |
| Voluntary return to work | 17 | 18 | 19 | 29 | 21 |
| Other | — | — | 4 | — | 1 |
| Totals | 50 | 51 | 49 | 73 | 60 |
| Number of Workers Involved | |||||
| Private negotiations between parties | 6,580 | 3,757 | 4,722 | 4,829 | 2,682 |
| Intervention of third party | 1,120 | 2,115 | 2,196 | 3,100 | 4,214 |
| Voluntary return to work | 5,879 | 9,673 | 5,806 | 10,833 | 6,390 |
| Other | — | — | 985 | — | 1,019 |
| Totals | 13,579 | 15,545 | 13,709 | 18,762 | 14,305 |
Further information for the year 1960 is given in the next table.
| Method of Settlement | Number of Stoppages | Number of Firms Affected | Number of Workers Involved | Number of Working Days Lost | Estimated Loss in Wages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | |||||
| Private negotiations between parties | 18 | 18 | 2,682 | 3,428 | 9,726 |
| Intervention of third party | 20 | 24 | 4,214 | 18,559 | 55,359 |
| Voluntary return to work | 21 | 34 | 6,390 | 7,582 | 30,947 |
| Other | 1 | 5 | 1,019 | 6,114 | 20,380 |
| Totals | 60 | 81 | 14,305 | 35,683 | 116,412 |
RESULTS — In compiling the table which follows no stoppage has been included as ending in favour of either employers or workers unless the result has been beyond question. In cases where workers have made more than one demand, succeeding in one or more and failing in one or more, or where they have made one or more demands and in respect of each have been partially successful only, the result has been treated as a compromise. Where stirkers have returned to work without any definite decision being arrived at regarding the demands made, or where (as in the case of a sympathetic strike) no definite demand has been made, or where a strike is merely by way of a protest, the result has been recorded as indeterminate.
RESULTS OF STOPPAGES
| Result | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Stoppages | |||||
| In favour of workers | 11 | 14 | 6 | 11 | 7 |
| In favour of employers | 9 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 10 |
| Compromise | 8 | 5 | 10 | 17 | 16 |
| Indeterminate | 22 | 26 | 28 | 35 | 27 |
| Totals | 50 | 51 | 49 | 73 | 60 |
| Number of Workers Involved | |||||
| In favour of workers | 1,465 | 2,434 | 1,497 | 874 | 1,497 |
| In favour of employers | 1,529 | 976 | 476 | 1,964 | 2,135 |
| Compromise | 2,930 | 406 | 3,807 | 2,307 | 3,604 |
| Indeterminate | 7,655 | 11,729 | 7,929 | 13,417 | 7,069 |
| Totals | 13,579 | 15,545 | 13,709 | 18,762 | 14,305 |
| Number of Working Days Lost | |||||
| In favour of workers | 2,992 | 10,102 | 2,961 | 827 | 3,447 |
| In favour of employers | 8,401 | 4,062 | 1,728 | 3,121 | 8,612 |
| Compromise | 5,400 | 1,144 | 5,109 | 8,993 | 13,901 |
| Indeterminate | 7,077 | 12,878 | 8,990 | 16,710 | 9,723 |
| Totals | 23,870 | 28,186 | 18,788 | 29,651 | 35,683 |
Of stoppages ending definitely in favour of one party or the other during the five years 1956–60 workers succeeded in 49 instances and employers in 40. In the previous five years (1951–55) workers were successful in 51 instances and employers in 23.
CAUSES AND RESULTS — In the following table the causes and results of stoppages occurring during 1960 are shown in conjunction.
| Result | Cause | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wages | Hours | Employment | Other Working Conditions | Sympathy | Other | Total | |
| Number of Stoppages | |||||||
| In favour of workers | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | — | — | 7 |
| In favour of employers | 5 | — | 4 | 1 | — | — | 10 |
| Compromise | 4 | — | 8 | 3 | — | 1 | 16 |
| Indeterminate | 6 | 1 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 27 |
| Totals | 18 | 2 | 23 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 60 |
| Number of Firms Affected | |||||||
| In favour of workers | 7 | 1 | 2 | 1 | — | — | 11 |
| In favour of employers | 7 | — | 4 | 1 | — | — | 12 |
| Compromise | 4 | — | 12 | 3 | — | 1 | 20 |
| Indeterminate | 6 | 1 | 9 | 13 | 6 | 3 | 38 |
| Totals | 24 | 2 | 27 | 18 | 6 | 4 | 81 |
| Number of Workers Involved | |||||||
| In favour of workers | 761 | 264 | 395 | 77 | — | — | 1,497 |
| In favour of employers | 740 | — | 1,386 | 9 | — | — | 2,135 |
| Compromise | 1,354 | — | 1,524 | 576 | — | 150 | 3,604 |
| Indeterminate | 1,354 | 250 | 2,044 | 2,150 | 382 | 889 | 7,069 |
| Totals | 4,209 | 514 | 5,349 | 2,812 | 382 | 1,039 | 14,305 |
| Number of Days Lost | |||||||
| In favour of workers | 1,772 | 86 | 1,550 | 39 | — | — | 3,447 |
| In favour of employers | 1,892 | — | 6,711 | 9 | — | — | 8,612 |
| Compromise | 5,786 | — | 7,439 | 226 | — | 450 | 13,901 |
| Indeterminate | 4,617 | 250 | 1,916 | 2,145 | 277 | 518 | 9,723 |
| Totals | 14,067 | 336 | 17,616 | 2,419 | 277 | 968 | 35,683 |
| Estimated Loss in Wages | |||||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| In favour of workers | 4,678 | 283 | 4,825 | 51 | — | — | 9,837 |
| In favour of employers | 4,924 | — | 22,523 | — | — | — | 27,447 |
| Compromise | 13,193 | — | 23,993 | 712 | — | 2,700 | 40,598 |
| Indeterminate | 15,051 | 1,260 | 8,093 | 11,075 | 1,075 | 1,976 | 38,530 |
| Totals | 37,846 | 1,543 | 59,434 | 11,838 | 1,075 | 4,676 | 116,412 |
In 1900 the first Workers' Compensation Act in New Zealand introduced the principle that where a worker suffered injury by accident arising out of and in the course of employment he was entitled to compensation from his employer, irrespective of whether the latter had been negligent. The Workers' Compensation Act 1956, with regulations made under it, represents the existing law on workers' compensation, subject to certain other relevant legislation mentioned later in this section. “Worker” for the purposes of the Act means any person who has entered into, or works under, a contract of service or apprenticeship with an employer, whether by way of manual labour, clerical work, or otherwise, and whether remunerated by wages, salary, or otherwise. Thus all workers (manual and non-manual) are afforded the protection of the Act, irrespective of the amount of remuneration. A worker who is the husband or wife of his or her employer is not a worker for the purposes of the Act, except for the provisions enabling employers to take out voluntary insurance cover in respect of certain classes of persons as if they were workers covered by the Act.
The worker is entitled to compensation from his employer where he suffers personal injury by accident arising out of and in the course of the employment, and this is so whether or not the employment is for the purposes of any trade or business carried on by the employer and whether or not the employment is of a casual nature. Even if the worker is working under an illegal contract of service at the time of an accident arising out of and in the course of employment, he is entitled to compensation if the illegality consists in evasion of a statutory minimum age provision, or if the Judge, Magistrate, or other person dealing with the matter decides, having regard to all the circumstances, to treat the contract as valid. No compensation is payable in respect of any accident which is attributable to the serious and wilful misconduct of the worker injured, unless the injury results in death or serious or permanent disablement. No compensation is payable in respect of the death of a worker following on, or incapacity resulting from or aggravated by, unreasonable refusal to submit to medical or surgical treatment. Certain accidents are deemed to arise out of and in the course of employment, provided that in each case the accident is of a type that would entitle the worker to compensation had it happened at his work place, namely:
Accidents to apprentices attending compulsory classes at technical schools.
Accidents to workers acting in breach of any Act, regulations, or orders affecting their employment or acting without instructions from the employer (provided that the worker would have been entitled to compensation had there been no breach of Act, etc.).
Accidents to workers travelling to or from work by transport provided by the employer primarily for conveyance of the workers, authorised by him, or arranged with the workers or their union, the employer meeting the whole or part of the cost.
Accidents to workers during meal or rest times, happening on premises occupied by the employer, on premises to which the workers have by virtue of their employment the right of access, or on premises where the workers are entitled to be by authorisation of the employer.
Diseases are deemed to be personal injuries by accident if they are due to the nature of any employment in which the worker was employed during a prescribed period before the date of commencement of the incapacity. In the case of diseases due to exposure to radioactivity the prescribed period is five years, and two years in all other cases. If the worker contracts any disease in respect of which he would be entitled to a miner's benefit under the Social Security Act he is not entitled to receive any compensation under the Workers' Compensation Act while receiving such benefit. Nor can a benefit be paid for any period during which the worker is receiving compensation, and no lump-sum compensation is to be paid for any incapacity caused by such diseases.
In assessing compensation, account is not to be taken of any money accruing to the claimant under any insurance policy, nor, in the case of a partial dependant of a deceased worker, of any gain to the estate or the dependant, nor of any money payable by or to a friendly society or other organisation.
The Act generally applies only to accidents happening in New Zealand, but also applies to accidents on New Zealand ships and aircraft and to accidents to seamen or airmen employed in New Zealand ships or aircraft.
All the maximum rates of compensation, whether for weekly payments or the various allowances, such as dependants' allowances and medical expenses, are fixed by Order in Council. The Act also adopts the method of having the various maximum total payments of compensation for death or incapacity expressed in terms of the current maximum weekly payment, so that any variation in the latter automatically varies the maxima for total payments. Compensation rates at present (by virtue of the Workers' Compensation Order 1957 and amendments) are as follows:
1. In case of death:
Where the worker leaves total dependants, a sum equal to the aggregate of the prescribed maximum weekly payments for 274 weeks (£2,740); or
Where the worker leaves partial dependants only, a sum reasonable and proportionate to the injury to these dependants, but not exceeding the sum specified in (a).
Compensation received prior to death by the injured person in respect of the accident which causes his death is deducted from the above amounts, to arrive at the amounts payable to dependants, to the extent that such prior compensation exceeds the aggregate of the prescribed maximum weekly payments for 39 weeks (£390).
2. In the case of injury:
During total incapacity, weekly payments equal to 80 per cent of the worker's weekly earnings (maximum £10 per week, minimum £2 10s.).
During partial incapacity, weekly payments equal to 80 per cent of the difference between the worker's pre-accident weekly earnings and the weekly amount he is earning or able to earn in suitable employment or business after the accident.
Weekly payments are payable for a maximum of six years. They are payable for all periods of incapacity. The workers' weekly earnings are deemed to be his ordinary weekly earnings (exclusive of overtime) at the time of the accident, increased or reduced during his incapacity according to increases or decreases in ordinary rates of pay, ruling rates of pay, or minimum rates of wages. As an alternative, the worker may elect to have his weekly payments based on his average weekly earnings (exclusive of overtime) over the last 12 months or some shorter period in the employment of the same employer, increased or decreased during incapacity according to increases or decreases in the minimum wage under the Minimum Wage Act 1945. Permanently incapacitated apprentices, trainees, or workers under 21 years of age have their weekly earnings computed on adult or journeymen's rates.
In the case of certain injuries involving permanent disability (e.g., dismemberment or loss of use) compensation is assessed in accordance with a schedule to the Act, representing a percentage (varying according to the nature of the dismemberment) of an amount equal to the aggregate of maximum weekly payments of compensation for six years (£3,130). In assessing the compensation payable for such injuries, any period of total incapacity due to illness resulting from the injury is deducted from the six years.
In addition to the ordinary compensation, dependants' allowances are payable under the Workers' Compensation Act 1956. Where the death of the worker results from the injury, an allowance of £50 is payable in respect of each total dependant under 16 years of age, and a proportionate amount in respect of each partial dependant under 16. Where the worker's total incapacity results from the injury, an allowance of £1 per week is payable in respect of his wife or dependent woman in a position of parent to children under 16 years of age maintained by the worker, provided that the combined amount of weekly payments and dependants' allowances is not to exceed 90 per cent of the worker's weekly earnings. A child over 16 and under 18 years of age is treated as being under 16 if still at school or undergoing training without pay.
Various other allowances and expenses are payable in addition to the ordinary compensation. An injured worker is entitled to an allowance of £2 per week for any period during which he requires constant personal attendance and is not being maintained free of charge in a hospital. In the case of death, reasonable expenses up to £100 are payable for medical and surgical attendance and the funeral. In the case of incapacity reasonable expenses of medical and surgical attendance are payable up to a maximum:
In respect of the total sum, £50 for inpatient treatment in any hospital and £50 for other treatment.
In respect of each occasion of attendance other than for inpatient treatment, 12s. 6d. (with certain variations in the case of specialist services, X-ray diagnostic services, and physiotherapeutic services).
Where as a result of the injury to a worker an artificial limb or aid is necessary, the employer must pay the reasonable cost of the artificial limb or aid, and the reasonable cost of keeping it in repair for three years up to a maximum of £25. Where, as a result of accident arising out of and in the course of employment, the worker suffers damage to teeth, an artificial limb or aid, clothing, or spectacles he is wearing (in this case the injury suffered must be one for which compensation is payable), the employer must pay for the reasonable cost of repair or replacement to a maximum of £50. Where the worker needs to be removed to a doctor or hospital after the accident, the employer must pay the costs of removal. Where a worker requires medical treatment in another town or at a place more than 5 miles from his residence, the employer must pay the expenses of transport and meals or lodging up to a maximum of £50.
Weekly payments of compensation may not be discontinued or diminished except in the following cases:
Where the weekly payment is in respect of total incapacity and the worker has actually returned to work.
By agreement with the worker.
By leave of the Compensation Court upon payment of a lump sum in lieu of weekly payments.
By leave of the Compensation Court or Magistrate's Court where a doctor certifies that the worker has wholly or partially recovered or that any incapacity is not due in whole or part to the accident. The Court will not grant such leave in the case of partial recovery unless the worker is working in some suitable employment or business, or some suitable employment has been provided by his employer.
By judgment or order of a Court of competent jurisdiction.
After the expiration of the maximum period of six years.
Where the weekly payment is in respect of total incapacity and the worker's doctor has certified he is fit to resume work and the worker has not done so. If in fact the Compensation Court is satisfied that the worker was not fit to resume work, it shall declare that the ending of payments was unlawful. The additional amount to be paid by way of penalty is in the discretion of the Court.
If the employer wrongfully terminates or diminishes weekly compensation payments, he is liable to pay double compensation to the worker.
Proceedings under the Act are taken in the Compensation Court. The Court consists of a Judge, and there is provision in the Act for the appointment of a Registrar for each industrial district under the Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act 1954. Procedure is determined by regulations — the Workers' Compensation Rules. No appeal lies to any other Court from any order made by the Compensation Court, nor may any such order be removed into another Court to be quashed or varied, except upon the ground of want or excess of jurisdiction. All proceedings for the recovery of compensation and the determination of any questions under the Act are, with certain exceptions, taken in the Compensation Court and not otherwise. Rights of indemnity conferred by the Act are enforceable in the Supreme Court or some other Court of competent jurisdiction, and not (except with the consent of the parties) in the Compensation Court. Where the parties agree or the amount claimed does not exceed £50, proceedings for the recovery of compensation in respect of any injury which has not caused the death of a worker may be taken in the Magistrate's Court. Medical, funeral, and surgical expenses and other allowances of a similar nature may be recovered in the Magistrate's Court equally with the Compensation Court.
Proceedings under the Act for the recovery of compensation are not maintainable unless written notice of the accident has been given to the employer as soon as practicable after its happening. Action for recovery must also be commenced within 12 months after the date of the accident or death, or date of the last payment of compensation or signing of admission of liability. The Court has power to excuse failure to give notice or to commence action within the limited time if the employer has not been prejudiced, or the failure was due to mistake, absence from New Zealand, or other reasonable cause.
Compensation is apportioned by the Compensation Court, and is to be paid to the dependants entitled, but where the dependant is an infant or of unsound mind or the Court so orders, the amount is to be held on trust subject to the directions of the Court. The Court may order that such amount be held on trust as a class fund to be applied for the benefit of the persons concerned, at the discretion of the trustee subject to directions from the Court. These provisions of the Act relating to apportionment in the case of death are applied to cases of incapacity where compensation is payable in the form of a lump sum and the injured worker is an infant or of unsound mind, or the Court orders that the whole or part of the lump sum be held on trust for the worker. In the case of an infant worker, the application of the provisions is subject to there being no settlement between the parties in writing approved by a Magistrate's Court, in which case the Magistrate may order that the compensation be paid to the infant or held on trust under the apportionment provisions of the Act.
With certain exceptions it is compulsory for all employers to insure against their liability to pay compensation or damages in respect of injuries to workers. The Secretary of Labour has power to grant exemption where the employer has adequate financial resources, or is a Commonwealth shipping company indemnified by a United Kingdom mutual protecting club or is employing workers domiciled outside New Zealand and adequately protected by compensation rights and insurance enforceable in the country of their domicile or in the country where they were engaged. The National Airways Corporation, the Linen Flax Corporation, and education boards and other school authorities are not required to insure their workers. The Secretary of Labour may grant exemption to the trustees of the General Trust Fund established under the New Zealand Rules of Racing. The insurance provisions of the Act do not apply with respect to overseas workers temporarily employed in New Zealand by overseas employers for a period of six months or less.
Insurance is effected by the delivery of wages statements by employers to authorised insurers (insurance companies who have notified the Secretary of Labour that they have made the necessary deposit under the Insurance Companies' Deposits Act 1953). Maximum rates of premiums for the different categories of workers are fixed by the Employers' Liability Insurance Regulations. The employer is required to give prompt notification of details of accidents causing death or personal injury to workers, to his insurer, and to an Inspector of Factories.
The Workers' Compensation Board consists of the General Manager of the State Fire Insurance Office and one other Government representative, two representatives of the Council of Fire and Accident Underwriters' Associations of New Zealand, one employers' representative, and one workers' representative. Its functions include recommending the maximum rates of premiums and rates of commission for insurance agents, administering the Workers' Compensation Account used in carrying out the Board's functions, undertaking and assisting accident prevention, research into causes, incidence, and prevention of accidents, and the care and assistance of injured workers. Penal rates up to 100 per cent in excess of the prescribed maximum rates may be imposed by the Board in cases where the risks to workers are unusually great. To finance the activities of the Board, levies are collected from authorised insurers and exempted employers. The Board also acts as the insurer of employers who have neglected to insure their workers with an authorised insurer, so that workers are protected in all cases. The Board may collect from delinquent employers moneys it pays out as insurer.
Various offences are recognised under the legislation. They include refusing or failing to give or deliver any statement or information as required by the Act, or reasonably required by the insurer or the Board, wilfully or negligently making any false return or giving any false or misleading information concerning liability to any premiums or in relation to any claim, and making any false or otherwise misleading statements to obtain benefits or avoid obligations under the Act. In the case of intentional evasion of liability to pay premiums there is the additional liability to a penal charge up to treble the deficient premium.
Damages received in respect of an accident may be set off against compensation recoverable in respect of the same accident, or vice versa. Where judgment has been recovered for compensation, no damages are thereafter recoverable unless the Court is satisfied that the judgment has not been satisfied though all reasonable steps have been taken to obtain satisfaction. The same rule applies with respect to compensation, where judgment has been recovered for damages.
Where the injury for which compensation is payable was caused under circumstances creating a legal liability in some person other than the employer to pay damages in respect thereof, the person by whom the compensation is paid or payable is entitled to indemnification by the person so liable.
Certain other statutes are relevant to the question of workers' compensation. By the Law Reform Act 1936, all causes of action (with certain exceptions) subsisting against or vested in a person who dies survive against or for the benefit of his estate. The Workers' Compensation Act makes it clear that this applies to rights to recover compensation. The Law Reform Act also provides that the amount of compensation or damages payable to a work shall be a charge on the insurance moneys payable in respect of liability to compensation or damages, so that the injured worker is protected in the event of an employer becoming bankrupt or, in the case of a corporation, being wound up. This Act also provides for contribution between joint tort-feasors. It completely abolished all remnants of the common law defence of common employment, whereby an injured worker could not recover damages from his employer where the injury was caused by the negligence of a fellow worker. The defence had been previously abrogated in the Workers' Compensation Act 1922, but subject to the condition that the injured worker could not recover more than £1,000 damages. The Contributory Negligence Act 1947 removed the common law disability on a plaintiff, guilty of contributory negligence, to sue for damages, and provided that in such case the damages recoverable should be reduced to such extent as the Court thought just, having regard to the plaintiff's share in the responsibility for the damage. Section 23 of the Tuberculosis Act 1948 creates a presumption in favour of a person who contracts tuberculosis while employed on nursing duties or the like, that the disease was contracted whilst so employed. By the Deaths by Accidents Compensation Act 1952, when the death of any person is caused by another's negligence the executor or administrator of the deceased person's estate, or certain relatives, have the right, which did not exist at common law, to bring an action for damages. Section 16 of the Finance Act (No. 2) 1952, amending section 29 of the Social Security Act 1938, provides that in any proceedings under the Deaths by Accidents Compensation Act or the Workers' Compensation Act for damages or compensation in respect of the death of any person, no account is to be taken in assessing the damages or compensation payable by or to any person of any family benefit under the Social Security Act. By provisions of the Companies Act 1955 and the Bankruptcy Amendment Act 1956 workers' compensation is given equal priority with wages in bankruptcy and the winding up of a company.
GENERAL — As a result of an international conference of official statisticians held at Geneva in 1923, under the auspices of the International Labour Office set up by the League of Nations, the collection and compilation of statistics of industrial accidents on substantially uniform lines was undertaken in the principal countries. Collection of statistics of industrial accidents in New Zealand commenced in 1924. The statistics in this subsection, which relates in particular to the years 1955–59, were all compiled by the Department of Statistics.
Before 1949 statistics were compiled from accident notifications made to the Department of Labour and supplemented by subsequent inquiry as to the final result of the accident.
Under the 1947 and 1950 amendments to the Workers' Compensation Act, there was introduced on 1 April 1949 and terminated on 31 March 1951 a State monopoly of workers' compensation insurance, and during this time, by arrangement with the State Fire and Accident Insurance Office, statistics were compiled from claims for compensation. It was found that reporting of accidents was far from being complete under the notifications system, for there was an apparent — but unreal — rise in accidents from 15,721 in 1948 to 30,075 in 1949. Thus the statistics from 1949 are not comparable with those for earlier years.
In 1951, on the termination of the monopoly, the Workers' Compensation Board came into being, and its assistance has enabled a continuation of the statistics on the basis of compensation claims, these being notified to the Department of Statistics by all authorised insurers. Coverage was, moreover, improved, with the addition of reports of accidents in marine and waterfront work, some local authorities, and a few businesses for which exemption has been authorised from the normal liability to insure.
A further increase in coverage (amounting to about 1,400 accidents in the first year) was caused by the repeal, effective from 1 December 1951, of the former provision that no compensation was payable for less than three days' absence from work. Since that date the statistics have included all accidents resulting in fatality, permanent disability, or absence from work beyond the day (or shift) in which the accident occurred.
Before 1956 the only Government Departments reporting accidents were the Ministry of Works, New Zealand Electricity Department, New Zealand Forest Service, New Zealand Government Railways Department, Post Office, Mines Department, and the Government Printing and Stationery Department, plus one or two other Departments which in a very few cases had taken outside insurance cover. From the beginning of 1956 all accidents in Government Departments became notifiable, resulting in an increase of about 400 reported accidents in that year.
The only limitation in the statistics now is that, because they are derived from claims made under the Workers' Compensation Act, they exclude accidents to working proprietors and similar persons not insurable under the Act. This limits the scope of the statistics in the farming industry especially.
Doubt has been expressed from time to time that all claims are being reported by insurers and self-insurers. Lengthy and careful investigations, however, have established no way in which a real discrepancy could occur, but a number of ways in which an illusory one might; and indeed there is positive proof of a tendency on the part of insurers to over-report. It will be seen from the later tables that accidents showed a startling increase in 1958 over 1957. A full discussion of the probable reasons for this increase will be found in the Report on the Industrial Accidents Statistics of New Zealand for 1958. Figures for the 1959 year showed marked decreases in the numbers of accidents resulting in fatality (28.3 per cent), permanent total disability (20 per cent), and permanent partial disability (3.6 per cent).
Claims resulting from the more serious accidents are frequently not settled for some considerable time after the occurrence of the accident, and a period is therefore allowed so that the bulk of such claims may be included in the statistics for the year in which the accidents occurred. The 1952 statistics covered claims notified to the Department up to November 1953, but from 1953 the closing date has been standardised at mid-August of the following year. Thus the 1952 statistics, especially for the more serious accidents, are not altogether comparable with other years. Even allowing this period of seven and a half months, it is inevitable that any year's statistics will include a small proportion of long-delayed claims from previous years. (In the 1959 statistics there were 2,556 such claims out of a total of 53,313.) But with the standardising of the closing date at mid-August, the effect of these late claims should be compensatory from year to year.
PRINCIPAL STATISTICS, 1955–59 — The following table gives a summary of the principal statistics for the latest five years. The concepts and calculation of frequency and severity rates and of calendar days lost are explained in a succeeding note, and changes in compensation rates are set out in a subsequent table.
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Calculated on a different basis from 1956; see explanation following. | ||||||
| Number of accidents resulting in — | ||||||
| Fatality | 63 | 97 | 86 | 92 | 66 | |
| Permanent total disability | 6 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 8 | |
| Permanent partial disability | 976 | 944 | 813 | 969 | 934 | |
| Temporary disability | 40,993 | 42,584 | 44,583 | 50,874 | 52,305 | |
| Totals | 42,038 | 43,630 | 45,490 | 51,945 | 53,313 | |
| Compensation paid (incl. damages) — | ||||||
| Total | £ | 1,974,281 | 2,342,623 | 2,422,288 | 2,947,405 | 2,950,580 |
| Average per accident | £ | 47.0 | 53.7 | 53.2 | 56.7 | 55.3 |
| Calendar days lost — | ||||||
| Temporary disability only | 831,693 | 909,879 | 921,226 | 975,440 | 964,872 | |
| Average per accident | 20 | 21 | 21 | 19 | 18 | |
| Total, on constant basis* | 3,021,663 | 3,234,584 | 2,918,546 | 3,377,730 | 2,915,240 | |
| Average per accident (time charge) | 72 | 74 | 64 | 65 | 55 | |
| Total, on actual basis* | 2,693,732 | 3,238,597 | 2,896,907 | 3,315,020 | 2,923,520 | |
| Average per accident | 64 | 74 | 64 | 64 | 55 | |
| Frequency and severity rates — | ||||||
| Frequency rate | 3.15 | 3.33 | 3.43 | 3.86 | 3.89 | |
| Physical injury severity rate* | 1,394 | 1,538 | 1,358 | 1,559 | 1,313 | |
| Economic loss severity rate* | 1,242 | 1,547 | 1,361 | 1,543 | 1,324 | |
FREQUENCY AND SEVERITY RATES AND CALENDAR DAYS LOST — Frequency rates are calculated according to the formula: Accidents per 100,000 man-hours worked. For severity rates the formula is: Man-hours lost through accidents per 100,000 man-hours worked.
The man-hours lost are derived from the calendar days lost. In the computation of the latter, an important point arises. Where an accident causes a fatality or permanent disability, the assessment of time lost may, or may not, take into account the variations (caused by the differences in the ages of the workers injured) in the expectation of working life destroyed by the accident. Now because the worker's age is not relevant to the character of the hazard from which his accident occurred, the true injury severity rate must ignore the factor of age. Therefore in calculating the physical injury severity rate in the foregoing table a constant allowance of time lost is made for all fatalities, with a percentage of this for each permanent disability according to the percentage of that disability as set out in the First Schedule to the Workers' Compensation Act 1956.
Before 1956 this allowance was 9,545 calendar days, but the production of the New Zealand Tables of Working Life 1951 enabled the more accurate figure of 9,263 calendar days to be set. This is the average working-life expectancy of workers in New Zealand who suffer accidents causing fatality or permanent disability.
To the calendar days lost through fatal and permanent disabling accidents are added the actual days lost through temporary disabilities, adjusted to allow for the different age distribution of workers suffering this kind of accident. From the total the man-hours lost are calculated.
A severity rate calculated similarly, but taking into account the worker's actual ages, is however not without interest. This rate is called the economic loss severity rate; further details will be found in the Report on the Industrial Accidents Statistics of New Zealand for 1959.
If the average severity of the individual accidents is required, it can be found by dividing the calendar days lost by the number of accidents. This rate, called the time charge, and calculated without reference to age, is also shown in the preceding table.
The frequency rate, obviously, measures the relative frequency of accidents within industries or groups of industries. The time charge measures the average severity of the individual accidents. The severity rate measures the relative total severities of all accidents occurring within the industries or groups. Though each of these measures is distinct and has its own appropriate application, the three are interrelated, for it will be found that the physical injury severity rate is the product of the frequency rate and the time charge in terms of man-hours.
COMPENSATION RATES — The maximum amount, irrespective of travelling, medical, legal, funeral, and similar expenses payable under the Workers' Compensation Act in respect of a fatality was raised from £1,000 to £1,500 in 1948, with the new provision that no deduction was to be made from this amount of any weekly payments prior to death unless the total of the principal amount and the weekly payments exceeded £1,750. The minimum amount was raised from £300 to £750. At the same time the maximum and minimum payments of weekly compensation became £5 10s. and £2.
The amounts payable under these headings from that date are set out in the next table.
| Effective Date | Maximum Principal | Maximum Before Reduction | Minimum Principal | Maximum Weekly | Minimum Weekly | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | s. | d. | £ | s. | d. | |
| 1 April 1948 | 1,500 | 1,750 | 750 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 September 1949 | 1,750 | 2,000 | 750 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 December 1950 | 1,750 | 2,000 | 750 | 6 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 July 1951 | 1,750 | 2,000 | 750 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 December 1951 | 2,000 | 2,300 | 750 | 7 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 19 September 1952 | 2,000 | 2,300 | 750 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 September 1953 | 2,150 | 2,450 | 750 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 December 1953 | 2,370 | 2,700 | 825 | 8 | 16 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 23 December 1954 | 2,430 | 2,770 | 850 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 |
| 13 December 1956 | 2,540 | 2,890 | 890 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
| 1 April 1957 | 2,590 | 2,958 | None | 9 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
| 19 November 1959 | 2,740 | 3,130 | None | 10 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 0 |
With the Workers' Compensation Act 1956, effective from 1 April 1957, there became payable for the first time an allowance of £1 a week for a dependent wife, and 10s. for each dependent child. An allowance of £50 is also payable on the death of a worker for each dependent child. More detailed information will be found in Section 37A.
The Act, it should be remembered, does not affect civil liability, and a worker or his dependants may take action at common law against negligent persons. The damages recoverable are consequently not limited to the statutory maximum under the Act.
INDUSTRY OF WORKER – In the table following, industrial accidents during the year 1959 are classified into certain important industrial groups. The New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification of all Economic Activities has been followed since 1951.
The figures for calendar days lost are arrived at by adding together the actual days lost through temporary incapacity; the expectation of working life (taken according to the age of the worker from the Tables of Working Life 1951) lost through each fatal accident; and a percentage of this for each accident resulting in permanent disability, according to the percentage of that disability.
For years before 1956 these figures were calculated without reference to the age of the worker, so that the figures for calendar days lost in the following table are not comparable with those in issues of the Yearbook before 1958. (In other tables in this section the time charge and physical injury severity rate are calculated without reference to the age of the worker, as explained under the earlier heading “Frequency and Severity Rates and Calendar Days Lost”.)
| Industrial Group | Total Accidents | Calendar Days Lost | Total Compensation (Including Damages) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Average | Total | Average | ||
| Agriculture, forestry, hunting, and fishing – | £ | £ | |||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 4,268 | 392,829 | 92 | 280,438 | 65.7 |
| Forestry and logging | 1,413 | 147,113 | 104 | 114,572 | 81.1 |
| Hunting, trapping, and game propagation | 78 | 4,595 | 59 | 9,671 | 124.0 |
| Fishing | 63 | 6,087 | 97 | 5,771 | 91.6 |
| Mining and quarrying – | |||||
| Coal mining | 2,425 | 69,208 | 29 | 104,398 | 431 |
| Metal mining | 16 | 283 | 18 | 515 | 32.2 |
| Crude petroleum and natural gas | 14 | 216 | 15 | 404 | 28.9 |
| Stone quarrying, clay and sand pits | 327 | 28,328 | 87 | 33,911 | 103.7 |
| Non-metallic mining and quarrying | 12 | 263 | 22 | 510 | 42.5 |
| Manufacturing— | |||||
| Food | 7,484 | 249,005 | 33 | 301,036 | 40.2 |
| Beverages | 283 | 6,289 | 22 | 10,500 | 37.1 |
| Tobacco | 54 | 629 | 12 | 952 | 17.6 |
| Textiles | 486 | 37,572 | 77 | 29,884 | 61.5 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 478 | 20,073 | 42 | 16,251 | 34.0 |
| Wood and cork (excluding furniture) | 2,582 | 193,731 | 75 | 171,621 | 66.5 |
| Furniture and fixtures | 365 | 24,301 | 67 | 18,894 | 51.8 |
| Paper and paper products | 594 | 52,592 | 89 | 46,739 | 78.7 |
| Printing, publishing, and allied industries | 328 | 13,038 | 40 | 17,915 | 54.6 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear) | -156 | 4,229 | 27 | 6,245 | 40.0 |
| Rubber products | 280 | 25,806 | 92 | 32,203 | 115.0 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 664 | 36,406 | 55 | 41,660 | 62.7 |
| Products of petroleum and coal | 40 | 1,151 | 29 | 1,682 | 42.1 |
| Non-metallic mineral products | 1,265 | 75,402 | 60 | 68,248 | 54.0 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 1,220 | 64,322 | 53 | 69,794 | 57.2 |
| Machinery (except electrical machinery) and general engineering | 2,157 | 92,856 | 43 | 88,353 | 41.0 |
| Electrical machinery, apparatus, appliances, and supplies | 304 | 9,226 | 30 | 13,110 | 43.1 |
| Transport equipment | 2,076 | 86,872 | 42 | 93,099 | 44.8 |
| Miscellaneous industries | 258 | 12,025 | 47 | 13,122 | 50.9 |
| Construction | 9,200 | 514,476 | 56 | 517,728 | 56.3 |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services – | |||||
| Electricity, gas, and steam | 1,027 | 123,830 | 121 | 120,334 | 117.2 |
| Water and sanitary services | 292 | 12,495 | 43 | 19,072 | 65.3 |
| Commerce – | |||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 3,351 | 158,133 | 47 | 151,899 | 45.3 |
| Banks and other financial institutions | 15 | 868 | 58 | 1,064 | 70.9 |
| Insurance | 11 | 2,343 | 213 | 3,820 | 347.3 |
| Real estate | 5 | 93 | 19 | 229 | 45.8 |
| Transport, storage, and communication – | |||||
| Transport | 6,097 | 286,597 | 47 | 390,196 | 64.0 |
| Storage and warehousing | 186 | 4,065 | 22 | 6,237 | 33.5 |
| Communication | 882 | 15,361 | 17 | 23,100 | 26.2 |
| Services – | |||||
| Government | 233 | 19,399 | 83 | 7,855 | 33.7 |
| Community and business | 1,138 | 33,135 | 29 | 43,243 | 38.0 |
| Recreation | 269 | 32,526 | 121 | 18,664 | 69.4 |
| Personal | 910 | 65,705 | 72 | 55,571 | 61.1 |
| Ill defined and not specified | 7 | 47 | 7 | 70 | 10.0 |
| Totals | 53,313 | 2,923,520 | 55 | 2,950,580 | 55.3 |
The numbers of accidents and the severity rates (hours lost per 100,000 man-hours worked) for the industrial groups, together with the labour force and frequency ratio (accidents per 100,000 man-hours worked) for the groups, are shown in the following diagrams.
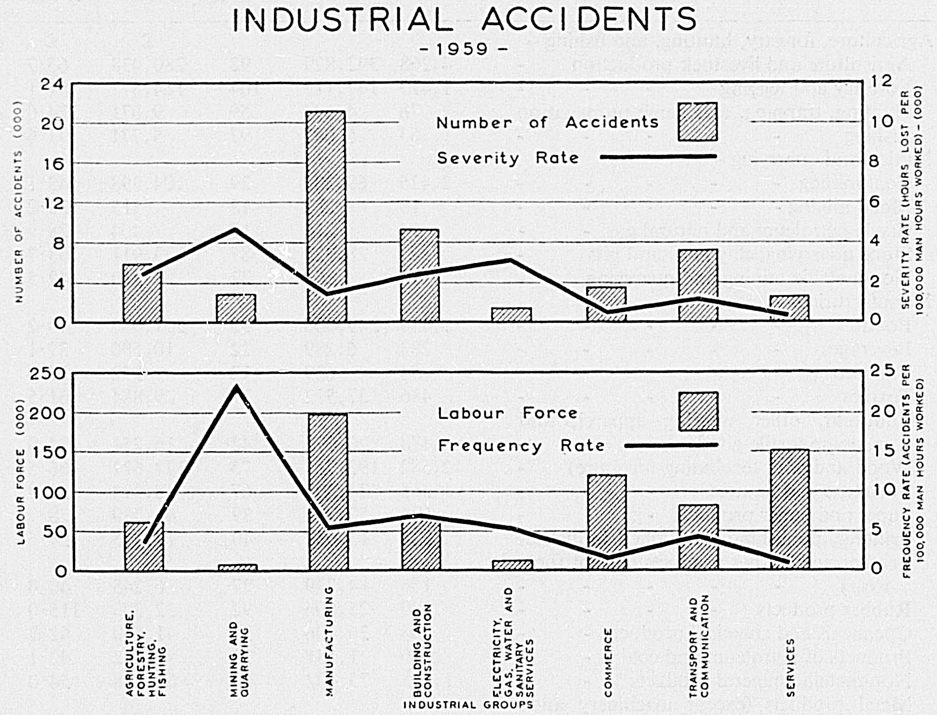
The same industrial groups are used in the following table, which gives the resulting disability and time charge and which covers the five years 1955–59.
| Industrial Group | Number of Accidents Resulting In – | Time Charge (in Calendar Days) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatality | Permanent Total Disability | Permanent Partial Disability | Temporary Disability | Total | ||
| Agriculture, forestry, hunting, and fishing – | ||||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 72 | 5 | 454 | 18,045 | 18,576 | 105 |
| Forestry and logging | 34 | 3 | 132 | 5,890 | 6,059 | 112 |
| Hunting, trapping, and game propagation | 2 | – | 8 | 317 | 327 | 154 |
| Fishing | 2 | 1 | 8 | 303 | 314 | 169 |
| Mining and quarrying – | ||||||
| Coal mining | 12 | 1 | 135 | 11,167 | 11,315 | 51 |
| Metal mining | 4 | 87 | 91 | 89 | ||
| Crude petroleum and natural gas | 1 | – | – | 38 | 39 | 256 |
| Stone quarrying, clay and sand pits | 11 | 1 | 43 | 1,517 | 1,572 | 159 |
| Non-metallic | 1 | 2 | 42 | 45 | 317 | |
| Manufacturing – | ||||||
| Food | 14 | 1 | 429 | 32,427 | 32,871 | 36 |
| Beverages | 4 | 1 | 29 | 1,366 | 1,400 | 75 |
| Tobacco, cigars, and cigarettes | 3 | 247 | 250 | 34 | ||
| Textiles | – | 1 | 79 | 1,905 | 1,985 | 74 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | – | – | 35 | 2,018 | 2,053 | 37 |
| Wood and cork | 12 | 1 | 388 | 11,088 | 11,489 | 79 |
| Furniture and fixtures | – | – | 95 | 1,507 | 1,602 | 77 |
| Paper and paper products | 2 | – | 79 | 2,647 | 2,728 | 61 |
| Printing, publishing, etc.- | 2 | – | 56 | 1,254 | 1,312 | 85 |
| Leather and leather products | – | – | 13 | 664 | 677 | 37 |
| Rubber products | 1 | – | 34 | 1,183 | 1,218 | 72 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 2 | 1 | 58 | 3,045 | 3,106 | 51 |
| Products of petroleum and coal | – | – | 4 | 205 | 209 | 67 |
| Non-metallic mineral products | 6 | – | 104 | 5,059 | 5,169 | 63 |
| Metal products | 3 | – | 141 | 4,470 | 4,614 | 61 |
| Machinery, founding and general engineering | 5 | – | 199 | 9,141 | 9,345 | 45 |
| Electrical machinery, appliances, and supplies | – | – | 32 | 1,293 | 1,325 | 53 |
| Transport equipment | 4 | 2 | 159 | 9,157 | 9,322 | 48 |
| Miscellaneous | – | – | 22 | 684 | 706 | 59 |
| Construction | 70 | 6 | 866 | 38,215 | 39,157 | 69 |
| Electricity, gas, water, and sanitary services – | ||||||
| Electricity, gas, and steam | 21 | 6 | 76 | 4,399 | 4,502 | 102 |
| Water and sanitary services | 3 | – | 17 | 1,244 | 1,264 | 63 |
| Commerce – | ||||||
| Wholesale and retail trade | 26 | 1 | 302 | 14,810 | 15,139 | 65 |
| Financial | 2 | – | 1 | 70 | 73 | 281 |
| Insurance | – | – | 3 | 55 | 58 | 93 |
| Real estate | – | – | 1 | 24 | 25 | 85 |
| Transport, storage, and communication – | ||||||
| Transport | 70 | 4 | 385 | 30,368 | 30,827 | 61 |
| Storage and warehousing | – | – | 11 | 899 | 910 | 29 |
| Communication | 5 | – | 6 | 4,216 | 4,227 | 28 |
| Services – | ||||||
| Government | 4 | – | 10 | 902 | 916 | 72 |
| Community and business | 5 | 1 | 71 | 4,287 | 4,364 | 59 |
| Recreational | 1 | – | 32 | 1,089 | 1,122 | 86 |
| Personal | 8 | – | 110 | 3,967 | 4,085 | 83 |
| Ill defined or not stated | – | – | – | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| Totals | 404 | 37 | 4,636 | 231,339 | 236,416 | 65 |
CAUSE OF ACCIDENT AND RESULTING DISABILITY – The following table relates cause of accident and degree of resulting disability for the five-year period 1955–59.
| Cause | Fatality | Permanent Disability* | Temporary Disability | Total | Percentage of Total Accidents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Including permanent total disability cases as follows: 1955, 6; 1956, 5; 1957, 8; 1958, 10; 1959, 8; total, 37. | |||||
| Machinery | 84 | 2,074 | 37,647 | 39,805 | 16.8 |
| Vehicle | 127 | 197 | 11,332 | 11,656 | 4.9 |
| Electricity, explosion, flames, hot substance | 41 | 72 | 5,729 | 5,842 | 2.5 |
| Poison, corrosive substance | 9 | 9 | 1,941 | 1,959 | 0.8 |
| Fall of person | 51 | 520 | 29,574 | 30,145 | 12.8 |
| Stepping on or striking against fixed or stationary object | 5 | 52 | 10,663 | 10,720 | 4.5 |
| Moving object (not being handled by person injured) | 41 | 150 | 8,353 | 8,544 | 3.6 |
| Fall of earth | 15 | 50 | 1,349 | 1,414 | 0.6 |
| Handling of object | 7 | 794 | 72,920 | 73,721 | 31.2 |
| Hand tools | 4 | 552 | 38,324 | 38,880 | 16.5 |
| Miscellaneous | 20 | 203 | 13,507 | 13,730 | 5.8 |
| Totals | 404 | 4,673 | 231,339 | 236,416 | 100.0 |
Further information on resulting disability, by industrial groups, will be found in the table on pages 1062–1063.
AGE OF WORKER – The following table supplies a percentage distribution of accidents, recorded during each of the years 1955 to 1959, according to age group of the person injured.
| Age (Completed Years) | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Cases | Per Cent of Total | Number of Cases | Per Cent of Total | Number of Cases | Per Cent of Total | Number of Cases | Per Cent of Total | Number of Cases | Per Cent of Total | ||
| Under 16 | 325 | 0.8 | 351 | 0.18 | 347 | 0.8 | 358 | 0.7 | 413 | 0.8 | |
| 16 – | 20 | 4,931 | 11.7 | 5,308 | 12.2 | 5,751 | 12.6 | 7,277 | 14.0 | 7,950 | 14.9 |
| 21 – | 24 | 4,933 | 11.7 | 5,119 | 11.7 | 5,003 | 11.0 | 6,060 | 11.7 | 6,092 | 11.4 |
| 25 – | 34 | 10,871 | 25.9 | 11,162 | 25.6 | 11,574 | 25.4 | 12,607 | 24.3 | 12,689 | 23.9 |
| 35 – | 44 | 8,306 | 19.7 | 8,665 | 19.9 | 8,945 | 19.7 | 9,684 | 18.6 | 9,675 | 18.2 |
| 45 – | 54 | 6,625 | 15.8 | 6,759 | 15.5 | 7,106 | 15.6 | 7,662 | 14.7 | 7,696 | 14.4 |
| 55 – | 64 | 3,054 | 7.3 | 3,325 | 7.6 | 3,400 | 7.5 | 3,618 | 7.0 | 3,596 | 6.7 |
| 65 and over | 744 | 1.8 | 650 | 1.5 | 673 | 1.5 | 726 | 1.4 | 609 | 1.1 | |
| Not stated | 2,249 | 5.3 | 2,291 | 5.2 | 2,691 | 5.9 | 3,953 | 7.6 | 4,593 | 8.6 | |
| Totals | 42,038 | 100.0 | 43,630 | 100.0 | 45,490 | 100.0 | 51,945 | 100.0 | 53,313 | 100.0 | |
NATURE OF INJURY – A classification of accidents according to injury sustained gives the following results for the years 1955 to 1959.
| Injury | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | Total, 1955–59 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bruises, contusions, and abrasions | 7,858 | 8,098 | 7,992 | 5,863 | 5,713 | 35,524 |
| Burns | 1,517 | 1,537 | 1,724 | 2,154 | 2,109 | 9,041 |
| Concussions | 246 | 289 | 274 | 308 | 255 | 1,372 |
| Lacerations, punctures, and open wounds | 12,101 | 12,237 | 13,233 | 14,024 | 14,573 | 66,168 |
| Ruptures | 355 | 380 | 353 | 421 | 457 | 1,966 |
| Amputations (traumatic) | 383 | 346 | 267 | 147 | 119 | 1,262 |
| Dislocations | 249 | 228 | 240 | 225 | 220 | 1,162 |
| Fractures | 4,257 | 4,311 | 4,376 | 4,685 | 4,404 | 22,033 |
| Sprains and strains | 12,232 | 13,333 | 13,995 | 15,559 | 16,321 | 71,440 |
| Occupational dermatitis | 613 | 521 | 495 | 563 | 526 | 2,718 |
| Other and ill defined | 2,227 | 2,350 | 2,541 | 7,996 | 8,616 | 23,730 |
| Totals | 42,038 | 43,630 | 45,490 | 51,945 | 53,313 | 236,416 |
| Cases where septic poisoning occurred – | ||||||
| Number | 5,529 | 5,645 | 7,054 | 8,889 | 9,598 | 36,715 |
| Percentage of all accidents | 13.2 | 12.9 | 15.5 | 17.1 | 180 | 15.5 |
Of the septic cases shown for 1959 in the preceding table, 31.7 per cent occurred in the handling of objects (including pricks and scratches by bones and thorns in slaughtering and packing operations), and 24.1 per cent in the use of hand tools.
PART OF BODY INJURED – The number and percentage of cases in which different parts of the body were injured in industrial accidents is given in the following table for the years 1955–59.
| Part of Body Injured | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | Total, 1955–59 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Per Cent | ||||||
| Head | 812 | 776 | 729 | 802 | 803 | 3,922 | 1.7 |
| Eye and orbit | 1,834 | 1,842 | 1,971 | 2,591 | 2,810 | 11,048 | 4.7 |
| Rest of face | 620 | 667 | 650 | 610 | 605 | 3,152 | 1.3 |
| Neck, back, and chest | 6,559 | 6,988 | 7,590 | 8,607 | 9,187 | 38,931 | 16.5 |
| Abdomen and contents | 461 | 533 | 478 | 926 | 993 | 3,391 | 1.4 |
| Upper limb – | |||||||
| Collarbone and shoulder | 1,425 | 1,355 | 1,397 | 1,441 | 1,461 | 7,079 | 3.0 |
| Arm | 2,432 | 2,535 | 2,617 | 2,682 | 2,581 | 12,847 | 5.4 |
| Hand and wrist | 14,102 | 14,363 | 15,098 | 18,052 | 18,376 | 79,989 | 33.8 |
| Lower limb – | |||||||
| Hip, thigh, and leg | 5,424 | 5,703 | 5,757 | 5,779 | 5,894 | 28,557 | 12.1 |
| Ankle and foot | 5,486 | 5,698 | 6,003 | 7,163 | 7,191 | 31,541 | 13.3 |
| Other, multiple, ill defined, not applicable | 2,883 | 3,172 | 3,200 | 3,292 | 3,412 | 15,959 | 6.8 |
| Totals | 42,038 | 43,630 | 45,490 | 51,945 | 53,313 | 236,416 | 100.0 |
DURATION OF INCAPACITY – A summary of the duration of incapacity and the number of cases of fatality, permanent total disability, and permanent partial disability is given below for the years 1956 to 1959, together with the totals for the five-year period 1955–59.
| Duration | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | Total, 1955–59 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | Number | Per Cent | |
| 1 or 2 days | 1,844 | 4.2 | 1,956 | 4.3 | 2,786 | 5.3 | 3,036 | 5.7 | 11,495 | 4.9 |
| Over 2 days to 1 week | 11,307 | 25.9 | 12,341 | 27.1 | 14,661 | 28.2 | 15,667 | 29.4 | 64,984 | 27.5 |
| Over 1 week to 2 weeks | 12,506 | 28.7 | 13,041 | 28.7 | 15,056 | 29.0 | 15,234 | 28.6 | 67,722 | 28.6 |
| Over 2 weeks to 4 weeks | 9,206 | 21.1 | 9,487 | 20.9 | 10,231 | 19.7 | 10,478 | 19.7 | 48,360 | 20.5 |
| Over 4 weeks to 6 weeks | 3,369 | 7.7 | 3,338 | 7.3 | 3,514 | 6.8 | 3,453 | 6.5 | 16,853 | 71 |
| Over 6 weeks to 13 weeks | 3,147 | 7.2 | 3,218 | 7.1 | 3,448 | 6.6 | 3,302 | 6.2 | 16,218 | 6.9 |
| Over 13 weeks | 1,205 | 2.8 | 1,202 | 2.6 | 1,178 | 2.3 | 1,135 | 2.1 | 5,707 | 2.4 |
| Number of accidents resulting in – | ||||||||||
| Temporary disability | 42,584 | 97.6 | 44,583 | 98.0 | 50,874 | 97.9 | 52,305 | 98.2 | 231,339 | 97.9 |
| Fatality | 97 | 0.2 | 86 | 0.2 | 92 | 0.2 | 66 | 0.1 | 404 | 0.2 |
| Permanent total disability | 5 | – | 8 | – | 10 | – | 8 | – | 37 | – |
| Permanent partial disability | 944 | 2.2 | 813 | 1.8 | 969 | 1.9 | 934 | 1.7 | 4,636 | 1.9 |
| Totals | 43,630 | 100.0 | 45,490 | 100.0 | 51,945 | 100.0 | 53,313 | 100.0 | 236,416 | 100.0 |
ACCIDENTS PRODUCING DELAYED ACTION – As the following table shows, in about one-third of all accidents there is a time lag between the accident and the time the worker ceases work.
| Complications of Injury | Delayed Action | No Delayed Action | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Week or Less | Over 1 Week and up to 2 Weeks | Over 2 Weeks | |||
| Sepsis | 5,486 | 757 | 447 | 2,685 | 9,375 |
| Surgical amputation | 1 | – | 2 | 243 | 246 |
| Sepsis and surgical amputation | 12 | 4 | 3 | 11 | 30 |
| Loss of function (excluding amputation) | 64 | 14 | 23 | 433 | 534 |
| Sepsis, both organs of a pair | 87 | 16 | 7 | 83 | 193 |
| Loss of function (excluding amputation), both organs of a pair | 2 | – | – | 9 | 11 |
| No complications, both organs of a pair | 91 | 1 | 2 | 395 | 489 |
| No complications, other | 9,929 | 676 | 839 | 30,991 | 42,435 |
| Totals | 15,672 | 1,468 | 1,323 | 34,850 | 53,313 |
Many employees suffering from minor injuries such as scratches and slight cuts, strains, and abrasions evidently fail to have them properly attended to. The result is often septic poisoning or more severe disablement, coupled with an enforced absence that is longer than would have been had the injury received immediate attention. Worse, permanent disability may be the result: 124 such cases are recorded in the above table.
One of the main responsibilities of the Workers' Compensation Board is the reduction of the accident rate in industry. It has sponsored the National Safety Association, comprised of representatives of industry and interested Government Departments, with an objective of preventing accidents and lessening human suffering and loss arising from injuries received at work and elsewhere.
Further, the Board, in conjunction with the Department of Health, has opened an Industrial Health Centre in Penrose, Auckland, and is prepared to assist in the establishment of further centres in areas of concentrated industrial activity. The Department of Health is also associated with other industrial health centres in Auckland, Wellington, Lyttelton, Christchurch, and Dunedin.
TIME OF OCCURRENCE – The following tabulation of industrial accidents, according to the hour of occurrence, shows the effects of fatigue during the working day.
| Time of Occurrence to Nearest Hour | Year | Cause, 1955–59 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | Machinery | Falls of Persons | Handling Objects | Hand Tools | Other | Total, 1955–59 | |
| 8 a.m. | 1,516 | 1,640 | 1,890 | 2,118 | 2,199 | 1,526 | 1,619 | 2,772 | 1,293 | 2,153 | 9,363 |
| 9 a.m. | 3,606 | 3,850 | 4,133 | 4,798 | 4,969 | 3,806 | 2,561 | 7,312 | 3,847 | 3,830 | 21,356 |
| 10 a.m. | 5,187 | 5,480 | 5,549 | 6,381 | 6,596 | 4,805 | 3,474 | 9,798 | 5,233 | 5,883 | 29,193 |
| 11 a.m. | 5,641 | 5,880 | 6,074 | 6,802 | 7,009 | 5,211 | 3.692 | 10,620 | 5,730 | 6,153 | 31,406 |
| 12 noon | 2,799 | 2,940 | 3,081 | 3,626 | 3,694 | 2,884 | 2,192 | 4,679 | 2,946 | 3,439 | 16,140 |
| 1 p.m. | 1.524 | 1,616 | 1,715 | 2,093 | 2,308 | 1,848 | 1,276 | 2,348 | 1,500 | 2,284 | 9,256 |
| 2 p.m. | 4,336 | 4,385 | 4,689 | 5,421 | 5,599 | 4,493 | 2,747 | 7,716 | 4,546 | 4,928 | 24,430 |
| 3 p.m. | 4,785 | 4,873 | 4,853 | 5,620 | 5,675 | 4,506 | 3,383 | 8,320 | 4,663 | 4,934 | 25,806 |
| 4 p.m. | 4,283 | 4,225 | 4,451 | 5,066 | 5,062 | 4,294 | 3,226 | 7,191 | 3,988 | 4,388 | 23,087 |
| 5 p.m. | 2,189 | 2,243 | 2,367 | 2,613 | 2,642 | 1,951 | 1,919 | 3,390 | 1,825 | 2,969 | 12,054 |
| Other hours | 3,154 | 3,499 | 3,587 | 3,917 | 3,957 | 2,980 | 3,212 | 5,027 | 1,596 | 5,299 | 18,114 |
| Not stated | 1,838 | 2,014 | 2,071 | 2,399 | 2,461 | 1,453 | 841 | 3,923 | 1,663 | 2,903 | 10,783 |
| Not applicable | 1,180 | 985 | 1,030 | 1,091 | 1,142 | 48 | 3 | 625 | 50 | 4,702 | 5,428 |
| Totals | 42,038 | 43,630 | 45,490 | 51,945 | 53,313 | 39,805 | 30,145 | 73,721 | 38,880 | 53,865 | 236,416 |
This table indicates that accidents are most numerous during the middle and later part of the morning; there is another peak in mid-afternoon, but this does not reach the same high point.
A more definite indication is given by the length of time the employee had worked on the day when the accident occurred.
| Number of Hours Already Worked | Year | Cause, 1955–59 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | Machinery | Falls of Persons | Handling Objects | Hand Tools | Other | Total, 1955–59 | |
| Under 1 | 2,190 | 2,381 | 2,588 | 2,964 | 3,021 | 2,333 | 2,251 | 3,918 | 1,860 | 2,782 | 13,144 |
| 1 and under 2 | 4,409 | 4,592 | 4,943 | 5,622 | 5,786 | 4,544 | 2,938 | 8,506 | 4,410 | 4,954 | 25,352 |
| 2 and under 3 | 5,081 | 5,267 | 5,490 | 6,262 | 6,490 | 4,811 | 3,466 | 9,325 | 4,881 | 6,107 | 28,590 |
| 3 and under 4 | 5,647 | 5,889 | 5,976 | 6,694 | 6,849 | 5,336 | 3,674 | 10,193 | 5,647 | 6,205 | 31,055 |
| 4 and under 5 | 3,282 | 3,386 | 3,566 | 4,235 | 4,274 | 3,367 | 2,606 | 5,372 | 3,341 | 4,057 | 18,743 |
| 5 and under 6 | 3,659 | 3,720 | 3,922 | 4,569 | 4,764 | 3,723 | 2,342 | 6.314 | 3,805 | 4,450 | 20,634 |
| 6 and under 7 | 4,760 | 4,797 | 4,916 | 5,770 | 5,779 | 4,498 | 3,419 | 8;259 | 4,621 | 5,225 | 26,022 |
| 7 and under 8 | 4,099 | 4,189 | 4,341 | 4,738 | 4,973 | 4,068 | 3,089 | 6,913 | 3,858 | 4,412 | 22,340 |
| 8 or over | 3,620 | 3,600 | 3,538 | 4,081 | 4,000 | 3,213 | 3,031 | 5,552 | 2,623 | 4,420 | 18,839 |
| Not stated | 4,111 | 4,824 | 5,180 | 5,919 | 6,235 | 3,865 | 3,326 | 8,743 | 3,784 | 6,551 | 26,269 |
| Not applicable | 1,180 | 985 | 1,030 | 1,091 | 1,142 | 47 | 3 | 626 | 50 | 4,702 | 5,428 |
| Totals | 42,038 | 43,630 | 45,490 | 51,945 | 53,313 | 39,805 | 30,145 | 73,721 | 38,880 | 53,865 | 236,416 |
The foregoing table shows that the greatest number of accidents occurred during the third and fourth hours worked in the day. Overtime accidents (eight hours or more already worked) represented 7.5 per cent of all accidents in 1959.
DAY OF THE WEEK – In 1958, for the first time, a table was prepared correlating the causes of accidents with the days of the week on which they occurred. Friday was shown to have significantly fewer accidents than the other days of the normal working week in all cause groups except two, in which the number of accidents was too small to have great significance. Accidents from Monday to Thursday showed a sharply decreasing trend, with three notable exceptions: in accidents caused by hand tools the trend, though downward, was only mildly so; in machinery accidents there was scarcely any difference among the four days; and in accidents caused by electricity, explosions, flames, and hot substances the trend was, surprisingly, an upward one.
The trends revealed by the 1958 figures have largely been maintained in 1959, although accidents caused by hand tools now show a greater decrease mid-week and machinery accidents a progressive and marked decrease from Monday to Thursday. The following table shows the number of accidents by day of the week and by cause for 1959.
| Cause | Sunday | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Not Stated or not Applicable | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machinery | 164 | 1,658 | 1,795 | 1,580 | 1,514 | 1,379 | 468 | 31 | 8,589 |
| Vehicle | 58 | 466 | 485 | 438 | 410 | 355 | 115 | 1 | 2,328 |
| Electricity, explosion, flames, hot substance | 59 | 220 | 245 | 199 | 234 | 239 | 94 | 2 | 1,292 |
| Poison, corrosive substance | 8 | 67 | 76 | 60 | 93 | 73 | 32 | 15 | 424 |
| Fall of person | 195 | 1,451 | 1,348 | 1,248 | 1,165 | 995 | 439 | 18 | 6,859 |
| Stepping on or striking against fixed or stationary object | 55 | 499 | 423 | 418 | 421 | 373 | 131 | 15 | 2,335 |
| Moving object (not being handled by person injured) | 43 | 428 | 432 | 418 | 378 | 320 | 95 | 2 | 2,116 |
| Fall of earth | – | 58 | 55 | 61 | 62 | 42 | 6 | – | 284 |
| Handling of object | 301 | 3,505 | 3,272 | 2,965 | 3,008 | 2,733 | 822 | 232 | 16,838 |
| Hand tool | 148 | 1,879 | 1,816 | 1,650 | 1,734 | 1,437 | 362 | 56 | 9,082 |
| Miscellaneous | 75 | 416 | 392 | 379 | 404 | 330 | 191 | 979 | 3,166 |
| Totals | 1,106 | 10,647 | 10,339 | 9,416 | 9,423 | 8,276 | 2,755 | 1,351 | 53,313 |
| Percentage of all accidents | 2.1 | 19.9 | 19.4 | 17.7 | 17.7 | 15.5 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
OCCUPATION OF WORKER – The following table gives the occupations of workers injured during 1959, by the resulting disability, with the 1958 totals for comparison.
| Occupation Group | 1959 | 1958 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatality | Permanent Total Disability | Permanent Partial Disability | Temporary Disability | Total | ||
| Professional, technical, and related workers | – | – | 5 | 502 | 507 | 373 |
| Managers, administrators, clerical and related workers | 2 | 1 | 11 | 409 | 423 | 397 |
| Sales workers | 1 | – | 19 | 1,087 | 1,107 | 1,130 |
| Farmers, fishermen, hunters, forestry and related workers - | ||||||
| Farm labourers and unspecialised workers | 8 | 1 | 49 | 2,848 | 2,906 | 2,933 |
| Forestry and related workers | 5 | 1 | 23 | 1,382 | 1,411 | 1,187 |
| Other | 3 | 1 | 31 | 1,555 | 1,590 | 1,440 |
| Workers in mine, quarry, and related occupations – | ||||||
| Miners and related workers | – | – | 12 | 1,496 | 1,508 | 1,414 |
| Other | 3 | – | 16 | 1,029 | 1,048 | 982 |
| Workers in transport and communication occupations – | ||||||
| Stevedores, dock and wharf labourers | 1 | – | 34 | 1,726 | 1,761 | 1,820 |
| Drivers (not railway) and deliverymen | 5 | – | 40 | 2,699 | 2,744 | 2,651 |
| Other | 6 | – | 4 | 1,395 | 1,405 | 1,388 |
| Craftsmen,production process workers, and labourers – | ||||||
| Carpenters, joiners, cabinet-makers, coopers, and related workers | 6 | 1 | 183 | 6,198 | 6,388 | 6,352 |
| Toolmakers, machinists, plumbers, welders, platers, and related workers | 1 | – | 134 | 5,954 | 6,089 | 5,604 |
| Electricians and related electric and electronics workers | 6 | 2 | 15 | 1,456 | 1,479 | 1,385 |
| Bakers, millers, brewmasters, and related food and beverage workers | 2 | – | 59 | 5,881 | 5,942 | 5,970 |
| Miscellaneous labourers | 4 | – | 106 | 7,927 | 8,037 | 8,448 |
| Other | 8 | 1 | 150 | 6,620 | 6,779 | 6,351 |
| Service workers and workers in entertainment, sport, and recreation | 5 | – | 43 | 2,141 | 2,189 | 2,104 |
| Occupations unidentifiable or not reported | – | – | – | – | – | 16 |
| Totals | 66 | 8 | 934 | 52,305 | 53,313 | 51,945 |
The legislation on occupational safety is principally contained in the following statutes (and the regulations made under them):
The Factories Act 1946, sections 41 to 79; the Machinery Act 1950; the Bush Workers Act 1945; the Construction Act 1959; the Shops and Offices Act 1955, First Schedule; the Workers' Compensation Act 1956; the Coal Mines Act 1925; the Mining Act 1926; the Explosives Act 1957; the Dangerous Goods Act 1957; the Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes Act 1950; the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952; the Quarries Act 1944; the Health Act 1956 so far as it relates to occupational health (see Section 5A).
Government Departments and other organisations concerned with the administration of the Acts, or who have responsibilities for occupational accident prevention, have the scope of their work summarised in the following pages, and legislative requirements are also covered.
Department of Labour – This Department has the largest overall responsibility for the prevention of accidents in industry. The two principal statutes it administers are the Factories Act 1946, of which a large section is concerned with safety, health, and welfare in factories, and the Machinery Act 1950, which is concerned with the inspection of all machinery (with some exceptions covered by other legislation) in work places and the safety of persons working with such machinery. The Department also administers regulations under these Acts, and other statutes dealing with specific spheres of occupational accident prevention – the Bush Workers Act 1945, the Construction Act 1959, and the Shops and Offices Act 1955. It also has administrative responsibility for the Workers' Compensation Act 1956. In addition, the Department supervises more than 600 awards and industrial agreements, many of which include specific safety, health, and welfare provisions relating to particular occupations and processes.
The administration of this safety legislation is based primarily on regular inspection of work places and requisitioning for improvements, together with investigation of reported breaches of legislation by employers and workers and investigation of a large number of accidents including serious and fatal accidents in industries coming within the scope of the legislation. Special attention is given to dangerous machinery. The Department employs some 110 Inspectors of Factories (including six who specialise in bush undertakings), together with 20 Safety Inspectors appointed under the Construction Act 1959, all of whom are qualified by special examination. Their work is substantially preventive. The Construction Regulations 1961 came into force on 1 March 1961.
The Department of Labour also engages in a large amount of occupational safety education. It collaborates with the Department of Education and with teacher training colleges and technical schools in the instruction of technical teachers in occupational safety and in the safety training of apprentices and senior school pupils. Further, it issues monthly occupational safety posters to industry and publishes a range of safety booklets, pamphlets, warning notices, and other printed publicity. Its library of occupational safety films, which is widely used by industry, Government Departments, trade unions, industrial organisations, etc., is believed to be the largest specialised film library of its kind in the world. The Department produces industrial safety displays and exhibits, and has its own specially fitted exhibition van by means of which the displays are taken on tour regularly through selected areas of the country and the exhibits used in the education and instruction of apprentices, school children, workers, employers, and the general public. The Department also publishes the Labour and Employment Gazette, a quarterly industrial periodical which includes a substantial amount of material relating to occupational safety.
In Wellington the Department has an Industrial Safety Training Institute, which it opened in 1960, consisting of a lecture room and a large display and demonstration area. The institute is used for safety courses for inspectors, teachers, trade and industry groups, post-graduate nurses doing work in the field of occupational health, and so on.
The Department cooperates with all other bodies working in this and related fields and seeks specialist advice from time to time from such other Departments as Health, Marine, Forestry, Mines, Railways, Works, Electricity, Agriculture, and Scientific and Industrial Research, and collaborates with them in matters of mutual concern.
A Joint Committee on Occupational Health and Safety Education of the Departments of Labour and Health ensures that the educational work of these Departments in this field is coordinated and wherever responsibility is shared that it is undertaken jointly. The National Safety Association of New Zealand (Inc.) is also associated with this Committee for the purpose of mutual sharing of information.
Safety of Machinery – The Machinery Act 1950 provides for the inspection of machinery by inspectors of the Department of Labour. The use of faulty, defective, and insufficiently guarded machinery may be prohibited as unsafe, and requisitions served on the owner to make a machine safe for use in a specified time. Inspectors of Factories, Safety Inspectors appointed under the Construction Act 1959, and inspectors under the Bush Workers Act 1945 have all the powers of an inspector under the Act, and Inspectors of Mines have powers of Inspectors of Machinery in respect of machinery in mines.
Where a person is killed or suffers serious bodily injury as the result of an accident caused by machinery the owner or person in charge of the machinery must inform an inspector within 48 hours, and the cause of the accident is investigated.
The Machinery Amendment Act 1956 placed on the manufacturer the responsibility to design and build machines incorporating guards which securely encase all dangerous parts. Sellers, agents, and persons who let on hire commit an offence against the Act if they sell or let on hire any machine which is not properly guarded. This has overcome complaints previously made by owners of machines when requested to guard dangerous parts – namely, that the machine had been recently purchased and that guards should have been provided with the machine.
The number of requisitions for machine guarding complied with during the latest five years ended 31 March, including figures for other statutes as well as the Machinery Act, were as follows: 1955–56, 3,046; 1956–57, 4,076; 1957–58, 21,895; 1958–59, 19,371; and 1959–60, 14,107.
The Workers' Compensation Act 1956 provides that, whenever any accident happens which causes personal injury to or the death of any worker, the employer shall report the matter to his insurer. The report has to be in the form prescribed by the Employers' Liability Insurance Regulations 1957.
Likewise any accident must be reported to an Inspector of Factories.
Under the Factories Act 1946 the occupier of a factory is required to keep a register in the prescribed form with details of all accidents which occur in the factory and of which he has knowledge. An Inspector of Factories must also be given notice of accidents in a factory causing death or injury which is likely to incapacitate the sufferer for work for at least 48 hours.
Under the Machinery Act 1950 the person in charge of machinery must also maintain a register of accidents in the prescribed form and notify an Inspector of Machinery where a person is killed or suffers severe bodily injury.
Department of Health – This Department has general responsibility under the Health Act 1956 and regulations made under that Act for occupational health as one sphere of public health, and, in addition, section 78 of the Factories Act 1946 gives to Medical Officers of Health and Inspectors of Health the same powers and responsibilities as Inspectors of Factories with regard to the health and welfare provisions of the Act. There is no distinct dividing line between occupational safety and occupational health, and therefore the responsibilities of the Departments of Labour and Health at some points tend to overlap. There is therefore the closest collaboration between the two Departments at Head Office administrative level and also between Medical Officers of Health and Inspectors of Factories at local district level. For this reason, certain regulations are issued jointly under both the Health Act and Factories Act. (See also the section on “Occupational Health” on pages 141–2).
Marine Department – This Department has overall responsibility for the safety of persons working on the waterfront, for physical conditions on ships affecting the safety of ships' crews, and for the Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes Act 1950.
Safety of Ships – A substantial portion of the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 is concerned with the safety of ships and those who sail in them. This Act contains the necessary authority for implementing the provisions of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea 1948 and the International Load Line Convention 1930, to both of which New Zealand is a signatory. Both conventions deal principally with ships engaged on international voyages, but the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 also contains provisions concerning the safety of all other ships plying in and about New Zealand coastal waters.
With the exception of fishing boats not exceeding 60 ft registered length, pleasure yachts not exceeding 50 tons register, missionary ships, and certain small vessels engaged in carrying agricultural or pastoral produce, the hull, machinery, and equipment of every New Zealand ship are required to be surveyed once in every 12 months by a Surveyor of Ships of the Marine Department. If in the opinion of the surveyor the hull, machinery, and equipment of the ship arc up to the standards of seaworthiness and efficiency required by the Marine Department, a certificate of survey is issued which is valid for a period not exceeding one year and which sets out the limits in which the vessel may ply, the number of passengers and/or crew she may carry, and the lifesaving appliances to be carried. Under certain circumstances this certificate may be extended for a further period not exceeding three months.
Rules and regulations have been made under the authority of the Shipping and Seamen Act prescribing the scales of lifesaving and fire appliances to be carried on the various classes of ships, the radio installations required, the number and type of compasses and their adjustment by competent persons, the standards of crew accommodation, and in the case of passenger ships, standards of watertight subdivision, fire protection, electrical and machinery installations, pumping arrangements, etc. The following rules and regulations are all concerned with the safety of life at sea; Shipping (Dangerous Goods) Rules 1953; Shipping (Grain) Rules 1953; Load Line Rules 1953; Shipping (Closing of Openings in Hulls and Watertight Bulkheads) Rules 1954; Shipping Construction Rules 1954; Shipping Direction Finders Rules 1954; Shipping Lifesaving Appliances Rules 1960; Shipping Musters Rules 1954; Shipping Navigational Warning Rules 1954; Shipping (Pilot Ladders) Rules 1954; Shipping Radio Rules 1954; Shipping Signals of Distress Rules 1954; Shipping Fire Appliances Rules 1958: Shipping Ballast Regulations 1937; Ships' Compasses Regulations 1947; Deck Cargo Regulations 1950; Transport of Radioactive Substances Regulations 1951; Shipping (Accepted Safety Convention Certificates) Regulations 1953; Collision Regulations Order 1953; Timber Cargo Regulations 1953; Shipping (Crew Accommodation) Regulations 1954; Shipping (Certificates of Competency as A.B.) Regulations 1954; Load Line (Particulars of Depth of Loading) Regulations 1954.
Provision is also made in the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 to ensure the competence of ships' masters, deck and engineer officers, and able-bodied seamen.
In the event of a shipping casualty involving material damage to a vessel through stranding, collision, fire, etc., or where any loss of life occurs, there is power under the Shipping and Seamen Act 1952 to hold a preliminary inquiry into the circumstances of the casualty. If this inquiry indicates the necessity for it, the Minister of Marine may order a formal investigation to be held by a Magistrate assisted by technical assessors. The function of the Court is to determine the facts concerning the casualty, to apportion blame if necessary, and to make recommendations as to any action which might reduce the likelihood of a recurrence of the casualty. Much of the existing legislation concerning the safety of life at sea has been the direct result of lessons learned from past casualties both in New Zealand and overseas.
Port Safety – The General Harbour Regulations and General Harbour (Safe Working Load) Regulations administered by the Marine Department are designed to promote the safety of life and limb in the waterfront industry. It is an obligation placed on employers of port workers to report accidents, occurring in New Zealand ports on official forms to the Marine Department.
All cargo gear used in working cargo must comply with the requirements of the General Harbour (Safe Working Loads) Regulations. Articles of cargo gear are tested and inspected by officers of the Marine Department before being put into use, and certificates of test and examination are issued in respect of them. Samples of wire and fibre ropes used for working cargoes are tested to destruction, and the respective breaking strengths must not be less than specified in departmental tables. Gear is afterwards inspected annually by officers of the Department, or in the case of repaired gear, is tested and inspected after repair.
Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes – The Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes Act 1950 is designed to promote the safety of life and limb in the operation of steam boilers, digesters, other steam-pressure vessels, and air receivers; hydraulic, electric, and other lifts; all types of power-driven cranes. Nothing in the Act applies to any machinery driven by manual or animal power, or to any machinery the motive power of which does not exceed 1 horsepower.
Boilers, air receivers, and other pressure vessels, lifts, and cranes are required to be of approved design and workmanship, and the moving parts of machinery must be adequately guarded.
All boilers and power cranes are inspected and certificated once per year and lifts twice per year. It is illegal to work a boiler or other pressure vessel or any crane or lift which does not carry a current certificate of inspection issued by the Marine Department. The Department publishes three books of rules on pressure vessels, boilers, and cranes.
Particulars of inspections of boilers and machinery by the Marine Department during the year ended 31 December 1959 were as follows.
| Boiler inspections – | |
| Fired boilers | 4,776 |
| Pressure vessels | 16,247 |
| Total | 21,023 |
| Machinery inspections – | |
| Lifts | 3,930 |
| Cranes | 2,006 |
| Total | 5,936 |
| Grand total | 26,959 |
The Acts provide that where loss of life or serious bodily injury to any person occurs by reason of the explosion of a boiler, or as a result of an accident caused by machinery, the explosion or accident must be reported by the owner, and the cause investigated by an engineer-surveyor.
The Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes Act 1950 also provides for the issue of certificates to those who pass the prescribed examinations for land engineers and enginedrivers in charge of boilers and machinery, for winding-engine drivers for mining purposes, for drivers employed on locomotives working on railway lines not under the control of the Government Railways Department, and for the drivers of steam traction engines on roads. Certificates are also issued to electric-tram drivers, as provided by the Tramways Amendment Act 1910, and cable-tram drivers' certificates in pursuance of section 75 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1946. The issue of these certificates is controlled by a Board of Examiners set up under the Act, the chairman being the Chief Engineer-Surveyor. The total number of candidates examined in 1959 was 430; of this number 342 were successful.
Mines Department – This Department is responsible for the safety of persons working in mines (both underground and opencast) and in quarries.
Mining Acts – The Mining Act 1926 requires that a person acting in the capacity of mine manager of any mine where there are more than 12 men employed at any one time above ground, or more than six underground, must hold a certificate granted after examination by a Board of Examiners empowered under the Act to grant such certificates. Provision is made for proper ventilation in mines, the air temperature must not exceed 80°F in any working place, special care is required to be taken in handling explosives, dangerous places must be properly timbered, and special regulations are made as to hauling machinery, etc.
All machinery used to supply motive power is subject to the provisions of the Boilers, Lifts, and Cranes Act 1950 and the Machinery Act 1950 so far as these provisions apply. Inspectors of Mines have the powers of Inspectors of Machinery under the former Act and, by the Mining Amendment Act 1953, they are also given the powers of Inspectors of Machinery under the latter Act. Sufficient water must be supplied where it is necessary for the laying of dust in a mine. The Mining Amendment Act 1927 provides, inter alia, that a mine where 20 men or over are employed on one shift must have two outlets.
Comprehensive amending regulations pursuant to the Mining Act were issued in August 1945.
Coal Mining Acts – For every coal mine there must be a duly qualified manager, who must be either the owner of the mine or some person appointed by the owner, and who is responsible for the control, management, and direction of the mine. Inspectors of Coal Mines must hold certificates as first-class mine managers under the Coal Mines Act 1925. Certain sections of the Act deal with the control of coal dust, the use of safety lamps, first-aid endorsement on certificates of competency, the prohibition of work in places where the presence of gas is suspected, and the inspection of the mine before the commencement of work, etc. All accidents in mines rendering a workman unfit for work are notifiable. Comprehensive regulations pursuant to the 1925 Act, and known as the Coal Mines Regulations, were issued in 1939. These regulations have been amended from time to time in subsequent years.
A levy at the rate of 9d. a ton on coal other than lignite and 71/2d. a ton for lignite is paid into a fund, called the Coal Mining Districts Welfare and Research Fund. This fund is used for the purposes of relief of miners injured in the course of employment, covers the cost of running and equipping mine rescue stations, and provides amenities in coal-mining districts, while moneys may be expended from the fund for research and otherwise generally for the benefit of the industry. The Coal Mining Districts Welfare and Research Council directs the expenditure.
Quarries Act – The Quarries Act 1944 contains provisions as to inspectors, and the appointment, qualifications, and duties of quarry managers. Adequate rules are provided for the safety of workers and the prevention of accidents. The Quarries Amendment Act 1951 placed opencast coal quarries under the authority of this Act and made consequential amendments to the Coal Mines Act 1925, certain provisions of which are now applied to opencast coal quarries. The 1954 amendment extends the definition of a quarry to cover hydro-electric works construction and a dam for water supply to the public.
Revised Quarries Regulations containing many new regulations and amendments to previous regulations were promulgated on 21 January 1959. These are framed to ensure proper standards of safety for all engaged in quarrying operations.
New Zealand Electricity Department – In addition to its major role of supplying bulk power, the New Zealand Electricity Department, amongst other things, administers the Electricity Act 1945, the Electrical Supply Regulations, the Electrical Wiring Regulations, the Electricians Act 1952, and the Electric Linemen Act 1959.
The Electrical Supply Regulations set out minimum requirements for the construction and maintenance of lines and equipment used for the generation and distribution of electricity. These regulations also state conditions in regard to the characteristics of the supply to electricity consumers. The Department provides inspecting services in the interests of safety to life and property.
The Electrical Wiring Regulations set out minimum requirements for electrical installations, apparatus, and appliances used on consumers' premises. It is the responsibility of Electrical Supply Authorities to inspect such installations to see that they comply with the Wiring Regulations, which are designed to promote safety to life and property.
The Electricians Act, through a Board set up under that Act, provides that electrical work be performed by registered persons, for the registration of Electrical Inspectors, and for legal proceedings to be taken where necessary. The aim of the Act is to promote safety to life and property.
The Electric Linemen Act set up the Electric Linemen Training Committee and provides for the training and certification of linemen and for work on overhead lines to be done only by authorised persons.
The Department is also actively engaged in promoting electrical safety through such bodies as the National Safety Association and committees of the New Zealand Standards Institute.
Air Department, Civil Aviation Administration – The Administration is responsible for the safety of aircraft and crews engaged in private and commercial carriage of the public and commercial carriage of goods, including agricultural aviation. The Administration lays down standards of aircraft construction and maintenance by means of Civil Airworthiness Requirements and by regulation controls the standards of crew competency and physical fitness. The Accidents Branch has a responsibility in regard to both service and civil flying to investigate all aircraft accidents to ascertain their causes and to advise on preventive measures. The Operations Division generally lays down standard limitations for aircraft operations according to aircraft performance and quality of airfields. Safety of aircraft engaged in all-weather flying is achieved by controlled separation exercised by Air Traffic Control.
With agricultural aviation now rivalling all other forms of aviation in New Zealand, and with the increasing use of toxic chemicals for control of pests and weeds, the Administration, in close collaboration with the Departments of Health and Agriculture, requires pilots engaged in the distribution of these chemicals to obtain a Chemical Rating by attendance at a special residential course at one of the agricultural colleges and the passing of a written examination.
Department of Internal Affairs – The Department of Internal Affairs, through its Explosives Branch, administers legislation which has as its purpose the protection of life and property from the hazards associated with the handling, storage, transport, and use of explosives, dangerous goods, and cinematograph film.
Explosives – The empowering legislation is the Explosives Act 1957 as amended by the Explosives Amendment Act 1958. The regulations in force are the Explosives Regulations 1959, and the Explosives Authorisation Order 1959 lists the explosives which may be imported into or manufactured in New Zealand. The explosives legislation is concerned solely with explosives proper, such as blasting powder, gelignite, and detonators which are used in blasting operations, explosive compositions used in ammunition, signals, or fireworks, and also ammunition, signals, and fireworks in their final manufactured form.
The main matters covered by the explosives legislation are (a) the authorisation and classification of explosives; (b) the licensing and control of importations, manufacture, conveyance (by air, sea, or land), storage, and sale of explosives; and (c) the promulgation of rules for the handling and use of explosives.
The regulations provide for the approval of the design, construction, and isolation of storage magazines and explosives factory buildings. In the case of factories, approval is also required of the manufacturing processes used in the production of explosives, and a general set of rules governing the safety of employees engaged in the industry are laid down in these regulations.
The legislation also deals with the conditions under which explosives may be transported and the type of vehicle which may be used for that purpose.
Dangerous Goods – The relevant legislation is the Dangerous Goods Act 1957 and the Dangerous Goods Regulations 1958. Substances controlled under the heading of dangerous goods embrace a wide range of inflammable materials, such as petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, calcium carbide, white phosphorus, ammonium nitrate, the chlorates of sodium, potassium, and calcium, compressed gases, and liquefied petroleum gas. While the Chief Inspector of Explosives has the overall responsibility for administration of this legislation, provision is made in the Act for the appointment of local bodies to act as local licensing authorities responsible for the issue of licences and the carrying out of regular inspections within their own districts. Over 160 local authorities, including all cities, almost all boroughs, a number of town boards, and a few counties, have been appointed as local licensing authorities under this provision.
As the regulations pertaining to dangerous goods are very comprehensive, a summary only of the more important requirements is given here. These are:
Premises for the storage of dangerous goods must be licensed.
Work rooms where dangerous goods are used industrially must be approved as to their construction and general layout.
The design and construction of tank wagons, aircraft-refuelling units, and other vehicles used for the conveyance of dangerous goods must be approved.
Types of containers, such as tins and drums for packing of dangerous goods, must be approved.
Vehicles and containers used for carrying or holding dangerous goods must be properly labelled.
Fuel-oil burners must be approved as to type and the installation of fuel-oil-consuming systems must also be approved.
Cylinders for holding compressed gases must be to an approved specification and the arrangements for filling and storage of the cylinders must also be subject to approval.
The installation of stationary petrol-driven internal combustion engines must be approved.
The repair and disposal of tanks and other containers which have held dangerous goods are controlled.
Adequate fire-extinguishing equipment must be provided in any place where dangerous goods are stored, handled, or used.
For the purpose of effective enforcement, inspectors appointed under the Act are given the power to enter and inspect premises where dangerous goods are stored under licence or where there is reason to believe that dangerous goods may be present; to seize goods or containers where such action is considered necessary; to take samples of dangerous goods for the purpose of testing; and to investigate the circumstances of any accident with dangerous goods.
Cinematograph Films – The Cinematograph Films Act 1928 and its associated regulations include provisions governing the storage, handling, and projection of cinematograph films and the licensing of theatres and other buildings in which cinematograph film is projected and of cinematograph-film projectionists. Control is exercised through a licensing system. Premises in which cinematograph film is stored or screened must be licensed and must comply with certain requirements as to construction, ventilation, and means of egress. Projectionists employed in cinematograph theatres are required to be the holders of an operator's licence of the requisite grade.
The Public Service Commission – Progress towards safety at work can come only from deliberate, informed, and organised effort in every work place. It is a recognised fact that most industrial accidents result from unsafe conditions, unsafe human acts, or from a combination of both. Consequently, occupational accidents, with their resultant loss of productive hours, suffering, and incapacity, will be kept to a minimum only if (a) safe working conditions are provided, and (b) safe working methods are adopted.
To this end the Public Service Commission has ensured that positive measures are adopted towards the prevention of accidents at work. It realises that safety at work is important to morale and efficiency. It accepts the fact that leadership in the organisation of safety measures must come from top management. It endeavours to have every worker assured that there is a definite policy for safety based on the best available knowledge and methods, and that organisation and resources are in existence to ensure the implementation of that policy.
Safety work must be, and is, in the hands of experienced people. The Commission itself watches statistics and trends and directs special attention to causes and localities with a high incidence of accidents. It encourages Departments to campaign for safety, and offers active assistance where needed. Also, on behalf of its associated Departments, the Commission is a member of the National Safety Association of New Zealand.
Ministry of Works – On each major construction project the Ministry of Works has appointed a senior technical officer to act in the capacity of Safety Officer. He is invariably an officer with considerable practical knowledge and experience of departmental construction works. It is his duty to see that every section of the work is safeguarded to the maximum extent.
There is a wide range of activities undertaken by the Department on a major construction job such as a hydro-electric power project. For instance there are the mechanical workshops with installed machinery on various types used to repair the machines used on the job. There are also scores of bulldozers carryall scrapers, huge mechanical shovels, cement hoppers, and cableways. The custody and distribution of tons of stores of all kinds is undertaken daily. Large numbers of men are transported daily in buses and trucks to and from their homes and the job sites. Electrical reticulation and maintenance is also a major task if the job is to proceed day and night without interruption.
In the actual carrying out of the work, tunnels are driven into the rock floor for foundation and survey purposes. Rivers are diverted, necessitating the excavation of thousands of tons of material, tons of explosives being used in these operations. Massive reinforced concrete structures are erected.
Safety requirements prescribed in various Government Acts and regulations play a major part in safety promotion on construction works. The Safety Officer is required to have a sound working knowledge of these requirements. In addition he is sent to training courses conducted periodically by the National Safety Association of New Zealand. From this training and with the help of Divisional Technical Staff (Mechanical, Civil Engineering, etc.) to whom he can look for specialised knowledge and assistance, the Safety Officer is well qualified to police the various sections of the works and ensure that the various safety regulations are complied with.
In the main it is the Department's foremen and overseers who can play the most important part in accident prevention on the job. These supervisors are in direct control of the day-to-day work, and by instructing their workers in the use of correct, efficient, and safe working methods, can prevent accidents. It is therefore an important part of the Safety Officer's job to make supervising staff safety conscious.
To do this, staff talks on safety are given, circulars, booklets, and extracts from safety regulations are distributed, posters are displayed on the works site, and film showings are made at regular intervals. In addition, with a view to safety, the Department encourages visits and inspections of the works by officials from other Government Departments, although these are not always required by law. The recommendations made in their reports are invariably acted upon.
All accident reports are examined by the Safety Officer. It is his responsibility to ensure that appropriate action is taken to prevent a recurrence of a similar accident on the job. He also reports to Head Office if the experience gained would be helpful on other works.
Protective clothing is supplied to many of the Department's workers employed on specific work. Welders are issued with goggles or helmets, gauntlets, and also leather aprons on special jobs. Operators on lathes, woodworking machinery, and other allied types of machines are supplied with goggles; spray painters with masks; and construction workers on projects with protective helmets. These are only a few of the items on issue to protect workers from injury, and work in this field is progressing as better and improved protective equipment becomes available.
Quite apart from accident-prevention activities on the job, a great deal of work is done by Head Office Divisions in safety promotion. In recent years much time has been devoted by the Mechanical Division to improve the safety of existing machinery in workshops by use of guards. Investigations into the use of cranes and other lifting machinery have also resulted in safety improvements.
Department of Agriculture – The high degree of mechanisation on the 90,000-odd farm holdings in New Zealand is responsible in large part for the high output per unit of labour engaged in primary production; but it has been responsible too for an increase in the hazards associated with life and work in the country. Nearly 4,000 threshing machines, 19,000 wool presses, 30,000 internal combustion engines, 140,000 electric motors, 78,400 agricultural tractors, 37,000 milking plants, 29,000 shearing plants, as well as farm trucks, cultivating and harvesting implements, and other farm equipment and installations have taken a high annual toll in accidents and deaths, especially in recent years when there has been rapid growth in the use of heavy machinery for both normal farm operations and for bringing new land into production.
The increasing use of chemicals in agriculture for weed control and as pesticides and therapeutants, and employment of aircraft in farm work (248 machines in 1960), have added to the hazards to which those engaged in the agricultural industry have been subjected.
For both humanitarian and economic reasons the Department of Agriculture has incorporated in its general extension service to farmers, advice on the proper operation of farm implements and equipment, and on safety precautions in farm management. Emphasis has been on education rather than coercion or regulation.
Personal efforts by departmental field officers to promote safety consciousness among farmers and other agricultural workers are assisted by machinery demonstrations, lectures, film showings, posters, field days, show exhibits, and publications.
The Department of Agriculture cooperates closely with other Departments, the National Safety Association, and other agencies in farm-safety extension work. It assisted with lecturers and material for the first course in farm safety in 1957 at Canterbury Agricultural College, Lincoln, and has helped to promote a scheme for the training and appointment of farm-safety officers from the ranks of the Young Farmers' Federation, which is supported by the Department.
Workers' Compensation Board – This Board is a statutory body set up under the provisions of the Workers' Compensation Act. One of its responsibilities is a general requirement to “prevent accidents to workers by such means as the Board thinks fit, and cooperate with any Government Department and other bodies and persons for that purpose”. It is also required to assist in providing facilities for the treatment and rehabilitation of injured persons. It has interpreted these requirements by sponsoring the formation of the National Safety Association of New Zealand (Inc.), and by making grants to the Department of Labour for safety education, the Department of Health for the construction of Industrial Health Centres at Penrose and Mt. Wellington (Auckland) and Woolston (Christchurch), and to the Auckland Hospital Board towards the cost of a rehabilitation centre for disabled civilians at Otara (Auckland). The Board also sponsors a scheme for first-aid instruction in remote areas by the Order of St. John.
National Safety Association of New Zealand (Inc.) – This organisation was sponsored and is largely financed by the Workers' Compensation Board. It comprises member firms interested in promoting occupational safety, and is controlled by an elected executive functioning through specialist committees, five branch committees, and a small headquarters staff, together with a number of field organisers. It seeks to stimulate firms and organisations in taking all possible measures to reduce accidents in their own establishments, and especially in establishing their own internal safety organisations, full-time or part-time safety officers, and where possible joint management-worker safety committees. The Association also issues safety education material, undertakes general safety instruction and supervisor training within firms through its field staff, and organises periodical courses for farm safety officers and industrial safety officers. Its field of interest is substantially limited to occupational safety.
ADMINISTRATION – Under the Island Territories Act 1943, the Cook Islands Act 1915, and the Samoa Act 1921, the Minister of Island Territories is charged with the administration of New Zealand's dependent territories, and the Department of Island Territories is the executive agency for that administration.
New Zealand's first administrative responsibility for dependent areas in the South Pacific was undertaken in 1901, when the Cook Islands (including Niue) were brought within the boundaries of New Zealand. In 1919 New Zealand was given a mandate over Western Samoa; this became a trusteeship in 1946 under the Trusteeship Council of United Nations, and is being terminated from 1 January 1962 with the granting of independence to Western Samoa. In 1949 the Tokelau Islands, formerly part of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony, legally became part of New Zealand, which had administered them on behalf of the United Kingdom since 1925. Annual reports are forwarded to the United Nations Committee on Information from Non-self-governing Territories regarding progress made in Cook Islands, Niue, and the Tokelau Islands.
The Chatham Islands, which comprise one of the 121 counties of New Zealand, have had their development seriously retarded by reason of their isolation and consequent lack of direct contact with the mainland. In order to assist in overcoming the disabilities suffered by the people of the Chatham Islands, and to promote the general welfare and development of the islands, the Government, in December 1949, placed their general administration under the Department of Island Territories. A Resident Commissioner is responsible for coordination of all Government activities in the islands and also acts as Resident Magistrate.
Besides administering the various island groups, the Department controls the operations of the N.Z.G.m.v. Moana Roa and the purchase and shipping of equipment, stores, etc., to island administrations. In addition, the Department takes an interest in the welfare of islanders in New Zealand, and is associated with the South Pacific Commission and the South Pacific Health Service. The former is an advisory and consultative body set up by the Governments of Australia, France, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America, all of which are responsible for the administration of non-self-governing territories in the Pacific. The functions of the Commission are to recommend to the member Governments means for promoting the social, economic, and medical welfare of the peoples in the region, and to this end several projects have been organised. The South Pacific Health Service advises member Governments on health matters, collects and distributes epidemiological information, assists in the maintenance of professional staffs, and encourages medical research and the training of indigenous people as assistant medical practitioners and nurses.
The Officer for Islands Education is responsible under the Department for the coordination of educational policies in the various island groups, the appointment of New Zealand teachers on secondment, the publication of School Journals in the vernacular of the different groups, and the supply of modern teaching equipment. An islands scholarship scheme instituted in 1945, under which selected students from all territories are given secondary and higher education in New Zealand, is under the Department's direction. Since the inauguration of the scheme 279 children have won scholarships, of whom 99 have already returned to employment in the islands. In 1960 three boys were awarded technical scholarships.
By arrangement between the Governments of Fiji and New Zealand, young Samoans, Cook Islanders, Niueans, and Tokelau Islanders receive training at the Central Medical School, Suva, Fiji, to equip them for duty in their own territories as assistant medical practitioners, assistant dental practitioners, pharmacy and laboratory assistants, and assistant sanitary inspectors.
New Zealand also exercises the administration of the Ross Dependency on behalf of the United Kingdom Government. The Ross Dependency is normally uninhabited but, at the 1956 census date, had a population of 166 males, and at 1 April 1960, 137 males, these men being members of scientific expeditions. Brief mention is also made in this section of Nauru Island, which is administered under a trusteeship, held jointly by the United Kingdom Government, the Government of Australia, and the New Zealand Government.
The term “island territories” does not include Stewart Island or the Chatham Islands, which form part of New Zealand, although, as mentioned earlier, the latter have been placed under the administrative direction of the Department of Island Territories. The following minor islands,which are referred to on page 1 of this Yearbook, are also excluded: Three Kings Islands, Auckland Islands, Campbell Island, Antipodes Islands, Bounty Islands, Snares Islands, and Solander Island. None of these islands is regularly inhabited, although meteorological stations were established on the Auckland and Campbell Islands in 1940. The station in the Auckland Islands was closed in June 1945, but a staff of 10 is still engaged on Campbell Island maintaining meteorological records and conducting ionospheric research. A radio station is also established on Campbell Island. The Kermadec Islands are also excluded, for, although they are in the same category as the Cook Islands in that they originally ranked as annexed islands, all New Zealand laws extend to them and there is no separate administration. A meteorological station and an aeradio station have been established on Raoul Island. The population, including the official staff of Raoul Island, at 31 March 1961 numbered 10. This is the only island of the Kermadec Group that is inhabited.
COOK ISLANDS Des – The Cook Islands were proclaimed a British Protectorate in 1888, and on 11 June 1901 they were annexed and proclaimed part of New Zealand under the Colonial Boundaries Act 1895. Niue, though one of the Cook Islands, has been under separate administration since 1903, and data relating to it are given later in this section. Not including Niue, there are 15 islands in the proclaimed territory, scattered over an area of some 850,000 square miles of ocean, and extending from Penrhyn, situated 9° south of the Equator, to Mangaia, which is just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. The Cook Islands are bounded on the east and west by the 156th and 167th meridians of west longitude respectively, and on the north and south by the 8th and 23rd parallels of south latitude. The total land area of the 15 islands is approximately 93 square miles, while Niue has an area slightly in excess of that figure.
Of the islands of the Southern Group, Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Atiu, Mitiaro, Mauke, and Mangaia are elevated and fertile, while Manuae and Takutea and the islands of the Northern Group, comprising Penrhyn, Manihiki, Rakahanga, Pukapuka, Palmerston, Nassau, and Suwarrow, are sea-level coral atolls. As a consequence the southern islands support the greater population. With one exception, Penrhyn, none of the islands possesses a good harbour.
The whole of the Cook Islands lie within the hurricane zone, and a number of destructive storms have been experienced. The Cook Islands are covered by a meteorological service with headquarters in Fiji, and advance warning of the intensity and path of tropical storms is available and enables precautions to be taken to protect life and property. From December to March the climate is warm and humid, and there is always the possibility of serious storms. In the remaining months of the year the climate of the Southern Group is mild and equable. The mean annual temperature in Rarotonga taken over the last 40 years was 74.5°F, and the average yearly rainfall over the same period was 84 in.
Following is a brief description of the individual islands.
SOUTHERN GROUP – Rarotonga (16,602 acres), the most fertile island of the territory, rises to a height of 2,140 ft. It is clothed to the tops of the mountains with splendid vegetation, and has abundant streams, considerable tracts of sloping land, and rich alluvial valleys. The town of Avarua is the centre of the local administration, and is 1,633 miles from Auckland. There is an airfield on the island. Tomatoes, oranges, and other citrus fruits are the chief exports.
Mangaia (12,800 acres, 110 miles from Rarotonga is the southeasternmost of the Group. Mangaia is not as fertile as Rarotonga, but produces quantities of coconuts, oranges, pineapples, other citrus fruits, etc. Mangaia is of volcanic origin and is surrounded by a barrier reef without passages. From a narrow sandy beach the shore rises in high cliffs to a mile-wide plateau, which descends again to almost sea level, enclosing an ancient crater holding several volcanic mounds, the highest of which exceeds 550 ft. The crater drains by subterranean channels.
Atiu (6,654 acres, 116 miles from Rarotonga) has a fertile plateau above steep cliffs. Citrus fruits and copra are the main exports.
Mauke (4,552 acres, 150 miles from Rarotonga) is a low circular island about 2 miles across, lying to the north-east of Rarotonga. Like Mangaia and Atiu, it is surrounded by an unbroken fringing reef. Mauke is very fertile. Oranges are the main export.
Aitutaki (4,461 acres, 140 miles from Rarotonga) is about 18 miles in circuit and one of the most fertile of the islands forming the Southern Group. It has an airfield and a flying-boat base which was used regularly by the Coral Route service to Tahiti up to September 1960. Tomatoes, oranges, and copra are the main exports.
Mitiaro (5,500 acres, 142 miles from Rarotonga) is a good example of an elevated coral reef, thinly coated with sand and gravel of the same material. The greater part of the surface is not more than 6 ft above high-water mark.
Manuae (1,524 acres, 124 miles from Rarotonga) consists of two small islands, Manuae and Te-Au-o-Tu, joined by a coral reef. The two islands are in general usage covered by the term Manuae; the name Hervey Islands is an alternative but rarely used title.
Takutea (302 acres, 118 miles from Rarotonga) is a small coral island, moderately fertile, but it is not regularly inhabited. It is owned by the people of Atiu and worked by them as a copra plantation.
NORTHERN GROUP – Penrhyn (2,432 acres, 737 miles from Rarotonga) is also sometimes known as Tongareva. The large lagoon with its two entrances affords the only land-locked shelter within the group for vessels other than fishing boats, and it is the refuge of trading schooners during the hurricane season. The island has a pearl-shell industry.
Manihiki (1,344 acres, 650 miles from Rarotonga) is an atoll about 30 miles in circumference, valuable for the extent of its coconut groves. It has a large pearl-shell industry. Fishing for shell was suspended from 1958 to 1960.
Pukapuka (1,250 acres, 715 miles from Rarotonga) is a small triangular-shaped atoll of about 3 miles in diameter, with its highest point about 15 ft above sea level. The people of this island have somewhat different customs and dialect from those of the remainder of the group.
Rakahanga (960 acres, 674 miles from Rarotonga) is also an atoll, and shares its Resident Agent with Manihiki, from which it is only 25 miles distant. Copra is the only export.
Palmerston (1,000 acres, 270 miles from Rarotonga) consists of eight islets threaded along a reef. Palmerston also bears the name of Avarau, and is noted as the “San Pablo” of Magellan, the first island discovered in the South Seas.
Suwarrow (600 acres, 513 miles from Rarotonga) is a coral atoll of triangular form possessing a land-locked lagoon 8 miles by 6, which is capable of being made into an excellent harbour. The island which has been much reduced in land area by storms, is a sanctuary for sea birds.
Nassau (300 acres, 673 miles from Rarotonga) is a small island well planted with coconut trees. It is owned by the people of Pukapuka, who utilise the island for its copra.
Administration – The executive government of the Cook Islands is vested in the Crown in right of the Government of New Zealand. There is a Resident Commissioner, who is charged, subject to the control of the Minister of Island Territories, with the administration of the executive government of the Cook Islands. The Resident Commissioner, who is stationed at Rarotonga, is represented in the outer islands by Resident Agents.
In each of the 10 main islands there is an Island Council consisting of ex officio members (officials, arikis, or leading chiefs) and elected members. Elections were first held in March 1947 and have since been conducted triennially in each constituency, the franchise extending to all Cook Island Maoris of 18 years of age or over. The councils, which must meet at least annually, and in practice meet much more frequently, are presided over by the Resident Commissioner, if present, or by the Resident Agents. Europeans in the Group are represented by one elected member on the Island Council of Rarotonga.
A major step forward in the constitutional development of the Cook Islands was the passing in October 1957 of the Cook Islands Amendment Act 1957. The most important provisions of this Act are those which provide for:
The establishment of a Legislative Assembly with an elected majority to replace the Legislative Council, which had a majority of official members. The Assembly is empowered to appropriate and authorise the expenditure of all revenue derived in the Cook Islands.
The setting up of an Executive Committee with elected and official representation to advise the Resident Commissioner in his administration of the executive government. This committee provides a valuable link between the legislature and executive.
The creation of village committees with limited police and judicial authority.
The appointment of Justices of the Peace.
In October 1958 elections for islands' representatives were held, and on 3 November 1958 the Assembly met for the first time.
The Legislative Assembly consists of 26 members, excluding the Resident Commissioner, 14 of whom are elected by secret ballot under a system of universal suffrage, seven (being in each case a member of an Island Council) elected by the various Island Councils, one member for the electing Europeans, and four official members.
Laws governing the Cook Islands axe made by Act of the New Zealand Parliament or by Orders in Council and regulations issued thereunder. Ordinances applicable to the whole of the Cook Islands are now made by the Legislative Assembly of the Cook Islands, subject to certain statutory restrictions. These ordinances require the assent of the Resident Commissioner, and may be disallowed either wholly or in part by the Governor-General within one year after the assent of the Resident Commissioner has been given. Ordinances restricted in their application to the islands in which they are made may be enacted by the local Island Councils. These local ordinances require the consent of the Resident Commissioner, or they may be reserved for the Governor-General's pleasure.
The administration of justice is in the hands of the High Court, the Native Land Court, and the Native Appellate Court. The High Court exercises civil and criminal jurisdiction throughout the Cook Islands, while the Native Land Court is concerned with litigation on lands and titles. The Native Appellate Court hears appeals and applications for rehearings in respect of judgments of the Native Land Court.
The Cook Islands Public Service comes under the control of the New Zealand Public Service Commission.
Population and Vital Statistics – The Cook Island Maori is a Polynesian and is closely related to the New Zealand Maori. There is a strong resemblance between the two peoples in tradition, language, and custom. Many of the tribes in both places are able to trace their descent back to a common ancestor. A census of the Cook Islands taken on 25 September 1956 recorded a total population (exclusive of Niue) of 16,680, an increase of 1,601, or 10.6 per cent, as compared with the census of 25 September 1951. Details of population of the islands of the group as at 31 December 1959 are set out in the following table.
ESTIMATED POPULATION AS AT 31 DECEMBER 1959
| Island | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rarotonga | 4,083 | 3,744 | 7,827 |
| Aitutaki | 1,253 | 1,385 | 2,638 |
| Mangaia | 1,132 | 1,053 | 2,185 |
| Atiu | 741 | 697 | 1,438 |
| Mauke | 470 | 425 | 895 |
| Mitiaro | 158 | 149 | 307 |
| Manuae | 30 | 13 | 43 |
| Palmerston | 50 | 42 | 92 |
| Pukapuka | 362 | 357 | 719 |
| Nassau | 49 | 41 | 90 |
| Manihiki | 356 | 389 | 745 |
| Rakahanga | 181 | 196 | 377 |
| Penrhyn | 353 | 332 | 685 |
| Suwarrow | – | – | – |
| Takutea | – | – | – |
| Totals | 9,218 | 8,823 | 18,041 |
During the year ended 31 December 1959 births numbered 813 and deaths 178. The number of deaths of children under one year of age in 1959 was 44.
Health – In accordance with the provisions of the Cook Islands Act 1915, all Cook Islanders receive free medical and surgical treatment in their villages, in the hospital, and in the tuberculosis sanatorium. Cook Island Maori patients in the hospital and the sanatorium, and all school children, receive free dental treatment.
Although lying within the tropics, the Cook Islands are singularly free from the common diseases prevalent in other tropical islands. Malaria is unknown, but filariasis is endemic, and this and tuberculosis provide the main health problems of the Group. The objective of the health services – to improve the health of the community – is being pursued by a system of village sanitary inspection and group medical examination, combined with modern treatment of disease in dispensary, clinic hospital, and sanatorium.
The staff of the Health Department during 1959–60 numbered 146. Only the Chief Medical Officer the Assistant Medical Officer, the Matron, and three or four certificated New Zealand nurses were Europeans. The dental clinic is staffed by a European dentist and two nurses, and six Cook Islands staff.
A general hospital (57 beds) equipped with dispensary, X-ray, and laboratory facilities, and a tuberculosis sanatorium (64 beds) are maintained in Rarotonga. In the outer islands, dispensaries with accommodation for a few patients are operated by assistant medical practitioners. A cottage hospital has been built at Aitutaki. Atiu, Penrhyn, and Mangaia also have small hospitals.
Education – Primary education in the Cook Islands is provided by the Administration, the Roman Catholic Mission, and the Seventh Day Adventist Mission, post-primary education being provided by the Administration for children selected from throughout the Group.
Education is free and compulsory between the ages of six and sixteen years. At 31 March 1960 the total number of pupils on the rolls was 4,760, comprising 4,302 pupils at Government schools and 458 at denominational schools. Under the Government Scholarship Scheme seven ordinary and three trade scholars proceeded to New Zealand early in 1960. The total number of scholarships granted since 1946 is now 90.
Labour and Employment – There is a wide variation in types of employment in the different islands. On the atolls in the Northern Group the island people subsist largely on coconuts and fish, and there is little opportunity for them to engage in other pursuits which would provide exports and a consequent higher living standard. In the islands of Manihiki and Penrhyn pearl diving is carried out under regulations which restrict this employment to Polynesians, and otherwise govern the industry. A strict control of this industry is enforced to ensure that the beds are not depleted. It is in the fertile islands of the Southern Group that most of the population is concentrated, and labour is required for the growing, harvesting, packing, and shipment of fruit and copra, the staple exports on which living standards depend. As most of the land in these islands is held by family groups under customary title, the bulk of the people are engaged in work on their own plantations. There is, however, opportunity for wage earners in the administrative departments, in plantation work, and in the handling of fruit for export.
In Rarotonga secondary industries have been established in the form of two clothing factories and a factory for manufacturing articles from paua shell. Products from both industries are exported to the New Zealand market. The manufacture of handicrafts is on a domestic basis.
A number of Cook Island Maoris go to New Zealand to engage in service or to learn trades. This migration is under supervision, and persons desiring to leave the islands are subject to examination for health and character.
Agriculture – The principal export crops of the Cook Islands are citrus fruits, copra, pineapples, and tomatoes. The following are the estimated areas planted in the principal crops: coconuts, 28,250 acres; citrus fruits, 767 acres; taro, 400 acres; bananas, 1,406 acres; tomatoes, 800 acres; pineapples, 473 acres; manioc, 325 acres; kumeras, 200 acres; yams, 50 acres. In order to aid the economy of the Cook Islands, the New Zealand Government arranged for an extension of the citrus replanting scheme and the erection of a central cool store and packing shed at Rarotonga.
There are 1,864 horses, 262 head of cattle, 10,273 pigs, and 2,248 goats in the islands.
Transport and Communications – For trading connections with other countries the islands are mainly dependent on a steamer service to and from New Zealand. This service makes calls at Rarotonga and occasional calls, for the purpose of loading cargoes of oranges in season, at the larger and more productive of the islands of the Southern Group. Occasional calls are made by trans-Pacific cargo vessels at Rarotonga.
Radio communication has largely removed the former isolation of the islands, there being now no permanently inhabited island without a radio station. The chief station is Rarotonga Radio, which maintains direct communication with the substations and with Wellington, Apia, and Suva. Postal and telegraph services are available in all the islands, and there is a telephone service in Rarotonga
Trade – A summary of exports by country of destination and imports by country of origin for each of the latest five years available is contained in the next table.
| Country of Origin | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imports (£) | |||||
| New Zealand | 425,237 | 557,023 | 564,171 | 641,926 | 495,806 |
| Australia | 7,657 | 19,060 | 25,715 | 38,421 | 47,752 |
| United Kingdom | 56,042 | 108,291 | 65,062 | 66,944 | 67,748 |
| Canada | 29,393 | 14,797 | 34,372 | 25,298 | 22,899 |
| United States of America | 23,927 | 15,301 | 48,055 | 31,942 | 15,405 |
| Other | 30,108 | 54,738 | 50,673 | 81,500 | 68,151 |
| Totals | 572,364 | 769,210 | 788,048 | 886,031 | 717,761 |
| Exports (£) | |||||
| New Zealand | 329,180 | 381,891 | 402,454 | 363,225 | 482,011 |
| Australia | 15,120 | 92 | 9,925 | 1,737 | 1 |
| United States of America | 51,710 | 47,236 | 59,041 | 17,184 | 8,907 |
| United Kingdom | 44 | 462 | 274 | 288 | 174 |
| Italy | 10,780 | 21,717 | 16,210 | 11,631 | – |
| Other | 13,219 | 33,719 | 53,021 | 11,193 | 8,242 |
| Totals | 420,053 | 485,117 | 540,925 | 405,258 | 499,335 |
The New Zealand Customs Tariff applies to the Cook Islands with special duties on sugar, cotton piece goods (except calico), linen piece goods, piece goods of mixed linen and cotton, and black-twist tobacco. During the war period, import, finance, and price controls were instituted and have been kept in force. Import licences are required for goods imported from countries other than New Zealand.
Details of the quantities and values of the principal commodities exported in 1959 with 1958 figures also given, are shown below.
| Commodity | 1958 | 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| Cases | £ | Cases | £ | |
| Citrus fruits | 78,279 | 112,927 | 106,951 | 155,037 |
| Bananas | 751 | 793 | 1,055 | 865 |
| Pineapples | 2,060 | 1,886 | 1,472 | 1,511 |
| boxes | boxes | |||
| Tomatoes | 71,866 | 53,676 | 85,959 | 58,238 |
| tons | tons | |||
| Copra | 944 | 48,486 | 1,321 | 99,565 |
| Mother-of-pearl shell | 97 | 49,580 | 61 | 18,586 |
| Handicrafts, grassware, etc. | – | – | 2,813 | |
| Manufactured goods (apparel) | 96,089 | 80,858 | ||
| Jewellery | 10,244 | 29,449 | ||
Foodstuffs continue to be the largest class of import; major imports for 1959, with comparative figures for 1958, are set out in the following table.
| Commodity | Value | Percentage of Total Imports | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| £ | £ | per cent | per cent | |
| Foodstuffs | 274,502 | 226,202 | 31.0 | 31.5 |
| Drapery and piece goods | 125,870 | 68,663 | 14.1 | 9.6 |
| Oils and petrol, etc. | 51,328 | 43,962 | 5.8 | 6.6 |
| Tobacco and cigarettes | 31,287 | 13,839 | 3.5 | 2.0 |
| Vehicles and parts | 33,058 | 31,957 | 3.7 | 4.5 |
| Fruit cases and sacks | 27,982 | 30,383 | 2.2 | 4.2 |
Public Finance – New Zealand currency is in use in the Group. The principal sources of revenue within the Group are import duties £75,740, export duties £6,921, stamp sales £5,607, and income tax £19,247. Apart from income tax, there is no direct taxation of the Maori community.
The New Zealand Government has continued to make subsidies and grants available on a generous scale for capital development in health, education, and other social services, and for meeting the budgetary deficits of the Group.
A comparative statement of revenue and expenditure for the latest five years is shown hereunder.
| Year | Subsidies from New Zealand | Revenue from Cook Islands | Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955–56 | 294,243 | 285,021 | 568,313 |
| 1956–57 | 275,000 | 305,940 | 622,745 |
| 1957–58 | 390,962 | 444,391 | 787,909 |
| 1958–59 | 365,425 | 432,261 | 836,232 |
| 1959–60 | 455,530 | 425,868 | 855,617 |
The principal items of expenditure in 1959–60 were £152,836 on education, £135,234 on health services, and £74,547 on public works. More detailed information in respect of the Cook Islands and Niue Island will be found in parliamentary paper A.3 for the year ended 31 March 1960.
NIUE: Descriptive – Niue Island, discovered by Captain Cook in 1774, became part of New Zealand in 1901, when the boundaries of New Zealand were extended to include the Cook Islands. As stated previously, Niue is part of the Cook Islands, but has been under separate administration since 1903. The island is situated in latitude 19° 02' south and longitude 169° 52' west, somewhat west of the centre of the irregular triangle formed by Samoa, Tonga, and the southern Cook Islands, and is 600 miles distant from the latter. The island, which has an area of 64,028 acres, is an elevated coral outcrop with a coral reef fringing a precipitous and broken coastline. The central saucer-shaped plateau, rising to a height of 220 ft, is encircled by a narrow terrace about 90 ft above sea level. There are no running streams, and the island is dependent on rainwater, which is stored in tanks. The soil, though fertile, is not plentiful, and this feature, combined with the rocky and broken nature of the country, makes cultivation difficult and has precluded the grazing of stock in the past, although some goats were recently introduced to provide milk. The climate is mild and equable, but the island is on the edge of the hurricane belt. (In February 1959 a hurricane struck the island and damage to administration buildings, houses, churches, crops, timber supplies, and personal possessions was estimated at £750,000, and a similar misfortune occurred in January 1960.) The mean annual temperature during the last 30 years was 76.6° F, and the average annual rainfall for a similar period was 79.4 in.
The port of Alofi has an open roadstead anchorage which is satisfactory in fair weather.
Administration – Provision for the administration of Niue is made in the Cook Islands Act 1915, which provides for the appointment of a Resident Commissioner charged with the administration of the executive government of Niue. Laws are made by Act of the New Zealand Parliament, or regulations issued thereunder, or by ordinance passed by the local Island Assembly. This body meets periodically under the presidency of the Resident Commissioner, and consists of up to 16 Niuean members appointed by the Governor-General, and representing all villages on the island.
Population and Vital Statistics – The Niuean is of Polynesian stock and the language a Polynesian dialect peculiar to the island, but closely related to that of Tonga, Samoa, and the Cook Islands. Population increase would be greater by 100 or more annually if it were not for the increasing emigration of Niueans to New Zealand. Totals of the 10 censuses taken since 11 June 1901 are as follows.
| Census | Population |
|---|---|
| 1902 | 4,079 |
| 1906 | 3,822 |
| 1911 | 3,943 |
| 1916 | 3,880 |
| 1921 | 3,750 |
| 1926 | 3,795 |
| 1936 | 4,104 |
| 1945 | 4,253 |
| 1951 | 4,553 |
| 1956 | 4,707 |
The following table shows the population as at the census of September 1956.
| Niuean | European | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | 2,246 | 33 | 2,279 |
| Females | 2,404 | 24 | 2,428 |
| Totals | 4,650 | 57 | 4,707 |
The inhabitants are distributed amongst 12 villages, of which Alofi is the largest. The inhabitants of Niue are British subjects and New Zealand citizens.
For the calendar year 1959 births totalled 203 and deaths 44. There were 10 deaths of children under one year of age, the infant mortality rate per 1,000 live births being 49.3.
Health – Niue, although situated in the tropics, is largely free from diseases prevalent in tropical countries. An energetic tuberculosis campaign is being carried out by the Chief Medical Officer and his staff. The Niuean standard of general hygiene is very good by Pacific standards.
All medical and dental treatment, including hospital services, is provided free of charge to the inhabitants, the money for this expenditure being provided out of subsidies from the New Zealand Government. There is a Government hospital. Attached to the hospital is an outpatients department, X-ray unit, laboratory, and dispensary. The staff at December 1960 numbered 50.
The amounts expended on public health during the past five years were as follows.
| 1955–56 | 1956–57 | 1957–58 | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount expended | £34,875 | £42,724 | £39,360 | £37,471 | £49,618 |
| Population | 4,679 | 4,707 | 4,735 | 4,718 | 4,781 |
| Amount per head of population | £7 9s. Od. | £9 0s. Od. | £8 6s. 6d. | £9 15s. Od. | £10 7s. 7d. |
Education – The seven primary schools, the two post-primary classes, an accelerate class, and the side school (European and selected Niuean pupils) are all under the control of the Administration. The Education Department is controlled by the European Education Officer with a staff of seven European and 89 Niuean teachers.
The total number of children attending school in Niue at the end of 1959 was 1,297, and scholarship pupils attending school or receiving training in New Zealand numbered 20. Education is free and compulsory for those aged from six to 14 years.
Labour and Employment – The only substantial employer of labour is the Administration, which employs Niueans in the Education, Police, Public Works, Transport, and other Departments, and in the loading or discharge of vessels. Apart from this, labour is engaged from time to time to prepare copra for shipment. During the last four years a large number of unskilled labourers has been employed on public works. The basic wage rates are 9s. 9d. per day for unskilled work, 1s. 6d. per hour for waterside work, and on a varying scale for other employment. There is no unemployment problem.
Agriculture – The Agriculture Department has now been functioning for over six years. Before any actual plant improvements could be made it was necessary for soil studies to be made, pilot trials commenced, and for the Department to be organised and staff trained. Much of this had been achieved when the hurricane of February 1959 destroyed practically all existing trials and experiments.
The principal agricultural exports are copra, bananas, and kumeras. All the copra exported is grown by the Niueans, there being no European planters. Most copra is shipped under a contract with a New Zealand firm.
The extremely rocky nature of the ground makes all agriculture difficult, as practically the whole of the arable land is confined to small pockets of soil among the coral rocks. Of the total area of some 65,000 acres, approximately 48,000 acres are more or less continuously cultivated, while some 8,000 acres are in forest. The remaining 9,000 acres are either in coastal forest and scrub, light forest, or heavy forest.
As the Niuean depends for his livelihood upon his family lands, alienation is prohibited, so that there are no landowners apart from the Niueans and the Administration.
Transport and Communication – There are no internal transport services. The transport of goods and produce to and from the port of Alofi is carried out by Administration and privately owned motor vehicles. There are some 72 miles of all-weather roads on the island.
At Alofi there is an open roadstead only, and cargo is handled by lighters.
Full postal services are provided at Alofi, where there is a Post Office Savings Bank. A single-line telephone system connects all villages on the island, and a radio station is maintained by the Administration for overseas communication.
Trade – During 1959 inward cargo totalled 3,266 tons, while outward cargo totalled 925 tons. As usual, the bulk of the trade was with New Zealand.
The values of exports and imports for the latest five years available are given below.
| Year | Exports | Imports | Total Trade |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955 | 78,360 | 158,082 | 236,442 |
| 1956 | 63,608 | 162,739 | 226,347 |
| 1957 | 58,667 | 153,598 | 212,265 |
| 1958 | 56,785 | 152,107 | 208,892 |
| 1959 | 25,753 | 171,659 | 197,412 |
Exports of principal commodities over the latest five years were as follows.
| Item | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | ||||||
| Copra (tons) | 952 | 62,050 | 831 | 48,978 | 740 | 40,104 | 715 | 36,760 | 123 | 7,782 |
| Bananas (cases) | 4,983 | 4,983 | 4,070 | 4,070 | 6,124 | 6,448 | 988 | 1,070 | 239 | 265 |
| Kumeras (bags) | 16 | 8 | 190 | 260 | 1,377 | 1,662 | 6,528 | 5,766 | 8,910 | 8,903 |
| Plaited ware | .. | 8,091 | .. | 6,321 | .. | 5,498 | .. | 5,183 | .. | 1,592 |
| Principal exports | .. | 75,132 | .. | 59,629 | .. | 53,712 | .. | 48,779 | .. | 18,542 |
| Total exports | .. | 78,360 | .. | 63,608 | .. | 58,667 | .. | 56,785 | .. | 25,753 |
The New Zealand Customs Tariff is in force, and there is free trade between the island and New Zealand. Local duties are, however, imposed on cotton piece goods, sugar, and twist tobaccos irrespective of country of origin.
Public Finance – Revenue within the island is raised principally from import and export duties. the sale of stamps, and High Court fines. Income tax at New Zealand rates is levied on those with taxable incomes, while a poll tax of £1 per annum is imposed on all Niuean males aged 18 years and over.
Deficits are met by a subsidy from New Zealand. A comparative statement of revenue and expenditure during the latest five financial years is given in the following table.
| Year | Revenue | Expenditure | Subsidy |
|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955–56 | 103,666 | 221,498 | 109,953 |
| 1956–57 | 101,761 | 243,951 | 137,172 |
| 1957–58 | 149,980 | 284,632 | 163,587 |
| 1958–59 | 139,747 | 297,831 | 150,000 |
| 1959–60 | 167,642 | 418,837 | 232,560 |
TOKELAU ISLANDS: Descriptive – Situated some 300 miles to the north of Western Samoa, between 8° and 10° south latitude and between 171° and 173° west longitude, are the three atoll islands of Atafu, Nukunono, and Fakaofo, of the Tokelau (Union) Group. A fourth island, Olosega, belonging to the United States of America and lying 100 miles to the south of Fakaofo, completes the group.
Each atoll is composed of a number of coral islets surrounding a central lagoon. These islets vary in size from 100 yards to 4 miles in length, while none is wider than 400 yards nor, with but few exceptions, higher than 10 ft above sea level. The land area of each atoll is approximately as follows: Fakaofo, 650 acres; Atafu, 500 acres; Nukunono, 1,350 acres. The atolls do not lie in close proximity, there being 40 miles of open sea between Fakaofo and Nukunono, and 57 miles between Nukunono and Atafu.
Owing to the absence of humus in the soil, the vegetation is practically restricted to coconut palms, although one islet of each atoll is reserved for growing the tauanave, or tausunu, a short stubby tree, which yields to the Tokelau Islanders their only timber for the construction of canoes and utensils.
The general isolation of the Tokelau Islands and the limited nature of the economy have combined to produce an extremely simple pattern of living and a stable society in which there is freedom from many social problems. The absence of such complicating factors as divergent economic interests, cultural differences, or racial conflict is conducive towards the maintenance of the present peaceful mode of life and outlook. Village affairs are managed by the Council of Elders, comprising representatives of the families, and this body also exerts some influence over the “aumaga” or village labour force. In this way the traditional form of patriarchal authority has been preserved and regulates Tokelau society, performing a service alongside, and also in addition to, the public duties of government which are carried out by local officials such as the Faipule and the Pulenu'u.
Administration – The first recorded European discovery of the Tokelau Islands was made by Quiros, the Spanish Navigator, who in 1606 made a landfall at Olosega. In 1765 Atafu was discovered by Commodore Byron, R.N., and the islands were included under the protection of Great Britain in 1877. In 1916 the islands, at the request of the inhabitants, were formally annexed to Great Britain by an Order in Council, which also extended the boundaries of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony to include the Tokelau Group (then known as the Union Islands) and their dependencies. The group was governed by the High Commissioner for the Western Pacific and administered by the District Officer at Funafuti, in the Ellice Group. In 1925 the New Zealand Government, at the request of the British Government, agreed to administer the islands. By Order in Council the group was separated from the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony, and by a further Order in Council in the same year the Governor-General of New Zealand was empowered to make laws for its peace, order, and good government, and authorised to delegate from time to time to the Administrator of Western Samoa so much of this power as might be considered desirable. The right was reserved to the Governor-General in Council to disallow any laws passed under this delegated power and to make any restriction deemed proper. The vesting of administrative powers in the Administrator of Western Samoa (now the High Commissioner) in 1926 was a matter of convenience, the Tokelau Group having no political connection with the Territory of Western Samoa.
The Tokelau Nomenclature Ordinance 1946 officially fixed the name of the group, hitherto sometimes referred to as the Union Islands, as the Tokelau Islands or the Tokelau Islands Dependency.
By the Tokelau Islands Act 1948 the Tokelau Group was included within the territorial boundaries of New Zealand; legislative powers are now vested in the Governor-General in Council, while executive powers remain with the High Commissioner of Western Samoa. The inhabitants of the Tokelau Islands are British subjects and New Zealand citizens.
There is no resident European administrative staff, but an administrative officer was appointed in 1955. He is based at Apia, Western Samoa, and coordinates administrative services for the group.
Population – The people, though closely allied to the Samoans, have not such a fine physique. Intermarriage with Gilbert and other Islanders has probably lessened the strain of pure Polynesian blood to a greater extent than in the case of the Samoans.
On 25 September 1956 a census showed a total population of 1,619. The indigenous population was as follows.
| Island | Males | Females | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fakaofo | 312 | 375 | 687 |
| Atafu | 226 | 241 | 467 |
| Nukunono | 199 | 266 | 465 |
| Totals | 737 | 882 | 1,619 |
Health – Health services in the Tokelau Islands are organised and supervised from Apia, from where also the supplies are drawn. The incidence of disease in the islands is slight.
Three Samoan medical practitioners are stationed in the group. Other medical staff consists of staff nurses, nurses, and dressers, who obtain their training at Apia hospital in Western Samoa. In addition, each atoll has an active women's committee, and to these committees much credit is due for their work in village health and sanitation.
Education – There are now 17 trained Tokelau teachers in the group. All the necessary school equipment, stationery, and textbooks are supplied by the New Zealand Government; the schools also receive copies of the Samoan Teachers Monthly Guide and of Samoan and New Zealand School Journals. In addition, they are equipped with filmstrip projectors and also with radio sets so that the daily educational broadcasts of the Western Samoan Education Department may be utilised. The mission school on Nukunono is equipped by the New Zealand Government in a similar fashion to the schools of the other islands.
The rolls of the three schools in March 1960 were as follows: Fakaofo, 235; Atafu, 145; Nukunono, 150. In addition, a number of Tokelau children attend Government and mission schools in Western Samoa.
Communications – Visits to the islands are made at approximately three-monthly intervals by aircraft of the Royal New Zealand Air Force stationed at Lauthala Bay, Fiji. Trading visits are made at fairly regular intervals by a vessel chartered by the Western Samoa Trust Estates Corporation.
Radiotelegraph receivers and transmitters are operated on each atoll, being housed in small radiotelegraph station buildings. In addition, receiving sets are installed in all villages and enable the people to listen to broadcasts from the Apia broadcasting station.
Trade and Finance – The quantity of copra shipped for the year ended 31 March 1960 amounted to 211 tons. Apart from copra the only exports are handicrafts.
Revenue is derived principally from export duty on copra, Customs duty of 121/2 per cent ad valorem on all goods entering the islands, trading profits, and the sale of postage stamps. Revenue for the year 1959 was £20,281 (including subsidy from New Zealand) and expenditure £20,281.
Under the Tokelau Islands Copra Regulations 1952 a Copra Stabilisation Fund was established by a levy on purchases of copra for export, and is used to supplement the prices received by the producers, or by the purchasers on resale after export, as may be necessary from time to time. At 31 March 1960 there was £5,543 in the fund.
WESTERN SAMOA: Independence – The attainment of independence by Western Samoa on 1 January 1962 will see the fulfilment of the objective of trusteeship. Information on administration must from this date be read in the light of this major constitutional change.
Descriptive – Western Samoa comprises the two large islands of Upolu and Savai'i, and islets of Apolima, Manono, Fanuatapu, Namu'a, Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, and Nu'usafe'e. The geographical boundaries are between latitude 13° and 15° south and longitude 171° and 173° west.
Savai'i is the larger of the two main islands, with a length of 46 miles, a breadth of 25 miles, and a total area of 660 square miles. The island is mountainous, rising to a height of 6,094 ft. Upolu, which extends some 45 miles in length and 13 in breadth, measures about 430 square miles in area, and rises to a height of 3,608 ft. Of the two, Upolu is the more fertile and contains two-thirds of the population. Only two of the smaller islands, Manono and Apolima, which are situated in the strait which separates Savai'i and Upolu, are inhabited. The remainder are within or near the fringing reef surrounding Upolu. The climate of the group is equable, the average temperatures during the last 60 years showing a mean daily maximum of 84.9° F, and a mean daily minimum of 74.0° F, while the average annual rainfall for a period of 60 years is 112.98 in.
Administration – Western Samoa was administered by Germany until 29 August 1914, when the Territory was occupied by a New Zealand military force. A Mandate for the administration of Western Samoa, conferred upon His Britannic Majesty to be exercised on his behalf by the New Zealand Government, was confirmed by the Council of the League of Nations on 17 December 1920. Following the establishment of an International Trusteeship System, under the Charter of the United Nations, New Zealand in 1946 communicated to the General Assembly of the United Nations its acceptance of the system in its application to Western Samoa. A draft trusteeship agreement submitted by the New Zealand Government to the United Nations in October 1946, was, with minor amendments, adopted by the General Assembly on 13 December of that year. In this agreement (printed as parliamentary paper A.26, 1947) the Government of New Zealand was designated the Administering Authority for Western Samoa.
As a result of a request by the Samoan people in 1947 for self-government, a Trusteeship Council Mission of Inquiry visited the Territory, publishing its report in October 1947. This report was found to be closely in line with the New Zealand Government proposals for political development outlined in the New Zealand Parliament in August 1947. The constitutional framework for implementing these proposals was established with the passing by the New Zealand Parliament of the Samoa Amendment Act 1947, which came into force on 10 March 1948.
The High Commissioner (appointed by the Governor-General and subject to the general control of the Minister of Island Territories) has been the representative in Western Samoa of the Government of New Zealand.
Under the Samoa Amendment Acts of 1956 and 1957 the Executive Council, first constituted in 1953 as an advisory body, became effectively “the principal instrument of policy” of the executive government of Western Samoa. The 1957 Act provided that members of the Executive Council (other than the High Commissioner and Fautua) should be designated Ministers.
Under the provision of the Samoa Amendment Act 1959 a form of Cabinet government was established on 1 October 1959. The seven elected Ministers and the two official members resigned from the Executive Council and were replaced by a Prime Minister designated by the Legislative Assembly and eight other Ministers (at least one of whom was required to be a person of European status) chosen by the Prime Minister from among the Legislative Assembly. The functions of the Cabinet are to “advise the Council of State in the exercise of its functions, powers, and authorities” and “the general direction and control of the Government of Western Samoa”.
The Council of State consists of the New Zealand High Commissioner and the two Fautua (representatives of the two royal lines of Tupua and Malietoa). Formerly an advisory body, the Council is now “the head of the executive government of Western Samoa”. Under the 1959 Amendment Act the Council is required to exercise powers vested in it “in accordance with the constitutional conventions for the time being applicable to the exercise of similar powers, functions, and authorities in the United Kingdom by Her Majesty”, i.e., in almost all cases on the advice of Ministers. The Council is also provided with a record of all decisions made by Cabinet, and any one member of the Council of State may request a discussion of a decision of Cabinet at a meeting of the full Executive Council (i.e., all Ministers and members of the Council of State). If, after such a discussion, a particular decision is disapproved by two members of the Council of State it may be referred back to Cabinet for reconsideration, but if the Cabinet adheres to its decision this is final.
The Legislative Assembly is composed of 41 elected Samoan members, five elected European members, and not more than three official members. For those persons possessing European status suffrage is universal but in the 41 Samoan constituencies (in accordance with the present wishes of the Samoan people) only persons whose names appear on the Register of Matai may register as electors or be nominated for election. Two ordinary sessions of the Legislative Assembly are held each year. The first session, at which the Budget is presented, is held in March, and the second in August, when most legislation is enacted. The duration of normal sessions is usually about three weeks. The Assembly has been competent to legislate on all matters except external affairs, defence, the title to New Zealand Government land, and matters provided for in certain “reserved enactments”.
The work of the Executive Government is carried on, under the general direction and control of the Cabinet, by 15 Departments. All staff including that of the Western Samoa Trust Estates Corporation is controlled by the Public Service Commission of Western Samoa.
The Citizenship of Western Samoa Ordinance 1959 established a nationality law for Western Samoan citizens of Western Samoa who also possess the status of New Zealand protected persons.
During 1959 a tentative timetable for the final stages of New Zealand's trusteeship of Western Samoa was agreed upon by the New Zealand Government, the Samoan leaders, and the Trusteeship Council of the United Nations. Important steps in this timetable were a Constitutional Convention late in 1960 and a plebiscite in May 1961.
On the attainment of independence by Western Samoa the Fautua will assume the position of Joint Heads of State and the office of High Commissioner as part of the Government will be abolished.
The Judiciary – The High Court of Western Samoa consists of the Chief Judge, a Puisne Judge, two part-time Commissioners, and five Samoan Associate Judges.
The High Court has full jurisdiction both civil and criminal for the administration of the law of Western Samoa. In more serious defended criminal cases, the High Court is constituted with four assessors and the Chief Judge, or Puisne Judge.
The Public Service – The Samoa Amendment Act 1949, which came into force on 1 April 1950, established a Western Samoan Public Service under the control of a Public Service Commissioner of Western Samoa, appointed by the Governor-General of New Zealand. The Samoa Amendment Act 1959 replaced the sole commissioner by a Commission of not more than three members appointed by the Council of State. At 31 December 1959 approximately 1,468 persons were employed in the Western Samoa Public Service, of whom 69 were domiciled overseas.
Population and Vital Statistics – The population census held in 1956 showed a total population of 97,327, an increase of 12,418 since the 1951 census.
The following table shows the summarised results, together with the corresponding figures for the 1951 census.
| 1951 Census | 1956 Census | |
|---|---|---|
| *Including other Polynesians. | ||
| Samoans | 80,153* | 88,036 |
| Part-Samoans | 4,142 | 7,900 |
| Europeans | 450 | 662 |
| Chinese | 164 | — |
| Other Pacific Islanders | – | 531 |
| Others | – | 149 |
| Not stated | – | 49 |
| Totals | 84,909 | 97,327 |
Apia, the only town in the Territory, is situated on the north coast of Upolu and, together with immediately adjoining villages, has a population approaching 19,000. It is the administrative headquarters and the only port of entry. The great majority of persons of European status live in or about Apia.
The estimated population at 31 December 1959 was 105,863 (males, 54,436; females, 51,427). During 1959 there were 4,041 births and 436 deaths, while arrivals in the Territory numbered 9,621 and departures 10,224. The Samoan infant-mortality rate was 22.27 per 1,000 live births.
Health – Western Samoa is free from many of the diseases which present the most serious health problems in large areas of the tropics. The climate is healthy even for Europeans unaccustomed to the heat and humidity, and the general level of nutrition is more satisfactory than in a great many tropical regions. The most prevalent diseases are hookworm, yaws, and filariasis, and diseases which result from faulty sanitation, such as typhoid, dysentry, and infantile diarrhoea. Tuberculosis is also a major problem, and chest diseases such as pneumonia are common. The death rate and infant-mortality rate in Western Samoa compare favourably with those in most other parts of the Pacific, but they are still high by western standards.
Apia Hospital has 250 beds, half in European-style buildings, the other half in Samoan fale-type wards. In 1955 a modern maternity block was opened accommodating 28 cases.
The Health Department is under the control of the Director of Health, who is assisted by a medical officer of health, four medical officers, and 43 Samoan medical practitioners.
Most villages have a women's village committee, and these committees, by their close cooperation with the Samoan medical practitioners and nurses, do much to promote the health and welfare of the people. Health education is also carried on by means of radio broadcasts in both Samoan and English.
During 1959 5,718 inpatients and 80,741 outpatients were treated at Apia hospital, where 727 major operations were performed.
Education – The Education Department of the Government of Western Samoa consists of a Director of Education, his assistant, a chief inspector, who is assisted in the supervision of the village schools by eight Samoan inspectors, and Samoan and European headmasters and staffs for the various schools.
The Government and mission schools function side by side, close cooperation being maintained by the controlling bodies. There are 330 mission schools throughout the Territory with some 8,735 pupils. In addition to the 113 Government primary schools, there are three advanced Government schools, manual and domestic training centres, and a teachers' training college.
Although there is as yet no provision for compulsory education, where there are Government schools there is free primary education for boys and girls. Secondary education is available for children selected by competitive examination at Samoa College (opened in February 1953), which in 1959 had a roll number of 225 in the secondary department. With the development of the educational system in Western Samoa, the scope of the Government scheme for providing scholarships to New Zealand secondary schools has been reduced. Selected secondary school pupils will receive scholarships for study at universities in New Zealand.
Educational Statistics – The figures given below record the number of scholars at the various schools in 1959.
| Number of Scholars, 1959 | |
|---|---|
| Government primary schools, 5–18 years | 16,055 |
| Government vocational, 16–21 years | 391 |
| Government secondary, 13–21 years | 215 |
| Total, Government schools | 16,661 |
| Mission primary schools, 5–18 years | 8,735 |
| Mission secondary, 13–21 years | 368 |
| Mission vocational, 16–21 years | 15 |
| Total, mission schools | 9,118 |
| Grand total | 25,779 |
NOTE – In the primary schools, few pupils attend before the age of six years and most have left by the age of 16 years.
Labour and Employment - There are about 8,000 persons who could be classed as wage and salary earners, and of these probably 7,000 are Samoans. At least half of these are employed in varying grades of skilled work by either the Government or the Western Samoa Trust Estates Corporation, which administers the former Reparation Estates. Many others are employed by trading firms and other businesses in Apia. Numbers of skilled or semi-skilled workers leave Samoa to work in New Zealand. A Trades Training Centre has been established to help meet the need for skilled labour in the territory and it is hoped that a modified system of apprenticeship will evolve. Community groups are employed by Government for unskilled work, such as road making, by planters for agricultural work, or in other occupations such as wharf labouring.
The basic minimum wage for Government employees in 1959 was 11s. 3d. per day, with higher rates for semi-skilled and skilled workers.
A cost of living index is maintained by the Samoan Government.
Agriculture and Animal Husbandry - Public services in connection with agriculture are organised under the Agriculture Department, which employs, in addition to clerical staff, a staff of Samoan field instructors and Samoan district plantation inspectors, the latter being resident in districts throughout Samoa.
The type of terrain on which export crops are grown precludes the widespread use of mechanical equipment, the soil being mixed with scoria and volcanic refuse in most areas. Domestic crops make adequate provision for village requirements under present methods of cultivation.
Livestock are of local importance. Pigs and poultry figure in the Samoan village economy, while cattle are raised on the Western Samoa Trust Estates and other plantations. Horses and donkeys are used for plantation work. Western Samoa Trust Estates cattle, which number approximately 9,500 head, besides grazing the plantations clear of undergrowth, provide fresh beef for consumption in the Territory and hides for export. The herds consist mainly of the Hereford and Aberdeen Angus breeds, and are maintained and improved in quality by rotational grazing and careful selection for breeding. A Zebu strain has been introduced from Fiji.
The land of Western Samoa is classified in law as Crown land, Samoan land, and European land there being some 80,000 acres of Crown land, 561,062 acres of Samoan land, 32,000 acres of Western Samoa Trust Estates land, and about 27,000 acres of European land. It is estimated that about 400,000 acres, or 55 per cent of the land area of the Territory, is made up of steep hillsides, lava beds, or other unproductive areas, although as time passes lava beds gradually begin to support vegetation. The areas of land devoted to the principal crops are as follows: coconuts, 38,721 acres; bananas, 3,939 acres; cocoa, 12,708 acres; food crops, 14,040 acres. Production by Samoans accounts for most of the copra exported, an increasing proportion of the cocoa exported, and nearly all of the bananas exported.
Forestry - The forests in Western Samoa are neither virgin nor densely stocked with valuable timber species. Savai'i has more extensive areas of forest than Upolu, but the rugged terrain precludes the economic extraction of the timber. Two milling concerns operate in Upolu, but together they supplied only one-sixth of the consumption of timber in 1959, which was about 1,556,000 superficial feet.
Industry - Apart from two sawmilling concerns, a soap factory established in 1953, and a tyre retreading plant, there are no industrial activities of any magnitude in the Territory. There are a few small enterprises for the processing of coffee and the manufacture of cordials, curios, and similar products. There are no known mineral resources available for development.
Communications - There is a twice-monthly passenger and cargo service from New Zealand to Western Samoa, via Fiji and Tonga, while a twice-weekly service operates between Apia and Pago Pago in American Samoa.
The present air service is by local airlines to American Samoa to connect with Pan American Airways' weekly service between Hawaii and Fiji via American Samoa.
There are 392 miles of road, of which 78 are of bitumen surface. At the end of 1959 there were 321 private cars, 82 buses, and 246 trucks, land rovers, and vans registered in the Territory.
There is only one telephone system, which has approximately 80 miles of local wires and 519 subscribers. The Government maintains a short-wave radio station for normal overseas communications.
Trade - The exports and imports of Western Samoa for each of the latest 14 years are as follows.
| Year | Exports | Imports | Year | Exports | Imports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1946 | 719,050 | 478,695 | 1953 | 1,954,689 | 1,312,769 |
| 1947 | 1,351,770 | 923,773 | 1954 | 2,211,847 | 1,710,494 |
| 1948 | 1,108,258 | 954,028 | 1955 | 2,511,899 | 1,894,542 |
| 1949 | 1,344,758 | 881,584 | 1956 | 1,805,696 | 1,860,420 |
| 1950 | 1,303,761 | 1,095,121 | 1957 | 1,882,323 | 1,827,878 |
| 1951 | 1,721,942 | 1,194,698 | 1958 | 2,947,628 | 2,220,976 |
| 1952 | 1,778,084 | 1,687,790 | 1959 | 3,320,096 | 2,560,420 |
The following table shows for the years 1958 and 1959 the value of exports and imports according to country of destination and country of origin.
| Country | Exports (Including Re-exports) | Imports | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 1959 | 1958 | 1959 | |
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| New Zealand | 1,287,184 | 1,315,753 | 738,420 | 726,207 |
| Australia | 55,823 | 60,111 | 391,001 | 434,502 |
| United Kingdom | 1,297,798 | 1,171,558 | 360,734 | 428,382 |
| Fiji | 31,738 | 27,774 | 93,232 | 118,424 |
| Japan | 5,168 | 89,973 | 126,483 | 130,254 |
| Indonesia | - | - | 73,515 | 60,011 |
| United States of America | 221,216 | 255,667 | 119,982 | 326,500 |
| Other | 48,701 | 399,260 | 317,609 | 336,140 |
| Totals | 2,947,628 | 3,320,096 | 2,220,976 | 2,560,420 |
The principal exports consisted of cocoa, 4,023 tons, £996,673; copra, 16,842 tons, £1,357,846; and bananas, 786,423 cases, £904,281. At the end of 1959 the Copra Reserve Fund stood at £490,000. This money is available to maintain the price of copra at an economic level if this becomes necessary.
The bulk of the Territory's copra is sold under contract; the price depends upon world market conditions.
The principal imports for 1959 were: 48,814 cwt of sugar, value £96,826; 1,109,336 yards of cotton piece goods, £51,383; meat in tins and kegs, 18,620 cwt, £251,152; and motor vehicles, parts, etc., £139,295.
Public Finance - The Legislative Assembly is empowered to authorise payments for public purposes out of the public moneys of Western Samoa. The Government financial year ends on 31 December. No public debt exists in the Territory.
The following table shows the total revenue and expenditure for the latest five years. The principal items of expenditure are also shown.
| Revenue | Expenditure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education | Public Health | Public Works | Total, Including Others | ||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1955 | 1,224,360 | 194,150 | 219,940 | 492,270 | 1,297,150 |
| 1956 | 1,232,000 | 236,000 | 230,000 | 323,000 | 1,349,000 |
| 1957 | 1,063,000 | 251,000 | 215,000 | 319,000 | 1,274,000 |
| 1958 | 1,305,000 | 204,000 | 191,000 | 280,000 | 1,037,000 |
| 1959 | 1,556,000 | 212,000 | 248,000 | 598,000 | 1,565,000 |
The policy of the New Zealand Government was to devote the trading profits derived from the former New Zealand Reparation Estates towards expenditure on social and economic developmental schemes for the benefit of the Territory. Since the transfer of the New Zealand Reparation Estates to the Western Samoa Trust Estates Corporation in 1957 the New Zealand Government has made direct grants to the Government of Western Samoa. In 1959 they totalled £46,000.
The public revenue of the Territory is derived from a combination of direct and indirect taxes. The principal indirect taxes are import and export duties, which provide a suitable method of obtaining revenue from a central source at a minimum cost, and are thus well suited to the present stage of development of the Territory. Store tax was abolished as from April 1955 and replaced by a graduated salary and company tax. There are no direct taxes imposed on individual Samoans other than the salary tax on incomes in excess of £200 per annum, payable in cash by individuals after deducting the normal exemptions.
Receipts of revenue from the various sources of taxation for the calendar years 1956, 1957, 1958, and 1959 were as follows.
| Source | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Arms licences | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Export duties | 159 | 155 | 217 | 279 |
| Import duties | 428 | 411 | 517 | 622 |
| Licences and fees | 9 | 11 | 28 | 26 |
| Income tax | 139 | 119 | 94 | 149 |
| Stamp duties | 7 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Water rates | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Vehicle licences | 11 | 11 | 12 | 14 |
| Shipping and port duties | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Totals | 760 | 715 | 879 | 1,105 |
Money and Banking - The only trading bank in the Territory is the Bank of Western Samoa, which came into being on 1 April 1959, replacing a branch of the Bank of New Zealand.
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| Amount of currency in circulation | 150,000 | 170,000 | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| Aggregate deposit money - | ||||
| Post Office Savings Bank | 365,000 | 345,000 | 375,000 | 367,000 |
| Bank of Western Samoa | 300,000 | 277,000 | 330,000 | 862,000 |
No gold resources are held. Foreign exchange is obtained from the common sterling pool. Currency is backed by New Zealand Government securities held by the Territorial Government.
CHATHAM ISLANDS - The Chatham Islands, which are composed of one main island, three small islands, and numerous reefs and islets within a radius of 30 miles, lie 467 nautical miles east of Lyttelton, and have an area of 372 square miles. There are approximately 500 people on the islands, which are part of New Zealand proper, being attached to the Lyttelton Electorate for Europeans and to the Western Maori Electorate for Maori electors.
The islands were constituted a county in 1901, but the first council was not elected until 1925. The council obtains its revenue not from rates, but from import and export duties. The revenue of the county council from this source for the year ended 31 March 1960 amounted to £9,609.
There is a cottage hospital at Waitangi, the main settlement and port of entry, and schools at Te Kairakau, Te Ore, Owenga, and Kaingaroa.
The island's major industry is sheep farming, there being no dairy farming. Some cattle are exported, but the islander's greatest source of revenue comes from the export of sheep and wool. For the year ended March 1960, 11,438 sheep and 2,817 bales of wool were exported. Imports totalled 1,237 tons.
Flying boats have been chartered from time to time as found necessary to transport passengers to and from New Zealand. There is an irregular shipping service for the greater part of the year. Internal communications are not good, road work being made difficult and expensive by the extensive peat swamps. There are six party-telephone lines on the island. Isolated sheep stations maintain contact with the radio station at Waitangi by means of radiotelephones. A radiotelephone service was established with New Zealand early in 1953.
NAURU - Nauru Island is about half a degree below the equator and lies 166° 56' east of Greenwich. It is an elevated island about 3 1/2 miles long and 2 1/2 miles wide, with a circumference of 12 miles, and an area of 5,263 acres. With the exception of a narrow coastal belt favourable for the growth of coconuts, and of a brackish lagoon, the island consists of phosphate deposits overlying a bed of coralliferous limestone. The island is completely surrounded by a coral reef, and beyond the reef the sea bed slopes sharply downwards at an angle of 45°. These two factors, together with the presence of the strong equatorial current of 2 knots, materially affect the shipping facilities of the island. The fact that the island lies in the latitude of the easterly trade winds, which blow from nine to 10 months of the year, is also significant, since it explains the comparative absence of rainfall, a condition necessary for the existence of phosphate deposits. Before the Japanese occupied it on 26 August 1942, the Island of Nauru was administered under a mandate, dated 17 December 1919, approved by the League of Nations. This mandate was held jointly by the Governments of Australia, Great Britain, and New Zealand, and by a mutual agreement the administration was in practice left to the Australian Government. On 13 September 1945 the Japanese garrison on the island surrendered, and civil administration was re-established on 1 November 1945. Nauru was brought under the International Trusteeship system by a trusteeship agreement which was approved by the General Assembly of the United Nations on 1 November 1947. The Governments of Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom were designated as the joint Administering Authority, and it was agreed that the Australian Government should continue to administer the island on their behalf.
In 1951 an ordinance provided for the abolition of the Nauruan Council of Chiefs, a body established by custom, and the creation of a Nauruan Local Government Council. The latter council is composed of nine Nauruans elected by all Nauruans, male or female, who are over 21 years of age. Voting is by secret ballot, and a preferential system of voting is employed. The council is an advisory body which, subject to the Administrator's approval, may make rules covering certain specified subjects.
Financial figures quoted hereunder are in Australian currency.
The mining rights are vested in the British Phosphate Commissioners, subject to the rights of the Nauruan landowners, and the deposits, as well as those on Ocean Island, about 165 miles to the east of Nauru, are worked by the Commissioners. The royalty payable on phosphate shipments to or on behalf of the Nauruans for 1959-60 amounted to £179,054. Administrative expenses are covered by direct payments by the Commissioners. These amounted to £408,906 for 1959-60.
The deposits do not appear to be simple guano, and some authorities consider them to be of a marine sedimentary origin raised from the sea bed and subjected to weathering. From the point of view of phosphate manufacture the deposits are of a very high grade, exports averaging 85.4 per cent tricalcic phosphate and 3.4 per cent calcium carbonate. Owing to the uneven nature of the outcrops of coralliferous limestone the extent of the deposits cannot be measured accurately, but it is estimated that there are between 65 and 70 million tons of phosphate rock available.
Of the 1,201,138 tons of phosphate exported in 1959-60 Australia received 704,632 tons and New Zealand 291,956 tons; the remainder was exported to the United Kingdom.
The following table shows the population of Nauru for the five latest years.
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Includes 784 Gilbert and Ellice Islanders employed under contract by the British Phosphate Commissioners. | |||||
| Nauruans | 1,935 | 1,976 | 2,093 | 2,158 | 2,196 |
| Immigrants - | |||||
| European | 262 | 286 | 373 | 363 | 382 |
| Chinese | 568 | 696 | 732 | 654 | 712 |
| Other Pacific Islands | 911 | 935 | 1,105 | 1,133* | 974 |
| Total Population | 3,676 | 3,893 | 4,303 | 4,308 | 4,264 |
Revenue and expenditure and trade of the Nauru Administration for five years are given in the following table.
| Year | Revenue | Expenditure | Exports | Imports |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| £ | £ | £ | £ | |
| 1954-55 | 303,674 | 276,783 | 2,165,163 | 706,238 |
| 1955-56 | 261,164 | 257,274 | 2,568,640 | 877,264 |
| 1956-57 | 218,916 | 302,349 | 2,236,808 | 1,170,218 |
| 1957-58 | 352,656 | 357,396 | 2,421,898 | 971,029 |
| 1958-59 | 350,344 | 357,759 | 2,492,361 | 1,013,674 |
| 1959-60 | 438,246 | 408,906 | 2,823,940 | 1,342,201 |
Imports consist almost entirely of food supplies and of machinery for the working of the phosphate deposits.
ROSS DEPENDENCY: Descriptive - The Ross Dependency comprises the sector of the Antarctic continent between 160° east and 150° west longitude, together with the islands lying between those degrees of longitude and south of latitude 60° south.
Within these boundaries there are an estimated 160,000-175,000 square miles of land and 130,000 square miles of permanent ice shelf. The land is virtually entirely covered by ice, but has bases inhabited by scientific personnel.
Administration - By Order in Council of 30 July 1923 under the British Settlements Act 1887 (Imp.) the territories of the Ross Dependency were brought within the jurisdiction of the New Zealand Government. From time to time laws for the Dependency have been made by regulations promulgated by the Governor-General of New Zealand.
Administrative powers are vested in the Governor-General of New Zealand, and administrative officers (commonly referred to as Administrators) have been appointed from time to time since 1923. In 1956 a Deputy Administrator was also appointed, and other officers were given the powers of Stipendiary Magistrate, coroner, and postmaster.
The New Zealand Geographic Board, which is the place-names authority for the Ross Dependency, has published a provisional Gazetteer of the Ross Dependency.
The New Zealand Government decided that the New Zealand bases in the Ross Dependency would continue to be operated after the conclusion of the International Geophysical Year. In March 1958 the Government appointed the Ross Dependency Research Committee to coordinate and supervise all New Zealand activity in the Ross Dependency, with particular reference to the scientific and technical programme.
The functions of the Committee are:
To advise the Minister in Charge of Scientific and Industrial Research on the organisation and administration of New Zealand activity in the Ross Dependency;
To present an annual report to the Minister in Charge of Scientific and Industrial Research;
To coordinate and supervise all New Zealand activity in the Ross Dependency with particular reference to the scientific and technical programme;
To coordinate New Zealand activity with that of other countries operating in Antarctica and, in particular, with any expeditions of such countries operating in the Ross Dependency;
To coordinate the publication and dissemination of the results of scientific research and investigation and the custody of records.
The implementation of the approved programme is the responsibility of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, in which an Antarctic Division has been formed to undertake this task. The specific functions of the Division are:
To be responsible for the execution and operation of Antarctic activities undertaken by the New Zealand Government;
To supervise approved non-Government expeditions to the Antarctic;
To maintain an information centre on Antarctic exploration and scientific research.
Responsibility for coordinating the scientific details of the approved programme, the procurement of scientific equipment and spares, and the working up of scientific data has been delegated as follows: Meteorology, Director, New Zealand Meteorological Service; Survey and Maps, Surveyor-General, Department of Lands and Survey; Geology and Glaciology, Director, Geological Survey; Special Upper Atmosphere Investigations and Aurora, Director, Dominion Physical Laboratory; Seismology, Geomagnetism, Ionosphere, Director, Geophysics Division; Oceanography, Director, Oceanographic Institute; Biology, Director, Dominion Museum.
Outside the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, several Government Departments provide important aid to New Zealand Antarctic activities. The Royal New Zealand Navy operates HMNZS Endeavour for the annual relief of Scott Base and for oceanographic surveys and provides ships for additional oceanographic work in Antarctic waters. The Post Office provides assistance on communication matters and by the secondment of staff. The Meteorological Service, Dominion Museum, and Department of Lands and Survey participate in the programme. The last-named provides surveyors and publishes all maps. The Army and Air Departments, the National Broad-casting Service, and the Marine Department assist in numerous ways, particularly with the secondment of staff. The Victoria University of Wellington and the University of Canterbury, Christchurch, are active participants in Antarctic work. Their projects are coordinated through the Ross Dependency Research Committee and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
Non-Government expeditions from New Zealand to the Antarctic are authorised by the Minister for Scientific and Industrial Research after prior examination by the Ross Dependency Research Committee as to their scientific worth, the competence of the members of the expedition to accomplish the objectives, the adequacy of the logistic arrangements, etc.
New Zealand's international relations on Antarctic affairs are conducted at the political level by the Department of External Affairs. Whilst scientific contact with other countries and institutions engaged in Antarctic research is maintained at all levels, the primary channel is the Ross Dependency Research Committee.
Exploration - Various expeditions have operated within the area of the Dependency since the coastline was explored by Sir James Ross in 1841. In the twentieth century British and American explorers have investigated parts of the territory, but much still remains to be done.
In December 1956 a New Zealand expedition under the leadership of Sir Edmund Hillary sailed for McMurdo Sound in HMNZS Endeavour. In January 1957 Scott Base was established near Cape Armitage on Ross Island. The purpose of the expedition was twofold: to take part in the crossing of the continent from the Weddell Sea to Scott Base by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, and to participate in the Antarctic programme of the International Geophysical Year. During the early months of 1957 the expedition was successful in finding a route and setting up depots across the Ross Ice Shelf and up the Skelton Glacier to the Polar Plateau.
In the summer of 1957-58 the expedition explored a route farther south and established depots for the use of the crossing party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition. Sir Edmund Hillary and four other New Zealanders reached the South Pole on 3 January 1958. The crossing of the continent was successfully achieved on 20 March 1958 when Sir Vivian Fuchs' party reached Scott Base. Further reference to these activities is made in Appendix (d) of the 1958 Yearbook, which also includes maps of the Ross Dependency.
Scientific Programme - For the purposes of the International Geophysical Year a joint New Zealand - United States scientific station, known as Hallett Station, was established at Cape Hallett in January 1957. Throughout the International Geophysical Year New Zealand maintained at Scott Base and Hallett Station a scientific programme in close accord with the aims and objects of the IGY. (References to these activities are contained in Appendix (d) of the 1958 Yearbook.) With the conclusion of the IGY synoptic and intensive programme of regular observations, and the widening scope of Antarctic research, the Ross Dependency Research Committee formulated a programme for 1959 to commence a reorientation of New Zealand Antarctic work.
Since then, at Scott Base, regular observations have been undertaken in seismology, geomagnetism, ionosphere, meteorology, aurora, and glaciology. Special research programmes have been carried out on “Whistlers” and associated phenomena, and on the D-region of the ionosphere. Sea-level recordings have also been made. At Hallett Station, which is a joint United States - New Zealand base, New Zealand scientists have conducted a programme in aurora, geomagnetism, ionosphere, and seismology.
In 1958-59 the New Zealand Geological and Survey Expedition made geological and topographical surveys in a number of areas in the McMurdo Sound region. The completion of this survey net work will make possible the construction of a detailed map from aerial photographs. Members of the expedition climbed Mts. Erebus, Terror, and Discovery (a first ascent). A four-man party from the Victoria University of Wellington spent seven weeks in the Wright Dry Valley area of Victoria Land, between 77° south and 77° 45' south. The party made a geological and topographical survey of the area, and carried out meteorological and biological work, as well as making gravity observations from the coast to within 4 miles of the polar plateau. Considerable biological work was also carried out at Scott Base by members of other field expeditions, and by biologists on HMNZS Endeavour. Emphasis was laid on the study of seals and skuas. Further oceanographic surveys between New Zealand and the Antarctic continent were carried out. The Antarctic Convergence was traversed eastwards from the vicinity of Macquarie Island to the pack ice north of the Ross Sea. An extensive carbon-dating sampling programme was carried out. Twenty oceanographic stations were occupied in the Ross Sea, each station comprising hydrology, bottom dredging, plankton trawls, and bottom-sediment cores.
For the 1959-60 summer, the programme of field work was further extended by:
Geological and mapping surveys south of Scott Base. Two four-man parties explored part of the Victoria Land coastal area. Air support was provided by the reactivated RNZAF Antarctic Flight.
An extended survey of the Victoria Land Dry Valley area by an expedition from the Victoria University of Wellington.
An eight-man New Zealand Alpine Club expedition, with a strong nucleus of scientists, working in the area east of the Beardmore Glacier.
A two-man party occupying Shackleton's old hut site at Cape Royds for a survey of the Adelie penguin rookery, and other biological work.
A party of two scientists of the Soil Bureau, investigating the soil potentialities of the McMurdo Sound area.
Oceanographic cruises by HMNZS Endeavour between New Zealand and Macquarie Island, and in the Ross Sea, involving hydrological, geological, and biological work, as well as seismic and magnetic surveys.
For the 1960-61 summer a similar programme of field work was followed, with the United States Navy flying relief teams to the Antarctic and undertaking the air drop of supplies to the field parties.
Whaling - To date there has been little development of the economic resources of the territory, and commercial activity has been restricted to whaling.
Regulations dated 24 October 1929 prohibit whaling in the territorial waters of the Ross Dependency without a licence. New Zealand is a member of the International Whaling Commission, the purpose of which is to enforce conservation of whale stocks.
Table of Contents
NEW ZEALAND'S TOURIST INDUSTRY - New Zealand has rightly been described as “the world's most exciting travel package”. With features such as the amazing thermal areas, magnificent lakes and fiords, glaciers, alpine regions, and unrivalled hunting, fishing, and other sporting opportunities, New Zealand combines in a comparatively small area a host of attractions, each one of which has made some other country famous. In addition to these natural attractions, the dignity and charm of the Maori race provides a cultural attraction which is unique to New Zealand.
In spite of these many and diverse attractions, for many years New Zealand remained beyond the reach of most potential tourists. Infrequent transport services and the time and cost involved in getting here often made the trip prohibitive. However, over recent years there have been spectacular changes. Increased and faster shipping services, the phenomenal patronage of air transport, and the more recent introduction of “time payment” travel has brought New Zealand within comparatively easy reach. Auckland is now only 27 hours by air from London or 22 hours by air from New York.
Improvements in transport services have not only increased the number of tourists coming to New Zealand, they have also extended the markets from which tourists are attracted.
Visitor Arrivals and Receipts from Travel - The increase in the total number of visitors to New Zealand since the year ended March 1950 has been steady and has averaged 14.8 per cent a year. Travel receipts show a slightly higher rate of increase of 19.0 per cent per year.
| March Year | Visitor* Arrivals | Through Passengers | Visitor and Through-passenger Arrivals | Travel Receipts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Excludes through passengers and tourists on cruise ships. | ||||
| £(000) | ||||
| 1950 | 14,716 | 2,489 | 17,205 | 1,128 |
| 1951 | 16,434 | 2,923 | 19,357 | 1,200 |
| 1952 | 17,150 | 2,744 | 19,894 | 1,471 |
| 1953 | 18,665 | 5,645 | 24,310 | 1,686 |
| 1954 | 19,506 | 7,448 | 26,954 | 1,606 |
| 1955 | 21,946 | 11,005 | 32,951 | 1,950 |
| 1956 | 23,679 | 8,264 | 31,943 | 2,396 |
| 1957 | 27,979 | 20,718 | 48,697 | 3,155 |
| 1958 | 29,772 | 31,468 | 61,240 | 3,471 |
| 1959 | 31,173 | 26,045 | 57,218 | 3,010 |
| 1960 | 36,557 | 35,637 | 72,194 | 3,264 |
In general, through passengers do not stay for more than three days in New Zealand, therefore the travel receipts are derived mainly from visitor arrivals. Crews of visiting ships also contribute towards the travel receipts and crew numbers have risen from 47,499 in 1950 to 93,860 in the year ended March 1960. In the years ended March 1957 and March 1958 abnormal receipts were derived from visitor movements caused by the Olympic Games in Australia and other international meetings in New Zealand such as the International Jaycee Conference, the Boy Scout Jamboree, and the International Geophysical Year. The fall-off in through passengers from 31,468 in the 1958 March year to 26,045 in the 1959 March year and the reduction in immigration from 26,254 to 24,852 over the same period accentuated the fall in receipts, since a small amount of travellers' cheques cashed by immigrants and through passengers is credited to travel receipts.
Receipts from travel for the year ended March 1960 were £3,263,755, and represented an increase of £254,240, or 8.5 per cent, on the previous year.
| Country or Area | March Year | Increase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | Actual | Percentage | |
| £ | £ | £ | per cent | |
| Canada | 48,917 | 63,944 | 15,027 | 30.7 |
| United States | 421,668 | 550,976 | 129,308 | 30.6 |
| Other non-sterling | 23,580 | 47,262 | 23,682 | 100.0 |
| Totals | 494,165 | 662,182 | 168,017 | 34.0 |
| United Kingdom | 999,338 | 991,651 | -7,687 | -0.8 |
| Australia | 1,424,863 | 1,518,046 | 93,183 | 6.5 |
| Other sterling | 91,149 | 91,876 | 727 | 0.8 |
| Totals | 2,515,350 | 2,601,573 | 86,223 | 3.5 |
| Grand totals | 3,009,515 | 3,263,755 | 254,240 | 8.5 |
For the year ended March 1960 total receipts from the non-sterling area rose by 34 per cent to £662,182, an increase of £168,017 on the previous year. While the percentage increase in sterling area receipts (3.5 per cent) was much lower than for the non-sterling area (34 per cent), the increase in Australian receipts of £93,183 was nevertheless substantial.
Countries of Origin - The country or area of origin of all visitors to New Zealand during the year ended 31 March 1960 is given in the following table. The increase over the previous year is also given for comparison purposes.
VISITOR ARRIVALS
| Country or Area | March Year | Increase 1960 over 1959 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | Number | Per Cent | |
| *Includes Middle Eastern countries. | ||||
| Australia | 16,415 | 17,569 | 1,154 | 7.0 |
| United Kingdom | 3,272 | 4,199 | 927 | 28.2 |
| Canada | 686 | 926 | 240 | 35.0 |
| Pacific Isles (Br.) | 2,703 | 3,328 | 635 | 23.3 |
| Other Commonwealth countries | 1,223 | 1,322 | 99 | 8.4 |
| United States | 5,018 | 6,402 | 1,384 | 28.0 |
| Other European countries* | 873 | 1,468 | 595 | 68.2 |
| Other countries | 983 | 1,343 | 360 | 36.6 |
| Total | 31,173 | 36,557 | 5,394 | 17.4 |
Traditionally Australia has always been the major source of tourists but other areas are now gaining in relative importance, notably the United States.
PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF VISITORS
| March Year | Australia | United Kingdom | Canada | United States | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 61 | 14 | 2 | 6 | 17 | 100 |
| 1955 | 59 | 13 | 2 | 8 | 18 | 100 |
| 1960 | 48 | 11 | 3 | 18 | 20 | 100 |
In 1955-56, 14,254 Australians constituted 61 per cent of all visitors, but, although by March 1960 their number had increased to 17,659, they represented only 48 per cent of all visitors. In the same period the number of United States visitors has increased from 1,950 to 6,402, and their proportion of the market from 8 to 18 per cent. The growth in visitor arrivals from the United States has been rapid since the year ended March 1956. Prior to that year a slow rate of growth had been maintained.
The influx of United States visitors since 1956 is attributable mainly to the growth in the number of cruise ships in the Pacific area. The surge of through-passenger arrivals from 1956 onwards is a measure of the greater availability of berths to New Zealand.
Tourist Length of Stay in New Zealand - Of the 36,557 visitors (excluding through passengers) who arrived in New Zealand in the year ended March 1960, 24,794 classified themselves as tourists. The tourists alone, according to their stated intended length of stay, spent approximately 1,229,000 days in New Zealand. In addition, 11,763 other visitors stayed an estimated 623,400 days in New Zealand. The 35,637 through passengers also spent from one to three days in this country, making the total length of stay in New Zealand for these classes of arrivals almost 2,000,000 days.
The average intended length of stay stated by the tourist on arrival tends to decrease each year as the speed of transportation improves.
TOURIST AVERAGE INTENDED LENGTH OF STAY IN DAYS
| Country | March Years | |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| United Kingdom | 76 | 76 (49) |
| Australia | 49 | 44(37) |
| United States | 31 | 27 (21) |
| Canada | 67 | 51 (34) |
| All countries | 57 | 54 (38) |
The figures in parentheses give the average intended length of stay for tourists staying less than four months in New Zealand; 86.7 per cent of all tourists intended to stay for less than four months in New Zealand and the average intended length of stay of these persons was 38 days.
Ports of Arrival in New Zealand and Seasonality - The ports of arrival for visitors and through passengers to New Zealand are given below for the year ended March 1960.
| Visitors | Through Passengers | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Resumption of flights from Australia to Wellington will alter the pattern for subsequent years. | |||
| Auckland: Air | 16,758 | 1,236 | 17,994 |
| Sea | 7,688 | 26,226 | 33,914 |
| Total | 24,446 | 27,462 | 51,908 |
| Wellington*: Sea | 4,586 | 7,293 | 11,879 |
| Christchurch: Air | 6,627 | - | 6,627 |
| Lyttelton: Sea | 473 | - | 473 |
| Other | 425 | 882 | 1,307 |
| Totals | 36,557 | 35,637 | 72,194 |
Auckland is the main port of arrival and receives over 72 per cent of all visitors and through passengers. This influx causes a high demand for hotel accommodation, but an analysis of the distribution pattern shows that there is a tendency for arrivals to spread more evenly throughout the year with the build-up of passenger-ship traffic to New Zealand.
SEASONALITY PATTERN OF VISITORS AND THROUGH PASSENGERS, YEAR ENDED MARCH 1960
| Visitors | Monthly Index No. | Through Passengers | Monthly Index No. | Total Visitors | Monthly Index No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | 2,238 | 41 | 2,197 | 53 | 4,435 | 51 |
| May | 1,551 | 29 | 2,925 | 71 | 4,476 | 51 |
| June | 1,351 | 25 | 4,102 | 99 | 5,453 | 62 |
| July | 1,515 | 28 | 2,951 | 71 | 4,466 | 51 |
| August | 1,787 | 33 | 1,645 | 40 | 3,432 | 39 |
| September | 2,931 | 54 | 2,860 | 69 | 5,791 | 66 |
| October | 3,367 | 62 | 2,033 | 49 | 5,400 | 62 |
| November | 3,482 | 65 | 3,215 | 78 | 6,697 | 77 |
| December | 5,395 | 100 | 3,251 | 79 | 8,646 | 99 |
| January | 4,391 | 81 | 3,479 | 84 | 7,870 | 90 |
| February | 4,598 | 85 | 4,129 | 100 | 8,727 | 100 |
| March | 3,951 | 73 | 2,850 | 69 | 6,801 | 78 |
| Totals | 36,557 | 35,637 | 72,194 |
The monthly index figure gives the monthly total of arrivals as a percentage of the peak month. Arrivals are highest in December (8,646) and February (8,727) and these arrivals, taken in conjunction with the demand arising from the New Zealand summer holiday period, impose a strain on available hotel accommodation during these months. There is a growing tendency for through passengers to make overland trips if the ship calls at, say, Auckland and Wellington. This means that hotels at inland centres benefit from the provision of accommodation to coach parties, who may spend from two to four days travelling overland.
Hotel Accommodation in New Zealand - In New Zealand hotels aim at providing good food and comfortable living, rather than the extra luxury services that are features of some American and Continental hotels.
Few New Zealand hotels have more than 100 rooms. In the main cities some provide a private bathroom or shower and toilet with every bedroom. Smaller hotels which have been recently built in secondary centres close to tourist resorts also have these facilities.
Most of the other hotels have a proportion of bedrooms with private bath and toilet attached, and many have telephones in bedrooms. All leading hotels have good furnishings that are comfortable and pleasing rather than ostentatious. At tourist resorts the leading tourist hotels offer good standards of accommodation and service.
Overseas visitors will find New Zealand hotel tariffs reasonable. In a top-grade hotel a room with bath and toilet (all meals included) costs about 65s. (about $9.00) a day. Rooms without private bathrooms range from 40s. ($5.00) a day. These tariffs are liable to alterations.
As in other parts of the world, reservations, especially at the main scenic areas, are often difficult to obtain if early application is not made. It is advisable, therefore, to arrange for reservations well ahead of the proposed visit to avoid possible disappointment.
Tourist Hotels - Since its inception the Tourist Department operated hotels and ancillary services at national tourist resorts. In the main, these hotels are situated in national parks or scenic reserves, whose administration, until the National Parks Act 1952, was the responsibility of the Department. Control of these hotels passed to the Tourist Hotel Corporation in 1956.
Tourist hotels are situated at the following places:
| North Island |
|---|
| Lake House, Waikaremoana |
| Chateau Tongariro |
| Waitomo |
| Wairakei |
| Tokaanu |
| South Island |
|---|
| *Under construction. |
| Hermitage, Mount Cook |
| Eichardt's, Queenstown |
| Te Anau |
| Milford |
| Franz Josef* |
| Wanaka* |
Including the Tourist Hotel Corporation hotels, there are 95 hotels exempted from price control in the North Island and 42 in the South Island, a total of 137. The majority of other hotels in New Zealand are graded from five star to one star, and the grade of the hotel determines the rate per day.
| Grade | Daily Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | |
| 5 star | 45 | 0 |
| 4 star plus | 41 | 6 |
| 4 star | 40 | 0 |
| 3 star plus | 38 | 0 |
| 3 star | 34 | 6 |
| 2 star | 30 | 6 |
| 1 star | 27 | 0 |
| Ungraded | 24 | 0 |
The numbers of hotels in each grade as at June 1960 are given for the North and South Island. The North Island has the preponderance of decontrolled hotels. The low number of hotels in the four- and five-star gradings is explained by the fact that a hotelier may apply for decontrol when the hotel reaches four-star grading and complies with certain other conditions
| Grade | North Island | South Island | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 62 | 112 |
| 2 | 103 | 126 | 229 |
| 3 | 86 | 77 | 163 |
| 3+ | 71 | 39 | 110 |
| 4 | 7 | 17 | 24 |
| 5 | 1 | - | 1 |
| 318 | 321 | 639 | |
| Decontrolled | 95 | 42 | 137 |
| Total | 413 | 363 | 776 |
In December 1958 there were 131 licensed hotels of tourist-class standard with a capacity of 6,765 beds throughout the country. Since that time a number of new hotels have been brought into operation and other major hotels are now in the planning stage. New tourist hotels are shortly to be constructed near the Franz Josef Glacier and at Wanaka. These hotels will provide 60 beds each initially. The Chevron-Hilton hotel to be built in Auckland will provide another 200 beds, bringing the total number of beds of tourist-class standard to over 7,000.
Climate - The summer season, which is the peak time for tourist travel, comes at the opposite time of the year to that of the Northern Hemisphere. The seasons are:
| Summer: | December, January, February. |
| Autumn: | March, April, May. |
| Winter: | June, July, August. |
| Spring: | September, October, November. |
With no violent summer or winter extremes, special clothing is not required for a visit to New Zealand. The relatively even temperatures make most of New Zealand's tourist centres “all the year round” holiday resorts.
Transport - All main cities, secondary centres, and tourist resorts are linked by road or rail services running to regular and frequent schedules and there are extensive internal air services. Rail travel is comfortable. Dining cars are not used but stops are made for meals at railway dining rooms. New diesel railcars are being progressively introduced on the main routes.
The New Zealand National Airways Corporation operates an efficient internal air service which links the leading cities and secondary centres and also some of the tourist resorts. Meals and refreshments are not usually served in the air because of the relatively short journeys, but there are cafeterias at the air centres. Vickers Viscount aircraft operate between the main cities and Fokker Friendships have recently been introduced. There are also several privately owned scenic and charter air services. The new international airport was opened in Christchurch in February 1960. Wellington Airport re-opened in July 1959, and construction work has commenced at Mangere on an international airport to serve Auckland.
The North and South Islands are linked by a 174 nautical mile steamer express service which operates nightly, except Sundays, between Wellington and Lyttelton, the port for Christchurch. There is also a steamer service across Cook Strait between Wellington and Picton, which is situated at the north end of the South Island.
Inter-Island traffic will receive a boost when the new car and passenger ferry comes into operation between Wellington and Picton in 1962. In conjunction with this, a new scenic road is being driven down the West Coast of the South Island. When completed in 1964 the new road will enable tourists to make a circular tour of the South Island viewing the alps, lakes, fiords, and glaciers which abound in this region.
Shopping - New Zealand shops are well stocked, both with imported lines and locally manufactured goods. Clothing costs are relatively slightly higher than in the United Kingdom; most foodstuffs are relatively cheaper.
Souvenirs - Attractive jewellery is made from the highly polished blue-green shell of the paua, a large shellfish similar to the North American abalone. Set in silver, paua-shell jewellery makes pleasing and distinctive mementos.
A type of jade, known in New Zealand as greenstone, has been for centuries the material out of which the Maori carved his ornaments and weapons. The quaint little tiki, featured on the New Zealand halfpenny, is often fashioned into attractive brooches, tiepins, and earrings.
New Zealand has many attractive woods, which are also made into interesting souvenirs. The Maori people are outstanding wood carvers, and beautifully ornamented objects, often inlaid with paua shell, are obtainable.
As a leading wool-producing country, New Zealand has a large woollen goods manufacturing industry. Fine locally manufactured travelling rugs (car robes) make useful souvenirs. New Zealand knitwear - sweaters, scarves, etc. - are attractive.
Cigarettes and Tobacco - New Zealand and English cigarettes are obtainable, but American cigarettes are not available.
Sporting Attractions - Angling - Most rivers, streams, and lakes in the country contain trout. The best area is that from Lake Taupo to Lake Rotorua in the North Island. Rainbow trout predominate, and the average weight is between 5 and 10 1b. There are numerous fishing lodges to cater for enthusiasts. The brown trout provides outstanding angling in the South Island. Quinnat salmon have been successfully introduced in the large glacier-fed rivers of the South Island. Atlantic salmon are found in the Waiau River system, particularly at the outlets of Lakes Te Anau and Manapouri.
Big-game Fishing - The warm waters off the eastern shores of North Auckland and in the Bay of Plenty are New Zealand's deep-sea fishing grounds. Swordfish, black and striped marlin, broadbill, hammerhead, mako, and thresher shark are the principal game fish. The main bases are at Otehei Bay and Russell. Other centres are Whangaroa, Whangarei, Whitianga, and Tauranga.
Ski-ing - New Zealand has good ski-ing grounds, both in the North and South Islands. Mt. Ruapehu is the main centre in the North Island. Skis and all necessary equipment can be hired from the Chateau Tongariro tourist hotel at the foot of the mountain. There are also good ski-ing slopes at Mt. Egmont in Taranaki.
In the South Island the Hermitage Hotel at Mt. Cook on the eastern slopes of the Southern Alps is an important ski-ing centre. The other main ski-ing area in the South Island is at Coronet Peak near Queenstown.
Hunting - Deer have become so numerous in New Zealand that they are classed as pests and can be shot all the year round. Some of the best deerstalking in the world can be found in the New Zealand forests. In the South Island deer are often found in the less accessible areas, such as Fiordland and on the higher slopes of the Southern Alps. This is the only region in the world where thar and chamois trophies can be obtained. In the North Island conditions are easier, and the sport is becoming increasingly popular in the Rotorua-Taupo area.
A brief description of the scenic attractions in New Zealand is to be found in the 1955 Yearbook, and the 1960 Yearbook contains a pictorial supplement entitled “Scenic New Zealand”.
Early History of the Tourist and Publicity Department - The Tourist and Publicity Department, established in 1901, was originally known as the Department of Tourist and Health Resorts. Its objectives were to provide facilities which would enable New Zealanders to enjoy the scenic and recreational resources of their own country and to develop overseas tourist traffic to and through New Zealand.
Tourist bureaus were opened in Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill in 1902, and in 1911 the first overseas offices were established in Sydney and Melbourne. Bureaus are now sited in Auckland, Te Aroha, Rotorua, Wellington, Christchurch, Dunedin, and Invercargill. There are also a further 20 agencies in other parts of New Zealand. Overseas offices are situated in Sydney, Melbourne, London, San Francisco, and New York.
Organisation of the Department - The Department now consists of a Tourist Division and a Publicity Division, both of which are responsible to the Minister in Charge of Tourist and Health Resorts and Publicity and Information. The Permanent Head of both Divisions is the General Manager of the Tourist and Publicity Department. The Head Office in Wellington provides accounting, staff, and staff training services for both Divisions and administrative and promotional services for its offices and agencies in New Zealand and overseas. The Publicity Division consists of three sections:
The Information Section, which provides editorial and public relations services to the Government and to most Government Departments and initiates and supplies New Zealand publicity of all kinds for use within New Zealand and overseas.
The National Publicity Studios, which combine photographic, artistic, design, display, modelling, workshop, and other services necessary for a wide range of publications, exhibitions, displays, and posters.
The National Film Unit, which produces news and feature films covering all aspects of New Zealand. Many of its films are made for purely tourist publicity purposes and these are widely distributed overseas.
Facilities Offered by the Tourist Department - The Department operates a comprehensive travel service and provides reservation of accommodation; bookings for seats on trains, service cars, aircraft, and inter-Island steamers, and hire of taxis. Officers of the Department meet overseas vessels and aircraft to help tourists clear their luggage through Customs and to aid them with travel arrangements. Individual tours can be arranged down to the last detail. Conducted party tours are available for those who prefer to travel in groups. Private motor tours and “drive yourself” tours can also be provided. New Zealand was the first country in the world to develop a complete Government-owned travel service, in addition to the normal function of publicising New Zealand as a tourist resort.
Association with Other Organisations - New Zealand is a member of the International Union of Official Travel Organisations, an association whose principal aims are to ease travel difficulties and obstacles and promote travel research. New Zealand sent observers to its annual conferences from 1946 to 1948 and became a member in 1949. In November 1959 a New Zealand delegate attended the Fourteenth General Assembly held in Manila, Philippines.
New Zealand is a foundation member of the Pacific Area Travel Association, which was formed in 1952 as a tourist promotional body for the Pacific area. Two of the Association's conferences have been held in this country - one in 1954 and another in Christchurch in February 1960.
The Tourist Department is also a member of the New Zealand Travel and Holidays Association - an organisation representing private travel interests in New Zealand.
ART GALLERIES AND MUSEUMS - New Zealand art galleries and museums follow progressive modern lines in endeavouring to cater for a wide range of artistic and scientific interests. While one of their primary aims is to feature New Zealand material, their collections, particularly those of the larger centres, include overseas subjects.
The Art Galleries and Museums Association of New Zealand (Incorporated) comprises 17 institutional members as follows: Auckland Institute and Museum; Auckland Art Gallery; Waikato Art Gallery, Hamilton; Gisborne Art Gallery and Museum; Hawke's Bay Art Gallery and Museum, Napier; Taranaki Museum, New Plymouth; Wanganui Public Museum; Sargeant Art Gallery, Wanganui; Dominion Museum, Wellington; New Zealand Geological Survey, Lower Hutt; Nelson Museum; Bishop Suter Art Gallery, Nelson; Canterbury Museum, Christchurch; South Canterbury Historical Museum, Timaru; Otago Museum, Dunedin; Hocken Library, Dunedin; and Southland Museum, Invercargill.
Other art galleries include the following: National Art Gallery, Wellington; Robert McDougall Art Gallery, Christchurch; and Dunedin Public Art Gallery.
New Zealand museums are particularly rich in New Zealand Maori and related Polynesian material. While the chief activities and qualifications of staff in New Zealand museums have in the past lain in the fields of natural history and Maori ethnology, in recent years they have had to take increasing responsibility for historical and technological material. The Art Galleries and Museums Association and the Royal Society of New Zealand have investigated the need for and possible organisation of technological museums, and their findings may determine a pattern of future development.
A steady increase in the artistic achievement of New Zealand artists progressively enriches the collections of New Zealand art galleries. In the art field the broadening of collections by the acquisition of more overseas material is a need which is engaging the attention of New Zealand's art galleries. The same need in the field of natural history, archaeology, and history is increasingly the concern of New Zealand museums.
While no uniform pattern for the control and financing of New Zealand's art galleries and museums applies, they are for the most part run by boards deriving their funds from bequests, local authority grants, public subscriptions, and donations. The Dominion Museum and National Art Gallery has for a number of years received a substantial Government subsidy.
International cooperation in the featuring in New Zealand of overseas exhibitions and in overseas countries of New Zealand exhibitions has been characteristic over recent years of the progressive policies of New Zealand's art galleries and museums.
CULTURAL AWARDS - A number of cultural awards are available in New Zealand, some being scholarships or bursaries or their equivalent, others being awards for achievement.
The literary field includes the following:
New Zealand Literary Fund - This fund is financed by a yearly appropriation on the vote of the Department of Internal Affairs, the amount in recent years being £2,000. Assistance from the fund is granted by the Minister of Internal Affairs, who is advised by the Literary Fund Advisory Committee. The approved categories of assistance are: (1) Grants towards the publishing costs (or by other appropriate means) to enable the publication of writing of literary merit in such fields as contemporary creative literature, historical writing, reprints of New Zealand classics, and Maori literature. (2) Grants to New Zealand authors undertaking creative work on approved projects. (3) Grants towards the cost of publication (or other appropriate means) of critical books and studies, to encourage the reading and study of New Zealand literature. (4) Such other assistance as the committee, with better knowledge gained by its experience, may deem desirable.
Scholarship in Letters - The scholarship is available annually for award to a New Zealand writer by the Minister of Internal Affairs on the recommendation of the Literary Fund Advisory Committee. It is of the value of £500. The scholarship is intended to enable the recipient to give all or most of his time to the project or projects nominated by him, either in New Zealand or abroad, during the year of tenure. Applications for tenure during the following calendar year are made before 31 August to the Secretary for Internal Affairs.
Robert Burns Fellowship in Literature - This fellowship in literature is tenable for one year, with provision for extension, at the University of Otago, a condition being that the fellow shall be resident for the academic year. The fellowship is open to New Zealand writers, preferably under 40 years. The fellow receives the equivalent of a lecturer's salary. Applications are made to the Registrar, University of Otago, Dunedin.
Award for Achievement - The Award for Achievement of £100 is available annually for award to a New Zealand writer by the Minister of Internal Affairs on the recommendation of the Literary Fund Advisory Committee. (Applications are not called for.)
Esther Glen Award - This award of the New Zealand Library Association is available annually for award to the author of the most distinguished children's book written by a New Zealander and published in New Zealand during the year. The award consists of a medal. (Applications are not called for.)
Hubert Church Prose Award - This award of PEN (New Zealand Centre) is available annually for the best prose writing by a New Zealand author during the year in question. The amount is £50. (Applications are not called for.)
Jessie Mackay Poetry Award - This award of PEN (New Zealand Centre) is available annually for the best poetry written by a New Zealand author during the year in question. The amount is £50. (Applications are not called for.)
Katherine Mansfield Memorial Award - This award of the New Zealand Women Writers' Society (Inc.) is financed from funds provided by the Bank of New Zealand. It is open to New Zealanders (both men and women) by birth or residence. In 1959 entries were called for in two sections, one for an essay or article and the other for a short story, the prizes being 50 guineas in each section. The next competition will be in 1961.
In the field of music, drama, ballet, and art, the New Zealand Government gives assistance through bursaries and scholarships to individuals and grants to professional and amateur organisations.
New Zealand has no advanced training institutions in music, drama, ballet, or art, and students must go overseas for such training. The Government offers bursaries of the value of £400 a year, plus £50 towards return passage, to promising students in music, drama, and ballet. The Association of New Zealand Art Societies and the National Art Gallery each award scholarships of the value of £500 a year financed from Government funds.
Each year grants are made to various national and local cultural groups. Substantial subsidies have been made to the New Zealand Players Company, the New Zealand Opera Company, and the New Zealand Ballet Company. Other organisations which have received assistance from Government funds include the New Zealand Drama Council, the New Zealand Film Institute, the British Drama League, the New Zealand Federation of Chamber Music Societies, the Alex Lindsay Orchestra, the Architectural Gallery, Wellington, the Auckland Junior Symphony Orchestra, and the Festival of the Pines, New Plymouth.
NATIONAL HISTORIC PLACES TRUST - Under the Historic Places Act 1954 a National Historic Places Trust was established for the purpose of preserving and marking and keeping permanent records of places and objects of national or local historic interest. The original members of the Trust were appointed as from 11 August 1955. Seventeen regional committees have been formed. The Trust is preparing a list of buildings throughout the country which it will be prepared to take action to preserve.
MAORI WELFARE - The legislative basis of the Maori welfare programme is the Maori Social and Economic Advancement Act of 1945. The aim of the Act is “The social and economic advancement and the promotion and maintenance of the health and general well-being of the Maori community”. It is also designed to facilitate the full integration of the Maori race into the social and economic structure of the country. An important feature of the Act is that it does not seek to impose standards from without; rather, it calls upon the Maori people to exercise control and direction of their own communities in the essentials of good citizenship and civic responsibility.
Under the above Act areas may be declared tribal districts or tribal committee areas. In such districts or areas tribal executives and committees have been set up by the Maori people to promote their development. At 31 March 1960 the numbers of such districts and areas were 84 and 492 respectively. A Controller, an Assistant Controller, seven district welfare officers, and 26 male and 22 female welfare officers, nearly all of the Maori race, have been appointed to advise and assist these bodies.
One of the major aspects of the recent development of Maori welfare is the emergence of women as an organised socialising factor. Thus, as at 31 March 1960 the Maori Women's Welfare League had a strength of approximately 3,200 members.
The Act provides for subsidies to be paid on moneys raised by the Maori people through their executives and committees for various social purposes set out in the Act, mainly in the improvement of local amenities. The subsidy granted in the financial year ended 31 March 1960 amounted to £40,203. Total subsidies paid under the Act amount to £292,436.
The Minister of Maori Affairs also appoints Maori wardens who have certain powers to ensure orderly behaviour among the Maori people within the tribal districts to which they are appointed. By 31 March 1960 wardens' certificates were held by 455 persons, all being Maoris.
The 1951 amendment to the principal Act, while similar to earlier provisions prohibiting the supply and consumption of liquor in or near dance halls, is somewhat wider in scope and prohibits the supply and consumption of liquor where any gathering of Maoris is being held at a “marae”. Provision is made for the issue of permits by tribal committees authorising the supply of liquor to Maori gatherings in certain circumstances. There are also provisions relating to applications for prohibition orders against Maoris.
PUBLIC TRUST OFFICE - In the early years of settlement in New Zealand those who wished to make provision for the administration of their estates on their death often experienced difficulty in selecting a suitable person competent and willing to act as trustee. That difficulty was natural in a new country where the colonists were fully occupied with their own affairs, and were unable to give to the property or business of another the close attention that was demanded. Even if an otherwise suitable trustee could be found, his solvency - an essential element in a trustee - might be in doubt, particularly when in those days the financial position of an individual could quickly change for the worse. Moreover, changes of residence were frequent, and the nominated trustee might have left the colony or have moved to another district at the time when his presence and services were most required.
In these circumstances the Public Trust Office was established in 1872 (it is now constituted under the Public Trust Office Act 1957) under the administration of the Public Trustee, a corporation sole with perpetual succession and a seal of office. The main purpose of the original Act was to provide a means of overcoming the difficulties that have been mentioned and to make available to the public a trustworthy administrator of the estates of deceased persons at a reasonable cost, the integrity of the Public Trustee and his officers being guaranteed by the State. That continues to be the chief function of the Office, but since its establishment the range of service has been very considerably extended. The Public Trustee now acts in many capacities, e.g., as administrator in intestate estate; executor and trustee under wills; trustee under marriage and other settlements; trustee of benefit or relief funds; agent or attorney for absentees or persons desiring to be relieved of business worries; sinking fund commissioner for local authorities; administrator of unclaimed lands and property; statutory administrator of the estates of mental patients (other than Maoris); manager (when so appointed by the Court) of the estates of aged and infirm persons unable to attend their own affairs; and administrator of compensation moneys payable in respect of the death of a worker. The wills of persons desiring the Public Trustee to act as their executor are prepared and held in safe custody by him, free of charge.
In lieu of obtaining probate or other grant of administration, the Public Trustee may file in an office of the Supreme Court an election by him to administer an estate (testate or intestate) if the gross value of the property in New Zealand is estimated not to exceed £1,000. If after the filing of the election the value of the property is found to exceed £1,500, the Public Trustee must obtain a grant of probate or administration in the ordinary way. This authority in many instances, by obviating the need for a grant of probate or administration, facilitates the administration and reduces costs.
The establishment of the Public Trust Office - one of the earliest examples of a State service - has proved an unqualified success. Ample evidence of this is to be found in the fact that 18,863 estates and funds of a total value of £77,046,102 were under the Public Trustee's administration at 31 March 1960. The beneficial results achieved did not pass unnoticed outside New Zealand and led to the establishment of similar offices in England and other parts of the British Commonwealth.
The progress that has been made in the present century is illustrated by the following table.
| Year Ended 31 March | Estates and Funds Under Administration | Wills of Living Persons on Deposit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Value | ||
| £ | No. | ||
| 1900 | 2,667 | 2,192,594 | 675 |
| 1920 | 14,679 | 20,860,686 | 25,792 |
| 1950 | 18,313 | 58,646,288 | 146,288 |
| 1960 | 18,863 | 77,046,102 | 190,258 |
During the year ended 31 March 1960, 4,595 estates valued at £16,410,743 were accepted for administration. The administration of 4,374 estates was completed.
Capital moneys becoming available for investment either form part of the Common Fund of the Office or, at the option of the testator or settler, are invested in such securities as he may specify. Interest is allowed on moneys in the Common Fund at the rate fixed from time to time by the Governor-General in Council (4 per cent from 1 January 1958) and is free of all commission and other charges. Both capital and interest are guaranteed by the State, thus affording the complete security that it is the object of the Office to provide. On the other hand, moneys directed to be invested in specified securities do not carry the State guarantee and, subject to the Public Trustee's ordinary liability as a trustee, any loss resulting from their investment falls upon the estate concerned. Commission is charged on the collection of the interest. Recognising that the safety of the moneys is thereby assured, the great majority of testators and settlors desire their funds to be placed in the Common Fund.
Charges and commission rates are contained in the Public Trust Office Regulations 1958.
New investments completed during the year ended 31 March 1960 totalled £2,240,000, the favourable terms offered by the Office again proving popular with borrowers. The investments held by the Office at 31 March 1960 totalled £22,866,354. These figures relate exclusively to Common Fund investments, and do not include other special investments made on behalf of estates or investments which constituted assets of estates when the latter came under the Public Trustee's administration and which are still held as assets of those estates.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, 11,794 wills appointing the Public Trustee executor were deposited with him for safe custody. The total number of such wills held on deposit at 31 March 1960 was 190,258. In addition to preparing the will of the testator in the first instance, the Public Trustee prepares any subsequent will or codicil that may be desired. During the year ended 31 March 1960 effect was given in 7,177 cases to changes desired by testators.
PATENTS, DESIGNS, TRADE MARKS, AND COPYRIGHT - The legislation concerned is the Patents Act 1953, the Trade Marks Act 1953, the Registered Designs Act 1953, and the Copyright Act 1913. The total number of applications for the grant of letters patent and for the registration of designs and trade marks during the financial year 1959-60 was 5,322, which was 824 more than the previous year.
The following table shows the number of applications for patents and for the registration of trade marks and designs in each of the last 12 years.
| Year | Patents | Trade Marks | Designs |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Year ended 31 March. | |||
| 1948 | 2,469 | 1,439 | 229 |
| 1949 | 1,984 | 1,292 | 255 |
| 1950 | 1,987 | 1,422 | 246 |
| 1951 | 2,047 | 1,439 | 165 |
| 1952 | 1,952 | 1,390 | 177 |
| 1953 | 2,124 | 1,358 | 216 |
| 1954-55* | 2,438 | 1,703 | 245 |
| 1955-56* | 2,298 | 1,631 | 261 |
| 1956-57* | 2,324 | 1,858 | 250 |
| 1957-58* | 2,398 | 1,956 | 261 |
| 1958-59* | 2,356 | 1,896 | 246 |
| 1959-60* | 2,784 | 2,258 | 280 |
Patents - The applications received during 1959-60 were broadly classified as follows: mechanical engineering, 793; chemistry, 604; electrical engineering, 372; primary industries, 327; building construction, 357; home science and miscellaneous, 331.
Great Britain with 721 applications was much less than New Zealand (1,012), followed by the United States of America (447), Australia (186), with the remainder (382) distributed among 21 other countries.
Trade Marks - In applications for trade marks in 1959-60 Classes 5 (pharmaceutical, veterinary, and sanitary substances) and 25 (clothing) again predominated with 364 and 294 applications respectively, and they were followed by Class 3 (soaps, detergents, cosmetics, etc.) 166; Class 1 (chemicals, etc.) 104; Class 30 (coffee, tea, cocoa, cereal products, etc.) 96; Class 7 (machines and machine tools, etc.) 84.
The countries from which the applications originated were: New Zealand, 773; Great Britain, 458; United States of America, 398; Australia, 196; with the remaining 433 distributed between 17 other countries.
Renewal of registration of 1,419 trade marks was effected during the year.
Designs - The total number of applications since the inception of design registration in New Zealand is 8,443.
Copyright - Copyright fees in 1959-60 amounted to £27, compared with £20 in the previous year.
BANKRUPTCY - The law relating to bankruptcy in New Zealand is contained in the main in the Bankruptcy Act 1908 and its amendments. Jurisdiction in bankruptcy matters is vested in the Supreme Court. The Governor-General, however, may by Proclamation confer similar jurisdiction on a Magistrate's Court in cases where the liabilities do not exceed £300.
All proceedings in bankruptcy are commenced by a petition filed in the Court. A petition may be filed either by the debtor or by a creditor, a fee of £6 being payable. The filing of a debtor's petition is equivalent to an order of the Court adjudging the debtor a bankrupt, no order being required in this case. Not less than £30 in the aggregate must be owing by the debtor to the creditor or creditors filing a petition.
Section 7 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1947 increased the value of furniture and household effects, including wearing apparel of himself and family, which a bankrupt may select and retain as his own property from £50 to £100.
Immediately on a debtor's petition being filed or adjudication being made on a creditor's petition, the Registrar of the Court gives notice to the Official Assignee in Bankruptcy, in whom all the property of the bankrupt thereupon vests. The bankrupt must hand over his books of account, papers, deeds, etc., to the Official Assignee, and furnish such information as is necessary to enable the Assignee to administer the estate to the best advantage. The bankrupt may also be required to produce statements of accounts, balance sheets, etc., covering the period of three years immediately prior to the commencement of his bankruptcy, give inventories of his property and debts, and generally assist in the realisation of his property. The Assignee may summon the bankrupt before himself, or before a Magistrate, to be examined on oath. The Bankruptcy Amendment Act 1927 forbids (save with the consent of the Court, on the application of the Official Assignee) the publication of a report of any examination of a bankrupt before the Assignee or of any matter arising in the course of such an examination.
The Official Assignee is empowered to sell the bankrupt's property, to claim debts due to the bankrupt estate, to carry on the business of the bankrupt so far as is necessary or expedient for its beneficial winding up, or to divide the property among the creditors. The bankrupt may be appointed by the Official Assignee to manage his estate or carry on his business on behalf of the creditors.
Creditors may accept a composition in satisfaction of the debts due to them. In such a case, after approval of the Court, a deed of composition is executed and filed, and the bankruptcy annulled.
On application being made by the bankrupt, the Court is empowered to grant him an order of discharge, either absolute, suspended, or conditional. The application may be opposed either by the Official Assignee or by any creditor who has proved his claim. A public examination of the bankrupt may be demanded by the Assignee on a resolution by creditors.
Undischarged Bankrupts - Section 14 of the Bankruptcy Amendment Act 1927 requires the annual compilation of a list showing the names, occupations, and other particulars of all persons who have been adjudged bankrupt since 31 March 1927, and who have not obtained an order of discharge, or whose order of discharge is suspended for a term, or is subject to conditions remaining unfulfilled.
Section 9 of the Statutes Amendment Act 1936 provides that the Minister of Justice may from time to time publish the list, or so much of it as relates to adjudications within any specified period ending on the date of the compilation of the list.
Transactions in Bankruptcy - The number of transactions in bankruptcy during the last five years is now given. A long-term record of the more important features will be found in the Statistical Summary given later in this volume. The number of Court orders for winding up companies by an Official Assignee is shown in addition to the figures of individual bankrupts, financial transactions on behalf of companies being included in the later tables.
| Year | Number of Bankruptcies | Petitions by Debtors | Adjudications on Petitions by Creditors | Orders of Discharge or Annulment Granted | Orders for Winding Up Companies by Assignee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1956 | 371 | 309 | 62 | 80 | 19 |
| 1957 | 421 | 364 | 57 | 74 | 16 |
| 1958 | 479 | 392 | 87 | 82 | 16 |
| 1959 | 594 | 511 | 83 | 131 | 24 |
| 1960 | 473 | 405 | 68 | 144 | 22 |
In the case of a partnership, not only the partnership but each partner is counted in the total of transactions.
During the later war and immediate post-war years the number of bankruptcies was exceptionally low, extremely buoyant business conditions prevailing throughout this period. Since 1955 there has been a decided upward trend, the annual average being 119 for the five years 1946-50, compared with an average of 487 for the years 1956-60, although the numbers in recent years are still below the average of the period 1920-40. Regard should be paid to the fact that the number of business units is also increasing.
The general bankruptcy statistics do not cover private assignments and compositions, but relate only to cases dealt with by Official Assignees. Certain statistics of private assignments are available, and details of these appear later.
Assets and Liabilities - Debtors are required to file a statement of the extent of their liabilities and assets, but there is usually a marked difference between these statements and the amounts actually realised by the Official Assignee or the debts subsequently proved by creditors.
It should be understood that in the following table the figures in each column refer to all transactions under the respective heads during the year, the amounts realised by Assignees and paid in dividends and preferential claims relating partly to the current year's bankruptcies (many of which, however, are not disposed of during the year) and partly to cases commenced in previous years. Time-lag variations of this nature account for the amounts paid during 1959 exceeding the figures for amounts realised. Since 1954 company windings-up are included in the totals.
| Year | Number of Bankruptcies | Amounts Realised by Official Assignees | Amounts of Debts Proved | Amounts Paid in Dividends, Preferential and Secured Claims | Amounts Paid in Government Commission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Including 1 deceased person's estate under Part IV of the Administration Act 1952. †Including 2 deceased persons' estates under Part IV of the Administration Act 1952. ‡Including 4 deceased persons' estates under Part IV of the Administration Act 1952. | |||||
| £ | £ | £ | £ | ||
| 1950 | 142 | 49,252 | 125,917 | 39,821 | 3,498 |
| 1951 | 145* | 48,269 | 136,822 | 46,897 | 3,916 |
| 1952 | 168* | 56,241 | 251,129 | 29,053 | 3,322 |
| 1953 | 215* | 72,162 | 381,016 | 46,916 | 4,597 |
| 1954 | 277 | 82,571 | 413,447 | 59,212 | 4,938 |
| 1955 | 304* | 112,418 | 382,322 | 96,484 | 9,337 |
| 1956 | 390 | 130,574 | 547,751 | 78,503 | 6,921 |
| 1957 | 437† | 180,364 | 782,226 | 100,488 | 8,134 |
| 1958 | 495‡ | 184,795 | 819,135 | 130,783 | 12,797 |
| 1959 | 618† | 194,877 | 755,193 | 200,775 | 12,596 |
| 1960 | 495 | 165,586 | 668,911 | 139,874 | 13,206 |
The table following shows for each of the last 11 years the average amount of debts proved per estate, and also the proportion of dividends, preferential claims, and secured claims, to debts.
| Year | Average Debts Proved per Estate | Proportion of Dividends, etc., to Debts |
|---|---|---|
| £ | per cent | |
| 1950 | 887 | 31.62 |
| 1951 | 944 | 34.28 |
| 1952 | 1,495 | 11.57 |
| 1953 | 1,772 | 12.31 |
| 1954 | 1,493 | 14.32 |
| 1955 | 1,258 | 25.24 |
| 1956 | 1,404 | 14.33 |
| 1957 | 1,790 | 12.85 |
| 1958 | 1,655 | 15.97 |
| 1959 | 1,222 | 26.59 |
| 1960 | 1,351 | 20.91 |
Apart from dividends, preferential and secured claims, and Government commission, payments made from assets realised include cost of actions, solicitors' fees, and expenses incurred in managing estates for the benefit of creditors.
Amount of Liabilities – The following table shows for each of the last five years a classification of bankruptcies according to the amount of stated liabilities. With all partnerships the liabilities for each partner are included, but not the partnership.
| Liabilities | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excludes 2 partnerships. †Excludes 3 partnerships. ‡Excludes 3 partnerships, also 2 companies for which no statement of liabilities has been filed. §Excludes 5 partnerships. ||Excludes 1 partnership. | |||||
| Under £250 | 75 | 159 | 94 | 138 | 113 |
| £250 and under £500 | 75 | 71 | 105 | 145 | 97 |
| £500 and under £1,000 | 97 | 79 | 112 | 124 | 94 |
| £1,000 and under £2,000 | 76 | 60 | 85 | 106 | 91 |
| £2,000 and under £5,000 | 46 | 46 | 69 | 74 | 73 |
| £5,000 and over | 19 | 19 | 25 | 26 | 26 |
| Totals | 388* | 434† | 490‡ | 613§ | 494|| |
Most failures are for comparatively small amounts. Of a total of 2,419 bankruptcies during the five years surveyed 24 per cent were for liabilities of less than £250 and 44 per cent for liabilities under £500.
Occupations of Bankrupts — The following table shows in broad groups the occupations by industry of those persons adjudged bankrupt in the last five years. The revised classification is based on the international standard industrial code. Companies are here excluded.
| 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Excludes 2 partnerships. †Excludes 3 partnerships. ‡Excludes 5 partnerships. §Excludes 1 partnership. | |||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 25 | 34 | 36 | 70 | 41 |
| Forestry, hunting, and fishing | 3 | 12 | 22 | 26 | 17 |
| Mining and quarrying | 2 | 1 | - | - | - |
| Manufacturing — | |||||
| Food and beverages | 8 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 12 |
| Footwear and textiles | 6 | 5 | - | 5 | 4 |
| Wood, furniture, and fixtures | 10 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| Printing and publishing | - | 1 | - | 4 | 3 |
| Machinery (not electrical) | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| Transport equipment | 10 | 6 | 22 | 21 | 19 |
| Other | 7 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 11 |
| Construction | 71 | 67 | 69 | 98 | 114 |
| Wholesale and retail trade | 50 | 64 | 82 | 90 | 68 |
| Other commerce | 3 | - | - | - | 1 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 63 | 66 | 72 | 66 | 30 |
| Personal and community services | 29 | 33 | 44 | 52 | 59 |
| Activities not adequately described— | |||||
| Contractor | 5 | 10 | 26 | 9 | 6 |
| Labourer | 26 | 54 | 51 | 87 | 41 |
| Other | 46 | 34 | 31 | 42 | 37 |
| Totals | 369* | 418† | 476† | 589‡ | 472§ |
The types of activity in which bankrupts were engaged at the time of failure frequently bear little relationship to the fact of insolvency. Personal extravagance or business incompetence are probably much more important factors in the majority of cases.
The occupational status of individual bankrupts during each of the calendar years 1950–60 is given in the following table. With all partnerships the occupation of each partner is included, but not the partnership. Under the heading “Working for Salary or Wages” are included small numbers returning no occupational status.
| Year | Occupational Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working for Salary or Wages | Employer of Labour | Working on Own Account But Not Employing Labour | Total | |
*Excludes 1 partnership. ‡Excludes 2 partnerships. ||Excludes 5 partnerships. †Includes 1 retired person. §Excludes 3 partnerships. | ||||
| 1950 | 44 | 43 | 55 | 142 |
| 1951 | 61 | 26 | 57 | 144* |
| 1952 | 64 | 40 | 63 | 167* |
| 1953 | 91 | 34 | 89 | 214* |
| 1954 | 103 | 37 | 123 | 263 |
| 1955 | 108 | 39 | 145 | 293† |
| 1956 | 188 | 49 | 132 | 369‡ |
| 1957 | 211 | 71 | 136 | 418§ |
| 1958 | 213 | 80 | 183 | 476§ |
| 1959 | 288 | 99 | 202 | 589|| |
| 1960 | 246 | 109 | 117 | 472* |
Private Assignments — Official bankruptcies, as explained earlier, do not comprise all financial failures and the bankruptcy statistics have been supplemented since 1928 by the collection of data relating to private assignments. The statistics cover all operations arising out of deeds of assignment made under section 150 (2) of the Stamp Duties Act 1954. Because of the difficulty in collecting the information, the figures include estimates in some cases and are therefore approximations.
Amount of Liabilities — The following table classifies estates assigned during the last five years according to the amount of liabilities.
| Liabilities | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes 3 estates in which the assignors were subsequently adjudged bankrupt. †Excludes 1 assignment not proceeded with and 1 assignment for which no information is available. ‡Excludes 1 estate in which the assignor was subsequently adjudged bankrupt, and 2 estates for which no information is available. §Excludes 10 assignments not proceeded with. | |||||
| Under £250 | - | - | - | - | - |
| £250 and under £500 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| £500 and under £1,000 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| £1,000 and under £2,000 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 7 |
| £2,000 and under £5,000 | 12 | 17 | 11 | 8 | 18 |
| £5,000 and over | 10 | 13 | 19 | 12 | 20 |
| Unspecified | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Totals | 33* | 38† | 36‡ | 24§ | 46 |
The amounts of liabilities involved are relatively much higher for private assignments than for bankruptcies. For the five years 1955–59, 98 per cent of privately assigned estates had liabilities of £1,000 and over. For bankruptcies, only 34 per cent of the total number fell into this category.
Occupations of Assignors — The occupations of assignors in broad industrial classes during the last five years available were as follows. The classification used follows that of the occupational table of bankrupts given earlier in this section.
| 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Includes 3 estates in which the assignors were subsequently adjudged bankrupt. †Excludes 1 assignment not proceeded with and 1 assignment for which no information was available. ‡Excludes 1 estate in which the assignor was subsequently adjudged bankrupt, and 2 estates for which no information is available. §Excludes 10 assignments not proceeded with. | |||||
| Agriculture and livestock production | 3 | 4 | 2 | - | 1 |
| Manufacturing | 2 | - | - | - | 4 |
| Construction | 16 | 12 | 17 | 8 | 19 |
| Wholesale and retail trade | 5 | 18 | 9 | 8 | 10 |
| Transport, storage, and communication | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Personal and community services | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Activities not adequately described | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 6 |
| Totals | 33* | 38† | 36‡ | 24§ | 46 |
Of the 1959 total, 23 were employers of labour, 4 were employees, and 19 were working on own account.
Provisional figures for 1960 show the number of private assignments as 29. Data relating to private assignments are normally collected much later than those for bankruptcies, as a longer period is necessary for settlement of the financial arrangements in the former case.
LOTTERIES — Under the Gaming Act 1908 the Minister of Internal Affairs may grant permission (subject to such conditions as he thinks fit) for the disposing by raffle or chance of any painting, drawing, sculpture, or other work of art, or literature, or mineral specimen, or mechanical model. The Gaming Amendment Act 1949 made several important changes in the law relating to raffles. Major changes include provisions enabling real and personal property to be raffled, licences being formerly issued only for works of art and mineral specimens; authority is given to authorised members of the Police to issue raffle licences where an individual prize does not exceed £10 in value, and where the total value of the prizes does not exceed £25; and authorised members of the Police may from time to time approve organisations to conduct raffles, provided the value of the prizes in any raffle does not exceed £5. By the Stamp Duties Act 1954, as amended in 1957, any such licence granted for the raffling of any real or personal property in excess of £500 value is subject to a lottery duty of 10 per cent of the value of the tickets sold in the lottery. Information as to receipts from this source will be found in Section 26B - Taxation.
The Gaming Act also permits sweepstakes and art unions (as defined) under certain specified conditions.
During the year ended 31 March 1960, 6,208 licences covering small raffles with prizes ranging from £25 to £500 in cash or goods were issued to local or national organisations. Raffles in which the prizes are less than £25 in total, and with no one prize exceeding £10, are licensed and supervised by the Police. In addition, 17 licences were issued in respect of the regular £10,000 art unions. The aggregate results of these regular art unions for the past seven years have been as follows.
| 1953-54 | 1954-55 | 1955-56 | 1956-57 | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of lotteries | 13 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| Gross sales £ | 418,279 | 404,449 | 608,620 | 605,738 | 588,258 | 606,256 | 594,157 |
| Commission on sales £ | 62,741 | 60,667 | 91,293 | 90,860 | 88,239 | 90,938 | 89,123 |
| Expenses £ | 48,608 | 49,952 | 64,060 | 62,919 | 55,573 | 59,817 | 60,082 |
| Prizes £ | 91,000 | 91,000 | 150,000 | 160,000 | 160,000 | 170,000 | 170,000 |
| Net proceeds £ | 215,930 | 202,830 | 303,267 | 291,959 | 284,446 | 285,501 | 274,952 |
| Lottery duty £ | 41,827 | 40,445 | 60,862 | 60,574 | 58,826 | 60,625 | 59,416 |
| Net profit £ | 174,103 | 162,385 | 242,405 | 231,385 | 225,620 | 224,876 | 215,536 |
Allocation of funds earned from the art unions in the preceding table during 1959–60 was as follows: £49,915 to charitable and philanthropic organisations; £14,674 to various mayoral or other recognised relief of distress funds; £49,489 to cultural purposes; £24,115 to sporting bodies; £3,200 to old folks' associations; £20,790 to youth organisations (YMCA, Boy Scouts, etc.); £4,300 to the bands' associations; national water safety, £15,500; and miscellaneous grants, £15,585.
GENERAL ELECTION RESULTS — A general election of parliamentary representatives was held on 26 November 1960, voting in New Zealand for both European and Maori electorates taking place on that day.
The strength of the political party representation among members of Parliament after the 1960 election was National 46, Labour 34. The relative strengths after the four preceding general elections were as follows: November 1949, National 46, Labour 34; September 1951, National 50, Labour 30; November 1954, National 45, Labour 35, and November 1957, Labour 41, National 39.
The total number of electors on the roll for the election was 1,303,955, comprising European, 1,255,488 and Maori, 48,467. The number of votes recorded, including informal, was 1,176,963 (European 1,139,090; Maori 37,873), this figure including 6,315 special votes cast by persons who were not on the roll.
Votes cast for candidates by political affiliations were as follows: National, 557,046; Labour, 508,179; Social Credit, 100,905; Communist, 2,423; Independent, 1,257; other parties 693.
The following table shows for the 1954, 1957, and the 1960 general elections the number of votes recorded by the main political parties, along with the percentages that the various party votes represent of the total votes recorded and of the total valid votes.
| Party | Votes Recorded | Percentage of Total Votes Recorded | Percentage of Total Valid Votes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1954 | 1957 | 1960 | 1954 | 1957 | 1960 | 1954 | 1957 | 1960 | |
| National | 485,630 | 511,699 | 557,046 | 43.93 | 43.99 | 47.33 | 44.28 | 44.21 | 47.59 |
| Labour | 484,082 | 559,096 | 508,179 | 43.78 | 48.07 | 43.18 | 44.13 | 48.31 | 43.42 |
| Social Credit | 122,068 | 83,498 | 100,905 | 11.04 | 7.18 | 8.57 | 11.13 | 7.22 | 8.62 |
| Communist | 1,134 | 706 | 2,423 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.21 |
| Other | 3,979 | 2,366 | 1,950 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| Total valid votes | 1,096,893 | 1,157,365 | 1,170,503 | 99.21 | 99.51 | 99.45 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Informal votes | 8,716 | 5,696 | 6,460 | 0.79 | 0.49 | 0.55 | ... | ... | ... |
| Total votes recorded | 1,105,609 | 1,163,061 | 1,176,963 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ... | ... | ... |
A statement of voting in individual electorates (both European and Maori) at the general election in 1960 is now given.
NOTE — Abbreviations used: C, Communist; I, Independent; I M M, Independent Maori Movement; K, Kauhanganui; L, Labour; N, National; P, People's Progressive Independent; S C, Social Credit; U, United New Zealand Political Movement.
| Electoral Districts, Names of Candidates, and Party Affiliations | Number of Votes Recorded | Number of Electors on Roll | Population at Census 1956 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ashburton - | |||
| Gerard (N) | 8,094 | ||
| Glassey (L) | 5,536 | ||
| Hayes (S C) | 948 | ||
| Informal | 29 | ||
| Totals | 14,607 | 16,007 | 25,862 |
| Auckland Central - | |||
| Douglas (L) | 6,915 | ||
| Liddle (S C) | 586 | ||
| McAra (C) | 164 | ||
| Presland (N) | 5,069 | ||
| Informal | 136 | ||
| Totals | 12,870 | 15,691 | 27,547 |
| Avon - | |||
| Edmonds (S C) | 1,973 | ||
| Mathison (L) | 8,683 | ||
| McNulty (C) | 126 | ||
| Pickering (N) | 4,467 | ||
| Informal | 69 | ||
| Totals | 15,318 | 17,334 | 26,806 |
| Awarua - | |||
| Grieve (N) | 7,772 | ||
| McNaughton (S C) | 1,117 | ||
| Wyatt (L) | 4,772 | ||
| Informal | 66 | ||
| Totals | 13,727 | 15,596 | 25,941 |
| Bay of Plenty- | |||
| Allen (N) | 6,920 | ||
| Knox (S C) | 1,334 | ||
| Santon (L) | 4,509 | ||
| Informal | 58 | ||
| Totals | 12,821 | 14,058 | 25,316 |
| Buller - | |||
| Bergh (I) | 210 | ||
| King (N) | 4,834 | ||
| Matthews (S C) | 1,984 | ||
| Skinner (L) | 6,380 | ||
| Informal | 72 | ||
| Totals | 13,480 | 14,603 | 26,814 |
| Christchurch Central - | |||
| Flint (N) | 4,851 | ||
| Green (S C) | 851 | ||
| Locke (C) | 133 | ||
| Macfarlane (L) | 6,786 | ||
| Informal | 83 | ||
| Totals | 12,704 | 14,833 | 26,092 |
| Clutha - | |||
| Fahey (L) | 4,312 | ||
| Gordon (N) | 8,175 | ||
| Lumsden (S C) | 1,166 | ||
| Informal | 72 | ||
| Totals | 13,725 | 15,178 | 26,813 |
| Dunedin Central - | |||
| Aberdeen (S C) | 951 | ||
| Connolly (L) | 7,175 | ||
| Scurr (N) | 6,333 | ||
| Taylor (I) | 471 | ||
| Informal | 78 | ||
| Totals | 15,008 | 16,611 | 26,413 |
| Eden- | |||
| Grove (S C) | 556 | ||
| Penney (L) | 6,730 | ||
| Rae (N) | 8,632 | ||
| Informal | 112 | ||
| Totals | 16,030 | 18,235 | 27,415 |
| Egmont - | |||
| Sheat (N) | 7,128 | ||
| Smith (S C) | 2,209 | ||
| Watson (L) | 3,195 | ||
| Informal | 49 | ||
| Totals | 12,581 | 13,959 | 25,301 |
| Fendalton - | |||
| Forster (S C) | 826 | ||
| Lake (N) | 9,500 | ||
| Rowling (L) | 6,778 | ||
| Informal | 43 | ||
| Totals | 17,147 | 18,790 | 26,112 |
| Franklin - | |||
| Allen (N) | 9,442 | ||
| Preston (L) | 4,245 | ||
| Wheeler (S C) | 1,219 | ||
| Informal | 61 | ||
| Totals | 14,967 | 16,633 | 26,984 |
| Gisborne - | |||
| Box (S C) | 994 | ||
| Keeling (L) | 6,993 | ||
| Tombleson (N) | 7,284 | ||
| Informal | 186 | ||
| Totals | 15,457 | 16,588 | 26,705 |
| Grey Lynn - | |||
| Hackett (L) | 8,761 | ||
| Morley (S C) | 693 | ||
| Wolf (C) | 117 | ||
| Zouch (N) | 4,165 | ||
| Informal | 64 | ||
| Totals | 13,800 | 15,478 | 25,108 |
| Hamilton - | |||
| Adams-Schneider (N) | 8,222 | ||
| Arthur (L) | 5,639 | ||
| Bethune (S C) | 1,117 | ||
| Informal | 32 | ||
| Totals | 15,010 | 16,719 | 26,786 |
| Hastings - | |||
| Keating (L) | 7,665 | ||
| MacIntyre (N) | 7,965 | ||
| Thew (S C) | 1,302 | ||
| Informal | 65 | ||
| Totals | 16,997 | 18,312 | 27,060 |
| Hauraki - | |||
| Donovan (S C) | 1,611 | ||
| Kinsella (N) | 7,401 | ||
| Tucker (L) | 4,766 | ||
| Informal | 49 | ||
| Totals | 13,827 | 15,194 | 26,546 |
| Hawke's Bay - | |||
| Bullock (S C) | 1,110 | ||
| Cheer (I) | 263 | ||
| Harker (N) | 7,508 | ||
| Woolf (L) | 3,826 | ||
| Informal | 99 | ||
| Totals | 12,806 | 14,233 | 25,021 |
| Heretaunga - | |||
| Bailey (L) | 8,265 | ||
| Hampson-Tindale (N) | 5,689 | ||
| Wall (S C) | 1,360 | ||
| Informal | 69 | ||
| Totals | 15,383 | 16,744 | 26,954 |
| Hobson - | |||
| Cracknell (S C) | 5,005 | ||
| Sloane (N) | 6,406 | ||
| Webber (L) | 2,335 | ||
| Informal | 57 | ||
| Totals | 13,803 | 15,386 | 27,176 |
| Hurunui - | |||
| Adcock (L) | 5,576 | ||
| Clark (S C) | 1,180 | ||
| Gillespie (N) | 8,307 | ||
| Informal | 49 | ||
| Totals | 15,112 | 16,680 | 25,838 |
| Hutt - | |||
| Barker (N) | 5,265 | ||
| Hegman (C) | 40 | ||
| Milne (S C) | 997 | ||
| Nash (L) | 7,614 | ||
| Wain (I) | 115 | ||
| Informal | 127 | ||
| Totals | 14,158 | 15,611 | 27,018 |
| Invercargill - | |||
| Hanan (N) | 8,128 | ||
| Henderson (L) | 6,202 | ||
| Steele (S C) | 624 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 15,005 | 16,451 | 26,181 |
| Island Bay - | |||
| Cameron (S C) | 748 | ||
| Curry (N) | 5,668 | ||
| Nordmeyer (L) | 7,459 | ||
| Smith (C) | 128 | ||
| Informal | 110 | ||
| Totals | 14,113 | 16,162 | 26,704 |
| Karori - | |||
| Marshall (N) | 9,841 | ||
| Smuts-Kennedy (L) | 5,528 | ||
| Wild (S C) | 505 | ||
| Informal | 158 | ||
| Totals | 16,032 | 17,943 | 26,683 |
| Lyttelton - | |||
| Hay (N) | 7,650 | ||
| Kirk (L) | 7,910 | ||
| Munnings (S C) | 1,040 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 16,651 | 17,869 | 27,484 |
| Manawatu - | |||
| Fischer (L) | 4,596 | ||
| O'Brien (S C) | 2,068 | ||
| Tennent (N) | 7,716 | ||
| Informal | 43 | ||
| Totals | 14,423 | 15,888 | 26,613 |
| Manukau - | |||
| Gotz (N) | 9,723 | ||
| Higham (S C) | 778 | ||
| Stamp (L) | 9,478 | ||
| Informal | 80 | ||
| Totals | 20,059 | 21,458 | 25,680 |
| Marlborough - | |||
| Hope (L) | 5,677 | ||
| Kerr (S C) | 1,680 | ||
| Shand(N) | 7,424 | ||
| Informal | 52 | ||
| Totals | 14,833 | 15,867 | 25,858 |
| Marsden - | |||
| McKay (N) | 8,704 | ||
| McQuillan (S C) | 2,132 | ||
| Reid (L) | 4,353 | ||
| Informal | 78 | ||
| Totals | 15,267 | 16,824 | 27,397 |
| Miramar - | |||
| Fox (L) | 7,186 | ||
| Johnson (S C) | 893 | ||
| Lyons (N) | 6,719 | ||
| Informal | 74 | ||
| Totals | 14,872 | 16,508 | 25,888 |
| Mornington - | |||
| Hudson (L) | 7,635 | ||
| Marton (C) | 70 | ||
| Milburn (S C) | 1,548 | ||
| Thorn (N) | 5,389 | ||
| Informal | 56 | ||
| Totals | 14,698 | 16,010 | 25,050 |
| Mt. Albert - | |||
| Anderson (N) | 6,229 | ||
| Freer (L) | 7,905 | ||
| Monteith (S C) | 690 | ||
| Pitcher (U) | 34 | ||
| Informal | 79 | ||
| Totals | 14,937 | 16,431 | 25,136 |
| Napier - | |||
| Edwards (L) | 8,838 | ||
| Frampton (S C) | 874 | ||
| Gunn (N) | 7,433 | ||
| Informal | 82 | ||
| Totals | 17,227 | 18,554 | 26,362 |
| Nelson - | |||
| Mahan (S C) | 1,223 | ||
| Martin (N) | 6,752 | ||
| Whitehead (L) | 8,519 | ||
| Informal | 76 | ||
| Totals | 16,570 | 17,721 | 27,053 |
| New Plymouth - | |||
| Aderman (N) | 9,063 | ||
| Barclay (L) | 7,370 | ||
| Lattimer (S C) | 1,068 | ||
| Informal | 72 | ||
| Totals | 17,573 | 19,031 | 27,552 |
| North Dunedin - | |||
| Bell (N) | 5,170 | ||
| Goddard (S C) | 1,265 | ||
| Hunter (C) | 73 | ||
| McMillan (L) | 7,645 | ||
| Informal | 104 | ||
| Totals | 14,257 | 15,558 | 26,066 |
| North Shore - | |||
| Eyre (N) | 8,727 | ||
| Holloway (I) | 97 | ||
| Richards (S C) | 431 | ||
| Smith (L) | 6,910 | ||
| Informal | 57 | ||
| Totals | 16,222 | 17,661 | 26,945 |
| Onehunga - | |||
| Leitch (S C) | 534 | ||
| McEwen (C) | 97 | ||
| Phillips (N) | 4,080 | ||
| Watt (L) | 8,785 | ||
| Informal | 63 | ||
| Totals | 13,559 | 15,145 | 25,353 |
| Onslow - | |||
| Clark (N) | 7,880 | ||
| Elliott (S C) | 920 | ||
| May (L) | 8,670 | ||
| Smith (C) | 101 | ||
| Informal | 61 | ||
| Totals | 17,632 | 19,039 | 26,915 |
| Otago Central - | |||
| George (N) | 7,320 | ||
| Jones (S C) | 1,372 | ||
| MacDonell (L) | 2,976 | ||
| Informal | 41 | ||
| Totals | 11,709 | 12,767 | 26,002 |
| Otahuhu - | |||
| Deas (L) | 9,247 | ||
| Donovan (S C) | 622 | ||
| Hieatt (C) | 114 | ||
| Tucker (N) | 6,473 | ||
| Informal | 98 | ||
| Totals | 16,554 | 17,959 | 26,025 |
| Otaki - | |||
| Cameron (L) | 6,894 | ||
| Clunie (S C) | 1,758 | ||
| McCready (N) | 8,938 | ||
| Informal | 83 | ||
| Totals | 17,673 | 18,948 | 25,747 |
| Pahiatua - | |||
| Dempsey (S C) | 1,298 | ||
| Holyoake (N) | 8,111 | ||
| McKane (L) | 3,177 | ||
| Informal | 59 | ||
| Totals | 12,645 | 13,909 | 25,091 |
| Palmerston North - | |||
| Brown (N) | 7,401 | ||
| Gunn (S C) | 1,186 | ||
| Manning (C) | 79 | ||
| Skoglund (L) | 7,268 | ||
| Informal | 80 | ||
| Totals | 16,014 | 17,445 | 25,604 |
| Patea - | |||
| Jack (N) | 6,420 | ||
| Mullins (S C) | 2,076 | ||
| Vallely (L) | 4,116 | ||
| Informal | 71 | ||
| Totals | 12,683 | 13,849 | 25,062 |
| Petone - | |||
| Long (S C) | 1,052 | ||
| Martin (N) | 5,820 | ||
| Moohan (L) | 8,738 | ||
| Informal | 100 | ||
| Totals | 15,710 | 17,356 | 26,963 |
| Piako - | |||
| Barrowclough (S C) | 1,555 | ||
| Goosman (N) | 8,500 | ||
| Uttinger (L) | 3,124 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 13,230 | 15,158 | 26,674 |
| Ponsonby - | |||
| Jackson (C) | 361 | ||
| Macdonald (L) | 9,138 | ||
| McLauchlan (N) | 4,394 | ||
| Ross (S C) | 612 | ||
| Informal | 102 | ||
| Totals | 14,607 | 16,959 | 27,375 |
| Raglan - | |||
| Baxter (L) | 5,548 | ||
| Carter (N) | 6,919 | ||
| Christie (I) | 101 | ||
| Thompson (S C) | 720 | ||
| Informal | 60 | ||
| Totals | 13,348 | 14,526 | 25,403 |
| Rangitikei - | |||
| Cameron (L) | 3,812 | ||
| Needham (S C) | 1,894 | ||
| Shelton (N) | 7,701 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 13,458 | 15,132 | 25,583 |
| Remuera - | |||
| Algie (N) | 10,212 | ||
| Gustafson (L) | 4,103 | ||
| Morley (S C) | 692 | ||
| Informal | 77 | ||
| Totals | 15,084 | 17,160 | 25,593 |
| Riccarton - | |||
| Connelly (L) | 8,342 | ||
| Cullen (S C) | 1,019 | ||
| Sergel (N) | 6,320 | ||
| Informal | 35 | ||
| Totals | 15,716 | 17,251 | 24,976 |
| Rodney - | |||
| Amos (L) | 3,571 | ||
| Hunter (S C) | 2,150 | ||
| Scott (N) | 7,728 | ||
| Informal | 75 | ||
| Totals | 13,524 | 14,986 | 25,114 |
| Roskill - | |||
| Ayo (C) | 68 | ||
| Faulkner (L) | 8,141 | ||
| Langstone (S C) | 575 | ||
| Taylor (N) | 6,767 | ||
| Informal | 129 | ||
| Totals | 15,680 | 17,014 | 24,983 |
| Rotorua - | |||
| Boord (L) | 7,473 | ||
| Lapwood (N) | 7,831 | ||
| Tunnicliffle (S C) | 1,416 | ||
| Informal | 76 | ||
| Totals | 16,796 | 18,400 | 27,523 |
| St. Albans - | |||
| Lynne (S C) | 746 | ||
| Pickering (L) | 7,511 | ||
| Walker (N) | 7,809 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 16,117 | 17,586 | 26,576 |
| St. Kilda - | |||
| Barnes (N) | 6,827 | ||
| Fraser (L) | 7,662 | ||
| Greenwood (S C) | 1,169 | ||
| Informal | 51 | ||
| Totals | 15,709 | 16,867 | 25,853 |
| Selwyn - | |||
| McAlpine (N) | 8,096 | ||
| Morton (S C) | 1,042 | ||
| Palmer (L) | 5,257 | ||
| Informal | 74 | ||
| Totals | 14,469 | 15,972 | 26,224 |
| Stratford - | |||
| Murray (N) | 7,638 | ||
| St. George (L) | 3,250 | ||
| Tuffery (S C) | 1,936 | ||
| Informal | 58 | ||
| Totals | 12,882 | 14,375 | 26,749 |
| Sydenham - | |||
| Howard (L) | 8,827 | ||
| Pounsford (S C) | 1,225 | ||
| Quigley (N) | 4,034 | ||
| Informal | 71 | ||
| Totals | 14,157 | 16,171 | 26,074 |
| Tamaki - | |||
| McGowan (S C) | 352 | ||
| Muldoon (N) | 8,728 | ||
| Smith (C) | 77 | ||
| Tizard (L) | 7,580 | ||
| Informal | 73 | ||
| Totals | 16,810 | 18,112 | 25,065 |
| Tauranga - | |||
| Goodfellow (L) | 3,881 | ||
| Walsh (N) | 9,120 | ||
| Young (S C) | 2,563 | ||
| Informal | 75 | ||
| Totals | 15,639 | 17,463 | 25,965 |
| Timaru - | |||
| Carr (L) | 7,617 | ||
| Isitt (S C) | 542 | ||
| Rae (P) | 90 | ||
| White (N) | 7,260 | ||
| Informal | 81 | ||
| Totals | 15,590 | 16,874 | 26,436 |
| Waikato - | |||
| Ingram (L) | 4,362 | ||
| Pemberton (S C) | 1,192 | ||
| Sim (N) | 7,403 | ||
| Informal | 64 | ||
| Totals | 13,021 | 14,751 | 25,838 |
| Waipa - | |||
| Bennett (S C) | 1,795 | ||
| Johnstone (N) | 8,544 | ||
| Reese (L) | 5,303 | ||
| Informal | 77 | ||
| Totals | 15,719 | 17,461 | 26,327 |
| Wairarapa - | |||
| Cooksley (N) | 7,887 | ||
| Crawford (S C) | 1,450 | ||
| Goldsmith (L) | 5,799 | ||
| Informal | 57 | ||
| Totals | 15,193 | 16,163 | 26,604 |
| Waitakere - | |||
| Mason (L) | 10,680 | ||
| Robertson (S C) | 1,239 | ||
| Wilcox (C) | 201 | ||
| Wilkinson (N) | 6,971 | ||
| Informal | 179 | ||
| Totals | 19,270 | 21,244 | 26,381 |
| Waitaki - | |||
| Barwood (S C) | 1,358 | ||
| Hayman (N) | 8,492 | ||
| McKay (L) | 6,520 | ||
| Informal | 69 | ||
| Totals | 16,439 | 17,289 | 26,726 |
| Waitemata - | |||
| Firth (N) | 7,992 | ||
| Jordan (S C) | 1,174 | ||
| King (L) | 9,241 | ||
| McLeod (C) | 139 | ||
| Informal | 52 | ||
| Totals | 18,598 | 20,258 | 26,395 |
| Waitomo - | |||
| Mason (S C) | 1,623 | ||
| McLaren (L) | 3,543 | ||
| Seath (N) | 7,494 | ||
| Informal | 56 | ||
| Totals | 12,716 | 14,425 | 26,843 |
| Wallace - | |||
| Harris (L) | 3,050 | ||
| Stack (S C) | 990 | ||
| Talboys (N) | 8,786 | ||
| Informal | 33 | ||
| Totals | 12,859 | 14,419 | 26,200 |
| Wanganui - | |||
| Crotty (N) | 5,911 | ||
| Marks (S C) | 3,132 | ||
| Spooner (L) | 6,071 | ||
| Informal | 81 | ||
| Totals | 15,195 | 16,241 | 25,078 |
| Wellington Central - | |||
| Kitts (L) | 6,992 | ||
| Norris (S C) | 526 | ||
| Riddiford (N) | 7,373 | ||
| Stanton (C) | 127 | ||
| Informal | 83 | ||
| Totals | 15,101 | 17,409 | 27,244 |
| Westland - | |||
| Blanchfield (L) | 8,153 | ||
| Fraser (S C) | 1,175 | ||
| Hogg (N) | 4,309 | ||
| Mitchell (C) | 208 | ||
| Informal | 62 | ||
| Totals | 13,907 | 14,996 | 26,780 |
| Maori Electorates | |||
| Eastern Maori - | |||
| Carter (I M M) | 191 | ||
| Omana (L) | 5,809 | ||
| Reedy (S C) | 2,784 | ||
| Vercoe (N) | 2,496 | ||
| Informal | 360 | ||
| Totals | 11,640 | 14,060 | |
| Northern Maori - | |||
| Clarke (S C) | 1,437 | ||
| Harrison (N) | 2,082 | ||
| Paikea (L) | 5,454 | ||
| Informal | 165 | ||
| Totals | 9,138 | 11,667 | |
| Southern Maori | |||
| Nia Nia (S C) | 474 | ||
| Tirikatene (L) | 5,132 | ||
| Tutaki (N) | 1,185 | ||
| Informal | 135 | ||
| Totals | 6,926 | 9,319 | |
| Western Maori - | |||
| Hurinui-Jones (N) | 2,029 | ||
| Rakena (K) | 378 | ||
| Ratana (L) | 6,695 | ||
| Tuwhangai (S C) | 874 | ||
| Informal | 193 | ||
| Totals | 10,169 | 13,421 | |
NATIONAL LICENSING POLLS — The licensing poll of 26 November 1960, held in conjunction with the parliamentary elections, was the eleventh at which the three issues — national continuance, State purchase and control, and national prohibition (without compensation) — were submitted to the electors. Official figures of the 1960 poll, together with those of the five preceding polls, were as follows.
| 1943 | 1946 | 1949 | 1954 | 1957 | 1960 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For national continuance | 529,386 | 542,681 | 660,573 | 672,754 | 723,059 | 765,952 |
| For State purchase and control | 123,701 | 202,664 | 135,982 | 164,380 | 160,483 | 138,644 |
| For national prohibition | 269,800 | 259,162 | 268,567 | 250,460 | 260,132 | 255,157 |
The percentage of votes recorded for State purchase and control was 13.4 of the total votes in 1943, 20.2 in 1946, 12.8 in 1949, 15.1 in 1954, 14.0 in 1957 and 11.95 in 1960. National continuance reached 63.4 per cent in 1935, since when it fell gradually to 54.0 per cent in 1946, recovered substantially at the expense largely of the State purchase and control vote to 62.0 per cent in 1949, was steady at 61.9 per cent in 1954, rose to 63.2 per cent in 1957 and to 66.04 in 1960. Votes cast in favour of national prohibition amounted to 47.3 per cent in 1925, but fell heavily at each of the next two polls, reaching 29.6 per cent in 1935. There was little variation in this percentage in 1938 and 1943, but further falls to 25.2 per cent, 23.0 per cent, 22.8 and 22.0 per cent were recorded in 1949, 1954, 1957, and 1960 respectively.
The voting results in each licensing district, and for the local restoration polls in 1960 are now given.
General Licensing Poll
| Electoral District | For National Continuance | For State Purchase and Control | For National Prohibition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ashburton | 9,400 | 1,398 | 3,687 |
| Auckland Central | 8,546 | 1,775 | 2,210 |
| Avon | 10,092 | 2,073 | 2,943 |
| Awarua | 9,055 | 868 | 3,677 |
| Bay of Plenty | 8,329 | 1,529 | 2,831 |
| Buller | 9,563 | 1,136 | 2,616 |
| Christchurch Central | 8,251 | 1,549 | 2,717 |
| Clutha | 8,453 | 1,012 | 4,101 |
| Dunedin Central | 9,515 | 1,847 | 3,436 |
| Eden | 9,652 | 1,935 | 4,094 |
| Egmont | 9,104 | 773 | 2,555 |
| Fendalton | 11,463 | 1,686 | 3,798 |
| Franklin | 9,545 | 1,546 | 3,695 |
| Gisborne | 10,431 | 1,528 | 3,320 |
| Grey Lynn | 8,644 | 2,039 | 2,855 |
| Hamilton | 9,190 | 1,719 | 3,907 |
| Hastings | 11,418 | 1,730 | 3,607 |
| Hauraki | 8,948 | 1,426 | 3,322 |
| Hawke's Bay | 9,263 | 1,126 | 2,276 |
| Heretaunga | 10,120 | 2,665 | 2,372 |
| Hobson | 8,642 | 1,525 | 3,501 |
| Hurunui | 10,215 | 1,252 | 3,493 |
| Hutt | 8,771 | 2,377 | 2,803 |
| Invercargill | 9,480 | 1,021 | 4,324 |
| Island Bay | 8,962 | 2,124 | 2,727 |
| Karori | 10,780 | 2,141 | 2,890 |
| Lyttelton | 10,728 | 2,141 | 3,555 |
| Manawatu | 9,678 | 1,272 | 3,317 |
| Manukau | 12,993 | 2,542 | 4,264 |
| Marlborough | 10,551 | 1,201 | 2,954 |
| Marsden | 9,532 | 1,882 | 3,661 |
| Miramar | 9,906 | 1,852 | 2,805 |
| Mornington | 9,043 | 2,003 | 3,522 |
| Mount Albert | 8,973 | 2,172 | 3,537 |
| Napier | 11,211 | 1,993 | 3,785 |
| Nelson | 10,507 | 1,581 | 4,313 |
| New Plymouth | 11,757 | 1,632 | 3,936 |
| North Dunedin | 8,569 | 2,005 | 3,548 |
| North Shore | 10,655 | 2,323 | 3,054 |
| Onehunga | 8,183 | 2,289 | 2,885 |
| Onslow | 11,555 | 2,660 | 3,194 |
| Otago Central | 8,009 | 1,146 | 2,429 |
| Otahuhu | 10,727 | 2,634 | 2,923 |
| Otaki | 11,354 | 2,124 | 3,916 |
| Pahiatua | 8,876 | 967 | 2,660 |
| Palmerston North | 10,581 | 1,558 | 3,665 |
| Patea | 9,228 | 975 | 2,303 |
| Petone | 9,984 | 2,761 | 2,752 |
| Piako | 8,629 | 1,100 | 3,375 |
| Ponsonby | 9,130 | 2,266 | 2,906 |
| Raglan | 8,701 | 1,755 | 2,678 |
| Rangitikei | 9,608 | 871 | 2,817 |
| Remuera | 10,062 | 1,514 | 3,293 |
| Riccarton | 10,612 | 1,848 | 3,094 |
| Rodney | 8,861 | 1,389 | 3,121 |
| Roskill | 9,885 | 2,092 | 3,487 |
| Rotorua | 11,253 | 2,443 | 2,836 |
| St. Albans | 10,265 | 1,822 | 3,856 |
| St. Kilda | 9,931 | 2,002 | 3,612 |
| Selwyn | 9,947 | 1,402 | 2,987 |
| Stratford | 9,584 | 744 | 2,437 |
| Sydenham | 8,979 | 1,796 | 3,230 |
| Tamaki | 11,092 | 2,281 | 3,221 |
| Tauranga | 9,984 | 1,595 | 3,884 |
| Timaru | 9,974 | 1,762 | 3,690 |
| Waikato | 8,622 | 1,378 | 2,856 |
| Waipa | 10,229 | 1,563 | 3,777 |
| Wairarapa | 10,022 | 1,536 | 3,449 |
| Waitakere | 12,620 | 2,641 | 3,677 |
| Waitaki | 10,163 | 2,034 | 4,049 |
| Waitemata | 11,615 | 2,918 | 3,487 |
| Waitomo | 9,104 | 1,188 | 2,286 |
| Wallace | 8,590 | 713 | 3,472 |
| Wanganui | 10,070 | 1,415 | 3,535 |
| Wellington Central | 10,394 | 1,995 | 2,422 |
| Westland | 10,413 | 1,274 | 2,093 |
| Eastern Maori | 6,187 | 2,291 | 2,487 |
| Northern Maori | 4,590 | 1,741 | 2,378 |
| Southern Maori | 3,767 | 1,603 | 1,273 |
| Western Maori | 4,637 | 2,159 | 2,657 |
| Totals | 765,952 | 138,644 | 255,157 |
Local Restoration Polls
| Licensing District | For Local Restoration of Licence | For Local No-licence | Number of Valid Votes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland Suburbs | 19,306 | 13,388 | 32,694 |
| Eden | 5,433 | 6,472 | 11,905 |
| Grey Lynn | 7,082 | 6,581 | 13,663 |
| Oamaru | 7,694 | 4,136 | 11,830 |
| Roskill | 11,574 | 13,433 | 25,007 |
| Wellington East | 6,897 | 6,805 | 13,702 |
| Wellington South | 5,262 | 4,156 | 9,418 |
| Wellington West | 6,812 | 7,311 | 14,123 |
| Totals | 70,060 | 62,282 | 132,342 |
Local restoration was carried in the Oamaru Licensing District.
LIQUOR LICENSING — The principal Act dealing with the sale of liquor is the Licensing Act 1908 and its amendments.
History — The earliest legislation relating to the sale of liquor in New Zealand was the Licensing Ordinance 1842. This required all persons selling liquor in quantities of less than 2 gallons to obtain a licence. It did not place any restrictions on the number of licences which might be granted, nor did it regulate the conduct of the trade generally. Under this Ordinance the hours during which liquor might be sold were from 6 in the morning until 10 at night on weekdays and from 1 to 7 in the afternoon on Sundays, with a proviso that Justices might grant an extension until midnight on working days.
The growth of the temperance and prohibition movements led to the passing of the Licensing Act 1881, which comprehensively regulated and controlled the liquor trade and is the source of many of the provisions of the present law. The Act created a system of licensing committees, which originally consisted of five members elected annually by ratepayers. The districts over which licensing committees had jurisdiction were small and fragmentary but they were extended by the Alcoholic Liquors Sale Control Act 1893 to coincide with parliamentary electoral boundaries. The same Act provided that the committees should consist of a Resident Magistrate as chairman and eight members (reduced to five in 1895) elected every three years by the electors of the district. Except for the substitution of Stipendiary Magistrates for Resident Magistrates, the constitution of licensing committees has remained unaltered up to the present.
In 1893 a system of local option was introduced. The electors of every licensing district were given the opportunity of voting periodically for the continuance, reduction, or abolution of licences in the district. In consequence of this many hotels lost their licences and a number of districts (the first being Clutha) carried “no licence”. The right to vote for reduction of licences was abolished in 1910 and the provisions relating to local option were repealed in 1918 and replaced by provisions for a periodical nation-wide vote on the issues of continuance, prohibition, and state purchase and control. Those areas which had carried no-licence were, however, to remain “dry” until a 60 per cent majority of the electors had voted for restoration of licences. Remaining districts with no-licence are Auckland Suburbs, Eden, Grey Lynn, Roskill, Wellington East, Wellington South, and Wellington West.
The most important developments in the law since 1920 have been the establishment in 1948 of the Licensing Control Commission and the introduction in certain former no-licence districts of a system of control through licensing trusts referred to later in this section.
The principal functions of the Licensing Control Commission are to authorise new publicans', tourist house, and wholesale licences, to deal with applications for the grant of club charters, to cancel unnecessary licences and to determine the compensation payable to their holders, to prescribe minimum standards of accommodation, amenities, and services, and generally to supervise the work of licensing committees. There is a right of appeal to the Supreme Court against any decision of the Commission cancelling licences on grounds that they are not needed, or determining appeals against a direction of a licensing committee to a licensee to rebuild, alter, or repair premises when the cost would be £5,000 or more. Where the Commission determines the amount of compensation payable on the cancellation or surrender of a licence, an appeal against that determination lies to the Land Valuation Court.
Principles of Licensing Law — The principles on which the licensing law of New Zealand rests are that no liquor may be sold without a licence, that apart from special cases (for instance, chartered clubs) liquor may not be sold for consumption on the premises unless accommodation for the travelling public is provided on the same premises, that the number of licences should be limited, and that there should be strict regulation of the conduct of the trade and of the provision of accommodation and services.
The following types of licence for the sale of liquor are authorised by law in New Zealand: publican's, accommodation, tourist house, packet, restaurant, New Zealand wine, works canteen, wholesale, wine reseller's, winemaker's, brewer's conditional. In addition, charters may be issued to certain clubs.
The publican's licence is the most important and numerous form of licence. It authorises the sale of liquor in any quantity for consumption on or off the premises. In return for the privilege of selling liquor the holder of a publican's licence must provide accommodation and amenities in accordance with the requirements of the Licensing Control Commission, with a minimum in boroughs of six rooms for guests.
The number of new publicans' licences which may be granted is limited by statute to a number equal to the total of:
The number of publicans' licences in force on the passing of the Licensing Amendment Act 1948, together with an additional 20;
The number granted in place of accommodation licences;
The number granted following the carrying of restoration in a no-licence district (including the King Country); and
One additional licence for every 10,000 increase in the population of New Zealand.
It should be made clear that the number of publicans' licences which may be authorised under these heads is in addition to the number of hotels existing in licensing trust districts.
Accommodation licences were granted in earlier times on the terms of keeping a road or bridge in repair or of providing accommodation or of performing some similar obligation. No new accommodation licences may be granted and this form of licence is not of significance at the present day.
Tourist house licences were first provided for in the Licensing Amendment Act 1948. They are authorised by the Licensing Control Commission and confer the right to sell liquor to guests staying or dining at the hotel for consumption on the premises.
Packet licences authorise the sale of liquor to passengers on ships.
A restaurant licence (first provided for by the 1960 amendment) authorises the licensee to sell and serve light wine, beer, and stout to persons dining at the restaurant for consumption with a meal. The licences are authorised by the Licensing Control Commission and their number may not exceed 10. The Commission may authorise dancing on restaurant premises if it is satisfied that the premises are not being used primarily for dancing and that the facilities are available only to people partaking of meals.
New Zealand wine licences authorise the sale of wine produced in New Zealand in quantities of not more than 2 gallons. Only three New Zealand wine licences are in operation and the law prohibits the grant of any further licences of this type.
A works canteen licence is a form of licence created in 1948. It authorises the sale of liquor for consumption on the premises at canteens in a public works camp. No works canteen licences have in fact been granted.
Wholesale licences authorise the sale of liquor in quantities of not less than 2 gallons to any one person at any one time. The holder of a wholesale licence is not required by law to, and in most cases does not in fact, confine his sales to the holders of other licences, and sales by wholesale licensees to the general public are extensive.
A wine reseller's licence authorises its holder to sell New Zealand wine for consumption off the premises in quantities of not less than 1 reputed quart.
Winemakers' licences are granted not by a licensing committee but by a Magistrate, and authorise the sale of New Zealand wine by producers in the same quantities as are permitted by a wine reseller's licence.
Brewers licences are not issued under the Licensing Act but under Customs legislation. A brewer's licence authorises the sale of beer, whether to the holders of licences or to the general public, in quantities of not less than 2 gallons. The licensing Control Commission has the power to grant new brewers' licences and, subject to appeal to the Supreme Court, to revoke existing ones.
Conditional licences authorise the sale of liquor at shows, races, and similar functions for any period not exceeding seven days. In the nature of things the number of conditional licences in force at any one time fluctuates considerably.
New Licences — The Licensing Control Commission determines after a public sitting whether a new publican's, tourist house, or wholesale licence should be authorised in any particular locality and (in the case of a publican's or tourist house licence) the minimum standards of accommodation and services which must be provided. There is provision for a poll of residents on the question whether a licence is desired in the locality, and if the majority of valid votes recorded at the poll is against a licence the Commission may not authorise one unless special circumstances exist.
In authorising any new licence the Commission fixes a fair price which a successful applicant for the licence must pay. Broadly speaking, the fair price represents the difference between the value of the proposed premises with a licence to sell liquor and without one. The amount received by way of fair price for new licences is paid into the Licensing Fund set up by the 1948 Amendment Act. Compensation for cancelled licences is paid out of this fund. The fund stood at £140,892 at 31 March 1960.
Once a licence has been authorised, the licensing committee having jurisdiction in respect of the locality calls for applications from persons who wish to establish premises on a site of their choosing which comply with the minimum standards laid down in the Commission's authorisation. The licensing committee determines between competing applicants for the licence, and its decision, in effect, fixes the exact site of the proposed premises. In the case of a publican's licence there is provision for 20 or more residents within a certain radius to object to the establishment of a hotel on the site, on the grounds that it is in the vicinity of a school, church, or hospital, or that the area is predominantly residential and a substantial number of residents object to a hotel there. This objection is heard by a Magistrate, who may uphold or dismiss it or direct a poll of residents.
Amending legislation in 1955 provides that if, following a special poll of residents which favours trust control, an application for a licence which has been authorised is made on behalf of a local licensing trust to be formed, the licence must, other things being equal, be granted to the proposed trust.
Licences either in force or authorised at 31 March 1960 comprised 1,107 publicans' and accommodation licences, 167 wholesale licences, and 21 tourist house licences. Licensed premises in the trust areas of Ashburton, Clutha, Geraldine, Invercargill, Masterton, Mataura, and Porirua are not included in these figures, as such areas are outside the jurisdiction of the Commission.
There were 48 permanent club charters and 116 renewable club charters in force at 31 March 1960.
Hours of Sale — In 1917 the Sale of Liquor Restriction Act provided for the closing of licensed premises, so far as the sale of liquor was concerned, on weekdays between the hours of 6 p.m. in the evening and 9 a.m. on the following morning, and all day on Sundays, Christmas Day, and Good Friday, except that wholesalers and brewers (also winemakers and wine resellers) might sell liquor between 7 a.m. and 9 a.m. on weekday mornings. This legislation was originally intended as a temporary wartime measure but was made permanent in 1918.
In 1949 a referendum was held pursuant to the provisions of the Licensing Amendment Act 1948 on the question of hours for the sale of liquor in hotel bars. The proposal for the retention of the existing hours was carried by a large majority, the vote in favour of the existing hours being 473,768 and the vote for the alternative proposal of a total of 9 hours between 10 a.m. and 10 p.m. being 153,854.
The Licensing Amendment Act 1955 removed the restrictions as to the hours during which holders of brewers' licences might sell and deliver to other licensed premises. The Licensing Amendment Act 1957 extended the hours during which holders of winemakers' licences might sell and deliver to other licensed premises to between 6 a.m. and 8 p.m.
The Licensing Amendment Act 1960 authorised hotels to serve liquor to guests and lodgers partaking of a meal for consumption with the meal up to 11.30 p.m. on any day and between 12 noon and 2.30 p.m. on Sunday, Christmas Day, and Good Friday. By the same Act the hours during which licensed restaurants may sell and serve liquor to diners were fixed as 12 noon to 2.30 p.m. and 6 p.m. to 11.30 p.m. on any day.
Licensing Trusts — The system of trust control in New Zealand is an alternative to the traditional means of controlling the sale of liquor through privately held licences supervised by licensing committees and since 1949 by the Licensing Control Commission. The system of licensing committees controlled by the Licensing Control Commission gives the public an indirect control over the conditions under which liquor is sold. In the case of trusts public control is direct, since the whole of the liquor trade in a trust district is conducted by the trust, which is elected by the residents and is responsible to them.
The first licensing trust in New Zealand was set up in 1944 following the carrying of restoration in the former Invercargill no-licence district. This trust was originally an appointed body but was made elective in 1950 to bring it into line with other licensing trusts.
Following the carrying of restoration in the Masterton no-licence district in 1946, the electors of that area were given the opportunity of recording their views as to whether they desired trust control. The district was divided into three areas, trust control being carried in the southern area (mainly comprising the borough of Masterton) and being defeated in the other two areas which are predominantly rural. Legislation providing for the constitution of the Masterton Licensing Trust to control the southern area was passed in 1947.
As a result of special licensing polls held on 9 March 1949 in the Ashburton and Geraldine areas, the restoration proposal was carried by the necessary majority in each case. A majority of the valid votes cast were also in favour of trust control and, by virtue of the Licensing Trusts Act 1949, trusts were established in these two districts.
The Licensing Trusts Act 1949 provides a general code for the taking of polls on the issue of trust control in former no-licence districts which have carried restoration, and for the constitution, functions, and powers of licensing trusts. An amendment in 1950 provided for the taking of polls in any area where the Licensing Control Commission has authorised a new licence to determine whether the majority of the residents wish that licence to be conducted by a local licensing trust. It may be mentioned that the powers of a local licensing trust operating an individual licence are more limited than those of a district licensing trust. The Licensing Act applies virtually in its entirety to a local licensing trust which, unlike district licensing trusts, is subject to supervision by the licensing committee and the Licensing Control Commission.
Following a vote in favour of trust control in the areas of Clutha and Mataura, provision was made in the Licensing Amendment Act 1955 for the division of districts into wards for the purpose of elections.
Pursuant to the provisions of the Licensing Amendment Act 1953, special polls were held in the King Country, Johnsonville, and Porirua areas in 1954 to determine whether liquor should be sold in those areas and if so whether its control should be in the hands of licensing trusts. In the King Country the necessary majority voted in favour of the sale of liquor and rejected the proposal for trust control; in Johnsonville the proposal for the sale of liquor was not carried; in Porirua the majority favoured the sale of liquor and the establishment of a trust.
The total number of district trusts in New Zealand is at present eight — Ashburton, Clutha, Geraldine, Invercargill, Masterton, Mataura, Oamaru, and Porirua. In addition, two local trusts at Cheviot in Canterbury and Mt. Wellington in the Auckland suburbs are operating hotels.
TIME-SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS — The following article on the New Zealand time-service arrangements was prepared by the New Zealand Time Service, Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
One uniform time is kept throughout New Zealand. The New Zealand Gazette of 31 October 1868 contained a Government announcement to the effect that the time corresponding to longitude 172° 30' east of Greenwich (exactly 11 1/2 hours in advance of Greenwich time) was to be adopted as the New Zealand Mean Time throughout the colony.
This New Zealand Mean Time, 11 h 30 min. in advance of Greenwich Mean Time (G.M.T.), was observed continuously up to 1927, when on 6 November clocks were advanced 1 hour until 4 March 1928. Summer Time, with clocks advanced only 30 minutes (to 12 h ahead of G.M.T.), became standard practice in the summer months under the Summer Time Act 1929.
The Daylight Saving Emergency Regulations of 1941 provided for the continuance of Summer Time throughout that year, and its continued observance during subsequent war years was provided for by regulations made annually.
By the Standard Time Act of 1945 the time of the meridian 180° east of Greenwich (12 h in advance of G.M.T.) was adopted as the Standard Time for New Zealand. Thus, what was formerly known as “Summer Time” became “New Zealand Standard Time” as from 1 January 1946. The times stated in this article are New Zealand Standard Time, unless otherwise stated.
The time throughout New Zealand is controlled by the New Zealand Time Service, Wellington. The Observatory signal clock is kept as correct as possible by means of astronomical observations, and by comparison with radio time signals from observatories in other parts of the world.
The Observatory provides the following time service:
These signals are transmitted between 10 h 55 min and 11 h 00 min a.m. daily, and are in accordance with the modified ONOGO system. The procedure is as follows:
At 10 h 55 min 30 sec the “Attention” call (—. —. —), followed by the Observatory call sign ZMO (— —.. — — — — —).
From 10 h 56 min 05 sec to 10 h 56 min 50 sec the letter O (— — —), repeated every 10 seconds, except that the third series from 25 sec to 30 sec consists of a single dash prolonged for five seconds.
From 10 h 57 min 00 sec to 10 h 57 min 49 sec the letter X (—,. —), repeated every five seconds.
From 10 h 57 min 55 sec to 10 h 58 min 00 sec, first time signal, consisting of six dots at intervals of one second.
From 10 h 58 min 08 sec to 10 h 58 min 50 sec the letter N (—.), repeated every 10 seconds.
From 10 h 58 min 55 sec to 10 h 59 min 00 sec, second time signal, consisting of six dots at intervals of one second.
From 10 h 59 min 06 sec to 10 h 59 min 50 sec the letter G (— —.), repeated every 10 seconds.
From 10 h 59 min 55 sec to 11 h 00 min 00 sec, third time signal, consisting of six dots at intervals of one second.
The series of six dots which constitute the actual time signals are transmitted directly from the Observatory signal clock, which is seldom more than one-tenth of a second in error. The remaining signals are for tuning and identification purposes only, and should not be used as precise time signals. Corrections to the time signals can be obtained on application to the Seismological Observatory.
Time signals from the Observatory are transmitted as follows:
| New Zealand | Standard Time |
|---|---|
| 5.00 a.m. | 2YA only (daily except Sundays) |
| 6.00 a.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily except Sundays) |
| 7.00 a.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
| 8.00 a.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
| 9.00 a.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
| 10.58 a.m. | 2YA only (daily) |
| 10.59 a.m. | |
| 11.00 a.m. | |
| 12.30 p.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
| 4.00 p.m. | 2YA only (daily) |
| 6.30 p.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
| 7.00 p.m. | 2YA only (daily) |
| 9.00 p.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily except Sundays) |
| 10.00 p.m. | 2YA only (daily) |
| 11.00 p.m. | All YA and YZ stations (daily) |
Each time signal consists of six dots, separated by intervals of one second, the last dot being the exact minute.
The Observatory sends time signals by telegraph to the General Post Office and the Railways Department, Wellington, at 9.00 a.m. daily. This signal is transmitted to all telegraph offices in New Zealand and to all railway stations in the North Island.
The Government Buildings clock (Wellington) is checked at 9.00 a.m. daily by means of a special circuit between the clock and the Observatory. The error of this clock is usually less than 15 seconds.
PUBLIC HOLIDAYS — These are listed below for 1961 and 1962:
| 1961 | 1962 | |
|---|---|---|
| *Date of Queen's birthday, 21 April 1926. | ||
| New Year's Day | 1 January | 1 January |
| Good Friday | 31 March | 20 April |
| Easter Monday | 3 April | 23 April |
| Anzac Day | 25 April | 25 April |
| Queen's Birthday* (observance) | 5 June | 4 June |
| Labour Day | 23 October | 22 October |
| Christmas Day | 25 December | 25 December |
| Boxing Day | 26 December | 26 December |
In addition to the above, there is in each provincial district a holiday for the provincial anniversary. The actual anniversary days are as follows: Auckland, 29 January; Canterbury, 16 December; Hawke's Bay, 1 November; Marlborough, 1 November; Nelson, 1 February; Otago and Southland, 23 March; Taranaki, 31 March; Wellington, 22 January; and Westland, 1 December.
When Anniversary Day falls on Friday or later, the holiday is observed on the next Monday; if earlier, it is observed on the preceding Monday. In some cases the holiday is taken on the local show day or some other day.
Table of Contents
His Excellency the Right Hon. Viscount Cobham, G.C.M.G., T.D.
Official Secretary — D. C. Williams, Esq.
Comptroller — Major I. M. Erskine, Grenadier Guards.
Aides-de-Camp — Captain D. H. Blundell-Hollinshead-Blundell, Grenadier Guards.
Lieutenant H. Y. La R. Beverley, Royal Marines.
(His Excellency assumed office on 5 September 1957)
Details of previous vice-regal representatives up to 1930 were listed in the 1931 issue of the Yearbook (pp. 59–60). Governors-General since 1930 are listed below.
| Assumed Office | Retired | |
|---|---|---|
| The Right Hon. Charles Bathurst, Viscount Bledisloe, P.C., G.C.M.G., K.B.E., M.A. (OXON.) | 19 Mar 1930 | 15 Mar 1935 |
| The Right Hon. George Vere Arundell, Viscount Galway, G.C.M.G., D.S.O., O.B.E. | 12 Apr 1935 | 3 Feb 1941 |
| Marshall of the Royal Air Force the Right Hon. Cyril Louis Norton, Baron Newall, G.C.B., O.M., G.C.M.G., C.B.E., A.M. | 22 Feb 1941 | 19 Apr 1946 |
| Lieutenant-General the Right Hon. Bernard Cyril, Baron Freyberg, V.C., G.C.M.G., K.C.B., K.B.E., D.S.O. | 17 Jun 1946 | 15 Aug 1952 |
| Lieutenant-General the Right Hon. Charles Willoughby Moke, Baron Norrie, G.C.M.G., G.C.V.O., C.B., D.S.O., M.C. | 2 Dec 1952 | 25 Jul 1957 |
SINCE THE ESTABLISHMENT OF RESPONSIBLE GOVERNMENT IN NEW ZEALAND IN 1856
| Name of Ministry | Name of Premier | Assumed Office | Retired |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Bell-Sewell | Henry Sewell | 7 May 1856 | 20 May 1856 |
| 2. Fox | William Fox | 20 May 1856 | 2 Jun 1856 |
| 3. Stafford | Edward William Stafford | 2 Jun 1856 | 12 Jul 1861 |
| 4. Fox | William Fox | 12 Jul 1861 | 6 Aug 1862 |
| 5. Domett | Alfred Domett | 6 Aug 1862 | 30 Oct 1863 |
| 6. Whitaker-Fox | Frederick Whitaker | 30 Oct 1863 | 24 Nov 1864 |
| 7. Weld | Frederick Aloysius Weld | 24 Nov 1864 | 16 Oct 1865 |
| 8. Stafford | Edward William Stafford | 16 Oct 1865 | 28 Jun 1869 |
| 9. Fox | William Fox | 28 Jun 1869 | 10 Sep 1872 |
| 10. Stafford | Edward William Stafford | 10 Sep 1872 | 11 Oct 1872 |
| 11. Waterhouse | George Marsden Waterhouse | 11 Oct 1872 | 3 Mar 1873 |
| 12. Fox | William Fox | 3 Mar 1873 | 8 Apr 1873 |
| 13. Vogel | Julius Vogel, C.M.G. | 8 Apr 1873 | 6 Jul 1875 |
| 14. Pollen | Daniel Pollen, M.L.C. | 6 Jul 1875 | 15 Feb 1876 |
| 15. Vogel | Sir Julius Vogel, K.C.M.G. | 15 Feb 1876 | 1 Sep 1876 |
| 16. Atkinson | Harry Albert Atkinson | 1 Sep 1876 | 13 Sep 1876 |
| 17. Atkinson (reconstituted) | Harry Albert Atkinson | 13 Sep 1876 | 13 Oct 1877 |
| 18. Grey | Sir George Grey, K.C.B. | 15 Oct 1877 | 8 Oct 1879 |
| 19. Hall | John Hall | 8 Oct 1879 | 21 Apr 1882 |
| 20. Whitaker | Frederick Whitaker, M.L.C. | 21 Apr 1882 | 25 Sep 1883 |
| 21. Atkinson | Harry Albert Atkinson | 25 Sep 1883 | 16 Aug 1884 |
| 22. Stout-Vogel | Robert Stout | 16 Aug 1884 | 28 Aug 1884 |
| 23. Atkinson | Harry Albert Atkinson | 28 Aug 1884 | 3 Sep 1884 |
| 24. Stout-Vogel | Sir Robert Stout, K.C.M.G. | 3 Sep 1884 | 8 Oct 1887 |
| 25. Atkinson | Sir Harry Albert Atkinson, K.C.M.G. | 8 Oct 1887 | 24 Jan 1891 |
| 26. Ballance | John Ballance | 24 Jan 1891 | 1 May 1893 |
| 27. Seddon | Right Hon. Richard John Seddon | 1 May 1893 | 21 Jun 1906 |
| 28. Hall-Jones | William Hall-Jones | 21 Jun 1906 | 6 Aug 1906 |
| 29. Ward | Right Hon. Sir Joseph George Ward, BART., K.C.M.G. | 6 Aug 1906 | 28 Mar 1912 |
| 30. Mackenzie | Thomas Mackenzie | 28 Mar 1912 | 10 Jul 1912 |
| 31. Massey | Right Hon. William Ferguson Massey | 10 Jul 1912 | 12 Aug 1915 |
| 32. National | Right Hon. William Ferguson Massey | 12 Aug 1915 | 25 Aug 1919 |
| 33. Massey | Right Hon. William Ferguson Massey | 25 Aug 1919 | 14 May 1925 |
| 34. Bell | Hon. Sir Francis Henry Dillon Bell, G.C.M.G., K.C. | 14 May 1925 | 30 May 1925 |
| 35. Coates | Right Hon. Joseph Gordon Coates, M.C. | 30 May 1925 | 10 Dec 1928 |
| 36. Ward | Right Hon. Sir Joseph George Ward, BART., G.C.M.G. | 10 Dec 1928 | 28 May 1930 |
| 37. Forbes | Right Hon. George William Forbes | 28 May 1930 | 22 Sep 1931 |
| 38. Coalition | Right Hon. George William Forbes | 22 Sep 1931 | 6 Dec 1935 |
| 39. Savage | Right Hon. Michael Joseph Savage | 6 Dec 1935 | 1 Apr 1940 |
| 40. Fraser | Hon. Peter Fraser | 1 Apr 1940 | 30 Apr 1940 |
| 41. Fraser | Right Hon. Peter Fraser, C.H. | 30 Apr 1940 | 13 Dec 1949 |
| 42. Holland | Right Hon. Sir Sidney George Holland, G.C.B., C.H. | 13 Dec 1949 | 26 Sep 1957 |
| 43. Holyoake | Right Hon. Keith Jacka Holyoake | 26 Sep 1957 | 12 Dec 1957 |
| 44. Nash | Right Hon. Walter Nash, C.H. | 12 Dec 1957 | 12 Dec 1960 |
| 45. Holyoake | Right Hon. Keith Jacka Holyoake | 12 Dec 1960 |
Table of Contents
Right Hon. K. J. HOLYOAKE, Prime Minister, Minister of External Affairs, Minister in Charge of the Legislative Department, Minister in Charge of the Audit Department.
Hon. J. R. MARSHALL, Deputy Prime Minister, Minister of Industries and Commerce, Minister of Customs, Minister of Overseas Trade.
Hon. J. R. HANAN, Attorney-General, Minister of Justice, Minister of Maori Affairs, Minister in Charge of the Electoral Department.
Hon. J. K. McALPINE, Minister of Transport, Minister of Railways, Minister in Charge of Civil Aviation.
Hon. T. P. SHAND, Minister of Labour, Minister of Immigration, Minister of Mines, Minister in Charge of Publicity and Information.
Hon. W. S. GOOSMAN, Minister of Works, Minister of Electricity.
Hon. H. R. LAKE, Minister of Finance, Minister in Charge of the Inland Revenue Department, Minister in Charge of the Department of Statistics, Minister in Charge of the National Provident Fund, Minister in Charge of the Government Superannuation Fund, Minister in Charge of Friendly Societies.
Hon. D. J. EYRE, Minister of Defence, Minister in Charge of Police, Minister in Charge of Tourist and Health Resorts.
Hon. R. G. GERARD, Minister of Lands, Minister of Forests, Minister of Marine, Minister in Charge of the Valuation Department.
Hon. F. L. A. GöTZ, Minister of Internal Affairs, Minister of Civil Defence, Minister of Island Territories.
Hon. J. RAE, Minister of Housing, Minister in Charge of the State Advances Corporation, Minister in Charge of the Public Trust Office, Minister in Charge of the Government Life Insurance Office, Minister in Charge of the Government Printing and Stationery Department.
Hon. W. B. TENNENT, Minister of Education, Minister in Charge of Scientific and Industrial Research.
Hon. T. L. HAYMAN, Minister of Agriculture.
Hon. N. L. SHELTON, Minister of Health, Minister of Social Security, Minister for e Welfare of Women and Children, Minister in Charge of the Child Welfare Division.
Hon. A. E. KINSELLA, Postmaster-General, Minister of Broadcasting, Minister in Charge of War Pensions, Minister in Charge of Rehabilitation, Minister in Charge of the State Fire Insurance Office, Minister in Charge of the Earthquake and War Damage Commission.
Clerk of the Executive Council, T. J. Sherrard, O.B.E., M.S.M., J.P.
Parliamentary Under-secretaries —
D. C. Seath (to Minister of Finance).
B. E. Talboys (to Minister of Industries and Commerce).
Prime Minister — Rt. Hon. K. J. Holyoake.
Leader of the Opposition — Rt. Hon. W. Nash, C.H.
Speaker — Hon. R. M. Algie. Chairman of Committees — R. E. Jack.
Clerk of the House — H. N. Dollimore, LL.B.
| Name | Electoral District |
|---|---|
*Government Member. †Elected 10 June 1961, following the death of the Hon. W. H. Gillespie, Minister of Agriculture, on 23 April 1961. | |
| For European Electorates | |
| Adams-Schneider, L. R.* | Hamilton |
| Aderman, E. P.* | N. Plymouth |
| Algie, Hon. R. M.* | Remuera |
| Allen, A. E.* | Franklin |
| Allen, P. B.* | Bay of Plenty |
| Bailey, R. L. | Heretaunga |
| Blanchfield, P. | Westland |
| Brown, W. H.* | Palmerston |
| North | |
| Carr, Rev. Clyde | Timaru |
| Carter, D.J.* | Raglan |
| Connelly, M. A. | Riccarton |
| Connolly, Hon. P. G., D.S.C., V.R.D. | Dunedin |
| Central | |
| Cooksley, B. V., M.M.*- | Wairarapa |
| Deas, J. M. | Otahuhu |
| Douglas, N. V. | Auckland |
| Central | |
| Edwards, J. G. | Napier |
| Eyre, Hon. D. J.* | North Shore |
| Faulkner, A. J. | Roskill |
| Fox. Hon. W. A. | Miramar |
| Fraser, W. A. | St. Kilda |
| Freer, W. W. | Mount Albert |
| George, J. H.* | Central Otago |
| Gerard, Hon. R. G.* | Ashburton |
| Goosman, Hon. W. S.* | Piako |
| Gordon, J. B.* | Clutha |
| Gotz, Hon. F. L. A.* | Manukau |
| Grieve, G. G.* | Awarua |
| Hackett, Hon. F. | Grey Lynn |
| Hanan, Hon. J. R.* | Invercargill |
| Harker, C G. E.* | Hawke's Bay |
| Hayman, Hon. T. L.* | Waitaki |
| Holyoake, Right Hon. K. J.* | Pahiatua |
| Howard, Hon. Miss M. B. | Sydenham |
| Hudson, W. A. | Mornington |
| Jack, R. E.* | Patea |
| Johnstone, H.* | Waipa |
| King, N.J. | Waitemata |
| Kinsella, Hon. A. E.* | Hauraki |
| Kirk, N. E. | Lyttelton |
| Lake, Hon. H. R.* | Fendalton |
| Lapwood, H. R.* | Rotorua |
| McAlpine, Hon. J. K.* | Selwyn |
| McCready, A.* | Otaki |
| Macdonald, R. | Ponsonby |
| Macfarlane, Hon. R. M., C.M.G. | Christchurch |
| Central | |
| MacIntyre, D.* | Hastings |
| McKay, D. N.* | Marsden |
| McMillan, Mrs E. E. | North |
| Dunedin | |
| Marshall, Hon. J. R.* | Karori |
| Mason, Hon. H. G. R., Q.C. | Waitakere |
| Mathison, Hon. J. | Avon |
| May, H. L. J. | Onslow |
| Moohan, Hon. M. | Petone |
| Muldoon, R. D.* | Tamaki |
| Murray, T. T., M.C., M.M.* | Stratford |
| Nash, Right Hon. W., C.H. | Hutt |
| Nordmeyer, Hon. A. H. | Island Bay |
| Pickering, H. E. L.*† | Hurunui |
| Rae, Hon. J.* | Eden |
| Riddiford, D. J.* | Wellington |
| Central | |
| Scott, W.J. * | Rodney |
| Seath, D.C.* | Waitomo |
| Shand, Hon. T. P.* | Marlborough |
| Sheat, W. A.* | Egmont |
| Shelton, Hon. N. L.* | Rangitikei |
| Sim, G. F.* | Waikato |
| Skinner, Hon. C. F., M.C. | Buller |
| Sloane, L. F.* | Hobson |
| Spooner, G. A. | Wanganui |
| Talboys, B. E.* | Wallace |
| Tennent, Hon. W. B.* | Manawatu |
| Tombleson, Mrs E. I.* | Gisborne |
| Walker, H. J.* | St. Albans |
| Walsh, G. A.* | Tauranga |
| Watt, Hon. H. | Onehunga |
| Whitehead, S. A. | Nelson |
| For Maori Electorates | |
| Omana, T. | Eastern Maori |
| Paikea, T. P. | Northern |
| Maori | |
| Ratana, Mrs I. M. | Western |
| Maori | |
| Tirikatene, Hon. Sir Eruera, K.C.M.G. | Southern |
| Maori | |
(For earlier Parliaments and sessions refer to pp 59–60 of the 1930, p 986 of the 1940, and p 1184 of the 1960 issues of the Yearbook.)
| Parliament | Date of Opening of Session | Date of Ending of Session |
|---|---|---|
| Twenty-ninth | 27 June 1950 | 1 December 1950 |
| 26 June 1951 | 13 July 1951 | |
| Thirtieth | 25 September 1951 | 6 December 1951 |
| 25 June 1952 | 24 October 1952 | |
| 8 April 1953 | 27 November 1953 | |
| 12 January 1954 | 13 January 1954 | |
| 22 June 1954 | 1 October 1954 | |
| Thirty-first | 22 March 1955 | 28 October 1955 |
| 4 April 1956 | 26 October 1956 | |
| 11 June 1957 | 25 October 1957 | |
| Thirty-second | 21 January 1958 | 31 January 1958 |
| 10 June 1958 | 3 October 1958 | |
| 24 June 1959 | 23 October 1959 | |
| 22 June 1960 | 28 October 1960 | |
| Thirty-third | 21 June 1961 | - |
LIST OF LEGISLATION, 1960 — During the parliamentary session of 1960, which commenced on 22 June, and which ended on 28 October, the General Assembly passed 123 public Acts, 15 local Acts, and 4 private Acts. The following is a list of public, local, and private Acts passed during the session, suffixed in each case as appropriate by “N.A.” — new Act, “A.A.” — amending Act, “C.A.” — consolidation Act, “C.A.A.” — consolidating and amending Act, or “V.C.A.” — validating and confirming Act.
PUBLIC ACTS
| Acts Interpretation Amendment (A.A.) |
| Administration Amendment (A.A.) |
| Agriculture (Emergency Regulations Confirmation) (V.C.A.) |
| Air Services Licensing Amendment (A.A.) |
| Amusement Tax (C.A.A.) |
| Animals Protection (N.A.) |
| Antarctica (N.A.) |
| Apple and Pear Marketing Amendment (A.A.) |
| Appropriation (N.A.) |
| Bankruptcy Amendment (A.A.) |
| Bauxite Amendment (A.A.) |
| Broadcasting Amendment (A.A.) |
| Cheques (A.A.) |
| Child Welfare Amendment (A.A.) |
| Chiropractors (N.A.) |
| Cinematograph Films Amendment (A.A.) |
| Civil Aviation Amendment (A.A.) |
| Coal Mines Amendment (A.A.) |
| Companies Amendment (A.A.) |
| Cook Islands Amendment (A.A.) |
| Cooperative Freezing Companies (N.A.) |
| Counties Amendment (A.A.) |
| Criminal Justice Amendment (A.A.) |
| Customs Acts Amendment (A.A.) |
| Dairy Products Marketing Commission Amendment (A.A.) |
| Dangerous Drugs Amendment (A.A.) |
| Disabled Persons Employment Promotion (N.A.) |
| Education Amendment (No. 2) (A.A.) |
| Education Lands Amendment (A.A.) |
| Electoral Amendment (A.A.) |
| Electrical Supply Authorities Association Amendment (A.A.) |
| Electricians Amendment (A.A.) |
| Electric Power Boards Amendment (A.A.) |
| Emergency Regulations Amendment (A.A.) |
| Estate and Gift Duties Amendment (A.A.) |
| Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Amendment (A.A.) |
| Fertilisers (C.A.A.) |
| Finance (N.A.) |
| Forests Amendment (A.A.) |
| Gaming Amendment (A.A.) |
| Gas Industry Amendment (A.A.) |
| Government Service Equal Pay (N.A.) |
| Health Amendment (A.A.) |
| Hydatids Amendment (A.A.) |
| Immigration Restriction Amendment (A.A.) |
| Imprest Supply (N.A.) |
| Imprest Supply (No. 2) (N.A.) |
| Imprest Supply (No. 3) (N.A.) |
| Imprest Supply (No. 4) (N.A.) |
| Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Amendment (A.A.) |
| Inland Revenue Department Amendment (A.A.) |
| Joint Family Homes Amendment (A.A.) |
| Judicature Amendment (A.A.) |
| Juries Amendment (A.A.) |
| King George the Fifth Memorial Children's Health Camps Amendment (A.A.) |
| Land Amendment (A.A.) |
| Land and Income Tax Amendment (A.A.) |
| Land and Income Tax (Annual) (N.A.) |
| Land Transfer Amendment (A.A.) |
| Land Valuation Court Amendment (A.A.) |
| Licensing Amendment (A.A.) |
| Local Authorities Empowering (Aviation Encouragement) Amendment (A.A.) |
| Local Elections and Polls Amendment (A.A.) |
| Local Legislation (N.A.) |
| Magistrates' Courts Amendment (A.A.) |
| Manapouri - Te Anau Development (V.A.) |
| Maori Purposes (A.A.) |
| Meat Export Control Amendment (A.A.) |
| Mining Amendment (A.A.) |
| Municipal Corporations Amendment (A.A.) |
| Municipal Insurance (N.A.) |
| Napier High School Amendment (A.A.) |
| National Expenditure Adjustment Amendment (A.A.) |
| National Provident Fund Amendment (A.A.) |
| National Roads Amendment (A.A.) |
| National Savings Amendment (A.A.) |
| Nelson Railway Authorisation (N.A.) |
| New Zealand Army Amendment (A.A.) |
| New Zealand National Airways Amendment (A.A.) |
| New Zealand University Amendment (A.A.) |
| Noxious Weeds Amendment (A.A.) |
| Nurses and Midwives Amendment (A.A.) |
| Patriotic and Canteen Funds Amendment (A.A.) |
| Poisons (C.A.A.) |
| Police Offences Amendment (A.A.) |
| Police Offences Amendment (No. 2) (A.A.) |
| Political Disabilities Removal (C.A.A.) |
| Post Office Amendment (A.A.) |
| Potato Growing Industry Amendment (A.A.) |
| Primary Products Marketing Regulations Confirmation (V.C.A.) |
| Public Revenues Amendment (A.A.) |
| Public Safety Conservation Amendment (A.A.) |
| Public Service Amendment (A.A.) |
| Public Works Amendment (A.A.) |
| Rabbits Amendment (A.A.) |
| Rangiora High School Amendment (A.A.) |
| Rating Amendment (A.A.) |
| Republic of Ghana (N.A.) |
| Reserve Bank of New Zealand Amendment (A.A.) |
| Reserves and Domains Amendment (A.A.) |
| Reserves and Other Lands Disposal (N.A.) |
| Royal New Zealand Air Force Amendment (A.A.) |
| Servants' Registry Offices Amendment (A.A.) |
| Social Security Amendment (A.A.) |
| Soil Conservation and Rivers Control Amendment (A.A.) |
| Stamp Duties Amendment (A.A.) |
| State Supply of Electrical Energy Amendment (A.A.) |
| Stock Amendment (A.A.) |
| Stock Remedies Amendment (A.A.) |
| Superannuation Amendment (A.A.) |
| Surveyors Amendment (A.A.) |
| Thames Boys' and Girls' High School Amendment (A.A.) |
| Transport Amendment (A.A.) |
| Trustee Amendment (A.A.) |
| Trustee Companies (N.A.) |
| Unit Trusts (N.A.) |
| University Grants Committee (N.A.) |
| Vegetables Levy Amendment (A.A.) |
| Waikato Valley Authority Amendment (A.A.) |
| Waitangi Day (N.A.) |
| War Pensions Amendment (A.A.) |
| Wills Amendment (A.A.) |
| Workers' Compensation Amendment (A.A.) |
LOCAL ACTS
| Auckland Harbour Board (Lynfield Development) Loan and Empowering (N.A.) |
| Auckland Metropolitan Drainage (N.A.) |
| Auckland Regional Authority Establishment (N.A.) |
| Auckland Transport Board Amendment (A.A.) |
| Awatere County Empowering (N.A.) |
| Christchurch District Drainage Amendment (A.A.) |
| Christchurch Tramway District Amendment (A.A.) |
| Dunedin City Empowering (N.A.) |
| Marlborough Harbour Amendment (A.A.) |
| Otago Harbour Board Empowering (N.A.) |
| Southland Harbour Board Empowering (N.A.) |
| Tamaki River Reclamation (N.A.) |
| Taranaki Harbour Board Empowering (N.A.) |
| Te Kauwhata Town Council Empowering (N.A.) |
| Whangarei Harbour Board Empowering (N.A.) |
PRIVATE ACTS
| Bryant House Trust Board Enabling (N.A.) |
| Church of England Trusts Amendment (A.A.) |
| University of Hawke's Bay Trust (N.A.) |
| Wanganui Orphanage Trust Extension (N.A.) |
Judges of the Court of Appeal and Supreme Court —
Chief Justice: Right Hon. Sir Harold Barrowclough, K.C.M.G., C.B., D.S.O., M.C., E.D.
Court of Appeal: Hon. Sir Kenneth Gresson, K.B.E., President; Hon. Sir Alfred North; Hon. Sir Timothy Cleary.
Supreme Court, Puisne Judges: Hon. Sir Douglas Hutchison; Hon. A. K. Turner; Hon. G. I. McGregor; Hon. T. E. Henry; Hon. T. A. Gresson; Hon. T. P. McCarthy; Hon. A. L. Haslam; Hon. R. Hardie Boys; Hon. I. H. Macarthur; Hon. C. P. Richmond; Hon. W. E. Leicester.
Judges of the Court of Arbitration — Hon. Sir Arthur Tyndall, K.B., C.M.G.; W. F. Stilwell.
Judges of Compensation Court — D. J. Dalglish; K. G. Archer.
Judge of Land Valuation Court — K. G. Archer.
Since the preceding issue of the Yearbook the following honours have been conferred by Her Majesty the Queen for services rendered in connection with New Zealand:
Knight Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (K.B.E.) —
Mr Guy Richardson Powles, C.M.G.
Knight Bachelor —
The Hon. Francis Boyd Adams.
Companion of the Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George (C.M.G.) —
Dr L. C. L. Averill, M.C.; Mr H. L. Bockett.
Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (C.B.E.)—
Mr J. Andrew; Mr K. N. Buttle; Mr G. E. Turney.
Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (O.B.E.) —
Mr N. R. Bain; Mr J. Cumming; Professor E. Gregory; Mr C. W. F. Hamilton; Mr J. McL. Hogben; Mr C. H. R. Jepsen; Mr G. Nevill; Mr M. R. Jones; Mr S. I. Russell; Mr A. H. Ward.
Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (M.B.E.) —
Mrs R. O. Chadfield; Mr W. Clayton; Mr W. Cole; Miss E. H. Elliott; Mr F. S. Grayling; Mr M. G. Halberg; Mr W. P. Hartstonge; Mr J. T. Head; Mr N. B. Hunt; Rev. N. Kukutai; Miss M. E. McLean; Miss C. J. Ovens; Mrs J. E. Phipps; Mr P. A. P. Pomau; Mr R. J. Runciman; Mr H. W. Smith; Mr G. Smith; Mr E. R. Spriggs; Mr H. T. Williams; Miss G. M. Wilson.
British Empire Medal (B.E.M.) —
Constable J. D. Cleeve; Mr D. Smith; Sergeant Tohovaka; Detective Senior Sergeant G. C. Urquhart.
Queen's Police Medal, for Distinguished Service —
Chief Superintendent F. J. Brady.
Queen's Fire Service Medal, for Distinguished Service —
Chief Fire Officer H. J. Hayward; Deputy Chief Fire Officer G. A. MacKenzie.
Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (C.B.E.) —
Brigadier F. L. Hutter, E.D., Q.H.S.; Air Commodore T. F. Gill, D.S.O.
Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (O.B.E.) —
Lieutenant-Colonel H. McK. Reid; Lieutenant-Colonel P. J. Oliver, E.D.; Wing Commander J. Hardy.
Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (M.B.E.) —
Temporary Lieutenant Commander (SP) F. J. Glanville; Captain (temporary Major) D. H. McLeod, E.D.; Captain M. H. Moore; Flight Lieutenant H. C. O'Loughlin; Lieutenant and Quartermaster H. Williamson; Warrant Officer (W) C. F. Bryers; Warrant Officer Second Class J. T. Dawson.
Air Force Cross (A.F.C.) —
Flight Lieutenant A. R. Campbell; Flight Lieutenant W. J. Cranfield; Flight Lieutenant, J. C. Evison.
Air Force Medal (A.F.M.) —
Flight Sergeant P. Antwis.
British Empire Medal (B.E.M.) —
Staff Sergeant (temporary Warrant Officer Second Class) I. McD. Russell; Staff Sergeant (temporary Warrant Officer Second Class) R. M. Urquhart; Chief Petty Officer J. Barker; Chief Ordnance Artificer S. Harris; Chief Engineering Mechanic T. A. Hardy; Chief Wren M. M. McCambridge; Staff Sergeant F. J. Kinley; Flight Sergeant J. V. W. Thomas; Sergeant P. Crowther; Sergeant G. G. S. Harvey; Corporal J. W. Carter.
Knight Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (K.B.E.) —
Mr Alfred Hayward, C.B.E.
Knight Bachelor —
Mr James Lawrence Hay, O.B.E.; Mr Roy Hunter Stevenson, M.B.E.
Companion of the Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George (C.M.G.) —
Mr F. H. M. Hanson, D.S.O., O.B.E., M.M., E.D.; Mr B. E. Keiller.
Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (C.B.E.) —
Mr G. B. Baker, M.B.E., D.C.M., M.M.; Mr G. P. Proctor; Mr F. F. Reid; Mr W. A. Whitlock.
Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (O.B.E.)—
Mr J. D. Aitchison; Mr M. S. Galloway, M.C.; Mr J. Houston; Mr Pei Te Hurinui Jones; Captain W. G. Kelsey; Mr M. R. Lawson; Mr R. W. McCredie; Mr H. McD. Scott; Mr J. Turnbull; Mr D. W. W. Williams; Mr P. M. E. Williams.
Companion of the Imperial Service Order (I.S.O.) —
Dr J. F. Filmer; Mr R. E. Kemp.
Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (M.B.E.) —
Miss M. M. Bain; Miss L. E. Cook; Mrs H. M. Downer; Mr E. Edwards; Brigadier H. C. Goffin (Salvation Army); Detective Chief Inspector J. J. Halcrow; Mr H. G. Hill; Mr B. Hundelby; Mrs K. G. Hurd-Wood; Mr C. W. S. Keinan; Mr C. Lassen; Rev. P. H. Leonard; Mr J. W. MacLeod; Mr H. A. Mildon; Mr A. G. Monahan; Mr N. McL. Speer; Mr S. J. Snow; Mrs C. E. Tulloch; Mr N. Webley.
British Empire Medal for Gallantry (B.E.M.) —
Constable K. M. Jones; Detective J. Sheehan.
Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (C.B.E.) —
Brigadier W. S. McKinnon, O.B.E.
Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (O.B.E.) —
Commander C. H. Hilliard, v.r.d.; Lieutenant Colonel L. A. Kermode; Wing Commander L. H. Edwards.
Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (M.B.E.) —
Lieutenant Commander D. G. Bamfield, A.D.C.; Major R. J. Moor, E.D.; Major R. E. Johnston; Squadron Leader L. J. McLean; Captain J. J. Ayton; Flight Officer E. G. Hume; Warrant Officer Second Class C. B. Fowler.
Bar to the Air Force Cross —
Wing Commander G. R. B. Highet, D.F.C., A.F.C.
Air Force Cross (A.F.C.)—
Flying Officer B. G. Anderson.
British Empire Medal (B.E.M.) —
Staff Sergeant, (temporary Warrant Officer Second Class), R. A. A. Burnett; Staff Sergeant, (temporary Warrant Officer Second Class) H. Preston; Chief Petty Officer E. C. F. Barnes; Chief Petty Officer H. C. M. Brock; Chief Petty Officer W. M. C. Gibbs; Chief Petty Officer Writer R. O. Smyth; Sergeant J. C. Hart; Corporal F. Murphy.
Queen's Commendation for Valuable Services in the Air —
Flight Lieutenant M. R. Breed; Flight Lieutenant W. R. Swap.
A complete list of the honours, decorations, etc., for distinguished or gallant conduct, devotion to duty, etc., awarded to New Zealand personnel serving with Her Majesty's Forces in Malaya up to mid-1960 was published in the 1959 and 1960 Yearbooks. Later awards are listed below.
Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (M.B.E.)—
Major F. A. Bishop; Major L. W. Wright.
British Empire Medal (B.E.M.)—
Sergeant D. I. Mackintosh.
Mention in Despatches (M.I.D.)—
Lieutenant A. R. Fraser; Sergeant P. W. J. Faulkner; Lance Corporal L. J. Ferguson.
Commander-in-Chief's Certificate for Good Service—
Sergeant R. S. Hurle.
LIST OF DEPARTMENTS OF THE NEW ZEALAND GOVERNMENT, WITH TITLES AND HOLDERS OF CHIEF ADMINISTRATIVE POSITIONS, APRIL 1961
| Department | Chief Administrative Positions | |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Name | |
| Agriculture | Director-General | P. W. Smallfield, M.AGR.SC. |
| Air | Chief of Air Staff and First Air Force Member of the Air Board | Air Vice-Marshall M. F. Calder, C.B., C.B.E., LL.B. |
| Air Secretary | B. R. Rae, M.B.E., B.COM. | |
| Civil Aviation | Director | Air Vice-Marshall Sir A. De. T. Nevill, K.B.E., C.B., M.SC., F.R.A.E.S. |
| Meteorological | Director | M. A. F. Barnett, O.B.E., M.SC., PH.D., F.INST.P., F.R.S.N.Z. |
| Army | Chief of the General Staff and First Military Member of the Army Board | Major-General L. W. Thornton, C.B.E. |
| Army Secretary | A. N. V. Dobbs, M.COM., ACCTS. PROF. | |
| Audit | Controller and Auditor-General | A. D. Burns, A.R.A.N.Z. |
| Broadcasting | Director | J. H. E. Schroder, M.A. |
| Crown Law | Solicitor-General | H. R. C. Wild, Q.C., LL.M. |
| Customs | Comptroller | J. F. Cummings. |
| Education | Director | A. E. Campbell, M.A., DIP.ED. |
| External Affairs | Secretary | A. D. M. Mcintosh, C.M.G., M.A. |
| Government Life Insurance | Commissioner | W. K. Watson, A.R.A.N.Z. |
| Health | Director-General | H. B. Turbott, I.S.O., M.B., CH.B., D.P.H. (N.Z.). |
| Mental Hygiene Division | Director | G. Blake-Palmer, M.R.C.S. (ENG.), L.R.C.P. (LOND.), D.P.M., L.D.S., R.C.S.(ENG.). |
| Industries and Commerce | Secretary | W. B. Sutch, M.A., B.COM., PH.D.(U.S.A.). |
| Inland Revenue | Commissioner | F. R. Macken, LL.M. |
| Chief Deputy Commissioner | J. F. Boyd, ACCTS. PROF. | |
| Deputy Commissioner (Taxes Division) | J. E. Curran, A.R.A.N.Z. | |
| Deputy Commissioner | A. L. Twhigg, LAW PROF. | |
| Internal Affairs | Secretary and Clerk of Writs | J. V. Meech. |
| Dominion Museum | Director | R. A. Falla, D.SC., M.A. |
| National Art Gallery | Director | S. B. Maclennan, A.R.C.A. |
| Island Territories | Secretary | J. M. McEwen, LL.B. |
| Justice | Secretary for Justice | J. L. Robson, LL.M., PH.D. |
| Registrar-General's Division | Registrar-General | J. G. A'Court. |
| Chief Electoral Officer | L. Irwin. | |
| Land and Deeds Division | Registrar-General of Land | E. K. Phillips, Solr. |
| Patent Office | Commissioner | A. D. McGregor, LL.B. |
| Labour | Secretary of Labour | H. L. Bockett, C.M.G., A.R.A.N.Z. |
| Lands and Survey | Director-General | D. N. R. Webb. |
| Law Drafting | Law Draftsman | D. A. S. Ward, B.A., LL.B. |
| Legislative | Clerk of House of Representatives | H. N. Dollimore, LL.B. |
| Maori Affairs | Secretary, and Maori Trustee | J. K. Hunn, LL.M. |
| Marine | Secretary | G. L. O'Halloran, LL.B. |
| Mines | Under-Secretary | P. M. Outhwaite, M.S.EX. |
| Navy | Chief of the Naval Staff and First Naval Member of the Naval Board | Rear-Admiral P. Phipps, D.S.C. AND BAR, V.R.D. |
| Navy Secretary | D. A. Wraight. | |
| New Zealand Electricity | General Manager | A. E. Davenport, B.E.(ELECT.), M.I.E.E. |
| New Zealand Forest Service | Director-General | A. L. Poole, M.SC, B.FOR.SC. |
| Police | Commissioner | W. S. Brown, M.V.O. |
| Post Office | Director-General | D. Donaldson, B.SC., M.I.E.E. |
| Prime Minister's | Permanent Head | A. D. M. McIntosh, C.M.G., M.A. |
| Joint Principal Private Secretaries | P. A. Barnes, ACCTS. PROF., | |
| R. B. Taylor, B.A. | ||
| Printing and Stationery | Government Printer | R. E. Owen. |
| Public Service Commission | Chairman of Commission | L. A. Atkinson, M.COM., D.P.A. |
| Members | A. G. Rodda, ACCTS. PROF., D.P.A. | |
| R. J. MacLachlan, B.A., B.COM., DIP. U.V. (AUCK.) | ||
| Public Trust | Public Trustee | W. Brown, LAW. PROF. |
| Railways | General Manager | A. T. Gandell, M.I.C.E., M.N.Z.I.E. |
| Scientific and Industrial Research | Secretary | W. M. Hamilton, D.SC., M. GRIC. SC., N.D.H. (N.Z.). |
| Social Security | Director, Chairman, Social Security Commission, and Secretary for War Pensions | A. E. T. Williams, ACCTS. PROF. |
| State Advances Corporation of New Zealand | Managing Director | J. D. R. Wood. |
| General Manager | W. Hay, LL.M. | |
| State Fire and Accident Insurance | General Manager | A. J. Martin, FIRE AND ACCID. INS. DIPS. |
| Statistics | Government Statistician | J. V. T. Baker, M.A., M.COM., F.R.A.N.Z., D.P.A. |
| Tourist and Publicity | General Manager | K. B. Longmore, ACCTS. PROF. |
| Transport | Commissioner | A. E. Forsyth, b.e. |
| Treasury | Secretary | E. L. Greensmith, M.COM., LAW PROF., A.R.A.N.Z. |
| Government Actuary's Branch | Government Actuary | V. Thompson, F.I.A. |
| Superannuation | Controller | M. Aldred, ACCTS. PROF. |
| National Provident Fund | Superintendent | |
| Valuation | Valuer-General | J. B. Brown, DIP. AG. (LIN.). |
| Works, Ministry of | Commissioner of Works | F. H. M. Hanson, D.S.O. AND BAR, O.B.E., M.M., E.D., M.S.I.N.Z., M.N.Z.I.E. |
| Engineer-in-Chief | C. W. O. Turner, B.SC.(ENG.) (LON.), M.ENG. (ILLINOIS), M.I.C.E. | |
| Government Architect | F. G. F. Sheppard, F.N.Z.I.A., A.R.I.B.A. | |
| Housing Division | Director | J. V. Jebson, F.N.Z.I.A. |
The Public Service comprises in the widest sense all servants of the Crown — other than those holding political or judicial office — who are employed in a civil capacity and whose remuneration is paid from parliamentary appropriations. They are employees of the various State Departments, commissions, and other agencies, and represent practically all occupations.
Thirty-eight State Departments are under the control of the Public Service Commission. They employed approximately 39,320 permanent officers and 2,328 temporary staff (excluding casuals) at 31 March 1961. Two other Departments, the Post Office and the Railways Department, are each independently controlled. Details of numbers of staff employed and general administrative organisation are contained elsewhere in this volume, as are the details of the Teaching Service, the uniformed branches of the Police, Navy, Army, and Air Departments, the Judiciary, and the Magistracy.
The Public Service Commission — The Commission is a body of up to four men each appointed by the Governor-General on the recommendation of Government for a period of five years and eligible for reappointment (Public Service Amendment Act 1954). At 1 April 1961 the Commission had three members.
Functions — The Commission's functions are defined in the Public Service Act 1912 and amendments, and are briefly as follows: (1) recruitment of staff, (2) classification of positions according to importance and character, (3) maintenance of a fair and efficient system of promotion, (4) protection of the independence and integrity of the Service, (5) maintenance of efficiency and economy, (6) maintenance of discipline, (7) regulation of various personnel matters, e.g., leave, hours of work, payment of allowances.
Recruitment — The recruitment of public servants is conducted by the Commission through its district representatives, its own officers, and by Departments in collaboration with the Commission. Details of career openings in the Service are regularly supplied to schools; careers booklets are published by some Departments.
All recruits, except with permission of the Governor-General, must be British subjects, and are appointed on probation normally for two years.
Classification — There are five statutory divisions into which positions may be classified, as follows:
Administrative — Those positions held by Permanent Heads and their Deputies.
Professional — Includes qualified officers employed in fields such as architecture, engineering, dentistry, law, medicine, and science.
Clerical — Includes qualified officers employed on duties ranging from routine clerical and accounting work to senior executive positions.
Educational — Includes teachers in Maori schools, the correspondence schools, and special institutions.
General — Includes a wide range of “field” positions, the trades, and similar occupations.
The Commission is required to grade officers in these divisions according to their fitness and the character and importance of the duties performed by them. A statutory regrading of the whole Service is required each five years.
Promotion — Promotion in the Public Service is based on merit. While the Service has clearly defined salary scales and avenues of promotion, it allows for and encourages quick promotion with special salary increases to officers of merit. All vacancies above the basic grade for first entry into the Service are widely advertised so that all persons in the Service, and sometimes persons outside the Service, may apply for higher positions. Appointments are given to the most suitable and efficient applicants and, as between Service personnel, seniority becomes a factor only when applicants have equal claims in other respects.
Public servants have certain rights of appeal to the Public Service Board of Appeal concerning (1) gradings fixed by the Commission in the statutory regrading year, (2) promotions approved by the Commission, and (3) decisions by the Commission concerning charges made against officers. The Board's decisions are final.
Independence and Integrity — One of the statutory functions of the Commission is to protect the independence and integrity of the Service. The Commission is not responsible to a Minister of the Crown. Subject to the statutory appeal rights of staff, the Commission is autonomous in matters of appointments to and promotions in the Service, except in respect of a few positions exempted from the provisions of the Public Service Act. It is, however, required to report annually to Parliament on the condition and efficiency of the Public Service.
By statute a person is liable to a penalty should he attempt to influence the Commission regarding a person's appointment, promotion, or salary.
Efficiency and Economy — The Commission is responsible for efficiency and economy in the Public Service. Its Inspectors carry out general inspections of Departments; and it has an Organisation and Methods (O and M) Section to give advisory service to Departments and to explore, in collaboration with Departments, problems of Service application with a view to finding model systems. Successful administration depends on the employment of the most efficient and up-to-date management techniques.
Complementary to the continuing search for improved organisation and methods is a formal suggestions scheme designed to stimulate suggestions for better methods from all ranks of public servants. This scheme produces a steady flow of suggestions, many of which are adopted in full or in part.
Staff Training and Education — A comprehensive Service training and education policy is pursued by the Commission's Staff Training Branch. The Branch organises central courses, instructs departmental training officers in training techniques, publishes training material, assists Departments to develop training to meet specific needs, and acts as a general clearing house for the exchange of information on training methods. It also administers the various bursary schemes operated by the Commission.
Office Accommodation — The Commission is represented on the Government Office Accommodation Board. The Board's Secretariat are members of, and attached to, the Commission's staff.
Statistics: Staff — The detailed distribution of staff among Departments under the Public Service Commission is shown in the Commission's annual reports to Parliament (parliamentary paper H. 14).
Salaries — The following general provisions are applicable:
Public Service Commissioners — Fixed by annual appropriation. Present rates are: Chairman, £3,750; members, £3,000.
Administrative Division — Various rates, according to position held; fixed by annual appropriation.
Other Divisions — As prescribed by Public Service Salary Order 1960 (Serial No. 1960/152). Salaries payable in the Professional and Clerical Divisions from 1 April 1961 were as set out below (various rates are payable in the General Division):
| Salary | Salary Incremental Range |
|---|---|
| VI | £315, £360, £415, £475, £535, £600, £650, £700, £745 £805, £850 |
| V | £745, £805, £850, £900, £940 |
| IV | £985, £1,030 |
| III | £1,075, £1,120 |
| II | £1,165, £1,210 |
| I | £1 300 |
| Sp. | £1,400, £1,500, £1,600, £1,700, £1,800, £1,900, £2,025, £2,150, £2,300, £2,450, £2,600, £2,800 |
The commencing salary for those with three years' secondary education is £360; with School Certificate, £415; with Endorsed School Certificate, £415, with increment to next step after six months' service; with University Entrance £475; and for those with University Entrance and Higher School Certificate, £475, with increment to next step after six months' service.
Argentina — Hon. Representative of Department of Industries and Commerce, T. E. B. Poole, Alsina, 1146, Buenos Aires.
Australia — High Commissioner, S. C. Johnston; Counsellor, J. Shepherd; Second Secretary, P. G. Milien; Third Secretary, J. C. Averill; Canberra, A.C.T.; Head, New Zealand Joint Services Liaison Staff, Brigadier J. R. Page, C.B.E., D.S.O.; Senior Trade Commissioner in Australia and Commercial Adviser, R. V. Jackson; Trade Commissioner and Assistant Commercial Adviser, W. K. Coad; Travel Manager (Tourist and Publicity), R. W. Coupland; Assistant Trade Commissioner, H. N. McCarthy; Trade Commissioner (Timber), T. A. Foley; Assistant Trade Commissioner (Timber), M. M. Pinfold, 14 Martin Place (P.O. Box 365F), Sydney; Trade Commissioner and Commercial Adviser, A. C. Davys; Assistant Trade Commissioner and Assistant Commercial Adviser, R. E. Tyrie; Travel Commissioner (Tourist and Publicity), A. N. Reid, 428 Collins Street (P.O. Box 2136), Melbourne.
Burma — Hon. New Zealand Government Agents, New Zealand Insurance Co., Rangoon.
Canada — High Commissioner, Foss Shanahan; First Secretary, W. G. Thorp; Third Secretary, C. D. Geary; Attaché (Administration), B. N. Leydon; Military, Naval and Air Adviser, Brigadier T. C. Campbell, C.B.E., D.S.O., M.C., E.D.; Assistant Military, Naval and Air Adviser, Wing Commander J. R. Claydon, A.F.C., R.N.Z.A.F., Suite 804, Commonwealth Buildings, 77 Metcalfe Street (P.O. Box 1222), Ottawa; Trade Commissioner, R. B. Gray; Assistant Trade Commissioner, J. D. Kerr, 708 Prudential Assurance Building, Montreal 2.
Ceylon — High Commissioner, Sir Guy Powles, K.B.E., C.M.G. (resident in New Delhi).
Federation of Malaya — High Commissioner, C. M. Bennett, D.S.O.; First Secretary, Dr R. A. Lochore; Trade Commissioner, W. L. Middlernass, M.V.O.; Second Secretary, B. M. Brown; Attaché (Administration), N. E. Parker, Police Cooperative Building, Suleiman Road, Kuala Lumpur.
Fiji — Hon. New Zealand Government Agents, W. R. Carpenter and Co. (Fiji) Ltd., Suva.
France — Ambassador, C. E. Beeby, C.M.G.; Counsellor, I. L. G. Stewart; Second Secretary, J. G. McArthur; Third Secretary, G. J. Young; Attaché (Administration), Miss J. J. Barnett, 9 Rue Leonard de Vinci, Paris.
Hong Kong — Trade Commissioner, J. P. Costello, Union House Phase 1, Chater Road, Hong Kong.
India — High Commissioner, Sir Guy Powles, K.B.E., C.M.G.; Trade Commissioner, R. T. C. de Lambert; Second Secretary, I. K. McGregor; Third Secretary, J. K. Cunningham, 39 Golf Links Road, New Delhi. Hon. New Zealand Government Agents, New Zealand Insurance Co., Calcutta.
Indonesia - Consul-General, D. M. Rae, Hotel Duta, Djakarta.
Japan — Ambassador, J. S. Reid; Counsellor, B. D. Zohrab; Trade Commissioner and Commercial Counsellor, J. S. Scott; Third Secretary, D. N. Atkins; Attaché (Administration), D. J. Robertson; Assistant Trade Commissioner and Attaché (Commercial), M. W. Craig, 26 Sanbancho Chiyodaku, Tokyo.
Netherlands — Consul, T. A. N. Johnson, C.V.O., 53 Anna Pavlownastraat, The Hague.
Singapore — Commissioner, R. L. Hutchens, D.S.O.; First Secretary, D. F. Dunlop; Military Liaison Officer, Commander J. F. McKenzie, R.N.Z.N.; Assistant Military Liaison Officer, Lieutenant Colonel, R. H. Dyson, E.D., R.N.Z.A.; Trade Commissioner, H. W. Shepherd; Third Secretary, D. Law; Attaché (Administration), G. A. Petterson, Asia Insurance Building, Finlayson Green, Singapore.
South-East Asia Treaty Organisation — Council Representative, C. Craw, Bangkok.
Thailand — Chargé d'Affaires, a.i., C. Craw; First Secretary, R. E. B. Peren; Third Secretary, J. M. R. Mansfield; Third Secretary, P. J. Te O. Gordon; Attaché (Administration), D. J. Robertson, New Zealand Embassy, 296 Phyathai Road, Bangkok.
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland — High Commissioner, Hon. T. L. Macdonald; Counsellor, G. D. L. White, M.V.O.; Counsellor (Economic), L. V. Castle; First Secretary, Miss H. N. Hampton; First Secretary (Economic), K. C. Durrant; Second Secretary, R. L. Jermyn; Third Secretary, I. P. Muir; Third Secretary, H. Freeman-Greene; Senior R.N.Z.A.F. Officer, Air Commodore I. G. Morrison, C.B.E., R.N.Z.A.F.; Senior Army Liaison Officer, Brigadier R. C. Queree, C.B.E., D.S.O.; Senior R.N.Z.N. Liaison Officer, Captain F. N. F. Johnston, D.S.C., R.N.Z.N.; Financial Secretary, R. J. Hogg; Senior Trade Commissioner and Commercial Counsellor, K. L. Press; Trade Commissioner and Commercial Secretary, G. H. Datson; Assistant Trade Commissioner and Commercial Secretary, W. E. B. Tucker; Trade Officer, D. Homewood; Trade Officer, M. Roberts; Public Relations Officer, A. T. Campbell; Senior Scientific Adviser, Dr V. Armstrong; Scientific Adviser, B. W. Collins; Agricultural Adviser, C. V. Dayus; Inspector of Dairy Products, J. J. Walker; Chief Migration Officer, J. V. Brennan; Customs Adviser, P. A. Bemrose; Travel Commissioner (Tourist and Publicity), J. E. Hartstonge; Deputy Travel Commissioner, W. F. Bern; Communications Adviser, H. W. Curtis; Representative of the Public Trust Office, J. D. L. Rose; Advisory Engineer, New Zealand Railways, R. F. Marriott.
United Nations — Permanent Representative, Foss Shanahan; Counsellor, R. Q. Quentin-Baxter; First Secretary (Economic), W. A. E. Green; First Secretary, P. K. Edmonds; Third Secretaries, W. B. Harland, L. G. Watt; Attaché, R. J. Lawrence; the Permanent Mission of New Zealand to the United Nations, Suite 530, International Building, Rockefeller Centre, New York.
United States of America — Ambassador, G. R. Laking; First Secretaries, R. M. Miller, Miss A. B. Souter; Second Secretary, R. M. Mullins; Third Secretary, D. B. G. McLean; Attache (Administration), S. J. V. Wilson; New Zealand Embassy, 19 Observatory Circle, Washington. Armed Forces Attaché, Brigadier T. C. Campbell, C.B.E., D.S.O., M.C., E.D.; Assistant Armed Forces Attaché, Wing Commander J. R. Claydon, A.F.C., R.N.Z.A.F., 3101 Cleveland Avenue, N.W., Washington. Senior Trade Commissioner and Commercial Counsellor, G. R. J. Hope; Trade Commissioner and Commercial Secretary, A. W. Broadbent; Assistant Trade Commissioner and Commercial Attaché, L. G. Donaldson, Suite 306, Associations Buildings, 1145 19th Street, N.W., Washington. Consul-General, O. P. Gabites; Consul (Commercial) and Trade Commissioner, J. L. Fenaughty, Assistant Trade Commissioner and Vice-Consul, (Commercial), A. K. Robinson; Travel Commissioner, N. S. Munro; Deputy Travel Commissioner, G. F. Swafford, Suite 530, International Building, Rockefeller Centre, New York. Consul-General, R. L. G. Challis, New Zealand Travel Commissioner for the United States and Canada, N. F. F. Gouffe; Deputy Travel Commissioner, W. Scott; Trade Commissioner and Consul (Commercial), R. J. Inglis; Vice-Consul, Miss A. J. Pearce, New Zealand Consulate-General, 153 Kearney Street, San Francisco.
West Indies Federation — Trade Commissioner, D. N. Hull, 27 Henry Street, Port of Spain.
Argentina — Consul, Dr L. M. Moreno-Quintana, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington.
Australia — High Commissioner, His Excellency Vice-Admiral Sir John Collins, K.B.E., C.B.; First Secretary, F. Truelove; Defence Representative, Colonel S. A. Fletcher; Third Secretary, R. D. Sturkey, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington; Commercial Counsellor, C. A. Allen; Commercial Secretary, J. A. Morey, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington. Trade Commissioner C. L. Steele, 56 Shortland Street, Auckland. Trade Commissioner, D. M. Walker, Phoenix Assurance Building, 89 Worcester Street, Christchurch.
Austria — Chargé d'Affaires (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), Dr W. de Comtes, Canberra, Hon. Consul, S. B. Clarke, Wellington.
Belgium — Chargé d'Affaires, a.i., Etienne Humblet, Dominion Farmers' Institute, Wellington. Hon. Consuls, J. B. Ferguson, Auckland; Sir Joseph Ward, Bart., Christchurch; A. H. Allen, Dunedin.
Brazil — Hon. Consul, C. A. L. Treadwell; Hon. Vice-Consul, P. J. Treadwell, Wellington.
Canada — High Commissioner, His Excellency Mr G. R. Heasman, o.b.e.; First Secretary (Commercial), J. H. Stone; Second Secretary, R. B. Edmonds; Second Secretary (Commercial), W. J. Collett, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington.
Ceylon — High Commissioner (with jurisdiction in New Zealand) (Vacant); Chargé d'Affaires, Mr Nesaratnam, Canberra; Commercial Attaché and Trade Commissioner, E. M. O.Martenstyn. Sydney; Hon. Trade Commissioner, D. H. Scott, Wellington.
Chile — Consul (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), J. R. Dundas Smith, Sydney; Hon. Consul, H. O. Taylor, Auckland.
China — Consul-General, Dr Daniel Yu-Tang Lew; Vice-Consul, Chen Che Yao, D.I.C. Buildings, Lambton Quay, Wellington.
Czechoslovakia — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary (Vacant); First Secretary and Chargé d'Affaires, a.i., Bretislav Matanoha; Second Secretary, O. Svihalek, 10 Brougham Ave., Wellington.
Denmark — Chargé d'Affaires, Thorkild Wegener-Clausen, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington. Hon. Consuls: A. A. Beuth, Wellington; L. J. Stevens, Auckland; A. C. Perry, Christchurch. Hon. Vice-Consul, G. C. Petersen, Palmerston North.
Dominican Republic — Hon. Consul, F. Russell Baker, Auckland.
Fiji — New Zealand Agents for the Colony of Fiji, L. D. Nathan and Co. Ltd., Auckland.
Finland — Chargé d'Affaires (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), Toivo Kala, Sydney. Hon. Consul, T. N. Gibbs, Wellington.
France — Ambassador, His Excellency Mr L. A. Félix; Counsellor, C. L. Béguin-Billecocq; First Secretary, A. Sicé; Commercial Counsellor, R. Maurice; Assistant Commercial Attaché, M. Baillard; Third Secretary, A. Coulaud, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington. Army, Naval, and Air Attaché, Captains de Frégate, J. P. E. Eschbach (Resident in Noumea). Hon. Consular Agents: R. G. McElroy, Auckland; F. Farrell, Christchurch; A. N. Haggitt, Dunedin; E. F. Paul, Apia, Western Samoa.
German Federal Republic —Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, His Excellency Dr H. Noehring; First Secretary, J. J. Blomeyer, 3 Claremont Grove, Wellington.
Greece — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr George Christodulo; First Secretary, N. Athanassiou, Canberra. Hon. Acting Consul-General, S. Garland, Wellington.
India — High Commissioner (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr Samarendranath Sen, Canberra; Press Attaché, Jagmohan Mahajan, Sydney; First Secretary (Commercial) and Acting High Commissioner, Mr V. C. Viajaya Raghavan, 49 Willis Street, Wellington.
Indonesia — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, Dr A. Y. Helmi, Canberra; Hon. Consul-General, G. E. L. Alderton, C.M.C., Auckland.
Israel — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr Moshe Yuval; First Secretary and Consul, Haim Raphael; Commercial Attaché, Oswald Sharef, Sydney.
Italy — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, His Excellency Dr Giuseppe Capece Galeota della Regina, 24 Grant Road, Wellington. Hon. Consular Agents, Renato Forti, Auckland; P. P. Amodeo, Christchurch; G. Monopoli, Nelson.
Japan — Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary, His Excellency Mr Kaoru Hara; Counsellor, T. Ngakawa; Third Secretary, Hiroshi Ando, 298 Oriental Parade, Wellington C. 4.
Lebanon — Consul-General (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), Dr Karim Azkoul, Sydney.
Malaya — High Commissioner, Dato Suleiman bin Dato Abdul Rahman, Canberra. Hon. Trade Commissioner, K. D. Butland, Auckland.
Netherlands — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, His Excellency Baron Bentinck van Schoonheten; First Secretary, C. G. Van Geest; Attaché of Legation, C. H. A. Plug; Emigration Attaché, C. A. Korndörffer, D.I.C. Building, Lambton Quay, Wellington. Hon. Consul, C. S. O. Hughes; Migration Officer, H. W. F. M. Knottenbelt, Auckland; Emigration Officer, J. J. A. de Moor, Christchurch. Hon. Vice-Consuls: G. N. Francis, Christchurch; J. M. Richie, Dunedin.
Norway — Consul-General (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), Olav Nordland, Sydney. Hon. Consul, Dr A. B. Andersen, Wellington. Hon. Vice-Consuls: D. Millar, Auckland; J. Heaton Rhodes, Christchurch; W. F. Edmond, Dunedin.
Pakistan — High Commissioner (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr J. G. Kharas; First Secretary, Ishanulla Khan; Second Secretary, Kaiser Rasheed, Canberra; First Secretary (Commercial), F. H. Choudhury, Sydney.
Panama — Consul, P. C. Griffiths, Dingwall Building, Auckland.
The Philippines — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr M. Ezpeleta; First Secretary and Consul-General, Bartolome Umayam; Attaché, A. Prats, jun., Sydney; Military Attaché, Colonel F. Liamas; Hon. Consul, E. O. Faber, Auckland.
Portugal — Hon. Consuls: L. D. Nathan, Auckland; W. S. Wheeler, Wellington. Hon. Vice-Consul, I. D. Reid, Wellington.
Sweden — Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary, His Excellency Mr Olof Ripa, 105 Customhouse Quay, Wellington; Hon. Acting Consul, C. E. Taylor, Wellington. Hon. Vice-Consuls: C. M. Richwhite, Auckland; I. Machin, Christchurch; R. S. Glendining, Dunedin; G. M. Corbet, Invercargill.
Switzerland — Consul-General, Dr O. Rossetti, D.I.C. Building, Wellington.
Thailand — Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary (with jurisdiction in New Zealand), His Excellency Mr Vadhana Isarabhakdi; Military Attaché, Colonel Bulrit Dadarananda, Canberra; Chargé d'Affairs, a.i., Lek Tantemsapya; Attaché, Subhadra Gajajiva, Wellington.
Tonga — New Zealand Agents for the Government of Tonga, Messrs Spedding Ltd., Auckland.
Turkey — Hon. Consul, E. G. Cowell, Auckland.
Union of South Africa — Hon. Trade Commissioner, M. G. C. McCaul, Wellington.
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics — Chargé d'Affaires, a.i., N. V. Ivanov; First Secretary, N. I. Evdokeyev; Commercial Counsellor, V. S. Andreev, Second Secretaries, E. P. Lutskij, S. N. Smirnov and W. I. Shtukov; Third Secretary, L.A.Filatov; Attachés, N. I. Kriuchenkov and L. V. Scherbakov, 57 Messines Road, Wellington.
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland — High Commissioner, His Excellency The Hon. Sir Francis Cumming-Bruce, K.C.M.G.; Deputy High Commissioner (Vacant); First Secretary (Information), J. L. Hayden, O.B.E.; First Secretaries, J. K. Hic man and J. R. Flaxman; Second Secretary, R. G. Beer; Information Officer, J. Shotter; Economic Adviser, C. G. Cruickshank; First Secretary (Commercial) and Trade Commissioner, G. C. Dick; Assistant Trade Commissioners, Miss D. F. Stuart, K. W. Neall; First Secretary (Agriculture and Food), J. Eaton, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington. Service Liaison Staff: Navy, Captain A. Turnbull, R.N.; Army, Colonel K. S. Wilson; Air, Group Captain J. H. L. Blount, D.F.C., R.A.F.; Secretary, Squadron-Leader L. Ayling, M.B.E., Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay, Wellington. Trade Commissioner, A. P. Timms; Assistant Trade Commissioner, D. P. Dick, Customs Street East, Auckland.
United States of America — Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary (designate), His Excellency Mr A. B. Akers; Counsellor, Miss R. Bacon; Army Attaché, Colonel Mabry G. Miller; Air Attaché, Colonel Andrew E. McDavid (resident in Canberra); Naval Attaché and Naval Attaché for Air, Commander L. C. Knowles; First Secretary and Consul, G. M. Fennemore; First Secretary (Economic) and Consul, F. Irving; Second Secretary and Consul (Administrative Officer), Robert R. Bliss; Attaché and Public Affairs Officer, John B. Lanum; Agricultural Attaché, Dr Daniel E. Brady; Second Secretary (Economic and Commercial), Peter W. Lande; Assistant Air Attaché, Major Mance C. Smith (resident in Canberra); Second Secretary and Consul, Mrs Edith A. Stensby, Government Life Insurance Building, Customhouse Quay Vellington. Vice-Consul, R. H. Thompson, Auckland. Consular Agent, William G. Quirk, Chriscnurch.
Venezuela — Hon. Consul, Dr L. Bennett, Dingwall Building, Auckland C. 1.
Yugoslavia — Acting Consul-General, R. Sarenac, 49 Hobson Street, Wellington.
Table of Contents
POPULATION AND EXTERNAL MIGRATION (INCLUDING MAORIS)
| Year | Population | Mean Population | Year Ended 31 March | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At 31 December | At 31 March | Year Ended 31 December | Year Ended 31 March | Overseas Passenger Arrivals* | Overseas Passenger Departures* | |
| *Excluding through passengers and tourists on cruising liners. | ||||||
| 1910 | 1,050,410 | 1,035,212 | 1,040,534 | 1,025,638 | 34,715 | 32,854 |
| 1911 | 1,075,250 | 1,056,199 | 1,063,887 | 1,045,706 | 37,049 | 34,375 |
| 1912 | 1,102,471 | 1,081,344 | 1,088,861 | 1,069,828 | 43,097 | 37,205 |
| 1913 | 1,134,506 | 1,111,589 | 1,118,488 | 1,096,467 | 46,892 | 34,935 |
| 1914 | 1,145,838 | 1,139,668 | 1,140,172 | 1,125,628 | 41,672 | 31,517 |
| 1915 | 1,152,638 | 1,150,386 | 1,149,238 | 1,145,027 | 33,377 | 27,254 |
| 1916 | 1,150,339 | 1,150,250 | 1,149,225 | 1,150,318 | 25,407 | 22,808 |
| 1917 | 1,147,448 | 1,150,938 | 1,148,893 | 1,149,225 | 20,470 | 20,047 |
| 1918 | 1,158,149 | 1,154,559 | 1,152,798 | 1,152,748 | 13,718 | 12,214 |
| 1919 | 1,227,181 | 1,178,406 | 1,192,665 | 1,166,482 | 11,978 | 11,473 |
| 1920 | 1,257,611 | 1,236,915 | 1,242,396 | 1,207,660 | 26,900 | 23,990 |
| 1921 | 1,292,892 | 1,267,498 | 1,274,917 | 1,252,206 | 46,090 | 31,908 |
| 1922 | 1,318,884 | 1,301,251 | 1,305,126 | 1,283,546 | 41,128 | 30,396 |
| 1923 | 1,343,02i | 1,325,301 | 1,328,193 | 1,311,382 | 34,108 | 28,581 |
| 1924 | 1,370,403 | 1,347,853 | 1,352,618 | 1,334,029 | 36,254 | 30,487 |
| 1925 | 1,401,230 | 1,379,487 | 1,384,428 | 1,359,995 | 42,211 | 29,913 |
| 1926 | 1,429,669 | 1,409,812 | 1,413,743 | 1,392,073 | 42,449 | 30,714 |
| 1927 | 1,450,356 | 1,438,132 | 1,439,004 | 1,420,838 | 45,682 | 34,018 |
| 1928 | 1,467,370 | 1,453,821 | 1,456,075 | 1,443,551 | 35,837 | 37,072 |
| 1929 | 1,486,134 | 1,471,110 | 1,473,419 | 1,460,363 | 34,799 | 34,088 |
| 1930 | l,506,8O9 | 1,489,203 | 1,493,019 | 1,478,027 | 33,839 | 31,454 |
| 1931 | 1,522,762 | 1,511,700 | 1,514,215 | 1,498,416 | 30,741 | 25,632 |
| 1932 | 1,534,735 | 1,525,545 | 1,527,062 | 1,517,940 | 17,891 | 21,063 |
| 1933 | 1,547,124 | 1,538,028 | 1,539,590 | 1,530,119 | 18,713 | 21,308 |
| 1934 | 1,558,373 | 1,550,125 | 1,551,532 | 1,542,651 | 19,687 | 22,022 |
| 1935 | 1,569,689 | 1,560,992 | 1,562,233 | 1,554,297 | 24,901 | 28,051 |
| 1936 | 1,584,617 | 1,573,927 | 1,575,231 | 1,565,263 | 26,936 | 28,050 |
| 1937 | 1,601,758 | 1,587,211 | 1,589,972 | 1,578,757 | 31,670 | 32,023 |
| 1938 | 1,618,313 | 1,604,479 | 1,606,763 | 1,594,275 | 38,738 | 36,352 |
| 1939 | 1,641,639 | 1,624,714 | 1,628,512 | 1,611,362 | 42,648 | 37,685 |
| 1940 | 1,633,645 | 1,640,901 | 1,637,305 | 1,633,447 | 31,432 | 25,404 |
| 1941 | 1,631,276 | 1,636,230 | 1,630,948 | 1,635,715 | 13,814 | 13,100 |
| 1942 | 1,636,403 | 1,634,338 | 1,639,572 | 1,630,419 | 7,102 | 6,893 |
| 1943 | 1,642,041 | 1,634,094 | 1,635,635 | 1,640,191 | 3,133 | 2,592 |
| 1944 | 1,676,286 | 1,643,900 | 1,655,795 | 1,637,570 | 3,747 | 3,640 |
| 1945 | 1,727,817 | 1,679,972 | 1,694,641 | 1,664,585 | 7,207 | 6,189 |
| 1946 | 1,781,214 | 1,756,756 | 1,759,526 | 1,710,680 | 13,309 | 10,966 |
| 1947 | 1,817,453 | 1,789,476 | 1,798,262 | 1,770,291 | 25,358 | 22,320 |
| 1948 | 1,853,806 | 1,828,025 | 1,834,655 | 1,807,611 | 33,144 | 27,388 |
| 1949 | 1,892,042 | 1,864,560 | 1,871,748 | 1,843,767 | 35,946 | 31,765 |
| 1950 | 1,927,629 | 1,902,883 | 1,909,092 | 1,881,317 | 50,880 | 43,000 |
| 1951 | 1,970,522 | 1,938,032 | 1,947,529 | 1,917,934 | 54,644 | 47,122 |
| 1952 | 2,024,556 | 1,984,730 | 1,996,149 | 1,958,729 | 62,498 | 46,834 |
| 1953 | 2,074,781 | 2,037,553 | 2,048,826 | 2,009,506 | 66,240 | 44,208 |
| 1954 | 2,118,434 | 2,087,740 | 2,094,910 | 2,061,376 | 61,845 | 46,404 |
| 1955 | 2,164,734 | 2,130,927 | 2,138,946 | 2,105,767 | 61,610 | 54,580 |
| 1956 | 2,209,132 | 2,175,373 | 2,182,833 | 2,150,290 | 66,472 | 58,380 |
| 1957 | 2,262,814 | 2,221,169 | 2,232,591 | 2,194,108 | 76,005 | 64,563 |
| 1958 | 2,315,900 | 2,275,515 | 2,285,852 | 2,246,093 | 79,666 | 64,258 |
| 1959 | 2,359,746 | 2,326,129 | 2,334,617 | 2,298,814 | 83,648 | 73,656 |
| 1960 | 2,403,488 | 2,370,166 | 2,376,984 | 2,345,602 | 89,377 | 86,164 |
| 1961 | 106,238 | 104,618 | ||||
VITAL STATISTICS (EXCLUDING MAORIS)
| Year | Numbers | Rates per 1,000 of Mean Population | Deaths Under 1 Year per 1,000 Live Births | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live Births | Marriages* | Deaths | Deaths Under 1 Year | Live Births | Marriages* | Deaths | ||
| *Maori marriages are included since 1942. | ||||||||
| 1910 | 25,984 | 8,236 | 9,639 | 1,760 | 26.17 | 8.30 | 9.71 | 67.73 |
| 1911 | 26,354 | 8,825 | 9,534 | 1,484 | 25.97 | 8.70 | 939 | 56.31 |
| 1912 | 27,508 | 9,149 | 9,214 | 1,409 | 26.48 | 8.81 | 8.87 | 51.22 |
| 1913 | 27,935 | 8,813 | 10,119 | 1,653 | 26.14 | 8.25 | 9.47 | 59.17 |
| 1914 | 28,338 | 9,280 | 10,148 | 1,456 | 25.99 | 8.51 | 9.31 | 51.38 |
| 1915 | 27,850 | 10,028 | 9,965 | 1,394 | 25.33 | 9.12 | 9.06 | 50.05 |
| 1916 | 28,509 | 8,213 | 10,596 | 1,446 | 25.94 | 7.47 | 9.64 | 50.72 |
| 1917 | 28,239 | 6,417 | 10,528 | 1,360 | 25.69 | 5.84 | 9.58 | 48.16 |
| 1918 | 25,860 | 6,227 | 16,364 | 1,252 | 23.44 | 5.65 | 14.84 | 48.41 |
| 1919 | 24,483 | 9,519 | 10,808 | 1,108 | 21.42 | 8.33 | 9.46 | 45.26 |
| 1920 | 29,921 | 12,175 | 12,109 | 1,513 | 25.09 | 10.21 | 10.15 | 50.57 |
| 1921 | 28,567 | 10,635 | 10,682 | 1,366 | 23.36 | 8.69 | 8.73 | 47.82 |
| 1922 | 29,006 | 9,556 | 10,977 | 1,215 | 23.18 | 7.64 | 8.77 | 41.89 |
| 1923 | 27,967 | 10,070 | 11,511 | 1,225 | 21.96 | 7.91 | 9.04 | 43.80 |
| 1924 | 28,014 | 10,259 | 10,767 | 1,127 | 21.60 | 7.91 | 8.30 | 40.23 |
| 1925 | 28,153 | 10,419 | 11,026 | 1,125 | 21.20 | 7.85 | 8.30 | 39.96 |
| 1926 | 28,473 | 10,680 | 11,819 | 1,132 | 21.06 | 7.90 | 8.74 | 39.76 |
| 1927 | 27,881 | 10,478 | 11,613 | 1,080 | 20.29 | 7.63 | 8.45 | 38.74 |
| 1928 | 27,200 | 10,537 | 11,811 | 984 | 19.57 | 7.58 | 8.50 | 36.18 |
| 1929 | 26,747 | 10,967 | 12,314 | 912 | 19.03 | 7.80 | 8.76 | 34.10 |
| 1930 | 26,797 | 11,075 | 12,199 | 924 | 18.83 | 7.78 | 8.57 | 34.48 |
| 1931 | 26,622 | 9,817 | 12,047 | 856 | 18.45 | 6.81 | 8.35 | 32.15 |
| 1932 | 24,884 | 9,896 | 11,683 | 777 | 17.12 | 6.81 | 8.04 | 31.22 |
| 1933 | 24,334 | 10,510 | 11,701 | 770 | 16.63 | 7.18 | 7.99 | 31.64 |
| 1934 | 24,322 | 11,256 | 12,527 | 781 | 16.51 | 7.64 | 8.50 | 32.11 |
| 1935 | 23,965 | 12,187 | 12,217 | 773 | 16.17 | 8.23 | 8.25 | 32.26 |
| 1936 | 24,837 | 13,808 | 13,056 | 769 | 16.64 | 9.25 | 8.75 | 30.96 |
| 1937 | 26,014 | 14,364 | 13,658 | 812 | 17.29 | 9.55 | 9.08 | 31.21 |
| 1938 | 27,249 | 15,328 | 14,754 | 971 | 17.93 | 10.09 | 9.71 | 35.63 |
| 1939 | 28,833 | 17,115 | 14,158 | 898 | 18.73 | 11.12 | 9.20 | 31.14 |
| 1940 | 32,771 | 17,448 | 14,282 | 990 | 21.19 | 11.28 | 9.24 | 30.21 |
| 1941 | 35,100 | 13,313 | 15,146 | 1,045 | 22.81 | 8.65 | 9.84 | 29.77 |
| 1942 | 33,574 | 12,775 | 16,385 | 964 | 21.73 | 7.79 | 10.60 | 28.71 |
| 1943 | 30,311 | 12,021 | 15,447 | 951 | 19.70 | 7.35 | 10.04 | 31.37 |
| 1944 | 33,599 | 13,646 | 15,363 | 1,012 | 21.59 | 8.24 | 9.87 | 30.12 |
| 1945 | 37,007 | 16,693 | 16,051 | 1,036 | 23.22 | 9.85 | 10.07 | 27.99 |
| 1946 | 41,871 | 21,096 | 16,093 | 1,093 | 25.26 | 11.99 | 9.71 | 26.10 |
| 1947 | 44,816 | 19,047 | 15,904 | 1,122 | 26.47 | 10.59 | 9.39 | 25.04 |
| 1948 | 44,193 | 17,750 | 15,812 | 970 | 25.59 | 9.67 | 9.16 | 21.95 |
| 1949 | 43,988 | 17,354 | 16,012 | 1,046 | 24.98 | 9.27 | 9.09 | 23.78 |
| 1950 | 44,309 | 17,099 | 16,715 | 1,008 | 24.67 | 8.96 | 9.31 | 22.75 |
| 1951 | 44,651 | 16,915 | 17,512 | 1,017 | 24.39 | 8.69 | 9.56 | 22.78 |
| 1952 | 46,469 | 17,061 | 17,413 | 1,014 | 24.77 | 8.55 | 9.28 | 21.82 |
| 1953 | 46,414 | 17,224 | 17,009 | 931 | 24.12 | 8.41 | 8.84 | 20.06 |
| 1954 | 48,431 | 17,557 | 17,667 | 968 | 24.63 | 8.38 | 8.98 | 19.99 |
| 1955 | 49,869 | 17,795 | 17,953 | 1,002 | 24.86 | 8.32 | 8.95 | 20.09 |
| 1956 | 50,430 | 17,531 | 18,403 | 978 | 24.67 | 8.03 | 9.00 | 19.39 |
| 1957 | 51,852 | 17,614 | 19,411 | 1,036 | 24.82 | 7.89 | 9.29 | 19.98 |
| 1958 | 53,774 | 18,305 | 19,014 | 1,043 | 25.16 | 8.01 | 8.90 | 19.40 |
| 1959 | 54,739 | 18,315 | 19,814 | 1,089 | 25.10 | 7.84 | 9.09 | 19.89 |
| 1960 | 55,433 | 18,909 | 19,524 | 1,090 | 25.00 | 7.96 | 8.81 | 19.66 |
EDUCATION
| Year | Number of Scholars* Receiving | University Students (Excluding Affiliated Agricultural Colleges) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Education at | Secondary Education at | |||||||
| Public Schools | Registered Private Schools | Maori Village Schools | Secondary (Including Endowed and Combined) Schools | District High Schools | Technical Schools | Registered Private Schools and Maori Secondary Schools | ||
| *Excludes those receiving tuition from the correspondence schools (primary and secondary). | ||||||||
| 1910 | 156,687 | 19,052 | 4,280 | 5,176 | 1,916 | 1,253 | 1,862 | |
| 1911 | 161,991 | 19,967 | 4,557 | 5,465 | 1,777 | 1,341 | 831 | 1,900 |
| 1912 | 166,645 | 20,350 | 4,694 | 5,831 | 1,815 | 1,526 | 883 | 2,228 |
| 1913 | 172,617 | 21,251 | 4,647 | 6,154 | 1,837 | 1,664 | 545 | 2,318 |
| 1914 | 178,969 | 22,247 | 5,072 | 6,418 | 1,896 | 1,839 | 850 | 2,257 |
| 1915 | 183,719 | 22,477 | 5,191 | 6,488 | 2,102 | 1,955 | 992 | 2,039 |
| 1916 | 186,350 | 23,635 | 5,132 | 7,052 | 2,115 | 2,105 | 1,004 | 1,985 |
| 1917 | 188,754 | 25,685 | 5,173 | 7,590 | 2,180 | 2,347 | 1,206 | 1,977 |
| 1918 | 193,345 | 26,371 | 5,064 | 8,384 | 2,283 | 2,747 | 1,366 | 2,226 |
| 1919 | 194,586 | 20,977 | 5,198 | 9,068 | 2,159 | 2,926 | 1,497 | 3,060 |
| 1920 | 198,460 | 22,193 | 5,508 | 9,196 | 2,157 | 2,766 | 1,439 | 3,822 |
| 1921 | 205,955 | 23,924 | 5,822 | 10,030 | 2,176 | 3,349 | 1,634 | 4,123 |
| 1922 | 211,081 | 24,861 | 6,161 | 10,736 | 2,606 | 4,202 | 1,998 | 3,958 |
| 1923 | 212,460 | 26,010 | 6,186 | 11,619 | 2,818 | 5,054 | 2,134 | 4,202 |
| 1924 | 213,768 | 26,302 | 6,310 | 12,010 | 2,900 | 5,369 | 2,473 | 4,236 |
| 1925 | 215,063 | 25,933 | 6,386 | 12,514 | 3,136 | 5,132 | 2,511 | 4,442 |
| 1926 | 219,017 | 26,778 | 6,591 | 13,651 | 3,299 | 5,700 | 2,794 | 4,653 |
| 1927 | 221,157 | 27,358 | 6,620 | 14,190 | 3,581 | 5,703 | 2,932 | 4,878 |
| 1928 | 219,950 | 26,596 | 6,671 | 15,038 | 3,880 | 6,061 | 3,430 | 4,802 |
| 1929 | 219,166 | 26,977 | 6,979 | 15,498 | 4,000 | 6,114 | 3,698 | 4,623 |
| 1930 | 219,235 | 26,451 | 7,070 | 16,149 | 4,240 | 6,953 | 3,825 | 4,801 |
| 1931 | 218,829 | 26,726 | 7,503 | 16,344 | 4,944 | 7,397 | 3,777 | 4,869 |
| 1932 | 207,635 | 26,410 | 7,313 | 15,948 | 4,486 | 7,106 | 3,616 | 4,912 |
| 1933 | 200,968 | 26,428 | 7,340 | 15,715 | 4,511 | 7,149 | 3,586 | 4,806 |
| 1934 | 200,070 | 26,636 | 7,587 | 15,901 | 4,365 | 7,183 | 3,651 | 4,721 |
| 1935 | 197,689 | 26,869 | 7,876 | 16,162 | 4,593 | 7,323 | 3,968 | 4,818 |
| 1936 | 210,552 | 27,709 | 9,175 | 16,556 | 4,070 | 7,422 | 4,241 | 4,967 |
| 1937 | 208,036 | 27,931 | 9,642 | 16,811 | 4,389 | 7,833 | 4,613 | 5,010 |
| 1938 | 206,375 | 28,386 | 9,832 | 17,764 | 4,905 | 8,149 | 4,902 | 5,219 |
| 1939 | 205,415 | 28,280 | 10,403 | 18,176 | 5,401 | 8,481 | 5,137 | 5,647 |
| 1940 | 204,276 | 28,454 | 10,730 | 17,710 | 5,253 | 8,009 | 5,207 | 5,197 |
| 1941 | 204,332 | 28,614 | 10,916 | 16,986 | 5,033 | 7,371 | 5,325 | 4,964 |
| 1942 | 204,200 | 28,467 | 11,009 | 16,805 | 4,852 | 7,923 | 5,357 | 4,292 |
| 1943 | 204,372 | 29,328 | 11,274 | 18,324 | 5,197 | 8,436 | 6,035 | 5,693 |
| 1944 | 206,220 | 29,717 | 11,793 | 20,829 | 6,187 | 10,233 | 6,927 | 6,986 |
| 1945 | 209,899 | 30,401 | 12,190 | 21,566 | 6,872 | 10,865 | 7,831 | 8,149 |
| 1946 | 218,614 | 31,506 | 12,654 | 21,936 | 6,656 | 11,712 | 8,419 | 10,993 |
| 1947 | 227,108 | 32,604 | 13,170 | 21,847 | 6,666 | 12,328 | 8,913 | 11,291 |
| 1948 | 233,304 | 33,360 | 13,254 | 22,059 | 6,895 | 12,136 | 8,809 | 11,380 |
| 1949 | 242,038 | 34,960 | 13,288 | 22,617 | 7,320 | 12,504 | 9,182 | 11,000 |
| 1950 | 254,533 | 36,748 | 13,426 | 23,539 | 6,992 | 13,859 | 9,439 | 10,936 |
| 1951 | 267,541 | 38,512 | 13,663 | 24,628 | 7,195 | 14,871 | 9,946 | 10,428 |
| 1952 | 285,040 | 40,444 | 14,076 | 26,411 | 7,946 | 16,179 | 10,558 | 10,225 |
| 1953 | 300,748 | 42,799 | 14,345 | 28,783 | 8,709 | 18,136 | 11,368 | 10,326 |
| 1954 | 314,944 | 44,240 | 14,086 | 35,616 | 8,364 | 18,268 | 12,568 | 10,304 |
| 1955 | 321,537 | 45,963 | 13,988 | 40,824 | 8,876 | 18,292 | 12,903 | 10,331 |
| 1956 | 335,645 | 48,434 | 13,996 | 43,111 | 8,618 | 19,069 | 14,534 | 10,493 |
| 1957 | 348,940 | 49,644 | 13,284 | 47,141 | 8,823 | 17,496 | 15,738 | 11,039 |
| 1958 | 364,181 | 51,063 | 14,135 | 51,573 | 8,720 | 17,406 | 16,557 | 12,085 |
| 1959 | 373,807 | 53,431 | 13,153 | 57,631 | 8,210 | 18,297 | 17,238 | 13,505 |
| 1960 | 378,927 | 54,168 | 13,187 | 64,434 | 7,542 | 20,985 | 18,684 | 14,934 |
NOTE - In addition, in 1960, 875 attended the affiliated agricultural colleges, 1,125 received tuition from the Primary Correspondence School, 551 from the Secondary Correspondence School, and 4,807 from the Technical Correspondence School.
JUSTICE
| Year | Summary Convictions in Magistrates' Courts* | Total Convictions or Sentences in Superior Courts | Total Distinct Persons Sentenced in Superior Courts | Prisoners in Gaol at End of Year (Undergoing Sentence) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Population | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Population | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Mean Population | Number | Rate per 1,000 of Population | |
*Excluding Children's Court cases from year 1914 onwards. †Change in legislation has resulted in more cases being dealt with in Magistrates' Courts. | ||||||||
| 1909 | 31,151 | 30.55 | 552 | 0.54 | 544 | 0.53 | 877 | 0.85 |
| 1910 | 32,435 | 31.17 | 495 | 0.48 | 494 | 0.47 | 843 | 0.80 |
| 1911 | 33,029 | 31.05 | 453 | 0.43 | 427 | 0.40 | 802 | 0.75 |
| 1912 | 36,191 | 33.24 | 480 | 0.44 | 428 | 0.39 | 821 | 0.75 |
| 1913 | 39,685 | 35.48 | 446 | 0.40 | 409 | 0.37 | 834 | 0.74 |
| 1914 | 40,673 | 35.67 | 522 | 0.46 | 483 | 0.42 | 981 | 0.86 |
| 1915 | 38,446 | 33.45 | 509 | 0.44 | 441 | 0.38 | 941 | 0.82 |
| 1916 | 34,324 | 29.87 | 448 | 0.39 | 401 | 0.35 | 834 | 0.73 |
| 1917 | 33,302 | 28.99 | 623 | 0.54 | 377 | 0.33 | 954 | 0.83 |
| 1918 | 28,421 | 24.65 | 632 | 0.55 | 355 | 0.31 | 1,005 | 0.87 |
| 1919 | 31,766 | 26.63 | 808 | 0.68 | 461 | 0.39 | 852 | 0.69 |
| 1920 | 34,740 | 27.96 | 1,011 | 0.81 | 459 | 0.37 | 996 | 0.79 |
| 1921 | 36,492 | 28.58 | 1,475 | 1.16 | 616 | 0.48 | 1,044 | 0.81 |
| 1922 | 33,995 | 26.05 | 1,417 | 1.09 | 601 | 0.46 | 1,052 | 0.83 |
| 1923 | 36,701 | 29.14 | 1,663 | 1.25 | 625 | 0.47 | 1,141 | 0.85 |
| 1924 | 38,982 | 28.82 | 1,388 | 1.03 | 555 | 0.41 | 1,197 | 0.87 |
| 1925 | 43,407 | 31.35 | 1,465 | 1.06 | 511 | 0.37 | 1,284 | 0.92 |
| 1926 | 44,887 | 31.75 | 1,562 | 1.10 | 569 | 0.40 | 1,388 | 0.97 |
| 1927 | 44,540 | 30.95 | 1,739 | 1.21 | 569 | 0.40 | 1,483 | 1.02 |
| 1928 | 43,419 | 29.82 | 1,368 | 0.94 | 478 | 0.33 | 1,435 | 0.98 |
| 1929 | 44,311 | 30.07 | 1,345 | 0.91 | 473 | 0.32 | 1,342 | 0.90 |
| 1930 | 45,544 | 30.50 | 1,524 | 1.02 | 538 | 0.36 | 1,523 | 1.01 |
| 1931 | 40,374 | 26.66 | 1,624 | 1.07 | 600 | 0.40 | 1,614 | 1.06 |
| 1932 | 40,591 | 26.58 | 1,710 | 1.12 | 636 | 0.42 | 1,522 | 0.99 |
| 1933 | 36,043 | 23.41 | 1,513 | 0.98 | 531 | 0.34 | 1,410 | 0.91 |
| 1934 | 35,752 | 23.04 | 1,213 | 0.78 | 490 | 0.32 | 1,199 | 0.77 |
| 1935 | 36,230 | 23.19 | 1,148 | 0.73 | 472 | 0.30 | 1,112 | 0.71 |
| 1936 | 39,517 | 25.09 | 1,178 | 0.75 | 462 | 0.29 | 915 | 0.58 |
| 1937 | 42,726 | 26.87 | 1,318 | 0.83 | 507 | 0.32 | 790 | 0.49 |
| 1938 | 49,651 | 30.90 | 1,322 | 0.82 | 488 | 0.30 | 777 | 0.48 |
| 1939 | 52,288 | 32.11 | 1,489 | 0.91 | 571 | 0.35 | 895 | 0.55 |
| 1940 | 46,110 | 28.16 | 1,394 | 0.85 | 547 | 0.33 | 863 | 0.53 |
| 1941 | 39,636 | 24.30 | 1,496 | 0.92 | 542 | 0.33 | 988 | 0.61 |
| 1942 | 1,460 | 0.89 | 457 | 0.28 | 1,034 | 0.63 | ||
| 1943 | 1,378 | 0.84 | 494 | 0.30 | 1,024 | 0.62 | ||
| 1944 | 1,441 | 0.87 | 560 | 0.34 | 945 | 0.56 | ||
| 1945 | 1,885 | 1.11 | 619 | 0.37 | 998 | 0.58 | ||
| 1946 | 1,713 | 0.97 | 655 | 0.37 | 992 | 0.56 | ||
| 1947 | 40,990 | 22.79 | 1,948 | 1.08 | 740 | 0.41 | 1,088 | 0.60 |
| 1948 | 44,119 | 24.05 | 2,323 | 1.27 | 717 | 0.39 | 986 | 0.53 |
| 1949 | 50,000 | 26.71 | 1,718 | 0.92 | 676 | 0.36 | 941 | 0.50 |
| 1950 | 51,606 | 27.03 | 1,583 | 0.83 | 642 | 0.34 | 1,043 | 0.54 |
| 1951 | 56,128 | 28.82 | 1,574 | 0.81 | 644 | 0.33 | 1,040 | 0.53 |
| 1952 | 73,960 | 37.05 | 1,706 | 0.85 | 704 | 0.35 | 1,083 | 0.54 |
| 1953 | 82,143 | 40.09 | 361† | 0.18 | 179† | 0.09 | 1,088 | 0.52 |
| 1954 | 80,210 | 38.29 | 326† | 0.16 | 148† | 0.07 | 1,196 | 0.57 |
| 1955 | 77,806 | 36.38 | 377† | 0.18 | 147† | 0.07 | 1,118 | 0.52 |
| 1956 | 87,394 | 40.40 | 601† | 0.28 | 204† | 0.09 | 1,362 | 0.62 |
| 1957 | 98,647 | 44.18 | 567† | 0.25 | 199† | 0.09 | 1,474 | 0.66 |
| 1958 | 108,791 | 47.59 | 558† | 0.24 | 206† | 0.09 | 1,642 | 0.72 |
| 1959 | 101,655 | 43.54 | 595† | 0.25 | 212† | 0.09 | 1,714 | 0.73 |
AGRICULTURE
| Season | Wheat for Threshing | Oats for Threshing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Yield | Yield per acre | Area | Yield | Yield per acre | |
| *Yield probably overstated for these four seasons, owing to total being obtained by applying ascertained averages to areas returned by farmers as sown for threshing. Some areas returned in these years as intended for threshing would appear to have been eventually utilized for other purposes. | ||||||
| acres | bushels | bushels | acres | bushels | bushels | |
| 1909–10 | 311,000 | 8,661,100 | 28.00 | 377,000 | 13,804,000 | 37.00 |
| 1910–11 | 322,167 | 8,290,221 | 25.73 | 302,827 | 10,118,917 | 33.41 |
| 1911–12 | 215,528 | 7,261,138 | 33.69 | 403,668 | 19,662,668* | 48.71 |
| 1912–13 | 189,869 | 5,179,626 | 27.28 | 386,786 | 13,583,924* | 35.12 |
| 1913–14 | 166,774 | 5,231,700 | 31.37 | 361,741 | 14,740,946* | 40.75 |
| 1914–15 | 229,600 | 6,644,336 | 28.94 | 287,561 | 11,436,301* | 39.77 |
| 1915–16 | 329,207 | 7,108,360 | 21.59 | 212,688 | 7,653,208 | 35.98 |
| 1916–17 | 217,743 | 5,051,227 | 23.19 | 177,524 | 5,371,436 | 30.26 |
| 1917–18 | 280,978 | 6,807,536 | 24.23 | 156,202 | 4,942,759 | 31.64 |
| 1918–19 | 208,030 | 6,567,629 | 31.57 | 172,686 | 6,884,609 | 39.87 |
| 1919–20 | 139,611 | 4,559,934 | 32.66 | 179,800 | 6,967,862 | 38.75 |
| 1920–21 | 219,985 | 6,872,262 | 31.24 | 147,559 | 5,225,115 | 35.41 |
| 1921–22 | 352,918 | 10,565,275 | 29.94 | 170,655 | 6,752,663 | 39.56 |
| 1922–23 | 275,775 | 8,395,023 | 30.44 | 143,090 | 5,688,157 | 39.75 |
| 1923–24 | 173,864 | 4,174,537 | 24.01 | 63,842 | 1,964,511 | 30.77 |
| 1924–25 | 166,964 | 5,447,758 | 32.62 | 147,387 | 5,707,174 | 38.72 |
| 1925–26 | 151,673 | 4,617,041 | 30.44 | 102,485 | 4,115,606 | 40.14 |
| 1926–27 | 220,083 | 7,952,442 | 36.13 | 117,326 | 4,997,535 | 42.58 |
| 1927–28 | 260,987 | 9,541,444 | 36.56 | 88,223 | 3,852,687 | 43.66 |
| 1928–29 | 255,312 | 8,832,864 | 34.60 | 73,101 | 3,065,113 | 41.93 |
| 1929–30 | 235,942 | 7,239,556 | 30.68 | 67,722 | 3,002,288 | 44.33 |
| 1930–31 | 249,014 | 7,579,153 | 30.44 | 87,152 | 3,376,609 | 38.74 |
| 1931–32 | 268,756 | 6,582,698 | 24.49 | 68,690 | 2,818,152 | 41.03 |
| 1932–33 | 302,531 | 11,054,972 | 36.54 | 116,206 | 5,132,183 | 44.16 |
| 1933–34 | 286,271 | 9,036,017 | 31.56 | 78,343 | 3,242,500 | 41.39 |
| 1934–35 | 225,389 | 5,933,245 | 26.32 | 52,516 | 1,890,145 | 35.99 |
| 1935–36 | 248,639 | 8,859,223 | 35.63 | 77,502 | 3,302,642 | 42.61 |
| 1936–37 | 221,790 | 7,168,963 | 32.32 | 74,772 | 3,525,430 | 47.15 |
| 1937–38 | 185,949 | 6,042,981 | 32.50 | 57,917 | 2,640,915 | 45.60 |
| 1938–39 | 189,281 | 5,564,136 | 29.40 | 54,422 | 2,604,817 | 47.86 |
| 1939–40 | 257,532 | 8,010,089 | 31.10 | 49,751 | 2,081,106 | 41.83 |
| 1940–41 | 243,197 | 8,305,865 | 34.15 | 71,758 | 3,114,946 | 43.41 |
| 1941–42 | 258,002 | 8,671,244 | 33.61 | 70,796 | 3,444,812 | 48.66 |
| 1942–43 | 286,998 | 9,819,342 | 34.21 | 56,291 | 2,808,774 | 49.90 |
| 1943–44 | 233,786 | 7,208,485 | 30.83 | 39,652 | 1,834,310 | 46.26 |
| 1944–45 | 183,886 | 6,992,204 | 38.02 | 77,684 | 4,209,143 | 54.18 |
| 1945–46 | 161,049 | 5,439,041 | 33.77 | 57,278 | 2,796,877 | 48.83 |
| 1946–47 | 141,407 | 5,368,120 | 37.96 | 55,297 | 2,686,211 | 48.58 |
| 1947–48 | 123,751 | 4,539,017 | 36.68 | 63,159 | 2,853,517 | 45.18 |
| 1948–49 | 146,707 | 5,958,026 | 40.61 | 78,300 | 3,718,597 | 47.49 |
| 1949–50 | 125,159 | 4,899,668 | 39.15 | 52,645 | 2,620,252 | 49.77 |
| 1950–51 | 144,763 | 6,271,928 | 43.33 | 35,808 | 1,827,953 | 51.05 |
| 1951–52 | 89,955 | 3,890,167 | 43.25 | 45,561 | 2,469,530 | 54.20 |
| 1952–53 | 127,225 | 4,525,298 | 35.57 | 49,087 | 2,385,129 | 48.59 |
| 1953–54 | 113,813 | 4,783,227 | 42.03 | 20,529 | 945,386 | 46.05 |
| 1954–55 | 103,989 | 4,113,444 | 39.56 | 31,164 | 1,602,058 | 51.41 |
| 1955–56 | 68,479 | 2,658,428 | 38.82 | 42,168 | 1,947,404 | 46.18 |
| 1956–57 | 65,743 | 2,950,273 | 44.88 | 56,496 | 2,888,310 | 51.12 |
| 1957–58 | 83,936 | 3,727,117 | 44.40 | 29,981 | 1,460,149 | 48.70 |
| 1958–59 | 132,913 | 6,038,822 | 45.43 | 34,011 | 1,575,755 | 46.33 |
| 1959–60 | 163,158 | 8,700,199 | 53.32 | 33,524 | 1,825,104 | 54.44 |
LIVESTOCK
| Year | Horses | Total Cattle | Dairy Cows* | Sheep | Pigs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Figures from 1917 onwards are for dairy cows in milk only. | |||||
| 1910 | .. | .. | .. | 24,269,620 | .. |
| 1911 | 404,284 | 2,020,171 | 633,733 | 23,996,126 | 348,754 |
| 1912 | .. | .. | .. | 23,750,153 | .. |
| 1913 | .. | .. | .. | 24,191,810 | .. |
| 1914 | .. | .. | .. | 24,798,763 | .. |
| 1915 | .. | .. | .. | 24,901,421 | .. |
| 1916 | 371,331 | 2,417,491 | 750,323 | 24,788,150 | 297,501 |
| 1917 | 373,600 | 2,575,230 | 684,032 | 25,270,386 | 283,770 |
| 1918 | 378,050 | 2,869,465 | 710,561 | 26,538,302 | 258,694 |
| 1919 | 363,188 | 3,035,478 | 732,253 | 25,828,554 | 235,347 |
| 1920 | 346,407 | 3,101,945 | 782,757 | 23,919,970 | 266,829 |
| 1921 | 337,259 | 3,139,223 | 890,220 | 23,285,031 | 349,892 |
| 1922 | 332,105 | 3,323,223 | 1,015,325 | 22,222,259 | 384,333 |
| 1923 | 330,818 | 3,480,694 | 1,124,671 | 23,081,439 | 400,889 |
| 1924 | 330,430 | 3,563,497 | 1,184,977 | 23,775,776 | 414,271 |
| 1925 | 326,830 | 3,503,744 | 1,195,567 | 24,547,955 | 440,115 |
| 1926 | 314,867 | 3,452,486 | 1,181,441 | 24,904,993 | 472,534 |
| 1927 | 303,713 | 3,257,729 | 1,181,545 | 25,649,016 | 520,143 |
| 1928 | 307,160 | 3,273,769 | 1,242,729 | 27,133,810 | 586,898 |
| 1929 | 298,986 | 3,445,790 | 1,291,204 | 29,051,382 | 556,732 |
| 1930 | 297,195 | 3,770,223 | 1,389,541 | 30,841,287 | 487,793 |
| 1931 | 282,729 | 4,043,560 | 1,478,947 | 29,792,516 | 468,533 |
| 1932 | 267,980 | 4,035,418 | 1,562,079 | 28,691,788 | 505,755 |
| 1933 | 263,883 | 4,155,058 | 1,703,328 | 27,755,966 | 583,921 |
| 1934 | 260,892 | 4,264,163 | 1,795,817 | 28,649,038 | 652,732 |
| 1935 | 259,972 | 4,256,534 | 1,807,377 | 29,076,754 | 755,094 |
| 1936 | 263,156 | 4,217,113 | 1,802,773 | 30,113,704 | 800,802 |
| 1937 | 264,785 | 4,352,136 | 1,784,820 | 31,305,818 | 794,758 |
| 1938 | 265,153 | 4,469,117 | 1,743,190 | 32,378,774 | 748,805 |
| 1939 | 261,789 | 4,527,983 | 1,723,893 | 31,897,091 | 675,802 |
| 1940 | 258,567 | 4,496,067 | 1,719,289 | 31,062,875 | 706,340 |
| 1941 | 253,052 | 4,538,908 | 1,759,018 | 31,751,660 | 761,519 |
| 1942 | 248,597 | 4,604,749 | 1,756,654 | .. | 681,016 |
| 1943 | 236,455 | 4,447,548 | 1,714,959 | .. | 604,574 |
| 1944 | 225,823 | 4,439,258 | 1,647,920 | 33,200,298 | 573,362 |
| 1945 | 217,689 | 4,590,926 | 1,678,943 | 33,974,612 | 593,828 |
| 1946 | 216,335 | 4,666,782 | 1,661,944 | .. | 549,391 |
| 1947 | 206,575 | 4,633,800 | 1,657,690 | 32,681,799 | 545,874 |
| 1948 | 203,885 | 4,716,287 | 1,713,532 | 32,483,138 | 548,177 |
| 1949 | 196,055 | 4,722,836 | 1,746,753 | 32,844,918 | 544,841 |
| 1950 | 194,877 | 4,954,906 | 1,850,089 | 33,856,558 | 555,245 |
| 1951 | 183,972 | 5,060,024 | 1,898,197 | 34,786,386 | 564,335 |
| 1952 | 173,922 | 5,164,689 | 1,905,534 | 35,384,270 | 565,723 |
| 1953 | 158,065 | 5,445,963 | 1,962,492 | 36,192,935 | 627,830 |
| 1954 | 158,280 | 5,744,878 | 1,999,140 | 38,010,954 | 648,902 |
| 1955 | 147,063 | 5,886,777 | 1,994,761 | 39,117,300 | 681,359 |
| 1956 | .. | .. | .. | 40,255,488 | .. |
| 1957 | 129,309 | 5,808,635 | 1,997,819 | 42,382,008 | 602,469 |
| 1958 | 123,261 | 5,885,584 | 1,966,547 | 46,025,930 | 627,812 |
| 1959 | 122,957 | 5,973,352 | 1,931,112 | 46,876,222 | 691,568 |
| 1960 | 104,995 | 5,991,938 | 1,886,772 | 47,133,557 | 660,261 |
NOTE - With the exception of sheep, figures from 1931 onwards exclude stock within boroughs, and the figures for 1960 are for stock on holdings of 10 acres or over outside borough boundaries.
| TRADE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Excluding Specie* | Specie† | ||||||
| Exports | Imports | Exports | Imports | |||||
| Total | Per Head of Mean Population | Total | Per Head of Mean Population | |||||
*Figures are in terms of New Zealand currency. †Specie exports and imports represent face value. ‡Increases mainly due to imports of defence materials and equipment. §Provisional. | ||||||||
| £(000) | £ | s. | £(000) | £ | s. | £(000) | ||
| 1910 | 22,152 | 21 | 6 | 16,748 | 16 | 2 | 28 | 303 |
| 1911 | 18,980 | 17 | 17 | 18,783 | 17 | 13 | 48 | 763 |
| 1912 | 21,512 | 19 | 15 | 20,577 | 18 | 18 | 259 | 400 |
| 1913 | 22,810 | 20 | 8 | 21,654 | 19 | 7 | 176 | 635 |
| 1914 | 26,254 | 23 | 1 | 21,144 | 18 | 11 | 8 | 712 |
| 1915 | 31,431 | 27 | 7 | 20,659 | 18 | 0 | 318 | 1,070 |
| 1916 | 33,281 | 28 | 19 | 25,045 | 21 | 16 | 6 | 1,294 |
| 1917 | 31,517 | 27 | 9 | 20,742 | 18 | 1 | 70 | 177 |
| 1918 | 28,481 | 24 | 14 | 24,132 | 20 | 19 | 36 | 102 |
| 1919 | 53,908 | 45 | 4 | 30,309 | 25 | 8 | 62 | 363 |
| 1920 | 46,405 | 37 | 7 | 61,554 | 49 | 11 | 37 | 42 |
| 1921 | 44,828 | 35 | 2 | 42,744 | 33 | 10 | -- | 198 |
| 1922 | 42,726 | 32 | 15 | 34,826 | 26 | 14 | -- | 186 |
| 1923 | 45,940 | 34 | 12 | 43,364 | 32 | 13 | 27 | 15 |
| 1924 | 52,509 | 38 | 16 | 48,528 | 35 | 18 | 103 | -- |
| 1925 | 55,243 | 39 | 18 | 52,426 | 37 | 17 | 19 | 31 |
| 1926 | 45,269 | 32 | 1 | 49,812 | 35 | 5 | 7 | 78 |
| 1927 | 48,496 | 33 | 14 | 44,783 | 31 | 2 | -- | -- |
| 1928 | 55,570 | 38 | 3 | 44,844 | 30 | 16 | 618 | 42 |
| 1929 | 54,930 | 37 | 6 | 48,734 | 33 | 2 | 649 | 64 |
| 1930 | 44,941 | 30 | 2 | 44,340 | 29 | 14 | -- | 363 |
| 1931 | 34,951 | 23 | 2 | 26,498 | 17 | 10 | 202 | 56 |
| 1932 | 35,610 | 23 | 6 | 24,646 | 16 | 3 | 1,356 | 55 |
| 1933 | 41,006 | 26 | 13 | 25,581 | 16 | 12 | 296 | 425 |
| 1934 | 47,343 | 30 | 10 | 31,340 | 20 | 4 | 2,284 | 1,242 |
| 1935 | 46,538 | 29 | 16 | 36,317 | 23 | 5 | 521 | 382 |
| 1936 | 56,752 | 36 | 1 | 44,259 | 28 | 2 | 45 | 37 |
| 1937 | 66,713 | 41 | 19 | 56,161 | 35 | 6 | 4 | 319 |
| 1938 | 58,376 | 36 | 7 | 55,422 | 34 | 10 | 32 | 31 |
| 1939 | 58,049 | 35 | 13 | 49,387 | 30 | 7 | 3 | 25 |
| 1940 | 73,741 | 45 | 1 | 48,998 | 29 | 19 | -- | 37 |
| 1941 | 67,479 | 41 | 8 | 49,167 | 30 | 3 | 10 | 205 |
| 1942 | 81,285 | 49 | 12 | 53,856‡ | 32 | 17 | 25 | 147 |
| 1943 | 71,863 | 43 | 19 | 95,242‡ | 58 | 5 | 1 | 462 |
| 1944 | 77,787 | 47 | 0 | 86,397‡ | 52 | 4 | -- | 160 |
| 1945 | 81,631 | 48 | 3 | 55,088 | 32 | 10 | 4 | 208 |
| 1946 | 101,302 | 57 | 12 | 71,571 | 40 | 14 | 5 | 419 |
| 1947 | 129,420 | 71 | 19 | 128,641 | 71 | 11 | 10 | 185 |
| 1948 | 147,821 | 80 | 11 | 128,534 | 70 | 1 | 55 | 625 |
| 1949 | 147,281 | 78 | 14 | 120,033 | 64 | 3 | 570 | 1,041 |
| 1950 | 183,752 | 96 | 5 | 157,943 | 82 | 15 | 514 | 170 |
| 1951 | 248,127 | 127 | 8 | 206,534 | 106 | 1 | 280 | 250 |
| 1952 | 240,561 | 120 | 10 | 229,447 | 114 | 19 | 27 | 85 |
| 1953 | 235,860 | 115 | 2 | 163,613 | 79 | 17 | 8 | 107 |
| 1954 | 244,466 | 116 | 14 | 213,155 | 101 | 15 | 8 | 21 |
| 1955 | 259,289 | 121 | 4 | 250,661 | 117 | 4 | 13 | 44 |
| 1956 | 277,483 | 127 | 2 | 234,779 | 107 | 11 | 2 | 12 |
| 1957 | 276,569 | 123 | 18 | 261,738 | 117 | 5 | 15 | 49 |
| 1958 | 250,173 | 109 | 9 | 252,800 | 110 | 12 | 162 | 98 |
| 1959 | 293,659 | 125 | 16 | 205,076 | 87 | 8 | 39 | 55 |
| 1960§ | 302,508 | 127 | 5 | 251,811 | 105 | 18 | 37 | 57 |
NOTE - As from 1 January 1952 imports were valued at c.d.v. Prior to that date the valuation used was c.d.v. plus 10 per cent.
| Year | Exports of New Zealand Produce | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wool | Frozen Meat* | Tallow | ||||
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
*Includes exports of chilled beef. †Provisional. | ||||||
| lb(m.) | £(000) | tons | £(000) | tons | £(000) | |
| 1910 | 204 | 8,308 | 132,710 | 3,850 | 26,009 | 757 |
| 1911 | 169 | 6,492 | 112,528 | 3,503 | 20,656 | 607 |
| 1912 | 188 | 7,105 | 128,662 | 3,910 | 23,545 | 685 |
| 1913 | 187 | 8,058 | 128,935 | 4,450 | 22,743 | 663 |
| 1914 | 220 | 9,318 | 161,498 | 5,863 | 24,515 | 694 |
| 1915 | 197 | 10,388 | 179,563 | 7,794 | 26,763 | 781 |
| 1916 | 186 | 12,386 | 166,302 | 7,271 | 22,472 | 785 |
| 1917 | 178 | 12,175 | 122,347 | 5,982 | 12,599 | 553 |
| 1918 | 109 | 7,527 | 101,845 | 4,958 | 16,421 | 848 |
| 1919 | 274 | 19,560 | 191,134 | 9,628 | 46,874 | 2,680 |
| 1920 | 162 | 11,864 | 231,464 | 11,674 | 27,041 | 1,749 |
| 1921 | 159 | 5,221 | 216,138 | 11,164 | 27,712 | 867 |
| 1922 | 322 | 11,882 | 175,900 | 8,387 | 26,495 | 751 |
| 1923 | 218 | 10,905 | 152,196 | 9,013 | 25,243 | 786 |
| 1924 | 206 | 15,268 | 160,679 | 9,500 | 23,988 | 799 |
| 1925 | 206 | 17,740 | 170,710 | 11,175 | 25,038 | 895 |
| 1926 | 213 | 11,830 | 151,718 | 8,656 | 21,128 | 741 |
| 1927 | 221 | 12,962 | 168,248 | 9,105 | 23,875 | 714 |
| 1928 | 227 | 16,679 | 189,691 | 10,310 | 25,748 | 804 |
| 1929 | 235 | 15,359 | 166,810 | 9,883 | 20,832 | 694 |
| 1930 | 197 | 7,664 | 201,832 | 10,937 | 24,628 | 684 |
| 1931 | 212 | 5,515 | 206,940 | 8,893 | 23,264 | 413 |
| 1932 | 238 | 5,743 | 232,274 | 8,436 | 25,377 | 462 |
| 1933 | 286 | 7,422 | 260,156 | 9,846 | 28,020 | 516 |
| 1934 | 256 | 12,516 | 248,472 | 11,887 | 27,662 | 480 |
| 1935 | 223 | 7,097 | 260,326 | 12,769 | 25,277 | 631 |
| 1936 | 314 | 13,294 | 255,990 | 13,239 | 26,095 | 628 |
| 1937 | 282 | 19,070 | 270,546 | 14,690 | 25,940 | 648 |
| 1938 | 271 | 12,185 | 268,665 | 15,092 | 29,613 | 525 |
| 1939 | 277 | 11,666 | 295,313 | 15,391 | 29,137 | 457 |
| 1940 | 300 | 16,875 | 348,831 | 19,681 | 34,138 | 708 |
| 1941 | 216 | 12,613 | 264,242 | 16,595 | 39,328 | 818 |
| 1942 | 308 | 18,337 | 287,069 | 17,777 | 51,779 | 1,144 |
| 1943 | 207 | 13,484 | 220,633 | 13,802 | 43,955 | 1,071 |
| 1944 | 189 | 12,711 | 207,803 | 12,482 | 26,624 | 608 |
| 1945 | 166 | 12,717 | 282,692 | 17,598 | 30,726 | 909 |
| 1946 | 365 | 26,596 | 337,669 | 23,240 | 24,756 | 1,063 |
| 1947 | 375 | 31,970 | 347,781 | 29,353 | 25,725 | 2,367 |
| 1948 | 421 | 44,505 | 343,496 | 28,624 | 20,063 | 2,154 |
| 1949 | 430 | 46,554 | 344,103 | 27,230 | 25,432 | 2,531 |
| 1950 | 394 | 74,653 | 338,084 | 28,629 | 29,596 | 2,161 |
| 1951 | 317 | 128,176 | 274,801 | 25,394 | 29,848 | 2,568 |
| 1952 | 438 | 81,998 | 385,561 | 40,475 | 48,951 | 4,752 |
| 1953 | 392 | 84,598 | 326,688 | 39,887 | 40,153 | 1,945 |
| 1954 | 393 | 88,437 | 370,792 | 51,906 | 39,112 | 2,577 |
| 1955 | 417 | 93,887 | 378,178 | 60,740 | 43,434 | 2,872 |
| 1956 | 428 | 91,532 | 414,152 | 63,892 | 39,618 | 2,655 |
| 1957 | 432 | 105,959 | 388,446 | 64,078 | 46,207 | 3,033 |
| 1958 | 457 | 80,037 | 405,401 | 73,490 | 51,260 | 3,414 |
| 1959 | 529 | 89,643 | 434,739 | 71,250 | 53,559 | 3,283 |
| 1960† | 521 | 102,320 | 467,020 | 76,167 | 59,303 | 2,921 |
| Year | Exports of New Zealand Produce | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butter | Cheese | Gold | ||||
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| tons | £(000) | tons | £(000) | oz | £(000) | |
| 1910 | 17,827 | 1,812 | 22,596 | 1,195 | 478,288 | 1,896 |
| 1911 | 15,119 | 1,577 | 21,959 | 1,192 | 455,226 | 1,817 |
| 1912 | 18,906 | 2,089 | 28,854 | 1,680 | 343,163 | 1,345 |
| 1913 | 18,613 | 2,062 | 30,583 | 1,770 | 376,161 | 1,459 |
| 1914 | 21,703 | 2,339 | 43,189 | 2,564 | 227,954 | 895 |
| 1915 | 21,007 | 2,701 | 40,863 | 2,730 | 422,825 | 1,695 |
| 1916 | 17,932 | 2,632 | 47,471 | 3,514 | 292,620 | 1,199 |
| 1917 | 12,720 | 2,032 | 44,287 | 3,949 | 218,624 | 904 |
| 1918 | 21,551 | 3,402 | 44,172 | 4,087 | 11,987 | 42 |
| 1919 | 17,291 | 3,080 | 78,616 | 7,791 | 320,207 | 1,334 |
| 1920 | 15,600 | 3,022 | 61,103 | 6,161 | 212,973 | 884 |
| 1921 | 44,924 | 11,170 | 68,439 | 8,199 | 149,595 | 612 |
| 1922 | 56,010 | 9,042 | 58,060 | 4,687 | 131,848 | 540 |
| 1923 | 62,507 | 10,689 | 72,073 | 6,870 | 169,512 | 699 |
| 1924 | 63,473 | 11,642 | 79,724 | 7,023 | 133,631 | 552 |
| 1925 | 62,266 | 10,240 | 68,838 | 5,801 | 114,696 | 472 |
| 1926 | 58,402 | 8,695 | 73,077 | 5,939 | 125,777 | 516 |
| 1927 | 72,777 | 10,915 | 74,640 | 5,583 | 130,171 | 535 |
| 1928 | 72,479 | 11,303 | 78,364 | 6,694 | 118,722 | 490 |
| 1929 | 82,690 | 13,228 | 88,955 | 7,017 | 116,848 | 480 |
| 1930 | 94,212 | 11,854 | 90,649 | 6,438 | 133,749 | 551 |
| 1931 | 99,428 | 10,650 | 81,817 | 4,461 | 140,970 | 581 |
| 1932 | 109,277 | 10,639 | 89,522 | 4,951 | 200,648 | 1,092 |
| 1933 | 131,762 | 11,649 | 99,147 | 4,766 | 177,241 | 1,282 |
| 1934 | 130,726 | 10,043 | 99,225 | 4,694 | 162,490 | 1,321 |
| 1935 | 139,465 | 13,617 | 86,378 | 4,377 | 171,283 | 1,442 |
| 1936 | 139,807 | 15,318 | 82,910 | 5,122 | 168,073 | 1,399 |
| 1937 | 148,804 | 16,986 | 82,358 | 5,372 | 172,317 | 1,435 |
| 1938 | 130,727 | 16,520 | 80,526 | 5,935 | 152,487 | 1,297 |
| 1939 | 122,165 | 16,111 | 83,863 | 5,870 | 176,370 | 1,629 |
| 1940 | 131,135 | 18,228 | 101,675 | 8,233 | 188,459 | 1,948 |
| 1941 | 113,157 | 15,778 | 118,312 | 9,834 | 176,242 | 1,830 |
| 1942 | 117,231 | 16,478 | 134,381 | 11,860 | 167,246 | 1,727 |
| 1943 | 99,259 | 14,393 | 100,497 | 9,126 | 149,563 | 1,543 |
| 1944 | 115,340 | 18,553 | 77,703 | 7,444 | 138,048 | 1,424 |
| 1945 | 103,477 | 19,278 | 87,426 | 9,519 | 121,084 | 1,263 |
| 1946 | 101,794 | 19,841 | 75,746 | 8,448 | 111,531 | 1,185 |
| 1947 | 127,708 | 29,058 | 87,044 | 11,621 | 98,557 | 1,035 |
| 1948 | 135,634 | 33,763 | 75,623 | 11,197 | 58,400 | 609 |
| 1949 | 147,670 | 35,474 | 93,938 | 12,674 | 63,854 | 608 |
| 1950 | 138,267 | 35,873 | 99,890 | 14,536 | 110,486 | 1,311 |
| 1951 | 147,964 | 41,490 | 106,619 | 16,650 | 68,929 | 844 |
| 1952 | 184,028 | 56,145 | 91,255 | 15,527 | 66,616 | 798 |
| 1953 | 159,106 | 51,461 | 101,360 | 18,373 | 29,674 | 365 |
| 1954 | 132,481 | 44,807 | 90,396 | 16,380 | 41,484 | 488 |
| 1955 | 150,965 | 51,022 | 85,042 | 13,682 | 21,840 | 261 |
| 1956 | 167,449 | 53,168 | 88,877 | 22,244 | 20,450 | 244 |
| 1957 | 145,075 | 38,456 | 88,476 | 17,923 | 26,769 | 311 |
| 1958 | 175,392 | 38,850 | 89,428 | 12,402 | 19,392 | 232 |
| 1959 | 192,978 | 55,808 | 83,452 | 22,103 | 30,333 | 364 |
| 1960* | 157,050 | 50,135 | 79,412 | 18,558 | 25,953 | 311 |
| Year | Exports of New Zealand Produce | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apples and Pears | Grass and Clover Seeds | Milk and Cream (Dried and Condensed) | ||||
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value | |
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| lb(000) | £ | cwt | £ | tons | £ | |
| 1910 | 215 | 1,590 | 54,946 | 113,568 | 105 | 5,326 |
| 1911 | 240 | 2,049 | 18,438 | 40,317 | 126 | 6,898 |
| 1912 | 589 | 4,979 | 36,344 | 69,694 | 14 | 671 |
| 1913 | 1,505 | 12,160 | 35,589 | 60,492 | 8 | 359 |
| 1914 | 2,554 | 22,412 | 39,572 | 73,551 | 21 | 791 |
| 1915 | 2,459 | 21,402 | 13,980 | 42,314 | 525 | 20,388 |
| 1916 | 865 | 7,465 | 9,841 | 34,266 | 439 | 23,780 |
| 1917 | 7 | 108 | 16,484 | 48,635 | 1,832 | 153,538 |
| 1918 | 12 | 160 | 15,995 | 42,215 | 3,153 | 341,797 |
| 1919 | 13 | 210 | 49,906 | 249,886 | 4,685 | 579,266 |
| 1920 | 1,405 | 15,073 | 23,821 | 147,369 | 6,228 | 795,612 |
| 1921 | 2,042 | 23,590 | 37,319 | 156,114 | 8,302 | 1,109,331 |
| 1922 | 4,741 | 65,732 | 70,120 | 285,451 | 5,099 | 529,650 |
| 1923 | 5,954 | 74,455 | 47,031 | 175,754 | 7,242 | 513,495 |
| 1924 | 9,784 | 122,721 | 36,331 | 149,083 | 6,018 | 505,098 |
| 1925 | 8,787 | 120,546 | 45,368 | 151,164 | 6,135 | 425,738 |
| 1926 | 29,350 | 369,664 | 57,726 | 200,380 | 5,056 | 345,072 |
| 1927 | 21,841 | 272,848 | 90,362 | 255,798 | 5,545 | 346,271 |
| 1928 | 40,618 | 514,992 | 50,238 | 162,452 | 7,687 | 392,452 |
| 1929 | 40,343 | 582,809 | 57,869 | 182,537 | 6,132 | 352,587 |
| 1930 | 53,091 | 669,214 | 36,560 | 166,221 | 6,786 | 351,339 |
| 1931 | 53,607 | 669,145 | 40,953 | 155,410 | 5,735 | 246,483 |
| 1932 | 63,222 | 799,420 | 34,337 | 109,632 | 7,158 | 269,121 |
| 1933 | 57,537 | 720,766 | 80,308 | 152,458 | 7,875 | 315,964 |
| 1934 | 62,679 | 778,840 | 48,751 | 166,511 | 9,626 | 407,708 |
| 1935 | 41,578 | 524,493 | 71,649 | 215,738 | 9,278 | 370,890 |
| 1936 | 49,337 | 608,430 | 79,982 | 249,861 | 10,599 | 405,801 |
| 1937 | 37,720 | 472,739 | 58,107 | 205,988 | 11,033 | 364,676 |
| 1938 | 61,847 | 772,096 | 45,484 | 233,372 | 9,168 | 307,603 |
| 1939 | 41,906 | 574,704 | 45,829 | 284,514 | 10,958 | 377,506 |
| 1940 | 23,709 | 226,002 | 45,742 | 369,035 | 10,464 | 419,176 |
| 1941 | 425 | 4,660 | 88,191 | 563,673 | 13,233 | 699,533 |
| 1942 | 327 | 3,511 | 82,499 | 592,681 | 12,315 | 683,578 |
| 1943 | 185 | 2,002 | 90,720 | 665,113 | 10,353 | 598,228 |
| 1944 | 20 | 303 | 158,475 | 1,453,090 | 8,228 | 534,716 |
| 1945 | 159 | 2,118 | 166,553 | 1,797,827 | 15,105 | 1,021,128 |
| 1946 | 12,159 | 153,408 | 150,598 | 1,942,072 | 16,995 | 1,202,323 |
| 1947 | 239 | 4,260 | 147,011 | 1,663,365 | 19,981 | 1,651,396 |
| 1948 | 40,204 | 873,627 | 174,843 | 1,700,644 | 26,540 | 2,209,805 |
| 1949 | 21,364 | 383,182 | 161,993 | 1,523,426 | 34,390 | 2,866,116 |
| 1950 | 38,603 | 679,243 | 164,114 | 2,083,630 | 40,632 | 3,321,883 |
| 1951 | 27,944 | 691,717 | 88,428 | 1,246,014 | 46,713 | 3,952,028 |
| 1952 | 55,278 | 2,060,089 | 163,452 | 2,106,627 | 62,732 | 6,563,941 |
| 1953 | 46,122 | 1,714,903 | 179,267 | 1,869,676 | 62,990 | 6,277,745 |
| 1954 | 49,693 | 1,549,342 | 184,253 | 2,802,421 | 45,223 | 4,091,835 |
| 1955 | 41,639 | 1,303,398 | 79,398 | 1,348,133 | 50,925 | 3,586,598 |
| 1956 | 64,486 | 2,029,327 | 146,403 | 1,597,467 | 52,080 | 4,384,527 |
| 1957 | 57,389 | 1,801,521 | 162,552 | 1,189,605 | 67,711 | 5,741,428 |
| 1958 | 73,137 | 2,289,340 | 148,230 | 1,517,716 | 89,428 | 3,806,182 |
| 1959 | 76,754 | 2,400,980 | 91,221 | 988,271 | 70,379 | 5,728,978 |
| 1960* | 76,806 | 2,402,889 | 128,325 | 1,679,427 | 60,313 | 5,532,348 |
| Year | Exports of New Zealand Produce | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle Hides and Calf Skins | Sheep Skins | |||||
| Cattle Hides | Calf Skins | Aggregate Value | With Wool | Without Wool | Aggregate Value | |
| *Provisional. | ||||||
| (thousand) | £(000) | (thousand) | £(000) | |||
| 1910 | .. | .. | .. | 983 | 6,827 | 741 |
| 1911 | .. | .. | .. | 901 | 6,719 | 634 |
| 1912 | .. | .. | .. | 920 | 7,001 | 707 |
| 1913 | .. | .. | .. | 933 | 7,238 | 800 |
| 1914 | 214 | 182 | 408 | 919 | 7,607 | 857 |
| 1915 | 270 | 234 | 572 | 499 | 8,595 | 827 |
| 1916 | 297 | 206 | 672 | 398 | 7,938 | 918 |
| 1917 | 177 | 51 | 454 | 3 | 6,525 | 1,300 |
| 1918 | 207 | 106 | 530 | - | 8,742 | 1,814 |
| 1919 | 319 | 107 | 964 | - | 8,502 | 1,695 |
| 1920 | 285 | 251 | 1,126 | - | 9,222 | 3,060 |
| 1921 | 329 | 441 | 569 | 86 | 8,351 | 972 |
| 1922 | 240 | 465 | 504 | 645 | 9,500 | 980 |
| 1923 | 340 | 609 | 746 | 706 | 7,541 | 1,122 |
| 1924 | 470 | 707 | 832 | 689 | 8,136 | 1,513 |
| 1925 | 496 | 702 | 940 | 471 | 8,224 | 1,989 |
| 1926 | 449 | 751 | 756 | 707 | 8,525 | 1,544 |
| 1927 | 398 | 774 | 923 | 973 | 8,946 | 1,551 |
| 1928 | 432 | 770 | 1,228 | 1,365 | 8,817 | 1,924 |
| 1929 | 291 | 668 | 678 | 1,072 | 8,560 | 1,812 |
| 1930 | 291 | 657 | 511 | 1,542 | 9,478 | 1,517 |
| 1931 | 309 | 653 | 337 | 1,666 | 10,420 | 806 |
| 1932 | 304 | 846 | 306 | 1,641 | 11,999 | 694 |
| 1933 | 401 | 891 | 544 | 3,380 | 11,814 | 1,403 |
| 1934 | 476 | 1,110 | 627 | 2,950 | 9,244 | 1,250 |
| 1935 | 522 | 1,266 | 686 | 2,405 | 11,765 | 1,275 |
| 1936 | 431 | 1,178 | 762 | 1,780 | 10,847 | 1,703 |
| 1937 | 506 | 1,163 | 1,031 | 1,744 | 10,759 | 2,246 |
| 1938 | 516 | 1,247 | 743 | 1,824 | 12,354 | 1,369 |
| 1939 | 528 | 1,103 | 781 | 1,933 | 13,224 | 1,460 |
| 1940 | 520 | 1,032 | 860 | 1,799 | 11,340 | 1,932 |
| 1941 | 385 | 1,016 | 1,003 | 770 | 17,744 | 2,007 |
| 1942 | 357 | 931 | 1,065 | 1,013 | 14,590 | 2,807 |
| 1943 | 418 | 944 | 1,129 | 777 | 14,000 | 2,264 |
| 1944 | 305 | 888 | 900 | 815 | 14,425 | 2,387 |
| 1945 | 329 | 795 | 1,040 | 905 | 14,324 | 2,402 |
| 1946 | 392 | 660 | 1,480 | 784 | 14,694 | 2,491 |
| 1947 | 473 | 757 | 2,917 | 1,416 | 15,624 | 6,014 |
| 1948 | 476 | 666 | 2,887 | 869 | 16,289 | 5,658 |
| 1949 | 328 | 1,122 | 2,340 | 795 | 16,620 | 3,856 |
| 1950 | 363 | 870 | 2,601 | 670 | 16,791 | 6,736 |
| 1951 | 336 | 977 | 2,992 | 719 | 13,986 | 9,033 |
| 1952 | 533 | 1,578 | 3,258 | 1,100 | 18,992 | 6,416 |
| 1953 | 400 | 961 | 2,402 | 1,254 | 17,032 | 7,934 |
| 1954 | 503 | 1,129 | 2,584 | 1,068 | 17,831 | 7,659 |
| 1955 | 654 | 1,304 | 2,822 | 1,064 | 19,249 | 6,082 |
| 1956 | 837 | 1,117 | 2,965 | 1,088 | '19,271 | 7,319 |
| 1957 | 906 | 1,280 | 3,241 | 1,066 | 18,745 | 6,645 |
| 1958 | 904 | 1,015 | 2,922 | 915 | 19,679 | 5,085 |
| 1959 | 880 | 963 | 4,468 | 1,250 | 24,618 | 8,457 |
| 1960* | 807 | 1,029 | 3,368 | 1,236 | 25,988 | 9,529 |
PRODUCTION
| Season | Wool Production | Butterfat Production | Timber Production | Meat Production | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Production (Greasy Basis) | Average Price per Pound (Greasy Wool) | Total Value | Total Production | Yield per Cow in Milk | Average Payout per Pound† | |||
*Provisional. †Excludes payment for butterfat in milk and cream consumed as such. | ||||||||
| lb (m.) | d. | £(m.) | lb (m.) | lb | d | bd. ft.(m.) | ton(000) | |
| 1914–15 | 229 | 11 | 10.5 | 112 | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| 1915–16 | 229 | 15 | 14.3 | 120 | 180 | 16.5 | 309 | .. |
| 1916–17 | 231 | 15 | 14.4 | 127 | 186 | .. | .. | .. |
| 1917–18 | 239 | 15 | 14.9 | 121 | 170 | .. | .. | .. |
| 1918–19 | 241 | 15 | 15.1 | 124 | 170 | .. | .. | .. |
| 1919–20 | 229 | 15 | 14.3 | 136 | 174 | 21.0 | 301 | .. |
| 1920–21 | 217 | 7 | 6.3 | 155 | 174 | 28.0 | 308 | .. |
| 1921–22 | 210 | 8 | 7.0 | 199 | 196 | 14.5 | 315 | .. |
| 1922–23 | 209 | 10.85 | 9.4 | 226 | 201 | 17.0 | 304 | .. |
| 1923–24 | 216 | 15.78 | 14.2 | 229 | 193 | 15.5 | 317 | .. |
| 1924–25 | 223 | 20.21 | 18.8 | 241 | 202 | 17.0 | 344 | .. |
| 1925–26 | 228 | 11.93 | 11.3 | 234 | 198 | 18.0 | 353 | .. |
| 1926–27 | 241 | 12.70 | 12.8 | 259 | 219 | 15.5 | 306 | .. |
| 1927–28 | 253 | 16.67 | 17.6 | 264 | 213 | 18.0 | 270 | .. |
| 1928–29 | 263 | 14.88 | 16.3 | 289 | 224 | 18.5 | 270 | .. |
| 1929–30 | 262 | 8.55 | 9.3 | 314 | 226 | 16.0 | 282 | .. |
| 1930–31 | 259 | 5.67 | 6.1 | 322 | 215 | 11.5 | 229 | .. |
| 1931–32 | 270 | 5.26 | 5.9 | 340 | 215 | 11.0 | 154 | .. |
| 1932–33 | 277 | 5.15 | 5.9 | 397 | 230 | 9.0 | 166 | .. |
| 1933–34 | 290 | 11.07 | 13.4 | 427 | 235 | 9.0 | 198 | .. |
| 1934–35 | 265 | 6.54 | 7.2 | 410 | 224 | 9.5 | 244 | .. |
| 1935–36 | 304 | 9.13 | 11.6 | 437 | 240 | 12.5 | 293 | .. |
| 1936–37 | 303 | 15.71 | 19.8 | 458 | 254 | 13.7 | 306 | .. |
| 1937–38 | 297 | 10.04 | 12.4 | 435 | 247 | 15.2 | 323 | .. |
| 1938–39 | 328 | 9.17 | 12.5 | 400 | 229 | 16.5 | 317 | .. |
| 1939–40 | 310 | 12.85 | 15.8 | 431 | 247 | 16.7 | 336 | .. |
| 1940–41 | 331 | 12.87 | 16.9 | 466 | 262 | 16.7 | 342 | .. |
| 1941–42 | 345 | 12.88 | 17.6 | 437 | 246 | 16.8 | 324 | .. |
| 1942–43 | 340 | 14.58 | 19.7 | 407 | 234 | 17.1 | 342 | .. |
| 1943–44 | 330 | 14.60 | 19.2 | 387 | 232 | 18.2 | 351 | .. |
| 1944–45 | 372 | 14.61 | 21.6 | 432 | 254 | 20.3 | 340 | .. |
| 1945–46 | 365 | 14.51 | 21.2 | 373 | 221 | 21.2 | 345 | 541 |
| 1946–47 | 367 | 17.83 | 27.5 | 408 | 243 | 23.7 | 354 | 560 |
| 1947–48 | 362 | 25.11 | 37.9 | 418 | 241 | 26.6 | 431 | 549 |
| 1948–49 | 367 | 25.81 | 39.5 | 457 | 259 | 27.8 | 470 | 556 |
| 1949–50 | 390 | 37.98 | 61.7 | 471 | 251 | 29.2 | 478 | 577 |
| 1950–51 | 390 | 87.84 | 142.7 | 495 | 258 | 31.0 | 528 | 530 |
| 1951–52 | 407 | 40.19 | 68.2 | 502 | 262 | 34.6 | 575 | 602 |
| 1952–53 | 418 | 46.19 | 80.4 | 535 | 272 | 37.2 | 575 | 578 |
| 1953–54 | 426 | 50.25 | 89.2 | 496 | 247 | 38.9 | 574 | 589 |
| 1954–55 | 455 | 49.67 | 94.2 | 505 | 253 | 38.2 | 616 | 637 |
| 1955–56 | 462 | 46.19 | 88.9 | 528 | 264 | 38.0 | 626 | 682 |
| 1956–57 | 491 | 54.76 | 112.0 | 523 | 261 | 38.1 | 597 | 670 |
| 1957–58 | 496 | 41.16 | 85.1 | 557 | 282 | 36.9 | 597 | 688 |
| 1958–59 | 540 | 36.07 | 81.2 | 556 | 287 | 32.8 | 637 | 736 |
| 1959–60 | 577 | 44.65 | 107.3 | 545 | 282* | 33.4* | 694* | 157* |
FACTORY PRODUCTION (REVISED SERIES)
| Year | Number of Establishments | Persons* Engaged | Salaries* and Wages Paid | Cost of Materials | Other Expenses of Production | Value of Output | Added Value | Value of Land and Buildings, Plant and Machinery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*For the year 1915–16 and earlier years, figures refer to productive employees only. †Estimates based on results of sample survey carried out during that year. | ||||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1877–78 | 1,093 | 10,604 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 2,382 |
| 1880–81 | 1,430 | 13,922 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 7,102 |
| 1885–86 | 1,833 | 19,653 | .. | .. | .. | 6,458 | .. | 4,069 |
| 1890–91 | 2,152 | 23,761 | 1,657 | .. | 8,558 | .. | 4,335 | |
| 1895–96 | 2,361 | 25,397 | 1,748 | 3,562 | .. | 9,264 | 5,703 | 4,777 |
| 1900–01 | 3,059 | 38,651 | 2,811 | 7,716 | .. | 16,485 | 8,769 | 6,546 |
| 1905–06 | 3,381 | 45,198 | 3,593 | 13,290 | .. | 21,610 | 8,320 | 9,537 |
| 1910–11 | 3,421 | 42,142 | 4,353 | 18,738 | .. | 28,569 | 9,831 | 11,989 |
| 1915–16 | 3,657 | 44,673 | 5,317 | 29,850 | .. | 41,924 | 12,073 | 15,799 |
| 1918–19 | 3,385 | 53,062 | 7,646 | 38,291 | .. | 53,806 | 15,515 | 19,144 |
| 1920–21 | 3,894 | 62,972 | 11,753 | 53,009 | .. | 75,489 | 22,479 | 25,696 |
| 1925–26 | 4,643 | 70,212 | 14,149 | 51,303 | 7,262 | 78,468 | 27,165 | 32,420 |
| 1930–31 | 5,047 | 70,625 | 13,885 | 45,314 | 8,448 | 71,721 | 26,407 | 34,496 |
| 1931–32 | 4,823 | 62,335 | 11,199 | 38,867 | 7,660 | 60,751 | 21,884 | 32,919 |
| 1932–33 | 4,847 | 62,583 | 10,674 | 38,945 | 7,519 | 60,159 | 21,214 | 32,945 |
| 1933–34 | 4,883 | 65,961 | 10,729 | 43,513 | 7,536 | 65,908 | 22,395 | 31,965 |
| 1934–35 | 5,126 | 72,095 | 11,694 | 48,835 | 8,163 | 73,320 | 24,485 | 32,415 |
| 1935–36 | 5,391 | 78,701 | 13,091 | 56,859 | 8,665 | 83,766 | 26,907 | 33,175 |
| 1936–37 | 5,584 | 87,822 | 16,296 | 67,496 | 9,778 | 99,379 | 31,883 | 34,386 |
| 1937–38 | 5,780 | 93,534 | 18,703 | 71,750 | 9,808 | 106,502 | 34,752 | 36,308 |
| 1938–39 | 6,002 | 93,638 | 19,927 | 71,173 | 9,316 | 106,608 | 35,435 | 38,597 |
| 1939–40 | 6,198 | 99,349 | 21,893 | 80,210 | 10,345 | 120,324 | 40,114 | 41,020 |
| 1940–41 | 6,252 | 104,784 | 24,306 | 93,013 | 11,203 | 137,399 | 44,386 | 42,165 |
| 1941–42 | 6,225 | 108,275 | 26,813 | 96,482 | 12,047 | 145,608 | 49,126 | 43,752 |
| 1942–43 | 5,985 | 106,179 | 29,427 | 101,900 | 12,541 | 155,779 | 53,879 | 44,674 |
| 1943–44 | 6,062 | 109,221 | 31,398 | 107,027 | 13,626 | 164,837 | 57,810 | 45,984 |
| 1944–45 | 6,340 | 113,534 | 34,197 | 116,476 | 14,556 | 178,586 | 62,110 | 48,765 |
| 1945–46 | 6,847 | 118,886 | 37,910 | 117,639 | 15,312 | 183,542 | 66,483 | 51,781 |
| 1946–47 | 7,498 | 124,925 | 41,488 | 131,348 | 17,279 | 205,649 | 74,301 | 55,775 |
| 1947–48 | 7,822 | 130,504 | 47,940 | 174,845 | 20,077 | 259,181 | 84,336 | 63,316 |
| 1948–49† | 7,852 | 132,427 | 51,402 | 195,053 | 21,955 | 286,396 | 91,343 | 73,585 |
| 1949–50 | 7,815 | 133,245 | 56,231 | 215,009 | 24,140 | 317,343 | 102,334 | 77,993 |
| 1950–51 | 8,113 | 138,435 | 65,005 | 266,885 | 28,867 | 380,200 | 113,316 | 87,617 |
| 1951–52 | 8,546 | 144,352 | 75,029 | 290,731 | 31,940 | 430,984 | 140,252 | 97,522 |
| 1952–53 | 8,511 | 143,164 | 78,483 | 318,949 | 35,258 | 463,940 | 144,912 | 109,100 |
| 1953–54 | 8,377 | 146,488 | 86,621 | 332,825 | 40,263 | 495,213 | 162,389 | 122,269 |
| 1954–55 | 8,366 | 153,575 | 98,413 | 365,299 | 47,853 | 550,618 | 185,318 | 138,274 |
| 1955–56 | 8,515 | 158,238 | 107,939 | 384,794 | 56,541 | 585,942 | 201,148 | 168,573 |
| 1956–57 | 8,488 | 156,752 | 110,948 | 394,988 | 59,902 | 602,041 | 207,053 | 180,123 |
| 1957–58 | 8,529 | 162,985 | 119,989 | 417,918 | 66,052 | 644,929 | 227,011 | 189,287 |
| 1958–59 | 8,565 | 168,742 | 128,278 | 418,647 | 70,321 | 659,455 | 240,807 | 205,886 |
| 1959–60 | 8,550 | 172,106 | 136,176 | 439,088 | 72,963 | 705,617 | 266,529 | 223,727 |
REVENUE AND EXPENDITURE OF GENERAL GOVERNMENT
| Year Ended 31 March | Consolidated Fund* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts | Payments | Deficit | Surplus | |||
| From Taxation | From Other Sources | Total | ||||
*See p. 791 for coverage of Consolidated Fund. †Excludes £20,000,000 loan portions of payment to Reserve Bank for liability due to alteration in the exchange rate as from 20 August 1948. ‡Excludes duty on motor spirits refunded under the Transport Amendment Act 1958 (£933,000 in 1958–59, £2,327,000 in 1959–60 and £993,000 in 1960–61). | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1911 | 4,837 | 5,460 | 10,297 | 9,343 | ... | 954 |
| 1912 | 5,297 | 5,765 | 11,061 | 10,340 | ... | 721 |
| 1913 | 5,607 | 6,127 | 11,734 | 11,082 | ... | 652 |
| 1914 | 5,918 | 6,312 | 12,230 | 11,826 | ... | 404 |
| 1915 | 5,882 | 6,570 | 12,452 | 12,380 | ... | 72 |
| 1916 | 7,267 | 7,243 | 14,510 | 12,493 | ... | 2,017 |
| 1917 | 10,550 | 7,818 | 18,368 | 14,059 | ... | 4,309 |
| 1918 | 12,341 | 7,865 | 20,206 | 15,120 | ... | 5,086 |
| 1919 | 13,802 | 8,551 | 22,352 | 18,674 | ... | 3,679 |
| 1920 | 16,257 | 9,825 | 26,081 | 23,782 | ... | 2,299 |
| 1921 | 22,184 | 12,077 | 34,261 | 28,129 | ... | 6,132 |
| 1922 | 16,371 | 11,756 | 28,127 | 28,467 | 340 | |
| 1923 | 15,594 | 11,985 | 27,579 | 26,264 | ... | 1,316 |
| 1924 | 16,417 | 11,544 | 27,960 | 26,148 | ... | 1,812 |
| 1925 | 16,555 | 12,088 | 28,643 | 27,399 | ... | 1,244 |
| 1926 | 16,978 | 7,747 | 24,726 | 23,570 | ... | 1,156 |
| 1927 | 16,900 | 8,044 | 24,943 | 24,356 | ... | 587 |
| 1928 | 16,849 | 8,275 | 25,124 | 24,945 | ... | 179 |
| 1929 | 17,835 | 5,765 | 23,600 | 24,177 | 577 | ... |
| 1930 | 19,474 | 5,876 | 25,350 | 25,201 | ... | 149 |
| 1931 | 18,597 | 4,471 | 23,069 | 24,708 | 1,639 | ... |
| 1932 | 16,188 | 6,532 | 22,720 | 24,861 | 2,141 | ... |
| 1933 | 15,604 | 6,964 | 22,569 | 22,528 | ... | 40 |
| 1934 | 17,060 | 6,433 | 23,493 | 24,202 | 709 | ... |
| 1935 | 20,178 | 5,948 | 26,126 | 24,500 | ... | 1,626 |
| 1936 | 21,556 | 4,616 | 26,172 | 25,891 | ... | 282 |
| 1937 | 26,941 | 4,206 | 31,147 | 30,675 | ... | 472 |
| 1938 | 31,664 | 13,145 | 44,810 | 43,999 | ... | 811 |
| 1939 | 32,306 | 11,393 | 43,699 | 42,889 | ... | 809 |
| 1940 | 32,811 | 14,109 | 46,919 | 46,600 | ... | 319 |
| 1941 | 34,874 | 16,107 | 50,981 | 49,254 | ... | 1,726 |
| 1942 | 35,162 | 19,391 | 54,553 | 52,880 | ... | 1,672 |
| 1943 | 36,196 | 18,880 | 55,076 | 50,921 | ... | 4,155 |
| 1944 | 42,018 | 15,544 | 57,561 | 55,329 | ... | 2,233 |
| 1945 | 45,689 | 14,239 | 59,929 | 58,714 | ... | 1,215 |
| 1946 | 48,371 | 15,543 | 63,914 | 62,659 | ... | 1,254 |
| 1947 | 90,715 | 17,579 | 108,294 | 103,683 | ... | 4,611 |
| 1948 | 96,099 | 21,017 | 117,116 | 115,330 | ... | 1,786 |
| 1949 | 101,062 | 20,462 | 121,524† | 118,893† | ... | 2,631 |
| 1950 | 103,853 | 21,143 | 124,997 | 120,689 | ... | 4,308 |
| 1951 | 122,181 | 21,576 | 143,757 | 135,504 | ... | 8,253 |
| 1952 | 156,937 | 23,851 | 180,788 | 168,153 | 12,636 | |
| 1953 | 154,262 | 23,560 | 177,822 | 174,515 | 3,307 | |
| 1954 | 156,196 | 26,124 | 182,319 | 180,516 | 1,803 | |
| 1955 | 162,509 | 28,708 | 191,216 | 184,376 | ... | 6,840 |
| 1956 | 167,419 | 30,014 | 197,433 | 193,282 | ... | 4,151 |
| 1957 | 172,795 | 33,482 | 206,276 | 202,951 | ... | 3,326 |
| 1958 | 158,925 | 34,655 | 193,580 | 193,736 | 155 | ... |
| 1959 | 204,830 | 35,547 | 240,377‡ | 239,955‡ | ... | 422 |
| 1960 | 276,446 | 38,402 | 314,848‡ | 314,217‡ | ... | 631 |
| 1961 | 237,378 | 46,975 | 284,354‡ | 283,958‡ | ... | 396 |
NOTE - Reference to Section 26A will indicate that the figures shown in the above table are by no means on a comparable basis over the period. The figures from 1937–38 onwards have been adjusted to bring them into line with present practice.
INDEBTEDNESS OF GENERAL GOVERNMENT - AMOUNT OF DEBENTURES AND STOCK IN CIRCULATION (Nominal Amounts)
| As at 31 March | Domiciled in | Total | Per Head of Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States of America | London | Australia | New Zealand | ||||
| £(thousand) | £ | s. | |||||
| 1911 | - | 62,222 | 4,214 | 14,642 | 81,078 | 76 | 15 |
| 1912 | - | 64,005 | 4,214 | 16,135 | 84,354 | 78 | 0 |
| 1913 | - | 68,929 | 4,214 | 16,917 | 90,061 | 81 | 0 |
| 1914 | - | 78,624 | 4,287 | 16,819 | 99,730 | 87 | 10 |
| 1915 | - | 76,410 | 3,979 | 19,671 | 100,060 | 87 | 0 |
| 1916 | - | 81,465 | 3,521 | 24,652 | 109,637 | 95 | 6 |
| 1917 | - | 83,878 | 3,386 | 42,573 | 129,836 | 112 | 10 |
| 1918 | - | 88,708 | 3,386 | 58,747 | 150,840 | 130 | 13 |
| 1919 | - | 95,708 | 3,386 | 76,982 | 176,076 | 149 | 8 |
| 1920 | - | 95,708 | 3,386 | 102,077 | 201,171 | 162 | 13 |
| 1921 | - | 99,692 | 1,655 | 104,977 | 206,324 | 162 | 16 |
| 1922 | - | 105,919 | 2,287 | 110,848 | 219,054 | 168 | 7 |
| 1923 | - | 110,668 | 2,159 | 106,126 | 218,953 | 165 | 4 |
| 1924 | - | 114,877 | 2,107 | 104,633 | 221,616 | 164 | 8 |
| 1925 | - | 120,818 | 2,952 | 104,044 | 227,815 | 165 | 3 |
| 1926 | - | 128,048 | 3,643 | 107,165 | 238,855 | 169 | 8 |
| 1927 | - | 132,513 | 4,042 | 109,296 | 245,851 | 170 | 19 |
| 1928 | - | 139,757 | 4,169 | 107,470 | 251,396 | 172 | 18 |
| 1929 | - | 149,346 | 4,168 | 110,677 | 264,192 | 179 | 12 |
| 1930 | - | 146,581 | 4,277 | 116,526 | 267,383 | 179 | 11 |
| 1931 | - | 154,547 | 4,175 | 117,311 | 276,033 | 182 | 12 |
| 1932 | - | 133,451 | 3,915 | 118,386 | 255,752 | 167 | 13 |
| 1933 | - | 135,210 | 2,869 | 118,354 | 256,432 | 166 | 15 |
| 1934 | - | 134,717 | 2,908 | 138,976 | 276,601 | 178 | 9 |
| 1935 | - | 134,781 | 2,184 | 117,425 | 254,390 | 162 | 19 |
| 1936 | - | 132,521 | 1,593 | 122,257 | 256,370 | 162 | 18 |
| 1937 | - | 130,546 | 892 | 130,041 | 261,479 | 164 | 15 |
| 1938 | - | 130,666 | 883 | 132,462 | 264,010 | 164 | 11 |
| 1939 | - | 130,662 | 880 | 146,238 | 277,779 | 170 | 19 |
| 1940 | - | 131,672 | 880 | 164,165 | 296,716 | 180 | 17 |
| 1941 | - | 132,180 | 880 | 190,176 | 323,236 | 197 | 11 |
| 1942 | - | 127,564 | 862 | 230,780 | 359,207 | 219 | 16 |
| 1943 | - | 132,083 | 862 | 304,689 | 437,634 | 267 | 16 |
| 1944 | - | 132,917 | 862 | 366,747 | 500,526 | 304 | 9 |
| 1945 | - | 133,091 | 861 | 403,274 | 537,227 | 319 | 16 |
| 1946 | - | 94,529 | 861 | 472,750 | 568,140 | 323 | 8 |
| 1947 | - | 94,529 | 861 | 482,990 | 578,380 | 323 | 4 |
| 1948 | - | 83,188 | 779 | 494,112 | 578,078 | 316 | 5 |
| 1949 | - | 79,962 | 628 | 534,395 | 614,986 | 329 | 17 |
| 1950 | - | 78,140 | 628 | 565,112 | 643,880 | 338 | 7 |
| 1951 | - | 77,808 | - | 589,425 | 667,233 | 344 | 6 |
| 1952 | - | 77,808 | - | 575,855 | 653,662 | 329 | 7 |
| 1953 | - | 77,790 | - | 589,898 | 667,688 | 327 | 14 |
| 1954 | - | 87,790 | - | 616,581 | 704,371 | 337 | 8 |
| 1955 | - | 97,789 | - | 630,804 | 728,593 | 341 | 18 |
| 1956 | - | 95,804 | - | 639,397 | 735,201 | 337 | 19 |
| 1957 | 4,429 | 100,425 | - | 652,265 | 757,120 | 340 | 17 |
| 1958 | 3,963 | 99,576 | - | 678,572 | 782,111 | 343 | 14 |
| 1959 | 23,548 | 118,277 | - | 674,728 | 816,552 | 351 | 1 |
| 1960 | 18,965 | 117,764 | - | 707,787 | 844,516 | 356 | 6 |
| 1961 | 18,499 | 108,163 | - | 741,511 | 868,173 | 363 | 11 |
NOTE - The figures for 1932 and later years exclude £26,191,000 contingent liability in respect of which interest payments have been suspended by agreement with the United Kingdom Government since 1931.
37—Ybk. + insets
| LOCAL AUTHORITIES* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Ended 31 March | Receipts | Payments | Total Gross Indebtedness† | |||
| Revenue | Other Receipts | Total | ||||
| From Rates | From Other Sources | |||||
*Exclusive of hospital boards. †Debt shown at its nominal amount, that portion domiciled overseas not being converted to its New Zealand currency equivalent. In terms of New Zealand currency, gross debt at 31 March 1960 amounted to £(N.Z.) 143,506,87O. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1910 | 1,526 | 1,934 | 2,362 | 5,823 | 4,898 | 17,810 |
| 1911 | 1,593 | 2,172 | 1,777 | 5,541 | 5,360 | 19,105 |
| 1912 | 1,678 | 2,299 | 2,425 | 6,402 | 6,074 | 20,763 |
| 1913 | 1,799 | 2,532 | 2,383 | 6,714 | 6,538 | 22,183 |
| 1914 | 2,006 | 2,719 | 2,412 | 7,136 | 6,796 | 23,773 |
| 1915 | 2,140 | 2,861 | 2,596 | 7,597 | 6,807 | 24,539 |
| 1916 | 2,355 | 2,968 | 2,469 | 7,792 | 6,921 | 26,045 |
| 1917 | 2,535 | 3,244 | 1,411 | 7,190 | 6,759 | 26,800 |
| 1918 | 2,675 | 3,284 | 1,250 | 7,208 | 7,103 | 27,653 |
| 1919 | 2,940 | 3,452 | 943 | 7,334 | 7,320 | 28,075 |
| 1920 | 3,144 | 4,487 | 3,329 | 10,960 | 10,884 | 30,188 |
| 1921 | 3,550 | 5,336 | 3,430 | 12,316 | 12,762 | 32,105 |
| 1922 | 3,780 | 6,075 | 5,487 | 15,342 | 15,092 | 36,745 |
| 1923 | 4,278 | 6,244 | 7,400 | 17,921 | 15,696 | 43,191 |
| 1924 | 4,446 | 6,704 | 5,685 | 16,835 | 16,521 | 46,538 |
| 1925 | 4,669 | 7,512 | 7,613 | 19,794 | 19,423 | 53,353 |
| 1926 | 5,040 | 8,334 | 7,506 | 20,879 | 20,916 | 59,420 |
| 1927 | 5,311 | 8,955 | 6,680 | 20,946 | 21,748 | 64,012 |
| 1928 | 5,616 | 9,786 | 5,668 | 21,070 | 22,423 | 66,404 |
| 1929 | 5,844 | 9,584 | 6,042 | 21,470 | 21,300 | 69,295 |
| 1930 | 6,011 | 10,747 | 5,495 | 22,253 | 22,061 | 71,208 |
| 1931 | 5,637 | 10,627 | 4,433 | 20,698 | 22,175 | 72,686 |
| 1932 | 5,512 | 9,682 | 4,374 | 19,568 | 20,087 | 72,402 |
| 1933 | 5,238 | 8,913 | 4,433 | 18,584 | 18,885 | 72,476 |
| 1934 | 5,541 | 8,688 | 3,822 | 18,051 | 17,738 | 61,969 |
| 1935 | 5,511 | 9,167 | 3,943 | 18,622 | 18,745 | 71,245 |
| 1936 | 5,586 | 9,553 | 4,349 | 19,487 | 19,337 | 70,400 |
| 1937 | 5,994 | 9,979 | 4,253 | 20,227 | 20,223 | 68,560 |
| 1938 | 6,541 | 11,005 | 4,390 | 21,936 | 22,051 | 68,061 |
| 1939 | 6,972 | 11,751 | 6,255 | 24,977 | 25,079 | 68,207 |
| 1940 | 7,289 | 12,670 | 6,772 | 26,731 | 25,709 | 69,487 |
| 1941 | 7,344 | 13,144 | 4,652 | 25,140 | 24,727 | 67,975 |
| 1942 | 7,442 | 13,399 | 3,175 | 24,017 | 24,072 | 66,646 |
| 1943 | 7,765 | 14,083 | 2,640 | 24,488 | 23,228 | 65,131 |
| 1944 | 7,824 | 15,145 | 2,054 | 25,022 | 23,801 | 63,263 |
| 1945 | 7,896 | 15,473 | 2,086 | 25,455 | 25,224 | 61,238 |
| 1946 | 8,633 | 15,844 | 2,744 | 27,221 | 27,355 | 60,026 |
| 1947 | 9,541 | 17,019 | 3,737 | 30,297 | 30,479 | 57,768 |
| 1948 | 9,807 | 17,824 | 4,408 | 32,039 | 32,457 | 57,117 |
| 1949 | 10,797 | 19,757 | 5,458 | 36,012 | 35,812 | 56,605 |
| 1950 | 11,645 | 21,079 | 7,367 | 40,091 | 39,664 | 56,302 |
| 1951 | 12,577 | 22,626 | 7,461 | 42,664 | 43,242 | 56,087 |
| 1952 | 14,514 | 25,155 | 9,543 | 49,212 | 48,846 | 57,869 |
| 1953 | 15,354 | 28,717 | 14,615 | 58,685 | 58,337 | 64,427 |
| 1954 | 16,421 | 33,522 | 19,307 | 69,250 | 68,289 | 73,446 |
| 1955 | 18,259 | 39,079 | 17,280 | 74,618 | 73,981 | 79,320 |
| 1956 | 18,883 | 42,395 | 21,424 | 82,702 | 83,559 | 87,984 |
| 1957 | 20,659 | 43,875 | 26,058 | 90,592 | 90,740 | 99,088 |
| 1958 | 22,707 | 46,859 | 31,051 | 100,618 | 98,288 | 114,675 |
| 1959 | 24,392 | 53,838 | 29,874 | 108,105 | 106,599 | 127,970 |
| 1960 | 25,744 | 50,858 | 41,780 | 118,382 | 115,596 | 143,557 |
LOCAL AUTHORITIES* - LOAN INDEBTEDNESS†(Exclusive of Inscribed Debt)
| As at 31 March | Counties | Boroughs | Harbour Boards | Electric Power Districts | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Exclusive of hospital boards. †Debt shown at its nominal amount, that portion domiciled overseas not being converted to its New Zealand currency equivalent. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1910 | 77 | 7,687 | 5,788 | ... | 1,385 | 14,938 |
| 1911 | 186 | 8,399 | 6,002 | ... | 1,544 | 16,132 |
| 1912 | 404 | 9,149 | 6,272 | ... | 1,953 | 17,777 |
| 1913 | 605 | 9,982 | 6,432 | ... | 2,176 | 19,195 |
| 1914 | 801 | 11,061 | 6,696 | ... | 2,373 | 20,931 |
| 1915 | 1,026 | 11,353 | 6,991 | ... | 2,389 | 21,758 |
| 1916 | 1,162 | 12,364 | 7,136 | ... | 2,655 | 23,317 |
| 1917 | 1,260 | 12,919 | 7,272 | ... | 2,658 | 24,109 |
| 1918 | 1,476 | 13,462 | 7,387 | ... | 2,698 | 25,023 |
| 1919 | 1,654 | 13,680 | 7,417 | ... | 2,770 | 25,521 |
| 1920 | 2,033 | 15,296 | 7,496 | ... | 2,892 | 27,717 |
| 1921 | 2,526 | 16,041 | 7,650 | 148 | 3,314 | 29,679 |
| 1922 | 3,007 | 18,060 | 8,250 | 1,480 | 3,566 | 34,363 |
| 1923 | 3,803 | 21,596 | 8,589 | 3,052 | 3,808 | 40,850 |
| 1924 | 3,997 | 22,075 | 9,173 | 4,741 | 4,237 | 44,224 |
| 1925 | 4,617 | 25,883 | 9,751 | 6,515 | 4,316 | 51,081 |
| 1926 | 5,390 | 28,026 | 9,993 | 8,746 | 5,025 | 57,180 |
| 1927 | 5,992 | 30,044 | 10,258 | 10,113 | 5,415 | 61,823 |
| 1928 | 6,205 | 31,599 | 10,477 | 10,175 | 5,817 | 64,274 |
| 1929 | 6,351 | 32,244 | 10,774 | 11,987 | 5,860 | 67,217 |
| 1930 | 6,533 | 31,521 | 10,461 | 12,636 | 8,029 | 69,180 |
| 1931 | 6,641 | 32,139 | 10,509 | 13,012 | 8,416 | 70,717 |
| 1932 | 6,686 | 31,683 | 10,549 | 13,122 | 8,437 | 70,478 |
| 1933 | 6,614 | 31,792 | 10,620 | 13,032 | 8,550 | 70,608 |
| 1934 | 6,558 | 31,359 | 10,497 | 13,213 | 8,522 | 70,148 |
| 1935 | 6,403 | 30,992 | 10,525 | 13,399 | 8,186 | 69,505 |
| 1936 | 6,229 | 30,773 | 10,219 | 13,485 | 8,040 | 68,746 |
| 1937 | 6,125 | 30,506 | 10,152 | 12,027 | 8,141 | 66,950 |
| 1938 | 6,083 | 30,542 | 9,894 | 11,890 | 8,078 | 66,487 |
| 1939 | 6,107 | 30,601 | 9,747 | 12,471 | 7,753 | 66,678 |
| 1940 | 6,184 | 30,769 | 9,961 | 13,115 | 7,978 | 68,006 |
| 1941 | 6,154 | 30,024 | 9,928 | 13,107 | 7,331 | 66,544 |
| 1942 | 6,101 | 29,647 | 9,797 | 12,499 | 7,289 | 65,333 |
| 1943 | 5,873 | 28,853 | 9,791 | 12,377 | 7,076 | 63,969 |
| 1944 | 5,633 | 28,212 | 9,701 | 11,829 | 6,934 | 62,308 |
| 1945 | 5,386 | 27,567 | 9,497 | 11,536 | 6,429 | 60,415 |
| 1946 | 5,196 | 27,231 | 9,365 | 11,191 | 6,360 | 59,342 |
| 1947 | 4,957 | 26,713 | 8,406 | 10,842 | 6,253 | 57,172 |
| 1948 | 4,763 | 26,479 | 8,234 | 11,094 | 6,043 | 56,613 |
| 1949 | 4,631 | 25,925 | 8,046 | 11,580 | 6,000 | 56,182 |
| 1950 | 4,466 | 26,075 | 7,785 | 11,997 | 5,719 | 56,043 |
| 1951 | 4,316 | 26,236 | 7,382 | 12,462 | 5,602 | 55,998 |
| 1952 | 4,276 | 27,158 | 7,496 | 13,004 | 5,919 | 57,853 |
| 1953 | 4,323 | 29,739 | 8,886 | 14,422 | 7,052 | 64,422 |
| 1954 | 4,313 | 34,005 | 10,362 | 15,970 | 8,795 | 73,445 |
| 1955 | 4,579 | 36,696 | 10,812 | 17,213 | 10,020 | 79,320 |
| 1956 | 5,120 | 40,104 | 11,619 | 18,827 | 12,313 | 87,984 |
| 1957 | 5,929 | 44,684 | 13,060 | 19,789 | 15,625 | 99,088 |
| 1958 | 6,772 | 51,414 | 15,689 | 21,300 | 19,500 | 114,675 |
| 1959 | 7,433 | 55,751 | 17,562 | 22,930 | 24,313 | 127,970 |
| 1960 | 8,721 | 62,056 | 20,033 | 23,884 | 28,862 | 143,557 |
TRADING BANKS - ASSETS AND LIABILITIES: NET NOTE CIRCULATION (Average of Four Quarters up to 1929, thereafter Weekly Averages)
| Year | Trading Banks - Assets | Trading Banks - Liabilities | Notes in Circulation* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advances | Coin and Bullion* | Total (All Assets)† | Deposits | Total (All Liabilities)† | ||
*Gold coin and bullion, and note-issue functions, taken over by Reserve Bank (August 1934). The Reserve Bank assumed liability for the outstanding notes of the trading banks as from 1 August 1936. †As at last balance day in December from 1934 onwards. | ||||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1910 | 18,440 | 5,036 | 26,399 | 24,969 | 26,742 | 1,626 |
| 1911 | 21,260 | 5,195 | 29,434 | 26,765 | 28,626 | 1,678 |
| 1912 | 22,908 | 5,338 | 31,196 | 25,622 | 27,508 | 1,715 |
| 1913 | 22,902 | 5,204 | 30,709 | 25,733 | 27,591 | 1,674 |
| 1914 | 24,250 | 5,713 | 32,502 | 27,641 | 29,808 | 1,998 |
| 1915 | 23,639 | 6,781 | 33,209 | 31,434 | 34,448 | 2,846 |
| 1916 | 24,912 | 7,394 | 37,015 | 37,508 | 41,978 | 4,050 |
| 1917 | 28,848 | 8,072 | 44,980 | 42,931 | 48,542 | 5,411 |
| 1918 | 31,711 | 8,086 | 48,570 | 45,563 | 52,049 | 6,267 |
| 1919 | 31,718 | 8,017 | 48,615 | 50,489 | 57,861 | 7,088 |
| 1920 | 38,242 | 7,729 | 56,111 | 59,405 | 67,818 | 7,890 |
| 1921 | 50,608 | 7,661 | 68,701 | 49,397 | 58,808 | 7,569 |
| 1922 | 44,768 | 7,823 | 61,780 | 45,913 | 53,869 | 7,019 |
| 1923 | 43,322 | 7,901 | 59,641 | 49,039 | 56,204 | 6,593 |
| 1924 | 44,537 | 7,816 | 61,326 | 49,502 | 57,131 | 6,588 |
| 1925 | 45,299 | 7,723 | 62,129 | 52,207 | 60,220 | 6,775 |
| 1926 | 49,149 | 7,797 | 65,765 | 50,135 | 58,008 | 6,730 |
| 1927 | 50,032 | 7,875 | 66,627 | 48,294 | 56,321 | 6,510 |
| 1928 | 46,179 | 7,512 | 62,819 | 53,799 | 61,851 | 6,374 |
| 1929 | 49,378 | 7,048 | 65,476 | 57,636 | 65,233 | 6,361 |
| 1930 | 53,657 | 6,799 | 69,748 | 56,425 | 63,984 | 6,187 |
| 1931 | 52,420 | 6,924 | 68,557 | 53,645 | 61,463 | 5,734 |
| 1932 | 50,256 | 5,958 | 69,015 | 52,852 | 60,649 | 5,917 |
| 1933 | 45,705 | 5,106 | 69,657 | 57,620 | 65,281 | 6,163 |
| 1934 | 41,410 | 3,423 | 73,509 | 63,382 | 69,259 | 6,286 |
| 1935 | 44,700 | 768 | 83,009 | 61,453 | 65,981 | 6,420 |
| 1936 | 45,918 | 720 | 83,866 | 65,154 | 65,940 | 7,500 |
| 1937 | 49,200 | 743 | 85,823 | 66,843 | 67,842 | 8,921 |
| 1938 | 55,650 | 876 | 85,072 | 65,039 | 66,821 | 9,989 |
| 1939 | 54,746 | 747 | 96,109 | 67,279 | 75,978 | 12,014 |
| 1940 | 47,954 | 718 | 101,496 | 77,364 | 82,033 | 14,791 |
| 1941 | 49,746 | 762 | 105,291 | 80,720 | 84,074 | 17,435 |
| 1942 | 45,440 | 687 | 118,949 | 90,880 | 100,768 | 21,497 |
| 1943 | 43,250 | 644 | 132,699 | 106,324 | 114,628 | 27,636 |
| 1944 | 46,773 | 713 | 140,939 | 117,568 | 122,214 | 32,102 |
| 1945 | 51,766 | 684 | 164,499 | 130,138 | 142,595 | 34,983 |
| 1946 | 58,271 | 727 | 179,028 | 149,777 | 160,504 | 38,198 |
| 1947 | 76,476 | 906 | 191,992 | 164,170 | 177,593 | 40,127 |
| 1948 | 88,160 | 1,393 | 193,458 | 175,669 | 190,538 | 40,796 |
| 1949 | 83,357 | 1,502 | 208,278 | 186,092 | 208,920 | 42,535 |
| 1950 | 94,715 | 1,688 | 225,349 | 202,200 | 233,969 | 45,228 |
| 1951 | 132,917 | 1,532 | 270,301 | 250,723 | 275,256 | 48,970 |
| 1952 | 169,841 | 1,471 | 268,151 | 252,968 | 255,083 | 50,978 |
| 1953 | 136,827 | 1,540 | 291,295 | 265,269 | 281,557 | 53,387 |
| 1954 | 156,973 | 1,455 | 301,633 | 281,750 | 305,827 | 57,692 |
| 1955 | 182,929 | 1,383 | 300,303 | 279,855 | 299,529 | 59,456 |
| 1956 | 170,648 | 1,338 | 287,681 | 268,734 | 284,368 | 59,987 |
| 1957 | 164,877 | 1,321 | 299,551 | 278,858 | 296,136 | 61,216 |
| 1958 | 175,417 | 1,416 | 288,538 | 279,030 | 280,143 | 62,095 |
| 1959 | 170,076 | 1,471 | 316,286 | 283,364 | 314,949 | 62,692 |
| 1960 | 177,745 | 1,444 | 350,290 | 323,920 | 360,330 | 65,630 |
POST OFFICE SAVINGS BANK
| Year | Number of Depositors at End of Year | Total Amount of Deposits During Year | Interest Credited to Depositors | Total Amount of Withdrawals During Year* | Excess of Deposits plus Interest over Withdrawals | Total Amount to Credit of Depositors at End of Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*From January 1958 includes interest paid out on investment accounts. †Fifteen months, 1 January 1920 to 31 March 1921. ‡Excess of withdrawals over deposits. §Does not include £11,448,000 from war gratuity accounts transferred to Post Office Savings Bank as from 31 March 1949, transactions in respect of which are shown in next line in italics. | ||||||
| Number | £(thousand) | |||||
| 1910 | 380,585 | 10,709 | 425 | 9,696 | 1,438 | 14,105 |
| 1911 | 405,566 | 11,627 | 473 | 10,662 | 1,438 | 15,543 |
| 1912 | 432,199 | 11,725 | 512 | 11,450 | 787 | 16,330 |
| 1913 | 458,594 | 11,287 | 556 | 11,041 | 801 | 17,131 |
| 1914 | 483,262 | 11,904 | 615 | 10,603 | 1,916 | 19,048 |
| 1915 | 509,085 | 13,706 | 707 | 11,295 | 3,118 | 22,166 |
| 1916 | 538,072 | 15,576 | 818 | 12,957 | 3,437 | 25,603 |
| 1917 | 566,351 | 17,107 | 948 | 14,461 | 3,593 | 29,196 |
| 1918 | 590,205 | 18,101 | 1,059 | 14,939 | 4,221 | 33,418 |
| 1919 | 630,783 | 29,758 | 1,179 | 25,962 | 4,975 | 38,393 |
| 1920–21† | 664,819 | 44,303 | 1,819 | 41,162 | 4,959 | 43,352 |
| 1921–22 | 678,930 | 29,126 | 1,600 | 30,236 | 490 | 43,842 |
| 1922–23 | 690,790 | 26,682 | 1,606 | 27,769 | 519 | 44,360 |
| 1923–24 | 710,157 | 29,598 | 1,650 | 29,510 | 1,738 | 46,098 |
| 1924–25 | 735,148 | 29,583 | 1,681 | 30,414 | 850 | 46,949 |
| 1925–26 | 758,155 | 31,834 | 1,732 | 32,603 | 962 | 47,911 |
| 1926–27 | 783,827 | 29,456 | 1,767 | 30,150 | 1,074 | 48,986 |
| 1927–28 | 804,725 | 27,611 | 1,747 | 30,585 | —1,227‡ | 47,759 |
| 1928–29 | 828,296 | 27,252 | 1,745 | 28,112 | 885 | 48,644 |
| 1929–30 | 852,757 | 28,562 | 1,806 | 29,576 | 792 | 49,436 |
| 1930–31 | 878,043 | 24,532 | 1,764 | 28,063 | —1,768‡ | 47,669 |
| 1931–32 | 877,090 | 19,464 | 1,611 | 25,488 | —4,413‡ | 43,255 |
| 1932–33 | 797,097 | 16,933 | 1,476 | 19,636 | —1,227‡ | 42,028 |
| 1933–34 | 798,262 | 19,429 | 1,231 | 17,818 | 2,842 | 44,870 |
| 1934–35 | 817,617 | 24,180 | 1,320 | 20,947 | 4,553 | 49,424 |
| 1935–36 | 840,671 | 25,620 | 1,406 | 23,534 | 3,492 | 52,916 |
| 1936–37 | 880,857 | 30,677 | 1,514 | 27,042 | 5,149 | 58,066 |
| 1937–38 | 920,805 | 33,041 | 1,669 | 29,629 | 5,081 | 63,147 |
| 1938–39 | 946,822 | 30,434 | 1,727 | 34,598 | —2,436‡ | 60,710 |
| 1939–40 | 960,565 | 25,151 | 1,603 | 29,463 | —2,709‡ | 58,002 |
| 1940–41 | 992,792 | 28,607 | 1,667 | 25,319 | 4,955 | 62,957 |
| 1941–42 | 1,039,783 | 32,045 | 1,821 | 25,377 | 8,489 | 71,445 |
| 1942–43 | 1,086,996 | 38,097 | 1,817 | 26,889 | 13,025 | 84,470 |
| 1943–44 | 1,128,936 | 47,649 | 2,076 | 35,580 | 14,145 | 98,614 |
| 1944–45 | 1,161,886 | 54,585 | 2,452 | 42,159 | 14,878 | 113,492 |
| 1945–46 | 1,203,181 | 67,861 | 2,787 | 55,626 | 15,022 | 128,514 |
| 1946–47 | 1,239,948 | 72,381 | 3,094 | 62,747 | 12,727 | 141,242 |
| 1947–48 | 1,277,265 | 72,553 | 3,307 | 68,660 | 7,200 | 148,442 |
| 1948–49 | 1,311,292 | 70,691 | 3,439 | 67,723 | 6,407 | 154,849§ |
| 1949–50 | 11,448 | 3,793 | 7,655 | 170,982 | ||
| 1,372,672 | 77,963 | 3,821 | 73,306 | 8,478 | ||
| 1950–51 | 1,407,241 | 86,395 | 3,915 | 85,190 | 5,120 | 176,103 |
| 1951–52 | 1,450,309 | 98,206 | 4,080 | 93,749 | 8,537 | 184,639 |
| 1952–53 | 1,485,852 | 99,126 | 4,208 | 96,700 | 6,634 | 191,274 |
| 1953–54 | 1,520,988 | 109,340 | 4,443 | 99,135 | 14,648 | 205,922 |
| 1954–55 | 1,554,549 | 117,881 | 4,711 | 112,842 | 9,749 | 215,671 |
| 1955–56 | 1,585,422 | 118,312 | 4,854 | 118,657 | 4,509 | 220,180 |
| 1956–57 | 1,650,331 | 131,444 | 6,301 | 121,319 | 16,425 | 236,606 |
| 1957–58 | 1,719,564 | 149,024 | 6,869 | 133,994 | 21,900 | 258,505 |
| 1958–59 | 1,778,426 | 141,837 | 7,274 | 143,703 | 5,408 | 263,913 |
| 1959–60 | 1,826,037 | 158,153 | 7,526 | 146,658 | 19,021 | 282,934 |
| 1960–61 | 1,883,675 | 182,130 | 8,189 | 166,785 | 23,533 | 306,467 |
POSTAL
| Year | Letters, Cards, etc., Posted and Delivered | Total Mail Matter (Including Parcels) Posted and Delivered | Money Orders Issued | Postal Notes Issued | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | |||
*Year ended 31 March following from 1946. †Counted once only from 1941. ‡Increase largely accounted for by withdrawals from savings-bank accounts for payment at sub-post-offices being paid by savings-bank money orders as from 31 March 1946. | ||||||
| (000) | (000) | (000) | £(000) | (000) | £(000) | |
| 1909 | 186,926 | 295,886 | 539 | 2,308 | 1,415 | 441 |
| 1910 | 196,769 | 310,237 | 570 | 2,458 | 1,667 | 517 |
| 1911 | 205,451 | 323,664 | 608 | 2,759 | 1,822 | 567 |
| 1912 | 214,184 | 333,621 | 666 | 3,231 | 1,971 | 627 |
| 1913 | 223,961 | 338,400 | 691 | 3,358 | 2,239 | 712 |
| 1914 | 233,901 | 359,031 | 692 | 3,428 | 2,314 | 715 |
| 1915 | 242,548 | 356,520 | 665 | 3,472 | 2,370 | 713 |
| 1916 | 242,121 | 347,017 | 669 | 3,607 | 2,286 | 686 |
| 1917 | 245,797 | 344,963 | 643 | 3,477 | 2,167 | 629 |
| 1918 | 242,527 | 333,827 | 639 | 3,649 | 2,091 | 611 |
| 1919 | 247,143 | 340,448 | 690 | 4,604 | 2,198 | 646 |
| 1920 | 259,743 | 360,747 | 700 | 5,277 | 2,280 | 691 |
| 1921 | 253,767 | 359,097 | 669 | 4,851 | 2,378 | 723 |
| 1922 | 239,997 | 356,188 | 660 | 4,279 | 2,435 | 730 |
| 1923 | 252,022 | 383,197 | 685 | 4,390 | 2,653 | 786 |
| 1924 | 272,312 | 426,908 | 732 | 4,693 | 2,846 | 841 |
| 1925 | 294,631 | 471,504 | 767 | 4,977 | 3,041 | 902 |
| 1926 | 298,617 | 486,381 | 793 | 5,033 | 3,330 | 965 |
| 1927 | 297,478 | 496,553 | 804 | 4,995 | 3,614 | 1,015 |
| 1928 | 298,548 | 517,750 | 808 | 4,978 | 3,576 | 1,058 |
| 1929 | 309,162 | 532,071 | 835 | 5,188 | 3,817 | 1,123 |
| 1930 | 313,148 | 542,003 | 834 | 5,070 | 3,907 | 1,129 |
| 1931 | 263,634 | 465,484 | 714 | 3,993 | 2,885 | 952 |
| 1932 | 246,395 | 436,615 | 649 | 3,336 | 2,687 | 958 |
| 1933 | 261,979 | 461,133 | 636 | 3,113 | 2,883 | 1,062 |
| 1934 | 275,064 | 486,831 | 655 | 3,210 | 3,326 | 1,141 |
| 1935 | 288,645 | 526,127 | 673 | 3,374 | 3,827 | 1,294 |
| 1936 | 292,099 | 534,097 | 734 | 3,795 | 3,833 | 1,378 |
| 1937 | 302,170 | 547,688 | 784 | 4,313 | 3,747 | 1,455 |
| 1938 | 316,309 | 608,682 | 848 | 4,802 | 3,835 | 1,485 |
| 1939 | 312,604 | 591,477 | 911 | 5,094 | 3,375 | 1,323 |
| 1940 | 296,684 | 531,942 | 813 | 4,435 | 2,559 | 1,021 |
| 1941 | 142,996† | 261,870† | 752 | 4,302 | 2,408 | 981 |
| 1942 | 817 | 4,961 | 2,242 | 934 | ||
| 1943 | 787 | 5,501 | 2,216 | 945 | ||
| 1944 | 762 | 5,989 | 2,223 | 952 | ||
| 1945 | 140,355 | 236,844 | 770 | 7,202 | 2,266 | 983 |
| 1946 | 160,680* | 294,326* | 903 | 10,624‡ | 2,354 | 1,028 |
| 1947 | 159,778 | 301,067 | 917 | 10,804 | 2,465 | 1,072 |
| 1948 | 162,131 | 319,229 | 943 | 10,843 | 2,484 | 1,106 |
| 1949 | 169,798 | 343,024 | 952 | 10,856 | 2,461 | 1,120 |
| 1950 | 178,857 | 358,183 | 977 | 11,638 | 2,372 | 1,084 |
| 1951 | 174,591 | 346,654 | 1,027 | 12,681 | 2,350 | 1,116 |
| 1952 | 176,895 | 357,611 | 1,091 | 14,374 | 2,297 | 1,101 |
| 1953 | 173,532 | 359,346 | 1,136 | 14,667 | 2,230 | 1,080 |
| 1954 | 180,105 | 386,381 | 1,236 | 20,587 | 2,278 | 1,101 |
| 1955 | 187,487 | 408,097 | 1,337 | 25,461 | 2,334 | 1,086 |
| 1956 | 191,979 | 412,379 | 1,383 | 26,300 | 2,230 | 1,072 |
| 1957 | 202,339 | 438,638 | 1,339 | 24,907 | 2,176 | 1,138 |
| 1958 | 204,660 | 446,403 | 1,353 | 25,039 | 2,240 | 1,230 |
| 1959 | 210,286 | 464,254 | 1,404 | 24,044 | 2,369 | 1,332 |
GOVERNMENT RAILWAYS
| Year Ended 31 March | Miles Open for Traffic | Capital Cost of Open Lines | Train-milage | Passengers Carried, Excluding Season-ticket Holders | Goods and Livestock* | Revenue† | Expenditure‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Equivalent tonnage of livestock. †From 1925–26, figures relate to railway operation only. ‡Capital cost written down by £10,400,000. | |||||||
| £(000) | (000) | (000) | tons(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| 1910 | 2,717 | 28,513 | 7,889 | 11,141 | 5,490 | 3,250 | 2,169 |
| 1911 | 2,753 | 29,607 | 8,141 | 11,201 | 5,864 | 3,494 | 2,303 |
| 1912 | 2,798 | 30,506 | 8,372 | 11,891 | 5,888 | 3,677 | 2,466 |
| 1913 | 2,851 | 31,611 | 9,016 | 13,124 | 6,246 | 3,971 | 2,706 |
| 1914 | 2,854 | 32,355 | 9,319 | 13,356 | 6,020 | 4,043 | 2,880 |
| 1915 | 2,945 | 34,134 | 9,383 | 13,566 | 6,453 | 4,105 | 2,920 |
| 1916 | 2,960 | 34,858 | 9,357 | 14,202 | 6,371 | 4,548 | 2,911 |
| 1917 | 2,960 | 35,379 | 9,146 | 14,173 | 6,239 | 4,801 | 2,927 |
| 1918 | 2,983 | 36,001 | 7,469 | 11,408 | 5,743 | 4,688 | 3,043 |
| 1919 | 2,983 | 36,168 | 7,478 | 11,375 | 5,612 | 4,989 | 3,309 |
| 1920 | 2,996 | 36,390 | 7,409 | 12,761 | 6,000 | 5,752 | 4,105 |
| 1921 | 3,009 | 37,235 | 9,03 | 15,316 | 6,487 | 6,909 | 5,637 |
| 1922 | 3,021 | 39,309 | 8,717 | 14,262 | 6,321 | 6,644 | 6,238 |
| 1923 | 3,028 | 40,275 | 8,347 | 14,257 | 6,619 | 6,728 | 5,502 |
| 1924 | 3,053 | 41,399 | 9,025 | 13,817 | 6,918 | 6,984 | 5,404 |
| 1925 | 3,085 | 44,571 | 9,084 | 12,397 | 7,025 | 7,113 | 5,545 |
| 1926 | 3,138 | 47,609 | 10,319 | 11,788 | 7,247 | 7,589 | 6,165 |
| 1927 | 3,164 | 49,184 | 10,724 | 10,275 | 7,300 | 7,423 | 6,158 |
| 1928 | 3,180 | 51,187 | 10,839 | 9,273 | 7,358 | 7,344 | 6,302 |
| 1929 | 3,287 | 56,569 | 11,113 | 9,047 | 7,613 | 7,525 | 6,375 |
| 1930 | 3,287 | 57,788 | 12,022 | 8,467 | 7,789 | 7,474 | 6,848 |
| 1931 | 3,322 | 60,545 | 11,282 | 7,266 | 6,958 | 6,781 | 6,406 |
| 1932 | 3,315 | 51,425‡ | 10,169 | 6,504 | 5,825 | 5,789 | 5,302 |
| 1933 | 3,315 | 51,481 | 9,829 | 6,871 | 5,491 | 5,339 | 4,834 |
| 1934 | 3,320 | 53,909 | 10,163 | 7,511 | 5,642 | 5,629 | 4,877 |
| 1935 | 3,320 | 54,089 | 10,626 | 7,809 | 6,024 | 5,908 | 5,139 |
| 1936 | 3,320 | 54,253 | 11,050 | 7,964 | 6,189 | 6,244 | 5,523 |
| 1937 | 3,320 | 54,696 | 11,868 | 8,285 | 6,813 | 6,904 | 6,338 |
| 1938 | 3,323 | 56,065 | 12,778 | 8,069 | 7,516 | 7,592 | 7,292 |
| 1939 | 3,319 | 58,677 | 13,073 | 7,813 | 7,539 | 8,005 | 7,664 |
| 1940 | 3,390 | 63,059 | 13,367 | 8,283 | 7,674 | 8,762 | 7,943 |
| 1941 | 3,390 | 64,763 | 13,560 | 9,440 | 8,426 | 9,694 | 8,407 |
| 1942 | 3,390 | 64,904 | 13,979 | 11,106 | 8,474 | 10,384 | 8,903 |
| 1943 | 3,460 | 68,685 | 15,140 | 17,171 | 8,887 | 12,415 | 10,020 |
| 1944 | 3,504 | 70,999 | 15,329 | 18,317 | 9,027 | 13,465 | 11,366 |
| 1945 | 3,504 | 71,354 | 12,803 | 13,630 | 8,954 | 12,448 | 11,697 |
| 1946 | 3,528 | 74,467 | 13,455 | 13,553 | 9,210 | 13,105 | 12,550 |
| 1947 | 3,528 | 75,354 | 13,169 | 10,222 | 9,329 | 12,824 | 13,645 |
| 1948 | 3,526 | 77,089 | 13,712 | 8,111 | 9,524 | 13,964 | 15,090 |
| 1949 | 3,526 | 78,796 | 13,895 | 7,708 | 9,666 | 15,339 | 16,788 |
| 1950 | 3,526 | 81,552 | 14,421 | 7,881 | 9,948 | 16,062 | 17,361 |
| 1951 | 3,531 | 84,992 | 14,153 | 7,574 | 9,616 | 18,500 | 18,725 |
| 1952 | 3,539 | 88,027 | 12,371 | 5,642 | 9,829 | 20,097 | 21,515 |
| 1953 | 3,535 | 93,330 | 13,409 | 5,779 | 10,026 | 22,589 | 22,755 |
| 1954 | 3,504 | 97,622 | 13,719 | 6,841 | 9,635 | 23,682 | 23,621 |
| 1955 | 3,489 | 103,554 | 14,420 | 7,804 | 10,336 | 27,009 | 25,542 |
| 1956 | 3,422 | 108,548 | 14,884 | 7,975 | 10,678 | 27,871 | 26,775 |
| 1957 | 3,418 | 120,101 | 15,102 | 8,132 | 10,325 | 28,507 | 28,694 |
| 1958 | 3,466 | 125,472 | 14,825 | 7,769 | 10,332 | 30,010 | 31,064 |
| 1959 | 3,420 | 133,943 | 14,605 | 8,070 | 10,367 | 29,823 | 30,505 |
| 1960 | 3,336 | 138,471 | 14,480 | 8,245 | 10,543 | 30,271 | 30,758 |
BANKRUPTCIES AND NEW COMPANY REGISTRATIONS
| Year | Bankruptcies | New Company Registrations* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Bankruptcies | Amount Realised by Official Assignee | Amount of Debts Proved | Number of New Registrations | Amount of Nominal Capital | |
*Public, private, and overseas. †The extraordinarily high figure for 1934 is due to the inclusion of all overseas companies (numbering 187 with an aggregate nominal capital of £193,023,000) which had previous to 1934 established places of business in New Zealand and which were reregistered in 1934 under Part XII of the Companies Act 1933. ‡Since 1954 company liquidations are included in the total. | |||||
| £ | £ | £(000) | |||
| 1910 | 393 | 79,100 | 176,001 | ... | ... |
| 1911 | 344 | 40,009 | 133,517 | ... | ... |
| 1912 | 312 | 39,965 | 120,325 | ... | ... |
| 1913 | 343 | 42,735 | 228,829 | ... | ... |
| 1914 | 391 | 64,153 | 199,251 | ... | ... |
| 1915 | 294 | 63,310 | 153,926 | ... | ... |
| 1916 | 304 | 56,416 | 172,774 | 258 | 4,073 |
| 1917 | 265 | 63,645 | 178,244 | 261 | 5,367 |
| 1918 | 164 | 67,729 | 88,607 | 200 | 3,055 |
| 1919 | 141 | 54,662 | 59,767 | 328 | 5,943 |
| 1920 | 145 | 47,897 | 77,752 | 501 | 9,564 |
| 1921 | 336 | 78,271 | 558,504 | 337 | 3,498 |
| 1922 | 690 | 126,145 | 834,356 | 417 | 13,125 |
| 1923 | 674 | 124,641 | 668,925 | 502 | 13,006 |
| 1924 | 670 | 118,641 | 703,995 | 565 | 21,367 |
| 1925 | 653 | 98,648 | 471,028 | 621 | 14,760 |
| 1926 | 752 | 102,899 | 585,687 | 655 | 10,748 |
| 1927 | 867 | 108,850 | 679,473 | 698 | 8,702 |
| 1928 | 806 | 116,613 | 767,327 | 736 | 10,985 |
| 1929 | 687 | 91,180 | 502,112 | 903 | 12,472 |
| 1930 | 780 | 83,308 | 827,345 | 893 | 6,703 |
| 1931 | 848 | 108,809 | 1,042,187 | 795 | 8,284 |
| 1932 | 661 | 75,657 | 624,892 | 812 | 6,866 |
| 1933 | 450 | 61,723 | 489,895 | 830 | 7,301 |
| 1934 | 326 | 44,533 | 258,920 | 933 | 200,739† |
| 1935 | 257 | 41,037 | 225,508 | 810 | 24,238 |
| 1936 | 260 | 32,983 | 169,866 | 942 | 9,935 |
| 1937 | 222 | 55,970 | 171,706 | 888 | 6,113 |
| 1938 | 267 | 64,511 | 230,463 | 824 | 6,576 |
| 1939 | 267 | 44,171 | 225,490 | 681 | 8,910 |
| 1940 | 213 | 42,418 | 125,289 | 391 | 3,779 |
| 1941 | 165 | 35,453 | 71,011 | 288 | 11,246 |
| 1942 | 82 | 29,753 | 32,227 | 198 | 961 |
| 1943 | 45 | 18,883 | 20,052 | 270 | 1,547 |
| 1944 | 51 | 13,466 | 51,035 | 464 | 1,490 |
| 1945 | 45 | 18,530 | 118,216 | 741 | 3,383 |
| 1946 | 52 | 20,942 | 48,506 | 1,435 | 11,064 |
| 1947 | 74 | 15,528 | 44,731 | 1,813 | 9,575 |
| 1948 | 148 | 50,280 | 143,282 | 1,751 | 8,684 |
| 1949 | 179 | 38,410 | 203,173 | 2,157 | 7,982 |
| 1950 | 142 | 49,252 | 125,917 | 2,074 | 10,178 |
| 1951 | 145 | 48,269 | 136,822 | 2,020 | 12,807 |
| 1952 | 168 | 56,241 | 251,129 | 1,744 | 33,408 |
| 1953 | 215 | 72,162 | 381,017 | 2,041 | 43,034 |
| 1954‡ | 277 | 82,571 | 413,447 | 2,685 | 27,746 |
| 1955 | 304 | 112,418 | 382,322 | 2,695 | 18,347 |
| 1956 | 390 | 130,574 | 547,751 | 3,255 | 20,608 |
| 1957 | 437 | 180,364 | 782,226 | 3,502 | 80,543 |
| 1958 | 495 | 184,795 | 819,135 | 3,034 | 30,764 |
| 1959 | 618 | 194,877 | 755,193 | 2,737 | 47,103 |
| 1960 | 495 | 165,586 | 668,911 | 3,767 | 36,996 |
INSURANCE
| Year | Life (Ordinary and Industrial) | Accident | Fire | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policies in Force† | Sum Assured† | Net Revenue* | Net Expenditure* | Net Revenue* | Net Expenditure* | |
*Excluding unexpired risks reserves. †Excludes annuities. | ||||||
| (000) | £(million) | £(thousand) | ||||
| 1911–12 | 216 | 37 | 272 | 228 | ... | ... |
| 1912–13 | 230 | 39 | 327 | 254 | ... | ... |
| 1913–14 | 241 | 41 | 342 | 261 | ... | ... |
| 1914–15 | 250 | 42 | 351 | 288 | ... | ... |
| 1915–16 | 260 | 44 | 345 | 292 | ... | ... |
| 1916–17 | 274 | 45 | 355 | 302 | ... | ... |
| 1917–18 | 283 | 46 | 356 | 321 | ... | ... |
| 1918–19 | 299 | 49 | 364 | 327 | 974 | 748 |
| 1919–20 | 318 | 54 | 456 | 399 | 1,101 | 770 |
| 1920–21 | 339 | 59 | 541 | 455 | 1,282 | 886 |
| 1921–22 | 357 | 63 | 715 | 619 | 1,404 | 1,159 |
| 1922–23 | 370 | 65 | 718 | 652 | 1,429 | 1,169 |
| 1923–24 | 389 | 70 | 767 | 707 | 1,435 | 1,207 |
| 1924–25 | 412 | 76 | 869 | 791 | 1,446 | 1,279 |
| 1925–26 | 433 | 81 | 1,158 | 980 | 1,517 | 1,224 |
| 1926–27 | 455 | 87 | 1,331 | 1,145 | 1,491 | 1,352 |
| 1927–28 | 480 | 92 | 1,341 | 1,224 | 1,497 | 1,445 |
| 1928–29 | 503 | 98 | 1,423 | 1,299 | 1,501 | 1,534 |
| 1929–30 | 532 | 105 | 1,663 | 1,449 | 1,516 | 1,333 |
| 1930–31 | 553 | 112 | 1,745 | 1,549 | 1,553 | 1,307 |
| 1931–32 | 546 | 113 | 1,526 | 1,456 | 1,554 | 1,452 |
| 1932–33 | 543 | 112 | 1,319 | 1,181 | 1,493 | 1,166 |
| 1933–34 | 558 | 113 | 1,266 | 1,112 | 1,428 | 1,079 |
| 1934–35 | 589 | 117 | 1,393 | 1,201 | 1,373 | 1,050 |
| 1935–36 | 628 | 124 | 1,513 | 1,404 | 1,375 | 1,019 |
| 1936–37 | 686 | 136 | 1,764 | 1,700 | 1,355 | 987 |
| 1937–38 | 751 | 151 | 2,223 | 2,135 | 1,295 | 933 |
| 1938–39 | 801 | 161 | 2,606 | 2,336 | 1,330 | 1,011 |
| 1939–40 | 836 | 170 | 2,820 | 2,392 | 1,392 | 1,059 |
| 1940–41 | 865 | 178 | 2,641 | 2,305 | 1,442 | 1,123 |
| 1941–42 | 900 | 187 | 2,605 | 2,228 | 1,507 | 1,167 |
| 1942–43 | 922 | 194 | 2,391 | 2,065 | 1,562 | 1,337 |
| 1943–44 | 954 | 204 | 2,680 | 2,292 | 1,679 | 1,324 |
| 1944–45 | 992 | 219 | 2,718 | 2,432 | 1,571 | 1,286 |
| 1945–46 | 1,036 | 239 | 2,961 | 2,652 | 1,640 | 1,353 |
| 1946–47 | 1,096 | 266 | 3,379 | 2,842 | 1,828 | 1,544 |
| 1947–48 | 1,151 | 296 | 4,037 | 3,461 | 2,043 | 1,674 |
| 1948–49 | 1,192 | 325 | 4,471 | 3,985 | 2,322 | 1,712 |
| 1949–50 | 1,226 | 353 | 5,054 | 4,495 | 2,554 | 1,922 |
| 1950–51 | 1,263 | 387 | 5,987 | 5,211 | 2,749 | 2,238 |
| 1951–52 | 1,304 | 433 | 6,830 | 6,060 | 3,053 | 2,429 |
| 1952–53 | 1,345 | 479 | 8,187 | 7,203 | 3,409 | 2,792 |
| 1953–54 | 1,381 | 529 | 9,183 | 8,031 | 3,755 | 3,084 |
| 1954–55 | 1,427 | 592 | 10,222 | 9,057 | 4,126 | 3,248 |
| 1955–56 | 1,463 | 662 | 11,378 | 10,387 | 4,224 | 3,555 |
| 1956–57 | 1,494 | 732 | 12,815 | 11,846 | 4,396 | 3,654 |
| 1957–58 | 1,528 | 812 | 14,168 | 13,225 | 4,648 | 4,029 |
| 1958–59 | 1,561 | 902 | 15,370 | 14,347 | 5,012 | 4,207 |
| 1959–60 | 1,598 | 1,013 | 16,681 | 15,263 | 5,574 | 4,424 |
Table of Contents
APPENDICES
1642 European discovery of New Zealand by Tasman.
1769 Captain Cook's first visit to New Zealand.
1791 Discovery of Snares and Chatham Islands.
1792 First sealing gang left on New Zealand coast.
1814 Arrival of Rev. Samuel Marsden, and introduction of Christianity. Horses, cattle, sheep, and poultry first brought to New Zealand.
1820 Hongi's visit to England. First vessel entered Auckland Harbour.
1823–28 Jurisdiction of Courts of Justice in New South Wales extended to British subjects in New Zealand.
1825 First attempt at colonisation, by an expedition under Captain Herd.
1827 Hongi's forces destroyed mission station at Whangaroa.
1831 Tory Channel whaling station established. Application of 13 chiefs for the protection of King William IV.
1833 Mr James Busby appointed British Resident at Bay of Islands.
1834 Waimate Pa, near Opunake, shelled and captured by British – first occasion on which HM troops employed in New Zealand.
1835 Declaration of independence of the whole of New Zealand as one nation, with title of “United Tribes of New Zealand”. Ngati-Awa tribes migrated to and conquered Chatham Islands.
1838 Pelorus Sound discovered.
1839 Governor of New South Wales authorised to include within the limits of that colony any territory that might be acquired in sovereignty by Her Majesty in New Zealand. Preliminary expedition of New Zealand Company under Colonel Wakefield arrived at Port Nicholson.
1840 Arrival of New Zealand Company's settlers at Port Nicholson. Treaty of Waitangi signed. British sovereignty proclaimed. Captain Hobson appointed Lieutenant-Governor, with residence at Auckland. Settlements formed at Petre (Wanganui) and Akaroa.
1841 Issue of charter of incorporation of New Zealand Company. New Zealand proclaimed independent of New South Wales. Arrival of New Plymouth settlers.
1842 Settlement founded at Nelson.
1843 Affray with Maoris at the Wairau.
1844 Royal flagstaff at Kororareka cut down by Heke.
1845 Destruction of Kororareka by Heke.
1846 Arrival of first steam vessel (HMS Driver) in New Zealand waters. Capture of pa at Ruapekapeka and termination of Heke's war. Maori hostilities near Wellington. Te Rauparaha captured and detained as a prisoner. New Zealand divided into two provinces, New Munster and New Ulster, and representative institutions conferred.
1847 Attack by Maoris on Wanganui.
1848 Suspension of that part of New Zealand Government Act which had conferred representative institutions. Otago founded.
1850 Surrender of New Zealand Company's charter, all its interests reverting to the Imperial Government. Canterbury founded.
1852 Discovery of gold at Coromandel. Constitution Act passed, granting representative institutions to New Zealand, and dividing country into six provinces.
1854 Opening at Auckland of first session of the General Assembly.
1855 First members elected to the House of Representatives under system of responsible Government. Very severe earthquake on both sides of Cook Strait.
1856 Appointment of first Ministry under system of responsible Government.
1857 Goldfield opened at Collingwood.
1858 New Provinces Act passed. Hawke's Bay Province constituted.
1859 Establishment of Marlborough Province.
1860 Hostilities in Waitara district.
1861 Truce arranged with Waitara Maoris. Bank of New Zealand incorporated. Southland Province established. Gold discovered at Gabriel's Gully, Otago.
1862 Coromandel proclaimed a goldfield. Wreck of S.S. White Swan, with loss of many public records. First electric-telegraph line opened – Christchurch to Lyttelton.
1863 Wreck of HMS Orpheus on Manukau bar, with loss of 181 lives. Control of Maori affairs transferred to Colonial Government. Commencement of Waikato War. Defeat of Maoris at Rangiriri, and occupation of Ngaruawahia. First railway in New Zealand, portion of Christchurch-Lyttelton line, opened.
1864 Severe fighting in Waikato and elsewhere, including battles of Rangiaohia, Orakau, Gate Pa, and Te Ranga. First major discovery of gold on West Coast of South Island.
1865 Seat of Government transferred to Wellington. Further fighting, followed by proclamation of peace. Activities of Hauhau fanatics, including murders of Europeans. Rebel Maoris defeated at Wairoa.
1866 Cook Strait submarine telegraph cable laid.
1867 Opening of Thames Goldfield. Lyttelton Tunnel completed. Admission of four Maori members to House of Representatives as direct representatives of Maori people.
1868 Maori prisoners, under leadership of Te Kooti, seized schooner Rifleman and escaped from Chatham Islands to mainland, where they massacred Europeans. Considerable fighting with these and other rebel Maoris.
1869 Continuation of fighting with rebels and of pursuit of Te Kooti. Visit of H.R.H. the Duke of Edinburgh. Government Life Insurance Office established.
1870 Further fighting with Te Kooti. Last of Imperial troops left New Zealand. Commencement of San Francisco mail service. Possession taken of Bounty Island. Inauguration of Vogel public works policy. Act passed to establish the New Zealand University. Southland Province reunited with Otago.
1871 Commencement of railway construction under public works policy.
1872 Resumption of friendly relations with Waitara Maoris. Appointment of Maori chiefs (two) to Legislative Council. Public Trust Office created.
1873 Establishment of New Zealand Shipping Co.
1874 In pursuance of immigration and public works policy, 31,774 assisted immigrants arrived. Westland Province established.
1875 Resumption of amicable relations with Maori King. Establishment of Union Steam Ship Company. Abolition of Provinces Act passed.
1876 New Zealand connected by cable with Australia. Abolition of Provinces Act came into operation, provincial institutions being abolished and the country divided into counties and boroughs.
1877 Education Act passed, providing for free and compulsory education.
1878 Completion of the Christchurch-Invercargill railway.
1879 Triennial Parliaments Act passed. Adult male suffrage introduced. Kaitangata coal mine explosion, whereby 34 lives lost.
1881 Wreck of S.S. Tararua, with loss of 130 lives.
1882 First shipment of frozen meat from New Zealand.
1883 Direct steam communication inaugurated between New Zealand and England.
1885 New Zealand Industrial Exhibition at Wellington.
1886 Tarawera eruption, involving loss of 101 lives and destruction of Pink and White Terraces.
1887 Annexation of Kermadec Islands. Members of House of Representatives reduced to 74, including four Maoris.
1888 British protectorate over Cook Islands proclaimed.
1889 South Seas Exhibition at Dunedin.
1890 Great maritime strike. First election of House of Representatives under one-man-one-vote principle.
1891 Inauguration of Liberal regime under Hon. John Ballance, succeeded on his death in 1893 by Mr Seddon. This and following years marked by passage of industrial and social legislation.
1892 Introduction of lease-in-perpetuity system of land tenure.
1893 Franchise extended to women. Special licensing poll introduced.
1894 Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Act passed. Government Advances to Settlers Act passed. Wreck of S.S. Wairarapa, with loss of 135 lives.
1896 Brunner Mine explosion, causing 67 deaths. Abolition of non-residential or property qualification to vote. Government Valuation of Land Act passed.
1898 Old-age Pensions Act passed.
1899 Labour Day instituted. New Zealand Contingent (the first of 10) sent to South Africa.
1900 Number of European representatives in Lower House increased to 76.
1901 T.R.H. the Duke and Duchess of York visited New Zealand. Penny postage adopted by New Zealand. Cook and other Pacific islands annexed.
1902 Pacific cable opened. Wreck of S.S. Elingamite, with loss of 43 lives. Conference of colonial Premiers in London.
1903 Empire Day proclaimed. State Fire Insurance Act passed.
1905 Workers' Dwellings Act passed. Title of New Zealand's representative in London altered to “High Commissioner”.
1906 Death of Right Hon. R. J. Seddon, Premier since 1893. Advances to Workers Act passed. New Zealand International Exhibition at Christchurch.
1907 New Zealand constituted a Dominion. Lease-in-perpetuity system of land tenure abolished. Parliament Buildings destroyed by fire.
1908 Through railway communication established between Wellington and Auckland. Wellington-Manawatu railway purchased by Government. Second Ballot Act passed.
1909 S.S.Penguin wrecked in Cook Strait, with loss of 75 lives. Battle cruiser presented by New Zealand to Imperial Government. System of compulsory military training introduced.
1910 Field-Marshal Lord Kitchener reported and advised on New Zealand defences. Public Debt Extinction Act and National Provident Fund Act passed.
1911 Wireless telegraphy installed in New Zealand. Widows' Pensions Act passed. First poll on national prohibition taken.
1912 Foundation stone of new Parliament Buildings laid. Public Service placed under Commissioner control.
1913 Extensive strikes. Second Ballot Act repealed.
1914 Western Samoa occupied by New Zealand Advance Expeditionary Force. Main Expeditionary Force left for Egypt. Huntly coal mine disaster, with loss of 43 lives.
1915 New Zealand Expeditionary Force engaged in operations on Gallipoli Peninsula. National Cabinet formed. National register of men compiled. Pensions for miners introduced.
1916 New Zealand Division transferred to Western Front, Mounted Brigade being retained in Egypt. Compulsory enrolment of men for war service introduced. Lake Coleridge electric-supply scheme opened.
1918 S.S. Wimmera sunk by enemy mine off New Zealand coast, with loss of 26 lives. Otira Tunnel pierced. End of First World War. Great influenza epidemic, causing nearly 7,000 deaths.
1919 Women made eligible for seats in Parliament. New Zealand represented at Peace Conference by Right Hon. W. F. Massey, Prime Minister.
1920 Visit of H.R.H. the Prince of Wales. Railway strike. First aeroplane flight over Cook Strait. League of Nations gave New Zealand mandate to administer Western Samoa. Anzac Day constituted.
1921 Samoa Act passed, making provision for government in terms of mandate. New Zealand represented at Disarmament Conference, Washington.
1922 Meat-export trade placed under control of a board.
1923 Opening of Otira Tunnel. Ross Dependency proclaimed, and placed under jurisdiction of Governor-General. Dairy Produce Export Control Act passed.
1924 Railway strike. Direct two-way radio communication effected with England. Motor Vehicles Act provided for registration and annual licensing of motor vehicles. Land Transfer (Compulsory Registration of Titles) Act passed. Pensions for blind persons introduced. S.S. Ripple foundered off Cape Palliser with loss of 16 lives.
1925 New Zealand and South Seas International Exhibition at Dunedin. Administration of Tokelau (Union) Islands transferred to New Zealand.
1926 Family Allowances Act passed.
1927 Visit of T.R.H. the Duke and Duchess of York. Summer Time Act passed.
1928 Kingsford Smith and party made first successful flight across Tasman Sea.
1929 Severe earthquake in Murchison-Karamea district caused 17 deaths. Daylight saving (half hour) permanently adopted for summer months.
1930 Legislation providing for relief of unemployment first passed.
1931 Worst earthquake in history of New Zealand occurred in Hawke's Bay, resulting in the loss of 255 lives. General reduction of 10 per cent in wages and salaries. Parliament approved draft Statute of Westminster. Mortgagors' relief legislation passed.
1932 Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration Amendment Act made important changes in industrial legislation. National Expenditure Adjustment Act made reductions in old-age and other pensions, in salaries of State employees, and in rentals, interest rates, and other fixed charges. The historic Waitangi Estate presented to the nation by Their Excellencies Lord and Lady Bledisloe. New Zealand represented at Ottawa Conference.
1933 Exchange raised at instance of Government to £125 N.Z. for £100 London (telegraphic transfers). Sales tax instituted. Conversion of internal public debt with reduction in interest rates, and provision made for local authorities interest reduction and loans conversion. Successful experimental shipments of chilled beef to England. Issue of New Zealand silver coinage.
1934 First official trans-Tasman air mail. Reserve Bank incorporated and commenced business. H.R.H. the Duke of Gloucester arrived on an official visit. First licensed air-transport service commenced operations.
1935 Bank notes of trading banks ceased to be legal tender. Rural Mortgagors Final Adjustment Act passed, and Court of Review established. National Government defeated at general election, and Labour Government assumed office for first of four successive terms.
1936 Inauguration of inter-Island trunk air services. Reserve Bank nationalised. System of guaranteed prices for butter and cheese introduced. Forty-hour week became operative. Powers of Court of Arbitration restored. Railcar services inaugurated. New Zealand elected to seat on League of Nations Council.
1937 New Zealand represented at Imperial Conference by Right Hon. M. J. Savage, Hon. W. Nash, and Mr W. J. Jordan. Death of Lord Rutherford of Nelson.
1938 Mr W. J. Jordan, New Zealand's representative on League of Nations, elected President of the League Assembly. Social Security Act passed. Introduction of import selection and control.
1939 Declaration of war with Germany. Recruitment for 2nd New Zealand Expeditionary Force. Arrangements for purchase of primary products by Imperial Government. New Zealand Centennial Exhibition opened at Wellington. Naval engagement off River Plate in which HMS Achilles, largely manned by New Zealand ratings, took part.
1940 Centennial celebrations. Departure of First Echelon of 2nd New Zealand Expeditionary Force. Death of the Prime Minister, the Right Hon. M. J. Savage; succeeded in office by Hon. P. Fraser. Declaration of war with Italy. RMS Niagara sunk off New Zealand coast by enemy mine. Ballots for military service. National savings scheme inaugurated.
1941 Daylight saving period extended to cover whole year. First enrolment of married men for military service. Death penalty abolished, also flogging and whipping. Declaration of war with Japan. Territorial Forces mobilised.
1942 Complete mobilisation of Military Forces ordered. Introduction of control of industrial manpower. Compulsory enrolment of all male British subjects between ages of 18 and 65 inclusive, in Emergency Reserve Corps. Lend-lease reciprocal aid extended to include Australia and New Zealand. Gold to value of £2,397,000 salvaged from RMS Niagara. Rationing introduced. Mobilisation of women for essential work.
1943 Death of Right Hon. J. G. Coates, M.C., member of War Cabinet and former Prime Minister. North African campaign brought to a successful conclusion. Railway accident near Hyde–21 persons killed. 2nd NZEF (3rd Division) took part in action against Japanese in the Pacific Area.
1944 Australian - New Zealand Agreement 1944, providing for collaboration on matters of mutual interest. Mutual-aid Agreement between Canadian and New Zealand Governments signed.
1945 War in Europe ended (8 May). Manpower controls in regard to women and young persons relaxed. Wartime press censorship abolished. War Cabinet dissolved. War in Pacific ended, Japan formally surrenders (15 August). Electoral Amendment Act providing for abolition of the “country quota” passed. South Island Main Trunk Railway opened, through rail connection from Picton to Bluff established.
1946 First women members of Legislative Council (two) appointed. Restrictions on consumption of electric power imposed in North Island. Remaining manpower controls lifted in June. Family benefit of 10S. per week made universal as from 1 April. Lieutenant-General Sir Bernard Freyberg, V.C., assumed office as Governor-General (17 June). Railways Department inaugurated inter-island air freight service.
1947 £12,500,000 presented to United Kingdom Government by New Zealand. Local Government Commission appointed. First woman Cabinet Minister in New Zealand appointed. Marketing of dairy produce and fixation of basic price taken over by Dairy Commission. Statute of Westminster adopted by New Zealand Parliament.
1948 Licensing Control Commission appointed. Mt. Ngauruhoe erupts after 22 years' quiescence. Adjustment of exchange rate to parity with sterling as from 20 August.
1949 Polls on the establishment of off-course betting and on an alteration in hotel hours held in March. Referendum on question of compulsory military training answered in the affirmative. Labour Government defeated and National Government assumed office on 13 December for first of three successive terms.
1950 British Empire Games held at Auckland. Control of land sales, except of farm land, lifted. Control of sterling funds and securities relaxed. Abolition of petrol and butter rationing. Two New Zealand frigates departed for Korean waters. Legislative Council Abolition Act passed. Kayforce sailed from Wellington for Korea on 10 December. Death of Right Hon. Peter Fraser, Prime Minister, 1940–49.
1951 Prolonged waterfront strike resulted in Proclamation of State of Emergency, and issue of regulations under the Public Safety Conservation Act. Servicemen kept essential cargoes moving. Waterfront unions deregistered, followed by deregistration of certain other unions – e.g., freezing workers – seamen and miners also involved. Establishment of Civil Emergency Reserve. Off-course betting operations commenced by Totalisator Agency Board. United States of America, Australia, and New Zealand signed Pacific Security Treaty.
1952 Royal Commission on Railways. Proclamation of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II read by the Governor-General at Parliament Buildings on 11 February. New Zealand team at Olympic Games at Helsinki most successful, one gold and two bronze medals won and one Olympic record made. Report of Royal Commission on the Waterfront Industry released.
1953 Power restrictions suspended in North Island, first time for 12 years. Coronation Day for Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth the Second marked in New Zealand by nation-wide civic programmes. Mt. Everest conquered on 29 May by British expedition, the summit being reached by the New Zealander Edmund Hillary and the Sherpa Tensing. Armistice agreement signed in Korea. The London-Christchurch air race won by RAF Canberra No. 3 in record time of 23 hours 51 minutes. New Zealand's worst railway disaster occurred at Tangiwai on Christmas Eve, with a death roll of 154 persons. Arrival of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth the Second and His Royal Highness the Duke of Edinburgh, on 23 December, the first occasion on which a reigning monarch had visited these shores. Her Majesty broadcast to the Commonwealth and Empire from Auckland on 25 December. The first Proclamation issued by a reigning Sovereign in New Zealand summoned Parliament for its opening by the Queen on 12 January 1954.
1954 Continuation of Royal Tour, including meetings of the Privy Council and Executive Council and opening of a special session of Parliament. New Zealand took seat on United Nations Security Council. New Zealand sent team to Vancouver for British Empire Games – most successful in New Zealand's history, winning seven gold, seven silver, and five bronze medals. The Executive Council and Cabinet held meetings at Auckland on 25 May to mark the centenary of parliamentary government in New Zealand. New Zealand signed the South-East Asia Treaty at Manila.
1955 New Zealand made contribution to defence of South-East Asia by sending squadron of fighter bombers and part transport squadron to Malaya and, later in the year, an Army Special Air Service Squadron. First train run from Murupara to Kawerau in April, this followed later in the year by the successful operation of newsprint mills at Kawerau. Rimutaka tunnel opened for traffic in November. Formal agreement signed for initiation of reciprocal N.Z.-U.K. social security scheme.
1956 Interest rates on Post Office Savings Bank accounts increased. Report of Royal Commission on Monetary, Banking, and Credit Systems released. Census taken. Roxburgh and Whakamaru power stations in operation. Guaranteed price scheme for potatoes announced. Petition for increased State aid to private schools rejected. Building controls abolished. Team of 53 competitors sent to Olympic Games at Melbourne wins two gold medals. Colombo Plan Conference held in Wellington. Duke of Edinburgh visited New Zealand.
1957 New Zealand Antarctic Expedition established Scott Base at Pram Point, McMurdo Sound. Trade discussions between New Zealand and United Kingdom Governments held during April and May in London. New Zealand shared fully in programme for International Geophysical Year, including Antarctic section. Dairy produce given unrestricted, duty-free right of entry to Britain till 1967. Plan announced to almost double generating capacity of New Zealand's power systems by 1970 at cost of £235 million, including the laying of a cable across Cook Strait. Restraints on credit continued. Lord Cobham succeeded Lord Norrie as Governor-General on 5 September. Separate Court of Appeal constituted. Sir Leslie Munro elected President of United Nations General Assembly. Start made on Benmore power station. National Government defeated and Labour Government assumed office on 12 December. Battalion sailed for service in Malaya.
1958 Import selection and exchange allocation brought into force to conserve overseas exchange. Sir Edmund Hillary and companions reached South Pole overland from Scott Base. Royal Tour of Her Majesty the Queen Mother. PA YE taxation on incomes introduced. Electric power restrictions in North Island. Increase in family and age benefits. Army reorganised as an operational regular brigade group. New Zealand won four gold, six silver, and nine bronze medals at Empire Games in Cardiff. Power generated from geothermal steam at Wairakei and from coal station at Mercer. Report made by Royal Commission on Local Authority Finance. Revised trade pact provided for variation of margins of preference on United Kingdom imports. Power restrictions lifted.
1959 Mr C. M. Bennett, a distinguished Maori, appointed High Commissioner in Malaya. New Zealand's contribution to Colombo Plan exceeds £8 million. Experimental television station began transmission in Auckland. National Consumer Council appointed and four regional consumer committees established. Institute of Nuclear Sciences established. Commission of inquiry into meat industry. Scheme provided for capitalisation of family benefit for housing purposes. Auckland Harbour Bridge opened (May). Reconstructed Wellington Airport opened for traffic (July). S.S. Holmglen foundered off Timaru with loss of 15 lives. Twelve nations, including New Zealand, signed treaty to preserve Antarctica for peaceful scientific research for all time.
1960 United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation regional seminar on publications for schools held in Wellington. Government signed agreement for company to use power from Te Anau - Manapouri Lakes system for large aluminium smelting industry with production planned for 1965. Report issued by Committee on New Zealand Universities chaired by Sir David Hughes Parry - salary increases followed. First High Commissioner appointed to India. Commission on Education appointed with Sir George Currie as chairman. Institute of Economic Research established. Export income exceeded £300 million for March year. Direct Wellington - Sydney air services resumed. Meat export development company formed. Industrial Development Conference held in Wellington. Increase in shipping freight rates. New Zealand athletes won two gold medals in one day at Olympic Games in Rome, also one bronze medal. Import licensing schedule eased. Government Service Equal Pay Act passed. Conference of British Commonwealth Statisticians held in Wellington. Labour Government defeated and National Government assumed office on 13 December.
| Subject | Year | Page |
|---|---|---|
| Building stones | 1892 | 194 |
| Varieties of soil | 1892 | 193 |
| Patents, designs, and trade marks | 1893 | 350 |
| Acclimatisation | 1894 | 430 |
| Cooperative system of constructing public works | 1894 | 234 |
| Frozen meat trade, the | 1894 | 311 |
| Labour in New Zealand | 1894 | 362 |
| Midland railway, the | 1894 | 386 |
| Railways in New Zealand: Their history and progress | 1894 | 377 |
| Sheep, crossbreeding of | 1894 | 308 |
| Sheep farming | 1894 | 302 |
| Southern Alps, the | 1894 | 474 |
| State farms | 1894 | 243 |
| West Coast Sounds, the | 1894 | 482 |
| Cheviot Estate, the | 1895 | 264 |
| Shipping companies– | ||
| New Zealand Shipping Co. | 1895 | 392 |
| Shaw, Savill, and Albion Co. | 1895 | 393 |
| Union Steam Ship Co. of New Zealand | 1895 | 389 |
| Wellington-Manawatu railway, the | 1895 | 381 |
| Laws of England and New Zealand, difference between | 1896 | 281 |
| Waihi Gold Mining Co. | 1897 | 432 |
| Wattle growing in the Auckland Provincial District | 1897 | 430 |
| Mount Cook: Its glaciers, and the Hermitage | 1898 | 552 |
| Scenic wonderland, a | 1898 | 565 |
| Christchurch to West Coast, journey from | 1899 | 548 |
| Forest trees and the timber industry | 1899 | 470 |
| Gold dredging industry, the | 1899 | 509 |
| Moa, heir of the | 1899 | 517 |
| Mount Cook district, the | 1899 | 554 |
| Tokaanu to Raetihi | 1899 | 539 |
| Tuhoeland | 1899 | 546 |
| Waikato district and through to Wanganui | 1899 | 520 |
| Waiouru to Mangaonoho | 1899 | 543 |
| Chatham Islands, the | 1900 | 531 |
| Coal deposits of New Zealand, the | 1900 | 479 |
| Hemp industry, the | 1900 | 477 |
| Kauri gum | 1900 | 489 |
| Maori mythology | 1900 | 536 |
| Mount Cook, a night on | 1900 | 525 |
| Mount Sefton, ascent of | 1900 | 519 |
| New Zealand contingents for South Africa | 1900 | 449 |
| Pumice-stone deposits of New Zealand | 1900 | 486 |
| Wanganui River, up the, to Tokaanu | 1900 | 509 |
| Maori religion | 1901 | 530 |
| Marlborough Sounds, the | 1901 | 517 |
| Otago lakes, the | 1901 | 523 |
| Sydney pageant, the | 1901 | 527 |
| Cook Islands, the laws of | 1902 | 573 |
| Maori, neolithic, the | 1902 | 578 |
| Maori sociology | 1903 | 641 |
| Timber trees of the world | 1903 | 605 |
| Exotic trees in Canterbury | 1904 | 569 |
| Hanmer thermal springs | 1905 | 631 |
| Maori, colour sense of the | 1905 | 637 |
| Thermal springs district | 1905 | 614 |
| Maori marriage customs | 1906 | 638 |
| Tree planting | 1906 | 611 |
| White Island, a day on | 1906 | 637 |
| Maori, ancient: His amusements, games, etc. | 1907 | 707 |
| Maori chant (tangi) | 1907 | 711 |
| New Zealand international exhibition | 1907 | 701 |
| Maori, ancient: His clothing | 1908 | 734 |
| Maori songs | 1908 | 739 |
| Agriculture in New Zealand | 1912 | 809 |
| Government training ship Amokura | 1913 | 942 |
| HMS New Zealand | 1913 | 932 |
| Land and income tax assessment | 1913 | 884 |
| Mineral waters of New Zealand | 1913 | 896 |
| External trade of New Zealand, the | 1915 | 858 |
| Maori, topographical nomenclature of the | 1919 | 936 |
| Wages and working hours in New Zealand | 1919 | 860 |
| Education system of New Zealand, the | 1925 | 816 |
| Effect of nativity order on infant mortality | 1925 | 835 |
| Local government in New Zealand | 1925 | 845 |
| Terman intelligence tests in New Zealand schools | 1925 | 823 |
| Wellington municipal milk supply | 1925 | 777 |
| Cancer in New Zealand: A statistical study | 1926 | 889 |
| Totalisator, the | 1926 | 838 |
| Britomart, mission of, at Akaroa, in August 1840 | 1927 | 1012 |
| Mortality rates, New Zealand | 1927 | 995 |
| Livestock production: A review based on standard values and units | 1929 | 990 |
| Lakes of New Zealand | 1932 | 11 |
| Rivers of New Zealand | 1932 | 6 |
| Dairy farm survey | 1938 | 429 |
| Ross Dependency | 1938 | 900 |
| Fauna, the | 1940 | 36 |
| Geology | 1940 | 7 |
| Libraries | 1940 | 928 |
| Mineral waters and spars | 1940 | 935 |
| Plants of New Zealand, the | 1940 | 28 |
| Tourist attractions | 1940 | 932 |
| Alexander Turnbull Library | 1946 | 914 |
| National Film Unit | 1946 | 724 |
| Retail prices in New Zealand, with special reference to the Consumers' Price Index | 1947–49 | 998 |
| Economic policy and national income | 1950 | 1033 |
| Department of Scientific and Industrial Research | 1951–52 | 1066 |
| Standardisation | 1951–52 | 1076 |
| Sources of statistical information | 1953 | 1016 |
| Royal Tour of New Zealand, 23 December 1953 to 31 January 1954 | 1954 | 1121 |
| New Zealand; Its tourist industry, tourist and sporting attractions, and travel information | 1955 | 1143 |
| Royal Commission on Monetary, Banking, and Credit Systems: Summary of report | 1956 | 1201 |
| Consumers' Price Index – 1955 Revision | 1957 | 1214 |
| New Zealand Activities in the Antarctic | 1958 | 1247 |
| New Zealand's International Activities | 1959 | 1221 |
| Grassland Research in New Zealand | 1960 | 1243 |
The following list, compiled by Mr C. R. H. Taylor, M.A., DIP. JOUR., F.N.Z.L.A. (Chief Librarian of the Alexander Turnbull Library), includes the more notable works in their fields issued from 1950 onwards. Earlier works are listed in the 1947–49 issue of the Yearbook (pages 979–998) and in the 1932 issue.
Apart from this listing, the following may be noted. Government Departments, municipalities, boards, church organisations, institutions, associations, councils, authorities, and banks commonly issue annual reports. Some, particularly Government Departments, issue information brochures and books. The Standards Institute produces standards for a wide range of products. A series of diplomatic brochures is issued by the Department of External Affairs. Maps of many kinds are available from the Department of Lands and Survey. Statistical publications, including census, are compiled by the Department of Statistics. Business and general directories are published by Wise, Universal Business Directories, and Stone.
Lists of current publications in New Zealand are issued by the General Assembly Library, and printed cards of accessions by the National Library Service may be purchased. The Government Printer carries a large stock of Government publications. Most books tend to remain in print for two or three years, but many earlier ones are only available in libraries and from second-hand sources.
ASSOCIATED BOOKSELLERSOF NEW ZEALAND. A list of New Zealand books in print 1957. Hamilton. Offset Printers, 1957.
BAGNALL, A. G. (editor). Union list of serials in New Zealand libraries. Wellington. New Zealand Library Service, 1953. Supplements have been issued.
DRUMMOND, Helen Margaret and LEATHAM, E. H. Bibliography of New Zealand tussock grasslands. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
FAIR, Andrew Peter Rasch. Guide to book values – New Zealand, Australia, Pacific, Antarctic: book auction records 1952–56. Wellington, 1956.
HARRIS, Wm. J. Guide to New Zealand reference material and other sources of information, 2nd edition. Wellington. New Zealand Library Association, 1950.
Index to New Zealand periodicals and current national bibliography of New Zealand books and pamphlets published in 1959. Wellington. New Zealand National Library Service, 1960. Annual supplements.
JENKINS, David Lloyd. Union list of theses of the University of New Zealand, 1910–1954. Wellington. New Zealand Library Association, 1956.
JOHNSTONE, Arthur H. Canterbury books, 1847–1955: a bibliography. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1956.
A Legal bibliography of the British Commonwealth of Nations, Vol. 6. Australia, New Zealand and their dependencies. London. Sweet and Maxwell, 1958. Part 5, New Zealand, compiled by J. O. Wilson.
MCCORMICK, Eric Hall. Tasman and New Zealand: a bibliographical study. Wellington. Government Printer, 1959. (Turnbull Library Bulletin No. 14.)
MILLER, David. Bibliography of New Zealand Entomology, 1775–1952. Wellington. Government Printer, 1956.
NEW ZEALAND NATIONAL LIBRARY SERVICE. New Zealand periodicals: a select list. Wellington, 1959.
NORTHERN ADVOCATE INDEX. (Quarterly.) Whangarei. Northern Publishing Co.
SCHOEN, Grace M. A list of references on New Zealand social services. Wellington. Library School, 1960.
TAYLOR, Clyde Romer Hughes. A Pacific bibliography: Printed matter relating to the native peoples of Polynesia, Melanesia, and Micronesia. (Includes classified bibliography on the Maori.) Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1951.
TAYLOR, David Mortimer. The oldest manuscripts in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1955.
GREY, Sir George. Polynesian mythology and ancient traditional history of the Maori. 3rd edition. Edited by W. W. Bird. Illustrated by Russell Clark. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1956.
JOHANSEN, J. Prytz. The Maori and his religion in its non-ritualistic aspects. Kobenhavn. Ejnar Munksgaard, 1954.
PAAR, Stephen. Canterbury pilgrimage: the first hundred years of the Church of England in Canterbury, New Zealand. Christchurch. Centennial Committee of the Diocese of Christchurch, 1952.
REED, Alexander Wyclif. Legends of Rotorua and the hot lakes. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
AIREY, Wellis Thomas Goodwin. New Zealand foreign policy related to New Zealand social development and current world trends. Wellington. New Zealand Student Labour Federation, 1954.
AMMUNDSEN, George Albert (comp.). Local body administration: a selection of articles… Wanganui. New Zealand Institute for Local Body Administrative Officers, 1960.
ANGUS, Norman Charles. The expert and administration in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1959.
AUSUBEL, David Paul. The fern and the tiki: an American view of New Zealand : national character, social attitudes and race relations. Sydney. Angus and Robertson, 1960.
BAKER, Richard St. B. Land of Tane: the threat of erosion. London. Butterworth, 1956.
BOLLINGER, Conrad V. I. Grog's own country: history of liquor licensing in New Zealand. Wellington. Price, 1959.
CAMPBELL, Richard M. The Public Service Commission in operation. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1950.
CONDLIFFE, John Bell. New Zealand in the making. 2nd edition. London. Allen and Unwin, 1959.—— The welfare state in New Zealand. London. Allen and Unwin, 1959.
CONFERENCEON CAPITAL DEVELOPMENTIN NEW ZEALAND DURINGTHE NEXT TEN YEARS. Christchurch, 1953. (Mimeographical.)
CONSUMER. A quarterly magazine issued by the Consumer Service. Wellington. 1959–61.
DOLLIMORE, H. N. The Parliament of New Zealand and Parliament House. Wellington. Government Printer, 1953.
EQUAL PAY IMPLEMENTATION COMMITTEE. Report by D. J. Dalglish, chairman. Wellington. Government Printer, 1960.
FONG, Ng Bickleen. The Chinese in New Zealand: a study in assimilation. Oxford University Press, 1959.
GREEN, William Albert Edward and others. Social services in New Zealand. A group report. Revised edition. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1954.
HUNN, Jack K. Report of Department of Maori Affairs. Wellington. Government Printer, 1960.
HUTTON, Leslie Bertram and STACE, F. N. (editors). The engineering history of electric supply in New Zealand, Vol. 1. Wellington. Electric Supply Authority Engineers Institute of New Zealand, 1958.
JONES, Frederick George Hall. The history and activities of Rotary in New Zealand. Invercargill. Southland Historical Committee, 1955.
LOCHORE, Reuel Anson. From Europe to New Zealand. An account of our continental European settlers. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
MACDONALD, Winifred. Auckland yesterday and today: an outline of the development and everyday life of New Zealand's largest city. Auckland. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
MACKAY, J. K. Broadcasting in New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
MANNING, Arthur Edward. The Bodgie. A study in abnormal psychology. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
MAPLES, E. Social security services in New Zealand. Oxford University Press, 1949.
MILNE, R. S. (editor). Bureaucracy in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1957.
NEALE, Edward Percy. Guide to New Zealand official statistics. Third edition. Auckland. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1955.
NEW ZEALAND COMMISSION of INQUIRY appointed to inquire into certain matters relating to the conduct of members of the Police Force. Final Report. Sir Robert Kennedy, Chairman. Wellington. Government Printer, 1955.
NEW ZEALAND GOVERNMENT. The New Zealand economy 1939–51. Wellington. Government Printer, 1951.
——Economic Survey. Annual since 1952. Wellington. Government Printer.
NEW ZEALAND SOIL CONSERVATIONAND RIVERS CONTROL COUNCIL. Catchments of New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1956.
NEW ZEALAND SPECIAL COMMITTEE on moral delinquency in children and adolescents. Report. O. C. Mazengarb, Chairman. Wellington. Government Printer, 1954.
NIXON, Allan Johnston. Divorce in New Zealand. Auckland. Auckland University College, 1954.
PARKER, R. S. (editor). Economic stability in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1953.
POLASCHEK, Raymond Joseph (editor). Government administration in New Zealand. Wellington, New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1958.
——Local Government in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1956.
PREECE, Cardew, and RIDER. Report on inter-island electric power transmission. Wellington. Government Printer, 1960.
REPORT of the royal commission on monetary, banking, and credit systems, presented to the House of Representatives. Wellington. Government Printer, 1956.
RESERVE BANKOF NEW ZEALAND. Overseas trade and finance, with particular reference to New Zealand. Wellington. Reserve Bank, 1960.
ROSENBERG, Wolfgang. Full employment: can the New Zealand economic miracle last? Wellington. Reed, 1960.
ROSENFELD, Max. The New Zealand house. 7th edition revised. Auckland. New Zealand House Design Publications, 1960.
SCHOLEFIELD, Guy Hardy. New Zealand parliamentary record 1840–1949. Wellington. Government Printer, 1950.
SCOTT, K. J. (editor). Welfare in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1955.
SIMKIN, C. G. F. The instability of a dependent economy: economic fluctuations in New Zealand, 1840–1914. Oxford University Press, 1951.
SOCIAL SECURITY DEPARTMENT. The growth and development of social security in New Zealand . . . (1898–1949). Wellington. Government Printer, 1950.
SUTCH, WILLIAM Ball. Economic changes of a quarter century. Wellington. Department of Industries and Commerce, 1959.
——The role of consumer industries. Wellington. Department of Industries and Commerce, 1960.
TOTALISATOR AGENCY BOARD. History and operation of off-course betting in New Zealand. Wellington. Totalisator Agency Board, 1958.
TYNDALL, Sir Arthur. The settlement of labour disputes in New Zealand. Cambridge, Mass. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1953.
WESTSTRATE, Cornelis. Portrait of a modern mixed economy: New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand University Press, 1959.
ALEXANDER, Robert Ritchie. The story of Te Aute College. (The leading secondary school for Maori boys.) Wellington. Reed, 1951.
ASHBRIDGE, George Richard. Teachers' legal and service handbook. 6th edition. Wellington. Educational Institute, 1959.
BARR, Janet R. Within sound of the bell. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1953.
BUTCHERS, A. G. Centennial history of education in Canterbury. Christchurch. Canterbury Education Board, 1953.
EWING, John Lithgow. Origins of the New Zealand primary schools curriculum, 1840–78. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1960.
NEW ZEALAND UNIVERSITY. Alphabetical roll of graduates. Wellington. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1951.
——The University of New Zealand Calendar. Wellington (Annual). Individual colleges issue separate calendars.
PARKYN, George William (editor). The administration of education in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Institute of Public Administration, 1954.
——Success and failure at the University. Vol. 1. Academic performance and the entrance standard. Wellington. Council for Educational Research, 1959.
SEARLE, ERNEST Johnstone. The teaching of science in post-primary schools. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1958.
SMITH, Sir David S. Devolution in academic matters: the Rhodes scholarships. Wellington. University of New Zealand, 1953.
——The quality and standing of the University. Wellington. University of New Zealand, 1954.
TURNER, Harold Walter. Halls of residence. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1953.
WHITE, Dorothy Mary. Books before five. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1954.
BEACHAM, A. The position of coal in the New Zealand economy. Dunedin. University of Otago, 1957.
BRIDGER, Grover Leon. Fertiliser production in New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1951.
BUCHANAN, Ruthven A. A breeding analysis concerning the dual-purpose Romney in New Zealand. Palmerston North, 1957.
ELPHICK, John Oliver. A users' directory of New Zealand coals. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1956.
FEDERATED FARMERSOF NEW ZEALAND OTAGO PROVINCIAL DISTRICT HYDATIDS COMMITTEE. The practical approach to the problem of hydatid disease. Dunedin, 1958.
FENNESSY, B. B. The control of the European rabbit in New Zealand. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation. Melbourne, 1958.
HADFIELD, J. W. Linen flax fibre production in New Zealand. Christchurch. Linen Flax Corporation of New Zealand, 1953.
HOWARD, Walter Wegner. The rabbit problem in New Zealand. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1958.
LEVY, Sir E. Bruce. Grasslands of New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1951.
MACDONALD, George Ranald. The Canterbury Frozen Meat Company Ltd., the first seventy-five years. Christchurch, 1958.
MCEWAN, John Martin. The wheat varieties of New Zealand. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
MCNULTY, Francis Edward. There's money in meat: the story of the freezing industry in New Zealand. Auckland. In Print Publishing Co., 1959.
MASSEY AGRICULTURAL COLLEGE. Dairy farming annual (since 1948). Palmerston North.
——Sheepfarming annual (since 1938). Palmerston North.
MILLS, Allan Robert. Sheep-o! the story of the world's fastest shearers. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
NEW ZEALAND DAIRY SCIENCE ASSOCIATION. The contribution of dairy scientists during the last 25 years to the advancement of the New Zealand dairy industry. Palmerston North, 1954.
ORCHISTON, H. D. Fertilisers, lime and farm production in New Zealand, 1900–1952. Christchurch. Canterbury Agricultural College, 1957.
PHILLIPPS, H. A survey of fellmongering calf skin and hide production and leather manufacture in New Zealand and Australia. British Leather Manufacturers' Research Association, 1957.
PHILPOTT, Bryan Passmore, and STEWART, J. D. Capital income and output in New Zealand agriculture 1922–56. Wellington. Meat and Wool Board's Economic Service, 1958.
SUTCH, William Ball. The oil industry of New Zealand. Wellington. Department of Industries and Commerce, 1959.
TEBB, Cuthbert Palmer. Aerial topdressing: review of five years' operation in Raglan - Waikato - King Country, 1953–58. Christchurch. New Zealand Meat and Wool Board's Economic Service, 1958.
WILD, L. J. The development of agricultural education in New Zealand. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1953. (The Macmillan Brown Lectures.)
WILSON, R. A. Fifty years farming on sand country. Palmerston North. Keeling and Mundy, 1959.
ANDERSON, H. E. The law relating to companies in New Zealand. 2nd edition. Edited by D. J. Dalglish and others. Wellington. Brooker, 1957.
BIRKS, Walter Richard. The legal relationship of parent and child. Wellington. Legal Publications, 1952.
BURTON, Robert C. C. Bankruptcy law in New Zealand, and the law relating to insolvent estates, private assignments, chattels, transfer hire purchase, and arbitration. Wellington. Sweet and Maxwell, 1959.
CHALMERS, Charles Clive. Chalmers' and Dixon's road traffic laws of New Zealand. 2nd edition. Wellington. Butterworth, 1952.
CUNNINGHAM, Herbert Adam. Taxation laws of New Zealand. 4th edition. Edited by M. I. Thompson and R. P. Kellaway. Wellington. Butterworth, 1960.
CURRIE, A. E. Crown and subject: A treatise on the rights and legal relationship of the Crown and the people of New Zealand. Wellington. Legal Publications, 1953.
DUGDALE, Donald Frederick. New Zealand hire purchase law. Wellington. Butterworth, 1960.
GARROW, James Mitchell Ellis. Garrow's law of real property in New Zealand. 4th edition. Edited by E. C. Adams. Wellington. Butterworth, 1954.
INGLIS, Brinsley Donald. Family law. Wellington. Sweet and Maxwell, 1960.
LUXFORD, J. H. Liquor laws of New Zealand. 2nd edition. Wellington. Butterworth, 1953.
MACDONALD, John William. Law relating to workers' compensation in New Zealand. 2nd edition Edited by C. H. Arndt. Wellington. Butterworth, 1954.
MARSHALL, John R. and PAGE, E. F. The law of watercourses and a handbook for catchment boards. Wellington. New Zealand Catchment Boards Association, 1957.
MERCANTILE GAZETTEOF NEW ZEALAND. Digest of legal, commercial, and statistical information. Christchurch. Trade Auxiliary, 1950.
NEW ZEALAND STATUTES 1908–1957. Reprint. 16 vols. Wellington. Government Printer, 1960.
Robson, John Lochiel (editor). New Zealand : the development of its laws and constitution. London. Stevens, 1954.
SIM, Sir Wilfrid Joseph. Sim's divorce law and practice in New Zealand. 6th edition. Assisted by P. Keesing. Wellington. Butterworth, 1954.
SMITH, Norman W. Maori land law. Wellington. Reed. 1960.
STAPLES, C. A. A guide to New Zealand income tax practice. 14th edition. Wellington. Financial Publications, 1954.
STEPHENS, A. C. The law relating to family protection in New Zealand. 2nd edition. Wellington. Butterworth, 1957.
WARD, Denzil Anthony Seaver, and WILD, Herbert Richard Churton. Mercantile law in New Zealand. 3rd edition. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
COLLINS, Raymond J. G. (editor). The postage stamps of New Zealand. Vol. 3. Wellington. Royal Philatelic Society of New Zealand, 1955.
FRANKS, L. J. S. Postal history catalogue of New Zealand. Vol. 1. Christchurch. 1958.
HAWKINS, Clifford William. A survey of the commercial sailing craft built in the Auckland Province, and in particular those sailing out of Auckland, with some account of their trade. Auckland. Pelorus Press for the Author, 1960.
NEWZEALAND PHILATELIC SOCIETY. Catalogue of New Zealand stamps. Vol. 2, 1951.
NEW ZEALAND POST OFFICE. One hundred years of postage stamps. 1855–1955. Wellington. New Zealand Post Office, 1955.
PALMER, A. N., and STEWART, W. W. Cavalcade of New Zealand locomotives… the railway engine since 1863. Wellington. Reed, 1956.
HARAWIRE, Kahi Takimoana. Teach yourself Maori. 2nd edition. Wellington. Reed, 1954.
KOHERE, Reweti Tuhorouta. Maori proverbs and sayings translated and explained. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
——He Konae Aronui. Proverbs and sayings of the Maori. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
MEAD, Sidney Moko. We speak Maori. First lessons in the Maori language. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
WALL, Arnold. New Zealand English: a guide to the correct pronunciation of English, with special reference to New Zealand. 3rd edition. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
——The Queen's English. A commentary for New Zealand. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1958.
WILLIAMS, H. W. Dictionary of the Maori language. 6th edition. Revised under the auspices of the Polynesian Society. Wellington. Government Printer, 1957.
WILLS, Webster H. Lessons in the Maori language. New Plymouth. Avery, 1950.
MATTHEWS, J. W. New Zealand trees. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
REED, A. H. The story of the kauri. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
SAINSBURY, George Osborne King. A handbook of the New Zealand mosses. Wellington. Royal Society, 1955.
STEVENSON, Greta Barbara. A book of ferns. Dunedin. John McIndoe, 1954.
WALL, Arnold. Botanical names of the flora of New Zealand. Auckland. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1950.
WESTON, G. C. Exotic forest trees in New Zealand. Wellington. New Zealand Forest Service, 1957.
ADKIN, G. Leslie. Horowhenua. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1949.
ARCHEY, Gilbert Edward. Sculpture and design, an outline of Maori Art. Auckland. War Memoria Museum, 1955.
BEATTIE, James Herries. Our southernmost Maoris. Dunedin. Otago Daily Times, 1954.
BEST, Elsdon. The Maori as he was. 2nd edition. Wellington. Government Printer, 1953.
BUCK, Sir Peter H. The coming of the Maori. Wellington. Maori Purposes Board, 1950.
——Sir Peter Henry. Vikings of the Pacific. Chicago. University of Chicago Press, 1959.
COWAN, James. The Caltex book of Maori lore, revised by J. B. Palmer. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
DEPARTMENTOF MAORI AFFAIRS. Te ao hou: The new world. (English and Maori journal.) Quarterly. Wellington.
DUFF, Roger S. Moa-hunter period of Maori culture. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1950.
FINLAYSON, Roderick David and SMITH, Joan. The Maoris of New Zealand. London. Oxford University Press, 1958.
FIRTH, Raymond William. Economics of the New Zealand Maori. 2nd edition. Wellington. Government Printer, 1959.
FREEMAN, J. D. and GEDDES, W. R. (editors). Anthropology in the South Seas. Essays presented to H. D. Skinner. New Plymouth. Avery, 1959.
GORST, Sir John Eldon. The Maori king, edited by Keith Sinclair. Hamilton. Paul, 1959.
GRACE, John Te H. Tuwharetoa: the history of the Maori people of the Taupo district. Wellington Reed, 1959.
JEFFERSON, Christina. Dendroglyphs of the Chatham Islands. Moriori designs. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1956.
KELLY, Leslie G. Tainui. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1949.
MEAD, Sidney Moko. Taniko weaving: How to make Maori belts and other useful articles. Wellington. Reed, 1952.
PADOVAN, Renzo. The Maori as an artist. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
PHILLIPPS, Wm. J. Maori carving. Wellington. Tombs, 1950.
—Maori houses and food stores. Wellington. Dominion Museum (Monograph No. 8), 1952.
—Carved Maori houses of western and northern areas of New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1955.
—The great carved house Mataatoa. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1956.
—Maori rafter and taniko designs. 3rd edition. Wellington. Tombs, 1960.
PRESBYTERIAN CHURCHOF NEW ZEALAND MAORI SYNOD. Maori and Pakeha in church and community: a symposium. Christchurch. Presbyterian Bookroom, 1960.
PRICE, A. G. White settlers and native peoples. Melbourne. Georgian House, 1949. (2 chapters on Maori race.)
REED, A. H. and A. W. Maori place names and their meanings. Wellington. Reed, 1950.
RUFF, Elsie. Jade of the Maori. London. Gemmological Association, 1950.
SHARP, C. Andrew. Ancient voyagers in the Pacific. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1956.
SUTHERLAND, I. L. G. Ngarimu hui. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1949.
TAYLOR, William Anderson. Lore and history of the South Island Maori. Christchurch. Bascands, 1952.
WAIARIKI YOUNG MAORI LEADERS' CONFERENCE: Whakatane 1960 Report. Auckland. Council of Adult Education, University of Auckland, 1960. (This is one of several such conferences in other areas.)
ALPERS, Antony. A book of dolphins, illus. by Erik Thorn. Hamilton. Paul, 1960.
BASTINGS, Lyndon (editor). Directory of New Zealand science. 3rd edition. Wellington. New Zealand Association of Scientific Workers, 1954.
COTTON, Charles Andrew. New Zealand geomorphology, 1912–25. Wellington. New Zealand University Press, 1955.
EIBY, George. Earthquakes. London. Muller, 1957.
GRAHAM, David. A treasury of New Zealand fishes. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
GRANGE, Leslie Issott. Prospecting for radioactive minerals in New Zealand. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1956.
GREGG, Donald Rowe. Volcanoes of Tongariro National Park. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1960.
HAMILTON, William Maxwell, and BAUMGART, I. L. White Island. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
HOCHSTETTER, Ferdinand von. Geology of New Zealand . . . the provinces of Auckland and Nelson, translated and edited by C. A. Fleming. Wellington. Government Printer, 1959.
NEW ZEALAND ASTRONOMICAL HANDBOOK. (Annual.) Wellington. Royal Astronomical Society of New Zealand.
NEW ZEALAND SOIL BUREAU. General survey of the soils of North Island, New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1954.
OLIVER, Walter Reginald Brook. New Zealand birds. 2nd edition. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
PACIFIC SCIENCE CONGRESS. Proceedings of the seventh Pacific Science Congress, 1949. Wellington. Royal Society of New Zealand, 1954.
PARROTT, Arthur Wilson. The queer and rare fishes of New Zealand. London. Hodder and Stoughton, 1960.
RICHDALE, L. E. A population study of penguins. Oxford. Clarendon Press, 1957.
RINEY, Thane A. Identification of big game animals in New Zealand. Wellington. Dominion Museum, 1955.
STIDOLPH, Robert Hector Donald (editor). The Takahe: Accounts of field investigations on notornis. Masterton. Ornithological Society of New Zealand, 1951.
SUGGATE, Richard Patrick. New Zealand coals: their geological setting and its influence on their properties. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
WILLIAMS, Gordon John. New mineral discoveries in the Nelson province. Nelson. Stiles, 1957.
BEAGLEHOLE, Ernest. Mental health in New Zealand. Wellington. University Press, 1951.
BROWN, Charles Maurice Bevan. Sources of love and fear. Wellington. Reed, 1950.
GORDON, Doris C. Doctor down under. London. Faber, 1957.
HEWAT, Robert Eric Tamlyn, and Eastcott, D. F. Dental caries in New Zealand: report of an epidemiological and racial study. Christchurch. Medical Research Council, 1956.
BRITTENDEN, Richard Trevor. Great days in New Zealand cricket. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
CRICKET ALMANACK of New Zealand 1959, edited by Arthur H. Carman. Wellington. Sporting Publications, 1959.
CARMAN, Arthur H. Ranfurly Shield rugby: the complete book of match reports. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
FAIRBURN, John (editor). The 1956 Springboks in New Zealand. Auckland. A. D. Organ, 1956.
MCCARTHY, Winston John. Round the world with the All Blacks, 1953–54. Wellington. Sporting Publications, 1954.
MCLEAN, Terence H. P. Great days in New Zealand rugby. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
—Kings of rugby. The British Lions' 1959 tour of New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
O'Brien, B. F. Kiwis with gloves on: a history and record book of New Zealand boxing. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
RUGBY ALMANACKOF NEW ZEALAND, 1960, edited by Arthur H. Carman, Read Masters, and Arthur C. Swan. Wellington. Sporting Publications, 1960.
SUTTON-SMITH, Brian. The games of New Zealand children. Berkeley. University of California Press, 1959.
SWAN, Arthur Cameron. History of New Zealand rugby football. Vol. 2. 1946–57. Wellington. New Zealand Rugby Football Union, 1958.
BAXTER, James Keir. Recent trends in New Zealand poetry. Christchurch. Caxton, 1951.
—The fallen house: poems. Christchurch. Caxton, 1953.
—In fires of no return: poems. London. Oxford University Press, 1958.
—Two Plays: The wide open cage and Jack Winter's dream. Hastings. Capricorn Press, 1959.
BETHELL, Mary Ursula. Collected poems. Christchurch. Caxton, 1950.
BRASH, Charles Orwell, The estate and other poems. Christchurch. Caxton, 1957.
CAMPBELL, Alistair. Mine eyes dazzle. Poems, 1947–49. Christchurch. Caxton, 1950.
CHAPMAN, Robert M., and BENNETT, Jonathan (editors). An anthology of New Zealand verse. Oxford University Press, 1956.
CURNOW, Thomas Allen Monro. The best of Whim Wham. Hamilton. Paul, 1959.
CURNOW, Thomas Allen Monro (editor). A book of New Zealand verse, 1923–50. Christchurch. Caxton, 1951.
CURNOW, Thomas A. M. The Penguin book of New Zealand verse, selected with an introduction. Harmondsworth. Penguin, 1960.
DALLAS, Ruth, Country road and other poems 1947–52. Christchurch. Caxton, 1953.
DOYLE, Charles Desmond. A splinter of glass: poems 1951–55. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1956.
DUGGAN, Eileen May. More poems. London. Allen and Unwin, 1951.
GLOVER, D. J. M. Arawata Bill: A sequence of poems. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1953.
—Since then. Wellington. Mermaid, 1957.
HART-SMITH, Wm. Poems of discovery. Sydney. Angus and Robertson, 1959.
JOHNSON, Louis (editor). New Zealand poetry yearbook. Vol. 9. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1960.
JOSEPH, Michael Kennedy. Imaginary islands: poems. Auckland. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1950.
—The living countries. Hamilton. Paul, 1959.
MASON, Bruce E. G. The pohutukawa tree: a play in three acts. Wellington. Price, 1960.
OLIVER, William Hosking. Fire without phoenix: poems 1946–54. Christchurch. Caxton, 1957.
REID, John Cowie (comp.). The Kiwi laughs: an anthology of New Zealand prose humour. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
SCHAFER, Adele. Hinemoa and Tutanekai and other . . . poems. Wellington, 1959.
SINCLAIR, Keith. Songs for a summer. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1952.
—Strangers or beasts. Christchurch. Caxton, 1954.
SMITHYMAN, William Kendrick. The blind mountain. Christchurch. Caxton, 1950.
The Night Shift. Poems … by J. K. Baxter, Chas. Doyle, Louis Johnson, and Kendrick Smithyman. Wellington. Capricorn, 1957.
WALL, Arnold. A century of New Zealand's praise. Christchurch. Simpson and Williams, 1950.
WILKINSON, Iris Guiver. Houses by the sea and the later poems of Robin Hyde (pseudonym). With an introduction by Gloria Rawlinson. Christchurch. Caxton, 1952.
WOODHOUSE, Airini E. New Zealand farm and station verse, 1850–1950. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1950.
ART GALLERIESAND MUSEUMS ASSOCIATIONOF NEW ZEALAND. Guide to the art galleries and museums of New Zealand, 1958.
BAXTER, James Keir. The fire and the anvil. Notes on modern poetry. Wellington. New Zealand University Press, 1955.
BERKMAN, Sylvia Leah. Katherine Mansfield: A critical study. New Haven. Yale University Press, 1951.
BURTON, Ormond Edward. Spring fires: a study in New Zealand writing. Auckland. Book Centre, 1956.
HOFMAN, Helen L. (editor). The puritan and the waif. Critical essays on the work of Frank Sargeson by Walter Allen and others. Auckland, 1954.
HOLCROFT, Montague Harry. Discovered isles: A trilogy (Second issue of three separate essays.) Christchurch. Caxton, 1950.
—The eye of the lizard: a selection of essays from the New Zealand Listener. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
HOWELL, Arthur R. Frances Hodgkins: Four vital years. London. Rockliff, 1951.
MCCORMICK, Eric Hall. Eric Lee-Johnson, with a biographical introduction. Hamilton. Paul, 1956.
—Frances Hodgkins and her circle. An exhibition. Auckland. Pelorus Press, 1954.
—New Zealand literature: a survey. London. Oxford University Press, 1959.
—Works of Frances Hodgkins in New Zealand. Auckland. City Art Gallery, 1954.
MALING, Peter B. Samuel Butler at Mesopotamia together with Butler's “Forest Creek” manuscript and his letters to Tripp and Acland. Wellington. Government Printer, 1960.
MANSFIELD, Katherine. Katherine Mansfield's letters to John Middleton Murry. London. Constable, 1951.
MARSH, Ngaio. Perspectives. The New Zealander and the visual arts. Auckland Gallery Associates, 1960.
THE NEW ZEALAND WRITERS' HANDBOOK, edited for the PEN, New Zealand Centre, by Stuart Perry. Wellington. Reed, 1952.
REED, A. H. and A. W. The House of Reed: fifty years of New Zealand publishing, 1907–57. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
REID (Joan and Russell), Ltd. Prompt book: a New Zealand theatre guide. 2nd edition. Wellington. 1959.
SCHOLEFIELD, Guy Hardy. Newspapers in New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
SCHRODER, John Henry Erle. Second appearances. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
STEWART, Douglas Alexander. Four plays. Sydney. Angus and Robertson, 1959.
TAYLOR, Ernest Mervyn. Engravings on wood. Wellington. Mermaid, 1957.
BULLOCK, Marie I. It's been nice not knowing you. Auckland. Collins, 1960.
CARMAN, Dulce. Dream of the dark. London. Wright and Brown, 1955.
COURAGE, James. The call home. London. Cape, 1956.
— A way of love. London. Cape, 1959.
— The young have secrets. London. Cape, 1954.
CROSS, Ian Robert. The God boy. London. Deutsch, 1958.
— The backward sex; a novel. London. Deutsch, 1960.
DAVIN, D. M. (editor). New Zealand short stories. Oxford University Press, 1953.
— The sullen bell. London. Michael Joseph, 1956.
DUCKWORTH, Marilyn R. The matchbox house. London. Hutchinson, 1960.
DUGGAN, Maurice. Immanuel's land. Auckland. Pilgrim Press, 1956.
EDEN, Dorothy. Listen to danger. London. Macdonald, 1958.
FOWLER, Leo. Brown conflict: a tale of white man and Maori 1861–62. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
FRANCE, Ruth. The race. London. Constable, 1958.
FRAME, Jane. Owls do cry. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1957.
GOULTER, Mary Catherine. Keeper of the sheep. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1955.
GUTHRIE, John. Paradise Bay. London. Werner Laurie, 1952.
Joseph, Michael Kennedy. I'll soldier no more. London. Gollancz, 1958.
MCLEOD, David. The tall tussock: stories of the high country. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
MANSFIELD, Katherine. Selected short stories, with an introduction by D. M. Davin. Oxford University Press, 1953.
MARSH, Ngaio. Opening night. London. Collins, 1951.
— Off with his head. London. Collins, 1957.
— False scent. London. Collins, 1960.
— Singing in the shrouds. London. Collins, 1958.
MASON, Henrietta. Fool's gold. London. Hale, 1960.
MASTERS, Lester. Back-country tales. Hastings, 1960.
MIDDLETON, Osman E. G. The stone and other stories. Auckland. Pilgrim Press, 1959.
MUIR, Macgregor Robin. Word for word. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1960.
PARK, Ruth. One-a-pecker, two-a-pecker. Sydney. Angus and Robertson, 1957.
REES, Rosemary Frances. Love in a lonely land. London. Harrap, 1958.
REYBURN, Wallace. The street that died. London. Cassell, 1960.
SARGESON, Frank. I for one. Christchurch. Caxton, 1954.
SCOTT, Mary E. The white elephant. Hamilton. Paul, 1959.
— No sad songs. Hamilton. Paul, 1960.
SCOTT, Mary E., and WEST, Joyce. Fatal lady. Hamilton. Paul, 1960.
SHADBOLT, Maurice. The New Zealanders: a sequence of stories. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
SLATTER, Gordon. A gun in my hand. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1959.
STRINGFELLOW, Olga. Mary Bravender. London. Collins, 1960.
SUMMERS, Essie. The lark in the meadow. London. Mills and Boon, 1959.
WARNER, Sylvia Ashton-. Spinster: a novel. London. Secker and Warburg, 1958.
— Incense to idols; a novel. London. Secker and Warburg, 1960.
WILSON, Guthrie Edward. Brave company. London. Hale, 1951.
— Julien Ware. London. Hale, 1952.
— The feared and the fearless. London. Hale, 1954.
— Sweet white wine. London. Hale, 1956.
— Strip Jack naked. London. Hale, 1957.
— The incorruptibles. London. Hutchinson, 1960.
ACRES, Thyna A. M. Opo the gay dolphin. Wellington. Reed, 1956.
ADKIN, George Leslie. The great harbour of Tara … Maori place names and sites of Wellington … environs. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1958.
AUCKLAND Provincial Public Relations Office. The story of the Auckland harbour bridge. Auckland, 1959.
BRUNNER, Thomas. The great journey. An expedition to explore the interior of the Middle Island, 1846–48. Edited by John D. Pascoe. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1952.
CLUNE, Frank. Roaming round New Zealand. Sydney. Angus and Robertson, 1956.
CRANWELL Publishing CO. FARMS AND STATIONS OF NEW ZEALAND. VOL. 1, 1957; VOL. 2, 1958. Auckland.
CUMBERLAND, Kenneth Brailey, and Fox, J. W. New Zealand: a regional view. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1958.
DOLLIMORE, Edward Stewart. New Zealand guide, incorporating Wise's every place in New Zealand. Dunedin. Wise, 1952.
DOUGLAS, Charles Edward. Mr Explorer Douglas. Edited by John D. Pascoe. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
DUFF, Oliver. New Zealand now. London. Allen and Unwin, 1956.
GOLDBLATT, David. Democracy at ease, a New Zealand profile. London. Pall Mall Press, 1957.
HALL, David Oswald William. Portrait of New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
HARDINGHAM, John Frederick Watson. New Zealand travel guide. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
HARDWICK, John M. D. Opportunity in New Zealand. London. Rockliff, 1955.
— The Royal visit to New Zealand, December 1953 – January 1954. Edited by J. H. Richards. Wellington. Reed, 1954.
HEWITT, Leonard Rodney and Mavis DAVIDSON. The mountains of New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1954.
HILLARY, Sir Edmund. High adventure. London. Hodder and Stoughton, 1955.
KEAM, Ronald Frank. Lake Taupo. Auckland, 1959.
LAUPER, Jakob. Over the Whitcombe Pass. Edited by John Pascoe. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
MCCLYMONT, William Graham. The exploration of New Zealand. 2nd edition. London. Oxford University Press, 1959.
MCLINTOCK, Alexander Hare (editor). A descriptive atlas of New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1959.
MEAD, Arthur D. Wanganui River. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
MORRELL, W. P., and HALL, D. O. W. A history of New Zealand life. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs. 1957.
NAN KIVELL, Rex de C. The Rex Nan Kivell collection of early New Zealand Pictures. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1953.
NEWTON, Peter. High country journey. Wellington. Reed, 1952.
NEW ZEALAND DEPARTMENTOF TOURISTAND PUBLICITY. A tour of New Zealand by Her Majesty the Queen and the Duke of Edinburgh, 1953–54. Wellington. Government Printer, 1953.
The Oxford Atlas for New Zealand. London. Oxford University Press, 1959.
PANTON, H. S. New Zealand. A preview of the land of the long white cloud. London. Rockliff, 1951.
PASCOE, John Dobree. Great days in New Zealand mountaineering. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
— Land uplifted high. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1952.
PETERSEN, G. C. Lake Taupo. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
REED, Alfred Hamish. Walks in Maoriland byways. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
REED, Arnold Wyclif. The story of New Zealand place names. Wellington. Reed, 1952.
REEVES, W. P. The long white cloud. Ao-tea-roa . . . with additional chapters by A. J. Harrop. London. Allen and Unwin, 1950.
RICHARDS, James Harray. Milford Sound. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
— Rangi and Rotorua. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
— Waitomo Caves. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
SALMON, John Tenison. Heritage destroyed: the crisis in scenery preservation in New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
STONE, Desmond (editor). Verdict on New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
SUTHERLAND, W. T. G. The golden bush. London. Michael Joseph, 1953. Also at Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1953.
WEBB, Beatrice. Visit to New Zealand in 1898 . . . with entries by Sidney Webb. Wellington. Price, 1958.
WHITE'S AVIATION LTD., Auckland. White's pictorial reference of New Zealand: Representative air views of New Zealand cities and boroughs. Auckland. White's Aviation, 1952.
WILKINSON, Alexander Stanley. Kapiti bird sanctuary. Masterton. Stidolph, 1952.
WILSON, Robert A. Bird islands of New Zealand. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
WINKS, Robin William. These New Zealanders. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1954.
WOOD, Frederick Loyd Whitfield. This New Zealand. 4th edition. London. Hammond, 1958.
BRYANT, L. V. New Zealanders and Everest. Foreword by Sir Edmund Hillary. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
BURDON, R. M. New Zealand notables: Series three. Christchurch. Caxton, 1951.
Furkert, F. W. Early New Zealand engineers, edited by W. L. Newnham. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
NEW ZEALAND BUSINESS WHO'S WHO, 1958–59. Wellington. Business Book Co., 1958.
SIMPSON, Frank A. (editor). Who's who in New Zealand. 6th edition. Wellington. Reed, 1956.
TILLMAN, Harry. Great men of New Zealand Rugby. Christchurch. Lancaster, 1957.
WHITE'S AIR DIRECTORYAND WHO'S WHOIN NEW ZEALAND AVIATION (including the South Pacific), 1956–57. Auckland. White's Aviation, 1956.
ALPERS, Antony. Katherine Mansfield, a biography. New York. Knapf, 1953.
ANDERSON, J. C., and PETERSEN, G. C. The Mair family. Wellington. Reed, 1956.
BURDON, Randal Mathews. Scholar errant: a biography of Professor A. W. Bickerton. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1956.
CARRINGTON, C. E. John Robert Godley of Canterbury. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1950.
CODY, J. F. Man of two worlds: Sir Maui Pomare. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
CRUMP, Barry J. A good keen man. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
DILLON, Constantine Augustus. The Dillon letters, 1842–53. Edited by C. A. Sharp. Wellington. Reed, 1954.
DOMETT, Alfred. The diary of Alfred Domett. Edited by E. A. Horsman. Oxford University Press, 1953.
FRY, A. S. The Aunt Daisy story. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
KEYS, Lillian G. The life and times of Bishop Pompallier. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1957.
HILLARY, Sir Edmund P., and LOWE, Geo. East of Everest. An account of the New Zealand Alpine Club Himalayan expedition, 1954. London. Hodder and Stoughton, 1956.
JONES, Pei te Hurinui. King Potatau: an account of the life of Potatau Te Wherowhero, the first Maori King. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1960.
MANSON, Cecil M. and Celia E. Doctor Agnes Bennett. Foreword by J. C. Beaglehole. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
MULGAN, Alan Edward. The making of a New Zealander. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
OPIE, June. Over my dead body. London. Methuen, 1957.
RAMSDEN, George Eric Oakes. A memoir – Te Rangihiroa: Memorial to Sir Peter Buck. Wellington. Department of Maori Affairs, 1954.
ROTH, Herbert Otto. George Hogben: a biography. Wellington. New Zealand Council for Educational Research, 1952.
RUTHERFORD, James. Sir George Grey, K.C.B. 1812–1898. A study in colonial development. London. Cassell, 1961.
STEVENS, Percival George William. John Grigg of Longbeach. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1952.
THORN, James. Peter Fraser, New Zealand's wartime Prime Minister. London. Odhams Press 1952.
WARD, Edward Robert. The journal of Edward Ward 1850–51. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1958.
WILD, L. J. The life and times of Sir James Wilson of Bulls. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1953.
WILLIAMS, John B. The New Zealand Journal, 1842–1844. Edited by Robert W. Kenny. Salem. Peabody Museum, 1956.
WILSON, Helen Mary. My first eighty years. Hamilton. Paul, 1950.
WOODHOUSE, Airini Elizabeth. Guthrie-Smith of Tutira. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
COCKS, Pamela S. Preliminary list of archives of local bodies in New Zealand 1960. Wellington. New Zealand Library Association, 1960.
CONDLIFFE, J. B., and AIREY, W. T. G. A short history of New Zealand. 9th edition. Christchurch Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
COOK, James. Journals on his voyages of discovery. Edited by J. C. Beaglehole (and others). Vol. 1: The voyage of the Endeavour, 1768–1771. Cambridge University Press for the Hakluyt Society, 1955.
— Charts and views drawn by Cook and his officers and reproduced from the original manuscripts. Edited by R. A. Skelton. Cambridge University Press for the Hakluyt Society, 1955.
CRUISE, Richard A. Journal of a ten months residence in New Zealand, 1820. Edited by A. G. Bagnall. Christchurch. Pegasus Press, 1957.
DUMONTD'URVILLE, Jules S. C. The voyage of the Astrolabe, 1840. An English version by Olive Wright. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
MCLINTOCK, Alexander Hare. Crown colony government in New Zealand. Wellington. Government Printer, 1958.
MILLER, Harold G. New Zealand. London. Hutchinson, 1950.
NEW ZEALAND DOMINION ARCHIVES. A guide to the Dominion archives. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1953.
— Archives of the Governor-General. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1953.
— Archives of the Army Department. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1953.
— Archives of the New Zealand Company. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1953.
NEW ZEALAND NATIONAL (formerly “DOMINION“) ARCHIVES. Archives of the Provinces of New Ulster and New Munster and of the Civil Secretary's Office. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1954.
NEW ZEALAND NATIONAL ARCHIVES. Archives of the provinces of Auckland and Taranaki. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1958.
— Archives of the provinces of Nelson and Marlborough and of the Nelson Trust Funds Board. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1958.
NEW ZEALAND NATIONAL HISTORICAL PLACES TRUST. Rules. Wellington. Government Printer, 1956.
OLIVER, William Hosking. The story of New Zealand. London. Faber, 1960.
SINCLAIR, Keith. A history of New Zealand. Harmondsworth. Penguin Books, 1959.
SUTHERLAND, Allan. New Zealand famous firsts and related records. Auckland. Zedfirst publications, 1960.
TAPP, Edwin John. Early New Zealand, a dependency of New South Wales 1788–1841. Carlton. Melbourne Univerity Press, 1958.
WILSON, James Oakley. A finding list of British Parliamentary papers relating to New Zealand 1817–1900. Wellington. General Assembly Library, 1960.
WRIGHT, Harrison M. New Zealand 1769–1840. Early years of Western contact. Cambridge Mass. Harvard University Press, 1960.
ACLAND, Leopold George Dyke. The early Canterbury runs and glossary of station terms. (Incorporating earlier volumes.) Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1951.
ALLAN, Ruth Mary. The history of Port Nelson. Wellington. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1954.
BAGNALL, A. G. Masterton's first hundred years. Masterton. Centennial Committee, 1954.
— Old Greytown, 1854–1954. Greytown Centennial Book Committee, 1953.
— A history of Carterton; the story of the first hundred years. Carterton. Borough Council, 1957.
BANKS, Sir Joseph. Sir Joseph Banks in New Zealand. Edited by W. P. Morrell. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
BEILBY, Geo. T. Roads to tomorrow . . . one hundred years of Baptist work in New Zealand. Christchurch. Baptist Union of New Zealand, 1957.
COLE, J. R. Pompallier, the house and the mission of Bishop Pompallier in early New Zealand. Wellington. Department of Internal Affairs, 1957.
COOK, JAMES. Captain Cook in New Zealand. Extracts from the journals, edited by A. H. and A. W. Reed. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
DRUMMOND, Alison E. H. Married and gone to New Zealand, being extracts from the writings of women pioneers. Hamilton. Paul, 1960.
ELVY, William John. Kei puta te Wairau: a history of Marlborough in Maori times. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1957.
GILLESPIE, Oliver Arthur. South Canterbury: a record of settlement. Timaru. South Canterbury Centennial History Committee, 1958.
GLASSON, H. A. The golden cobweb: a saga of the Otago goldfields, 1861–64. Dunedin. Otago Daily Times, 1957.
GODLEY, Charlotte (Wynne). Letters from early New Zealand, 1850–1853. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1951.
GOLDMAN, Lazarus Morris. The history of the Jews in New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
GORST, John. The Maori King. Edited by K. Sinclair. Hamilton. Paul, 1959.
GOULTER, Mary C. Sons of France. A forgotton influence on New Zealand History. Wellington. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1957.
GRAINGER, John. The Auckland story . . . through the years. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
GRAYLAND, Eugene C. New Zealand disasters. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
HARPER, Barbara O. History of the Country Women's Institutes of New Zealand 1921–58. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1960.
HASSALL, Charles Edward. A short history of the Port of Timaru, 1852–1955. Timaru. Harbour Board, 1955.
HIGHT, Sir James, and STRAUBEL, C. R. A history of Canterbury. Christchurch. Canterbury Centennial Association, 1957.
HOBBS, Leslie Raymond. The wild west coast. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1959.
INGRAM, Charles William Nepean, and WHEATLEY, P. Owen. Shipwrecks: New Zealand disasters, 1795–1950. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
JILLETT, J. W. L. Wings across the Tasman, 1928–53. Wellington. Reed, 1953.
JOHNSON, John. The Story of Lyttelton. Lyttelton. Lyttelton Borough Council, 1952.
Kelly, Leslie George. Marion Dufresne at the Bay of Islands. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
MACKAY, Joseph Angus. Historic Poverty Bay and the East Coast. Gisborne. The Author, 1949.
MCLINTOCK, A. H. Liquor and the King Country. Wellington. Government Printer, 1953.
MCNEISH, Jas. Taverns in the town. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
MANSON, Cecil M., and Cecilia E. Tides of Hokianga. Wellington. Wingfield Press, 1956.
MEIKLEJOHN, G. M. Early conflicts of press and government. A story of the first New Zealand Herald and of the founding of Auckland. Auckland. Wilson and Horton, 1953.
MILLAR, John Halket. Death round the bend. Nelson. Stiles, 1955.
MILLER, Frederick Walter Gascoyne. Beyond the blue mountains. A history of the West Otago district. Dunedin. Otago Centennial Historical Publications, 1954.
MILLER, John Owen. Early Victorian New Zealand: racial tension and social attitudes, 1839–52. London. Oxford, 1958.
MONAGHAN, Harold W. From age to age: the story of the Church of England in the Diocese of Wellington 1858–1958. Wellington. Diocesan Committee of Wellington, 1957.
MORRELL, William Parke. Britain in the Pacific Islands. Oxford. Clarendon, 1960.
MULGAN, David Kennaway. The Kiwi's first wings: the story of the Walsh brothers and the New Zealand Flying School 1910–1924. Wellington. Wingfield, 1960.
NEW ZEALAND TANGIWAI RAILWAY Disaster BOARDOF ENQUIRY. Report. Wellington. Government Printer, 1954.
PETERSEN, George Conrad. The pioneering days of Palmerston North. Levin. Kerslake, Billens, and Humphrey, 1952.
RAMSDEN, George Eric Oakes. Rangiatea: The story of Otaki church. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
REED, Alfred Hamish. Historic Bay of Islands. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
— The story of Hawke's Bay. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
REED, Arnold Wyclif. Auckland, city of the seas. Wellington. Reed, 1955.
REED, Vernon H. The gift of Waitangi. Wellington. Reed, 1957.
RHODES, William Barnard. The whaling journal of Captain W. B. Rhodes. Barque Australian, 1836–38. Notes by C. R. Straubel. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1954.
RYAN, Archie Bruce. Gold discoveries in New Zealand. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
SCOTT, R. G. The Parihaka story. Auckland. Southern Cross Books, 1954.
SHARP, Charles Andrew. Crisis at Kerikeri. Wellington. Reed, 1958.
— The discovery of the Pacific Islands. Oxford. Clarendon Press, 1960.
SINCLAIR, Keith. Maori land league. Auckland University College, 1950.
— The origins of the Maori Wars. Wellington. New Zealand University Press, 1957.
Smith, R. A. Printing in Canterbury. A history of newspapers and printing houses. Christchurch Club of Printing House Craftsmen, 1953.
STEWART, George Gordon. The romance of New Zealand railways. Wellington. Reed, 1951.
SUTHERLAND, Allan. Flags of New Zealand. Auckland. 1958.
TAYLOR, Nancy M. Early travellers in New Zealand. Oxford. Clarendon Press, 1959.
TORLESSE, Charles Obins. The Torlesse papers . . . concerning the founding of the Canterbury settlement in New Zealand 1848–51. Edited by Peter P. Maling. Christchurch. Pegasus, 1958.
TRACY, Mona (Mackay). West Coast yesterdays. Wellington. Reed, 1960.
TURNBULL, Michael R. M. The New Zealand bubble: the Wakefield theory in practice. Wellington. Price Milburn, 1959.
WAKEFIELD, Edward Jerningham. Adventure in New Zealand. An abridgment by Joan Stevens, Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1955.
WATERS, Sydney David. Union Line: A short history of the Union Steam Ship Company of New Zealand. Wellington. The Company, 1952.
WOOD, Russell George. From Plymouth to New Plymouth. Wellington. Reed, 1959.
WYNYARD, Montague Harrison. The story of Maungakiekie the ancient Maori fortress and now One Tree Hill. Auckland. One Tree Hill Domain Board, 1958.
WATERS, S. D. Ordeal by sea. New Zealand shipping in the Second World War, 1939–45. London. New Zealand Shipping Company, 1949.
The following have been published by the War History Branch, Department of Internal Affairs, Wellington.
ANSON, T. V. The New Zealand Dental services. 1960.
BATES, P. W. Supply Company. 1955.
BORMAN, C. A. Divisional Signals. 1954.
BURDON, R. M. 24 Battalion. 1953.
CODY, J. F. 21 Battalion. 1953.
— 28 (Maori) Battalion. 1957.
DAVIN, D. M. Crete. 1953.
GILLESPIE, O. A. The Pacific. (Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War.) 1952.
HALL, D. O. W. New Zealanders in South Africa, 1899–1902. 1949.
HENDERSON, James Herbert. R.M.T. 1954.
— 22 Battalion. Wellington. 1958.
KAY, Robin Langford. 27 (Machine Gun) Battalion. Wellington. 1957.
LLEWELLYN, S. P. Journey towards Christmas. (Official History of the 1st Ammunition Company, 2nd N.Z.E.F.) 1949.
MASON, W. W. Prisoners of war. 1954.
MCCLYMONT, W. G. To Greece. 1959.
MCKINNEY, J. B. Medical units of 2nd N.Z.E.F. in Middle East and Italy. 1952.
NEW ZEALAND ARMY JOURNAL. Vol. 1, No. 1, 1954. Wellington.
NORTON, F. D. 26 Battalion. 1952.
PHILLIPS, N. C. Italy. Vol. 1. The Sangro to Cassino. 1957.
PRINGLE, D. J. C., and GLUE, W. A. 20 Battalion and Armoured Regiment. 1957.
ROSS, Angus. 23 Battalion. 1959.
ROSS, John Macaulay Sutherland. Royal New Zealand Air Force. 1955.
SCOULLAR, J. L. Battle for Egypt. 1955.
Sinclair, D. W. 19 Battalion and Armoured Regiment. 1954.
STEVENS, W. G. Problems of 2 N.Z.E.F. 1958.
STOUT, T. D. M. War surgery and medicine. 1954.
— Medical services in New Zealand and the Pacific. 1958.
— New Zealand medical services in Middle East and Italy. 1957.
THOMSPON, H. L. New Zealanders with the Royal Air Force. 3 vols. 1953–59.
UNDERHILL, Rev. M. L., and others. New Zealand chaplains in the Second World War. 1950.
WAR HISTORY BRANCH. Documents relating to New Zealand's participation in the Second World War, 1939–45 –
Vol. I. 1950.
Vol. II. 1951.
WATERS, Sydney David. The Royal New Zealand Navy. 1956.
WOOD, Frederick L. W. The New Zealand people at war; political and external affairs. 1958.
Episodes and Studies
The following is the complete range of Episodes and Studies published by War History Branch, Department of Internal Affairs, Wellington, from 1948–55.
CLARE, B. G. Early operations with Bomber Command. 1950.
DEAN, H. R. The Royal New Zealand Air Force in South-East Asia, 1941–42. 1952.
FAIRCLOTH, N. W. New Zealanders in the Battle of Britain. 1950.
HALL, D. O. W. Women at war. 1948. Prisoners of Germany. 1949. Prisoners of Italy. 1949. Prisoners of Japan. 1949. Coastwatchers. 1951. Escapes. 1954.
KAY, R. L. Long range desert group in Libya, 1940. 1949. Long range desert group in the Mediterranean. 1950.
LLEWELLYN, S. P. Troopships. 1949.
MCGLYNN, M. B. Special service in Greece. 1953.
MCKINNEY, J. B. Wounded in battle. 1950.
MURPHY, W. E. Point 175. 1954.
ROSS, J. M. S. The assault on Rabaul. 1949.
SMITH, E. H. Guns against tanks. 1948.
THOMPSON, H. L. Aircraft against U-boat. 1950.
WARDS, I. MCL. Takrouna. 1951.
WAR HISTORY BRANCH STAFF. “The other side of the hill”. 1952.
WATERS, S. D. Achilles at River Plate. 1948. German raiders in the Pacific. 1949. Leander. 1950.
WHELAN, J. A. Malta airmen, 1951.
COOK AND OTHER ISLANDS
AIKMAN, Colin Campbell. First report on constitutional survey of the Cook Islands. Wellington. Department of Island Territories, 1956.
BEAGLEHOLE, Ernest. Social change in the South Pacific: Rarotonga and Aitutaki. London. Allen and Unwin, 1957.
COOK ISLANDS REGISTRAROF COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES. Cooperation for the Maoris of the Cook Islands. Wellington. Government Printer, 1956.
CUMBERLAND, Kenneth Brailey. South-west Pacific. A geography. Christchurch. Whitcombe and Tombs, 1954.
DAVIS, Thomas R. A. H. Doctor to the islands, by Tom and Lydia Davis. London. M. Joseph, 1955.
EDEN, Allan William. Islands of despair . . . the subantarctic islands of New Zealand. London. Melrose, 1955.
MCCARTHY, Dennis Douglas (editor). New Zealand medical research in the South-West Pacific . . . Western Samoa, Rarotonga, and Pukapuka. Dunedin. Coulls, Somerville, Wilkie, 1954.
SCHOFIELD, James Cecil. The geology and hydrology of Niue Island. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
SIMPSON, Frank A. Chatham Islands, Wellington. Reed, 1950.
THOMAS, Marjory C. J. Forgotten islands of the South Pacific, by Rosaline Redwood (pseud.). (Solander, Codfish, Ruapuke, Macquarie, and Chatham Islands.) Wellington. Reed, 1950.
UNIVERSAL business directory for Pacific Islands. Auckland. Universal Business Directories, 1958.
VICTORIA UNIVERSITYOF WELLINGTON Department OF GEOGRAPHY. Western Pacific. Studies of man and environment in the Western Pacific. Wellington. 1958.
WRIGHT, Alfred C. S. Soils of Chatham Island (Rekohu). Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
SAMOA CHURCHWARD, Spencer. A Samoan grammar. 2nd edition. Spectator Publishing Co., Melbourne, for Methodist Church of Australasia, 1951.
JAMES, Clifford Samuel. Diseases commonly met with in Melanesia and Polynesia. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Auckland. Institute Print, 1956.
JUPP, Kathleen M. Report on the population census of Western Samoa 1956. Wellington. Government Printer, 1958.
KEAR, David and WOOD, B. L. The geology and hydrology of Western Samoa. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1959.
KEESING, Felix M., and M. M. Elite communication in Samoa. A study of leadership. Stanford. University Press, 1956.
MARSHALL, Colin, and THOMPSON, T. S. Forestry in Western Samoa. Wellington. Government Printer, 1953.
SCHULTZ, E. Proverbial expressions of the Samoans. Translated by Brother Herman. Wellington. Polynesian Society, 1953.
STACE, Vernon Desmond. Western Samoa, an economic survey. Noumea. South Pacific Commission, 1956.
ROSS DEPENDENCY
THE ANTARCTIC TODAY. Compiled by members of the New Zealand Antarctic Society. Wellington. Reed, 1952.
FUCHS, Sir Vivian Ernest, and HILLARY, Sir Edmund. The crossing of Antarctica, the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition 1955–58. London. Cassell, 1958.
GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF NEW ZEALAND ANTARCTIC RESEARCH COMMITTEE. Preliminary bibliography of the geology of the Ross Dependency, 1956 (duplicated). (These were followed by a series of geological and biological reports.)
HATHERTON, T. New Zealand IGY Antarctic Expeditions, Scott Base and Hallett Station. Wellington. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 1961. Bulletin 140.
HELM, A. S. Provisional gazetteer of the Ross Dependency. Wellington. New Zealand Geographic Board, 1957. Supplement 1960.
ROSS SEA COMMITTEE. New Zealand Antarctic Manual, 1956–58. Scott Base, Ross Dependency, 1958.
Extracts from the Report of the Committee on New Zealand Universities, chaired by Sir David Hughes Parry.*
THE ROLE OF THE UNIVERSITY IN THE NEW ZEALAND COMMUNITY - What role the universities should play in the New Zealand community will depend in large measure upon the kind of society New Zealand wants and is willing to pay for.
We have received submissions from Departments of Government, from professional groups, from voluntary societies, as well as from the University of New Zealand and its constituent universities and agricultural colleges, all of which indicate that many New Zealanders want, and feel that New Zealand must have, a more diversified and more industrialised economy if it is to maintain its population at the present standard of living, and if possible improve it; that they want a wider variety and a progressive improvement of social and professional services; and that they want to foster a better and deeper understanding of New Zealand's own life and problems in order to provide a more varied and interesting life for the community.
How much public support these representations have we are not in a position to say. But if New Zealand does want and is willing to pay for a more developed economic, social, and cultural life, then the universities must play a much greater role in the New Zealand community, and must be much better supported financially than they have been in the past.
If, for example, New Zealand is to develop more secondary industry, then she will have to educate-or import-more chemical, physical, and biological scientists; more engineers; more chemical, building, and food technologists; more economists, and more people trained in the arts and skills of management. The world-wide demand for such persons is currently so great - and is growing so rapidly - that the opportunities to import them in the numbers required are limited. The alternative is to import or educate the teachers in these fields and with their help and guidance to develop the skills required, in universities and/or technological institutions. Even if the decision is made to educate the required personnel locally, there will be a further question to answer, namely: What part shall the universities and agricultural colleges play in the development of these new skills and emerging professions ?
A second example illustrates the concern which has been expressed to us for New Zealand's social development. If New Zealand wants to continue to supply her population with health, welfare, and public educational services of a high order, and to continue to improve them, then she must induce a sufficient number of the best qualified of her young people to offer and equip themselves for this work. At the moment, in common with other countries, New Zealand is trying to staff her schools and other public services from a low-birthrate generation in order to cater for a very high-birthrate generation, and this has brought about - again in common with other countries - a lowering of academic standards for entrance to some of the public services, notably teaching. We mention teaching specifically because the Department of Education has drawn public attention to the present critical shortage of teachers - and particularly to the shortage of those with full qualifications. The Department is concerned, as are the teachers of New Zealand and the public, that the country's most valuable resource, its young people, shall not have their vision and skill limited by being educated by those whose own education is inadequate. With this in mind, the Department, with the support of the teaching profession, is trying to stimulate as many as possible of those now taking primary, as well as post-primary, teacher training, who have the requisite qualifications, to pursue university studies.
When the supply of those coming into teacher training who possess university entrance qualifications catches up with the demand, as it is expected to do in four or five years, the present demand for university programmes of study will be much increased. Here again the quality of excellence the public wants - and is willing to pay for - in the training of those who educate their children, and who perform other social services, will affect the role of the university in the community.
One further illustration may be offered. It has been represented to us that New Zealand should introduce into university studies, or develop to a higher level, more of those subjects which have a direct bearing on New Zealand's own life and problems, which are designed to foster the growth of national self-understanding, and to increase delight in life. It is suggested to us that more attention should be paid at the universities, at the appropriate level, to New Zealand's own history, life, and literature, the arts (with particular emphasis on design), economic problems, social organisation, marine environment, soil science, and forest problems, to name only some from very diverse fields. It is argued by those making the representations that such studies would widen the vision of promising students regarding the possibilities of life in New Zealand; and would strengthen their roots in the New Zealand environment before they go abroad, if they do go, with the result that more of them would have stronger incentives to return to fields of study into which they had already penetrated or in which they had already achieved some degree of authority.
* Report of the Committee on New Zealand Universities 1959. Government Printer, Wellington. See reference on page 240 of this Yearbook.
The purpose here again is to show the relationship between the university's role and the community's aspiration. If New Zealand wants to foster more, and more advanced, study of its own life and problems, then the universities will have to be equipped to carry out such study, much of it at the more expensive graduate level.
In all three of the illustrations given here the universities' role in the community will be vitally affected by the image the community has of its own economic, social, and cultural future, and by its view of the universities' part in shaping that future.
At the moment New Zealand's attitude towards its universities and colleges is similar to that of most other young and developing countries, not far removed from a pioneer tradition which is prepared to cater to the needs of today and tomorrow but doubts the value of planning too far ahead, and which tends to prefer practice without theory. To say this is not to be critical of the pioneer tradition in its time and place, but to doubt whether the continuance of that tradition will longer serve New Zealand's needs in a world where scientific, social, and technological change have become the norm, and where planning ahead is as accepted a part of public policy as it is of personal policy.
In keeping with this pioneer tradition the universities of New Zealand are not widely regarded as having a primary responsibility for original investigation and research. “They should stick to their teaching,” it has been said. To say this, to advocate the separation of teaching from research, is to invite social and cultural, no less than scientific and technological, stagnation. Society, if it is to make advances, must have institutions in which teaching and research go hand in hand, in which students can come in contact with, and become excited by, the possibilities of research and its relation to human progress.
The universities of New Zealand are aware of the need to combine teaching with research and, indeed, a certain amount of research is being carried on, despite heavy teaching loads, inadequate facilities, and little financial support. Unless the universities' teaching staffs are provided with the time, money, and facilities to think about the future of their society in relation to its past, to compare and relate the contributions of other cultures to those of their own, to investigate the nature of the physical world and to keep abreast of the investigations of others, they will not be in a position to serve their society as, in recent years, in most developing countries, they have been asked to serve it.
The traditional view of the university in the British conception of higher education has undergone substantial modifications and adaptations in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, consequent upon new social requirements which brought into being many of the civic universities in the United Kingdom, and the equivalent needs which prompted the development of similar institutions in the United States and throughout the Commonwealth. The monastic tradition in which the ancient universities were founded, to prepare young men “for service in Church and State”, has had to accommodate itself to the idea of co-education and also to broaden its programme of studies beyond the traditional disciplines of theology, law, arts, science, and medicine, in order to provide the wider range of professional skills that the new societies required: agricultural science, architecture, dentistry, education, engineering, forestry, home science, pharmacy, business administration, public administration, social work, and librarianship, to name only some.
In addition to the increase in specifically professional studies the nineteenth and twentieth centuries have also seen a thorough overhauling of the traditional arts and science curricula, a great enlargement in the area of general studies, and an increased emphasis on “liberal” education, partly for its own sake and partly as the intellectual equipment of those who proposed to follow a “career” in public service, politics, journalism, or teaching, rather than one of the traditional “professions”.
Paralleling the emphasis on liberal education and the renovation of the science curriculum, and related to both, there has developed a much greater emphasis on the responsibility of the universities for research, both pure and applied, in part as a service to society and in part to invigorate both teaching and learning. There can be no doubt that the stimulus which research has given to university life has been in large measure responsible for the greatly increased contemporary recognition of the importance of the universities as centres of independent thought; as guardians of the accumulated culture of the past; as social and scientific laboratories for the accumulation of new knowledge; and as “pilot plants” for the experimental applications of new knowledge to the solution of economic, technological, social, and cultural problems. . . .
NEEDS OF THE COMMUNITY - We regard the encouragement and development of science and technology as vital to the economy and well-being of the country. We do not, however, feel that the New Zealand community has yet become fully aware of the implication of its neglect of these essentials to material progress. This is all the more surprising because New Zealand has already benefited handsomely from its own discoveries in the field of agricultural science and from the wide application of these discoveries by the farming community and agricultural industries. New Zealand has also taken advantage of, and derived great benefits from, the application of engineering knowledge and techniques to the supply and service of electric power from its water resources. There is, however, an awakening realisation in New Zealand that secondary or manufacturing industries must be expanded and developed beyond the assembling and servicing type of industry into the realm of production of capital goods, such as machinery, and of more consumer goods, in order to maintain the people's standards of living and to employ the increasing population.
We have noticed the tendency to decry New Zealand's lack of raw materials and its small population and markets as disadvantages weighing against the possibility of developing industries on an economic basis. It has not been our specific task to study this problem, but we have been able to discern promising possibilities and potentialities in secondary industries built around the primary industries. Food processing is an example of such a secondary industry. The canning of fruit, vegetables, meat, and fish offers opportunities for expansion, since New Zealand has great natural advantages in the growing of the raw materials for these. Paper pulp and timber and other wood products are emerging as valuable exports. There are raw materials for the manufacturing of woollen textiles, leather, and other goods. If the technologies for the manufacture of these products had been studied earlier in New Zealand, and they had then been developed under the pressure of economic facts and growing population, there is no saying how flourishing such secondary industries would have been by now. Such developments could have been facilitated not only by the availability of raw materials but also, and at least equally, by the knowledge and resourcefulness of the people, and by the ability, enterprise, and technological expertise of individuals.
The expansion in New Zealand of secondary industries, and the further improvement of primary industries, call for the development of human and material resources, with scientific, engineering, and technological skills and enterprise of the highest quality; and this not in a small number of very clever people, and not by imitation of overseas practice, but in a large number of highly qualified, well educated people who will invent, adapt, and improve manufactures suitable and peculiar to the New Zealand environment. Most of these advances stem from university-educated persons; in short, from scientists, technologists, economists, and administrators.
The role of the university in all this is pre-eminent; its task and responsibility are clear and unmistakable. It also concerns every man and woman in New Zealand, whether he or she belongs to a trade union or a profession; all have a vital stake in the results of scientific discoveries and their application. And in so far as the universities foster such discoveries and educate persons in scientific techniques, no employed person in New Zealand can afford not to be interested in university education although he may not wish to have, or cannot have, such an education for himself. It is a national responsibility. Fortunately, there are encouraging signs from the past that when the New Zealand community is fully seized of an important national responsibility its response is rapid and unequivocal.
A great responsibility is, therefore, thrown on those concerned with university education. The difficulties in the way of the universities in New Zealand as they face the progressive demands upon them of science and technology are manifold. One difficulty is the high cost of educating scientists and technologists; laboratories and equipment are expensive; the competition for qualified teachers, professors, scientists, and technologists is world-wide and keen. Another difficulty is that of defining the relative spheres of operation of the universities and the technical colleges in the expanding field of technological education.
In the last decade or so research and development in New Zealand have been concentrated upon the problems of the primary industries and have come mainly through the agricultural colleges and the Government research institutions of the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research under the stimulus of the need to produce more wool, meat, dairy products, and timber products. Secondary industry's contribution and participation in research and development have been small and sadly lacking in many fields. Industrialists are now awakening to the fact that more qualified personnel and more complex skills are essential to their progress. They have, in the past, put little pressure on the universities for professional engineers and scientists, and even now seem to find it difficult to prescribe the sorts of educated persons and complex skills they need. The universities, too, have been slow to grasp the fact that it is a matter of concern for them, and as a consequence, have been slow to develop teaching and research in the applied sciences and technologies.
It has been said that one of the great sources of the strength of a nation is its scientific and technological manpower. New Zealand can be no exception to this. Nor, we think, would New Zealanders consciously subscribe to the idea that they should be an exception, for by so doing they would, in effect, be contributing to the lowering of their present standard of living and bringing about their own decline. We feel that New Zealand is not fully that one of the main causes of its lack of progress in the development of secondary industries is its tardiness in developing technological education.
DEMAND FOR ENGINEERING AND SCIENTIFIC PERSONNEL-At present about 120 engineers per annum, of whom about 15 reach the Master of Engineering level, and 180 scientists per annum, of whom some 50 reach the Master of Science level, graduate from the universities. Some go overseas but the majority are available for teaching, for the various public services, and for industry. We have not had before us any general assessment of the demand for engineering and scientific personnel except that the Public Service Commission and other Government institutions and the teaching services have indicated that they would like more. We have seen the report, H. of 1949, to the Minister of Education on Education and Supply of Professional Engineers, and in it is the recommendation: “That the number of professional engineers be increased to 850 per million of the population in 10 years, and thereafter, as opportunity offers, to 950 per million during the following 15 years”.
A review by the Department of Education in 1958 showed that to increase the 1958 aggregate of 1,650 graduate engineers, or 730 per million of population, to an aggregate of 2,125, or 827 per million of population, by 1964, and of 3,050, or 950 per million of population, by 1975, the outturn from the universities has to increase from the actual figure of 120 for 1958 to 170 per annum for 1964, and to 190 per annum for 1975; and that this was within the capabilities of the two schools of engineering at Canterbury and Auckland. We think these increased numbers of engineers to be trained and employed are reasonable; if anything, they may be even on the low side.
Unfortunately, no such survey seems to have been made of the needs of the community for scientists and it would appear desirable that such a survey be carried out. But, if the employment of scientists were to be increased at to same rate as engineers, the outturn from the universities would have to increase from the prese in 1958 to 205 per annum by 1964, when the total employed would be about 2,300; and to per annum by 1975. However, having regard to the very low figure of scientists and technologists now employed in industry, and the fact that secondary industries are beginning to expand, we feel that the rate of increase of demand for scientists and technologists could easily exceed that predicted for engineers. If it is assumed that, instead of there being 460 out of 2,300 scientists in industry in 1964, 690 will be required, i.e., 50 per cent more in industry than now, making a total of 2,530 by 1964, then the outturn from the universities would have to be about 280 per annum by 1964.
We think that 2,530 scientists by 1964, or soon after that, is a conservative estimate of the needs of the country, for even if industry does not attract the additional numbers, greater numbers are obviously required as teachers in the schools and universities. The number of university entrants coming forward should provide sufficient science enrolments but the university facilities as regards staff, buildings, and equipment will have to be improved and expanded and that as a matter of urgency.
The above estimates take no account of the demand for graduates in agricultural science. We were informed that up to 100 such graduates could be absorbed without difficulty each year for the next few years.
TECHNOLOGY - Technology, briefly, is the application of the discoveries of science to industry and commerce - their translation to usable products and services. A good technologist has a high level of knowledge of science and engineering, a high degree of skill in applying these to the economic production of usable products and services and, further, he should know how to manage people. Scientific and technological advances of this century have created a great demand for technologists and technicians. This demand has caught educational institutions and industry unprepared, both in their philosophy and in their facilities.
The description of a technologist generally accepted is that given in the British White Paper on Technical Education 1956:
“A technologist has the qualifications and experience required for membership of a professional institution. Most university graduates in engineering and other applied sciences, and a good proportion of holders of higher national diplomas or certificates or similar qualifications, become technologists.
“A technologist has studied the fundamental principles of his chosen technology and should be able to use his knowledge and experience to initiate practical developments. He is expected to accept a high degree of responsibility and in many cases to push forward the boundaries of knowledge in his own particular field.”
The technologist therefore has to acquire three skills - technical, managerial, and what is sometimes described as conceptual skill or the ability to see the pattern as a whole, so that improvement and development and expansion can be made to fit this whole into a progressive economy for the country. This third skill in particular, “conceptual” skill, is one that is not likely to be acquired except in a university atmosphere. It is unlikely to be developed by a technical college education. In the words of Kelvin “pure science and technology flourish best in close collaboration”.
Categories of Technical Men in Industry - Industry requires several categories of technically skilled men. It is unwise to try to divide them into watertight compartments. The numbers in each category vary according to the type of industry; and the work and responsibility of the various groups merge one into the other. In general it can be said that there are four such categories:
Graduates in engineering and science, and particularly in the applied sciences.
A rather hard to define “near-graduate” or middle-range technologist class.
Technicians.
Tradesmen or artisans.
Graduates-Graduates from a university in engineering and the applied sciences are generally immediately effective for some important work in industry such as design and development, industrial research, and the control and testing of process and plant. They should qualify with a few years' experience for higher technical and administrative posts.
The university graduate in pure science usually finds employment in one of three fields: in the educational institutions (school and university), in special research institutions (Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Department of Agriculture, industry), and in industry and commerce. His university education in pure science prepares him to apply himself more quickly and effectively to teaching and to research than to work in industry, especially manufacturing work in industry. He has been closely associated with teachers and has picked up something of the teaching process from their example and methods at school and university, even if he has not been instructed in methods of teaching. In research for his masterate he will have received instruction in the principles of research and will have carried out some research under the guidance of his professor. But when the graduate in the pure sciences goes into industry he enters into a new and different environment hitherto unfamiliar to him and also often unfamiliar to his professor. To become effective, he has to acquire much new knowledge, especially with regard to the operation of factory (instead of laboratory) equipment and processes, and the management of factory personnel. Probably only in the factory laboratory, where testing and analysing are done, will he feel initially at home.
Many universities overseas include applied sciences in their curricula, for example, industrial chemistry, industrial physics, and industrial biology, bacteriology, biochemistry, and chemical engineering, in which study is made of the principles and methods of applying scientific knowledge to manufacturing processes and equipment. Although this education in applied science is still largely of a theoretical and classroom and laboratory nature, it gives a good lead into factory work. There is still to be acquired skill in the application of this knowledge to actual factory operation.
The “Near Graduate” or Middle-range Group - In the more industrialised countries there is a large group of technically skilled men, in between the technician and the technologist, with university degree qualifications, merging on either side into both of these. This class of technologist has generally been educated at a college of advanced technology or other technical college, often as a part-time student. Some have acquired degrees in technology, but most have taken diplomas in engineering, in one of the applied sciences, or in some branch of technology.
Industry has engaged this group in much greater numbers than university graduates of higher academic qualifications. For one thing, larger numbers of this class of technically trained persons are required, and for another, industry has favoured these persons because of their quicker adjustment to industrial conditions because of the greater amount of practical experience gained during training. While such part-time education at university or college develops simultaneously both technical and managerial skills, it has the disadvantage of leaving the student somewhat rigid and narrow because he has little time or energy for activities or interests that broaden his development. One of the main questions this poses is where and how this group is to be educated in New Zealand; in the university or technical school system of the Department of Education.
Technicians - The British White Paper defined a technician thus: “A technician is qualified by specialist technical education and practical training to work under the general direction of a technologist. Consequently, he will require a good knowledge of mathematics and science related to his own speciality. Examples of technicians in the factory are assistant designers and junior ranks of management on the shop floor.”
A technician has reached a good standard in some specialisations such as chemical testing, biological, and other laboratory assistance. New Zealand offers a Certificate in Engineering for technicians. The technician should show aptitude for practical work and is a valuable assistant to the research worker and to the more highly qualified professional technologist, scientist, or engineer. Because of his restricted field of education, where little emphasis has been placed on basic science and engineering, although much emphasis has been placed on practical skill with tools, machines, and equipment, he is not usually capable of making technical advances or pushing forward the boundaries of knowledge in the field in which he is working. The British White Paper states that in Great Britian as many as five or six technicians may be required for every technologist, over a range of industries.
The position concerning education for technicians in New Zealand is described in pages 1-18 of the Department of Education annual report for 1956. In 1954 the Government set up a controlling authority for New Zealand Certificates in Engineering. This authority now issues two grades of certificates, a lower and a senior. The grade of the senior course is such that the controlling authority and the university are discussing the allowing of credits to holders of the certificate of outstanding merit to enable them to enter university at the second professional year for a degree in engineering. A similar type of course and controlling authority for chemical and scientific technicians is almost ready to begin, and a course for the building industry is being actively investigated.
In 1958 the Government established a New Zealand Council for Technical Education with functions, inter alia, “to foster close relations between technical education and industry and commerce and more particularly:
“(i) To ascertain the needs of industry and commerce and of sections thereof for technical education;
“(ii) To promote coordination between technical education, industry and commerce, workers' organisations, and Government Departments in various ways, including research, exchange of staff, provision of visiting lecturers, loans and gifts of equipment, consulting services to industry, advanced lecture courses, and seminars.
“To consider the coordination of the work of senior technical colleges and the technological activities of the universities”.
Tradesmen are generally trained by apprenticeship, supplemented by part-time instruction at technical schools.
Development of Technological Education Overseas-In Great Britain the education of middle-range technologists originally was built around technical colleges where students acquired their technical and managerial skills by working part-time in industry and part-time at college. Therefore, in Great Britain, learning by doing became a tradition in the development of this type of skill. The system obviously encouraged part-time study and so fell short of instilling fundamental scientific and engineering knowledge, and left the student poorly equipped for research and development. The attitude in Great Britain has changed since the last war and technological education has become recognised as a higher educational responsibility.
In Europe, on the other hand, technology was from the beginning built around special universities such as the Techniscne Hochschule in Berlin, founded in 1799 and granted university status in 1875; and Zurich, 1855, from which Einstein announced his theory of relativity. In both the United States and Canada, technological education has been an integral part of university education. The special institutions, such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology and California Institute of Technology, are elite institutions apart from the general streams of technological education.
In Australia the University of New South Wales was founded as a University of Technology in 1953 and later took over the diploma classes of the Sydney Technical College. This institution now grants degrees in engineering, applied sciences, and technology and also diplomas in the same disciplines.
It would seem prudent for New Zealand, as a relatively small economy just beginning its industrial development, to avoid a multiplicity of types of institutions and base the technological education of its first and second grades of technologists on the universities. By following this pattern the New Zealand universities will cover more fully the requirements of all the main avenues of employment -education, public service, and industry-and provide a wide range of complex skills, scientific, technological, and managerial, called for in the development of the country.
The Present Position of Technology in New Zealand Universities and Agricultural Colleges - New Zealand is unique among the agricultural countries of the world in its great dependence on grassland farming; the teachers in soil, plant, and animal science have been able to draw to only a limited degree on the principles and practices developed overseas. The effective application of new knowledge on New Zealand farms has resulted in a rise of about 75 per cent in the volume of farm production since 1928-29, although the area farmed is virtually unchanged and the farm labour force is actually smaller. New Zealand can indeed be proud of the technological advances which have brought about such an increase in productivity. The two agricultural colleges, Massey and Canterbury, which are traditionally residential colleges, provide both degree and diploma courses in the agricultural sciences and technologies and, in addition, an assortment of university extension short courses ranging from refresher courses for those already qualified to application courses for young farmer groups. The system turns out persons qualified for university teaching and research, for research in the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, for the advisory services to farmers supplied by Government and industrial organisations, and produces also many diplomates who take up farming as a career. It therefore covers both the scientific and the technological fields in a sound and comprehensive manner.
Technologies based on engineering are well provided for at the University of Canterbury, where the school of engineering includes chemical engineering in addition to the usual civil, mechanical, and electrical engineering.
The school of engineering at Auckland is handicapped by its temporary location at Ardmore and has no chemical engineering. Its transfer to a permanent site, in close proximity to the science and other faculties, the addition of chemical engineering, and whether or not aeronautical engineering should be continued are all matters that should be given urgent consideration.
The school of mines at Otago is carrying on under difficulties. It is doing some much needed training in metallurgy, but we feel that consideration should be given to concentrating education for engineering technologies for the South Island at the University of Canterbury.
In the sciences not nearly enough is being done from the technological point of view. Scientific education is still predominantly in the pure sciences and only to a very small extent in the applied sciences. Biochemistry at the University of Otago and Victoria University of Wellington, and industrial chemistry at the University of Canterbury and Victoria University of Wellington are moves in this direction, but it seems clear that the universities have not yet sufficiently recognised that, in addition to teaching pure sciences, there is great need to teach how to apply these to manufacturing processes.
That some professors in the universities recognise this inadequa in the teaching of technology is brought out in a report by Dr Llewellyn and Professor Packer of Canterbury on “Technology in the Universities. This report was prepared for the University Senate and was submitted to us by the University of Canterbury. From it we quote:
“The situation at the present time is then that the Education Department has, quite properly, taken preliminary steps to broaden the scope of technical training in New Zealand and has established machinery with which to examine the part which technical colleges may be called upon to play in collaboration or otherwise with the university in technological education. On the other hand the university has not yet fully examined or collated its own functions in technological education, nor has it made any progress in determining the adequacy or otherwise of its existing courses for the training of technologists. The university has certainly not, to our knowledge, attempted to formulate any forward thinking policy of development of university technological education either on its own or in collaboration with the technical colleges.”
The report also says:
“In its degree courses for science and engineering, the university provides comprehensive study of fundamentals of science and mathematics, it provides opportunity for the acquisition by the student of sufficient technical skill wherewith he could examine the validity of his theoretical deductions or hypotheses and, particularly in engineering courses, it provides opportunities for the application of these fundamental principles in a range of particularised technologies.”
This report, inter alia, recommends that microbiology, biochemistry, metallurgy, industrial design, and building technology be included in certain degree courses and that consideration be given to the introduction of post-graduate short courses in certain technologies.
We have no doubt whatever that the training of the professional technologist requiring the usua university qualifications should be done at the university. We have no doubt either that much, if not most, of the education of the middle-range technologist should also be done by the university, for degree or diploma credit, depending on which is appropriate, and not by the technical school system. It will not be sufficient as heretofore to reach general agreement with the Department of Education that the university's field is the training of the technologist and the Department's field is the training of the technician, and at the same time for the Department to extend the training of the technician upwards in grade and for the university to do little about technology. It seems to us that the respective responsibilities and work of the universities and of the Department of Education in this rather blurred field should be more clearly defined by a joint University - Department of Education liaison group consisting of equal numbers from each, with a chairman from the Grants Committee; and we recommend the setting up of such a liaison committee.
Having regard to the foregoing, we make the following recommendations:
That the science departments of the universities be expanded as a matter of urgency to provide for the increased number of scientists required by the schools, universities, and industry.
That the universities should include more of the applied sciences, such as industrial chemistry, applied physics, industrial microbiology, biochemistry, and metallurgy in their degree courses.
That the universities should include more technological subjects such as industrial design, food, wood, wool, leather, and building technology in their degree courses.
That the universities give consideration to the increasing need for courses in the principles and techniques of business and industrial management, at both the degree and diploma levels, and as a special need, at the advanced business management level.
That consideration be given to the introduction of chemical engineering at the Auckland Engineering School, and the possible elimination of aeronautical engineering if on inquiry future demand would not seem to justify its continuance.
That consideration be given to concentrating all engineering education in the South Island at the University of Canterbury.
That a joint University - Department of Education liaison committee be set up, of equal numbers from each, with a chairman from the Grants Committee, to define the respective responsibilities of each in the education of the middle-range technologist group.
RESEARCH AT THE UNIVERSITIES AND AGRICULTURAL COLLEGES - One of the acknowledged purposes of a university is to extend the frontiers of knowledge. Research stimulates the intellect and endeavours of staff and students alike, makes the university a live, exciting community wherein leadership germinates and is cultivated and tended. To ensure both material and cultural progress, this vigorous pursuit of knowledge is equally as important in the humanities and the social sciences as it is recognised to be in the natural sciences. One of the greatest benefits derived from research in universities is the stimulation and broadening which staff and students get from close contact and association with men engaged in research in different fields. Opportunities for such association are lacking in the specialist research institutions such as those of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and Department of Agriculture.
We have investigated and given much attention to this part of the life of the universities and agricultural colleges and we have found centres of vigour, some in science, others in the social sciences and humanities, but practically all hindered, often frustrated, by lack of finance, of facilities, and of time. More crippling perhaps than lack of space and money is the lack of time on the part of the professors and other teachers now overloaded with teaching duties.
Further, and in particular, we think that the agricultural colleges are not used enough as research centres. We fully recognise the importance to New Zealand of the research activities of the Department of Agriculture's research division and the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research. In view of the importance of agriculture in the New Zealand economy it is only appropriate that substantial sums of money should be spent on research relating to New Zealand's soils, crops, animals, and agricultural technology. Because of the variety and multitude of the problems, however, it would seem to us highly desirable to use the existing institutions to greater advantage, partly by increasing direct grants, partly by having the universities assume the responsibility for some of the problems for which the research institutes are now seeking solutions. Some research problems more than others lend themselves to being pursued in a teaching environment and it is these that we think should be allocated to the colleges. There is another reason why it is only good economy to make available to the colleges opportunities for further research. They are the training ground for many of the future agricultural research scientists and technologists and it is important for the future of research itself that both should be taught where research is being conducted.
It is true that the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research has made some move towards facilitating coordination by locating some of its experimental stations alongside the agricultural colleges, for example, the Grasslands Division and the Plant Chemistry Divisions and the Dairy Research Institute near Massey Agricultural College; the Crop Research and Botany Divisions near Canterbury Agricultural College. What we would urge is that serious consideration be given by the Government and its two great research institutions, the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and the Department of Agriculture, to the effect the present policy has on the university system as a whole and especially on the agricultural colleges.
Financing of Research - Financial support for research at present comes from a variety of sources, the University Research Committee, the Medical Research Council, the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Carnegie Corporation, and private donations.
Research in the constituent universities has been stimulated by an annual grant made by the Government direct to the University of New Zealand and administered by a special committee, the Research Committee, appointed by Senate. The grant was £10,000 when first made in 1946 and has subsequently been increased to £25,000 for the current year. The personnel of the Research Committee has comprised a representative of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and university officials and teachers, chosen to cover the main fields of research - the physical and biological sciences, the humanities, and social sciences - rather than to represent the several universities. The advantage of this central administration is that the Research Committee has been able to apply money to make the greatest impact where most urgently needed.
The principles adopted by the committee, inter alia, make provision for research fellowships, support for research students, visits between constituent universities, maintenance for research workers. purchase of materials and special equipment, and employment of special assistants.
The chairman of the Research Committee, in his submission, stated:
”… the establishment of research fund fellowships, open to those with first or second class honours, has greatly helped to stimulate research in the universities . . . Over the years 102 of these fellowships have been awarded, 12 being current, and some 50 fellows have been awarded the degree of Ph.D….
“The grant of £25,000 is not enough. On behalf of the Research Committee, I put forward the case for a considerably larger grant, at least £100,000 per annum.
The Research Committee in its requests to the Grants Committee for the third quinquennium which was to have started on 1 April 1960 asked for a research grant of £100,000 per annum, but the Grants Committee reduced this to £40,000 for the first year rising to £80,000 for the last year of the quinquennium. One of its reasons for doing so was that it had proposed that additional funds should be made available under the block grants for employment of extra technical assistants in all departments.
From the 1958-59 report of the Research Committee to Senate, we have seen that of £26,385 disbursed, about £15,000 went to the chemistry and physics departments, and £6,695 to fellowships, leaving from this grant a most insignificant amount of £1,500 for the other departments and subjects in the four universities. Of this the agricultural colleges receive nothing. Research at Massey Agricultural College subsists on an annual grant of £8,000 per annum from the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and a smaller grant from the Wool Board. Both grants are on an annual basis with no guarantee of continuity. Further, the grants are not entirely free and can be used to limited extent only in financing the work of students preparing for the degrees of master or doctor.
Canterbury Agricultural College also receives limited grants annually; in 1958, £8,500 from the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, £3,000 from the Wool Board, and £2,500 from the Department of Agriculture.
The Medical Research Council disbursed about £100,000 in 1958, mainly to the Medical School. A special grant by Government to the universities for nuclear science is at present under negotiation. The Carnegie Corporation granted 60,000 dollars during the period 1953-57 for work in the social sciences and has advised that it is unable to agree to a further grant as its policy is to initiate research and then leave it to the local institution to continue. We consider that provision ought to be made for the continuance of this work.
The Department of Scientific and Industrial Research in 1958 granted £34,000 for special projects such as the Industrial Development Department at the University of Canterbury, ironsands research at Victoria University of Wellington, Seagrove radio station at the University of Auckland, and special work at Massey and Lincoln Agricultural Colleges.
There have been, from time to time, a number of private donations for equipment, scholarships, and research. We consider such donations should be sought and encouraged and in another part of this report we deal with the effect that taxation has on such donations.
In addition to the inadequacy of the finance for research, the machinery for the approval of the money is cumbersome and frustrating. It seems that at present before any piece of research can be undertaken the description of the project and the estimate of the sum required have to go through a long and perilous journey.
Excluding special grants such as those from the Medical Research Council or for nuclear science, Government finance directly distributed for research at the universities is £25,000 per annum. This is in striking contrast to the amount of money spent by Government Departments, where some £1,500,000 per annum are spent on agricultural research alone by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research and the Department of Agriculture. We are aware of the work of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research in other than the agricultural field, but the disproportion between departmental expenditure on research and research expenditure in the universities reflects a failure to make full use of the good talent to be found among the staff and students of the universities. It also fails to take account of the stimulating effect on both staff and students of being in contact with research.
One has no need to recall that some of the significant advances, especially in science and technology, have been and are being made by men who had their origins in New Zealand universities, and who could have continued there had research been given its due recognition as an activity of the universities and colleges.
Coordination and Balancing of Research - Not only is the expenditure on research in New Zealand disproportionate as between the Government research institutions and the universities, but there is also, in our opinion, insufficient collaboration at top level and insufficient coordination of policy among Government Departments and between Government institutions and the universities.
We are of the opinion that it would be to the great advantage of the New Zealand community if a National Scientific Research Council were to be constituted. Such a body could study the scientific and technological problems of New Zealand; it could inform the public how the material resources of the country could be developed, to promote the industrial and social well-being of the nation, and advise the Government and the universities on these matters. Such a council, drawn from persons of the highest standing in industry, commerce, the professions, the universities, and Government, and covering the fields of health, economics, science, engineering, and the technologies, should be able to make most valuable contributions to the coordination of balanced research programmes and to the stimulation of national development in every area that science touches.
In the light of the foregoing considerations, we make the following recommendations:
That additional finance be made available to the universities for the purposes of research and that the machinery for the approval and financing of projects be overhauled and simplified. We think this recommendation can be implemented in two stages: (a) as an immediate matter of urgency, and then (b) as a long-term plan.
Interim Plan - The first and most urgent requirement is that the £25,000 research grant be increased immediately to £65,000 per annum and to £100,000 for 1961. These sums should be administered as heretofore by the Research Committee until the new University Grants Committee is ready to take the function over.
Longer-term Plan - The chief source of money for research at the universities should be from Government through the block grants to the universities and colleges. Supplementary assistance from the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, the Department of Agriculture, the Medical Research Council, and from industry and private donations should continue and every encouragement should be given to increase them. The direct grant for research, excluding any supplementary assistance and special funds such as those for nuclear science and medical research, should rise over the next few years from the £100,000 per annum which we have already recommended as interim assistance to at least £150,000 per annum. Money granted by the Government for research would then come to the universities through two channels:
The block grants to the universities and colleges; and
Through the post-graduate scholarships and research grants subcommittee which we are recommending in another chapter of this report, to be set up as a subcommittee of the University Grants Committee. This money should be used for special projects and equipment not covered by the block grants.
That a National Scientific Research Council should be set up to coordinate and administer the scientific research services of the State and to make grants to the universities in fields of their particular responsibility.
For some of the statistical series included in this issue of the Yearbook later information is available than is included in the body of the book. This later information is given in the following paragraphs, with references to the appropriate portion of the Yearbook containing more detailed information for earlier periods.
Population (p. 49) - Recent population changes are given in the following table. Preliminary figures of the Population Census of 18 April 1961 are set out on pages 1225-1228.
| Date | Males | Females | Total | Mean Population for Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Population (Including Maoris) | ||||
| 30 June 1960 | 1,191,867 | 1,179,879 | 2,371,746 | 2,356,186 |
| 30 September 1960 | 1,198,534 | 1,185,935 | 2,384,469 | 2,366,398 |
| 31 December 1960 | 1,207,946 | 1,195,621 | 2,403,567 | 2,377,010 |
| Maori Population | ||||
| 30 June 1960 | 81,237 | 78,472 | 159,709 | 156,914 |
| 30 September 1960 | 81,991 | 79,259 | 161,250 | 158,325 |
| 31 December 1960 | 82,723 | 79,952 | 162,675 | 159,768 |
The above figures are exclusive of the population of the Cook Islands, 18,174 (at 31 March 1960); Niue Island, 4,890 (at 31 December 1960); Tokelau Islands, 1,938 (at 31 December 1960); and Western Samoa, 108,403 (at 31 December 1960).
Natural Increase - Owing to the uniformly high levels in births in the last few years and the relative stability in the number of deaths, population gains from natural increase - i.e., excess of births over deaths - have been particularly marked in recent years, the excess of births over deaths for the calendar year 1960 being 41,956.
Migration (pp. 62-64)-The total number of arrivals in New Zealand during the year ended 31 March 1961 was 242,814, while the total number of departures in the same year was 240,867. Excluding crews, through passengers and tourists on cruising liners, arrivals totalled 106,238 and departures 104,618, making the net excess of arrivals 1,620, as compared with 3,213 in 1959-60. A classification of total arrivals and departures gives the following results.
| Category | Year Ended 31 March | |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 1961 | |
| Migration: Arrivals | ||
| Immigrants intending permanent residence | 20,294 | 21,424 |
| New Zealand residents returning | 32,526 | 43,890 |
| Visitors- | ||
| Tourists | 24,794 | 27,299 |
| Others | 11,763 | 13,625 |
| Through passengers and tourists on cruising liners | 35,637 | 36,386 |
| Crew | 93,860 | 100,190 |
| Total arrivals | 218,874 | 242,814 |
| Migration: Departures | ||
| New Zealand residents departing - | ||
| Permanently | 13,420 | 14,848 |
| Temporarily | 34,667 | 47,204 |
| Temporary residents departing | 38,077 | 42,566 |
| Through passengers and tourists on cruising liners | 35,637 | 36,386 |
| Crews | 94,274 | 99,863 |
| Total departures | 216,075 | 240,867 |
Passenger arrivals for the year ended 31 March 1961 reached a record level, as did passenger departures. While arrivals showed an increase of 23,940, or 10.94 per cent, over the previous year, departures increased by 24,792 or 11-47 per cent.
Immigrants intending permanent residence numbered 21,424, an increase of 1,130 on the previous year. The 2,231 assisted immigrants included in the 21,424 arrivals in 1960-61 show a decrease of 318 on the 1959-60 figure of 2,549.
New Zealand residents departing permanently showed an increase of 1,428, or 11 per cent, over the 1959-60 figure.
Shipping and Trade of Ports (pp. 315-330)-Statistics of entrances and clearances of vessels in the foreign trade in 1959 and 1960, and the total calls made in the foreign and coastal trade for the same years, are shown in the following table. The tonnage of cargo handled is also given.
| Item | Calendar Year | |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | |
| Entrances - | ||
| Overseas - | ||
| Number of vessels | 883 | 972 |
| Net tonnage | 4,027,125 | 4,500,892 |
| Clearances - | ||
| Overseas - | ||
| Number of vessels | 903 | 961 |
| Net tonnage | 4,114,739 | 4,408,425 |
| Total calls made - | ||
| Overseas - | ||
| Number of vessels | 2,875 | 3,124 |
| Net tonnage | 12,699,652 | 13,548,761 |
| Coastal - | ||
| Number of vessels | 10,999 | 10,249 |
| Net tonnage | 4,972,529 | 4,978,142 |
| Total- | ||
| Number of vessels | 13,874 | 13,373 |
| Net tonnage | 17,672,181 | 18,526,903 |
| Tonnage of cargo handled - | ||
| Inwards | 6,674,316 | 7,342,051 |
| Outwards | 3,842,680 | 3,928,364 |
| Transhipped | 255,266 | 219,926 |
| Total manifest tonnage | 10,772,262 | 11,490,341 |
Statistics of shipping movement and cargo handled at New Zealand ports in 1959 and 1960 are given below.
| Port | Total Shipping Movement | Total Cargo Handled | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 Net Tonnage | 1960 Net Tonnage | 1959 | 1960 | |
| tons (thousand) | ||||
| Auckland | 7,858 | 8,265 | 3,092 | 3,290 |
| Wellington | 8,810 | 8,640 | 2,238 | 2,436 |
| Lyttelton | 6,016 | 6,253 | 1,296 | 1,399 |
| Otago | 2,644 | 2,720 | 546 | 589 |
| Tauranga | 1,013 | 1,186 | 570 | 643 |
| Other ports | 9,080 | 9,901 | 3,030 | 3,133 |
| Totals | 35,421 | 36,965 | 10,772 | 11,490 |
Railway Transport (pp. 330-341) - Summarised statistics of railway transport in the years ended 31 March 1959,1960, and 1961 follow.
| Item | Unit | Year Ended 31 March | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | ||
| *Including road motor and other subsidiary services. | ||||
| Passenger journeys - | ||||
| Railways | (000) | 25,437 | 26,134 | 26,233 |
| Railway road motor services | (000) | 20,032 | 21,201 | 21,370 |
| Tonnage of goods carried- | ||||
| Timber | tons (000) | 1,468 | 1,570 | 1,652 |
| Livestock | tons (000) | 643 | 657 | 639 |
| Other goods | tons (000) | 8,256 | 8,316 | 8,539 |
| Totals | tons (000) | 10,367 | 10,543 | 10,830 |
| Net ton-miles run | millions | 1,158 | 1,171 | 1,205 |
| Revenue- | ||||
| Railway operation | £(000) | 29,823 | 30,271 | 31,429 |
| Total* | £(000) | 34,373 | 34,937 | 36,239 |
| Expenditure- | ||||
| Railway operation | £(000) | 30,505 | 30,758 | 31,488 |
| Total* | £(000) | 35,137 | 35,500 | 36,302 |
Road Transport (p. 347) - Statistics of motor vehicles licensed at 31 March 1960 and 1961 are as follows.
| Class | As at 31 March | |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 1961 | |
| Cars | 502,574 | 523,847. |
| Trucks- | ||
| Light | 49,724 | 51,025 |
| Heavy | 69,686 | 73,382 |
| Contract vehicles | 1,679 | 1,706 |
| Omnibuses | 2,317 | 2,255 |
| Taxis | 2,445 | 2,491 |
| Rental cars | 2,225 | 2,423 |
| Private-hire cars | 174 | 158 |
| Service cars | 628 | 586 |
| Trailers | 100,855 | 117,597 |
| Vehicles exempted from payment of licence fees (other than exempted Government-owned vehicles) | 57,224 | 62,169 |
| Government vehicles | 16,683 | 17,480 |
| Motor cycles | 26,874 | 28,436 |
| Power cycles | 9,937 | 10,854 |
| Totals | 843,025 | 894,409 |
| Dealers' cars | 3,054 | 3,135 |
| Dealers' motor cycles | 152 | 145 |
| Totals | 846,231 | 897,689 |
Timber: Production (p. 466) - Provisional figures issued by the New Zealand Forest Service indicate a record level of timber production for the year ended 31 March 1961, the output of rough-sawn timber being given as 714,090,000 board feet, substantially above the output of the previous year. The output of the principal species was as follows: rimu and miro, 219,713,000 board feet; matai, 31,501,000 board feet; kahikatea, 20,674,000 board feet; beech, 12,470,000 board feet; totara, 12,803,000 board feet; tawa, 17,108,000 board feet; and exotic pine, 374,125,000 board feet. Indigenous species totalled 318,708,000 board feet, and exotics, 395,382,000 board feet.
Production totals for 1959-60 rose by 4.4 per cent in volume of output over the previous year. The annual increases in volume of output for the two previous years were 7.2 per cent in 1957-58 and 5.5 per cent in 1958-59. Production of three groups of industries dropped in volume in 1959-60, namely, footwear and apparel (-3.7 per cent), leather and leather products (-4.1 per cent), and rubber products (-0.6 per cent). In five groups the volume index rose by over 10 per cent compared with the previous year - printing and publishing, 12.8 per cent; chemicals and chemical products, 11.9 per cent; non-metallic mineral products, 10.9 per cent; textiles, 10.8 per cent; and tobacco manufactures, 10.5 per cent. In the several groups without individual volume indexes employment and added-value figures indicate a substantial increase in volume for the following groups - basic metal manufactures, metal products, machinery, and miscellaneous products.
The number of factories surveyed decreased from 8,565 in 1958-59 to 8,550 in 1959-60, while the total number of persons engaged in factories rose from 168,742 to 172,106, or by 2.0 per cent. Overtime worked by wage earners in 1959-60, at 22,724,082 hours, represented an increase of 4.6 per cent on 1958-59. Average overtime hours worked by all wage earners in 1959-60 were 193 hours for males and 45 hours for females, as against 188 and 47 respectively in the previous year. In 13 of the 20 industrial groups total overtime hours were higher and six groups reported increases of over 10 per cent - petroleum and coal products, 31.4 per cent; printing and publishing, 14.2 per cent; non-metallic mineral products, 13.7 per cent; miscellaneous products, 11.1 per cent; metal products, 10.3 per cent; and machinery, 12.5 per cent. Three groups of industries showed substantial declines in overtime - beverages, 27.5 per cent; rubber products, 16.5 per cent: and footwear and clothing, 15.4 per cent.
Of the additional 3,364 persons engaged, 3,146 were males and 218 were females. Engineering groups engaged 12 per cent of the added persons - metal products (600) and machinery (460)-while six other groups recorded increases of 300 or more - textiles, 470 (4.9 per cent); wood products, 420 (3.3 per cent); printing and publishing, 420 (4.1 per cent); non-metallic mineral products, 390 (5.7 per cent); miscellaneous products, 380 (11.1 per cent); and chemicals and products, 370 (7.2 per cent). Of the five groups showing decreases in persons engaged two stand out-footwear and clothing, 940 (3.6 per cent), and beverages, 100 (4.5 per cent)
Total salaries and wages paid during the year, at £136,175,840, were £7.9 million higher than in 1958-59, an increase of 6.2 per cent. Wages paid in industry during 1959-60 averaged £853 for males and £450 for females as against £821 and £441 during the previous year, increases of 3.9 and 2.0 per cent respectively. These averages include overtime payments and bonuses.
Added value, at £266,529,200, represents the total contribution to New Zealand's production for 1959-60 by manufacturers covered in this series and shows a rise of 10.7 per cent over 1958-59. Only two groups recorded declines in added value - beverages and footwear-clothing. Of the remainder, eight had increases of over 10 per cent-food 23.4 per cent, chemicals and chemical products 20.0 per cent, textiles 15.0 per cent, basic metal products 16.3 per cent, miscellaneous products 14.1 per cent, metal products 14.0 per cent, petroleum and coal products 11.6 per cent, and machinery 10.0 per cent. In 1959-60 salaries and wages represented 51.1 per cent of added value (53.3 per cent in the previous year) while manufacturers' surplus was 21.5 per cent of added value (17.5 per cent in 1958-59).
Capital expenditure during 1959-60 amounted to £26.9 million, compared with £23.2 million in 1957-58 and £27.8 million in 1958-59. These amounts cannot be taken as the total capital expended by New Zealand manufacturers during the year, as they do not take into account capital expenditure on units not yet in production.
This series of industrial production statistics compiled by the Department of Statistics covers 80 per cent of the labour force engaged in manufacturing activity. Actually the proportion of industrial production covered by the survey would be greater than 80 per cent, in that all establishments of any considerable size are included.
The year covered by these statistics is in general that ended 31 March 1960, although concerns are permitted to furnish returns covering financial years most closely corresponding to that period. In the case of dairy factories and meat-freezing works the years correspond to the respective seasons ended June and September 1960.
Summary (p. 499) - Following are the principal statistics of factory production for 1959-60, with comparable figures for the two preceding years.
| General Summary | 1957-58 | 1958-59 | 1959-60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of establishments | 8,529 | 8,565 | 8,550 | |
| Persons engaged | No. | 162,985 | 168,742 | 172,106 |
| Production costs- | ||||
| Salaries, wages | £ | 119,989,253 | 128,278,259 | 136,175,840 |
| Materials | £ | 417,918,274 | 418,647,288 | 439,087,799 |
| Other expenses | £ | 66,052,015 | 70,320,610 | 72,963,276 |
| Totals | £ | 603,959,542 | 617,246,157 | 648,226,915 |
| Value of output | £ | 644,928,872 | 659,454,543 | 705,616,999 |
| Manufacturers' surplus | £ | 40,969,330 | 42,208,386 | 57,390,084 |
| Value added in manufacture | £ | 227,010,598 | 240,807,255 | 266,529,200 |
| Overtime worked by wage earners | h | 20,431,809 | 21,724,241 | 22,724,082 |
| Volume index for industry: Base 1956-57 (=1000) | 1072 | 1130 | 1180 | |
| Premises and plant - | ||||
| Value at end of year - | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 112,758,584 | 123,629,077 | 136,549,586 |
| Plant and machinery | £ | 76,528,492 | 82,257,290 | 87,177,462 |
| Capital expenditure during year- | ||||
| Land and buildings | £ | 9,420,308 | 11,184,624 | 10,364,662 |
| Plant and machinery | £ | 13,801,687 | 16,653,921 | 16,574,857 |
| Coal consumption as fuel | tons | 1,014,390 | 1,029,974 | 988,504 |
Principal Statistics 1959–60 (p. 527) - The following table gives the number of persons engaged, production costs, value of output, and added value for the year 1959–60, classified according to industry groups.
| Industry Group | Number of Persons Engaged | Production Costs | Value of Output | Added Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salaries and Wages | Materials | Other Expenses | Total | ||||
| £(000) | |||||||
| Food | 31,084 | 28,769 | 200,953 | 16,271 | 245,992 | 258,807 | 57,855 |
| Beverages | 2,099 | 1,831 | 5,209 | 2,085 | 9,125 | 11,030 | 5,822 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 1,244 | 796 | 5,611 | 622 | 7,029 | 7,646 | 2,035 |
| Textiles | 10,024 | 6,871 | 25,221 | 3,517 | 35,609 | 38,303 | 13,082 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 25,089 | 13,908 | 24,960 | 3,659 | 42,527 | 45,172 | 20,212 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 13,209 | 11,024 | 23,979 | 6,265 | 41,267 | 45,363 | 21,384 |
| Furniture and fittings | 4,960 | 3,847 | 6,596 | 1,015 | 11,459 | 12,419 | 5,823 |
| Paper and paper products | 5,313 | 4,761 | 14,487 | 7,447 | 26,695 | 31,218 | 16,731 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 10,832 | 9,020 | 9,449 | 4,013 | 22,482 | 26,179 | 16,730 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1,625 | 1,124 | 3,185 | 403 | 4,712 | 5,182 | 1,997 |
| Rubber products | 2,872 | 2,694 | 5,378 | 1,643 | 9,715 | 11,529 | 6,151 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 5,596 | 4,558 | 20,854 | 4,016 | 29,428 | 33,891 | 13,037 |
| Petroleum and coal products | 421 | 378 | 2,348 | 378 | 3,104 | 3,416 | 1,068 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 7,211 | 6,083 | 8,359 | 6,106 | 20,549 | 23,725 | 15,366 |
| Basic metal manufactures | 1,020 | 917 | 2,442 | 446 | 3,805 | 4,228 | 1,786 |
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | 8,903 | 7,667 | 14,773 | 3,018 | 25,458 | 28,702 | 13,929 |
| Machinery (except electrical) | 9,869 | 8,497 | 15,890 | 3,061 | 27,447 | 29,718 | 13,828 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 4,711 | 3,512 | 8,714 | 1,529 | 13,755 | 15,102 | 6,389 |
| Transport equipment | 22,199 | 17,163 | 35,823 | 6,222 | 59,207 | 63,883 | 28,060 |
| Miscellaneous products | 3,825 | 2,756 | 4,858 | 1,249 | 8,863 | 10,104 | 5,247 |
| Totals | 172,106 | 136,176 | 439,088 | 72,963 | 648,227 | 705,617 | 266,529 |
Volume of Industrial Production (p. 525) - The following analysis shows the variations in the volume of industrial production in the several industrial groups. The series is based on the volume of production in 1956–57.
GROUP INDICES: BASE 1956–57 (= 1000)
| Industry Group | 1957–58 Index | 1958–59 Index | 1959–60 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | (+) or (-) Over 1958–59 | |||
| Per Cent | ||||
| Food | 1061 | 1121 | 1156 | + 3.2 |
| Beverages | 1048 | 993 | 1002 | + 0.9 |
| Tobacco manufactures | 1108 | 1148 | 1268 | + 10.5 |
| Textiles | 1114 | 1287 | 1426 | + 10.8 |
| Footwear, other wearing apparel, and made-up textile goods | 1053 | 1148 | 1106 | - 3.7 |
| Wood and cork products (except furniture) | 987 | 1053 | 1103 | + 4.8 |
| Paper and paper products | 1220 | 1306 | 1402 | + 7.3 |
| Printing, publishing, etc. | 1057 | 1093 | 1232 | + 12.8 |
| Leather and leather products (except footwear and apparel) | 1015 | 1172 | 1124 | - 4.1 |
| Rubber products | 1098 | 1144 | 1137 | - 0.6 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 1047 | 1040 | 1163 | + 11.9 |
| Non-metallic mineral products n.e.i. | 1078 | 1121 | 1243 | + 10.9 |
| Electrical machinery and appliances | 1153 | 1293 | 1348 | + 4.3 |
| Furniture and fittings | 1073 | 1117 | 1142 | + 2.3 |
| Petroleum and coal products | ||||
| Basic metal manufactures | ||||
| Metal products (except machinery and transport equipment) | ||||
| Machinery (except electrical) | ||||
| Transport equipment | ||||
| Miscellaneous products | ||||
| Totals, all groups | 1072 | 1130 | 1180 | + 4.4 |
Regional Distribution of Factory Production, 1959–60 (p. 499) - The table following gives a general summary by employment districts and shows a comparison of the manufacturing strengths of each district. The fairest guide to actual volume of production is the column in the subsequent part of this table on “Added Value”. This shows Auckland district's dominance in the manufacturing world, its production now being more than the total for the South Island.
FACTORIES: SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS BY EMPLOYMENT DISTRICTS, 1959–60
| Employment District | Number of Factories | Persons Engaged | Salaries and Wages Paid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| £(000) | £(000) | ||||
| Whangarei | 222 | 2,607 | 217 | 2,046 | 95 |
| Auckland | 2,148 | 36,219 | 16,612 | 33,206 | 7,811 |
| Hamilton | 535 | 6,490 | 940 | 5,628 | 407 |
| Paeroa | 121 | 1,312 | 332 | 1,081 | 135 |
| Tauranga | 119 | 1,108 | 189 | 898 | 77 |
| Rotorua | 219 | 5,694 | 424 | 5,692 | 204 |
| Gisborne | 120 | 1,359 | 372 | 1,129 | 164 |
| Napier | 167 | 1,762 | 496 | 1,498 | 208 |
| Hastings | 164 | 3,135 | 630 | 2,893 | 302 |
| New Plymouth | 339 | 4,128 | 817 | 3,601 | 327 |
| Wanganui | 237 | 2,898 | 837 | 2,596 | 361 |
| Palmerston North | 447 | 4,829 | 1,641 | 4,179 | 710 |
| Masterton | 144 | 1,709 | 321 | 1,464 | 133 |
| Lower Hutt | 324 | 7,767 | 2,743 | 7,652 | 1,388 |
| Wellington | 710 | 8,806 | 4,716 | 8,385 | 2,373 |
| Totals, North Island | 6,016 | 89,823 | 31,287 | 81,950 | 14,696 |
| Blenheim | 90 | 846 | 210 | 718 | 95 |
| Nelson | 174 | 1,891 | 350 | 1,548 | 146 |
| Greymouth | 156 | 1,342 | 233 | 1,138 | 100 |
| Christchurch | 1,013 | 17,405 | 6,994 | 15,180 | 3,186 |
| Ashburton | 67 | 966 | 227 | 880 | 92 |
| Timaru | 154 | 2,224 | 375 | 1,993 | 176 |
| Oamaru | 58 | 975 | 210 | 850 | 88 |
| Dunedin | 485 | 8,437 | 3,047 | 7,220 | 1,337 |
| Invercargill | 337 | 4,851 | 413 | 4,600 | 184 |
| Totals, South Island | 2,534 | 38,937 | 12,059 | 34,126 | 5,404 |
| Totals, New Zealand | 8,550 | 128,760 | 43,346 | 116,076 | 20,100 |
| Employment District | Cost of Materials | Value of Output | Added Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Percentage of Total* | ||||
| * Figures in parentheses are percentages in previous year (1958–59). | |||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | |||
| Whangarei | 13,125 | 17,888 | 4,763 | 1.8 | (2.1) |
| Auckland | 117,672 | 194,229 | 76,557 | 28.7 | (28.9) |
| Hamilton | 34,924 | 47,255 | 12,331 | 4.6 | (4.4) |
| Paeroa | 8,973 | 11,377 | 2,403 | 0.9 | (1.1) |
| Tauranga | 5,449 | 7,577 | 2,129 | 0.8 | (0.7) |
| Rotorua | 15,426 | 33,337 | 17,911 | 6.7 | (6.8) |
| Gisborne | 3,843 | 6,170 | 2,327 | 0.9 | (0.9) |
| Napier | 6,306 | 9,763 | 3,457 | 1.3 | (1.2) |
| Hastings | 12,260 | 17,701 | 5,440 | 2.0 | (2.0) |
| New Plymouth | 22,306 | 29,818 | 7,513 | 2.8 | (2.8) |
| Wanganui | 10,644 | 16,123 | 5,479 | 2.1 | (2.0) |
| Palmerston North | 20,520 | 30,269 | 9,749 | 3.7 | (3.4) |
| Masterton | 6,889 | 9,917 | 3,028 | 1.1 | (1.1) |
| Lower Hutt | 33,507 | 52,056 | 18,550 | 7.0 | (7.6) |
| Wellington | 21,279 | 40,461 | 19,182 | 7.2 | (7.8) |
| Totals, North Island | 333,123 | 523,942 | 190,819 | 71.6 | (72.7) |
| Blenheim | 2,090 | 3,514 | 1,424 | 0.5 | (0.5) |
| Nelson | 4,459 | 8,073 | 3,614 | 1.4 | (1.5) |
| Greymouth | 2,678 | 5,051 | 2,373 | 0.9 | (0.8) |
| Christchurch | 43,216 | 77,019 | 33,804 | 12.7 | (12.9) |
| Ashburton | 2,828 | 4,489 | 1,661 | 0.6 | (0.6) |
| Timaru | 8,534 | 12,505 | 3,972 | 1.5 | (1.3) |
| Oamaru | 3,376 | 5,361 | 1,985 | 0.8 | (0.5) |
| Dunedin | 21,709 | 38,103 | 16,394 | 6.2 | (6.4) |
| Invercargill | 17,076 | 27,559 | 10,483 | 3.9 | (2.8) |
| Totals, South Island | 105,965 | 181,675 | 75,710 | 28.4 | (27.3) |
| Totals, New Zealand | 439,088 | 705,617 | 266,529 | 100.0 | (100.0) |
Wool - Weight, sale value, and average value per pound of greasy wool sold at auction in New Zealand.
| Season | Weight of Greasy Wool Sold | Sale Value | Value per Pound | Average Minimum Floor Price per Pound of Greasy Wool | Price per Pound on Floor, Greasy* | Index Numbers† Base: 1949–50 (=1000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*Average of selected types. †Based on price on floor, clean. | ||||||
| lb (000) | £(000) | d. | d. | d. | ||
| 1959–60 | 409,199 | 76,121 | 44.65 | 33.00 | 46.05 | 1179 |
| 1960–61 | 420,941 | 70,753 | 40.34 | 33.00 | 42.29 | 1082 |
Dairy Produce - The following table shows the average weekly sterling price for New Zealand butter and cheese ex-store, and the average weekly sales on the London market.
| Month | Butter | Cheese | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Finest and First Grades) Average Price per Cwt | (All Grades) Weekly Average Sales | (Finest and First Grades, White) Average Price per Cwt (Crated) | (All Grades) Weekly Average Sales | |
| 1961- | s. | tons | s. | tons |
| May | 250 | 3,400 | 230 | 1,196 |
| June | 250 | 3,267 | 230 | 1,490 |
Quarterly Sales or Turnover - Values of quarterly sales or turnover for all retail stores, corrected for seasonal fluctuations and for price and population changes, are shown in the following table for December 1960 and March 1961 quarters.
QUARTERLY SALES OR TURNOVER—ALL STORE TYPES
| Quarter Ended | In Current £s | In Constant 1957–58 £s | In Current £s | In Constant 1957–58 £s | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As Recorded | Seasonally Corrected | Before Seasonal Correction | Seasonally Corrected | As Recorded | Seasonally Corrected | Before Seasonal Correction | Seasonally Corrected | |||||
| Value | Index* | Value | Index* | Value | Index* | Value | Index* | |||||
| * Base: Average quarterly values during the year ended March 1958 (= 1000). | ||||||||||||
| total turnover £(m) | total turnover £(m) | turnover per head of population £ | turnover per head of population £ | |||||||||
| 1960—Dec | 159.8 | 143.5 | 1173 | 149.7 | 134.5 | 1100 | 66.7 | 60.0 | 1102 | 62.5 | 56.2 | 1032 |
| 1961—Mar | 140.4 | 150.0 | 1226 | 132.4 | 141.5 | 1157 | 58.3 | 62.3 | 1144 | 55.0 | 58.7 | 1078 |
Statistics of external trade in the calendar year 1960, are given below.
Total Commodity Trade - Following are statistics of exports and imports in 1958, 1959, and 1960.
| Calendar Year | Exports | Imports (c.d.v.) | Excess of Exports Over Imports | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand' Produce | Total Exports | |||
| * The corresponding c.i.f. values were £285,077,000 in 1958, £231,417,000 in 1959, and £280,764,000 in 1960. | ||||
| £(thousand) | ||||
| 1958 | 247,984 | 250,173 | 252,800* | - 2,627 |
| 1959 | 290,998 | 293,659 | 205,076* | 88,583 |
| 1960 | 299,791 | 302,508 | 251,811 | 50,697 |
The total trade per head of mean population in 1960 was £233 (exports £127 and imports £106).
Exports - New Zealand's export commodity trade in 1960 was valued at £302.5 million, an increase of £8.8 million over the previous year. An indication of the movement in the value of exports in the main groups of commodities is afforded by the following table.
VALUE OF EXPORTS
| Calendar Year | Butter | Cheese | Frozen Meat | Wool | Hides, Pelts, an Skins |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||
| 1958 | 38,850 | 12,402 | 73,490 | 80,037 | 8,317 |
| 1959 | 55,808 | 22,103 | 71,250 | 89,643 | 13,254 |
| 1960 | 50,135 | 18,558 | 76,167 | 102,320 | 13,291 |
Apart from the question of values, a special interest attaches to progress in the volume of our export trade in major export commodities. In the following table the fluctuations in the quantities of exports of butter, cheese, meat, and wool since 1950 are shown.
| Calendar Year | Butter | Cheese | Frozen Meat | Wool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tons (thousand) | ||||
| 1950 | 138.3 | 99.9 | 338.1 | 175.9 |
| 1951 | 147.5 | 106.6 | 274.8 | 141.5 |
| 1952 | 184.0 | 91.3 | 385.6 | 195.6 |
| 1953 | 159.1 | 101.4 | 326.7 | 174.8 |
| 1954 | 132.5 | 90.4 | 370.8 | 175.4 |
| 1955 | 151.0 | 85.1 | 378.2 | 186.3 |
| 1956 | 167.5 | 88.9 | 414.2 | 191.0 |
| 1957 | 145.1 | 88.5 | 388.5 | 192.7 |
| 1958 | 175.4 | 89.5 | 405.4 | 204.0 |
| 1959 | 193.0 | 83.5 | 436.9 | 236.0 |
| 1960 | 157.1 | 79.4 | 467.0 | 232.8 |
Direction of Export Trade - The table below shows the main destinations of New Zealand exports in 1960.
| Country | Total Exports* |
|---|---|
| * Provisional figures. | |
| £(000) | |
| United Kingdom | 160,257 |
| India | 1,029 |
| Ceylon | 461 |
| Malaya | 428 |
| Singapore | 490 |
| Hong Kong | 481 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 99 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 121 |
| Union of South Africa | 797 |
| Bahamas | 78 |
| Barbados | 226 |
| Bermuda | 193 |
| Canada | 3,645 |
| Jamaica | 1,564 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 1,086 |
| Australia | 13,477 |
| Fiji | 1,080 |
| Tonga | 304 |
| Western Samoa | 791 |
| Other Commonwealth countries | 433 |
| Totals, Commonwealth countries | 187,040 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 7,674 |
| Bulgaria | 196 |
| Czechoslovakia | 1,745 |
| Denmark | 516 |
| Finland | 194 |
| France | 20,320 |
| German Democratic Republic | 132 |
| German Federal Republic | 10,633 |
| Greece | 384 |
| Republic of Ireland | 244 |
| Italy | 7,552 |
| Netherlands | 4,179 |
| Norway | 109 |
| Poland | 2,376 |
| Portugal | 534 |
| Russia | 2,511 |
| Sweden | 811 |
| Yugoslavia | 220 |
| Burma | 138 |
| China | 2,335 |
| Philippines | 615 |
| Japan | 8,893 |
| Egypt | 256 |
| Mexico | 116 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 274 |
| Panama Republic | 291 |
| Peru | 628 |
| United States of America | 38,480 |
| Venezuela | 498 |
| Hawaii | 1,078 |
| American Samoa | 136 |
| Other countries | 847 |
| Totals, all other countries | 114,915 |
| Ships' stores | 554 |
| Totals, all countries | 302,508 |
Exports to Commonwealth countries in 1960 accounted for 62 per cent of the total exports, excluding ships' stores.
Imports - The table following classifies imports by broad divisions.
IMPORTS VALUED AT CURRENT DOMESTIC VALUE IN COUNTRY OF EXPORT
| Calendar Year | Food, Beverages, and Tobacco | Mineral Fuels | Chemicals (Including Manufactured Fertilisers) | Base Metals and Manufactures of Metal | Machinery and Transport Equipment | Textiles, Clothing, and Footwear | Total* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Including classes not listed. | |||||||
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| 1958 | 24,769 | 19,952 | 20,703 | 38,588 | 71,238 | 36,786 | 252,800 |
| 1959 | 19,289 | 18,499 | 16,725 | 32,367 | 54,967 | 28,168 | 205,076 |
| 1960 | 20,132 | 20,827 | 19,937 | 39,105 | 71,801 | 35,560 | 251,811 |
Direction of Import Trade - The next table shows the main sources (origin) of New Zealand's imports in 1960.
| Country | Total Imports* |
|---|---|
| * Provisional figures. | |
| £(000) | |
| United Kingdom | 109,596 |
| Aden | 531 |
| Singapore | 1,243 |
| Bahrain | 1,308 |
| Ceylon | 2,391 |
| Hong Kong | 1,963 |
| India | 5,638 |
| Malaya | 2,172 |
| Pakistan | 140 |
| Sarawak | 253 |
| Ghana | 590 |
| Kenya and Uganda | 479 |
| Rhodesia-Nyasaland Federation | 142 |
| Tanganyika | 365 |
| Union of South Africa | 1,650 |
| Canada | 7,945 |
| Jamaica | 181 |
| Australia | 45,366 |
| Fiji | 479 |
| Gilbert and Ellice Islands | 170 |
| Nauru Island | 727 |
| Western Samoa | 576 |
| Other Commonwealth countries | 566 |
| Totals, Commonwealth countries | 184,471 |
| Austria | 391 |
| Belgium and Luxemburg | 2,311 |
| Czechoslovakia | 439 |
| Denmark | 410 |
| Finland | 367 |
| France | 2,091 |
| German Democratic Republic | 103 |
| German Federal Republic | 7,768 |
| Republic of Ireland | 136 |
| Italy | 1,845 |
| Netherlands | 3,353 |
| Norway | 678 |
| Portugal | 168 |
| Spain | 163 |
| Sweden | 1,987 |
| Switzerland | 2,333 |
| China | 433 |
| Indonesia | 2,349 |
| Iran | 2,042 |
| Japan | 7,184 |
| Saudi Arabia | 985 |
| Dominican Republic | 245 |
| Mexico | 200 |
| Netherlands Antilles | 925 |
| Peru | 240 |
| United States of America | 26,202 |
| Venezuela | 1,242 |
| French Oceania | 242 |
| Other countries | 508 |
| Totals, all other countries | 67,340 |
| Totals, all countries | 251,811 |
Imports from Commonwealth countries in 1960 comprised 73 per cent of the total.
Retail Prices (pp. 715–717) - Details of the consumers' price index for the calendar year 1960 and for the quarter ended 31 March 1961, are given below.
CONSUMERS' PRICE INDEX
| Base: Weighted average 21 towns, 1955 (= 1000) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Calendar Year 1960 | Quarter Ended 31 March 1961 | |
| Food- | ||
| Meat and fish | 1176 | 1185 |
| Fruits, vegetables, and eggs | 1109 | 1112 |
| Other foods | 1041 | 1047 |
| All foods | 1092 | 1098 |
| Housing - | ||
| Rent | 1232 | 1250 |
| Home ownership | 1309 | 1347 |
| All housing | 1286 | 1318 |
| Household operation - | ||
| Fuel and light | 1128 | 1129 |
| Home furnishing | 1088 | 1090 |
| Domestic supplies and services | 1114 | 1118 |
| All household operation | 1107 | 1109 |
| Apparel - | ||
| Clothing | 1030 | 1039 |
| Footwear | 1242 | 1266 |
| All apparel | 1063 | 1074 |
| Transportation - | ||
| Public transport | 1203 | 1204 |
| Private transport | 1217 | 1203 |
| All transportation | 1213 | 1204 |
| Miscellaneous - | ||
| Tobacco and alcohol | 1285 | 1272 |
| Other supplies | 1130 | 1141 |
| Other services | 1245 | 1271 |
| All miscellaneous | 1232 | 1235 |
| All groups | 1154 | 1163 |
Revision of Share Prices Index Numbers - The series of monthly and annual share price index numbers have been reviewed and a new series on base year 1960 (= 1000) has been commenced. An account of the revision is included in a supplement to the Monthly Abstract of Statistics for March 1961.
To enable longer term comparisons embracing the new series, the older group and all group series have been converted to base 1960 (= 1000) and are presented in the following table. There is no old series comparable with the Distribution group of the new series.
SHARE PRICES INDEX NUMBERS
| Base: Average for each group, 1960 (= 1000) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Industrial | Finance | All Groups |
| 1950 | 620 | 571 | 592 |
| 1951 | 647 | 645 | 646 |
| 1952 | 526 | 540 | 534 |
| 1953 | 503 | 556 | 533 |
| 1954 | 561 | 652 | 612 |
| 1955 | 599 | 689 | 650 |
| 1956 | 608 | 719 | 670 |
| 1957 | 680 | 770 | 731 |
| 1958 | 659 | 716 | 691 |
| 1959 | 749 | 809 | 783 |
| 1960 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
Monthly statistics for the first five months of 1961 are given below.
SHARE PRICES MONTHLY INDEX NUMBERS, BASE YEAR 1960 (= 1000)
| Month | Industrial Group | Distribution Group | Finance Group | All Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961— | ||||
| January | 1043 | 1026 | 1001 | 1029 |
| February | 1032 | 994 | 969 | 1009 |
| March | 1035 | 974 | 965 | 1006 |
| April | 1037 | 974 | 990 | 1014 |
| May | 1047 | 978 | 982 | 1018 |
Consolidated Fund (pp. 792–794) - The following table contains a summary of the receipts and payments of the Consolidated Fund for the financial years ended 31 March 1960 and 1961.
| 1959–60 | 1960–61 | |
|---|---|---|
*Excludes £2,326,000 in 1959–60 and £993,000 in 1960–61 of duty on motor spirits refunded under the Transport Amendment Act 1958; this comprises refunds to persons entitled to exemption from the additional payment of Customs duty from 27 June 1958. †Includes social security income tax and also £2,420,000 social security charge on 1957–58 income. ‡Includes £2,224,000 social security charge on 1957–58 income. | ||
| Receipts | £(thousand) | |
| Taxation | 276,446*† | 237,378*‡ |
| Interest on capital liability - | ||
| Post Office | 2,654 | 2,899 |
| Electric supply | 6,559 | 7,105 |
| Housing and housing construction | 1,697 | 1,800 |
| Land settlement | 2,131 | 2,328 |
| New Zealand National Airways Corporation | 95 | 122 |
| State Advances Corporation | 348 | |
| Interest on other public moneys | 1,840 | 1,701 |
| Profits on trading undertakings | 3,355 | 4,741 |
| Departmental receipts | 20,070 | 25,930 |
| Totals, receipts | 314,848*† | 284,354*‡ |
| Payments | ||
| Permanent appropriations - | ||
| Civil list | 194 | 201 |
| Debt services - | ||
| Interest | 28,759 | 30,085 |
| Amortisation | 9,343 | 9,830 |
| Administration and management | 333 | 450 |
| Superannuation (subsidy and contribution) | 4,971 | 5,381 |
| Advance to Dairy Products Marketing Commission | 3,000 | |
| Miscellaneous | 952* | 694* |
| Totals, permanent appropriations | 44,553* | 49,642* |
| Annual appropriations - | ||
| Legislative | 269 | 284 |
| Prime Minister's Office | 24 | 26 |
| External Affairs | 2,665 | 2,765 |
| Finance - | ||
| Treasury | 524 | 566 |
| Stabilisation | 12,601 | 15,351 |
| Customs | 643 | 691 |
| Inland Revenue | 1,992 | 2,138 |
| Audit | 251 | 268 |
| Totals, finance | 16,012 | 19,014 |
| General administration - | ||
| Public Service Commission | 152 | 164 |
| Internal Affairs | 2,204 | 2,286 |
| Island Territories | 1,534 | 1,692 |
| Printing and Stationery | 1,609 | 1,678 |
| Marine | 748 | 915 |
| Labour | 1,819 | 1,614 |
| Maori Affairs | 1,054 | 1,107 |
| Valuation | 432 | 469 |
| Statistics | 226 | 278 |
| Totals, general administration | 9,778 | 10,202 |
| Law and order - | ||
| Justice | 2,224 | 2,695 |
| Crown Law | 39 | 50 |
| Police | 3,298 | 3,455 |
| Totals, law and order | 5,562 | 6,200 |
| Defence - | ||
| Navy | 4,326 | 4,481 |
| Army | 6,585 | 7,270 |
| Air | 6,214 | 6,294 |
| Defence construction and maintenance | 2,097 | 2,293 |
| Totals, defence | 19,222 | 20,337 |
| Maintenance - | ||
| Public works and services | 11,509 | 12,363 |
| Roads | 2,026 | 1,938 |
| Totals, maintenance | 13,535 | 14,300 |
| Development of primary and secondary industries - | ||
| Lands and Survey | 2,114 | 2,278 |
| Forest Service | 2,951 | 3,268 |
| Agriculture | 5,661 | 5,603 |
| Industries and Commerce | 528 | 624 |
| Tourist and Publicity | 1,162 | 1,240 |
| Scientific and Industrial Research | 1,812 | 2,028 |
| Mines | 130 | 89 |
| Transport | 751 | 847 |
| Civil Aviation and Meteorological Services | 3,441 | 3,217 |
| Totals, development of primary and secondary industries | 18,550 | 19,194 |
| Social services - | ||
| Health | 8,335 | 8,709 |
| Public hospitals | 17,205 | 19,561 |
| Education | 39,445 | 43,825 |
| Rehabilitation | 917 | 1,355 |
| War and other pensions | 11,576 | 12,330 |
| Contribution to Social Security Fund | 106,500 | 34,700 |
| Totals, social services | 183,977 | 120,481 |
| Totals, annual appropriations | 269,594 | 212,803 |
| Unauthorised expenditure | 70 | 13 |
| Transfer to Loans Redemption Account | - | 10,000 |
| Transfer to Public Works Account | - | 6,500 |
| Transfer to Reserve Fund | - | 5,000 |
| Totals, payments | 314,217* | 283,958* |
| Surplus or deficit from current year's operations | +631 | +396 |
| Balance in Fund at end of year | 8,038 | 8,434 |
Taxation (pp. 801–802) - Particulars of revenue from taxation for the financial years 1958–59, 1959–60, and 1960–61 are contained in the following table.
| Item of Revenue | 1958–59 | 1959–60 | 1960–61 |
|---|---|---|---|
* See footnote on page 1210. †Includes social security income tax and also £2,420,000 social security charge on 1957–58 income. ‡Includes £2,224,000 social security charge on 1957–58 income. | |||
| £(thousand) | |||
| Consolidated Fund - | |||
| Customs | 39,099* | 41,090* | 42,692* |
| Beer duty | 11,258 | 13,350 | 14,529 |
| Sales tax | 25,751 | 24,241 | 23,744 |
| Film-hire tax | 169 | 166 | 179 |
| Milage tax | 82 | 190 | 60 |
| Other duties and racing taxation | 7,193 | 7,625 | 9,003 |
| Death (including gift) duties | 10,426 | 12,335 | 33,823 |
| Land tax | 1,448 | 1,526 | 1,817 |
| Income tax | 109,406 | 175,923† | 131,530‡ |
| Social security taxation - | |||
| Social security charge 1957–58 income | 10,366 | - | - |
| Social security income tax | 70,249 | - | 75,390 |
| National Roads Fund taxation - | |||
| Highways revenue (less rebates) | 19,798 | 20,842 | 21,695 |
| Totals | 305,243* | 297,288* | 334,463* |
A summary showing the amounts received from direct taxes on income and from all sources during the latest two years is now given.
| Year | Direct Taxes on Income (i.e., Income Tax and Social Security Charges on Income) | Total Taxation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Per Head of Mean Population | Percentage of Total Taxation | Amount | Per Head of Mean Population | |||
| £(000) | £ | s. | £(000) | £ | s. | ||
| 1959–60 | 175,923 | 75 | 0 | 59.2 | 297,288 | 126 | 15 |
| 1960–61 | 206,920 | 86 | 13 | 61.9 | 334,463 | 140 | 1 |
State Indebtedness (pp. 828–831) - The public debt as at 31 March 1961 amounted to £868,200,000, an increase of £23,700,000 as compared with a year earlier. Of the 1961 debt figure, £108,200,000 was held in the United Kingdom, £18,500,000 in the United States of America, and £741,500,000 in New Zealand.
Financial statistics of local government for the year ended 31 March 1960 now follow.
Receipts
| Year Ended 31 March | Rates | Public Utilities, Licences, Rents, Interest | Government Grants and Subsidies | Loans | Other Receipts | Total Receipts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1958 | 22,707 | 42,343 | 12,002 | 21,662 | 1,903 | 100,618 |
| 1959 | 24,392 | 48,903 | 12,287 | 19,691 | 2,832 | 108,105 |
| 1960 | 25,744 | 50,858 | 12,714 | 22,933 | 6,133 | 118,382 |
Expenditure
| Year Ended 31 March | Works and Utilities (Construction and Maintenance) | Administration | Interest on Loans | Amortisation of Debt | Other | Total Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1958 | 79,619 | 5,857 | 4,225 | 5,843 | 2,744 | 98,288 |
| 1959 | 85,869 | 6,191 | 5,133 | 6,238 | 3,169 | 106,599 |
| 1960 | 90,092 | 6,232 | 5,726 | 7,281 | 6,265 | 115,596 |
Expenditure on New Works out of Loan Money (Boroughs Only)
| Year Ended 31 March | Roads, Streets, and Bridges | Drainage and Sewerage | Water Supply | Parks, Gardens, Town Halls, Libraries, Art Galleries, and Places of Public Recreation | Gasworks and Electrical Works | Other Public Works | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | |||||||
| 1958 | 1,828 | 772 | 3,358 | 621 | 541 | 1,313 | 8,433 |
| 1959 | 1,803 | 986 | 1,523 | 704 | 728 | 1,520 | 7,264 |
| 1960 | 2,079 | 1,340 | 1,372 | 606 | 730 | 1,902 | 8,030 |
Assets and Liabilities
| As at 31 March | Assets | Liabilities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Assets | Other Assets (Estimated) | Total Debt | Other Liabilities | Total Liabilities | ||
| Gross Debt | Net Debt | |||||
| £(thousand) | ||||||
| 1958 | 37,101 | 213,686 | 114,675 | 107,239 | 11,010 | 118,249 |
| 1959 | 40,251 | 235,249 | 127,970 | 120,495 | 11,911 | 132,405 |
| 1960 | 38,955 | 275,917 | 143,557 | 136,504 | 13,296 | 149,800 |
Gross Debt of Local Authorities per Head of Population and Annual Charge
| At 31 March | Population | Gross Debt | Annual Loan Charge | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Rate per Head | Amount | Rate per Head | ||||||
| £(000) | £ | s. | d. | £(000) | £ | s. | d. | ||
| 1958 | 2,275,515 | 114,675 | 50 | 7 | 11 | 10,811 | 4 | 15 | 0 |
| 1959 | 2,326,129 | 127,970 | 55 | 0 | 3 | 12,047 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| 1960 | 2,370,166 | 143,557 | 60 | 11 | 4 | 13,304 | 5 | 12 | 3 |
Gross Loan Indebtedness
| At 31 March | Counties and Road Districts | Boroughs and Town Districts | Urban Drainage Districts | Urban Transport Districts | Electric Power Districts | Harbour Boards | Other Districts | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| £(thousand) | ||||||||
| 1958 | 6,790 | 51,581 | 8,988 | 4,149 | 21,300 | 15,689 | 6,178 | 114,675 |
| 1959 | 7,429 | 55,909 | 12,127 | 3,909 | 22,930 | 17,562 | 8,104 | 127,970 |
| 1960 | 8,735 | 62,215 | 16,092 | 3,803 | 23,884 | 20,033 | 8,793 | 143,557 |
Domicile of Debt
| At 31 March | Amount | Percentage of Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | United Kingdom | Australia | New Zealand | United Kingdom | Australia | |
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | Per Cent | Per Cent | Per Cent | |
| 1958 | 111,435 | 2,963 | 278 | 97.18 | 2.58 | 0.24 |
| 1959 | 125,813 | 1,883 | 275 | 98.31 | 1.48 | 0.21 |
| 1960 | 141,975 | 1,333 | 248 | 98.90 | 0.93 | 0.17 |
Debt Charges and Loans Sanctioned
| At 31 March | Debt Charges | Loans Sanctioned | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On Debentures and Other Securities | On Inscribed Debt | Total | Year | Total Applications | Sanctioned | ||
| New Works | Redemption Loans | ||||||
| £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | £(000) | ||
| 1958 | 10,811 | - | 10,811 | 1958–59 | 21,510 | 20,538 | 542 |
| 1959 | 12,047 | - | 12,047 | 1959–60 | 32,848 | 28,973 | 237 |
| 1960 | 13,304 | - | 13,304 | 1960–61 | 37,686 | 34,648 | 475 |
Reserve Bank (p. 884) - Data showing the liabilities and assets of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand at the last balance day in May 1961 are shown below, together with the corresponding figures for the last balance day in March 1961.
| Item | As at Last Balance Day in | |
|---|---|---|
| March 1961 | May 1961 | |
* Expressed in New Zealand currency. † An increase in investments in New Zealand and a matching decrease in advances to State, follow from a change in the Government's method of borrowing from the Reserve Bank; holdings of 1 per cent three-month Treasury Bills have been exchanged for 1 per cent Government stock. | ||
| Liabilities | £(000) | |
| Total liabilities (including other) | 174,782 | 177,014 |
| Bank notes | 83,950 | 82,065 |
| Demand liabilities - | ||
| State | 27,597 | 12,152 |
| Marketing | 1,378 | 893 |
| Banks | 49,010 | 67,899 |
| Other | 920 | 1,375 |
| Assets - | ||
| Total assets (including other) | 174,782 | 177,014 |
| Investments - | ||
| Overseas* | 33,297 | 31,267 |
| In New Zealand | 71,308† | 71,308† |
| Reserve* - | ||
| Sterling exchange | 11,176 | 9,555 |
| Other exchange | 477 | 593 |
| Advances - | ||
| State | 29 | 173 |
| Marketing organisations | 40,212 | 37,423 |
| Other | 9,190 | 18,050 |
Trading Banks (pp. 885–896) - The principal statistics of trading banks for the months of March and May are given below. Debits and clearings cover the weekly periods ended on the last Wednesday of the respective months, while the remaining figures are as at those dates.
| Item | As at Last Balance Day in | |
|---|---|---|
| March 1961 | May 1961 | |
| *Includes certain current accounts, operated by non-profit organisations, for which interest is payable on monthly minimum balances; these accounts were previously included in “deposits not bearing interest” column. | ||
| Bank debits during week - | ||
| Government £(000) | 36,835 | 14,070 |
| Other £(000) | 199,686 | 146,265 |
| Advances including notes and bills discounted £(000) | 233,284 | 233,507 |
| Unexercised overdrafts £(000) | 115,697 | 120,797 |
| Deposits - | ||
| Total £(000) | 331,530 | 333,026 |
| Government £(000) | 8,401 | 4,962 |
| Not bearing interest £(000) | 255,288 | 258,930 |
| Bearing interest* £(000) | 67,841 | 69,134 |
| Reserve Bank notes - | ||
| Notes held by trading banks £(000) | 13,362 | 14,945 |
| Net note circulation £(000) | 70,588 | 67,120 |
| Ratio of advances to deposits Per Cent | 70.37 | 67.11 |
Overseas Assets of Banks (p. 897) - In the following table overseas assets of banks (on account of New Zealand business only) are shown.
| Item | Overseas Assets at End of | |
|---|---|---|
| March 1960 | March 1961 | |
| £(000) | ||
| Trading banks' overseas assets— | ||
| In London | 28,649 | 17,108 |
| Elsewhere | 6,011 | 6,778 |
| Reserve Bank's overseas assets— | ||
| Sterling exchange | 59,368 | 11,176 |
| Other overseas assets | 12,360 | 34,025 |
| Total gross overseas assets | 106,388 | 69,088 |
| Overseas liabilities of trading banks | 8,745 | 15,430 |
| Overseas liabilities of Reserve Bank | 57 | 140 |
| Net overseas assets | 97,586 | 53,518 |
Net overseas assets at 7 June 1961 totalled £57.2 million, compared with £114.1 million on 8 June 1960.
Savings Banks (pp. 902–908) - A summary of statistics of savings banks at 31 March 1961 is given below.
| Item | Post Office Savings Bank | Trustee Savings Banks | National Savings Accounts |
|---|---|---|---|
*Includes interest paid out on investment accounts. †On deposits held during year ended 30 June 1960. ‡Excess of deposits plus investment account interest over withdrawals. | |||
| Number of depositors | 1,883,675 £(000) | 462,949 £(000) | £(000) |
| Total amount of deposits during year | 182,130 | 55,933 | 5,864 |
| Total amount of withdrawals during year | 166,785* | 49,067* | 9,259 |
| Interest | 8,189‡ | 1,940 | 2,046† |
| Total amount to credit of depositors at end of March 1961 | 306,467‡ | 73,852 | 57,559 |
Post Office Savings Bank Accounts Classified by Amount Groups (p. 904) - The following is a classification of the balances in Post Office Savings Bank accounts at 31 March 1959, 1960, and 1961, shown by amount groups and percentage of accounts within each group.
| Amount | At 31 March 1959 | At 31 March 1960 | At 31 March 1961 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | Number of Accounts | Percentage of Total | ||
| £ | £ | ||||||
| Under 1- | |||||||
| Inoperative | 158,904 | 8.94 | 161,131 | 8.82 | 166,447 | 8.84 | |
| Operative | 200,189 | 11.26 | 198,420 | 10.87 | 212,854 | 11.30 | |
| 1 and under | 10 | 455,409 | 25.61 | 457,129 | 25.03 | 476,389 | 25.29 |
| 10 ,, | 50 | 359,532 | 20.21 | 376,050 | 20.59 | 376,925 | 20.01 |
| 50 ,, | 100 | 147,746 | 8.31 | 153,506 | 8.40 | 156,533 | 8.31 |
| 100 ,, | 200 | 139,620 | 7.85 | 145,630 | 7.98 | 146,775 | 7.79 |
| 200 ,, | 300 | 78,484 | 4.41 | 82,007 | 4.49 | 82,285 | 4.37 |
| 300 ,, | 400 | 51,180 | 2.88 | 52,984 | 2.90 | 54,151 | 2.87 |
| 400 ,, | 500 | 38,833 | 2.18 | 40,506 | 2.22 | 41,262 | 2.19 |
| 500 ,, | 600 | 29,617 | 1.67 | 30,771 | 1.69 | 32,419 | 1.72 |
| 600 ,, | 700 | 18,939 | 1.06 | 20,635 | 1.13 | 22,211 | 1.18 |
| 700 ,, | 800 | 14,802 | 0.83 | 16,510 | 0.91 | 17,220 | 0.91 |
| 800 ,, | 900 | 12,070 | 0.68 | 12,702 | 0.70 | 13,471 | 0.72 |
| 900 ,, | 1,000 | 10,470 | 0.59 | 11,030 | 0.60 | 11,703 | 0.62 |
| 1,000 ,, | 1,500 | 31,444 | 1.77 | 33,617 | 1.84 | 36,590 | 1.94 |
| 1,500 ,, | 2,000 | 12,873 | 0.72 | 13,385 | 0.73 | 14,482 | 0.77 |
| 2,000 ,, | 3,000 | 11,641 | 0.65 | 12,125 | 0.67 | 13,192 | 0.70 |
| 3,000 ,, | 4,000 | 3,782 | 0.21 | 4,353 | 0.24 | 4,337 | 0.23 |
| 4,000 ,, | 5,000 | 1,710 | 0.10 | 1,862 | 0.10 | 2,411 | 0.13 |
| 5,000 and over | 1,181 | 0.07 | 1,684 | 0.09 | 2,018 | 0.11 | |
| Total number of accounts | 1,778,426 | 100.00 | 1,826,037 | 100.00 | 1,883,675 | 100.00 | |
Overseas Exchange Transactions - The following statement gives statistics of overseas exchange transactions for the years ended 31 March 1960 and 1961. Comparable items for the calendar years 1959 and 1960 are, however, given on pages 899–900. All figures quoted are taken from Reserve Bank sources.
| Item | Year Ended 31 March 1960 | Year Ended 31 March 1961 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receipts | Payments | Receipts | Payments | |
| £(thousand) | ||||
| Exports - | ||||
| Butter | 62,455 | 40,530 | ||
| Cheese | 20,862 | 19,480 | ||
| Meat | 71,697 | 79,656 | ||
| Wool | 106,884 | 101,963 | ||
| Totals (including other) | 314,219 | 296,568 | ||
| Imports - | ||||
| Licensed | 209,560 | 251,674 | ||
| Decontrolled | 4,621 | 19,216 | ||
| Government | 27,159 | 28,583 | ||
| Totals (including other) | 241,340 | 299,473 | ||
| Transport: Freights, fares, ships' charters | 5,279 | 11,943 | 5,988 | 13,639 |
| Travel: Private and business (exclusive of fares) | 3,264 | 9,604 | 3,759 | 13,883 |
| Insurance - | ||||
| Insurance, reinsurance, other transfers | 968 | 2,605 | 1,574 | 2,860 |
| International investment income - | ||||
| Interest, dividends, and other private investment income | 5,106 | 9.234 | 6,206 | 11,299 |
| Interest on Government and local authority loans | 5,711 | 5,331 | ||
| Totals, international investment income | 5,106 | 14,945 | 6,206 | 16,630 |
| Government transactions - | ||||
| Current expenditure by New Zealand Government overseas | 8,988 | 9,437 | ||
| Current receipts by New Zealand Government and expenditure by other governments in New Zealand | 2,472 | 2,458 | ||
| Totals, Government transactions | 2,472 | 8,988 | 2,458 | 9,437 |
| Miscellaneous current transactions - | ||||
| Commissions, royalties, rebates, etc. | 1,043 | 2,991 | 1,491 | 3,285 |
| Films and entertainments | - | 1,197 | - | 1,178 |
| Unilateral transfers (immigrants' transfers, personal remittances, charitable, legacies, etc.) | 7,641 | 10,184 | 7,841 | 10,766 |
| Expenses of business firms | 722 | 4,334 | 889 | 4,811 |
| Other current transactions | 698 | 1,757 | 968 | 1,416 |
| Totals, miscellaneous current transactions | 10,105 | 20,462 | 11,189 | 21,455 |
| Capital transfers - | ||||
| Private | 11,481 | 3,077 | 8,711 | 5,544 |
| Government | 100 | 20,210 | 8,320 | 8,631 |
| Bank drawings on Australian Bank Credit | 7,455 | - | ||
| Local authority | 506 | 639 | ||
| Totals, capital transfers | 11,582 | 31,247 | 17,031 | 14,814 |
| Cook Islands exports or imports | 20 | 187 | 43 | 158 |
| Unidentified | 58 | - | 79 | - |
| Grand totals | 353,072 | 341,321 | 344,896 | 392,348 |
Receipts of the Social Security Fund for the year ended 31 March 1961 consisted of £75,390,000 in social security income tax, and a contribution of £34,700,000 from the Consolidated Fund. Included in this latter amount was £2,223,926 received as social security charge on 1957–58 income. Miscellaneous receipts totalled £372,306, making the total receipts of the Fund £110,462,306.
Payments from the Fund in 1960–61, with 1959–60 payments in parentheses, were: Monetary benefits, £87,539,316 (£83,843,190) including emergency benefits and supplementary assistance, £1,240,317 (£1,204,439); medical, etc., benefits £21,148,431 (£19,891,627); administration expenses, £1,704,672 (£1,522,130); Family Benefits (Home Ownership) Act 1958 - advances under section 4 (1), £6,941,089 (£3,879,889); other payments £46,761 (£57,498). Total payments from the Fund were therefore £117,380,269 (£109,194,334). The balance in the Fund at the end of March 1961 was £11,222,524.
Particulars of the various social security benefits (monetary and health) and war pensions in force at the end of March 1961, together with total payments during the financial year 1960–61, are shown in the following table.
| Class of Benefit or Pension | As at 31 March 1961 | Payments During Year Ended 31 March 1961 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number in Force | Annual Value | ||
| Social security benefits | £(000) | £(000) | |
| Monetary - | |||
| Superannuation | 97,528 | 18,650 | 20,087 |
| Age | 106,673 | 24,631 | 27,036 |
| Widows' | 13,328 | 4,186 | 4,200 |
| Orphans' | 274 | 45 | 43 |
| Family | 348,004 | 29,859 | 30,900 |
| Invalids' | 8,157 | 2,237 | 2,149 |
| Miners' | 318 | 103 | 118 |
| Unemployment | 140 | ... | 93 |
| Sickness | 3,929 | ... | 1,673 |
| Emergency | 2,802 | ... | 932 |
| Supplementary assistance | 6,998 | ... | 308 |
| Advances for repairs to homes | 308 | ... | 38 |
| Capitalisation of family benefit | 10,044 | ... | 6,941 |
| Totals | 598,503 | ... | 94,518 |
| Medical - | |||
| Medical | ... | ... | 4,245 |
| Hospital | ... | ... | 5,670 |
| Maternity | ... | ... | 1,672 |
| Pharmaceutical | ... | ... | 6,798 |
| Supplementary | ... | ... | 2,764 |
| Totals | ... | ... | 21,148 |
| War pensions - | |||
| First World War | 14,339 | 3,579 | 3,319 |
| Second World War | 24,518 | 3,205 | 2,879 |
| War Veterans' Allowances | 14,251 | 6,373 | 5,705 |
| South African War | 19 | 5 | 5 |
| Mercantile Marine | 28 | 4 | 4 |
| Emergency Reserve Corps | 9 | 2 | 2 |
| K Force | 197 | 17 | 18 |
| War Pensions supplementary assistance | 221 | ... | 10 |
| Totals | 53,582 | ... | 11,942 |
| Sundry pensions and annuities | 677 | 93 | 96 |
| Grand totals | 652,762 | ... | 127,704 |
Wage Rates (pp. 994–1009) - Index numbers of average nominal weekly wage rates of adult male and adult female wage earners in 1959 and 1960, and of adult male wage earners as at 31 March 1961, are as follows.
| Industrial Group | Base: All Groups (1954 = 1000) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult Males | Adult Females | ||||
| Average for Year | As at 31 March 1961* | Average for Year | |||
| 1959 | 1960 | 1959 | 1960 | ||
| *Provisional. | |||||
| Provision of - | |||||
| Food, drink, etc. | 1212 | 1272 | 1283 | 1028 | 1082 |
| Clothing, footwear, and textiles | 1125 | 1182 | 1205 | 1118 | 1178 |
| Building and construction | 1093 | 1149 | 1162 | ||
| Power, heat, and light | 1062 | 1120 | 1145 | ||
| Transport by water and air | 1340 | 1407 | 1419 | ||
| Transport by land | 1147 | 1214 | 1228 | ||
| Accommodation, meals, and personal service | 1098 | 1157 | 1200 | 1254 | 1326 |
| Working in or on - | |||||
| Wood, wicker, seagrass, etc. | 1158 | 1221 | 1227 | ||
| Metal | 1204 | 1267 | 1271 | ||
| Stone, clay, glass, chemicals, etc. | 1087 | 1136 | 1154 | ||
| Paper, printing, etc. | 1227 | 1294 | 1298 | 1090 | 1164 |
| Skins, leather, etc. | 1079 | 1142 | 1151 | ||
| Mines and quarries | 1144 | 1201 | 1207 | ||
| The land (farming pursuits) | 994 | 1029 | 1038 | ||
| All groups combined | 1136 | 1193 | 1205 | 1146 | 1210 |
Effective Weekly Wage Rates (p. 1001) - The following table shows nominal and effective weekly wage rates of adult workers for the years 1959 and 1960, and of males only for the first quarter of 1961. The base of the index numbers is in each case the calendar year 1954 (= 1000).
| Year | Retail Prices (All Groups) | Nominal Weekly Wage Rates | Effective Weekly Wage Rates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | ||
| * Provisional. | |||||
| 1959 | 1175 | 1136 | 1146 | 967 | 975 |
| 1960 | 1183 | 1193 | 1210 | 1008 | 1023 |
| 1961- | |||||
| March quarter | 1192 | 1205* | 1011* | ||
Average Rates of Wages (pp. 1002–1005) - The following table gives the prescribed minimum average weekly wage rates as at 31 March 1961, the series being confined to adult males.
| Occupation | Average Wage (Four Principal Districts) at 31 March 1961 | |
|---|---|---|
| Adult Males | s. | d. |
| Bakers - | ||
| Journeymen | 273 | 5 |
| Labourers | 229 | 10 |
| Butchers - | ||
| First shopmen | 284 | 8 |
| Second shopmen | 265 | 5 |
| Butter-factory employees - | ||
| Churning and butter making: Others | 261 | 3 |
| Flourmilling - | ||
| Kilnmen | 264 | 2 |
| Assistant smuttermen | 250 | 0 |
| Rollermen | 290 | 0 |
| Meat freezing - | ||
| Slaughtermen per 100 sheep | 118 | 4 |
| Workers not otherwise specified | 277 | 0 |
| Meat preserving - | ||
| Boners | 330 | 10 |
| Others | 285 | 3 |
| Sausage-casing making: Workers not otherwise specified | 295 | 10 |
| Aerated water and cordial making - | ||
| Cordial makers | 252 | 0 |
| Others | 243 | 7 |
| Brewing: Others | 267 | 6 |
| Tailors - | ||
| Journeymen | 265 | 0 |
| Stock cutters (factory) | 264 | 2 |
| Footwear manufacturing workers | 272 | 3 |
| Woollen mills - | ||
| Spinners | 274 | 1 |
| Others | 247 | 4 |
| Building - | ||
| Bricklayers | 277 | 6 |
| Carpenters and joiners | 273 | 4 |
| Plasterers | 281 | 6 |
| Plumbers | 285 | 0 |
| Builders' labourers | 246 | 8 |
| General labourers | 228 | 6 |
| Sawmilling - | ||
| Sawyers | 287 | 5 |
| Tailers-out | 263 | 10 |
| Yardmen head | 282 | 0 |
| Workers not specified | 258 | 10 |
| Boatbuilding: Shipwrights | 279 | 0 |
| Metal works etc. - | ||
| Boilermakers journeymen | 273 | 4 |
| Iron and brass moulders | 276 | 0 |
| Tinsmiths journeymen | 278 | 4 |
| Engineering fitters etc. | 280 | 0 |
| Electrical wiremen | 283 | 4 |
| Motor mechanics | 274 | 2 |
| Printing - | ||
| Linotype operators (day) | 289 | 4 |
| Letterpress machinists (day) | 279 | 0 |
| Skin and leather workers - | ||
| Curriers | 255 | 0 |
| All other workers | 227 | 9 |
| Mineral and stone workers - | ||
| Flangers and moulders | 260 | 10 |
| All other workers | 237 | 6 |
| Mining (coal) - | ||
| Surface: Tippers | 292 | 11 |
| Miners (on day wages per shift) | 56 | 4 |
| Truckers | 255 | 5 |
| Quarrymen | 228 | 1 |
| Agricultural and pastoral workers - | ||
| General farm hands | 168 | 3 |
| Threshing mill: Other workers per hour | 5 | 11 |
| Ploughmen | 168 | 3 |
| Shearers (per 100 sheep shorn) | 71 | 6 |
| Shepherds | 168 | 3 |
| Wool pressers | 284 | 2 |
| Dairy-farm workers | 205 | 6 |
| Railways - | ||
| Enginedrivers average third and sixth years | 318 | 9 |
| Locomotive assistant average second and eighth years | 283 | 4 |
| Guards average first and third years | 305 | 10 |
| Tramways - | ||
| Drivers | 270 | 0 |
| Conductors (after six months) | 260 | 0 |
| Shipping and cargo working - | ||
| Assistant stewards, first grade | 251 | 2 |
| Assistant stewards, second grade | 247 | 1 |
| Chief cooks | 305 | 3 |
| Second cooks | 277 | 2 |
| Able seamen | 269 | 6 |
| Ordinary seamen 18 years or over | 206 | 10 |
| Waterside workers: Ordinary cargo | 283 | 4 |
| Hotel workers- | ||
| First cooks | 259 | 7 |
| Waiters | 192 | 8 |
| Miscellaneous | ||
| Retailing of apparel: Shop assistants | 257 | 4 |
| Grocers' assistants | 256 | 1 |
| Warehouse storemen | 249 | 6 |
NOTE - The following perquisities (as assessed for statistical purposes), as at 31 March 1961, should be added to the listed occupations: General farm hands, ploughmen, and shepherds, 42s. 6d., and dairy-farm workers, 42s. 6d. per week for board and lodging; shearers and wool pressers, 8s. per day for rations; assistant stewards (first and second grade), chief and second cooks, able and ordinary seamen, 55s. 7d. per week as value of board and lodging; and hotel first cooks and waiters, 63s. 2d. per week as value of board and lodging.
Estimated Distribution of the Labour Force (p. 1013) - The following table supplies an estimated distribution of the total labour force at 15 October 1960 and 15 April 1961.
| Industrial Group | Males | Females | Totals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 1960 | April 1961 | October 1960 | April 1961 | October 1960 | April 1961 | |
| thousand | ||||||
| Primary industry | 134.0 | 132.5 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 144.8 | 143.3 |
| Manufacturing industry | 168.2 | 177.7 | 52.9 | 54.7 | 221.1 | 232.4 |
| Power, water, and sanitary services | 11.9 | 11.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 12.7 | 12.6 |
| Building and construction | 81.7 | 82.7 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 83.2 | 84.3 |
| Transport and communication | 74.5 | 75.5 | 10.4 | 11.0 | 84.9 | 86.5 |
| Distribution and finance | 99.8 | 102.4 | 50.3 | 52.7 | 150.1 | 155.1 |
| Domestic and personal services | 20.4 | 20.5 | 25.6 | 26.1 | 46.0 | 46.6 |
| Administration and professional | 66.3 | 67.8 | 62.2 | 63.4 | 128.5 | 131.2 |
| Totals in industry | 656.8 | 670.9 | 214.5 | 221.1 | 871.3 | 892.0 |
| Armed forces | 9.6 | 9.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 10.1 | 9.6 |
| Unemployed | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Totals labour force | 666.8 | 680.2 | 215.0 | 221.7 | 881.8 | 901.9 |
Half-yearly Surveys of Employment (pp. 1014–1020) - Following is a summary of the employment statistics as returned for 15 April 1961. These statistics are provisional.
| Item | Primary Industry (Other than Farming, Fishing, and Hunting) | Manufacturing Industry | Power, Water, and Sanitary Services | Building and Construction | Transport and Communication | Distribution and Finance | Domestic and Personal Services | Administration and Professional | Total, all Industries Covered |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male employees (full time) | 10,414 | 158,545 | 11,755 | 54,643 | 55,307 | 75,224 | 11,692 | 53,611 | 431,191 |
| Male working proprietors | 444 | 10.495 | 6 | 7,294 | 2,314 | 12,043 | 3,704 | 622 | 36,922 |
| Female employees (full time) | 302 | 50,279 | 842 | 1,356 | 9,874 | 42,571 | 14,735 | 51,448 | 171,407 |
| Female working proprietors | 12 | 1,437 | - | - | 125 | .4,517 | 2,472 | 211 | 8,774 |
| Number of establishments | 603 | 12,742 | 266 | 6,621 | 2,709 | 17,141 | 4,994 | 4,032 | 49,108 |
The figures shown in the manufacturing industry column are further subdivided as follows.
| Food, Drink, and Tobacco | Textiles, Clothing, and Leather | Building Materials and Furnishings | Engineering and Metal Working | Miscellaneous Manufacturing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male employees (full time) | 35,686 | 13,373 | 27,408 | 58,535 | 23,543 |
| Male working proprietors | 1,153 | 1,173 | 2,040 | 5,036 | 1,093 |
| Female employees (full time) | 7,460 | 25,547 | 1,927 | 6,821 | 8,524 |
| Female working proprietors | 475 | 531 | 48 | 252 | 131 |
| Number of establishments | 1,707 | 1,810 | 2,530 | 5,263 | 1,432 |
Limitations in the coverage of the figures shown above are noted on page 1014.
Summary of Vacancies, Placements, and Disengaged Persons - This table gives additional figures to those presented on page 1022.
| Item | Vacancies at End of Month | Placements During Month | Disengaged Persons at End of Month | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | Males | Females | Total | |
| *From and including May 1959 vacancies notified by Railways Department were reduced following a re-assessment of their staffing requirements. | |||||||||
| Monthly average over calendar year - | |||||||||
| 1959* | 3,046 | 2,254 | 5,300 | 1,025 | 389 | 1,414 | 1,096 | 92 | 1,188 |
| 1960 | 4,076 | 2,688 | 6,764 | 793 | 329 | 1,122 | 569 | 64 | 633 |
| Monthly total - | |||||||||
| 1961 | |||||||||
| January | 5,502 | 3,342 | 8,844 | 668 | 614 | 1,282 | 288 | 45 | 333 |
| February | 5,762 | 3,499 | 9,261 | 910 | 666 | 1,576 | 223 | 43 | 266 |
| March | 6,148 | 3,514 | 9,662 | 586 | 334 | 920 | 205 | 29 | 234 |
| April | 6,080 | 3,458 | 9,538 | 593 | 291 | 884 | 220 | 43 | 263 |
| May | 5,770 | 3,340 | 9,110 | 652 | 216 | 868 | 285 | 34 | 319 |
Radio Licences (p. 385) - The number of radio licences in force for receiving stations on 31 March 1961 was 587,168, and for all classes of radio licences 593,220, compared with 577,403 and 583,214 respectively at 31 March 1960.
Television Licences (p. 385) - At 31 May 1961 there were 5,630 television receiving licences in force.
Horse Racing (pp. 823–824) - The number of racing days in the calendar year 1960 was 383. Totalisator turnover totalled £50,186,000 in 1960 (£43,717,000 in 1959) while Government taxation totalled £4,643,000 in 1960 (£4,037,000 in 1959).
Land Transfers (pp. 290–292) - Transactions under the Land Transfer Act showed increases in both number and consideration. The average amount per transaction (town and suburban properties) in 1960–61 was £2,295, as compared with £2,102 in 1959–60 and £2,036 in 1958–59.
| Item | Year Ended 31 March | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | ||
| Town and suburban properties - | ||||
| Number | 41,854 | 45,125 | 52,233 | |
| Area | acres | 10,283 | 10,999 | 16,000 |
| Consideration | £(000) | 85,216 | 94,866 | 119,894 |
| Country properties - | ||||
| Freehold - | ||||
| Number | 6,796 | 7,204 | 8,403 | |
| Area | acres (000) | 1,072 | 1,264 | 1,710 |
| Consideration | £(000) | 39,619 | 44,576 | 62,176 |
| Total freehold and leasehold - | ||||
| Number | 7,299 | 7,730 | 9,179 | |
| Consideration | £(000) | 42,400 | 47,859 | 67,888 |
| All properties: Total consideration | £(000) | 127,616 | 142,725 | 187,782 |
Mortgages (pp. 922–932) - Particulars of gross totals of mortgages registered and discharged during the last three financial years are shown below. Mortgage registrations have again shown an increase in number, and the increase of £33,048,000 in the total amount of consideration compared with an increase of £11,819,000 in 1959–60. Mortgages discharged have also shown increases both in number and amount of consideration.
| Year Ended 31 March | Registered* | Discharged* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Amount | Number | Amount | |
| *Inclusive of duplicate registrations and discharges. | ||||
| £(000) | £(000) | |||
| 1959 | 56,218 | 109,187 | 36,925 | 44,418 |
| 1960 | 57,867 | 121,006 | 39,935 | 51,758 |
| 1961 | 64,637 | 154,054 | 46,474 | 68,313 |
Justice (p. 264) - Prisoners in jails at end of calendar year: 1959, 1,746, or 7.40 per 10,000 of population; 1960, 1,828, or 7.60 per 10,000 of population.
Registration of Aliens (p. 70) - The number of aliens on the register at 1 April 1961 totalled 27,294 (16,649 males, 10,645 females), compared with 1 April 1960 figures of 27,643 (17,072 males, 10,571 females).
Naturalisations (p. 69) - The number of certificates of naturalisation issued to former aliens during the year ended 31 March 1961 was 930, compared with a total of 1,017 in the previous year. Certificates of registration as a New Zealand citizen were granted to 847 citizens of other countries of the Commonwealth or former aliens (735 in 1959–60), and 372 certificates of registration (301 in 1959–60) to minor children (either citizens of other countries of the Commonwealth or former aliens).
Wholesale Trade - A quarterly survey is now made of stocks held by stores conducting predominantly wholesale business. The following table shows, by store-type group, for stores covered by the quarterly survey, the values of stocks held by wholesalers at 31 March for the last three years. The value of stocks increased by 1.7 percent between 1959 and 1960, and by 11.5 percent between 1960 and 1961.
| Store-type Group | As at | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 31 March 1959 | 31 March 1960 | 31 March 1961 | |
| £(thousand) | |||
| Food and drink | 4,710 | 4,985 | 5,046 |
| Apparel | 6,233 | 5,932 | 6,071 |
| Furniture | 2,349 | 2,493 | 2,982 |
| Automotive | 7,306 | 7,288 | 8,054 |
| Hardware | 8,726 | 9,373 | 10,305 |
| Chemicals | 3,289 | 3,369 | 3,621 |
| General merchants | 8,871 | 9,025 | 10,193 |
| Miscellaneous | 20,950 | 21,003 | 24,481 |
| Totals | 62,434 | 63,468 | 70,753 |
A population census of New Zealand was taken on the night of Tuesday, 18 April 1961. Preliminary population figures are given in the following tables. The 1956 census totals (adjusted, where necessary, to correspond with the 1961 boundaries) are shown for the purposes of comparison.
POPULATION (INCLUSIVE OF MAORIS) IN COUNTIES, CITIES AND BOROUGHS, TOWN DISTRICTS, ETC.
| County (Excluding Town Districts, but Including County Towns) | 1956 Census | 1961 Census (Preliminary Figures) |
|---|---|---|
| North Island | ||
| Mangonui | 7,754 | 7,573 |
| Whangaroa | 2,503 | 2,312 |
| Hokianga | 6,623 | 5,236 |
| Bay of Islands | 11,693 | 12,233 |
| Whangaret | 13,643 | 13,822 |
| Hobson | 6,709 | 6,374 |
| Otamatea | 6,826 | 6,934 |
| Rodney | 6,532 | 6,804 |
| Waitemata | 32,224 | 53,064 |
| Great Barrier Island | 271 | 264 |
| Manukau | 20,435 | 28,166 |
| Franklin | 17,606 | 18,254 |
| Raglan | 12,078 | 12,077 |
| Waikato | 14,894 | 17,801 |
| Waipa | 16,621 | 20,189 |
| Otorohanga | 7,881 | 8,205 |
| Waitomo | 9,126 | 8,788 |
| Taumarunui | 8,974 | 8,863 |
| Coromandel | 2,761 | 2,842 |
| Thames | 3,209 | 3,207 |
| Hauraki Plains | 5,752 | 5,689 |
| Ohinemuri | 4,401 | 4,171 |
| Piako | 12,162 | 12,471 |
| Matamata | 19,303 | 22,343 |
| Tauranga | 17,354 | 19,985 |
| Rotorua | 12,230 | 14,305 |
| Taupo | 9,616 | 12,976 |
| Whakatane | 15,123 | 16,214 |
| Opotiki | 5,152 | 4,883 |
| Matakaoa | 1,834 | 1,828 |
| Waiapu | 6,228 | 5,636 |
| Uawa | 1,707 | 1,725 |
| Waikohu | 3,343 | 3,035 |
| Cook | 8,649 | 8,868 |
| Wairoa | 8,000 | 7,699 |
| Hawke's Bay | 18,706 | 21,050 |
| Waipawa | 3,962 | 4,021 |
| Waipukurau | 1,291 | 1,278 |
| Patangata | 3,522 | 3,431 |
| Dannevirke | 4,838 | 4,596 |
| Woodville | 1,840 | 1,736 |
| Clifton | 2,772 | 2,602 |
| Taranaki | 7,418 | 7,905 |
| Inglewood | 3,322 | 3,212 |
| Egmont | 6,347 | 6,243 |
| Stratford | 6,219 | 6,028 |
| Eltham | 3,121 | 3,102 |
| Waimate West | 2,998 | 2,883 |
| Hawera | 4,772 | 4,852 |
| Patea | 4,007 | 3,837 |
| Waimarino | 2,688 | 2,320 |
| Waitotara | 3,303 | 3,301 |
| Wanganui | 3,614 | 3,504 |
| Rangitikei | 14,000 | 13,954 |
| Kiwitea | 2,362 | 2,338 |
| Pohangina | 1,297 | 1,197 |
| Oroua | 4,610 | 4,561 |
| Manawatu | 7,215 | 7,285 |
| Kairanga | 6,098 | 6,153 |
| Horowhenua | 9,284 | 10,559 |
| Hutt | 20,412 | 29,679 |
| Makara | 10,191 | 16,955 |
| Pahiatua | 2,837 | 2,741 |
| Akitio | 1,189 | 1,182 |
| Eketahuna | 1,923 | 1,819 |
| Mauriceville | 546 | 514 |
| Masterton | 4,125 | 4,129 |
| Wairarapa South | 3,090 | 3,041 |
| Featherston | 3,825 | 3,676 |
| Totals, North Island | 516,961 | 580,520 |
| South Island | ||
| Sounds | 951 | 857 |
| Marlborough | 7,621 | 7,955 |
| Awatere | 1,692 | 1,739 |
| Kaikoura | 3,243 | 3,133 |
| Amuri | 2,981 | 2,931 |
| Cheviot | 1,466 | 1,533 |
| Waimea | 13,511 | 14,101 |
| Golden Bay | 4,057 | 3,676 |
| Buller | 4,568 | 4,089 |
| Murchison | 1,472 | 1,448 |
| Inangahua | 3,357 | 3,083 |
| Grey | 4,969 | 4,765 |
| Westland | 4,537 | 4,407 |
| Waipara | 2,813 | 2,922 |
| Kowai | 2,100 | 2,220 |
| Ashley | 692 | 665 |
| Rangiora | 3,644 | 3,782 |
| Eyre | 1,626 | 1,885 |
| Oxford | 1,637 | 1,582 |
| Tawera | 754 | 746 |
| Malvern | 4,578 | 4,231 |
| Paparua | 13,095 | 15,894 |
| Waimairi | 25,297 | 39,479 |
| Heathcote | 4,824 | 6,074 |
| Halswell | 1,554 | 2,866 |
| Mount Herbert | 605 | 627 |
| Akaroa | 1,962 | 1,823 |
| Chatham Islands | 524 | 487 |
| Wairewa | 915 | 797 |
| Springs | 2,398 | 2,625 |
| Ellesmere | 3,599 | 3,705 |
| Selwyn | 1,658 | 1,703 |
| Ashburton | 11,222 | 11,599 |
| Geraldine | 5,313 | 5,148 |
| Levels | 5,215 | 5,726 |
| Mackenzie | 3,144 | 3,309 |
| Waimate | 6,399 | 6,059 |
| Waitaki | 8,062 | 11,018 |
| Waihemo | 1,099 | 1,003 |
| Waikouaiti | 3,767 | 3,599 |
| Peninsula | 3,677 | 3,677 |
| Taieri | 7,204 | 7,832 |
| Bruce | 3,958 | 3,981 |
| Clutha | 6,121 | 6,118 |
| Tuapeka | 7,579 | 4,746 |
| Maniototo | 2,753 | 2,794 |
| Vincent | 4,807 | 4,008 |
| Lake | 1,812 | 1,830 |
| Southland | 26,674 | 28,669 |
| Wallace | 9,789 | 10,107 |
| Fiord | 11 | 51 |
| Stewart Island | 541 | 536 |
| Totals, South Island | 247,847 | 269,648 |
| Totals, New Zealand counties | 764,808 | 850,168 |
| North Island | ||
| Kaitaia | 2,358 | 2,704 |
| Kaikohe | 2,122 | 2,733 |
| Whangarei | 15,588 | 17,865 |
| Dargaville | 3,306 | 3,737 |
| Helensville | 1,151 | 1,215 |
| East Coast Bays | 7,498 | 9,494 |
| Birkenhead | 5,644 | 7,245 |
| Northcote | 3,777 | 5,183 |
| Takapuna | 18,724 | 20,406 |
| Devonport | 11,179 | 10,949 |
| Henderson | 2,623 | 3,956 |
| Glen Eden | 4,096 | 5,175 |
| New Lynn | 7,547 | 8,773 |
| Auckland (City) | 136,540 | 143,426 |
| Mount Albert | 25,644 | 25,869 |
| Mount Eden | 18,635 | 18,358 |
| Mount Wellington | 11,990 | 16,029 |
| Newmarket | 2,217 | 1,852 |
| Ellerslie | 4,501 | 4,406 |
| One Tree Hill | 12,889 | 12,931 |
| Mount Roskill | 25,549 | 29,910 |
| Howick | 3,974 | 6,394 |
| Onehunga | 16,702 | 16,375 |
| Otahuhu | 8,555 | 8,768 |
| Papatoetoe | 12,021 | 17,912 |
| Manurewa | 4,664 | 10,981 |
| Papakura | 5,235 | 7,999 |
| Pukekohe | 4,689 | 5,787 |
| Waiuku | 1,417 | 1,611 |
| Tuakau | 1,326 | 1,524 |
| Huntly | 4,187 | 4,617 |
| Ngaruawahia | 2,703 | 3,275 |
| Hamilton (City) | 36,629 | 42,166 |
| Cambridge | 4,604 | 5,284 |
| Te Awamutu | 4,614 | 5,423 |
| Otorohanga | 1,917 | 1,997 |
| Te Kuiti | 3,781 | 4,494 |
| Taumarunui | 4,343 | 4,961 |
| Thames | 5,001 | 5,314 |
| Paeroa | 2,871 | 2,896 |
| Waihi | 3,075 | 3,164 |
| Te Aroha | 2,854 | 3,058 |
| Morrinsville | 3,764 | 4,111 |
| Matamata | 2,703 | 3,292 |
| Putaruru | 2,815 | 3,550 |
| Mount Maunganui | 3,432 | 5,082 |
| Tauranga | 11,071 | 13,435 |
| Te Puke | 1,925 | 2,299 |
| Rotorua | 14,579 | 19,362 |
| Taupo | 2,849 | 5,251 |
| Whakatane | 5,525 | 7,169 |
| Kawerau | 2,740 | 4,413 |
| Opotiki | 2,346 | 2,559 |
| Gisborne (City) | 19,661 | 21,769 |
| Wairoa | 3,796 | 4,301 |
| Napier (City) | 21,287 | 24,618 |
| Hastings (City) | 20,244 | 23,371 |
| Taradale | 3,398 | 4,854 |
| Havelock North | 2,643 | 3,621 |
| Waipawa | 1,607 | 1,712 |
| Waipukurau | 2,886 | 3,250 |
| Dannevirke | 5,294 | 5,517 |
| Woodville | 1,439 | 1,529 |
| Waitara | 3,675 | 4,369 |
| New Plymouth (City) | 25,725 | 29,354 |
| Inglewood | 1,682 | 1,884 |
| Stratford | 4,811 | 5,273 |
| Eltham | 2,192 | 2,255 |
| Hawera | 6,973 | 7,537 |
| Patea | 1,898 | 1,991 |
| Ohakune | 1,626 | 1,542 |
| Raetihi | 1,186 | 1,344 |
| Wanganui (City) | 29,864 | 33,341 |
| Taihape | 2,464 | 2,684 |
| Marton | 4,001 | 4,317 |
| Feilding | 6,790 | 8,160 |
| Foxton | 2,525 | 2,627 |
| Palmerston North (City) | 35,792 | 40,998 |
| Shannon | 1,189 | 1,398 |
| Levin | 6,488 | 7,940 |
| Otaki | 2,722 | 2,981 |
| Upper Hutt | 12,226 | 16,894 |
| Lower Hutt (City) | 50,667 | 53,010 |
| Petone | 10,374 | 9,888 |
| Eastbourne | 2,724 | 2,645 |
| Wellington (City) | 122,244 | 123,948 |
| Tawa | 4,043 | 7,192 |
| Pahiatua | 2,322 | 2,577 |
| Eketahuna | 774 | 771 |
| Masterton | 13,000 | 15,121 |
| Carterton | 2,590 | 3,077 |
| Greytown | 1,391 | 1,579 |
| Featherston | 1,197 | 1,476 |
| Martinborough | 1,192 | 1,422 |
| Totals, North Island | 961,091 | 1,080,876 |
| South Island | ||
| Picton | 2,079 | 2,320 |
| Blenheim | 10,366 | 11,942 |
| Nelson (City) | 21,228 | 23,959 |
| Richmond | 2,515 | 3,472 |
| Motueka | 2,824 | 3,310 |
| Westport | 5,522 | 5,464 |
| Runanga | 1,844 | 1,734 |
| Greymouth | 8,948 | 8,877 |
| Brunner | 1,144 | 1,072 |
| Kumara | 505 | 435 |
| Hokitika | 3,032 | 3,005 |
| Ross | 549 | 503 |
| Rangiora | 3,150 | 3,540 |
| Kaiapoi | 2,738 | 3,109 |
| Riccarton | 7,914 | 7,348 |
| Christchurch (City) | 143,115 | 151,333 |
| Lyttelton | 3,589 | 3,403 |
| Ashburton | 10,243 | 11,604 |
| Geraldine | 1,640 | 1,832 |
| Temuka | 2,254 | 2,430 |
| Timaru (City) | 23,336 | 24,816 |
| Waimate | 3,107 | 3,308 |
| Oamaru | 11,088 | 12,401 |
| Hampden | 307 | 303 |
| Palmerston | 878 | 868 |
| Waikouaiti | 631 | 687 |
| Port Chalmers | 3,143 | 3,120 |
| West Harbour | 2,182 | 2,291 |
| Dunedin (City) | 71,277 | 73,226 |
| St. Kilda | 6,946 | 6,633 |
| Green Island | 4,482 | 5,163 |
| Mosgiel | 4,050 | 6,463 |
| Milton | 1,904 | 1,922 |
| Kaitangata | 1,286 | 1,249 |
| Balclutha | 3,323 | 3,928 |
| Tapanui | 669 | 767 |
| Lawrence | 589 | 594 |
| Roxburgh | 794 | 769 |
| Naseby | 189 | 155 |
| Alexandra | 1,823 | 2,292 |
| Cromwell | 885 | 942 |
| Arrowtown | 186 | 171 |
| Queenstown | 1,198 | 1,322 |
| Gore | 6,567 | 7,270 |
| Mataura | 1,850 | 2,085 |
| Winton | 1,287 | 1,473 |
| Invercargill (City) | 31,148 | 35,604 |
| Bluff | 2,693 | 3,003 |
| Riverton | 1,171 | 1,225 |
| Totals, South Island | 424,188 | 454,742 |
| Totals, New Zealand cities and boroughs | 1,385,279 | 1,535,618 |
| (a) TOWN DISTRICTS NOT FORMING PARTS OF COUNTIES | ||
| North Island | ||
| Kawakawa | 758 | 935 |
| Hikurangi | 1,007 | 966 |
| Kamo | 1,013 | 1,598 |
| Warkworth | 883 | 989 |
| Murupara | 762 | 1,560 |
| Ohura | 575 | 656 |
| Manaia | 718 | 815 |
| Waverley | 859 | 890 |
| Manunui | 877 | 950 |
| Mangaweka | 342 | 332 |
| Hunterville | 581 | 596 |
| Totals, North Island | 8,375 | 10,287 |
| South Island | ||
| Wyndham | 636 | 679 |
| Lumsden | 592 | 666 |
| Nightcaps | 650 | 686 |
| Otautau | 796 | 806 |
| Totals, South Island | 2,674 | 2,837 |
| Totals, New Zealand independent town districts | 11,049 | 13,124 |
| (b) TOWN DISTRICTS FORMING PARTS OF COUNTIES | ||
| (The parent county is shown in parentheses) | ||
| North Island | ||
| Kohukohu (Hokianga) | 239 | 194 |
| Rawene (Hokianga) | 463 | 472 |
| Russell (Bay or Islands) | 617 | 569 |
| Mercer (Franklin) | 310 | 234 |
| Te Kauwhata (Waikato) | 677 | 758 |
| Ohaupo (Waipa) | 323 | 329 |
| Kihikihi (Waipa) | 747 | 1,026 |
| Te Karaka (Waikohu) | 392 | 473 |
| Patutahi (Cook) | 254 | 244 |
| Kaponga (Eltham) | 510 | 517 |
| Normanby (Hawera) | 478 | 528 |
| Totals, North Island | 5,010 | 5,344 |
| South Island | ||
| Edendale (Southland) | 561 | 600 |
| Totals, South Island | 561 | 600 |
| Totals, New Zealand dependent town districts | 5,571 | 5,944 |
| County Town | 1961 Census* (Preliminary Figures) |
|---|---|
| * No comparable figures available for 1956. | |
| (Population is also included in that of the parent county, which is given in parentheses) | |
| North Island | |
| Awanui (Mangonui) | 151 |
| Kerikeri (Bay of Islands) | 278 |
| Moerewa (Bay of Islands) | 757 |
| Paihia (Bay of Islands) | 448 |
| Te Kopuru (Hobson) | 582 |
| Kaiwaka (Otamatea) | 318 |
| Maungaturoto (Otamatea) | 565 |
| Ruawai (Otamatea) | 590 |
| Leigh (Rodney) | 163 |
| Wellsford (Rodney) | 1,136 |
| Green Bay (Waitemata) | 1,198 |
| Kelston West (Waitemata) | 2,545 |
| Titirangi (Waitemata) | 4,482 |
| Glenfield (Waitemata) | 5,706 |
| Beachlands (Manukau) | 465 |
| Bucklands and Eastern Beaches (Manukau) | 1,943 |
| Mangere Bridge (Manukau) | 4,029 |
| Mangere East (Manukau) | 4,869 |
| Pakuranga (Manukau) | 1,596 |
| Raglan (Raglan) | 1,022 |
| Rotowaro (Raglan) | 527 |
| Kawhia (Otorohanga) | 324 |
| Piopio (Waitomo) | 457 |
| Whitianga (Coromandel) | 610 |
| Whangamata (Thames) | 393 |
| Waihi Beach (Ohinemuri) | 545 |
| Tirau (Matamata) | 602 |
| Tokoroa (Matamata) | 7,054 |
| Athenree (Tauranga) | 83 |
| Greerton (Tauranga) | 4,680 |
| Katikati (Tauranga) | 995 |
| Maketu (Tauranga) | 509 |
| Ngongotaha (Rotorua) | 1,628 |
| Takapau (Waipawa) | 558 |
| Otane (Patangata) | 395 |
| Porangahau (Patangata) | 225 |
| Urenui (Clifton) | 265 |
| Oakura (Taranaki) | 283 |
| Okato (Taranaki) | 369 |
| Midhurst (Stratford) | 347 |
| Waitotara (Patea) | 149 |
| Otamatea (Wanganui vicinity) (Waitotara) | 349 |
| Putiki (Wanganui) | 348 |
| Ratana (Rangitikei) | 429 |
| Bulls (Rangitikei) | 1,215 |
| Ashhurst (Oroua) | 641 |
| Foxton Beach (Manawatu) | 819 |
| Himatangi Beach (Manawatu) | 81 |
| Rongotea (Manawatu) | 369 |
| Sanson (Manawatu) | 325 |
| Tangimoana Beach (Manawatu) | 185 |
| Waikanae (Horowhenua) | 1,090 |
| Waitarere (Horowhenua) | 232 |
| Paekakariki (Hutt) | 1,679 |
| Plimmerton-Paremata (Hutt) | 2,964 |
| Wainuiomata (Hutt) | 8,038 |
| Porirua (Makara) | 9,618 |
| Takapuwahia (Porirua Pa) (Makara) | 373 |
| Titahi Bay (Makara) | 5,867 |
| Totals, North Island | 88,463 |
| South Island | |
| Havelock (Marlborough) | 290 |
| Kaikoura (Kaikoura) | 1,328 |
| Waimangaroa (Buller) | 338 |
| Karoro (Grey) | 428 |
| Hornby (Paparua) | 5,669 |
| Sockburn (Paparua) | 4,793 |
| Akaroa (Akaroa) | 630 |
| Leeston (Ellesmere) | 769 |
| Southbridge (Ellesmere) | 477 |
| Andrewville (Geraldine) | 324 |
| Winchester (Geraldine) | 247 |
| Fairlie (Mackenzie) | 844 |
| Brighton (Taieri) | 885 |
| Fairfield (Taieri) | 914 |
| Middlemarch (Taieri) | 240 |
| Waldronville (Taieri) | 506 |
| Benhar (Bruce) | 277 |
| Stirling (Bruce) | 243 |
| Owaka (Clutha) | 403 |
| Clinton (Clutha) | 489 |
| Kaka Point (Clutha) | 90 |
| Ranfurly (Maniototo) | 850 |
| Wanaka (Lake) | 360 |
| Balfour (Southland) | 246 |
| Grassmere (Southland) | 1,245 |
| Waikiwi (Southland) | 1,962 |
| Ohai (Wallace) | 967 |
| Tuatapere (Wallace) | 869 |
| Totals, South Island | 26,683 |
| Totals, New Zealand county towns | 115,146 |
In addition to the above population there were 9,210 people on islands outside county boundaries, on board ships, or in transit on night express trains and steamer expresses.
The islands outside county boundaries include Waiheke Island (Waiheke Road District) with a population of 2,053.
The total population of New Zealand as recorded at the 1961 census was 2,414,064.
For the North Island the total was 1,684,139, and for the South Island 729,925.
[Obtainable from the Government Printer, Corner of Rutland and Lorne Streets (P.O. Box 5344) Auckland; Lambton Quay, Wellington; and 112 Gloucester Street (P.O. Box 1721), Christchurch.]
| Title | Latest No. | Date of Issue | Price per Copy (Post Free) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * £2 10s. a year (post free). | ||||
| s. | d. | |||
| Annual Report of the Department of Statistics (H. 39) | 1961 | June 1961 | 1 | 6 |
| New Zealand Official Yearbook | 1961 | August 1961 | 17 | 6 |
| Pocket Digest of New Zealand Statistics | 1961 | May 1961 | 5 | 0 |
| Statistical Publications 1840–1960 | April 1961 | 9 | 6 | |
| Annual Statistical Reports: | ||||
| Balance of Payments | 1959–60 | October 1960 | 5 | 6 |
| External Trade Statistics, Report on and Analysis of | 1958 | May 1960 | 15 | 6 |
| Farm Production Statistics | 1958–59 | June 1960 | 11 | 6 |
| Income and Income Tax Statistics for the Income Year | 1957–58 | January 1961 | 10 | 6 |
| Industrial Accidents Statistics | 1959 | March 1961 | 7 | 6 |
| Industrial Production Statistics | 1958–59 | October 1960 | 30 | 0 |
| Insurance Statistics | 1959–60 | February 1961 | 5 | 6 |
| Justice Statistics | 1959 | December 1960 | 10 | 6 |
| National Income and Expenditure | 1959–60 | September 1960 | 4 | 6 |
| Special Supplement: The Accounts of the Government Sector | 1956–57 to 1959–60 | January 1961 | 6 | 6 |
| Population, Migration, and Buildings Statistics | 1959–60 | December 1960 | 8 | 6 |
| Prices, Wages, and Labour Statistics | 1959 | October 1960 | 13 | 6 |
| Shipping and Other Transport Statistics | 1959 | June 1960 | 8 | 6 |
| Vital Statistics | 1960 | July 1961 | 7 | 6 |
| Inter-industry Study of the New Zealand Economy | 1954–55 | June 1959 | 5 | 6 |
| Local Authorities Handbook of New Zealand | 1958–59 | September 1960 | 17 | 6 |
| Monthly Abstract of Statistics* | 5 | 0 | ||
| Supplements: | ||||
| Changes in Age Distribution of New Zealand Male Population (September Abstract) | ... | October 1958 | - | - |
| Compound Interest Tables (October Abstract) | ... | November 1959 | - | - |
| Factory Production Statistics (March Abstract) | 1959–60 | April 1961 | - | - |
| Import Prices and Volume Index Numbers (June Abstract) | July 1961 | - | - | |
| Industrial Classification of Salary and Wage Payments (June Abstract) | 1959–60 | July 1961 | - | - |
| Livestock Numbers and Other Farm Statistics (February Abstract) | 1960 | March 1961 | - | - |
| Manufacturers' Stocks (Quarterly Issue) | Mar Quarter | June 1961 | - | - |
| National Income and Expenditure (August Abstract) | 1959–60 | August 1960 | - | - |
| New Zealand Prices and Wages Index Numbers 1913–1957 (April Abstract) | ... | May 1958 | - | - |
| Normal Seasonal Variation of Temperature in New Zealand (March Abstract) | ... | April 1959 | - | - |
| Retail Trading Statistics (Quarterly Issue) | Mar Quarter | June 1961 | - | - |
| Survey of Dairy Farmers' Incomes (May Abstract) | 1958–59 | August 1960 | - | - |
| Survey of Sheep Farmers' Incomes (March Abstract) | 1958–59 | March 1961 | - | - |
| Survey of Town Milk Producers' Incomes (May Abstract) | 1958–59 | October 1960 | - | - |
| Wholesale Trading Statistics (Quarterly Issue) | Mar Quarter | June 1961 | - | - |
| Special Supplements: | ||||
| Consumer's Price Index, 1955 Revision (November Abstract) | ... | December 1956 | 3 | 0 |
| New Zealand Tables of Working Life (February Abstract) | 1951 | March 1957 | 2 | 0 |
| Remarriage and Length of Widowhood of New Zealand Widows, 1955–57 (May Abstract) | ... | June 1961 | 2 | 0 |
| Agricultural and Pastoral Statistics of New Zealand, 1861–1954 | ... | July 1956 | 2 | 0 |
| Final Report on the Census of Farm Production | 1949–50 | May 1956 | 11 | 6 |
| Census of Distribution, 1958 | 1958 | August 1959 | 10 | 6 |
| Census of Libraries, 1959 | 1959 | March 1960 | 7 | 6 |
| Volumes of 1956 Census Results: | ||||
| Vol. I. Increase and Location of Population | 1956 | March 1958 | 16 | 6 |
| Vol. II. Ages and Marital Status | 1956 | February 1959 | 17 | 6 |
| Vol. III. Religious Professions | 1956 | February 1959 | 5 | 6 |
| Vol. IV. Industries and Occupations | 1956 | January 1960 | 19 | 6 |
| Vol. V. Incomes | 1956 | June 1959 | 5 | 6 |
| Vol. VI. Birthplace and Duration of Residence of Overseas-born | 1956 | May 1959 | 4 | 6 |
| Vol. VII. Race | 1956 | October 1959 | 5 | 6 |
| Vol. VIII. Maori Population and Dwellings | 1956 | April 1960 | 13 | 6 |
| Vol. IX. Dwellings and Households | 1956 | April 1959 | 12 | 6 |
| Vol. X. General Report (including Details of War Service, Dependent Children, and Usual Place of Residence) | 1956 | December 1960 | 17 | 6 |
| Appendix A. Census of Poultry | 1956 | February 1958 | 4 | 6 |
| Appendix B. New Zealand Life Tables, 1955–57 | 1956 | January 1961 | 4 | 6 |
| Interim Returns of Population and Dwellings | 1956 | November 1956 | 4 | 6 |
NOTE - Where more than one reference to a subject is given, the chief reference, wherever it has been possible to determine it, is indicated by bold type. Two or more references to a subject so indicated signify major, and approximately equal, importance.
A
- Abortion, 116, 127, 133, 139.
- Accident Insurance, 962–966, 1161.
- State, 976–977.
- Accidents -
- Aircraft, 118, 136.
- Cases Treated in Hospitals, 136.
- Causes of, 1058.
- Deaths from, 78, 112, 117–119, 124, 341, 355–357, 484, 1056–1057, 1060–1063.
- Farming, 119.
- Frequency Rates, 1052–1053.
- Industrial, 1047–1063.
- Mining, 119, 484, 485, 1055, 1056, 1062.
- Motor-vehicle, 78, 112, 117, 118, 124, 353–357.
- Railway, 118, 136, 341, 355.
- Time Lost Through, 1060.
- Tramway, 118, 355.
- Transport, 117, 118, 136, 355–357.
- Acclimatisation of Fishes, 5, 479.
- Accommodation, Financial Assistance for, 161–162.
- Accommodation Licences, 1116–1119.
- Accounts of the Government Sector, 764.
- Accounts, Public, 788–801.
- Accounts, Sector, and Inter-Industry Studies, 787.
- Acreage and Yield of Crops, 422–439, 1143.
- Acreage of Holdings, 285–286.
- Acts Passed in 1960, 1125–1127.
- Added Value in Manufacturing, 497–505, 518–520, 523, 524, 525, 529–545, 1151.
- Administration, 35–36.
- Cook Islands, 1074–1075.
- Niue Island, 1079.
- Western Samoa, 1083–1084.
- Adolescent Dental Service, 145.
- Adoptions, 89–90.
- Adult Education, 243–244.
- Adultery, 96, 98.
- Advances -
- Bank, 884, 887–893, 1156.
- Bank Control Policy, 891–893.
- Building Societies, 939–943.
- Rural, 293–294, 932–938.
- State (see State Advances and State Aid).
- Advertisements, Medical, 141.
- Advertising by Radio, 379–384.
- Aerated Water and Cordial Industry, 502, 533.
- Aerial Land, Surveys, 306, 366.
- Aerial Work Operations, 365–366.
- Aero Clubs, 369.
- Aerodromes, 274, 275, 369.
- Afforestation, 450–458, 462.
- Companies, 450, 462.
- Age Benefits, 176, 177, 178–179, 193.
- Age Distribution of Population, 59.
- Ages of -
- Cancer Decedents, 115.
- Infants Dying, 106–107, 125.
- Injured Employees, 1058.
- Maoris Dying, 122, 125.
- Mental Hospital Patients, 166, 170.
- Migrants, 63.
- Mothers or Parents, 85, 86, 88, 89.
- Offenders Probationed, 260.
- Patients in Public Hospitals, 131.
- Persons Dying, 101–103, 122, 125.
- Persons Married, 93–95.
- Population, 59.
- Prisoners, 263.
- Public School Pupils, 224, 226.
- Tubercular Decedents, 113.
- Aggregation of Incomes, 866.
- Agricultural and Pastoral Production, 395–449, 1143, 1144.
- Persons Engaged in, 1025.
- Value of, 395–401.
- Volume of, 397, 401.
- Agricultural Aviation, 295, 365–366.
- Agricultural Machinery, 421–422, 505, 545.
- Imports of, 692.
- Agricultural Produce -
- Consumed Locally, 399, 739–741.
- Exported, 399, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675.
- Gross Farming Income, 395–398.
- Agricultural Workers Act, 984.
- Agriculture, 395–422.
- Department of, 415–416.
- Occupational Safety, 1070–1071.
- Research in, 415–418, 428, 429, 439.
- Aids, Artificial, 192, 194.
- Aids, Nursing, 151.
- Air Force, 273–275, 276, 277.
- Casualties, 277.
- Expenditure on, 275, 794.
- Air Mails, 362–368, 371.
- Air Pollution, 142.
- Air Training Corps, 274.
- Air Transport and Aviation, 273–275, 361–369.
- Aircraft, 275, 361–369.
- Accidents, 118, 136.
- Licensing and Control, 361–369.
- Aitutaki Island, 2, 1073, 1075.
- Alcoholic Liquors -
- Consumption of, 740.
- Duty on, 699–703, 802, 805.
- Exports of, 653, 655.
- Imports of, 678, 686, 694.
- Sale of, 1116–1119.
- Alexander Turnbull Library, 1169.
- Aliens, Naturalisation and Registration of, 68–70, 1224.
- Alps, 2–3.
- Aluminium Industry, 494.
- Ambassadors, 1134–1138.
- Ambulance, St. John, 154.
- Amortisation of Debt, 793, 797, 836–837, 845.
- Amputees, 197.
- Amusement Tax, 391, 393, 394, 802, 823, 825.
- Angling, 479, 1098.
- Animal Life, 17.
- Animals, Noxious, 455, 459.
- Anniversary Days, 1120.
- Annual Holidays Act, 981.
- Annuities, 193, 203–205, 958.
- Antarctic, New Zealand Activities in the, 1090–1092, 1169.
- Ante-natal Services, 161.
- Antimony Ore, 487.
- Antipodes Islands, 1, 1073.
- AnzacDay, 981.
- Apiaries or Apiculture, 434, 449.
- Apparel, Duty on, 700.
- Apples, 425, 436–437.
- Consumption of, 739.
- Exported, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148.
- Fixation of Prices of, 594–595.
- Marketing of, 594–595.
- Apprentices, 279, 1011–1012.
- Appropriation, Expenditure under, 793–794.
- Arbitration (see Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration).
- Area-
- In Crops, 422–439, 1143.
- In Cultivation, 286, 424–433.
- Of Land Holdings, 285, 286.
- Of New Zealand, 1–2, 60, 285, 405.
- Of Properties Transferred, 290–292.
- Of Provincial Districts, 50.
- Top-dressed, 419.
- Armed Forces-
- Casualties in, 277.
- Demobilisation of, 284.
- Honours and Awards Conferred, 1128, 1129.
- Overseas at Census Dates, 45.
- Pay and Allowances, 748, 757, 761, 762.
- Serving Overseas, 268, 270, 272–273, 275.
- Strengths of, 267, 269, 273, 275, 276, 1013.
- Army, 270–273, 275–277.
- Expenditure on, 273, 794.
- Arrivals (see Migration).
- Arson and Incendiarism, 973.
- Art Galleries, 1099.
- Art Unions, 1109.
- Articles on Special Subjects in Previous Issues, 1168–1169.
- Artificial Aids, 192, 194.
- Artificial Limbs, 192.
- Asbestos, 489.
- Assessable Income, 856–877.
- Assessment of-
- Income Tax, 806–816, 856–872.
- Land Tax, 816.
- Land Values, 311.
- Assets of-
- Bankrupts, 1105, 1160.
- Banks, 884, 887, 896–898, 908, 1156, 1216.
- Building Societies, 943.
- Companies, 878–879.
- Electric-power Undertakings, 580.
- Fire Insurance Companies, 967–968.
- Friendly Societies, 210.
- Life Assurance Companies, 961.
- Local Government, 847–848, 1213.
- Manufacturing Industries, 521–522.
- Atafu Islands, 2, 1081–1082.
- Atiu Island, 2, 1073, 1075.
- Auckland -
- Broadcasting Stations, 380, 381.
- Building Values, 562.
- Climate, 15, 16.
- Houses and Flats, New State, 563.
- Population, 53, 54, 56.
- Sales Tax Receipts, 826.
- Shipping, 318, 321–325, 673, 696.
- Television Station, 385.
- Trustee Savings Bank, 906–908.
- University of, 236–237.
- Urban Transport, 359, 360.
- Auckland Islands, 1, 1073.
- Audit of Expenditure, 788.
- Australia -
- Birth and Natural Increase Rates, 83.
- Consumption of Foodstuffs, 738, 741.
- Debt Domiciled in, 833, 851, 1153.
- Libraries, 389.
- Motor Accident Death and Injury Rates, 357.
- New Zealand Representatives in, 1134.
- Population, 75.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices in, 712.
- Reciprocal Trade with, 705.
- Representatives in New Zealand, 1136.
- Social Security Reciprocity with, 174, 175, 176, 187.
- Automobiles (see Motor Vehicles).
- Aviation, Agricultural, 295, 365–366.
- Aviation and Air Transport, 273–275, 361–369.
- Awards; Cultural, 1100–1101.
- Awards to Armed Forces Personnel, 1130.
B
- Bachelors Marrying, 93.
- Bacon and Ham, Consumption of, 739.
- Bacon and Ham Curing, 502, 530.
- Balance of Payments, 764–787.
- Capital Account, 765, 772, 775, 777, 779, 781.
- Current Account, 765, 769–771, 776, 778, 780.
- Merchandise Transactions, 773–774.
- Regional Accounts, 774–782.
- Survey of Companies with Overseas Affiliations, 782–787.
- Balance of Trade, 636.
- Bananas, 596, 1076, 1077, 1080, 1087.
- Consumption of, 739.
- Imports of, 685, 694, 697.
- Bank Notes, 882–887, 895–896, 918–919.
- Denominations of, 896, 919.
- In Circulation, 895–896, 912–913, 1156.
- Bank of New Zealand, 830, 838, 885–886.
- Banking and Currency, 880–922, 1156, 1157, 1215–1217.
- Bankruptcy, 994, 1104–1109, 1160.
- Banks, Overseas Assets of, 887, 896–898, 1216.
- Banks, Savings-
- Post Office, 902–906, 915–916, 1157, 1216.
- School, 905–906.
- Trustee, 906–908, 1216.
- Barley, 424–427, 430–431, 439.
- Beds, Hospital, 159, 160.
- Beef-
- Cattle, 444.
- Cattle Farms, 446.
- Chilled, 608, 609, 674, 675.
- Consumption of, 738, 739.
- Export of, 592, 674, 675.
- Slaughterings for, 413, 529.
- Beer-
- Consumption of, 740.
- Duty on, 700, 701, 703, 792, 802, 805.
- Production of, 533.
- Bees, 449.
- Benefits, Social Security, 145, 173, 176–195, 744, 755, 757, 799.
- Bentonite, 480, 489.
- Beverages, Production of, 506–527, 533.
- Bibliography-
- General, 1170–1185.
- New Zealand Flora and Fauna, 16–17.
- Bills, Treasury, 828, 833.
- Births, 76, 80–90, 1140.
- Excess of, over Deaths, 50, 77, 82.
- In Cook Islands, 1075.
- In Niue Island, 1079.
- In Western Samoa, 1084.
- Of Maoris, 76, 120–121.
- Biscuit Industry, 502, 532.
- Bituminous Coal, 480–483.
- Blind, Benefits for and Education of, 182, 187, 221, 279.
- Board of School Children, 232.
- Board of Trade, 649–650, 698.
- Bobby Calves, 413.
- Boilers, Inspection of, 1066.
- Bonds, National Savings, 827–828, 908–909.
- Books, Library, 387–389.
- Boroughs, 40, 41, 840–855.
- Area of, 56–57.
- Bridges in, 342.
- Capital and Unimproved Values, 313.
- Debt, 847, 850, 851, 1155.
- Employees of, 855.
- Housing, 551, 563.
- Milage of Streets, 341.
- Population, 56–58.
- Borstal Institutions, 253, 256, 261, 263.
- Boundaries of New Zealand, 1.
- Bounty Islands, 1, 1073.
- Bread Subsidy, 742.
- Breeding Bulls, 444.
- Breeding Ewes, 440.
- Breeding Sows, 440, 441, 446.
- Breweries, 502, 533.
- Brick Production, 541.
- Brides and Grooms, 92–95.
- Bridges, 332, 342.
- Bridle-tracks, 341.
- Brigades, Fire, 459, 975.
- British Countries, Representatives in New Zealand, 1136–1138.
- British Nationality, 68.
- British Phosphate Commission, 838, 1089.
- British Postal Orders, 373.
- British Preference, 703–706.
- British Sovereignty, 22.
- British Trade Representatives, 1138.
- Broadcasting, Radio, 379–385.
- For Schools, 236, 382.
- Time Signals, 382, 1120.
- Bronze Coinage, 917.
- Building, 546–568.
- Persons Engaged in, 1013, 1015, 1016.
- Wages and Hours Worked of Employees, 1002, 1008.
- Building and Housing Construction and Tenancy, 546–568, 932–939.
- Group Building Scheme, 549.
- Building Costs, 546, 558.
- Building Materials, 546–549.
- Imports of, 548–549, 680.
- Building Permits, 558–564.
- Building Societies, 939–943.
- Deposits, 916, 941, 943.
- Buildings, Education, 222–223.
- Bulk Purchase Agreement, 593.
- Bullion, Exports of, 652, 654, 674, 675, 1147.
- Bullion Production, 5, 487.
- Burials, 99, 141.
- Bursaries-
- Dental, 145, 239.
- Department of Health, 138.
- Ex-servicemen's, 239, 280.
- Ex-servicemen's Children, 199, 280.
- Medical, 239.
- Physical Education, 234.
- Post-primary Teachers', 234.
- Secondary Schools, 231.
- Technical Schools, 231.
- University, 238–240.
- Bush, 16, 287, 450–456.
- Bushel Units, Weights of, 425.
- Business, Census of, 611–620.
- Business Failures, 994, 1104–1109, 1160.
- Business Loans, 935–937.
- For Ex-servicemen, 287–284.
- Butter (see Dairy Produce).
- Butterfat Production, 408–410 530, 1150.
- Butterfat Yields, 408, 409.
C
- Cabinet, 35–36.
- Cable Tramway, 360.
- Cables, Ocean, 376.
- Cadets-
- Army, 272.
- Navy, 269.
- Calf-skins Exported, 653, 654, 669, 674, 675, 1149.
- Calves Slaughtered, 413.
- Campbell Island, 1, 44, 1073.
- Camps, Health, 143, 153.
- Canada-
- Consumption of Foodstuffs, 738, 741.
- Exchange Rate with, 920.
- Libraries, 389.
- New Zealand Representatives in, 1134.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices in, 712.
- Reciprocal Trade with, 705.
- Representatives in New Zealand, 1136.
- Canadian Pacific Air Lines, 368.
- Cancer, 78, 112, 113–115, 123, 132.
- Candle and Soap Industry, 504, 539.
- Canned and Preserved Meats, etc., Production of, 529.
- Canned Fish-
- Exports of, 477.
- Imports of, 685, 694.
- Canned Fruits-
- Consumption of, 739.
- Imports of, 685, 694.
- Production of, 533.
- Canned Meat Exported, 653, 654, 666, 674, 675.
- Canned Vegetables-
- Consumption of, 739.
- Exports of, 653, 655, 674, 675.
- Production of, 533.
- Canterbury Agricultural College, 216, 218, 240.
- Capital-
- Expenditure of Government, 795.
- Invested in Electric-power Undertakings, 577–580.
- Invested in Manufacturing Industries, 521–522.
- Invested in Railways, 332, 1159.
- Invested in Telegraph Construction, 373.
- Invested in Telephone Construction, 375.
- Of Banks, 880, 885.
- Of Companies, 944–945.
- Capital Formation, 745–752.
- Capital Issues Control, 921.
- Capital Transfers, 899, 900.
- Capital Value of Land, 309–314.
- Rating on, 840–841.
- Cargo Carried by Air Transport, 362–368.
- Cargo Handled at Ports, 315–327.
- Carnegie Corporation, 243.
- Carpets and Rugs, Imports of, 687.
- Carton, Paper Bags, etc., Industry, 537.
- Casein Exported, 653, 654, 670, 674, 675.
- Casein Produced, 410, 530.
- Cash Order Trading, 629.
- Cassiterite, 487.
- Casualties in War, 277.
- Casualties, Shipping, 330.
- Catchment Boards, 41, 294, 458, 840–855.
- Cattle, 440, 444–446, 1144.
- Cattle Hides Exported, 653, 654, 669, 674, 675, 1149.
- Cattle Slaughtered, 413.
- Causes of-
- Accidents, 1058.
- Deaths, 78, 106–120, 123–126.
- Fires, 973.
- Industrial Disputes, 1043–1044, 1046.
- Infant Mortality, 108–110.
- Maori Deaths, 123–126.
- Mental Disorders, 169.
- Still-birth, 110.
- Cement-
- Carried on Railways, 339.
- Exports of, 652, 654.
- Imports of, 688, 695.
- Industry, 504, 541.
- Production of, 541.
- Cemeteries, 141.
- Census, 37, 45, 50–53, 60–61, 88, 1225–1228.
- Employment Statistics, 1024–1025.
- Incomes of Individuals, 879.
- Of Agriculture, 286, 407–408, 423, 434, 442.
- Of Distribution, 611–620.
- Of Dwellings, 552–554.
- Of Libraries, 387–389.
- Of Poultry, 447–448.
- Of Religions, 73–74.
- Publications, 1230.
- Unemployment Statistics, 1023.
- Central Reserve Bank (see Reserve Bank).
- Cereals, 422–431, 1143.
- Consumption of, 741.
- Certificates-
- Dentists' Practising, 150–151.
- Enginedrivers' 1067.
- Land titles, 289.
- Marine Officers', 328–329, 987.
- Medical Practitioners', 150.
- Mine Officials', 1067.
- Naturalisation, 68–69.
- Occupational Therapists', 152.
- Opticians', 152.
- Physiotherapists', 151.
- Plumbers', 152.
- Teachers', 220.
- Certification of Seed, 439.
- Certification of Trades, 220, 221.
- Charitable Aids, 161.
- Chatham Islands, 1, 376, 1088–1089, 1185.
- Schools, 218, 232.
- Cheese (see Dairy Produce).
- Chemicals and Chemical Products Industry, 504, 506–527, 539–540.
- Chemists, Registration of, 153.
- Child Health, 142–144.
- Child Migration, 65.
- Child Welfare, 142–144, 153–154, 221, 240–242, 258.
- Childbirth, Accidents, etc., of, 78, 108, 110–111, 112, 116–117, 124, 127, 133, 139.
- Children-
- Adopted, 89–90.
- Affected by Divorce Proceedings, 98.
- Allowances in Respect of, 174–197.
- Born, Numbers and Rates, 76, 81–82, 121.
- Born, Sexes of, 83–85, 90, 121.
- Crippled, 153, 231.
- Dental Treatment of, 144.
- Dependent, 72–73.
- Fathers' Income Group, 868.
- Handicapped, 143, 217, 240–242.
- Intellectually Handicapped, 162.
- Legitimated, 89.
- Medical Inspection of, 143.
- Offences by, 240–242, 258–259.
- Under One, Deaths of, 79, 101, 102, 105–110, 124–126, 1140.
- Children's Courts, 240–242, 258–259.
- Children's Homes, 162, 241.
- Chilled Beef, 608, 609, 674, 675.
- Chinese, 1084, 1089.
- Christchurch-
- Broadcasting Stations, 380, 381.
- Building Values, 562.
- Climate, 15, 16.
- Houses and Flats, New State, 563.
- Population, 53, 54, 57.
- Sales Tax Receipts, 826.
- University of Canterbury, 236–237.
- Urban Transport, 357, 358, 359.
- Churches, 95–96.
- Cigarettes and Tobacco-
- Duty on, 699, 701, 703.
- Imports of, 678, 686, 694.
- Production of, 438, 502, 506–527, 534.
- Cinematograph Film-hire Tax, 792, 802, 825.
- Cinematograph Films, 1069.
- Cinematograph Theatres, 390–394.
- Cinnabar, 487.
- Cities, Population of, 54, 56, 57.
- Citizenship, 68.
- Citrus Fruits, 425, 436–437, 596, 1076, 1077.
- Consumption of, 739.
- Imports of, 694, 697.
- Civil Aviation, 361–369.
- Civil Law Cases, 247–251.
- Civil List, 34, 35, 793.
- Claims, Insurance, 955–978.
- Clays, 404, 480.
- Clergy of Each Church, and Marriages by, 95–96.
- Climate, 2–3, 8–16, 1097.
- Cook Islands, 1073.
- Niue Island, 1078.
- Western Samoa, 1083.
- Clinics-
- Ante-natal, 161.
- School Dental, 144.
- Clocks, Public, 1120.
- Closing Hours of Shops, 983.
- Clothing and Footwear, Retail Prices of, 710–711.
- Clothing, Imports of, 679.
- Clothing Industry, 502–503, 534–535.
- Clover Seed (see Grass and Clover Seed).
- Club Charters, 1118.
- Clubs, Aero, 369.
- Clubs, Agricultural, 233.
- Clubs, Rifle, 273.
- Clubs, Working-men's, 209.
- Coal-
- Carried on Railways, 339, 340.
- Consumption of, 485, 514–515, 585.
- Exports of, 652, 654, 674, 675.
- Production of, 480, 484.
- Research, 486, 490.
- Resources, 482–483.
- Coal Mines Act, 482, 1067.
- Coal Mining, 454, 480–486.
- Disputes, 1042, 1043.
- Wages and Hours Worked of Employees, 1003, 1007.
- Welfare and Research Fund, 486.
- Coastline, 2.
- Coastal Shipping, 320, 323–326.
- Coastal Vessels Registered, 328.
- Cocoa Beans, Imports of, 686, 694.
- Coffee Beans, Imports of, 686, 694.
- Coin Held by Banks, 884, 887.
- Coin Imported and Exported, 646, 1145.
- Coin in Circulation, 913.
- Coinage and Currency, 917–919.
- Colleges-
- Agricultural, 216, 218, 240.
- Military, 271.
- Naval, 269.
- Pharmacy, 153.
- Teachers' Training, 216, 220, 233–234.
- Collieries, 480–486.
- State, 485.
- Colombo Plan, 29–30.
- Commerce, Overseas, 632–707, 1145–1149, 1205–1207.
- Commercial Failures, 994, 1104–1109, 1160.
- Commodities, Consumption of, 734–742.
- Commodity Sales, Retail, 614, 621–623.
- Commodity Sales, Wholesale, 617.
- Community Centres, 154, 244.
- Companies-
- Assets of, 878–879.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Bank Advances to, 890.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Cooperative Dairy, 411.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Deposits with, 911–912, 916.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Financial Statements, Analysis of, 946–954.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Income of, 748–763, 857, 870–877.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Joint Stock, 876, 944–954.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Overseas, 945, 968, 971.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Paid-up Capital, 875–877.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Private, 876, 945–946.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Registered, 944–945, 1160.
- Share Prices Indices, 729–733.
- Taxation of, 175, 813, 857, 870–877.
- Comparisons with Other Countries-
- Birth and Natural Increase Rates, 83.
- Cinema Attendance, 392.
- Consumption of Foodstuffs, 740–741.
- Dairy Produce Consumption, 738.
- Death Rates, 78, 101.
- Expectation of Life, 105.
- External Trade Per Head, 636.
- Infant-mortality Rates, 79, 105–106.
- Libraries, 389.
- Marriage Rates, 92.
- Motor Accident Death and Injury Rates, 357.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices, 712.
- Suicide Rates, 120.
- Telephones to Population, 374.
- Compensation, Workers', 1047–1055.
- Compulsory Insurance, 977, 1050.
- Compulsory Unionism, 1031.
- Conciliation Council, 1034–1035.
- Concrete Products Industry, 504, 542.
- Confectionery Industry, 532.
- Confinement, Deaths in, 78, 108, 112, 116–117, 124, 133.
- Confinements, 84, 86, 89.
- Conjugal Condition of Persons Marrying, 92–93.
- Conjugal Rights, Restitution of, 96, 98.
- Conservation of Forests, 450–451.
- Conservation of Soil, 294–295, 458.
- Consolidated Fund, 175, 791–794, 802–804, 1152, 1210–1211.
- Constitution, 30.
- Of Local Districts, 39–40.
- Construction Act, 985–986.
- Construction, Building, and Housing, 546–568, 932–939.
- Wages and Hours Worked of Employees, 1002, 1008.
- Consuls, 1135–1138.
- Consumer Council, 709–710.
- Consumer Credit, Survey of, 628–631.
- Consumers' Goods, Imports of, 680, 681, 682.
- Consumers' Price Index, 713–722, 1169, 1208.
- Consumption of-
- Coal, 485, 514–515, 585.
- Commodities, 734–742.
- Electricity, 569, 580–581.
- Farm Produce, 398–399, 411, 412, 429, 738–741.
- Motor Spirits, 348–349.
- Wheat, 429.
- Wool, 413, 534.
- Contact Lenses, 192.
- Contagious Diseases, 78, 108, 109, 112, 123, 123, 127–133, 139.
- Contractors' Liens, 993.
- Contributory Negligence Act, 1051.
- Control of-
- Bank Advances, 891–893.
- Capital Issues, 921.
- Exchange, 642, 898, 919.
- Exports, 593, 646.
- Imports, 646–649, 701.
- Poultry, 448.
- Prices, 708–709.
- Rivers, 294–295.
- Convictions-
- For Drunkenness, 252, 253, 254, 257.
- For Traffic Offences, 252, 253–254.
- Of Juveniles, 258–259.
- Of Maoris, 258.
- Of Women, 251, 254, 255, 258.
- Convictions in Magistrates' Courts, 250–254, 258, 1142.
- Convictions in Supreme Court, 255–256, 258, 1142.
- Cook Islands, 1–2, 66, 203, 1073–1078.
- Bibliography, 1184.
- Exports to, 676–677.
- Imports from, 696–697.
- Population, 44, 1075.
- Public Finance, 1078.
- Radio Stations, 376, 1077.
- Shipping, 326–327.
- Trade, 1077–1078.
- Cook Strait Submarine Power Cable, 572.
- Cooperative Credit Associations, 938.
- Cooperative Dairy Companies, 411.
- Copper Fabricating Industry, 495.
- Copper, Ore, 487.
- Cordial and Aerated-water Industry, 533.
- Corn Crops, 424.
- Correspondence Classes, 218, 229, 232–233.
- Cosmetics, Manufacture of, 540.
- Cost of Living, 708–722.
- Costs-
- Railway Construction, 332, 1159.
- Roading, 343–346, 796.
- Cotton Mill, 495.
- Cotton Piece-goods, Imports of, 687.
- Council, Consumer, 709–710.
- Council, Dental, 150.
- Council, Executive, 35.
- Members of, 1123.
- Council, Fire Service, 844, 975.
- Council for Educational Research, 243.
- Council, Legislative, Abolition of, 31.
- Council, Medical, 149–150.
- Council, Medical Research, 149.
- Council of Adult Education, 243.
- Council of Legal Education, 237.
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, 416.
- Counties, 39–40, 840–855.
- Area of, 55–56.
- Bridges in, 342.
- Building Values, 562.
- Capital and Unimproved Values, 313.
- Debt, 847, 850, 851, 1155.
- Employees of, 855.
- Milage of Roads, 341.
- Population, 54–56.
- Country Lands, Mortgages on, 925–926, 928, 935.
- Courts-
- Appeal, 247–248, 251, 257, 1127.
- Arbitration, 248, 979–981, 994, 1029, 1034–1037, 1127.
- Bankruptcy, 1104.
- Children's, 240–242, 258–259.
- Compensation, 248, 1049–1051, 1127.
- Divorce, 96, 97.
- Judges of, 1127.
- Land Valuation, 248, 293, 311, 1127.
- Magistrates', 248, 249–250, 258, 1142.
- Maori Appellate, 303.
- Maori Land, 303.
- Supreme, 96, 97, 248, 250, 255–256, 1142.
- Cover, Fire, 969.
- Cow Testing, 416, 420.
- Cranes, Inspection of, 1066.
- Crayfish, 474, 477, 478.
- Exports of, 652, 654.
- Cream, Consumption of, 738.
- Cream Separators on Farms, 421.
- Credit, Consumer, Survey of, 628–631.
- Credit, Letters of, Post Office Savings Bank, 905.
- Credit, Rural Intermediate, 938.
- Creditors' Petitions, 1104.
- Crematoria, 141.
- Crews of Overseas Vessels, 63.
- Crime, Law and, 247–265, 1142.
- Criminals, Habitual, 263.
- Crippled Children, 153, 231.
- Crops, 286, 422–439, 1143.
- Research, 418.
- Crown Land, 287, 296–301, 798.
- Rates Paid to Local Authorities, 844.
- Crown Tenants, 297–299.
- Cultivation, Area in, 286, 424–433.
- Cultural Awards, 1100–1101.
- Cupro-nickel Coinage, 917.
- Currency and Banking, 880–922, 1156, 1157, 1215–1217.
- Customary Land, 302.
- Customs, Representatives Overseas, 1135.
- Customs Tariff and Revenue, 697–707.
- Customs Taxation, 697–707, 754, 792, 802, 805.
D
- Dairy Board, 410–411, 602–604.
- Dairy Cows, 421, 440, 444–446, 1144.
- Dairy Farms, 408, 445.
- Dairy Industry, 395–400, 421, 444–446, 502, 530, 598–607, 890, 984, 1007.
- Dairy Industry Stabilisation Account, 610.
- Dairy Produce, 408–410, 598–607.
- Bulk Purchases of, 593.
- Carried on Railways, 339, 340.
- Consumption of, 738.
- Export of, 324, 591, 651–656, 667–668, 674, 675, 738, 1147.
- Factories, 408–410, 530.
- Grading of, 411, 416,
- Gross Farming Income, 395–397.
- Guaranteed Prices for, 601–607.
- Levy on, 411.
- Marketing of, 589–590.
- Prices Paid for, 598–607, 1205.
- Production of, 408–410, 530.
- Subsidy on, 741, 742.
- Dairy Products Marketing Commission, 593, 601–604.
- Dairying Machinery, 421.
- Exports of, 655.
- Damage (Earthquake and War) Insurance, 800, 977–978.
- Daylight Saving, 1119.
- Death Duties, 754, 792, 802, 817–818.
- Estates Passed for, 820–822.
- Death Penalty Abolished and Restored, 256.
- Deaths, 77–78, 82, 99–120, 121–126, 132–134, 341, 355–357, 484, 1140.
- Accidental (see Accidents).
- Distribution Over Year, 101.
- Due to Earthquakes, 8.
- Foetal, 90.
- From External Causes, 117–120.
- From Puerperal Causes, 78, 111, 112, 116–117, 124, 133.
- In Cook Islands, 1075.
- In Hospitals, 132–134.
- In Mental Hospitals, 173.
- In Niue Island, 1079.
- In Western Samoa, 1084.
- Inquests on, 80.
- Neo-natal, 101, 106–111, 125–126.
- Of Friendly Society Members, 210.
- Of Infants, 79, 101–103, 105–110, 122, 124–126, 1140.
- Of Insured Persons, 957–959.
- Of Maoris, 77–78, 120, 121–126.
- Of Servicemen Overseas, 99, 277.
- Violent, 78, 80, 112, 117–120, 124, 355–357, 484.
- Debenture Tax, 813.
- Debentures, 827, 848–851, 908, 1153.
- Debits, Bank, 894.
- Debt, Conversion of, 831–832.
- Debt, Location of, 833, 851, 1153.
- Debt of Local Government, 158, 838, 848–854, 1154, 1155, 1214.
- Debt, Public, 793, 827–838, 1153.
- Debtors' Petitions, 1104.
- Deceased Persons' Estates, 820–822.
- Decrees in Divorce, 96–98.
- Deeds Registration, 289, 922.
- Defence, 266–277.
- Committee, 266.
- Expenditure on, 270, 273, 275, 755, 794.
- Fund, 800–801.
- Science, 266–267.
- Degrees, University, 150, 237.
- Demobilisation of Servicemen, 284.
- Demography, 44–75, 1139, 1140.
- Density of Population, 60.
- Dental Benefits (Social Security), 145, 192, 194.
- Dental Services, Hygiene, etc., 144–145, 150–151, 192.
- Department of Agriculture, 415–416.
- Department of External Affairs, 25–26.
- Department of Health, 137–138.
- Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, 416–418, 1169.
- Departments, Government, 36, 1102, 1123, 1130–1132.
- Departures (see Migration).
- Dependants of Soldiers, Pensions for, 195–203.
- Dependent Children, 72–73.
- Dependent Children, Care of, 221, 240–242.
- Deposits-
- By Insurance Companies, 955, 967.
- Interest Rates on, 914–916.
- With Building Societies, 916, 941, 943.
- With Local Authorities, 916.
- With Reserve Bank, 884.
- With Savings Banks, 902–909, 1157.
- With Stock and Station Agencies, 909.
- With Trading Banks, 887–889, 912, 915, 1156.
- With Trading Companies, 916,
- Depreciation Allowances, 521, 744, 752, 806.
- Depreciation of New Zealand Currency, 919.
- Desertion, 96, 98, 180.
- Desertion, Ship, 252.
- Designs, Registration of, 1104.
- Detention, Reformative, 256, 260.
- Diagnostic, Laboratory, Services, 191.
- Diagnostic, X-ray, Services, 190–191, 194.
- Diagrams and Graphs-
- Aviation, Civil, 364.
- By Monetary Areas, 782.
- Changes in Overseas Direct Investment, 784.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Balance of Payments-
- By Monetary Areas, 782.
- Changes in Overseas Direct Investment, 784.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Banking, 888, 891, 895, 898.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Building Permits, 560.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Butterfat Production, 410.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Dairy Produce, Prices and Sales of, 600–601.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Dairy Production, 410.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Electricity Generation, 581.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Experts, 635, 641.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Factory Production, 520.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Farming Income, Gross, 397.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Imports, 635, 641.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Industrial Accidents, 1056.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Infant Death Rates, 107.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Life Assurance, 955, 962.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Manufacturing Industries, 520.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Mortgages, 931.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Motor Vehicles Licensed, 349.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Motor Spirits Consumption, 349.
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- National Income and Expenditure -
- Expenditure, 749.
- Private Outlay, 750.
- Note Circulation, 895.
- Overseas Assets of Banks, 898.
- Population, 47.
- Price Indices, 714, 730.
- Production, 410, 428, 520.
- Pulp and Paper, etc., Production, 467.
- Railways, Tonnage of Goods, etc., 340.
- Rates of Interest on Mortgages, 931.
- Retail Prices Indices, 714.
- Retail Trading, 612.
- School Population, 219.
- Share Prices Indices, 730.
- Taxation Revenue, 804.
- Temperature Pattern, 14.
- Timber Production, 465.
- Trading Banks, 888, 891, 898.
- Union Membership, 1031.
- Vital Statistics, 83, 114.
- Wheat Production, 428.
- Wool Production, 414.
- Dietitians, 152.
- Diphtheria, 78, 108, 112, 127, 128, 139, 143.
- Diplomas, 150, 220, 238.
- Diplomatic Representatives, 1134–1138.
- Disabilities from Industrial Accidents, 1051–1058.
- Disability War Pensions, 202.
- Disabled Servicemen, 195–203, 279.
- Discharged Soldiers' Settlement, 277–284, 300–301, 937.
- Discount Rates, 914–915.
- Disease, Prevention of, 143.
- Diseases, Notifications of, 127–130, 139.
- Diseases, Principal, Deaths from, 78, 111–117, 123–126, 132–133.
- Diseases Treated in Hospitals, 131–133.
- Diseases, Tropical, 1076, 1085.
- Disengaged Persons, 1022.
- Displaced Persons, 66.
- Disputes, Industrial, 1034–1046.
- Distribution, Census of, 611–620.
- Distribution of Population, 50–59.
- By Ages, 59.
- By Industries, 1025.
- Distribution of Private Income, 757–763.
- Distribution Statistics, 611–631.
- District High Schools, 218, 227–230, 235, 1141.
- Districts-
- Electoral, 37, 1124.
- Land, 287, 296.
- List of Local, 41.
- Roads Councils, 342–343.
- Dividends, Bankruptcy, 1105.
- Dividends, Companies, 785–786.
- Dividends, Totalisator, 824.
- Divorce, 96–98.
- Divorced Persons Remarrying, 92–93.
- Dogs, 447.
- Domains, Public, 287–288.
- Domestic Assistance, 187, 191, 194.
- Domestic Trade, 611–631, 1205.
- Domicile of Debt, 833, 851, 1153.
- Drainage Districts, 41, 843–855.
- Dredging, Gold, 487.
- Drivers' Licences, 347, 844.
- Drowning Accidents, 117.
- Drugs, 140, 189.
- Drunkenness, 96, 98, 252, 253, 254, 257.
- Ducks, 447.
- Dunedin-
- Broadcasting Stations, 380, 381.
- Building Values, 562.
- Climate, 15, 16.
- Population, 53, 54, 57.
- Sales Tax Receipts, 826.
- Shipping, 318, 321–325, 673, 696.
- Trustee Savings Bank, 906–908.
- University of Otago, 236–237.
- Urban Transport, 359, 360.
- Duties-
- Customs and Excise, 697–707, 754, 792, 802, 805.
- Death, 754, 792, 802, 817–818.
- Export, 702, 1088.
- Gift, 802, 818–819.
- On Instruments, 802, 823.
- On Lottery Tickets, 823, 1109.
- Stamp, 792, 802, 823.
- Dwellings (see also Houses and Flats), 552.
- Amenities of, 553–554.
- Materials of Outer Walls, 554.
- Means of Cooking, 553.
- Tenure of, 553.
E
- Earthquake and War Damage Insurance, 800, 977–978.
- Earthquakes, 7–8.
- Earths, Types of, 403–405.
- Economic Pensions, 198.
- Economic Stabilisation, 709.
- Education, 212–246, 1076, 1079, 1082, 1085, 1141.
- Adult, 243–244.
- Boards, 212, 213, 214.
- Buildings, 222–223.
- Buildings, Debt on, 830.
- Commission on, 214.
- Endowments, 213, 222.
- Expenditure on, 221–222, 232, 755, 794.
- Of Ex-servicemen, 280, 284.
- Of New Settlers, 244.
- Pacific Islands, 245–246.
- Physical, 154, 234.
- Educational Association, Workers', 244.
- Educational Research, 243.
- Effective Weekly Wage-rates, 1001, 1219.
- Eggs, 448.
- Consumption of, 740.
- Marketing of, 596.
- Retail Price of, 710.
- Subsidy on, 742.
- Elections, General, 33, 1109–1115.
- Representation Commission, 37.
- Electoral Districts, 37, 1124.
- Electoral Provisions, 37–38.
- Electoral Qualifications, 38–39, 41–42.
- Electors, Registration of, 38, 41.
- Electric-
- Motors on Farms, 421.
- Steam Stations, 485, 571–572.
- Power Boards, 41, 576, 578, 843–855, 1155.
- Steam Stations, 485, 571–572.
- Power, Development of, 569–572.
- Steam Stations, 485, 571–572.
- Power, Generation and Supply, 569–583.
- Steam Stations, 485, 571–572.
- Power in Manufacturing Industries, 513–514.
- Power, Review of Operations, 577–583.
- Railways, 331–334.
- Supply Account, 797.
- Tramways, 357, 360.
- Electrical Machinery and Appliances Industry, 505, 506–527, 543.
- Electricity, Consumption of, 569, 580–581.
- Emergency Benefits, 176, 186, 193.
- Emergency Reserve Corps, 276.
- Pensions for, 193, 199, 201.
- Emigration, 62–64.
- Employees-
- Electric Supply, 577–579.
- Farm, 1025.
- Fire Brigade, 975.
- Forest Industries, 470.
- Government, 1019–1020.
- Hospital Boards, 855.
- In Industry, 1013, 1015–1020.
- Legislation Affecting, 979–989.
- Local Government, 855, 1019–1020, 1027.
- Manufacturing Industries, 497–510, 523, 529–545, 1013, 1015–1020, 1025, 1151.
- Mining, 484, 485.
- Picture Theatres, 390, 394.
- Post Office, 378, 1020.
- Public Service, 1133.
- Public Works, 1026.
- Railway, 340–341, 1020.
- Retail Trading, 613.
- Service Establishments, 618.
- State Coal Mines, 485.
- Unions of, 1029–1033.
- Wholesale Trading, 617.
- Employers, 1030, 1033.
- Employers' Liability Insurance, 962–964, 977, 1047–1050.
- Employers' Unions, 1030, 1033.
- Employment, 1010–1028.
- Employment Districts, Manufacturing Industries, Production in, 499.
- Employment Placement Scheme, 1021.
- Employment Promotion, 1010–1012.
- Taxation, 825, 996.
- Employment, Seasonal Fluctuations in, 1025.
- Employment Service, National, 1010.
- Employment, Subsidised, 1010.
- Employment, Survey of, 1014–1023, 1222.
- Employment Vacancies, 1018, 1021, 1022.
- Endowment Land, 297–300.
- Endowments, Education, 213, 222.
- Enginedrivers' Certificates, 1067.
- Engineering Industries, 543–545.
- Engines-
- Employed in Manufacturing Industries, 513–514.
- Employed on Farms, 421.
- Railway, 332, 333.
- Ensilage (see Silage).
- Entertainments Tax, 391, 393, 394, 802, 823, 825.
- Erosion, 458.
- Estate Duty, 802, 817–818.
- Estates-
- Administered by Public Trust Office, 1102–1103.
- Assigned, 1104–1109.
- Passed for Death Duty, 820–822.
- European Economic Community, 590–591.
- Ewes, Breeding, 440.
- Examinations-
- Education Department, 220.
- Electric-tram Drivers', 1067.
- Enginedrivers', 1067.
- Marine Officers', 328–329.
- Medical, of School Children, 143.
- Medical Practitioners, 150.
- Teachers', 220.
- Trades, 221.
- University, 150,220.
- Exchange Allocation, 649, 901–902.
- Exchange (Currency), 919–920.
- Control of, 642, 898, 919.
- Expenditure on, 828.
- New Zealand - London, 919–920.
- Rates of, 919–920.
- Reserve, 884, 896–898.
- Exchange Transactions, Overseas, 642–644, 898–902, 1217.
- Exchanges, Telephone, 373–375.
- Excise Duties, 701–702, 703, 754, 802, 805.
- Executive Council, 35.
- Members of, 1123.
- Exemptions from Taxation-
- Income Tax, 806–816, 867–868.
- Land Tax, 816.
- Ex-nuptial Infants-
- Births of, 88–89.
- Legitimation of, 89.
- Protection of, 242.
- Exotic Plantations, 453–454, 456–458.
- Expectation of Life, 104–105, 122.
- Expeditionary Forces, 276, 1164, 1165.
- Expenditure-
- Air Force, 275, 794.
- Army, 273, 794.
- Audit of, 788.
- Broadcasting, 383.
- Civil Aviation, 361–362.
- Defence, 270, 273, 275, 755, 794.
- Education, 221–222, 232, 755, 794.
- Electric Power, 577–580, 582–583.
- Forest Service, 462–463.
- Government, 753–757, 788–801, 1152, 1210.
- Health, 138, 794.
- Insurance Companies, 958, 960, 963, 970–971, 975–978, 1161.
- Local Government, 158, 576, 578, 756, 845–846. 1154, 1213.
- Mental Hospitals, 173.
- National, 743–764.
- National Roads Fund, 344, 796.
- Naval, 270, 794.
- Picture Theatres, 391, 393, 394.
- Post Office, 373, 375, 377–378.
- Railway, 334–336, 796, 1159.
- Rehabilitation, 281–284, 793.
- Roads, 344.
- Urban Transport, 358–361.
- War, 830.
- Explosives, 1068.
- Export Control, 593, 646.
- Dairy Produce, 411, 593.
- Honey, 596.
- Meat, 593.
- Export Duties, 702, 1088.
- Export Licences, 646.
- Export Prices, 598–601.
- Index Numbers of, 725–727.
- By Classes, 726.
- By Commodity Groups, 726.
- By Destination, 726.
- Exports, 632–677, 704–705, 734–736, 773, 1145–1149, 1205–1206.
- Apples, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148. By Ports, 673.
- By Section and Division, 655–657.
- Casein, 653, 654, 670, 674, 675.
- Classification of, 651–657.
- Crayfish, 652–654.
- Currency, Restrictions on, 917.
- Dairy Produce, 324, 591, 651–656, 667–668, 674, 675, 738, 1147.
- Destination of, 657–672.
- Excess over Imports, 636.
- Fats, 324, 653, 655, 668–669, 674, 675.
- Fish, 477, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Gold, 652, 654, 674, 675, 1147.
- Hides, Skins, and Pelts, 324, 651, 653, 654, 669–670, 674, 675, 1149.
- List of, 652–655.
- Meat, 324, 592, 651–656, 664–666, 674, 675, 738, 1146.
- Metal, Scrap, 653, 655.
- Milk, Dried and Condensed, 653, 654, 668, 674, 675, 1148.
- Newsprint, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Receipts from, 899, 900.
- Sausage Casings, 653, 654, 670, 674, 675.
- Seeds (Grass and Clover), 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148.
- Specie, 646, 1145.
- Timber, 324, 470–472, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Valuation of, 637, 651.
- Values, Index Numbers, 735.
- Volume, Index Numbers, 645, 736.
- Wood Pulp, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Wool, 324, 651, 653, 655, 663–664, 674, 675, 1146.
- External Affairs, Department of, 25–26.
- External Migration, 62–66, 1139, 1197–1198.
- External Trade, 632–707, 1145–1149, 1205–1207.
F
- Factories, 491–545, 1151.
- Accidents in, 1051–1063.
- Act, 141, 981–982.
- Classification of, 496–497, 502–505.
- Classified by Size, 509–510.
- Coal Consumed in, 514–515.
- Dairy, 408–410, 530.
- Employees, 497–510, 523, 529–545, 1013, 1015–1020, 1025, 1151.
- Fire Losses on, 974.
- Registered, 497.
- Summary of Operations, 526–545.
- Factory Production, 399–401, 491–545, 1151, 1200–1204.
- By Employment Districts, 499.
- By Provincial Districts, 498.
- Fakaofo Island, 2, 1081–1082.
- Fallow Land, 286, 425.
- Family Benefits, 174, 176, 177, 181–182, 193, 816.
- Capitalisation of, 176, 182, 934.
- Family Homes, Joint, 565.
- Farm Employees, 1025.
- Farm Employees, Wage-rates, etc., 984, 996, 997, 1003, 1005.
- Farm Finance, Provision of, 281–282, 296–300, 890, 932–938.
- Farm Holdings, 285–286.
- Classification of, 407–408.
- Farm Implements, 421–422.
- Manufacture of, 545.
- Farm Industry Reserves, 610.
- Farm Loans for Ex-servicemen, 281–284.
- Farm Machinery, 421–422.
- Imports of, 680, 690, 692.
- Farm Produce-
- Consumption of, 398–399, 411, 412, 429, 738–741.
- Export of, 324, 398–399, 651–656, 663–671, 674, 675, 1146–1149.
- Marketing of, 588–610.
- Farm Subsidies, 419–421.
- Farm Training and Settlement of Discharged Servicemen, 279–280, 284, 300–301.
- Farmers-
- Advice for, 415–418.
- Financial Assistance to, 293–294, 890, 932–938.
- Mutual Insurance Associations, 974.
- Farming, 395–449.
- Farming Income, Gross, 395–398.
- Farming Lands, Mortgages on, 925–926, 928, 935.
- Fathers, Ages of, 85.
- Fats Exported, 653, 655, 668–669, 674, 675, 1146.
- Fauna, 17.
- Female Suffrage, 38, 1164.
- Female Wage Rates, 993, 999–1001, 1004, 1005.
- Ferns, 16.
- Fertiliser Industry, 504, 539.
- Fertiliser, Land Top-dressed with, 419.
- Fertiliser Used in Aerial Top-dressing, 366.
- Fertilisers, Imports of, 679, 691, 695.
- Fertilisers, Subsidy on Imported, 420.
- Fertilisers, Subsidy on Transport of, 420.
- Fever, Scarlet, 78, 112.
- Field Crops, 422–439.
- Film Library, National, 236.
- Film Unit, National, 1169.
- Film-hire Tax, 792, 802, 825.
- Finance and Investment, 922–954.
- Finance, Farm, 281–282, 293–294, 296–300, 890, 932–938.
- Finance, Government, 753–757, 788–838, 1152, 1153, 1210–1212.
- Finance, Local Government, 156-258, 578, 755–756, 839–855, 1154–1155.
- Hospital Boards, 156–158.
- Fire Boards, 41.
- Fire Brigades, 459, 975.
- Fire Districts, 455, 843–855.
- Fire Insurance, 967–975, 1161.
- State, 834, 977.
- Fire Losses, 969–974, 977.
- Fire Prevention in Forests, 455, 459.
- Fires on Vessels, 330.
- First Births, 86–88.
- Fish, 5, 473–479.
- Canned-
- Exports of, 477.
- Imports of, 685, 694.
- Consumption of, 740.
- Exported, 477, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Value of Production, 400, 474.
- Fishing, Big-game, 478, 1098.
- Fish-liver Oil, 477.
- Fixed Deposits, 887, 915.
- Flats, 552, 556.
- Pensioners', 162.
- Flax Lands, 287, 438.
- Flax, Linen, 426, 439, 838.
- Exports of, 653, 655.
- Flax, Phormium (see Phormium).
- Floating Debt, 828, 831.
- Flogging Abolished, 256.
- Flora, 16.
- Flour-
- Consumption of, 740.
- Production of, 531.
- Subsidy, 742.
- Fodder Crops, 424, 429, 432–433.
- Foetal Deaths, 90.
- Fog Signals, 329.
- Food and Drugs, Sale of, 140.
- Food Consumption, 734–742.
- Food Poisoning, 127, 129, 139.
- Food Production, 502, 506–527, 529–533.
- Food, Retail Prices of, 710, 712.
- Food Subsidies, 741–742.
- Footwear and Clothing, Retail Prices of, 710–711.
- Footwear, Imports of, 679, 687, 694.
- Footwear Industry, 503, 535, 1008.
- Foreign Vessels, 319.
- Foreigners, Naturalisation of, 68–69.
- Forest Fire Prevention, 455, 459.
- Forest Produce Exported, 470–472, 652, 654, 672, 674. 675.
- Forest Trees, 16, 472.
- Forestry, 450–472.
- Persons Engaged in, 470, 1019.
- Research, 460–461.
- Value of Production, 400.
- Forty-hour Week, 981,
- Fowls, 447.
- Franchise, General Government, 38–39.
- Franchise, Local Government, 41–42.
- Freehold, Crown Land Made, 300.
- Freehold Land, 287.
- Freight-
- Carried by Air Transport, 362–368.
- Carried by Shipping, 315–327.
- Carried by Trains, 336–340, 1159.
- Subsidy, 420.
- Train-miles, 339.
- Frequency Rates of Accidents, 1052–1053.
- Friendly Societies, 209–211.
- Frost, 10, 12.
- Fruit-
- Consumption of, 739, 740.
- Export of, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148.
- Fixation of Prices of, 594–595, 596.
- Imports of, 685, 694, 697.
- Industry, 286, 424, 436–438.
- Fruit and Vegetable Preserving Industry, 502, 532–533.
- Fuels and Lubricants, Imports of, 680, 681, 688, 695.
- Funds of Public Account, 788–801.
- Funeral and Sick Funds, 210.
- Furniture and Fittings Industry, 503, 506–527, 536.
- Furniture Loans, 281, 284, 937.
G
- Gaming Act, 823, 1109.
- Gaols, Prisoners in, 263–265, 1142.
- Gardens, Acreage in, 286, 435.
- Gardens (Commercial), Registration of, 435.
- Gardens, Production in Home, 436.
- Gas District, 843–855.
- Gas Generation and Supply, 583–587.
- Gas Price, 583.
- Gas Subsidy, 583, 742.
- Geese, 447.
- General Assembly, 31–34, 1124.
- Generating Stations, 570–571.
- Geographic Board, 307.
- Geographical Features, 2–6.
- Geology, 7, 489–490.
- Geophysical Year, International, 1091.
- Geothermal Steam, Electric Power Stations, 571–572.
- Geysers, 2.
- Gift Duty, 802, 818–819.
- Glaciers, 4.
- Glass and Glass Products Industry, 495, 504.
- Gold, Discovery of, 5, 1162.
- Gold Exported, 652, 654, 674, 675, 1147.
- Gold Mining and Production, 5, 487.
- Gold Reserve, 884.
- Gonorrhoea, 132, 140.
- Goods Available for Use, 734–737.
- Goods Carried on Railways, 337–340, 1159.
- Goods, Dangerous, 1068–1069.
- Goods-service Licences, 350–352.
- Government Departments, 36, 1102, 1123, 1130–1132.
- Government Finance, 753–757, 788–838, 1152, 1153, 1210–1212.
- Government Housing, 546, 554–558, 563, 795, 830, 938–939.
- Government Insurance, 975–978.
- Government Marketing, 593.
- Government Railways, 330–341, 1159.
- Industrial Tribunal, 341, 988.
- Superannuation Fund, 203.
- Government Representatives Overseas, 1134–1135.
- Government Roads, 346–347.
- Government Sector, Accounts of the, 764.
- Government Service Tribunal Act, 987.
- Government Superannuation Fund, 203–205.
- Government, System of, 31–36.
- Governments, Provincial, 39, 212.
- Governor-General, 1121.
- Powers, Duties, etc., 31.
- Grading of-
- Dairy Produce, 411, 416.
- Public Servants, 1133, 1134.
- Graduates, University, 237.
- Grain Crops, 424–431, 1143.
- Grain Milling, 502, 531, 1002, 1007.
- Grapes and Vineyards, 434, 436.
- Graphs (see Diagrams).
- Grass and Clover Seed, 423, 424, 426, 433–434.
- Exports of, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148.
- Grass Lands, 286, 287, 405, 418, 425.
- Grassland Research in New Zealand, 1169.
- Gratuities, Ex-servicemen's, 903.
- Gravel and Sand, 480.
- Greenstone, 489.
- Groceries, Retail Prices of, 710.
- Gross Farming Income, 395–398.
- Gross Indebtedness, 828–829, 1153.
- Of Local Government, 838, 848–850, 1154.
- Of Local Government, Purpose for Which Raised, 851.
- Of Local Government to Government Departments, 849.
- Gross National Product, 744–748.
- Gross Reproduction Rate, 45.
- Guaranteed Prices for Dairy Produce, 601–607.
- Guidance, Vocational, 231, 1011.
- Gum, Kauri, 489.
- Exported, 489, 652, 654, 674, 675.
H
- Half-castes, 61, 121.
- Ham and Bacon, Consumption of, 739.
- Ham and Bacon Curing, 502, 530.
- Harbour Boards, 41, 843–855, 1155.
- Harbour Bridge Authority, 41, 843–855.
- Harbour-ferry Services, 350–352.
- Harbours (see also Ports), 2.
- Hardwoods, Imported, 471.
- Harvests, 422–439, 1143.
- Hay, 433.
- Header Harvesters, 422.
- Heads of Government Departments, 1130–1132.
- Health Camps, 143, 153.
- Health, Child, 142–144.
- Health, Dental, 144–145.
- Health, Department of, 137–138, 1065.
- Health, Education, 145–146.
- Health, Insurance, 174,182–193.
- Health, Occupational, 141–142.
- Health, Public, 137–173.
- Hearing Aids, 192.
- Heavy Traffic Fees, 344, 350.
- Hepatitis, 127, 128, 129, 139.
- Herd Testing, 416.
- Hides, Skins, and Pelts Exported, 324, 651, 653, 654, 655, 669–670, 674, 675, 1149.
- High Commissioners, 1134–1138.
- High Schools, 218, 227–230, 235, 1141.
- Higher Education, 218, 236–240, 1141.
- Highways, 346.
- Taxation, 343–344, 802, 805.
- Hire Purchase Trading, 614, 629–631.
- Historic Places Trust, National, 1101.
- History, Early and From 1870, 18–22.
- History of New Zealand, 18–22, 1162–1167.
- Hoes, Rotary, and Garden Tractors, 421.
- Holdings (see Land Holdings).
- Holidays, 981, 982, 983, 984, 1120.
- Home Garden Vegetable Production, 436.
- Home Lay-by Accounts, Post Office Savings Bank, 905.
- Home-nursing Services, 191.
- Homes, Benevolent, 161.
- Homes, Children's, 162, 241.
- Homicide, 78, 80, 112, 117, 124, 256.
- Honey, 449.
- Consumption of, 740.
- Exported, 449, 653, 654, 674, 675.
- Marketing of, 596.
- Honours Conferred, 1127–1129.
- Hops, 438, 533.
- Exports of, 653, 655.
- Horse-racing, 823–825, 1223.
- Horses, 408, 440, 447, 1144.
- Exported, 653, 655.
- Horticulture, 408, 416, 434.
- Hosiery and Other Knitting Mills, 534.
- Hosiery, Imports of, 686, 694.
- Hospital Benefits, 176, 188–194.
- Hospital Boards, 41, 155–161, 189.
- Employees of, 855.
- Employees' Superannuation, 206.
- Finances of, 156–158.
- Indebtedness of, 838.
- Levies on Local Government, 156, 157, 845.
- Hospital Districts, 155.
- Hospitals, 130–136, 155–173, 189–194, 1076, 1079, 1085.
- Accommodation of, 159–160.
- Maternity, 146, 160–161, 190.
- Mental, 162–173, 190.
- Private, 160, 189, 190, 194.
- Private Mental, 162.
- Public, 130–136, 190, 194.
- St. Helens, 146, 160, 190.
- Staff of, 855.
- Hostels, 162, 1010.
- Hot Springs, 2.
- Hotels and Restaurants, Fire Losses on, 974.
- Hotels, Licensed, 1096–1097, 1116–1119.
- Hourly Wage Rates, 997–998.
- Hours of Labour, 525–526, 981, 983, 986, 1005–1009.
- House of Representatives, 31–34, 1124.
- Broadcast of Proceedings of, 382.
- Members of, 1124.
- House Rents, 565–568.
- Houses and Flats, 546–568.
- Advances for, 281–284, 932–939.
- Census Enumerations, 552–554.
- Completed, 556–557, 564–565.
- Fire Losses on, 974.
- In Course of Erection, 563.
- Maori, 284, 555.
- Rents, 565–568.
- Sale of State, 938–939.
- State, 546, 555–558, 563.
- Housing, 546–568, 795, 932–939.
- Conference, 549.
- Debt, 830.
- Group Building Scheme, 549.
- Home Lay-by Scheme, 550.
- Local Government, 846.
- Of Ex-servicemen, 281–284.
- Of Maoris, 284, 555.
- State, 546, 554–558, 563, 795, 830, 938–939.
- Hungarian Refugees, 66.
- Hunting, 1098.
- Hydatids, 127, 128, 139, 141.
- Hydro-electric Power, 4, 5, 570–571.
- Development of, 569–571.
- Hygiene-
- Environmental, 140.
- Industrial, 141.
- Mental, 162.
- Social, 140.
I
- Ice-cream, Consumption of, 738.
- Ice-cream Industry, 502, 531.
- Illegitimacy (see Ex-nuptial).
- Immigration, 62–67, 1010, 1139.
- Assisted, 65.
- Hostels, 1010.
- Restriction on, 67.
- Implements, Farm, 421–422.
- Manufacture of, 545.
- Import Control and Licences, 646–649, 701.
- Cook Islands, 1077.
- Import Price Indices, 728, 732.
- Importers, Bank Advances to, 890.
- Imports, 632–649, 677–697, 704–705, 734–737, 773–774, 1145, 1205, 1207.
- By Ports, 696.
- Classification of, 677–682.
- Currency, Restrictions on, 917.
- Excess of Exports over, 636.
- Free and Dutiable, 697–707.
- Licensing and Control of, 646–649, 701.
- List of, 685–695.
- Origin of, 682–693.
- Payments on Account of, 899, 900.
- Purpose or Use of, 677–682.
- Restrictions on, 646–649, 701.
- Cook Islands, 1077.
- Specie, 646, 917, 1145.
- Valuation of, 637, 677.
- Value of, Index Numbers, 735.
- Volume of Index Numbers, 645, 736.
- Income-
- Company, 748–763, 857, 870–877.
- Gross Farming, 395–398.
- National, 743–764.
- Of Individuals, 857–869.
- Personal, 748, 749.
- Private, 744–750, 757–763.
- Returnable, 857, 871, 872.
- Income tax, 754, 792, 802, 806–816, 856–879.
- Increase of Population, 44–45, 50–53, 76–77, 82.
- Indebtedness of Local Government, 158, 838, 848–854,1154, 1155.
- Indebtedness, State, 827–838, 1153.
- Index Numbers-
- Consumers' Price, 715–722.
- By Classes, 726.
- By Commodity Groups, 726.
- By Destination, 726.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Deaths, Sex-ratio, 100.
- By Classes, 726.
- By Commodity Groups, 726.
- By Destination, 726.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Electricity Generated, 569.
- By Classes, 726.
- By Commodity Groups, 726.
- By Destination, 726.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Export Prices, 725–727, 732.
- By Classes, 726.
- By Commodity Groups, 726.
- By Destination, 726.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Factory Production-
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Farm Production, Value and Volume, 397, 401.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Gross Farming Income, 397.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Hours of Labour, 1009.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- House Rent, 715.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Import Prices, 728, 732.
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Manufacturing Industries Production-
- Value and Volume, 401, 524–525.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Private Income, 758, 763.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Production, 397, 401.
- Farm, Value and Volume of, 397, 401.
- Manufacturing Industries, Value of, 401, 524–525.
- Retail Prices, 713–722, 732, 733.
- Share Prices, 729–733.
- Value of Goods Available for Use, 735.
- Value of Imports, 735.
- Value of Production, 397, 401–402.
- Volume of Exports, 645, 736.
- Volume of Goods Available for Use, 736.
- Volume of Imports, 645, 736.
- Volume of Production, 397, 401–402, 524–525.
- Volume of Trade, 645.
- Wage Rates, 733, 994–1001, 1009.
- Wholesale Prices, 722–725, 732, 733.
- Wool Prices, 597.
- Indigenous Forests, 287, 453.
- Industrial Accidents, 1047–1063.
- Compensation Rates, 1053–1054.
- Frequency and Severity Rates, 1053.
- Nature and Location of, 1059.
- Time Charge of, 1060.
- Industrial Associations, 1033.
- Industrial Conciliation and Arbitration, 979–980, 1029–1037, 1044–1045.
- Industrial Development Conference, 493–494.
- Industrial Distribution of Population, 1025.
- Industrial Efficiency, 493.
- Industrial Hygiene, 141.
- Industrial Relations Act, 1037.
- Industrial Unions, 1029–1033.
- Industries-
- Bank Advances to, 890.
- Classification of, 496–497, 502–505.
- Licensing of, 493.
- Manufacturing, 399–401, 491–545, 1151, 1200–1204.
- Industry-
- Earnings and Hours Worked in, 1005–1009.
- Fatigue in, 1061.
- Organisation of, 523–524.
- Persons Engaged in, 497–510, 523, 529–545, 1013, 1015–1020.
- Sector Accounts, 787.
- State Aid to, 935–937.
- Infancy, Diseases of, 78, 108–109, 124–126, 133.
- Infant Mortality, 79, 101–103, 105–110, 124–126, 1140.
- Maori, 79, 124–126.
- Infantile Paralysis (Poliomyelitis), 78, 108, 112, 123, 127, 128, 179.
- Infectious Diseases-
- Control of, in Schools, 143.
- Deaths from, 78, 112, 113, 123, 132.
- Hospital Cases, 132.
- Notification of, 127–130, 139.
- Injuries (see Accidents).
- Inquests, 80, 99.
- Insanity, 96, 97, 98, 162–173.
- Insolvency, 994, 1104–1109, 1160.
- Instalment Sales, 629.
- Instruments, Duty on, 802, 823.
- Instruments, Registration of, 289.
- Insurance, 955–978, 1161.
- Accident, 962–966, 1161.
- Earthquake and War Damage, 800, 977–978.
- Fire, 967–975, 1161.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 521.
- Life, 955–962, 975–976, 1161.
- Motor-vehicles, Third-party Risks, 962–966.
- State, 975–978.
- Inter-Industry Studies and Accounts, 787.
- Interest-
- Credited by Savings Banks, 903, 906–909, 1157.
- On Local Government Debt, 158, 756, 851–852, 854.
- On Mortgages, 927–931, 937, 938.
- On Post Office Capital Liability, 377, 792.
- On Public Debt, 744, 748, 755, 793, 835–836.
- On Railways Capital Liability, 334.
- Payments Overseas, 835, 851.
- Payments to Consolidated Fund, 792.
- Rates (see Rates of Interest).
- Reduction of, 914–916.
- Intermediate Credit, Rural, 938.
- Intermediate Schools, 215, 218, 225, 226, 232, 235.
- International Activities, New Zealand's, 22–30, 1169.
- International Air Services, 366–368.
- International Geophysical Year, 1091.
- International Investment Income, 899.
- International Refugee Organisation, 66.
- Intoxicating Liquor-
- Duty on, 699–703, 802, 805.
- Sale of, 1116–1119.
- Invalid's Benefits, 176, 177, 182–183, 193.
- Investment Accounts, Post Office Savings Bank, 905.
- Investment and Finance, 922–954.
- Investment Certificates, 827.
- Investment in New Zealand and Overseas, 782–787.
- Investment Pool, National Provident Fund, 207.
- Investment Societies, 939–943.
- Deposits, 916, 941, 943.
- Investments, Reserve Bank, 884.
- Investments, State, 830, 834.
- Invisible Imports and Exports, 898–900.
- Iron and Steel, Imports of, 689, 695.
- Iron and Steel Industry, 494.
- Iron Ores and Ironsands, 480, 486.
- Irrigation, 1026.
- Island Territories, 2, 44, 1072–1092.
- Islands-
- Administered on Trust, 1–2, 1083–1088, 1089.
- Annexed, 1072–1082.
- Outlying, 1, 1072–1073.
J
- Joinery Industry, 503, 536.
- Joint Family Homes, 565.
- Joint-stock Companies, 876, 944–954.
- In Manufacturing Industries, 523.
- Journal of Agriculture, 416, 418.
- Journal, School, 236, 1072.
- Judiciary, 37, 247–248.
- Members of, 1127.
- Superannuation of, 204.
- June Year Exports, 638, 673–675.
- June Year Imports, 638.
- Juries, 249.
- Justice, 247–265, 793, 1142, 1224.
- Justices of the Peace, 251.
- Juvenile Offenders, 240–242, 258–259.
- Juvenile Wage-rates, 1004–1005, 1009.
K
- Kale, 424, 433, 439.
- Kauri Gum, 489.
- Exported, 489, 652, 654, 674, 675.
- Kea, Destruction of, 420.
- Kermadec Islands, 1, 44, 1073.
- Kindergarten Schools, 214, 218, 223.
- Knitting Mills and Hosiery Industry, 534.
L
- Laboratory Diagnostic Services, 191–192, 194.
- Labour, Department of, 1010, 1011, 1014–1023, 1063–1065.
- Labour Disputes Investigation Act, 1037.
- Labour Force, 1013, 1221.
- Projections, 1013–1014.
- Labour, Hours of, 525–526, 981, 983, 986, 1005–1009.
- Labour Laws and Working Conditions, 979–989.
- Lakes, 5–6, 570–571.
- Lamb, Consumption of, 412, 738, 739.
- Lamb Exported, 592, 674, 675, 738.
- Lamb Produced, 411, 412.
- Lambs, 440, 441.
- Slaughtered, 413, 529.
- Land Act, 222, 296–301.
- Land Development, 296–301, 304.
- Land Districts, 287, 296.
- Land Drainage Districts, 41, 843–855.
- Land for Ex-servicemen, 279–280, 300–301.
- Land Holdings, 285–286.
- Classification by Farm Types, 407–408.
- Mortgages on, 922–926, 935.
- Land, Marginal, 293–294.
- Land, Occupation of, 285–287, 405.
- Land, Purchase of, 296–301.
- Land Sales, Control of, 292.
- Land Settlement, 285–304.
- Land Settlement Account, 798.
- Land Settlement Board, 296.
- Land Settlement Promotion Act, 292–293.
- Land Surveys, 305–308.
- Land Tax, 754, 792, 802, 806, 816.
- Land Tenure and Settlement, 285–304.
- Land Titles, Registration of, 289.
- Land Transfers, 289–292, 1223.
- Land, Valuation of, 308–314.
- Lands Open for Selection, 297.
- Latest Statistical Information, 1197–1228.
- Law and Crime, 247–265, 1142.
- Law, Mortgage, 922–923.
- Law, Revision of, 247.
- Laws Affecting Labour, 979–989.
- Laws Enacted in 1960, 1125–1127.
- Leasehold Landholdings, 287, 297–300.
- Leases, Renewable, 296–299.
- Leather and Leather Products Industry, 504, 506–527, 538.
- Legacy Duty, 817–819.
- Legal Education, 237.
- Legal Tender, 918.
- Legations, 1136–1138.
- Legislation-
- Labour and Allied, 979–989.
- Passed in 1960, 1125–1127.
- Legislative Authority, 31–34.
- Legislative Council, Abolition of, 31.
- Legitimation, 89.
- Letter Boxes, 371.
- Letter Telegrams, 374.
- Letters, etc., Posted, 370, 371, 1158.
- Letters of Credit, Post Office Savings Bank, 905.
- Levies by Fire Authorities, 970.
- Levies by Hospital Boards, 156, 157, 845.
- Levy-
- Coal Production, 486, 1067.
- Dairy Produce, 411.
- Electric Power, 576.
- Honey, 596.
- Meat, 702.
- Orchard, 436.
- Potato, 431.
- Totalisator, 823, 824.
- Vegetable Growers, 435.
- Wool, 415, 594, 702.
- Liabilities of-
- Bankrupts, 1105–1108, 1160.
- Banks, 884, 886, 1156.
- Building Societies, 943.
- Electric-power Undertakings, 580.
- Fire Insurance Companies, 967–968.
- Friendly Societies, 210.
- Life Assurance Companies, 961.
- Local Government, 847, 1213.
- Reserve Bank, 884.
- Library, Alexander Turnbull, 1169.
- Library Services, 221, 244–245, 262, 386–389.
- Licences-
- Aerodrome, 369.
- By Local Authorities, 844.
- Drivers', 347, 844.
- Export, 646.
- Fishing, 479.
- Fishing Vessels, 473.
- Flight Crew, etc., 369.
- Import, 646–649, 701.
- Motor Vehicle, 347–349.
- Petroleum Prospecting, 488.
- Publicans', 844, 1116–1119.
- Radio, 384–385.
- Raffle, 1109.
- Ross Sea Whaling, 1092.
- Transport, 350–353.
- Licensing, 1116–1119.
- Authority, 351–352.
- Control Commission, 1116–1119.
- Poll, 1114–1115.
- Trusts, 1118–1119.
- Licensing of-
- Commercial Air Services, 362.
- Industries, 493.
- Lotteries, 1109.
- Motor Vehicles, 347–349.
- Private Hospitals, 160.
- Sale of Alcoholic Liquor, 1116–1119.
- Liens, Contractors', 993.
- Life Assurance, 955–962, 975–976, 1161.
- Death-rates, 960.
- State, 975–976.
- Life, Expectation of, 104–105, 122.
- Lifts, Inspection of, 1066.
- Lighthouses, 329.
- Lignite, 480–483.
- Lime Industry, 504.
- Lime, Land Top-dressed with, 419.
- Lime, Subsidy on Transport of, 420.
- Limestone, 480.
- Linen Flax, 426, 439, 502, 838.
- Exports of, 653, 655.
- Linseed, 426, 432.
- Liquor Licensing, 1116–1119.
- Literature, New Zealand, 1170–1184.
- Livestock, 439–449, 1144.
- Carried on Railways, 337, 339.
- Slaughterings of, 413.
- Loans-
- Allocation of, 830.
- By Building Societies, 939–943.
- Conversion of, 831–832.
- Dates of Maturity of, 831–833, 852.
- Domicile of, 833, 851, 1153.
- Guaranteed, 829.
- National Development, 799–800, 832.
- Of Hospital Boards, 157.
- Of Local Government, 157, 839, 848–854, 1154, 1155.
- On Assurance Policies, 961, 976.
- Raised for War Purposes, 830.
- Redemption of, 793, 797, 831–832, 845.
- Rehabilitation, 281–284, 934–937.
- State Advances, 549–550, 844, 932–939.
- Supplementary, 281, 935, 936.
- Suspensory, 281, 933, 935, 936.
- Local Government, 39–43, 155–161, 576, 578, 755–756, 839–855, 1154–1155, 1213–1214.
- Advances to, 345–346, 844, 935–937.
- Assets of, 847–848.
- Borrowing, 839.
- Commission, 41.
- Debt of, 158, 838, 848–854, 1154–1155.
- Deposits with, 916.
- Employees of, 855, 1019–1020, 1027.
- Expenditure of, 158, 576, 578, 756, 845–846, 1154.
- Finance, 839–855, 1213–1214.
- Forestry, 462.
- History of, 39.
- Housing by, 551.
- Investment Pool, 207.
- Levies on, by Hospital Boards, 156, 157, 845.
- Liabilities of, 847.
- Obligations under Health Act, 137.
- Pensioners' Flats, 162.
- Receipts of, 157, 578, 756, 841–844, 1154.
- Registered Stock, 848.
- Superannuation, 206.
- Taxation by, 756, 827, 839–841.
- Urban Transport Operated by, 357–361.
- Local Railway District, 41, 843–855.
- Local Restoration Polls, 1115.
- Lockouts, 1034–1038.
- Locomotives, 332, 333.
- Lodges, Friendly Societies, 209–211.
- London Prices for Dairy Produce, 599–601.
- London Prices for Meat, 608.
- Losses from Fire, 969–974, 977.
- In Forests, 459.
- Lotteries, 1109.
- Duty on, 823, 1109.
- Lubricants and Fuels, Imports of, 680, 681, 688, 695.
- Lucerne, 424.
- Lump-sum Payments, 744.
M
- Machinery-
- Accidents, 1058.
- Farm, 421–422.
- Imports of, 679, 690, 692.
- Industry, 505, 506–527, 545.
- Manufacturing Industries, 513–514, 522.
- Safety of, 1064–1065.
- Magistrates, Stipendiary, 248.
- Superannuation of, 204.
- Mails, 370–372, 1158.
- Air, 362–368, 371.
- Maize, 424–427.
- Malaya, Federation of, Reciprocal Trade with, 705.
- Malting Barley, 431.
- Malting Industry, 502.
- Mangaia Island, 2, 1073, 1075.
- Manganese Ore, 480, 487.
- Mangolds, 426.
- Manihiki Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Manuae Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Manufacturing Industries, 399–401, 491–545, 1151, 1267–1271.
- By Employment Districts, 499, 1203–1204.
- By Provincial Districts, 498.
- Classification of, 502–505.
- Coal Consumed in, 514–515.
- Persons Engaged in, 497–510, 523, 529–545, 1013, 1015–1020, 1025.
- Registered, 497.
- Stocks, 522–523.
- Summary of Operations, 526–545.
- Manure Industry, 539.
- Manures, Imports of, 679, 691, 695.
- Manures, Land Top-dressed with, 419.
- Manures Used for Aerial Top-dressing, 366.
- Maori Affairs, Board of, 303.
- Maori Electorates, 1124.
- Maori Housing, 284, 555.
- Maori Lands, 302–304.
- Maori Trustee, 303–304, 834.
- Maori Welfare, 1101.
- Maoris-
- Births of, 76, 121.
- Children Attending Schools, 218, 226–228, 230–231, 232.
- Deaths of, 77–78, 120, 121–126.
- Employment, 1010.
- Expectation of Life, 122.
- Franchise, 38.
- Half-castes, 61, 121.
- In Prisons, 258, 263.
- Infant Mortality of, 79, 124–126.
- Marriages of, 121.
- Members of Parliament, 33, 1124.
- Natural Increase of, 77.
- Offences by, 257–258.
- Population, 44, 51–53, 60–61, 1197.
- Rehabilitation of, 280, 284.
- Schools for, 216, 221, 223, 226–228, 230–231, 232.
- Sex Proportions of, 48.
- Still-births, 90.
- Map of New Zealand (End of Volume).
- Maps and Charts, 307–308.
- Maps, Factory Production, 500–501.
- Maps, Geological, 490.
- Maps, Rainfall, 11.
- Maps Showing Mineral Resources, 481.
- Maps Showing Power Stations, etc., 574–575.
- Marine Department, Occupational Safety, 1065–1067.
- Marine Officers' Certificates, 328–329, 987.
- Marital Status, 71–72, 92–93.
- Market Gardens, 434–435, 984.
- Registration of, 435.
- Marketing of Primary Produce, 588–610.
- Marriages, 77, 90–98, 121, 1140.
- Masculinity Rate, 84, 90.
- Masseurs (see Physiotherapists).
- Massey Agricultural College, 216, 218, 240.
- Materials Used in Manufacturing Industries, 497–501, 515–516, 523, 527–545, 1151.
- Maternal Mortality, 78, 111, 112, 116–117, 124, 133.
- Maternal Welfare, 139, 146.
- Maternity Benefits, 160, 176, 190, 193, 194.
- Maternity Hospitals, 146, 159, 160–161, 190.
- Maternity Nurses, 151, 160, 190.
- Maternity Services, 160–161, 190, 193.
- Maturity Dates of Loans, 831–833, 852.
- Mauke Island, 2, 1073, 1075.
- Mean Population, 49, 402, 1139.
- Mean Time, 1119.
- Measures and Weights, 305, 425.
- Meat-
- Bulk-purchase of, 593.
- Consumption of, 411, 412, 738, 739.
- Export Control, 593.
- Export of, 324, 592, 651–656, 664–666, 674, 675–1146.
- Export Price Index, 726.
- Freezing and Preserving Industry, 502, 529, 890.
- Industry Reserve Account, 610.
- Inspection of, 416.
- Levy on Exports of, 702.
- Marketing of, 588–589, 594.
- Prices for, 594, 607–610.
- Production, 411–413, 529–530, 1150.
- Retail Prices of, 710.
- Meat Producers Board, 594, 608.
- Medical Advertisements, 141.
- Medical Benefits, 176, 188–189, 193, 194.
- Medical Bursaries, 239.
- Medical Council, 149–150.
- Medical Practitioners, 150, 189.
- Medical Research Council, 149.
- Medical Services, 137–173, 188–194.
- In Cook Islands, 1076.
- In Niue Island, 1079.
- In Western Samoa, 1085.
- Medical Statistics, 127–136, 149, 210.
- Medicine, Physical, 147–148.
- Members of Parliament, 31–34, 1124.
- Superannuation of, 34, 204.
- Meningitis, 139.
- Meningococcal Infections, 78, 108, 112, 123, 127.
- Mental Hospitals, 162–173, 190.
- Mercantile Marine, 277, 315–330.
- Pensions, 193, 199, 201.
- Merchandise, Exports of, 632–677, 704–705, 734–736, 773, 1145–1149, 1205–1206.
- Merchandise, Imports of, 632–649, 677–697, 704–705, 734–737, 773–774, 1145, 1205, 1207.
- Merchandise Transhipped, 323–326.
- Mercury, 487.
- Metal Products Industry, 505, 506–527, 545.
- Metal, Scrap, Exports of, 653, 655.
- Meteorology, 8–16.
- Cook Islands, 1073.
- Niue Island, 1078.
- Western Samoa, 1083.
- Midwives, 148, 151, 160, 190.
- Migration, External, 62–66, 1139, 1197–1198.
- Child, 65.
- Milage of-
- Bus, etc., Routes, 359, 360.
- Commercial Air Services, 363, 367.
- Highways, 345, 347.
- Railways, 330–331, 337, 341, 1159.
- Roads, 341.
- Milage Tax, 344, 792, 802.
- Military Colleges, 271.
- Military Forces, 270–273.
- Military Pensions, 195–203.
- Milk-
- Boards, 41.
- Consumption, 738, 741.
- Control of Prices and Sale of, 595–596.
- Districts, 843–855.
- Dried and Condensed, Exports of, 653, 654, 668, 674, 675, 1148.
- Dried and Condensed, Production of, 410.
- Examination and Testing of, 411, 416.
- For School Children, 143, 233.
- Marketing of, 595–596.
- Subsidy, 742.
- Milk Products (see Dairy Produce).
- Milking Machines, 421.
- Mills, 491–545.
- Minerals and Mineral Production, 480–490.
- Miners' Benefits, 176, 177, 183–184, 193, 486.
- Miners' Phthisis, 183.
- Mining, 480–490, 830.
- Accidents, 119, 484, 1055, 1056, 1062.
- Disputes, 1042, 1043.
- Legislation, 986.
- Persons Engaged in, 484, 485, 1019.
- Produce Exported, 652, 654, 674, 675.
- Value of Production, 400, 480.
- Ministers of Each Church, and Marriages by, 95–96.
- Ministers Plenipotentiary, 1136–1138.
- Ministries, Successive, 1121–1122.
- Minors, Marriages of, 95.
- Mission Schools, 1082, 1085.
- Mitiaro Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Monarch, The, 31.
- Monetary, Banking, and Credit Systems, Royal Commission on, 880, 1169.
- Monetary Benefits, Social Security, 176–188, 193, 799.
- Money Orders Issued and Paid, 372–373, 1158.
- Money, Volume of, in Circulation, 912–913.
- Morbidity, 127–136, 210.
- Mortality (see Deaths).
- Mortgage Corporation, 932.
- Mortgage Exemption, 816.
- Mortgagee, Rights of, 923.
- Mortgages, 922–932, 935, 961, 1223.
- Rates of Interest on, 927–931, 937, 938.
- State Advances, 932–939.
- Mothers, Ages of, 85, 86, 88.
- In Ex-nuptial Cases, 89.
- Mothers, Average Issue of, 86.
- Mothers, Previous Issue of, 86.
- Motive Power in Manufacturing Industries, 513–514.
- Motor Body Building and Repairs Industry, 544.
- Motor Spirits-
- Consumption of, 348–349.
- Imports of, 688–695.
- Retail Price of, 712.
- Taxation on, 343, 350, 701, 805, 844.
- Motor Transport, 335, 347–361.
- Motor Vehicles-
- Accidents, 78, 112, 117, 118, 124, 353–357.
- Assembly of, 505, 543.
- Drivers' Licences, 347, 844.
- Duty on, 700.
- Imports of, 692, 695.
- Insurance, 962–966.
- Methods of Purchasing, 630.
- Post Office, 378.
- Registration and Licensing of, 347–349, 1200.
- Repairs Industry, 505.
- Taxation, 343, 700, 754, 805.
- Traffic Offences, 252, 253–254, 354.
- Motor Vessels Registered, 328.
- Motor-engineering Industry, 543–544.
- Motorways, 346–347.
- Mountains, 2–3.
- Multiple Births, 84–85.
- Murder, 78, 80, 96, 112, 117, 124, 256.
- Abolition and Restoration of Death Penalty for, 256.
- Museums, 236, 1099.
- Mussels, 474, 477.
- Mutton, Consumption of, 412, 739, 740.
- Mutton Exported, 592, 674–675, 738.
- Mutton Produced, 411, 412, 529.
- Mutual Insurance Associations, 974.
N
- Nassau Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Nassella Tussock Districts, 41, 843–855.
- National Accounts, 743–787.
- National Airways Corporation, 362, 363, 792, 830, 838.
- National Council of Adult Education, 243.
- National Development Loans, 799–800, 832.
- National Employment Service, 1010.
- National Film Library, 236.
- National Film Unit, 1169.
- National Health Institute, 149.
- National Historic Places Trust, 1101.
- National Income and Expenditure, 743–764.
- National Library Service, 221, 244–245, 262.
- National Licensing Polls, 1114–1115.
- National Provident Fund, 206–208, 834.
- National Roads Board, 342–343, 805.
- National Roads Fund, 342–344, 795–796, 805, 1212.
- National Safety Association, 1071.
- National Savings, 827–828, 834, 908–909, 1216.
- National Service Registration Act, 267.
- Nationality, 68–69.
- Of Naturalised Persons, 69.
- Of Overseas Shipping, 318–319.
- Of Registered Aliens, 70.
- Native Animals, 17.
- Native Bush, 16, 287, 450–456.
- Native Fresh-water Fishes, 479.
- Native Grasses, 16.
- Natural Increase of Population, 45, 50, 77, 82–83, 1197.
- Naturalisation, 68–69, 1224.
- Nauru Island, 1089–1090.
- Naval Defence, 267–270, 276.
- Naval Expenditure, 270, 794.
- Neo-natal Deaths, 101, 106–111, 125–126.
- Nephrite, 489.
- Net Note Circulation, 895–896.
- Net Reproduction Rate, 45.
- New Zealand Broadcasting Service, 236, 379–385, 834.
- New Zealand Dairy Board, 410–411, 602–604.
- New Zealand Electricity Department, 569, 1026.
- Occupational Safety, 1067–1068.
- New Zealand Forest Products Ltd., 468.
- New Zealand Mean Time, 1119.
- New Zealand Red Cross Society, 154.
- New Zealand Representatives Overseas, 1134–1135.
- New Zealand's International Activities, 22–30, 1169.
- Newspapers, 386.
- Produced, 528.
- Registered, 372.
- Newsprint, Exports of, 472, 672, 674, 675.
- Newsprint, Imports of, 472, 691.
- Newsprint, Production of, 467.
- Niue Island, 1, 2, 44, 326–327, 376, 676, 1078–1081.
- Note Issue, 884, 887, 895–896, 918–919.
- Notes in Circulation, 895–896, 912–913, 1156.
- Notification of Births, 80, 120–121.
- Notification of Diseases, 127–130, 139.
- Nukunono Island, 2, 1081–1082.
- Nullity of Marriage, 97.
- Nurseries, 434, 435.
- Nurses-
- Dental, 144, 192.
- District, 191.
- In Public Hospitals, 855.
- Industrial, 142.
- Male, 151.
- Maternity, 151, 160, 190.
- Plunket, 143, 153, 161.
- Psychiatric, 151.
- Public Health, 143, 153.
- Registration of, 151.
- Superannuation for, 206.
- Nursing, 148–149, 191.
- Nursing Aids, 151.
- Nylon Piece-goods, Imports of, 687.
O
- Oatmeal, etc., Consumption of, 740.
- Oatmeal, etc., Production of, 531.
- Oats, 424–427, 429–430, 433, 439, 1143.
- Observatory, Time Signals From, 382, 1120.
- Occupation of Land, 285–287, 405.
- Occupational Health, 141–142.
- Occupational Safety, 1063–1071.
- Occupational Therapists, 152.
- Occupational Training of Discharged Servicemen, 278–279, 282.
- Occupations of Bankrupts, 1106–1107.
- Ocean Island, 1089.
- Offences, 251–259.
- By Children, 240–242, 258–259.
- By Maoris, 257–258.
- By Women, 257.
- Offenders Probation Act, 259.
- Officers' Certificates (Marine), 328–329, 987.
- Offices Act, Shops and, 982–984.
- Official Representatives, 1134–1138.
- Oil and Tar, Production from Coal, 485.
- Oil, Fish-liver, 477.
- Oil Refinery, 494.
- Oil Wells, 488.
- Oil, Whale, 474, 478, 652, 654.
- Old People's Homes, 161–162.
- Omnibuses Licensed, 347.
- Onions, 426, 432, 439.
- Exports of, 653, 655.
- Opencast Mining, 484.
- Opium, Prohibition of, 140.
- Opossum Skins Exported, 653, 654, 674, 675.
- Opticians, Registration of, 152.
- Oranges, Imports of, 685, 694, 697.
- Orchards, 434, 436–438, 984.
- Orchestra, National, 382, 383.
- Origin of Immigrants, 64.
- Origin of Imports, 682–693.
- Orphans' Benefits, 176, 177, 181, 193.
- Ottawa Agreement, 698, 704.
- Outlying Islands, 1, 1072.
- Out-patients, 159.
- Maternity Hospitals, 160.
- Overdraft Authorities, Unexercised, 894.
- Overdraft Rates, 914.
- Overtime, 525–526, 981, 983, 986, 1007–1009.
- Owner-occupied Houses, Rental Value of, 743, 748, 757.
- Oysters, 474, 477.
P
- Pacific Islands, Annexed, 1072–1082.
- Bibliography, 1185.
- Education, 245–246.
- Radio Communication, 376, 1077, 1080.
- Paint and Varnish Industry, 504, 540.
- Palmerston Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Pan American World Airways, 368.
- Paper and Paper Products Industry, 503, 506–527, 536–537.
- Paper and Pulp, External Trade in, 472.
- Paper, Imports of, 691, 695.
- Paralysis, Infantile (Poliomyelitis), 78, 108, 112, 123, 127, 128, 139.
- Parcels-post, 371, 372, 673.
- Parents-
- Ages of, 85, 86.
- Duration of Marriage of, 87.
- Parks, National, 288.
- Parliament, 31–34.
- Members of, 31–34, 1124.
- Parliamentary Elections, 33, 1109–1114.
- Parliaments, Successive, 1125.
- Parole Board, 261, 262–263.
- Passenger Milage-
- Air Services, 364–367.
- Railways, 337.
- Passenger Services, 350–353.
- Passengers-
- Buses, etc., 357–361.
- Commercial Aircraft, 364–368.
- Motor Vehicle, 353.
- Overseas, 62–63, 1139.
- Railway, 336–338, 1159.
- Shipping, 320.
- Passports, 66.
- Pastoral and Agricultural Production, 395–449, 1143, 1144.
- Persons Engaged in, 1025.
- Value of, 395–401.
- Volume of, 397, 401.
- Pastoral Produce-
- Consumed Locally, 399, 738–739, 741.
- Export of, 399, 449, 651–675, 1146–1149.
- Gross Farming Income, 395–397.
- Pasture Grasses, 286, 418, 425.
- Patents, Designs, Trade Marks, and Copyright, 1103–1104.
- Patients in Hospitals, 130–131, 159–160.
- Patients in Mental Hospitals, 163–171.
- PAYE Taxation, 175, 809–816.
- Payments, Balance of, 764–787.
- Peaks, Altitude of, 3.
- Pears, 425, 436–437.
- Export of, 653, 655, 1148.
- Marketing of, 594–595.
- Peas, 424–427, 431.
- Export of, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675.
- Pelts, Hides, and Skins, Export of, 324, 651, 653, 654, 655, 669–670, 674, 675, 1149.
- Penrhyn (Tongareva) Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Pensions, 174–211, 744, 757.
- Perinatal Mortality and Prematurity, 110–111.
- Perlite, 489.
- Permanent Building Societies, 940–943.
- Permanent Heads of Government Departments, 1130–1132.
- Permits, Building, 558–564.
- Petitions-
- Bankruptcy, 1104.
- Divorce, 96–98.
- Petrol (see Motor Spirits).
- Petroleum, 480, 488.
- Imports of, 695.
- Pharmaceutical Benefits, 176, 189, 193, 194.
- Pharmaceutical Chemists, 153.
- Pharmaceuticals, Manufacture of, 540.
- Pharmacy, 153.
- Phormium, 287, 408, 438.
- Industry, 502.
- Phosphate Rock, 489, 539.
- From Nauru Island, 1089.
- Imports of, 691, 695.
- Phthisis (see Tuberculosis).
- Miners', 183.
- Physical Welfare and Recreation, 154.
- Physiography, 1–17.
- Physiotherapists, 151.
- Physiotherapy Benefits, 191, 194.
- Picture Theatres, 390–394.
- Pig-meats-
- Consumption of, 738, 739.
- Export of, 674, 675, 738.
- Prices for, 609.
- Production of, 529.
- Pigs, 408, 440, 441, 446, 1144.
- Slaughtered, 413.
- Pilots, Air, 369.
- Pisciculture, 479.
- Placement Service, 1010, 1021–1022.
- Plaints, 250.
- Planing Mills, 503, 536.
- Planning, Town and Country, 42–43.
- Plantations, 286, 405, 408, 425, 435, 450–452.
- State, 452.
- Plants, New Zealand, 16.
- Platinum, 488.
- Plumbers, Registration of, 152.
- Plunket System, 153, 161.
- Plywood and Veneer, 468–469, 503, 542.
- Poisoning, 117, 127, 129, 133, 139, 1059.
- Poisons, 140.
- Police, 265, 793.
- Superannuation, 203.
- Policies, Insurance, 955–975, 1161.
- Poliomyelitis, 78, 108, 112, 123, 127, 128, 139.
- Vaccination, 128, 143.
- Polling at-
- General Elections, 1109–1115.
- Licensing Polls, 1114–1115.
- Pollution, Air, 142.
- Population, 44–75, 402, 1139, 1197, 1225–1228.
- Age Distribution of, 59.
- Distribution of, 50–59.
- Industrial Distribution of, 1025.
- Method of Compilation of, 48.
- Of Campbell Island, 44.
- Of Cook Islands, 44, 1075.
- Of Kermadec Islands, 44, 1073.
- Of Nauru Island, 1089.
- Of Niue Island, 44, 1079.
- Of Ross Dependency, 44.
- Of Tokelau Islands, 44, 1082.
- Of Western Samoa, 44, 1084.
- Projections, 45–47.
- World, 74–75.
- Pork Consumed, 412, 739.
- Pork Exported, 674, 675, 738.
- Pork Produced, 411, 412, 529.
- Portfolios of Ministers, 1123.
- Ports-
- Fishing, 476.
- Of Arrival and Departure, 318.
- Of Registry, 328.
- Safety of, 1066.
- Shipping and Trade of, 315–325, 673, 696.
- Post Office, 370–378, 834, 1158.
- Account, 800.
- Superannuation of, 203.
- Wages and Hours Worked of, 1008.
- Debt, 830.
- Superannuation of, 203.
- Wages and Hours Worked of, 1008.
- Employees, 378, 1020.
- Superannuation of, 203.
- Wages and Hours Worked of, 1008.
- Interest on Capital Liability, 792.
- Savings Bank, 902–906, 915–916, 1157, 1216.
- Staff Tribunal, 988, 993.
- Postal Notes, 373, 1158.
- Post-primary Education, 213–220, 227–231, 1141.
- Potatoes, 424, 426, 431–432.
- Consumption of, 739, 741.
- Export of, 653, 655, 674, 675.
- Marketing of, 595.
- Pottery, China, and Earthenware Industry, 504, 541.
- Poultry, 408, 447–448.
- Consumption of, 740.
- Poultry Runs Registration, 448.
- Pounamu (Greenstone), 489.
- Power Boards, 41, 576, 578, 843–855, 1155.
- Power, Electric (see Electric).
- Power Used in Manufacturing Industries, 513.
- Preferential Tariff, 697–701, 703–706.
- Pregnancy, Diseases, etc., of, 78, 108, 110–111, 112, 116–117, 124, 127, 133.
- Premiers, Successive, 1121–1122.
- Premium Income, 955–978.
- Preserved Meats, etc., Production of, 529.
- Prevention of Forest Fires, 455, 459.
- Price Tribunal, 708–709.
- Prices, 708–733.
- Collection of, 713.
- Comparisons with Other Countries, 712.
- Effect on Exports and Imports, 729.
- Fixation of, 708.
- Guaranteed for Dairy Produce, 601–607.
- Of New Zealand Stocks, 834.
- Regulation of, 708–709.
- Stabilisation of, 708–709.
- Trade Practices Act, 1958, 709.
- Primage Duty, 698, 702.
- Primary Products-
- Consumption of, 398–399, 738–741.
- Export of, 324, 398–399, 651–675, 1146–1149.
- Marketing of, 588–610.
- Primary Schools, 214–219, 223–227, 232–235, 1085, 1141.
- Prime Ministers, Successive, 1121–1122.
- Principal Events, 1162–1167.
- Printing and Publishing Industry, 503, 506–527, 537.
- Prisoners of War, 277.
- Prisons and Prisoners, 258, 260–265, 1142.
- Private Assignments, 1108–1109.
- Probation, 252, 256, 259–260, 262.
- Producers' Equipment, Imports of, 680, 681, 682.
- Producers' Materials, Imports of, 680, 681.
- Production-
- Agricultural and Pastoral, 395–449, 1143, 1144.
- Clothing, 534–535.
- Dairy, 408–411, 530, 1150.
- Fisheries, 474–476.
- Forestry, 400.
- Local Consumption of, 398–399, 738–740.
- Manufacturing Industries, 400, 401, 491–545, 1151, 1200–1204.
- Meat, 411–413, 529–530, 1150.
- Mineral, 400, 480–490.
- Per Head of Population, 402.
- Pulp and Paper, etc., 466–468.
- Timber, 464–466, 535, 1150, 1200.
- Value of, 395–401, 735.
- Volume of, 397, 401–402, 524–525, 736–737.
- Wool, 396, 413–415, 1150.
- Prohibition Issue, 1114–1115.
- Prohibition Orders, 252.
- Projections-
- Labour Force, 1013–1014.
- Population, 45–47.
- School Population, 219.
- Promotion of Employment, 1010–1012.
- Properties Transferred, 289–292.
- Proprietors, Working, 1015–1017.
- Protection of Wages, 993–994.
- Provident Fund, National, 206–208, 834.
- Provincial Districts, 39.
- Area and Population of, 50.
- Density of Population in, 60.
- Manufacturing Industries in, 498.
- Public Accounts, 788–801, 1210–1211.
- Public Buildings, Expenditure on, 795.
- Public Debt, 827–838, 1153.
- Repayment of, 793, 827–832, 836–837.
- Public Finance, 788–838, 1152, 1153, 1210–1212.
- Public Health, 137–173.
- Public Holidays, 1120.
- Public Service, 987, 1132–1134.
- Board of Appeal, 1133.
- Occupational Safety, 1069.
- Classification, 1133, 1134.
- Occupational Safety, 1069.
- Commission, 1132–1133.
- Occupational Safety, 1069.
- Employees, 1133.
- Superannuation, 203.
- Public Trust Office, 1102–1103.
- Public Works-
- Account, 795, 800.
- Employees, 1026.
- Housing Construction, 555–558, 563, 795.
- Occupational Safety, 1070.
- Railway Construction, 331.
- Road Construction, 342.
- Public Works and Services, Maintenance of, 755, 794.
- Publicans' Licences, 844, 1116–1119.
- Publications-
- A Descriptive Atlas of New Zealand, 403.
- Agriculture, Department of, 416, 418.
- Census, 1230.
- Education, Department of, 236, 1072.
- General Bibliography, 1170–1185.
- Labour and Employment Gazette, 1014, 1064.
- Lands and Survey, Department of, 307–308.
- New Zealand Flora and Fauna, 16–17.
- New Zealand Listener, 381, 383.
- Register of Newspapers, 372.
- Statistics, Department of, 1229–1230.
- Publishing and Printing Industry, 503, 506–527, 537.
- Puerperal Accidents, etc., 78, 108, 110–111, 112, 116–117, 124, 127, 133.
- Puisne Judges, 1127.
- Pukapuka (Danger) Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Pulp and Paper, External Trade in, 472.
- Pulp and Paper Industry, 466–468, 536–537.
- Pulp and Paperboard, Imports of, 695.
- Pumice, 480, 652, 654.
- Pupils, School, 218–233, 1141.
Q
- Quarries, 986.
- Accidents at, 119, 1055, 1056, 1062.
- Persons Engaged in, 1019.
- Safety in, 1067.
- Quartz Mining, 487.
- Quicksilver, 487.
- Quorum-
- Executive Council, 35.
- House of Representatives, 32.
- Quotations, New Zealand Stocks, 834.
R
- Rabbit Boards, 421.
- Rabbit Districts, 41, 843–855.
- Rabbit Skins Exported, 653, 654.
- Rabbits, Destruction of, 366, 420.
- Racing Taxation, 802, 823–825.
- Radiation Protection, 146–147.
- Radio Advertising, 379–384.
- Radio Assembly and Manufacture, 505, 528, 543.
- Radio Beacons, 329.
- Radio Broadcasting, 236, 379–385.
- Radio Communication, 376–377, 1077, 1080.
- Radio Licences, 384–385, 1223.
- Radio Stations, 376, 377, 379–382, 1073, 1077, 1080.
- Radio Time Signals, 382, 1120.
- Radioactive Substances Act, 146.
- Radiologists, 146–147, 190, 194.
- Radiotelephone Services, 377.
- Raffles, 1109.
- Railcars, 332.
- Railway and Tramway Equipment, Imports of, 680, 692.
- Railways, 330–341, 1159, 1199.
- Accidents, 118, 136, 341, 355.
- Air Freight Service, 364–365.
- Debt, 830.
- Employees, 340, 1020.
- Private, 330, 341.
- Revenue and Expenditure, 334–336, 796, 1159.
- School Children's Transport, 232.
- Superannuation, 203, 341.
- Tribunal, 341, 988, 993.
- Wages and Hours Worked of Employees, 1003, 1008.
- Rainfall, 9, 10–11, 14–16.
- Rakahanga (Reirson) Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Rangemaking Industry, 505, 543.
- Ranges, Mountain, 2–3.
- Raoul Island, 1073.
- Rape, 424, 439.
- Rarotonga Island, 2, 1073, 1075–1077.
- Rateable Value of Land, 314.
- Rates, Local Government, 756, 827, 839–841, 1154.
- Rates of Exchange, 919–920.
- Rates of Interest-
- On Building Societies' Deposits, 916.
- On Company Deposits, 916.
- On Fixed Deposits, 915.
- On Local Government Debt, 852, 854.
- On Mortgages, 927–931, 937, 938.
- On Public Debt, 831–832, 835.
- On Rehabilitation Loans, 281.
- On Rural Intermediate Credit, 938.
- Paid by Savings Banks, 915–916.
- Rates of Tax, 806–816, 869, 872.
- Rates of Wages, 733, 982–984, 990–1009, 1220–1221.
- Rates of War Pensions, 196–199.
- Rating by Local Government, 156, 157, 839–841.
- On Unimproved Value, 840–841.
- On Urban Farm Lands, 311.
- Rayon Piece-goods, Imports of, 687.
- Receipts Overseas, 642–644, 1217.
- Reciprocal Benefits, Social Security, 174, 175, 176, 187–188, 799.
- Reciprocal Tariff and Trade, 703–706.
- Recreation and Physical Welfare, 154.
- Recreation in Forests, 456.
- Recruiting-
- Air Force, 274.
- Army, 271.
- Navy, 269.
- Police, 265.
- Red Cross Society, 154.
- Redemption of Loans, 793, 797, 831–832, 845.
- Redemption of Mortgages, 922–923, 931–932.
- Redemption of Savings Bonds, 909.
- Re-exports, 676.
- Reformative Detention, 256, 260.
- Refrigerators, 528, 553.
- Refugee Organisation, International, 66.
- Refugees, 66.
- Registrars, Marriages Before, 90–91, 95.
- Registration of-
- Adopted Children, 89.
- Aliens, 69–70, 1224.
- Apiaries, 449.
- Apprenticeships, 012.
- Births, 76, 80–81, 120.
- Building Societies, 939.
- Chemists, 153.
- Companies, 944–945, 1160.
- Dairy Companies, 411.
- Deaths, 99, 120, 121–122.
- Deeds, 289, 922.
- Dentists, 150–151.
- Designs, 1104.
- Electors, 38, 41.
- Ex-nuptial Births, 81, 88.
- Fishing Vessels, 473.
- Friendly Societies, 209.
- Hospital Dietitians, 152.
- Industrial Unions, 1029.
- Land Owners, 289.
- Land Titles, 289.
- Male Nurses, 151.
- Maori Births, 120–121.
- Maori Deaths, 99, 120, 121–122.
- Maori Electors, 38.
- Market Gardens, 435.
- Marriages, 90–91, 121.
- Maternity Nurses, 151.
- Medical Practitioners, 150.
- Midwives, 151.
- Mortgages, 922–926.
- Motor Vehicles, 347–349.
- Newspapers, 372.
- Nurseries, 435.
- Nurses, 151.
- Nursing Aids, 151.
- Occupational Therapists, 152.
- Opticians, 152.
- Patents, 1103.
- Pharmaceutical Chemists, 153.
- Physiotherapists, 151.
- Plumbers, 152.
- Poultry-runs, 448.
- Private Schools, 226.
- Psychiatric Nurses, 151.
- Still-births, 90, 99, 110.
- Trade Marks, 1103.
- Trade Unions, 1029.
- Unemployed, 1023.
- Vessels, 327–328.
- Registry, Ports of, 328.
- Regulation of Prices, 708–709.
- Rehabilitation, 239, 277–284, 755, 793, 934–937.
- Relief Institutions, 155–162.
- Relief of Unemployment, 184.
- Religious Professions, 73–74.
- Marriages by Ministers of, 95–96.
- Officiating Ministers, 90–91, 95–96.
- Renewable Leases, 296–299.
- Rent Restrictions, 565–568.
- Rental Cars; 347.
- Rental Value, Owner-occupied Houses, 743, 748, 757.
- Renters, Film, Taxation of, 825.
- Rents, House, 565–568.
- Rents, Stabilisation of, 566.
- Repayment of Public Debt, 793, 831–832, 836–837.
- Representation Commission, 37.
- Representatives, House of, 31–34, 1124.
- Broadcast of Proceedings of, 382.
- Election of, 33, 1109–1114.
- Members of, 1124.
- Representatives in New Zealand, 1136–1138.
- Representatives Overseas, 1134–1135.
- Reproduction Rate, 45.
- Research, Agricultural, 415–418, 428, 429, 439.
- Research Associations in Industry, 496.
- Research, Dental, 145.
- Research, Educational, 243.
- Research for Industry, 495–496.
- Research, Forestry, 460–461.
- Research, Grassland, 1169.
- Research Institute, Wheat, 428–429.
- Research, Medical, 149.
- Research, Mining, 489–490.
- Research Scholarships, 238.
- Reserve Bank, 642–644, 834, 838, 880–885, 918–919, 1215.
- Reserves, Air Force, 275.
- Reserves, Farm Industry, 610.
- Reserves, Military, 273.
- Reserves, Naval, 269.
- Reserves, Public or Scenic, 287–288.
- Restrictions on Employment, 982, 984, 986.
- Retail Prices, 710–712, 1208.
- Retail Trading, 611–615, 620–628, 1205.
- Retailers, Bank Advances to, 890.
- Revaluations, Land, 311–312.
- Revenue, 788–827, 1152.
- Broadcasting, 383, 384.
- Customs, 702–703, 802, 805.
- Electric Power, 577–579, 581, 844.
- Forest Service, 462–463.
- Government (see Government Finance).
- Insurance Companies, 958, 960, 963, 970–971, 975–978, 1161.
- Local Government, 157, 578, 756, 841–844, 1154, 1213.
- National Roads Fund, 343–344, 796.
- Picture Theatres, 391, 393, 394.
- Post Office, 373, 376, 377–378.
- Railway, 334–336, 339, 796, 1159.
- Social Security Fund, 175, 799, 802, 825.
- Urban Transport, 358–361.
- Rice, Imports of, 694.
- Rivers, 4–5, 570–571.
- Control of, 294–295.
- Road Districts, 41, 843–855.
- Bridges in, 342.
- Debt of, 847.
- Milage of Roads, 341.
- Road Goods Services, 350–352.
- Road Passenger Services, 350–353, 357–360.
- Road Safety, 353–354.
- Road Transport, 349–353, 357–361, 1200.
- Roads, 341–361.
- Accidents on, 78, 112, 117, 118, 124, 355–357.
- Expenditure on, 343–346, 796, 830.
- Taxation, 343–344, 350, 802, 805.
- Roll, Valuation, 309–210, 840.
- Rolling Stock-
- Buses, etc., 358–360.
- Railway, 332–333.
- Roman Catholic Schools, 217, 227, 1076.
- Ross Dependency, 1, 2, 44, 1090–1092, 1185.
- Whaling, 1092.
- Royal New Zealand Air Force, 273–275, 276, 277.
- Royal New Zealand Navy, 267–270, 276, 277.
- Rubber Products Industry, 504, 506–527, 538, 1008.
- Rural Advances, 293–294, 932–938.
- Rural Education, 231–233.
- Rural Housing, 551, 559, 562, 935.
- Rural Intermediate Credit, 938.
- Rural Mail Deliveries, 371.
- Rural Mortgages, 925–926, 928, 935.
- Rural Population, 51–52.
- Ryecorn, 425, 439.
S
- St. Helens Hospitals, 146, 160, 190.
- St. John Ambulance, 154.
- Safety, Occupational, 1063–1071.
- Safety of Machinery, 1064–1065.
- Safety of Workers, 985–986.
- Salaries and Wages, 377, 391, 497–505, 510–513, 527–545, 577–579, 585–587, 613, 617, 618, 748, 757, 761, 762, 866, 1151.
- Charge on, 156, 175, 799, 802, 825, 996.
- Salaries of Members of-
- Executive Council, 34.
- House of Representatives, 34.
- Public Service, 1134.
- Sales Tax, 754, 792, 802, 826.
- Salmon, 479.
- Salt, 480, 489, 838.
- Samoa (see Western Samoa).
- Sanatoria, 159.
- Sanctuaries, Wildlife, 289.
- Sand and Gravel, 480.
- Sand Dunes, Stabilisation of, 458.
- Sanitation, 137–142.
- Sausage Casings, Export of, 653, 654, 670, 674, 675.
- Savai'i Island, 1083.
- Savings Accounts and Bonds (National), 827–828, 908–909.
- Savings Banks, 902–909, 915–916, 1157, 1216.
- Savings, Private, 745–752.
- Savings, Small, 909.
- Sawmills, etc., 464–470, 503, 535.
- Wages and Hours Worked of Employees, 1002, 1007.
- Scheelite, 487, 652, 654.
- Scholarships, 238–239, 1085.
- School Certificate, 215, 220.
- School Children, 218–233, 1141.
- Dental Treatment of, 144.
- Medical Inspection of, 143.
- Milk for, 143, 233.
- Transport and Board of, 231–232.
- School Committees, 212, 213.
- School Inspectors, 224, 226, 228.
- School Journal, 236, 1072.
- School Savings Bank, 905–906.
- School System, 214–217.
- School Teachers, 212–214, 226, 227, 233–236.
- Superannuation, 203.
- Schools, 212–246, 1076, 1079, 1085.
- Combined, 218, 227–230, 232, 235.
- Consolidation of, 231.
- Denominational, 217, 227, 1076, 1085.
- Dental Clinics, 144.
- Free Text-books in, 236.
- Military, 272.
- Of Mining, 237, 489.
- Private, 226–227, 232, 1141.
- Public, 212–236, 1141.
- Special, 221, 241.
- Science and Technology, University Education for, 1186–1196.
- Science, Defence, 266–267.
- Scientific and Industrial Research, Department of, 416–418, 1169.
- Scientific Research for Industry, 495–496.
- Sea Fisheries, 473–478.
- Seals, 478.
- Seamen, 193, 199, 201, 986–987.
- Seamen Act, Shipping and, 986–987.
- Secondary Education, 213–220, 227–231, 235–236, 1141.
- Sector Accounts and Inter-Industry Studies, 787.
- Seed Certification, 439.
- Seed Sowing, Aerial, 366.
- Seeds, Grass and Clover, 424, 433–434.
- Exported, 653, 655, 671, 674, 675, 1148.
- Seismology, 7–8.
- Sentences on Criminals, 255–256, 1142.
- Separate Rates, 839.
- Separation, Judicial, 96, 97.
- Separators, Cream, 421.
- Serpentine, 480, 489, 539.
- Service, Public (see Public Service).
- Service-car Licences, 347.
- Servicemen-
- Acquisition of Land by Ex-, 279–280, 300–301.
- Casualties Overseas, 277.
- Demobilisation of, 284.
- Educational Facilities for Ex-, 280.
- Financial Assistance to Ex-, 281–284, 300–301, 934–937.
- Pensions for Ex-, 193, 195–203.
- Registration of Deaths of, 99.
- Rehabilitation of Ex-, 239, 277–284, 755, 934–937.
- Services-
- Air Force, 273–275, 276, 277.
- Army, 270–273, 275–277.
- Navy, 267–270, 276, 277.
- Sessions, Parliamentary, Successive, 1125.
- Settlement of Industrial Disputes, 1034–1037, 1044–1045.
- Settlement of Land, 285–304.
- Settlement, Ex-servicemen's, 279–280, 281–282, 300–301.
- Settlement, Small Farms, 297–299.
- Sex Proportions, 48.
- Sexes of-
- Children Born, 83–85, 90, 121.
- Factory Employees, 507–510.
- Patients in Mental Hospitals, 164–166.
- Patients in Public Hospitals, 131.
- Prisoners, 263, 264.
- Scholars and Students, 224, 226–230, 237–238.
- School Teachers, 226, 227, 233–236.
- Twin Births, 85.
- Sexual Offences, 252, 256, 258, 259.
- Share Prices, Index Numbers, 729–733, 1209.
- Sharemilking Agreements, 984.
- Shares in Building Societies, 940, 941.
- Sharks, 478.
- Shearers' Wage Rates, 993, 1003.
- Shearing Machines on Farms, 421.
- Sheep, 439–444, 1144.
- Sheep and Lambs Slaughtered, 413, 529.
- Sheep Farms, 408.
- Sheep Skins and Pelts Exported, 653, 655, 670, 674, 675, 1149.
- Sheetmetal Working Industry, 505, 544.
- Shipping, 315–330.
- On Inland Waters, 327.
- Shipping and Seamen Act, 986–987.
- Ships (see Vessels).
- Shoe and Boot Industry, 535.
- Shops and Offices Act, 982–984.
- Shops, Fire Losses on, 974.
- Short-wave Radio Broadcasting, 381.
- Sick Funds, 210, 377.
- Sickness, 127–136, 210.
- Benefits, 176, 177, 185–186, 193.
- Insurance, 210, 962.
- Signals, Time, 382, 1119.
- Silage, 433.
- Silica Sand, 480.
- Silver, 480, 487.
- Coins, New Zealand, 917.
- Silviculture, 455–458, 461.
- Sinking Fund, Electric Power, 582.
- Ski-ing, 1098.
- Skins, Hides, and Pelts, Export of, 324, 651, 653, 654, 655, 669–670, 674, 675, 1149.
- Slaughter of Animals for Food, 413.
- Snares Islands, 1, 1073.
- Snow, 12.
- Soap and Candle Industry, 504, 539.
- Social Security, 156, 174–195, 1218.
- Benefits, 145, 173, 176–195, 744, 755, 757, 799.
- Charge, etc., 156, 175, 799, 802, 825, 871, 872, 996.
- Fund, 145, 175, 799, 803, 825.
- Income Tax, 175, 799, 802.
- Reciprocity with Australia, 174, 175, 176, 187.
- Reciprocity with United Kingdom, 174, 176, 187–188.
- Supplementary Assistance, 186, 193.
- Taxation, 175, 754, 799, 802, 825, 996, 1212.
- Soil Conservation, 294–295, 458.
- Soil Survey, 417.
- Soils, 403–405.
- Solander Island, 1, 1073.
- Soldiers, 270–273, 275–277.
- Sources of Income, 866.
- South Africa, Union of-
- Birth and Natural Increase Rates, 83.
- Libraries, 389.
- Population, 75.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices in, 712.
- Reciprocal Trade with, 704.
- South African War Pensions, 193, 201.
- South-East Asia Treaty Organisation (SEATO), 29.
- Southern Alps, 3.
- Souvenirs, 1098.
- Sovereignty, 22.
- Specialist Services, 194.
- Specie, Movement of, 646, 1145.
- Speed Limit, 353.
- Spinsters Marrying, 93.
- Spirits, Consumption of, 740.
- Spirits, Duty on, 699, 700, 702, 703.
- Spirits, Imports of, 686, 694.
- Sports, 154, 1098.
- Stabilisation of-
- Prices, 708–709.
- Rents, 566.
- Sand Dunes, 458.
- Stabilisation Subsidies, 741–742, 744, 755, 793.
- Stakes, Tax on, 824.
- Stamp Duties, 792, 802, 823.
- Standard Time, 1119.
- Standardised Death Rates for Cancer, 114.
- State Advances, 844, 932–939.
- Corporation, 549–550, 834, 838, 849, 932–939.
- State Aid to-
- Afforestation, 460–461.
- Building, 549–551, 932–939.
- Cook Islands, 1078.
- Discharged Servicemen, 277–284, 300–301, 934–937.
- Farming Industry, 296–301, 415–418, 932–938.
- Hospital Boards, 156, 157.
- Housing, 932–939.
- Immigrants, 65.
- Local Government, 156, 157, 345–346, 755, 934–937.
- Manufacturing, 935–937.
- Mining, 489–490.
- Niue Island, 1081.
- Prospecting, 489.
- Purchases of Private Land, 300.
- Superannuation Funds, 205, 208.
- Unemployed, 184, 193, 1023.
- Wheat Growing, 428, 429.
- State Coal Mines, 485, 830.
- Account, 797.
- Persons Employed in, 485.
- State Departments, 36, 1102, 1123, 1130–1132.
- State Electricity Department, 569, 1026.
- Occupational Safety, 1067–1068.
- State Finance, 753–757, 788–838, 1152, 1153.
- State Forests, 550–452, 830.
- State Housing, 546, 554–558, 563, 795, 830.
- Sale of, 938–939.
- State Indebtedness, 827–838, 1153, 1212.
- State Insurance-
- Accident, 834, 976–977.
- Earthquake and War Damage, 800, 977–978.
- Fire, 834, 977.
- Life, 975–976.
- State Marketing, 593.
- State Maternity Hospitals, 160, 190.
- State Placement Service, 1010, 1021–1022.
- Stations-
- Air Force, 274, 275.
- Electric Power, 570–572.
- Fire Brigade, 975.
- Meteorological, 15, 16, 1073.
- Naval, 268.
- Radio, 376, 377, 379–382, 1073, 1077, 1080.
- Telephone, 374.
- Statistical Information, Latest, 1197–1228.
- Statistical Publications, 1229–1230.
- Statistical Summary, 1139–1161.
- Statutes of 1960, 1125–1127.
- Steam Electric Power Stations, 571–572.
- Steam, Geothermal, Electric Power Stations, 571–572.
- Steel and Iron, Imports of, 689, 695.
- Steel Industry, 494.
- Sterling Exchange-
- Holdings of, 884, 897.
- Rates, 919–920.
- Sterling Values of Currency, 919–920.
- Stewart Island, 1.
- Oysters, 477.
- Population, 56.
- Still-births, 84, 85, 90, 110–111.
- Registration of, 90, 99, 110.
- Stock and Station Agents-
- Advances to, 890.
- Deposits, etc., with, 909–910.
- Stock, Live (see Livestock).
- Stock, Quotations for, 834.
- Stock, Registered, Local Government, 848.
- Stocks, Manufacturers', 522–523.
- Stocks, Retail, 611–615, 623.
- Stone Fruits, 425, 436, 739.
- Stones, Building and Ornamental, 480, 489.
- Stranding of Vessels, 330.
- Streets and Roads, Length of, 341.
- Strikes, 1034–1046.
- Students, 218–220.
- Students, University, 218, 220, 237–238, 1141.
- Subscribers, Telephone, 374.
- Subsidies-
- Highways, 345–346.
- On Food and Clothing, 741–742, 755.
- Stabilisation, 741–742, 744, 755, 793.
- To Gasworks, 583, 741, 742.
- To Hospital Boards, 156, 157.
- To Local Government, 844.
- To Mining, 489.
- To National Provident Fund, 208.
- To Superannuation Fund, 205, 377, 796, 797.
- Succession Duty, 819.
- Suffrage, 33, 38, 41–42.
- Sugar-
- Consumption of, 740, 741.
- Duty on, 699, 702, 703.
- Exported, 653, 655.
- Imports of, 686, 694.
- International Agreement, 707.
- Used by Factories, 531, 532, 533.
- Sugar of Milk Exported, 653, 654, 674, 675.
- Suicide, 78, 80, 112, 119–120, 124.
- Sulphur, Imports of, 695.
- Sulphur, Used in Fertiliser Industry, 539.
- Summary Convictions, 251–254, 258, 1142.
- Summer Time (Daylight Saving), 1119.
- Sunshine, 12–13, 15, 16.
- Superannuation, 34, 158, 203–205, 341, 793.
- Benefits, Social Security, 176, 178, 193.
- Private Funds, 205.
- Superphosphate and Fertiliser Industry, 539.
- Supplementary Medical, etc., Benefits, 176, 190–194.
- Surtax, 698, 699.
- Survey of Companies with Overseas Affiliations, 782–787.
- Survey Publications, Land, 307–308.
- Survey System, Land, 305.
- Surveys-
- Aerial, Land, 306, 366.
- Geodetic, Land, 305.
- Geological, 489–490.
- National Forest, 451.
- Of Coal Resources, 482–483.
- Of Consumer Credit, 628–631.
- Of Employment, 1014–1023.
- Of Land, 305–308.
- Of Retail Prices, 713.
- Of Retail Trading, Quarterly, 620–628, 1205.
- Of Ships, 329.
- Soil, 417.
- Standard Land, 305.
- Tidal, 306–307.
- Sustenance Allowances, 1023.
- Suwarrow (Anchorage) Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Swedes, 424, 433, 439.
- Sweepstakes, 1109.
- Swimming, 154.
- Drowning Accidents, 117.
- Swordfish, 478.
- Syphilis, 78, 108, 112, 123, 132, 140, 169.
T
- Takutea Island, 2, 1074, 1075.
- Tallow Exported, 324, 653, 655, 668–669, 674, 675, 1146.
- Tallow Produced, 529.
- Tanning Industry, 504, 538, 1008.
- Tariff, Customs, 697–707.
- Tariffs and Trade Agreement (GATT), 706.
- Tasman Empire Airways Ltd., 366–367, 838.
- Tasman Pulp and Paper Co., 467, 838.
- Tax, Income, 754, 792, 802, 806–816, 856–879.
- Tax, Land, 754, 792, 802, 806, 816.
- Taxation, 702, 744–762, 792, 801–827, 1152, 1212.
- Amusement, 391, 393, 394, 802, 825.
- Customs, 697–707, 754, 802, 805.
- Direct, 750, 751, 754, 756, 759, 761, 801.
- Employment Promotion, 825, 996.
- Film Hire, 792, 802, 825.
- Forest, 462.
- Highways, 343–344, 802, 805.
- Indirect, 744, 751, 754, 759.
- Local Government, 756, 827, 839–841.
- Motor Spirits, 343, 350, 701, 805, 844.
- Motor Vehicles, 343, 700, 754, 805.
- Orchards, 436.
- Racing, 802, 823–825.
- Roads, 343–344, 802, 805.
- Sales, 754, 792, 802, 826.
- Social Security, 175, 754, 799, 802, 825, 996, 1212.
- Taxis, 347.
- Taxpayers, Incomes of, 856–879.
- Tea-
- Consumption of, 740.
- Duty on, 699.
- Imports of, 686, 694.
- Teachers' Grading, 213.
- Teachers' Superannuation, 203.
- Teachers' Training Colleges, 216, 233–234.
- Teaching Aids, 236.
- Teaching Profession, 233–236.
- Technical Correspondence School, 218, 229.
- Technical Education, 218, 227–231, 235, 1141.
- Telegraph Services, 373–374, 376.
- Telephones, 373–375.
- Television, 379, 385, 1223.
- Temperature, 13, 15, 16.
- Tenancy Act, 565–568.
- Tenancy and Rents, 565–568.
- Tenure of Crown Lands, 296–301.
- Tenure of Dwellings, 553.
- Tenure of Occupied Land, 287, 297–299.
- Terminating Building Societies, 940–943.
- Terms of Trade, 729.
- Territorial Air Force, 273–275.
- Territorial Forces, 270–273.
- Text-books in Schools, Free, 236.
- Textiles, Duty on, 700.
- Textiles, Production of, 502, 506–527, 534.
- Theatres, etc., Fire Losses on, 974.
- Theatres, Picture, 390–394.
- Theft, 252, 256, 257, 259.
- Therapists, Occupational, 152.
- Thermal Electric Power Stations, 571.
- Third-party Risks Insurance, 962–966.
- Thorium, 486.
- Three Kings Islands, 1, 1073.
- Threshing Mills, 422.
- Thrift Club Accounts, Post Office Savings Bank, 904–905.
- Tidal Survey, 306–307.
- Timber-
- Carried on Railways, 339, 340.
- Export Duty on, 702.
- Export of, 470–472, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Import Duty on, 700.
- Imports of, 470–471, 690, 695.
- Output, 464–466, 535, 1150, 1200.
- Value of, 400.
- Plantations, 286, 408, 425, 435, 450–452.
- Preservation of, 469–470.
- Resources, 450–452.
- Sales, 463.
- Trees, 16, 472.
- Timbers, Strengths of, 472.
- Time Lost-
- Through Industrial Accidents, 1060.
- Through Industrial Disputes, 1038–1046.
- Time Service, 382, 1119–1120.
- Tin, 487.
- Title, Certificates of, Issued, 289–290.
- Titles, Compulsory Registration of, 289.
- Tobacco, 426, 438.
- Consumption of, 740.
- Duty on, 699, 701, 703.
- Factories, 502, 506–527, 534, 1007.
- Imports of, 678, 686, 694.
- Tokelau (Union) Islands, 1–2, 44, 66, 1081–1082.
- Toll Communications, 374, 375.
- Ton-miles Flown, 364–367.
- Tonnage of Registered Vessels, 327–328.
- Tonnage of Shipping and Cargo, 315–328.
- Tons, One-mile, Railway, 339.
- Topdressing, 366, 419.
- Topographical Mapping, 306.
- Totalisator Taxation, 823–824.
- Totalisator, Turnover on, 823–825.
- Tourist Agents Overseas, 1134–1135.
- Tourist and Publicity Department, 1098–1099.
- Tourist Attractions, 1169.
- Tourist Industry, 1093–1099.
- Tourists, 63.
- Tourists' Rail Tickets Issued, 338.
- Town and Country Planning, 42–43.
- Town Districts, 40, 843–855.
- Area of, 58.
- Bridges in, 342.
- Capital and Unimproved Values, 313.
- Debt, 847, 850.
- Milage of Streets, 341.
- Population, 58.
- Tractors, Imports of, 690, 695.
- Tractors on Farms, 421–422.
- Trade, 632–707, 1145–1149, 1205–1207.
- Agreements, 590–591, 703–707.
- Balance of, 636.
- Board of, 649–650, 698.
- Commissioner Service, 650–651.
- Cook Islands, 676–677, 696–697, 1077–1078.
- Direction of, 639–641.
- Nauru Island, 1090.
- Niue Island, 676, 1080.
- Of Ports, 315–325, 673, 696.
- Representatives, 1134–1138.
- Terms of, 729.
- Volume of, 645, 736.
- Western Samoa, 1087.
- Trade Marks, 1103.
- Trade Practices Act 1958, 709.
- Trade Training of Discharged Servicemen, 278–279, 284.
- Trade Unions, 1029–1033.
- Trades Certification, 220, 221.
- Trading Accounts, State, 796–798.
- Trading Banks, 885–894, 913, 1156, 1215.
- Trading Companies, Deposits with, 916.
- Trading, Retail, 611–615, 620–628.
- Traffic-
- Accidents, 78, 112, 117, 118, 124, 136, 341, 353–357.
- Air, 361–369.
- Motor, 347–361.
- Offences, 252, 253–254.
- Railway, 336–340, 1159.
- Training of-
- Defence Forces, 268–275.
- Dental Nurses, 144.
- Discharged Servicemen, 278–279, 284.
- Forestry Employees, 461.
- Nurses, 148.
- Police Recruits, 265.
- Teachers, 220, 221, 233–235.
- Tramways, etc., 357.
- Accidents, 118, 355.
- Cable, 360.
- Transhipment of Cargo, 323–326.
- Transport, 315–369, 1198–1200.
- Accidents, 117, 118, 136.
- Districts, Urban, 41, 843–855.
- Equipment, Imports of, 680, 681, 682.
- Equipment Industry, 505, 506–527, 543–544.
- Licensing, 350–353.
- Of School Children, 231–232.
- Persons Engaged in, 1020.
- Urban, 357–361.
- Travel Allowances, Overseas, 900.
- Trawling, 473, 476.
- Treasury Bills, 828, 833.
- Treaty of Waitangi, 22.
- Tree Planting, 450–458.
- Trees, Forest, 16, 472.
- Triplets Born, 84, 85.
- Trolley-buses, 359–360.
- Trout, 5, 479.
- Trust (Liquor) Control, 1118–1119.
- Trust Territory, 1–2, 44, 1083–1088, 1089.
- Trustee, Maori, 303–304, 834.
- Trustee, Public, 1102–1103.
- Trustee Savings Banks, 906–908, 916, 1216.
- Tuberculin Tests, 130.
- Tuberculosis, 78, 108, 109, 112, 113, 114, 125, 127, 130, 132, 138, 139, 142, 154, 159, 169, 1076.
- Maori Deaths from, 123, 125.
- Register, 130.
- Vaccination, 130, 142.
- Tungsten Ore, 480, 487.
- Tunnels, Railway, 330–331.
- Turkeys, 447.
- Turnbull, Alexander, Library, 1169.
- Turnips, 424, 433, 439.
- Tussock Boards, Nassella, 41, 843–855.
- Tussock, etc., Land, 418.
- Twins and Triplets Born, 84–85, 89.
- Tyre Tax, 344, 701, 805.
U
- Undergraduates, 237.
- Under-Secretaries, Parliamentary, 34.
- Unemployment, 1023.
- Benefits, 176, 177, 184, 193, 1023.
- Taxation, 996.
- Unexercised Overdraft Authorities, 894.
- Unimproved Occupied Land, 287.
- Unimproved Value of Land, 309–314.
- Land Tax Assessed on, 816.
- Rating on, 840–841.
- Unions, Trade, 1029–1033.
- United Kingdom-
- Birth and Natural Increase Rates, 83.
- Consumption of Foodstuffs, 738, 741.
- Dairy Produce and Meat Imported into, 591–592.
- Debt Domiciled in, 832, 833, 851, 1153.
- Libraries, 389.
- Motor Accident Death and Injury Rates, 357.
- New Zealand Representatives in, 1135.
- Population, 75.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices in, 712.
- Representatives in New Zealand, 1138.
- Social Security Reciprocity, 174, 176, 187–188.
- United Nations, 26–29, 83, 92, 101, 105, 120, 1083.
- United States of America-
- Birth and Natural Increase Rates, 83.
- Consumption of Foodstuffs, 738, 741.
- Debt Domiciled in, 833, 1153.
- Exchange Rate with, 920.
- Libraries, 389.
- Motor Accident Death and Injury Rates, 357.
- New Zealand Representatives in, 1135.
- Population, 75.
- Population, Annual Average Increase, 47.
- Prices in, 712.
- Representatives in New Zealand, 1138.
- University Education, 216, 218, 220, 230, 236–240, 1141.
- Committee on, 240.
- University Education for Science and Technology, 1186–1196.
- University Libraries, 387, 388.
- University Scholarships, 238–239.
- Unpaid Fractions, Totalisator, 824.
- Upolu Island, 1083.
- Uranium, 486, 490.
- Urban Drainage Districts, 41, 843–855.
- Urban Drift, 51.
- Urban Farm Lands, Rating on, 311.
- Urban Housing, 558–564.
- Urban Mortgages, 925–926, 928, 935.
- Urban Population, 51–54.
- Urban Transport, 357–361.
- Urban Transport Districts, 843–855.
V
- Vacancies, Employment, 1018, 1021, 1022.
- Vaccination, 130, 142, 143.
- Valuation-
- Of Exports, 637, 651.
- Of Imports, 637, 677.
- Of Land, 308–314.
- Of Personal Expenditure, 745.
- Roll, 309–310, 840.
- Value Added in Manufacturing, 497–505, 518–520, 523, 524, 525, 529–545, 1151.
- Value of-
- Currency, 919–920.
- Farm Production, 395–401.
- Goods Available for Use, 734–735.
- Manufacturing Production, 399–401, 497–545, 1151.
- Materials Used in Manufacturing Industries, 497–545, 1151.
- Production, 395–401, 735.
- Veal-
- Consumption of, 412, 739.
- Export of, 674, 675.
- Production of, 411, 412, 529.
- Vegetable Gardens, 435.
- Home Production in, 436.
- Vegetables-
- Consumption of, 739, 740.
- Exported, Canned and Frozen, 653, 655.
- Retail Prices of, 710.
- Vegetation, 16.
- Vehicles-
- Buses, 357–360.
- Motor (see Motor Vehicles).
- Railway, 332.
- Veneer and Plywood, 468–469, 503, 542.
- Venereal Diseases, 78, 108, 112, 123, 132, 140, 169.
- Vessels-
- Crews of, 63.
- Entered and Cleared, 315–322.
- Fishing, 474.
- Nationality of, 318–319.
- Naval, 268, 270.
- Radio Communication with, 377.
- Registered, 327–328.
- Safety of, 1065–1066.
- Survey of, 329.
- Wrecked, 330.
- Veterans' Allowances, 193, 197, 198–199, 201.
- Veterinary Services, 416, 420.
- Vineyards and Grapes, 434, 436.
- Visitors to New Zealand, 63, 1093–1096.
- Visual Aids in Teaching, 236.
- Vital Statistics, 76–136, 1140.
- Cook Islands, 1075.
- Niue Island, 1079.
- Western Samoa, 1084.
- Vocational Guidance, 231, 1011.
- Volcanoes, 2, 3, 404, 405.
- Volume of-
- Exports, 645, 736.
- Farm Production, 397, 401–402.
- Goods Available for Use, 736.
- Imports, 645, 736.
- Manufacturing Industries Production, 401–402, 524–525.
- Money in Circulation, 912–913.
- Production, 397, 401–402, 524–525.
- Trade, 645, 736.
- Voluntary Welfare Organisations, 153.
- Voting-
- At General Elections, 1109–1115.
- At Licensing Polls, 1114–1115.
- Qualifications, 38–39, 41–42.
- Vouchers, Audit of, 788.
W
- Wage and Salary Earners, 497–505, 855, 1033.
- Wage, Basic, 993.
- Wage, Minimum, 982, 983, 984, 992–993.
- Wage Rates, 733, 982–984, 990–1009, 1219.
- Wages-
- And Salary Payments, 377, 391, 497–505, 510–513, 527–545, 577–579, 585–587, 613, 617, 618, 748, 757, 761, 762, 866, 1151.
- And Wage Rate Legislation, 990–994.
- Average Hourly Wage in Industry, 1007–1009.
- Increases in, 982, 990–1007.
- Legislative Changes in, 990–994.
- Lost Through Industrial Disputes, 1038–1046.
- Minimum Weekly Rates, 1002–1005.
- Of Electric-supply Employees, 577–579.
- Of Manufacturing Industry Employees, 497–505, 510–513, 527–545, 1151.
- Of Picture Theatre Employees, 391.
- Protection of, 993–994.
- Shearers', 993, 1003.
- Tax on, 156, 175, 799, 802, 825, 996.
- Waitangi, Treaty of, 22.
- War, 275–277.
- Bursaries for Ex-servicemen's Children, 199, 280.
- Casualties, 277.
- Damage and Earthquake Insurance, 800, 977–978.
- Deaths Register, 99.
- Debt, 830.
- Loans, 830.
- Pensions, 193, 195–203, 1218.
- Pensions Appeal Board, 200.
- Pensions Supplementary Assistance, 199.
- Publications Pertaining to, 1183–1184.
- Veterans' Allowances, 193, 197, 198–199, 201.
- Warships, 268, 270.
- Washing Machines, 528, 553.
- Water Power, 570–571.
- Waterfront Control, 988–989.
- Weather, 8–16.
- Cook Islands, 1073.
- Niue Island, 1078.
- Western Samoa, 1083.
- Weights and Measures, 305, 425.
- Welfare, Maori, 1101.
- Welfare, Maternal, 139, 146.
- Welfare of Workers, 982, 984, 985–986, 987.
- Welfare Organisations, 153.
- Wellington-
- Broadcasting Stations, 380, 381.
- Building Values, 562.
- Climate, 15, 16.
- Population, 53, 54, 57.
- Sales Tax Receipts, 826.
- Shipping, 318, 321–325, 673, 696.
- Urban Transport, 360.
- Victoria University of, 236–237.
- Western Samoa, 1, 2, 66, 203, 1083–1088.
- Bibliography, 1185.
- Education, 1085.
- Population of, 44, 1084.
- Radio Communications, 376, 1086.
- Trade, 1087.
- Whale Oil, 474, 478, 652, 654.
- Whales and Whaling, 478, 1092.
- Wheat, 424–429, 1143.
- Imports of, 686, 694.
- International Agreement, 707.
- Milled, 531.
- Research, 417, 418.
- Whey Butter, 410, 530.
- Whipping Abolished, 256.
- Whitebait, 474, 478.
- Wholesale Liquor Licences, 1116–1118.
- Wholesale Prices, 712, 722–725.
- Wholesale Trading, 615–617, 1224.
- Whooping-cough, 78, 108, 112, 123, 125, 143.
- Widowers, Remarriages of, 93, 94.
- Widows-
- Benefits, 176, 177, 180–181, 193.
- Remarriages of, 93, 94.
- War Pensions, 196–203.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries, 289.
- Wills Administered by Public Trust Office, 1102–1103.
- Winds, 9–10.
- Wine, Consumption of, 740.
- Wine, Duty on, 699–700.
- Wine Licences, 1116–1118.
- Wine-making Industry, 502.
- Wire Rope Industry, 495.
- Withdrawals from Savings Banks, 902–909, 1157.
- Wives, Aggregation of Income, 866.
- Wives, Allowances in Respect of, 178–204.
- Women-
- Air Force, Royal New Zealand, 273, 275.
- Army Corps, Royal New Zealand, 270.
- Deaths of, in Childbirth, 78, 112, 116–117, 124, 133.
- Eligible for Parliament, 33.
- Employed in Factories, 507–510, 1013, 1015–1020.
- Nationality Laws, re, 68.
- Naval Service, Royal New Zealand, 269.
- Of Child-bearing Ages, 82.
- Offences by, 257.
- Police, 265.
- Wage Rates of, 993, 999–1001, 1004, 1005.
- Working Conditions of, 981, 983.
- Working Hours of, 1009.
- Wood Preservation, 469–470.
- Wood Pulp, Exports of, 472, 652, 654, 672, 674, 675.
- Wood Pulp, Production of, 466.
- Wool-
- Capital Account, 610.
- Carried on Railways, 339, 340.
- Commission Account, 610.
- Commissions, 594.
- Export Price Index, 726.
- Exports of, 324, 651, 653, 655, 663–664, 674, 675, 1146.
- Imports of, 686.
- Levy, 415, 594, 702.
- Marketing of, 589, 594.
- Prices for, 597, 1150, 1204.
- Production, 396, 413–415, 529, 1150.
- Retention Moneys, 610, 749.
- Used at Local Mills, 413, 534.
- Woollen Mills, 502, 534, 1008.
- Woollen Piece-goods, Imports of, 687.
- Woolscouring Industry, 502.
- Workers' Compensation, 1047–1055.
- Board, 1050, 1071.
- Insurance, 962, 977.
- Workers' Educational Association, 244.
- Workers, Safety of, 985–986.
- Working Conditions, 979–989.
- Working Conditions in the Government Service, 987–988.
- Working Days Lost Through Industrial Disputes, 1038–1046.
- Working Hours, 525–526, 981, 983–986, 1005–1009.
- Working Life Expectancies, 1027–1028.
- Working Proprietors, 1015–1017.
- World Population, 74–75.
- Wrecks, 330.
X
- X-ray, 146–147.
- Diagnostic Services, 190–191, 194.
- Examinations, 130, 142, 190–191.
Y
- Yields-
- Butterfat, 408, 409.
- Crops, 427–432, 1143.
- Youth Centres, 231, 1011.
- Youth Hostels, 162.
- Youths-
- Wage Rates of, 1004–1005, 1009.
- Working Conditions of, 981, 983, 986.
Z
- Zoology, 17.
